User login
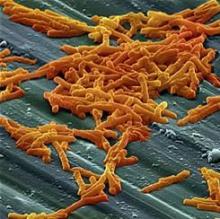
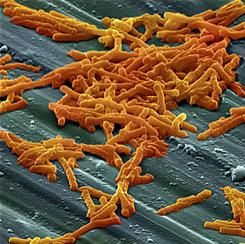
Dentist-prescribed antibiotics implicated in community-acquired C. diff
SAN DIEGO – Antibiotic prescriptions written by dentists make a substantial but largely unrecognized contribution to the risk of community-acquired Clostridium difficile (CA-CDI) infections, according to results of a public health initiative that was presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
When nearly 1,000 cases of CA-CDI suspected of being the result of antibiotic exposure were evaluated, it was found that 15% of the prescriptions were written by dentists, often for indications that are counter to current guidelines, reported Maria Bye, MPH, an officer in the Infectious Disease Epidemiology, Prevention, and Control Division of the Minnesota Department of Health, St. Paul.
In another finding from this study relevant to infection control, a substantial proportion of dentist-prescribed antibiotics associated with CA-CDI were not in the medical record. Rather, they were discovered in interviews conducted to isolate risk factors. “This is concerning since clinicians unaware of these exposures will not think about CA-CDI or other complications of antibiotic use, possibly delaying therapy,” Ms. Bye said.
The importance of dental antibiotic prescriptions in CA-CDI was identified in an ongoing infectious disease program managed by the Minnesota Department of Health in collaboration with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. In the years 2009-2015, medical records and interviews were conducted to identify risk factors in 1,626 confirmed cases of CA-CDI in five Minnesota counties. All cases were among patients without an overnight stay in a health care facility in the previous 12 weeks, which was an exclusion criterion.
After the review of medical records and patient interviews, 926 (57%) of the CA-CDI cases were deemed likely to be related to antibiotic exposure. Of these antibiotic exposures, 136 (15%) were from prescriptions written by dentists, a figure reached only when patients were interviewed. According to Ms. Bye, 34% of the antibiotics prescribed by dentists were not in the medical record.
There were also notable differences in antibiotic exposures stemming from dentist prescriptions relative to prescriptions from other sources. Perhaps most significantly, dental-related antibiotic prescriptions were far more likely to be for clindamycin (50% vs. 10%; P less than .001), which is commonly associated with increased risk of C. difficile, according to Ms. Bye. Fluoroquinolones (6% vs. 19%; P less than .001) and cephalosporins (7% vs. 30%; P less than .001) were significantly less likely to be prescribed by dentists. Patients who developed CA-CDI associated with antibiotics prescribed by dentists were also significantly older than were those receiving antibiotics from another source (mean age 57 years vs. 45 years; P less than .001).
For the first years of this analysis, information on the indication for dentist-prescribed antibiotics was not collected, but these data were collected beginning in 2015. In the data collected so far, a substantial proportion of prescriptions were written for prophylaxis against systemic infections, including prevention of endocarditis or infection of prosthetic joints. However, few of these prescriptions were indicated.
“The American Dental Association stated that antibiotic prophylaxis is not generally recommended in patients with prosthetic joints,” said Ms. Bye, noting that this is consistent with similar statements issued by the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgery. In 2007, the American Heart Association narrowed its recommendations for prophylactic antibiotics to patients at the highest risk of adverse consequences from endocarditis.
Of the four patients who received prophylactic antibiotics from their dentists for a cardiovascular or orthopedic indication, only one met current criteria, Ms. Bye reported.
The contribution of antibiotic exposures from dentist prescriptions to CA-CDI should not be surprising, according to Ms. Bye. In the United States, dentists prescribe 10% of all outpatient antibiotics. Although there are many valid indications for these prescriptions, Ms. Bye cited a survey that found that the proportion of dentists familiar with current guidelines and the risks of adverse events produced by antibiotics, including CA-CDI, is less than 50%.
“Dentists need to be included in antibiotic stewardship programs,” she advised. This will include educating dentists about the indications for antibiotic prophylaxis for medical conditions. She also suggested that clinicians should routinely ask patients about whether they have received antibiotics from a dentist so that this information gets into the medical record.
The event was the combined annual meetings of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America, the HIV Medicine Association, and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society.
SAN DIEGO – Antibiotic prescriptions written by dentists make a substantial but largely unrecognized contribution to the risk of community-acquired Clostridium difficile (CA-CDI) infections, according to results of a public health initiative that was presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
When nearly 1,000 cases of CA-CDI suspected of being the result of antibiotic exposure were evaluated, it was found that 15% of the prescriptions were written by dentists, often for indications that are counter to current guidelines, reported Maria Bye, MPH, an officer in the Infectious Disease Epidemiology, Prevention, and Control Division of the Minnesota Department of Health, St. Paul.
In another finding from this study relevant to infection control, a substantial proportion of dentist-prescribed antibiotics associated with CA-CDI were not in the medical record. Rather, they were discovered in interviews conducted to isolate risk factors. “This is concerning since clinicians unaware of these exposures will not think about CA-CDI or other complications of antibiotic use, possibly delaying therapy,” Ms. Bye said.
The importance of dental antibiotic prescriptions in CA-CDI was identified in an ongoing infectious disease program managed by the Minnesota Department of Health in collaboration with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. In the years 2009-2015, medical records and interviews were conducted to identify risk factors in 1,626 confirmed cases of CA-CDI in five Minnesota counties. All cases were among patients without an overnight stay in a health care facility in the previous 12 weeks, which was an exclusion criterion.
After the review of medical records and patient interviews, 926 (57%) of the CA-CDI cases were deemed likely to be related to antibiotic exposure. Of these antibiotic exposures, 136 (15%) were from prescriptions written by dentists, a figure reached only when patients were interviewed. According to Ms. Bye, 34% of the antibiotics prescribed by dentists were not in the medical record.
There were also notable differences in antibiotic exposures stemming from dentist prescriptions relative to prescriptions from other sources. Perhaps most significantly, dental-related antibiotic prescriptions were far more likely to be for clindamycin (50% vs. 10%; P less than .001), which is commonly associated with increased risk of C. difficile, according to Ms. Bye. Fluoroquinolones (6% vs. 19%; P less than .001) and cephalosporins (7% vs. 30%; P less than .001) were significantly less likely to be prescribed by dentists. Patients who developed CA-CDI associated with antibiotics prescribed by dentists were also significantly older than were those receiving antibiotics from another source (mean age 57 years vs. 45 years; P less than .001).
For the first years of this analysis, information on the indication for dentist-prescribed antibiotics was not collected, but these data were collected beginning in 2015. In the data collected so far, a substantial proportion of prescriptions were written for prophylaxis against systemic infections, including prevention of endocarditis or infection of prosthetic joints. However, few of these prescriptions were indicated.
“The American Dental Association stated that antibiotic prophylaxis is not generally recommended in patients with prosthetic joints,” said Ms. Bye, noting that this is consistent with similar statements issued by the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgery. In 2007, the American Heart Association narrowed its recommendations for prophylactic antibiotics to patients at the highest risk of adverse consequences from endocarditis.
Of the four patients who received prophylactic antibiotics from their dentists for a cardiovascular or orthopedic indication, only one met current criteria, Ms. Bye reported.
The contribution of antibiotic exposures from dentist prescriptions to CA-CDI should not be surprising, according to Ms. Bye. In the United States, dentists prescribe 10% of all outpatient antibiotics. Although there are many valid indications for these prescriptions, Ms. Bye cited a survey that found that the proportion of dentists familiar with current guidelines and the risks of adverse events produced by antibiotics, including CA-CDI, is less than 50%.
“Dentists need to be included in antibiotic stewardship programs,” she advised. This will include educating dentists about the indications for antibiotic prophylaxis for medical conditions. She also suggested that clinicians should routinely ask patients about whether they have received antibiotics from a dentist so that this information gets into the medical record.
The event was the combined annual meetings of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America, the HIV Medicine Association, and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society.
SAN DIEGO – Antibiotic prescriptions written by dentists make a substantial but largely unrecognized contribution to the risk of community-acquired Clostridium difficile (CA-CDI) infections, according to results of a public health initiative that was presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
When nearly 1,000 cases of CA-CDI suspected of being the result of antibiotic exposure were evaluated, it was found that 15% of the prescriptions were written by dentists, often for indications that are counter to current guidelines, reported Maria Bye, MPH, an officer in the Infectious Disease Epidemiology, Prevention, and Control Division of the Minnesota Department of Health, St. Paul.
In another finding from this study relevant to infection control, a substantial proportion of dentist-prescribed antibiotics associated with CA-CDI were not in the medical record. Rather, they were discovered in interviews conducted to isolate risk factors. “This is concerning since clinicians unaware of these exposures will not think about CA-CDI or other complications of antibiotic use, possibly delaying therapy,” Ms. Bye said.
The importance of dental antibiotic prescriptions in CA-CDI was identified in an ongoing infectious disease program managed by the Minnesota Department of Health in collaboration with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. In the years 2009-2015, medical records and interviews were conducted to identify risk factors in 1,626 confirmed cases of CA-CDI in five Minnesota counties. All cases were among patients without an overnight stay in a health care facility in the previous 12 weeks, which was an exclusion criterion.
After the review of medical records and patient interviews, 926 (57%) of the CA-CDI cases were deemed likely to be related to antibiotic exposure. Of these antibiotic exposures, 136 (15%) were from prescriptions written by dentists, a figure reached only when patients were interviewed. According to Ms. Bye, 34% of the antibiotics prescribed by dentists were not in the medical record.
There were also notable differences in antibiotic exposures stemming from dentist prescriptions relative to prescriptions from other sources. Perhaps most significantly, dental-related antibiotic prescriptions were far more likely to be for clindamycin (50% vs. 10%; P less than .001), which is commonly associated with increased risk of C. difficile, according to Ms. Bye. Fluoroquinolones (6% vs. 19%; P less than .001) and cephalosporins (7% vs. 30%; P less than .001) were significantly less likely to be prescribed by dentists. Patients who developed CA-CDI associated with antibiotics prescribed by dentists were also significantly older than were those receiving antibiotics from another source (mean age 57 years vs. 45 years; P less than .001).
For the first years of this analysis, information on the indication for dentist-prescribed antibiotics was not collected, but these data were collected beginning in 2015. In the data collected so far, a substantial proportion of prescriptions were written for prophylaxis against systemic infections, including prevention of endocarditis or infection of prosthetic joints. However, few of these prescriptions were indicated.
“The American Dental Association stated that antibiotic prophylaxis is not generally recommended in patients with prosthetic joints,” said Ms. Bye, noting that this is consistent with similar statements issued by the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgery. In 2007, the American Heart Association narrowed its recommendations for prophylactic antibiotics to patients at the highest risk of adverse consequences from endocarditis.
Of the four patients who received prophylactic antibiotics from their dentists for a cardiovascular or orthopedic indication, only one met current criteria, Ms. Bye reported.
The contribution of antibiotic exposures from dentist prescriptions to CA-CDI should not be surprising, according to Ms. Bye. In the United States, dentists prescribe 10% of all outpatient antibiotics. Although there are many valid indications for these prescriptions, Ms. Bye cited a survey that found that the proportion of dentists familiar with current guidelines and the risks of adverse events produced by antibiotics, including CA-CDI, is less than 50%.
“Dentists need to be included in antibiotic stewardship programs,” she advised. This will include educating dentists about the indications for antibiotic prophylaxis for medical conditions. She also suggested that clinicians should routinely ask patients about whether they have received antibiotics from a dentist so that this information gets into the medical record.
The event was the combined annual meetings of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America, the HIV Medicine Association, and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society.
AT ID WEEK 2017
Key clinical point: A public health initiative tracking community-acquired Clostridium difficile infections suggests dental antibiotic prescribing is a significant source.
Major finding: When traced, 15% of the antibiotics related to community-acquired C. difficile infections were from a dentist prescription.
Data source: Population-based surveillance study.
Disclosures: Ms. Bye reported that she has no financial relationships relevant to this topic.
In the reemergence of typhus, the challenge is early diagnosis
SAN DIEGO – Typhus in many forms, particularly scrub typhus, has reemerged worldwide, but none of these rickettsial infections poses a significant public health threat if promptly diagnosed, according to an update presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
Scrub typhus, which is spread by several species of trombiculid mites or chiggers, poses a large threat in regard to typhus epidemics, particularly in Asia, but sporadic cases of different types of typhus are being seen everywhere, including in the United States, according to George M. Varghese, MD, department of infectious diseases, Christian Medical College, Vellore, India.
“The typhus diseases are clinically similar but epidemiologically and etiologically distinct,” reported Dr. Varghese, “but doxycycline is the drug of choice for almost all of the rickettsial infections.”

The bacteria responsible for scrub typhus is Orientia tsutsugamushi, which is no longer included in the genus Rickettsia, but Dr. Varghese, who has published frequently on the epidemiology of scrub typhus, said that it is still appropriately grouped among rickettsial infections. It shares many features with the other rickettsioses, which were considered to be fading but are now resurging after the large epidemics that occurred prior to the introduction of antibiotics.
In the World Wars, Rickettsia prowazekii – which is carried and spread by body lice – was the most well known typhus threat. According to Dr. Varghese, this bacterium may have killed more soldiers in these conflicts than did firearms. Although R. prowazekii has not disappeared as a source of typhus outbreaks, particularly in South America and Africa, there are current epidemics produced from rickettsial infections carried by fleas, such as R. typhi, or ticks, like R. rickettsii, or mice, like R. felis.
For clinical detection of these forms of typhus, there are differences. Although all are associated with a rapid onset of fever, headache, and myalgia, subtle signs can be helpful in making a diagnosis while waiting for laboratory confirmation. For example, scrub typhus, unlike Rocky Mountain Fever, which is caused by tick bites, does not generally include a rash. Rather, eschars, which are small patches of necrotic skin, are far more characteristic.
“Serological tests are the most common diagnostic tool for typhus, but serology may not allow early diagnosis. You can obtain a false positive in the early stages of disease,” Dr. Varghese warned. To speed the diagnosis, he said that looking for the clinical clues characteristic of the suspected form of typhus, such as the scrub typhus-associated eschar, “is valuable.” However, he also emphasized that even with positive serology results, “good epidemiology and history is helpful for laboratory interpretation.”
A variety of serological tests can identify typhus pathogens, but ELISA is now the most widely used, according to Dr. Varghese, noting that this test offers a sensitivity of 93% and a specificity of 91%. Both are higher than those provided by alternatives. As a result of improved sensitivity of diagnostic tests, prevalence rates of some forms of typhus have proved to be unexpectedly high. For example, in a study undertaken in his region of India, the seroprevalence of scrub typhus was 31.8% (Trop Med Int Health. 2017;22:576-82. doi: 10.1111/tmi.12853).
Of unmet needs in the clinical management of typhus, Dr. Varghese listed better strategies for point-of-care diagnosis and treatment and better data on how to manage patients who are severely ill. Advanced disease, which is common to rural areas with limited access to health care, is the source of almost all typhus mortality, according to Dr. Varghese. He described a trial now being initiated in severe disease that will compare intravenous doxycycline to IV azithromycin and to a combination of both IV doxycycline and azithromycin.
Although Dr. Varghese cautioned that reports of resistant typhus infections, particularly in Thailand, might prove to be the next big clinical challenge in typhus, he said that progress is being made toward reducing the burden of this disease in his area of the world. In a disease associated with a mortality of 50% if left untreated, he attributes gains to earlier diagnosis and prompt treatment.
At his medical center, “we have been working with this disease for a decade and a half,” he said, referring to scrub typhus. “When we started off, the mortality was around 15% after diagnosis. Today, the mortality is about 5%-7%.”
Dr. Varghese reported that he has no financial relationships relevant to this topic. The event was the combined annual meetings of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America, the HIV Medicine Association, and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society.
SAN DIEGO – Typhus in many forms, particularly scrub typhus, has reemerged worldwide, but none of these rickettsial infections poses a significant public health threat if promptly diagnosed, according to an update presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
Scrub typhus, which is spread by several species of trombiculid mites or chiggers, poses a large threat in regard to typhus epidemics, particularly in Asia, but sporadic cases of different types of typhus are being seen everywhere, including in the United States, according to George M. Varghese, MD, department of infectious diseases, Christian Medical College, Vellore, India.
“The typhus diseases are clinically similar but epidemiologically and etiologically distinct,” reported Dr. Varghese, “but doxycycline is the drug of choice for almost all of the rickettsial infections.”

The bacteria responsible for scrub typhus is Orientia tsutsugamushi, which is no longer included in the genus Rickettsia, but Dr. Varghese, who has published frequently on the epidemiology of scrub typhus, said that it is still appropriately grouped among rickettsial infections. It shares many features with the other rickettsioses, which were considered to be fading but are now resurging after the large epidemics that occurred prior to the introduction of antibiotics.
In the World Wars, Rickettsia prowazekii – which is carried and spread by body lice – was the most well known typhus threat. According to Dr. Varghese, this bacterium may have killed more soldiers in these conflicts than did firearms. Although R. prowazekii has not disappeared as a source of typhus outbreaks, particularly in South America and Africa, there are current epidemics produced from rickettsial infections carried by fleas, such as R. typhi, or ticks, like R. rickettsii, or mice, like R. felis.
For clinical detection of these forms of typhus, there are differences. Although all are associated with a rapid onset of fever, headache, and myalgia, subtle signs can be helpful in making a diagnosis while waiting for laboratory confirmation. For example, scrub typhus, unlike Rocky Mountain Fever, which is caused by tick bites, does not generally include a rash. Rather, eschars, which are small patches of necrotic skin, are far more characteristic.
“Serological tests are the most common diagnostic tool for typhus, but serology may not allow early diagnosis. You can obtain a false positive in the early stages of disease,” Dr. Varghese warned. To speed the diagnosis, he said that looking for the clinical clues characteristic of the suspected form of typhus, such as the scrub typhus-associated eschar, “is valuable.” However, he also emphasized that even with positive serology results, “good epidemiology and history is helpful for laboratory interpretation.”
A variety of serological tests can identify typhus pathogens, but ELISA is now the most widely used, according to Dr. Varghese, noting that this test offers a sensitivity of 93% and a specificity of 91%. Both are higher than those provided by alternatives. As a result of improved sensitivity of diagnostic tests, prevalence rates of some forms of typhus have proved to be unexpectedly high. For example, in a study undertaken in his region of India, the seroprevalence of scrub typhus was 31.8% (Trop Med Int Health. 2017;22:576-82. doi: 10.1111/tmi.12853).
Of unmet needs in the clinical management of typhus, Dr. Varghese listed better strategies for point-of-care diagnosis and treatment and better data on how to manage patients who are severely ill. Advanced disease, which is common to rural areas with limited access to health care, is the source of almost all typhus mortality, according to Dr. Varghese. He described a trial now being initiated in severe disease that will compare intravenous doxycycline to IV azithromycin and to a combination of both IV doxycycline and azithromycin.
Although Dr. Varghese cautioned that reports of resistant typhus infections, particularly in Thailand, might prove to be the next big clinical challenge in typhus, he said that progress is being made toward reducing the burden of this disease in his area of the world. In a disease associated with a mortality of 50% if left untreated, he attributes gains to earlier diagnosis and prompt treatment.
At his medical center, “we have been working with this disease for a decade and a half,” he said, referring to scrub typhus. “When we started off, the mortality was around 15% after diagnosis. Today, the mortality is about 5%-7%.”
Dr. Varghese reported that he has no financial relationships relevant to this topic. The event was the combined annual meetings of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America, the HIV Medicine Association, and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society.
SAN DIEGO – Typhus in many forms, particularly scrub typhus, has reemerged worldwide, but none of these rickettsial infections poses a significant public health threat if promptly diagnosed, according to an update presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
Scrub typhus, which is spread by several species of trombiculid mites or chiggers, poses a large threat in regard to typhus epidemics, particularly in Asia, but sporadic cases of different types of typhus are being seen everywhere, including in the United States, according to George M. Varghese, MD, department of infectious diseases, Christian Medical College, Vellore, India.
“The typhus diseases are clinically similar but epidemiologically and etiologically distinct,” reported Dr. Varghese, “but doxycycline is the drug of choice for almost all of the rickettsial infections.”

The bacteria responsible for scrub typhus is Orientia tsutsugamushi, which is no longer included in the genus Rickettsia, but Dr. Varghese, who has published frequently on the epidemiology of scrub typhus, said that it is still appropriately grouped among rickettsial infections. It shares many features with the other rickettsioses, which were considered to be fading but are now resurging after the large epidemics that occurred prior to the introduction of antibiotics.
In the World Wars, Rickettsia prowazekii – which is carried and spread by body lice – was the most well known typhus threat. According to Dr. Varghese, this bacterium may have killed more soldiers in these conflicts than did firearms. Although R. prowazekii has not disappeared as a source of typhus outbreaks, particularly in South America and Africa, there are current epidemics produced from rickettsial infections carried by fleas, such as R. typhi, or ticks, like R. rickettsii, or mice, like R. felis.
For clinical detection of these forms of typhus, there are differences. Although all are associated with a rapid onset of fever, headache, and myalgia, subtle signs can be helpful in making a diagnosis while waiting for laboratory confirmation. For example, scrub typhus, unlike Rocky Mountain Fever, which is caused by tick bites, does not generally include a rash. Rather, eschars, which are small patches of necrotic skin, are far more characteristic.
“Serological tests are the most common diagnostic tool for typhus, but serology may not allow early diagnosis. You can obtain a false positive in the early stages of disease,” Dr. Varghese warned. To speed the diagnosis, he said that looking for the clinical clues characteristic of the suspected form of typhus, such as the scrub typhus-associated eschar, “is valuable.” However, he also emphasized that even with positive serology results, “good epidemiology and history is helpful for laboratory interpretation.”
A variety of serological tests can identify typhus pathogens, but ELISA is now the most widely used, according to Dr. Varghese, noting that this test offers a sensitivity of 93% and a specificity of 91%. Both are higher than those provided by alternatives. As a result of improved sensitivity of diagnostic tests, prevalence rates of some forms of typhus have proved to be unexpectedly high. For example, in a study undertaken in his region of India, the seroprevalence of scrub typhus was 31.8% (Trop Med Int Health. 2017;22:576-82. doi: 10.1111/tmi.12853).
Of unmet needs in the clinical management of typhus, Dr. Varghese listed better strategies for point-of-care diagnosis and treatment and better data on how to manage patients who are severely ill. Advanced disease, which is common to rural areas with limited access to health care, is the source of almost all typhus mortality, according to Dr. Varghese. He described a trial now being initiated in severe disease that will compare intravenous doxycycline to IV azithromycin and to a combination of both IV doxycycline and azithromycin.
Although Dr. Varghese cautioned that reports of resistant typhus infections, particularly in Thailand, might prove to be the next big clinical challenge in typhus, he said that progress is being made toward reducing the burden of this disease in his area of the world. In a disease associated with a mortality of 50% if left untreated, he attributes gains to earlier diagnosis and prompt treatment.
At his medical center, “we have been working with this disease for a decade and a half,” he said, referring to scrub typhus. “When we started off, the mortality was around 15% after diagnosis. Today, the mortality is about 5%-7%.”
Dr. Varghese reported that he has no financial relationships relevant to this topic. The event was the combined annual meetings of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America, the HIV Medicine Association, and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society.
AT IDWEEK 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Almost all of the estimated 15,000 annual global deaths attributed to rickettsial infections could be eliminated with prompt doxycycline therapy.
Data source: Topic review.
Disclosures: Dr. Varghese reported that he has no relevant conflicts to disclose.
IDWeek 2017 opens in San Diego
facing infectious diseases clinicians and researchers in the 21st century.
Premeeting workshops and symposia occupy most of the first 2 days of the event, with highlights including a session on managing infections in opioid users and a “late breaker” symposium addressing the latest on the H7N9 outbreak in China, the current findings and recommendations regarding Candida auris, and the epidemiology of the recent Legionella outbreaks in the United States. Another late breaker session focuses on the recent spate of hepatitis A outbreaks, including one in conference host city San Diego, primarily among the homeless population.
IDWeek is the combined annual meeting of the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA), the HIV Medicine Association (HIVMA), and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society (PIDS). The first IDWeek was held in 2012.
One intriguing interactive session – aptly-titled “Nightmare Bugs” – will investigate the problems posed by multidrug-resistant organisms and the need for new antimicrobials to defeat them.
There are many sessions and posters addressing evergreen clinical topics for ID clinicians, such as antimicrobial resistance, antibiotic stewardship, surgical site infections, bacteremia and sepsis, Clostridium difficile, hepatitis care, and HIV care. But the education committee at IDWeek always manages to touch on topics in the news. For instance, one late breaker session will feature a discussion of the nexus between the opioid crisis and infectious diseases, the outbreak of cholera in Yemen, and the epidemiology of the yellow fever outbreak in Brazil.
Featured speakers at the event include James M. Hughes, MD, professor of medicine at Emory University, Atlanta, who will discuss the importance of a One Health approach to emerging microbial threats, and Connie Celum, MD, MPH, professor of global health and medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, who intends to describe the progress in effective HIV prevention interventions and lessons learned in implementation. Neil O. Fishman, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, is delivering the annual SHEA lecture at IDWeek, and will explain how ID physicians and epidemiologists can promote interventions to achieve high reliability in health care. Renowned ID researcher Janet Englund, MD, of Seattle Children’s Hospital, will discuss the potential future therapies to prevent or treat respiratory viral infections in high-risk pediatric patients.
The 2017 conference will close with a three-part plenary – “21st Century Cures” – featuring ID luminaries Christopher Karp, MD, of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, James E. Crowe Jr., MD, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn., and David Thomas, MD, MPH, of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore.
[email protected]
On Twitter @richpizzi
facing infectious diseases clinicians and researchers in the 21st century.
Premeeting workshops and symposia occupy most of the first 2 days of the event, with highlights including a session on managing infections in opioid users and a “late breaker” symposium addressing the latest on the H7N9 outbreak in China, the current findings and recommendations regarding Candida auris, and the epidemiology of the recent Legionella outbreaks in the United States. Another late breaker session focuses on the recent spate of hepatitis A outbreaks, including one in conference host city San Diego, primarily among the homeless population.
IDWeek is the combined annual meeting of the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA), the HIV Medicine Association (HIVMA), and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society (PIDS). The first IDWeek was held in 2012.
One intriguing interactive session – aptly-titled “Nightmare Bugs” – will investigate the problems posed by multidrug-resistant organisms and the need for new antimicrobials to defeat them.
There are many sessions and posters addressing evergreen clinical topics for ID clinicians, such as antimicrobial resistance, antibiotic stewardship, surgical site infections, bacteremia and sepsis, Clostridium difficile, hepatitis care, and HIV care. But the education committee at IDWeek always manages to touch on topics in the news. For instance, one late breaker session will feature a discussion of the nexus between the opioid crisis and infectious diseases, the outbreak of cholera in Yemen, and the epidemiology of the yellow fever outbreak in Brazil.
Featured speakers at the event include James M. Hughes, MD, professor of medicine at Emory University, Atlanta, who will discuss the importance of a One Health approach to emerging microbial threats, and Connie Celum, MD, MPH, professor of global health and medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, who intends to describe the progress in effective HIV prevention interventions and lessons learned in implementation. Neil O. Fishman, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, is delivering the annual SHEA lecture at IDWeek, and will explain how ID physicians and epidemiologists can promote interventions to achieve high reliability in health care. Renowned ID researcher Janet Englund, MD, of Seattle Children’s Hospital, will discuss the potential future therapies to prevent or treat respiratory viral infections in high-risk pediatric patients.
The 2017 conference will close with a three-part plenary – “21st Century Cures” – featuring ID luminaries Christopher Karp, MD, of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, James E. Crowe Jr., MD, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn., and David Thomas, MD, MPH, of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore.
[email protected]
On Twitter @richpizzi
facing infectious diseases clinicians and researchers in the 21st century.
Premeeting workshops and symposia occupy most of the first 2 days of the event, with highlights including a session on managing infections in opioid users and a “late breaker” symposium addressing the latest on the H7N9 outbreak in China, the current findings and recommendations regarding Candida auris, and the epidemiology of the recent Legionella outbreaks in the United States. Another late breaker session focuses on the recent spate of hepatitis A outbreaks, including one in conference host city San Diego, primarily among the homeless population.
IDWeek is the combined annual meeting of the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA), the HIV Medicine Association (HIVMA), and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society (PIDS). The first IDWeek was held in 2012.
One intriguing interactive session – aptly-titled “Nightmare Bugs” – will investigate the problems posed by multidrug-resistant organisms and the need for new antimicrobials to defeat them.
There are many sessions and posters addressing evergreen clinical topics for ID clinicians, such as antimicrobial resistance, antibiotic stewardship, surgical site infections, bacteremia and sepsis, Clostridium difficile, hepatitis care, and HIV care. But the education committee at IDWeek always manages to touch on topics in the news. For instance, one late breaker session will feature a discussion of the nexus between the opioid crisis and infectious diseases, the outbreak of cholera in Yemen, and the epidemiology of the yellow fever outbreak in Brazil.
Featured speakers at the event include James M. Hughes, MD, professor of medicine at Emory University, Atlanta, who will discuss the importance of a One Health approach to emerging microbial threats, and Connie Celum, MD, MPH, professor of global health and medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, who intends to describe the progress in effective HIV prevention interventions and lessons learned in implementation. Neil O. Fishman, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, is delivering the annual SHEA lecture at IDWeek, and will explain how ID physicians and epidemiologists can promote interventions to achieve high reliability in health care. Renowned ID researcher Janet Englund, MD, of Seattle Children’s Hospital, will discuss the potential future therapies to prevent or treat respiratory viral infections in high-risk pediatric patients.
The 2017 conference will close with a three-part plenary – “21st Century Cures” – featuring ID luminaries Christopher Karp, MD, of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, James E. Crowe Jr., MD, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn., and David Thomas, MD, MPH, of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore.
[email protected]
On Twitter @richpizzi
Bezlotoxumab may lower risk of C. difficile readmissions
Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) patients treated with bezlotoxumab were less likely to be readmitted for recurring symptoms within 30 days of discharge, according to a phase 3 trial funded by Merck.
Recurrent CDI is a burden on both patients and providers, increasing health risks with each recurrence and eating through hospital resources, according to Vimalanand S. Prabhu, PhD, associate principal scientist for Merck.
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, study of 1,050 CDI patients, a total of 27 (5%) of 530 of those given bezlotoxumab were re-hospitalized 30 days after discharge, compared with 58 (11%) of 520 patients in the placebo group (Clin Infect Dis. 2017 Aug 11. doi. 10.1093/cid/cix523).
Patients were gathered from 322 sites across 30 countries between November 2011 and May 2015.
When measuring CDI-related readmissions, the investigators found use of bezlotoxumab reduced rCDI hospitalizations by 6%, and by approximately 8% in high-risk patients, such as those over 65 years old or with severe CDI.
Bezlotoxumab works by binding to CDI toxin B, a primary cause of CDI symptoms, according to Dr. Prabhu and fellow investigators. The researchers suggested that bezlotoxumab could be a prevailing factor in fighting the rate of CDI infections, which accounted for 29,000 deaths in 2011 (N Engl J Med. 2015 Jun 11;372[24]:2368-9).
Investigators acknowledged that patients admitted for the study may be healthier than the real-world CDI population.
All investigators reported some financial involvement, whether being a full-time employee or acting as a consultant, for Merck, which funded the study. Individually, investigators reported financial ties to similar medical companies, such as Pfizer and AstraZeneca.
[email protected]
On Twitter @eaztweets
Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) patients treated with bezlotoxumab were less likely to be readmitted for recurring symptoms within 30 days of discharge, according to a phase 3 trial funded by Merck.
Recurrent CDI is a burden on both patients and providers, increasing health risks with each recurrence and eating through hospital resources, according to Vimalanand S. Prabhu, PhD, associate principal scientist for Merck.
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, study of 1,050 CDI patients, a total of 27 (5%) of 530 of those given bezlotoxumab were re-hospitalized 30 days after discharge, compared with 58 (11%) of 520 patients in the placebo group (Clin Infect Dis. 2017 Aug 11. doi. 10.1093/cid/cix523).
Patients were gathered from 322 sites across 30 countries between November 2011 and May 2015.
When measuring CDI-related readmissions, the investigators found use of bezlotoxumab reduced rCDI hospitalizations by 6%, and by approximately 8% in high-risk patients, such as those over 65 years old or with severe CDI.
Bezlotoxumab works by binding to CDI toxin B, a primary cause of CDI symptoms, according to Dr. Prabhu and fellow investigators. The researchers suggested that bezlotoxumab could be a prevailing factor in fighting the rate of CDI infections, which accounted for 29,000 deaths in 2011 (N Engl J Med. 2015 Jun 11;372[24]:2368-9).
Investigators acknowledged that patients admitted for the study may be healthier than the real-world CDI population.
All investigators reported some financial involvement, whether being a full-time employee or acting as a consultant, for Merck, which funded the study. Individually, investigators reported financial ties to similar medical companies, such as Pfizer and AstraZeneca.
[email protected]
On Twitter @eaztweets
Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) patients treated with bezlotoxumab were less likely to be readmitted for recurring symptoms within 30 days of discharge, according to a phase 3 trial funded by Merck.
Recurrent CDI is a burden on both patients and providers, increasing health risks with each recurrence and eating through hospital resources, according to Vimalanand S. Prabhu, PhD, associate principal scientist for Merck.
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, study of 1,050 CDI patients, a total of 27 (5%) of 530 of those given bezlotoxumab were re-hospitalized 30 days after discharge, compared with 58 (11%) of 520 patients in the placebo group (Clin Infect Dis. 2017 Aug 11. doi. 10.1093/cid/cix523).
Patients were gathered from 322 sites across 30 countries between November 2011 and May 2015.
When measuring CDI-related readmissions, the investigators found use of bezlotoxumab reduced rCDI hospitalizations by 6%, and by approximately 8% in high-risk patients, such as those over 65 years old or with severe CDI.
Bezlotoxumab works by binding to CDI toxin B, a primary cause of CDI symptoms, according to Dr. Prabhu and fellow investigators. The researchers suggested that bezlotoxumab could be a prevailing factor in fighting the rate of CDI infections, which accounted for 29,000 deaths in 2011 (N Engl J Med. 2015 Jun 11;372[24]:2368-9).
Investigators acknowledged that patients admitted for the study may be healthier than the real-world CDI population.
All investigators reported some financial involvement, whether being a full-time employee or acting as a consultant, for Merck, which funded the study. Individually, investigators reported financial ties to similar medical companies, such as Pfizer and AstraZeneca.
[email protected]
On Twitter @eaztweets
FROM CLINICAL INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Key clinical point:
Major finding: A total of 27 of 530 (5%) bezlotoxumab patients were readmitted within 30 days of discharge compared with 58 of 520 (11%) placebo patients.
Data source: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, global phase 3 trials conducted from November 2011-May 2015 at 322 sites in 30 countries.
Disclosures: All investigators report employment or financial support with Merck and have individually reported financial ties to similar companies like Astellas, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, and others.
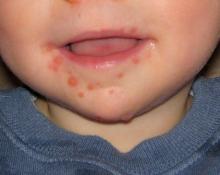
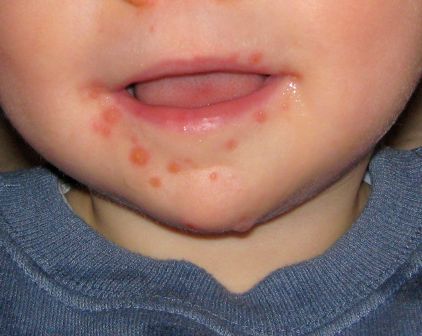
Developing vaccines against enterovirus-A71 called a priority
MADRID – Is there a need for an enterovirus-A71 vaccine?
This is a new question for North American and European physicians, but not so new in Asia.
“China says yes, with more than 15 million cases of hand, foot, and mouth disease resulting in 3,500 deaths since surveillance started in 2009,” Heli Harvala, MD, said at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
Seroconversion rates 28 days after the second dose of these vaccines, both directed specifically against viral subgenotype C-4, are 92%-100%. Vaccine efficacy is 91%-97%, according to Dr. Harvala, a consultant medical virologist at University College London.
It remains a mystery why major outbreaks of severe EV-A71 disease have mostly occurred in Asia, with the notable exception of a Spanish outbreak of EV-A71 encephalitis in 2016. The possibility of much wider spread is concerning.
The Chinese monovalent EV-A71 vaccines, however, are seen as a stopgap. For one thing, recent evidence suggests that it’s probably not the specific EV-A71 C-4 viral subgenotype that accounts for all severe disease.
“I think we have to aim for a multivalent vaccine,” Dr. Harvala said.
Now in clinical trials, investigational bivalent vaccines are directed against other EV-A71 subgenotypes in addition to C-4, and also against another enterovirus, coxsackievirus serotype A16, the most common cause of classic hand, foot, and mouth disease in the United States. But that’s probably not enough, according to Dr. Harvala. She noted that coxsackievirus A6, which was first identified more than 50 years ago, abruptly became the main cause of mild hand, foot, and mouth disease in China in 2013 and again in 2015. Moreover, its role in severe cases is growing, and there have been important outbreaks in the United States in recent years. These severe cases come in three main presentations, resembling either erythema multiforme, chicken pox, or eczema herpeticum.
Dr. Harvala added that a next-generation vaccine probably also should offer protection against enterovirus-D68. In 2014, there were 1,153 laboratory-confirmed EV-D68 infections and 14 deaths in the United States and Canada. This infection poses a diagnostic challenge: while the virus is readily detectable on throat swabs, it’s only rarely present in stool or cerebrospinal fluid samples.
“It’s important to keep in mind that this infection is still underdiagnosed. We are not really looking for it,” she said.
No specific treatment for enterovirus infections is available. Three capsid-binding antiviral agents now are in clinical trials: pleconaril, vapendavir, and pocapavir. In addition, translational studies have demonstrated that the SSRI fluoxetine inhibits enterovirus replication, but there have been no clinical trials as yet.
Although development of antivirals effective against enterovirus is an active area of research, Dr. Harvala thinks drug resistance will be an issue, underscoring the importance of vaccine development.
She reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding her presentation.
MADRID – Is there a need for an enterovirus-A71 vaccine?
This is a new question for North American and European physicians, but not so new in Asia.
“China says yes, with more than 15 million cases of hand, foot, and mouth disease resulting in 3,500 deaths since surveillance started in 2009,” Heli Harvala, MD, said at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
Seroconversion rates 28 days after the second dose of these vaccines, both directed specifically against viral subgenotype C-4, are 92%-100%. Vaccine efficacy is 91%-97%, according to Dr. Harvala, a consultant medical virologist at University College London.
It remains a mystery why major outbreaks of severe EV-A71 disease have mostly occurred in Asia, with the notable exception of a Spanish outbreak of EV-A71 encephalitis in 2016. The possibility of much wider spread is concerning.
The Chinese monovalent EV-A71 vaccines, however, are seen as a stopgap. For one thing, recent evidence suggests that it’s probably not the specific EV-A71 C-4 viral subgenotype that accounts for all severe disease.
“I think we have to aim for a multivalent vaccine,” Dr. Harvala said.
Now in clinical trials, investigational bivalent vaccines are directed against other EV-A71 subgenotypes in addition to C-4, and also against another enterovirus, coxsackievirus serotype A16, the most common cause of classic hand, foot, and mouth disease in the United States. But that’s probably not enough, according to Dr. Harvala. She noted that coxsackievirus A6, which was first identified more than 50 years ago, abruptly became the main cause of mild hand, foot, and mouth disease in China in 2013 and again in 2015. Moreover, its role in severe cases is growing, and there have been important outbreaks in the United States in recent years. These severe cases come in three main presentations, resembling either erythema multiforme, chicken pox, or eczema herpeticum.
Dr. Harvala added that a next-generation vaccine probably also should offer protection against enterovirus-D68. In 2014, there were 1,153 laboratory-confirmed EV-D68 infections and 14 deaths in the United States and Canada. This infection poses a diagnostic challenge: while the virus is readily detectable on throat swabs, it’s only rarely present in stool or cerebrospinal fluid samples.
“It’s important to keep in mind that this infection is still underdiagnosed. We are not really looking for it,” she said.
No specific treatment for enterovirus infections is available. Three capsid-binding antiviral agents now are in clinical trials: pleconaril, vapendavir, and pocapavir. In addition, translational studies have demonstrated that the SSRI fluoxetine inhibits enterovirus replication, but there have been no clinical trials as yet.
Although development of antivirals effective against enterovirus is an active area of research, Dr. Harvala thinks drug resistance will be an issue, underscoring the importance of vaccine development.
She reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding her presentation.
MADRID – Is there a need for an enterovirus-A71 vaccine?
This is a new question for North American and European physicians, but not so new in Asia.
“China says yes, with more than 15 million cases of hand, foot, and mouth disease resulting in 3,500 deaths since surveillance started in 2009,” Heli Harvala, MD, said at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
Seroconversion rates 28 days after the second dose of these vaccines, both directed specifically against viral subgenotype C-4, are 92%-100%. Vaccine efficacy is 91%-97%, according to Dr. Harvala, a consultant medical virologist at University College London.
It remains a mystery why major outbreaks of severe EV-A71 disease have mostly occurred in Asia, with the notable exception of a Spanish outbreak of EV-A71 encephalitis in 2016. The possibility of much wider spread is concerning.
The Chinese monovalent EV-A71 vaccines, however, are seen as a stopgap. For one thing, recent evidence suggests that it’s probably not the specific EV-A71 C-4 viral subgenotype that accounts for all severe disease.
“I think we have to aim for a multivalent vaccine,” Dr. Harvala said.
Now in clinical trials, investigational bivalent vaccines are directed against other EV-A71 subgenotypes in addition to C-4, and also against another enterovirus, coxsackievirus serotype A16, the most common cause of classic hand, foot, and mouth disease in the United States. But that’s probably not enough, according to Dr. Harvala. She noted that coxsackievirus A6, which was first identified more than 50 years ago, abruptly became the main cause of mild hand, foot, and mouth disease in China in 2013 and again in 2015. Moreover, its role in severe cases is growing, and there have been important outbreaks in the United States in recent years. These severe cases come in three main presentations, resembling either erythema multiforme, chicken pox, or eczema herpeticum.
Dr. Harvala added that a next-generation vaccine probably also should offer protection against enterovirus-D68. In 2014, there were 1,153 laboratory-confirmed EV-D68 infections and 14 deaths in the United States and Canada. This infection poses a diagnostic challenge: while the virus is readily detectable on throat swabs, it’s only rarely present in stool or cerebrospinal fluid samples.
“It’s important to keep in mind that this infection is still underdiagnosed. We are not really looking for it,” she said.
No specific treatment for enterovirus infections is available. Three capsid-binding antiviral agents now are in clinical trials: pleconaril, vapendavir, and pocapavir. In addition, translational studies have demonstrated that the SSRI fluoxetine inhibits enterovirus replication, but there have been no clinical trials as yet.
Although development of antivirals effective against enterovirus is an active area of research, Dr. Harvala thinks drug resistance will be an issue, underscoring the importance of vaccine development.
She reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding her presentation.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ESPID 2017
Researchers develop 30-min antibiotic susceptibility test for UTI
Researchers in Sweden have developed a 30-minute test capable of determining whether a bacterial urinary tract infection is susceptible or resistant to nine antibiotics. Their findings suggest that it is possible to develop a point-of-care test for patients with UTI.
Most phenotypic and genotypic antibiotic susceptibility tests are too slow to guide treatment, ranging from 2 days to 1 hour. The researchers at Uppsala (Sweden) University cut the testing time down to less than 30 minutes by using a microfluidic chip and direct single-cell imaging.
The chip traps the bacterial cells and allows growth media with different antibiotics (or none) to flow around them. “With this setup, we could detect the differential growth rate between treatment and reference populations in 3 min for ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, mecillinam, nitrofurantoin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole; 7 min for amoxicillin-clavulanate and doripenem; 9 min for fosfomycin; and 11 min for ampicillin based on 99.9% confidence intervals,” wrote Özden Baltekin and his coauthors.
That test specifically used Escherichia coli cells; comparable speed and accuracy was replicated using Klebsiella pneumoniae and Staphylococcus saprophyticus. For the development of a point-of-care test for patients, the researchers said all that would be needed are about 100 bacteria cells.
“We have here focused on bacterial species and antibiotics related to UTIs, but it is likely that the same principles would work for sepsis, mastitis, or meningitis,” they suggested (Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2017 Aug 8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1708558114).
Researchers in Sweden have developed a 30-minute test capable of determining whether a bacterial urinary tract infection is susceptible or resistant to nine antibiotics. Their findings suggest that it is possible to develop a point-of-care test for patients with UTI.
Most phenotypic and genotypic antibiotic susceptibility tests are too slow to guide treatment, ranging from 2 days to 1 hour. The researchers at Uppsala (Sweden) University cut the testing time down to less than 30 minutes by using a microfluidic chip and direct single-cell imaging.
The chip traps the bacterial cells and allows growth media with different antibiotics (or none) to flow around them. “With this setup, we could detect the differential growth rate between treatment and reference populations in 3 min for ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, mecillinam, nitrofurantoin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole; 7 min for amoxicillin-clavulanate and doripenem; 9 min for fosfomycin; and 11 min for ampicillin based on 99.9% confidence intervals,” wrote Özden Baltekin and his coauthors.
That test specifically used Escherichia coli cells; comparable speed and accuracy was replicated using Klebsiella pneumoniae and Staphylococcus saprophyticus. For the development of a point-of-care test for patients, the researchers said all that would be needed are about 100 bacteria cells.
“We have here focused on bacterial species and antibiotics related to UTIs, but it is likely that the same principles would work for sepsis, mastitis, or meningitis,” they suggested (Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2017 Aug 8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1708558114).
Researchers in Sweden have developed a 30-minute test capable of determining whether a bacterial urinary tract infection is susceptible or resistant to nine antibiotics. Their findings suggest that it is possible to develop a point-of-care test for patients with UTI.
Most phenotypic and genotypic antibiotic susceptibility tests are too slow to guide treatment, ranging from 2 days to 1 hour. The researchers at Uppsala (Sweden) University cut the testing time down to less than 30 minutes by using a microfluidic chip and direct single-cell imaging.
The chip traps the bacterial cells and allows growth media with different antibiotics (or none) to flow around them. “With this setup, we could detect the differential growth rate between treatment and reference populations in 3 min for ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, mecillinam, nitrofurantoin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole; 7 min for amoxicillin-clavulanate and doripenem; 9 min for fosfomycin; and 11 min for ampicillin based on 99.9% confidence intervals,” wrote Özden Baltekin and his coauthors.
That test specifically used Escherichia coli cells; comparable speed and accuracy was replicated using Klebsiella pneumoniae and Staphylococcus saprophyticus. For the development of a point-of-care test for patients, the researchers said all that would be needed are about 100 bacteria cells.
“We have here focused on bacterial species and antibiotics related to UTIs, but it is likely that the same principles would work for sepsis, mastitis, or meningitis,” they suggested (Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2017 Aug 8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1708558114).
FROM PNAS
VIDEO: When to turn to surgery in postpartum uterine infection
PARK CITY, UTAH – When postpartum infections don’t respond to antibiotics, doctors and surgeons need to move fast; surgery – often hysterectomy – is the only thing that will save the woman’s life.
The problem is that with today’s antibiotics, doctors may have never encountered the situation, and sometimes continue to treat with antibiotics until it’s too late.
In Seattle, physicians turn to David Eschenbach, MD, chair of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, for advice on when it’s time to give up on antibiotics and go to the OR. It’s a difficult decision, especially when patients are young.
In an interview at the annual scientific meeting of the Infectious Diseases Society for Obstetrics and Gynecology, Dr. Eschenbach shared what he’s learned from decades of experience in dealing with one of the most devastating postpartum complications.
PARK CITY, UTAH – When postpartum infections don’t respond to antibiotics, doctors and surgeons need to move fast; surgery – often hysterectomy – is the only thing that will save the woman’s life.
The problem is that with today’s antibiotics, doctors may have never encountered the situation, and sometimes continue to treat with antibiotics until it’s too late.
In Seattle, physicians turn to David Eschenbach, MD, chair of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, for advice on when it’s time to give up on antibiotics and go to the OR. It’s a difficult decision, especially when patients are young.
In an interview at the annual scientific meeting of the Infectious Diseases Society for Obstetrics and Gynecology, Dr. Eschenbach shared what he’s learned from decades of experience in dealing with one of the most devastating postpartum complications.
PARK CITY, UTAH – When postpartum infections don’t respond to antibiotics, doctors and surgeons need to move fast; surgery – often hysterectomy – is the only thing that will save the woman’s life.
The problem is that with today’s antibiotics, doctors may have never encountered the situation, and sometimes continue to treat with antibiotics until it’s too late.
In Seattle, physicians turn to David Eschenbach, MD, chair of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, for advice on when it’s time to give up on antibiotics and go to the OR. It’s a difficult decision, especially when patients are young.
In an interview at the annual scientific meeting of the Infectious Diseases Society for Obstetrics and Gynecology, Dr. Eschenbach shared what he’s learned from decades of experience in dealing with one of the most devastating postpartum complications.
AT IDSOG
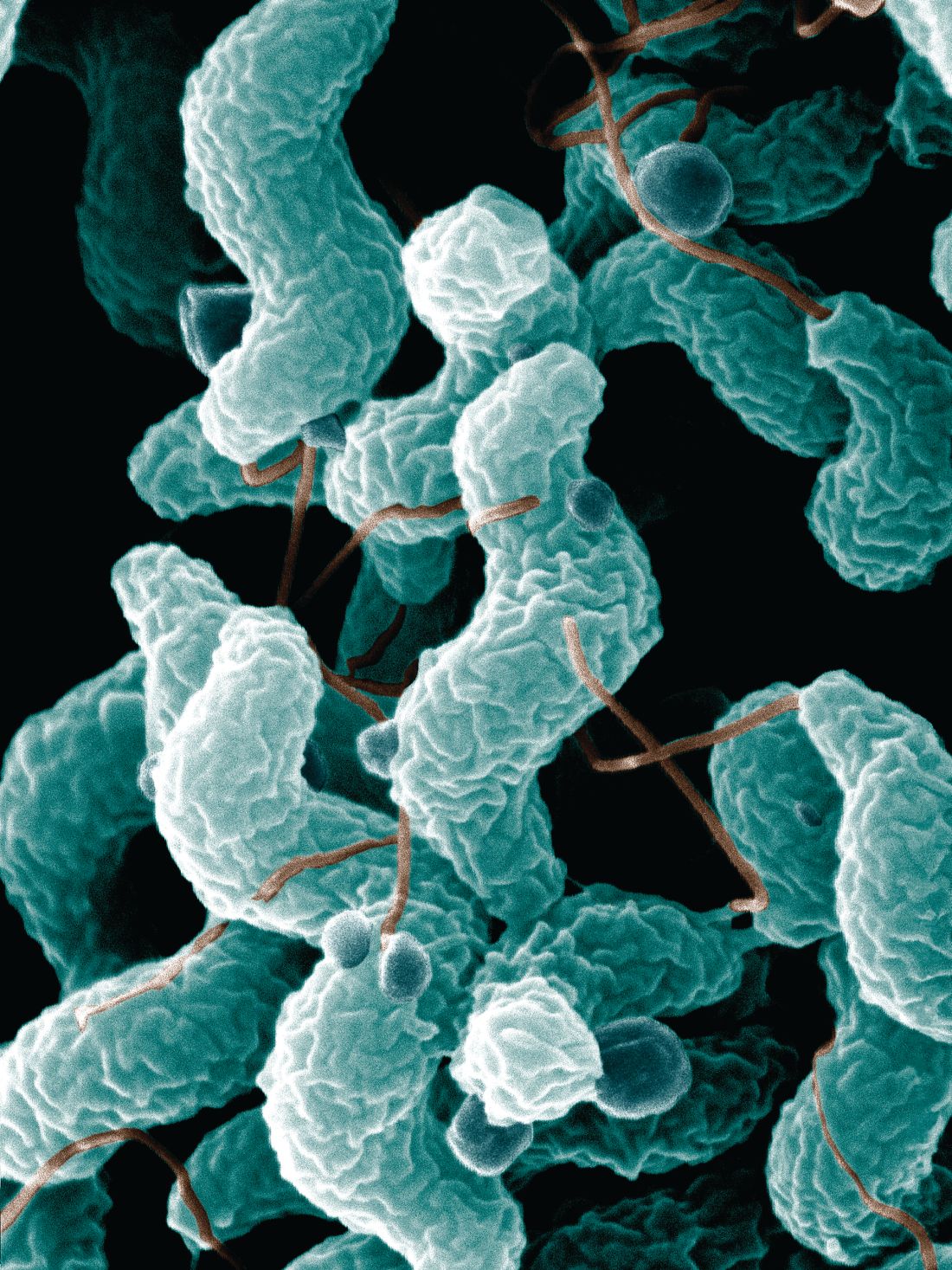
Campylobacteriosis incidence rises in U.S. from 2004 to 2012
Incidence of campylobacteriosis increased significantly in the United States from 2004 to 2012, according to Aimee Geissler, PhD, and her associates.
A total of 303,520 cases of campylobacteriosis were reported during the study period, with the average incidence rate growing from 10.5 cases per 100,000 persons during 2004-2006 to 12.7 cases per 100,000 persons during 2010-2012, an increase of 21%. The median number of Camplyobacter outbreaks doubled from 28 during 2004-2006 to 56 during 2010-2012; in total, 347 outbreaks were reported. Campylobacteriosis is the nation’s most common bacterial diarrheal illness.
The study findings “underscore the importance of standardizing national surveillance for campylobacteriosis, which is important in understanding the burden of infection, better describing geographic variations and differences among species, elucidating risk factors, and targeting prevention and control measures,” the investigators concluded.
Find the full study in Clinical Infectious Diseases (2017 Jul 20. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix624).
Incidence of campylobacteriosis increased significantly in the United States from 2004 to 2012, according to Aimee Geissler, PhD, and her associates.
A total of 303,520 cases of campylobacteriosis were reported during the study period, with the average incidence rate growing from 10.5 cases per 100,000 persons during 2004-2006 to 12.7 cases per 100,000 persons during 2010-2012, an increase of 21%. The median number of Camplyobacter outbreaks doubled from 28 during 2004-2006 to 56 during 2010-2012; in total, 347 outbreaks were reported. Campylobacteriosis is the nation’s most common bacterial diarrheal illness.
The study findings “underscore the importance of standardizing national surveillance for campylobacteriosis, which is important in understanding the burden of infection, better describing geographic variations and differences among species, elucidating risk factors, and targeting prevention and control measures,” the investigators concluded.
Find the full study in Clinical Infectious Diseases (2017 Jul 20. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix624).
Incidence of campylobacteriosis increased significantly in the United States from 2004 to 2012, according to Aimee Geissler, PhD, and her associates.
A total of 303,520 cases of campylobacteriosis were reported during the study period, with the average incidence rate growing from 10.5 cases per 100,000 persons during 2004-2006 to 12.7 cases per 100,000 persons during 2010-2012, an increase of 21%. The median number of Camplyobacter outbreaks doubled from 28 during 2004-2006 to 56 during 2010-2012; in total, 347 outbreaks were reported. Campylobacteriosis is the nation’s most common bacterial diarrheal illness.
The study findings “underscore the importance of standardizing national surveillance for campylobacteriosis, which is important in understanding the burden of infection, better describing geographic variations and differences among species, elucidating risk factors, and targeting prevention and control measures,” the investigators concluded.
Find the full study in Clinical Infectious Diseases (2017 Jul 20. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix624).
FROM CLINICAL INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Lessons emerge from Europe’s first enterovirus-related brain stem encephalitis outbreak
MADRID – Ninety-two percent of Spanish children sickened during the first-ever outbreak of enterovirus-associated brain stem encephalitis in western Europe survived with no long-term sequelae, Nuria Worner, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
“We think that aggressive treatments should be restricted to those patients with important neurologic involvement,” declared Dr. Worner of Vall d’Hebron University Hospital in Barcelona. “We can say that no patients with milder involvement and without warning signs during the first 24 hours after onset of neurologic involvement went on to develop fulminant symptoms.”
Notable outbreaks of enterovirus A71 (EV-A71)-associated brain stem encephalitis occurred in Southeast Asia, Australia, and China in the late 1990s.
Dr. Worner reported on 196 children treated for laboratory-confirmed EV-A71–associated brain stem encephalitis at 16 Spanish hospitals in April-December 2016. Their median age was 25 months, 57% were male, and a median of 2 days of symptoms of mild viral illness transpired before neurologic symptoms arose. Prior to presenting to a hospital, 21% of the children had been diagnosed with hand-foot-and-mouth disease, and 13% with herpangina.
Initial preadmission symptoms included fever in 94% of cases, sleepiness in 86%, ataxia in 75%, tremor in 47%, myoclonus in 40%, and a rash in 26%.
Fifty-five percent of the children had EV RNA isolated from both throat and feces, 26% from the throat only, and 19% only from their feces. Eighty-seven percent of serotyped EV were EV-A71.
Ninety percent of children underwent lumbar puncture. Particularly noteworthy was the finding that EV was detected in the cerebrospinal fluid of a mere 3% of patients, although pleocytosis was present in 84%.
Brain MRI showed brain stem encephalitis along with myelitis in 50% of patients, brain stem myelitis without encephalitis in 29%, myelitis elsewhere in 2%, and normal findings in 19%.
Ground zero for the outbreak was Barcelona and the surrounding region of Catalonia; indeed, 130 of the 196 (66%) affected children came from there. The Catalan health department and pediatric infectious disease specialists quickly created standardized case severity definitions and treatment recommendations; they distributed them nationally.
Mild EV-A71–associated brain stem disease was defined as two or more of the following: tremor, myoclonus, mild ataxia, and/or significant drowsiness. The recommendation in these mild cases was for no treatment other than supportive care and careful in-hospital monitoring.
Patients with moderate involvement had to meet the definition for mild disease plus more pronounced ataxia or bulbar motor neuron involvement marked by slurred speech, drooling, dysphagia, apnea, abolition of the gag reflex, and/or an abnormal respiratory pattern. Moderately affected patients received two doses of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), each dosed at 1 g/kg per 24 hours. Admission to the pediatric ICU was individualized for patients with moderate EV-A71–associated brain stem encephalitis.
Severe disease was categorized as bulbar motor neuron involvement plus neurogenic cardiorespiratory failure. Those patients were uniformly admitted to a pediatric ICU and given the two doses of IVIG. The need for systemic steroids was determined on an individual basis.
Forty percent of patients received IVIG and systemic steroids, 24% received IVIG only, 2% systemic steroids only, and 34% received no treatment other than supportive care.
Twenty-six percent of children were admitted to a pediatric ICU for a median stay of 3.5 days. Nine percent of children were placed on mechanical ventilation.
As the disease evolved, the most frequent neurologic complications included slurred speech in 15% of children, abnormal breathing pattern in 11%, seizures in 10%, acute flaccid paralysis in 9%, and cardiorespiratory failure with pulmonary edema in 9%, all occurring within the first hours after hospital admission.
The median hospital length of stay for the full study population was 6 days. The survival rate was 99.5%, with the sole death being due to cardiorespiratory failure.
With 1-6 months of follow-up since the acute episode of EV-A71–associated brain stem encephalitis, the long-term sequelae included two cases of limb paresis and two cases of paresis of a cranial nerve, one child with residual seizures, and one with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy.
Asked why the fatality rate in the Spanish outbreak was so much lower than in the earlier Australasian outbreaks, Dr. Worner cited Catalan physicians’ quick recognition of what was underway – and, more importantly, a difference in the EV-A71 viral subgenotype. Most of the most severe cases in Asia and Australia involved the C-4 subgenotype, while in Spain, the predominant subgenotype involved in the outbreak was C-1.
As for the curious finding that EV was detectable in the cerebrospinal fluid of a mere 3% of the Spanish children, she said the explanation is unknown. The two main possibilities are that the CNS symptoms were due to a parenchymal brain infection rather than to EV-A71 infection of meningeal tissue. Alternatively, the CNS involvement may have been a manifestation of an immunologic response to the infection, rather than being due to the virus itself.
Dr. Worner reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
MADRID – Ninety-two percent of Spanish children sickened during the first-ever outbreak of enterovirus-associated brain stem encephalitis in western Europe survived with no long-term sequelae, Nuria Worner, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
“We think that aggressive treatments should be restricted to those patients with important neurologic involvement,” declared Dr. Worner of Vall d’Hebron University Hospital in Barcelona. “We can say that no patients with milder involvement and without warning signs during the first 24 hours after onset of neurologic involvement went on to develop fulminant symptoms.”
Notable outbreaks of enterovirus A71 (EV-A71)-associated brain stem encephalitis occurred in Southeast Asia, Australia, and China in the late 1990s.
Dr. Worner reported on 196 children treated for laboratory-confirmed EV-A71–associated brain stem encephalitis at 16 Spanish hospitals in April-December 2016. Their median age was 25 months, 57% were male, and a median of 2 days of symptoms of mild viral illness transpired before neurologic symptoms arose. Prior to presenting to a hospital, 21% of the children had been diagnosed with hand-foot-and-mouth disease, and 13% with herpangina.
Initial preadmission symptoms included fever in 94% of cases, sleepiness in 86%, ataxia in 75%, tremor in 47%, myoclonus in 40%, and a rash in 26%.
Fifty-five percent of the children had EV RNA isolated from both throat and feces, 26% from the throat only, and 19% only from their feces. Eighty-seven percent of serotyped EV were EV-A71.
Ninety percent of children underwent lumbar puncture. Particularly noteworthy was the finding that EV was detected in the cerebrospinal fluid of a mere 3% of patients, although pleocytosis was present in 84%.
Brain MRI showed brain stem encephalitis along with myelitis in 50% of patients, brain stem myelitis without encephalitis in 29%, myelitis elsewhere in 2%, and normal findings in 19%.
Ground zero for the outbreak was Barcelona and the surrounding region of Catalonia; indeed, 130 of the 196 (66%) affected children came from there. The Catalan health department and pediatric infectious disease specialists quickly created standardized case severity definitions and treatment recommendations; they distributed them nationally.
Mild EV-A71–associated brain stem disease was defined as two or more of the following: tremor, myoclonus, mild ataxia, and/or significant drowsiness. The recommendation in these mild cases was for no treatment other than supportive care and careful in-hospital monitoring.
Patients with moderate involvement had to meet the definition for mild disease plus more pronounced ataxia or bulbar motor neuron involvement marked by slurred speech, drooling, dysphagia, apnea, abolition of the gag reflex, and/or an abnormal respiratory pattern. Moderately affected patients received two doses of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), each dosed at 1 g/kg per 24 hours. Admission to the pediatric ICU was individualized for patients with moderate EV-A71–associated brain stem encephalitis.
Severe disease was categorized as bulbar motor neuron involvement plus neurogenic cardiorespiratory failure. Those patients were uniformly admitted to a pediatric ICU and given the two doses of IVIG. The need for systemic steroids was determined on an individual basis.
Forty percent of patients received IVIG and systemic steroids, 24% received IVIG only, 2% systemic steroids only, and 34% received no treatment other than supportive care.
Twenty-six percent of children were admitted to a pediatric ICU for a median stay of 3.5 days. Nine percent of children were placed on mechanical ventilation.
As the disease evolved, the most frequent neurologic complications included slurred speech in 15% of children, abnormal breathing pattern in 11%, seizures in 10%, acute flaccid paralysis in 9%, and cardiorespiratory failure with pulmonary edema in 9%, all occurring within the first hours after hospital admission.
The median hospital length of stay for the full study population was 6 days. The survival rate was 99.5%, with the sole death being due to cardiorespiratory failure.
With 1-6 months of follow-up since the acute episode of EV-A71–associated brain stem encephalitis, the long-term sequelae included two cases of limb paresis and two cases of paresis of a cranial nerve, one child with residual seizures, and one with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy.
Asked why the fatality rate in the Spanish outbreak was so much lower than in the earlier Australasian outbreaks, Dr. Worner cited Catalan physicians’ quick recognition of what was underway – and, more importantly, a difference in the EV-A71 viral subgenotype. Most of the most severe cases in Asia and Australia involved the C-4 subgenotype, while in Spain, the predominant subgenotype involved in the outbreak was C-1.
As for the curious finding that EV was detectable in the cerebrospinal fluid of a mere 3% of the Spanish children, she said the explanation is unknown. The two main possibilities are that the CNS symptoms were due to a parenchymal brain infection rather than to EV-A71 infection of meningeal tissue. Alternatively, the CNS involvement may have been a manifestation of an immunologic response to the infection, rather than being due to the virus itself.
Dr. Worner reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
MADRID – Ninety-two percent of Spanish children sickened during the first-ever outbreak of enterovirus-associated brain stem encephalitis in western Europe survived with no long-term sequelae, Nuria Worner, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
“We think that aggressive treatments should be restricted to those patients with important neurologic involvement,” declared Dr. Worner of Vall d’Hebron University Hospital in Barcelona. “We can say that no patients with milder involvement and without warning signs during the first 24 hours after onset of neurologic involvement went on to develop fulminant symptoms.”
Notable outbreaks of enterovirus A71 (EV-A71)-associated brain stem encephalitis occurred in Southeast Asia, Australia, and China in the late 1990s.
Dr. Worner reported on 196 children treated for laboratory-confirmed EV-A71–associated brain stem encephalitis at 16 Spanish hospitals in April-December 2016. Their median age was 25 months, 57% were male, and a median of 2 days of symptoms of mild viral illness transpired before neurologic symptoms arose. Prior to presenting to a hospital, 21% of the children had been diagnosed with hand-foot-and-mouth disease, and 13% with herpangina.
Initial preadmission symptoms included fever in 94% of cases, sleepiness in 86%, ataxia in 75%, tremor in 47%, myoclonus in 40%, and a rash in 26%.
Fifty-five percent of the children had EV RNA isolated from both throat and feces, 26% from the throat only, and 19% only from their feces. Eighty-seven percent of serotyped EV were EV-A71.
Ninety percent of children underwent lumbar puncture. Particularly noteworthy was the finding that EV was detected in the cerebrospinal fluid of a mere 3% of patients, although pleocytosis was present in 84%.
Brain MRI showed brain stem encephalitis along with myelitis in 50% of patients, brain stem myelitis without encephalitis in 29%, myelitis elsewhere in 2%, and normal findings in 19%.
Ground zero for the outbreak was Barcelona and the surrounding region of Catalonia; indeed, 130 of the 196 (66%) affected children came from there. The Catalan health department and pediatric infectious disease specialists quickly created standardized case severity definitions and treatment recommendations; they distributed them nationally.
Mild EV-A71–associated brain stem disease was defined as two or more of the following: tremor, myoclonus, mild ataxia, and/or significant drowsiness. The recommendation in these mild cases was for no treatment other than supportive care and careful in-hospital monitoring.
Patients with moderate involvement had to meet the definition for mild disease plus more pronounced ataxia or bulbar motor neuron involvement marked by slurred speech, drooling, dysphagia, apnea, abolition of the gag reflex, and/or an abnormal respiratory pattern. Moderately affected patients received two doses of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), each dosed at 1 g/kg per 24 hours. Admission to the pediatric ICU was individualized for patients with moderate EV-A71–associated brain stem encephalitis.
Severe disease was categorized as bulbar motor neuron involvement plus neurogenic cardiorespiratory failure. Those patients were uniformly admitted to a pediatric ICU and given the two doses of IVIG. The need for systemic steroids was determined on an individual basis.
Forty percent of patients received IVIG and systemic steroids, 24% received IVIG only, 2% systemic steroids only, and 34% received no treatment other than supportive care.
Twenty-six percent of children were admitted to a pediatric ICU for a median stay of 3.5 days. Nine percent of children were placed on mechanical ventilation.
As the disease evolved, the most frequent neurologic complications included slurred speech in 15% of children, abnormal breathing pattern in 11%, seizures in 10%, acute flaccid paralysis in 9%, and cardiorespiratory failure with pulmonary edema in 9%, all occurring within the first hours after hospital admission.
The median hospital length of stay for the full study population was 6 days. The survival rate was 99.5%, with the sole death being due to cardiorespiratory failure.
With 1-6 months of follow-up since the acute episode of EV-A71–associated brain stem encephalitis, the long-term sequelae included two cases of limb paresis and two cases of paresis of a cranial nerve, one child with residual seizures, and one with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy.
Asked why the fatality rate in the Spanish outbreak was so much lower than in the earlier Australasian outbreaks, Dr. Worner cited Catalan physicians’ quick recognition of what was underway – and, more importantly, a difference in the EV-A71 viral subgenotype. Most of the most severe cases in Asia and Australia involved the C-4 subgenotype, while in Spain, the predominant subgenotype involved in the outbreak was C-1.
As for the curious finding that EV was detectable in the cerebrospinal fluid of a mere 3% of the Spanish children, she said the explanation is unknown. The two main possibilities are that the CNS symptoms were due to a parenchymal brain infection rather than to EV-A71 infection of meningeal tissue. Alternatively, the CNS involvement may have been a manifestation of an immunologic response to the infection, rather than being due to the virus itself.
Dr. Worner reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
AT ESPID 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Ninety-two percent of Spanish children involved in an outbreak of enterovirus-associated brain stem encephalitis survived with no long-term sequelae.
Data source: A retrospective review of 196 children treated for laboratory-confirmed EV-A71–associated brain stem encephalitis at 16 Spanish hospitals in April-December 2016 during the first-ever outbreak of this condition in western Europe.
Disclosures: Dr. Worner reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
CDC refocuses Zika testing recommendations in pregnancy
, including those who may have been exposed before pregnancy through travel or sexual contact.
In updated guidance released July 24, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cited a combination of factors behind the change in recommendations, including the declining prevalence of Zika virus across the Americas and a high likelihood of false positives associated with the use of a common serologic assay (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub 2017 Jul 24. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6629e1).
Positive IgM results can also occur after previous exposure to other flaviviruses besides Zika, Dr. Oduyebo and her colleagues noted.
The CDC now recommends that pregnant women with likely continuing – not previous – exposure to the Zika virus and those with symptoms suggestive of Zika virus disease be tested. Those higher-risk groups should receive nucleic acid testing (NAT).
The new guidance presents two updated testing algorithms, one for each group.
Any pregnant woman with symptoms suggestive of Zika should be tested “as soon as possible through 12 weeks after symptom onset,” the CDC said, with both NAT (serum and urine) and IgM serology testing.
Women with likely ongoing exposure to Zika – such as those living in or traveling to an area of mosquito-borne Zika transmission or those whose partners are living in or traveling to such an area – should be tested up to three times during the pregnancy using NAT serum and urine tests. IgM testing is not recommended for that group.
All pregnant women should be asked about their potential Zika exposures before and during the current pregnancy, the CDC said. That discussion, which covers potential travel and partner exposures along with questions about symptoms, should be repeated at every prenatal visit.
While routine testing of asymptomatic women without ongoing exposure is not recommended, patient preferences, clinical judgment, and a “balanced assessment of risks and expected outcomes” should guide decisions about testing, according to the CDC.
, including those who may have been exposed before pregnancy through travel or sexual contact.
In updated guidance released July 24, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cited a combination of factors behind the change in recommendations, including the declining prevalence of Zika virus across the Americas and a high likelihood of false positives associated with the use of a common serologic assay (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub 2017 Jul 24. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6629e1).
Positive IgM results can also occur after previous exposure to other flaviviruses besides Zika, Dr. Oduyebo and her colleagues noted.
The CDC now recommends that pregnant women with likely continuing – not previous – exposure to the Zika virus and those with symptoms suggestive of Zika virus disease be tested. Those higher-risk groups should receive nucleic acid testing (NAT).
The new guidance presents two updated testing algorithms, one for each group.
Any pregnant woman with symptoms suggestive of Zika should be tested “as soon as possible through 12 weeks after symptom onset,” the CDC said, with both NAT (serum and urine) and IgM serology testing.
Women with likely ongoing exposure to Zika – such as those living in or traveling to an area of mosquito-borne Zika transmission or those whose partners are living in or traveling to such an area – should be tested up to three times during the pregnancy using NAT serum and urine tests. IgM testing is not recommended for that group.
All pregnant women should be asked about their potential Zika exposures before and during the current pregnancy, the CDC said. That discussion, which covers potential travel and partner exposures along with questions about symptoms, should be repeated at every prenatal visit.
While routine testing of asymptomatic women without ongoing exposure is not recommended, patient preferences, clinical judgment, and a “balanced assessment of risks and expected outcomes” should guide decisions about testing, according to the CDC.
, including those who may have been exposed before pregnancy through travel or sexual contact.
In updated guidance released July 24, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cited a combination of factors behind the change in recommendations, including the declining prevalence of Zika virus across the Americas and a high likelihood of false positives associated with the use of a common serologic assay (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub 2017 Jul 24. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6629e1).
Positive IgM results can also occur after previous exposure to other flaviviruses besides Zika, Dr. Oduyebo and her colleagues noted.
The CDC now recommends that pregnant women with likely continuing – not previous – exposure to the Zika virus and those with symptoms suggestive of Zika virus disease be tested. Those higher-risk groups should receive nucleic acid testing (NAT).
The new guidance presents two updated testing algorithms, one for each group.
Any pregnant woman with symptoms suggestive of Zika should be tested “as soon as possible through 12 weeks after symptom onset,” the CDC said, with both NAT (serum and urine) and IgM serology testing.
Women with likely ongoing exposure to Zika – such as those living in or traveling to an area of mosquito-borne Zika transmission or those whose partners are living in or traveling to such an area – should be tested up to three times during the pregnancy using NAT serum and urine tests. IgM testing is not recommended for that group.
All pregnant women should be asked about their potential Zika exposures before and during the current pregnancy, the CDC said. That discussion, which covers potential travel and partner exposures along with questions about symptoms, should be repeated at every prenatal visit.
While routine testing of asymptomatic women without ongoing exposure is not recommended, patient preferences, clinical judgment, and a “balanced assessment of risks and expected outcomes” should guide decisions about testing, according to the CDC.
FROM MMWR