User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Children’s share of new COVID-19 cases is on the rise
The cumulative percentage of COVID-19 cases reported in children continues to climb, but “the history behind that cumulative number shows substantial change,” according to a new analysis of state health department data.
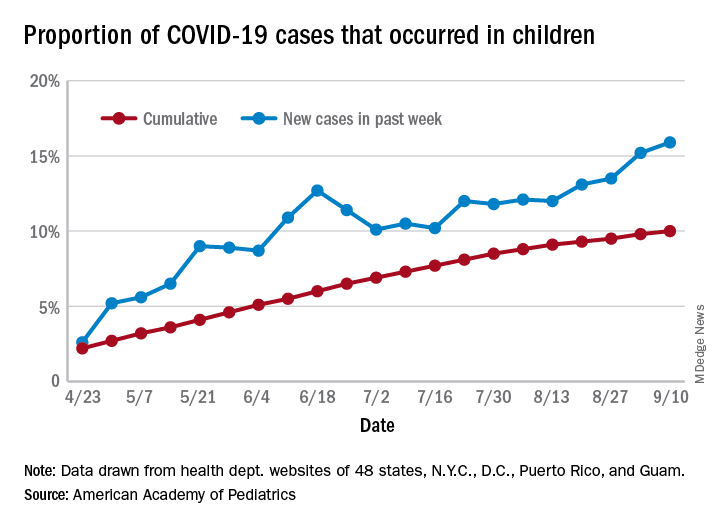
As of Sept. 10, the 549,432 cases in children represented 10.0% of all reported COVID-19 cases in the United States following a substantial rise over the course of the pandemic – the figure was 7.7% on July 16 and 3.2% on May 7, Blake Sisk, PhD, of the American Academy of Pediatrics and associates reported Sept. 29 in Pediatrics.
Unlike the cumulative number, the weekly proportion of cases in children fell early in the summer but then started climbing again in late July. Dr. Sisk and associates wrote.
Despite the increase, however, the proportion of pediatric COVID-19 cases is still well below children’s share of the overall population (22.6%). Also, “it is unclear how much of the increase in child cases is due to increased testing capacity, although CDC data from public and commercial laboratories show the share of all tests administered to children ages 0-17 has remained stable at 5%-7% since late April,” they said.
Data for the current report were drawn from 49 state health department websites (New York state does not report ages for COVID-19 cases), along with New York City, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam. Alabama changed its definition of a child case in August and was not included in the trend analysis (see graph), the investigators explained.
Those data show “substantial variation in case growth by region: in April, a preponderance of cases was in the Northeast. In June, cases surged in the South and West, followed by mid-July increases in the Midwest,” Dr. Sisk and associates said.
The increase among children in Midwest states is ongoing with the number of new cases reaching its highest level yet during the week ending Sept. 10, they reported.
SOURCE: Sisk B et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Sep 29. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-027425.
The cumulative percentage of COVID-19 cases reported in children continues to climb, but “the history behind that cumulative number shows substantial change,” according to a new analysis of state health department data.

As of Sept. 10, the 549,432 cases in children represented 10.0% of all reported COVID-19 cases in the United States following a substantial rise over the course of the pandemic – the figure was 7.7% on July 16 and 3.2% on May 7, Blake Sisk, PhD, of the American Academy of Pediatrics and associates reported Sept. 29 in Pediatrics.
Unlike the cumulative number, the weekly proportion of cases in children fell early in the summer but then started climbing again in late July. Dr. Sisk and associates wrote.
Despite the increase, however, the proportion of pediatric COVID-19 cases is still well below children’s share of the overall population (22.6%). Also, “it is unclear how much of the increase in child cases is due to increased testing capacity, although CDC data from public and commercial laboratories show the share of all tests administered to children ages 0-17 has remained stable at 5%-7% since late April,” they said.
Data for the current report were drawn from 49 state health department websites (New York state does not report ages for COVID-19 cases), along with New York City, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam. Alabama changed its definition of a child case in August and was not included in the trend analysis (see graph), the investigators explained.
Those data show “substantial variation in case growth by region: in April, a preponderance of cases was in the Northeast. In June, cases surged in the South and West, followed by mid-July increases in the Midwest,” Dr. Sisk and associates said.
The increase among children in Midwest states is ongoing with the number of new cases reaching its highest level yet during the week ending Sept. 10, they reported.
SOURCE: Sisk B et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Sep 29. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-027425.
The cumulative percentage of COVID-19 cases reported in children continues to climb, but “the history behind that cumulative number shows substantial change,” according to a new analysis of state health department data.

As of Sept. 10, the 549,432 cases in children represented 10.0% of all reported COVID-19 cases in the United States following a substantial rise over the course of the pandemic – the figure was 7.7% on July 16 and 3.2% on May 7, Blake Sisk, PhD, of the American Academy of Pediatrics and associates reported Sept. 29 in Pediatrics.
Unlike the cumulative number, the weekly proportion of cases in children fell early in the summer but then started climbing again in late July. Dr. Sisk and associates wrote.
Despite the increase, however, the proportion of pediatric COVID-19 cases is still well below children’s share of the overall population (22.6%). Also, “it is unclear how much of the increase in child cases is due to increased testing capacity, although CDC data from public and commercial laboratories show the share of all tests administered to children ages 0-17 has remained stable at 5%-7% since late April,” they said.
Data for the current report were drawn from 49 state health department websites (New York state does not report ages for COVID-19 cases), along with New York City, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam. Alabama changed its definition of a child case in August and was not included in the trend analysis (see graph), the investigators explained.
Those data show “substantial variation in case growth by region: in April, a preponderance of cases was in the Northeast. In June, cases surged in the South and West, followed by mid-July increases in the Midwest,” Dr. Sisk and associates said.
The increase among children in Midwest states is ongoing with the number of new cases reaching its highest level yet during the week ending Sept. 10, they reported.
SOURCE: Sisk B et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Sep 29. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-027425.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Pandemic poses new challenges for rural doctors
These include struggling with seeing patients virtually and treating patients who have politicized the virus. Additionally, the pandemic has exposed rural practices to greater financial difficulties.
Before the pandemic some rurally based primary care physicians were already working through big challenges, such as having few local medical colleagues to consult and working in small practices with lean budgets. In fact, data gathered by the National Rural Health Association showed that there are only 40 primary care physicians per 100,000 patients in rural regions, compared with 53 in urban areas – and the number of physicians overall is 13 per 10,000 in rural areas, compared with 31 in cities.
In the prepandemic world, for some doctors, the challenges were balanced by the benefits of practicing in these sparsely populated communities with scenic, low-traffic roads. Some perks of practicing in rural areas touted by doctors included having a fast commute, being able to swim in a lake near the office before work, having a low cost of living, and feeling like they are making a difference in their communities as they treat generations of the families they see around town.
But today, new hurdles to practicing medicine in rural America created by the COVID-19 pandemic have caused the hardships to feel heavier than the joys at times for some physicians interviewed by MDedge.
Many independent rural practices in need of assistance were not able to get much from the federal Provider Relief Funds, said John M. Westfall, MD, who is director of the Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies in Family Medicine and Primary Care, in an interview.
“Rural primary care doctors function independently or in smaller critical access hospitals and community health centers,” said Dr. Westfall, who previously practiced family medicine in a small town in Colorado. “Many of these have much less financial reserves so are at risk of cutbacks and closure.”
Jacqueline W. Fincher, MD, an internist based in a tiny Georgia community along the highway between Atlanta and Augusta, said her small practice works on really thin margins and doesn’t have much cushion. At the beginning of the pandemic, all visits were down, and her practice operated at a loss. To help, Dr. Fincher and her colleagues applied for funding from the Small Business Administration’s Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) through the CARES Act.
“COVID-19 has had a tremendous impact especially on primary care practices. We live and die by volume. … Our volume in mid-March to mid-May really dropped dramatically,” explained Dr. Fincher, who is also president of the American College of Physicians. “The PPP sustained us for 2 months, enabling us to pay our staff and to remain open and get us up and running on telehealth.”
Starting up telemedicine
Experiencing spotty or no access to broadband Internet is nothing new to rural physicians, but having this problem interfere with their ability to provide care to patients is.
As much of the American health system rapidly embraced telehealth during the pandemic, obtaining access to high-speed Internet has been a major challenge for rural patients, noted Dr. Westfall.
“Some practices were able to quickly adopt some telehealth capacity with phone and video. Changes in payment for telehealth helped. But in some rural communities there was not adequate Internet bandwidth for quality video connections. And some patients did not have the means for high-speed video connections,” Dr. Westfall said.
Indeed, according to a 2019 Pew Research Center survey, 63% of rural Americans say they can access the Internet through a broadband connection at home, compared with 75% and 79% in suburban and urban areas, respectively.
In the Appalachian town of Zanesville, Ohio, for example, family physician Shelly L. Dunmyer, MD, and her colleagues discovered that many patients don’t have Internet access at home. Dr. Fincher has to go to the office to conduct telehealth visits because her own Internet access at home is unpredictable. As for patients, it may take 15 minutes for them to work out technical glitches and find good Internet reception, said Dr. Fincher. For internist Y. Ki Shin, MD, who practices in the coastal town of Montesano in Washington state, about 25% of his practice’s telehealth visits must be conducted by phone because of limitations on video, such as lack of high-speed access.
But telephone visits are often insufficient replacements for appointments via video, according to several rural physicians interviewed for this piece.
“Telehealth can be frustrating at times due to connectivity issues which can be difficult at times in the rural areas,” said Dr. Fincher. “In order for telehealth to be reasonably helpful to patients and physicians to care for people with chronic problems, the patients must have things like blood pressure monitors, glucometers, and scales to address problems like hypertension, diabetes myelitis, and congestive heart failure.”
“If you have the audio and video and the data from these devices, you’re good. If you don’t have these data, and/or don’t have the video you just can’t provide good care,” she explained.
Dr. Dunmyer and her colleagues at Medical Home Primary Care Center in Zanesville, Ohio, found a way to get around the problem of patients not being able to access Internet to participate in video visits from their homes. This involved having her patients drive into her practice’s parking lot to participate in modified telehealth visits. Staffers gave iPads to patients in their cars, and Dr. Dunmyer conducted visits from her office, about 50 yards away.
“We were even doing Medicare wellness visits: Instead of asking them to get up and move around the room, we would sit at the window and wave at them, ask them to get out, walk around the car. We were able to check mobility and all kinds of things that we’d normally do in the office,” Dr. Dunmyer explained in an interview.
The family physician noted that her practice is now conducting fewer parking lot visits since her office is allowing in-person appointments, but that they’re still an option for her patients.
Treating political adversaries
Some rural physicians have experienced strained relationships with patients for reasons other than technology – stark differences in opinion over the pandemic itself. Certain patients are following President Trump’s lead and questioning everything from the pandemic death toll to preventive measures recommended by scientists and medical experts, physicians interviewed by MDedge said.
Patients everywhere share these viewpoints, of course, but research and election results confirm that rural areas are more receptive to conservative viewpoints. In 2018, a Pew Research Center survey reported that rural and urban areas are “becoming more polarized politically,” and “rural areas tend to have a higher concentration of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents.” For example, 40% of rural respondents reported “very warm” or “somewhat warm” feelings toward Donald Trump, compared with just 19% in urban areas.
Dr. Shin has struggled to cope with patients who want to argue about pandemic safety precautions like wearing masks and seem to question whether systemic racism exists.
“We are seeing a lot more people who feel that this pandemic is not real, that it’s a political and not-true infection,” he said in an interview. “We’ve had patients who were angry at us because we made them wear masks, and some were demanding hydroxychloroquine and wanted to have an argument because we’re not going to prescribe it for them.”
In one situation, which he found especially disturbing, Dr. Shin had to leave the exam room because a patient wouldn’t stop challenging him regarding the pandemic. Things have gotten so bad that Dr. Shin has even questioned whether he wants to continue his long career in his small town because of local political attitudes such as opposition to mask-wearing and social distancing.
“Mr. Trump’s misinformation on this pandemic made my job much more difficult. As a minority, I feel less safe in my community than ever,” said Dr. Shin, who described himself as Asian American.
Despite these new stressors, Dr. Shin has experienced some joyful moments while practicing medicine in the pandemic.
He said a recent home visit to a patient who had been hospitalized for over 3 months and nearly died helped him put political disputes with his patients into perspective.
“He was discharged home but is bedbound. He had gangrene on his toes, and I could not fully examine him using video,” Dr. Shin recalled. “It was tricky to find the house, but a very large Trump sign was very helpful in locating it. It was a good visit: He was happy to see me, and I was happy to see that he was doing okay at home.”
“I need to remind myself that supporting Mr. Trump does not always mean that my patient supports Mr. Trump’s view on the pandemic and the race issues in our country,” Dr. Shin added.
The Washington-based internist said he also tells himself that, even if his patients refuse to follow his strong advice regarding pandemic precautions, it does not mean he has failed as a doctor.
“I need to continue to educate patients about the dangers of COVID infection but cannot be angry if they don’t choose to follow my recommendations,” he noted.
Dr. Fincher says her close connection with patients has allowed her to smooth over politically charged claims about the pandemic in the town of Thomson, Georgia, with a population 6,800.
“I have a sense that, even though we may differ in our understanding of some basic facts, they appreciate what I say since we have a long-term relationship built on trust,” she said. This kind of trust, Dr. Fincher suggested, may be more common than in urban areas where there’s a larger supply of physicians, and patients don’t see the same doctors for long periods of time.
“It’s more meaningful when it comes from me, rather than doctors who are [new to patients] every year when their employer changes their insurance,” she noted.
These include struggling with seeing patients virtually and treating patients who have politicized the virus. Additionally, the pandemic has exposed rural practices to greater financial difficulties.
Before the pandemic some rurally based primary care physicians were already working through big challenges, such as having few local medical colleagues to consult and working in small practices with lean budgets. In fact, data gathered by the National Rural Health Association showed that there are only 40 primary care physicians per 100,000 patients in rural regions, compared with 53 in urban areas – and the number of physicians overall is 13 per 10,000 in rural areas, compared with 31 in cities.
In the prepandemic world, for some doctors, the challenges were balanced by the benefits of practicing in these sparsely populated communities with scenic, low-traffic roads. Some perks of practicing in rural areas touted by doctors included having a fast commute, being able to swim in a lake near the office before work, having a low cost of living, and feeling like they are making a difference in their communities as they treat generations of the families they see around town.
But today, new hurdles to practicing medicine in rural America created by the COVID-19 pandemic have caused the hardships to feel heavier than the joys at times for some physicians interviewed by MDedge.
Many independent rural practices in need of assistance were not able to get much from the federal Provider Relief Funds, said John M. Westfall, MD, who is director of the Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies in Family Medicine and Primary Care, in an interview.
“Rural primary care doctors function independently or in smaller critical access hospitals and community health centers,” said Dr. Westfall, who previously practiced family medicine in a small town in Colorado. “Many of these have much less financial reserves so are at risk of cutbacks and closure.”
Jacqueline W. Fincher, MD, an internist based in a tiny Georgia community along the highway between Atlanta and Augusta, said her small practice works on really thin margins and doesn’t have much cushion. At the beginning of the pandemic, all visits were down, and her practice operated at a loss. To help, Dr. Fincher and her colleagues applied for funding from the Small Business Administration’s Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) through the CARES Act.
“COVID-19 has had a tremendous impact especially on primary care practices. We live and die by volume. … Our volume in mid-March to mid-May really dropped dramatically,” explained Dr. Fincher, who is also president of the American College of Physicians. “The PPP sustained us for 2 months, enabling us to pay our staff and to remain open and get us up and running on telehealth.”
Starting up telemedicine
Experiencing spotty or no access to broadband Internet is nothing new to rural physicians, but having this problem interfere with their ability to provide care to patients is.
As much of the American health system rapidly embraced telehealth during the pandemic, obtaining access to high-speed Internet has been a major challenge for rural patients, noted Dr. Westfall.
“Some practices were able to quickly adopt some telehealth capacity with phone and video. Changes in payment for telehealth helped. But in some rural communities there was not adequate Internet bandwidth for quality video connections. And some patients did not have the means for high-speed video connections,” Dr. Westfall said.
Indeed, according to a 2019 Pew Research Center survey, 63% of rural Americans say they can access the Internet through a broadband connection at home, compared with 75% and 79% in suburban and urban areas, respectively.
In the Appalachian town of Zanesville, Ohio, for example, family physician Shelly L. Dunmyer, MD, and her colleagues discovered that many patients don’t have Internet access at home. Dr. Fincher has to go to the office to conduct telehealth visits because her own Internet access at home is unpredictable. As for patients, it may take 15 minutes for them to work out technical glitches and find good Internet reception, said Dr. Fincher. For internist Y. Ki Shin, MD, who practices in the coastal town of Montesano in Washington state, about 25% of his practice’s telehealth visits must be conducted by phone because of limitations on video, such as lack of high-speed access.
But telephone visits are often insufficient replacements for appointments via video, according to several rural physicians interviewed for this piece.
“Telehealth can be frustrating at times due to connectivity issues which can be difficult at times in the rural areas,” said Dr. Fincher. “In order for telehealth to be reasonably helpful to patients and physicians to care for people with chronic problems, the patients must have things like blood pressure monitors, glucometers, and scales to address problems like hypertension, diabetes myelitis, and congestive heart failure.”
“If you have the audio and video and the data from these devices, you’re good. If you don’t have these data, and/or don’t have the video you just can’t provide good care,” she explained.
Dr. Dunmyer and her colleagues at Medical Home Primary Care Center in Zanesville, Ohio, found a way to get around the problem of patients not being able to access Internet to participate in video visits from their homes. This involved having her patients drive into her practice’s parking lot to participate in modified telehealth visits. Staffers gave iPads to patients in their cars, and Dr. Dunmyer conducted visits from her office, about 50 yards away.
“We were even doing Medicare wellness visits: Instead of asking them to get up and move around the room, we would sit at the window and wave at them, ask them to get out, walk around the car. We were able to check mobility and all kinds of things that we’d normally do in the office,” Dr. Dunmyer explained in an interview.
The family physician noted that her practice is now conducting fewer parking lot visits since her office is allowing in-person appointments, but that they’re still an option for her patients.
Treating political adversaries
Some rural physicians have experienced strained relationships with patients for reasons other than technology – stark differences in opinion over the pandemic itself. Certain patients are following President Trump’s lead and questioning everything from the pandemic death toll to preventive measures recommended by scientists and medical experts, physicians interviewed by MDedge said.
Patients everywhere share these viewpoints, of course, but research and election results confirm that rural areas are more receptive to conservative viewpoints. In 2018, a Pew Research Center survey reported that rural and urban areas are “becoming more polarized politically,” and “rural areas tend to have a higher concentration of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents.” For example, 40% of rural respondents reported “very warm” or “somewhat warm” feelings toward Donald Trump, compared with just 19% in urban areas.
Dr. Shin has struggled to cope with patients who want to argue about pandemic safety precautions like wearing masks and seem to question whether systemic racism exists.
“We are seeing a lot more people who feel that this pandemic is not real, that it’s a political and not-true infection,” he said in an interview. “We’ve had patients who were angry at us because we made them wear masks, and some were demanding hydroxychloroquine and wanted to have an argument because we’re not going to prescribe it for them.”
In one situation, which he found especially disturbing, Dr. Shin had to leave the exam room because a patient wouldn’t stop challenging him regarding the pandemic. Things have gotten so bad that Dr. Shin has even questioned whether he wants to continue his long career in his small town because of local political attitudes such as opposition to mask-wearing and social distancing.
“Mr. Trump’s misinformation on this pandemic made my job much more difficult. As a minority, I feel less safe in my community than ever,” said Dr. Shin, who described himself as Asian American.
Despite these new stressors, Dr. Shin has experienced some joyful moments while practicing medicine in the pandemic.
He said a recent home visit to a patient who had been hospitalized for over 3 months and nearly died helped him put political disputes with his patients into perspective.
“He was discharged home but is bedbound. He had gangrene on his toes, and I could not fully examine him using video,” Dr. Shin recalled. “It was tricky to find the house, but a very large Trump sign was very helpful in locating it. It was a good visit: He was happy to see me, and I was happy to see that he was doing okay at home.”
“I need to remind myself that supporting Mr. Trump does not always mean that my patient supports Mr. Trump’s view on the pandemic and the race issues in our country,” Dr. Shin added.
The Washington-based internist said he also tells himself that, even if his patients refuse to follow his strong advice regarding pandemic precautions, it does not mean he has failed as a doctor.
“I need to continue to educate patients about the dangers of COVID infection but cannot be angry if they don’t choose to follow my recommendations,” he noted.
Dr. Fincher says her close connection with patients has allowed her to smooth over politically charged claims about the pandemic in the town of Thomson, Georgia, with a population 6,800.
“I have a sense that, even though we may differ in our understanding of some basic facts, they appreciate what I say since we have a long-term relationship built on trust,” she said. This kind of trust, Dr. Fincher suggested, may be more common than in urban areas where there’s a larger supply of physicians, and patients don’t see the same doctors for long periods of time.
“It’s more meaningful when it comes from me, rather than doctors who are [new to patients] every year when their employer changes their insurance,” she noted.
These include struggling with seeing patients virtually and treating patients who have politicized the virus. Additionally, the pandemic has exposed rural practices to greater financial difficulties.
Before the pandemic some rurally based primary care physicians were already working through big challenges, such as having few local medical colleagues to consult and working in small practices with lean budgets. In fact, data gathered by the National Rural Health Association showed that there are only 40 primary care physicians per 100,000 patients in rural regions, compared with 53 in urban areas – and the number of physicians overall is 13 per 10,000 in rural areas, compared with 31 in cities.
In the prepandemic world, for some doctors, the challenges were balanced by the benefits of practicing in these sparsely populated communities with scenic, low-traffic roads. Some perks of practicing in rural areas touted by doctors included having a fast commute, being able to swim in a lake near the office before work, having a low cost of living, and feeling like they are making a difference in their communities as they treat generations of the families they see around town.
But today, new hurdles to practicing medicine in rural America created by the COVID-19 pandemic have caused the hardships to feel heavier than the joys at times for some physicians interviewed by MDedge.
Many independent rural practices in need of assistance were not able to get much from the federal Provider Relief Funds, said John M. Westfall, MD, who is director of the Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies in Family Medicine and Primary Care, in an interview.
“Rural primary care doctors function independently or in smaller critical access hospitals and community health centers,” said Dr. Westfall, who previously practiced family medicine in a small town in Colorado. “Many of these have much less financial reserves so are at risk of cutbacks and closure.”
Jacqueline W. Fincher, MD, an internist based in a tiny Georgia community along the highway between Atlanta and Augusta, said her small practice works on really thin margins and doesn’t have much cushion. At the beginning of the pandemic, all visits were down, and her practice operated at a loss. To help, Dr. Fincher and her colleagues applied for funding from the Small Business Administration’s Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) through the CARES Act.
“COVID-19 has had a tremendous impact especially on primary care practices. We live and die by volume. … Our volume in mid-March to mid-May really dropped dramatically,” explained Dr. Fincher, who is also president of the American College of Physicians. “The PPP sustained us for 2 months, enabling us to pay our staff and to remain open and get us up and running on telehealth.”
Starting up telemedicine
Experiencing spotty or no access to broadband Internet is nothing new to rural physicians, but having this problem interfere with their ability to provide care to patients is.
As much of the American health system rapidly embraced telehealth during the pandemic, obtaining access to high-speed Internet has been a major challenge for rural patients, noted Dr. Westfall.
“Some practices were able to quickly adopt some telehealth capacity with phone and video. Changes in payment for telehealth helped. But in some rural communities there was not adequate Internet bandwidth for quality video connections. And some patients did not have the means for high-speed video connections,” Dr. Westfall said.
Indeed, according to a 2019 Pew Research Center survey, 63% of rural Americans say they can access the Internet through a broadband connection at home, compared with 75% and 79% in suburban and urban areas, respectively.
In the Appalachian town of Zanesville, Ohio, for example, family physician Shelly L. Dunmyer, MD, and her colleagues discovered that many patients don’t have Internet access at home. Dr. Fincher has to go to the office to conduct telehealth visits because her own Internet access at home is unpredictable. As for patients, it may take 15 minutes for them to work out technical glitches and find good Internet reception, said Dr. Fincher. For internist Y. Ki Shin, MD, who practices in the coastal town of Montesano in Washington state, about 25% of his practice’s telehealth visits must be conducted by phone because of limitations on video, such as lack of high-speed access.
But telephone visits are often insufficient replacements for appointments via video, according to several rural physicians interviewed for this piece.
“Telehealth can be frustrating at times due to connectivity issues which can be difficult at times in the rural areas,” said Dr. Fincher. “In order for telehealth to be reasonably helpful to patients and physicians to care for people with chronic problems, the patients must have things like blood pressure monitors, glucometers, and scales to address problems like hypertension, diabetes myelitis, and congestive heart failure.”
“If you have the audio and video and the data from these devices, you’re good. If you don’t have these data, and/or don’t have the video you just can’t provide good care,” she explained.
Dr. Dunmyer and her colleagues at Medical Home Primary Care Center in Zanesville, Ohio, found a way to get around the problem of patients not being able to access Internet to participate in video visits from their homes. This involved having her patients drive into her practice’s parking lot to participate in modified telehealth visits. Staffers gave iPads to patients in their cars, and Dr. Dunmyer conducted visits from her office, about 50 yards away.
“We were even doing Medicare wellness visits: Instead of asking them to get up and move around the room, we would sit at the window and wave at them, ask them to get out, walk around the car. We were able to check mobility and all kinds of things that we’d normally do in the office,” Dr. Dunmyer explained in an interview.
The family physician noted that her practice is now conducting fewer parking lot visits since her office is allowing in-person appointments, but that they’re still an option for her patients.
Treating political adversaries
Some rural physicians have experienced strained relationships with patients for reasons other than technology – stark differences in opinion over the pandemic itself. Certain patients are following President Trump’s lead and questioning everything from the pandemic death toll to preventive measures recommended by scientists and medical experts, physicians interviewed by MDedge said.
Patients everywhere share these viewpoints, of course, but research and election results confirm that rural areas are more receptive to conservative viewpoints. In 2018, a Pew Research Center survey reported that rural and urban areas are “becoming more polarized politically,” and “rural areas tend to have a higher concentration of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents.” For example, 40% of rural respondents reported “very warm” or “somewhat warm” feelings toward Donald Trump, compared with just 19% in urban areas.
Dr. Shin has struggled to cope with patients who want to argue about pandemic safety precautions like wearing masks and seem to question whether systemic racism exists.
“We are seeing a lot more people who feel that this pandemic is not real, that it’s a political and not-true infection,” he said in an interview. “We’ve had patients who were angry at us because we made them wear masks, and some were demanding hydroxychloroquine and wanted to have an argument because we’re not going to prescribe it for them.”
In one situation, which he found especially disturbing, Dr. Shin had to leave the exam room because a patient wouldn’t stop challenging him regarding the pandemic. Things have gotten so bad that Dr. Shin has even questioned whether he wants to continue his long career in his small town because of local political attitudes such as opposition to mask-wearing and social distancing.
“Mr. Trump’s misinformation on this pandemic made my job much more difficult. As a minority, I feel less safe in my community than ever,” said Dr. Shin, who described himself as Asian American.
Despite these new stressors, Dr. Shin has experienced some joyful moments while practicing medicine in the pandemic.
He said a recent home visit to a patient who had been hospitalized for over 3 months and nearly died helped him put political disputes with his patients into perspective.
“He was discharged home but is bedbound. He had gangrene on his toes, and I could not fully examine him using video,” Dr. Shin recalled. “It was tricky to find the house, but a very large Trump sign was very helpful in locating it. It was a good visit: He was happy to see me, and I was happy to see that he was doing okay at home.”
“I need to remind myself that supporting Mr. Trump does not always mean that my patient supports Mr. Trump’s view on the pandemic and the race issues in our country,” Dr. Shin added.
The Washington-based internist said he also tells himself that, even if his patients refuse to follow his strong advice regarding pandemic precautions, it does not mean he has failed as a doctor.
“I need to continue to educate patients about the dangers of COVID infection but cannot be angry if they don’t choose to follow my recommendations,” he noted.
Dr. Fincher says her close connection with patients has allowed her to smooth over politically charged claims about the pandemic in the town of Thomson, Georgia, with a population 6,800.
“I have a sense that, even though we may differ in our understanding of some basic facts, they appreciate what I say since we have a long-term relationship built on trust,” she said. This kind of trust, Dr. Fincher suggested, may be more common than in urban areas where there’s a larger supply of physicians, and patients don’t see the same doctors for long periods of time.
“It’s more meaningful when it comes from me, rather than doctors who are [new to patients] every year when their employer changes their insurance,” she noted.
Higher glycemic time in range may benefit T2D patients
Patients with type 2 or type 1 diabetes who stay in a blood glucose range of 70-180 mg/dL at least 70% of the time have the lowest rates of major adverse coronary events, severe hypoglycemic episodes, and microvascular events, according to a post hoc analysis of data collected from 5,774 patients with type 2 diabetes.
Data collected by the DEVOTE trial showed that every additional 10% of the time that a patient with type 2 diabetes (T2D) spent in their target range for blood glucose linked with a significant 6% reduced rate for developing a major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE), Richard M. Bergenstal, MD, said at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
For every 10% increase in time in range (TIR), patients showed an average 10% drop in their incidence of severe hypoglycemic episodes.
Increasing evidence from post hoc analyses
These findings confirmed a prior post hoc analysis of data collected in the DCCT trial (NCT00360815), which were published in the New England Journal of Medicine, although those results showed significant relationships between increased TIR and decreased rates of retinopathy and microalbuminuria. For every 10% drop in TIR, retinopathy rose by 64% and microalbuminuria increased by 40%, according to a post hoc analysis of the DCCT data that Dr. Bergenstal helped run and was published in Diabetes Care.
“It’s becoming clear that time in range is an important metric for diabetes management, and our new findings and those previously reported with the DCCT data make it look like time in range is becoming a good marker for clinical outcomes as well,” said Dr. Bergenstal, an endocrinologist at the Park Nicollet Clinic in Minneapolis.
“It’s a new concept, getting time-in-range data,” said Dr. Bergenstal, who was a coauthor of recommendations from Diabetes Care that were made in 2019 by an expert panel organized by the Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes Congress. “We think this will be a good marker to keep glycemia in a safe range, and the results look positive.” Patients who stay in the blood glucose range of 70-180 mg/dL (3.9-10.0 mmol/L) at least 70% of the time generally have an hemoglobin A1c of about 7%, which is what makes it a good target for patients and clinicians to focus on. Patients with a 50% TIR rate generally have an HbA1c of about 8%.
But a TIR assessment can be more informative than HbA1c, said the 2019 recommendations document. It called TIR assessments “appropriate and useful as clinical targets and outcome measurements that complement A1c for a wide range of people with diabetes.”
Data mining from DEVOTE
The analysis run by Dr. Bergenstal and his associates used data from 5,774 of the 7,637 patients enrolled in the DEVOTE trial, for whom adequate longitudinal blood glucose data were available to derive and track TIR. DEVOTE had the primary aim of comparing two different types of insulin in patients with T2D, according to its explanation in the New England Journal of Medicine. The DEVOTE patients did not undergo routine continuous blood glucose monitoring, so derivation of TIR was the only option with the dataset, Dr. Bergenstal said. “We’re trying to get continuous blood monitoring into T2D trials,” he said.
The post hoc analysis showed that, during the study’s follow-up of just under 2 years, patients who maintained a derived TIR of 70%-100% had about a 6% MACE rate, which peaked at nearly twice that in patients whose TIR was 30% or less. The analysis showed a roughly positive linear relationship between TIR and MACE rates across the range of TIR values. In an adjusted analysis, patients with at least a 70% TIR had a significant 31% lower rate of MACE events, compared with patients whose TIR was 50% or less.
A second analysis that looked for the association between TIR and incidence of hypoglycemic episodes showed a somewhat similar positive relationship, with incidence rates of severe hypoglycemia episodes of about 4%-5% among patients with a TIR of 70% or greater, and a rate of about 7% in patients with a TIR of 30% or less, spiking to 14% among patients with a TIR of 10% or less. In an adjusted analysis, patients with a TIR of at least 70% had a significant 46% lower rate of severe hypoglycemic events, compared with patients whose TIR was 50% or less. This finding belies a common misconception that the tighter glycemic control that produces a higher TIR will lead to increased episodes of severe hypoglycemia, Dr. Bergenstal noted.
He also reported less extensive data on microvascular events. In an adjusted analysis, patients with a TIR of at least 70% had a significant 40% cut in these events compared with patients with 50% or less TIR.
DEVOTE was funded by Novo Nordisk. Dr. Bergenstal has had financial relationships with Novo Nordisk and several other companies.
SOURCE: Bergenstal R et al. EASD 2020, abstract 159.
Patients with type 2 or type 1 diabetes who stay in a blood glucose range of 70-180 mg/dL at least 70% of the time have the lowest rates of major adverse coronary events, severe hypoglycemic episodes, and microvascular events, according to a post hoc analysis of data collected from 5,774 patients with type 2 diabetes.
Data collected by the DEVOTE trial showed that every additional 10% of the time that a patient with type 2 diabetes (T2D) spent in their target range for blood glucose linked with a significant 6% reduced rate for developing a major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE), Richard M. Bergenstal, MD, said at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
For every 10% increase in time in range (TIR), patients showed an average 10% drop in their incidence of severe hypoglycemic episodes.
Increasing evidence from post hoc analyses
These findings confirmed a prior post hoc analysis of data collected in the DCCT trial (NCT00360815), which were published in the New England Journal of Medicine, although those results showed significant relationships between increased TIR and decreased rates of retinopathy and microalbuminuria. For every 10% drop in TIR, retinopathy rose by 64% and microalbuminuria increased by 40%, according to a post hoc analysis of the DCCT data that Dr. Bergenstal helped run and was published in Diabetes Care.
“It’s becoming clear that time in range is an important metric for diabetes management, and our new findings and those previously reported with the DCCT data make it look like time in range is becoming a good marker for clinical outcomes as well,” said Dr. Bergenstal, an endocrinologist at the Park Nicollet Clinic in Minneapolis.
“It’s a new concept, getting time-in-range data,” said Dr. Bergenstal, who was a coauthor of recommendations from Diabetes Care that were made in 2019 by an expert panel organized by the Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes Congress. “We think this will be a good marker to keep glycemia in a safe range, and the results look positive.” Patients who stay in the blood glucose range of 70-180 mg/dL (3.9-10.0 mmol/L) at least 70% of the time generally have an hemoglobin A1c of about 7%, which is what makes it a good target for patients and clinicians to focus on. Patients with a 50% TIR rate generally have an HbA1c of about 8%.
But a TIR assessment can be more informative than HbA1c, said the 2019 recommendations document. It called TIR assessments “appropriate and useful as clinical targets and outcome measurements that complement A1c for a wide range of people with diabetes.”
Data mining from DEVOTE
The analysis run by Dr. Bergenstal and his associates used data from 5,774 of the 7,637 patients enrolled in the DEVOTE trial, for whom adequate longitudinal blood glucose data were available to derive and track TIR. DEVOTE had the primary aim of comparing two different types of insulin in patients with T2D, according to its explanation in the New England Journal of Medicine. The DEVOTE patients did not undergo routine continuous blood glucose monitoring, so derivation of TIR was the only option with the dataset, Dr. Bergenstal said. “We’re trying to get continuous blood monitoring into T2D trials,” he said.
The post hoc analysis showed that, during the study’s follow-up of just under 2 years, patients who maintained a derived TIR of 70%-100% had about a 6% MACE rate, which peaked at nearly twice that in patients whose TIR was 30% or less. The analysis showed a roughly positive linear relationship between TIR and MACE rates across the range of TIR values. In an adjusted analysis, patients with at least a 70% TIR had a significant 31% lower rate of MACE events, compared with patients whose TIR was 50% or less.
A second analysis that looked for the association between TIR and incidence of hypoglycemic episodes showed a somewhat similar positive relationship, with incidence rates of severe hypoglycemia episodes of about 4%-5% among patients with a TIR of 70% or greater, and a rate of about 7% in patients with a TIR of 30% or less, spiking to 14% among patients with a TIR of 10% or less. In an adjusted analysis, patients with a TIR of at least 70% had a significant 46% lower rate of severe hypoglycemic events, compared with patients whose TIR was 50% or less. This finding belies a common misconception that the tighter glycemic control that produces a higher TIR will lead to increased episodes of severe hypoglycemia, Dr. Bergenstal noted.
He also reported less extensive data on microvascular events. In an adjusted analysis, patients with a TIR of at least 70% had a significant 40% cut in these events compared with patients with 50% or less TIR.
DEVOTE was funded by Novo Nordisk. Dr. Bergenstal has had financial relationships with Novo Nordisk and several other companies.
SOURCE: Bergenstal R et al. EASD 2020, abstract 159.
Patients with type 2 or type 1 diabetes who stay in a blood glucose range of 70-180 mg/dL at least 70% of the time have the lowest rates of major adverse coronary events, severe hypoglycemic episodes, and microvascular events, according to a post hoc analysis of data collected from 5,774 patients with type 2 diabetes.
Data collected by the DEVOTE trial showed that every additional 10% of the time that a patient with type 2 diabetes (T2D) spent in their target range for blood glucose linked with a significant 6% reduced rate for developing a major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE), Richard M. Bergenstal, MD, said at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
For every 10% increase in time in range (TIR), patients showed an average 10% drop in their incidence of severe hypoglycemic episodes.
Increasing evidence from post hoc analyses
These findings confirmed a prior post hoc analysis of data collected in the DCCT trial (NCT00360815), which were published in the New England Journal of Medicine, although those results showed significant relationships between increased TIR and decreased rates of retinopathy and microalbuminuria. For every 10% drop in TIR, retinopathy rose by 64% and microalbuminuria increased by 40%, according to a post hoc analysis of the DCCT data that Dr. Bergenstal helped run and was published in Diabetes Care.
“It’s becoming clear that time in range is an important metric for diabetes management, and our new findings and those previously reported with the DCCT data make it look like time in range is becoming a good marker for clinical outcomes as well,” said Dr. Bergenstal, an endocrinologist at the Park Nicollet Clinic in Minneapolis.
“It’s a new concept, getting time-in-range data,” said Dr. Bergenstal, who was a coauthor of recommendations from Diabetes Care that were made in 2019 by an expert panel organized by the Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes Congress. “We think this will be a good marker to keep glycemia in a safe range, and the results look positive.” Patients who stay in the blood glucose range of 70-180 mg/dL (3.9-10.0 mmol/L) at least 70% of the time generally have an hemoglobin A1c of about 7%, which is what makes it a good target for patients and clinicians to focus on. Patients with a 50% TIR rate generally have an HbA1c of about 8%.
But a TIR assessment can be more informative than HbA1c, said the 2019 recommendations document. It called TIR assessments “appropriate and useful as clinical targets and outcome measurements that complement A1c for a wide range of people with diabetes.”
Data mining from DEVOTE
The analysis run by Dr. Bergenstal and his associates used data from 5,774 of the 7,637 patients enrolled in the DEVOTE trial, for whom adequate longitudinal blood glucose data were available to derive and track TIR. DEVOTE had the primary aim of comparing two different types of insulin in patients with T2D, according to its explanation in the New England Journal of Medicine. The DEVOTE patients did not undergo routine continuous blood glucose monitoring, so derivation of TIR was the only option with the dataset, Dr. Bergenstal said. “We’re trying to get continuous blood monitoring into T2D trials,” he said.
The post hoc analysis showed that, during the study’s follow-up of just under 2 years, patients who maintained a derived TIR of 70%-100% had about a 6% MACE rate, which peaked at nearly twice that in patients whose TIR was 30% or less. The analysis showed a roughly positive linear relationship between TIR and MACE rates across the range of TIR values. In an adjusted analysis, patients with at least a 70% TIR had a significant 31% lower rate of MACE events, compared with patients whose TIR was 50% or less.
A second analysis that looked for the association between TIR and incidence of hypoglycemic episodes showed a somewhat similar positive relationship, with incidence rates of severe hypoglycemia episodes of about 4%-5% among patients with a TIR of 70% or greater, and a rate of about 7% in patients with a TIR of 30% or less, spiking to 14% among patients with a TIR of 10% or less. In an adjusted analysis, patients with a TIR of at least 70% had a significant 46% lower rate of severe hypoglycemic events, compared with patients whose TIR was 50% or less. This finding belies a common misconception that the tighter glycemic control that produces a higher TIR will lead to increased episodes of severe hypoglycemia, Dr. Bergenstal noted.
He also reported less extensive data on microvascular events. In an adjusted analysis, patients with a TIR of at least 70% had a significant 40% cut in these events compared with patients with 50% or less TIR.
DEVOTE was funded by Novo Nordisk. Dr. Bergenstal has had financial relationships with Novo Nordisk and several other companies.
SOURCE: Bergenstal R et al. EASD 2020, abstract 159.
FROM EASD 2020
Exercise cuts diabetes death risk by a third in two studies
Type 2 diabetes patients could lower their risk for death from any cause by up to a third by exercising at a moderate to high level or by cycling, according to data from two studies reported at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Yun-Ju Lai, MD, and colleagues from the Puli branch of Taichung Veterans General Hospital in Nantou, Taiwan, found that persons with type 2 diabetes who exercised at moderate to high intensity had a 25%-32% decreased risk for death, compared with those who did not exercise.
In a separate study, Mathias Ried-Larsen, MSc, PhD, group leader at the Centre for Physical Activity Research, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, and associates found that cycling was associated with a 25%-31% decreased risk for all-cause death compared to no cycling, and that cycling also reduced cardiovascular mortality.
Results fit with ADA recommendations
“There is really nothing surprising about these results as others have shown that regular participation in physical activity lowers both overall mortality rates and morbidity,” commented Sheri Colberg-Ochs, PhD, professor emerita in exercise science at Old Dominion University in Norfolk, Va., in an interview.
“Regular exercise participation lowers the risk of mortality in almost all populations with many different health conditions. It is not specific to people with type 2 diabetes,” Dr. Colberg-Ochs said. “These data add further support to the ADA [American Diabetes Association] recommendations by again suggesting that being more active leads to many health benefits for people with type 2 diabetes.”
Dr. Colberg-Ochs, who was not involved in either study, is recognized by the ADA as an Outstanding Educator in Diabetes. She was also involved in writing the ADA’s position statement on physical activity/exercise in diabetes, which advocate that adults with type 2 diabetes should reduce sedentary time and undertake both aerobic and resistance exercise training to help optimize their glycemic and general health outcomes.
Asian population understudied
In an interview Dr. Lai acknowledged that epidemiologic studies had shown that exercise reduced the risk of cardiovascular events and mortality in subjects with type 2 diabetes. “However, the dose of exercise capacity for reducing mortality risk in people with type 2 diabetes was not yet well investigated, especially in the Asian population.”
Dr. Lai and colleagues analyzed data on 4,859 subjects drawn from two Taiwanese databases – the National Health Interview Survey and the National Health Insurance research database – to study what effect exercise “capacity” had on the risk for death in those with type 2 diabetes.
“Information about physical activity during leisure time was collected by asking the questions: ‘How often do you exercise every week? What kind of exercise do you do? How long do you do the exercise?’, Dr. Lai said. “We included nearly all kinds of exercise in the analysis, such as jogging, swimming, walking, dancing, riding, and so on.”
Each exercise had an activity intensity code expressed as kilocalories per minute. This was used to determine the exercise “capacity” by multiplying it by how frequently the exercise was performed per week and for how long each time.
“I don’t think ‘capacity’ is the right word to use here. The equation they used describes their exercise ‘volume,’ not their capacity. Self-reported exercise is notoriously inaccurate,” Dr. Colberg-Ochs observed. Furthermore, “just asking people how much they exercise and at what intensity [without using a validated exercise questionnaire] gives questionable results.”
The study’s findings, however, were clear: Those who exercised at a higher level had a significantly decreased risk for all-cause mortality than did those with no exercise habits. The hazard ratio for death by any cause was 0.75 for those who undertook a moderate level of exercise, burning 0-800 kcal per week. Exercising at a higher level burned more than 800 kcal had a HR of 0.68. A significant (P < .01) trend in favor of more exercise was noted.
Cycling reduces all-cause and cardiovascular mortality
In their prospective cohort study, Dr. Ried-Larsen and associates took a more specific look at the effects of exercise on mortality in diabetes by studying a single exercise: cycling. They sampled data on more than 5,000 people collected as part of the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition study. First, they identified participants with diabetes – although they couldn’t distinguish type 1 from type 2 forms because this was self-reported or obtained from registries. They then identified those who reported cycling at their baseline assessment and those who reported a change in cycling habits at their second examination around 5 years later.
At baseline, 38% of participants reported that they cycled every week. The mean age was 56 years, diabetes duration was 8 years, one-fifth were smokers, and the average body mass index was 29 kg/m2.
Participants who reported cycling up to 1 hour every week at baseline had a 25% reduction in all-cause mortality, compared with those who did not cycle. The biggest reduction (31%) in all-cause mortality was seen for cycling 2.5-5 hours a week; cycling for 1-2.5 hours, and for more than 5 hours, yielded 23% and 24% risk reductions, respectively.
A reverse J–shaped relationship between cycling duration and reduction in all-cause mortality was seen, Dr. Ried-Larsen noted during a live oral session at the virtual meeting. “The maximum benefit [was at] around 5 hours per week, and the benefits persisted until around 9 hours per week.” Adjustment for the prevalence of stroke, MI, cancer, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and central obesity did not alter the findings.
“The direction of the association was the same for cardiovascular mortality as all-cause mortality, although a bit weaker, with the maximum benefit being around 4 hours per week, and that persisted up until around 8 hours per week,” Dr. Ried-Larsen said.
The benefits of cycling on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality were lost, however, if those who cycled at baseline stopped by the second examination. Those who did not cycle at the first but did at the second examination got a benefit on both, as did those who continued cycling.
“Cycling is among one of the preferred activities for diabetes patients, so it actually may help them to achieve the recommend level of physical activity,” Dr. Ried-Larsen said.
Tailored exercise program important
Advice for exercise “should be tailored to the individual and based on starting fitness levels and activity levels,” Dr. Colberg-Ochs recommended.
“Those who are the most sedentary and the least fit have the most to gain from doing any activity. They should be advised to start out slowly and progress slowly with both aerobic activities and some resistance training,” Dr. Colberg-Ochs said.
She added: “In addition, individuals over 40 should engage in regular balance training, and all individuals should do some flexibility exercises.”
The studies received no commercial funding and all those mentioned in this article had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Lai Y-J et al. EASD 2020, Poster presentation 267; Ried-Larsen M et al. EASD 2020, Oral presentation 194.
Type 2 diabetes patients could lower their risk for death from any cause by up to a third by exercising at a moderate to high level or by cycling, according to data from two studies reported at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Yun-Ju Lai, MD, and colleagues from the Puli branch of Taichung Veterans General Hospital in Nantou, Taiwan, found that persons with type 2 diabetes who exercised at moderate to high intensity had a 25%-32% decreased risk for death, compared with those who did not exercise.
In a separate study, Mathias Ried-Larsen, MSc, PhD, group leader at the Centre for Physical Activity Research, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, and associates found that cycling was associated with a 25%-31% decreased risk for all-cause death compared to no cycling, and that cycling also reduced cardiovascular mortality.
Results fit with ADA recommendations
“There is really nothing surprising about these results as others have shown that regular participation in physical activity lowers both overall mortality rates and morbidity,” commented Sheri Colberg-Ochs, PhD, professor emerita in exercise science at Old Dominion University in Norfolk, Va., in an interview.
“Regular exercise participation lowers the risk of mortality in almost all populations with many different health conditions. It is not specific to people with type 2 diabetes,” Dr. Colberg-Ochs said. “These data add further support to the ADA [American Diabetes Association] recommendations by again suggesting that being more active leads to many health benefits for people with type 2 diabetes.”
Dr. Colberg-Ochs, who was not involved in either study, is recognized by the ADA as an Outstanding Educator in Diabetes. She was also involved in writing the ADA’s position statement on physical activity/exercise in diabetes, which advocate that adults with type 2 diabetes should reduce sedentary time and undertake both aerobic and resistance exercise training to help optimize their glycemic and general health outcomes.
Asian population understudied
In an interview Dr. Lai acknowledged that epidemiologic studies had shown that exercise reduced the risk of cardiovascular events and mortality in subjects with type 2 diabetes. “However, the dose of exercise capacity for reducing mortality risk in people with type 2 diabetes was not yet well investigated, especially in the Asian population.”
Dr. Lai and colleagues analyzed data on 4,859 subjects drawn from two Taiwanese databases – the National Health Interview Survey and the National Health Insurance research database – to study what effect exercise “capacity” had on the risk for death in those with type 2 diabetes.
“Information about physical activity during leisure time was collected by asking the questions: ‘How often do you exercise every week? What kind of exercise do you do? How long do you do the exercise?’, Dr. Lai said. “We included nearly all kinds of exercise in the analysis, such as jogging, swimming, walking, dancing, riding, and so on.”
Each exercise had an activity intensity code expressed as kilocalories per minute. This was used to determine the exercise “capacity” by multiplying it by how frequently the exercise was performed per week and for how long each time.
“I don’t think ‘capacity’ is the right word to use here. The equation they used describes their exercise ‘volume,’ not their capacity. Self-reported exercise is notoriously inaccurate,” Dr. Colberg-Ochs observed. Furthermore, “just asking people how much they exercise and at what intensity [without using a validated exercise questionnaire] gives questionable results.”
The study’s findings, however, were clear: Those who exercised at a higher level had a significantly decreased risk for all-cause mortality than did those with no exercise habits. The hazard ratio for death by any cause was 0.75 for those who undertook a moderate level of exercise, burning 0-800 kcal per week. Exercising at a higher level burned more than 800 kcal had a HR of 0.68. A significant (P < .01) trend in favor of more exercise was noted.
Cycling reduces all-cause and cardiovascular mortality
In their prospective cohort study, Dr. Ried-Larsen and associates took a more specific look at the effects of exercise on mortality in diabetes by studying a single exercise: cycling. They sampled data on more than 5,000 people collected as part of the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition study. First, they identified participants with diabetes – although they couldn’t distinguish type 1 from type 2 forms because this was self-reported or obtained from registries. They then identified those who reported cycling at their baseline assessment and those who reported a change in cycling habits at their second examination around 5 years later.
At baseline, 38% of participants reported that they cycled every week. The mean age was 56 years, diabetes duration was 8 years, one-fifth were smokers, and the average body mass index was 29 kg/m2.
Participants who reported cycling up to 1 hour every week at baseline had a 25% reduction in all-cause mortality, compared with those who did not cycle. The biggest reduction (31%) in all-cause mortality was seen for cycling 2.5-5 hours a week; cycling for 1-2.5 hours, and for more than 5 hours, yielded 23% and 24% risk reductions, respectively.
A reverse J–shaped relationship between cycling duration and reduction in all-cause mortality was seen, Dr. Ried-Larsen noted during a live oral session at the virtual meeting. “The maximum benefit [was at] around 5 hours per week, and the benefits persisted until around 9 hours per week.” Adjustment for the prevalence of stroke, MI, cancer, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and central obesity did not alter the findings.
“The direction of the association was the same for cardiovascular mortality as all-cause mortality, although a bit weaker, with the maximum benefit being around 4 hours per week, and that persisted up until around 8 hours per week,” Dr. Ried-Larsen said.
The benefits of cycling on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality were lost, however, if those who cycled at baseline stopped by the second examination. Those who did not cycle at the first but did at the second examination got a benefit on both, as did those who continued cycling.
“Cycling is among one of the preferred activities for diabetes patients, so it actually may help them to achieve the recommend level of physical activity,” Dr. Ried-Larsen said.
Tailored exercise program important
Advice for exercise “should be tailored to the individual and based on starting fitness levels and activity levels,” Dr. Colberg-Ochs recommended.
“Those who are the most sedentary and the least fit have the most to gain from doing any activity. They should be advised to start out slowly and progress slowly with both aerobic activities and some resistance training,” Dr. Colberg-Ochs said.
She added: “In addition, individuals over 40 should engage in regular balance training, and all individuals should do some flexibility exercises.”
The studies received no commercial funding and all those mentioned in this article had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Lai Y-J et al. EASD 2020, Poster presentation 267; Ried-Larsen M et al. EASD 2020, Oral presentation 194.
Type 2 diabetes patients could lower their risk for death from any cause by up to a third by exercising at a moderate to high level or by cycling, according to data from two studies reported at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Yun-Ju Lai, MD, and colleagues from the Puli branch of Taichung Veterans General Hospital in Nantou, Taiwan, found that persons with type 2 diabetes who exercised at moderate to high intensity had a 25%-32% decreased risk for death, compared with those who did not exercise.
In a separate study, Mathias Ried-Larsen, MSc, PhD, group leader at the Centre for Physical Activity Research, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, and associates found that cycling was associated with a 25%-31% decreased risk for all-cause death compared to no cycling, and that cycling also reduced cardiovascular mortality.
Results fit with ADA recommendations
“There is really nothing surprising about these results as others have shown that regular participation in physical activity lowers both overall mortality rates and morbidity,” commented Sheri Colberg-Ochs, PhD, professor emerita in exercise science at Old Dominion University in Norfolk, Va., in an interview.
“Regular exercise participation lowers the risk of mortality in almost all populations with many different health conditions. It is not specific to people with type 2 diabetes,” Dr. Colberg-Ochs said. “These data add further support to the ADA [American Diabetes Association] recommendations by again suggesting that being more active leads to many health benefits for people with type 2 diabetes.”
Dr. Colberg-Ochs, who was not involved in either study, is recognized by the ADA as an Outstanding Educator in Diabetes. She was also involved in writing the ADA’s position statement on physical activity/exercise in diabetes, which advocate that adults with type 2 diabetes should reduce sedentary time and undertake both aerobic and resistance exercise training to help optimize their glycemic and general health outcomes.
Asian population understudied
In an interview Dr. Lai acknowledged that epidemiologic studies had shown that exercise reduced the risk of cardiovascular events and mortality in subjects with type 2 diabetes. “However, the dose of exercise capacity for reducing mortality risk in people with type 2 diabetes was not yet well investigated, especially in the Asian population.”
Dr. Lai and colleagues analyzed data on 4,859 subjects drawn from two Taiwanese databases – the National Health Interview Survey and the National Health Insurance research database – to study what effect exercise “capacity” had on the risk for death in those with type 2 diabetes.
“Information about physical activity during leisure time was collected by asking the questions: ‘How often do you exercise every week? What kind of exercise do you do? How long do you do the exercise?’, Dr. Lai said. “We included nearly all kinds of exercise in the analysis, such as jogging, swimming, walking, dancing, riding, and so on.”
Each exercise had an activity intensity code expressed as kilocalories per minute. This was used to determine the exercise “capacity” by multiplying it by how frequently the exercise was performed per week and for how long each time.
“I don’t think ‘capacity’ is the right word to use here. The equation they used describes their exercise ‘volume,’ not their capacity. Self-reported exercise is notoriously inaccurate,” Dr. Colberg-Ochs observed. Furthermore, “just asking people how much they exercise and at what intensity [without using a validated exercise questionnaire] gives questionable results.”
The study’s findings, however, were clear: Those who exercised at a higher level had a significantly decreased risk for all-cause mortality than did those with no exercise habits. The hazard ratio for death by any cause was 0.75 for those who undertook a moderate level of exercise, burning 0-800 kcal per week. Exercising at a higher level burned more than 800 kcal had a HR of 0.68. A significant (P < .01) trend in favor of more exercise was noted.
Cycling reduces all-cause and cardiovascular mortality
In their prospective cohort study, Dr. Ried-Larsen and associates took a more specific look at the effects of exercise on mortality in diabetes by studying a single exercise: cycling. They sampled data on more than 5,000 people collected as part of the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition study. First, they identified participants with diabetes – although they couldn’t distinguish type 1 from type 2 forms because this was self-reported or obtained from registries. They then identified those who reported cycling at their baseline assessment and those who reported a change in cycling habits at their second examination around 5 years later.
At baseline, 38% of participants reported that they cycled every week. The mean age was 56 years, diabetes duration was 8 years, one-fifth were smokers, and the average body mass index was 29 kg/m2.
Participants who reported cycling up to 1 hour every week at baseline had a 25% reduction in all-cause mortality, compared with those who did not cycle. The biggest reduction (31%) in all-cause mortality was seen for cycling 2.5-5 hours a week; cycling for 1-2.5 hours, and for more than 5 hours, yielded 23% and 24% risk reductions, respectively.
A reverse J–shaped relationship between cycling duration and reduction in all-cause mortality was seen, Dr. Ried-Larsen noted during a live oral session at the virtual meeting. “The maximum benefit [was at] around 5 hours per week, and the benefits persisted until around 9 hours per week.” Adjustment for the prevalence of stroke, MI, cancer, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and central obesity did not alter the findings.
“The direction of the association was the same for cardiovascular mortality as all-cause mortality, although a bit weaker, with the maximum benefit being around 4 hours per week, and that persisted up until around 8 hours per week,” Dr. Ried-Larsen said.
The benefits of cycling on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality were lost, however, if those who cycled at baseline stopped by the second examination. Those who did not cycle at the first but did at the second examination got a benefit on both, as did those who continued cycling.
“Cycling is among one of the preferred activities for diabetes patients, so it actually may help them to achieve the recommend level of physical activity,” Dr. Ried-Larsen said.
Tailored exercise program important
Advice for exercise “should be tailored to the individual and based on starting fitness levels and activity levels,” Dr. Colberg-Ochs recommended.
“Those who are the most sedentary and the least fit have the most to gain from doing any activity. They should be advised to start out slowly and progress slowly with both aerobic activities and some resistance training,” Dr. Colberg-Ochs said.
She added: “In addition, individuals over 40 should engage in regular balance training, and all individuals should do some flexibility exercises.”
The studies received no commercial funding and all those mentioned in this article had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Lai Y-J et al. EASD 2020, Poster presentation 267; Ried-Larsen M et al. EASD 2020, Oral presentation 194.
FROM EASD 2020
Revamping mentorship in medicine
Why the current system fails underrepresented physicians — and tips to improve it
Mentoring is often promoted as an organizational practice to promote diversity and inclusion. New or established group members who want to further their careers look for a mentor to guide them toward success within a system by amplifying their strengths and accomplishments and defending and promoting them when necessary. But how can mentoring work if there isn’t a mentor?
For underrepresented groups or marginalized physicians, it too often looks as if there are no mentors who understand the struggles of being a racial or ethnic minority group member or mentors who are even cognizant of those struggles. Mentoring is a practice that occurs within the overarching systems of practice groups, academic departments, hospitals, medicine, and society at large. These systems frequently carry the legacies of bias, discrimination, and exclusion. The mentoring itself that takes place within a biased system risks perpetuating institutional bias, exclusion, or a sense of unworthiness in the mentee. It is stressful for any person with a minority background or even a minority interest to feel that there’s no one to emulate in their immediate working environment. When that is the case, a natural question follows: “Do I even belong here?”
Before departments and psychiatric practices turn to old, surface-level solutions like using mentorship to appear more welcoming to underrepresented groups, leaders must explicitly evaluate their track record of mentorship within their system and determine whether mentorship has been used to protect the status quo or move the culture forward. As mentorship is inherently an imbalanced relationship, there must be department- or group-level reflection about the diversity of mentors and also their examinations of mentors’ own preconceived notions of who will make a “good” mentee.
At the most basic level, leaders can examine whether there are gaps in who is mentored and who is not. Other parts of mentoring relationships should also be examined: a) How can mentoring happen if there is a dearth of underrepresented groups in the department? b) What type of mentoring style is favored? Do departments/groups look for a natural fit between mentor and mentee or are they matched based on interests, ideals, and goals? and c) How is the worthiness for mentorship determined?
One example is the fraught process of evaluating “worthiness” among residents. Prospective mentors frequently divide trainees unofficially into a top-tier candidates, middle-tier performers who may be overlooked, and a bottom tier who are avoided when it comes to mentorship. Because this division is informal and usually based on extremely early perceptions of trainees’ aptitude and openness, the process can be subject to an individual mentor’s conscious and unconscious bias, which then plays a large role in perpetuating systemic racism. When it comes to these informal but often rigid divisions, it can be hard to fall from the top when mentees are buoyed by good will, frequent opportunities to shine, and the mentor’s reputation. Likewise,
Below are three recommendations to consider for improving mentorship within departments:
1) Consider opportunities for senior mentors and potential mentees to interact with one another outside of assigned duties so that some mentorship relationships can be formed organically.
2) Review when mentorship relationships have been ineffective or unsuccessful versus productive and useful for both participants.
3) Increase opportunities for adjunct or former faculty who remain connected to the institution to also be mentors. This approach would open up more possibilities and could increase the diversity of available mentors.
If mentorship is to be part of the armamentarium for promoting equity within academia and workplaces alike, it must be examined and changed to meet the new reality.
Dr. Posada is assistant clinical professor, department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at George Washington University in Washington. She also serves as staff physician at George Washington Medical Faculty Associates, also in Washington. She disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Forrester is consultation-liaison psychiatry fellowship training director at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. She disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Why the current system fails underrepresented physicians — and tips to improve it
Why the current system fails underrepresented physicians — and tips to improve it
Mentoring is often promoted as an organizational practice to promote diversity and inclusion. New or established group members who want to further their careers look for a mentor to guide them toward success within a system by amplifying their strengths and accomplishments and defending and promoting them when necessary. But how can mentoring work if there isn’t a mentor?
For underrepresented groups or marginalized physicians, it too often looks as if there are no mentors who understand the struggles of being a racial or ethnic minority group member or mentors who are even cognizant of those struggles. Mentoring is a practice that occurs within the overarching systems of practice groups, academic departments, hospitals, medicine, and society at large. These systems frequently carry the legacies of bias, discrimination, and exclusion. The mentoring itself that takes place within a biased system risks perpetuating institutional bias, exclusion, or a sense of unworthiness in the mentee. It is stressful for any person with a minority background or even a minority interest to feel that there’s no one to emulate in their immediate working environment. When that is the case, a natural question follows: “Do I even belong here?”
Before departments and psychiatric practices turn to old, surface-level solutions like using mentorship to appear more welcoming to underrepresented groups, leaders must explicitly evaluate their track record of mentorship within their system and determine whether mentorship has been used to protect the status quo or move the culture forward. As mentorship is inherently an imbalanced relationship, there must be department- or group-level reflection about the diversity of mentors and also their examinations of mentors’ own preconceived notions of who will make a “good” mentee.
At the most basic level, leaders can examine whether there are gaps in who is mentored and who is not. Other parts of mentoring relationships should also be examined: a) How can mentoring happen if there is a dearth of underrepresented groups in the department? b) What type of mentoring style is favored? Do departments/groups look for a natural fit between mentor and mentee or are they matched based on interests, ideals, and goals? and c) How is the worthiness for mentorship determined?
One example is the fraught process of evaluating “worthiness” among residents. Prospective mentors frequently divide trainees unofficially into a top-tier candidates, middle-tier performers who may be overlooked, and a bottom tier who are avoided when it comes to mentorship. Because this division is informal and usually based on extremely early perceptions of trainees’ aptitude and openness, the process can be subject to an individual mentor’s conscious and unconscious bias, which then plays a large role in perpetuating systemic racism. When it comes to these informal but often rigid divisions, it can be hard to fall from the top when mentees are buoyed by good will, frequent opportunities to shine, and the mentor’s reputation. Likewise,
Below are three recommendations to consider for improving mentorship within departments:
1) Consider opportunities for senior mentors and potential mentees to interact with one another outside of assigned duties so that some mentorship relationships can be formed organically.
2) Review when mentorship relationships have been ineffective or unsuccessful versus productive and useful for both participants.
3) Increase opportunities for adjunct or former faculty who remain connected to the institution to also be mentors. This approach would open up more possibilities and could increase the diversity of available mentors.
If mentorship is to be part of the armamentarium for promoting equity within academia and workplaces alike, it must be examined and changed to meet the new reality.
Dr. Posada is assistant clinical professor, department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at George Washington University in Washington. She also serves as staff physician at George Washington Medical Faculty Associates, also in Washington. She disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Forrester is consultation-liaison psychiatry fellowship training director at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. She disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Mentoring is often promoted as an organizational practice to promote diversity and inclusion. New or established group members who want to further their careers look for a mentor to guide them toward success within a system by amplifying their strengths and accomplishments and defending and promoting them when necessary. But how can mentoring work if there isn’t a mentor?
For underrepresented groups or marginalized physicians, it too often looks as if there are no mentors who understand the struggles of being a racial or ethnic minority group member or mentors who are even cognizant of those struggles. Mentoring is a practice that occurs within the overarching systems of practice groups, academic departments, hospitals, medicine, and society at large. These systems frequently carry the legacies of bias, discrimination, and exclusion. The mentoring itself that takes place within a biased system risks perpetuating institutional bias, exclusion, or a sense of unworthiness in the mentee. It is stressful for any person with a minority background or even a minority interest to feel that there’s no one to emulate in their immediate working environment. When that is the case, a natural question follows: “Do I even belong here?”
Before departments and psychiatric practices turn to old, surface-level solutions like using mentorship to appear more welcoming to underrepresented groups, leaders must explicitly evaluate their track record of mentorship within their system and determine whether mentorship has been used to protect the status quo or move the culture forward. As mentorship is inherently an imbalanced relationship, there must be department- or group-level reflection about the diversity of mentors and also their examinations of mentors’ own preconceived notions of who will make a “good” mentee.
At the most basic level, leaders can examine whether there are gaps in who is mentored and who is not. Other parts of mentoring relationships should also be examined: a) How can mentoring happen if there is a dearth of underrepresented groups in the department? b) What type of mentoring style is favored? Do departments/groups look for a natural fit between mentor and mentee or are they matched based on interests, ideals, and goals? and c) How is the worthiness for mentorship determined?
One example is the fraught process of evaluating “worthiness” among residents. Prospective mentors frequently divide trainees unofficially into a top-tier candidates, middle-tier performers who may be overlooked, and a bottom tier who are avoided when it comes to mentorship. Because this division is informal and usually based on extremely early perceptions of trainees’ aptitude and openness, the process can be subject to an individual mentor’s conscious and unconscious bias, which then plays a large role in perpetuating systemic racism. When it comes to these informal but often rigid divisions, it can be hard to fall from the top when mentees are buoyed by good will, frequent opportunities to shine, and the mentor’s reputation. Likewise,
Below are three recommendations to consider for improving mentorship within departments:
1) Consider opportunities for senior mentors and potential mentees to interact with one another outside of assigned duties so that some mentorship relationships can be formed organically.
2) Review when mentorship relationships have been ineffective or unsuccessful versus productive and useful for both participants.
3) Increase opportunities for adjunct or former faculty who remain connected to the institution to also be mentors. This approach would open up more possibilities and could increase the diversity of available mentors.
If mentorship is to be part of the armamentarium for promoting equity within academia and workplaces alike, it must be examined and changed to meet the new reality.
Dr. Posada is assistant clinical professor, department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at George Washington University in Washington. She also serves as staff physician at George Washington Medical Faculty Associates, also in Washington. She disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Forrester is consultation-liaison psychiatry fellowship training director at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. She disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
DAPA-CKD resets eGFR floor for safe SGLT2 inhibitor use
The dramatically positive safety and efficacy results from the DAPA-CKD trial, which showed that treatment with the sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor dapagliflozin significantly cut both chronic kidney disease progression and all-cause death in patients with or without type 2 diabetes, were also notable for broadening the population of patients eligible for this treatment to those in the upper range of stage 4 CKD.
Of the 4,304 CKD patients enrolled in DAPA-CKD, 624 (14%) had an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 25-29 mL/min per 1.73m2, an unprecedented population to receive a drug from the SGLT2 inhibitor class in a reported study. The results provided definitive evidence for efficacy and safety in this range of renal function, said Hiddo J.L. Heerspink, Ph.D., at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Until now, the widely accepted lowest level for starting an SGLT2 inhibitor in routine practice has been an eGFR as low as 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
Using SGLT2 inhibitors when eGFR is as low as 25
“It’s time to reduce the eGFR level for initiating an SGLT2 inhibitor to as low as 25,” said Dr. Heerspink, a professor of clinical pharmacology at the University of Groningen (the Netherlands).
While conceding that this is primarily a decision to be made by guideline writers and regulatory bodies, he declared what he believed was established by the DAPA-CKD findings: “We’ve shown that dapagliflozin can be safely used in these patients. It is effective across the spectrum of kidney function.”
Other experts not associated with the study agreed.
The trial researchers were “brave” to enroll patients with eGFRs as low as 25 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and “we urgently need these agents in patients with an eGFR this low,” commented Chantal Mathieu, MD, an endocrinologist and professor of medicine at Catholic University in Leuven, Belgium, and designated discussant for the report. Overall, she called the findings “spectacular,” a “landmark trial,” and a “winner.”
The study also set an new, lower floor for the level of albuminuria that can be usefully treated with dapagliflozin (Farxiga) by enrolling patients with a urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio as low as 200 mg/g; the previous lower limit had been 300 mg/g, noted Dr. Mathieu. The new findings pose challenges to guideline writers, regulators who approve drug labels, and payers to a quickly make changes that will bring dapagliflozin to a wider number of patients with CKD.
Once the full DAPA-CKD results are reported, “it will change practice, and push the eGFR needle down” to as low as 25. It will also lower the albuminuria threshold for using dapagliflozin or other drugs in the class, commented David Z.I. Cherney, MD, a nephrologist at the University of Toronto. “It’s just one study,” he admitted, but the consistent renal benefits seen across several studies involving all four drugs in the SGLT2 inhibitor class will help hasten this change in identifying treatable patients, as well as expand the drug class to patients with CKD but no type 2 diabetes (T2D).
“I don’t think we’ve ever had stronger evidence” for drugs that can benefit both heart and renal function, plus the drug class is “very safe, and really easy to start” and maintain in patients, Dr. Cherney said in an interview. “It’s wonderful for these patients that we now have something new for treatment,” a drug with a “very favorable benefit-to-risk ratio.”
Results show many dapagliflozin benefits
While this broadening of the range of patients proven to tolerate and benefit from an SGLT2 inhibitor was an important consequence of DAPA-CKD, the study’s primary finding – that dapagliflozin was as safe and effective for slowing CKD progression in patients regardless of whether they also had T2D – will have an even bigger impact on expanding the target patient population. Showing efficacy in patients with CKD but without a T2D etiology, the status of about a third of the enrolled 4,304 patients, makes this treatment an option for “millions” of additional patients worldwide, said Dr. Heerspink. “These are the most common patients nephrologists see.” A major challenge now will be to do a better job finding patients with CKD who could benefit from dapagliflozin.
DAPA-CKD enrolled CKD patients based primarily on prespecified albuminuria and eGFR levels at more than 300 centers in 34 countries, including the United States. Virtually all patients, 97%, were on the only treatment now available with proven efficacy for slowing CKD, either an ACE inhibitor or an angiotensin receptor blocker. The small number of patients not on one of these drugs was because of poor tolerance.
The study’s primary endpoint was the combined rate of cardiovascular death, renal death, end-stage renal disease, or a drop in eGFR of at least 50% from baseline. This occurred in 14.5% of patients who received placebo and in 9.2% of those who received dapagliflozin during a median follow-up of 2.4 years, a highly significant 39% relative risk reduction. Concurrently with the report at the virtual meeting the results also appeared online in the New England Journal of Medicine. This 5.3% cut in the absolute rate of the combined, primary adverse outcome converted into a number needed to treat of 19 to prevent 1 event during 2.4 years, a “much lower” number needed to treat than reported for renin-angiotensin system inhibitors in these types of patients, Dr. Heerspink said.
Notable positive secondary outcomes included a significant 31% relative cut (a 2% absolute decline) in all-cause mortality, “a major highlight” of the findings, Dr. Heerspink said. Dapagliflozin treatment also linked with a significant 29% relative cut in the incidence of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure.
“Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death in patients with CKD,” explained David C. Wheeler, MD, a coinvestigator on the study and professor of kidney medicine at University College London. “The heart and kidney are intertwined. This is about cardiorenal disease.”
DAPA-CKD was funded by AstraZeneca, the company that markets dapagliflozin. Dr. Heerspink has been a consultant to and received research funding from AstraZeneca. He has also received personal fees from Mundipharma and Novo Nordisk, and he has also served as consultant to several other companies with the honoraria being paid to his institution. Dr. Mathieu has had relationships with AstraZeneca and several other companies. Dr. Cherney has been a consultant to and has received research funding from AstraZeneca and several other companies. Dr. Wheeler has received personal fees from AstraZeneca and from several other companies.
SOURCE: Heerspink HJL et al. EASD 2020 and N Engl J Med. 2020 Sep 24. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2024816.
The dramatically positive safety and efficacy results from the DAPA-CKD trial, which showed that treatment with the sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor dapagliflozin significantly cut both chronic kidney disease progression and all-cause death in patients with or without type 2 diabetes, were also notable for broadening the population of patients eligible for this treatment to those in the upper range of stage 4 CKD.
Of the 4,304 CKD patients enrolled in DAPA-CKD, 624 (14%) had an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 25-29 mL/min per 1.73m2, an unprecedented population to receive a drug from the SGLT2 inhibitor class in a reported study. The results provided definitive evidence for efficacy and safety in this range of renal function, said Hiddo J.L. Heerspink, Ph.D., at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Until now, the widely accepted lowest level for starting an SGLT2 inhibitor in routine practice has been an eGFR as low as 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
Using SGLT2 inhibitors when eGFR is as low as 25
“It’s time to reduce the eGFR level for initiating an SGLT2 inhibitor to as low as 25,” said Dr. Heerspink, a professor of clinical pharmacology at the University of Groningen (the Netherlands).
While conceding that this is primarily a decision to be made by guideline writers and regulatory bodies, he declared what he believed was established by the DAPA-CKD findings: “We’ve shown that dapagliflozin can be safely used in these patients. It is effective across the spectrum of kidney function.”
Other experts not associated with the study agreed.
The trial researchers were “brave” to enroll patients with eGFRs as low as 25 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and “we urgently need these agents in patients with an eGFR this low,” commented Chantal Mathieu, MD, an endocrinologist and professor of medicine at Catholic University in Leuven, Belgium, and designated discussant for the report. Overall, she called the findings “spectacular,” a “landmark trial,” and a “winner.”
The study also set an new, lower floor for the level of albuminuria that can be usefully treated with dapagliflozin (Farxiga) by enrolling patients with a urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio as low as 200 mg/g; the previous lower limit had been 300 mg/g, noted Dr. Mathieu. The new findings pose challenges to guideline writers, regulators who approve drug labels, and payers to a quickly make changes that will bring dapagliflozin to a wider number of patients with CKD.
Once the full DAPA-CKD results are reported, “it will change practice, and push the eGFR needle down” to as low as 25. It will also lower the albuminuria threshold for using dapagliflozin or other drugs in the class, commented David Z.I. Cherney, MD, a nephrologist at the University of Toronto. “It’s just one study,” he admitted, but the consistent renal benefits seen across several studies involving all four drugs in the SGLT2 inhibitor class will help hasten this change in identifying treatable patients, as well as expand the drug class to patients with CKD but no type 2 diabetes (T2D).
“I don’t think we’ve ever had stronger evidence” for drugs that can benefit both heart and renal function, plus the drug class is “very safe, and really easy to start” and maintain in patients, Dr. Cherney said in an interview. “It’s wonderful for these patients that we now have something new for treatment,” a drug with a “very favorable benefit-to-risk ratio.”
Results show many dapagliflozin benefits
While this broadening of the range of patients proven to tolerate and benefit from an SGLT2 inhibitor was an important consequence of DAPA-CKD, the study’s primary finding – that dapagliflozin was as safe and effective for slowing CKD progression in patients regardless of whether they also had T2D – will have an even bigger impact on expanding the target patient population. Showing efficacy in patients with CKD but without a T2D etiology, the status of about a third of the enrolled 4,304 patients, makes this treatment an option for “millions” of additional patients worldwide, said Dr. Heerspink. “These are the most common patients nephrologists see.” A major challenge now will be to do a better job finding patients with CKD who could benefit from dapagliflozin.
DAPA-CKD enrolled CKD patients based primarily on prespecified albuminuria and eGFR levels at more than 300 centers in 34 countries, including the United States. Virtually all patients, 97%, were on the only treatment now available with proven efficacy for slowing CKD, either an ACE inhibitor or an angiotensin receptor blocker. The small number of patients not on one of these drugs was because of poor tolerance.
The study’s primary endpoint was the combined rate of cardiovascular death, renal death, end-stage renal disease, or a drop in eGFR of at least 50% from baseline. This occurred in 14.5% of patients who received placebo and in 9.2% of those who received dapagliflozin during a median follow-up of 2.4 years, a highly significant 39% relative risk reduction. Concurrently with the report at the virtual meeting the results also appeared online in the New England Journal of Medicine. This 5.3% cut in the absolute rate of the combined, primary adverse outcome converted into a number needed to treat of 19 to prevent 1 event during 2.4 years, a “much lower” number needed to treat than reported for renin-angiotensin system inhibitors in these types of patients, Dr. Heerspink said.
Notable positive secondary outcomes included a significant 31% relative cut (a 2% absolute decline) in all-cause mortality, “a major highlight” of the findings, Dr. Heerspink said. Dapagliflozin treatment also linked with a significant 29% relative cut in the incidence of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure.
“Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death in patients with CKD,” explained David C. Wheeler, MD, a coinvestigator on the study and professor of kidney medicine at University College London. “The heart and kidney are intertwined. This is about cardiorenal disease.”
DAPA-CKD was funded by AstraZeneca, the company that markets dapagliflozin. Dr. Heerspink has been a consultant to and received research funding from AstraZeneca. He has also received personal fees from Mundipharma and Novo Nordisk, and he has also served as consultant to several other companies with the honoraria being paid to his institution. Dr. Mathieu has had relationships with AstraZeneca and several other companies. Dr. Cherney has been a consultant to and has received research funding from AstraZeneca and several other companies. Dr. Wheeler has received personal fees from AstraZeneca and from several other companies.
SOURCE: Heerspink HJL et al. EASD 2020 and N Engl J Med. 2020 Sep 24. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2024816.
The dramatically positive safety and efficacy results from the DAPA-CKD trial, which showed that treatment with the sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor dapagliflozin significantly cut both chronic kidney disease progression and all-cause death in patients with or without type 2 diabetes, were also notable for broadening the population of patients eligible for this treatment to those in the upper range of stage 4 CKD.
Of the 4,304 CKD patients enrolled in DAPA-CKD, 624 (14%) had an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 25-29 mL/min per 1.73m2, an unprecedented population to receive a drug from the SGLT2 inhibitor class in a reported study. The results provided definitive evidence for efficacy and safety in this range of renal function, said Hiddo J.L. Heerspink, Ph.D., at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Until now, the widely accepted lowest level for starting an SGLT2 inhibitor in routine practice has been an eGFR as low as 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
Using SGLT2 inhibitors when eGFR is as low as 25
“It’s time to reduce the eGFR level for initiating an SGLT2 inhibitor to as low as 25,” said Dr. Heerspink, a professor of clinical pharmacology at the University of Groningen (the Netherlands).
While conceding that this is primarily a decision to be made by guideline writers and regulatory bodies, he declared what he believed was established by the DAPA-CKD findings: “We’ve shown that dapagliflozin can be safely used in these patients. It is effective across the spectrum of kidney function.”
Other experts not associated with the study agreed.
The trial researchers were “brave” to enroll patients with eGFRs as low as 25 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and “we urgently need these agents in patients with an eGFR this low,” commented Chantal Mathieu, MD, an endocrinologist and professor of medicine at Catholic University in Leuven, Belgium, and designated discussant for the report. Overall, she called the findings “spectacular,” a “landmark trial,” and a “winner.”
The study also set an new, lower floor for the level of albuminuria that can be usefully treated with dapagliflozin (Farxiga) by enrolling patients with a urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio as low as 200 mg/g; the previous lower limit had been 300 mg/g, noted Dr. Mathieu. The new findings pose challenges to guideline writers, regulators who approve drug labels, and payers to a quickly make changes that will bring dapagliflozin to a wider number of patients with CKD.
Once the full DAPA-CKD results are reported, “it will change practice, and push the eGFR needle down” to as low as 25. It will also lower the albuminuria threshold for using dapagliflozin or other drugs in the class, commented David Z.I. Cherney, MD, a nephrologist at the University of Toronto. “It’s just one study,” he admitted, but the consistent renal benefits seen across several studies involving all four drugs in the SGLT2 inhibitor class will help hasten this change in identifying treatable patients, as well as expand the drug class to patients with CKD but no type 2 diabetes (T2D).
“I don’t think we’ve ever had stronger evidence” for drugs that can benefit both heart and renal function, plus the drug class is “very safe, and really easy to start” and maintain in patients, Dr. Cherney said in an interview. “It’s wonderful for these patients that we now have something new for treatment,” a drug with a “very favorable benefit-to-risk ratio.”
Results show many dapagliflozin benefits
While this broadening of the range of patients proven to tolerate and benefit from an SGLT2 inhibitor was an important consequence of DAPA-CKD, the study’s primary finding – that dapagliflozin was as safe and effective for slowing CKD progression in patients regardless of whether they also had T2D – will have an even bigger impact on expanding the target patient population. Showing efficacy in patients with CKD but without a T2D etiology, the status of about a third of the enrolled 4,304 patients, makes this treatment an option for “millions” of additional patients worldwide, said Dr. Heerspink. “These are the most common patients nephrologists see.” A major challenge now will be to do a better job finding patients with CKD who could benefit from dapagliflozin.
DAPA-CKD enrolled CKD patients based primarily on prespecified albuminuria and eGFR levels at more than 300 centers in 34 countries, including the United States. Virtually all patients, 97%, were on the only treatment now available with proven efficacy for slowing CKD, either an ACE inhibitor or an angiotensin receptor blocker. The small number of patients not on one of these drugs was because of poor tolerance.
The study’s primary endpoint was the combined rate of cardiovascular death, renal death, end-stage renal disease, or a drop in eGFR of at least 50% from baseline. This occurred in 14.5% of patients who received placebo and in 9.2% of those who received dapagliflozin during a median follow-up of 2.4 years, a highly significant 39% relative risk reduction. Concurrently with the report at the virtual meeting the results also appeared online in the New England Journal of Medicine. This 5.3% cut in the absolute rate of the combined, primary adverse outcome converted into a number needed to treat of 19 to prevent 1 event during 2.4 years, a “much lower” number needed to treat than reported for renin-angiotensin system inhibitors in these types of patients, Dr. Heerspink said.
Notable positive secondary outcomes included a significant 31% relative cut (a 2% absolute decline) in all-cause mortality, “a major highlight” of the findings, Dr. Heerspink said. Dapagliflozin treatment also linked with a significant 29% relative cut in the incidence of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure.
“Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death in patients with CKD,” explained David C. Wheeler, MD, a coinvestigator on the study and professor of kidney medicine at University College London. “The heart and kidney are intertwined. This is about cardiorenal disease.”
DAPA-CKD was funded by AstraZeneca, the company that markets dapagliflozin. Dr. Heerspink has been a consultant to and received research funding from AstraZeneca. He has also received personal fees from Mundipharma and Novo Nordisk, and he has also served as consultant to several other companies with the honoraria being paid to his institution. Dr. Mathieu has had relationships with AstraZeneca and several other companies. Dr. Cherney has been a consultant to and has received research funding from AstraZeneca and several other companies. Dr. Wheeler has received personal fees from AstraZeneca and from several other companies.
SOURCE: Heerspink HJL et al. EASD 2020 and N Engl J Med. 2020 Sep 24. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2024816.
FROM EASD 2020
J&J’s one-shot COVID-19 vaccine advances to phase 3 testing
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, which is aiding Johnson & Johnson with development, described this in a news release as the fourth phase 3 clinical trial of evaluating an investigational vaccine for coronavirus disease.
This NIAID tally tracks products likely to be presented soon for Food and Drug Administration approval. (The World Health Organization’s COVID vaccine tracker lists nine candidates as having reached this stage, including products developed in Russia and China.)
As many as 60,000 volunteers will be enrolled in the trial, with about 215 clinical research sites expected to participate, NIAID said. The vaccine will be tested in the United States and abroad.
The start of this test, known as the ENSEMBLE trial, follows positive results from a Phase 1/2a clinical study, which involved a single vaccination. The results of this study have been submitted to medRxiv and are set to be published online imminently.
New Brunswick, N.J–based J&J said it intends to offer the vaccine on “a not-for-profit basis for emergency pandemic use.” If testing proceeds well, J&J might seek an emergency use clearance for the vaccine, which could possibly allow the first batches to be made available in early 2021.
J&J’s vaccine is unusual in that it will be tested based on a single dose, while other advanced candidates have been tested in two-dose regimens.
J&J on Wednesday also released the study protocol for its phase 3 test. The developers of the other late-stage COVID vaccine candidates also have done this, as reported by Medscape Medical News. Because of the great interest in the COVID vaccine, the American Medical Association had last month asked the FDA to keep physicians informed of their COVID-19 vaccine review process.
Trials and tribulations
One of these experimental COVID vaccines already has had a setback in phase 3 testing, which is a fairly routine occurrence in drug development. But with a pandemic still causing deaths and disrupting lives around the world, there has been intense interest in each step of the effort to develop a COVID vaccine.
AstraZeneca PLC earlier this month announced a temporary cessation of all their coronavirus vaccine trials to investigate an “unexplained illness” that arose in a participant, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
On September 12, AstraZeneca announced that clinical trials for the AZD1222, which it developed with Oxford University, had resumed in the United Kingdom. On Wednesday, CNBC said Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar told the news station that AstraZeneca’s late-stage coronavirus vaccine trial in the United States remains on hold until safety concerns are resolved, a critical issue with all the fast-track COVID vaccines now being tested.
“Look at the AstraZeneca program, phase 3 clinical trial, a lot of hope. [A] single serious adverse event report in the United Kingdom, global shutdown, and [a] hold of the clinical trials,” Mr. Azar told CNBC.
The New York Times has reported on concerns stemming from serious neurologic illnesses in two participants, both women, who received AstraZeneca’s experimental vaccine in Britain.
The Senate Health, Education, Labor and Pensions Committee on Wednesday separately held a hearing with the leaders of the FDA and the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention, allowing an airing of lawmakers’ concerns about a potential rush to approve a COVID vaccine.
Details of J&J trial
The J&J trial is designed primarily to determine if the investigational vaccine can prevent moderate to severe COVID-19 after a single dose. It also is designed to examine whether the vaccine can prevent COVID-19 requiring medical intervention and if the vaccine can prevent milder cases of COVID-19 and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection, NIAID said.
Principal investigators for the phase 3 trial of the J & J vaccine are Paul A. Goepfert, MD, director of the Alabama Vaccine Research Clinic at the University of Alabama in Birmingham; Beatriz Grinsztejn, MD, PhD, director of the Laboratory of Clinical Research on HIV/AIDS at the Evandro Chagas National Institute of Infectious Diseases-Oswaldo Cruz Foundation in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; and Glenda E. Gray, MBBCh, president and chief executive officer of the South African Medical Research Council and coprincipal investigator of the HIV Vaccine Trials Network.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, which is aiding Johnson & Johnson with development, described this in a news release as the fourth phase 3 clinical trial of evaluating an investigational vaccine for coronavirus disease.
This NIAID tally tracks products likely to be presented soon for Food and Drug Administration approval. (The World Health Organization’s COVID vaccine tracker lists nine candidates as having reached this stage, including products developed in Russia and China.)
As many as 60,000 volunteers will be enrolled in the trial, with about 215 clinical research sites expected to participate, NIAID said. The vaccine will be tested in the United States and abroad.
The start of this test, known as the ENSEMBLE trial, follows positive results from a Phase 1/2a clinical study, which involved a single vaccination. The results of this study have been submitted to medRxiv and are set to be published online imminently.
New Brunswick, N.J–based J&J said it intends to offer the vaccine on “a not-for-profit basis for emergency pandemic use.” If testing proceeds well, J&J might seek an emergency use clearance for the vaccine, which could possibly allow the first batches to be made available in early 2021.
J&J’s vaccine is unusual in that it will be tested based on a single dose, while other advanced candidates have been tested in two-dose regimens.
J&J on Wednesday also released the study protocol for its phase 3 test. The developers of the other late-stage COVID vaccine candidates also have done this, as reported by Medscape Medical News. Because of the great interest in the COVID vaccine, the American Medical Association had last month asked the FDA to keep physicians informed of their COVID-19 vaccine review process.
Trials and tribulations
One of these experimental COVID vaccines already has had a setback in phase 3 testing, which is a fairly routine occurrence in drug development. But with a pandemic still causing deaths and disrupting lives around the world, there has been intense interest in each step of the effort to develop a COVID vaccine.
AstraZeneca PLC earlier this month announced a temporary cessation of all their coronavirus vaccine trials to investigate an “unexplained illness” that arose in a participant, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
On September 12, AstraZeneca announced that clinical trials for the AZD1222, which it developed with Oxford University, had resumed in the United Kingdom. On Wednesday, CNBC said Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar told the news station that AstraZeneca’s late-stage coronavirus vaccine trial in the United States remains on hold until safety concerns are resolved, a critical issue with all the fast-track COVID vaccines now being tested.
“Look at the AstraZeneca program, phase 3 clinical trial, a lot of hope. [A] single serious adverse event report in the United Kingdom, global shutdown, and [a] hold of the clinical trials,” Mr. Azar told CNBC.
The New York Times has reported on concerns stemming from serious neurologic illnesses in two participants, both women, who received AstraZeneca’s experimental vaccine in Britain.
The Senate Health, Education, Labor and Pensions Committee on Wednesday separately held a hearing with the leaders of the FDA and the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention, allowing an airing of lawmakers’ concerns about a potential rush to approve a COVID vaccine.
Details of J&J trial
The J&J trial is designed primarily to determine if the investigational vaccine can prevent moderate to severe COVID-19 after a single dose. It also is designed to examine whether the vaccine can prevent COVID-19 requiring medical intervention and if the vaccine can prevent milder cases of COVID-19 and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection, NIAID said.
Principal investigators for the phase 3 trial of the J & J vaccine are Paul A. Goepfert, MD, director of the Alabama Vaccine Research Clinic at the University of Alabama in Birmingham; Beatriz Grinsztejn, MD, PhD, director of the Laboratory of Clinical Research on HIV/AIDS at the Evandro Chagas National Institute of Infectious Diseases-Oswaldo Cruz Foundation in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; and Glenda E. Gray, MBBCh, president and chief executive officer of the South African Medical Research Council and coprincipal investigator of the HIV Vaccine Trials Network.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, which is aiding Johnson & Johnson with development, described this in a news release as the fourth phase 3 clinical trial of evaluating an investigational vaccine for coronavirus disease.
This NIAID tally tracks products likely to be presented soon for Food and Drug Administration approval. (The World Health Organization’s COVID vaccine tracker lists nine candidates as having reached this stage, including products developed in Russia and China.)
As many as 60,000 volunteers will be enrolled in the trial, with about 215 clinical research sites expected to participate, NIAID said. The vaccine will be tested in the United States and abroad.
The start of this test, known as the ENSEMBLE trial, follows positive results from a Phase 1/2a clinical study, which involved a single vaccination. The results of this study have been submitted to medRxiv and are set to be published online imminently.
New Brunswick, N.J–based J&J said it intends to offer the vaccine on “a not-for-profit basis for emergency pandemic use.” If testing proceeds well, J&J might seek an emergency use clearance for the vaccine, which could possibly allow the first batches to be made available in early 2021.
J&J’s vaccine is unusual in that it will be tested based on a single dose, while other advanced candidates have been tested in two-dose regimens.
J&J on Wednesday also released the study protocol for its phase 3 test. The developers of the other late-stage COVID vaccine candidates also have done this, as reported by Medscape Medical News. Because of the great interest in the COVID vaccine, the American Medical Association had last month asked the FDA to keep physicians informed of their COVID-19 vaccine review process.
Trials and tribulations
One of these experimental COVID vaccines already has had a setback in phase 3 testing, which is a fairly routine occurrence in drug development. But with a pandemic still causing deaths and disrupting lives around the world, there has been intense interest in each step of the effort to develop a COVID vaccine.
AstraZeneca PLC earlier this month announced a temporary cessation of all their coronavirus vaccine trials to investigate an “unexplained illness” that arose in a participant, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
On September 12, AstraZeneca announced that clinical trials for the AZD1222, which it developed with Oxford University, had resumed in the United Kingdom. On Wednesday, CNBC said Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar told the news station that AstraZeneca’s late-stage coronavirus vaccine trial in the United States remains on hold until safety concerns are resolved, a critical issue with all the fast-track COVID vaccines now being tested.
“Look at the AstraZeneca program, phase 3 clinical trial, a lot of hope. [A] single serious adverse event report in the United Kingdom, global shutdown, and [a] hold of the clinical trials,” Mr. Azar told CNBC.
The New York Times has reported on concerns stemming from serious neurologic illnesses in two participants, both women, who received AstraZeneca’s experimental vaccine in Britain.
The Senate Health, Education, Labor and Pensions Committee on Wednesday separately held a hearing with the leaders of the FDA and the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention, allowing an airing of lawmakers’ concerns about a potential rush to approve a COVID vaccine.
Details of J&J trial
The J&J trial is designed primarily to determine if the investigational vaccine can prevent moderate to severe COVID-19 after a single dose. It also is designed to examine whether the vaccine can prevent COVID-19 requiring medical intervention and if the vaccine can prevent milder cases of COVID-19 and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection, NIAID said.
Principal investigators for the phase 3 trial of the J & J vaccine are Paul A. Goepfert, MD, director of the Alabama Vaccine Research Clinic at the University of Alabama in Birmingham; Beatriz Grinsztejn, MD, PhD, director of the Laboratory of Clinical Research on HIV/AIDS at the Evandro Chagas National Institute of Infectious Diseases-Oswaldo Cruz Foundation in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; and Glenda E. Gray, MBBCh, president and chief executive officer of the South African Medical Research Council and coprincipal investigator of the HIV Vaccine Trials Network.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VERTIS CV: Ertugliflozin’s proven benefits fall short of other SGLT2 inhibitors
Further analyses from the cardiovascular outcome trial of the sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitor ertugliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes helped better define positive effects the drug had on preserving renal function, and also gave a tantalizing hint that this drug, and hence possibly the entire SGLT2 inhibitor drug class, may benefit patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
But the underlying problem for ertugliflozin (Steglatro) – first seen when results from the VERTIS CV trial initially came out in June 2020 at the annual meeting of the American Diabetes Association – was that, while the trial met its primary endpoint of proving noninferiority to placebo for the combined endpoint of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke, treatment with ertugliflozin showed no suggestion of benefit, compared with placebo for reducing this endpoint, producing a nonsignificant 3% relative cut in the combined rate of these adverse events, compared with placebo treatment.
‘Somewhat disappointing’ trial performance
Overall, results from VERTIS CV with ertugliflozin were “somewhat disappointing,” commented Melanie J. Davies, MD, who was not involved with the study and chaired a session at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes that reviewed the main results, put them into perspective, and added a few new exploratory analyses.
Although the results from 8,246-patient VERTIS CV (Evaluation of Ertugliflozin Efficacy and Safety Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial) put ertugliflozin in the same league as other drugs from its class for safety, “we do not see the significant benefits observed in many of the previous cardiovascular outcomes trials” for other drugs in the SGLT2 inhibitor class, specifically canagliflozin (Invokana), dapagliflozin (Farxiga), and empagliflozin (Jardiance), Dr. Davies said in an interview. The upshot, for at least the time being, is that ertugliflozin “is unlikely to receive a label for any new indications,” she predicted. In contrast, the other drugs in the class have, for example, received a U.S. labeled indication to reduce cardiovascular death (empagliflozin) or major cardiovascular disease events (canagliflozin) in adults with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and cardiovascular disease, or to reduce heart failure hospitalizations (dapagliflozin).
The main results from VERTIS CV, posted online in the New England Journal of Medicine after the EASD session, showed a single significant outcome difference between treatment with ertugliflozin and placebo over a median of 3.0 years of follow-up from among 10 reported secondary outcomes: a 30% relative reduction (a 1.1% absolute reduction) in the rate of hospitalization for heart failure, the sole criterion in the report by which ertugliflozin matched the benefits of the other SGLT2 inhibitors.
But the prespecified design of VERTIS CV called for a hierarchical sequence of secondary analyses. The statistically significant noninferiority of the primary endpoint allowed calculation of the initial secondary endpoint, a reduction in the combined rate of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure. Ertugliflozin treatment cut this outcome by a relative 12%, compared with placebo, a difference that was not significant.
This neutral finding brought to a stop further statistical testing of any of the other secondary endpoints, including impact on hospitalization for heart failure by itself. It also guaranteed that no beneficial effect inferred from the trial’s data would qualify for statistical validity, making it unlikely that ertugliflozin would gain any new label indications from these results. The drug carries a U.S. label that is limited to providing glycemic control.
Choosing among the SGLT2 inhibitors
“What we can say for sure is that there is a glycemic benefit and a heart failure hospitalization benefit” across all four of the SGLT2 inhibitors. “Beyond that, the best we can say today [about using these drugs in practice] is to follow regulatory indications and guidelines recommendations,” commented Javed Butler, MD, a cardiologist and professor and chair of medicine at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson.
“These results are going to lead to some serious discussions among the research, clinical, and regulatory communities about class effects versus drug effects, and specific trial data versus the totality of evidence,” he said in an interview.
“I think it will influence prescribing ertugliflozin, particularly in patients with established cardiovascular disease, or when the goal is to improve heart failure outcomes of reduce chronic kidney disease,” added Dr. Davies, a professor of diabetes medicine at the University of Leicester (England). “We already have positive benefits [proven for these outcomes] using other agents in the class.”
Perhaps one feature potentially in ertugliflozin’s favor is its price, and whatever impact that might have for payers or patients with inadequate coverage for their drug costs. U.S. websites show a typical retail price for ertugliflozin that is roughly 40% below the three other agents in the class, a difference that can add up to an annual cost savings of about $2,500.
A major consideration for clinicians deciding which SGLT2 inhibitor to prescribe should be “what can the patient afford,” noted Darren K. McGuire, MD, a coinvestigator for VERTIS CV, during discussion of the trial at the EASD virtual meeting.
New analyses show more renal-effect consistency
One surprise in the initial VERTIS CV report was in the study’s key renal outcome, a composite of renal death, need for dialysis, or a doubling of the serum creatinine level, which reflects a cut of at least a 50% in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). This composite outcome trended toward a significant benefit but fell short, producing a nominal 19% relative reduction. This combined endpoint probably “set the bar too high,” said David Z.I. Cherney, MD, a nephrologist who led the renal assessments run in the trial. He presented several exploratory analyses during the virtual EASD session that provided reassuring evidence that ertugliflozin was not an outlier among the SGLT2 inhibitors when it came to kidney benefits.
Perhaps the most compelling analysis he reported was a slight tweak to the main renal composite endpoint that substituted prevention of a 40% or greater reduction in eGFR for prevention of a 50% or greater reduction. By this somewhat lower bar for efficacy, treatment with ertugliflozin in VERTIS CV linked with a 34% relative risk reduction, compared with placebo (a roughly 1% absolute reduction) that was statistically significant, and importantly came out very close to the effect for this revised endpoint that had been seen for the other three SGLT2 inhibitor drugs.
Focusing on prevention of a 40% or greater drop in eGFR “gives a much more robust measure of renal protection,” Dr. Cherney, a clinician and researcher at the University of Toronto, said in an interview. “The key message is that renal protection is much more uniform” with the rest of the drugs in the class when looked at this way or by some of the other alternative parameters he reported. But the new renal analyses do not address disparities seen among the drugs in the class for several cardiovascular disease effects.
“The overall impression from VERTIS CV is that there was less cardiovascular disease benefit,” except for prevention of heart failure hospitalization, he said.
A teaser for HFpEF
One additional notable new finding discussed during the EASD session stemmed from the investigators ability to mine the medical records of enrolled patients for information about their heart failure history and left ventricular ejection fractions, a data set that was “unique,” compared with the other cardiovascular outcome trials for the drugs in the class, noted Francesco Cosentino, MD, another VERTIS CV coinvestigator and professor of cardiology at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm.
Roughly a quarter of the enrolled patients had a history of heart failure, and about half of these patients had heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, about 1,000 total patients. In this subgroup treatment with ertugliflozin linked with a 30% relative reduction in hospitalization for heart failure, compared with placebo, a roughly 0.5% absolute reduction. The numbers were small and underpowered for producing convincing evidence, but it provided an intriguing hint of benefit for an unmet need that is currently undergoing further testing in studies designed to specifically explore benefit in this type of heart failure patient, said Dr. Cosentino.
VERTIS CV was sponsored by Merck and Pfizer, the companies that market ertugliflozin. Dr. Davies has been a speaker on behalf of Merck and has had relationships with several other companies. Dr. Butler is a consultant to Merck and several other companies. Dr. McGuire has received honoraria from Merck, nonfinancial support from Pfizer, and has had relationships with several other companies. Dr. Cherney has received honoraria from Merck, nonfinancial research support from Pfizer, and has also had relationships with several other companies. Dr. Cosentino has received fees from Merck and Pfizer, and also from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Novo Nordisk
Further analyses from the cardiovascular outcome trial of the sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitor ertugliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes helped better define positive effects the drug had on preserving renal function, and also gave a tantalizing hint that this drug, and hence possibly the entire SGLT2 inhibitor drug class, may benefit patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
But the underlying problem for ertugliflozin (Steglatro) – first seen when results from the VERTIS CV trial initially came out in June 2020 at the annual meeting of the American Diabetes Association – was that, while the trial met its primary endpoint of proving noninferiority to placebo for the combined endpoint of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke, treatment with ertugliflozin showed no suggestion of benefit, compared with placebo for reducing this endpoint, producing a nonsignificant 3% relative cut in the combined rate of these adverse events, compared with placebo treatment.
‘Somewhat disappointing’ trial performance
Overall, results from VERTIS CV with ertugliflozin were “somewhat disappointing,” commented Melanie J. Davies, MD, who was not involved with the study and chaired a session at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes that reviewed the main results, put them into perspective, and added a few new exploratory analyses.
Although the results from 8,246-patient VERTIS CV (Evaluation of Ertugliflozin Efficacy and Safety Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial) put ertugliflozin in the same league as other drugs from its class for safety, “we do not see the significant benefits observed in many of the previous cardiovascular outcomes trials” for other drugs in the SGLT2 inhibitor class, specifically canagliflozin (Invokana), dapagliflozin (Farxiga), and empagliflozin (Jardiance), Dr. Davies said in an interview. The upshot, for at least the time being, is that ertugliflozin “is unlikely to receive a label for any new indications,” she predicted. In contrast, the other drugs in the class have, for example, received a U.S. labeled indication to reduce cardiovascular death (empagliflozin) or major cardiovascular disease events (canagliflozin) in adults with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and cardiovascular disease, or to reduce heart failure hospitalizations (dapagliflozin).
The main results from VERTIS CV, posted online in the New England Journal of Medicine after the EASD session, showed a single significant outcome difference between treatment with ertugliflozin and placebo over a median of 3.0 years of follow-up from among 10 reported secondary outcomes: a 30% relative reduction (a 1.1% absolute reduction) in the rate of hospitalization for heart failure, the sole criterion in the report by which ertugliflozin matched the benefits of the other SGLT2 inhibitors.
But the prespecified design of VERTIS CV called for a hierarchical sequence of secondary analyses. The statistically significant noninferiority of the primary endpoint allowed calculation of the initial secondary endpoint, a reduction in the combined rate of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure. Ertugliflozin treatment cut this outcome by a relative 12%, compared with placebo, a difference that was not significant.
This neutral finding brought to a stop further statistical testing of any of the other secondary endpoints, including impact on hospitalization for heart failure by itself. It also guaranteed that no beneficial effect inferred from the trial’s data would qualify for statistical validity, making it unlikely that ertugliflozin would gain any new label indications from these results. The drug carries a U.S. label that is limited to providing glycemic control.
Choosing among the SGLT2 inhibitors
“What we can say for sure is that there is a glycemic benefit and a heart failure hospitalization benefit” across all four of the SGLT2 inhibitors. “Beyond that, the best we can say today [about using these drugs in practice] is to follow regulatory indications and guidelines recommendations,” commented Javed Butler, MD, a cardiologist and professor and chair of medicine at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson.
“These results are going to lead to some serious discussions among the research, clinical, and regulatory communities about class effects versus drug effects, and specific trial data versus the totality of evidence,” he said in an interview.
“I think it will influence prescribing ertugliflozin, particularly in patients with established cardiovascular disease, or when the goal is to improve heart failure outcomes of reduce chronic kidney disease,” added Dr. Davies, a professor of diabetes medicine at the University of Leicester (England). “We already have positive benefits [proven for these outcomes] using other agents in the class.”
Perhaps one feature potentially in ertugliflozin’s favor is its price, and whatever impact that might have for payers or patients with inadequate coverage for their drug costs. U.S. websites show a typical retail price for ertugliflozin that is roughly 40% below the three other agents in the class, a difference that can add up to an annual cost savings of about $2,500.
A major consideration for clinicians deciding which SGLT2 inhibitor to prescribe should be “what can the patient afford,” noted Darren K. McGuire, MD, a coinvestigator for VERTIS CV, during discussion of the trial at the EASD virtual meeting.
New analyses show more renal-effect consistency
One surprise in the initial VERTIS CV report was in the study’s key renal outcome, a composite of renal death, need for dialysis, or a doubling of the serum creatinine level, which reflects a cut of at least a 50% in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). This composite outcome trended toward a significant benefit but fell short, producing a nominal 19% relative reduction. This combined endpoint probably “set the bar too high,” said David Z.I. Cherney, MD, a nephrologist who led the renal assessments run in the trial. He presented several exploratory analyses during the virtual EASD session that provided reassuring evidence that ertugliflozin was not an outlier among the SGLT2 inhibitors when it came to kidney benefits.
Perhaps the most compelling analysis he reported was a slight tweak to the main renal composite endpoint that substituted prevention of a 40% or greater reduction in eGFR for prevention of a 50% or greater reduction. By this somewhat lower bar for efficacy, treatment with ertugliflozin in VERTIS CV linked with a 34% relative risk reduction, compared with placebo (a roughly 1% absolute reduction) that was statistically significant, and importantly came out very close to the effect for this revised endpoint that had been seen for the other three SGLT2 inhibitor drugs.
Focusing on prevention of a 40% or greater drop in eGFR “gives a much more robust measure of renal protection,” Dr. Cherney, a clinician and researcher at the University of Toronto, said in an interview. “The key message is that renal protection is much more uniform” with the rest of the drugs in the class when looked at this way or by some of the other alternative parameters he reported. But the new renal analyses do not address disparities seen among the drugs in the class for several cardiovascular disease effects.
“The overall impression from VERTIS CV is that there was less cardiovascular disease benefit,” except for prevention of heart failure hospitalization, he said.
A teaser for HFpEF
One additional notable new finding discussed during the EASD session stemmed from the investigators ability to mine the medical records of enrolled patients for information about their heart failure history and left ventricular ejection fractions, a data set that was “unique,” compared with the other cardiovascular outcome trials for the drugs in the class, noted Francesco Cosentino, MD, another VERTIS CV coinvestigator and professor of cardiology at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm.
Roughly a quarter of the enrolled patients had a history of heart failure, and about half of these patients had heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, about 1,000 total patients. In this subgroup treatment with ertugliflozin linked with a 30% relative reduction in hospitalization for heart failure, compared with placebo, a roughly 0.5% absolute reduction. The numbers were small and underpowered for producing convincing evidence, but it provided an intriguing hint of benefit for an unmet need that is currently undergoing further testing in studies designed to specifically explore benefit in this type of heart failure patient, said Dr. Cosentino.
VERTIS CV was sponsored by Merck and Pfizer, the companies that market ertugliflozin. Dr. Davies has been a speaker on behalf of Merck and has had relationships with several other companies. Dr. Butler is a consultant to Merck and several other companies. Dr. McGuire has received honoraria from Merck, nonfinancial support from Pfizer, and has had relationships with several other companies. Dr. Cherney has received honoraria from Merck, nonfinancial research support from Pfizer, and has also had relationships with several other companies. Dr. Cosentino has received fees from Merck and Pfizer, and also from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Novo Nordisk
Further analyses from the cardiovascular outcome trial of the sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitor ertugliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes helped better define positive effects the drug had on preserving renal function, and also gave a tantalizing hint that this drug, and hence possibly the entire SGLT2 inhibitor drug class, may benefit patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
But the underlying problem for ertugliflozin (Steglatro) – first seen when results from the VERTIS CV trial initially came out in June 2020 at the annual meeting of the American Diabetes Association – was that, while the trial met its primary endpoint of proving noninferiority to placebo for the combined endpoint of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke, treatment with ertugliflozin showed no suggestion of benefit, compared with placebo for reducing this endpoint, producing a nonsignificant 3% relative cut in the combined rate of these adverse events, compared with placebo treatment.
‘Somewhat disappointing’ trial performance
Overall, results from VERTIS CV with ertugliflozin were “somewhat disappointing,” commented Melanie J. Davies, MD, who was not involved with the study and chaired a session at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes that reviewed the main results, put them into perspective, and added a few new exploratory analyses.
Although the results from 8,246-patient VERTIS CV (Evaluation of Ertugliflozin Efficacy and Safety Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial) put ertugliflozin in the same league as other drugs from its class for safety, “we do not see the significant benefits observed in many of the previous cardiovascular outcomes trials” for other drugs in the SGLT2 inhibitor class, specifically canagliflozin (Invokana), dapagliflozin (Farxiga), and empagliflozin (Jardiance), Dr. Davies said in an interview. The upshot, for at least the time being, is that ertugliflozin “is unlikely to receive a label for any new indications,” she predicted. In contrast, the other drugs in the class have, for example, received a U.S. labeled indication to reduce cardiovascular death (empagliflozin) or major cardiovascular disease events (canagliflozin) in adults with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and cardiovascular disease, or to reduce heart failure hospitalizations (dapagliflozin).
The main results from VERTIS CV, posted online in the New England Journal of Medicine after the EASD session, showed a single significant outcome difference between treatment with ertugliflozin and placebo over a median of 3.0 years of follow-up from among 10 reported secondary outcomes: a 30% relative reduction (a 1.1% absolute reduction) in the rate of hospitalization for heart failure, the sole criterion in the report by which ertugliflozin matched the benefits of the other SGLT2 inhibitors.
But the prespecified design of VERTIS CV called for a hierarchical sequence of secondary analyses. The statistically significant noninferiority of the primary endpoint allowed calculation of the initial secondary endpoint, a reduction in the combined rate of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure. Ertugliflozin treatment cut this outcome by a relative 12%, compared with placebo, a difference that was not significant.
This neutral finding brought to a stop further statistical testing of any of the other secondary endpoints, including impact on hospitalization for heart failure by itself. It also guaranteed that no beneficial effect inferred from the trial’s data would qualify for statistical validity, making it unlikely that ertugliflozin would gain any new label indications from these results. The drug carries a U.S. label that is limited to providing glycemic control.
Choosing among the SGLT2 inhibitors
“What we can say for sure is that there is a glycemic benefit and a heart failure hospitalization benefit” across all four of the SGLT2 inhibitors. “Beyond that, the best we can say today [about using these drugs in practice] is to follow regulatory indications and guidelines recommendations,” commented Javed Butler, MD, a cardiologist and professor and chair of medicine at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson.
“These results are going to lead to some serious discussions among the research, clinical, and regulatory communities about class effects versus drug effects, and specific trial data versus the totality of evidence,” he said in an interview.
“I think it will influence prescribing ertugliflozin, particularly in patients with established cardiovascular disease, or when the goal is to improve heart failure outcomes of reduce chronic kidney disease,” added Dr. Davies, a professor of diabetes medicine at the University of Leicester (England). “We already have positive benefits [proven for these outcomes] using other agents in the class.”
Perhaps one feature potentially in ertugliflozin’s favor is its price, and whatever impact that might have for payers or patients with inadequate coverage for their drug costs. U.S. websites show a typical retail price for ertugliflozin that is roughly 40% below the three other agents in the class, a difference that can add up to an annual cost savings of about $2,500.
A major consideration for clinicians deciding which SGLT2 inhibitor to prescribe should be “what can the patient afford,” noted Darren K. McGuire, MD, a coinvestigator for VERTIS CV, during discussion of the trial at the EASD virtual meeting.
New analyses show more renal-effect consistency
One surprise in the initial VERTIS CV report was in the study’s key renal outcome, a composite of renal death, need for dialysis, or a doubling of the serum creatinine level, which reflects a cut of at least a 50% in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). This composite outcome trended toward a significant benefit but fell short, producing a nominal 19% relative reduction. This combined endpoint probably “set the bar too high,” said David Z.I. Cherney, MD, a nephrologist who led the renal assessments run in the trial. He presented several exploratory analyses during the virtual EASD session that provided reassuring evidence that ertugliflozin was not an outlier among the SGLT2 inhibitors when it came to kidney benefits.
Perhaps the most compelling analysis he reported was a slight tweak to the main renal composite endpoint that substituted prevention of a 40% or greater reduction in eGFR for prevention of a 50% or greater reduction. By this somewhat lower bar for efficacy, treatment with ertugliflozin in VERTIS CV linked with a 34% relative risk reduction, compared with placebo (a roughly 1% absolute reduction) that was statistically significant, and importantly came out very close to the effect for this revised endpoint that had been seen for the other three SGLT2 inhibitor drugs.
Focusing on prevention of a 40% or greater drop in eGFR “gives a much more robust measure of renal protection,” Dr. Cherney, a clinician and researcher at the University of Toronto, said in an interview. “The key message is that renal protection is much more uniform” with the rest of the drugs in the class when looked at this way or by some of the other alternative parameters he reported. But the new renal analyses do not address disparities seen among the drugs in the class for several cardiovascular disease effects.
“The overall impression from VERTIS CV is that there was less cardiovascular disease benefit,” except for prevention of heart failure hospitalization, he said.
A teaser for HFpEF
One additional notable new finding discussed during the EASD session stemmed from the investigators ability to mine the medical records of enrolled patients for information about their heart failure history and left ventricular ejection fractions, a data set that was “unique,” compared with the other cardiovascular outcome trials for the drugs in the class, noted Francesco Cosentino, MD, another VERTIS CV coinvestigator and professor of cardiology at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm.
Roughly a quarter of the enrolled patients had a history of heart failure, and about half of these patients had heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, about 1,000 total patients. In this subgroup treatment with ertugliflozin linked with a 30% relative reduction in hospitalization for heart failure, compared with placebo, a roughly 0.5% absolute reduction. The numbers were small and underpowered for producing convincing evidence, but it provided an intriguing hint of benefit for an unmet need that is currently undergoing further testing in studies designed to specifically explore benefit in this type of heart failure patient, said Dr. Cosentino.
VERTIS CV was sponsored by Merck and Pfizer, the companies that market ertugliflozin. Dr. Davies has been a speaker on behalf of Merck and has had relationships with several other companies. Dr. Butler is a consultant to Merck and several other companies. Dr. McGuire has received honoraria from Merck, nonfinancial support from Pfizer, and has had relationships with several other companies. Dr. Cherney has received honoraria from Merck, nonfinancial research support from Pfizer, and has also had relationships with several other companies. Dr. Cosentino has received fees from Merck and Pfizer, and also from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Novo Nordisk
FROM EASD 2020
No prior use of insulin predicts postsurgical diabetes remission
Type 2 diabetes patients who had never used insulin showed sustained remission 10 years after bariatric surgery in a prospective study of 85 patients.
Having diabetes for less than 5 years was also predictive of achieving long-term diabetes remission, Diego Moriconi, MD, of the University of Pisa (Italy) and presenting study investigator, reported at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
“Weight loss was associated with type 2 diabetes remission 1 year after surgery, but it had no impact on the long-term relapse of diabetes,” Dr. Moriconi said.
The findings are important, commented Tina Vilsbøll, MD, DMSc, chief consultant at the Steno Diabetes Centre Copenhagen, who chaired the session. They’re important because they would help “to set the expectations for patients before they have surgery, what to expect in respect to resolution or remission of diabetes.”
If patients were taking insulin, for instance, the take home would seem to be not to expect too much in terms of remission of their diabetes, Dr. Vilsbøll said. She added: “Usually I am not a big fan of [relying on] diabetes duration, because often we know that patients with type 2 diabetes have had diabetes for a long time before they’re actually diagnosed.” However, “it seems to be very important here.”
Dr. Moriconi reported the findings of an observational study that had started in 2006 and recruited individuals about to undergo bariatric surgery for type 2 diabetes. Participants were evaluated before surgery and every 6-12 months after, undergoing various clinical and laboratory investigations, for a period of 10 years.
The majority of the recruited patients (76%) were women. Most (also 76%) had undergone gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y) surgery, and the remainder had undergone sleeve gastrectomy. Both types of surgery were equally as good at getting people into remission, as defined by the American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes, Dr. Moriconi said. As such, remission was achieved if the fasting blood glucose fell below 100 mg/dL and the hemoglobin A1c below 5.7%.
In the first year following surgery, 75% of patients had met diabetes remission criteria. This fell to 61% of patients after 5 years, and to 55% at 10 years. At each of these time points, 25% of patients had type 2 diabetes, with 14% relapsing back at 5 years and 20% at 10 years.
Dr. Moriconi pointed out some of the different characteristics of the 47 patients who had achieved diabetes remission at 10 years, compared with the 17 who had “relapsed” back to having type 2 diabetes and the 21 who had remained with type 2 diabetes.
The decrease in body mass index achieved at 10 years was no different between the three groups. However, 1 year after surgery, there had been a significantly greater drop in body in those who achieved remission, compared with those who did not (P = .04).
“Glycemic control improved with time in all the three groups after bariatric surgery, although more markedly so in the remission group,” Dr. Moriconi said.
He highlighted how none of the patients who had achieved remission had used insulin, whereas 12% of those who had relapsed and half (52%) of those who remained with type 2 diabetes had used insulin (P < .0001).
Patients who achieved remission at 1, 5, and 10 years were more likely to have had diabetes for less than 5 years than those who remained with type 2 diabetes. The average duration of diabetes was 2 years in those achieving remission versus 8 years in those who had relapsed and 13 years in those who had remained diabetic (P < .0001).
Logistic regression analysis, which adjusted for all major confounding factors such as age, sex, and type of surgery, showed that only the duration of diabetes and insulin therapy before surgery were the only predictors of long-term diabetes remission.
The study had no commercial funding. Dr. Moriconi and Dr. Vilsbøll had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Moriconi D. EASD 2020, Oral presentation 120.
Type 2 diabetes patients who had never used insulin showed sustained remission 10 years after bariatric surgery in a prospective study of 85 patients.
Having diabetes for less than 5 years was also predictive of achieving long-term diabetes remission, Diego Moriconi, MD, of the University of Pisa (Italy) and presenting study investigator, reported at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
“Weight loss was associated with type 2 diabetes remission 1 year after surgery, but it had no impact on the long-term relapse of diabetes,” Dr. Moriconi said.
The findings are important, commented Tina Vilsbøll, MD, DMSc, chief consultant at the Steno Diabetes Centre Copenhagen, who chaired the session. They’re important because they would help “to set the expectations for patients before they have surgery, what to expect in respect to resolution or remission of diabetes.”
If patients were taking insulin, for instance, the take home would seem to be not to expect too much in terms of remission of their diabetes, Dr. Vilsbøll said. She added: “Usually I am not a big fan of [relying on] diabetes duration, because often we know that patients with type 2 diabetes have had diabetes for a long time before they’re actually diagnosed.” However, “it seems to be very important here.”
Dr. Moriconi reported the findings of an observational study that had started in 2006 and recruited individuals about to undergo bariatric surgery for type 2 diabetes. Participants were evaluated before surgery and every 6-12 months after, undergoing various clinical and laboratory investigations, for a period of 10 years.
The majority of the recruited patients (76%) were women. Most (also 76%) had undergone gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y) surgery, and the remainder had undergone sleeve gastrectomy. Both types of surgery were equally as good at getting people into remission, as defined by the American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes, Dr. Moriconi said. As such, remission was achieved if the fasting blood glucose fell below 100 mg/dL and the hemoglobin A1c below 5.7%.
In the first year following surgery, 75% of patients had met diabetes remission criteria. This fell to 61% of patients after 5 years, and to 55% at 10 years. At each of these time points, 25% of patients had type 2 diabetes, with 14% relapsing back at 5 years and 20% at 10 years.
Dr. Moriconi pointed out some of the different characteristics of the 47 patients who had achieved diabetes remission at 10 years, compared with the 17 who had “relapsed” back to having type 2 diabetes and the 21 who had remained with type 2 diabetes.
The decrease in body mass index achieved at 10 years was no different between the three groups. However, 1 year after surgery, there had been a significantly greater drop in body in those who achieved remission, compared with those who did not (P = .04).
“Glycemic control improved with time in all the three groups after bariatric surgery, although more markedly so in the remission group,” Dr. Moriconi said.
He highlighted how none of the patients who had achieved remission had used insulin, whereas 12% of those who had relapsed and half (52%) of those who remained with type 2 diabetes had used insulin (P < .0001).
Patients who achieved remission at 1, 5, and 10 years were more likely to have had diabetes for less than 5 years than those who remained with type 2 diabetes. The average duration of diabetes was 2 years in those achieving remission versus 8 years in those who had relapsed and 13 years in those who had remained diabetic (P < .0001).
Logistic regression analysis, which adjusted for all major confounding factors such as age, sex, and type of surgery, showed that only the duration of diabetes and insulin therapy before surgery were the only predictors of long-term diabetes remission.
The study had no commercial funding. Dr. Moriconi and Dr. Vilsbøll had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Moriconi D. EASD 2020, Oral presentation 120.
Type 2 diabetes patients who had never used insulin showed sustained remission 10 years after bariatric surgery in a prospective study of 85 patients.
Having diabetes for less than 5 years was also predictive of achieving long-term diabetes remission, Diego Moriconi, MD, of the University of Pisa (Italy) and presenting study investigator, reported at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
“Weight loss was associated with type 2 diabetes remission 1 year after surgery, but it had no impact on the long-term relapse of diabetes,” Dr. Moriconi said.
The findings are important, commented Tina Vilsbøll, MD, DMSc, chief consultant at the Steno Diabetes Centre Copenhagen, who chaired the session. They’re important because they would help “to set the expectations for patients before they have surgery, what to expect in respect to resolution or remission of diabetes.”
If patients were taking insulin, for instance, the take home would seem to be not to expect too much in terms of remission of their diabetes, Dr. Vilsbøll said. She added: “Usually I am not a big fan of [relying on] diabetes duration, because often we know that patients with type 2 diabetes have had diabetes for a long time before they’re actually diagnosed.” However, “it seems to be very important here.”
Dr. Moriconi reported the findings of an observational study that had started in 2006 and recruited individuals about to undergo bariatric surgery for type 2 diabetes. Participants were evaluated before surgery and every 6-12 months after, undergoing various clinical and laboratory investigations, for a period of 10 years.
The majority of the recruited patients (76%) were women. Most (also 76%) had undergone gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y) surgery, and the remainder had undergone sleeve gastrectomy. Both types of surgery were equally as good at getting people into remission, as defined by the American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes, Dr. Moriconi said. As such, remission was achieved if the fasting blood glucose fell below 100 mg/dL and the hemoglobin A1c below 5.7%.
In the first year following surgery, 75% of patients had met diabetes remission criteria. This fell to 61% of patients after 5 years, and to 55% at 10 years. At each of these time points, 25% of patients had type 2 diabetes, with 14% relapsing back at 5 years and 20% at 10 years.
Dr. Moriconi pointed out some of the different characteristics of the 47 patients who had achieved diabetes remission at 10 years, compared with the 17 who had “relapsed” back to having type 2 diabetes and the 21 who had remained with type 2 diabetes.
The decrease in body mass index achieved at 10 years was no different between the three groups. However, 1 year after surgery, there had been a significantly greater drop in body in those who achieved remission, compared with those who did not (P = .04).
“Glycemic control improved with time in all the three groups after bariatric surgery, although more markedly so in the remission group,” Dr. Moriconi said.
He highlighted how none of the patients who had achieved remission had used insulin, whereas 12% of those who had relapsed and half (52%) of those who remained with type 2 diabetes had used insulin (P < .0001).
Patients who achieved remission at 1, 5, and 10 years were more likely to have had diabetes for less than 5 years than those who remained with type 2 diabetes. The average duration of diabetes was 2 years in those achieving remission versus 8 years in those who had relapsed and 13 years in those who had remained diabetic (P < .0001).
Logistic regression analysis, which adjusted for all major confounding factors such as age, sex, and type of surgery, showed that only the duration of diabetes and insulin therapy before surgery were the only predictors of long-term diabetes remission.
The study had no commercial funding. Dr. Moriconi and Dr. Vilsbøll had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Moriconi D. EASD 2020, Oral presentation 120.
FROM EASD 2020
CDC playbook prepares states for rollout of COVID-19 vaccine if one is approved
States have begun preparing to distribute a COVID-19 vaccine if one is approved, a CDC official said today.
The CDC released guidance for states on Sept. 16 titled COVID-19 Vaccination Program Interim Playbook for Jurisdiction Operations. The document discusses vaccine ordering, storage, and handling and says that states should submit their plans for vaccine distribution to the agency by Oct. 16.
“Every jurisdiction is heavily involved right now in their plan development,” CDC official Janell Routh, MD, told the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices during its Sept. 22 meeting. “It was really impressive to me that, even though the playbook only went out last week, states and jurisdictions have been thinking about this for quite some time.”
However, one committee member suggested that setting a deadline before more safety, efficacy, and storage information is known may be premature.
“I cannot imagine that we will actually know the final storage requirements for this vaccine by Oct. 16, which makes me a little concerned about finalizing state plans,” said Helen “Keipp” Talbot, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn. “We also don’t know the best populations yet when it comes to efficacy and safety.”
Dr. Routh said the CDC is asking states to plan on the basis of assumptions. “We know those plans will constantly be improving, changing, as we learn more information,” Dr. Routh said. States agreed to return a plan 30 days after the playbook was released, which is how the Oct. 16 deadline was established, she said.
States are encouraged to think broadly. Plans may include contingencies for a product that requires ultracold storage or for distributing more than one vaccine product, Dr. Routh said.
“One goal is to be ready on the first day that we can actually distribute vaccine,” Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said during the meeting. “Our colleagues in Operation Warp Speed say that they expect there will be vaccine as early as November, and therefore we need to be ready so there is no delay in distributing that vaccine. And that phase, that early phase, is really close upon us.”
Many states have already developed plans, and the CDC is providing technical assistance as needed to monitor the plans regularly, Dr. Routh said.
Key issues identified
From holding pilot meetings with five jurisdictions, officials learned that public confidence in the vaccine is among states’ greatest concerns, Dr. Routh said. In addition, distribution is resource intensive, and social distancing adds logistical complexity.
Specific guidance on whom to vaccinate in the early stages will smooth the process, officials suggested during the pilot meetings. For the first several weeks, vaccine doses may be limited to priority populations, such as health care workers.
“This interim playbook is a living document,” Dr. Routh emphasized. “We definitely plan to update the content regularly as we learn more information about what vaccines and when they will be released.”
During the early stages of COVID-19 vaccination, officials plan to implement an enhanced monitoring program in which vaccine recipients would complete surveys about adverse events, in addition to the traditional vaccine safety monitoring programs that already exist, officials said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
States have begun preparing to distribute a COVID-19 vaccine if one is approved, a CDC official said today.
The CDC released guidance for states on Sept. 16 titled COVID-19 Vaccination Program Interim Playbook for Jurisdiction Operations. The document discusses vaccine ordering, storage, and handling and says that states should submit their plans for vaccine distribution to the agency by Oct. 16.
“Every jurisdiction is heavily involved right now in their plan development,” CDC official Janell Routh, MD, told the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices during its Sept. 22 meeting. “It was really impressive to me that, even though the playbook only went out last week, states and jurisdictions have been thinking about this for quite some time.”
However, one committee member suggested that setting a deadline before more safety, efficacy, and storage information is known may be premature.
“I cannot imagine that we will actually know the final storage requirements for this vaccine by Oct. 16, which makes me a little concerned about finalizing state plans,” said Helen “Keipp” Talbot, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn. “We also don’t know the best populations yet when it comes to efficacy and safety.”
Dr. Routh said the CDC is asking states to plan on the basis of assumptions. “We know those plans will constantly be improving, changing, as we learn more information,” Dr. Routh said. States agreed to return a plan 30 days after the playbook was released, which is how the Oct. 16 deadline was established, she said.
States are encouraged to think broadly. Plans may include contingencies for a product that requires ultracold storage or for distributing more than one vaccine product, Dr. Routh said.
“One goal is to be ready on the first day that we can actually distribute vaccine,” Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said during the meeting. “Our colleagues in Operation Warp Speed say that they expect there will be vaccine as early as November, and therefore we need to be ready so there is no delay in distributing that vaccine. And that phase, that early phase, is really close upon us.”
Many states have already developed plans, and the CDC is providing technical assistance as needed to monitor the plans regularly, Dr. Routh said.
Key issues identified
From holding pilot meetings with five jurisdictions, officials learned that public confidence in the vaccine is among states’ greatest concerns, Dr. Routh said. In addition, distribution is resource intensive, and social distancing adds logistical complexity.
Specific guidance on whom to vaccinate in the early stages will smooth the process, officials suggested during the pilot meetings. For the first several weeks, vaccine doses may be limited to priority populations, such as health care workers.
“This interim playbook is a living document,” Dr. Routh emphasized. “We definitely plan to update the content regularly as we learn more information about what vaccines and when they will be released.”
During the early stages of COVID-19 vaccination, officials plan to implement an enhanced monitoring program in which vaccine recipients would complete surveys about adverse events, in addition to the traditional vaccine safety monitoring programs that already exist, officials said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
States have begun preparing to distribute a COVID-19 vaccine if one is approved, a CDC official said today.
The CDC released guidance for states on Sept. 16 titled COVID-19 Vaccination Program Interim Playbook for Jurisdiction Operations. The document discusses vaccine ordering, storage, and handling and says that states should submit their plans for vaccine distribution to the agency by Oct. 16.
“Every jurisdiction is heavily involved right now in their plan development,” CDC official Janell Routh, MD, told the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices during its Sept. 22 meeting. “It was really impressive to me that, even though the playbook only went out last week, states and jurisdictions have been thinking about this for quite some time.”
However, one committee member suggested that setting a deadline before more safety, efficacy, and storage information is known may be premature.
“I cannot imagine that we will actually know the final storage requirements for this vaccine by Oct. 16, which makes me a little concerned about finalizing state plans,” said Helen “Keipp” Talbot, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn. “We also don’t know the best populations yet when it comes to efficacy and safety.”
Dr. Routh said the CDC is asking states to plan on the basis of assumptions. “We know those plans will constantly be improving, changing, as we learn more information,” Dr. Routh said. States agreed to return a plan 30 days after the playbook was released, which is how the Oct. 16 deadline was established, she said.
States are encouraged to think broadly. Plans may include contingencies for a product that requires ultracold storage or for distributing more than one vaccine product, Dr. Routh said.
“One goal is to be ready on the first day that we can actually distribute vaccine,” Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said during the meeting. “Our colleagues in Operation Warp Speed say that they expect there will be vaccine as early as November, and therefore we need to be ready so there is no delay in distributing that vaccine. And that phase, that early phase, is really close upon us.”
Many states have already developed plans, and the CDC is providing technical assistance as needed to monitor the plans regularly, Dr. Routh said.
Key issues identified
From holding pilot meetings with five jurisdictions, officials learned that public confidence in the vaccine is among states’ greatest concerns, Dr. Routh said. In addition, distribution is resource intensive, and social distancing adds logistical complexity.
Specific guidance on whom to vaccinate in the early stages will smooth the process, officials suggested during the pilot meetings. For the first several weeks, vaccine doses may be limited to priority populations, such as health care workers.
“This interim playbook is a living document,” Dr. Routh emphasized. “We definitely plan to update the content regularly as we learn more information about what vaccines and when they will be released.”
During the early stages of COVID-19 vaccination, officials plan to implement an enhanced monitoring program in which vaccine recipients would complete surveys about adverse events, in addition to the traditional vaccine safety monitoring programs that already exist, officials said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.



















