User login
Ultrasound improves specificity of psoriatic arthritis referrals
The use of ultrasound in screening for psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis could reduce the number of unnecessary referrals to rheumatologists, according to a research letter published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
Up to one-third of patients with psoriasis have underlying psoriatic arthritis (PsA), but half of all patients with psoriasis experience nonspecific musculoskeletal complaints.
“Different screening tools have been developed for the dermatology practice to distinguish patients with a higher likelihood of having PsA; however, the low specificities of these tools limit their use in clinical practice,” wrote Dilek Solmaz, MD, and colleagues at the University of Ottawa.
In this prospective study, 51 patients with psoriasis were screened for referral to a rheumatologist using the Early Arthritis for Psoriatic Patients and Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool questionnaires. They also underwent a limited ultrasound scanning of wrists, hands, feet, and the most painful joint, which was reviewed by experienced rheumatologists.
A dermatologist was asked to make a decision on referral based on the questionnaire data alone, then invited to revisit that decision after viewing the ultrasound results. When basing their decision on the questionnaires only, the dermatologist decided to refer 92% of patients to a rheumatologist. Of these patients, 40% were subsequently diagnosed with PsA, which represented a sensitivity of 95% but specificity of just 9%.
After reviewing the ultrasound data, the dermatologist revised their recommendations and only referred 43% of patients. Of these, 68% were later diagnosed with psoriatic arthritis. Among the patients who were not referred after the ultrasound review, five were diagnosed with PsA, but two had isolated axial involvement with no peripheral joint disease. Excluding these two cases, the sensitivity decreased to 88% but specificity increased to 77%.
“Screening tools in psoriasis that have high sensitivities usually have low specificities, which means a higher number of patients to be referred to rheumatology than needed,” the authors wrote. “Our study demonstrated that a musculoskeletal [ultrasound] based on a predefined protocol improves the referrals made to rheumatology.”
The authors did note that the ultrasounds were reviewed by experienced rheumatologists, so the results might not be generalizable to less-experienced sonographers without experience in musculoskeletal disorders.
The study was funded by AbbVie. One author declared receiving funding for a fellowship from UCB. Two authors declared honoraria and advisory consultancies with the pharmaceutical sector, including AbbVie.
SOURCE: Solmaz D et al. Br J Dermatol. 2019 Nov 28. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18515.
The use of ultrasound in screening for psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis could reduce the number of unnecessary referrals to rheumatologists, according to a research letter published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
Up to one-third of patients with psoriasis have underlying psoriatic arthritis (PsA), but half of all patients with psoriasis experience nonspecific musculoskeletal complaints.
“Different screening tools have been developed for the dermatology practice to distinguish patients with a higher likelihood of having PsA; however, the low specificities of these tools limit their use in clinical practice,” wrote Dilek Solmaz, MD, and colleagues at the University of Ottawa.
In this prospective study, 51 patients with psoriasis were screened for referral to a rheumatologist using the Early Arthritis for Psoriatic Patients and Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool questionnaires. They also underwent a limited ultrasound scanning of wrists, hands, feet, and the most painful joint, which was reviewed by experienced rheumatologists.
A dermatologist was asked to make a decision on referral based on the questionnaire data alone, then invited to revisit that decision after viewing the ultrasound results. When basing their decision on the questionnaires only, the dermatologist decided to refer 92% of patients to a rheumatologist. Of these patients, 40% were subsequently diagnosed with PsA, which represented a sensitivity of 95% but specificity of just 9%.
After reviewing the ultrasound data, the dermatologist revised their recommendations and only referred 43% of patients. Of these, 68% were later diagnosed with psoriatic arthritis. Among the patients who were not referred after the ultrasound review, five were diagnosed with PsA, but two had isolated axial involvement with no peripheral joint disease. Excluding these two cases, the sensitivity decreased to 88% but specificity increased to 77%.
“Screening tools in psoriasis that have high sensitivities usually have low specificities, which means a higher number of patients to be referred to rheumatology than needed,” the authors wrote. “Our study demonstrated that a musculoskeletal [ultrasound] based on a predefined protocol improves the referrals made to rheumatology.”
The authors did note that the ultrasounds were reviewed by experienced rheumatologists, so the results might not be generalizable to less-experienced sonographers without experience in musculoskeletal disorders.
The study was funded by AbbVie. One author declared receiving funding for a fellowship from UCB. Two authors declared honoraria and advisory consultancies with the pharmaceutical sector, including AbbVie.
SOURCE: Solmaz D et al. Br J Dermatol. 2019 Nov 28. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18515.
The use of ultrasound in screening for psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis could reduce the number of unnecessary referrals to rheumatologists, according to a research letter published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
Up to one-third of patients with psoriasis have underlying psoriatic arthritis (PsA), but half of all patients with psoriasis experience nonspecific musculoskeletal complaints.
“Different screening tools have been developed for the dermatology practice to distinguish patients with a higher likelihood of having PsA; however, the low specificities of these tools limit their use in clinical practice,” wrote Dilek Solmaz, MD, and colleagues at the University of Ottawa.
In this prospective study, 51 patients with psoriasis were screened for referral to a rheumatologist using the Early Arthritis for Psoriatic Patients and Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool questionnaires. They also underwent a limited ultrasound scanning of wrists, hands, feet, and the most painful joint, which was reviewed by experienced rheumatologists.
A dermatologist was asked to make a decision on referral based on the questionnaire data alone, then invited to revisit that decision after viewing the ultrasound results. When basing their decision on the questionnaires only, the dermatologist decided to refer 92% of patients to a rheumatologist. Of these patients, 40% were subsequently diagnosed with PsA, which represented a sensitivity of 95% but specificity of just 9%.
After reviewing the ultrasound data, the dermatologist revised their recommendations and only referred 43% of patients. Of these, 68% were later diagnosed with psoriatic arthritis. Among the patients who were not referred after the ultrasound review, five were diagnosed with PsA, but two had isolated axial involvement with no peripheral joint disease. Excluding these two cases, the sensitivity decreased to 88% but specificity increased to 77%.
“Screening tools in psoriasis that have high sensitivities usually have low specificities, which means a higher number of patients to be referred to rheumatology than needed,” the authors wrote. “Our study demonstrated that a musculoskeletal [ultrasound] based on a predefined protocol improves the referrals made to rheumatology.”
The authors did note that the ultrasounds were reviewed by experienced rheumatologists, so the results might not be generalizable to less-experienced sonographers without experience in musculoskeletal disorders.
The study was funded by AbbVie. One author declared receiving funding for a fellowship from UCB. Two authors declared honoraria and advisory consultancies with the pharmaceutical sector, including AbbVie.
SOURCE: Solmaz D et al. Br J Dermatol. 2019 Nov 28. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18515.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGY
Verrucous Psoriasis Treated With Methotrexate and Acitretin Combination Therapy
To the Editor:
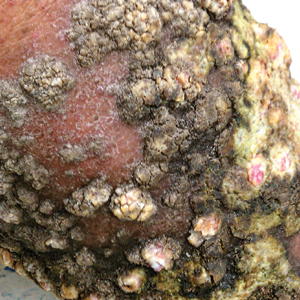
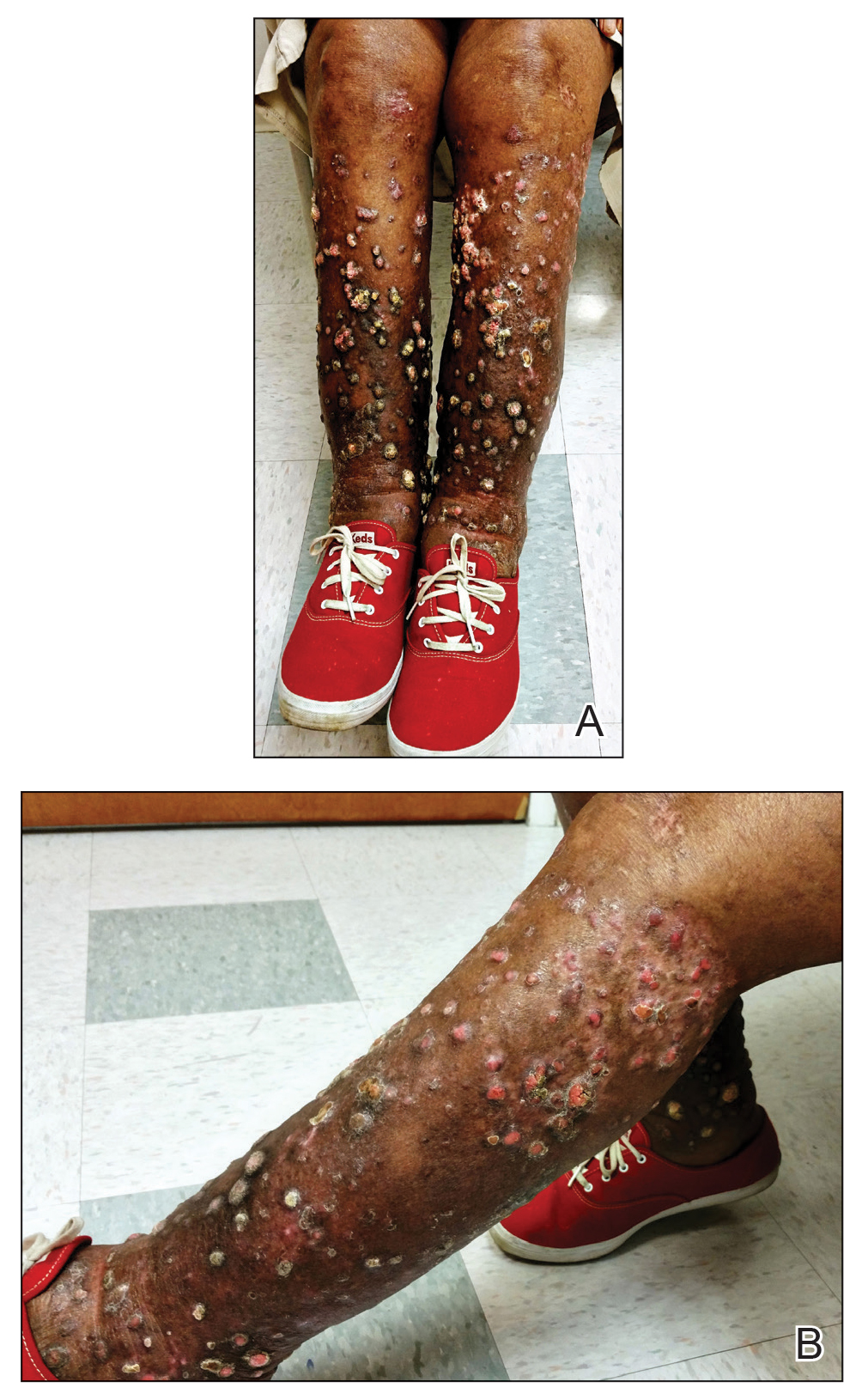
A 76-year-old woman with venous insufficiency presented with numerous thick, hyperkeratotic, confluent papules and plaques involving both legs and thighs as well as the lower back. She initially developed lesions on the distal legs, which progressed to involve the thighs and lower back, slowly enlarging over 7 years (Figure 1). The eruption was associated with pruritus and was profoundly malodorous. The patient had been unsuccessfully treated with triamcinolone ointment, bleach baths, and several courses of oral antibiotics. Her history was remarkable for marked venous insufficiency and mild anemia, with a hemoglobin level of 11.9 g/dL (reference range, 14.0–17.5 g/dL). She had no other abnormalities on a comprehensive blood test, basic metabolic panel, or liver function test.
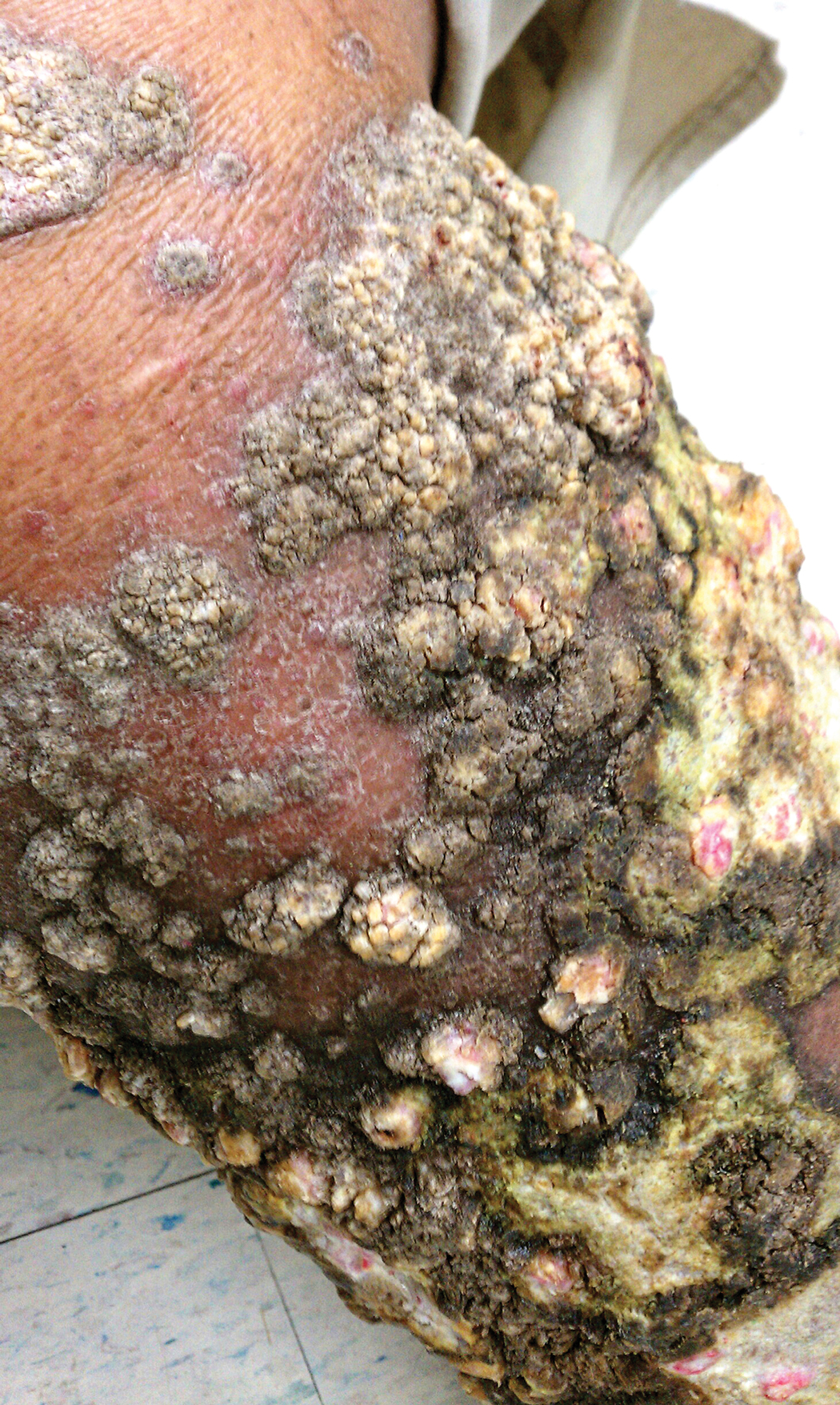
A punch biopsy specimen from the left lower back was obtained and demonstrated papillomatous psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with broad parakeratosis, few intracorneal neutrophils, hypogranulosis, and suprapapillary thinning (Figure 2). She was initially treated with oral methotrexate (20 mg weekly), resulting in partial improvement of plaques and complete resolution of pruritus and malodor. After 15 months of treatment with methotrexate, low-dose methotrexate (10 mg weekly) in combination with acitretin 25 mg daily was started, resulting in further improvement of hyperkeratosis (Figure 3). The patient also was given a compounded corticosteroid ointment containing liquor carbonis detergens, salicylic acid, and fluocinonide ointment, achieving minor additional benefit. Comprehensive metabolic panel, lipid panel, and liver function tests were obtained quarterly. Hemoglobin levels remained low, similar to baseline (11.3–12.5 g/dL), while all other values were within reference range. The patient tolerated treatment well, reporting mild dryness of lips on review of systems, which was attributed to acitretin and was treated with emollients.
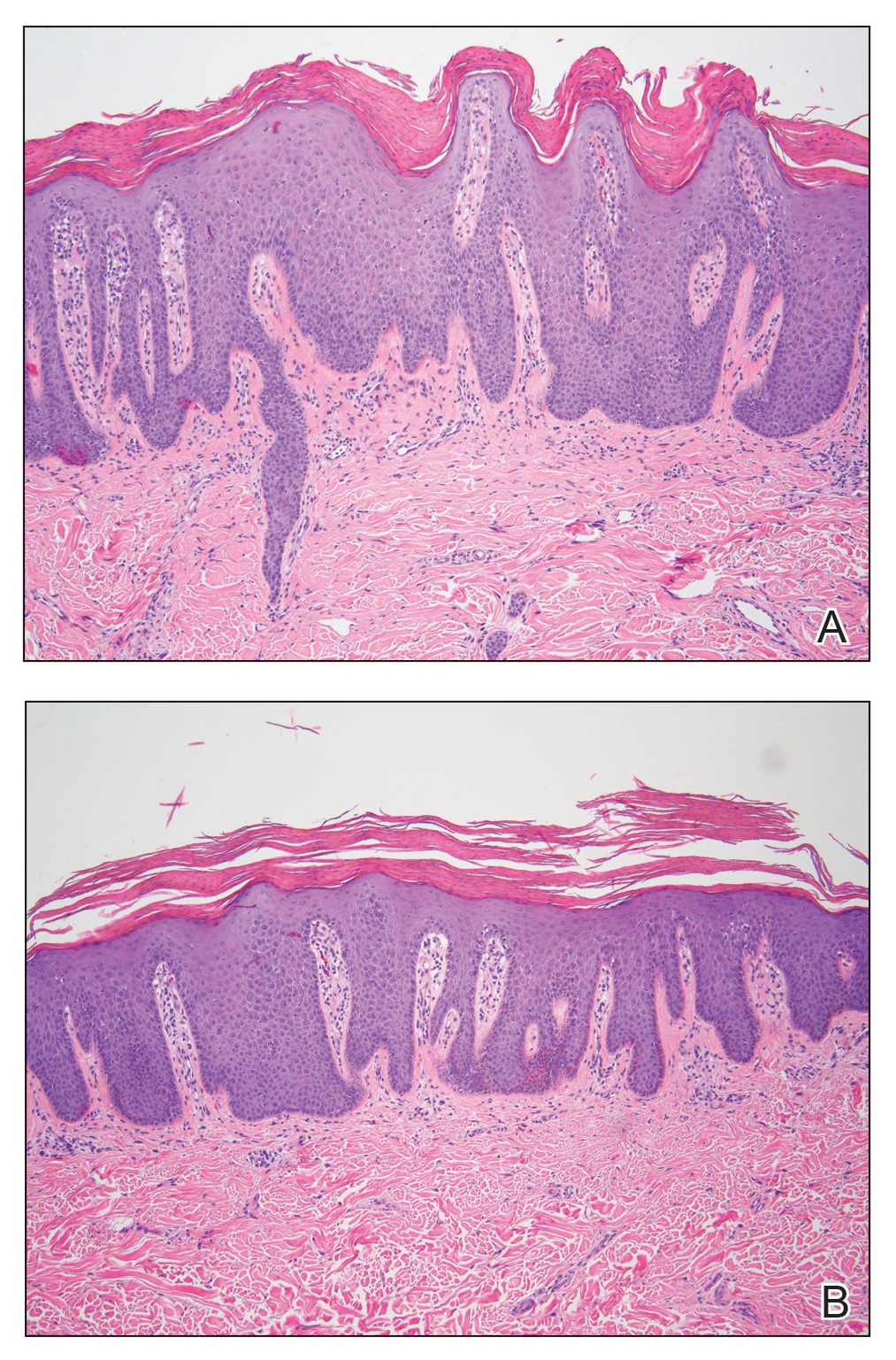
Verrucous psoriasis is an uncommon variant of psoriasis that presents as localized annular, erythrodermic, or drug-induced disease, as reported in a patient with preexisting psoriasis after interferon treatment of hepatitis C.1,2 It is characterized by symmetric hypertrophic verrucous plaques that may have an erythematous base and involve the legs, arms, trunk, and dorsal aspect of the hands3; malodor is frequent.1 Histopathologically, overlapping features of verruca vulgaris and psoriasis have been described. Specifically, lesions display typical psoriasiform changes, including parakeratosis, epidermal acanthosis with elongation of rete ridges, suprapapillary thinning, epidermal hypogranulosis, dilated or tortuous capillaries, and neutrophil collections in the stratum corneum (Munro microabscesses) or stratum spinosum (spongiform pustules of Kogoj).3 Additional findings of papillomatosis and epithelial buttressing are highly suggestive of verrucous psoriasis,3 though epithelial buttressing is not universally present.4-6 Similarly, although eosinophils and plasma cells have been described in some patients with verrucous psoriasis, this finding has not been consistently reported.4-6 Our biopsy specimen (Figure 2) lacks the epithelial buttressing but does exhibit subtle papillomatous hyperplasia consistent with the diagnosis of psoriasis.
The etiology of this entity is unknown. An association with diabetes mellitus, pulmonary disease, lymphatic circulation disorders, and immunosuppression has been proposed. Others have reported repeated trauma as contributing to the pathogenesis.1 For our patient, trauma secondary to scratching, long-standing venous insufficiency, and neglect likely contributed to the development of verrucous plaques.
The diagnosis of verrucous psoriasis can be challenging because of its similarity to several other entities, including verruca vulgaris; epidermal nevus; and squamous cell carcinoma, particularly verrucous carcinoma.4,6,7 The diagnosis has been less challenging in areas where prior typical psoriatic lesions evolved into a verrucous morphology. Our patient presented a diagnostic challenge and draws attention to this unique variant of psoriasis that could easily be misdiagnosed and lead to inappropriate treatment.
Verrucous psoriasis can be recalcitrant to therapy. Although studies addressing treatment modalities are lacking, several recommendations can be derived from case reports and our patient. The use of topical therapies, including topical corticosteroids (eg, fluocinonide, clobetasol, halobetasol), keratolytic agents (eg, urea, salicylic acid), and calcipotriene, provide only minimal improvement when used as monotherapy.1 Better success has been reported with systemic therapies, mainly methotrexate and acitretin, with anecdotal reports favoring the use of oral retinoids.1,6 Conversely, biologic medications such as etanercept, ustekinumab, adalimumab, and infliximab have only provided a partial response.1 Combination therapies including intralesional triamcinolone plus methotrexate4 or methotrexate plus acitretin, as in our patient, seem to provide additional benefit. Methotrexate and acitretin combination therapy has traditionally been avoided because of the risk for hepatotoxicity. However, a case series has demonstrated a moderate safety profile with concurrent use of these drugs in treatment-resistant psoriasis.8 In our case, clinical response was most pronounced with combination therapy of methotrexate 10 mg weekly and acitretin 25 mg daily. Thus, strong consideration should be given for combination methotrexate-acitretin therapy in patients with recalcitrant verrucous psoriasis who lack comorbid conditions.
We present a case of verrucous psoriasis, a variant of psoriasis characterized by hypertrophic plaques. We propose that venous insufficiency and long-standing untreated disease was instrumental to the development of these lesions. Furthermore, retinoids, particularly in combination with methotrexate, provided the most benefit for our patient.
Acknowledgment
We thank Stephen Somach, MD (Cleveland, Ohio), for his help interpreting the microscopic findings in our biopsy specimen. He received no compensation.
- Curtis AR, Yosipovitch G. Erythrodermic verrucous psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2012;23:215-218.
- Scavo S, Gurrera A, Mazzaglia C, et al. Verrucous psoriasis in a patient with chronic C hepatitis treated with interferon. Clin Drug Investig. 2004;24:427-429.
- Khalil FK, Keehn CA, Saeed S, et al. Verrucous psoriasis: a distinctive clinicopathologic variant of psoriasis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:204-207.
- Hall L, Marks V, Tyler W. Verrucous psoriasis: a clinical and histopathologic mimicker of verruca vulgaris [abstract]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68(suppl 1):AB218.
- Monroe HR, Hillman JD, Chiu MW. A case of verrucous psoriasis. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:10.
- Larsen F, Susa JS, Cockerell CJ, et al. Case of multiple verrucous carcinomas responding to treatment with acetretin more likely to have been a case of verrucous psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:534-535.
- Kuan YZ, Hsu HC, Kuo TT, et al. Multiple verrucous carcinomas treated with acitretin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56(2 suppl):S29-S32.
- Lowenthal KE, Horn PJ, Kalb RE. Concurrent use of methotrexate and acitretin revisited. J Dermatolog Treat. 2008;19:22-26.
To the Editor:
A 76-year-old woman with venous insufficiency presented with numerous thick, hyperkeratotic, confluent papules and plaques involving both legs and thighs as well as the lower back. She initially developed lesions on the distal legs, which progressed to involve the thighs and lower back, slowly enlarging over 7 years (Figure 1). The eruption was associated with pruritus and was profoundly malodorous. The patient had been unsuccessfully treated with triamcinolone ointment, bleach baths, and several courses of oral antibiotics. Her history was remarkable for marked venous insufficiency and mild anemia, with a hemoglobin level of 11.9 g/dL (reference range, 14.0–17.5 g/dL). She had no other abnormalities on a comprehensive blood test, basic metabolic panel, or liver function test.

A punch biopsy specimen from the left lower back was obtained and demonstrated papillomatous psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with broad parakeratosis, few intracorneal neutrophils, hypogranulosis, and suprapapillary thinning (Figure 2). She was initially treated with oral methotrexate (20 mg weekly), resulting in partial improvement of plaques and complete resolution of pruritus and malodor. After 15 months of treatment with methotrexate, low-dose methotrexate (10 mg weekly) in combination with acitretin 25 mg daily was started, resulting in further improvement of hyperkeratosis (Figure 3). The patient also was given a compounded corticosteroid ointment containing liquor carbonis detergens, salicylic acid, and fluocinonide ointment, achieving minor additional benefit. Comprehensive metabolic panel, lipid panel, and liver function tests were obtained quarterly. Hemoglobin levels remained low, similar to baseline (11.3–12.5 g/dL), while all other values were within reference range. The patient tolerated treatment well, reporting mild dryness of lips on review of systems, which was attributed to acitretin and was treated with emollients.


Verrucous psoriasis is an uncommon variant of psoriasis that presents as localized annular, erythrodermic, or drug-induced disease, as reported in a patient with preexisting psoriasis after interferon treatment of hepatitis C.1,2 It is characterized by symmetric hypertrophic verrucous plaques that may have an erythematous base and involve the legs, arms, trunk, and dorsal aspect of the hands3; malodor is frequent.1 Histopathologically, overlapping features of verruca vulgaris and psoriasis have been described. Specifically, lesions display typical psoriasiform changes, including parakeratosis, epidermal acanthosis with elongation of rete ridges, suprapapillary thinning, epidermal hypogranulosis, dilated or tortuous capillaries, and neutrophil collections in the stratum corneum (Munro microabscesses) or stratum spinosum (spongiform pustules of Kogoj).3 Additional findings of papillomatosis and epithelial buttressing are highly suggestive of verrucous psoriasis,3 though epithelial buttressing is not universally present.4-6 Similarly, although eosinophils and plasma cells have been described in some patients with verrucous psoriasis, this finding has not been consistently reported.4-6 Our biopsy specimen (Figure 2) lacks the epithelial buttressing but does exhibit subtle papillomatous hyperplasia consistent with the diagnosis of psoriasis.
The etiology of this entity is unknown. An association with diabetes mellitus, pulmonary disease, lymphatic circulation disorders, and immunosuppression has been proposed. Others have reported repeated trauma as contributing to the pathogenesis.1 For our patient, trauma secondary to scratching, long-standing venous insufficiency, and neglect likely contributed to the development of verrucous plaques.
The diagnosis of verrucous psoriasis can be challenging because of its similarity to several other entities, including verruca vulgaris; epidermal nevus; and squamous cell carcinoma, particularly verrucous carcinoma.4,6,7 The diagnosis has been less challenging in areas where prior typical psoriatic lesions evolved into a verrucous morphology. Our patient presented a diagnostic challenge and draws attention to this unique variant of psoriasis that could easily be misdiagnosed and lead to inappropriate treatment.
Verrucous psoriasis can be recalcitrant to therapy. Although studies addressing treatment modalities are lacking, several recommendations can be derived from case reports and our patient. The use of topical therapies, including topical corticosteroids (eg, fluocinonide, clobetasol, halobetasol), keratolytic agents (eg, urea, salicylic acid), and calcipotriene, provide only minimal improvement when used as monotherapy.1 Better success has been reported with systemic therapies, mainly methotrexate and acitretin, with anecdotal reports favoring the use of oral retinoids.1,6 Conversely, biologic medications such as etanercept, ustekinumab, adalimumab, and infliximab have only provided a partial response.1 Combination therapies including intralesional triamcinolone plus methotrexate4 or methotrexate plus acitretin, as in our patient, seem to provide additional benefit. Methotrexate and acitretin combination therapy has traditionally been avoided because of the risk for hepatotoxicity. However, a case series has demonstrated a moderate safety profile with concurrent use of these drugs in treatment-resistant psoriasis.8 In our case, clinical response was most pronounced with combination therapy of methotrexate 10 mg weekly and acitretin 25 mg daily. Thus, strong consideration should be given for combination methotrexate-acitretin therapy in patients with recalcitrant verrucous psoriasis who lack comorbid conditions.
We present a case of verrucous psoriasis, a variant of psoriasis characterized by hypertrophic plaques. We propose that venous insufficiency and long-standing untreated disease was instrumental to the development of these lesions. Furthermore, retinoids, particularly in combination with methotrexate, provided the most benefit for our patient.
Acknowledgment
We thank Stephen Somach, MD (Cleveland, Ohio), for his help interpreting the microscopic findings in our biopsy specimen. He received no compensation.
To the Editor:
A 76-year-old woman with venous insufficiency presented with numerous thick, hyperkeratotic, confluent papules and plaques involving both legs and thighs as well as the lower back. She initially developed lesions on the distal legs, which progressed to involve the thighs and lower back, slowly enlarging over 7 years (Figure 1). The eruption was associated with pruritus and was profoundly malodorous. The patient had been unsuccessfully treated with triamcinolone ointment, bleach baths, and several courses of oral antibiotics. Her history was remarkable for marked venous insufficiency and mild anemia, with a hemoglobin level of 11.9 g/dL (reference range, 14.0–17.5 g/dL). She had no other abnormalities on a comprehensive blood test, basic metabolic panel, or liver function test.

A punch biopsy specimen from the left lower back was obtained and demonstrated papillomatous psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with broad parakeratosis, few intracorneal neutrophils, hypogranulosis, and suprapapillary thinning (Figure 2). She was initially treated with oral methotrexate (20 mg weekly), resulting in partial improvement of plaques and complete resolution of pruritus and malodor. After 15 months of treatment with methotrexate, low-dose methotrexate (10 mg weekly) in combination with acitretin 25 mg daily was started, resulting in further improvement of hyperkeratosis (Figure 3). The patient also was given a compounded corticosteroid ointment containing liquor carbonis detergens, salicylic acid, and fluocinonide ointment, achieving minor additional benefit. Comprehensive metabolic panel, lipid panel, and liver function tests were obtained quarterly. Hemoglobin levels remained low, similar to baseline (11.3–12.5 g/dL), while all other values were within reference range. The patient tolerated treatment well, reporting mild dryness of lips on review of systems, which was attributed to acitretin and was treated with emollients.


Verrucous psoriasis is an uncommon variant of psoriasis that presents as localized annular, erythrodermic, or drug-induced disease, as reported in a patient with preexisting psoriasis after interferon treatment of hepatitis C.1,2 It is characterized by symmetric hypertrophic verrucous plaques that may have an erythematous base and involve the legs, arms, trunk, and dorsal aspect of the hands3; malodor is frequent.1 Histopathologically, overlapping features of verruca vulgaris and psoriasis have been described. Specifically, lesions display typical psoriasiform changes, including parakeratosis, epidermal acanthosis with elongation of rete ridges, suprapapillary thinning, epidermal hypogranulosis, dilated or tortuous capillaries, and neutrophil collections in the stratum corneum (Munro microabscesses) or stratum spinosum (spongiform pustules of Kogoj).3 Additional findings of papillomatosis and epithelial buttressing are highly suggestive of verrucous psoriasis,3 though epithelial buttressing is not universally present.4-6 Similarly, although eosinophils and plasma cells have been described in some patients with verrucous psoriasis, this finding has not been consistently reported.4-6 Our biopsy specimen (Figure 2) lacks the epithelial buttressing but does exhibit subtle papillomatous hyperplasia consistent with the diagnosis of psoriasis.
The etiology of this entity is unknown. An association with diabetes mellitus, pulmonary disease, lymphatic circulation disorders, and immunosuppression has been proposed. Others have reported repeated trauma as contributing to the pathogenesis.1 For our patient, trauma secondary to scratching, long-standing venous insufficiency, and neglect likely contributed to the development of verrucous plaques.
The diagnosis of verrucous psoriasis can be challenging because of its similarity to several other entities, including verruca vulgaris; epidermal nevus; and squamous cell carcinoma, particularly verrucous carcinoma.4,6,7 The diagnosis has been less challenging in areas where prior typical psoriatic lesions evolved into a verrucous morphology. Our patient presented a diagnostic challenge and draws attention to this unique variant of psoriasis that could easily be misdiagnosed and lead to inappropriate treatment.
Verrucous psoriasis can be recalcitrant to therapy. Although studies addressing treatment modalities are lacking, several recommendations can be derived from case reports and our patient. The use of topical therapies, including topical corticosteroids (eg, fluocinonide, clobetasol, halobetasol), keratolytic agents (eg, urea, salicylic acid), and calcipotriene, provide only minimal improvement when used as monotherapy.1 Better success has been reported with systemic therapies, mainly methotrexate and acitretin, with anecdotal reports favoring the use of oral retinoids.1,6 Conversely, biologic medications such as etanercept, ustekinumab, adalimumab, and infliximab have only provided a partial response.1 Combination therapies including intralesional triamcinolone plus methotrexate4 or methotrexate plus acitretin, as in our patient, seem to provide additional benefit. Methotrexate and acitretin combination therapy has traditionally been avoided because of the risk for hepatotoxicity. However, a case series has demonstrated a moderate safety profile with concurrent use of these drugs in treatment-resistant psoriasis.8 In our case, clinical response was most pronounced with combination therapy of methotrexate 10 mg weekly and acitretin 25 mg daily. Thus, strong consideration should be given for combination methotrexate-acitretin therapy in patients with recalcitrant verrucous psoriasis who lack comorbid conditions.
We present a case of verrucous psoriasis, a variant of psoriasis characterized by hypertrophic plaques. We propose that venous insufficiency and long-standing untreated disease was instrumental to the development of these lesions. Furthermore, retinoids, particularly in combination with methotrexate, provided the most benefit for our patient.
Acknowledgment
We thank Stephen Somach, MD (Cleveland, Ohio), for his help interpreting the microscopic findings in our biopsy specimen. He received no compensation.
- Curtis AR, Yosipovitch G. Erythrodermic verrucous psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2012;23:215-218.
- Scavo S, Gurrera A, Mazzaglia C, et al. Verrucous psoriasis in a patient with chronic C hepatitis treated with interferon. Clin Drug Investig. 2004;24:427-429.
- Khalil FK, Keehn CA, Saeed S, et al. Verrucous psoriasis: a distinctive clinicopathologic variant of psoriasis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:204-207.
- Hall L, Marks V, Tyler W. Verrucous psoriasis: a clinical and histopathologic mimicker of verruca vulgaris [abstract]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68(suppl 1):AB218.
- Monroe HR, Hillman JD, Chiu MW. A case of verrucous psoriasis. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:10.
- Larsen F, Susa JS, Cockerell CJ, et al. Case of multiple verrucous carcinomas responding to treatment with acetretin more likely to have been a case of verrucous psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:534-535.
- Kuan YZ, Hsu HC, Kuo TT, et al. Multiple verrucous carcinomas treated with acitretin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56(2 suppl):S29-S32.
- Lowenthal KE, Horn PJ, Kalb RE. Concurrent use of methotrexate and acitretin revisited. J Dermatolog Treat. 2008;19:22-26.
- Curtis AR, Yosipovitch G. Erythrodermic verrucous psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2012;23:215-218.
- Scavo S, Gurrera A, Mazzaglia C, et al. Verrucous psoriasis in a patient with chronic C hepatitis treated with interferon. Clin Drug Investig. 2004;24:427-429.
- Khalil FK, Keehn CA, Saeed S, et al. Verrucous psoriasis: a distinctive clinicopathologic variant of psoriasis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:204-207.
- Hall L, Marks V, Tyler W. Verrucous psoriasis: a clinical and histopathologic mimicker of verruca vulgaris [abstract]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68(suppl 1):AB218.
- Monroe HR, Hillman JD, Chiu MW. A case of verrucous psoriasis. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:10.
- Larsen F, Susa JS, Cockerell CJ, et al. Case of multiple verrucous carcinomas responding to treatment with acetretin more likely to have been a case of verrucous psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:534-535.
- Kuan YZ, Hsu HC, Kuo TT, et al. Multiple verrucous carcinomas treated with acitretin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56(2 suppl):S29-S32.
- Lowenthal KE, Horn PJ, Kalb RE. Concurrent use of methotrexate and acitretin revisited. J Dermatolog Treat. 2008;19:22-26.
Practice Points
- Verrucous psoriasis in an uncommon but recalcitrant-to-treatment variant of psoriasis that is characterized by hypertrophic plaques.
- The diagnosis of verrucous psoriasis is challenging, as it can mimic other entities such as verruca vulgaris and squamous cell carcinoma.
- Although the etiology of this entity is unknown, an association with diabetes mellitus, pulmonary disease, lymphatic circulation disorders, and immunosuppression has been described.
- The combination of methotrexate and acitretin is a safe and effective option for these patients in the absence of comorbid conditions.
Repeat LTBI testing best in patients taking biologics with new risk factors
ATLANTA – Patients taking biologics who received latent tuberculosis testing on an annual basis were unlikely to convert from a negative QuantiFERON test to a positive result, which suggests that the test may be unnecessary for patients without new tuberculosis risk factors, according to research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
In addition, nearly all of the cost of repeat testing for latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) went to patients who were not diagnosed with or treated for LTBI, noted Urmi Khanna, MD, a dermatologist with the Cleveland Clinic.
“All in all, about $1.4 million U.S. dollars was spent just on additional QuantiFERON testing, and only 1% of this additional cost was actually spent on testing patients who were diagnosed with and treated for latent tuberculosis,” Dr. Khanna said in her presentation at the meeting.
“Based on this study, we would like to propose that, in low incidence TB regions such as the United States, repeat LTBI testing in patients on biologic therapies should be focused on patients who have new risk factors for TB infection since their last screening,” she said.
The National Psoriasis Foundation has recommended patients be screened annually for LTBI, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the ACR have recommended patients taking biologics be screened annually for LTBI if they have new risk factors for TB, such as coming into contact with immigrants, a person infected with TB, immunosuppressed individuals, or persons working in areas where TB might be present. Annual screening was also recently added to the Medicare Merit-Based Incentive Payment System (MIPS), which will affect physician reimbursement. “Based on [the addition of this quality outcome measure], we expect that more and more physicians will adopt this practice of annual LTBI screening in all patients on biologics,” Dr. Khanna said.
She and her colleagues examined QuantiFERON tuberculosis test (QFT) results of 10,914 patients from the Cleveland Clinic Foundation between August 2007 and March 2019 where patients were receiving systemic biologic therapy for inflammatory or autoimmune conditions, including nearly 32% with inflammatory bowel disease, 29% with rheumatoid arthritis, and 25% with psoriatic disease. Overall, 5,212 patients were included in the final analysis, and patients had a median of three QFT results. Patients had a median age of 41 years, had taken an average of 1.80 biologics during follow-up, and had a median biologic therapy duration of about 49 months. The most common biologics used were adalimumab (33%), etanercept (17%), and infliximab (17%).
Of these patients, 4,561 patients had negative QFTs (88%), 172 patients had one or more positive QFTs (3%), and 479 patients had one or more indeterminate QFTs (9%). For patients who converted from a negative QFT to a positive QFT, the most common risk factors were exposure to someone with TB (26%), immigrating or traveling to an endemic area (26%), and occupational exposure (16%).
Within the group with one or more positive QFTs, there were 108 patients with baseline positive QFTs prior to starting biologic therapy (2.1%), 61 patients who converted from a baseline negative QFT to a positive QFT (1.2%), and 3 patients where a positive result overlapped with a negative result (0.1%). The majority of patients who converted to a positive QFT result had borderline positive results (70.5%), defined as 0.35 to 1 IU/mL, compared with 29.5% of converters who had a positive QFT result of more than 1.0 IU/mL.
Among the 61 patients who converted to a positive QFT result, 28 patients with LTBI (46%) and 1 patient with an active case of TB (2%) were diagnosed and treated. The active TB case was a 29-year-old patient with inflammatory bowel disease and ankylosing spondylitis receiving adalimumab who had recently traveled to India.
The researchers also examined the cost of additional QFTs in each group. Among negative QFTs, the cost of an additional 9,611 tests was $1,201,375. The cost of additional tests for indeterminate QFTs was $136,200, but Dr. Khanna noted that 99.99% of additional tests in this group were for patients never diagnosed with or treated for LTBI. Additional tests for positive QFTs cost another $47,700, and 26.1% of patients in this group were diagnosed and received treatment for LTBI, compared with 73.9% who did not receive an LTBI diagnosis or treatment.
In the discussion session following the presentation, Dr. Khanna emphasized that discontinuing annual screening in low-risk patients was not standard of care at the Cleveland Clinic, and this study was conducted to raise awareness of focusing testing on patients with new TB risk factors.
Dr. Khanna reported no relevant financial disclosures. A few of her coauthors reported financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Khanna U et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract 1802.
ATLANTA – Patients taking biologics who received latent tuberculosis testing on an annual basis were unlikely to convert from a negative QuantiFERON test to a positive result, which suggests that the test may be unnecessary for patients without new tuberculosis risk factors, according to research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
In addition, nearly all of the cost of repeat testing for latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) went to patients who were not diagnosed with or treated for LTBI, noted Urmi Khanna, MD, a dermatologist with the Cleveland Clinic.
“All in all, about $1.4 million U.S. dollars was spent just on additional QuantiFERON testing, and only 1% of this additional cost was actually spent on testing patients who were diagnosed with and treated for latent tuberculosis,” Dr. Khanna said in her presentation at the meeting.
“Based on this study, we would like to propose that, in low incidence TB regions such as the United States, repeat LTBI testing in patients on biologic therapies should be focused on patients who have new risk factors for TB infection since their last screening,” she said.
The National Psoriasis Foundation has recommended patients be screened annually for LTBI, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the ACR have recommended patients taking biologics be screened annually for LTBI if they have new risk factors for TB, such as coming into contact with immigrants, a person infected with TB, immunosuppressed individuals, or persons working in areas where TB might be present. Annual screening was also recently added to the Medicare Merit-Based Incentive Payment System (MIPS), which will affect physician reimbursement. “Based on [the addition of this quality outcome measure], we expect that more and more physicians will adopt this practice of annual LTBI screening in all patients on biologics,” Dr. Khanna said.
She and her colleagues examined QuantiFERON tuberculosis test (QFT) results of 10,914 patients from the Cleveland Clinic Foundation between August 2007 and March 2019 where patients were receiving systemic biologic therapy for inflammatory or autoimmune conditions, including nearly 32% with inflammatory bowel disease, 29% with rheumatoid arthritis, and 25% with psoriatic disease. Overall, 5,212 patients were included in the final analysis, and patients had a median of three QFT results. Patients had a median age of 41 years, had taken an average of 1.80 biologics during follow-up, and had a median biologic therapy duration of about 49 months. The most common biologics used were adalimumab (33%), etanercept (17%), and infliximab (17%).
Of these patients, 4,561 patients had negative QFTs (88%), 172 patients had one or more positive QFTs (3%), and 479 patients had one or more indeterminate QFTs (9%). For patients who converted from a negative QFT to a positive QFT, the most common risk factors were exposure to someone with TB (26%), immigrating or traveling to an endemic area (26%), and occupational exposure (16%).
Within the group with one or more positive QFTs, there were 108 patients with baseline positive QFTs prior to starting biologic therapy (2.1%), 61 patients who converted from a baseline negative QFT to a positive QFT (1.2%), and 3 patients where a positive result overlapped with a negative result (0.1%). The majority of patients who converted to a positive QFT result had borderline positive results (70.5%), defined as 0.35 to 1 IU/mL, compared with 29.5% of converters who had a positive QFT result of more than 1.0 IU/mL.
Among the 61 patients who converted to a positive QFT result, 28 patients with LTBI (46%) and 1 patient with an active case of TB (2%) were diagnosed and treated. The active TB case was a 29-year-old patient with inflammatory bowel disease and ankylosing spondylitis receiving adalimumab who had recently traveled to India.
The researchers also examined the cost of additional QFTs in each group. Among negative QFTs, the cost of an additional 9,611 tests was $1,201,375. The cost of additional tests for indeterminate QFTs was $136,200, but Dr. Khanna noted that 99.99% of additional tests in this group were for patients never diagnosed with or treated for LTBI. Additional tests for positive QFTs cost another $47,700, and 26.1% of patients in this group were diagnosed and received treatment for LTBI, compared with 73.9% who did not receive an LTBI diagnosis or treatment.
In the discussion session following the presentation, Dr. Khanna emphasized that discontinuing annual screening in low-risk patients was not standard of care at the Cleveland Clinic, and this study was conducted to raise awareness of focusing testing on patients with new TB risk factors.
Dr. Khanna reported no relevant financial disclosures. A few of her coauthors reported financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Khanna U et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract 1802.
ATLANTA – Patients taking biologics who received latent tuberculosis testing on an annual basis were unlikely to convert from a negative QuantiFERON test to a positive result, which suggests that the test may be unnecessary for patients without new tuberculosis risk factors, according to research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
In addition, nearly all of the cost of repeat testing for latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) went to patients who were not diagnosed with or treated for LTBI, noted Urmi Khanna, MD, a dermatologist with the Cleveland Clinic.
“All in all, about $1.4 million U.S. dollars was spent just on additional QuantiFERON testing, and only 1% of this additional cost was actually spent on testing patients who were diagnosed with and treated for latent tuberculosis,” Dr. Khanna said in her presentation at the meeting.
“Based on this study, we would like to propose that, in low incidence TB regions such as the United States, repeat LTBI testing in patients on biologic therapies should be focused on patients who have new risk factors for TB infection since their last screening,” she said.
The National Psoriasis Foundation has recommended patients be screened annually for LTBI, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the ACR have recommended patients taking biologics be screened annually for LTBI if they have new risk factors for TB, such as coming into contact with immigrants, a person infected with TB, immunosuppressed individuals, or persons working in areas where TB might be present. Annual screening was also recently added to the Medicare Merit-Based Incentive Payment System (MIPS), which will affect physician reimbursement. “Based on [the addition of this quality outcome measure], we expect that more and more physicians will adopt this practice of annual LTBI screening in all patients on biologics,” Dr. Khanna said.
She and her colleagues examined QuantiFERON tuberculosis test (QFT) results of 10,914 patients from the Cleveland Clinic Foundation between August 2007 and March 2019 where patients were receiving systemic biologic therapy for inflammatory or autoimmune conditions, including nearly 32% with inflammatory bowel disease, 29% with rheumatoid arthritis, and 25% with psoriatic disease. Overall, 5,212 patients were included in the final analysis, and patients had a median of three QFT results. Patients had a median age of 41 years, had taken an average of 1.80 biologics during follow-up, and had a median biologic therapy duration of about 49 months. The most common biologics used were adalimumab (33%), etanercept (17%), and infliximab (17%).
Of these patients, 4,561 patients had negative QFTs (88%), 172 patients had one or more positive QFTs (3%), and 479 patients had one or more indeterminate QFTs (9%). For patients who converted from a negative QFT to a positive QFT, the most common risk factors were exposure to someone with TB (26%), immigrating or traveling to an endemic area (26%), and occupational exposure (16%).
Within the group with one or more positive QFTs, there were 108 patients with baseline positive QFTs prior to starting biologic therapy (2.1%), 61 patients who converted from a baseline negative QFT to a positive QFT (1.2%), and 3 patients where a positive result overlapped with a negative result (0.1%). The majority of patients who converted to a positive QFT result had borderline positive results (70.5%), defined as 0.35 to 1 IU/mL, compared with 29.5% of converters who had a positive QFT result of more than 1.0 IU/mL.
Among the 61 patients who converted to a positive QFT result, 28 patients with LTBI (46%) and 1 patient with an active case of TB (2%) were diagnosed and treated. The active TB case was a 29-year-old patient with inflammatory bowel disease and ankylosing spondylitis receiving adalimumab who had recently traveled to India.
The researchers also examined the cost of additional QFTs in each group. Among negative QFTs, the cost of an additional 9,611 tests was $1,201,375. The cost of additional tests for indeterminate QFTs was $136,200, but Dr. Khanna noted that 99.99% of additional tests in this group were for patients never diagnosed with or treated for LTBI. Additional tests for positive QFTs cost another $47,700, and 26.1% of patients in this group were diagnosed and received treatment for LTBI, compared with 73.9% who did not receive an LTBI diagnosis or treatment.
In the discussion session following the presentation, Dr. Khanna emphasized that discontinuing annual screening in low-risk patients was not standard of care at the Cleveland Clinic, and this study was conducted to raise awareness of focusing testing on patients with new TB risk factors.
Dr. Khanna reported no relevant financial disclosures. A few of her coauthors reported financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Khanna U et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract 1802.
REPORTING FROM ACR 2019
Depression and Suicidality in Psoriasis and Clinical Studies of Brodalumab: A Narrative Review
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder that affects patients’ quality of life and social interactions.1 Several studies have shown a strong consistent association between psoriasis and depression as well as possible suicidal ideation and behavior (SIB).1-13 Notable findings from a 2018 review found depression prevalence ranged from 2.1% to 33.7% among patients with psoriasis vs 0% to 22.7% among unaffected patients.7 In a 2017 meta-analysis, Singh et al2 found increased odds of SIB (odds ratio [OR], 2.05), attempted suicide (OR, 1.32), and completed suicide (OR, 1.20) in patients with psoriasis compared to those without psoriasis. In 2018, Wu and colleagues7 reported that odds of SIB among patients with psoriasis ranged from 1.01 to 1.94 times those of patients without psoriasis, and SIB and suicide attempts were more common than in patients with other dermatologic conditions. Koo and colleagues1 reached similar conclusions. At the same time, the occurrence of attempted and completed suicides among patients in psoriasis clinical trials has raised concerns about whether psoriasis medications also may increase the risk for SIB.7
We review research on the effects of psoriasis treatment on patients’ symptoms of depression and SIB, with a focus on recent analyses of depressive symptoms and SIB among patients with psoriasis who received brodalumab in clinical trials. Finally, we suggest approaches clinicians may consider when caring for patients with psoriasis who may be at risk for depression and SIB.
We reviewed research on the effects of biologic therapy for psoriasis on depression and SIB, with a primary focus on recent large meta-analyses. Published findings on the pattern of SIB in brodalumab clinical trials and effects of brodalumab treatment on symptoms of depression and anxiety are summarized. The most recent evidence (January 2014–December 2018) regarding the mental health comorbidities of psoriasis was assessed using published English-language research data and review articles according to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the following terms: depression, anxiety, suicide, suicidal ideation and behavior, SIB, brodalumab, or psoriasis. We also reviewed citations within articles to identify relevant sources. Implications for clinical care of patients with psoriasis are discussed based on expert recommendations and the authors’ clinical experience.
RESULTS
Effects of Psoriasis Treatment on Symptoms of Depression and Suicidality
Occurrences of attempted suicide and completed suicide have been reported during treatment with several psoriasis medications,7,9 raising concerns about whether these medications increase the risk for depression and SIB in an already vulnerable population. Wu and colleagues7 reviewed 11 studies published from 2006 to 2017 reporting the effects of medications for the treatment of psoriasis—adalimumab, apremilast, brodalumab, etanercept, and ustekinumab—on measures of depression and anxiety such as the Beck Depression Inventory, the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), and the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) 8. In each of the 11 studies, symptoms of depression improved after treatment, over time, or compared to placebo. Notably, the magnitude of improvement in symptoms of depression was not strongly linked to the magnitude of clinical improvement.7 Other recent studies have reported reductions in symptoms of depression with biologic therapies, including adalimumab, etanercept, guselkumab, ixekizumab, secukinumab, and ustekinumab.14-21
With respect to suicidality, an analysis of publicly available data found low rates of completed and attempted suicides (point estimates of 0.0–0.15 per 100 patient-years) in clinical development programs of apremilast, brodalumab, ixekizumab, and secukinumab. Patient suicidality in these trials often occurred in the context of risk factors or stressors such as work, financial difficulties, depression, and substance abuse.7 In a detailed 2016 analysis of suicidal behaviors during clinical trials of apremilast, brodalumab, etanercept, infliximab, ixekizumab, secukinumab, tofacitinib, ustekinumab, and other investigational agents, Gooderham and colleagues9 concluded that the behaviors may have resulted from the disease or patients’ psychosocial status rather than from treatment and that treatment with biologics does not increase the risk for SIB. Improvements in symptoms of depression during treatment suggest the potential to improve patients’ psychiatric outcomes with biologic treatment.9
Evidence From Brodalumab Studies
Intensive efforts have been made to assess the effect of brodalumab, a fully human anti–IL-17RA monoclonal antibody shown to be efficacious in the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, on symptoms of depression and to understand the incidence of SIB among patients receiving brodalumab in clinical trials.22-27
To examine the effects of brodalumab on symptoms of depression, the HADS questionnaire28 was administered to patients in 1 of 3 phase 3 clinical trials of brodalumab.23 A HADS score of 0 to 7 is considered normal, 8 to 10 is mild, 11 to 14 is moderate, and 15 to 21 is severe.23 The HADS questionnaire was administered to evaluate the presence and severity of depression and anxiety symptoms at baseline and at weeks 12, 24, 36, and 52.25 This scale was not used in the other 2 phase 3 studies of brodalumab because at the time those studies were initiated, there was no indication to include mental health screenings as part of the study protocol.
Patients were initially randomized to placebo (n=220), brodalumab 140 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W; n=219), or brodalumab 210 mg Q2W (the eventual approved dose; n=222) for 12 weeks.23 At week 12, patients initially randomized to placebo were switched to brodalumab through week 52. Patients initially randomized to brodalumab 210 mg Q2W were re-randomized to either placebo or brodalumab 210 mg Q2W.23 Depression and anxiety were common at baseline. Based on HADS scores, depression occurred among 27% and 26% of patients randomized to brodalumab and placebo, respectively; anxiety occurred in 36% of patients in each group.22 Among patients receiving brodalumab 210 mg Q2W from baseline to week 12, HADS depression scores improved in 67% of patients and worsened in 19%. In contrast, the proportion of patients receiving placebo whose depression scores improved (45%) was similar to the proportion whose scores worsened (38%). Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale anxiety scores also improved more often with brodalumab than with placebo.22
Furthermore, among patients who had moderate or severe depression or anxiety at baseline, a greater percentage experienced improvement with brodalumab than placebo.23 Among 30 patients with moderate to severe HADS depression scores at baseline who were treated with brodalumab 210 mg Q2W, 22 (73%) improved by at least 1 depression category by week 12; in the placebo group, 10 of 22 (45%) improved. Among patients with moderate or severe anxiety scores, 28 of 42 patients (67%) treated with brodalumab 210 mg Q2W improved by at least 1 anxiety category compared to 8 of 27 (30%) placebo-treated patients.23
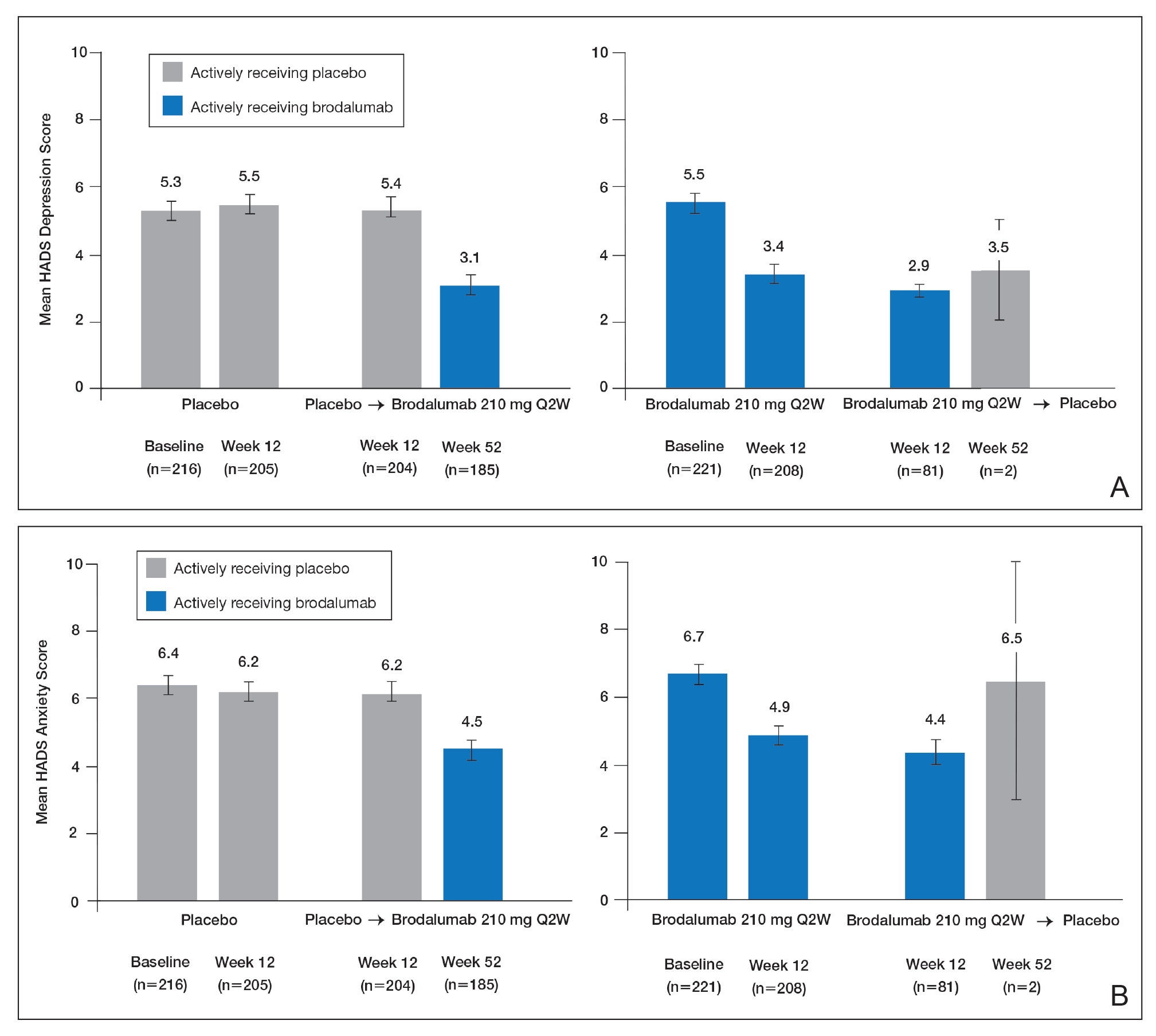
Over 52 weeks, HADS depression and anxiety scores continued to show a pattern of improvement among patients receiving brodalumab vs placebo.25 Among patients initially receiving placebo, mean HADS depression scores were unchanged from baseline (5.3) to week 12 (5.5). After patients were switched to brodalumab 210 mg Q2W, there was a trend toward improvement between week 12 (5.4) and week 52 (3.1). Among patients initially treated with brodalumab 210 mg Q2W, mean depression scores fell from baseline (5.5) to week 12 (3.4), then rose again between weeks 12 (2.9) and 52 (3.5) in patients switched to placebo (Figure, A). The pattern of findings was similar for HADS anxiety scores (Figure, B).25 Overall,
SIB in Studies of Brodalumab
In addition to assessing the effect of brodalumab treatment on symptoms of depression and anxiety in patients with psoriasis, the brodalumab clinical trial program also tracked patterns of SIB among enrolled patients. In contrast with other clinical trials in which patients with a history of psychiatric disorders or substance abuse were excluded, clinical trials of brodalumab did not exclude patients with psychiatric disorders (eg, SIB, depression) and were therefore reflective of the real-world population of patients with moderate to severe psoriasis.22
In a recently published, detailed analysis of psychiatric adverse events (AEs) in the brodalumab clinical trials, data related to SIB in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis were analyzed from the placebo-controlled phases and open-label, long-term extensions of a placebo-controlled phase 2 clinical trial and from the previously mentioned 3 phase 3 clinical trials.22 From the initiation of the clinical trial program, AEs were monitored during all trials. In response to completed suicides during some studies, additional SIB evaluations were later added at the request of the US Food and Drug Administration, including the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale, the PHQ-8, and the Columbia Classification Algorithm for Suicide Assessment, to independently adjudicate SIB events.22
In total, 4464 patients in the brodalumab clinical trials received at least 1 dose of brodalumab, and 4126 of these patients received at least 1 dose of brodalumab 210 mg Q2W.22 Total exposure was 9174 patient-years of brodalumab, and mean exposure was 23 months. During the 52-week controlled phases of the clinical trials, 7 patients receiving brodalumab experienced any form of SIB event, representing a time-adjusted incidence rate of 0.20 events (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.08-0.41 events) per 100 patient-years of exposure. During the same 52-week period, patients receiving the comparator drug ustekinumab had an SIB rate of 0.60 events (95% CI, 0.12-1.74 events) per 100 patient-years, which was numerically higher than the rate with brodalumab. Inferential statistical analyses were not performed, but overlapping 95% CIs around these point estimates imply a similar level of SIB risk associated with each agent in these studies. During controlled and uncontrolled treatment periods in all studies, the SIB rate among brodalumab-treated patients was 0.37 events per 100 patient-years.22
Over all study phases, 3 completed suicides and 1 case adjudicated as indeterminate by the Columbia Classification Algorithm for Suicide Assessment review board were reported.22 All occurred in men aged 39 to 59 years. Of 6 patients with an AE of suicide attempt, all patients had at least 1 SIB risk factor and 3 had a history of SIB. The rate of SIB events was greater in patients with a history of depression (1.42) or suicidality (3.21) compared to those without any history of depression or suicidality (0.21 and 0.20, respectively).22 An examination of the regions in which the brodalumab studies were conducted showed generally consistent SIB incidence rates: 0.52, 0.29, 0.77, and 0 events per 100 patient-years in North America, Europe, Australia, and Russia, respectively.24
As previously described, depression and other risk factors for SIB are prevalent among patients with psoriasis. In addition, the rate of suicide mortality has increased substantially over the last decade in the general population, particularly among middle-aged white men,29 who made up much of the brodalumab clinical trial population.22 Therefore, even without treatment, it would not be surprising that SIB events occurred during the brodalumab trials. Most patients with SIB events during the trials had a history of predisposing risk factors.22 Prescribing information for brodalumab in the United States includes a boxed warning advising physicians to be aware of the risk of SIB as well as a statement that a causal relationship between SIB and brodalumab treatment has not been established.27
Despite the boxed warning in the brodalumab package insert concerning suicidality, a causal relationship between brodalumab treatment and increased risk of SIB has not been firmly established.27 The US boxed warning is based on 3 completed suicides and 1 case adjudicated as indeterminate among more than 4000 patients who received at least 1 dose of brodalumab during global clinical trials (0.07% [3/4464]). Compliance in the Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program is mandatory, and patient screening and counseling should not be minimized.27 The 3 completed suicides occurred in patients who reported a history of financial stressors, legal difficulties, or depression and anxiety, and they occurred at least 140 days after initiation of treatment with brodalumab, a chronology that does not support a strong association between brodalumab exposure and SIB.22 Taking into consideration the increased risk for depression among individuals with psoriasis and the details surrounding the 3 completed suicides, an evidence-based causal relationship between brodalumab and increased risk for suicidality cannot be concluded. However, physicians must assess risks and benefits of any therapy in the context of the individual patient’s preferences, risk factors, and response to treatment.
Dermatologists who are aware of the comorbidity between psoriasis and mood disorders play an important role in evaluating patients with psoriasis for psychiatric risk factors.30-32 The dermatologist should discuss with patients the relationship between psoriasis and depression, assess for any history of depression and SIB, and evaluate for signs and symptoms of depression and current SIB.33 Screening tools, including the HADS or the short, easily administered PHQ-234 or PHQ-4,35 can be used to assess whether patients have symptoms of depression.1,36,37 Patients at risk for depression or SIB should be referred to their primary care physician or a mental health care practitioner.37 Currently, there is a gap in knowledge in screening patients for psychiatric issues within the dermatology community33,38; however, health care providers can give support to help bridge this gap.
Acknowledgments
This study was sponsored by Amgen Inc. Medical writing support was provided under the direction of the authors by Lisa Baker, PhD, and Rebecca E. Slager, PhD, of MedThink SciCom (Cary, North Carolina) and funded by Ortho Dermatologics, a division of Bausch Health US, LLC.
- Koo J, Marangell LB, Nakamura M, et al. Depression and suicidality in psoriasis: review of the literature including the cytokine theory of depression. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:1999-2009.
- Singh S, Taylor C, Kornmehl H, et al. Psoriasis and suicidality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:425-440.e2.
- Chi CC, Chen TH, Wang SH, et al. Risk of suicidality in people with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:621-627.
- Dalgard FJ, Gieler U, Tomas-Aragones L, et al. The psychological burden of skin diseases: a cross-sectional multicenter study among dermatological out-patients in 13 European countries. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:984-991.
- Pompili M, Innamorati M, Trovarelli S, et al. Suicide risk and psychiatric comorbidity in patients with psoriasis. J Int Med Res. 2016;44:61-66.
- Pompili M, Innamorati M, Forte A, et al. Psychiatric comorbidity and suicidal ideation in psoriasis, melanoma and allergic disorders. Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract. 2017;21:209-214.
- Wu JJ, Feldman SR, Koo J, et al. Epidemiology of mental health comorbidity in psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2018;29:487-495.
- Dowlatshahi EA, Wakkee M, Arends LR, et al. The prevalence and odds of depressive symptoms and clinical depression in psoriasis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:1542-1551.
- Gooderham M, Gavino-Velasco J, Clifford C, et al. A review of psoriasis, therapies, and suicide. J Cutan Med Surg. 2016;20:293-303.
- Shah K, Mellars L, Changolkar A, et al. Real-world burden of comorbidities in US patients with psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:287-292.e4.
- Cohen BE, Martires KJ, Ho RS. Psoriasis and the risk of depression in the US population: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009-2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:73-79.
- Wu JJ, Penfold RB, Primatesta P, et al. The risk of depression, suicidal ideation and suicide attempt in patients with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:1168-1175.
- Pietrzak D, Pietrzak A, Krasowska D, et al. Depressiveness, measured with Beck Depression Inventory, in patients with psoriasis. J Affect Disord. 2017;209:229-234.
- Sator P. Safety and tolerability of adalimumab for the treatment of psoriasis: a review summarizing 15 years of real-life experience. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2018;9:147-158.
- Wu CY, Chang YT, Juan CK, et al. Depression and insomnia in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis taking tumor necrosis factor antagonists. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:E3816.
- Gordon KB, Blauvelt A, Foley P, et al. Efficacy of guselkumab in subpopulations of patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: a pooled analysis of the phase III VOYAGE 1 and VOYAGE 2 studies. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:132-139.
- Strober B, Gooderham M, de Jong EMGJ, et al. Depressive symptoms, depression, and the effect of biologic therapy among patients in Psoriasis Longitudinal Assessment and Registry (PSOLAR). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:70-80.
- Griffiths CEM, Fava M, Miller AH, et al. Impact of ixekizumab treatment on depressive symptoms and systemic inflammation in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis: an integrated analysis of three phase 3 clinical studies. Psychother Psychosom. 2017;86:260-267.
- Salame N, Ehsani-Chimeh N, Armstrong AW. Comparison of mental health outcomes among adults with psoriasis on biologic versus oral therapies: a population-based study. J Dermatolog Treat. 2019;30:135-140.
- Strober BE, Langley RGB, Menter A, et al. No elevated risk for depression, anxiety or suicidality with secukinumab in a pooled analysis of data from 10 clinical studies in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:E105-E107.
- Kim SJ, Park MY, Pak K, et al. Improvement of depressive symptoms in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis treated with ustekinumab: an open label trial validated using Beck Depression Inventory, Hamilton Depression Rating scale measures and 18fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET). J Dermatolog Treat. 2018;29:761-768.
- Lebwohl MG, Papp KA, Marangell LB, et al. Psychiatric adverse events during treatment with brodalumab: analysis of psoriasis clinical trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:81-89.e5.
- Papp KA, Reich K, Paul C, et al. A prospective phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of brodalumab in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:273-286.
- Feldman SR, Harris S, Rastogi S, et al. Distribution of depression and suicidality in a psoriasis clinical trial population. Poster presented at: Winter Clinical Dermatology Conference; January 12-17, 2018; Lahaina, HI.
- Gooderham M, Feldman SR, Harris S, et al. Effects of brodalumab on anxiety and depression in patients with psoriasis: results from a phase 3, randomized, controlled clinical trial (AMAGINE-1). Poster presented at: 76th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology; February 16-20, 2018; San Diego, CA.
- Lebwohl M, Strober B, Menter A, et al. Phase 3 studies comparing brodalumab with ustekinumab in psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1318-1328.
- Siliq (brodalumab)[package insert]. Bridgewater, NJ: Bausch Health US, LLC; 2017.
- Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1983;67:361-370.
- Hashim PW, Chen T, Lebwohl MG, et al. What lies beneath the face value of a box warning: a deeper look at brodalumab. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:S29-S34.
- Roubille C, Richer V, Starnino T, et al. Evidence-based recommendations for the management of comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis: expert opinion of the Canadian Dermatology-Rheumatology Comorbidity Initiative. J Rheumatol. 2015;42:1767-1780.
- Takeshita J, Grewal S, Langan SM, et al. Psoriasis and comorbid diseases: implications for management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:393-403.
- Gupta MA, Pur DR, Vujcic B, et al. Suicidal behaviors in the dermatology patient. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:302-311.
- Wu JJ. Contemporary management of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Am J Manag Care. 2017;23(21 suppl):S403-S416.
- Manea L, Gilbody S, Hewitt C, et al. Identifying depression with the PHQ-2: a diagnostic meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2016;203:382-395.
- Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB, et al. An ultra-brief screening scale for anxiety and depression: the PHQ-4. Psychosomatics. 2009;50:613-621.
- Lamb RC, Matcham F, Turner MA, et al. Screening for anxiety and depression in people with psoriasis: a cross-sectional study in a tertiary referral setting. Br J Dermatol. 2017;176:1028-1034.
- Dauden E, Blasco AJ, Bonanad C, et al. Position statement for the management of comorbidities in psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:2058-2073.
- Moon HS, Mizara A, McBride SR. Psoriasis and psycho-dermatology. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2013;3:117-130.
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder that affects patients’ quality of life and social interactions.1 Several studies have shown a strong consistent association between psoriasis and depression as well as possible suicidal ideation and behavior (SIB).1-13 Notable findings from a 2018 review found depression prevalence ranged from 2.1% to 33.7% among patients with psoriasis vs 0% to 22.7% among unaffected patients.7 In a 2017 meta-analysis, Singh et al2 found increased odds of SIB (odds ratio [OR], 2.05), attempted suicide (OR, 1.32), and completed suicide (OR, 1.20) in patients with psoriasis compared to those without psoriasis. In 2018, Wu and colleagues7 reported that odds of SIB among patients with psoriasis ranged from 1.01 to 1.94 times those of patients without psoriasis, and SIB and suicide attempts were more common than in patients with other dermatologic conditions. Koo and colleagues1 reached similar conclusions. At the same time, the occurrence of attempted and completed suicides among patients in psoriasis clinical trials has raised concerns about whether psoriasis medications also may increase the risk for SIB.7
We review research on the effects of psoriasis treatment on patients’ symptoms of depression and SIB, with a focus on recent analyses of depressive symptoms and SIB among patients with psoriasis who received brodalumab in clinical trials. Finally, we suggest approaches clinicians may consider when caring for patients with psoriasis who may be at risk for depression and SIB.
We reviewed research on the effects of biologic therapy for psoriasis on depression and SIB, with a primary focus on recent large meta-analyses. Published findings on the pattern of SIB in brodalumab clinical trials and effects of brodalumab treatment on symptoms of depression and anxiety are summarized. The most recent evidence (January 2014–December 2018) regarding the mental health comorbidities of psoriasis was assessed using published English-language research data and review articles according to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the following terms: depression, anxiety, suicide, suicidal ideation and behavior, SIB, brodalumab, or psoriasis. We also reviewed citations within articles to identify relevant sources. Implications for clinical care of patients with psoriasis are discussed based on expert recommendations and the authors’ clinical experience.
RESULTS
Effects of Psoriasis Treatment on Symptoms of Depression and Suicidality
Occurrences of attempted suicide and completed suicide have been reported during treatment with several psoriasis medications,7,9 raising concerns about whether these medications increase the risk for depression and SIB in an already vulnerable population. Wu and colleagues7 reviewed 11 studies published from 2006 to 2017 reporting the effects of medications for the treatment of psoriasis—adalimumab, apremilast, brodalumab, etanercept, and ustekinumab—on measures of depression and anxiety such as the Beck Depression Inventory, the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), and the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) 8. In each of the 11 studies, symptoms of depression improved after treatment, over time, or compared to placebo. Notably, the magnitude of improvement in symptoms of depression was not strongly linked to the magnitude of clinical improvement.7 Other recent studies have reported reductions in symptoms of depression with biologic therapies, including adalimumab, etanercept, guselkumab, ixekizumab, secukinumab, and ustekinumab.14-21
With respect to suicidality, an analysis of publicly available data found low rates of completed and attempted suicides (point estimates of 0.0–0.15 per 100 patient-years) in clinical development programs of apremilast, brodalumab, ixekizumab, and secukinumab. Patient suicidality in these trials often occurred in the context of risk factors or stressors such as work, financial difficulties, depression, and substance abuse.7 In a detailed 2016 analysis of suicidal behaviors during clinical trials of apremilast, brodalumab, etanercept, infliximab, ixekizumab, secukinumab, tofacitinib, ustekinumab, and other investigational agents, Gooderham and colleagues9 concluded that the behaviors may have resulted from the disease or patients’ psychosocial status rather than from treatment and that treatment with biologics does not increase the risk for SIB. Improvements in symptoms of depression during treatment suggest the potential to improve patients’ psychiatric outcomes with biologic treatment.9
Evidence From Brodalumab Studies
Intensive efforts have been made to assess the effect of brodalumab, a fully human anti–IL-17RA monoclonal antibody shown to be efficacious in the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, on symptoms of depression and to understand the incidence of SIB among patients receiving brodalumab in clinical trials.22-27
To examine the effects of brodalumab on symptoms of depression, the HADS questionnaire28 was administered to patients in 1 of 3 phase 3 clinical trials of brodalumab.23 A HADS score of 0 to 7 is considered normal, 8 to 10 is mild, 11 to 14 is moderate, and 15 to 21 is severe.23 The HADS questionnaire was administered to evaluate the presence and severity of depression and anxiety symptoms at baseline and at weeks 12, 24, 36, and 52.25 This scale was not used in the other 2 phase 3 studies of brodalumab because at the time those studies were initiated, there was no indication to include mental health screenings as part of the study protocol.
Patients were initially randomized to placebo (n=220), brodalumab 140 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W; n=219), or brodalumab 210 mg Q2W (the eventual approved dose; n=222) for 12 weeks.23 At week 12, patients initially randomized to placebo were switched to brodalumab through week 52. Patients initially randomized to brodalumab 210 mg Q2W were re-randomized to either placebo or brodalumab 210 mg Q2W.23 Depression and anxiety were common at baseline. Based on HADS scores, depression occurred among 27% and 26% of patients randomized to brodalumab and placebo, respectively; anxiety occurred in 36% of patients in each group.22 Among patients receiving brodalumab 210 mg Q2W from baseline to week 12, HADS depression scores improved in 67% of patients and worsened in 19%. In contrast, the proportion of patients receiving placebo whose depression scores improved (45%) was similar to the proportion whose scores worsened (38%). Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale anxiety scores also improved more often with brodalumab than with placebo.22
Furthermore, among patients who had moderate or severe depression or anxiety at baseline, a greater percentage experienced improvement with brodalumab than placebo.23 Among 30 patients with moderate to severe HADS depression scores at baseline who were treated with brodalumab 210 mg Q2W, 22 (73%) improved by at least 1 depression category by week 12; in the placebo group, 10 of 22 (45%) improved. Among patients with moderate or severe anxiety scores, 28 of 42 patients (67%) treated with brodalumab 210 mg Q2W improved by at least 1 anxiety category compared to 8 of 27 (30%) placebo-treated patients.23
Over 52 weeks, HADS depression and anxiety scores continued to show a pattern of improvement among patients receiving brodalumab vs placebo.25 Among patients initially receiving placebo, mean HADS depression scores were unchanged from baseline (5.3) to week 12 (5.5). After patients were switched to brodalumab 210 mg Q2W, there was a trend toward improvement between week 12 (5.4) and week 52 (3.1). Among patients initially treated with brodalumab 210 mg Q2W, mean depression scores fell from baseline (5.5) to week 12 (3.4), then rose again between weeks 12 (2.9) and 52 (3.5) in patients switched to placebo (Figure, A). The pattern of findings was similar for HADS anxiety scores (Figure, B).25 Overall,

SIB in Studies of Brodalumab
In addition to assessing the effect of brodalumab treatment on symptoms of depression and anxiety in patients with psoriasis, the brodalumab clinical trial program also tracked patterns of SIB among enrolled patients. In contrast with other clinical trials in which patients with a history of psychiatric disorders or substance abuse were excluded, clinical trials of brodalumab did not exclude patients with psychiatric disorders (eg, SIB, depression) and were therefore reflective of the real-world population of patients with moderate to severe psoriasis.22
In a recently published, detailed analysis of psychiatric adverse events (AEs) in the brodalumab clinical trials, data related to SIB in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis were analyzed from the placebo-controlled phases and open-label, long-term extensions of a placebo-controlled phase 2 clinical trial and from the previously mentioned 3 phase 3 clinical trials.22 From the initiation of the clinical trial program, AEs were monitored during all trials. In response to completed suicides during some studies, additional SIB evaluations were later added at the request of the US Food and Drug Administration, including the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale, the PHQ-8, and the Columbia Classification Algorithm for Suicide Assessment, to independently adjudicate SIB events.22
In total, 4464 patients in the brodalumab clinical trials received at least 1 dose of brodalumab, and 4126 of these patients received at least 1 dose of brodalumab 210 mg Q2W.22 Total exposure was 9174 patient-years of brodalumab, and mean exposure was 23 months. During the 52-week controlled phases of the clinical trials, 7 patients receiving brodalumab experienced any form of SIB event, representing a time-adjusted incidence rate of 0.20 events (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.08-0.41 events) per 100 patient-years of exposure. During the same 52-week period, patients receiving the comparator drug ustekinumab had an SIB rate of 0.60 events (95% CI, 0.12-1.74 events) per 100 patient-years, which was numerically higher than the rate with brodalumab. Inferential statistical analyses were not performed, but overlapping 95% CIs around these point estimates imply a similar level of SIB risk associated with each agent in these studies. During controlled and uncontrolled treatment periods in all studies, the SIB rate among brodalumab-treated patients was 0.37 events per 100 patient-years.22
Over all study phases, 3 completed suicides and 1 case adjudicated as indeterminate by the Columbia Classification Algorithm for Suicide Assessment review board were reported.22 All occurred in men aged 39 to 59 years. Of 6 patients with an AE of suicide attempt, all patients had at least 1 SIB risk factor and 3 had a history of SIB. The rate of SIB events was greater in patients with a history of depression (1.42) or suicidality (3.21) compared to those without any history of depression or suicidality (0.21 and 0.20, respectively).22 An examination of the regions in which the brodalumab studies were conducted showed generally consistent SIB incidence rates: 0.52, 0.29, 0.77, and 0 events per 100 patient-years in North America, Europe, Australia, and Russia, respectively.24
As previously described, depression and other risk factors for SIB are prevalent among patients with psoriasis. In addition, the rate of suicide mortality has increased substantially over the last decade in the general population, particularly among middle-aged white men,29 who made up much of the brodalumab clinical trial population.22 Therefore, even without treatment, it would not be surprising that SIB events occurred during the brodalumab trials. Most patients with SIB events during the trials had a history of predisposing risk factors.22 Prescribing information for brodalumab in the United States includes a boxed warning advising physicians to be aware of the risk of SIB as well as a statement that a causal relationship between SIB and brodalumab treatment has not been established.27
Despite the boxed warning in the brodalumab package insert concerning suicidality, a causal relationship between brodalumab treatment and increased risk of SIB has not been firmly established.27 The US boxed warning is based on 3 completed suicides and 1 case adjudicated as indeterminate among more than 4000 patients who received at least 1 dose of brodalumab during global clinical trials (0.07% [3/4464]). Compliance in the Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program is mandatory, and patient screening and counseling should not be minimized.27 The 3 completed suicides occurred in patients who reported a history of financial stressors, legal difficulties, or depression and anxiety, and they occurred at least 140 days after initiation of treatment with brodalumab, a chronology that does not support a strong association between brodalumab exposure and SIB.22 Taking into consideration the increased risk for depression among individuals with psoriasis and the details surrounding the 3 completed suicides, an evidence-based causal relationship between brodalumab and increased risk for suicidality cannot be concluded. However, physicians must assess risks and benefits of any therapy in the context of the individual patient’s preferences, risk factors, and response to treatment.
Dermatologists who are aware of the comorbidity between psoriasis and mood disorders play an important role in evaluating patients with psoriasis for psychiatric risk factors.30-32 The dermatologist should discuss with patients the relationship between psoriasis and depression, assess for any history of depression and SIB, and evaluate for signs and symptoms of depression and current SIB.33 Screening tools, including the HADS or the short, easily administered PHQ-234 or PHQ-4,35 can be used to assess whether patients have symptoms of depression.1,36,37 Patients at risk for depression or SIB should be referred to their primary care physician or a mental health care practitioner.37 Currently, there is a gap in knowledge in screening patients for psychiatric issues within the dermatology community33,38; however, health care providers can give support to help bridge this gap.
Acknowledgments
This study was sponsored by Amgen Inc. Medical writing support was provided under the direction of the authors by Lisa Baker, PhD, and Rebecca E. Slager, PhD, of MedThink SciCom (Cary, North Carolina) and funded by Ortho Dermatologics, a division of Bausch Health US, LLC.
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder that affects patients’ quality of life and social interactions.1 Several studies have shown a strong consistent association between psoriasis and depression as well as possible suicidal ideation and behavior (SIB).1-13 Notable findings from a 2018 review found depression prevalence ranged from 2.1% to 33.7% among patients with psoriasis vs 0% to 22.7% among unaffected patients.7 In a 2017 meta-analysis, Singh et al2 found increased odds of SIB (odds ratio [OR], 2.05), attempted suicide (OR, 1.32), and completed suicide (OR, 1.20) in patients with psoriasis compared to those without psoriasis. In 2018, Wu and colleagues7 reported that odds of SIB among patients with psoriasis ranged from 1.01 to 1.94 times those of patients without psoriasis, and SIB and suicide attempts were more common than in patients with other dermatologic conditions. Koo and colleagues1 reached similar conclusions. At the same time, the occurrence of attempted and completed suicides among patients in psoriasis clinical trials has raised concerns about whether psoriasis medications also may increase the risk for SIB.7
We review research on the effects of psoriasis treatment on patients’ symptoms of depression and SIB, with a focus on recent analyses of depressive symptoms and SIB among patients with psoriasis who received brodalumab in clinical trials. Finally, we suggest approaches clinicians may consider when caring for patients with psoriasis who may be at risk for depression and SIB.
We reviewed research on the effects of biologic therapy for psoriasis on depression and SIB, with a primary focus on recent large meta-analyses. Published findings on the pattern of SIB in brodalumab clinical trials and effects of brodalumab treatment on symptoms of depression and anxiety are summarized. The most recent evidence (January 2014–December 2018) regarding the mental health comorbidities of psoriasis was assessed using published English-language research data and review articles according to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the following terms: depression, anxiety, suicide, suicidal ideation and behavior, SIB, brodalumab, or psoriasis. We also reviewed citations within articles to identify relevant sources. Implications for clinical care of patients with psoriasis are discussed based on expert recommendations and the authors’ clinical experience.
RESULTS
Effects of Psoriasis Treatment on Symptoms of Depression and Suicidality
Occurrences of attempted suicide and completed suicide have been reported during treatment with several psoriasis medications,7,9 raising concerns about whether these medications increase the risk for depression and SIB in an already vulnerable population. Wu and colleagues7 reviewed 11 studies published from 2006 to 2017 reporting the effects of medications for the treatment of psoriasis—adalimumab, apremilast, brodalumab, etanercept, and ustekinumab—on measures of depression and anxiety such as the Beck Depression Inventory, the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), and the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) 8. In each of the 11 studies, symptoms of depression improved after treatment, over time, or compared to placebo. Notably, the magnitude of improvement in symptoms of depression was not strongly linked to the magnitude of clinical improvement.7 Other recent studies have reported reductions in symptoms of depression with biologic therapies, including adalimumab, etanercept, guselkumab, ixekizumab, secukinumab, and ustekinumab.14-21
With respect to suicidality, an analysis of publicly available data found low rates of completed and attempted suicides (point estimates of 0.0–0.15 per 100 patient-years) in clinical development programs of apremilast, brodalumab, ixekizumab, and secukinumab. Patient suicidality in these trials often occurred in the context of risk factors or stressors such as work, financial difficulties, depression, and substance abuse.7 In a detailed 2016 analysis of suicidal behaviors during clinical trials of apremilast, brodalumab, etanercept, infliximab, ixekizumab, secukinumab, tofacitinib, ustekinumab, and other investigational agents, Gooderham and colleagues9 concluded that the behaviors may have resulted from the disease or patients’ psychosocial status rather than from treatment and that treatment with biologics does not increase the risk for SIB. Improvements in symptoms of depression during treatment suggest the potential to improve patients’ psychiatric outcomes with biologic treatment.9
Evidence From Brodalumab Studies
Intensive efforts have been made to assess the effect of brodalumab, a fully human anti–IL-17RA monoclonal antibody shown to be efficacious in the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, on symptoms of depression and to understand the incidence of SIB among patients receiving brodalumab in clinical trials.22-27
To examine the effects of brodalumab on symptoms of depression, the HADS questionnaire28 was administered to patients in 1 of 3 phase 3 clinical trials of brodalumab.23 A HADS score of 0 to 7 is considered normal, 8 to 10 is mild, 11 to 14 is moderate, and 15 to 21 is severe.23 The HADS questionnaire was administered to evaluate the presence and severity of depression and anxiety symptoms at baseline and at weeks 12, 24, 36, and 52.25 This scale was not used in the other 2 phase 3 studies of brodalumab because at the time those studies were initiated, there was no indication to include mental health screenings as part of the study protocol.
Patients were initially randomized to placebo (n=220), brodalumab 140 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W; n=219), or brodalumab 210 mg Q2W (the eventual approved dose; n=222) for 12 weeks.23 At week 12, patients initially randomized to placebo were switched to brodalumab through week 52. Patients initially randomized to brodalumab 210 mg Q2W were re-randomized to either placebo or brodalumab 210 mg Q2W.23 Depression and anxiety were common at baseline. Based on HADS scores, depression occurred among 27% and 26% of patients randomized to brodalumab and placebo, respectively; anxiety occurred in 36% of patients in each group.22 Among patients receiving brodalumab 210 mg Q2W from baseline to week 12, HADS depression scores improved in 67% of patients and worsened in 19%. In contrast, the proportion of patients receiving placebo whose depression scores improved (45%) was similar to the proportion whose scores worsened (38%). Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale anxiety scores also improved more often with brodalumab than with placebo.22
Furthermore, among patients who had moderate or severe depression or anxiety at baseline, a greater percentage experienced improvement with brodalumab than placebo.23 Among 30 patients with moderate to severe HADS depression scores at baseline who were treated with brodalumab 210 mg Q2W, 22 (73%) improved by at least 1 depression category by week 12; in the placebo group, 10 of 22 (45%) improved. Among patients with moderate or severe anxiety scores, 28 of 42 patients (67%) treated with brodalumab 210 mg Q2W improved by at least 1 anxiety category compared to 8 of 27 (30%) placebo-treated patients.23
Over 52 weeks, HADS depression and anxiety scores continued to show a pattern of improvement among patients receiving brodalumab vs placebo.25 Among patients initially receiving placebo, mean HADS depression scores were unchanged from baseline (5.3) to week 12 (5.5). After patients were switched to brodalumab 210 mg Q2W, there was a trend toward improvement between week 12 (5.4) and week 52 (3.1). Among patients initially treated with brodalumab 210 mg Q2W, mean depression scores fell from baseline (5.5) to week 12 (3.4), then rose again between weeks 12 (2.9) and 52 (3.5) in patients switched to placebo (Figure, A). The pattern of findings was similar for HADS anxiety scores (Figure, B).25 Overall,

SIB in Studies of Brodalumab
In addition to assessing the effect of brodalumab treatment on symptoms of depression and anxiety in patients with psoriasis, the brodalumab clinical trial program also tracked patterns of SIB among enrolled patients. In contrast with other clinical trials in which patients with a history of psychiatric disorders or substance abuse were excluded, clinical trials of brodalumab did not exclude patients with psychiatric disorders (eg, SIB, depression) and were therefore reflective of the real-world population of patients with moderate to severe psoriasis.22
In a recently published, detailed analysis of psychiatric adverse events (AEs) in the brodalumab clinical trials, data related to SIB in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis were analyzed from the placebo-controlled phases and open-label, long-term extensions of a placebo-controlled phase 2 clinical trial and from the previously mentioned 3 phase 3 clinical trials.22 From the initiation of the clinical trial program, AEs were monitored during all trials. In response to completed suicides during some studies, additional SIB evaluations were later added at the request of the US Food and Drug Administration, including the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale, the PHQ-8, and the Columbia Classification Algorithm for Suicide Assessment, to independently adjudicate SIB events.22
In total, 4464 patients in the brodalumab clinical trials received at least 1 dose of brodalumab, and 4126 of these patients received at least 1 dose of brodalumab 210 mg Q2W.22 Total exposure was 9174 patient-years of brodalumab, and mean exposure was 23 months. During the 52-week controlled phases of the clinical trials, 7 patients receiving brodalumab experienced any form of SIB event, representing a time-adjusted incidence rate of 0.20 events (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.08-0.41 events) per 100 patient-years of exposure. During the same 52-week period, patients receiving the comparator drug ustekinumab had an SIB rate of 0.60 events (95% CI, 0.12-1.74 events) per 100 patient-years, which was numerically higher than the rate with brodalumab. Inferential statistical analyses were not performed, but overlapping 95% CIs around these point estimates imply a similar level of SIB risk associated with each agent in these studies. During controlled and uncontrolled treatment periods in all studies, the SIB rate among brodalumab-treated patients was 0.37 events per 100 patient-years.22
Over all study phases, 3 completed suicides and 1 case adjudicated as indeterminate by the Columbia Classification Algorithm for Suicide Assessment review board were reported.22 All occurred in men aged 39 to 59 years. Of 6 patients with an AE of suicide attempt, all patients had at least 1 SIB risk factor and 3 had a history of SIB. The rate of SIB events was greater in patients with a history of depression (1.42) or suicidality (3.21) compared to those without any history of depression or suicidality (0.21 and 0.20, respectively).22 An examination of the regions in which the brodalumab studies were conducted showed generally consistent SIB incidence rates: 0.52, 0.29, 0.77, and 0 events per 100 patient-years in North America, Europe, Australia, and Russia, respectively.24
As previously described, depression and other risk factors for SIB are prevalent among patients with psoriasis. In addition, the rate of suicide mortality has increased substantially over the last decade in the general population, particularly among middle-aged white men,29 who made up much of the brodalumab clinical trial population.22 Therefore, even without treatment, it would not be surprising that SIB events occurred during the brodalumab trials. Most patients with SIB events during the trials had a history of predisposing risk factors.22 Prescribing information for brodalumab in the United States includes a boxed warning advising physicians to be aware of the risk of SIB as well as a statement that a causal relationship between SIB and brodalumab treatment has not been established.27
Despite the boxed warning in the brodalumab package insert concerning suicidality, a causal relationship between brodalumab treatment and increased risk of SIB has not been firmly established.27 The US boxed warning is based on 3 completed suicides and 1 case adjudicated as indeterminate among more than 4000 patients who received at least 1 dose of brodalumab during global clinical trials (0.07% [3/4464]). Compliance in the Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program is mandatory, and patient screening and counseling should not be minimized.27 The 3 completed suicides occurred in patients who reported a history of financial stressors, legal difficulties, or depression and anxiety, and they occurred at least 140 days after initiation of treatment with brodalumab, a chronology that does not support a strong association between brodalumab exposure and SIB.22 Taking into consideration the increased risk for depression among individuals with psoriasis and the details surrounding the 3 completed suicides, an evidence-based causal relationship between brodalumab and increased risk for suicidality cannot be concluded. However, physicians must assess risks and benefits of any therapy in the context of the individual patient’s preferences, risk factors, and response to treatment.
Dermatologists who are aware of the comorbidity between psoriasis and mood disorders play an important role in evaluating patients with psoriasis for psychiatric risk factors.30-32 The dermatologist should discuss with patients the relationship between psoriasis and depression, assess for any history of depression and SIB, and evaluate for signs and symptoms of depression and current SIB.33 Screening tools, including the HADS or the short, easily administered PHQ-234 or PHQ-4,35 can be used to assess whether patients have symptoms of depression.1,36,37 Patients at risk for depression or SIB should be referred to their primary care physician or a mental health care practitioner.37 Currently, there is a gap in knowledge in screening patients for psychiatric issues within the dermatology community33,38; however, health care providers can give support to help bridge this gap.
Acknowledgments
This study was sponsored by Amgen Inc. Medical writing support was provided under the direction of the authors by Lisa Baker, PhD, and Rebecca E. Slager, PhD, of MedThink SciCom (Cary, North Carolina) and funded by Ortho Dermatologics, a division of Bausch Health US, LLC.
- Koo J, Marangell LB, Nakamura M, et al. Depression and suicidality in psoriasis: review of the literature including the cytokine theory of depression. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:1999-2009.
- Singh S, Taylor C, Kornmehl H, et al. Psoriasis and suicidality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:425-440.e2.
- Chi CC, Chen TH, Wang SH, et al. Risk of suicidality in people with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:621-627.
- Dalgard FJ, Gieler U, Tomas-Aragones L, et al. The psychological burden of skin diseases: a cross-sectional multicenter study among dermatological out-patients in 13 European countries. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:984-991.
- Pompili M, Innamorati M, Trovarelli S, et al. Suicide risk and psychiatric comorbidity in patients with psoriasis. J Int Med Res. 2016;44:61-66.
- Pompili M, Innamorati M, Forte A, et al. Psychiatric comorbidity and suicidal ideation in psoriasis, melanoma and allergic disorders. Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract. 2017;21:209-214.
- Wu JJ, Feldman SR, Koo J, et al. Epidemiology of mental health comorbidity in psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2018;29:487-495.
- Dowlatshahi EA, Wakkee M, Arends LR, et al. The prevalence and odds of depressive symptoms and clinical depression in psoriasis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:1542-1551.
- Gooderham M, Gavino-Velasco J, Clifford C, et al. A review of psoriasis, therapies, and suicide. J Cutan Med Surg. 2016;20:293-303.
- Shah K, Mellars L, Changolkar A, et al. Real-world burden of comorbidities in US patients with psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:287-292.e4.
- Cohen BE, Martires KJ, Ho RS. Psoriasis and the risk of depression in the US population: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009-2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:73-79.
- Wu JJ, Penfold RB, Primatesta P, et al. The risk of depression, suicidal ideation and suicide attempt in patients with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:1168-1175.
- Pietrzak D, Pietrzak A, Krasowska D, et al. Depressiveness, measured with Beck Depression Inventory, in patients with psoriasis. J Affect Disord. 2017;209:229-234.
- Sator P. Safety and tolerability of adalimumab for the treatment of psoriasis: a review summarizing 15 years of real-life experience. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2018;9:147-158.
- Wu CY, Chang YT, Juan CK, et al. Depression and insomnia in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis taking tumor necrosis factor antagonists. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:E3816.
- Gordon KB, Blauvelt A, Foley P, et al. Efficacy of guselkumab in subpopulations of patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: a pooled analysis of the phase III VOYAGE 1 and VOYAGE 2 studies. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:132-139.
- Strober B, Gooderham M, de Jong EMGJ, et al. Depressive symptoms, depression, and the effect of biologic therapy among patients in Psoriasis Longitudinal Assessment and Registry (PSOLAR). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:70-80.
- Griffiths CEM, Fava M, Miller AH, et al. Impact of ixekizumab treatment on depressive symptoms and systemic inflammation in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis: an integrated analysis of three phase 3 clinical studies. Psychother Psychosom. 2017;86:260-267.
- Salame N, Ehsani-Chimeh N, Armstrong AW. Comparison of mental health outcomes among adults with psoriasis on biologic versus oral therapies: a population-based study. J Dermatolog Treat. 2019;30:135-140.
- Strober BE, Langley RGB, Menter A, et al. No elevated risk for depression, anxiety or suicidality with secukinumab in a pooled analysis of data from 10 clinical studies in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:E105-E107.
- Kim SJ, Park MY, Pak K, et al. Improvement of depressive symptoms in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis treated with ustekinumab: an open label trial validated using Beck Depression Inventory, Hamilton Depression Rating scale measures and 18fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET). J Dermatolog Treat. 2018;29:761-768.
- Lebwohl MG, Papp KA, Marangell LB, et al. Psychiatric adverse events during treatment with brodalumab: analysis of psoriasis clinical trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:81-89.e5.
- Papp KA, Reich K, Paul C, et al. A prospective phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of brodalumab in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:273-286.
- Feldman SR, Harris S, Rastogi S, et al. Distribution of depression and suicidality in a psoriasis clinical trial population. Poster presented at: Winter Clinical Dermatology Conference; January 12-17, 2018; Lahaina, HI.
- Gooderham M, Feldman SR, Harris S, et al. Effects of brodalumab on anxiety and depression in patients with psoriasis: results from a phase 3, randomized, controlled clinical trial (AMAGINE-1). Poster presented at: 76th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology; February 16-20, 2018; San Diego, CA.
- Lebwohl M, Strober B, Menter A, et al. Phase 3 studies comparing brodalumab with ustekinumab in psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1318-1328.
- Siliq (brodalumab)[package insert]. Bridgewater, NJ: Bausch Health US, LLC; 2017.
- Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1983;67:361-370.
- Hashim PW, Chen T, Lebwohl MG, et al. What lies beneath the face value of a box warning: a deeper look at brodalumab. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:S29-S34.
- Roubille C, Richer V, Starnino T, et al. Evidence-based recommendations for the management of comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis: expert opinion of the Canadian Dermatology-Rheumatology Comorbidity Initiative. J Rheumatol. 2015;42:1767-1780.
- Takeshita J, Grewal S, Langan SM, et al. Psoriasis and comorbid diseases: implications for management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:393-403.
- Gupta MA, Pur DR, Vujcic B, et al. Suicidal behaviors in the dermatology patient. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:302-311.
- Wu JJ. Contemporary management of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Am J Manag Care. 2017;23(21 suppl):S403-S416.
- Manea L, Gilbody S, Hewitt C, et al. Identifying depression with the PHQ-2: a diagnostic meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2016;203:382-395.
- Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB, et al. An ultra-brief screening scale for anxiety and depression: the PHQ-4. Psychosomatics. 2009;50:613-621.
- Lamb RC, Matcham F, Turner MA, et al. Screening for anxiety and depression in people with psoriasis: a cross-sectional study in a tertiary referral setting. Br J Dermatol. 2017;176:1028-1034.
- Dauden E, Blasco AJ, Bonanad C, et al. Position statement for the management of comorbidities in psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:2058-2073.
- Moon HS, Mizara A, McBride SR. Psoriasis and psycho-dermatology. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2013;3:117-130.
- Koo J, Marangell LB, Nakamura M, et al. Depression and suicidality in psoriasis: review of the literature including the cytokine theory of depression. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:1999-2009.
- Singh S, Taylor C, Kornmehl H, et al. Psoriasis and suicidality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:425-440.e2.
- Chi CC, Chen TH, Wang SH, et al. Risk of suicidality in people with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:621-627.
- Dalgard FJ, Gieler U, Tomas-Aragones L, et al. The psychological burden of skin diseases: a cross-sectional multicenter study among dermatological out-patients in 13 European countries. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:984-991.
- Pompili M, Innamorati M, Trovarelli S, et al. Suicide risk and psychiatric comorbidity in patients with psoriasis. J Int Med Res. 2016;44:61-66.
- Pompili M, Innamorati M, Forte A, et al. Psychiatric comorbidity and suicidal ideation in psoriasis, melanoma and allergic disorders. Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract. 2017;21:209-214.
- Wu JJ, Feldman SR, Koo J, et al. Epidemiology of mental health comorbidity in psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2018;29:487-495.
- Dowlatshahi EA, Wakkee M, Arends LR, et al. The prevalence and odds of depressive symptoms and clinical depression in psoriasis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:1542-1551.
- Gooderham M, Gavino-Velasco J, Clifford C, et al. A review of psoriasis, therapies, and suicide. J Cutan Med Surg. 2016;20:293-303.
- Shah K, Mellars L, Changolkar A, et al. Real-world burden of comorbidities in US patients with psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:287-292.e4.
- Cohen BE, Martires KJ, Ho RS. Psoriasis and the risk of depression in the US population: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009-2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:73-79.
- Wu JJ, Penfold RB, Primatesta P, et al. The risk of depression, suicidal ideation and suicide attempt in patients with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:1168-1175.
- Pietrzak D, Pietrzak A, Krasowska D, et al. Depressiveness, measured with Beck Depression Inventory, in patients with psoriasis. J Affect Disord. 2017;209:229-234.
- Sator P. Safety and tolerability of adalimumab for the treatment of psoriasis: a review summarizing 15 years of real-life experience. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2018;9:147-158.
- Wu CY, Chang YT, Juan CK, et al. Depression and insomnia in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis taking tumor necrosis factor antagonists. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:E3816.
- Gordon KB, Blauvelt A, Foley P, et al. Efficacy of guselkumab in subpopulations of patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: a pooled analysis of the phase III VOYAGE 1 and VOYAGE 2 studies. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:132-139.
- Strober B, Gooderham M, de Jong EMGJ, et al. Depressive symptoms, depression, and the effect of biologic therapy among patients in Psoriasis Longitudinal Assessment and Registry (PSOLAR). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:70-80.
- Griffiths CEM, Fava M, Miller AH, et al. Impact of ixekizumab treatment on depressive symptoms and systemic inflammation in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis: an integrated analysis of three phase 3 clinical studies. Psychother Psychosom. 2017;86:260-267.
- Salame N, Ehsani-Chimeh N, Armstrong AW. Comparison of mental health outcomes among adults with psoriasis on biologic versus oral therapies: a population-based study. J Dermatolog Treat. 2019;30:135-140.
- Strober BE, Langley RGB, Menter A, et al. No elevated risk for depression, anxiety or suicidality with secukinumab in a pooled analysis of data from 10 clinical studies in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:E105-E107.
- Kim SJ, Park MY, Pak K, et al. Improvement of depressive symptoms in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis treated with ustekinumab: an open label trial validated using Beck Depression Inventory, Hamilton Depression Rating scale measures and 18fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET). J Dermatolog Treat. 2018;29:761-768.
- Lebwohl MG, Papp KA, Marangell LB, et al. Psychiatric adverse events during treatment with brodalumab: analysis of psoriasis clinical trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:81-89.e5.
- Papp KA, Reich K, Paul C, et al. A prospective phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of brodalumab in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:273-286.
- Feldman SR, Harris S, Rastogi S, et al. Distribution of depression and suicidality in a psoriasis clinical trial population. Poster presented at: Winter Clinical Dermatology Conference; January 12-17, 2018; Lahaina, HI.
- Gooderham M, Feldman SR, Harris S, et al. Effects of brodalumab on anxiety and depression in patients with psoriasis: results from a phase 3, randomized, controlled clinical trial (AMAGINE-1). Poster presented at: 76th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology; February 16-20, 2018; San Diego, CA.
- Lebwohl M, Strober B, Menter A, et al. Phase 3 studies comparing brodalumab with ustekinumab in psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1318-1328.
- Siliq (brodalumab)[package insert]. Bridgewater, NJ: Bausch Health US, LLC; 2017.
- Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1983;67:361-370.
- Hashim PW, Chen T, Lebwohl MG, et al. What lies beneath the face value of a box warning: a deeper look at brodalumab. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:S29-S34.
- Roubille C, Richer V, Starnino T, et al. Evidence-based recommendations for the management of comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis: expert opinion of the Canadian Dermatology-Rheumatology Comorbidity Initiative. J Rheumatol. 2015;42:1767-1780.
- Takeshita J, Grewal S, Langan SM, et al. Psoriasis and comorbid diseases: implications for management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:393-403.
- Gupta MA, Pur DR, Vujcic B, et al. Suicidal behaviors in the dermatology patient. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:302-311.
- Wu JJ. Contemporary management of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Am J Manag Care. 2017;23(21 suppl):S403-S416.
- Manea L, Gilbody S, Hewitt C, et al. Identifying depression with the PHQ-2: a diagnostic meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2016;203:382-395.
- Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB, et al. An ultra-brief screening scale for anxiety and depression: the PHQ-4. Psychosomatics. 2009;50:613-621.
- Lamb RC, Matcham F, Turner MA, et al. Screening for anxiety and depression in people with psoriasis: a cross-sectional study in a tertiary referral setting. Br J Dermatol. 2017;176:1028-1034.
- Dauden E, Blasco AJ, Bonanad C, et al. Position statement for the management of comorbidities in psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:2058-2073.
- Moon HS, Mizara A, McBride SR. Psoriasis and psycho-dermatology. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2013;3:117-130.
Practice Points
- Psoriasis elevates the risk for depression and possible suicide.
- Dermatologists should be aware that the brodalumab package insert has a boxed warning stating that there is no established causal association between treatment with brodalumab and increased risk for suicidal ideation and behavior.
- Clinicians are urged to evaluate patients with psoriasis for psychiatric risk factors regardless of their therapy.
FDA approves infliximab-axxq for numerous indications
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the biosimilar infliximab-axxq (Avsola) for various indications, making it the fourth biosimilar of infliximab (Remicade) to be cleared for marketing by the agency.
The tumor necrosis factor inhibitor is indicated for patients with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis who are aged 6 years and older, RA in combination with methotrexate, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, and plaque psoriasis. The approval is based on numerous trials. The most common adverse reactions are infections, infusion-related reactions, headache, and abdominal pain.
Full prescribing information can be found on the FDA website, as can more information about biosimilars.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the biosimilar infliximab-axxq (Avsola) for various indications, making it the fourth biosimilar of infliximab (Remicade) to be cleared for marketing by the agency.
The tumor necrosis factor inhibitor is indicated for patients with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis who are aged 6 years and older, RA in combination with methotrexate, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, and plaque psoriasis. The approval is based on numerous trials. The most common adverse reactions are infections, infusion-related reactions, headache, and abdominal pain.
Full prescribing information can be found on the FDA website, as can more information about biosimilars.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the biosimilar infliximab-axxq (Avsola) for various indications, making it the fourth biosimilar of infliximab (Remicade) to be cleared for marketing by the agency.
The tumor necrosis factor inhibitor is indicated for patients with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis who are aged 6 years and older, RA in combination with methotrexate, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, and plaque psoriasis. The approval is based on numerous trials. The most common adverse reactions are infections, infusion-related reactions, headache, and abdominal pain.
Full prescribing information can be found on the FDA website, as can more information about biosimilars.
Certolizumab safety profile varies widely across indications
MADRID – , Andrew Blauvelt, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
He presented a comprehensive analysis of safety data from all 49 clinical trials of the tumor necrosis factor inhibitor for its approved indications. The data set included 11,317 patients who received certolizumab for a collective 21,695 person-years in 27 trials in rheumatoid arthritis patients, 5 in psoriasis, 15 for Crohn’s disease, and one trial each for axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis.
“It’s not real-world data, but it is a large group of patients [studied] over many years,” noted Dr. Blauvelt, a dermatologist and president of the Oregon Medical Research Center, Portland.
As a renowned authority on psoriasis, he was part of a multidisciplinary expert panel commissioned by UCB to analyze serious adverse events in the complete clinical trials experience involving the company’s tumor necrosis factor inhibitor certolizumab (Cimzia). The panel included experts from rheumatology, gastroenterology, epidemiology, and other disciplines.
The key takeaway: “When you think about the serious side effects of the drug, you have to think about what the indication is, whether the patients are on systemic corticosteroids, and whether they’re heavy or not,” Dr. Blauvelt said.
Take, for example, the risk of serious infections requiring treatment with intravenous antibiotics. The incidence rates ranged from a low of 1.5 per 100 patient-years in psoriasis patients on certolizumab to a high of 5.97 in those with Crohn’s disease, with rates of 3.44 cases per 100 patient-years among rheumatoid arthritis patients and 1.64-1.67 in those with psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis, respectively. Patients with Crohn’s disease were 2.22-fold more likely than were those with rheumatoid arthritis to experience a serious infection during their clinical trial experience on certolizumab. In contrast, psoriasis patients had a 52% relative risk reduction and those with psoriatic arthritis were 31% less likely to develop a serious infection compared with those with rheumatoid arthritis.
The explanation for these highly variable serious infection rates lies in part on the huge differences in the concurrent use of systemic corticosteroids with certolizumab across indications. A mere 3.3% of psoriasis patients were also on steroids, compared with 46.2% of rheumatoid arthritis patients, 50.8% of those with ankylosing spondylitis, and about 25% of the Crohn’s disease and psoriatic arthritis patients, he noted.
Advanced age was independently associated with increased risk of serious infections. Patients aged 65 or older were 1.68-fold more likely to experience this event than were those under age 45. And patients whose disease duration was 10 years or more at baseline had a 1.36-fold increased serious infection risk compared with those who had less than a 1-year-long disease history, independent of which disease they had.
The prevalence of baseline obesity varied by indication. The mean body mass index was 30.1 kg/m2 in the psoriasis patients, 29.8 kg/m2 in those with psoriatic arthritis, lowest at 24 kg/m2 in Crohn’s disease patients, and a bit over 27 kg/m2 in those with rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis.
Obesity alone was not an independent risk factor for serious infection in certolizumab-treated patients; however, the combination of a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or more plus systemic corticosteroid use was associated with a greater risk than with steroids alone.
Based upon a multivariate regression analysis adjusted for age, sex, indication, disease duration, use of methotrexate, and prior use of other TNF inhibitors, the investigators calculated that in patients with Crohn’s disease 16.6% of serious infections in patients on certolizumab were attributable to systemic corticosteroid use.
Risks of major adverse cardiovascular events and cancer on certolizumab
The risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) while on certolizumab ranged from a high of 0.62 MACE events per 100 patient-years in the rheumatoid arthritis population to a low of 0.1 per 100 patient-years in patients treated for Crohn’s disease or ankylosing spondylitis. Psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis patients had MACE rates of 0.27 and 0.54, respectively.
Obesity was independently associated with increased risk of an acute MI and other MACEs. So was advanced age. No surprises there. The investigators calculated that 16.7% of MACEs in patients on certolizumab were attributable to obesity and another 20.9% were attributable to use of systemic corticosteroids.
The incidence rate for all malignancies, including nonmelanoma skin cancer, ranged from a low of 0.46 cases per 100 patient-years in the psoriatic arthritis cohort on certolizumab to a high of 0.93 in those with rheumatoid arthritis, with rates of 0.68, 0.73, and 0.51 in patients with psoriasis, Crohn’s disease, and ankylosing spondylitis, respectively.
Neither systemic corticosteroids, obesity, disease duration, or prior exposure to a TNF inhibitor was linked to increased risk of cancer in patients on certolizumab. The standout risk factor was age: Patients who were 65 or older at baseline were 11.4-fold more likely to develop cancer during participation in their clinical trial than were those younger than 45. Those who were 45 to 65 years old were 4.3-fold more likely to be diagnosed with a malignancy than were those younger than age 45.
Of note, concomitant use of methotrexate was associated with a statistically significant 28% reduction in malignancy risk.
Dr. Blauvelt reported serving as a consultant to and receiving research funding from UCB, the study sponsor, as well as more than two dozen other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Blauvelt A. EADV Congress, Abstract FC04.06.
MADRID – , Andrew Blauvelt, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
He presented a comprehensive analysis of safety data from all 49 clinical trials of the tumor necrosis factor inhibitor for its approved indications. The data set included 11,317 patients who received certolizumab for a collective 21,695 person-years in 27 trials in rheumatoid arthritis patients, 5 in psoriasis, 15 for Crohn’s disease, and one trial each for axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis.
“It’s not real-world data, but it is a large group of patients [studied] over many years,” noted Dr. Blauvelt, a dermatologist and president of the Oregon Medical Research Center, Portland.
As a renowned authority on psoriasis, he was part of a multidisciplinary expert panel commissioned by UCB to analyze serious adverse events in the complete clinical trials experience involving the company’s tumor necrosis factor inhibitor certolizumab (Cimzia). The panel included experts from rheumatology, gastroenterology, epidemiology, and other disciplines.
The key takeaway: “When you think about the serious side effects of the drug, you have to think about what the indication is, whether the patients are on systemic corticosteroids, and whether they’re heavy or not,” Dr. Blauvelt said.
Take, for example, the risk of serious infections requiring treatment with intravenous antibiotics. The incidence rates ranged from a low of 1.5 per 100 patient-years in psoriasis patients on certolizumab to a high of 5.97 in those with Crohn’s disease, with rates of 3.44 cases per 100 patient-years among rheumatoid arthritis patients and 1.64-1.67 in those with psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis, respectively. Patients with Crohn’s disease were 2.22-fold more likely than were those with rheumatoid arthritis to experience a serious infection during their clinical trial experience on certolizumab. In contrast, psoriasis patients had a 52% relative risk reduction and those with psoriatic arthritis were 31% less likely to develop a serious infection compared with those with rheumatoid arthritis.
The explanation for these highly variable serious infection rates lies in part on the huge differences in the concurrent use of systemic corticosteroids with certolizumab across indications. A mere 3.3% of psoriasis patients were also on steroids, compared with 46.2% of rheumatoid arthritis patients, 50.8% of those with ankylosing spondylitis, and about 25% of the Crohn’s disease and psoriatic arthritis patients, he noted.
Advanced age was independently associated with increased risk of serious infections. Patients aged 65 or older were 1.68-fold more likely to experience this event than were those under age 45. And patients whose disease duration was 10 years or more at baseline had a 1.36-fold increased serious infection risk compared with those who had less than a 1-year-long disease history, independent of which disease they had.
The prevalence of baseline obesity varied by indication. The mean body mass index was 30.1 kg/m2 in the psoriasis patients, 29.8 kg/m2 in those with psoriatic arthritis, lowest at 24 kg/m2 in Crohn’s disease patients, and a bit over 27 kg/m2 in those with rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis.
Obesity alone was not an independent risk factor for serious infection in certolizumab-treated patients; however, the combination of a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or more plus systemic corticosteroid use was associated with a greater risk than with steroids alone.
Based upon a multivariate regression analysis adjusted for age, sex, indication, disease duration, use of methotrexate, and prior use of other TNF inhibitors, the investigators calculated that in patients with Crohn’s disease 16.6% of serious infections in patients on certolizumab were attributable to systemic corticosteroid use.
Risks of major adverse cardiovascular events and cancer on certolizumab
The risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) while on certolizumab ranged from a high of 0.62 MACE events per 100 patient-years in the rheumatoid arthritis population to a low of 0.1 per 100 patient-years in patients treated for Crohn’s disease or ankylosing spondylitis. Psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis patients had MACE rates of 0.27 and 0.54, respectively.
Obesity was independently associated with increased risk of an acute MI and other MACEs. So was advanced age. No surprises there. The investigators calculated that 16.7% of MACEs in patients on certolizumab were attributable to obesity and another 20.9% were attributable to use of systemic corticosteroids.
The incidence rate for all malignancies, including nonmelanoma skin cancer, ranged from a low of 0.46 cases per 100 patient-years in the psoriatic arthritis cohort on certolizumab to a high of 0.93 in those with rheumatoid arthritis, with rates of 0.68, 0.73, and 0.51 in patients with psoriasis, Crohn’s disease, and ankylosing spondylitis, respectively.
Neither systemic corticosteroids, obesity, disease duration, or prior exposure to a TNF inhibitor was linked to increased risk of cancer in patients on certolizumab. The standout risk factor was age: Patients who were 65 or older at baseline were 11.4-fold more likely to develop cancer during participation in their clinical trial than were those younger than 45. Those who were 45 to 65 years old were 4.3-fold more likely to be diagnosed with a malignancy than were those younger than age 45.
Of note, concomitant use of methotrexate was associated with a statistically significant 28% reduction in malignancy risk.
Dr. Blauvelt reported serving as a consultant to and receiving research funding from UCB, the study sponsor, as well as more than two dozen other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Blauvelt A. EADV Congress, Abstract FC04.06.
MADRID – , Andrew Blauvelt, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
He presented a comprehensive analysis of safety data from all 49 clinical trials of the tumor necrosis factor inhibitor for its approved indications. The data set included 11,317 patients who received certolizumab for a collective 21,695 person-years in 27 trials in rheumatoid arthritis patients, 5 in psoriasis, 15 for Crohn’s disease, and one trial each for axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis.
“It’s not real-world data, but it is a large group of patients [studied] over many years,” noted Dr. Blauvelt, a dermatologist and president of the Oregon Medical Research Center, Portland.
As a renowned authority on psoriasis, he was part of a multidisciplinary expert panel commissioned by UCB to analyze serious adverse events in the complete clinical trials experience involving the company’s tumor necrosis factor inhibitor certolizumab (Cimzia). The panel included experts from rheumatology, gastroenterology, epidemiology, and other disciplines.
The key takeaway: “When you think about the serious side effects of the drug, you have to think about what the indication is, whether the patients are on systemic corticosteroids, and whether they’re heavy or not,” Dr. Blauvelt said.
Take, for example, the risk of serious infections requiring treatment with intravenous antibiotics. The incidence rates ranged from a low of 1.5 per 100 patient-years in psoriasis patients on certolizumab to a high of 5.97 in those with Crohn’s disease, with rates of 3.44 cases per 100 patient-years among rheumatoid arthritis patients and 1.64-1.67 in those with psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis, respectively. Patients with Crohn’s disease were 2.22-fold more likely than were those with rheumatoid arthritis to experience a serious infection during their clinical trial experience on certolizumab. In contrast, psoriasis patients had a 52% relative risk reduction and those with psoriatic arthritis were 31% less likely to develop a serious infection compared with those with rheumatoid arthritis.
The explanation for these highly variable serious infection rates lies in part on the huge differences in the concurrent use of systemic corticosteroids with certolizumab across indications. A mere 3.3% of psoriasis patients were also on steroids, compared with 46.2% of rheumatoid arthritis patients, 50.8% of those with ankylosing spondylitis, and about 25% of the Crohn’s disease and psoriatic arthritis patients, he noted.
Advanced age was independently associated with increased risk of serious infections. Patients aged 65 or older were 1.68-fold more likely to experience this event than were those under age 45. And patients whose disease duration was 10 years or more at baseline had a 1.36-fold increased serious infection risk compared with those who had less than a 1-year-long disease history, independent of which disease they had.
The prevalence of baseline obesity varied by indication. The mean body mass index was 30.1 kg/m2 in the psoriasis patients, 29.8 kg/m2 in those with psoriatic arthritis, lowest at 24 kg/m2 in Crohn’s disease patients, and a bit over 27 kg/m2 in those with rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis.
Obesity alone was not an independent risk factor for serious infection in certolizumab-treated patients; however, the combination of a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or more plus systemic corticosteroid use was associated with a greater risk than with steroids alone.
Based upon a multivariate regression analysis adjusted for age, sex, indication, disease duration, use of methotrexate, and prior use of other TNF inhibitors, the investigators calculated that in patients with Crohn’s disease 16.6% of serious infections in patients on certolizumab were attributable to systemic corticosteroid use.
Risks of major adverse cardiovascular events and cancer on certolizumab
The risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) while on certolizumab ranged from a high of 0.62 MACE events per 100 patient-years in the rheumatoid arthritis population to a low of 0.1 per 100 patient-years in patients treated for Crohn’s disease or ankylosing spondylitis. Psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis patients had MACE rates of 0.27 and 0.54, respectively.
Obesity was independently associated with increased risk of an acute MI and other MACEs. So was advanced age. No surprises there. The investigators calculated that 16.7% of MACEs in patients on certolizumab were attributable to obesity and another 20.9% were attributable to use of systemic corticosteroids.
The incidence rate for all malignancies, including nonmelanoma skin cancer, ranged from a low of 0.46 cases per 100 patient-years in the psoriatic arthritis cohort on certolizumab to a high of 0.93 in those with rheumatoid arthritis, with rates of 0.68, 0.73, and 0.51 in patients with psoriasis, Crohn’s disease, and ankylosing spondylitis, respectively.
Neither systemic corticosteroids, obesity, disease duration, or prior exposure to a TNF inhibitor was linked to increased risk of cancer in patients on certolizumab. The standout risk factor was age: Patients who were 65 or older at baseline were 11.4-fold more likely to develop cancer during participation in their clinical trial than were those younger than 45. Those who were 45 to 65 years old were 4.3-fold more likely to be diagnosed with a malignancy than were those younger than age 45.
Of note, concomitant use of methotrexate was associated with a statistically significant 28% reduction in malignancy risk.
Dr. Blauvelt reported serving as a consultant to and receiving research funding from UCB, the study sponsor, as well as more than two dozen other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Blauvelt A. EADV Congress, Abstract FC04.06.
REPORTING FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
Pediatric dermatology update: New research offers insight into psoriasis, alopecia
LAS VEGAS – Recent research is offering new insights into psoriasis and alopecia in the pediatric population, a dermatologist told colleagues, and it’s time to be on the lookout for psoriasis linked to treatment with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors.
Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, at the University of California, San Diego, offered these tips and comments in a presentation at Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar:
Psoriasis
It’s a brand new day for adult psoriasis sufferers, but it seems to be only a brand new morning for their pediatric counterparts. “Kids and teenagers were left behind in the biologic revolution,” Dr. Eichenfield said. “Only two systemic biologics have been approved for psoriasis in children.” They are ustekinumab (Stelara), approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating psoriasis in children aged 12 years and older, and etanercept, approved for aged 4 years and older.
The good news, he said, is that “our new biologic agents are now being studied in children.”
Research is also providing new insight into pediatric psoriasis, said Dr. Eichenfield, who is also chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego. It’s now clear that “there’s a lot more facial involvement, and a high involvement of scalp and nail,” he noted.
It’s also clear, he said, that inflammation begins early in pediatric psoriasis. That raises the question of whether it’s a good idea to launch aggressive treatment to stop the “psoriatic march” toward cardiovascular and other medical problems down the line, he commented.
“Keep an open mind to getting aggressive in therapy,” he advised, although he acknowledged that “it’s hard to get beyond the two biologics, and only one is approved for children under 12.”
Dr. Eichenfield advised colleagues to keep an eye out for TNF inhibitor–induced psoriasis. “We’re seeing it pretty regularly,” he said, commonly in children who are treated with TNF inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis or Crohn’s disease.
The lesions “look like dermatitis but are very psoriasiform,” he said, and research suggests this can appear after a single dose or after as many as 63 months of treatment. Topical and light therapy can be helpful. But if those treatments do not help, he said, it’s time to consider changing the biologic that the patient is taking. “Is the biologic adequately controlling their underlying disease? If not, you can help find one that would be great for their underlying disease and clear up their psoriasis.”
Alopecia
Pediatric alopecia “is a problem I see pretty regularly in practice,” Dr. Eichenfield said. When he sees patients with alopecia, he says that, “‘if your child doesn’t have 50% hair loss, you’re in the good group. It will generally heal up and never come back again.’ ”
He referred to a recent study, where investigators at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia retrospectively studied 125 children under age 4 years who were diagnosed with alopecia areata and followed for 2 years. Over time, those children with over 50% of hair loss initially were more likely to have worsening Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) scores over the follow-up period. But a high proportion of those with mild alopecia initially continued to have mild alopecia at follow-up (Pediatr Dermatol. 2019 Aug 29. doi: 10.1111/pde.13990).
Dr. Eichenfield noted that the study found that 41% of the patients also had atopic dermatitis.
He also highlighted two other recent studies on pediatric alopecia: One found that while vitamin D levels were low in a majority of children with alopecia in the study, the proportion who had a deficiency was similar to the proportion in a larger pediatric population, at about 22% in both groups (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Sep;79(3):e43-e44). Supplementation doesn’t seem to help. “It’s not important to test levels,” he said.
Another study examined whether it’s a good idea to test patients for celiac disease in children with alopecia (Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jul;35[4]:535-8). Some parents may ask this question, but the answer, he said, is generally no.
What’s next? “We were hoping oral and topical JAK inhibitors would work well” in this population, Dr. Eichenfield said, but study findings haven’t been promising.
Still, oral tofacitinib (Xeljanz) showed some “pretty impressive” success in a recent study in four children, he noted. Based on the results, the authors wrote that “we suggest that, after proper counseling regarding the risks, including severe infection and malignancy, the use of tofacitinib may be considered for preadolescent children with AA [alopecia areata] who are experiencing psychosocial impairment” (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Feb;80[2]:568-70).
In general, Dr. Eichenfield said, research on pediatric alopecia “will be secondary, especially with JAK inhibitors because of the risk of side effects. But [children will] probably tolerate them better than adults do because they have fewer medical problems.”
Meanwhile, he added, controversy continues to swirl around how to treat children over age 10 years who have lost 50% or more of their hair. “I’ve seen hundreds of kids with alopecia areata,” he said, “and I can’t predict what the course may be.”
Dr. Eichenfield reports multiple relationships (consultant or investigator) with various pharmaceutical companies, including Abbvie, Allergan, Lilly, Novartis, and others. SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – Recent research is offering new insights into psoriasis and alopecia in the pediatric population, a dermatologist told colleagues, and it’s time to be on the lookout for psoriasis linked to treatment with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors.
Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, at the University of California, San Diego, offered these tips and comments in a presentation at Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar:
Psoriasis
It’s a brand new day for adult psoriasis sufferers, but it seems to be only a brand new morning for their pediatric counterparts. “Kids and teenagers were left behind in the biologic revolution,” Dr. Eichenfield said. “Only two systemic biologics have been approved for psoriasis in children.” They are ustekinumab (Stelara), approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating psoriasis in children aged 12 years and older, and etanercept, approved for aged 4 years and older.
The good news, he said, is that “our new biologic agents are now being studied in children.”
Research is also providing new insight into pediatric psoriasis, said Dr. Eichenfield, who is also chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego. It’s now clear that “there’s a lot more facial involvement, and a high involvement of scalp and nail,” he noted.
It’s also clear, he said, that inflammation begins early in pediatric psoriasis. That raises the question of whether it’s a good idea to launch aggressive treatment to stop the “psoriatic march” toward cardiovascular and other medical problems down the line, he commented.
“Keep an open mind to getting aggressive in therapy,” he advised, although he acknowledged that “it’s hard to get beyond the two biologics, and only one is approved for children under 12.”
Dr. Eichenfield advised colleagues to keep an eye out for TNF inhibitor–induced psoriasis. “We’re seeing it pretty regularly,” he said, commonly in children who are treated with TNF inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis or Crohn’s disease.
The lesions “look like dermatitis but are very psoriasiform,” he said, and research suggests this can appear after a single dose or after as many as 63 months of treatment. Topical and light therapy can be helpful. But if those treatments do not help, he said, it’s time to consider changing the biologic that the patient is taking. “Is the biologic adequately controlling their underlying disease? If not, you can help find one that would be great for their underlying disease and clear up their psoriasis.”
Alopecia
Pediatric alopecia “is a problem I see pretty regularly in practice,” Dr. Eichenfield said. When he sees patients with alopecia, he says that, “‘if your child doesn’t have 50% hair loss, you’re in the good group. It will generally heal up and never come back again.’ ”
He referred to a recent study, where investigators at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia retrospectively studied 125 children under age 4 years who were diagnosed with alopecia areata and followed for 2 years. Over time, those children with over 50% of hair loss initially were more likely to have worsening Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) scores over the follow-up period. But a high proportion of those with mild alopecia initially continued to have mild alopecia at follow-up (Pediatr Dermatol. 2019 Aug 29. doi: 10.1111/pde.13990).
Dr. Eichenfield noted that the study found that 41% of the patients also had atopic dermatitis.
He also highlighted two other recent studies on pediatric alopecia: One found that while vitamin D levels were low in a majority of children with alopecia in the study, the proportion who had a deficiency was similar to the proportion in a larger pediatric population, at about 22% in both groups (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Sep;79(3):e43-e44). Supplementation doesn’t seem to help. “It’s not important to test levels,” he said.
Another study examined whether it’s a good idea to test patients for celiac disease in children with alopecia (Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jul;35[4]:535-8). Some parents may ask this question, but the answer, he said, is generally no.
What’s next? “We were hoping oral and topical JAK inhibitors would work well” in this population, Dr. Eichenfield said, but study findings haven’t been promising.
Still, oral tofacitinib (Xeljanz) showed some “pretty impressive” success in a recent study in four children, he noted. Based on the results, the authors wrote that “we suggest that, after proper counseling regarding the risks, including severe infection and malignancy, the use of tofacitinib may be considered for preadolescent children with AA [alopecia areata] who are experiencing psychosocial impairment” (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Feb;80[2]:568-70).
In general, Dr. Eichenfield said, research on pediatric alopecia “will be secondary, especially with JAK inhibitors because of the risk of side effects. But [children will] probably tolerate them better than adults do because they have fewer medical problems.”
Meanwhile, he added, controversy continues to swirl around how to treat children over age 10 years who have lost 50% or more of their hair. “I’ve seen hundreds of kids with alopecia areata,” he said, “and I can’t predict what the course may be.”
Dr. Eichenfield reports multiple relationships (consultant or investigator) with various pharmaceutical companies, including Abbvie, Allergan, Lilly, Novartis, and others. SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – Recent research is offering new insights into psoriasis and alopecia in the pediatric population, a dermatologist told colleagues, and it’s time to be on the lookout for psoriasis linked to treatment with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors.
Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, at the University of California, San Diego, offered these tips and comments in a presentation at Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar:
Psoriasis
It’s a brand new day for adult psoriasis sufferers, but it seems to be only a brand new morning for their pediatric counterparts. “Kids and teenagers were left behind in the biologic revolution,” Dr. Eichenfield said. “Only two systemic biologics have been approved for psoriasis in children.” They are ustekinumab (Stelara), approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating psoriasis in children aged 12 years and older, and etanercept, approved for aged 4 years and older.
The good news, he said, is that “our new biologic agents are now being studied in children.”
Research is also providing new insight into pediatric psoriasis, said Dr. Eichenfield, who is also chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego. It’s now clear that “there’s a lot more facial involvement, and a high involvement of scalp and nail,” he noted.
It’s also clear, he said, that inflammation begins early in pediatric psoriasis. That raises the question of whether it’s a good idea to launch aggressive treatment to stop the “psoriatic march” toward cardiovascular and other medical problems down the line, he commented.
“Keep an open mind to getting aggressive in therapy,” he advised, although he acknowledged that “it’s hard to get beyond the two biologics, and only one is approved for children under 12.”
Dr. Eichenfield advised colleagues to keep an eye out for TNF inhibitor–induced psoriasis. “We’re seeing it pretty regularly,” he said, commonly in children who are treated with TNF inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis or Crohn’s disease.
The lesions “look like dermatitis but are very psoriasiform,” he said, and research suggests this can appear after a single dose or after as many as 63 months of treatment. Topical and light therapy can be helpful. But if those treatments do not help, he said, it’s time to consider changing the biologic that the patient is taking. “Is the biologic adequately controlling their underlying disease? If not, you can help find one that would be great for their underlying disease and clear up their psoriasis.”
Alopecia
Pediatric alopecia “is a problem I see pretty regularly in practice,” Dr. Eichenfield said. When he sees patients with alopecia, he says that, “‘if your child doesn’t have 50% hair loss, you’re in the good group. It will generally heal up and never come back again.’ ”
He referred to a recent study, where investigators at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia retrospectively studied 125 children under age 4 years who were diagnosed with alopecia areata and followed for 2 years. Over time, those children with over 50% of hair loss initially were more likely to have worsening Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) scores over the follow-up period. But a high proportion of those with mild alopecia initially continued to have mild alopecia at follow-up (Pediatr Dermatol. 2019 Aug 29. doi: 10.1111/pde.13990).
Dr. Eichenfield noted that the study found that 41% of the patients also had atopic dermatitis.
He also highlighted two other recent studies on pediatric alopecia: One found that while vitamin D levels were low in a majority of children with alopecia in the study, the proportion who had a deficiency was similar to the proportion in a larger pediatric population, at about 22% in both groups (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Sep;79(3):e43-e44). Supplementation doesn’t seem to help. “It’s not important to test levels,” he said.
Another study examined whether it’s a good idea to test patients for celiac disease in children with alopecia (Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jul;35[4]:535-8). Some parents may ask this question, but the answer, he said, is generally no.
What’s next? “We were hoping oral and topical JAK inhibitors would work well” in this population, Dr. Eichenfield said, but study findings haven’t been promising.
Still, oral tofacitinib (Xeljanz) showed some “pretty impressive” success in a recent study in four children, he noted. Based on the results, the authors wrote that “we suggest that, after proper counseling regarding the risks, including severe infection and malignancy, the use of tofacitinib may be considered for preadolescent children with AA [alopecia areata] who are experiencing psychosocial impairment” (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Feb;80[2]:568-70).
In general, Dr. Eichenfield said, research on pediatric alopecia “will be secondary, especially with JAK inhibitors because of the risk of side effects. But [children will] probably tolerate them better than adults do because they have fewer medical problems.”
Meanwhile, he added, controversy continues to swirl around how to treat children over age 10 years who have lost 50% or more of their hair. “I’ve seen hundreds of kids with alopecia areata,” he said, “and I can’t predict what the course may be.”
Dr. Eichenfield reports multiple relationships (consultant or investigator) with various pharmaceutical companies, including Abbvie, Allergan, Lilly, Novartis, and others. SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM SDEF LAS VEGAS DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
In psoriasis, methotrexate and other older drugs can still be useful
LAS VEGAS – While biologics have dramatically changed the picture, drugs like , a dermatologist told colleagues.
However, caution is necessary, especially when the drugs are used in combination with biologics, Bruce E. Strober, MD, PhD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and Central Connecticut Dermatology, Cromwell, Conn., said at Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
Dr. Strober offered these tips about the proper use of these four drugs in psoriasis patients:
Acitretin (Soriatane). “This was used as monotherapy initially, but at this point in history, fewer and fewer patients are getting it as monotherapy,” he said. A dose of 25 mg/day appears to provide the best mix of efficacy and side-effect control, “although it’s not a high-efficacy drug, especially at 25 mg a day. It’s a slow-acting drug, and you may need 4 if not 6 months to see the maximum effect before you give up on it.”
What about using acitretin in combination with other therapies? Studies examining its use with phototherapy haven’t been promising, Dr. Strober said. The drug can be used with methotrexate, he said, even though the combination will worry pharmacists. “Follow the liver, and you’ll be fine” he noted. “That combination can be successful. Laboratory monitoring is not onerous: Discontinue after a few months if you’ve not seen any movement.” The drug can also be used with biologics, he said.
Apremilast (Otezla). This drug will bring about a third of patients to a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75. “That’s not the most impressive efficacy. Rarely do we clear patients with this drug, and it has tolerability issues in some patients,” Dr. Strober said. Side effects can include diarrhea, nausea, headache, and depression. “Warn patients of these possibilities,” he added.
Methotrexate. “It’s very helpful and not a drug to be feared if it’s monitored correctly,” Dr. Strober said. “It’s certainly not a biologic, but it’s not a bad drug from an efficacy standpoint, and it does have efficacy in psoriatic arthritis.”
The drug’s low cost can make it a good alternative to biologics in patients with limited insurance options – such as those on Medicare – or those who don’t have insurance, he said.
“Psoriasis is often controlled at a mean dose of 15 mg/week [orally], with no test dose; start at 15-mg weekly,” he said. “It’s an interesting drug that allows you to dose weekly and still get efficacy,” especially when dosed subcutaneously.
Beware the many contraindications such as pregnancy, possible pregnancy, and high alcohol intake, he added. Dr. Strober doesn’t recommend liver biopsies to monitor hepatic effects. “It’s a poor test with risk and sampling error,” he said.
Cyclosporine. This drug is best “in severe patients in need of a quick response,” said Dr. Strober, who added that biologics are often a better option even in patients who are sensitive to price since samples and free-drug programs are available. “It’s in and out of the body quickly, and most people skip doses and get recurrence of their disease quickly,” he said.
Blood tests are a hassle for patients, he said, and “people often don’t feel great on the drug,” said Dr. Strober, who added, however, that he still does occasionally use it.
Dr. Strober reported multiple disclosures including consultant/advisory board (AbbVie, Amgen, Lilly, Pfizer, among others) and investigator relationships. SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – While biologics have dramatically changed the picture, drugs like , a dermatologist told colleagues.
However, caution is necessary, especially when the drugs are used in combination with biologics, Bruce E. Strober, MD, PhD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and Central Connecticut Dermatology, Cromwell, Conn., said at Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
Dr. Strober offered these tips about the proper use of these four drugs in psoriasis patients:
Acitretin (Soriatane). “This was used as monotherapy initially, but at this point in history, fewer and fewer patients are getting it as monotherapy,” he said. A dose of 25 mg/day appears to provide the best mix of efficacy and side-effect control, “although it’s not a high-efficacy drug, especially at 25 mg a day. It’s a slow-acting drug, and you may need 4 if not 6 months to see the maximum effect before you give up on it.”
What about using acitretin in combination with other therapies? Studies examining its use with phototherapy haven’t been promising, Dr. Strober said. The drug can be used with methotrexate, he said, even though the combination will worry pharmacists. “Follow the liver, and you’ll be fine” he noted. “That combination can be successful. Laboratory monitoring is not onerous: Discontinue after a few months if you’ve not seen any movement.” The drug can also be used with biologics, he said.
Apremilast (Otezla). This drug will bring about a third of patients to a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75. “That’s not the most impressive efficacy. Rarely do we clear patients with this drug, and it has tolerability issues in some patients,” Dr. Strober said. Side effects can include diarrhea, nausea, headache, and depression. “Warn patients of these possibilities,” he added.
Methotrexate. “It’s very helpful and not a drug to be feared if it’s monitored correctly,” Dr. Strober said. “It’s certainly not a biologic, but it’s not a bad drug from an efficacy standpoint, and it does have efficacy in psoriatic arthritis.”
The drug’s low cost can make it a good alternative to biologics in patients with limited insurance options – such as those on Medicare – or those who don’t have insurance, he said.
“Psoriasis is often controlled at a mean dose of 15 mg/week [orally], with no test dose; start at 15-mg weekly,” he said. “It’s an interesting drug that allows you to dose weekly and still get efficacy,” especially when dosed subcutaneously.
Beware the many contraindications such as pregnancy, possible pregnancy, and high alcohol intake, he added. Dr. Strober doesn’t recommend liver biopsies to monitor hepatic effects. “It’s a poor test with risk and sampling error,” he said.
Cyclosporine. This drug is best “in severe patients in need of a quick response,” said Dr. Strober, who added that biologics are often a better option even in patients who are sensitive to price since samples and free-drug programs are available. “It’s in and out of the body quickly, and most people skip doses and get recurrence of their disease quickly,” he said.
Blood tests are a hassle for patients, he said, and “people often don’t feel great on the drug,” said Dr. Strober, who added, however, that he still does occasionally use it.
Dr. Strober reported multiple disclosures including consultant/advisory board (AbbVie, Amgen, Lilly, Pfizer, among others) and investigator relationships. SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – While biologics have dramatically changed the picture, drugs like , a dermatologist told colleagues.
However, caution is necessary, especially when the drugs are used in combination with biologics, Bruce E. Strober, MD, PhD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and Central Connecticut Dermatology, Cromwell, Conn., said at Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
Dr. Strober offered these tips about the proper use of these four drugs in psoriasis patients:
Acitretin (Soriatane). “This was used as monotherapy initially, but at this point in history, fewer and fewer patients are getting it as monotherapy,” he said. A dose of 25 mg/day appears to provide the best mix of efficacy and side-effect control, “although it’s not a high-efficacy drug, especially at 25 mg a day. It’s a slow-acting drug, and you may need 4 if not 6 months to see the maximum effect before you give up on it.”
What about using acitretin in combination with other therapies? Studies examining its use with phototherapy haven’t been promising, Dr. Strober said. The drug can be used with methotrexate, he said, even though the combination will worry pharmacists. “Follow the liver, and you’ll be fine” he noted. “That combination can be successful. Laboratory monitoring is not onerous: Discontinue after a few months if you’ve not seen any movement.” The drug can also be used with biologics, he said.
Apremilast (Otezla). This drug will bring about a third of patients to a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75. “That’s not the most impressive efficacy. Rarely do we clear patients with this drug, and it has tolerability issues in some patients,” Dr. Strober said. Side effects can include diarrhea, nausea, headache, and depression. “Warn patients of these possibilities,” he added.
Methotrexate. “It’s very helpful and not a drug to be feared if it’s monitored correctly,” Dr. Strober said. “It’s certainly not a biologic, but it’s not a bad drug from an efficacy standpoint, and it does have efficacy in psoriatic arthritis.”
The drug’s low cost can make it a good alternative to biologics in patients with limited insurance options – such as those on Medicare – or those who don’t have insurance, he said.
“Psoriasis is often controlled at a mean dose of 15 mg/week [orally], with no test dose; start at 15-mg weekly,” he said. “It’s an interesting drug that allows you to dose weekly and still get efficacy,” especially when dosed subcutaneously.
Beware the many contraindications such as pregnancy, possible pregnancy, and high alcohol intake, he added. Dr. Strober doesn’t recommend liver biopsies to monitor hepatic effects. “It’s a poor test with risk and sampling error,” he said.
Cyclosporine. This drug is best “in severe patients in need of a quick response,” said Dr. Strober, who added that biologics are often a better option even in patients who are sensitive to price since samples and free-drug programs are available. “It’s in and out of the body quickly, and most people skip doses and get recurrence of their disease quickly,” he said.
Blood tests are a hassle for patients, he said, and “people often don’t feel great on the drug,” said Dr. Strober, who added, however, that he still does occasionally use it.
Dr. Strober reported multiple disclosures including consultant/advisory board (AbbVie, Amgen, Lilly, Pfizer, among others) and investigator relationships. SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
REPORTING FROM SDEF LAS VEGAS DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
SPIRIT-H2H results confirm superiority of ixekizumab over adalimumab for PsA
ATLANTA – Ixekizumab (Taltz) provided significantly greater improvement in joint and skin symptoms, compared with adalimumab (Humira), in biologic-naive patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA), according to final 52-week safety and efficacy results from the randomized SPIRIT-H2H study.
The high-affinity monoclonal antibody against interleukin-17A also performed at least as well as the tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–inhibitor adalimumab across multiple PsA domains and regardless of methotrexate use, Josef Smolen, MD, reported during a late-breaking abstract session at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Multiple biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) are available for the treatment of PsA, but few studies have directly compared their efficacy and safety, said Dr. Smolen of the Medical University of Vienna. He noted that the SPIRIT-H2H study aimed to compare ixekizumab and adalimumab and also to address “one of the most clinically relevant questions for clinicians,” which relates to the efficacy of bDMARDs with and without concomitant methotrexate.
Ixekizumab is approved for adults with active PsA and moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, but TNF inhibitors like adalimumab have long been considered the gold standard for PsA treatment, he explained.
Of 283 patients with PsA randomized to receive ixekizumab and 283 randomized to receive adalimumab, 87% and 84%, respectively, completed week 52 of the head-to-head, open-label study comparing the bDMARDs. Treatment with ixekizumab achieved the primary endpoint of simultaneous improvement of 50% on ACR response criteria (ACR50) and 100% on the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI100) in 39% of patients, which was significantly higher than the rate of 26% with adalimumab, Dr. Smolen said.
Ixekizumab also performed at least as well as adalimumab for the secondary outcome measures of ACR50 response (50% in both groups) and PASI100 response (64% vs. 41%), as well as for all other outcomes measures, including multiple musculoskeletal PsA domains, he said.
“Remarkably ... at 1 year, more than one-third of the patients achieved an ACR70 in both groups, and half of the patients achieved an ACR50,” he added, noting that the ACR100 responses were in line with previous investigations.
Stratification by methotrexate use showed that the simultaneous ACR50 and PASI100 response rates were improved with ixekizumab versus adalimumab both in users and nonusers of methotrexate (39% vs. 30% and 40% vs. 20%, respectively). This finding highlights the ongoing debate about whether TNF inhibitors should or should not be used with methotrexate for PsA.
“This study was not adequately powered to say that, but there is some indication, and I think that this is food for thought for future further analysis because the data in the literature are discrepant in this respect,” Dr. Smolen said.
In non-methotrexate users in SPIRIT-H2H, the ACR20 responses were 53% with ixekinumab vs. 40% with adalimumab, ACR50 responses were 72% vs. 60%, and ACR70 responses were 41% vs. 27%, respectively, he said noting that the difference for ACR70 was statistically significant, and that the ACR70 response with ixekinumab was about the same as the ACR50 for adalimumab.
As for ACR20, ACR50, and ACR70 responses in methotrexate users, “the lines criss-crossed” early on, he said, but all were “slightly superior” with adalimumab than with ixekizumab at 52 weeks (75% vs. 68%, 56% vs. 48%, and 39% vs. 32%, respectively).
Study participants had a mean age of 48 years and had active PsA with at least 3/66 tender joints, at least 3/68 swollen joints, at least 3% psoriasis body surface area involvement, no prior treatment with bDMARDs, and prior inadequate response to one or more conventional synthetic DMARDs. Treatment was dosed according to drug labeling through 52 weeks.
The safety profiles of both agents were consistent with previous reports; treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 73.9% of ixekizumab and 68.6% of adalimumab patients, and serious adverse events occurred in 4.2% and 12.4%, respectively.
“On the other hand, ixekizumab had more injection site reactions: 11% vs. close to 4%,” he said, noting that 4.2% of the ixekizumab patients and 7.4% of the adalimumab patients discontinued treatment because of adverse events. No deaths occurred in either group.
As reported previously in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, ixekizumab was superior to adalimumab for simultaneous achievement of ACR50 and PASI100 at 24 weeks, and these final 52-week results confirm those results, he said.
The study was funded by Eli Lilly, which markets ixekizumab. Dr. Smolen reported research grants and/or honoraria from Eli Lilly and AbbVie, which markets adalimumab, as well as many other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Smolen J et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract L20.
ATLANTA – Ixekizumab (Taltz) provided significantly greater improvement in joint and skin symptoms, compared with adalimumab (Humira), in biologic-naive patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA), according to final 52-week safety and efficacy results from the randomized SPIRIT-H2H study.
The high-affinity monoclonal antibody against interleukin-17A also performed at least as well as the tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–inhibitor adalimumab across multiple PsA domains and regardless of methotrexate use, Josef Smolen, MD, reported during a late-breaking abstract session at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Multiple biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) are available for the treatment of PsA, but few studies have directly compared their efficacy and safety, said Dr. Smolen of the Medical University of Vienna. He noted that the SPIRIT-H2H study aimed to compare ixekizumab and adalimumab and also to address “one of the most clinically relevant questions for clinicians,” which relates to the efficacy of bDMARDs with and without concomitant methotrexate.
Ixekizumab is approved for adults with active PsA and moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, but TNF inhibitors like adalimumab have long been considered the gold standard for PsA treatment, he explained.
Of 283 patients with PsA randomized to receive ixekizumab and 283 randomized to receive adalimumab, 87% and 84%, respectively, completed week 52 of the head-to-head, open-label study comparing the bDMARDs. Treatment with ixekizumab achieved the primary endpoint of simultaneous improvement of 50% on ACR response criteria (ACR50) and 100% on the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI100) in 39% of patients, which was significantly higher than the rate of 26% with adalimumab, Dr. Smolen said.
Ixekizumab also performed at least as well as adalimumab for the secondary outcome measures of ACR50 response (50% in both groups) and PASI100 response (64% vs. 41%), as well as for all other outcomes measures, including multiple musculoskeletal PsA domains, he said.
“Remarkably ... at 1 year, more than one-third of the patients achieved an ACR70 in both groups, and half of the patients achieved an ACR50,” he added, noting that the ACR100 responses were in line with previous investigations.
Stratification by methotrexate use showed that the simultaneous ACR50 and PASI100 response rates were improved with ixekizumab versus adalimumab both in users and nonusers of methotrexate (39% vs. 30% and 40% vs. 20%, respectively). This finding highlights the ongoing debate about whether TNF inhibitors should or should not be used with methotrexate for PsA.
“This study was not adequately powered to say that, but there is some indication, and I think that this is food for thought for future further analysis because the data in the literature are discrepant in this respect,” Dr. Smolen said.
In non-methotrexate users in SPIRIT-H2H, the ACR20 responses were 53% with ixekinumab vs. 40% with adalimumab, ACR50 responses were 72% vs. 60%, and ACR70 responses were 41% vs. 27%, respectively, he said noting that the difference for ACR70 was statistically significant, and that the ACR70 response with ixekinumab was about the same as the ACR50 for adalimumab.
As for ACR20, ACR50, and ACR70 responses in methotrexate users, “the lines criss-crossed” early on, he said, but all were “slightly superior” with adalimumab than with ixekizumab at 52 weeks (75% vs. 68%, 56% vs. 48%, and 39% vs. 32%, respectively).
Study participants had a mean age of 48 years and had active PsA with at least 3/66 tender joints, at least 3/68 swollen joints, at least 3% psoriasis body surface area involvement, no prior treatment with bDMARDs, and prior inadequate response to one or more conventional synthetic DMARDs. Treatment was dosed according to drug labeling through 52 weeks.
The safety profiles of both agents were consistent with previous reports; treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 73.9% of ixekizumab and 68.6% of adalimumab patients, and serious adverse events occurred in 4.2% and 12.4%, respectively.
“On the other hand, ixekizumab had more injection site reactions: 11% vs. close to 4%,” he said, noting that 4.2% of the ixekizumab patients and 7.4% of the adalimumab patients discontinued treatment because of adverse events. No deaths occurred in either group.
As reported previously in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, ixekizumab was superior to adalimumab for simultaneous achievement of ACR50 and PASI100 at 24 weeks, and these final 52-week results confirm those results, he said.
The study was funded by Eli Lilly, which markets ixekizumab. Dr. Smolen reported research grants and/or honoraria from Eli Lilly and AbbVie, which markets adalimumab, as well as many other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Smolen J et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract L20.
ATLANTA – Ixekizumab (Taltz) provided significantly greater improvement in joint and skin symptoms, compared with adalimumab (Humira), in biologic-naive patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA), according to final 52-week safety and efficacy results from the randomized SPIRIT-H2H study.
The high-affinity monoclonal antibody against interleukin-17A also performed at least as well as the tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–inhibitor adalimumab across multiple PsA domains and regardless of methotrexate use, Josef Smolen, MD, reported during a late-breaking abstract session at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Multiple biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) are available for the treatment of PsA, but few studies have directly compared their efficacy and safety, said Dr. Smolen of the Medical University of Vienna. He noted that the SPIRIT-H2H study aimed to compare ixekizumab and adalimumab and also to address “one of the most clinically relevant questions for clinicians,” which relates to the efficacy of bDMARDs with and without concomitant methotrexate.
Ixekizumab is approved for adults with active PsA and moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, but TNF inhibitors like adalimumab have long been considered the gold standard for PsA treatment, he explained.
Of 283 patients with PsA randomized to receive ixekizumab and 283 randomized to receive adalimumab, 87% and 84%, respectively, completed week 52 of the head-to-head, open-label study comparing the bDMARDs. Treatment with ixekizumab achieved the primary endpoint of simultaneous improvement of 50% on ACR response criteria (ACR50) and 100% on the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI100) in 39% of patients, which was significantly higher than the rate of 26% with adalimumab, Dr. Smolen said.
Ixekizumab also performed at least as well as adalimumab for the secondary outcome measures of ACR50 response (50% in both groups) and PASI100 response (64% vs. 41%), as well as for all other outcomes measures, including multiple musculoskeletal PsA domains, he said.
“Remarkably ... at 1 year, more than one-third of the patients achieved an ACR70 in both groups, and half of the patients achieved an ACR50,” he added, noting that the ACR100 responses were in line with previous investigations.
Stratification by methotrexate use showed that the simultaneous ACR50 and PASI100 response rates were improved with ixekizumab versus adalimumab both in users and nonusers of methotrexate (39% vs. 30% and 40% vs. 20%, respectively). This finding highlights the ongoing debate about whether TNF inhibitors should or should not be used with methotrexate for PsA.
“This study was not adequately powered to say that, but there is some indication, and I think that this is food for thought for future further analysis because the data in the literature are discrepant in this respect,” Dr. Smolen said.
In non-methotrexate users in SPIRIT-H2H, the ACR20 responses were 53% with ixekinumab vs. 40% with adalimumab, ACR50 responses were 72% vs. 60%, and ACR70 responses were 41% vs. 27%, respectively, he said noting that the difference for ACR70 was statistically significant, and that the ACR70 response with ixekinumab was about the same as the ACR50 for adalimumab.
As for ACR20, ACR50, and ACR70 responses in methotrexate users, “the lines criss-crossed” early on, he said, but all were “slightly superior” with adalimumab than with ixekizumab at 52 weeks (75% vs. 68%, 56% vs. 48%, and 39% vs. 32%, respectively).
Study participants had a mean age of 48 years and had active PsA with at least 3/66 tender joints, at least 3/68 swollen joints, at least 3% psoriasis body surface area involvement, no prior treatment with bDMARDs, and prior inadequate response to one or more conventional synthetic DMARDs. Treatment was dosed according to drug labeling through 52 weeks.
The safety profiles of both agents were consistent with previous reports; treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 73.9% of ixekizumab and 68.6% of adalimumab patients, and serious adverse events occurred in 4.2% and 12.4%, respectively.
“On the other hand, ixekizumab had more injection site reactions: 11% vs. close to 4%,” he said, noting that 4.2% of the ixekizumab patients and 7.4% of the adalimumab patients discontinued treatment because of adverse events. No deaths occurred in either group.
As reported previously in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, ixekizumab was superior to adalimumab for simultaneous achievement of ACR50 and PASI100 at 24 weeks, and these final 52-week results confirm those results, he said.
The study was funded by Eli Lilly, which markets ixekizumab. Dr. Smolen reported research grants and/or honoraria from Eli Lilly and AbbVie, which markets adalimumab, as well as many other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Smolen J et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract L20.
REPORTING FROM ACR 2019
Scalp Psoriasis Considerations
1. Blakely K, Gooderham M. Management of scalp psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2016;6:33-40.
2. Krueger G, Koo J, Lebwohl M, et al. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life: results of a 1998 National Psoriasis Foundation patient-membership survey. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:280-284.
3. Merola JF, Li T, Li WQ, et al. Prevalence of psoriasis phenotypes among men and women in the USA. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:486-489.
4. Frez ML, Asawanonda P, Gunasekara C, et al. Recommendations for a patient-centered approach to the assessment and treatment of scalp psoriasis: a consensus statement from the Asia Scalp Psoriasis Study Group. J Dermatol Treat. 2014;25:38-45.
5. van de Kerkhof PC, Franssen ME. Psoriasis of the scalp. diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2001;2:159-165.
6. Chan CS, Van Voorhees AS, Lebwohl MG, et al. Treatment of severe scalp psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:962-971.
7. Aldredge LM, Higham RC. Manifestations and management of difficult-to-treat psoriasis. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2018;10:189-197.
8. Dopytalska K, Sobolewski P, Blaszczak A, et al. Psoriasis in special localizations. Reumatologia. 2018;56:392-398.
9. Papp K, Berth-Jones J, Kragballe K, et al. Scalp psoriasis: a review of current topical treatment options. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007;21:1151-1160.
10. Kircik LH, Kumar S. Scalp psoriasis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9(8 suppl):S101-S105.
11. Wozel G. Psoriasis treatment in difficult locations: scalp, nails, and intertriginous areas. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:448-459.
12. Sampogna F, Linder D, Piaserico S, et al. Quality of life assessment of patients with scalp dermatitis using the Italian version of the Scalpdex. Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 2014;94:411-414.
13. Crowley J. Scalp psoriasis: an overview of the disease and available therapies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:912-918.
14. Shah VV, Lee EB, Reddy SP, et al. Scalp psoriasis with increased hair density. Cutis. 2018;102:63-64.
15. George SM, Taylor MR, Farrant PB. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721.
16. Shuster S. Psoriatic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:73-77.
17. Wyatt E, Bottoms E, Comaish S. Abnormal hair shafts in psoriasis on scanning electron microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:368-373.
18. Schoorl WJ, van Baar HJ, van de Kerkhof PC. The hair root pattern in psoriasis of the scalp. Acta Derm Venereol. 1992;72:141-142.
1. Blakely K, Gooderham M. Management of scalp psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2016;6:33-40.
2. Krueger G, Koo J, Lebwohl M, et al. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life: results of a 1998 National Psoriasis Foundation patient-membership survey. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:280-284.
3. Merola JF, Li T, Li WQ, et al. Prevalence of psoriasis phenotypes among men and women in the USA. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:486-489.
4. Frez ML, Asawanonda P, Gunasekara C, et al. Recommendations for a patient-centered approach to the assessment and treatment of scalp psoriasis: a consensus statement from the Asia Scalp Psoriasis Study Group. J Dermatol Treat. 2014;25:38-45.
5. van de Kerkhof PC, Franssen ME. Psoriasis of the scalp. diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2001;2:159-165.
6. Chan CS, Van Voorhees AS, Lebwohl MG, et al. Treatment of severe scalp psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:962-971.
7. Aldredge LM, Higham RC. Manifestations and management of difficult-to-treat psoriasis. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2018;10:189-197.
8. Dopytalska K, Sobolewski P, Blaszczak A, et al. Psoriasis in special localizations. Reumatologia. 2018;56:392-398.
9. Papp K, Berth-Jones J, Kragballe K, et al. Scalp psoriasis: a review of current topical treatment options. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007;21:1151-1160.
10. Kircik LH, Kumar S. Scalp psoriasis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9(8 suppl):S101-S105.
11. Wozel G. Psoriasis treatment in difficult locations: scalp, nails, and intertriginous areas. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:448-459.
12. Sampogna F, Linder D, Piaserico S, et al. Quality of life assessment of patients with scalp dermatitis using the Italian version of the Scalpdex. Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 2014;94:411-414.
13. Crowley J. Scalp psoriasis: an overview of the disease and available therapies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:912-918.
14. Shah VV, Lee EB, Reddy SP, et al. Scalp psoriasis with increased hair density. Cutis. 2018;102:63-64.
15. George SM, Taylor MR, Farrant PB. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721.
16. Shuster S. Psoriatic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:73-77.
17. Wyatt E, Bottoms E, Comaish S. Abnormal hair shafts in psoriasis on scanning electron microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:368-373.
18. Schoorl WJ, van Baar HJ, van de Kerkhof PC. The hair root pattern in psoriasis of the scalp. Acta Derm Venereol. 1992;72:141-142.
1. Blakely K, Gooderham M. Management of scalp psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2016;6:33-40.
2. Krueger G, Koo J, Lebwohl M, et al. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life: results of a 1998 National Psoriasis Foundation patient-membership survey. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:280-284.
3. Merola JF, Li T, Li WQ, et al. Prevalence of psoriasis phenotypes among men and women in the USA. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:486-489.
4. Frez ML, Asawanonda P, Gunasekara C, et al. Recommendations for a patient-centered approach to the assessment and treatment of scalp psoriasis: a consensus statement from the Asia Scalp Psoriasis Study Group. J Dermatol Treat. 2014;25:38-45.
5. van de Kerkhof PC, Franssen ME. Psoriasis of the scalp. diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2001;2:159-165.
6. Chan CS, Van Voorhees AS, Lebwohl MG, et al. Treatment of severe scalp psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:962-971.
7. Aldredge LM, Higham RC. Manifestations and management of difficult-to-treat psoriasis. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2018;10:189-197.
8. Dopytalska K, Sobolewski P, Blaszczak A, et al. Psoriasis in special localizations. Reumatologia. 2018;56:392-398.
9. Papp K, Berth-Jones J, Kragballe K, et al. Scalp psoriasis: a review of current topical treatment options. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007;21:1151-1160.
10. Kircik LH, Kumar S. Scalp psoriasis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9(8 suppl):S101-S105.
11. Wozel G. Psoriasis treatment in difficult locations: scalp, nails, and intertriginous areas. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:448-459.
12. Sampogna F, Linder D, Piaserico S, et al. Quality of life assessment of patients with scalp dermatitis using the Italian version of the Scalpdex. Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 2014;94:411-414.
13. Crowley J. Scalp psoriasis: an overview of the disease and available therapies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:912-918.
14. Shah VV, Lee EB, Reddy SP, et al. Scalp psoriasis with increased hair density. Cutis. 2018;102:63-64.
15. George SM, Taylor MR, Farrant PB. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721.
16. Shuster S. Psoriatic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:73-77.
17. Wyatt E, Bottoms E, Comaish S. Abnormal hair shafts in psoriasis on scanning electron microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:368-373.
18. Schoorl WJ, van Baar HJ, van de Kerkhof PC. The hair root pattern in psoriasis of the scalp. Acta Derm Venereol. 1992;72:141-142.