User login
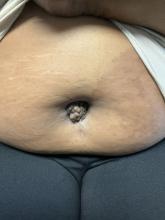
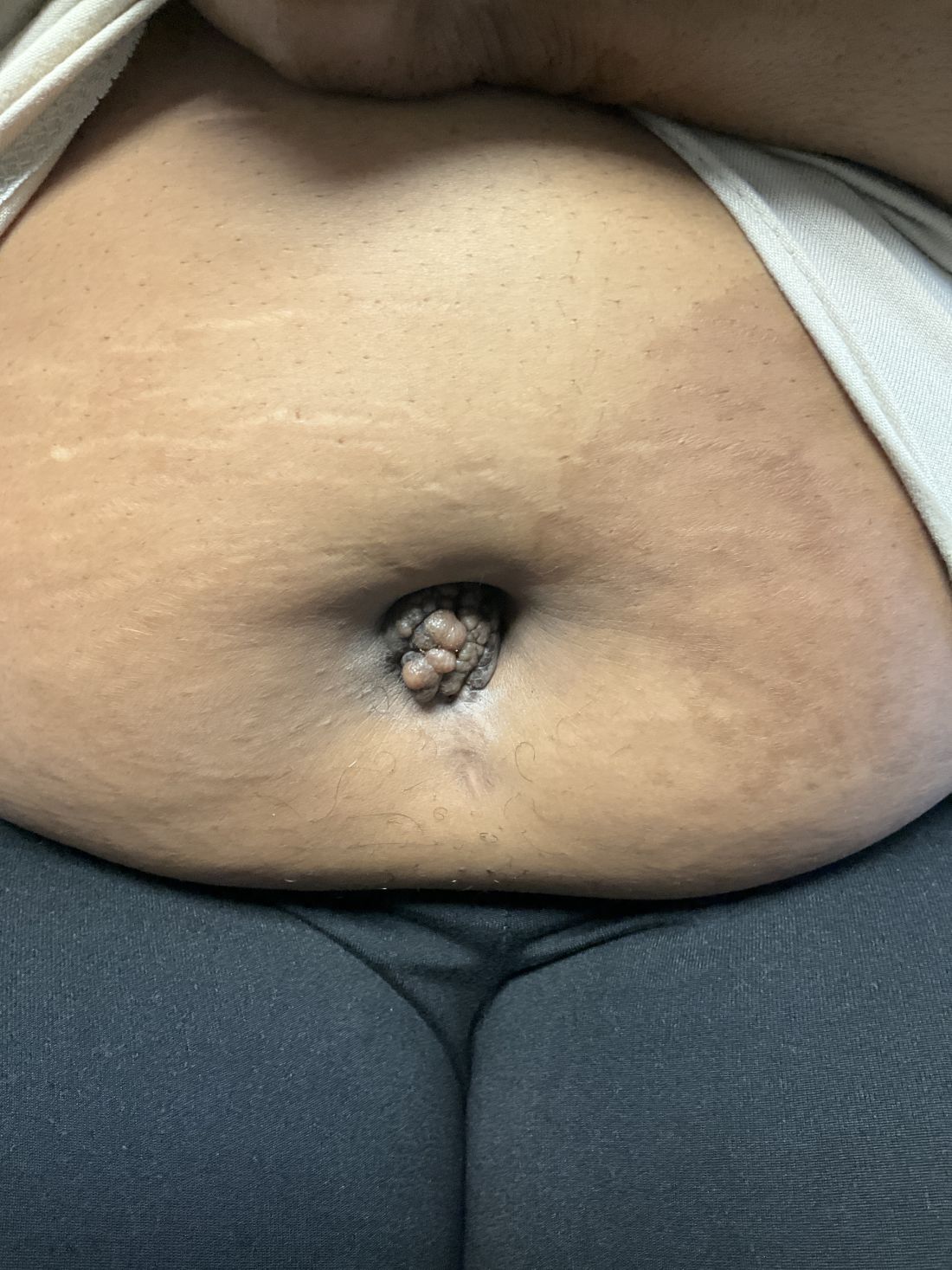
A 27-year-old Haitian woman presented with a painful umbilical mass which had been growing in size for 5 months
Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside of the uterine cavity, commonly occurring in women of reproductive age. The condition usually affects the adnexa (ovaries, Fallopian tubes, and associated ligaments and connective tissue) but can also be seen in extrapelvic structures.
Cutaneous endometriosis is an uncommon subtype that accounts for 1% of endometriosis cases and occurs when endometrial tissue is found on the surface of the skin. It is divided into primary and secondary cutaneous endometriosis. The that may lead to seeding of endometrial tissue on the skin. In the case of our patient, it appears that her laparoscopic procedure 2 years ago was the cause of endometrial seeding in the umbilicus.
Clinically, the condition may present with a palpable mass, cyclic pain, and bloody discharge from the affected area. Due to the rarity of cutaneous endometriosis, it may be hard to distinguish from other diagnoses such as keloids, dermatofibromas, hernias, or cutaneous metastasis of cancers (Sister Mary Joseph nodules).
The definitive diagnosis can be made by biopsy and histopathological assessment showing a mixture of endometrial glands and stromal tissue. Imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are helpful in excluding more common diagnoses such as hernia or cutaneous metastasis. In this patient, the mass was surgically excised. Histopathological assessment established the diagnosis of cutaneous endometriosis.
Treatment options include surgical excision and medical therapy. Medical therapy entails the use of hormonal agents such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, danazol (a pituitary gonadotropin inhibitor), and oral contraceptives, which reduce the cyclical proliferation of endothelial tissue. These agents can be used preoperatively to reduce the size of the cutaneous mass before surgical excision, or as an alternative treatment for patients who wish to avoid surgery. The rate of recurrence is observed to be higher with medical therapy rather than surgical treatment.
The case and photo were submitted by Mina Ahmed, MBBS, Brooke Resh Sateesh MD, and Nathan Uebelhoer MD, of San Diego Family Dermatology, San Diego, California. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Gonzalez RH et al. Am J Case Rep. 2021;22:e932493-1–e932493-4.
2. Raffi L et al. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019 Dec;5(5):384-386.
3. Sharma A, Apostol R. Cutaneous endometriosis. Treasure Island, Fla: Statpearls Publishing, 2023.
Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside of the uterine cavity, commonly occurring in women of reproductive age. The condition usually affects the adnexa (ovaries, Fallopian tubes, and associated ligaments and connective tissue) but can also be seen in extrapelvic structures.
Cutaneous endometriosis is an uncommon subtype that accounts for 1% of endometriosis cases and occurs when endometrial tissue is found on the surface of the skin. It is divided into primary and secondary cutaneous endometriosis. The that may lead to seeding of endometrial tissue on the skin. In the case of our patient, it appears that her laparoscopic procedure 2 years ago was the cause of endometrial seeding in the umbilicus.
Clinically, the condition may present with a palpable mass, cyclic pain, and bloody discharge from the affected area. Due to the rarity of cutaneous endometriosis, it may be hard to distinguish from other diagnoses such as keloids, dermatofibromas, hernias, or cutaneous metastasis of cancers (Sister Mary Joseph nodules).
The definitive diagnosis can be made by biopsy and histopathological assessment showing a mixture of endometrial glands and stromal tissue. Imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are helpful in excluding more common diagnoses such as hernia or cutaneous metastasis. In this patient, the mass was surgically excised. Histopathological assessment established the diagnosis of cutaneous endometriosis.
Treatment options include surgical excision and medical therapy. Medical therapy entails the use of hormonal agents such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, danazol (a pituitary gonadotropin inhibitor), and oral contraceptives, which reduce the cyclical proliferation of endothelial tissue. These agents can be used preoperatively to reduce the size of the cutaneous mass before surgical excision, or as an alternative treatment for patients who wish to avoid surgery. The rate of recurrence is observed to be higher with medical therapy rather than surgical treatment.
The case and photo were submitted by Mina Ahmed, MBBS, Brooke Resh Sateesh MD, and Nathan Uebelhoer MD, of San Diego Family Dermatology, San Diego, California. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Gonzalez RH et al. Am J Case Rep. 2021;22:e932493-1–e932493-4.
2. Raffi L et al. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019 Dec;5(5):384-386.
3. Sharma A, Apostol R. Cutaneous endometriosis. Treasure Island, Fla: Statpearls Publishing, 2023.
Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside of the uterine cavity, commonly occurring in women of reproductive age. The condition usually affects the adnexa (ovaries, Fallopian tubes, and associated ligaments and connective tissue) but can also be seen in extrapelvic structures.
Cutaneous endometriosis is an uncommon subtype that accounts for 1% of endometriosis cases and occurs when endometrial tissue is found on the surface of the skin. It is divided into primary and secondary cutaneous endometriosis. The that may lead to seeding of endometrial tissue on the skin. In the case of our patient, it appears that her laparoscopic procedure 2 years ago was the cause of endometrial seeding in the umbilicus.
Clinically, the condition may present with a palpable mass, cyclic pain, and bloody discharge from the affected area. Due to the rarity of cutaneous endometriosis, it may be hard to distinguish from other diagnoses such as keloids, dermatofibromas, hernias, or cutaneous metastasis of cancers (Sister Mary Joseph nodules).
The definitive diagnosis can be made by biopsy and histopathological assessment showing a mixture of endometrial glands and stromal tissue. Imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are helpful in excluding more common diagnoses such as hernia or cutaneous metastasis. In this patient, the mass was surgically excised. Histopathological assessment established the diagnosis of cutaneous endometriosis.
Treatment options include surgical excision and medical therapy. Medical therapy entails the use of hormonal agents such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, danazol (a pituitary gonadotropin inhibitor), and oral contraceptives, which reduce the cyclical proliferation of endothelial tissue. These agents can be used preoperatively to reduce the size of the cutaneous mass before surgical excision, or as an alternative treatment for patients who wish to avoid surgery. The rate of recurrence is observed to be higher with medical therapy rather than surgical treatment.
The case and photo were submitted by Mina Ahmed, MBBS, Brooke Resh Sateesh MD, and Nathan Uebelhoer MD, of San Diego Family Dermatology, San Diego, California. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Gonzalez RH et al. Am J Case Rep. 2021;22:e932493-1–e932493-4.
2. Raffi L et al. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019 Dec;5(5):384-386.
3. Sharma A, Apostol R. Cutaneous endometriosis. Treasure Island, Fla: Statpearls Publishing, 2023.
Study Identifies Cardiovascular Comorbidities Associated With Dermatomyositis
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- DM is associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD), but US-based data studies on CVD comorbidities in patients with DM are lacking.
- In a cross-sectional analysis of participants in the All of Us research program aged 18 years and older with at least 1 year of electronic health record (EHR) data, researchers identified DM cases and controls with nearest neighbor propensity score matching by age, sex, race/ethnicity, EHR duration, and healthcare visit quantity.
- They used the Pearson’s chi-squared test, Fisher’s exact test, unpaired t-test, or Mann-Whitney U test to compare clinical characteristics and traditional CV comorbidities.
- Multivariable conditional logistic regression was used with backward elimination of comorbidities with P > .1 or evidence of collinearity.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among 235,161 All of Us participants, researchers identified 206 DM cases and 824 matched controls with largely similar demographic characteristics, including smoking status, obesity, and indicators of socioeconomic status.
- Participants with DM were more likely to have a history of atrial fibrillation (10.1% vs 16.0%, respectively), chronic kidney disease (15.2% vs 29.1%), congestive heart failure (9.6% vs 18.0%), coronary artery disease (CAD) (18.2% vs 34.0%), hypertension (52.5% vs 60.7%), myocardial infarction (7.4% vs 15.0), type 2 diabetes (27.3% vs 47.6%), and valvular heart disease (8.7% vs 16.5%) than matched controls.
- In a multivariable analysis that adjusted for potential confounders, three comorbidities remained associated with DM: CAD (odds ratio [OR], 2.0; P < .001), type 2 diabetes (OR, 2.2; P < .001), and chronic kidney disease (OR, 1.7; P = .015).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings are important both for prognosis and clinical care, suggesting DM patients should be screened for CVD risk factors to potentially reduce the increased risk for cardiovascular events and CVD-related mortality in DM,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
Corresponding author Alisa N. Femia, MD, of the department of dermatology at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, led the research. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
How DM treatments might influence CVD development was not addressed. EHRs may have diagnostic inaccuracies and omissions and lack data on clinical features and severity.
DISCLOSURES:
The project was supported by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Institutes of Health. Dr. Femia reported consulting fees from Octagon Therapeutics, Timber Pharmaceuticals, and Guidepoint. Study author Michael S. Garshick, MD, reported consulting fees from AbbVie and Horizon Therapeutics. The remaining authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- DM is associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD), but US-based data studies on CVD comorbidities in patients with DM are lacking.
- In a cross-sectional analysis of participants in the All of Us research program aged 18 years and older with at least 1 year of electronic health record (EHR) data, researchers identified DM cases and controls with nearest neighbor propensity score matching by age, sex, race/ethnicity, EHR duration, and healthcare visit quantity.
- They used the Pearson’s chi-squared test, Fisher’s exact test, unpaired t-test, or Mann-Whitney U test to compare clinical characteristics and traditional CV comorbidities.
- Multivariable conditional logistic regression was used with backward elimination of comorbidities with P > .1 or evidence of collinearity.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among 235,161 All of Us participants, researchers identified 206 DM cases and 824 matched controls with largely similar demographic characteristics, including smoking status, obesity, and indicators of socioeconomic status.
- Participants with DM were more likely to have a history of atrial fibrillation (10.1% vs 16.0%, respectively), chronic kidney disease (15.2% vs 29.1%), congestive heart failure (9.6% vs 18.0%), coronary artery disease (CAD) (18.2% vs 34.0%), hypertension (52.5% vs 60.7%), myocardial infarction (7.4% vs 15.0), type 2 diabetes (27.3% vs 47.6%), and valvular heart disease (8.7% vs 16.5%) than matched controls.
- In a multivariable analysis that adjusted for potential confounders, three comorbidities remained associated with DM: CAD (odds ratio [OR], 2.0; P < .001), type 2 diabetes (OR, 2.2; P < .001), and chronic kidney disease (OR, 1.7; P = .015).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings are important both for prognosis and clinical care, suggesting DM patients should be screened for CVD risk factors to potentially reduce the increased risk for cardiovascular events and CVD-related mortality in DM,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
Corresponding author Alisa N. Femia, MD, of the department of dermatology at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, led the research. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
How DM treatments might influence CVD development was not addressed. EHRs may have diagnostic inaccuracies and omissions and lack data on clinical features and severity.
DISCLOSURES:
The project was supported by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Institutes of Health. Dr. Femia reported consulting fees from Octagon Therapeutics, Timber Pharmaceuticals, and Guidepoint. Study author Michael S. Garshick, MD, reported consulting fees from AbbVie and Horizon Therapeutics. The remaining authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- DM is associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD), but US-based data studies on CVD comorbidities in patients with DM are lacking.
- In a cross-sectional analysis of participants in the All of Us research program aged 18 years and older with at least 1 year of electronic health record (EHR) data, researchers identified DM cases and controls with nearest neighbor propensity score matching by age, sex, race/ethnicity, EHR duration, and healthcare visit quantity.
- They used the Pearson’s chi-squared test, Fisher’s exact test, unpaired t-test, or Mann-Whitney U test to compare clinical characteristics and traditional CV comorbidities.
- Multivariable conditional logistic regression was used with backward elimination of comorbidities with P > .1 or evidence of collinearity.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among 235,161 All of Us participants, researchers identified 206 DM cases and 824 matched controls with largely similar demographic characteristics, including smoking status, obesity, and indicators of socioeconomic status.
- Participants with DM were more likely to have a history of atrial fibrillation (10.1% vs 16.0%, respectively), chronic kidney disease (15.2% vs 29.1%), congestive heart failure (9.6% vs 18.0%), coronary artery disease (CAD) (18.2% vs 34.0%), hypertension (52.5% vs 60.7%), myocardial infarction (7.4% vs 15.0), type 2 diabetes (27.3% vs 47.6%), and valvular heart disease (8.7% vs 16.5%) than matched controls.
- In a multivariable analysis that adjusted for potential confounders, three comorbidities remained associated with DM: CAD (odds ratio [OR], 2.0; P < .001), type 2 diabetes (OR, 2.2; P < .001), and chronic kidney disease (OR, 1.7; P = .015).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings are important both for prognosis and clinical care, suggesting DM patients should be screened for CVD risk factors to potentially reduce the increased risk for cardiovascular events and CVD-related mortality in DM,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
Corresponding author Alisa N. Femia, MD, of the department of dermatology at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, led the research. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
How DM treatments might influence CVD development was not addressed. EHRs may have diagnostic inaccuracies and omissions and lack data on clinical features and severity.
DISCLOSURES:
The project was supported by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Institutes of Health. Dr. Femia reported consulting fees from Octagon Therapeutics, Timber Pharmaceuticals, and Guidepoint. Study author Michael S. Garshick, MD, reported consulting fees from AbbVie and Horizon Therapeutics. The remaining authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA Gives Nod to Berdazimer Gel for Molluscum Contagiosum
On January 5, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved berdazimer gel 10.3% for the treatment of molluscum contagiosum (MC) in adults and children aged 1 year or older.
Approval of berdazimer, a topical nitric oxide–releasing agent, was based largely on a 12-week pivotal phase 3 trial known as B-SIMPLE4, in which 891 patients with a mean age of 6.6 years (range, 0.9-47.5 years) were randomly assigned to treatment with berdazimer gel 10.3% or a vehicle gel applied in a thin layer to all lesions once daily. At 12 weeks, 32.4% of patients in the berdazimer group achieved complete clearance of MC lesions compared with 19.7% of those in the vehicle group (P < .001).
Only 4.1% of patients on berdazimer and 0.7% of those on the vehicle experienced adverse events that led to discontinuation of treatment. The most common adverse events in both groups were application-site pain and erythema, and most of these were mild or moderate.
According to a press release announcing the approval from Ligand Pharmaceuticals, which acquired berdazimer topical gel from Novan in September 2023, the development makes berdazimer topical gel 10.3% the first and only topical prescription medication that can be applied by patients, parents, or caregivers at home; outside of a physician›s office; or outside of other medical settings to treat MC. Nitric oxide has been shown to have antiviral effects, although the mechanism of action of berdazimer for treating molluscum “is unknown,” the company said in the release.
The drug will be marketed under the name Zelsuvmi and is expected to be available in the second half of 2024.
On July 21, 2023, topical cantharidin became the first approved treatment of MC for adults and pediatric patients aged 2 years or older, with the FDA approval of a drug-device combination (Ycanth) that contains a formulation of cantharidin solution 0.7% and is administered by healthcare professionals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
On January 5, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved berdazimer gel 10.3% for the treatment of molluscum contagiosum (MC) in adults and children aged 1 year or older.
Approval of berdazimer, a topical nitric oxide–releasing agent, was based largely on a 12-week pivotal phase 3 trial known as B-SIMPLE4, in which 891 patients with a mean age of 6.6 years (range, 0.9-47.5 years) were randomly assigned to treatment with berdazimer gel 10.3% or a vehicle gel applied in a thin layer to all lesions once daily. At 12 weeks, 32.4% of patients in the berdazimer group achieved complete clearance of MC lesions compared with 19.7% of those in the vehicle group (P < .001).
Only 4.1% of patients on berdazimer and 0.7% of those on the vehicle experienced adverse events that led to discontinuation of treatment. The most common adverse events in both groups were application-site pain and erythema, and most of these were mild or moderate.
According to a press release announcing the approval from Ligand Pharmaceuticals, which acquired berdazimer topical gel from Novan in September 2023, the development makes berdazimer topical gel 10.3% the first and only topical prescription medication that can be applied by patients, parents, or caregivers at home; outside of a physician›s office; or outside of other medical settings to treat MC. Nitric oxide has been shown to have antiviral effects, although the mechanism of action of berdazimer for treating molluscum “is unknown,” the company said in the release.
The drug will be marketed under the name Zelsuvmi and is expected to be available in the second half of 2024.
On July 21, 2023, topical cantharidin became the first approved treatment of MC for adults and pediatric patients aged 2 years or older, with the FDA approval of a drug-device combination (Ycanth) that contains a formulation of cantharidin solution 0.7% and is administered by healthcare professionals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
On January 5, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved berdazimer gel 10.3% for the treatment of molluscum contagiosum (MC) in adults and children aged 1 year or older.
Approval of berdazimer, a topical nitric oxide–releasing agent, was based largely on a 12-week pivotal phase 3 trial known as B-SIMPLE4, in which 891 patients with a mean age of 6.6 years (range, 0.9-47.5 years) were randomly assigned to treatment with berdazimer gel 10.3% or a vehicle gel applied in a thin layer to all lesions once daily. At 12 weeks, 32.4% of patients in the berdazimer group achieved complete clearance of MC lesions compared with 19.7% of those in the vehicle group (P < .001).
Only 4.1% of patients on berdazimer and 0.7% of those on the vehicle experienced adverse events that led to discontinuation of treatment. The most common adverse events in both groups were application-site pain and erythema, and most of these were mild or moderate.
According to a press release announcing the approval from Ligand Pharmaceuticals, which acquired berdazimer topical gel from Novan in September 2023, the development makes berdazimer topical gel 10.3% the first and only topical prescription medication that can be applied by patients, parents, or caregivers at home; outside of a physician›s office; or outside of other medical settings to treat MC. Nitric oxide has been shown to have antiviral effects, although the mechanism of action of berdazimer for treating molluscum “is unknown,” the company said in the release.
The drug will be marketed under the name Zelsuvmi and is expected to be available in the second half of 2024.
On July 21, 2023, topical cantharidin became the first approved treatment of MC for adults and pediatric patients aged 2 years or older, with the FDA approval of a drug-device combination (Ycanth) that contains a formulation of cantharidin solution 0.7% and is administered by healthcare professionals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
US Dermatologic Drug Approvals Rose Between 2012 and 2022
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Only five new drugs for diseases treated mostly by dermatologists were approved by the FDA between 1999 and 2009.
- In a cross-sectional analysis to characterize the frequency and degree of innovation of dermatologic drugs approved more recently, researchers identified new and supplemental dermatologic drugs approved between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2022, from FDA lists, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services CenterWatch, and peer-reviewed articles.
- They used five proxy measures to estimate each drug’s degree of innovation: FDA designation (first in class, advance in class, or addition to class), independent clinical usefulness ratings, and benefit ratings by health technology assessment organizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- The study authors identified 52 new drug applications and 26 supplemental new indications approved by the FDA for dermatologic indications between 2012 and 2022.
- Of the 52 new drugs, the researchers categorized 11 (21%) as first in class and 13 (25%) as first in indication.
- An analysis of benefit ratings available for 38 of the drugs showed that 15 (39%) were rated as being clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
- Of the 10 supplemental new indications with ratings by any organization, 3 (30%) were rated as clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
IN PRACTICE:
While innovative drug development in dermatology may have increased, “these findings also highlight opportunities to develop more truly innovative dermatologic agents, particularly for diseases with unmet therapeutic need,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Samir Kamat, MD, of the Medical Education Department at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, and corresponding author Ravi Gupta, MD, MSHP, of the Internal Medicine Division at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, led the research. The study was published online as a research letter on December 20, 2023, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
They include the use of individual indications to assess clinical usefulness and benefit ratings. Many drugs, particularly supplemental indications, lacked such ratings. Reformulations of already marketed drugs or indications were not included.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Kamat and Dr. Gupta had no relevant disclosures. Three coauthors reported having received financial support outside of the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Only five new drugs for diseases treated mostly by dermatologists were approved by the FDA between 1999 and 2009.
- In a cross-sectional analysis to characterize the frequency and degree of innovation of dermatologic drugs approved more recently, researchers identified new and supplemental dermatologic drugs approved between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2022, from FDA lists, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services CenterWatch, and peer-reviewed articles.
- They used five proxy measures to estimate each drug’s degree of innovation: FDA designation (first in class, advance in class, or addition to class), independent clinical usefulness ratings, and benefit ratings by health technology assessment organizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- The study authors identified 52 new drug applications and 26 supplemental new indications approved by the FDA for dermatologic indications between 2012 and 2022.
- Of the 52 new drugs, the researchers categorized 11 (21%) as first in class and 13 (25%) as first in indication.
- An analysis of benefit ratings available for 38 of the drugs showed that 15 (39%) were rated as being clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
- Of the 10 supplemental new indications with ratings by any organization, 3 (30%) were rated as clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
IN PRACTICE:
While innovative drug development in dermatology may have increased, “these findings also highlight opportunities to develop more truly innovative dermatologic agents, particularly for diseases with unmet therapeutic need,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Samir Kamat, MD, of the Medical Education Department at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, and corresponding author Ravi Gupta, MD, MSHP, of the Internal Medicine Division at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, led the research. The study was published online as a research letter on December 20, 2023, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
They include the use of individual indications to assess clinical usefulness and benefit ratings. Many drugs, particularly supplemental indications, lacked such ratings. Reformulations of already marketed drugs or indications were not included.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Kamat and Dr. Gupta had no relevant disclosures. Three coauthors reported having received financial support outside of the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Only five new drugs for diseases treated mostly by dermatologists were approved by the FDA between 1999 and 2009.
- In a cross-sectional analysis to characterize the frequency and degree of innovation of dermatologic drugs approved more recently, researchers identified new and supplemental dermatologic drugs approved between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2022, from FDA lists, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services CenterWatch, and peer-reviewed articles.
- They used five proxy measures to estimate each drug’s degree of innovation: FDA designation (first in class, advance in class, or addition to class), independent clinical usefulness ratings, and benefit ratings by health technology assessment organizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- The study authors identified 52 new drug applications and 26 supplemental new indications approved by the FDA for dermatologic indications between 2012 and 2022.
- Of the 52 new drugs, the researchers categorized 11 (21%) as first in class and 13 (25%) as first in indication.
- An analysis of benefit ratings available for 38 of the drugs showed that 15 (39%) were rated as being clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
- Of the 10 supplemental new indications with ratings by any organization, 3 (30%) were rated as clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
IN PRACTICE:
While innovative drug development in dermatology may have increased, “these findings also highlight opportunities to develop more truly innovative dermatologic agents, particularly for diseases with unmet therapeutic need,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Samir Kamat, MD, of the Medical Education Department at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, and corresponding author Ravi Gupta, MD, MSHP, of the Internal Medicine Division at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, led the research. The study was published online as a research letter on December 20, 2023, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
They include the use of individual indications to assess clinical usefulness and benefit ratings. Many drugs, particularly supplemental indications, lacked such ratings. Reformulations of already marketed drugs or indications were not included.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Kamat and Dr. Gupta had no relevant disclosures. Three coauthors reported having received financial support outside of the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
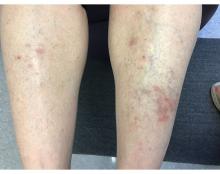
A 55-year-old female presented a with few years' history of pruritic plaques on her shins and wrists
. Lesions may have a covering of scale. HLP commonly affects middle aged men and women. Lesions are most commonly located bilaterally on the shins and ankles and can be painful or pruritic. The differential diagnosis for the condition includes lichen simplex chronicus, connective tissue disease, and other skin disorders that cause hyperkeratosis. This wide differential makes histopathological analysis a useful tool in confirming the diagnosis of HLP.
A definitive diagnosis can be made via skin biopsy. Histopathology reveals hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and a band-like lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis. An eosinophilic infiltrate may be present. Other common features include saw tooth rete ridges and Civatte bodies, which are apoptotic keratinocytes. The lymphocytic infiltrate may indicate an autoimmune etiology in which the body’s immune system erroneously attacks itself. However, the exact cause is not known and genetic and environmental factors may play a role.
The treatment of HLP includes symptomatic management and control of inflammation. Topical steroids can be prescribed to manage the inflammation and associated pruritus, and emollient creams and moisturizers are helpful in controlling the dryness. Oral steroids, immunosuppressant medications, or retinoids may be necessary in more severe cases. In addition, psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA) light therapy has been found to be beneficial in some cases. Squamous cell carcinoma may arise in lesions.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Donna Bilu Martin, MD; Premier Dermatology, MD, Aventura, Florida. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Arnold DL, Krishnamurthy K. Lichen Planus. [Updated 2023 Jun 1]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526126/
Jaime TJ et al. An Bras Dermatol. 2011 Jul-Aug;86(4 Suppl 1):S96-9.
Mirchandani S et al. Med Pharm Rep. 2020 Apr;93(2):210-2. .
Whittington CP et al. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2023 Jun 19. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2022-0515-RA.
. Lesions may have a covering of scale. HLP commonly affects middle aged men and women. Lesions are most commonly located bilaterally on the shins and ankles and can be painful or pruritic. The differential diagnosis for the condition includes lichen simplex chronicus, connective tissue disease, and other skin disorders that cause hyperkeratosis. This wide differential makes histopathological analysis a useful tool in confirming the diagnosis of HLP.
A definitive diagnosis can be made via skin biopsy. Histopathology reveals hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and a band-like lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis. An eosinophilic infiltrate may be present. Other common features include saw tooth rete ridges and Civatte bodies, which are apoptotic keratinocytes. The lymphocytic infiltrate may indicate an autoimmune etiology in which the body’s immune system erroneously attacks itself. However, the exact cause is not known and genetic and environmental factors may play a role.
The treatment of HLP includes symptomatic management and control of inflammation. Topical steroids can be prescribed to manage the inflammation and associated pruritus, and emollient creams and moisturizers are helpful in controlling the dryness. Oral steroids, immunosuppressant medications, or retinoids may be necessary in more severe cases. In addition, psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA) light therapy has been found to be beneficial in some cases. Squamous cell carcinoma may arise in lesions.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Donna Bilu Martin, MD; Premier Dermatology, MD, Aventura, Florida. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Arnold DL, Krishnamurthy K. Lichen Planus. [Updated 2023 Jun 1]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526126/
Jaime TJ et al. An Bras Dermatol. 2011 Jul-Aug;86(4 Suppl 1):S96-9.
Mirchandani S et al. Med Pharm Rep. 2020 Apr;93(2):210-2. .
Whittington CP et al. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2023 Jun 19. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2022-0515-RA.
. Lesions may have a covering of scale. HLP commonly affects middle aged men and women. Lesions are most commonly located bilaterally on the shins and ankles and can be painful or pruritic. The differential diagnosis for the condition includes lichen simplex chronicus, connective tissue disease, and other skin disorders that cause hyperkeratosis. This wide differential makes histopathological analysis a useful tool in confirming the diagnosis of HLP.
A definitive diagnosis can be made via skin biopsy. Histopathology reveals hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and a band-like lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis. An eosinophilic infiltrate may be present. Other common features include saw tooth rete ridges and Civatte bodies, which are apoptotic keratinocytes. The lymphocytic infiltrate may indicate an autoimmune etiology in which the body’s immune system erroneously attacks itself. However, the exact cause is not known and genetic and environmental factors may play a role.
The treatment of HLP includes symptomatic management and control of inflammation. Topical steroids can be prescribed to manage the inflammation and associated pruritus, and emollient creams and moisturizers are helpful in controlling the dryness. Oral steroids, immunosuppressant medications, or retinoids may be necessary in more severe cases. In addition, psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA) light therapy has been found to be beneficial in some cases. Squamous cell carcinoma may arise in lesions.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Donna Bilu Martin, MD; Premier Dermatology, MD, Aventura, Florida. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Arnold DL, Krishnamurthy K. Lichen Planus. [Updated 2023 Jun 1]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526126/
Jaime TJ et al. An Bras Dermatol. 2011 Jul-Aug;86(4 Suppl 1):S96-9.
Mirchandani S et al. Med Pharm Rep. 2020 Apr;93(2):210-2. .
Whittington CP et al. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2023 Jun 19. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2022-0515-RA.
Tape strips detect hidradenitis suppurativa biomarkers, novel study shows
, results from a novel study showed.
“Tape strips can provide important clues to when and which drugs to use in HS in patients with both early and late disease, which can change clinical practice,” corresponding study author Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, professor and chair of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, said in an interview. “It is noninvasive and nonscarring,” she added.
Tape stripping has been validated in atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and other dermatologic conditions in recent years. For the current study, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, and is believed to be the first of its kind, Dr. Guttman-Yassky and colleagues performed RNA sequencing from large D-Squame tape strips collected from lesional and nonlesional skin of 22 patients with HS and from 21 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. They correlated the expression of skin biomarkers between tape strips and a previously published gene-signature of HS biopsies. The mean age of patients with HS was 43 years, while the mean age of healthy controls was 35. The average International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System (IHS4) score of the HS cohort was 36.
Consistent with published studies, the researchers found that tape strips identified an overall higher inflammatory burden in HS. Specifically, they observed an upregulation of known cytokines within the following pathways: Th1 (such as IFNG, CXCL9/10/11, and CCR5); Th17 (such as interleukin [IL]-17A/F, IL12B, IL23A, CAMP, and CCL20); Th2 (such as IL4R, IL13/IL31/IL10, CCR4, CCL7/CCL13/CCL24, TNFSF4/OX40L, and TNFRSF4/OX40); and Th22 (such as IL22 and IL32).
The researchers also found that the expression of Th17 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha pathways were highly correlated between tape strips and biopsies and that HS clinical severity was significantly associated with expression of biomarkers, such as TNF-alpha, IL17A/F, OX40, JAK1-3, and IL4R in HS lesional and/or nonlesional skin.
“It was quite unexpected that we are able to identify, using a minimally invasive approach that samples only the upper layers of the epidermis, products and processes that are considered to be deeper-situated, such as IL-17, and other immune markers,” Dr. Guttman-Yassky said in the interview. “We were also surprised to see how well the tape-stripped–derived skin molecular profile correlated with that of biopsies, as well as how well it correlated with the clinical disease severity of HS.”
Also surprising, she added, was that the biomarkers in nonlesional tape-stripped skin, such as IL-17 and TNF alpha, “show high correlations with disease severity and provide clues to early disease.”
If using tape strips in HS is validated in larger cohort studies, the potential cost implications of using this approach in practice remain unclear, Dr. Guttman-Yassky said. “It is currently not cheap, but we are hoping that one day, we can provide a means to diagnose the disease and treat it early, and appropriately, utilizing this approach,” she commented. “We are excited about the applicability of this study to the early treatment and longitudinal follow up of HS with drugs that are targeting specific immune molecules and pathways,” she said, adding that it will also be useful for helping determine which drug should be used for which patient.
She and her co-authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its small sample size and the fact that tape stripping is limited to the epidermis.
Asked to comment on the study, Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, a dermatologist who directs the HS clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said the findings “have important potential implications for our ability to one day personalize treatments for a patient with early HS in a minimally invasive way.”
As the study authors point out, she added, “tape strips only allow sampling of the epidermis, which is limiting in a disease like HS where much of the disruption is in the dermis with deep nodules and dermal tunnels. However, our overall goal should be to catch patients in the early stages of their disease before the occurrence of irreversible tissue damage such as dermal tunnels. Thus, the ongoing campaign for early diagnosis and early intervention by various stakeholders in the field of HS can help mitigate the impact of this inherent limitation of tape strips. It will be exciting to see larger studies that investigate tape strip results in relation to clinical phenotypes, disease progression, and therapeutic responses.”
The study was funded by an International Dermatology Outcome Measures Hidradenitis Suppurativa Grant. Dr. Guttman-Yassky disclosed that she has been a consultant to, an adviser for, and has received research grants from many pharmaceutical companies. Of the remaining authors, 2 also had multiple disclosures and 11 had no disclosures. Dr. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of the board of directors for the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation. She has also served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Novartis, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie; and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte.
, results from a novel study showed.
“Tape strips can provide important clues to when and which drugs to use in HS in patients with both early and late disease, which can change clinical practice,” corresponding study author Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, professor and chair of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, said in an interview. “It is noninvasive and nonscarring,” she added.
Tape stripping has been validated in atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and other dermatologic conditions in recent years. For the current study, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, and is believed to be the first of its kind, Dr. Guttman-Yassky and colleagues performed RNA sequencing from large D-Squame tape strips collected from lesional and nonlesional skin of 22 patients with HS and from 21 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. They correlated the expression of skin biomarkers between tape strips and a previously published gene-signature of HS biopsies. The mean age of patients with HS was 43 years, while the mean age of healthy controls was 35. The average International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System (IHS4) score of the HS cohort was 36.
Consistent with published studies, the researchers found that tape strips identified an overall higher inflammatory burden in HS. Specifically, they observed an upregulation of known cytokines within the following pathways: Th1 (such as IFNG, CXCL9/10/11, and CCR5); Th17 (such as interleukin [IL]-17A/F, IL12B, IL23A, CAMP, and CCL20); Th2 (such as IL4R, IL13/IL31/IL10, CCR4, CCL7/CCL13/CCL24, TNFSF4/OX40L, and TNFRSF4/OX40); and Th22 (such as IL22 and IL32).
The researchers also found that the expression of Th17 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha pathways were highly correlated between tape strips and biopsies and that HS clinical severity was significantly associated with expression of biomarkers, such as TNF-alpha, IL17A/F, OX40, JAK1-3, and IL4R in HS lesional and/or nonlesional skin.
“It was quite unexpected that we are able to identify, using a minimally invasive approach that samples only the upper layers of the epidermis, products and processes that are considered to be deeper-situated, such as IL-17, and other immune markers,” Dr. Guttman-Yassky said in the interview. “We were also surprised to see how well the tape-stripped–derived skin molecular profile correlated with that of biopsies, as well as how well it correlated with the clinical disease severity of HS.”
Also surprising, she added, was that the biomarkers in nonlesional tape-stripped skin, such as IL-17 and TNF alpha, “show high correlations with disease severity and provide clues to early disease.”
If using tape strips in HS is validated in larger cohort studies, the potential cost implications of using this approach in practice remain unclear, Dr. Guttman-Yassky said. “It is currently not cheap, but we are hoping that one day, we can provide a means to diagnose the disease and treat it early, and appropriately, utilizing this approach,” she commented. “We are excited about the applicability of this study to the early treatment and longitudinal follow up of HS with drugs that are targeting specific immune molecules and pathways,” she said, adding that it will also be useful for helping determine which drug should be used for which patient.
She and her co-authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its small sample size and the fact that tape stripping is limited to the epidermis.
Asked to comment on the study, Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, a dermatologist who directs the HS clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said the findings “have important potential implications for our ability to one day personalize treatments for a patient with early HS in a minimally invasive way.”
As the study authors point out, she added, “tape strips only allow sampling of the epidermis, which is limiting in a disease like HS where much of the disruption is in the dermis with deep nodules and dermal tunnels. However, our overall goal should be to catch patients in the early stages of their disease before the occurrence of irreversible tissue damage such as dermal tunnels. Thus, the ongoing campaign for early diagnosis and early intervention by various stakeholders in the field of HS can help mitigate the impact of this inherent limitation of tape strips. It will be exciting to see larger studies that investigate tape strip results in relation to clinical phenotypes, disease progression, and therapeutic responses.”
The study was funded by an International Dermatology Outcome Measures Hidradenitis Suppurativa Grant. Dr. Guttman-Yassky disclosed that she has been a consultant to, an adviser for, and has received research grants from many pharmaceutical companies. Of the remaining authors, 2 also had multiple disclosures and 11 had no disclosures. Dr. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of the board of directors for the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation. She has also served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Novartis, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie; and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte.
, results from a novel study showed.
“Tape strips can provide important clues to when and which drugs to use in HS in patients with both early and late disease, which can change clinical practice,” corresponding study author Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, professor and chair of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, said in an interview. “It is noninvasive and nonscarring,” she added.
Tape stripping has been validated in atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and other dermatologic conditions in recent years. For the current study, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, and is believed to be the first of its kind, Dr. Guttman-Yassky and colleagues performed RNA sequencing from large D-Squame tape strips collected from lesional and nonlesional skin of 22 patients with HS and from 21 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. They correlated the expression of skin biomarkers between tape strips and a previously published gene-signature of HS biopsies. The mean age of patients with HS was 43 years, while the mean age of healthy controls was 35. The average International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System (IHS4) score of the HS cohort was 36.
Consistent with published studies, the researchers found that tape strips identified an overall higher inflammatory burden in HS. Specifically, they observed an upregulation of known cytokines within the following pathways: Th1 (such as IFNG, CXCL9/10/11, and CCR5); Th17 (such as interleukin [IL]-17A/F, IL12B, IL23A, CAMP, and CCL20); Th2 (such as IL4R, IL13/IL31/IL10, CCR4, CCL7/CCL13/CCL24, TNFSF4/OX40L, and TNFRSF4/OX40); and Th22 (such as IL22 and IL32).
The researchers also found that the expression of Th17 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha pathways were highly correlated between tape strips and biopsies and that HS clinical severity was significantly associated with expression of biomarkers, such as TNF-alpha, IL17A/F, OX40, JAK1-3, and IL4R in HS lesional and/or nonlesional skin.
“It was quite unexpected that we are able to identify, using a minimally invasive approach that samples only the upper layers of the epidermis, products and processes that are considered to be deeper-situated, such as IL-17, and other immune markers,” Dr. Guttman-Yassky said in the interview. “We were also surprised to see how well the tape-stripped–derived skin molecular profile correlated with that of biopsies, as well as how well it correlated with the clinical disease severity of HS.”
Also surprising, she added, was that the biomarkers in nonlesional tape-stripped skin, such as IL-17 and TNF alpha, “show high correlations with disease severity and provide clues to early disease.”
If using tape strips in HS is validated in larger cohort studies, the potential cost implications of using this approach in practice remain unclear, Dr. Guttman-Yassky said. “It is currently not cheap, but we are hoping that one day, we can provide a means to diagnose the disease and treat it early, and appropriately, utilizing this approach,” she commented. “We are excited about the applicability of this study to the early treatment and longitudinal follow up of HS with drugs that are targeting specific immune molecules and pathways,” she said, adding that it will also be useful for helping determine which drug should be used for which patient.
She and her co-authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its small sample size and the fact that tape stripping is limited to the epidermis.
Asked to comment on the study, Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, a dermatologist who directs the HS clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said the findings “have important potential implications for our ability to one day personalize treatments for a patient with early HS in a minimally invasive way.”
As the study authors point out, she added, “tape strips only allow sampling of the epidermis, which is limiting in a disease like HS where much of the disruption is in the dermis with deep nodules and dermal tunnels. However, our overall goal should be to catch patients in the early stages of their disease before the occurrence of irreversible tissue damage such as dermal tunnels. Thus, the ongoing campaign for early diagnosis and early intervention by various stakeholders in the field of HS can help mitigate the impact of this inherent limitation of tape strips. It will be exciting to see larger studies that investigate tape strip results in relation to clinical phenotypes, disease progression, and therapeutic responses.”
The study was funded by an International Dermatology Outcome Measures Hidradenitis Suppurativa Grant. Dr. Guttman-Yassky disclosed that she has been a consultant to, an adviser for, and has received research grants from many pharmaceutical companies. Of the remaining authors, 2 also had multiple disclosures and 11 had no disclosures. Dr. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of the board of directors for the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation. She has also served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Novartis, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie; and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Combined rituximab and omalizumab promising for refractory bullous pemphigoid
who do not respond to rituximab alone, results of a case series suggest.
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is a rare, chronic, inflammatory, blistering disease that mainly occurs in people in their 50s through their 70s. BP has high morbidity and mortality, especially in people with comorbidities common to the elderly, yet no Food and Drug Administration–approved therapies for BP exist, Stephanie T. Le, MD, a dermatologist in the department of dermatology of the University of California, Davis, told this publication.
“BP is typically thought of as an IgG-mediated disease, but many BP patients also have elevated levels of total circulating IgE levels, which has been linked to hallmarks of bullous pemphigoid, including blisters,” Dr. Le said. “These findings suggest that ideal BP treatments, such as rituximab and omalizumab, should target both IgG and IgE.”
In a study published in JAMA Dermatology, Dr. Le and her coauthors analyzed the electronic medical record data of adult patients with BP who were treated with combined rituximab and omalizumab at UC Davis between 2015 and 2022. The 10 patients who met their selection criteria averaged 62 years of age. Most were female, and most were non-Hispanic White. All had severe BP, with an initial mean BP Disease Area index score of 170, and all applied whole-body topical corticosteroid for treatment.
All participants received 1000 mg intravenous rituximab on days 0 and 15. In addition to rituximab, seven patients received subcutaneous high-dose omalizumab (300 mg every 2 weeks); and three patients received low-dose omalizumab (300 mg every 4 weeks or 150 mg every 2 weeks).
After a mean of 2.1 months, all patients in the high-dose omalizumab-plus-rituximab group had achieved complete remission. By contrast, all patients in the low-dose omalizumab-plus-rituximab group improved after a mean of 13 months, and none achieved complete remission.
At 3 months, all study participants were rated as being very much improved. All four patients in the high-dose omalizumab group who tapered omalizumab dosage or frequency had flare-ups within 1-3 months that resolved when they restarted the medication. Among patients who achieved complete remission, 4 of 7 required rituximab redosing between 6 and 16 months later. Rituximab alone did not achieve remission: Three patients needed to add high-dose omalizumab. All reported adverse effects were mild.
Alternatives to Corticosteroids Are Needed
For BP, “with no FDA-approved therapies available, corticosteroids remain first line for acute flares. However, prolonged corticosteroid use is associated with multiple adverse effects, including increased susceptibility to infection, osteoporosis, and diabetes mellitus,” Dr. Le pointed out. “Patients with BP who are treated with high-dose corticosteroids have significantly increased mortality and have very poor 1-year survival.
“Rituximab and omalizumab dual therapy offers another potential treatment option for severe or treatment-refractory BP,” she added. “We are hopeful that other physicians will adopt this therapy.”
The authors acknowledged limitations of the study, including its retrospective design, small sample size, lack of standardized intervals between rituximab and omalizumab, and variation in concurrent therapies, and they recommended further related research.
No conflicts of interest were reported. No funding details were provided.
who do not respond to rituximab alone, results of a case series suggest.
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is a rare, chronic, inflammatory, blistering disease that mainly occurs in people in their 50s through their 70s. BP has high morbidity and mortality, especially in people with comorbidities common to the elderly, yet no Food and Drug Administration–approved therapies for BP exist, Stephanie T. Le, MD, a dermatologist in the department of dermatology of the University of California, Davis, told this publication.
“BP is typically thought of as an IgG-mediated disease, but many BP patients also have elevated levels of total circulating IgE levels, which has been linked to hallmarks of bullous pemphigoid, including blisters,” Dr. Le said. “These findings suggest that ideal BP treatments, such as rituximab and omalizumab, should target both IgG and IgE.”
In a study published in JAMA Dermatology, Dr. Le and her coauthors analyzed the electronic medical record data of adult patients with BP who were treated with combined rituximab and omalizumab at UC Davis between 2015 and 2022. The 10 patients who met their selection criteria averaged 62 years of age. Most were female, and most were non-Hispanic White. All had severe BP, with an initial mean BP Disease Area index score of 170, and all applied whole-body topical corticosteroid for treatment.
All participants received 1000 mg intravenous rituximab on days 0 and 15. In addition to rituximab, seven patients received subcutaneous high-dose omalizumab (300 mg every 2 weeks); and three patients received low-dose omalizumab (300 mg every 4 weeks or 150 mg every 2 weeks).
After a mean of 2.1 months, all patients in the high-dose omalizumab-plus-rituximab group had achieved complete remission. By contrast, all patients in the low-dose omalizumab-plus-rituximab group improved after a mean of 13 months, and none achieved complete remission.
At 3 months, all study participants were rated as being very much improved. All four patients in the high-dose omalizumab group who tapered omalizumab dosage or frequency had flare-ups within 1-3 months that resolved when they restarted the medication. Among patients who achieved complete remission, 4 of 7 required rituximab redosing between 6 and 16 months later. Rituximab alone did not achieve remission: Three patients needed to add high-dose omalizumab. All reported adverse effects were mild.
Alternatives to Corticosteroids Are Needed
For BP, “with no FDA-approved therapies available, corticosteroids remain first line for acute flares. However, prolonged corticosteroid use is associated with multiple adverse effects, including increased susceptibility to infection, osteoporosis, and diabetes mellitus,” Dr. Le pointed out. “Patients with BP who are treated with high-dose corticosteroids have significantly increased mortality and have very poor 1-year survival.
“Rituximab and omalizumab dual therapy offers another potential treatment option for severe or treatment-refractory BP,” she added. “We are hopeful that other physicians will adopt this therapy.”
The authors acknowledged limitations of the study, including its retrospective design, small sample size, lack of standardized intervals between rituximab and omalizumab, and variation in concurrent therapies, and they recommended further related research.
No conflicts of interest were reported. No funding details were provided.
who do not respond to rituximab alone, results of a case series suggest.
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is a rare, chronic, inflammatory, blistering disease that mainly occurs in people in their 50s through their 70s. BP has high morbidity and mortality, especially in people with comorbidities common to the elderly, yet no Food and Drug Administration–approved therapies for BP exist, Stephanie T. Le, MD, a dermatologist in the department of dermatology of the University of California, Davis, told this publication.
“BP is typically thought of as an IgG-mediated disease, but many BP patients also have elevated levels of total circulating IgE levels, which has been linked to hallmarks of bullous pemphigoid, including blisters,” Dr. Le said. “These findings suggest that ideal BP treatments, such as rituximab and omalizumab, should target both IgG and IgE.”
In a study published in JAMA Dermatology, Dr. Le and her coauthors analyzed the electronic medical record data of adult patients with BP who were treated with combined rituximab and omalizumab at UC Davis between 2015 and 2022. The 10 patients who met their selection criteria averaged 62 years of age. Most were female, and most were non-Hispanic White. All had severe BP, with an initial mean BP Disease Area index score of 170, and all applied whole-body topical corticosteroid for treatment.
All participants received 1000 mg intravenous rituximab on days 0 and 15. In addition to rituximab, seven patients received subcutaneous high-dose omalizumab (300 mg every 2 weeks); and three patients received low-dose omalizumab (300 mg every 4 weeks or 150 mg every 2 weeks).
After a mean of 2.1 months, all patients in the high-dose omalizumab-plus-rituximab group had achieved complete remission. By contrast, all patients in the low-dose omalizumab-plus-rituximab group improved after a mean of 13 months, and none achieved complete remission.
At 3 months, all study participants were rated as being very much improved. All four patients in the high-dose omalizumab group who tapered omalizumab dosage or frequency had flare-ups within 1-3 months that resolved when they restarted the medication. Among patients who achieved complete remission, 4 of 7 required rituximab redosing between 6 and 16 months later. Rituximab alone did not achieve remission: Three patients needed to add high-dose omalizumab. All reported adverse effects were mild.
Alternatives to Corticosteroids Are Needed
For BP, “with no FDA-approved therapies available, corticosteroids remain first line for acute flares. However, prolonged corticosteroid use is associated with multiple adverse effects, including increased susceptibility to infection, osteoporosis, and diabetes mellitus,” Dr. Le pointed out. “Patients with BP who are treated with high-dose corticosteroids have significantly increased mortality and have very poor 1-year survival.
“Rituximab and omalizumab dual therapy offers another potential treatment option for severe or treatment-refractory BP,” she added. “We are hopeful that other physicians will adopt this therapy.”
The authors acknowledged limitations of the study, including its retrospective design, small sample size, lack of standardized intervals between rituximab and omalizumab, and variation in concurrent therapies, and they recommended further related research.
No conflicts of interest were reported. No funding details were provided.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
New consensus guide on rare drug hypersensitivity reaction
TOPLINE:
).
METHODOLOGY:
Data on the evaluation, assessment, and treatment of the rare but potentially life-threatening drug hypersensitivity reaction are lacking.
To support clinicians in diagnosing and managing DRESS, a steering committee conducted a literature review to examine current research, identify evidence, and develop consensus statements. They invited experts from 21 countries across four continents to participate in a Delphi consensus process.
An international panel of 54 experts (including 45 dermatologists) initially assessed 100 statements related to baseline workup, severity of the condition, and treatment. Two more statements were added in the second round.
After revisions and the second round, the group reached consensus for 93 statements overall.
TAKEAWAY:
The statements generating the most disagreement involved diagnosis. The group ultimately supported the value of measuring the viral load of Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, and human herpesvirus 6 in all patients with suspected DRESS. The group also agreed on screening for hepatitis A, B, and C in cases of liver involvement and screening for hepatitis B and C before starting systemic therapy.
The group agreed with previous severity criteria that differentiate between mild, moderate, and severe DRESS based on the extent of liver, kidney, and blood involvement and the damage of other organs.
Consensus on treatment was reached for all 12 relevant statements in the first Delphi round. Recommendations included the use of corticosteroids and immediate discontinuation of the drugs causing the reaction.
IN PRACTICE:
“This Delphi exercise aimed to provide a common ground of consensus,” the authors noted. However, “each of the addressed categories needs more in-depth follow-up studies to improve the clinical management of patients.”
SOURCE:
The DRESS Delphi consensus group conducted its exercise under the leadership of Marie-Charlotte Brüggen, MD, of the University Hospital of Zürich. The consensus was published online in the JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Published evidence was limited because of the low prevalence of DRESS. The consensus statements should therefore be considered with caution and in the context of a clinician’s expertise and available resources. Research gaps also persist in how DRESS may vary with region and ethnicity. The severity thresholds need validation in a revised multicenter statement.
DISCLOSURES:
The consensus review received no outside funding. Dr. Brüggen disclosed relationships with the Swiss National Science Foundation, Christine Kühne – Center for Allergy Research and Education, FreeNovation, LEO Foundation, Olga Mayenfisch Foundation, University of Zürich, LEO Pharma, Pierre Fabre Eczema Foundation, Eli Lilly, AbbVie, GSK, and AstraZeneca. Coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies, foundations, and medical publishing companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
).
METHODOLOGY:
Data on the evaluation, assessment, and treatment of the rare but potentially life-threatening drug hypersensitivity reaction are lacking.
To support clinicians in diagnosing and managing DRESS, a steering committee conducted a literature review to examine current research, identify evidence, and develop consensus statements. They invited experts from 21 countries across four continents to participate in a Delphi consensus process.
An international panel of 54 experts (including 45 dermatologists) initially assessed 100 statements related to baseline workup, severity of the condition, and treatment. Two more statements were added in the second round.
After revisions and the second round, the group reached consensus for 93 statements overall.
TAKEAWAY:
The statements generating the most disagreement involved diagnosis. The group ultimately supported the value of measuring the viral load of Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, and human herpesvirus 6 in all patients with suspected DRESS. The group also agreed on screening for hepatitis A, B, and C in cases of liver involvement and screening for hepatitis B and C before starting systemic therapy.
The group agreed with previous severity criteria that differentiate between mild, moderate, and severe DRESS based on the extent of liver, kidney, and blood involvement and the damage of other organs.
Consensus on treatment was reached for all 12 relevant statements in the first Delphi round. Recommendations included the use of corticosteroids and immediate discontinuation of the drugs causing the reaction.
IN PRACTICE:
“This Delphi exercise aimed to provide a common ground of consensus,” the authors noted. However, “each of the addressed categories needs more in-depth follow-up studies to improve the clinical management of patients.”
SOURCE:
The DRESS Delphi consensus group conducted its exercise under the leadership of Marie-Charlotte Brüggen, MD, of the University Hospital of Zürich. The consensus was published online in the JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Published evidence was limited because of the low prevalence of DRESS. The consensus statements should therefore be considered with caution and in the context of a clinician’s expertise and available resources. Research gaps also persist in how DRESS may vary with region and ethnicity. The severity thresholds need validation in a revised multicenter statement.
DISCLOSURES:
The consensus review received no outside funding. Dr. Brüggen disclosed relationships with the Swiss National Science Foundation, Christine Kühne – Center for Allergy Research and Education, FreeNovation, LEO Foundation, Olga Mayenfisch Foundation, University of Zürich, LEO Pharma, Pierre Fabre Eczema Foundation, Eli Lilly, AbbVie, GSK, and AstraZeneca. Coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies, foundations, and medical publishing companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
).
METHODOLOGY:
Data on the evaluation, assessment, and treatment of the rare but potentially life-threatening drug hypersensitivity reaction are lacking.
To support clinicians in diagnosing and managing DRESS, a steering committee conducted a literature review to examine current research, identify evidence, and develop consensus statements. They invited experts from 21 countries across four continents to participate in a Delphi consensus process.
An international panel of 54 experts (including 45 dermatologists) initially assessed 100 statements related to baseline workup, severity of the condition, and treatment. Two more statements were added in the second round.
After revisions and the second round, the group reached consensus for 93 statements overall.
TAKEAWAY:
The statements generating the most disagreement involved diagnosis. The group ultimately supported the value of measuring the viral load of Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, and human herpesvirus 6 in all patients with suspected DRESS. The group also agreed on screening for hepatitis A, B, and C in cases of liver involvement and screening for hepatitis B and C before starting systemic therapy.
The group agreed with previous severity criteria that differentiate between mild, moderate, and severe DRESS based on the extent of liver, kidney, and blood involvement and the damage of other organs.
Consensus on treatment was reached for all 12 relevant statements in the first Delphi round. Recommendations included the use of corticosteroids and immediate discontinuation of the drugs causing the reaction.
IN PRACTICE:
“This Delphi exercise aimed to provide a common ground of consensus,” the authors noted. However, “each of the addressed categories needs more in-depth follow-up studies to improve the clinical management of patients.”
SOURCE:
The DRESS Delphi consensus group conducted its exercise under the leadership of Marie-Charlotte Brüggen, MD, of the University Hospital of Zürich. The consensus was published online in the JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Published evidence was limited because of the low prevalence of DRESS. The consensus statements should therefore be considered with caution and in the context of a clinician’s expertise and available resources. Research gaps also persist in how DRESS may vary with region and ethnicity. The severity thresholds need validation in a revised multicenter statement.
DISCLOSURES:
The consensus review received no outside funding. Dr. Brüggen disclosed relationships with the Swiss National Science Foundation, Christine Kühne – Center for Allergy Research and Education, FreeNovation, LEO Foundation, Olga Mayenfisch Foundation, University of Zürich, LEO Pharma, Pierre Fabre Eczema Foundation, Eli Lilly, AbbVie, GSK, and AstraZeneca. Coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies, foundations, and medical publishing companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Hidradenitis suppurativa: Two anti-IL17A/F therapies yield positive results
BERLIN – In separate trials conducted in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), two biologics that inhibit the activity of interleukin-17A (IL-17A) and IL-17F were associated with highly encouraging rates of control.
One of the trials evaluated a nanobody inhibitor, sonelokimab, a molecule with a substantially smaller size than traditional monoclonal antibodies (40 kilodaltons vs. 150 kilodaltons). After 24 weeks of treatment, the most effective of the two study doses almost doubled the proportion of patients with complete resolution of draining tunnels (41.1% vs. 23.8%; P < .05) relative to placebo.
“I think the size of sonelokimab is important,” Brian Kirby, MD, a consultant dermatologist at St. Vincent’s Hospital, Dublin, said at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. “We think the smaller size results in better penetration of inflamed tissue,” he added, noting that penetration of abscesses, fistulae, and tunnels has been recognized in the past as a potential weakness of the larger monoclonal antibodies.
The other set of anti-17-A/F set of data were generated by a pooled 48-week maintenance from the BE HEARD I and II trials with bimekizumab. The 16-week data from these two trials were presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology earlier this year.
IL-17A/F trials
Both the
In the sonelokimab trial, called MIRA, 234 adults with HS were randomized in a 2:2:2:1 ratio to one of the two experimental arms, placebo, or a reference arm with the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor adalimumab. Nearly 64% had Hurley stage II HS.
The primary endpoint was a 75% or greater reduction in total abscesses and nodules with no increase in draining tunnel count (HiSCR75) from baseline. Dr. Kirby said that this is more rigorous than the HiSCR50 endpoint more commonly used in HS clinical trials. Treatments were administered every 2 weeks for the first 8 weeks of a planned follow-up of 24 weeks and then every 4 weeks thereafter.
At 16 weeks, according to the data Dr. Kirby presented, both doses of sonelokimab were more active than placebo, but Dr. Kirby reported that the lower dose performed better for most objective endpoints.
For example, the HiSCR75 was reached by 43.3% of those randomized to the 120-mg dose (P < .001 vs. placebo), 34.8% of those randomized to the 240-mg dose (P <.01), and 14.7% of those randomized to placebo.
For HiSCR50, response rates were 65.7%, 53.0%, and 27.9%, for the 120-mg, 240-mg, and placebo arms, respectively. Again, both the lower dose (P < .001) and the higher dose (P < .01) were significantly superior to placebo.
On the International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System (IHS4), which counts nodules and abscesses, score reductions were 19.3, 14.5, and 7.9 for the lower dose, higher dose, and placebo, respectively, with a greater statistical advantage for the lower relative to the higher dose over placebo (P <.001 vs. P <.01).
However, patient-focused outcomes were not necessarily greater for the lower dose. For the patient-completed measure, the Numerical Rating Scale 50% reduction in skin pain (NRS50), the proportion of patients responding at 12 weeks was numerically greater for the 240-mg dose (41.3%) than with the 120-mg dose (32.0%), although both reached the same statistical advantage (P < .001) over the 4.3% who reached this level of response on placebo.
For the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) and the Patient Global Impression of Severity (PGI-S), improvements from baseline were similar for the lower and higher dose, although there was a modest numerical and statistical advantage for the higher dose over placebo (P < .001 vs. P <.01).
The HiSCR50 (57.6%) and HiSCR75 (36.4%) responses were both lower for those randomized to the TNF inhibitor adalimumab relative to sonelokimab, but the smaller number of patients in this arm prohibited a statistical comparison.
Although oral candidiasis was more common among patients receiving either dose of sonelokimab than placebo, these were of mild to moderate severity. Dr. Kirby said that there were no unexpected safety issues, and sonelokimab was generally well tolerated.
The results are encouraging, but Dr. Kirby acknowledged that data are now needed to confirm that resolution of tunnels and fistulae is greater with a nanobody inhibitor of IL-17A/F than other targeted therapies. Even if this is validated, he said studies are needed to prove that the small relative molecule size is the reason behind the benefits.
Forty-eight–week bimekizumab data
From the pooled BE HEARD I and BE HEARD II maintenance data, the major message is that the robust responses observed at 16 weeks versus placebo were maintained at 48 weeks. More than 75% of patients retained a HiSCR50 response and more than 55% achieved a HiSCR75 response at the 48-week follow-up. The durable response was also reflected in other measures, according to Christos C. Zouboulis, MD, PhD, director of the department of dermatology, Brandenburg Medical School, Neuruppin, Germany.
“Improvements in disease severity were seen over time,” Dr. Zouboulis reported. “The majority of patients with severe HS at baseline shifted to mild to moderate disease according to the IHS4 classification.”
To the degree that both sonelokimab and bimekizumab target IL-17A/F, these data are mutually reinforcing. Dr. Kirby said that there is a sizable body of data implicating IL-17A/F in driving HS, and the activity of inhibitors in support the clinical value of IL-17A/F suppression.
On Oct. 18, shortly after the EADV meeting concluded, the Food and Drug Administration approved bimekizumab for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, the first approved indication in the United States. In the European Union, it was approved for psoriasis in 2021, and for psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis in June 2023.
Dr. Kirby has financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies, including MoonLake, which is developing sonelokimab and sponsored the MIRA trial. Dr. Christos, president of the European HS Foundation, has financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies, including UCB, which makes bimekizumab and provided funding for the BE HEARD I and II trials.
BERLIN – In separate trials conducted in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), two biologics that inhibit the activity of interleukin-17A (IL-17A) and IL-17F were associated with highly encouraging rates of control.
One of the trials evaluated a nanobody inhibitor, sonelokimab, a molecule with a substantially smaller size than traditional monoclonal antibodies (40 kilodaltons vs. 150 kilodaltons). After 24 weeks of treatment, the most effective of the two study doses almost doubled the proportion of patients with complete resolution of draining tunnels (41.1% vs. 23.8%; P < .05) relative to placebo.
“I think the size of sonelokimab is important,” Brian Kirby, MD, a consultant dermatologist at St. Vincent’s Hospital, Dublin, said at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. “We think the smaller size results in better penetration of inflamed tissue,” he added, noting that penetration of abscesses, fistulae, and tunnels has been recognized in the past as a potential weakness of the larger monoclonal antibodies.
The other set of anti-17-A/F set of data were generated by a pooled 48-week maintenance from the BE HEARD I and II trials with bimekizumab. The 16-week data from these two trials were presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology earlier this year.
IL-17A/F trials
Both the
In the sonelokimab trial, called MIRA, 234 adults with HS were randomized in a 2:2:2:1 ratio to one of the two experimental arms, placebo, or a reference arm with the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor adalimumab. Nearly 64% had Hurley stage II HS.
The primary endpoint was a 75% or greater reduction in total abscesses and nodules with no increase in draining tunnel count (HiSCR75) from baseline. Dr. Kirby said that this is more rigorous than the HiSCR50 endpoint more commonly used in HS clinical trials. Treatments were administered every 2 weeks for the first 8 weeks of a planned follow-up of 24 weeks and then every 4 weeks thereafter.
At 16 weeks, according to the data Dr. Kirby presented, both doses of sonelokimab were more active than placebo, but Dr. Kirby reported that the lower dose performed better for most objective endpoints.
For example, the HiSCR75 was reached by 43.3% of those randomized to the 120-mg dose (P < .001 vs. placebo), 34.8% of those randomized to the 240-mg dose (P <.01), and 14.7% of those randomized to placebo.
For HiSCR50, response rates were 65.7%, 53.0%, and 27.9%, for the 120-mg, 240-mg, and placebo arms, respectively. Again, both the lower dose (P < .001) and the higher dose (P < .01) were significantly superior to placebo.
On the International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System (IHS4), which counts nodules and abscesses, score reductions were 19.3, 14.5, and 7.9 for the lower dose, higher dose, and placebo, respectively, with a greater statistical advantage for the lower relative to the higher dose over placebo (P <.001 vs. P <.01).
However, patient-focused outcomes were not necessarily greater for the lower dose. For the patient-completed measure, the Numerical Rating Scale 50% reduction in skin pain (NRS50), the proportion of patients responding at 12 weeks was numerically greater for the 240-mg dose (41.3%) than with the 120-mg dose (32.0%), although both reached the same statistical advantage (P < .001) over the 4.3% who reached this level of response on placebo.
For the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) and the Patient Global Impression of Severity (PGI-S), improvements from baseline were similar for the lower and higher dose, although there was a modest numerical and statistical advantage for the higher dose over placebo (P < .001 vs. P <.01).
The HiSCR50 (57.6%) and HiSCR75 (36.4%) responses were both lower for those randomized to the TNF inhibitor adalimumab relative to sonelokimab, but the smaller number of patients in this arm prohibited a statistical comparison.
Although oral candidiasis was more common among patients receiving either dose of sonelokimab than placebo, these were of mild to moderate severity. Dr. Kirby said that there were no unexpected safety issues, and sonelokimab was generally well tolerated.
The results are encouraging, but Dr. Kirby acknowledged that data are now needed to confirm that resolution of tunnels and fistulae is greater with a nanobody inhibitor of IL-17A/F than other targeted therapies. Even if this is validated, he said studies are needed to prove that the small relative molecule size is the reason behind the benefits.
Forty-eight–week bimekizumab data
From the pooled BE HEARD I and BE HEARD II maintenance data, the major message is that the robust responses observed at 16 weeks versus placebo were maintained at 48 weeks. More than 75% of patients retained a HiSCR50 response and more than 55% achieved a HiSCR75 response at the 48-week follow-up. The durable response was also reflected in other measures, according to Christos C. Zouboulis, MD, PhD, director of the department of dermatology, Brandenburg Medical School, Neuruppin, Germany.
“Improvements in disease severity were seen over time,” Dr. Zouboulis reported. “The majority of patients with severe HS at baseline shifted to mild to moderate disease according to the IHS4 classification.”
To the degree that both sonelokimab and bimekizumab target IL-17A/F, these data are mutually reinforcing. Dr. Kirby said that there is a sizable body of data implicating IL-17A/F in driving HS, and the activity of inhibitors in support the clinical value of IL-17A/F suppression.
On Oct. 18, shortly after the EADV meeting concluded, the Food and Drug Administration approved bimekizumab for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, the first approved indication in the United States. In the European Union, it was approved for psoriasis in 2021, and for psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis in June 2023.
Dr. Kirby has financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies, including MoonLake, which is developing sonelokimab and sponsored the MIRA trial. Dr. Christos, president of the European HS Foundation, has financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies, including UCB, which makes bimekizumab and provided funding for the BE HEARD I and II trials.
BERLIN – In separate trials conducted in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), two biologics that inhibit the activity of interleukin-17A (IL-17A) and IL-17F were associated with highly encouraging rates of control.
One of the trials evaluated a nanobody inhibitor, sonelokimab, a molecule with a substantially smaller size than traditional monoclonal antibodies (40 kilodaltons vs. 150 kilodaltons). After 24 weeks of treatment, the most effective of the two study doses almost doubled the proportion of patients with complete resolution of draining tunnels (41.1% vs. 23.8%; P < .05) relative to placebo.
“I think the size of sonelokimab is important,” Brian Kirby, MD, a consultant dermatologist at St. Vincent’s Hospital, Dublin, said at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. “We think the smaller size results in better penetration of inflamed tissue,” he added, noting that penetration of abscesses, fistulae, and tunnels has been recognized in the past as a potential weakness of the larger monoclonal antibodies.
The other set of anti-17-A/F set of data were generated by a pooled 48-week maintenance from the BE HEARD I and II trials with bimekizumab. The 16-week data from these two trials were presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology earlier this year.
IL-17A/F trials
Both the
In the sonelokimab trial, called MIRA, 234 adults with HS were randomized in a 2:2:2:1 ratio to one of the two experimental arms, placebo, or a reference arm with the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor adalimumab. Nearly 64% had Hurley stage II HS.
The primary endpoint was a 75% or greater reduction in total abscesses and nodules with no increase in draining tunnel count (HiSCR75) from baseline. Dr. Kirby said that this is more rigorous than the HiSCR50 endpoint more commonly used in HS clinical trials. Treatments were administered every 2 weeks for the first 8 weeks of a planned follow-up of 24 weeks and then every 4 weeks thereafter.
At 16 weeks, according to the data Dr. Kirby presented, both doses of sonelokimab were more active than placebo, but Dr. Kirby reported that the lower dose performed better for most objective endpoints.
For example, the HiSCR75 was reached by 43.3% of those randomized to the 120-mg dose (P < .001 vs. placebo), 34.8% of those randomized to the 240-mg dose (P <.01), and 14.7% of those randomized to placebo.
For HiSCR50, response rates were 65.7%, 53.0%, and 27.9%, for the 120-mg, 240-mg, and placebo arms, respectively. Again, both the lower dose (P < .001) and the higher dose (P < .01) were significantly superior to placebo.
On the International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System (IHS4), which counts nodules and abscesses, score reductions were 19.3, 14.5, and 7.9 for the lower dose, higher dose, and placebo, respectively, with a greater statistical advantage for the lower relative to the higher dose over placebo (P <.001 vs. P <.01).
However, patient-focused outcomes were not necessarily greater for the lower dose. For the patient-completed measure, the Numerical Rating Scale 50% reduction in skin pain (NRS50), the proportion of patients responding at 12 weeks was numerically greater for the 240-mg dose (41.3%) than with the 120-mg dose (32.0%), although both reached the same statistical advantage (P < .001) over the 4.3% who reached this level of response on placebo.
For the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) and the Patient Global Impression of Severity (PGI-S), improvements from baseline were similar for the lower and higher dose, although there was a modest numerical and statistical advantage for the higher dose over placebo (P < .001 vs. P <.01).
The HiSCR50 (57.6%) and HiSCR75 (36.4%) responses were both lower for those randomized to the TNF inhibitor adalimumab relative to sonelokimab, but the smaller number of patients in this arm prohibited a statistical comparison.
Although oral candidiasis was more common among patients receiving either dose of sonelokimab than placebo, these were of mild to moderate severity. Dr. Kirby said that there were no unexpected safety issues, and sonelokimab was generally well tolerated.
The results are encouraging, but Dr. Kirby acknowledged that data are now needed to confirm that resolution of tunnels and fistulae is greater with a nanobody inhibitor of IL-17A/F than other targeted therapies. Even if this is validated, he said studies are needed to prove that the small relative molecule size is the reason behind the benefits.
Forty-eight–week bimekizumab data
From the pooled BE HEARD I and BE HEARD II maintenance data, the major message is that the robust responses observed at 16 weeks versus placebo were maintained at 48 weeks. More than 75% of patients retained a HiSCR50 response and more than 55% achieved a HiSCR75 response at the 48-week follow-up. The durable response was also reflected in other measures, according to Christos C. Zouboulis, MD, PhD, director of the department of dermatology, Brandenburg Medical School, Neuruppin, Germany.
“Improvements in disease severity were seen over time,” Dr. Zouboulis reported. “The majority of patients with severe HS at baseline shifted to mild to moderate disease according to the IHS4 classification.”
To the degree that both sonelokimab and bimekizumab target IL-17A/F, these data are mutually reinforcing. Dr. Kirby said that there is a sizable body of data implicating IL-17A/F in driving HS, and the activity of inhibitors in support the clinical value of IL-17A/F suppression.
On Oct. 18, shortly after the EADV meeting concluded, the Food and Drug Administration approved bimekizumab for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, the first approved indication in the United States. In the European Union, it was approved for psoriasis in 2021, and for psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis in June 2023.
Dr. Kirby has financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies, including MoonLake, which is developing sonelokimab and sponsored the MIRA trial. Dr. Christos, president of the European HS Foundation, has financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies, including UCB, which makes bimekizumab and provided funding for the BE HEARD I and II trials.
AT THE EADV CONGRESS
Prurigo nodularis diagnosis delay in skin of color gains added significance
NEW YORK – according to an expert evaluating current approaches at the Skin of Color Update 2023.
“As dermatologists, prurigo nodularis is one of the most severe diseases we treat, said Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Itch Center, Baltimore. Now with one approved therapy and more coming, “it offers one of the most important opportunities we have to dramatically improve someone’s entire life.”
Prior to the September 2022 approval of dupilumab for the treatment of prurigo nodularis (the first treatment approved for this indication), Dr. Kwatra said that the limited options for control of pruritus made him anxious. Prurigo nodularis is characterized by highly itchy nodules that can produce symptoms patients describe as unbearable.
Itch typically severe
On a scale for which 10 represents the worst itch imaginable, scores of 8 or greater are not unusual, according to Dr. Kwatra. Nodules on the trunk and the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs are characteristic, but the persistent itch is the immediate target of treatment once the diagnosis is made. For that reason, he urged clinicians to be familiar with the presentation in patients with darker skin types to reduce time to treatment.
In addition to the difficulty of seeing the characteristic red that is typical of erythema in lighter skin, patients with darker skin types tend to have larger nodules that might vary in shape relative to lighter skin types, Dr. Kwatra said. Given that the presentation of prurigo nodularis is highly heterogeneous even among the same skin types, the nuances in patients with darker skin can be that much more confusing for those without prior experience.
Among Blacks in particular, the nodules in some cases “can be huge,” he added. “They can almost look like keloids due to their thickened and fibrotic appearance.”
Phenotypes appear to be racially linked
In Black patients, the appearance can vary enough relative to lighter skin individuals, that “there seems to be something a little bit different going on,” he said, and this is, in fact, supported by a cluster analysis of circulating biomarkers reported by Dr. Kwatra and colleagues in 2022, in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
In that study, the biomarker profile distinguished two distinct groups. Whites were more common in a cluster with relatively low expression of inflammatory markers (cluster 1), while Blacks were more common in a cluster with an inflammatory plasma profile (cluster 2), with higher relative expression of multiple cytokines, C-reactive protein, eosinophils, and other markers of up-regulated inflammation.
In addition to a lower rate of myelopathy in cluster 2 than cluster 1 (18% vs. 67%; P = .028), patients in cluster 2 had a significantly worse itch than those in cluster 1 on the Numeric Rating Scale for itch and a significantly lower quality of life based on the Dermatology Life Quality Index score.
Other work at Dr. Kwatra’s center that is based on genetic sequencing has provided evidence that Blacks – and Asians to a lesser extent – are predisposed genetically to develop nodules, perhaps explaining why the nodules tend to be larger than those seen in Whites.
The significance of the evidence that prurigo nodularis is associated with a more up-regulated inflammatory profile in Blacks than in Whites is that they might be particularly likely to respond to dupilumab or other targeted immunomodulating therapies that are in development, according to Dr. Kwatra. Although he did not provide data on response by race, he did provide several case examples of complete itch control following dupilumab therapy in Black patients.
In his experience, high levels of blood eosinophils and other inflammatory markers are predictors of response to dupilumab regardless of skin type, but he expressed concern that time to diagnosis is sometimes longer in Black patients if the nuances of disease expression are not appreciated.
For treating prurigo nodularis in Blacks as well as Whites, Dr. Kwatra suggested that clinicians stay current with what he predicted will be a growing array of treatment options. He did not discuss nemolizumab, an interleukin-31 receptor alpha antagonist. Soon after the meeting, results of a phase 3 trial of nemolizumab in patients with moderate to severe prurigo nodularis were published in the New England Journal of Medicine. (Dr. Kwatra is the lead author of the study but did not specifically discuss this treatment at the meeting.)
In the international placebo-controlled trial, called OLYMPIA 2, treatment was associated with a significant reduction in the signs and symptoms of prurigo nodularis, including reductions in itch, at 16 weeks, although only 4% of patients in the study were Black.
Given the expanding array of therapies, the message of considering prurigo nodularis in Black patients in order to accelerate the time to diagnosis is timely, Andrew F. Alexis, MD, MPH, professor of clinical dermatology and vice-chair for diversity and inclusion for the department of dermatology, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
“Current studies suggest a higher prevalence and greater severity of prurigo nodularis among Black patients compared to White patients,” said Dr. Alexis, agreeing with Dr. Kwatra. Referring to evidence that Blacks might mount a greater inflammatory response to prurigo nodularis than Whites, Dr. Alexis called for “a better understanding of the pathomechanisms” of this disease in order “to address unmet needs and reduce disparities for our diverse population of patients who suffer from prurigo nodularis.’
Dr. Kwatra reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis, ASLAN, Cara, Castle Biosciences, Celldex, Galderma, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, LEO pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
NEW YORK – according to an expert evaluating current approaches at the Skin of Color Update 2023.
“As dermatologists, prurigo nodularis is one of the most severe diseases we treat, said Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Itch Center, Baltimore. Now with one approved therapy and more coming, “it offers one of the most important opportunities we have to dramatically improve someone’s entire life.”
Prior to the September 2022 approval of dupilumab for the treatment of prurigo nodularis (the first treatment approved for this indication), Dr. Kwatra said that the limited options for control of pruritus made him anxious. Prurigo nodularis is characterized by highly itchy nodules that can produce symptoms patients describe as unbearable.
Itch typically severe
On a scale for which 10 represents the worst itch imaginable, scores of 8 or greater are not unusual, according to Dr. Kwatra. Nodules on the trunk and the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs are characteristic, but the persistent itch is the immediate target of treatment once the diagnosis is made. For that reason, he urged clinicians to be familiar with the presentation in patients with darker skin types to reduce time to treatment.
In addition to the difficulty of seeing the characteristic red that is typical of erythema in lighter skin, patients with darker skin types tend to have larger nodules that might vary in shape relative to lighter skin types, Dr. Kwatra said. Given that the presentation of prurigo nodularis is highly heterogeneous even among the same skin types, the nuances in patients with darker skin can be that much more confusing for those without prior experience.
Among Blacks in particular, the nodules in some cases “can be huge,” he added. “They can almost look like keloids due to their thickened and fibrotic appearance.”
Phenotypes appear to be racially linked
In Black patients, the appearance can vary enough relative to lighter skin individuals, that “there seems to be something a little bit different going on,” he said, and this is, in fact, supported by a cluster analysis of circulating biomarkers reported by Dr. Kwatra and colleagues in 2022, in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
In that study, the biomarker profile distinguished two distinct groups. Whites were more common in a cluster with relatively low expression of inflammatory markers (cluster 1), while Blacks were more common in a cluster with an inflammatory plasma profile (cluster 2), with higher relative expression of multiple cytokines, C-reactive protein, eosinophils, and other markers of up-regulated inflammation.
In addition to a lower rate of myelopathy in cluster 2 than cluster 1 (18% vs. 67%; P = .028), patients in cluster 2 had a significantly worse itch than those in cluster 1 on the Numeric Rating Scale for itch and a significantly lower quality of life based on the Dermatology Life Quality Index score.
Other work at Dr. Kwatra’s center that is based on genetic sequencing has provided evidence that Blacks – and Asians to a lesser extent – are predisposed genetically to develop nodules, perhaps explaining why the nodules tend to be larger than those seen in Whites.
The significance of the evidence that prurigo nodularis is associated with a more up-regulated inflammatory profile in Blacks than in Whites is that they might be particularly likely to respond to dupilumab or other targeted immunomodulating therapies that are in development, according to Dr. Kwatra. Although he did not provide data on response by race, he did provide several case examples of complete itch control following dupilumab therapy in Black patients.
In his experience, high levels of blood eosinophils and other inflammatory markers are predictors of response to dupilumab regardless of skin type, but he expressed concern that time to diagnosis is sometimes longer in Black patients if the nuances of disease expression are not appreciated.
For treating prurigo nodularis in Blacks as well as Whites, Dr. Kwatra suggested that clinicians stay current with what he predicted will be a growing array of treatment options. He did not discuss nemolizumab, an interleukin-31 receptor alpha antagonist. Soon after the meeting, results of a phase 3 trial of nemolizumab in patients with moderate to severe prurigo nodularis were published in the New England Journal of Medicine. (Dr. Kwatra is the lead author of the study but did not specifically discuss this treatment at the meeting.)
In the international placebo-controlled trial, called OLYMPIA 2, treatment was associated with a significant reduction in the signs and symptoms of prurigo nodularis, including reductions in itch, at 16 weeks, although only 4% of patients in the study were Black.
Given the expanding array of therapies, the message of considering prurigo nodularis in Black patients in order to accelerate the time to diagnosis is timely, Andrew F. Alexis, MD, MPH, professor of clinical dermatology and vice-chair for diversity and inclusion for the department of dermatology, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
“Current studies suggest a higher prevalence and greater severity of prurigo nodularis among Black patients compared to White patients,” said Dr. Alexis, agreeing with Dr. Kwatra. Referring to evidence that Blacks might mount a greater inflammatory response to prurigo nodularis than Whites, Dr. Alexis called for “a better understanding of the pathomechanisms” of this disease in order “to address unmet needs and reduce disparities for our diverse population of patients who suffer from prurigo nodularis.’
Dr. Kwatra reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis, ASLAN, Cara, Castle Biosciences, Celldex, Galderma, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, LEO pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
NEW YORK – according to an expert evaluating current approaches at the Skin of Color Update 2023.
“As dermatologists, prurigo nodularis is one of the most severe diseases we treat, said Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Itch Center, Baltimore. Now with one approved therapy and more coming, “it offers one of the most important opportunities we have to dramatically improve someone’s entire life.”
Prior to the September 2022 approval of dupilumab for the treatment of prurigo nodularis (the first treatment approved for this indication), Dr. Kwatra said that the limited options for control of pruritus made him anxious. Prurigo nodularis is characterized by highly itchy nodules that can produce symptoms patients describe as unbearable.
Itch typically severe
On a scale for which 10 represents the worst itch imaginable, scores of 8 or greater are not unusual, according to Dr. Kwatra. Nodules on the trunk and the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs are characteristic, but the persistent itch is the immediate target of treatment once the diagnosis is made. For that reason, he urged clinicians to be familiar with the presentation in patients with darker skin types to reduce time to treatment.
In addition to the difficulty of seeing the characteristic red that is typical of erythema in lighter skin, patients with darker skin types tend to have larger nodules that might vary in shape relative to lighter skin types, Dr. Kwatra said. Given that the presentation of prurigo nodularis is highly heterogeneous even among the same skin types, the nuances in patients with darker skin can be that much more confusing for those without prior experience.
Among Blacks in particular, the nodules in some cases “can be huge,” he added. “They can almost look like keloids due to their thickened and fibrotic appearance.”
Phenotypes appear to be racially linked
In Black patients, the appearance can vary enough relative to lighter skin individuals, that “there seems to be something a little bit different going on,” he said, and this is, in fact, supported by a cluster analysis of circulating biomarkers reported by Dr. Kwatra and colleagues in 2022, in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
In that study, the biomarker profile distinguished two distinct groups. Whites were more common in a cluster with relatively low expression of inflammatory markers (cluster 1), while Blacks were more common in a cluster with an inflammatory plasma profile (cluster 2), with higher relative expression of multiple cytokines, C-reactive protein, eosinophils, and other markers of up-regulated inflammation.
In addition to a lower rate of myelopathy in cluster 2 than cluster 1 (18% vs. 67%; P = .028), patients in cluster 2 had a significantly worse itch than those in cluster 1 on the Numeric Rating Scale for itch and a significantly lower quality of life based on the Dermatology Life Quality Index score.
Other work at Dr. Kwatra’s center that is based on genetic sequencing has provided evidence that Blacks – and Asians to a lesser extent – are predisposed genetically to develop nodules, perhaps explaining why the nodules tend to be larger than those seen in Whites.
The significance of the evidence that prurigo nodularis is associated with a more up-regulated inflammatory profile in Blacks than in Whites is that they might be particularly likely to respond to dupilumab or other targeted immunomodulating therapies that are in development, according to Dr. Kwatra. Although he did not provide data on response by race, he did provide several case examples of complete itch control following dupilumab therapy in Black patients.
In his experience, high levels of blood eosinophils and other inflammatory markers are predictors of response to dupilumab regardless of skin type, but he expressed concern that time to diagnosis is sometimes longer in Black patients if the nuances of disease expression are not appreciated.
For treating prurigo nodularis in Blacks as well as Whites, Dr. Kwatra suggested that clinicians stay current with what he predicted will be a growing array of treatment options. He did not discuss nemolizumab, an interleukin-31 receptor alpha antagonist. Soon after the meeting, results of a phase 3 trial of nemolizumab in patients with moderate to severe prurigo nodularis were published in the New England Journal of Medicine. (Dr. Kwatra is the lead author of the study but did not specifically discuss this treatment at the meeting.)
In the international placebo-controlled trial, called OLYMPIA 2, treatment was associated with a significant reduction in the signs and symptoms of prurigo nodularis, including reductions in itch, at 16 weeks, although only 4% of patients in the study were Black.
Given the expanding array of therapies, the message of considering prurigo nodularis in Black patients in order to accelerate the time to diagnosis is timely, Andrew F. Alexis, MD, MPH, professor of clinical dermatology and vice-chair for diversity and inclusion for the department of dermatology, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
“Current studies suggest a higher prevalence and greater severity of prurigo nodularis among Black patients compared to White patients,” said Dr. Alexis, agreeing with Dr. Kwatra. Referring to evidence that Blacks might mount a greater inflammatory response to prurigo nodularis than Whites, Dr. Alexis called for “a better understanding of the pathomechanisms” of this disease in order “to address unmet needs and reduce disparities for our diverse population of patients who suffer from prurigo nodularis.’
Dr. Kwatra reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis, ASLAN, Cara, Castle Biosciences, Celldex, Galderma, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, LEO pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
AT SOC 2023