User login
Addressing supply-demand mismatch in GI
Impacts of this supply-demand mismatch are felt daily in our GI practices as we strive to expand access in our clinics and endoscopy suites, particularly in rural and urban underserved communities. In gastroenterology, increased demand for care has been driven by a perfect storm of population growth, increased patient awareness of GI health, and rising incidence of digestive diseases.
Between 2019 and 2034, the U.S. population is expected to grow by 10.6%, while the population aged 65 and older expands by over 42%. Recent increases in the CRC screening–eligible population also have contributed to unprecedented demand for GI care. Furthermore, care delivery has become more complex and time-consuming with the evolution of personalized medicine and high prevalence of comorbid conditions. At the same time, we are faced with a dwindling supply of gastroenterology providers. In 2021, there were 15,678 practicing gastroenterologists in the U.S., over half of whom were 55 years or older. This translates to 1 gastroenterologist per 20,830 people captured in the U.S. Census.
Addressing this striking supply-demand mismatch in GI requires a multi-pronged approach that addresses its complex drivers. First and foremost, we must expand the number of GI fellowship training slots to boost our pipeline. There are approximately 1,840 GI fellows currently in training, a third of whom enter the workforce each year. While the number of GI fellowship slots in the GI fellowship match has slowly increased over time (from 525 available slots across 199 programs in 2019 to 657 slots across 230 programs in 2023), this incremental growth is dwarfed by overall need. Continued advocacy for increased funding to support expansion of training slots is necessary to further move the needle – such lobbying recently led to the addition of 1,000 new Medicare-supported graduate medical education positions across specialties over a 5-year period starting in 2020, illustrating that change is possible. At the same time, we must address the factors that are causing gastroenterologists to leave the workforce prematurely through early retirement or part-time work by investing in innovative solutions to address burnout, reduce administrative burdens, enhance the efficiency of care delivery, and maintain financial viability. By investing in our physician workforce and its sustainability, we can ensure that our profession is better prepared to meet the needs of our growing and increasingly complex patient population now and in the future.
We hope you enjoy the November issue of GI & Hepatology News and have a wonderful Thanksgiving.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor-in-Chief
Impacts of this supply-demand mismatch are felt daily in our GI practices as we strive to expand access in our clinics and endoscopy suites, particularly in rural and urban underserved communities. In gastroenterology, increased demand for care has been driven by a perfect storm of population growth, increased patient awareness of GI health, and rising incidence of digestive diseases.
Between 2019 and 2034, the U.S. population is expected to grow by 10.6%, while the population aged 65 and older expands by over 42%. Recent increases in the CRC screening–eligible population also have contributed to unprecedented demand for GI care. Furthermore, care delivery has become more complex and time-consuming with the evolution of personalized medicine and high prevalence of comorbid conditions. At the same time, we are faced with a dwindling supply of gastroenterology providers. In 2021, there were 15,678 practicing gastroenterologists in the U.S., over half of whom were 55 years or older. This translates to 1 gastroenterologist per 20,830 people captured in the U.S. Census.
Addressing this striking supply-demand mismatch in GI requires a multi-pronged approach that addresses its complex drivers. First and foremost, we must expand the number of GI fellowship training slots to boost our pipeline. There are approximately 1,840 GI fellows currently in training, a third of whom enter the workforce each year. While the number of GI fellowship slots in the GI fellowship match has slowly increased over time (from 525 available slots across 199 programs in 2019 to 657 slots across 230 programs in 2023), this incremental growth is dwarfed by overall need. Continued advocacy for increased funding to support expansion of training slots is necessary to further move the needle – such lobbying recently led to the addition of 1,000 new Medicare-supported graduate medical education positions across specialties over a 5-year period starting in 2020, illustrating that change is possible. At the same time, we must address the factors that are causing gastroenterologists to leave the workforce prematurely through early retirement or part-time work by investing in innovative solutions to address burnout, reduce administrative burdens, enhance the efficiency of care delivery, and maintain financial viability. By investing in our physician workforce and its sustainability, we can ensure that our profession is better prepared to meet the needs of our growing and increasingly complex patient population now and in the future.
We hope you enjoy the November issue of GI & Hepatology News and have a wonderful Thanksgiving.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor-in-Chief
Impacts of this supply-demand mismatch are felt daily in our GI practices as we strive to expand access in our clinics and endoscopy suites, particularly in rural and urban underserved communities. In gastroenterology, increased demand for care has been driven by a perfect storm of population growth, increased patient awareness of GI health, and rising incidence of digestive diseases.
Between 2019 and 2034, the U.S. population is expected to grow by 10.6%, while the population aged 65 and older expands by over 42%. Recent increases in the CRC screening–eligible population also have contributed to unprecedented demand for GI care. Furthermore, care delivery has become more complex and time-consuming with the evolution of personalized medicine and high prevalence of comorbid conditions. At the same time, we are faced with a dwindling supply of gastroenterology providers. In 2021, there were 15,678 practicing gastroenterologists in the U.S., over half of whom were 55 years or older. This translates to 1 gastroenterologist per 20,830 people captured in the U.S. Census.
Addressing this striking supply-demand mismatch in GI requires a multi-pronged approach that addresses its complex drivers. First and foremost, we must expand the number of GI fellowship training slots to boost our pipeline. There are approximately 1,840 GI fellows currently in training, a third of whom enter the workforce each year. While the number of GI fellowship slots in the GI fellowship match has slowly increased over time (from 525 available slots across 199 programs in 2019 to 657 slots across 230 programs in 2023), this incremental growth is dwarfed by overall need. Continued advocacy for increased funding to support expansion of training slots is necessary to further move the needle – such lobbying recently led to the addition of 1,000 new Medicare-supported graduate medical education positions across specialties over a 5-year period starting in 2020, illustrating that change is possible. At the same time, we must address the factors that are causing gastroenterologists to leave the workforce prematurely through early retirement or part-time work by investing in innovative solutions to address burnout, reduce administrative burdens, enhance the efficiency of care delivery, and maintain financial viability. By investing in our physician workforce and its sustainability, we can ensure that our profession is better prepared to meet the needs of our growing and increasingly complex patient population now and in the future.
We hope you enjoy the November issue of GI & Hepatology News and have a wonderful Thanksgiving.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor-in-Chief
Seven metrics oncology practices can track to be successful
and see how they measure up against their peers.
“Once practices figure out what they want to measure, and obviously they want to measure things that they’re not doing so well, they can look for opportunities for improvement,” said Diana Berich Brieva, DHA, MBA, CPC-A, the CEO of Ambulatory Care Consultants, which partners with medical practices to optimize operations and increase revenue.
Benchmarking your practice against others shows you how your numbers stack up to other practices’ metrics by percentile – for instance, whether your revenue is in the 25th, 50th, or 75th percentile against similar practices.
The 2024 MIPS Value Pathways (MVP) for Advancing Cancer Care is a new CMS program with specific metric criteria. The voluntary program has a Nov. 30, 2023, deadline for practices to sign up. The purpose of the program is to help practices identify areas where they can improve. Also, oncology societies such as the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) have developed metrics for this specialty.
Still, for many practices, it’s essential to develop your own metrics according to your patient population and available resources, explained Dr. Brieva.
Here are seven popular oncology metrics that many practices track to measure success.
1. Productivity
Every practice may think about productivity differently depending on whether it focuses on new patients, revenue, business development, or a combination. You can measure physician productivity in many ways: by the number of new patients per full-time employee (FTE), work relative value units (wRVU) per FTE, which measures physician work, and established patient visits.
Some clinics measure for wRVU for chemotherapy administration and per-hospital visits as a percentage of total patients as well. “We’re a community-based oncology practice, so we don’t use RVUs, but we do use other production numbers,” said Emily Touloukian, DO, an oncologist-hematologist and president of Coastal Cancer Center with four locations around South Carolina. She is assistant professor of internal medicine at the University of South Carolina, Columbia.
“There are lots of quality programs out there that measure how well oncology practices are meeting guidelines. The one we’ve participated with since its inception is [the] Quality Oncology Practice Initiative (QOPI) through [the] American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO),” said Dr. Touloukian. “Basically, it’s a chart review and extraction of various indicators in accordance with quality measures.”
Pontchartrain Cancer Center, with four locations around Louisiana, tracks the number of new patients in hematology and oncology by location and provider. They also track follow-up patients. New and follow-up patient metrics are broken down by visit code.
“The E&M code tells me the level of acuity that the physician coded for,” said Kathy Oubre, MS, the CEO of Pontchartrain. Patients with complicated cases get a higher-paying code since clinics get paid differently for each code. Ms. Oubre tracks the codes by provider and says if they bill every patient with the same code, it can put your practice at risk for an audit, even when it’s the lowest billable code.
In the 2019 ASCO survey, the number of new patient visits reported by participants averaged 301 visits per FTE. Established patient visits averaged 3,334.
“When we talk about metrics and how we measure things and how successful our practice is, productivity also has to do with how satisfied the people working for you and with you are,” said Dr. Touloukian.
“If you’re not providing a supportive workplace for your physicians and employees, you’re not going to be successful,” she said. “You’ll end up with doctors coming and going every 2 years, employees quitting all the time, and a need for retraining.” Instead, if you can create a welcoming, sustainable environment where people are happy to come to work, physicians aren’t burnt out, and get to spend time away from the clinic to recharge, productivity will be more successful.
2. Revenue
When participating in their voluntary survey, practices can get a copy of revenue metric data annually from the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA). It collects the number of FTEs, gross revenue, net revenue, and collection rate and is broken down by specialties so your practice can benchmark against others. Total revenue, including oncologists’ salaries per FTE from the ASCO survey, was $7,323,900, but comparisons are difficult since practices differ in services.
Revenue metrics can consist of total revenue (cash collections), net medical excluding radiation services, drug revenue for infusion services, cash expenses including salaries, net accounts receivable, and gross accounts receivable minus contractual allowances and bad debt. Practices can differ on bad debt collection because of the emotional nature of cancer treatment. However, some use revenue cycle management companies with debt collection services; others find charity foundation funds for patients who can’t pay.
Pontchartrain also tracks when its clinic gets paid. Ms. Oubre said the best practice is that your claims receive payment within 21 days. They send claims out every 24 hours. “For example, most of that money is in drugs we’ve administered to patients we’ve likely already paid for.” Since there is a gap between paying their wholesaler for drugs and receiving reimbursement, they closely track claims and payment metrics.
Any claims that get sent back are refiled and sent out again within 24 hours. When claims hit 31 days without a response, the practice reaches out to learn the problem. “We’re proactive rather than waiting for the denial to come,” Ms. Oubre told this news organization. Dr. Brieva said for every revenue metric a practice tracks in which they’re not performing well, the practice has to find a solution. Are too many claims being denied? Do claim forms contain errors? Are most claims being paid in the 21-day window? Is the problem a user error, an issue with the clearinghouse, or an intake error on the other end? The key to successful metric use is to drill down for answers to these questions.
3. Patient satisfaction
Patient satisfaction may be one of the more straightforward metrics practices can track, though not specific to oncology. Dr. Brieva said most metric programs include patient satisfaction surveys against which you can benchmark your practice. You can also create your own emailed patient surveys. The metric can show how satisfied your patients are and how you compare against other practices.
Ms. Oubre said Pontchartrain also tracks metrics around participating in advanced care planning, survivorship care, and transitional care management. Even though most insurers require copays for these services, they’ve found patients who participate in them have an overall better experience.
“The Biden administration also has a Cancer Moon Shot initiative, which intends to reduce cancer deaths by 50% by 2047,” said Dr. Brieva. “They want to reduce deaths and improve the experience of patients. So, tracking survival rates will also be key for this program.”
4. Referrals
Oncology is typically a referral business. So, keeping track of the top referring physicians every quarter is the best way to ensure your referring clinicians are happy with your practice’s service. A best practice is that all new oncology referrals are seen within 48 hours. If your referral metric drops off, especially for top referrers, a physician from your practice should check in with the referrer.
Ms. Oubre runs reports out of the EMR and scrubs for referring providers, so she’s alerted to any issues. “It can be as simple as a front office staff who was rude on the phone,” she said. “We had an issue years ago with one of our schedulers who didn’t want to risk staying after 5:00 p.m., so she wouldn’t put anyone on the schedule after 3:00. But if I hadn’t called and identified that from the referring practitioner, I wouldn’t have known that they couldn’t get late-afternoon appointments at our clinic.”
5. No-show appointments
Practices track no-shows per week to determine which patients did not show up for their visits vs. those who rescheduled. If a patient on active treatment starts no-showing, practices must find out why. Is it a social or a transportation issue, or do they want to discontinue treatment? Often, you can help with the problem if you know what it is.
“Sometimes we can help from a social determinants of health perspective, helping to provide services like transportation, financial assistance, or other things, and patients appreciate that we would care enough to reach out to see if we can help,” said Ms. Oubre.
For recurring no-shows, practices should notify the referring provider. Letting the referring clinician know that the patient stopped coming is a professional courtesy that helps strengthen your referral relationships. You wouldn’t want the referring physician to think the patient is being treated for cancer only to find out later that they discontinued treatment.
6. Injections and infusions
By tracking the number of injections and infusions per location per week, clinics can assess how busy their chemo chairs are and how many injections they give. Benchmarks include the number of initial intravenous infusions/injections and the total number of drug administration services per patient per chair. Similar metrics in radiation oncology are helpful.
7. Pharmacy prescriptions
For practices with an in-house pharmacy, tracking how many prescriptions are written per week by each provider and whether they could fill them in-house or had to send them out to a specialty pharmacy because of an insurance issue tells you the volume of drugs your pharmacy is fulfilling. Point-of-care dispensing pharmacy revenue averaged $1,843,342 in the ASCO survey.
Dr. Brieva mentioned many other trackable metrics, such as the time to start treatment, adherence to treatment guidelines, rates of side effects and complications, patient retention rates, treatment completion rates, and coordination of care with other providers, which may be additional metrics your practice wants to track.
Dr. Touloukian said that practices must be careful how they measure some metrics because if you’re extracting data from the EMR and someone hasn’t entered it correctly, you won’t get accurate information. “I like programs like QOPI because while it’s a little labor intensive, my staff actually goes in and extracts the data from the charts and shows the proof.
“Comparing yourself to other [oncology] practices across the nation helps to ensure you’re achieving a certain level of success on some of these traditional metrics,” said Dr. Touloukian.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
and see how they measure up against their peers.
“Once practices figure out what they want to measure, and obviously they want to measure things that they’re not doing so well, they can look for opportunities for improvement,” said Diana Berich Brieva, DHA, MBA, CPC-A, the CEO of Ambulatory Care Consultants, which partners with medical practices to optimize operations and increase revenue.
Benchmarking your practice against others shows you how your numbers stack up to other practices’ metrics by percentile – for instance, whether your revenue is in the 25th, 50th, or 75th percentile against similar practices.
The 2024 MIPS Value Pathways (MVP) for Advancing Cancer Care is a new CMS program with specific metric criteria. The voluntary program has a Nov. 30, 2023, deadline for practices to sign up. The purpose of the program is to help practices identify areas where they can improve. Also, oncology societies such as the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) have developed metrics for this specialty.
Still, for many practices, it’s essential to develop your own metrics according to your patient population and available resources, explained Dr. Brieva.
Here are seven popular oncology metrics that many practices track to measure success.
1. Productivity
Every practice may think about productivity differently depending on whether it focuses on new patients, revenue, business development, or a combination. You can measure physician productivity in many ways: by the number of new patients per full-time employee (FTE), work relative value units (wRVU) per FTE, which measures physician work, and established patient visits.
Some clinics measure for wRVU for chemotherapy administration and per-hospital visits as a percentage of total patients as well. “We’re a community-based oncology practice, so we don’t use RVUs, but we do use other production numbers,” said Emily Touloukian, DO, an oncologist-hematologist and president of Coastal Cancer Center with four locations around South Carolina. She is assistant professor of internal medicine at the University of South Carolina, Columbia.
“There are lots of quality programs out there that measure how well oncology practices are meeting guidelines. The one we’ve participated with since its inception is [the] Quality Oncology Practice Initiative (QOPI) through [the] American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO),” said Dr. Touloukian. “Basically, it’s a chart review and extraction of various indicators in accordance with quality measures.”
Pontchartrain Cancer Center, with four locations around Louisiana, tracks the number of new patients in hematology and oncology by location and provider. They also track follow-up patients. New and follow-up patient metrics are broken down by visit code.
“The E&M code tells me the level of acuity that the physician coded for,” said Kathy Oubre, MS, the CEO of Pontchartrain. Patients with complicated cases get a higher-paying code since clinics get paid differently for each code. Ms. Oubre tracks the codes by provider and says if they bill every patient with the same code, it can put your practice at risk for an audit, even when it’s the lowest billable code.
In the 2019 ASCO survey, the number of new patient visits reported by participants averaged 301 visits per FTE. Established patient visits averaged 3,334.
“When we talk about metrics and how we measure things and how successful our practice is, productivity also has to do with how satisfied the people working for you and with you are,” said Dr. Touloukian.
“If you’re not providing a supportive workplace for your physicians and employees, you’re not going to be successful,” she said. “You’ll end up with doctors coming and going every 2 years, employees quitting all the time, and a need for retraining.” Instead, if you can create a welcoming, sustainable environment where people are happy to come to work, physicians aren’t burnt out, and get to spend time away from the clinic to recharge, productivity will be more successful.
2. Revenue
When participating in their voluntary survey, practices can get a copy of revenue metric data annually from the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA). It collects the number of FTEs, gross revenue, net revenue, and collection rate and is broken down by specialties so your practice can benchmark against others. Total revenue, including oncologists’ salaries per FTE from the ASCO survey, was $7,323,900, but comparisons are difficult since practices differ in services.
Revenue metrics can consist of total revenue (cash collections), net medical excluding radiation services, drug revenue for infusion services, cash expenses including salaries, net accounts receivable, and gross accounts receivable minus contractual allowances and bad debt. Practices can differ on bad debt collection because of the emotional nature of cancer treatment. However, some use revenue cycle management companies with debt collection services; others find charity foundation funds for patients who can’t pay.
Pontchartrain also tracks when its clinic gets paid. Ms. Oubre said the best practice is that your claims receive payment within 21 days. They send claims out every 24 hours. “For example, most of that money is in drugs we’ve administered to patients we’ve likely already paid for.” Since there is a gap between paying their wholesaler for drugs and receiving reimbursement, they closely track claims and payment metrics.
Any claims that get sent back are refiled and sent out again within 24 hours. When claims hit 31 days without a response, the practice reaches out to learn the problem. “We’re proactive rather than waiting for the denial to come,” Ms. Oubre told this news organization. Dr. Brieva said for every revenue metric a practice tracks in which they’re not performing well, the practice has to find a solution. Are too many claims being denied? Do claim forms contain errors? Are most claims being paid in the 21-day window? Is the problem a user error, an issue with the clearinghouse, or an intake error on the other end? The key to successful metric use is to drill down for answers to these questions.
3. Patient satisfaction
Patient satisfaction may be one of the more straightforward metrics practices can track, though not specific to oncology. Dr. Brieva said most metric programs include patient satisfaction surveys against which you can benchmark your practice. You can also create your own emailed patient surveys. The metric can show how satisfied your patients are and how you compare against other practices.
Ms. Oubre said Pontchartrain also tracks metrics around participating in advanced care planning, survivorship care, and transitional care management. Even though most insurers require copays for these services, they’ve found patients who participate in them have an overall better experience.
“The Biden administration also has a Cancer Moon Shot initiative, which intends to reduce cancer deaths by 50% by 2047,” said Dr. Brieva. “They want to reduce deaths and improve the experience of patients. So, tracking survival rates will also be key for this program.”
4. Referrals
Oncology is typically a referral business. So, keeping track of the top referring physicians every quarter is the best way to ensure your referring clinicians are happy with your practice’s service. A best practice is that all new oncology referrals are seen within 48 hours. If your referral metric drops off, especially for top referrers, a physician from your practice should check in with the referrer.
Ms. Oubre runs reports out of the EMR and scrubs for referring providers, so she’s alerted to any issues. “It can be as simple as a front office staff who was rude on the phone,” she said. “We had an issue years ago with one of our schedulers who didn’t want to risk staying after 5:00 p.m., so she wouldn’t put anyone on the schedule after 3:00. But if I hadn’t called and identified that from the referring practitioner, I wouldn’t have known that they couldn’t get late-afternoon appointments at our clinic.”
5. No-show appointments
Practices track no-shows per week to determine which patients did not show up for their visits vs. those who rescheduled. If a patient on active treatment starts no-showing, practices must find out why. Is it a social or a transportation issue, or do they want to discontinue treatment? Often, you can help with the problem if you know what it is.
“Sometimes we can help from a social determinants of health perspective, helping to provide services like transportation, financial assistance, or other things, and patients appreciate that we would care enough to reach out to see if we can help,” said Ms. Oubre.
For recurring no-shows, practices should notify the referring provider. Letting the referring clinician know that the patient stopped coming is a professional courtesy that helps strengthen your referral relationships. You wouldn’t want the referring physician to think the patient is being treated for cancer only to find out later that they discontinued treatment.
6. Injections and infusions
By tracking the number of injections and infusions per location per week, clinics can assess how busy their chemo chairs are and how many injections they give. Benchmarks include the number of initial intravenous infusions/injections and the total number of drug administration services per patient per chair. Similar metrics in radiation oncology are helpful.
7. Pharmacy prescriptions
For practices with an in-house pharmacy, tracking how many prescriptions are written per week by each provider and whether they could fill them in-house or had to send them out to a specialty pharmacy because of an insurance issue tells you the volume of drugs your pharmacy is fulfilling. Point-of-care dispensing pharmacy revenue averaged $1,843,342 in the ASCO survey.
Dr. Brieva mentioned many other trackable metrics, such as the time to start treatment, adherence to treatment guidelines, rates of side effects and complications, patient retention rates, treatment completion rates, and coordination of care with other providers, which may be additional metrics your practice wants to track.
Dr. Touloukian said that practices must be careful how they measure some metrics because if you’re extracting data from the EMR and someone hasn’t entered it correctly, you won’t get accurate information. “I like programs like QOPI because while it’s a little labor intensive, my staff actually goes in and extracts the data from the charts and shows the proof.
“Comparing yourself to other [oncology] practices across the nation helps to ensure you’re achieving a certain level of success on some of these traditional metrics,” said Dr. Touloukian.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
and see how they measure up against their peers.
“Once practices figure out what they want to measure, and obviously they want to measure things that they’re not doing so well, they can look for opportunities for improvement,” said Diana Berich Brieva, DHA, MBA, CPC-A, the CEO of Ambulatory Care Consultants, which partners with medical practices to optimize operations and increase revenue.
Benchmarking your practice against others shows you how your numbers stack up to other practices’ metrics by percentile – for instance, whether your revenue is in the 25th, 50th, or 75th percentile against similar practices.
The 2024 MIPS Value Pathways (MVP) for Advancing Cancer Care is a new CMS program with specific metric criteria. The voluntary program has a Nov. 30, 2023, deadline for practices to sign up. The purpose of the program is to help practices identify areas where they can improve. Also, oncology societies such as the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) have developed metrics for this specialty.
Still, for many practices, it’s essential to develop your own metrics according to your patient population and available resources, explained Dr. Brieva.
Here are seven popular oncology metrics that many practices track to measure success.
1. Productivity
Every practice may think about productivity differently depending on whether it focuses on new patients, revenue, business development, or a combination. You can measure physician productivity in many ways: by the number of new patients per full-time employee (FTE), work relative value units (wRVU) per FTE, which measures physician work, and established patient visits.
Some clinics measure for wRVU for chemotherapy administration and per-hospital visits as a percentage of total patients as well. “We’re a community-based oncology practice, so we don’t use RVUs, but we do use other production numbers,” said Emily Touloukian, DO, an oncologist-hematologist and president of Coastal Cancer Center with four locations around South Carolina. She is assistant professor of internal medicine at the University of South Carolina, Columbia.
“There are lots of quality programs out there that measure how well oncology practices are meeting guidelines. The one we’ve participated with since its inception is [the] Quality Oncology Practice Initiative (QOPI) through [the] American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO),” said Dr. Touloukian. “Basically, it’s a chart review and extraction of various indicators in accordance with quality measures.”
Pontchartrain Cancer Center, with four locations around Louisiana, tracks the number of new patients in hematology and oncology by location and provider. They also track follow-up patients. New and follow-up patient metrics are broken down by visit code.
“The E&M code tells me the level of acuity that the physician coded for,” said Kathy Oubre, MS, the CEO of Pontchartrain. Patients with complicated cases get a higher-paying code since clinics get paid differently for each code. Ms. Oubre tracks the codes by provider and says if they bill every patient with the same code, it can put your practice at risk for an audit, even when it’s the lowest billable code.
In the 2019 ASCO survey, the number of new patient visits reported by participants averaged 301 visits per FTE. Established patient visits averaged 3,334.
“When we talk about metrics and how we measure things and how successful our practice is, productivity also has to do with how satisfied the people working for you and with you are,” said Dr. Touloukian.
“If you’re not providing a supportive workplace for your physicians and employees, you’re not going to be successful,” she said. “You’ll end up with doctors coming and going every 2 years, employees quitting all the time, and a need for retraining.” Instead, if you can create a welcoming, sustainable environment where people are happy to come to work, physicians aren’t burnt out, and get to spend time away from the clinic to recharge, productivity will be more successful.
2. Revenue
When participating in their voluntary survey, practices can get a copy of revenue metric data annually from the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA). It collects the number of FTEs, gross revenue, net revenue, and collection rate and is broken down by specialties so your practice can benchmark against others. Total revenue, including oncologists’ salaries per FTE from the ASCO survey, was $7,323,900, but comparisons are difficult since practices differ in services.
Revenue metrics can consist of total revenue (cash collections), net medical excluding radiation services, drug revenue for infusion services, cash expenses including salaries, net accounts receivable, and gross accounts receivable minus contractual allowances and bad debt. Practices can differ on bad debt collection because of the emotional nature of cancer treatment. However, some use revenue cycle management companies with debt collection services; others find charity foundation funds for patients who can’t pay.
Pontchartrain also tracks when its clinic gets paid. Ms. Oubre said the best practice is that your claims receive payment within 21 days. They send claims out every 24 hours. “For example, most of that money is in drugs we’ve administered to patients we’ve likely already paid for.” Since there is a gap between paying their wholesaler for drugs and receiving reimbursement, they closely track claims and payment metrics.
Any claims that get sent back are refiled and sent out again within 24 hours. When claims hit 31 days without a response, the practice reaches out to learn the problem. “We’re proactive rather than waiting for the denial to come,” Ms. Oubre told this news organization. Dr. Brieva said for every revenue metric a practice tracks in which they’re not performing well, the practice has to find a solution. Are too many claims being denied? Do claim forms contain errors? Are most claims being paid in the 21-day window? Is the problem a user error, an issue with the clearinghouse, or an intake error on the other end? The key to successful metric use is to drill down for answers to these questions.
3. Patient satisfaction
Patient satisfaction may be one of the more straightforward metrics practices can track, though not specific to oncology. Dr. Brieva said most metric programs include patient satisfaction surveys against which you can benchmark your practice. You can also create your own emailed patient surveys. The metric can show how satisfied your patients are and how you compare against other practices.
Ms. Oubre said Pontchartrain also tracks metrics around participating in advanced care planning, survivorship care, and transitional care management. Even though most insurers require copays for these services, they’ve found patients who participate in them have an overall better experience.
“The Biden administration also has a Cancer Moon Shot initiative, which intends to reduce cancer deaths by 50% by 2047,” said Dr. Brieva. “They want to reduce deaths and improve the experience of patients. So, tracking survival rates will also be key for this program.”
4. Referrals
Oncology is typically a referral business. So, keeping track of the top referring physicians every quarter is the best way to ensure your referring clinicians are happy with your practice’s service. A best practice is that all new oncology referrals are seen within 48 hours. If your referral metric drops off, especially for top referrers, a physician from your practice should check in with the referrer.
Ms. Oubre runs reports out of the EMR and scrubs for referring providers, so she’s alerted to any issues. “It can be as simple as a front office staff who was rude on the phone,” she said. “We had an issue years ago with one of our schedulers who didn’t want to risk staying after 5:00 p.m., so she wouldn’t put anyone on the schedule after 3:00. But if I hadn’t called and identified that from the referring practitioner, I wouldn’t have known that they couldn’t get late-afternoon appointments at our clinic.”
5. No-show appointments
Practices track no-shows per week to determine which patients did not show up for their visits vs. those who rescheduled. If a patient on active treatment starts no-showing, practices must find out why. Is it a social or a transportation issue, or do they want to discontinue treatment? Often, you can help with the problem if you know what it is.
“Sometimes we can help from a social determinants of health perspective, helping to provide services like transportation, financial assistance, or other things, and patients appreciate that we would care enough to reach out to see if we can help,” said Ms. Oubre.
For recurring no-shows, practices should notify the referring provider. Letting the referring clinician know that the patient stopped coming is a professional courtesy that helps strengthen your referral relationships. You wouldn’t want the referring physician to think the patient is being treated for cancer only to find out later that they discontinued treatment.
6. Injections and infusions
By tracking the number of injections and infusions per location per week, clinics can assess how busy their chemo chairs are and how many injections they give. Benchmarks include the number of initial intravenous infusions/injections and the total number of drug administration services per patient per chair. Similar metrics in radiation oncology are helpful.
7. Pharmacy prescriptions
For practices with an in-house pharmacy, tracking how many prescriptions are written per week by each provider and whether they could fill them in-house or had to send them out to a specialty pharmacy because of an insurance issue tells you the volume of drugs your pharmacy is fulfilling. Point-of-care dispensing pharmacy revenue averaged $1,843,342 in the ASCO survey.
Dr. Brieva mentioned many other trackable metrics, such as the time to start treatment, adherence to treatment guidelines, rates of side effects and complications, patient retention rates, treatment completion rates, and coordination of care with other providers, which may be additional metrics your practice wants to track.
Dr. Touloukian said that practices must be careful how they measure some metrics because if you’re extracting data from the EMR and someone hasn’t entered it correctly, you won’t get accurate information. “I like programs like QOPI because while it’s a little labor intensive, my staff actually goes in and extracts the data from the charts and shows the proof.
“Comparing yourself to other [oncology] practices across the nation helps to ensure you’re achieving a certain level of success on some of these traditional metrics,” said Dr. Touloukian.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Teledermatology: A Postpandemic Update
The rapid expansion of teledermatology in the United States due to the COVID-19 pandemic has been well documented, 1 but where do we stand now that health care and society as a whole are back to a new version of normal? It is important to consider why telemedicine was able to grow so quickly during that period—the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) unilaterally changed policies related to provision of services and reimbursement thereof due to the public health emergency (PHE), which was declared by the Department of Health and Human Services in January 2020 to provide increased access to care for patients. Under the PHE, reimbursement rates for virtual visits improved, providers could care for patients from their homes and across state lines, and the use of video platforms that were not Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act compliant was allowed. 2,3
The trajectory of teledermatology after the pandemic, however, remains unclear. In a survey assessing dermatologists’ perceptions of telemedicine (N=4356), 97% used telemedicine during the pandemic but only 58% reported that they intended to continue using teledermatology postpandemic,1 which is driven, at least in part, by the potential concern that dermatologists will again experience the same regulatory and logistical barriers that limited teledermatology utilization prepandemic.
What has changed in reimbursement for teledermatology since the PHE ended?
The PHE ended on May 11, 2023, and already video platforms that were used during the pandemic to provide telemedicine visits but are not Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act compliant are now forbidden,2 Medicare virtual check-in appointments can only be conducted with established patients,4 and medical licensing requirements have been reinstated in most states such that patients must be located in the state where the provider is licensed to practice medicine at the time of a virtual visit.3 Although the CMS was granted wide freedoms to waive and suspend certain rules, this was only in the context of the PHE, and any lasting changes must be established by Congress.
Reassuringly, recent legislation via the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2023, authorized an extension of many of the CMS telehealth flexibilities that were in place during the PHE through December 31, 2024 (Table),2 such as allowing access to telehealth services in any geographic area in the United States rather than only rural areas, allowing patients to stay in their homes for telehealth visits rather than traveling to an approved health care facility, and allowing the delivery of telemedicine via audio-only technology if a patient is unable to use both audio and video. As of now, the place of service (POS) designation for telehealth visits will not revert back to the former code (POS 02) but will remain at POS 11 with the telehealth modifier -95 so physicians will be reimbursed at the full level of a non-facility physician’s office rate.4 The CMS has indicated that there will be no change in the reimbursement policy until after December 31, 20234; however, the sense of uncertainty around what happens after this date has made it hard for organizations and practices to fully commit to teledermatology services without knowing what the long-term financial impact may be. Some organizations have already noted that they plan to continue supporting telemedicine after the CMS flexibilities expire. Accountable Care Organizations have the ability to offer services that allow participating practitioners to continue the use of telemedicine visits to expand access to care. Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program policies vary by state and private health insurance policies vary by individual plans, but it should be noted that commercial coverage for telemedicine visits was already strong prior to the pandemic.2
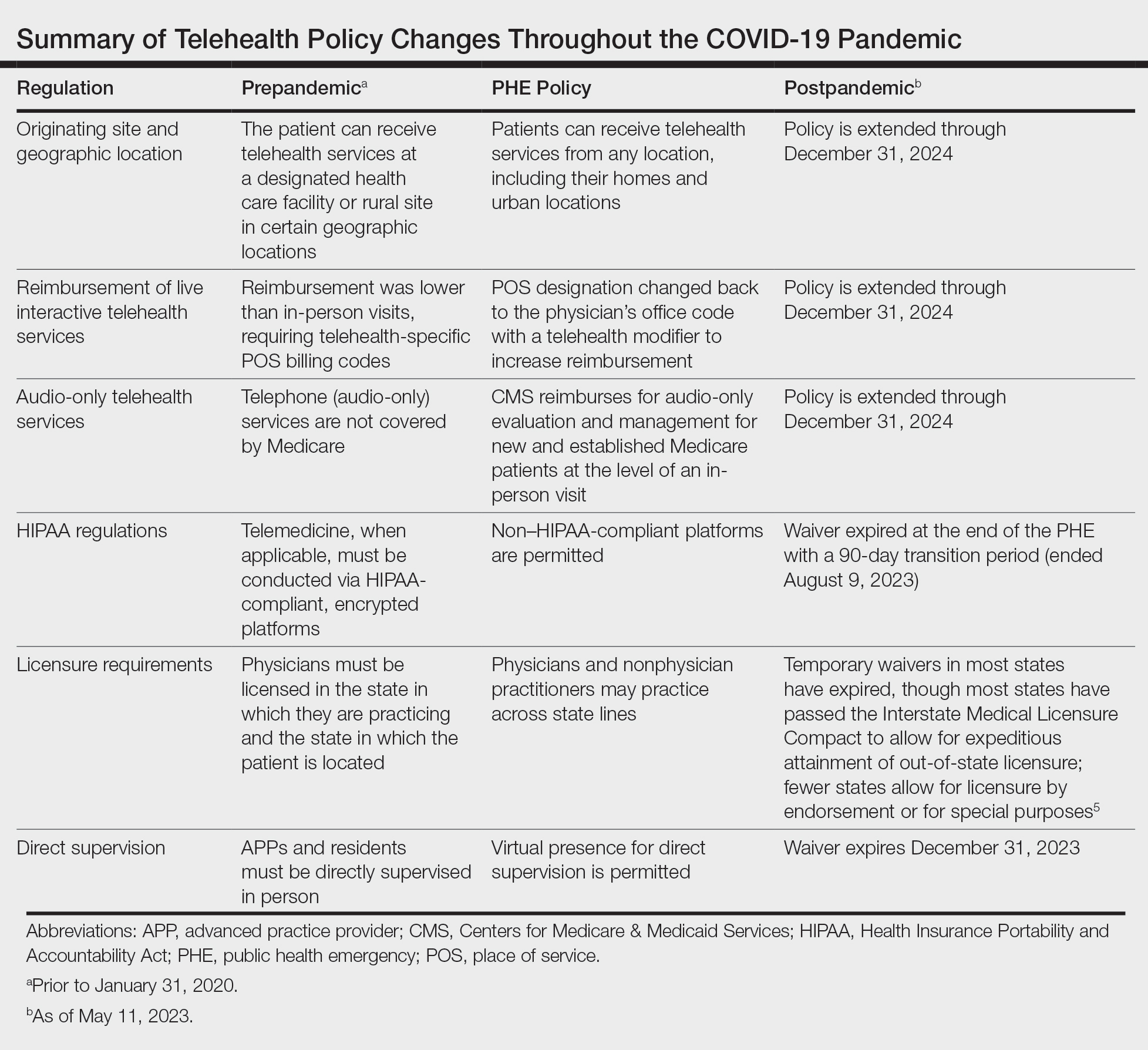
What medical licensing requirements are in place now for telehealth?
During the PHE, medical licensing requirements also were relaxed, enabling providers to deliver telemedicine service in states where they were not licensed.3 As the PHE orders ended, some states including New York discontinued cross-state licensing waivers altogether,6 whereas others have enacted legislation to make them permanent or extend them for brief periods of time.3,6 One potential solution is the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact (https://www.imlcc.org/), which includes 39 states as of October 2023. This program expedites the process for physicians already licensed in participating states to obtain their medical license in another participating state, though licensing fees are required for each state in which a physician wants to practice. Furthermore, some states such as North Dakota, Hawaii, and Virginia have licensure by endorsement policies, which enable licensed physicians with specific qualifications to provide telehealth services in the endorsing state. Other states such as Florida, New Jersey, Louisiana, Minnesota, Nevada, and New Mexico have special telehealth registries that allow physicians in good standing who are licensed in other states to deliver telehealth services to in-state residents barring they do not provide in-person, in-state services.6 Lastly, some states have temporary practice laws to allow existing patients who need medical attention while traveling out of state to see their home providers virtually or in person under certain circumstances for a limited period of time.3,5 In Hawaii and New Hampshire, physicians with out-of-state licenses can provide consultative services in some circumstances.5
What changes have been made to make it easier for patients to use telehealth?
As the legislation around telemedicine is shifting postpandemic, it is important to address additional logistical barriers to teledermatology on a larger scale if the discipline is to stay in practice. On November 15, 2021, the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act provided $65 billion in funding for broadband to expand access to high-speed internet. Some of this money was allocated to the Affordable Connectivity Program, which provides eligible households with a discount on broadband service and internet-connected devices. Eligible patrons can qualify for a discount of up to $75 per month for internet service and a one-time discount up to $100 on a laptop, desktop computer, or tablet purchased through a participating provider.6 Although a step in the right direction, the effects of this program on telemedicine encounters remains to be proven. Additionally, these programs do not address educational barriers to understanding how to utilize telemedicine platforms or provide incentives for practitioners to offer telemedicine services.
Final Thoughts
The pandemic taught our specialty a great deal about how to utilize telemedicine. For many dermatologists a return to in-person business as usual could not come fast enough; however, many practices have continued to offer at least some teledermatology services. Although the PHE waivers have ended, the extension of numerous CMS flexibilities through the end of 2024 allows us more time to develop sustainable policies to support the long-term health of telemedicine as a whole, both to sustain practices and to expand access to care in dermatology. The favorable attitudes of both patients and physicians about teledermatology have been clearly documented,1,7 and we should continue to safely expand the use of this technology.
- Kennedy J, Arey S, Hopkins Z, et al. Dermatologist perceptions of teledermatology implementation and future use after COVID-19: demographics, barriers, and insights. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:595-597.
- US Department of Health and Human Services. HHS fact sheet: telehealth flexibilities and resources and the COVID-19 public health emergency. Published May 10, 2023. Accessed October 18, 2023. https://www.hhs.gov/aboutnews/2023/05/10/hhs-fact-sheet-telehealth-flexibilities-resources-covid-19-public-health-emergency.html
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Licensing across state lines. Updated May 11, 2023. Accessed October 25, 2023. https://telehealth.hhs.gov/licensure/licensing-across-state-lines
- American Academy of Dermatology. Teledermatology and the COVID-19 pandemic. Accessed October 12, 2023. https://www.aad.org/member/practice/telederm/covid-19
- American Medical Association. Licensure & Telehealth. Accessed October 12, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/issue-brief-licensure-telehealth.pdf
- Federal Communications Commission. Affordable Connectivity Program. Updated June 29, 2023. Accessed October 12, 2023. https://www.fcc.gov/affordable-connectivity-program
- Tensen E, van der Heijden JP, Jaspers MWM, et al. Two decades of teledermatology: current status and integration in national healthcare systems. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2016;5:96-104.
The rapid expansion of teledermatology in the United States due to the COVID-19 pandemic has been well documented, 1 but where do we stand now that health care and society as a whole are back to a new version of normal? It is important to consider why telemedicine was able to grow so quickly during that period—the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) unilaterally changed policies related to provision of services and reimbursement thereof due to the public health emergency (PHE), which was declared by the Department of Health and Human Services in January 2020 to provide increased access to care for patients. Under the PHE, reimbursement rates for virtual visits improved, providers could care for patients from their homes and across state lines, and the use of video platforms that were not Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act compliant was allowed. 2,3
The trajectory of teledermatology after the pandemic, however, remains unclear. In a survey assessing dermatologists’ perceptions of telemedicine (N=4356), 97% used telemedicine during the pandemic but only 58% reported that they intended to continue using teledermatology postpandemic,1 which is driven, at least in part, by the potential concern that dermatologists will again experience the same regulatory and logistical barriers that limited teledermatology utilization prepandemic.
What has changed in reimbursement for teledermatology since the PHE ended?
The PHE ended on May 11, 2023, and already video platforms that were used during the pandemic to provide telemedicine visits but are not Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act compliant are now forbidden,2 Medicare virtual check-in appointments can only be conducted with established patients,4 and medical licensing requirements have been reinstated in most states such that patients must be located in the state where the provider is licensed to practice medicine at the time of a virtual visit.3 Although the CMS was granted wide freedoms to waive and suspend certain rules, this was only in the context of the PHE, and any lasting changes must be established by Congress.
Reassuringly, recent legislation via the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2023, authorized an extension of many of the CMS telehealth flexibilities that were in place during the PHE through December 31, 2024 (Table),2 such as allowing access to telehealth services in any geographic area in the United States rather than only rural areas, allowing patients to stay in their homes for telehealth visits rather than traveling to an approved health care facility, and allowing the delivery of telemedicine via audio-only technology if a patient is unable to use both audio and video. As of now, the place of service (POS) designation for telehealth visits will not revert back to the former code (POS 02) but will remain at POS 11 with the telehealth modifier -95 so physicians will be reimbursed at the full level of a non-facility physician’s office rate.4 The CMS has indicated that there will be no change in the reimbursement policy until after December 31, 20234; however, the sense of uncertainty around what happens after this date has made it hard for organizations and practices to fully commit to teledermatology services without knowing what the long-term financial impact may be. Some organizations have already noted that they plan to continue supporting telemedicine after the CMS flexibilities expire. Accountable Care Organizations have the ability to offer services that allow participating practitioners to continue the use of telemedicine visits to expand access to care. Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program policies vary by state and private health insurance policies vary by individual plans, but it should be noted that commercial coverage for telemedicine visits was already strong prior to the pandemic.2

What medical licensing requirements are in place now for telehealth?
During the PHE, medical licensing requirements also were relaxed, enabling providers to deliver telemedicine service in states where they were not licensed.3 As the PHE orders ended, some states including New York discontinued cross-state licensing waivers altogether,6 whereas others have enacted legislation to make them permanent or extend them for brief periods of time.3,6 One potential solution is the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact (https://www.imlcc.org/), which includes 39 states as of October 2023. This program expedites the process for physicians already licensed in participating states to obtain their medical license in another participating state, though licensing fees are required for each state in which a physician wants to practice. Furthermore, some states such as North Dakota, Hawaii, and Virginia have licensure by endorsement policies, which enable licensed physicians with specific qualifications to provide telehealth services in the endorsing state. Other states such as Florida, New Jersey, Louisiana, Minnesota, Nevada, and New Mexico have special telehealth registries that allow physicians in good standing who are licensed in other states to deliver telehealth services to in-state residents barring they do not provide in-person, in-state services.6 Lastly, some states have temporary practice laws to allow existing patients who need medical attention while traveling out of state to see their home providers virtually or in person under certain circumstances for a limited period of time.3,5 In Hawaii and New Hampshire, physicians with out-of-state licenses can provide consultative services in some circumstances.5
What changes have been made to make it easier for patients to use telehealth?
As the legislation around telemedicine is shifting postpandemic, it is important to address additional logistical barriers to teledermatology on a larger scale if the discipline is to stay in practice. On November 15, 2021, the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act provided $65 billion in funding for broadband to expand access to high-speed internet. Some of this money was allocated to the Affordable Connectivity Program, which provides eligible households with a discount on broadband service and internet-connected devices. Eligible patrons can qualify for a discount of up to $75 per month for internet service and a one-time discount up to $100 on a laptop, desktop computer, or tablet purchased through a participating provider.6 Although a step in the right direction, the effects of this program on telemedicine encounters remains to be proven. Additionally, these programs do not address educational barriers to understanding how to utilize telemedicine platforms or provide incentives for practitioners to offer telemedicine services.
Final Thoughts
The pandemic taught our specialty a great deal about how to utilize telemedicine. For many dermatologists a return to in-person business as usual could not come fast enough; however, many practices have continued to offer at least some teledermatology services. Although the PHE waivers have ended, the extension of numerous CMS flexibilities through the end of 2024 allows us more time to develop sustainable policies to support the long-term health of telemedicine as a whole, both to sustain practices and to expand access to care in dermatology. The favorable attitudes of both patients and physicians about teledermatology have been clearly documented,1,7 and we should continue to safely expand the use of this technology.
The rapid expansion of teledermatology in the United States due to the COVID-19 pandemic has been well documented, 1 but where do we stand now that health care and society as a whole are back to a new version of normal? It is important to consider why telemedicine was able to grow so quickly during that period—the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) unilaterally changed policies related to provision of services and reimbursement thereof due to the public health emergency (PHE), which was declared by the Department of Health and Human Services in January 2020 to provide increased access to care for patients. Under the PHE, reimbursement rates for virtual visits improved, providers could care for patients from their homes and across state lines, and the use of video platforms that were not Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act compliant was allowed. 2,3
The trajectory of teledermatology after the pandemic, however, remains unclear. In a survey assessing dermatologists’ perceptions of telemedicine (N=4356), 97% used telemedicine during the pandemic but only 58% reported that they intended to continue using teledermatology postpandemic,1 which is driven, at least in part, by the potential concern that dermatologists will again experience the same regulatory and logistical barriers that limited teledermatology utilization prepandemic.
What has changed in reimbursement for teledermatology since the PHE ended?
The PHE ended on May 11, 2023, and already video platforms that were used during the pandemic to provide telemedicine visits but are not Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act compliant are now forbidden,2 Medicare virtual check-in appointments can only be conducted with established patients,4 and medical licensing requirements have been reinstated in most states such that patients must be located in the state where the provider is licensed to practice medicine at the time of a virtual visit.3 Although the CMS was granted wide freedoms to waive and suspend certain rules, this was only in the context of the PHE, and any lasting changes must be established by Congress.
Reassuringly, recent legislation via the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2023, authorized an extension of many of the CMS telehealth flexibilities that were in place during the PHE through December 31, 2024 (Table),2 such as allowing access to telehealth services in any geographic area in the United States rather than only rural areas, allowing patients to stay in their homes for telehealth visits rather than traveling to an approved health care facility, and allowing the delivery of telemedicine via audio-only technology if a patient is unable to use both audio and video. As of now, the place of service (POS) designation for telehealth visits will not revert back to the former code (POS 02) but will remain at POS 11 with the telehealth modifier -95 so physicians will be reimbursed at the full level of a non-facility physician’s office rate.4 The CMS has indicated that there will be no change in the reimbursement policy until after December 31, 20234; however, the sense of uncertainty around what happens after this date has made it hard for organizations and practices to fully commit to teledermatology services without knowing what the long-term financial impact may be. Some organizations have already noted that they plan to continue supporting telemedicine after the CMS flexibilities expire. Accountable Care Organizations have the ability to offer services that allow participating practitioners to continue the use of telemedicine visits to expand access to care. Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program policies vary by state and private health insurance policies vary by individual plans, but it should be noted that commercial coverage for telemedicine visits was already strong prior to the pandemic.2

What medical licensing requirements are in place now for telehealth?
During the PHE, medical licensing requirements also were relaxed, enabling providers to deliver telemedicine service in states where they were not licensed.3 As the PHE orders ended, some states including New York discontinued cross-state licensing waivers altogether,6 whereas others have enacted legislation to make them permanent or extend them for brief periods of time.3,6 One potential solution is the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact (https://www.imlcc.org/), which includes 39 states as of October 2023. This program expedites the process for physicians already licensed in participating states to obtain their medical license in another participating state, though licensing fees are required for each state in which a physician wants to practice. Furthermore, some states such as North Dakota, Hawaii, and Virginia have licensure by endorsement policies, which enable licensed physicians with specific qualifications to provide telehealth services in the endorsing state. Other states such as Florida, New Jersey, Louisiana, Minnesota, Nevada, and New Mexico have special telehealth registries that allow physicians in good standing who are licensed in other states to deliver telehealth services to in-state residents barring they do not provide in-person, in-state services.6 Lastly, some states have temporary practice laws to allow existing patients who need medical attention while traveling out of state to see their home providers virtually or in person under certain circumstances for a limited period of time.3,5 In Hawaii and New Hampshire, physicians with out-of-state licenses can provide consultative services in some circumstances.5
What changes have been made to make it easier for patients to use telehealth?
As the legislation around telemedicine is shifting postpandemic, it is important to address additional logistical barriers to teledermatology on a larger scale if the discipline is to stay in practice. On November 15, 2021, the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act provided $65 billion in funding for broadband to expand access to high-speed internet. Some of this money was allocated to the Affordable Connectivity Program, which provides eligible households with a discount on broadband service and internet-connected devices. Eligible patrons can qualify for a discount of up to $75 per month for internet service and a one-time discount up to $100 on a laptop, desktop computer, or tablet purchased through a participating provider.6 Although a step in the right direction, the effects of this program on telemedicine encounters remains to be proven. Additionally, these programs do not address educational barriers to understanding how to utilize telemedicine platforms or provide incentives for practitioners to offer telemedicine services.
Final Thoughts
The pandemic taught our specialty a great deal about how to utilize telemedicine. For many dermatologists a return to in-person business as usual could not come fast enough; however, many practices have continued to offer at least some teledermatology services. Although the PHE waivers have ended, the extension of numerous CMS flexibilities through the end of 2024 allows us more time to develop sustainable policies to support the long-term health of telemedicine as a whole, both to sustain practices and to expand access to care in dermatology. The favorable attitudes of both patients and physicians about teledermatology have been clearly documented,1,7 and we should continue to safely expand the use of this technology.
- Kennedy J, Arey S, Hopkins Z, et al. Dermatologist perceptions of teledermatology implementation and future use after COVID-19: demographics, barriers, and insights. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:595-597.
- US Department of Health and Human Services. HHS fact sheet: telehealth flexibilities and resources and the COVID-19 public health emergency. Published May 10, 2023. Accessed October 18, 2023. https://www.hhs.gov/aboutnews/2023/05/10/hhs-fact-sheet-telehealth-flexibilities-resources-covid-19-public-health-emergency.html
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Licensing across state lines. Updated May 11, 2023. Accessed October 25, 2023. https://telehealth.hhs.gov/licensure/licensing-across-state-lines
- American Academy of Dermatology. Teledermatology and the COVID-19 pandemic. Accessed October 12, 2023. https://www.aad.org/member/practice/telederm/covid-19
- American Medical Association. Licensure & Telehealth. Accessed October 12, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/issue-brief-licensure-telehealth.pdf
- Federal Communications Commission. Affordable Connectivity Program. Updated June 29, 2023. Accessed October 12, 2023. https://www.fcc.gov/affordable-connectivity-program
- Tensen E, van der Heijden JP, Jaspers MWM, et al. Two decades of teledermatology: current status and integration in national healthcare systems. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2016;5:96-104.
- Kennedy J, Arey S, Hopkins Z, et al. Dermatologist perceptions of teledermatology implementation and future use after COVID-19: demographics, barriers, and insights. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:595-597.
- US Department of Health and Human Services. HHS fact sheet: telehealth flexibilities and resources and the COVID-19 public health emergency. Published May 10, 2023. Accessed October 18, 2023. https://www.hhs.gov/aboutnews/2023/05/10/hhs-fact-sheet-telehealth-flexibilities-resources-covid-19-public-health-emergency.html
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Licensing across state lines. Updated May 11, 2023. Accessed October 25, 2023. https://telehealth.hhs.gov/licensure/licensing-across-state-lines
- American Academy of Dermatology. Teledermatology and the COVID-19 pandemic. Accessed October 12, 2023. https://www.aad.org/member/practice/telederm/covid-19
- American Medical Association. Licensure & Telehealth. Accessed October 12, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/issue-brief-licensure-telehealth.pdf
- Federal Communications Commission. Affordable Connectivity Program. Updated June 29, 2023. Accessed October 12, 2023. https://www.fcc.gov/affordable-connectivity-program
- Tensen E, van der Heijden JP, Jaspers MWM, et al. Two decades of teledermatology: current status and integration in national healthcare systems. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2016;5:96-104.
‘Why did I choose this?’ Tackling burnout in oncology
MADRID – “Why did I choose this?”
That is the core question a Portuguese oncologist posed from the audience during a session at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) that was dedicated to building a sustainable oncology workforce.
“Ten, twenty years ago, being a doctor was a dream,” she said, but right now doctors are underpaid, under strain, and have very few resources.
This oncologist is hardly alone.
A survey from ESMO conducted almost a decade ago found that more than 50% of oncologists across Europe, many of whom were early in their careers, reported being burned out.
This, Dr. Lim said, “was the starting point,” well before the COVID pandemic struck.
More recently, the pandemic has taken its own toll on the well-being of oncologists. A survey presented at ESMO 2020 revealed that 38% of participants, spanning 101 countries, reported experiencing burnout, and 66% said they were not able to perform their job.
Medscape’s 2023 Physician Burnout and Depression Report highlighted similar burnout rates, with 53% of U.S. physicians and 52% of oncologists saying they felt burned out, compared with about 42% in 2018, before the pandemic.
The oncology workforce is in crisis in every country, said Dr. Lim, from the Cancer Dynamics Lab, the Francis Crick Institute, London.
Burnout, characterized by emotional exhaustion, depersonalization or feelings of cynicism, and a low sense of personal accomplishment, can result in a poor work-life balance as well as poor mental and physical health. Factors linked to burnout include social isolation, increased workload, reduced quality of work, lack of control over work, and stressful professional experiences.
Together, these factors can affect patient care and further exacerbate staffing issues, Dr. Lim said.
Staffing shortages are common. Oncologists often work long hours or on weekends to cover gaps caused by staffing shortages. Recent data revealed that in high-income countries, there are on average 0.65 medical oncologists and 0.25 radiation oncologists per 100 patients — a situation made worse by professionals taking early retirement or leaving medicine during the pandemic.
“We have seen that the shortage of human resources in many countries as well as the increasing workload related to the increasing number of cancers,” as well as patients surviving longer, have increased pressures on the healthcare system, Andrés Cervantes, MD, PhD, president of ESMO, explained in a press conference.
While tackling these oncology workforce problems requires smaller, local changes to a physician’s daily routine, “the real change,” Dr. Lim said, lies at an infrastructure level.
In response to this chronic and growing problem, ESMO launched its Resilience Task Force in 2020 to evaluate burnout and well-being. The task force plans to publish a position paper in which it will propose a set of recommendations regarding the psychosocial risks of burnout as well as flexible work patterns, well-being resources, and targeted support.
A panel of experts at the meeting touched on some of these solutions.
Dealing with staff shortages is a must, said Jean-Yves Blay, MD, PhD, during the session. “It’s a simple mathematical equation,” Dr. Blay said. “We must increase the number of doctors in medical schools and the number of nurses and healthcare professionals in all schools.” Improving staffing would also help reduce chronic workload issues.
Resilience training should also be incorporated into physician training starting in medical school. Teaching oncologists how to deal with bad news and to cope when patients dies is particularly important.
“I was not taught that,” said the oncologist from Portugal. “I had to learn that at my own cost.”
The good news is that it’s possible to develop resiliency skills over time, said Claire Hardy, PhD, from Lancaster University, United Kingdom, who agreed that training programs could be one approach to improve oncologists’ work life.
However, a person’s needs are determined by their institution and personal responsibilities. “No one knows your job better than you,” Dr. Hardy said. “No one knows better than you where the inefficiencies are, where the bureaucracy is that could be taken away, or it could be done by somebody whose role it is to sort all that out.”
But having this understanding is not enough. Physician also need to feel “psychological safety to be able to speak out and say that something isn’t working right now or is too much,” or, “I’m spending too much time doing this.”
In other words, oncologists need to be able to set boundaries and say no.
Dr. Hardy said this concept “has been around a while, but it’s really gaining momentum,” and being able to discuss these issues in a forum such as the ESMO Congress is a promising start.
Dr. Lim has relationships with Janseen and SEOM. No other relevant financial relationships were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MADRID – “Why did I choose this?”
That is the core question a Portuguese oncologist posed from the audience during a session at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) that was dedicated to building a sustainable oncology workforce.
“Ten, twenty years ago, being a doctor was a dream,” she said, but right now doctors are underpaid, under strain, and have very few resources.
This oncologist is hardly alone.
A survey from ESMO conducted almost a decade ago found that more than 50% of oncologists across Europe, many of whom were early in their careers, reported being burned out.
This, Dr. Lim said, “was the starting point,” well before the COVID pandemic struck.
More recently, the pandemic has taken its own toll on the well-being of oncologists. A survey presented at ESMO 2020 revealed that 38% of participants, spanning 101 countries, reported experiencing burnout, and 66% said they were not able to perform their job.
Medscape’s 2023 Physician Burnout and Depression Report highlighted similar burnout rates, with 53% of U.S. physicians and 52% of oncologists saying they felt burned out, compared with about 42% in 2018, before the pandemic.
The oncology workforce is in crisis in every country, said Dr. Lim, from the Cancer Dynamics Lab, the Francis Crick Institute, London.
Burnout, characterized by emotional exhaustion, depersonalization or feelings of cynicism, and a low sense of personal accomplishment, can result in a poor work-life balance as well as poor mental and physical health. Factors linked to burnout include social isolation, increased workload, reduced quality of work, lack of control over work, and stressful professional experiences.
Together, these factors can affect patient care and further exacerbate staffing issues, Dr. Lim said.
Staffing shortages are common. Oncologists often work long hours or on weekends to cover gaps caused by staffing shortages. Recent data revealed that in high-income countries, there are on average 0.65 medical oncologists and 0.25 radiation oncologists per 100 patients — a situation made worse by professionals taking early retirement or leaving medicine during the pandemic.
“We have seen that the shortage of human resources in many countries as well as the increasing workload related to the increasing number of cancers,” as well as patients surviving longer, have increased pressures on the healthcare system, Andrés Cervantes, MD, PhD, president of ESMO, explained in a press conference.
While tackling these oncology workforce problems requires smaller, local changes to a physician’s daily routine, “the real change,” Dr. Lim said, lies at an infrastructure level.
In response to this chronic and growing problem, ESMO launched its Resilience Task Force in 2020 to evaluate burnout and well-being. The task force plans to publish a position paper in which it will propose a set of recommendations regarding the psychosocial risks of burnout as well as flexible work patterns, well-being resources, and targeted support.
A panel of experts at the meeting touched on some of these solutions.
Dealing with staff shortages is a must, said Jean-Yves Blay, MD, PhD, during the session. “It’s a simple mathematical equation,” Dr. Blay said. “We must increase the number of doctors in medical schools and the number of nurses and healthcare professionals in all schools.” Improving staffing would also help reduce chronic workload issues.
Resilience training should also be incorporated into physician training starting in medical school. Teaching oncologists how to deal with bad news and to cope when patients dies is particularly important.
“I was not taught that,” said the oncologist from Portugal. “I had to learn that at my own cost.”
The good news is that it’s possible to develop resiliency skills over time, said Claire Hardy, PhD, from Lancaster University, United Kingdom, who agreed that training programs could be one approach to improve oncologists’ work life.
However, a person’s needs are determined by their institution and personal responsibilities. “No one knows your job better than you,” Dr. Hardy said. “No one knows better than you where the inefficiencies are, where the bureaucracy is that could be taken away, or it could be done by somebody whose role it is to sort all that out.”
But having this understanding is not enough. Physician also need to feel “psychological safety to be able to speak out and say that something isn’t working right now or is too much,” or, “I’m spending too much time doing this.”
In other words, oncologists need to be able to set boundaries and say no.
Dr. Hardy said this concept “has been around a while, but it’s really gaining momentum,” and being able to discuss these issues in a forum such as the ESMO Congress is a promising start.
Dr. Lim has relationships with Janseen and SEOM. No other relevant financial relationships were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MADRID – “Why did I choose this?”
That is the core question a Portuguese oncologist posed from the audience during a session at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) that was dedicated to building a sustainable oncology workforce.
“Ten, twenty years ago, being a doctor was a dream,” she said, but right now doctors are underpaid, under strain, and have very few resources.
This oncologist is hardly alone.
A survey from ESMO conducted almost a decade ago found that more than 50% of oncologists across Europe, many of whom were early in their careers, reported being burned out.
This, Dr. Lim said, “was the starting point,” well before the COVID pandemic struck.
More recently, the pandemic has taken its own toll on the well-being of oncologists. A survey presented at ESMO 2020 revealed that 38% of participants, spanning 101 countries, reported experiencing burnout, and 66% said they were not able to perform their job.
Medscape’s 2023 Physician Burnout and Depression Report highlighted similar burnout rates, with 53% of U.S. physicians and 52% of oncologists saying they felt burned out, compared with about 42% in 2018, before the pandemic.
The oncology workforce is in crisis in every country, said Dr. Lim, from the Cancer Dynamics Lab, the Francis Crick Institute, London.
Burnout, characterized by emotional exhaustion, depersonalization or feelings of cynicism, and a low sense of personal accomplishment, can result in a poor work-life balance as well as poor mental and physical health. Factors linked to burnout include social isolation, increased workload, reduced quality of work, lack of control over work, and stressful professional experiences.
Together, these factors can affect patient care and further exacerbate staffing issues, Dr. Lim said.
Staffing shortages are common. Oncologists often work long hours or on weekends to cover gaps caused by staffing shortages. Recent data revealed that in high-income countries, there are on average 0.65 medical oncologists and 0.25 radiation oncologists per 100 patients — a situation made worse by professionals taking early retirement or leaving medicine during the pandemic.
“We have seen that the shortage of human resources in many countries as well as the increasing workload related to the increasing number of cancers,” as well as patients surviving longer, have increased pressures on the healthcare system, Andrés Cervantes, MD, PhD, president of ESMO, explained in a press conference.
While tackling these oncology workforce problems requires smaller, local changes to a physician’s daily routine, “the real change,” Dr. Lim said, lies at an infrastructure level.
In response to this chronic and growing problem, ESMO launched its Resilience Task Force in 2020 to evaluate burnout and well-being. The task force plans to publish a position paper in which it will propose a set of recommendations regarding the psychosocial risks of burnout as well as flexible work patterns, well-being resources, and targeted support.
A panel of experts at the meeting touched on some of these solutions.
Dealing with staff shortages is a must, said Jean-Yves Blay, MD, PhD, during the session. “It’s a simple mathematical equation,” Dr. Blay said. “We must increase the number of doctors in medical schools and the number of nurses and healthcare professionals in all schools.” Improving staffing would also help reduce chronic workload issues.
Resilience training should also be incorporated into physician training starting in medical school. Teaching oncologists how to deal with bad news and to cope when patients dies is particularly important.
“I was not taught that,” said the oncologist from Portugal. “I had to learn that at my own cost.”
The good news is that it’s possible to develop resiliency skills over time, said Claire Hardy, PhD, from Lancaster University, United Kingdom, who agreed that training programs could be one approach to improve oncologists’ work life.
However, a person’s needs are determined by their institution and personal responsibilities. “No one knows your job better than you,” Dr. Hardy said. “No one knows better than you where the inefficiencies are, where the bureaucracy is that could be taken away, or it could be done by somebody whose role it is to sort all that out.”
But having this understanding is not enough. Physician also need to feel “psychological safety to be able to speak out and say that something isn’t working right now or is too much,” or, “I’m spending too much time doing this.”
In other words, oncologists need to be able to set boundaries and say no.
Dr. Hardy said this concept “has been around a while, but it’s really gaining momentum,” and being able to discuss these issues in a forum such as the ESMO Congress is a promising start.
Dr. Lim has relationships with Janseen and SEOM. No other relevant financial relationships were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESMO 2023
Employment vs. private practice: Who’s happier?
Alexandra Kharazi, MD, a California-based cardiothoracic surgeon, previously worked as an employed physician and is now in private practice. Though she appreciates that there are some trade-offs to working with her small group of three surgeons, Dr. Kharazi has no qualms about her choice.
“For me, it’s an issue of autonomy,” she said. “While I have to work a lot of hours, I don’t have to adhere to a strict schedule. I also don’t have to follow specific policies and rules.”
In contrast, Cassandra Boduch, MD, an employed psychiatrist with PsychPlus in Houston, is very satisfied with working as an employee. “I looked into private practice, but no one really prepares you for the complications that come with it,” she said. “There’s a lot more that goes into it than people realize.”
By hanging up her own shingle, Dr. Kharazi may be living a rapidly shrinking dream. According to the American Medical Association, between 2012 and 2022, the share of physicians working in private practice fell from 60% to 47%. The share of physicians working in hospitals as direct employees or contractors increased from about 6% to about 10% during the same time period.
, according to the AMA.
Though the traditional dream of owning your own practice may be slipping away, are employed physicians less happy than are their self-employed peers? By many measures, the answer is no.
In Medscape’s Employed Physicians Report 2023, doctors weighed in on the pros and cons of their jobs.
When asked what they like most about their jobs, employed physician respondents reported “not having to run a business” as their number-one benefit, followed closely by a stable income. The fact that employers pay for malpractice insurance ranked third, followed by work-life balance.
“We get no business classes in medical school or residency,” said one employed physician. “Having a good salary feels good,” said another. Yet another respondent chimed in: “Running a practice as a small business has become undoable over the past 10-12 years.”
And 50% of employed physicians said that they were “very satisfied/satisfied” with their degree of autonomy.
Still, employed physicians also had plenty to say about the downsides of their jobs.
Many pointed to “feeling like a cog in the machine,” and one doctor pointed to the hassle of dealing with bureaucracy. Others complained about the fact that nonphysicians ran the business and lacked an understanding of what physicians really need from their jobs. When asked whether administrative rules made sense, 63% of physician respondents said that yes, the rules make sense for the business; but, only 52% said that the rules make sense for the doctors themselves.
Other complaints included the requirement to reach high productivity targets and too low an income potential. In the 9 years since Medscape’s 2104 Employed Physicians Report, the share of employed doctors paid on a straight salary has declined from 46% to 31%. Those compensated on a base salary plus productivity targets and other performance metrics rose from 13% in 2014 to 32% now.
“Many doctors go into private practice because of the freedom it brings and the potential financial incentives,” added Dr. Boduch. “I know that many doctors have a dream of working for themselves, and in many cases, that works out great for them.”
Dr. Boduch noted that in her job as chief medical officer at PsychPlus, she still has flexibility plus the perks of working with a bigger practice. In this scenario, Dr. Boduch said, the company can negotiate with insurance companies, allowing her the financial rewards of private practice.
What’s right for you?
“I think it might be somewhat generational,” said Cody Futch, senior recruiting executive at AMN Healthcare. “It used to be that fewer hospitals offered employment, so private practice was the way to go. Now, there are fewer privates because hospitals and corporations are buying them up.”
This reality has potentially shaped the way younger generations approach their workplace. Also, Gen Z tends to have less intention to stay with a current employer for the long term than did their parents. “Older physicians were trained to expect they’d run their own business and build it over the years,” said Mr. Futch. “The younger generations look at it as a job, something they may want to switch in a few years. It’s a combination of candidates wanting more options, and also the fact that there are more options to be employed.”
Along those lines, younger generations in general tend to place work-life balance as a higher priority than do older generations, and employed physicians place this equation high on the list as well. In the Employed Physicians Report 2023, 54% said that they are satisfied or better with their work-life balance, up from 51% in the 2022 report.
With that in mind, Dr. Kharazi noted that flexibility is one of the chief reasons why she likes private practice. “If my kid has an event I want to attend, I don’t have to adhere to a strict schedule,” she said.
Satisfaction as an employee vs. employed doctor sometimes changes based on the type of medicine you practice too. With specialties that tend to be primarily outpatient, such as dermatology and allergy, private practice may be the best option regardless. “Hospitals don’t seek out those specialists as much and the specialists can operate successfully without a hospital,” said Mr. Futch.
Hospitals try to incentivize doctors with perks like hefty sign-on bonuses, student loan forgiveness, plenty of vacation time, and more. They also put money into marketing their doctors, a time-consuming and expensive aspect that is tough to shoulder in private practice, especially in the early years. Mr. Futch adds that many doctors view employment as a more stable option. “As the government changes reimbursement policies, the income from private practice fluctuates,” he said. “So many doctors worry that if they buy into a private practice, it is a risky endeavor.”
Hospitals aren’t always a sure bet in that regard, either: They go through tough financial times, lay off staff, or make salary cuts. Historically, however, employment tends to be the safer route, which can make it an attractive option.
Ultimately, the pros and cons of each scenario are individual. It’s up to physicians to do their own math and balance sheet before making a decision.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Alexandra Kharazi, MD, a California-based cardiothoracic surgeon, previously worked as an employed physician and is now in private practice. Though she appreciates that there are some trade-offs to working with her small group of three surgeons, Dr. Kharazi has no qualms about her choice.
“For me, it’s an issue of autonomy,” she said. “While I have to work a lot of hours, I don’t have to adhere to a strict schedule. I also don’t have to follow specific policies and rules.”
In contrast, Cassandra Boduch, MD, an employed psychiatrist with PsychPlus in Houston, is very satisfied with working as an employee. “I looked into private practice, but no one really prepares you for the complications that come with it,” she said. “There’s a lot more that goes into it than people realize.”
By hanging up her own shingle, Dr. Kharazi may be living a rapidly shrinking dream. According to the American Medical Association, between 2012 and 2022, the share of physicians working in private practice fell from 60% to 47%. The share of physicians working in hospitals as direct employees or contractors increased from about 6% to about 10% during the same time period.
, according to the AMA.
Though the traditional dream of owning your own practice may be slipping away, are employed physicians less happy than are their self-employed peers? By many measures, the answer is no.
In Medscape’s Employed Physicians Report 2023, doctors weighed in on the pros and cons of their jobs.
When asked what they like most about their jobs, employed physician respondents reported “not having to run a business” as their number-one benefit, followed closely by a stable income. The fact that employers pay for malpractice insurance ranked third, followed by work-life balance.
“We get no business classes in medical school or residency,” said one employed physician. “Having a good salary feels good,” said another. Yet another respondent chimed in: “Running a practice as a small business has become undoable over the past 10-12 years.”
And 50% of employed physicians said that they were “very satisfied/satisfied” with their degree of autonomy.
Still, employed physicians also had plenty to say about the downsides of their jobs.
Many pointed to “feeling like a cog in the machine,” and one doctor pointed to the hassle of dealing with bureaucracy. Others complained about the fact that nonphysicians ran the business and lacked an understanding of what physicians really need from their jobs. When asked whether administrative rules made sense, 63% of physician respondents said that yes, the rules make sense for the business; but, only 52% said that the rules make sense for the doctors themselves.
Other complaints included the requirement to reach high productivity targets and too low an income potential. In the 9 years since Medscape’s 2104 Employed Physicians Report, the share of employed doctors paid on a straight salary has declined from 46% to 31%. Those compensated on a base salary plus productivity targets and other performance metrics rose from 13% in 2014 to 32% now.
“Many doctors go into private practice because of the freedom it brings and the potential financial incentives,” added Dr. Boduch. “I know that many doctors have a dream of working for themselves, and in many cases, that works out great for them.”
Dr. Boduch noted that in her job as chief medical officer at PsychPlus, she still has flexibility plus the perks of working with a bigger practice. In this scenario, Dr. Boduch said, the company can negotiate with insurance companies, allowing her the financial rewards of private practice.
What’s right for you?
“I think it might be somewhat generational,” said Cody Futch, senior recruiting executive at AMN Healthcare. “It used to be that fewer hospitals offered employment, so private practice was the way to go. Now, there are fewer privates because hospitals and corporations are buying them up.”
This reality has potentially shaped the way younger generations approach their workplace. Also, Gen Z tends to have less intention to stay with a current employer for the long term than did their parents. “Older physicians were trained to expect they’d run their own business and build it over the years,” said Mr. Futch. “The younger generations look at it as a job, something they may want to switch in a few years. It’s a combination of candidates wanting more options, and also the fact that there are more options to be employed.”
Along those lines, younger generations in general tend to place work-life balance as a higher priority than do older generations, and employed physicians place this equation high on the list as well. In the Employed Physicians Report 2023, 54% said that they are satisfied or better with their work-life balance, up from 51% in the 2022 report.
With that in mind, Dr. Kharazi noted that flexibility is one of the chief reasons why she likes private practice. “If my kid has an event I want to attend, I don’t have to adhere to a strict schedule,” she said.
Satisfaction as an employee vs. employed doctor sometimes changes based on the type of medicine you practice too. With specialties that tend to be primarily outpatient, such as dermatology and allergy, private practice may be the best option regardless. “Hospitals don’t seek out those specialists as much and the specialists can operate successfully without a hospital,” said Mr. Futch.
Hospitals try to incentivize doctors with perks like hefty sign-on bonuses, student loan forgiveness, plenty of vacation time, and more. They also put money into marketing their doctors, a time-consuming and expensive aspect that is tough to shoulder in private practice, especially in the early years. Mr. Futch adds that many doctors view employment as a more stable option. “As the government changes reimbursement policies, the income from private practice fluctuates,” he said. “So many doctors worry that if they buy into a private practice, it is a risky endeavor.”
Hospitals aren’t always a sure bet in that regard, either: They go through tough financial times, lay off staff, or make salary cuts. Historically, however, employment tends to be the safer route, which can make it an attractive option.
Ultimately, the pros and cons of each scenario are individual. It’s up to physicians to do their own math and balance sheet before making a decision.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Alexandra Kharazi, MD, a California-based cardiothoracic surgeon, previously worked as an employed physician and is now in private practice. Though she appreciates that there are some trade-offs to working with her small group of three surgeons, Dr. Kharazi has no qualms about her choice.
“For me, it’s an issue of autonomy,” she said. “While I have to work a lot of hours, I don’t have to adhere to a strict schedule. I also don’t have to follow specific policies and rules.”
In contrast, Cassandra Boduch, MD, an employed psychiatrist with PsychPlus in Houston, is very satisfied with working as an employee. “I looked into private practice, but no one really prepares you for the complications that come with it,” she said. “There’s a lot more that goes into it than people realize.”
By hanging up her own shingle, Dr. Kharazi may be living a rapidly shrinking dream. According to the American Medical Association, between 2012 and 2022, the share of physicians working in private practice fell from 60% to 47%. The share of physicians working in hospitals as direct employees or contractors increased from about 6% to about 10% during the same time period.
, according to the AMA.
Though the traditional dream of owning your own practice may be slipping away, are employed physicians less happy than are their self-employed peers? By many measures, the answer is no.
In Medscape’s Employed Physicians Report 2023, doctors weighed in on the pros and cons of their jobs.
When asked what they like most about their jobs, employed physician respondents reported “not having to run a business” as their number-one benefit, followed closely by a stable income. The fact that employers pay for malpractice insurance ranked third, followed by work-life balance.
“We get no business classes in medical school or residency,” said one employed physician. “Having a good salary feels good,” said another. Yet another respondent chimed in: “Running a practice as a small business has become undoable over the past 10-12 years.”
And 50% of employed physicians said that they were “very satisfied/satisfied” with their degree of autonomy.
Still, employed physicians also had plenty to say about the downsides of their jobs.
Many pointed to “feeling like a cog in the machine,” and one doctor pointed to the hassle of dealing with bureaucracy. Others complained about the fact that nonphysicians ran the business and lacked an understanding of what physicians really need from their jobs. When asked whether administrative rules made sense, 63% of physician respondents said that yes, the rules make sense for the business; but, only 52% said that the rules make sense for the doctors themselves.
Other complaints included the requirement to reach high productivity targets and too low an income potential. In the 9 years since Medscape’s 2104 Employed Physicians Report, the share of employed doctors paid on a straight salary has declined from 46% to 31%. Those compensated on a base salary plus productivity targets and other performance metrics rose from 13% in 2014 to 32% now.
“Many doctors go into private practice because of the freedom it brings and the potential financial incentives,” added Dr. Boduch. “I know that many doctors have a dream of working for themselves, and in many cases, that works out great for them.”
Dr. Boduch noted that in her job as chief medical officer at PsychPlus, she still has flexibility plus the perks of working with a bigger practice. In this scenario, Dr. Boduch said, the company can negotiate with insurance companies, allowing her the financial rewards of private practice.
What’s right for you?
“I think it might be somewhat generational,” said Cody Futch, senior recruiting executive at AMN Healthcare. “It used to be that fewer hospitals offered employment, so private practice was the way to go. Now, there are fewer privates because hospitals and corporations are buying them up.”
This reality has potentially shaped the way younger generations approach their workplace. Also, Gen Z tends to have less intention to stay with a current employer for the long term than did their parents. “Older physicians were trained to expect they’d run their own business and build it over the years,” said Mr. Futch. “The younger generations look at it as a job, something they may want to switch in a few years. It’s a combination of candidates wanting more options, and also the fact that there are more options to be employed.”
Along those lines, younger generations in general tend to place work-life balance as a higher priority than do older generations, and employed physicians place this equation high on the list as well. In the Employed Physicians Report 2023, 54% said that they are satisfied or better with their work-life balance, up from 51% in the 2022 report.
With that in mind, Dr. Kharazi noted that flexibility is one of the chief reasons why she likes private practice. “If my kid has an event I want to attend, I don’t have to adhere to a strict schedule,” she said.
Satisfaction as an employee vs. employed doctor sometimes changes based on the type of medicine you practice too. With specialties that tend to be primarily outpatient, such as dermatology and allergy, private practice may be the best option regardless. “Hospitals don’t seek out those specialists as much and the specialists can operate successfully without a hospital,” said Mr. Futch.
Hospitals try to incentivize doctors with perks like hefty sign-on bonuses, student loan forgiveness, plenty of vacation time, and more. They also put money into marketing their doctors, a time-consuming and expensive aspect that is tough to shoulder in private practice, especially in the early years. Mr. Futch adds that many doctors view employment as a more stable option. “As the government changes reimbursement policies, the income from private practice fluctuates,” he said. “So many doctors worry that if they buy into a private practice, it is a risky endeavor.”
Hospitals aren’t always a sure bet in that regard, either: They go through tough financial times, lay off staff, or make salary cuts. Historically, however, employment tends to be the safer route, which can make it an attractive option.
Ultimately, the pros and cons of each scenario are individual. It’s up to physicians to do their own math and balance sheet before making a decision.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Employed physicians: A survival guide
The strike by health care workers at Kaiser Permanente may not involve physicians (yet). But as more doctors in the United States are finding themselves working as salaried employees, physicians can – and probably will – become a powerful force for change in a health care system that has shown itself to be increasingly hostile to employee concerns over issues involving patient care, wages and benefits, safety, and well-being.
Salaried employment has its challenges. Physician-employees may have less autonomy and voice in decision-making that affects patients. They may splinter into fragmented work groups; feel isolated; and have different imperatives based on who they are, what they want, and where they work. They may feel more removed from their patients and struggle to build strong relationships, with their employers in the way.
Yet important opportunities exist for doctors when embracing their employee side. Examples of these interests include adequate compensation, wellness, job security, patient and worker safety, health care quality, reasonable workloads and schedules, and fair treatment by employers, including the need to exhibit a strong collective voice in organizational decision-making.
Some believe that physician-employees must be unionized to maximize their rights and power as employees. Many expect physician unionization to take hold more fully over time. Medical residents, the doctors of tomorrow, are already considering unionization in greater numbers. Some are also doing it in the same employment setting alongside other health professionals, such as nurses.
Having studied doctors and their employment situations for years, I am convinced that whether through unionization or another approach, physicians must also change how they think about control; train and learn alongside other health care workers who share similar interests; and elevate at an early career stage their knowledge of the business side of health care.
Adopt a more pragmatic definition of autonomy
Doctors must embrace an updated definition of autonomy – one that matches their status as highly paid labor.
When I have spoken to physicians in my research about what autonomy means to them, many seem unable to reconceptualize it from a vague and absolute form of their profession’s strategic control over their economic fates and technical skills toward an individualized control that is situation-specific, one centered on winning the daily fights about workplace bread-and-butter issues such as those mentioned above.
But a more pragmatic definition of autonomy could get doctors focused on influencing important issues of the patient-care day and enhance their negotiating power with employers. It would allow physicians to break out of what often seems a paralysis of inaction – waiting for employers, insurers, or the government to reinstate the profession’s idealized version of control by handing it back the keys to the health care system through major regulatory, structural, and reimbursement-related changes. This fantasy is unlikely to become reality.
Physician-employees I’ve talked to over the years understand their everyday challenges. But when it comes to engaging in localized and sustained action to overcome them, they often perform less well, leading to feelings of helplessness and burnout. Valuing tactical control over their jobs and work setting will yield smaller but more impactful wins as employees intent on making their everyday work lives better.
Train alongside other health care professionals
Physicians must accept that how they are trained no longer prepares them for the employee world into which most are dropped. For instance, unless doctors are trained collaboratively alongside other health care professionals – such as nurses – they are less likely to identify closely with these colleagues once in practice. There is strength in numbers, so this mutual identification empowers both groups of employees. Yet, medical education remains largely the same: training young medical students in isolation for the first couple of years, then placing them into clerkships and residencies where true interprofessional care opportunities remain stunted and secondary to the “physician as captain of the team” mantra.
Unfortunately, the “hidden curriculum” of medicine helps convince medical students and residents early in their careers that they are the unquestioned leaders in patient care settings. This hierarchy encourages some doctors to keep their psychological distance from other members of the health care team and to resist sharing power, concerns, or insights with less skilled health care workers. This socialization harms the ability of physicians to act in a unified fashion alongside these other workers. Having physicians learn and train alongside other health professionals yields positive benefits for collective advocacy, including a shared sense of purpose, positive views on collaboration with others in the health setting, and greater development of bonds with nonphysician coworkers.
Integrate business with medical training in real time
Medical students and residents generally lack exposure to the everyday business realities of the U.S. health care system. This gap hinders their ability to understand the employee world and push for the types of changes and work conditions that benefit all health care workers. Formal business and management training should be a required part of every U.S. medical school and residency curriculum from day one. If you see it at all in medical schools now, it is mostly by accident, or given separate treatment in the form of standalone MBA or MPH degrees that rarely integrate organically and in real time with actual medical training. Not every doctor needs an MBA or MPH degree. However, all of them require a stronger contextual understanding of how the medicine they wish to practice is shaped by the economic and fiscal circumstances surrounding it – circumstances they do not control.
This is another reason why young doctors are unhappy and burned out. They cannot push for specific changes or properly critique the pros and cons of how their work is structured because they have not been made aware, in real time as they learn clinical practice, how their jobs are shaped by realities such as insurance coverage and reimbursement, the fragmentation of the care delivery system, their employer’s financial health , and the socioeconomic circumstances of their patients. They aren’t given the methods and tools related to process and quality improvement, budgeting, negotiation, risk management, leadership, and talent management that might help them navigate these undermining forces. They also get little advance exposure in their training to important workplace “soft” skills in such areas as how to work in teams, networking, communication and listening, empathy, and problem-solving – all necessary foci for bringing them closer to other health care workers and advocating alongside them effectively with health care employers.
Now is the time for physicians to embrace their identity as employees. Doing so is in their own best interest as professionals. It will help others in the health care workforce as well as patients. Moreover, it provides a needed counterbalance to the powerful corporate ethos now ascendant in U.S. health care.
Timothy Hoff, PhD, is a professor of management and healthcare systems at Northeastern University, Boston, and an associate fellow at the University of Oxford, England. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The strike by health care workers at Kaiser Permanente may not involve physicians (yet). But as more doctors in the United States are finding themselves working as salaried employees, physicians can – and probably will – become a powerful force for change in a health care system that has shown itself to be increasingly hostile to employee concerns over issues involving patient care, wages and benefits, safety, and well-being.
Salaried employment has its challenges. Physician-employees may have less autonomy and voice in decision-making that affects patients. They may splinter into fragmented work groups; feel isolated; and have different imperatives based on who they are, what they want, and where they work. They may feel more removed from their patients and struggle to build strong relationships, with their employers in the way.
Yet important opportunities exist for doctors when embracing their employee side. Examples of these interests include adequate compensation, wellness, job security, patient and worker safety, health care quality, reasonable workloads and schedules, and fair treatment by employers, including the need to exhibit a strong collective voice in organizational decision-making.
Some believe that physician-employees must be unionized to maximize their rights and power as employees. Many expect physician unionization to take hold more fully over time. Medical residents, the doctors of tomorrow, are already considering unionization in greater numbers. Some are also doing it in the same employment setting alongside other health professionals, such as nurses.
Having studied doctors and their employment situations for years, I am convinced that whether through unionization or another approach, physicians must also change how they think about control; train and learn alongside other health care workers who share similar interests; and elevate at an early career stage their knowledge of the business side of health care.
Adopt a more pragmatic definition of autonomy
Doctors must embrace an updated definition of autonomy – one that matches their status as highly paid labor.
When I have spoken to physicians in my research about what autonomy means to them, many seem unable to reconceptualize it from a vague and absolute form of their profession’s strategic control over their economic fates and technical skills toward an individualized control that is situation-specific, one centered on winning the daily fights about workplace bread-and-butter issues such as those mentioned above.
But a more pragmatic definition of autonomy could get doctors focused on influencing important issues of the patient-care day and enhance their negotiating power with employers. It would allow physicians to break out of what often seems a paralysis of inaction – waiting for employers, insurers, or the government to reinstate the profession’s idealized version of control by handing it back the keys to the health care system through major regulatory, structural, and reimbursement-related changes. This fantasy is unlikely to become reality.
Physician-employees I’ve talked to over the years understand their everyday challenges. But when it comes to engaging in localized and sustained action to overcome them, they often perform less well, leading to feelings of helplessness and burnout. Valuing tactical control over their jobs and work setting will yield smaller but more impactful wins as employees intent on making their everyday work lives better.
Train alongside other health care professionals
Physicians must accept that how they are trained no longer prepares them for the employee world into which most are dropped. For instance, unless doctors are trained collaboratively alongside other health care professionals – such as nurses – they are less likely to identify closely with these colleagues once in practice. There is strength in numbers, so this mutual identification empowers both groups of employees. Yet, medical education remains largely the same: training young medical students in isolation for the first couple of years, then placing them into clerkships and residencies where true interprofessional care opportunities remain stunted and secondary to the “physician as captain of the team” mantra.
Unfortunately, the “hidden curriculum” of medicine helps convince medical students and residents early in their careers that they are the unquestioned leaders in patient care settings. This hierarchy encourages some doctors to keep their psychological distance from other members of the health care team and to resist sharing power, concerns, or insights with less skilled health care workers. This socialization harms the ability of physicians to act in a unified fashion alongside these other workers. Having physicians learn and train alongside other health professionals yields positive benefits for collective advocacy, including a shared sense of purpose, positive views on collaboration with others in the health setting, and greater development of bonds with nonphysician coworkers.
Integrate business with medical training in real time
Medical students and residents generally lack exposure to the everyday business realities of the U.S. health care system. This gap hinders their ability to understand the employee world and push for the types of changes and work conditions that benefit all health care workers. Formal business and management training should be a required part of every U.S. medical school and residency curriculum from day one. If you see it at all in medical schools now, it is mostly by accident, or given separate treatment in the form of standalone MBA or MPH degrees that rarely integrate organically and in real time with actual medical training. Not every doctor needs an MBA or MPH degree. However, all of them require a stronger contextual understanding of how the medicine they wish to practice is shaped by the economic and fiscal circumstances surrounding it – circumstances they do not control.
This is another reason why young doctors are unhappy and burned out. They cannot push for specific changes or properly critique the pros and cons of how their work is structured because they have not been made aware, in real time as they learn clinical practice, how their jobs are shaped by realities such as insurance coverage and reimbursement, the fragmentation of the care delivery system, their employer’s financial health , and the socioeconomic circumstances of their patients. They aren’t given the methods and tools related to process and quality improvement, budgeting, negotiation, risk management, leadership, and talent management that might help them navigate these undermining forces. They also get little advance exposure in their training to important workplace “soft” skills in such areas as how to work in teams, networking, communication and listening, empathy, and problem-solving – all necessary foci for bringing them closer to other health care workers and advocating alongside them effectively with health care employers.
Now is the time for physicians to embrace their identity as employees. Doing so is in their own best interest as professionals. It will help others in the health care workforce as well as patients. Moreover, it provides a needed counterbalance to the powerful corporate ethos now ascendant in U.S. health care.
Timothy Hoff, PhD, is a professor of management and healthcare systems at Northeastern University, Boston, and an associate fellow at the University of Oxford, England. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The strike by health care workers at Kaiser Permanente may not involve physicians (yet). But as more doctors in the United States are finding themselves working as salaried employees, physicians can – and probably will – become a powerful force for change in a health care system that has shown itself to be increasingly hostile to employee concerns over issues involving patient care, wages and benefits, safety, and well-being.
Salaried employment has its challenges. Physician-employees may have less autonomy and voice in decision-making that affects patients. They may splinter into fragmented work groups; feel isolated; and have different imperatives based on who they are, what they want, and where they work. They may feel more removed from their patients and struggle to build strong relationships, with their employers in the way.
Yet important opportunities exist for doctors when embracing their employee side. Examples of these interests include adequate compensation, wellness, job security, patient and worker safety, health care quality, reasonable workloads and schedules, and fair treatment by employers, including the need to exhibit a strong collective voice in organizational decision-making.
Some believe that physician-employees must be unionized to maximize their rights and power as employees. Many expect physician unionization to take hold more fully over time. Medical residents, the doctors of tomorrow, are already considering unionization in greater numbers. Some are also doing it in the same employment setting alongside other health professionals, such as nurses.
Having studied doctors and their employment situations for years, I am convinced that whether through unionization or another approach, physicians must also change how they think about control; train and learn alongside other health care workers who share similar interests; and elevate at an early career stage their knowledge of the business side of health care.
Adopt a more pragmatic definition of autonomy
Doctors must embrace an updated definition of autonomy – one that matches their status as highly paid labor.
When I have spoken to physicians in my research about what autonomy means to them, many seem unable to reconceptualize it from a vague and absolute form of their profession’s strategic control over their economic fates and technical skills toward an individualized control that is situation-specific, one centered on winning the daily fights about workplace bread-and-butter issues such as those mentioned above.
But a more pragmatic definition of autonomy could get doctors focused on influencing important issues of the patient-care day and enhance their negotiating power with employers. It would allow physicians to break out of what often seems a paralysis of inaction – waiting for employers, insurers, or the government to reinstate the profession’s idealized version of control by handing it back the keys to the health care system through major regulatory, structural, and reimbursement-related changes. This fantasy is unlikely to become reality.
Physician-employees I’ve talked to over the years understand their everyday challenges. But when it comes to engaging in localized and sustained action to overcome them, they often perform less well, leading to feelings of helplessness and burnout. Valuing tactical control over their jobs and work setting will yield smaller but more impactful wins as employees intent on making their everyday work lives better.
Train alongside other health care professionals
Physicians must accept that how they are trained no longer prepares them for the employee world into which most are dropped. For instance, unless doctors are trained collaboratively alongside other health care professionals – such as nurses – they are less likely to identify closely with these colleagues once in practice. There is strength in numbers, so this mutual identification empowers both groups of employees. Yet, medical education remains largely the same: training young medical students in isolation for the first couple of years, then placing them into clerkships and residencies where true interprofessional care opportunities remain stunted and secondary to the “physician as captain of the team” mantra.
Unfortunately, the “hidden curriculum” of medicine helps convince medical students and residents early in their careers that they are the unquestioned leaders in patient care settings. This hierarchy encourages some doctors to keep their psychological distance from other members of the health care team and to resist sharing power, concerns, or insights with less skilled health care workers. This socialization harms the ability of physicians to act in a unified fashion alongside these other workers. Having physicians learn and train alongside other health professionals yields positive benefits for collective advocacy, including a shared sense of purpose, positive views on collaboration with others in the health setting, and greater development of bonds with nonphysician coworkers.
Integrate business with medical training in real time
Medical students and residents generally lack exposure to the everyday business realities of the U.S. health care system. This gap hinders their ability to understand the employee world and push for the types of changes and work conditions that benefit all health care workers. Formal business and management training should be a required part of every U.S. medical school and residency curriculum from day one. If you see it at all in medical schools now, it is mostly by accident, or given separate treatment in the form of standalone MBA or MPH degrees that rarely integrate organically and in real time with actual medical training. Not every doctor needs an MBA or MPH degree. However, all of them require a stronger contextual understanding of how the medicine they wish to practice is shaped by the economic and fiscal circumstances surrounding it – circumstances they do not control.
This is another reason why young doctors are unhappy and burned out. They cannot push for specific changes or properly critique the pros and cons of how their work is structured because they have not been made aware, in real time as they learn clinical practice, how their jobs are shaped by realities such as insurance coverage and reimbursement, the fragmentation of the care delivery system, their employer’s financial health , and the socioeconomic circumstances of their patients. They aren’t given the methods and tools related to process and quality improvement, budgeting, negotiation, risk management, leadership, and talent management that might help them navigate these undermining forces. They also get little advance exposure in their training to important workplace “soft” skills in such areas as how to work in teams, networking, communication and listening, empathy, and problem-solving – all necessary foci for bringing them closer to other health care workers and advocating alongside them effectively with health care employers.
Now is the time for physicians to embrace their identity as employees. Doing so is in their own best interest as professionals. It will help others in the health care workforce as well as patients. Moreover, it provides a needed counterbalance to the powerful corporate ethos now ascendant in U.S. health care.
Timothy Hoff, PhD, is a professor of management and healthcare systems at Northeastern University, Boston, and an associate fellow at the University of Oxford, England. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Prior authorization software: Saves time but hurdles remain
New England Baptist Hospital has been grappling with a serious problem facing health care today: insurers demanding prior authorizations for services ordered by physicians. Meeting payers’ requirements eats up time, delays treatment, and can be a costly drain on doctors’ practices.
To deal with this problem, the Boston orthopedic hospital has opted to automate submission of prior authorization requests on behalf of more than 100 mostly orthopedic surgeons on staff.
After 5 years using this system, “we can say that automation definitely works,” said Lidiya Hadzhieva, director of patient access at the hospital. The software has reduced write-offs by 30% and staff costs by 25%. Prior authorization gets approved 3 days after scheduling, compared with 11 days previously, she said.
“This software not only saves staff time, but it can also more accurately predict when prior authorization is needed,” she added.
For practices deluged with required prior authorizations by insurers, automation is emerging as a way for practices to make the process less time-consuming and save money. However, the software can be costly and may not be adoptable to many practices, and many physicians are not even aware it exists.
So far, the software is mainly used at large organizations like hospital systems. But as word gets out and the software becomes easier to use, private practices and other smaller entities may join the automation trend.
There is definitely a need to automate prior authorization. The American Medical Association reports that physicians spend 16 hours per week on prior authorizations. In a recent AMA survey, more than 60% of physicians indicated that it’s difficult to know when prior authorization is needed. And 93% of physicians reported care delays while waiting for authorization, the AMA said.
Experts estimate that 80% of prior authorization work could be automated, but most practices still use the phone or fax, even as numbers of prior authorizations continue to increase.
How it works
Automation software connects directly to the practice’s electronic health record (EHR). “When the doctor places an order in the EHR, the process starts automatically,” Ms. Hadzhieva said. “The doctor may not even notice it.”
In addition to using an EHR connection, many software products can communicate with the payer through its portal or by fax or phone, while still automating other parts of the process.
The software’s first step is to decide whether prior authorization is needed. This requires having an updated list of the rules that each payer uses for prior authorization. Manually keeping track of payer rules is very time-consuming, but automation uses bots to visit each payer site to look for rules changes. One vendor, Infinitus, uses a voice-based bot called Eva that calls up each payer and speaks with a representative.
“Automatically updating payer rules is not a new technology,” said YiDing Yu, MD, chief product officer at Olive, the automation vendor for New England Baptist. “What is new in the last 5 years is extracting the information needed for the prior authorization out of the clinical notes.”
This is challenging because each doctor has different ways to describe each step of clinical work. To identify this shorthand, Dr. Yu said Olive uses natural language processing, which is a form of artificial intelligence that learns how each doctor describes things.
Dr. Yu asserts that Olive is actually better than a practice’s staff at digging out clinical information. She said staff without much clinical training may miss terms that the software can catch, and they don’t have the time to go back many months into the record to find valuable information. But automation can do that.
In some instances, however, the software may not be able to find the information, in which case it alerts staff through a prompt in the EHR and the information is retrieved manually, Dr. Yu said.
Next, the Olive software puts the information it found into the request form and sends it to the payer. After submission, the software constantly checks on the status of each request, again visiting payer sites with a bot.
At New England Baptist, the software is used mainly by physicians in fairly small private practices who are on staff. They are using the software on the hospital’s dime, but it only works inside the hospital, Ms. Hadzhieva said. For their work outside of the hospital, they would have to purchase the Olive software on their own, she said.
Automation hasn’t spread to practices yet
Despite the promising outcomes for products like Olive, automation software is still primarily used by large organizations. Vendors say very few private practices have bought it yet. “The technology works, but it is still in the early-adopter phase,” Dr. Yu said.
For one thing, the software can be expensive. Very few vendors reveal their prices, but Dr. Yu did so. She said Olive normally costs about $50,000 a year for even a small organization. She insisted, however, that the savings from avoiding just one denial each month for a hip surgery would justify the expense.
On the other hand, some automation software is free, such as the Surescripts product for prior authorization of prescriptions. But it is unclear whether Surescripts does as much as Olive. Vendors’ descriptions of their products tend to be vague.
Also, Surescripts and Olive have entirely separate functions. Dr. Yu said Olive is limited to procedures, so it benefits specialties like oncology, neurosurgery, colorectal surgery, vascular surgery, and cardiology. Olive does not cover prescriptions, because they operate on a different technology.
Dr. Yu said another hurdle for adopting the software is the kind of EHR systems that doctors use. At this point, only a few EHR systems – such as Epic, Cerner, and Athena – are compatible with Olive. Large organizations tend to use Epic and Cerner, while many practices often use Athena or a variety of other systems, she said.
Despite stunted demand, there is no shortage of companies offering automation software for medical (that is, non-prescription) prior authorization. One compilation lists 25 such vendors, including companies like Myndshft, Rhyme, Infinitus, Infinx, and Waystar. As with any start-up technology, companies occasionally buy each other out.
In addition to issues like cost, specialty, and EHR compatibility, another hurdle is that few doctors even know the technology exists. Vendors say marketing focuses on larger provider organizations, not smaller practices.
Even many tech-savvy doctors, like Adam Bruggeman, MD, an orthopedist and CEO of Texas Spine Care Center in San Antonio, say they know little about the technology. “There is definitely a need to automate prior authorization,” he said. “But I don’t know of any colleagues who use it.” He has only just begun to explore vendors, he said.
Many medical practice consultants also have not yet explored the technology. “Automation makes a lot of sense, because there are a lot of repetitive tasks in prior authorization,” said Jill Arena, CEO of Portland, Ore.–based Health e Practices. “But I haven’t looked into it yet, and none of my clients has even asked about it.”
“I could see how it could be an easier sell for large organizations,” she added. “They have an IT person and a CFO who can explore the issue. Smaller practices usually don’t have that kind of expertise.”
Where does automation go from here?
Until now, clinicians who want to fully automate prior authorizations would have to buy two products – one for medical procedures and one for prescriptions. This has to do with incompatible electronic transmission standards, which are used to digitize information, said Susan Lawson-Dawson, content marketing strategist for the vendor Myndshft Health.
Myndshft has long been selling automation software for medical prior authorizations, but now it is introducing a product for prescriptions, Ms. Lawson-Dawson said. She said Myndshft will then be the only vendor to automate both kinds of prior authorizations.
Ms. Lawson-Dawson said Myndshft has 685 customers to date and is looking for more business. Recently the company entered the Google Cloud Marketplace. Google Cloud customers can now direct their committed spend with Google to purchasing Myndshft, meaning they could get it at a discount.
Software like Olive and Myndshft can operate independently of payers, but a vendor called Rhyme depends on payers for its software to function, said Rhyme CEO Joe Anstine. He said more than 300 payers have agreed to install the Rhyme system, and Rhyme has signed up a number of large health systems to use the product. Initially, he said, clinicians paid for the service, but now Rhyme is beginning to find payers to foot the costs and to let clinicians use it for free, which would open Rhyme up to smaller practices.
EHR companies themselves are beginning to offer automation, too. Epic, for example, has created a tool for prior authorization as part of its Epic Payer Platform. Like Rhyme, it requires payer cooperation, because information goes back and forth between clinician and payer in what is called bi-directional exchange.
The Epic product is still in its pilot phase. Epic reported that several large health systems were using its product in conjunction with a specific payer – for instance, Mayo Clinic with Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota and Ochsner Health with Humana. According to Epic, the arrangement reduced Mayo’s denials due to additional documentation requests by 63% for professional billing.
Automating with just one payer still means the clinician has to deal with manual processes at other payers, but a large clinician could have sufficient volume with that one payer to make the arrangement useful.
Will payers automate prior authorization?
Ultimately, payers may take the automation business away from vendors, offering a free product to all clinicians. But don’t hold your breath. Payers first have to rebuild their electronic systems to accommodate an electronic connection with providers. Even then, some payers might hold back from automating, forcing practices to continue manually processing some prior authorizations.
Efforts are underway, however, to mandate payers to support prior authorization automation. For this to happen, payers would have to revamp their data so that it could be easily read by practices’ EHRs. This would mean adopting a specific interoperability standard called Health Level 7 Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR).
Toward this goal, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services proposes to require payers to adopt FHIR by January 2026. (CMS still has to finalize the rule.) Experts say the two-year ramp-up time is needed because it takes extensive work for payers to translate their data into FHIR.
The only payer so far to switch to FHIR for prior authorization is Regence in Washington state. In a pilot project, it has automated prior authorization with just one provider, MultiCare Connected Care, an accountable care organization (ACO), also in Washington state.
Anna Taylor, associate vice president of population health and value-based care at MultiCare, explained how the arrangement works. “Two separate entities are sharing one operational process,” she told this news organization. “That means they can have a digital conversation back and forth, so it is much easier to resolve prior authorization issues.”
Unlike many vendor products, the Regence service is free. And while the vendors market only to large organizations, most doctors in the MultiCare arrangement are in independent practices. Ms. Taylor said these doctors have been “enthusiastic” about the arrangement.
The results of the pilot are impressive. Ms. Taylor said automation has resulted in a 233% productivity gain for MultiCare clinicians, and 89% of submissions to Regence get an immediate response.
There is a potential downside, however, to working directly with payers. A direct connection to clinicians allows payers to access the doctor’s clinical notes, which could make many doctors uneasy. But Ms. Taylor said Regence only has access to the “discrete data fields” on MultiCare’s EHR dashboard, not to the notes themselves.
The ultimate goal of the Regence-Multicare project is to include more payers and clinicians. Ms. Taylor said two of the 27 other payers that MultiCare works with are “highly interested,” but it would take a lot of work for them to get connected with practices and other clinicians.
Ultimately, payers could offer automation and third-party vendors might then fade away. However, physicians may resist working directly with payers if the arrangement requires full access to their medical records.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New England Baptist Hospital has been grappling with a serious problem facing health care today: insurers demanding prior authorizations for services ordered by physicians. Meeting payers’ requirements eats up time, delays treatment, and can be a costly drain on doctors’ practices.
To deal with this problem, the Boston orthopedic hospital has opted to automate submission of prior authorization requests on behalf of more than 100 mostly orthopedic surgeons on staff.
After 5 years using this system, “we can say that automation definitely works,” said Lidiya Hadzhieva, director of patient access at the hospital. The software has reduced write-offs by 30% and staff costs by 25%. Prior authorization gets approved 3 days after scheduling, compared with 11 days previously, she said.
“This software not only saves staff time, but it can also more accurately predict when prior authorization is needed,” she added.
For practices deluged with required prior authorizations by insurers, automation is emerging as a way for practices to make the process less time-consuming and save money. However, the software can be costly and may not be adoptable to many practices, and many physicians are not even aware it exists.
So far, the software is mainly used at large organizations like hospital systems. But as word gets out and the software becomes easier to use, private practices and other smaller entities may join the automation trend.
There is definitely a need to automate prior authorization. The American Medical Association reports that physicians spend 16 hours per week on prior authorizations. In a recent AMA survey, more than 60% of physicians indicated that it’s difficult to know when prior authorization is needed. And 93% of physicians reported care delays while waiting for authorization, the AMA said.
Experts estimate that 80% of prior authorization work could be automated, but most practices still use the phone or fax, even as numbers of prior authorizations continue to increase.
How it works
Automation software connects directly to the practice’s electronic health record (EHR). “When the doctor places an order in the EHR, the process starts automatically,” Ms. Hadzhieva said. “The doctor may not even notice it.”
In addition to using an EHR connection, many software products can communicate with the payer through its portal or by fax or phone, while still automating other parts of the process.
The software’s first step is to decide whether prior authorization is needed. This requires having an updated list of the rules that each payer uses for prior authorization. Manually keeping track of payer rules is very time-consuming, but automation uses bots to visit each payer site to look for rules changes. One vendor, Infinitus, uses a voice-based bot called Eva that calls up each payer and speaks with a representative.
“Automatically updating payer rules is not a new technology,” said YiDing Yu, MD, chief product officer at Olive, the automation vendor for New England Baptist. “What is new in the last 5 years is extracting the information needed for the prior authorization out of the clinical notes.”
This is challenging because each doctor has different ways to describe each step of clinical work. To identify this shorthand, Dr. Yu said Olive uses natural language processing, which is a form of artificial intelligence that learns how each doctor describes things.
Dr. Yu asserts that Olive is actually better than a practice’s staff at digging out clinical information. She said staff without much clinical training may miss terms that the software can catch, and they don’t have the time to go back many months into the record to find valuable information. But automation can do that.
In some instances, however, the software may not be able to find the information, in which case it alerts staff through a prompt in the EHR and the information is retrieved manually, Dr. Yu said.
Next, the Olive software puts the information it found into the request form and sends it to the payer. After submission, the software constantly checks on the status of each request, again visiting payer sites with a bot.
At New England Baptist, the software is used mainly by physicians in fairly small private practices who are on staff. They are using the software on the hospital’s dime, but it only works inside the hospital, Ms. Hadzhieva said. For their work outside of the hospital, they would have to purchase the Olive software on their own, she said.
Automation hasn’t spread to practices yet
Despite the promising outcomes for products like Olive, automation software is still primarily used by large organizations. Vendors say very few private practices have bought it yet. “The technology works, but it is still in the early-adopter phase,” Dr. Yu said.
For one thing, the software can be expensive. Very few vendors reveal their prices, but Dr. Yu did so. She said Olive normally costs about $50,000 a year for even a small organization. She insisted, however, that the savings from avoiding just one denial each month for a hip surgery would justify the expense.
On the other hand, some automation software is free, such as the Surescripts product for prior authorization of prescriptions. But it is unclear whether Surescripts does as much as Olive. Vendors’ descriptions of their products tend to be vague.
Also, Surescripts and Olive have entirely separate functions. Dr. Yu said Olive is limited to procedures, so it benefits specialties like oncology, neurosurgery, colorectal surgery, vascular surgery, and cardiology. Olive does not cover prescriptions, because they operate on a different technology.
Dr. Yu said another hurdle for adopting the software is the kind of EHR systems that doctors use. At this point, only a few EHR systems – such as Epic, Cerner, and Athena – are compatible with Olive. Large organizations tend to use Epic and Cerner, while many practices often use Athena or a variety of other systems, she said.
Despite stunted demand, there is no shortage of companies offering automation software for medical (that is, non-prescription) prior authorization. One compilation lists 25 such vendors, including companies like Myndshft, Rhyme, Infinitus, Infinx, and Waystar. As with any start-up technology, companies occasionally buy each other out.
In addition to issues like cost, specialty, and EHR compatibility, another hurdle is that few doctors even know the technology exists. Vendors say marketing focuses on larger provider organizations, not smaller practices.
Even many tech-savvy doctors, like Adam Bruggeman, MD, an orthopedist and CEO of Texas Spine Care Center in San Antonio, say they know little about the technology. “There is definitely a need to automate prior authorization,” he said. “But I don’t know of any colleagues who use it.” He has only just begun to explore vendors, he said.
Many medical practice consultants also have not yet explored the technology. “Automation makes a lot of sense, because there are a lot of repetitive tasks in prior authorization,” said Jill Arena, CEO of Portland, Ore.–based Health e Practices. “But I haven’t looked into it yet, and none of my clients has even asked about it.”
“I could see how it could be an easier sell for large organizations,” she added. “They have an IT person and a CFO who can explore the issue. Smaller practices usually don’t have that kind of expertise.”
Where does automation go from here?
Until now, clinicians who want to fully automate prior authorizations would have to buy two products – one for medical procedures and one for prescriptions. This has to do with incompatible electronic transmission standards, which are used to digitize information, said Susan Lawson-Dawson, content marketing strategist for the vendor Myndshft Health.
Myndshft has long been selling automation software for medical prior authorizations, but now it is introducing a product for prescriptions, Ms. Lawson-Dawson said. She said Myndshft will then be the only vendor to automate both kinds of prior authorizations.
Ms. Lawson-Dawson said Myndshft has 685 customers to date and is looking for more business. Recently the company entered the Google Cloud Marketplace. Google Cloud customers can now direct their committed spend with Google to purchasing Myndshft, meaning they could get it at a discount.
Software like Olive and Myndshft can operate independently of payers, but a vendor called Rhyme depends on payers for its software to function, said Rhyme CEO Joe Anstine. He said more than 300 payers have agreed to install the Rhyme system, and Rhyme has signed up a number of large health systems to use the product. Initially, he said, clinicians paid for the service, but now Rhyme is beginning to find payers to foot the costs and to let clinicians use it for free, which would open Rhyme up to smaller practices.
EHR companies themselves are beginning to offer automation, too. Epic, for example, has created a tool for prior authorization as part of its Epic Payer Platform. Like Rhyme, it requires payer cooperation, because information goes back and forth between clinician and payer in what is called bi-directional exchange.
The Epic product is still in its pilot phase. Epic reported that several large health systems were using its product in conjunction with a specific payer – for instance, Mayo Clinic with Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota and Ochsner Health with Humana. According to Epic, the arrangement reduced Mayo’s denials due to additional documentation requests by 63% for professional billing.
Automating with just one payer still means the clinician has to deal with manual processes at other payers, but a large clinician could have sufficient volume with that one payer to make the arrangement useful.
Will payers automate prior authorization?
Ultimately, payers may take the automation business away from vendors, offering a free product to all clinicians. But don’t hold your breath. Payers first have to rebuild their electronic systems to accommodate an electronic connection with providers. Even then, some payers might hold back from automating, forcing practices to continue manually processing some prior authorizations.
Efforts are underway, however, to mandate payers to support prior authorization automation. For this to happen, payers would have to revamp their data so that it could be easily read by practices’ EHRs. This would mean adopting a specific interoperability standard called Health Level 7 Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR).
Toward this goal, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services proposes to require payers to adopt FHIR by January 2026. (CMS still has to finalize the rule.) Experts say the two-year ramp-up time is needed because it takes extensive work for payers to translate their data into FHIR.
The only payer so far to switch to FHIR for prior authorization is Regence in Washington state. In a pilot project, it has automated prior authorization with just one provider, MultiCare Connected Care, an accountable care organization (ACO), also in Washington state.
Anna Taylor, associate vice president of population health and value-based care at MultiCare, explained how the arrangement works. “Two separate entities are sharing one operational process,” she told this news organization. “That means they can have a digital conversation back and forth, so it is much easier to resolve prior authorization issues.”
Unlike many vendor products, the Regence service is free. And while the vendors market only to large organizations, most doctors in the MultiCare arrangement are in independent practices. Ms. Taylor said these doctors have been “enthusiastic” about the arrangement.
The results of the pilot are impressive. Ms. Taylor said automation has resulted in a 233% productivity gain for MultiCare clinicians, and 89% of submissions to Regence get an immediate response.
There is a potential downside, however, to working directly with payers. A direct connection to clinicians allows payers to access the doctor’s clinical notes, which could make many doctors uneasy. But Ms. Taylor said Regence only has access to the “discrete data fields” on MultiCare’s EHR dashboard, not to the notes themselves.
The ultimate goal of the Regence-Multicare project is to include more payers and clinicians. Ms. Taylor said two of the 27 other payers that MultiCare works with are “highly interested,” but it would take a lot of work for them to get connected with practices and other clinicians.
Ultimately, payers could offer automation and third-party vendors might then fade away. However, physicians may resist working directly with payers if the arrangement requires full access to their medical records.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New England Baptist Hospital has been grappling with a serious problem facing health care today: insurers demanding prior authorizations for services ordered by physicians. Meeting payers’ requirements eats up time, delays treatment, and can be a costly drain on doctors’ practices.
To deal with this problem, the Boston orthopedic hospital has opted to automate submission of prior authorization requests on behalf of more than 100 mostly orthopedic surgeons on staff.
After 5 years using this system, “we can say that automation definitely works,” said Lidiya Hadzhieva, director of patient access at the hospital. The software has reduced write-offs by 30% and staff costs by 25%. Prior authorization gets approved 3 days after scheduling, compared with 11 days previously, she said.
“This software not only saves staff time, but it can also more accurately predict when prior authorization is needed,” she added.
For practices deluged with required prior authorizations by insurers, automation is emerging as a way for practices to make the process less time-consuming and save money. However, the software can be costly and may not be adoptable to many practices, and many physicians are not even aware it exists.
So far, the software is mainly used at large organizations like hospital systems. But as word gets out and the software becomes easier to use, private practices and other smaller entities may join the automation trend.
There is definitely a need to automate prior authorization. The American Medical Association reports that physicians spend 16 hours per week on prior authorizations. In a recent AMA survey, more than 60% of physicians indicated that it’s difficult to know when prior authorization is needed. And 93% of physicians reported care delays while waiting for authorization, the AMA said.
Experts estimate that 80% of prior authorization work could be automated, but most practices still use the phone or fax, even as numbers of prior authorizations continue to increase.
How it works
Automation software connects directly to the practice’s electronic health record (EHR). “When the doctor places an order in the EHR, the process starts automatically,” Ms. Hadzhieva said. “The doctor may not even notice it.”
In addition to using an EHR connection, many software products can communicate with the payer through its portal or by fax or phone, while still automating other parts of the process.
The software’s first step is to decide whether prior authorization is needed. This requires having an updated list of the rules that each payer uses for prior authorization. Manually keeping track of payer rules is very time-consuming, but automation uses bots to visit each payer site to look for rules changes. One vendor, Infinitus, uses a voice-based bot called Eva that calls up each payer and speaks with a representative.
“Automatically updating payer rules is not a new technology,” said YiDing Yu, MD, chief product officer at Olive, the automation vendor for New England Baptist. “What is new in the last 5 years is extracting the information needed for the prior authorization out of the clinical notes.”
This is challenging because each doctor has different ways to describe each step of clinical work. To identify this shorthand, Dr. Yu said Olive uses natural language processing, which is a form of artificial intelligence that learns how each doctor describes things.
Dr. Yu asserts that Olive is actually better than a practice’s staff at digging out clinical information. She said staff without much clinical training may miss terms that the software can catch, and they don’t have the time to go back many months into the record to find valuable information. But automation can do that.
In some instances, however, the software may not be able to find the information, in which case it alerts staff through a prompt in the EHR and the information is retrieved manually, Dr. Yu said.
Next, the Olive software puts the information it found into the request form and sends it to the payer. After submission, the software constantly checks on the status of each request, again visiting payer sites with a bot.
At New England Baptist, the software is used mainly by physicians in fairly small private practices who are on staff. They are using the software on the hospital’s dime, but it only works inside the hospital, Ms. Hadzhieva said. For their work outside of the hospital, they would have to purchase the Olive software on their own, she said.
Automation hasn’t spread to practices yet
Despite the promising outcomes for products like Olive, automation software is still primarily used by large organizations. Vendors say very few private practices have bought it yet. “The technology works, but it is still in the early-adopter phase,” Dr. Yu said.
For one thing, the software can be expensive. Very few vendors reveal their prices, but Dr. Yu did so. She said Olive normally costs about $50,000 a year for even a small organization. She insisted, however, that the savings from avoiding just one denial each month for a hip surgery would justify the expense.
On the other hand, some automation software is free, such as the Surescripts product for prior authorization of prescriptions. But it is unclear whether Surescripts does as much as Olive. Vendors’ descriptions of their products tend to be vague.
Also, Surescripts and Olive have entirely separate functions. Dr. Yu said Olive is limited to procedures, so it benefits specialties like oncology, neurosurgery, colorectal surgery, vascular surgery, and cardiology. Olive does not cover prescriptions, because they operate on a different technology.
Dr. Yu said another hurdle for adopting the software is the kind of EHR systems that doctors use. At this point, only a few EHR systems – such as Epic, Cerner, and Athena – are compatible with Olive. Large organizations tend to use Epic and Cerner, while many practices often use Athena or a variety of other systems, she said.
Despite stunted demand, there is no shortage of companies offering automation software for medical (that is, non-prescription) prior authorization. One compilation lists 25 such vendors, including companies like Myndshft, Rhyme, Infinitus, Infinx, and Waystar. As with any start-up technology, companies occasionally buy each other out.
In addition to issues like cost, specialty, and EHR compatibility, another hurdle is that few doctors even know the technology exists. Vendors say marketing focuses on larger provider organizations, not smaller practices.
Even many tech-savvy doctors, like Adam Bruggeman, MD, an orthopedist and CEO of Texas Spine Care Center in San Antonio, say they know little about the technology. “There is definitely a need to automate prior authorization,” he said. “But I don’t know of any colleagues who use it.” He has only just begun to explore vendors, he said.
Many medical practice consultants also have not yet explored the technology. “Automation makes a lot of sense, because there are a lot of repetitive tasks in prior authorization,” said Jill Arena, CEO of Portland, Ore.–based Health e Practices. “But I haven’t looked into it yet, and none of my clients has even asked about it.”
“I could see how it could be an easier sell for large organizations,” she added. “They have an IT person and a CFO who can explore the issue. Smaller practices usually don’t have that kind of expertise.”
Where does automation go from here?
Until now, clinicians who want to fully automate prior authorizations would have to buy two products – one for medical procedures and one for prescriptions. This has to do with incompatible electronic transmission standards, which are used to digitize information, said Susan Lawson-Dawson, content marketing strategist for the vendor Myndshft Health.
Myndshft has long been selling automation software for medical prior authorizations, but now it is introducing a product for prescriptions, Ms. Lawson-Dawson said. She said Myndshft will then be the only vendor to automate both kinds of prior authorizations.
Ms. Lawson-Dawson said Myndshft has 685 customers to date and is looking for more business. Recently the company entered the Google Cloud Marketplace. Google Cloud customers can now direct their committed spend with Google to purchasing Myndshft, meaning they could get it at a discount.
Software like Olive and Myndshft can operate independently of payers, but a vendor called Rhyme depends on payers for its software to function, said Rhyme CEO Joe Anstine. He said more than 300 payers have agreed to install the Rhyme system, and Rhyme has signed up a number of large health systems to use the product. Initially, he said, clinicians paid for the service, but now Rhyme is beginning to find payers to foot the costs and to let clinicians use it for free, which would open Rhyme up to smaller practices.
EHR companies themselves are beginning to offer automation, too. Epic, for example, has created a tool for prior authorization as part of its Epic Payer Platform. Like Rhyme, it requires payer cooperation, because information goes back and forth between clinician and payer in what is called bi-directional exchange.
The Epic product is still in its pilot phase. Epic reported that several large health systems were using its product in conjunction with a specific payer – for instance, Mayo Clinic with Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota and Ochsner Health with Humana. According to Epic, the arrangement reduced Mayo’s denials due to additional documentation requests by 63% for professional billing.
Automating with just one payer still means the clinician has to deal with manual processes at other payers, but a large clinician could have sufficient volume with that one payer to make the arrangement useful.
Will payers automate prior authorization?
Ultimately, payers may take the automation business away from vendors, offering a free product to all clinicians. But don’t hold your breath. Payers first have to rebuild their electronic systems to accommodate an electronic connection with providers. Even then, some payers might hold back from automating, forcing practices to continue manually processing some prior authorizations.
Efforts are underway, however, to mandate payers to support prior authorization automation. For this to happen, payers would have to revamp their data so that it could be easily read by practices’ EHRs. This would mean adopting a specific interoperability standard called Health Level 7 Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR).
Toward this goal, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services proposes to require payers to adopt FHIR by January 2026. (CMS still has to finalize the rule.) Experts say the two-year ramp-up time is needed because it takes extensive work for payers to translate their data into FHIR.
The only payer so far to switch to FHIR for prior authorization is Regence in Washington state. In a pilot project, it has automated prior authorization with just one provider, MultiCare Connected Care, an accountable care organization (ACO), also in Washington state.
Anna Taylor, associate vice president of population health and value-based care at MultiCare, explained how the arrangement works. “Two separate entities are sharing one operational process,” she told this news organization. “That means they can have a digital conversation back and forth, so it is much easier to resolve prior authorization issues.”
Unlike many vendor products, the Regence service is free. And while the vendors market only to large organizations, most doctors in the MultiCare arrangement are in independent practices. Ms. Taylor said these doctors have been “enthusiastic” about the arrangement.
The results of the pilot are impressive. Ms. Taylor said automation has resulted in a 233% productivity gain for MultiCare clinicians, and 89% of submissions to Regence get an immediate response.
There is a potential downside, however, to working directly with payers. A direct connection to clinicians allows payers to access the doctor’s clinical notes, which could make many doctors uneasy. But Ms. Taylor said Regence only has access to the “discrete data fields” on MultiCare’s EHR dashboard, not to the notes themselves.
The ultimate goal of the Regence-Multicare project is to include more payers and clinicians. Ms. Taylor said two of the 27 other payers that MultiCare works with are “highly interested,” but it would take a lot of work for them to get connected with practices and other clinicians.
Ultimately, payers could offer automation and third-party vendors might then fade away. However, physicians may resist working directly with payers if the arrangement requires full access to their medical records.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Working with industry in private practice gastroenterology
In this video, Dr. Nadeem Baig of Allied Digestive Health in West Long Branck, N.J., discusses why he chose private practice gastroenterology and how his organization works with industry to support its mission of providing the best care for patients.
He has no financial conflicts relative to the topics in this video.

In this video, Dr. Nadeem Baig of Allied Digestive Health in West Long Branck, N.J., discusses why he chose private practice gastroenterology and how his organization works with industry to support its mission of providing the best care for patients.
He has no financial conflicts relative to the topics in this video.

In this video, Dr. Nadeem Baig of Allied Digestive Health in West Long Branck, N.J., discusses why he chose private practice gastroenterology and how his organization works with industry to support its mission of providing the best care for patients.
He has no financial conflicts relative to the topics in this video.

CHEST philanthropy: Moving into the future
In an ideal world, change would be progressive, the direction would be clear, and adoption would be easy. We learned in these past few years that sometimes change cannot wait. The vulnerabilities of the health care system were laid bare by the pandemic, including vast disparities in treatment and the urgent need to grow our profession.
In the light of these truths, CHEST looked within and asked a difficult question: Are we doing everything we can? This question probably sounds very familiar – one you ask every day, one you know the importance of asking. It was time we asked it of ourselves.
Milestones are a good time to reevaluate
Philanthropy is not new to CHEST. We celebrated 25 years of the CHEST Foundation in Nashville during CHEST 2022. Stories about community and clinical research grants were circulated in website blogs, emails, and newsletters and on social media for years. Our committee member volunteers worked hard developing accurate and credible patient education content for the CHEST Foundation website. Because of our faithful donors, communities around the world had access to better medical care and healthier environments.
This is amazing work, but it was time to ask:
- What can CHEST provide that others cannot?
- Where are the gaps we can fill?
- What is our community passionate about changing?
Working collectively, CHEST and CHEST Foundation leadership, along with staff, rigorously reviewed the success of our past fundraising efforts, areas of commitment our donors had specified, and the direction of interest our membership was leading us toward – like social accountability, growth and diversification of our profession, grassroots community impact, and partnerships to expand our reach. The process took nearly a year to complete – but, in the realm of big changes, that’s equal to the time needed for one good, deep breath.
Focusing on significant change means narrowing our scope
Meeting these goals would mean changing how we worked and letting go of areas better served elsewhere. CHEST needed to:
1. Align philanthropy with our mission to elevate the value placed on giving, making it a core priority and responsibility of CHEST as an organization.
2. Consolidate philanthropy under CHEST to reduce administrative costs and create efficiencies, allowing more funds to go directly to our philanthropic efforts.
3. Establish clear and transparent areas of giving that resonate with our members as a way to grow our impact and make real change.
With the full support of the CHEST Board of Regents, the CHEST Foundation Board of Advisors – under the guidance of Advisory Chair, Robert De Marco, MD, FCCP, and CHEST Foundation President, Ian Nathanson, MD, FCCP – approved a merger of the CHEST Foundation with CHEST.
In order to increase our impact and create greater awareness of CHEST philanthropic efforts, the Board of Advisors got to work defining a giving strategy that would meet the philanthropic goals and priorities of the CHEST membership. Four areas were defined and are referred to as our philanthropic pillars: clinical research, community impact, support of the profession, and dedication to education.
These pillars were approved by the Board of Regents at their spring leadership meeting.
Giving goals without support are just dreams
This transition puts the responsibility for funding the giving pillars in the hands of CHEST. The first step is ensuring the members see the impact of their donations.
“When you see your donation in action, you never doubt that you made a good decision,” said CHEST CEO, Robert A. Musacchio, PhD. “If we can show that to every member, the next 25 years of CHEST philanthropy are limitless.”
Helping connect donors to that experience is Meggie Cramer, the new Director of Philanthropy and Advancement , who has experience working directly with health care systems like Rush University Medical Center in Chicago and Hospital Sister Health System in Green Bay, Wisconsin.
“When you are giving to programs you are passionate about, you feel good about being a part of making a difference,” explained Cramer. “That’s my goal – to help our members find areas they care about and know their gift is part of creating real change.”
For frequently asked questions about the transition, please visit our website.
In an ideal world, change would be progressive, the direction would be clear, and adoption would be easy. We learned in these past few years that sometimes change cannot wait. The vulnerabilities of the health care system were laid bare by the pandemic, including vast disparities in treatment and the urgent need to grow our profession.
In the light of these truths, CHEST looked within and asked a difficult question: Are we doing everything we can? This question probably sounds very familiar – one you ask every day, one you know the importance of asking. It was time we asked it of ourselves.
Milestones are a good time to reevaluate
Philanthropy is not new to CHEST. We celebrated 25 years of the CHEST Foundation in Nashville during CHEST 2022. Stories about community and clinical research grants were circulated in website blogs, emails, and newsletters and on social media for years. Our committee member volunteers worked hard developing accurate and credible patient education content for the CHEST Foundation website. Because of our faithful donors, communities around the world had access to better medical care and healthier environments.
This is amazing work, but it was time to ask:
- What can CHEST provide that others cannot?
- Where are the gaps we can fill?
- What is our community passionate about changing?
Working collectively, CHEST and CHEST Foundation leadership, along with staff, rigorously reviewed the success of our past fundraising efforts, areas of commitment our donors had specified, and the direction of interest our membership was leading us toward – like social accountability, growth and diversification of our profession, grassroots community impact, and partnerships to expand our reach. The process took nearly a year to complete – but, in the realm of big changes, that’s equal to the time needed for one good, deep breath.
Focusing on significant change means narrowing our scope
Meeting these goals would mean changing how we worked and letting go of areas better served elsewhere. CHEST needed to:
1. Align philanthropy with our mission to elevate the value placed on giving, making it a core priority and responsibility of CHEST as an organization.
2. Consolidate philanthropy under CHEST to reduce administrative costs and create efficiencies, allowing more funds to go directly to our philanthropic efforts.
3. Establish clear and transparent areas of giving that resonate with our members as a way to grow our impact and make real change.
With the full support of the CHEST Board of Regents, the CHEST Foundation Board of Advisors – under the guidance of Advisory Chair, Robert De Marco, MD, FCCP, and CHEST Foundation President, Ian Nathanson, MD, FCCP – approved a merger of the CHEST Foundation with CHEST.
In order to increase our impact and create greater awareness of CHEST philanthropic efforts, the Board of Advisors got to work defining a giving strategy that would meet the philanthropic goals and priorities of the CHEST membership. Four areas were defined and are referred to as our philanthropic pillars: clinical research, community impact, support of the profession, and dedication to education.
These pillars were approved by the Board of Regents at their spring leadership meeting.
Giving goals without support are just dreams
This transition puts the responsibility for funding the giving pillars in the hands of CHEST. The first step is ensuring the members see the impact of their donations.
“When you see your donation in action, you never doubt that you made a good decision,” said CHEST CEO, Robert A. Musacchio, PhD. “If we can show that to every member, the next 25 years of CHEST philanthropy are limitless.”
Helping connect donors to that experience is Meggie Cramer, the new Director of Philanthropy and Advancement , who has experience working directly with health care systems like Rush University Medical Center in Chicago and Hospital Sister Health System in Green Bay, Wisconsin.
“When you are giving to programs you are passionate about, you feel good about being a part of making a difference,” explained Cramer. “That’s my goal – to help our members find areas they care about and know their gift is part of creating real change.”
For frequently asked questions about the transition, please visit our website.
In an ideal world, change would be progressive, the direction would be clear, and adoption would be easy. We learned in these past few years that sometimes change cannot wait. The vulnerabilities of the health care system were laid bare by the pandemic, including vast disparities in treatment and the urgent need to grow our profession.
In the light of these truths, CHEST looked within and asked a difficult question: Are we doing everything we can? This question probably sounds very familiar – one you ask every day, one you know the importance of asking. It was time we asked it of ourselves.
Milestones are a good time to reevaluate
Philanthropy is not new to CHEST. We celebrated 25 years of the CHEST Foundation in Nashville during CHEST 2022. Stories about community and clinical research grants were circulated in website blogs, emails, and newsletters and on social media for years. Our committee member volunteers worked hard developing accurate and credible patient education content for the CHEST Foundation website. Because of our faithful donors, communities around the world had access to better medical care and healthier environments.
This is amazing work, but it was time to ask:
- What can CHEST provide that others cannot?
- Where are the gaps we can fill?
- What is our community passionate about changing?
Working collectively, CHEST and CHEST Foundation leadership, along with staff, rigorously reviewed the success of our past fundraising efforts, areas of commitment our donors had specified, and the direction of interest our membership was leading us toward – like social accountability, growth and diversification of our profession, grassroots community impact, and partnerships to expand our reach. The process took nearly a year to complete – but, in the realm of big changes, that’s equal to the time needed for one good, deep breath.
Focusing on significant change means narrowing our scope
Meeting these goals would mean changing how we worked and letting go of areas better served elsewhere. CHEST needed to:
1. Align philanthropy with our mission to elevate the value placed on giving, making it a core priority and responsibility of CHEST as an organization.
2. Consolidate philanthropy under CHEST to reduce administrative costs and create efficiencies, allowing more funds to go directly to our philanthropic efforts.
3. Establish clear and transparent areas of giving that resonate with our members as a way to grow our impact and make real change.
With the full support of the CHEST Board of Regents, the CHEST Foundation Board of Advisors – under the guidance of Advisory Chair, Robert De Marco, MD, FCCP, and CHEST Foundation President, Ian Nathanson, MD, FCCP – approved a merger of the CHEST Foundation with CHEST.
In order to increase our impact and create greater awareness of CHEST philanthropic efforts, the Board of Advisors got to work defining a giving strategy that would meet the philanthropic goals and priorities of the CHEST membership. Four areas were defined and are referred to as our philanthropic pillars: clinical research, community impact, support of the profession, and dedication to education.
These pillars were approved by the Board of Regents at their spring leadership meeting.
Giving goals without support are just dreams
This transition puts the responsibility for funding the giving pillars in the hands of CHEST. The first step is ensuring the members see the impact of their donations.
“When you see your donation in action, you never doubt that you made a good decision,” said CHEST CEO, Robert A. Musacchio, PhD. “If we can show that to every member, the next 25 years of CHEST philanthropy are limitless.”
Helping connect donors to that experience is Meggie Cramer, the new Director of Philanthropy and Advancement , who has experience working directly with health care systems like Rush University Medical Center in Chicago and Hospital Sister Health System in Green Bay, Wisconsin.
“When you are giving to programs you are passionate about, you feel good about being a part of making a difference,” explained Cramer. “That’s my goal – to help our members find areas they care about and know their gift is part of creating real change.”
For frequently asked questions about the transition, please visit our website.
CT simulation not needed in palliative radiotherapy planning
, according to a results from a randomized trial presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Radiation Oncology.
The aim of this same-day CT scan, called a CT simulation scan, is to optimize radiation targeting by mimicking the conditions under which radiation is delivered using the latest information on the size and location of lesions.
But investigators reported that skipping the CT simulation scan saves patients hours in the clinic, allows patients to experience pain relief faster, and saves radiation oncologists time without compromising dosimetric coverage of cancerous lesions.
“This is huge in a symptomatic patient population,” said Melissa O’Neil, an advanced practice radiation therapist at the London, Ont., Health Sciences Centre and the lead investigator on the trial, dubbed DART (Diagnostic CT-Enabled Radiation Therapy).
“Diagnostic CT-based radiation planning substantially reduces time in the [treatment] center without a detriment in plan deliverability or quality,” Ms. O’Neil said.
In addition, patients are exposed to less radiation, and staff doesn’t have to spend as much time tending to symptomatic patients before treatment. Omitting this scan “should be considered for patients with a recent diagnostic CT scan who are undergoing simple palliative radiation,” Ms. O’Neil said.
CT simulation scans are standard of care in cases involving palliative radiation, but they create bottlenecks in the workflow. When a CT simulation is performed on the day of treatment, patients must wait hours as the results are translated into a treatment plan.
In the DART analysis, 33 patients with 42 treatment sites were randomly assigned to CT simulation planning or diagnostic CT planning.
Patients received up to 30 Gy in up to 10 fractions for bone or soft tissue metastases or primary tumor targets in the thorax, abdomen, pelvis, or proximal limbs. Single-fraction treatments were most common.
Three-quarters of the patients were men (median age, 72 years). Lung cancer was the most common type of primary tumor, followed by prostate and breast cancer.
The eight participants for whom the CT simulation approach was used waited 3-4 hours for treatment planning and overall spent a median of 4.8 hours in the cancer center on their day of treatment.
The 25 patients for whom diagnostic CT planning was used spent a median of 0.4 hours, or about 24 minutes, in the center on their day of treatment because radiation plans were completed before they arrived. The median time between their diagnostic CTs and radiation treatment was 13 days (range, 8-22 days).
Ms. O’Neil and her team found that if the original diagnostic CT was performed within 28 days, lesion anatomy would not have changed enough to warrant a new scan.
On the day of treatment, the study team used surface-guided radiation therapy techniques to ensure patients in the diagnostic CT planning group were positioned within 3 mm of where they were during their diagnostic scans, an essential step to ensure that radiation is delivered to the correct location. Ms. O’Neil noted that other investigators have used anatomic landmarks, a simpler approach, to achieve these results.
Overall, radiation oncologists rated radiation dose distribution as “acceptable” in about 80% of cases in both arms of DART and “acceptable with minor deviation” in the remaining 20% of cases.
Every radiation oncologist and medical physicists in the trial gave the workflow with diagnostic CT planning a 5 out of 5 rating for acceptability, and 90% of patients in this group rated the amount of time they spent for treatment as “acceptable.”
In contrast, only half of patients in the simulation arm said the amount of time spent was acceptable.
These findings align with several previous studies that support the diagnostic approach.
Jacob Scott, MD, a radiation oncologist at the Cleveland Clinic, said, “The comparable results using a recent diagnostic CT in place of a CT simulation for palliative radiation is an exciting step forward in radiation oncology. We may soon be in a world where we no longer need simulations.”
Dr. Scott also noted that combining diagnostic scans with cone beam or surface-guided positioning in lieu of CT simulations could further save “the health system and patients time and money.”
No external funding for the study was reported. The investigators, Ms. O’Neil, and Dr. Scott have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. One investigator reported receiving honoraria from Knight Therapeutics, AbbVie, Tersera, and Eisai and owns stock in Myovant.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a results from a randomized trial presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Radiation Oncology.
The aim of this same-day CT scan, called a CT simulation scan, is to optimize radiation targeting by mimicking the conditions under which radiation is delivered using the latest information on the size and location of lesions.
But investigators reported that skipping the CT simulation scan saves patients hours in the clinic, allows patients to experience pain relief faster, and saves radiation oncologists time without compromising dosimetric coverage of cancerous lesions.
“This is huge in a symptomatic patient population,” said Melissa O’Neil, an advanced practice radiation therapist at the London, Ont., Health Sciences Centre and the lead investigator on the trial, dubbed DART (Diagnostic CT-Enabled Radiation Therapy).
“Diagnostic CT-based radiation planning substantially reduces time in the [treatment] center without a detriment in plan deliverability or quality,” Ms. O’Neil said.
In addition, patients are exposed to less radiation, and staff doesn’t have to spend as much time tending to symptomatic patients before treatment. Omitting this scan “should be considered for patients with a recent diagnostic CT scan who are undergoing simple palliative radiation,” Ms. O’Neil said.
CT simulation scans are standard of care in cases involving palliative radiation, but they create bottlenecks in the workflow. When a CT simulation is performed on the day of treatment, patients must wait hours as the results are translated into a treatment plan.
In the DART analysis, 33 patients with 42 treatment sites were randomly assigned to CT simulation planning or diagnostic CT planning.
Patients received up to 30 Gy in up to 10 fractions for bone or soft tissue metastases or primary tumor targets in the thorax, abdomen, pelvis, or proximal limbs. Single-fraction treatments were most common.
Three-quarters of the patients were men (median age, 72 years). Lung cancer was the most common type of primary tumor, followed by prostate and breast cancer.
The eight participants for whom the CT simulation approach was used waited 3-4 hours for treatment planning and overall spent a median of 4.8 hours in the cancer center on their day of treatment.
The 25 patients for whom diagnostic CT planning was used spent a median of 0.4 hours, or about 24 minutes, in the center on their day of treatment because radiation plans were completed before they arrived. The median time between their diagnostic CTs and radiation treatment was 13 days (range, 8-22 days).
Ms. O’Neil and her team found that if the original diagnostic CT was performed within 28 days, lesion anatomy would not have changed enough to warrant a new scan.
On the day of treatment, the study team used surface-guided radiation therapy techniques to ensure patients in the diagnostic CT planning group were positioned within 3 mm of where they were during their diagnostic scans, an essential step to ensure that radiation is delivered to the correct location. Ms. O’Neil noted that other investigators have used anatomic landmarks, a simpler approach, to achieve these results.
Overall, radiation oncologists rated radiation dose distribution as “acceptable” in about 80% of cases in both arms of DART and “acceptable with minor deviation” in the remaining 20% of cases.
Every radiation oncologist and medical physicists in the trial gave the workflow with diagnostic CT planning a 5 out of 5 rating for acceptability, and 90% of patients in this group rated the amount of time they spent for treatment as “acceptable.”
In contrast, only half of patients in the simulation arm said the amount of time spent was acceptable.
These findings align with several previous studies that support the diagnostic approach.
Jacob Scott, MD, a radiation oncologist at the Cleveland Clinic, said, “The comparable results using a recent diagnostic CT in place of a CT simulation for palliative radiation is an exciting step forward in radiation oncology. We may soon be in a world where we no longer need simulations.”
Dr. Scott also noted that combining diagnostic scans with cone beam or surface-guided positioning in lieu of CT simulations could further save “the health system and patients time and money.”
No external funding for the study was reported. The investigators, Ms. O’Neil, and Dr. Scott have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. One investigator reported receiving honoraria from Knight Therapeutics, AbbVie, Tersera, and Eisai and owns stock in Myovant.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a results from a randomized trial presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Radiation Oncology.
The aim of this same-day CT scan, called a CT simulation scan, is to optimize radiation targeting by mimicking the conditions under which radiation is delivered using the latest information on the size and location of lesions.
But investigators reported that skipping the CT simulation scan saves patients hours in the clinic, allows patients to experience pain relief faster, and saves radiation oncologists time without compromising dosimetric coverage of cancerous lesions.
“This is huge in a symptomatic patient population,” said Melissa O’Neil, an advanced practice radiation therapist at the London, Ont., Health Sciences Centre and the lead investigator on the trial, dubbed DART (Diagnostic CT-Enabled Radiation Therapy).
“Diagnostic CT-based radiation planning substantially reduces time in the [treatment] center without a detriment in plan deliverability or quality,” Ms. O’Neil said.
In addition, patients are exposed to less radiation, and staff doesn’t have to spend as much time tending to symptomatic patients before treatment. Omitting this scan “should be considered for patients with a recent diagnostic CT scan who are undergoing simple palliative radiation,” Ms. O’Neil said.
CT simulation scans are standard of care in cases involving palliative radiation, but they create bottlenecks in the workflow. When a CT simulation is performed on the day of treatment, patients must wait hours as the results are translated into a treatment plan.
In the DART analysis, 33 patients with 42 treatment sites were randomly assigned to CT simulation planning or diagnostic CT planning.
Patients received up to 30 Gy in up to 10 fractions for bone or soft tissue metastases or primary tumor targets in the thorax, abdomen, pelvis, or proximal limbs. Single-fraction treatments were most common.
Three-quarters of the patients were men (median age, 72 years). Lung cancer was the most common type of primary tumor, followed by prostate and breast cancer.
The eight participants for whom the CT simulation approach was used waited 3-4 hours for treatment planning and overall spent a median of 4.8 hours in the cancer center on their day of treatment.
The 25 patients for whom diagnostic CT planning was used spent a median of 0.4 hours, or about 24 minutes, in the center on their day of treatment because radiation plans were completed before they arrived. The median time between their diagnostic CTs and radiation treatment was 13 days (range, 8-22 days).
Ms. O’Neil and her team found that if the original diagnostic CT was performed within 28 days, lesion anatomy would not have changed enough to warrant a new scan.
On the day of treatment, the study team used surface-guided radiation therapy techniques to ensure patients in the diagnostic CT planning group were positioned within 3 mm of where they were during their diagnostic scans, an essential step to ensure that radiation is delivered to the correct location. Ms. O’Neil noted that other investigators have used anatomic landmarks, a simpler approach, to achieve these results.
Overall, radiation oncologists rated radiation dose distribution as “acceptable” in about 80% of cases in both arms of DART and “acceptable with minor deviation” in the remaining 20% of cases.
Every radiation oncologist and medical physicists in the trial gave the workflow with diagnostic CT planning a 5 out of 5 rating for acceptability, and 90% of patients in this group rated the amount of time they spent for treatment as “acceptable.”
In contrast, only half of patients in the simulation arm said the amount of time spent was acceptable.
These findings align with several previous studies that support the diagnostic approach.
Jacob Scott, MD, a radiation oncologist at the Cleveland Clinic, said, “The comparable results using a recent diagnostic CT in place of a CT simulation for palliative radiation is an exciting step forward in radiation oncology. We may soon be in a world where we no longer need simulations.”
Dr. Scott also noted that combining diagnostic scans with cone beam or surface-guided positioning in lieu of CT simulations could further save “the health system and patients time and money.”
No external funding for the study was reported. The investigators, Ms. O’Neil, and Dr. Scott have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. One investigator reported receiving honoraria from Knight Therapeutics, AbbVie, Tersera, and Eisai and owns stock in Myovant.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ASTRO 2023



