User login
SSaSS: Salt substitute shows clear reduction in stroke, CV events, death
Switching from regular salt to a low-sodium salt substitute has major public health benefits, including a reduction in stroke, cardiovascular events, and death, a new landmark study shows.
The Salt Substitute and Stroke Study (SSaSS) was conducted in 21,000 people with a history of stroke or high blood pressure in rural China, with half of them using a lower-sodium salt substitute instead of regular salt.
Results showed that after 5 years, those using the salt substitute had a 14% reduction in stroke, a 13% reduction in major cardiovascular events, and a 12% reduction in death. These benefits were achieved without any apparent adverse effects.
The trial was presented by Bruce Neal, MB, George Institute for Global Health, Sydney, Australia, on Aug. 29 at the virtual European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress 2021. They were simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“This is one of the largest dietary intervention trials ever conducted and has shown very clear evidence of protection against stroke, cardiovascular events, and premature death, with no adverse effects with a very simple and low-cost intervention,” Dr. Neal concluded. “This is a very easy thing to work into the diet. You just replace regular salt with a substitute that looks and tastes almost identical,” he added.
Addressing the issue of whether these results are generalizable to other populations, Dr. Neal said, “We believe the results are relevant to everyone who eats salt.
“The way the body manages sodium and potassium and their association with blood pressure is highly consistent across different populations,” he said. “Almost everyone, with the exception of a few people with serious kidney disease, should be avoiding salt or switching to a salt substitute and expect to see some benefit of this.”
Commentators at the ESC presentation lauded the study as “magnificent,” with “extraordinary” results and “very powerful implications.”
Designated discussant, hypertension expert Bryan Williams, MD, University College London, said the SSaSS was “probably the most important study with regards to public health that we will see.” He described the reductions in stroke, cardiovascular events, and death as “extraordinary for such a simple intervention.”
Dr. Williams added: “Those who have doubted the benefits of salt restriction must now admit they were wrong. The debate stops here. The data are in. Global health interventions to implement these findings must now begin.”
He also highlighted the large number of events in the trial. “This was a large, pragmatic, long-duration study in a high-risk population, and with 5,000 cardiovascular events it gives enormous power to show benefits.”
Chair of the ESC session, Barbara Casadei, MD, DPhil, John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford (England), said the SSaSS “will change the way we think about salt and be remembered for years to come.”
Noting that the benefits were seen in all subgroups across the study, Bertram Pitt, MD, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, was particularly excited about the stroke reduction seen in patients with diabetes, noting that several recent trials of new diabetes drugs have not managed to show a reduction in stroke.
“For patients with diabetes, this is a really important intervention,” he stated.
However, an editorial accompanying the NEJM publication gave a somewhat less enthusiastic response to the study than the ESC commentators.
Julie R. Ingelfinger, MD, deputy editor of the journal, points out that serial monitoring of potassium levels was not performed in the trial, so it is possible that hyperkalemic episodes were not detected, and persons with a history of medical conditions that may be associated with hyperkalemia were not studied.
She also noted that because the salt substitute was distributed to families, it would have been instructive to have data on the household members without risk factors, but no such data were obtained.
“Overall, the SSaSS provides some intriguing hints, but wider effectiveness is hard to predict, given limited generalizability,” she concluded.
Cluster-randomized trial
The SSaSS was an open-label, cluster-randomized trial involving 20,995 people from 600 villages in rural China who had a history of stroke or were 60 years of age or older and had uncontrolled hypertension. Patients with a history of severe kidney disease and those taking potassium supplements or potassium-sparing diuretics were excluded.
They were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to the intervention group, in which the participants used a salt substitute (roughly 75% sodium chloride and 25% potassium chloride), or to the control group, in which the participants continued to use regular salt (100% sodium chloride).
Results showed that after a mean follow-up of 4.74 years, systolic blood pressure was reduced by 3.3 mm Hg in the salt substitute group.
The rate of stroke, the primary endpoint, was 29.14 events per 1,000 person-years in the salt substitute group vs. 33.65 events per 1,000 person-years with regular salt (rate ratio, 0.86; 95% confidence interval, 0.77-0.96; P = .006).
The rates of major cardiovascular events were 49.09 events per 1,000 person-years in the salt substitute group vs. 56.29 events per 1,000 person-years in those using regular salt (rate ratio, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.80-0.94; P < .001).
And the rate of death was 39.28 events per 1,000 person-years with the salt substitute vs. 44.61 events per 1,000 person-years with regular salt (rate ratio, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.82-0.95; P < .001).
The rate of serious adverse events attributed to hyperkalemia was not significantly higher with the salt substitute than with regular salt (3.35 events vs. 3.30 events per 1,000 person-years; rate ratio, 1.04; 95% CI, 0.80-1.37; P = .76).
Dr. Neal reported that 7%-8% of the control group started using salt substitute over the study period, so these results have likely underestimated the true effect of switching to a salt substitute product.
Noting that about 10 million cardiovascular events occur each year in China, he said the study results suggested that using salt substitute instead of regular salt could prevent about 10% of these events.
Food manufacturers must make changes
Dr. Neal acknowledged that a limitation of the study was the fact it was conducted in a single country, which would raise issues of generalizability. But he said he believes the results are generalizable to other populations.
Those who would get the most benefit from switching to a salt substitute are those who consume large amounts of discretionary salt – salt added at home at the time of cooking for preservation of food or seasoning. “This is salt that is easy to replace with salt substitute,” Dr. Neal noted.
“There are more than 5 billion people in the world that consume more than 50% of their salt intake as discretionary salt – mainly in the developing world. These people would expect to get significant health benefits from a switch to salt substitute.”
He pointed out that salt substitute is low cost and is easy to manufacture. “Salt substitutes cost around 50% more than regular salt, but this translates into just a dollar or two per person per year to make the switch.”
Dr. Neal said the results also apply to higher-income countries but must be implemented by governments and food manufactures, as most salt in these countries comes from processed foods.
“This study provides strong evidence to take to the food industry,” he concluded. “We would like to see food manufacturers switch to using salt substitute and for salt substitute products to be widely available on supermarket shelves. We also urge governments to take action to promote use of salt substitutes over regular salt. This could take the form of taxing regular salt or subsidies for use of salt substitutes.”
The SSaSS was supported by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. Dr. Neal reports no disclosures. Dr. Ingelfinger is employed by the New England Journal of Medicine as deputy editor.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Switching from regular salt to a low-sodium salt substitute has major public health benefits, including a reduction in stroke, cardiovascular events, and death, a new landmark study shows.
The Salt Substitute and Stroke Study (SSaSS) was conducted in 21,000 people with a history of stroke or high blood pressure in rural China, with half of them using a lower-sodium salt substitute instead of regular salt.
Results showed that after 5 years, those using the salt substitute had a 14% reduction in stroke, a 13% reduction in major cardiovascular events, and a 12% reduction in death. These benefits were achieved without any apparent adverse effects.
The trial was presented by Bruce Neal, MB, George Institute for Global Health, Sydney, Australia, on Aug. 29 at the virtual European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress 2021. They were simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“This is one of the largest dietary intervention trials ever conducted and has shown very clear evidence of protection against stroke, cardiovascular events, and premature death, with no adverse effects with a very simple and low-cost intervention,” Dr. Neal concluded. “This is a very easy thing to work into the diet. You just replace regular salt with a substitute that looks and tastes almost identical,” he added.
Addressing the issue of whether these results are generalizable to other populations, Dr. Neal said, “We believe the results are relevant to everyone who eats salt.
“The way the body manages sodium and potassium and their association with blood pressure is highly consistent across different populations,” he said. “Almost everyone, with the exception of a few people with serious kidney disease, should be avoiding salt or switching to a salt substitute and expect to see some benefit of this.”
Commentators at the ESC presentation lauded the study as “magnificent,” with “extraordinary” results and “very powerful implications.”
Designated discussant, hypertension expert Bryan Williams, MD, University College London, said the SSaSS was “probably the most important study with regards to public health that we will see.” He described the reductions in stroke, cardiovascular events, and death as “extraordinary for such a simple intervention.”
Dr. Williams added: “Those who have doubted the benefits of salt restriction must now admit they were wrong. The debate stops here. The data are in. Global health interventions to implement these findings must now begin.”
He also highlighted the large number of events in the trial. “This was a large, pragmatic, long-duration study in a high-risk population, and with 5,000 cardiovascular events it gives enormous power to show benefits.”
Chair of the ESC session, Barbara Casadei, MD, DPhil, John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford (England), said the SSaSS “will change the way we think about salt and be remembered for years to come.”
Noting that the benefits were seen in all subgroups across the study, Bertram Pitt, MD, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, was particularly excited about the stroke reduction seen in patients with diabetes, noting that several recent trials of new diabetes drugs have not managed to show a reduction in stroke.
“For patients with diabetes, this is a really important intervention,” he stated.
However, an editorial accompanying the NEJM publication gave a somewhat less enthusiastic response to the study than the ESC commentators.
Julie R. Ingelfinger, MD, deputy editor of the journal, points out that serial monitoring of potassium levels was not performed in the trial, so it is possible that hyperkalemic episodes were not detected, and persons with a history of medical conditions that may be associated with hyperkalemia were not studied.
She also noted that because the salt substitute was distributed to families, it would have been instructive to have data on the household members without risk factors, but no such data were obtained.
“Overall, the SSaSS provides some intriguing hints, but wider effectiveness is hard to predict, given limited generalizability,” she concluded.
Cluster-randomized trial
The SSaSS was an open-label, cluster-randomized trial involving 20,995 people from 600 villages in rural China who had a history of stroke or were 60 years of age or older and had uncontrolled hypertension. Patients with a history of severe kidney disease and those taking potassium supplements or potassium-sparing diuretics were excluded.
They were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to the intervention group, in which the participants used a salt substitute (roughly 75% sodium chloride and 25% potassium chloride), or to the control group, in which the participants continued to use regular salt (100% sodium chloride).
Results showed that after a mean follow-up of 4.74 years, systolic blood pressure was reduced by 3.3 mm Hg in the salt substitute group.
The rate of stroke, the primary endpoint, was 29.14 events per 1,000 person-years in the salt substitute group vs. 33.65 events per 1,000 person-years with regular salt (rate ratio, 0.86; 95% confidence interval, 0.77-0.96; P = .006).
The rates of major cardiovascular events were 49.09 events per 1,000 person-years in the salt substitute group vs. 56.29 events per 1,000 person-years in those using regular salt (rate ratio, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.80-0.94; P < .001).
And the rate of death was 39.28 events per 1,000 person-years with the salt substitute vs. 44.61 events per 1,000 person-years with regular salt (rate ratio, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.82-0.95; P < .001).
The rate of serious adverse events attributed to hyperkalemia was not significantly higher with the salt substitute than with regular salt (3.35 events vs. 3.30 events per 1,000 person-years; rate ratio, 1.04; 95% CI, 0.80-1.37; P = .76).
Dr. Neal reported that 7%-8% of the control group started using salt substitute over the study period, so these results have likely underestimated the true effect of switching to a salt substitute product.
Noting that about 10 million cardiovascular events occur each year in China, he said the study results suggested that using salt substitute instead of regular salt could prevent about 10% of these events.
Food manufacturers must make changes
Dr. Neal acknowledged that a limitation of the study was the fact it was conducted in a single country, which would raise issues of generalizability. But he said he believes the results are generalizable to other populations.
Those who would get the most benefit from switching to a salt substitute are those who consume large amounts of discretionary salt – salt added at home at the time of cooking for preservation of food or seasoning. “This is salt that is easy to replace with salt substitute,” Dr. Neal noted.
“There are more than 5 billion people in the world that consume more than 50% of their salt intake as discretionary salt – mainly in the developing world. These people would expect to get significant health benefits from a switch to salt substitute.”
He pointed out that salt substitute is low cost and is easy to manufacture. “Salt substitutes cost around 50% more than regular salt, but this translates into just a dollar or two per person per year to make the switch.”
Dr. Neal said the results also apply to higher-income countries but must be implemented by governments and food manufactures, as most salt in these countries comes from processed foods.
“This study provides strong evidence to take to the food industry,” he concluded. “We would like to see food manufacturers switch to using salt substitute and for salt substitute products to be widely available on supermarket shelves. We also urge governments to take action to promote use of salt substitutes over regular salt. This could take the form of taxing regular salt or subsidies for use of salt substitutes.”
The SSaSS was supported by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. Dr. Neal reports no disclosures. Dr. Ingelfinger is employed by the New England Journal of Medicine as deputy editor.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Switching from regular salt to a low-sodium salt substitute has major public health benefits, including a reduction in stroke, cardiovascular events, and death, a new landmark study shows.
The Salt Substitute and Stroke Study (SSaSS) was conducted in 21,000 people with a history of stroke or high blood pressure in rural China, with half of them using a lower-sodium salt substitute instead of regular salt.
Results showed that after 5 years, those using the salt substitute had a 14% reduction in stroke, a 13% reduction in major cardiovascular events, and a 12% reduction in death. These benefits were achieved without any apparent adverse effects.
The trial was presented by Bruce Neal, MB, George Institute for Global Health, Sydney, Australia, on Aug. 29 at the virtual European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress 2021. They were simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“This is one of the largest dietary intervention trials ever conducted and has shown very clear evidence of protection against stroke, cardiovascular events, and premature death, with no adverse effects with a very simple and low-cost intervention,” Dr. Neal concluded. “This is a very easy thing to work into the diet. You just replace regular salt with a substitute that looks and tastes almost identical,” he added.
Addressing the issue of whether these results are generalizable to other populations, Dr. Neal said, “We believe the results are relevant to everyone who eats salt.
“The way the body manages sodium and potassium and their association with blood pressure is highly consistent across different populations,” he said. “Almost everyone, with the exception of a few people with serious kidney disease, should be avoiding salt or switching to a salt substitute and expect to see some benefit of this.”
Commentators at the ESC presentation lauded the study as “magnificent,” with “extraordinary” results and “very powerful implications.”
Designated discussant, hypertension expert Bryan Williams, MD, University College London, said the SSaSS was “probably the most important study with regards to public health that we will see.” He described the reductions in stroke, cardiovascular events, and death as “extraordinary for such a simple intervention.”
Dr. Williams added: “Those who have doubted the benefits of salt restriction must now admit they were wrong. The debate stops here. The data are in. Global health interventions to implement these findings must now begin.”
He also highlighted the large number of events in the trial. “This was a large, pragmatic, long-duration study in a high-risk population, and with 5,000 cardiovascular events it gives enormous power to show benefits.”
Chair of the ESC session, Barbara Casadei, MD, DPhil, John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford (England), said the SSaSS “will change the way we think about salt and be remembered for years to come.”
Noting that the benefits were seen in all subgroups across the study, Bertram Pitt, MD, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, was particularly excited about the stroke reduction seen in patients with diabetes, noting that several recent trials of new diabetes drugs have not managed to show a reduction in stroke.
“For patients with diabetes, this is a really important intervention,” he stated.
However, an editorial accompanying the NEJM publication gave a somewhat less enthusiastic response to the study than the ESC commentators.
Julie R. Ingelfinger, MD, deputy editor of the journal, points out that serial monitoring of potassium levels was not performed in the trial, so it is possible that hyperkalemic episodes were not detected, and persons with a history of medical conditions that may be associated with hyperkalemia were not studied.
She also noted that because the salt substitute was distributed to families, it would have been instructive to have data on the household members without risk factors, but no such data were obtained.
“Overall, the SSaSS provides some intriguing hints, but wider effectiveness is hard to predict, given limited generalizability,” she concluded.
Cluster-randomized trial
The SSaSS was an open-label, cluster-randomized trial involving 20,995 people from 600 villages in rural China who had a history of stroke or were 60 years of age or older and had uncontrolled hypertension. Patients with a history of severe kidney disease and those taking potassium supplements or potassium-sparing diuretics were excluded.
They were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to the intervention group, in which the participants used a salt substitute (roughly 75% sodium chloride and 25% potassium chloride), or to the control group, in which the participants continued to use regular salt (100% sodium chloride).
Results showed that after a mean follow-up of 4.74 years, systolic blood pressure was reduced by 3.3 mm Hg in the salt substitute group.
The rate of stroke, the primary endpoint, was 29.14 events per 1,000 person-years in the salt substitute group vs. 33.65 events per 1,000 person-years with regular salt (rate ratio, 0.86; 95% confidence interval, 0.77-0.96; P = .006).
The rates of major cardiovascular events were 49.09 events per 1,000 person-years in the salt substitute group vs. 56.29 events per 1,000 person-years in those using regular salt (rate ratio, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.80-0.94; P < .001).
And the rate of death was 39.28 events per 1,000 person-years with the salt substitute vs. 44.61 events per 1,000 person-years with regular salt (rate ratio, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.82-0.95; P < .001).
The rate of serious adverse events attributed to hyperkalemia was not significantly higher with the salt substitute than with regular salt (3.35 events vs. 3.30 events per 1,000 person-years; rate ratio, 1.04; 95% CI, 0.80-1.37; P = .76).
Dr. Neal reported that 7%-8% of the control group started using salt substitute over the study period, so these results have likely underestimated the true effect of switching to a salt substitute product.
Noting that about 10 million cardiovascular events occur each year in China, he said the study results suggested that using salt substitute instead of regular salt could prevent about 10% of these events.
Food manufacturers must make changes
Dr. Neal acknowledged that a limitation of the study was the fact it was conducted in a single country, which would raise issues of generalizability. But he said he believes the results are generalizable to other populations.
Those who would get the most benefit from switching to a salt substitute are those who consume large amounts of discretionary salt – salt added at home at the time of cooking for preservation of food or seasoning. “This is salt that is easy to replace with salt substitute,” Dr. Neal noted.
“There are more than 5 billion people in the world that consume more than 50% of their salt intake as discretionary salt – mainly in the developing world. These people would expect to get significant health benefits from a switch to salt substitute.”
He pointed out that salt substitute is low cost and is easy to manufacture. “Salt substitutes cost around 50% more than regular salt, but this translates into just a dollar or two per person per year to make the switch.”
Dr. Neal said the results also apply to higher-income countries but must be implemented by governments and food manufactures, as most salt in these countries comes from processed foods.
“This study provides strong evidence to take to the food industry,” he concluded. “We would like to see food manufacturers switch to using salt substitute and for salt substitute products to be widely available on supermarket shelves. We also urge governments to take action to promote use of salt substitutes over regular salt. This could take the form of taxing regular salt or subsidies for use of salt substitutes.”
The SSaSS was supported by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. Dr. Neal reports no disclosures. Dr. Ingelfinger is employed by the New England Journal of Medicine as deputy editor.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Coffee drinking in midlife tied to heart benefits
Among middle-aged people without heart disease, drinking up to three cups of coffee per day was linked with a lower risk for stroke or death over the next decade, along with better heart structure and function, in a large, observational study.
Specifically, light-to-moderate coffee drinking, defined as 0.5 to 3 cups per day, was associated with a 21% lower risk for stroke, a 17% lower risk for death from cardiovascular disease (CVD), and a 12% lower risk for death from all causes, as well as more favorable cardiac MRI findings, compared with nondrinkers (< 0.5 cup per day) during a median 11-year follow-up.
Heavy coffee drinkers, defined as those consuming more than three cups per day, on the other hand, likewise had more favorable cardiac MRI findings, but with similar (not lower) rates of stroke and CVD or all-cause mortality compared with nondrinkers.
Judit Simon, MD, presented these findings, from close to 500,000 participants in the UK Biobank study, at a press conference before an e-poster session at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“To our knowledge, this is the largest study to systematically assess the cardiovascular effects of regular coffee consumption in a population without diagnosed heart disease,” Dr. Simon, a PhD student at the Heart and Vascular Centre, Semmelweis University, Budapest, Hungary, said in an ESC press release.
The results “suggest that regular coffee consumption is safe, as even high daily intake was not associated with adverse cardiovascular outcomes and all-cause mortality after a follow-up of 10 to 15 years,” she said.
The imaging analysis showed that “compared with participants who did not drink coffee regularly, daily consumers had healthier sized and better functioning hearts,” Dr. Simon continued, “consistent with reversing the detrimental effects of aging on the heart.”
“The observed benefits might be partly explained by positive alterations in cardiac structure and function,” she speculated, adding that further studies are needed to explain the underlying mechanisms.
Instant coffee most popular
In this population, the coffee drinkers mostly drank instant coffee (55%), followed by filtered/ground (23%), decaffeinated (20%), or other types of coffee (2%), Dr. Simon said in an interview.
Risk for myocardial infarction (MI) or heart failure did not significantly differ for different categories of coffee intake, she added. The researchers did not study the effect of coffee consumption on atrial fibrillation (AF), she noted.
Study limitations, Dr. Simon acknowledged, include that it was observational, so it cannot show causation, and that coffee consumption was self-reported in a questionnaire.
Invited to comment, Alice H. Lichtenstein, DSc, who was not involved with the research, said, “Consistent with prior data, this new study indicates there is no adverse effect of coffee consumption on cardiovascular health and there may be a benefit.”
However, “because of the nature of the data, it would not be recommended that an individual starting drinking coffee to improve cardiovascular health,” added Dr. Lichtenstein, director and senior scientist at the Cardiovascular Nutrition Laboratory at Tufts University, Boston.
But if people already drink coffee, “it is fine to continue, assuming that the coffee drinks are not high in added sugar and cream,” she said in an interview.
Coffee intake, CVD outcomes, and heart structure
To study the relationship between coffee intake and incident MI, stroke, and death, as well as heart structure, the researchers examined data from the UK Biobank, which recruited 500,000 people aged 40-69 years in 2006-2010 from across the United Kingdom.
They identified 468,629 participants with no signs of heart disease at recruitment and an average age of 56 years, of whom 56% were women.
The participants were divided into three groups based on usual coffee intake: none (22% of participants), light-to-moderate (58%), and high (20%).
Median tea intake was three cups per day overall, four cups per day in noncoffee drinkers, three cups per day in light-to-moderate coffee drinkers, and one cup per day in high coffee drinkers.
Compared to not drinking coffee, light-to-moderate coffee consumption was associated with lower risks for all-cause death (hazard ratio [HR], 0.88; P < .001), CVD death (HR, 0.83; P = .006), and stroke (HR, 0.79; P = .037), over a median follow-up of 11 years, after adjustment for sex; weight; height; smoking status; physical activity; high blood pressure; diabetes; cholesterol level; socioeconomic status; and usual intake of alcohol, meat, tea, fruit, and vegetables.
In the 30,650 participants who had cardiac MRI data, the study found that compared with not drinking coffee, both light-to-moderate and high coffee consumption were associated with significantly increased left and right ventricular end-systolic and end-diastolic volumes, and with greater left ventricular mass (all P < .001).
These differences were small but significant, Dr. Simon stressed, because this was a cohort of healthy patients who did not have CVD (heart failure, MI, stroke, AF) at baseline, although some had hypertension or diabetes.
Press conference chairperson, Steen Dalby Kristensen, MD, professor and cardiologist, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark, a coffee lover himself, wanted to know if an amount such as two, three, or four cups of coffee was optimal to see these heart benefits, and whether there were differences in benefits seen with drinking different types of coffee.
The analysis did not identify an optimal coffee intake, Dr. Simon said. Compared with not drinking coffee, she continued, drinking instant coffee was associated with a lower risk for all-cause mortality, but not CVD mortality or stroke.
Drinking filtered coffee was associated with lower risks for all three outcomes, but there was no significant difference in risk for MI. Drinking decaffeinated coffee was associated with a lower risk for all-cause and CVD mortality.
“Decaffeinated coffee contains a small amount of caffeine,” Dr. Simon pointed out. “Something other than caffeine might have this protective impact,” she suggested.
The researchers and Dr. Lichtenstein declared having no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among middle-aged people without heart disease, drinking up to three cups of coffee per day was linked with a lower risk for stroke or death over the next decade, along with better heart structure and function, in a large, observational study.
Specifically, light-to-moderate coffee drinking, defined as 0.5 to 3 cups per day, was associated with a 21% lower risk for stroke, a 17% lower risk for death from cardiovascular disease (CVD), and a 12% lower risk for death from all causes, as well as more favorable cardiac MRI findings, compared with nondrinkers (< 0.5 cup per day) during a median 11-year follow-up.
Heavy coffee drinkers, defined as those consuming more than three cups per day, on the other hand, likewise had more favorable cardiac MRI findings, but with similar (not lower) rates of stroke and CVD or all-cause mortality compared with nondrinkers.
Judit Simon, MD, presented these findings, from close to 500,000 participants in the UK Biobank study, at a press conference before an e-poster session at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“To our knowledge, this is the largest study to systematically assess the cardiovascular effects of regular coffee consumption in a population without diagnosed heart disease,” Dr. Simon, a PhD student at the Heart and Vascular Centre, Semmelweis University, Budapest, Hungary, said in an ESC press release.
The results “suggest that regular coffee consumption is safe, as even high daily intake was not associated with adverse cardiovascular outcomes and all-cause mortality after a follow-up of 10 to 15 years,” she said.
The imaging analysis showed that “compared with participants who did not drink coffee regularly, daily consumers had healthier sized and better functioning hearts,” Dr. Simon continued, “consistent with reversing the detrimental effects of aging on the heart.”
“The observed benefits might be partly explained by positive alterations in cardiac structure and function,” she speculated, adding that further studies are needed to explain the underlying mechanisms.
Instant coffee most popular
In this population, the coffee drinkers mostly drank instant coffee (55%), followed by filtered/ground (23%), decaffeinated (20%), or other types of coffee (2%), Dr. Simon said in an interview.
Risk for myocardial infarction (MI) or heart failure did not significantly differ for different categories of coffee intake, she added. The researchers did not study the effect of coffee consumption on atrial fibrillation (AF), she noted.
Study limitations, Dr. Simon acknowledged, include that it was observational, so it cannot show causation, and that coffee consumption was self-reported in a questionnaire.
Invited to comment, Alice H. Lichtenstein, DSc, who was not involved with the research, said, “Consistent with prior data, this new study indicates there is no adverse effect of coffee consumption on cardiovascular health and there may be a benefit.”
However, “because of the nature of the data, it would not be recommended that an individual starting drinking coffee to improve cardiovascular health,” added Dr. Lichtenstein, director and senior scientist at the Cardiovascular Nutrition Laboratory at Tufts University, Boston.
But if people already drink coffee, “it is fine to continue, assuming that the coffee drinks are not high in added sugar and cream,” she said in an interview.
Coffee intake, CVD outcomes, and heart structure
To study the relationship between coffee intake and incident MI, stroke, and death, as well as heart structure, the researchers examined data from the UK Biobank, which recruited 500,000 people aged 40-69 years in 2006-2010 from across the United Kingdom.
They identified 468,629 participants with no signs of heart disease at recruitment and an average age of 56 years, of whom 56% were women.
The participants were divided into three groups based on usual coffee intake: none (22% of participants), light-to-moderate (58%), and high (20%).
Median tea intake was three cups per day overall, four cups per day in noncoffee drinkers, three cups per day in light-to-moderate coffee drinkers, and one cup per day in high coffee drinkers.
Compared to not drinking coffee, light-to-moderate coffee consumption was associated with lower risks for all-cause death (hazard ratio [HR], 0.88; P < .001), CVD death (HR, 0.83; P = .006), and stroke (HR, 0.79; P = .037), over a median follow-up of 11 years, after adjustment for sex; weight; height; smoking status; physical activity; high blood pressure; diabetes; cholesterol level; socioeconomic status; and usual intake of alcohol, meat, tea, fruit, and vegetables.
In the 30,650 participants who had cardiac MRI data, the study found that compared with not drinking coffee, both light-to-moderate and high coffee consumption were associated with significantly increased left and right ventricular end-systolic and end-diastolic volumes, and with greater left ventricular mass (all P < .001).
These differences were small but significant, Dr. Simon stressed, because this was a cohort of healthy patients who did not have CVD (heart failure, MI, stroke, AF) at baseline, although some had hypertension or diabetes.
Press conference chairperson, Steen Dalby Kristensen, MD, professor and cardiologist, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark, a coffee lover himself, wanted to know if an amount such as two, three, or four cups of coffee was optimal to see these heart benefits, and whether there were differences in benefits seen with drinking different types of coffee.
The analysis did not identify an optimal coffee intake, Dr. Simon said. Compared with not drinking coffee, she continued, drinking instant coffee was associated with a lower risk for all-cause mortality, but not CVD mortality or stroke.
Drinking filtered coffee was associated with lower risks for all three outcomes, but there was no significant difference in risk for MI. Drinking decaffeinated coffee was associated with a lower risk for all-cause and CVD mortality.
“Decaffeinated coffee contains a small amount of caffeine,” Dr. Simon pointed out. “Something other than caffeine might have this protective impact,” she suggested.
The researchers and Dr. Lichtenstein declared having no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among middle-aged people without heart disease, drinking up to three cups of coffee per day was linked with a lower risk for stroke or death over the next decade, along with better heart structure and function, in a large, observational study.
Specifically, light-to-moderate coffee drinking, defined as 0.5 to 3 cups per day, was associated with a 21% lower risk for stroke, a 17% lower risk for death from cardiovascular disease (CVD), and a 12% lower risk for death from all causes, as well as more favorable cardiac MRI findings, compared with nondrinkers (< 0.5 cup per day) during a median 11-year follow-up.
Heavy coffee drinkers, defined as those consuming more than three cups per day, on the other hand, likewise had more favorable cardiac MRI findings, but with similar (not lower) rates of stroke and CVD or all-cause mortality compared with nondrinkers.
Judit Simon, MD, presented these findings, from close to 500,000 participants in the UK Biobank study, at a press conference before an e-poster session at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“To our knowledge, this is the largest study to systematically assess the cardiovascular effects of regular coffee consumption in a population without diagnosed heart disease,” Dr. Simon, a PhD student at the Heart and Vascular Centre, Semmelweis University, Budapest, Hungary, said in an ESC press release.
The results “suggest that regular coffee consumption is safe, as even high daily intake was not associated with adverse cardiovascular outcomes and all-cause mortality after a follow-up of 10 to 15 years,” she said.
The imaging analysis showed that “compared with participants who did not drink coffee regularly, daily consumers had healthier sized and better functioning hearts,” Dr. Simon continued, “consistent with reversing the detrimental effects of aging on the heart.”
“The observed benefits might be partly explained by positive alterations in cardiac structure and function,” she speculated, adding that further studies are needed to explain the underlying mechanisms.
Instant coffee most popular
In this population, the coffee drinkers mostly drank instant coffee (55%), followed by filtered/ground (23%), decaffeinated (20%), or other types of coffee (2%), Dr. Simon said in an interview.
Risk for myocardial infarction (MI) or heart failure did not significantly differ for different categories of coffee intake, she added. The researchers did not study the effect of coffee consumption on atrial fibrillation (AF), she noted.
Study limitations, Dr. Simon acknowledged, include that it was observational, so it cannot show causation, and that coffee consumption was self-reported in a questionnaire.
Invited to comment, Alice H. Lichtenstein, DSc, who was not involved with the research, said, “Consistent with prior data, this new study indicates there is no adverse effect of coffee consumption on cardiovascular health and there may be a benefit.”
However, “because of the nature of the data, it would not be recommended that an individual starting drinking coffee to improve cardiovascular health,” added Dr. Lichtenstein, director and senior scientist at the Cardiovascular Nutrition Laboratory at Tufts University, Boston.
But if people already drink coffee, “it is fine to continue, assuming that the coffee drinks are not high in added sugar and cream,” she said in an interview.
Coffee intake, CVD outcomes, and heart structure
To study the relationship between coffee intake and incident MI, stroke, and death, as well as heart structure, the researchers examined data from the UK Biobank, which recruited 500,000 people aged 40-69 years in 2006-2010 from across the United Kingdom.
They identified 468,629 participants with no signs of heart disease at recruitment and an average age of 56 years, of whom 56% were women.
The participants were divided into three groups based on usual coffee intake: none (22% of participants), light-to-moderate (58%), and high (20%).
Median tea intake was three cups per day overall, four cups per day in noncoffee drinkers, three cups per day in light-to-moderate coffee drinkers, and one cup per day in high coffee drinkers.
Compared to not drinking coffee, light-to-moderate coffee consumption was associated with lower risks for all-cause death (hazard ratio [HR], 0.88; P < .001), CVD death (HR, 0.83; P = .006), and stroke (HR, 0.79; P = .037), over a median follow-up of 11 years, after adjustment for sex; weight; height; smoking status; physical activity; high blood pressure; diabetes; cholesterol level; socioeconomic status; and usual intake of alcohol, meat, tea, fruit, and vegetables.
In the 30,650 participants who had cardiac MRI data, the study found that compared with not drinking coffee, both light-to-moderate and high coffee consumption were associated with significantly increased left and right ventricular end-systolic and end-diastolic volumes, and with greater left ventricular mass (all P < .001).
These differences were small but significant, Dr. Simon stressed, because this was a cohort of healthy patients who did not have CVD (heart failure, MI, stroke, AF) at baseline, although some had hypertension or diabetes.
Press conference chairperson, Steen Dalby Kristensen, MD, professor and cardiologist, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark, a coffee lover himself, wanted to know if an amount such as two, three, or four cups of coffee was optimal to see these heart benefits, and whether there were differences in benefits seen with drinking different types of coffee.
The analysis did not identify an optimal coffee intake, Dr. Simon said. Compared with not drinking coffee, she continued, drinking instant coffee was associated with a lower risk for all-cause mortality, but not CVD mortality or stroke.
Drinking filtered coffee was associated with lower risks for all three outcomes, but there was no significant difference in risk for MI. Drinking decaffeinated coffee was associated with a lower risk for all-cause and CVD mortality.
“Decaffeinated coffee contains a small amount of caffeine,” Dr. Simon pointed out. “Something other than caffeine might have this protective impact,” she suggested.
The researchers and Dr. Lichtenstein declared having no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FIDELITY: Finerenone benefits patients with T2D across CKD spectrum
New data on using the nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) finerenone to treat patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease did more than further confirm this new drug’s efficacy in these patients for slowing progression to end-stage renal disease and reducing hospitalizations for heart failure.
It also strengthened the case for clinicians to be much more proactive in collecting urine specimens from patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) to find those with albuminuria whose kidney function has not yet dropped below 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, a population that the data show finerenone can help.
The FIDELITY prespecified meta-analysis combined data from two related pivotal trials of finerenone (Kerendia) in a total of more than 13,000 patients with T2D and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Each of these two trials, FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD, identified patients with CKD by either of two methods, or a total of four different criteria.
In sum, the two trials enrolled patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 25-90 mL/min per 1.73 m2 and a urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) of 30-299, or an eGFR of 25-75 mL/min per 1.73 m2 and a UACR of 300-5,000. The result was that 40% of enrolled patients had an eGFR of at least 60, levels that are considered normal, but they also had some level of albuminuria that defined them as having CKD.
The results showed that during a median follow-up of 36 months, patients with a normal eGFR and albuminuria had their combined incidence of cardiovascular disease events (cardiovascular death, MI, stroke, or hospitalization for heart failure) reduced by roughly the same amount as seen in patients with lower levels of eGFR and renal function, a finding that reimagines how clinicians need to routinely screen patients with T2D for CKD, Gerasimos Filippatos, MD, reported at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“Measuring UACR in patients with type 2 diabetes is important to identify patients who will benefit from finerenone treatment independent of their eGFR,” said Dr. Filippatos, professor of medicine at the University of Athens and director of the heart failure unit at Attikon University Hospital in Athens.
The combined FIDELITY analysis showed a significant overall cut in the combined cardiovascular disease endpoint of 14% relative to placebo, which reflected a 1.7% absolute reduction in events between the two arms during 3 years of treatment. The primary driver of this benefit was the significant drop in hospitalizations for heart failure on finerenone compared with placebo, which fell by a relative 22% and by an absolute 1.1%, Dr. Filippatos reported.
Routinely screening for albuminuria is ‘practice changing’
“This is really practice changing information for cardiologists,” said Rajiv L. Agarwal, MD, a copresenter of the FIDELITY analysis and a lead investigator of the two finerenone trials.
When cardiologists and possibly other specialists see patients with T2D, they traditionally have focused on measuring left ventricular ejection fraction and checking for other indications of heart failure. The new results from FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD showed that finerenone treatment can prevent heart failure onset or worsening in patients with T2D with finerenone, which clinicians can accomplish by “simply measuring UACR,” as well as eGFR, and then treating patients with abnormal levels of either, explained Dr. Agarwal, a nephrologist and professor of medicine at Indiana University in Indianapolis.
“Diabetologists know that when they see patients with diabetes they need to collect a urine sample to check for albuminuria. But when some other clinicians see a patient with type 2 diabetes and a normal eGFR, they often think that the patient is okay and don’t get a urine specimen,” noted Bertram Pitt, MD, another collaborator of the finerenone trials and a heart failure specialist affiliated with the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor.
“We need to pay more attention to UACR and albuminuria; traditionally clinicians have mostly looked at eGFR,” agreed Dipti Itchhaporia, MD, a cardiologist at the Carlton Heart and Vascular Institute of Hoag Hospital in Newport Beach, Calif. UACR “is a marker that should be shared” between endocrinologists, nephrologists, and cardiologists as they together care for patients with T2D, suggested Dr. Itchhaporia, president of the American College of Cardiology.
Two pivotal trials with consistent findings
The FIDELITY analysis combined data from the FIDELIO-DKD trial, reported in 2020, and from the FIGARO-DKD trial that was first reported during the current congress as well as in a simultaneous report published online.
Results from the two trials were very consistent, although the primary endpoint in FIDELIO-DKD was a composite measure of renal disease with the combined cardiovascular disease metric a secondary endpoint, while this got flipped in FIGARO-DKD which had the cardiovascular disease composite as its primary endpoint as the combined renal outcomes as a secondary endpoint.
In addition to showing a consistent, significant reduction in both combined cardiovascular disease events and in the specific endpoint of hospitalization for heart failure, the two trials also showed a consistent benefit for slowing renal disease progression, including significantly fewer patients developing end-stage kidney disease. In the combined FIDELITY analysis, treatment with finerenone cut the incidence of end-stage kidney disease by a significant 20% compared with placebo, and by an absolute reduction of 0.6%.
Another common finding was a relatively low incidence of hyperkalemia compared with what’s usually seen using a steroidal MRA, spironolactone or eplerenone. In the combined analysis treatment with finerenone produced a 14% incidence of any hyperkalemia compared with 7% among placebo-treated patients, and the rate of patients stopping their treatment because of hyperkalemia was 1.7% on finerenone and 0.6% on placebo.
“Finerenone is much better tolerated” than the steroidal MRAs in causing clinically significant hyperkalemia, noted Dr. Pitt. “There are a lot of misconceptions” about the potassium-raising potential of MRAs, and “people get frightened” by the potential. Spreading the message of finerenone’s relative safety “will take a lot of education,” he acknowledged. Routine monitoring of potassium levels is a key step to minimizing the risk for hyperkalemia when using finerenone, he added.
Suggested benefit from combination treatment
Another intriguing observation from FIDELITY derived from the fact that roughly 7% of enrolled patients were also on treatment with a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor at entry, and about 7% were on treatment with a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, and in both subgroups the incidence of the composite cardiovascular disease endpoint appeared to suggest additive effects of agents from either of these classes when combined with finerenone. Although the numbers of patients on combined treatment were too low to show a definitive result, “our expectation is that we will see an additive effect,” said Dr. Pitt. Ideally, patients with T2D and CKD “should be on both” an SGLT2 inhibitor and finerenone, he predicted.
SGLT2 inhibitors have now been embraced as a key treatment for patients with T2D or with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, and the preliminary data suggest that combining these agents with finerenone can provide additional benefit, agreed Dr. Itchhaporia. Aside from the need for more evidence to prove this, there are also practical considerations of “How do we pay for all these fantastic therapies?” She expressed optimism that cost-benefit analyses will eventually show that the additive benefits justify the added cost.
Based largely on results from FIDELIO-DKD, finerenone received marketing approval from the Food and Drug Administration in July 2021 for the indication of treating patients with T2D and chronic kidney disease.
FIGARO-DKD, FIDELIO-DKD, and FIDELITY were sponsored by Bayer, the company that markets finerenone. Dr. Filippatos has received lecture fees from Bayer, and has had financial relationships with Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medtronic, Novartis, Servier, and Vifor. Dr. Agarwal received travel support from and has been a consultant to Bayer and to numerous other companies. Dr. Pitt has been a consultant to Bayer and to numerous other companies. Dr. Itchhaporia had no disclosures.
New data on using the nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) finerenone to treat patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease did more than further confirm this new drug’s efficacy in these patients for slowing progression to end-stage renal disease and reducing hospitalizations for heart failure.
It also strengthened the case for clinicians to be much more proactive in collecting urine specimens from patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) to find those with albuminuria whose kidney function has not yet dropped below 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, a population that the data show finerenone can help.
The FIDELITY prespecified meta-analysis combined data from two related pivotal trials of finerenone (Kerendia) in a total of more than 13,000 patients with T2D and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Each of these two trials, FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD, identified patients with CKD by either of two methods, or a total of four different criteria.
In sum, the two trials enrolled patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 25-90 mL/min per 1.73 m2 and a urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) of 30-299, or an eGFR of 25-75 mL/min per 1.73 m2 and a UACR of 300-5,000. The result was that 40% of enrolled patients had an eGFR of at least 60, levels that are considered normal, but they also had some level of albuminuria that defined them as having CKD.
The results showed that during a median follow-up of 36 months, patients with a normal eGFR and albuminuria had their combined incidence of cardiovascular disease events (cardiovascular death, MI, stroke, or hospitalization for heart failure) reduced by roughly the same amount as seen in patients with lower levels of eGFR and renal function, a finding that reimagines how clinicians need to routinely screen patients with T2D for CKD, Gerasimos Filippatos, MD, reported at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“Measuring UACR in patients with type 2 diabetes is important to identify patients who will benefit from finerenone treatment independent of their eGFR,” said Dr. Filippatos, professor of medicine at the University of Athens and director of the heart failure unit at Attikon University Hospital in Athens.
The combined FIDELITY analysis showed a significant overall cut in the combined cardiovascular disease endpoint of 14% relative to placebo, which reflected a 1.7% absolute reduction in events between the two arms during 3 years of treatment. The primary driver of this benefit was the significant drop in hospitalizations for heart failure on finerenone compared with placebo, which fell by a relative 22% and by an absolute 1.1%, Dr. Filippatos reported.
Routinely screening for albuminuria is ‘practice changing’
“This is really practice changing information for cardiologists,” said Rajiv L. Agarwal, MD, a copresenter of the FIDELITY analysis and a lead investigator of the two finerenone trials.
When cardiologists and possibly other specialists see patients with T2D, they traditionally have focused on measuring left ventricular ejection fraction and checking for other indications of heart failure. The new results from FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD showed that finerenone treatment can prevent heart failure onset or worsening in patients with T2D with finerenone, which clinicians can accomplish by “simply measuring UACR,” as well as eGFR, and then treating patients with abnormal levels of either, explained Dr. Agarwal, a nephrologist and professor of medicine at Indiana University in Indianapolis.
“Diabetologists know that when they see patients with diabetes they need to collect a urine sample to check for albuminuria. But when some other clinicians see a patient with type 2 diabetes and a normal eGFR, they often think that the patient is okay and don’t get a urine specimen,” noted Bertram Pitt, MD, another collaborator of the finerenone trials and a heart failure specialist affiliated with the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor.
“We need to pay more attention to UACR and albuminuria; traditionally clinicians have mostly looked at eGFR,” agreed Dipti Itchhaporia, MD, a cardiologist at the Carlton Heart and Vascular Institute of Hoag Hospital in Newport Beach, Calif. UACR “is a marker that should be shared” between endocrinologists, nephrologists, and cardiologists as they together care for patients with T2D, suggested Dr. Itchhaporia, president of the American College of Cardiology.
Two pivotal trials with consistent findings
The FIDELITY analysis combined data from the FIDELIO-DKD trial, reported in 2020, and from the FIGARO-DKD trial that was first reported during the current congress as well as in a simultaneous report published online.
Results from the two trials were very consistent, although the primary endpoint in FIDELIO-DKD was a composite measure of renal disease with the combined cardiovascular disease metric a secondary endpoint, while this got flipped in FIGARO-DKD which had the cardiovascular disease composite as its primary endpoint as the combined renal outcomes as a secondary endpoint.
In addition to showing a consistent, significant reduction in both combined cardiovascular disease events and in the specific endpoint of hospitalization for heart failure, the two trials also showed a consistent benefit for slowing renal disease progression, including significantly fewer patients developing end-stage kidney disease. In the combined FIDELITY analysis, treatment with finerenone cut the incidence of end-stage kidney disease by a significant 20% compared with placebo, and by an absolute reduction of 0.6%.
Another common finding was a relatively low incidence of hyperkalemia compared with what’s usually seen using a steroidal MRA, spironolactone or eplerenone. In the combined analysis treatment with finerenone produced a 14% incidence of any hyperkalemia compared with 7% among placebo-treated patients, and the rate of patients stopping their treatment because of hyperkalemia was 1.7% on finerenone and 0.6% on placebo.
“Finerenone is much better tolerated” than the steroidal MRAs in causing clinically significant hyperkalemia, noted Dr. Pitt. “There are a lot of misconceptions” about the potassium-raising potential of MRAs, and “people get frightened” by the potential. Spreading the message of finerenone’s relative safety “will take a lot of education,” he acknowledged. Routine monitoring of potassium levels is a key step to minimizing the risk for hyperkalemia when using finerenone, he added.
Suggested benefit from combination treatment
Another intriguing observation from FIDELITY derived from the fact that roughly 7% of enrolled patients were also on treatment with a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor at entry, and about 7% were on treatment with a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, and in both subgroups the incidence of the composite cardiovascular disease endpoint appeared to suggest additive effects of agents from either of these classes when combined with finerenone. Although the numbers of patients on combined treatment were too low to show a definitive result, “our expectation is that we will see an additive effect,” said Dr. Pitt. Ideally, patients with T2D and CKD “should be on both” an SGLT2 inhibitor and finerenone, he predicted.
SGLT2 inhibitors have now been embraced as a key treatment for patients with T2D or with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, and the preliminary data suggest that combining these agents with finerenone can provide additional benefit, agreed Dr. Itchhaporia. Aside from the need for more evidence to prove this, there are also practical considerations of “How do we pay for all these fantastic therapies?” She expressed optimism that cost-benefit analyses will eventually show that the additive benefits justify the added cost.
Based largely on results from FIDELIO-DKD, finerenone received marketing approval from the Food and Drug Administration in July 2021 for the indication of treating patients with T2D and chronic kidney disease.
FIGARO-DKD, FIDELIO-DKD, and FIDELITY were sponsored by Bayer, the company that markets finerenone. Dr. Filippatos has received lecture fees from Bayer, and has had financial relationships with Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medtronic, Novartis, Servier, and Vifor. Dr. Agarwal received travel support from and has been a consultant to Bayer and to numerous other companies. Dr. Pitt has been a consultant to Bayer and to numerous other companies. Dr. Itchhaporia had no disclosures.
New data on using the nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) finerenone to treat patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease did more than further confirm this new drug’s efficacy in these patients for slowing progression to end-stage renal disease and reducing hospitalizations for heart failure.
It also strengthened the case for clinicians to be much more proactive in collecting urine specimens from patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) to find those with albuminuria whose kidney function has not yet dropped below 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, a population that the data show finerenone can help.
The FIDELITY prespecified meta-analysis combined data from two related pivotal trials of finerenone (Kerendia) in a total of more than 13,000 patients with T2D and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Each of these two trials, FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD, identified patients with CKD by either of two methods, or a total of four different criteria.
In sum, the two trials enrolled patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 25-90 mL/min per 1.73 m2 and a urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) of 30-299, or an eGFR of 25-75 mL/min per 1.73 m2 and a UACR of 300-5,000. The result was that 40% of enrolled patients had an eGFR of at least 60, levels that are considered normal, but they also had some level of albuminuria that defined them as having CKD.
The results showed that during a median follow-up of 36 months, patients with a normal eGFR and albuminuria had their combined incidence of cardiovascular disease events (cardiovascular death, MI, stroke, or hospitalization for heart failure) reduced by roughly the same amount as seen in patients with lower levels of eGFR and renal function, a finding that reimagines how clinicians need to routinely screen patients with T2D for CKD, Gerasimos Filippatos, MD, reported at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“Measuring UACR in patients with type 2 diabetes is important to identify patients who will benefit from finerenone treatment independent of their eGFR,” said Dr. Filippatos, professor of medicine at the University of Athens and director of the heart failure unit at Attikon University Hospital in Athens.
The combined FIDELITY analysis showed a significant overall cut in the combined cardiovascular disease endpoint of 14% relative to placebo, which reflected a 1.7% absolute reduction in events between the two arms during 3 years of treatment. The primary driver of this benefit was the significant drop in hospitalizations for heart failure on finerenone compared with placebo, which fell by a relative 22% and by an absolute 1.1%, Dr. Filippatos reported.
Routinely screening for albuminuria is ‘practice changing’
“This is really practice changing information for cardiologists,” said Rajiv L. Agarwal, MD, a copresenter of the FIDELITY analysis and a lead investigator of the two finerenone trials.
When cardiologists and possibly other specialists see patients with T2D, they traditionally have focused on measuring left ventricular ejection fraction and checking for other indications of heart failure. The new results from FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD showed that finerenone treatment can prevent heart failure onset or worsening in patients with T2D with finerenone, which clinicians can accomplish by “simply measuring UACR,” as well as eGFR, and then treating patients with abnormal levels of either, explained Dr. Agarwal, a nephrologist and professor of medicine at Indiana University in Indianapolis.
“Diabetologists know that when they see patients with diabetes they need to collect a urine sample to check for albuminuria. But when some other clinicians see a patient with type 2 diabetes and a normal eGFR, they often think that the patient is okay and don’t get a urine specimen,” noted Bertram Pitt, MD, another collaborator of the finerenone trials and a heart failure specialist affiliated with the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor.
“We need to pay more attention to UACR and albuminuria; traditionally clinicians have mostly looked at eGFR,” agreed Dipti Itchhaporia, MD, a cardiologist at the Carlton Heart and Vascular Institute of Hoag Hospital in Newport Beach, Calif. UACR “is a marker that should be shared” between endocrinologists, nephrologists, and cardiologists as they together care for patients with T2D, suggested Dr. Itchhaporia, president of the American College of Cardiology.
Two pivotal trials with consistent findings
The FIDELITY analysis combined data from the FIDELIO-DKD trial, reported in 2020, and from the FIGARO-DKD trial that was first reported during the current congress as well as in a simultaneous report published online.
Results from the two trials were very consistent, although the primary endpoint in FIDELIO-DKD was a composite measure of renal disease with the combined cardiovascular disease metric a secondary endpoint, while this got flipped in FIGARO-DKD which had the cardiovascular disease composite as its primary endpoint as the combined renal outcomes as a secondary endpoint.
In addition to showing a consistent, significant reduction in both combined cardiovascular disease events and in the specific endpoint of hospitalization for heart failure, the two trials also showed a consistent benefit for slowing renal disease progression, including significantly fewer patients developing end-stage kidney disease. In the combined FIDELITY analysis, treatment with finerenone cut the incidence of end-stage kidney disease by a significant 20% compared with placebo, and by an absolute reduction of 0.6%.
Another common finding was a relatively low incidence of hyperkalemia compared with what’s usually seen using a steroidal MRA, spironolactone or eplerenone. In the combined analysis treatment with finerenone produced a 14% incidence of any hyperkalemia compared with 7% among placebo-treated patients, and the rate of patients stopping their treatment because of hyperkalemia was 1.7% on finerenone and 0.6% on placebo.
“Finerenone is much better tolerated” than the steroidal MRAs in causing clinically significant hyperkalemia, noted Dr. Pitt. “There are a lot of misconceptions” about the potassium-raising potential of MRAs, and “people get frightened” by the potential. Spreading the message of finerenone’s relative safety “will take a lot of education,” he acknowledged. Routine monitoring of potassium levels is a key step to minimizing the risk for hyperkalemia when using finerenone, he added.
Suggested benefit from combination treatment
Another intriguing observation from FIDELITY derived from the fact that roughly 7% of enrolled patients were also on treatment with a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor at entry, and about 7% were on treatment with a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, and in both subgroups the incidence of the composite cardiovascular disease endpoint appeared to suggest additive effects of agents from either of these classes when combined with finerenone. Although the numbers of patients on combined treatment were too low to show a definitive result, “our expectation is that we will see an additive effect,” said Dr. Pitt. Ideally, patients with T2D and CKD “should be on both” an SGLT2 inhibitor and finerenone, he predicted.
SGLT2 inhibitors have now been embraced as a key treatment for patients with T2D or with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, and the preliminary data suggest that combining these agents with finerenone can provide additional benefit, agreed Dr. Itchhaporia. Aside from the need for more evidence to prove this, there are also practical considerations of “How do we pay for all these fantastic therapies?” She expressed optimism that cost-benefit analyses will eventually show that the additive benefits justify the added cost.
Based largely on results from FIDELIO-DKD, finerenone received marketing approval from the Food and Drug Administration in July 2021 for the indication of treating patients with T2D and chronic kidney disease.
FIGARO-DKD, FIDELIO-DKD, and FIDELITY were sponsored by Bayer, the company that markets finerenone. Dr. Filippatos has received lecture fees from Bayer, and has had financial relationships with Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medtronic, Novartis, Servier, and Vifor. Dr. Agarwal received travel support from and has been a consultant to Bayer and to numerous other companies. Dr. Pitt has been a consultant to Bayer and to numerous other companies. Dr. Itchhaporia had no disclosures.
FROM ESC CONGRESS 2021
Dapagliflozin in HFrEF may cut arrhythmias, sudden death: DAPA-HF
Dapagliflozin might reduce the risk for ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), a post hoc analysis of the DAPA-HF trial suggests.
The addition of dapagliflozin to standard therapy reduced the relative risk for the primary composite endpoint of any serious ventricular arrhythmia, resuscitated cardiac arrest, or sudden death by 21%, compared with placebo (hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.63-0.99). The absolute risk reduction was 1.5% (5.9% vs. 7.4%).
The benefit was consistent in a competing-risks analysis that included all-cause mortality (HR, 0.80; P = .043) and across the individual components of the composite outcome, James Curtain, MD, Cardiovascular Research Centre of Glasgow, said at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
As previously reported from the main trial, treatment with the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor cut the primary endpoint of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure by 26% among 4,744 patients with HFrEF and in New York Heart Association functional class 2-4.
Cochair of the late-breaking science session, Lars Lund, MD, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, pointed out that dapagliflozin reduced sudden cardiac deaths and related events to an extent similar to that observed for cardiovascular deaths, total mortality, and the main trial’s primary endpoint.
“So does that mean it has any particular effect on arrhythmic events or does it mean, such as a beta-blocker, for example, [it] reduces calcium transience and improves handling of calcium, or does it have an effect simply by improving heart failure?” he asked.
Dr. Curtain replied they are still trying to understand the effects of this new class of drug but that studies have shown dapagliflozin and other SGLT2 inhibitors have favorable effects on adverse cardiac remodeling, which contributes to sudden death and ventricular arrhythmia. They’ve also been shown to reduce cardiac chamber size, left ventricular hypertrophy, and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels over time, consistent with a reduction in myocardial wall stress. “So it could indeed be one of several mechanisms by which they may exert a beneficial cardiac effect.”
Speaking with this news organization, Dr. Curtain pointed out that the Kaplan-Meier curves for the composite outcome began to separate early on, but that the clearest separation was after 9 months, suggestive of a positive action on adverse cardiac remodeling over time.
“This would improve the patients’ heart failure situation, but also thick ventricles are a key risk factor for the occurrence of sudden death and ventricular arrhythmias,” he said. “The effects on adverse cardiac remodeling, given its plausibility in terms of our Kaplan-Meier curves, are one [mechanism] that I’d look to in the first instance, but I’m sure there are more than one actions at play.”
According to the new analysis, the primary outcome occurred in 315 (6.6%) patients; there were 203 adjudicated sudden deaths (64%), 104 investigator-reported ventricular arrhythmias (33%), and 8 resuscitated cardiac arrests (3%). Independent predictors of the primary outcome were higher NT-proBNP levels (odds ratio, 1.54), previous ventricular arrhythmia (OR, 1.93), previous myocardial infarction (OR, 1.42), male sex (OR, 1.53), and higher body mass index (OR, 1.03).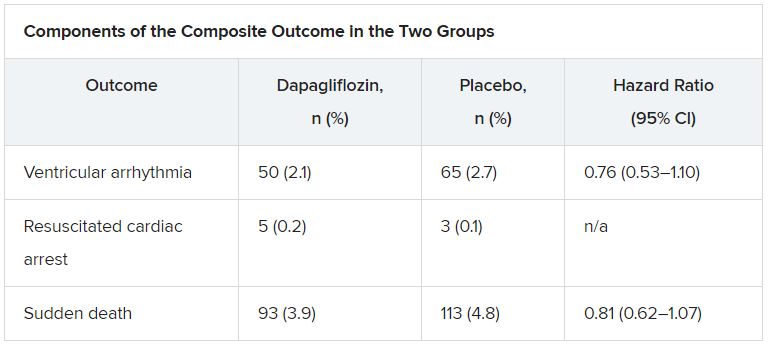
The effect of dapagliflozin on the primary outcome was consistent in several sensitivity analyses and “generally consistent” across key subgroups, Dr. Curtain said.
During a discussion of the results, session cochair Mitja Lainscak, MD, General Hospital Murska Sobota, Slovenia, called out two exceptions. “With regard to patients with implanted ICDs, the effect was neutral, and in the patients without diabetes, the benefit was less than in diabetic patients. Any explanations for that?”
Dr. Curtain responded that “it’s important to note that in the subgroup analyses the point estimates were all on the side favoring dapagliflozin and the interaction test was not significant in that subgroup. The numbers of patients who were in the defibrillator group were modest, and there was a relatively smaller number of events, so it may be harder to show benefit in that group.”
In the dapagliflozin and placebo groups, the event rates per 100 person-years were 3.9 and 5.8, respectively, in patients with diabetes, and 4.1 and 4.7, respectively, in those without diabetes (P for interaction = .273).
Event rates per 100 person-years were 5.8 and 5.9, respectively, in patients with a defibrillator at baseline, and 3.5 and 4.9, respectively, in those without a defibrillator (P for interaction = .174).
Asked to comment on the study, which was simultaneously published in the European Heart Journal, Milton Packer, MD, Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, said he had “very little confidence” in the findings.
“This was entirely post hoc and the investigators combined events – with markedly different levels of clinical importance – in order to achieve a P value less than 0.05,” he told this news organization. “If one takes asymptomatic ventricular arrhythmias out of the analysis, the effect is no longer statistically significant. Furthermore, half of sudden deaths in patients with heart failure are not related to a ventricular arrhythmia.”
The authors note in their report that the analysis was not prespecified and the findings should be regarded as “hypothesis generating and require confirmation,” but also point out that a recent meta-analysis showed that SGLT2 inhibitor use was associated with a lower risk for ventricular tachycardia. Other limitations to the post hoc analysis are that adverse-event reporting likely underestimated the true prevalence of ventricular arrhythmias, and that these events were not adjudicated.
DAPA-HF was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr. Curtain reports no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the coauthors are listed in the paper.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dapagliflozin might reduce the risk for ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), a post hoc analysis of the DAPA-HF trial suggests.
The addition of dapagliflozin to standard therapy reduced the relative risk for the primary composite endpoint of any serious ventricular arrhythmia, resuscitated cardiac arrest, or sudden death by 21%, compared with placebo (hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.63-0.99). The absolute risk reduction was 1.5% (5.9% vs. 7.4%).
The benefit was consistent in a competing-risks analysis that included all-cause mortality (HR, 0.80; P = .043) and across the individual components of the composite outcome, James Curtain, MD, Cardiovascular Research Centre of Glasgow, said at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
As previously reported from the main trial, treatment with the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor cut the primary endpoint of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure by 26% among 4,744 patients with HFrEF and in New York Heart Association functional class 2-4.
Cochair of the late-breaking science session, Lars Lund, MD, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, pointed out that dapagliflozin reduced sudden cardiac deaths and related events to an extent similar to that observed for cardiovascular deaths, total mortality, and the main trial’s primary endpoint.
“So does that mean it has any particular effect on arrhythmic events or does it mean, such as a beta-blocker, for example, [it] reduces calcium transience and improves handling of calcium, or does it have an effect simply by improving heart failure?” he asked.
Dr. Curtain replied they are still trying to understand the effects of this new class of drug but that studies have shown dapagliflozin and other SGLT2 inhibitors have favorable effects on adverse cardiac remodeling, which contributes to sudden death and ventricular arrhythmia. They’ve also been shown to reduce cardiac chamber size, left ventricular hypertrophy, and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels over time, consistent with a reduction in myocardial wall stress. “So it could indeed be one of several mechanisms by which they may exert a beneficial cardiac effect.”
Speaking with this news organization, Dr. Curtain pointed out that the Kaplan-Meier curves for the composite outcome began to separate early on, but that the clearest separation was after 9 months, suggestive of a positive action on adverse cardiac remodeling over time.
“This would improve the patients’ heart failure situation, but also thick ventricles are a key risk factor for the occurrence of sudden death and ventricular arrhythmias,” he said. “The effects on adverse cardiac remodeling, given its plausibility in terms of our Kaplan-Meier curves, are one [mechanism] that I’d look to in the first instance, but I’m sure there are more than one actions at play.”
According to the new analysis, the primary outcome occurred in 315 (6.6%) patients; there were 203 adjudicated sudden deaths (64%), 104 investigator-reported ventricular arrhythmias (33%), and 8 resuscitated cardiac arrests (3%). Independent predictors of the primary outcome were higher NT-proBNP levels (odds ratio, 1.54), previous ventricular arrhythmia (OR, 1.93), previous myocardial infarction (OR, 1.42), male sex (OR, 1.53), and higher body mass index (OR, 1.03).
The effect of dapagliflozin on the primary outcome was consistent in several sensitivity analyses and “generally consistent” across key subgroups, Dr. Curtain said.
During a discussion of the results, session cochair Mitja Lainscak, MD, General Hospital Murska Sobota, Slovenia, called out two exceptions. “With regard to patients with implanted ICDs, the effect was neutral, and in the patients without diabetes, the benefit was less than in diabetic patients. Any explanations for that?”
Dr. Curtain responded that “it’s important to note that in the subgroup analyses the point estimates were all on the side favoring dapagliflozin and the interaction test was not significant in that subgroup. The numbers of patients who were in the defibrillator group were modest, and there was a relatively smaller number of events, so it may be harder to show benefit in that group.”
In the dapagliflozin and placebo groups, the event rates per 100 person-years were 3.9 and 5.8, respectively, in patients with diabetes, and 4.1 and 4.7, respectively, in those without diabetes (P for interaction = .273).
Event rates per 100 person-years were 5.8 and 5.9, respectively, in patients with a defibrillator at baseline, and 3.5 and 4.9, respectively, in those without a defibrillator (P for interaction = .174).
Asked to comment on the study, which was simultaneously published in the European Heart Journal, Milton Packer, MD, Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, said he had “very little confidence” in the findings.
“This was entirely post hoc and the investigators combined events – with markedly different levels of clinical importance – in order to achieve a P value less than 0.05,” he told this news organization. “If one takes asymptomatic ventricular arrhythmias out of the analysis, the effect is no longer statistically significant. Furthermore, half of sudden deaths in patients with heart failure are not related to a ventricular arrhythmia.”
The authors note in their report that the analysis was not prespecified and the findings should be regarded as “hypothesis generating and require confirmation,” but also point out that a recent meta-analysis showed that SGLT2 inhibitor use was associated with a lower risk for ventricular tachycardia. Other limitations to the post hoc analysis are that adverse-event reporting likely underestimated the true prevalence of ventricular arrhythmias, and that these events were not adjudicated.
DAPA-HF was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr. Curtain reports no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the coauthors are listed in the paper.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dapagliflozin might reduce the risk for ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), a post hoc analysis of the DAPA-HF trial suggests.
The addition of dapagliflozin to standard therapy reduced the relative risk for the primary composite endpoint of any serious ventricular arrhythmia, resuscitated cardiac arrest, or sudden death by 21%, compared with placebo (hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.63-0.99). The absolute risk reduction was 1.5% (5.9% vs. 7.4%).
The benefit was consistent in a competing-risks analysis that included all-cause mortality (HR, 0.80; P = .043) and across the individual components of the composite outcome, James Curtain, MD, Cardiovascular Research Centre of Glasgow, said at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
As previously reported from the main trial, treatment with the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor cut the primary endpoint of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure by 26% among 4,744 patients with HFrEF and in New York Heart Association functional class 2-4.
Cochair of the late-breaking science session, Lars Lund, MD, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, pointed out that dapagliflozin reduced sudden cardiac deaths and related events to an extent similar to that observed for cardiovascular deaths, total mortality, and the main trial’s primary endpoint.
“So does that mean it has any particular effect on arrhythmic events or does it mean, such as a beta-blocker, for example, [it] reduces calcium transience and improves handling of calcium, or does it have an effect simply by improving heart failure?” he asked.
Dr. Curtain replied they are still trying to understand the effects of this new class of drug but that studies have shown dapagliflozin and other SGLT2 inhibitors have favorable effects on adverse cardiac remodeling, which contributes to sudden death and ventricular arrhythmia. They’ve also been shown to reduce cardiac chamber size, left ventricular hypertrophy, and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels over time, consistent with a reduction in myocardial wall stress. “So it could indeed be one of several mechanisms by which they may exert a beneficial cardiac effect.”
Speaking with this news organization, Dr. Curtain pointed out that the Kaplan-Meier curves for the composite outcome began to separate early on, but that the clearest separation was after 9 months, suggestive of a positive action on adverse cardiac remodeling over time.
“This would improve the patients’ heart failure situation, but also thick ventricles are a key risk factor for the occurrence of sudden death and ventricular arrhythmias,” he said. “The effects on adverse cardiac remodeling, given its plausibility in terms of our Kaplan-Meier curves, are one [mechanism] that I’d look to in the first instance, but I’m sure there are more than one actions at play.”
According to the new analysis, the primary outcome occurred in 315 (6.6%) patients; there were 203 adjudicated sudden deaths (64%), 104 investigator-reported ventricular arrhythmias (33%), and 8 resuscitated cardiac arrests (3%). Independent predictors of the primary outcome were higher NT-proBNP levels (odds ratio, 1.54), previous ventricular arrhythmia (OR, 1.93), previous myocardial infarction (OR, 1.42), male sex (OR, 1.53), and higher body mass index (OR, 1.03).
The effect of dapagliflozin on the primary outcome was consistent in several sensitivity analyses and “generally consistent” across key subgroups, Dr. Curtain said.
During a discussion of the results, session cochair Mitja Lainscak, MD, General Hospital Murska Sobota, Slovenia, called out two exceptions. “With regard to patients with implanted ICDs, the effect was neutral, and in the patients without diabetes, the benefit was less than in diabetic patients. Any explanations for that?”
Dr. Curtain responded that “it’s important to note that in the subgroup analyses the point estimates were all on the side favoring dapagliflozin and the interaction test was not significant in that subgroup. The numbers of patients who were in the defibrillator group were modest, and there was a relatively smaller number of events, so it may be harder to show benefit in that group.”
In the dapagliflozin and placebo groups, the event rates per 100 person-years were 3.9 and 5.8, respectively, in patients with diabetes, and 4.1 and 4.7, respectively, in those without diabetes (P for interaction = .273).
Event rates per 100 person-years were 5.8 and 5.9, respectively, in patients with a defibrillator at baseline, and 3.5 and 4.9, respectively, in those without a defibrillator (P for interaction = .174).
Asked to comment on the study, which was simultaneously published in the European Heart Journal, Milton Packer, MD, Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, said he had “very little confidence” in the findings.
“This was entirely post hoc and the investigators combined events – with markedly different levels of clinical importance – in order to achieve a P value less than 0.05,” he told this news organization. “If one takes asymptomatic ventricular arrhythmias out of the analysis, the effect is no longer statistically significant. Furthermore, half of sudden deaths in patients with heart failure are not related to a ventricular arrhythmia.”
The authors note in their report that the analysis was not prespecified and the findings should be regarded as “hypothesis generating and require confirmation,” but also point out that a recent meta-analysis showed that SGLT2 inhibitor use was associated with a lower risk for ventricular tachycardia. Other limitations to the post hoc analysis are that adverse-event reporting likely underestimated the true prevalence of ventricular arrhythmias, and that these events were not adjudicated.
DAPA-HF was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr. Curtain reports no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the coauthors are listed in the paper.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESC CONGRESS 2021
EMPEROR-Preserved: Empagliflozin scores HFpEF breakthrough
Updated August 30, 2021
The SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin achieved in EMPEROR-Preserved what no other agent could previously do: unequivocally cut the incidence of cardiovascular death or hospitalization in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Treatment with empagliflozin (Jardiance) led to a significant 21% relative reduction in the rate of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure (HHF), compared with placebo, among 5,988 randomized patients with HFpEF during a median 26 months of follow-up, proving that patients with HFpEF finally have a treatment that gives them clinically meaningful benefit, and paving the way to an abrupt change in management of these patients, experts said.
“This is the first trial to show unequivocal benefits of any drug on major heart failure outcomes in patients with HFpEF,” Stefan D. Anker, MD, PhD, declared at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
The 21% relative reduction, which reflected a cut in the absolute rate of the trial’s primary composite endpoint of 3.3% compared with placebo, was driven mainly by a significant 27% relative reduction in the incidence of HHF (P < .001). Empagliflozin treatment, on top of standard therapy for patients with HFpEF, also resulted in a nonsignificant 9% relative risk reduction in the incidence of cardiovascular death, but it had no discernible impact on the rate of death from any cause, said Dr. Anker, professor of cardiology at Charité Medical University in Berlin.
Concurrently with his talk at the meeting, the results were published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Practice will change ‘quickly’
“This will definitely change our practice, and quite quickly,” said Carlos Aguiar, MD, chair of the Advanced Heart Failure and Heart Transplantation Unit at Hospital Santa Cruz in Carnaxide, Portugal, who was not involved in the study.
Transition to routine use of empagliflozin in patients with HFpEF should be swift because it has already become a mainstay of treatment for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) based on evidence for empagliflozin in EMPEROR-Reduced. A second sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2 ) inhibitor, dapagliflozin (Farxiga), is also an option for treating HFrEF based on results in the DAPA-HF trial, and the DELIVER trial, still in progress, is testing dapagliflozin as a HFpEF treatment in about 6,000 patients, with results expected in 2022.
About half of the patients in EMPEROR-Preserved had diabetes, and the treatment effects on HFpEF were similar regardless of patients’ diabetes status. Empagliflozin, like other members of the SGLT2 inhibitor class, boosts urinary excretion of glucose and received initial regulatory approval as an agent for glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Empagliflozin also has U.S.-approved marketing indications for treating patients with HFrEF whether or not they also have diabetes, and for reducing cardiovascular death in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
“We already use this drug class in cardiovascular medicine and to treat patients with type 2 diabetes, and we have been eager to find a treatment for patients with HFpEF. This is something that will be really significant,” said Dr. Aguiar.
Heart failure clinicians have “become familiar prescribing” SGLT2 inhibitors following approval of HFrEF indications for some of these agents, noted Mary Norine Walsh, MD, a heart failure specialist with Ascension Medical Group in Indianapolis. The new results “are good news because there have been so few options” for patients with HFpEF, she said in an interview.
EMPEROR-Preserved “is the first phase 3 clinical trial that exclusively enrolled patients with heart failure and an ejection fraction of more than 40% to meet its primary outcome,” and the results “represent a major win against a medical condition that had previously proven formidable,” Mark H. Drazner, MD, said in an editorial that accompanied the published results.
The trial’s findings “should contribute to a change in clinical practice given the paucity of therapeutic options available for patients with HFpEF,” wrote Dr. Drazner, a heart failure specialist who is professor and clinical chief of cardiology at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas.
Theresa A, McDonagh, MD, MBChB, who chaired the panel that just released revised guidelines from the European Society of Cardiology for managing patients with heart failure, predicted that empagliflozin treatment for patients with HFpEF will soon show up in guidelines. It will likely receive a “should be considered” ranking despite being a single study because of the impressive size of the treatment effect and lack of well-supported alternative treatments, she commented as a discussant of the trial during its presentation at the congress. If the DELIVER trial with dapagliflozin shows a similar effect, the recommendation would likely become even stronger, added Dr. McDonagh, a heart failure specialist and professor of cardiology at King’s College, London.
More women enrolled than ever before
EMPEROR-Preserved enrolled adults with chronic HFpEF in New York Heart Association functional class II-IV and a left ventricular ejection fraction greater than 40% starting in 2017 at more than 600 sites in more than 20 countries worldwide including the United States. As background therapy, more than 80% of patients received treatment with either an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker (in some instances in the form of sacubitril/valsartan), more than 80% were on a beta-blocker, and about a third were taking a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, making them “very well treated HFpEF patients,” Dr. Anker said.
One of the most notable features of enrollment was that 45% of participants were women, giving this trial the highest inclusion of women compared with all prior studies in patients with HFpEF or with HFrEF, said Dr. Walsh. “HFpEF is very prevalent in woman,” she noted, and having this high participation rate of women in the study increases its relevance to these patients. “It’s important to be able to tell women that patients like you were in the study so we can more easily apply the lessons from the trial to you. That can’t be stressed enough,” she said.
The primary outcome occurred in 415 (13.8%) of the 2,997 patients in the empagliflozin group and in 511 (17.1%) of 2,991 patients who received placebo (hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.69-0.90; P < .001).
The study showed a safety profile consistent with prior experience with empagliflozin, Dr. Anker added.
Pooling EMPEROR-Preserved with EMPEROR-Reduced
The investigators who ran EMPEROR-Preserved designed the trial to closely parallel the EMPEROR-Reduced trial in patients with HFrEF, and they included a prespecified analysis (EMPEROR-Pooled) that combined the more than 9,700 patients in the two studies. This showed a consistent and robust benefit from empagliflozin for reducing HHF across a wide spectrum of patients with heart failure, ranging from patients with left ventricular ejection fractions of less than 25% to patients with ejection fractions as high as 64%. However, the analysis also showed that patients with ejection fractions of 65% or greater received no discernible benefit from empagliflozin, Milton Packer, MD, reported in a separate talk at the congress.
“The findings demonstrate the benefits of empagliflozin across a broad range of patients with heart failure who have ejection fractions of less than 60%-65%,” said Dr. Packer, a researcher at Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas.
This apparent attenuation of an effect at higher ejection fractions “has been observed in other HFpEF trials, most recently in the PARAGON-HF trial” of sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto), he noted. Additional analyses led by Dr. Packer showed that in patients with ejection fractions below 65% the HHF benefit from empagliflozin consistently surpassed the benefit seen with sacubitril/valsartan in PARAGON-HF. But he recommended using both drugs in patients with HFpEF and an ejection fraction up to about 60%.
“If I had a patient with HFpEF I would use both drugs as well as beta-blockers and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists,” he said during a press briefing.
Another finding from analysis of the EMPEROR-Reduced and EMPEROR-Preserved trials together was that patients with reduced ejection fractions showed a significant 49% relative reduction in the incidence of serious renal outcomes, but this effect was completely blunted in EMPEROR-Preserved.
“Ejection fraction influences the effects of empagliflozin on major renal outcomes,” concluded Dr. Packer in a report on this analysis published simultaneously with the main EMPEROR-Preserved findings (N Engl J Med. 2021 Aug 27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2112411). “These data from the EMPEROR trials are unique. We have no comparable data” from any of the other reported studies of SGLT2 inhibitors,” he said.
EMPEROR-Preserved was sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim and by Eli Lilly, the two companies that jointly market empagliflozin (Jardiance). Dr. Anker has received personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and from several other companies, and he has received grants and personal fees from Abbott Vascular and Vifor. Dr. Packer has received consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and from numerous other companies. Dr. McDonagh has has recent financial relationships with AstraZeneca, Cprpus, Novartis, Pfizer, and Vifor. Dr. Aguiar and Dr. Walsh had no disclosures.
Updated August 30, 2021
The SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin achieved in EMPEROR-Preserved what no other agent could previously do: unequivocally cut the incidence of cardiovascular death or hospitalization in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Treatment with empagliflozin (Jardiance) led to a significant 21% relative reduction in the rate of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure (HHF), compared with placebo, among 5,988 randomized patients with HFpEF during a median 26 months of follow-up, proving that patients with HFpEF finally have a treatment that gives them clinically meaningful benefit, and paving the way to an abrupt change in management of these patients, experts said.
“This is the first trial to show unequivocal benefits of any drug on major heart failure outcomes in patients with HFpEF,” Stefan D. Anker, MD, PhD, declared at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
The 21% relative reduction, which reflected a cut in the absolute rate of the trial’s primary composite endpoint of 3.3% compared with placebo, was driven mainly by a significant 27% relative reduction in the incidence of HHF (P < .001). Empagliflozin treatment, on top of standard therapy for patients with HFpEF, also resulted in a nonsignificant 9% relative risk reduction in the incidence of cardiovascular death, but it had no discernible impact on the rate of death from any cause, said Dr. Anker, professor of cardiology at Charité Medical University in Berlin.
Concurrently with his talk at the meeting, the results were published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Practice will change ‘quickly’
“This will definitely change our practice, and quite quickly,” said Carlos Aguiar, MD, chair of the Advanced Heart Failure and Heart Transplantation Unit at Hospital Santa Cruz in Carnaxide, Portugal, who was not involved in the study.
Transition to routine use of empagliflozin in patients with HFpEF should be swift because it has already become a mainstay of treatment for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) based on evidence for empagliflozin in EMPEROR-Reduced. A second sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2 ) inhibitor, dapagliflozin (Farxiga), is also an option for treating HFrEF based on results in the DAPA-HF trial, and the DELIVER trial, still in progress, is testing dapagliflozin as a HFpEF treatment in about 6,000 patients, with results expected in 2022.
About half of the patients in EMPEROR-Preserved had diabetes, and the treatment effects on HFpEF were similar regardless of patients’ diabetes status. Empagliflozin, like other members of the SGLT2 inhibitor class, boosts urinary excretion of glucose and received initial regulatory approval as an agent for glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Empagliflozin also has U.S.-approved marketing indications for treating patients with HFrEF whether or not they also have diabetes, and for reducing cardiovascular death in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
“We already use this drug class in cardiovascular medicine and to treat patients with type 2 diabetes, and we have been eager to find a treatment for patients with HFpEF. This is something that will be really significant,” said Dr. Aguiar.
Heart failure clinicians have “become familiar prescribing” SGLT2 inhibitors following approval of HFrEF indications for some of these agents, noted Mary Norine Walsh, MD, a heart failure specialist with Ascension Medical Group in Indianapolis. The new results “are good news because there have been so few options” for patients with HFpEF, she said in an interview.
EMPEROR-Preserved “is the first phase 3 clinical trial that exclusively enrolled patients with heart failure and an ejection fraction of more than 40% to meet its primary outcome,” and the results “represent a major win against a medical condition that had previously proven formidable,” Mark H. Drazner, MD, said in an editorial that accompanied the published results.
The trial’s findings “should contribute to a change in clinical practice given the paucity of therapeutic options available for patients with HFpEF,” wrote Dr. Drazner, a heart failure specialist who is professor and clinical chief of cardiology at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas.
Theresa A, McDonagh, MD, MBChB, who chaired the panel that just released revised guidelines from the European Society of Cardiology for managing patients with heart failure, predicted that empagliflozin treatment for patients with HFpEF will soon show up in guidelines. It will likely receive a “should be considered” ranking despite being a single study because of the impressive size of the treatment effect and lack of well-supported alternative treatments, she commented as a discussant of the trial during its presentation at the congress. If the DELIVER trial with dapagliflozin shows a similar effect, the recommendation would likely become even stronger, added Dr. McDonagh, a heart failure specialist and professor of cardiology at King’s College, London.
More women enrolled than ever before
EMPEROR-Preserved enrolled adults with chronic HFpEF in New York Heart Association functional class II-IV and a left ventricular ejection fraction greater than 40% starting in 2017 at more than 600 sites in more than 20 countries worldwide including the United States. As background therapy, more than 80% of patients received treatment with either an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker (in some instances in the form of sacubitril/valsartan), more than 80% were on a beta-blocker, and about a third were taking a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, making them “very well treated HFpEF patients,” Dr. Anker said.
One of the most notable features of enrollment was that 45% of participants were women, giving this trial the highest inclusion of women compared with all prior studies in patients with HFpEF or with HFrEF, said Dr. Walsh. “HFpEF is very prevalent in woman,” she noted, and having this high participation rate of women in the study increases its relevance to these patients. “It’s important to be able to tell women that patients like you were in the study so we can more easily apply the lessons from the trial to you. That can’t be stressed enough,” she said.
The primary outcome occurred in 415 (13.8%) of the 2,997 patients in the empagliflozin group and in 511 (17.1%) of 2,991 patients who received placebo (hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.69-0.90; P < .001).
The study showed a safety profile consistent with prior experience with empagliflozin, Dr. Anker added.
Pooling EMPEROR-Preserved with EMPEROR-Reduced
The investigators who ran EMPEROR-Preserved designed the trial to closely parallel the EMPEROR-Reduced trial in patients with HFrEF, and they included a prespecified analysis (EMPEROR-Pooled) that combined the more than 9,700 patients in the two studies. This showed a consistent and robust benefit from empagliflozin for reducing HHF across a wide spectrum of patients with heart failure, ranging from patients with left ventricular ejection fractions of less than 25% to patients with ejection fractions as high as 64%. However, the analysis also showed that patients with ejection fractions of 65% or greater received no discernible benefit from empagliflozin, Milton Packer, MD, reported in a separate talk at the congress.
“The findings demonstrate the benefits of empagliflozin across a broad range of patients with heart failure who have ejection fractions of less than 60%-65%,” said Dr. Packer, a researcher at Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas.
This apparent attenuation of an effect at higher ejection fractions “has been observed in other HFpEF trials, most recently in the PARAGON-HF trial” of sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto), he noted. Additional analyses led by Dr. Packer showed that in patients with ejection fractions below 65% the HHF benefit from empagliflozin consistently surpassed the benefit seen with sacubitril/valsartan in PARAGON-HF. But he recommended using both drugs in patients with HFpEF and an ejection fraction up to about 60%.
“If I had a patient with HFpEF I would use both drugs as well as beta-blockers and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists,” he said during a press briefing.
Another finding from analysis of the EMPEROR-Reduced and EMPEROR-Preserved trials together was that patients with reduced ejection fractions showed a significant 49% relative reduction in the incidence of serious renal outcomes, but this effect was completely blunted in EMPEROR-Preserved.
“Ejection fraction influences the effects of empagliflozin on major renal outcomes,” concluded Dr. Packer in a report on this analysis published simultaneously with the main EMPEROR-Preserved findings (N Engl J Med. 2021 Aug 27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2112411). “These data from the EMPEROR trials are unique. We have no comparable data” from any of the other reported studies of SGLT2 inhibitors,” he said.
EMPEROR-Preserved was sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim and by Eli Lilly, the two companies that jointly market empagliflozin (Jardiance). Dr. Anker has received personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and from several other companies, and he has received grants and personal fees from Abbott Vascular and Vifor. Dr. Packer has received consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and from numerous other companies. Dr. McDonagh has has recent financial relationships with AstraZeneca, Cprpus, Novartis, Pfizer, and Vifor. Dr. Aguiar and Dr. Walsh had no disclosures.
Updated August 30, 2021
The SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin achieved in EMPEROR-Preserved what no other agent could previously do: unequivocally cut the incidence of cardiovascular death or hospitalization in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Treatment with empagliflozin (Jardiance) led to a significant 21% relative reduction in the rate of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure (HHF), compared with placebo, among 5,988 randomized patients with HFpEF during a median 26 months of follow-up, proving that patients with HFpEF finally have a treatment that gives them clinically meaningful benefit, and paving the way to an abrupt change in management of these patients, experts said.
“This is the first trial to show unequivocal benefits of any drug on major heart failure outcomes in patients with HFpEF,” Stefan D. Anker, MD, PhD, declared at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
The 21% relative reduction, which reflected a cut in the absolute rate of the trial’s primary composite endpoint of 3.3% compared with placebo, was driven mainly by a significant 27% relative reduction in the incidence of HHF (P < .001). Empagliflozin treatment, on top of standard therapy for patients with HFpEF, also resulted in a nonsignificant 9% relative risk reduction in the incidence of cardiovascular death, but it had no discernible impact on the rate of death from any cause, said Dr. Anker, professor of cardiology at Charité Medical University in Berlin.
Concurrently with his talk at the meeting, the results were published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Practice will change ‘quickly’
“This will definitely change our practice, and quite quickly,” said Carlos Aguiar, MD, chair of the Advanced Heart Failure and Heart Transplantation Unit at Hospital Santa Cruz in Carnaxide, Portugal, who was not involved in the study.
Transition to routine use of empagliflozin in patients with HFpEF should be swift because it has already become a mainstay of treatment for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) based on evidence for empagliflozin in EMPEROR-Reduced. A second sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2 ) inhibitor, dapagliflozin (Farxiga), is also an option for treating HFrEF based on results in the DAPA-HF trial, and the DELIVER trial, still in progress, is testing dapagliflozin as a HFpEF treatment in about 6,000 patients, with results expected in 2022.
About half of the patients in EMPEROR-Preserved had diabetes, and the treatment effects on HFpEF were similar regardless of patients’ diabetes status. Empagliflozin, like other members of the SGLT2 inhibitor class, boosts urinary excretion of glucose and received initial regulatory approval as an agent for glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Empagliflozin also has U.S.-approved marketing indications for treating patients with HFrEF whether or not they also have diabetes, and for reducing cardiovascular death in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
“We already use this drug class in cardiovascular medicine and to treat patients with type 2 diabetes, and we have been eager to find a treatment for patients with HFpEF. This is something that will be really significant,” said Dr. Aguiar.
Heart failure clinicians have “become familiar prescribing” SGLT2 inhibitors following approval of HFrEF indications for some of these agents, noted Mary Norine Walsh, MD, a heart failure specialist with Ascension Medical Group in Indianapolis. The new results “are good news because there have been so few options” for patients with HFpEF, she said in an interview.
EMPEROR-Preserved “is the first phase 3 clinical trial that exclusively enrolled patients with heart failure and an ejection fraction of more than 40% to meet its primary outcome,” and the results “represent a major win against a medical condition that had previously proven formidable,” Mark H. Drazner, MD, said in an editorial that accompanied the published results.
The trial’s findings “should contribute to a change in clinical practice given the paucity of therapeutic options available for patients with HFpEF,” wrote Dr. Drazner, a heart failure specialist who is professor and clinical chief of cardiology at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas.
Theresa A, McDonagh, MD, MBChB, who chaired the panel that just released revised guidelines from the European Society of Cardiology for managing patients with heart failure, predicted that empagliflozin treatment for patients with HFpEF will soon show up in guidelines. It will likely receive a “should be considered” ranking despite being a single study because of the impressive size of the treatment effect and lack of well-supported alternative treatments, she commented as a discussant of the trial during its presentation at the congress. If the DELIVER trial with dapagliflozin shows a similar effect, the recommendation would likely become even stronger, added Dr. McDonagh, a heart failure specialist and professor of cardiology at King’s College, London.
More women enrolled than ever before
EMPEROR-Preserved enrolled adults with chronic HFpEF in New York Heart Association functional class II-IV and a left ventricular ejection fraction greater than 40% starting in 2017 at more than 600 sites in more than 20 countries worldwide including the United States. As background therapy, more than 80% of patients received treatment with either an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker (in some instances in the form of sacubitril/valsartan), more than 80% were on a beta-blocker, and about a third were taking a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, making them “very well treated HFpEF patients,” Dr. Anker said.
One of the most notable features of enrollment was that 45% of participants were women, giving this trial the highest inclusion of women compared with all prior studies in patients with HFpEF or with HFrEF, said Dr. Walsh. “HFpEF is very prevalent in woman,” she noted, and having this high participation rate of women in the study increases its relevance to these patients. “It’s important to be able to tell women that patients like you were in the study so we can more easily apply the lessons from the trial to you. That can’t be stressed enough,” she said.
The primary outcome occurred in 415 (13.8%) of the 2,997 patients in the empagliflozin group and in 511 (17.1%) of 2,991 patients who received placebo (hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.69-0.90; P < .001).
The study showed a safety profile consistent with prior experience with empagliflozin, Dr. Anker added.
Pooling EMPEROR-Preserved with EMPEROR-Reduced
The investigators who ran EMPEROR-Preserved designed the trial to closely parallel the EMPEROR-Reduced trial in patients with HFrEF, and they included a prespecified analysis (EMPEROR-Pooled) that combined the more than 9,700 patients in the two studies. This showed a consistent and robust benefit from empagliflozin for reducing HHF across a wide spectrum of patients with heart failure, ranging from patients with left ventricular ejection fractions of less than 25% to patients with ejection fractions as high as 64%. However, the analysis also showed that patients with ejection fractions of 65% or greater received no discernible benefit from empagliflozin, Milton Packer, MD, reported in a separate talk at the congress.
“The findings demonstrate the benefits of empagliflozin across a broad range of patients with heart failure who have ejection fractions of less than 60%-65%,” said Dr. Packer, a researcher at Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas.
This apparent attenuation of an effect at higher ejection fractions “has been observed in other HFpEF trials, most recently in the PARAGON-HF trial” of sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto), he noted. Additional analyses led by Dr. Packer showed that in patients with ejection fractions below 65% the HHF benefit from empagliflozin consistently surpassed the benefit seen with sacubitril/valsartan in PARAGON-HF. But he recommended using both drugs in patients with HFpEF and an ejection fraction up to about 60%.
“If I had a patient with HFpEF I would use both drugs as well as beta-blockers and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists,” he said during a press briefing.
Another finding from analysis of the EMPEROR-Reduced and EMPEROR-Preserved trials together was that patients with reduced ejection fractions showed a significant 49% relative reduction in the incidence of serious renal outcomes, but this effect was completely blunted in EMPEROR-Preserved.
“Ejection fraction influences the effects of empagliflozin on major renal outcomes,” concluded Dr. Packer in a report on this analysis published simultaneously with the main EMPEROR-Preserved findings (N Engl J Med. 2021 Aug 27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2112411). “These data from the EMPEROR trials are unique. We have no comparable data” from any of the other reported studies of SGLT2 inhibitors,” he said.
EMPEROR-Preserved was sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim and by Eli Lilly, the two companies that jointly market empagliflozin (Jardiance). Dr. Anker has received personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and from several other companies, and he has received grants and personal fees from Abbott Vascular and Vifor. Dr. Packer has received consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and from numerous other companies. Dr. McDonagh has has recent financial relationships with AstraZeneca, Cprpus, Novartis, Pfizer, and Vifor. Dr. Aguiar and Dr. Walsh had no disclosures.
FROM ESC CONGRESS 2021
FDA okays difelikefalin for dialysis-associated pruritus in patients with CKD
Some nephrologists welcomed the Aug. 23 approval of this new option for treating pruritus, a relatively common and often hard-to-resolve complication of dialysis in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) that can substantially impinge on quality of life for some patients, but also voiced uncertainty about the role of a new agent with a modest trial track record that may be expensive and face insurance-coverage hurdles.
“Uptake of difelikefalin will depend on awareness of itch among patients dependent on hemodialysis, and on payment policies,” predicted Daniel E. Weiner, MD, a nephrologist at Tufts Medical Center in Boston. “Pruritus is underdiagnosed among people with kidney failure, and in some patients ongoing pruritus can be highly impactful on sleep and quality of life. The clinical trial results were very encouraging that difelikefalin is effective and safe,” which makes recognition of pruritus as a significant issue for patients a key factor in uptake of the new drug, Dr. Weiner, an investigator in a difelikefalin clinical study, said in an interview.
Other nephrologists acknowledged the substantial problem that itch can pose for many patients with CKD on dialysis but questioned the weight of evidence behind difelikefalin’s approval.
Two pivotal trials with fewer than 900 total randomized patients
The data considered by the FDA primarily featured results from two pivotal trials, KALM-1 and KALM-2. KALM-1 randomized 378 patients with CKD and on hemodialysis and with moderate to severe pruritus to intravenous treatment with difelikefalin or placebo three times a week for 12 weeks with a primary endpoint of an improvement (decrease) of at least 3 points from baseline in their Worst Itching Intensity Numerical Rating Scale (WI-NRS) score, which averaged just over 7 points at baseline. After 12 weeks on treatment, 52% of patients who received difelikefalin had at least a 3-point drop, compared with 31% of patients who received placebo, a significant difference. The results appeared in a 2020 report in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Confirmatory results came in the second pivotal trial, KALM-2, a similarly designed, 12-week study that randomized 473 patients, with 54% of those in the active arm achieving at least a 3-point cut in their baseline WI-NRS score, compared with 42% of patients who received placebo, a significant difference. A report at the Kidney Week meeting sponsored by the National Kidney Foundation in October 2020 presented the KALM-2 results, but the findings have not yet appeared in a published article.
In sum, the data suggest that treatment with difelikefalin will, on average, produce a clinically meaningful effect on itch compared with placebo in about 20% of patients, with nearly half the patients who receive the active drug having a less robust response and many patients who receive no active treatment also show a meaningful cut in their pruritus severity in a trial setting, noted Paul Palevsky, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh and chief of the renal section at the Veterans Affairs Pittsburgh Healthcare System.
The upshot is that questions linger over which patients are the best candidates for this drug and how it might perform in real-world practice given difelikefalin’s limited track record, Dr. Palevsky said in an interview.
In addition, the labeling specifies the indication is for patients with moderate to severe pruritus, but itching severity is not routinely quantified in these patients in current practice, added Dr. Palevsky, who is also president of the National Kidney Foundation.
Dr. Weiner noted that another unknown is the appropriate duration of treatment in real-world use.
What will it cost, and will it be covered?
The drug’s price and insurance coverage will likely be a major factor in uptake of the new drug, agreed both Dr. Weiner and Dr. Palevsky, especially the coverage decision for Medicare patients by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. A corollary is whether or not coverage for difelikefalin, which patients receive as an intravenous infusion during each of their usual three-times-a-week dialysis sessions, will lie outside of the bundled dialysis reimbursement payment. If is no mechanism exists to pay for difelikefalin separately beyond the current bundled dialysis rate, “I suspect it will not get used very much unless it is very inexpensive,” predicted Dr. Weiner.
Another issue is where difelikefalin fits within the lineup of standard treatment options. “A lot of people receiving hemodialysis suffer from pruritus and have not been successfully treated. For these individuals difelikefalin could be a game changer,” Dr. Weiner said.
Other nephrologists have a more positive take on the existing treatment options.
“Start systemic therapy for patients with itch that is significantly affecting quality of life; stepping up from topical therapy just delays effective treatment,” advised Hugh C. Rayner, MD, a nephrologist affiliated with Birmingham (England) Heartland’s Hospital who was lead author on a review of pruritus treatments for patients with CKD on hemodialysis.
“Standard systemic therapy is gabapentin or pregabalin,” an approach “supported by robust evidence confirmed in a Cochrane review,” he said in an interview. The impact of difelikefalin “will be limited as its effectiveness in reducing itch is modest at best and far inferior to gabapentin and pregabalin,” Dr. Rayner added. Difelikefalin’s “main downsides will be its cost, compared with gabapentin, and its gastrointestinal side effects.”
Adverse-event profiles
In KALM-1, the most frequent adverse effects from difelikefalin treatment was diarrhea, in 10% of patients, compared with a 4% rate among patients who received placebo. Vomiting occurred at a 5% incidence on difelikefalin and in 3% of patients on placebo. All serious adverse events occurred in 26% of patients on difelikefalin and in 22% of those who received placebo. Discontinuations because of an adverse event occurred in 8% of patients on difelikefalin and in 5% of the placebo patients.
An editorial that accompanied the published KALM-1 report in 2020 said “the findings are compelling, although diarrhea, dizziness, and vomiting were frequent side effects.”
Both Dr. Weiner and Dr. Palevsky were more reserved than Dr. Rayner in their appraisal of gabapentin and pregabalin, although Dr. Palevsky admitted that he has prescribed one or the other of these two drugs to “lots of patients,” especially gabapentin. “But they are not completely benign drugs,” he cautioned, a concern echoed by Dr. Weiner.
“Antihistamines, gabapentin, and pregabalin have a high side-effect burden in patients on hemodialysis and limited efficacy, and are poor options for chronic pruritus management,” explained Dr. Weiner. “I would favor difelikefalin to chronic prescription of these other agents” because difelikefalin “appears effective and has a very low side effect burden. Very few effective treatments for pruritus do not have side effects.”
Difelikefalin is a peripherally restricted, selective kappa opioid receptor agonist that exerts antipruritic effects by activating kappa opioid receptors on peripheral neurons and immune cells. The drug’s hydrophilic, small-peptide structure restricts passive diffusion across membranes, which limits the drug’s access to kappa opioid receptors in the central nervous system and hence reduces potential adverse effects.
The FDA made this approval decision without consulting an advisory committee. The companies that will market difelikefalin (Korsuva), Cara Therapeutics and Vifor Pharma, announced that their U.S. promotional launch of the drug starts early in 2022.
The KALM-1 and KALM-2 studies were sponsored by Cara Therapeutics and Vifor Pharma, the two companies that have been jointly developing difelikefalin. Dr. Pavelsky and Dr. Rayner had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Weiner was previously an adviser to Cara and Vifor and participated as an investigator in a difelikefalin clinical study, but more recently has had no relationships with the companies.
Some nephrologists welcomed the Aug. 23 approval of this new option for treating pruritus, a relatively common and often hard-to-resolve complication of dialysis in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) that can substantially impinge on quality of life for some patients, but also voiced uncertainty about the role of a new agent with a modest trial track record that may be expensive and face insurance-coverage hurdles.
“Uptake of difelikefalin will depend on awareness of itch among patients dependent on hemodialysis, and on payment policies,” predicted Daniel E. Weiner, MD, a nephrologist at Tufts Medical Center in Boston. “Pruritus is underdiagnosed among people with kidney failure, and in some patients ongoing pruritus can be highly impactful on sleep and quality of life. The clinical trial results were very encouraging that difelikefalin is effective and safe,” which makes recognition of pruritus as a significant issue for patients a key factor in uptake of the new drug, Dr. Weiner, an investigator in a difelikefalin clinical study, said in an interview.
Other nephrologists acknowledged the substantial problem that itch can pose for many patients with CKD on dialysis but questioned the weight of evidence behind difelikefalin’s approval.
Two pivotal trials with fewer than 900 total randomized patients
The data considered by the FDA primarily featured results from two pivotal trials, KALM-1 and KALM-2. KALM-1 randomized 378 patients with CKD and on hemodialysis and with moderate to severe pruritus to intravenous treatment with difelikefalin or placebo three times a week for 12 weeks with a primary endpoint of an improvement (decrease) of at least 3 points from baseline in their Worst Itching Intensity Numerical Rating Scale (WI-NRS) score, which averaged just over 7 points at baseline. After 12 weeks on treatment, 52% of patients who received difelikefalin had at least a 3-point drop, compared with 31% of patients who received placebo, a significant difference. The results appeared in a 2020 report in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Confirmatory results came in the second pivotal trial, KALM-2, a similarly designed, 12-week study that randomized 473 patients, with 54% of those in the active arm achieving at least a 3-point cut in their baseline WI-NRS score, compared with 42% of patients who received placebo, a significant difference. A report at the Kidney Week meeting sponsored by the National Kidney Foundation in October 2020 presented the KALM-2 results, but the findings have not yet appeared in a published article.
In sum, the data suggest that treatment with difelikefalin will, on average, produce a clinically meaningful effect on itch compared with placebo in about 20% of patients, with nearly half the patients who receive the active drug having a less robust response and many patients who receive no active treatment also show a meaningful cut in their pruritus severity in a trial setting, noted Paul Palevsky, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh and chief of the renal section at the Veterans Affairs Pittsburgh Healthcare System.
The upshot is that questions linger over which patients are the best candidates for this drug and how it might perform in real-world practice given difelikefalin’s limited track record, Dr. Palevsky said in an interview.
In addition, the labeling specifies the indication is for patients with moderate to severe pruritus, but itching severity is not routinely quantified in these patients in current practice, added Dr. Palevsky, who is also president of the National Kidney Foundation.
Dr. Weiner noted that another unknown is the appropriate duration of treatment in real-world use.
What will it cost, and will it be covered?
The drug’s price and insurance coverage will likely be a major factor in uptake of the new drug, agreed both Dr. Weiner and Dr. Palevsky, especially the coverage decision for Medicare patients by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. A corollary is whether or not coverage for difelikefalin, which patients receive as an intravenous infusion during each of their usual three-times-a-week dialysis sessions, will lie outside of the bundled dialysis reimbursement payment. If is no mechanism exists to pay for difelikefalin separately beyond the current bundled dialysis rate, “I suspect it will not get used very much unless it is very inexpensive,” predicted Dr. Weiner.
Another issue is where difelikefalin fits within the lineup of standard treatment options. “A lot of people receiving hemodialysis suffer from pruritus and have not been successfully treated. For these individuals difelikefalin could be a game changer,” Dr. Weiner said.
Other nephrologists have a more positive take on the existing treatment options.
“Start systemic therapy for patients with itch that is significantly affecting quality of life; stepping up from topical therapy just delays effective treatment,” advised Hugh C. Rayner, MD, a nephrologist affiliated with Birmingham (England) Heartland’s Hospital who was lead author on a review of pruritus treatments for patients with CKD on hemodialysis.
“Standard systemic therapy is gabapentin or pregabalin,” an approach “supported by robust evidence confirmed in a Cochrane review,” he said in an interview. The impact of difelikefalin “will be limited as its effectiveness in reducing itch is modest at best and far inferior to gabapentin and pregabalin,” Dr. Rayner added. Difelikefalin’s “main downsides will be its cost, compared with gabapentin, and its gastrointestinal side effects.”
Adverse-event profiles
In KALM-1, the most frequent adverse effects from difelikefalin treatment was diarrhea, in 10% of patients, compared with a 4% rate among patients who received placebo. Vomiting occurred at a 5% incidence on difelikefalin and in 3% of patients on placebo. All serious adverse events occurred in 26% of patients on difelikefalin and in 22% of those who received placebo. Discontinuations because of an adverse event occurred in 8% of patients on difelikefalin and in 5% of the placebo patients.
An editorial that accompanied the published KALM-1 report in 2020 said “the findings are compelling, although diarrhea, dizziness, and vomiting were frequent side effects.”
Both Dr. Weiner and Dr. Palevsky were more reserved than Dr. Rayner in their appraisal of gabapentin and pregabalin, although Dr. Palevsky admitted that he has prescribed one or the other of these two drugs to “lots of patients,” especially gabapentin. “But they are not completely benign drugs,” he cautioned, a concern echoed by Dr. Weiner.
“Antihistamines, gabapentin, and pregabalin have a high side-effect burden in patients on hemodialysis and limited efficacy, and are poor options for chronic pruritus management,” explained Dr. Weiner. “I would favor difelikefalin to chronic prescription of these other agents” because difelikefalin “appears effective and has a very low side effect burden. Very few effective treatments for pruritus do not have side effects.”
Difelikefalin is a peripherally restricted, selective kappa opioid receptor agonist that exerts antipruritic effects by activating kappa opioid receptors on peripheral neurons and immune cells. The drug’s hydrophilic, small-peptide structure restricts passive diffusion across membranes, which limits the drug’s access to kappa opioid receptors in the central nervous system and hence reduces potential adverse effects.
The FDA made this approval decision without consulting an advisory committee. The companies that will market difelikefalin (Korsuva), Cara Therapeutics and Vifor Pharma, announced that their U.S. promotional launch of the drug starts early in 2022.
The KALM-1 and KALM-2 studies were sponsored by Cara Therapeutics and Vifor Pharma, the two companies that have been jointly developing difelikefalin. Dr. Pavelsky and Dr. Rayner had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Weiner was previously an adviser to Cara and Vifor and participated as an investigator in a difelikefalin clinical study, but more recently has had no relationships with the companies.
Some nephrologists welcomed the Aug. 23 approval of this new option for treating pruritus, a relatively common and often hard-to-resolve complication of dialysis in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) that can substantially impinge on quality of life for some patients, but also voiced uncertainty about the role of a new agent with a modest trial track record that may be expensive and face insurance-coverage hurdles.
“Uptake of difelikefalin will depend on awareness of itch among patients dependent on hemodialysis, and on payment policies,” predicted Daniel E. Weiner, MD, a nephrologist at Tufts Medical Center in Boston. “Pruritus is underdiagnosed among people with kidney failure, and in some patients ongoing pruritus can be highly impactful on sleep and quality of life. The clinical trial results were very encouraging that difelikefalin is effective and safe,” which makes recognition of pruritus as a significant issue for patients a key factor in uptake of the new drug, Dr. Weiner, an investigator in a difelikefalin clinical study, said in an interview.
Other nephrologists acknowledged the substantial problem that itch can pose for many patients with CKD on dialysis but questioned the weight of evidence behind difelikefalin’s approval.
Two pivotal trials with fewer than 900 total randomized patients
The data considered by the FDA primarily featured results from two pivotal trials, KALM-1 and KALM-2. KALM-1 randomized 378 patients with CKD and on hemodialysis and with moderate to severe pruritus to intravenous treatment with difelikefalin or placebo three times a week for 12 weeks with a primary endpoint of an improvement (decrease) of at least 3 points from baseline in their Worst Itching Intensity Numerical Rating Scale (WI-NRS) score, which averaged just over 7 points at baseline. After 12 weeks on treatment, 52% of patients who received difelikefalin had at least a 3-point drop, compared with 31% of patients who received placebo, a significant difference. The results appeared in a 2020 report in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Confirmatory results came in the second pivotal trial, KALM-2, a similarly designed, 12-week study that randomized 473 patients, with 54% of those in the active arm achieving at least a 3-point cut in their baseline WI-NRS score, compared with 42% of patients who received placebo, a significant difference. A report at the Kidney Week meeting sponsored by the National Kidney Foundation in October 2020 presented the KALM-2 results, but the findings have not yet appeared in a published article.
In sum, the data suggest that treatment with difelikefalin will, on average, produce a clinically meaningful effect on itch compared with placebo in about 20% of patients, with nearly half the patients who receive the active drug having a less robust response and many patients who receive no active treatment also show a meaningful cut in their pruritus severity in a trial setting, noted Paul Palevsky, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh and chief of the renal section at the Veterans Affairs Pittsburgh Healthcare System.
The upshot is that questions linger over which patients are the best candidates for this drug and how it might perform in real-world practice given difelikefalin’s limited track record, Dr. Palevsky said in an interview.
In addition, the labeling specifies the indication is for patients with moderate to severe pruritus, but itching severity is not routinely quantified in these patients in current practice, added Dr. Palevsky, who is also president of the National Kidney Foundation.
Dr. Weiner noted that another unknown is the appropriate duration of treatment in real-world use.
What will it cost, and will it be covered?
The drug’s price and insurance coverage will likely be a major factor in uptake of the new drug, agreed both Dr. Weiner and Dr. Palevsky, especially the coverage decision for Medicare patients by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. A corollary is whether or not coverage for difelikefalin, which patients receive as an intravenous infusion during each of their usual three-times-a-week dialysis sessions, will lie outside of the bundled dialysis reimbursement payment. If is no mechanism exists to pay for difelikefalin separately beyond the current bundled dialysis rate, “I suspect it will not get used very much unless it is very inexpensive,” predicted Dr. Weiner.
Another issue is where difelikefalin fits within the lineup of standard treatment options. “A lot of people receiving hemodialysis suffer from pruritus and have not been successfully treated. For these individuals difelikefalin could be a game changer,” Dr. Weiner said.
Other nephrologists have a more positive take on the existing treatment options.
“Start systemic therapy for patients with itch that is significantly affecting quality of life; stepping up from topical therapy just delays effective treatment,” advised Hugh C. Rayner, MD, a nephrologist affiliated with Birmingham (England) Heartland’s Hospital who was lead author on a review of pruritus treatments for patients with CKD on hemodialysis.
“Standard systemic therapy is gabapentin or pregabalin,” an approach “supported by robust evidence confirmed in a Cochrane review,” he said in an interview. The impact of difelikefalin “will be limited as its effectiveness in reducing itch is modest at best and far inferior to gabapentin and pregabalin,” Dr. Rayner added. Difelikefalin’s “main downsides will be its cost, compared with gabapentin, and its gastrointestinal side effects.”
Adverse-event profiles
In KALM-1, the most frequent adverse effects from difelikefalin treatment was diarrhea, in 10% of patients, compared with a 4% rate among patients who received placebo. Vomiting occurred at a 5% incidence on difelikefalin and in 3% of patients on placebo. All serious adverse events occurred in 26% of patients on difelikefalin and in 22% of those who received placebo. Discontinuations because of an adverse event occurred in 8% of patients on difelikefalin and in 5% of the placebo patients.
An editorial that accompanied the published KALM-1 report in 2020 said “the findings are compelling, although diarrhea, dizziness, and vomiting were frequent side effects.”
Both Dr. Weiner and Dr. Palevsky were more reserved than Dr. Rayner in their appraisal of gabapentin and pregabalin, although Dr. Palevsky admitted that he has prescribed one or the other of these two drugs to “lots of patients,” especially gabapentin. “But they are not completely benign drugs,” he cautioned, a concern echoed by Dr. Weiner.
“Antihistamines, gabapentin, and pregabalin have a high side-effect burden in patients on hemodialysis and limited efficacy, and are poor options for chronic pruritus management,” explained Dr. Weiner. “I would favor difelikefalin to chronic prescription of these other agents” because difelikefalin “appears effective and has a very low side effect burden. Very few effective treatments for pruritus do not have side effects.”
Difelikefalin is a peripherally restricted, selective kappa opioid receptor agonist that exerts antipruritic effects by activating kappa opioid receptors on peripheral neurons and immune cells. The drug’s hydrophilic, small-peptide structure restricts passive diffusion across membranes, which limits the drug’s access to kappa opioid receptors in the central nervous system and hence reduces potential adverse effects.
The FDA made this approval decision without consulting an advisory committee. The companies that will market difelikefalin (Korsuva), Cara Therapeutics and Vifor Pharma, announced that their U.S. promotional launch of the drug starts early in 2022.
The KALM-1 and KALM-2 studies were sponsored by Cara Therapeutics and Vifor Pharma, the two companies that have been jointly developing difelikefalin. Dr. Pavelsky and Dr. Rayner had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Weiner was previously an adviser to Cara and Vifor and participated as an investigator in a difelikefalin clinical study, but more recently has had no relationships with the companies.
Eyes on ESC ‘21: Hope for EMPEROR-Preserved, guidelines remade
There will be so much more to the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology, which begins Aug. 27 with an all-virtual format, than detailed primary results of EMPEROR-Preserved, a trial that could mark a turning point for heart failure (HF) medical therapy.
Also among the featured Hot Line and Late-Breaking Science sessions are – along with many other studies – explorations of arrhythmia management (ablation or guided by loop recorder); secondary prevention, including by vaccination; oral anticoagulation, notably after transcatheter valve procedures; and colchicine or thrombosis prophylaxis in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
There will even be a head-to-head comparison of two long-familiar left atrial appendage (LAA) occluders, and a population-based, randomized trial of sodium restriction through wide-scale use of a potassium-based salt substitute.
The congress will also introduce four guideline documents at sessions throughout the Congress, one on each day. They cover new and modified recommendations for heart failure; pacing, including cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT); cardiovascular (CV) disease prevention; and, with cosponsorship from the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, valvular heart disease.
The virtues of virtual
That next year’s Congress is slated for Aug. 27-30 in Barcelona should be welcome news for anyone whose “what if” curiosity about all-virtual conferences has already been satisfied. But with experience comes wisdom, as the medical societies have learned that online scientific meetings have some winning qualities that may be worth keeping, as least for a while.
“I think there is no doubt that the digital format will continue, for several reasons. One is that this pandemic is not over,” ESC Congress program committee chair Stephan Windecker, MD, Bern (Switzerland) University Hospital, , told this news organization. “As long as it is not over, the digital format is here to stay.”
But it also appears that people who haven’t been able to attend the congress in person are keen to log in and engage online, Dr. Windecker said. The 2020 all-virtual conference drew a much younger pool of registrants, on average, than did the live conferences before the pandemic.
“I think that’s an indication of people that may be in training, in early stages of their career, or they don’t have the support from departments or from their practice, or other financial means.” But they are able to participate via computer, tablet, or smartphone, he said.
“Another advantage is that the recorded content can be replayed at the convenience of whoever wants to consume it at a later point in time,” he added. “Those are just some examples why the digital format is likely to stay,” on its own or in a new age of hybrid meetings.
New and updated guidelines
Leading off the guideline series is the document on diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic HF, which leveraged the past few busy years of HF clinical trials to arrive at a number of new recommendations and strengthened level-of-evidence ratings. It covers both drug and device therapy of HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and acute decompensated HF, and tweaks and further enshrines the concept of HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF).
Several updated recommendations for both long-used and novel medications, notably the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, will be included because of the recently appreciated evidence-based impact in HFrEF, Dr. Windecker noted.
“I think it will be particularly interesting to look for the SGLT2 inhibitors as not a completely new class of drugs, but certainly one where there has been a lot of new evidence, to look at how those drugs will be integrated in the overall care pathway.”
A top-line preview of the new HF guideline limited to drug therapy, presented at July’s Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA), provided a simple answer to a common question in the new, bountiful age of HFrEF medications: Which meds, initiated in what order?
As it happens, the new recommendation for first-line HFrEF drug therapy is not a silver bullet, but a shotgun – prompt initiation of at least four meds, one from each of four drug classes: renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), and SGLT2 inhibitors. Each class, as described in the document, is to be started as soon as safely feasible, in a sequence deemed appropriate for each individual patient.
Spotlight on EMPEROR-Preserved
The world already knows that the trial, which tested the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly) on top of standard therapy, “met” its primary endpoint in almost 6,000 patients with HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), who included some with HFmrEF by more contemporary definitions.
That means patients in EMPEROR-Preserved assigned to take empagliflozin showed significantly fewer events that made up the study’s primary endpoint, a composite of CV death or HF hospitalization. It appears to be the first clearly significant overall medical therapy benefit for a clinical primary endpoint in a major randomized HFpEF drug trial.
And that, pending fuller presentation of trial results at the Congress on Aug. 27, could be a huge deal for the half of HF patients with left ventricular ejection fractions (LVEF) higher than the HFrEF range.
Those early top-line results weren’t a decisive bombshell for a field now filled with hope for a practice-changing empagliflozin outcome in EMPEROR-Preserved, which isn’t a certainty. They were more like the “boom” of a mortar launching a rocket of fireworks that may explode into a chrysanthemum or green comet or, sometimes, turn out to be no more than a dud. The promise of the early cursory results critically depends on further details.
“Provided there is a compelling benefit, this is what everyone has been waiting for in this condition for decades,” Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, director of cardiometabolic research at Saint Luke’s Mid-America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Mo., said.
“Already knowing that the trial met the primary endpoint is obviously very intriguing and encouraging,” he added. “But there are things we don’t know, such as: What is the magnitude of benefit? And whether that benefit, whatever the magnitude, is driven by reductions in both heart failure hospitalizations and cardiovascular death, or only one of the two.”
For example: “If we see an impressive benefit for reduction of hospitalizations, but not a significant reduction in death, that would still be a huge advance. That’s because, to date, we don’t have any drug for HFpEF that has convincingly demonstrated a compelling reduction in heart failure hospitalization or improvement in symptoms, function, or quality of life,” observed Dr. Kosiborod, who wasn’t part of EMPEROR-Preserved.
There have been “suggestions” from HFrEF trials that empagliflozin and dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) “have very comparable effects on at least the endpoint of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure,” he said. “So, my expectation would be that whatever is observed in EMPEROR-Preserved is likely a class effect, as well.”
Following EMPEROR-Preserved on the agenda is EMPEROR-Pooled, a patient-level combined analysis of the EMPEROR series of trials that spans the range of HF, regardless of ejection fraction or diabetes status, primarily exploring the effects of empagliflozin on renal function.
Other offerings, Friday, Aug. 27
Scheduled immediately after EMPEROR-Preserved is a presentation on the SMART-MI trial, which should clarify whether management guided by continuous ambulatory monitoring is effective in patients considered at especially high arrhythmic risk. Entry called for recent myocardial infarction and an LVEF of 36%-50% with evidence of cardiac autonomic dysfunction.
The trial randomly assigned 400 such patients to be or not be implanted with a Reveal LINQ (Medtronic) loop recorder and followed them for up to 18 months, primarily for detection of potentially serious arrhythmic events. Endpoints that involved mortality, hospitalization or other clinical events were secondary.
In a time slot preceding both SMART-MI and EMPEROR-Preserved, the GUIDE-HF trial is following a projected 3,600 patients with HF implanted with a CardioMEMS HF System (Abbott) pulmonary artery (PA) pressure sensor to explore the its value for guiding management.
The trial’s three cohorts, followed for at least 12 months, include randomized sensor-monitored and control groups of patients with New York Heart Association class 2-4 symptoms, as well as a third observational set of patients in NYHA class 3. That’s the indication for which the CardioMEMS monitor gained approval in the United States in 2014 based on the 2011 CHAMPION trial, and which fared just as well in the 2017 CHAMPION Post-Approval Study.
The Friday Hot Lines also include Dal-GenE, which has entered about 6,000 patients with recent MI to test the once-abandoned cholesterol ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor dalcetrapib (DalCor) for any secondary-prevention benefits when used selectively. The trial’s hook: All its patients are confirmed to have the AA genotype of the rs1967309 variant in the ADCY9 gene, which has been associated with a pronounced clinical response to CETP inhibition.
Saturday, Aug. 28
The direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) have largely replaced vitamin K antagonists in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AFib). But whether DOACs are similarly preferable in the growing world population of people who have undergone transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR or TAVI), an issue explored with variable results in the ATLANTIS and GALILEO trials, is far from settled.
The ENVISAGE-TAVI AF trial explored the question for the factor X inhibitor edoxaban (Savaysa, Lixiana, Daiichi-Sankyo) in 1,400 patients with AFib and a transfemoral TAVR in the previous 5 days, who were randomly assigned to the DOAC or standard management along with discretionary antiplatelet therapy. They’ve been followed for up to 3 years for a composite endpoint of clinical events – including death, MI, and stroke – and for major bleeding.
The day will also feature MASTER DAPT, a comparison of two dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) regimens in an estimated 4,300 patients considered to be high-risk for bleeding who had received the sirolimus-eluting Ultimaster (Terumo) coronary stent, which has a bioresorbable polymer coating.
Investigators have randomly assigned patients to receive either very-short-duration DAPT, for about a month after stenting, followed by a P2Y12 inhibitor alone for up to a year after the procedure; or a more conventional regimen of a P2Y12 inhibitor for 6-12 months with aspirin maintained for a total of 12 months.
Later that day, investigators from the FIGARO-DKD trial will present their results based on 7,437 patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD), a much fuller version than the top-line findings announced by sponsor Bayer 3 months ago.
Those top-line results suggested that patients assigned to receive the nonsteroidal nonselective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) finerenone (Kerendia) on top of standard care benefited with a drop in risk for the primary endpoint of CV death or nonfatal CV events.
Finerenone was recently approved in the United States for treating patients with both type 2 diabetes and CKD based on the published FIDELIO-DKD trial, which had seen less CKD progression and fewer CV events in such patients who took the novel MRA.
Although similar in design to FIGARO-DKD, FIDELIO-DKD had entered fewer patients with early-stage diabetic kidney disease (DKD). That led researchers to pool the two trials’ populations to create a cohort that spans the spectrum of DKD severity. An analysis of the pooled cohort, dubbed FIDELITY, is on the schedule after FIGARO-DKD.
After FIDELITY is the prospective APAF-CRT trial that is following a projected 1,830 patients with permanent, symptomatic AFib and a recent hospitalization for AFib or HF and who were not good candidates for standard ablation. They were assigned to receive either atrioventricular junctional ablation followed by CRT, with or without a defibrillation, on top of optimal meds – a so-called “ablate-and-pace” strategy – or an implantable cardioverter defibrillator with rate-control drug therapy.
The new analysis represents the trial’s second phase in which mortality was followed for 4 years as the primary endpoint, in contrast to the previously reported initial phase that followed the first 102 patients for 2 years for the composite primary endpoint of death, worsening HF, and HF hospitalization. The first phase had halted enrollment before reaching its planned target of 280 patients after an interim analysis showed a significant benefit for ablate and pace.
Next up: DECAAF 2, a randomized assessment of whether catheter ablation for AFib guided by delayed gadolinium enhancement on MRI, a proxy for scar tissue, can be more effective than standard AFib ablation by pulmonary vein isolation alone. An estimated 900 patients with persistent AFib who had never before undergone ablation for the arrhythmia were randomly assigned to one strategy or the other and followed for AFib recurrence over 18 months.
Sunday, Aug. 29
The TOMAHAWK trial aimed to clarify the optimal timing of invasive coronary angiography for resuscitated patients with non–ST-segment elevation out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, a broad population in a setting for which there is little randomized-trial guidance. Investigators randomly assigned 558 such patients to undergo immediate invasive angiography or to direct intensive care unit admission for initial standard care with discretionary delayed angiography. Patients were followed for all-cause mortality, with other clinical events and neurologic outcomes as secondary endpoints.
Next on the schedule, the RIPCORD-2 trial randomly assigned 1,100 patients with stable known or suspected coronary artery disease (CAD) to undergo conventional angiography alone or with added direct pressure-wire measurement of fractional flow reserve to guide management decisions. Primary outcomes include health care costs and patient-reported quality of life at 1 year.
Slated for later that day, the Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial-2 (ACST-2) has entered an estimated 3600 patients with a substantial carotid artery narrowing not associated with symptoms but for which either carotid endarterectomy (CEA) or carotid artery stenting (CAS) was considered anatomically feasible. There also must have been “substantial uncertainty” regarding the optimal procedure choice.
The trial, conducted in 40 countries primarily in Europe and North America and launched in 2008, randomly assigned the patients to undergo either CEA or CAS, in both cases with appropriate medical therapy, and followed them for periprocedural events and up to 10 years for strokes and stroke-related events.
The LOOP study, which is to directly follow ACST-2, has explored whether screening for AFib using the Medtronic Reveal LINQ monitor in older patients with non-AFib stroke risk factors – with oral anticoagulation prescribed for those who test positive – can lower their risk for stroke or systemic embolism. It randomly assigned 6,000 such patients to care guided by the loop recorder or to standard care.
On a somewhat larger scale, the Salt Substitute and Stroke Study (SSaSS) randomly assigned a total of 20,996 people in about 600 villages across northern China and Tibet to sodium-restriction intervention and control groups by village. All participants had a history of stroke or were aged at least 60 years with uncontrolled hypertension.
As described by the trial’s online portal, participants in villages assigned to the intervention group were given a supply of a low-sodium, potassium-supplementing salt substitute to replace their own salt supplies, along with education on the health benefits of sodium restriction. Participants in control villages continued their normal diets and, at the trial’s beginning, received “advice to reduce their salt intake.” All were required to own a telephone.
Clinical events, including strokes and hospitalizations throughout a 5-year follow-up, were tracked by phone calls made to all participants every 6 months and were documented at follow-up home visits.
Sunday is also to feature a Late-Breaking Trials session with a focus on COVID-19, which leads off with COLCOVID, a test of colchicine in patients hospitalized for suspected SARS-CoV-2 infection and in acute respiratory distress.
The 1,279 participants in Argentina were randomly assigned to receive or not receive the potent anti-inflammatory agent on top of antivirals and other standard management and followed for death or new need for mechanical ventilation. A successful outcome would contrast with the RECOVERY trial, which terminated a colchicine group of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 because of a lack of efficacy earlier this year.
COLCOVID is to be followed by the MICHELLE trial of rivaroxaban (Xarelto, Bayer/Janssen) prophylaxis, compared with no preventive oral anticoagulant, in 320 patients who, when hospitalized with COVID-19, had been on parenteral anticoagulants because of an elevated risk for venous thromboembolism. The trial, conducted in Brazil, called for postdischarge rivaroxaban at a once-daily dosage of 10 mg for about 1 month.
The session also includes a presentation called “Insights into the Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Comprehensive Analysis from the GUIDE-HF Trial,” the primary outcomes of which will be reported on the first day of the Congress.
Following is a presentation on the PREPARE-IT study of icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), given at high dosages intended to be anti-inflammatory, compared with placebo, in an estimated 4,000 adults. The trial has two groups: A prevention group of adults living and circulating in the community; and a treatment group of patients aged at least 40 years with confirmed symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection for whom the need for hospitalization isn’t clear.
Monday, Aug. 30
The final day of the Congress features a trial called Influenza Vaccination after Myocardial Infarction (IAMI), which has tested the secondary preventive effect of influenza vaccination by randomly assigning 2,571 patients to receive a standard vaccine or a saline placebo injection on one occasion.
Entry to the international trial called for a diagnosis of MI with or without ST-segment elevation, or stable CAD and age at least 75 years with other risk factors. The patients were followed for death, MI, stent thrombosis, and a slew of secondary endpoints over 12 months.
Monday offerings continue later in a time block leading off with the STEP trial, which has randomly assigned an estimated 8,000 patients at 40 centers in China who are 60 to 80 years of age with a systolic blood pressure of 140 to <190 mm Hg to be on standard guideline-based therapy or an intensive drug-management strategy.
The systolic BP goals are 130 to <150 mm Hg for standard care and 110 to <130 mm Hg for the intensive regimen. The composite primary endpoint includes death and clinical events related to acute coronary syndromes, HF, revascularization, and stroke.
Following on heels of STEP, the Amulet IDE trial – the first major randomized comparison of two transcatheter LAA closure devices – entered 1,878 patients with nonvalvular AFib who were considered high-risk for bleeding and stroke or systemic embolism.
They were randomly assigned in the noninferiority trial to receive either the AMPLATZER Amulet (Abbott Medical Devices) or the WATCHMAN (Boston Scientific) closure devices and were followed for safety and efficacy for up to 5 years.
Both LAA closure devices, intended to make patients with AFib less reliant on oral anticoagulation, are now available on both sides of the Atlantic – as well as many other countries – after the Amulet’s United States market approval on Aug. 16, based largely on the Amulet IDE trial.
Rounding out the final Hot Line set is one of the latest efforts to show the efficacy and safety of a very short DAPT period after coronary stenting in patients with acute coronary syndromes, the STOPDAPT-2 ACS trial.
The study assigned 3,008 patients in Japan to receive aspirin and clopidogrel for either 1 month or 1 year after implantation with an everolimus-eluting cobalt-chromium stent and followed them for up to 5 years for a composite of MI, CV death, stent thrombosis, stroke, and bleeding.
The trial follows the published STOPDAPT-2 trial that showed superiority for the 1-month DAPT regimen in a predominantly stable-CAD population treated with the same kind of stent.
Program structure and format
A total of 15 online channels are to be available in the morning, European time, their schedules running in parallel. Presentations often are prerecorded, but also include live sessions at 8:00 a.m. Central time and 12 p.m. CET (2:00 a.m. and 6:00 a.m. Eastern time) to liven up the channel offerings, Dr. Windecker observed, and to make them more immediate and potentially interactive.
Many of the parallel channels are devoted throughout the Congress to particular silos of cardiology; for example, arrhythmias and device therapy is on channel 3; CAD and acute care is on 5; HF is on 6; and preventive cardiology is on 9.
Other channels swing across different topics from day to day, such as channel 1, which covers COVID-19 topics on the first and third day of the meeting, “advances in science” on day 2, and “digital health, public health, health economics” on day 4.
The focus each day, starting at 2:00 p.m. CET (8:00 a.m. ET) and continuing into the evening in Europe, shifts over to the Prime Time live program, which features the Hot Line and guideline presentations and many of the live abstract presentations.
Dr. Kosiborod, not a researcher with the EMPEROR trials, is chair of the Dapagliflozin in Preserved Ejection Fraction Heart Failure ( PRESERVED-HF ) trial, which is scheduled for presentation at the September 2021 Heart Failure Society of American meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There will be so much more to the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology, which begins Aug. 27 with an all-virtual format, than detailed primary results of EMPEROR-Preserved, a trial that could mark a turning point for heart failure (HF) medical therapy.
Also among the featured Hot Line and Late-Breaking Science sessions are – along with many other studies – explorations of arrhythmia management (ablation or guided by loop recorder); secondary prevention, including by vaccination; oral anticoagulation, notably after transcatheter valve procedures; and colchicine or thrombosis prophylaxis in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
There will even be a head-to-head comparison of two long-familiar left atrial appendage (LAA) occluders, and a population-based, randomized trial of sodium restriction through wide-scale use of a potassium-based salt substitute.
The congress will also introduce four guideline documents at sessions throughout the Congress, one on each day. They cover new and modified recommendations for heart failure; pacing, including cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT); cardiovascular (CV) disease prevention; and, with cosponsorship from the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, valvular heart disease.
The virtues of virtual
That next year’s Congress is slated for Aug. 27-30 in Barcelona should be welcome news for anyone whose “what if” curiosity about all-virtual conferences has already been satisfied. But with experience comes wisdom, as the medical societies have learned that online scientific meetings have some winning qualities that may be worth keeping, as least for a while.
“I think there is no doubt that the digital format will continue, for several reasons. One is that this pandemic is not over,” ESC Congress program committee chair Stephan Windecker, MD, Bern (Switzerland) University Hospital, , told this news organization. “As long as it is not over, the digital format is here to stay.”
But it also appears that people who haven’t been able to attend the congress in person are keen to log in and engage online, Dr. Windecker said. The 2020 all-virtual conference drew a much younger pool of registrants, on average, than did the live conferences before the pandemic.
“I think that’s an indication of people that may be in training, in early stages of their career, or they don’t have the support from departments or from their practice, or other financial means.” But they are able to participate via computer, tablet, or smartphone, he said.
“Another advantage is that the recorded content can be replayed at the convenience of whoever wants to consume it at a later point in time,” he added. “Those are just some examples why the digital format is likely to stay,” on its own or in a new age of hybrid meetings.
New and updated guidelines
Leading off the guideline series is the document on diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic HF, which leveraged the past few busy years of HF clinical trials to arrive at a number of new recommendations and strengthened level-of-evidence ratings. It covers both drug and device therapy of HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and acute decompensated HF, and tweaks and further enshrines the concept of HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF).
Several updated recommendations for both long-used and novel medications, notably the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, will be included because of the recently appreciated evidence-based impact in HFrEF, Dr. Windecker noted.
“I think it will be particularly interesting to look for the SGLT2 inhibitors as not a completely new class of drugs, but certainly one where there has been a lot of new evidence, to look at how those drugs will be integrated in the overall care pathway.”
A top-line preview of the new HF guideline limited to drug therapy, presented at July’s Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA), provided a simple answer to a common question in the new, bountiful age of HFrEF medications: Which meds, initiated in what order?
As it happens, the new recommendation for first-line HFrEF drug therapy is not a silver bullet, but a shotgun – prompt initiation of at least four meds, one from each of four drug classes: renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), and SGLT2 inhibitors. Each class, as described in the document, is to be started as soon as safely feasible, in a sequence deemed appropriate for each individual patient.
Spotlight on EMPEROR-Preserved
The world already knows that the trial, which tested the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly) on top of standard therapy, “met” its primary endpoint in almost 6,000 patients with HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), who included some with HFmrEF by more contemporary definitions.
That means patients in EMPEROR-Preserved assigned to take empagliflozin showed significantly fewer events that made up the study’s primary endpoint, a composite of CV death or HF hospitalization. It appears to be the first clearly significant overall medical therapy benefit for a clinical primary endpoint in a major randomized HFpEF drug trial.
And that, pending fuller presentation of trial results at the Congress on Aug. 27, could be a huge deal for the half of HF patients with left ventricular ejection fractions (LVEF) higher than the HFrEF range.
Those early top-line results weren’t a decisive bombshell for a field now filled with hope for a practice-changing empagliflozin outcome in EMPEROR-Preserved, which isn’t a certainty. They were more like the “boom” of a mortar launching a rocket of fireworks that may explode into a chrysanthemum or green comet or, sometimes, turn out to be no more than a dud. The promise of the early cursory results critically depends on further details.
“Provided there is a compelling benefit, this is what everyone has been waiting for in this condition for decades,” Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, director of cardiometabolic research at Saint Luke’s Mid-America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Mo., said.
“Already knowing that the trial met the primary endpoint is obviously very intriguing and encouraging,” he added. “But there are things we don’t know, such as: What is the magnitude of benefit? And whether that benefit, whatever the magnitude, is driven by reductions in both heart failure hospitalizations and cardiovascular death, or only one of the two.”
For example: “If we see an impressive benefit for reduction of hospitalizations, but not a significant reduction in death, that would still be a huge advance. That’s because, to date, we don’t have any drug for HFpEF that has convincingly demonstrated a compelling reduction in heart failure hospitalization or improvement in symptoms, function, or quality of life,” observed Dr. Kosiborod, who wasn’t part of EMPEROR-Preserved.
There have been “suggestions” from HFrEF trials that empagliflozin and dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) “have very comparable effects on at least the endpoint of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure,” he said. “So, my expectation would be that whatever is observed in EMPEROR-Preserved is likely a class effect, as well.”
Following EMPEROR-Preserved on the agenda is EMPEROR-Pooled, a patient-level combined analysis of the EMPEROR series of trials that spans the range of HF, regardless of ejection fraction or diabetes status, primarily exploring the effects of empagliflozin on renal function.
Other offerings, Friday, Aug. 27
Scheduled immediately after EMPEROR-Preserved is a presentation on the SMART-MI trial, which should clarify whether management guided by continuous ambulatory monitoring is effective in patients considered at especially high arrhythmic risk. Entry called for recent myocardial infarction and an LVEF of 36%-50% with evidence of cardiac autonomic dysfunction.
The trial randomly assigned 400 such patients to be or not be implanted with a Reveal LINQ (Medtronic) loop recorder and followed them for up to 18 months, primarily for detection of potentially serious arrhythmic events. Endpoints that involved mortality, hospitalization or other clinical events were secondary.
In a time slot preceding both SMART-MI and EMPEROR-Preserved, the GUIDE-HF trial is following a projected 3,600 patients with HF implanted with a CardioMEMS HF System (Abbott) pulmonary artery (PA) pressure sensor to explore the its value for guiding management.
The trial’s three cohorts, followed for at least 12 months, include randomized sensor-monitored and control groups of patients with New York Heart Association class 2-4 symptoms, as well as a third observational set of patients in NYHA class 3. That’s the indication for which the CardioMEMS monitor gained approval in the United States in 2014 based on the 2011 CHAMPION trial, and which fared just as well in the 2017 CHAMPION Post-Approval Study.
The Friday Hot Lines also include Dal-GenE, which has entered about 6,000 patients with recent MI to test the once-abandoned cholesterol ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor dalcetrapib (DalCor) for any secondary-prevention benefits when used selectively. The trial’s hook: All its patients are confirmed to have the AA genotype of the rs1967309 variant in the ADCY9 gene, which has been associated with a pronounced clinical response to CETP inhibition.
Saturday, Aug. 28
The direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) have largely replaced vitamin K antagonists in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AFib). But whether DOACs are similarly preferable in the growing world population of people who have undergone transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR or TAVI), an issue explored with variable results in the ATLANTIS and GALILEO trials, is far from settled.
The ENVISAGE-TAVI AF trial explored the question for the factor X inhibitor edoxaban (Savaysa, Lixiana, Daiichi-Sankyo) in 1,400 patients with AFib and a transfemoral TAVR in the previous 5 days, who were randomly assigned to the DOAC or standard management along with discretionary antiplatelet therapy. They’ve been followed for up to 3 years for a composite endpoint of clinical events – including death, MI, and stroke – and for major bleeding.
The day will also feature MASTER DAPT, a comparison of two dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) regimens in an estimated 4,300 patients considered to be high-risk for bleeding who had received the sirolimus-eluting Ultimaster (Terumo) coronary stent, which has a bioresorbable polymer coating.
Investigators have randomly assigned patients to receive either very-short-duration DAPT, for about a month after stenting, followed by a P2Y12 inhibitor alone for up to a year after the procedure; or a more conventional regimen of a P2Y12 inhibitor for 6-12 months with aspirin maintained for a total of 12 months.
Later that day, investigators from the FIGARO-DKD trial will present their results based on 7,437 patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD), a much fuller version than the top-line findings announced by sponsor Bayer 3 months ago.
Those top-line results suggested that patients assigned to receive the nonsteroidal nonselective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) finerenone (Kerendia) on top of standard care benefited with a drop in risk for the primary endpoint of CV death or nonfatal CV events.
Finerenone was recently approved in the United States for treating patients with both type 2 diabetes and CKD based on the published FIDELIO-DKD trial, which had seen less CKD progression and fewer CV events in such patients who took the novel MRA.
Although similar in design to FIGARO-DKD, FIDELIO-DKD had entered fewer patients with early-stage diabetic kidney disease (DKD). That led researchers to pool the two trials’ populations to create a cohort that spans the spectrum of DKD severity. An analysis of the pooled cohort, dubbed FIDELITY, is on the schedule after FIGARO-DKD.
After FIDELITY is the prospective APAF-CRT trial that is following a projected 1,830 patients with permanent, symptomatic AFib and a recent hospitalization for AFib or HF and who were not good candidates for standard ablation. They were assigned to receive either atrioventricular junctional ablation followed by CRT, with or without a defibrillation, on top of optimal meds – a so-called “ablate-and-pace” strategy – or an implantable cardioverter defibrillator with rate-control drug therapy.
The new analysis represents the trial’s second phase in which mortality was followed for 4 years as the primary endpoint, in contrast to the previously reported initial phase that followed the first 102 patients for 2 years for the composite primary endpoint of death, worsening HF, and HF hospitalization. The first phase had halted enrollment before reaching its planned target of 280 patients after an interim analysis showed a significant benefit for ablate and pace.
Next up: DECAAF 2, a randomized assessment of whether catheter ablation for AFib guided by delayed gadolinium enhancement on MRI, a proxy for scar tissue, can be more effective than standard AFib ablation by pulmonary vein isolation alone. An estimated 900 patients with persistent AFib who had never before undergone ablation for the arrhythmia were randomly assigned to one strategy or the other and followed for AFib recurrence over 18 months.
Sunday, Aug. 29
The TOMAHAWK trial aimed to clarify the optimal timing of invasive coronary angiography for resuscitated patients with non–ST-segment elevation out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, a broad population in a setting for which there is little randomized-trial guidance. Investigators randomly assigned 558 such patients to undergo immediate invasive angiography or to direct intensive care unit admission for initial standard care with discretionary delayed angiography. Patients were followed for all-cause mortality, with other clinical events and neurologic outcomes as secondary endpoints.
Next on the schedule, the RIPCORD-2 trial randomly assigned 1,100 patients with stable known or suspected coronary artery disease (CAD) to undergo conventional angiography alone or with added direct pressure-wire measurement of fractional flow reserve to guide management decisions. Primary outcomes include health care costs and patient-reported quality of life at 1 year.
Slated for later that day, the Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial-2 (ACST-2) has entered an estimated 3600 patients with a substantial carotid artery narrowing not associated with symptoms but for which either carotid endarterectomy (CEA) or carotid artery stenting (CAS) was considered anatomically feasible. There also must have been “substantial uncertainty” regarding the optimal procedure choice.
The trial, conducted in 40 countries primarily in Europe and North America and launched in 2008, randomly assigned the patients to undergo either CEA or CAS, in both cases with appropriate medical therapy, and followed them for periprocedural events and up to 10 years for strokes and stroke-related events.
The LOOP study, which is to directly follow ACST-2, has explored whether screening for AFib using the Medtronic Reveal LINQ monitor in older patients with non-AFib stroke risk factors – with oral anticoagulation prescribed for those who test positive – can lower their risk for stroke or systemic embolism. It randomly assigned 6,000 such patients to care guided by the loop recorder or to standard care.
On a somewhat larger scale, the Salt Substitute and Stroke Study (SSaSS) randomly assigned a total of 20,996 people in about 600 villages across northern China and Tibet to sodium-restriction intervention and control groups by village. All participants had a history of stroke or were aged at least 60 years with uncontrolled hypertension.
As described by the trial’s online portal, participants in villages assigned to the intervention group were given a supply of a low-sodium, potassium-supplementing salt substitute to replace their own salt supplies, along with education on the health benefits of sodium restriction. Participants in control villages continued their normal diets and, at the trial’s beginning, received “advice to reduce their salt intake.” All were required to own a telephone.
Clinical events, including strokes and hospitalizations throughout a 5-year follow-up, were tracked by phone calls made to all participants every 6 months and were documented at follow-up home visits.
Sunday is also to feature a Late-Breaking Trials session with a focus on COVID-19, which leads off with COLCOVID, a test of colchicine in patients hospitalized for suspected SARS-CoV-2 infection and in acute respiratory distress.
The 1,279 participants in Argentina were randomly assigned to receive or not receive the potent anti-inflammatory agent on top of antivirals and other standard management and followed for death or new need for mechanical ventilation. A successful outcome would contrast with the RECOVERY trial, which terminated a colchicine group of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 because of a lack of efficacy earlier this year.
COLCOVID is to be followed by the MICHELLE trial of rivaroxaban (Xarelto, Bayer/Janssen) prophylaxis, compared with no preventive oral anticoagulant, in 320 patients who, when hospitalized with COVID-19, had been on parenteral anticoagulants because of an elevated risk for venous thromboembolism. The trial, conducted in Brazil, called for postdischarge rivaroxaban at a once-daily dosage of 10 mg for about 1 month.
The session also includes a presentation called “Insights into the Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Comprehensive Analysis from the GUIDE-HF Trial,” the primary outcomes of which will be reported on the first day of the Congress.
Following is a presentation on the PREPARE-IT study of icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), given at high dosages intended to be anti-inflammatory, compared with placebo, in an estimated 4,000 adults. The trial has two groups: A prevention group of adults living and circulating in the community; and a treatment group of patients aged at least 40 years with confirmed symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection for whom the need for hospitalization isn’t clear.
Monday, Aug. 30
The final day of the Congress features a trial called Influenza Vaccination after Myocardial Infarction (IAMI), which has tested the secondary preventive effect of influenza vaccination by randomly assigning 2,571 patients to receive a standard vaccine or a saline placebo injection on one occasion.
Entry to the international trial called for a diagnosis of MI with or without ST-segment elevation, or stable CAD and age at least 75 years with other risk factors. The patients were followed for death, MI, stent thrombosis, and a slew of secondary endpoints over 12 months.
Monday offerings continue later in a time block leading off with the STEP trial, which has randomly assigned an estimated 8,000 patients at 40 centers in China who are 60 to 80 years of age with a systolic blood pressure of 140 to <190 mm Hg to be on standard guideline-based therapy or an intensive drug-management strategy.
The systolic BP goals are 130 to <150 mm Hg for standard care and 110 to <130 mm Hg for the intensive regimen. The composite primary endpoint includes death and clinical events related to acute coronary syndromes, HF, revascularization, and stroke.
Following on heels of STEP, the Amulet IDE trial – the first major randomized comparison of two transcatheter LAA closure devices – entered 1,878 patients with nonvalvular AFib who were considered high-risk for bleeding and stroke or systemic embolism.
They were randomly assigned in the noninferiority trial to receive either the AMPLATZER Amulet (Abbott Medical Devices) or the WATCHMAN (Boston Scientific) closure devices and were followed for safety and efficacy for up to 5 years.
Both LAA closure devices, intended to make patients with AFib less reliant on oral anticoagulation, are now available on both sides of the Atlantic – as well as many other countries – after the Amulet’s United States market approval on Aug. 16, based largely on the Amulet IDE trial.
Rounding out the final Hot Line set is one of the latest efforts to show the efficacy and safety of a very short DAPT period after coronary stenting in patients with acute coronary syndromes, the STOPDAPT-2 ACS trial.
The study assigned 3,008 patients in Japan to receive aspirin and clopidogrel for either 1 month or 1 year after implantation with an everolimus-eluting cobalt-chromium stent and followed them for up to 5 years for a composite of MI, CV death, stent thrombosis, stroke, and bleeding.
The trial follows the published STOPDAPT-2 trial that showed superiority for the 1-month DAPT regimen in a predominantly stable-CAD population treated with the same kind of stent.
Program structure and format
A total of 15 online channels are to be available in the morning, European time, their schedules running in parallel. Presentations often are prerecorded, but also include live sessions at 8:00 a.m. Central time and 12 p.m. CET (2:00 a.m. and 6:00 a.m. Eastern time) to liven up the channel offerings, Dr. Windecker observed, and to make them more immediate and potentially interactive.
Many of the parallel channels are devoted throughout the Congress to particular silos of cardiology; for example, arrhythmias and device therapy is on channel 3; CAD and acute care is on 5; HF is on 6; and preventive cardiology is on 9.
Other channels swing across different topics from day to day, such as channel 1, which covers COVID-19 topics on the first and third day of the meeting, “advances in science” on day 2, and “digital health, public health, health economics” on day 4.
The focus each day, starting at 2:00 p.m. CET (8:00 a.m. ET) and continuing into the evening in Europe, shifts over to the Prime Time live program, which features the Hot Line and guideline presentations and many of the live abstract presentations.
Dr. Kosiborod, not a researcher with the EMPEROR trials, is chair of the Dapagliflozin in Preserved Ejection Fraction Heart Failure ( PRESERVED-HF ) trial, which is scheduled for presentation at the September 2021 Heart Failure Society of American meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There will be so much more to the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology, which begins Aug. 27 with an all-virtual format, than detailed primary results of EMPEROR-Preserved, a trial that could mark a turning point for heart failure (HF) medical therapy.
Also among the featured Hot Line and Late-Breaking Science sessions are – along with many other studies – explorations of arrhythmia management (ablation or guided by loop recorder); secondary prevention, including by vaccination; oral anticoagulation, notably after transcatheter valve procedures; and colchicine or thrombosis prophylaxis in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
There will even be a head-to-head comparison of two long-familiar left atrial appendage (LAA) occluders, and a population-based, randomized trial of sodium restriction through wide-scale use of a potassium-based salt substitute.
The congress will also introduce four guideline documents at sessions throughout the Congress, one on each day. They cover new and modified recommendations for heart failure; pacing, including cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT); cardiovascular (CV) disease prevention; and, with cosponsorship from the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, valvular heart disease.
The virtues of virtual
That next year’s Congress is slated for Aug. 27-30 in Barcelona should be welcome news for anyone whose “what if” curiosity about all-virtual conferences has already been satisfied. But with experience comes wisdom, as the medical societies have learned that online scientific meetings have some winning qualities that may be worth keeping, as least for a while.
“I think there is no doubt that the digital format will continue, for several reasons. One is that this pandemic is not over,” ESC Congress program committee chair Stephan Windecker, MD, Bern (Switzerland) University Hospital, , told this news organization. “As long as it is not over, the digital format is here to stay.”
But it also appears that people who haven’t been able to attend the congress in person are keen to log in and engage online, Dr. Windecker said. The 2020 all-virtual conference drew a much younger pool of registrants, on average, than did the live conferences before the pandemic.
“I think that’s an indication of people that may be in training, in early stages of their career, or they don’t have the support from departments or from their practice, or other financial means.” But they are able to participate via computer, tablet, or smartphone, he said.
“Another advantage is that the recorded content can be replayed at the convenience of whoever wants to consume it at a later point in time,” he added. “Those are just some examples why the digital format is likely to stay,” on its own or in a new age of hybrid meetings.
New and updated guidelines
Leading off the guideline series is the document on diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic HF, which leveraged the past few busy years of HF clinical trials to arrive at a number of new recommendations and strengthened level-of-evidence ratings. It covers both drug and device therapy of HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and acute decompensated HF, and tweaks and further enshrines the concept of HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF).
Several updated recommendations for both long-used and novel medications, notably the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, will be included because of the recently appreciated evidence-based impact in HFrEF, Dr. Windecker noted.
“I think it will be particularly interesting to look for the SGLT2 inhibitors as not a completely new class of drugs, but certainly one where there has been a lot of new evidence, to look at how those drugs will be integrated in the overall care pathway.”
A top-line preview of the new HF guideline limited to drug therapy, presented at July’s Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA), provided a simple answer to a common question in the new, bountiful age of HFrEF medications: Which meds, initiated in what order?
As it happens, the new recommendation for first-line HFrEF drug therapy is not a silver bullet, but a shotgun – prompt initiation of at least four meds, one from each of four drug classes: renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), and SGLT2 inhibitors. Each class, as described in the document, is to be started as soon as safely feasible, in a sequence deemed appropriate for each individual patient.
Spotlight on EMPEROR-Preserved
The world already knows that the trial, which tested the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly) on top of standard therapy, “met” its primary endpoint in almost 6,000 patients with HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), who included some with HFmrEF by more contemporary definitions.
That means patients in EMPEROR-Preserved assigned to take empagliflozin showed significantly fewer events that made up the study’s primary endpoint, a composite of CV death or HF hospitalization. It appears to be the first clearly significant overall medical therapy benefit for a clinical primary endpoint in a major randomized HFpEF drug trial.
And that, pending fuller presentation of trial results at the Congress on Aug. 27, could be a huge deal for the half of HF patients with left ventricular ejection fractions (LVEF) higher than the HFrEF range.
Those early top-line results weren’t a decisive bombshell for a field now filled with hope for a practice-changing empagliflozin outcome in EMPEROR-Preserved, which isn’t a certainty. They were more like the “boom” of a mortar launching a rocket of fireworks that may explode into a chrysanthemum or green comet or, sometimes, turn out to be no more than a dud. The promise of the early cursory results critically depends on further details.
“Provided there is a compelling benefit, this is what everyone has been waiting for in this condition for decades,” Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, director of cardiometabolic research at Saint Luke’s Mid-America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Mo., said.
“Already knowing that the trial met the primary endpoint is obviously very intriguing and encouraging,” he added. “But there are things we don’t know, such as: What is the magnitude of benefit? And whether that benefit, whatever the magnitude, is driven by reductions in both heart failure hospitalizations and cardiovascular death, or only one of the two.”
For example: “If we see an impressive benefit for reduction of hospitalizations, but not a significant reduction in death, that would still be a huge advance. That’s because, to date, we don’t have any drug for HFpEF that has convincingly demonstrated a compelling reduction in heart failure hospitalization or improvement in symptoms, function, or quality of life,” observed Dr. Kosiborod, who wasn’t part of EMPEROR-Preserved.
There have been “suggestions” from HFrEF trials that empagliflozin and dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) “have very comparable effects on at least the endpoint of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure,” he said. “So, my expectation would be that whatever is observed in EMPEROR-Preserved is likely a class effect, as well.”
Following EMPEROR-Preserved on the agenda is EMPEROR-Pooled, a patient-level combined analysis of the EMPEROR series of trials that spans the range of HF, regardless of ejection fraction or diabetes status, primarily exploring the effects of empagliflozin on renal function.
Other offerings, Friday, Aug. 27
Scheduled immediately after EMPEROR-Preserved is a presentation on the SMART-MI trial, which should clarify whether management guided by continuous ambulatory monitoring is effective in patients considered at especially high arrhythmic risk. Entry called for recent myocardial infarction and an LVEF of 36%-50% with evidence of cardiac autonomic dysfunction.
The trial randomly assigned 400 such patients to be or not be implanted with a Reveal LINQ (Medtronic) loop recorder and followed them for up to 18 months, primarily for detection of potentially serious arrhythmic events. Endpoints that involved mortality, hospitalization or other clinical events were secondary.
In a time slot preceding both SMART-MI and EMPEROR-Preserved, the GUIDE-HF trial is following a projected 3,600 patients with HF implanted with a CardioMEMS HF System (Abbott) pulmonary artery (PA) pressure sensor to explore the its value for guiding management.
The trial’s three cohorts, followed for at least 12 months, include randomized sensor-monitored and control groups of patients with New York Heart Association class 2-4 symptoms, as well as a third observational set of patients in NYHA class 3. That’s the indication for which the CardioMEMS monitor gained approval in the United States in 2014 based on the 2011 CHAMPION trial, and which fared just as well in the 2017 CHAMPION Post-Approval Study.
The Friday Hot Lines also include Dal-GenE, which has entered about 6,000 patients with recent MI to test the once-abandoned cholesterol ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor dalcetrapib (DalCor) for any secondary-prevention benefits when used selectively. The trial’s hook: All its patients are confirmed to have the AA genotype of the rs1967309 variant in the ADCY9 gene, which has been associated with a pronounced clinical response to CETP inhibition.
Saturday, Aug. 28
The direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) have largely replaced vitamin K antagonists in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AFib). But whether DOACs are similarly preferable in the growing world population of people who have undergone transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR or TAVI), an issue explored with variable results in the ATLANTIS and GALILEO trials, is far from settled.
The ENVISAGE-TAVI AF trial explored the question for the factor X inhibitor edoxaban (Savaysa, Lixiana, Daiichi-Sankyo) in 1,400 patients with AFib and a transfemoral TAVR in the previous 5 days, who were randomly assigned to the DOAC or standard management along with discretionary antiplatelet therapy. They’ve been followed for up to 3 years for a composite endpoint of clinical events – including death, MI, and stroke – and for major bleeding.
The day will also feature MASTER DAPT, a comparison of two dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) regimens in an estimated 4,300 patients considered to be high-risk for bleeding who had received the sirolimus-eluting Ultimaster (Terumo) coronary stent, which has a bioresorbable polymer coating.
Investigators have randomly assigned patients to receive either very-short-duration DAPT, for about a month after stenting, followed by a P2Y12 inhibitor alone for up to a year after the procedure; or a more conventional regimen of a P2Y12 inhibitor for 6-12 months with aspirin maintained for a total of 12 months.
Later that day, investigators from the FIGARO-DKD trial will present their results based on 7,437 patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD), a much fuller version than the top-line findings announced by sponsor Bayer 3 months ago.
Those top-line results suggested that patients assigned to receive the nonsteroidal nonselective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) finerenone (Kerendia) on top of standard care benefited with a drop in risk for the primary endpoint of CV death or nonfatal CV events.
Finerenone was recently approved in the United States for treating patients with both type 2 diabetes and CKD based on the published FIDELIO-DKD trial, which had seen less CKD progression and fewer CV events in such patients who took the novel MRA.
Although similar in design to FIGARO-DKD, FIDELIO-DKD had entered fewer patients with early-stage diabetic kidney disease (DKD). That led researchers to pool the two trials’ populations to create a cohort that spans the spectrum of DKD severity. An analysis of the pooled cohort, dubbed FIDELITY, is on the schedule after FIGARO-DKD.
After FIDELITY is the prospective APAF-CRT trial that is following a projected 1,830 patients with permanent, symptomatic AFib and a recent hospitalization for AFib or HF and who were not good candidates for standard ablation. They were assigned to receive either atrioventricular junctional ablation followed by CRT, with or without a defibrillation, on top of optimal meds – a so-called “ablate-and-pace” strategy – or an implantable cardioverter defibrillator with rate-control drug therapy.
The new analysis represents the trial’s second phase in which mortality was followed for 4 years as the primary endpoint, in contrast to the previously reported initial phase that followed the first 102 patients for 2 years for the composite primary endpoint of death, worsening HF, and HF hospitalization. The first phase had halted enrollment before reaching its planned target of 280 patients after an interim analysis showed a significant benefit for ablate and pace.
Next up: DECAAF 2, a randomized assessment of whether catheter ablation for AFib guided by delayed gadolinium enhancement on MRI, a proxy for scar tissue, can be more effective than standard AFib ablation by pulmonary vein isolation alone. An estimated 900 patients with persistent AFib who had never before undergone ablation for the arrhythmia were randomly assigned to one strategy or the other and followed for AFib recurrence over 18 months.
Sunday, Aug. 29
The TOMAHAWK trial aimed to clarify the optimal timing of invasive coronary angiography for resuscitated patients with non–ST-segment elevation out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, a broad population in a setting for which there is little randomized-trial guidance. Investigators randomly assigned 558 such patients to undergo immediate invasive angiography or to direct intensive care unit admission for initial standard care with discretionary delayed angiography. Patients were followed for all-cause mortality, with other clinical events and neurologic outcomes as secondary endpoints.
Next on the schedule, the RIPCORD-2 trial randomly assigned 1,100 patients with stable known or suspected coronary artery disease (CAD) to undergo conventional angiography alone or with added direct pressure-wire measurement of fractional flow reserve to guide management decisions. Primary outcomes include health care costs and patient-reported quality of life at 1 year.
Slated for later that day, the Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial-2 (ACST-2) has entered an estimated 3600 patients with a substantial carotid artery narrowing not associated with symptoms but for which either carotid endarterectomy (CEA) or carotid artery stenting (CAS) was considered anatomically feasible. There also must have been “substantial uncertainty” regarding the optimal procedure choice.
The trial, conducted in 40 countries primarily in Europe and North America and launched in 2008, randomly assigned the patients to undergo either CEA or CAS, in both cases with appropriate medical therapy, and followed them for periprocedural events and up to 10 years for strokes and stroke-related events.
The LOOP study, which is to directly follow ACST-2, has explored whether screening for AFib using the Medtronic Reveal LINQ monitor in older patients with non-AFib stroke risk factors – with oral anticoagulation prescribed for those who test positive – can lower their risk for stroke or systemic embolism. It randomly assigned 6,000 such patients to care guided by the loop recorder or to standard care.
On a somewhat larger scale, the Salt Substitute and Stroke Study (SSaSS) randomly assigned a total of 20,996 people in about 600 villages across northern China and Tibet to sodium-restriction intervention and control groups by village. All participants had a history of stroke or were aged at least 60 years with uncontrolled hypertension.
As described by the trial’s online portal, participants in villages assigned to the intervention group were given a supply of a low-sodium, potassium-supplementing salt substitute to replace their own salt supplies, along with education on the health benefits of sodium restriction. Participants in control villages continued their normal diets and, at the trial’s beginning, received “advice to reduce their salt intake.” All were required to own a telephone.
Clinical events, including strokes and hospitalizations throughout a 5-year follow-up, were tracked by phone calls made to all participants every 6 months and were documented at follow-up home visits.
Sunday is also to feature a Late-Breaking Trials session with a focus on COVID-19, which leads off with COLCOVID, a test of colchicine in patients hospitalized for suspected SARS-CoV-2 infection and in acute respiratory distress.
The 1,279 participants in Argentina were randomly assigned to receive or not receive the potent anti-inflammatory agent on top of antivirals and other standard management and followed for death or new need for mechanical ventilation. A successful outcome would contrast with the RECOVERY trial, which terminated a colchicine group of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 because of a lack of efficacy earlier this year.
COLCOVID is to be followed by the MICHELLE trial of rivaroxaban (Xarelto, Bayer/Janssen) prophylaxis, compared with no preventive oral anticoagulant, in 320 patients who, when hospitalized with COVID-19, had been on parenteral anticoagulants because of an elevated risk for venous thromboembolism. The trial, conducted in Brazil, called for postdischarge rivaroxaban at a once-daily dosage of 10 mg for about 1 month.
The session also includes a presentation called “Insights into the Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Comprehensive Analysis from the GUIDE-HF Trial,” the primary outcomes of which will be reported on the first day of the Congress.
Following is a presentation on the PREPARE-IT study of icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), given at high dosages intended to be anti-inflammatory, compared with placebo, in an estimated 4,000 adults. The trial has two groups: A prevention group of adults living and circulating in the community; and a treatment group of patients aged at least 40 years with confirmed symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection for whom the need for hospitalization isn’t clear.
Monday, Aug. 30
The final day of the Congress features a trial called Influenza Vaccination after Myocardial Infarction (IAMI), which has tested the secondary preventive effect of influenza vaccination by randomly assigning 2,571 patients to receive a standard vaccine or a saline placebo injection on one occasion.
Entry to the international trial called for a diagnosis of MI with or without ST-segment elevation, or stable CAD and age at least 75 years with other risk factors. The patients were followed for death, MI, stent thrombosis, and a slew of secondary endpoints over 12 months.
Monday offerings continue later in a time block leading off with the STEP trial, which has randomly assigned an estimated 8,000 patients at 40 centers in China who are 60 to 80 years of age with a systolic blood pressure of 140 to <190 mm Hg to be on standard guideline-based therapy or an intensive drug-management strategy.
The systolic BP goals are 130 to <150 mm Hg for standard care and 110 to <130 mm Hg for the intensive regimen. The composite primary endpoint includes death and clinical events related to acute coronary syndromes, HF, revascularization, and stroke.
Following on heels of STEP, the Amulet IDE trial – the first major randomized comparison of two transcatheter LAA closure devices – entered 1,878 patients with nonvalvular AFib who were considered high-risk for bleeding and stroke or systemic embolism.
They were randomly assigned in the noninferiority trial to receive either the AMPLATZER Amulet (Abbott Medical Devices) or the WATCHMAN (Boston Scientific) closure devices and were followed for safety and efficacy for up to 5 years.
Both LAA closure devices, intended to make patients with AFib less reliant on oral anticoagulation, are now available on both sides of the Atlantic – as well as many other countries – after the Amulet’s United States market approval on Aug. 16, based largely on the Amulet IDE trial.
Rounding out the final Hot Line set is one of the latest efforts to show the efficacy and safety of a very short DAPT period after coronary stenting in patients with acute coronary syndromes, the STOPDAPT-2 ACS trial.
The study assigned 3,008 patients in Japan to receive aspirin and clopidogrel for either 1 month or 1 year after implantation with an everolimus-eluting cobalt-chromium stent and followed them for up to 5 years for a composite of MI, CV death, stent thrombosis, stroke, and bleeding.
The trial follows the published STOPDAPT-2 trial that showed superiority for the 1-month DAPT regimen in a predominantly stable-CAD population treated with the same kind of stent.
Program structure and format
A total of 15 online channels are to be available in the morning, European time, their schedules running in parallel. Presentations often are prerecorded, but also include live sessions at 8:00 a.m. Central time and 12 p.m. CET (2:00 a.m. and 6:00 a.m. Eastern time) to liven up the channel offerings, Dr. Windecker observed, and to make them more immediate and potentially interactive.
Many of the parallel channels are devoted throughout the Congress to particular silos of cardiology; for example, arrhythmias and device therapy is on channel 3; CAD and acute care is on 5; HF is on 6; and preventive cardiology is on 9.
Other channels swing across different topics from day to day, such as channel 1, which covers COVID-19 topics on the first and third day of the meeting, “advances in science” on day 2, and “digital health, public health, health economics” on day 4.
The focus each day, starting at 2:00 p.m. CET (8:00 a.m. ET) and continuing into the evening in Europe, shifts over to the Prime Time live program, which features the Hot Line and guideline presentations and many of the live abstract presentations.
Dr. Kosiborod, not a researcher with the EMPEROR trials, is chair of the Dapagliflozin in Preserved Ejection Fraction Heart Failure ( PRESERVED-HF ) trial, which is scheduled for presentation at the September 2021 Heart Failure Society of American meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
U.S. kidney transplants grow in number and success
During 2016-2019, U.S. centers performed kidney transplants in nearly 77,000 patients, a jump of almost 25% compared with 4-year averages of about 62,000 patients throughout 2004-2015. That works out to about 15,000 more patients receiving donor kidneys, Sundaram Hariharan, MD, and associates reported in the New England Journal of Medicine in a review of all U.S. renal transplantations performed during 1996-2019.
Coupled with the volume uptick during this 24-year period were new lows in graft losses and patient deaths. By 2018, mortality during the first year following transplantation occurred at about a 1% rate among patients who had received a kidney from a living donor, and at about a 3% rate when the organ came from a deceased donor, nearly half the rate of 2 decades earlier, in 1996. Rates of first-year graft loss during 2017 were also about half of what they had been in 1996, occurring in about 2% of patients who received a living donor organ and in about 6% of those who got a kidney from a deceased donor during 2017.
“Twenty years ago, kidney transplantation was the preferred option compared with dialysis, and even more so now,” summed up Dr. Hariharan, a senior transplant nephrologist and professor of medicine and surgery at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center and first author of the report. Kidney transplantation survival at U.S. centers “improved steadily over the past 24 years, despite patient variables becoming worse,” he said in an interview.
Kidney recipients are older, more obese, and have more prevalent diabetes
During the period studied, kidney transplant recipients became on average older and more obese, and had a higher prevalence of diabetes; the age of organ donors grew as well. The prevalence of diabetes among patients who received a kidney from a deceased donor increased from 24% during 1996-1999 to 36% during 2016-2019, while diabetes prevalence among recipients of an organ from a living donor rose from 25% in 1996-1999 to 29% during 2016-2019.
The improved graft and patient survival numbers “are very encouraging trends,” said Michelle A. Josephson, MD, professor and medical director of kidney transplantation at the University of Chicago, who was not involved with the report. “We have been hearing for a number of years that short-term graft survival had improved, but I’m thrilled to learn that long-term survival has also improved.”
The report documented 10-year survival of graft recipients during 2008-2011 of 67%, up from 61% during 1996-1999, and a 10-year overall graft survival rate of 54% in the 2008-2011 cohort, an improvement from the 42% rate in patients who received their organs in 1996-1999, changes Dr. Hariharan characterized as “modest.”
These improvements in long-term graft and patient survival are “meaningful, and particularly notable that outcomes improved despite increased complexity of the transplant population,” said Krista L. Lentine, MD, PhD, professor and medical director of living donation at Saint Louis University. But “despite these improvements, long-term graft survival remains limited,” she cautioned, especially because of risks for substantial complications from chronic immunosuppressive treatment including infection, cancer, glucose intolerance, and dyslipidemia.
The analysis reported by Dr. Hariharan and his associates used data collected by the Scientific Registry of Transplant Patients, run under contract with the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, which has tracked all patients who have had kidney transplants at U.S. centers since the late 1980s, said Dr. Hariharan. The database included just over 362,000 total transplants during the 24-year period studied, with 36% of all transplants involving organs from living donors with the remaining patients receiving kidneys from deceased donors.
Living donations still stagnant; deceased-donor kidneys rise
The data showed that the rate of transplants from living donors was stagnant for 2 decades, with 22,525 patients transplanted during 2000-2003, and 23,746 transplanted during 2016-2019, with very similar rates during the intervening years. The recent spurt in transplants during 2016-2019 compared with the preceding decade depended almost entirely on kidneys from deceased donors. This rate jumped from the steady, slow rise it showed during 1996-2015, when deceased-donor transplants rose from about 30,000 during 1996-1999 to about 41,000 during 2012-2015, to a more dramatic increase of about 12,000 additional transplants during the most recent period, adding up to a total of more than 53,000 transplants from deceased donors during 2016-2019.
“I strongly recommend organs from living donors” when feasible, said Dr. Hariharan. “At some centers, a high proportion of transplants use living donors, but not at other centers,” he said.
It’s unknown why transplants using organs from deceased donors has shown this growth, but Dr. Hariharan suggested a multifactorial explanation. Those factors include growth in the number of patients with end-stage renal disease who require dialysis, increased numbers of patients listed for kidney transplant, new approaches that allow organs from older donors and those infected with pathogens such as hepatitis C virus or HIV, greater numbers of people and families agreeing to donate organs, and possibly the opioid crisis that may have led to increased organ donation. The number of U.S. centers performing kidney transplants rose from fewer than 200 about a quarter of a century ago to about 250 today, he added.
‘Immuno Bill’ guarantees Medicare coverage for immunosuppression
Dr. Hariharan voiced optimism that graft and patient survival rates will continue to improve going forward. One factor will likely be the passage in late 2020 of the “Immuno Bill” by the U.S. Congress, which among other things mandated ongoing coverage starting in 2023 for immunosuppressive drugs for all Medicare beneficiaries with a kidney transplant. Until then, Medicare provides coverage for only 36 months, a time limit that has resulted in nearly 400 kidney recipients annually losing coverage of their immunosuppression medications.
Dr. Hariharan and coauthors called the existing potential for discontinuation of immunosuppressive drug an “unnecessary impediment to long-term survival for which patients and society paid a heavy price.”
“Kidney transplantation, especially from living donors, offers patients with kidney failure the best chance for long-term survival and improved quality of life, with lower cost to the health care system,” Dr. Lentine said in an interview. Despite the many positive trends detailed in the report from Dr. Hariharan and coauthors, “the vast majority of the more than 700,000 people in the United States with kidney failure will not have an opportunity to receive a transplant due to limitations in organ supply.” And many patients who receive a kidney transplant eventually must resume dialysis because of “limited long-term graft survival resulting from allograft nephropathy, recurrent native disease, medication nonadherence, or other causes.” Plus many potentially transplantable organs go unused.
Dr. Lentine cited a position statement issued in July 2021 by the National Kidney Foundation that made several recommendations on how to improve access to kidney transplants and improve outcomes. “Expanding opportunities for safe living donation, eliminating racial disparities in living-donor access, improving wait-list access and transport readiness, maximizing use of deceased-donor organs, and extending graft longevity are critical priorities,” said Dr. Lentine, lead author on the statement.
“For many or even most patients with kidney failure transplantation is the optimal form of renal replacement. The better recent outcomes and evolving management strategies make transplantation an even more attractive option,” said Dr. Josephson. Improved outcomes among U.S. transplant patients also highlights the “importance of increasing access to kidney transplantation” for all people with kidney failure who could benefit from this treatment, she added.
Dr. Hariharan and Dr. Lentine had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Josephson has been a consultant to UCB and has an ownership interest in Seagen.
During 2016-2019, U.S. centers performed kidney transplants in nearly 77,000 patients, a jump of almost 25% compared with 4-year averages of about 62,000 patients throughout 2004-2015. That works out to about 15,000 more patients receiving donor kidneys, Sundaram Hariharan, MD, and associates reported in the New England Journal of Medicine in a review of all U.S. renal transplantations performed during 1996-2019.
Coupled with the volume uptick during this 24-year period were new lows in graft losses and patient deaths. By 2018, mortality during the first year following transplantation occurred at about a 1% rate among patients who had received a kidney from a living donor, and at about a 3% rate when the organ came from a deceased donor, nearly half the rate of 2 decades earlier, in 1996. Rates of first-year graft loss during 2017 were also about half of what they had been in 1996, occurring in about 2% of patients who received a living donor organ and in about 6% of those who got a kidney from a deceased donor during 2017.
“Twenty years ago, kidney transplantation was the preferred option compared with dialysis, and even more so now,” summed up Dr. Hariharan, a senior transplant nephrologist and professor of medicine and surgery at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center and first author of the report. Kidney transplantation survival at U.S. centers “improved steadily over the past 24 years, despite patient variables becoming worse,” he said in an interview.
Kidney recipients are older, more obese, and have more prevalent diabetes
During the period studied, kidney transplant recipients became on average older and more obese, and had a higher prevalence of diabetes; the age of organ donors grew as well. The prevalence of diabetes among patients who received a kidney from a deceased donor increased from 24% during 1996-1999 to 36% during 2016-2019, while diabetes prevalence among recipients of an organ from a living donor rose from 25% in 1996-1999 to 29% during 2016-2019.
The improved graft and patient survival numbers “are very encouraging trends,” said Michelle A. Josephson, MD, professor and medical director of kidney transplantation at the University of Chicago, who was not involved with the report. “We have been hearing for a number of years that short-term graft survival had improved, but I’m thrilled to learn that long-term survival has also improved.”
The report documented 10-year survival of graft recipients during 2008-2011 of 67%, up from 61% during 1996-1999, and a 10-year overall graft survival rate of 54% in the 2008-2011 cohort, an improvement from the 42% rate in patients who received their organs in 1996-1999, changes Dr. Hariharan characterized as “modest.”
These improvements in long-term graft and patient survival are “meaningful, and particularly notable that outcomes improved despite increased complexity of the transplant population,” said Krista L. Lentine, MD, PhD, professor and medical director of living donation at Saint Louis University. But “despite these improvements, long-term graft survival remains limited,” she cautioned, especially because of risks for substantial complications from chronic immunosuppressive treatment including infection, cancer, glucose intolerance, and dyslipidemia.
The analysis reported by Dr. Hariharan and his associates used data collected by the Scientific Registry of Transplant Patients, run under contract with the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, which has tracked all patients who have had kidney transplants at U.S. centers since the late 1980s, said Dr. Hariharan. The database included just over 362,000 total transplants during the 24-year period studied, with 36% of all transplants involving organs from living donors with the remaining patients receiving kidneys from deceased donors.
Living donations still stagnant; deceased-donor kidneys rise
The data showed that the rate of transplants from living donors was stagnant for 2 decades, with 22,525 patients transplanted during 2000-2003, and 23,746 transplanted during 2016-2019, with very similar rates during the intervening years. The recent spurt in transplants during 2016-2019 compared with the preceding decade depended almost entirely on kidneys from deceased donors. This rate jumped from the steady, slow rise it showed during 1996-2015, when deceased-donor transplants rose from about 30,000 during 1996-1999 to about 41,000 during 2012-2015, to a more dramatic increase of about 12,000 additional transplants during the most recent period, adding up to a total of more than 53,000 transplants from deceased donors during 2016-2019.
“I strongly recommend organs from living donors” when feasible, said Dr. Hariharan. “At some centers, a high proportion of transplants use living donors, but not at other centers,” he said.
It’s unknown why transplants using organs from deceased donors has shown this growth, but Dr. Hariharan suggested a multifactorial explanation. Those factors include growth in the number of patients with end-stage renal disease who require dialysis, increased numbers of patients listed for kidney transplant, new approaches that allow organs from older donors and those infected with pathogens such as hepatitis C virus or HIV, greater numbers of people and families agreeing to donate organs, and possibly the opioid crisis that may have led to increased organ donation. The number of U.S. centers performing kidney transplants rose from fewer than 200 about a quarter of a century ago to about 250 today, he added.
‘Immuno Bill’ guarantees Medicare coverage for immunosuppression
Dr. Hariharan voiced optimism that graft and patient survival rates will continue to improve going forward. One factor will likely be the passage in late 2020 of the “Immuno Bill” by the U.S. Congress, which among other things mandated ongoing coverage starting in 2023 for immunosuppressive drugs for all Medicare beneficiaries with a kidney transplant. Until then, Medicare provides coverage for only 36 months, a time limit that has resulted in nearly 400 kidney recipients annually losing coverage of their immunosuppression medications.
Dr. Hariharan and coauthors called the existing potential for discontinuation of immunosuppressive drug an “unnecessary impediment to long-term survival for which patients and society paid a heavy price.”
“Kidney transplantation, especially from living donors, offers patients with kidney failure the best chance for long-term survival and improved quality of life, with lower cost to the health care system,” Dr. Lentine said in an interview. Despite the many positive trends detailed in the report from Dr. Hariharan and coauthors, “the vast majority of the more than 700,000 people in the United States with kidney failure will not have an opportunity to receive a transplant due to limitations in organ supply.” And many patients who receive a kidney transplant eventually must resume dialysis because of “limited long-term graft survival resulting from allograft nephropathy, recurrent native disease, medication nonadherence, or other causes.” Plus many potentially transplantable organs go unused.
Dr. Lentine cited a position statement issued in July 2021 by the National Kidney Foundation that made several recommendations on how to improve access to kidney transplants and improve outcomes. “Expanding opportunities for safe living donation, eliminating racial disparities in living-donor access, improving wait-list access and transport readiness, maximizing use of deceased-donor organs, and extending graft longevity are critical priorities,” said Dr. Lentine, lead author on the statement.
“For many or even most patients with kidney failure transplantation is the optimal form of renal replacement. The better recent outcomes and evolving management strategies make transplantation an even more attractive option,” said Dr. Josephson. Improved outcomes among U.S. transplant patients also highlights the “importance of increasing access to kidney transplantation” for all people with kidney failure who could benefit from this treatment, she added.
Dr. Hariharan and Dr. Lentine had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Josephson has been a consultant to UCB and has an ownership interest in Seagen.
During 2016-2019, U.S. centers performed kidney transplants in nearly 77,000 patients, a jump of almost 25% compared with 4-year averages of about 62,000 patients throughout 2004-2015. That works out to about 15,000 more patients receiving donor kidneys, Sundaram Hariharan, MD, and associates reported in the New England Journal of Medicine in a review of all U.S. renal transplantations performed during 1996-2019.
Coupled with the volume uptick during this 24-year period were new lows in graft losses and patient deaths. By 2018, mortality during the first year following transplantation occurred at about a 1% rate among patients who had received a kidney from a living donor, and at about a 3% rate when the organ came from a deceased donor, nearly half the rate of 2 decades earlier, in 1996. Rates of first-year graft loss during 2017 were also about half of what they had been in 1996, occurring in about 2% of patients who received a living donor organ and in about 6% of those who got a kidney from a deceased donor during 2017.
“Twenty years ago, kidney transplantation was the preferred option compared with dialysis, and even more so now,” summed up Dr. Hariharan, a senior transplant nephrologist and professor of medicine and surgery at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center and first author of the report. Kidney transplantation survival at U.S. centers “improved steadily over the past 24 years, despite patient variables becoming worse,” he said in an interview.
Kidney recipients are older, more obese, and have more prevalent diabetes
During the period studied, kidney transplant recipients became on average older and more obese, and had a higher prevalence of diabetes; the age of organ donors grew as well. The prevalence of diabetes among patients who received a kidney from a deceased donor increased from 24% during 1996-1999 to 36% during 2016-2019, while diabetes prevalence among recipients of an organ from a living donor rose from 25% in 1996-1999 to 29% during 2016-2019.
The improved graft and patient survival numbers “are very encouraging trends,” said Michelle A. Josephson, MD, professor and medical director of kidney transplantation at the University of Chicago, who was not involved with the report. “We have been hearing for a number of years that short-term graft survival had improved, but I’m thrilled to learn that long-term survival has also improved.”
The report documented 10-year survival of graft recipients during 2008-2011 of 67%, up from 61% during 1996-1999, and a 10-year overall graft survival rate of 54% in the 2008-2011 cohort, an improvement from the 42% rate in patients who received their organs in 1996-1999, changes Dr. Hariharan characterized as “modest.”
These improvements in long-term graft and patient survival are “meaningful, and particularly notable that outcomes improved despite increased complexity of the transplant population,” said Krista L. Lentine, MD, PhD, professor and medical director of living donation at Saint Louis University. But “despite these improvements, long-term graft survival remains limited,” she cautioned, especially because of risks for substantial complications from chronic immunosuppressive treatment including infection, cancer, glucose intolerance, and dyslipidemia.
The analysis reported by Dr. Hariharan and his associates used data collected by the Scientific Registry of Transplant Patients, run under contract with the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, which has tracked all patients who have had kidney transplants at U.S. centers since the late 1980s, said Dr. Hariharan. The database included just over 362,000 total transplants during the 24-year period studied, with 36% of all transplants involving organs from living donors with the remaining patients receiving kidneys from deceased donors.
Living donations still stagnant; deceased-donor kidneys rise
The data showed that the rate of transplants from living donors was stagnant for 2 decades, with 22,525 patients transplanted during 2000-2003, and 23,746 transplanted during 2016-2019, with very similar rates during the intervening years. The recent spurt in transplants during 2016-2019 compared with the preceding decade depended almost entirely on kidneys from deceased donors. This rate jumped from the steady, slow rise it showed during 1996-2015, when deceased-donor transplants rose from about 30,000 during 1996-1999 to about 41,000 during 2012-2015, to a more dramatic increase of about 12,000 additional transplants during the most recent period, adding up to a total of more than 53,000 transplants from deceased donors during 2016-2019.
“I strongly recommend organs from living donors” when feasible, said Dr. Hariharan. “At some centers, a high proportion of transplants use living donors, but not at other centers,” he said.
It’s unknown why transplants using organs from deceased donors has shown this growth, but Dr. Hariharan suggested a multifactorial explanation. Those factors include growth in the number of patients with end-stage renal disease who require dialysis, increased numbers of patients listed for kidney transplant, new approaches that allow organs from older donors and those infected with pathogens such as hepatitis C virus or HIV, greater numbers of people and families agreeing to donate organs, and possibly the opioid crisis that may have led to increased organ donation. The number of U.S. centers performing kidney transplants rose from fewer than 200 about a quarter of a century ago to about 250 today, he added.
‘Immuno Bill’ guarantees Medicare coverage for immunosuppression
Dr. Hariharan voiced optimism that graft and patient survival rates will continue to improve going forward. One factor will likely be the passage in late 2020 of the “Immuno Bill” by the U.S. Congress, which among other things mandated ongoing coverage starting in 2023 for immunosuppressive drugs for all Medicare beneficiaries with a kidney transplant. Until then, Medicare provides coverage for only 36 months, a time limit that has resulted in nearly 400 kidney recipients annually losing coverage of their immunosuppression medications.
Dr. Hariharan and coauthors called the existing potential for discontinuation of immunosuppressive drug an “unnecessary impediment to long-term survival for which patients and society paid a heavy price.”
“Kidney transplantation, especially from living donors, offers patients with kidney failure the best chance for long-term survival and improved quality of life, with lower cost to the health care system,” Dr. Lentine said in an interview. Despite the many positive trends detailed in the report from Dr. Hariharan and coauthors, “the vast majority of the more than 700,000 people in the United States with kidney failure will not have an opportunity to receive a transplant due to limitations in organ supply.” And many patients who receive a kidney transplant eventually must resume dialysis because of “limited long-term graft survival resulting from allograft nephropathy, recurrent native disease, medication nonadherence, or other causes.” Plus many potentially transplantable organs go unused.
Dr. Lentine cited a position statement issued in July 2021 by the National Kidney Foundation that made several recommendations on how to improve access to kidney transplants and improve outcomes. “Expanding opportunities for safe living donation, eliminating racial disparities in living-donor access, improving wait-list access and transport readiness, maximizing use of deceased-donor organs, and extending graft longevity are critical priorities,” said Dr. Lentine, lead author on the statement.
“For many or even most patients with kidney failure transplantation is the optimal form of renal replacement. The better recent outcomes and evolving management strategies make transplantation an even more attractive option,” said Dr. Josephson. Improved outcomes among U.S. transplant patients also highlights the “importance of increasing access to kidney transplantation” for all people with kidney failure who could benefit from this treatment, she added.
Dr. Hariharan and Dr. Lentine had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Josephson has been a consultant to UCB and has an ownership interest in Seagen.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Prevalence of youth-onset diabetes climbing, type 2 disease more so in racial/ethnic minorities
The prevalence of youth-onset diabetes in the United States rose significantly from 2001 to 2017, with rates of type 2 diabetes climbing disproportionately among racial/ethnic minorities, according to investigators.
In individuals aged 19 years or younger, prevalence rates of type 1 and type 2 diabetes increased 45.1% and 95.3%, respectively, reported lead author Jean M. Lawrence, ScD, MPH, MSSA, program director of the division of diabetes, endocrinology, and metabolic diseases at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., and colleagues.
“Elucidating differences in diabetes prevalence trends by diabetes type and demographic characteristics is essential to describe the burden of disease and to estimate current and future resource needs,” Dr. Lawrence and colleagues wrote in JAMA.
The retrospective analysis was a part of the ongoing SEARCH study, which includes data from individuals in six areas across the United States: Colorado, California, Ohio, South Carolina, Washington state, and Arizona/New Mexico (Indian Health Services). In the present report, three prevalence years were evaluated: 2001, 2009, and 2017. For each year, approximately 3.5 million youths were included. Findings were reported in terms of diabetes type, race/ethnicity, age at diagnosis, and sex.
Absolute prevalence of type 1 diabetes per 1,000 youths increased from 1.48 in 2001, to 1.93 in 2009, and finally 2.15 in 2017. Across the 16-year period, this represents an absolute increase of 0.67 (95% confidence interval, 0.64-0.70), and a relative increase of 45.1% (95% CI, 40.0%-50.4%). In absolute terms, prevalence increased most among non-Hispanic White (0.93 per 1,000) and non-Hispanic Black (0.89 per 1,000) youths.
While type 2 diabetes was comparatively less common than type 1 diabetes, absolute prevalence per 1,000 youths increased to a greater degree, rising from 0.34 in 2001 to 0.46 in 2009 and to 0.67 in 2017. This amounts to relative increase across the period of 95.3% (95% CI, 77.0%-115.4%). Absolute increases were disproportionate among racial/ethnic minorities, particularly Black and Hispanic youths, who had absolute increases per 1,000 youths of 0.85 (95% CI, 0.74-0.97) and 0.57 (95% CI, 0.51-0.64), respectively, compared with 0.05 (95% CI, 0.03-0.07) for White youths.
“Increases [among Black and Hispanic youths] were not linear,” the investigators noted. “Hispanic youths had a significantly greater increase in the first interval compared with the second interval, while Black youths had no significant increase in the first interval and a significant increase in the second interval.”
Dr. Lawrence and colleagues offered several possible factors driving these trends in type 2 diabetes.
“Changes in anthropometric risk factors appear to play a significant role,” they wrote, noting that “Black and Mexican American teenagers experienced the greatest increase in prevalence of obesity/severe obesity from 1999 to 2018, which may contribute to race and ethnicity differences. Other contributing factors may include increases in exposure to maternal obesity and diabetes (gestational and type 2 diabetes) and exposure to environmental chemicals.”
According to Megan Kelsey, MD, associate professor of pediatric endocrinology, director of lifestyle medicine endocrinology, and medical director of the bariatric surgery center at Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora, the increased rates of type 2 diabetes reported by the study are alarming, yet they pale in comparison with what’s been happening since the pandemic began.
“Individual institutions have reported anywhere between a 50% – which is basically what we’re seeing at our hospital – to a 300% increase in new diagnoses [of type 2 diabetes] in a single-year time period,” Dr. Kelsey said in an interview. “So what is reported [in the present study] doesn’t even get at what’s been going on over the past year and a half.”
Dr. Kelsey offered some speculative drivers of this recent surge in cases, including stress, weight gain caused by sedentary behavior and more access to food, and the possibility that SARS-CoV-2 may infect pancreatic islet beta cells, thereby interfering with insulin production.
Type 2 diabetes is particularly concerning among young people, Dr. Kelsey noted, as it is more challenging to manage than adult-onset disease.
Young patients “also develop complications much sooner than you’d expect,” she added. “So we really need to understand why these rates are increasing, how we can identify kids at risk, and how we can better prevent it, so we aren’t stuck with a disease that’s really difficult to treat.”
To this end, the NIH recently opened applications for investigators to participate in a prospective longitudinal study of youth-onset type 2 diabetes. Young people at risk of diabetes will be followed through puberty, a period of increased risk, according to Dr. Kelsey.
“The goal will be to take kids who don’t yet have [type 2] diabetes, but are at risk, and try to better understand, as some of them progress to developing diabetes, what is going on,” Dr. Kelsey said. “What are other factors that we can use to better predict who’s going to develop diabetes? And can we use the information from this [upcoming] study to understand how to better prevent it? Because nothing that has been tried so far has worked.”
The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, NIDDK, and others. The investigators and Dr. Kelsey reported no conflicts of interest.
The prevalence of youth-onset diabetes in the United States rose significantly from 2001 to 2017, with rates of type 2 diabetes climbing disproportionately among racial/ethnic minorities, according to investigators.
In individuals aged 19 years or younger, prevalence rates of type 1 and type 2 diabetes increased 45.1% and 95.3%, respectively, reported lead author Jean M. Lawrence, ScD, MPH, MSSA, program director of the division of diabetes, endocrinology, and metabolic diseases at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., and colleagues.
“Elucidating differences in diabetes prevalence trends by diabetes type and demographic characteristics is essential to describe the burden of disease and to estimate current and future resource needs,” Dr. Lawrence and colleagues wrote in JAMA.
The retrospective analysis was a part of the ongoing SEARCH study, which includes data from individuals in six areas across the United States: Colorado, California, Ohio, South Carolina, Washington state, and Arizona/New Mexico (Indian Health Services). In the present report, three prevalence years were evaluated: 2001, 2009, and 2017. For each year, approximately 3.5 million youths were included. Findings were reported in terms of diabetes type, race/ethnicity, age at diagnosis, and sex.
Absolute prevalence of type 1 diabetes per 1,000 youths increased from 1.48 in 2001, to 1.93 in 2009, and finally 2.15 in 2017. Across the 16-year period, this represents an absolute increase of 0.67 (95% confidence interval, 0.64-0.70), and a relative increase of 45.1% (95% CI, 40.0%-50.4%). In absolute terms, prevalence increased most among non-Hispanic White (0.93 per 1,000) and non-Hispanic Black (0.89 per 1,000) youths.
While type 2 diabetes was comparatively less common than type 1 diabetes, absolute prevalence per 1,000 youths increased to a greater degree, rising from 0.34 in 2001 to 0.46 in 2009 and to 0.67 in 2017. This amounts to relative increase across the period of 95.3% (95% CI, 77.0%-115.4%). Absolute increases were disproportionate among racial/ethnic minorities, particularly Black and Hispanic youths, who had absolute increases per 1,000 youths of 0.85 (95% CI, 0.74-0.97) and 0.57 (95% CI, 0.51-0.64), respectively, compared with 0.05 (95% CI, 0.03-0.07) for White youths.
“Increases [among Black and Hispanic youths] were not linear,” the investigators noted. “Hispanic youths had a significantly greater increase in the first interval compared with the second interval, while Black youths had no significant increase in the first interval and a significant increase in the second interval.”
Dr. Lawrence and colleagues offered several possible factors driving these trends in type 2 diabetes.
“Changes in anthropometric risk factors appear to play a significant role,” they wrote, noting that “Black and Mexican American teenagers experienced the greatest increase in prevalence of obesity/severe obesity from 1999 to 2018, which may contribute to race and ethnicity differences. Other contributing factors may include increases in exposure to maternal obesity and diabetes (gestational and type 2 diabetes) and exposure to environmental chemicals.”
According to Megan Kelsey, MD, associate professor of pediatric endocrinology, director of lifestyle medicine endocrinology, and medical director of the bariatric surgery center at Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora, the increased rates of type 2 diabetes reported by the study are alarming, yet they pale in comparison with what’s been happening since the pandemic began.
“Individual institutions have reported anywhere between a 50% – which is basically what we’re seeing at our hospital – to a 300% increase in new diagnoses [of type 2 diabetes] in a single-year time period,” Dr. Kelsey said in an interview. “So what is reported [in the present study] doesn’t even get at what’s been going on over the past year and a half.”
Dr. Kelsey offered some speculative drivers of this recent surge in cases, including stress, weight gain caused by sedentary behavior and more access to food, and the possibility that SARS-CoV-2 may infect pancreatic islet beta cells, thereby interfering with insulin production.
Type 2 diabetes is particularly concerning among young people, Dr. Kelsey noted, as it is more challenging to manage than adult-onset disease.
Young patients “also develop complications much sooner than you’d expect,” she added. “So we really need to understand why these rates are increasing, how we can identify kids at risk, and how we can better prevent it, so we aren’t stuck with a disease that’s really difficult to treat.”
To this end, the NIH recently opened applications for investigators to participate in a prospective longitudinal study of youth-onset type 2 diabetes. Young people at risk of diabetes will be followed through puberty, a period of increased risk, according to Dr. Kelsey.
“The goal will be to take kids who don’t yet have [type 2] diabetes, but are at risk, and try to better understand, as some of them progress to developing diabetes, what is going on,” Dr. Kelsey said. “What are other factors that we can use to better predict who’s going to develop diabetes? And can we use the information from this [upcoming] study to understand how to better prevent it? Because nothing that has been tried so far has worked.”
The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, NIDDK, and others. The investigators and Dr. Kelsey reported no conflicts of interest.
The prevalence of youth-onset diabetes in the United States rose significantly from 2001 to 2017, with rates of type 2 diabetes climbing disproportionately among racial/ethnic minorities, according to investigators.
In individuals aged 19 years or younger, prevalence rates of type 1 and type 2 diabetes increased 45.1% and 95.3%, respectively, reported lead author Jean M. Lawrence, ScD, MPH, MSSA, program director of the division of diabetes, endocrinology, and metabolic diseases at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., and colleagues.
“Elucidating differences in diabetes prevalence trends by diabetes type and demographic characteristics is essential to describe the burden of disease and to estimate current and future resource needs,” Dr. Lawrence and colleagues wrote in JAMA.
The retrospective analysis was a part of the ongoing SEARCH study, which includes data from individuals in six areas across the United States: Colorado, California, Ohio, South Carolina, Washington state, and Arizona/New Mexico (Indian Health Services). In the present report, three prevalence years were evaluated: 2001, 2009, and 2017. For each year, approximately 3.5 million youths were included. Findings were reported in terms of diabetes type, race/ethnicity, age at diagnosis, and sex.
Absolute prevalence of type 1 diabetes per 1,000 youths increased from 1.48 in 2001, to 1.93 in 2009, and finally 2.15 in 2017. Across the 16-year period, this represents an absolute increase of 0.67 (95% confidence interval, 0.64-0.70), and a relative increase of 45.1% (95% CI, 40.0%-50.4%). In absolute terms, prevalence increased most among non-Hispanic White (0.93 per 1,000) and non-Hispanic Black (0.89 per 1,000) youths.
While type 2 diabetes was comparatively less common than type 1 diabetes, absolute prevalence per 1,000 youths increased to a greater degree, rising from 0.34 in 2001 to 0.46 in 2009 and to 0.67 in 2017. This amounts to relative increase across the period of 95.3% (95% CI, 77.0%-115.4%). Absolute increases were disproportionate among racial/ethnic minorities, particularly Black and Hispanic youths, who had absolute increases per 1,000 youths of 0.85 (95% CI, 0.74-0.97) and 0.57 (95% CI, 0.51-0.64), respectively, compared with 0.05 (95% CI, 0.03-0.07) for White youths.
“Increases [among Black and Hispanic youths] were not linear,” the investigators noted. “Hispanic youths had a significantly greater increase in the first interval compared with the second interval, while Black youths had no significant increase in the first interval and a significant increase in the second interval.”
Dr. Lawrence and colleagues offered several possible factors driving these trends in type 2 diabetes.
“Changes in anthropometric risk factors appear to play a significant role,” they wrote, noting that “Black and Mexican American teenagers experienced the greatest increase in prevalence of obesity/severe obesity from 1999 to 2018, which may contribute to race and ethnicity differences. Other contributing factors may include increases in exposure to maternal obesity and diabetes (gestational and type 2 diabetes) and exposure to environmental chemicals.”
According to Megan Kelsey, MD, associate professor of pediatric endocrinology, director of lifestyle medicine endocrinology, and medical director of the bariatric surgery center at Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora, the increased rates of type 2 diabetes reported by the study are alarming, yet they pale in comparison with what’s been happening since the pandemic began.
“Individual institutions have reported anywhere between a 50% – which is basically what we’re seeing at our hospital – to a 300% increase in new diagnoses [of type 2 diabetes] in a single-year time period,” Dr. Kelsey said in an interview. “So what is reported [in the present study] doesn’t even get at what’s been going on over the past year and a half.”
Dr. Kelsey offered some speculative drivers of this recent surge in cases, including stress, weight gain caused by sedentary behavior and more access to food, and the possibility that SARS-CoV-2 may infect pancreatic islet beta cells, thereby interfering with insulin production.
Type 2 diabetes is particularly concerning among young people, Dr. Kelsey noted, as it is more challenging to manage than adult-onset disease.
Young patients “also develop complications much sooner than you’d expect,” she added. “So we really need to understand why these rates are increasing, how we can identify kids at risk, and how we can better prevent it, so we aren’t stuck with a disease that’s really difficult to treat.”
To this end, the NIH recently opened applications for investigators to participate in a prospective longitudinal study of youth-onset type 2 diabetes. Young people at risk of diabetes will be followed through puberty, a period of increased risk, according to Dr. Kelsey.
“The goal will be to take kids who don’t yet have [type 2] diabetes, but are at risk, and try to better understand, as some of them progress to developing diabetes, what is going on,” Dr. Kelsey said. “What are other factors that we can use to better predict who’s going to develop diabetes? And can we use the information from this [upcoming] study to understand how to better prevent it? Because nothing that has been tried so far has worked.”
The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, NIDDK, and others. The investigators and Dr. Kelsey reported no conflicts of interest.
FROM JAMA
US Preventive Services Task Force lowers diabetes screening age for overweight
The United States Preventive Services Task Force has updated its recommendation on the age of screening for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in the primary care setting – lowering the age from 40 to 35 years for asymptomatic patients who are overweight or obese and encouraging greater interventions when patients do show a risk.
“The USPSTF concludes with moderate certainty that screening for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes and offering or referring patients with prediabetes to effective preventive interventions has a moderate net benefit,” the task force concludes in its recommendation, published Aug. 24 in JAMA.
“Clinicians should offer or refer patients with prediabetes to effective preventive interventions,” they write.
Experts commenting on the issue strongly emphasize that it’s not just the screening, but the subsequent intervention that is needed to make a difference.
“If young adults newly identified with abnormal glucose metabolism do not receive the needed intensive behavioral change support, screening may provide no benefit,” write Richard W. Grant, MD, MPH, and colleagues in an editorial published with the recommendation.
“Given the role of our obesogenic and physically inactive society in the shift toward earlier onset of diabetes, efforts to increase screening and recognition of abnormal glucose metabolism must be coupled with robust public health measures to address the underlying contributors.”
BMI cutoff lower for at-risk ethnic populations
The recommendation, which updates the task force’s 2015 guideline, carries a “B” classification, meaning the USPSTF has high certainty that the net benefit is moderate. It now specifies screening from age 35to 70 for persons classified as overweight (body mass index at least 25) or obese (BMI at least 30) and recommends referral to preventive interventions when patients are found to have prediabetes.
In addition to recommendations of lifestyle changes, such as diet and physical activity, the task force also endorses the diabetes drug metformin as a beneficial intervention in the prevention or delay of diabetes, while noting fewer overall health benefits from metformin than from the lifestyle changes.
A lower BMI cutoff of at least 23 is recommended for diabetes screening of Asian Americans, and, importantly, screening for prediabetes and diabetes should be considered at an even earlier age if the patient is from a population with a disproportionately high prevalence of diabetes, including American Indian/Alaska Native, Black, Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, Hispanic/Latino, the task force recommends.
Screening tests should include fasting plasma glucose, hemoglobin A1c, or an oral glucose tolerance test. Although screening every 3 years “may be a reasonable approach for adults with normal blood glucose levels,” the task force adds that “the optimal screening interval for adults with an initial normal glucose test result is uncertain.”
Data review: Few with prediabetes know they have it
The need for the update was prompted by troubling data showing increasing diabetes rates despite early signs that can and should be identified and acted upon in the primary care setting to prevent disease progression.
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, for instance, show that while 13% of all U.S. adults 18 years or older have diabetes and 35% meet criteria for prediabetes, as many as 21% of those with diabetes were not aware of or did not report having the disease. Furthermore, only a small fraction – 15% of those with prediabetes – said they had been told by a health professional that they had this condition, the task force notes.
The task force’s final recommendation was based on a systematic review of evidence regarding the screening of asymptomatic, nonpregnant adults and the harms and benefits of interventions, such as physical activity, behavioral counseling, or pharmacotherapy.
Among key evidence supporting the lower age was a 2014 study showing that the number of people necessary to obtain one positive test for diabetes with screening sharply drops from 80 among those aged 30-34 years to just 31 among those aged 36-39.
Opportunistic universal screening of eligible people aged 35 and older would yield a ratio of 1 out of just 15 to spot a positive test, the authors of that study reported.
In addition, a large cohort study in more than 77,000 people with prediabetes strongly links the risk of developing diabetes with increases in A1c level and with increasing BMI.
ADA recommendations differ
The new recommendations differ from American Diabetes Association guidelines, which call for diabetes screening at all ages for people who are overweight or obese and who have one or more risk factors, such as physical inactivity or a first-degree relative with diabetes. If results are normal, repeat screening at least every 3 years is recommended.
The ADA further recommends universal screening for all adults 45 years and older, regardless of their risk factors.
For the screening of adults over 45, the ADA recommends using a fasting plasma glucose level, 2-hour plasma glucose level during a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test, or A1c level, regardless of risk factors.
The American Association of Clinical Endocrinology also recommends universal screening for prediabetes and diabetes for all adults 45 years or older, regardless of risk factors, and also advises screening those who have risk factors for diabetes regardless of age.
Screening of little benefit without behavior change support
In an interview, Dr. Grant added that broad efforts are essential as those at the practice level have clearly not succeeded.
“The medical model of individual counseling and referral has not really been effective, and so we really need to think in terms of large-scale public health action,” said Dr. Grant, of the division of research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Oakland.
His editorial details the sweeping, multifactorial efforts that are needed.
“To turn this recommendation into action – that is, to translate screening activities into improved clinical outcomes – change is needed at the patient-clinician level (recognizing and encouraging eligible individuals to be screened), health care system level (reducing screening barriers and ensuring access to robust lifestyle programs), and societal level (applying effective public health interventions to reduce obesity and increase exercise),” they write.
A top priority has to be a focus on individuals of diverse backgrounds and issues such as access to healthy programs in minority communities, Dr. Grant noted.
“Newly diagnosed adults are more likely to be African-American and Latinx,” he said.
“We really need to invest in healthier communities for low-income, non-White communities to reverse the persistent health care disparities in these communities.”
While the challenges may appear daunting, history shows they are not necessarily insurmountable – as evidenced in the campaign to discourage tobacco smoking.
“National smoking cessation efforts are one example of a mostly successful public health campaign that has made a difference in health behaviors,” Grant noted.
The recommendation is also posted on the USPSTF web site .
Dr. Grant reports receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
The United States Preventive Services Task Force has updated its recommendation on the age of screening for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in the primary care setting – lowering the age from 40 to 35 years for asymptomatic patients who are overweight or obese and encouraging greater interventions when patients do show a risk.
“The USPSTF concludes with moderate certainty that screening for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes and offering or referring patients with prediabetes to effective preventive interventions has a moderate net benefit,” the task force concludes in its recommendation, published Aug. 24 in JAMA.
“Clinicians should offer or refer patients with prediabetes to effective preventive interventions,” they write.
Experts commenting on the issue strongly emphasize that it’s not just the screening, but the subsequent intervention that is needed to make a difference.
“If young adults newly identified with abnormal glucose metabolism do not receive the needed intensive behavioral change support, screening may provide no benefit,” write Richard W. Grant, MD, MPH, and colleagues in an editorial published with the recommendation.
“Given the role of our obesogenic and physically inactive society in the shift toward earlier onset of diabetes, efforts to increase screening and recognition of abnormal glucose metabolism must be coupled with robust public health measures to address the underlying contributors.”
BMI cutoff lower for at-risk ethnic populations
The recommendation, which updates the task force’s 2015 guideline, carries a “B” classification, meaning the USPSTF has high certainty that the net benefit is moderate. It now specifies screening from age 35to 70 for persons classified as overweight (body mass index at least 25) or obese (BMI at least 30) and recommends referral to preventive interventions when patients are found to have prediabetes.
In addition to recommendations of lifestyle changes, such as diet and physical activity, the task force also endorses the diabetes drug metformin as a beneficial intervention in the prevention or delay of diabetes, while noting fewer overall health benefits from metformin than from the lifestyle changes.
A lower BMI cutoff of at least 23 is recommended for diabetes screening of Asian Americans, and, importantly, screening for prediabetes and diabetes should be considered at an even earlier age if the patient is from a population with a disproportionately high prevalence of diabetes, including American Indian/Alaska Native, Black, Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, Hispanic/Latino, the task force recommends.
Screening tests should include fasting plasma glucose, hemoglobin A1c, or an oral glucose tolerance test. Although screening every 3 years “may be a reasonable approach for adults with normal blood glucose levels,” the task force adds that “the optimal screening interval for adults with an initial normal glucose test result is uncertain.”
Data review: Few with prediabetes know they have it
The need for the update was prompted by troubling data showing increasing diabetes rates despite early signs that can and should be identified and acted upon in the primary care setting to prevent disease progression.
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, for instance, show that while 13% of all U.S. adults 18 years or older have diabetes and 35% meet criteria for prediabetes, as many as 21% of those with diabetes were not aware of or did not report having the disease. Furthermore, only a small fraction – 15% of those with prediabetes – said they had been told by a health professional that they had this condition, the task force notes.
The task force’s final recommendation was based on a systematic review of evidence regarding the screening of asymptomatic, nonpregnant adults and the harms and benefits of interventions, such as physical activity, behavioral counseling, or pharmacotherapy.
Among key evidence supporting the lower age was a 2014 study showing that the number of people necessary to obtain one positive test for diabetes with screening sharply drops from 80 among those aged 30-34 years to just 31 among those aged 36-39.
Opportunistic universal screening of eligible people aged 35 and older would yield a ratio of 1 out of just 15 to spot a positive test, the authors of that study reported.
In addition, a large cohort study in more than 77,000 people with prediabetes strongly links the risk of developing diabetes with increases in A1c level and with increasing BMI.
ADA recommendations differ
The new recommendations differ from American Diabetes Association guidelines, which call for diabetes screening at all ages for people who are overweight or obese and who have one or more risk factors, such as physical inactivity or a first-degree relative with diabetes. If results are normal, repeat screening at least every 3 years is recommended.
The ADA further recommends universal screening for all adults 45 years and older, regardless of their risk factors.
For the screening of adults over 45, the ADA recommends using a fasting plasma glucose level, 2-hour plasma glucose level during a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test, or A1c level, regardless of risk factors.
The American Association of Clinical Endocrinology also recommends universal screening for prediabetes and diabetes for all adults 45 years or older, regardless of risk factors, and also advises screening those who have risk factors for diabetes regardless of age.
Screening of little benefit without behavior change support
In an interview, Dr. Grant added that broad efforts are essential as those at the practice level have clearly not succeeded.
“The medical model of individual counseling and referral has not really been effective, and so we really need to think in terms of large-scale public health action,” said Dr. Grant, of the division of research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Oakland.
His editorial details the sweeping, multifactorial efforts that are needed.
“To turn this recommendation into action – that is, to translate screening activities into improved clinical outcomes – change is needed at the patient-clinician level (recognizing and encouraging eligible individuals to be screened), health care system level (reducing screening barriers and ensuring access to robust lifestyle programs), and societal level (applying effective public health interventions to reduce obesity and increase exercise),” they write.
A top priority has to be a focus on individuals of diverse backgrounds and issues such as access to healthy programs in minority communities, Dr. Grant noted.
“Newly diagnosed adults are more likely to be African-American and Latinx,” he said.
“We really need to invest in healthier communities for low-income, non-White communities to reverse the persistent health care disparities in these communities.”
While the challenges may appear daunting, history shows they are not necessarily insurmountable – as evidenced in the campaign to discourage tobacco smoking.
“National smoking cessation efforts are one example of a mostly successful public health campaign that has made a difference in health behaviors,” Grant noted.
The recommendation is also posted on the USPSTF web site .
Dr. Grant reports receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
The United States Preventive Services Task Force has updated its recommendation on the age of screening for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in the primary care setting – lowering the age from 40 to 35 years for asymptomatic patients who are overweight or obese and encouraging greater interventions when patients do show a risk.
“The USPSTF concludes with moderate certainty that screening for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes and offering or referring patients with prediabetes to effective preventive interventions has a moderate net benefit,” the task force concludes in its recommendation, published Aug. 24 in JAMA.
“Clinicians should offer or refer patients with prediabetes to effective preventive interventions,” they write.
Experts commenting on the issue strongly emphasize that it’s not just the screening, but the subsequent intervention that is needed to make a difference.
“If young adults newly identified with abnormal glucose metabolism do not receive the needed intensive behavioral change support, screening may provide no benefit,” write Richard W. Grant, MD, MPH, and colleagues in an editorial published with the recommendation.
“Given the role of our obesogenic and physically inactive society in the shift toward earlier onset of diabetes, efforts to increase screening and recognition of abnormal glucose metabolism must be coupled with robust public health measures to address the underlying contributors.”
BMI cutoff lower for at-risk ethnic populations
The recommendation, which updates the task force’s 2015 guideline, carries a “B” classification, meaning the USPSTF has high certainty that the net benefit is moderate. It now specifies screening from age 35to 70 for persons classified as overweight (body mass index at least 25) or obese (BMI at least 30) and recommends referral to preventive interventions when patients are found to have prediabetes.
In addition to recommendations of lifestyle changes, such as diet and physical activity, the task force also endorses the diabetes drug metformin as a beneficial intervention in the prevention or delay of diabetes, while noting fewer overall health benefits from metformin than from the lifestyle changes.
A lower BMI cutoff of at least 23 is recommended for diabetes screening of Asian Americans, and, importantly, screening for prediabetes and diabetes should be considered at an even earlier age if the patient is from a population with a disproportionately high prevalence of diabetes, including American Indian/Alaska Native, Black, Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, Hispanic/Latino, the task force recommends.
Screening tests should include fasting plasma glucose, hemoglobin A1c, or an oral glucose tolerance test. Although screening every 3 years “may be a reasonable approach for adults with normal blood glucose levels,” the task force adds that “the optimal screening interval for adults with an initial normal glucose test result is uncertain.”
Data review: Few with prediabetes know they have it
The need for the update was prompted by troubling data showing increasing diabetes rates despite early signs that can and should be identified and acted upon in the primary care setting to prevent disease progression.
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, for instance, show that while 13% of all U.S. adults 18 years or older have diabetes and 35% meet criteria for prediabetes, as many as 21% of those with diabetes were not aware of or did not report having the disease. Furthermore, only a small fraction – 15% of those with prediabetes – said they had been told by a health professional that they had this condition, the task force notes.
The task force’s final recommendation was based on a systematic review of evidence regarding the screening of asymptomatic, nonpregnant adults and the harms and benefits of interventions, such as physical activity, behavioral counseling, or pharmacotherapy.
Among key evidence supporting the lower age was a 2014 study showing that the number of people necessary to obtain one positive test for diabetes with screening sharply drops from 80 among those aged 30-34 years to just 31 among those aged 36-39.
Opportunistic universal screening of eligible people aged 35 and older would yield a ratio of 1 out of just 15 to spot a positive test, the authors of that study reported.
In addition, a large cohort study in more than 77,000 people with prediabetes strongly links the risk of developing diabetes with increases in A1c level and with increasing BMI.
ADA recommendations differ
The new recommendations differ from American Diabetes Association guidelines, which call for diabetes screening at all ages for people who are overweight or obese and who have one or more risk factors, such as physical inactivity or a first-degree relative with diabetes. If results are normal, repeat screening at least every 3 years is recommended.
The ADA further recommends universal screening for all adults 45 years and older, regardless of their risk factors.
For the screening of adults over 45, the ADA recommends using a fasting plasma glucose level, 2-hour plasma glucose level during a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test, or A1c level, regardless of risk factors.
The American Association of Clinical Endocrinology also recommends universal screening for prediabetes and diabetes for all adults 45 years or older, regardless of risk factors, and also advises screening those who have risk factors for diabetes regardless of age.
Screening of little benefit without behavior change support
In an interview, Dr. Grant added that broad efforts are essential as those at the practice level have clearly not succeeded.
“The medical model of individual counseling and referral has not really been effective, and so we really need to think in terms of large-scale public health action,” said Dr. Grant, of the division of research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Oakland.
His editorial details the sweeping, multifactorial efforts that are needed.
“To turn this recommendation into action – that is, to translate screening activities into improved clinical outcomes – change is needed at the patient-clinician level (recognizing and encouraging eligible individuals to be screened), health care system level (reducing screening barriers and ensuring access to robust lifestyle programs), and societal level (applying effective public health interventions to reduce obesity and increase exercise),” they write.
A top priority has to be a focus on individuals of diverse backgrounds and issues such as access to healthy programs in minority communities, Dr. Grant noted.
“Newly diagnosed adults are more likely to be African-American and Latinx,” he said.
“We really need to invest in healthier communities for low-income, non-White communities to reverse the persistent health care disparities in these communities.”
While the challenges may appear daunting, history shows they are not necessarily insurmountable – as evidenced in the campaign to discourage tobacco smoking.
“National smoking cessation efforts are one example of a mostly successful public health campaign that has made a difference in health behaviors,” Grant noted.
The recommendation is also posted on the USPSTF web site .
Dr. Grant reports receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
FROM JAMA