User login
Not just a bad dream: Nightmares may predict dementia
Results from a large cohort study showed that healthy middle-aged adults who had bad dreams at least once a week were four times more likely to experience cognitive decline over the following decade, and older adults were twice as likely to be diagnosed with dementia, compared with peers who never had bad dreams.
Frequent nightmares may “identify people who are at high risk of developing dementia in the future, several years or decades before the characteristic memory and thinking problems emerge,” study investigator Abidemi Otaiku, BMBS, University of Birmingham, England, said in an interview.
“This would be the optimum time for doctors to intervene to try and slow down or prevent dementia from developing,” Dr. Otaiku said.
The findings were published online in The Lancet journal eClinicalMedicine).
Distressing dreams
Distressing dreams have been previously associated with faster cognitive decline and increased dementia risk in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD), but whether the same holds for individuals from the general population without PD is unknown.
To investigate, Dr. Otaiku examined data from three community-based cohorts in the United States. This included 605 middle-aged adults (aged 35-64 years) who were followed for up to 13 years and 2,600 adults aged 79 and older who were followed for up to 7 years. All were considered cognitively normal at baseline.
The prevalence of frequent distressing dreams, defined as occurring “once a week or more,” was higher in the older cohort compared with the middle-aged cohort (6.9% vs. 6.0%, respectively).
This is in line with other research that showed distressing dreams remain relatively stable throughout early adulthood and then progressively increase in prevalence from middle to older adulthood.
After adjustment for all covariates, a higher frequency of distressing dreams was linearly and statistically significantly associated with a higher risk for cognitive decline in middle-aged adults (P = .016) and a higher risk for dementia in older adults (P = .001).
In the fully adjusted model, compared with middle-aged adults who never had bad dreams, those who reported having one or more bad dreams weekly had a fourfold risk for cognitive decline (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 3.99; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.07-14.85).
Older adults who had one or more bad dreams weekly had a greater than twofold increased risk for developing dementia (aOR, 2.21; 95% CI, 1.35-3.62).
Early days
In sex-stratified analyses, distressing dreams were strongly and statistically significantly associated with cognitive decline and dementia in men, but were only weakly and nonsignificantly associated with cognitive decline and dementia in women.
Dr. Otaiku said he suspects some individuals in the preclinical phase of dementia have “subtle neurodegeneration occurring over time in the right frontal lobe: the area of the brain that helps to downregulate negative emotions whilst we are awake, and also whilst we are dreaming.”
This could result in “depression and anxiety in the day, and nightmares and bad dreams during the night,” he said.
It is possible that treatment for frequent nightmares may help to slow cognitive decline and delay or prevent dementia, Dr. Otaiku added.
He noted that prazosin is used to treat nightmares and has been shown to prevent memory decline and reduce amyloid B generation in preclinical studies of Alzheimer’s disease.
“This is an exciting prospect [but] it is still early days and we will need research to see whether treating nightmares might help to reduce dementia risk down the line,” Dr. Otaiku said.
Credible research
In an interview regarding these findings, Maria C. Carrillo, PhD, chief science officer for the Alzheimer’s Association, said: “This is credible research consistent with the idea that sleep disturbances may be a risk factor or warning sign of cognitive decline.”
She added that “what’s novel here” is the researchers examined distressing dreams – not more physical sleep disturbances and disorders such as insomnia or apnea.
“However, nightmares can disturb sleep in the same way these disorders do by waking people up in the middle of the night,” said Dr. Carrillo, who was not involved with the study.
“Previous research has pointed to nightmares being indicative of potential changes in the brain that can precede other dementias like Parkinson’s disease. More research is needed to tease out what exactly is happening in the brain during nightmares that may be contributing to this increased risk,” she said.
Dr. Carrillo noted that “getting good sleep” is important for overall health, which includes brain health.
“The good news is there are treatments – both drug and nondrug – that can help address sleep disturbances,” she added.
This study received no external funding. Dr. Otaiku and Dr. Carrillo have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Results from a large cohort study showed that healthy middle-aged adults who had bad dreams at least once a week were four times more likely to experience cognitive decline over the following decade, and older adults were twice as likely to be diagnosed with dementia, compared with peers who never had bad dreams.
Frequent nightmares may “identify people who are at high risk of developing dementia in the future, several years or decades before the characteristic memory and thinking problems emerge,” study investigator Abidemi Otaiku, BMBS, University of Birmingham, England, said in an interview.
“This would be the optimum time for doctors to intervene to try and slow down or prevent dementia from developing,” Dr. Otaiku said.
The findings were published online in The Lancet journal eClinicalMedicine).
Distressing dreams
Distressing dreams have been previously associated with faster cognitive decline and increased dementia risk in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD), but whether the same holds for individuals from the general population without PD is unknown.
To investigate, Dr. Otaiku examined data from three community-based cohorts in the United States. This included 605 middle-aged adults (aged 35-64 years) who were followed for up to 13 years and 2,600 adults aged 79 and older who were followed for up to 7 years. All were considered cognitively normal at baseline.
The prevalence of frequent distressing dreams, defined as occurring “once a week or more,” was higher in the older cohort compared with the middle-aged cohort (6.9% vs. 6.0%, respectively).
This is in line with other research that showed distressing dreams remain relatively stable throughout early adulthood and then progressively increase in prevalence from middle to older adulthood.
After adjustment for all covariates, a higher frequency of distressing dreams was linearly and statistically significantly associated with a higher risk for cognitive decline in middle-aged adults (P = .016) and a higher risk for dementia in older adults (P = .001).
In the fully adjusted model, compared with middle-aged adults who never had bad dreams, those who reported having one or more bad dreams weekly had a fourfold risk for cognitive decline (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 3.99; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.07-14.85).
Older adults who had one or more bad dreams weekly had a greater than twofold increased risk for developing dementia (aOR, 2.21; 95% CI, 1.35-3.62).
Early days
In sex-stratified analyses, distressing dreams were strongly and statistically significantly associated with cognitive decline and dementia in men, but were only weakly and nonsignificantly associated with cognitive decline and dementia in women.
Dr. Otaiku said he suspects some individuals in the preclinical phase of dementia have “subtle neurodegeneration occurring over time in the right frontal lobe: the area of the brain that helps to downregulate negative emotions whilst we are awake, and also whilst we are dreaming.”
This could result in “depression and anxiety in the day, and nightmares and bad dreams during the night,” he said.
It is possible that treatment for frequent nightmares may help to slow cognitive decline and delay or prevent dementia, Dr. Otaiku added.
He noted that prazosin is used to treat nightmares and has been shown to prevent memory decline and reduce amyloid B generation in preclinical studies of Alzheimer’s disease.
“This is an exciting prospect [but] it is still early days and we will need research to see whether treating nightmares might help to reduce dementia risk down the line,” Dr. Otaiku said.
Credible research
In an interview regarding these findings, Maria C. Carrillo, PhD, chief science officer for the Alzheimer’s Association, said: “This is credible research consistent with the idea that sleep disturbances may be a risk factor or warning sign of cognitive decline.”
She added that “what’s novel here” is the researchers examined distressing dreams – not more physical sleep disturbances and disorders such as insomnia or apnea.
“However, nightmares can disturb sleep in the same way these disorders do by waking people up in the middle of the night,” said Dr. Carrillo, who was not involved with the study.
“Previous research has pointed to nightmares being indicative of potential changes in the brain that can precede other dementias like Parkinson’s disease. More research is needed to tease out what exactly is happening in the brain during nightmares that may be contributing to this increased risk,” she said.
Dr. Carrillo noted that “getting good sleep” is important for overall health, which includes brain health.
“The good news is there are treatments – both drug and nondrug – that can help address sleep disturbances,” she added.
This study received no external funding. Dr. Otaiku and Dr. Carrillo have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Results from a large cohort study showed that healthy middle-aged adults who had bad dreams at least once a week were four times more likely to experience cognitive decline over the following decade, and older adults were twice as likely to be diagnosed with dementia, compared with peers who never had bad dreams.
Frequent nightmares may “identify people who are at high risk of developing dementia in the future, several years or decades before the characteristic memory and thinking problems emerge,” study investigator Abidemi Otaiku, BMBS, University of Birmingham, England, said in an interview.
“This would be the optimum time for doctors to intervene to try and slow down or prevent dementia from developing,” Dr. Otaiku said.
The findings were published online in The Lancet journal eClinicalMedicine).
Distressing dreams
Distressing dreams have been previously associated with faster cognitive decline and increased dementia risk in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD), but whether the same holds for individuals from the general population without PD is unknown.
To investigate, Dr. Otaiku examined data from three community-based cohorts in the United States. This included 605 middle-aged adults (aged 35-64 years) who were followed for up to 13 years and 2,600 adults aged 79 and older who were followed for up to 7 years. All were considered cognitively normal at baseline.
The prevalence of frequent distressing dreams, defined as occurring “once a week or more,” was higher in the older cohort compared with the middle-aged cohort (6.9% vs. 6.0%, respectively).
This is in line with other research that showed distressing dreams remain relatively stable throughout early adulthood and then progressively increase in prevalence from middle to older adulthood.
After adjustment for all covariates, a higher frequency of distressing dreams was linearly and statistically significantly associated with a higher risk for cognitive decline in middle-aged adults (P = .016) and a higher risk for dementia in older adults (P = .001).
In the fully adjusted model, compared with middle-aged adults who never had bad dreams, those who reported having one or more bad dreams weekly had a fourfold risk for cognitive decline (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 3.99; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.07-14.85).
Older adults who had one or more bad dreams weekly had a greater than twofold increased risk for developing dementia (aOR, 2.21; 95% CI, 1.35-3.62).
Early days
In sex-stratified analyses, distressing dreams were strongly and statistically significantly associated with cognitive decline and dementia in men, but were only weakly and nonsignificantly associated with cognitive decline and dementia in women.
Dr. Otaiku said he suspects some individuals in the preclinical phase of dementia have “subtle neurodegeneration occurring over time in the right frontal lobe: the area of the brain that helps to downregulate negative emotions whilst we are awake, and also whilst we are dreaming.”
This could result in “depression and anxiety in the day, and nightmares and bad dreams during the night,” he said.
It is possible that treatment for frequent nightmares may help to slow cognitive decline and delay or prevent dementia, Dr. Otaiku added.
He noted that prazosin is used to treat nightmares and has been shown to prevent memory decline and reduce amyloid B generation in preclinical studies of Alzheimer’s disease.
“This is an exciting prospect [but] it is still early days and we will need research to see whether treating nightmares might help to reduce dementia risk down the line,” Dr. Otaiku said.
Credible research
In an interview regarding these findings, Maria C. Carrillo, PhD, chief science officer for the Alzheimer’s Association, said: “This is credible research consistent with the idea that sleep disturbances may be a risk factor or warning sign of cognitive decline.”
She added that “what’s novel here” is the researchers examined distressing dreams – not more physical sleep disturbances and disorders such as insomnia or apnea.
“However, nightmares can disturb sleep in the same way these disorders do by waking people up in the middle of the night,” said Dr. Carrillo, who was not involved with the study.
“Previous research has pointed to nightmares being indicative of potential changes in the brain that can precede other dementias like Parkinson’s disease. More research is needed to tease out what exactly is happening in the brain during nightmares that may be contributing to this increased risk,” she said.
Dr. Carrillo noted that “getting good sleep” is important for overall health, which includes brain health.
“The good news is there are treatments – both drug and nondrug – that can help address sleep disturbances,” she added.
This study received no external funding. Dr. Otaiku and Dr. Carrillo have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ECLINICALMEDICINE
FDA OKs selpercatinib for adults with RET-fusion+ solid tumors
that have progressed during or following systemic treatment, or for patients for whom there are no good alternative treatments.
In 2020, selpercatinib received accelerated approval for lung and thyroid RET-positive tumors; that approval transitioned to a regular approval for non–small cell lung cancer on Sept. 21. The latest approval expands the drug label to include an array of RET-positive tumor types, including pancreatic and colorectal cancers.
The approval was based on data from the phase 1/2 LIBRETTO-001 trial, which evaluated 41 patients with RET fusion–positive tumors. Thirty-seven patients (90%) had received prior systemic therapy, with almost one-third receiving three or more. Primary efficacy measures were overall response rate and duration of response.
Among the 41 patients, the overall response rate was 44%, with a duration of response of 24.5 months. Additionally, for 67% of patients, results lasted at least 6 months.
“In the LIBRETTO-001 trial, selpercatinib demonstrated clinically meaningful and durable responses across a variety of tumor types in patients with RET-driven cancers,” Vivek Subbiah, MD, coinvestigator for the trial, said in a press release. “These data and FDA approval of the tumor-agnostic indication underscore the importance of routine, comprehensive genomic testing for patients across a wide variety of tumor types.”
The most common cancers in the study were pancreatic adenocarcinoma (27%), colorectal cancer (24%), and salivary cancer (10%).
The recommended selpercatinib dose, based on body weight, is 120 mg orally twice daily for people who weigh less than 110 pounds or 160 mg orally twice daily for who weigh 110 pounds or more.
The most common adverse reactions were edema, diarrhea, fatigue, dry mouth, hypertension, abdominal pain, constipation, rash, nausea, and headache.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
that have progressed during or following systemic treatment, or for patients for whom there are no good alternative treatments.
In 2020, selpercatinib received accelerated approval for lung and thyroid RET-positive tumors; that approval transitioned to a regular approval for non–small cell lung cancer on Sept. 21. The latest approval expands the drug label to include an array of RET-positive tumor types, including pancreatic and colorectal cancers.
The approval was based on data from the phase 1/2 LIBRETTO-001 trial, which evaluated 41 patients with RET fusion–positive tumors. Thirty-seven patients (90%) had received prior systemic therapy, with almost one-third receiving three or more. Primary efficacy measures were overall response rate and duration of response.
Among the 41 patients, the overall response rate was 44%, with a duration of response of 24.5 months. Additionally, for 67% of patients, results lasted at least 6 months.
“In the LIBRETTO-001 trial, selpercatinib demonstrated clinically meaningful and durable responses across a variety of tumor types in patients with RET-driven cancers,” Vivek Subbiah, MD, coinvestigator for the trial, said in a press release. “These data and FDA approval of the tumor-agnostic indication underscore the importance of routine, comprehensive genomic testing for patients across a wide variety of tumor types.”
The most common cancers in the study were pancreatic adenocarcinoma (27%), colorectal cancer (24%), and salivary cancer (10%).
The recommended selpercatinib dose, based on body weight, is 120 mg orally twice daily for people who weigh less than 110 pounds or 160 mg orally twice daily for who weigh 110 pounds or more.
The most common adverse reactions were edema, diarrhea, fatigue, dry mouth, hypertension, abdominal pain, constipation, rash, nausea, and headache.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
that have progressed during or following systemic treatment, or for patients for whom there are no good alternative treatments.
In 2020, selpercatinib received accelerated approval for lung and thyroid RET-positive tumors; that approval transitioned to a regular approval for non–small cell lung cancer on Sept. 21. The latest approval expands the drug label to include an array of RET-positive tumor types, including pancreatic and colorectal cancers.
The approval was based on data from the phase 1/2 LIBRETTO-001 trial, which evaluated 41 patients with RET fusion–positive tumors. Thirty-seven patients (90%) had received prior systemic therapy, with almost one-third receiving three or more. Primary efficacy measures were overall response rate and duration of response.
Among the 41 patients, the overall response rate was 44%, with a duration of response of 24.5 months. Additionally, for 67% of patients, results lasted at least 6 months.
“In the LIBRETTO-001 trial, selpercatinib demonstrated clinically meaningful and durable responses across a variety of tumor types in patients with RET-driven cancers,” Vivek Subbiah, MD, coinvestigator for the trial, said in a press release. “These data and FDA approval of the tumor-agnostic indication underscore the importance of routine, comprehensive genomic testing for patients across a wide variety of tumor types.”
The most common cancers in the study were pancreatic adenocarcinoma (27%), colorectal cancer (24%), and salivary cancer (10%).
The recommended selpercatinib dose, based on body weight, is 120 mg orally twice daily for people who weigh less than 110 pounds or 160 mg orally twice daily for who weigh 110 pounds or more.
The most common adverse reactions were edema, diarrhea, fatigue, dry mouth, hypertension, abdominal pain, constipation, rash, nausea, and headache.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Unsure on the best T2D drug choice? Let patients decide
STOCKHOLM – When a clinician is unsure which of several equally viable drug options is best for a specific patient with type 2 diabetes, a rational approach is to run a serial trial with each one and then let each patient decide which agent works best for them.
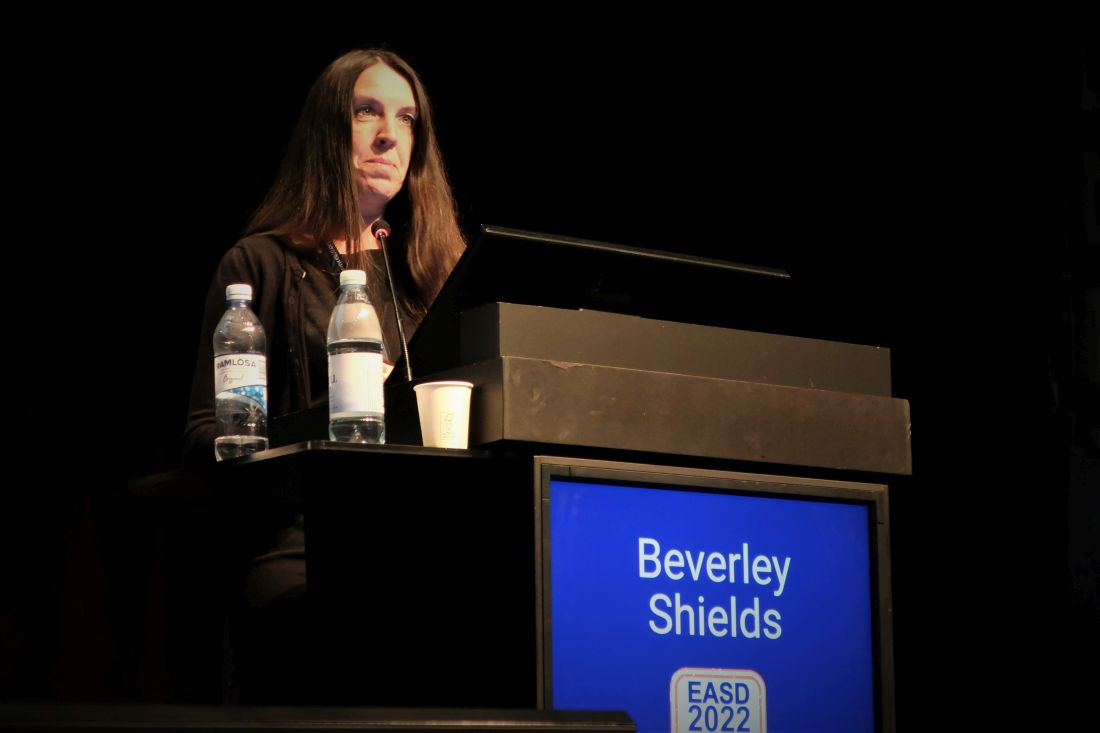
That concept underwent successful testing in a recent trial with 457 patients with type 2 diabetes and already on treatment with metformin or metformin plus a sulfonylurea but needed further glycemic control. After cycling through 4-month trials (when tolerated) of canagliflozin (Invokana), pioglitazone (Actos), and sitagliptin (Januvia), 24% identified pioglitazone as the one that made them feel best, 33% favored sitagliptin, 37% said canagliflozin was tops, and 6% had no preference, Beverley Shields, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
After making these selections based on just their qualitative self-appraisals, researchers told patients about their hemoglobin A1c status on each of the three agents. It barely budged their choices, which became 25% calling pioglitazone best, 35% naming sitagliptin their preference, 38% opting for canagliflozin, with 2% having no preference.
Further analysis showed that the drug patients preferred was also the one that produced their lowest A1c level when compared with their 8 months on each of the two other agents tested, showing a link between lower A1c levels and improved well-being. The same relationship existed for the drug that caused the fewest adverse events for each patient.
Patients prefer feeling better
“Patients tended to prefer the drug that they ‘felt better’ on, with the lowest A1c level and the lowest number of side effects,” explained Dr. Shields, a medical statistician at the University of Exeter (England). Changes in weight appeared less important to patients for establishing a preference.
“This is for when there is equipoise” among drug options, Andrew Hattersley, BMBCh, DM, the study’s principal investigator, said in an interview. “When you are unsure what to prescribe and there is no clear indication for one drug over another, try 4 months of one and 4 months of the other, then let the patient decide.
“Patients had overwhelming positivity about being able to choose their drug,” added Dr. Hattersley, who is also professor of molecular medicine at the University of Exeter.
“This has implications across medicine,” he added. “Whenever you’re not sure how to balance adverse effects and positive effects the best person to decide is the one who experiences the effects.”
“I’m a bit worried by this approach, but it is something new” and worth considering, commented Drazenka P. Barlovic, MD, an endocrinologist at the University Medical Center in Ljubljana, Slovenia, who chaired the session where Dr. Shields gave her report. “We should also have the courage to challenge metformin, as there is no longer an obligation to make it the first drug,” she said in an interview.
The study ran as a secondary analysis of the TriMaster study, which had the primary objective of identifying patient characteristics that could predict which of the three drug options tested worked best for certain patient subgroups. That analysis, presented at the 2021 EASD annual meeting, found that factors such as body mass index and kidney function significantly linked with the clinical responses patients had to each of the three tested agents.
The new analysis focused on 457 of the TriMaster participants who had provided preference information after they had tried all three agents. By design, none of the participants enrolled in the study had a contraindication for any of the tested drugs.
Patients quickly identify adverse effects
“We picked 4 months because it not too long, but long enough to see adverse effects, and to measure on-treatment A1c. Patients quickly identify their adverse events,” Dr. Shields said in an interview.
“This could come into practice now; there is no cost involved. Do it when you’re not certain which drug to prescribe,” Dr. Hattersley suggested. “We can’t know which drug a patient might prefer.” He also stressed telling patients to return quicker than 4 months if they can’t tolerate a new drug.
The findings have already changed Dr. Hattersley’s practice, and he believes it will catch on as he introduces it to local primary care physicians.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Shields, Dr. Hattersley, and Dr. Barlovic had no disclosures.
STOCKHOLM – When a clinician is unsure which of several equally viable drug options is best for a specific patient with type 2 diabetes, a rational approach is to run a serial trial with each one and then let each patient decide which agent works best for them.
That concept underwent successful testing in a recent trial with 457 patients with type 2 diabetes and already on treatment with metformin or metformin plus a sulfonylurea but needed further glycemic control. After cycling through 4-month trials (when tolerated) of canagliflozin (Invokana), pioglitazone (Actos), and sitagliptin (Januvia), 24% identified pioglitazone as the one that made them feel best, 33% favored sitagliptin, 37% said canagliflozin was tops, and 6% had no preference, Beverley Shields, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
After making these selections based on just their qualitative self-appraisals, researchers told patients about their hemoglobin A1c status on each of the three agents. It barely budged their choices, which became 25% calling pioglitazone best, 35% naming sitagliptin their preference, 38% opting for canagliflozin, with 2% having no preference.
Further analysis showed that the drug patients preferred was also the one that produced their lowest A1c level when compared with their 8 months on each of the two other agents tested, showing a link between lower A1c levels and improved well-being. The same relationship existed for the drug that caused the fewest adverse events for each patient.
Patients prefer feeling better
“Patients tended to prefer the drug that they ‘felt better’ on, with the lowest A1c level and the lowest number of side effects,” explained Dr. Shields, a medical statistician at the University of Exeter (England). Changes in weight appeared less important to patients for establishing a preference.
“This is for when there is equipoise” among drug options, Andrew Hattersley, BMBCh, DM, the study’s principal investigator, said in an interview. “When you are unsure what to prescribe and there is no clear indication for one drug over another, try 4 months of one and 4 months of the other, then let the patient decide.
“Patients had overwhelming positivity about being able to choose their drug,” added Dr. Hattersley, who is also professor of molecular medicine at the University of Exeter.
“This has implications across medicine,” he added. “Whenever you’re not sure how to balance adverse effects and positive effects the best person to decide is the one who experiences the effects.”
“I’m a bit worried by this approach, but it is something new” and worth considering, commented Drazenka P. Barlovic, MD, an endocrinologist at the University Medical Center in Ljubljana, Slovenia, who chaired the session where Dr. Shields gave her report. “We should also have the courage to challenge metformin, as there is no longer an obligation to make it the first drug,” she said in an interview.
The study ran as a secondary analysis of the TriMaster study, which had the primary objective of identifying patient characteristics that could predict which of the three drug options tested worked best for certain patient subgroups. That analysis, presented at the 2021 EASD annual meeting, found that factors such as body mass index and kidney function significantly linked with the clinical responses patients had to each of the three tested agents.
The new analysis focused on 457 of the TriMaster participants who had provided preference information after they had tried all three agents. By design, none of the participants enrolled in the study had a contraindication for any of the tested drugs.
Patients quickly identify adverse effects
“We picked 4 months because it not too long, but long enough to see adverse effects, and to measure on-treatment A1c. Patients quickly identify their adverse events,” Dr. Shields said in an interview.
“This could come into practice now; there is no cost involved. Do it when you’re not certain which drug to prescribe,” Dr. Hattersley suggested. “We can’t know which drug a patient might prefer.” He also stressed telling patients to return quicker than 4 months if they can’t tolerate a new drug.
The findings have already changed Dr. Hattersley’s practice, and he believes it will catch on as he introduces it to local primary care physicians.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Shields, Dr. Hattersley, and Dr. Barlovic had no disclosures.
STOCKHOLM – When a clinician is unsure which of several equally viable drug options is best for a specific patient with type 2 diabetes, a rational approach is to run a serial trial with each one and then let each patient decide which agent works best for them.
That concept underwent successful testing in a recent trial with 457 patients with type 2 diabetes and already on treatment with metformin or metformin plus a sulfonylurea but needed further glycemic control. After cycling through 4-month trials (when tolerated) of canagliflozin (Invokana), pioglitazone (Actos), and sitagliptin (Januvia), 24% identified pioglitazone as the one that made them feel best, 33% favored sitagliptin, 37% said canagliflozin was tops, and 6% had no preference, Beverley Shields, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
After making these selections based on just their qualitative self-appraisals, researchers told patients about their hemoglobin A1c status on each of the three agents. It barely budged their choices, which became 25% calling pioglitazone best, 35% naming sitagliptin their preference, 38% opting for canagliflozin, with 2% having no preference.
Further analysis showed that the drug patients preferred was also the one that produced their lowest A1c level when compared with their 8 months on each of the two other agents tested, showing a link between lower A1c levels and improved well-being. The same relationship existed for the drug that caused the fewest adverse events for each patient.
Patients prefer feeling better
“Patients tended to prefer the drug that they ‘felt better’ on, with the lowest A1c level and the lowest number of side effects,” explained Dr. Shields, a medical statistician at the University of Exeter (England). Changes in weight appeared less important to patients for establishing a preference.
“This is for when there is equipoise” among drug options, Andrew Hattersley, BMBCh, DM, the study’s principal investigator, said in an interview. “When you are unsure what to prescribe and there is no clear indication for one drug over another, try 4 months of one and 4 months of the other, then let the patient decide.
“Patients had overwhelming positivity about being able to choose their drug,” added Dr. Hattersley, who is also professor of molecular medicine at the University of Exeter.
“This has implications across medicine,” he added. “Whenever you’re not sure how to balance adverse effects and positive effects the best person to decide is the one who experiences the effects.”
“I’m a bit worried by this approach, but it is something new” and worth considering, commented Drazenka P. Barlovic, MD, an endocrinologist at the University Medical Center in Ljubljana, Slovenia, who chaired the session where Dr. Shields gave her report. “We should also have the courage to challenge metformin, as there is no longer an obligation to make it the first drug,” she said in an interview.
The study ran as a secondary analysis of the TriMaster study, which had the primary objective of identifying patient characteristics that could predict which of the three drug options tested worked best for certain patient subgroups. That analysis, presented at the 2021 EASD annual meeting, found that factors such as body mass index and kidney function significantly linked with the clinical responses patients had to each of the three tested agents.
The new analysis focused on 457 of the TriMaster participants who had provided preference information after they had tried all three agents. By design, none of the participants enrolled in the study had a contraindication for any of the tested drugs.
Patients quickly identify adverse effects
“We picked 4 months because it not too long, but long enough to see adverse effects, and to measure on-treatment A1c. Patients quickly identify their adverse events,” Dr. Shields said in an interview.
“This could come into practice now; there is no cost involved. Do it when you’re not certain which drug to prescribe,” Dr. Hattersley suggested. “We can’t know which drug a patient might prefer.” He also stressed telling patients to return quicker than 4 months if they can’t tolerate a new drug.
The findings have already changed Dr. Hattersley’s practice, and he believes it will catch on as he introduces it to local primary care physicians.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Shields, Dr. Hattersley, and Dr. Barlovic had no disclosures.
AT EASD 2022
Early age at hysterectomy ups type 2 diabetes risk
Data from a large French cohort study suggest that women who have a hysterectomy before 40-45 years of age may be at particular risk of subsequently developing type 2 diabetes.
A 20% increase in the risk for incident diabetes was found comparing women of all ages who had and had not had a hysterectomy (P = .0003).
This risk jumped to a 52% increase when only women below the age of 45 were considered (P < .0001) and was still 38% higher if only women under 40 years were analyzed (P = .005).
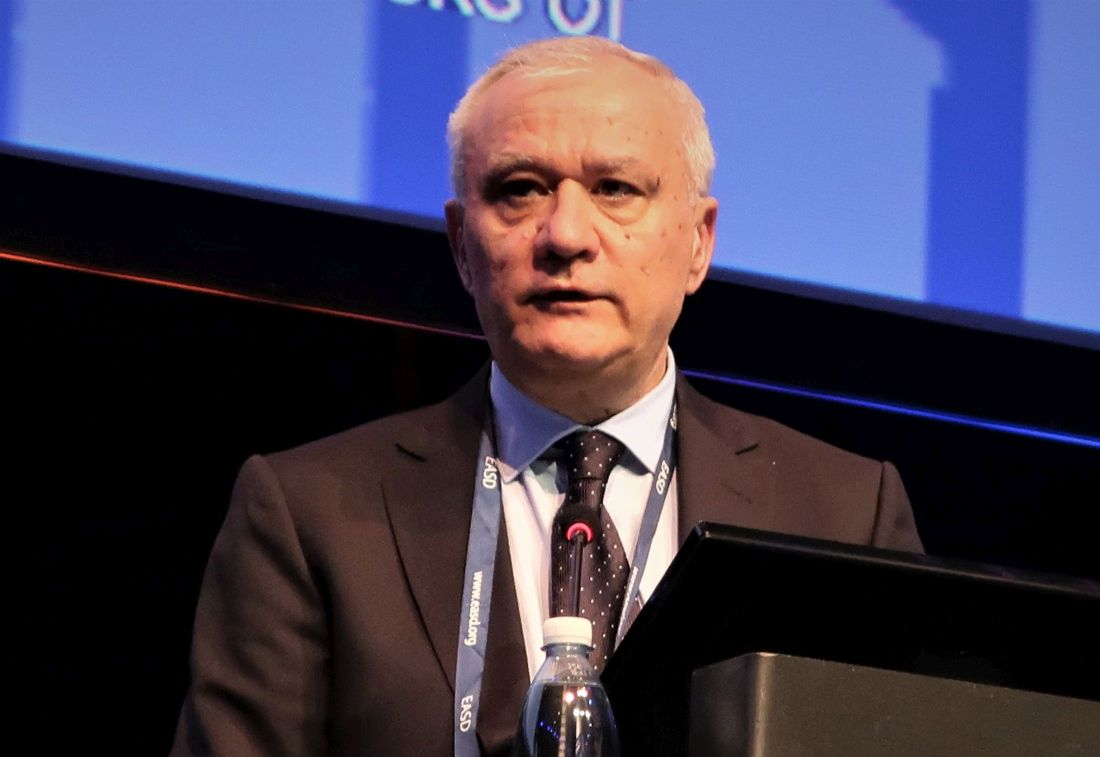
“Our findings clearly show that hysterectomy is a risk marker for diabetes,” Fabrice Bonnet, MD, PhD, of Centre Hospitalier Universitaire (CHU) de Rennes (France), said at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Importantly, this risk appears to occur “independently of any hormonal therapy, any reproductive factors, physical activity, and diet,” Dr. Bonnet added.
Findings challenged
“I would like to challenge your findings,” said Peter Nilsson, MD, PhD, a professor at Lund (Sweden) University, during the postpresentation discussion period.
“Could there be a detection bias?” queried Dr. Nilsson. “If you undergo surgery like this, there will be several postoperative visits to a physician and there’s a higher likelihood of somebody taking blood samples and detecting diabetes.
“So, if this is true, it could mean that postoperative controls of goiter or thyroid surgery would bring the same findings,” Dr. Nilsson suggested.
“It is an epidemiological cohort of woman followed for a long time,” Dr. Bonnet responded. “So of course, there probably was more blood testing than in the usual population, but we did not observe the association for another type of surgery and type 2 diabetes.”
Clarifying further, Dr. Bonnet said that they had looked at thyroid surgery but not any other types of abdominal surgery.
Assessing the risk of incident diabetes
Hysterectomy is a common surgery among women – more than 400,000 are estimated to be performed every year in the United States, and 80,000 in France, with a rising rate in developing countries, Dr. Bonnet said in an interview.
“We don’t know exactly why that is, but it could have long-term consequences in terms of metabolic effects and the incidence of diabetes,” he said.
Prior research has linked having a hysterectomy with an increased rate of hypertension and cardiovascular risk, and there have also been a few studies linking it to diabetes.
“Our aim was to analyze the relationship between the past history of hysterectomies and the risk of incident diabetes; and specifically, we assessed the influence of age,” Dr. Bonnet said.
To do so, data on more than 83,000 women who had participated in The French E3N Prospective Cohort Study (E3N) were obtained. This large epidemiologic study is the French component of the long-running EPIC study.
For inclusion in the analysis, women had to have no diabetes at baseline, to have had their uterus, ovaries, or both removed for benign gynecologic reasons, and to have had their surgeries performed before any diagnosis of diabetes had been made. A diagnosis of diabetes was identified through the women’s responses to self-report questionnaires and prescriptions for antidiabetic medications.
In all, 2,672 women were found to have developed diabetes during the 16-year follow-up period.
The hazard ratio for the risk of diabetes in women who had and had not had a hysterectomy was 1.30 (95% confidence interval, 1.17-1.43; P < .0001), taking age into account and stratifying for birth generation.
The association held, when there was adjustment for other factors such as smoking status, physical activity, history of diabetes, weight, and adherence to a Mediterranean diet (HR 1.27; 95% CI 1.02-1.05; P = .02).
And, after adjustment for age at menarche, menopausal status, age at which menopause was reached, oral contraceptive and hormone therapy use, and the number of pregnancies, the risk for type 2 diabetes was still apparent in those who had undergoing a hysterectomy (HR, 1.20; 95% CI, 1.09-1.33; P = .0003).
Risk increased with oophorectomy
“Women who had both hysterectomy with bilateral oophorectomy had the highest rates of incident diabetes, as compared to women without hysterectomy and no oophorectomy,” said Dr. Bonnet (HR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.11-1.42; P = .0003).
“This suggests preserving ovarian function is of importance,” he added. “Try to keep the ovaries in place, so just have hysterectomy alone,” he suggested might be the advice to fellow clinicians.
“So, identifying women at higher risk could be followed by a prevention program,” he suggested. “We do this for women who have gestational diabetes,” but for women who have had a hysterectomy, “we didn’t pay attention to this until now.”
No increased risk for endometriosis
While hysterectomy appears to up the risk for diabetes, having endometriosis does not. In a separate analysis of data from the E3N cohort, no effect was seen despite the association between endometriosis and other cardiometabolic risk factors.
The HR for incident type 2 diabetes comparing women with and without endometriosis was 10.06 in a fully adjusted statistical model (95% CI, 0.87-1.29). While there was an increase in the risk for diabetes if a woman had endometriosis and had also had a hysterectomy, this was not significant (HR, 1.22; 95% CI, 0.96-1.54).
The E3N study was sponsored by the French Institute for Health and Research. Dr. Bonnet and Dr. Nilsson had no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Data from a large French cohort study suggest that women who have a hysterectomy before 40-45 years of age may be at particular risk of subsequently developing type 2 diabetes.
A 20% increase in the risk for incident diabetes was found comparing women of all ages who had and had not had a hysterectomy (P = .0003).
This risk jumped to a 52% increase when only women below the age of 45 were considered (P < .0001) and was still 38% higher if only women under 40 years were analyzed (P = .005).
“Our findings clearly show that hysterectomy is a risk marker for diabetes,” Fabrice Bonnet, MD, PhD, of Centre Hospitalier Universitaire (CHU) de Rennes (France), said at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Importantly, this risk appears to occur “independently of any hormonal therapy, any reproductive factors, physical activity, and diet,” Dr. Bonnet added.
Findings challenged
“I would like to challenge your findings,” said Peter Nilsson, MD, PhD, a professor at Lund (Sweden) University, during the postpresentation discussion period.
“Could there be a detection bias?” queried Dr. Nilsson. “If you undergo surgery like this, there will be several postoperative visits to a physician and there’s a higher likelihood of somebody taking blood samples and detecting diabetes.
“So, if this is true, it could mean that postoperative controls of goiter or thyroid surgery would bring the same findings,” Dr. Nilsson suggested.
“It is an epidemiological cohort of woman followed for a long time,” Dr. Bonnet responded. “So of course, there probably was more blood testing than in the usual population, but we did not observe the association for another type of surgery and type 2 diabetes.”
Clarifying further, Dr. Bonnet said that they had looked at thyroid surgery but not any other types of abdominal surgery.
Assessing the risk of incident diabetes
Hysterectomy is a common surgery among women – more than 400,000 are estimated to be performed every year in the United States, and 80,000 in France, with a rising rate in developing countries, Dr. Bonnet said in an interview.
“We don’t know exactly why that is, but it could have long-term consequences in terms of metabolic effects and the incidence of diabetes,” he said.
Prior research has linked having a hysterectomy with an increased rate of hypertension and cardiovascular risk, and there have also been a few studies linking it to diabetes.
“Our aim was to analyze the relationship between the past history of hysterectomies and the risk of incident diabetes; and specifically, we assessed the influence of age,” Dr. Bonnet said.
To do so, data on more than 83,000 women who had participated in The French E3N Prospective Cohort Study (E3N) were obtained. This large epidemiologic study is the French component of the long-running EPIC study.
For inclusion in the analysis, women had to have no diabetes at baseline, to have had their uterus, ovaries, or both removed for benign gynecologic reasons, and to have had their surgeries performed before any diagnosis of diabetes had been made. A diagnosis of diabetes was identified through the women’s responses to self-report questionnaires and prescriptions for antidiabetic medications.
In all, 2,672 women were found to have developed diabetes during the 16-year follow-up period.
The hazard ratio for the risk of diabetes in women who had and had not had a hysterectomy was 1.30 (95% confidence interval, 1.17-1.43; P < .0001), taking age into account and stratifying for birth generation.
The association held, when there was adjustment for other factors such as smoking status, physical activity, history of diabetes, weight, and adherence to a Mediterranean diet (HR 1.27; 95% CI 1.02-1.05; P = .02).
And, after adjustment for age at menarche, menopausal status, age at which menopause was reached, oral contraceptive and hormone therapy use, and the number of pregnancies, the risk for type 2 diabetes was still apparent in those who had undergoing a hysterectomy (HR, 1.20; 95% CI, 1.09-1.33; P = .0003).
Risk increased with oophorectomy
“Women who had both hysterectomy with bilateral oophorectomy had the highest rates of incident diabetes, as compared to women without hysterectomy and no oophorectomy,” said Dr. Bonnet (HR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.11-1.42; P = .0003).
“This suggests preserving ovarian function is of importance,” he added. “Try to keep the ovaries in place, so just have hysterectomy alone,” he suggested might be the advice to fellow clinicians.
“So, identifying women at higher risk could be followed by a prevention program,” he suggested. “We do this for women who have gestational diabetes,” but for women who have had a hysterectomy, “we didn’t pay attention to this until now.”
No increased risk for endometriosis
While hysterectomy appears to up the risk for diabetes, having endometriosis does not. In a separate analysis of data from the E3N cohort, no effect was seen despite the association between endometriosis and other cardiometabolic risk factors.
The HR for incident type 2 diabetes comparing women with and without endometriosis was 10.06 in a fully adjusted statistical model (95% CI, 0.87-1.29). While there was an increase in the risk for diabetes if a woman had endometriosis and had also had a hysterectomy, this was not significant (HR, 1.22; 95% CI, 0.96-1.54).
The E3N study was sponsored by the French Institute for Health and Research. Dr. Bonnet and Dr. Nilsson had no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Data from a large French cohort study suggest that women who have a hysterectomy before 40-45 years of age may be at particular risk of subsequently developing type 2 diabetes.
A 20% increase in the risk for incident diabetes was found comparing women of all ages who had and had not had a hysterectomy (P = .0003).
This risk jumped to a 52% increase when only women below the age of 45 were considered (P < .0001) and was still 38% higher if only women under 40 years were analyzed (P = .005).
“Our findings clearly show that hysterectomy is a risk marker for diabetes,” Fabrice Bonnet, MD, PhD, of Centre Hospitalier Universitaire (CHU) de Rennes (France), said at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Importantly, this risk appears to occur “independently of any hormonal therapy, any reproductive factors, physical activity, and diet,” Dr. Bonnet added.
Findings challenged
“I would like to challenge your findings,” said Peter Nilsson, MD, PhD, a professor at Lund (Sweden) University, during the postpresentation discussion period.
“Could there be a detection bias?” queried Dr. Nilsson. “If you undergo surgery like this, there will be several postoperative visits to a physician and there’s a higher likelihood of somebody taking blood samples and detecting diabetes.
“So, if this is true, it could mean that postoperative controls of goiter or thyroid surgery would bring the same findings,” Dr. Nilsson suggested.
“It is an epidemiological cohort of woman followed for a long time,” Dr. Bonnet responded. “So of course, there probably was more blood testing than in the usual population, but we did not observe the association for another type of surgery and type 2 diabetes.”
Clarifying further, Dr. Bonnet said that they had looked at thyroid surgery but not any other types of abdominal surgery.
Assessing the risk of incident diabetes
Hysterectomy is a common surgery among women – more than 400,000 are estimated to be performed every year in the United States, and 80,000 in France, with a rising rate in developing countries, Dr. Bonnet said in an interview.
“We don’t know exactly why that is, but it could have long-term consequences in terms of metabolic effects and the incidence of diabetes,” he said.
Prior research has linked having a hysterectomy with an increased rate of hypertension and cardiovascular risk, and there have also been a few studies linking it to diabetes.
“Our aim was to analyze the relationship between the past history of hysterectomies and the risk of incident diabetes; and specifically, we assessed the influence of age,” Dr. Bonnet said.
To do so, data on more than 83,000 women who had participated in The French E3N Prospective Cohort Study (E3N) were obtained. This large epidemiologic study is the French component of the long-running EPIC study.
For inclusion in the analysis, women had to have no diabetes at baseline, to have had their uterus, ovaries, or both removed for benign gynecologic reasons, and to have had their surgeries performed before any diagnosis of diabetes had been made. A diagnosis of diabetes was identified through the women’s responses to self-report questionnaires and prescriptions for antidiabetic medications.
In all, 2,672 women were found to have developed diabetes during the 16-year follow-up period.
The hazard ratio for the risk of diabetes in women who had and had not had a hysterectomy was 1.30 (95% confidence interval, 1.17-1.43; P < .0001), taking age into account and stratifying for birth generation.
The association held, when there was adjustment for other factors such as smoking status, physical activity, history of diabetes, weight, and adherence to a Mediterranean diet (HR 1.27; 95% CI 1.02-1.05; P = .02).
And, after adjustment for age at menarche, menopausal status, age at which menopause was reached, oral contraceptive and hormone therapy use, and the number of pregnancies, the risk for type 2 diabetes was still apparent in those who had undergoing a hysterectomy (HR, 1.20; 95% CI, 1.09-1.33; P = .0003).
Risk increased with oophorectomy
“Women who had both hysterectomy with bilateral oophorectomy had the highest rates of incident diabetes, as compared to women without hysterectomy and no oophorectomy,” said Dr. Bonnet (HR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.11-1.42; P = .0003).
“This suggests preserving ovarian function is of importance,” he added. “Try to keep the ovaries in place, so just have hysterectomy alone,” he suggested might be the advice to fellow clinicians.
“So, identifying women at higher risk could be followed by a prevention program,” he suggested. “We do this for women who have gestational diabetes,” but for women who have had a hysterectomy, “we didn’t pay attention to this until now.”
No increased risk for endometriosis
While hysterectomy appears to up the risk for diabetes, having endometriosis does not. In a separate analysis of data from the E3N cohort, no effect was seen despite the association between endometriosis and other cardiometabolic risk factors.
The HR for incident type 2 diabetes comparing women with and without endometriosis was 10.06 in a fully adjusted statistical model (95% CI, 0.87-1.29). While there was an increase in the risk for diabetes if a woman had endometriosis and had also had a hysterectomy, this was not significant (HR, 1.22; 95% CI, 0.96-1.54).
The E3N study was sponsored by the French Institute for Health and Research. Dr. Bonnet and Dr. Nilsson had no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
FROM EASD 2022
Shift in child hospice care is a lifeline for parents seeking a measure of comfort and hope
POMONA, CALIF. – When you first meet 17-month-old Aaron Martinez, it’s not obvious that something is catastrophically wrong.
What you see is a beautiful little boy with smooth, lustrous skin, an abundance of glossy brown hair, and a disarming smile. What you hear are coos and cries that don’t immediately signal anything is horribly awry.
But his parents, Adriana Pinedo and Hector Martinez, know the truth painfully well.
Although Ms. Pinedo’s doctors and midwife had described the pregnancy as “perfect” for all 9 months, Aaron was born with most of his brain cells dead, the result of two strokes and a massive bleed he sustained while in utero.
Doctors aren’t sure what caused the anomalies that left Aaron with virtually no cognitive function or physical mobility. His voluminous hair hides a head whose circumference is too small for his age. He has epilepsy that triggers multiple seizures each day, and his smile is not always what it seems. “It could be a smile; it could be a seizure,” Ms. Pinedo said.
Shortly after Aaron was born, doctors told Ms. Pinedo, 34, and Mr. Martinez, 35, there was no hope and they should “let nature take its course.” They would learn months later that the doctors had not expected the boy to live more than 5 days. It was on Day 5 that his parents put him in home hospice care, an arrangement that has continued into his second year of life.
The family gets weekly visits from hospice nurses, therapists, social workers, and a chaplain in the cramped one-bedroom apartment they rent from the people who live in the main house on the same lot on a quiet residential street in this Inland Empire city.
One of the main criteria for hospice care, established by Medicare largely for seniors but also applied to children, is a diagnosis of 6 months or less to live. Yet over the course of 17 months, Aaron’s medical team has repeatedly recertified his hospice eligibility.
Under a provision of the 2010 Affordable Care Act, children enrolled in Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program are allowed, unlike adults, to be in hospice while continuing to receive curative or life-extending care. Commercial insurers are not required to cover this “concurrent care,” but many now do.
More than a decade since its inception, concurrent care is widely credited with improving the quality of life for many terminally ill children, easing stress on the family and, in some cases, sustaining hope for a cure. But the arrangement can contribute to a painful dilemma for parents like Ms. Pinedo and Mr. Martinez, who are torn between their fierce commitment to their son and the futility of knowing that his condition leaves him with no future worth hoping for.
“We could lose a life, but if he continues to live this way, we’ll lose three,” said Ms. Pinedo. “There’s no quality of life for him or for us.”
Aaron’s doctors now say he could conceivably live for years. His body hasn’t stopped growing since he was born. He’s in the 96th percentile for height for his age, and his weight is about average.
His parents have talked about “graduating” him from hospice. But he is never stable for long, and they welcome the visits from their hospice team. The seizures, sometimes 30 a day, are a persistent assault on his brain and, as he grows, the medications intended to control them must be changed or the doses recalibrated. He is at continual risk of gastrointestinal problems and potentially deadly fluid buildup in his lungs.
Ms. Pinedo, who works from home for a nonprofit public health organization, spends much of her time with Aaron, while Mr. Martinez works as a landscaper. She has chosen to live in the moment, she said, because otherwise her mind wanders to a future in which either “he could die – or he won’t, and I’ll end up changing the diapers of a 40-year-old man.” Either of those “are going to suck.”
While cancer is one of the major illnesses afflicting children in hospice, many others, like Aaron, have rare congenital defects, severe neurological impairments, or uncommon metabolic deficiencies.
“We have diseases that families tell us are 1 of 10 cases in the world,” said Glen Komatsu, MD, medical director of Torrance, Calif.–based TrinityKids Care, which provides home hospice services to Aaron and more than 70 other kids in Los Angeles and Orange counties.
In the years leading up to the ACA’s implementation, pediatric health advocates lobbied hard for the concurrent care provision. Without the possibility of life-extending care or hope for a cure, many parents refused to put their terminally ill kids in hospice, thinking it was tantamount to giving up on them. That meant the whole family missed out on the support hospice can provide, not just pain relief and comfort for the dying child, but emotional and spiritual care for parents and siblings under extreme duress.
TrinityKids Care, run by the large national Catholic health system Providence, doesn’t just send nurses, social workers, and chaplains into homes. For patients able to participate, and their siblings, it also offers art and science projects, exercise classes, movies, and music. During the pandemic, these activities have been conducted via Zoom, and volunteers deliver needed supplies to the children’s homes.
The ability to get treatments that prolong their lives is a major reason children in concurrent care are more likely than adults to outlive the 6-months-to-live diagnosis required for hospice.
“Concurrent care, by its very intention, very clearly is going to extend their lives, and by extending their lives they’re no longer going to be hospice-eligible if you use the 6-month life expectancy criteria,” said David Steinhorn, MD, a pediatric intensive care physician in Virginia, who has helped develop numerous children’s hospice programs across the United States.
Another factor is that kids, even sick ones, are simply more robust than many older people.
“Sick kids are often otherwise healthy, except for one organ,” said Debra Lotstein, MD, chief of the division of comfort and palliative care at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles. “They may have cancer in their body, but their hearts are good and their lungs are good, compared to a 90-year-old who at baseline is just not as resilient.”
All of Aaron Martinez’s vital organs, except for his brain, seem to be working. “There have been times when we’ve brought him in, and the nurse looks at the chart and looks at him, and she can’t believe it’s that child,” said Mr. Martinez.
When kids live past the 6-month life expectancy, they must be recertified to stay in hospice. In many cases, Dr. Steinhorn said, he is willing to recertify his pediatric patients indefinitely.
Even with doctors advocating for them, it’s not always easy for children to get into hospice care. Most hospices care primarily for adults and are reluctant to take kids.
“The hospice will say: ‘We don’t have the capacity to treat children. Our nurses aren’t trained. It’s different. We just can’t do it,’ ” said Lori Butterworth, cofounder of the Children’s Hospice and Palliative Care Coalition of California in Watsonville. “The other reason is not wanting to, because it’s existentially devastating and sad and hard.”
Finances also play a role. Home hospice care is paid at a per diem rate set by Medicare – slightly over $200 a day for the first 2 months, about $161 a day after that – and it is typically the same for kids and adults. Children, particularly those with rare conditions, often require more intensive and innovative care, so the per diem doesn’t stretch as far.
The concurrent care provision has made taking pediatric patients more viable for hospice organizations, Dr. Steinhorn and others said. Under the ACA, many of the expenses for certain medications and medical services can be shifted to the patient’s primary insurance, leaving hospices responsible for pain relief and comfort care.
Even so, the relatively small number of kids who die each year from protracted ailments hardly makes pediatric hospice an appealing line of business in an industry craving growth, especially one in which private equity investors are active and seeking a big payday.
In California, only 21 of 1,336 hospices reported having a specialized pediatric hospice program, and 59 said they served at least one patient under age 21, according to an analysis of 2020 state data by Cordt Kassner, CEO of Hospice Analytics in Colorado Springs.
Hospice providers that do cater to children often face a more basic challenge: Even with the possibility of concurrent care, many parents still equate hospice with acceptance of death. That was the case initially for Matt and Reese Sonnen, Los Angeles residents whose daughter, Layla, was born with a seizure disorder that had no name: Her brain had simply failed to develop in the womb, and an MRI showed “fluid taking up space where the brain wasn’t,” her mother said.
When Layla’s team first mentioned hospice, “I was in the car on my phone, and I almost crashed the car,” Mrs. Sonnen recalled. “The first thought that came to mind was: ‘It is just the end,’ but we felt she was nowhere near it, because she was strong, she was mighty. She was my little girl. She was going to get through this.”
About 3 months later, as Layla’s nervous system deteriorated, causing her to writhe in pain, her parents agreed to enroll her in hospice with TrinityKids Care. She died weeks later, not long after her second birthday. She was in her mother’s arms, with Mr. Sonnen close by.
“All of a sudden, Layla breathed out a big rush of air. The nurse looked at me and said: ‘That was her last breath.’ I was literally breathing in her last breath,” Mrs. Sonnen recounted. “I never wanted to breathe again, because now I felt I had her in my lungs. Don’t make me laugh, don’t make me exhale.”
Layla’s parents have no regrets about their decision to put her in hospice. “It was the absolute right decision, and in hindsight we should have done it sooner,” Mr. Sonnen said. “She was suffering, and we had blinders on.”
Ms. Pinedo said she is “infinitely grateful” for hospice, despite the heartache of Aaron’s condition. Sometimes the social worker will stop by, she said, just to say hello and drop off a latte, a small gesture that can feel very uplifting. “They’ve been our lifeline,” she said.
Ms. Pinedo talks about a friend of hers with a healthy baby, also named Aaron, who is pregnant with her second child. “All the stuff that was on our list, they’re living. And I love them dearly. But it’s almost hard to look, because it’s like looking at the stuff that you didn’t get. It’s like Christmas Day, staring through the window at the neighbor’s house, and you’re sitting there in the cold.”
Yet she seems palpably torn between that bleak remorse and the unconditional love parents feel toward their children. At one point, Ms. Pinedo interrupted herself midsentence and turned to her son, who was in Mr. Martinez’s arms: “Yes, Papi, you are so stinking cute, and you are still my dream come true.”
This story was produced by KHN, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
POMONA, CALIF. – When you first meet 17-month-old Aaron Martinez, it’s not obvious that something is catastrophically wrong.
What you see is a beautiful little boy with smooth, lustrous skin, an abundance of glossy brown hair, and a disarming smile. What you hear are coos and cries that don’t immediately signal anything is horribly awry.
But his parents, Adriana Pinedo and Hector Martinez, know the truth painfully well.
Although Ms. Pinedo’s doctors and midwife had described the pregnancy as “perfect” for all 9 months, Aaron was born with most of his brain cells dead, the result of two strokes and a massive bleed he sustained while in utero.
Doctors aren’t sure what caused the anomalies that left Aaron with virtually no cognitive function or physical mobility. His voluminous hair hides a head whose circumference is too small for his age. He has epilepsy that triggers multiple seizures each day, and his smile is not always what it seems. “It could be a smile; it could be a seizure,” Ms. Pinedo said.
Shortly after Aaron was born, doctors told Ms. Pinedo, 34, and Mr. Martinez, 35, there was no hope and they should “let nature take its course.” They would learn months later that the doctors had not expected the boy to live more than 5 days. It was on Day 5 that his parents put him in home hospice care, an arrangement that has continued into his second year of life.
The family gets weekly visits from hospice nurses, therapists, social workers, and a chaplain in the cramped one-bedroom apartment they rent from the people who live in the main house on the same lot on a quiet residential street in this Inland Empire city.
One of the main criteria for hospice care, established by Medicare largely for seniors but also applied to children, is a diagnosis of 6 months or less to live. Yet over the course of 17 months, Aaron’s medical team has repeatedly recertified his hospice eligibility.
Under a provision of the 2010 Affordable Care Act, children enrolled in Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program are allowed, unlike adults, to be in hospice while continuing to receive curative or life-extending care. Commercial insurers are not required to cover this “concurrent care,” but many now do.
More than a decade since its inception, concurrent care is widely credited with improving the quality of life for many terminally ill children, easing stress on the family and, in some cases, sustaining hope for a cure. But the arrangement can contribute to a painful dilemma for parents like Ms. Pinedo and Mr. Martinez, who are torn between their fierce commitment to their son and the futility of knowing that his condition leaves him with no future worth hoping for.
“We could lose a life, but if he continues to live this way, we’ll lose three,” said Ms. Pinedo. “There’s no quality of life for him or for us.”
Aaron’s doctors now say he could conceivably live for years. His body hasn’t stopped growing since he was born. He’s in the 96th percentile for height for his age, and his weight is about average.
His parents have talked about “graduating” him from hospice. But he is never stable for long, and they welcome the visits from their hospice team. The seizures, sometimes 30 a day, are a persistent assault on his brain and, as he grows, the medications intended to control them must be changed or the doses recalibrated. He is at continual risk of gastrointestinal problems and potentially deadly fluid buildup in his lungs.
Ms. Pinedo, who works from home for a nonprofit public health organization, spends much of her time with Aaron, while Mr. Martinez works as a landscaper. She has chosen to live in the moment, she said, because otherwise her mind wanders to a future in which either “he could die – or he won’t, and I’ll end up changing the diapers of a 40-year-old man.” Either of those “are going to suck.”
While cancer is one of the major illnesses afflicting children in hospice, many others, like Aaron, have rare congenital defects, severe neurological impairments, or uncommon metabolic deficiencies.
“We have diseases that families tell us are 1 of 10 cases in the world,” said Glen Komatsu, MD, medical director of Torrance, Calif.–based TrinityKids Care, which provides home hospice services to Aaron and more than 70 other kids in Los Angeles and Orange counties.
In the years leading up to the ACA’s implementation, pediatric health advocates lobbied hard for the concurrent care provision. Without the possibility of life-extending care or hope for a cure, many parents refused to put their terminally ill kids in hospice, thinking it was tantamount to giving up on them. That meant the whole family missed out on the support hospice can provide, not just pain relief and comfort for the dying child, but emotional and spiritual care for parents and siblings under extreme duress.
TrinityKids Care, run by the large national Catholic health system Providence, doesn’t just send nurses, social workers, and chaplains into homes. For patients able to participate, and their siblings, it also offers art and science projects, exercise classes, movies, and music. During the pandemic, these activities have been conducted via Zoom, and volunteers deliver needed supplies to the children’s homes.
The ability to get treatments that prolong their lives is a major reason children in concurrent care are more likely than adults to outlive the 6-months-to-live diagnosis required for hospice.
“Concurrent care, by its very intention, very clearly is going to extend their lives, and by extending their lives they’re no longer going to be hospice-eligible if you use the 6-month life expectancy criteria,” said David Steinhorn, MD, a pediatric intensive care physician in Virginia, who has helped develop numerous children’s hospice programs across the United States.
Another factor is that kids, even sick ones, are simply more robust than many older people.
“Sick kids are often otherwise healthy, except for one organ,” said Debra Lotstein, MD, chief of the division of comfort and palliative care at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles. “They may have cancer in their body, but their hearts are good and their lungs are good, compared to a 90-year-old who at baseline is just not as resilient.”
All of Aaron Martinez’s vital organs, except for his brain, seem to be working. “There have been times when we’ve brought him in, and the nurse looks at the chart and looks at him, and she can’t believe it’s that child,” said Mr. Martinez.
When kids live past the 6-month life expectancy, they must be recertified to stay in hospice. In many cases, Dr. Steinhorn said, he is willing to recertify his pediatric patients indefinitely.
Even with doctors advocating for them, it’s not always easy for children to get into hospice care. Most hospices care primarily for adults and are reluctant to take kids.
“The hospice will say: ‘We don’t have the capacity to treat children. Our nurses aren’t trained. It’s different. We just can’t do it,’ ” said Lori Butterworth, cofounder of the Children’s Hospice and Palliative Care Coalition of California in Watsonville. “The other reason is not wanting to, because it’s existentially devastating and sad and hard.”
Finances also play a role. Home hospice care is paid at a per diem rate set by Medicare – slightly over $200 a day for the first 2 months, about $161 a day after that – and it is typically the same for kids and adults. Children, particularly those with rare conditions, often require more intensive and innovative care, so the per diem doesn’t stretch as far.
The concurrent care provision has made taking pediatric patients more viable for hospice organizations, Dr. Steinhorn and others said. Under the ACA, many of the expenses for certain medications and medical services can be shifted to the patient’s primary insurance, leaving hospices responsible for pain relief and comfort care.
Even so, the relatively small number of kids who die each year from protracted ailments hardly makes pediatric hospice an appealing line of business in an industry craving growth, especially one in which private equity investors are active and seeking a big payday.
In California, only 21 of 1,336 hospices reported having a specialized pediatric hospice program, and 59 said they served at least one patient under age 21, according to an analysis of 2020 state data by Cordt Kassner, CEO of Hospice Analytics in Colorado Springs.
Hospice providers that do cater to children often face a more basic challenge: Even with the possibility of concurrent care, many parents still equate hospice with acceptance of death. That was the case initially for Matt and Reese Sonnen, Los Angeles residents whose daughter, Layla, was born with a seizure disorder that had no name: Her brain had simply failed to develop in the womb, and an MRI showed “fluid taking up space where the brain wasn’t,” her mother said.
When Layla’s team first mentioned hospice, “I was in the car on my phone, and I almost crashed the car,” Mrs. Sonnen recalled. “The first thought that came to mind was: ‘It is just the end,’ but we felt she was nowhere near it, because she was strong, she was mighty. She was my little girl. She was going to get through this.”
About 3 months later, as Layla’s nervous system deteriorated, causing her to writhe in pain, her parents agreed to enroll her in hospice with TrinityKids Care. She died weeks later, not long after her second birthday. She was in her mother’s arms, with Mr. Sonnen close by.
“All of a sudden, Layla breathed out a big rush of air. The nurse looked at me and said: ‘That was her last breath.’ I was literally breathing in her last breath,” Mrs. Sonnen recounted. “I never wanted to breathe again, because now I felt I had her in my lungs. Don’t make me laugh, don’t make me exhale.”
Layla’s parents have no regrets about their decision to put her in hospice. “It was the absolute right decision, and in hindsight we should have done it sooner,” Mr. Sonnen said. “She was suffering, and we had blinders on.”
Ms. Pinedo said she is “infinitely grateful” for hospice, despite the heartache of Aaron’s condition. Sometimes the social worker will stop by, she said, just to say hello and drop off a latte, a small gesture that can feel very uplifting. “They’ve been our lifeline,” she said.
Ms. Pinedo talks about a friend of hers with a healthy baby, also named Aaron, who is pregnant with her second child. “All the stuff that was on our list, they’re living. And I love them dearly. But it’s almost hard to look, because it’s like looking at the stuff that you didn’t get. It’s like Christmas Day, staring through the window at the neighbor’s house, and you’re sitting there in the cold.”
Yet she seems palpably torn between that bleak remorse and the unconditional love parents feel toward their children. At one point, Ms. Pinedo interrupted herself midsentence and turned to her son, who was in Mr. Martinez’s arms: “Yes, Papi, you are so stinking cute, and you are still my dream come true.”
This story was produced by KHN, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
POMONA, CALIF. – When you first meet 17-month-old Aaron Martinez, it’s not obvious that something is catastrophically wrong.
What you see is a beautiful little boy with smooth, lustrous skin, an abundance of glossy brown hair, and a disarming smile. What you hear are coos and cries that don’t immediately signal anything is horribly awry.
But his parents, Adriana Pinedo and Hector Martinez, know the truth painfully well.
Although Ms. Pinedo’s doctors and midwife had described the pregnancy as “perfect” for all 9 months, Aaron was born with most of his brain cells dead, the result of two strokes and a massive bleed he sustained while in utero.
Doctors aren’t sure what caused the anomalies that left Aaron with virtually no cognitive function or physical mobility. His voluminous hair hides a head whose circumference is too small for his age. He has epilepsy that triggers multiple seizures each day, and his smile is not always what it seems. “It could be a smile; it could be a seizure,” Ms. Pinedo said.
Shortly after Aaron was born, doctors told Ms. Pinedo, 34, and Mr. Martinez, 35, there was no hope and they should “let nature take its course.” They would learn months later that the doctors had not expected the boy to live more than 5 days. It was on Day 5 that his parents put him in home hospice care, an arrangement that has continued into his second year of life.
The family gets weekly visits from hospice nurses, therapists, social workers, and a chaplain in the cramped one-bedroom apartment they rent from the people who live in the main house on the same lot on a quiet residential street in this Inland Empire city.
One of the main criteria for hospice care, established by Medicare largely for seniors but also applied to children, is a diagnosis of 6 months or less to live. Yet over the course of 17 months, Aaron’s medical team has repeatedly recertified his hospice eligibility.
Under a provision of the 2010 Affordable Care Act, children enrolled in Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program are allowed, unlike adults, to be in hospice while continuing to receive curative or life-extending care. Commercial insurers are not required to cover this “concurrent care,” but many now do.
More than a decade since its inception, concurrent care is widely credited with improving the quality of life for many terminally ill children, easing stress on the family and, in some cases, sustaining hope for a cure. But the arrangement can contribute to a painful dilemma for parents like Ms. Pinedo and Mr. Martinez, who are torn between their fierce commitment to their son and the futility of knowing that his condition leaves him with no future worth hoping for.
“We could lose a life, but if he continues to live this way, we’ll lose three,” said Ms. Pinedo. “There’s no quality of life for him or for us.”
Aaron’s doctors now say he could conceivably live for years. His body hasn’t stopped growing since he was born. He’s in the 96th percentile for height for his age, and his weight is about average.
His parents have talked about “graduating” him from hospice. But he is never stable for long, and they welcome the visits from their hospice team. The seizures, sometimes 30 a day, are a persistent assault on his brain and, as he grows, the medications intended to control them must be changed or the doses recalibrated. He is at continual risk of gastrointestinal problems and potentially deadly fluid buildup in his lungs.
Ms. Pinedo, who works from home for a nonprofit public health organization, spends much of her time with Aaron, while Mr. Martinez works as a landscaper. She has chosen to live in the moment, she said, because otherwise her mind wanders to a future in which either “he could die – or he won’t, and I’ll end up changing the diapers of a 40-year-old man.” Either of those “are going to suck.”
While cancer is one of the major illnesses afflicting children in hospice, many others, like Aaron, have rare congenital defects, severe neurological impairments, or uncommon metabolic deficiencies.
“We have diseases that families tell us are 1 of 10 cases in the world,” said Glen Komatsu, MD, medical director of Torrance, Calif.–based TrinityKids Care, which provides home hospice services to Aaron and more than 70 other kids in Los Angeles and Orange counties.
In the years leading up to the ACA’s implementation, pediatric health advocates lobbied hard for the concurrent care provision. Without the possibility of life-extending care or hope for a cure, many parents refused to put their terminally ill kids in hospice, thinking it was tantamount to giving up on them. That meant the whole family missed out on the support hospice can provide, not just pain relief and comfort for the dying child, but emotional and spiritual care for parents and siblings under extreme duress.
TrinityKids Care, run by the large national Catholic health system Providence, doesn’t just send nurses, social workers, and chaplains into homes. For patients able to participate, and their siblings, it also offers art and science projects, exercise classes, movies, and music. During the pandemic, these activities have been conducted via Zoom, and volunteers deliver needed supplies to the children’s homes.
The ability to get treatments that prolong their lives is a major reason children in concurrent care are more likely than adults to outlive the 6-months-to-live diagnosis required for hospice.
“Concurrent care, by its very intention, very clearly is going to extend their lives, and by extending their lives they’re no longer going to be hospice-eligible if you use the 6-month life expectancy criteria,” said David Steinhorn, MD, a pediatric intensive care physician in Virginia, who has helped develop numerous children’s hospice programs across the United States.
Another factor is that kids, even sick ones, are simply more robust than many older people.
“Sick kids are often otherwise healthy, except for one organ,” said Debra Lotstein, MD, chief of the division of comfort and palliative care at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles. “They may have cancer in their body, but their hearts are good and their lungs are good, compared to a 90-year-old who at baseline is just not as resilient.”
All of Aaron Martinez’s vital organs, except for his brain, seem to be working. “There have been times when we’ve brought him in, and the nurse looks at the chart and looks at him, and she can’t believe it’s that child,” said Mr. Martinez.
When kids live past the 6-month life expectancy, they must be recertified to stay in hospice. In many cases, Dr. Steinhorn said, he is willing to recertify his pediatric patients indefinitely.
Even with doctors advocating for them, it’s not always easy for children to get into hospice care. Most hospices care primarily for adults and are reluctant to take kids.
“The hospice will say: ‘We don’t have the capacity to treat children. Our nurses aren’t trained. It’s different. We just can’t do it,’ ” said Lori Butterworth, cofounder of the Children’s Hospice and Palliative Care Coalition of California in Watsonville. “The other reason is not wanting to, because it’s existentially devastating and sad and hard.”
Finances also play a role. Home hospice care is paid at a per diem rate set by Medicare – slightly over $200 a day for the first 2 months, about $161 a day after that – and it is typically the same for kids and adults. Children, particularly those with rare conditions, often require more intensive and innovative care, so the per diem doesn’t stretch as far.
The concurrent care provision has made taking pediatric patients more viable for hospice organizations, Dr. Steinhorn and others said. Under the ACA, many of the expenses for certain medications and medical services can be shifted to the patient’s primary insurance, leaving hospices responsible for pain relief and comfort care.
Even so, the relatively small number of kids who die each year from protracted ailments hardly makes pediatric hospice an appealing line of business in an industry craving growth, especially one in which private equity investors are active and seeking a big payday.
In California, only 21 of 1,336 hospices reported having a specialized pediatric hospice program, and 59 said they served at least one patient under age 21, according to an analysis of 2020 state data by Cordt Kassner, CEO of Hospice Analytics in Colorado Springs.
Hospice providers that do cater to children often face a more basic challenge: Even with the possibility of concurrent care, many parents still equate hospice with acceptance of death. That was the case initially for Matt and Reese Sonnen, Los Angeles residents whose daughter, Layla, was born with a seizure disorder that had no name: Her brain had simply failed to develop in the womb, and an MRI showed “fluid taking up space where the brain wasn’t,” her mother said.
When Layla’s team first mentioned hospice, “I was in the car on my phone, and I almost crashed the car,” Mrs. Sonnen recalled. “The first thought that came to mind was: ‘It is just the end,’ but we felt she was nowhere near it, because she was strong, she was mighty. She was my little girl. She was going to get through this.”
About 3 months later, as Layla’s nervous system deteriorated, causing her to writhe in pain, her parents agreed to enroll her in hospice with TrinityKids Care. She died weeks later, not long after her second birthday. She was in her mother’s arms, with Mr. Sonnen close by.
“All of a sudden, Layla breathed out a big rush of air. The nurse looked at me and said: ‘That was her last breath.’ I was literally breathing in her last breath,” Mrs. Sonnen recounted. “I never wanted to breathe again, because now I felt I had her in my lungs. Don’t make me laugh, don’t make me exhale.”
Layla’s parents have no regrets about their decision to put her in hospice. “It was the absolute right decision, and in hindsight we should have done it sooner,” Mr. Sonnen said. “She was suffering, and we had blinders on.”
Ms. Pinedo said she is “infinitely grateful” for hospice, despite the heartache of Aaron’s condition. Sometimes the social worker will stop by, she said, just to say hello and drop off a latte, a small gesture that can feel very uplifting. “They’ve been our lifeline,” she said.
Ms. Pinedo talks about a friend of hers with a healthy baby, also named Aaron, who is pregnant with her second child. “All the stuff that was on our list, they’re living. And I love them dearly. But it’s almost hard to look, because it’s like looking at the stuff that you didn’t get. It’s like Christmas Day, staring through the window at the neighbor’s house, and you’re sitting there in the cold.”
Yet she seems palpably torn between that bleak remorse and the unconditional love parents feel toward their children. At one point, Ms. Pinedo interrupted herself midsentence and turned to her son, who was in Mr. Martinez’s arms: “Yes, Papi, you are so stinking cute, and you are still my dream come true.”
This story was produced by KHN, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Genetic tests create treatment opportunities and confusion for breast cancer patients
The past decade has witnessed a rapid expansion of genetic tests, including new instruments to inform patients who have been diagnosed with breast cancer about the risk of recurrence and to guide their treatment.
Patients are sometimes left paying out-of-pocket for exams that are not yet the standard of care, and even the most up-to-date oncologists may be uncertain how to incorporate the flood of new information into what used to be standard treatment protocols.
A quarter-century ago, Myriad Genetics introduced the first breast cancer genetic test for BRCA mutations, two genes associated with a substantially elevated risk of getting breast cancer, opening the door to a new era in genetic testing. BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations account for as many as half of all hereditary breast cancers, and people with a problematic mutation on one of those genes have a 45%-72% chance of developing breast cancer during their lifetimes. They may also be at higher risk for ovarian and other cancers than people without harmful BRCA mutations.
But the clinical significance is murkier for many other genetic tests.
Testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes used to cost thousands of dollars. Now, for a fraction of that, doctors can order multigene test panels from commercial labs that look for mutations in dozens of genes. Some direct-to-consumer companies offer screening panels for a few hundred dollars, though their reliability varies.
When Jen Carbary was diagnosed with breast cancer in 2017 at age 44, genetic testing identified a mutation in a gene called PALB2 that significantly increases the risk of developing breast cancer. Guidelines suggest that breast cancer patients with a PALB2 mutation, much like those with BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations, consider having a mastectomy to reduce the chance of a breast cancer recurrence.
“I wish genetic testing was the standard of care,” said Ms. Carbary, who owed nothing for the test because her insurer covered the cost.
Ms. Carbary, who lives in Sterling Heights, Mich., said the test results affirmed the decision she had already made to have a double mastectomy and provided important information for family members, including her 21-year-old daughter and 18-year-old son, who will likely be tested in their mid-20s or early 30s.
But some breast cancer experts are concerned that widespread testing may also identify genetic mutations whose impact is unclear, creating anxiety and leading to further testing and to treatment of questionable value that could raise costs for the health care system.
It can also confuse patients.
“It happens a lot, that patients find their way to us after getting confusing results elsewhere,” said Mark Robson, MD, chief of the breast medicine service at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York. Robson said the cancer center has a clinical genetics service, staffed by doctors and genetic counselors, that helps people make decisions about how to manage genetic testing results.
For people diagnosed with breast cancer, many professional groups, including the influential National Comprehensive Cancer Network, recommend limiting testing to certain people, including those with high-risk factors, such as a family history of breast cancer; those who are 45 or younger when they’re diagnosed; and those with Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry.
But in 2019, the American Society of Breast Surgeons recommended a different approach: Offer genetic testing to all patients who are diagnosed with or have a personal history of breast cancer. The recommendation was controversial.
“The NCCN guidelines [cover] most of the women who needed testing, but we wanted to get them all,” said Eric Manahan, MD, a general surgeon in Dalton, Georgia, and a member of the surgeons group’s board of directors.
Mutations on other genes that are associated with breast cancer are much less common than BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations and generally don’t increase the risk of developing breast cancer as much. The cancer-causing impact of these genes may be less clear than that of the BRCA genes, which have been tested for since the mid-1990s.
And the appropriate response to the less common mutations – whether to consider a risk-reducing mastectomy or stepped-up screening – is often unclear.
“Things get sloppier and sloppier when you look at other genes,” said Steven Katz, MD, MPH, a professor of medicine and health management and policy at the University of Michigan. “The risks tend to be lower for different cancers, and less certain and more variable. You might walk away wondering: ‘Why’d I have to know that?’ ”
After people are diagnosed with breast cancer, genetic testing can help inform their decisions about the types of surgery to pursue – for example, a high risk of recurrence or a new breast cancer might persuade some to opt for more extensive surgery, such as a double mastectomy. Testing can also provide important information to family members about their potential cancer risk.
(This type of “germline” genetic testing, as it’s called, looks at mutations in the genes that people inherit from their parents. It is different from genomic tumor tests that look at specific genes or proteins in the cancer cells and can help doctors understand the rate at which the cancer cells are dividing, for example, and the likelihood of a cancer recurrence.)
Increasingly, germline genetic testing can also help guide other treatment decisions. Some patients with metastatic breast cancer who have BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations may be good candidates for poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors, cancer drugs that target tumors with mutations in those genes.
But genetic testing that uncovers inherited mutations in many other genes yields less clearly actionable information, even though positive results may alarm people.
At Memorial Sloan Kettering, cancer specialists focus on “therapeutic actionability,” said Dr. Robson. Will testing help someone decide whether she should get a double mastectomy or provide other important guidance? “A policy of testing everyone will identify very few additional BRCA breast mutations but will cost a lot.”
As a result, doctors are debating how best to deploy and incorporate new genetic knowledge. Insurers are trying to figure out which to pay for.
There is both underuse of tests that science says are relevant and overuse of tests that experts say provide information that can’t be interpreted with any scientific certainty.
The result may be confusion for patients newly diagnosed with breast cancer as they confront the expense of genetic tests and sometimes little guidance on the proper treatment.
Some doctors say the first step is to make sure that the small group of people who would clearly benefit are getting the genetic tests whose meaning is clearly understood. Only 15% of breast cancer patients who met select NCCN testing guidelines for inherited cancer received genetic testing, according to a 2017 study that examined data from a national household health survey between 2005 and 2015.
“I would argue that our focus needs to be on the people who are at high risk for breast cancer that aren’t even identified yet,” said Tuya Pal, MD, associate director for cancer health disparities at Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center and vice chair of the NCCN guidelines panel for genetic/familial high-risk assessment of breast, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers.
Patients may fall through the cracks because no one tells them they should be tested. In one analysis, 56% of high-risk breast cancer patients who didn’t get genetic testing said their doctors didn’t recommend it.
Even if doctors recommend genetic testing, they may lack the expertise to determine which tests people need and how to interpret the results. That’s the role of genetic counselors, but their ranks are stretched thin.
The consequences can be serious. In a study of 666 breast cancer patients who received genetic testing, half of those at average risk for inherited cancer got double mastectomies based on test results that found “variants of uncertain significance,” which aren’t clinically actionable. As many as half of surgeons reported managing such patients the same way as those with cancer-causing mutations.
“The bulk of our research would say that there is still room for improvement in terms of clinicians getting the understanding they need,” said Allison Kurian, MD, director of the women’s clinical cancer genetics program at Stanford (Calif.) University and a coauthor of the study.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
The past decade has witnessed a rapid expansion of genetic tests, including new instruments to inform patients who have been diagnosed with breast cancer about the risk of recurrence and to guide their treatment.
Patients are sometimes left paying out-of-pocket for exams that are not yet the standard of care, and even the most up-to-date oncologists may be uncertain how to incorporate the flood of new information into what used to be standard treatment protocols.
A quarter-century ago, Myriad Genetics introduced the first breast cancer genetic test for BRCA mutations, two genes associated with a substantially elevated risk of getting breast cancer, opening the door to a new era in genetic testing. BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations account for as many as half of all hereditary breast cancers, and people with a problematic mutation on one of those genes have a 45%-72% chance of developing breast cancer during their lifetimes. They may also be at higher risk for ovarian and other cancers than people without harmful BRCA mutations.
But the clinical significance is murkier for many other genetic tests.
Testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes used to cost thousands of dollars. Now, for a fraction of that, doctors can order multigene test panels from commercial labs that look for mutations in dozens of genes. Some direct-to-consumer companies offer screening panels for a few hundred dollars, though their reliability varies.
When Jen Carbary was diagnosed with breast cancer in 2017 at age 44, genetic testing identified a mutation in a gene called PALB2 that significantly increases the risk of developing breast cancer. Guidelines suggest that breast cancer patients with a PALB2 mutation, much like those with BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations, consider having a mastectomy to reduce the chance of a breast cancer recurrence.
“I wish genetic testing was the standard of care,” said Ms. Carbary, who owed nothing for the test because her insurer covered the cost.
Ms. Carbary, who lives in Sterling Heights, Mich., said the test results affirmed the decision she had already made to have a double mastectomy and provided important information for family members, including her 21-year-old daughter and 18-year-old son, who will likely be tested in their mid-20s or early 30s.
But some breast cancer experts are concerned that widespread testing may also identify genetic mutations whose impact is unclear, creating anxiety and leading to further testing and to treatment of questionable value that could raise costs for the health care system.
It can also confuse patients.
“It happens a lot, that patients find their way to us after getting confusing results elsewhere,” said Mark Robson, MD, chief of the breast medicine service at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York. Robson said the cancer center has a clinical genetics service, staffed by doctors and genetic counselors, that helps people make decisions about how to manage genetic testing results.
For people diagnosed with breast cancer, many professional groups, including the influential National Comprehensive Cancer Network, recommend limiting testing to certain people, including those with high-risk factors, such as a family history of breast cancer; those who are 45 or younger when they’re diagnosed; and those with Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry.
But in 2019, the American Society of Breast Surgeons recommended a different approach: Offer genetic testing to all patients who are diagnosed with or have a personal history of breast cancer. The recommendation was controversial.
“The NCCN guidelines [cover] most of the women who needed testing, but we wanted to get them all,” said Eric Manahan, MD, a general surgeon in Dalton, Georgia, and a member of the surgeons group’s board of directors.
Mutations on other genes that are associated with breast cancer are much less common than BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations and generally don’t increase the risk of developing breast cancer as much. The cancer-causing impact of these genes may be less clear than that of the BRCA genes, which have been tested for since the mid-1990s.
And the appropriate response to the less common mutations – whether to consider a risk-reducing mastectomy or stepped-up screening – is often unclear.
“Things get sloppier and sloppier when you look at other genes,” said Steven Katz, MD, MPH, a professor of medicine and health management and policy at the University of Michigan. “The risks tend to be lower for different cancers, and less certain and more variable. You might walk away wondering: ‘Why’d I have to know that?’ ”
After people are diagnosed with breast cancer, genetic testing can help inform their decisions about the types of surgery to pursue – for example, a high risk of recurrence or a new breast cancer might persuade some to opt for more extensive surgery, such as a double mastectomy. Testing can also provide important information to family members about their potential cancer risk.
(This type of “germline” genetic testing, as it’s called, looks at mutations in the genes that people inherit from their parents. It is different from genomic tumor tests that look at specific genes or proteins in the cancer cells and can help doctors understand the rate at which the cancer cells are dividing, for example, and the likelihood of a cancer recurrence.)
Increasingly, germline genetic testing can also help guide other treatment decisions. Some patients with metastatic breast cancer who have BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations may be good candidates for poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors, cancer drugs that target tumors with mutations in those genes.
But genetic testing that uncovers inherited mutations in many other genes yields less clearly actionable information, even though positive results may alarm people.
At Memorial Sloan Kettering, cancer specialists focus on “therapeutic actionability,” said Dr. Robson. Will testing help someone decide whether she should get a double mastectomy or provide other important guidance? “A policy of testing everyone will identify very few additional BRCA breast mutations but will cost a lot.”
As a result, doctors are debating how best to deploy and incorporate new genetic knowledge. Insurers are trying to figure out which to pay for.
There is both underuse of tests that science says are relevant and overuse of tests that experts say provide information that can’t be interpreted with any scientific certainty.
The result may be confusion for patients newly diagnosed with breast cancer as they confront the expense of genetic tests and sometimes little guidance on the proper treatment.
Some doctors say the first step is to make sure that the small group of people who would clearly benefit are getting the genetic tests whose meaning is clearly understood. Only 15% of breast cancer patients who met select NCCN testing guidelines for inherited cancer received genetic testing, according to a 2017 study that examined data from a national household health survey between 2005 and 2015.
“I would argue that our focus needs to be on the people who are at high risk for breast cancer that aren’t even identified yet,” said Tuya Pal, MD, associate director for cancer health disparities at Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center and vice chair of the NCCN guidelines panel for genetic/familial high-risk assessment of breast, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers.
Patients may fall through the cracks because no one tells them they should be tested. In one analysis, 56% of high-risk breast cancer patients who didn’t get genetic testing said their doctors didn’t recommend it.
Even if doctors recommend genetic testing, they may lack the expertise to determine which tests people need and how to interpret the results. That’s the role of genetic counselors, but their ranks are stretched thin.
The consequences can be serious. In a study of 666 breast cancer patients who received genetic testing, half of those at average risk for inherited cancer got double mastectomies based on test results that found “variants of uncertain significance,” which aren’t clinically actionable. As many as half of surgeons reported managing such patients the same way as those with cancer-causing mutations.
“The bulk of our research would say that there is still room for improvement in terms of clinicians getting the understanding they need,” said Allison Kurian, MD, director of the women’s clinical cancer genetics program at Stanford (Calif.) University and a coauthor of the study.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
The past decade has witnessed a rapid expansion of genetic tests, including new instruments to inform patients who have been diagnosed with breast cancer about the risk of recurrence and to guide their treatment.
Patients are sometimes left paying out-of-pocket for exams that are not yet the standard of care, and even the most up-to-date oncologists may be uncertain how to incorporate the flood of new information into what used to be standard treatment protocols.
A quarter-century ago, Myriad Genetics introduced the first breast cancer genetic test for BRCA mutations, two genes associated with a substantially elevated risk of getting breast cancer, opening the door to a new era in genetic testing. BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations account for as many as half of all hereditary breast cancers, and people with a problematic mutation on one of those genes have a 45%-72% chance of developing breast cancer during their lifetimes. They may also be at higher risk for ovarian and other cancers than people without harmful BRCA mutations.
But the clinical significance is murkier for many other genetic tests.
Testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes used to cost thousands of dollars. Now, for a fraction of that, doctors can order multigene test panels from commercial labs that look for mutations in dozens of genes. Some direct-to-consumer companies offer screening panels for a few hundred dollars, though their reliability varies.
When Jen Carbary was diagnosed with breast cancer in 2017 at age 44, genetic testing identified a mutation in a gene called PALB2 that significantly increases the risk of developing breast cancer. Guidelines suggest that breast cancer patients with a PALB2 mutation, much like those with BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations, consider having a mastectomy to reduce the chance of a breast cancer recurrence.
“I wish genetic testing was the standard of care,” said Ms. Carbary, who owed nothing for the test because her insurer covered the cost.
Ms. Carbary, who lives in Sterling Heights, Mich., said the test results affirmed the decision she had already made to have a double mastectomy and provided important information for family members, including her 21-year-old daughter and 18-year-old son, who will likely be tested in their mid-20s or early 30s.
But some breast cancer experts are concerned that widespread testing may also identify genetic mutations whose impact is unclear, creating anxiety and leading to further testing and to treatment of questionable value that could raise costs for the health care system.
It can also confuse patients.
“It happens a lot, that patients find their way to us after getting confusing results elsewhere,” said Mark Robson, MD, chief of the breast medicine service at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York. Robson said the cancer center has a clinical genetics service, staffed by doctors and genetic counselors, that helps people make decisions about how to manage genetic testing results.
For people diagnosed with breast cancer, many professional groups, including the influential National Comprehensive Cancer Network, recommend limiting testing to certain people, including those with high-risk factors, such as a family history of breast cancer; those who are 45 or younger when they’re diagnosed; and those with Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry.
But in 2019, the American Society of Breast Surgeons recommended a different approach: Offer genetic testing to all patients who are diagnosed with or have a personal history of breast cancer. The recommendation was controversial.
“The NCCN guidelines [cover] most of the women who needed testing, but we wanted to get them all,” said Eric Manahan, MD, a general surgeon in Dalton, Georgia, and a member of the surgeons group’s board of directors.
Mutations on other genes that are associated with breast cancer are much less common than BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations and generally don’t increase the risk of developing breast cancer as much. The cancer-causing impact of these genes may be less clear than that of the BRCA genes, which have been tested for since the mid-1990s.
And the appropriate response to the less common mutations – whether to consider a risk-reducing mastectomy or stepped-up screening – is often unclear.
“Things get sloppier and sloppier when you look at other genes,” said Steven Katz, MD, MPH, a professor of medicine and health management and policy at the University of Michigan. “The risks tend to be lower for different cancers, and less certain and more variable. You might walk away wondering: ‘Why’d I have to know that?’ ”
After people are diagnosed with breast cancer, genetic testing can help inform their decisions about the types of surgery to pursue – for example, a high risk of recurrence or a new breast cancer might persuade some to opt for more extensive surgery, such as a double mastectomy. Testing can also provide important information to family members about their potential cancer risk.
(This type of “germline” genetic testing, as it’s called, looks at mutations in the genes that people inherit from their parents. It is different from genomic tumor tests that look at specific genes or proteins in the cancer cells and can help doctors understand the rate at which the cancer cells are dividing, for example, and the likelihood of a cancer recurrence.)
Increasingly, germline genetic testing can also help guide other treatment decisions. Some patients with metastatic breast cancer who have BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations may be good candidates for poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors, cancer drugs that target tumors with mutations in those genes.
But genetic testing that uncovers inherited mutations in many other genes yields less clearly actionable information, even though positive results may alarm people.
At Memorial Sloan Kettering, cancer specialists focus on “therapeutic actionability,” said Dr. Robson. Will testing help someone decide whether she should get a double mastectomy or provide other important guidance? “A policy of testing everyone will identify very few additional BRCA breast mutations but will cost a lot.”
As a result, doctors are debating how best to deploy and incorporate new genetic knowledge. Insurers are trying to figure out which to pay for.
There is both underuse of tests that science says are relevant and overuse of tests that experts say provide information that can’t be interpreted with any scientific certainty.
The result may be confusion for patients newly diagnosed with breast cancer as they confront the expense of genetic tests and sometimes little guidance on the proper treatment.
Some doctors say the first step is to make sure that the small group of people who would clearly benefit are getting the genetic tests whose meaning is clearly understood. Only 15% of breast cancer patients who met select NCCN testing guidelines for inherited cancer received genetic testing, according to a 2017 study that examined data from a national household health survey between 2005 and 2015.
“I would argue that our focus needs to be on the people who are at high risk for breast cancer that aren’t even identified yet,” said Tuya Pal, MD, associate director for cancer health disparities at Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center and vice chair of the NCCN guidelines panel for genetic/familial high-risk assessment of breast, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers.
Patients may fall through the cracks because no one tells them they should be tested. In one analysis, 56% of high-risk breast cancer patients who didn’t get genetic testing said their doctors didn’t recommend it.
Even if doctors recommend genetic testing, they may lack the expertise to determine which tests people need and how to interpret the results. That’s the role of genetic counselors, but their ranks are stretched thin.
The consequences can be serious. In a study of 666 breast cancer patients who received genetic testing, half of those at average risk for inherited cancer got double mastectomies based on test results that found “variants of uncertain significance,” which aren’t clinically actionable. As many as half of surgeons reported managing such patients the same way as those with cancer-causing mutations.
“The bulk of our research would say that there is still room for improvement in terms of clinicians getting the understanding they need,” said Allison Kurian, MD, director of the women’s clinical cancer genetics program at Stanford (Calif.) University and a coauthor of the study.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Mothers’ diabetes linked to ADHD in their children
Children born to women who develop diabetes either before or during their pregnancy could be at risk for developing attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, data from a large multinational cohort study appear to show.
Considering more than 4.5 million mother-child pairs, it was found that children whose mothers had diabetes around the time of their pregnancy were 16% more likely to have ADHD diagnosed than were those whose mothers did not.
An increased risk was seen regardless of the type of diabetes, and regardless of whether or not the diabetes was present before or appeared during the pregnancy.
“We found a small increased risk of ADHD in children born to mothers with diabetes, including pregestational diabetes and gestational diabetes,” Carolyn Cesta, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Dr. Cesta, a postdoctoral researcher in the Centre for Pharmacoepidemiology at the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm noted that the effect sizes seen were lower than had been reported previously.
“This may be because we adjusted for a large number of covariates, including maternal ADHD and psychiatric disorders,” Dr. Cesta said.
ADHD and diabetes
“Previous studies have reported an increase in the risk of ADHD in children born to mothers with diabetes,” explained Dr. Cesta.
However, “these studies have been limited by the use of self-reported data, small sample sizes, lack of adjustment for important confounders, and they’re often limited to [White] populations,” she added. “There’s a lot of heterogeneity between these studies,” she said.
To try to iron out the differences seen in the prior studies, Dr. Cesta and associates looked at data from several databases based in Hong Kong (Clinical Data Analysis and Reporting System), four Nordic countries (Population Health Registers for Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden), and Taiwan (National Health Insurance Database).
To create the matched mother-child pairs, the databases were searched to find women who had children born between 2001 and 2018, and who had follow-up data available up to 2020 on not only their diabetes status and child’s ADHD status, but also other parameters, such as other maternal diagnoses, maternal medications, and a host of sociodemographic factors.
More than 24 potentially confounding or covariates were considered in the analysis, which used Cox proportional hazard regression modeling and propensity score analysis to calculate hazard ratios with 95% confidence intervals.
“We looked at whether [mothers] had a diagnosis of ADHD themselves, or other psychiatric disorders, because there is high heritability for these disorders,” Dr. Cesta said, indicating that all bases had endeavored to be covered.
Main findings
Results showed some differences in the prevalence of diabetes and ADHD between the three cohorts used in the analysis. The prevalence of any maternal diabetes ranged from 8.8% in the Hong Kong cohort to 3.3% in the Taiwan cohort, with a prevalence of 6.8% for the Nordic cohort.
Rates of pregestational diabetes were lowest in the Taiwan and Hong Kong cohorts, at 0.2% and 0.5%, respectively, and 2.2% in the Nordic cohort. Gestational diabetes rates were a respective 3.1%, 7.8%, and 4.6%.
The highest rate of ADHD in children was seen in the Taiwan cohort, at 9.6%, followed by 4.2% for the Hong Kong cohort, and 2.6% for the Nordic cohort.
The hazard ratio for having childhood ADHD was 1.16 when comparing any maternal diabetes to no maternal diabetes, 1.40 comparing mothers with and without pregestational diabetes, and a respective 1.36 and 1.37 comparing those with and without type 1 diabetes, and those with and without type 2 diabetes.
The HR for childhood ADHD comparing mothers with and without gestational diabetes was 1.13.
“Within the analysis for gestational diabetes, we had enough numbers to look at siblings that are discordant for maternal gestational diabetes,” Dr. Cesta said. Essentially “we’re comparing two siblings from the same mother, one that was exposed to gestational diabetes, one that wasn’t,” she explained.
Interestingly there was no association between ADHD and maternal gestational diabetes in the sibling analysis (HR, 1.0).
“When it comes to gestational diabetes, the evidence from our sibling analysis indicate that the association may actually be confounded by shared genetics and environmental factors,” said Dr. Cesta.
“So, future studies should explore the role of specific genetic factors in glycemic control during pregnancy and the relationship between maternal diabetes and ADHD.”
Answering long-standing questions
These data will help a lot in answering questions that clinicians have been asking themselves a long time, commented Jardena Puder, MD, who chaired the session.
“It still remains a bit puzzling that genetic and environmental factors could be responsible, if you see the same effect in type 1 [diabetes], and in type 2 [diabetes], and gestational diabetes,” said Dr. Puder, who is an endocrinologist and diabetologist at the woman-mother-child department at the Vaud University Hospital Center, Lausanne, Switzerland.
Type 1 and type 2 are “very distinct” in terms of the genetic and environmental factors involved, “so, the fact that you see [the effect] in both remains a bit puzzling,” said Dr. Puder.
“I wish we had the numbers to be able to do the sibling analysis for type 1 and type 2, just to see if we could tease anything out,” said Dr. Cesta.
“I do think this is part of the bigger question of what the relationship is between, like, metabolic disorders and psychiatric disorders, because even outside of pregnancy, we see that there’s often a comorbidity with them. So, it’s a good point.”
The next step is to look at the role of treatment and what effects glycemic control might have on the small, but still apparent, association between maternal diabetes and ADHD.
The study had multiple funders including the Hong Kong Research Grant Council, NordForsk, the Research Council of Norway, the Norwegian ADHD Research Network, the Hong Kong Innovation and Technology Commission, and European Horizon 2020.
Dr. Cesta had no conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Puder chaired the session in which the findings were presented and made no specific disclosures.
Children born to women who develop diabetes either before or during their pregnancy could be at risk for developing attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, data from a large multinational cohort study appear to show.
Considering more than 4.5 million mother-child pairs, it was found that children whose mothers had diabetes around the time of their pregnancy were 16% more likely to have ADHD diagnosed than were those whose mothers did not.
An increased risk was seen regardless of the type of diabetes, and regardless of whether or not the diabetes was present before or appeared during the pregnancy.
“We found a small increased risk of ADHD in children born to mothers with diabetes, including pregestational diabetes and gestational diabetes,” Carolyn Cesta, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Dr. Cesta, a postdoctoral researcher in the Centre for Pharmacoepidemiology at the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm noted that the effect sizes seen were lower than had been reported previously.
“This may be because we adjusted for a large number of covariates, including maternal ADHD and psychiatric disorders,” Dr. Cesta said.
ADHD and diabetes
“Previous studies have reported an increase in the risk of ADHD in children born to mothers with diabetes,” explained Dr. Cesta.
However, “these studies have been limited by the use of self-reported data, small sample sizes, lack of adjustment for important confounders, and they’re often limited to [White] populations,” she added. “There’s a lot of heterogeneity between these studies,” she said.
To try to iron out the differences seen in the prior studies, Dr. Cesta and associates looked at data from several databases based in Hong Kong (Clinical Data Analysis and Reporting System), four Nordic countries (Population Health Registers for Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden), and Taiwan (National Health Insurance Database).
To create the matched mother-child pairs, the databases were searched to find women who had children born between 2001 and 2018, and who had follow-up data available up to 2020 on not only their diabetes status and child’s ADHD status, but also other parameters, such as other maternal diagnoses, maternal medications, and a host of sociodemographic factors.
More than 24 potentially confounding or covariates were considered in the analysis, which used Cox proportional hazard regression modeling and propensity score analysis to calculate hazard ratios with 95% confidence intervals.
“We looked at whether [mothers] had a diagnosis of ADHD themselves, or other psychiatric disorders, because there is high heritability for these disorders,” Dr. Cesta said, indicating that all bases had endeavored to be covered.
Main findings
Results showed some differences in the prevalence of diabetes and ADHD between the three cohorts used in the analysis. The prevalence of any maternal diabetes ranged from 8.8% in the Hong Kong cohort to 3.3% in the Taiwan cohort, with a prevalence of 6.8% for the Nordic cohort.
Rates of pregestational diabetes were lowest in the Taiwan and Hong Kong cohorts, at 0.2% and 0.5%, respectively, and 2.2% in the Nordic cohort. Gestational diabetes rates were a respective 3.1%, 7.8%, and 4.6%.
The highest rate of ADHD in children was seen in the Taiwan cohort, at 9.6%, followed by 4.2% for the Hong Kong cohort, and 2.6% for the Nordic cohort.
The hazard ratio for having childhood ADHD was 1.16 when comparing any maternal diabetes to no maternal diabetes, 1.40 comparing mothers with and without pregestational diabetes, and a respective 1.36 and 1.37 comparing those with and without type 1 diabetes, and those with and without type 2 diabetes.
The HR for childhood ADHD comparing mothers with and without gestational diabetes was 1.13.
“Within the analysis for gestational diabetes, we had enough numbers to look at siblings that are discordant for maternal gestational diabetes,” Dr. Cesta said. Essentially “we’re comparing two siblings from the same mother, one that was exposed to gestational diabetes, one that wasn’t,” she explained.
Interestingly there was no association between ADHD and maternal gestational diabetes in the sibling analysis (HR, 1.0).
“When it comes to gestational diabetes, the evidence from our sibling analysis indicate that the association may actually be confounded by shared genetics and environmental factors,” said Dr. Cesta.
“So, future studies should explore the role of specific genetic factors in glycemic control during pregnancy and the relationship between maternal diabetes and ADHD.”
Answering long-standing questions
These data will help a lot in answering questions that clinicians have been asking themselves a long time, commented Jardena Puder, MD, who chaired the session.
“It still remains a bit puzzling that genetic and environmental factors could be responsible, if you see the same effect in type 1 [diabetes], and in type 2 [diabetes], and gestational diabetes,” said Dr. Puder, who is an endocrinologist and diabetologist at the woman-mother-child department at the Vaud University Hospital Center, Lausanne, Switzerland.
Type 1 and type 2 are “very distinct” in terms of the genetic and environmental factors involved, “so, the fact that you see [the effect] in both remains a bit puzzling,” said Dr. Puder.
“I wish we had the numbers to be able to do the sibling analysis for type 1 and type 2, just to see if we could tease anything out,” said Dr. Cesta.
“I do think this is part of the bigger question of what the relationship is between, like, metabolic disorders and psychiatric disorders, because even outside of pregnancy, we see that there’s often a comorbidity with them. So, it’s a good point.”
The next step is to look at the role of treatment and what effects glycemic control might have on the small, but still apparent, association between maternal diabetes and ADHD.
The study had multiple funders including the Hong Kong Research Grant Council, NordForsk, the Research Council of Norway, the Norwegian ADHD Research Network, the Hong Kong Innovation and Technology Commission, and European Horizon 2020.
Dr. Cesta had no conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Puder chaired the session in which the findings were presented and made no specific disclosures.
Children born to women who develop diabetes either before or during their pregnancy could be at risk for developing attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, data from a large multinational cohort study appear to show.
Considering more than 4.5 million mother-child pairs, it was found that children whose mothers had diabetes around the time of their pregnancy were 16% more likely to have ADHD diagnosed than were those whose mothers did not.
An increased risk was seen regardless of the type of diabetes, and regardless of whether or not the diabetes was present before or appeared during the pregnancy.
“We found a small increased risk of ADHD in children born to mothers with diabetes, including pregestational diabetes and gestational diabetes,” Carolyn Cesta, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Dr. Cesta, a postdoctoral researcher in the Centre for Pharmacoepidemiology at the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm noted that the effect sizes seen were lower than had been reported previously.
“This may be because we adjusted for a large number of covariates, including maternal ADHD and psychiatric disorders,” Dr. Cesta said.
ADHD and diabetes
“Previous studies have reported an increase in the risk of ADHD in children born to mothers with diabetes,” explained Dr. Cesta.
However, “these studies have been limited by the use of self-reported data, small sample sizes, lack of adjustment for important confounders, and they’re often limited to [White] populations,” she added. “There’s a lot of heterogeneity between these studies,” she said.
To try to iron out the differences seen in the prior studies, Dr. Cesta and associates looked at data from several databases based in Hong Kong (Clinical Data Analysis and Reporting System), four Nordic countries (Population Health Registers for Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden), and Taiwan (National Health Insurance Database).
To create the matched mother-child pairs, the databases were searched to find women who had children born between 2001 and 2018, and who had follow-up data available up to 2020 on not only their diabetes status and child’s ADHD status, but also other parameters, such as other maternal diagnoses, maternal medications, and a host of sociodemographic factors.
More than 24 potentially confounding or covariates were considered in the analysis, which used Cox proportional hazard regression modeling and propensity score analysis to calculate hazard ratios with 95% confidence intervals.
“We looked at whether [mothers] had a diagnosis of ADHD themselves, or other psychiatric disorders, because there is high heritability for these disorders,” Dr. Cesta said, indicating that all bases had endeavored to be covered.
Main findings
Results showed some differences in the prevalence of diabetes and ADHD between the three cohorts used in the analysis. The prevalence of any maternal diabetes ranged from 8.8% in the Hong Kong cohort to 3.3% in the Taiwan cohort, with a prevalence of 6.8% for the Nordic cohort.
Rates of pregestational diabetes were lowest in the Taiwan and Hong Kong cohorts, at 0.2% and 0.5%, respectively, and 2.2% in the Nordic cohort. Gestational diabetes rates were a respective 3.1%, 7.8%, and 4.6%.
The highest rate of ADHD in children was seen in the Taiwan cohort, at 9.6%, followed by 4.2% for the Hong Kong cohort, and 2.6% for the Nordic cohort.
The hazard ratio for having childhood ADHD was 1.16 when comparing any maternal diabetes to no maternal diabetes, 1.40 comparing mothers with and without pregestational diabetes, and a respective 1.36 and 1.37 comparing those with and without type 1 diabetes, and those with and without type 2 diabetes.
The HR for childhood ADHD comparing mothers with and without gestational diabetes was 1.13.
“Within the analysis for gestational diabetes, we had enough numbers to look at siblings that are discordant for maternal gestational diabetes,” Dr. Cesta said. Essentially “we’re comparing two siblings from the same mother, one that was exposed to gestational diabetes, one that wasn’t,” she explained.
Interestingly there was no association between ADHD and maternal gestational diabetes in the sibling analysis (HR, 1.0).
“When it comes to gestational diabetes, the evidence from our sibling analysis indicate that the association may actually be confounded by shared genetics and environmental factors,” said Dr. Cesta.
“So, future studies should explore the role of specific genetic factors in glycemic control during pregnancy and the relationship between maternal diabetes and ADHD.”
Answering long-standing questions
These data will help a lot in answering questions that clinicians have been asking themselves a long time, commented Jardena Puder, MD, who chaired the session.
“It still remains a bit puzzling that genetic and environmental factors could be responsible, if you see the same effect in type 1 [diabetes], and in type 2 [diabetes], and gestational diabetes,” said Dr. Puder, who is an endocrinologist and diabetologist at the woman-mother-child department at the Vaud University Hospital Center, Lausanne, Switzerland.
Type 1 and type 2 are “very distinct” in terms of the genetic and environmental factors involved, “so, the fact that you see [the effect] in both remains a bit puzzling,” said Dr. Puder.
“I wish we had the numbers to be able to do the sibling analysis for type 1 and type 2, just to see if we could tease anything out,” said Dr. Cesta.
“I do think this is part of the bigger question of what the relationship is between, like, metabolic disorders and psychiatric disorders, because even outside of pregnancy, we see that there’s often a comorbidity with them. So, it’s a good point.”
The next step is to look at the role of treatment and what effects glycemic control might have on the small, but still apparent, association between maternal diabetes and ADHD.
The study had multiple funders including the Hong Kong Research Grant Council, NordForsk, the Research Council of Norway, the Norwegian ADHD Research Network, the Hong Kong Innovation and Technology Commission, and European Horizon 2020.
Dr. Cesta had no conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Puder chaired the session in which the findings were presented and made no specific disclosures.
FROM EASD 2022
Triple threat: Novel agent shows potent T2D weight loss in phase 1
STOCKHOLM – First came the GLP-1 receptor agonists as treatments for patients with type 2 diabetes, then came tirzepatide (Mounjaro) which added a second incretin agonism for the receptor to the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Now coming onto the clinical scene is a molecule with triple agonism to the GLP-1 receptor, the GIP receptor, and to the glucagon receptor.
That molecule, LY3437943, showed reasonable safety and tolerability and an apparent incremental uptick in weight loss compared with the approved incretin-based agents for people with type 2 diabetes in a 12-week, dose-ranging study involving a 52 patients with type 2 diabetes who received the new agent.
The 12 people who uptitrated for a total of 12 weeks and reached the highest tested dose of LY3437943, 12 mg, injected once weekly during the final 4 weeks, showed an average weight loss of 8.65 kg, while the 11 patients who maxed out at a weekly dose of 6 mg of LY3437943 had an average 12-week weight loss of 7.52 kg, Zvonko Milicevic, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Fifteen more participants received placebo and five received a comparator GLP-1 receptor agonist. All 72 patients in the study were also already on treatment with metformin when they entered, and they were maintained on metformin throughout the study period.
The new agent showed “greater weight loss efficacy than currently approved medications,” said Dr. Milicevic, a staff researcher who works in Vienna for Eli Lilly, the company developing LY3437943.
‘Really impressive’ weight loss
Martin Haluzik, MD, who chaired the session where Dr. Milicevic spoke, agreed. “The data, especially for weight reduction, were really impressive,” Dr. Haluzik said in an interview. “It looks stronger than the best we have at the moment,” the dual incretin agonist tirzepatide, he added.
Cross-study comparisons are very unreliable, but to put the weight loss seen with LY3437943 in perspective, the 12-week weight reduction that occurred with the highest dose of tirzepatide tested (15 mg/weekly) in the pivotal SURPASS-2 trial with 1,879 randomized patients with type 2 diabetes was an average of roughly 5 kg, while the comparator of 1 mg weekly of semaglutide (Ozempic) tested in the same study produced an average weight loss of about 4 kg.
Other notable efficacy results for LY3437943 after 12 weeks on treatment included an average reduction in hemoglobin A1c from baseline of 1.90%, achieved in the group that received 6 mg weekly as their maximum dose for 8 weeks after a 4-week run-in at a lower dose; a reduction in systolic blood pressure of 7.99 mm Hg on the 6-mg maximum weekly dose and of 12.06 mm Hg on the maximum 12-mg weekly dose; and “robust” reductions in lipids including cuts from baseline of about 40% for both triglycerides and very-LDL cholesterol, Dr. Milicevic reported.
Adverse effects resemble approved incretin-based agents
The study, which ran at four U.S. sites, had a primary objective of safety assessment, and Dr. Milicevic said the results showed acceptable safety and tolerability consistent with the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and tirzepatide. Like those agents, LY3437943 caused primarily mild gastrointestinal adverse effects such as nausea and diarrhea. Of the 52 patients in the study who received the triple agonist, 4 discontinued treatment because of a treatment-emergent adverse effect, including 1 patient in the subgroup who received the maximum dose.
The only concerning adverse effect noted by Dr. Haluzik was the average increase in heart rate from baseline of 10.26 beats/min in the subgroup that received the maximum dose, roughly twice the increase seen with tirzepatide and semaglutide in SURPASS-2. The average heart rate increase was about half that, 5.30 beats/min compared with baseline, in the subgroup that received a maximum weekly dose of 6 mg.
Overall, the results showed “no major adverse effects that might hamper use,” said Dr. Haluzik, an endocrinologist and professor at Charles University in Prague.
Two phase 2 studies of LY3437943 are underway and are scheduled to finish before the end of 2022. They include a study of about 300 people with type 2 diabetes that’s running at 43 U.S. sites, and a second study of about 500 people with overweight or obesity running at 28 U.S. sites.
The study was sponsored by Eli Lilly, the company developing LY3437943. Dr. Milicevic is an employee of and stockholder of Eli Lilly. Dr. Haluzik has been an adviser to, consultant to, and received honoraria and research support from Eli Lilly. He has had similar relationships with Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, BristolMyersSquibb, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, Mundipharma, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.
STOCKHOLM – First came the GLP-1 receptor agonists as treatments for patients with type 2 diabetes, then came tirzepatide (Mounjaro) which added a second incretin agonism for the receptor to the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Now coming onto the clinical scene is a molecule with triple agonism to the GLP-1 receptor, the GIP receptor, and to the glucagon receptor.
That molecule, LY3437943, showed reasonable safety and tolerability and an apparent incremental uptick in weight loss compared with the approved incretin-based agents for people with type 2 diabetes in a 12-week, dose-ranging study involving a 52 patients with type 2 diabetes who received the new agent.
The 12 people who uptitrated for a total of 12 weeks and reached the highest tested dose of LY3437943, 12 mg, injected once weekly during the final 4 weeks, showed an average weight loss of 8.65 kg, while the 11 patients who maxed out at a weekly dose of 6 mg of LY3437943 had an average 12-week weight loss of 7.52 kg, Zvonko Milicevic, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Fifteen more participants received placebo and five received a comparator GLP-1 receptor agonist. All 72 patients in the study were also already on treatment with metformin when they entered, and they were maintained on metformin throughout the study period.
The new agent showed “greater weight loss efficacy than currently approved medications,” said Dr. Milicevic, a staff researcher who works in Vienna for Eli Lilly, the company developing LY3437943.
‘Really impressive’ weight loss
Martin Haluzik, MD, who chaired the session where Dr. Milicevic spoke, agreed. “The data, especially for weight reduction, were really impressive,” Dr. Haluzik said in an interview. “It looks stronger than the best we have at the moment,” the dual incretin agonist tirzepatide, he added.
Cross-study comparisons are very unreliable, but to put the weight loss seen with LY3437943 in perspective, the 12-week weight reduction that occurred with the highest dose of tirzepatide tested (15 mg/weekly) in the pivotal SURPASS-2 trial with 1,879 randomized patients with type 2 diabetes was an average of roughly 5 kg, while the comparator of 1 mg weekly of semaglutide (Ozempic) tested in the same study produced an average weight loss of about 4 kg.
Other notable efficacy results for LY3437943 after 12 weeks on treatment included an average reduction in hemoglobin A1c from baseline of 1.90%, achieved in the group that received 6 mg weekly as their maximum dose for 8 weeks after a 4-week run-in at a lower dose; a reduction in systolic blood pressure of 7.99 mm Hg on the 6-mg maximum weekly dose and of 12.06 mm Hg on the maximum 12-mg weekly dose; and “robust” reductions in lipids including cuts from baseline of about 40% for both triglycerides and very-LDL cholesterol, Dr. Milicevic reported.
Adverse effects resemble approved incretin-based agents
The study, which ran at four U.S. sites, had a primary objective of safety assessment, and Dr. Milicevic said the results showed acceptable safety and tolerability consistent with the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and tirzepatide. Like those agents, LY3437943 caused primarily mild gastrointestinal adverse effects such as nausea and diarrhea. Of the 52 patients in the study who received the triple agonist, 4 discontinued treatment because of a treatment-emergent adverse effect, including 1 patient in the subgroup who received the maximum dose.
The only concerning adverse effect noted by Dr. Haluzik was the average increase in heart rate from baseline of 10.26 beats/min in the subgroup that received the maximum dose, roughly twice the increase seen with tirzepatide and semaglutide in SURPASS-2. The average heart rate increase was about half that, 5.30 beats/min compared with baseline, in the subgroup that received a maximum weekly dose of 6 mg.
Overall, the results showed “no major adverse effects that might hamper use,” said Dr. Haluzik, an endocrinologist and professor at Charles University in Prague.
Two phase 2 studies of LY3437943 are underway and are scheduled to finish before the end of 2022. They include a study of about 300 people with type 2 diabetes that’s running at 43 U.S. sites, and a second study of about 500 people with overweight or obesity running at 28 U.S. sites.
The study was sponsored by Eli Lilly, the company developing LY3437943. Dr. Milicevic is an employee of and stockholder of Eli Lilly. Dr. Haluzik has been an adviser to, consultant to, and received honoraria and research support from Eli Lilly. He has had similar relationships with Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, BristolMyersSquibb, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, Mundipharma, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.
STOCKHOLM – First came the GLP-1 receptor agonists as treatments for patients with type 2 diabetes, then came tirzepatide (Mounjaro) which added a second incretin agonism for the receptor to the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Now coming onto the clinical scene is a molecule with triple agonism to the GLP-1 receptor, the GIP receptor, and to the glucagon receptor.
That molecule, LY3437943, showed reasonable safety and tolerability and an apparent incremental uptick in weight loss compared with the approved incretin-based agents for people with type 2 diabetes in a 12-week, dose-ranging study involving a 52 patients with type 2 diabetes who received the new agent.
The 12 people who uptitrated for a total of 12 weeks and reached the highest tested dose of LY3437943, 12 mg, injected once weekly during the final 4 weeks, showed an average weight loss of 8.65 kg, while the 11 patients who maxed out at a weekly dose of 6 mg of LY3437943 had an average 12-week weight loss of 7.52 kg, Zvonko Milicevic, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Fifteen more participants received placebo and five received a comparator GLP-1 receptor agonist. All 72 patients in the study were also already on treatment with metformin when they entered, and they were maintained on metformin throughout the study period.
The new agent showed “greater weight loss efficacy than currently approved medications,” said Dr. Milicevic, a staff researcher who works in Vienna for Eli Lilly, the company developing LY3437943.
‘Really impressive’ weight loss
Martin Haluzik, MD, who chaired the session where Dr. Milicevic spoke, agreed. “The data, especially for weight reduction, were really impressive,” Dr. Haluzik said in an interview. “It looks stronger than the best we have at the moment,” the dual incretin agonist tirzepatide, he added.
Cross-study comparisons are very unreliable, but to put the weight loss seen with LY3437943 in perspective, the 12-week weight reduction that occurred with the highest dose of tirzepatide tested (15 mg/weekly) in the pivotal SURPASS-2 trial with 1,879 randomized patients with type 2 diabetes was an average of roughly 5 kg, while the comparator of 1 mg weekly of semaglutide (Ozempic) tested in the same study produced an average weight loss of about 4 kg.
Other notable efficacy results for LY3437943 after 12 weeks on treatment included an average reduction in hemoglobin A1c from baseline of 1.90%, achieved in the group that received 6 mg weekly as their maximum dose for 8 weeks after a 4-week run-in at a lower dose; a reduction in systolic blood pressure of 7.99 mm Hg on the 6-mg maximum weekly dose and of 12.06 mm Hg on the maximum 12-mg weekly dose; and “robust” reductions in lipids including cuts from baseline of about 40% for both triglycerides and very-LDL cholesterol, Dr. Milicevic reported.
Adverse effects resemble approved incretin-based agents
The study, which ran at four U.S. sites, had a primary objective of safety assessment, and Dr. Milicevic said the results showed acceptable safety and tolerability consistent with the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and tirzepatide. Like those agents, LY3437943 caused primarily mild gastrointestinal adverse effects such as nausea and diarrhea. Of the 52 patients in the study who received the triple agonist, 4 discontinued treatment because of a treatment-emergent adverse effect, including 1 patient in the subgroup who received the maximum dose.
The only concerning adverse effect noted by Dr. Haluzik was the average increase in heart rate from baseline of 10.26 beats/min in the subgroup that received the maximum dose, roughly twice the increase seen with tirzepatide and semaglutide in SURPASS-2. The average heart rate increase was about half that, 5.30 beats/min compared with baseline, in the subgroup that received a maximum weekly dose of 6 mg.
Overall, the results showed “no major adverse effects that might hamper use,” said Dr. Haluzik, an endocrinologist and professor at Charles University in Prague.
Two phase 2 studies of LY3437943 are underway and are scheduled to finish before the end of 2022. They include a study of about 300 people with type 2 diabetes that’s running at 43 U.S. sites, and a second study of about 500 people with overweight or obesity running at 28 U.S. sites.
The study was sponsored by Eli Lilly, the company developing LY3437943. Dr. Milicevic is an employee of and stockholder of Eli Lilly. Dr. Haluzik has been an adviser to, consultant to, and received honoraria and research support from Eli Lilly. He has had similar relationships with Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, BristolMyersSquibb, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, Mundipharma, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.
AT EASD 2022
High BMI linked to better survival for cancer patients treated with ICI, but for men only
That is the conclusion of a new retrospective analysis presented during a poster session given at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology. The study sought to better understand ICI outcomes. “These are complex new treatments and, because they harness the immune system, no two patients are likely to respond in the same way. BMI has previously been associated with improved survival in patients with advanced lung cancer treated with immunotherapy. However, the reasons behind this observation, and the implications for treatment are unknown, as is whether this observation is specific for patients with only certain types of cancers,” study author Dwight Owen, MD, said in an email.
He pointed out that the retrospective nature of the findings means that they have no immediate clinical implications. “The reason for the discrepancy in males remains unclear. Although our study included a relatively large number of patients, it is a heterogenous cohort and there may be confounding factors that we haven’t recognized, so these findings need to be replicated in larger cohorts,” said Dr. Owen, a medical oncologist with The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus.
Asked if there is a potential biological explanation for a difference between males and females, Dr. Owen said that this is an area of intense research. One recent study examined whether androgen could help explain why men are more likely than women to both develop and have more aggressive nonreproductive cancers. They concluded that androgen receptor signaling may be leading to loss of effector and proliferative potential of CD8+ T cells in the tumor microenvironment. Once exhausted, these cells do not respond well to stimulation that can occur after ICI treatment.
On the opposite end of the spectrum, cancer cachexia is also a key subject of study. It is characterized by weight loss and is associated with worse clinical outcomes. A cachexia mouse model found that weight loss can lead to more clearance of immune checkpoint antibodies.
Still, much more work needs to be done. “For now, how BMI, obesity, and cachexia relate to other factors, for instance the microbiome and tumor immunogenicity, are still not fully understood,” Dr. Owen said.
The study data
The researchers analyzed data from 688 patients with metastatic cancer treated at their center between 2011 and 2017. 94% were White and 5% were Black. 41% were female and the mean age was 61.9 years. The mean BMI was 28.8 kg/m2; 40% of patients had melanoma, 23% had non–small cell lung cancer, 10% had renal cancer, and 27% had another form of cancer.
For every unit decrease in BMI, the researchers observed a 1.8% decrease in mortality (hazard ratio, 0.982; P = .007). Patients with a BMI of 40 or above had better survival than all other patients grouped by 5 BMI increments (that is, 35-40, 30-35, etc.). When separated by sex, males had a significant decrease in mortality for every increase in BMI unit (HR, 0.964; P = .004), but there was no significant difference among women (HR, 1.003; P = .706). The relationship in men held up after adjustment for Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group score, line of therapy, and cancer type (HR, 0.979; P = .0308). The researchers also looked at a separate cohort of 185 normal weight and 15 obese (BMI ≥ 40) NSCLC patients. Median survival was 27.5 months in the obese group and 9.1 months in the normal weight group (HR, 0.474; 95% CI, 0.232-0.969).
Dr. Owen has received research funding through his institution from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, Pfizer, Palobiofarma, and Onc.AI.
That is the conclusion of a new retrospective analysis presented during a poster session given at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology. The study sought to better understand ICI outcomes. “These are complex new treatments and, because they harness the immune system, no two patients are likely to respond in the same way. BMI has previously been associated with improved survival in patients with advanced lung cancer treated with immunotherapy. However, the reasons behind this observation, and the implications for treatment are unknown, as is whether this observation is specific for patients with only certain types of cancers,” study author Dwight Owen, MD, said in an email.
He pointed out that the retrospective nature of the findings means that they have no immediate clinical implications. “The reason for the discrepancy in males remains unclear. Although our study included a relatively large number of patients, it is a heterogenous cohort and there may be confounding factors that we haven’t recognized, so these findings need to be replicated in larger cohorts,” said Dr. Owen, a medical oncologist with The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus.
Asked if there is a potential biological explanation for a difference between males and females, Dr. Owen said that this is an area of intense research. One recent study examined whether androgen could help explain why men are more likely than women to both develop and have more aggressive nonreproductive cancers. They concluded that androgen receptor signaling may be leading to loss of effector and proliferative potential of CD8+ T cells in the tumor microenvironment. Once exhausted, these cells do not respond well to stimulation that can occur after ICI treatment.
On the opposite end of the spectrum, cancer cachexia is also a key subject of study. It is characterized by weight loss and is associated with worse clinical outcomes. A cachexia mouse model found that weight loss can lead to more clearance of immune checkpoint antibodies.
Still, much more work needs to be done. “For now, how BMI, obesity, and cachexia relate to other factors, for instance the microbiome and tumor immunogenicity, are still not fully understood,” Dr. Owen said.
The study data
The researchers analyzed data from 688 patients with metastatic cancer treated at their center between 2011 and 2017. 94% were White and 5% were Black. 41% were female and the mean age was 61.9 years. The mean BMI was 28.8 kg/m2; 40% of patients had melanoma, 23% had non–small cell lung cancer, 10% had renal cancer, and 27% had another form of cancer.
For every unit decrease in BMI, the researchers observed a 1.8% decrease in mortality (hazard ratio, 0.982; P = .007). Patients with a BMI of 40 or above had better survival than all other patients grouped by 5 BMI increments (that is, 35-40, 30-35, etc.). When separated by sex, males had a significant decrease in mortality for every increase in BMI unit (HR, 0.964; P = .004), but there was no significant difference among women (HR, 1.003; P = .706). The relationship in men held up after adjustment for Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group score, line of therapy, and cancer type (HR, 0.979; P = .0308). The researchers also looked at a separate cohort of 185 normal weight and 15 obese (BMI ≥ 40) NSCLC patients. Median survival was 27.5 months in the obese group and 9.1 months in the normal weight group (HR, 0.474; 95% CI, 0.232-0.969).
Dr. Owen has received research funding through his institution from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, Pfizer, Palobiofarma, and Onc.AI.
That is the conclusion of a new retrospective analysis presented during a poster session given at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology. The study sought to better understand ICI outcomes. “These are complex new treatments and, because they harness the immune system, no two patients are likely to respond in the same way. BMI has previously been associated with improved survival in patients with advanced lung cancer treated with immunotherapy. However, the reasons behind this observation, and the implications for treatment are unknown, as is whether this observation is specific for patients with only certain types of cancers,” study author Dwight Owen, MD, said in an email.
He pointed out that the retrospective nature of the findings means that they have no immediate clinical implications. “The reason for the discrepancy in males remains unclear. Although our study included a relatively large number of patients, it is a heterogenous cohort and there may be confounding factors that we haven’t recognized, so these findings need to be replicated in larger cohorts,” said Dr. Owen, a medical oncologist with The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus.
Asked if there is a potential biological explanation for a difference between males and females, Dr. Owen said that this is an area of intense research. One recent study examined whether androgen could help explain why men are more likely than women to both develop and have more aggressive nonreproductive cancers. They concluded that androgen receptor signaling may be leading to loss of effector and proliferative potential of CD8+ T cells in the tumor microenvironment. Once exhausted, these cells do not respond well to stimulation that can occur after ICI treatment.
On the opposite end of the spectrum, cancer cachexia is also a key subject of study. It is characterized by weight loss and is associated with worse clinical outcomes. A cachexia mouse model found that weight loss can lead to more clearance of immune checkpoint antibodies.
Still, much more work needs to be done. “For now, how BMI, obesity, and cachexia relate to other factors, for instance the microbiome and tumor immunogenicity, are still not fully understood,” Dr. Owen said.
The study data
The researchers analyzed data from 688 patients with metastatic cancer treated at their center between 2011 and 2017. 94% were White and 5% were Black. 41% were female and the mean age was 61.9 years. The mean BMI was 28.8 kg/m2; 40% of patients had melanoma, 23% had non–small cell lung cancer, 10% had renal cancer, and 27% had another form of cancer.
For every unit decrease in BMI, the researchers observed a 1.8% decrease in mortality (hazard ratio, 0.982; P = .007). Patients with a BMI of 40 or above had better survival than all other patients grouped by 5 BMI increments (that is, 35-40, 30-35, etc.). When separated by sex, males had a significant decrease in mortality for every increase in BMI unit (HR, 0.964; P = .004), but there was no significant difference among women (HR, 1.003; P = .706). The relationship in men held up after adjustment for Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group score, line of therapy, and cancer type (HR, 0.979; P = .0308). The researchers also looked at a separate cohort of 185 normal weight and 15 obese (BMI ≥ 40) NSCLC patients. Median survival was 27.5 months in the obese group and 9.1 months in the normal weight group (HR, 0.474; 95% CI, 0.232-0.969).
Dr. Owen has received research funding through his institution from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, Pfizer, Palobiofarma, and Onc.AI.
FROM ESMO CONGRESS 2022
‘Amazing’ data for cheap beta-blocker gel for diabetic foot ulcers
STOCKHOLM – Esmolol hydrochloride gel (Galnobax, NovoLead) appears to be a safe and effective novel topical treatment option for diabetic foot ulcers, according to results from a new trial of the drug, which is widely available as a generic and is inexpensive.
Of note, the proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure at 12 weeks with esmolol (plus standard of care) was around 60% compared with just over 40% in patients who received standard of care alone.
Presenting the findings at this year’s annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes was Ashu Rastogi, MD, a professor of endocrinology at the Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research in Chandigarh, India.
“Esmolol can be given topically as a 14% gel and is a novel treatment option in diabetic foot ulcer,” said Dr. Rastogi.
Esmolol, a short-acting beta-adrenergic blocker, is currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for cardiac indications only, such as short-term use for controlling supraventricular tachycardia. Beta-blockers are also used to treat hypertension.
However, esmolol has also been repurposed and formulated as a topical gel for the treatment of hard-to-heal diabetic foot ulcers (mainly neuropathic grade 1).
Audience member Ketan Dhatariya, MBBS, MD, PhD, a National Health Service consultant in diabetes, endocrinology, and general medicine and honorary senior lecturer at Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals, England, enthused about the findings.
“This is an amazing study. I’m part of a working group looking at the updating of a guideline for the International Working Group of the Diabetic Foot, reviewing all the studies on wound healing, specifically pharmacological interventions. This is way beyond anything shown to date in terms of medical intervention. [The authors] should be congratulated; this is really astounding,” he told this news organization.
“Right now, there is very little out there in terms of pharmacological interventions that have shown benefit,” he added. “Once this study has been peer-reviewed and is published properly, it is potentially game-changing because it is a generic, worldwide, cheap, and freely available medication.”
Study across 27 sites in India
Prior phase 1/2 data have shown that 60% of ulcers completely closed with esmolol (14% gel) compared with 39% with standard of care. Encouraged by these findings, a phase 3 randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study was conducted across 27 sites in India.
Patients were a mean age of 56 years, and had a body mass index (BMI) of 25-26 kg/m2 and mean hemoglobin A1c of 8.4%-8.7%. Around 70% of participants were men. Mean ulcer area was approximately 460-500 mm2, two-thirds of the ulcers were plantar, and mean ulcer duration was 40-50 weeks.
After screening and discontinuations (39 participants), a 12-week treatment phase began with patients randomized to one of three groups: esmolol (14% gel) along with standard of care administered twice daily (57 completers); standard of care only (63 completers); or vehicle gel (placebo) along with standard of care administered twice daily (17 completers).
Standard of care comprised wound cleaning, debridement, maintenance of moist wound environment, twice-daily fresh bandages, and off-loading footwear as needed, and was provided to all participants irrespective of study group.
The 12-week treatment period was followed by an observation period of 12 weeks up to the 24-week study endpoint.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure (100% re-epithelialization without drainage or dressing requirement) within the 12-week treatment phase.
Secondary endpoints included time to target ulcer closure during the 12-week treatment phase and proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure by 24 weeks (end of study). Investigators were blinded throughout.
Subanalyses were conducted based on ulcer location, size, and age, as well as estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 90 mL/min and ankle-brachial index under 0.9 but greater than 0.7.
50% more patients on esmolol had complete ulcer closure
The proportion of participants with complete ulcer closure at 12 weeks was 60.3% in the esmolol plus standard of care group, compared with 41.7% with standard of care only, a difference of 18.6% (odds ratio, 2.13; P = .0276).
“The 24-week end-of-study data show what happened in the 12 weeks following end of treatment,” said Dr. Rastogi, turning to results showing that by 24 weeks the proportion of participants with complete ulcer closure was 77.2% versus 55.6%, respectively, with a difference of 21.6% (OR, 2.71; P = .013).
Time to ulcer closure (a secondary endpoint) was similar between the esmolol plus standard of care vs. standard of care groups (74.3 vs. 72.5 days).
The impact of ulcer location on complete ulcer closure, a subanalysis, showed a higher proportion of patients experienced complete ulcer closure with esmolol plus standard of care versus standard of care. For example, in plantar-based ulcers, esmolol led to complete closure in 58.7% vs. 43.1%, while for nonplantar ulcers, complete closure was found in 63.6% vs. 38.1%.
In wounds less than 5 cm2, the proportion of complete closures was 66.0% vs. 50.0% for esmolol compared with standard of care alone, while in wounds over 5 cm2, these proportions were 47.6% vs. 26.9%.
Subanalyses also showed that esmolol was substantially better in patients with BMI greater than 25, ulcer duration over 12 weeks, and A1c above 8%.
Also, a subanalysis stratified by “real-life” situations favored esmolol, showing a 50.9% difference in the proportion of patients with diabetic foot ulcer healing in those with a history of hypertension and a 31.8% difference favoring esmolol in those with an abnormal electrocardiogram.
Overall, the proportions of patients who had an adverse event were 13.2%, 18.4%, and 37.5% in the esmolol plus standard of care, standard of care alone, and vehicle plus standard of care groups, respectively, and the vast majority were unrelated to study drug. There were no serious adverse events in the esmolol plus standard of care group.
A class effect of beta blockers?
The proposed mechanism of action of esmolol relates to a sequence of reducing inflammation (via vasodilation, fibroblast migration, and cytokine reduction); proliferation by beta-blockade (improves keratinocyte migration and epithelialization); and remodeling (increases collagen turnover).
Asked by an audience member if the observations were a class effect and systemic effect of beta-blockers, Dr. Rastogi said he could not say for sure that it was a class effect, but they deliberately used a beta-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist.
“It may not be a systemic effect because we have some patients who use beta-blockers systemically and they still have diabetic foot ulcers,” he said.
Dr. Rastogi and Dr. Dhatariya have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM – Esmolol hydrochloride gel (Galnobax, NovoLead) appears to be a safe and effective novel topical treatment option for diabetic foot ulcers, according to results from a new trial of the drug, which is widely available as a generic and is inexpensive.
Of note, the proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure at 12 weeks with esmolol (plus standard of care) was around 60% compared with just over 40% in patients who received standard of care alone.
Presenting the findings at this year’s annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes was Ashu Rastogi, MD, a professor of endocrinology at the Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research in Chandigarh, India.
“Esmolol can be given topically as a 14% gel and is a novel treatment option in diabetic foot ulcer,” said Dr. Rastogi.
Esmolol, a short-acting beta-adrenergic blocker, is currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for cardiac indications only, such as short-term use for controlling supraventricular tachycardia. Beta-blockers are also used to treat hypertension.
However, esmolol has also been repurposed and formulated as a topical gel for the treatment of hard-to-heal diabetic foot ulcers (mainly neuropathic grade 1).
Audience member Ketan Dhatariya, MBBS, MD, PhD, a National Health Service consultant in diabetes, endocrinology, and general medicine and honorary senior lecturer at Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals, England, enthused about the findings.
“This is an amazing study. I’m part of a working group looking at the updating of a guideline for the International Working Group of the Diabetic Foot, reviewing all the studies on wound healing, specifically pharmacological interventions. This is way beyond anything shown to date in terms of medical intervention. [The authors] should be congratulated; this is really astounding,” he told this news organization.
“Right now, there is very little out there in terms of pharmacological interventions that have shown benefit,” he added. “Once this study has been peer-reviewed and is published properly, it is potentially game-changing because it is a generic, worldwide, cheap, and freely available medication.”
Study across 27 sites in India
Prior phase 1/2 data have shown that 60% of ulcers completely closed with esmolol (14% gel) compared with 39% with standard of care. Encouraged by these findings, a phase 3 randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study was conducted across 27 sites in India.
Patients were a mean age of 56 years, and had a body mass index (BMI) of 25-26 kg/m2 and mean hemoglobin A1c of 8.4%-8.7%. Around 70% of participants were men. Mean ulcer area was approximately 460-500 mm2, two-thirds of the ulcers were plantar, and mean ulcer duration was 40-50 weeks.
After screening and discontinuations (39 participants), a 12-week treatment phase began with patients randomized to one of three groups: esmolol (14% gel) along with standard of care administered twice daily (57 completers); standard of care only (63 completers); or vehicle gel (placebo) along with standard of care administered twice daily (17 completers).
Standard of care comprised wound cleaning, debridement, maintenance of moist wound environment, twice-daily fresh bandages, and off-loading footwear as needed, and was provided to all participants irrespective of study group.
The 12-week treatment period was followed by an observation period of 12 weeks up to the 24-week study endpoint.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure (100% re-epithelialization without drainage or dressing requirement) within the 12-week treatment phase.
Secondary endpoints included time to target ulcer closure during the 12-week treatment phase and proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure by 24 weeks (end of study). Investigators were blinded throughout.
Subanalyses were conducted based on ulcer location, size, and age, as well as estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 90 mL/min and ankle-brachial index under 0.9 but greater than 0.7.
50% more patients on esmolol had complete ulcer closure
The proportion of participants with complete ulcer closure at 12 weeks was 60.3% in the esmolol plus standard of care group, compared with 41.7% with standard of care only, a difference of 18.6% (odds ratio, 2.13; P = .0276).
“The 24-week end-of-study data show what happened in the 12 weeks following end of treatment,” said Dr. Rastogi, turning to results showing that by 24 weeks the proportion of participants with complete ulcer closure was 77.2% versus 55.6%, respectively, with a difference of 21.6% (OR, 2.71; P = .013).
Time to ulcer closure (a secondary endpoint) was similar between the esmolol plus standard of care vs. standard of care groups (74.3 vs. 72.5 days).
The impact of ulcer location on complete ulcer closure, a subanalysis, showed a higher proportion of patients experienced complete ulcer closure with esmolol plus standard of care versus standard of care. For example, in plantar-based ulcers, esmolol led to complete closure in 58.7% vs. 43.1%, while for nonplantar ulcers, complete closure was found in 63.6% vs. 38.1%.
In wounds less than 5 cm2, the proportion of complete closures was 66.0% vs. 50.0% for esmolol compared with standard of care alone, while in wounds over 5 cm2, these proportions were 47.6% vs. 26.9%.
Subanalyses also showed that esmolol was substantially better in patients with BMI greater than 25, ulcer duration over 12 weeks, and A1c above 8%.
Also, a subanalysis stratified by “real-life” situations favored esmolol, showing a 50.9% difference in the proportion of patients with diabetic foot ulcer healing in those with a history of hypertension and a 31.8% difference favoring esmolol in those with an abnormal electrocardiogram.
Overall, the proportions of patients who had an adverse event were 13.2%, 18.4%, and 37.5% in the esmolol plus standard of care, standard of care alone, and vehicle plus standard of care groups, respectively, and the vast majority were unrelated to study drug. There were no serious adverse events in the esmolol plus standard of care group.
A class effect of beta blockers?
The proposed mechanism of action of esmolol relates to a sequence of reducing inflammation (via vasodilation, fibroblast migration, and cytokine reduction); proliferation by beta-blockade (improves keratinocyte migration and epithelialization); and remodeling (increases collagen turnover).
Asked by an audience member if the observations were a class effect and systemic effect of beta-blockers, Dr. Rastogi said he could not say for sure that it was a class effect, but they deliberately used a beta-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist.
“It may not be a systemic effect because we have some patients who use beta-blockers systemically and they still have diabetic foot ulcers,” he said.
Dr. Rastogi and Dr. Dhatariya have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM – Esmolol hydrochloride gel (Galnobax, NovoLead) appears to be a safe and effective novel topical treatment option for diabetic foot ulcers, according to results from a new trial of the drug, which is widely available as a generic and is inexpensive.
Of note, the proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure at 12 weeks with esmolol (plus standard of care) was around 60% compared with just over 40% in patients who received standard of care alone.
Presenting the findings at this year’s annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes was Ashu Rastogi, MD, a professor of endocrinology at the Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research in Chandigarh, India.
“Esmolol can be given topically as a 14% gel and is a novel treatment option in diabetic foot ulcer,” said Dr. Rastogi.
Esmolol, a short-acting beta-adrenergic blocker, is currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for cardiac indications only, such as short-term use for controlling supraventricular tachycardia. Beta-blockers are also used to treat hypertension.
However, esmolol has also been repurposed and formulated as a topical gel for the treatment of hard-to-heal diabetic foot ulcers (mainly neuropathic grade 1).
Audience member Ketan Dhatariya, MBBS, MD, PhD, a National Health Service consultant in diabetes, endocrinology, and general medicine and honorary senior lecturer at Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals, England, enthused about the findings.
“This is an amazing study. I’m part of a working group looking at the updating of a guideline for the International Working Group of the Diabetic Foot, reviewing all the studies on wound healing, specifically pharmacological interventions. This is way beyond anything shown to date in terms of medical intervention. [The authors] should be congratulated; this is really astounding,” he told this news organization.
“Right now, there is very little out there in terms of pharmacological interventions that have shown benefit,” he added. “Once this study has been peer-reviewed and is published properly, it is potentially game-changing because it is a generic, worldwide, cheap, and freely available medication.”
Study across 27 sites in India
Prior phase 1/2 data have shown that 60% of ulcers completely closed with esmolol (14% gel) compared with 39% with standard of care. Encouraged by these findings, a phase 3 randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study was conducted across 27 sites in India.
Patients were a mean age of 56 years, and had a body mass index (BMI) of 25-26 kg/m2 and mean hemoglobin A1c of 8.4%-8.7%. Around 70% of participants were men. Mean ulcer area was approximately 460-500 mm2, two-thirds of the ulcers were plantar, and mean ulcer duration was 40-50 weeks.
After screening and discontinuations (39 participants), a 12-week treatment phase began with patients randomized to one of three groups: esmolol (14% gel) along with standard of care administered twice daily (57 completers); standard of care only (63 completers); or vehicle gel (placebo) along with standard of care administered twice daily (17 completers).
Standard of care comprised wound cleaning, debridement, maintenance of moist wound environment, twice-daily fresh bandages, and off-loading footwear as needed, and was provided to all participants irrespective of study group.
The 12-week treatment period was followed by an observation period of 12 weeks up to the 24-week study endpoint.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure (100% re-epithelialization without drainage or dressing requirement) within the 12-week treatment phase.
Secondary endpoints included time to target ulcer closure during the 12-week treatment phase and proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure by 24 weeks (end of study). Investigators were blinded throughout.
Subanalyses were conducted based on ulcer location, size, and age, as well as estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 90 mL/min and ankle-brachial index under 0.9 but greater than 0.7.
50% more patients on esmolol had complete ulcer closure
The proportion of participants with complete ulcer closure at 12 weeks was 60.3% in the esmolol plus standard of care group, compared with 41.7% with standard of care only, a difference of 18.6% (odds ratio, 2.13; P = .0276).
“The 24-week end-of-study data show what happened in the 12 weeks following end of treatment,” said Dr. Rastogi, turning to results showing that by 24 weeks the proportion of participants with complete ulcer closure was 77.2% versus 55.6%, respectively, with a difference of 21.6% (OR, 2.71; P = .013).
Time to ulcer closure (a secondary endpoint) was similar between the esmolol plus standard of care vs. standard of care groups (74.3 vs. 72.5 days).
The impact of ulcer location on complete ulcer closure, a subanalysis, showed a higher proportion of patients experienced complete ulcer closure with esmolol plus standard of care versus standard of care. For example, in plantar-based ulcers, esmolol led to complete closure in 58.7% vs. 43.1%, while for nonplantar ulcers, complete closure was found in 63.6% vs. 38.1%.
In wounds less than 5 cm2, the proportion of complete closures was 66.0% vs. 50.0% for esmolol compared with standard of care alone, while in wounds over 5 cm2, these proportions were 47.6% vs. 26.9%.
Subanalyses also showed that esmolol was substantially better in patients with BMI greater than 25, ulcer duration over 12 weeks, and A1c above 8%.
Also, a subanalysis stratified by “real-life” situations favored esmolol, showing a 50.9% difference in the proportion of patients with diabetic foot ulcer healing in those with a history of hypertension and a 31.8% difference favoring esmolol in those with an abnormal electrocardiogram.
Overall, the proportions of patients who had an adverse event were 13.2%, 18.4%, and 37.5% in the esmolol plus standard of care, standard of care alone, and vehicle plus standard of care groups, respectively, and the vast majority were unrelated to study drug. There were no serious adverse events in the esmolol plus standard of care group.
A class effect of beta blockers?
The proposed mechanism of action of esmolol relates to a sequence of reducing inflammation (via vasodilation, fibroblast migration, and cytokine reduction); proliferation by beta-blockade (improves keratinocyte migration and epithelialization); and remodeling (increases collagen turnover).
Asked by an audience member if the observations were a class effect and systemic effect of beta-blockers, Dr. Rastogi said he could not say for sure that it was a class effect, but they deliberately used a beta-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist.
“It may not be a systemic effect because we have some patients who use beta-blockers systemically and they still have diabetic foot ulcers,” he said.
Dr. Rastogi and Dr. Dhatariya have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EASD 2022