User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Psychological intervention looks promising in Crohn’s disease
SAN DIEGO – A combination of cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness meditation could reduce pain and fatigue from Crohn’s disease, researchers say.
Patients who followed the program not only felt better but were also more often able to show up for work and leisure activities, compared with a control group assigned to a wait list, said Shmuel Odes, MD, a professor of internal medicine at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev in Beersheba, Israel. He presented the finding at Digestive Diseases Week® (DDW) 2022.
Psychological and social factors affect the gut and vice versa, Dr. Odes said. Yet many inflammatory bowel disease clinics overlook psychological interventions.
To address these issues, Dr. Odes and colleagues developed cognitive-behavioral– and mindfulness-based stress reduction (COBMINDEX) training, which can be taught by clinical social workers over the Internet. “The patient learns to relax,” Dr. Odes told MDedge News. “He learns not to fight his condition.”
In a previous paper, published in the journal Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Dr. Odes and colleagues reported that patients who learned the technique showed improvement on a variety of psychological and quality-of-life measures, accompanied by changes in inflammatory cytokines and cortisol.
In a follow-up analysis presented here, the researchers looked at measures of pain and fatigue and then examined whether these were associated with productivity at work and other daily activities.
The study investigators randomly assigned 72 patients to an intervention group who got COBMINDEX training right away, and another 70 to a control group assigned to a wait list of 12 weeks before they could get the training. At baseline, the two groups were not significantly different in any demographic or clinical variable the researchers could find.
Social workers provided COBMINDEX training for the patients in seven 60-minute session over 12 weeks. Five of the sessions were devoted to cognitive-behavioral therapy and two to mindfulness-based stress reduction. The social workers asked the patients to do exercises at least once a day and report outcomes through an app.
Twelve patients dropped out of the COBMINDEX group and four dropped from the wait-list group because of lack of interest, time constraints, pregnancy, or illness.
The researchers created a composite score with a 0-15 scale (with higher scores indicating greater pain) from three pain items from the Harvey-Bradshaw Index for Crohn’s Disease, the Short Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire, and the 12-Item Short Form Survey.
To measure fatigue, they used the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue, which has a 0-52 scale, with lower scores indicating greater fatigue.
To measure impairment while working and other daily activities, they used the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire: Crohn’s Disease. Scores on this measure are expressed as a percentage, with higher values indicating greater impairment.
Both the COBMINDEX and the wait-list groups improved on all these scales, but the improvements were significantly greater for the COBMINDEX group.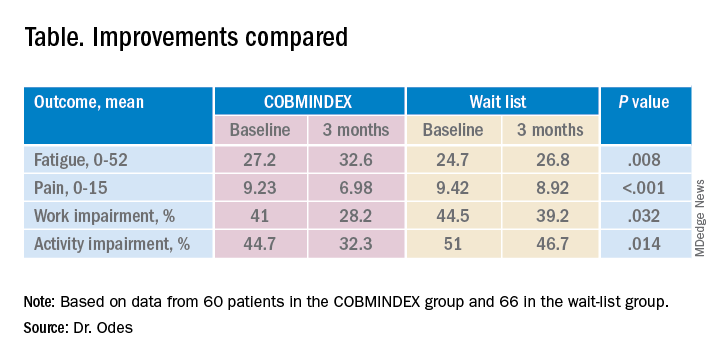
Through statistical analysis, the researchers found that the improvements in pain and fatigue indirectly caused the improvements in work and activity impairment, and that pain and fatigue improvements made independent contributions of similar magnitudes. COBMINDEX did not directly improve work or activity.
Psychological interventions are too often overlooked in Crohn’s disease, said the session comoderator Paul Moayyedi, MD, a professor of gastroenterology at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont. “We need to realize how important this is to patients and urgently make this available,” he told MDedge.
A variety of interventions are being researched, and this study makes an important contribution, he said. However, he questioned whether people on a wait list can serve as an adequate control. “If you have to wait for something, you tend to have more pain, and you could have less productivity just because of waiting,” he said. “Ideally they should do a randomized trial with a sham intervention, not a wait list.”
Dr. Odes responded that it is very difficult to recruit people to a trial if they only have a 50% chance of getting a real treatment. And he noted that the people on the wait list in this trial did not show any signs of increased symptoms.
Physicians wanting to provide psychological help to their Crohn’s disease patients can refer them to social workers or psychotherapists, Dr. Odes said, but these professionals may lack training for applying cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness-based stress reduction to patients with Crohn’s disease. His team hopes to make an app publicly available soon.
Neither Dr. Odes nor Dr. Moayyedi reported any relevant financial interests. The study was supported by a grant from the Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust.
SAN DIEGO – A combination of cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness meditation could reduce pain and fatigue from Crohn’s disease, researchers say.
Patients who followed the program not only felt better but were also more often able to show up for work and leisure activities, compared with a control group assigned to a wait list, said Shmuel Odes, MD, a professor of internal medicine at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev in Beersheba, Israel. He presented the finding at Digestive Diseases Week® (DDW) 2022.
Psychological and social factors affect the gut and vice versa, Dr. Odes said. Yet many inflammatory bowel disease clinics overlook psychological interventions.
To address these issues, Dr. Odes and colleagues developed cognitive-behavioral– and mindfulness-based stress reduction (COBMINDEX) training, which can be taught by clinical social workers over the Internet. “The patient learns to relax,” Dr. Odes told MDedge News. “He learns not to fight his condition.”
In a previous paper, published in the journal Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Dr. Odes and colleagues reported that patients who learned the technique showed improvement on a variety of psychological and quality-of-life measures, accompanied by changes in inflammatory cytokines and cortisol.
In a follow-up analysis presented here, the researchers looked at measures of pain and fatigue and then examined whether these were associated with productivity at work and other daily activities.
The study investigators randomly assigned 72 patients to an intervention group who got COBMINDEX training right away, and another 70 to a control group assigned to a wait list of 12 weeks before they could get the training. At baseline, the two groups were not significantly different in any demographic or clinical variable the researchers could find.
Social workers provided COBMINDEX training for the patients in seven 60-minute session over 12 weeks. Five of the sessions were devoted to cognitive-behavioral therapy and two to mindfulness-based stress reduction. The social workers asked the patients to do exercises at least once a day and report outcomes through an app.
Twelve patients dropped out of the COBMINDEX group and four dropped from the wait-list group because of lack of interest, time constraints, pregnancy, or illness.
The researchers created a composite score with a 0-15 scale (with higher scores indicating greater pain) from three pain items from the Harvey-Bradshaw Index for Crohn’s Disease, the Short Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire, and the 12-Item Short Form Survey.
To measure fatigue, they used the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue, which has a 0-52 scale, with lower scores indicating greater fatigue.
To measure impairment while working and other daily activities, they used the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire: Crohn’s Disease. Scores on this measure are expressed as a percentage, with higher values indicating greater impairment.
Both the COBMINDEX and the wait-list groups improved on all these scales, but the improvements were significantly greater for the COBMINDEX group.
Through statistical analysis, the researchers found that the improvements in pain and fatigue indirectly caused the improvements in work and activity impairment, and that pain and fatigue improvements made independent contributions of similar magnitudes. COBMINDEX did not directly improve work or activity.
Psychological interventions are too often overlooked in Crohn’s disease, said the session comoderator Paul Moayyedi, MD, a professor of gastroenterology at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont. “We need to realize how important this is to patients and urgently make this available,” he told MDedge.
A variety of interventions are being researched, and this study makes an important contribution, he said. However, he questioned whether people on a wait list can serve as an adequate control. “If you have to wait for something, you tend to have more pain, and you could have less productivity just because of waiting,” he said. “Ideally they should do a randomized trial with a sham intervention, not a wait list.”
Dr. Odes responded that it is very difficult to recruit people to a trial if they only have a 50% chance of getting a real treatment. And he noted that the people on the wait list in this trial did not show any signs of increased symptoms.
Physicians wanting to provide psychological help to their Crohn’s disease patients can refer them to social workers or psychotherapists, Dr. Odes said, but these professionals may lack training for applying cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness-based stress reduction to patients with Crohn’s disease. His team hopes to make an app publicly available soon.
Neither Dr. Odes nor Dr. Moayyedi reported any relevant financial interests. The study was supported by a grant from the Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust.
SAN DIEGO – A combination of cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness meditation could reduce pain and fatigue from Crohn’s disease, researchers say.
Patients who followed the program not only felt better but were also more often able to show up for work and leisure activities, compared with a control group assigned to a wait list, said Shmuel Odes, MD, a professor of internal medicine at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev in Beersheba, Israel. He presented the finding at Digestive Diseases Week® (DDW) 2022.
Psychological and social factors affect the gut and vice versa, Dr. Odes said. Yet many inflammatory bowel disease clinics overlook psychological interventions.
To address these issues, Dr. Odes and colleagues developed cognitive-behavioral– and mindfulness-based stress reduction (COBMINDEX) training, which can be taught by clinical social workers over the Internet. “The patient learns to relax,” Dr. Odes told MDedge News. “He learns not to fight his condition.”
In a previous paper, published in the journal Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Dr. Odes and colleagues reported that patients who learned the technique showed improvement on a variety of psychological and quality-of-life measures, accompanied by changes in inflammatory cytokines and cortisol.
In a follow-up analysis presented here, the researchers looked at measures of pain and fatigue and then examined whether these were associated with productivity at work and other daily activities.
The study investigators randomly assigned 72 patients to an intervention group who got COBMINDEX training right away, and another 70 to a control group assigned to a wait list of 12 weeks before they could get the training. At baseline, the two groups were not significantly different in any demographic or clinical variable the researchers could find.
Social workers provided COBMINDEX training for the patients in seven 60-minute session over 12 weeks. Five of the sessions were devoted to cognitive-behavioral therapy and two to mindfulness-based stress reduction. The social workers asked the patients to do exercises at least once a day and report outcomes through an app.
Twelve patients dropped out of the COBMINDEX group and four dropped from the wait-list group because of lack of interest, time constraints, pregnancy, or illness.
The researchers created a composite score with a 0-15 scale (with higher scores indicating greater pain) from three pain items from the Harvey-Bradshaw Index for Crohn’s Disease, the Short Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire, and the 12-Item Short Form Survey.
To measure fatigue, they used the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue, which has a 0-52 scale, with lower scores indicating greater fatigue.
To measure impairment while working and other daily activities, they used the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire: Crohn’s Disease. Scores on this measure are expressed as a percentage, with higher values indicating greater impairment.
Both the COBMINDEX and the wait-list groups improved on all these scales, but the improvements were significantly greater for the COBMINDEX group.
Through statistical analysis, the researchers found that the improvements in pain and fatigue indirectly caused the improvements in work and activity impairment, and that pain and fatigue improvements made independent contributions of similar magnitudes. COBMINDEX did not directly improve work or activity.
Psychological interventions are too often overlooked in Crohn’s disease, said the session comoderator Paul Moayyedi, MD, a professor of gastroenterology at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont. “We need to realize how important this is to patients and urgently make this available,” he told MDedge.
A variety of interventions are being researched, and this study makes an important contribution, he said. However, he questioned whether people on a wait list can serve as an adequate control. “If you have to wait for something, you tend to have more pain, and you could have less productivity just because of waiting,” he said. “Ideally they should do a randomized trial with a sham intervention, not a wait list.”
Dr. Odes responded that it is very difficult to recruit people to a trial if they only have a 50% chance of getting a real treatment. And he noted that the people on the wait list in this trial did not show any signs of increased symptoms.
Physicians wanting to provide psychological help to their Crohn’s disease patients can refer them to social workers or psychotherapists, Dr. Odes said, but these professionals may lack training for applying cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness-based stress reduction to patients with Crohn’s disease. His team hopes to make an app publicly available soon.
Neither Dr. Odes nor Dr. Moayyedi reported any relevant financial interests. The study was supported by a grant from the Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust.
AT DDW 2022
Does taking isotretinoin worsen a patient’s baseline IBD symptoms?
A , results from a small retrospective study suggests.
“Early studies of isotretinoin for use in severe acne suggested the drug may serve as a trigger for new-onset inflammatory bowel disease (IBD),” researchers led by Christina G. Lopez, MD, of the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, wrote in an article published online , in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. “While more recent studies have suggested no such causal relationship, little is known about the medication’s effect on patients with a preexisting IBD diagnosis.”
To investigate this topic further, the researchers identified 19 patients who were diagnosed with IBD and treated with isotretinoin between Jan. 1, 2006, and Jan. 1, 2020, at Mass General Brigham Hospitals, Boston. They determined severity of disease and degree of antecedent management of IBD by evaluating flaring two years prior to starting isotretinoin. The patients were considered to have a flare caused by isotretinoin if the IBD flare occurred during or up to 3 months following course completion.
The mean age of the 19 patients was 35 years, 26% were female, and 95% were White. Nearly half of the patients (42%) had ulcerative colitis, 37% had Crohn’s disease, and 21% had both. The researchers found that nine patients had flared two years before starting isotretinoin. Of these, five (56%) flared and four (44%) did not flare during treatment or within three months of completing the course of isotretinoin.
Of the 10 patients who did not flare two years before starting isotretinoin, seven (70%) did not flare during treatment and three (30%) flared during or within three months following completion of isotretinoin use. The researchers found no statistically significant association between isotretinoin use and flaring among patients with IBD (P = .76).
Dr. Lopez and her colleagues also assessed IBD maintenance therapy with respect to IBD flares in the study population. They observed no statistically significant association between the use of maintenance IBD therapy and the likelihood of having flares during isotretinoin treatment (P = .15).
“The results suggest limited association between isotretinoin and the worsening of a patient’s baseline IBD,” the authors concluded. They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its small sample size and retrospective design, and they called for larger and prospective studies to assess the relationship of IBD flaring in this population of patients.
Pooja Sodha, MD, director of the Center for Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the results, characterized the trial as “an important study highlighting how we continue to understand the safe use of isotretinoin in the IBD cohort.”
Isotretinoin, she added, “continues to be a highly important treatment for acne and in patients such as these where oral antibiotics are relatively contraindicated due to risk of exacerbating their bowel disease.” Such data are reassuring, “albeit future studies with larger patient pools are desirable,” she added. “Future studies could also help to elucidate if diet, smoking, sleep, exercise, and medication adherence are potential confounding factors along with whether the cumulative isotretinoin dose has any effect on IBD flares in those who are susceptible.”
Neither the researchers nor Dr. Sodha had financial conflicts. The other authors were from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard University, Boston, and the University of Massachusetts, Worcester.
A , results from a small retrospective study suggests.
“Early studies of isotretinoin for use in severe acne suggested the drug may serve as a trigger for new-onset inflammatory bowel disease (IBD),” researchers led by Christina G. Lopez, MD, of the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, wrote in an article published online , in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. “While more recent studies have suggested no such causal relationship, little is known about the medication’s effect on patients with a preexisting IBD diagnosis.”
To investigate this topic further, the researchers identified 19 patients who were diagnosed with IBD and treated with isotretinoin between Jan. 1, 2006, and Jan. 1, 2020, at Mass General Brigham Hospitals, Boston. They determined severity of disease and degree of antecedent management of IBD by evaluating flaring two years prior to starting isotretinoin. The patients were considered to have a flare caused by isotretinoin if the IBD flare occurred during or up to 3 months following course completion.
The mean age of the 19 patients was 35 years, 26% were female, and 95% were White. Nearly half of the patients (42%) had ulcerative colitis, 37% had Crohn’s disease, and 21% had both. The researchers found that nine patients had flared two years before starting isotretinoin. Of these, five (56%) flared and four (44%) did not flare during treatment or within three months of completing the course of isotretinoin.
Of the 10 patients who did not flare two years before starting isotretinoin, seven (70%) did not flare during treatment and three (30%) flared during or within three months following completion of isotretinoin use. The researchers found no statistically significant association between isotretinoin use and flaring among patients with IBD (P = .76).
Dr. Lopez and her colleagues also assessed IBD maintenance therapy with respect to IBD flares in the study population. They observed no statistically significant association between the use of maintenance IBD therapy and the likelihood of having flares during isotretinoin treatment (P = .15).
“The results suggest limited association between isotretinoin and the worsening of a patient’s baseline IBD,” the authors concluded. They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its small sample size and retrospective design, and they called for larger and prospective studies to assess the relationship of IBD flaring in this population of patients.
Pooja Sodha, MD, director of the Center for Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the results, characterized the trial as “an important study highlighting how we continue to understand the safe use of isotretinoin in the IBD cohort.”
Isotretinoin, she added, “continues to be a highly important treatment for acne and in patients such as these where oral antibiotics are relatively contraindicated due to risk of exacerbating their bowel disease.” Such data are reassuring, “albeit future studies with larger patient pools are desirable,” she added. “Future studies could also help to elucidate if diet, smoking, sleep, exercise, and medication adherence are potential confounding factors along with whether the cumulative isotretinoin dose has any effect on IBD flares in those who are susceptible.”
Neither the researchers nor Dr. Sodha had financial conflicts. The other authors were from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard University, Boston, and the University of Massachusetts, Worcester.
A , results from a small retrospective study suggests.
“Early studies of isotretinoin for use in severe acne suggested the drug may serve as a trigger for new-onset inflammatory bowel disease (IBD),” researchers led by Christina G. Lopez, MD, of the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, wrote in an article published online , in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. “While more recent studies have suggested no such causal relationship, little is known about the medication’s effect on patients with a preexisting IBD diagnosis.”
To investigate this topic further, the researchers identified 19 patients who were diagnosed with IBD and treated with isotretinoin between Jan. 1, 2006, and Jan. 1, 2020, at Mass General Brigham Hospitals, Boston. They determined severity of disease and degree of antecedent management of IBD by evaluating flaring two years prior to starting isotretinoin. The patients were considered to have a flare caused by isotretinoin if the IBD flare occurred during or up to 3 months following course completion.
The mean age of the 19 patients was 35 years, 26% were female, and 95% were White. Nearly half of the patients (42%) had ulcerative colitis, 37% had Crohn’s disease, and 21% had both. The researchers found that nine patients had flared two years before starting isotretinoin. Of these, five (56%) flared and four (44%) did not flare during treatment or within three months of completing the course of isotretinoin.
Of the 10 patients who did not flare two years before starting isotretinoin, seven (70%) did not flare during treatment and three (30%) flared during or within three months following completion of isotretinoin use. The researchers found no statistically significant association between isotretinoin use and flaring among patients with IBD (P = .76).
Dr. Lopez and her colleagues also assessed IBD maintenance therapy with respect to IBD flares in the study population. They observed no statistically significant association between the use of maintenance IBD therapy and the likelihood of having flares during isotretinoin treatment (P = .15).
“The results suggest limited association between isotretinoin and the worsening of a patient’s baseline IBD,” the authors concluded. They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its small sample size and retrospective design, and they called for larger and prospective studies to assess the relationship of IBD flaring in this population of patients.
Pooja Sodha, MD, director of the Center for Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the results, characterized the trial as “an important study highlighting how we continue to understand the safe use of isotretinoin in the IBD cohort.”
Isotretinoin, she added, “continues to be a highly important treatment for acne and in patients such as these where oral antibiotics are relatively contraindicated due to risk of exacerbating their bowel disease.” Such data are reassuring, “albeit future studies with larger patient pools are desirable,” she added. “Future studies could also help to elucidate if diet, smoking, sleep, exercise, and medication adherence are potential confounding factors along with whether the cumulative isotretinoin dose has any effect on IBD flares in those who are susceptible.”
Neither the researchers nor Dr. Sodha had financial conflicts. The other authors were from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard University, Boston, and the University of Massachusetts, Worcester.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Exercise response divides COPD patients into four groups
Not all patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) respond equally well to pulmonary rehabilitation (PR).
Now, physicians can better categorize which patients will do well with PR and which ones less well or not well at all based on a new system of clustering of COPD patients according to their response to exercise therapy.
“We identified four clusters of COPD patients and their response to PR in the aim to better understand PR outcome and [adapt] it to patients’ profiles and needs,” lead author Yara Al Chikhanie, MD, of the cardiopulmonary rehabilitation center Dieulefit Sante (France), and colleagues observed.
“Identification of patients likely to show smaller responses to PR may help to target patients benefiting the most and to adapt PR settings for nonresponders to standard PR,” they suggested.
The study was published online in Respiratory Medicine.
Single-center cohort
The cohort consisted of 835 patients from a single center who had been admitted to a cardiopulmonary rehabilitation center over a 6-year period from 2021 to 2017. “The PR program used in the center was the same over the 6-year period,” the authors note – consisting of a 3- to 4-week, inpatient program with activities 5 days a week.
Each day, patients attended a 25-minute aerobic training session on a cycling ergometer or a treadmill; a 30-minute low-intensity gym session; a 30-minute group walk outdoors, and 30 minutes of strength training. “We aimed to cluster patients with COPD admitted to PR based on patients’ clinical characteristics and 6-meter walk test results (6MWT), pulse oxygen saturation (SPO2), heart rate (HR), and dyspnea,” the authors explained.
They then evaluated patient response to PR in each of these clusters based on the amount of improvement in the 6-meter walk distance (6MWD), lung function, and quality of life observed, they added.
The population consisted of seniors, equally men and women, mostly GOLD II and III patients (a measure of lung function) with a limited walking capacity, some 84% of the cohort having a 6MWD <80% predicted. The characteristics of the four identified clusters were as follows:
- Cluster 1: Consisted of younger men, GOLD I to II, average walkers, obese. The average 6MWD was 430 meters and patients had a large exercise HR response to PR. This cluster had a 76 meter improvement in their 6MWD, although 16% of the same cluster still did not respond to PR.
- Cluster 2: Consisted of older women, GOLD II-III, who were slow walkers. This cluster had a reduced 6MWD of 362 meters, but they also had a significant 97-meter improvement in their 6MWD following PR. Some 18% were still nonresponders to PR.
- Cluster 3: Consisted of older men, GOLD II to III, dyspneic, slow walkers, some 32% of whom responded to PR. This cluster also had a reduced 6MWD at 388 meters, but again, they also had a significant improvement of 79 meters in their 6MWD following the introduction of PR. Some 11% were nonresponders to PR.
- Cluster 4: Consisted of older men, GOLD III to IV, very slow walkers, oxygen-dependent, very dyspneic. This cluster had a severely reduced 6MWD of only 290 meters with severe exercise desaturation and dyspnea, and almost all of them were on long-term oxygen therapy. Nevertheless, this cluster also had a significant, 66-meter improvement in their 6MWD. Twenty-eight percent of them were nonresponders to PR.
Clinical practice
“The highly heterogeneous nature of the enrolled patient population reflects clinical practice,” the authors point out. For example, cluster 1 included patients with the best lung function, compared with those in clusters 2, 3, and 4 – which may be due, at least in part, to the aggravation in disease severity with age given that patients in cluster 1 were the youngest overall.
The fact that those in cluster 4 had the worst performance may also have been because of age and disease severity, the authors note, as those in cluster 4 had the highest proportion of patients on long-term oxygen therapy, again suggestive of disease severity. “Of note, these patients show the most impaired 6MWT responses despite the use of oxygen supplementation during walking,” the researchers added.
The authors also suggest that patients such as those in cluster 4 may require specific PR modalities in order to optimize their functional benefits. In contrast, those in cluster 1 had a significantly higher body mass index, compared with those in the other 3 clusters, which, interestingly enough, was not associated with more severe functional exercise impairment. The fact that older age participants, such as those in cluster 3 as well as those with high BMI in cluster 1, were both able to improve their 6MWD post-PR to the same extent as younger patients without obesity suggests that most older or overweight/obese patients can still show clinically significant improvement in 6MWD post PR, as the authors suggest.
Notably, the 6MWT was the only test available both pre-and post PR, making this an important limitation of the study, because only one aspect of the effect of PR was evaluated, omitting other physical and psychosocial benefits of PR, investigators suggest.
Adds to the literature
Asked to comment on the findings, Sachin Gupta, MD, attending physician, pulmonary & critical care medicine, Alameda Health System, Highland Hospital, Oakland, Calif., felt that these data add to the literature in defining COPD patient profiles, helping to categorize those in whom to expect greater walk distance improvements with PR versus those who will respond less well.
“Because 6MWD is a surrogate marker for quality of life (QOL) and mortality, further analysis in the form of a randomized controlled trial to determine long-term outcomes among the four clusters with adjustment for baseline characteristics would help determine the extent to which certain patient clusters may respond to PR,” Dr. Gupta told this news organization in an email.
At the same time, he suggested that while patients may not experience much net benefit in their 6MWD, their QOL or mortality risk may still improve with PR. “I cannot recall a patient ever describing their experience with PR as anything other than positive,” Dr. Gupta stressed.
“And as the authors [themselves] note, because PR serves to benefit patients beyond the 6MWD, I would not recommend limiting PR referrals based on the patient clusters identified,” he said.
The authors had no conflicts of interest to declare. Dr. Gupta declared that he is an employee and shareholder at Genentech.
Not all patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) respond equally well to pulmonary rehabilitation (PR).
Now, physicians can better categorize which patients will do well with PR and which ones less well or not well at all based on a new system of clustering of COPD patients according to their response to exercise therapy.
“We identified four clusters of COPD patients and their response to PR in the aim to better understand PR outcome and [adapt] it to patients’ profiles and needs,” lead author Yara Al Chikhanie, MD, of the cardiopulmonary rehabilitation center Dieulefit Sante (France), and colleagues observed.
“Identification of patients likely to show smaller responses to PR may help to target patients benefiting the most and to adapt PR settings for nonresponders to standard PR,” they suggested.
The study was published online in Respiratory Medicine.
Single-center cohort
The cohort consisted of 835 patients from a single center who had been admitted to a cardiopulmonary rehabilitation center over a 6-year period from 2021 to 2017. “The PR program used in the center was the same over the 6-year period,” the authors note – consisting of a 3- to 4-week, inpatient program with activities 5 days a week.
Each day, patients attended a 25-minute aerobic training session on a cycling ergometer or a treadmill; a 30-minute low-intensity gym session; a 30-minute group walk outdoors, and 30 minutes of strength training. “We aimed to cluster patients with COPD admitted to PR based on patients’ clinical characteristics and 6-meter walk test results (6MWT), pulse oxygen saturation (SPO2), heart rate (HR), and dyspnea,” the authors explained.
They then evaluated patient response to PR in each of these clusters based on the amount of improvement in the 6-meter walk distance (6MWD), lung function, and quality of life observed, they added.
The population consisted of seniors, equally men and women, mostly GOLD II and III patients (a measure of lung function) with a limited walking capacity, some 84% of the cohort having a 6MWD <80% predicted. The characteristics of the four identified clusters were as follows:
- Cluster 1: Consisted of younger men, GOLD I to II, average walkers, obese. The average 6MWD was 430 meters and patients had a large exercise HR response to PR. This cluster had a 76 meter improvement in their 6MWD, although 16% of the same cluster still did not respond to PR.
- Cluster 2: Consisted of older women, GOLD II-III, who were slow walkers. This cluster had a reduced 6MWD of 362 meters, but they also had a significant 97-meter improvement in their 6MWD following PR. Some 18% were still nonresponders to PR.
- Cluster 3: Consisted of older men, GOLD II to III, dyspneic, slow walkers, some 32% of whom responded to PR. This cluster also had a reduced 6MWD at 388 meters, but again, they also had a significant improvement of 79 meters in their 6MWD following the introduction of PR. Some 11% were nonresponders to PR.
- Cluster 4: Consisted of older men, GOLD III to IV, very slow walkers, oxygen-dependent, very dyspneic. This cluster had a severely reduced 6MWD of only 290 meters with severe exercise desaturation and dyspnea, and almost all of them were on long-term oxygen therapy. Nevertheless, this cluster also had a significant, 66-meter improvement in their 6MWD. Twenty-eight percent of them were nonresponders to PR.
Clinical practice
“The highly heterogeneous nature of the enrolled patient population reflects clinical practice,” the authors point out. For example, cluster 1 included patients with the best lung function, compared with those in clusters 2, 3, and 4 – which may be due, at least in part, to the aggravation in disease severity with age given that patients in cluster 1 were the youngest overall.
The fact that those in cluster 4 had the worst performance may also have been because of age and disease severity, the authors note, as those in cluster 4 had the highest proportion of patients on long-term oxygen therapy, again suggestive of disease severity. “Of note, these patients show the most impaired 6MWT responses despite the use of oxygen supplementation during walking,” the researchers added.
The authors also suggest that patients such as those in cluster 4 may require specific PR modalities in order to optimize their functional benefits. In contrast, those in cluster 1 had a significantly higher body mass index, compared with those in the other 3 clusters, which, interestingly enough, was not associated with more severe functional exercise impairment. The fact that older age participants, such as those in cluster 3 as well as those with high BMI in cluster 1, were both able to improve their 6MWD post-PR to the same extent as younger patients without obesity suggests that most older or overweight/obese patients can still show clinically significant improvement in 6MWD post PR, as the authors suggest.
Notably, the 6MWT was the only test available both pre-and post PR, making this an important limitation of the study, because only one aspect of the effect of PR was evaluated, omitting other physical and psychosocial benefits of PR, investigators suggest.
Adds to the literature
Asked to comment on the findings, Sachin Gupta, MD, attending physician, pulmonary & critical care medicine, Alameda Health System, Highland Hospital, Oakland, Calif., felt that these data add to the literature in defining COPD patient profiles, helping to categorize those in whom to expect greater walk distance improvements with PR versus those who will respond less well.
“Because 6MWD is a surrogate marker for quality of life (QOL) and mortality, further analysis in the form of a randomized controlled trial to determine long-term outcomes among the four clusters with adjustment for baseline characteristics would help determine the extent to which certain patient clusters may respond to PR,” Dr. Gupta told this news organization in an email.
At the same time, he suggested that while patients may not experience much net benefit in their 6MWD, their QOL or mortality risk may still improve with PR. “I cannot recall a patient ever describing their experience with PR as anything other than positive,” Dr. Gupta stressed.
“And as the authors [themselves] note, because PR serves to benefit patients beyond the 6MWD, I would not recommend limiting PR referrals based on the patient clusters identified,” he said.
The authors had no conflicts of interest to declare. Dr. Gupta declared that he is an employee and shareholder at Genentech.
Not all patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) respond equally well to pulmonary rehabilitation (PR).
Now, physicians can better categorize which patients will do well with PR and which ones less well or not well at all based on a new system of clustering of COPD patients according to their response to exercise therapy.
“We identified four clusters of COPD patients and their response to PR in the aim to better understand PR outcome and [adapt] it to patients’ profiles and needs,” lead author Yara Al Chikhanie, MD, of the cardiopulmonary rehabilitation center Dieulefit Sante (France), and colleagues observed.
“Identification of patients likely to show smaller responses to PR may help to target patients benefiting the most and to adapt PR settings for nonresponders to standard PR,” they suggested.
The study was published online in Respiratory Medicine.
Single-center cohort
The cohort consisted of 835 patients from a single center who had been admitted to a cardiopulmonary rehabilitation center over a 6-year period from 2021 to 2017. “The PR program used in the center was the same over the 6-year period,” the authors note – consisting of a 3- to 4-week, inpatient program with activities 5 days a week.
Each day, patients attended a 25-minute aerobic training session on a cycling ergometer or a treadmill; a 30-minute low-intensity gym session; a 30-minute group walk outdoors, and 30 minutes of strength training. “We aimed to cluster patients with COPD admitted to PR based on patients’ clinical characteristics and 6-meter walk test results (6MWT), pulse oxygen saturation (SPO2), heart rate (HR), and dyspnea,” the authors explained.
They then evaluated patient response to PR in each of these clusters based on the amount of improvement in the 6-meter walk distance (6MWD), lung function, and quality of life observed, they added.
The population consisted of seniors, equally men and women, mostly GOLD II and III patients (a measure of lung function) with a limited walking capacity, some 84% of the cohort having a 6MWD <80% predicted. The characteristics of the four identified clusters were as follows:
- Cluster 1: Consisted of younger men, GOLD I to II, average walkers, obese. The average 6MWD was 430 meters and patients had a large exercise HR response to PR. This cluster had a 76 meter improvement in their 6MWD, although 16% of the same cluster still did not respond to PR.
- Cluster 2: Consisted of older women, GOLD II-III, who were slow walkers. This cluster had a reduced 6MWD of 362 meters, but they also had a significant 97-meter improvement in their 6MWD following PR. Some 18% were still nonresponders to PR.
- Cluster 3: Consisted of older men, GOLD II to III, dyspneic, slow walkers, some 32% of whom responded to PR. This cluster also had a reduced 6MWD at 388 meters, but again, they also had a significant improvement of 79 meters in their 6MWD following the introduction of PR. Some 11% were nonresponders to PR.
- Cluster 4: Consisted of older men, GOLD III to IV, very slow walkers, oxygen-dependent, very dyspneic. This cluster had a severely reduced 6MWD of only 290 meters with severe exercise desaturation and dyspnea, and almost all of them were on long-term oxygen therapy. Nevertheless, this cluster also had a significant, 66-meter improvement in their 6MWD. Twenty-eight percent of them were nonresponders to PR.
Clinical practice
“The highly heterogeneous nature of the enrolled patient population reflects clinical practice,” the authors point out. For example, cluster 1 included patients with the best lung function, compared with those in clusters 2, 3, and 4 – which may be due, at least in part, to the aggravation in disease severity with age given that patients in cluster 1 were the youngest overall.
The fact that those in cluster 4 had the worst performance may also have been because of age and disease severity, the authors note, as those in cluster 4 had the highest proportion of patients on long-term oxygen therapy, again suggestive of disease severity. “Of note, these patients show the most impaired 6MWT responses despite the use of oxygen supplementation during walking,” the researchers added.
The authors also suggest that patients such as those in cluster 4 may require specific PR modalities in order to optimize their functional benefits. In contrast, those in cluster 1 had a significantly higher body mass index, compared with those in the other 3 clusters, which, interestingly enough, was not associated with more severe functional exercise impairment. The fact that older age participants, such as those in cluster 3 as well as those with high BMI in cluster 1, were both able to improve their 6MWD post-PR to the same extent as younger patients without obesity suggests that most older or overweight/obese patients can still show clinically significant improvement in 6MWD post PR, as the authors suggest.
Notably, the 6MWT was the only test available both pre-and post PR, making this an important limitation of the study, because only one aspect of the effect of PR was evaluated, omitting other physical and psychosocial benefits of PR, investigators suggest.
Adds to the literature
Asked to comment on the findings, Sachin Gupta, MD, attending physician, pulmonary & critical care medicine, Alameda Health System, Highland Hospital, Oakland, Calif., felt that these data add to the literature in defining COPD patient profiles, helping to categorize those in whom to expect greater walk distance improvements with PR versus those who will respond less well.
“Because 6MWD is a surrogate marker for quality of life (QOL) and mortality, further analysis in the form of a randomized controlled trial to determine long-term outcomes among the four clusters with adjustment for baseline characteristics would help determine the extent to which certain patient clusters may respond to PR,” Dr. Gupta told this news organization in an email.
At the same time, he suggested that while patients may not experience much net benefit in their 6MWD, their QOL or mortality risk may still improve with PR. “I cannot recall a patient ever describing their experience with PR as anything other than positive,” Dr. Gupta stressed.
“And as the authors [themselves] note, because PR serves to benefit patients beyond the 6MWD, I would not recommend limiting PR referrals based on the patient clusters identified,” he said.
The authors had no conflicts of interest to declare. Dr. Gupta declared that he is an employee and shareholder at Genentech.
FROM RESPIRATORY MEDICINE
SGLT2 inhibitors as first-line therapy in type 2 diabetes?
Use of sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors rather than metformin as first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes appears to cut the risk for heart failure hospitalization but not myocardial infarction, stroke, or all-cause mortality, a new analysis of real-world data suggests.
Safety findings were similar, except for the fact that genital infections were more common with SGLT-2 inhibitors.
The study was conducted using claims data from two large U.S. insurance databases and Medicare. Propensity score matching was used to account for baseline differences.
The study was conducted by HoJin Shin, BPharm, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and colleagues. The findings were published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Those who start SGLT-2 inhibitors as first line show similar risks, compared with metformin in MI, stroke, and all-cause mortality outcomes. Strikingly and consistently, SGLT-2 inhibitors show lower risk for hospitalization for heart failure, which is consistent with the findings from cardiovascular outcomes trials,” Dr. Shin said in an interview.
Just a beginning step, although trial probably wasn’t long enough
However, she added, “I don’t want to overstate anything. ... We aren’t powered enough to investigate who would benefit the most. ... As a pharmacoepidemiologist, I think it’s my duty to provide high-quality evidence so we can actually help physicians and patients make better decisions on their medication. Our current research is just a beginning step.”
Asked to comment, Simeon I. Taylor, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, told this news organization, “This study generally confirmed conclusions from published RCTs [randomized clinical trials]. No real surprises, albeit the conclusions may not fully support some of the most enthusiastic claims for SGLT-2 inhibitors with respect to MI, stroke, and cardiovascular death.”
Indeed, Dr. Taylor noted that only two SGLT-2 inhibitors, canagliflozin and empagliflozin, were shown to have a statistically significant association with decreased major adverse cardiovascular events.
In contrast, neither dapagliflozin nor ertugliflozin showed significant benefit regarding those outcomes.
He also pointed out that those four major SLGT-2 inhibitor cardiovascular outcomes trials were placebo-controlled rather than head-to-head trials in which they were compared to an active comparator such as metformin.
“Viewed in this light, it’s probably not surprising that the present study did not demonstrate a robust benefit for SGLT-2 inhibitors to decrease [major adverse CV events].”
The duration of follow-up in the current study is also a limitation, he added.
“The majority of patients were followed for a year or less. This is probably sufficient to assess the impact of some pharmacological mechanisms, for example, the beneficial impact to decrease risk of heart failure by promoting urinary sodium excretion. However, it’s probably insufficient time to observe a beneficial impact on atherosclerosis. For example, there is typically a lag of several years before statins demonstrate efficacy with respect to adverse cardiovascular events.”
Nevertheless, he said, “it provides strong support for benefit with respect to decreasing risk of hospitalization for heart failure.”
He noted that while metformin is currently significantly cheaper than any SGLT-2 inhibitors, once the latter become available as generics, they will be cheaper, and this will likely have a bearing on prescribing decisions.
“Availability of generic SGLT-2 inhibitors offers potential to transform prescribing patterns for type 2 diabetes,” he noted.
First-line SGLT2 inhibitors versus metformin: Most outcomes similar
The study data came from two commercial U.S. health insurance databases, Optum Clinfomatics Data Mart and IBM Marketscan, and from Medicare fee-for-service enrollees.
From April 2013 through March 2020, a total of 9,334 patients began treatment with first-line SGLT-2 inhibitors; 819,973 patients began taking metformin. After 1:2 propensity score matching for confounders, there were 8,613 participants in the SGLT-2 inhibitor group and 17,226 in the group that began treatment with metformin.
The mean follow-up times were 10.7 months for patients taking SGLT-2 inhibitors and 12.2 months for patients taking metformin.
Incidence rates per 1,000 person-years for the composite of hospitalization for MI, hospitalization for ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, or all-cause mortality (MI/stroke/mortality) were 15.0 versus 16.2 for SLGT-2 inhibitors versus metformin, not a significant difference (hazard ratio, 0.96).
However, for the composite of heart failure hospitalization or all-cause mortality, the rates were 18.3 versus 23.5, a significant difference, with an HR of 0.80. The benefit was seen beginning at about 6 months.
Compared with metformin, SGLT-2 inhibitors showed a significantly lower risk for heart failure hospitalization (HR, 0.78), a numerically (but not significantly) lower risk for MI (HR, 0.70), and similar risks for stroke, mortality, and MI/stroke/HHF/mortality.
Genital infections were significantly more common with SGLT-2 inhibitors (54.1 vs. 23.7 per 1,000 person-years; HR, 2.19). Other safety measures were similar, including acute kidney injury, bone fractures, severe hypoglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, and lower-limb amputations.
How does cost factor in?
A sensitivity analysis aimed at examining the possible effect of unmeasured socioeconomic status showed no difference in cardiovascular benefit for first-line SGLT-2 inhibitors and metformin, compared with first-line dipeptidyl peptidase–4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, which cost more than metformin; it is not known what effect DPP-4 inhibitors have on the cardiovascular outcomes of interest.
Cost and insurance coverage factor into the benefit/risk calculation. Metformin is far less costly than any of the SGLT-2 inhibitors – roughly $10 to $20 per month, compared with more than $500 a month.
However, “for some fortunate patients with the most generous pharmacy benefit insurance coverage, the out-of-pocket cost of brand name drugs like SGLT-2 inhibitors is substantially lower,” Dr. Taylor noted.
He said that the current study “raises questions about whether the clinical benefits of SGLT-2 inhibitors as initial monotherapy justify the higher price relative to metformin. The data in this paper suggest that the value case for SGLT-2 inhibitors is strongest for patients with the greatest risk to be hospitalized for heart failure.”
Indeed, Dr. Shin said, “Once we get more information, it may just help in extending the coverage from insurance companies and Medicare/Medicaid, to lower the barrier to access.”
Dr. Taylor reiterated that patents on some of the early SGLT-2 inhibitors are expected to expire in the next few years, which would make it possible for generic versions to be approved. “At that point, prices would likely fall, possibly to levels similar to metformin.”
The study was funded by grant support from the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, department of medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Harvard Medical School, the National Institute on Aging, and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Dr. Shin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Taylor is a consultant for Ionis Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Use of sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors rather than metformin as first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes appears to cut the risk for heart failure hospitalization but not myocardial infarction, stroke, or all-cause mortality, a new analysis of real-world data suggests.
Safety findings were similar, except for the fact that genital infections were more common with SGLT-2 inhibitors.
The study was conducted using claims data from two large U.S. insurance databases and Medicare. Propensity score matching was used to account for baseline differences.
The study was conducted by HoJin Shin, BPharm, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and colleagues. The findings were published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Those who start SGLT-2 inhibitors as first line show similar risks, compared with metformin in MI, stroke, and all-cause mortality outcomes. Strikingly and consistently, SGLT-2 inhibitors show lower risk for hospitalization for heart failure, which is consistent with the findings from cardiovascular outcomes trials,” Dr. Shin said in an interview.
Just a beginning step, although trial probably wasn’t long enough
However, she added, “I don’t want to overstate anything. ... We aren’t powered enough to investigate who would benefit the most. ... As a pharmacoepidemiologist, I think it’s my duty to provide high-quality evidence so we can actually help physicians and patients make better decisions on their medication. Our current research is just a beginning step.”
Asked to comment, Simeon I. Taylor, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, told this news organization, “This study generally confirmed conclusions from published RCTs [randomized clinical trials]. No real surprises, albeit the conclusions may not fully support some of the most enthusiastic claims for SGLT-2 inhibitors with respect to MI, stroke, and cardiovascular death.”
Indeed, Dr. Taylor noted that only two SGLT-2 inhibitors, canagliflozin and empagliflozin, were shown to have a statistically significant association with decreased major adverse cardiovascular events.
In contrast, neither dapagliflozin nor ertugliflozin showed significant benefit regarding those outcomes.
He also pointed out that those four major SLGT-2 inhibitor cardiovascular outcomes trials were placebo-controlled rather than head-to-head trials in which they were compared to an active comparator such as metformin.
“Viewed in this light, it’s probably not surprising that the present study did not demonstrate a robust benefit for SGLT-2 inhibitors to decrease [major adverse CV events].”
The duration of follow-up in the current study is also a limitation, he added.
“The majority of patients were followed for a year or less. This is probably sufficient to assess the impact of some pharmacological mechanisms, for example, the beneficial impact to decrease risk of heart failure by promoting urinary sodium excretion. However, it’s probably insufficient time to observe a beneficial impact on atherosclerosis. For example, there is typically a lag of several years before statins demonstrate efficacy with respect to adverse cardiovascular events.”
Nevertheless, he said, “it provides strong support for benefit with respect to decreasing risk of hospitalization for heart failure.”
He noted that while metformin is currently significantly cheaper than any SGLT-2 inhibitors, once the latter become available as generics, they will be cheaper, and this will likely have a bearing on prescribing decisions.
“Availability of generic SGLT-2 inhibitors offers potential to transform prescribing patterns for type 2 diabetes,” he noted.
First-line SGLT2 inhibitors versus metformin: Most outcomes similar
The study data came from two commercial U.S. health insurance databases, Optum Clinfomatics Data Mart and IBM Marketscan, and from Medicare fee-for-service enrollees.
From April 2013 through March 2020, a total of 9,334 patients began treatment with first-line SGLT-2 inhibitors; 819,973 patients began taking metformin. After 1:2 propensity score matching for confounders, there were 8,613 participants in the SGLT-2 inhibitor group and 17,226 in the group that began treatment with metformin.
The mean follow-up times were 10.7 months for patients taking SGLT-2 inhibitors and 12.2 months for patients taking metformin.
Incidence rates per 1,000 person-years for the composite of hospitalization for MI, hospitalization for ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, or all-cause mortality (MI/stroke/mortality) were 15.0 versus 16.2 for SLGT-2 inhibitors versus metformin, not a significant difference (hazard ratio, 0.96).
However, for the composite of heart failure hospitalization or all-cause mortality, the rates were 18.3 versus 23.5, a significant difference, with an HR of 0.80. The benefit was seen beginning at about 6 months.
Compared with metformin, SGLT-2 inhibitors showed a significantly lower risk for heart failure hospitalization (HR, 0.78), a numerically (but not significantly) lower risk for MI (HR, 0.70), and similar risks for stroke, mortality, and MI/stroke/HHF/mortality.
Genital infections were significantly more common with SGLT-2 inhibitors (54.1 vs. 23.7 per 1,000 person-years; HR, 2.19). Other safety measures were similar, including acute kidney injury, bone fractures, severe hypoglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, and lower-limb amputations.
How does cost factor in?
A sensitivity analysis aimed at examining the possible effect of unmeasured socioeconomic status showed no difference in cardiovascular benefit for first-line SGLT-2 inhibitors and metformin, compared with first-line dipeptidyl peptidase–4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, which cost more than metformin; it is not known what effect DPP-4 inhibitors have on the cardiovascular outcomes of interest.
Cost and insurance coverage factor into the benefit/risk calculation. Metformin is far less costly than any of the SGLT-2 inhibitors – roughly $10 to $20 per month, compared with more than $500 a month.
However, “for some fortunate patients with the most generous pharmacy benefit insurance coverage, the out-of-pocket cost of brand name drugs like SGLT-2 inhibitors is substantially lower,” Dr. Taylor noted.
He said that the current study “raises questions about whether the clinical benefits of SGLT-2 inhibitors as initial monotherapy justify the higher price relative to metformin. The data in this paper suggest that the value case for SGLT-2 inhibitors is strongest for patients with the greatest risk to be hospitalized for heart failure.”
Indeed, Dr. Shin said, “Once we get more information, it may just help in extending the coverage from insurance companies and Medicare/Medicaid, to lower the barrier to access.”
Dr. Taylor reiterated that patents on some of the early SGLT-2 inhibitors are expected to expire in the next few years, which would make it possible for generic versions to be approved. “At that point, prices would likely fall, possibly to levels similar to metformin.”
The study was funded by grant support from the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, department of medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Harvard Medical School, the National Institute on Aging, and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Dr. Shin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Taylor is a consultant for Ionis Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Use of sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors rather than metformin as first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes appears to cut the risk for heart failure hospitalization but not myocardial infarction, stroke, or all-cause mortality, a new analysis of real-world data suggests.
Safety findings were similar, except for the fact that genital infections were more common with SGLT-2 inhibitors.
The study was conducted using claims data from two large U.S. insurance databases and Medicare. Propensity score matching was used to account for baseline differences.
The study was conducted by HoJin Shin, BPharm, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and colleagues. The findings were published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Those who start SGLT-2 inhibitors as first line show similar risks, compared with metformin in MI, stroke, and all-cause mortality outcomes. Strikingly and consistently, SGLT-2 inhibitors show lower risk for hospitalization for heart failure, which is consistent with the findings from cardiovascular outcomes trials,” Dr. Shin said in an interview.
Just a beginning step, although trial probably wasn’t long enough
However, she added, “I don’t want to overstate anything. ... We aren’t powered enough to investigate who would benefit the most. ... As a pharmacoepidemiologist, I think it’s my duty to provide high-quality evidence so we can actually help physicians and patients make better decisions on their medication. Our current research is just a beginning step.”
Asked to comment, Simeon I. Taylor, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, told this news organization, “This study generally confirmed conclusions from published RCTs [randomized clinical trials]. No real surprises, albeit the conclusions may not fully support some of the most enthusiastic claims for SGLT-2 inhibitors with respect to MI, stroke, and cardiovascular death.”
Indeed, Dr. Taylor noted that only two SGLT-2 inhibitors, canagliflozin and empagliflozin, were shown to have a statistically significant association with decreased major adverse cardiovascular events.
In contrast, neither dapagliflozin nor ertugliflozin showed significant benefit regarding those outcomes.
He also pointed out that those four major SLGT-2 inhibitor cardiovascular outcomes trials were placebo-controlled rather than head-to-head trials in which they were compared to an active comparator such as metformin.
“Viewed in this light, it’s probably not surprising that the present study did not demonstrate a robust benefit for SGLT-2 inhibitors to decrease [major adverse CV events].”
The duration of follow-up in the current study is also a limitation, he added.
“The majority of patients were followed for a year or less. This is probably sufficient to assess the impact of some pharmacological mechanisms, for example, the beneficial impact to decrease risk of heart failure by promoting urinary sodium excretion. However, it’s probably insufficient time to observe a beneficial impact on atherosclerosis. For example, there is typically a lag of several years before statins demonstrate efficacy with respect to adverse cardiovascular events.”
Nevertheless, he said, “it provides strong support for benefit with respect to decreasing risk of hospitalization for heart failure.”
He noted that while metformin is currently significantly cheaper than any SGLT-2 inhibitors, once the latter become available as generics, they will be cheaper, and this will likely have a bearing on prescribing decisions.
“Availability of generic SGLT-2 inhibitors offers potential to transform prescribing patterns for type 2 diabetes,” he noted.
First-line SGLT2 inhibitors versus metformin: Most outcomes similar
The study data came from two commercial U.S. health insurance databases, Optum Clinfomatics Data Mart and IBM Marketscan, and from Medicare fee-for-service enrollees.
From April 2013 through March 2020, a total of 9,334 patients began treatment with first-line SGLT-2 inhibitors; 819,973 patients began taking metformin. After 1:2 propensity score matching for confounders, there were 8,613 participants in the SGLT-2 inhibitor group and 17,226 in the group that began treatment with metformin.
The mean follow-up times were 10.7 months for patients taking SGLT-2 inhibitors and 12.2 months for patients taking metformin.
Incidence rates per 1,000 person-years for the composite of hospitalization for MI, hospitalization for ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, or all-cause mortality (MI/stroke/mortality) were 15.0 versus 16.2 for SLGT-2 inhibitors versus metformin, not a significant difference (hazard ratio, 0.96).
However, for the composite of heart failure hospitalization or all-cause mortality, the rates were 18.3 versus 23.5, a significant difference, with an HR of 0.80. The benefit was seen beginning at about 6 months.
Compared with metformin, SGLT-2 inhibitors showed a significantly lower risk for heart failure hospitalization (HR, 0.78), a numerically (but not significantly) lower risk for MI (HR, 0.70), and similar risks for stroke, mortality, and MI/stroke/HHF/mortality.
Genital infections were significantly more common with SGLT-2 inhibitors (54.1 vs. 23.7 per 1,000 person-years; HR, 2.19). Other safety measures were similar, including acute kidney injury, bone fractures, severe hypoglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, and lower-limb amputations.
How does cost factor in?
A sensitivity analysis aimed at examining the possible effect of unmeasured socioeconomic status showed no difference in cardiovascular benefit for first-line SGLT-2 inhibitors and metformin, compared with first-line dipeptidyl peptidase–4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, which cost more than metformin; it is not known what effect DPP-4 inhibitors have on the cardiovascular outcomes of interest.
Cost and insurance coverage factor into the benefit/risk calculation. Metformin is far less costly than any of the SGLT-2 inhibitors – roughly $10 to $20 per month, compared with more than $500 a month.
However, “for some fortunate patients with the most generous pharmacy benefit insurance coverage, the out-of-pocket cost of brand name drugs like SGLT-2 inhibitors is substantially lower,” Dr. Taylor noted.
He said that the current study “raises questions about whether the clinical benefits of SGLT-2 inhibitors as initial monotherapy justify the higher price relative to metformin. The data in this paper suggest that the value case for SGLT-2 inhibitors is strongest for patients with the greatest risk to be hospitalized for heart failure.”
Indeed, Dr. Shin said, “Once we get more information, it may just help in extending the coverage from insurance companies and Medicare/Medicaid, to lower the barrier to access.”
Dr. Taylor reiterated that patents on some of the early SGLT-2 inhibitors are expected to expire in the next few years, which would make it possible for generic versions to be approved. “At that point, prices would likely fall, possibly to levels similar to metformin.”
The study was funded by grant support from the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, department of medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Harvard Medical School, the National Institute on Aging, and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Dr. Shin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Taylor is a consultant for Ionis Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Eosinophilic diseases often overlap, raising costs
Eosinophilic GI diseases (EGIDs) often overlap with other eosinophil-associated diseases (EADs), which leads to greater health care costs, according to an analysis of the U.S. Optum Clinformatics claims database.
EADs have gained increased attention in recent years. They include eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), eosinophilic asthma, bullous pemphigoid, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, eosinophilic gastritis/gastroenteritis (EG/EGE), and a subset of non–cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis. All involve infiltration of eosinophils, but the exact immune mechanisms behind them seem to vary and are poorly understood, according to Justin Kwiatek, PharmD, who presented the results at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
“We do know that the suitable course of treatment is dependent on the organs impacted. From this study, we also know that EoE mostly exists on its own, with only a small portion also being diagnosed with asthma, while overlap with other EGIDs tends to be higher. This could be because EoE appears to be pathologically different from other EGIDs in the gastrointestinal tract such as eosinophilic gastritis in the stomach or eosinophilic gastroenteritis in the stomach and small bowel. Eosinophils are not normally present in the esophagus but are often found in the stomach or small bowel without inflammation,” said Dr. Kwiatek, who is senior global medical affairs leader, respiratory & immunology, at AstraZeneca.
The study is important, said Dhyanesh Patel, MD, who was asked to comment on the study. “There’s been a lot of interest in eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases recently because there is lack of a clear definition. We need to define it better because we need to figure out treatment options for the patients,” said Dr. Patel, who is an assistant professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
“It highlights that a lot of the patients that have one eosinophilic disease might have other concomitant atopic diseases. [It may be that] you can use one drug to treat all of them together, so I think it’s important to have a multidisciplinary approach where you work with an allergist and you work with an immunologist and treat their eosinophilic gastritis and their asthma together with one drug. That may help reduce medication burden,” said Dr. Patel.
The researchers analyzed records from 1,326,645 diagnosed patients with at least one EAD and at least 2 years following treatment. There were 13,872 patients with EoE, 38.4% of whom had at least one overlapping EAD. Of 1,365 patients with EG/EGE, 57.9% had at least one overlapping EAD.
EADs were associated with higher Charlson Comorbidity Index scores and high blood eosinophil levels (≥ 300 cells/mcL) among EoE patients, but not among EG/EGE patients. Within the EoE group, female gender was linked to more EAD comorbidities: 35% of patients with only EoE were female; 45% of patients with one comorbidity were female, as were 55% of those with two comorbidities and 57% of those with three or more comorbidities. There was no such trend among patients with EG/EGE.
Total health care costs were lower in the absence of one overlapping EAD among both EoE ($2,061 vs. $3,766 per patient per month) and EG/EGE patients ($2,860 vs. $4,053). Costs went up with more overlap: $8,572 for EoE and three or more other EADs, and $10,397 for EG/EGE and three or more other EADs. These costs were largely driven by outpatient care.
“The data shows that patients with eosinophilic gastritis and eosinophilic gastroenteritis are more likely to have overlapping eosinophilic conditions, such as asthma. When diagnosing a patient with EG or EGE, it’s important to monitor any new symptoms closely and to educate them about the risk factors. This is particularly true for patients with elevated blood eosinophil counts. Accounting for comorbidities and establishing a treatment plan early can help to manage the higher health care spend for patients with overlapping conditions,” said Dr. Kwiatek.
Dr. Kwiatek is an employee and stockholder of AstraZeneca, which funded the study and developed benralizumab, a drug that has been granted orphan drug status for EG/EGE and EoE. Optum Clinformatics is a longitudinal database of deidentified data formed by UnitedHealth Group. Dr. Patel has no relevant financial disclosures.
Eosinophilic GI diseases (EGIDs) often overlap with other eosinophil-associated diseases (EADs), which leads to greater health care costs, according to an analysis of the U.S. Optum Clinformatics claims database.
EADs have gained increased attention in recent years. They include eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), eosinophilic asthma, bullous pemphigoid, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, eosinophilic gastritis/gastroenteritis (EG/EGE), and a subset of non–cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis. All involve infiltration of eosinophils, but the exact immune mechanisms behind them seem to vary and are poorly understood, according to Justin Kwiatek, PharmD, who presented the results at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
“We do know that the suitable course of treatment is dependent on the organs impacted. From this study, we also know that EoE mostly exists on its own, with only a small portion also being diagnosed with asthma, while overlap with other EGIDs tends to be higher. This could be because EoE appears to be pathologically different from other EGIDs in the gastrointestinal tract such as eosinophilic gastritis in the stomach or eosinophilic gastroenteritis in the stomach and small bowel. Eosinophils are not normally present in the esophagus but are often found in the stomach or small bowel without inflammation,” said Dr. Kwiatek, who is senior global medical affairs leader, respiratory & immunology, at AstraZeneca.
The study is important, said Dhyanesh Patel, MD, who was asked to comment on the study. “There’s been a lot of interest in eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases recently because there is lack of a clear definition. We need to define it better because we need to figure out treatment options for the patients,” said Dr. Patel, who is an assistant professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
“It highlights that a lot of the patients that have one eosinophilic disease might have other concomitant atopic diseases. [It may be that] you can use one drug to treat all of them together, so I think it’s important to have a multidisciplinary approach where you work with an allergist and you work with an immunologist and treat their eosinophilic gastritis and their asthma together with one drug. That may help reduce medication burden,” said Dr. Patel.
The researchers analyzed records from 1,326,645 diagnosed patients with at least one EAD and at least 2 years following treatment. There were 13,872 patients with EoE, 38.4% of whom had at least one overlapping EAD. Of 1,365 patients with EG/EGE, 57.9% had at least one overlapping EAD.
EADs were associated with higher Charlson Comorbidity Index scores and high blood eosinophil levels (≥ 300 cells/mcL) among EoE patients, but not among EG/EGE patients. Within the EoE group, female gender was linked to more EAD comorbidities: 35% of patients with only EoE were female; 45% of patients with one comorbidity were female, as were 55% of those with two comorbidities and 57% of those with three or more comorbidities. There was no such trend among patients with EG/EGE.
Total health care costs were lower in the absence of one overlapping EAD among both EoE ($2,061 vs. $3,766 per patient per month) and EG/EGE patients ($2,860 vs. $4,053). Costs went up with more overlap: $8,572 for EoE and three or more other EADs, and $10,397 for EG/EGE and three or more other EADs. These costs were largely driven by outpatient care.
“The data shows that patients with eosinophilic gastritis and eosinophilic gastroenteritis are more likely to have overlapping eosinophilic conditions, such as asthma. When diagnosing a patient with EG or EGE, it’s important to monitor any new symptoms closely and to educate them about the risk factors. This is particularly true for patients with elevated blood eosinophil counts. Accounting for comorbidities and establishing a treatment plan early can help to manage the higher health care spend for patients with overlapping conditions,” said Dr. Kwiatek.
Dr. Kwiatek is an employee and stockholder of AstraZeneca, which funded the study and developed benralizumab, a drug that has been granted orphan drug status for EG/EGE and EoE. Optum Clinformatics is a longitudinal database of deidentified data formed by UnitedHealth Group. Dr. Patel has no relevant financial disclosures.
Eosinophilic GI diseases (EGIDs) often overlap with other eosinophil-associated diseases (EADs), which leads to greater health care costs, according to an analysis of the U.S. Optum Clinformatics claims database.
EADs have gained increased attention in recent years. They include eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), eosinophilic asthma, bullous pemphigoid, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, eosinophilic gastritis/gastroenteritis (EG/EGE), and a subset of non–cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis. All involve infiltration of eosinophils, but the exact immune mechanisms behind them seem to vary and are poorly understood, according to Justin Kwiatek, PharmD, who presented the results at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
“We do know that the suitable course of treatment is dependent on the organs impacted. From this study, we also know that EoE mostly exists on its own, with only a small portion also being diagnosed with asthma, while overlap with other EGIDs tends to be higher. This could be because EoE appears to be pathologically different from other EGIDs in the gastrointestinal tract such as eosinophilic gastritis in the stomach or eosinophilic gastroenteritis in the stomach and small bowel. Eosinophils are not normally present in the esophagus but are often found in the stomach or small bowel without inflammation,” said Dr. Kwiatek, who is senior global medical affairs leader, respiratory & immunology, at AstraZeneca.
The study is important, said Dhyanesh Patel, MD, who was asked to comment on the study. “There’s been a lot of interest in eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases recently because there is lack of a clear definition. We need to define it better because we need to figure out treatment options for the patients,” said Dr. Patel, who is an assistant professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
“It highlights that a lot of the patients that have one eosinophilic disease might have other concomitant atopic diseases. [It may be that] you can use one drug to treat all of them together, so I think it’s important to have a multidisciplinary approach where you work with an allergist and you work with an immunologist and treat their eosinophilic gastritis and their asthma together with one drug. That may help reduce medication burden,” said Dr. Patel.
The researchers analyzed records from 1,326,645 diagnosed patients with at least one EAD and at least 2 years following treatment. There were 13,872 patients with EoE, 38.4% of whom had at least one overlapping EAD. Of 1,365 patients with EG/EGE, 57.9% had at least one overlapping EAD.
EADs were associated with higher Charlson Comorbidity Index scores and high blood eosinophil levels (≥ 300 cells/mcL) among EoE patients, but not among EG/EGE patients. Within the EoE group, female gender was linked to more EAD comorbidities: 35% of patients with only EoE were female; 45% of patients with one comorbidity were female, as were 55% of those with two comorbidities and 57% of those with three or more comorbidities. There was no such trend among patients with EG/EGE.
Total health care costs were lower in the absence of one overlapping EAD among both EoE ($2,061 vs. $3,766 per patient per month) and EG/EGE patients ($2,860 vs. $4,053). Costs went up with more overlap: $8,572 for EoE and three or more other EADs, and $10,397 for EG/EGE and three or more other EADs. These costs were largely driven by outpatient care.
“The data shows that patients with eosinophilic gastritis and eosinophilic gastroenteritis are more likely to have overlapping eosinophilic conditions, such as asthma. When diagnosing a patient with EG or EGE, it’s important to monitor any new symptoms closely and to educate them about the risk factors. This is particularly true for patients with elevated blood eosinophil counts. Accounting for comorbidities and establishing a treatment plan early can help to manage the higher health care spend for patients with overlapping conditions,” said Dr. Kwiatek.
Dr. Kwiatek is an employee and stockholder of AstraZeneca, which funded the study and developed benralizumab, a drug that has been granted orphan drug status for EG/EGE and EoE. Optum Clinformatics is a longitudinal database of deidentified data formed by UnitedHealth Group. Dr. Patel has no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM DDW 2022
Most COVID long-haulers suffer long-term debilitating neurologic symptoms
Most COVID-19 long-haulers continue to have brain fog, fatigue, and compromised quality of life more than a year after the initial infection, results from the most extensive follow-up to date of a group of long COVID patients show.
Most patients continue to experience debilitating neurologic symptoms an average of 15 months from symptom onset, Igor Koralnik, MD, who oversees the Neuro COVID-19 Clinic at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, said during a press briefing.
Surprisingly, in some cases, new symptoms appear that didn’t exist before, including variation of heart rate and blood pressure, and gastrointestinal symptoms, indicating there may be a late appearance in dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system in those patients, Dr. Koralnik said.
The study was published online in Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology.
Evolving symptoms
The investigators evaluated the evolution of neurologic symptoms in 52 adults who had mild COVID-19 symptoms and were not admitted to the hospital.
Their mean age was 43 years, 73% were women and 77% had received a COVID-19 vaccine. These patients have now been followed for between 11 and 18 months since their initial infection.
Overall, between first and follow-up evaluations, there was no significant change in the frequency of most neurologic symptoms, including brain fog (81% vs. 71%), numbness/tingling (69% vs. 65%), headache (67% vs. 54%), dizziness (50% vs. 54%), blurred vision (34% vs. 44%), tinnitus (33% vs. 42%), and fatigue (87% vs. 81%).
The only neurologic symptoms that decreased over time were loss of taste (63% vs. 27%) and smell (58% vs. 21%).
Conversely, heart rate and blood pressure variation (35% vs. 56%) and gastrointestinal symptoms (27% vs. 48%; P = .04) increased at follow-up evaluations.
Patients reported subjective improvements in their recovery, cognitive function and fatigue, but quality of life measures remained lower than the average population of the United States.
There was a neutral effect of COVID vaccination on long COVID symptoms – it didn’t cure long COVID or make long COVID worse, which is a reason given by some long-haulers for not getting vaccinated, Dr. Koralnik told the briefing.
Therefore, “we continue to encourage our patients to get vaccinated and boosted according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendation,” he said.
Escape from the ‘pit of despair’
To date, the Northwestern Medicine Neuro COVID-19 Clinic has treated nearly 1,400 COVID long-haulers from across the United States.
Emily Caffee, a physical therapist from Wheaton, Ill., is one of them.
Speaking at the briefing, the 36-year-old described her saga and roller coaster of recovering from long COVID in three acts: her initial infection, followed by a descent into a pit of physical and emotional despair, followed by her eventual escape from that pit more than two years later.
Following a fairly mild case of COVID, Ms. Caffee said worsening neurologic symptoms forced her to take medical leave from her very physical and cognitively demanding job.
Ms. Caffee said she experienced crushing fatigue and brain fog, as well as rapid heart rate and blood pressure changes going from sitting to standing position.
She went from being a competitive athlete to someone who could barely get off the couch or empty the dishwasher.
With the ongoing help of her medical team, she slowly returned to daily activities and eventually to work on a limited basis.
Today, Ms. Caffee says she’s 90%-95% better but still she has some lingering symptoms and does not yet feel like her pre-COVID self.
It’s been a very slow climb out of the pit, Ms. Caffee said.
This study has no specific funding. The authors disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most COVID-19 long-haulers continue to have brain fog, fatigue, and compromised quality of life more than a year after the initial infection, results from the most extensive follow-up to date of a group of long COVID patients show.
Most patients continue to experience debilitating neurologic symptoms an average of 15 months from symptom onset, Igor Koralnik, MD, who oversees the Neuro COVID-19 Clinic at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, said during a press briefing.
Surprisingly, in some cases, new symptoms appear that didn’t exist before, including variation of heart rate and blood pressure, and gastrointestinal symptoms, indicating there may be a late appearance in dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system in those patients, Dr. Koralnik said.
The study was published online in Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology.
Evolving symptoms
The investigators evaluated the evolution of neurologic symptoms in 52 adults who had mild COVID-19 symptoms and were not admitted to the hospital.
Their mean age was 43 years, 73% were women and 77% had received a COVID-19 vaccine. These patients have now been followed for between 11 and 18 months since their initial infection.
Overall, between first and follow-up evaluations, there was no significant change in the frequency of most neurologic symptoms, including brain fog (81% vs. 71%), numbness/tingling (69% vs. 65%), headache (67% vs. 54%), dizziness (50% vs. 54%), blurred vision (34% vs. 44%), tinnitus (33% vs. 42%), and fatigue (87% vs. 81%).
The only neurologic symptoms that decreased over time were loss of taste (63% vs. 27%) and smell (58% vs. 21%).
Conversely, heart rate and blood pressure variation (35% vs. 56%) and gastrointestinal symptoms (27% vs. 48%; P = .04) increased at follow-up evaluations.
Patients reported subjective improvements in their recovery, cognitive function and fatigue, but quality of life measures remained lower than the average population of the United States.
There was a neutral effect of COVID vaccination on long COVID symptoms – it didn’t cure long COVID or make long COVID worse, which is a reason given by some long-haulers for not getting vaccinated, Dr. Koralnik told the briefing.
Therefore, “we continue to encourage our patients to get vaccinated and boosted according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendation,” he said.
Escape from the ‘pit of despair’
To date, the Northwestern Medicine Neuro COVID-19 Clinic has treated nearly 1,400 COVID long-haulers from across the United States.
Emily Caffee, a physical therapist from Wheaton, Ill., is one of them.
Speaking at the briefing, the 36-year-old described her saga and roller coaster of recovering from long COVID in three acts: her initial infection, followed by a descent into a pit of physical and emotional despair, followed by her eventual escape from that pit more than two years later.
Following a fairly mild case of COVID, Ms. Caffee said worsening neurologic symptoms forced her to take medical leave from her very physical and cognitively demanding job.
Ms. Caffee said she experienced crushing fatigue and brain fog, as well as rapid heart rate and blood pressure changes going from sitting to standing position.
She went from being a competitive athlete to someone who could barely get off the couch or empty the dishwasher.
With the ongoing help of her medical team, she slowly returned to daily activities and eventually to work on a limited basis.
Today, Ms. Caffee says she’s 90%-95% better but still she has some lingering symptoms and does not yet feel like her pre-COVID self.
It’s been a very slow climb out of the pit, Ms. Caffee said.
This study has no specific funding. The authors disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most COVID-19 long-haulers continue to have brain fog, fatigue, and compromised quality of life more than a year after the initial infection, results from the most extensive follow-up to date of a group of long COVID patients show.
Most patients continue to experience debilitating neurologic symptoms an average of 15 months from symptom onset, Igor Koralnik, MD, who oversees the Neuro COVID-19 Clinic at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, said during a press briefing.
Surprisingly, in some cases, new symptoms appear that didn’t exist before, including variation of heart rate and blood pressure, and gastrointestinal symptoms, indicating there may be a late appearance in dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system in those patients, Dr. Koralnik said.
The study was published online in Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology.
Evolving symptoms
The investigators evaluated the evolution of neurologic symptoms in 52 adults who had mild COVID-19 symptoms and were not admitted to the hospital.
Their mean age was 43 years, 73% were women and 77% had received a COVID-19 vaccine. These patients have now been followed for between 11 and 18 months since their initial infection.
Overall, between first and follow-up evaluations, there was no significant change in the frequency of most neurologic symptoms, including brain fog (81% vs. 71%), numbness/tingling (69% vs. 65%), headache (67% vs. 54%), dizziness (50% vs. 54%), blurred vision (34% vs. 44%), tinnitus (33% vs. 42%), and fatigue (87% vs. 81%).
The only neurologic symptoms that decreased over time were loss of taste (63% vs. 27%) and smell (58% vs. 21%).
Conversely, heart rate and blood pressure variation (35% vs. 56%) and gastrointestinal symptoms (27% vs. 48%; P = .04) increased at follow-up evaluations.
Patients reported subjective improvements in their recovery, cognitive function and fatigue, but quality of life measures remained lower than the average population of the United States.
There was a neutral effect of COVID vaccination on long COVID symptoms – it didn’t cure long COVID or make long COVID worse, which is a reason given by some long-haulers for not getting vaccinated, Dr. Koralnik told the briefing.
Therefore, “we continue to encourage our patients to get vaccinated and boosted according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendation,” he said.
Escape from the ‘pit of despair’
To date, the Northwestern Medicine Neuro COVID-19 Clinic has treated nearly 1,400 COVID long-haulers from across the United States.
Emily Caffee, a physical therapist from Wheaton, Ill., is one of them.
Speaking at the briefing, the 36-year-old described her saga and roller coaster of recovering from long COVID in three acts: her initial infection, followed by a descent into a pit of physical and emotional despair, followed by her eventual escape from that pit more than two years later.
Following a fairly mild case of COVID, Ms. Caffee said worsening neurologic symptoms forced her to take medical leave from her very physical and cognitively demanding job.
Ms. Caffee said she experienced crushing fatigue and brain fog, as well as rapid heart rate and blood pressure changes going from sitting to standing position.
She went from being a competitive athlete to someone who could barely get off the couch or empty the dishwasher.
With the ongoing help of her medical team, she slowly returned to daily activities and eventually to work on a limited basis.
Today, Ms. Caffee says she’s 90%-95% better but still she has some lingering symptoms and does not yet feel like her pre-COVID self.
It’s been a very slow climb out of the pit, Ms. Caffee said.
This study has no specific funding. The authors disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF CLINICAL AND TRANSLATIONAL NEUROLOGY
H. pylori antibiotics briefly disrupt gut microbiome
SAN DIEGO – Treatments to eradicate Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infections do increase the antibiotic resistance of the gut microbiota, but for only a few months, researchers reported at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
The finding applies similarly to levofloxacin quadruple therapy and bismuth quadruple therapy, both of which are equally efficacious as second-line treatments, said Jyh-Ming Liou, MD, PhD, clinical professor of internal medicine at National Taiwan University in Taipei.
This provides some reassurance that increased use of antibiotics to treat these infections won’t cause long-term disruptions to the patients’ microbiomes, said Dr. Liou.
“Maybe if we have indications for antibiotic treatment, then we don’t worry about the emergence of resistance in our bodies,” he said. “But the accumulation of antibodies in the environment may induce bacteria to mutate, so maybe we still need cautious use of antibiotics.”
H. pylori infections are becoming harder to treat as more strains develop resistance to antibiotics, leading physicians to use regimens with multiple agents. This in turn has raised concerns that gut microbiota could be disrupted, with pathogens potentially developing their own resistance.
To explore these risks, Dr. Liou and colleagues recruited adults whose H. pylori infections were not successfully eradicated.
They randomly assigned 280 patients each to one of two second-line therapies, levofloxacin quadruple or bismuth quadruple. At baseline, the researchers could not find any statistically significant differences in the two groups’ demographics, cigarette and alcohol use, or ulcers, as well as antibiotic resistance in patients’ microbiome between the groups.
Levofloxacin quadruple therapy consisted of esomeprazole 40 mg and amoxicillin 1 g for the first 7 days, followed by esomeprazole 40 mg, metronidazole 500 mg, and levofloxacin 250 mg for another 7 days (all twice daily).
Bismuth quadruple therapy consisted of esomeprazole 40 mg twice daily, bismuth tripotassium dicitrate 300 mg four times a day, tetracycline 500 mg four times a day, and metronidazole 500 mg three times a day, for 10 days.
The researchers collected stool samples at baseline, week 2, week 8, and 1 year after eradication therapy and analyzed them for microbiota diversity and antibiotic susceptibility.
The H. pylori eradication rates were almost the same in the two second-line therapies: 87.9% for levofloxacin quadruple and 87.5% for bismuth quadruple. When they were used as third-line (rescue) therapies, the success rates were also statistically the same, and the cumulative second-line and third-line eradication rate was 95.6% for levofloxacin quadruple and 96.6% for bismuth quadruple.
The two treatments did differ in adverse events with 48.4% for levofloxacin quadruple and 77.3% for bismuth quadruple, which was statistically significant (P < .0001).
After a year, H. pylori reinfected 2.5% of the levofloxacin group and 3% of the bismuth quadruple group.
The researchers used metagenomic sequencing to examine the bacteria in the patients’ microbiome for antibiotic resistance. Using 16S rRNA sequencing, they found that the proportion of genera and species with significant changes in abundance at 2 weeks after treatment compared with baseline was 52.4% for levofloxacin quadruple therapy versus 45.1% for bismuth quadruple therapy.
However, 8 weeks after treatment, the proportion with significant changes had dropped to 5.8% for the levofloxacin group and 21.5% for the bismuth group. And at the end of a year, they had further dropped to 0.9% for the levofloxacin group and 8.4% for the bismuth group.
“It was generally reassuring that, even after giving these combinations of different antibiotics, eventually it doesn’t seem to affect the resistance pattern in bacteria lower down in the gut,” said session moderator Steven Moss, MD, professor of medicine at Brown University in Providence, R.I.
Still, continuing to pile on more and more antibiotics to treat H. pylori infections won’t work forever because H. pylori strains are themselves developing resistance so rapidly, he said. “We’re certainly going to have worse eradications in the future unless we can come up with new tricks.”
A hopeful development are new techniques to test H. pylori for resistance to specific antibiotics before initiating treatment, said Dr. Moss.
Dr. Moss consults with companies developing H. pylori therapies and diagnostics. Dr. Liou reported no relevant financial interests.
SAN DIEGO – Treatments to eradicate Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infections do increase the antibiotic resistance of the gut microbiota, but for only a few months, researchers reported at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
The finding applies similarly to levofloxacin quadruple therapy and bismuth quadruple therapy, both of which are equally efficacious as second-line treatments, said Jyh-Ming Liou, MD, PhD, clinical professor of internal medicine at National Taiwan University in Taipei.
This provides some reassurance that increased use of antibiotics to treat these infections won’t cause long-term disruptions to the patients’ microbiomes, said Dr. Liou.
“Maybe if we have indications for antibiotic treatment, then we don’t worry about the emergence of resistance in our bodies,” he said. “But the accumulation of antibodies in the environment may induce bacteria to mutate, so maybe we still need cautious use of antibiotics.”
H. pylori infections are becoming harder to treat as more strains develop resistance to antibiotics, leading physicians to use regimens with multiple agents. This in turn has raised concerns that gut microbiota could be disrupted, with pathogens potentially developing their own resistance.
To explore these risks, Dr. Liou and colleagues recruited adults whose H. pylori infections were not successfully eradicated.
They randomly assigned 280 patients each to one of two second-line therapies, levofloxacin quadruple or bismuth quadruple. At baseline, the researchers could not find any statistically significant differences in the two groups’ demographics, cigarette and alcohol use, or ulcers, as well as antibiotic resistance in patients’ microbiome between the groups.
Levofloxacin quadruple therapy consisted of esomeprazole 40 mg and amoxicillin 1 g for the first 7 days, followed by esomeprazole 40 mg, metronidazole 500 mg, and levofloxacin 250 mg for another 7 days (all twice daily).
Bismuth quadruple therapy consisted of esomeprazole 40 mg twice daily, bismuth tripotassium dicitrate 300 mg four times a day, tetracycline 500 mg four times a day, and metronidazole 500 mg three times a day, for 10 days.
The researchers collected stool samples at baseline, week 2, week 8, and 1 year after eradication therapy and analyzed them for microbiota diversity and antibiotic susceptibility.
The H. pylori eradication rates were almost the same in the two second-line therapies: 87.9% for levofloxacin quadruple and 87.5% for bismuth quadruple. When they were used as third-line (rescue) therapies, the success rates were also statistically the same, and the cumulative second-line and third-line eradication rate was 95.6% for levofloxacin quadruple and 96.6% for bismuth quadruple.
The two treatments did differ in adverse events with 48.4% for levofloxacin quadruple and 77.3% for bismuth quadruple, which was statistically significant (P < .0001).
After a year, H. pylori reinfected 2.5% of the levofloxacin group and 3% of the bismuth quadruple group.
The researchers used metagenomic sequencing to examine the bacteria in the patients’ microbiome for antibiotic resistance. Using 16S rRNA sequencing, they found that the proportion of genera and species with significant changes in abundance at 2 weeks after treatment compared with baseline was 52.4% for levofloxacin quadruple therapy versus 45.1% for bismuth quadruple therapy.
However, 8 weeks after treatment, the proportion with significant changes had dropped to 5.8% for the levofloxacin group and 21.5% for the bismuth group. And at the end of a year, they had further dropped to 0.9% for the levofloxacin group and 8.4% for the bismuth group.
“It was generally reassuring that, even after giving these combinations of different antibiotics, eventually it doesn’t seem to affect the resistance pattern in bacteria lower down in the gut,” said session moderator Steven Moss, MD, professor of medicine at Brown University in Providence, R.I.
Still, continuing to pile on more and more antibiotics to treat H. pylori infections won’t work forever because H. pylori strains are themselves developing resistance so rapidly, he said. “We’re certainly going to have worse eradications in the future unless we can come up with new tricks.”
A hopeful development are new techniques to test H. pylori for resistance to specific antibiotics before initiating treatment, said Dr. Moss.
Dr. Moss consults with companies developing H. pylori therapies and diagnostics. Dr. Liou reported no relevant financial interests.
SAN DIEGO – Treatments to eradicate Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infections do increase the antibiotic resistance of the gut microbiota, but for only a few months, researchers reported at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
The finding applies similarly to levofloxacin quadruple therapy and bismuth quadruple therapy, both of which are equally efficacious as second-line treatments, said Jyh-Ming Liou, MD, PhD, clinical professor of internal medicine at National Taiwan University in Taipei.
This provides some reassurance that increased use of antibiotics to treat these infections won’t cause long-term disruptions to the patients’ microbiomes, said Dr. Liou.
“Maybe if we have indications for antibiotic treatment, then we don’t worry about the emergence of resistance in our bodies,” he said. “But the accumulation of antibodies in the environment may induce bacteria to mutate, so maybe we still need cautious use of antibiotics.”
H. pylori infections are becoming harder to treat as more strains develop resistance to antibiotics, leading physicians to use regimens with multiple agents. This in turn has raised concerns that gut microbiota could be disrupted, with pathogens potentially developing their own resistance.
To explore these risks, Dr. Liou and colleagues recruited adults whose H. pylori infections were not successfully eradicated.
They randomly assigned 280 patients each to one of two second-line therapies, levofloxacin quadruple or bismuth quadruple. At baseline, the researchers could not find any statistically significant differences in the two groups’ demographics, cigarette and alcohol use, or ulcers, as well as antibiotic resistance in patients’ microbiome between the groups.
Levofloxacin quadruple therapy consisted of esomeprazole 40 mg and amoxicillin 1 g for the first 7 days, followed by esomeprazole 40 mg, metronidazole 500 mg, and levofloxacin 250 mg for another 7 days (all twice daily).
Bismuth quadruple therapy consisted of esomeprazole 40 mg twice daily, bismuth tripotassium dicitrate 300 mg four times a day, tetracycline 500 mg four times a day, and metronidazole 500 mg three times a day, for 10 days.
The researchers collected stool samples at baseline, week 2, week 8, and 1 year after eradication therapy and analyzed them for microbiota diversity and antibiotic susceptibility.
The H. pylori eradication rates were almost the same in the two second-line therapies: 87.9% for levofloxacin quadruple and 87.5% for bismuth quadruple. When they were used as third-line (rescue) therapies, the success rates were also statistically the same, and the cumulative second-line and third-line eradication rate was 95.6% for levofloxacin quadruple and 96.6% for bismuth quadruple.
The two treatments did differ in adverse events with 48.4% for levofloxacin quadruple and 77.3% for bismuth quadruple, which was statistically significant (P < .0001).
After a year, H. pylori reinfected 2.5% of the levofloxacin group and 3% of the bismuth quadruple group.
The researchers used metagenomic sequencing to examine the bacteria in the patients’ microbiome for antibiotic resistance. Using 16S rRNA sequencing, they found that the proportion of genera and species with significant changes in abundance at 2 weeks after treatment compared with baseline was 52.4% for levofloxacin quadruple therapy versus 45.1% for bismuth quadruple therapy.
However, 8 weeks after treatment, the proportion with significant changes had dropped to 5.8% for the levofloxacin group and 21.5% for the bismuth group. And at the end of a year, they had further dropped to 0.9% for the levofloxacin group and 8.4% for the bismuth group.
“It was generally reassuring that, even after giving these combinations of different antibiotics, eventually it doesn’t seem to affect the resistance pattern in bacteria lower down in the gut,” said session moderator Steven Moss, MD, professor of medicine at Brown University in Providence, R.I.
Still, continuing to pile on more and more antibiotics to treat H. pylori infections won’t work forever because H. pylori strains are themselves developing resistance so rapidly, he said. “We’re certainly going to have worse eradications in the future unless we can come up with new tricks.”
A hopeful development are new techniques to test H. pylori for resistance to specific antibiotics before initiating treatment, said Dr. Moss.
Dr. Moss consults with companies developing H. pylori therapies and diagnostics. Dr. Liou reported no relevant financial interests.
AT DDW 2022
Vitamin D doesn’t reduce type 2 diabetes risk ... or does it?
Yet another study has found that vitamin D supplementation doesn’t reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the general population with prediabetes, but it does leave the door open for benefit in those with low insulin secretion.
The new findings come from the prospective Diabetes Prevention With Active Vitamin D (DPVD) trial of more than 1,200 Japanese participants with impaired glucose tolerance.
The data were published online in The BMJ by Tetsuya Kawahara, MD, PhD, of Shin Komonji Hospital, Kitakyushu, Japan, and colleagues.
Treatment with 0.75 μg/day of eldecalcitol, an active vitamin D analogue, for 3 years did not prevent progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes, nor did it improve the rate of regression to normoglycemia, compared with placebo.
However, “we showed a preventive effect of eldecalcitol after adjusting for covariables ... ,” wrote Dr. Kawahara and colleagues.
‘Remarkably similar’ results in several trials
The new trial is “well conducted, with rigorously defined and tested diagnostic criteria, and of sufficient duration, but it may have been underpowered to detect a small effect,” Tatiana Christides, MD, PhD, of Queen Mary University of London, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Dr. Christides notes that a recent meta-analysis of intervention trials did find a significant 10% reduction in risk of type 2 diabetes with vitamin D supplementation, “a difference too small to be detected by the new trial ... Although a 10% risk reduction is modest, it may be valuable at the population level and justifies further study.”
The new finding, a nonsignificant 13% relative reduction in risk, is similar to the 13% relative risk reduction found in the Vitamin D and Type 2 Diabetes (D2d) trial reported in 2019.
But in that study as in this one, there was a suggested benefit in a subset of people. In D2d, it was in those who were vitamin D deficient.
Asked to comment, D2d lead investigator Anastassios G. Pittas, MD, chief of the division of diabetes, endocrinology, and metabolism at Tufts University, Boston, pointed out that the results were also “remarkably similar” to those of a third study from Norway published in 2014, which also found a 13% relative risk reduction.
“The nearly identical results from the three trials that were specifically designed and conducted to test whether vitamin D supplementation lowers diabetes clearly points to a beneficial effect of vitamin D for diabetes risk reduction. However, the overall effect in people not selected for vitamin D insufficiency seems to be less than hypothesized in each trial,” Dr. Pittas said in an interview.
He added, “there will be no more specific vitamin D and diabetes prevention trials, so we need to continue gaining insights from these three trials.”
Some patients with prediabetes may benefit from vitamin D
Dr. Pittas advised that although the overall effect is modest in people with prediabetes who aren’t selected for vitamin D deficiency, “given how prevalent prediabetes and type 2 diabetes are, clinicians and patients should consider vitamin D supplementation as an adjunct to weight loss for diabetes prevention. Based on analyses from the D2d study, people with prediabetes who have low levels of vitamin D and are nonobese derive the most benefit.”
He noted that secondary analyses from D2d also suggest greater benefit among those achieving higher blood levels of vitamin D, but that high supplemental doses could cause adverse musculoskeletal outcomes in older adults, “so the benefit–harm ratio needs to be ascertained individually.”
Dr. Christides advised, “Until further data are available from high-quality randomized trials, health care professionals should continue to discuss with patients the musculoskeletal health benefits of vitamin D and support them to achieve and maintain lifestyle changes that, although challenging to sustain, are known to decrease development of [type 2 diabetes].”
DPVD: Hint of benefit in those with greater insulin resistance
The double-blind, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled DPVD trial took place from June 1, 2013, through Aug. 31, 2015, and involved 1,256 participants with impaired glucose tolerance (with or without impaired fasting glucose) from 32 institutions in Japan. They were randomized 1:1 to receive eldecalcitol or placebo for 3 years.
During the 3-year period, 12.5% of the 630 patients in the eldecalcitol group and 14.2% of the 626 patients in the placebo group developed diabetes. The difference was not significant, with a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.87 (P = .39). There was no difference in regression to normoglycemia, which had occurred in 23.0% with eldecalcitol versus 20.1% with placebo by the end of the study (P = .21).
However, eldecalcitol was effective for preventing the development of type 2 diabetes after adjustment for prespecified variables, including age, sex, hypertension, body mass index, family history of diabetes, 2-hour plasma glucose, 25-hydroxyvitamin D, and insulin resistance (HR, 0.69; P = .02).
In a post hoc analysis, eldecalcitol significantly prevented the development of type 2 diabetes among those with the lowest divisions of homeostatic model assessment (HOMA)-β (HR, 0.35; P < .001), HOMA-insulin resistance (HR, 0.37; P = .001), and fasting immunoreactive insulin (HR, 0.41; P = .001).
“These results indicate that eldecalcitol had a beneficial effect on insufficient basal insulin secretion,” Dr. Kawahara and colleagues wrote.
Discontinuations due to adverse events occurred in 4.1% with eldecalcitol and 3.4% in the placebo group (HR, 1.23; P = .47). Rates and types of adverse events didn’t differ significantly between the two groups.
The study was supported by a grant from the Kitakyushu Medical Association. The authors had no further disclosures. Dr. Christides had no disclosures. Dr. Pittas has reported receiving funding from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Yet another study has found that vitamin D supplementation doesn’t reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the general population with prediabetes, but it does leave the door open for benefit in those with low insulin secretion.
The new findings come from the prospective Diabetes Prevention With Active Vitamin D (DPVD) trial of more than 1,200 Japanese participants with impaired glucose tolerance.
The data were published online in The BMJ by Tetsuya Kawahara, MD, PhD, of Shin Komonji Hospital, Kitakyushu, Japan, and colleagues.
Treatment with 0.75 μg/day of eldecalcitol, an active vitamin D analogue, for 3 years did not prevent progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes, nor did it improve the rate of regression to normoglycemia, compared with placebo.
However, “we showed a preventive effect of eldecalcitol after adjusting for covariables ... ,” wrote Dr. Kawahara and colleagues.
‘Remarkably similar’ results in several trials
The new trial is “well conducted, with rigorously defined and tested diagnostic criteria, and of sufficient duration, but it may have been underpowered to detect a small effect,” Tatiana Christides, MD, PhD, of Queen Mary University of London, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Dr. Christides notes that a recent meta-analysis of intervention trials did find a significant 10% reduction in risk of type 2 diabetes with vitamin D supplementation, “a difference too small to be detected by the new trial ... Although a 10% risk reduction is modest, it may be valuable at the population level and justifies further study.”
The new finding, a nonsignificant 13% relative reduction in risk, is similar to the 13% relative risk reduction found in the Vitamin D and Type 2 Diabetes (D2d) trial reported in 2019.
But in that study as in this one, there was a suggested benefit in a subset of people. In D2d, it was in those who were vitamin D deficient.
Asked to comment, D2d lead investigator Anastassios G. Pittas, MD, chief of the division of diabetes, endocrinology, and metabolism at Tufts University, Boston, pointed out that the results were also “remarkably similar” to those of a third study from Norway published in 2014, which also found a 13% relative risk reduction.
“The nearly identical results from the three trials that were specifically designed and conducted to test whether vitamin D supplementation lowers diabetes clearly points to a beneficial effect of vitamin D for diabetes risk reduction. However, the overall effect in people not selected for vitamin D insufficiency seems to be less than hypothesized in each trial,” Dr. Pittas said in an interview.
He added, “there will be no more specific vitamin D and diabetes prevention trials, so we need to continue gaining insights from these three trials.”
Some patients with prediabetes may benefit from vitamin D
Dr. Pittas advised that although the overall effect is modest in people with prediabetes who aren’t selected for vitamin D deficiency, “given how prevalent prediabetes and type 2 diabetes are, clinicians and patients should consider vitamin D supplementation as an adjunct to weight loss for diabetes prevention. Based on analyses from the D2d study, people with prediabetes who have low levels of vitamin D and are nonobese derive the most benefit.”
He noted that secondary analyses from D2d also suggest greater benefit among those achieving higher blood levels of vitamin D, but that high supplemental doses could cause adverse musculoskeletal outcomes in older adults, “so the benefit–harm ratio needs to be ascertained individually.”
Dr. Christides advised, “Until further data are available from high-quality randomized trials, health care professionals should continue to discuss with patients the musculoskeletal health benefits of vitamin D and support them to achieve and maintain lifestyle changes that, although challenging to sustain, are known to decrease development of [type 2 diabetes].”
DPVD: Hint of benefit in those with greater insulin resistance
The double-blind, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled DPVD trial took place from June 1, 2013, through Aug. 31, 2015, and involved 1,256 participants with impaired glucose tolerance (with or without impaired fasting glucose) from 32 institutions in Japan. They were randomized 1:1 to receive eldecalcitol or placebo for 3 years.
During the 3-year period, 12.5% of the 630 patients in the eldecalcitol group and 14.2% of the 626 patients in the placebo group developed diabetes. The difference was not significant, with a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.87 (P = .39). There was no difference in regression to normoglycemia, which had occurred in 23.0% with eldecalcitol versus 20.1% with placebo by the end of the study (P = .21).
However, eldecalcitol was effective for preventing the development of type 2 diabetes after adjustment for prespecified variables, including age, sex, hypertension, body mass index, family history of diabetes, 2-hour plasma glucose, 25-hydroxyvitamin D, and insulin resistance (HR, 0.69; P = .02).
In a post hoc analysis, eldecalcitol significantly prevented the development of type 2 diabetes among those with the lowest divisions of homeostatic model assessment (HOMA)-β (HR, 0.35; P < .001), HOMA-insulin resistance (HR, 0.37; P = .001), and fasting immunoreactive insulin (HR, 0.41; P = .001).
“These results indicate that eldecalcitol had a beneficial effect on insufficient basal insulin secretion,” Dr. Kawahara and colleagues wrote.
Discontinuations due to adverse events occurred in 4.1% with eldecalcitol and 3.4% in the placebo group (HR, 1.23; P = .47). Rates and types of adverse events didn’t differ significantly between the two groups.
The study was supported by a grant from the Kitakyushu Medical Association. The authors had no further disclosures. Dr. Christides had no disclosures. Dr. Pittas has reported receiving funding from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Yet another study has found that vitamin D supplementation doesn’t reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the general population with prediabetes, but it does leave the door open for benefit in those with low insulin secretion.
The new findings come from the prospective Diabetes Prevention With Active Vitamin D (DPVD) trial of more than 1,200 Japanese participants with impaired glucose tolerance.
The data were published online in The BMJ by Tetsuya Kawahara, MD, PhD, of Shin Komonji Hospital, Kitakyushu, Japan, and colleagues.
Treatment with 0.75 μg/day of eldecalcitol, an active vitamin D analogue, for 3 years did not prevent progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes, nor did it improve the rate of regression to normoglycemia, compared with placebo.
However, “we showed a preventive effect of eldecalcitol after adjusting for covariables ... ,” wrote Dr. Kawahara and colleagues.
‘Remarkably similar’ results in several trials
The new trial is “well conducted, with rigorously defined and tested diagnostic criteria, and of sufficient duration, but it may have been underpowered to detect a small effect,” Tatiana Christides, MD, PhD, of Queen Mary University of London, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Dr. Christides notes that a recent meta-analysis of intervention trials did find a significant 10% reduction in risk of type 2 diabetes with vitamin D supplementation, “a difference too small to be detected by the new trial ... Although a 10% risk reduction is modest, it may be valuable at the population level and justifies further study.”
The new finding, a nonsignificant 13% relative reduction in risk, is similar to the 13% relative risk reduction found in the Vitamin D and Type 2 Diabetes (D2d) trial reported in 2019.
But in that study as in this one, there was a suggested benefit in a subset of people. In D2d, it was in those who were vitamin D deficient.
Asked to comment, D2d lead investigator Anastassios G. Pittas, MD, chief of the division of diabetes, endocrinology, and metabolism at Tufts University, Boston, pointed out that the results were also “remarkably similar” to those of a third study from Norway published in 2014, which also found a 13% relative risk reduction.
“The nearly identical results from the three trials that were specifically designed and conducted to test whether vitamin D supplementation lowers diabetes clearly points to a beneficial effect of vitamin D for diabetes risk reduction. However, the overall effect in people not selected for vitamin D insufficiency seems to be less than hypothesized in each trial,” Dr. Pittas said in an interview.
He added, “there will be no more specific vitamin D and diabetes prevention trials, so we need to continue gaining insights from these three trials.”
Some patients with prediabetes may benefit from vitamin D
Dr. Pittas advised that although the overall effect is modest in people with prediabetes who aren’t selected for vitamin D deficiency, “given how prevalent prediabetes and type 2 diabetes are, clinicians and patients should consider vitamin D supplementation as an adjunct to weight loss for diabetes prevention. Based on analyses from the D2d study, people with prediabetes who have low levels of vitamin D and are nonobese derive the most benefit.”
He noted that secondary analyses from D2d also suggest greater benefit among those achieving higher blood levels of vitamin D, but that high supplemental doses could cause adverse musculoskeletal outcomes in older adults, “so the benefit–harm ratio needs to be ascertained individually.”
Dr. Christides advised, “Until further data are available from high-quality randomized trials, health care professionals should continue to discuss with patients the musculoskeletal health benefits of vitamin D and support them to achieve and maintain lifestyle changes that, although challenging to sustain, are known to decrease development of [type 2 diabetes].”
DPVD: Hint of benefit in those with greater insulin resistance
The double-blind, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled DPVD trial took place from June 1, 2013, through Aug. 31, 2015, and involved 1,256 participants with impaired glucose tolerance (with or without impaired fasting glucose) from 32 institutions in Japan. They were randomized 1:1 to receive eldecalcitol or placebo for 3 years.
During the 3-year period, 12.5% of the 630 patients in the eldecalcitol group and 14.2% of the 626 patients in the placebo group developed diabetes. The difference was not significant, with a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.87 (P = .39). There was no difference in regression to normoglycemia, which had occurred in 23.0% with eldecalcitol versus 20.1% with placebo by the end of the study (P = .21).
However, eldecalcitol was effective for preventing the development of type 2 diabetes after adjustment for prespecified variables, including age, sex, hypertension, body mass index, family history of diabetes, 2-hour plasma glucose, 25-hydroxyvitamin D, and insulin resistance (HR, 0.69; P = .02).
In a post hoc analysis, eldecalcitol significantly prevented the development of type 2 diabetes among those with the lowest divisions of homeostatic model assessment (HOMA)-β (HR, 0.35; P < .001), HOMA-insulin resistance (HR, 0.37; P = .001), and fasting immunoreactive insulin (HR, 0.41; P = .001).
“These results indicate that eldecalcitol had a beneficial effect on insufficient basal insulin secretion,” Dr. Kawahara and colleagues wrote.
Discontinuations due to adverse events occurred in 4.1% with eldecalcitol and 3.4% in the placebo group (HR, 1.23; P = .47). Rates and types of adverse events didn’t differ significantly between the two groups.
The study was supported by a grant from the Kitakyushu Medical Association. The authors had no further disclosures. Dr. Christides had no disclosures. Dr. Pittas has reported receiving funding from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE BMJ
Researchers find a pathway to prevent COVID infection
What’s more, they have succeeded in closing the lock to block the virus and prevent it from interacting with the cell, thereby preventing infection.
UCLouvain emphasized that this discovery, which was published in Nature Communications, is sparking hope that an aerosol antiviral therapy can be developed that would eradicate the virus in the case of an infection or a high-risk contact.
For 2 years, the team under David Alsteens, PhD, a researcher at the UCLouvain Institute of Biomolecular Science and Technology, has been working hard to understand the precise molecular mechanisms the virus uses to infect a cell. They investigated the interaction between sialic acids, a kind of sugar residue present on the surface of cells, and the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein to clarify its role in the infection process.
It was already known that the function of the sugar residues that coat the cells is to promote cell recognition, thus enabling, in particular, viruses to identify their targets more easily, but also to provide them with a point of attachment and to facilitate infection of the cells.
The researchers have now revealed a variant of these sugars that interacts more strongly with the S protein than other sugars do.
In other words, the university explained, they found the set of keys that allows the virus to open the cell door. So, the researchers decided to catch the virus in its own trap, by preventing it from attaching to its host cell. To do this, they blocked the S protein’s points of attachment, thus suppressing any interaction with the cell surface, as if a padlock had been placed on the lock on the cell’s entry door.
Th researchers added that the advantage of this discovery is that it acts on the virus, irrespective of mutations.
The team of researchers will now conduct tests on mice to apply this blocking of virus binding sites and observe whether it works on the body. The results should make it possible to develop an antiviral therapy administered by aerosol in the case of infection or at-risk contact.
This discovery is also of interest for the future to counter other viruses with similar attachment factors.
This article was translated from MediQuality; a version appeared on Medscape.com.
What’s more, they have succeeded in closing the lock to block the virus and prevent it from interacting with the cell, thereby preventing infection.
UCLouvain emphasized that this discovery, which was published in Nature Communications, is sparking hope that an aerosol antiviral therapy can be developed that would eradicate the virus in the case of an infection or a high-risk contact.
For 2 years, the team under David Alsteens, PhD, a researcher at the UCLouvain Institute of Biomolecular Science and Technology, has been working hard to understand the precise molecular mechanisms the virus uses to infect a cell. They investigated the interaction between sialic acids, a kind of sugar residue present on the surface of cells, and the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein to clarify its role in the infection process.
It was already known that the function of the sugar residues that coat the cells is to promote cell recognition, thus enabling, in particular, viruses to identify their targets more easily, but also to provide them with a point of attachment and to facilitate infection of the cells.
The researchers have now revealed a variant of these sugars that interacts more strongly with the S protein than other sugars do.
In other words, the university explained, they found the set of keys that allows the virus to open the cell door. So, the researchers decided to catch the virus in its own trap, by preventing it from attaching to its host cell. To do this, they blocked the S protein’s points of attachment, thus suppressing any interaction with the cell surface, as if a padlock had been placed on the lock on the cell’s entry door.
Th researchers added that the advantage of this discovery is that it acts on the virus, irrespective of mutations.
The team of researchers will now conduct tests on mice to apply this blocking of virus binding sites and observe whether it works on the body. The results should make it possible to develop an antiviral therapy administered by aerosol in the case of infection or at-risk contact.
This discovery is also of interest for the future to counter other viruses with similar attachment factors.
This article was translated from MediQuality; a version appeared on Medscape.com.
What’s more, they have succeeded in closing the lock to block the virus and prevent it from interacting with the cell, thereby preventing infection.
UCLouvain emphasized that this discovery, which was published in Nature Communications, is sparking hope that an aerosol antiviral therapy can be developed that would eradicate the virus in the case of an infection or a high-risk contact.
For 2 years, the team under David Alsteens, PhD, a researcher at the UCLouvain Institute of Biomolecular Science and Technology, has been working hard to understand the precise molecular mechanisms the virus uses to infect a cell. They investigated the interaction between sialic acids, a kind of sugar residue present on the surface of cells, and the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein to clarify its role in the infection process.
It was already known that the function of the sugar residues that coat the cells is to promote cell recognition, thus enabling, in particular, viruses to identify their targets more easily, but also to provide them with a point of attachment and to facilitate infection of the cells.
The researchers have now revealed a variant of these sugars that interacts more strongly with the S protein than other sugars do.
In other words, the university explained, they found the set of keys that allows the virus to open the cell door. So, the researchers decided to catch the virus in its own trap, by preventing it from attaching to its host cell. To do this, they blocked the S protein’s points of attachment, thus suppressing any interaction with the cell surface, as if a padlock had been placed on the lock on the cell’s entry door.
Th researchers added that the advantage of this discovery is that it acts on the virus, irrespective of mutations.
The team of researchers will now conduct tests on mice to apply this blocking of virus binding sites and observe whether it works on the body. The results should make it possible to develop an antiviral therapy administered by aerosol in the case of infection or at-risk contact.
This discovery is also of interest for the future to counter other viruses with similar attachment factors.
This article was translated from MediQuality; a version appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE COMMUNICATIONS
Gout app improves treat to target, reduces flares
Self-management of gout using a smartphone app to record self-test urate levels and flares, and communicate those results to clinicians, could see more patients reaching target urate levels and even reducing flare frequency, a study has found.
Writing in The Lancet Rheumatology, Philip Riches, PhD, of the rheumatic disease unit at Western General Hospital in Edinburgh, and coauthors presented the findings of their randomized, controlled feasibility study of a new gout self-management approach aimed at helping patients treat to target.
While current rheumatology guidelines stress the importance of keeping urate below target levels to reduce flares and improve clinical outcomes, this isn’t always achieved in clinical practice. A previous trial of a nurse-led treat-to-target intervention did show a reduced incidence of flares and tophaceous disease, but the authors said, despite its cost-effectiveness, this approach has yet to be implemented in the United Kingdom.
Dr. Riches and colleagues developed a self-management strategy in which all 60 patients in the study self-tested their urate levels and were prompted to enter that data into the GoutSMART smartphone app once a month or opportunistically, along with information on disease severity and quality of life. All patients had been recommended for initiation or escalation of urate-lowering therapy, and had a serum urate of 0.36 mmol/L (6 mg/dL) or higher at baseline, and all received a gout management plan at the start of the study.
Patients in the intervention group who recorded a urate level above 0.30 mmol/L (5 mg/dL) via the app during the study were prompted to do a self-test every 2 weeks and given daily reminders in the app. Their urate levels were transmitted securely to the study team who then advised on dose escalation or treatment change. Those in the usual-care group also used the app but it only prompted them to record gout flares, keep quality of life diaries, or message the researchers.
At 24 weeks after the start of the study, 73% of 40 participants in the self-management group had reached the urate target of 0.30 mmol/L or below, compared with 15% of the 20 participants in the usual-care group (P < .0001).
The difference between the two groups was sustained even 1 year after starting the intervention, when 80% of those in the self-management group had reached that target, compared with 45% of those in the usual-care group.
Patients in the intervention group also had fewer flares, experiencing a mean of 2.03 flares in the first 24 weeks, compared with a mean of 3 among the control group, although the study didn’t report any difference in the rates of tophaceous disease.
Those in the self-management group had fewer medical appointments, but were prescribed higher doses of allopurinol at the 24- and 52-week visits.
“Qualitative feedback suggests that the self-monitoring approach was accepted by most participants and was enthusiastically endorsed by many,” the authors wrote. “The approach empowers patients and provides feedback on the effect of medication.”
It will be important to determine if the success of this self-management intervention can be replicated in an even broader patient population, Lisa K. Stamp, MBChB, PhD, of University of Otago, Christchurch, New Zealand, and Angelo L. Gaffo, MD, of University of Alabama at Birmingham, noted in an accompanying editorial. They wrote it was encouraging that only 7% of the 92 people screened for the trial did not have a smartphone and that it the patient sample had a mean age of 53 years. However, the trial did not include people with chronic kidney disease who make up nearly a quarter of all people with gout.
“It remains unknown whether the characteristics of those who did not reach target urate are the same or different as those who did, and a head-to-head comparison of these interventions would be of interest,” Dr. Stamp and Dr. Gaffo wrote. “A key challenge in managing gout is to determine which treatment strategy will be best suited to an individual with gout and to identify those for whom more support might be required.”
This study was supported by the University of Edinburgh and funded by NHS Lothian Health Foundation. No conflicts of interest were declared.
Self-management of gout using a smartphone app to record self-test urate levels and flares, and communicate those results to clinicians, could see more patients reaching target urate levels and even reducing flare frequency, a study has found.
Writing in The Lancet Rheumatology, Philip Riches, PhD, of the rheumatic disease unit at Western General Hospital in Edinburgh, and coauthors presented the findings of their randomized, controlled feasibility study of a new gout self-management approach aimed at helping patients treat to target.
While current rheumatology guidelines stress the importance of keeping urate below target levels to reduce flares and improve clinical outcomes, this isn’t always achieved in clinical practice. A previous trial of a nurse-led treat-to-target intervention did show a reduced incidence of flares and tophaceous disease, but the authors said, despite its cost-effectiveness, this approach has yet to be implemented in the United Kingdom.
Dr. Riches and colleagues developed a self-management strategy in which all 60 patients in the study self-tested their urate levels and were prompted to enter that data into the GoutSMART smartphone app once a month or opportunistically, along with information on disease severity and quality of life. All patients had been recommended for initiation or escalation of urate-lowering therapy, and had a serum urate of 0.36 mmol/L (6 mg/dL) or higher at baseline, and all received a gout management plan at the start of the study.
Patients in the intervention group who recorded a urate level above 0.30 mmol/L (5 mg/dL) via the app during the study were prompted to do a self-test every 2 weeks and given daily reminders in the app. Their urate levels were transmitted securely to the study team who then advised on dose escalation or treatment change. Those in the usual-care group also used the app but it only prompted them to record gout flares, keep quality of life diaries, or message the researchers.
At 24 weeks after the start of the study, 73% of 40 participants in the self-management group had reached the urate target of 0.30 mmol/L or below, compared with 15% of the 20 participants in the usual-care group (P < .0001).
The difference between the two groups was sustained even 1 year after starting the intervention, when 80% of those in the self-management group had reached that target, compared with 45% of those in the usual-care group.
Patients in the intervention group also had fewer flares, experiencing a mean of 2.03 flares in the first 24 weeks, compared with a mean of 3 among the control group, although the study didn’t report any difference in the rates of tophaceous disease.
Those in the self-management group had fewer medical appointments, but were prescribed higher doses of allopurinol at the 24- and 52-week visits.
“Qualitative feedback suggests that the self-monitoring approach was accepted by most participants and was enthusiastically endorsed by many,” the authors wrote. “The approach empowers patients and provides feedback on the effect of medication.”
It will be important to determine if the success of this self-management intervention can be replicated in an even broader patient population, Lisa K. Stamp, MBChB, PhD, of University of Otago, Christchurch, New Zealand, and Angelo L. Gaffo, MD, of University of Alabama at Birmingham, noted in an accompanying editorial. They wrote it was encouraging that only 7% of the 92 people screened for the trial did not have a smartphone and that it the patient sample had a mean age of 53 years. However, the trial did not include people with chronic kidney disease who make up nearly a quarter of all people with gout.
“It remains unknown whether the characteristics of those who did not reach target urate are the same or different as those who did, and a head-to-head comparison of these interventions would be of interest,” Dr. Stamp and Dr. Gaffo wrote. “A key challenge in managing gout is to determine which treatment strategy will be best suited to an individual with gout and to identify those for whom more support might be required.”
This study was supported by the University of Edinburgh and funded by NHS Lothian Health Foundation. No conflicts of interest were declared.
Self-management of gout using a smartphone app to record self-test urate levels and flares, and communicate those results to clinicians, could see more patients reaching target urate levels and even reducing flare frequency, a study has found.
Writing in The Lancet Rheumatology, Philip Riches, PhD, of the rheumatic disease unit at Western General Hospital in Edinburgh, and coauthors presented the findings of their randomized, controlled feasibility study of a new gout self-management approach aimed at helping patients treat to target.
While current rheumatology guidelines stress the importance of keeping urate below target levels to reduce flares and improve clinical outcomes, this isn’t always achieved in clinical practice. A previous trial of a nurse-led treat-to-target intervention did show a reduced incidence of flares and tophaceous disease, but the authors said, despite its cost-effectiveness, this approach has yet to be implemented in the United Kingdom.
Dr. Riches and colleagues developed a self-management strategy in which all 60 patients in the study self-tested their urate levels and were prompted to enter that data into the GoutSMART smartphone app once a month or opportunistically, along with information on disease severity and quality of life. All patients had been recommended for initiation or escalation of urate-lowering therapy, and had a serum urate of 0.36 mmol/L (6 mg/dL) or higher at baseline, and all received a gout management plan at the start of the study.
Patients in the intervention group who recorded a urate level above 0.30 mmol/L (5 mg/dL) via the app during the study were prompted to do a self-test every 2 weeks and given daily reminders in the app. Their urate levels were transmitted securely to the study team who then advised on dose escalation or treatment change. Those in the usual-care group also used the app but it only prompted them to record gout flares, keep quality of life diaries, or message the researchers.
At 24 weeks after the start of the study, 73% of 40 participants in the self-management group had reached the urate target of 0.30 mmol/L or below, compared with 15% of the 20 participants in the usual-care group (P < .0001).
The difference between the two groups was sustained even 1 year after starting the intervention, when 80% of those in the self-management group had reached that target, compared with 45% of those in the usual-care group.
Patients in the intervention group also had fewer flares, experiencing a mean of 2.03 flares in the first 24 weeks, compared with a mean of 3 among the control group, although the study didn’t report any difference in the rates of tophaceous disease.
Those in the self-management group had fewer medical appointments, but were prescribed higher doses of allopurinol at the 24- and 52-week visits.
“Qualitative feedback suggests that the self-monitoring approach was accepted by most participants and was enthusiastically endorsed by many,” the authors wrote. “The approach empowers patients and provides feedback on the effect of medication.”
It will be important to determine if the success of this self-management intervention can be replicated in an even broader patient population, Lisa K. Stamp, MBChB, PhD, of University of Otago, Christchurch, New Zealand, and Angelo L. Gaffo, MD, of University of Alabama at Birmingham, noted in an accompanying editorial. They wrote it was encouraging that only 7% of the 92 people screened for the trial did not have a smartphone and that it the patient sample had a mean age of 53 years. However, the trial did not include people with chronic kidney disease who make up nearly a quarter of all people with gout.
“It remains unknown whether the characteristics of those who did not reach target urate are the same or different as those who did, and a head-to-head comparison of these interventions would be of interest,” Dr. Stamp and Dr. Gaffo wrote. “A key challenge in managing gout is to determine which treatment strategy will be best suited to an individual with gout and to identify those for whom more support might be required.”
This study was supported by the University of Edinburgh and funded by NHS Lothian Health Foundation. No conflicts of interest were declared.
FROM THE LANCET RHEUMATOLOGY

