User login
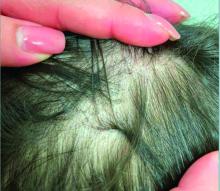
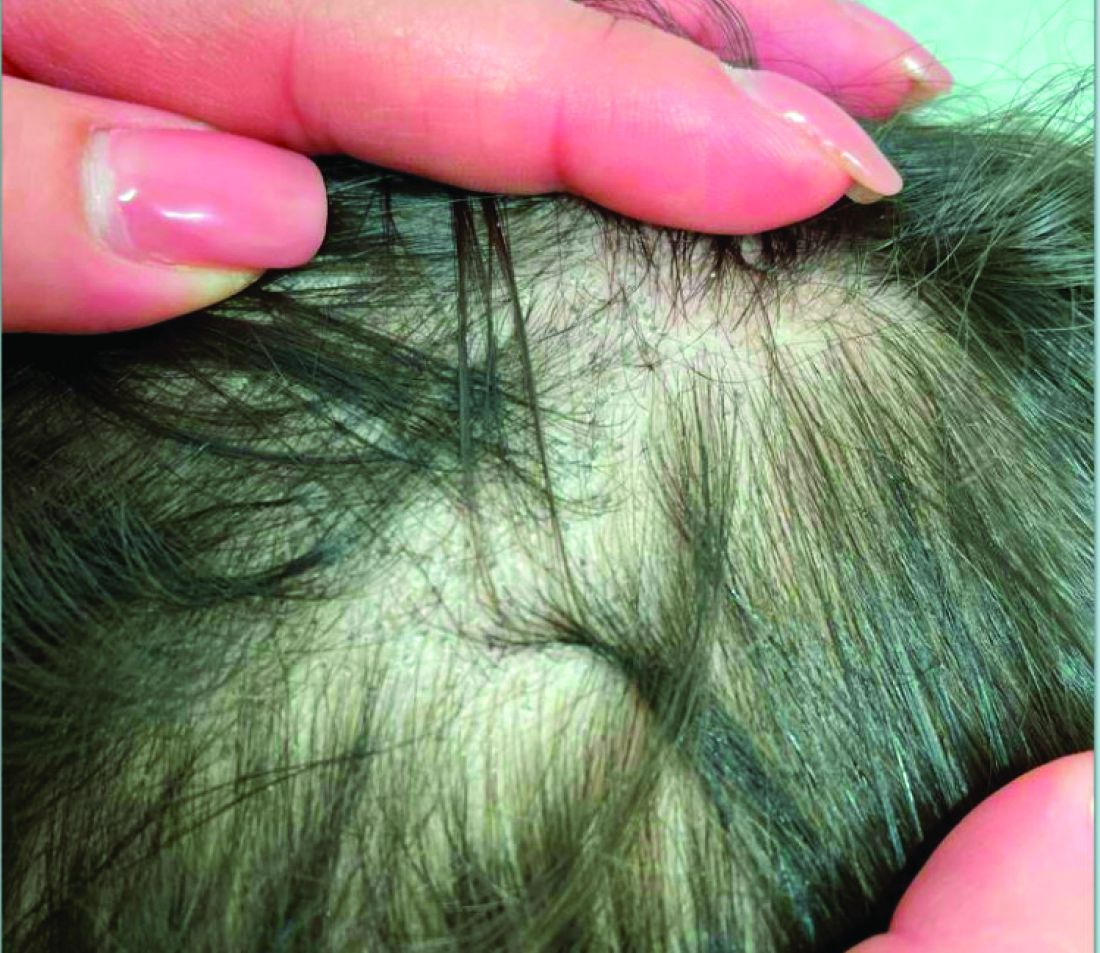
A 7-Year-Old Boy Presents With Dark Spots on His Scalp and Areas of Poor Hair Growth
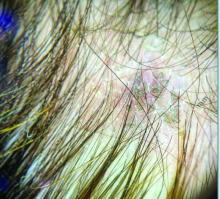
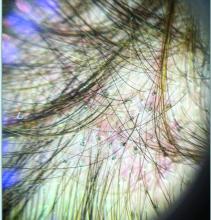
Given the trichoscopic findings, scrapings from the scaly areas were taken and revealed hyphae, confirming the diagnosis of tinea capitis. A fungal culture identified Trichophyton tonsurans as the causative organism.
Tinea capitis is the most common dermatophyte infection in children. Risk factors include participation in close-contact sports like wrestling or jiu-jitsu, attendance at daycare for younger children, African American hair care practices, pet ownership (particularly cats and rodents), and living in overcrowded conditions.
Diagnosis of tinea capitis requires a thorough clinical history to identify potential risk factors. On physical examination, patchy hair loss with associated scaling should raise suspicion for tinea capitis. Inflammatory signs, such as pustules and swelling, may suggest the presence of a kerion, further supporting the diagnosis. Although some practitioners use Wood’s lamp to help with diagnosis, its utility is limited. It detects fluorescence in Microsporum species (exothrix infections) but not in Trichophyton species (endothrix infections).
Trichoscopy can be a valuable tool when inflammation is minimal, and only hair loss and scaling are observed. Trichoscopic findings suggestive of tinea capitis include comma hairs, corkscrew hairs (as seen in this patient), Morse code-like hairs, zigzag hairs, bent hairs, block hairs, and i-hairs. Other common, though not characteristic, findings include broken hairs, black dots, perifollicular scaling, and diffuse scaling.
KOH (potassium hydroxide) analysis is another useful method for detecting fungal elements, though it does not identify the specific fungus and may not be available in all clinical settings. Mycologic culture remains the gold standard for diagnosing tinea capitis, though results can take 3-4 weeks. Newer diagnostic techniques, such as PCR analysis and MALDI-TOF/MS, offer more rapid identification of the causative organism.
The differential diagnosis includes:
- Seborrheic dermatitis, which presents with greasy, yellowish scales and itching, with trichoscopy showing twisted, coiled hairs and yellowish scaling.
- Psoriasis, which can mimic tinea capitis but presents with well-demarcated red plaques and silvery-white scales. Trichoscopy shows red dots and uniform scaling.
- Alopecia areata, which causes patchy hair loss without inflammation or scaling, with trichoscopic findings of exclamation mark hairs, black dots, and yellow dots.
- Trichotillomania, a hair-pulling disorder, which results in irregular patches of hair loss. Trichoscopy shows broken hairs of varying lengths, V-sign hairs, and flame-shaped residues at follicular openings.
Treatment of tinea capitis requires systemic antifungals and topical agents to prevent fungal spore spread. Several treatment guidelines are available from different institutions. Griseofulvin (FDA-approved for patients > 2 years of age) has been widely used, particularly for Microsporum canis infections. However, due to limited availability in many countries, terbinafine (FDA-approved for patients > 4 years of age) is now commonly used as first-line therapy, especially for Trichophyton species. Treatment typically lasts 4-6 weeks, and post-treatment cultures may be recommended to confirm mycologic cure.
Concerns about drug resistance have emerged, particularly for terbinafine-resistant dermatophytes linked to mutations in the squalene epoxidase enzyme. Resistance may be driven by limited antifungal availability and poor adherence to prolonged treatment regimens. While fluconazole and itraconazole are used off-label, growing evidence supports their effectiveness, although one large trial showed suboptimal cure rates with fluconazole.
Though systemic antifungals are generally safe, hepatotoxicity remains a concern, especially in patients with hepatic conditions or other comorbidities. Lab monitoring is advised for patients on prolonged or multiple therapies, or for those with coexisting conditions. The decision to conduct lab monitoring should be discussed with parents, balancing the very low risk of hepatotoxicity in healthy children against their comfort level.
An alternative to systemic therapy is photodynamic therapy (PDT), which has been reported as successful in treating tinea capitis infections, particularly in cases of T. mentagrophytes and M. canis. However, large-scale trials are needed to confirm PDT’s efficacy and safety.
In conclusion, children presenting with hair loss, scaling, and associated dark spots on the scalp should be evaluated for fungal infection. While trichoscopy can aid in diagnosis, fungal culture remains the gold standard for confirmation.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
Rudnicka L et al. Hair shafts in trichoscopy: clues for diagnosis of hair and scalp diseases. Dermatol Clin. 2013 Oct;31(4):695-708, x. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2013.06.007.
Gupta AK et al. An update on tinea capitis in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2024 Aug 7. doi: 10.1111/pde.15708.
Anna Waskiel-Burnat et al. Trichoscopy of tinea capitis: A systematic review. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020 Feb;10(1):43-52. doi: 10.1007/s13555-019-00350-1.
Given the trichoscopic findings, scrapings from the scaly areas were taken and revealed hyphae, confirming the diagnosis of tinea capitis. A fungal culture identified Trichophyton tonsurans as the causative organism.
Tinea capitis is the most common dermatophyte infection in children. Risk factors include participation in close-contact sports like wrestling or jiu-jitsu, attendance at daycare for younger children, African American hair care practices, pet ownership (particularly cats and rodents), and living in overcrowded conditions.
Diagnosis of tinea capitis requires a thorough clinical history to identify potential risk factors. On physical examination, patchy hair loss with associated scaling should raise suspicion for tinea capitis. Inflammatory signs, such as pustules and swelling, may suggest the presence of a kerion, further supporting the diagnosis. Although some practitioners use Wood’s lamp to help with diagnosis, its utility is limited. It detects fluorescence in Microsporum species (exothrix infections) but not in Trichophyton species (endothrix infections).
Trichoscopy can be a valuable tool when inflammation is minimal, and only hair loss and scaling are observed. Trichoscopic findings suggestive of tinea capitis include comma hairs, corkscrew hairs (as seen in this patient), Morse code-like hairs, zigzag hairs, bent hairs, block hairs, and i-hairs. Other common, though not characteristic, findings include broken hairs, black dots, perifollicular scaling, and diffuse scaling.
KOH (potassium hydroxide) analysis is another useful method for detecting fungal elements, though it does not identify the specific fungus and may not be available in all clinical settings. Mycologic culture remains the gold standard for diagnosing tinea capitis, though results can take 3-4 weeks. Newer diagnostic techniques, such as PCR analysis and MALDI-TOF/MS, offer more rapid identification of the causative organism.
The differential diagnosis includes:
- Seborrheic dermatitis, which presents with greasy, yellowish scales and itching, with trichoscopy showing twisted, coiled hairs and yellowish scaling.
- Psoriasis, which can mimic tinea capitis but presents with well-demarcated red plaques and silvery-white scales. Trichoscopy shows red dots and uniform scaling.
- Alopecia areata, which causes patchy hair loss without inflammation or scaling, with trichoscopic findings of exclamation mark hairs, black dots, and yellow dots.
- Trichotillomania, a hair-pulling disorder, which results in irregular patches of hair loss. Trichoscopy shows broken hairs of varying lengths, V-sign hairs, and flame-shaped residues at follicular openings.
Treatment of tinea capitis requires systemic antifungals and topical agents to prevent fungal spore spread. Several treatment guidelines are available from different institutions. Griseofulvin (FDA-approved for patients > 2 years of age) has been widely used, particularly for Microsporum canis infections. However, due to limited availability in many countries, terbinafine (FDA-approved for patients > 4 years of age) is now commonly used as first-line therapy, especially for Trichophyton species. Treatment typically lasts 4-6 weeks, and post-treatment cultures may be recommended to confirm mycologic cure.
Concerns about drug resistance have emerged, particularly for terbinafine-resistant dermatophytes linked to mutations in the squalene epoxidase enzyme. Resistance may be driven by limited antifungal availability and poor adherence to prolonged treatment regimens. While fluconazole and itraconazole are used off-label, growing evidence supports their effectiveness, although one large trial showed suboptimal cure rates with fluconazole.
Though systemic antifungals are generally safe, hepatotoxicity remains a concern, especially in patients with hepatic conditions or other comorbidities. Lab monitoring is advised for patients on prolonged or multiple therapies, or for those with coexisting conditions. The decision to conduct lab monitoring should be discussed with parents, balancing the very low risk of hepatotoxicity in healthy children against their comfort level.
An alternative to systemic therapy is photodynamic therapy (PDT), which has been reported as successful in treating tinea capitis infections, particularly in cases of T. mentagrophytes and M. canis. However, large-scale trials are needed to confirm PDT’s efficacy and safety.
In conclusion, children presenting with hair loss, scaling, and associated dark spots on the scalp should be evaluated for fungal infection. While trichoscopy can aid in diagnosis, fungal culture remains the gold standard for confirmation.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
Rudnicka L et al. Hair shafts in trichoscopy: clues for diagnosis of hair and scalp diseases. Dermatol Clin. 2013 Oct;31(4):695-708, x. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2013.06.007.
Gupta AK et al. An update on tinea capitis in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2024 Aug 7. doi: 10.1111/pde.15708.
Anna Waskiel-Burnat et al. Trichoscopy of tinea capitis: A systematic review. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020 Feb;10(1):43-52. doi: 10.1007/s13555-019-00350-1.
Given the trichoscopic findings, scrapings from the scaly areas were taken and revealed hyphae, confirming the diagnosis of tinea capitis. A fungal culture identified Trichophyton tonsurans as the causative organism.
Tinea capitis is the most common dermatophyte infection in children. Risk factors include participation in close-contact sports like wrestling or jiu-jitsu, attendance at daycare for younger children, African American hair care practices, pet ownership (particularly cats and rodents), and living in overcrowded conditions.
Diagnosis of tinea capitis requires a thorough clinical history to identify potential risk factors. On physical examination, patchy hair loss with associated scaling should raise suspicion for tinea capitis. Inflammatory signs, such as pustules and swelling, may suggest the presence of a kerion, further supporting the diagnosis. Although some practitioners use Wood’s lamp to help with diagnosis, its utility is limited. It detects fluorescence in Microsporum species (exothrix infections) but not in Trichophyton species (endothrix infections).
Trichoscopy can be a valuable tool when inflammation is minimal, and only hair loss and scaling are observed. Trichoscopic findings suggestive of tinea capitis include comma hairs, corkscrew hairs (as seen in this patient), Morse code-like hairs, zigzag hairs, bent hairs, block hairs, and i-hairs. Other common, though not characteristic, findings include broken hairs, black dots, perifollicular scaling, and diffuse scaling.
KOH (potassium hydroxide) analysis is another useful method for detecting fungal elements, though it does not identify the specific fungus and may not be available in all clinical settings. Mycologic culture remains the gold standard for diagnosing tinea capitis, though results can take 3-4 weeks. Newer diagnostic techniques, such as PCR analysis and MALDI-TOF/MS, offer more rapid identification of the causative organism.
The differential diagnosis includes:
- Seborrheic dermatitis, which presents with greasy, yellowish scales and itching, with trichoscopy showing twisted, coiled hairs and yellowish scaling.
- Psoriasis, which can mimic tinea capitis but presents with well-demarcated red plaques and silvery-white scales. Trichoscopy shows red dots and uniform scaling.
- Alopecia areata, which causes patchy hair loss without inflammation or scaling, with trichoscopic findings of exclamation mark hairs, black dots, and yellow dots.
- Trichotillomania, a hair-pulling disorder, which results in irregular patches of hair loss. Trichoscopy shows broken hairs of varying lengths, V-sign hairs, and flame-shaped residues at follicular openings.
Treatment of tinea capitis requires systemic antifungals and topical agents to prevent fungal spore spread. Several treatment guidelines are available from different institutions. Griseofulvin (FDA-approved for patients > 2 years of age) has been widely used, particularly for Microsporum canis infections. However, due to limited availability in many countries, terbinafine (FDA-approved for patients > 4 years of age) is now commonly used as first-line therapy, especially for Trichophyton species. Treatment typically lasts 4-6 weeks, and post-treatment cultures may be recommended to confirm mycologic cure.
Concerns about drug resistance have emerged, particularly for terbinafine-resistant dermatophytes linked to mutations in the squalene epoxidase enzyme. Resistance may be driven by limited antifungal availability and poor adherence to prolonged treatment regimens. While fluconazole and itraconazole are used off-label, growing evidence supports their effectiveness, although one large trial showed suboptimal cure rates with fluconazole.
Though systemic antifungals are generally safe, hepatotoxicity remains a concern, especially in patients with hepatic conditions or other comorbidities. Lab monitoring is advised for patients on prolonged or multiple therapies, or for those with coexisting conditions. The decision to conduct lab monitoring should be discussed with parents, balancing the very low risk of hepatotoxicity in healthy children against their comfort level.
An alternative to systemic therapy is photodynamic therapy (PDT), which has been reported as successful in treating tinea capitis infections, particularly in cases of T. mentagrophytes and M. canis. However, large-scale trials are needed to confirm PDT’s efficacy and safety.
In conclusion, children presenting with hair loss, scaling, and associated dark spots on the scalp should be evaluated for fungal infection. While trichoscopy can aid in diagnosis, fungal culture remains the gold standard for confirmation.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
Rudnicka L et al. Hair shafts in trichoscopy: clues for diagnosis of hair and scalp diseases. Dermatol Clin. 2013 Oct;31(4):695-708, x. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2013.06.007.
Gupta AK et al. An update on tinea capitis in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2024 Aug 7. doi: 10.1111/pde.15708.
Anna Waskiel-Burnat et al. Trichoscopy of tinea capitis: A systematic review. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020 Feb;10(1):43-52. doi: 10.1007/s13555-019-00350-1.
What Are the Best Tools for Early Childhood Developmental Concerns?
Early recognition of neurodevelopmental concerns and timely access to services have been shown to result in better outcomes for young children. But not all instruments are of equal value, and new research has sought to identify the most useful among them.
For their research, published online in Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology, Andrea Burgess, PhD, of the University of Queensland in Brisbane, Australia, and her colleagues looked at two decades’ worth of systematic reviews of screening, assessment, and diagnostic tools used in children younger than 6 years.
Eighty-six clinical reviews and six practice guidelines, all published between 2000 and 2023, were included in the scoping review, which covered nearly 250 different multi-domain and domain- and disorder-specific tools.
The diagnostic instruments were those used to diagnose the most common early childhood disorders, including intellectual disability, global developmental delay, communication disorders, autism spectrum disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, cerebral palsy, movement disorders, and fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Burgess and her colleagues sought to determine which tools had the strongest evidence behind them, noting that comparisons were inherently limited by differences in the tested populations, cutoff values, and other factors.
Burgess and her colleagues identified 67 instruments — about a third of those analyzed in the study — “with good discriminative or predictive validity for the screening and assessment of developmental concerns or disability.” Recommended tools were classified by tool type and by patient age groups.
The reason a tool might not be recommended, Burgess said in an email, was for lack of psychometric testing or published evidence, or because the tool was very narrow in scope (eg, covering only a single aspect of a domain), had a small time window for use, or was too new to have been captured in published systematic reviews.
Top Recommendations
Among multi-domain assessment tools, the Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development, the Battelle Developmental Inventory, and the Mullen Scales of Early Learning all emerged as highly recommended. The top diagnostic screening tool for autism was the revised version of Social Attention and Communication Surveillance. For cerebral palsy, the top-rated diagnostic assessment tools were Prechtl’s Qualitative Assessment of General Movements and the Hammersmith Infant Neurological Examination.
Ratifying findings by other groups, the researchers determined the Ages & Stages Questionnaires, Third Edition (ASQ-3) to be the best overall multi-domain screening instrument for early childhood development, thanks to its simplicity and ease of use by a wide range of practitioner types. Burgess and her colleagues noted, however, that the ASQ-3 “will not identify all children with developmental concerns and may incorrectly identify others,” and that it may be more accurate in children 2 years or older.
Patient Care Setting and Cultural, Socioeconomic Factors Are Key
This news organization spoke to two clinicians working with these and similar tools in the United States. Both said that the care setting can also influence the utility of tools, with cultural and socioeconomic factors playing important roles.
Liz Schwandt, PsyD, an early intervention specialist in Los Angeles, said in an interview that children living in high-risk communities in the United States have a larger burden of developmental delays. But for many families in these communities, accessing care can be complex, which is why well-designed, efficient screening tools like ASQ-3 are especially valuable in practice.
“The reality is you have 10 minutes with a lot of families, and if it’s an emergency, you need to know,” she said. “The ASQ-3 has a very broad age range for this type of instrument and can be used by different practitioner types. The reason it’s successful lies in its parent-centric approach and inherent ease of use. It’s quick, and you can score it using pencil and paper while chatting with the parent, and you can use it for multiple siblings in the space of one appointment.”
With very young children, in whom neurodevelopmental concerns often overlap domains, Schwandt said it can be more important to flag a potential problem early and initiate a nonspecific developmental intervention than wait for results from more precise assessments using more specialized tools. These often require multiple, multi-hour appointments, which can be difficult to attain in lower-resource settings in the United States and can delay care, she said.
Liza Mackintosh, MD, a pediatrician at a federally funded healthcare center in Los Angeles that serves mostly publicly insured families, called validated first-line screening tools “incredibly important.” While rates of developmental screenings in pediatric clinics are increasing, there is still room for improvement, she said.
Mackintosh’s institution does not currently use the ASQ-3 but a different screening tool, called the Survey of Well-Being of Young Children (SWYC), that is embedded into the electronic health record. (The SWYC was not among the tools highlighted in Burgess and colleagues’ review.) Like the ASQ-3, it is short and efficient, she said, and it is used in all children in the recommended age ranges.
“Our visits are on average only 20 minutes,” Mackintosh said. “There’s not enough time for an in-depth developmental assessment. We will flag things such as a speech delay, gross motor delay, or fine motor delay” and refer to early intervention centers for more in-depth developmental assessments as needed, she said.
“The biggest job of pediatricians working in communities that are under-resourced is advocating for those early intervention services,” Mackintosh added. “We really see our job as doing the recommended screening, putting that together with what we’re seeing clinically and on history, and then advocating for the right next step or early intervention. Because sometimes the diagnosis is — I don’t want to say irrelevant, but your treatment plan is still going to be the same. So while I don’t have a formal diagnosis yet, the child definitely needs therapies and we’re still going to get those therapies.”
Burgess and her colleagues stressed in their paper the importance of selecting tools that are culturally appropriate for Indigenous communities in Australia, noting that “inappropriate tools may lead to over- or under-recognition of children with developmental concerns.”
Schwandt and Mackintosh said that the same applies in US settings.
“We’ve done a good job translating screening tools into Chinese, Spanish, Vietnamese, and Russian,” Schwandt said. “But some of them assume a way of taking care of children that is not always shared across cultures. The expectations of how children should play and interact with adults can be very different, and there needs to be an understanding of that. Just putting something in Vietnamese doesn’t mean that there are obvious analogues to understanding what the questionnaire is asking.”
Mackintosh concurred. “A lot of times our patients will not do well on screening, even though they’re fine, because they don’t have the exposure to that activity that’s being asked about. So — is the child scribbling with crayons? Is she climbing up a ladder at a playground? In order to be able to do that, you need to have an environment that you are doing it in. The screeners have to really be appropriate for what the child is exposed to. And sometimes our patients just don’t have that exposure.”
Burgess and colleagues’ study was funded by the Australian government and the Merchant Charitable Foundation. The authors disclosed no financial conflicts of interest. Schwandt and Mackintosh disclosed no conflicts of interest related to their comments.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Early recognition of neurodevelopmental concerns and timely access to services have been shown to result in better outcomes for young children. But not all instruments are of equal value, and new research has sought to identify the most useful among them.
For their research, published online in Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology, Andrea Burgess, PhD, of the University of Queensland in Brisbane, Australia, and her colleagues looked at two decades’ worth of systematic reviews of screening, assessment, and diagnostic tools used in children younger than 6 years.
Eighty-six clinical reviews and six practice guidelines, all published between 2000 and 2023, were included in the scoping review, which covered nearly 250 different multi-domain and domain- and disorder-specific tools.
The diagnostic instruments were those used to diagnose the most common early childhood disorders, including intellectual disability, global developmental delay, communication disorders, autism spectrum disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, cerebral palsy, movement disorders, and fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Burgess and her colleagues sought to determine which tools had the strongest evidence behind them, noting that comparisons were inherently limited by differences in the tested populations, cutoff values, and other factors.
Burgess and her colleagues identified 67 instruments — about a third of those analyzed in the study — “with good discriminative or predictive validity for the screening and assessment of developmental concerns or disability.” Recommended tools were classified by tool type and by patient age groups.
The reason a tool might not be recommended, Burgess said in an email, was for lack of psychometric testing or published evidence, or because the tool was very narrow in scope (eg, covering only a single aspect of a domain), had a small time window for use, or was too new to have been captured in published systematic reviews.
Top Recommendations
Among multi-domain assessment tools, the Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development, the Battelle Developmental Inventory, and the Mullen Scales of Early Learning all emerged as highly recommended. The top diagnostic screening tool for autism was the revised version of Social Attention and Communication Surveillance. For cerebral palsy, the top-rated diagnostic assessment tools were Prechtl’s Qualitative Assessment of General Movements and the Hammersmith Infant Neurological Examination.
Ratifying findings by other groups, the researchers determined the Ages & Stages Questionnaires, Third Edition (ASQ-3) to be the best overall multi-domain screening instrument for early childhood development, thanks to its simplicity and ease of use by a wide range of practitioner types. Burgess and her colleagues noted, however, that the ASQ-3 “will not identify all children with developmental concerns and may incorrectly identify others,” and that it may be more accurate in children 2 years or older.
Patient Care Setting and Cultural, Socioeconomic Factors Are Key
This news organization spoke to two clinicians working with these and similar tools in the United States. Both said that the care setting can also influence the utility of tools, with cultural and socioeconomic factors playing important roles.
Liz Schwandt, PsyD, an early intervention specialist in Los Angeles, said in an interview that children living in high-risk communities in the United States have a larger burden of developmental delays. But for many families in these communities, accessing care can be complex, which is why well-designed, efficient screening tools like ASQ-3 are especially valuable in practice.
“The reality is you have 10 minutes with a lot of families, and if it’s an emergency, you need to know,” she said. “The ASQ-3 has a very broad age range for this type of instrument and can be used by different practitioner types. The reason it’s successful lies in its parent-centric approach and inherent ease of use. It’s quick, and you can score it using pencil and paper while chatting with the parent, and you can use it for multiple siblings in the space of one appointment.”
With very young children, in whom neurodevelopmental concerns often overlap domains, Schwandt said it can be more important to flag a potential problem early and initiate a nonspecific developmental intervention than wait for results from more precise assessments using more specialized tools. These often require multiple, multi-hour appointments, which can be difficult to attain in lower-resource settings in the United States and can delay care, she said.
Liza Mackintosh, MD, a pediatrician at a federally funded healthcare center in Los Angeles that serves mostly publicly insured families, called validated first-line screening tools “incredibly important.” While rates of developmental screenings in pediatric clinics are increasing, there is still room for improvement, she said.
Mackintosh’s institution does not currently use the ASQ-3 but a different screening tool, called the Survey of Well-Being of Young Children (SWYC), that is embedded into the electronic health record. (The SWYC was not among the tools highlighted in Burgess and colleagues’ review.) Like the ASQ-3, it is short and efficient, she said, and it is used in all children in the recommended age ranges.
“Our visits are on average only 20 minutes,” Mackintosh said. “There’s not enough time for an in-depth developmental assessment. We will flag things such as a speech delay, gross motor delay, or fine motor delay” and refer to early intervention centers for more in-depth developmental assessments as needed, she said.
“The biggest job of pediatricians working in communities that are under-resourced is advocating for those early intervention services,” Mackintosh added. “We really see our job as doing the recommended screening, putting that together with what we’re seeing clinically and on history, and then advocating for the right next step or early intervention. Because sometimes the diagnosis is — I don’t want to say irrelevant, but your treatment plan is still going to be the same. So while I don’t have a formal diagnosis yet, the child definitely needs therapies and we’re still going to get those therapies.”
Burgess and her colleagues stressed in their paper the importance of selecting tools that are culturally appropriate for Indigenous communities in Australia, noting that “inappropriate tools may lead to over- or under-recognition of children with developmental concerns.”
Schwandt and Mackintosh said that the same applies in US settings.
“We’ve done a good job translating screening tools into Chinese, Spanish, Vietnamese, and Russian,” Schwandt said. “But some of them assume a way of taking care of children that is not always shared across cultures. The expectations of how children should play and interact with adults can be very different, and there needs to be an understanding of that. Just putting something in Vietnamese doesn’t mean that there are obvious analogues to understanding what the questionnaire is asking.”
Mackintosh concurred. “A lot of times our patients will not do well on screening, even though they’re fine, because they don’t have the exposure to that activity that’s being asked about. So — is the child scribbling with crayons? Is she climbing up a ladder at a playground? In order to be able to do that, you need to have an environment that you are doing it in. The screeners have to really be appropriate for what the child is exposed to. And sometimes our patients just don’t have that exposure.”
Burgess and colleagues’ study was funded by the Australian government and the Merchant Charitable Foundation. The authors disclosed no financial conflicts of interest. Schwandt and Mackintosh disclosed no conflicts of interest related to their comments.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Early recognition of neurodevelopmental concerns and timely access to services have been shown to result in better outcomes for young children. But not all instruments are of equal value, and new research has sought to identify the most useful among them.
For their research, published online in Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology, Andrea Burgess, PhD, of the University of Queensland in Brisbane, Australia, and her colleagues looked at two decades’ worth of systematic reviews of screening, assessment, and diagnostic tools used in children younger than 6 years.
Eighty-six clinical reviews and six practice guidelines, all published between 2000 and 2023, were included in the scoping review, which covered nearly 250 different multi-domain and domain- and disorder-specific tools.
The diagnostic instruments were those used to diagnose the most common early childhood disorders, including intellectual disability, global developmental delay, communication disorders, autism spectrum disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, cerebral palsy, movement disorders, and fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Burgess and her colleagues sought to determine which tools had the strongest evidence behind them, noting that comparisons were inherently limited by differences in the tested populations, cutoff values, and other factors.
Burgess and her colleagues identified 67 instruments — about a third of those analyzed in the study — “with good discriminative or predictive validity for the screening and assessment of developmental concerns or disability.” Recommended tools were classified by tool type and by patient age groups.
The reason a tool might not be recommended, Burgess said in an email, was for lack of psychometric testing or published evidence, or because the tool was very narrow in scope (eg, covering only a single aspect of a domain), had a small time window for use, or was too new to have been captured in published systematic reviews.
Top Recommendations
Among multi-domain assessment tools, the Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development, the Battelle Developmental Inventory, and the Mullen Scales of Early Learning all emerged as highly recommended. The top diagnostic screening tool for autism was the revised version of Social Attention and Communication Surveillance. For cerebral palsy, the top-rated diagnostic assessment tools were Prechtl’s Qualitative Assessment of General Movements and the Hammersmith Infant Neurological Examination.
Ratifying findings by other groups, the researchers determined the Ages & Stages Questionnaires, Third Edition (ASQ-3) to be the best overall multi-domain screening instrument for early childhood development, thanks to its simplicity and ease of use by a wide range of practitioner types. Burgess and her colleagues noted, however, that the ASQ-3 “will not identify all children with developmental concerns and may incorrectly identify others,” and that it may be more accurate in children 2 years or older.
Patient Care Setting and Cultural, Socioeconomic Factors Are Key
This news organization spoke to two clinicians working with these and similar tools in the United States. Both said that the care setting can also influence the utility of tools, with cultural and socioeconomic factors playing important roles.
Liz Schwandt, PsyD, an early intervention specialist in Los Angeles, said in an interview that children living in high-risk communities in the United States have a larger burden of developmental delays. But for many families in these communities, accessing care can be complex, which is why well-designed, efficient screening tools like ASQ-3 are especially valuable in practice.
“The reality is you have 10 minutes with a lot of families, and if it’s an emergency, you need to know,” she said. “The ASQ-3 has a very broad age range for this type of instrument and can be used by different practitioner types. The reason it’s successful lies in its parent-centric approach and inherent ease of use. It’s quick, and you can score it using pencil and paper while chatting with the parent, and you can use it for multiple siblings in the space of one appointment.”
With very young children, in whom neurodevelopmental concerns often overlap domains, Schwandt said it can be more important to flag a potential problem early and initiate a nonspecific developmental intervention than wait for results from more precise assessments using more specialized tools. These often require multiple, multi-hour appointments, which can be difficult to attain in lower-resource settings in the United States and can delay care, she said.
Liza Mackintosh, MD, a pediatrician at a federally funded healthcare center in Los Angeles that serves mostly publicly insured families, called validated first-line screening tools “incredibly important.” While rates of developmental screenings in pediatric clinics are increasing, there is still room for improvement, she said.
Mackintosh’s institution does not currently use the ASQ-3 but a different screening tool, called the Survey of Well-Being of Young Children (SWYC), that is embedded into the electronic health record. (The SWYC was not among the tools highlighted in Burgess and colleagues’ review.) Like the ASQ-3, it is short and efficient, she said, and it is used in all children in the recommended age ranges.
“Our visits are on average only 20 minutes,” Mackintosh said. “There’s not enough time for an in-depth developmental assessment. We will flag things such as a speech delay, gross motor delay, or fine motor delay” and refer to early intervention centers for more in-depth developmental assessments as needed, she said.
“The biggest job of pediatricians working in communities that are under-resourced is advocating for those early intervention services,” Mackintosh added. “We really see our job as doing the recommended screening, putting that together with what we’re seeing clinically and on history, and then advocating for the right next step or early intervention. Because sometimes the diagnosis is — I don’t want to say irrelevant, but your treatment plan is still going to be the same. So while I don’t have a formal diagnosis yet, the child definitely needs therapies and we’re still going to get those therapies.”
Burgess and her colleagues stressed in their paper the importance of selecting tools that are culturally appropriate for Indigenous communities in Australia, noting that “inappropriate tools may lead to over- or under-recognition of children with developmental concerns.”
Schwandt and Mackintosh said that the same applies in US settings.
“We’ve done a good job translating screening tools into Chinese, Spanish, Vietnamese, and Russian,” Schwandt said. “But some of them assume a way of taking care of children that is not always shared across cultures. The expectations of how children should play and interact with adults can be very different, and there needs to be an understanding of that. Just putting something in Vietnamese doesn’t mean that there are obvious analogues to understanding what the questionnaire is asking.”
Mackintosh concurred. “A lot of times our patients will not do well on screening, even though they’re fine, because they don’t have the exposure to that activity that’s being asked about. So — is the child scribbling with crayons? Is she climbing up a ladder at a playground? In order to be able to do that, you need to have an environment that you are doing it in. The screeners have to really be appropriate for what the child is exposed to. And sometimes our patients just don’t have that exposure.”
Burgess and colleagues’ study was funded by the Australian government and the Merchant Charitable Foundation. The authors disclosed no financial conflicts of interest. Schwandt and Mackintosh disclosed no conflicts of interest related to their comments.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Artificial Intelligence Helps Diagnose Lung Disease in Infants and Outperforms Trainee Doctors
VIENNA — Artificial Intelligence (AI) can assist doctors in assessing and diagnosing respiratory illnesses in infants and children, according to two new studies presented at the European Respiratory Society (ERS) 2024 Congress.
Researchers can train artificial neural networks (ANNs) to detect lung disease in premature babies by analyzing their breathing patterns while they sleep. “Our noninvasive test is less distressing for the baby and their parents, meaning they can access treatment more quickly, and may also be relevant for their long-term prognosis,” said Edgar Delgado-Eckert, PhD, adjunct professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at The University of Basel, Switzerland, and a research group leader at the University Children’s Hospital, Switzerland.
Manjith Narayanan, MD, a consultant in pediatric pulmonology at the Royal Hospital for Children and Young People, Edinburgh, and honorary senior clinical lecturer at The University of Edinburgh, United Kingdom, said chatbots such as ChatGPT, Bard, and Bing can perform as well as or better than trainee doctors when assessing children with respiratory issues. He said chatbots could triage patients more quickly and ease pressure on health services.
Chatbots Show Promise in Triage of Pediatric Respiratory Illnesses
Researchers at The University of Edinburgh provided 10 trainee doctors with less than 4 months of clinical experience in pediatrics with clinical scenarios that covered topics such as cystic fibrosis, asthma, sleep-disordered breathing, breathlessness, chest infections, or no obvious diagnosis.
The trainee doctors had 1 hour to use the internet, although they were not allowed to use chatbots to solve each scenario with a descriptive answer.
Each scenario was also presented to the three large language models (LLMs): OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google’s Bard, and Microsoft’s Bing.
Six pediatric respiratory experts assessed all responses, scoring correctness, comprehensiveness, usefulness, plausibility, and coherence on a scale of 0-9. They were also asked to say whether they thought a human or a chatbot generated each response.
ChatGPT scored an average of 7 out of 9 overall and was believed to be more human-like than responses from the other chatbots. Bard scored an average of 6 out of 9 and was more “coherent” than trainee doctors, but in other respects, it was no better or worse than trainee doctors. Bing and trainee doctors scored an average of 4 out of 9.
“Our study is the first, to our knowledge, to test LLMs against trainee doctors in situations that reflect real-life clinical practice,” Narayanan said. “We did this by allowing the trainee doctors to have full access to resources available on the internet, as they would in real life. This moves the focus away from testing memory, where LLMs have a clear advantage.”
Narayanan said that these models could help nurses, trainee doctors, and primary care physicians triage patients quickly and assist medical professionals in their studies by summarizing their thought processes. “The key word, though, is “assist.” They cannot replace conventional medical training yet,” he told Medscape Medical News.
The researchers found no obvious hallucinations — seemingly made-up information — with any of the three LLMs. Still, Narayanan said, “We need to be aware of this possibility and build mitigations.”
Hilary Pinnock, ERS education council chair and professor of primary care respiratory medicine at The University of Edinburgh who was not involved in the research, said seeing how widely available AI tools can provide solutions to complex cases of respiratory illness in children is exciting and worrying at the same time. “It certainly points the way to a brave new world of AI-supported care.”
“However, before we start to use AI in routine clinical practice, we need to be confident that it will not create errors either through ‘hallucinating’ fake information or because it has been trained on data that does not equitably represent the population we serve,” she said.
AI Predicts Lung Disease in Premature Babies
Identifying bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) in premature babies remains a challenge. Lung function tests usually require blowing out on request, which is a task babies cannot perform. Current techniques require sophisticated equipment to measure an infant’s lung ventilation characteristics, so doctors usually diagnose BPD by the presence of its leading causes, prematurity and the need for respiratory support.
Researchers at the University of Basel in Switzerland trained an ANN model to predict BPD in premature babies.
The team studied a group of 139 full-term and 190 premature infants who had been assessed for BPD, recording their breathing for 10 minutes while they slept. For each baby, 100 consecutive regular breaths, carefully inspected to exclude sighs or other artifacts, were used to train, validate, and test an ANN called a Long Short-Term Memory model (LSTM), which is particularly effective at classifying sequential data such as tidal breathing.
Researchers used 60% of the data to teach the network how to recognize BPD, 20% to validate the model, and then fed the remaining 20% of the data to the model to see if it could correctly identify those babies with BPD.
The LSTM model classified a series of flow values in the unseen test data set as belonging to a patient diagnosed with BPD or not with 96% accuracy.
“Until recently, this need for large amounts of data has hindered efforts to create accurate models for lung disease in infants because it is so difficult to assess their lung function,” Delgado-Eckert said. “Our research delivers, for the first time, a comprehensive way of analyzing infants’ breathing and allows us to detect which babies have BPD as early as 1 month of corrected age.”
The study presented by Delgado-Eckert received funding from the Swiss National Science Foundation. Narayanan and Pinnock reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — Artificial Intelligence (AI) can assist doctors in assessing and diagnosing respiratory illnesses in infants and children, according to two new studies presented at the European Respiratory Society (ERS) 2024 Congress.
Researchers can train artificial neural networks (ANNs) to detect lung disease in premature babies by analyzing their breathing patterns while they sleep. “Our noninvasive test is less distressing for the baby and their parents, meaning they can access treatment more quickly, and may also be relevant for their long-term prognosis,” said Edgar Delgado-Eckert, PhD, adjunct professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at The University of Basel, Switzerland, and a research group leader at the University Children’s Hospital, Switzerland.
Manjith Narayanan, MD, a consultant in pediatric pulmonology at the Royal Hospital for Children and Young People, Edinburgh, and honorary senior clinical lecturer at The University of Edinburgh, United Kingdom, said chatbots such as ChatGPT, Bard, and Bing can perform as well as or better than trainee doctors when assessing children with respiratory issues. He said chatbots could triage patients more quickly and ease pressure on health services.
Chatbots Show Promise in Triage of Pediatric Respiratory Illnesses
Researchers at The University of Edinburgh provided 10 trainee doctors with less than 4 months of clinical experience in pediatrics with clinical scenarios that covered topics such as cystic fibrosis, asthma, sleep-disordered breathing, breathlessness, chest infections, or no obvious diagnosis.
The trainee doctors had 1 hour to use the internet, although they were not allowed to use chatbots to solve each scenario with a descriptive answer.
Each scenario was also presented to the three large language models (LLMs): OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google’s Bard, and Microsoft’s Bing.
Six pediatric respiratory experts assessed all responses, scoring correctness, comprehensiveness, usefulness, plausibility, and coherence on a scale of 0-9. They were also asked to say whether they thought a human or a chatbot generated each response.
ChatGPT scored an average of 7 out of 9 overall and was believed to be more human-like than responses from the other chatbots. Bard scored an average of 6 out of 9 and was more “coherent” than trainee doctors, but in other respects, it was no better or worse than trainee doctors. Bing and trainee doctors scored an average of 4 out of 9.
“Our study is the first, to our knowledge, to test LLMs against trainee doctors in situations that reflect real-life clinical practice,” Narayanan said. “We did this by allowing the trainee doctors to have full access to resources available on the internet, as they would in real life. This moves the focus away from testing memory, where LLMs have a clear advantage.”
Narayanan said that these models could help nurses, trainee doctors, and primary care physicians triage patients quickly and assist medical professionals in their studies by summarizing their thought processes. “The key word, though, is “assist.” They cannot replace conventional medical training yet,” he told Medscape Medical News.
The researchers found no obvious hallucinations — seemingly made-up information — with any of the three LLMs. Still, Narayanan said, “We need to be aware of this possibility and build mitigations.”
Hilary Pinnock, ERS education council chair and professor of primary care respiratory medicine at The University of Edinburgh who was not involved in the research, said seeing how widely available AI tools can provide solutions to complex cases of respiratory illness in children is exciting and worrying at the same time. “It certainly points the way to a brave new world of AI-supported care.”
“However, before we start to use AI in routine clinical practice, we need to be confident that it will not create errors either through ‘hallucinating’ fake information or because it has been trained on data that does not equitably represent the population we serve,” she said.
AI Predicts Lung Disease in Premature Babies
Identifying bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) in premature babies remains a challenge. Lung function tests usually require blowing out on request, which is a task babies cannot perform. Current techniques require sophisticated equipment to measure an infant’s lung ventilation characteristics, so doctors usually diagnose BPD by the presence of its leading causes, prematurity and the need for respiratory support.
Researchers at the University of Basel in Switzerland trained an ANN model to predict BPD in premature babies.
The team studied a group of 139 full-term and 190 premature infants who had been assessed for BPD, recording their breathing for 10 minutes while they slept. For each baby, 100 consecutive regular breaths, carefully inspected to exclude sighs or other artifacts, were used to train, validate, and test an ANN called a Long Short-Term Memory model (LSTM), which is particularly effective at classifying sequential data such as tidal breathing.
Researchers used 60% of the data to teach the network how to recognize BPD, 20% to validate the model, and then fed the remaining 20% of the data to the model to see if it could correctly identify those babies with BPD.
The LSTM model classified a series of flow values in the unseen test data set as belonging to a patient diagnosed with BPD or not with 96% accuracy.
“Until recently, this need for large amounts of data has hindered efforts to create accurate models for lung disease in infants because it is so difficult to assess their lung function,” Delgado-Eckert said. “Our research delivers, for the first time, a comprehensive way of analyzing infants’ breathing and allows us to detect which babies have BPD as early as 1 month of corrected age.”
The study presented by Delgado-Eckert received funding from the Swiss National Science Foundation. Narayanan and Pinnock reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — Artificial Intelligence (AI) can assist doctors in assessing and diagnosing respiratory illnesses in infants and children, according to two new studies presented at the European Respiratory Society (ERS) 2024 Congress.
Researchers can train artificial neural networks (ANNs) to detect lung disease in premature babies by analyzing their breathing patterns while they sleep. “Our noninvasive test is less distressing for the baby and their parents, meaning they can access treatment more quickly, and may also be relevant for their long-term prognosis,” said Edgar Delgado-Eckert, PhD, adjunct professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at The University of Basel, Switzerland, and a research group leader at the University Children’s Hospital, Switzerland.
Manjith Narayanan, MD, a consultant in pediatric pulmonology at the Royal Hospital for Children and Young People, Edinburgh, and honorary senior clinical lecturer at The University of Edinburgh, United Kingdom, said chatbots such as ChatGPT, Bard, and Bing can perform as well as or better than trainee doctors when assessing children with respiratory issues. He said chatbots could triage patients more quickly and ease pressure on health services.
Chatbots Show Promise in Triage of Pediatric Respiratory Illnesses
Researchers at The University of Edinburgh provided 10 trainee doctors with less than 4 months of clinical experience in pediatrics with clinical scenarios that covered topics such as cystic fibrosis, asthma, sleep-disordered breathing, breathlessness, chest infections, or no obvious diagnosis.
The trainee doctors had 1 hour to use the internet, although they were not allowed to use chatbots to solve each scenario with a descriptive answer.
Each scenario was also presented to the three large language models (LLMs): OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google’s Bard, and Microsoft’s Bing.
Six pediatric respiratory experts assessed all responses, scoring correctness, comprehensiveness, usefulness, plausibility, and coherence on a scale of 0-9. They were also asked to say whether they thought a human or a chatbot generated each response.
ChatGPT scored an average of 7 out of 9 overall and was believed to be more human-like than responses from the other chatbots. Bard scored an average of 6 out of 9 and was more “coherent” than trainee doctors, but in other respects, it was no better or worse than trainee doctors. Bing and trainee doctors scored an average of 4 out of 9.
“Our study is the first, to our knowledge, to test LLMs against trainee doctors in situations that reflect real-life clinical practice,” Narayanan said. “We did this by allowing the trainee doctors to have full access to resources available on the internet, as they would in real life. This moves the focus away from testing memory, where LLMs have a clear advantage.”
Narayanan said that these models could help nurses, trainee doctors, and primary care physicians triage patients quickly and assist medical professionals in their studies by summarizing their thought processes. “The key word, though, is “assist.” They cannot replace conventional medical training yet,” he told Medscape Medical News.
The researchers found no obvious hallucinations — seemingly made-up information — with any of the three LLMs. Still, Narayanan said, “We need to be aware of this possibility and build mitigations.”
Hilary Pinnock, ERS education council chair and professor of primary care respiratory medicine at The University of Edinburgh who was not involved in the research, said seeing how widely available AI tools can provide solutions to complex cases of respiratory illness in children is exciting and worrying at the same time. “It certainly points the way to a brave new world of AI-supported care.”
“However, before we start to use AI in routine clinical practice, we need to be confident that it will not create errors either through ‘hallucinating’ fake information or because it has been trained on data that does not equitably represent the population we serve,” she said.
AI Predicts Lung Disease in Premature Babies
Identifying bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) in premature babies remains a challenge. Lung function tests usually require blowing out on request, which is a task babies cannot perform. Current techniques require sophisticated equipment to measure an infant’s lung ventilation characteristics, so doctors usually diagnose BPD by the presence of its leading causes, prematurity and the need for respiratory support.
Researchers at the University of Basel in Switzerland trained an ANN model to predict BPD in premature babies.
The team studied a group of 139 full-term and 190 premature infants who had been assessed for BPD, recording their breathing for 10 minutes while they slept. For each baby, 100 consecutive regular breaths, carefully inspected to exclude sighs or other artifacts, were used to train, validate, and test an ANN called a Long Short-Term Memory model (LSTM), which is particularly effective at classifying sequential data such as tidal breathing.
Researchers used 60% of the data to teach the network how to recognize BPD, 20% to validate the model, and then fed the remaining 20% of the data to the model to see if it could correctly identify those babies with BPD.
The LSTM model classified a series of flow values in the unseen test data set as belonging to a patient diagnosed with BPD or not with 96% accuracy.
“Until recently, this need for large amounts of data has hindered efforts to create accurate models for lung disease in infants because it is so difficult to assess their lung function,” Delgado-Eckert said. “Our research delivers, for the first time, a comprehensive way of analyzing infants’ breathing and allows us to detect which babies have BPD as early as 1 month of corrected age.”
The study presented by Delgado-Eckert received funding from the Swiss National Science Foundation. Narayanan and Pinnock reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ERS 2024
Pediatricians Must Prepare for Impact on Allergies and Asthma From Climate Change
ORLANDO — It’s important for pediatricians not only to understand the causes and effects of climate change but also to know how to discuss this issue with families and make risk-based adjustments to their clinical practice based on the individual health and circumstances of each patient. That’s one of the key messages delivered at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) by Elizabeth C. Matsui, MD, MHS, professor of population health and pediatrics and director of the Center for Health and Environment Education and Research at the University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School.
“Even though climate change has been here and has been affecting health already for a while, it’s just really impossible to ignore right now,” she told attendees in a session focused on climate change impacts on allergies and asthma. “The challenge is connecting the dots between something that is much larger, or feels much larger, than the patient and the family that’s in front of you.”
The reality, however, is that climate change is now impacting patients’ health on an individual level, and pediatricians have a responsibility to understand how that’s happening and to help their families prepare for it.
“From the perspective of someone who went into medicine to practice and take care of the individual patient, I think it has been more difficult to connect those dots, and for the people in this room, it’s our job to connect those dots,” Matsui said. She also acknowledged that many of the solutions are frustratingly limited to the policy level and challenging to implement, “but it doesn’t mean that we can’t make a difference for the patients who are in front of us.”
Charles Moon, MD, a pediatrician and Pediatric Environmental Health Fellow at the Children’s Environmental Health Center, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, found the talk particularly helpful in providing information about both the broader issue and what it means on a local practice level.
“The biggest takeaway is that more people and more pediatricians are tuning in to this issue and realizing the dangers,” Moon said. “It’s clear that a larger community is forming around this, and I think we are at the cusp where more and more people will be coming in. We are really focusing on taking all the data and trying to figure out solutions. I think the solutions orientation is the most important part.”
Understanding the Big Picture
Matsui opened with a general discussion of the human causes of climate change and the effects on a global scale presently and in the future. For example, over the past 800,000 years, carbon dioxide levels have never been above 300 ppm, but they surpassed that threshold in 1911 and have reached 420 ppm today. The trapping of heat in Earth’s atmosphere caused by the increase in carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases is leading to multiple phenomena that impact health, such as longer growing seasons; increased droughts, heat waves, and wildfire seasons; and higher temperatures. These changes, in turn, affect allergens and asthma.
, Matsui said. Childhood is a critical period for lung and immune development, and the Environmental Protection Agency’s 2023 Climate Change and Children’s Health and Well-Being report projects that an increase of 2° C in global warming will result in an additional 34,500 pediatric asthma cases and 228,000 allergic rhinitis cases per year, driven largely by predicted increases in ozone and 2.5-µm particulate matter. The report also forecasts an increase in 6240 asthma emergency department visits and 332 additional respiratory hospitalizations per year.
“We know that these associations that we see between climate change exposures and poor respiratory health outcomes in kids are biologically plausible,” Matsui said. “They’re not just correlation without causation. A lot of the mechanisms for how air pollution, allergies, and other factors directly affect the lungs of the airway epithelium have been worked out.”
An Increase in Allergens and Viral Infections
Pediatricians should prepare for anticipated growth in allergens and viral infections. The longer growing seasons mean that pollen seasons will also lengthen. Meanwhile, higher concentrations of carbon dioxide cause individual plants to produce more pollen.
“As the winters get warmer, mice that might not be able to survive during the winter are surviving, and mice reproduce at a very rapid rate,” she said. “The increase in moisture means that dust mites, which absorb their water — they drink by absorbing humidity that’s in the air — will be present in higher concentrations, and their range will expand.”
Fungal and mold exposures are also increasing, not just outdoors but also indoors, “and there are all sorts of allergic and respiratory health consequences of fungal exposure,” Matsui said. As hurricanes and flooding increase, storm damage can also make indoor environments more conducive to fungal and mold growth.
Extreme weather from climate change also affects infrastructure. “When there’s healthcare infrastructure disruption and other infrastructure disruption, it adds to the challenge,” she said. “It compounds all the other threat to health from climate change, so this overall problem of climate change and health is multidimensional and very complicated.”
Then there’s the impact of climate change on respiratory viruses, which are a major driver of asthma exacerbations, Matsui said. The greater variability in daytime temperatures affects environmental reservoirs, transmission patterns, geographical ranges, and seasonality of various respiratory pathogens. The prevalence of respiratory syncytial virus infections, for example, increases during humid periods.
“This is coupled with the fact that the projected increases in air pollution increase susceptibility to respiratory virus infections,” Matsui said. “In fact, climate change and air pollution are inextricably linked.”
Climate Change and Air Pollution
Climate disruption creates extreme weather patterns that then lead to worsening air quality due to high temperatures; heavier precipitation; and more forest fires, droughts, dust storms, thunderstorms, hurricanes, stagnation events, and other extreme weather. Matsui shared a map showing the substantial increase in days with stagnant air since 1973. During stagnation events, air pollution builds up in the atmosphere because of a stable air mass that remains over a region for several days, with low-level winds and no precipitation.
The pollutants can then contribute to rising temperatures. Black carbon particulate matter released from the burning of forests and other biomass absorbs more solar radiation, further contributing to temperature increases. Data from the National Bureau of Economic Research has shown that the US made big strides in reducing air pollution from 2009 through 2016, but it began to reverse in 2016 as severe weather events picked up.
Pediatricians need to be cognizant of the synergistic effect of these different impacts as well. “We oftentimes talk about these problems in a silo, so we may talk about air pollution and health effects, or allergens and health effects, or heat and health effects, but all of these interact with each other and further compound the health effects,” compared to just one of them in isolation, Matsui said.
For example, air pollution increases sensitivity to allergen exposure and increases reaction severity, which disrupts the immune tolerance to allergens. “Heat and air pollution also interact, and the combination of the two is more deadly than either one alone,” she said.
Air pollution from wildfire smoke is also more toxic to the lungs than air pollution from other sources, so if there’s wildfire-based air pollution, the impact on respiratory hospitalizations is significantly greater. Even in places that would not otherwise be at risk for wildfires, the threat remains of air pollution from more distant fires, as New York City experienced from Canadian wildfires last year.
“This is a problem that is not just isolated to the parts of the world where the wildfires are located,” Matsui said.
Moon, who practices in New York City, said he really appreciated Matsui’s perspectives and nuanced advice as a subspecialist “because it’s obvious that the way we deliver healthcare is going to have to change based on climate change.” He hopes to see more subspecialists from other pediatric areas getting involved in looking at climate impacts and providing nuanced advice about changing clinical care similar to the examples Matsui provided.
Air pollution can also be deadly, as a landmark case in the United Kingdom revealed a few years ago when the court ruled that a child’s death from an asthma attack was directly due to air pollution. In addition to causing worse asthma symptoms and exacerbations, air pollution also adds to the risk of developing asthma and impedes lung growth, all of which disproportionately affects disadvantaged and minoritized communities, she said.
Greater Impact on Disadvantaged Populations
Matsui called attention to the equity implications of climate change impacts on health.
“If you have a community that does not have the infrastructure and access to resources, and that same community has a prevalence of asthma that is double that of their more advantaged and white counterparts, then the impacts of climate change are going to be amplified even more,” she said.
For example, a 2019 study found that the biggest predictor of the location of ragweed plants has to do with vacant lots and demolition of housing. Ragweed plants being more common in neighborhoods with vacant lots will disproportionately affect disadvantaged neighborhoods, she said. Another study found in Baltimore that mouse allergens — specifically urine — were a bigger cause of asthma in low-income children than were cockroach allergens.
“It’s important to consider context,” including age, gender and social and behavioral context, she said. “We as pediatricians know that children are particularly vulnerable, and what happens to them has an effect across the lifespan.”
Furthermore, pediatricians are aware that disadvantaged and minoritized communities lack infrastructure; often live in areas with greater air pollution; often have heat islands in their communities without protection, such as tree canopy; and may be at greater flooding risk. “Poverty is also associated with increased vulnerability” because of poorer housing and infrastructure, less education, less access to care, more preexisting health conditions and greater discrimination, she said.
Three Cornerstone Interventions
Interventions fall into three main buckets, Matsui said: mitigation, adaption, and resilience.
“Mitigation means reducing greenhouse gas and air pollution production and trying to enhance sinks for greenhouse gases,” she said. Mitigation strategies primarily occur at the policy level, with improved regulation, treaties, and market-based approaches, such as carbon tax and cap and trade.
Adaptation includes actions that lessen the impact on health and environment, such as infrastructure changes and implementation of air conditioning. Examples of climate change adaptation strategies also mostly come from policy but largely at state and local levels, where individual pediatricians have a greater voice and influence. These can include changes in urban planning to address heat islands, flooding risk, and public transportation’s contribution to air pollution and climate change. It can also include changes in housing regulation and policy and investments in healthcare, such as expanded Medicaid and health insurance and investing in disaster planning and readiness.
“Resilience is a more holistic concept,” Matsui said, “which advocates for system-wide, multilevel changes and involves a range of strategies to enhance social, human, natural, physical, and financial capacities.”
What Pediatricians Can Do
Pediatricians have an important role to play when it comes to climate change and health impacts.
“The first step is sort of understanding the complexity of climate change in terms of its potential health effects, but also being prepared to talk with our patients and their families about it,” Matsui said. “The second step is advocacy.” She drew attention to the February policy statement in Pediatrics that discusses precisely the ways in which pediatricians can leverage their expertise and credibility.
“Pediatricians are ideal advocates with whom to partner and uplift youth and community voices working to advance zero-carbon energy policy and climate justice,” she said. “There are many opportunities to advocate for climate solution policies at the local, state, national, and even international level.”
These roles can include educating elected officials and health insurance entities about the risks that climate change poses to allergies, asthma, and child health more broadly, as well as the benefits of local solutions, including improved air quality, tree canopy, and green space. “There are lots of opportunities to engage with the community, including speaking at public hearings, serving as an expert testimony, and writing letters to the editor,” she said.
The impact of these efforts can be further maximized by working with other healthcare professionals. Lori Byron, MD, a pediatrician from Red Lodge, Montana, who heads the AAP Chapter Climate Advocates program, noted during Q&A that every AAP chapter in the country has climate advocates. She added that the AAP is the first medical board to have climate modules in their maintenance of certification specifically designed to incorporate climate change education into well visits.
Adjusting Clinical Care
Meanwhile, in patient care, Matsui acknowledged it can be frustrating to think about what a massive impact climate has and simultaneously challenging to engage families in discussions about it. However, a wide range of resources are available that can be provided to patients.
“For a patient in front of you, being informed and prepared to talk about it is the first step to being able to assess their climate change risk and provide tailored guidance,” she said. Tailored guidance takes into account the child’s specific health situation and the risks they’re most likely to encounter, such as wildfire smoke, air pollution, longer pollen seasons, environmental allergens, or disruption of infrastructure.
“If I am seeing a patient with asthma who is allergic to a particular pollen, I can anticipate that pollen may be present in higher levels of the future, and that the season for that pollen may be longer,” Matsui said. “So if I’m thinking about allergen immunotherapy for that patient, future risk may be something that would push the conversation and the shared decision-making” from possible consideration to more serious consideration, depending on the child’s age.
“Another example is a patient with asthma, thinking about wildfire risk and having them prepared, because we know from data that wildfire air pollution is going to be worse for that child than pollution from other sources, and there are ways for them to be prepared,” Matsui said. For instance, having an HVAC system with a high-grade air filter (at least a MERV 13) will filter the air better if a wildfire causes smoke to descend over an area. Portable, less expensive HEPA filters are also an option if a family cannot upgrade their system, and wearing an N95 or N95-equivalent mask can also reduce the impact of high air pollution levels.
An example of thinking about the impact of potential infrastructure disruption could be ensuring patients have enough of all their medications if they’re close to running out. “It’s important for them to always have think about their medications and get those refills ahead of a storm,” she said.
Additional Resources
Understanding that pediatricians may not have time to discuss all these issues or have broader conversations about climate change during visits, Matsui highlighted the AAP website of resources on climate change. In addition to resources for pediatricians, such as a basic fact sheet about climate change impacts on children’s health and the technical report that informed the policy statement, the site has multiple resources for families:
- Climate Change Impact: Safeguarding Your Family’s Health and Well-being (video), How to Talk With Children About Climate Change, Climate Change & Children’s Health: AAP Policy Explained, Climate Checkup for Children’s Health: Little Changes With Big Impact, How Climate Change Can Make Children Sick: What Parents Need to Know, Climate Change & Wildfires: Why Kids Are Most at Risk, Climate Change, Extreme Weather & Children: What Families Need to Know, Extreme Heat & Air Pollution: Health Effects on Babies & Pregnant People, and
The following resources can also be helpful to pediatricians and/or families:
- Ready.gov, AirNow, Patient Exposure and the Air Quality Index, Protecting Vulnerable Patient Populations from Climate Hazards: A Referral Guide for Health Professionals from the US Department of Health and Human Services, Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP), Weatherization Assistance Program, and the Disaster Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (D-SNAP)
In some states, Medicaid will provide or cover the cost of air conditioning and/or air filters.
The presentation did not involve external funding. Drs. Matsui and Moon had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO — It’s important for pediatricians not only to understand the causes and effects of climate change but also to know how to discuss this issue with families and make risk-based adjustments to their clinical practice based on the individual health and circumstances of each patient. That’s one of the key messages delivered at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) by Elizabeth C. Matsui, MD, MHS, professor of population health and pediatrics and director of the Center for Health and Environment Education and Research at the University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School.
“Even though climate change has been here and has been affecting health already for a while, it’s just really impossible to ignore right now,” she told attendees in a session focused on climate change impacts on allergies and asthma. “The challenge is connecting the dots between something that is much larger, or feels much larger, than the patient and the family that’s in front of you.”
The reality, however, is that climate change is now impacting patients’ health on an individual level, and pediatricians have a responsibility to understand how that’s happening and to help their families prepare for it.
“From the perspective of someone who went into medicine to practice and take care of the individual patient, I think it has been more difficult to connect those dots, and for the people in this room, it’s our job to connect those dots,” Matsui said. She also acknowledged that many of the solutions are frustratingly limited to the policy level and challenging to implement, “but it doesn’t mean that we can’t make a difference for the patients who are in front of us.”
Charles Moon, MD, a pediatrician and Pediatric Environmental Health Fellow at the Children’s Environmental Health Center, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, found the talk particularly helpful in providing information about both the broader issue and what it means on a local practice level.
“The biggest takeaway is that more people and more pediatricians are tuning in to this issue and realizing the dangers,” Moon said. “It’s clear that a larger community is forming around this, and I think we are at the cusp where more and more people will be coming in. We are really focusing on taking all the data and trying to figure out solutions. I think the solutions orientation is the most important part.”
Understanding the Big Picture
Matsui opened with a general discussion of the human causes of climate change and the effects on a global scale presently and in the future. For example, over the past 800,000 years, carbon dioxide levels have never been above 300 ppm, but they surpassed that threshold in 1911 and have reached 420 ppm today. The trapping of heat in Earth’s atmosphere caused by the increase in carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases is leading to multiple phenomena that impact health, such as longer growing seasons; increased droughts, heat waves, and wildfire seasons; and higher temperatures. These changes, in turn, affect allergens and asthma.
, Matsui said. Childhood is a critical period for lung and immune development, and the Environmental Protection Agency’s 2023 Climate Change and Children’s Health and Well-Being report projects that an increase of 2° C in global warming will result in an additional 34,500 pediatric asthma cases and 228,000 allergic rhinitis cases per year, driven largely by predicted increases in ozone and 2.5-µm particulate matter. The report also forecasts an increase in 6240 asthma emergency department visits and 332 additional respiratory hospitalizations per year.
“We know that these associations that we see between climate change exposures and poor respiratory health outcomes in kids are biologically plausible,” Matsui said. “They’re not just correlation without causation. A lot of the mechanisms for how air pollution, allergies, and other factors directly affect the lungs of the airway epithelium have been worked out.”
An Increase in Allergens and Viral Infections
Pediatricians should prepare for anticipated growth in allergens and viral infections. The longer growing seasons mean that pollen seasons will also lengthen. Meanwhile, higher concentrations of carbon dioxide cause individual plants to produce more pollen.
“As the winters get warmer, mice that might not be able to survive during the winter are surviving, and mice reproduce at a very rapid rate,” she said. “The increase in moisture means that dust mites, which absorb their water — they drink by absorbing humidity that’s in the air — will be present in higher concentrations, and their range will expand.”
Fungal and mold exposures are also increasing, not just outdoors but also indoors, “and there are all sorts of allergic and respiratory health consequences of fungal exposure,” Matsui said. As hurricanes and flooding increase, storm damage can also make indoor environments more conducive to fungal and mold growth.
Extreme weather from climate change also affects infrastructure. “When there’s healthcare infrastructure disruption and other infrastructure disruption, it adds to the challenge,” she said. “It compounds all the other threat to health from climate change, so this overall problem of climate change and health is multidimensional and very complicated.”
Then there’s the impact of climate change on respiratory viruses, which are a major driver of asthma exacerbations, Matsui said. The greater variability in daytime temperatures affects environmental reservoirs, transmission patterns, geographical ranges, and seasonality of various respiratory pathogens. The prevalence of respiratory syncytial virus infections, for example, increases during humid periods.
“This is coupled with the fact that the projected increases in air pollution increase susceptibility to respiratory virus infections,” Matsui said. “In fact, climate change and air pollution are inextricably linked.”
Climate Change and Air Pollution
Climate disruption creates extreme weather patterns that then lead to worsening air quality due to high temperatures; heavier precipitation; and more forest fires, droughts, dust storms, thunderstorms, hurricanes, stagnation events, and other extreme weather. Matsui shared a map showing the substantial increase in days with stagnant air since 1973. During stagnation events, air pollution builds up in the atmosphere because of a stable air mass that remains over a region for several days, with low-level winds and no precipitation.
The pollutants can then contribute to rising temperatures. Black carbon particulate matter released from the burning of forests and other biomass absorbs more solar radiation, further contributing to temperature increases. Data from the National Bureau of Economic Research has shown that the US made big strides in reducing air pollution from 2009 through 2016, but it began to reverse in 2016 as severe weather events picked up.
Pediatricians need to be cognizant of the synergistic effect of these different impacts as well. “We oftentimes talk about these problems in a silo, so we may talk about air pollution and health effects, or allergens and health effects, or heat and health effects, but all of these interact with each other and further compound the health effects,” compared to just one of them in isolation, Matsui said.
For example, air pollution increases sensitivity to allergen exposure and increases reaction severity, which disrupts the immune tolerance to allergens. “Heat and air pollution also interact, and the combination of the two is more deadly than either one alone,” she said.
Air pollution from wildfire smoke is also more toxic to the lungs than air pollution from other sources, so if there’s wildfire-based air pollution, the impact on respiratory hospitalizations is significantly greater. Even in places that would not otherwise be at risk for wildfires, the threat remains of air pollution from more distant fires, as New York City experienced from Canadian wildfires last year.
“This is a problem that is not just isolated to the parts of the world where the wildfires are located,” Matsui said.
Moon, who practices in New York City, said he really appreciated Matsui’s perspectives and nuanced advice as a subspecialist “because it’s obvious that the way we deliver healthcare is going to have to change based on climate change.” He hopes to see more subspecialists from other pediatric areas getting involved in looking at climate impacts and providing nuanced advice about changing clinical care similar to the examples Matsui provided.
Air pollution can also be deadly, as a landmark case in the United Kingdom revealed a few years ago when the court ruled that a child’s death from an asthma attack was directly due to air pollution. In addition to causing worse asthma symptoms and exacerbations, air pollution also adds to the risk of developing asthma and impedes lung growth, all of which disproportionately affects disadvantaged and minoritized communities, she said.
Greater Impact on Disadvantaged Populations
Matsui called attention to the equity implications of climate change impacts on health.
“If you have a community that does not have the infrastructure and access to resources, and that same community has a prevalence of asthma that is double that of their more advantaged and white counterparts, then the impacts of climate change are going to be amplified even more,” she said.
For example, a 2019 study found that the biggest predictor of the location of ragweed plants has to do with vacant lots and demolition of housing. Ragweed plants being more common in neighborhoods with vacant lots will disproportionately affect disadvantaged neighborhoods, she said. Another study found in Baltimore that mouse allergens — specifically urine — were a bigger cause of asthma in low-income children than were cockroach allergens.
“It’s important to consider context,” including age, gender and social and behavioral context, she said. “We as pediatricians know that children are particularly vulnerable, and what happens to them has an effect across the lifespan.”
Furthermore, pediatricians are aware that disadvantaged and minoritized communities lack infrastructure; often live in areas with greater air pollution; often have heat islands in their communities without protection, such as tree canopy; and may be at greater flooding risk. “Poverty is also associated with increased vulnerability” because of poorer housing and infrastructure, less education, less access to care, more preexisting health conditions and greater discrimination, she said.
Three Cornerstone Interventions
Interventions fall into three main buckets, Matsui said: mitigation, adaption, and resilience.
“Mitigation means reducing greenhouse gas and air pollution production and trying to enhance sinks for greenhouse gases,” she said. Mitigation strategies primarily occur at the policy level, with improved regulation, treaties, and market-based approaches, such as carbon tax and cap and trade.
Adaptation includes actions that lessen the impact on health and environment, such as infrastructure changes and implementation of air conditioning. Examples of climate change adaptation strategies also mostly come from policy but largely at state and local levels, where individual pediatricians have a greater voice and influence. These can include changes in urban planning to address heat islands, flooding risk, and public transportation’s contribution to air pollution and climate change. It can also include changes in housing regulation and policy and investments in healthcare, such as expanded Medicaid and health insurance and investing in disaster planning and readiness.
“Resilience is a more holistic concept,” Matsui said, “which advocates for system-wide, multilevel changes and involves a range of strategies to enhance social, human, natural, physical, and financial capacities.”
What Pediatricians Can Do
Pediatricians have an important role to play when it comes to climate change and health impacts.
“The first step is sort of understanding the complexity of climate change in terms of its potential health effects, but also being prepared to talk with our patients and their families about it,” Matsui said. “The second step is advocacy.” She drew attention to the February policy statement in Pediatrics that discusses precisely the ways in which pediatricians can leverage their expertise and credibility.
“Pediatricians are ideal advocates with whom to partner and uplift youth and community voices working to advance zero-carbon energy policy and climate justice,” she said. “There are many opportunities to advocate for climate solution policies at the local, state, national, and even international level.”
These roles can include educating elected officials and health insurance entities about the risks that climate change poses to allergies, asthma, and child health more broadly, as well as the benefits of local solutions, including improved air quality, tree canopy, and green space. “There are lots of opportunities to engage with the community, including speaking at public hearings, serving as an expert testimony, and writing letters to the editor,” she said.
The impact of these efforts can be further maximized by working with other healthcare professionals. Lori Byron, MD, a pediatrician from Red Lodge, Montana, who heads the AAP Chapter Climate Advocates program, noted during Q&A that every AAP chapter in the country has climate advocates. She added that the AAP is the first medical board to have climate modules in their maintenance of certification specifically designed to incorporate climate change education into well visits.
Adjusting Clinical Care
Meanwhile, in patient care, Matsui acknowledged it can be frustrating to think about what a massive impact climate has and simultaneously challenging to engage families in discussions about it. However, a wide range of resources are available that can be provided to patients.
“For a patient in front of you, being informed and prepared to talk about it is the first step to being able to assess their climate change risk and provide tailored guidance,” she said. Tailored guidance takes into account the child’s specific health situation and the risks they’re most likely to encounter, such as wildfire smoke, air pollution, longer pollen seasons, environmental allergens, or disruption of infrastructure.
“If I am seeing a patient with asthma who is allergic to a particular pollen, I can anticipate that pollen may be present in higher levels of the future, and that the season for that pollen may be longer,” Matsui said. “So if I’m thinking about allergen immunotherapy for that patient, future risk may be something that would push the conversation and the shared decision-making” from possible consideration to more serious consideration, depending on the child’s age.
“Another example is a patient with asthma, thinking about wildfire risk and having them prepared, because we know from data that wildfire air pollution is going to be worse for that child than pollution from other sources, and there are ways for them to be prepared,” Matsui said. For instance, having an HVAC system with a high-grade air filter (at least a MERV 13) will filter the air better if a wildfire causes smoke to descend over an area. Portable, less expensive HEPA filters are also an option if a family cannot upgrade their system, and wearing an N95 or N95-equivalent mask can also reduce the impact of high air pollution levels.
An example of thinking about the impact of potential infrastructure disruption could be ensuring patients have enough of all their medications if they’re close to running out. “It’s important for them to always have think about their medications and get those refills ahead of a storm,” she said.
Additional Resources
Understanding that pediatricians may not have time to discuss all these issues or have broader conversations about climate change during visits, Matsui highlighted the AAP website of resources on climate change. In addition to resources for pediatricians, such as a basic fact sheet about climate change impacts on children’s health and the technical report that informed the policy statement, the site has multiple resources for families:
- Climate Change Impact: Safeguarding Your Family’s Health and Well-being (video), How to Talk With Children About Climate Change, Climate Change & Children’s Health: AAP Policy Explained, Climate Checkup for Children’s Health: Little Changes With Big Impact, How Climate Change Can Make Children Sick: What Parents Need to Know, Climate Change & Wildfires: Why Kids Are Most at Risk, Climate Change, Extreme Weather & Children: What Families Need to Know, Extreme Heat & Air Pollution: Health Effects on Babies & Pregnant People, and
The following resources can also be helpful to pediatricians and/or families:
- Ready.gov, AirNow, Patient Exposure and the Air Quality Index, Protecting Vulnerable Patient Populations from Climate Hazards: A Referral Guide for Health Professionals from the US Department of Health and Human Services, Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP), Weatherization Assistance Program, and the Disaster Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (D-SNAP)
In some states, Medicaid will provide or cover the cost of air conditioning and/or air filters.
The presentation did not involve external funding. Drs. Matsui and Moon had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO — It’s important for pediatricians not only to understand the causes and effects of climate change but also to know how to discuss this issue with families and make risk-based adjustments to their clinical practice based on the individual health and circumstances of each patient. That’s one of the key messages delivered at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) by Elizabeth C. Matsui, MD, MHS, professor of population health and pediatrics and director of the Center for Health and Environment Education and Research at the University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School.
“Even though climate change has been here and has been affecting health already for a while, it’s just really impossible to ignore right now,” she told attendees in a session focused on climate change impacts on allergies and asthma. “The challenge is connecting the dots between something that is much larger, or feels much larger, than the patient and the family that’s in front of you.”
The reality, however, is that climate change is now impacting patients’ health on an individual level, and pediatricians have a responsibility to understand how that’s happening and to help their families prepare for it.
“From the perspective of someone who went into medicine to practice and take care of the individual patient, I think it has been more difficult to connect those dots, and for the people in this room, it’s our job to connect those dots,” Matsui said. She also acknowledged that many of the solutions are frustratingly limited to the policy level and challenging to implement, “but it doesn’t mean that we can’t make a difference for the patients who are in front of us.”
Charles Moon, MD, a pediatrician and Pediatric Environmental Health Fellow at the Children’s Environmental Health Center, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, found the talk particularly helpful in providing information about both the broader issue and what it means on a local practice level.
“The biggest takeaway is that more people and more pediatricians are tuning in to this issue and realizing the dangers,” Moon said. “It’s clear that a larger community is forming around this, and I think we are at the cusp where more and more people will be coming in. We are really focusing on taking all the data and trying to figure out solutions. I think the solutions orientation is the most important part.”
Understanding the Big Picture
Matsui opened with a general discussion of the human causes of climate change and the effects on a global scale presently and in the future. For example, over the past 800,000 years, carbon dioxide levels have never been above 300 ppm, but they surpassed that threshold in 1911 and have reached 420 ppm today. The trapping of heat in Earth’s atmosphere caused by the increase in carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases is leading to multiple phenomena that impact health, such as longer growing seasons; increased droughts, heat waves, and wildfire seasons; and higher temperatures. These changes, in turn, affect allergens and asthma.
, Matsui said. Childhood is a critical period for lung and immune development, and the Environmental Protection Agency’s 2023 Climate Change and Children’s Health and Well-Being report projects that an increase of 2° C in global warming will result in an additional 34,500 pediatric asthma cases and 228,000 allergic rhinitis cases per year, driven largely by predicted increases in ozone and 2.5-µm particulate matter. The report also forecasts an increase in 6240 asthma emergency department visits and 332 additional respiratory hospitalizations per year.
“We know that these associations that we see between climate change exposures and poor respiratory health outcomes in kids are biologically plausible,” Matsui said. “They’re not just correlation without causation. A lot of the mechanisms for how air pollution, allergies, and other factors directly affect the lungs of the airway epithelium have been worked out.”
An Increase in Allergens and Viral Infections
Pediatricians should prepare for anticipated growth in allergens and viral infections. The longer growing seasons mean that pollen seasons will also lengthen. Meanwhile, higher concentrations of carbon dioxide cause individual plants to produce more pollen.
“As the winters get warmer, mice that might not be able to survive during the winter are surviving, and mice reproduce at a very rapid rate,” she said. “The increase in moisture means that dust mites, which absorb their water — they drink by absorbing humidity that’s in the air — will be present in higher concentrations, and their range will expand.”
Fungal and mold exposures are also increasing, not just outdoors but also indoors, “and there are all sorts of allergic and respiratory health consequences of fungal exposure,” Matsui said. As hurricanes and flooding increase, storm damage can also make indoor environments more conducive to fungal and mold growth.
Extreme weather from climate change also affects infrastructure. “When there’s healthcare infrastructure disruption and other infrastructure disruption, it adds to the challenge,” she said. “It compounds all the other threat to health from climate change, so this overall problem of climate change and health is multidimensional and very complicated.”
Then there’s the impact of climate change on respiratory viruses, which are a major driver of asthma exacerbations, Matsui said. The greater variability in daytime temperatures affects environmental reservoirs, transmission patterns, geographical ranges, and seasonality of various respiratory pathogens. The prevalence of respiratory syncytial virus infections, for example, increases during humid periods.
“This is coupled with the fact that the projected increases in air pollution increase susceptibility to respiratory virus infections,” Matsui said. “In fact, climate change and air pollution are inextricably linked.”
Climate Change and Air Pollution
Climate disruption creates extreme weather patterns that then lead to worsening air quality due to high temperatures; heavier precipitation; and more forest fires, droughts, dust storms, thunderstorms, hurricanes, stagnation events, and other extreme weather. Matsui shared a map showing the substantial increase in days with stagnant air since 1973. During stagnation events, air pollution builds up in the atmosphere because of a stable air mass that remains over a region for several days, with low-level winds and no precipitation.
The pollutants can then contribute to rising temperatures. Black carbon particulate matter released from the burning of forests and other biomass absorbs more solar radiation, further contributing to temperature increases. Data from the National Bureau of Economic Research has shown that the US made big strides in reducing air pollution from 2009 through 2016, but it began to reverse in 2016 as severe weather events picked up.
Pediatricians need to be cognizant of the synergistic effect of these different impacts as well. “We oftentimes talk about these problems in a silo, so we may talk about air pollution and health effects, or allergens and health effects, or heat and health effects, but all of these interact with each other and further compound the health effects,” compared to just one of them in isolation, Matsui said.
For example, air pollution increases sensitivity to allergen exposure and increases reaction severity, which disrupts the immune tolerance to allergens. “Heat and air pollution also interact, and the combination of the two is more deadly than either one alone,” she said.
Air pollution from wildfire smoke is also more toxic to the lungs than air pollution from other sources, so if there’s wildfire-based air pollution, the impact on respiratory hospitalizations is significantly greater. Even in places that would not otherwise be at risk for wildfires, the threat remains of air pollution from more distant fires, as New York City experienced from Canadian wildfires last year.
“This is a problem that is not just isolated to the parts of the world where the wildfires are located,” Matsui said.
Moon, who practices in New York City, said he really appreciated Matsui’s perspectives and nuanced advice as a subspecialist “because it’s obvious that the way we deliver healthcare is going to have to change based on climate change.” He hopes to see more subspecialists from other pediatric areas getting involved in looking at climate impacts and providing nuanced advice about changing clinical care similar to the examples Matsui provided.
Air pollution can also be deadly, as a landmark case in the United Kingdom revealed a few years ago when the court ruled that a child’s death from an asthma attack was directly due to air pollution. In addition to causing worse asthma symptoms and exacerbations, air pollution also adds to the risk of developing asthma and impedes lung growth, all of which disproportionately affects disadvantaged and minoritized communities, she said.
Greater Impact on Disadvantaged Populations
Matsui called attention to the equity implications of climate change impacts on health.
“If you have a community that does not have the infrastructure and access to resources, and that same community has a prevalence of asthma that is double that of their more advantaged and white counterparts, then the impacts of climate change are going to be amplified even more,” she said.
For example, a 2019 study found that the biggest predictor of the location of ragweed plants has to do with vacant lots and demolition of housing. Ragweed plants being more common in neighborhoods with vacant lots will disproportionately affect disadvantaged neighborhoods, she said. Another study found in Baltimore that mouse allergens — specifically urine — were a bigger cause of asthma in low-income children than were cockroach allergens.
“It’s important to consider context,” including age, gender and social and behavioral context, she said. “We as pediatricians know that children are particularly vulnerable, and what happens to them has an effect across the lifespan.”
Furthermore, pediatricians are aware that disadvantaged and minoritized communities lack infrastructure; often live in areas with greater air pollution; often have heat islands in their communities without protection, such as tree canopy; and may be at greater flooding risk. “Poverty is also associated with increased vulnerability” because of poorer housing and infrastructure, less education, less access to care, more preexisting health conditions and greater discrimination, she said.
Three Cornerstone Interventions
Interventions fall into three main buckets, Matsui said: mitigation, adaption, and resilience.
“Mitigation means reducing greenhouse gas and air pollution production and trying to enhance sinks for greenhouse gases,” she said. Mitigation strategies primarily occur at the policy level, with improved regulation, treaties, and market-based approaches, such as carbon tax and cap and trade.
Adaptation includes actions that lessen the impact on health and environment, such as infrastructure changes and implementation of air conditioning. Examples of climate change adaptation strategies also mostly come from policy but largely at state and local levels, where individual pediatricians have a greater voice and influence. These can include changes in urban planning to address heat islands, flooding risk, and public transportation’s contribution to air pollution and climate change. It can also include changes in housing regulation and policy and investments in healthcare, such as expanded Medicaid and health insurance and investing in disaster planning and readiness.
“Resilience is a more holistic concept,” Matsui said, “which advocates for system-wide, multilevel changes and involves a range of strategies to enhance social, human, natural, physical, and financial capacities.”
What Pediatricians Can Do
Pediatricians have an important role to play when it comes to climate change and health impacts.
“The first step is sort of understanding the complexity of climate change in terms of its potential health effects, but also being prepared to talk with our patients and their families about it,” Matsui said. “The second step is advocacy.” She drew attention to the February policy statement in Pediatrics that discusses precisely the ways in which pediatricians can leverage their expertise and credibility.
“Pediatricians are ideal advocates with whom to partner and uplift youth and community voices working to advance zero-carbon energy policy and climate justice,” she said. “There are many opportunities to advocate for climate solution policies at the local, state, national, and even international level.”
These roles can include educating elected officials and health insurance entities about the risks that climate change poses to allergies, asthma, and child health more broadly, as well as the benefits of local solutions, including improved air quality, tree canopy, and green space. “There are lots of opportunities to engage with the community, including speaking at public hearings, serving as an expert testimony, and writing letters to the editor,” she said.
The impact of these efforts can be further maximized by working with other healthcare professionals. Lori Byron, MD, a pediatrician from Red Lodge, Montana, who heads the AAP Chapter Climate Advocates program, noted during Q&A that every AAP chapter in the country has climate advocates. She added that the AAP is the first medical board to have climate modules in their maintenance of certification specifically designed to incorporate climate change education into well visits.
Adjusting Clinical Care
Meanwhile, in patient care, Matsui acknowledged it can be frustrating to think about what a massive impact climate has and simultaneously challenging to engage families in discussions about it. However, a wide range of resources are available that can be provided to patients.
“For a patient in front of you, being informed and prepared to talk about it is the first step to being able to assess their climate change risk and provide tailored guidance,” she said. Tailored guidance takes into account the child’s specific health situation and the risks they’re most likely to encounter, such as wildfire smoke, air pollution, longer pollen seasons, environmental allergens, or disruption of infrastructure.
“If I am seeing a patient with asthma who is allergic to a particular pollen, I can anticipate that pollen may be present in higher levels of the future, and that the season for that pollen may be longer,” Matsui said. “So if I’m thinking about allergen immunotherapy for that patient, future risk may be something that would push the conversation and the shared decision-making” from possible consideration to more serious consideration, depending on the child’s age.
“Another example is a patient with asthma, thinking about wildfire risk and having them prepared, because we know from data that wildfire air pollution is going to be worse for that child than pollution from other sources, and there are ways for them to be prepared,” Matsui said. For instance, having an HVAC system with a high-grade air filter (at least a MERV 13) will filter the air better if a wildfire causes smoke to descend over an area. Portable, less expensive HEPA filters are also an option if a family cannot upgrade their system, and wearing an N95 or N95-equivalent mask can also reduce the impact of high air pollution levels.
An example of thinking about the impact of potential infrastructure disruption could be ensuring patients have enough of all their medications if they’re close to running out. “It’s important for them to always have think about their medications and get those refills ahead of a storm,” she said.
Additional Resources
Understanding that pediatricians may not have time to discuss all these issues or have broader conversations about climate change during visits, Matsui highlighted the AAP website of resources on climate change. In addition to resources for pediatricians, such as a basic fact sheet about climate change impacts on children’s health and the technical report that informed the policy statement, the site has multiple resources for families:
- Climate Change Impact: Safeguarding Your Family’s Health and Well-being (video), How to Talk With Children About Climate Change, Climate Change & Children’s Health: AAP Policy Explained, Climate Checkup for Children’s Health: Little Changes With Big Impact, How Climate Change Can Make Children Sick: What Parents Need to Know, Climate Change & Wildfires: Why Kids Are Most at Risk, Climate Change, Extreme Weather & Children: What Families Need to Know, Extreme Heat & Air Pollution: Health Effects on Babies & Pregnant People, and
The following resources can also be helpful to pediatricians and/or families:
- Ready.gov, AirNow, Patient Exposure and the Air Quality Index, Protecting Vulnerable Patient Populations from Climate Hazards: A Referral Guide for Health Professionals from the US Department of Health and Human Services, Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP), Weatherization Assistance Program, and the Disaster Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (D-SNAP)
In some states, Medicaid will provide or cover the cost of air conditioning and/or air filters.
The presentation did not involve external funding. Drs. Matsui and Moon had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAP 2024
High Levels of Indoor Pollutants Promote Wheezing in Preschoolers
“There is an increasing concern about of the role of Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) in development of respiratory disorders like asthma, especially in children whose immune system is under development, and they are more vulnerable to the effects of poor air quality,” lead author Ioannis Sakellaris, PhD, of Université Paris-Saclay, Villejuif, France, said in an interview. However, the effects of specific pollutants on the health of young children in daycare settings has not been examined, he said.
In a presentation at the European Respiratory Society Congress, Sakellaris reviewed data from the French CRESPI cohort study, an epidemiological study of the impact of exposures to disinfectants and cleaning products on workers and children in daycare centers in France.
The study population included 532 children (47.4% girls) with a mean age of 22.3 months (aged 3 months to 4 years) in 106 daycare centers. A total of 171 children reportedly experienced at least one episode of wheezing since birth.
A total of 67 VOCs were measured during one day, and concentrations were studied in four categories based on quartiles. The researchers evaluated three child wheezing outcomes based on parental questionnaires: Ever wheeze since birth, recurrent wheeze (≥ 3 times since birth), and ever wheeze with inhaled corticosteroid use. The researchers adjusted for factors including child age and parental smoking status and education level.
Overall, ever wheezing was significantly associated with higher concentrations of 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene (odds ratio [OR] for Q4 vs Q1, 1.56; P = .08 for trend), 1-methoxy-2-propylacetate (OR, 1.62; P = .01), decamethylcyclopentasiloxane (OR, 2.12; P = .004), and methylisobutylcetone (OR, 1.85; P < .001).
The results emphasize the significant role of IAQ in respiratory health, said Sakellaris. “Further efforts to reduce pollutant concentrations and limit sources are needed,” he said. In addition, more studies on the combined effect of multiple VOCs are necessary for a deeper understanding of the complex relations between IAQ and children’s respiratory health, he said.
Pay Attention to Indoor Pollutants
“Since the COVID-19 pandemic, the use of cleaning products and disinfectants has exploded,” Alexander S. Rabin, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, said in an interview. Although many of these cleaning agents contain chemicals, including VOCs, that are known respiratory irritants, little is known about the relationship between VOCs and children’s respiratory outcomes in daycare settings, said Rabin, who was not involved in the study.
“I was struck by the wide array of VOCs detected in daycare settings,” Rabin said. However, the relationship to childhood wheeze was not entirely surprising as the VOCs included the known irritants benzene and toluene, he added.
The results suggest that exposure to VOCs, not only in cleaning agents but also building materials and other consumer products in daycare settings, may be associated with an increased risk for wheeze in children, said Rabin.
However, “it is important to know more about confounding variables, including concurrent rates of respiratory infection that are common among children,” said Rabin. “As the authors highlight, further work on the compound effects of multiple pollutants would be of interest. Lastly, it would be helpful to clearly identify the most common sources of VOCs that place children at greatest risk for wheeze, so that appropriate steps can be taken to mitigate risk,” he said.
The original CRESPI cohort study was supported by ANSES, ADEME, Fondation de France, and ARS Ile-de-France. Sakellaris and Rabin had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
“There is an increasing concern about of the role of Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) in development of respiratory disorders like asthma, especially in children whose immune system is under development, and they are more vulnerable to the effects of poor air quality,” lead author Ioannis Sakellaris, PhD, of Université Paris-Saclay, Villejuif, France, said in an interview. However, the effects of specific pollutants on the health of young children in daycare settings has not been examined, he said.
In a presentation at the European Respiratory Society Congress, Sakellaris reviewed data from the French CRESPI cohort study, an epidemiological study of the impact of exposures to disinfectants and cleaning products on workers and children in daycare centers in France.
The study population included 532 children (47.4% girls) with a mean age of 22.3 months (aged 3 months to 4 years) in 106 daycare centers. A total of 171 children reportedly experienced at least one episode of wheezing since birth.
A total of 67 VOCs were measured during one day, and concentrations were studied in four categories based on quartiles. The researchers evaluated three child wheezing outcomes based on parental questionnaires: Ever wheeze since birth, recurrent wheeze (≥ 3 times since birth), and ever wheeze with inhaled corticosteroid use. The researchers adjusted for factors including child age and parental smoking status and education level.
Overall, ever wheezing was significantly associated with higher concentrations of 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene (odds ratio [OR] for Q4 vs Q1, 1.56; P = .08 for trend), 1-methoxy-2-propylacetate (OR, 1.62; P = .01), decamethylcyclopentasiloxane (OR, 2.12; P = .004), and methylisobutylcetone (OR, 1.85; P < .001).
The results emphasize the significant role of IAQ in respiratory health, said Sakellaris. “Further efforts to reduce pollutant concentrations and limit sources are needed,” he said. In addition, more studies on the combined effect of multiple VOCs are necessary for a deeper understanding of the complex relations between IAQ and children’s respiratory health, he said.
Pay Attention to Indoor Pollutants
“Since the COVID-19 pandemic, the use of cleaning products and disinfectants has exploded,” Alexander S. Rabin, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, said in an interview. Although many of these cleaning agents contain chemicals, including VOCs, that are known respiratory irritants, little is known about the relationship between VOCs and children’s respiratory outcomes in daycare settings, said Rabin, who was not involved in the study.
“I was struck by the wide array of VOCs detected in daycare settings,” Rabin said. However, the relationship to childhood wheeze was not entirely surprising as the VOCs included the known irritants benzene and toluene, he added.
The results suggest that exposure to VOCs, not only in cleaning agents but also building materials and other consumer products in daycare settings, may be associated with an increased risk for wheeze in children, said Rabin.
However, “it is important to know more about confounding variables, including concurrent rates of respiratory infection that are common among children,” said Rabin. “As the authors highlight, further work on the compound effects of multiple pollutants would be of interest. Lastly, it would be helpful to clearly identify the most common sources of VOCs that place children at greatest risk for wheeze, so that appropriate steps can be taken to mitigate risk,” he said.
The original CRESPI cohort study was supported by ANSES, ADEME, Fondation de France, and ARS Ile-de-France. Sakellaris and Rabin had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
“There is an increasing concern about of the role of Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) in development of respiratory disorders like asthma, especially in children whose immune system is under development, and they are more vulnerable to the effects of poor air quality,” lead author Ioannis Sakellaris, PhD, of Université Paris-Saclay, Villejuif, France, said in an interview. However, the effects of specific pollutants on the health of young children in daycare settings has not been examined, he said.
In a presentation at the European Respiratory Society Congress, Sakellaris reviewed data from the French CRESPI cohort study, an epidemiological study of the impact of exposures to disinfectants and cleaning products on workers and children in daycare centers in France.
The study population included 532 children (47.4% girls) with a mean age of 22.3 months (aged 3 months to 4 years) in 106 daycare centers. A total of 171 children reportedly experienced at least one episode of wheezing since birth.
A total of 67 VOCs were measured during one day, and concentrations were studied in four categories based on quartiles. The researchers evaluated three child wheezing outcomes based on parental questionnaires: Ever wheeze since birth, recurrent wheeze (≥ 3 times since birth), and ever wheeze with inhaled corticosteroid use. The researchers adjusted for factors including child age and parental smoking status and education level.
Overall, ever wheezing was significantly associated with higher concentrations of 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene (odds ratio [OR] for Q4 vs Q1, 1.56; P = .08 for trend), 1-methoxy-2-propylacetate (OR, 1.62; P = .01), decamethylcyclopentasiloxane (OR, 2.12; P = .004), and methylisobutylcetone (OR, 1.85; P < .001).
The results emphasize the significant role of IAQ in respiratory health, said Sakellaris. “Further efforts to reduce pollutant concentrations and limit sources are needed,” he said. In addition, more studies on the combined effect of multiple VOCs are necessary for a deeper understanding of the complex relations between IAQ and children’s respiratory health, he said.
Pay Attention to Indoor Pollutants
“Since the COVID-19 pandemic, the use of cleaning products and disinfectants has exploded,” Alexander S. Rabin, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, said in an interview. Although many of these cleaning agents contain chemicals, including VOCs, that are known respiratory irritants, little is known about the relationship between VOCs and children’s respiratory outcomes in daycare settings, said Rabin, who was not involved in the study.
“I was struck by the wide array of VOCs detected in daycare settings,” Rabin said. However, the relationship to childhood wheeze was not entirely surprising as the VOCs included the known irritants benzene and toluene, he added.
The results suggest that exposure to VOCs, not only in cleaning agents but also building materials and other consumer products in daycare settings, may be associated with an increased risk for wheeze in children, said Rabin.
However, “it is important to know more about confounding variables, including concurrent rates of respiratory infection that are common among children,” said Rabin. “As the authors highlight, further work on the compound effects of multiple pollutants would be of interest. Lastly, it would be helpful to clearly identify the most common sources of VOCs that place children at greatest risk for wheeze, so that appropriate steps can be taken to mitigate risk,” he said.
The original CRESPI cohort study was supported by ANSES, ADEME, Fondation de France, and ARS Ile-de-France. Sakellaris and Rabin had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ERS 2024
SAFE: Ensuring Access for Children With Neurodevelopmental Disabilities
We pediatricians consider ourselves as compassionate professionals, optimistic about the potential of all children. This is reflected in the American Academy of Pediatrics’ equity statement of “its mission to ensure the health and well-being of all children. This includes promoting nurturing, inclusive environments and actively opposing intolerance, bigotry, bias, and discrimination.”
A committee of the Developmental Behavioral Pediatric Network developed and published a consensus statement specifically about problems in the care of individuals with neurodevelopmental disabilities (NDD) called the Supporting Access for Everyone (SAFE) initiative. All of us care for children with NDD as one in six are affected with these conditions that impact cognition, communication, motor, social, and/or behavior skills such as autism, ADHD, intellectual disabilities (ID), learning disorders, hearing or vision impairment, and motor disabilities such as cerebral palsy. Children with NDD are overrepresented in our daily practice schedule due to their multiple medical, behavioral, and social needs. NDD are also more common among marginalized children with racial, ethnic, sexual, or gender identity minority status compounding their difficulties in accessing quality care.
NDD present similar challenges to care as other chronic conditions that also require longer visits, more documentation, long-term monitoring, team-based care, care coordination, and often referrals. But most chronic medical conditions we care for such as asthma, diabetes, cancer, hypertension, and renal disease have clear national guidelines and appropriate billing codes and are not stigmatizing. Most also do not intrinsically affect the nervous system or cause disability as for NDD that alter the behavioral presentation of the individual in a way that changes their care.
Discrimination against individuals with NDD and other disabilities, called “ableism,” can take many forms: assuming a child with communication difficulty or ID is unable to understand explanations about their care; the presence of one NDD condition ending the clinician’s search for other issues; complicated problems or difficult behaviors in the medical setting truncating care, etc.
Adjustments Needed for Special Needs
As pediatricians we already adjust our interactions, starting instinctively, to the development level of the child we perceive before us. We approach infants slowly and softly, we speak in shorter sentences to toddlers, we joke around with school-aged children, and we take extra care about privacy with teens. This serves the relationships well for neurotypical children. But our (and our staff’s) perceptions of children with autism, ID, genetic syndromes that include NDD, or motor disabilities based on their behavioral presentation may not accurately recognize or accommodate their abilities or needs. Communication and environmental adjustments may need to be much more individualized to provide respectful care, comfort and even safety.
As an example, at this time 1 in 36 children have autism with or without ID. Defining features of autism include differences in social communication, repetitive or restrictive interests or behaviors, and hypersensitivity to the environment plus any coexisting conditions such as anxiety and hyperactivity. But most children with autism have completely age appropriate and typical physical appearance and their underlying condition may not even be known. The office setting, without special attention to the needs of a child with autism, may be frightening, loud, too bright, too crowded, fast paced, and confusing. The result of their sensitivities and difficulty communicating may lead to increased agitation, repetitive behaviors (sometimes called “stimming”), shrieking, attempts to escape the room, refusal to allow for vital signs or undressing, even aggression. Strategies for calming a neurotypical child such as talking or touching may make matters worse instead of better. We need help from the child and family and a plan to optimize their medical encounters.
If not adequately accommodated, children with many varieties of NDD end up not getting all the routine healthcare they need (eg vaccinations, blood tests, vital signs, even complete physical exams including dental) as well as having more adverse events during health care, including traumatizing seclusion, not allowing a support person to be present, restraint, injuries, and accidents. When more complex procedures are needed, eg x-ray, MRI, EEG, lab studies, or surgery, successful outcomes may be lower. Children with NDD have higher rates of often avoidable morbidity and mortality than those without, in part due to these barriers to complete care. While environmental accommodations to wheelchair users for accessibility has greatly improved in recent years, access to other kinds of individualized accommodations have lagged behind.
Accommodation Planning
There are a variety of factors that need to be taken into consideration in accommodating an individual with NDD. The family becomes the expert, along with the child, in knowing the child’s triggers, preferences, abilities, and level of understanding to accept and consent for care. An accommodation plan should be created using shared and supported decision making with the family and child and allowing for child preferences, regardless of their ability level, whenever possible. Development of an accommodation plan may benefit from multidisciplinary input, eg psychology, physical therapy, speech pathology, depending on the child’s needs and the practice’s ability to adapt.
The SAFE initiative is in the process of creating a checklist aiming to facilitate a description being created for each individual to help plan for a successful medical encounter while optimizing the child’s comfort, participation, and safety. While the checklist is not yet ready, we can start now by asking families and children in preparation for or at the start of a visit about their needs and writing a shared document that can also be placed in the electronic health record for the entire care team for informing care going forward.
It is especially important for the family to keep a copy of the care plan and for it to be sent as part of referrals for procedures or specialty visits so that the professionals can prepare and adapt the encounter. An excellent example is a how some hospitals schedule a practice visit for the child to experience the sights and sounds and people the child will encounter, for example, before an EEG, when nothing is required of the child. Scheduling the actual procedure at times of day when clinics are less crowded and wait times are shorter can improve the chances of success.
Some categories and details that might be included in an accommodation plan are listed below:
You might start the plan with the child’s preferred name/nickname, family member or support person names, and diagnoses along with a brief overview of the child’s level of functioning. Then list categories of needs and preferences along with suggestions or requests.
- Motor: Does the child have or need assistance entering the building, visit room, bathroom, or transferring to the exam table? What kind of assistance, if any, and by whom?
- Sensory: Is the child disturbed by noise, lights, or being touched? Does the child want to use equipment to be comfortable such as headphones, earplugs, or sunglasses or need a quiet room, care without perfumes, or dimmed lighting? Does the child typically refuse aspects of the physical examination?
- Behavioral regulation: What helps the child to stay calm? Are there certain triggers to becoming upset? Are there early cues that an upset is coming? What and who can help in the case of an upset?
- Habits/preferences: Are there certain comfort objects or habits your child needs? Are there habits your child needs to do, such as a certain order of events, or use of social stories or pictures, to cooperate or feel comfortable?
- Communication: How does the child make his/her needs known? Does the child/family speak English or another language? Does he/she use sign language or an augmentative communication device? What level of understanding does your child have; for example, similar to what age for a typical child? Is there a care plan with accommodations already available that needs review or needs revision with the child’s development or is a new one needed? Was the care plan developed including the child’s participation and assent or is more collaboration needed?
- History: Has your child had any very upsetting experiences in healthcare settings? What happened? Has the trauma been addressed? Are there reminders of the trauma that should be avoided?
- Other: Are there other things we should know about your child as an individual to provide the best care?
There are many actions needed to do better at ensuring equitable care for individuals with NDD. We should educate our office and medical staff about NDD in children and the importance of accommodating their needs, and ways to do it. The morning huddle can be used to remind staff of upcoming visits of children who may need accommodations. We then need to use quality improvement methods to check in periodically on how the changes are working for the children, families, and practice in order to continually improve.
The overall healthcare system also needs to change. Billing codes should reflect the time, complexity of accommodations, and documentation that were required for care. Episodes of the visit may need to be broken up within the day or over several days to allow the child to practice, calm down, and cooperate and this should be accounted for in billing. Given that NDD are generally lifelong conditions, payment systems that require measures of progress such as value-based payment based on improved outcomes will need to be adjusted to measure quality of care rather than significant progress.
We need to advocate for both individual children and for system changes to work toward equity of care for those with disabilities to make their lives more comfortable as well as ours.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
We pediatricians consider ourselves as compassionate professionals, optimistic about the potential of all children. This is reflected in the American Academy of Pediatrics’ equity statement of “its mission to ensure the health and well-being of all children. This includes promoting nurturing, inclusive environments and actively opposing intolerance, bigotry, bias, and discrimination.”
A committee of the Developmental Behavioral Pediatric Network developed and published a consensus statement specifically about problems in the care of individuals with neurodevelopmental disabilities (NDD) called the Supporting Access for Everyone (SAFE) initiative. All of us care for children with NDD as one in six are affected with these conditions that impact cognition, communication, motor, social, and/or behavior skills such as autism, ADHD, intellectual disabilities (ID), learning disorders, hearing or vision impairment, and motor disabilities such as cerebral palsy. Children with NDD are overrepresented in our daily practice schedule due to their multiple medical, behavioral, and social needs. NDD are also more common among marginalized children with racial, ethnic, sexual, or gender identity minority status compounding their difficulties in accessing quality care.
NDD present similar challenges to care as other chronic conditions that also require longer visits, more documentation, long-term monitoring, team-based care, care coordination, and often referrals. But most chronic medical conditions we care for such as asthma, diabetes, cancer, hypertension, and renal disease have clear national guidelines and appropriate billing codes and are not stigmatizing. Most also do not intrinsically affect the nervous system or cause disability as for NDD that alter the behavioral presentation of the individual in a way that changes their care.
Discrimination against individuals with NDD and other disabilities, called “ableism,” can take many forms: assuming a child with communication difficulty or ID is unable to understand explanations about their care; the presence of one NDD condition ending the clinician’s search for other issues; complicated problems or difficult behaviors in the medical setting truncating care, etc.
Adjustments Needed for Special Needs
As pediatricians we already adjust our interactions, starting instinctively, to the development level of the child we perceive before us. We approach infants slowly and softly, we speak in shorter sentences to toddlers, we joke around with school-aged children, and we take extra care about privacy with teens. This serves the relationships well for neurotypical children. But our (and our staff’s) perceptions of children with autism, ID, genetic syndromes that include NDD, or motor disabilities based on their behavioral presentation may not accurately recognize or accommodate their abilities or needs. Communication and environmental adjustments may need to be much more individualized to provide respectful care, comfort and even safety.
As an example, at this time 1 in 36 children have autism with or without ID. Defining features of autism include differences in social communication, repetitive or restrictive interests or behaviors, and hypersensitivity to the environment plus any coexisting conditions such as anxiety and hyperactivity. But most children with autism have completely age appropriate and typical physical appearance and their underlying condition may not even be known. The office setting, without special attention to the needs of a child with autism, may be frightening, loud, too bright, too crowded, fast paced, and confusing. The result of their sensitivities and difficulty communicating may lead to increased agitation, repetitive behaviors (sometimes called “stimming”), shrieking, attempts to escape the room, refusal to allow for vital signs or undressing, even aggression. Strategies for calming a neurotypical child such as talking or touching may make matters worse instead of better. We need help from the child and family and a plan to optimize their medical encounters.
If not adequately accommodated, children with many varieties of NDD end up not getting all the routine healthcare they need (eg vaccinations, blood tests, vital signs, even complete physical exams including dental) as well as having more adverse events during health care, including traumatizing seclusion, not allowing a support person to be present, restraint, injuries, and accidents. When more complex procedures are needed, eg x-ray, MRI, EEG, lab studies, or surgery, successful outcomes may be lower. Children with NDD have higher rates of often avoidable morbidity and mortality than those without, in part due to these barriers to complete care. While environmental accommodations to wheelchair users for accessibility has greatly improved in recent years, access to other kinds of individualized accommodations have lagged behind.
Accommodation Planning
There are a variety of factors that need to be taken into consideration in accommodating an individual with NDD. The family becomes the expert, along with the child, in knowing the child’s triggers, preferences, abilities, and level of understanding to accept and consent for care. An accommodation plan should be created using shared and supported decision making with the family and child and allowing for child preferences, regardless of their ability level, whenever possible. Development of an accommodation plan may benefit from multidisciplinary input, eg psychology, physical therapy, speech pathology, depending on the child’s needs and the practice’s ability to adapt.
The SAFE initiative is in the process of creating a checklist aiming to facilitate a description being created for each individual to help plan for a successful medical encounter while optimizing the child’s comfort, participation, and safety. While the checklist is not yet ready, we can start now by asking families and children in preparation for or at the start of a visit about their needs and writing a shared document that can also be placed in the electronic health record for the entire care team for informing care going forward.
It is especially important for the family to keep a copy of the care plan and for it to be sent as part of referrals for procedures or specialty visits so that the professionals can prepare and adapt the encounter. An excellent example is a how some hospitals schedule a practice visit for the child to experience the sights and sounds and people the child will encounter, for example, before an EEG, when nothing is required of the child. Scheduling the actual procedure at times of day when clinics are less crowded and wait times are shorter can improve the chances of success.
Some categories and details that might be included in an accommodation plan are listed below:
You might start the plan with the child’s preferred name/nickname, family member or support person names, and diagnoses along with a brief overview of the child’s level of functioning. Then list categories of needs and preferences along with suggestions or requests.
- Motor: Does the child have or need assistance entering the building, visit room, bathroom, or transferring to the exam table? What kind of assistance, if any, and by whom?
- Sensory: Is the child disturbed by noise, lights, or being touched? Does the child want to use equipment to be comfortable such as headphones, earplugs, or sunglasses or need a quiet room, care without perfumes, or dimmed lighting? Does the child typically refuse aspects of the physical examination?
- Behavioral regulation: What helps the child to stay calm? Are there certain triggers to becoming upset? Are there early cues that an upset is coming? What and who can help in the case of an upset?
- Habits/preferences: Are there certain comfort objects or habits your child needs? Are there habits your child needs to do, such as a certain order of events, or use of social stories or pictures, to cooperate or feel comfortable?
- Communication: How does the child make his/her needs known? Does the child/family speak English or another language? Does he/she use sign language or an augmentative communication device? What level of understanding does your child have; for example, similar to what age for a typical child? Is there a care plan with accommodations already available that needs review or needs revision with the child’s development or is a new one needed? Was the care plan developed including the child’s participation and assent or is more collaboration needed?
- History: Has your child had any very upsetting experiences in healthcare settings? What happened? Has the trauma been addressed? Are there reminders of the trauma that should be avoided?
- Other: Are there other things we should know about your child as an individual to provide the best care?
There are many actions needed to do better at ensuring equitable care for individuals with NDD. We should educate our office and medical staff about NDD in children and the importance of accommodating their needs, and ways to do it. The morning huddle can be used to remind staff of upcoming visits of children who may need accommodations. We then need to use quality improvement methods to check in periodically on how the changes are working for the children, families, and practice in order to continually improve.
The overall healthcare system also needs to change. Billing codes should reflect the time, complexity of accommodations, and documentation that were required for care. Episodes of the visit may need to be broken up within the day or over several days to allow the child to practice, calm down, and cooperate and this should be accounted for in billing. Given that NDD are generally lifelong conditions, payment systems that require measures of progress such as value-based payment based on improved outcomes will need to be adjusted to measure quality of care rather than significant progress.
We need to advocate for both individual children and for system changes to work toward equity of care for those with disabilities to make their lives more comfortable as well as ours.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
We pediatricians consider ourselves as compassionate professionals, optimistic about the potential of all children. This is reflected in the American Academy of Pediatrics’ equity statement of “its mission to ensure the health and well-being of all children. This includes promoting nurturing, inclusive environments and actively opposing intolerance, bigotry, bias, and discrimination.”
A committee of the Developmental Behavioral Pediatric Network developed and published a consensus statement specifically about problems in the care of individuals with neurodevelopmental disabilities (NDD) called the Supporting Access for Everyone (SAFE) initiative. All of us care for children with NDD as one in six are affected with these conditions that impact cognition, communication, motor, social, and/or behavior skills such as autism, ADHD, intellectual disabilities (ID), learning disorders, hearing or vision impairment, and motor disabilities such as cerebral palsy. Children with NDD are overrepresented in our daily practice schedule due to their multiple medical, behavioral, and social needs. NDD are also more common among marginalized children with racial, ethnic, sexual, or gender identity minority status compounding their difficulties in accessing quality care.
NDD present similar challenges to care as other chronic conditions that also require longer visits, more documentation, long-term monitoring, team-based care, care coordination, and often referrals. But most chronic medical conditions we care for such as asthma, diabetes, cancer, hypertension, and renal disease have clear national guidelines and appropriate billing codes and are not stigmatizing. Most also do not intrinsically affect the nervous system or cause disability as for NDD that alter the behavioral presentation of the individual in a way that changes their care.
Discrimination against individuals with NDD and other disabilities, called “ableism,” can take many forms: assuming a child with communication difficulty or ID is unable to understand explanations about their care; the presence of one NDD condition ending the clinician’s search for other issues; complicated problems or difficult behaviors in the medical setting truncating care, etc.
Adjustments Needed for Special Needs
As pediatricians we already adjust our interactions, starting instinctively, to the development level of the child we perceive before us. We approach infants slowly and softly, we speak in shorter sentences to toddlers, we joke around with school-aged children, and we take extra care about privacy with teens. This serves the relationships well for neurotypical children. But our (and our staff’s) perceptions of children with autism, ID, genetic syndromes that include NDD, or motor disabilities based on their behavioral presentation may not accurately recognize or accommodate their abilities or needs. Communication and environmental adjustments may need to be much more individualized to provide respectful care, comfort and even safety.
As an example, at this time 1 in 36 children have autism with or without ID. Defining features of autism include differences in social communication, repetitive or restrictive interests or behaviors, and hypersensitivity to the environment plus any coexisting conditions such as anxiety and hyperactivity. But most children with autism have completely age appropriate and typical physical appearance and their underlying condition may not even be known. The office setting, without special attention to the needs of a child with autism, may be frightening, loud, too bright, too crowded, fast paced, and confusing. The result of their sensitivities and difficulty communicating may lead to increased agitation, repetitive behaviors (sometimes called “stimming”), shrieking, attempts to escape the room, refusal to allow for vital signs or undressing, even aggression. Strategies for calming a neurotypical child such as talking or touching may make matters worse instead of better. We need help from the child and family and a plan to optimize their medical encounters.
If not adequately accommodated, children with many varieties of NDD end up not getting all the routine healthcare they need (eg vaccinations, blood tests, vital signs, even complete physical exams including dental) as well as having more adverse events during health care, including traumatizing seclusion, not allowing a support person to be present, restraint, injuries, and accidents. When more complex procedures are needed, eg x-ray, MRI, EEG, lab studies, or surgery, successful outcomes may be lower. Children with NDD have higher rates of often avoidable morbidity and mortality than those without, in part due to these barriers to complete care. While environmental accommodations to wheelchair users for accessibility has greatly improved in recent years, access to other kinds of individualized accommodations have lagged behind.
Accommodation Planning
There are a variety of factors that need to be taken into consideration in accommodating an individual with NDD. The family becomes the expert, along with the child, in knowing the child’s triggers, preferences, abilities, and level of understanding to accept and consent for care. An accommodation plan should be created using shared and supported decision making with the family and child and allowing for child preferences, regardless of their ability level, whenever possible. Development of an accommodation plan may benefit from multidisciplinary input, eg psychology, physical therapy, speech pathology, depending on the child’s needs and the practice’s ability to adapt.
The SAFE initiative is in the process of creating a checklist aiming to facilitate a description being created for each individual to help plan for a successful medical encounter while optimizing the child’s comfort, participation, and safety. While the checklist is not yet ready, we can start now by asking families and children in preparation for or at the start of a visit about their needs and writing a shared document that can also be placed in the electronic health record for the entire care team for informing care going forward.
It is especially important for the family to keep a copy of the care plan and for it to be sent as part of referrals for procedures or specialty visits so that the professionals can prepare and adapt the encounter. An excellent example is a how some hospitals schedule a practice visit for the child to experience the sights and sounds and people the child will encounter, for example, before an EEG, when nothing is required of the child. Scheduling the actual procedure at times of day when clinics are less crowded and wait times are shorter can improve the chances of success.
Some categories and details that might be included in an accommodation plan are listed below:
You might start the plan with the child’s preferred name/nickname, family member or support person names, and diagnoses along with a brief overview of the child’s level of functioning. Then list categories of needs and preferences along with suggestions or requests.
- Motor: Does the child have or need assistance entering the building, visit room, bathroom, or transferring to the exam table? What kind of assistance, if any, and by whom?
- Sensory: Is the child disturbed by noise, lights, or being touched? Does the child want to use equipment to be comfortable such as headphones, earplugs, or sunglasses or need a quiet room, care without perfumes, or dimmed lighting? Does the child typically refuse aspects of the physical examination?
- Behavioral regulation: What helps the child to stay calm? Are there certain triggers to becoming upset? Are there early cues that an upset is coming? What and who can help in the case of an upset?
- Habits/preferences: Are there certain comfort objects or habits your child needs? Are there habits your child needs to do, such as a certain order of events, or use of social stories or pictures, to cooperate or feel comfortable?
- Communication: How does the child make his/her needs known? Does the child/family speak English or another language? Does he/she use sign language or an augmentative communication device? What level of understanding does your child have; for example, similar to what age for a typical child? Is there a care plan with accommodations already available that needs review or needs revision with the child’s development or is a new one needed? Was the care plan developed including the child’s participation and assent or is more collaboration needed?
- History: Has your child had any very upsetting experiences in healthcare settings? What happened? Has the trauma been addressed? Are there reminders of the trauma that should be avoided?
- Other: Are there other things we should know about your child as an individual to provide the best care?
There are many actions needed to do better at ensuring equitable care for individuals with NDD. We should educate our office and medical staff about NDD in children and the importance of accommodating their needs, and ways to do it. The morning huddle can be used to remind staff of upcoming visits of children who may need accommodations. We then need to use quality improvement methods to check in periodically on how the changes are working for the children, families, and practice in order to continually improve.
The overall healthcare system also needs to change. Billing codes should reflect the time, complexity of accommodations, and documentation that were required for care. Episodes of the visit may need to be broken up within the day or over several days to allow the child to practice, calm down, and cooperate and this should be accounted for in billing. Given that NDD are generally lifelong conditions, payment systems that require measures of progress such as value-based payment based on improved outcomes will need to be adjusted to measure quality of care rather than significant progress.
We need to advocate for both individual children and for system changes to work toward equity of care for those with disabilities to make their lives more comfortable as well as ours.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
Vitamin D in Pregnancy Results in Stronger Bones for Kids
TOPLINE:
Gestational supplementation of 1000 IU/d cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) from early pregnancy until delivery increases the bone mineral content, bone mineral density (BMD), and bone mineral apparent density in children at age 6-7 years.
METHODOLOGY:
- The double-blinded, placebo-controlled MAVIDOS trial of gestational vitamin D supplementation previously showed increased BMD at age 4 years (but no difference at birth), and it is unclear how the effect may persist or change over time.
- In the original trial, researchers randomized 1134 pregnant women with singleton pregnancy from three UK hospitals from 2008 to 2014, and the 723 children born to mothers recruited in Southampton were invited to continue in offspring follow-up.
- Mothers were randomly assigned to receive either 1000-IU/d vitamin D or placebo from 14-17 weeks’ gestation until delivery; women in the placebo arm could take up to 400-IU/d vitamin D.
- In this post hoc analysis, among 454 children who were followed up at age 6-7 years, 447 had a usable whole body and lumbar spine dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scan (placebo group: n = 216; 48% boys; 98% White mothers and vitamin D group: n = 231; 56% boys; 96% White mothers).
- Offspring follow-up measures at birth and 4 and 6-7 years were bone area, bone mineral content, BMD, and bone mineral apparent density, derived from a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scan of whole body less head (WBLH), as well as fat and lean mass.
TAKEAWAY:
- The effect of gestational vitamin D supplementation on bone outcomes in children was similar at ages 4 and 6-7 years.
- At age 6-7 years, gestational vitamin D supplementation resulted in higher WBLH bone mineral content (0.15 SD; 95% CI, 0.04-0.26) and BMD (0.18 SD; 95% CI, 0.06-0.31) than placebo.
- The WBLH bone mineral apparent density (0.18 SD; 95% CI, 0.04-0.32) was also higher in the vitamin D group.
- The lean mass was greater in the vitamin D group (0.09 SD; 95% CI, 0.00-0.17) than in the placebo group.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings suggest that pregnancy vitamin D supplementation may be an important population health strategy to improve bone health,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Rebecca J. Moon, PhD, MRC Lifecourse Epidemiology Centre, University of Southampton, Southampton General Hospital, England. It was published online in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
LIMITATIONS:
Only individuals with baseline vitamin D levels of 25-100 nmol/L were eligible, excluding those with severe deficiency who might have benefited the most from supplementation. The participants were mostly White and well-educated, commonly overweight, which may have limited generalizability to other populations. Only 47% of the original cohort participated in the follow-up phase. Differences in maternal age, smoking status, and education between participants who remained in the study and those who did not may have introduced bias and affected generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by Versus Arthritis UK, Medical Research Council, Bupa Foundation, and National Institute for Health and Care Research, Southampton Biomedical Research Centre, and other sources. Some authors disclosed receiving travel reimbursement, speaker or lecture fees, honoraria, research funding, or personal or consultancy fees from Alliance for Better Bone Health and various pharmaceutical, biotechnology, medical device, healthcare, and food and nutrition companies outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Gestational supplementation of 1000 IU/d cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) from early pregnancy until delivery increases the bone mineral content, bone mineral density (BMD), and bone mineral apparent density in children at age 6-7 years.
METHODOLOGY:
- The double-blinded, placebo-controlled MAVIDOS trial of gestational vitamin D supplementation previously showed increased BMD at age 4 years (but no difference at birth), and it is unclear how the effect may persist or change over time.
- In the original trial, researchers randomized 1134 pregnant women with singleton pregnancy from three UK hospitals from 2008 to 2014, and the 723 children born to mothers recruited in Southampton were invited to continue in offspring follow-up.
- Mothers were randomly assigned to receive either 1000-IU/d vitamin D or placebo from 14-17 weeks’ gestation until delivery; women in the placebo arm could take up to 400-IU/d vitamin D.
- In this post hoc analysis, among 454 children who were followed up at age 6-7 years, 447 had a usable whole body and lumbar spine dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scan (placebo group: n = 216; 48% boys; 98% White mothers and vitamin D group: n = 231; 56% boys; 96% White mothers).
- Offspring follow-up measures at birth and 4 and 6-7 years were bone area, bone mineral content, BMD, and bone mineral apparent density, derived from a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scan of whole body less head (WBLH), as well as fat and lean mass.
TAKEAWAY:
- The effect of gestational vitamin D supplementation on bone outcomes in children was similar at ages 4 and 6-7 years.
- At age 6-7 years, gestational vitamin D supplementation resulted in higher WBLH bone mineral content (0.15 SD; 95% CI, 0.04-0.26) and BMD (0.18 SD; 95% CI, 0.06-0.31) than placebo.
- The WBLH bone mineral apparent density (0.18 SD; 95% CI, 0.04-0.32) was also higher in the vitamin D group.
- The lean mass was greater in the vitamin D group (0.09 SD; 95% CI, 0.00-0.17) than in the placebo group.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings suggest that pregnancy vitamin D supplementation may be an important population health strategy to improve bone health,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Rebecca J. Moon, PhD, MRC Lifecourse Epidemiology Centre, University of Southampton, Southampton General Hospital, England. It was published online in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
LIMITATIONS:
Only individuals with baseline vitamin D levels of 25-100 nmol/L were eligible, excluding those with severe deficiency who might have benefited the most from supplementation. The participants were mostly White and well-educated, commonly overweight, which may have limited generalizability to other populations. Only 47% of the original cohort participated in the follow-up phase. Differences in maternal age, smoking status, and education between participants who remained in the study and those who did not may have introduced bias and affected generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by Versus Arthritis UK, Medical Research Council, Bupa Foundation, and National Institute for Health and Care Research, Southampton Biomedical Research Centre, and other sources. Some authors disclosed receiving travel reimbursement, speaker or lecture fees, honoraria, research funding, or personal or consultancy fees from Alliance for Better Bone Health and various pharmaceutical, biotechnology, medical device, healthcare, and food and nutrition companies outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Gestational supplementation of 1000 IU/d cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) from early pregnancy until delivery increases the bone mineral content, bone mineral density (BMD), and bone mineral apparent density in children at age 6-7 years.
METHODOLOGY:
- The double-blinded, placebo-controlled MAVIDOS trial of gestational vitamin D supplementation previously showed increased BMD at age 4 years (but no difference at birth), and it is unclear how the effect may persist or change over time.
- In the original trial, researchers randomized 1134 pregnant women with singleton pregnancy from three UK hospitals from 2008 to 2014, and the 723 children born to mothers recruited in Southampton were invited to continue in offspring follow-up.
- Mothers were randomly assigned to receive either 1000-IU/d vitamin D or placebo from 14-17 weeks’ gestation until delivery; women in the placebo arm could take up to 400-IU/d vitamin D.
- In this post hoc analysis, among 454 children who were followed up at age 6-7 years, 447 had a usable whole body and lumbar spine dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scan (placebo group: n = 216; 48% boys; 98% White mothers and vitamin D group: n = 231; 56% boys; 96% White mothers).
- Offspring follow-up measures at birth and 4 and 6-7 years were bone area, bone mineral content, BMD, and bone mineral apparent density, derived from a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scan of whole body less head (WBLH), as well as fat and lean mass.
TAKEAWAY:
- The effect of gestational vitamin D supplementation on bone outcomes in children was similar at ages 4 and 6-7 years.
- At age 6-7 years, gestational vitamin D supplementation resulted in higher WBLH bone mineral content (0.15 SD; 95% CI, 0.04-0.26) and BMD (0.18 SD; 95% CI, 0.06-0.31) than placebo.
- The WBLH bone mineral apparent density (0.18 SD; 95% CI, 0.04-0.32) was also higher in the vitamin D group.
- The lean mass was greater in the vitamin D group (0.09 SD; 95% CI, 0.00-0.17) than in the placebo group.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings suggest that pregnancy vitamin D supplementation may be an important population health strategy to improve bone health,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Rebecca J. Moon, PhD, MRC Lifecourse Epidemiology Centre, University of Southampton, Southampton General Hospital, England. It was published online in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
LIMITATIONS:
Only individuals with baseline vitamin D levels of 25-100 nmol/L were eligible, excluding those with severe deficiency who might have benefited the most from supplementation. The participants were mostly White and well-educated, commonly overweight, which may have limited generalizability to other populations. Only 47% of the original cohort participated in the follow-up phase. Differences in maternal age, smoking status, and education between participants who remained in the study and those who did not may have introduced bias and affected generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by Versus Arthritis UK, Medical Research Council, Bupa Foundation, and National Institute for Health and Care Research, Southampton Biomedical Research Centre, and other sources. Some authors disclosed receiving travel reimbursement, speaker or lecture fees, honoraria, research funding, or personal or consultancy fees from Alliance for Better Bone Health and various pharmaceutical, biotechnology, medical device, healthcare, and food and nutrition companies outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nonalcoholic Beer and Underage Drinking
Several months ago in a letter about healthcare providers and the decision to use alcohol and other mind-altering substances on the job, I waxed enthusiastically about the new wave of no alcohol (NA) and zero (00) alcohol beers that have come on the market. In the last 2 years our local grocery store’s cooler space for nonalcoholic beer has grown from less than 24 inches to something approaching the height of the average sixth grader.
In a bold act of chivalry at the beginning of the pandemic I accepted the mantle of designated grocery shopper and over the last 3 years have become uncommonly proud of my ability to bring home the groceries efficiently and cost effectively, without catching COVID in the process. I have developed a sixth sense of choosing which human checker/bagger combination is fastest or whether the self-checkout is the way to go.
For obvious reasons the human checkers don’t ask for my ID when I am buying adult beverages. However, the self-check register freezes up instantly when I scan my 12-pack of Run Wild nonalcoholic. This necessitates a search for the MIA store person assigned to patrol the self-check corral, ever on the lookout for shoplifters, underage drinkers, and other generally shifty looking characters.
When I find one of the grocery store detectives (who is likely to have been a former patient), I say: “You know, this doesn’t have any alcohol in it.” They invariably reply with a shrug. “I know. But, the rules are the rules.” Occasionally, they may add: “It doesn’t make sense, does it?”
At first blush checking IDs for a nonalcoholic beverage may sound dumb, certainly to someone who is just a few years on either side of the legal drinking age. Why are we trying to protect some crazy teenager from the futility of getting high on a six-pack of something that at worst will make him spend most of the next couple of hours peeing?
But, there is concern in some corners that nonalcoholic drinks pose a significant threat to teenagers. Two PhDs at Stanford University have recently published a paper in which they worry that the dramatic rise in US sales of nonalcoholic drinks from 15% to 30% since 2018 may be socializing “users of alcohol drinking experiences by exposing them to the taste, look, and even brands of alcoholic beverages”.
Is there evidence to support their concern? I could only find one brief report in the Japanese literature that states that among young people “who experienced the nonalcoholic beverage intake, interest in or motivation for drinking alcoholic beverages, and/or smoking is higher than [among] those who did not.” The study didn’t appear to clearly separate the exposure in a family setting from the actual intake.
Beer is an acquired taste. If someone offered you your first taste of beer after a hot-weather set of tennis most of you would reject it and ask for water or lemonade. I can recall my first taste of beer. For some reason my father thought at age 11 or 12 I might like to try some from his glass. I’m not sure of his motivation, but he tried the same thing with oysters. I didn’t drink beer again until I was 16, motivated at that time by a group dynamic. The oyster trial, however, backfired on him and from then on he had to share his coveted dozen with me. Alcohol, unless heavily disguised by a mixer, is also not a taste that most young people find appealing.
It is unlikely that the average thrill-seeking teenager is going to ask his older-appearing buddy with a fake ID to buy him some nonalcoholic beer. Nor would he go to the effort or risk of acquiring his own fake ID just to see how it tastes. It just doesn’t compute, especially to a self-check corral patroller.
I guess one could envision a scenario in which a teenager wanting to fit in with the fast crowd would ask a trusted adult (or clueless parent) to buy him some nonalcoholic beer to bring to a party. He is running a serious risk of being laughed at by his friends if they find he’s drinking the fake stuff. It also seems unlikely that a parent would buy nonalcoholic beer to introduce his teenager to the taste of beer.
So,
Although it runs counter to my usual commitment to evidence-based decisions, making it difficult for adolescents to buy nonalcoholic beverages feels like the right think to do. As long as alcoholic and nonalcoholic beverages share the same display space and are packaged in nearly identical containers, there is ample opportunity for confusion. Recent evidence suggesting that even small amounts of alcohol increases some health risks should strengthen our resolve to minimize that confusion.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Several months ago in a letter about healthcare providers and the decision to use alcohol and other mind-altering substances on the job, I waxed enthusiastically about the new wave of no alcohol (NA) and zero (00) alcohol beers that have come on the market. In the last 2 years our local grocery store’s cooler space for nonalcoholic beer has grown from less than 24 inches to something approaching the height of the average sixth grader.
In a bold act of chivalry at the beginning of the pandemic I accepted the mantle of designated grocery shopper and over the last 3 years have become uncommonly proud of my ability to bring home the groceries efficiently and cost effectively, without catching COVID in the process. I have developed a sixth sense of choosing which human checker/bagger combination is fastest or whether the self-checkout is the way to go.
For obvious reasons the human checkers don’t ask for my ID when I am buying adult beverages. However, the self-check register freezes up instantly when I scan my 12-pack of Run Wild nonalcoholic. This necessitates a search for the MIA store person assigned to patrol the self-check corral, ever on the lookout for shoplifters, underage drinkers, and other generally shifty looking characters.
When I find one of the grocery store detectives (who is likely to have been a former patient), I say: “You know, this doesn’t have any alcohol in it.” They invariably reply with a shrug. “I know. But, the rules are the rules.” Occasionally, they may add: “It doesn’t make sense, does it?”
At first blush checking IDs for a nonalcoholic beverage may sound dumb, certainly to someone who is just a few years on either side of the legal drinking age. Why are we trying to protect some crazy teenager from the futility of getting high on a six-pack of something that at worst will make him spend most of the next couple of hours peeing?
But, there is concern in some corners that nonalcoholic drinks pose a significant threat to teenagers. Two PhDs at Stanford University have recently published a paper in which they worry that the dramatic rise in US sales of nonalcoholic drinks from 15% to 30% since 2018 may be socializing “users of alcohol drinking experiences by exposing them to the taste, look, and even brands of alcoholic beverages”.
Is there evidence to support their concern? I could only find one brief report in the Japanese literature that states that among young people “who experienced the nonalcoholic beverage intake, interest in or motivation for drinking alcoholic beverages, and/or smoking is higher than [among] those who did not.” The study didn’t appear to clearly separate the exposure in a family setting from the actual intake.
Beer is an acquired taste. If someone offered you your first taste of beer after a hot-weather set of tennis most of you would reject it and ask for water or lemonade. I can recall my first taste of beer. For some reason my father thought at age 11 or 12 I might like to try some from his glass. I’m not sure of his motivation, but he tried the same thing with oysters. I didn’t drink beer again until I was 16, motivated at that time by a group dynamic. The oyster trial, however, backfired on him and from then on he had to share his coveted dozen with me. Alcohol, unless heavily disguised by a mixer, is also not a taste that most young people find appealing.
It is unlikely that the average thrill-seeking teenager is going to ask his older-appearing buddy with a fake ID to buy him some nonalcoholic beer. Nor would he go to the effort or risk of acquiring his own fake ID just to see how it tastes. It just doesn’t compute, especially to a self-check corral patroller.
I guess one could envision a scenario in which a teenager wanting to fit in with the fast crowd would ask a trusted adult (or clueless parent) to buy him some nonalcoholic beer to bring to a party. He is running a serious risk of being laughed at by his friends if they find he’s drinking the fake stuff. It also seems unlikely that a parent would buy nonalcoholic beer to introduce his teenager to the taste of beer.
So,
Although it runs counter to my usual commitment to evidence-based decisions, making it difficult for adolescents to buy nonalcoholic beverages feels like the right think to do. As long as alcoholic and nonalcoholic beverages share the same display space and are packaged in nearly identical containers, there is ample opportunity for confusion. Recent evidence suggesting that even small amounts of alcohol increases some health risks should strengthen our resolve to minimize that confusion.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Several months ago in a letter about healthcare providers and the decision to use alcohol and other mind-altering substances on the job, I waxed enthusiastically about the new wave of no alcohol (NA) and zero (00) alcohol beers that have come on the market. In the last 2 years our local grocery store’s cooler space for nonalcoholic beer has grown from less than 24 inches to something approaching the height of the average sixth grader.
In a bold act of chivalry at the beginning of the pandemic I accepted the mantle of designated grocery shopper and over the last 3 years have become uncommonly proud of my ability to bring home the groceries efficiently and cost effectively, without catching COVID in the process. I have developed a sixth sense of choosing which human checker/bagger combination is fastest or whether the self-checkout is the way to go.
For obvious reasons the human checkers don’t ask for my ID when I am buying adult beverages. However, the self-check register freezes up instantly when I scan my 12-pack of Run Wild nonalcoholic. This necessitates a search for the MIA store person assigned to patrol the self-check corral, ever on the lookout for shoplifters, underage drinkers, and other generally shifty looking characters.
When I find one of the grocery store detectives (who is likely to have been a former patient), I say: “You know, this doesn’t have any alcohol in it.” They invariably reply with a shrug. “I know. But, the rules are the rules.” Occasionally, they may add: “It doesn’t make sense, does it?”
At first blush checking IDs for a nonalcoholic beverage may sound dumb, certainly to someone who is just a few years on either side of the legal drinking age. Why are we trying to protect some crazy teenager from the futility of getting high on a six-pack of something that at worst will make him spend most of the next couple of hours peeing?
But, there is concern in some corners that nonalcoholic drinks pose a significant threat to teenagers. Two PhDs at Stanford University have recently published a paper in which they worry that the dramatic rise in US sales of nonalcoholic drinks from 15% to 30% since 2018 may be socializing “users of alcohol drinking experiences by exposing them to the taste, look, and even brands of alcoholic beverages”.
Is there evidence to support their concern? I could only find one brief report in the Japanese literature that states that among young people “who experienced the nonalcoholic beverage intake, interest in or motivation for drinking alcoholic beverages, and/or smoking is higher than [among] those who did not.” The study didn’t appear to clearly separate the exposure in a family setting from the actual intake.
Beer is an acquired taste. If someone offered you your first taste of beer after a hot-weather set of tennis most of you would reject it and ask for water or lemonade. I can recall my first taste of beer. For some reason my father thought at age 11 or 12 I might like to try some from his glass. I’m not sure of his motivation, but he tried the same thing with oysters. I didn’t drink beer again until I was 16, motivated at that time by a group dynamic. The oyster trial, however, backfired on him and from then on he had to share his coveted dozen with me. Alcohol, unless heavily disguised by a mixer, is also not a taste that most young people find appealing.
It is unlikely that the average thrill-seeking teenager is going to ask his older-appearing buddy with a fake ID to buy him some nonalcoholic beer. Nor would he go to the effort or risk of acquiring his own fake ID just to see how it tastes. It just doesn’t compute, especially to a self-check corral patroller.
I guess one could envision a scenario in which a teenager wanting to fit in with the fast crowd would ask a trusted adult (or clueless parent) to buy him some nonalcoholic beer to bring to a party. He is running a serious risk of being laughed at by his friends if they find he’s drinking the fake stuff. It also seems unlikely that a parent would buy nonalcoholic beer to introduce his teenager to the taste of beer.
So,
Although it runs counter to my usual commitment to evidence-based decisions, making it difficult for adolescents to buy nonalcoholic beverages feels like the right think to do. As long as alcoholic and nonalcoholic beverages share the same display space and are packaged in nearly identical containers, there is ample opportunity for confusion. Recent evidence suggesting that even small amounts of alcohol increases some health risks should strengthen our resolve to minimize that confusion.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Anticipated Effects of Pneumococcal Vaccines on Otitis
Acute otitis media (AOM) is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis. Since the introduction of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs) shifts in the proportion of these three bacteria as causes of AOM and their antibiotic susceptibility profiles and strain diversity have occurred due to multiple factors including the PCVs and antibiotic selection pressure.
The 7-valent PCV (PCV7) was introduced in 2000 and was proven to be efficacious in preventing AOM, but no subsequent PCV has received an indication for prevention of AOM because the FDA required a tympanocentesis study to prove efficacy and that approval was not achieved for PCV13, PCV15, or PCV20. This is a little known fact. After introduction of PCV7, replacement pneumococcal strains expressing serotypes not in PCV7 emerged and antibiotic non-susceptible strains became predominant causes of AOM, especially antibiotic-resistant serotype 19A. To address the phenomena of pneumococcal serotype replacement, PCV13 was introduced in 2010. But serotype replacement continued to occur under PCV13 pressure, replacement serotypes increasingly caused AOM, and antibiotic-resistant serotype 35B emerged. Now we have two new higher valency PCVs: PCV15 (Merck) where serotypes 22F and 33F were added to the PCV13 serotypes and PCV20 (Pfizer) where 22F, 33F, 8, 10A, 11A, 12F, 15B were added to PCV13. Note that neither PCV15 nor PCV20 includes the most common serotype causing AOM – serotype 35B.1
While PCV15 and PCV20 should provide protection against more pneumococcal serotypes, increasing serotypes in both vaccines decreased immunogenicity of certain shared serotypes, more so with the addition of seven more in PCV20 than two more in PCV15, compared with PCV13. Whether lower antibody concentrations will make a difference clinically in terms of vaccine failure to prevent nasopharyngeal colonization, AOM, and/or invasive pneumococcal infections is currently unknown.
Our group from greater Rochester, New York, is the only one in the United States performing tympanocentesis to determine the etiology of AOM infections. Children between ages 6 and 36 months are studied. We recently reported our results for the time span September 2021 to September 2023, the immediate 2 years prior to recommendations for use of PCV15 and PCV20 in young children.2 Tympanocentesis was performed in 139 (78%) of 179 episodes of AOM, yielding 216 middle ear fluid samples (the higher number of middle ear fluids was due to bilateral tympanocentesis in some children). H. influenzae (40%) was the most common bacterial isolate, followed by S. pneumonia (19%) and M. catarrhalis (17%), with the remainder no growth. Polymerase chain reactions (PCR) was positive in many of those culture negative samples, suggesting prior use of antibiotics before tympanocentesis was performed. Among the pneumococcal isolates, 46% were oxacillin non-susceptible. Among the H. influenzae isolates, 27% were beta-lactamase producing and all M. catarrhalis were beta-lactamase-producing.
As we previously reported,1 we once again found that serotype 35B was the most frequent non-PCV15, non-PCV20, serotype. Other frequently detected non-PCV20 pneumococcal serotypes were 23A, 23B, 35D, 35F and 15C.2
Projected Pneumococcal Serotype Coverage by PCV15 and PCV20
PCV13 serotypes were identified in 9% of middle ear fluids, consistent with vaccine failure. Assuming 100% vaccine-type effectiveness, PCV15 will provide about 11% coverage of pneumococci causing AOM, the same PCV13 and PCV20 will provide 30% coverage, leaving 70% of pneumococci causing AOM in young children uncovered (Figure).
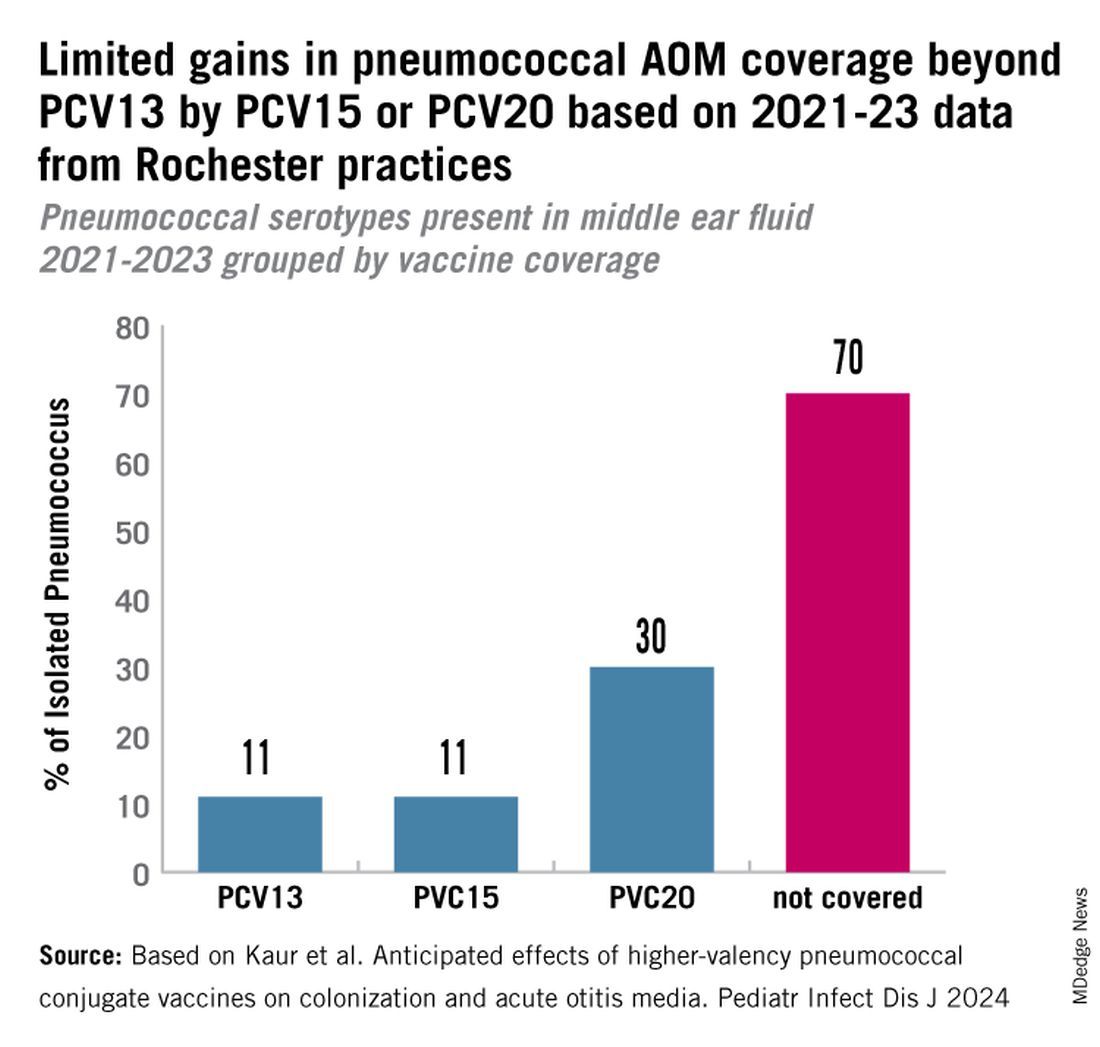
Thus, the high proportion of pneumococcal serotype 35B and other non-PCV15 or non-PCV20 serotypes will result in a relatively small incremental benefit over PCV13 in young children for AOM.
AOM is the most common cause of pediatric outpatient visits and antibiotic prescriptions in the United States that contributes to selection of antibiotic-resistant microbes.3 The economic burden of AOM is high, estimated at about $3 billion annually in the United States, when direct and indirect costs are calculated,4 thereby making AOM a major factor in calculations of cost effectiveness analyses of PCV immunizations in children.
While PCV15 and PCV20 include common serotypes associated with invasive pneumococcal diseases, their effectiveness in preventing AOM, acute sinusitis, and non-bacteremic community-acquired pneumonia is currently unknown because these vaccines were licensed based on safety and immunogenicity data, not proven efficacy.
The data on antibiotic susceptibility of pneumococci and H. influenza and M. catarrhalis isolated in the late post PCV13 era from young children in a pediatric primary-care setting raise a question about empiric antibiotic choice for AOM today. For penicillin non-susceptible pneumococcal strains, higher dosages of amoxicillin can improve eradication. However, higher dosages of amoxicillin cannot overcome beta-lactamase production by H. influenza and M. catarrhalis. Based on the mix of pathogens causing AOM and the antibiotic susceptibility of those bacteria, high-dose amoxicillin/clavulanate or alternative cephalosporin drugs active against pneumococci and beta-lactamase producing H. influenza and M. catarrhalis would be a better empiric choice over high-dose amoxicillin.
Limitations of our study include that it occurred in one center in New York, although we have previously shown results of tympanocentesis at our center are similar to those in Virginia and Pennsylvania5 and our study population was composed of children living in urban, suburban, and rural households of all economic levels. Because this study was conducted during a relatively short time frame (2021-2023), the numbers of subjects and samples were sometimes insufficient to identify statistically significant differences in some comparisons. Some children were lost to follow-up, and not every participant was consented for tympanocentesis. Some participants received antibiotics prior to middle ear fluid specimen collection.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute, at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
1. Kaur R et al. Dynamic Changes in Otopathogens Colonizing the Nasopharynx and Causing Acute Otitis Media in Children After 13-Valent (PCV13) Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccination During 2015-2019. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2022 Jan;41(1):37-44. doi: 10.1007/s10096-021-04324-0.
2. Kaur R et al. Anticipated Effects of Higher-valency Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines on Colonization and Acute Otitis Media. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2024 Oct 1;43(10):1004-1010. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000004413.
3. King LM et al. Pediatric Outpatient Visits and Antibiotic Use Attributable to Higher Valency Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine Serotypes. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 25:2023.08.24.23294570. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.24.23294570.
4. Ahmed S et al. Incremental Health Care Utilization and Costs for Acute Otitis Media in Children. Laryngoscope. 2014 Jan;124(1):301-5. doi: 10.1002/lary.24190.
5. Pichichero ME et al. Pathogens Causing Recurrent and Difficult-to-Treat Acute Otitis Media, 2003-2006. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2008 Nov;47(9):901-6. doi: 10.1177/0009922808319966.
Acute otitis media (AOM) is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis. Since the introduction of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs) shifts in the proportion of these three bacteria as causes of AOM and their antibiotic susceptibility profiles and strain diversity have occurred due to multiple factors including the PCVs and antibiotic selection pressure.
The 7-valent PCV (PCV7) was introduced in 2000 and was proven to be efficacious in preventing AOM, but no subsequent PCV has received an indication for prevention of AOM because the FDA required a tympanocentesis study to prove efficacy and that approval was not achieved for PCV13, PCV15, or PCV20. This is a little known fact. After introduction of PCV7, replacement pneumococcal strains expressing serotypes not in PCV7 emerged and antibiotic non-susceptible strains became predominant causes of AOM, especially antibiotic-resistant serotype 19A. To address the phenomena of pneumococcal serotype replacement, PCV13 was introduced in 2010. But serotype replacement continued to occur under PCV13 pressure, replacement serotypes increasingly caused AOM, and antibiotic-resistant serotype 35B emerged. Now we have two new higher valency PCVs: PCV15 (Merck) where serotypes 22F and 33F were added to the PCV13 serotypes and PCV20 (Pfizer) where 22F, 33F, 8, 10A, 11A, 12F, 15B were added to PCV13. Note that neither PCV15 nor PCV20 includes the most common serotype causing AOM – serotype 35B.1
While PCV15 and PCV20 should provide protection against more pneumococcal serotypes, increasing serotypes in both vaccines decreased immunogenicity of certain shared serotypes, more so with the addition of seven more in PCV20 than two more in PCV15, compared with PCV13. Whether lower antibody concentrations will make a difference clinically in terms of vaccine failure to prevent nasopharyngeal colonization, AOM, and/or invasive pneumococcal infections is currently unknown.
Our group from greater Rochester, New York, is the only one in the United States performing tympanocentesis to determine the etiology of AOM infections. Children between ages 6 and 36 months are studied. We recently reported our results for the time span September 2021 to September 2023, the immediate 2 years prior to recommendations for use of PCV15 and PCV20 in young children.2 Tympanocentesis was performed in 139 (78%) of 179 episodes of AOM, yielding 216 middle ear fluid samples (the higher number of middle ear fluids was due to bilateral tympanocentesis in some children). H. influenzae (40%) was the most common bacterial isolate, followed by S. pneumonia (19%) and M. catarrhalis (17%), with the remainder no growth. Polymerase chain reactions (PCR) was positive in many of those culture negative samples, suggesting prior use of antibiotics before tympanocentesis was performed. Among the pneumococcal isolates, 46% were oxacillin non-susceptible. Among the H. influenzae isolates, 27% were beta-lactamase producing and all M. catarrhalis were beta-lactamase-producing.
As we previously reported,1 we once again found that serotype 35B was the most frequent non-PCV15, non-PCV20, serotype. Other frequently detected non-PCV20 pneumococcal serotypes were 23A, 23B, 35D, 35F and 15C.2
Projected Pneumococcal Serotype Coverage by PCV15 and PCV20
PCV13 serotypes were identified in 9% of middle ear fluids, consistent with vaccine failure. Assuming 100% vaccine-type effectiveness, PCV15 will provide about 11% coverage of pneumococci causing AOM, the same PCV13 and PCV20 will provide 30% coverage, leaving 70% of pneumococci causing AOM in young children uncovered (Figure).

Thus, the high proportion of pneumococcal serotype 35B and other non-PCV15 or non-PCV20 serotypes will result in a relatively small incremental benefit over PCV13 in young children for AOM.
AOM is the most common cause of pediatric outpatient visits and antibiotic prescriptions in the United States that contributes to selection of antibiotic-resistant microbes.3 The economic burden of AOM is high, estimated at about $3 billion annually in the United States, when direct and indirect costs are calculated,4 thereby making AOM a major factor in calculations of cost effectiveness analyses of PCV immunizations in children.
While PCV15 and PCV20 include common serotypes associated with invasive pneumococcal diseases, their effectiveness in preventing AOM, acute sinusitis, and non-bacteremic community-acquired pneumonia is currently unknown because these vaccines were licensed based on safety and immunogenicity data, not proven efficacy.
The data on antibiotic susceptibility of pneumococci and H. influenza and M. catarrhalis isolated in the late post PCV13 era from young children in a pediatric primary-care setting raise a question about empiric antibiotic choice for AOM today. For penicillin non-susceptible pneumococcal strains, higher dosages of amoxicillin can improve eradication. However, higher dosages of amoxicillin cannot overcome beta-lactamase production by H. influenza and M. catarrhalis. Based on the mix of pathogens causing AOM and the antibiotic susceptibility of those bacteria, high-dose amoxicillin/clavulanate or alternative cephalosporin drugs active against pneumococci and beta-lactamase producing H. influenza and M. catarrhalis would be a better empiric choice over high-dose amoxicillin.
Limitations of our study include that it occurred in one center in New York, although we have previously shown results of tympanocentesis at our center are similar to those in Virginia and Pennsylvania5 and our study population was composed of children living in urban, suburban, and rural households of all economic levels. Because this study was conducted during a relatively short time frame (2021-2023), the numbers of subjects and samples were sometimes insufficient to identify statistically significant differences in some comparisons. Some children were lost to follow-up, and not every participant was consented for tympanocentesis. Some participants received antibiotics prior to middle ear fluid specimen collection.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute, at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
1. Kaur R et al. Dynamic Changes in Otopathogens Colonizing the Nasopharynx and Causing Acute Otitis Media in Children After 13-Valent (PCV13) Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccination During 2015-2019. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2022 Jan;41(1):37-44. doi: 10.1007/s10096-021-04324-0.
2. Kaur R et al. Anticipated Effects of Higher-valency Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines on Colonization and Acute Otitis Media. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2024 Oct 1;43(10):1004-1010. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000004413.
3. King LM et al. Pediatric Outpatient Visits and Antibiotic Use Attributable to Higher Valency Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine Serotypes. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 25:2023.08.24.23294570. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.24.23294570.
4. Ahmed S et al. Incremental Health Care Utilization and Costs for Acute Otitis Media in Children. Laryngoscope. 2014 Jan;124(1):301-5. doi: 10.1002/lary.24190.
5. Pichichero ME et al. Pathogens Causing Recurrent and Difficult-to-Treat Acute Otitis Media, 2003-2006. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2008 Nov;47(9):901-6. doi: 10.1177/0009922808319966.
Acute otitis media (AOM) is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis. Since the introduction of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs) shifts in the proportion of these three bacteria as causes of AOM and their antibiotic susceptibility profiles and strain diversity have occurred due to multiple factors including the PCVs and antibiotic selection pressure.
The 7-valent PCV (PCV7) was introduced in 2000 and was proven to be efficacious in preventing AOM, but no subsequent PCV has received an indication for prevention of AOM because the FDA required a tympanocentesis study to prove efficacy and that approval was not achieved for PCV13, PCV15, or PCV20. This is a little known fact. After introduction of PCV7, replacement pneumococcal strains expressing serotypes not in PCV7 emerged and antibiotic non-susceptible strains became predominant causes of AOM, especially antibiotic-resistant serotype 19A. To address the phenomena of pneumococcal serotype replacement, PCV13 was introduced in 2010. But serotype replacement continued to occur under PCV13 pressure, replacement serotypes increasingly caused AOM, and antibiotic-resistant serotype 35B emerged. Now we have two new higher valency PCVs: PCV15 (Merck) where serotypes 22F and 33F were added to the PCV13 serotypes and PCV20 (Pfizer) where 22F, 33F, 8, 10A, 11A, 12F, 15B were added to PCV13. Note that neither PCV15 nor PCV20 includes the most common serotype causing AOM – serotype 35B.1
While PCV15 and PCV20 should provide protection against more pneumococcal serotypes, increasing serotypes in both vaccines decreased immunogenicity of certain shared serotypes, more so with the addition of seven more in PCV20 than two more in PCV15, compared with PCV13. Whether lower antibody concentrations will make a difference clinically in terms of vaccine failure to prevent nasopharyngeal colonization, AOM, and/or invasive pneumococcal infections is currently unknown.
Our group from greater Rochester, New York, is the only one in the United States performing tympanocentesis to determine the etiology of AOM infections. Children between ages 6 and 36 months are studied. We recently reported our results for the time span September 2021 to September 2023, the immediate 2 years prior to recommendations for use of PCV15 and PCV20 in young children.2 Tympanocentesis was performed in 139 (78%) of 179 episodes of AOM, yielding 216 middle ear fluid samples (the higher number of middle ear fluids was due to bilateral tympanocentesis in some children). H. influenzae (40%) was the most common bacterial isolate, followed by S. pneumonia (19%) and M. catarrhalis (17%), with the remainder no growth. Polymerase chain reactions (PCR) was positive in many of those culture negative samples, suggesting prior use of antibiotics before tympanocentesis was performed. Among the pneumococcal isolates, 46% were oxacillin non-susceptible. Among the H. influenzae isolates, 27% were beta-lactamase producing and all M. catarrhalis were beta-lactamase-producing.
As we previously reported,1 we once again found that serotype 35B was the most frequent non-PCV15, non-PCV20, serotype. Other frequently detected non-PCV20 pneumococcal serotypes were 23A, 23B, 35D, 35F and 15C.2
Projected Pneumococcal Serotype Coverage by PCV15 and PCV20
PCV13 serotypes were identified in 9% of middle ear fluids, consistent with vaccine failure. Assuming 100% vaccine-type effectiveness, PCV15 will provide about 11% coverage of pneumococci causing AOM, the same PCV13 and PCV20 will provide 30% coverage, leaving 70% of pneumococci causing AOM in young children uncovered (Figure).

Thus, the high proportion of pneumococcal serotype 35B and other non-PCV15 or non-PCV20 serotypes will result in a relatively small incremental benefit over PCV13 in young children for AOM.
AOM is the most common cause of pediatric outpatient visits and antibiotic prescriptions in the United States that contributes to selection of antibiotic-resistant microbes.3 The economic burden of AOM is high, estimated at about $3 billion annually in the United States, when direct and indirect costs are calculated,4 thereby making AOM a major factor in calculations of cost effectiveness analyses of PCV immunizations in children.
While PCV15 and PCV20 include common serotypes associated with invasive pneumococcal diseases, their effectiveness in preventing AOM, acute sinusitis, and non-bacteremic community-acquired pneumonia is currently unknown because these vaccines were licensed based on safety and immunogenicity data, not proven efficacy.
The data on antibiotic susceptibility of pneumococci and H. influenza and M. catarrhalis isolated in the late post PCV13 era from young children in a pediatric primary-care setting raise a question about empiric antibiotic choice for AOM today. For penicillin non-susceptible pneumococcal strains, higher dosages of amoxicillin can improve eradication. However, higher dosages of amoxicillin cannot overcome beta-lactamase production by H. influenza and M. catarrhalis. Based on the mix of pathogens causing AOM and the antibiotic susceptibility of those bacteria, high-dose amoxicillin/clavulanate or alternative cephalosporin drugs active against pneumococci and beta-lactamase producing H. influenza and M. catarrhalis would be a better empiric choice over high-dose amoxicillin.
Limitations of our study include that it occurred in one center in New York, although we have previously shown results of tympanocentesis at our center are similar to those in Virginia and Pennsylvania5 and our study population was composed of children living in urban, suburban, and rural households of all economic levels. Because this study was conducted during a relatively short time frame (2021-2023), the numbers of subjects and samples were sometimes insufficient to identify statistically significant differences in some comparisons. Some children were lost to follow-up, and not every participant was consented for tympanocentesis. Some participants received antibiotics prior to middle ear fluid specimen collection.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute, at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
1. Kaur R et al. Dynamic Changes in Otopathogens Colonizing the Nasopharynx and Causing Acute Otitis Media in Children After 13-Valent (PCV13) Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccination During 2015-2019. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2022 Jan;41(1):37-44. doi: 10.1007/s10096-021-04324-0.
2. Kaur R et al. Anticipated Effects of Higher-valency Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines on Colonization and Acute Otitis Media. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2024 Oct 1;43(10):1004-1010. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000004413.
3. King LM et al. Pediatric Outpatient Visits and Antibiotic Use Attributable to Higher Valency Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine Serotypes. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 25:2023.08.24.23294570. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.24.23294570.
4. Ahmed S et al. Incremental Health Care Utilization and Costs for Acute Otitis Media in Children. Laryngoscope. 2014 Jan;124(1):301-5. doi: 10.1002/lary.24190.
5. Pichichero ME et al. Pathogens Causing Recurrent and Difficult-to-Treat Acute Otitis Media, 2003-2006. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2008 Nov;47(9):901-6. doi: 10.1177/0009922808319966.
Down Syndrome: Several Cutaneous Conditions Common, Study Finds
TOPLINE:
(DS) in a 10-year retrospective study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a multicenter retrospective study of 1529 patients with DS from eight outpatient dermatology clinics in the United States and Canada between 2011 and 2021.
- In total, 50.8% of patients were children (0-12 years), 25.2% were adolescents (13-17 years), and 24% were adults (≥ 18 years).
- The researchers evaluated skin conditions in the patients.
TAKEAWAY:
- Eczematous dermatitis was the most common diagnosis, affecting 26% of patients, followed by folliculitis (19.3%) and seborrheic dermatitis (15.6%). Dermatophyte infections were diagnosed in 13%.
- Alopecia areata was the most common autoimmune skin condition, diagnosed in 178 patients (11.6%); 135 (75.8%) were children. Vitiligo was diagnosed in 66 patients (4.3%).
- The most common cutaneous infections were onychomycosis (5.9%), tinea pedis (5%), and verruca vulgaris/other viral warts (5%).
- High-risk medication use was reported in 4.3% of patients; acne vulgaris, hidradenitis suppurativa, and eczematous dermatitis were the most common associated conditions with such medications.
IN PRACTICE:
“Children, adolescents, and adults with DS are most often found to have eczematous, adnexal, and autoimmune skin conditions at outpatient dermatology visits,” the authors wrote. Their findings, they added, “offer valuable insights for clinicians and researchers, aiding in the improved prioritization of screening, diagnosis, and management, as well as facilitating both basic science and clinical research into prevalent skin conditions in individuals with DS.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Tasya Rakasiwi, of the Department of Dermatology, Dartmouth Health, Manchester, New Hampshire, and was published online in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Over 50% of the patients were children, potentially resulting in bias toward pediatric diagnoses and younger ages of presentation. Race, ethnicity, and sociodemographic factors were not captured, limiting the generalizability of the findings. Medical codes often do not capture disease phenotype or severity, and the manual conversion of International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 9 to ICD-10 codes may introduce potential conversion errors.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance. The authors declared no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
(DS) in a 10-year retrospective study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a multicenter retrospective study of 1529 patients with DS from eight outpatient dermatology clinics in the United States and Canada between 2011 and 2021.
- In total, 50.8% of patients were children (0-12 years), 25.2% were adolescents (13-17 years), and 24% were adults (≥ 18 years).
- The researchers evaluated skin conditions in the patients.
TAKEAWAY:
- Eczematous dermatitis was the most common diagnosis, affecting 26% of patients, followed by folliculitis (19.3%) and seborrheic dermatitis (15.6%). Dermatophyte infections were diagnosed in 13%.
- Alopecia areata was the most common autoimmune skin condition, diagnosed in 178 patients (11.6%); 135 (75.8%) were children. Vitiligo was diagnosed in 66 patients (4.3%).
- The most common cutaneous infections were onychomycosis (5.9%), tinea pedis (5%), and verruca vulgaris/other viral warts (5%).
- High-risk medication use was reported in 4.3% of patients; acne vulgaris, hidradenitis suppurativa, and eczematous dermatitis were the most common associated conditions with such medications.
IN PRACTICE:
“Children, adolescents, and adults with DS are most often found to have eczematous, adnexal, and autoimmune skin conditions at outpatient dermatology visits,” the authors wrote. Their findings, they added, “offer valuable insights for clinicians and researchers, aiding in the improved prioritization of screening, diagnosis, and management, as well as facilitating both basic science and clinical research into prevalent skin conditions in individuals with DS.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Tasya Rakasiwi, of the Department of Dermatology, Dartmouth Health, Manchester, New Hampshire, and was published online in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Over 50% of the patients were children, potentially resulting in bias toward pediatric diagnoses and younger ages of presentation. Race, ethnicity, and sociodemographic factors were not captured, limiting the generalizability of the findings. Medical codes often do not capture disease phenotype or severity, and the manual conversion of International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 9 to ICD-10 codes may introduce potential conversion errors.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance. The authors declared no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
(DS) in a 10-year retrospective study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a multicenter retrospective study of 1529 patients with DS from eight outpatient dermatology clinics in the United States and Canada between 2011 and 2021.
- In total, 50.8% of patients were children (0-12 years), 25.2% were adolescents (13-17 years), and 24% were adults (≥ 18 years).
- The researchers evaluated skin conditions in the patients.
TAKEAWAY:
- Eczematous dermatitis was the most common diagnosis, affecting 26% of patients, followed by folliculitis (19.3%) and seborrheic dermatitis (15.6%). Dermatophyte infections were diagnosed in 13%.
- Alopecia areata was the most common autoimmune skin condition, diagnosed in 178 patients (11.6%); 135 (75.8%) were children. Vitiligo was diagnosed in 66 patients (4.3%).
- The most common cutaneous infections were onychomycosis (5.9%), tinea pedis (5%), and verruca vulgaris/other viral warts (5%).
- High-risk medication use was reported in 4.3% of patients; acne vulgaris, hidradenitis suppurativa, and eczematous dermatitis were the most common associated conditions with such medications.
IN PRACTICE:
“Children, adolescents, and adults with DS are most often found to have eczematous, adnexal, and autoimmune skin conditions at outpatient dermatology visits,” the authors wrote. Their findings, they added, “offer valuable insights for clinicians and researchers, aiding in the improved prioritization of screening, diagnosis, and management, as well as facilitating both basic science and clinical research into prevalent skin conditions in individuals with DS.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Tasya Rakasiwi, of the Department of Dermatology, Dartmouth Health, Manchester, New Hampshire, and was published online in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Over 50% of the patients were children, potentially resulting in bias toward pediatric diagnoses and younger ages of presentation. Race, ethnicity, and sociodemographic factors were not captured, limiting the generalizability of the findings. Medical codes often do not capture disease phenotype or severity, and the manual conversion of International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 9 to ICD-10 codes may introduce potential conversion errors.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance. The authors declared no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.