User login
Flesh-Colored Pinpoint Papules With Fine White Spicules on the Upper Body
The Diagnosis: Trichodysplasia Spinulosa
A diagnosis of trichodysplasia spinulosa (TS) was rendered based on the clinical presentation— diffuse folliculocentric keratotic papules with spicules and leonine facies—coinciding with cyclosporine initiation. Biopsy was deferred given the classic presentation. The patient applied cidofovir cream 1% daily to lesions on the face. She was prescribed leflunomide 10 mg daily, which was later increased to 20 mg daily, for polyarthritis associated with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Her transplant physician increased her cyclosporine dosage from 50 mg twice daily to 75 mg each morning and 50 mg each evening due to rising creatinine and donor-specific antibodies from the renal transplant. The patient’s TS eruption mildly improved 3 months after the cyclosporine dose was increased. To treat persistent lesions, oral valganciclovir was started at 450 mg once daily and later reduced to every other day due to leukopenia. After 3 months of taking valganciclovir 450 mg every other day, the patient’s TS rash resolved.
Trichodysplasia spinulosa is a rare condition caused by TS-associated polyomavirus1 that may arise in immunosuppressed patients, especially in solid organ transplant recipients.2 It is characterized by spiculated and folliculocentric papules, mainly on the face,1 and often is diagnosed clinically, but if the presentation is not classic, a skin biopsy can help to confirm the diagnosis. Because of its rarity, treatment options do not have well-established efficacy1 but include reducing immunosuppression and using the antivirals cidofovir1 or valganciclovir3 to treat the polyomavirus. Topical retinoids,3 photodynamic therapy, 4 and leflunomide5 also may be effective.
Although the typical approach to treating TS is to reduce immunosuppression, this was not an option for our patient, as she required increased immunosuppression for the treatment of active SLE. Leflunomide can be used for SLE, and in some reports it can be effective for BK viremia in kidney transplant recipients5 as well as for TS in solid organ transplant recipients.6 Our patient showed improvement of the TS, BK viremia, renal function, and SLE while taking leflunomide and valganciclovir.
The differential diagnosis includes keratosis pilaris, lichen nitidus, scleromyxedema, and trichostasis spinulosa. Keratosis pilaris is a benign skin disorder consisting of patches of keratotic papules with varying degrees of erythema and inflammation that are formed by dead keratinocytes plugging the hair follicles and often are seen on the extremities, face, and trunk.7 Our patient’s papules were flesh colored with no notable background erythema. Additionally, the presence of leonine facies was atypical for keratosis pilaris. Acids, steroids, and kinase inhibitors are the most frequently used treatments for keratosis pilaris.8
Lichen nitidus is a skin condition characterized by multiple shiny, dome-shaped, flesh-colored papules usually found on the flexor surfaces of the arms, anterior trunk, and genitalia. It is mostly asymptomatic, but patients may experience pruritus. Most cases occur in children and young adults, with no obvious racial or gender predilection. The diagnosis often is clinical, but biopsy shows downward enlargement of the epidermal rete ridges surrounding a focal inflammatory infiltrate, known as a ball-in-claw configuration.9-11 Lichen nitidus spontaneously resolves within a few years without treatment. Our patient did have flesh-colored papules on the arms and chest; however, major involvement of the face is not typical in lichen nitidus. Additionally, fine white spicules would not be seen in lichen nitidus. For severe generalized lichen nitidus, treatment options include topical corticosteroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors, oral antihistamines, or UV light to decrease inflammation.9-11
Scleromyxedema is a rare condition involving the deposition of mucinous material in the papillary dermis to cause the formation of infiltrative skin lesions.12 It is thought that immunoglobulins and cytokines secreted by inflammatory cells lead to the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans, which then causes deposition of mucin in the dermis.13 The classic cutaneous features of scleromyxedema include waxy indurated papules and plaques with skin thickening throughout the entire body.12 Our patient’s papules were not notably indurated and involved less than 50% of the total body surface area. An important diagnostic feature of scleromyxedema is monoclonal gammopathy, which our patient did not have. Intravenous immunoglobulin is the first-line treatment of scleromyxedema, and second-line treatments include systemic corticosteroids and thalidomide.14 Our patient also did not require treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin, as her rash improved with antiviral medication, which would not address the underlying inflammatory processes associated with scleromyxedema.
Trichostasis spinulosa is a rare hair follicle disorder consisting of dark, spiny, hyperkeratotic follicular papules that can be found on the extremities and face, especially the nose. The etiology is unknown, but risk factors include congenital dysplasia of hair follicles; exposure to UV light, dust, oil, or heat; chronic renal failure; Malassezia yeast; and Propionibacterium acnes. Adult women with darker skin types are most commonly affected by trichostasis spinulosa.15,16 Our patient fit the epidemiologic demographic of trichostasis spinulosa, including a history of chronic renal failure. Her rash covered the face, nose, and arms; however, the papules were flesh colored, whereas trichostasis spinulosa would appear as black papules. Furthermore, yeast and bacterial infections have been identified as potential agents associated with trichostasis spinulosa; therefore, antiviral agents would be ineffective. Viable treatments for trichostasis spinulosa include emollients, topical keratolytic agents, retinoic acids, and lasers to remove abnormal hair follicles.15,16
- Curman P, Näsman A, Brauner H. Trichodysplasia spinulosa: a comprehensive disease and its treatment. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:1067-1076.
- Fischer MK, Kao GF, Nguyen HP, et al. Specific detection of trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus DNA in skin and renal allograft tissues in a patient with trichodysplasia spinulosa. Arch Dermatol. 2021;148:726-733.
- Shah PR, Esaa FS, Gupta P, et al. Trichodysplasia spinulosa successfully treated with adapalene 0.1% gel and oral valganciclovir in a renal transplant recipient. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:23-25.
- Liew YCC, Kee TYS, Kwek JL, et al. Photodynamic therapy for the treatment of trichodysplasia spinulosa in an Asian renal transplant recipient: a case report and review of the literature. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;7:74-83.
- Pierrotti LC, Urbano PRP, da Silva Nali LH, et al. Viremia and viuria of trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus before the development of clinical disease in a kidney transplant recipient. Transpl Infect Dis. 2019;21:E13133.
- Kassar R, Chang J, Chan AW, et al. Leflunomide for the treatment of trichodysplasia spinulosa in a liver transplant recipient. Transpl Infect Dis. 2017;19:E12702.
- Eckburg A, Kazemi T, Maguiness S. Keratosis pilaris rubra successfully treated with topical sirolimus: report of a case and review of the literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2022;39:429-431.
- Reddy S, Brahmbhatt H. A narrative review on the role of acids, steroids, and kinase inhibitors in the treatment of keratosis pilaris. Cureus. 2021;13:E18917.
- Jordan AS, Green MC, Sulit DJ. Lichen nitidus. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2019;119:704.
- Arizaga AT, Gaughan MD, Bang RH. Generalized lichen nitidus. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2002;27:115-117.
- Chu J, Lam JM. Lichen nitidus. CMAJ. 2014;186:E688.
- Haber R, Bachour J, El Gemayel M. Scleromyxedema treatment: a systematic review and update. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:1191-1201.
- Christman MP, Sukhdeo K, Kim RH, et al. Papular mucinosis, or localized lichen myxedematosis (LM) (discrete papular type). Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:8.
- Hoffman JHO, Enk AH. Scleromyxedema. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2020;18:1449-1467.
- Kositkuljorn C, Suchonwanit P. Trichostasis spinulosa: a case report with an unusual presentation. Case Rep Dermatol. 2020;12:178-185.
- Ramteke MN, Bhide AA. Trichostasis spinulosa at an unusual site. Int J Trichology. 2016;8:78-80.
The Diagnosis: Trichodysplasia Spinulosa
A diagnosis of trichodysplasia spinulosa (TS) was rendered based on the clinical presentation— diffuse folliculocentric keratotic papules with spicules and leonine facies—coinciding with cyclosporine initiation. Biopsy was deferred given the classic presentation. The patient applied cidofovir cream 1% daily to lesions on the face. She was prescribed leflunomide 10 mg daily, which was later increased to 20 mg daily, for polyarthritis associated with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Her transplant physician increased her cyclosporine dosage from 50 mg twice daily to 75 mg each morning and 50 mg each evening due to rising creatinine and donor-specific antibodies from the renal transplant. The patient’s TS eruption mildly improved 3 months after the cyclosporine dose was increased. To treat persistent lesions, oral valganciclovir was started at 450 mg once daily and later reduced to every other day due to leukopenia. After 3 months of taking valganciclovir 450 mg every other day, the patient’s TS rash resolved.
Trichodysplasia spinulosa is a rare condition caused by TS-associated polyomavirus1 that may arise in immunosuppressed patients, especially in solid organ transplant recipients.2 It is characterized by spiculated and folliculocentric papules, mainly on the face,1 and often is diagnosed clinically, but if the presentation is not classic, a skin biopsy can help to confirm the diagnosis. Because of its rarity, treatment options do not have well-established efficacy1 but include reducing immunosuppression and using the antivirals cidofovir1 or valganciclovir3 to treat the polyomavirus. Topical retinoids,3 photodynamic therapy, 4 and leflunomide5 also may be effective.
Although the typical approach to treating TS is to reduce immunosuppression, this was not an option for our patient, as she required increased immunosuppression for the treatment of active SLE. Leflunomide can be used for SLE, and in some reports it can be effective for BK viremia in kidney transplant recipients5 as well as for TS in solid organ transplant recipients.6 Our patient showed improvement of the TS, BK viremia, renal function, and SLE while taking leflunomide and valganciclovir.
The differential diagnosis includes keratosis pilaris, lichen nitidus, scleromyxedema, and trichostasis spinulosa. Keratosis pilaris is a benign skin disorder consisting of patches of keratotic papules with varying degrees of erythema and inflammation that are formed by dead keratinocytes plugging the hair follicles and often are seen on the extremities, face, and trunk.7 Our patient’s papules were flesh colored with no notable background erythema. Additionally, the presence of leonine facies was atypical for keratosis pilaris. Acids, steroids, and kinase inhibitors are the most frequently used treatments for keratosis pilaris.8
Lichen nitidus is a skin condition characterized by multiple shiny, dome-shaped, flesh-colored papules usually found on the flexor surfaces of the arms, anterior trunk, and genitalia. It is mostly asymptomatic, but patients may experience pruritus. Most cases occur in children and young adults, with no obvious racial or gender predilection. The diagnosis often is clinical, but biopsy shows downward enlargement of the epidermal rete ridges surrounding a focal inflammatory infiltrate, known as a ball-in-claw configuration.9-11 Lichen nitidus spontaneously resolves within a few years without treatment. Our patient did have flesh-colored papules on the arms and chest; however, major involvement of the face is not typical in lichen nitidus. Additionally, fine white spicules would not be seen in lichen nitidus. For severe generalized lichen nitidus, treatment options include topical corticosteroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors, oral antihistamines, or UV light to decrease inflammation.9-11
Scleromyxedema is a rare condition involving the deposition of mucinous material in the papillary dermis to cause the formation of infiltrative skin lesions.12 It is thought that immunoglobulins and cytokines secreted by inflammatory cells lead to the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans, which then causes deposition of mucin in the dermis.13 The classic cutaneous features of scleromyxedema include waxy indurated papules and plaques with skin thickening throughout the entire body.12 Our patient’s papules were not notably indurated and involved less than 50% of the total body surface area. An important diagnostic feature of scleromyxedema is monoclonal gammopathy, which our patient did not have. Intravenous immunoglobulin is the first-line treatment of scleromyxedema, and second-line treatments include systemic corticosteroids and thalidomide.14 Our patient also did not require treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin, as her rash improved with antiviral medication, which would not address the underlying inflammatory processes associated with scleromyxedema.
Trichostasis spinulosa is a rare hair follicle disorder consisting of dark, spiny, hyperkeratotic follicular papules that can be found on the extremities and face, especially the nose. The etiology is unknown, but risk factors include congenital dysplasia of hair follicles; exposure to UV light, dust, oil, or heat; chronic renal failure; Malassezia yeast; and Propionibacterium acnes. Adult women with darker skin types are most commonly affected by trichostasis spinulosa.15,16 Our patient fit the epidemiologic demographic of trichostasis spinulosa, including a history of chronic renal failure. Her rash covered the face, nose, and arms; however, the papules were flesh colored, whereas trichostasis spinulosa would appear as black papules. Furthermore, yeast and bacterial infections have been identified as potential agents associated with trichostasis spinulosa; therefore, antiviral agents would be ineffective. Viable treatments for trichostasis spinulosa include emollients, topical keratolytic agents, retinoic acids, and lasers to remove abnormal hair follicles.15,16
The Diagnosis: Trichodysplasia Spinulosa
A diagnosis of trichodysplasia spinulosa (TS) was rendered based on the clinical presentation— diffuse folliculocentric keratotic papules with spicules and leonine facies—coinciding with cyclosporine initiation. Biopsy was deferred given the classic presentation. The patient applied cidofovir cream 1% daily to lesions on the face. She was prescribed leflunomide 10 mg daily, which was later increased to 20 mg daily, for polyarthritis associated with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Her transplant physician increased her cyclosporine dosage from 50 mg twice daily to 75 mg each morning and 50 mg each evening due to rising creatinine and donor-specific antibodies from the renal transplant. The patient’s TS eruption mildly improved 3 months after the cyclosporine dose was increased. To treat persistent lesions, oral valganciclovir was started at 450 mg once daily and later reduced to every other day due to leukopenia. After 3 months of taking valganciclovir 450 mg every other day, the patient’s TS rash resolved.
Trichodysplasia spinulosa is a rare condition caused by TS-associated polyomavirus1 that may arise in immunosuppressed patients, especially in solid organ transplant recipients.2 It is characterized by spiculated and folliculocentric papules, mainly on the face,1 and often is diagnosed clinically, but if the presentation is not classic, a skin biopsy can help to confirm the diagnosis. Because of its rarity, treatment options do not have well-established efficacy1 but include reducing immunosuppression and using the antivirals cidofovir1 or valganciclovir3 to treat the polyomavirus. Topical retinoids,3 photodynamic therapy, 4 and leflunomide5 also may be effective.
Although the typical approach to treating TS is to reduce immunosuppression, this was not an option for our patient, as she required increased immunosuppression for the treatment of active SLE. Leflunomide can be used for SLE, and in some reports it can be effective for BK viremia in kidney transplant recipients5 as well as for TS in solid organ transplant recipients.6 Our patient showed improvement of the TS, BK viremia, renal function, and SLE while taking leflunomide and valganciclovir.
The differential diagnosis includes keratosis pilaris, lichen nitidus, scleromyxedema, and trichostasis spinulosa. Keratosis pilaris is a benign skin disorder consisting of patches of keratotic papules with varying degrees of erythema and inflammation that are formed by dead keratinocytes plugging the hair follicles and often are seen on the extremities, face, and trunk.7 Our patient’s papules were flesh colored with no notable background erythema. Additionally, the presence of leonine facies was atypical for keratosis pilaris. Acids, steroids, and kinase inhibitors are the most frequently used treatments for keratosis pilaris.8
Lichen nitidus is a skin condition characterized by multiple shiny, dome-shaped, flesh-colored papules usually found on the flexor surfaces of the arms, anterior trunk, and genitalia. It is mostly asymptomatic, but patients may experience pruritus. Most cases occur in children and young adults, with no obvious racial or gender predilection. The diagnosis often is clinical, but biopsy shows downward enlargement of the epidermal rete ridges surrounding a focal inflammatory infiltrate, known as a ball-in-claw configuration.9-11 Lichen nitidus spontaneously resolves within a few years without treatment. Our patient did have flesh-colored papules on the arms and chest; however, major involvement of the face is not typical in lichen nitidus. Additionally, fine white spicules would not be seen in lichen nitidus. For severe generalized lichen nitidus, treatment options include topical corticosteroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors, oral antihistamines, or UV light to decrease inflammation.9-11
Scleromyxedema is a rare condition involving the deposition of mucinous material in the papillary dermis to cause the formation of infiltrative skin lesions.12 It is thought that immunoglobulins and cytokines secreted by inflammatory cells lead to the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans, which then causes deposition of mucin in the dermis.13 The classic cutaneous features of scleromyxedema include waxy indurated papules and plaques with skin thickening throughout the entire body.12 Our patient’s papules were not notably indurated and involved less than 50% of the total body surface area. An important diagnostic feature of scleromyxedema is monoclonal gammopathy, which our patient did not have. Intravenous immunoglobulin is the first-line treatment of scleromyxedema, and second-line treatments include systemic corticosteroids and thalidomide.14 Our patient also did not require treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin, as her rash improved with antiviral medication, which would not address the underlying inflammatory processes associated with scleromyxedema.
Trichostasis spinulosa is a rare hair follicle disorder consisting of dark, spiny, hyperkeratotic follicular papules that can be found on the extremities and face, especially the nose. The etiology is unknown, but risk factors include congenital dysplasia of hair follicles; exposure to UV light, dust, oil, or heat; chronic renal failure; Malassezia yeast; and Propionibacterium acnes. Adult women with darker skin types are most commonly affected by trichostasis spinulosa.15,16 Our patient fit the epidemiologic demographic of trichostasis spinulosa, including a history of chronic renal failure. Her rash covered the face, nose, and arms; however, the papules were flesh colored, whereas trichostasis spinulosa would appear as black papules. Furthermore, yeast and bacterial infections have been identified as potential agents associated with trichostasis spinulosa; therefore, antiviral agents would be ineffective. Viable treatments for trichostasis spinulosa include emollients, topical keratolytic agents, retinoic acids, and lasers to remove abnormal hair follicles.15,16
- Curman P, Näsman A, Brauner H. Trichodysplasia spinulosa: a comprehensive disease and its treatment. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:1067-1076.
- Fischer MK, Kao GF, Nguyen HP, et al. Specific detection of trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus DNA in skin and renal allograft tissues in a patient with trichodysplasia spinulosa. Arch Dermatol. 2021;148:726-733.
- Shah PR, Esaa FS, Gupta P, et al. Trichodysplasia spinulosa successfully treated with adapalene 0.1% gel and oral valganciclovir in a renal transplant recipient. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:23-25.
- Liew YCC, Kee TYS, Kwek JL, et al. Photodynamic therapy for the treatment of trichodysplasia spinulosa in an Asian renal transplant recipient: a case report and review of the literature. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;7:74-83.
- Pierrotti LC, Urbano PRP, da Silva Nali LH, et al. Viremia and viuria of trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus before the development of clinical disease in a kidney transplant recipient. Transpl Infect Dis. 2019;21:E13133.
- Kassar R, Chang J, Chan AW, et al. Leflunomide for the treatment of trichodysplasia spinulosa in a liver transplant recipient. Transpl Infect Dis. 2017;19:E12702.
- Eckburg A, Kazemi T, Maguiness S. Keratosis pilaris rubra successfully treated with topical sirolimus: report of a case and review of the literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2022;39:429-431.
- Reddy S, Brahmbhatt H. A narrative review on the role of acids, steroids, and kinase inhibitors in the treatment of keratosis pilaris. Cureus. 2021;13:E18917.
- Jordan AS, Green MC, Sulit DJ. Lichen nitidus. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2019;119:704.
- Arizaga AT, Gaughan MD, Bang RH. Generalized lichen nitidus. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2002;27:115-117.
- Chu J, Lam JM. Lichen nitidus. CMAJ. 2014;186:E688.
- Haber R, Bachour J, El Gemayel M. Scleromyxedema treatment: a systematic review and update. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:1191-1201.
- Christman MP, Sukhdeo K, Kim RH, et al. Papular mucinosis, or localized lichen myxedematosis (LM) (discrete papular type). Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:8.
- Hoffman JHO, Enk AH. Scleromyxedema. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2020;18:1449-1467.
- Kositkuljorn C, Suchonwanit P. Trichostasis spinulosa: a case report with an unusual presentation. Case Rep Dermatol. 2020;12:178-185.
- Ramteke MN, Bhide AA. Trichostasis spinulosa at an unusual site. Int J Trichology. 2016;8:78-80.
- Curman P, Näsman A, Brauner H. Trichodysplasia spinulosa: a comprehensive disease and its treatment. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:1067-1076.
- Fischer MK, Kao GF, Nguyen HP, et al. Specific detection of trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus DNA in skin and renal allograft tissues in a patient with trichodysplasia spinulosa. Arch Dermatol. 2021;148:726-733.
- Shah PR, Esaa FS, Gupta P, et al. Trichodysplasia spinulosa successfully treated with adapalene 0.1% gel and oral valganciclovir in a renal transplant recipient. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:23-25.
- Liew YCC, Kee TYS, Kwek JL, et al. Photodynamic therapy for the treatment of trichodysplasia spinulosa in an Asian renal transplant recipient: a case report and review of the literature. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;7:74-83.
- Pierrotti LC, Urbano PRP, da Silva Nali LH, et al. Viremia and viuria of trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus before the development of clinical disease in a kidney transplant recipient. Transpl Infect Dis. 2019;21:E13133.
- Kassar R, Chang J, Chan AW, et al. Leflunomide for the treatment of trichodysplasia spinulosa in a liver transplant recipient. Transpl Infect Dis. 2017;19:E12702.
- Eckburg A, Kazemi T, Maguiness S. Keratosis pilaris rubra successfully treated with topical sirolimus: report of a case and review of the literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2022;39:429-431.
- Reddy S, Brahmbhatt H. A narrative review on the role of acids, steroids, and kinase inhibitors in the treatment of keratosis pilaris. Cureus. 2021;13:E18917.
- Jordan AS, Green MC, Sulit DJ. Lichen nitidus. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2019;119:704.
- Arizaga AT, Gaughan MD, Bang RH. Generalized lichen nitidus. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2002;27:115-117.
- Chu J, Lam JM. Lichen nitidus. CMAJ. 2014;186:E688.
- Haber R, Bachour J, El Gemayel M. Scleromyxedema treatment: a systematic review and update. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:1191-1201.
- Christman MP, Sukhdeo K, Kim RH, et al. Papular mucinosis, or localized lichen myxedematosis (LM) (discrete papular type). Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:8.
- Hoffman JHO, Enk AH. Scleromyxedema. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2020;18:1449-1467.
- Kositkuljorn C, Suchonwanit P. Trichostasis spinulosa: a case report with an unusual presentation. Case Rep Dermatol. 2020;12:178-185.
- Ramteke MN, Bhide AA. Trichostasis spinulosa at an unusual site. Int J Trichology. 2016;8:78-80.
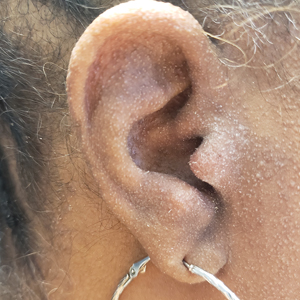
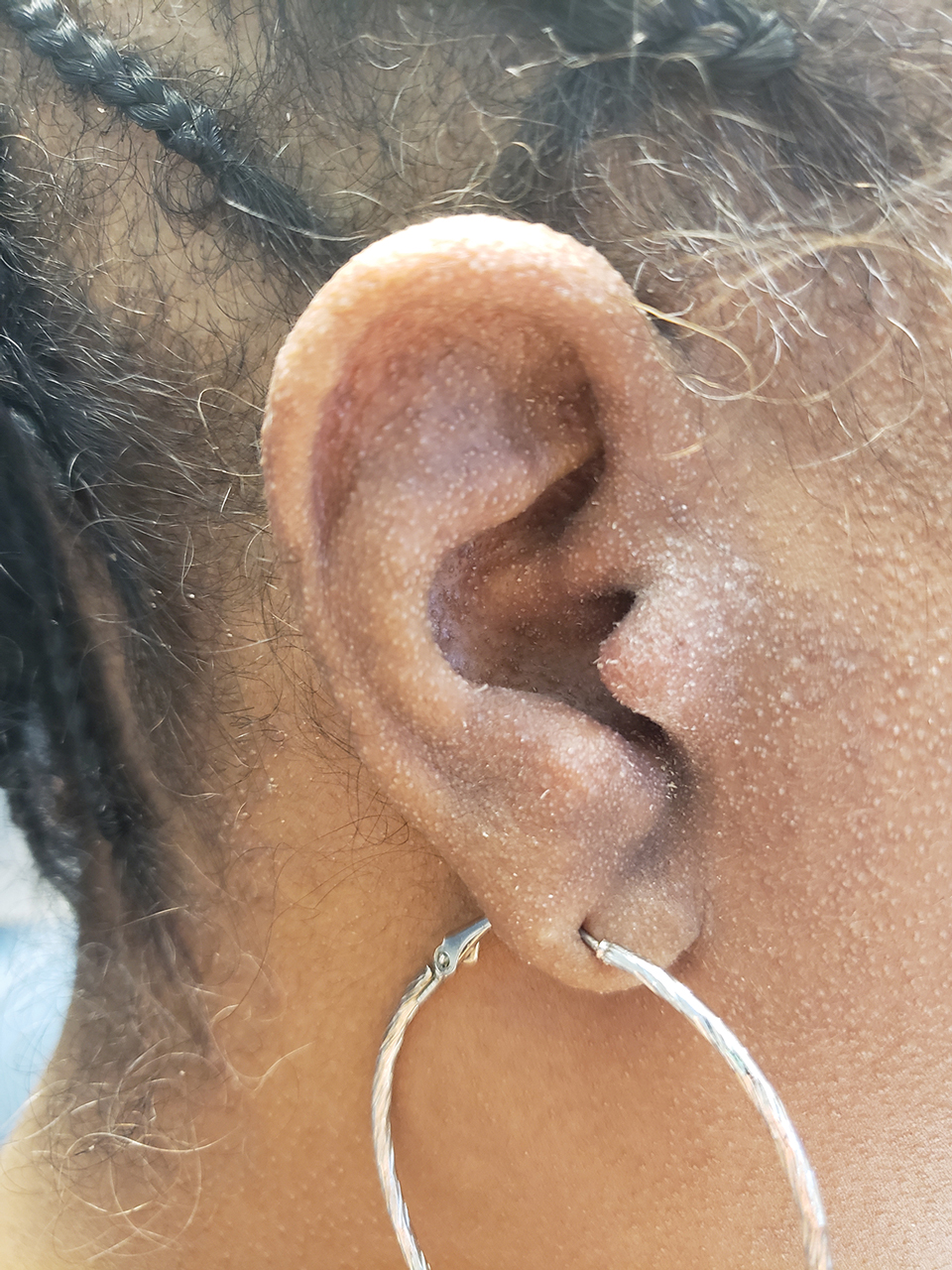
A 54-year-old Black woman presented with a rash that developed 6 months after a renal transplant due to a history of systemic lupus erythematosus with lupus nephritis. She was started on mycophenolate mofetil and tacrolimus after the transplant but was switched to cyclosporine because of BK viremia. The rash developed 1 week after cyclosporine was initiated and consisted of pruritic papules that started on the face and spread to the trunk and arms. Physical examination revealed innumerable follicular-based, keratotic, flesh-colored, pinpoint papules with fine white spicules on the face (top), neck, chest, arms, and back. Leonine facies was seen along the glabella with madarosis of the lateral eyebrows (top) and ears (bottom).
Predicting and Understanding Vaccine Response Determinants
In this column, I recently discussed the impact of the microbiome on childhood vaccine responses. My group has been expanding our research on the topic of childhood vaccine response and its relationship to infection proneness. Therefore, I want to share new research findings.
Immune responsiveness to vaccines varies among children, leaving some susceptible to infections. We also have evidence that the immune deficiencies that contribute to poor vaccine responsiveness also manifest in children as respiratory infection proneness.
Predicting Vaccine Response in the Neonatal Period
The first 100 days of life is an amazing transition time in early life. During that time, the immune system is highly influenced by environmental factors that generate epigenetic changes affecting vaccine responsiveness. Some publications have used the term “window of opportunity,” because it is thought that interventions to change a negative trajectory to a positive one for vaccine responsiveness have a better potential to be effective. Predicting which children will be poorly responsive to vaccines would be desirable, so those children could be specifically identified for intervention. Doing so in the neonatal age time frame using easy-to-obtain clinical samples would be a bonus.
In our most recent study, we sought to identify cytokine biosignatures in the neonatal period, measured in convenient nasopharyngeal secretions, that predict vaccine responses, measured as antibody levels to various vaccines at 1 year of life. Secondly, we assessed the effect of antibiotic exposures on vaccine responses in the study cohort. Third, we tested for induction of CD4+ T-cell vaccine-specific immune memory at infant age 1 year. Fourth, we studied antigen presenting cells (APCs) at rest and in response to an adjuvant called R848, known to stimulate toll-like receptor (TLR) 7/8 agonist, to assess its effects on the immune cells of low vaccine responder children, compared with other children.1
The study population consisted of 101 infants recruited from two primary care pediatric practices in/near Rochester, New York. Children lived in suburban and rural environments. Enrollment and sampling occurred during 2017-2020. All participants received regularly scheduled childhood vaccinations according to the recommendations by US Centers for Disease Control. Nasopharyngeal swabs were used to collect nasal secretions. Antibody titers against six antigens were measured at approximately 1 year of age from all 72 available blood samples. The protective threshold of the corresponding vaccine antigen divided each vaccine-induced antibody level and the ratio considered a normalized titer. The normalized antibody titers were used to define vaccine responsiveness groups as Low Vaccine Responder (bottom 25th percentile of vaccine responders, n = 18 children), as Normal Vaccine Responder (25-75th percentile of vaccine responders, n = 36 children) and as High Vaccine Responder (top 25th percentile of vaccine responders, n = 18 children).
We found that specific nasal cytokine levels measured at newborn age 1 week old, 2 weeks old, and 3 weeks old were predictive of the vaccine response groupings measured at child age 1 year old, following their primary series of vaccinations. The P values varied between less than .05 to .001.
Five newborns had antibiotic exposure at/near the time of birth; 4 [80%] of the 5 were Low Vaccine Responders vs 1 [2%] of 60 Normal+High Vaccine Responder children, P = .006. Also, the cumulative days of antibiotic exposure up to 1 year was highly associated with low vaccine responders, compared with Normal+High Vaccine Responder children (P = 2 x 10-16).
We found that Low Vaccine Responder infants had reduced vaccine-specific T-helper memory cells producing INFg and IL-2 (Th1 cytokines) and IL-4 (Th2 cytokines), compared with Normal+High Vaccine Responder children. In the absence of sufficient numbers of antigen-specific memory CD4+ T-cells, a child would become unprotected from the target infection that the vaccines were intended to prevent after the antibody levels wane.
We found that Low Vaccine Responder antigen-presenting cells are different from those in normal vaccine responders and they can be distinguished when at rest and when stimulated by a specific adjuvant — R848. Our previous findings suggested that Low Vaccine Responder children have a prolonged neonatal-like immune profile (PNIP).2 Therefore, stimulating the immune system of a Low Vaccine Responder could shift their cellular immune responses to behave like cells of Normal+High Vaccine Responder children.
In summary, we identified cytokine biosignatures measured in nasopharyngeal secretions in the neonatal period that predicted vaccine response groups measured as antibody levels at 1 year of life. We showed that reduced vaccine responsiveness was associated with antibiotic exposure at/near birth and with cumulative exposure during the first year of life. We found that Low Vaccine Responder children at 1 year old have fewer vaccine-specific memory CD4+ Th1 and Th2-cells and that antigen-presenting cells at rest and in response to R848 antigen stimulation differ, compared with Normal+High Vaccine Responder children.
Future work by our group will focus on exploring early-life risk factors that influence differences in vaccine responsiveness and interventions that might shift a child’s responsiveness from low to normal or high.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute, at Rochester (New York) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
1. Pichichero ME et al. Variability of Vaccine Responsiveness in Young Children. J Infect Dis. 2023 Nov 22:jiad524. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad524.
2. Pichichero ME et al. Functional Immune Cell Differences Associated with Low Vaccine Responses in Infants. J Infect Dis. 2016 Jun 15;213(12):2014-2019. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw053.
In this column, I recently discussed the impact of the microbiome on childhood vaccine responses. My group has been expanding our research on the topic of childhood vaccine response and its relationship to infection proneness. Therefore, I want to share new research findings.
Immune responsiveness to vaccines varies among children, leaving some susceptible to infections. We also have evidence that the immune deficiencies that contribute to poor vaccine responsiveness also manifest in children as respiratory infection proneness.
Predicting Vaccine Response in the Neonatal Period
The first 100 days of life is an amazing transition time in early life. During that time, the immune system is highly influenced by environmental factors that generate epigenetic changes affecting vaccine responsiveness. Some publications have used the term “window of opportunity,” because it is thought that interventions to change a negative trajectory to a positive one for vaccine responsiveness have a better potential to be effective. Predicting which children will be poorly responsive to vaccines would be desirable, so those children could be specifically identified for intervention. Doing so in the neonatal age time frame using easy-to-obtain clinical samples would be a bonus.
In our most recent study, we sought to identify cytokine biosignatures in the neonatal period, measured in convenient nasopharyngeal secretions, that predict vaccine responses, measured as antibody levels to various vaccines at 1 year of life. Secondly, we assessed the effect of antibiotic exposures on vaccine responses in the study cohort. Third, we tested for induction of CD4+ T-cell vaccine-specific immune memory at infant age 1 year. Fourth, we studied antigen presenting cells (APCs) at rest and in response to an adjuvant called R848, known to stimulate toll-like receptor (TLR) 7/8 agonist, to assess its effects on the immune cells of low vaccine responder children, compared with other children.1
The study population consisted of 101 infants recruited from two primary care pediatric practices in/near Rochester, New York. Children lived in suburban and rural environments. Enrollment and sampling occurred during 2017-2020. All participants received regularly scheduled childhood vaccinations according to the recommendations by US Centers for Disease Control. Nasopharyngeal swabs were used to collect nasal secretions. Antibody titers against six antigens were measured at approximately 1 year of age from all 72 available blood samples. The protective threshold of the corresponding vaccine antigen divided each vaccine-induced antibody level and the ratio considered a normalized titer. The normalized antibody titers were used to define vaccine responsiveness groups as Low Vaccine Responder (bottom 25th percentile of vaccine responders, n = 18 children), as Normal Vaccine Responder (25-75th percentile of vaccine responders, n = 36 children) and as High Vaccine Responder (top 25th percentile of vaccine responders, n = 18 children).
We found that specific nasal cytokine levels measured at newborn age 1 week old, 2 weeks old, and 3 weeks old were predictive of the vaccine response groupings measured at child age 1 year old, following their primary series of vaccinations. The P values varied between less than .05 to .001.
Five newborns had antibiotic exposure at/near the time of birth; 4 [80%] of the 5 were Low Vaccine Responders vs 1 [2%] of 60 Normal+High Vaccine Responder children, P = .006. Also, the cumulative days of antibiotic exposure up to 1 year was highly associated with low vaccine responders, compared with Normal+High Vaccine Responder children (P = 2 x 10-16).
We found that Low Vaccine Responder infants had reduced vaccine-specific T-helper memory cells producing INFg and IL-2 (Th1 cytokines) and IL-4 (Th2 cytokines), compared with Normal+High Vaccine Responder children. In the absence of sufficient numbers of antigen-specific memory CD4+ T-cells, a child would become unprotected from the target infection that the vaccines were intended to prevent after the antibody levels wane.
We found that Low Vaccine Responder antigen-presenting cells are different from those in normal vaccine responders and they can be distinguished when at rest and when stimulated by a specific adjuvant — R848. Our previous findings suggested that Low Vaccine Responder children have a prolonged neonatal-like immune profile (PNIP).2 Therefore, stimulating the immune system of a Low Vaccine Responder could shift their cellular immune responses to behave like cells of Normal+High Vaccine Responder children.
In summary, we identified cytokine biosignatures measured in nasopharyngeal secretions in the neonatal period that predicted vaccine response groups measured as antibody levels at 1 year of life. We showed that reduced vaccine responsiveness was associated with antibiotic exposure at/near birth and with cumulative exposure during the first year of life. We found that Low Vaccine Responder children at 1 year old have fewer vaccine-specific memory CD4+ Th1 and Th2-cells and that antigen-presenting cells at rest and in response to R848 antigen stimulation differ, compared with Normal+High Vaccine Responder children.
Future work by our group will focus on exploring early-life risk factors that influence differences in vaccine responsiveness and interventions that might shift a child’s responsiveness from low to normal or high.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute, at Rochester (New York) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
1. Pichichero ME et al. Variability of Vaccine Responsiveness in Young Children. J Infect Dis. 2023 Nov 22:jiad524. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad524.
2. Pichichero ME et al. Functional Immune Cell Differences Associated with Low Vaccine Responses in Infants. J Infect Dis. 2016 Jun 15;213(12):2014-2019. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw053.
In this column, I recently discussed the impact of the microbiome on childhood vaccine responses. My group has been expanding our research on the topic of childhood vaccine response and its relationship to infection proneness. Therefore, I want to share new research findings.
Immune responsiveness to vaccines varies among children, leaving some susceptible to infections. We also have evidence that the immune deficiencies that contribute to poor vaccine responsiveness also manifest in children as respiratory infection proneness.
Predicting Vaccine Response in the Neonatal Period
The first 100 days of life is an amazing transition time in early life. During that time, the immune system is highly influenced by environmental factors that generate epigenetic changes affecting vaccine responsiveness. Some publications have used the term “window of opportunity,” because it is thought that interventions to change a negative trajectory to a positive one for vaccine responsiveness have a better potential to be effective. Predicting which children will be poorly responsive to vaccines would be desirable, so those children could be specifically identified for intervention. Doing so in the neonatal age time frame using easy-to-obtain clinical samples would be a bonus.
In our most recent study, we sought to identify cytokine biosignatures in the neonatal period, measured in convenient nasopharyngeal secretions, that predict vaccine responses, measured as antibody levels to various vaccines at 1 year of life. Secondly, we assessed the effect of antibiotic exposures on vaccine responses in the study cohort. Third, we tested for induction of CD4+ T-cell vaccine-specific immune memory at infant age 1 year. Fourth, we studied antigen presenting cells (APCs) at rest and in response to an adjuvant called R848, known to stimulate toll-like receptor (TLR) 7/8 agonist, to assess its effects on the immune cells of low vaccine responder children, compared with other children.1
The study population consisted of 101 infants recruited from two primary care pediatric practices in/near Rochester, New York. Children lived in suburban and rural environments. Enrollment and sampling occurred during 2017-2020. All participants received regularly scheduled childhood vaccinations according to the recommendations by US Centers for Disease Control. Nasopharyngeal swabs were used to collect nasal secretions. Antibody titers against six antigens were measured at approximately 1 year of age from all 72 available blood samples. The protective threshold of the corresponding vaccine antigen divided each vaccine-induced antibody level and the ratio considered a normalized titer. The normalized antibody titers were used to define vaccine responsiveness groups as Low Vaccine Responder (bottom 25th percentile of vaccine responders, n = 18 children), as Normal Vaccine Responder (25-75th percentile of vaccine responders, n = 36 children) and as High Vaccine Responder (top 25th percentile of vaccine responders, n = 18 children).
We found that specific nasal cytokine levels measured at newborn age 1 week old, 2 weeks old, and 3 weeks old were predictive of the vaccine response groupings measured at child age 1 year old, following their primary series of vaccinations. The P values varied between less than .05 to .001.
Five newborns had antibiotic exposure at/near the time of birth; 4 [80%] of the 5 were Low Vaccine Responders vs 1 [2%] of 60 Normal+High Vaccine Responder children, P = .006. Also, the cumulative days of antibiotic exposure up to 1 year was highly associated with low vaccine responders, compared with Normal+High Vaccine Responder children (P = 2 x 10-16).
We found that Low Vaccine Responder infants had reduced vaccine-specific T-helper memory cells producing INFg and IL-2 (Th1 cytokines) and IL-4 (Th2 cytokines), compared with Normal+High Vaccine Responder children. In the absence of sufficient numbers of antigen-specific memory CD4+ T-cells, a child would become unprotected from the target infection that the vaccines were intended to prevent after the antibody levels wane.
We found that Low Vaccine Responder antigen-presenting cells are different from those in normal vaccine responders and they can be distinguished when at rest and when stimulated by a specific adjuvant — R848. Our previous findings suggested that Low Vaccine Responder children have a prolonged neonatal-like immune profile (PNIP).2 Therefore, stimulating the immune system of a Low Vaccine Responder could shift their cellular immune responses to behave like cells of Normal+High Vaccine Responder children.
In summary, we identified cytokine biosignatures measured in nasopharyngeal secretions in the neonatal period that predicted vaccine response groups measured as antibody levels at 1 year of life. We showed that reduced vaccine responsiveness was associated with antibiotic exposure at/near birth and with cumulative exposure during the first year of life. We found that Low Vaccine Responder children at 1 year old have fewer vaccine-specific memory CD4+ Th1 and Th2-cells and that antigen-presenting cells at rest and in response to R848 antigen stimulation differ, compared with Normal+High Vaccine Responder children.
Future work by our group will focus on exploring early-life risk factors that influence differences in vaccine responsiveness and interventions that might shift a child’s responsiveness from low to normal or high.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute, at Rochester (New York) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
1. Pichichero ME et al. Variability of Vaccine Responsiveness in Young Children. J Infect Dis. 2023 Nov 22:jiad524. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad524.
2. Pichichero ME et al. Functional Immune Cell Differences Associated with Low Vaccine Responses in Infants. J Infect Dis. 2016 Jun 15;213(12):2014-2019. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw053.
Latest Breakthroughs in Molluscum Contagiosum Therapy
Molluscum contagiosum (ie, molluscum) is a ubiquitous infection caused by the poxvirus molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV). Although skin deep, molluscum shares many factors with the more virulent poxviridae. Moisture and trauma can cause viral material to be released from the pearly papules through a small opening, which also allows entry of bacteria and medications into the lesion. The MCV is transmitted by direct contact with skin or via fomites.1
Molluscum can affect children of any age, with MCV type 1 peaking in toddlers and school-aged children and MCV type 2 after the sexual debut. The prevalence of molluscum has increased since the 1980s. It is stressful for children and caregivers and poses challenges in schools as well as sports such as swimming, wrestling, and karate.1,2
For the first time, we have US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved products to treat MCV infections. Previously, only off-label agents were used. Therefore, we have to contemplate why treatment is important to our patients.
What type of care is required for molluscum?
Counseling is the first and only mandatory treatment, which consists of 3 parts: natural history, risk factors for spread, and options for therapy. The natural history of molluscum in children is early spread, contagion to oneself and others (as high as 60% of sibling co-bathers3), triggering of dermatitis, eventual onset of the beginning-of-the-end (BOTE) sign, and eventually clearance. The natural history in adults is poorly understood.
Early clearance is uncommon; reports have suggested 45.6% to 48.4% of affected patients are clear at 1 year and 69.5% to 72.6% at 1.5 years.4 For many children, especially those with atopic dermatitis (AD), lesions linger and often spread, with many experiencing disease for 3 to 4 years. Fomites such as towels, washcloths, and sponges can transfer the virus and spread lesions; therefore, I advise patients to gently pat their skin dry, wash towels frequently, and avoid sharing bathing equipment.1,3,5 Children and adults with immunosuppression may have a greater number of lesions and more prolonged course of disease, including those with HIV as well as DOC8 and CARD11 mutations.6 The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) emphasizes that children should not be excluded from attending child care/school or from swimming in public pools but lesions should be covered.6 Lesions, especially those in the antecubital region, can trigger new-onset AD or AD flares.3 In response, gentle skin care including fragrance-free cleansers and periodic application of moisturizers may ward off AD. Topical corticosteroids are preferred.
Dermatitis in MCV is a great mimicker and can resemble erythema multiforme, Gianotti-Crosti syndrome, impetigo, and AD.1 Superinfection recently has been reported; however, in a retrospective analysis of 56 patients with inflamed lesions secondary to molluscum infection, only 7 had positive bacterial cultures, which supports the idea of the swelling and redness of inflammation as a mimic for infection.7 When true infection does occur, tender, swollen, pus-filled lesions should be lanced and cultured.1,7,8
When should we consider therapy?
Therapy is highly dependent on the child, the caregiver, and the social circumstances.1 More than 80% of parents are anxious about molluscum, and countless children are embarrassed or ashamed.1 Ultimately, an unhappy child merits care. The AAP cites the following as reasons to treat: “(1) alleviate discomfort, including itching; (2) reduce autoinoculation; (3) limit transmission of the virus to close contacts; (4) reduce cosmetic concerns; and (5) prevent secondary infection.”6 For adults, we should consider limitations to intimacy and reduction of sexual transmission risk.6
Treatment can be based on the number of lesions. With a few lesions (<3), therapy is worthwhile if they are unsightly; appear on exposed skin causing embarrassment; and/or are itchy, uncomfortable, or large. In a report of 300 children with molluscum treated with cantharidin, most patients choosing therapy had 10 to 20 lesions, but this was over multiple visits.8 Looking at a 2018 data set of 50 patients (all-comers) with molluscum,3 the mean number of lesions was 10 (median, 7); 3 lesions were 1 SD below, while 14, 17, and 45 were 1, 2, and 3 SDs above, respectively. This data set shows that patients can develop more lesions rapidly, and most children have many visible lesions (N.B. Silverberg, MD, unpublished data).
Because each lesion contains infectious viral particles and patients scratch, more lesions are equated to greater autoinoculation and contagion. In addition to the AAP criteria, treatment can be considered for households with immunocompromised individuals, children at risk for new-onset AD, or those with AD at risk for flare. For patients with 45 lesions or more (3 SDs), clearance is harder to achieve with 2 sessions of in-office therapy, and multiple methods or the addition of immunomodulatory therapeutics should be considered.
Do we have to clear every lesion?
New molluscum lesions may arise until a patient achieves immunity, and they may appear more than a month after inoculation, making it difficult to keep up with the rapid spread. Latency between exposure and lesion development usually is 2 to 7 weeks but may be as long as 6 months, making it difficult to prevent spread.6 Therefore, when we treat, we should not promise full clearance to patients and parents. Rather, we should inform them that new lesions may develop later, and therapy is only effective on visible lesions. In a recent study, a 50% clearance of lesions was the satisfactory threshold for parents, demonstrating that satisfaction is possible with partial clearance.9
What is new in therapeutics for molluscum?
Molluscum therapies are either destructive, immunomodulatory, or antiviral. Two agents now are approved by the FDA for the treatment of molluscum infections.
Berdazimer gel 10.3% is approved for patients 1 year or older, but it is not yet available. This agent has both immunomodulatory and antiviral properties.10 It features a home therapy that is mixed on a small palette, then painted on by the patient or parent once daily for 12 weeks. Study outcomes demonstrated more than 50% lesional clearance.11,12 Complete clearance was achieved in at least 30% of patients.12A proprietary topical version of cantharidin 0.7% in flexible collodion is now FDA approved for patients 2 years and older. This vesicant-triggering iatrogenic is targeted at creating blisters overlying molluscum lesions. It is conceptually similar to older versions but with some enhanced features.5,13,14 This version was used for therapy every 3 weeks for up to 4 sessions in clinical trials. Safety is similar across all body sites treated (nonmucosal and not near the mucosal surfaces) but not for mucosa, the mid face, or eyelids.13 Complete lesion clearance was 46.3% to 54% and statistically greater than placebo (P<.001).14Both agents are well tolerated in children with AD; adverse effects include blistering with cantharidin and dermatitislike symptoms with berdazimer.15,16 These therapies have the advantage of being easy to use.
Final Thoughts
We have entered an era of high-quality molluscum therapy. Patient care involves developing a good knowledge of the agents, incorporating shared decision-making with patients and caregivers, and addressing therapy in the context of comorbid diseases such as AD.
- Silverberg NB. Pediatric molluscum: an update. Cutis. 2019;104:301-305, E1-E2.
- Thompson AJ, Matinpour K, Hardin J, et al. Molluscum gladiatorum. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:13030/qt0nj121n1.
- Silverberg NB. Molluscum contagiosum virus infection can trigger atopic dermatitis disease onset or flare. Cutis. 2018;102:191-194.
- Basdag H, Rainer BM, Cohen BA. Molluscum contagiosum: to treat or not to treat? experience with 170 children in an outpatient clinic setting in the northeastern United States. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:353-357. doi:10.1111/pde.12504
- Silverberg NB. Warts and molluscum in children. Adv Dermatol. 2004;20:23-73.
- Molluscum contagiosum. In: Kimberlin DW, Lynfield R, Barnett ED, et al (eds). Red Book: 2021–2024 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases. 32nd edition. American Academy of Pediatrics. May 26, 2021. Accessed May 20, 2024. https://publications.aap.org/redbook/book/347/chapter/5754264/Molluscum-Contagiosum
- Gross I, Ben Nachum N, Molho-Pessach V, et al. The molluscum contagiosum BOTE sign—infected or inflamed? Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:476-479. doi:10.1111/pde.14124
- Silverberg NB, Sidbury R, Mancini AJ. Childhood molluscum contagiosum: experience with cantharidin therapy in 300 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:503-507. doi:10.1067/mjd.2000.106370
- Maeda-Chubachi T, McLeod L, Enloe C, et al. Defining clinically meaningful improvement in molluscum contagiosum. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;90:443-445. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.033
- Guttman-Yassky E, Gallo RL, Pavel AB, et al. A nitric oxide-releasing topical medication as a potential treatment option for atopic dermatitis through antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activity. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140:2531-2535.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2020.04.013
- Browning JC, Cartwright M, Thorla I Jr, et al. A patient-centered perspective of molluscum contagiosum as reported by B-SIMPLE4 Clinical Trial patients and caregivers: Global Impression of Change and Exit Interview substudy results. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023;24:119-133. doi:10.1007/s40257-022-00733-9
- Sugarman JL, Hebert A, Browning JC, et al. Berdazimer gel for molluscum contagiosum: an integrated analysis of 3 randomized controlled trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;90:299-308. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.09.066
- Eichenfield LF, Kwong P, Gonzalez ME, et al. Safety and efficacy of VP-102 (cantharidin, 0.7% w/v) in molluscum contagiosum by body region: post hoc pooled analyses from two phase III randomized trials. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14:42-47.
- Eichenfield LF, McFalda W, Brabec B, et al. Safety and efficacy of VP-102, a proprietary, drug-device combination product containing cantharidin, 0.7% (w/v), in children and adults with molluscum contagiosum: two phase 3 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:1315-1323. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.3238
- Paller AS, Green LJ, Silverberg N, et al. Berdazimer gel for molluscum contagiosum in patients with atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol.Published online February 27, 2024. doi:10.1111/pde.15575
- Eichenfield L, Hebert A, Mancini A, et al. Therapeutic approaches and special considerations for treating molluscum contagiosum. J Drugs Dermatol. 2021;20:1185-1190. doi:10.36849/jdd.6383
Molluscum contagiosum (ie, molluscum) is a ubiquitous infection caused by the poxvirus molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV). Although skin deep, molluscum shares many factors with the more virulent poxviridae. Moisture and trauma can cause viral material to be released from the pearly papules through a small opening, which also allows entry of bacteria and medications into the lesion. The MCV is transmitted by direct contact with skin or via fomites.1
Molluscum can affect children of any age, with MCV type 1 peaking in toddlers and school-aged children and MCV type 2 after the sexual debut. The prevalence of molluscum has increased since the 1980s. It is stressful for children and caregivers and poses challenges in schools as well as sports such as swimming, wrestling, and karate.1,2
For the first time, we have US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved products to treat MCV infections. Previously, only off-label agents were used. Therefore, we have to contemplate why treatment is important to our patients.
What type of care is required for molluscum?
Counseling is the first and only mandatory treatment, which consists of 3 parts: natural history, risk factors for spread, and options for therapy. The natural history of molluscum in children is early spread, contagion to oneself and others (as high as 60% of sibling co-bathers3), triggering of dermatitis, eventual onset of the beginning-of-the-end (BOTE) sign, and eventually clearance. The natural history in adults is poorly understood.
Early clearance is uncommon; reports have suggested 45.6% to 48.4% of affected patients are clear at 1 year and 69.5% to 72.6% at 1.5 years.4 For many children, especially those with atopic dermatitis (AD), lesions linger and often spread, with many experiencing disease for 3 to 4 years. Fomites such as towels, washcloths, and sponges can transfer the virus and spread lesions; therefore, I advise patients to gently pat their skin dry, wash towels frequently, and avoid sharing bathing equipment.1,3,5 Children and adults with immunosuppression may have a greater number of lesions and more prolonged course of disease, including those with HIV as well as DOC8 and CARD11 mutations.6 The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) emphasizes that children should not be excluded from attending child care/school or from swimming in public pools but lesions should be covered.6 Lesions, especially those in the antecubital region, can trigger new-onset AD or AD flares.3 In response, gentle skin care including fragrance-free cleansers and periodic application of moisturizers may ward off AD. Topical corticosteroids are preferred.
Dermatitis in MCV is a great mimicker and can resemble erythema multiforme, Gianotti-Crosti syndrome, impetigo, and AD.1 Superinfection recently has been reported; however, in a retrospective analysis of 56 patients with inflamed lesions secondary to molluscum infection, only 7 had positive bacterial cultures, which supports the idea of the swelling and redness of inflammation as a mimic for infection.7 When true infection does occur, tender, swollen, pus-filled lesions should be lanced and cultured.1,7,8
When should we consider therapy?
Therapy is highly dependent on the child, the caregiver, and the social circumstances.1 More than 80% of parents are anxious about molluscum, and countless children are embarrassed or ashamed.1 Ultimately, an unhappy child merits care. The AAP cites the following as reasons to treat: “(1) alleviate discomfort, including itching; (2) reduce autoinoculation; (3) limit transmission of the virus to close contacts; (4) reduce cosmetic concerns; and (5) prevent secondary infection.”6 For adults, we should consider limitations to intimacy and reduction of sexual transmission risk.6
Treatment can be based on the number of lesions. With a few lesions (<3), therapy is worthwhile if they are unsightly; appear on exposed skin causing embarrassment; and/or are itchy, uncomfortable, or large. In a report of 300 children with molluscum treated with cantharidin, most patients choosing therapy had 10 to 20 lesions, but this was over multiple visits.8 Looking at a 2018 data set of 50 patients (all-comers) with molluscum,3 the mean number of lesions was 10 (median, 7); 3 lesions were 1 SD below, while 14, 17, and 45 were 1, 2, and 3 SDs above, respectively. This data set shows that patients can develop more lesions rapidly, and most children have many visible lesions (N.B. Silverberg, MD, unpublished data).
Because each lesion contains infectious viral particles and patients scratch, more lesions are equated to greater autoinoculation and contagion. In addition to the AAP criteria, treatment can be considered for households with immunocompromised individuals, children at risk for new-onset AD, or those with AD at risk for flare. For patients with 45 lesions or more (3 SDs), clearance is harder to achieve with 2 sessions of in-office therapy, and multiple methods or the addition of immunomodulatory therapeutics should be considered.
Do we have to clear every lesion?
New molluscum lesions may arise until a patient achieves immunity, and they may appear more than a month after inoculation, making it difficult to keep up with the rapid spread. Latency between exposure and lesion development usually is 2 to 7 weeks but may be as long as 6 months, making it difficult to prevent spread.6 Therefore, when we treat, we should not promise full clearance to patients and parents. Rather, we should inform them that new lesions may develop later, and therapy is only effective on visible lesions. In a recent study, a 50% clearance of lesions was the satisfactory threshold for parents, demonstrating that satisfaction is possible with partial clearance.9
What is new in therapeutics for molluscum?
Molluscum therapies are either destructive, immunomodulatory, or antiviral. Two agents now are approved by the FDA for the treatment of molluscum infections.
Berdazimer gel 10.3% is approved for patients 1 year or older, but it is not yet available. This agent has both immunomodulatory and antiviral properties.10 It features a home therapy that is mixed on a small palette, then painted on by the patient or parent once daily for 12 weeks. Study outcomes demonstrated more than 50% lesional clearance.11,12 Complete clearance was achieved in at least 30% of patients.12A proprietary topical version of cantharidin 0.7% in flexible collodion is now FDA approved for patients 2 years and older. This vesicant-triggering iatrogenic is targeted at creating blisters overlying molluscum lesions. It is conceptually similar to older versions but with some enhanced features.5,13,14 This version was used for therapy every 3 weeks for up to 4 sessions in clinical trials. Safety is similar across all body sites treated (nonmucosal and not near the mucosal surfaces) but not for mucosa, the mid face, or eyelids.13 Complete lesion clearance was 46.3% to 54% and statistically greater than placebo (P<.001).14Both agents are well tolerated in children with AD; adverse effects include blistering with cantharidin and dermatitislike symptoms with berdazimer.15,16 These therapies have the advantage of being easy to use.
Final Thoughts
We have entered an era of high-quality molluscum therapy. Patient care involves developing a good knowledge of the agents, incorporating shared decision-making with patients and caregivers, and addressing therapy in the context of comorbid diseases such as AD.
Molluscum contagiosum (ie, molluscum) is a ubiquitous infection caused by the poxvirus molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV). Although skin deep, molluscum shares many factors with the more virulent poxviridae. Moisture and trauma can cause viral material to be released from the pearly papules through a small opening, which also allows entry of bacteria and medications into the lesion. The MCV is transmitted by direct contact with skin or via fomites.1
Molluscum can affect children of any age, with MCV type 1 peaking in toddlers and school-aged children and MCV type 2 after the sexual debut. The prevalence of molluscum has increased since the 1980s. It is stressful for children and caregivers and poses challenges in schools as well as sports such as swimming, wrestling, and karate.1,2
For the first time, we have US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved products to treat MCV infections. Previously, only off-label agents were used. Therefore, we have to contemplate why treatment is important to our patients.
What type of care is required for molluscum?
Counseling is the first and only mandatory treatment, which consists of 3 parts: natural history, risk factors for spread, and options for therapy. The natural history of molluscum in children is early spread, contagion to oneself and others (as high as 60% of sibling co-bathers3), triggering of dermatitis, eventual onset of the beginning-of-the-end (BOTE) sign, and eventually clearance. The natural history in adults is poorly understood.
Early clearance is uncommon; reports have suggested 45.6% to 48.4% of affected patients are clear at 1 year and 69.5% to 72.6% at 1.5 years.4 For many children, especially those with atopic dermatitis (AD), lesions linger and often spread, with many experiencing disease for 3 to 4 years. Fomites such as towels, washcloths, and sponges can transfer the virus and spread lesions; therefore, I advise patients to gently pat their skin dry, wash towels frequently, and avoid sharing bathing equipment.1,3,5 Children and adults with immunosuppression may have a greater number of lesions and more prolonged course of disease, including those with HIV as well as DOC8 and CARD11 mutations.6 The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) emphasizes that children should not be excluded from attending child care/school or from swimming in public pools but lesions should be covered.6 Lesions, especially those in the antecubital region, can trigger new-onset AD or AD flares.3 In response, gentle skin care including fragrance-free cleansers and periodic application of moisturizers may ward off AD. Topical corticosteroids are preferred.
Dermatitis in MCV is a great mimicker and can resemble erythema multiforme, Gianotti-Crosti syndrome, impetigo, and AD.1 Superinfection recently has been reported; however, in a retrospective analysis of 56 patients with inflamed lesions secondary to molluscum infection, only 7 had positive bacterial cultures, which supports the idea of the swelling and redness of inflammation as a mimic for infection.7 When true infection does occur, tender, swollen, pus-filled lesions should be lanced and cultured.1,7,8
When should we consider therapy?
Therapy is highly dependent on the child, the caregiver, and the social circumstances.1 More than 80% of parents are anxious about molluscum, and countless children are embarrassed or ashamed.1 Ultimately, an unhappy child merits care. The AAP cites the following as reasons to treat: “(1) alleviate discomfort, including itching; (2) reduce autoinoculation; (3) limit transmission of the virus to close contacts; (4) reduce cosmetic concerns; and (5) prevent secondary infection.”6 For adults, we should consider limitations to intimacy and reduction of sexual transmission risk.6
Treatment can be based on the number of lesions. With a few lesions (<3), therapy is worthwhile if they are unsightly; appear on exposed skin causing embarrassment; and/or are itchy, uncomfortable, or large. In a report of 300 children with molluscum treated with cantharidin, most patients choosing therapy had 10 to 20 lesions, but this was over multiple visits.8 Looking at a 2018 data set of 50 patients (all-comers) with molluscum,3 the mean number of lesions was 10 (median, 7); 3 lesions were 1 SD below, while 14, 17, and 45 were 1, 2, and 3 SDs above, respectively. This data set shows that patients can develop more lesions rapidly, and most children have many visible lesions (N.B. Silverberg, MD, unpublished data).
Because each lesion contains infectious viral particles and patients scratch, more lesions are equated to greater autoinoculation and contagion. In addition to the AAP criteria, treatment can be considered for households with immunocompromised individuals, children at risk for new-onset AD, or those with AD at risk for flare. For patients with 45 lesions or more (3 SDs), clearance is harder to achieve with 2 sessions of in-office therapy, and multiple methods or the addition of immunomodulatory therapeutics should be considered.
Do we have to clear every lesion?
New molluscum lesions may arise until a patient achieves immunity, and they may appear more than a month after inoculation, making it difficult to keep up with the rapid spread. Latency between exposure and lesion development usually is 2 to 7 weeks but may be as long as 6 months, making it difficult to prevent spread.6 Therefore, when we treat, we should not promise full clearance to patients and parents. Rather, we should inform them that new lesions may develop later, and therapy is only effective on visible lesions. In a recent study, a 50% clearance of lesions was the satisfactory threshold for parents, demonstrating that satisfaction is possible with partial clearance.9
What is new in therapeutics for molluscum?
Molluscum therapies are either destructive, immunomodulatory, or antiviral. Two agents now are approved by the FDA for the treatment of molluscum infections.
Berdazimer gel 10.3% is approved for patients 1 year or older, but it is not yet available. This agent has both immunomodulatory and antiviral properties.10 It features a home therapy that is mixed on a small palette, then painted on by the patient or parent once daily for 12 weeks. Study outcomes demonstrated more than 50% lesional clearance.11,12 Complete clearance was achieved in at least 30% of patients.12A proprietary topical version of cantharidin 0.7% in flexible collodion is now FDA approved for patients 2 years and older. This vesicant-triggering iatrogenic is targeted at creating blisters overlying molluscum lesions. It is conceptually similar to older versions but with some enhanced features.5,13,14 This version was used for therapy every 3 weeks for up to 4 sessions in clinical trials. Safety is similar across all body sites treated (nonmucosal and not near the mucosal surfaces) but not for mucosa, the mid face, or eyelids.13 Complete lesion clearance was 46.3% to 54% and statistically greater than placebo (P<.001).14Both agents are well tolerated in children with AD; adverse effects include blistering with cantharidin and dermatitislike symptoms with berdazimer.15,16 These therapies have the advantage of being easy to use.
Final Thoughts
We have entered an era of high-quality molluscum therapy. Patient care involves developing a good knowledge of the agents, incorporating shared decision-making with patients and caregivers, and addressing therapy in the context of comorbid diseases such as AD.
- Silverberg NB. Pediatric molluscum: an update. Cutis. 2019;104:301-305, E1-E2.
- Thompson AJ, Matinpour K, Hardin J, et al. Molluscum gladiatorum. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:13030/qt0nj121n1.
- Silverberg NB. Molluscum contagiosum virus infection can trigger atopic dermatitis disease onset or flare. Cutis. 2018;102:191-194.
- Basdag H, Rainer BM, Cohen BA. Molluscum contagiosum: to treat or not to treat? experience with 170 children in an outpatient clinic setting in the northeastern United States. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:353-357. doi:10.1111/pde.12504
- Silverberg NB. Warts and molluscum in children. Adv Dermatol. 2004;20:23-73.
- Molluscum contagiosum. In: Kimberlin DW, Lynfield R, Barnett ED, et al (eds). Red Book: 2021–2024 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases. 32nd edition. American Academy of Pediatrics. May 26, 2021. Accessed May 20, 2024. https://publications.aap.org/redbook/book/347/chapter/5754264/Molluscum-Contagiosum
- Gross I, Ben Nachum N, Molho-Pessach V, et al. The molluscum contagiosum BOTE sign—infected or inflamed? Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:476-479. doi:10.1111/pde.14124
- Silverberg NB, Sidbury R, Mancini AJ. Childhood molluscum contagiosum: experience with cantharidin therapy in 300 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:503-507. doi:10.1067/mjd.2000.106370
- Maeda-Chubachi T, McLeod L, Enloe C, et al. Defining clinically meaningful improvement in molluscum contagiosum. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;90:443-445. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.033
- Guttman-Yassky E, Gallo RL, Pavel AB, et al. A nitric oxide-releasing topical medication as a potential treatment option for atopic dermatitis through antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activity. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140:2531-2535.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2020.04.013
- Browning JC, Cartwright M, Thorla I Jr, et al. A patient-centered perspective of molluscum contagiosum as reported by B-SIMPLE4 Clinical Trial patients and caregivers: Global Impression of Change and Exit Interview substudy results. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023;24:119-133. doi:10.1007/s40257-022-00733-9
- Sugarman JL, Hebert A, Browning JC, et al. Berdazimer gel for molluscum contagiosum: an integrated analysis of 3 randomized controlled trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;90:299-308. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.09.066
- Eichenfield LF, Kwong P, Gonzalez ME, et al. Safety and efficacy of VP-102 (cantharidin, 0.7% w/v) in molluscum contagiosum by body region: post hoc pooled analyses from two phase III randomized trials. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14:42-47.
- Eichenfield LF, McFalda W, Brabec B, et al. Safety and efficacy of VP-102, a proprietary, drug-device combination product containing cantharidin, 0.7% (w/v), in children and adults with molluscum contagiosum: two phase 3 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:1315-1323. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.3238
- Paller AS, Green LJ, Silverberg N, et al. Berdazimer gel for molluscum contagiosum in patients with atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol.Published online February 27, 2024. doi:10.1111/pde.15575
- Eichenfield L, Hebert A, Mancini A, et al. Therapeutic approaches and special considerations for treating molluscum contagiosum. J Drugs Dermatol. 2021;20:1185-1190. doi:10.36849/jdd.6383
- Silverberg NB. Pediatric molluscum: an update. Cutis. 2019;104:301-305, E1-E2.
- Thompson AJ, Matinpour K, Hardin J, et al. Molluscum gladiatorum. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:13030/qt0nj121n1.
- Silverberg NB. Molluscum contagiosum virus infection can trigger atopic dermatitis disease onset or flare. Cutis. 2018;102:191-194.
- Basdag H, Rainer BM, Cohen BA. Molluscum contagiosum: to treat or not to treat? experience with 170 children in an outpatient clinic setting in the northeastern United States. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:353-357. doi:10.1111/pde.12504
- Silverberg NB. Warts and molluscum in children. Adv Dermatol. 2004;20:23-73.
- Molluscum contagiosum. In: Kimberlin DW, Lynfield R, Barnett ED, et al (eds). Red Book: 2021–2024 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases. 32nd edition. American Academy of Pediatrics. May 26, 2021. Accessed May 20, 2024. https://publications.aap.org/redbook/book/347/chapter/5754264/Molluscum-Contagiosum
- Gross I, Ben Nachum N, Molho-Pessach V, et al. The molluscum contagiosum BOTE sign—infected or inflamed? Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:476-479. doi:10.1111/pde.14124
- Silverberg NB, Sidbury R, Mancini AJ. Childhood molluscum contagiosum: experience with cantharidin therapy in 300 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:503-507. doi:10.1067/mjd.2000.106370
- Maeda-Chubachi T, McLeod L, Enloe C, et al. Defining clinically meaningful improvement in molluscum contagiosum. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;90:443-445. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.033
- Guttman-Yassky E, Gallo RL, Pavel AB, et al. A nitric oxide-releasing topical medication as a potential treatment option for atopic dermatitis through antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activity. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140:2531-2535.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2020.04.013
- Browning JC, Cartwright M, Thorla I Jr, et al. A patient-centered perspective of molluscum contagiosum as reported by B-SIMPLE4 Clinical Trial patients and caregivers: Global Impression of Change and Exit Interview substudy results. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023;24:119-133. doi:10.1007/s40257-022-00733-9
- Sugarman JL, Hebert A, Browning JC, et al. Berdazimer gel for molluscum contagiosum: an integrated analysis of 3 randomized controlled trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;90:299-308. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.09.066
- Eichenfield LF, Kwong P, Gonzalez ME, et al. Safety and efficacy of VP-102 (cantharidin, 0.7% w/v) in molluscum contagiosum by body region: post hoc pooled analyses from two phase III randomized trials. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14:42-47.
- Eichenfield LF, McFalda W, Brabec B, et al. Safety and efficacy of VP-102, a proprietary, drug-device combination product containing cantharidin, 0.7% (w/v), in children and adults with molluscum contagiosum: two phase 3 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:1315-1323. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.3238
- Paller AS, Green LJ, Silverberg N, et al. Berdazimer gel for molluscum contagiosum in patients with atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol.Published online February 27, 2024. doi:10.1111/pde.15575
- Eichenfield L, Hebert A, Mancini A, et al. Therapeutic approaches and special considerations for treating molluscum contagiosum. J Drugs Dermatol. 2021;20:1185-1190. doi:10.36849/jdd.6383
Seniors in Households with Children Have Sixfold Higher Risk for Pneumococcal Disease
BARCELONA, SPAIN — Streptococcus pneumoniae, the bacteria that causes pneumococcal disease, is sixfold more likely to colonize adults older than 60 years who have regular contact with children than those who do not, data from a community-based study showed.
However, there is “no clear evidence of adult-to-adult transmission,” and the researchers, led by Anne L. Wyllie, PhD, from the Yale School of Public Health, New Haven, Connecticut, noted that the study results suggest “the main benefit of adult pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) immunization is to directly protect adults who are exposed to children, who still carry and transmit some vaccine-type pneumococci despite successful pediatric national immunization programs.”
The data show that relatively high pneumococcus carriage rates are seen in people who have regular contact with children, who have had contact in the previous 2 weeks, and who have had contact for extended periods, Dr. Wyllie explained.
Preschoolers in particular were found to be most likely to transmit pneumococcus to older adults. “It is the 24- to 59-month-olds who are most associated with pneumococcal carriage, more than 1- to 2-year-olds,” she reported. However, transmission rates from children younger than 1 year are higher than those from children aged 1-2 years, she added.
The findings were presented at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) 2024 global conference, formerly known as the ECCMID conference.
Originally Designed to Investigate Adult-to-Adult Transmission
The researchers wanted to understand the sources and dynamics of transmission, as well as the risk factors for pneumococcal disease in older adults, to help predict the effect of PCVs in people older than 60 years.
Although “we designed the study to specifically look at transmission between adults, in the end, we were presented with a very unique scenario” — restricted social mixing as a result of the COVID pandemic — during which “no community activities were happening,” Dr. Wyllie said. Because of this, the team was able to determine “the source of acquisition or transmission to the older adults was, very likely, coming from contact with children.”
Pneumococci are commonly found in respiratory tracts of healthy people. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimated that 20%-60% of school-aged children may be colonized compared with only 5%-10% of adults without children.
The longitudinal study was conducted among household pairs, such as married couples who were both aged at least 60 years and who did not have people younger than 60 years living in the household, in New Haven over two winter seasons: 2020-2021 and 2021-2022.
Self-collected saliva samples were assessed, and surveys on social behaviors and health were completed every 2 weeks for a 10-week period (with six study visits). The saliva sampling method was used because the researchers considered it to be more effective than samples from nasopharyngeal swabs. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction assays were used to test the saliva samples for the presence of pneumococcal DNA (pneumococcus genes piaB and lytA) and the diversity of pneumococcal strains (36 serotypes were targeted).
Strongly Suggestive of Transmission From Children to Older Adults
Of the 121 adults living in 61 households who were enrolled in the study, 62 adults participated in both seasons. Mean age was 70.9 years (range, 60-86 years), 51% of participants were women, and 85% were White.
Overall, 52 of 1088 (4.8%) samples tested positive for pneumococcus, and 27 of 121 (22.3%) adults were colonized on at least one sampling visit. Some were colonized at multiple timepoints, and two were colonized throughout the 10-week sampling period. Of the two participants who were colonized at five of six timepoints, one reported daily contact with children younger than 5 years and children aged 5-9 years in the two study seasons. This person was also positive at three of six sampling points during the first study season.
There were five instances in which both members of the household were carriers in the same season, although not necessarily at the same timepoint. Numbers were too small to determine whether transmission had occurred between the household pairs.
Contact with a 24- to 59-month-old child (older than 2 years but younger than 5 years) had the strongest association with elevated odds of carrying pneumococcus, the authors reported in their preprint, although the frequency and intensity of contact also mattered.
At any sampled time (point prevalence), pneumococcal carriage was substantially — just over sixfold — higher among older adults who had contact with children daily or every few days (10%) than among those who had no contact with children (1.6%).
In particular, contact between adults and children younger than 5 years and children aged 5-9 years was found to lead to elevated point prevalences of 13.8% and 14.1%, respectively. Pneumococcal carriage in children older than 10 years was lower, with a point prevalence of 8.3%.
The younger the child, the greater the point prevalence; point prevalences were 13.8% for samples from children aged 1 year and younger, 10.5% for samples from children aged 1-2 years, and 17.8% for children aged 2-5 years.
Carriage prevalence was higher in older adults who reported daily contact with children (15.7%) or contact every few days (14.0%) than in those who reported contact with children only once or twice a month (4.5%) or never (1.8%), they wrote.
“Older people who have a lot of contact with kids and are more susceptible to respiratory viruses can get a secondary infection from pneumococcus, especially during the cold and flu seasons. Vaccination can help to protect them or lessen severity of the illness,” Wyllie pointed out.
However, adult PCV immunization may not have a major impact on onward transmission to other adults, the authors wrote in their preprint.
This study supports prior work demonstrating that pneumococcal colonization is greater in households with children than in those without, said Stephen Pelton, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist from Boston University schools of medicine and public health. “The unique aspect is that Dr. Wyllie’s group has looked at individuals over age 60 and used the most sensitive methods currently available to detect pneumococcal carriage.”
“At the most recent ISPPD [International Society of Pneumonia and Pneumococcal Diseases conference], the role of adult-to-adult transmission in the community was discussed. This study confirms the critical role children play in community transmission of the pneumococcus,” Dr. Pelton noted.
Dr. Wyllie received consulting and/or advisory board fees from Pfizer, Merck, Diasorin, PPS Health, Primary Health, Co-Diagnostics, and Global Diagnostic Systems for work unrelated to this project and is the principal investigator on research grants from Pfizer, Merck, NIH RADx-UP, and SalivaDirect, Inc. to Yale University and from NIH RADx, Balvi.io, and Shield T3 to SalivaDirect, Inc. Dr. Pelton received honoraria from Merck, Pfizer, Sanofi, and GSK for participation in Pneumococcal Advisory Boards and DSMB (Sanofi). Boston Medical Center received grant funding for investigator-initiated research from Merck and Pfizer.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
BARCELONA, SPAIN — Streptococcus pneumoniae, the bacteria that causes pneumococcal disease, is sixfold more likely to colonize adults older than 60 years who have regular contact with children than those who do not, data from a community-based study showed.
However, there is “no clear evidence of adult-to-adult transmission,” and the researchers, led by Anne L. Wyllie, PhD, from the Yale School of Public Health, New Haven, Connecticut, noted that the study results suggest “the main benefit of adult pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) immunization is to directly protect adults who are exposed to children, who still carry and transmit some vaccine-type pneumococci despite successful pediatric national immunization programs.”
The data show that relatively high pneumococcus carriage rates are seen in people who have regular contact with children, who have had contact in the previous 2 weeks, and who have had contact for extended periods, Dr. Wyllie explained.
Preschoolers in particular were found to be most likely to transmit pneumococcus to older adults. “It is the 24- to 59-month-olds who are most associated with pneumococcal carriage, more than 1- to 2-year-olds,” she reported. However, transmission rates from children younger than 1 year are higher than those from children aged 1-2 years, she added.
The findings were presented at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) 2024 global conference, formerly known as the ECCMID conference.
Originally Designed to Investigate Adult-to-Adult Transmission
The researchers wanted to understand the sources and dynamics of transmission, as well as the risk factors for pneumococcal disease in older adults, to help predict the effect of PCVs in people older than 60 years.
Although “we designed the study to specifically look at transmission between adults, in the end, we were presented with a very unique scenario” — restricted social mixing as a result of the COVID pandemic — during which “no community activities were happening,” Dr. Wyllie said. Because of this, the team was able to determine “the source of acquisition or transmission to the older adults was, very likely, coming from contact with children.”
Pneumococci are commonly found in respiratory tracts of healthy people. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimated that 20%-60% of school-aged children may be colonized compared with only 5%-10% of adults without children.
The longitudinal study was conducted among household pairs, such as married couples who were both aged at least 60 years and who did not have people younger than 60 years living in the household, in New Haven over two winter seasons: 2020-2021 and 2021-2022.
Self-collected saliva samples were assessed, and surveys on social behaviors and health were completed every 2 weeks for a 10-week period (with six study visits). The saliva sampling method was used because the researchers considered it to be more effective than samples from nasopharyngeal swabs. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction assays were used to test the saliva samples for the presence of pneumococcal DNA (pneumococcus genes piaB and lytA) and the diversity of pneumococcal strains (36 serotypes were targeted).
Strongly Suggestive of Transmission From Children to Older Adults
Of the 121 adults living in 61 households who were enrolled in the study, 62 adults participated in both seasons. Mean age was 70.9 years (range, 60-86 years), 51% of participants were women, and 85% were White.
Overall, 52 of 1088 (4.8%) samples tested positive for pneumococcus, and 27 of 121 (22.3%) adults were colonized on at least one sampling visit. Some were colonized at multiple timepoints, and two were colonized throughout the 10-week sampling period. Of the two participants who were colonized at five of six timepoints, one reported daily contact with children younger than 5 years and children aged 5-9 years in the two study seasons. This person was also positive at three of six sampling points during the first study season.
There were five instances in which both members of the household were carriers in the same season, although not necessarily at the same timepoint. Numbers were too small to determine whether transmission had occurred between the household pairs.
Contact with a 24- to 59-month-old child (older than 2 years but younger than 5 years) had the strongest association with elevated odds of carrying pneumococcus, the authors reported in their preprint, although the frequency and intensity of contact also mattered.
At any sampled time (point prevalence), pneumococcal carriage was substantially — just over sixfold — higher among older adults who had contact with children daily or every few days (10%) than among those who had no contact with children (1.6%).
In particular, contact between adults and children younger than 5 years and children aged 5-9 years was found to lead to elevated point prevalences of 13.8% and 14.1%, respectively. Pneumococcal carriage in children older than 10 years was lower, with a point prevalence of 8.3%.
The younger the child, the greater the point prevalence; point prevalences were 13.8% for samples from children aged 1 year and younger, 10.5% for samples from children aged 1-2 years, and 17.8% for children aged 2-5 years.
Carriage prevalence was higher in older adults who reported daily contact with children (15.7%) or contact every few days (14.0%) than in those who reported contact with children only once or twice a month (4.5%) or never (1.8%), they wrote.
“Older people who have a lot of contact with kids and are more susceptible to respiratory viruses can get a secondary infection from pneumococcus, especially during the cold and flu seasons. Vaccination can help to protect them or lessen severity of the illness,” Wyllie pointed out.
However, adult PCV immunization may not have a major impact on onward transmission to other adults, the authors wrote in their preprint.
This study supports prior work demonstrating that pneumococcal colonization is greater in households with children than in those without, said Stephen Pelton, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist from Boston University schools of medicine and public health. “The unique aspect is that Dr. Wyllie’s group has looked at individuals over age 60 and used the most sensitive methods currently available to detect pneumococcal carriage.”
“At the most recent ISPPD [International Society of Pneumonia and Pneumococcal Diseases conference], the role of adult-to-adult transmission in the community was discussed. This study confirms the critical role children play in community transmission of the pneumococcus,” Dr. Pelton noted.
Dr. Wyllie received consulting and/or advisory board fees from Pfizer, Merck, Diasorin, PPS Health, Primary Health, Co-Diagnostics, and Global Diagnostic Systems for work unrelated to this project and is the principal investigator on research grants from Pfizer, Merck, NIH RADx-UP, and SalivaDirect, Inc. to Yale University and from NIH RADx, Balvi.io, and Shield T3 to SalivaDirect, Inc. Dr. Pelton received honoraria from Merck, Pfizer, Sanofi, and GSK for participation in Pneumococcal Advisory Boards and DSMB (Sanofi). Boston Medical Center received grant funding for investigator-initiated research from Merck and Pfizer.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
BARCELONA, SPAIN — Streptococcus pneumoniae, the bacteria that causes pneumococcal disease, is sixfold more likely to colonize adults older than 60 years who have regular contact with children than those who do not, data from a community-based study showed.
However, there is “no clear evidence of adult-to-adult transmission,” and the researchers, led by Anne L. Wyllie, PhD, from the Yale School of Public Health, New Haven, Connecticut, noted that the study results suggest “the main benefit of adult pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) immunization is to directly protect adults who are exposed to children, who still carry and transmit some vaccine-type pneumococci despite successful pediatric national immunization programs.”
The data show that relatively high pneumococcus carriage rates are seen in people who have regular contact with children, who have had contact in the previous 2 weeks, and who have had contact for extended periods, Dr. Wyllie explained.
Preschoolers in particular were found to be most likely to transmit pneumococcus to older adults. “It is the 24- to 59-month-olds who are most associated with pneumococcal carriage, more than 1- to 2-year-olds,” she reported. However, transmission rates from children younger than 1 year are higher than those from children aged 1-2 years, she added.
The findings were presented at the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) 2024 global conference, formerly known as the ECCMID conference.
Originally Designed to Investigate Adult-to-Adult Transmission
The researchers wanted to understand the sources and dynamics of transmission, as well as the risk factors for pneumococcal disease in older adults, to help predict the effect of PCVs in people older than 60 years.
Although “we designed the study to specifically look at transmission between adults, in the end, we were presented with a very unique scenario” — restricted social mixing as a result of the COVID pandemic — during which “no community activities were happening,” Dr. Wyllie said. Because of this, the team was able to determine “the source of acquisition or transmission to the older adults was, very likely, coming from contact with children.”
Pneumococci are commonly found in respiratory tracts of healthy people. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimated that 20%-60% of school-aged children may be colonized compared with only 5%-10% of adults without children.
The longitudinal study was conducted among household pairs, such as married couples who were both aged at least 60 years and who did not have people younger than 60 years living in the household, in New Haven over two winter seasons: 2020-2021 and 2021-2022.
Self-collected saliva samples were assessed, and surveys on social behaviors and health were completed every 2 weeks for a 10-week period (with six study visits). The saliva sampling method was used because the researchers considered it to be more effective than samples from nasopharyngeal swabs. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction assays were used to test the saliva samples for the presence of pneumococcal DNA (pneumococcus genes piaB and lytA) and the diversity of pneumococcal strains (36 serotypes were targeted).
Strongly Suggestive of Transmission From Children to Older Adults
Of the 121 adults living in 61 households who were enrolled in the study, 62 adults participated in both seasons. Mean age was 70.9 years (range, 60-86 years), 51% of participants were women, and 85% were White.
Overall, 52 of 1088 (4.8%) samples tested positive for pneumococcus, and 27 of 121 (22.3%) adults were colonized on at least one sampling visit. Some were colonized at multiple timepoints, and two were colonized throughout the 10-week sampling period. Of the two participants who were colonized at five of six timepoints, one reported daily contact with children younger than 5 years and children aged 5-9 years in the two study seasons. This person was also positive at three of six sampling points during the first study season.
There were five instances in which both members of the household were carriers in the same season, although not necessarily at the same timepoint. Numbers were too small to determine whether transmission had occurred between the household pairs.
Contact with a 24- to 59-month-old child (older than 2 years but younger than 5 years) had the strongest association with elevated odds of carrying pneumococcus, the authors reported in their preprint, although the frequency and intensity of contact also mattered.
At any sampled time (point prevalence), pneumococcal carriage was substantially — just over sixfold — higher among older adults who had contact with children daily or every few days (10%) than among those who had no contact with children (1.6%).
In particular, contact between adults and children younger than 5 years and children aged 5-9 years was found to lead to elevated point prevalences of 13.8% and 14.1%, respectively. Pneumococcal carriage in children older than 10 years was lower, with a point prevalence of 8.3%.
The younger the child, the greater the point prevalence; point prevalences were 13.8% for samples from children aged 1 year and younger, 10.5% for samples from children aged 1-2 years, and 17.8% for children aged 2-5 years.
Carriage prevalence was higher in older adults who reported daily contact with children (15.7%) or contact every few days (14.0%) than in those who reported contact with children only once or twice a month (4.5%) or never (1.8%), they wrote.
“Older people who have a lot of contact with kids and are more susceptible to respiratory viruses can get a secondary infection from pneumococcus, especially during the cold and flu seasons. Vaccination can help to protect them or lessen severity of the illness,” Wyllie pointed out.
However, adult PCV immunization may not have a major impact on onward transmission to other adults, the authors wrote in their preprint.
This study supports prior work demonstrating that pneumococcal colonization is greater in households with children than in those without, said Stephen Pelton, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist from Boston University schools of medicine and public health. “The unique aspect is that Dr. Wyllie’s group has looked at individuals over age 60 and used the most sensitive methods currently available to detect pneumococcal carriage.”
“At the most recent ISPPD [International Society of Pneumonia and Pneumococcal Diseases conference], the role of adult-to-adult transmission in the community was discussed. This study confirms the critical role children play in community transmission of the pneumococcus,” Dr. Pelton noted.
Dr. Wyllie received consulting and/or advisory board fees from Pfizer, Merck, Diasorin, PPS Health, Primary Health, Co-Diagnostics, and Global Diagnostic Systems for work unrelated to this project and is the principal investigator on research grants from Pfizer, Merck, NIH RADx-UP, and SalivaDirect, Inc. to Yale University and from NIH RADx, Balvi.io, and Shield T3 to SalivaDirect, Inc. Dr. Pelton received honoraria from Merck, Pfizer, Sanofi, and GSK for participation in Pneumococcal Advisory Boards and DSMB (Sanofi). Boston Medical Center received grant funding for investigator-initiated research from Merck and Pfizer.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESCMID GLOBAL 2024
The Appendix: Is It ’Useless,’ or a Safe House and Immune Training Ground?
When doctors and patients consider the appendix, it’s often with urgency. In cases of appendicitis, the clock could be ticking down to a life-threatening burst. Thus, despite recent research suggesting antibiotics could be an alternative therapy, appendectomy remains standard for uncomplicated appendicitis.
But what if removing the appendix could raise the risk for gastrointestinal (GI) diseases like irritable bowel syndrome and colorectal cancer? That’s what some emerging science suggests. And though the research is early and mixed, it’s enough to give some health professionals pause.
“If there’s no reason to remove the appendix, then it’s better to have one,” said Heather Smith, PhD, a comparative anatomist at Midwestern University, Glendale, Arizona. Preemptive removal is not supported by the evidence, she said.
To be fair, we’ve come a long way since 1928, when American physician Miles Breuer, MD, suggested that people with infected appendixes should be left to perish, so as to remove their inferior DNA from the gene pool (he called such people “uncivilized” and “candidates for extinction”). Charles Darwin, while less radical, believed the appendix was at best useless — a mere vestige of our ancestors switching diets from leaves to fruits.
What we know now is that the appendix isn’t just a troublesome piece of worthless flesh. Instead, it may act as a safe house for friendly gut bacteria and a training camp for the immune system. It also appears to play a role in several medical conditions, from ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer to Parkinson’s disease and lupus. The roughly 300,000 Americans who undergo appendectomy each year should be made aware of this, some experts say. But the frustrating truth is, scientists are still trying to figure out in which cases having an appendix is protective and in which we may be better off without it.
A ‘Worm’ as Intestinal Protection
The appendix is a blind pouch (meaning its ending is closed off) that extends from the large intestine. Not all mammals have one; it’s been found in several species of primates and rodents, as well as in rabbits, wombats, and Florida manatees, among others (dogs and cats don’t have it). While a human appendix “looks like a little worm,” Dr. Smith said, these anatomical structures come in various sizes and shapes. Some are thick, as in a beaver, while others are long and spiraling, like a rabbit’s.
Comparative anatomy studies reveal that the appendix has evolved independently at least 29 times throughout mammalian evolution. This suggests that “it has some kind of an adaptive function,” Dr. Smith said. When French scientists analyzed data from 258 species of mammals, they discovered that those that possess an appendix live longer than those without one. A possible explanation, the researchers wrote, may lie with the appendix’s role in preventing diarrhea.
Their 2023 study supported this hypothesis. Based on veterinary records of 45 different species of primates housed in a French zoo, the scientists established that primates with appendixes are far less likely to suffer severe diarrhea than those that don’t possess this organ. The appendix, it appears, might be our tiny weapon against bowel troubles.
For immunologist William Parker, PhD, a visiting scholar at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, these data are “about as good as we could hope for” in support of the idea that the appendix might protect mammals from GI problems. An experiment on humans would be unethical, Dr. Parker said. But observational studies offer clues.
One study showed that compared with people with an intact appendix, young adults with a history of appendectomy have more than double the risk of developing a serious infection with non-typhoidal Salmonella of the kind that would require hospitalization.
A ‘Safe House’ for Bacteria
Such studies add weight to a theory that Dr. Parker and his colleagues developed back in 2007: That the appendix acts as a “safe house” for beneficial gut bacteria.
Think of the colon as a wide pipe, Dr. Parker said, that may become contaminated with a pathogen such as Salmonella. Diarrhea follows, and the pipe gets repeatedly flushed, wiping everything clean, including your friendly gut microbiome. Luckily, “you’ve got this little offshoot of that pipe,” where the flow can’t really get in “because it’s so constricted,” Dr. Parker said. The friendly gut microbes can survive inside the appendix and repopulate the colon once diarrhea is over. Dr. Parker and his colleagues found that the human appendix contains a thick layer of beneficial bacteria. “They were right where we predicted they would be,” he said.
This safe house hypothesis could explain why the gut microbiome may be different in people who no longer have an appendix. In one small study, people who’d had an appendectomy had a less diverse microbiome, with a lower abundance of beneficial strains such as Butyricicoccus and Barnesiella, than did those with intact appendixes.
The appendix likely has a second function, too, Dr. Smith said: It may serve as a training camp for the immune system. “When there is an invading pathogen in the gut, it helps the GI system to mount the immune response,” she said. The human appendix is rich in special cells known as M cells. These act as scouts, detecting and capturing invasive bacteria and viruses and presenting them to the body’s defense team, such as the T lymphocytes.
If the appendix shelters beneficial bacteria and boosts immune response, that may explain its links to various diseases. According to an epidemiological study from Taiwan,patients who underwent an appendectomy have a 46% higher risk of developing irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) — a disease associated with a low abundance of Butyricicoccus bacteria. This is why, the study authors wrote, doctors should pay careful attention to people who’ve had their appendixes removed, monitoring them for potential symptoms of IBS.
The same database helped uncover other connections between appendectomy and disease. For one, there was type 2 diabetes: Within 3 years of the surgery, patients under 30 had double the risk of developing this disorder. Then there was lupus: While those who underwent appendectomy generally had higher risk for this autoimmune disease, women were particularly affected.
The Contentious Connections
The most heated scientific discussion surrounds the links between the appendix and conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and colorectal cancer. A small 2019 study showed, for example, that appendectomy may improve symptoms of certain forms of ulcerative colitis that don’t respond to standard medical treatments. A third of patients improved after their appendix was removed, and 17% fully recovered.
Why? According to Dr. Parker, appendectomy may work for ulcerative colitis because it’s “a way of suppressing the immune system, especially in the lower intestinal areas.” A 2023 meta-analysis found that people who’d had their appendix removed before being diagnosed with ulcerative colitis were less likely to need their colon removed later on.
Such a procedure may have a serious side effect, however: Colorectal cancer. French scientists discovered that removing the appendix may reduce the numbers of certain immune cells called CD3+ and CD8+ T cells, causing a weakened immune surveillance. As a result, tumor cells might escape detection.
Yet the links between appendix removal and cancer are far from clear. A recent meta-analysis found that while people with appendectomies generally had a higher risk for colorectal cancer, for Europeans, these effects were insignificant. In fact, removal of the appendix actually protected European women from this particular form of cancer. For Parker, such mixed results may stem from the fact that treatments and populations vary widely. The issue “may depend on complex social and medical factors,” Dr. Parker said.
Things also appear complicated with Parkinson’s disease — another condition linked to the appendix. A large epidemiological study showed that appendectomy is associated with a lower risk for Parkinson’s disease and a delayed age of Parkinson’s onset. It also found that a normal appendix contains α-synuclein, a protein that may accumulate in the brain and contribute to the development of Parkinson’s. “Although α-synuclein is toxic when in the brain, it appears to be quite normal when present in the appendix,” said Luis Vitetta, PhD, MD, a clinical epidemiologist at the University of Sydney, Camperdown, Australia. Yet, not all studies find that removing the appendix lowers the risk for Parkinson’s. In fact, some show the opposite results.
How Should Doctors View the Appendix?
Even with these mysteries and contradictions, Dr. Vitetta said, a healthy appendix in a healthy body appears to be protective. This is why, he said, when someone is diagnosed with appendicitis, careful assessment is essential before surgery is performed.
“Perhaps an antibiotic can actually help fix it,” he said. A 2020 study published in The New England Journal of Medicine showed that antibiotics may indeed be a good alternative to surgery for the treatment of appendicitis. “We don’t want necessarily to remove an appendix that could be beneficial,” Dr. Smith said.
The many links between the appendix and various diseases mean that doctors should be more vigilant when treating patients who’ve had this organ removed, Dr. Parker said. “When a patient loses an appendix, depending on their environment, there may be effects on infection and cancer. So they might need more regular checkups,” he said. This could include monitoring for IBS and colorectal cancer.
What’s more, Dr. Parker believes that research on the appendix puts even more emphasis on the need to protect the gut microbiome — such as taking probiotics with antibiotics. And while we are still a long way from understanding how exactly this worm-like structure affects various diseases, one thing appears quite certain: The appendix is not useless. “If Darwin had the information that we have, he would not have drawn these conclusions,” Dr. Parker said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When doctors and patients consider the appendix, it’s often with urgency. In cases of appendicitis, the clock could be ticking down to a life-threatening burst. Thus, despite recent research suggesting antibiotics could be an alternative therapy, appendectomy remains standard for uncomplicated appendicitis.
But what if removing the appendix could raise the risk for gastrointestinal (GI) diseases like irritable bowel syndrome and colorectal cancer? That’s what some emerging science suggests. And though the research is early and mixed, it’s enough to give some health professionals pause.
“If there’s no reason to remove the appendix, then it’s better to have one,” said Heather Smith, PhD, a comparative anatomist at Midwestern University, Glendale, Arizona. Preemptive removal is not supported by the evidence, she said.
To be fair, we’ve come a long way since 1928, when American physician Miles Breuer, MD, suggested that people with infected appendixes should be left to perish, so as to remove their inferior DNA from the gene pool (he called such people “uncivilized” and “candidates for extinction”). Charles Darwin, while less radical, believed the appendix was at best useless — a mere vestige of our ancestors switching diets from leaves to fruits.
What we know now is that the appendix isn’t just a troublesome piece of worthless flesh. Instead, it may act as a safe house for friendly gut bacteria and a training camp for the immune system. It also appears to play a role in several medical conditions, from ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer to Parkinson’s disease and lupus. The roughly 300,000 Americans who undergo appendectomy each year should be made aware of this, some experts say. But the frustrating truth is, scientists are still trying to figure out in which cases having an appendix is protective and in which we may be better off without it.
A ‘Worm’ as Intestinal Protection
The appendix is a blind pouch (meaning its ending is closed off) that extends from the large intestine. Not all mammals have one; it’s been found in several species of primates and rodents, as well as in rabbits, wombats, and Florida manatees, among others (dogs and cats don’t have it). While a human appendix “looks like a little worm,” Dr. Smith said, these anatomical structures come in various sizes and shapes. Some are thick, as in a beaver, while others are long and spiraling, like a rabbit’s.
Comparative anatomy studies reveal that the appendix has evolved independently at least 29 times throughout mammalian evolution. This suggests that “it has some kind of an adaptive function,” Dr. Smith said. When French scientists analyzed data from 258 species of mammals, they discovered that those that possess an appendix live longer than those without one. A possible explanation, the researchers wrote, may lie with the appendix’s role in preventing diarrhea.
Their 2023 study supported this hypothesis. Based on veterinary records of 45 different species of primates housed in a French zoo, the scientists established that primates with appendixes are far less likely to suffer severe diarrhea than those that don’t possess this organ. The appendix, it appears, might be our tiny weapon against bowel troubles.
For immunologist William Parker, PhD, a visiting scholar at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, these data are “about as good as we could hope for” in support of the idea that the appendix might protect mammals from GI problems. An experiment on humans would be unethical, Dr. Parker said. But observational studies offer clues.
One study showed that compared with people with an intact appendix, young adults with a history of appendectomy have more than double the risk of developing a serious infection with non-typhoidal Salmonella of the kind that would require hospitalization.
A ‘Safe House’ for Bacteria
Such studies add weight to a theory that Dr. Parker and his colleagues developed back in 2007: That the appendix acts as a “safe house” for beneficial gut bacteria.
Think of the colon as a wide pipe, Dr. Parker said, that may become contaminated with a pathogen such as Salmonella. Diarrhea follows, and the pipe gets repeatedly flushed, wiping everything clean, including your friendly gut microbiome. Luckily, “you’ve got this little offshoot of that pipe,” where the flow can’t really get in “because it’s so constricted,” Dr. Parker said. The friendly gut microbes can survive inside the appendix and repopulate the colon once diarrhea is over. Dr. Parker and his colleagues found that the human appendix contains a thick layer of beneficial bacteria. “They were right where we predicted they would be,” he said.
This safe house hypothesis could explain why the gut microbiome may be different in people who no longer have an appendix. In one small study, people who’d had an appendectomy had a less diverse microbiome, with a lower abundance of beneficial strains such as Butyricicoccus and Barnesiella, than did those with intact appendixes.
The appendix likely has a second function, too, Dr. Smith said: It may serve as a training camp for the immune system. “When there is an invading pathogen in the gut, it helps the GI system to mount the immune response,” she said. The human appendix is rich in special cells known as M cells. These act as scouts, detecting and capturing invasive bacteria and viruses and presenting them to the body’s defense team, such as the T lymphocytes.
If the appendix shelters beneficial bacteria and boosts immune response, that may explain its links to various diseases. According to an epidemiological study from Taiwan,patients who underwent an appendectomy have a 46% higher risk of developing irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) — a disease associated with a low abundance of Butyricicoccus bacteria. This is why, the study authors wrote, doctors should pay careful attention to people who’ve had their appendixes removed, monitoring them for potential symptoms of IBS.
The same database helped uncover other connections between appendectomy and disease. For one, there was type 2 diabetes: Within 3 years of the surgery, patients under 30 had double the risk of developing this disorder. Then there was lupus: While those who underwent appendectomy generally had higher risk for this autoimmune disease, women were particularly affected.
The Contentious Connections
The most heated scientific discussion surrounds the links between the appendix and conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and colorectal cancer. A small 2019 study showed, for example, that appendectomy may improve symptoms of certain forms of ulcerative colitis that don’t respond to standard medical treatments. A third of patients improved after their appendix was removed, and 17% fully recovered.
Why? According to Dr. Parker, appendectomy may work for ulcerative colitis because it’s “a way of suppressing the immune system, especially in the lower intestinal areas.” A 2023 meta-analysis found that people who’d had their appendix removed before being diagnosed with ulcerative colitis were less likely to need their colon removed later on.
Such a procedure may have a serious side effect, however: Colorectal cancer. French scientists discovered that removing the appendix may reduce the numbers of certain immune cells called CD3+ and CD8+ T cells, causing a weakened immune surveillance. As a result, tumor cells might escape detection.
Yet the links between appendix removal and cancer are far from clear. A recent meta-analysis found that while people with appendectomies generally had a higher risk for colorectal cancer, for Europeans, these effects were insignificant. In fact, removal of the appendix actually protected European women from this particular form of cancer. For Parker, such mixed results may stem from the fact that treatments and populations vary widely. The issue “may depend on complex social and medical factors,” Dr. Parker said.
Things also appear complicated with Parkinson’s disease — another condition linked to the appendix. A large epidemiological study showed that appendectomy is associated with a lower risk for Parkinson’s disease and a delayed age of Parkinson’s onset. It also found that a normal appendix contains α-synuclein, a protein that may accumulate in the brain and contribute to the development of Parkinson’s. “Although α-synuclein is toxic when in the brain, it appears to be quite normal when present in the appendix,” said Luis Vitetta, PhD, MD, a clinical epidemiologist at the University of Sydney, Camperdown, Australia. Yet, not all studies find that removing the appendix lowers the risk for Parkinson’s. In fact, some show the opposite results.
How Should Doctors View the Appendix?
Even with these mysteries and contradictions, Dr. Vitetta said, a healthy appendix in a healthy body appears to be protective. This is why, he said, when someone is diagnosed with appendicitis, careful assessment is essential before surgery is performed.
“Perhaps an antibiotic can actually help fix it,” he said. A 2020 study published in The New England Journal of Medicine showed that antibiotics may indeed be a good alternative to surgery for the treatment of appendicitis. “We don’t want necessarily to remove an appendix that could be beneficial,” Dr. Smith said.
The many links between the appendix and various diseases mean that doctors should be more vigilant when treating patients who’ve had this organ removed, Dr. Parker said. “When a patient loses an appendix, depending on their environment, there may be effects on infection and cancer. So they might need more regular checkups,” he said. This could include monitoring for IBS and colorectal cancer.
What’s more, Dr. Parker believes that research on the appendix puts even more emphasis on the need to protect the gut microbiome — such as taking probiotics with antibiotics. And while we are still a long way from understanding how exactly this worm-like structure affects various diseases, one thing appears quite certain: The appendix is not useless. “If Darwin had the information that we have, he would not have drawn these conclusions,” Dr. Parker said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When doctors and patients consider the appendix, it’s often with urgency. In cases of appendicitis, the clock could be ticking down to a life-threatening burst. Thus, despite recent research suggesting antibiotics could be an alternative therapy, appendectomy remains standard for uncomplicated appendicitis.
But what if removing the appendix could raise the risk for gastrointestinal (GI) diseases like irritable bowel syndrome and colorectal cancer? That’s what some emerging science suggests. And though the research is early and mixed, it’s enough to give some health professionals pause.
“If there’s no reason to remove the appendix, then it’s better to have one,” said Heather Smith, PhD, a comparative anatomist at Midwestern University, Glendale, Arizona. Preemptive removal is not supported by the evidence, she said.
To be fair, we’ve come a long way since 1928, when American physician Miles Breuer, MD, suggested that people with infected appendixes should be left to perish, so as to remove their inferior DNA from the gene pool (he called such people “uncivilized” and “candidates for extinction”). Charles Darwin, while less radical, believed the appendix was at best useless — a mere vestige of our ancestors switching diets from leaves to fruits.
What we know now is that the appendix isn’t just a troublesome piece of worthless flesh. Instead, it may act as a safe house for friendly gut bacteria and a training camp for the immune system. It also appears to play a role in several medical conditions, from ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer to Parkinson’s disease and lupus. The roughly 300,000 Americans who undergo appendectomy each year should be made aware of this, some experts say. But the frustrating truth is, scientists are still trying to figure out in which cases having an appendix is protective and in which we may be better off without it.
A ‘Worm’ as Intestinal Protection
The appendix is a blind pouch (meaning its ending is closed off) that extends from the large intestine. Not all mammals have one; it’s been found in several species of primates and rodents, as well as in rabbits, wombats, and Florida manatees, among others (dogs and cats don’t have it). While a human appendix “looks like a little worm,” Dr. Smith said, these anatomical structures come in various sizes and shapes. Some are thick, as in a beaver, while others are long and spiraling, like a rabbit’s.
Comparative anatomy studies reveal that the appendix has evolved independently at least 29 times throughout mammalian evolution. This suggests that “it has some kind of an adaptive function,” Dr. Smith said. When French scientists analyzed data from 258 species of mammals, they discovered that those that possess an appendix live longer than those without one. A possible explanation, the researchers wrote, may lie with the appendix’s role in preventing diarrhea.
Their 2023 study supported this hypothesis. Based on veterinary records of 45 different species of primates housed in a French zoo, the scientists established that primates with appendixes are far less likely to suffer severe diarrhea than those that don’t possess this organ. The appendix, it appears, might be our tiny weapon against bowel troubles.
For immunologist William Parker, PhD, a visiting scholar at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, these data are “about as good as we could hope for” in support of the idea that the appendix might protect mammals from GI problems. An experiment on humans would be unethical, Dr. Parker said. But observational studies offer clues.
One study showed that compared with people with an intact appendix, young adults with a history of appendectomy have more than double the risk of developing a serious infection with non-typhoidal Salmonella of the kind that would require hospitalization.
A ‘Safe House’ for Bacteria
Such studies add weight to a theory that Dr. Parker and his colleagues developed back in 2007: That the appendix acts as a “safe house” for beneficial gut bacteria.
Think of the colon as a wide pipe, Dr. Parker said, that may become contaminated with a pathogen such as Salmonella. Diarrhea follows, and the pipe gets repeatedly flushed, wiping everything clean, including your friendly gut microbiome. Luckily, “you’ve got this little offshoot of that pipe,” where the flow can’t really get in “because it’s so constricted,” Dr. Parker said. The friendly gut microbes can survive inside the appendix and repopulate the colon once diarrhea is over. Dr. Parker and his colleagues found that the human appendix contains a thick layer of beneficial bacteria. “They were right where we predicted they would be,” he said.
This safe house hypothesis could explain why the gut microbiome may be different in people who no longer have an appendix. In one small study, people who’d had an appendectomy had a less diverse microbiome, with a lower abundance of beneficial strains such as Butyricicoccus and Barnesiella, than did those with intact appendixes.
The appendix likely has a second function, too, Dr. Smith said: It may serve as a training camp for the immune system. “When there is an invading pathogen in the gut, it helps the GI system to mount the immune response,” she said. The human appendix is rich in special cells known as M cells. These act as scouts, detecting and capturing invasive bacteria and viruses and presenting them to the body’s defense team, such as the T lymphocytes.
If the appendix shelters beneficial bacteria and boosts immune response, that may explain its links to various diseases. According to an epidemiological study from Taiwan,patients who underwent an appendectomy have a 46% higher risk of developing irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) — a disease associated with a low abundance of Butyricicoccus bacteria. This is why, the study authors wrote, doctors should pay careful attention to people who’ve had their appendixes removed, monitoring them for potential symptoms of IBS.
The same database helped uncover other connections between appendectomy and disease. For one, there was type 2 diabetes: Within 3 years of the surgery, patients under 30 had double the risk of developing this disorder. Then there was lupus: While those who underwent appendectomy generally had higher risk for this autoimmune disease, women were particularly affected.
The Contentious Connections
The most heated scientific discussion surrounds the links between the appendix and conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and colorectal cancer. A small 2019 study showed, for example, that appendectomy may improve symptoms of certain forms of ulcerative colitis that don’t respond to standard medical treatments. A third of patients improved after their appendix was removed, and 17% fully recovered.
Why? According to Dr. Parker, appendectomy may work for ulcerative colitis because it’s “a way of suppressing the immune system, especially in the lower intestinal areas.” A 2023 meta-analysis found that people who’d had their appendix removed before being diagnosed with ulcerative colitis were less likely to need their colon removed later on.
Such a procedure may have a serious side effect, however: Colorectal cancer. French scientists discovered that removing the appendix may reduce the numbers of certain immune cells called CD3+ and CD8+ T cells, causing a weakened immune surveillance. As a result, tumor cells might escape detection.
Yet the links between appendix removal and cancer are far from clear. A recent meta-analysis found that while people with appendectomies generally had a higher risk for colorectal cancer, for Europeans, these effects were insignificant. In fact, removal of the appendix actually protected European women from this particular form of cancer. For Parker, such mixed results may stem from the fact that treatments and populations vary widely. The issue “may depend on complex social and medical factors,” Dr. Parker said.
Things also appear complicated with Parkinson’s disease — another condition linked to the appendix. A large epidemiological study showed that appendectomy is associated with a lower risk for Parkinson’s disease and a delayed age of Parkinson’s onset. It also found that a normal appendix contains α-synuclein, a protein that may accumulate in the brain and contribute to the development of Parkinson’s. “Although α-synuclein is toxic when in the brain, it appears to be quite normal when present in the appendix,” said Luis Vitetta, PhD, MD, a clinical epidemiologist at the University of Sydney, Camperdown, Australia. Yet, not all studies find that removing the appendix lowers the risk for Parkinson’s. In fact, some show the opposite results.
How Should Doctors View the Appendix?
Even with these mysteries and contradictions, Dr. Vitetta said, a healthy appendix in a healthy body appears to be protective. This is why, he said, when someone is diagnosed with appendicitis, careful assessment is essential before surgery is performed.
“Perhaps an antibiotic can actually help fix it,” he said. A 2020 study published in The New England Journal of Medicine showed that antibiotics may indeed be a good alternative to surgery for the treatment of appendicitis. “We don’t want necessarily to remove an appendix that could be beneficial,” Dr. Smith said.
The many links between the appendix and various diseases mean that doctors should be more vigilant when treating patients who’ve had this organ removed, Dr. Parker said. “When a patient loses an appendix, depending on their environment, there may be effects on infection and cancer. So they might need more regular checkups,” he said. This could include monitoring for IBS and colorectal cancer.
What’s more, Dr. Parker believes that research on the appendix puts even more emphasis on the need to protect the gut microbiome — such as taking probiotics with antibiotics. And while we are still a long way from understanding how exactly this worm-like structure affects various diseases, one thing appears quite certain: The appendix is not useless. “If Darwin had the information that we have, he would not have drawn these conclusions,” Dr. Parker said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New Era? ‘Double Selective’ Antibiotic Spares the Microbiome
A new antibiotic uses a never-before-seen mechanism to deliver a direct hit on tough-to-treat infections while leaving beneficial microbes alone. The strategy could lead to a new class of antibiotics that attack dangerous bacteria in a powerful new way, overcoming current drug resistance while sparing the gut microbiome.
“The biggest takeaway is the double-selective component,” said co-lead author Kristen A. Muñoz, PhD, who performed the research as a doctoral student at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC). “We were able to develop a drug that not only targets problematic pathogens, but because it is selective for these pathogens only, we can spare the good bacteria and preserve the integrity of the microbiome.”
The drug goes after Gram-negative bacteria — pathogens responsible for debilitating and even fatal infections like gastroenteritis, urinary tract infections, pneumonia, sepsis, and cholera. The arsenal of antibiotics against them is old, with no new classes specifically targeting these bacteria coming on the market since 1968.
Many of these bugs have become resistant to one or more antibiotics, with deadly consequences. And antibiotics against them can also wipe out beneficial gut bacteria, allowing serious secondary infections to flare up.
In a study published in Nature, the drug lolamicin knocked out or reduced 130 strains of antibiotic-resistant Gram-negative bacteria in cell cultures. It also successfully treated drug-resistant bloodstream infections and pneumonia in mice while sparing their gut microbiome.
With their microbiomes intact, the mice then fought off secondary infection with Clostridioides difficile (a leading cause of opportunistic and sometimes fatal infections in US health care facilities), while mice treated with other compounds that damaged their microbiome succumbed.
How It Works
Like a well-built medieval castle, Gram-negative bacteria are encased in two protective walls, or membranes. Dr. Muñoz and her team at UIUC set out to breach this defense by finding compounds that hinder the “Lol system,” which ferries lipoproteins between them.
From one compound they constructed lolamicin, which can stop Gram-negative pathogens — with little effect on Gram-negative beneficial bacteria and no effect on Gram-positive bacteria.
“Gram-positive bacteria do not have an outer membrane, so they do not possess the Lol system,” Dr. Muñoz said. “When we compared the sequences of the Lol system in certain Gram-negative pathogens to Gram-negative commensal [beneficial] gut bacteria, we saw that the Lol systems were pretty different.”
Tossing a monkey wrench into the Lol system may be the study’s biggest contribution to future antibiotic development, said Kim Lewis, PhD, professor of Biology and director of Antimicrobial Discovery Center at Northeastern University, Boston, who has discovered several antibiotics now in preclinical research. One, darobactin, targets Gram-negative bugs without affecting the gut microbiome. Another, teixobactin, takes down Gram-positive bacteria without causing drug resistance.
“Lolamicin hits a novel target. I would say that’s the most significant study finding,” said Dr. Lewis, who was not involved in the study. “That is rare. If you look at antibiotics introduced since 1968, they have been modifications of existing antibiotics or, rarely, new chemically but hitting the same proven targets. This one hits something properly new, and [that’s] what I found perhaps the most original and interesting.”
Kirk E. Hevener, PharmD, PhD, associate professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, Tennessee, agreed. (Dr. Hevener also was not involved in the study.) “Lolamicin works by targeting a unique Gram-negative transport system. No currently approved antibacterials work in this way, meaning it potentially represents the first of a new class of antibacterials with narrow-spectrum Gram-negative activity and low gastrointestinal disturbance,” said Dr. Hevener, whose research looks at new antimicrobial drug targets.
The UIUC researchers noted that lolamicin has one drawback: Bacteria frequently developed resistance to it. But in future work, it could be tweaked, combined with other antibiotics, or used as a template for finding other Lol system attackers, they said.
“There is still a good amount of work cut out for us in terms of assessing the clinical translatability of lolamicin, but we are hopeful for the future of this drug,” Dr. Muñoz said.
Addressing a Dire Need
Bringing such a drug to market — from discovery to Food and Drug Administration approval — could take more than a decade, said Dr. Hevener. And new agents, especially for Gram-negative bugs, are sorely needed.
Not only do these bacteria shield themselves with a double membrane but they also “have more complex resistance mechanisms including special pumps that can remove antibacterial drugs from the cell before they can be effective,” Dr. Hevener said.
As a result, drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria are making treatment of severe infections such as sepsis and pneumonia in health care settings difficult.
Bloodstream infections with drug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae have a 40% mortality rate, Dr. Lewis said. And microbiome damage caused by antibiotics is also widespread and deadly, wiping out communities of helpful, protective gut bacteria. That contributes to over half of the C. difficile infections that affect 500,000 people and kill 30,000 a year in the United States.
“Our arsenal of antibacterials that can be used to treat Gram-negative infections is dangerously low,” Dr. Hevener said. “Research will always be needed to develop new antibacterials with novel mechanisms of activity that can bypass bacterial resistance mechanisms.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A new antibiotic uses a never-before-seen mechanism to deliver a direct hit on tough-to-treat infections while leaving beneficial microbes alone. The strategy could lead to a new class of antibiotics that attack dangerous bacteria in a powerful new way, overcoming current drug resistance while sparing the gut microbiome.
“The biggest takeaway is the double-selective component,” said co-lead author Kristen A. Muñoz, PhD, who performed the research as a doctoral student at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC). “We were able to develop a drug that not only targets problematic pathogens, but because it is selective for these pathogens only, we can spare the good bacteria and preserve the integrity of the microbiome.”
The drug goes after Gram-negative bacteria — pathogens responsible for debilitating and even fatal infections like gastroenteritis, urinary tract infections, pneumonia, sepsis, and cholera. The arsenal of antibiotics against them is old, with no new classes specifically targeting these bacteria coming on the market since 1968.
Many of these bugs have become resistant to one or more antibiotics, with deadly consequences. And antibiotics against them can also wipe out beneficial gut bacteria, allowing serious secondary infections to flare up.
In a study published in Nature, the drug lolamicin knocked out or reduced 130 strains of antibiotic-resistant Gram-negative bacteria in cell cultures. It also successfully treated drug-resistant bloodstream infections and pneumonia in mice while sparing their gut microbiome.
With their microbiomes intact, the mice then fought off secondary infection with Clostridioides difficile (a leading cause of opportunistic and sometimes fatal infections in US health care facilities), while mice treated with other compounds that damaged their microbiome succumbed.
How It Works
Like a well-built medieval castle, Gram-negative bacteria are encased in two protective walls, or membranes. Dr. Muñoz and her team at UIUC set out to breach this defense by finding compounds that hinder the “Lol system,” which ferries lipoproteins between them.
From one compound they constructed lolamicin, which can stop Gram-negative pathogens — with little effect on Gram-negative beneficial bacteria and no effect on Gram-positive bacteria.
“Gram-positive bacteria do not have an outer membrane, so they do not possess the Lol system,” Dr. Muñoz said. “When we compared the sequences of the Lol system in certain Gram-negative pathogens to Gram-negative commensal [beneficial] gut bacteria, we saw that the Lol systems were pretty different.”
Tossing a monkey wrench into the Lol system may be the study’s biggest contribution to future antibiotic development, said Kim Lewis, PhD, professor of Biology and director of Antimicrobial Discovery Center at Northeastern University, Boston, who has discovered several antibiotics now in preclinical research. One, darobactin, targets Gram-negative bugs without affecting the gut microbiome. Another, teixobactin, takes down Gram-positive bacteria without causing drug resistance.
“Lolamicin hits a novel target. I would say that’s the most significant study finding,” said Dr. Lewis, who was not involved in the study. “That is rare. If you look at antibiotics introduced since 1968, they have been modifications of existing antibiotics or, rarely, new chemically but hitting the same proven targets. This one hits something properly new, and [that’s] what I found perhaps the most original and interesting.”
Kirk E. Hevener, PharmD, PhD, associate professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, Tennessee, agreed. (Dr. Hevener also was not involved in the study.) “Lolamicin works by targeting a unique Gram-negative transport system. No currently approved antibacterials work in this way, meaning it potentially represents the first of a new class of antibacterials with narrow-spectrum Gram-negative activity and low gastrointestinal disturbance,” said Dr. Hevener, whose research looks at new antimicrobial drug targets.
The UIUC researchers noted that lolamicin has one drawback: Bacteria frequently developed resistance to it. But in future work, it could be tweaked, combined with other antibiotics, or used as a template for finding other Lol system attackers, they said.
“There is still a good amount of work cut out for us in terms of assessing the clinical translatability of lolamicin, but we are hopeful for the future of this drug,” Dr. Muñoz said.
Addressing a Dire Need
Bringing such a drug to market — from discovery to Food and Drug Administration approval — could take more than a decade, said Dr. Hevener. And new agents, especially for Gram-negative bugs, are sorely needed.
Not only do these bacteria shield themselves with a double membrane but they also “have more complex resistance mechanisms including special pumps that can remove antibacterial drugs from the cell before they can be effective,” Dr. Hevener said.
As a result, drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria are making treatment of severe infections such as sepsis and pneumonia in health care settings difficult.
Bloodstream infections with drug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae have a 40% mortality rate, Dr. Lewis said. And microbiome damage caused by antibiotics is also widespread and deadly, wiping out communities of helpful, protective gut bacteria. That contributes to over half of the C. difficile infections that affect 500,000 people and kill 30,000 a year in the United States.
“Our arsenal of antibacterials that can be used to treat Gram-negative infections is dangerously low,” Dr. Hevener said. “Research will always be needed to develop new antibacterials with novel mechanisms of activity that can bypass bacterial resistance mechanisms.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A new antibiotic uses a never-before-seen mechanism to deliver a direct hit on tough-to-treat infections while leaving beneficial microbes alone. The strategy could lead to a new class of antibiotics that attack dangerous bacteria in a powerful new way, overcoming current drug resistance while sparing the gut microbiome.
“The biggest takeaway is the double-selective component,” said co-lead author Kristen A. Muñoz, PhD, who performed the research as a doctoral student at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC). “We were able to develop a drug that not only targets problematic pathogens, but because it is selective for these pathogens only, we can spare the good bacteria and preserve the integrity of the microbiome.”
The drug goes after Gram-negative bacteria — pathogens responsible for debilitating and even fatal infections like gastroenteritis, urinary tract infections, pneumonia, sepsis, and cholera. The arsenal of antibiotics against them is old, with no new classes specifically targeting these bacteria coming on the market since 1968.
Many of these bugs have become resistant to one or more antibiotics, with deadly consequences. And antibiotics against them can also wipe out beneficial gut bacteria, allowing serious secondary infections to flare up.
In a study published in Nature, the drug lolamicin knocked out or reduced 130 strains of antibiotic-resistant Gram-negative bacteria in cell cultures. It also successfully treated drug-resistant bloodstream infections and pneumonia in mice while sparing their gut microbiome.
With their microbiomes intact, the mice then fought off secondary infection with Clostridioides difficile (a leading cause of opportunistic and sometimes fatal infections in US health care facilities), while mice treated with other compounds that damaged their microbiome succumbed.
How It Works
Like a well-built medieval castle, Gram-negative bacteria are encased in two protective walls, or membranes. Dr. Muñoz and her team at UIUC set out to breach this defense by finding compounds that hinder the “Lol system,” which ferries lipoproteins between them.
From one compound they constructed lolamicin, which can stop Gram-negative pathogens — with little effect on Gram-negative beneficial bacteria and no effect on Gram-positive bacteria.
“Gram-positive bacteria do not have an outer membrane, so they do not possess the Lol system,” Dr. Muñoz said. “When we compared the sequences of the Lol system in certain Gram-negative pathogens to Gram-negative commensal [beneficial] gut bacteria, we saw that the Lol systems were pretty different.”
Tossing a monkey wrench into the Lol system may be the study’s biggest contribution to future antibiotic development, said Kim Lewis, PhD, professor of Biology and director of Antimicrobial Discovery Center at Northeastern University, Boston, who has discovered several antibiotics now in preclinical research. One, darobactin, targets Gram-negative bugs without affecting the gut microbiome. Another, teixobactin, takes down Gram-positive bacteria without causing drug resistance.
“Lolamicin hits a novel target. I would say that’s the most significant study finding,” said Dr. Lewis, who was not involved in the study. “That is rare. If you look at antibiotics introduced since 1968, they have been modifications of existing antibiotics or, rarely, new chemically but hitting the same proven targets. This one hits something properly new, and [that’s] what I found perhaps the most original and interesting.”
Kirk E. Hevener, PharmD, PhD, associate professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, Tennessee, agreed. (Dr. Hevener also was not involved in the study.) “Lolamicin works by targeting a unique Gram-negative transport system. No currently approved antibacterials work in this way, meaning it potentially represents the first of a new class of antibacterials with narrow-spectrum Gram-negative activity and low gastrointestinal disturbance,” said Dr. Hevener, whose research looks at new antimicrobial drug targets.
The UIUC researchers noted that lolamicin has one drawback: Bacteria frequently developed resistance to it. But in future work, it could be tweaked, combined with other antibiotics, or used as a template for finding other Lol system attackers, they said.
“There is still a good amount of work cut out for us in terms of assessing the clinical translatability of lolamicin, but we are hopeful for the future of this drug,” Dr. Muñoz said.
Addressing a Dire Need
Bringing such a drug to market — from discovery to Food and Drug Administration approval — could take more than a decade, said Dr. Hevener. And new agents, especially for Gram-negative bugs, are sorely needed.
Not only do these bacteria shield themselves with a double membrane but they also “have more complex resistance mechanisms including special pumps that can remove antibacterial drugs from the cell before they can be effective,” Dr. Hevener said.
As a result, drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria are making treatment of severe infections such as sepsis and pneumonia in health care settings difficult.
Bloodstream infections with drug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae have a 40% mortality rate, Dr. Lewis said. And microbiome damage caused by antibiotics is also widespread and deadly, wiping out communities of helpful, protective gut bacteria. That contributes to over half of the C. difficile infections that affect 500,000 people and kill 30,000 a year in the United States.
“Our arsenal of antibacterials that can be used to treat Gram-negative infections is dangerously low,” Dr. Hevener said. “Research will always be needed to develop new antibacterials with novel mechanisms of activity that can bypass bacterial resistance mechanisms.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Moderna’s RSV Vaccine Approved by FDA
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved mRESVIA (mRNA-1345, Moderna), a vaccine for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
“The FDA approval of our second product, mRESVIA, builds on the strength and versatility of our mRNA platform,” Stéphane Bancel, chief executive officer of Moderna, said in a news release. “mRESVIA protects older adults from the severe outcomes of RSV infection. This approval is also the first time an mRNA vaccine has been approved for a disease other than COVID-19.”
mRESVIA is a single-dose vaccine available in prefilled syringes, which the company says are designed to maximize ease of administration, saving vaccinators’ time, and reducing the risk for administrative errors.
The approval is based on the positive results from the phase 3 ConquerRSV clinical trial, published in The New England Journal of Medicine in December 2023. The study, conducted in approximately 37,000 adults aged 60 years or older in 22 countries, found a vaccine efficacy against RSV lower respiratory tract disease of 83.7% after a median 3.7 months of follow-up.
An additional longer-term analysis showed continued protection over 8.6 months median follow-up. No serious safety concerns were identified. The most reported adverse reactions were injection site pain, fatigue, headache, myalgia, and arthralgia.
Moderna has also filed for approval in multiple markets around the world, and says it expects mRESVIA to be available in the United States in time for the 2024-2025 respiratory virus season.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved mRESVIA (mRNA-1345, Moderna), a vaccine for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
“The FDA approval of our second product, mRESVIA, builds on the strength and versatility of our mRNA platform,” Stéphane Bancel, chief executive officer of Moderna, said in a news release. “mRESVIA protects older adults from the severe outcomes of RSV infection. This approval is also the first time an mRNA vaccine has been approved for a disease other than COVID-19.”
mRESVIA is a single-dose vaccine available in prefilled syringes, which the company says are designed to maximize ease of administration, saving vaccinators’ time, and reducing the risk for administrative errors.
The approval is based on the positive results from the phase 3 ConquerRSV clinical trial, published in The New England Journal of Medicine in December 2023. The study, conducted in approximately 37,000 adults aged 60 years or older in 22 countries, found a vaccine efficacy against RSV lower respiratory tract disease of 83.7% after a median 3.7 months of follow-up.
An additional longer-term analysis showed continued protection over 8.6 months median follow-up. No serious safety concerns were identified. The most reported adverse reactions were injection site pain, fatigue, headache, myalgia, and arthralgia.
Moderna has also filed for approval in multiple markets around the world, and says it expects mRESVIA to be available in the United States in time for the 2024-2025 respiratory virus season.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved mRESVIA (mRNA-1345, Moderna), a vaccine for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
“The FDA approval of our second product, mRESVIA, builds on the strength and versatility of our mRNA platform,” Stéphane Bancel, chief executive officer of Moderna, said in a news release. “mRESVIA protects older adults from the severe outcomes of RSV infection. This approval is also the first time an mRNA vaccine has been approved for a disease other than COVID-19.”
mRESVIA is a single-dose vaccine available in prefilled syringes, which the company says are designed to maximize ease of administration, saving vaccinators’ time, and reducing the risk for administrative errors.
The approval is based on the positive results from the phase 3 ConquerRSV clinical trial, published in The New England Journal of Medicine in December 2023. The study, conducted in approximately 37,000 adults aged 60 years or older in 22 countries, found a vaccine efficacy against RSV lower respiratory tract disease of 83.7% after a median 3.7 months of follow-up.
An additional longer-term analysis showed continued protection over 8.6 months median follow-up. No serious safety concerns were identified. The most reported adverse reactions were injection site pain, fatigue, headache, myalgia, and arthralgia.
Moderna has also filed for approval in multiple markets around the world, and says it expects mRESVIA to be available in the United States in time for the 2024-2025 respiratory virus season.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
5 Vaccinations Adults Need Beyond COVID and Flu
Many adults are complacent about vaccinations, believing that annual COVID and flu shots aside, they had all the immunizations they need as children and teens. But adults need vaccines as well, especially if they have missed earlier doses. And older and health-compromised adults, in particular, can benefit from newer vaccines that were not part of the childhood schedule.
“The question is whether adults had the vaccinations they need in the first place,” Sandra Adamson Fryhofer, MD, an internist in Atlanta and the American Medical Association’s liaison to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said in an interview. “Many do not even have reliable records of vaccination.”
Primary care physicians are ideally positioned to get adult patients to update their vaccination status on older vaccines and obtain newer ones as needed. “ACIP recommendations for adult vaccines are getting longer and more complicated and the way they’re administered is more complex, too, in that they’re not all given in the primary care office but sometimes in pharmacies,” Dr. Fryhofer said.
Not all adult patients want to update their vaccinations. “Vaccine hesitancy among many adults is accelerated by the several new vaccines that have been recommended in recent years,” Lauren Block, MD, MPH, an internist at Northwell Health and assistant professor in the Institute of Health System Science at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research in metropolitan New York City, said in an interview.
Physicians are rightly concerned about the lagging rates of adult vaccination, Dr. Block said. “Given the prevalence of conditions like pneumonia and shingles and the morbidity associated with them, healthcare providers should take every opportunity to discuss vaccination with patients, from well visits to hospital visits,” Dr. Block added.
She pointed to several obstacles to broader uptake, including product shortages, financial barriers, and, increasingly, the negative vocal messaging from media outlets and social media.
Current Recommendations
The main vaccines recommended for adults, besides flu and COVID shots, are for respiratory syncytial virus (RVS); shingles; pneumococcal disease; measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR); and tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (Tdap). Less commonly, booster vaccines for MM, and hepatitis are recommended when titers are proven to be low.
ACIP’s updated 2024 Adult Immunization Schedule can be downloaded from the website of the CDC.
The newest additions to the schedule include RSV vaccines, the mpox vaccine (Jynneos), a new MenACWY-MenB combo vaccine (Penbraya), and the new 2023-2024 formulation of updated COVID vaccines (both mRNA and protein-based adjuvanted versions).
1. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccines
There are two licensed RSV vaccines, Arexvy and Abrysvo. The CDC schedule recommends a single-dose RSV vaccine for adults age 60 years and older, especially those at high risk of contracting the virus — but after shared decision-making based on a discussion of the risk-harm balance since this vaccine carries a small increased chance of developing the neurological symptoms of Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Chronic health conditions associated with a higher risk of severe RVS include cardiopulmonary disease, diabetes, and kidney, liver, and hematologic disorders, as well as compromised immunity, older age, and frailty.
2. Shingles Vaccines
This painful disease carries the potential complication of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), which leads to long-term nerve pain in 10%-18% of patients, especially those over age 40. ACIP recommends two doses of the recombinant zoster vaccine (Shingrix) for individuals 50 years and older. Those 19 years and older with weakened immune systems due to disease or medical treatments should get two doses of the recombinant vaccine, as they have a higher risk of getting shingles and its complications, including neurological problems and skin and eye infections.
3 Pneumococcal Vaccines
There are three approved pneumococcal vaccines: PCV15 (Vaxneuvance), PCV20 (Prevnar20), and PPSV23 (Pneumovax23).
“The pneumococcal vaccine schedule is the most complicated one as higher-valent products continue to become available,” Dr. Fryhofer said.
The two types are pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs, specifically PCV15 and PCV20) and the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23). “While PPSV23 covers 23 strains, it doesn’t give the long-term immunity of the conjugate vaccine,” said Dr. Fryhofer. “A patient may have completed their vaccination with the polysaccharide vaccine but 5 years out may no longer be protected. So we offer the option of getting a dose of PCV20 to round out the protection and confer greater immune memory.”
The ACIP schedule recommends immunization against the Streptococcus pneumoniae pathogen for all older and all at-risk adults. Routine administration of PCV15 or PCV20 is advised for those 65 years or older who have never received any pneumococcal conjugate vaccine or whose previous vaccination history is unknown. If PCV15 is used, it should be followed by PPSV23. Those 65 years or older should get PPSV23 even if they already had one or more doses of pneumococcal vaccine before turning 65.
Further vaccination is recommended for younger at-risk adults aged 19-64 years who have received both PCV13 and PPSV23 but have incomplete vaccination status. These individuals are advised to complete their pneumococcal series by receiving either a single dose of PCV20 at an interval of at least 5 years after the last pneumococcal vaccine dose or more than one dose of PPSV23.
See Pneumococcal Vaccination: Summary of Who and When to Vaccinate for CDC guidance on vaccination options for adults who have previously received a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Or, to sort out quickly who gets what and when based on their age, concurrent conditions, and vaccination history, the CDC offers a type-in app called the PneumoRecs VaxAdvisor.
4. Measles, Mumps, and Rubella, and Varicella Vaccines
The two approved MMR vaccines are M-M-R II and PRIORIX. A third vaccine, ProQuad, adds varicella.
Adults lacking presumptive evidence of immunity should get at least one dose of the MMR combination vaccine.
Those born before 1957 are deemed to be immune, Dr. Fryhofer noted.
Two doses are recommended for adults entering high-risk settings for measles or mumps transmission such as healthcare personnel, students away at college, and international travelers. The two doses should be separated by at least 28 days. It’s no secret that measles, though preventable, is making a comeback, with 146 reported cases (48 in adults) across 21 states as of May 31 — most linked to international travel.
Women who plan to get pregnant should be vaccinated before but not during each pregnancy. (The vaccine is safe during lactation.) And those of childbearing age with no presumptive evidence of immunity are advised to get at least one dose of the MMR vaccine.
5. Tetanus, Diphtheria, and Pertussis Vaccine
Adults with no previous Tdap vaccination should receive a single dose of Adacel or Boostrix followed by a booster every 10 years. Boostrix is recommended for adults over 64 years.
During every pregnancy, women should have a single dose of Tdap, preferably in gestational weeks 27 through 36.
As to the immediate postpartum period, Tdap is recommended only for mothers who did not receive it during their current pregnancy and never received a prior dose. If a woman did not receive Tdap during her current pregnancy but did receive a prior dose of Tdap, she does not need Tdap postpartum.
The Challenges
According to Dr. Fryhofer, widespread disinformation about the risks of immunization against vaccine-preventable diseases has brought us to a flashpoint. “It’s now more important than ever to keep telling patients that vaccination is one of the most effective tools for preventing individual illness and protecting public health.”
She recommends that doctors follow the National Institutes of Health’s AIMS method to broach the subject of adult vaccination and increase participation in an inquiring, reassuring, and low-pressure way. Standing for Announce, Inquire, Mirror, and Secure, AIMS structures a nonjudgmental, patient-friendly conversation around immunization to elicit and acknowledge the reasons for hesitancy while explaining the safety and efficacy of vaccines.
Dr. Fryhofer frequently uses AIMS to bring inoculation-averse patients around. “Keep the conversation open with reluctant patients but leave them where they are. They need to see you as a reliable source and nonjudgmental source of information,” she said.
Dr. Block recommends outlining the diseases that have been eliminated through vaccines, from polio to measles, as well as the dangers of vaccine refusal, as indicated by recent outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases in areas with low immunization rates. “This approach highlights the opportunity we all have to get vaccinated to protect ourselves and our communities,” she said.
In Dr. Fryhofer’s view, the situation is urgent and doctors need to be proactive. “We’re now at a public-health tipping point where we may see a sliding back and a reversing of many years of progress.”
Dr. Fryhofer and Dr. Block disclosed no competing interests relevant to their comments.
Many adults are complacent about vaccinations, believing that annual COVID and flu shots aside, they had all the immunizations they need as children and teens. But adults need vaccines as well, especially if they have missed earlier doses. And older and health-compromised adults, in particular, can benefit from newer vaccines that were not part of the childhood schedule.
“The question is whether adults had the vaccinations they need in the first place,” Sandra Adamson Fryhofer, MD, an internist in Atlanta and the American Medical Association’s liaison to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said in an interview. “Many do not even have reliable records of vaccination.”
Primary care physicians are ideally positioned to get adult patients to update their vaccination status on older vaccines and obtain newer ones as needed. “ACIP recommendations for adult vaccines are getting longer and more complicated and the way they’re administered is more complex, too, in that they’re not all given in the primary care office but sometimes in pharmacies,” Dr. Fryhofer said.
Not all adult patients want to update their vaccinations. “Vaccine hesitancy among many adults is accelerated by the several new vaccines that have been recommended in recent years,” Lauren Block, MD, MPH, an internist at Northwell Health and assistant professor in the Institute of Health System Science at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research in metropolitan New York City, said in an interview.
Physicians are rightly concerned about the lagging rates of adult vaccination, Dr. Block said. “Given the prevalence of conditions like pneumonia and shingles and the morbidity associated with them, healthcare providers should take every opportunity to discuss vaccination with patients, from well visits to hospital visits,” Dr. Block added.
She pointed to several obstacles to broader uptake, including product shortages, financial barriers, and, increasingly, the negative vocal messaging from media outlets and social media.
Current Recommendations
The main vaccines recommended for adults, besides flu and COVID shots, are for respiratory syncytial virus (RVS); shingles; pneumococcal disease; measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR); and tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (Tdap). Less commonly, booster vaccines for MM, and hepatitis are recommended when titers are proven to be low.
ACIP’s updated 2024 Adult Immunization Schedule can be downloaded from the website of the CDC.
The newest additions to the schedule include RSV vaccines, the mpox vaccine (Jynneos), a new MenACWY-MenB combo vaccine (Penbraya), and the new 2023-2024 formulation of updated COVID vaccines (both mRNA and protein-based adjuvanted versions).
1. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccines
There are two licensed RSV vaccines, Arexvy and Abrysvo. The CDC schedule recommends a single-dose RSV vaccine for adults age 60 years and older, especially those at high risk of contracting the virus — but after shared decision-making based on a discussion of the risk-harm balance since this vaccine carries a small increased chance of developing the neurological symptoms of Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Chronic health conditions associated with a higher risk of severe RVS include cardiopulmonary disease, diabetes, and kidney, liver, and hematologic disorders, as well as compromised immunity, older age, and frailty.
2. Shingles Vaccines
This painful disease carries the potential complication of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), which leads to long-term nerve pain in 10%-18% of patients, especially those over age 40. ACIP recommends two doses of the recombinant zoster vaccine (Shingrix) for individuals 50 years and older. Those 19 years and older with weakened immune systems due to disease or medical treatments should get two doses of the recombinant vaccine, as they have a higher risk of getting shingles and its complications, including neurological problems and skin and eye infections.
3 Pneumococcal Vaccines
There are three approved pneumococcal vaccines: PCV15 (Vaxneuvance), PCV20 (Prevnar20), and PPSV23 (Pneumovax23).
“The pneumococcal vaccine schedule is the most complicated one as higher-valent products continue to become available,” Dr. Fryhofer said.
The two types are pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs, specifically PCV15 and PCV20) and the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23). “While PPSV23 covers 23 strains, it doesn’t give the long-term immunity of the conjugate vaccine,” said Dr. Fryhofer. “A patient may have completed their vaccination with the polysaccharide vaccine but 5 years out may no longer be protected. So we offer the option of getting a dose of PCV20 to round out the protection and confer greater immune memory.”
The ACIP schedule recommends immunization against the Streptococcus pneumoniae pathogen for all older and all at-risk adults. Routine administration of PCV15 or PCV20 is advised for those 65 years or older who have never received any pneumococcal conjugate vaccine or whose previous vaccination history is unknown. If PCV15 is used, it should be followed by PPSV23. Those 65 years or older should get PPSV23 even if they already had one or more doses of pneumococcal vaccine before turning 65.
Further vaccination is recommended for younger at-risk adults aged 19-64 years who have received both PCV13 and PPSV23 but have incomplete vaccination status. These individuals are advised to complete their pneumococcal series by receiving either a single dose of PCV20 at an interval of at least 5 years after the last pneumococcal vaccine dose or more than one dose of PPSV23.
See Pneumococcal Vaccination: Summary of Who and When to Vaccinate for CDC guidance on vaccination options for adults who have previously received a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Or, to sort out quickly who gets what and when based on their age, concurrent conditions, and vaccination history, the CDC offers a type-in app called the PneumoRecs VaxAdvisor.
4. Measles, Mumps, and Rubella, and Varicella Vaccines
The two approved MMR vaccines are M-M-R II and PRIORIX. A third vaccine, ProQuad, adds varicella.
Adults lacking presumptive evidence of immunity should get at least one dose of the MMR combination vaccine.
Those born before 1957 are deemed to be immune, Dr. Fryhofer noted.
Two doses are recommended for adults entering high-risk settings for measles or mumps transmission such as healthcare personnel, students away at college, and international travelers. The two doses should be separated by at least 28 days. It’s no secret that measles, though preventable, is making a comeback, with 146 reported cases (48 in adults) across 21 states as of May 31 — most linked to international travel.
Women who plan to get pregnant should be vaccinated before but not during each pregnancy. (The vaccine is safe during lactation.) And those of childbearing age with no presumptive evidence of immunity are advised to get at least one dose of the MMR vaccine.
5. Tetanus, Diphtheria, and Pertussis Vaccine
Adults with no previous Tdap vaccination should receive a single dose of Adacel or Boostrix followed by a booster every 10 years. Boostrix is recommended for adults over 64 years.
During every pregnancy, women should have a single dose of Tdap, preferably in gestational weeks 27 through 36.
As to the immediate postpartum period, Tdap is recommended only for mothers who did not receive it during their current pregnancy and never received a prior dose. If a woman did not receive Tdap during her current pregnancy but did receive a prior dose of Tdap, she does not need Tdap postpartum.
The Challenges
According to Dr. Fryhofer, widespread disinformation about the risks of immunization against vaccine-preventable diseases has brought us to a flashpoint. “It’s now more important than ever to keep telling patients that vaccination is one of the most effective tools for preventing individual illness and protecting public health.”
She recommends that doctors follow the National Institutes of Health’s AIMS method to broach the subject of adult vaccination and increase participation in an inquiring, reassuring, and low-pressure way. Standing for Announce, Inquire, Mirror, and Secure, AIMS structures a nonjudgmental, patient-friendly conversation around immunization to elicit and acknowledge the reasons for hesitancy while explaining the safety and efficacy of vaccines.
Dr. Fryhofer frequently uses AIMS to bring inoculation-averse patients around. “Keep the conversation open with reluctant patients but leave them where they are. They need to see you as a reliable source and nonjudgmental source of information,” she said.
Dr. Block recommends outlining the diseases that have been eliminated through vaccines, from polio to measles, as well as the dangers of vaccine refusal, as indicated by recent outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases in areas with low immunization rates. “This approach highlights the opportunity we all have to get vaccinated to protect ourselves and our communities,” she said.
In Dr. Fryhofer’s view, the situation is urgent and doctors need to be proactive. “We’re now at a public-health tipping point where we may see a sliding back and a reversing of many years of progress.”
Dr. Fryhofer and Dr. Block disclosed no competing interests relevant to their comments.
Many adults are complacent about vaccinations, believing that annual COVID and flu shots aside, they had all the immunizations they need as children and teens. But adults need vaccines as well, especially if they have missed earlier doses. And older and health-compromised adults, in particular, can benefit from newer vaccines that were not part of the childhood schedule.
“The question is whether adults had the vaccinations they need in the first place,” Sandra Adamson Fryhofer, MD, an internist in Atlanta and the American Medical Association’s liaison to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said in an interview. “Many do not even have reliable records of vaccination.”
Primary care physicians are ideally positioned to get adult patients to update their vaccination status on older vaccines and obtain newer ones as needed. “ACIP recommendations for adult vaccines are getting longer and more complicated and the way they’re administered is more complex, too, in that they’re not all given in the primary care office but sometimes in pharmacies,” Dr. Fryhofer said.
Not all adult patients want to update their vaccinations. “Vaccine hesitancy among many adults is accelerated by the several new vaccines that have been recommended in recent years,” Lauren Block, MD, MPH, an internist at Northwell Health and assistant professor in the Institute of Health System Science at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research in metropolitan New York City, said in an interview.
Physicians are rightly concerned about the lagging rates of adult vaccination, Dr. Block said. “Given the prevalence of conditions like pneumonia and shingles and the morbidity associated with them, healthcare providers should take every opportunity to discuss vaccination with patients, from well visits to hospital visits,” Dr. Block added.
She pointed to several obstacles to broader uptake, including product shortages, financial barriers, and, increasingly, the negative vocal messaging from media outlets and social media.
Current Recommendations
The main vaccines recommended for adults, besides flu and COVID shots, are for respiratory syncytial virus (RVS); shingles; pneumococcal disease; measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR); and tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (Tdap). Less commonly, booster vaccines for MM, and hepatitis are recommended when titers are proven to be low.
ACIP’s updated 2024 Adult Immunization Schedule can be downloaded from the website of the CDC.
The newest additions to the schedule include RSV vaccines, the mpox vaccine (Jynneos), a new MenACWY-MenB combo vaccine (Penbraya), and the new 2023-2024 formulation of updated COVID vaccines (both mRNA and protein-based adjuvanted versions).
1. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccines
There are two licensed RSV vaccines, Arexvy and Abrysvo. The CDC schedule recommends a single-dose RSV vaccine for adults age 60 years and older, especially those at high risk of contracting the virus — but after shared decision-making based on a discussion of the risk-harm balance since this vaccine carries a small increased chance of developing the neurological symptoms of Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Chronic health conditions associated with a higher risk of severe RVS include cardiopulmonary disease, diabetes, and kidney, liver, and hematologic disorders, as well as compromised immunity, older age, and frailty.
2. Shingles Vaccines
This painful disease carries the potential complication of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), which leads to long-term nerve pain in 10%-18% of patients, especially those over age 40. ACIP recommends two doses of the recombinant zoster vaccine (Shingrix) for individuals 50 years and older. Those 19 years and older with weakened immune systems due to disease or medical treatments should get two doses of the recombinant vaccine, as they have a higher risk of getting shingles and its complications, including neurological problems and skin and eye infections.
3 Pneumococcal Vaccines
There are three approved pneumococcal vaccines: PCV15 (Vaxneuvance), PCV20 (Prevnar20), and PPSV23 (Pneumovax23).
“The pneumococcal vaccine schedule is the most complicated one as higher-valent products continue to become available,” Dr. Fryhofer said.
The two types are pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs, specifically PCV15 and PCV20) and the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23). “While PPSV23 covers 23 strains, it doesn’t give the long-term immunity of the conjugate vaccine,” said Dr. Fryhofer. “A patient may have completed their vaccination with the polysaccharide vaccine but 5 years out may no longer be protected. So we offer the option of getting a dose of PCV20 to round out the protection and confer greater immune memory.”
The ACIP schedule recommends immunization against the Streptococcus pneumoniae pathogen for all older and all at-risk adults. Routine administration of PCV15 or PCV20 is advised for those 65 years or older who have never received any pneumococcal conjugate vaccine or whose previous vaccination history is unknown. If PCV15 is used, it should be followed by PPSV23. Those 65 years or older should get PPSV23 even if they already had one or more doses of pneumococcal vaccine before turning 65.
Further vaccination is recommended for younger at-risk adults aged 19-64 years who have received both PCV13 and PPSV23 but have incomplete vaccination status. These individuals are advised to complete their pneumococcal series by receiving either a single dose of PCV20 at an interval of at least 5 years after the last pneumococcal vaccine dose or more than one dose of PPSV23.
See Pneumococcal Vaccination: Summary of Who and When to Vaccinate for CDC guidance on vaccination options for adults who have previously received a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Or, to sort out quickly who gets what and when based on their age, concurrent conditions, and vaccination history, the CDC offers a type-in app called the PneumoRecs VaxAdvisor.
4. Measles, Mumps, and Rubella, and Varicella Vaccines
The two approved MMR vaccines are M-M-R II and PRIORIX. A third vaccine, ProQuad, adds varicella.
Adults lacking presumptive evidence of immunity should get at least one dose of the MMR combination vaccine.
Those born before 1957 are deemed to be immune, Dr. Fryhofer noted.
Two doses are recommended for adults entering high-risk settings for measles or mumps transmission such as healthcare personnel, students away at college, and international travelers. The two doses should be separated by at least 28 days. It’s no secret that measles, though preventable, is making a comeback, with 146 reported cases (48 in adults) across 21 states as of May 31 — most linked to international travel.
Women who plan to get pregnant should be vaccinated before but not during each pregnancy. (The vaccine is safe during lactation.) And those of childbearing age with no presumptive evidence of immunity are advised to get at least one dose of the MMR vaccine.
5. Tetanus, Diphtheria, and Pertussis Vaccine
Adults with no previous Tdap vaccination should receive a single dose of Adacel or Boostrix followed by a booster every 10 years. Boostrix is recommended for adults over 64 years.
During every pregnancy, women should have a single dose of Tdap, preferably in gestational weeks 27 through 36.
As to the immediate postpartum period, Tdap is recommended only for mothers who did not receive it during their current pregnancy and never received a prior dose. If a woman did not receive Tdap during her current pregnancy but did receive a prior dose of Tdap, she does not need Tdap postpartum.
The Challenges
According to Dr. Fryhofer, widespread disinformation about the risks of immunization against vaccine-preventable diseases has brought us to a flashpoint. “It’s now more important than ever to keep telling patients that vaccination is one of the most effective tools for preventing individual illness and protecting public health.”
She recommends that doctors follow the National Institutes of Health’s AIMS method to broach the subject of adult vaccination and increase participation in an inquiring, reassuring, and low-pressure way. Standing for Announce, Inquire, Mirror, and Secure, AIMS structures a nonjudgmental, patient-friendly conversation around immunization to elicit and acknowledge the reasons for hesitancy while explaining the safety and efficacy of vaccines.
Dr. Fryhofer frequently uses AIMS to bring inoculation-averse patients around. “Keep the conversation open with reluctant patients but leave them where they are. They need to see you as a reliable source and nonjudgmental source of information,” she said.
Dr. Block recommends outlining the diseases that have been eliminated through vaccines, from polio to measles, as well as the dangers of vaccine refusal, as indicated by recent outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases in areas with low immunization rates. “This approach highlights the opportunity we all have to get vaccinated to protect ourselves and our communities,” she said.
In Dr. Fryhofer’s view, the situation is urgent and doctors need to be proactive. “We’re now at a public-health tipping point where we may see a sliding back and a reversing of many years of progress.”
Dr. Fryhofer and Dr. Block disclosed no competing interests relevant to their comments.
‘Don’t Screen’ for Vitamin D: New Endo Society Guideline
BOSTON —
The evidence-based document was presented on June 3, 2024, at the Endocrine Society annual meeting, and simultaneously published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. It advises that people who may benefit from vitamin D supplementation include:
- Children aged 1-18 years to prevent rickets and to potentially lower the risk for respiratory tract infections
- Pregnant people to lower the risk for maternal and fetal or neonatal complications
- Adults older than 75 years to lower the risk for mortality
- Adults with prediabetes to lower the risk for type 2 diabetes
In those groups, the recommendation is for daily (rather than intermittent) empiric vitamin D supplementation of more than what was recommended in 2011 by the National Academy of Medicine (NAM), which was then called the Institute of Medicine (IOM): 600 IU/d for those aged 1-70 years and 800 IU/d for those older than 70 years. The document acknowledges that the optimal dose for these populations isn’t known, but it provides the dose ranges that were used in the trials cited as evidence for the recommendations.
In contrast, the document advises against more vitamin D than the recommended daily intake for most healthier adults younger than 75 years and recommends against testing for blood vitamin D levels in the general population, including those with obesity or darker complexions.
Guideline author Anastassios G. Pittas, MD, professor of medicine at Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, told this news organization, “this guideline refers to people who are otherwise healthy, and there’s no clear indication for vitamin D, such as people with already established osteoporosis. This guideline is not relevant to them.”
Dr. Pittas also noted, “there’s no single question and single answer about the role of vitamin D in health and disease, which is what people often want to know. There are many questions, and we cannot answer all of them.”
Panel Chair Marie B. Demay, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, told this news organization that indeed the panel was limited by lack of randomized clinical trial evidence to answer many important questions. “There is a paucity of data regarding definition of optimal levels and optimal intake of vitamin D for preventing specific diseases ... What we really need are large scale clinical trials and biomarkers so we can predict disease outcome before it happens.”
Overall, Dr. Demay said, “The recommendations are that populations adhere to the [NAM/IOM] dietary recommended intakes, and there are certain populations that will likely benefit from levels of intake above [those].”
Asked to comment, session moderator Clifford J. Rosen, MD, director of Clinical and Translational Research and senior scientist at Maine Medical Center Research Institute, Scarborough, Maine, noted that screening for vitamin D is quite common in clinical practice, but the recommendation against doing so makes sense.
“When clinicians measure vitamin D, then they’re forced to make a decision what to do about it. That’s where questions about the levels come in. And that’s a big problem. So what the panel’s saying is, don’t screen ... This really gets to the heart of the issue, because we have no data that there’s anything about screening that allows us to improve quality of life ... Screening is probably not worthwhile in any age group.”
Dr. Rosen, who was an author on the 2011 NAM/IOM dietary reference intakes, said that since then, new data have come out regarding the role of vitamin D in mortality in people older than 75 years, benefit in children with regard to respiratory illness, and the potential benefit of vitamin D in pregnancy. “Otherwise, I think we’re going over a lot of the same stuff that we’ve talked about since I was on the IOM panel 15 years ago ... But I think the level of evidence and rigor with which they did it is really impressive.”
However, Simeon I. Taylor, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, expressed disappointment that the document was limited to healthy people. “Although acknowledging challenges in managing vitamin D status in patients with several diseases, [such as] chronic kidney disease or inflammatory bowel disease, the new guidelines do not provide sufficient guidance for practicing physicians about how to manage these complex patients.”
In addition, Dr. Taylor said that the guidelines “do not explicitly consider the literature suggesting that alternative testing strategies may provide more relevant insights into vitamin D status. Just as variation in levels of thyroid-binding globulin have convinced endocrinologists not to rely on measurement of total thyroxine; interindividual variation in levels of vitamin D binding protein must be accounted for to interpret measurements of total levels of 25(OH)D. It would have been useful to explicitly consider the possible value of measuring vitamin D binding protein-independent indices of vitamin D status.”
Dr. Taylor also raised the same point as an audience member did during the Q&A period regarding patients with osteoporosis or osteopenia. “The value and utility of the new guidelines would be greatly strengthened by providing guidance for how to approach this important and very large group of individuals.”
Dr. Taylor did say that the document has “several strengths, including the fact that they acknowledge the major limitations of the quality of relevant evidence derived from clinical trials.”
In an accompanying commentary, the guideline authors delve into the issues of skin pigmentation and race as they pertain to vitamin D metabolism, writing:
The panel discovered that no randomized clinical trials have directly assessed vitamin D related patient-important outcomes based on participants’ skin pigmentation, although race and ethnicity often served as presumed proxies for skin pigmentation in the literature. In their deliberations, guideline panel members and selected Endocrine Society leaders underscored the critical need to distinguish between skin pigmentation as a biological variable and race and ethnicity as socially determined constructs. This differentiation is vital to maximize scientific rigor and, thus, the validity of resulting recommendations.
Dr. Pittas and Dr. Demay have no disclosures relevant to this clinical practice guideline. Dr. Rosen has no disclosures. Dr. Taylor serves as a consultant for Ionis Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON —
The evidence-based document was presented on June 3, 2024, at the Endocrine Society annual meeting, and simultaneously published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. It advises that people who may benefit from vitamin D supplementation include:
- Children aged 1-18 years to prevent rickets and to potentially lower the risk for respiratory tract infections
- Pregnant people to lower the risk for maternal and fetal or neonatal complications
- Adults older than 75 years to lower the risk for mortality
- Adults with prediabetes to lower the risk for type 2 diabetes
In those groups, the recommendation is for daily (rather than intermittent) empiric vitamin D supplementation of more than what was recommended in 2011 by the National Academy of Medicine (NAM), which was then called the Institute of Medicine (IOM): 600 IU/d for those aged 1-70 years and 800 IU/d for those older than 70 years. The document acknowledges that the optimal dose for these populations isn’t known, but it provides the dose ranges that were used in the trials cited as evidence for the recommendations.
In contrast, the document advises against more vitamin D than the recommended daily intake for most healthier adults younger than 75 years and recommends against testing for blood vitamin D levels in the general population, including those with obesity or darker complexions.
Guideline author Anastassios G. Pittas, MD, professor of medicine at Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, told this news organization, “this guideline refers to people who are otherwise healthy, and there’s no clear indication for vitamin D, such as people with already established osteoporosis. This guideline is not relevant to them.”
Dr. Pittas also noted, “there’s no single question and single answer about the role of vitamin D in health and disease, which is what people often want to know. There are many questions, and we cannot answer all of them.”
Panel Chair Marie B. Demay, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, told this news organization that indeed the panel was limited by lack of randomized clinical trial evidence to answer many important questions. “There is a paucity of data regarding definition of optimal levels and optimal intake of vitamin D for preventing specific diseases ... What we really need are large scale clinical trials and biomarkers so we can predict disease outcome before it happens.”
Overall, Dr. Demay said, “The recommendations are that populations adhere to the [NAM/IOM] dietary recommended intakes, and there are certain populations that will likely benefit from levels of intake above [those].”
Asked to comment, session moderator Clifford J. Rosen, MD, director of Clinical and Translational Research and senior scientist at Maine Medical Center Research Institute, Scarborough, Maine, noted that screening for vitamin D is quite common in clinical practice, but the recommendation against doing so makes sense.
“When clinicians measure vitamin D, then they’re forced to make a decision what to do about it. That’s where questions about the levels come in. And that’s a big problem. So what the panel’s saying is, don’t screen ... This really gets to the heart of the issue, because we have no data that there’s anything about screening that allows us to improve quality of life ... Screening is probably not worthwhile in any age group.”
Dr. Rosen, who was an author on the 2011 NAM/IOM dietary reference intakes, said that since then, new data have come out regarding the role of vitamin D in mortality in people older than 75 years, benefit in children with regard to respiratory illness, and the potential benefit of vitamin D in pregnancy. “Otherwise, I think we’re going over a lot of the same stuff that we’ve talked about since I was on the IOM panel 15 years ago ... But I think the level of evidence and rigor with which they did it is really impressive.”
However, Simeon I. Taylor, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, expressed disappointment that the document was limited to healthy people. “Although acknowledging challenges in managing vitamin D status in patients with several diseases, [such as] chronic kidney disease or inflammatory bowel disease, the new guidelines do not provide sufficient guidance for practicing physicians about how to manage these complex patients.”
In addition, Dr. Taylor said that the guidelines “do not explicitly consider the literature suggesting that alternative testing strategies may provide more relevant insights into vitamin D status. Just as variation in levels of thyroid-binding globulin have convinced endocrinologists not to rely on measurement of total thyroxine; interindividual variation in levels of vitamin D binding protein must be accounted for to interpret measurements of total levels of 25(OH)D. It would have been useful to explicitly consider the possible value of measuring vitamin D binding protein-independent indices of vitamin D status.”
Dr. Taylor also raised the same point as an audience member did during the Q&A period regarding patients with osteoporosis or osteopenia. “The value and utility of the new guidelines would be greatly strengthened by providing guidance for how to approach this important and very large group of individuals.”
Dr. Taylor did say that the document has “several strengths, including the fact that they acknowledge the major limitations of the quality of relevant evidence derived from clinical trials.”
In an accompanying commentary, the guideline authors delve into the issues of skin pigmentation and race as they pertain to vitamin D metabolism, writing:
The panel discovered that no randomized clinical trials have directly assessed vitamin D related patient-important outcomes based on participants’ skin pigmentation, although race and ethnicity often served as presumed proxies for skin pigmentation in the literature. In their deliberations, guideline panel members and selected Endocrine Society leaders underscored the critical need to distinguish between skin pigmentation as a biological variable and race and ethnicity as socially determined constructs. This differentiation is vital to maximize scientific rigor and, thus, the validity of resulting recommendations.
Dr. Pittas and Dr. Demay have no disclosures relevant to this clinical practice guideline. Dr. Rosen has no disclosures. Dr. Taylor serves as a consultant for Ionis Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON —
The evidence-based document was presented on June 3, 2024, at the Endocrine Society annual meeting, and simultaneously published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. It advises that people who may benefit from vitamin D supplementation include:
- Children aged 1-18 years to prevent rickets and to potentially lower the risk for respiratory tract infections
- Pregnant people to lower the risk for maternal and fetal or neonatal complications
- Adults older than 75 years to lower the risk for mortality
- Adults with prediabetes to lower the risk for type 2 diabetes
In those groups, the recommendation is for daily (rather than intermittent) empiric vitamin D supplementation of more than what was recommended in 2011 by the National Academy of Medicine (NAM), which was then called the Institute of Medicine (IOM): 600 IU/d for those aged 1-70 years and 800 IU/d for those older than 70 years. The document acknowledges that the optimal dose for these populations isn’t known, but it provides the dose ranges that were used in the trials cited as evidence for the recommendations.
In contrast, the document advises against more vitamin D than the recommended daily intake for most healthier adults younger than 75 years and recommends against testing for blood vitamin D levels in the general population, including those with obesity or darker complexions.
Guideline author Anastassios G. Pittas, MD, professor of medicine at Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, told this news organization, “this guideline refers to people who are otherwise healthy, and there’s no clear indication for vitamin D, such as people with already established osteoporosis. This guideline is not relevant to them.”
Dr. Pittas also noted, “there’s no single question and single answer about the role of vitamin D in health and disease, which is what people often want to know. There are many questions, and we cannot answer all of them.”
Panel Chair Marie B. Demay, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, told this news organization that indeed the panel was limited by lack of randomized clinical trial evidence to answer many important questions. “There is a paucity of data regarding definition of optimal levels and optimal intake of vitamin D for preventing specific diseases ... What we really need are large scale clinical trials and biomarkers so we can predict disease outcome before it happens.”
Overall, Dr. Demay said, “The recommendations are that populations adhere to the [NAM/IOM] dietary recommended intakes, and there are certain populations that will likely benefit from levels of intake above [those].”
Asked to comment, session moderator Clifford J. Rosen, MD, director of Clinical and Translational Research and senior scientist at Maine Medical Center Research Institute, Scarborough, Maine, noted that screening for vitamin D is quite common in clinical practice, but the recommendation against doing so makes sense.
“When clinicians measure vitamin D, then they’re forced to make a decision what to do about it. That’s where questions about the levels come in. And that’s a big problem. So what the panel’s saying is, don’t screen ... This really gets to the heart of the issue, because we have no data that there’s anything about screening that allows us to improve quality of life ... Screening is probably not worthwhile in any age group.”
Dr. Rosen, who was an author on the 2011 NAM/IOM dietary reference intakes, said that since then, new data have come out regarding the role of vitamin D in mortality in people older than 75 years, benefit in children with regard to respiratory illness, and the potential benefit of vitamin D in pregnancy. “Otherwise, I think we’re going over a lot of the same stuff that we’ve talked about since I was on the IOM panel 15 years ago ... But I think the level of evidence and rigor with which they did it is really impressive.”
However, Simeon I. Taylor, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, expressed disappointment that the document was limited to healthy people. “Although acknowledging challenges in managing vitamin D status in patients with several diseases, [such as] chronic kidney disease or inflammatory bowel disease, the new guidelines do not provide sufficient guidance for practicing physicians about how to manage these complex patients.”
In addition, Dr. Taylor said that the guidelines “do not explicitly consider the literature suggesting that alternative testing strategies may provide more relevant insights into vitamin D status. Just as variation in levels of thyroid-binding globulin have convinced endocrinologists not to rely on measurement of total thyroxine; interindividual variation in levels of vitamin D binding protein must be accounted for to interpret measurements of total levels of 25(OH)D. It would have been useful to explicitly consider the possible value of measuring vitamin D binding protein-independent indices of vitamin D status.”
Dr. Taylor also raised the same point as an audience member did during the Q&A period regarding patients with osteoporosis or osteopenia. “The value and utility of the new guidelines would be greatly strengthened by providing guidance for how to approach this important and very large group of individuals.”
Dr. Taylor did say that the document has “several strengths, including the fact that they acknowledge the major limitations of the quality of relevant evidence derived from clinical trials.”
In an accompanying commentary, the guideline authors delve into the issues of skin pigmentation and race as they pertain to vitamin D metabolism, writing:
The panel discovered that no randomized clinical trials have directly assessed vitamin D related patient-important outcomes based on participants’ skin pigmentation, although race and ethnicity often served as presumed proxies for skin pigmentation in the literature. In their deliberations, guideline panel members and selected Endocrine Society leaders underscored the critical need to distinguish between skin pigmentation as a biological variable and race and ethnicity as socially determined constructs. This differentiation is vital to maximize scientific rigor and, thus, the validity of resulting recommendations.
Dr. Pittas and Dr. Demay have no disclosures relevant to this clinical practice guideline. Dr. Rosen has no disclosures. Dr. Taylor serves as a consultant for Ionis Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Analysis Finds Minority of Chronic Wounds Treated by Dermatologists
. However, fewer than 8% of chronic wounds were managed by dermatologists during this time.
Those are among key findings from an analysis of National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NAMCS) data between 2011 and 2019 presented as a late-breaking abstract at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology. “Cutaneous wounds were estimated to account for 28.1 to 96.1 billion dollars in US health care costs in 2014,” one of the study authors, Rithi Chandy, MD, MS, a research fellow at the Center for Dermatology Research at Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, North Carolina, said in an interview following the meeting. “By examining national trends in patient visits and treatment, we may be able to better inform health care utilization for cutaneous wounds.”
Dr. Chandy and colleagues analyzed de-identified patient data from the 2011 to 2019 NAMCS for acute and chronic wound diagnoses, medications prescribed, and physician specialty categories. During the time studied, 5.76 billion patient visits were made, including 45.1 million visits for cutaneous wounds. Of these, the most common diagnoses were open wounds of the thumb without nail damage (7.96%), the lower leg (5.75%), nonpressure chronic ulcers of other parts of the foot (5.08%), and open wounds of the ear (5%).
Among all visits for cutaneous wounds, about one third were chronic cutaneous wounds, with the following descriptions: “Nonpressure chronic ulcer of other part of foot” (17.8%); “nonpressure chronic ulcer of skin, not elsewhere classified” (9.38%); and “ulcer of lower limbs, excluding decubitus, unspecified” (8.72%). “The frequency of patient visits per year during the study period remained stable for both acute and chronic wounds,” Dr. Chandy said. The number of visits for which antimicrobials were used was stable over time for both acute and chronic cutaneous wounds, with the exception of increased use of antivirals for chronic cutaneous wounds, he added.
Specifically, prescriptions were issued in 156 million visits over the time studied, most commonly cephalexin (4.22%), topical silver sulfadiazine (1.59%), topical mupirocin (1.12%), and miscellaneous antibiotics (1.18%).
“Our data shows that topical mupirocin is the most commonly used topical antimicrobial for cutaneous wounds,” Dr. Chandy said. “However, there are reports of emerging bacterial resistance to mupirocin. Our data can inform ongoing efforts to promote antimicrobial stewardship and drug development to provide alternative options that are less likely to induce antimicrobial resistance.”
In findings limited to specialty-specific NAMCS data available from 2011 and from 2013 to 2016, dermatologists managed 3.85% of overall cutaneous wounds, 2.35% of acute wounds, and 7.39% of chronic wounds. By contrast, Dr. Chandy said, 21.1% of chronic wounds were managed by general/family practice physicians, 20.7% by internists, 6.84% by general surgeons, and 5.65% by orthopedic surgeons.
“As dermatologists are experts in the structure and function of the skin and are trained to manage cutaneous disorders including wound healing, we [believe that] dermatologists are equipped with the skill set” for managing wounds, especially for chronic ulcers, he said. The decline in dermatologists who specialize in wound care, he added, “underscores the need for structured dermatology fellowship programs to prepare next-generation dermatologists to address this shortage and ensure dermatology leadership in cutaneous wound healing.”
Dr. Chandy acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the potential for misclassification of diagnoses or medications prescribed and the fact that the NAMCS database is unable to provide insight into individual patient experiences such as continual cutaneous wound management for the same patient over time.
In the opinion of Shari R. Lipner, MD, PhD, associate professor of clinical dermatology and director of the Nail Division at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, who was asked to comment on the study, the most interesting finding was that dermatologists cared for a small minority of patients with cutaneous wounds. “It would be interesting to know whether this is due to dermatologist shortages or knowledge gaps on the part of primary care physicians or patients that dermatologists are trained to care for wounds,” Dr. Lipner told this news organization. Other unanswered questions, she noted, “are patient demographics, geographic locations, and comorbidities.”
One of the study authors, Steven R. Feldman, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at Wake Forest University, disclosed that he has received research, speaking and/or consulting support from numerous pharmaceutical companies. No other authors reported having relevant disclosures. Dr. Lipner reported having no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
. However, fewer than 8% of chronic wounds were managed by dermatologists during this time.
Those are among key findings from an analysis of National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NAMCS) data between 2011 and 2019 presented as a late-breaking abstract at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology. “Cutaneous wounds were estimated to account for 28.1 to 96.1 billion dollars in US health care costs in 2014,” one of the study authors, Rithi Chandy, MD, MS, a research fellow at the Center for Dermatology Research at Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, North Carolina, said in an interview following the meeting. “By examining national trends in patient visits and treatment, we may be able to better inform health care utilization for cutaneous wounds.”
Dr. Chandy and colleagues analyzed de-identified patient data from the 2011 to 2019 NAMCS for acute and chronic wound diagnoses, medications prescribed, and physician specialty categories. During the time studied, 5.76 billion patient visits were made, including 45.1 million visits for cutaneous wounds. Of these, the most common diagnoses were open wounds of the thumb without nail damage (7.96%), the lower leg (5.75%), nonpressure chronic ulcers of other parts of the foot (5.08%), and open wounds of the ear (5%).
Among all visits for cutaneous wounds, about one third were chronic cutaneous wounds, with the following descriptions: “Nonpressure chronic ulcer of other part of foot” (17.8%); “nonpressure chronic ulcer of skin, not elsewhere classified” (9.38%); and “ulcer of lower limbs, excluding decubitus, unspecified” (8.72%). “The frequency of patient visits per year during the study period remained stable for both acute and chronic wounds,” Dr. Chandy said. The number of visits for which antimicrobials were used was stable over time for both acute and chronic cutaneous wounds, with the exception of increased use of antivirals for chronic cutaneous wounds, he added.
Specifically, prescriptions were issued in 156 million visits over the time studied, most commonly cephalexin (4.22%), topical silver sulfadiazine (1.59%), topical mupirocin (1.12%), and miscellaneous antibiotics (1.18%).
“Our data shows that topical mupirocin is the most commonly used topical antimicrobial for cutaneous wounds,” Dr. Chandy said. “However, there are reports of emerging bacterial resistance to mupirocin. Our data can inform ongoing efforts to promote antimicrobial stewardship and drug development to provide alternative options that are less likely to induce antimicrobial resistance.”
In findings limited to specialty-specific NAMCS data available from 2011 and from 2013 to 2016, dermatologists managed 3.85% of overall cutaneous wounds, 2.35% of acute wounds, and 7.39% of chronic wounds. By contrast, Dr. Chandy said, 21.1% of chronic wounds were managed by general/family practice physicians, 20.7% by internists, 6.84% by general surgeons, and 5.65% by orthopedic surgeons.
“As dermatologists are experts in the structure and function of the skin and are trained to manage cutaneous disorders including wound healing, we [believe that] dermatologists are equipped with the skill set” for managing wounds, especially for chronic ulcers, he said. The decline in dermatologists who specialize in wound care, he added, “underscores the need for structured dermatology fellowship programs to prepare next-generation dermatologists to address this shortage and ensure dermatology leadership in cutaneous wound healing.”
Dr. Chandy acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the potential for misclassification of diagnoses or medications prescribed and the fact that the NAMCS database is unable to provide insight into individual patient experiences such as continual cutaneous wound management for the same patient over time.
In the opinion of Shari R. Lipner, MD, PhD, associate professor of clinical dermatology and director of the Nail Division at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, who was asked to comment on the study, the most interesting finding was that dermatologists cared for a small minority of patients with cutaneous wounds. “It would be interesting to know whether this is due to dermatologist shortages or knowledge gaps on the part of primary care physicians or patients that dermatologists are trained to care for wounds,” Dr. Lipner told this news organization. Other unanswered questions, she noted, “are patient demographics, geographic locations, and comorbidities.”
One of the study authors, Steven R. Feldman, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at Wake Forest University, disclosed that he has received research, speaking and/or consulting support from numerous pharmaceutical companies. No other authors reported having relevant disclosures. Dr. Lipner reported having no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
. However, fewer than 8% of chronic wounds were managed by dermatologists during this time.
Those are among key findings from an analysis of National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NAMCS) data between 2011 and 2019 presented as a late-breaking abstract at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology. “Cutaneous wounds were estimated to account for 28.1 to 96.1 billion dollars in US health care costs in 2014,” one of the study authors, Rithi Chandy, MD, MS, a research fellow at the Center for Dermatology Research at Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, North Carolina, said in an interview following the meeting. “By examining national trends in patient visits and treatment, we may be able to better inform health care utilization for cutaneous wounds.”
Dr. Chandy and colleagues analyzed de-identified patient data from the 2011 to 2019 NAMCS for acute and chronic wound diagnoses, medications prescribed, and physician specialty categories. During the time studied, 5.76 billion patient visits were made, including 45.1 million visits for cutaneous wounds. Of these, the most common diagnoses were open wounds of the thumb without nail damage (7.96%), the lower leg (5.75%), nonpressure chronic ulcers of other parts of the foot (5.08%), and open wounds of the ear (5%).
Among all visits for cutaneous wounds, about one third were chronic cutaneous wounds, with the following descriptions: “Nonpressure chronic ulcer of other part of foot” (17.8%); “nonpressure chronic ulcer of skin, not elsewhere classified” (9.38%); and “ulcer of lower limbs, excluding decubitus, unspecified” (8.72%). “The frequency of patient visits per year during the study period remained stable for both acute and chronic wounds,” Dr. Chandy said. The number of visits for which antimicrobials were used was stable over time for both acute and chronic cutaneous wounds, with the exception of increased use of antivirals for chronic cutaneous wounds, he added.
Specifically, prescriptions were issued in 156 million visits over the time studied, most commonly cephalexin (4.22%), topical silver sulfadiazine (1.59%), topical mupirocin (1.12%), and miscellaneous antibiotics (1.18%).
“Our data shows that topical mupirocin is the most commonly used topical antimicrobial for cutaneous wounds,” Dr. Chandy said. “However, there are reports of emerging bacterial resistance to mupirocin. Our data can inform ongoing efforts to promote antimicrobial stewardship and drug development to provide alternative options that are less likely to induce antimicrobial resistance.”
In findings limited to specialty-specific NAMCS data available from 2011 and from 2013 to 2016, dermatologists managed 3.85% of overall cutaneous wounds, 2.35% of acute wounds, and 7.39% of chronic wounds. By contrast, Dr. Chandy said, 21.1% of chronic wounds were managed by general/family practice physicians, 20.7% by internists, 6.84% by general surgeons, and 5.65% by orthopedic surgeons.
“As dermatologists are experts in the structure and function of the skin and are trained to manage cutaneous disorders including wound healing, we [believe that] dermatologists are equipped with the skill set” for managing wounds, especially for chronic ulcers, he said. The decline in dermatologists who specialize in wound care, he added, “underscores the need for structured dermatology fellowship programs to prepare next-generation dermatologists to address this shortage and ensure dermatology leadership in cutaneous wound healing.”
Dr. Chandy acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the potential for misclassification of diagnoses or medications prescribed and the fact that the NAMCS database is unable to provide insight into individual patient experiences such as continual cutaneous wound management for the same patient over time.
In the opinion of Shari R. Lipner, MD, PhD, associate professor of clinical dermatology and director of the Nail Division at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, who was asked to comment on the study, the most interesting finding was that dermatologists cared for a small minority of patients with cutaneous wounds. “It would be interesting to know whether this is due to dermatologist shortages or knowledge gaps on the part of primary care physicians or patients that dermatologists are trained to care for wounds,” Dr. Lipner told this news organization. Other unanswered questions, she noted, “are patient demographics, geographic locations, and comorbidities.”
One of the study authors, Steven R. Feldman, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at Wake Forest University, disclosed that he has received research, speaking and/or consulting support from numerous pharmaceutical companies. No other authors reported having relevant disclosures. Dr. Lipner reported having no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
FROM SID 2024