User login
Neutrophilic Dermatosis of the Dorsal Hand: A Distinctive Variant of Sweet Syndrome
To the Editor:
Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand (NDDH) is an uncommon reactive neutrophilic dermatosis that presents as a painful, enlarging, ulcerative nodule. It often is misdiagnosed and initially treated as an infection. Similar to other neutrophilic dermatoses, it is associated with underlying infections, inflammatory conditions, and malignancies. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand is considered a subset of Sweet syndrome (SS); we highlight similarities and differences between NDDH and SS, reporting the case of a 66-year-old man without systemic symptoms who developed NDDH on the right hand.
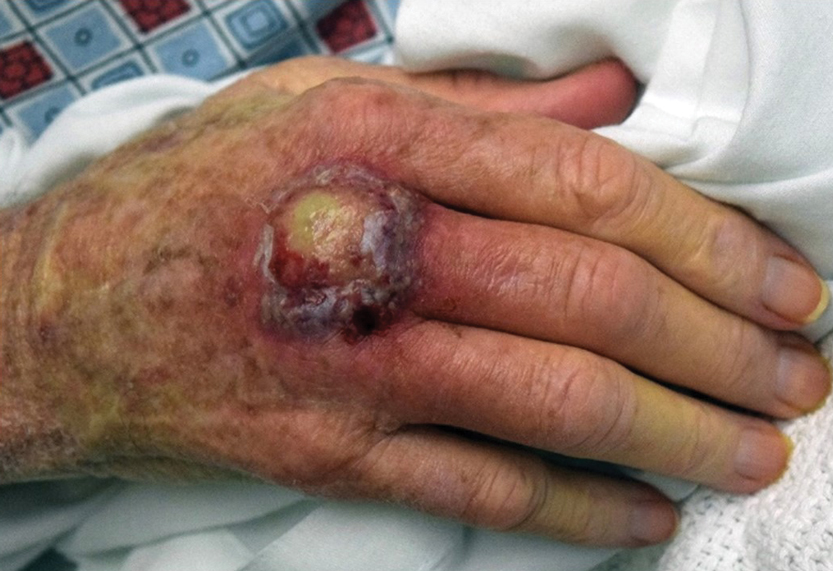
A 66-year-old man presented with a progressively enlarging, painful, ulcerative, 2-cm nodule on the right hand following mechanical trauma 2 weeks prior (Figure 1). He was afebrile with no remarkable medical history. Laboratory evaluation revealed an erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of 20 mm/h (reference range, 0-10 mm/h) and C-reactive protein (CRP) level of 3.52 mg/dL (reference range, 0-0.5 mg/dL) without leukocytosis; both were not remarkably elevated when adjusted for age.1,2 The clinical differential diagnosis was broad and included pyoderma with evolving cellulitis, neutrophilic dermatosis, atypical mycobacterial infection, subcutaneous or deep fungal infection, squamous cell carcinoma, cutaneous lymphoma, and metastasis. Due to the rapid development of the lesion, initial treatment focused on a bacterial infection, but there was no improvement on antibiotics and wound cultures were negative. The ulcerative nodule was biopsied, and histopathology demonstrated abundant neutrophilic inflammation, endothelial swelling, and leukocytoclasis without microorganisms (Figure 2). Tissue cultures for bacteria, fungi, and atypical mycobacteria were negative. A diagnosis of NDDH was made based on clinical and histologic findings. The wound improved with a 3-week course of oral prednisone.
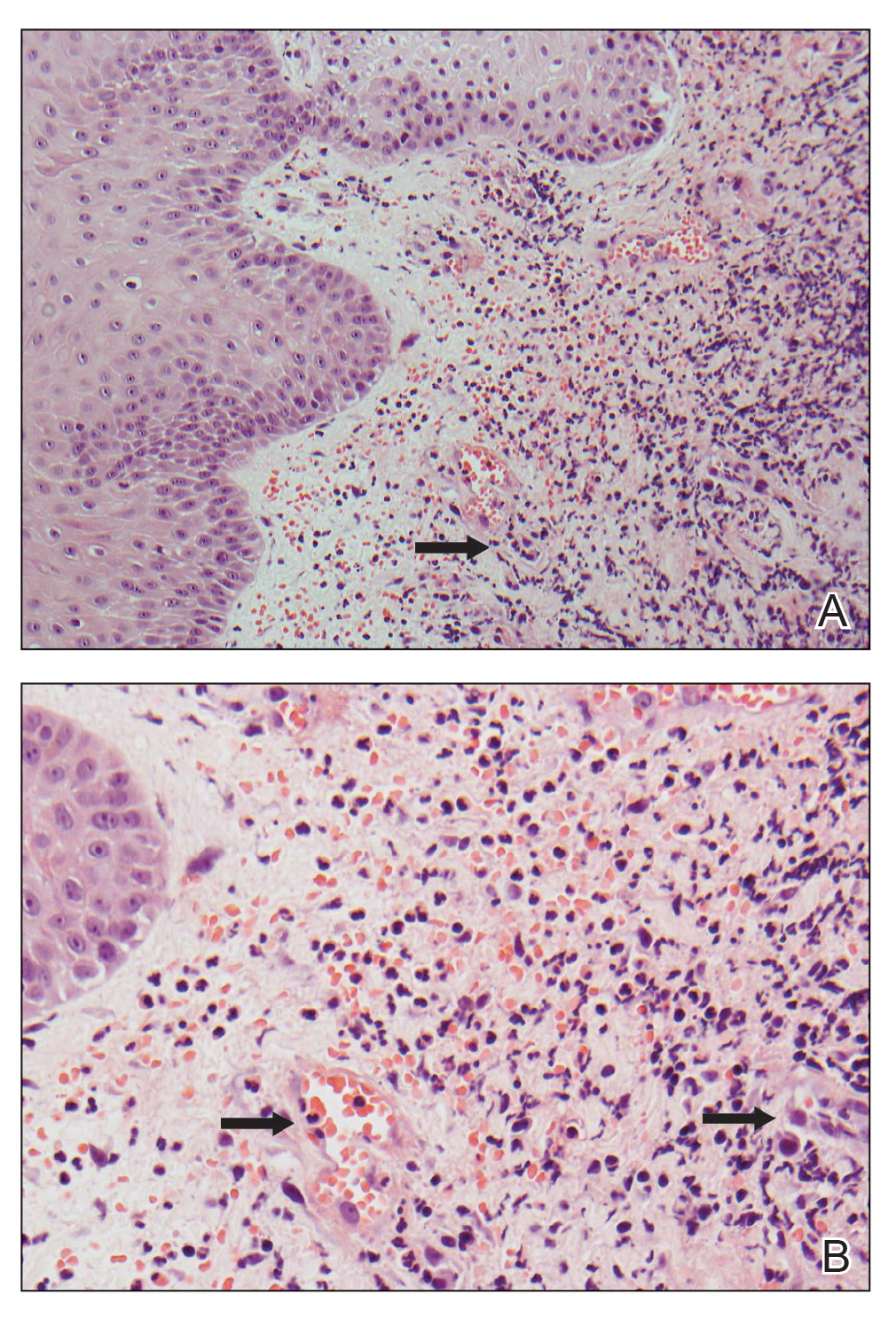
Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand is a subset of reactive neutrophilic dermatoses, which includes SS (acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) and pyoderma gangrenosum. It is described as a localized variant of SS, with similar associated underlying inflammatory, neoplastic conditions and laboratory findings.3 However, NDDH has characteristic features that differ from classic SS. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand typically presents as painful papules, pustules, or ulcers that progress to become larger ulcers, plaques, and nodules. The clinical appearance may more closely resemble pyoderma gangrenosum or atypical SS, with ulceration frequently present. Pathergy also may be demonstrated in NDDH, similar to our patient. The average age of presentation for NDDH is 60 years, which is older than the average age for SS or pyoderma gangrenosum.3 Similar to other neutrophilic dermatoses, NDDH responds well to oral steroids or steroid-sparing immunosuppressants such as dapsone, colchicine, azathioprine, or tetracycline antibiotics.4
The criteria for SS are well established5,6 and may be used for the diagnosis of NDDH, taking into account the localization of lesions to the dorsal aspect of the hands. The diagnostic criteria for SS include fulfillment of both major and at least 2 of 4 minor criteria. The 2 major criteria include rapid presentation of skin lesions and neutrophilic dermal infiltrate on biopsy. Minor criteria are defined as the following: (1) preceding nonspecific respiratory or gastrointestinal tract infection, inflammatory conditions, underlying malignancy, or pregnancy; (2) fever; (3) excellent response to steroids; and (4) 3 of the 4 of the following laboratory abnormalities: elevated CRP, ESR, leukocytosis, or left shift in complete blood cell count. Our patient met both major criteria and only 1 minor criterion—excellent response to systemic corticosteroids. Nofal et al7 advocated for revised diagnostic criteria for SS, with one suggestion utilizing only the 2 major criteria being necessary for diagnosis. Given that serum inflammatory markers may not be as elevated in NDDH compared to SS,3,7,8 meeting the major criteria alone may be a better way to diagnose NDDH, as in our patient.
Our patient presented with an expanding ulcerating nodule on the hand that elicited a wide list of differential diagnoses to include infections and neoplasms. Rapid development, localization to the dorsal aspect of the hand, and treatment resistance to antibiotics may help the clinician consider a diagnosis of NDDH, which should be confirmed by a biopsy. Similar to other neutrophilic dermatoses, an underlying malignancy or inflammatory condition should be sought out. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand responds well to systemic steroids, though recurrences may occur.
- Miller A, Green M, Robinson D. Simple rule for calculating normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Br Med (Clinical Res Ed). 1983;286:226.
- Wyczalkowska-Tomasik A, Czarkowska-Paczek B, Zielenkiewicz M, et al. Inflammatory markers change with age, but do not fall beyond reported normal ranges. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016;64:249-254.
- Walling HW, Snipes CJ, Gerami P, et al. The relationship between neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands and Sweet syndrome: report of 9 cases and comparison to atypical pyoderma gangrenosum. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:57-63.
- Gaulding J, Kohen LL. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017; 76(6 suppl 1):AB178.
- Sweet RD. An acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis. Br J Dermatol. 1964;76:349-356.
- Su WP, Liu HN. Diagnostic criteria for Sweet’s syndrome. Cutis. 1986;37:167-174.
- Nofal A, Abdelmaksoud A, Amer H, et al. Sweet’s syndrome: diagnostic criteria revisited. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2017;15:1081-1088.
- Wolf R, Tüzün Y. Acral manifestations of Sweet syndrome (neutrophilic dermatosis of the hands). Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:81-84.
To the Editor:
Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand (NDDH) is an uncommon reactive neutrophilic dermatosis that presents as a painful, enlarging, ulcerative nodule. It often is misdiagnosed and initially treated as an infection. Similar to other neutrophilic dermatoses, it is associated with underlying infections, inflammatory conditions, and malignancies. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand is considered a subset of Sweet syndrome (SS); we highlight similarities and differences between NDDH and SS, reporting the case of a 66-year-old man without systemic symptoms who developed NDDH on the right hand.

A 66-year-old man presented with a progressively enlarging, painful, ulcerative, 2-cm nodule on the right hand following mechanical trauma 2 weeks prior (Figure 1). He was afebrile with no remarkable medical history. Laboratory evaluation revealed an erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of 20 mm/h (reference range, 0-10 mm/h) and C-reactive protein (CRP) level of 3.52 mg/dL (reference range, 0-0.5 mg/dL) without leukocytosis; both were not remarkably elevated when adjusted for age.1,2 The clinical differential diagnosis was broad and included pyoderma with evolving cellulitis, neutrophilic dermatosis, atypical mycobacterial infection, subcutaneous or deep fungal infection, squamous cell carcinoma, cutaneous lymphoma, and metastasis. Due to the rapid development of the lesion, initial treatment focused on a bacterial infection, but there was no improvement on antibiotics and wound cultures were negative. The ulcerative nodule was biopsied, and histopathology demonstrated abundant neutrophilic inflammation, endothelial swelling, and leukocytoclasis without microorganisms (Figure 2). Tissue cultures for bacteria, fungi, and atypical mycobacteria were negative. A diagnosis of NDDH was made based on clinical and histologic findings. The wound improved with a 3-week course of oral prednisone.

Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand is a subset of reactive neutrophilic dermatoses, which includes SS (acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) and pyoderma gangrenosum. It is described as a localized variant of SS, with similar associated underlying inflammatory, neoplastic conditions and laboratory findings.3 However, NDDH has characteristic features that differ from classic SS. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand typically presents as painful papules, pustules, or ulcers that progress to become larger ulcers, plaques, and nodules. The clinical appearance may more closely resemble pyoderma gangrenosum or atypical SS, with ulceration frequently present. Pathergy also may be demonstrated in NDDH, similar to our patient. The average age of presentation for NDDH is 60 years, which is older than the average age for SS or pyoderma gangrenosum.3 Similar to other neutrophilic dermatoses, NDDH responds well to oral steroids or steroid-sparing immunosuppressants such as dapsone, colchicine, azathioprine, or tetracycline antibiotics.4
The criteria for SS are well established5,6 and may be used for the diagnosis of NDDH, taking into account the localization of lesions to the dorsal aspect of the hands. The diagnostic criteria for SS include fulfillment of both major and at least 2 of 4 minor criteria. The 2 major criteria include rapid presentation of skin lesions and neutrophilic dermal infiltrate on biopsy. Minor criteria are defined as the following: (1) preceding nonspecific respiratory or gastrointestinal tract infection, inflammatory conditions, underlying malignancy, or pregnancy; (2) fever; (3) excellent response to steroids; and (4) 3 of the 4 of the following laboratory abnormalities: elevated CRP, ESR, leukocytosis, or left shift in complete blood cell count. Our patient met both major criteria and only 1 minor criterion—excellent response to systemic corticosteroids. Nofal et al7 advocated for revised diagnostic criteria for SS, with one suggestion utilizing only the 2 major criteria being necessary for diagnosis. Given that serum inflammatory markers may not be as elevated in NDDH compared to SS,3,7,8 meeting the major criteria alone may be a better way to diagnose NDDH, as in our patient.
Our patient presented with an expanding ulcerating nodule on the hand that elicited a wide list of differential diagnoses to include infections and neoplasms. Rapid development, localization to the dorsal aspect of the hand, and treatment resistance to antibiotics may help the clinician consider a diagnosis of NDDH, which should be confirmed by a biopsy. Similar to other neutrophilic dermatoses, an underlying malignancy or inflammatory condition should be sought out. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand responds well to systemic steroids, though recurrences may occur.
To the Editor:
Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand (NDDH) is an uncommon reactive neutrophilic dermatosis that presents as a painful, enlarging, ulcerative nodule. It often is misdiagnosed and initially treated as an infection. Similar to other neutrophilic dermatoses, it is associated with underlying infections, inflammatory conditions, and malignancies. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand is considered a subset of Sweet syndrome (SS); we highlight similarities and differences between NDDH and SS, reporting the case of a 66-year-old man without systemic symptoms who developed NDDH on the right hand.

A 66-year-old man presented with a progressively enlarging, painful, ulcerative, 2-cm nodule on the right hand following mechanical trauma 2 weeks prior (Figure 1). He was afebrile with no remarkable medical history. Laboratory evaluation revealed an erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of 20 mm/h (reference range, 0-10 mm/h) and C-reactive protein (CRP) level of 3.52 mg/dL (reference range, 0-0.5 mg/dL) without leukocytosis; both were not remarkably elevated when adjusted for age.1,2 The clinical differential diagnosis was broad and included pyoderma with evolving cellulitis, neutrophilic dermatosis, atypical mycobacterial infection, subcutaneous or deep fungal infection, squamous cell carcinoma, cutaneous lymphoma, and metastasis. Due to the rapid development of the lesion, initial treatment focused on a bacterial infection, but there was no improvement on antibiotics and wound cultures were negative. The ulcerative nodule was biopsied, and histopathology demonstrated abundant neutrophilic inflammation, endothelial swelling, and leukocytoclasis without microorganisms (Figure 2). Tissue cultures for bacteria, fungi, and atypical mycobacteria were negative. A diagnosis of NDDH was made based on clinical and histologic findings. The wound improved with a 3-week course of oral prednisone.

Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand is a subset of reactive neutrophilic dermatoses, which includes SS (acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) and pyoderma gangrenosum. It is described as a localized variant of SS, with similar associated underlying inflammatory, neoplastic conditions and laboratory findings.3 However, NDDH has characteristic features that differ from classic SS. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand typically presents as painful papules, pustules, or ulcers that progress to become larger ulcers, plaques, and nodules. The clinical appearance may more closely resemble pyoderma gangrenosum or atypical SS, with ulceration frequently present. Pathergy also may be demonstrated in NDDH, similar to our patient. The average age of presentation for NDDH is 60 years, which is older than the average age for SS or pyoderma gangrenosum.3 Similar to other neutrophilic dermatoses, NDDH responds well to oral steroids or steroid-sparing immunosuppressants such as dapsone, colchicine, azathioprine, or tetracycline antibiotics.4
The criteria for SS are well established5,6 and may be used for the diagnosis of NDDH, taking into account the localization of lesions to the dorsal aspect of the hands. The diagnostic criteria for SS include fulfillment of both major and at least 2 of 4 minor criteria. The 2 major criteria include rapid presentation of skin lesions and neutrophilic dermal infiltrate on biopsy. Minor criteria are defined as the following: (1) preceding nonspecific respiratory or gastrointestinal tract infection, inflammatory conditions, underlying malignancy, or pregnancy; (2) fever; (3) excellent response to steroids; and (4) 3 of the 4 of the following laboratory abnormalities: elevated CRP, ESR, leukocytosis, or left shift in complete blood cell count. Our patient met both major criteria and only 1 minor criterion—excellent response to systemic corticosteroids. Nofal et al7 advocated for revised diagnostic criteria for SS, with one suggestion utilizing only the 2 major criteria being necessary for diagnosis. Given that serum inflammatory markers may not be as elevated in NDDH compared to SS,3,7,8 meeting the major criteria alone may be a better way to diagnose NDDH, as in our patient.
Our patient presented with an expanding ulcerating nodule on the hand that elicited a wide list of differential diagnoses to include infections and neoplasms. Rapid development, localization to the dorsal aspect of the hand, and treatment resistance to antibiotics may help the clinician consider a diagnosis of NDDH, which should be confirmed by a biopsy. Similar to other neutrophilic dermatoses, an underlying malignancy or inflammatory condition should be sought out. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand responds well to systemic steroids, though recurrences may occur.
- Miller A, Green M, Robinson D. Simple rule for calculating normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Br Med (Clinical Res Ed). 1983;286:226.
- Wyczalkowska-Tomasik A, Czarkowska-Paczek B, Zielenkiewicz M, et al. Inflammatory markers change with age, but do not fall beyond reported normal ranges. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016;64:249-254.
- Walling HW, Snipes CJ, Gerami P, et al. The relationship between neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands and Sweet syndrome: report of 9 cases and comparison to atypical pyoderma gangrenosum. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:57-63.
- Gaulding J, Kohen LL. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017; 76(6 suppl 1):AB178.
- Sweet RD. An acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis. Br J Dermatol. 1964;76:349-356.
- Su WP, Liu HN. Diagnostic criteria for Sweet’s syndrome. Cutis. 1986;37:167-174.
- Nofal A, Abdelmaksoud A, Amer H, et al. Sweet’s syndrome: diagnostic criteria revisited. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2017;15:1081-1088.
- Wolf R, Tüzün Y. Acral manifestations of Sweet syndrome (neutrophilic dermatosis of the hands). Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:81-84.
- Miller A, Green M, Robinson D. Simple rule for calculating normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Br Med (Clinical Res Ed). 1983;286:226.
- Wyczalkowska-Tomasik A, Czarkowska-Paczek B, Zielenkiewicz M, et al. Inflammatory markers change with age, but do not fall beyond reported normal ranges. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016;64:249-254.
- Walling HW, Snipes CJ, Gerami P, et al. The relationship between neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands and Sweet syndrome: report of 9 cases and comparison to atypical pyoderma gangrenosum. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:57-63.
- Gaulding J, Kohen LL. Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017; 76(6 suppl 1):AB178.
- Sweet RD. An acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis. Br J Dermatol. 1964;76:349-356.
- Su WP, Liu HN. Diagnostic criteria for Sweet’s syndrome. Cutis. 1986;37:167-174.
- Nofal A, Abdelmaksoud A, Amer H, et al. Sweet’s syndrome: diagnostic criteria revisited. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2017;15:1081-1088.
- Wolf R, Tüzün Y. Acral manifestations of Sweet syndrome (neutrophilic dermatosis of the hands). Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:81-84.
Practice Points
- Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hand (NDDH) is a reactive neutrophilic dermatosis that includes Sweet syndrome (SS) and pyoderma gangrenosum.
- Localization to the dorsal aspect of the hand, presence of ulcerative nodules, and older age at onset are characteristic features of NDDH.
- Meeting the major criteria alone for SS may be a more sensitive way to diagnose NDDH, as serum inflammatory markers may not be remarkably elevated in this condition.
All-oral regimen succeeds for rifampin-resistant tuberculosis
A combination oral-only therapy of bedaquiline, pretomanid, and linezolid was significantly more effective than standard care in preventing unfavorable outcomes in patients with treatment-resistant tuberculosis, based on data from more than 500 individuals.
, and data on the use of new and repurposed drug combinations are lacking, wrote Bern-Thomas Nyang’wa, MBBS, of Médecins Sans Frontières, Amsterdam, and colleagues.
In a study known as the TB-PRACTECAL trial, the researchers enrolled 552 pulmonary rifampin-resistant tuberculosis patients aged 15 years and older to examine several new and repurposed drug combinations. The participants were randomized in a 1:1:1:1 ratio to treatment with 36-80 weeks of standard care; 24-week oral bedaquiline, pretomanid, and linezolid (BPaL); BPaL plus clofazimine (BPaLC); or BPaL plus moxifloxacin (BPaLM) . This was followed by stage two of the trial, in which participants were randomized 1:1 to receive standard care or BPaLM. The current study, published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, reported the stage two findings; the primary outcome was a composite of unfavorable outcomes at 72 weeks including death, treatment failure, treatment discontinuation, recurrence of tuberculosis, or loss to follow-up.
The modified intent-to-treat population included 138 patients in the BPaLM group and 137 patients in the standard care group. In this population, 56 (41%) of 137 participants in the standard care group and 16 (12%) of 137 participants in the BPaLM group met criteria for the unfavorable outcome at 72 weeks; noninferiority and superiority were significantly greater in the BPaLM group (P < .0001).
Early discontinuation was the main reason patients met the unfavorable outcome criteria (89% of standard care patients and 69% of BPaLM patients); adverse events accounted for 23% of discontinuations in the standard care group and 64% of discontinuations in the BPaLM group.
However, fewer patients in the BPaLM group experienced grade 3 or higher adverse events compared with the standard care group (23% vs. 48%). The most common adverse events included hepatic disorders, cardiac disorders, and anemia.
In addition, all subgroup analyses favored BPaLM over standard care at 72 weeks including subgroups based on sex, age, disease severity, re-treatment status, and smoking status.
The findings were limited by several factors including the changes to standard of care over the course of the study, potential bias because the study was stopped for efficacy, and inclusion of loss to follow-up as part of the composite unfavorable outcome, the researchers noted.
Remaining research questions include the optimal dose of linezolid, whether use of alternative fluoroquinolones would yield similar results, and whether the results would generalize to populations including children, pregnant women, and patients with extrapulmonary tuberculosis, they added.
However, the results support BPaLM as the preferred treatment for adults and adolescents with pulmonary rifampin-resistant TB, the researchers concluded.
BPaLM poised to improve TB care
Before 2020, treatment for rifampin-resistant tuberculosis was 9-20 months in duration, toxic, and inadequately effective, and new treatment regimens are urgently needed, Mary Jo Farmer, MD, a pulmonary and critical care specialist at the University of Massachusetts Baystate Health Regional Campus, Springfield, said in an interview.
“The BPaL-based regimens perform better than the 9- to 20-month standard of care, are shorter in duration, have a lower pill burden, improve quality of life, and are cost-effective,” she said. “The BPaL regimens have the potential to improve outcomes for thousands of patients with rifampin-resistant tuberculosis.”
“The 24-week oral regimen consisting of bedaquiline, pretomanid, linezolid and moxifloxacin is noninferior to standard of care for treatment of patients with pulmonary rifampin-resistant tuberculosis, and this BPaLM regimen was added to the WHO guidance for treatment of this condition in 2022,” said Dr. Farmer, who was not involved in the study. “It remains to be seen if BPaLM will become the preferred regimen for adolescents and adults with pulmonary rifampin-resistant tuberculosis,” she said.
Dr. Farmer agreed with the study authors that the optimal dose of linezolid, optimal duration of treatment, and the role of dose reduction remain unknown, and pharmacokinetic studies are needed to identify these parameters.
The study was supported by Médecins Sans Frontières. TB Alliance donated pretomanid to the study prior to its commercialization. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Farmer had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the editorial advisory board of CHEST Physician.
A combination oral-only therapy of bedaquiline, pretomanid, and linezolid was significantly more effective than standard care in preventing unfavorable outcomes in patients with treatment-resistant tuberculosis, based on data from more than 500 individuals.
, and data on the use of new and repurposed drug combinations are lacking, wrote Bern-Thomas Nyang’wa, MBBS, of Médecins Sans Frontières, Amsterdam, and colleagues.
In a study known as the TB-PRACTECAL trial, the researchers enrolled 552 pulmonary rifampin-resistant tuberculosis patients aged 15 years and older to examine several new and repurposed drug combinations. The participants were randomized in a 1:1:1:1 ratio to treatment with 36-80 weeks of standard care; 24-week oral bedaquiline, pretomanid, and linezolid (BPaL); BPaL plus clofazimine (BPaLC); or BPaL plus moxifloxacin (BPaLM) . This was followed by stage two of the trial, in which participants were randomized 1:1 to receive standard care or BPaLM. The current study, published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, reported the stage two findings; the primary outcome was a composite of unfavorable outcomes at 72 weeks including death, treatment failure, treatment discontinuation, recurrence of tuberculosis, or loss to follow-up.
The modified intent-to-treat population included 138 patients in the BPaLM group and 137 patients in the standard care group. In this population, 56 (41%) of 137 participants in the standard care group and 16 (12%) of 137 participants in the BPaLM group met criteria for the unfavorable outcome at 72 weeks; noninferiority and superiority were significantly greater in the BPaLM group (P < .0001).
Early discontinuation was the main reason patients met the unfavorable outcome criteria (89% of standard care patients and 69% of BPaLM patients); adverse events accounted for 23% of discontinuations in the standard care group and 64% of discontinuations in the BPaLM group.
However, fewer patients in the BPaLM group experienced grade 3 or higher adverse events compared with the standard care group (23% vs. 48%). The most common adverse events included hepatic disorders, cardiac disorders, and anemia.
In addition, all subgroup analyses favored BPaLM over standard care at 72 weeks including subgroups based on sex, age, disease severity, re-treatment status, and smoking status.
The findings were limited by several factors including the changes to standard of care over the course of the study, potential bias because the study was stopped for efficacy, and inclusion of loss to follow-up as part of the composite unfavorable outcome, the researchers noted.
Remaining research questions include the optimal dose of linezolid, whether use of alternative fluoroquinolones would yield similar results, and whether the results would generalize to populations including children, pregnant women, and patients with extrapulmonary tuberculosis, they added.
However, the results support BPaLM as the preferred treatment for adults and adolescents with pulmonary rifampin-resistant TB, the researchers concluded.
BPaLM poised to improve TB care
Before 2020, treatment for rifampin-resistant tuberculosis was 9-20 months in duration, toxic, and inadequately effective, and new treatment regimens are urgently needed, Mary Jo Farmer, MD, a pulmonary and critical care specialist at the University of Massachusetts Baystate Health Regional Campus, Springfield, said in an interview.
“The BPaL-based regimens perform better than the 9- to 20-month standard of care, are shorter in duration, have a lower pill burden, improve quality of life, and are cost-effective,” she said. “The BPaL regimens have the potential to improve outcomes for thousands of patients with rifampin-resistant tuberculosis.”
“The 24-week oral regimen consisting of bedaquiline, pretomanid, linezolid and moxifloxacin is noninferior to standard of care for treatment of patients with pulmonary rifampin-resistant tuberculosis, and this BPaLM regimen was added to the WHO guidance for treatment of this condition in 2022,” said Dr. Farmer, who was not involved in the study. “It remains to be seen if BPaLM will become the preferred regimen for adolescents and adults with pulmonary rifampin-resistant tuberculosis,” she said.
Dr. Farmer agreed with the study authors that the optimal dose of linezolid, optimal duration of treatment, and the role of dose reduction remain unknown, and pharmacokinetic studies are needed to identify these parameters.
The study was supported by Médecins Sans Frontières. TB Alliance donated pretomanid to the study prior to its commercialization. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Farmer had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the editorial advisory board of CHEST Physician.
A combination oral-only therapy of bedaquiline, pretomanid, and linezolid was significantly more effective than standard care in preventing unfavorable outcomes in patients with treatment-resistant tuberculosis, based on data from more than 500 individuals.
, and data on the use of new and repurposed drug combinations are lacking, wrote Bern-Thomas Nyang’wa, MBBS, of Médecins Sans Frontières, Amsterdam, and colleagues.
In a study known as the TB-PRACTECAL trial, the researchers enrolled 552 pulmonary rifampin-resistant tuberculosis patients aged 15 years and older to examine several new and repurposed drug combinations. The participants were randomized in a 1:1:1:1 ratio to treatment with 36-80 weeks of standard care; 24-week oral bedaquiline, pretomanid, and linezolid (BPaL); BPaL plus clofazimine (BPaLC); or BPaL plus moxifloxacin (BPaLM) . This was followed by stage two of the trial, in which participants were randomized 1:1 to receive standard care or BPaLM. The current study, published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, reported the stage two findings; the primary outcome was a composite of unfavorable outcomes at 72 weeks including death, treatment failure, treatment discontinuation, recurrence of tuberculosis, or loss to follow-up.
The modified intent-to-treat population included 138 patients in the BPaLM group and 137 patients in the standard care group. In this population, 56 (41%) of 137 participants in the standard care group and 16 (12%) of 137 participants in the BPaLM group met criteria for the unfavorable outcome at 72 weeks; noninferiority and superiority were significantly greater in the BPaLM group (P < .0001).
Early discontinuation was the main reason patients met the unfavorable outcome criteria (89% of standard care patients and 69% of BPaLM patients); adverse events accounted for 23% of discontinuations in the standard care group and 64% of discontinuations in the BPaLM group.
However, fewer patients in the BPaLM group experienced grade 3 or higher adverse events compared with the standard care group (23% vs. 48%). The most common adverse events included hepatic disorders, cardiac disorders, and anemia.
In addition, all subgroup analyses favored BPaLM over standard care at 72 weeks including subgroups based on sex, age, disease severity, re-treatment status, and smoking status.
The findings were limited by several factors including the changes to standard of care over the course of the study, potential bias because the study was stopped for efficacy, and inclusion of loss to follow-up as part of the composite unfavorable outcome, the researchers noted.
Remaining research questions include the optimal dose of linezolid, whether use of alternative fluoroquinolones would yield similar results, and whether the results would generalize to populations including children, pregnant women, and patients with extrapulmonary tuberculosis, they added.
However, the results support BPaLM as the preferred treatment for adults and adolescents with pulmonary rifampin-resistant TB, the researchers concluded.
BPaLM poised to improve TB care
Before 2020, treatment for rifampin-resistant tuberculosis was 9-20 months in duration, toxic, and inadequately effective, and new treatment regimens are urgently needed, Mary Jo Farmer, MD, a pulmonary and critical care specialist at the University of Massachusetts Baystate Health Regional Campus, Springfield, said in an interview.
“The BPaL-based regimens perform better than the 9- to 20-month standard of care, are shorter in duration, have a lower pill burden, improve quality of life, and are cost-effective,” she said. “The BPaL regimens have the potential to improve outcomes for thousands of patients with rifampin-resistant tuberculosis.”
“The 24-week oral regimen consisting of bedaquiline, pretomanid, linezolid and moxifloxacin is noninferior to standard of care for treatment of patients with pulmonary rifampin-resistant tuberculosis, and this BPaLM regimen was added to the WHO guidance for treatment of this condition in 2022,” said Dr. Farmer, who was not involved in the study. “It remains to be seen if BPaLM will become the preferred regimen for adolescents and adults with pulmonary rifampin-resistant tuberculosis,” she said.
Dr. Farmer agreed with the study authors that the optimal dose of linezolid, optimal duration of treatment, and the role of dose reduction remain unknown, and pharmacokinetic studies are needed to identify these parameters.
The study was supported by Médecins Sans Frontières. TB Alliance donated pretomanid to the study prior to its commercialization. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Farmer had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the editorial advisory board of CHEST Physician.
FROM LANCET RESPIRATORY MEDICINE
New CDC advisory once again flags BA.2.86 COVID variant
An emerging variant of COVID-19 called BA.2.86 that caused alarm in the summer of 2023 has landed on the Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s radar again.
The variant accounted for nearly 9% of cases during the 2-week period ending Nov. 25, up from 3% during the previous 2 weeks, according to data published Nov. 27 by the CDC. The estimates are not exact, and the CDC indicated the actual percentage of cases may range from 5% to 15%.
The CDC took the unusual step of publishing a specific statement about the rise in BA.2.86 cases. The variant drew worldwide attention during the summer because of how different its makeup is, compared with other prominent variants of the virus that causes COVID-19, raising the potential for the new variant to be more capable of causing infection. But after a flurry of interest in BA.2.86, it didn’t end up being as widespread as expected, so for months it wasn’t listed as a standalone variant on the CDC’s variant tracker list.
“At this time, BA.2.86 does not appear to be driving increases in infections or hospitalizations in the United States,” the CDC wrote in its advisory. “It is not possible at this time to know whether BA.2.86 infection produces different symptoms from other variants. In general, symptoms of COVID-19 tend to be similar across variants. The types of symptoms and how severe they are usually depend more on a person’s immunity than which variant causes the infection.”
BA.2.86 is now the third-most prominent variant circulating the United States, behind HV.1 and EG.5, which combined account for about 45% of all U.S. COVID-19 cases. All three are from the Omicron lineage of the virus.
About 8% of all COVID tests reported to the CDC were positive for the week ending Nov. 18, which is a decline, compared with recent weeks. But indicators for severe cases of the illness have ticked up lately, including rises among ED visits for COVID, hospitalizations, and deaths.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
An emerging variant of COVID-19 called BA.2.86 that caused alarm in the summer of 2023 has landed on the Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s radar again.
The variant accounted for nearly 9% of cases during the 2-week period ending Nov. 25, up from 3% during the previous 2 weeks, according to data published Nov. 27 by the CDC. The estimates are not exact, and the CDC indicated the actual percentage of cases may range from 5% to 15%.
The CDC took the unusual step of publishing a specific statement about the rise in BA.2.86 cases. The variant drew worldwide attention during the summer because of how different its makeup is, compared with other prominent variants of the virus that causes COVID-19, raising the potential for the new variant to be more capable of causing infection. But after a flurry of interest in BA.2.86, it didn’t end up being as widespread as expected, so for months it wasn’t listed as a standalone variant on the CDC’s variant tracker list.
“At this time, BA.2.86 does not appear to be driving increases in infections or hospitalizations in the United States,” the CDC wrote in its advisory. “It is not possible at this time to know whether BA.2.86 infection produces different symptoms from other variants. In general, symptoms of COVID-19 tend to be similar across variants. The types of symptoms and how severe they are usually depend more on a person’s immunity than which variant causes the infection.”
BA.2.86 is now the third-most prominent variant circulating the United States, behind HV.1 and EG.5, which combined account for about 45% of all U.S. COVID-19 cases. All three are from the Omicron lineage of the virus.
About 8% of all COVID tests reported to the CDC were positive for the week ending Nov. 18, which is a decline, compared with recent weeks. But indicators for severe cases of the illness have ticked up lately, including rises among ED visits for COVID, hospitalizations, and deaths.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
An emerging variant of COVID-19 called BA.2.86 that caused alarm in the summer of 2023 has landed on the Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s radar again.
The variant accounted for nearly 9% of cases during the 2-week period ending Nov. 25, up from 3% during the previous 2 weeks, according to data published Nov. 27 by the CDC. The estimates are not exact, and the CDC indicated the actual percentage of cases may range from 5% to 15%.
The CDC took the unusual step of publishing a specific statement about the rise in BA.2.86 cases. The variant drew worldwide attention during the summer because of how different its makeup is, compared with other prominent variants of the virus that causes COVID-19, raising the potential for the new variant to be more capable of causing infection. But after a flurry of interest in BA.2.86, it didn’t end up being as widespread as expected, so for months it wasn’t listed as a standalone variant on the CDC’s variant tracker list.
“At this time, BA.2.86 does not appear to be driving increases in infections or hospitalizations in the United States,” the CDC wrote in its advisory. “It is not possible at this time to know whether BA.2.86 infection produces different symptoms from other variants. In general, symptoms of COVID-19 tend to be similar across variants. The types of symptoms and how severe they are usually depend more on a person’s immunity than which variant causes the infection.”
BA.2.86 is now the third-most prominent variant circulating the United States, behind HV.1 and EG.5, which combined account for about 45% of all U.S. COVID-19 cases. All three are from the Omicron lineage of the virus.
About 8% of all COVID tests reported to the CDC were positive for the week ending Nov. 18, which is a decline, compared with recent weeks. But indicators for severe cases of the illness have ticked up lately, including rises among ED visits for COVID, hospitalizations, and deaths.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Is air filtration the best public health intervention against respiratory viruses?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
When it comes to the public health fight against respiratory viruses – COVID, flu, RSV, and so on – it has always struck me as strange how staunchly basically any intervention is opposed. Masking was, of course, the prototypical entrenched warfare of opposing ideologies, with advocates pointing to studies suggesting the efficacy of masking to prevent transmission and advocating for broad masking recommendations, and detractors citing studies that suggested masks were ineffective and characterizing masking policies as fascist overreach. I’ll admit that I was always perplexed by this a bit, as that particular intervention seemed so benign – a bit annoying, I guess, but not crazy.
I have come to appreciate what I call status quo bias, which is the tendency to reject any policy, advice, or intervention that would force you, as an individual, to change your usual behavior. We just don’t like to do that. It has made me think that the most successful public health interventions might be the ones that take the individual out of the loop. And air quality control seems an ideal fit here. Here is a potential intervention where you, the individual, have to do precisely nothing. The status quo is preserved. We just, you know, have cleaner indoor air.
But even the suggestion of air treatment systems as a bulwark against respiratory virus transmission has been met with not just skepticism but cynicism, and perhaps even defeatism. It seems that there are those out there who think there really is nothing we can do. Sickness is interpreted in a Calvinistic framework: You become ill because it is your pre-destiny. But maybe air treatment could actually work. It seems like it might, if a new paper from PLOS One is to be believed.
What we’re talking about is a study titled “Bipolar Ionization Rapidly Inactivates Real-World, Airborne Concentrations of Infective Respiratory Viruses” – a highly controlled, laboratory-based analysis of a bipolar ionization system which seems to rapidly reduce viral counts in the air.
The proposed mechanism of action is pretty simple. The ionization system – which, don’t worry, has been shown not to produce ozone – spits out positively and negatively charged particles, which float around the test chamber, designed to look like a pretty standard room that you might find in an office or a school.
Virus is then injected into the chamber through an aerosolization machine, to achieve concentrations on the order of what you might get standing within 6 feet or so of someone actively infected with COVID while they are breathing and talking.
The idea is that those ions stick to the virus particles, similar to how a balloon sticks to the wall after you rub it on your hair, and that tends to cause them to clump together and settle on surfaces more rapidly, and thus get farther away from their ports of entry to the human system: nose, mouth, and eyes. But the ions may also interfere with viruses’ ability to bind to cellular receptors, even in the air.
To quantify viral infectivity, the researchers used a biological system. Basically, you take air samples and expose a petri dish of cells to them and see how many cells die. Fewer cells dying, less infective. Under control conditions, you can see that virus infectivity does decrease over time. Time zero here is the end of a SARS-CoV-2 aerosolization.
This may simply reflect the fact that virus particles settle out of the air. But As you can see, within about an hour, you have almost no infective virus detectable. That’s fairly impressive.
Now, I’m not saying that this is a panacea, but it is certainly worth considering the use of technologies like these if we are going to revamp the infrastructure of our offices and schools. And, of course, it would be nice to see this tested in a rigorous clinical trial with actual infected people, not cells, as the outcome. But I continue to be encouraged by interventions like this which, to be honest, ask very little of us as individuals. Maybe it’s time we accept the things, or people, that we cannot change.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
When it comes to the public health fight against respiratory viruses – COVID, flu, RSV, and so on – it has always struck me as strange how staunchly basically any intervention is opposed. Masking was, of course, the prototypical entrenched warfare of opposing ideologies, with advocates pointing to studies suggesting the efficacy of masking to prevent transmission and advocating for broad masking recommendations, and detractors citing studies that suggested masks were ineffective and characterizing masking policies as fascist overreach. I’ll admit that I was always perplexed by this a bit, as that particular intervention seemed so benign – a bit annoying, I guess, but not crazy.
I have come to appreciate what I call status quo bias, which is the tendency to reject any policy, advice, or intervention that would force you, as an individual, to change your usual behavior. We just don’t like to do that. It has made me think that the most successful public health interventions might be the ones that take the individual out of the loop. And air quality control seems an ideal fit here. Here is a potential intervention where you, the individual, have to do precisely nothing. The status quo is preserved. We just, you know, have cleaner indoor air.
But even the suggestion of air treatment systems as a bulwark against respiratory virus transmission has been met with not just skepticism but cynicism, and perhaps even defeatism. It seems that there are those out there who think there really is nothing we can do. Sickness is interpreted in a Calvinistic framework: You become ill because it is your pre-destiny. But maybe air treatment could actually work. It seems like it might, if a new paper from PLOS One is to be believed.
What we’re talking about is a study titled “Bipolar Ionization Rapidly Inactivates Real-World, Airborne Concentrations of Infective Respiratory Viruses” – a highly controlled, laboratory-based analysis of a bipolar ionization system which seems to rapidly reduce viral counts in the air.
The proposed mechanism of action is pretty simple. The ionization system – which, don’t worry, has been shown not to produce ozone – spits out positively and negatively charged particles, which float around the test chamber, designed to look like a pretty standard room that you might find in an office or a school.
Virus is then injected into the chamber through an aerosolization machine, to achieve concentrations on the order of what you might get standing within 6 feet or so of someone actively infected with COVID while they are breathing and talking.
The idea is that those ions stick to the virus particles, similar to how a balloon sticks to the wall after you rub it on your hair, and that tends to cause them to clump together and settle on surfaces more rapidly, and thus get farther away from their ports of entry to the human system: nose, mouth, and eyes. But the ions may also interfere with viruses’ ability to bind to cellular receptors, even in the air.
To quantify viral infectivity, the researchers used a biological system. Basically, you take air samples and expose a petri dish of cells to them and see how many cells die. Fewer cells dying, less infective. Under control conditions, you can see that virus infectivity does decrease over time. Time zero here is the end of a SARS-CoV-2 aerosolization.
This may simply reflect the fact that virus particles settle out of the air. But As you can see, within about an hour, you have almost no infective virus detectable. That’s fairly impressive.
Now, I’m not saying that this is a panacea, but it is certainly worth considering the use of technologies like these if we are going to revamp the infrastructure of our offices and schools. And, of course, it would be nice to see this tested in a rigorous clinical trial with actual infected people, not cells, as the outcome. But I continue to be encouraged by interventions like this which, to be honest, ask very little of us as individuals. Maybe it’s time we accept the things, or people, that we cannot change.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
When it comes to the public health fight against respiratory viruses – COVID, flu, RSV, and so on – it has always struck me as strange how staunchly basically any intervention is opposed. Masking was, of course, the prototypical entrenched warfare of opposing ideologies, with advocates pointing to studies suggesting the efficacy of masking to prevent transmission and advocating for broad masking recommendations, and detractors citing studies that suggested masks were ineffective and characterizing masking policies as fascist overreach. I’ll admit that I was always perplexed by this a bit, as that particular intervention seemed so benign – a bit annoying, I guess, but not crazy.
I have come to appreciate what I call status quo bias, which is the tendency to reject any policy, advice, or intervention that would force you, as an individual, to change your usual behavior. We just don’t like to do that. It has made me think that the most successful public health interventions might be the ones that take the individual out of the loop. And air quality control seems an ideal fit here. Here is a potential intervention where you, the individual, have to do precisely nothing. The status quo is preserved. We just, you know, have cleaner indoor air.
But even the suggestion of air treatment systems as a bulwark against respiratory virus transmission has been met with not just skepticism but cynicism, and perhaps even defeatism. It seems that there are those out there who think there really is nothing we can do. Sickness is interpreted in a Calvinistic framework: You become ill because it is your pre-destiny. But maybe air treatment could actually work. It seems like it might, if a new paper from PLOS One is to be believed.
What we’re talking about is a study titled “Bipolar Ionization Rapidly Inactivates Real-World, Airborne Concentrations of Infective Respiratory Viruses” – a highly controlled, laboratory-based analysis of a bipolar ionization system which seems to rapidly reduce viral counts in the air.
The proposed mechanism of action is pretty simple. The ionization system – which, don’t worry, has been shown not to produce ozone – spits out positively and negatively charged particles, which float around the test chamber, designed to look like a pretty standard room that you might find in an office or a school.
Virus is then injected into the chamber through an aerosolization machine, to achieve concentrations on the order of what you might get standing within 6 feet or so of someone actively infected with COVID while they are breathing and talking.
The idea is that those ions stick to the virus particles, similar to how a balloon sticks to the wall after you rub it on your hair, and that tends to cause them to clump together and settle on surfaces more rapidly, and thus get farther away from their ports of entry to the human system: nose, mouth, and eyes. But the ions may also interfere with viruses’ ability to bind to cellular receptors, even in the air.
To quantify viral infectivity, the researchers used a biological system. Basically, you take air samples and expose a petri dish of cells to them and see how many cells die. Fewer cells dying, less infective. Under control conditions, you can see that virus infectivity does decrease over time. Time zero here is the end of a SARS-CoV-2 aerosolization.
This may simply reflect the fact that virus particles settle out of the air. But As you can see, within about an hour, you have almost no infective virus detectable. That’s fairly impressive.
Now, I’m not saying that this is a panacea, but it is certainly worth considering the use of technologies like these if we are going to revamp the infrastructure of our offices and schools. And, of course, it would be nice to see this tested in a rigorous clinical trial with actual infected people, not cells, as the outcome. But I continue to be encouraged by interventions like this which, to be honest, ask very little of us as individuals. Maybe it’s time we accept the things, or people, that we cannot change.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chest pain with long COVID common but undertreated
And chronic chest discomfort may persist in some individuals for years after COVID, warranting future studies of reliable treatments and pain management in this population, a new study shows.
“Recent studies have shown that chest pain occurs in as many as 89% of patients who qualify as having long COVID,” said Ansley Poole, an undergraduate student at the University of South Florida, Tampa, who conducted the research under the supervision of Christine Hunt, DO, and her colleagues at Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Fla.
The findings, though preliminary, shed light on the prevalence, current treatments, and ongoing challenges in managing symptoms of long COVID, said Ms. Poole, who presented the research at the annual Pain Medicine Meeting sponsored by the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine.
Long COVID, which affects an estimated 18 million Americans, manifests approximately 12 weeks after the initial infection and can persist for 2 months or more. Ms. Poole and her team set out to identify risk factors, treatment options, and outcomes for patients dealing with post-COVID chest discomfort.
The study involved a retrospective chart review of 520 patients from the Mayo Clinic network, narrowed down to a final sample of 104. To be included, patients had to report chest discomfort 3-6 months post COVID that continued for 3-6 months after presentation, with no history of chronic chest pain before the infection.
The researchers identified no standardized method for the treatment or management of chest pain linked to long COVID. “Patients were prescribed multiple different treatments, including opioids, post-COVID treatment programs, anticoagulants, steroids, and even psychological programs,” Ms. Poole said.
The median age of the patients was around 50 years; more than 65% were female and over 90% identified as White. More than half (55%) had received one or more vaccine doses at the time of infection. The majority were classified as overweight or obese at the time of their SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Of the 104 patients analyzed, 30 were referred to one or more subspecialties within the pain medicine department, 23 were hospitalized, and 9 were admitted to the intensive care unit or critical care.
“Fifty-three of our patients visited the ER one or more times after COVID because of chest discomfort; however, only six were admitted for over 24 hours, indicating possible overuse of emergency services,” Ms. Poole noted.
Overall, chest pain was described as intermittent instead of constant, which may have been a barrier to providing adequate and timely treatment. The inconsistent presence of pain contributed to the prolonged suffering some patients experienced, Ms. Poole noted.
The study identified several comorbidities, potentially complicating the treatment and etiology of chest pain. These comorbidities – when combined with COVID-related chest pain – contributed to the wide array of prescribed treatments, including steroids, anticoagulants, beta blockers, and physical therapy. Chest pain also seldom stood alone; it was often accompanied by other long COVID–related symptoms, such as shortness of breath.
“Our current analysis indicates that chest pain continues on for years in many individuals, suggesting that COVID-related chest pain may be resistant to treatment,” Ms. Poole reported.
The observed heterogeneity in treatments and outcomes in patients experiencing long-term chest discomfort after COVID infection underscores the need for future studies to establish reliable treatment and management protocols for this population, said Dalia Elmofty, MD, an associate professor of anesthesia and critical care at the University of Chicago, who was not involved in the study. “There are things about COVID that we don’t fully understand. As we’re seeing its consequences and trying to understand its etiology, we recognize the need for further research,” Dr. Elmofty said.
“So many different disease pathologies came out of COVID, whether it’s organ pathology, myofascial pathology, or autoimmune pathology, and all of that is obviously linked to pain,” Dr. Elmofty told this news organization. “It’s an area of research that we are going to have to devote a lot of time to in order to understand, but I think we’re still in the very early phases, trying to fit the pieces of the puzzle together.”
Ms. Poole and Dr. Elmofty report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
And chronic chest discomfort may persist in some individuals for years after COVID, warranting future studies of reliable treatments and pain management in this population, a new study shows.
“Recent studies have shown that chest pain occurs in as many as 89% of patients who qualify as having long COVID,” said Ansley Poole, an undergraduate student at the University of South Florida, Tampa, who conducted the research under the supervision of Christine Hunt, DO, and her colleagues at Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Fla.
The findings, though preliminary, shed light on the prevalence, current treatments, and ongoing challenges in managing symptoms of long COVID, said Ms. Poole, who presented the research at the annual Pain Medicine Meeting sponsored by the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine.
Long COVID, which affects an estimated 18 million Americans, manifests approximately 12 weeks after the initial infection and can persist for 2 months or more. Ms. Poole and her team set out to identify risk factors, treatment options, and outcomes for patients dealing with post-COVID chest discomfort.
The study involved a retrospective chart review of 520 patients from the Mayo Clinic network, narrowed down to a final sample of 104. To be included, patients had to report chest discomfort 3-6 months post COVID that continued for 3-6 months after presentation, with no history of chronic chest pain before the infection.
The researchers identified no standardized method for the treatment or management of chest pain linked to long COVID. “Patients were prescribed multiple different treatments, including opioids, post-COVID treatment programs, anticoagulants, steroids, and even psychological programs,” Ms. Poole said.
The median age of the patients was around 50 years; more than 65% were female and over 90% identified as White. More than half (55%) had received one or more vaccine doses at the time of infection. The majority were classified as overweight or obese at the time of their SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Of the 104 patients analyzed, 30 were referred to one or more subspecialties within the pain medicine department, 23 were hospitalized, and 9 were admitted to the intensive care unit or critical care.
“Fifty-three of our patients visited the ER one or more times after COVID because of chest discomfort; however, only six were admitted for over 24 hours, indicating possible overuse of emergency services,” Ms. Poole noted.
Overall, chest pain was described as intermittent instead of constant, which may have been a barrier to providing adequate and timely treatment. The inconsistent presence of pain contributed to the prolonged suffering some patients experienced, Ms. Poole noted.
The study identified several comorbidities, potentially complicating the treatment and etiology of chest pain. These comorbidities – when combined with COVID-related chest pain – contributed to the wide array of prescribed treatments, including steroids, anticoagulants, beta blockers, and physical therapy. Chest pain also seldom stood alone; it was often accompanied by other long COVID–related symptoms, such as shortness of breath.
“Our current analysis indicates that chest pain continues on for years in many individuals, suggesting that COVID-related chest pain may be resistant to treatment,” Ms. Poole reported.
The observed heterogeneity in treatments and outcomes in patients experiencing long-term chest discomfort after COVID infection underscores the need for future studies to establish reliable treatment and management protocols for this population, said Dalia Elmofty, MD, an associate professor of anesthesia and critical care at the University of Chicago, who was not involved in the study. “There are things about COVID that we don’t fully understand. As we’re seeing its consequences and trying to understand its etiology, we recognize the need for further research,” Dr. Elmofty said.
“So many different disease pathologies came out of COVID, whether it’s organ pathology, myofascial pathology, or autoimmune pathology, and all of that is obviously linked to pain,” Dr. Elmofty told this news organization. “It’s an area of research that we are going to have to devote a lot of time to in order to understand, but I think we’re still in the very early phases, trying to fit the pieces of the puzzle together.”
Ms. Poole and Dr. Elmofty report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
And chronic chest discomfort may persist in some individuals for years after COVID, warranting future studies of reliable treatments and pain management in this population, a new study shows.
“Recent studies have shown that chest pain occurs in as many as 89% of patients who qualify as having long COVID,” said Ansley Poole, an undergraduate student at the University of South Florida, Tampa, who conducted the research under the supervision of Christine Hunt, DO, and her colleagues at Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Fla.
The findings, though preliminary, shed light on the prevalence, current treatments, and ongoing challenges in managing symptoms of long COVID, said Ms. Poole, who presented the research at the annual Pain Medicine Meeting sponsored by the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine.
Long COVID, which affects an estimated 18 million Americans, manifests approximately 12 weeks after the initial infection and can persist for 2 months or more. Ms. Poole and her team set out to identify risk factors, treatment options, and outcomes for patients dealing with post-COVID chest discomfort.
The study involved a retrospective chart review of 520 patients from the Mayo Clinic network, narrowed down to a final sample of 104. To be included, patients had to report chest discomfort 3-6 months post COVID that continued for 3-6 months after presentation, with no history of chronic chest pain before the infection.
The researchers identified no standardized method for the treatment or management of chest pain linked to long COVID. “Patients were prescribed multiple different treatments, including opioids, post-COVID treatment programs, anticoagulants, steroids, and even psychological programs,” Ms. Poole said.
The median age of the patients was around 50 years; more than 65% were female and over 90% identified as White. More than half (55%) had received one or more vaccine doses at the time of infection. The majority were classified as overweight or obese at the time of their SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Of the 104 patients analyzed, 30 were referred to one or more subspecialties within the pain medicine department, 23 were hospitalized, and 9 were admitted to the intensive care unit or critical care.
“Fifty-three of our patients visited the ER one or more times after COVID because of chest discomfort; however, only six were admitted for over 24 hours, indicating possible overuse of emergency services,” Ms. Poole noted.
Overall, chest pain was described as intermittent instead of constant, which may have been a barrier to providing adequate and timely treatment. The inconsistent presence of pain contributed to the prolonged suffering some patients experienced, Ms. Poole noted.
The study identified several comorbidities, potentially complicating the treatment and etiology of chest pain. These comorbidities – when combined with COVID-related chest pain – contributed to the wide array of prescribed treatments, including steroids, anticoagulants, beta blockers, and physical therapy. Chest pain also seldom stood alone; it was often accompanied by other long COVID–related symptoms, such as shortness of breath.
“Our current analysis indicates that chest pain continues on for years in many individuals, suggesting that COVID-related chest pain may be resistant to treatment,” Ms. Poole reported.
The observed heterogeneity in treatments and outcomes in patients experiencing long-term chest discomfort after COVID infection underscores the need for future studies to establish reliable treatment and management protocols for this population, said Dalia Elmofty, MD, an associate professor of anesthesia and critical care at the University of Chicago, who was not involved in the study. “There are things about COVID that we don’t fully understand. As we’re seeing its consequences and trying to understand its etiology, we recognize the need for further research,” Dr. Elmofty said.
“So many different disease pathologies came out of COVID, whether it’s organ pathology, myofascial pathology, or autoimmune pathology, and all of that is obviously linked to pain,” Dr. Elmofty told this news organization. “It’s an area of research that we are going to have to devote a lot of time to in order to understand, but I think we’re still in the very early phases, trying to fit the pieces of the puzzle together.”
Ms. Poole and Dr. Elmofty report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Intense exercise may lead to colds. A new study tells us why
Can too much of a healthy habit become bad?
Lots of evidence shows that regular exercise wards off respiratory infections such as colds, flu, and COVID-19. However, according to a new study.
The findings come as we enter another possible tripledemic this winter, with an increase in COVID, flu, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Public health officials are on alert for a potentially severe flu season, following high flu activity this year in Australia (which can help predict how bad the U.S. flu season will be).
Studies show that the risk for acute respiratory infections is lower in people who exercise regularly. Physically active people are also less likely to suffer severe outcomes from COVID.
But while inactivity has emerged as a potential risk factor for respiratory infections, scientists have long proposed that too much activity, particularly of a prolonged and highly intense nature, may also increase susceptibility.
“The theory suggests that a short-term suppression of the immune system following intense exercise leads to an increase in susceptibility to infection, especially upper respiratory illness,” said Choukri Ben Mamoun, PhD, professor of medicine (infectious diseases) and microbial pathogenesis at the Yale Institute for Global Health, New Haven, Conn. Researchers have documented a greater incidence of upper respiratory illness “among both highly trained and healthy untrained individuals following increased activity during competition or heaving training blocks.”
That’s important if you treat athletes or patients with physically demanding jobs that push them to their physical limits, such as firefighters, police officers, or military personnel.
The new study was small but sheds light on a possible mechanism. Researchers tested blood, saliva, and urine samples from 11 firefighters before and 10 minutes after intense exercise designed to mimic wildfire fighting. The firefighters hiked over hilly terrain for 45 minutes in humid weather wearing up to 44 pounds of wildland gear.
After the workout, subjects had fewer proinflammatory cytokines and ceramides, and more antimicrobial peptides, changes that indicate a greater susceptibility to infection, researchers said. A systematic review adds weight to their findings, revealing a handful of studies in marathon runners, firefighters, soldiers, and soccer players that found an increase in respiratory symptoms after strenuous workouts.
“The relationship between exercise and the immune system is complex and varies from person to person,” said Dr. Mamoun, who was not part of the study. “Physicians can use this study’s findings to provide individualized exercise recommendations.”
An adaptive mechanism gone awry
During intense exercise, the body may reduce airway inflammation to help you breathe, say the authors. The boost in antimicrobial peptides found in the saliva samples could be the body’s way of compensating for the diminished immune function.
Antimicrobial peptides are part of the immune response but they’re “usually not very effective for viral infections,” said lead author Ernesto Nakayasu, PhD, senior research scientist at the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, a U.S. Department of Energy lab in Richland, Washington. “That’s why we think it may make you more exposed to respiratory infections.”
The drop in proinflammatory molecules had an inverse relationship with opiorphin, a peripheral tissue vasodilator thought to increase blood flow and improve oxygen delivery to the muscles during exercise. This may be an adaptive mechanism to improve gas exchange in response to greater oxygen demand.
But as with many adaptive mechanisms, this one may have an unintended consequence. Fewer proinflammatory molecules on patrol may leave you more vulnerable to infection. Plus, during intense exercise, people tend to breathe through their mouths, bypassing the nasal barriers and allowing more microbes – including viruses – to penetrate and deposit in the distal airways of the lungs.
Advice for patients
More research is needed to know exactly how long and how strenuously one needs to exercise to trigger these immune changes, Dr. Nakayasu said.
As shown by their lactate accumulation (an indicator of anaerobic metabolism), the firefighters in the study outpaced the average person’s aerobic respiratory capacity, meaning the average person doing moderate exercise likely wouldn’t trigger these changes.
“Regular moderate exercise is generally associated with better health outcomes [and] improved immune function,” said Dr. Mamoun. For those who exercise to the extreme, proper rest and recovery are “essential for maintaining a robust immune system,” Dr. Mamoun said.
And of course, you can encourage patients to get vaccinated. Young, healthy patients may assume they don’t need COVID-19 or flu shots, as indicated by a recent survey that found one-third of Americans feel they don’t need these vaccinations if they’re not high risk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can too much of a healthy habit become bad?
Lots of evidence shows that regular exercise wards off respiratory infections such as colds, flu, and COVID-19. However, according to a new study.
The findings come as we enter another possible tripledemic this winter, with an increase in COVID, flu, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Public health officials are on alert for a potentially severe flu season, following high flu activity this year in Australia (which can help predict how bad the U.S. flu season will be).
Studies show that the risk for acute respiratory infections is lower in people who exercise regularly. Physically active people are also less likely to suffer severe outcomes from COVID.
But while inactivity has emerged as a potential risk factor for respiratory infections, scientists have long proposed that too much activity, particularly of a prolonged and highly intense nature, may also increase susceptibility.
“The theory suggests that a short-term suppression of the immune system following intense exercise leads to an increase in susceptibility to infection, especially upper respiratory illness,” said Choukri Ben Mamoun, PhD, professor of medicine (infectious diseases) and microbial pathogenesis at the Yale Institute for Global Health, New Haven, Conn. Researchers have documented a greater incidence of upper respiratory illness “among both highly trained and healthy untrained individuals following increased activity during competition or heaving training blocks.”
That’s important if you treat athletes or patients with physically demanding jobs that push them to their physical limits, such as firefighters, police officers, or military personnel.
The new study was small but sheds light on a possible mechanism. Researchers tested blood, saliva, and urine samples from 11 firefighters before and 10 minutes after intense exercise designed to mimic wildfire fighting. The firefighters hiked over hilly terrain for 45 minutes in humid weather wearing up to 44 pounds of wildland gear.
After the workout, subjects had fewer proinflammatory cytokines and ceramides, and more antimicrobial peptides, changes that indicate a greater susceptibility to infection, researchers said. A systematic review adds weight to their findings, revealing a handful of studies in marathon runners, firefighters, soldiers, and soccer players that found an increase in respiratory symptoms after strenuous workouts.
“The relationship between exercise and the immune system is complex and varies from person to person,” said Dr. Mamoun, who was not part of the study. “Physicians can use this study’s findings to provide individualized exercise recommendations.”
An adaptive mechanism gone awry
During intense exercise, the body may reduce airway inflammation to help you breathe, say the authors. The boost in antimicrobial peptides found in the saliva samples could be the body’s way of compensating for the diminished immune function.
Antimicrobial peptides are part of the immune response but they’re “usually not very effective for viral infections,” said lead author Ernesto Nakayasu, PhD, senior research scientist at the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, a U.S. Department of Energy lab in Richland, Washington. “That’s why we think it may make you more exposed to respiratory infections.”
The drop in proinflammatory molecules had an inverse relationship with opiorphin, a peripheral tissue vasodilator thought to increase blood flow and improve oxygen delivery to the muscles during exercise. This may be an adaptive mechanism to improve gas exchange in response to greater oxygen demand.
But as with many adaptive mechanisms, this one may have an unintended consequence. Fewer proinflammatory molecules on patrol may leave you more vulnerable to infection. Plus, during intense exercise, people tend to breathe through their mouths, bypassing the nasal barriers and allowing more microbes – including viruses – to penetrate and deposit in the distal airways of the lungs.
Advice for patients
More research is needed to know exactly how long and how strenuously one needs to exercise to trigger these immune changes, Dr. Nakayasu said.
As shown by their lactate accumulation (an indicator of anaerobic metabolism), the firefighters in the study outpaced the average person’s aerobic respiratory capacity, meaning the average person doing moderate exercise likely wouldn’t trigger these changes.
“Regular moderate exercise is generally associated with better health outcomes [and] improved immune function,” said Dr. Mamoun. For those who exercise to the extreme, proper rest and recovery are “essential for maintaining a robust immune system,” Dr. Mamoun said.
And of course, you can encourage patients to get vaccinated. Young, healthy patients may assume they don’t need COVID-19 or flu shots, as indicated by a recent survey that found one-third of Americans feel they don’t need these vaccinations if they’re not high risk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can too much of a healthy habit become bad?
Lots of evidence shows that regular exercise wards off respiratory infections such as colds, flu, and COVID-19. However, according to a new study.
The findings come as we enter another possible tripledemic this winter, with an increase in COVID, flu, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Public health officials are on alert for a potentially severe flu season, following high flu activity this year in Australia (which can help predict how bad the U.S. flu season will be).
Studies show that the risk for acute respiratory infections is lower in people who exercise regularly. Physically active people are also less likely to suffer severe outcomes from COVID.
But while inactivity has emerged as a potential risk factor for respiratory infections, scientists have long proposed that too much activity, particularly of a prolonged and highly intense nature, may also increase susceptibility.
“The theory suggests that a short-term suppression of the immune system following intense exercise leads to an increase in susceptibility to infection, especially upper respiratory illness,” said Choukri Ben Mamoun, PhD, professor of medicine (infectious diseases) and microbial pathogenesis at the Yale Institute for Global Health, New Haven, Conn. Researchers have documented a greater incidence of upper respiratory illness “among both highly trained and healthy untrained individuals following increased activity during competition or heaving training blocks.”
That’s important if you treat athletes or patients with physically demanding jobs that push them to their physical limits, such as firefighters, police officers, or military personnel.
The new study was small but sheds light on a possible mechanism. Researchers tested blood, saliva, and urine samples from 11 firefighters before and 10 minutes after intense exercise designed to mimic wildfire fighting. The firefighters hiked over hilly terrain for 45 minutes in humid weather wearing up to 44 pounds of wildland gear.
After the workout, subjects had fewer proinflammatory cytokines and ceramides, and more antimicrobial peptides, changes that indicate a greater susceptibility to infection, researchers said. A systematic review adds weight to their findings, revealing a handful of studies in marathon runners, firefighters, soldiers, and soccer players that found an increase in respiratory symptoms after strenuous workouts.
“The relationship between exercise and the immune system is complex and varies from person to person,” said Dr. Mamoun, who was not part of the study. “Physicians can use this study’s findings to provide individualized exercise recommendations.”
An adaptive mechanism gone awry
During intense exercise, the body may reduce airway inflammation to help you breathe, say the authors. The boost in antimicrobial peptides found in the saliva samples could be the body’s way of compensating for the diminished immune function.
Antimicrobial peptides are part of the immune response but they’re “usually not very effective for viral infections,” said lead author Ernesto Nakayasu, PhD, senior research scientist at the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, a U.S. Department of Energy lab in Richland, Washington. “That’s why we think it may make you more exposed to respiratory infections.”
The drop in proinflammatory molecules had an inverse relationship with opiorphin, a peripheral tissue vasodilator thought to increase blood flow and improve oxygen delivery to the muscles during exercise. This may be an adaptive mechanism to improve gas exchange in response to greater oxygen demand.
But as with many adaptive mechanisms, this one may have an unintended consequence. Fewer proinflammatory molecules on patrol may leave you more vulnerable to infection. Plus, during intense exercise, people tend to breathe through their mouths, bypassing the nasal barriers and allowing more microbes – including viruses – to penetrate and deposit in the distal airways of the lungs.
Advice for patients
More research is needed to know exactly how long and how strenuously one needs to exercise to trigger these immune changes, Dr. Nakayasu said.
As shown by their lactate accumulation (an indicator of anaerobic metabolism), the firefighters in the study outpaced the average person’s aerobic respiratory capacity, meaning the average person doing moderate exercise likely wouldn’t trigger these changes.
“Regular moderate exercise is generally associated with better health outcomes [and] improved immune function,” said Dr. Mamoun. For those who exercise to the extreme, proper rest and recovery are “essential for maintaining a robust immune system,” Dr. Mamoun said.
And of course, you can encourage patients to get vaccinated. Young, healthy patients may assume they don’t need COVID-19 or flu shots, as indicated by a recent survey that found one-third of Americans feel they don’t need these vaccinations if they’re not high risk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MILITARY MEDICAL RESEARCH
Childhood immunization schedule includes new RSV, mpox, meningococcal, and pneumococcal vaccines
The immunization schedule for children and adolescents, summarized as an American Academy of Pediatrics policy statement in the journal Pediatrics, contains new entries for the monoclonal antibody immunization nirsevimab for respiratory syncytial virus in infants, the maternal RSV vaccine RSVpreF for pregnant people, the mpox vaccine for adolescents, the 2023-2024 COVID-19 vaccine, the 20-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV20), and the pentavalent meningococcal vaccine (MenACWY-TT/MenB-FHbp).
A number of immunizations have been deleted from the 2024 schedule, including the pentavalent meningococcal vaccine MenABCWY because of a discontinuation in its distribution in the United States, the bivalent mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, the diphtheria and tetanus toxoids adsorbed vaccine, the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13), and the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23).
The 2024 childhood and adolescent immunization schedule, also approved by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, American Academy of Family Physicians, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, American College of Nurse-Midwives, American Academy of Physician Associates, and National Association of Pediatric Nurse Practitioners, is published each year based on current recommendations that have been approved for use by the Food and Drug Administration.
In a press release, the AAP said the CDC decided to publish the recommendations early to ensure health providers are able to administer immunizations and that they are covered by insurance. They also referenced CDC reports that found vaccination rates for kindergarteners have not bounced back since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, and vaccine exemptions for the 2022-2023 school year were at an “all-time high.”
RSV
New to the schedule are the recently approved RSV monoclonal antibody nirsevimab for infants and the RSV vaccine RSVpreF for pregnant people. According to the CDC’s combined immunization schedule for 2024, the timing of the infant RSV immunization is heavily dependent upon when and whether a RSV vaccine was administered during pregnancy. The RSV vaccine should be routinely given between 32 weeks and 36 weeks of gestation between September and January in most of the United States with the caveat that either the maternal vaccine or the infant immunization is recommended.
Infants born between October and March in most of the United States are eligible for the RSV immunization within 14 days of birth if the pregnant parent did not receive an RSV vaccine during pregnancy, or if the parent received the vaccine in the 14 days prior to birth. For infants born between April and September RSV immunization is recommended prior to the start of RSV season.
The immunization is also recommended for infants who were hospitalized for conditions such as prematurity after birth between October and March, infants aged 8-19 months who are undergoing medical support related to prematurity, infants aged 8-19 months who are severely immunocompromised, and infants aged 9-19 months who are American Indian or Alaska Native, and infants undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass.
Mpox
Another new addition to the schedule is mpox, which is recommended for adolescents 18 years or older who are at risk for mpox infection, including gay, bisexual, nonbinary, transgender, or other individuals who have developed a sexually transmitted disease within the last 6 months, had more than one sexual partner, or engaged in sex in a commercial sex venue or public space with confirmed mpox transmission.
Currently, mpox vaccination during pregnancy is not recommended due to a lack of safety data on the vaccine during pregnancy; however, the CDC noted pregnant persons who have been exposed to any of the risk factors above may receive the vaccine.
COVID, influenza, pneumococcal vaccines
The COVID-19 vaccine recommendations were updated to reflect the 2023-2023 formulation of the vaccine. Unvaccinated children between 6 months and 4 years of age will now receive the 2023-2024 formula mRNA vaccines, which includes the two-dose Moderna vaccine and three-dose Pfizer vaccine for use in that age group. Children with a previous history of COVID-19 vaccination are eligible to receive an age-appropriate COVID-19 vaccine from the 2023-2024 formulation, and children between 5-11 years old and 12-18 years old can receive a single dose of an mRNA vaccine regardless of vaccine history; unvaccinated children 12-18 years old are also eligible to receive the two-dose Novavax vaccine.
For influenza, the schedule refers to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommendations released in August, with a note indicating that individuals with an egg allergy can receive another vaccine recommended for their age group without concerns for safety.
The pneumococcal vaccine recommendations have removed PCV13 completely, with updates on the PCV15, PCV20, and PPSV23 in sections on routine vaccination, catch-up vaccination, and special situations. The poliovirus section has also seen its catch-up section revised with a recommendation to complete a vaccination series in adolescents 18 years old known or suspected to have an incomplete series, and to count trivalent oral poliovirus vaccines and OPV administered before April 2016 toward U.S. vaccination requirements.
‘Timely and necessary’ changes
Michael Pichichero, MD, director of the Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital Research Institute, said in an interview that the committee that developed the immunization schedule was thorough in its recommendations for children and adolescents.
“The additions are timely and necessary as the landscape of vaccines for children changes,” he said.
Bonnie M. Word, MD, director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic, said that the immunization schedule “sets the standard and provides clarification and uniformity for administration of all recommended vaccines for U.S. children.”
The U.S. immunization program “is one of the best success stories in medicine,” Dr. Wood said. She noted it is important for providers to become familiar with these vaccines and their indications “to provide advice and be able to respond to questions of parents and/or patients.
“Often patients spend more time with office staff than the physician. It is helpful to make sure everyone in the office understands the importance of and the rationale for immunizing, so families hear consistent messaging,” she said.
Dr. Pichichero and Dr. Word reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
The immunization schedule for children and adolescents, summarized as an American Academy of Pediatrics policy statement in the journal Pediatrics, contains new entries for the monoclonal antibody immunization nirsevimab for respiratory syncytial virus in infants, the maternal RSV vaccine RSVpreF for pregnant people, the mpox vaccine for adolescents, the 2023-2024 COVID-19 vaccine, the 20-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV20), and the pentavalent meningococcal vaccine (MenACWY-TT/MenB-FHbp).
A number of immunizations have been deleted from the 2024 schedule, including the pentavalent meningococcal vaccine MenABCWY because of a discontinuation in its distribution in the United States, the bivalent mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, the diphtheria and tetanus toxoids adsorbed vaccine, the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13), and the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23).
The 2024 childhood and adolescent immunization schedule, also approved by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, American Academy of Family Physicians, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, American College of Nurse-Midwives, American Academy of Physician Associates, and National Association of Pediatric Nurse Practitioners, is published each year based on current recommendations that have been approved for use by the Food and Drug Administration.
In a press release, the AAP said the CDC decided to publish the recommendations early to ensure health providers are able to administer immunizations and that they are covered by insurance. They also referenced CDC reports that found vaccination rates for kindergarteners have not bounced back since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, and vaccine exemptions for the 2022-2023 school year were at an “all-time high.”
RSV
New to the schedule are the recently approved RSV monoclonal antibody nirsevimab for infants and the RSV vaccine RSVpreF for pregnant people. According to the CDC’s combined immunization schedule for 2024, the timing of the infant RSV immunization is heavily dependent upon when and whether a RSV vaccine was administered during pregnancy. The RSV vaccine should be routinely given between 32 weeks and 36 weeks of gestation between September and January in most of the United States with the caveat that either the maternal vaccine or the infant immunization is recommended.
Infants born between October and March in most of the United States are eligible for the RSV immunization within 14 days of birth if the pregnant parent did not receive an RSV vaccine during pregnancy, or if the parent received the vaccine in the 14 days prior to birth. For infants born between April and September RSV immunization is recommended prior to the start of RSV season.
The immunization is also recommended for infants who were hospitalized for conditions such as prematurity after birth between October and March, infants aged 8-19 months who are undergoing medical support related to prematurity, infants aged 8-19 months who are severely immunocompromised, and infants aged 9-19 months who are American Indian or Alaska Native, and infants undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass.
Mpox
Another new addition to the schedule is mpox, which is recommended for adolescents 18 years or older who are at risk for mpox infection, including gay, bisexual, nonbinary, transgender, or other individuals who have developed a sexually transmitted disease within the last 6 months, had more than one sexual partner, or engaged in sex in a commercial sex venue or public space with confirmed mpox transmission.
Currently, mpox vaccination during pregnancy is not recommended due to a lack of safety data on the vaccine during pregnancy; however, the CDC noted pregnant persons who have been exposed to any of the risk factors above may receive the vaccine.
COVID, influenza, pneumococcal vaccines
The COVID-19 vaccine recommendations were updated to reflect the 2023-2023 formulation of the vaccine. Unvaccinated children between 6 months and 4 years of age will now receive the 2023-2024 formula mRNA vaccines, which includes the two-dose Moderna vaccine and three-dose Pfizer vaccine for use in that age group. Children with a previous history of COVID-19 vaccination are eligible to receive an age-appropriate COVID-19 vaccine from the 2023-2024 formulation, and children between 5-11 years old and 12-18 years old can receive a single dose of an mRNA vaccine regardless of vaccine history; unvaccinated children 12-18 years old are also eligible to receive the two-dose Novavax vaccine.
For influenza, the schedule refers to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommendations released in August, with a note indicating that individuals with an egg allergy can receive another vaccine recommended for their age group without concerns for safety.
The pneumococcal vaccine recommendations have removed PCV13 completely, with updates on the PCV15, PCV20, and PPSV23 in sections on routine vaccination, catch-up vaccination, and special situations. The poliovirus section has also seen its catch-up section revised with a recommendation to complete a vaccination series in adolescents 18 years old known or suspected to have an incomplete series, and to count trivalent oral poliovirus vaccines and OPV administered before April 2016 toward U.S. vaccination requirements.
‘Timely and necessary’ changes
Michael Pichichero, MD, director of the Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital Research Institute, said in an interview that the committee that developed the immunization schedule was thorough in its recommendations for children and adolescents.
“The additions are timely and necessary as the landscape of vaccines for children changes,” he said.
Bonnie M. Word, MD, director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic, said that the immunization schedule “sets the standard and provides clarification and uniformity for administration of all recommended vaccines for U.S. children.”
The U.S. immunization program “is one of the best success stories in medicine,” Dr. Wood said. She noted it is important for providers to become familiar with these vaccines and their indications “to provide advice and be able to respond to questions of parents and/or patients.
“Often patients spend more time with office staff than the physician. It is helpful to make sure everyone in the office understands the importance of and the rationale for immunizing, so families hear consistent messaging,” she said.
Dr. Pichichero and Dr. Word reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
The immunization schedule for children and adolescents, summarized as an American Academy of Pediatrics policy statement in the journal Pediatrics, contains new entries for the monoclonal antibody immunization nirsevimab for respiratory syncytial virus in infants, the maternal RSV vaccine RSVpreF for pregnant people, the mpox vaccine for adolescents, the 2023-2024 COVID-19 vaccine, the 20-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV20), and the pentavalent meningococcal vaccine (MenACWY-TT/MenB-FHbp).
A number of immunizations have been deleted from the 2024 schedule, including the pentavalent meningococcal vaccine MenABCWY because of a discontinuation in its distribution in the United States, the bivalent mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, the diphtheria and tetanus toxoids adsorbed vaccine, the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13), and the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23).
The 2024 childhood and adolescent immunization schedule, also approved by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, American Academy of Family Physicians, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, American College of Nurse-Midwives, American Academy of Physician Associates, and National Association of Pediatric Nurse Practitioners, is published each year based on current recommendations that have been approved for use by the Food and Drug Administration.
In a press release, the AAP said the CDC decided to publish the recommendations early to ensure health providers are able to administer immunizations and that they are covered by insurance. They also referenced CDC reports that found vaccination rates for kindergarteners have not bounced back since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, and vaccine exemptions for the 2022-2023 school year were at an “all-time high.”
RSV
New to the schedule are the recently approved RSV monoclonal antibody nirsevimab for infants and the RSV vaccine RSVpreF for pregnant people. According to the CDC’s combined immunization schedule for 2024, the timing of the infant RSV immunization is heavily dependent upon when and whether a RSV vaccine was administered during pregnancy. The RSV vaccine should be routinely given between 32 weeks and 36 weeks of gestation between September and January in most of the United States with the caveat that either the maternal vaccine or the infant immunization is recommended.
Infants born between October and March in most of the United States are eligible for the RSV immunization within 14 days of birth if the pregnant parent did not receive an RSV vaccine during pregnancy, or if the parent received the vaccine in the 14 days prior to birth. For infants born between April and September RSV immunization is recommended prior to the start of RSV season.
The immunization is also recommended for infants who were hospitalized for conditions such as prematurity after birth between October and March, infants aged 8-19 months who are undergoing medical support related to prematurity, infants aged 8-19 months who are severely immunocompromised, and infants aged 9-19 months who are American Indian or Alaska Native, and infants undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass.
Mpox
Another new addition to the schedule is mpox, which is recommended for adolescents 18 years or older who are at risk for mpox infection, including gay, bisexual, nonbinary, transgender, or other individuals who have developed a sexually transmitted disease within the last 6 months, had more than one sexual partner, or engaged in sex in a commercial sex venue or public space with confirmed mpox transmission.
Currently, mpox vaccination during pregnancy is not recommended due to a lack of safety data on the vaccine during pregnancy; however, the CDC noted pregnant persons who have been exposed to any of the risk factors above may receive the vaccine.
COVID, influenza, pneumococcal vaccines
The COVID-19 vaccine recommendations were updated to reflect the 2023-2023 formulation of the vaccine. Unvaccinated children between 6 months and 4 years of age will now receive the 2023-2024 formula mRNA vaccines, which includes the two-dose Moderna vaccine and three-dose Pfizer vaccine for use in that age group. Children with a previous history of COVID-19 vaccination are eligible to receive an age-appropriate COVID-19 vaccine from the 2023-2024 formulation, and children between 5-11 years old and 12-18 years old can receive a single dose of an mRNA vaccine regardless of vaccine history; unvaccinated children 12-18 years old are also eligible to receive the two-dose Novavax vaccine.
For influenza, the schedule refers to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommendations released in August, with a note indicating that individuals with an egg allergy can receive another vaccine recommended for their age group without concerns for safety.
The pneumococcal vaccine recommendations have removed PCV13 completely, with updates on the PCV15, PCV20, and PPSV23 in sections on routine vaccination, catch-up vaccination, and special situations. The poliovirus section has also seen its catch-up section revised with a recommendation to complete a vaccination series in adolescents 18 years old known or suspected to have an incomplete series, and to count trivalent oral poliovirus vaccines and OPV administered before April 2016 toward U.S. vaccination requirements.
‘Timely and necessary’ changes
Michael Pichichero, MD, director of the Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital Research Institute, said in an interview that the committee that developed the immunization schedule was thorough in its recommendations for children and adolescents.
“The additions are timely and necessary as the landscape of vaccines for children changes,” he said.
Bonnie M. Word, MD, director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic, said that the immunization schedule “sets the standard and provides clarification and uniformity for administration of all recommended vaccines for U.S. children.”
The U.S. immunization program “is one of the best success stories in medicine,” Dr. Wood said. She noted it is important for providers to become familiar with these vaccines and their indications “to provide advice and be able to respond to questions of parents and/or patients.
“Often patients spend more time with office staff than the physician. It is helpful to make sure everyone in the office understands the importance of and the rationale for immunizing, so families hear consistent messaging,” she said.
Dr. Pichichero and Dr. Word reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Use the stool! Fecal microbiota transplants help kids with diarrheal infection
(AAP).
However, fecal microbiota transplants (FMTs) should not be used to treat other gastrointestinal ailments such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, because scientific evidence falls short on effectiveness in treating these conditions, the group said.
C. difficile infections (CDIs) are major contributors to hospital-associated diarrhea and diarrhea caused by antibiotics. An FMT involves introducing the feces of a healthy person into the gastrointestinal tract, usually through a nasogastric tube but sometimes in capsules containing healthy stool. Serious adverse reactions associated with an FMT, such as hospitalization, are rare, occuring in roughly 2% of case, the AAP said.
An FMT “does have a place for treatment of recurrent CDIs in children,” said Maria Oliva-Hemker, MD, a pediatric gastroenterologist at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore and the lead author of the report, which was online in Pediatrics.
The AAP strongly encourages people not to perform an FMT at home, although caregivers may be tempted due to a lack of medical facilities located nearby to deliver this care.
“People might see a video on YouTube and think they can do this themselves,” Dr. Oliva-Hemker said.
An FMT requires screening of donors for any infections, which involves administering questionnaires and analyzing donor blood and stool, which are tasks better suited for medical facilities than for a living room.
No controlled or prospective clinical trials on the efficacy of FMT for children exist, according to the AAP. But a retrospective study published in 2020 showed that one or two courses of FMT prevented CDI recurrence in children 87% of the time. Researchers defined the eradication of CDIs as no recurrence for at least 2 months after an FMT and noted the success rates in children were comaparable to those reported in adults.
Unlike pediatric data, adult data come from a randomized clinical trial.
“Sometimes, kids are the last people to be enrolled in these trials,” said Maribeth Nicholson, MD, MPH, a pediatric gastroenterologist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn., an author of the 2020 study.
Dr. Nicholson, who was not involved in the AAP report, said that the retrospective data are strong enough to justify using FMT to eradicate CDIs in children. But researchers are unclear about the biologic mechanisms that make FMTs work.
Dr. Nicholson said that many therapeutics meant to produce a healthier microbiome are being studied in clinical trials. Any clinical trials of such products should include children, Dr. Nicholson said. A child’s gastrointestinal microbiome is actively developing, Dr. Nicholson added, compared with the relatively stable microbiome of an adult.
“When we think about the microbiome it makes sense to target kids, because they’re more apt to respond to these therapies. I worry that somebody will say ‘this doesn’t work in adults,’ and it just stops there,” Dr. Nicholson said.
Though the AAP said that the benefits of FMT for treating CDIs are clear, the data available for treating other conditions such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease are less convincing. Any child receiving an FMT for these ailments should only do so as part of a clinical trial, the group said.
The AAP report endorses a joint position paper, published in 2019, about the benefits of FMTs for CDIs from North American and European pediatric gastroenterology societies. Dr. Nicholson was an author of this joint statement and hopes that the AAP report raises further awareness among pediatricians that FMTs are a safe and effective treatment for recurrent CDIs.
“This is something that maybe is not as discussed in pediatric circles. Kids need FMTs sometimes,” Dr. Nicholson said.
Dr. Oliva-Hemker and Dr. Nicholson report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
(AAP).
However, fecal microbiota transplants (FMTs) should not be used to treat other gastrointestinal ailments such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, because scientific evidence falls short on effectiveness in treating these conditions, the group said.
C. difficile infections (CDIs) are major contributors to hospital-associated diarrhea and diarrhea caused by antibiotics. An FMT involves introducing the feces of a healthy person into the gastrointestinal tract, usually through a nasogastric tube but sometimes in capsules containing healthy stool. Serious adverse reactions associated with an FMT, such as hospitalization, are rare, occuring in roughly 2% of case, the AAP said.
An FMT “does have a place for treatment of recurrent CDIs in children,” said Maria Oliva-Hemker, MD, a pediatric gastroenterologist at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore and the lead author of the report, which was online in Pediatrics.
The AAP strongly encourages people not to perform an FMT at home, although caregivers may be tempted due to a lack of medical facilities located nearby to deliver this care.
“People might see a video on YouTube and think they can do this themselves,” Dr. Oliva-Hemker said.
An FMT requires screening of donors for any infections, which involves administering questionnaires and analyzing donor blood and stool, which are tasks better suited for medical facilities than for a living room.
No controlled or prospective clinical trials on the efficacy of FMT for children exist, according to the AAP. But a retrospective study published in 2020 showed that one or two courses of FMT prevented CDI recurrence in children 87% of the time. Researchers defined the eradication of CDIs as no recurrence for at least 2 months after an FMT and noted the success rates in children were comaparable to those reported in adults.
Unlike pediatric data, adult data come from a randomized clinical trial.
“Sometimes, kids are the last people to be enrolled in these trials,” said Maribeth Nicholson, MD, MPH, a pediatric gastroenterologist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn., an author of the 2020 study.
Dr. Nicholson, who was not involved in the AAP report, said that the retrospective data are strong enough to justify using FMT to eradicate CDIs in children. But researchers are unclear about the biologic mechanisms that make FMTs work.
Dr. Nicholson said that many therapeutics meant to produce a healthier microbiome are being studied in clinical trials. Any clinical trials of such products should include children, Dr. Nicholson said. A child’s gastrointestinal microbiome is actively developing, Dr. Nicholson added, compared with the relatively stable microbiome of an adult.
“When we think about the microbiome it makes sense to target kids, because they’re more apt to respond to these therapies. I worry that somebody will say ‘this doesn’t work in adults,’ and it just stops there,” Dr. Nicholson said.
Though the AAP said that the benefits of FMT for treating CDIs are clear, the data available for treating other conditions such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease are less convincing. Any child receiving an FMT for these ailments should only do so as part of a clinical trial, the group said.
The AAP report endorses a joint position paper, published in 2019, about the benefits of FMTs for CDIs from North American and European pediatric gastroenterology societies. Dr. Nicholson was an author of this joint statement and hopes that the AAP report raises further awareness among pediatricians that FMTs are a safe and effective treatment for recurrent CDIs.
“This is something that maybe is not as discussed in pediatric circles. Kids need FMTs sometimes,” Dr. Nicholson said.
Dr. Oliva-Hemker and Dr. Nicholson report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
(AAP).
However, fecal microbiota transplants (FMTs) should not be used to treat other gastrointestinal ailments such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, because scientific evidence falls short on effectiveness in treating these conditions, the group said.
C. difficile infections (CDIs) are major contributors to hospital-associated diarrhea and diarrhea caused by antibiotics. An FMT involves introducing the feces of a healthy person into the gastrointestinal tract, usually through a nasogastric tube but sometimes in capsules containing healthy stool. Serious adverse reactions associated with an FMT, such as hospitalization, are rare, occuring in roughly 2% of case, the AAP said.
An FMT “does have a place for treatment of recurrent CDIs in children,” said Maria Oliva-Hemker, MD, a pediatric gastroenterologist at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore and the lead author of the report, which was online in Pediatrics.
The AAP strongly encourages people not to perform an FMT at home, although caregivers may be tempted due to a lack of medical facilities located nearby to deliver this care.
“People might see a video on YouTube and think they can do this themselves,” Dr. Oliva-Hemker said.
An FMT requires screening of donors for any infections, which involves administering questionnaires and analyzing donor blood and stool, which are tasks better suited for medical facilities than for a living room.
No controlled or prospective clinical trials on the efficacy of FMT for children exist, according to the AAP. But a retrospective study published in 2020 showed that one or two courses of FMT prevented CDI recurrence in children 87% of the time. Researchers defined the eradication of CDIs as no recurrence for at least 2 months after an FMT and noted the success rates in children were comaparable to those reported in adults.
Unlike pediatric data, adult data come from a randomized clinical trial.
“Sometimes, kids are the last people to be enrolled in these trials,” said Maribeth Nicholson, MD, MPH, a pediatric gastroenterologist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn., an author of the 2020 study.
Dr. Nicholson, who was not involved in the AAP report, said that the retrospective data are strong enough to justify using FMT to eradicate CDIs in children. But researchers are unclear about the biologic mechanisms that make FMTs work.
Dr. Nicholson said that many therapeutics meant to produce a healthier microbiome are being studied in clinical trials. Any clinical trials of such products should include children, Dr. Nicholson said. A child’s gastrointestinal microbiome is actively developing, Dr. Nicholson added, compared with the relatively stable microbiome of an adult.
“When we think about the microbiome it makes sense to target kids, because they’re more apt to respond to these therapies. I worry that somebody will say ‘this doesn’t work in adults,’ and it just stops there,” Dr. Nicholson said.
Though the AAP said that the benefits of FMT for treating CDIs are clear, the data available for treating other conditions such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease are less convincing. Any child receiving an FMT for these ailments should only do so as part of a clinical trial, the group said.
The AAP report endorses a joint position paper, published in 2019, about the benefits of FMTs for CDIs from North American and European pediatric gastroenterology societies. Dr. Nicholson was an author of this joint statement and hopes that the AAP report raises further awareness among pediatricians that FMTs are a safe and effective treatment for recurrent CDIs.
“This is something that maybe is not as discussed in pediatric circles. Kids need FMTs sometimes,” Dr. Nicholson said.
Dr. Oliva-Hemker and Dr. Nicholson report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PEDIATRICS
New at-home test approved for chlamydia and gonorrhea
Called Simple 2, it’s the first test approved by the Food and Drug Administration that uses a sample collected at home to test for an STD, other than tests for HIV. The test can be purchased over-the-counter in stores or ordered online and delivered in discreet packaging. A vaginal swab or urine sample is collected and then sent for laboratory testing using a prepaid shipping label.
The FDA issued the final needed approval on Nov. 15, and the product is already for sale on the website of the manufacturer, LetsGetChecked. The listed price is $99 with free shipping for a single test kit, and the site offers a discounted subscription to receive a kit every 3 months for $69.30 per kit.
Gonorrhea cases have surged 28% since 2017, reaching 700,000 cases during 2021, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data show. Chlamydia has also been on the rise, up 4% from 2020 to 2021, with 1.6 million annual infections.
Previously, tests for the two STDs required that samples be taken at a health care location such as a doctor’s office. The Simple 2 test results can be retrieved online, and a health care provider will reach out to people whose tests are positive or invalid. Results are typically received in 2-5 days, according to a press release from LetsGetChecked, which also offers treatment services.
“This authorization marks an important public health milestone, giving patients more information about their health from the privacy of their own home,” said Jeff Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, in a statement. “We are eager to continue supporting greater consumer access to diagnostic tests, which helps further our goal of bringing more health care into the home.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Called Simple 2, it’s the first test approved by the Food and Drug Administration that uses a sample collected at home to test for an STD, other than tests for HIV. The test can be purchased over-the-counter in stores or ordered online and delivered in discreet packaging. A vaginal swab or urine sample is collected and then sent for laboratory testing using a prepaid shipping label.
The FDA issued the final needed approval on Nov. 15, and the product is already for sale on the website of the manufacturer, LetsGetChecked. The listed price is $99 with free shipping for a single test kit, and the site offers a discounted subscription to receive a kit every 3 months for $69.30 per kit.
Gonorrhea cases have surged 28% since 2017, reaching 700,000 cases during 2021, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data show. Chlamydia has also been on the rise, up 4% from 2020 to 2021, with 1.6 million annual infections.
Previously, tests for the two STDs required that samples be taken at a health care location such as a doctor’s office. The Simple 2 test results can be retrieved online, and a health care provider will reach out to people whose tests are positive or invalid. Results are typically received in 2-5 days, according to a press release from LetsGetChecked, which also offers treatment services.
“This authorization marks an important public health milestone, giving patients more information about their health from the privacy of their own home,” said Jeff Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, in a statement. “We are eager to continue supporting greater consumer access to diagnostic tests, which helps further our goal of bringing more health care into the home.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Called Simple 2, it’s the first test approved by the Food and Drug Administration that uses a sample collected at home to test for an STD, other than tests for HIV. The test can be purchased over-the-counter in stores or ordered online and delivered in discreet packaging. A vaginal swab or urine sample is collected and then sent for laboratory testing using a prepaid shipping label.
The FDA issued the final needed approval on Nov. 15, and the product is already for sale on the website of the manufacturer, LetsGetChecked. The listed price is $99 with free shipping for a single test kit, and the site offers a discounted subscription to receive a kit every 3 months for $69.30 per kit.
Gonorrhea cases have surged 28% since 2017, reaching 700,000 cases during 2021, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data show. Chlamydia has also been on the rise, up 4% from 2020 to 2021, with 1.6 million annual infections.
Previously, tests for the two STDs required that samples be taken at a health care location such as a doctor’s office. The Simple 2 test results can be retrieved online, and a health care provider will reach out to people whose tests are positive or invalid. Results are typically received in 2-5 days, according to a press release from LetsGetChecked, which also offers treatment services.
“This authorization marks an important public health milestone, giving patients more information about their health from the privacy of their own home,” said Jeff Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, in a statement. “We are eager to continue supporting greater consumer access to diagnostic tests, which helps further our goal of bringing more health care into the home.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Breast implants used in double lung transplant post infection
An innovative surgical procedure combining breast implants and an artificial lung may help more patients with severe lung disease survive to receive transplants. The case was described in a press conference sponsored by Northwestern University, Evanston, Ill.
In May 2023, a surgical team at Northwestern removed both infected lungs from David “Davey” Bauer, aged 34 years, and temporarily used breast implants to hold his heart in place until new lungs were available.
In April 2023, Mr. Bauer, a longtime smoker and vaper, experienced shortness of breath. His girlfriend, Susan Gore, took him to an urgent care center, and he returned home, but “the next morning he couldn’t walk,” Ms. Gore said in the press conference. A trip to the ED yielded a diagnosis of influenza A, followed rapidly by a bacterial lung infection that proved resistant to antibiotics. Mr. Bauer had no prior medical history of serious illness, but he was soon in an intensive care unit. His condition continued to decline, and a double lung transplant was his only option.
The Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute specializes in challenging cases, and Mr. Bauer was transferred there.
Back from the brink
Mr. Bauer made the transfer to Chicago despite being critically ill. He was in dire need of a lung transplant, and the only way to resolve his infection was to remove the lungs, said Ankit Bharat, MD, chief of thoracic surgery and director of Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute, in the press conference.
“Something needed to be done right away,” Dr. Bharat said. Mr. Bauer’s lungs were removed and the chest cavity was extensively debrided to remove the infection.
Then it was time for outside-the-box thinking. “With the lungs taken out, we needed something to support the heart,” he said. Breast implants came to mind, and double Ds were the largest available.
In addition, the surgeons created an artificial lung system of conduits to keep Mr. Bauer’s blood pumping. “We wanted to maintain the natural blood flow in the body that would be present if the lungs were there,” Dr. Bharat explained.
Plastic surgeons at Northwestern gave Mr. Bauer’s surgical team “a crash course” in managing the breast implants, Dr. Bharat said. The team anticipated that their novel surgical solution would need to last for weeks, but Mr. Bauer’s condition improved immediately once the infected lungs were removed. He was placed on a double-lung transplant list, and the team received an offer of new lungs within 24 hours.
The breast implants were removed, the new lungs were implanted, and Bauer spent several months in the ICU before his discharge to rehabilitation therapy at the end of September, according to a Northwestern press release.
This type of procedure could help patients with infections who need transplants but are too sick to undergo them, Dr. Bharat said in the press conference. In Mr. Bauer’s case, “a lot of stars aligned,” including Bauer’s rapid improvement and the quick availability of a perfect lung match, Dr. Bharat said. Many patients don’t survive to the point of transplant.
“We were surprised how quickly he recovered once we removed the infected lungs,” Dr. Bharat noted. The quick recovery may be in part because of Bauer’s youth and relative good health, but “this was uncharted territory.”
Mr. Bauer’s case is the first use of this particular surgical technique, although the team drew on lessons learned in other surgical settings, such as removal of both lungs to prevent cross-contamination in patients with cancer, he added.
Causes and effects
As for the factors that contributed to Mr. Bauer’s initial infection, “there is a lot we don’t know, but we can try to put things together,” said Dr. Bharat. Just as many factors lined up to promote Mr. Bauer’s recovery, many factors lined up to cause the problem, including long-standing smoking and vaping. Although some still view vaping as a safer alternative to smoking, patient data and experiences do not support this claim. “We know for a fact that both of them cause harm,” he added.
Mr. Bauer started smoking cigarettes at age 21 and typically smoked a pack of cigarettes each day before switching to vaping in 2014. In addition, Mr. Bauer had not been vaccinated against the flu, and his flu infection was followed by a bacterial infection.
Bacterial infections followed by hospitalizations are not new as an effect of vaping; a series of articles described the ongoing epidemic of e-cigarette or vaping product use–associated lung injury (EVALI). Patients with EVALI often present at urgent care centers, as Bauer did, with symptoms of flu or pneumonia, and they are often given medication and sent home.
Looking ahead: “We expect that Davey will fully recover and live a normal life,” although he will remain in Chicago for another year for monitoring, said Rade Tomic, MD, pulmonologist and medical director of the Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute lung transplant program, in the press conference.
Mr. Bauer expressed his thanks to the surgical team, who also presented him with another gift: a T-shirt with his newly chosen nickname, “DD Davey.” “I feel so blessed, I got a second chance at life,” Mr. Bauer said in the press conference. “You should not inhale anything into your lungs except oxygen.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An innovative surgical procedure combining breast implants and an artificial lung may help more patients with severe lung disease survive to receive transplants. The case was described in a press conference sponsored by Northwestern University, Evanston, Ill.
In May 2023, a surgical team at Northwestern removed both infected lungs from David “Davey” Bauer, aged 34 years, and temporarily used breast implants to hold his heart in place until new lungs were available.
In April 2023, Mr. Bauer, a longtime smoker and vaper, experienced shortness of breath. His girlfriend, Susan Gore, took him to an urgent care center, and he returned home, but “the next morning he couldn’t walk,” Ms. Gore said in the press conference. A trip to the ED yielded a diagnosis of influenza A, followed rapidly by a bacterial lung infection that proved resistant to antibiotics. Mr. Bauer had no prior medical history of serious illness, but he was soon in an intensive care unit. His condition continued to decline, and a double lung transplant was his only option.

The Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute specializes in challenging cases, and Mr. Bauer was transferred there.
Back from the brink
Mr. Bauer made the transfer to Chicago despite being critically ill. He was in dire need of a lung transplant, and the only way to resolve his infection was to remove the lungs, said Ankit Bharat, MD, chief of thoracic surgery and director of Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute, in the press conference.
“Something needed to be done right away,” Dr. Bharat said. Mr. Bauer’s lungs were removed and the chest cavity was extensively debrided to remove the infection.
Then it was time for outside-the-box thinking. “With the lungs taken out, we needed something to support the heart,” he said. Breast implants came to mind, and double Ds were the largest available.
In addition, the surgeons created an artificial lung system of conduits to keep Mr. Bauer’s blood pumping. “We wanted to maintain the natural blood flow in the body that would be present if the lungs were there,” Dr. Bharat explained.
Plastic surgeons at Northwestern gave Mr. Bauer’s surgical team “a crash course” in managing the breast implants, Dr. Bharat said. The team anticipated that their novel surgical solution would need to last for weeks, but Mr. Bauer’s condition improved immediately once the infected lungs were removed. He was placed on a double-lung transplant list, and the team received an offer of new lungs within 24 hours.
The breast implants were removed, the new lungs were implanted, and Bauer spent several months in the ICU before his discharge to rehabilitation therapy at the end of September, according to a Northwestern press release.
This type of procedure could help patients with infections who need transplants but are too sick to undergo them, Dr. Bharat said in the press conference. In Mr. Bauer’s case, “a lot of stars aligned,” including Bauer’s rapid improvement and the quick availability of a perfect lung match, Dr. Bharat said. Many patients don’t survive to the point of transplant.
“We were surprised how quickly he recovered once we removed the infected lungs,” Dr. Bharat noted. The quick recovery may be in part because of Bauer’s youth and relative good health, but “this was uncharted territory.”
Mr. Bauer’s case is the first use of this particular surgical technique, although the team drew on lessons learned in other surgical settings, such as removal of both lungs to prevent cross-contamination in patients with cancer, he added.
Causes and effects
As for the factors that contributed to Mr. Bauer’s initial infection, “there is a lot we don’t know, but we can try to put things together,” said Dr. Bharat. Just as many factors lined up to promote Mr. Bauer’s recovery, many factors lined up to cause the problem, including long-standing smoking and vaping. Although some still view vaping as a safer alternative to smoking, patient data and experiences do not support this claim. “We know for a fact that both of them cause harm,” he added.
Mr. Bauer started smoking cigarettes at age 21 and typically smoked a pack of cigarettes each day before switching to vaping in 2014. In addition, Mr. Bauer had not been vaccinated against the flu, and his flu infection was followed by a bacterial infection.
Bacterial infections followed by hospitalizations are not new as an effect of vaping; a series of articles described the ongoing epidemic of e-cigarette or vaping product use–associated lung injury (EVALI). Patients with EVALI often present at urgent care centers, as Bauer did, with symptoms of flu or pneumonia, and they are often given medication and sent home.
Looking ahead: “We expect that Davey will fully recover and live a normal life,” although he will remain in Chicago for another year for monitoring, said Rade Tomic, MD, pulmonologist and medical director of the Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute lung transplant program, in the press conference.
Mr. Bauer expressed his thanks to the surgical team, who also presented him with another gift: a T-shirt with his newly chosen nickname, “DD Davey.” “I feel so blessed, I got a second chance at life,” Mr. Bauer said in the press conference. “You should not inhale anything into your lungs except oxygen.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An innovative surgical procedure combining breast implants and an artificial lung may help more patients with severe lung disease survive to receive transplants. The case was described in a press conference sponsored by Northwestern University, Evanston, Ill.
In May 2023, a surgical team at Northwestern removed both infected lungs from David “Davey” Bauer, aged 34 years, and temporarily used breast implants to hold his heart in place until new lungs were available.
In April 2023, Mr. Bauer, a longtime smoker and vaper, experienced shortness of breath. His girlfriend, Susan Gore, took him to an urgent care center, and he returned home, but “the next morning he couldn’t walk,” Ms. Gore said in the press conference. A trip to the ED yielded a diagnosis of influenza A, followed rapidly by a bacterial lung infection that proved resistant to antibiotics. Mr. Bauer had no prior medical history of serious illness, but he was soon in an intensive care unit. His condition continued to decline, and a double lung transplant was his only option.

The Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute specializes in challenging cases, and Mr. Bauer was transferred there.
Back from the brink
Mr. Bauer made the transfer to Chicago despite being critically ill. He was in dire need of a lung transplant, and the only way to resolve his infection was to remove the lungs, said Ankit Bharat, MD, chief of thoracic surgery and director of Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute, in the press conference.
“Something needed to be done right away,” Dr. Bharat said. Mr. Bauer’s lungs were removed and the chest cavity was extensively debrided to remove the infection.
Then it was time for outside-the-box thinking. “With the lungs taken out, we needed something to support the heart,” he said. Breast implants came to mind, and double Ds were the largest available.
In addition, the surgeons created an artificial lung system of conduits to keep Mr. Bauer’s blood pumping. “We wanted to maintain the natural blood flow in the body that would be present if the lungs were there,” Dr. Bharat explained.
Plastic surgeons at Northwestern gave Mr. Bauer’s surgical team “a crash course” in managing the breast implants, Dr. Bharat said. The team anticipated that their novel surgical solution would need to last for weeks, but Mr. Bauer’s condition improved immediately once the infected lungs were removed. He was placed on a double-lung transplant list, and the team received an offer of new lungs within 24 hours.
The breast implants were removed, the new lungs were implanted, and Bauer spent several months in the ICU before his discharge to rehabilitation therapy at the end of September, according to a Northwestern press release.
This type of procedure could help patients with infections who need transplants but are too sick to undergo them, Dr. Bharat said in the press conference. In Mr. Bauer’s case, “a lot of stars aligned,” including Bauer’s rapid improvement and the quick availability of a perfect lung match, Dr. Bharat said. Many patients don’t survive to the point of transplant.
“We were surprised how quickly he recovered once we removed the infected lungs,” Dr. Bharat noted. The quick recovery may be in part because of Bauer’s youth and relative good health, but “this was uncharted territory.”
Mr. Bauer’s case is the first use of this particular surgical technique, although the team drew on lessons learned in other surgical settings, such as removal of both lungs to prevent cross-contamination in patients with cancer, he added.
Causes and effects
As for the factors that contributed to Mr. Bauer’s initial infection, “there is a lot we don’t know, but we can try to put things together,” said Dr. Bharat. Just as many factors lined up to promote Mr. Bauer’s recovery, many factors lined up to cause the problem, including long-standing smoking and vaping. Although some still view vaping as a safer alternative to smoking, patient data and experiences do not support this claim. “We know for a fact that both of them cause harm,” he added.
Mr. Bauer started smoking cigarettes at age 21 and typically smoked a pack of cigarettes each day before switching to vaping in 2014. In addition, Mr. Bauer had not been vaccinated against the flu, and his flu infection was followed by a bacterial infection.
Bacterial infections followed by hospitalizations are not new as an effect of vaping; a series of articles described the ongoing epidemic of e-cigarette or vaping product use–associated lung injury (EVALI). Patients with EVALI often present at urgent care centers, as Bauer did, with symptoms of flu or pneumonia, and they are often given medication and sent home.
Looking ahead: “We expect that Davey will fully recover and live a normal life,” although he will remain in Chicago for another year for monitoring, said Rade Tomic, MD, pulmonologist and medical director of the Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute lung transplant program, in the press conference.
Mr. Bauer expressed his thanks to the surgical team, who also presented him with another gift: a T-shirt with his newly chosen nickname, “DD Davey.” “I feel so blessed, I got a second chance at life,” Mr. Bauer said in the press conference. “You should not inhale anything into your lungs except oxygen.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.