User login
Guselkumab improves effector cytokine levels in PsA patients with inadequate response to TNFi
Key clinical point: Guselkumab led to early reduction of inflammatory cytokines, which was sustained through 48 weeks, with subsequent improvements in clinical response in patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and an inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi-IR).
Major finding: Serum levels of interleukin (IL)-17A, IL-17F, IL-22, and serum amyloid A reduced significantly by week 4 and were sustained through week 48 in the guselkumab (P < .05) vs placebo group when compared with control individuals without PsA. Patients who achieved a clinical response to guselkumab at week 24 showed significant reduction in IL-6 levels at week 4 compared with non-responders (P < .05).
Study details: Findings are from the phase 3b COSMOS study including patients with active PsA and TNFi-IR who were randomly assigned to receive either guselkumab (n = 189) or placebo (n = 96) and compared with matched control individuals.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Janssen Research & Development (R&D), LLC, USA. Seven authors declared being employees of Janssen R&D, LLC, or others or owning stocks or stock options in Johnson & Johnson. Several authors declared ties with various sources, including Janssen.
Source: Schett G et al. Effect of guselkumab on serum biomarkers in patients with active psoriatic arthritis and inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors: Results from the COSMOS phase 3b study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023;25:150 (Aug 16, corrected Sep 15). doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03125-4
Key clinical point: Guselkumab led to early reduction of inflammatory cytokines, which was sustained through 48 weeks, with subsequent improvements in clinical response in patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and an inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi-IR).
Major finding: Serum levels of interleukin (IL)-17A, IL-17F, IL-22, and serum amyloid A reduced significantly by week 4 and were sustained through week 48 in the guselkumab (P < .05) vs placebo group when compared with control individuals without PsA. Patients who achieved a clinical response to guselkumab at week 24 showed significant reduction in IL-6 levels at week 4 compared with non-responders (P < .05).
Study details: Findings are from the phase 3b COSMOS study including patients with active PsA and TNFi-IR who were randomly assigned to receive either guselkumab (n = 189) or placebo (n = 96) and compared with matched control individuals.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Janssen Research & Development (R&D), LLC, USA. Seven authors declared being employees of Janssen R&D, LLC, or others or owning stocks or stock options in Johnson & Johnson. Several authors declared ties with various sources, including Janssen.
Source: Schett G et al. Effect of guselkumab on serum biomarkers in patients with active psoriatic arthritis and inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors: Results from the COSMOS phase 3b study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023;25:150 (Aug 16, corrected Sep 15). doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03125-4
Key clinical point: Guselkumab led to early reduction of inflammatory cytokines, which was sustained through 48 weeks, with subsequent improvements in clinical response in patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and an inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi-IR).
Major finding: Serum levels of interleukin (IL)-17A, IL-17F, IL-22, and serum amyloid A reduced significantly by week 4 and were sustained through week 48 in the guselkumab (P < .05) vs placebo group when compared with control individuals without PsA. Patients who achieved a clinical response to guselkumab at week 24 showed significant reduction in IL-6 levels at week 4 compared with non-responders (P < .05).
Study details: Findings are from the phase 3b COSMOS study including patients with active PsA and TNFi-IR who were randomly assigned to receive either guselkumab (n = 189) or placebo (n = 96) and compared with matched control individuals.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Janssen Research & Development (R&D), LLC, USA. Seven authors declared being employees of Janssen R&D, LLC, or others or owning stocks or stock options in Johnson & Johnson. Several authors declared ties with various sources, including Janssen.
Source: Schett G et al. Effect of guselkumab on serum biomarkers in patients with active psoriatic arthritis and inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors: Results from the COSMOS phase 3b study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023;25:150 (Aug 16, corrected Sep 15). doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03125-4
Cat Scratch Disease Presenting With Concurrent Pityriasis Rosea in a 10-Year-Old Girl
To the Editor:
Cat scratch disease (CSD) is caused by Bartonella henselae and Bartonella clarridgeiae bacteria transferred from cats to humans that results in an inflamed inoculation site and tender lymphadenopathy. Pityriasis rosea (PR) and PR-like eruptions are self-limited, acute exanthems that have been associated with infections, vaccinations, and medications. We report a case of PR occurring in a 10-year-old girl with CSD, which may suggest an association between the 2 diseases.

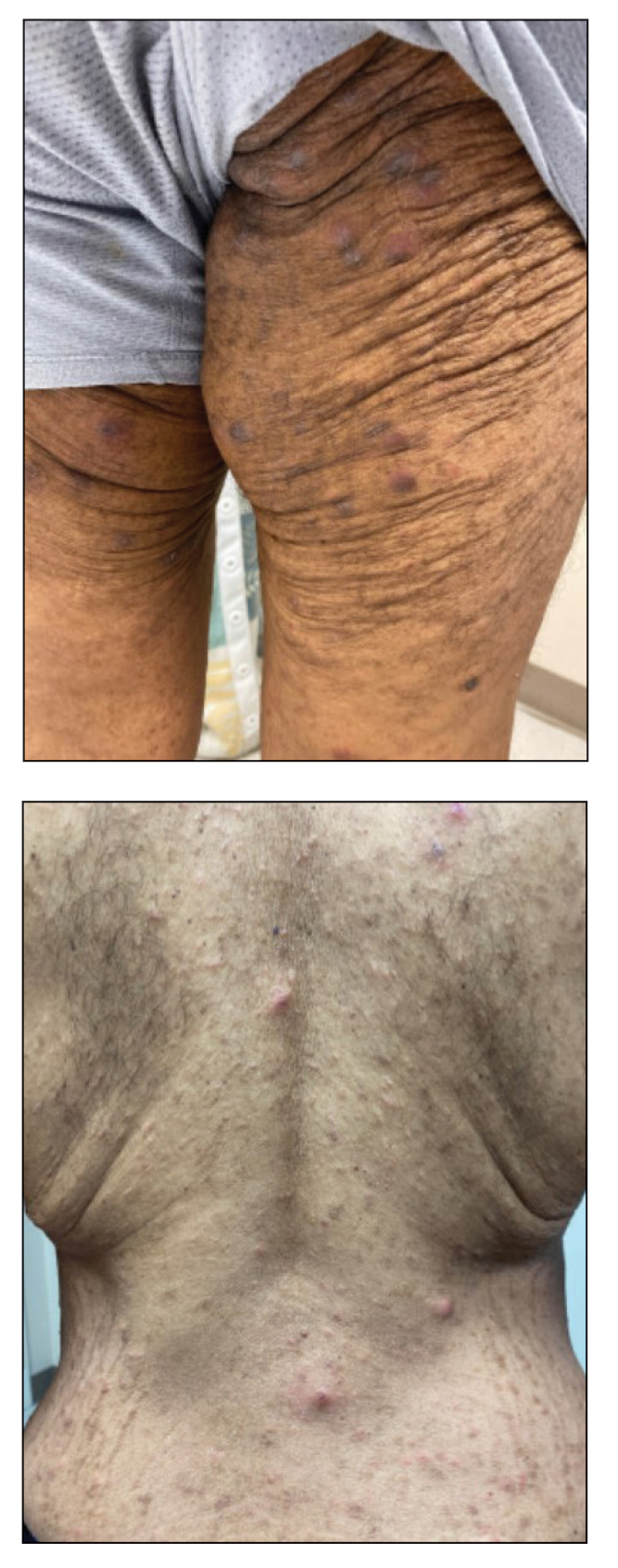
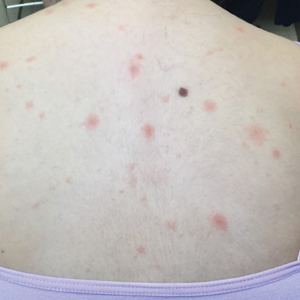
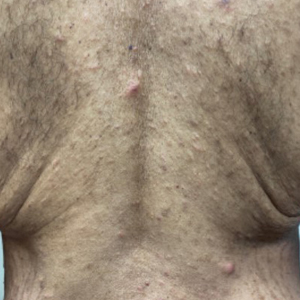
A 10-year-old girl who was otherwise healthy presented in the winter with a rash of 5 days’ duration. Fourteen days prior to the rash, the patient reported being scratched by a new kitten and noted a pinpoint “puncture” on the left forearm that developed into a red papule over the following week. Seven days after the cat scratch, the patient experienced pain and swelling in the left axilla. Approximately 1 week after the onset of lymphadenopathy, the patient developed an asymptomatic rash that started with a large spot on the left chest, followed by smaller spots appearing over the next 2 days and spreading to the rest of the trunk. Four days after the rash onset, the patient experienced a mild headache, low-grade subjective fever, and chills. She denied any recent travel, bug bites, sore throat, and diarrhea. She was up-to-date on all vaccinations and had not received any vaccines preceding the symptoms. Physical examination revealed a 2-cm pink, scaly, thin plaque with a collarette of scale on the left upper chest (herald patch), along with multiple thin pink papules and small plaques with central scale on the trunk (Figure 1). A pustule with adjacent linear erosion was present on the left ventral forearm (Figure 2). The patient had a tender subcutaneous nodule in the left axilla as well as bilateral anterior and posterior cervical-chain subcutaneous tender nodules. There was no involvement of the palms, soles, or mucosae.
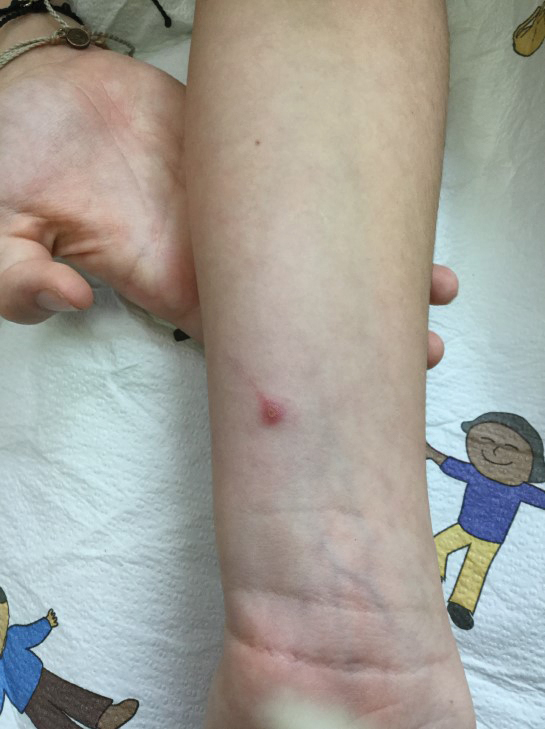
The patient was empirically treated for CSD with azithromycin (200 mg/5 mL), 404 mg on day 1 followed by 202 mg daily for 4 days. The rash was treated with hydrocortisone cream 2.5% twice daily for 2 weeks. A wound culture of the pustule on the left forearm was negative for neutrophils and organisms. Antibody serologies obtained 4 weeks after presentation were notable for an elevated B henselae IgG titer of 1:640, confirming the diagnosis of CSD. Following treatment with azithromycin and hydrocortisone, all of the patient’s symptoms resolved after 1 to 2 weeks.
Cat scratch disease is a zoonotic infection caused by the bacteria B henselae and the more recently described pathogen B clarridgeiae. Cat fleas spread these bacteria among cats, which subsequently inoculate the bacteria into humans through bites and scratches. The incidence of CSD in the United States is estimated to be 4.5 to 9.3 per 100,000 individuals in the outpatient setting and 0.19 to 0.86 per 100,000 individuals in the inpatient setting.1 Geographic variance can occur based on flea populations, resulting in higher incidence in warm humid climates and lower incidence in mountainous arid climates. The incidence of CSD in the pediatric population is highest in children aged 5 to 9 years. A national representative survey (N=3011) from 2017 revealed that 37.2% of primary care providers had diagnosed CSD in the prior year.1
Classic CSD presents as an erythematous papule at the inoculation site lasting days to weeks, with progression to tender lymphadenopathy lasting weeks to months. Fever, malaise, and chills also can be seen. Atypical CSD occurs in up to 24% of cases in immunocompetent patients.1 Atypical and systemic presentations are varied and can include fever of unknown origin, neuroretinitis, uveitis, retinal vessel occlusion, encephalitis, hepatosplenic lesions, Parinaud oculoglandular syndrome, osteomyelitis, and endocarditis.1,2 Atypical dermatologic presentations of CSD include maculopapular rash in 7% of cases and erythema nodosum in 2.5% of cases, as well as rare reports of cutaneous vasculitis, urticaria, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, and papuloedematous eruption.3 Treatment guidelines for CSD vary widely depending on the clinical presentation as well as the immunocompetence of the infected individual. Our patient had limited regional lymphadenopathy with no signs of dissemination or neurologic involvement and was successfully treated with a 5-day course of oral azithromycin (weight based, 10 mg/kg). More extensive disease such as hepatosplenic or neurologic CSD may require multiple antibiotics for up to 6 weeks. Alternative or additional antibiotics used for CSD include rifampin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, gentamicin, and clarithromycin. Opinions vary as to whether all patients or just those with complicated infections warrant antibiotic therapy.4-6
Pityriasis rosea is a self-limited acute exanthematous disease that is classically associated with a systemic reactivation of human herpesvirus (HHV) 6 and/or HHV-7. The incidence of PR is estimated to be 480 per 100,000 dermatologic patients. It is slightly more common in females and occurs most often in patients aged 10 to 35 years.7 Clinically, PR appears with the abrupt onset of a single erythematous scaly patch (termed the herald patch), followed by a secondary eruption of smaller erythematous scaly macules and patches along the trunk’s cleavage lines. The secondary eruption on the back is sometimes termed a Christmas or fir tree pattern.7,8
In addition to the classic presentation of PR, there have been reports of numerous atypical clinical presentations. The herald patch, which classically presents on the trunk, also has been reported to present on the extremities; PR of the extremities is defined by lesions that appear as large scaly plaques on the extremities only. Inverse PR presents with lesions occurring in flexural areas and acral surfaces but not on the trunk. There also is an acral PR variant in which lesions appear only on the palms, wrists, and soles. Purpuric or hemorrhagic PR has been described and presents with purpura and petechiae with or without collarettes of scale in diffuse locations, including the palate. Oral PR presents more commonly in patients of color as erosions, ulcers, hemorrhagic lesions, bullae, or geographic tongue. Erythema multiforme–like PR appears with targetoid lesions on the trunk, face, neck, and arms without a history of herpes simplex virus infection. A large pear-shaped herald patch has been reported and characterizes the gigantea PR of Darier variant. Irritated PR occurs with typical PR findings, but afflicted patients report severe pain and burning with diaphoresis. Relapsing PR can occur within 1 year of a prior episode of PR and presents without a herald patch. Persistent PR is defined by PR lasting more than 3 months, and most reported cases have included oral lesions. Finally, other PR variants that have been described include urticarial, papular, follicular, vesicular, and hypopigmented types.7-9
Furthermore, there have been reports of multiple atypical presentations occurring simultaneously in the same patient.10 Although PR classically has been associated with HHV-6 and/or HHV-7 reactivation, it has been reported with a few other clinical situations and conditions. Pityriasislike eruption specifically refers to an exanthem secondary to drugs or vaccination that resembles PR but shows clinical differences, including diffuse and confluent dusky-red macules and/or plaques with or without desquamation on the trunk, extremities, and face. Drugs that have been implicated as triggers include ACE inhibitors, gold, isotretinoin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, omeprazole, terbinafine, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Smallpox, tuberculosis, poliomyelitis, influenza, diphtheria, tetanus, hepatitis B virus, pneumococcus, papillomavirus, yellow fever, and pertussis vaccinations also have been associated with PR.7,11,12 Additionally, PR has been reported to occur with active systemic infections, specifically H1N1 influenza, though it is rare.13 Because of its self-limited course, treatment of PR most often involves only reassurance. Topical corticosteroids may be appropriate for pruritus.7,8
Pediatric health care providers including dermatologists should be familiar with both CSD and PR because they are common diseases that more often are encountered in the pediatric population. We present a unique case of CSD presenting with concurrent PR, which highlights a potential new etiology for PR and a rare cutaneous manifestation of CSD. Further investigation into a possible relationship between CSD and PR may be warranted. Patients with any signs and symptoms of fever, tender lymphadenopathy, worsening rash, or exposure to cats warrant a thorough history and physical examination to ensure that neither entity is overlooked.
- Nelson CA, Moore AR, Perea AE, et al. Cat scratch disease: U.S. clinicians’ experience and knowledge [published online July 14, 2017]. Zoonoses Public Health. 2018;65:67-73. doi:10.1111/zph.12368
- Habot-Wilner Z, Trivizki O, Goldstein M, et al. Cat-scratch disease: ocular manifestations and treatment outcome. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018;96:E524-E532. doi:10.1111/aos.13684
- Schattner A, Uliel L, Dubin I. The cat did it: erythema nodosum and additional atypical presentations of Bartonella henselae infection in immunocompetent hosts [published online February 16, 2018]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-222511
- Shorbatli L, Koranyi K, Nahata M. Effectiveness of antibiotic therapy in pediatric patients with cat scratch disease. Int J Clin Pharm. 2018;40:1458-1461. doi: 10.1007/s11096-018-0746-1
- Bass JW, Freitas BC, Freitas AD, et al. Prospective randomized double blind placebo-controlled evaluation of azithromycin for treatment of cat-scratch disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998;17:447-452. doi:10.1097/00006454-199806000-00002
- Spach DH, Kaplan SL. Treatment of cat scratch disease. UpToDate. Updated December 9, 2021. Accessed September 12, 2023. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-of-cat-scratch-disease
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Rebora A, et al. Pityriasis rosea: a comprehensive classification. Dermatology. 2016;232:431-437. doi:10.1159/000445375
- Urbina F, Das A, Sudy E. Clinical variants of pityriasis rosea. World J Clin Cases. 2017;5:203-211. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v5.i6.203
- Alzahrani NA, Al Jasser MI. Geographic tonguelike presentation in a child with pityriasis rosea: case report and review of oral manifestations of pityriasis rosea. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:E124-E127. doi:10.1111/pde.13417
- Sinha S, Sardana K, Garg V. Coexistence of two atypical variants of pityriasis rosea: a case report and review of literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:538-540. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2011.01549.x
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Parodi A. Pityriasis rosea and pityriasis rosea-like eruptions: how to distinguish them? JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:800-801. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2018.04.002
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Javor S, et al. Vaccine-induced pityriasis rosea and pityriasis rosea-like eruptions: a review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:544-545. doi:10.1111/jdv.12942
- Mubki TF, Bin Dayel SA, Kadry R. A case of pityriasis rosea concurrent with the novel influenza A (H1N1) infection. Pediatr Dermatol. 2011;28:341-342. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2010.01090.x
To the Editor:
Cat scratch disease (CSD) is caused by Bartonella henselae and Bartonella clarridgeiae bacteria transferred from cats to humans that results in an inflamed inoculation site and tender lymphadenopathy. Pityriasis rosea (PR) and PR-like eruptions are self-limited, acute exanthems that have been associated with infections, vaccinations, and medications. We report a case of PR occurring in a 10-year-old girl with CSD, which may suggest an association between the 2 diseases.

A 10-year-old girl who was otherwise healthy presented in the winter with a rash of 5 days’ duration. Fourteen days prior to the rash, the patient reported being scratched by a new kitten and noted a pinpoint “puncture” on the left forearm that developed into a red papule over the following week. Seven days after the cat scratch, the patient experienced pain and swelling in the left axilla. Approximately 1 week after the onset of lymphadenopathy, the patient developed an asymptomatic rash that started with a large spot on the left chest, followed by smaller spots appearing over the next 2 days and spreading to the rest of the trunk. Four days after the rash onset, the patient experienced a mild headache, low-grade subjective fever, and chills. She denied any recent travel, bug bites, sore throat, and diarrhea. She was up-to-date on all vaccinations and had not received any vaccines preceding the symptoms. Physical examination revealed a 2-cm pink, scaly, thin plaque with a collarette of scale on the left upper chest (herald patch), along with multiple thin pink papules and small plaques with central scale on the trunk (Figure 1). A pustule with adjacent linear erosion was present on the left ventral forearm (Figure 2). The patient had a tender subcutaneous nodule in the left axilla as well as bilateral anterior and posterior cervical-chain subcutaneous tender nodules. There was no involvement of the palms, soles, or mucosae.

The patient was empirically treated for CSD with azithromycin (200 mg/5 mL), 404 mg on day 1 followed by 202 mg daily for 4 days. The rash was treated with hydrocortisone cream 2.5% twice daily for 2 weeks. A wound culture of the pustule on the left forearm was negative for neutrophils and organisms. Antibody serologies obtained 4 weeks after presentation were notable for an elevated B henselae IgG titer of 1:640, confirming the diagnosis of CSD. Following treatment with azithromycin and hydrocortisone, all of the patient’s symptoms resolved after 1 to 2 weeks.
Cat scratch disease is a zoonotic infection caused by the bacteria B henselae and the more recently described pathogen B clarridgeiae. Cat fleas spread these bacteria among cats, which subsequently inoculate the bacteria into humans through bites and scratches. The incidence of CSD in the United States is estimated to be 4.5 to 9.3 per 100,000 individuals in the outpatient setting and 0.19 to 0.86 per 100,000 individuals in the inpatient setting.1 Geographic variance can occur based on flea populations, resulting in higher incidence in warm humid climates and lower incidence in mountainous arid climates. The incidence of CSD in the pediatric population is highest in children aged 5 to 9 years. A national representative survey (N=3011) from 2017 revealed that 37.2% of primary care providers had diagnosed CSD in the prior year.1
Classic CSD presents as an erythematous papule at the inoculation site lasting days to weeks, with progression to tender lymphadenopathy lasting weeks to months. Fever, malaise, and chills also can be seen. Atypical CSD occurs in up to 24% of cases in immunocompetent patients.1 Atypical and systemic presentations are varied and can include fever of unknown origin, neuroretinitis, uveitis, retinal vessel occlusion, encephalitis, hepatosplenic lesions, Parinaud oculoglandular syndrome, osteomyelitis, and endocarditis.1,2 Atypical dermatologic presentations of CSD include maculopapular rash in 7% of cases and erythema nodosum in 2.5% of cases, as well as rare reports of cutaneous vasculitis, urticaria, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, and papuloedematous eruption.3 Treatment guidelines for CSD vary widely depending on the clinical presentation as well as the immunocompetence of the infected individual. Our patient had limited regional lymphadenopathy with no signs of dissemination or neurologic involvement and was successfully treated with a 5-day course of oral azithromycin (weight based, 10 mg/kg). More extensive disease such as hepatosplenic or neurologic CSD may require multiple antibiotics for up to 6 weeks. Alternative or additional antibiotics used for CSD include rifampin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, gentamicin, and clarithromycin. Opinions vary as to whether all patients or just those with complicated infections warrant antibiotic therapy.4-6
Pityriasis rosea is a self-limited acute exanthematous disease that is classically associated with a systemic reactivation of human herpesvirus (HHV) 6 and/or HHV-7. The incidence of PR is estimated to be 480 per 100,000 dermatologic patients. It is slightly more common in females and occurs most often in patients aged 10 to 35 years.7 Clinically, PR appears with the abrupt onset of a single erythematous scaly patch (termed the herald patch), followed by a secondary eruption of smaller erythematous scaly macules and patches along the trunk’s cleavage lines. The secondary eruption on the back is sometimes termed a Christmas or fir tree pattern.7,8
In addition to the classic presentation of PR, there have been reports of numerous atypical clinical presentations. The herald patch, which classically presents on the trunk, also has been reported to present on the extremities; PR of the extremities is defined by lesions that appear as large scaly plaques on the extremities only. Inverse PR presents with lesions occurring in flexural areas and acral surfaces but not on the trunk. There also is an acral PR variant in which lesions appear only on the palms, wrists, and soles. Purpuric or hemorrhagic PR has been described and presents with purpura and petechiae with or without collarettes of scale in diffuse locations, including the palate. Oral PR presents more commonly in patients of color as erosions, ulcers, hemorrhagic lesions, bullae, or geographic tongue. Erythema multiforme–like PR appears with targetoid lesions on the trunk, face, neck, and arms without a history of herpes simplex virus infection. A large pear-shaped herald patch has been reported and characterizes the gigantea PR of Darier variant. Irritated PR occurs with typical PR findings, but afflicted patients report severe pain and burning with diaphoresis. Relapsing PR can occur within 1 year of a prior episode of PR and presents without a herald patch. Persistent PR is defined by PR lasting more than 3 months, and most reported cases have included oral lesions. Finally, other PR variants that have been described include urticarial, papular, follicular, vesicular, and hypopigmented types.7-9
Furthermore, there have been reports of multiple atypical presentations occurring simultaneously in the same patient.10 Although PR classically has been associated with HHV-6 and/or HHV-7 reactivation, it has been reported with a few other clinical situations and conditions. Pityriasislike eruption specifically refers to an exanthem secondary to drugs or vaccination that resembles PR but shows clinical differences, including diffuse and confluent dusky-red macules and/or plaques with or without desquamation on the trunk, extremities, and face. Drugs that have been implicated as triggers include ACE inhibitors, gold, isotretinoin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, omeprazole, terbinafine, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Smallpox, tuberculosis, poliomyelitis, influenza, diphtheria, tetanus, hepatitis B virus, pneumococcus, papillomavirus, yellow fever, and pertussis vaccinations also have been associated with PR.7,11,12 Additionally, PR has been reported to occur with active systemic infections, specifically H1N1 influenza, though it is rare.13 Because of its self-limited course, treatment of PR most often involves only reassurance. Topical corticosteroids may be appropriate for pruritus.7,8
Pediatric health care providers including dermatologists should be familiar with both CSD and PR because they are common diseases that more often are encountered in the pediatric population. We present a unique case of CSD presenting with concurrent PR, which highlights a potential new etiology for PR and a rare cutaneous manifestation of CSD. Further investigation into a possible relationship between CSD and PR may be warranted. Patients with any signs and symptoms of fever, tender lymphadenopathy, worsening rash, or exposure to cats warrant a thorough history and physical examination to ensure that neither entity is overlooked.
To the Editor:
Cat scratch disease (CSD) is caused by Bartonella henselae and Bartonella clarridgeiae bacteria transferred from cats to humans that results in an inflamed inoculation site and tender lymphadenopathy. Pityriasis rosea (PR) and PR-like eruptions are self-limited, acute exanthems that have been associated with infections, vaccinations, and medications. We report a case of PR occurring in a 10-year-old girl with CSD, which may suggest an association between the 2 diseases.

A 10-year-old girl who was otherwise healthy presented in the winter with a rash of 5 days’ duration. Fourteen days prior to the rash, the patient reported being scratched by a new kitten and noted a pinpoint “puncture” on the left forearm that developed into a red papule over the following week. Seven days after the cat scratch, the patient experienced pain and swelling in the left axilla. Approximately 1 week after the onset of lymphadenopathy, the patient developed an asymptomatic rash that started with a large spot on the left chest, followed by smaller spots appearing over the next 2 days and spreading to the rest of the trunk. Four days after the rash onset, the patient experienced a mild headache, low-grade subjective fever, and chills. She denied any recent travel, bug bites, sore throat, and diarrhea. She was up-to-date on all vaccinations and had not received any vaccines preceding the symptoms. Physical examination revealed a 2-cm pink, scaly, thin plaque with a collarette of scale on the left upper chest (herald patch), along with multiple thin pink papules and small plaques with central scale on the trunk (Figure 1). A pustule with adjacent linear erosion was present on the left ventral forearm (Figure 2). The patient had a tender subcutaneous nodule in the left axilla as well as bilateral anterior and posterior cervical-chain subcutaneous tender nodules. There was no involvement of the palms, soles, or mucosae.

The patient was empirically treated for CSD with azithromycin (200 mg/5 mL), 404 mg on day 1 followed by 202 mg daily for 4 days. The rash was treated with hydrocortisone cream 2.5% twice daily for 2 weeks. A wound culture of the pustule on the left forearm was negative for neutrophils and organisms. Antibody serologies obtained 4 weeks after presentation were notable for an elevated B henselae IgG titer of 1:640, confirming the diagnosis of CSD. Following treatment with azithromycin and hydrocortisone, all of the patient’s symptoms resolved after 1 to 2 weeks.
Cat scratch disease is a zoonotic infection caused by the bacteria B henselae and the more recently described pathogen B clarridgeiae. Cat fleas spread these bacteria among cats, which subsequently inoculate the bacteria into humans through bites and scratches. The incidence of CSD in the United States is estimated to be 4.5 to 9.3 per 100,000 individuals in the outpatient setting and 0.19 to 0.86 per 100,000 individuals in the inpatient setting.1 Geographic variance can occur based on flea populations, resulting in higher incidence in warm humid climates and lower incidence in mountainous arid climates. The incidence of CSD in the pediatric population is highest in children aged 5 to 9 years. A national representative survey (N=3011) from 2017 revealed that 37.2% of primary care providers had diagnosed CSD in the prior year.1
Classic CSD presents as an erythematous papule at the inoculation site lasting days to weeks, with progression to tender lymphadenopathy lasting weeks to months. Fever, malaise, and chills also can be seen. Atypical CSD occurs in up to 24% of cases in immunocompetent patients.1 Atypical and systemic presentations are varied and can include fever of unknown origin, neuroretinitis, uveitis, retinal vessel occlusion, encephalitis, hepatosplenic lesions, Parinaud oculoglandular syndrome, osteomyelitis, and endocarditis.1,2 Atypical dermatologic presentations of CSD include maculopapular rash in 7% of cases and erythema nodosum in 2.5% of cases, as well as rare reports of cutaneous vasculitis, urticaria, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, and papuloedematous eruption.3 Treatment guidelines for CSD vary widely depending on the clinical presentation as well as the immunocompetence of the infected individual. Our patient had limited regional lymphadenopathy with no signs of dissemination or neurologic involvement and was successfully treated with a 5-day course of oral azithromycin (weight based, 10 mg/kg). More extensive disease such as hepatosplenic or neurologic CSD may require multiple antibiotics for up to 6 weeks. Alternative or additional antibiotics used for CSD include rifampin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, gentamicin, and clarithromycin. Opinions vary as to whether all patients or just those with complicated infections warrant antibiotic therapy.4-6
Pityriasis rosea is a self-limited acute exanthematous disease that is classically associated with a systemic reactivation of human herpesvirus (HHV) 6 and/or HHV-7. The incidence of PR is estimated to be 480 per 100,000 dermatologic patients. It is slightly more common in females and occurs most often in patients aged 10 to 35 years.7 Clinically, PR appears with the abrupt onset of a single erythematous scaly patch (termed the herald patch), followed by a secondary eruption of smaller erythematous scaly macules and patches along the trunk’s cleavage lines. The secondary eruption on the back is sometimes termed a Christmas or fir tree pattern.7,8
In addition to the classic presentation of PR, there have been reports of numerous atypical clinical presentations. The herald patch, which classically presents on the trunk, also has been reported to present on the extremities; PR of the extremities is defined by lesions that appear as large scaly plaques on the extremities only. Inverse PR presents with lesions occurring in flexural areas and acral surfaces but not on the trunk. There also is an acral PR variant in which lesions appear only on the palms, wrists, and soles. Purpuric or hemorrhagic PR has been described and presents with purpura and petechiae with or without collarettes of scale in diffuse locations, including the palate. Oral PR presents more commonly in patients of color as erosions, ulcers, hemorrhagic lesions, bullae, or geographic tongue. Erythema multiforme–like PR appears with targetoid lesions on the trunk, face, neck, and arms without a history of herpes simplex virus infection. A large pear-shaped herald patch has been reported and characterizes the gigantea PR of Darier variant. Irritated PR occurs with typical PR findings, but afflicted patients report severe pain and burning with diaphoresis. Relapsing PR can occur within 1 year of a prior episode of PR and presents without a herald patch. Persistent PR is defined by PR lasting more than 3 months, and most reported cases have included oral lesions. Finally, other PR variants that have been described include urticarial, papular, follicular, vesicular, and hypopigmented types.7-9
Furthermore, there have been reports of multiple atypical presentations occurring simultaneously in the same patient.10 Although PR classically has been associated with HHV-6 and/or HHV-7 reactivation, it has been reported with a few other clinical situations and conditions. Pityriasislike eruption specifically refers to an exanthem secondary to drugs or vaccination that resembles PR but shows clinical differences, including diffuse and confluent dusky-red macules and/or plaques with or without desquamation on the trunk, extremities, and face. Drugs that have been implicated as triggers include ACE inhibitors, gold, isotretinoin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, omeprazole, terbinafine, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Smallpox, tuberculosis, poliomyelitis, influenza, diphtheria, tetanus, hepatitis B virus, pneumococcus, papillomavirus, yellow fever, and pertussis vaccinations also have been associated with PR.7,11,12 Additionally, PR has been reported to occur with active systemic infections, specifically H1N1 influenza, though it is rare.13 Because of its self-limited course, treatment of PR most often involves only reassurance. Topical corticosteroids may be appropriate for pruritus.7,8
Pediatric health care providers including dermatologists should be familiar with both CSD and PR because they are common diseases that more often are encountered in the pediatric population. We present a unique case of CSD presenting with concurrent PR, which highlights a potential new etiology for PR and a rare cutaneous manifestation of CSD. Further investigation into a possible relationship between CSD and PR may be warranted. Patients with any signs and symptoms of fever, tender lymphadenopathy, worsening rash, or exposure to cats warrant a thorough history and physical examination to ensure that neither entity is overlooked.
- Nelson CA, Moore AR, Perea AE, et al. Cat scratch disease: U.S. clinicians’ experience and knowledge [published online July 14, 2017]. Zoonoses Public Health. 2018;65:67-73. doi:10.1111/zph.12368
- Habot-Wilner Z, Trivizki O, Goldstein M, et al. Cat-scratch disease: ocular manifestations and treatment outcome. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018;96:E524-E532. doi:10.1111/aos.13684
- Schattner A, Uliel L, Dubin I. The cat did it: erythema nodosum and additional atypical presentations of Bartonella henselae infection in immunocompetent hosts [published online February 16, 2018]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-222511
- Shorbatli L, Koranyi K, Nahata M. Effectiveness of antibiotic therapy in pediatric patients with cat scratch disease. Int J Clin Pharm. 2018;40:1458-1461. doi: 10.1007/s11096-018-0746-1
- Bass JW, Freitas BC, Freitas AD, et al. Prospective randomized double blind placebo-controlled evaluation of azithromycin for treatment of cat-scratch disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998;17:447-452. doi:10.1097/00006454-199806000-00002
- Spach DH, Kaplan SL. Treatment of cat scratch disease. UpToDate. Updated December 9, 2021. Accessed September 12, 2023. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-of-cat-scratch-disease
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Rebora A, et al. Pityriasis rosea: a comprehensive classification. Dermatology. 2016;232:431-437. doi:10.1159/000445375
- Urbina F, Das A, Sudy E. Clinical variants of pityriasis rosea. World J Clin Cases. 2017;5:203-211. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v5.i6.203
- Alzahrani NA, Al Jasser MI. Geographic tonguelike presentation in a child with pityriasis rosea: case report and review of oral manifestations of pityriasis rosea. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:E124-E127. doi:10.1111/pde.13417
- Sinha S, Sardana K, Garg V. Coexistence of two atypical variants of pityriasis rosea: a case report and review of literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:538-540. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2011.01549.x
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Parodi A. Pityriasis rosea and pityriasis rosea-like eruptions: how to distinguish them? JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:800-801. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2018.04.002
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Javor S, et al. Vaccine-induced pityriasis rosea and pityriasis rosea-like eruptions: a review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:544-545. doi:10.1111/jdv.12942
- Mubki TF, Bin Dayel SA, Kadry R. A case of pityriasis rosea concurrent with the novel influenza A (H1N1) infection. Pediatr Dermatol. 2011;28:341-342. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2010.01090.x
- Nelson CA, Moore AR, Perea AE, et al. Cat scratch disease: U.S. clinicians’ experience and knowledge [published online July 14, 2017]. Zoonoses Public Health. 2018;65:67-73. doi:10.1111/zph.12368
- Habot-Wilner Z, Trivizki O, Goldstein M, et al. Cat-scratch disease: ocular manifestations and treatment outcome. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018;96:E524-E532. doi:10.1111/aos.13684
- Schattner A, Uliel L, Dubin I. The cat did it: erythema nodosum and additional atypical presentations of Bartonella henselae infection in immunocompetent hosts [published online February 16, 2018]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-222511
- Shorbatli L, Koranyi K, Nahata M. Effectiveness of antibiotic therapy in pediatric patients with cat scratch disease. Int J Clin Pharm. 2018;40:1458-1461. doi: 10.1007/s11096-018-0746-1
- Bass JW, Freitas BC, Freitas AD, et al. Prospective randomized double blind placebo-controlled evaluation of azithromycin for treatment of cat-scratch disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998;17:447-452. doi:10.1097/00006454-199806000-00002
- Spach DH, Kaplan SL. Treatment of cat scratch disease. UpToDate. Updated December 9, 2021. Accessed September 12, 2023. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-of-cat-scratch-disease
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Rebora A, et al. Pityriasis rosea: a comprehensive classification. Dermatology. 2016;232:431-437. doi:10.1159/000445375
- Urbina F, Das A, Sudy E. Clinical variants of pityriasis rosea. World J Clin Cases. 2017;5:203-211. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v5.i6.203
- Alzahrani NA, Al Jasser MI. Geographic tonguelike presentation in a child with pityriasis rosea: case report and review of oral manifestations of pityriasis rosea. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:E124-E127. doi:10.1111/pde.13417
- Sinha S, Sardana K, Garg V. Coexistence of two atypical variants of pityriasis rosea: a case report and review of literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:538-540. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2011.01549.x
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Parodi A. Pityriasis rosea and pityriasis rosea-like eruptions: how to distinguish them? JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:800-801. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2018.04.002
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Javor S, et al. Vaccine-induced pityriasis rosea and pityriasis rosea-like eruptions: a review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:544-545. doi:10.1111/jdv.12942
- Mubki TF, Bin Dayel SA, Kadry R. A case of pityriasis rosea concurrent with the novel influenza A (H1N1) infection. Pediatr Dermatol. 2011;28:341-342. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2010.01090.x
Practice Points
- Dermatologists should familiarize themselves with the physical examination findings of cat scratch disease.
- There are numerous clinical variants and triggers of pityriasis rosea (PR).
- There may be a new infectious trigger for PR, and exposure to cats prior to a classic PR eruption should raise one’s suspicion as a possible cause.
AVAHO 2023: A New View of Women's Health and Clinician Wellness
Sirisha Manyam, DO, eagerly looks forward to attending Association of VA Hematology and Oncology (AVAHO) 2023 and participating in discussion concerning two central topics: women's health and clinician wellness. Recognizing and meeting the distinctive stressors faced by healthcare workers, which have produced alarming rates of burnout, is an apt priority for Veterans Affairs systems, Dr Maryam suggests, and one which is paralleled by the need to engage the unique challenges faced by women, specifically the cluster of considerations surrounding breast cancer treatment.
Sirisha Manyam, DO, eagerly looks forward to attending Association of VA Hematology and Oncology (AVAHO) 2023 and participating in discussion concerning two central topics: women's health and clinician wellness. Recognizing and meeting the distinctive stressors faced by healthcare workers, which have produced alarming rates of burnout, is an apt priority for Veterans Affairs systems, Dr Maryam suggests, and one which is paralleled by the need to engage the unique challenges faced by women, specifically the cluster of considerations surrounding breast cancer treatment.
Sirisha Manyam, DO, eagerly looks forward to attending Association of VA Hematology and Oncology (AVAHO) 2023 and participating in discussion concerning two central topics: women's health and clinician wellness. Recognizing and meeting the distinctive stressors faced by healthcare workers, which have produced alarming rates of burnout, is an apt priority for Veterans Affairs systems, Dr Maryam suggests, and one which is paralleled by the need to engage the unique challenges faced by women, specifically the cluster of considerations surrounding breast cancer treatment.
AVAHO 2023: Expanding Opportunities for Veteran Care
Timothy O'Brien, MD, shares his expectations for the upcoming 2023 AVAHO conference. Dr O'Brien highlights four key areas of interest: networking with providers from other VA systems; creating more clinical trial opportunities; exploring educational sessions on topics like AI in oncology and geriatric oncology; and fostering team building within the local VA group. With an area of focus in malignant hematology, particularly multiple myeloma, Dr O'Brien sees learning opportunities within the education sessions on geriatric oncology. Considering that the average age of patients with multiple myeloma at his institution is 70 years, he looks forward to gaining valuable strategies for geriatric assessment.
Timothy O'Brien, MD, shares his expectations for the upcoming 2023 AVAHO conference. Dr O'Brien highlights four key areas of interest: networking with providers from other VA systems; creating more clinical trial opportunities; exploring educational sessions on topics like AI in oncology and geriatric oncology; and fostering team building within the local VA group. With an area of focus in malignant hematology, particularly multiple myeloma, Dr O'Brien sees learning opportunities within the education sessions on geriatric oncology. Considering that the average age of patients with multiple myeloma at his institution is 70 years, he looks forward to gaining valuable strategies for geriatric assessment.
Timothy O'Brien, MD, shares his expectations for the upcoming 2023 AVAHO conference. Dr O'Brien highlights four key areas of interest: networking with providers from other VA systems; creating more clinical trial opportunities; exploring educational sessions on topics like AI in oncology and geriatric oncology; and fostering team building within the local VA group. With an area of focus in malignant hematology, particularly multiple myeloma, Dr O'Brien sees learning opportunities within the education sessions on geriatric oncology. Considering that the average age of patients with multiple myeloma at his institution is 70 years, he looks forward to gaining valuable strategies for geriatric assessment.


AVAHO 2023: Exploring AI and Cancer Navigation for Veterans
Soo Park, MD, discusses her expectations for the upcoming 2023 AVAHO meeting in Chicago. Two items on the agenda particularly stand out: the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in oncology and the importance of cancer patient navigation. Dr Park acknowledges AI's potential to transform cancer diagnostics and drug discovery, particularly in aiding molecular profiling. Additionally, she highlights the value of cancer patient navigators in optimizing veteran care, particularly in the setting of geriatric oncology.
Soo Park, MD, discusses her expectations for the upcoming 2023 AVAHO meeting in Chicago. Two items on the agenda particularly stand out: the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in oncology and the importance of cancer patient navigation. Dr Park acknowledges AI's potential to transform cancer diagnostics and drug discovery, particularly in aiding molecular profiling. Additionally, she highlights the value of cancer patient navigators in optimizing veteran care, particularly in the setting of geriatric oncology.
Soo Park, MD, discusses her expectations for the upcoming 2023 AVAHO meeting in Chicago. Two items on the agenda particularly stand out: the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in oncology and the importance of cancer patient navigation. Dr Park acknowledges AI's potential to transform cancer diagnostics and drug discovery, particularly in aiding molecular profiling. Additionally, she highlights the value of cancer patient navigators in optimizing veteran care, particularly in the setting of geriatric oncology.


2023 Update on abnormal uterine bleeding
Endometrial ablation continues to be performed in significant numbers in the United States, with an estimated 500,000 cases annually. Several nonresectoscopic endometrial ablation devices have been approved for use, and some are now discontinued. The newest endometrial ablation therapy to gain US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval and to have published outcomes is the Cerene cryotherapy ablation device (Channel Medsystems, Inc). The results of 36-month outcomes from the CLARITY study were published last year, and we have chosen to review these long-term data in addition to that of a second study in which investigators assessed the ability to access the endometrial cavity postcryoablation. We believe this is important because of concerns about the inability to access the endometrial cavity after ablation, as well as the potential for delay in the diagnosis of endometrial cancer. It is interesting that 2 publications simultaneously reviewed the incidence of endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation within the past 12 months, and we therefore present those findings as they provide valuable information.
Our second focus in this year’s Update is to provide additional information about the burgeoning data on gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonists. We review evidence on linzagolix from the PRIMROSE 1 and PRIMROSE 2 trials and longer-term data on relugolix combination therapy for symptomatic uterine fibroids.
Three-year follow-up after endometrial cryoablation with the Cerene device found high patient satisfaction, low hysterectomy rates
Curlin HL, Cintron LC, Anderson TL. A prospective, multicenter, clinical trial evaluating the safety and effectiveness of the Cerene device to treat heavy menstrual bleeding. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2021;28;899-908.
Curlin HL, Anderson TL. Endometrial cryoablation for the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding: 36-month outcomes from the CLARITY study. Int J Womens Health. 2022;14:1083-1092.
The 12-month data on the clinical safety and effectiveness of the Cerene cryoablation device were published in 2021 in the CLARITY trial.1 The 36-month outcomes were published in 2022 and showed sustained clinical effects through month 36 with a low risk of adverse outcomes.2 The interesting aspect of this trial is that although the amenorrhea rate was relatively low at 12 months (6.5%), it continued to remain relatively low compared with rates found with other devices, but the amenorrhea rate increased at 36 months (14.4%). This was the percentage of patients who reported, “I no longer get my period.”
Patient satisfaction was high
Despite a relatively low amenorrhea rate, study participants had a high satisfaction rate and a low 3-year hysterectomy rate. Eighty-five percent of the participants were satisfied or very satisfied, and the cumulative hysterectomy rate was low at 5%.
The overall reintervention rate was 8.7%. Six patients were treated with medications, 2 patients underwent repeat endometrial ablation, 1 received a levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device, and 12 underwent hysterectomy.
At 36 months, 201 of the original 242 participants were available for assessment. Unfortunately, 5 pregnancies were reported through the 6-month posttreatment period, which emphasizes the importance of having reliable contraception. However, there were no reports of hematometra or postablation tubal sterilization syndrome (PATSS).
Effect on bleeding was long term
The main finding of the CLARITY study is that the Cerene cryoablation device appears to have a relatively stable effect on bleedingfor the first 3 years after therapy, with minimal risk of hematometra and PATSS. What we find interesting is that despite Cerene cryoablation having one of the lowest amenorrhea rates, it not only had a satisfaction rate in line with that of other devices but also had a low hysterectomy rate—only 5%—at 3 years.
The study authors pointed out that there is a lack of scarring within the endometrial cavity with the Cerene device. Some may find less endometrial scarring worth a low amenorrhea rate in the context of a favorable satisfaction rate. This begs the question, how well can the endometrial cavity be assessed? For answers, keep reading.
Can the endometrial cavity be reliably accessed after Cerene cryoablation?
Endometrial ablation has been associated with intracavitary scarring that results in hematometra, PATSS, and a concern for difficulty in performing an adequate endometrial assessment in patients who develop postablation abnormal uterine bleeding.
In a prospective study, 230 participants (of an initial 242) treated with Cerene cyroablation were studied with hysteroscopic evaluation of the endometrial cavity 12 months after surgery.3 The uterine cavity was accessible in 98.7% of participants. The cavity was not accessible in 3 participants due to pain or cervical stenosis.
Visualization of the uterine cavity was possible by hysteroscopy in 92.7% of study participants (204 of 220), with 1 or both tubal ostia identified in 89.2%. Both tubal ostia were visible in 78.4% and 1 ostium was visible in 10.8%. The cavity was not visualized in 16 of the 220 patients (7.2%) due to intrauterine adhesions, technical difficulties, or menstruation. Also of note, 97 of the 230 participants available at the 12-month follow-up had undergone tubal sterilization before cryoablation and none reported symptoms of PATSS or hematometra, which may be considered surrogate markers for adhesions.
Results of the CLARITY study demonstrated the clinical safety and effectiveness of the Cerene cryoablation device at 12 months, with sustained clinical effects through 36 months and a low risk of adverse outcomes. Patient satisfaction rates were high, and the hysterectomy rate was low. In addition, in a prospective study of patients treated with Cerene cryoablation, hysteroscopic evaluation at 12 months found the uterine cavity accessible in more than 98% of participants, and uterine visualization also was high. Therefore, the Cerene cryoablation device may provide the advantage of an easier evaluation of patients who eventually develop abnormal bleeding after endometrial ablation.
Continue to: Tissue effects differ with ablation technique...
Tissue effects differ with ablation technique
The study authors suggested that different tissue effects occur with freezing compared with heating ablation techniques. With freezing, over weeks to months the chronic inflammatory tissue is eventually replaced by a fibrous scar of collagen, with some preservation of the collagen matrix during tissue repair. This may be different from the charring and boiling of heated tissue that results in architectural tissue loss and may interfere with wound repair and tissue remodeling. Although the incidence of postoperative adhesions after endometrial ablation is not well studied, it is encouraging that most patients who received cryoablation with the Cerene device were able to undergo an evaluation of the endometrium without general anesthesia.
Key takeaway
The main idea from this study is that the endometrium can be assessed by office hysteroscopy in most patients who undergo cryoablation with the Cerene device. This may have advantages in terms of reducing the risk of PATSS and hematometra, and it may allow easier evaluation of the endometrium for patients who have postablation abnormal uterine bleeding. This begs the question, does intrauterine scarring influence the detection of endometrial cancer? For answers, keep reading.
Does endometrial ablation place a patient at higher risk for a delay in the diagnosis of endometrial cancer?
Radestad AF, Dahm-Kahler P, Holmberg E, et al. Long-term incidence of endometrial cancer after endometrial resection and ablation: a population based Swedish gynecologic cancer group (SweGCG) study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2022;101:923-930.
Oderkerk TJ, van de Kar MRD, Cornel KMC, et al. Endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation: a systematic review. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2022;32:1555-1560.
The answer to this question appears to be no, based on 2 different types of studies. One study was a 20-year population database review from Sweden,4 and the other was a systematic review of 11 cohort studies.5
Population-based study findings
The data from the Swedish population database is interesting because since 1994 all Swedish citizens have been allocated a unique personal identification number at birth or immigration that enables official registries and research. In reviewing their data from 1997 through 2017, Radestad and colleagues compared transcervical resection of the endometrium (TCRE) and other forms of endometrial ablation against the Swedish National Patient Register data for endometrial cancer.4 They found no increase in the incidence of endometrial cancer after TCRE (0.3%) or after endometrial ablation (0.02%) and suggested a significantly lower incidence of endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation.
This study is beneficial because it is the largest study to explore the long-term incidence of endometrial cancer after TCRE and endometrial ablation. The investigators hypothesized that, as an explanation for the difference between rates, ablation may burn deeper into the myometrium and treat adenomyosis compared with TCRE. However, they also were cautious to note that although this was a 20-year study, the incidence of endometrial carcinoma likely will reach a peak in the next few years.
Systematic review conclusions
In the systematic review, out of 890 publications from the authors’ database search, 11 articles were eventually included for review.5 A total of 29,102 patients with endometrial ablation were followed for a period of up to 25 years, and the incidence of endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation varied from 0.0% to 1.6%. A total of 38 cases of endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation have been described in the literature. Of those cases, bleeding was the most common presenting symptom of the disease. Endometrial sampling was successful in 89% of cases, and in 90% of cases, histological exam showed an early-stage endometrial adenocarcinoma.
Based on their review, the authors concluded that the incidence of endometrial cancer was not increased in patients who received endometrial ablation, and more importantly, there was no apparent delay in the diagnosis of endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation. They further suggested that diagnostic management with endometrial sampling did not appear to be a barrier.
The main findings from these 2 studies by Radestad and colleagues and Oderkerk and associates are that endometrial cancer does not appear to be more common after endometrial ablation, and it appears to be diagnosed with endometrial sampling in most cases.4,5 There may be some protection against endometrial cancer with nonresectoscopic endometrial ablation, although this needs to be verified by additional studies. To juxtapose this information with the prior information about cryotherapy, it emphasizes that the scarring within the endometrium will likely reduce the incidence of PATSS and hematometra, which are relatively low-incidence occurrences at 5% to 7%, but it likely does not affect the detection of endometrial cancer.
Longer-term data for relugolix combination treatment of symptomatic uterine bleeding from fibroids shows sustained efficacy
Al-Hendy A, Lukes AS, Poindexter AN, et al. Long-term relugolix combination therapy for symptomatic uterine leiomyomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2022;140:920-930.
Relugolix combination therapy was previously reported to be effective for the treatment of fibroids based on the 24-week trials LIBERTY 1 and LIBERTY 2. We now have information about longer-term therapy for up to 52 weeks of treatment.6
Relugolix combination therapy is a once-daily single tablet for the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding thought to be due to uterine fibroids in premenopausal women. It is comprised of relugolix 40 mg (a GnRH antagonist), estradiol 1.0 mg, and norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg.
Continue to: Extension study showed sustained efficacy...
Extension study showed sustained efficacy
The study by Al-Hendy and colleagues showed that the relugolix combination not only was well tolerated but also that there was sustained improvement in heavy bleeding, with the average patient having an approximately 90% decrease in menstrual bleeding from baseline.6 It was noted that 70.6% of patients achieved amenorrhea over the last 35 days of treatment.
Importantly, the treatment effect was independent of race, body mass index, baseline menstrual blood loss, and uterine fibroid volume. The bone mineral density (BMD) change trajectory was similar to what was observed in the pivotal study. No new safety concerns were identified, and BMD generally was preserved.
The extension study by Al-Hendy and colleagues demonstrated that that the reduced fibroid-associated bleeding treated with relugolix combination therapy is sustained throughout the 52-week period, with no new safety concerns.
Linzagolix is the newest GnRH antagonist to be studied in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial
Donnez J, Taylor HS, Stewart EA, et al. Linzagolix with and without hormonal add-back therapy for the treatment of symptomatic uterine fibroids: two randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2022;400:896-907.
At the time of this writing, linzagolix was not approved by the FDA. The results of the PRIMROSE 1 (P1) and PRIMROSE 2 (P2) trials were published last year as 2 identical 52-week randomized, parallel, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials.7 The difference between the development of linzagolix as a GnRH antagonist and other similar medications is the strategy of potential partial hypothalamic pituitary ovarian axis suppression at 100 mg versus complete suppression at 200 mg. In this trial by Donnez and colleagues, both linzagolix doses were evaluated with and without add-back hormonal therapy and also were compared with placebo in a 1:1:1:1:1 ratio.7
Study details and results
To be eligible for this study, participants had to have heavy menstrual bleeding, defined as more than 80 mL for at least 2 cycles, and have at least 1 fibroid that was 2 cm in diameter or multiple small fibroids with the calculated uterine volume of more than 200 cm3. No fibroid larger than 12 cm in diameter was included.
The primary end point was a menstrual blood loss of 80 mL or less and a 50% or more reduction in menstrual blood loss from baseline in the 28 days before week 24. Uterine fibroid volume reduction and a safety assessment, including BMD assessment, also were studied.
In the P1 trial, which was conducted in US sites, the response rate for the primary objective was 56.4% in the linzagolix 100-mg group, 66.4% in the 100-mg plus add-back therapy group, 71.4% in the 200-mg group, and 75.5% in the 200-mg plus add-back group, compared with 35.0% in the placebo group.
In the P2 trial, which included sites in both Europe and the United States, the response rates were 56.7% in the 100-mg group, 77.2% in the 100-mg plus add-back therapy group, 77.7% in the 200-mg group, and 93.9% in the 200-mg plus add-back therapy group, compared with 29.4% in the placebo group. Thus, in both trials a significantly higher proportion of menstrual reduction occurred in all linzagolix treatment groups compared with placebo.
As expected, the incidence of hot flushes was the highest in participants taking the linzagolix 200-mg dose without add-back hormonal therapy, with hot flushes occurring in 35% (P1) and 32% (P2) of patients, compared with all other groups, which was 3% to 14%. All treatment groups showed improvement in quality-of-life scores compared with placebo. Of note, to achieve reduction of fibroid volume in the 40% to 50% range, this was observed consistently only with the linzagolix 200-mg alone dose.
Linzagolix effect on bone
Decreases in BMD appeared to be dose dependent, as lumbar spine losses of up to 4% were noted with the linzgolix 200-mg dose, and a 2% loss was observed with the 100-mg dose at 24 weeks. However, these were improved with add-back therapy. There were continued BMD decreases at 52 weeks, with up to 2.4% with 100 mg of linzagolix and up to 1.5% with 100 mg plus add-back therapy, and up to 2% with 200 mg of linzagolix plus add-back therapy. ●
Results of the P1 and P2 trials suggest that there could be a potential niche for linzagolix in patients who need chronic use (> 6 months) without the need for concomitant add-back hormone therapy at lower doses. The non-add-back option may be a possibility for women who have both a contraindication to estrogen and an increased risk for hormone-related adverse events.
- Curlin HL, Cintron LC, Anderson TL. A prospective, multicenter, clinical trial evaluating the safety and effectiveness of the Cerene device to treat heavy menstrual bleeding. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2021;28;899-908.
- Curlin HL, Anderson TL. Endometrial cryoablation for the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding: 36-month outcomes from the CLARITY study. Int J Womens Health. 2022;14:1083-1092.
- Curlin H, Cholkeri-Singh A, Leal JGG, et al. Hysteroscopic access and uterine cavity evaluation 12 months after endometrial ablation with the Cerene cryotherapy device. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2022;29:440-447.
- Radestad AF, Dahm-Kahler P, Holmberg E, et al. Longterm incidence of endometrial cancer after endometrial resection and ablation: a population based Swedish gynecologic cancer group (SweGCG) study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2022;101:923-930.
- Oderkerk TJ, van de Kar MRD, Cornel KMC, et al. Endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation: a systematic review. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2022;32:1555-1560.
- Al-Hendy A, Lukes AS, Poindexter AN, et al. Long-term relugolix combination therapy for symptomatic uterine leiomyomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2022;140:920-930.
- Donnez J, Taylor HS, Stewart EA, et al. Linzagolix with and without hormonal add-back therapy for the treatment of symptomatic uterine fibroids: two randomised, placebo- controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2022;400:896-907.
Endometrial ablation continues to be performed in significant numbers in the United States, with an estimated 500,000 cases annually. Several nonresectoscopic endometrial ablation devices have been approved for use, and some are now discontinued. The newest endometrial ablation therapy to gain US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval and to have published outcomes is the Cerene cryotherapy ablation device (Channel Medsystems, Inc). The results of 36-month outcomes from the CLARITY study were published last year, and we have chosen to review these long-term data in addition to that of a second study in which investigators assessed the ability to access the endometrial cavity postcryoablation. We believe this is important because of concerns about the inability to access the endometrial cavity after ablation, as well as the potential for delay in the diagnosis of endometrial cancer. It is interesting that 2 publications simultaneously reviewed the incidence of endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation within the past 12 months, and we therefore present those findings as they provide valuable information.
Our second focus in this year’s Update is to provide additional information about the burgeoning data on gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonists. We review evidence on linzagolix from the PRIMROSE 1 and PRIMROSE 2 trials and longer-term data on relugolix combination therapy for symptomatic uterine fibroids.
Three-year follow-up after endometrial cryoablation with the Cerene device found high patient satisfaction, low hysterectomy rates
Curlin HL, Cintron LC, Anderson TL. A prospective, multicenter, clinical trial evaluating the safety and effectiveness of the Cerene device to treat heavy menstrual bleeding. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2021;28;899-908.
Curlin HL, Anderson TL. Endometrial cryoablation for the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding: 36-month outcomes from the CLARITY study. Int J Womens Health. 2022;14:1083-1092.
The 12-month data on the clinical safety and effectiveness of the Cerene cryoablation device were published in 2021 in the CLARITY trial.1 The 36-month outcomes were published in 2022 and showed sustained clinical effects through month 36 with a low risk of adverse outcomes.2 The interesting aspect of this trial is that although the amenorrhea rate was relatively low at 12 months (6.5%), it continued to remain relatively low compared with rates found with other devices, but the amenorrhea rate increased at 36 months (14.4%). This was the percentage of patients who reported, “I no longer get my period.”
Patient satisfaction was high
Despite a relatively low amenorrhea rate, study participants had a high satisfaction rate and a low 3-year hysterectomy rate. Eighty-five percent of the participants were satisfied or very satisfied, and the cumulative hysterectomy rate was low at 5%.
The overall reintervention rate was 8.7%. Six patients were treated with medications, 2 patients underwent repeat endometrial ablation, 1 received a levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device, and 12 underwent hysterectomy.
At 36 months, 201 of the original 242 participants were available for assessment. Unfortunately, 5 pregnancies were reported through the 6-month posttreatment period, which emphasizes the importance of having reliable contraception. However, there were no reports of hematometra or postablation tubal sterilization syndrome (PATSS).
Effect on bleeding was long term
The main finding of the CLARITY study is that the Cerene cryoablation device appears to have a relatively stable effect on bleedingfor the first 3 years after therapy, with minimal risk of hematometra and PATSS. What we find interesting is that despite Cerene cryoablation having one of the lowest amenorrhea rates, it not only had a satisfaction rate in line with that of other devices but also had a low hysterectomy rate—only 5%—at 3 years.
The study authors pointed out that there is a lack of scarring within the endometrial cavity with the Cerene device. Some may find less endometrial scarring worth a low amenorrhea rate in the context of a favorable satisfaction rate. This begs the question, how well can the endometrial cavity be assessed? For answers, keep reading.
Can the endometrial cavity be reliably accessed after Cerene cryoablation?
Endometrial ablation has been associated with intracavitary scarring that results in hematometra, PATSS, and a concern for difficulty in performing an adequate endometrial assessment in patients who develop postablation abnormal uterine bleeding.
In a prospective study, 230 participants (of an initial 242) treated with Cerene cyroablation were studied with hysteroscopic evaluation of the endometrial cavity 12 months after surgery.3 The uterine cavity was accessible in 98.7% of participants. The cavity was not accessible in 3 participants due to pain or cervical stenosis.
Visualization of the uterine cavity was possible by hysteroscopy in 92.7% of study participants (204 of 220), with 1 or both tubal ostia identified in 89.2%. Both tubal ostia were visible in 78.4% and 1 ostium was visible in 10.8%. The cavity was not visualized in 16 of the 220 patients (7.2%) due to intrauterine adhesions, technical difficulties, or menstruation. Also of note, 97 of the 230 participants available at the 12-month follow-up had undergone tubal sterilization before cryoablation and none reported symptoms of PATSS or hematometra, which may be considered surrogate markers for adhesions.
Results of the CLARITY study demonstrated the clinical safety and effectiveness of the Cerene cryoablation device at 12 months, with sustained clinical effects through 36 months and a low risk of adverse outcomes. Patient satisfaction rates were high, and the hysterectomy rate was low. In addition, in a prospective study of patients treated with Cerene cryoablation, hysteroscopic evaluation at 12 months found the uterine cavity accessible in more than 98% of participants, and uterine visualization also was high. Therefore, the Cerene cryoablation device may provide the advantage of an easier evaluation of patients who eventually develop abnormal bleeding after endometrial ablation.
Continue to: Tissue effects differ with ablation technique...
Tissue effects differ with ablation technique
The study authors suggested that different tissue effects occur with freezing compared with heating ablation techniques. With freezing, over weeks to months the chronic inflammatory tissue is eventually replaced by a fibrous scar of collagen, with some preservation of the collagen matrix during tissue repair. This may be different from the charring and boiling of heated tissue that results in architectural tissue loss and may interfere with wound repair and tissue remodeling. Although the incidence of postoperative adhesions after endometrial ablation is not well studied, it is encouraging that most patients who received cryoablation with the Cerene device were able to undergo an evaluation of the endometrium without general anesthesia.
Key takeaway
The main idea from this study is that the endometrium can be assessed by office hysteroscopy in most patients who undergo cryoablation with the Cerene device. This may have advantages in terms of reducing the risk of PATSS and hematometra, and it may allow easier evaluation of the endometrium for patients who have postablation abnormal uterine bleeding. This begs the question, does intrauterine scarring influence the detection of endometrial cancer? For answers, keep reading.
Does endometrial ablation place a patient at higher risk for a delay in the diagnosis of endometrial cancer?
Radestad AF, Dahm-Kahler P, Holmberg E, et al. Long-term incidence of endometrial cancer after endometrial resection and ablation: a population based Swedish gynecologic cancer group (SweGCG) study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2022;101:923-930.
Oderkerk TJ, van de Kar MRD, Cornel KMC, et al. Endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation: a systematic review. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2022;32:1555-1560.
The answer to this question appears to be no, based on 2 different types of studies. One study was a 20-year population database review from Sweden,4 and the other was a systematic review of 11 cohort studies.5
Population-based study findings
The data from the Swedish population database is interesting because since 1994 all Swedish citizens have been allocated a unique personal identification number at birth or immigration that enables official registries and research. In reviewing their data from 1997 through 2017, Radestad and colleagues compared transcervical resection of the endometrium (TCRE) and other forms of endometrial ablation against the Swedish National Patient Register data for endometrial cancer.4 They found no increase in the incidence of endometrial cancer after TCRE (0.3%) or after endometrial ablation (0.02%) and suggested a significantly lower incidence of endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation.
This study is beneficial because it is the largest study to explore the long-term incidence of endometrial cancer after TCRE and endometrial ablation. The investigators hypothesized that, as an explanation for the difference between rates, ablation may burn deeper into the myometrium and treat adenomyosis compared with TCRE. However, they also were cautious to note that although this was a 20-year study, the incidence of endometrial carcinoma likely will reach a peak in the next few years.
Systematic review conclusions
In the systematic review, out of 890 publications from the authors’ database search, 11 articles were eventually included for review.5 A total of 29,102 patients with endometrial ablation were followed for a period of up to 25 years, and the incidence of endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation varied from 0.0% to 1.6%. A total of 38 cases of endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation have been described in the literature. Of those cases, bleeding was the most common presenting symptom of the disease. Endometrial sampling was successful in 89% of cases, and in 90% of cases, histological exam showed an early-stage endometrial adenocarcinoma.
Based on their review, the authors concluded that the incidence of endometrial cancer was not increased in patients who received endometrial ablation, and more importantly, there was no apparent delay in the diagnosis of endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation. They further suggested that diagnostic management with endometrial sampling did not appear to be a barrier.
The main findings from these 2 studies by Radestad and colleagues and Oderkerk and associates are that endometrial cancer does not appear to be more common after endometrial ablation, and it appears to be diagnosed with endometrial sampling in most cases.4,5 There may be some protection against endometrial cancer with nonresectoscopic endometrial ablation, although this needs to be verified by additional studies. To juxtapose this information with the prior information about cryotherapy, it emphasizes that the scarring within the endometrium will likely reduce the incidence of PATSS and hematometra, which are relatively low-incidence occurrences at 5% to 7%, but it likely does not affect the detection of endometrial cancer.
Longer-term data for relugolix combination treatment of symptomatic uterine bleeding from fibroids shows sustained efficacy
Al-Hendy A, Lukes AS, Poindexter AN, et al. Long-term relugolix combination therapy for symptomatic uterine leiomyomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2022;140:920-930.
Relugolix combination therapy was previously reported to be effective for the treatment of fibroids based on the 24-week trials LIBERTY 1 and LIBERTY 2. We now have information about longer-term therapy for up to 52 weeks of treatment.6
Relugolix combination therapy is a once-daily single tablet for the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding thought to be due to uterine fibroids in premenopausal women. It is comprised of relugolix 40 mg (a GnRH antagonist), estradiol 1.0 mg, and norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg.
Continue to: Extension study showed sustained efficacy...
Extension study showed sustained efficacy
The study by Al-Hendy and colleagues showed that the relugolix combination not only was well tolerated but also that there was sustained improvement in heavy bleeding, with the average patient having an approximately 90% decrease in menstrual bleeding from baseline.6 It was noted that 70.6% of patients achieved amenorrhea over the last 35 days of treatment.
Importantly, the treatment effect was independent of race, body mass index, baseline menstrual blood loss, and uterine fibroid volume. The bone mineral density (BMD) change trajectory was similar to what was observed in the pivotal study. No new safety concerns were identified, and BMD generally was preserved.
The extension study by Al-Hendy and colleagues demonstrated that that the reduced fibroid-associated bleeding treated with relugolix combination therapy is sustained throughout the 52-week period, with no new safety concerns.
Linzagolix is the newest GnRH antagonist to be studied in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial
Donnez J, Taylor HS, Stewart EA, et al. Linzagolix with and without hormonal add-back therapy for the treatment of symptomatic uterine fibroids: two randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2022;400:896-907.
At the time of this writing, linzagolix was not approved by the FDA. The results of the PRIMROSE 1 (P1) and PRIMROSE 2 (P2) trials were published last year as 2 identical 52-week randomized, parallel, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials.7 The difference between the development of linzagolix as a GnRH antagonist and other similar medications is the strategy of potential partial hypothalamic pituitary ovarian axis suppression at 100 mg versus complete suppression at 200 mg. In this trial by Donnez and colleagues, both linzagolix doses were evaluated with and without add-back hormonal therapy and also were compared with placebo in a 1:1:1:1:1 ratio.7
Study details and results
To be eligible for this study, participants had to have heavy menstrual bleeding, defined as more than 80 mL for at least 2 cycles, and have at least 1 fibroid that was 2 cm in diameter or multiple small fibroids with the calculated uterine volume of more than 200 cm3. No fibroid larger than 12 cm in diameter was included.
The primary end point was a menstrual blood loss of 80 mL or less and a 50% or more reduction in menstrual blood loss from baseline in the 28 days before week 24. Uterine fibroid volume reduction and a safety assessment, including BMD assessment, also were studied.
In the P1 trial, which was conducted in US sites, the response rate for the primary objective was 56.4% in the linzagolix 100-mg group, 66.4% in the 100-mg plus add-back therapy group, 71.4% in the 200-mg group, and 75.5% in the 200-mg plus add-back group, compared with 35.0% in the placebo group.
In the P2 trial, which included sites in both Europe and the United States, the response rates were 56.7% in the 100-mg group, 77.2% in the 100-mg plus add-back therapy group, 77.7% in the 200-mg group, and 93.9% in the 200-mg plus add-back therapy group, compared with 29.4% in the placebo group. Thus, in both trials a significantly higher proportion of menstrual reduction occurred in all linzagolix treatment groups compared with placebo.
As expected, the incidence of hot flushes was the highest in participants taking the linzagolix 200-mg dose without add-back hormonal therapy, with hot flushes occurring in 35% (P1) and 32% (P2) of patients, compared with all other groups, which was 3% to 14%. All treatment groups showed improvement in quality-of-life scores compared with placebo. Of note, to achieve reduction of fibroid volume in the 40% to 50% range, this was observed consistently only with the linzagolix 200-mg alone dose.
Linzagolix effect on bone
Decreases in BMD appeared to be dose dependent, as lumbar spine losses of up to 4% were noted with the linzgolix 200-mg dose, and a 2% loss was observed with the 100-mg dose at 24 weeks. However, these were improved with add-back therapy. There were continued BMD decreases at 52 weeks, with up to 2.4% with 100 mg of linzagolix and up to 1.5% with 100 mg plus add-back therapy, and up to 2% with 200 mg of linzagolix plus add-back therapy. ●
Results of the P1 and P2 trials suggest that there could be a potential niche for linzagolix in patients who need chronic use (> 6 months) without the need for concomitant add-back hormone therapy at lower doses. The non-add-back option may be a possibility for women who have both a contraindication to estrogen and an increased risk for hormone-related adverse events.
Endometrial ablation continues to be performed in significant numbers in the United States, with an estimated 500,000 cases annually. Several nonresectoscopic endometrial ablation devices have been approved for use, and some are now discontinued. The newest endometrial ablation therapy to gain US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval and to have published outcomes is the Cerene cryotherapy ablation device (Channel Medsystems, Inc). The results of 36-month outcomes from the CLARITY study were published last year, and we have chosen to review these long-term data in addition to that of a second study in which investigators assessed the ability to access the endometrial cavity postcryoablation. We believe this is important because of concerns about the inability to access the endometrial cavity after ablation, as well as the potential for delay in the diagnosis of endometrial cancer. It is interesting that 2 publications simultaneously reviewed the incidence of endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation within the past 12 months, and we therefore present those findings as they provide valuable information.
Our second focus in this year’s Update is to provide additional information about the burgeoning data on gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonists. We review evidence on linzagolix from the PRIMROSE 1 and PRIMROSE 2 trials and longer-term data on relugolix combination therapy for symptomatic uterine fibroids.
Three-year follow-up after endometrial cryoablation with the Cerene device found high patient satisfaction, low hysterectomy rates
Curlin HL, Cintron LC, Anderson TL. A prospective, multicenter, clinical trial evaluating the safety and effectiveness of the Cerene device to treat heavy menstrual bleeding. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2021;28;899-908.
Curlin HL, Anderson TL. Endometrial cryoablation for the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding: 36-month outcomes from the CLARITY study. Int J Womens Health. 2022;14:1083-1092.
The 12-month data on the clinical safety and effectiveness of the Cerene cryoablation device were published in 2021 in the CLARITY trial.1 The 36-month outcomes were published in 2022 and showed sustained clinical effects through month 36 with a low risk of adverse outcomes.2 The interesting aspect of this trial is that although the amenorrhea rate was relatively low at 12 months (6.5%), it continued to remain relatively low compared with rates found with other devices, but the amenorrhea rate increased at 36 months (14.4%). This was the percentage of patients who reported, “I no longer get my period.”
Patient satisfaction was high
Despite a relatively low amenorrhea rate, study participants had a high satisfaction rate and a low 3-year hysterectomy rate. Eighty-five percent of the participants were satisfied or very satisfied, and the cumulative hysterectomy rate was low at 5%.
The overall reintervention rate was 8.7%. Six patients were treated with medications, 2 patients underwent repeat endometrial ablation, 1 received a levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device, and 12 underwent hysterectomy.
At 36 months, 201 of the original 242 participants were available for assessment. Unfortunately, 5 pregnancies were reported through the 6-month posttreatment period, which emphasizes the importance of having reliable contraception. However, there were no reports of hematometra or postablation tubal sterilization syndrome (PATSS).
Effect on bleeding was long term
The main finding of the CLARITY study is that the Cerene cryoablation device appears to have a relatively stable effect on bleedingfor the first 3 years after therapy, with minimal risk of hematometra and PATSS. What we find interesting is that despite Cerene cryoablation having one of the lowest amenorrhea rates, it not only had a satisfaction rate in line with that of other devices but also had a low hysterectomy rate—only 5%—at 3 years.
The study authors pointed out that there is a lack of scarring within the endometrial cavity with the Cerene device. Some may find less endometrial scarring worth a low amenorrhea rate in the context of a favorable satisfaction rate. This begs the question, how well can the endometrial cavity be assessed? For answers, keep reading.
Can the endometrial cavity be reliably accessed after Cerene cryoablation?
Endometrial ablation has been associated with intracavitary scarring that results in hematometra, PATSS, and a concern for difficulty in performing an adequate endometrial assessment in patients who develop postablation abnormal uterine bleeding.
In a prospective study, 230 participants (of an initial 242) treated with Cerene cyroablation were studied with hysteroscopic evaluation of the endometrial cavity 12 months after surgery.3 The uterine cavity was accessible in 98.7% of participants. The cavity was not accessible in 3 participants due to pain or cervical stenosis.
Visualization of the uterine cavity was possible by hysteroscopy in 92.7% of study participants (204 of 220), with 1 or both tubal ostia identified in 89.2%. Both tubal ostia were visible in 78.4% and 1 ostium was visible in 10.8%. The cavity was not visualized in 16 of the 220 patients (7.2%) due to intrauterine adhesions, technical difficulties, or menstruation. Also of note, 97 of the 230 participants available at the 12-month follow-up had undergone tubal sterilization before cryoablation and none reported symptoms of PATSS or hematometra, which may be considered surrogate markers for adhesions.
Results of the CLARITY study demonstrated the clinical safety and effectiveness of the Cerene cryoablation device at 12 months, with sustained clinical effects through 36 months and a low risk of adverse outcomes. Patient satisfaction rates were high, and the hysterectomy rate was low. In addition, in a prospective study of patients treated with Cerene cryoablation, hysteroscopic evaluation at 12 months found the uterine cavity accessible in more than 98% of participants, and uterine visualization also was high. Therefore, the Cerene cryoablation device may provide the advantage of an easier evaluation of patients who eventually develop abnormal bleeding after endometrial ablation.
Continue to: Tissue effects differ with ablation technique...
Tissue effects differ with ablation technique
The study authors suggested that different tissue effects occur with freezing compared with heating ablation techniques. With freezing, over weeks to months the chronic inflammatory tissue is eventually replaced by a fibrous scar of collagen, with some preservation of the collagen matrix during tissue repair. This may be different from the charring and boiling of heated tissue that results in architectural tissue loss and may interfere with wound repair and tissue remodeling. Although the incidence of postoperative adhesions after endometrial ablation is not well studied, it is encouraging that most patients who received cryoablation with the Cerene device were able to undergo an evaluation of the endometrium without general anesthesia.
Key takeaway
The main idea from this study is that the endometrium can be assessed by office hysteroscopy in most patients who undergo cryoablation with the Cerene device. This may have advantages in terms of reducing the risk of PATSS and hematometra, and it may allow easier evaluation of the endometrium for patients who have postablation abnormal uterine bleeding. This begs the question, does intrauterine scarring influence the detection of endometrial cancer? For answers, keep reading.
Does endometrial ablation place a patient at higher risk for a delay in the diagnosis of endometrial cancer?
Radestad AF, Dahm-Kahler P, Holmberg E, et al. Long-term incidence of endometrial cancer after endometrial resection and ablation: a population based Swedish gynecologic cancer group (SweGCG) study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2022;101:923-930.
Oderkerk TJ, van de Kar MRD, Cornel KMC, et al. Endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation: a systematic review. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2022;32:1555-1560.
The answer to this question appears to be no, based on 2 different types of studies. One study was a 20-year population database review from Sweden,4 and the other was a systematic review of 11 cohort studies.5
Population-based study findings
The data from the Swedish population database is interesting because since 1994 all Swedish citizens have been allocated a unique personal identification number at birth or immigration that enables official registries and research. In reviewing their data from 1997 through 2017, Radestad and colleagues compared transcervical resection of the endometrium (TCRE) and other forms of endometrial ablation against the Swedish National Patient Register data for endometrial cancer.4 They found no increase in the incidence of endometrial cancer after TCRE (0.3%) or after endometrial ablation (0.02%) and suggested a significantly lower incidence of endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation.
This study is beneficial because it is the largest study to explore the long-term incidence of endometrial cancer after TCRE and endometrial ablation. The investigators hypothesized that, as an explanation for the difference between rates, ablation may burn deeper into the myometrium and treat adenomyosis compared with TCRE. However, they also were cautious to note that although this was a 20-year study, the incidence of endometrial carcinoma likely will reach a peak in the next few years.
Systematic review conclusions
In the systematic review, out of 890 publications from the authors’ database search, 11 articles were eventually included for review.5 A total of 29,102 patients with endometrial ablation were followed for a period of up to 25 years, and the incidence of endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation varied from 0.0% to 1.6%. A total of 38 cases of endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation have been described in the literature. Of those cases, bleeding was the most common presenting symptom of the disease. Endometrial sampling was successful in 89% of cases, and in 90% of cases, histological exam showed an early-stage endometrial adenocarcinoma.
Based on their review, the authors concluded that the incidence of endometrial cancer was not increased in patients who received endometrial ablation, and more importantly, there was no apparent delay in the diagnosis of endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation. They further suggested that diagnostic management with endometrial sampling did not appear to be a barrier.
The main findings from these 2 studies by Radestad and colleagues and Oderkerk and associates are that endometrial cancer does not appear to be more common after endometrial ablation, and it appears to be diagnosed with endometrial sampling in most cases.4,5 There may be some protection against endometrial cancer with nonresectoscopic endometrial ablation, although this needs to be verified by additional studies. To juxtapose this information with the prior information about cryotherapy, it emphasizes that the scarring within the endometrium will likely reduce the incidence of PATSS and hematometra, which are relatively low-incidence occurrences at 5% to 7%, but it likely does not affect the detection of endometrial cancer.
Longer-term data for relugolix combination treatment of symptomatic uterine bleeding from fibroids shows sustained efficacy
Al-Hendy A, Lukes AS, Poindexter AN, et al. Long-term relugolix combination therapy for symptomatic uterine leiomyomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2022;140:920-930.
Relugolix combination therapy was previously reported to be effective for the treatment of fibroids based on the 24-week trials LIBERTY 1 and LIBERTY 2. We now have information about longer-term therapy for up to 52 weeks of treatment.6
Relugolix combination therapy is a once-daily single tablet for the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding thought to be due to uterine fibroids in premenopausal women. It is comprised of relugolix 40 mg (a GnRH antagonist), estradiol 1.0 mg, and norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg.
Continue to: Extension study showed sustained efficacy...
Extension study showed sustained efficacy
The study by Al-Hendy and colleagues showed that the relugolix combination not only was well tolerated but also that there was sustained improvement in heavy bleeding, with the average patient having an approximately 90% decrease in menstrual bleeding from baseline.6 It was noted that 70.6% of patients achieved amenorrhea over the last 35 days of treatment.
Importantly, the treatment effect was independent of race, body mass index, baseline menstrual blood loss, and uterine fibroid volume. The bone mineral density (BMD) change trajectory was similar to what was observed in the pivotal study. No new safety concerns were identified, and BMD generally was preserved.
The extension study by Al-Hendy and colleagues demonstrated that that the reduced fibroid-associated bleeding treated with relugolix combination therapy is sustained throughout the 52-week period, with no new safety concerns.
Linzagolix is the newest GnRH antagonist to be studied in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial
Donnez J, Taylor HS, Stewart EA, et al. Linzagolix with and without hormonal add-back therapy for the treatment of symptomatic uterine fibroids: two randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2022;400:896-907.
At the time of this writing, linzagolix was not approved by the FDA. The results of the PRIMROSE 1 (P1) and PRIMROSE 2 (P2) trials were published last year as 2 identical 52-week randomized, parallel, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials.7 The difference between the development of linzagolix as a GnRH antagonist and other similar medications is the strategy of potential partial hypothalamic pituitary ovarian axis suppression at 100 mg versus complete suppression at 200 mg. In this trial by Donnez and colleagues, both linzagolix doses were evaluated with and without add-back hormonal therapy and also were compared with placebo in a 1:1:1:1:1 ratio.7
Study details and results
To be eligible for this study, participants had to have heavy menstrual bleeding, defined as more than 80 mL for at least 2 cycles, and have at least 1 fibroid that was 2 cm in diameter or multiple small fibroids with the calculated uterine volume of more than 200 cm3. No fibroid larger than 12 cm in diameter was included.
The primary end point was a menstrual blood loss of 80 mL or less and a 50% or more reduction in menstrual blood loss from baseline in the 28 days before week 24. Uterine fibroid volume reduction and a safety assessment, including BMD assessment, also were studied.
In the P1 trial, which was conducted in US sites, the response rate for the primary objective was 56.4% in the linzagolix 100-mg group, 66.4% in the 100-mg plus add-back therapy group, 71.4% in the 200-mg group, and 75.5% in the 200-mg plus add-back group, compared with 35.0% in the placebo group.
In the P2 trial, which included sites in both Europe and the United States, the response rates were 56.7% in the 100-mg group, 77.2% in the 100-mg plus add-back therapy group, 77.7% in the 200-mg group, and 93.9% in the 200-mg plus add-back therapy group, compared with 29.4% in the placebo group. Thus, in both trials a significantly higher proportion of menstrual reduction occurred in all linzagolix treatment groups compared with placebo.
As expected, the incidence of hot flushes was the highest in participants taking the linzagolix 200-mg dose without add-back hormonal therapy, with hot flushes occurring in 35% (P1) and 32% (P2) of patients, compared with all other groups, which was 3% to 14%. All treatment groups showed improvement in quality-of-life scores compared with placebo. Of note, to achieve reduction of fibroid volume in the 40% to 50% range, this was observed consistently only with the linzagolix 200-mg alone dose.
Linzagolix effect on bone
Decreases in BMD appeared to be dose dependent, as lumbar spine losses of up to 4% were noted with the linzgolix 200-mg dose, and a 2% loss was observed with the 100-mg dose at 24 weeks. However, these were improved with add-back therapy. There were continued BMD decreases at 52 weeks, with up to 2.4% with 100 mg of linzagolix and up to 1.5% with 100 mg plus add-back therapy, and up to 2% with 200 mg of linzagolix plus add-back therapy. ●
Results of the P1 and P2 trials suggest that there could be a potential niche for linzagolix in patients who need chronic use (> 6 months) without the need for concomitant add-back hormone therapy at lower doses. The non-add-back option may be a possibility for women who have both a contraindication to estrogen and an increased risk for hormone-related adverse events.
- Curlin HL, Cintron LC, Anderson TL. A prospective, multicenter, clinical trial evaluating the safety and effectiveness of the Cerene device to treat heavy menstrual bleeding. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2021;28;899-908.
- Curlin HL, Anderson TL. Endometrial cryoablation for the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding: 36-month outcomes from the CLARITY study. Int J Womens Health. 2022;14:1083-1092.
- Curlin H, Cholkeri-Singh A, Leal JGG, et al. Hysteroscopic access and uterine cavity evaluation 12 months after endometrial ablation with the Cerene cryotherapy device. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2022;29:440-447.
- Radestad AF, Dahm-Kahler P, Holmberg E, et al. Longterm incidence of endometrial cancer after endometrial resection and ablation: a population based Swedish gynecologic cancer group (SweGCG) study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2022;101:923-930.
- Oderkerk TJ, van de Kar MRD, Cornel KMC, et al. Endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation: a systematic review. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2022;32:1555-1560.
- Al-Hendy A, Lukes AS, Poindexter AN, et al. Long-term relugolix combination therapy for symptomatic uterine leiomyomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2022;140:920-930.
- Donnez J, Taylor HS, Stewart EA, et al. Linzagolix with and without hormonal add-back therapy for the treatment of symptomatic uterine fibroids: two randomised, placebo- controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2022;400:896-907.
- Curlin HL, Cintron LC, Anderson TL. A prospective, multicenter, clinical trial evaluating the safety and effectiveness of the Cerene device to treat heavy menstrual bleeding. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2021;28;899-908.
- Curlin HL, Anderson TL. Endometrial cryoablation for the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding: 36-month outcomes from the CLARITY study. Int J Womens Health. 2022;14:1083-1092.
- Curlin H, Cholkeri-Singh A, Leal JGG, et al. Hysteroscopic access and uterine cavity evaluation 12 months after endometrial ablation with the Cerene cryotherapy device. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2022;29:440-447.
- Radestad AF, Dahm-Kahler P, Holmberg E, et al. Longterm incidence of endometrial cancer after endometrial resection and ablation: a population based Swedish gynecologic cancer group (SweGCG) study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2022;101:923-930.
- Oderkerk TJ, van de Kar MRD, Cornel KMC, et al. Endometrial cancer after endometrial ablation: a systematic review. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2022;32:1555-1560.
- Al-Hendy A, Lukes AS, Poindexter AN, et al. Long-term relugolix combination therapy for symptomatic uterine leiomyomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2022;140:920-930.
- Donnez J, Taylor HS, Stewart EA, et al. Linzagolix with and without hormonal add-back therapy for the treatment of symptomatic uterine fibroids: two randomised, placebo- controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2022;400:896-907.
News & Perspectives from Ob.Gyn. News
COMMENTARY
Answering the protein question when prescribing plant-based diets
Science supports the use of a whole food, predominantly plant-based dietary pattern for optimal health, including reduced risk for chronic disease, and best practice in treatment of leading chronic disease.
But clinicians who prescribe such eating patterns encounter a common concern from patients whose health may benefit.
“Where will I get my protein?”
We’ve all heard it, and it’s understandable
To ensure that patients have all the facts when making dietary decisions, clinicians need to be prepared to respond to concerns about protein adequacy and quality with evidence-based information. A good starting point for these conversations is to assess how much protein patients are already consuming. A review of the 2015-2016 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey found that women normally consume an average of 69 g and men an average of 97 g of protein daily.
As a general point of reference, the recommended dietary allowance for protein is about 0.8 g/kg of bodyweight (or 0.36 g/lb), which equates to about 52 g of protein per day for a 145-lb woman and 65 g for a 180-lb man. But for many patients, it may be best to get a more precise recommendation based upon age, gender and physical activity level by using a handy Department of Agriculture tool for health care professionals to calculate daily protein and other nutrient needs. Patients can also use one of countless apps to track their protein and other nutrient intake. By using the tool and a tracking app, both clinician and patients can be fully informed whether protein needs are being met.
LATEST NEWS
Continuous glucose monitors for pregnant patients?
Patients with pregestational diabetes may benefit from use of a continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump paired with a continuous glucose monitor. Use of the tools has been associated with a reduction in maternal and neonatal morbidity, a recent study found.
“We were seeing an unacceptable burden of both maternal and fetal disease in our diabetic population,” said Neil Hamill, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Methodist Women’s Hospital, Omaha, Neb., and an author of the study. “We thought the success with this technology in the nonpregnant population would and should translate into the pregnant population.”
Dr. Hamill and his colleagues analyzed data from 55 pregnant patients who received care at the Women’s Hospital Perinatal Center at the Nebraska Methodist Health System between October 2019 and October 2022. Everyone in the cohort had pregestational diabetes and required insulin prior to week 20 of pregnancy. They used CGMs for more than 2 weeks. The study set blood glucose levels of less than 140 mg/dL as a healthy benchmark.
Participants who had severe preeclampsia, who had delivered preterm, who had delivered a neonate with respiratory distress syndrome, and/or who had given birth to a larger-than-expected infant spent less time in the safe zone — having a blood glucose level below 140 mg/dL—than women who did not have those risk factors.
“When blood sugar control is better, maternal and fetal outcomes are improved,” Dr. Hamill said.
Neetu Sodhi, MD, an ob.gyn. at Providence Cedars-Sinai Tarzana Medical Center, Los Angeles, expressed optimism that use of blood glucose monitors and insulin pumps can improve outcomes for pregnant patients with pregestational diabetes.
“This is just another case for why it’s so important for patients to have access to these types of devices that really, really improve their outcomes and their health, and now it’s proven in the case of pregnancy outcomes too – or at least suggested strongly with this data,” Dr. Sodhi said.
Continue to: It may be time to pay attention to COVID again...
It may be time to pay attention to COVID again
More than 3 years into the COVID-19 era, most Americans have settled back into their prepandemic lifestyles. But a new dominant variant and rising hospitalization numbers may give way to another summer surge.
Since April, a new COVID variant has cropped up. According to recent Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, EG.5—from the Omicron family—now makes up 17% of all cases in the United States, up from 7.5% in the first week of July.
A summary from the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota says that EG.5, nicknamed “Eris” by health trackers, is nearly the same as its parent strain, XBB.1.9.2, but has one extra spike mutation.
Along with the news of EG.5’s growing prevalence, COVID-related hospitalization rates have increased by 12.5% during the week ending on July 29—the most significant uptick since December. Still, no connection has been made between the new variant and rising hospital admissions. And so far, experts have found no difference in the severity of illness or symptoms between Eris and the strains that came before it.
Cause for concern?
The COVID virus has a great tendency to mutate, said William Schaffner, MD, a professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
“Fortunately, these are relatively minor mutations.” Even so, SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, continues to be highly contagious. “There isn’t any doubt that it’s spreading—but it’s not more serious.”
So, Dr. Schaffner doesn’t think it’s time to panic. He prefers calling it an “uptick” in cases instead of a “surge,” because a surge “sounds too big.”
While the numbers are still low, compared with 2022’s summer surge, experts still urge people to stay aware of changes in the virus. “I do not think that there is any cause for alarm,” agreed Bernard Camins, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York.
So why the higher number of cases? “There has been an increase in COVID cases this summer, probably related to travel, socializing, and dwindling masking,” said Anne Liu, MD, an allergy, immunology, and infectious disease specialist at Stanford (Calif.) University. Even so, “because of an existing level of immunity from vaccination and prior infections, it has been limited and case severity has been lower than in prior surges.” ●
COMMENTARY
Answering the protein question when prescribing plant-based diets
Science supports the use of a whole food, predominantly plant-based dietary pattern for optimal health, including reduced risk for chronic disease, and best practice in treatment of leading chronic disease.
But clinicians who prescribe such eating patterns encounter a common concern from patients whose health may benefit.
“Where will I get my protein?”
We’ve all heard it, and it’s understandable
To ensure that patients have all the facts when making dietary decisions, clinicians need to be prepared to respond to concerns about protein adequacy and quality with evidence-based information. A good starting point for these conversations is to assess how much protein patients are already consuming. A review of the 2015-2016 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey found that women normally consume an average of 69 g and men an average of 97 g of protein daily.
As a general point of reference, the recommended dietary allowance for protein is about 0.8 g/kg of bodyweight (or 0.36 g/lb), which equates to about 52 g of protein per day for a 145-lb woman and 65 g for a 180-lb man. But for many patients, it may be best to get a more precise recommendation based upon age, gender and physical activity level by using a handy Department of Agriculture tool for health care professionals to calculate daily protein and other nutrient needs. Patients can also use one of countless apps to track their protein and other nutrient intake. By using the tool and a tracking app, both clinician and patients can be fully informed whether protein needs are being met.
LATEST NEWS
Continuous glucose monitors for pregnant patients?
Patients with pregestational diabetes may benefit from use of a continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump paired with a continuous glucose monitor. Use of the tools has been associated with a reduction in maternal and neonatal morbidity, a recent study found.
“We were seeing an unacceptable burden of both maternal and fetal disease in our diabetic population,” said Neil Hamill, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Methodist Women’s Hospital, Omaha, Neb., and an author of the study. “We thought the success with this technology in the nonpregnant population would and should translate into the pregnant population.”
Dr. Hamill and his colleagues analyzed data from 55 pregnant patients who received care at the Women’s Hospital Perinatal Center at the Nebraska Methodist Health System between October 2019 and October 2022. Everyone in the cohort had pregestational diabetes and required insulin prior to week 20 of pregnancy. They used CGMs for more than 2 weeks. The study set blood glucose levels of less than 140 mg/dL as a healthy benchmark.
Participants who had severe preeclampsia, who had delivered preterm, who had delivered a neonate with respiratory distress syndrome, and/or who had given birth to a larger-than-expected infant spent less time in the safe zone — having a blood glucose level below 140 mg/dL—than women who did not have those risk factors.
“When blood sugar control is better, maternal and fetal outcomes are improved,” Dr. Hamill said.
Neetu Sodhi, MD, an ob.gyn. at Providence Cedars-Sinai Tarzana Medical Center, Los Angeles, expressed optimism that use of blood glucose monitors and insulin pumps can improve outcomes for pregnant patients with pregestational diabetes.
“This is just another case for why it’s so important for patients to have access to these types of devices that really, really improve their outcomes and their health, and now it’s proven in the case of pregnancy outcomes too – or at least suggested strongly with this data,” Dr. Sodhi said.
Continue to: It may be time to pay attention to COVID again...
It may be time to pay attention to COVID again
More than 3 years into the COVID-19 era, most Americans have settled back into their prepandemic lifestyles. But a new dominant variant and rising hospitalization numbers may give way to another summer surge.
Since April, a new COVID variant has cropped up. According to recent Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, EG.5—from the Omicron family—now makes up 17% of all cases in the United States, up from 7.5% in the first week of July.
A summary from the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota says that EG.5, nicknamed “Eris” by health trackers, is nearly the same as its parent strain, XBB.1.9.2, but has one extra spike mutation.
Along with the news of EG.5’s growing prevalence, COVID-related hospitalization rates have increased by 12.5% during the week ending on July 29—the most significant uptick since December. Still, no connection has been made between the new variant and rising hospital admissions. And so far, experts have found no difference in the severity of illness or symptoms between Eris and the strains that came before it.
Cause for concern?
The COVID virus has a great tendency to mutate, said William Schaffner, MD, a professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
“Fortunately, these are relatively minor mutations.” Even so, SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, continues to be highly contagious. “There isn’t any doubt that it’s spreading—but it’s not more serious.”
So, Dr. Schaffner doesn’t think it’s time to panic. He prefers calling it an “uptick” in cases instead of a “surge,” because a surge “sounds too big.”
While the numbers are still low, compared with 2022’s summer surge, experts still urge people to stay aware of changes in the virus. “I do not think that there is any cause for alarm,” agreed Bernard Camins, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York.
So why the higher number of cases? “There has been an increase in COVID cases this summer, probably related to travel, socializing, and dwindling masking,” said Anne Liu, MD, an allergy, immunology, and infectious disease specialist at Stanford (Calif.) University. Even so, “because of an existing level of immunity from vaccination and prior infections, it has been limited and case severity has been lower than in prior surges.” ●
COMMENTARY
Answering the protein question when prescribing plant-based diets
Science supports the use of a whole food, predominantly plant-based dietary pattern for optimal health, including reduced risk for chronic disease, and best practice in treatment of leading chronic disease.
But clinicians who prescribe such eating patterns encounter a common concern from patients whose health may benefit.
“Where will I get my protein?”
We’ve all heard it, and it’s understandable
To ensure that patients have all the facts when making dietary decisions, clinicians need to be prepared to respond to concerns about protein adequacy and quality with evidence-based information. A good starting point for these conversations is to assess how much protein patients are already consuming. A review of the 2015-2016 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey found that women normally consume an average of 69 g and men an average of 97 g of protein daily.
As a general point of reference, the recommended dietary allowance for protein is about 0.8 g/kg of bodyweight (or 0.36 g/lb), which equates to about 52 g of protein per day for a 145-lb woman and 65 g for a 180-lb man. But for many patients, it may be best to get a more precise recommendation based upon age, gender and physical activity level by using a handy Department of Agriculture tool for health care professionals to calculate daily protein and other nutrient needs. Patients can also use one of countless apps to track their protein and other nutrient intake. By using the tool and a tracking app, both clinician and patients can be fully informed whether protein needs are being met.
LATEST NEWS
Continuous glucose monitors for pregnant patients?
Patients with pregestational diabetes may benefit from use of a continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump paired with a continuous glucose monitor. Use of the tools has been associated with a reduction in maternal and neonatal morbidity, a recent study found.
“We were seeing an unacceptable burden of both maternal and fetal disease in our diabetic population,” said Neil Hamill, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Methodist Women’s Hospital, Omaha, Neb., and an author of the study. “We thought the success with this technology in the nonpregnant population would and should translate into the pregnant population.”
Dr. Hamill and his colleagues analyzed data from 55 pregnant patients who received care at the Women’s Hospital Perinatal Center at the Nebraska Methodist Health System between October 2019 and October 2022. Everyone in the cohort had pregestational diabetes and required insulin prior to week 20 of pregnancy. They used CGMs for more than 2 weeks. The study set blood glucose levels of less than 140 mg/dL as a healthy benchmark.
Participants who had severe preeclampsia, who had delivered preterm, who had delivered a neonate with respiratory distress syndrome, and/or who had given birth to a larger-than-expected infant spent less time in the safe zone — having a blood glucose level below 140 mg/dL—than women who did not have those risk factors.
“When blood sugar control is better, maternal and fetal outcomes are improved,” Dr. Hamill said.
Neetu Sodhi, MD, an ob.gyn. at Providence Cedars-Sinai Tarzana Medical Center, Los Angeles, expressed optimism that use of blood glucose monitors and insulin pumps can improve outcomes for pregnant patients with pregestational diabetes.
“This is just another case for why it’s so important for patients to have access to these types of devices that really, really improve their outcomes and their health, and now it’s proven in the case of pregnancy outcomes too – or at least suggested strongly with this data,” Dr. Sodhi said.
Continue to: It may be time to pay attention to COVID again...
It may be time to pay attention to COVID again
More than 3 years into the COVID-19 era, most Americans have settled back into their prepandemic lifestyles. But a new dominant variant and rising hospitalization numbers may give way to another summer surge.
Since April, a new COVID variant has cropped up. According to recent Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, EG.5—from the Omicron family—now makes up 17% of all cases in the United States, up from 7.5% in the first week of July.
A summary from the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota says that EG.5, nicknamed “Eris” by health trackers, is nearly the same as its parent strain, XBB.1.9.2, but has one extra spike mutation.
Along with the news of EG.5’s growing prevalence, COVID-related hospitalization rates have increased by 12.5% during the week ending on July 29—the most significant uptick since December. Still, no connection has been made between the new variant and rising hospital admissions. And so far, experts have found no difference in the severity of illness or symptoms between Eris and the strains that came before it.
Cause for concern?
The COVID virus has a great tendency to mutate, said William Schaffner, MD, a professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
“Fortunately, these are relatively minor mutations.” Even so, SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, continues to be highly contagious. “There isn’t any doubt that it’s spreading—but it’s not more serious.”
So, Dr. Schaffner doesn’t think it’s time to panic. He prefers calling it an “uptick” in cases instead of a “surge,” because a surge “sounds too big.”
While the numbers are still low, compared with 2022’s summer surge, experts still urge people to stay aware of changes in the virus. “I do not think that there is any cause for alarm,” agreed Bernard Camins, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York.
So why the higher number of cases? “There has been an increase in COVID cases this summer, probably related to travel, socializing, and dwindling masking,” said Anne Liu, MD, an allergy, immunology, and infectious disease specialist at Stanford (Calif.) University. Even so, “because of an existing level of immunity from vaccination and prior infections, it has been limited and case severity has been lower than in prior surges.” ●
Commentary: Are "significant" results necessarily clinically meaningful? October 2023
I was excited to see that the study included the use of objective electronic monitoring of sleep quality. This was done using wrist actigraphy, devices on the wrist that measure acceleration movements. What a great tool this could be for measuring how much scratching our patients are doing! With devices like these measuring movements objectively, we wouldn't have to rely on patients' self-report of itch or sleep quality. Sadly, these monitors did not show any meaningful differences between the dupilumab and placebo groups. This technology holds great promise but it isn't yet ready for prime-time assessment of scratching or sleep.
The title of Chiesa Fuxench and colleagues' article, "Risk of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Patients With Atopic Dermatitis," might be scary to our patients. The authors reported that "children and adults with AD had an increased risk of IBD [inflammatory bowel disease]." The authors concluded, "Clinicians should be aware of these risks, particularly when selecting systemic treatments for AD in patients who may have coincident gastrointestinal symptoms." Bah, humbug, I say!
Be careful when someone tells you there is increased risk. This study was done exceptionally well by an exceptionally good research team. They were working with a huge database and included many controls to ensure that their findings weren't due to chance. And while they did find an "increased risk," they proved — rather conclusively, I believe — that the increased risk is tiny and not something we need to worry about.
The results of this study suggest that there is a scientific link between AD and IBD, probably some genetic inflammatory signaling contributing to both conditions. But even in the highest-risk group, it would take seeing well over 1000 patients for a year to see one more case of IBD due to AD. This article is a good foundation for researchers who want to explore the underlying connection between AD and IBD. The study is an even better foundation for physicians who want to reassure patients that there is little to no meaningful increased risk for IBD in patients with AD.
Am I allowed to just say "Ditto!"? Wan and colleagues' article "Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease and Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis" does show a statistically significant increased risk for cardiovascular (CV) disease in patients with AD. Is that increase clinically significant? This study was also exceptionally well done by an exceptionally good research team. They concluded, "Atopic dermatitis, particularly when severe, is associated with increased risks of venous thromboembolism and CV disease, which may influence the monitoring of patients and selection of treatments for AD." I look at their findings and conclude that AD, even when severe, is associated with little if any clinically meaningful increased risks for venous thromboembolism or CV disease, and we don't need to add any special CV monitoring of AD patients.
The key data are presented in Table 2 of their manuscript. In children, the risk for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in those with severe AD was about 3 times (0.16) that of those with no AD (0.05). But those numbers are per 1000 patient-years. Therefore, the increased risk is 0.16 - 0.05 = 0.11/1000 patient-years. Thus, you'd expect to see one more case of DVT per year in every 9000 children with severe AD. Does that mean we need to monitor all 9000 for DVT? Would that be cost-effective? Might the monitoring cause more problems than it would solve?
CV disease is much more common in adults than in children, but still, with a difference in risk of about 0.5-1 per 1000 patient-years, you'd only expect one more event due to AD in every 1000-2000 patients, and even that is assuming that the entire risk difference was due to AD and not to some other variable that wasn't measured.
With so much drug development for AD, I think we are going to be inundated with companies wanting us to hear their message over and over again. One way to do that is to mine clinical trial data for more papers. In Merola and colleagues' article "Safety and Efficacy of Tralokinumab in Older Adults With Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis" we see just that. We already know that tralokinumab is effective for moderate to severe AD from past publications of clinical trial data. Here, the investigators report on a subset of the clinical trial data — the data on older adults — and, not surprisingly, the drug worked. The efficacy rate, 17% getting clear or almost clear, doesn't sound particularly exciting compared with the higher rates we've seen for other products, but perhaps that lower rate is due in part to differences in studies. Instead of more cuts of data from the same trials, it would be nice to see how tralokinumab compares with other AD treatments on a head-to-head basis.
I was excited to see that the study included the use of objective electronic monitoring of sleep quality. This was done using wrist actigraphy, devices on the wrist that measure acceleration movements. What a great tool this could be for measuring how much scratching our patients are doing! With devices like these measuring movements objectively, we wouldn't have to rely on patients' self-report of itch or sleep quality. Sadly, these monitors did not show any meaningful differences between the dupilumab and placebo groups. This technology holds great promise but it isn't yet ready for prime-time assessment of scratching or sleep.
The title of Chiesa Fuxench and colleagues' article, "Risk of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Patients With Atopic Dermatitis," might be scary to our patients. The authors reported that "children and adults with AD had an increased risk of IBD [inflammatory bowel disease]." The authors concluded, "Clinicians should be aware of these risks, particularly when selecting systemic treatments for AD in patients who may have coincident gastrointestinal symptoms." Bah, humbug, I say!
Be careful when someone tells you there is increased risk. This study was done exceptionally well by an exceptionally good research team. They were working with a huge database and included many controls to ensure that their findings weren't due to chance. And while they did find an "increased risk," they proved — rather conclusively, I believe — that the increased risk is tiny and not something we need to worry about.
The results of this study suggest that there is a scientific link between AD and IBD, probably some genetic inflammatory signaling contributing to both conditions. But even in the highest-risk group, it would take seeing well over 1000 patients for a year to see one more case of IBD due to AD. This article is a good foundation for researchers who want to explore the underlying connection between AD and IBD. The study is an even better foundation for physicians who want to reassure patients that there is little to no meaningful increased risk for IBD in patients with AD.
Am I allowed to just say "Ditto!"? Wan and colleagues' article "Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease and Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis" does show a statistically significant increased risk for cardiovascular (CV) disease in patients with AD. Is that increase clinically significant? This study was also exceptionally well done by an exceptionally good research team. They concluded, "Atopic dermatitis, particularly when severe, is associated with increased risks of venous thromboembolism and CV disease, which may influence the monitoring of patients and selection of treatments for AD." I look at their findings and conclude that AD, even when severe, is associated with little if any clinically meaningful increased risks for venous thromboembolism or CV disease, and we don't need to add any special CV monitoring of AD patients.
The key data are presented in Table 2 of their manuscript. In children, the risk for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in those with severe AD was about 3 times (0.16) that of those with no AD (0.05). But those numbers are per 1000 patient-years. Therefore, the increased risk is 0.16 - 0.05 = 0.11/1000 patient-years. Thus, you'd expect to see one more case of DVT per year in every 9000 children with severe AD. Does that mean we need to monitor all 9000 for DVT? Would that be cost-effective? Might the monitoring cause more problems than it would solve?
CV disease is much more common in adults than in children, but still, with a difference in risk of about 0.5-1 per 1000 patient-years, you'd only expect one more event due to AD in every 1000-2000 patients, and even that is assuming that the entire risk difference was due to AD and not to some other variable that wasn't measured.
With so much drug development for AD, I think we are going to be inundated with companies wanting us to hear their message over and over again. One way to do that is to mine clinical trial data for more papers. In Merola and colleagues' article "Safety and Efficacy of Tralokinumab in Older Adults With Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis" we see just that. We already know that tralokinumab is effective for moderate to severe AD from past publications of clinical trial data. Here, the investigators report on a subset of the clinical trial data — the data on older adults — and, not surprisingly, the drug worked. The efficacy rate, 17% getting clear or almost clear, doesn't sound particularly exciting compared with the higher rates we've seen for other products, but perhaps that lower rate is due in part to differences in studies. Instead of more cuts of data from the same trials, it would be nice to see how tralokinumab compares with other AD treatments on a head-to-head basis.
I was excited to see that the study included the use of objective electronic monitoring of sleep quality. This was done using wrist actigraphy, devices on the wrist that measure acceleration movements. What a great tool this could be for measuring how much scratching our patients are doing! With devices like these measuring movements objectively, we wouldn't have to rely on patients' self-report of itch or sleep quality. Sadly, these monitors did not show any meaningful differences between the dupilumab and placebo groups. This technology holds great promise but it isn't yet ready for prime-time assessment of scratching or sleep.
The title of Chiesa Fuxench and colleagues' article, "Risk of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Patients With Atopic Dermatitis," might be scary to our patients. The authors reported that "children and adults with AD had an increased risk of IBD [inflammatory bowel disease]." The authors concluded, "Clinicians should be aware of these risks, particularly when selecting systemic treatments for AD in patients who may have coincident gastrointestinal symptoms." Bah, humbug, I say!
Be careful when someone tells you there is increased risk. This study was done exceptionally well by an exceptionally good research team. They were working with a huge database and included many controls to ensure that their findings weren't due to chance. And while they did find an "increased risk," they proved — rather conclusively, I believe — that the increased risk is tiny and not something we need to worry about.
The results of this study suggest that there is a scientific link between AD and IBD, probably some genetic inflammatory signaling contributing to both conditions. But even in the highest-risk group, it would take seeing well over 1000 patients for a year to see one more case of IBD due to AD. This article is a good foundation for researchers who want to explore the underlying connection between AD and IBD. The study is an even better foundation for physicians who want to reassure patients that there is little to no meaningful increased risk for IBD in patients with AD.
Am I allowed to just say "Ditto!"? Wan and colleagues' article "Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease and Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis" does show a statistically significant increased risk for cardiovascular (CV) disease in patients with AD. Is that increase clinically significant? This study was also exceptionally well done by an exceptionally good research team. They concluded, "Atopic dermatitis, particularly when severe, is associated with increased risks of venous thromboembolism and CV disease, which may influence the monitoring of patients and selection of treatments for AD." I look at their findings and conclude that AD, even when severe, is associated with little if any clinically meaningful increased risks for venous thromboembolism or CV disease, and we don't need to add any special CV monitoring of AD patients.
The key data are presented in Table 2 of their manuscript. In children, the risk for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in those with severe AD was about 3 times (0.16) that of those with no AD (0.05). But those numbers are per 1000 patient-years. Therefore, the increased risk is 0.16 - 0.05 = 0.11/1000 patient-years. Thus, you'd expect to see one more case of DVT per year in every 9000 children with severe AD. Does that mean we need to monitor all 9000 for DVT? Would that be cost-effective? Might the monitoring cause more problems than it would solve?
CV disease is much more common in adults than in children, but still, with a difference in risk of about 0.5-1 per 1000 patient-years, you'd only expect one more event due to AD in every 1000-2000 patients, and even that is assuming that the entire risk difference was due to AD and not to some other variable that wasn't measured.
With so much drug development for AD, I think we are going to be inundated with companies wanting us to hear their message over and over again. One way to do that is to mine clinical trial data for more papers. In Merola and colleagues' article "Safety and Efficacy of Tralokinumab in Older Adults With Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis" we see just that. We already know that tralokinumab is effective for moderate to severe AD from past publications of clinical trial data. Here, the investigators report on a subset of the clinical trial data — the data on older adults — and, not surprisingly, the drug worked. The efficacy rate, 17% getting clear or almost clear, doesn't sound particularly exciting compared with the higher rates we've seen for other products, but perhaps that lower rate is due in part to differences in studies. Instead of more cuts of data from the same trials, it would be nice to see how tralokinumab compares with other AD treatments on a head-to-head basis.
Diffuse Pruritic Eruption in an Immunocompromised Patient
The Diagnosis: Scabies Infestation
Direct microscopy revealed the presence of a live scabies mite and numerous eggs (Figure), confirming the diagnosis of a scabies infestation. Scabies, caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis mite, characteristically presents in adults as pruritic hyperkeratotic plaques of the interdigital web spaces of the hands, flexor surfaces of the wrists and elbows, axillae, male genitalia, and breasts; however, an atypical presentation is common in immunocompromised or immunosuppressed individuals, such as our patient. In children, the palms, soles, and head (ie, face, scalp, neck) are common sites of involvement. Although dermatologists generally are familiar with severe atypical presentations such as Norwegian crusted scabies or bullous scabies, it is important that they are aware of other atypical presentations, such as the diffuse papulonodular variant observed in our patient.1 As such, a low threshold of suspicion for scabies infestations should be employed in immunocompromised patients with new-onset pruritic eruptions.
Direct microscopy is widely accepted as the gold standard for the diagnosis of scabies infestations; it is a fast and low-cost diagnostic tool. However, this technique displays variable sensitivity in clinical practice, requiring experience and a skilled hand.1,2 Other more sensitive diagnostic options for suspected scabies infestations include histopathology, serology, and molecular-based techniques such as DNA isolation and polymerase chain reaction. Although these tests do demonstrate greater sensitivity, they also are more invasive, time intensive, and costly.2 Therefore, they typically are not the first choice for a suspected scabies infestation. Dermoscopy has emerged as another tool to aid in the diagnosis of a suspected scabies infestation, enabling visualization of scaly burrows, eggs, and live mites. Classically, findings resembling a delta wing with contrail are seen on dermoscopic examination. The delta wing represents the brown triangular structure of the pigmented scabies mite head and anterior legs; the contrail is the lighter linear structures streaming behind the scabies mite (similar to visible vapor streams occurring behind flying jets), representing the burrow of the mite.
Although treatment of scabies infestations typically can be accomplished with permethrin cream 5%, the diffuse nature of our patient’s lesions in combination with his immunocompromised state made oral therapy a more appropriate choice. Based on Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendations, the patient received 2 doses of oral weight-based ivermectin (200 μg/kg per dose) administered 1 week apart.1,3 The initial dose at day 1 serves to eliminate any scabies mites that are present, while the second dose 1 week later eliminates any residual eggs. Our patient experienced complete resolution of the symptoms following this treatment regimen.
It was important to differentiate our patient’s scabies infestation from other intensely pruritic conditions and morphologic mimics including papular urticaria, lichenoid drug eruptions, tinea corporis, and prurigo nodularis. Papular urticaria is an intensely pruritic hypersensitivity reaction to insect bites that commonly affects the extremities or other exposed areas. Visible puncta may be present.4 Our patient’s lesion distribution involved areas covered by clothing, no puncta were present, and he had no history of a recent arthropod assault, making the diagnosis of papular urticaria less likely.
Lichenoid drug eruptions classically present with symmetric, diffuse, pruritic, violaceous, scaling papules and plaques that present 2 to 3 months after exposure to an offending agent.5 Our patient’s eruption was papulonodular with no violaceous plaques, and he did not report changes to his medications, making a lichenoid drug eruption less likely.
Tinea corporis is another intensely pruritic condition that should be considered, especially in immunocompromised patients. It is caused by dermatophytes and classically presents as erythematous pruritic plaques with an annular, advancing, scaling border.6 Although immunocompromised patients may display extensive involvement, our patient’s lesions were papulonodular with no annular morphology or scale, rendering tinea corporis less likely.
Prurigo nodularis is a chronic condition characterized by pruritic, violaceous, dome-shaped, smooth or crusted nodules secondary to repeated scratching or pressure. Although prurigo nodules can develop as a secondary change due to chronic excoriations in scabies infestations, prurigo nodules usually do not develop in areas such as the midline of the back that are not easily reached by the fingernails,7 which made prurigo nodularis less likely in our patient.
This case describes a unique papulonodular variant of scabies presenting in an immunocompromised cancer patient. Timely recognition and diagnosis of atypical scabies infestations can decrease morbidity and improve the quality of life of these patients.
- Chandler DJ, Fuller LC. A review of scabies: an infestation more than skin deep. Dermatology. 2019;235:79-90. doi:10.1159/000495290
- Siddig EE, Hay R. Laboratory-based diagnosis of scabies: a review of the current status. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2022;116:4-9. doi:10.1093/trstmh/trab049
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Parasites—scabies. medications. Accessed September 19, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/ scabies/health_professionals/meds.html
- Örnek S, Zuberbier T, Kocatürk E. Annular urticarial lesions. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:480-504. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol .2021.12.010
- Cheraghlou S, Levy LL. Fixed drug eruptions, bullous drug eruptions, and lichenoid drug eruptions. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:679-692. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.06.010
- Leung AK, Lam JM, Leong KF, et al. Tinea corporis: an updated review. Drugs Context. 2020;9:2020-5-6. doi:10.7573/dic.2020-5-6
- Kwon CD, Khanna R, Williams KA, et al. Diagnostic workup and evaluation of patients with prurigo nodularis. Medicines (Basel). 2019;6:97. doi:10.3390/medicines6040097
The Diagnosis: Scabies Infestation
Direct microscopy revealed the presence of a live scabies mite and numerous eggs (Figure), confirming the diagnosis of a scabies infestation. Scabies, caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis mite, characteristically presents in adults as pruritic hyperkeratotic plaques of the interdigital web spaces of the hands, flexor surfaces of the wrists and elbows, axillae, male genitalia, and breasts; however, an atypical presentation is common in immunocompromised or immunosuppressed individuals, such as our patient. In children, the palms, soles, and head (ie, face, scalp, neck) are common sites of involvement. Although dermatologists generally are familiar with severe atypical presentations such as Norwegian crusted scabies or bullous scabies, it is important that they are aware of other atypical presentations, such as the diffuse papulonodular variant observed in our patient.1 As such, a low threshold of suspicion for scabies infestations should be employed in immunocompromised patients with new-onset pruritic eruptions.

Direct microscopy is widely accepted as the gold standard for the diagnosis of scabies infestations; it is a fast and low-cost diagnostic tool. However, this technique displays variable sensitivity in clinical practice, requiring experience and a skilled hand.1,2 Other more sensitive diagnostic options for suspected scabies infestations include histopathology, serology, and molecular-based techniques such as DNA isolation and polymerase chain reaction. Although these tests do demonstrate greater sensitivity, they also are more invasive, time intensive, and costly.2 Therefore, they typically are not the first choice for a suspected scabies infestation. Dermoscopy has emerged as another tool to aid in the diagnosis of a suspected scabies infestation, enabling visualization of scaly burrows, eggs, and live mites. Classically, findings resembling a delta wing with contrail are seen on dermoscopic examination. The delta wing represents the brown triangular structure of the pigmented scabies mite head and anterior legs; the contrail is the lighter linear structures streaming behind the scabies mite (similar to visible vapor streams occurring behind flying jets), representing the burrow of the mite.
Although treatment of scabies infestations typically can be accomplished with permethrin cream 5%, the diffuse nature of our patient’s lesions in combination with his immunocompromised state made oral therapy a more appropriate choice. Based on Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendations, the patient received 2 doses of oral weight-based ivermectin (200 μg/kg per dose) administered 1 week apart.1,3 The initial dose at day 1 serves to eliminate any scabies mites that are present, while the second dose 1 week later eliminates any residual eggs. Our patient experienced complete resolution of the symptoms following this treatment regimen.
It was important to differentiate our patient’s scabies infestation from other intensely pruritic conditions and morphologic mimics including papular urticaria, lichenoid drug eruptions, tinea corporis, and prurigo nodularis. Papular urticaria is an intensely pruritic hypersensitivity reaction to insect bites that commonly affects the extremities or other exposed areas. Visible puncta may be present.4 Our patient’s lesion distribution involved areas covered by clothing, no puncta were present, and he had no history of a recent arthropod assault, making the diagnosis of papular urticaria less likely.
Lichenoid drug eruptions classically present with symmetric, diffuse, pruritic, violaceous, scaling papules and plaques that present 2 to 3 months after exposure to an offending agent.5 Our patient’s eruption was papulonodular with no violaceous plaques, and he did not report changes to his medications, making a lichenoid drug eruption less likely.
Tinea corporis is another intensely pruritic condition that should be considered, especially in immunocompromised patients. It is caused by dermatophytes and classically presents as erythematous pruritic plaques with an annular, advancing, scaling border.6 Although immunocompromised patients may display extensive involvement, our patient’s lesions were papulonodular with no annular morphology or scale, rendering tinea corporis less likely.
Prurigo nodularis is a chronic condition characterized by pruritic, violaceous, dome-shaped, smooth or crusted nodules secondary to repeated scratching or pressure. Although prurigo nodules can develop as a secondary change due to chronic excoriations in scabies infestations, prurigo nodules usually do not develop in areas such as the midline of the back that are not easily reached by the fingernails,7 which made prurigo nodularis less likely in our patient.
This case describes a unique papulonodular variant of scabies presenting in an immunocompromised cancer patient. Timely recognition and diagnosis of atypical scabies infestations can decrease morbidity and improve the quality of life of these patients.
The Diagnosis: Scabies Infestation
Direct microscopy revealed the presence of a live scabies mite and numerous eggs (Figure), confirming the diagnosis of a scabies infestation. Scabies, caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis mite, characteristically presents in adults as pruritic hyperkeratotic plaques of the interdigital web spaces of the hands, flexor surfaces of the wrists and elbows, axillae, male genitalia, and breasts; however, an atypical presentation is common in immunocompromised or immunosuppressed individuals, such as our patient. In children, the palms, soles, and head (ie, face, scalp, neck) are common sites of involvement. Although dermatologists generally are familiar with severe atypical presentations such as Norwegian crusted scabies or bullous scabies, it is important that they are aware of other atypical presentations, such as the diffuse papulonodular variant observed in our patient.1 As such, a low threshold of suspicion for scabies infestations should be employed in immunocompromised patients with new-onset pruritic eruptions.

Direct microscopy is widely accepted as the gold standard for the diagnosis of scabies infestations; it is a fast and low-cost diagnostic tool. However, this technique displays variable sensitivity in clinical practice, requiring experience and a skilled hand.1,2 Other more sensitive diagnostic options for suspected scabies infestations include histopathology, serology, and molecular-based techniques such as DNA isolation and polymerase chain reaction. Although these tests do demonstrate greater sensitivity, they also are more invasive, time intensive, and costly.2 Therefore, they typically are not the first choice for a suspected scabies infestation. Dermoscopy has emerged as another tool to aid in the diagnosis of a suspected scabies infestation, enabling visualization of scaly burrows, eggs, and live mites. Classically, findings resembling a delta wing with contrail are seen on dermoscopic examination. The delta wing represents the brown triangular structure of the pigmented scabies mite head and anterior legs; the contrail is the lighter linear structures streaming behind the scabies mite (similar to visible vapor streams occurring behind flying jets), representing the burrow of the mite.
Although treatment of scabies infestations typically can be accomplished with permethrin cream 5%, the diffuse nature of our patient’s lesions in combination with his immunocompromised state made oral therapy a more appropriate choice. Based on Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendations, the patient received 2 doses of oral weight-based ivermectin (200 μg/kg per dose) administered 1 week apart.1,3 The initial dose at day 1 serves to eliminate any scabies mites that are present, while the second dose 1 week later eliminates any residual eggs. Our patient experienced complete resolution of the symptoms following this treatment regimen.
It was important to differentiate our patient’s scabies infestation from other intensely pruritic conditions and morphologic mimics including papular urticaria, lichenoid drug eruptions, tinea corporis, and prurigo nodularis. Papular urticaria is an intensely pruritic hypersensitivity reaction to insect bites that commonly affects the extremities or other exposed areas. Visible puncta may be present.4 Our patient’s lesion distribution involved areas covered by clothing, no puncta were present, and he had no history of a recent arthropod assault, making the diagnosis of papular urticaria less likely.
Lichenoid drug eruptions classically present with symmetric, diffuse, pruritic, violaceous, scaling papules and plaques that present 2 to 3 months after exposure to an offending agent.5 Our patient’s eruption was papulonodular with no violaceous plaques, and he did not report changes to his medications, making a lichenoid drug eruption less likely.
Tinea corporis is another intensely pruritic condition that should be considered, especially in immunocompromised patients. It is caused by dermatophytes and classically presents as erythematous pruritic plaques with an annular, advancing, scaling border.6 Although immunocompromised patients may display extensive involvement, our patient’s lesions were papulonodular with no annular morphology or scale, rendering tinea corporis less likely.
Prurigo nodularis is a chronic condition characterized by pruritic, violaceous, dome-shaped, smooth or crusted nodules secondary to repeated scratching or pressure. Although prurigo nodules can develop as a secondary change due to chronic excoriations in scabies infestations, prurigo nodules usually do not develop in areas such as the midline of the back that are not easily reached by the fingernails,7 which made prurigo nodularis less likely in our patient.
This case describes a unique papulonodular variant of scabies presenting in an immunocompromised cancer patient. Timely recognition and diagnosis of atypical scabies infestations can decrease morbidity and improve the quality of life of these patients.
- Chandler DJ, Fuller LC. A review of scabies: an infestation more than skin deep. Dermatology. 2019;235:79-90. doi:10.1159/000495290
- Siddig EE, Hay R. Laboratory-based diagnosis of scabies: a review of the current status. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2022;116:4-9. doi:10.1093/trstmh/trab049
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Parasites—scabies. medications. Accessed September 19, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/ scabies/health_professionals/meds.html
- Örnek S, Zuberbier T, Kocatürk E. Annular urticarial lesions. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:480-504. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol .2021.12.010
- Cheraghlou S, Levy LL. Fixed drug eruptions, bullous drug eruptions, and lichenoid drug eruptions. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:679-692. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.06.010
- Leung AK, Lam JM, Leong KF, et al. Tinea corporis: an updated review. Drugs Context. 2020;9:2020-5-6. doi:10.7573/dic.2020-5-6
- Kwon CD, Khanna R, Williams KA, et al. Diagnostic workup and evaluation of patients with prurigo nodularis. Medicines (Basel). 2019;6:97. doi:10.3390/medicines6040097
- Chandler DJ, Fuller LC. A review of scabies: an infestation more than skin deep. Dermatology. 2019;235:79-90. doi:10.1159/000495290
- Siddig EE, Hay R. Laboratory-based diagnosis of scabies: a review of the current status. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2022;116:4-9. doi:10.1093/trstmh/trab049
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Parasites—scabies. medications. Accessed September 19, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/ scabies/health_professionals/meds.html
- Örnek S, Zuberbier T, Kocatürk E. Annular urticarial lesions. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:480-504. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol .2021.12.010
- Cheraghlou S, Levy LL. Fixed drug eruptions, bullous drug eruptions, and lichenoid drug eruptions. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:679-692. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.06.010
- Leung AK, Lam JM, Leong KF, et al. Tinea corporis: an updated review. Drugs Context. 2020;9:2020-5-6. doi:10.7573/dic.2020-5-6
- Kwon CD, Khanna R, Williams KA, et al. Diagnostic workup and evaluation of patients with prurigo nodularis. Medicines (Basel). 2019;6:97. doi:10.3390/medicines6040097
A 54-year-old man presented to our dermatology clinic for evaluation of a widespread intensely pruritic rash of 4 weeks’ duration. Calamine lotion and oral hydroxyzine provided minimal relief. He was being treated for a myeloproliferative disorder with immunosuppressive therapy consisting of a combination of cladribine, low-dose cytarabine, and fedratinib. Physical examination revealed multiple excoriated papules and indurated nodules on the extensor and flexor surfaces of the arms and legs (top), chest, midline of the back (bottom), and groin. No lesions were noted on the volar aspect of the patient’s wrists or interdigital spaces, and no central puncta or scales were present. He denied any preceding arthropod bites, trauma, new environmental exposures, or changes to his medications. Scrapings from several representative lesions were obtained for mineral oil preparation and microscopic evaluation.