User login
Is EVAR for ruptured AAA worth revisiting?
CHICAGO – Numerous studies have shown conflicting results for endovascular repair in ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA), but an analysis of 4,000-plus cases from a national registry has found a 41% reduction in mortality with endovascular repair vs. open repair, according to a presentation at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
“EVAR is becoming an increasingly popular strategy for treatment of AAA,” said Samer Alharthi, MD, MPH, of the University of Toledo in Ohio. “As surgeon experience and endovascular technology have improved, a greater percentage of ruptured AAA are being treated by EVAR.”
Dr. Alharthi reported on a retrospective analysis of 4,133 patients who had repair for ruptured AAA in the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database from 2010 to 2016. Notably, the number of EVAR repairs continue to increase and peaked in 2015, with 53% of ruptured AAA treated by EVAR.
Over the term of the study, the overall mortality rate was 22.6% for EVAR and 33.2% for open repair (P less than .001), Dr. Alharthi said. “After adjusting for cofounders, there was a 41% reduction in the mortality rate with the EVAR approach,” he said.
The only appreciable significant difference in demographics between the two groups was a higher percentage of smokers with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease having open repair – 942 (49.2%) vs. 701 (36.2%) – and a higher percentage of patients with end-stage renal disease having EVAR, Dr. Alharthi said. Other comorbidities had no statistically significant difference.
“Complications – pneumonia, reintubation, and acute renal failure – were higher in the open than the EVAR group,” he said. For example, rates of acute renal failure were 15.4% and 8.2% (P less than.001), respectively. Rates of myocardial infarction were similar between the two groups: 6.3% and 6% (P = .74), respectively.
Dr. Alharthi had no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Alharthi S et al. Midwestern Vascular 2019, Abstract 13.
CHICAGO – Numerous studies have shown conflicting results for endovascular repair in ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA), but an analysis of 4,000-plus cases from a national registry has found a 41% reduction in mortality with endovascular repair vs. open repair, according to a presentation at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
“EVAR is becoming an increasingly popular strategy for treatment of AAA,” said Samer Alharthi, MD, MPH, of the University of Toledo in Ohio. “As surgeon experience and endovascular technology have improved, a greater percentage of ruptured AAA are being treated by EVAR.”
Dr. Alharthi reported on a retrospective analysis of 4,133 patients who had repair for ruptured AAA in the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database from 2010 to 2016. Notably, the number of EVAR repairs continue to increase and peaked in 2015, with 53% of ruptured AAA treated by EVAR.
Over the term of the study, the overall mortality rate was 22.6% for EVAR and 33.2% for open repair (P less than .001), Dr. Alharthi said. “After adjusting for cofounders, there was a 41% reduction in the mortality rate with the EVAR approach,” he said.
The only appreciable significant difference in demographics between the two groups was a higher percentage of smokers with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease having open repair – 942 (49.2%) vs. 701 (36.2%) – and a higher percentage of patients with end-stage renal disease having EVAR, Dr. Alharthi said. Other comorbidities had no statistically significant difference.
“Complications – pneumonia, reintubation, and acute renal failure – were higher in the open than the EVAR group,” he said. For example, rates of acute renal failure were 15.4% and 8.2% (P less than.001), respectively. Rates of myocardial infarction were similar between the two groups: 6.3% and 6% (P = .74), respectively.
Dr. Alharthi had no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Alharthi S et al. Midwestern Vascular 2019, Abstract 13.
CHICAGO – Numerous studies have shown conflicting results for endovascular repair in ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA), but an analysis of 4,000-plus cases from a national registry has found a 41% reduction in mortality with endovascular repair vs. open repair, according to a presentation at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
“EVAR is becoming an increasingly popular strategy for treatment of AAA,” said Samer Alharthi, MD, MPH, of the University of Toledo in Ohio. “As surgeon experience and endovascular technology have improved, a greater percentage of ruptured AAA are being treated by EVAR.”
Dr. Alharthi reported on a retrospective analysis of 4,133 patients who had repair for ruptured AAA in the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database from 2010 to 2016. Notably, the number of EVAR repairs continue to increase and peaked in 2015, with 53% of ruptured AAA treated by EVAR.
Over the term of the study, the overall mortality rate was 22.6% for EVAR and 33.2% for open repair (P less than .001), Dr. Alharthi said. “After adjusting for cofounders, there was a 41% reduction in the mortality rate with the EVAR approach,” he said.
The only appreciable significant difference in demographics between the two groups was a higher percentage of smokers with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease having open repair – 942 (49.2%) vs. 701 (36.2%) – and a higher percentage of patients with end-stage renal disease having EVAR, Dr. Alharthi said. Other comorbidities had no statistically significant difference.
“Complications – pneumonia, reintubation, and acute renal failure – were higher in the open than the EVAR group,” he said. For example, rates of acute renal failure were 15.4% and 8.2% (P less than.001), respectively. Rates of myocardial infarction were similar between the two groups: 6.3% and 6% (P = .74), respectively.
Dr. Alharthi had no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Alharthi S et al. Midwestern Vascular 2019, Abstract 13.
REPORTING FROM MIDWESTERN VASCULAR 2019
FDA grants sirolimus-eluting balloon breakthrough device designation for PAD
The Food and Drug Administration has granted the Breakthrough Device Designation to the Virtue sirolimus-eluting balloon (SEB) for below-the-knee peripheral arterial disease, according to a statement from Orchestra BioMed.
According to the FDA, this designation indicates that the Virtue SEB could provide a “more effective treatment option ... for a life-threatening or irreversibly debilitating disease”; as the release notes, below-the-knee atherosclerosis presents a high rate of amputation and poor survival outcomes but has limited treatment options. The designation leads to expedited development, assessment, and review.
Darren R. Sherman, president, CEO, and cofounder of Orchestra BioMed, noted that the Virtue SEB “has the potential to improve long-term outcomes and reduce periprocedural complications” that can “extend hospital stay and increase cost of treatment.” The system had previously received this designation for coronary in-stent restenosis based upon the 3-year results of the European SABRE trial.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted the Breakthrough Device Designation to the Virtue sirolimus-eluting balloon (SEB) for below-the-knee peripheral arterial disease, according to a statement from Orchestra BioMed.
According to the FDA, this designation indicates that the Virtue SEB could provide a “more effective treatment option ... for a life-threatening or irreversibly debilitating disease”; as the release notes, below-the-knee atherosclerosis presents a high rate of amputation and poor survival outcomes but has limited treatment options. The designation leads to expedited development, assessment, and review.
Darren R. Sherman, president, CEO, and cofounder of Orchestra BioMed, noted that the Virtue SEB “has the potential to improve long-term outcomes and reduce periprocedural complications” that can “extend hospital stay and increase cost of treatment.” The system had previously received this designation for coronary in-stent restenosis based upon the 3-year results of the European SABRE trial.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted the Breakthrough Device Designation to the Virtue sirolimus-eluting balloon (SEB) for below-the-knee peripheral arterial disease, according to a statement from Orchestra BioMed.
According to the FDA, this designation indicates that the Virtue SEB could provide a “more effective treatment option ... for a life-threatening or irreversibly debilitating disease”; as the release notes, below-the-knee atherosclerosis presents a high rate of amputation and poor survival outcomes but has limited treatment options. The designation leads to expedited development, assessment, and review.
Darren R. Sherman, president, CEO, and cofounder of Orchestra BioMed, noted that the Virtue SEB “has the potential to improve long-term outcomes and reduce periprocedural complications” that can “extend hospital stay and increase cost of treatment.” The system had previously received this designation for coronary in-stent restenosis based upon the 3-year results of the European SABRE trial.
Apply for the Travel Advocacy Scholarship by Oct. 31
Oct. 31 is the deadline for the Vascular Surgery Trainee Advocacy Travel Scholarship. The primary purpose of this award is to provide the recipient with an opportunity to participate in Capitol Hill visits and learn more about the SVS’ health policy and advocacy activities. The awardee will receive $1,500 that can be used toward the cost of travel, housing and subsistence during the visits. Reports from past recipients are available on the SVS website here. For questions, email [email protected] or telephone 800-258-7188.
Oct. 31 is the deadline for the Vascular Surgery Trainee Advocacy Travel Scholarship. The primary purpose of this award is to provide the recipient with an opportunity to participate in Capitol Hill visits and learn more about the SVS’ health policy and advocacy activities. The awardee will receive $1,500 that can be used toward the cost of travel, housing and subsistence during the visits. Reports from past recipients are available on the SVS website here. For questions, email [email protected] or telephone 800-258-7188.
Oct. 31 is the deadline for the Vascular Surgery Trainee Advocacy Travel Scholarship. The primary purpose of this award is to provide the recipient with an opportunity to participate in Capitol Hill visits and learn more about the SVS’ health policy and advocacy activities. The awardee will receive $1,500 that can be used toward the cost of travel, housing and subsistence during the visits. Reports from past recipients are available on the SVS website here. For questions, email [email protected] or telephone 800-258-7188.
States pass record number of laws to reel in drug prices
Whether Congress will act this year to address the affordability of prescription drugs – a high priority among voters – remains uncertain. But states aren’t waiting.
So far this year, 33 states have enacted a record 51 laws to address drug prices, affordability, and access. That tops the previous record of 45 laws enacted in 28 states set just last year, according to the National Academy for State Health Policy, a nonprofit advocacy group that develops model legislation and promotes such laws.
Among the new measures are those that authorize importing prescription drugs, screen for excessive price increases by drug companies, and establish oversight boards to set the prices that states will pay for drugs.
“Legislative activity in this area is escalating,” said Trish Riley, NASHP’s executive director. “This year, some states moved to launch programs that directly impact what they and consumers pay for high-cost drugs.”
And more laws could be coming before year’s end. Of the handful of states still in legislative session – including California, Massachusetts, Michigan, New Jersey, Ohio, and Pennsylvania – debate continues on dozens of prescription drug bills. In New Jersey alone, some 20 proposed laws are under consideration.
“Both Democrat and Republican leaders have shown a willingness to pursue strong measures that help consumers but also protect state taxpayer dollars,” said Hemi Tewarson, director of the National Governors Association’s health programs.
Ms. Riley, Ms. Tewarson, and others note, however, that states can go only so far in addressing rising drug prices, and that federal legislation would be necessary to have a major effect on the way the marketplace works.
Federal lawmakers are keeping a close eye on the state initiatives, Ms. Tewarson said, to gauge where legislative compromise may lie – even as Congress debates more than a dozen bills that target drug costs. Political divisiveness, a packed congressional schedule and a looming election year could stall momentum at the federal level.
The pharmaceutical industry has opposed most – though not all – state bills, said Priscilla VanderVeer, a spokeswoman for the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America, the industry’s main trade group.
“We agree that what consumers now pay for drugs out-of-pocket is a serious problem,” said Ms. VanderVeer. “Many states have passed bills that look good on paper but that we don’t believe will save consumers money.”
Limiting gag rules for pharmacists
At least 16 states have enacted 20 laws governing the behavior of pharmacy benefit managers. The so-called PBMs serve as middlemen among drugmakers, insurance companies, and pharmacies, largely with pharmaceutical industry support.
Those laws add to the 28 passed in 2018. Most of the new laws ban “gag clauses” that some PBMs impose on pharmacists. The clauses, written into pharmacy contracts, stop pharmacists from discussing with customers whether a drug’s cash price would be lower than its out-of-pocket cost under insurance.
With widespread public outrage over gag clauses pushing states to act, federal lawmakers got the message. In October, Congress passed a federal law banning such clauses in PBM-pharmacy contracts nationwide and under the Medicare Part D prescription drug benefit. The Senate passed it 98-2.
Even so, many of this year’s PBM laws contain additional gag clause limitations that go beyond the 2018 federal law.
Importing cheaper drugs
Four states – Colorado, Florida, Maine, and Vermont – this year have enacted measures to establish programs to import cheaper prescription drugs from Canada and, in Florida’s case, potentially other countries. Six other states are considering such legislation.
Medicines from Canada and other countries are less expensive because those nations negotiate directly with drugmakers to set prices.
“This is an area where states once feared to tread,” said Jane Horvath, a consultant with NASHP who has advised Maryland and Oregon, among other states, on prescription drug policy. “Now both Republicans and Democrats view it as a way to infuse more price competition into the marketplace.”
Hurdles remain, however. A 2003 law allows states to import cheaper drugs from Canada but only if the federal Health & Human Services Department approves a state’s plan and certifies its safety. During 2004-2009, the federal government halted nascent drug import efforts in five states.
Even so, momentum for importation has built in recent years in states and Congress as drug prices have continued to rise. And the Trump administration this summer threw its support behind the idea.
Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis, a Republican and close ally of President Donald Trump, signed his state’s measure into law on June 11, claiming he did so after Trump personally promised him that the White House would back the initiative.
On July 31, HHS announced an “action plan” to “lay the foundation for safe importation of certain prescription drugs.” The plan includes a process to authorize state initiatives. It also requires formal regulatory review, including establishing Food and Drug Administration safety criteria. That process could take up to 2 years.
Two big problems remain: In the weeks since the announcement, the Canadian government has opposed any plan that would rely solely on Canada as a source of imported drugs. The pharmaceutical industry also opposes the plan.
Creating drug affordability boards
Maryland and Maine enacted laws this year that establish state agencies to review the costs of drugs and take action against those whose price increases exceed a certain threshold.
New Jersey and Massachusetts are debating similar legislation this year.
Maryland’s law establishes a five-member board to review the list prices and costs of drugs purchased by the state and Maryland’s county and local governments. The board will probe drugs that increase in price by $3,000 or more per year and new medicines that enter the market costing $30,000 or more per year or over the course of treatment.
If approved by future legislation, upper payment limits on drugs with excessive price increases or annual costs would take effect in January 2022.
“My constituents have signaled loud and clear that bringing drug prices down is one of their top priorities,” said state Sen. Katherine Klausmeier, a Democrat representing Baltimore, who sponsored the legislation.
Maine’s law also establishes a five-member board. Beginning in 2021, the board will set annual spending targets for drugs purchased by the state and local governments.
Increasing price transparency
This year, four states – Colorado, Oregon, Texas, and Washington – became the latest to enact laws requiring drug companies to provide information to states and consumers on the list prices of drugs and planned price increases.
The majority of states now have such transparency laws, and most post the data on public websites. The details vary, but all states with such laws seek to identify drugs with price increases above 10% or more a year, and drugs with price increases above set dollar values.
Oregon’s new law, for example, requires manufacturers to notify the state 60 days in advance of any planned increase of 10% or more in the price of brand-name drugs, and any 25% or greater increase in the price of generic drugs.
“That 60-days’ notice was very important to us,” said state Rep. Andrea Salinas, a Democrat and chair of the Oregon House’s health committee, who represents Lake Oswego. “It gives doctors and patients advance notice and a chance to adjust and consider what to do.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Whether Congress will act this year to address the affordability of prescription drugs – a high priority among voters – remains uncertain. But states aren’t waiting.
So far this year, 33 states have enacted a record 51 laws to address drug prices, affordability, and access. That tops the previous record of 45 laws enacted in 28 states set just last year, according to the National Academy for State Health Policy, a nonprofit advocacy group that develops model legislation and promotes such laws.
Among the new measures are those that authorize importing prescription drugs, screen for excessive price increases by drug companies, and establish oversight boards to set the prices that states will pay for drugs.
“Legislative activity in this area is escalating,” said Trish Riley, NASHP’s executive director. “This year, some states moved to launch programs that directly impact what they and consumers pay for high-cost drugs.”
And more laws could be coming before year’s end. Of the handful of states still in legislative session – including California, Massachusetts, Michigan, New Jersey, Ohio, and Pennsylvania – debate continues on dozens of prescription drug bills. In New Jersey alone, some 20 proposed laws are under consideration.
“Both Democrat and Republican leaders have shown a willingness to pursue strong measures that help consumers but also protect state taxpayer dollars,” said Hemi Tewarson, director of the National Governors Association’s health programs.
Ms. Riley, Ms. Tewarson, and others note, however, that states can go only so far in addressing rising drug prices, and that federal legislation would be necessary to have a major effect on the way the marketplace works.
Federal lawmakers are keeping a close eye on the state initiatives, Ms. Tewarson said, to gauge where legislative compromise may lie – even as Congress debates more than a dozen bills that target drug costs. Political divisiveness, a packed congressional schedule and a looming election year could stall momentum at the federal level.
The pharmaceutical industry has opposed most – though not all – state bills, said Priscilla VanderVeer, a spokeswoman for the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America, the industry’s main trade group.
“We agree that what consumers now pay for drugs out-of-pocket is a serious problem,” said Ms. VanderVeer. “Many states have passed bills that look good on paper but that we don’t believe will save consumers money.”
Limiting gag rules for pharmacists
At least 16 states have enacted 20 laws governing the behavior of pharmacy benefit managers. The so-called PBMs serve as middlemen among drugmakers, insurance companies, and pharmacies, largely with pharmaceutical industry support.
Those laws add to the 28 passed in 2018. Most of the new laws ban “gag clauses” that some PBMs impose on pharmacists. The clauses, written into pharmacy contracts, stop pharmacists from discussing with customers whether a drug’s cash price would be lower than its out-of-pocket cost under insurance.
With widespread public outrage over gag clauses pushing states to act, federal lawmakers got the message. In October, Congress passed a federal law banning such clauses in PBM-pharmacy contracts nationwide and under the Medicare Part D prescription drug benefit. The Senate passed it 98-2.
Even so, many of this year’s PBM laws contain additional gag clause limitations that go beyond the 2018 federal law.
Importing cheaper drugs
Four states – Colorado, Florida, Maine, and Vermont – this year have enacted measures to establish programs to import cheaper prescription drugs from Canada and, in Florida’s case, potentially other countries. Six other states are considering such legislation.
Medicines from Canada and other countries are less expensive because those nations negotiate directly with drugmakers to set prices.
“This is an area where states once feared to tread,” said Jane Horvath, a consultant with NASHP who has advised Maryland and Oregon, among other states, on prescription drug policy. “Now both Republicans and Democrats view it as a way to infuse more price competition into the marketplace.”
Hurdles remain, however. A 2003 law allows states to import cheaper drugs from Canada but only if the federal Health & Human Services Department approves a state’s plan and certifies its safety. During 2004-2009, the federal government halted nascent drug import efforts in five states.
Even so, momentum for importation has built in recent years in states and Congress as drug prices have continued to rise. And the Trump administration this summer threw its support behind the idea.
Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis, a Republican and close ally of President Donald Trump, signed his state’s measure into law on June 11, claiming he did so after Trump personally promised him that the White House would back the initiative.
On July 31, HHS announced an “action plan” to “lay the foundation for safe importation of certain prescription drugs.” The plan includes a process to authorize state initiatives. It also requires formal regulatory review, including establishing Food and Drug Administration safety criteria. That process could take up to 2 years.
Two big problems remain: In the weeks since the announcement, the Canadian government has opposed any plan that would rely solely on Canada as a source of imported drugs. The pharmaceutical industry also opposes the plan.
Creating drug affordability boards
Maryland and Maine enacted laws this year that establish state agencies to review the costs of drugs and take action against those whose price increases exceed a certain threshold.
New Jersey and Massachusetts are debating similar legislation this year.
Maryland’s law establishes a five-member board to review the list prices and costs of drugs purchased by the state and Maryland’s county and local governments. The board will probe drugs that increase in price by $3,000 or more per year and new medicines that enter the market costing $30,000 or more per year or over the course of treatment.
If approved by future legislation, upper payment limits on drugs with excessive price increases or annual costs would take effect in January 2022.
“My constituents have signaled loud and clear that bringing drug prices down is one of their top priorities,” said state Sen. Katherine Klausmeier, a Democrat representing Baltimore, who sponsored the legislation.
Maine’s law also establishes a five-member board. Beginning in 2021, the board will set annual spending targets for drugs purchased by the state and local governments.
Increasing price transparency
This year, four states – Colorado, Oregon, Texas, and Washington – became the latest to enact laws requiring drug companies to provide information to states and consumers on the list prices of drugs and planned price increases.
The majority of states now have such transparency laws, and most post the data on public websites. The details vary, but all states with such laws seek to identify drugs with price increases above 10% or more a year, and drugs with price increases above set dollar values.
Oregon’s new law, for example, requires manufacturers to notify the state 60 days in advance of any planned increase of 10% or more in the price of brand-name drugs, and any 25% or greater increase in the price of generic drugs.
“That 60-days’ notice was very important to us,” said state Rep. Andrea Salinas, a Democrat and chair of the Oregon House’s health committee, who represents Lake Oswego. “It gives doctors and patients advance notice and a chance to adjust and consider what to do.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Whether Congress will act this year to address the affordability of prescription drugs – a high priority among voters – remains uncertain. But states aren’t waiting.
So far this year, 33 states have enacted a record 51 laws to address drug prices, affordability, and access. That tops the previous record of 45 laws enacted in 28 states set just last year, according to the National Academy for State Health Policy, a nonprofit advocacy group that develops model legislation and promotes such laws.
Among the new measures are those that authorize importing prescription drugs, screen for excessive price increases by drug companies, and establish oversight boards to set the prices that states will pay for drugs.
“Legislative activity in this area is escalating,” said Trish Riley, NASHP’s executive director. “This year, some states moved to launch programs that directly impact what they and consumers pay for high-cost drugs.”
And more laws could be coming before year’s end. Of the handful of states still in legislative session – including California, Massachusetts, Michigan, New Jersey, Ohio, and Pennsylvania – debate continues on dozens of prescription drug bills. In New Jersey alone, some 20 proposed laws are under consideration.
“Both Democrat and Republican leaders have shown a willingness to pursue strong measures that help consumers but also protect state taxpayer dollars,” said Hemi Tewarson, director of the National Governors Association’s health programs.
Ms. Riley, Ms. Tewarson, and others note, however, that states can go only so far in addressing rising drug prices, and that federal legislation would be necessary to have a major effect on the way the marketplace works.
Federal lawmakers are keeping a close eye on the state initiatives, Ms. Tewarson said, to gauge where legislative compromise may lie – even as Congress debates more than a dozen bills that target drug costs. Political divisiveness, a packed congressional schedule and a looming election year could stall momentum at the federal level.
The pharmaceutical industry has opposed most – though not all – state bills, said Priscilla VanderVeer, a spokeswoman for the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America, the industry’s main trade group.
“We agree that what consumers now pay for drugs out-of-pocket is a serious problem,” said Ms. VanderVeer. “Many states have passed bills that look good on paper but that we don’t believe will save consumers money.”
Limiting gag rules for pharmacists
At least 16 states have enacted 20 laws governing the behavior of pharmacy benefit managers. The so-called PBMs serve as middlemen among drugmakers, insurance companies, and pharmacies, largely with pharmaceutical industry support.
Those laws add to the 28 passed in 2018. Most of the new laws ban “gag clauses” that some PBMs impose on pharmacists. The clauses, written into pharmacy contracts, stop pharmacists from discussing with customers whether a drug’s cash price would be lower than its out-of-pocket cost under insurance.
With widespread public outrage over gag clauses pushing states to act, federal lawmakers got the message. In October, Congress passed a federal law banning such clauses in PBM-pharmacy contracts nationwide and under the Medicare Part D prescription drug benefit. The Senate passed it 98-2.
Even so, many of this year’s PBM laws contain additional gag clause limitations that go beyond the 2018 federal law.
Importing cheaper drugs
Four states – Colorado, Florida, Maine, and Vermont – this year have enacted measures to establish programs to import cheaper prescription drugs from Canada and, in Florida’s case, potentially other countries. Six other states are considering such legislation.
Medicines from Canada and other countries are less expensive because those nations negotiate directly with drugmakers to set prices.
“This is an area where states once feared to tread,” said Jane Horvath, a consultant with NASHP who has advised Maryland and Oregon, among other states, on prescription drug policy. “Now both Republicans and Democrats view it as a way to infuse more price competition into the marketplace.”
Hurdles remain, however. A 2003 law allows states to import cheaper drugs from Canada but only if the federal Health & Human Services Department approves a state’s plan and certifies its safety. During 2004-2009, the federal government halted nascent drug import efforts in five states.
Even so, momentum for importation has built in recent years in states and Congress as drug prices have continued to rise. And the Trump administration this summer threw its support behind the idea.
Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis, a Republican and close ally of President Donald Trump, signed his state’s measure into law on June 11, claiming he did so after Trump personally promised him that the White House would back the initiative.
On July 31, HHS announced an “action plan” to “lay the foundation for safe importation of certain prescription drugs.” The plan includes a process to authorize state initiatives. It also requires formal regulatory review, including establishing Food and Drug Administration safety criteria. That process could take up to 2 years.
Two big problems remain: In the weeks since the announcement, the Canadian government has opposed any plan that would rely solely on Canada as a source of imported drugs. The pharmaceutical industry also opposes the plan.
Creating drug affordability boards
Maryland and Maine enacted laws this year that establish state agencies to review the costs of drugs and take action against those whose price increases exceed a certain threshold.
New Jersey and Massachusetts are debating similar legislation this year.
Maryland’s law establishes a five-member board to review the list prices and costs of drugs purchased by the state and Maryland’s county and local governments. The board will probe drugs that increase in price by $3,000 or more per year and new medicines that enter the market costing $30,000 or more per year or over the course of treatment.
If approved by future legislation, upper payment limits on drugs with excessive price increases or annual costs would take effect in January 2022.
“My constituents have signaled loud and clear that bringing drug prices down is one of their top priorities,” said state Sen. Katherine Klausmeier, a Democrat representing Baltimore, who sponsored the legislation.
Maine’s law also establishes a five-member board. Beginning in 2021, the board will set annual spending targets for drugs purchased by the state and local governments.
Increasing price transparency
This year, four states – Colorado, Oregon, Texas, and Washington – became the latest to enact laws requiring drug companies to provide information to states and consumers on the list prices of drugs and planned price increases.
The majority of states now have such transparency laws, and most post the data on public websites. The details vary, but all states with such laws seek to identify drugs with price increases above 10% or more a year, and drugs with price increases above set dollar values.
Oregon’s new law, for example, requires manufacturers to notify the state 60 days in advance of any planned increase of 10% or more in the price of brand-name drugs, and any 25% or greater increase in the price of generic drugs.
“That 60-days’ notice was very important to us,” said state Rep. Andrea Salinas, a Democrat and chair of the Oregon House’s health committee, who represents Lake Oswego. “It gives doctors and patients advance notice and a chance to adjust and consider what to do.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Insurers to pay record number of rebates to patients
Health insurance companies are getting ready to disburse a record $1.3 billion in medical loss ratio (MLR) rebates, according to an analysis by the Kaiser Family Foundation.
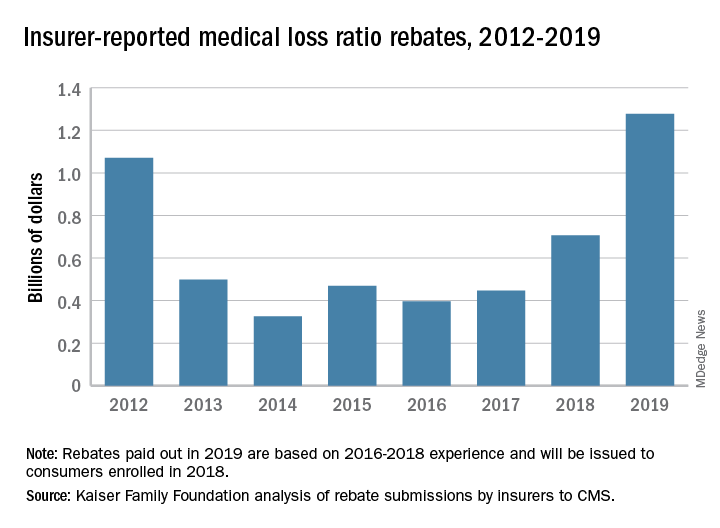
The $1.3 billion surpasses the previous rebate record of $1.1 billion, issued in 2012.
The increase is driven largely by individual market insurers who will pay $743 million in rebates this year, according to the report, which analyzed insurer data submitted to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Rebates in the small-group and large-group insurance markets are similar to previous years, with expected paybacks of $250 million from small- and $284 million from large-group markets, according to the Kaiser report. Insurance companies have until September 30, 2019, to start issuing rebates.
The rebates stem from the MLR requirement imposed by the Affordable Care Act (ACA), which limits the amount of premium dollars that can be used for administration, marketing, and profit. Under the health law, companies are required to publicly report how much they spend on health care, quality improvement, and other activities using premium funds. Individual and small-group market insurers must spend at least 80% on health care claims and quality improvement,while large-group plans must spend at least 85%. Rebates are based on a 3-year average of financial data by each insurer.
Patients in the individual insurance market can expect their rebate in either a premium credit or a check. In the large and small group markets, rebates may be split between employee and employer depending on the plan contract.
The volume of rebates differed greatly across the states, with some states paying zero rebates and others paying millions. Virginia insurers for example, will pay the highest number of total rebates ($150 million), followed by Pennsylvania ($130 million) and Florida ($107 million), according to the report. Payments by insurers in the individual market alone ranged from zero dollars in 13 states to $111 million in Virginia. Individual market insurers in Arizona will pay $92 million in rebates to patients, while individual plans in Texas will pay $80 million. Florida insurers will pay the highest in rebates in both the small-group and large-group market at $44 million and $42 million respectively.
The largest rebates within the individual market will come from Centene, HCSC, Cigna, and Highmark. Authors of the report noted that these insurers tend to have higher enrollment and are active in multiple states.
Individual marketplace insurers will likely pay high rebates against next year, based on an individual market that remains strong and profitable, despite the recent elimination of the individual mandate penalty, according to the authors.
Health insurance companies are getting ready to disburse a record $1.3 billion in medical loss ratio (MLR) rebates, according to an analysis by the Kaiser Family Foundation.

The $1.3 billion surpasses the previous rebate record of $1.1 billion, issued in 2012.
The increase is driven largely by individual market insurers who will pay $743 million in rebates this year, according to the report, which analyzed insurer data submitted to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Rebates in the small-group and large-group insurance markets are similar to previous years, with expected paybacks of $250 million from small- and $284 million from large-group markets, according to the Kaiser report. Insurance companies have until September 30, 2019, to start issuing rebates.
The rebates stem from the MLR requirement imposed by the Affordable Care Act (ACA), which limits the amount of premium dollars that can be used for administration, marketing, and profit. Under the health law, companies are required to publicly report how much they spend on health care, quality improvement, and other activities using premium funds. Individual and small-group market insurers must spend at least 80% on health care claims and quality improvement,while large-group plans must spend at least 85%. Rebates are based on a 3-year average of financial data by each insurer.
Patients in the individual insurance market can expect their rebate in either a premium credit or a check. In the large and small group markets, rebates may be split between employee and employer depending on the plan contract.
The volume of rebates differed greatly across the states, with some states paying zero rebates and others paying millions. Virginia insurers for example, will pay the highest number of total rebates ($150 million), followed by Pennsylvania ($130 million) and Florida ($107 million), according to the report. Payments by insurers in the individual market alone ranged from zero dollars in 13 states to $111 million in Virginia. Individual market insurers in Arizona will pay $92 million in rebates to patients, while individual plans in Texas will pay $80 million. Florida insurers will pay the highest in rebates in both the small-group and large-group market at $44 million and $42 million respectively.
The largest rebates within the individual market will come from Centene, HCSC, Cigna, and Highmark. Authors of the report noted that these insurers tend to have higher enrollment and are active in multiple states.
Individual marketplace insurers will likely pay high rebates against next year, based on an individual market that remains strong and profitable, despite the recent elimination of the individual mandate penalty, according to the authors.
Health insurance companies are getting ready to disburse a record $1.3 billion in medical loss ratio (MLR) rebates, according to an analysis by the Kaiser Family Foundation.

The $1.3 billion surpasses the previous rebate record of $1.1 billion, issued in 2012.
The increase is driven largely by individual market insurers who will pay $743 million in rebates this year, according to the report, which analyzed insurer data submitted to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Rebates in the small-group and large-group insurance markets are similar to previous years, with expected paybacks of $250 million from small- and $284 million from large-group markets, according to the Kaiser report. Insurance companies have until September 30, 2019, to start issuing rebates.
The rebates stem from the MLR requirement imposed by the Affordable Care Act (ACA), which limits the amount of premium dollars that can be used for administration, marketing, and profit. Under the health law, companies are required to publicly report how much they spend on health care, quality improvement, and other activities using premium funds. Individual and small-group market insurers must spend at least 80% on health care claims and quality improvement,while large-group plans must spend at least 85%. Rebates are based on a 3-year average of financial data by each insurer.
Patients in the individual insurance market can expect their rebate in either a premium credit or a check. In the large and small group markets, rebates may be split between employee and employer depending on the plan contract.
The volume of rebates differed greatly across the states, with some states paying zero rebates and others paying millions. Virginia insurers for example, will pay the highest number of total rebates ($150 million), followed by Pennsylvania ($130 million) and Florida ($107 million), according to the report. Payments by insurers in the individual market alone ranged from zero dollars in 13 states to $111 million in Virginia. Individual market insurers in Arizona will pay $92 million in rebates to patients, while individual plans in Texas will pay $80 million. Florida insurers will pay the highest in rebates in both the small-group and large-group market at $44 million and $42 million respectively.
The largest rebates within the individual market will come from Centene, HCSC, Cigna, and Highmark. Authors of the report noted that these insurers tend to have higher enrollment and are active in multiple states.
Individual marketplace insurers will likely pay high rebates against next year, based on an individual market that remains strong and profitable, despite the recent elimination of the individual mandate penalty, according to the authors.
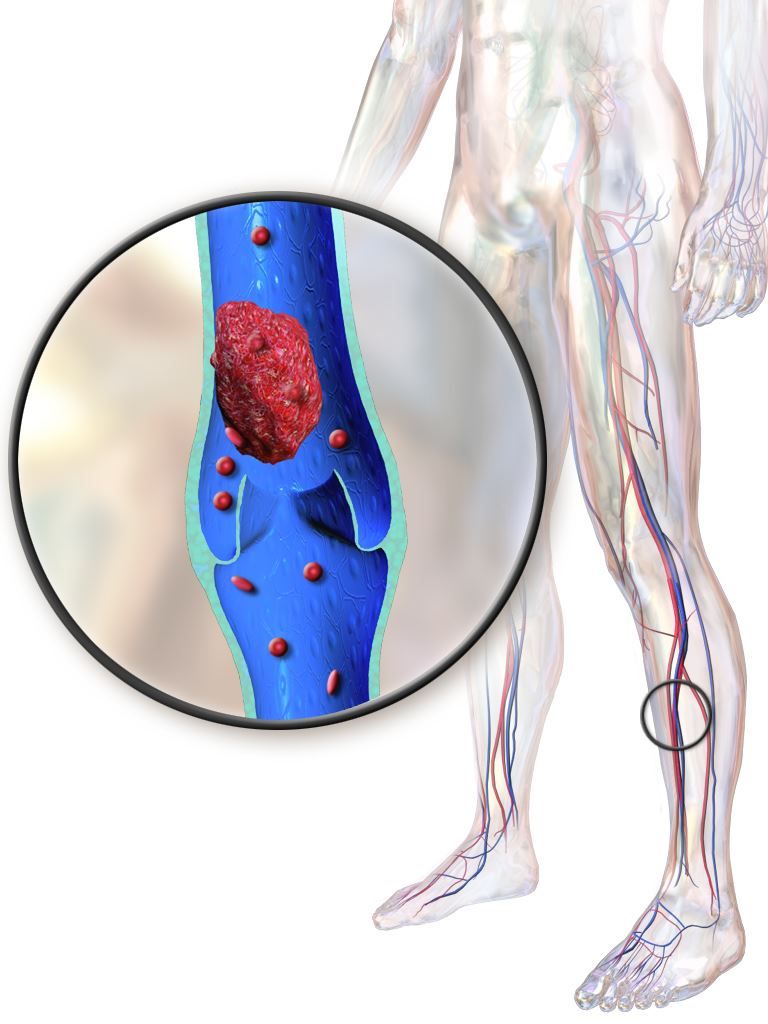
Older IBD patients are most at risk of postdischarge VTE
Hospitalized patients with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are most likely to be readmitted for venous thromboembolism (VTE) within 60 days of discharge, according to a new study that analyzed 5 years of U.S. readmissions data.
“Given increased thrombotic risk postdischarge, as well as overall safety of VTE prophylaxis, extending prophylaxis for those at highest risk may have significant benefits,” wrote Adam S. Faye, MD, of Columbia University, and coauthors. The study was published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
To determine which IBD patients would be most in need of postdischarge VTE prophylaxis, as well as when to administer it, the researchers analyzed 2010-2014 data from the Nationwide Readmissions Database (NRD). They found a total of 872,122 index admissions for IBD patients; 4% of those patients had a prior VTE. Of the index admissions, 1,160 led to a VTE readmission within 90 days. Readmitted patients had a relatively equal proportion of ulcerative colitis (n = 522) and Crohn’s disease (n = 638).
More than 90% of VTE readmissions occurred within 60 days of discharge; the risk was highest over the first 10 days and then decreased in each ensuing 10-day period until a slight increase at the 81- to 90-day period. All patients over age 30 had higher rates of readmission than those of patients under age 18, with the highest risk in patients between the ages of 66 and 80 years (risk ratio 4.04; 95% confidence interval, 2.54-6.44, P less than .01). Women were at lower risk (RR 0.82; 95% CI, 0.73-0.92, P less than .01). Higher risks of readmission were also associated with being on Medicare (RR 1.39; 95% CI, 1.23-1.58, P less than .01) compared with being on private insurance and being cared for at a large hospital (RR 1.26; 95% CI, 1.04-1.52, P = .02) compared with a small hospital.
The highest risk of VTE readmission was associated with a prior history of VTE (RR 2.89; 95% CI, 2.40-3.48, P less than .01), having two or more comorbidities (RR 2.57; 95% CI, 2.11-3.12, P less than .01) and having a Clostridioides difficile infection as of index admission (RR 1.90; 95% CI, 1.51-2.38, P less than .01). In addition, increased risk was associated with being discharged to a nursing or care facility (RR 1.85; 95% CI, 1.56-2.20, P less than .01) or home with health services (RR 2.05; 95% CI, 1.78-2.38, P less than .01) compared with a routine discharge.
In their multivariable analysis, similar factors such as a history of VTE (adjusted RR 2.41; 95% CI, 1.99-2.90, P less than .01), two or more comorbidities (aRR 1.78; 95% CI, 1.44-2.20, P less than .01) and C. difficile infection (aRR 1.47; 95% CI, 1.17-1.85, P less than.01) continued to be associated with higher risk of VTE readmission.
Though they emphasized that the use of NRD data offered the impressive ability to “review over 15 million discharges across the U.S. annually,” Dr. Faye and coauthors acknowledged that their study did have limitations. These included the inability to verify via chart review the study’s outcomes and covariates. In addition, they were unable to assess potential contributing risk factors such as medication use, use of VTE prophylaxis during hospitalization, disease severity, and family history. Finally, though unlikely, they admitted the possibility that patients could be counted more than once if they were readmitted with a VTE each year of the study.
The authors reported being supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health and various pharmaceutical companies, as well as receiving honoraria and serving as consultants.
SOURCE: Faye AS et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 July 20. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.028.
Hospitalized patients with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are most likely to be readmitted for venous thromboembolism (VTE) within 60 days of discharge, according to a new study that analyzed 5 years of U.S. readmissions data.
“Given increased thrombotic risk postdischarge, as well as overall safety of VTE prophylaxis, extending prophylaxis for those at highest risk may have significant benefits,” wrote Adam S. Faye, MD, of Columbia University, and coauthors. The study was published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
To determine which IBD patients would be most in need of postdischarge VTE prophylaxis, as well as when to administer it, the researchers analyzed 2010-2014 data from the Nationwide Readmissions Database (NRD). They found a total of 872,122 index admissions for IBD patients; 4% of those patients had a prior VTE. Of the index admissions, 1,160 led to a VTE readmission within 90 days. Readmitted patients had a relatively equal proportion of ulcerative colitis (n = 522) and Crohn’s disease (n = 638).
More than 90% of VTE readmissions occurred within 60 days of discharge; the risk was highest over the first 10 days and then decreased in each ensuing 10-day period until a slight increase at the 81- to 90-day period. All patients over age 30 had higher rates of readmission than those of patients under age 18, with the highest risk in patients between the ages of 66 and 80 years (risk ratio 4.04; 95% confidence interval, 2.54-6.44, P less than .01). Women were at lower risk (RR 0.82; 95% CI, 0.73-0.92, P less than .01). Higher risks of readmission were also associated with being on Medicare (RR 1.39; 95% CI, 1.23-1.58, P less than .01) compared with being on private insurance and being cared for at a large hospital (RR 1.26; 95% CI, 1.04-1.52, P = .02) compared with a small hospital.
The highest risk of VTE readmission was associated with a prior history of VTE (RR 2.89; 95% CI, 2.40-3.48, P less than .01), having two or more comorbidities (RR 2.57; 95% CI, 2.11-3.12, P less than .01) and having a Clostridioides difficile infection as of index admission (RR 1.90; 95% CI, 1.51-2.38, P less than .01). In addition, increased risk was associated with being discharged to a nursing or care facility (RR 1.85; 95% CI, 1.56-2.20, P less than .01) or home with health services (RR 2.05; 95% CI, 1.78-2.38, P less than .01) compared with a routine discharge.
In their multivariable analysis, similar factors such as a history of VTE (adjusted RR 2.41; 95% CI, 1.99-2.90, P less than .01), two or more comorbidities (aRR 1.78; 95% CI, 1.44-2.20, P less than .01) and C. difficile infection (aRR 1.47; 95% CI, 1.17-1.85, P less than.01) continued to be associated with higher risk of VTE readmission.
Though they emphasized that the use of NRD data offered the impressive ability to “review over 15 million discharges across the U.S. annually,” Dr. Faye and coauthors acknowledged that their study did have limitations. These included the inability to verify via chart review the study’s outcomes and covariates. In addition, they were unable to assess potential contributing risk factors such as medication use, use of VTE prophylaxis during hospitalization, disease severity, and family history. Finally, though unlikely, they admitted the possibility that patients could be counted more than once if they were readmitted with a VTE each year of the study.
The authors reported being supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health and various pharmaceutical companies, as well as receiving honoraria and serving as consultants.
SOURCE: Faye AS et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 July 20. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.028.
Hospitalized patients with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are most likely to be readmitted for venous thromboembolism (VTE) within 60 days of discharge, according to a new study that analyzed 5 years of U.S. readmissions data.
“Given increased thrombotic risk postdischarge, as well as overall safety of VTE prophylaxis, extending prophylaxis for those at highest risk may have significant benefits,” wrote Adam S. Faye, MD, of Columbia University, and coauthors. The study was published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
To determine which IBD patients would be most in need of postdischarge VTE prophylaxis, as well as when to administer it, the researchers analyzed 2010-2014 data from the Nationwide Readmissions Database (NRD). They found a total of 872,122 index admissions for IBD patients; 4% of those patients had a prior VTE. Of the index admissions, 1,160 led to a VTE readmission within 90 days. Readmitted patients had a relatively equal proportion of ulcerative colitis (n = 522) and Crohn’s disease (n = 638).
More than 90% of VTE readmissions occurred within 60 days of discharge; the risk was highest over the first 10 days and then decreased in each ensuing 10-day period until a slight increase at the 81- to 90-day period. All patients over age 30 had higher rates of readmission than those of patients under age 18, with the highest risk in patients between the ages of 66 and 80 years (risk ratio 4.04; 95% confidence interval, 2.54-6.44, P less than .01). Women were at lower risk (RR 0.82; 95% CI, 0.73-0.92, P less than .01). Higher risks of readmission were also associated with being on Medicare (RR 1.39; 95% CI, 1.23-1.58, P less than .01) compared with being on private insurance and being cared for at a large hospital (RR 1.26; 95% CI, 1.04-1.52, P = .02) compared with a small hospital.
The highest risk of VTE readmission was associated with a prior history of VTE (RR 2.89; 95% CI, 2.40-3.48, P less than .01), having two or more comorbidities (RR 2.57; 95% CI, 2.11-3.12, P less than .01) and having a Clostridioides difficile infection as of index admission (RR 1.90; 95% CI, 1.51-2.38, P less than .01). In addition, increased risk was associated with being discharged to a nursing or care facility (RR 1.85; 95% CI, 1.56-2.20, P less than .01) or home with health services (RR 2.05; 95% CI, 1.78-2.38, P less than .01) compared with a routine discharge.
In their multivariable analysis, similar factors such as a history of VTE (adjusted RR 2.41; 95% CI, 1.99-2.90, P less than .01), two or more comorbidities (aRR 1.78; 95% CI, 1.44-2.20, P less than .01) and C. difficile infection (aRR 1.47; 95% CI, 1.17-1.85, P less than.01) continued to be associated with higher risk of VTE readmission.
Though they emphasized that the use of NRD data offered the impressive ability to “review over 15 million discharges across the U.S. annually,” Dr. Faye and coauthors acknowledged that their study did have limitations. These included the inability to verify via chart review the study’s outcomes and covariates. In addition, they were unable to assess potential contributing risk factors such as medication use, use of VTE prophylaxis during hospitalization, disease severity, and family history. Finally, though unlikely, they admitted the possibility that patients could be counted more than once if they were readmitted with a VTE each year of the study.
The authors reported being supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health and various pharmaceutical companies, as well as receiving honoraria and serving as consultants.
SOURCE: Faye AS et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 July 20. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.028.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Readmission for VTE in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases most often occurs within 60 days of discharge.
Major finding: The highest readmission risk was in patients between the ages of 66 and 80 (risk ratio 4.04; 95% confidence interval, 2.54-6.44, P less than .01).
Study details: A retrospective cohort study of 1,160 IBD patients who had VTE readmissions via 2010-2014 data from the Nationwide Readmissions Database.
Disclosures: The authors reported being supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health and various pharmaceutical companies, as well as receiving honoraria and serving as consultants.
Source: Faye AS et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 July 20. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.028.
Apply to become the next SVS PSO Associate Medical Director
The SVS PSO is looking for a part-time Associate Medical Director. This person will be responsible for assisting the SVS PSO Medical Director and the SVS PSO staff, with guidance and over site in its clinical operations. The new associate director will be nominated by the SVS PSO Executive Committee and approved the SVS and the SVS Executive Board. He or she will serve a one-year term, with the opportunity to serve two additional one-year terms. There is a modest honorary associated with this position and the potential to advance into the role of SVS PSO Medical Director. Submit your application before Oct. 11 to be considered. Read the full job description here. Please email your completed resume to [email protected].
The SVS PSO is looking for a part-time Associate Medical Director. This person will be responsible for assisting the SVS PSO Medical Director and the SVS PSO staff, with guidance and over site in its clinical operations. The new associate director will be nominated by the SVS PSO Executive Committee and approved the SVS and the SVS Executive Board. He or she will serve a one-year term, with the opportunity to serve two additional one-year terms. There is a modest honorary associated with this position and the potential to advance into the role of SVS PSO Medical Director. Submit your application before Oct. 11 to be considered. Read the full job description here. Please email your completed resume to [email protected].
The SVS PSO is looking for a part-time Associate Medical Director. This person will be responsible for assisting the SVS PSO Medical Director and the SVS PSO staff, with guidance and over site in its clinical operations. The new associate director will be nominated by the SVS PSO Executive Committee and approved the SVS and the SVS Executive Board. He or she will serve a one-year term, with the opportunity to serve two additional one-year terms. There is a modest honorary associated with this position and the potential to advance into the role of SVS PSO Medical Director. Submit your application before Oct. 11 to be considered. Read the full job description here. Please email your completed resume to [email protected].
SVS Now Accepting International Scholar Applications
If you are a young vascular surgeon from outside North America, consider applying for the International Scholars Program. Recipients of the award will receive a $5,000 stipend, spend two weeks in the U.S, visiting universities and clinics, and attend the 2020 VAM in Toronto. Scholars will work with a mentor to schedule various vascular program visits, including clinical, teaching and research programs. Apply before Sept. 16 to be considered. Learn more.
If you are a young vascular surgeon from outside North America, consider applying for the International Scholars Program. Recipients of the award will receive a $5,000 stipend, spend two weeks in the U.S, visiting universities and clinics, and attend the 2020 VAM in Toronto. Scholars will work with a mentor to schedule various vascular program visits, including clinical, teaching and research programs. Apply before Sept. 16 to be considered. Learn more.
If you are a young vascular surgeon from outside North America, consider applying for the International Scholars Program. Recipients of the award will receive a $5,000 stipend, spend two weeks in the U.S, visiting universities and clinics, and attend the 2020 VAM in Toronto. Scholars will work with a mentor to schedule various vascular program visits, including clinical, teaching and research programs. Apply before Sept. 16 to be considered. Learn more.
Become a mentor on SVSConnect
The SVS has officially announced its new Mentor Match program on its online community, SVSConnect. This program provides a simple way to match general surgery residents and medical students with vascular surgeons who will, ideally, help guide them on their career path. Our resident and student members have been awaiting a program like this, and it will only be successful if we have a large pool of Active SVS members enrolled as mentors. Mentees will be able to enroll soon, at which time the matching process will begin. Please look out for communication from us for when that occurs. Questions? Reach out to [email protected].
The SVS has officially announced its new Mentor Match program on its online community, SVSConnect. This program provides a simple way to match general surgery residents and medical students with vascular surgeons who will, ideally, help guide them on their career path. Our resident and student members have been awaiting a program like this, and it will only be successful if we have a large pool of Active SVS members enrolled as mentors. Mentees will be able to enroll soon, at which time the matching process will begin. Please look out for communication from us for when that occurs. Questions? Reach out to [email protected].
The SVS has officially announced its new Mentor Match program on its online community, SVSConnect. This program provides a simple way to match general surgery residents and medical students with vascular surgeons who will, ideally, help guide them on their career path. Our resident and student members have been awaiting a program like this, and it will only be successful if we have a large pool of Active SVS members enrolled as mentors. Mentees will be able to enroll soon, at which time the matching process will begin. Please look out for communication from us for when that occurs. Questions? Reach out to [email protected].
Celebrate Vascular Nurses Week of September 8
Join us as we celebrate all vascular nurses September 8 to 14 during Vascular Nurses Week. Be sure to let your nurses know how much you value them and their important contributions to your vascular team. You may also encourage your vascular nurses to join the SVS as affiliate members. Membership benefits include discounted meeting registrations, scholarship opportunities, leadership opportunities and more. Read more about Affiliate membership for vascular nurses here.
Join us as we celebrate all vascular nurses September 8 to 14 during Vascular Nurses Week. Be sure to let your nurses know how much you value them and their important contributions to your vascular team. You may also encourage your vascular nurses to join the SVS as affiliate members. Membership benefits include discounted meeting registrations, scholarship opportunities, leadership opportunities and more. Read more about Affiliate membership for vascular nurses here.
Join us as we celebrate all vascular nurses September 8 to 14 during Vascular Nurses Week. Be sure to let your nurses know how much you value them and their important contributions to your vascular team. You may also encourage your vascular nurses to join the SVS as affiliate members. Membership benefits include discounted meeting registrations, scholarship opportunities, leadership opportunities and more. Read more about Affiliate membership for vascular nurses here.