User login
Common gut bacteria linked to Parkinson’s disease
, a small study suggests.
Environmental factors as well as genetics are also suspected to play a role in PD etiology, although the exact cause remains unknown.
“Our findings indicate that specific strains of Desulfovibrio bacteria are likely to cause Parkinson’s disease,” study investigator Per Erik Saris, PhD, from the University of Helsinki, Finland, says in a news release.
The study was published online in Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.
Screen and treat?
It builds on earlier work by the researchers that showed that Desulfovibrio bacteria were more prevalent and more abundant in quantity in patients with PD, especially patients with more severe disease, than in healthy individuals.
Desulfovibrio is a genus of gram-negative bacteria commonly found in aquatic environments in which levels of organic material are elevated, as well as in waterlogged soils.
In their latest study, Dr. Saris and colleagues looked for Desulfovibrio species in fecal samples from 10 patients with PD and their healthy spouses. Isolated Desulfovibrio strains were fed to a strain of Caenorhabditis elegans roundworms that expressed human alpha-syn fused with yellow fluorescent protein.
They found that worms fed Desulfovibrio bacteria from patients with PD harbored significantly more (P < .001) and larger alpha-syn aggregates (P < .001) than worms fed Desulfovibrio bacteria from healthy individuals or worms fed Escherichia coli strains.
In addition, worms fed Desulfovibrio strains from patients with PD died in significantly higher quantities than worms fed E. coli bacteria (P < .01).
Desulfovibrio strains isolated from patients with PD and strains isolated from healthy individuals appear to have different traits. Comparative genomics studies are needed to identify genetic differences and pathogenic genes from Desulfovibrio strains from patients with PD, the researchers note.
“Taking into account that aggregation of alpha-syn is a hallmark of PD, the ability of Desulfovibrio bacteria to induce alpha-syn aggregation in large numbers and sizes, as demonstrated in the present study, provides further evidence for the pathogenic role of Desulfovibrio bacteria in PD, as previously suggested,” they add.
The findings highlight the potential for screening and targeted removal of harmful Desulfovibrio bacteria, Dr. Saris suggests in the news release.
No clinical implications
In a comment, James Beck, PhD, chief scientific officer at the Parkinson’s Foundation, cautioned that “this research is in a very early stage, uses a nonvertebrate animal model, and the number of participants is small.
“Understanding the role of the gut microbiome in influencing PD is in its infancy. These are important steps to determining what – if any – link may be between gut bacteria and PD,” Dr. Beck said.
“Right now, there are no implications for the screening/treatment of carriers,” Dr. Beck said.
“It seems that a lot of people, whether with PD or not, harbor Desulfovibrio bacteria in their gut. More research is needed to understand what is different between the Desulfovibrio bacteria of people with PD vs. those who do not have PD,” Dr. Beck added.
The study was supported by the Magnus Ehrnrooth Foundation and the Jane and Aatos Erkko Foundation. Dr. Saris and Dr. Beck have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a small study suggests.
Environmental factors as well as genetics are also suspected to play a role in PD etiology, although the exact cause remains unknown.
“Our findings indicate that specific strains of Desulfovibrio bacteria are likely to cause Parkinson’s disease,” study investigator Per Erik Saris, PhD, from the University of Helsinki, Finland, says in a news release.
The study was published online in Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.
Screen and treat?
It builds on earlier work by the researchers that showed that Desulfovibrio bacteria were more prevalent and more abundant in quantity in patients with PD, especially patients with more severe disease, than in healthy individuals.
Desulfovibrio is a genus of gram-negative bacteria commonly found in aquatic environments in which levels of organic material are elevated, as well as in waterlogged soils.
In their latest study, Dr. Saris and colleagues looked for Desulfovibrio species in fecal samples from 10 patients with PD and their healthy spouses. Isolated Desulfovibrio strains were fed to a strain of Caenorhabditis elegans roundworms that expressed human alpha-syn fused with yellow fluorescent protein.
They found that worms fed Desulfovibrio bacteria from patients with PD harbored significantly more (P < .001) and larger alpha-syn aggregates (P < .001) than worms fed Desulfovibrio bacteria from healthy individuals or worms fed Escherichia coli strains.
In addition, worms fed Desulfovibrio strains from patients with PD died in significantly higher quantities than worms fed E. coli bacteria (P < .01).
Desulfovibrio strains isolated from patients with PD and strains isolated from healthy individuals appear to have different traits. Comparative genomics studies are needed to identify genetic differences and pathogenic genes from Desulfovibrio strains from patients with PD, the researchers note.
“Taking into account that aggregation of alpha-syn is a hallmark of PD, the ability of Desulfovibrio bacteria to induce alpha-syn aggregation in large numbers and sizes, as demonstrated in the present study, provides further evidence for the pathogenic role of Desulfovibrio bacteria in PD, as previously suggested,” they add.
The findings highlight the potential for screening and targeted removal of harmful Desulfovibrio bacteria, Dr. Saris suggests in the news release.
No clinical implications
In a comment, James Beck, PhD, chief scientific officer at the Parkinson’s Foundation, cautioned that “this research is in a very early stage, uses a nonvertebrate animal model, and the number of participants is small.
“Understanding the role of the gut microbiome in influencing PD is in its infancy. These are important steps to determining what – if any – link may be between gut bacteria and PD,” Dr. Beck said.
“Right now, there are no implications for the screening/treatment of carriers,” Dr. Beck said.
“It seems that a lot of people, whether with PD or not, harbor Desulfovibrio bacteria in their gut. More research is needed to understand what is different between the Desulfovibrio bacteria of people with PD vs. those who do not have PD,” Dr. Beck added.
The study was supported by the Magnus Ehrnrooth Foundation and the Jane and Aatos Erkko Foundation. Dr. Saris and Dr. Beck have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a small study suggests.
Environmental factors as well as genetics are also suspected to play a role in PD etiology, although the exact cause remains unknown.
“Our findings indicate that specific strains of Desulfovibrio bacteria are likely to cause Parkinson’s disease,” study investigator Per Erik Saris, PhD, from the University of Helsinki, Finland, says in a news release.
The study was published online in Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.
Screen and treat?
It builds on earlier work by the researchers that showed that Desulfovibrio bacteria were more prevalent and more abundant in quantity in patients with PD, especially patients with more severe disease, than in healthy individuals.
Desulfovibrio is a genus of gram-negative bacteria commonly found in aquatic environments in which levels of organic material are elevated, as well as in waterlogged soils.
In their latest study, Dr. Saris and colleagues looked for Desulfovibrio species in fecal samples from 10 patients with PD and their healthy spouses. Isolated Desulfovibrio strains were fed to a strain of Caenorhabditis elegans roundworms that expressed human alpha-syn fused with yellow fluorescent protein.
They found that worms fed Desulfovibrio bacteria from patients with PD harbored significantly more (P < .001) and larger alpha-syn aggregates (P < .001) than worms fed Desulfovibrio bacteria from healthy individuals or worms fed Escherichia coli strains.
In addition, worms fed Desulfovibrio strains from patients with PD died in significantly higher quantities than worms fed E. coli bacteria (P < .01).
Desulfovibrio strains isolated from patients with PD and strains isolated from healthy individuals appear to have different traits. Comparative genomics studies are needed to identify genetic differences and pathogenic genes from Desulfovibrio strains from patients with PD, the researchers note.
“Taking into account that aggregation of alpha-syn is a hallmark of PD, the ability of Desulfovibrio bacteria to induce alpha-syn aggregation in large numbers and sizes, as demonstrated in the present study, provides further evidence for the pathogenic role of Desulfovibrio bacteria in PD, as previously suggested,” they add.
The findings highlight the potential for screening and targeted removal of harmful Desulfovibrio bacteria, Dr. Saris suggests in the news release.
No clinical implications
In a comment, James Beck, PhD, chief scientific officer at the Parkinson’s Foundation, cautioned that “this research is in a very early stage, uses a nonvertebrate animal model, and the number of participants is small.
“Understanding the role of the gut microbiome in influencing PD is in its infancy. These are important steps to determining what – if any – link may be between gut bacteria and PD,” Dr. Beck said.
“Right now, there are no implications for the screening/treatment of carriers,” Dr. Beck said.
“It seems that a lot of people, whether with PD or not, harbor Desulfovibrio bacteria in their gut. More research is needed to understand what is different between the Desulfovibrio bacteria of people with PD vs. those who do not have PD,” Dr. Beck added.
The study was supported by the Magnus Ehrnrooth Foundation and the Jane and Aatos Erkko Foundation. Dr. Saris and Dr. Beck have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM FRONTIERS IN CELLULAR AND INFECTION MICROBIOLOGY
Rheumatoid arthritis linked to increased Parkinson’s risk
Claims data in 55,000 patients with RA and 273,000 age- and sex-matched controls show that those with RA were 1.74 times more likely than controls to be diagnosed with PD.
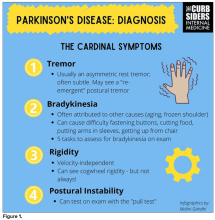
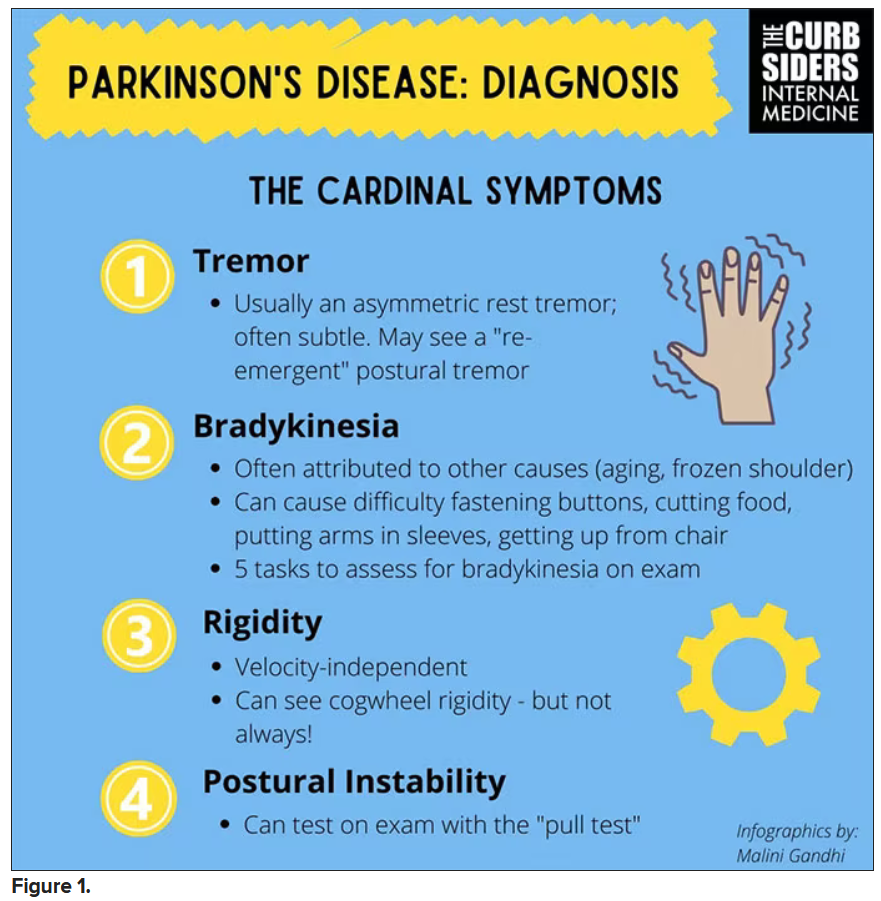
“If patients with rheumatoid arthritis begin exhibiting motor symptoms such as muscle rigidity, tremors, or slowed movement, it is imperative that they be evaluated by a qualified neurologist to rule out the possibility of developing Parkinson’s disease,” study investigator Hyungjin Kim, MD, PhD, told this news organization.
Dr. Kim is an associate professor in the department of medical humanities at Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine in Seoul, South Korea.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
Conflicting findings
The investigators note that a number of studies have examined the link between RA and PD, with conflicting results – one even showing a 35% reduced risk for PD for individuals with RA. A more recent population-based study in Taiwan showed a 37% higher rate of PD in patients with rheumatic disease.
However, previous studies did not control for important variables such as body mass index or diabetes.
For the current study, the investigators analyzed claims on about 55,000 patients diagnosed with RA between 2010 and 2017, with follow-up until 2019, and compared the outcomes of this group vs. those of 273,000 controls.
The mean age of claimants was 58 years, and 75% were female.
Results showed that those diagnosed with seropositive RA were about twice as likely as controls to be diagnosed with PD. Those with seronegative RA were 1.2 times as likely as controls to be diagnosed with PD.
Dr. Kim noted that although the pathogenic link between RA and PD remains elusive, inflammation probably plays an important role. “Inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6, which are increased in RA patients, can induce microglial activation, leading to neuroinflammation,” he stated.
“These inflammatory cytokines are known to be associated with the dysfunction and degeneration of nigral dopaminergic neurons, which are important in the pathogenesis of PD,” he added.
The investigators noted that patients with RA may have been subject to more frequent health care services than controls and so were more likely to obtain a PD diagnosis.
Another possibility was that because patients with health check-ups were included in the analysis, the findings may have been biased toward those who were older and who had a higher income.
Dr. Kim noted that additional research is required to clarify the pathogenic connection between RA and PD.
“Moreover, additional studies are necessary to explore the potential influence of novel therapeutic treatments for RA on Parkinson’s disease susceptibility in patients with RA,” he said.
Commenting on the findings for this news organization, David Sulzer, PhD, professor of psychiatry, neurology, and pharmacology at Columbia University in New York, said that the study adds to the growing body of evidence showing there is an autoimmune component to PD.
Dr. Sulzer pointed to data in several papers he published with others to this effect, including one showing higher rates of PD in people with inflammatory bowel disease.
The study had no specific funding. The study investigators and Dr. Sulzer report no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Claims data in 55,000 patients with RA and 273,000 age- and sex-matched controls show that those with RA were 1.74 times more likely than controls to be diagnosed with PD.
“If patients with rheumatoid arthritis begin exhibiting motor symptoms such as muscle rigidity, tremors, or slowed movement, it is imperative that they be evaluated by a qualified neurologist to rule out the possibility of developing Parkinson’s disease,” study investigator Hyungjin Kim, MD, PhD, told this news organization.
Dr. Kim is an associate professor in the department of medical humanities at Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine in Seoul, South Korea.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
Conflicting findings
The investigators note that a number of studies have examined the link between RA and PD, with conflicting results – one even showing a 35% reduced risk for PD for individuals with RA. A more recent population-based study in Taiwan showed a 37% higher rate of PD in patients with rheumatic disease.
However, previous studies did not control for important variables such as body mass index or diabetes.
For the current study, the investigators analyzed claims on about 55,000 patients diagnosed with RA between 2010 and 2017, with follow-up until 2019, and compared the outcomes of this group vs. those of 273,000 controls.
The mean age of claimants was 58 years, and 75% were female.
Results showed that those diagnosed with seropositive RA were about twice as likely as controls to be diagnosed with PD. Those with seronegative RA were 1.2 times as likely as controls to be diagnosed with PD.
Dr. Kim noted that although the pathogenic link between RA and PD remains elusive, inflammation probably plays an important role. “Inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6, which are increased in RA patients, can induce microglial activation, leading to neuroinflammation,” he stated.
“These inflammatory cytokines are known to be associated with the dysfunction and degeneration of nigral dopaminergic neurons, which are important in the pathogenesis of PD,” he added.
The investigators noted that patients with RA may have been subject to more frequent health care services than controls and so were more likely to obtain a PD diagnosis.
Another possibility was that because patients with health check-ups were included in the analysis, the findings may have been biased toward those who were older and who had a higher income.
Dr. Kim noted that additional research is required to clarify the pathogenic connection between RA and PD.
“Moreover, additional studies are necessary to explore the potential influence of novel therapeutic treatments for RA on Parkinson’s disease susceptibility in patients with RA,” he said.
Commenting on the findings for this news organization, David Sulzer, PhD, professor of psychiatry, neurology, and pharmacology at Columbia University in New York, said that the study adds to the growing body of evidence showing there is an autoimmune component to PD.
Dr. Sulzer pointed to data in several papers he published with others to this effect, including one showing higher rates of PD in people with inflammatory bowel disease.
The study had no specific funding. The study investigators and Dr. Sulzer report no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Claims data in 55,000 patients with RA and 273,000 age- and sex-matched controls show that those with RA were 1.74 times more likely than controls to be diagnosed with PD.
“If patients with rheumatoid arthritis begin exhibiting motor symptoms such as muscle rigidity, tremors, or slowed movement, it is imperative that they be evaluated by a qualified neurologist to rule out the possibility of developing Parkinson’s disease,” study investigator Hyungjin Kim, MD, PhD, told this news organization.
Dr. Kim is an associate professor in the department of medical humanities at Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine in Seoul, South Korea.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
Conflicting findings
The investigators note that a number of studies have examined the link between RA and PD, with conflicting results – one even showing a 35% reduced risk for PD for individuals with RA. A more recent population-based study in Taiwan showed a 37% higher rate of PD in patients with rheumatic disease.
However, previous studies did not control for important variables such as body mass index or diabetes.
For the current study, the investigators analyzed claims on about 55,000 patients diagnosed with RA between 2010 and 2017, with follow-up until 2019, and compared the outcomes of this group vs. those of 273,000 controls.
The mean age of claimants was 58 years, and 75% were female.
Results showed that those diagnosed with seropositive RA were about twice as likely as controls to be diagnosed with PD. Those with seronegative RA were 1.2 times as likely as controls to be diagnosed with PD.
Dr. Kim noted that although the pathogenic link between RA and PD remains elusive, inflammation probably plays an important role. “Inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6, which are increased in RA patients, can induce microglial activation, leading to neuroinflammation,” he stated.
“These inflammatory cytokines are known to be associated with the dysfunction and degeneration of nigral dopaminergic neurons, which are important in the pathogenesis of PD,” he added.
The investigators noted that patients with RA may have been subject to more frequent health care services than controls and so were more likely to obtain a PD diagnosis.
Another possibility was that because patients with health check-ups were included in the analysis, the findings may have been biased toward those who were older and who had a higher income.
Dr. Kim noted that additional research is required to clarify the pathogenic connection between RA and PD.
“Moreover, additional studies are necessary to explore the potential influence of novel therapeutic treatments for RA on Parkinson’s disease susceptibility in patients with RA,” he said.
Commenting on the findings for this news organization, David Sulzer, PhD, professor of psychiatry, neurology, and pharmacology at Columbia University in New York, said that the study adds to the growing body of evidence showing there is an autoimmune component to PD.
Dr. Sulzer pointed to data in several papers he published with others to this effect, including one showing higher rates of PD in people with inflammatory bowel disease.
The study had no specific funding. The study investigators and Dr. Sulzer report no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
Novel levodopa delivery system promises continuous dosing without surgery or pump
BOSTON – , according to an early clinical experience described in the Emerging Science session at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
On this device, the attenuation of levodopa fluctuations “translated into dramatic improvements in clinical behavior, including highly significant reductions in OFF time and an increase in ON time with no dyskinesias,” reported C. Warren Olanow, MD, who is a chairman emeritus of the department of neurology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and now an employee of the company developing this new device.
A novel strategy
Numerous studies have demonstrated that reductions in the troughs of plasma levodopa associated with oral dosing result in longer ON time with fewer dyskinesias, according to Dr. Olanow, who explained this has led to strategies for numerous strategies to achieve continuous delivery. A device that delivers levodopa into the stomach through a surgically implanted catheter has already received regulatory approval. Other devices delivering levodopa subcutaneously are in development, but Dr. Olanow said each of these has had limitations.
“The problem with these approaches is they are associated with potentially serious side effects and they require the patient to wear a cumbersome device,” he explained. Relative to the subcutaneous delivery systems, which have been associated with injection site reactions that include painful nodules, and the surgically implanted devices, which also require an external pump, the latest strategy avoids both disadvantages.
Called DopaFuse, the experimental device is designed to deliver the levodopa and carbidopa into the mouth through a micropump within a wearable retainer. Dr. Olanow said that previous experimental studies demonstrated that small doses of levodopa delivered by mouth to the gastrointestinal system reduce levodopa plasma variability. This early clinical study supports that premise. Levodopa delivered into the mouth by way of a propellant in the retainer-mounted pump improved clinical endpoints.
Encouraging trial results
In the study, 16 patients between the ages of 30 and 75 with Parkinson’s disease were enrolled. On day 1, they received an oral dose of levodopa/carbidopa consistent with their current treatment. On day 2, levodopa/carbidopa was delivered through the retainer-mounted device at equivalent doses. On day 3, they received a single morning oral dose and the received the remainder of their levodopa/carbidopa regimen through the device. On days 4 to 14, they received treatment in the same schedule as day 3.
When pharmacokinetics of levodopa on day 3 were compared with those on day 1, the fluctuation index and coefficient of levodopa concentration variability was reduced to a degree that was highly statistically significant (P < .0001). This, in turn, correlated with “striking” reductions in OFF time with equally statistically significant improvement in ON time and ON time without dyskinesias, according to Dr. Olanow.
Relative to an OFF time of 3.2 hours on day 1, the OFF time of 1.6 hours on day 3 represented a 50% reduction (P < .0001). ON time improved from 12.8 hours to 14.5 hours (P < .001). ON time without dyskinesias improved numerically from 8.8 hours to 9.6 hours.
“There were also improvements in activities of daily living when patients were on DopaFuse, which is a hard endpoint to reach in a study with such a small sample size,” Dr. Olanow reported.
There were no serious adverse events. Three patients reported vomiting and two patients each reported headache, but these events were mild and all resolved within a day. Three patients reported buccal lesions, but these also resolved within a day.
“Some patients reported trouble with speaking in the beginning but at the end of the study, patients were reporting that it was easier to speak because of the motor improvements,” Dr. Olanow said.
Overall, the device was well tolerated by the subjects, providing the evidence for the next stages of clinical studies, reported Dr. Olanow.
“If this turns out to be what we hope it is, it will allow us to deliver levodopa without motor complications, without need for a surgical procedure, and without the risk of subcutaneous lesions,” Dr. Olanow said.
More delivery strategies are needed
This device is in an early phase of development, but several specialists in Parkinson’s disease agreed that there is a need for more strategies to provide continuous levodopa in patients with advancing symptoms. Stuart Isaacson, MD, director, Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Center of Boca Raton, Fla., is among them.
“Novel delivery devices that can provide more continuous levodopa delivery would be an important therapeutic advance,” Dr. Isaacson said. He called levodopa “the cornerstone of treatment through the course of Parkinson’s disease,” but more physiologic dosing in advancing disease has been a challenge.
“While there are many therapies currently available to manage OFF time, many people living with Parkinson’s disease continue to spend only half of their waking day with good ON time,” he added.
The currently approved method of delivering continuous levodopa through a surgically placed catheter into the gastrointestinal system is effective, but has limitations, according to Aaron L. Ellenbogen, MD, a neurologist at Beaumont Hospital, Farmington Hills, Mich.
“One of the challenges with the current treatment landscape of Parkinson’s disease is that medication can be absorbed variably through the gastrointestinal system,” he said. “As the disease progresses, this often becomes more troublesome.” Although this new device is likely to share this issue, Dr. Ellenbogen said that several devices might be useful to match patients with the one that works best for them.
Dr. Olanow is the founder and CEO of Clintrex Research Corporation, through which he also serves as chief medical officer of SynAgile, the company developing DopaFuse. Dr. Isaacson has financial relationships with more than 30 companies, including those that produce levodopa and levodopa delivery systems. Dr. Ellenbogen has financial relationships with Allergan, Acorda, Supernus, and Teva.
BOSTON – , according to an early clinical experience described in the Emerging Science session at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
On this device, the attenuation of levodopa fluctuations “translated into dramatic improvements in clinical behavior, including highly significant reductions in OFF time and an increase in ON time with no dyskinesias,” reported C. Warren Olanow, MD, who is a chairman emeritus of the department of neurology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and now an employee of the company developing this new device.
A novel strategy
Numerous studies have demonstrated that reductions in the troughs of plasma levodopa associated with oral dosing result in longer ON time with fewer dyskinesias, according to Dr. Olanow, who explained this has led to strategies for numerous strategies to achieve continuous delivery. A device that delivers levodopa into the stomach through a surgically implanted catheter has already received regulatory approval. Other devices delivering levodopa subcutaneously are in development, but Dr. Olanow said each of these has had limitations.
“The problem with these approaches is they are associated with potentially serious side effects and they require the patient to wear a cumbersome device,” he explained. Relative to the subcutaneous delivery systems, which have been associated with injection site reactions that include painful nodules, and the surgically implanted devices, which also require an external pump, the latest strategy avoids both disadvantages.
Called DopaFuse, the experimental device is designed to deliver the levodopa and carbidopa into the mouth through a micropump within a wearable retainer. Dr. Olanow said that previous experimental studies demonstrated that small doses of levodopa delivered by mouth to the gastrointestinal system reduce levodopa plasma variability. This early clinical study supports that premise. Levodopa delivered into the mouth by way of a propellant in the retainer-mounted pump improved clinical endpoints.
Encouraging trial results
In the study, 16 patients between the ages of 30 and 75 with Parkinson’s disease were enrolled. On day 1, they received an oral dose of levodopa/carbidopa consistent with their current treatment. On day 2, levodopa/carbidopa was delivered through the retainer-mounted device at equivalent doses. On day 3, they received a single morning oral dose and the received the remainder of their levodopa/carbidopa regimen through the device. On days 4 to 14, they received treatment in the same schedule as day 3.
When pharmacokinetics of levodopa on day 3 were compared with those on day 1, the fluctuation index and coefficient of levodopa concentration variability was reduced to a degree that was highly statistically significant (P < .0001). This, in turn, correlated with “striking” reductions in OFF time with equally statistically significant improvement in ON time and ON time without dyskinesias, according to Dr. Olanow.
Relative to an OFF time of 3.2 hours on day 1, the OFF time of 1.6 hours on day 3 represented a 50% reduction (P < .0001). ON time improved from 12.8 hours to 14.5 hours (P < .001). ON time without dyskinesias improved numerically from 8.8 hours to 9.6 hours.
“There were also improvements in activities of daily living when patients were on DopaFuse, which is a hard endpoint to reach in a study with such a small sample size,” Dr. Olanow reported.
There were no serious adverse events. Three patients reported vomiting and two patients each reported headache, but these events were mild and all resolved within a day. Three patients reported buccal lesions, but these also resolved within a day.
“Some patients reported trouble with speaking in the beginning but at the end of the study, patients were reporting that it was easier to speak because of the motor improvements,” Dr. Olanow said.
Overall, the device was well tolerated by the subjects, providing the evidence for the next stages of clinical studies, reported Dr. Olanow.
“If this turns out to be what we hope it is, it will allow us to deliver levodopa without motor complications, without need for a surgical procedure, and without the risk of subcutaneous lesions,” Dr. Olanow said.
More delivery strategies are needed
This device is in an early phase of development, but several specialists in Parkinson’s disease agreed that there is a need for more strategies to provide continuous levodopa in patients with advancing symptoms. Stuart Isaacson, MD, director, Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Center of Boca Raton, Fla., is among them.
“Novel delivery devices that can provide more continuous levodopa delivery would be an important therapeutic advance,” Dr. Isaacson said. He called levodopa “the cornerstone of treatment through the course of Parkinson’s disease,” but more physiologic dosing in advancing disease has been a challenge.
“While there are many therapies currently available to manage OFF time, many people living with Parkinson’s disease continue to spend only half of their waking day with good ON time,” he added.
The currently approved method of delivering continuous levodopa through a surgically placed catheter into the gastrointestinal system is effective, but has limitations, according to Aaron L. Ellenbogen, MD, a neurologist at Beaumont Hospital, Farmington Hills, Mich.
“One of the challenges with the current treatment landscape of Parkinson’s disease is that medication can be absorbed variably through the gastrointestinal system,” he said. “As the disease progresses, this often becomes more troublesome.” Although this new device is likely to share this issue, Dr. Ellenbogen said that several devices might be useful to match patients with the one that works best for them.
Dr. Olanow is the founder and CEO of Clintrex Research Corporation, through which he also serves as chief medical officer of SynAgile, the company developing DopaFuse. Dr. Isaacson has financial relationships with more than 30 companies, including those that produce levodopa and levodopa delivery systems. Dr. Ellenbogen has financial relationships with Allergan, Acorda, Supernus, and Teva.
BOSTON – , according to an early clinical experience described in the Emerging Science session at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
On this device, the attenuation of levodopa fluctuations “translated into dramatic improvements in clinical behavior, including highly significant reductions in OFF time and an increase in ON time with no dyskinesias,” reported C. Warren Olanow, MD, who is a chairman emeritus of the department of neurology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and now an employee of the company developing this new device.
A novel strategy
Numerous studies have demonstrated that reductions in the troughs of plasma levodopa associated with oral dosing result in longer ON time with fewer dyskinesias, according to Dr. Olanow, who explained this has led to strategies for numerous strategies to achieve continuous delivery. A device that delivers levodopa into the stomach through a surgically implanted catheter has already received regulatory approval. Other devices delivering levodopa subcutaneously are in development, but Dr. Olanow said each of these has had limitations.
“The problem with these approaches is they are associated with potentially serious side effects and they require the patient to wear a cumbersome device,” he explained. Relative to the subcutaneous delivery systems, which have been associated with injection site reactions that include painful nodules, and the surgically implanted devices, which also require an external pump, the latest strategy avoids both disadvantages.
Called DopaFuse, the experimental device is designed to deliver the levodopa and carbidopa into the mouth through a micropump within a wearable retainer. Dr. Olanow said that previous experimental studies demonstrated that small doses of levodopa delivered by mouth to the gastrointestinal system reduce levodopa plasma variability. This early clinical study supports that premise. Levodopa delivered into the mouth by way of a propellant in the retainer-mounted pump improved clinical endpoints.
Encouraging trial results
In the study, 16 patients between the ages of 30 and 75 with Parkinson’s disease were enrolled. On day 1, they received an oral dose of levodopa/carbidopa consistent with their current treatment. On day 2, levodopa/carbidopa was delivered through the retainer-mounted device at equivalent doses. On day 3, they received a single morning oral dose and the received the remainder of their levodopa/carbidopa regimen through the device. On days 4 to 14, they received treatment in the same schedule as day 3.
When pharmacokinetics of levodopa on day 3 were compared with those on day 1, the fluctuation index and coefficient of levodopa concentration variability was reduced to a degree that was highly statistically significant (P < .0001). This, in turn, correlated with “striking” reductions in OFF time with equally statistically significant improvement in ON time and ON time without dyskinesias, according to Dr. Olanow.
Relative to an OFF time of 3.2 hours on day 1, the OFF time of 1.6 hours on day 3 represented a 50% reduction (P < .0001). ON time improved from 12.8 hours to 14.5 hours (P < .001). ON time without dyskinesias improved numerically from 8.8 hours to 9.6 hours.
“There were also improvements in activities of daily living when patients were on DopaFuse, which is a hard endpoint to reach in a study with such a small sample size,” Dr. Olanow reported.
There were no serious adverse events. Three patients reported vomiting and two patients each reported headache, but these events were mild and all resolved within a day. Three patients reported buccal lesions, but these also resolved within a day.
“Some patients reported trouble with speaking in the beginning but at the end of the study, patients were reporting that it was easier to speak because of the motor improvements,” Dr. Olanow said.
Overall, the device was well tolerated by the subjects, providing the evidence for the next stages of clinical studies, reported Dr. Olanow.
“If this turns out to be what we hope it is, it will allow us to deliver levodopa without motor complications, without need for a surgical procedure, and without the risk of subcutaneous lesions,” Dr. Olanow said.
More delivery strategies are needed
This device is in an early phase of development, but several specialists in Parkinson’s disease agreed that there is a need for more strategies to provide continuous levodopa in patients with advancing symptoms. Stuart Isaacson, MD, director, Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Center of Boca Raton, Fla., is among them.
“Novel delivery devices that can provide more continuous levodopa delivery would be an important therapeutic advance,” Dr. Isaacson said. He called levodopa “the cornerstone of treatment through the course of Parkinson’s disease,” but more physiologic dosing in advancing disease has been a challenge.
“While there are many therapies currently available to manage OFF time, many people living with Parkinson’s disease continue to spend only half of their waking day with good ON time,” he added.
The currently approved method of delivering continuous levodopa through a surgically placed catheter into the gastrointestinal system is effective, but has limitations, according to Aaron L. Ellenbogen, MD, a neurologist at Beaumont Hospital, Farmington Hills, Mich.
“One of the challenges with the current treatment landscape of Parkinson’s disease is that medication can be absorbed variably through the gastrointestinal system,” he said. “As the disease progresses, this often becomes more troublesome.” Although this new device is likely to share this issue, Dr. Ellenbogen said that several devices might be useful to match patients with the one that works best for them.
Dr. Olanow is the founder and CEO of Clintrex Research Corporation, through which he also serves as chief medical officer of SynAgile, the company developing DopaFuse. Dr. Isaacson has financial relationships with more than 30 companies, including those that produce levodopa and levodopa delivery systems. Dr. Ellenbogen has financial relationships with Allergan, Acorda, Supernus, and Teva.
FROM AAN 2023
Phase 3 study of new levodopa/carbidopa delivery system meets all efficacy endpoints
BOSTON – presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
When compared with optimized oral immediate-release medication, the delivery system, called ND0612 (NeuroDerm, Rehovot, Israel), improved ON time without troublesome dyskinesias while improving symptoms according to ratings from both patients and clinicians, according to Alberto J. Espay, MD, professor of neurology and director of the Gardner Family Center for Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders, University of Cincinnati.
The new delivery system addresses the challenge of reducing the variability in levodopa plasma concentrations, a major factor in motor fluctuations and diminishing benefit from orally administered drug, according to Dr. Espay. He said that continuous infusion strategies have long been sought as a method to preserve levodopa efficacy.
BouNDless findings
There were two phases to this multinational trial, called BouNDless. In the first, an open-label run-in phase, 381 patients with Parkinson’s disease were dose titrated for optimization of oral immediate-release levodopa and carbidopa. They were then optimized for the same drugs delivered with ND0612. The study was conducted over 12 weeks; 122 patients left the study after this phase due to adverse events, lack of efficacy, or withdrawal of consent.
In the second phase, the 259 remaining patients were randomized to the continuous infusion arm or to immediate release oral therapy. In this double-blind, double-dummy phase, those randomized to the ND0612 infusion also received oral placebos. Those randomized to oral therapy received a placebo infusion. Efficacy and safety were assessed at the end of 12 weeks.
At the end of phase 1, the ON time increased by about 3 hours when levodopa-carbidopa dosing was optimized on either delivery method. Dr. Espay attributed the improvement to the value of optimized dosing even in patients with relatively advanced disease.
However, for the purposes of the double-blind comparison, this improvement in ON time provided a new baseline for comparison of the two delivery methods. This is important for interpreting the primary result, which was a 1.72-hour difference in ON time at the end of the study. The difference was created when ON time was maintained with ND0612 continuous drug delivery but eroded in the group randomized to oral immediate-release treatment.
Several secondary endpoints supported the greater efficacy of continuous subcutaneous delivery. These included lower OFF time (0.50 vs. 1.90 hours), less accumulation of disability on the United Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale part II-M-EDL (-0.30 vs. +2.75 points), and greater improvement on the Patient Global Impression of Change (+0.31 vs. +0.70 points), and the Clinical Global Impression of change (+0.31 vs. +0.77 points). The differences were highly statistically significant (all P < .0001).
The patients participating in the double-blind phase of the study were similar with a mean age of 63.5 years in both groups and time since Parkinson’s disease diagnosis (> 9 years). The median ON time without troublesome dyskinesias was about 12 hours at baseline in both groups and the median OFF time was about 3.5 hours.
The higher rate of treatment-related adverse events in the ND0612 group (67.2% vs. 52.7%) was largely explained by the greater rate of infusion site reactions (57.0% vs. 42.7%). The rates of severe reactions in the two groups were the same (0.8%), but both mild (43.8% vs. 36.6%) and moderate (12.5% vs. 5.3%) reactions occurred more commonly in the group receiving active therapy.
“Infusion reactions are the Achilles heel of all subcutaneous therapies,” acknowledged Dr. Espay, who expects other infusion systems in development to share this risk. He suggested that the clinical impact can be attenuated to some degree by rotating infusion sites.
BeyoND extension study
Data from an open-label extension (OLE) of the phase 2b BeyoND trial were also presented at the AAN meeting and generated generally similar results. Largely a safety study, there was no active control in the initial BeyoND or the BeyoND OLE. In BeyoND, the improvement in ON time from baseline was even greater than that seen in BouNDless, but, again, the optimization of dosing in the BouNDless run-in established a greater baseline of disease control.
In the OLE of BeyoND, presented by Aaron Ellenbogen, DO, a neurologist in Farmington, Mich., one of the notable findings was the retention of patients. After 2 years of follow-up, 82% completed at least 2 years of follow-up and 66.7% have now remained on treatment for at least 3 years. Dr. Ellenbogen maintains that this retention rate provides compelling evidence of a favorable benefit-to-risk ratio.
Fulfilling an unmet need
The favorable efficacy data from this trial represent “a big advance,” according to Ihtsham Ul Haq, MD, chief, movement disorders division, University of Miami, who was reached for comment. He noted that continuous infusion delivery has been anticipated for some time, and he expects these types of systems to fulfill an unmet need.
“This will be a useful option in a carefully selected group of patients,” said Dr. Haq, who considers the types of improvement in ON time to be highly clinically meaningful.
However, he cautioned that the nodules created by injection site reactions might limit the utility of this treatment option in at least some patients. Wearing the external device might also be a limiting factor for some patients.
In complex Parkinson’s disease, a stage that can be reached fairly rapidly in some patients but might take 15 years or more in others, all of the options involve a careful benefit-to-risk calculation, according to Dr. Haq. Deep brain stimulation is among the most effective options, but continuous infusion might appeal to some patients for delaying this procedure or as an alternative.
“We need multiple options for these types of patients, and it appears that continuous infusion will be one of them,” Dr. Haq said.
Dr. Espay has financial relationships with Acadia, Acorda, Amneal, AskBio, Bexion, Kyowa Kirin, Neuroderm, Neurocrine, and Sunovion. Dr. Ellenbogen has financial relationships with Allergan, Acorda, Supernus, and Teva. Dr. Haq reports no potential conflicts of interest.
BOSTON – presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
When compared with optimized oral immediate-release medication, the delivery system, called ND0612 (NeuroDerm, Rehovot, Israel), improved ON time without troublesome dyskinesias while improving symptoms according to ratings from both patients and clinicians, according to Alberto J. Espay, MD, professor of neurology and director of the Gardner Family Center for Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders, University of Cincinnati.
The new delivery system addresses the challenge of reducing the variability in levodopa plasma concentrations, a major factor in motor fluctuations and diminishing benefit from orally administered drug, according to Dr. Espay. He said that continuous infusion strategies have long been sought as a method to preserve levodopa efficacy.
BouNDless findings
There were two phases to this multinational trial, called BouNDless. In the first, an open-label run-in phase, 381 patients with Parkinson’s disease were dose titrated for optimization of oral immediate-release levodopa and carbidopa. They were then optimized for the same drugs delivered with ND0612. The study was conducted over 12 weeks; 122 patients left the study after this phase due to adverse events, lack of efficacy, or withdrawal of consent.
In the second phase, the 259 remaining patients were randomized to the continuous infusion arm or to immediate release oral therapy. In this double-blind, double-dummy phase, those randomized to the ND0612 infusion also received oral placebos. Those randomized to oral therapy received a placebo infusion. Efficacy and safety were assessed at the end of 12 weeks.
At the end of phase 1, the ON time increased by about 3 hours when levodopa-carbidopa dosing was optimized on either delivery method. Dr. Espay attributed the improvement to the value of optimized dosing even in patients with relatively advanced disease.
However, for the purposes of the double-blind comparison, this improvement in ON time provided a new baseline for comparison of the two delivery methods. This is important for interpreting the primary result, which was a 1.72-hour difference in ON time at the end of the study. The difference was created when ON time was maintained with ND0612 continuous drug delivery but eroded in the group randomized to oral immediate-release treatment.
Several secondary endpoints supported the greater efficacy of continuous subcutaneous delivery. These included lower OFF time (0.50 vs. 1.90 hours), less accumulation of disability on the United Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale part II-M-EDL (-0.30 vs. +2.75 points), and greater improvement on the Patient Global Impression of Change (+0.31 vs. +0.70 points), and the Clinical Global Impression of change (+0.31 vs. +0.77 points). The differences were highly statistically significant (all P < .0001).
The patients participating in the double-blind phase of the study were similar with a mean age of 63.5 years in both groups and time since Parkinson’s disease diagnosis (> 9 years). The median ON time without troublesome dyskinesias was about 12 hours at baseline in both groups and the median OFF time was about 3.5 hours.
The higher rate of treatment-related adverse events in the ND0612 group (67.2% vs. 52.7%) was largely explained by the greater rate of infusion site reactions (57.0% vs. 42.7%). The rates of severe reactions in the two groups were the same (0.8%), but both mild (43.8% vs. 36.6%) and moderate (12.5% vs. 5.3%) reactions occurred more commonly in the group receiving active therapy.
“Infusion reactions are the Achilles heel of all subcutaneous therapies,” acknowledged Dr. Espay, who expects other infusion systems in development to share this risk. He suggested that the clinical impact can be attenuated to some degree by rotating infusion sites.
BeyoND extension study
Data from an open-label extension (OLE) of the phase 2b BeyoND trial were also presented at the AAN meeting and generated generally similar results. Largely a safety study, there was no active control in the initial BeyoND or the BeyoND OLE. In BeyoND, the improvement in ON time from baseline was even greater than that seen in BouNDless, but, again, the optimization of dosing in the BouNDless run-in established a greater baseline of disease control.
In the OLE of BeyoND, presented by Aaron Ellenbogen, DO, a neurologist in Farmington, Mich., one of the notable findings was the retention of patients. After 2 years of follow-up, 82% completed at least 2 years of follow-up and 66.7% have now remained on treatment for at least 3 years. Dr. Ellenbogen maintains that this retention rate provides compelling evidence of a favorable benefit-to-risk ratio.
Fulfilling an unmet need
The favorable efficacy data from this trial represent “a big advance,” according to Ihtsham Ul Haq, MD, chief, movement disorders division, University of Miami, who was reached for comment. He noted that continuous infusion delivery has been anticipated for some time, and he expects these types of systems to fulfill an unmet need.
“This will be a useful option in a carefully selected group of patients,” said Dr. Haq, who considers the types of improvement in ON time to be highly clinically meaningful.
However, he cautioned that the nodules created by injection site reactions might limit the utility of this treatment option in at least some patients. Wearing the external device might also be a limiting factor for some patients.
In complex Parkinson’s disease, a stage that can be reached fairly rapidly in some patients but might take 15 years or more in others, all of the options involve a careful benefit-to-risk calculation, according to Dr. Haq. Deep brain stimulation is among the most effective options, but continuous infusion might appeal to some patients for delaying this procedure or as an alternative.
“We need multiple options for these types of patients, and it appears that continuous infusion will be one of them,” Dr. Haq said.
Dr. Espay has financial relationships with Acadia, Acorda, Amneal, AskBio, Bexion, Kyowa Kirin, Neuroderm, Neurocrine, and Sunovion. Dr. Ellenbogen has financial relationships with Allergan, Acorda, Supernus, and Teva. Dr. Haq reports no potential conflicts of interest.
BOSTON – presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
When compared with optimized oral immediate-release medication, the delivery system, called ND0612 (NeuroDerm, Rehovot, Israel), improved ON time without troublesome dyskinesias while improving symptoms according to ratings from both patients and clinicians, according to Alberto J. Espay, MD, professor of neurology and director of the Gardner Family Center for Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders, University of Cincinnati.
The new delivery system addresses the challenge of reducing the variability in levodopa plasma concentrations, a major factor in motor fluctuations and diminishing benefit from orally administered drug, according to Dr. Espay. He said that continuous infusion strategies have long been sought as a method to preserve levodopa efficacy.
BouNDless findings
There were two phases to this multinational trial, called BouNDless. In the first, an open-label run-in phase, 381 patients with Parkinson’s disease were dose titrated for optimization of oral immediate-release levodopa and carbidopa. They were then optimized for the same drugs delivered with ND0612. The study was conducted over 12 weeks; 122 patients left the study after this phase due to adverse events, lack of efficacy, or withdrawal of consent.
In the second phase, the 259 remaining patients were randomized to the continuous infusion arm or to immediate release oral therapy. In this double-blind, double-dummy phase, those randomized to the ND0612 infusion also received oral placebos. Those randomized to oral therapy received a placebo infusion. Efficacy and safety were assessed at the end of 12 weeks.
At the end of phase 1, the ON time increased by about 3 hours when levodopa-carbidopa dosing was optimized on either delivery method. Dr. Espay attributed the improvement to the value of optimized dosing even in patients with relatively advanced disease.
However, for the purposes of the double-blind comparison, this improvement in ON time provided a new baseline for comparison of the two delivery methods. This is important for interpreting the primary result, which was a 1.72-hour difference in ON time at the end of the study. The difference was created when ON time was maintained with ND0612 continuous drug delivery but eroded in the group randomized to oral immediate-release treatment.
Several secondary endpoints supported the greater efficacy of continuous subcutaneous delivery. These included lower OFF time (0.50 vs. 1.90 hours), less accumulation of disability on the United Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale part II-M-EDL (-0.30 vs. +2.75 points), and greater improvement on the Patient Global Impression of Change (+0.31 vs. +0.70 points), and the Clinical Global Impression of change (+0.31 vs. +0.77 points). The differences were highly statistically significant (all P < .0001).
The patients participating in the double-blind phase of the study were similar with a mean age of 63.5 years in both groups and time since Parkinson’s disease diagnosis (> 9 years). The median ON time without troublesome dyskinesias was about 12 hours at baseline in both groups and the median OFF time was about 3.5 hours.
The higher rate of treatment-related adverse events in the ND0612 group (67.2% vs. 52.7%) was largely explained by the greater rate of infusion site reactions (57.0% vs. 42.7%). The rates of severe reactions in the two groups were the same (0.8%), but both mild (43.8% vs. 36.6%) and moderate (12.5% vs. 5.3%) reactions occurred more commonly in the group receiving active therapy.
“Infusion reactions are the Achilles heel of all subcutaneous therapies,” acknowledged Dr. Espay, who expects other infusion systems in development to share this risk. He suggested that the clinical impact can be attenuated to some degree by rotating infusion sites.
BeyoND extension study
Data from an open-label extension (OLE) of the phase 2b BeyoND trial were also presented at the AAN meeting and generated generally similar results. Largely a safety study, there was no active control in the initial BeyoND or the BeyoND OLE. In BeyoND, the improvement in ON time from baseline was even greater than that seen in BouNDless, but, again, the optimization of dosing in the BouNDless run-in established a greater baseline of disease control.
In the OLE of BeyoND, presented by Aaron Ellenbogen, DO, a neurologist in Farmington, Mich., one of the notable findings was the retention of patients. After 2 years of follow-up, 82% completed at least 2 years of follow-up and 66.7% have now remained on treatment for at least 3 years. Dr. Ellenbogen maintains that this retention rate provides compelling evidence of a favorable benefit-to-risk ratio.
Fulfilling an unmet need
The favorable efficacy data from this trial represent “a big advance,” according to Ihtsham Ul Haq, MD, chief, movement disorders division, University of Miami, who was reached for comment. He noted that continuous infusion delivery has been anticipated for some time, and he expects these types of systems to fulfill an unmet need.
“This will be a useful option in a carefully selected group of patients,” said Dr. Haq, who considers the types of improvement in ON time to be highly clinically meaningful.
However, he cautioned that the nodules created by injection site reactions might limit the utility of this treatment option in at least some patients. Wearing the external device might also be a limiting factor for some patients.
In complex Parkinson’s disease, a stage that can be reached fairly rapidly in some patients but might take 15 years or more in others, all of the options involve a careful benefit-to-risk calculation, according to Dr. Haq. Deep brain stimulation is among the most effective options, but continuous infusion might appeal to some patients for delaying this procedure or as an alternative.
“We need multiple options for these types of patients, and it appears that continuous infusion will be one of them,” Dr. Haq said.
Dr. Espay has financial relationships with Acadia, Acorda, Amneal, AskBio, Bexion, Kyowa Kirin, Neuroderm, Neurocrine, and Sunovion. Dr. Ellenbogen has financial relationships with Allergan, Acorda, Supernus, and Teva. Dr. Haq reports no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM AAN 2023
New assay hailed as a game changer for early Parkinson’s diagnosis
, and provides information on molecular subtypes, new research indicates.
“Identifying an effective biomarker for Parkinson’s disease pathology could have profound implications for the way we treat the condition, potentially making it possible to diagnose people earlier, identify the best treatments for different subsets of patients, and speed up clinical trials,” the study’s co-lead author Andrew Siderowf, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in a news release.
“Our findings suggest that the αSyn-SAA technique is highly accurate at detecting the biomarker for Parkinson’s disease regardless of the clinical features, making it possible to accurately diagnose the disease in patients at early stages,” added co-lead author Luis Concha-Marambio, PhD, director of research and development at Amprion, San Diego, Calif.
The study was published online in The Lancet Neurology.
‘New era’ in Parkinson’s disease
The researchers assessed the usefulness of αSyn-SAA in a cross-sectional analysis of 1,123 participants in the Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI) cohort from 33 participating academic neurology outpatient practices in 12 countries.
The cohort included individuals with sporadic Parkinson’s disease from LRRK2 or GBA variants, healthy controls, individuals with clinical syndromes prodromal to Parkinson’s disease (rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder [RBD] or hyposmia), and nonmanifesting carriers of LRRK2 and GBA variants. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples from each participant were analyzed using αSyn-SAA.
Overall, αSyn-SAA differentiated Parkinson’s disease from healthy controls with 87.7% sensitivity and 96.3% specificity.
Sensitivity of the assay varied across subgroups based on genetic and clinical features. Among genetic Parkinson’s disease subgroups, sensitivity was highest for GBA Parkinson’s disease (95.9%), followed by sporadic Parkinson’s disease (93.3%), and lowest for LRRK2 Parkinson’s disease (67.5%). Among clinical features, hyposmia was the most robust predictor of a positive assay result.
Among all Parkinson’s disease cases with hyposmia, the sensitivity of the assay was 97.2%, compared with 63.0% for Parkinson’s disease without olfactory dysfunction. Combining genetic and clinical features, the sensitivity of positive αSyn-SAA in sporadic Parkinson’s disease with olfactory deficit was 98.6%, compared with 78.3% in sporadic Parkinson’s disease without hyposmia. Most prodromal participants (86%) with RBD and hyposmia had positive αSyn-SAA results, indicating they had α-synuclein aggregates despite not yet being diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease.
Among those recruited based on their loss of smell, 89% (16 of 18 participants) had positive αSyn-SAA results. Similarly, in those with RBD, positive αSyn-SAA results were present in 85% of cases (28 of 33). No other clinical features were associated with a positive αSyn-SAA result.
In participants who carried LRRK2 or GBA variants but had no Parkinson’s disease diagnosis or prodromal symptoms (nonmanifesting carriers), 9% (14 of 159) and 7% (11 of 151), respectively, had positive αSyn-SAA results.
To date, this is the largest analysis of α-Syn-SAA for the biochemical diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease, the researchers said.
The results show that the assay classifies people with Parkinson’s disease with “high sensitivity and specificity, provides information about molecular heterogeneity, and detects prodromal individuals before diagnosis,” they wrote.
“These findings suggest a crucial role for the α-synuclein SAA in therapeutic development, both to identify pathologically defined subgroups of people with Parkinson’s disease and to establish biomarker-defined at-risk cohorts,” they added.
Amprion has commercialized the assay (SYNTap test), which can be ordered online.
‘Seminal development’
The authors of an accompanying editorial noted the study “lays the foundation for a biological diagnosis” of Parkinson’s disease. “We have entered a new era of biomarker and treatment development for Parkinson’s disease. The possibility of detecting a misfolded α-synuclein, the pathological hallmark of Parkinson’s disease, by employing an SSA, is a seminal development,” wrote Daniela Berg, MD, PhD, and Christine Klein, MD, with University Hospital Schleswig-Holstein, Germany.
“However, to fully leverage the enormous potential of the α-synuclein seed amplification, the test would have to be performed in blood rather than the CSF, a less invasive approach that has proven to be viable,” they added.
“Although the blood-based method needs to be further elaborated for scalability, α-synuclein SAA is a game changer in Parkinson’s disease diagnostics, research, and treatment trials,” they concluded.
The study was funded by The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research and a consortium of more than 40 private and philanthropic partners. Dr. Siderowf has declared consulting for Merck and Parkinson Study Group, and receiving honoraria from Bial. A full list of author disclosures is available with the original article. Dr. Berg and Dr. Klein have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, and provides information on molecular subtypes, new research indicates.
“Identifying an effective biomarker for Parkinson’s disease pathology could have profound implications for the way we treat the condition, potentially making it possible to diagnose people earlier, identify the best treatments for different subsets of patients, and speed up clinical trials,” the study’s co-lead author Andrew Siderowf, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in a news release.
“Our findings suggest that the αSyn-SAA technique is highly accurate at detecting the biomarker for Parkinson’s disease regardless of the clinical features, making it possible to accurately diagnose the disease in patients at early stages,” added co-lead author Luis Concha-Marambio, PhD, director of research and development at Amprion, San Diego, Calif.
The study was published online in The Lancet Neurology.
‘New era’ in Parkinson’s disease
The researchers assessed the usefulness of αSyn-SAA in a cross-sectional analysis of 1,123 participants in the Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI) cohort from 33 participating academic neurology outpatient practices in 12 countries.
The cohort included individuals with sporadic Parkinson’s disease from LRRK2 or GBA variants, healthy controls, individuals with clinical syndromes prodromal to Parkinson’s disease (rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder [RBD] or hyposmia), and nonmanifesting carriers of LRRK2 and GBA variants. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples from each participant were analyzed using αSyn-SAA.
Overall, αSyn-SAA differentiated Parkinson’s disease from healthy controls with 87.7% sensitivity and 96.3% specificity.
Sensitivity of the assay varied across subgroups based on genetic and clinical features. Among genetic Parkinson’s disease subgroups, sensitivity was highest for GBA Parkinson’s disease (95.9%), followed by sporadic Parkinson’s disease (93.3%), and lowest for LRRK2 Parkinson’s disease (67.5%). Among clinical features, hyposmia was the most robust predictor of a positive assay result.
Among all Parkinson’s disease cases with hyposmia, the sensitivity of the assay was 97.2%, compared with 63.0% for Parkinson’s disease without olfactory dysfunction. Combining genetic and clinical features, the sensitivity of positive αSyn-SAA in sporadic Parkinson’s disease with olfactory deficit was 98.6%, compared with 78.3% in sporadic Parkinson’s disease without hyposmia. Most prodromal participants (86%) with RBD and hyposmia had positive αSyn-SAA results, indicating they had α-synuclein aggregates despite not yet being diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease.
Among those recruited based on their loss of smell, 89% (16 of 18 participants) had positive αSyn-SAA results. Similarly, in those with RBD, positive αSyn-SAA results were present in 85% of cases (28 of 33). No other clinical features were associated with a positive αSyn-SAA result.
In participants who carried LRRK2 or GBA variants but had no Parkinson’s disease diagnosis or prodromal symptoms (nonmanifesting carriers), 9% (14 of 159) and 7% (11 of 151), respectively, had positive αSyn-SAA results.
To date, this is the largest analysis of α-Syn-SAA for the biochemical diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease, the researchers said.
The results show that the assay classifies people with Parkinson’s disease with “high sensitivity and specificity, provides information about molecular heterogeneity, and detects prodromal individuals before diagnosis,” they wrote.
“These findings suggest a crucial role for the α-synuclein SAA in therapeutic development, both to identify pathologically defined subgroups of people with Parkinson’s disease and to establish biomarker-defined at-risk cohorts,” they added.
Amprion has commercialized the assay (SYNTap test), which can be ordered online.
‘Seminal development’
The authors of an accompanying editorial noted the study “lays the foundation for a biological diagnosis” of Parkinson’s disease. “We have entered a new era of biomarker and treatment development for Parkinson’s disease. The possibility of detecting a misfolded α-synuclein, the pathological hallmark of Parkinson’s disease, by employing an SSA, is a seminal development,” wrote Daniela Berg, MD, PhD, and Christine Klein, MD, with University Hospital Schleswig-Holstein, Germany.
“However, to fully leverage the enormous potential of the α-synuclein seed amplification, the test would have to be performed in blood rather than the CSF, a less invasive approach that has proven to be viable,” they added.
“Although the blood-based method needs to be further elaborated for scalability, α-synuclein SAA is a game changer in Parkinson’s disease diagnostics, research, and treatment trials,” they concluded.
The study was funded by The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research and a consortium of more than 40 private and philanthropic partners. Dr. Siderowf has declared consulting for Merck and Parkinson Study Group, and receiving honoraria from Bial. A full list of author disclosures is available with the original article. Dr. Berg and Dr. Klein have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, and provides information on molecular subtypes, new research indicates.
“Identifying an effective biomarker for Parkinson’s disease pathology could have profound implications for the way we treat the condition, potentially making it possible to diagnose people earlier, identify the best treatments for different subsets of patients, and speed up clinical trials,” the study’s co-lead author Andrew Siderowf, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in a news release.
“Our findings suggest that the αSyn-SAA technique is highly accurate at detecting the biomarker for Parkinson’s disease regardless of the clinical features, making it possible to accurately diagnose the disease in patients at early stages,” added co-lead author Luis Concha-Marambio, PhD, director of research and development at Amprion, San Diego, Calif.
The study was published online in The Lancet Neurology.
‘New era’ in Parkinson’s disease
The researchers assessed the usefulness of αSyn-SAA in a cross-sectional analysis of 1,123 participants in the Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI) cohort from 33 participating academic neurology outpatient practices in 12 countries.
The cohort included individuals with sporadic Parkinson’s disease from LRRK2 or GBA variants, healthy controls, individuals with clinical syndromes prodromal to Parkinson’s disease (rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder [RBD] or hyposmia), and nonmanifesting carriers of LRRK2 and GBA variants. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples from each participant were analyzed using αSyn-SAA.
Overall, αSyn-SAA differentiated Parkinson’s disease from healthy controls with 87.7% sensitivity and 96.3% specificity.
Sensitivity of the assay varied across subgroups based on genetic and clinical features. Among genetic Parkinson’s disease subgroups, sensitivity was highest for GBA Parkinson’s disease (95.9%), followed by sporadic Parkinson’s disease (93.3%), and lowest for LRRK2 Parkinson’s disease (67.5%). Among clinical features, hyposmia was the most robust predictor of a positive assay result.
Among all Parkinson’s disease cases with hyposmia, the sensitivity of the assay was 97.2%, compared with 63.0% for Parkinson’s disease without olfactory dysfunction. Combining genetic and clinical features, the sensitivity of positive αSyn-SAA in sporadic Parkinson’s disease with olfactory deficit was 98.6%, compared with 78.3% in sporadic Parkinson’s disease without hyposmia. Most prodromal participants (86%) with RBD and hyposmia had positive αSyn-SAA results, indicating they had α-synuclein aggregates despite not yet being diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease.
Among those recruited based on their loss of smell, 89% (16 of 18 participants) had positive αSyn-SAA results. Similarly, in those with RBD, positive αSyn-SAA results were present in 85% of cases (28 of 33). No other clinical features were associated with a positive αSyn-SAA result.
In participants who carried LRRK2 or GBA variants but had no Parkinson’s disease diagnosis or prodromal symptoms (nonmanifesting carriers), 9% (14 of 159) and 7% (11 of 151), respectively, had positive αSyn-SAA results.
To date, this is the largest analysis of α-Syn-SAA for the biochemical diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease, the researchers said.
The results show that the assay classifies people with Parkinson’s disease with “high sensitivity and specificity, provides information about molecular heterogeneity, and detects prodromal individuals before diagnosis,” they wrote.
“These findings suggest a crucial role for the α-synuclein SAA in therapeutic development, both to identify pathologically defined subgroups of people with Parkinson’s disease and to establish biomarker-defined at-risk cohorts,” they added.
Amprion has commercialized the assay (SYNTap test), which can be ordered online.
‘Seminal development’
The authors of an accompanying editorial noted the study “lays the foundation for a biological diagnosis” of Parkinson’s disease. “We have entered a new era of biomarker and treatment development for Parkinson’s disease. The possibility of detecting a misfolded α-synuclein, the pathological hallmark of Parkinson’s disease, by employing an SSA, is a seminal development,” wrote Daniela Berg, MD, PhD, and Christine Klein, MD, with University Hospital Schleswig-Holstein, Germany.
“However, to fully leverage the enormous potential of the α-synuclein seed amplification, the test would have to be performed in blood rather than the CSF, a less invasive approach that has proven to be viable,” they added.
“Although the blood-based method needs to be further elaborated for scalability, α-synuclein SAA is a game changer in Parkinson’s disease diagnostics, research, and treatment trials,” they concluded.
The study was funded by The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research and a consortium of more than 40 private and philanthropic partners. Dr. Siderowf has declared consulting for Merck and Parkinson Study Group, and receiving honoraria from Bial. A full list of author disclosures is available with the original article. Dr. Berg and Dr. Klein have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET NEUROLOGY
Mississippi–Ohio River valley linked to higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
according to findings from a study that was released ahead of its scheduled presentation at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
The association was attributed to concentrations of particulate matter (PM) 2.5 in the Mississippi–Ohio River valley, which was on average higher than in other areas, but that didn’t entirely explain the increase in Parkinson’s disease in that region, Brittany Krzyzanowski, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow in the neuroepidemiology research program of the department of neurology at Barrow Neurological Institute, Dignity Health St. Joseph’s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, said in an interview.
“This study revealed Parkinson’s disease hot spots in the Mississippi–Ohio River valley, a region that has some of the highest levels of air pollution in the nation,” she said, “but we also still find a relationship between air pollution and Parkinson’s risk in the regions in the western half of the United States where Parkinson’s disease and air pollution levels are relatively low.”
Dr. Krzyzanowski and colleagues evaluated 22,546,965 Medicare beneficiaries in 2009, using a multimethod approach that included geospatial analytical techniques to categorize their exposure to PM2.5 based on age, sex, race, smoking status, and health care usage. The researchers also performed individual-level case-control analysis to assess PM2.5 results at the county level. The Medicare beneficiaries were grouped according to average exposure, with the lowest group having an average annual exposure of 5 mcg/m3 and the group with the highest exposure having an average annual exposure of 19 mcg/m3.
In total, researchers identified 83,674 Medicare beneficiaries with incident Parkinson’s disease, with 434 new cases per 100,000 people in the highest exposure group, compared with 359 new cases per 100,000 people in the lowest-exposure group. The relative risk for Parkinson’s disease increased in the highest quartile of PM2.5 by 25%, compared with the lowest quartile after adjusting for factors such as age, smoking status, and health care usage (95% confidence interval, 20%–29%).
The results showed the nationwide average annual PM2.5 was associated with incident Parkinson’s disease, and the Rocky Mountain region carried a strong association between PM2.5 and Parkson’s disease with a 16% increase in risk per level of exposure to PM2.5. While the Mississippi-Ohio River valley was also associated with Parkinson’s disease, there was a weaker association between PM2.5 and Parkinson’s disease, which the researchers attributed to a “ceiling effect” of PM2.5 between approximately 12-19 mcg/m3.
Dr. Krzyzanowski said that use of a large-population-based dataset and high-resolution location data were major strengths of the study. “Having this level of information leaves less room for uncertainty in our measures and analyses,” she said. “Our study also leveraged innovative geographic information systems which allowed us to refine local patterns of disease by using population behavior and demographic information (such as smoking and age) to ensure that we could provide the most accurate map representation available to date.”
A focus on air pollution
Existing research in examining the etiology of Parkinson’s mainly focused on exposure to pesticides,* Dr. Krzyzanowski explained, and “consists of studies using relatively small populations and low-resolution air pollution data.” Genetics is another possible cause, she noted, but only explains some Parkinson’s disease cases.
“Our work suggests that we should also be looking at air pollution as a contributor in the development of Parkinson’s disease,” she said.
Ray Dorsey, MD, professor of neurology at the University of Rochester (N.Y.), who was not involved with the study, said that evidence is mounting that “air pollution may be an important causal factor in Parkinson’s and especially Alzheimer’s disease.”
“This study by a well-regarded group of researchers adds epidemiological evidence for that association,” he said. Another strength is that the study was conducted in the United States, as many epidemiological studies evaluating air pollution and Parkinson’s disease have been performed outside the country because of “a dearth of reliable data sources.”
“This study, along with others, suggest that some of the important environmental toxicants tied to brain disease may be inhaled,” Dr. Dorsey said. “The nose may be the front door to the brain.”
Dr. Krzyzanowski said the next step in their research is further examination of different types of air pollution. “Air pollution contains a variety of toxic components which vary from region to region. Understanding the different components in air pollution and how they interact with climate, temperature, and topography could help explain the regional differences we observed.”
One potential limitation in the study is a lag between air pollution exposure and development of Parkinson’s disease, Dr. Dorsey noted.
“Here, it looks like (but I am not certain) that the investigators looked at current air pollution levels and new cases of Parkinson’s. Ideally, for incident cases of Parkinson’s disease, we would want to know historical data on exposure to air pollution,” he said.
Future studies should include prospective evaluation of adults as well as babies and children who have been exposed to both high and low levels of air pollution. That kind of study “would be incredibly valuable for determining the role of an important environmental toxicant in many brain diseases, including stroke, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s,” he said.
Dr. Krzyzanowski and Dr. Dorsey reported no relevant financial disclosures. This study was supported by grants from the Department of Defense, the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, and The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research.
*Correction, 4/14/23: An earlier version of this article mischaracterized the disease that was the subject of this research.
according to findings from a study that was released ahead of its scheduled presentation at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
The association was attributed to concentrations of particulate matter (PM) 2.5 in the Mississippi–Ohio River valley, which was on average higher than in other areas, but that didn’t entirely explain the increase in Parkinson’s disease in that region, Brittany Krzyzanowski, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow in the neuroepidemiology research program of the department of neurology at Barrow Neurological Institute, Dignity Health St. Joseph’s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, said in an interview.
“This study revealed Parkinson’s disease hot spots in the Mississippi–Ohio River valley, a region that has some of the highest levels of air pollution in the nation,” she said, “but we also still find a relationship between air pollution and Parkinson’s risk in the regions in the western half of the United States where Parkinson’s disease and air pollution levels are relatively low.”
Dr. Krzyzanowski and colleagues evaluated 22,546,965 Medicare beneficiaries in 2009, using a multimethod approach that included geospatial analytical techniques to categorize their exposure to PM2.5 based on age, sex, race, smoking status, and health care usage. The researchers also performed individual-level case-control analysis to assess PM2.5 results at the county level. The Medicare beneficiaries were grouped according to average exposure, with the lowest group having an average annual exposure of 5 mcg/m3 and the group with the highest exposure having an average annual exposure of 19 mcg/m3.
In total, researchers identified 83,674 Medicare beneficiaries with incident Parkinson’s disease, with 434 new cases per 100,000 people in the highest exposure group, compared with 359 new cases per 100,000 people in the lowest-exposure group. The relative risk for Parkinson’s disease increased in the highest quartile of PM2.5 by 25%, compared with the lowest quartile after adjusting for factors such as age, smoking status, and health care usage (95% confidence interval, 20%–29%).
The results showed the nationwide average annual PM2.5 was associated with incident Parkinson’s disease, and the Rocky Mountain region carried a strong association between PM2.5 and Parkson’s disease with a 16% increase in risk per level of exposure to PM2.5. While the Mississippi-Ohio River valley was also associated with Parkinson’s disease, there was a weaker association between PM2.5 and Parkinson’s disease, which the researchers attributed to a “ceiling effect” of PM2.5 between approximately 12-19 mcg/m3.
Dr. Krzyzanowski said that use of a large-population-based dataset and high-resolution location data were major strengths of the study. “Having this level of information leaves less room for uncertainty in our measures and analyses,” she said. “Our study also leveraged innovative geographic information systems which allowed us to refine local patterns of disease by using population behavior and demographic information (such as smoking and age) to ensure that we could provide the most accurate map representation available to date.”
A focus on air pollution
Existing research in examining the etiology of Parkinson’s mainly focused on exposure to pesticides,* Dr. Krzyzanowski explained, and “consists of studies using relatively small populations and low-resolution air pollution data.” Genetics is another possible cause, she noted, but only explains some Parkinson’s disease cases.
“Our work suggests that we should also be looking at air pollution as a contributor in the development of Parkinson’s disease,” she said.
Ray Dorsey, MD, professor of neurology at the University of Rochester (N.Y.), who was not involved with the study, said that evidence is mounting that “air pollution may be an important causal factor in Parkinson’s and especially Alzheimer’s disease.”
“This study by a well-regarded group of researchers adds epidemiological evidence for that association,” he said. Another strength is that the study was conducted in the United States, as many epidemiological studies evaluating air pollution and Parkinson’s disease have been performed outside the country because of “a dearth of reliable data sources.”
“This study, along with others, suggest that some of the important environmental toxicants tied to brain disease may be inhaled,” Dr. Dorsey said. “The nose may be the front door to the brain.”
Dr. Krzyzanowski said the next step in their research is further examination of different types of air pollution. “Air pollution contains a variety of toxic components which vary from region to region. Understanding the different components in air pollution and how they interact with climate, temperature, and topography could help explain the regional differences we observed.”
One potential limitation in the study is a lag between air pollution exposure and development of Parkinson’s disease, Dr. Dorsey noted.
“Here, it looks like (but I am not certain) that the investigators looked at current air pollution levels and new cases of Parkinson’s. Ideally, for incident cases of Parkinson’s disease, we would want to know historical data on exposure to air pollution,” he said.
Future studies should include prospective evaluation of adults as well as babies and children who have been exposed to both high and low levels of air pollution. That kind of study “would be incredibly valuable for determining the role of an important environmental toxicant in many brain diseases, including stroke, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s,” he said.
Dr. Krzyzanowski and Dr. Dorsey reported no relevant financial disclosures. This study was supported by grants from the Department of Defense, the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, and The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research.
*Correction, 4/14/23: An earlier version of this article mischaracterized the disease that was the subject of this research.
according to findings from a study that was released ahead of its scheduled presentation at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
The association was attributed to concentrations of particulate matter (PM) 2.5 in the Mississippi–Ohio River valley, which was on average higher than in other areas, but that didn’t entirely explain the increase in Parkinson’s disease in that region, Brittany Krzyzanowski, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow in the neuroepidemiology research program of the department of neurology at Barrow Neurological Institute, Dignity Health St. Joseph’s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, said in an interview.
“This study revealed Parkinson’s disease hot spots in the Mississippi–Ohio River valley, a region that has some of the highest levels of air pollution in the nation,” she said, “but we also still find a relationship between air pollution and Parkinson’s risk in the regions in the western half of the United States where Parkinson’s disease and air pollution levels are relatively low.”
Dr. Krzyzanowski and colleagues evaluated 22,546,965 Medicare beneficiaries in 2009, using a multimethod approach that included geospatial analytical techniques to categorize their exposure to PM2.5 based on age, sex, race, smoking status, and health care usage. The researchers also performed individual-level case-control analysis to assess PM2.5 results at the county level. The Medicare beneficiaries were grouped according to average exposure, with the lowest group having an average annual exposure of 5 mcg/m3 and the group with the highest exposure having an average annual exposure of 19 mcg/m3.
In total, researchers identified 83,674 Medicare beneficiaries with incident Parkinson’s disease, with 434 new cases per 100,000 people in the highest exposure group, compared with 359 new cases per 100,000 people in the lowest-exposure group. The relative risk for Parkinson’s disease increased in the highest quartile of PM2.5 by 25%, compared with the lowest quartile after adjusting for factors such as age, smoking status, and health care usage (95% confidence interval, 20%–29%).
The results showed the nationwide average annual PM2.5 was associated with incident Parkinson’s disease, and the Rocky Mountain region carried a strong association between PM2.5 and Parkson’s disease with a 16% increase in risk per level of exposure to PM2.5. While the Mississippi-Ohio River valley was also associated with Parkinson’s disease, there was a weaker association between PM2.5 and Parkinson’s disease, which the researchers attributed to a “ceiling effect” of PM2.5 between approximately 12-19 mcg/m3.
Dr. Krzyzanowski said that use of a large-population-based dataset and high-resolution location data were major strengths of the study. “Having this level of information leaves less room for uncertainty in our measures and analyses,” she said. “Our study also leveraged innovative geographic information systems which allowed us to refine local patterns of disease by using population behavior and demographic information (such as smoking and age) to ensure that we could provide the most accurate map representation available to date.”
A focus on air pollution
Existing research in examining the etiology of Parkinson’s mainly focused on exposure to pesticides,* Dr. Krzyzanowski explained, and “consists of studies using relatively small populations and low-resolution air pollution data.” Genetics is another possible cause, she noted, but only explains some Parkinson’s disease cases.
“Our work suggests that we should also be looking at air pollution as a contributor in the development of Parkinson’s disease,” she said.
Ray Dorsey, MD, professor of neurology at the University of Rochester (N.Y.), who was not involved with the study, said that evidence is mounting that “air pollution may be an important causal factor in Parkinson’s and especially Alzheimer’s disease.”
“This study by a well-regarded group of researchers adds epidemiological evidence for that association,” he said. Another strength is that the study was conducted in the United States, as many epidemiological studies evaluating air pollution and Parkinson’s disease have been performed outside the country because of “a dearth of reliable data sources.”
“This study, along with others, suggest that some of the important environmental toxicants tied to brain disease may be inhaled,” Dr. Dorsey said. “The nose may be the front door to the brain.”
Dr. Krzyzanowski said the next step in their research is further examination of different types of air pollution. “Air pollution contains a variety of toxic components which vary from region to region. Understanding the different components in air pollution and how they interact with climate, temperature, and topography could help explain the regional differences we observed.”
One potential limitation in the study is a lag between air pollution exposure and development of Parkinson’s disease, Dr. Dorsey noted.
“Here, it looks like (but I am not certain) that the investigators looked at current air pollution levels and new cases of Parkinson’s. Ideally, for incident cases of Parkinson’s disease, we would want to know historical data on exposure to air pollution,” he said.
Future studies should include prospective evaluation of adults as well as babies and children who have been exposed to both high and low levels of air pollution. That kind of study “would be incredibly valuable for determining the role of an important environmental toxicant in many brain diseases, including stroke, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s,” he said.
Dr. Krzyzanowski and Dr. Dorsey reported no relevant financial disclosures. This study was supported by grants from the Department of Defense, the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, and The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research.
*Correction, 4/14/23: An earlier version of this article mischaracterized the disease that was the subject of this research.
FROM AAN 2023
Picking up the premotor symptoms of Parkinson’s
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. We had a great discussion on Parkinson’s Disease for Primary Care with Dr. Albert Hung. Paul, this was something that really made me nervous. I didn’t have a lot of comfort with it. But he taught us a lot of tips about how to recognize Parkinson’s.
I hadn’t been as aware of the premotor symptoms: constipation, hyposmia (loss of sense of smell), and rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. If patients have those early on and they aren’t explained by other things (especially the REM sleep behavior disorder), you should really key in because those patients are at risk of developing Parkinson’s years down the line. Those symptoms could present first, which just kind of blew my mind.
What tips do you have about how to recognize Parkinson’s? Do you want to talk about the physical exam?
Paul N. Williams, MD: You know I love the physical exam stuff, so I’m happy to talk about that.
You were deeply upset that cogwheel rigidity was not pathognomonic for Parkinson’s, but you made the point – and our guest agreed – that asymmetry tends to be the key here. And I really appreciated the point about reemergent tremor. This is this idea of a resting tremor. If someone has more parkinsonian features, you might see an intention tremor with essential tremor. If they reach out, it might seem steady at first, but if they hold long enough, then the tremor may kind of reemerge. I thought that was a neat distinction.
And this idea of cogwheel rigidity is a combination of some of the cardinal features of Parkinson’s – it’s a little bit of tremor and a little bit of rigidity too. There’s a baseline increase in tone, and then the tremor is superimposed on top of that. When you’re feeling cogwheeling, that’s actually what you’re feeling on examination. Parkinson’s, with all of its physical exam findings has always fascinated me.
Dr. Watto: He also told us about some red flags.
With classic idiopathic parkinsonism, there’s asymmetric involvement of the tremor. So red flags include a symmetric tremor, which might be something other than idiopathic parkinsonism. He also mentioned that one of the reasons you may want to get imaging (which is not always necessary if someone has a classic presentation), is if you see lower body–predominant symptoms of parkinsonism. These patients have rigidity or slowness of movement in their legs, but their upper bodies are not affected. They don’t have masked facies or the tremor in their hands. You might get an MRI in that case because that could be presentation of vascular dementia or vascular disease in the brain or even normal pressure hydrocephalus, which is a treatable condition. That would be one reason to get imaging.
What if the patient was exposed to a drug like a dopamine antagonist? They will get better in a couple of days, right?
Dr. Williams: This was a really fascinating point because we typically think if a patient’s symptoms are related to a drug exposure – in this case, drug-induced parkinsonism – we can just stop the medication and the symptoms will disappear in a couple of days as the drug leaves the system. But as it turns out, it might take much longer. A mistake that Dr Hung often sees is that the clinician stops the possibly offending agent, but when they don’t see an immediate relief of symptoms, they assume the drug wasn’t causing them. You really have to give the patient a fair shot off the medication to experience recovery because those symptoms can last weeks or even months after the drug is discontinued.
Dr. Watto: Dr Hung looks at the patient’s problem list and asks whether is there any reason this patient might have been exposed to one of these medications?
We’re not going to get too much into specific Parkinson’s treatment, but I was glad to hear that exercise actually improves mobility and may even have some neuroprotective effects. He mentioned ongoing trials looking at that. We always love an excuse to tell patients that they should be moving around more and being physically active.
Dr. Williams: That was one of the more shocking things I learned, that exercise might actually be good for you. That will deeply inform my practice. Many of the treatments that we use for Parkinson’s only address symptoms. They don’t address progression or fix anything, but exercise can help with that.
Dr. Watto: Paul, the last question I wanted to ask you is about our role in primary care. Patients with Parkinson’s have autonomic symptoms. They have neurocognitive symptoms. What is our role in that as primary care physicians?
Dr. Williams: Myriad symptoms can accompany Parkinson’s, and we have experience with most of them. We should all feel fairly comfortable dealing with constipation, which can be a very bothersome symptom. And we can use our full arsenal for symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and even apathy – the anhedonia, which apparently can be the predominant feature. We do have the tools to address these problems.
This might be a situation where we might reach for bupropion or a tricyclic antidepressant, which might not be your initial choice for a patient with a possibly annoying mood disorder. But for someone with Parkinson’s disease, this actually may be very helpful. We know how to manage a lot of the symptoms that come along with Parkinson’s that are not just the motor symptoms, and we should take ownership of those things.
Dr. Watto: You can hear the rest of this podcast here. This has been another episode of The Curbsiders bringing you a little knowledge food for your brain hole. Until next time, I’ve been Dr Matthew Frank Watto.
Dr. Williams: And I’m Dr Paul Nelson Williams.
Dr. Watto is a clinical assistant professor, department of medicine, at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. Williams is Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, at Temple University, Philadelphia. Neither Dr. Watto nor Dr. Williams reported any relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. We had a great discussion on Parkinson’s Disease for Primary Care with Dr. Albert Hung. Paul, this was something that really made me nervous. I didn’t have a lot of comfort with it. But he taught us a lot of tips about how to recognize Parkinson’s.
I hadn’t been as aware of the premotor symptoms: constipation, hyposmia (loss of sense of smell), and rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. If patients have those early on and they aren’t explained by other things (especially the REM sleep behavior disorder), you should really key in because those patients are at risk of developing Parkinson’s years down the line. Those symptoms could present first, which just kind of blew my mind.
What tips do you have about how to recognize Parkinson’s? Do you want to talk about the physical exam?
Paul N. Williams, MD: You know I love the physical exam stuff, so I’m happy to talk about that.
You were deeply upset that cogwheel rigidity was not pathognomonic for Parkinson’s, but you made the point – and our guest agreed – that asymmetry tends to be the key here. And I really appreciated the point about reemergent tremor. This is this idea of a resting tremor. If someone has more parkinsonian features, you might see an intention tremor with essential tremor. If they reach out, it might seem steady at first, but if they hold long enough, then the tremor may kind of reemerge. I thought that was a neat distinction.
And this idea of cogwheel rigidity is a combination of some of the cardinal features of Parkinson’s – it’s a little bit of tremor and a little bit of rigidity too. There’s a baseline increase in tone, and then the tremor is superimposed on top of that. When you’re feeling cogwheeling, that’s actually what you’re feeling on examination. Parkinson’s, with all of its physical exam findings has always fascinated me.
Dr. Watto: He also told us about some red flags.
With classic idiopathic parkinsonism, there’s asymmetric involvement of the tremor. So red flags include a symmetric tremor, which might be something other than idiopathic parkinsonism. He also mentioned that one of the reasons you may want to get imaging (which is not always necessary if someone has a classic presentation), is if you see lower body–predominant symptoms of parkinsonism. These patients have rigidity or slowness of movement in their legs, but their upper bodies are not affected. They don’t have masked facies or the tremor in their hands. You might get an MRI in that case because that could be presentation of vascular dementia or vascular disease in the brain or even normal pressure hydrocephalus, which is a treatable condition. That would be one reason to get imaging.
What if the patient was exposed to a drug like a dopamine antagonist? They will get better in a couple of days, right?
Dr. Williams: This was a really fascinating point because we typically think if a patient’s symptoms are related to a drug exposure – in this case, drug-induced parkinsonism – we can just stop the medication and the symptoms will disappear in a couple of days as the drug leaves the system. But as it turns out, it might take much longer. A mistake that Dr Hung often sees is that the clinician stops the possibly offending agent, but when they don’t see an immediate relief of symptoms, they assume the drug wasn’t causing them. You really have to give the patient a fair shot off the medication to experience recovery because those symptoms can last weeks or even months after the drug is discontinued.
Dr. Watto: Dr Hung looks at the patient’s problem list and asks whether is there any reason this patient might have been exposed to one of these medications?
We’re not going to get too much into specific Parkinson’s treatment, but I was glad to hear that exercise actually improves mobility and may even have some neuroprotective effects. He mentioned ongoing trials looking at that. We always love an excuse to tell patients that they should be moving around more and being physically active.
Dr. Williams: That was one of the more shocking things I learned, that exercise might actually be good for you. That will deeply inform my practice. Many of the treatments that we use for Parkinson’s only address symptoms. They don’t address progression or fix anything, but exercise can help with that.
Dr. Watto: Paul, the last question I wanted to ask you is about our role in primary care. Patients with Parkinson’s have autonomic symptoms. They have neurocognitive symptoms. What is our role in that as primary care physicians?
Dr. Williams: Myriad symptoms can accompany Parkinson’s, and we have experience with most of them. We should all feel fairly comfortable dealing with constipation, which can be a very bothersome symptom. And we can use our full arsenal for symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and even apathy – the anhedonia, which apparently can be the predominant feature. We do have the tools to address these problems.
This might be a situation where we might reach for bupropion or a tricyclic antidepressant, which might not be your initial choice for a patient with a possibly annoying mood disorder. But for someone with Parkinson’s disease, this actually may be very helpful. We know how to manage a lot of the symptoms that come along with Parkinson’s that are not just the motor symptoms, and we should take ownership of those things.
Dr. Watto: You can hear the rest of this podcast here. This has been another episode of The Curbsiders bringing you a little knowledge food for your brain hole. Until next time, I’ve been Dr Matthew Frank Watto.
Dr. Williams: And I’m Dr Paul Nelson Williams.
Dr. Watto is a clinical assistant professor, department of medicine, at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. Williams is Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, at Temple University, Philadelphia. Neither Dr. Watto nor Dr. Williams reported any relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. We had a great discussion on Parkinson’s Disease for Primary Care with Dr. Albert Hung. Paul, this was something that really made me nervous. I didn’t have a lot of comfort with it. But he taught us a lot of tips about how to recognize Parkinson’s.
I hadn’t been as aware of the premotor symptoms: constipation, hyposmia (loss of sense of smell), and rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. If patients have those early on and they aren’t explained by other things (especially the REM sleep behavior disorder), you should really key in because those patients are at risk of developing Parkinson’s years down the line. Those symptoms could present first, which just kind of blew my mind.
What tips do you have about how to recognize Parkinson’s? Do you want to talk about the physical exam?
Paul N. Williams, MD: You know I love the physical exam stuff, so I’m happy to talk about that.
You were deeply upset that cogwheel rigidity was not pathognomonic for Parkinson’s, but you made the point – and our guest agreed – that asymmetry tends to be the key here. And I really appreciated the point about reemergent tremor. This is this idea of a resting tremor. If someone has more parkinsonian features, you might see an intention tremor with essential tremor. If they reach out, it might seem steady at first, but if they hold long enough, then the tremor may kind of reemerge. I thought that was a neat distinction.
And this idea of cogwheel rigidity is a combination of some of the cardinal features of Parkinson’s – it’s a little bit of tremor and a little bit of rigidity too. There’s a baseline increase in tone, and then the tremor is superimposed on top of that. When you’re feeling cogwheeling, that’s actually what you’re feeling on examination. Parkinson’s, with all of its physical exam findings has always fascinated me.
Dr. Watto: He also told us about some red flags.
With classic idiopathic parkinsonism, there’s asymmetric involvement of the tremor. So red flags include a symmetric tremor, which might be something other than idiopathic parkinsonism. He also mentioned that one of the reasons you may want to get imaging (which is not always necessary if someone has a classic presentation), is if you see lower body–predominant symptoms of parkinsonism. These patients have rigidity or slowness of movement in their legs, but their upper bodies are not affected. They don’t have masked facies or the tremor in their hands. You might get an MRI in that case because that could be presentation of vascular dementia or vascular disease in the brain or even normal pressure hydrocephalus, which is a treatable condition. That would be one reason to get imaging.
What if the patient was exposed to a drug like a dopamine antagonist? They will get better in a couple of days, right?
Dr. Williams: This was a really fascinating point because we typically think if a patient’s symptoms are related to a drug exposure – in this case, drug-induced parkinsonism – we can just stop the medication and the symptoms will disappear in a couple of days as the drug leaves the system. But as it turns out, it might take much longer. A mistake that Dr Hung often sees is that the clinician stops the possibly offending agent, but when they don’t see an immediate relief of symptoms, they assume the drug wasn’t causing them. You really have to give the patient a fair shot off the medication to experience recovery because those symptoms can last weeks or even months after the drug is discontinued.
Dr. Watto: Dr Hung looks at the patient’s problem list and asks whether is there any reason this patient might have been exposed to one of these medications?
We’re not going to get too much into specific Parkinson’s treatment, but I was glad to hear that exercise actually improves mobility and may even have some neuroprotective effects. He mentioned ongoing trials looking at that. We always love an excuse to tell patients that they should be moving around more and being physically active.
Dr. Williams: That was one of the more shocking things I learned, that exercise might actually be good for you. That will deeply inform my practice. Many of the treatments that we use for Parkinson’s only address symptoms. They don’t address progression or fix anything, but exercise can help with that.
Dr. Watto: Paul, the last question I wanted to ask you is about our role in primary care. Patients with Parkinson’s have autonomic symptoms. They have neurocognitive symptoms. What is our role in that as primary care physicians?
Dr. Williams: Myriad symptoms can accompany Parkinson’s, and we have experience with most of them. We should all feel fairly comfortable dealing with constipation, which can be a very bothersome symptom. And we can use our full arsenal for symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and even apathy – the anhedonia, which apparently can be the predominant feature. We do have the tools to address these problems.
This might be a situation where we might reach for bupropion or a tricyclic antidepressant, which might not be your initial choice for a patient with a possibly annoying mood disorder. But for someone with Parkinson’s disease, this actually may be very helpful. We know how to manage a lot of the symptoms that come along with Parkinson’s that are not just the motor symptoms, and we should take ownership of those things.
Dr. Watto: You can hear the rest of this podcast here. This has been another episode of The Curbsiders bringing you a little knowledge food for your brain hole. Until next time, I’ve been Dr Matthew Frank Watto.
Dr. Williams: And I’m Dr Paul Nelson Williams.
Dr. Watto is a clinical assistant professor, department of medicine, at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. Williams is Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, at Temple University, Philadelphia. Neither Dr. Watto nor Dr. Williams reported any relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Parkinson’s disease: What’s trauma got to do with it?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Kathrin LaFaver, MD: Hello. I’m happy to talk today to Dr. Indu Subramanian, clinical professor at University of California, Los Angeles, and director of the Parkinson’s Disease Research, Education and Clinical Center in Los Angeles. I am a neurologist in Saratoga Springs, New York, and we will be talking today about Indu’s new paper on childhood trauma and Parkinson’s disease. Welcome and thanks for taking the time.
Indu Subramanian, MD: Thank you so much for letting us highlight this important topic.
Dr. LaFaver: There are many papers published every month on Parkinson’s disease, but this topic stands out because it’s not a thing that has been commonly looked at. What gave you the idea to study this?
Neurology behind other specialties
Dr. Subramanian: Kathrin, you and I have been looking at things that can inform us about our patients – the person who’s standing in front of us when they come in and we’re giving them this diagnosis. I think that so much of what we’ve done [in the past] is a cookie cutter approach to giving everybody the standard treatment. [We’ve been assuming that] It doesn’t matter if they’re a man or woman. It doesn’t matter if they’re a veteran. It doesn’t matter if they may be from a minoritized population.
We’ve also been interested in approaches that are outside the box, right? We have this integrative medicine and lifestyle medicine background. I’ve been going to those meetings and really been struck by the mounting evidence on the importance of things like early adverse childhood events (ACEs), what zip code you live in, what your pollution index is, and how these things can affect people through their life and their health.
I think that it is high time neurologists pay attention to this. There’s been mounting evidence throughout many disease states, various types of cancers, and mental health. Cardiology is much more advanced, but we haven’t had much data in neurology. In fact, when we went to write this paper, there were just one or two papers that were looking at multiple sclerosis or general neurologic issues, but really nothing in Parkinson’s disease.
We know that Parkinson’s disease is not only a motor disease that affects mental health, but that it also affects nonmotor issues. Childhood adversity may affect how people progress or how quickly they may get a disease, and we were interested in how it may manifest in a disease like Parkinson’s disease.
That was the framework going to meetings. As we wrote this paper and were in various editing stages, there was a beautiful paper that came out by Nadine Burke Harris and team that really was a call to action for neurologists and caring about trauma.
Dr. LaFaver: I couldn’t agree more. It’s really an underrecognized issue. With my own background, being very interested in functional movement disorders, psychosomatic disorders, and so on, it becomes much more evident how common a trauma background is, not only for people we were traditionally asking about.
Why don’t you summarize your findings for us?
Adverse childhood events
Dr. Subramanian: This is a web-based survey, so obviously, these are patient self-reports of their disease. We have a large cohort of people that we’ve been following over 7 years. I’m looking at modifiable variables and what really impacts Parkinson’s disease. Some of our previous papers have looked at diet, exercise, and loneliness. This is the same cohort.
We ended up putting the ACEs questionnaire, which is 10 questions looking at whether you were exposed to certain things in your household below the age of 18. This is a relatively standard questionnaire that’s administered one time, and you get a score out of 10. This is something that has been pushed, at least in the state of California, as something that we should be checking more in all people coming in.
We introduced the survey, and we didn’t force everyone to take it. Unfortunately, there was 20% or so of our patients who chose not to answer these questions. One has to ask, who are those people that didn’t answer the questions? Are they the ones that may have had trauma and these questions were triggering? It was a gap. We didn’t add extra questions to explore why people didn’t answer those questions.
We have to also put this in context. We have a patient population that’s largely quite affluent, who are able to access web-based surveys through their computer, and largely Caucasian; there are not many minoritized populations in our cohort. We want to do better with that. We actually were able to gather a decent number of women. We represent women quite well in our survey. I think that’s because of this online approach and some of the things that we’re studying.
In our survey, we broke it down into people who had no ACEs, one to three ACEs, or four or more ACEs. This is a standard way to break down ACEs so that we’re able to categorize what to do with these patient populations.
What we saw – and it’s preliminary evidence – is that people who had higher ACE scores seemed to have more symptom severity when we controlled for things like years since diagnosis, age, and gender. They also seem to have a worse quality of life. There was some indication that there were more nonmotor issues in those populations, as you might expect, such as anxiety, depression, and things that presumably ACEs can affect separately.
There are some confounders, but I think we really want to use this as the first piece of evidence to hopefully pave the way for caring about trauma in Parkinson’s disease moving forward.
Dr. LaFaver: Thank you so much for that summary. You already mentioned the main methodology you used.
What is the next step for you? How do you see these findings informing our clinical care? Do you have suggestions for all of the neurologists listening in this regard?
PD not yet considered ACE-related
Dr. Subramanian: Dr. Burke Harris was the former surgeon general in California. She’s a woman of color and a brilliant speaker, and she had worked in inner cities, I think in San Francisco, with pediatric populations, seeing these effects of adversity in that time frame.
You see this population at risk, and then you’re following this cohort, which we knew from the Kaiser cohort determines earlier morbidity and mortality across a number of disease states. We’re seeing things like more heart attacks, more diabetes, and all kinds of things in these populations. This is not new news; we just have not been focusing on this.
In her paper, this call to action, they had talked about some ACE-related conditions that currently do not include Parkinson’s disease. There are three ACE-related neurologic conditions that people should be aware of. One is in the headache/pain universe. Another is in the stroke universe, and that’s understandable, given cardiovascular risk factors . Then the third is in this dementia risk category. I think Parkinson’s disease, as we know, can be associated with dementia. A large percentage of our patients get dementia, but we don’t have Parkinson’s disease called out in this framework.
What people are talking about is if you have no ACEs or are in this middle category of one to three ACEs and you don’t have an ACE-related diagnosis – which Parkinson’s disease is not currently – we just give some basic counseling about the importance of lifestyle. I think we would love to see that anyway. They’re talking about things like exercise, diet, sleep, social connection, getting out in nature, things like that, so just general counseling on the importance of that.
Then if you’re in this higher-risk category, and so with these ACE-related neurologic conditions, including dementia, headache, and stroke, if you had this middle range of one to three ACEs, they’re getting additional resources. Some of them may be referred for social work help or mental health support and things like that.
I’d really love to see that happening in Parkinson’s disease, because I think we have so many needs in our population. I’m always hoping to advocate for more mental health needs that are scarce and resources in the social support realm because I believe that social connection and social support is a huge buffer for this trauma.
ACEs are just one type of trauma. I take care of veterans in the Veterans [Affairs Department]. We have some information now coming out about posttraumatic stress disorder, predisposing to certain things in Parkinson’s disease, possibly head injury, and things like that. I think we have populations at risk that we can hopefully screen at intake, and I’m really pushing for that.
Maybe it’s not the neurologist that does this intake. It might be someone else on the team that can spend some time doing these questionnaires and understand if your patient has a high ACE score. Unless you ask, many patients don’t necessarily come forward to talk about this. I really am pushing for trying to screen and trying to advocate for more research in this area so that we can classify Parkinson’s disease as an ACE-related condition and thus give more resources from the mental health world, and also the social support world, to our patients.
Dr. LaFaver: Thank you. There are many important points, and I think it’s a very important thing to recognize that it may not be only trauma in childhood but also throughout life, as you said, and might really influence nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease in particular, including anxiety and pain, which are often difficult to treat.
I think there’s much more to do in research, advocacy, and education. We’re going to educate patients about this, and also educate other neurologists and providers. I think you mentioned that trauma-informed care is getting its spotlight in primary care and other specialties. I think we have catching up to do in neurology, and I think this is a really important work toward that goal.
Thank you so much for your work and for taking the time to share your thoughts. I hope to talk to you again soon.
Dr. Subramanian: Thank you so much, Kathrin.
Dr. LaFaver has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Subramanian disclosed ties with Acorda Therapeutics.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Kathrin LaFaver, MD: Hello. I’m happy to talk today to Dr. Indu Subramanian, clinical professor at University of California, Los Angeles, and director of the Parkinson’s Disease Research, Education and Clinical Center in Los Angeles. I am a neurologist in Saratoga Springs, New York, and we will be talking today about Indu’s new paper on childhood trauma and Parkinson’s disease. Welcome and thanks for taking the time.
Indu Subramanian, MD: Thank you so much for letting us highlight this important topic.
Dr. LaFaver: There are many papers published every month on Parkinson’s disease, but this topic stands out because it’s not a thing that has been commonly looked at. What gave you the idea to study this?
Neurology behind other specialties
Dr. Subramanian: Kathrin, you and I have been looking at things that can inform us about our patients – the person who’s standing in front of us when they come in and we’re giving them this diagnosis. I think that so much of what we’ve done [in the past] is a cookie cutter approach to giving everybody the standard treatment. [We’ve been assuming that] It doesn’t matter if they’re a man or woman. It doesn’t matter if they’re a veteran. It doesn’t matter if they may be from a minoritized population.
We’ve also been interested in approaches that are outside the box, right? We have this integrative medicine and lifestyle medicine background. I’ve been going to those meetings and really been struck by the mounting evidence on the importance of things like early adverse childhood events (ACEs), what zip code you live in, what your pollution index is, and how these things can affect people through their life and their health.
I think that it is high time neurologists pay attention to this. There’s been mounting evidence throughout many disease states, various types of cancers, and mental health. Cardiology is much more advanced, but we haven’t had much data in neurology. In fact, when we went to write this paper, there were just one or two papers that were looking at multiple sclerosis or general neurologic issues, but really nothing in Parkinson’s disease.
We know that Parkinson’s disease is not only a motor disease that affects mental health, but that it also affects nonmotor issues. Childhood adversity may affect how people progress or how quickly they may get a disease, and we were interested in how it may manifest in a disease like Parkinson’s disease.
That was the framework going to meetings. As we wrote this paper and were in various editing stages, there was a beautiful paper that came out by Nadine Burke Harris and team that really was a call to action for neurologists and caring about trauma.
Dr. LaFaver: I couldn’t agree more. It’s really an underrecognized issue. With my own background, being very interested in functional movement disorders, psychosomatic disorders, and so on, it becomes much more evident how common a trauma background is, not only for people we were traditionally asking about.
Why don’t you summarize your findings for us?
Adverse childhood events
Dr. Subramanian: This is a web-based survey, so obviously, these are patient self-reports of their disease. We have a large cohort of people that we’ve been following over 7 years. I’m looking at modifiable variables and what really impacts Parkinson’s disease. Some of our previous papers have looked at diet, exercise, and loneliness. This is the same cohort.
We ended up putting the ACEs questionnaire, which is 10 questions looking at whether you were exposed to certain things in your household below the age of 18. This is a relatively standard questionnaire that’s administered one time, and you get a score out of 10. This is something that has been pushed, at least in the state of California, as something that we should be checking more in all people coming in.
We introduced the survey, and we didn’t force everyone to take it. Unfortunately, there was 20% or so of our patients who chose not to answer these questions. One has to ask, who are those people that didn’t answer the questions? Are they the ones that may have had trauma and these questions were triggering? It was a gap. We didn’t add extra questions to explore why people didn’t answer those questions.
We have to also put this in context. We have a patient population that’s largely quite affluent, who are able to access web-based surveys through their computer, and largely Caucasian; there are not many minoritized populations in our cohort. We want to do better with that. We actually were able to gather a decent number of women. We represent women quite well in our survey. I think that’s because of this online approach and some of the things that we’re studying.
In our survey, we broke it down into people who had no ACEs, one to three ACEs, or four or more ACEs. This is a standard way to break down ACEs so that we’re able to categorize what to do with these patient populations.
What we saw – and it’s preliminary evidence – is that people who had higher ACE scores seemed to have more symptom severity when we controlled for things like years since diagnosis, age, and gender. They also seem to have a worse quality of life. There was some indication that there were more nonmotor issues in those populations, as you might expect, such as anxiety, depression, and things that presumably ACEs can affect separately.
There are some confounders, but I think we really want to use this as the first piece of evidence to hopefully pave the way for caring about trauma in Parkinson’s disease moving forward.
Dr. LaFaver: Thank you so much for that summary. You already mentioned the main methodology you used.
What is the next step for you? How do you see these findings informing our clinical care? Do you have suggestions for all of the neurologists listening in this regard?
PD not yet considered ACE-related
Dr. Subramanian: Dr. Burke Harris was the former surgeon general in California. She’s a woman of color and a brilliant speaker, and she had worked in inner cities, I think in San Francisco, with pediatric populations, seeing these effects of adversity in that time frame.
You see this population at risk, and then you’re following this cohort, which we knew from the Kaiser cohort determines earlier morbidity and mortality across a number of disease states. We’re seeing things like more heart attacks, more diabetes, and all kinds of things in these populations. This is not new news; we just have not been focusing on this.
In her paper, this call to action, they had talked about some ACE-related conditions that currently do not include Parkinson’s disease. There are three ACE-related neurologic conditions that people should be aware of. One is in the headache/pain universe. Another is in the stroke universe, and that’s understandable, given cardiovascular risk factors . Then the third is in this dementia risk category. I think Parkinson’s disease, as we know, can be associated with dementia. A large percentage of our patients get dementia, but we don’t have Parkinson’s disease called out in this framework.
What people are talking about is if you have no ACEs or are in this middle category of one to three ACEs and you don’t have an ACE-related diagnosis – which Parkinson’s disease is not currently – we just give some basic counseling about the importance of lifestyle. I think we would love to see that anyway. They’re talking about things like exercise, diet, sleep, social connection, getting out in nature, things like that, so just general counseling on the importance of that.
Then if you’re in this higher-risk category, and so with these ACE-related neurologic conditions, including dementia, headache, and stroke, if you had this middle range of one to three ACEs, they’re getting additional resources. Some of them may be referred for social work help or mental health support and things like that.
I’d really love to see that happening in Parkinson’s disease, because I think we have so many needs in our population. I’m always hoping to advocate for more mental health needs that are scarce and resources in the social support realm because I believe that social connection and social support is a huge buffer for this trauma.
ACEs are just one type of trauma. I take care of veterans in the Veterans [Affairs Department]. We have some information now coming out about posttraumatic stress disorder, predisposing to certain things in Parkinson’s disease, possibly head injury, and things like that. I think we have populations at risk that we can hopefully screen at intake, and I’m really pushing for that.
Maybe it’s not the neurologist that does this intake. It might be someone else on the team that can spend some time doing these questionnaires and understand if your patient has a high ACE score. Unless you ask, many patients don’t necessarily come forward to talk about this. I really am pushing for trying to screen and trying to advocate for more research in this area so that we can classify Parkinson’s disease as an ACE-related condition and thus give more resources from the mental health world, and also the social support world, to our patients.
Dr. LaFaver: Thank you. There are many important points, and I think it’s a very important thing to recognize that it may not be only trauma in childhood but also throughout life, as you said, and might really influence nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease in particular, including anxiety and pain, which are often difficult to treat.
I think there’s much more to do in research, advocacy, and education. We’re going to educate patients about this, and also educate other neurologists and providers. I think you mentioned that trauma-informed care is getting its spotlight in primary care and other specialties. I think we have catching up to do in neurology, and I think this is a really important work toward that goal.
Thank you so much for your work and for taking the time to share your thoughts. I hope to talk to you again soon.
Dr. Subramanian: Thank you so much, Kathrin.
Dr. LaFaver has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Subramanian disclosed ties with Acorda Therapeutics.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Kathrin LaFaver, MD: Hello. I’m happy to talk today to Dr. Indu Subramanian, clinical professor at University of California, Los Angeles, and director of the Parkinson’s Disease Research, Education and Clinical Center in Los Angeles. I am a neurologist in Saratoga Springs, New York, and we will be talking today about Indu’s new paper on childhood trauma and Parkinson’s disease. Welcome and thanks for taking the time.
Indu Subramanian, MD: Thank you so much for letting us highlight this important topic.
Dr. LaFaver: There are many papers published every month on Parkinson’s disease, but this topic stands out because it’s not a thing that has been commonly looked at. What gave you the idea to study this?
Neurology behind other specialties
Dr. Subramanian: Kathrin, you and I have been looking at things that can inform us about our patients – the person who’s standing in front of us when they come in and we’re giving them this diagnosis. I think that so much of what we’ve done [in the past] is a cookie cutter approach to giving everybody the standard treatment. [We’ve been assuming that] It doesn’t matter if they’re a man or woman. It doesn’t matter if they’re a veteran. It doesn’t matter if they may be from a minoritized population.
We’ve also been interested in approaches that are outside the box, right? We have this integrative medicine and lifestyle medicine background. I’ve been going to those meetings and really been struck by the mounting evidence on the importance of things like early adverse childhood events (ACEs), what zip code you live in, what your pollution index is, and how these things can affect people through their life and their health.
I think that it is high time neurologists pay attention to this. There’s been mounting evidence throughout many disease states, various types of cancers, and mental health. Cardiology is much more advanced, but we haven’t had much data in neurology. In fact, when we went to write this paper, there were just one or two papers that were looking at multiple sclerosis or general neurologic issues, but really nothing in Parkinson’s disease.
We know that Parkinson’s disease is not only a motor disease that affects mental health, but that it also affects nonmotor issues. Childhood adversity may affect how people progress or how quickly they may get a disease, and we were interested in how it may manifest in a disease like Parkinson’s disease.
That was the framework going to meetings. As we wrote this paper and were in various editing stages, there was a beautiful paper that came out by Nadine Burke Harris and team that really was a call to action for neurologists and caring about trauma.
Dr. LaFaver: I couldn’t agree more. It’s really an underrecognized issue. With my own background, being very interested in functional movement disorders, psychosomatic disorders, and so on, it becomes much more evident how common a trauma background is, not only for people we were traditionally asking about.
Why don’t you summarize your findings for us?
Adverse childhood events
Dr. Subramanian: This is a web-based survey, so obviously, these are patient self-reports of their disease. We have a large cohort of people that we’ve been following over 7 years. I’m looking at modifiable variables and what really impacts Parkinson’s disease. Some of our previous papers have looked at diet, exercise, and loneliness. This is the same cohort.
We ended up putting the ACEs questionnaire, which is 10 questions looking at whether you were exposed to certain things in your household below the age of 18. This is a relatively standard questionnaire that’s administered one time, and you get a score out of 10. This is something that has been pushed, at least in the state of California, as something that we should be checking more in all people coming in.
We introduced the survey, and we didn’t force everyone to take it. Unfortunately, there was 20% or so of our patients who chose not to answer these questions. One has to ask, who are those people that didn’t answer the questions? Are they the ones that may have had trauma and these questions were triggering? It was a gap. We didn’t add extra questions to explore why people didn’t answer those questions.
We have to also put this in context. We have a patient population that’s largely quite affluent, who are able to access web-based surveys through their computer, and largely Caucasian; there are not many minoritized populations in our cohort. We want to do better with that. We actually were able to gather a decent number of women. We represent women quite well in our survey. I think that’s because of this online approach and some of the things that we’re studying.
In our survey, we broke it down into people who had no ACEs, one to three ACEs, or four or more ACEs. This is a standard way to break down ACEs so that we’re able to categorize what to do with these patient populations.
What we saw – and it’s preliminary evidence – is that people who had higher ACE scores seemed to have more symptom severity when we controlled for things like years since diagnosis, age, and gender. They also seem to have a worse quality of life. There was some indication that there were more nonmotor issues in those populations, as you might expect, such as anxiety, depression, and things that presumably ACEs can affect separately.
There are some confounders, but I think we really want to use this as the first piece of evidence to hopefully pave the way for caring about trauma in Parkinson’s disease moving forward.
Dr. LaFaver: Thank you so much for that summary. You already mentioned the main methodology you used.
What is the next step for you? How do you see these findings informing our clinical care? Do you have suggestions for all of the neurologists listening in this regard?
PD not yet considered ACE-related
Dr. Subramanian: Dr. Burke Harris was the former surgeon general in California. She’s a woman of color and a brilliant speaker, and she had worked in inner cities, I think in San Francisco, with pediatric populations, seeing these effects of adversity in that time frame.
You see this population at risk, and then you’re following this cohort, which we knew from the Kaiser cohort determines earlier morbidity and mortality across a number of disease states. We’re seeing things like more heart attacks, more diabetes, and all kinds of things in these populations. This is not new news; we just have not been focusing on this.
In her paper, this call to action, they had talked about some ACE-related conditions that currently do not include Parkinson’s disease. There are three ACE-related neurologic conditions that people should be aware of. One is in the headache/pain universe. Another is in the stroke universe, and that’s understandable, given cardiovascular risk factors . Then the third is in this dementia risk category. I think Parkinson’s disease, as we know, can be associated with dementia. A large percentage of our patients get dementia, but we don’t have Parkinson’s disease called out in this framework.
What people are talking about is if you have no ACEs or are in this middle category of one to three ACEs and you don’t have an ACE-related diagnosis – which Parkinson’s disease is not currently – we just give some basic counseling about the importance of lifestyle. I think we would love to see that anyway. They’re talking about things like exercise, diet, sleep, social connection, getting out in nature, things like that, so just general counseling on the importance of that.
Then if you’re in this higher-risk category, and so with these ACE-related neurologic conditions, including dementia, headache, and stroke, if you had this middle range of one to three ACEs, they’re getting additional resources. Some of them may be referred for social work help or mental health support and things like that.
I’d really love to see that happening in Parkinson’s disease, because I think we have so many needs in our population. I’m always hoping to advocate for more mental health needs that are scarce and resources in the social support realm because I believe that social connection and social support is a huge buffer for this trauma.
ACEs are just one type of trauma. I take care of veterans in the Veterans [Affairs Department]. We have some information now coming out about posttraumatic stress disorder, predisposing to certain things in Parkinson’s disease, possibly head injury, and things like that. I think we have populations at risk that we can hopefully screen at intake, and I’m really pushing for that.
Maybe it’s not the neurologist that does this intake. It might be someone else on the team that can spend some time doing these questionnaires and understand if your patient has a high ACE score. Unless you ask, many patients don’t necessarily come forward to talk about this. I really am pushing for trying to screen and trying to advocate for more research in this area so that we can classify Parkinson’s disease as an ACE-related condition and thus give more resources from the mental health world, and also the social support world, to our patients.
Dr. LaFaver: Thank you. There are many important points, and I think it’s a very important thing to recognize that it may not be only trauma in childhood but also throughout life, as you said, and might really influence nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease in particular, including anxiety and pain, which are often difficult to treat.
I think there’s much more to do in research, advocacy, and education. We’re going to educate patients about this, and also educate other neurologists and providers. I think you mentioned that trauma-informed care is getting its spotlight in primary care and other specialties. I think we have catching up to do in neurology, and I think this is a really important work toward that goal.
Thank you so much for your work and for taking the time to share your thoughts. I hope to talk to you again soon.
Dr. Subramanian: Thank you so much, Kathrin.
Dr. LaFaver has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Subramanian disclosed ties with Acorda Therapeutics.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Do B vitamins reduce Parkinson’s risk?
Though there was some evidence that vitamin B12 early in life was associated with decreased PD risk, the findings were inconsistent and were observed only in people whose daily intake was 10 times the recommended level.
“The results of this large prospective study do not support the hypothesis that increasing folate or vitamin B6 intakes above the current levels would reduce PD risk in this population of mostly White U.S. health professionals,” lead investigator Mario H. Flores-Torres, MD, PhD, a research scientist in the department of nutrition at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, said in an interview.
However, he added, the study “leaves open the possibility that in some individuals the intake of vitamin B12 contributes to PD risk – a finding that warrants further research.”
The findings were published online in Movement Disorders.
Mixed findings
Previous studies have suggested B vitamins – including folate, B6 and B12 – might affect PD risk, but results have been mixed.
The new study included 80,965 women from the Nurses’ Health Study (1984-2016) and 48,837 men from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study (1986-2016). The average age at baseline was 50 years in women and 54 years in men, and participants were followed for about 30 years.
Participants completed questionnaires about diet at the beginning of the study and again every 4 years.
To account for the possibility of reverse causation due to the long prodromal phase of PD, investigators conducted lagged analyses at 8, 12, 16, and 20 years.
During the follow-up period, 1,426 incident cases of PD were diagnosed (687 in women and 739 in men).
Researchers found no link between reduced PD risk and intake of vitamin B6 or folate.
Though the total cumulative average intake of vitamin B12 was not associated with PD risk, investigators noted a modest decrease in risk between those with highest baseline of B12 and participants with the lowest baseline levels (hazard ratio, 0.80; P = .01).
Individuals in the highest quintile of B12 intake at baseline had an average intake of 21-22 mcg/d, close to 10 times the recommended daily intake of 2.4 mcg/d.
“Although some of our results suggest that a higher intake of vitamin B12 may decrease the risk of PD in a population of U.S. health professionals, the associations we observed were modest and not entirely consistent,” Dr. Flores-Torres said.
“Additional studies need to confirm our findings to better understand whether people who take higher amounts of B12 younger in life may have a protective benefit against PD,” he added.
The whole picture?
Commenting on the findings for this article, Rebecca Gilbert, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer of the American Parkinson Disease Association, New York, noted that checking B vitamin levels is a fairly standard practice for most clinicians. In that regard, this study highlights why this is important.
“Neurologists will often test B12 levels and recommend a supplement if your level is below the normal range,” she said. “No one is questioning the value of B12 for nerves and recommend that B12 is in the normal to high normal range.”
But understanding how B vitamins may or may not affect PD risk might require a different kind of study.
“This analysis, much like many others, is trying so hard to figure out what is it in diets that affects Parkinson’s disease risk,” Dr. Gilbert said. “But we have yet to say these are the nutrients that prevent Parkinson’s or increase the risk.”
One reason for the conflicting results in studies such as this could be that the explanation for the link between diet and PD risk may not be in specific minerals consumed but rather in the diet as a whole.
“Focusing on specific elements of a diet may not give us the answer,” Dr. Gilbert said. “We should be analyzing diet as a complete holistic picture because it’s not just the elements but how everything in what we eat works together.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Parkinson’s Foundation. Dr. Flores-Torres and Dr. Gilbert report no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Though there was some evidence that vitamin B12 early in life was associated with decreased PD risk, the findings were inconsistent and were observed only in people whose daily intake was 10 times the recommended level.
“The results of this large prospective study do not support the hypothesis that increasing folate or vitamin B6 intakes above the current levels would reduce PD risk in this population of mostly White U.S. health professionals,” lead investigator Mario H. Flores-Torres, MD, PhD, a research scientist in the department of nutrition at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, said in an interview.
However, he added, the study “leaves open the possibility that in some individuals the intake of vitamin B12 contributes to PD risk – a finding that warrants further research.”
The findings were published online in Movement Disorders.
Mixed findings
Previous studies have suggested B vitamins – including folate, B6 and B12 – might affect PD risk, but results have been mixed.
The new study included 80,965 women from the Nurses’ Health Study (1984-2016) and 48,837 men from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study (1986-2016). The average age at baseline was 50 years in women and 54 years in men, and participants were followed for about 30 years.
Participants completed questionnaires about diet at the beginning of the study and again every 4 years.
To account for the possibility of reverse causation due to the long prodromal phase of PD, investigators conducted lagged analyses at 8, 12, 16, and 20 years.
During the follow-up period, 1,426 incident cases of PD were diagnosed (687 in women and 739 in men).
Researchers found no link between reduced PD risk and intake of vitamin B6 or folate.
Though the total cumulative average intake of vitamin B12 was not associated with PD risk, investigators noted a modest decrease in risk between those with highest baseline of B12 and participants with the lowest baseline levels (hazard ratio, 0.80; P = .01).
Individuals in the highest quintile of B12 intake at baseline had an average intake of 21-22 mcg/d, close to 10 times the recommended daily intake of 2.4 mcg/d.
“Although some of our results suggest that a higher intake of vitamin B12 may decrease the risk of PD in a population of U.S. health professionals, the associations we observed were modest and not entirely consistent,” Dr. Flores-Torres said.
“Additional studies need to confirm our findings to better understand whether people who take higher amounts of B12 younger in life may have a protective benefit against PD,” he added.
The whole picture?
Commenting on the findings for this article, Rebecca Gilbert, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer of the American Parkinson Disease Association, New York, noted that checking B vitamin levels is a fairly standard practice for most clinicians. In that regard, this study highlights why this is important.
“Neurologists will often test B12 levels and recommend a supplement if your level is below the normal range,” she said. “No one is questioning the value of B12 for nerves and recommend that B12 is in the normal to high normal range.”
But understanding how B vitamins may or may not affect PD risk might require a different kind of study.
“This analysis, much like many others, is trying so hard to figure out what is it in diets that affects Parkinson’s disease risk,” Dr. Gilbert said. “But we have yet to say these are the nutrients that prevent Parkinson’s or increase the risk.”
One reason for the conflicting results in studies such as this could be that the explanation for the link between diet and PD risk may not be in specific minerals consumed but rather in the diet as a whole.
“Focusing on specific elements of a diet may not give us the answer,” Dr. Gilbert said. “We should be analyzing diet as a complete holistic picture because it’s not just the elements but how everything in what we eat works together.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Parkinson’s Foundation. Dr. Flores-Torres and Dr. Gilbert report no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Though there was some evidence that vitamin B12 early in life was associated with decreased PD risk, the findings were inconsistent and were observed only in people whose daily intake was 10 times the recommended level.
“The results of this large prospective study do not support the hypothesis that increasing folate or vitamin B6 intakes above the current levels would reduce PD risk in this population of mostly White U.S. health professionals,” lead investigator Mario H. Flores-Torres, MD, PhD, a research scientist in the department of nutrition at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, said in an interview.
However, he added, the study “leaves open the possibility that in some individuals the intake of vitamin B12 contributes to PD risk – a finding that warrants further research.”
The findings were published online in Movement Disorders.
Mixed findings
Previous studies have suggested B vitamins – including folate, B6 and B12 – might affect PD risk, but results have been mixed.
The new study included 80,965 women from the Nurses’ Health Study (1984-2016) and 48,837 men from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study (1986-2016). The average age at baseline was 50 years in women and 54 years in men, and participants were followed for about 30 years.
Participants completed questionnaires about diet at the beginning of the study and again every 4 years.
To account for the possibility of reverse causation due to the long prodromal phase of PD, investigators conducted lagged analyses at 8, 12, 16, and 20 years.
During the follow-up period, 1,426 incident cases of PD were diagnosed (687 in women and 739 in men).
Researchers found no link between reduced PD risk and intake of vitamin B6 or folate.
Though the total cumulative average intake of vitamin B12 was not associated with PD risk, investigators noted a modest decrease in risk between those with highest baseline of B12 and participants with the lowest baseline levels (hazard ratio, 0.80; P = .01).
Individuals in the highest quintile of B12 intake at baseline had an average intake of 21-22 mcg/d, close to 10 times the recommended daily intake of 2.4 mcg/d.
“Although some of our results suggest that a higher intake of vitamin B12 may decrease the risk of PD in a population of U.S. health professionals, the associations we observed were modest and not entirely consistent,” Dr. Flores-Torres said.
“Additional studies need to confirm our findings to better understand whether people who take higher amounts of B12 younger in life may have a protective benefit against PD,” he added.
The whole picture?
Commenting on the findings for this article, Rebecca Gilbert, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer of the American Parkinson Disease Association, New York, noted that checking B vitamin levels is a fairly standard practice for most clinicians. In that regard, this study highlights why this is important.
“Neurologists will often test B12 levels and recommend a supplement if your level is below the normal range,” she said. “No one is questioning the value of B12 for nerves and recommend that B12 is in the normal to high normal range.”
But understanding how B vitamins may or may not affect PD risk might require a different kind of study.
“This analysis, much like many others, is trying so hard to figure out what is it in diets that affects Parkinson’s disease risk,” Dr. Gilbert said. “But we have yet to say these are the nutrients that prevent Parkinson’s or increase the risk.”
One reason for the conflicting results in studies such as this could be that the explanation for the link between diet and PD risk may not be in specific minerals consumed but rather in the diet as a whole.
“Focusing on specific elements of a diet may not give us the answer,” Dr. Gilbert said. “We should be analyzing diet as a complete holistic picture because it’s not just the elements but how everything in what we eat works together.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Parkinson’s Foundation. Dr. Flores-Torres and Dr. Gilbert report no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MOVEMENT DISORDERS
Exercise tied to reduced Parkinson’s motor symptoms and increased well-being
A systematic review of 156 clinical trials involving 8,000 patients with Parkinson’s disease showed dancing and aquatic exercise, in particular, were most likely to improve motor symptoms, while swimming, endurance training, and mind-body training were most likely to benefit quality of life.
“For most types of exercise we studied, we observed positive effects on both the severity of motor signs and quality of life. These results highlight the importance of exercise in general, as they suggest people with Parkinson’s disease can benefit from a variety of exercises,” said study investigator Moritz Ernst, MSc, deputy head of the working group on evidence-based medicine at the University Hospital Cologne (Germany).
“Clinicians and people with Parkinson’s disease may have several options of exercise programs to choose from when establishing an individual training routine,” he added, emphasizing that overall those with Parkinson’s disease should seek professional advice, including assessment of motor and nonmotor symptoms, to develop a training agenda based on their individual needs.
The study was published online in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.
May I have this dance?
The investigators analyzed data from randomized, controlled trials comparing different types of exercise and no exercise and the subsequent effect on Parkinson’s disease symptoms. Exercise included dance, strength-resistance training, mind-body training such as tai chi and yoga, water-based training, resistance training, gait/balance/functional training, and endurance training.
The average age of study participants ranged from 60 to 74 years, and most of the studies included patients with mild to moderate Parkinson’s disease. The mean length of the various interventions was 12 weeks.
When the researchers examined the effect of exercise on motor symptoms, they found that dance (P = .88), aqua-based training (P = .69), and gait/balance/functional training (P = .67) were most likely to reduce symptom severity.
Aqua-based training (P = .95), endurance training (P = .77), and mind-body training (P = .75) were most were most likely to benefit quality of life, although the investigators caution that these findings were at risk of bias because quality of life was self-reported.
The investigators noted other study limitations including the fact that most of the studies included in the review had small sample sizes and their study only included patients with mild to moderate versus severe Parkinson’s disease.
The authors said that future research should include larger samples, report intent-to-treat analyses, and involve participants with more advanced forms of Parkinson’s disease who may also have cognitive difficulties.
Prescribe exercise
“We should be giving our patients, no matter where they are in their disease stage, a ‘prescription’ to exercise,” said Mitra Afshari, MD, MPH. Dr. Afshari was not involved in the study but leads her own research on Parkinson’s disease and exercise as the site principal investigator on the National Institutes of Health–funded SPARX3 Study in Parkinson’s Disease and Exercise at Rush University in Chicago. She said that, based on her experience caring for patients with Parkinson’s disease at all disease stages, “patients who have been physically active their whole lives and can maintain that activity despite their diagnosis fare the best.”
However, she added, those who initiate physical exercise after diagnosis can also do very well and reap benefits, including improved motor symptoms.
The study was funded by University Hospital of Cologne, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital, University of Cologne, and the German Ministry of Education and Research. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A systematic review of 156 clinical trials involving 8,000 patients with Parkinson’s disease showed dancing and aquatic exercise, in particular, were most likely to improve motor symptoms, while swimming, endurance training, and mind-body training were most likely to benefit quality of life.
“For most types of exercise we studied, we observed positive effects on both the severity of motor signs and quality of life. These results highlight the importance of exercise in general, as they suggest people with Parkinson’s disease can benefit from a variety of exercises,” said study investigator Moritz Ernst, MSc, deputy head of the working group on evidence-based medicine at the University Hospital Cologne (Germany).
“Clinicians and people with Parkinson’s disease may have several options of exercise programs to choose from when establishing an individual training routine,” he added, emphasizing that overall those with Parkinson’s disease should seek professional advice, including assessment of motor and nonmotor symptoms, to develop a training agenda based on their individual needs.
The study was published online in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.
May I have this dance?
The investigators analyzed data from randomized, controlled trials comparing different types of exercise and no exercise and the subsequent effect on Parkinson’s disease symptoms. Exercise included dance, strength-resistance training, mind-body training such as tai chi and yoga, water-based training, resistance training, gait/balance/functional training, and endurance training.
The average age of study participants ranged from 60 to 74 years, and most of the studies included patients with mild to moderate Parkinson’s disease. The mean length of the various interventions was 12 weeks.
When the researchers examined the effect of exercise on motor symptoms, they found that dance (P = .88), aqua-based training (P = .69), and gait/balance/functional training (P = .67) were most likely to reduce symptom severity.
Aqua-based training (P = .95), endurance training (P = .77), and mind-body training (P = .75) were most were most likely to benefit quality of life, although the investigators caution that these findings were at risk of bias because quality of life was self-reported.
The investigators noted other study limitations including the fact that most of the studies included in the review had small sample sizes and their study only included patients with mild to moderate versus severe Parkinson’s disease.
The authors said that future research should include larger samples, report intent-to-treat analyses, and involve participants with more advanced forms of Parkinson’s disease who may also have cognitive difficulties.
Prescribe exercise
“We should be giving our patients, no matter where they are in their disease stage, a ‘prescription’ to exercise,” said Mitra Afshari, MD, MPH. Dr. Afshari was not involved in the study but leads her own research on Parkinson’s disease and exercise as the site principal investigator on the National Institutes of Health–funded SPARX3 Study in Parkinson’s Disease and Exercise at Rush University in Chicago. She said that, based on her experience caring for patients with Parkinson’s disease at all disease stages, “patients who have been physically active their whole lives and can maintain that activity despite their diagnosis fare the best.”
However, she added, those who initiate physical exercise after diagnosis can also do very well and reap benefits, including improved motor symptoms.
The study was funded by University Hospital of Cologne, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital, University of Cologne, and the German Ministry of Education and Research. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A systematic review of 156 clinical trials involving 8,000 patients with Parkinson’s disease showed dancing and aquatic exercise, in particular, were most likely to improve motor symptoms, while swimming, endurance training, and mind-body training were most likely to benefit quality of life.
“For most types of exercise we studied, we observed positive effects on both the severity of motor signs and quality of life. These results highlight the importance of exercise in general, as they suggest people with Parkinson’s disease can benefit from a variety of exercises,” said study investigator Moritz Ernst, MSc, deputy head of the working group on evidence-based medicine at the University Hospital Cologne (Germany).
“Clinicians and people with Parkinson’s disease may have several options of exercise programs to choose from when establishing an individual training routine,” he added, emphasizing that overall those with Parkinson’s disease should seek professional advice, including assessment of motor and nonmotor symptoms, to develop a training agenda based on their individual needs.
The study was published online in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.
May I have this dance?
The investigators analyzed data from randomized, controlled trials comparing different types of exercise and no exercise and the subsequent effect on Parkinson’s disease symptoms. Exercise included dance, strength-resistance training, mind-body training such as tai chi and yoga, water-based training, resistance training, gait/balance/functional training, and endurance training.
The average age of study participants ranged from 60 to 74 years, and most of the studies included patients with mild to moderate Parkinson’s disease. The mean length of the various interventions was 12 weeks.
When the researchers examined the effect of exercise on motor symptoms, they found that dance (P = .88), aqua-based training (P = .69), and gait/balance/functional training (P = .67) were most likely to reduce symptom severity.
Aqua-based training (P = .95), endurance training (P = .77), and mind-body training (P = .75) were most were most likely to benefit quality of life, although the investigators caution that these findings were at risk of bias because quality of life was self-reported.
The investigators noted other study limitations including the fact that most of the studies included in the review had small sample sizes and their study only included patients with mild to moderate versus severe Parkinson’s disease.
The authors said that future research should include larger samples, report intent-to-treat analyses, and involve participants with more advanced forms of Parkinson’s disease who may also have cognitive difficulties.
Prescribe exercise
“We should be giving our patients, no matter where they are in their disease stage, a ‘prescription’ to exercise,” said Mitra Afshari, MD, MPH. Dr. Afshari was not involved in the study but leads her own research on Parkinson’s disease and exercise as the site principal investigator on the National Institutes of Health–funded SPARX3 Study in Parkinson’s Disease and Exercise at Rush University in Chicago. She said that, based on her experience caring for patients with Parkinson’s disease at all disease stages, “patients who have been physically active their whole lives and can maintain that activity despite their diagnosis fare the best.”
However, she added, those who initiate physical exercise after diagnosis can also do very well and reap benefits, including improved motor symptoms.
The study was funded by University Hospital of Cologne, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital, University of Cologne, and the German Ministry of Education and Research. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE COCHRANE DATABASE OF SYSTEMATIC REVIEWS