User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


Follow-Up Outcomes Data Often Missing for FDA Drug Approvals Based on Surrogate Markers
Over the past few decades, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has increasingly relied on surrogate measures such as blood tests instead of clinical outcomes for medication approvals. But critics say the agency lacks consistent standards to ensure the surrogate aligns with clinical outcomes that matter to patients — things like improvements in symptoms and gains in function.
Sometimes those decisions backfire. Consider: In July 2021, the FDA approved aducanumab for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, bucking the advice of an advisory panel for the agency that questioned the effectiveness of the medication. Regulators relied on data from the drugmaker, Biogen, showing the monoclonal antibody could reduce levels of amyloid beta plaques in blood — a surrogate marker officials hoped would translate to clinical benefit.
The FDA’s decision triggered significant controversy, and Biogen in January announced it is pulling it from the market this year, citing disappointing sales.
Although the case of aducanumab might seem extreme, given the stakes — Alzheimer’s remains a disease without an effective treatment — it’s far from unusual.
“When we prescribe a drug, there is an underlying assumption that the FDA has done its due diligence to confirm the drug is safe and of benefit,” said Reshma Ramachandran, MD, MPP, MHS, a researcher at Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, and a coauthor of a recent review of surrogate outcomes. “In fact, we found either no evidence or low-quality evidence.” Such markers are associated with clinical outcomes. “We just don’t know if they work meaningfully to treat the patient’s condition. The results were pretty shocking for us,” she said.
The FDA in 2018 released an Adult Surrogate Endpoint Table listing markers that can be used as substitutes for clinical outcomes to more quickly test, review, and approve new therapies. The analysis found the majority of these endpoints lacked subsequent confirmations, defined as published meta-analyses of clinical studies to validate the association between the marker and a clinical outcome important to patients.
In a paper published in JAMA, Dr. Ramachandran and her colleagues looked at 37 surrogate endpoints for nearly 3 dozen nononcologic diseases in the table.
Approval with surrogate markers implies responsibility for postapproval or validation studies — not just lab measures or imaging findings but mortality, morbidity, or improved quality of life, said Joshua D. Wallach, PhD, MS, assistant professor in the department of epidemiology at the Emory Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta and lead author of the JAMA review.
Dr. Wallach said surrogate markers are easier to measure and do not require large and long trials. But the FDA has not provided clear rules for what makes a surrogate marker valid in clinical trials.
“They’ve said that at a minimum, it requires meta-analytical evidence from studies that have looked at the correlation or the association between the surrogate and the clinical outcome,” Dr. Wallach said. “Our understanding was that if that’s a minimum expectation, we should be able to find those studies in the literature. And the reality is that we were unable to find evidence from those types of studies supporting the association between the surrogate and the clinical outcome.”
Physicians generally do not receive training about the FDA approval process and the difference between biomarkers, surrogate markers, and clinical endpoints, Dr. Ramachandran said. “Our study shows that things are much more uncertain than we thought when it comes to the prescribing of new drugs,” she said.
Surrogate Markers on the Rise
Dr. Wallach’s group looked for published meta-analyses compiling randomized controlled trials reporting surrogate endpoints for more than 3 dozen chronic nononcologic conditions, including type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer’s, kidney disease, HIV, gout, and lupus. They found no meta-analyses at all for 59% of the surrogate markers, while for those that were studied, few reported high-strength evidence of an association with clinical outcomes.
The findings echo previous research. In a 2020 study in JAMA Network Open, researchers tallied primary endpoints for all FDA approvals of new drugs and therapies during three 3-year periods: 1995-1997, 2005-2007, and 2015-2017. The proportion of products whose approvals were based on the use of clinical endpoints decreased from 43.8% in 1995-1997 to 28.4% in 2005-2007 to 23.3% in 2015-2017. The share based on surrogate endpoints rose from 43.3% to roughly 60% over the same interval.
A 2017 study in the Journal of Health Economics found the use of “imperfect” surrogate endpoints helped support the approval of an average of 16 new drugs per year between 2010 and 2014 compared with six per year from 1998 to 2008.
Similar concerns about weak associations between surrogate markers and drugs used to treat cancer have been documented before, including in a 2020 study published in eClinicalMedicine. The researchers found the surrogate endpoints in the FDA table either were not tested or were tested but proven to be weak surrogates.
“And yet the FDA considered these as good enough not only for accelerated approval but also for regular approval,” said Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, associate professor in the department of oncology at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, who led the group.
The use of surrogate endpoints is also increasing in Europe, said Huseyin Naci, MHS, PhD, associate professor of health policy at the London School of Economics and Political Science in England. He cited a cohort study of 298 randomized clinical trials (RCTs) in JAMA Oncology suggesting “contemporary oncology RCTs now largely measure putative surrogate endpoints.” Dr. Wallach called the FDA’s surrogate table “a great first step toward transparency. But a key column is missing from that table, telling us what is the basis for which the FDA allows drug companies to use the recognized surrogate markers. What is the evidence they are considering?”
If the agency allows companies the flexibility to validate surrogate endpoints, postmarketing studies designed to confirm the clinical utility of those endpoints should follow.
“We obviously want physicians to be guided by evidence when they’re selecting treatments, and they need to be able to interpret the clinical benefits of the drug that they’re prescribing,” he said. “This is really about having the research consumer, patients, and physicians, as well as industry, understand why certain markers are considered and not considered.”
Dr. Wallach reported receiving grants from the FDA (through the Yale University — Mayo Clinic Center of Excellence in Regulatory Science and Innovation), National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (1K01AA028258), and Johnson & Johnson (through the Yale University Open Data Access Project); and consulting fees from Hagens Berman Sobol Shapiro LLP and Dugan Law Firm APLC outside the submitted work. Dr. Ramachandran reported receiving grants from the Stavros Niarchos Foundation and FDA; receiving consulting fees from ReAct Action on Antibiotic Resistance strategy policy program outside the submitted work; and serving in an unpaid capacity as chair of the FDA task force for the nonprofit organization Doctors for America and in an unpaid capacity as board president for Universities Allied for Essential Medicines North America.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Over the past few decades, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has increasingly relied on surrogate measures such as blood tests instead of clinical outcomes for medication approvals. But critics say the agency lacks consistent standards to ensure the surrogate aligns with clinical outcomes that matter to patients — things like improvements in symptoms and gains in function.
Sometimes those decisions backfire. Consider: In July 2021, the FDA approved aducanumab for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, bucking the advice of an advisory panel for the agency that questioned the effectiveness of the medication. Regulators relied on data from the drugmaker, Biogen, showing the monoclonal antibody could reduce levels of amyloid beta plaques in blood — a surrogate marker officials hoped would translate to clinical benefit.
The FDA’s decision triggered significant controversy, and Biogen in January announced it is pulling it from the market this year, citing disappointing sales.
Although the case of aducanumab might seem extreme, given the stakes — Alzheimer’s remains a disease without an effective treatment — it’s far from unusual.
“When we prescribe a drug, there is an underlying assumption that the FDA has done its due diligence to confirm the drug is safe and of benefit,” said Reshma Ramachandran, MD, MPP, MHS, a researcher at Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, and a coauthor of a recent review of surrogate outcomes. “In fact, we found either no evidence or low-quality evidence.” Such markers are associated with clinical outcomes. “We just don’t know if they work meaningfully to treat the patient’s condition. The results were pretty shocking for us,” she said.
The FDA in 2018 released an Adult Surrogate Endpoint Table listing markers that can be used as substitutes for clinical outcomes to more quickly test, review, and approve new therapies. The analysis found the majority of these endpoints lacked subsequent confirmations, defined as published meta-analyses of clinical studies to validate the association between the marker and a clinical outcome important to patients.
In a paper published in JAMA, Dr. Ramachandran and her colleagues looked at 37 surrogate endpoints for nearly 3 dozen nononcologic diseases in the table.
Approval with surrogate markers implies responsibility for postapproval or validation studies — not just lab measures or imaging findings but mortality, morbidity, or improved quality of life, said Joshua D. Wallach, PhD, MS, assistant professor in the department of epidemiology at the Emory Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta and lead author of the JAMA review.
Dr. Wallach said surrogate markers are easier to measure and do not require large and long trials. But the FDA has not provided clear rules for what makes a surrogate marker valid in clinical trials.
“They’ve said that at a minimum, it requires meta-analytical evidence from studies that have looked at the correlation or the association between the surrogate and the clinical outcome,” Dr. Wallach said. “Our understanding was that if that’s a minimum expectation, we should be able to find those studies in the literature. And the reality is that we were unable to find evidence from those types of studies supporting the association between the surrogate and the clinical outcome.”
Physicians generally do not receive training about the FDA approval process and the difference between biomarkers, surrogate markers, and clinical endpoints, Dr. Ramachandran said. “Our study shows that things are much more uncertain than we thought when it comes to the prescribing of new drugs,” she said.
Surrogate Markers on the Rise
Dr. Wallach’s group looked for published meta-analyses compiling randomized controlled trials reporting surrogate endpoints for more than 3 dozen chronic nononcologic conditions, including type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer’s, kidney disease, HIV, gout, and lupus. They found no meta-analyses at all for 59% of the surrogate markers, while for those that were studied, few reported high-strength evidence of an association with clinical outcomes.
The findings echo previous research. In a 2020 study in JAMA Network Open, researchers tallied primary endpoints for all FDA approvals of new drugs and therapies during three 3-year periods: 1995-1997, 2005-2007, and 2015-2017. The proportion of products whose approvals were based on the use of clinical endpoints decreased from 43.8% in 1995-1997 to 28.4% in 2005-2007 to 23.3% in 2015-2017. The share based on surrogate endpoints rose from 43.3% to roughly 60% over the same interval.
A 2017 study in the Journal of Health Economics found the use of “imperfect” surrogate endpoints helped support the approval of an average of 16 new drugs per year between 2010 and 2014 compared with six per year from 1998 to 2008.
Similar concerns about weak associations between surrogate markers and drugs used to treat cancer have been documented before, including in a 2020 study published in eClinicalMedicine. The researchers found the surrogate endpoints in the FDA table either were not tested or were tested but proven to be weak surrogates.
“And yet the FDA considered these as good enough not only for accelerated approval but also for regular approval,” said Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, associate professor in the department of oncology at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, who led the group.
The use of surrogate endpoints is also increasing in Europe, said Huseyin Naci, MHS, PhD, associate professor of health policy at the London School of Economics and Political Science in England. He cited a cohort study of 298 randomized clinical trials (RCTs) in JAMA Oncology suggesting “contemporary oncology RCTs now largely measure putative surrogate endpoints.” Dr. Wallach called the FDA’s surrogate table “a great first step toward transparency. But a key column is missing from that table, telling us what is the basis for which the FDA allows drug companies to use the recognized surrogate markers. What is the evidence they are considering?”
If the agency allows companies the flexibility to validate surrogate endpoints, postmarketing studies designed to confirm the clinical utility of those endpoints should follow.
“We obviously want physicians to be guided by evidence when they’re selecting treatments, and they need to be able to interpret the clinical benefits of the drug that they’re prescribing,” he said. “This is really about having the research consumer, patients, and physicians, as well as industry, understand why certain markers are considered and not considered.”
Dr. Wallach reported receiving grants from the FDA (through the Yale University — Mayo Clinic Center of Excellence in Regulatory Science and Innovation), National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (1K01AA028258), and Johnson & Johnson (through the Yale University Open Data Access Project); and consulting fees from Hagens Berman Sobol Shapiro LLP and Dugan Law Firm APLC outside the submitted work. Dr. Ramachandran reported receiving grants from the Stavros Niarchos Foundation and FDA; receiving consulting fees from ReAct Action on Antibiotic Resistance strategy policy program outside the submitted work; and serving in an unpaid capacity as chair of the FDA task force for the nonprofit organization Doctors for America and in an unpaid capacity as board president for Universities Allied for Essential Medicines North America.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Over the past few decades, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has increasingly relied on surrogate measures such as blood tests instead of clinical outcomes for medication approvals. But critics say the agency lacks consistent standards to ensure the surrogate aligns with clinical outcomes that matter to patients — things like improvements in symptoms and gains in function.
Sometimes those decisions backfire. Consider: In July 2021, the FDA approved aducanumab for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, bucking the advice of an advisory panel for the agency that questioned the effectiveness of the medication. Regulators relied on data from the drugmaker, Biogen, showing the monoclonal antibody could reduce levels of amyloid beta plaques in blood — a surrogate marker officials hoped would translate to clinical benefit.
The FDA’s decision triggered significant controversy, and Biogen in January announced it is pulling it from the market this year, citing disappointing sales.
Although the case of aducanumab might seem extreme, given the stakes — Alzheimer’s remains a disease without an effective treatment — it’s far from unusual.
“When we prescribe a drug, there is an underlying assumption that the FDA has done its due diligence to confirm the drug is safe and of benefit,” said Reshma Ramachandran, MD, MPP, MHS, a researcher at Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, and a coauthor of a recent review of surrogate outcomes. “In fact, we found either no evidence or low-quality evidence.” Such markers are associated with clinical outcomes. “We just don’t know if they work meaningfully to treat the patient’s condition. The results were pretty shocking for us,” she said.
The FDA in 2018 released an Adult Surrogate Endpoint Table listing markers that can be used as substitutes for clinical outcomes to more quickly test, review, and approve new therapies. The analysis found the majority of these endpoints lacked subsequent confirmations, defined as published meta-analyses of clinical studies to validate the association between the marker and a clinical outcome important to patients.
In a paper published in JAMA, Dr. Ramachandran and her colleagues looked at 37 surrogate endpoints for nearly 3 dozen nononcologic diseases in the table.
Approval with surrogate markers implies responsibility for postapproval or validation studies — not just lab measures or imaging findings but mortality, morbidity, or improved quality of life, said Joshua D. Wallach, PhD, MS, assistant professor in the department of epidemiology at the Emory Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta and lead author of the JAMA review.
Dr. Wallach said surrogate markers are easier to measure and do not require large and long trials. But the FDA has not provided clear rules for what makes a surrogate marker valid in clinical trials.
“They’ve said that at a minimum, it requires meta-analytical evidence from studies that have looked at the correlation or the association between the surrogate and the clinical outcome,” Dr. Wallach said. “Our understanding was that if that’s a minimum expectation, we should be able to find those studies in the literature. And the reality is that we were unable to find evidence from those types of studies supporting the association between the surrogate and the clinical outcome.”
Physicians generally do not receive training about the FDA approval process and the difference between biomarkers, surrogate markers, and clinical endpoints, Dr. Ramachandran said. “Our study shows that things are much more uncertain than we thought when it comes to the prescribing of new drugs,” she said.
Surrogate Markers on the Rise
Dr. Wallach’s group looked for published meta-analyses compiling randomized controlled trials reporting surrogate endpoints for more than 3 dozen chronic nononcologic conditions, including type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer’s, kidney disease, HIV, gout, and lupus. They found no meta-analyses at all for 59% of the surrogate markers, while for those that were studied, few reported high-strength evidence of an association with clinical outcomes.
The findings echo previous research. In a 2020 study in JAMA Network Open, researchers tallied primary endpoints for all FDA approvals of new drugs and therapies during three 3-year periods: 1995-1997, 2005-2007, and 2015-2017. The proportion of products whose approvals were based on the use of clinical endpoints decreased from 43.8% in 1995-1997 to 28.4% in 2005-2007 to 23.3% in 2015-2017. The share based on surrogate endpoints rose from 43.3% to roughly 60% over the same interval.
A 2017 study in the Journal of Health Economics found the use of “imperfect” surrogate endpoints helped support the approval of an average of 16 new drugs per year between 2010 and 2014 compared with six per year from 1998 to 2008.
Similar concerns about weak associations between surrogate markers and drugs used to treat cancer have been documented before, including in a 2020 study published in eClinicalMedicine. The researchers found the surrogate endpoints in the FDA table either were not tested or were tested but proven to be weak surrogates.
“And yet the FDA considered these as good enough not only for accelerated approval but also for regular approval,” said Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, associate professor in the department of oncology at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, who led the group.
The use of surrogate endpoints is also increasing in Europe, said Huseyin Naci, MHS, PhD, associate professor of health policy at the London School of Economics and Political Science in England. He cited a cohort study of 298 randomized clinical trials (RCTs) in JAMA Oncology suggesting “contemporary oncology RCTs now largely measure putative surrogate endpoints.” Dr. Wallach called the FDA’s surrogate table “a great first step toward transparency. But a key column is missing from that table, telling us what is the basis for which the FDA allows drug companies to use the recognized surrogate markers. What is the evidence they are considering?”
If the agency allows companies the flexibility to validate surrogate endpoints, postmarketing studies designed to confirm the clinical utility of those endpoints should follow.
“We obviously want physicians to be guided by evidence when they’re selecting treatments, and they need to be able to interpret the clinical benefits of the drug that they’re prescribing,” he said. “This is really about having the research consumer, patients, and physicians, as well as industry, understand why certain markers are considered and not considered.”
Dr. Wallach reported receiving grants from the FDA (through the Yale University — Mayo Clinic Center of Excellence in Regulatory Science and Innovation), National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (1K01AA028258), and Johnson & Johnson (through the Yale University Open Data Access Project); and consulting fees from Hagens Berman Sobol Shapiro LLP and Dugan Law Firm APLC outside the submitted work. Dr. Ramachandran reported receiving grants from the Stavros Niarchos Foundation and FDA; receiving consulting fees from ReAct Action on Antibiotic Resistance strategy policy program outside the submitted work; and serving in an unpaid capacity as chair of the FDA task force for the nonprofit organization Doctors for America and in an unpaid capacity as board president for Universities Allied for Essential Medicines North America.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA
FDA Approves Tarlatamab for Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer
Tarlatamab is a first-in-class bispecific T-cell engager (BiTE) that binds delta-like ligand 3 on the surface of cells, including tumor cells, and CD3 expressed on the surface of T cells. It causes T-cell activation, release of inflammatory cytokines, and lysis of DLL3-expressing cells, according to labeling.
Approval was based on data from 99 patients in the DeLLphi-301 trial with relapsed/refractory extensive-stage SCLC who had progressed after platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients with symptomatic brain metastases, interstitial lung disease, noninfectious pneumonitis, and active immunodeficiency were excluded.
The overall response rate was 40%, and median duration of response 9.7 months. The overall response rate was 52% in 27 patients with platinum-resistant SCLC and 31% in 42 with platinum-sensitive disease.
Continued approval may depend on verification of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
Labeling includes a box warning of serious or life-threatening cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxicity, including immune effector cell–associated neurotoxicity syndrome.
The most common adverse events, occurring in 20% or more of patients, were cytokine release syndrome, fatigue, pyrexia, dysgeusia, decreased appetite, musculoskeletal pain, constipation, anemia, and nausea.
The most common grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities included decreased lymphocytes, decreased sodium, increased uric acid, decreased total neutrophils, decreased hemoglobin, increased activated partial thromboplastin time, and decreased potassium.
The starting dose is 1 mg given intravenously over 1 hour on the first day of the first cycle followed by 10 mg on day 8 and day 15 of the first cycle, then every 2 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
M. Alexander Otto is a physician assistant with a master’s degree in medical science and a journalism degree from Newhouse. He is an award-winning medical journalist who worked for several major news outlets before joining Medscape. Alex is also an MIT Knight Science Journalism fellow. Email: [email protected]
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Tarlatamab is a first-in-class bispecific T-cell engager (BiTE) that binds delta-like ligand 3 on the surface of cells, including tumor cells, and CD3 expressed on the surface of T cells. It causes T-cell activation, release of inflammatory cytokines, and lysis of DLL3-expressing cells, according to labeling.
Approval was based on data from 99 patients in the DeLLphi-301 trial with relapsed/refractory extensive-stage SCLC who had progressed after platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients with symptomatic brain metastases, interstitial lung disease, noninfectious pneumonitis, and active immunodeficiency were excluded.
The overall response rate was 40%, and median duration of response 9.7 months. The overall response rate was 52% in 27 patients with platinum-resistant SCLC and 31% in 42 with platinum-sensitive disease.
Continued approval may depend on verification of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
Labeling includes a box warning of serious or life-threatening cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxicity, including immune effector cell–associated neurotoxicity syndrome.
The most common adverse events, occurring in 20% or more of patients, were cytokine release syndrome, fatigue, pyrexia, dysgeusia, decreased appetite, musculoskeletal pain, constipation, anemia, and nausea.
The most common grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities included decreased lymphocytes, decreased sodium, increased uric acid, decreased total neutrophils, decreased hemoglobin, increased activated partial thromboplastin time, and decreased potassium.
The starting dose is 1 mg given intravenously over 1 hour on the first day of the first cycle followed by 10 mg on day 8 and day 15 of the first cycle, then every 2 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
M. Alexander Otto is a physician assistant with a master’s degree in medical science and a journalism degree from Newhouse. He is an award-winning medical journalist who worked for several major news outlets before joining Medscape. Alex is also an MIT Knight Science Journalism fellow. Email: [email protected]
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Tarlatamab is a first-in-class bispecific T-cell engager (BiTE) that binds delta-like ligand 3 on the surface of cells, including tumor cells, and CD3 expressed on the surface of T cells. It causes T-cell activation, release of inflammatory cytokines, and lysis of DLL3-expressing cells, according to labeling.
Approval was based on data from 99 patients in the DeLLphi-301 trial with relapsed/refractory extensive-stage SCLC who had progressed after platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients with symptomatic brain metastases, interstitial lung disease, noninfectious pneumonitis, and active immunodeficiency were excluded.
The overall response rate was 40%, and median duration of response 9.7 months. The overall response rate was 52% in 27 patients with platinum-resistant SCLC and 31% in 42 with platinum-sensitive disease.
Continued approval may depend on verification of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
Labeling includes a box warning of serious or life-threatening cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxicity, including immune effector cell–associated neurotoxicity syndrome.
The most common adverse events, occurring in 20% or more of patients, were cytokine release syndrome, fatigue, pyrexia, dysgeusia, decreased appetite, musculoskeletal pain, constipation, anemia, and nausea.
The most common grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities included decreased lymphocytes, decreased sodium, increased uric acid, decreased total neutrophils, decreased hemoglobin, increased activated partial thromboplastin time, and decreased potassium.
The starting dose is 1 mg given intravenously over 1 hour on the first day of the first cycle followed by 10 mg on day 8 and day 15 of the first cycle, then every 2 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
M. Alexander Otto is a physician assistant with a master’s degree in medical science and a journalism degree from Newhouse. He is an award-winning medical journalist who worked for several major news outlets before joining Medscape. Alex is also an MIT Knight Science Journalism fellow. Email: [email protected]
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Chatbots Seem More Empathetic Than Docs in Cancer Discussions
Large language models (LLM) such as ChatGPT have shown mixed results in the quality of their responses to consumer questions about cancer.
One recent study found AI chatbots to churn out incomplete, inaccurate, or even nonsensical cancer treatment recommendations, while another found them to generate largely accurate — if technical — responses to the most common cancer questions.
While researchers have seen success with purpose-built chatbots created to address patient concerns about specific cancers, the consensus to date has been that the generalized models like ChatGPT remain works in progress and that physicians should avoid pointing patients to them, for now.
Yet new findings suggest that these chatbots may do better than individual physicians, at least on some measures, when it comes to answering queries about cancer. For research published May 16 in JAMA Oncology (doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.0836), David Chen, a medical student at the University of Toronto, and his colleagues, isolated a random sample of 200 questions related to cancer care addressed to doctors on the public online forum Reddit. They then compared responses from oncologists with responses generated by three different AI chatbots. The blinded responses were rated for quality, readability, and empathy by six physicians, including oncologists and palliative and supportive care specialists.
Mr. Chen and colleagues’ research was modeled after a 2023 study that measured the quality of physician responses compared with chatbots for general medicine questions addressed to doctors on Reddit. That study found that the chatbots produced more empathetic-sounding answers, something Mr. Chen’s study also found. : quality, empathy, and readability.
Q&A With Author of New Research
Mr. Chen discussed his new study’s implications during an interview with this news organization.
Question: What is novel about this study?
Mr. Chen: We’ve seen many evaluations of chatbots that test for medical accuracy, but this study occurs in the domain of oncology care, where there are unique psychosocial and emotional considerations that are not precisely reflected in a general medicine setting. In effect, this study is putting these chatbots through a harder challenge.
Question: Why would chatbot responses seem more empathetic than those of physicians?
Mr. Chen: With the physician responses that we observed in our sample data set, we saw that there was very high variation of amount of apparent effort [in the physician responses]. Some physicians would put in a lot of time and effort, thinking through their response, and others wouldn’t do so as much. These chatbots don’t face fatigue the way humans do, or burnout. So they’re able to consistently provide responses with less variation in empathy.
Question: Do chatbots just seem empathetic because they are chattier?
Mr. Chen: We did think of verbosity as a potential confounder in this study. So we set a word count limit for the chatbot responses to keep it in the range of the physician responses. That way, verbosity was no longer a significant factor.
Question: How were quality and empathy measured by the reviewers?
Mr. Chen: For our study we used two teams of readers, each team composed of three physicians. In terms of the actual metrics we used, they were pilot metrics. There are no well-defined measurement scales or checklists that we could use to measure empathy. This is an emerging field of research. So we came up by consensus with our own set of ratings, and we feel that this is an area for the research to define a standardized set of guidelines.
Another novel aspect of this study is that we separated out different dimensions of quality and empathy. A quality response didn’t just mean it was medically accurate — quality also had to do with the focus and completeness of the response.
With empathy there are cognitive and emotional dimensions. Cognitive empathy uses critical thinking to understand the person’s emotions and thoughts and then adjusting a response to fit that. A patient may not want the best medically indicated treatment for their condition, because they want to preserve their quality of life. The chatbot may be able to adjust its recommendation with consideration of some of those humanistic elements that the patient is presenting with.
Emotional empathy is more about being supportive of the patient’s emotions by using expressions like ‘I understand where you’re coming from.’ or, ‘I can see how that makes you feel.’
Question: Why would physicians, not patients, be the best evaluators of empathy?
Mr. Chen: We’re actually very interested in evaluating patient ratings of empathy. We are conducting a follow-up study that evaluates patient ratings of empathy to the same set of chatbot and physician responses,to see if there are differences.
Question: Should cancer patients go ahead and consult chatbots?
Mr. Chen: Although we did observe increases in all of the metrics compared with physicians, this is a very specialized evaluation scenario where we’re using these Reddit questions and responses.
Naturally, we would need to do a trial, a head to head randomized comparison of physicians versus chatbots.
This pilot study does highlight the promising potential of these chatbots to suggest responses. But we can’t fully recommend that they should be used as standalone clinical tools without physicians.
This Q&A was edited for clarity.
Large language models (LLM) such as ChatGPT have shown mixed results in the quality of their responses to consumer questions about cancer.
One recent study found AI chatbots to churn out incomplete, inaccurate, or even nonsensical cancer treatment recommendations, while another found them to generate largely accurate — if technical — responses to the most common cancer questions.
While researchers have seen success with purpose-built chatbots created to address patient concerns about specific cancers, the consensus to date has been that the generalized models like ChatGPT remain works in progress and that physicians should avoid pointing patients to them, for now.
Yet new findings suggest that these chatbots may do better than individual physicians, at least on some measures, when it comes to answering queries about cancer. For research published May 16 in JAMA Oncology (doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.0836), David Chen, a medical student at the University of Toronto, and his colleagues, isolated a random sample of 200 questions related to cancer care addressed to doctors on the public online forum Reddit. They then compared responses from oncologists with responses generated by three different AI chatbots. The blinded responses were rated for quality, readability, and empathy by six physicians, including oncologists and palliative and supportive care specialists.
Mr. Chen and colleagues’ research was modeled after a 2023 study that measured the quality of physician responses compared with chatbots for general medicine questions addressed to doctors on Reddit. That study found that the chatbots produced more empathetic-sounding answers, something Mr. Chen’s study also found. : quality, empathy, and readability.
Q&A With Author of New Research
Mr. Chen discussed his new study’s implications during an interview with this news organization.
Question: What is novel about this study?
Mr. Chen: We’ve seen many evaluations of chatbots that test for medical accuracy, but this study occurs in the domain of oncology care, where there are unique psychosocial and emotional considerations that are not precisely reflected in a general medicine setting. In effect, this study is putting these chatbots through a harder challenge.
Question: Why would chatbot responses seem more empathetic than those of physicians?
Mr. Chen: With the physician responses that we observed in our sample data set, we saw that there was very high variation of amount of apparent effort [in the physician responses]. Some physicians would put in a lot of time and effort, thinking through their response, and others wouldn’t do so as much. These chatbots don’t face fatigue the way humans do, or burnout. So they’re able to consistently provide responses with less variation in empathy.
Question: Do chatbots just seem empathetic because they are chattier?
Mr. Chen: We did think of verbosity as a potential confounder in this study. So we set a word count limit for the chatbot responses to keep it in the range of the physician responses. That way, verbosity was no longer a significant factor.
Question: How were quality and empathy measured by the reviewers?
Mr. Chen: For our study we used two teams of readers, each team composed of three physicians. In terms of the actual metrics we used, they were pilot metrics. There are no well-defined measurement scales or checklists that we could use to measure empathy. This is an emerging field of research. So we came up by consensus with our own set of ratings, and we feel that this is an area for the research to define a standardized set of guidelines.
Another novel aspect of this study is that we separated out different dimensions of quality and empathy. A quality response didn’t just mean it was medically accurate — quality also had to do with the focus and completeness of the response.
With empathy there are cognitive and emotional dimensions. Cognitive empathy uses critical thinking to understand the person’s emotions and thoughts and then adjusting a response to fit that. A patient may not want the best medically indicated treatment for their condition, because they want to preserve their quality of life. The chatbot may be able to adjust its recommendation with consideration of some of those humanistic elements that the patient is presenting with.
Emotional empathy is more about being supportive of the patient’s emotions by using expressions like ‘I understand where you’re coming from.’ or, ‘I can see how that makes you feel.’
Question: Why would physicians, not patients, be the best evaluators of empathy?
Mr. Chen: We’re actually very interested in evaluating patient ratings of empathy. We are conducting a follow-up study that evaluates patient ratings of empathy to the same set of chatbot and physician responses,to see if there are differences.
Question: Should cancer patients go ahead and consult chatbots?
Mr. Chen: Although we did observe increases in all of the metrics compared with physicians, this is a very specialized evaluation scenario where we’re using these Reddit questions and responses.
Naturally, we would need to do a trial, a head to head randomized comparison of physicians versus chatbots.
This pilot study does highlight the promising potential of these chatbots to suggest responses. But we can’t fully recommend that they should be used as standalone clinical tools without physicians.
This Q&A was edited for clarity.
Large language models (LLM) such as ChatGPT have shown mixed results in the quality of their responses to consumer questions about cancer.
One recent study found AI chatbots to churn out incomplete, inaccurate, or even nonsensical cancer treatment recommendations, while another found them to generate largely accurate — if technical — responses to the most common cancer questions.
While researchers have seen success with purpose-built chatbots created to address patient concerns about specific cancers, the consensus to date has been that the generalized models like ChatGPT remain works in progress and that physicians should avoid pointing patients to them, for now.
Yet new findings suggest that these chatbots may do better than individual physicians, at least on some measures, when it comes to answering queries about cancer. For research published May 16 in JAMA Oncology (doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.0836), David Chen, a medical student at the University of Toronto, and his colleagues, isolated a random sample of 200 questions related to cancer care addressed to doctors on the public online forum Reddit. They then compared responses from oncologists with responses generated by three different AI chatbots. The blinded responses were rated for quality, readability, and empathy by six physicians, including oncologists and palliative and supportive care specialists.
Mr. Chen and colleagues’ research was modeled after a 2023 study that measured the quality of physician responses compared with chatbots for general medicine questions addressed to doctors on Reddit. That study found that the chatbots produced more empathetic-sounding answers, something Mr. Chen’s study also found. : quality, empathy, and readability.
Q&A With Author of New Research
Mr. Chen discussed his new study’s implications during an interview with this news organization.
Question: What is novel about this study?
Mr. Chen: We’ve seen many evaluations of chatbots that test for medical accuracy, but this study occurs in the domain of oncology care, where there are unique psychosocial and emotional considerations that are not precisely reflected in a general medicine setting. In effect, this study is putting these chatbots through a harder challenge.
Question: Why would chatbot responses seem more empathetic than those of physicians?
Mr. Chen: With the physician responses that we observed in our sample data set, we saw that there was very high variation of amount of apparent effort [in the physician responses]. Some physicians would put in a lot of time and effort, thinking through their response, and others wouldn’t do so as much. These chatbots don’t face fatigue the way humans do, or burnout. So they’re able to consistently provide responses with less variation in empathy.
Question: Do chatbots just seem empathetic because they are chattier?
Mr. Chen: We did think of verbosity as a potential confounder in this study. So we set a word count limit for the chatbot responses to keep it in the range of the physician responses. That way, verbosity was no longer a significant factor.
Question: How were quality and empathy measured by the reviewers?
Mr. Chen: For our study we used two teams of readers, each team composed of three physicians. In terms of the actual metrics we used, they were pilot metrics. There are no well-defined measurement scales or checklists that we could use to measure empathy. This is an emerging field of research. So we came up by consensus with our own set of ratings, and we feel that this is an area for the research to define a standardized set of guidelines.
Another novel aspect of this study is that we separated out different dimensions of quality and empathy. A quality response didn’t just mean it was medically accurate — quality also had to do with the focus and completeness of the response.
With empathy there are cognitive and emotional dimensions. Cognitive empathy uses critical thinking to understand the person’s emotions and thoughts and then adjusting a response to fit that. A patient may not want the best medically indicated treatment for their condition, because they want to preserve their quality of life. The chatbot may be able to adjust its recommendation with consideration of some of those humanistic elements that the patient is presenting with.
Emotional empathy is more about being supportive of the patient’s emotions by using expressions like ‘I understand where you’re coming from.’ or, ‘I can see how that makes you feel.’
Question: Why would physicians, not patients, be the best evaluators of empathy?
Mr. Chen: We’re actually very interested in evaluating patient ratings of empathy. We are conducting a follow-up study that evaluates patient ratings of empathy to the same set of chatbot and physician responses,to see if there are differences.
Question: Should cancer patients go ahead and consult chatbots?
Mr. Chen: Although we did observe increases in all of the metrics compared with physicians, this is a very specialized evaluation scenario where we’re using these Reddit questions and responses.
Naturally, we would need to do a trial, a head to head randomized comparison of physicians versus chatbots.
This pilot study does highlight the promising potential of these chatbots to suggest responses. But we can’t fully recommend that they should be used as standalone clinical tools without physicians.
This Q&A was edited for clarity.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
CPAP Underperforms: The Sequel
A few months ago, I posted a column on continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) with the title, “CPAP Oversells and Underperforms.” To date, it has 299 likes and 90 comments, which are almost all negative. I’m glad to see that it’s generated interest, and I’d like to address some of the themes expressed in the posts.
Most comments were personal testimonies to the miracles of CPAP. These are important, and the point deserves emphasis. CPAP can provide significant improvements in daytime sleepiness and quality of life. I closed the original piece by acknowledging this important fact. Readers can be forgiven for missing it given that the title and text were otherwise disparaging of CPAP.
But several comments warrant a more in-depth discussion. The original piece focuses on CPAP and cardiovascular (CV) outcomes but made no mention of atrial fibrillation (AF) or ejection fraction (EF). The effects of CPAP on each are touted by cardiologists and PAP-pushers alike and are drivers of frequent referrals. It›s my fault for omitting them from the discussion.
AF is easy. The data is identical to all other things CPAP and CV. Based on biologic plausibility alone, the likelihood of a relationship between AF and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is similar to the odds that the Celtics raise an 18th banner come June. There’s hypoxia, intrathoracic pressure swings, sympathetic surges, and sleep state disruptions. It’s easy to get from there to arrhythmogenesis. There’s lots of observational noise, too, but no randomized proof that CPAP alters this relationship.
I found four randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that tested CPAP’s effect on AF. I’ll save you the suspense; they were all negative. One even found a signal for more adverse events in the CPAP group. These studies have several positive qualities: They enrolled patients with moderate to severe sleep apnea and high oxygen desaturation indices, adherence averaged more than 4 hours across all groups in all trials, and the methods for assessing the AF outcomes differed slightly. There’s also a lot not to like: The sample sizes were small, only one trial enrolled “sleepy” patients (as assessed by the Epworth Sleepiness Score), and follow-up was short.
To paraphrase Carl Sagan, “absence of evidence does not equal evidence of absence.” As a statistician would say, type II error cannot be excluded by these RCTs. In medicine, however, the burden of proof falls on demonstrating efficacy. If we treat before concluding that a therapy works, we risk wasting time, money, medical resources, and the most precious of patient commodities: the energy required for behavior change. In their response to letters to the editor, the authors of the third RCT summarize the CPAP, AF, and CV disease data far better than I ever could. They sound the same words of caution and come out against screening patients with AF for OSA.
The story for CPAP’s effects on EF is similar though muddier. The American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines for heart failure cite a meta-analysis showing that CPAP improves left ventricular EF. In 2019, the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) CPAP guidelines included a systematic review and meta-analysis that found that CPAP has no effect on left ventricular EF in patients with or without heart failure.
There are a million reasons why two systematic reviews on the same topic might come to different conclusions. In this case, the included studies only partially overlap, and broadly speaking, it appears the authors made trade-offs. The review cited by the ACC/AHA had broader inclusion and significantly more patients and paid for it in heterogeneity (I2 in the 80%-90% range). The AASM analysis achieved 0% heterogeneity but limited inclusion to fewer than 100 patients. Across both, the improvement in EF was 2%- 5% at a minimally clinically important difference of 4%. Hardly convincing.
In summary, the road to negative trials and patient harm has always been paved with observational signal and biologic plausibility. Throw in some intellectual and academic bias, and you’ve created the perfect storm of therapeutic overconfidence.
Dr. Holley is a professor in the department of medicine, Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Maryland, and a physician at Pulmonary/Sleep and Critical Care Medicine, MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington. He disclosed ties to Metapharm Inc., CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
A few months ago, I posted a column on continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) with the title, “CPAP Oversells and Underperforms.” To date, it has 299 likes and 90 comments, which are almost all negative. I’m glad to see that it’s generated interest, and I’d like to address some of the themes expressed in the posts.
Most comments were personal testimonies to the miracles of CPAP. These are important, and the point deserves emphasis. CPAP can provide significant improvements in daytime sleepiness and quality of life. I closed the original piece by acknowledging this important fact. Readers can be forgiven for missing it given that the title and text were otherwise disparaging of CPAP.
But several comments warrant a more in-depth discussion. The original piece focuses on CPAP and cardiovascular (CV) outcomes but made no mention of atrial fibrillation (AF) or ejection fraction (EF). The effects of CPAP on each are touted by cardiologists and PAP-pushers alike and are drivers of frequent referrals. It›s my fault for omitting them from the discussion.
AF is easy. The data is identical to all other things CPAP and CV. Based on biologic plausibility alone, the likelihood of a relationship between AF and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is similar to the odds that the Celtics raise an 18th banner come June. There’s hypoxia, intrathoracic pressure swings, sympathetic surges, and sleep state disruptions. It’s easy to get from there to arrhythmogenesis. There’s lots of observational noise, too, but no randomized proof that CPAP alters this relationship.
I found four randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that tested CPAP’s effect on AF. I’ll save you the suspense; they were all negative. One even found a signal for more adverse events in the CPAP group. These studies have several positive qualities: They enrolled patients with moderate to severe sleep apnea and high oxygen desaturation indices, adherence averaged more than 4 hours across all groups in all trials, and the methods for assessing the AF outcomes differed slightly. There’s also a lot not to like: The sample sizes were small, only one trial enrolled “sleepy” patients (as assessed by the Epworth Sleepiness Score), and follow-up was short.
To paraphrase Carl Sagan, “absence of evidence does not equal evidence of absence.” As a statistician would say, type II error cannot be excluded by these RCTs. In medicine, however, the burden of proof falls on demonstrating efficacy. If we treat before concluding that a therapy works, we risk wasting time, money, medical resources, and the most precious of patient commodities: the energy required for behavior change. In their response to letters to the editor, the authors of the third RCT summarize the CPAP, AF, and CV disease data far better than I ever could. They sound the same words of caution and come out against screening patients with AF for OSA.
The story for CPAP’s effects on EF is similar though muddier. The American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines for heart failure cite a meta-analysis showing that CPAP improves left ventricular EF. In 2019, the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) CPAP guidelines included a systematic review and meta-analysis that found that CPAP has no effect on left ventricular EF in patients with or without heart failure.
There are a million reasons why two systematic reviews on the same topic might come to different conclusions. In this case, the included studies only partially overlap, and broadly speaking, it appears the authors made trade-offs. The review cited by the ACC/AHA had broader inclusion and significantly more patients and paid for it in heterogeneity (I2 in the 80%-90% range). The AASM analysis achieved 0% heterogeneity but limited inclusion to fewer than 100 patients. Across both, the improvement in EF was 2%- 5% at a minimally clinically important difference of 4%. Hardly convincing.
In summary, the road to negative trials and patient harm has always been paved with observational signal and biologic plausibility. Throw in some intellectual and academic bias, and you’ve created the perfect storm of therapeutic overconfidence.
Dr. Holley is a professor in the department of medicine, Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Maryland, and a physician at Pulmonary/Sleep and Critical Care Medicine, MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington. He disclosed ties to Metapharm Inc., CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
A few months ago, I posted a column on continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) with the title, “CPAP Oversells and Underperforms.” To date, it has 299 likes and 90 comments, which are almost all negative. I’m glad to see that it’s generated interest, and I’d like to address some of the themes expressed in the posts.
Most comments were personal testimonies to the miracles of CPAP. These are important, and the point deserves emphasis. CPAP can provide significant improvements in daytime sleepiness and quality of life. I closed the original piece by acknowledging this important fact. Readers can be forgiven for missing it given that the title and text were otherwise disparaging of CPAP.
But several comments warrant a more in-depth discussion. The original piece focuses on CPAP and cardiovascular (CV) outcomes but made no mention of atrial fibrillation (AF) or ejection fraction (EF). The effects of CPAP on each are touted by cardiologists and PAP-pushers alike and are drivers of frequent referrals. It›s my fault for omitting them from the discussion.
AF is easy. The data is identical to all other things CPAP and CV. Based on biologic plausibility alone, the likelihood of a relationship between AF and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is similar to the odds that the Celtics raise an 18th banner come June. There’s hypoxia, intrathoracic pressure swings, sympathetic surges, and sleep state disruptions. It’s easy to get from there to arrhythmogenesis. There’s lots of observational noise, too, but no randomized proof that CPAP alters this relationship.
I found four randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that tested CPAP’s effect on AF. I’ll save you the suspense; they were all negative. One even found a signal for more adverse events in the CPAP group. These studies have several positive qualities: They enrolled patients with moderate to severe sleep apnea and high oxygen desaturation indices, adherence averaged more than 4 hours across all groups in all trials, and the methods for assessing the AF outcomes differed slightly. There’s also a lot not to like: The sample sizes were small, only one trial enrolled “sleepy” patients (as assessed by the Epworth Sleepiness Score), and follow-up was short.
To paraphrase Carl Sagan, “absence of evidence does not equal evidence of absence.” As a statistician would say, type II error cannot be excluded by these RCTs. In medicine, however, the burden of proof falls on demonstrating efficacy. If we treat before concluding that a therapy works, we risk wasting time, money, medical resources, and the most precious of patient commodities: the energy required for behavior change. In their response to letters to the editor, the authors of the third RCT summarize the CPAP, AF, and CV disease data far better than I ever could. They sound the same words of caution and come out against screening patients with AF for OSA.
The story for CPAP’s effects on EF is similar though muddier. The American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines for heart failure cite a meta-analysis showing that CPAP improves left ventricular EF. In 2019, the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) CPAP guidelines included a systematic review and meta-analysis that found that CPAP has no effect on left ventricular EF in patients with or without heart failure.
There are a million reasons why two systematic reviews on the same topic might come to different conclusions. In this case, the included studies only partially overlap, and broadly speaking, it appears the authors made trade-offs. The review cited by the ACC/AHA had broader inclusion and significantly more patients and paid for it in heterogeneity (I2 in the 80%-90% range). The AASM analysis achieved 0% heterogeneity but limited inclusion to fewer than 100 patients. Across both, the improvement in EF was 2%- 5% at a minimally clinically important difference of 4%. Hardly convincing.
In summary, the road to negative trials and patient harm has always been paved with observational signal and biologic plausibility. Throw in some intellectual and academic bias, and you’ve created the perfect storm of therapeutic overconfidence.
Dr. Holley is a professor in the department of medicine, Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Maryland, and a physician at Pulmonary/Sleep and Critical Care Medicine, MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington. He disclosed ties to Metapharm Inc., CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Aquagenic Wrinkling Among Skin-Related Signs of Cystic Fibrosis
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients with CF, caused by a mutation in the CF Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) gene, can develop diverse dermatologic manifestations.
- Researchers reviewed the literature and provided their own clinical experience regarding dermatologic manifestations of CF.
- They also reviewed the cutaneous side effects of CFTR modulators and antibiotics used to treat CF.
TAKEAWAY:
- Aquagenic wrinkling of the palm is common in individuals with CF, affecting up to 80% of patients (and 25% of CF gene carriers), and can be an early manifestation of CF. Treatments include topical medications (such as aluminum chloride, corticosteroids, and salicylic acid), botulinum toxin injections, and recently, CFTR-modulating treatments.
- CF nutrient deficiency dermatitis, often in a diaper distribution, usually appears in infancy and, before newborn screening was available, was sometimes the first sign of CF in some cases. It usually resolves with an adequate diet, pancreatic enzymes, and/or nutritional supplements. Zinc and essential fatty acid deficiencies can lead to acrodermatitis enteropathica–like symptoms and psoriasiform rashes, respectively.
- CF is also associated with vascular disorders, including cutaneous and, rarely, systemic vasculitis. Treatment includes topical and oral steroids and immune-modulating therapies.
- CFTR modulators, now the most common and highly effective treatment for CF, are associated with several skin reactions, which can be managed with treatments that include topical steroids and oral antihistamines. Frequent antibiotic treatment can also trigger skin reactions.
IN PRACTICE:
“Recognition and familiarity with dermatologic clinical manifestations of CF are important for multidisciplinary care” for patients with CF, the authors wrote, adding that “dermatology providers may play a significant role in the diagnosis and management of CF cutaneous comorbidities.”
SOURCE:
Aaron D. Smith, BS, from the University of Virginia (UVA) School of Medicine, Charlottesville, and coauthors were from the departments of dermatology and pulmonology/critical care medicine at UVA. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The authors did not make a comment about the limitations of their review.
DISCLOSURES:
No funding was received for the review. The authors had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients with CF, caused by a mutation in the CF Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) gene, can develop diverse dermatologic manifestations.
- Researchers reviewed the literature and provided their own clinical experience regarding dermatologic manifestations of CF.
- They also reviewed the cutaneous side effects of CFTR modulators and antibiotics used to treat CF.
TAKEAWAY:
- Aquagenic wrinkling of the palm is common in individuals with CF, affecting up to 80% of patients (and 25% of CF gene carriers), and can be an early manifestation of CF. Treatments include topical medications (such as aluminum chloride, corticosteroids, and salicylic acid), botulinum toxin injections, and recently, CFTR-modulating treatments.
- CF nutrient deficiency dermatitis, often in a diaper distribution, usually appears in infancy and, before newborn screening was available, was sometimes the first sign of CF in some cases. It usually resolves with an adequate diet, pancreatic enzymes, and/or nutritional supplements. Zinc and essential fatty acid deficiencies can lead to acrodermatitis enteropathica–like symptoms and psoriasiform rashes, respectively.
- CF is also associated with vascular disorders, including cutaneous and, rarely, systemic vasculitis. Treatment includes topical and oral steroids and immune-modulating therapies.
- CFTR modulators, now the most common and highly effective treatment for CF, are associated with several skin reactions, which can be managed with treatments that include topical steroids and oral antihistamines. Frequent antibiotic treatment can also trigger skin reactions.
IN PRACTICE:
“Recognition and familiarity with dermatologic clinical manifestations of CF are important for multidisciplinary care” for patients with CF, the authors wrote, adding that “dermatology providers may play a significant role in the diagnosis and management of CF cutaneous comorbidities.”
SOURCE:
Aaron D. Smith, BS, from the University of Virginia (UVA) School of Medicine, Charlottesville, and coauthors were from the departments of dermatology and pulmonology/critical care medicine at UVA. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The authors did not make a comment about the limitations of their review.
DISCLOSURES:
No funding was received for the review. The authors had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients with CF, caused by a mutation in the CF Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) gene, can develop diverse dermatologic manifestations.
- Researchers reviewed the literature and provided their own clinical experience regarding dermatologic manifestations of CF.
- They also reviewed the cutaneous side effects of CFTR modulators and antibiotics used to treat CF.
TAKEAWAY:
- Aquagenic wrinkling of the palm is common in individuals with CF, affecting up to 80% of patients (and 25% of CF gene carriers), and can be an early manifestation of CF. Treatments include topical medications (such as aluminum chloride, corticosteroids, and salicylic acid), botulinum toxin injections, and recently, CFTR-modulating treatments.
- CF nutrient deficiency dermatitis, often in a diaper distribution, usually appears in infancy and, before newborn screening was available, was sometimes the first sign of CF in some cases. It usually resolves with an adequate diet, pancreatic enzymes, and/or nutritional supplements. Zinc and essential fatty acid deficiencies can lead to acrodermatitis enteropathica–like symptoms and psoriasiform rashes, respectively.
- CF is also associated with vascular disorders, including cutaneous and, rarely, systemic vasculitis. Treatment includes topical and oral steroids and immune-modulating therapies.
- CFTR modulators, now the most common and highly effective treatment for CF, are associated with several skin reactions, which can be managed with treatments that include topical steroids and oral antihistamines. Frequent antibiotic treatment can also trigger skin reactions.
IN PRACTICE:
“Recognition and familiarity with dermatologic clinical manifestations of CF are important for multidisciplinary care” for patients with CF, the authors wrote, adding that “dermatology providers may play a significant role in the diagnosis and management of CF cutaneous comorbidities.”
SOURCE:
Aaron D. Smith, BS, from the University of Virginia (UVA) School of Medicine, Charlottesville, and coauthors were from the departments of dermatology and pulmonology/critical care medicine at UVA. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The authors did not make a comment about the limitations of their review.
DISCLOSURES:
No funding was received for the review. The authors had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Why Cardiac Biomarkers Don’t Help Predict Heart Disease
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s the counterintuitive stuff in epidemiology that always really interests me. One intuition many of us have is that if a risk factor is significantly associated with an outcome, knowledge of that risk factor would help to predict that outcome. Makes sense. Feels right.
But it’s not right. Not always.
Here’s a fake example to illustrate my point. Let’s say we have 10,000 individuals who we follow for 10 years and 2000 of them die. (It’s been a rough decade.) At baseline, I measured a novel biomarker, the Perry Factor, in everyone. To keep it simple, the Perry Factor has only two values: 0 or 1.
I then do a standard associational analysis and find that individuals who are positive for the Perry Factor have a 40-fold higher odds of death than those who are negative for it. I am beginning to reconsider ascribing my good name to this biomarker. This is a highly statistically significant result — a P value <.001.
Clearly, knowledge of the Perry Factor should help me predict who will die in the cohort. I evaluate predictive power using a metric called the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC, referred to as the C-statistic in time-to-event studies). It tells you, given two people — one who dies and one who doesn’t — how frequently you “pick” the right person, given the knowledge of their Perry Factor.
A C-statistic of 0.5, or 50%, would mean the Perry Factor gives you no better results than a coin flip; it’s chance. A C-statistic of 1 is perfect prediction. So, what will the C-statistic be, given the incredibly strong association of the Perry Factor with outcomes? 0.9? 0.95?
0.5024. Almost useless.

Let’s figure out why strength of association and usefulness for prediction are not always the same thing.
I constructed my fake Perry Factor dataset quite carefully to illustrate this point. Let me show you what happened. What you see here is a breakdown of the patients in my fake study. You can see that just 11 of them were Perry Factor positive, but 10 of those 11 ended up dying.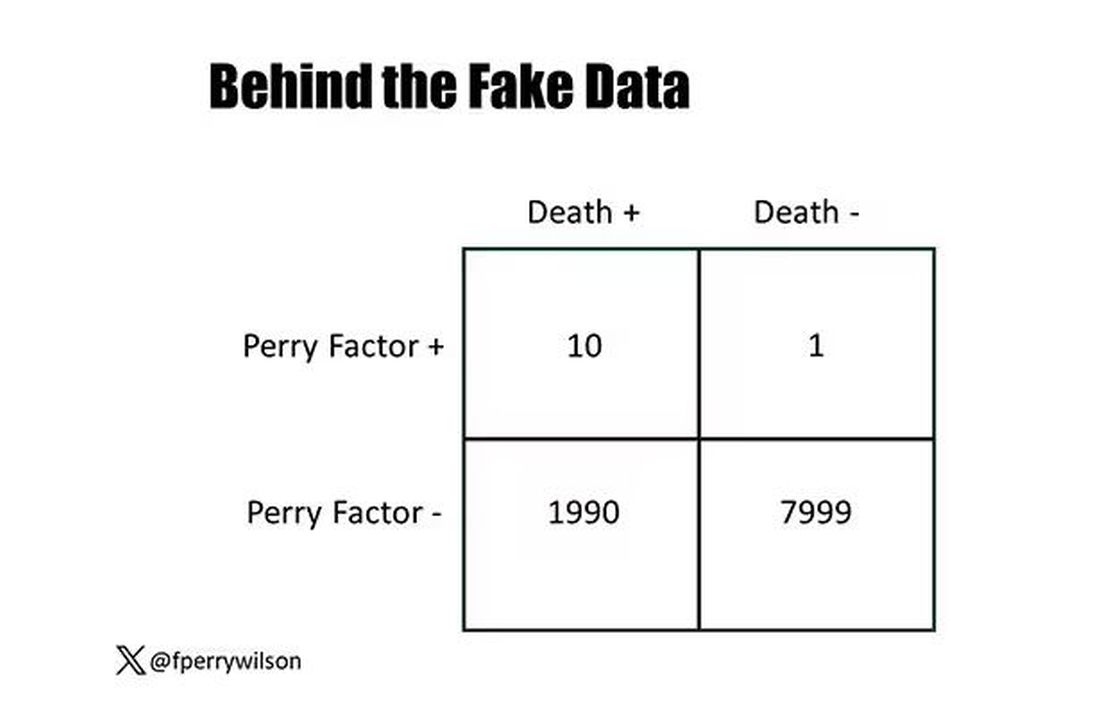
That’s quite unlikely by chance alone. It really does appear that if you have Perry Factor, your risk for death is much higher. But the reason that Perry Factor is a bad predictor is because it is so rare in the population. Sure, you can use it to correctly predict the outcome of 10 of the 11 people who have it, but the vast majority of people don’t have Perry Factor. It’s useless to distinguish who will die vs who will live in that population.
Why have I spent so much time trying to reverse our intuition that strength of association and strength of predictive power must be related? Because it helps to explain this paper, “Prognostic Value of Cardiovascular Biomarkers in the Population,” appearing in JAMA, which is a very nice piece of work trying to help us better predict cardiovascular disease.
I don’t need to tell you that cardiovascular disease is the number-one killer in this country and most of the world. I don’t need to tell you that we have really good preventive therapies and lifestyle interventions that can reduce the risk. But it would be nice to know in whom, specifically, we should use those interventions.
Cardiovascular risk scores, to date, are pretty simple. The most common one in use in the United States, the pooled cohort risk equation, has nine variables, two of which require a cholesterol panel and one a blood pressure test. It’s easy and it’s pretty accurate.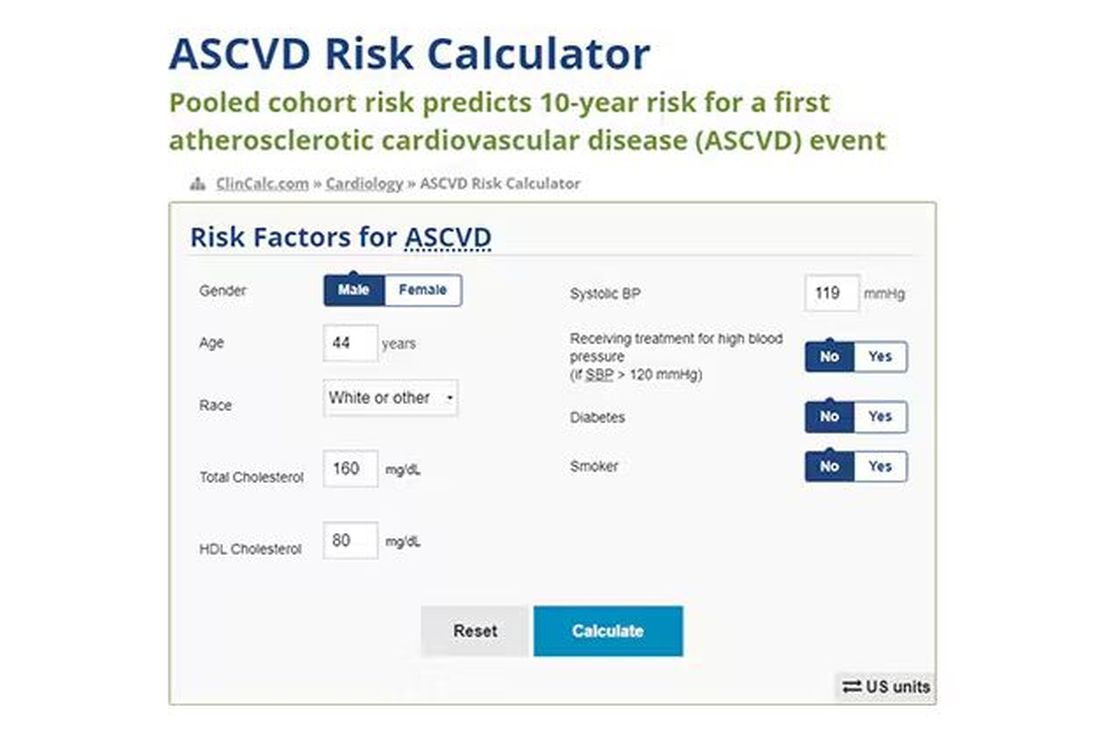
Using the score from the pooled cohort risk calculator, you get a C-statistic as high as 0.82 when applied to Black women, a low of 0.71 when applied to Black men. Non-Black individuals are in the middle. Not bad. But, clearly, not perfect.
And aren’t we in the era of big data, the era of personalized medicine? We have dozens, maybe hundreds, of quantifiable biomarkers that are associated with subsequent heart disease. Surely, by adding these biomarkers into the risk equation, we can improve prediction. Right?
The JAMA study includes 164,054 patients pooled from 28 cohort studies from 12 countries. All the studies measured various key biomarkers at baseline and followed their participants for cardiovascular events like heart attack, stroke, coronary revascularization, and so on.
The biomarkers in question are really the big guns in this space: troponin, a marker of stress on the heart muscle; NT-proBNP, a marker of stretch on the heart muscle; and C-reactive protein, a marker of inflammation. In every case, higher levels of these markers at baseline were associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular disease in the future.
Troponin T, shown here, has a basically linear risk with subsequent cardiovascular disease.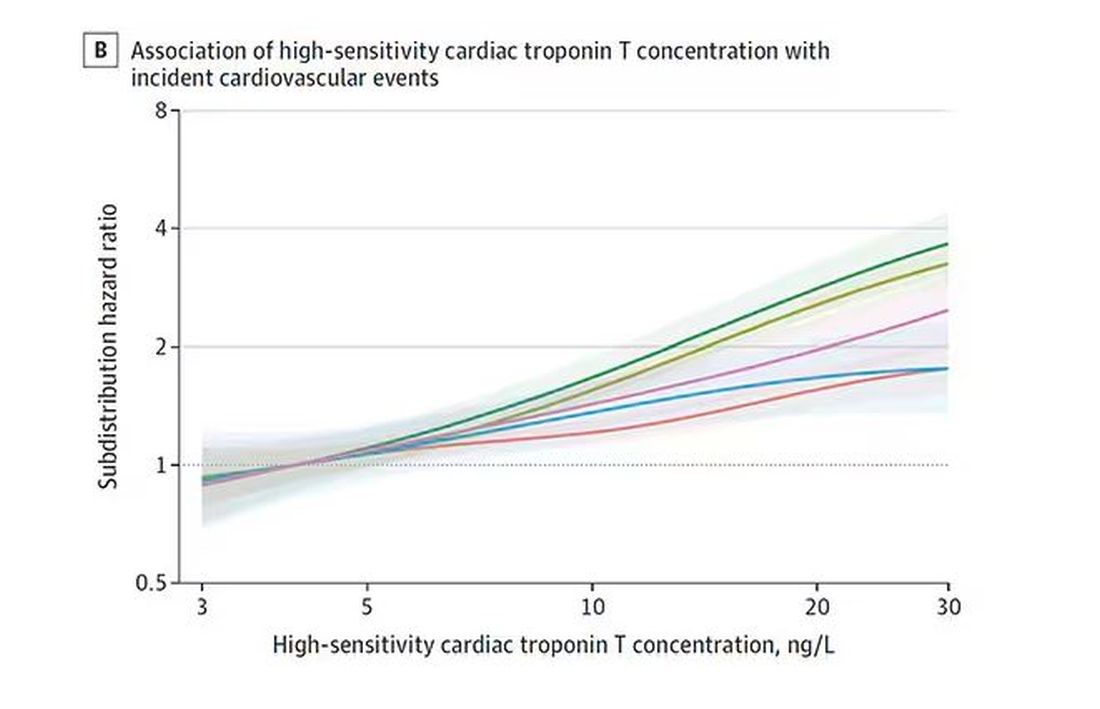
BNP seems to demonstrate more of a threshold effect, where levels above 60 start to associate with problems.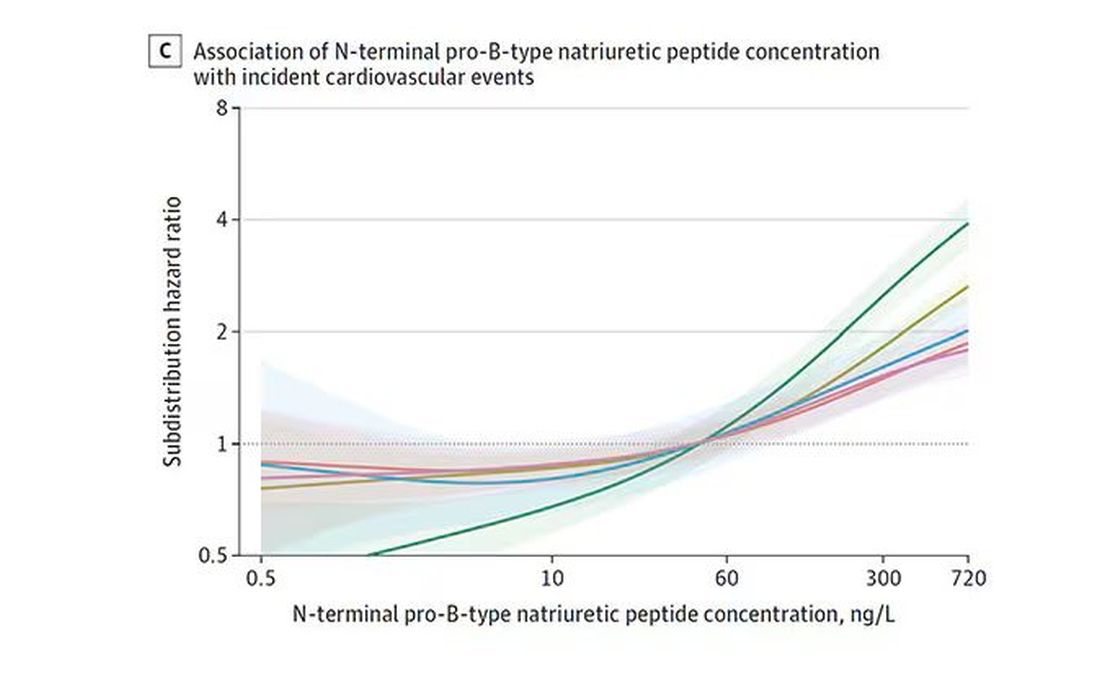
And CRP does a similar thing, with levels above 1.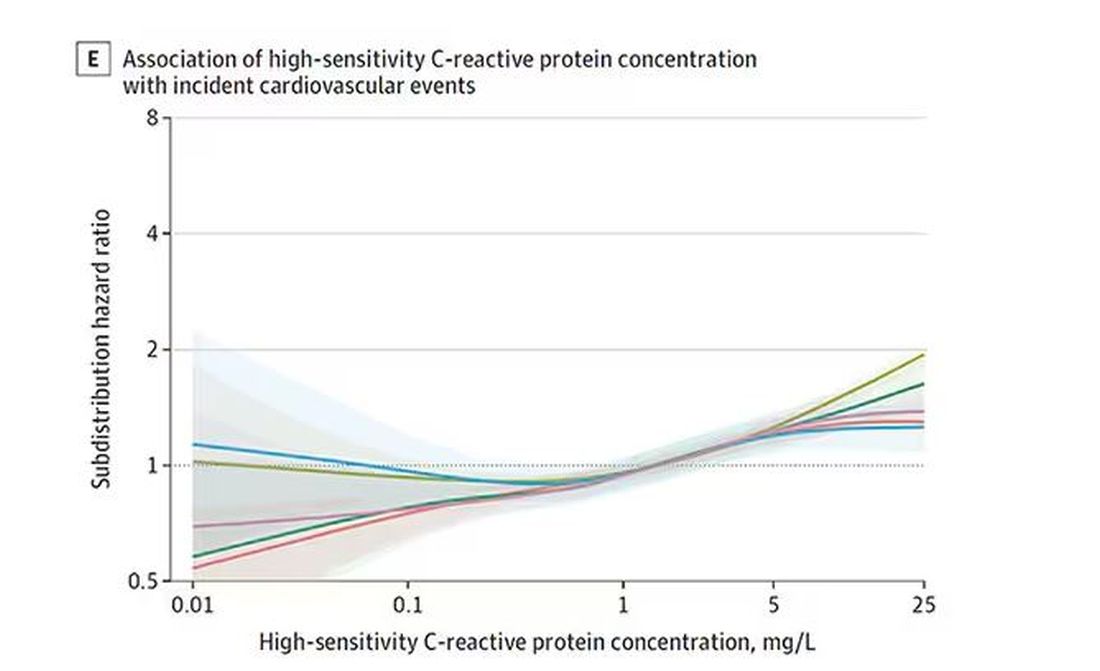
All of these findings were statistically significant. If you have higher levels of one or more of these biomarkers, you are more likely to have cardiovascular disease in the future.
Of course, our old friend the pooled cohort risk equation is still here — in the background — requiring just that one blood test and measurement of blood pressure. Let’s talk about predictive power.
The pooled cohort risk equation score, in this study, had a C-statistic of 0.812.
By adding troponin, BNP, and CRP to the equation, the new C-statistic is 0.819. Barely any change.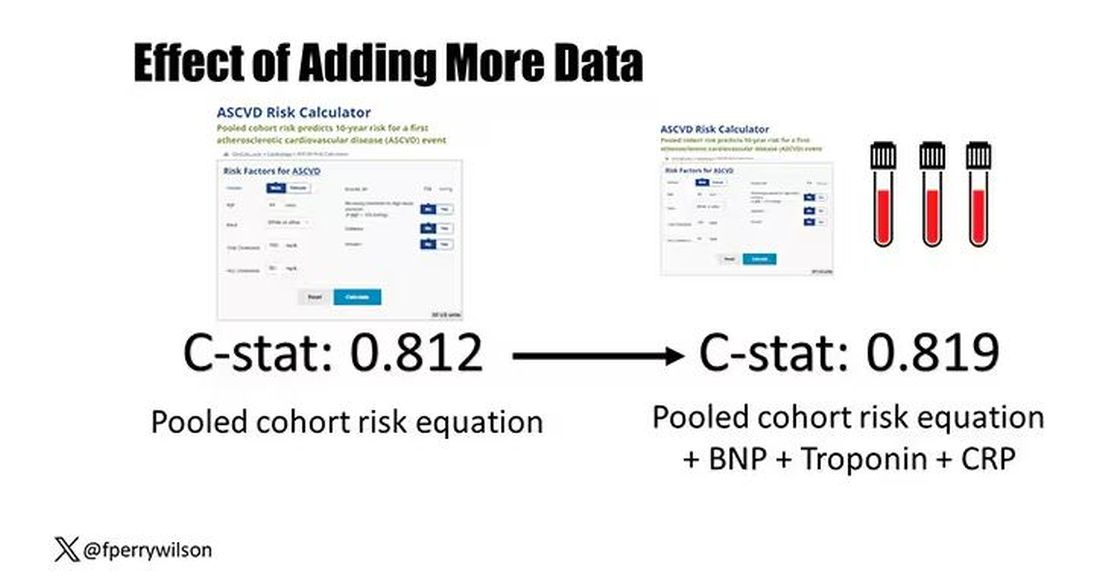
Now, the authors looked at different types of prediction here. The greatest improvement in the AUC was seen when they tried to predict heart failure within 1 year of measurement; there the AUC improved by 0.04. But the presence of BNP as a biomarker and the short time window of 1 year makes me wonder whether this is really prediction at all or whether they were essentially just diagnosing people with existing heart failure.
Why does this happen? Why do these promising biomarkers, clearly associated with bad outcomes, fail to improve our ability to predict the future? I already gave one example, which has to do with how the markers are distributed in the population. But even more relevant here is that the new markers will only improve prediction insofar as they are not already represented in the old predictive model.
Of course, BNP, for example, wasn’t in the old model. But smoking was. Diabetes was. Blood pressure was. All of that data might actually tell you something about the patient’s BNP through their mutual correlation. And improvement in prediction requires new information.
This is actually why I consider this a really successful study. We need to do studies like this to help us find what those new sources of information might be.
We will never get to a C-statistic of 1. Perfect prediction is the domain of palm readers and astrophysicists. But better prediction is always possible through data. The big question, of course, is which data?
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s the counterintuitive stuff in epidemiology that always really interests me. One intuition many of us have is that if a risk factor is significantly associated with an outcome, knowledge of that risk factor would help to predict that outcome. Makes sense. Feels right.
But it’s not right. Not always.
Here’s a fake example to illustrate my point. Let’s say we have 10,000 individuals who we follow for 10 years and 2000 of them die. (It’s been a rough decade.) At baseline, I measured a novel biomarker, the Perry Factor, in everyone. To keep it simple, the Perry Factor has only two values: 0 or 1.
I then do a standard associational analysis and find that individuals who are positive for the Perry Factor have a 40-fold higher odds of death than those who are negative for it. I am beginning to reconsider ascribing my good name to this biomarker. This is a highly statistically significant result — a P value <.001.
Clearly, knowledge of the Perry Factor should help me predict who will die in the cohort. I evaluate predictive power using a metric called the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC, referred to as the C-statistic in time-to-event studies). It tells you, given two people — one who dies and one who doesn’t — how frequently you “pick” the right person, given the knowledge of their Perry Factor.
A C-statistic of 0.5, or 50%, would mean the Perry Factor gives you no better results than a coin flip; it’s chance. A C-statistic of 1 is perfect prediction. So, what will the C-statistic be, given the incredibly strong association of the Perry Factor with outcomes? 0.9? 0.95?
0.5024. Almost useless.

Let’s figure out why strength of association and usefulness for prediction are not always the same thing.
I constructed my fake Perry Factor dataset quite carefully to illustrate this point. Let me show you what happened. What you see here is a breakdown of the patients in my fake study. You can see that just 11 of them were Perry Factor positive, but 10 of those 11 ended up dying.
That’s quite unlikely by chance alone. It really does appear that if you have Perry Factor, your risk for death is much higher. But the reason that Perry Factor is a bad predictor is because it is so rare in the population. Sure, you can use it to correctly predict the outcome of 10 of the 11 people who have it, but the vast majority of people don’t have Perry Factor. It’s useless to distinguish who will die vs who will live in that population.
Why have I spent so much time trying to reverse our intuition that strength of association and strength of predictive power must be related? Because it helps to explain this paper, “Prognostic Value of Cardiovascular Biomarkers in the Population,” appearing in JAMA, which is a very nice piece of work trying to help us better predict cardiovascular disease.
I don’t need to tell you that cardiovascular disease is the number-one killer in this country and most of the world. I don’t need to tell you that we have really good preventive therapies and lifestyle interventions that can reduce the risk. But it would be nice to know in whom, specifically, we should use those interventions.
Cardiovascular risk scores, to date, are pretty simple. The most common one in use in the United States, the pooled cohort risk equation, has nine variables, two of which require a cholesterol panel and one a blood pressure test. It’s easy and it’s pretty accurate.
Using the score from the pooled cohort risk calculator, you get a C-statistic as high as 0.82 when applied to Black women, a low of 0.71 when applied to Black men. Non-Black individuals are in the middle. Not bad. But, clearly, not perfect.
And aren’t we in the era of big data, the era of personalized medicine? We have dozens, maybe hundreds, of quantifiable biomarkers that are associated with subsequent heart disease. Surely, by adding these biomarkers into the risk equation, we can improve prediction. Right?
The JAMA study includes 164,054 patients pooled from 28 cohort studies from 12 countries. All the studies measured various key biomarkers at baseline and followed their participants for cardiovascular events like heart attack, stroke, coronary revascularization, and so on.
The biomarkers in question are really the big guns in this space: troponin, a marker of stress on the heart muscle; NT-proBNP, a marker of stretch on the heart muscle; and C-reactive protein, a marker of inflammation. In every case, higher levels of these markers at baseline were associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular disease in the future.
Troponin T, shown here, has a basically linear risk with subsequent cardiovascular disease.
BNP seems to demonstrate more of a threshold effect, where levels above 60 start to associate with problems.
And CRP does a similar thing, with levels above 1.
All of these findings were statistically significant. If you have higher levels of one or more of these biomarkers, you are more likely to have cardiovascular disease in the future.
Of course, our old friend the pooled cohort risk equation is still here — in the background — requiring just that one blood test and measurement of blood pressure. Let’s talk about predictive power.
The pooled cohort risk equation score, in this study, had a C-statistic of 0.812.
By adding troponin, BNP, and CRP to the equation, the new C-statistic is 0.819. Barely any change.
Now, the authors looked at different types of prediction here. The greatest improvement in the AUC was seen when they tried to predict heart failure within 1 year of measurement; there the AUC improved by 0.04. But the presence of BNP as a biomarker and the short time window of 1 year makes me wonder whether this is really prediction at all or whether they were essentially just diagnosing people with existing heart failure.
Why does this happen? Why do these promising biomarkers, clearly associated with bad outcomes, fail to improve our ability to predict the future? I already gave one example, which has to do with how the markers are distributed in the population. But even more relevant here is that the new markers will only improve prediction insofar as they are not already represented in the old predictive model.
Of course, BNP, for example, wasn’t in the old model. But smoking was. Diabetes was. Blood pressure was. All of that data might actually tell you something about the patient’s BNP through their mutual correlation. And improvement in prediction requires new information.
This is actually why I consider this a really successful study. We need to do studies like this to help us find what those new sources of information might be.
We will never get to a C-statistic of 1. Perfect prediction is the domain of palm readers and astrophysicists. But better prediction is always possible through data. The big question, of course, is which data?
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s the counterintuitive stuff in epidemiology that always really interests me. One intuition many of us have is that if a risk factor is significantly associated with an outcome, knowledge of that risk factor would help to predict that outcome. Makes sense. Feels right.
But it’s not right. Not always.
Here’s a fake example to illustrate my point. Let’s say we have 10,000 individuals who we follow for 10 years and 2000 of them die. (It’s been a rough decade.) At baseline, I measured a novel biomarker, the Perry Factor, in everyone. To keep it simple, the Perry Factor has only two values: 0 or 1.
I then do a standard associational analysis and find that individuals who are positive for the Perry Factor have a 40-fold higher odds of death than those who are negative for it. I am beginning to reconsider ascribing my good name to this biomarker. This is a highly statistically significant result — a P value <.001.
Clearly, knowledge of the Perry Factor should help me predict who will die in the cohort. I evaluate predictive power using a metric called the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC, referred to as the C-statistic in time-to-event studies). It tells you, given two people — one who dies and one who doesn’t — how frequently you “pick” the right person, given the knowledge of their Perry Factor.
A C-statistic of 0.5, or 50%, would mean the Perry Factor gives you no better results than a coin flip; it’s chance. A C-statistic of 1 is perfect prediction. So, what will the C-statistic be, given the incredibly strong association of the Perry Factor with outcomes? 0.9? 0.95?
0.5024. Almost useless.

Let’s figure out why strength of association and usefulness for prediction are not always the same thing.
I constructed my fake Perry Factor dataset quite carefully to illustrate this point. Let me show you what happened. What you see here is a breakdown of the patients in my fake study. You can see that just 11 of them were Perry Factor positive, but 10 of those 11 ended up dying.
That’s quite unlikely by chance alone. It really does appear that if you have Perry Factor, your risk for death is much higher. But the reason that Perry Factor is a bad predictor is because it is so rare in the population. Sure, you can use it to correctly predict the outcome of 10 of the 11 people who have it, but the vast majority of people don’t have Perry Factor. It’s useless to distinguish who will die vs who will live in that population.
Why have I spent so much time trying to reverse our intuition that strength of association and strength of predictive power must be related? Because it helps to explain this paper, “Prognostic Value of Cardiovascular Biomarkers in the Population,” appearing in JAMA, which is a very nice piece of work trying to help us better predict cardiovascular disease.
I don’t need to tell you that cardiovascular disease is the number-one killer in this country and most of the world. I don’t need to tell you that we have really good preventive therapies and lifestyle interventions that can reduce the risk. But it would be nice to know in whom, specifically, we should use those interventions.
Cardiovascular risk scores, to date, are pretty simple. The most common one in use in the United States, the pooled cohort risk equation, has nine variables, two of which require a cholesterol panel and one a blood pressure test. It’s easy and it’s pretty accurate.
Using the score from the pooled cohort risk calculator, you get a C-statistic as high as 0.82 when applied to Black women, a low of 0.71 when applied to Black men. Non-Black individuals are in the middle. Not bad. But, clearly, not perfect.
And aren’t we in the era of big data, the era of personalized medicine? We have dozens, maybe hundreds, of quantifiable biomarkers that are associated with subsequent heart disease. Surely, by adding these biomarkers into the risk equation, we can improve prediction. Right?
The JAMA study includes 164,054 patients pooled from 28 cohort studies from 12 countries. All the studies measured various key biomarkers at baseline and followed their participants for cardiovascular events like heart attack, stroke, coronary revascularization, and so on.
The biomarkers in question are really the big guns in this space: troponin, a marker of stress on the heart muscle; NT-proBNP, a marker of stretch on the heart muscle; and C-reactive protein, a marker of inflammation. In every case, higher levels of these markers at baseline were associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular disease in the future.
Troponin T, shown here, has a basically linear risk with subsequent cardiovascular disease.
BNP seems to demonstrate more of a threshold effect, where levels above 60 start to associate with problems.
And CRP does a similar thing, with levels above 1.
All of these findings were statistically significant. If you have higher levels of one or more of these biomarkers, you are more likely to have cardiovascular disease in the future.
Of course, our old friend the pooled cohort risk equation is still here — in the background — requiring just that one blood test and measurement of blood pressure. Let’s talk about predictive power.
The pooled cohort risk equation score, in this study, had a C-statistic of 0.812.
By adding troponin, BNP, and CRP to the equation, the new C-statistic is 0.819. Barely any change.
Now, the authors looked at different types of prediction here. The greatest improvement in the AUC was seen when they tried to predict heart failure within 1 year of measurement; there the AUC improved by 0.04. But the presence of BNP as a biomarker and the short time window of 1 year makes me wonder whether this is really prediction at all or whether they were essentially just diagnosing people with existing heart failure.
Why does this happen? Why do these promising biomarkers, clearly associated with bad outcomes, fail to improve our ability to predict the future? I already gave one example, which has to do with how the markers are distributed in the population. But even more relevant here is that the new markers will only improve prediction insofar as they are not already represented in the old predictive model.
Of course, BNP, for example, wasn’t in the old model. But smoking was. Diabetes was. Blood pressure was. All of that data might actually tell you something about the patient’s BNP through their mutual correlation. And improvement in prediction requires new information.
This is actually why I consider this a really successful study. We need to do studies like this to help us find what those new sources of information might be.
We will never get to a C-statistic of 1. Perfect prediction is the domain of palm readers and astrophysicists. But better prediction is always possible through data. The big question, of course, is which data?
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Self-Monitoring Better Than Usual Care Among Patients With Hypertension
TOPLINE:
Blood pressure (BP) self-monitoring and medication management may be better than usual care for controlling hypertension, a new study published in JAMA Network Open suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- The secondary analysis of a randomized, unblinded clinical trial included patients aged ≥ 40 years with uncontrolled hypertension in Valencia, Spain, between 2017 and 2020.
- The 111 patients in the intervention group received educational materials and instructions for self-monitoring of BP with a home monitor and medication adjustment as needed without contacting their healthcare clinicians.
- The 108 patients in the control group received usual care, including education on BP control.
- After 24 months, researchers recorded BP levels, the number of people who achieved a target BP (systolic BP < 140 mm Hg and diastolic BP < 90 mm Hg), adverse events, quality of life, behavioral changes, and health service use.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients in the intervention group had a lower average systolic BP reading at 24 months than patients who received usual care (adjusted mean difference, -3.4 mm Hg).
- Patients in the intervention group also had a lower average diastolic BP reading than usual care (adjusted mean difference, -2.5 mm Hg).
- The percentage of people who achieved the target BP was similar in both groups (64% in the intervention group compared with 54% in the control group).
- Researchers found no difference between groups in terms of adverse events, use of health services, behavioral changes such as smoking status or body weight, or quality of life.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results suggest that simple, inexpensive, and easy-to-implement self-management interventions have the potential to improve the long-term control of hypertension in routine clinical practice.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Gabriel Sanfélix-Gimeno, PhD, Pharm D, head of the Health Services Research & Pharmacoepidemiology Unit at Fisabio Research Institute in Valencia, Spain.
LIMITATIONS:
Some study participants were lost to follow-up due to COVID-19 restrictions. The trial was unblinded, which may have led to biases among patients and clinicians. Clinicians treated both the control and intervention groups. The results may not be extrapolated to those with controlled hypertension, very high BP, or people who are pregnant because they were not included in the study.
DISCLOSURES:
Various authors reported receiving grants from RTI Health Solutions or personal fees from GSK and MSD outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. The study was funded by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III at the Spanish Ministry of Research, Innovation and Universities, the European Regional Development Fund, and Spanish Clinical Research Network.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Blood pressure (BP) self-monitoring and medication management may be better than usual care for controlling hypertension, a new study published in JAMA Network Open suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- The secondary analysis of a randomized, unblinded clinical trial included patients aged ≥ 40 years with uncontrolled hypertension in Valencia, Spain, between 2017 and 2020.
- The 111 patients in the intervention group received educational materials and instructions for self-monitoring of BP with a home monitor and medication adjustment as needed without contacting their healthcare clinicians.
- The 108 patients in the control group received usual care, including education on BP control.
- After 24 months, researchers recorded BP levels, the number of people who achieved a target BP (systolic BP < 140 mm Hg and diastolic BP < 90 mm Hg), adverse events, quality of life, behavioral changes, and health service use.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients in the intervention group had a lower average systolic BP reading at 24 months than patients who received usual care (adjusted mean difference, -3.4 mm Hg).
- Patients in the intervention group also had a lower average diastolic BP reading than usual care (adjusted mean difference, -2.5 mm Hg).
- The percentage of people who achieved the target BP was similar in both groups (64% in the intervention group compared with 54% in the control group).
- Researchers found no difference between groups in terms of adverse events, use of health services, behavioral changes such as smoking status or body weight, or quality of life.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results suggest that simple, inexpensive, and easy-to-implement self-management interventions have the potential to improve the long-term control of hypertension in routine clinical practice.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Gabriel Sanfélix-Gimeno, PhD, Pharm D, head of the Health Services Research & Pharmacoepidemiology Unit at Fisabio Research Institute in Valencia, Spain.
LIMITATIONS:
Some study participants were lost to follow-up due to COVID-19 restrictions. The trial was unblinded, which may have led to biases among patients and clinicians. Clinicians treated both the control and intervention groups. The results may not be extrapolated to those with controlled hypertension, very high BP, or people who are pregnant because they were not included in the study.
DISCLOSURES:
Various authors reported receiving grants from RTI Health Solutions or personal fees from GSK and MSD outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. The study was funded by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III at the Spanish Ministry of Research, Innovation and Universities, the European Regional Development Fund, and Spanish Clinical Research Network.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Blood pressure (BP) self-monitoring and medication management may be better than usual care for controlling hypertension, a new study published in JAMA Network Open suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- The secondary analysis of a randomized, unblinded clinical trial included patients aged ≥ 40 years with uncontrolled hypertension in Valencia, Spain, between 2017 and 2020.
- The 111 patients in the intervention group received educational materials and instructions for self-monitoring of BP with a home monitor and medication adjustment as needed without contacting their healthcare clinicians.
- The 108 patients in the control group received usual care, including education on BP control.
- After 24 months, researchers recorded BP levels, the number of people who achieved a target BP (systolic BP < 140 mm Hg and diastolic BP < 90 mm Hg), adverse events, quality of life, behavioral changes, and health service use.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients in the intervention group had a lower average systolic BP reading at 24 months than patients who received usual care (adjusted mean difference, -3.4 mm Hg).
- Patients in the intervention group also had a lower average diastolic BP reading than usual care (adjusted mean difference, -2.5 mm Hg).
- The percentage of people who achieved the target BP was similar in both groups (64% in the intervention group compared with 54% in the control group).
- Researchers found no difference between groups in terms of adverse events, use of health services, behavioral changes such as smoking status or body weight, or quality of life.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results suggest that simple, inexpensive, and easy-to-implement self-management interventions have the potential to improve the long-term control of hypertension in routine clinical practice.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Gabriel Sanfélix-Gimeno, PhD, Pharm D, head of the Health Services Research & Pharmacoepidemiology Unit at Fisabio Research Institute in Valencia, Spain.
LIMITATIONS:
Some study participants were lost to follow-up due to COVID-19 restrictions. The trial was unblinded, which may have led to biases among patients and clinicians. Clinicians treated both the control and intervention groups. The results may not be extrapolated to those with controlled hypertension, very high BP, or people who are pregnant because they were not included in the study.
DISCLOSURES:
Various authors reported receiving grants from RTI Health Solutions or personal fees from GSK and MSD outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. The study was funded by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III at the Spanish Ministry of Research, Innovation and Universities, the European Regional Development Fund, and Spanish Clinical Research Network.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI)
Imagine this: A 15-year-old male presents to an urgent care center with a one-day history of fever, cough, and shortness of breath. He is mildly tachypneic with bilateral scattered crackles on lung exam. A rapid test for COVID-19 and influenza is positive for influenza A — a surprising result in June.
An oxygen saturation of 90% prompts transfer to the emergency department at the local children’s hospital. The emergency medicine fellow is skeptical of the presumptive diagnosis. Influenza in the summer in a boy who had not traveled outside his small hometown in the southeastern United States? A respiratory viral panel also detected influenza A, but the specimen did not type as influenza A H1 or H3. This result prompted the laboratory technician to place a call to the ordering physician. “Does this patient have risk factors for avian flu?” the tech asked.
Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) A(H5N1) is not a new virus. It was discovered in waterfowl in China in 1996 and has since evolved into multiple clades and subclades, spreading to every continent on the globe except Oceania. It is called highly pathogenic because it kills a large number of the birds that it infects. In 2021, Clade 2.3.4.4b HPAI A(H5N1) viruses emerged in North America, causing large outbreaks in wild birds and farmed poultry populations, including backyard flocks. Sporadic infections have been identified in a diverse group of mammals, including foxes, raccoons, baby goats, bears, and harbor seals. In March of this year, HPAI A(H5N1) was detected for the first time in United States dairy cattle. As we go to press, the United States Department of Agriculture has detected HPAI A(H5N1) in dairy cattle on 36 farms in 9 states.
Human infections are rare, but often severe. Following a 1997 outbreak of HPAI A(H5N1) in Hong Kong, 18 people were infected and 6 died. Since then, more than 900 cases have been reported in humans and approximately half of these have been fatal. The spectrum of disease includes asymptomatic infection and mild disease, as occurred recently in Texas. A dairy farm worker who was exposed to dairy cattle presumed to be infected with HPAI A(H5N1) developed conjunctivitis and no other symptoms. An individual infected in Colorado in 2022 had no symptoms other than fatigue and recovered.
Human-to-human transmission was not identified with either of these cases, although very limited, non-sustained transmission has been observed in the past, usually in family members of infected people after prolonged close exposure.
Right now, most people in the United States are not at risk for HPAI A(H5N1) infection.
Careful history taking with our illustrative and hypothetical case revealed exposure to farm animals but in a state without known cases of HPAI A(H5N1) in dairy cattle. State health department officials nevertheless agreed with further testing of the patient. Some influenza diagnostic tests cleared by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) can detect some novel influenza A viruses such as HPAI A(H5N1) but cannot distinguish between infection with seasonal influenza A or novel influenza A viruses. Molecular assays may give an “influenza A untypeable” result, as in our case. The CDC urges further testing on these untypeable specimens at local or state public health laboratories. When HPAI A(H5N1) is suspected, a negative result on a commercially available test is not considered sufficient to exclude the possibility of infection.
Our patient was admitted to the hospital and droplet, contact, and airborne precautions were instituted along with antiviral treatment with oseltamivir. Preliminary analysis of HPAI A(H5N1) viruses predicts susceptibility to currently available antivirals. The admitting physician confirmed that the boy had received influenza vaccine in the preceding season but, unfortunately, seasonal vaccines do not protect against HPAI A(H5N1) infection.
Advice for Clinicians
Given the recent media attention and public health focus on HPAI A(H5N1), frontline clinicians may start receiving questions from patients and families and perhaps requests for testing. At this point, testing is generally recommended only for individuals with risk factors or known exposures. Healthcare providers with questions about testing are encouraged to reach out to their local or state health departments.
Public health authorities have provided recommendations for protection from HPAI. These include avoiding unprotected exposures to sick or dead wild birds, poultry, other domesticated birds, and wild or domesticated animals (including cattle). People should avoid unprotected contact with animals with suspected or confirmed HPAI A(H5N1)-virus infection or products from these animals, including raw or unpasteurized milk and raw milk products.
We can, however, reassure families that the commercial milk supply is safe. In late April, the FDA reported that HPAI viral fragments were found in one of five retail milk samples by polymerase chain reaction testing. Additional testing did not detect any live, infectious virus, indicating the effectiveness of pasteurization at inactivating the virus. Of importance to pediatricians and others pediatric clinicians, limited sampling of retail powdered infant formula and powdered milk products marketed as toddler formula revealed no viral fragments or viable virus.
The million-dollar question is whether HPAI A(H5N1) could start a new pandemic. To date, the virus has not acquired the mutations that would make it easily transmissible from person to person. If that changes and the virus does start spreading more widely, candidate vaccines that could protect against HPAI A(H5N1) have been developed and are part of the national stockpile. Let’s hope we don’t need them.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She is a member of the American Academy of Pediatrics’ Committee on Infectious Diseases and the physician lead for Red Book Online. The opinions expressed in this article are her own. Dr. Bryant discloses that she has served as an investigator on clinical trials funded by Pfizer, Enanta and Gilead. Email her at [email protected]. (Also [email protected].)
Imagine this: A 15-year-old male presents to an urgent care center with a one-day history of fever, cough, and shortness of breath. He is mildly tachypneic with bilateral scattered crackles on lung exam. A rapid test for COVID-19 and influenza is positive for influenza A — a surprising result in June.
An oxygen saturation of 90% prompts transfer to the emergency department at the local children’s hospital. The emergency medicine fellow is skeptical of the presumptive diagnosis. Influenza in the summer in a boy who had not traveled outside his small hometown in the southeastern United States? A respiratory viral panel also detected influenza A, but the specimen did not type as influenza A H1 or H3. This result prompted the laboratory technician to place a call to the ordering physician. “Does this patient have risk factors for avian flu?” the tech asked.
Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) A(H5N1) is not a new virus. It was discovered in waterfowl in China in 1996 and has since evolved into multiple clades and subclades, spreading to every continent on the globe except Oceania. It is called highly pathogenic because it kills a large number of the birds that it infects. In 2021, Clade 2.3.4.4b HPAI A(H5N1) viruses emerged in North America, causing large outbreaks in wild birds and farmed poultry populations, including backyard flocks. Sporadic infections have been identified in a diverse group of mammals, including foxes, raccoons, baby goats, bears, and harbor seals. In March of this year, HPAI A(H5N1) was detected for the first time in United States dairy cattle. As we go to press, the United States Department of Agriculture has detected HPAI A(H5N1) in dairy cattle on 36 farms in 9 states.
Human infections are rare, but often severe. Following a 1997 outbreak of HPAI A(H5N1) in Hong Kong, 18 people were infected and 6 died. Since then, more than 900 cases have been reported in humans and approximately half of these have been fatal. The spectrum of disease includes asymptomatic infection and mild disease, as occurred recently in Texas. A dairy farm worker who was exposed to dairy cattle presumed to be infected with HPAI A(H5N1) developed conjunctivitis and no other symptoms. An individual infected in Colorado in 2022 had no symptoms other than fatigue and recovered.
Human-to-human transmission was not identified with either of these cases, although very limited, non-sustained transmission has been observed in the past, usually in family members of infected people after prolonged close exposure.
Right now, most people in the United States are not at risk for HPAI A(H5N1) infection.
Careful history taking with our illustrative and hypothetical case revealed exposure to farm animals but in a state without known cases of HPAI A(H5N1) in dairy cattle. State health department officials nevertheless agreed with further testing of the patient. Some influenza diagnostic tests cleared by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) can detect some novel influenza A viruses such as HPAI A(H5N1) but cannot distinguish between infection with seasonal influenza A or novel influenza A viruses. Molecular assays may give an “influenza A untypeable” result, as in our case. The CDC urges further testing on these untypeable specimens at local or state public health laboratories. When HPAI A(H5N1) is suspected, a negative result on a commercially available test is not considered sufficient to exclude the possibility of infection.
Our patient was admitted to the hospital and droplet, contact, and airborne precautions were instituted along with antiviral treatment with oseltamivir. Preliminary analysis of HPAI A(H5N1) viruses predicts susceptibility to currently available antivirals. The admitting physician confirmed that the boy had received influenza vaccine in the preceding season but, unfortunately, seasonal vaccines do not protect against HPAI A(H5N1) infection.
Advice for Clinicians
Given the recent media attention and public health focus on HPAI A(H5N1), frontline clinicians may start receiving questions from patients and families and perhaps requests for testing. At this point, testing is generally recommended only for individuals with risk factors or known exposures. Healthcare providers with questions about testing are encouraged to reach out to their local or state health departments.
Public health authorities have provided recommendations for protection from HPAI. These include avoiding unprotected exposures to sick or dead wild birds, poultry, other domesticated birds, and wild or domesticated animals (including cattle). People should avoid unprotected contact with animals with suspected or confirmed HPAI A(H5N1)-virus infection or products from these animals, including raw or unpasteurized milk and raw milk products.
We can, however, reassure families that the commercial milk supply is safe. In late April, the FDA reported that HPAI viral fragments were found in one of five retail milk samples by polymerase chain reaction testing. Additional testing did not detect any live, infectious virus, indicating the effectiveness of pasteurization at inactivating the virus. Of importance to pediatricians and others pediatric clinicians, limited sampling of retail powdered infant formula and powdered milk products marketed as toddler formula revealed no viral fragments or viable virus.
The million-dollar question is whether HPAI A(H5N1) could start a new pandemic. To date, the virus has not acquired the mutations that would make it easily transmissible from person to person. If that changes and the virus does start spreading more widely, candidate vaccines that could protect against HPAI A(H5N1) have been developed and are part of the national stockpile. Let’s hope we don’t need them.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She is a member of the American Academy of Pediatrics’ Committee on Infectious Diseases and the physician lead for Red Book Online. The opinions expressed in this article are her own. Dr. Bryant discloses that she has served as an investigator on clinical trials funded by Pfizer, Enanta and Gilead. Email her at [email protected]. (Also [email protected].)
Imagine this: A 15-year-old male presents to an urgent care center with a one-day history of fever, cough, and shortness of breath. He is mildly tachypneic with bilateral scattered crackles on lung exam. A rapid test for COVID-19 and influenza is positive for influenza A — a surprising result in June.
An oxygen saturation of 90% prompts transfer to the emergency department at the local children’s hospital. The emergency medicine fellow is skeptical of the presumptive diagnosis. Influenza in the summer in a boy who had not traveled outside his small hometown in the southeastern United States? A respiratory viral panel also detected influenza A, but the specimen did not type as influenza A H1 or H3. This result prompted the laboratory technician to place a call to the ordering physician. “Does this patient have risk factors for avian flu?” the tech asked.
Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) A(H5N1) is not a new virus. It was discovered in waterfowl in China in 1996 and has since evolved into multiple clades and subclades, spreading to every continent on the globe except Oceania. It is called highly pathogenic because it kills a large number of the birds that it infects. In 2021, Clade 2.3.4.4b HPAI A(H5N1) viruses emerged in North America, causing large outbreaks in wild birds and farmed poultry populations, including backyard flocks. Sporadic infections have been identified in a diverse group of mammals, including foxes, raccoons, baby goats, bears, and harbor seals. In March of this year, HPAI A(H5N1) was detected for the first time in United States dairy cattle. As we go to press, the United States Department of Agriculture has detected HPAI A(H5N1) in dairy cattle on 36 farms in 9 states.
Human infections are rare, but often severe. Following a 1997 outbreak of HPAI A(H5N1) in Hong Kong, 18 people were infected and 6 died. Since then, more than 900 cases have been reported in humans and approximately half of these have been fatal. The spectrum of disease includes asymptomatic infection and mild disease, as occurred recently in Texas. A dairy farm worker who was exposed to dairy cattle presumed to be infected with HPAI A(H5N1) developed conjunctivitis and no other symptoms. An individual infected in Colorado in 2022 had no symptoms other than fatigue and recovered.
Human-to-human transmission was not identified with either of these cases, although very limited, non-sustained transmission has been observed in the past, usually in family members of infected people after prolonged close exposure.
Right now, most people in the United States are not at risk for HPAI A(H5N1) infection.
Careful history taking with our illustrative and hypothetical case revealed exposure to farm animals but in a state without known cases of HPAI A(H5N1) in dairy cattle. State health department officials nevertheless agreed with further testing of the patient. Some influenza diagnostic tests cleared by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) can detect some novel influenza A viruses such as HPAI A(H5N1) but cannot distinguish between infection with seasonal influenza A or novel influenza A viruses. Molecular assays may give an “influenza A untypeable” result, as in our case. The CDC urges further testing on these untypeable specimens at local or state public health laboratories. When HPAI A(H5N1) is suspected, a negative result on a commercially available test is not considered sufficient to exclude the possibility of infection.
Our patient was admitted to the hospital and droplet, contact, and airborne precautions were instituted along with antiviral treatment with oseltamivir. Preliminary analysis of HPAI A(H5N1) viruses predicts susceptibility to currently available antivirals. The admitting physician confirmed that the boy had received influenza vaccine in the preceding season but, unfortunately, seasonal vaccines do not protect against HPAI A(H5N1) infection.
Advice for Clinicians
Given the recent media attention and public health focus on HPAI A(H5N1), frontline clinicians may start receiving questions from patients and families and perhaps requests for testing. At this point, testing is generally recommended only for individuals with risk factors or known exposures. Healthcare providers with questions about testing are encouraged to reach out to their local or state health departments.
Public health authorities have provided recommendations for protection from HPAI. These include avoiding unprotected exposures to sick or dead wild birds, poultry, other domesticated birds, and wild or domesticated animals (including cattle). People should avoid unprotected contact with animals with suspected or confirmed HPAI A(H5N1)-virus infection or products from these animals, including raw or unpasteurized milk and raw milk products.
We can, however, reassure families that the commercial milk supply is safe. In late April, the FDA reported that HPAI viral fragments were found in one of five retail milk samples by polymerase chain reaction testing. Additional testing did not detect any live, infectious virus, indicating the effectiveness of pasteurization at inactivating the virus. Of importance to pediatricians and others pediatric clinicians, limited sampling of retail powdered infant formula and powdered milk products marketed as toddler formula revealed no viral fragments or viable virus.
The million-dollar question is whether HPAI A(H5N1) could start a new pandemic. To date, the virus has not acquired the mutations that would make it easily transmissible from person to person. If that changes and the virus does start spreading more widely, candidate vaccines that could protect against HPAI A(H5N1) have been developed and are part of the national stockpile. Let’s hope we don’t need them.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She is a member of the American Academy of Pediatrics’ Committee on Infectious Diseases and the physician lead for Red Book Online. The opinions expressed in this article are her own. Dr. Bryant discloses that she has served as an investigator on clinical trials funded by Pfizer, Enanta and Gilead. Email her at [email protected]. (Also [email protected].)
Survey Spotlights Identification of Dermatologic Adverse Events From Cancer Therapies
“New cancer therapies have brought a diversity of treatment-related dermatologic adverse events (dAEs) beyond those experienced with conventional chemotherapy, which has demanded an evolving assessment of toxicities,” researchers led by Nicole R. LeBoeuf, MD, MPH, of the Department of Dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the Center for Cutaneous Oncology at the Dana-Farber Brigham Cancer Center, Boston, wrote in a poster presented at the American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting.
The authors noted that “Version 5.0 of the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE v5.0)” serves as the current, broadly accepted criteria for classification and grading during routine medical care and clinical trials. But despite extensive utilization of CTCAE, there is little data regarding its application.”
To evaluate how CTCAE is being used in clinical practice, they sent a four-case survey of dAEs to 81 dermatologists and 182 medical oncologists at six US-based academic institutions. For three of the cases, respondents were asked to classify and grade morbilliform, psoriasiform, and papulopustular rashes based on a review of photographs and text descriptions. For the fourth case, respondents were asked to grade a dAE using only a clinic note text description. The researchers used chi-square tests in R software to compare survey responses.
Compared with medical oncologists, dermatologists were significantly more likely to provide correct responses in characterizing morbilliform and psoriasiform eruptions. “As low as 12%” of medical oncologists were correct, and “as low as 87%” of dermatologists were correct (P < .001). Similarly, dermatologists were significantly more likely to grade the psoriasiform, papulopustular, and written cases correctly compared with medical oncologists (P < .001 for all associations).
“These cases demonstrated poor concordance of classification and grading between specialties and across medical oncology,” the authors concluded in their poster, noting that 87% of medical oncologists were interested in additional educational tools on dAEs. “With correct classification as low as 12%, medical oncologists may have more difficulty delivering appropriate, toxicity-specific therapy and may consider banal eruptions dangerous.”
Poor concordance of grading among the two groups of clinicians “raises the question of whether CTCAE v5.0 is an appropriate determinant for patient continuation on therapy or in trials,” they added. “As anticancer therapy becomes more complex — with new toxicities from novel agents and combinations — we must ensure we have a grading system that is valid across investigators and does not harm patients by instituting unnecessary treatment stops.”
Future studies, they said, “can explore what interventions beyond involvement of dermatologists improve classification and grading in practice.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study, noted that with the continued expansion and introduction of new targeted and immunotherapies in the oncology space, “you can be sure we will continue to appreciate the importance and value of the field of supportive oncodermatology, as hair, skin, and nails are almost guaranteed collateral damage in this story.
“Ensuring early identification and consistent grading severity is not only important for the plethora of patients who are currently developing the litany of cutaneous adverse events but to evaluate potential mitigation strategies and even push along countermeasures down the FDA approval pathway,” Dr. Friedman said. In this study, the investigators demonstrated that work “is sorely needed, not just in dermatology but even more so for our colleagues across the aisle. A central tenet of supportive oncodermatology must also be education for all stakeholders, and the good news is our oncology partners will welcome it.”
Dr. LeBoeuf disclosed that she is a consultant to and has received honoraria from Bayer, Seattle Genetics, Sanofi, Silverback, Fortress Biotech, and Synox Therapeutics outside the submitted work. No other authors reported having financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman directs the supportive oncodermatology program at GW that received independent funding from La Roche-Posay.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“New cancer therapies have brought a diversity of treatment-related dermatologic adverse events (dAEs) beyond those experienced with conventional chemotherapy, which has demanded an evolving assessment of toxicities,” researchers led by Nicole R. LeBoeuf, MD, MPH, of the Department of Dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the Center for Cutaneous Oncology at the Dana-Farber Brigham Cancer Center, Boston, wrote in a poster presented at the American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting.
The authors noted that “Version 5.0 of the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE v5.0)” serves as the current, broadly accepted criteria for classification and grading during routine medical care and clinical trials. But despite extensive utilization of CTCAE, there is little data regarding its application.”
To evaluate how CTCAE is being used in clinical practice, they sent a four-case survey of dAEs to 81 dermatologists and 182 medical oncologists at six US-based academic institutions. For three of the cases, respondents were asked to classify and grade morbilliform, psoriasiform, and papulopustular rashes based on a review of photographs and text descriptions. For the fourth case, respondents were asked to grade a dAE using only a clinic note text description. The researchers used chi-square tests in R software to compare survey responses.
Compared with medical oncologists, dermatologists were significantly more likely to provide correct responses in characterizing morbilliform and psoriasiform eruptions. “As low as 12%” of medical oncologists were correct, and “as low as 87%” of dermatologists were correct (P < .001). Similarly, dermatologists were significantly more likely to grade the psoriasiform, papulopustular, and written cases correctly compared with medical oncologists (P < .001 for all associations).
“These cases demonstrated poor concordance of classification and grading between specialties and across medical oncology,” the authors concluded in their poster, noting that 87% of medical oncologists were interested in additional educational tools on dAEs. “With correct classification as low as 12%, medical oncologists may have more difficulty delivering appropriate, toxicity-specific therapy and may consider banal eruptions dangerous.”
Poor concordance of grading among the two groups of clinicians “raises the question of whether CTCAE v5.0 is an appropriate determinant for patient continuation on therapy or in trials,” they added. “As anticancer therapy becomes more complex — with new toxicities from novel agents and combinations — we must ensure we have a grading system that is valid across investigators and does not harm patients by instituting unnecessary treatment stops.”
Future studies, they said, “can explore what interventions beyond involvement of dermatologists improve classification and grading in practice.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study, noted that with the continued expansion and introduction of new targeted and immunotherapies in the oncology space, “you can be sure we will continue to appreciate the importance and value of the field of supportive oncodermatology, as hair, skin, and nails are almost guaranteed collateral damage in this story.
“Ensuring early identification and consistent grading severity is not only important for the plethora of patients who are currently developing the litany of cutaneous adverse events but to evaluate potential mitigation strategies and even push along countermeasures down the FDA approval pathway,” Dr. Friedman said. In this study, the investigators demonstrated that work “is sorely needed, not just in dermatology but even more so for our colleagues across the aisle. A central tenet of supportive oncodermatology must also be education for all stakeholders, and the good news is our oncology partners will welcome it.”
Dr. LeBoeuf disclosed that she is a consultant to and has received honoraria from Bayer, Seattle Genetics, Sanofi, Silverback, Fortress Biotech, and Synox Therapeutics outside the submitted work. No other authors reported having financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman directs the supportive oncodermatology program at GW that received independent funding from La Roche-Posay.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“New cancer therapies have brought a diversity of treatment-related dermatologic adverse events (dAEs) beyond those experienced with conventional chemotherapy, which has demanded an evolving assessment of toxicities,” researchers led by Nicole R. LeBoeuf, MD, MPH, of the Department of Dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the Center for Cutaneous Oncology at the Dana-Farber Brigham Cancer Center, Boston, wrote in a poster presented at the American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting.
The authors noted that “Version 5.0 of the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE v5.0)” serves as the current, broadly accepted criteria for classification and grading during routine medical care and clinical trials. But despite extensive utilization of CTCAE, there is little data regarding its application.”
To evaluate how CTCAE is being used in clinical practice, they sent a four-case survey of dAEs to 81 dermatologists and 182 medical oncologists at six US-based academic institutions. For three of the cases, respondents were asked to classify and grade morbilliform, psoriasiform, and papulopustular rashes based on a review of photographs and text descriptions. For the fourth case, respondents were asked to grade a dAE using only a clinic note text description. The researchers used chi-square tests in R software to compare survey responses.
Compared with medical oncologists, dermatologists were significantly more likely to provide correct responses in characterizing morbilliform and psoriasiform eruptions. “As low as 12%” of medical oncologists were correct, and “as low as 87%” of dermatologists were correct (P < .001). Similarly, dermatologists were significantly more likely to grade the psoriasiform, papulopustular, and written cases correctly compared with medical oncologists (P < .001 for all associations).
“These cases demonstrated poor concordance of classification and grading between specialties and across medical oncology,” the authors concluded in their poster, noting that 87% of medical oncologists were interested in additional educational tools on dAEs. “With correct classification as low as 12%, medical oncologists may have more difficulty delivering appropriate, toxicity-specific therapy and may consider banal eruptions dangerous.”
Poor concordance of grading among the two groups of clinicians “raises the question of whether CTCAE v5.0 is an appropriate determinant for patient continuation on therapy or in trials,” they added. “As anticancer therapy becomes more complex — with new toxicities from novel agents and combinations — we must ensure we have a grading system that is valid across investigators and does not harm patients by instituting unnecessary treatment stops.”
Future studies, they said, “can explore what interventions beyond involvement of dermatologists improve classification and grading in practice.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study, noted that with the continued expansion and introduction of new targeted and immunotherapies in the oncology space, “you can be sure we will continue to appreciate the importance and value of the field of supportive oncodermatology, as hair, skin, and nails are almost guaranteed collateral damage in this story.
“Ensuring early identification and consistent grading severity is not only important for the plethora of patients who are currently developing the litany of cutaneous adverse events but to evaluate potential mitigation strategies and even push along countermeasures down the FDA approval pathway,” Dr. Friedman said. In this study, the investigators demonstrated that work “is sorely needed, not just in dermatology but even more so for our colleagues across the aisle. A central tenet of supportive oncodermatology must also be education for all stakeholders, and the good news is our oncology partners will welcome it.”
Dr. LeBoeuf disclosed that she is a consultant to and has received honoraria from Bayer, Seattle Genetics, Sanofi, Silverback, Fortress Biotech, and Synox Therapeutics outside the submitted work. No other authors reported having financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman directs the supportive oncodermatology program at GW that received independent funding from La Roche-Posay.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAD 2024
Traffic Noise Negatively Impacts Health
New research by Thomas Münzel, MD, senior professor of cardiology at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz in Mainz, Germany, and colleagues again emphasized the harmful effects of noise on the heart and blood vessels. An analysis of current epidemiologic data provided strong indications that transportation noise is closely related to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, according to a statement on the data analysis. The results were published in Circulation Research.
Morbidity and Mortality
Epidemiologic studies have shown that road, rail, or air traffic noise increases the risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, with strong evidence for ischemic heart disease, heart failure, and stroke, according to the scientists. These factors could favor vascular (endothelial) dysfunction, inflammation, and hypertension, thereby increasing cardiovascular risk.
Consequences and Pathomechanisms
In the current publication, the authors provided an overview of epidemiologic research on the effects of transportation noise on cardiovascular risk factors and diseases, discussed mechanistic insights from the latest clinical and experimental studies, and proposed new risk markers to address noise-induced cardiovascular effects in the general population. An integrated analysis in the article demonstrated that for every 10 dB(A) increase, the risk for cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack, stroke, and heart failure significantly increases by 3.2%.
The authors also explained the possible effects of noise on changes in gene networks, epigenetic pathways, circadian rhythms, signal transmission along the neuronal-cardiovascular axis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and metabolism. Finally, current and future noise protection strategies are described, and the existing evidence on noise as a cardiovascular risk factor is discussed.
Confirmed Cardiovascular Risk Factor
“As an increasing proportion of the population is exposed to harmful traffic noise, efforts to reduce noise and laws for noise reduction are of great importance for future public health,” said Dr. Münzel. “It is also important for us that due to the strong evidence, traffic noise is finally recognized as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.”
Heart Attack Outcomes
Dr. Münzel and other researchers from Mainz have been studying the cardiovascular consequences of air pollution and traffic noise for several years. For example, they found that heart attacks in people and animals exposed to high noise levels earlier in life healed poorly. These results were published last year in Cardiovascular Research. According to the authors, the findings suggest that traffic noise may play a significant role in the development and course of coronary heart disease, such as after a heart attack.
The scientists initially found in animal experiments that exposure to aircraft noise for 4 days led to increased inflammation in the vessels. Compared with mice not exposed to aircraft noise, the noise-exposed animals showed an increase in free radicals; these animals exhibited a significant inflammatory response and had impaired vessel function.
The researchers explained that the experimental data showed aircraft noise alone triggers a proinflammatory transcription program that promotes the infiltration of immune cells into cardiovascular tissue in animals with acute myocardial infarction. They noted an increased infiltration of CD45+ cells into the vessels and heart, dominated by neutrophils in vessel tissue and Ly6Chigh monocytes in heart tissue. This infiltration creates a proinflammatory milieu that adversely affects the outcome after myocardial infarction by predisposing the heart tissue to greater ischemic damage and functional impairment. Exposure of animals to aircraft noise before induction of myocardial infarction by left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery ligation impaired left ventricular function and increased infarct size after cardiac ischemia. In addition, noise exposure exacerbated infarct-induced endothelial dysfunction of peripheral vessels as early as 24 hours after LAD ligation.
Clinical Confirmation
These experimental results were confirmed by observations in the population-based Gutenberg Health Study. The researchers analyzed data from 100 patients with heart attack. The lead and senior authors of the study Michael Molitor, MD, and Philip Wenzel, MD, of the University of Mainz, explained, “From our studies, we have learned that exposure to aircraft noise before a heart attack significantly amplifies subsequent cardiovascular inflammation and exacerbates ischemic heart failure, which is favored by inflammation-promoting vascular conditioning. Our translational results show that people who have been exposed to noise in the past have a worse course if they experience a heart attack later in life.”
Study participants who had experienced a heart attack in their medical history had elevated levels of C-reactive protein if they had been exposed to aircraft noise in the past and subsequently developed noise annoyance reactions (0.305 vs 1.5; P = .0094). In addition, left ventricular ejection fraction in these patients after a heart attack was worse than that in patients with infarction without noise exposure in their medical history (62.5 vs 65.6; P = .0053).
The results suggest that measures to reduce environmental noise could help improve the clinical outcomes of heart attack patients, according to the authors.
Mental Health Effects
Traffic noise also may be associated with an increased risk for depression and anxiety disorders, as reported 2 years ago by the German Society for Psychosomatic Medicine and Medical Psychotherapy. Evolution has programmed the human organism to perceive noises as indicators of potential sources of danger — even during sleep. “Noise puts the body on alert,” explained Manfred E. Beutel, MD, director of the Clinic for Psychosomatic Medicine and Psychotherapy at the University of Mainz. As a result, the autonomic nervous system activates stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, leading to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. If noise becomes chronic, chronic diseases can develop. “Indeed, observational and experimental studies have shown that persistent noise annoyance promotes incident hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Beutel.
Depression Risk Doubled
Among the negative effects of noise annoyance are also mental illnesses, as has become increasingly clear. “Noise annoyance disrupts daily activities and interferes with feelings and thoughts, sleep, and recovery,” said Dr. Beutel. The interruptions trigger negative emotional reactions such as anger, distress, exhaustion, flight impulses, and stress symptoms. “Such conditions promote the development of depression over time,” said Dr. Beutel. This observation was confirmed by the large-scale Gutenberg Health Study using the example of the Mainz population, which suffers to a large extent from noise annoyance because of the nearby Frankfurt Airport. “With increasing noise annoyance, the rates of depression and anxiety disorders steadily increased, until the risks eventually doubled with extreme annoyance,” said Dr. Beutel. Other studies point in the same direction. For example, a meta-analysis found a 12% increase in the risk for depression per 10-dB increase in noise. Another study found an association between nocturnal noise annoyance and the use of antidepressants.
Fine Particulate Matter
According to an evaluation of the Gutenberg Study, people perceive noise annoyance from aircraft noise as the most pronounced, followed by road, neighborhood, industrial, and railway noise. Noise occurs most frequently in urban areas that also produce air pollution such as fine particulate matter. “Fine particulate matter is also suspected of promoting anxiety and depression,” said Dr. Beutel, “because the small particles of fine particulate matter can enter the bloodstream and trigger inflammatory processes there, which in turn are closely related to depression.”
This story was translated from Univadis Germany, which is part of the Medscape professional network, using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New research by Thomas Münzel, MD, senior professor of cardiology at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz in Mainz, Germany, and colleagues again emphasized the harmful effects of noise on the heart and blood vessels. An analysis of current epidemiologic data provided strong indications that transportation noise is closely related to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, according to a statement on the data analysis. The results were published in Circulation Research.
Morbidity and Mortality
Epidemiologic studies have shown that road, rail, or air traffic noise increases the risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, with strong evidence for ischemic heart disease, heart failure, and stroke, according to the scientists. These factors could favor vascular (endothelial) dysfunction, inflammation, and hypertension, thereby increasing cardiovascular risk.
Consequences and Pathomechanisms
In the current publication, the authors provided an overview of epidemiologic research on the effects of transportation noise on cardiovascular risk factors and diseases, discussed mechanistic insights from the latest clinical and experimental studies, and proposed new risk markers to address noise-induced cardiovascular effects in the general population. An integrated analysis in the article demonstrated that for every 10 dB(A) increase, the risk for cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack, stroke, and heart failure significantly increases by 3.2%.
The authors also explained the possible effects of noise on changes in gene networks, epigenetic pathways, circadian rhythms, signal transmission along the neuronal-cardiovascular axis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and metabolism. Finally, current and future noise protection strategies are described, and the existing evidence on noise as a cardiovascular risk factor is discussed.
Confirmed Cardiovascular Risk Factor
“As an increasing proportion of the population is exposed to harmful traffic noise, efforts to reduce noise and laws for noise reduction are of great importance for future public health,” said Dr. Münzel. “It is also important for us that due to the strong evidence, traffic noise is finally recognized as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.”
Heart Attack Outcomes
Dr. Münzel and other researchers from Mainz have been studying the cardiovascular consequences of air pollution and traffic noise for several years. For example, they found that heart attacks in people and animals exposed to high noise levels earlier in life healed poorly. These results were published last year in Cardiovascular Research. According to the authors, the findings suggest that traffic noise may play a significant role in the development and course of coronary heart disease, such as after a heart attack.
The scientists initially found in animal experiments that exposure to aircraft noise for 4 days led to increased inflammation in the vessels. Compared with mice not exposed to aircraft noise, the noise-exposed animals showed an increase in free radicals; these animals exhibited a significant inflammatory response and had impaired vessel function.
The researchers explained that the experimental data showed aircraft noise alone triggers a proinflammatory transcription program that promotes the infiltration of immune cells into cardiovascular tissue in animals with acute myocardial infarction. They noted an increased infiltration of CD45+ cells into the vessels and heart, dominated by neutrophils in vessel tissue and Ly6Chigh monocytes in heart tissue. This infiltration creates a proinflammatory milieu that adversely affects the outcome after myocardial infarction by predisposing the heart tissue to greater ischemic damage and functional impairment. Exposure of animals to aircraft noise before induction of myocardial infarction by left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery ligation impaired left ventricular function and increased infarct size after cardiac ischemia. In addition, noise exposure exacerbated infarct-induced endothelial dysfunction of peripheral vessels as early as 24 hours after LAD ligation.
Clinical Confirmation
These experimental results were confirmed by observations in the population-based Gutenberg Health Study. The researchers analyzed data from 100 patients with heart attack. The lead and senior authors of the study Michael Molitor, MD, and Philip Wenzel, MD, of the University of Mainz, explained, “From our studies, we have learned that exposure to aircraft noise before a heart attack significantly amplifies subsequent cardiovascular inflammation and exacerbates ischemic heart failure, which is favored by inflammation-promoting vascular conditioning. Our translational results show that people who have been exposed to noise in the past have a worse course if they experience a heart attack later in life.”
Study participants who had experienced a heart attack in their medical history had elevated levels of C-reactive protein if they had been exposed to aircraft noise in the past and subsequently developed noise annoyance reactions (0.305 vs 1.5; P = .0094). In addition, left ventricular ejection fraction in these patients after a heart attack was worse than that in patients with infarction without noise exposure in their medical history (62.5 vs 65.6; P = .0053).
The results suggest that measures to reduce environmental noise could help improve the clinical outcomes of heart attack patients, according to the authors.
Mental Health Effects
Traffic noise also may be associated with an increased risk for depression and anxiety disorders, as reported 2 years ago by the German Society for Psychosomatic Medicine and Medical Psychotherapy. Evolution has programmed the human organism to perceive noises as indicators of potential sources of danger — even during sleep. “Noise puts the body on alert,” explained Manfred E. Beutel, MD, director of the Clinic for Psychosomatic Medicine and Psychotherapy at the University of Mainz. As a result, the autonomic nervous system activates stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, leading to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. If noise becomes chronic, chronic diseases can develop. “Indeed, observational and experimental studies have shown that persistent noise annoyance promotes incident hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Beutel.
Depression Risk Doubled
Among the negative effects of noise annoyance are also mental illnesses, as has become increasingly clear. “Noise annoyance disrupts daily activities and interferes with feelings and thoughts, sleep, and recovery,” said Dr. Beutel. The interruptions trigger negative emotional reactions such as anger, distress, exhaustion, flight impulses, and stress symptoms. “Such conditions promote the development of depression over time,” said Dr. Beutel. This observation was confirmed by the large-scale Gutenberg Health Study using the example of the Mainz population, which suffers to a large extent from noise annoyance because of the nearby Frankfurt Airport. “With increasing noise annoyance, the rates of depression and anxiety disorders steadily increased, until the risks eventually doubled with extreme annoyance,” said Dr. Beutel. Other studies point in the same direction. For example, a meta-analysis found a 12% increase in the risk for depression per 10-dB increase in noise. Another study found an association between nocturnal noise annoyance and the use of antidepressants.
Fine Particulate Matter
According to an evaluation of the Gutenberg Study, people perceive noise annoyance from aircraft noise as the most pronounced, followed by road, neighborhood, industrial, and railway noise. Noise occurs most frequently in urban areas that also produce air pollution such as fine particulate matter. “Fine particulate matter is also suspected of promoting anxiety and depression,” said Dr. Beutel, “because the small particles of fine particulate matter can enter the bloodstream and trigger inflammatory processes there, which in turn are closely related to depression.”
This story was translated from Univadis Germany, which is part of the Medscape professional network, using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New research by Thomas Münzel, MD, senior professor of cardiology at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz in Mainz, Germany, and colleagues again emphasized the harmful effects of noise on the heart and blood vessels. An analysis of current epidemiologic data provided strong indications that transportation noise is closely related to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, according to a statement on the data analysis. The results were published in Circulation Research.
Morbidity and Mortality
Epidemiologic studies have shown that road, rail, or air traffic noise increases the risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, with strong evidence for ischemic heart disease, heart failure, and stroke, according to the scientists. These factors could favor vascular (endothelial) dysfunction, inflammation, and hypertension, thereby increasing cardiovascular risk.
Consequences and Pathomechanisms
In the current publication, the authors provided an overview of epidemiologic research on the effects of transportation noise on cardiovascular risk factors and diseases, discussed mechanistic insights from the latest clinical and experimental studies, and proposed new risk markers to address noise-induced cardiovascular effects in the general population. An integrated analysis in the article demonstrated that for every 10 dB(A) increase, the risk for cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack, stroke, and heart failure significantly increases by 3.2%.
The authors also explained the possible effects of noise on changes in gene networks, epigenetic pathways, circadian rhythms, signal transmission along the neuronal-cardiovascular axis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and metabolism. Finally, current and future noise protection strategies are described, and the existing evidence on noise as a cardiovascular risk factor is discussed.
Confirmed Cardiovascular Risk Factor
“As an increasing proportion of the population is exposed to harmful traffic noise, efforts to reduce noise and laws for noise reduction are of great importance for future public health,” said Dr. Münzel. “It is also important for us that due to the strong evidence, traffic noise is finally recognized as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.”
Heart Attack Outcomes
Dr. Münzel and other researchers from Mainz have been studying the cardiovascular consequences of air pollution and traffic noise for several years. For example, they found that heart attacks in people and animals exposed to high noise levels earlier in life healed poorly. These results were published last year in Cardiovascular Research. According to the authors, the findings suggest that traffic noise may play a significant role in the development and course of coronary heart disease, such as after a heart attack.
The scientists initially found in animal experiments that exposure to aircraft noise for 4 days led to increased inflammation in the vessels. Compared with mice not exposed to aircraft noise, the noise-exposed animals showed an increase in free radicals; these animals exhibited a significant inflammatory response and had impaired vessel function.
The researchers explained that the experimental data showed aircraft noise alone triggers a proinflammatory transcription program that promotes the infiltration of immune cells into cardiovascular tissue in animals with acute myocardial infarction. They noted an increased infiltration of CD45+ cells into the vessels and heart, dominated by neutrophils in vessel tissue and Ly6Chigh monocytes in heart tissue. This infiltration creates a proinflammatory milieu that adversely affects the outcome after myocardial infarction by predisposing the heart tissue to greater ischemic damage and functional impairment. Exposure of animals to aircraft noise before induction of myocardial infarction by left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery ligation impaired left ventricular function and increased infarct size after cardiac ischemia. In addition, noise exposure exacerbated infarct-induced endothelial dysfunction of peripheral vessels as early as 24 hours after LAD ligation.
Clinical Confirmation
These experimental results were confirmed by observations in the population-based Gutenberg Health Study. The researchers analyzed data from 100 patients with heart attack. The lead and senior authors of the study Michael Molitor, MD, and Philip Wenzel, MD, of the University of Mainz, explained, “From our studies, we have learned that exposure to aircraft noise before a heart attack significantly amplifies subsequent cardiovascular inflammation and exacerbates ischemic heart failure, which is favored by inflammation-promoting vascular conditioning. Our translational results show that people who have been exposed to noise in the past have a worse course if they experience a heart attack later in life.”
Study participants who had experienced a heart attack in their medical history had elevated levels of C-reactive protein if they had been exposed to aircraft noise in the past and subsequently developed noise annoyance reactions (0.305 vs 1.5; P = .0094). In addition, left ventricular ejection fraction in these patients after a heart attack was worse than that in patients with infarction without noise exposure in their medical history (62.5 vs 65.6; P = .0053).
The results suggest that measures to reduce environmental noise could help improve the clinical outcomes of heart attack patients, according to the authors.
Mental Health Effects
Traffic noise also may be associated with an increased risk for depression and anxiety disorders, as reported 2 years ago by the German Society for Psychosomatic Medicine and Medical Psychotherapy. Evolution has programmed the human organism to perceive noises as indicators of potential sources of danger — even during sleep. “Noise puts the body on alert,” explained Manfred E. Beutel, MD, director of the Clinic for Psychosomatic Medicine and Psychotherapy at the University of Mainz. As a result, the autonomic nervous system activates stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, leading to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. If noise becomes chronic, chronic diseases can develop. “Indeed, observational and experimental studies have shown that persistent noise annoyance promotes incident hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Beutel.
Depression Risk Doubled
Among the negative effects of noise annoyance are also mental illnesses, as has become increasingly clear. “Noise annoyance disrupts daily activities and interferes with feelings and thoughts, sleep, and recovery,” said Dr. Beutel. The interruptions trigger negative emotional reactions such as anger, distress, exhaustion, flight impulses, and stress symptoms. “Such conditions promote the development of depression over time,” said Dr. Beutel. This observation was confirmed by the large-scale Gutenberg Health Study using the example of the Mainz population, which suffers to a large extent from noise annoyance because of the nearby Frankfurt Airport. “With increasing noise annoyance, the rates of depression and anxiety disorders steadily increased, until the risks eventually doubled with extreme annoyance,” said Dr. Beutel. Other studies point in the same direction. For example, a meta-analysis found a 12% increase in the risk for depression per 10-dB increase in noise. Another study found an association between nocturnal noise annoyance and the use of antidepressants.
Fine Particulate Matter
According to an evaluation of the Gutenberg Study, people perceive noise annoyance from aircraft noise as the most pronounced, followed by road, neighborhood, industrial, and railway noise. Noise occurs most frequently in urban areas that also produce air pollution such as fine particulate matter. “Fine particulate matter is also suspected of promoting anxiety and depression,” said Dr. Beutel, “because the small particles of fine particulate matter can enter the bloodstream and trigger inflammatory processes there, which in turn are closely related to depression.”
This story was translated from Univadis Germany, which is part of the Medscape professional network, using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.

