User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Feds launch COVID-19 worker vaccine mandates
The Biden administration on Nov. 4 unveiled its rule to require most of the country’s larger employers to mandate workers be fully vaccinated against COVID-19, but set a Jan. 4 deadline, avoiding the busy holiday season.
The White House also shifted the time lines for earlier mandates applying to federal workers and contractors to Jan. 4. And the same deadline applies to a new separate rule for health care workers.
The new rules are meant to preempt “any inconsistent state or local laws,” including bans and limits on employers’ authority to require vaccination, masks, or testing, the White House said in a statement.
The rule on employers from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration will apply to organizations with 100 or more employees. These employers will need to make sure each worker is fully vaccinated or tests for COVID-19 on at least a weekly basis. The OSHA rule will also require that employers provide paid time for employees to get vaccinated and ensure that all unvaccinated workers wear a face mask in the workplace. This rule will cover 84 million employees. The OSHA rule will not apply to workplaces covered by either the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services rule or the federal contractor vaccination requirement
“The virus will not go away by itself, or because we wish it away: We have to act,” President Joe Biden said in a statement. “Vaccination is the single best pathway out of this pandemic.”
Mandates were not the preferred route to managing the pandemic, he said.
“Too many people remain unvaccinated for us to get out of this pandemic for good,” he said. “So I instituted requirements – and they are working.”
The White House said 70% percent of U.S. adults are now fully vaccinated – up from less than 1% when Mr. Biden took office in January.
The CMS vaccine rule is meant to cover more than 17 million workers and about 76,000 medical care sites, including hospitals, ambulatory surgery centers, nursing homes, dialysis facilities, home health agencies, and long-term care facilities. The rule will apply to employees whether their positions involve patient care or not.
Unlike the OSHA mandate, the one for health care workers will not offer the option of frequent COVID-19 testing instead of vaccination. There is a “higher bar” for health care workers, given their role in treating patients, so the mandate allows only for vaccination or limited exemptions, a senior administration official said on Nov. 3 during a call with reporters.
The CMS rule includes a “range of remedies,” including penalties and denial of payment for health care facilities that fail to meet the vaccine mandate. CMS could theoretically cut off hospitals and other medical organizations for failure to comply, but that would be a “last resort,” a senior administration official said. CMS will instead work with health care facilities to help them comply with the federal rule on vaccination of medical workers.
The new CMS rules apply only to Medicare- and Medicaid-certified centers and organizations. The rule does not directly apply to other health care entities, such as doctor’s offices, that are not regulated by CMS.
“Most states have separate licensing requirements for health care staff and health care providers that would be applicable to physician office staff and other staff in small health care entities that are not subject to vaccination requirements under this IFC,” CMS said in the rule.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Biden administration on Nov. 4 unveiled its rule to require most of the country’s larger employers to mandate workers be fully vaccinated against COVID-19, but set a Jan. 4 deadline, avoiding the busy holiday season.
The White House also shifted the time lines for earlier mandates applying to federal workers and contractors to Jan. 4. And the same deadline applies to a new separate rule for health care workers.
The new rules are meant to preempt “any inconsistent state or local laws,” including bans and limits on employers’ authority to require vaccination, masks, or testing, the White House said in a statement.
The rule on employers from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration will apply to organizations with 100 or more employees. These employers will need to make sure each worker is fully vaccinated or tests for COVID-19 on at least a weekly basis. The OSHA rule will also require that employers provide paid time for employees to get vaccinated and ensure that all unvaccinated workers wear a face mask in the workplace. This rule will cover 84 million employees. The OSHA rule will not apply to workplaces covered by either the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services rule or the federal contractor vaccination requirement
“The virus will not go away by itself, or because we wish it away: We have to act,” President Joe Biden said in a statement. “Vaccination is the single best pathway out of this pandemic.”
Mandates were not the preferred route to managing the pandemic, he said.
“Too many people remain unvaccinated for us to get out of this pandemic for good,” he said. “So I instituted requirements – and they are working.”
The White House said 70% percent of U.S. adults are now fully vaccinated – up from less than 1% when Mr. Biden took office in January.
The CMS vaccine rule is meant to cover more than 17 million workers and about 76,000 medical care sites, including hospitals, ambulatory surgery centers, nursing homes, dialysis facilities, home health agencies, and long-term care facilities. The rule will apply to employees whether their positions involve patient care or not.
Unlike the OSHA mandate, the one for health care workers will not offer the option of frequent COVID-19 testing instead of vaccination. There is a “higher bar” for health care workers, given their role in treating patients, so the mandate allows only for vaccination or limited exemptions, a senior administration official said on Nov. 3 during a call with reporters.
The CMS rule includes a “range of remedies,” including penalties and denial of payment for health care facilities that fail to meet the vaccine mandate. CMS could theoretically cut off hospitals and other medical organizations for failure to comply, but that would be a “last resort,” a senior administration official said. CMS will instead work with health care facilities to help them comply with the federal rule on vaccination of medical workers.
The new CMS rules apply only to Medicare- and Medicaid-certified centers and organizations. The rule does not directly apply to other health care entities, such as doctor’s offices, that are not regulated by CMS.
“Most states have separate licensing requirements for health care staff and health care providers that would be applicable to physician office staff and other staff in small health care entities that are not subject to vaccination requirements under this IFC,” CMS said in the rule.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Biden administration on Nov. 4 unveiled its rule to require most of the country’s larger employers to mandate workers be fully vaccinated against COVID-19, but set a Jan. 4 deadline, avoiding the busy holiday season.
The White House also shifted the time lines for earlier mandates applying to federal workers and contractors to Jan. 4. And the same deadline applies to a new separate rule for health care workers.
The new rules are meant to preempt “any inconsistent state or local laws,” including bans and limits on employers’ authority to require vaccination, masks, or testing, the White House said in a statement.
The rule on employers from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration will apply to organizations with 100 or more employees. These employers will need to make sure each worker is fully vaccinated or tests for COVID-19 on at least a weekly basis. The OSHA rule will also require that employers provide paid time for employees to get vaccinated and ensure that all unvaccinated workers wear a face mask in the workplace. This rule will cover 84 million employees. The OSHA rule will not apply to workplaces covered by either the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services rule or the federal contractor vaccination requirement
“The virus will not go away by itself, or because we wish it away: We have to act,” President Joe Biden said in a statement. “Vaccination is the single best pathway out of this pandemic.”
Mandates were not the preferred route to managing the pandemic, he said.
“Too many people remain unvaccinated for us to get out of this pandemic for good,” he said. “So I instituted requirements – and they are working.”
The White House said 70% percent of U.S. adults are now fully vaccinated – up from less than 1% when Mr. Biden took office in January.
The CMS vaccine rule is meant to cover more than 17 million workers and about 76,000 medical care sites, including hospitals, ambulatory surgery centers, nursing homes, dialysis facilities, home health agencies, and long-term care facilities. The rule will apply to employees whether their positions involve patient care or not.
Unlike the OSHA mandate, the one for health care workers will not offer the option of frequent COVID-19 testing instead of vaccination. There is a “higher bar” for health care workers, given their role in treating patients, so the mandate allows only for vaccination or limited exemptions, a senior administration official said on Nov. 3 during a call with reporters.
The CMS rule includes a “range of remedies,” including penalties and denial of payment for health care facilities that fail to meet the vaccine mandate. CMS could theoretically cut off hospitals and other medical organizations for failure to comply, but that would be a “last resort,” a senior administration official said. CMS will instead work with health care facilities to help them comply with the federal rule on vaccination of medical workers.
The new CMS rules apply only to Medicare- and Medicaid-certified centers and organizations. The rule does not directly apply to other health care entities, such as doctor’s offices, that are not regulated by CMS.
“Most states have separate licensing requirements for health care staff and health care providers that would be applicable to physician office staff and other staff in small health care entities that are not subject to vaccination requirements under this IFC,” CMS said in the rule.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
James Bond taken down by an epidemiologist
No, Mr. Bond, I expect you to die
Movie watching usually requires a certain suspension of disbelief, and it’s safe to say James Bond movies require this more than most. Between the impossible gadgets and ludicrous doomsday plans, very few have ever stopped to consider the health risks of the James Bond universe.
Now, however, Bond, James Bond, has met his most formidable opponent: Wouter Graumans, a graduate student in epidemiology from the Netherlands. During a foray to Burkina Faso to study infectious diseases, Mr. Graumans came down with a case of food poisoning, which led him to wonder how 007 is able to trot across this big world of ours without contracting so much as a sinus infection.
Because Mr. Graumans is a man of science and conviction, mere speculation wasn’t enough. He and a group of coauthors wrote an entire paper on the health risks of the James Bond universe.
Doing so required watching over 3,000 minutes of numerous movies and analyzing Bond’s 86 total trips to 46 different countries based on current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advice for travel to those countries. Time which, the authors state in the abstract, “could easily have been spent on more pressing societal issues or forms of relaxation that are more acceptable in academic circles.”
Naturally, Mr. Bond’s line of work entails exposure to unpleasant things, such as poison, dehydration, heatstroke, and dangerous wildlife (everything from ticks to crocodiles), though oddly enough he never succumbs to any of it. He’s also curiously immune to hangovers, despite rarely drinking anything nonalcoholic. There are also less obvious risks: For one, 007 rarely washes his hands. During one movie, he handles raw chicken to lure away a pack of crocodiles but fails to wash his hands afterward, leaving him at risk for multiple food-borne illnesses.
Of course, we must address the elephant in the bedroom: Mr. Bond’s numerous, er, encounters with women. One would imagine the biggest risk to those women would be from the various STDs that likely course through Bond’s body, but of the 27% who died shortly after … encountering … him, all involved violence, with disease playing no obvious role. Who knows, maybe he’s clean? Stranger things have happened.
The timing of this article may seem a bit suspicious. Was it a PR stunt by the studio? Rest assured, the authors addressed this, noting that they received no funding for the study, and that, “given the futility of its academic value, this is deemed entirely appropriate by all authors.” We love when a punchline writes itself.
How to see Atlanta on $688.35 a day
The world is always changing, so we have to change with it. This week, LOTME becomes a travel guide, and our first stop is the Big A, the Big Peach, Dogwood City, Empire City of the South, Wakanda.
There’s lots to do in Atlanta: Celebrate a World Series win, visit the College Football Hall of Fame or the World of Coca Cola, or take the Stranger Things/Upside Down film locations tour. Serious adventurers, however, get out of the city and go to Emory Decatur Hospital in – you guessed it – Decatur (unofficial motto: “Everything is Greater in Decatur”).
Find the emergency room and ask for Taylor Davis, who will be your personal guide. She’ll show you how to check in at the desk, sit in the waiting room for 7 hours, and then leave without seeing any medical personnel or receiving any sort of attention whatsoever. All the things she did when she went there in July for a head injury.
Ms. Davis told Fox5 Atlanta: “I didn’t get my vitals taken, nobody called my name. I wasn’t seen at all.”
But wait! There’s more! By booking your trip through LOTMEgo* and using the code “Decatur,” you’ll get the Taylor Davis special, which includes a bill/cover charge for $688.35 from the hospital. An Emory Healthcare patient financial services employee told Ms. Davis that “you get charged before you are seen. Not for being seen.”
If all this has you ready to hop in your car (really?), then check out LOTMEgo* on Twittbook and InstaTok. You’ll also find trick-or-treating tips and discounts on haunted hospital tours.
*Does not actually exist
Breaking down the hot flash
Do you ever wonder why we scramble for cold things when we’re feeling nauseous? Whether it’s the cool air that needs to hit your face in the car or a cold, damp towel on the back of your neck, scientists think it could possibly be an evolutionary mechanism at the cellular level.
Motion sickness it’s actually a battle of body temperature, according to an article from LiveScience. Capillaries in the skin dilate, allowing for more blood flow near the skin’s surface and causing core temperature to fall. Once body temperature drops, the hypothalamus, which regulates temperature, tries to do its job by raising body temperature. Thus the hot flash!
The cold compress and cool air help fight the battle by counteracting the hypothalamus, but why the drop in body temperature to begin with?
There are a few theories. Dr. Robert Glatter, an emergency physician at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York, told LiveScience that the lack of oxygen needed in body tissue to survive at lower temperatures could be making it difficult to get oxygen to the body when a person is ill, and is “more likely an adaptive response influenced by poorly understood mechanisms at the cellular level.”
Another theory is that the nausea and body temperature shift is the body’s natural response to help people vomit.
Then there’s the theory of “defensive hypothermia,” which suggests that cold sweats are a possible mechanism to conserve energy so the body can fight off an intruder, which was supported by a 2014 study and a 2016 review.
It’s another one of the body’s many survival tricks.
Teachers were right: Pupils can do the math
Teachers liked to preach that we wouldn’t have calculators with us all the time, but that wound up not being true. Our phones have calculators at the press of a button. But maybe even calculators aren’t always needed because our pupils do more math than you think.
The pupil light reflex – constrict in light and dilate in darkness – is well known, but recent work shows that pupil size is also regulated by cognitive and perceptual factors. By presenting subjects with images of various numbers of dots and measuring pupil size, the investigators were able to show “that numerical information is intrinsically related to perception,” lead author Dr. Elisa Castaldi of Florence University noted in a written statement.
The researchers found that pupils are responsible for important survival techniques. Coauthor David Burr of the University of Sydney and the University of Florence gave an evolutionary perspective: “When we look around, we spontaneously perceive the form, size, movement and colour of a scene. Equally spontaneously, we perceive the number of items before us. This ability, shared with most other animals, is an evolutionary fundamental: It reveals immediately important quantities, such as how many apples there are on the tree, or how many enemies are attacking.”
Useful information, indeed, but our pupils seem to be more interested in the quantity of beers in the refrigerator.
No, Mr. Bond, I expect you to die
Movie watching usually requires a certain suspension of disbelief, and it’s safe to say James Bond movies require this more than most. Between the impossible gadgets and ludicrous doomsday plans, very few have ever stopped to consider the health risks of the James Bond universe.
Now, however, Bond, James Bond, has met his most formidable opponent: Wouter Graumans, a graduate student in epidemiology from the Netherlands. During a foray to Burkina Faso to study infectious diseases, Mr. Graumans came down with a case of food poisoning, which led him to wonder how 007 is able to trot across this big world of ours without contracting so much as a sinus infection.
Because Mr. Graumans is a man of science and conviction, mere speculation wasn’t enough. He and a group of coauthors wrote an entire paper on the health risks of the James Bond universe.
Doing so required watching over 3,000 minutes of numerous movies and analyzing Bond’s 86 total trips to 46 different countries based on current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advice for travel to those countries. Time which, the authors state in the abstract, “could easily have been spent on more pressing societal issues or forms of relaxation that are more acceptable in academic circles.”
Naturally, Mr. Bond’s line of work entails exposure to unpleasant things, such as poison, dehydration, heatstroke, and dangerous wildlife (everything from ticks to crocodiles), though oddly enough he never succumbs to any of it. He’s also curiously immune to hangovers, despite rarely drinking anything nonalcoholic. There are also less obvious risks: For one, 007 rarely washes his hands. During one movie, he handles raw chicken to lure away a pack of crocodiles but fails to wash his hands afterward, leaving him at risk for multiple food-borne illnesses.
Of course, we must address the elephant in the bedroom: Mr. Bond’s numerous, er, encounters with women. One would imagine the biggest risk to those women would be from the various STDs that likely course through Bond’s body, but of the 27% who died shortly after … encountering … him, all involved violence, with disease playing no obvious role. Who knows, maybe he’s clean? Stranger things have happened.
The timing of this article may seem a bit suspicious. Was it a PR stunt by the studio? Rest assured, the authors addressed this, noting that they received no funding for the study, and that, “given the futility of its academic value, this is deemed entirely appropriate by all authors.” We love when a punchline writes itself.
How to see Atlanta on $688.35 a day
The world is always changing, so we have to change with it. This week, LOTME becomes a travel guide, and our first stop is the Big A, the Big Peach, Dogwood City, Empire City of the South, Wakanda.
There’s lots to do in Atlanta: Celebrate a World Series win, visit the College Football Hall of Fame or the World of Coca Cola, or take the Stranger Things/Upside Down film locations tour. Serious adventurers, however, get out of the city and go to Emory Decatur Hospital in – you guessed it – Decatur (unofficial motto: “Everything is Greater in Decatur”).
Find the emergency room and ask for Taylor Davis, who will be your personal guide. She’ll show you how to check in at the desk, sit in the waiting room for 7 hours, and then leave without seeing any medical personnel or receiving any sort of attention whatsoever. All the things she did when she went there in July for a head injury.
Ms. Davis told Fox5 Atlanta: “I didn’t get my vitals taken, nobody called my name. I wasn’t seen at all.”
But wait! There’s more! By booking your trip through LOTMEgo* and using the code “Decatur,” you’ll get the Taylor Davis special, which includes a bill/cover charge for $688.35 from the hospital. An Emory Healthcare patient financial services employee told Ms. Davis that “you get charged before you are seen. Not for being seen.”
If all this has you ready to hop in your car (really?), then check out LOTMEgo* on Twittbook and InstaTok. You’ll also find trick-or-treating tips and discounts on haunted hospital tours.
*Does not actually exist
Breaking down the hot flash
Do you ever wonder why we scramble for cold things when we’re feeling nauseous? Whether it’s the cool air that needs to hit your face in the car or a cold, damp towel on the back of your neck, scientists think it could possibly be an evolutionary mechanism at the cellular level.
Motion sickness it’s actually a battle of body temperature, according to an article from LiveScience. Capillaries in the skin dilate, allowing for more blood flow near the skin’s surface and causing core temperature to fall. Once body temperature drops, the hypothalamus, which regulates temperature, tries to do its job by raising body temperature. Thus the hot flash!
The cold compress and cool air help fight the battle by counteracting the hypothalamus, but why the drop in body temperature to begin with?
There are a few theories. Dr. Robert Glatter, an emergency physician at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York, told LiveScience that the lack of oxygen needed in body tissue to survive at lower temperatures could be making it difficult to get oxygen to the body when a person is ill, and is “more likely an adaptive response influenced by poorly understood mechanisms at the cellular level.”
Another theory is that the nausea and body temperature shift is the body’s natural response to help people vomit.
Then there’s the theory of “defensive hypothermia,” which suggests that cold sweats are a possible mechanism to conserve energy so the body can fight off an intruder, which was supported by a 2014 study and a 2016 review.
It’s another one of the body’s many survival tricks.
Teachers were right: Pupils can do the math
Teachers liked to preach that we wouldn’t have calculators with us all the time, but that wound up not being true. Our phones have calculators at the press of a button. But maybe even calculators aren’t always needed because our pupils do more math than you think.
The pupil light reflex – constrict in light and dilate in darkness – is well known, but recent work shows that pupil size is also regulated by cognitive and perceptual factors. By presenting subjects with images of various numbers of dots and measuring pupil size, the investigators were able to show “that numerical information is intrinsically related to perception,” lead author Dr. Elisa Castaldi of Florence University noted in a written statement.
The researchers found that pupils are responsible for important survival techniques. Coauthor David Burr of the University of Sydney and the University of Florence gave an evolutionary perspective: “When we look around, we spontaneously perceive the form, size, movement and colour of a scene. Equally spontaneously, we perceive the number of items before us. This ability, shared with most other animals, is an evolutionary fundamental: It reveals immediately important quantities, such as how many apples there are on the tree, or how many enemies are attacking.”
Useful information, indeed, but our pupils seem to be more interested in the quantity of beers in the refrigerator.
No, Mr. Bond, I expect you to die
Movie watching usually requires a certain suspension of disbelief, and it’s safe to say James Bond movies require this more than most. Between the impossible gadgets and ludicrous doomsday plans, very few have ever stopped to consider the health risks of the James Bond universe.
Now, however, Bond, James Bond, has met his most formidable opponent: Wouter Graumans, a graduate student in epidemiology from the Netherlands. During a foray to Burkina Faso to study infectious diseases, Mr. Graumans came down with a case of food poisoning, which led him to wonder how 007 is able to trot across this big world of ours without contracting so much as a sinus infection.
Because Mr. Graumans is a man of science and conviction, mere speculation wasn’t enough. He and a group of coauthors wrote an entire paper on the health risks of the James Bond universe.
Doing so required watching over 3,000 minutes of numerous movies and analyzing Bond’s 86 total trips to 46 different countries based on current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advice for travel to those countries. Time which, the authors state in the abstract, “could easily have been spent on more pressing societal issues or forms of relaxation that are more acceptable in academic circles.”
Naturally, Mr. Bond’s line of work entails exposure to unpleasant things, such as poison, dehydration, heatstroke, and dangerous wildlife (everything from ticks to crocodiles), though oddly enough he never succumbs to any of it. He’s also curiously immune to hangovers, despite rarely drinking anything nonalcoholic. There are also less obvious risks: For one, 007 rarely washes his hands. During one movie, he handles raw chicken to lure away a pack of crocodiles but fails to wash his hands afterward, leaving him at risk for multiple food-borne illnesses.
Of course, we must address the elephant in the bedroom: Mr. Bond’s numerous, er, encounters with women. One would imagine the biggest risk to those women would be from the various STDs that likely course through Bond’s body, but of the 27% who died shortly after … encountering … him, all involved violence, with disease playing no obvious role. Who knows, maybe he’s clean? Stranger things have happened.
The timing of this article may seem a bit suspicious. Was it a PR stunt by the studio? Rest assured, the authors addressed this, noting that they received no funding for the study, and that, “given the futility of its academic value, this is deemed entirely appropriate by all authors.” We love when a punchline writes itself.
How to see Atlanta on $688.35 a day
The world is always changing, so we have to change with it. This week, LOTME becomes a travel guide, and our first stop is the Big A, the Big Peach, Dogwood City, Empire City of the South, Wakanda.
There’s lots to do in Atlanta: Celebrate a World Series win, visit the College Football Hall of Fame or the World of Coca Cola, or take the Stranger Things/Upside Down film locations tour. Serious adventurers, however, get out of the city and go to Emory Decatur Hospital in – you guessed it – Decatur (unofficial motto: “Everything is Greater in Decatur”).
Find the emergency room and ask for Taylor Davis, who will be your personal guide. She’ll show you how to check in at the desk, sit in the waiting room for 7 hours, and then leave without seeing any medical personnel or receiving any sort of attention whatsoever. All the things she did when she went there in July for a head injury.
Ms. Davis told Fox5 Atlanta: “I didn’t get my vitals taken, nobody called my name. I wasn’t seen at all.”
But wait! There’s more! By booking your trip through LOTMEgo* and using the code “Decatur,” you’ll get the Taylor Davis special, which includes a bill/cover charge for $688.35 from the hospital. An Emory Healthcare patient financial services employee told Ms. Davis that “you get charged before you are seen. Not for being seen.”
If all this has you ready to hop in your car (really?), then check out LOTMEgo* on Twittbook and InstaTok. You’ll also find trick-or-treating tips and discounts on haunted hospital tours.
*Does not actually exist
Breaking down the hot flash
Do you ever wonder why we scramble for cold things when we’re feeling nauseous? Whether it’s the cool air that needs to hit your face in the car or a cold, damp towel on the back of your neck, scientists think it could possibly be an evolutionary mechanism at the cellular level.
Motion sickness it’s actually a battle of body temperature, according to an article from LiveScience. Capillaries in the skin dilate, allowing for more blood flow near the skin’s surface and causing core temperature to fall. Once body temperature drops, the hypothalamus, which regulates temperature, tries to do its job by raising body temperature. Thus the hot flash!
The cold compress and cool air help fight the battle by counteracting the hypothalamus, but why the drop in body temperature to begin with?
There are a few theories. Dr. Robert Glatter, an emergency physician at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York, told LiveScience that the lack of oxygen needed in body tissue to survive at lower temperatures could be making it difficult to get oxygen to the body when a person is ill, and is “more likely an adaptive response influenced by poorly understood mechanisms at the cellular level.”
Another theory is that the nausea and body temperature shift is the body’s natural response to help people vomit.
Then there’s the theory of “defensive hypothermia,” which suggests that cold sweats are a possible mechanism to conserve energy so the body can fight off an intruder, which was supported by a 2014 study and a 2016 review.
It’s another one of the body’s many survival tricks.
Teachers were right: Pupils can do the math
Teachers liked to preach that we wouldn’t have calculators with us all the time, but that wound up not being true. Our phones have calculators at the press of a button. But maybe even calculators aren’t always needed because our pupils do more math than you think.
The pupil light reflex – constrict in light and dilate in darkness – is well known, but recent work shows that pupil size is also regulated by cognitive and perceptual factors. By presenting subjects with images of various numbers of dots and measuring pupil size, the investigators were able to show “that numerical information is intrinsically related to perception,” lead author Dr. Elisa Castaldi of Florence University noted in a written statement.
The researchers found that pupils are responsible for important survival techniques. Coauthor David Burr of the University of Sydney and the University of Florence gave an evolutionary perspective: “When we look around, we spontaneously perceive the form, size, movement and colour of a scene. Equally spontaneously, we perceive the number of items before us. This ability, shared with most other animals, is an evolutionary fundamental: It reveals immediately important quantities, such as how many apples there are on the tree, or how many enemies are attacking.”
Useful information, indeed, but our pupils seem to be more interested in the quantity of beers in the refrigerator.
Phototoxicity Secondary to Home Fireplace Exposure After Photodynamic Therapy for Actinic Keratosis
To the Editor:
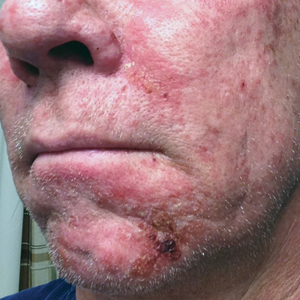
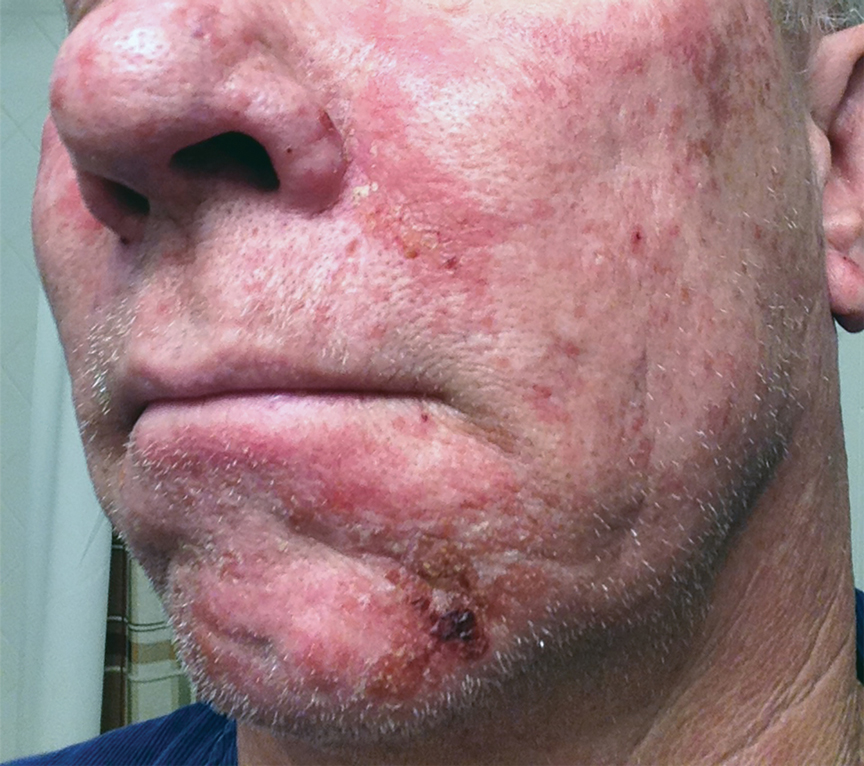
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a US Food and Drug Administration–approved treatment for actinic keratosis (AK). It also commonly is administered off label for basal cell carcinoma, Bowen disease, photoaging, and acne vulgaris and is being investigated for other applications.1,2 In the context of treating AK, the mechanism employed in PDT most commonly involves the application of exogenous aminolevulinic acid (ALA), which is metabolized to the endogenous photosensitizer protoporphyrin IX (PpIX) in skin cells by enzymes in the heme biosynthetic pathway.3 The preferential uptake of ALA and conversion to PpIX is due to the altered and increased permeability of abnormal keratin layers of aging, sun-damaged cells, and skin tumors. Selectivity of ALA also occurs due to the preferential intracellular accumulation of PpIX in proliferating, relatively iron–deficient, precancerous and cancerous cells. The therapeutic effect is achieved with light exposure to blue light wavelength at 417 nm and corresponds to the excitation peak of PpIX,4 which activates PpIX and forms reactive oxygen species in the presence of oxygen that ultimately cause cell necrosis and apoptosis.5 Because it takes approximately 24 hours for PpIX to be completely metabolized from the skin, patients are counseled to avoid sun or artificial light exposure in the first 24 hours post-PDT, regardless of the indication, to avoid a severe phototoxic reaction.3,6,7 Although it is normal and desirable for patients to experience some form of a phototoxic reaction, which may include erythema, edema, crusting, vesiculation, or erosion in most patients, these types of reactions most often are secondary to the intended exposure and incidental natural or artificial light exposures.6 We report a case of a severe phototoxic reaction in which a patient experienced painful erythema and purulence on the left side of the chin after being within an arm’s length of a flame in a fireplace following PDT treatment.
A 59-year-old man presented to our dermatology clinic for his second of 3 PDT sessions to treat AKs on the face. He had a history of a basal cell carcinoma on the left nasolabial fold that previously was treated with Mohs micrographic surgery and melanoma on the left ear that was previously treated with excision. The patient received the initial PDT session 1 month prior and experienced a mild reaction with minimal redness and peeling that resolved in 4 to 5 days. For the second treatment, per standard protocol at our clinic, ALA was applied to the face, after which the patient incubated for 1 hour prior to blue light exposure (mean [SD] peak output of 417 [5] nm for 1000 seconds and 10 J/cm2).
After blue light exposure, broad-spectrum sunscreen (sun protection factor 47) was applied to our patient’s face, and he wore a wide-brimmed hat upon leaving the clinic and walking to his car. Similar to the first PDT session 1 month prior, he experienced minimal pain immediately after treatment. Once home and approximately 4 to 5 hours after PDT, he tended to a fire using his left hand and leaned into the fireplace with the left side of his face, which was within an arm’s length of the flames. Although his skin did not come in direct contact with the flames, the brief 2- to 3-minute exposure to the flame’s light and heat produced an immediate intense burning pain that the patient likened to the pain of blue light exposure. Within 24 hours, he developed a severe inflammatory reaction that included erythema, edema, desquamation, and pustules on the left side of the chin and cheek that produced a purulent discharge (Figure). The purulence resolved the next day; however, the other clinical manifestations persisted for 1 week. Despite the discomfort and symptoms, our patient did not seek medical attention and instead managed his symptoms conservatively with cold compresses. Although he noticed an overall subjective improvement in the appearance of his face after this second treatment, he received a third treatment with PDT approximately 1 month later, which resulted in a response that was similar to his first visit.
Photodynamic therapy is an increasingly accepted treatment modality for a plethora of benign and malignant dermatologic conditions. Although blue and red light are the most common light sources utilized with PDT because their wavelengths (404–420 nm and 635 nm, respectively) correspond to the excitation peaks of photosensitizers, alternative light sources increasingly are being explored. There is increasing interest in utilizing infrared (IR) light sources (700–1,000,000 nm) to penetrate deeper into the skin in the treatment of precancerous and cancerous lesions. Exposure to IR radiation is known to raise skin temperature via inside-out dermal water absorption and is thought to be useful in PDT-ALA by promoting ALA penetration and its conversion to PpIX.8 In a randomized controlled trial by Giehl et al,9 visible light plus water-filtered IR-A light was shown to produce considerably less pain in ALA-PDT compared to placebo, though efficacy was not statistically affected. There are burgeoning trials examining the role of IR in treating dermatologic conditions such as acne, but research is still needed on ALA-PDT activated by IR radiation to target AKs.
Although the PDT side-effect profile of phototoxicity, dyspigmentation, and hypersensitivity is well documented, phototoxicity secondary to flame exposure is rare. In our patient, the synergistic effect of light and heat produced an exuberant phototoxic reaction. As the applications for PDT continue to broaden, this case may represent the importance of addressing additional precautions, such as avoiding open flames in the house or while camping, in the PDT aftercare instructions to maximize patient safety.
- Fritsch C, Ruzicka T. Fluorescence diagnosis and photodynamic therapy in dermatology from experimental state to clinic standard methods. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2006;25:425-439.
- Lang K, Schulte KW, Ruzicka T, et al. Aminolevulinic acid (Levulan)in photodynamic therapy of actinic keratoses. Skin Therapy Lett. 2001;6:1-2, 5.
- Kennedy JC, Pottier RH. Endogenous protoporphyrin IX, a clinically useful photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy. J Photochem Photobiol B. 1992;14:275-292.
- Wan MT, Lin JY. Current evidence and applications of photodynamic therapy in dermatology. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2014;7:145-163.
- Gad F, Viau G, Boushira M, et al. Photodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid induces apoptosis and caspase activation in malignant T cells. J Cutan Med Surg. 2001;5:8-13.
- Piacquadio DJ, Chen DM, Farber HF, et al. Photodynamic therapy with aminolevulinic acid topical solution and visible blue light in the treatment of multiple actinic keratoses of the face and scalp: investigator-blinded, phase 3, multicenter trials. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:41-46.
- Rhodes LE, Tsoukas MM, Anderson RR, et al. Iontophoretic delivery of ALA provides a quantitative model for ALA pharmacokinetics and PpIX phototoxicity in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1997;108:87-91.
- Dover JS, Phillips TJ, Arndt KA. Cutaneous effects and therapeutic uses of heat with emphasis on infrared radiation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20(2, pt 1):278-286.
- Giehl KA, Kriz M, Grahovac M, et al. A controlled trial of photodynamic therapy of actinic keratosis comparing different red light sources. Eur J Dermatol. 2014;24:335-341.
To the Editor:
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a US Food and Drug Administration–approved treatment for actinic keratosis (AK). It also commonly is administered off label for basal cell carcinoma, Bowen disease, photoaging, and acne vulgaris and is being investigated for other applications.1,2 In the context of treating AK, the mechanism employed in PDT most commonly involves the application of exogenous aminolevulinic acid (ALA), which is metabolized to the endogenous photosensitizer protoporphyrin IX (PpIX) in skin cells by enzymes in the heme biosynthetic pathway.3 The preferential uptake of ALA and conversion to PpIX is due to the altered and increased permeability of abnormal keratin layers of aging, sun-damaged cells, and skin tumors. Selectivity of ALA also occurs due to the preferential intracellular accumulation of PpIX in proliferating, relatively iron–deficient, precancerous and cancerous cells. The therapeutic effect is achieved with light exposure to blue light wavelength at 417 nm and corresponds to the excitation peak of PpIX,4 which activates PpIX and forms reactive oxygen species in the presence of oxygen that ultimately cause cell necrosis and apoptosis.5 Because it takes approximately 24 hours for PpIX to be completely metabolized from the skin, patients are counseled to avoid sun or artificial light exposure in the first 24 hours post-PDT, regardless of the indication, to avoid a severe phototoxic reaction.3,6,7 Although it is normal and desirable for patients to experience some form of a phototoxic reaction, which may include erythema, edema, crusting, vesiculation, or erosion in most patients, these types of reactions most often are secondary to the intended exposure and incidental natural or artificial light exposures.6 We report a case of a severe phototoxic reaction in which a patient experienced painful erythema and purulence on the left side of the chin after being within an arm’s length of a flame in a fireplace following PDT treatment.
A 59-year-old man presented to our dermatology clinic for his second of 3 PDT sessions to treat AKs on the face. He had a history of a basal cell carcinoma on the left nasolabial fold that previously was treated with Mohs micrographic surgery and melanoma on the left ear that was previously treated with excision. The patient received the initial PDT session 1 month prior and experienced a mild reaction with minimal redness and peeling that resolved in 4 to 5 days. For the second treatment, per standard protocol at our clinic, ALA was applied to the face, after which the patient incubated for 1 hour prior to blue light exposure (mean [SD] peak output of 417 [5] nm for 1000 seconds and 10 J/cm2).
After blue light exposure, broad-spectrum sunscreen (sun protection factor 47) was applied to our patient’s face, and he wore a wide-brimmed hat upon leaving the clinic and walking to his car. Similar to the first PDT session 1 month prior, he experienced minimal pain immediately after treatment. Once home and approximately 4 to 5 hours after PDT, he tended to a fire using his left hand and leaned into the fireplace with the left side of his face, which was within an arm’s length of the flames. Although his skin did not come in direct contact with the flames, the brief 2- to 3-minute exposure to the flame’s light and heat produced an immediate intense burning pain that the patient likened to the pain of blue light exposure. Within 24 hours, he developed a severe inflammatory reaction that included erythema, edema, desquamation, and pustules on the left side of the chin and cheek that produced a purulent discharge (Figure). The purulence resolved the next day; however, the other clinical manifestations persisted for 1 week. Despite the discomfort and symptoms, our patient did not seek medical attention and instead managed his symptoms conservatively with cold compresses. Although he noticed an overall subjective improvement in the appearance of his face after this second treatment, he received a third treatment with PDT approximately 1 month later, which resulted in a response that was similar to his first visit.

Photodynamic therapy is an increasingly accepted treatment modality for a plethora of benign and malignant dermatologic conditions. Although blue and red light are the most common light sources utilized with PDT because their wavelengths (404–420 nm and 635 nm, respectively) correspond to the excitation peaks of photosensitizers, alternative light sources increasingly are being explored. There is increasing interest in utilizing infrared (IR) light sources (700–1,000,000 nm) to penetrate deeper into the skin in the treatment of precancerous and cancerous lesions. Exposure to IR radiation is known to raise skin temperature via inside-out dermal water absorption and is thought to be useful in PDT-ALA by promoting ALA penetration and its conversion to PpIX.8 In a randomized controlled trial by Giehl et al,9 visible light plus water-filtered IR-A light was shown to produce considerably less pain in ALA-PDT compared to placebo, though efficacy was not statistically affected. There are burgeoning trials examining the role of IR in treating dermatologic conditions such as acne, but research is still needed on ALA-PDT activated by IR radiation to target AKs.
Although the PDT side-effect profile of phototoxicity, dyspigmentation, and hypersensitivity is well documented, phototoxicity secondary to flame exposure is rare. In our patient, the synergistic effect of light and heat produced an exuberant phototoxic reaction. As the applications for PDT continue to broaden, this case may represent the importance of addressing additional precautions, such as avoiding open flames in the house or while camping, in the PDT aftercare instructions to maximize patient safety.
To the Editor:
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a US Food and Drug Administration–approved treatment for actinic keratosis (AK). It also commonly is administered off label for basal cell carcinoma, Bowen disease, photoaging, and acne vulgaris and is being investigated for other applications.1,2 In the context of treating AK, the mechanism employed in PDT most commonly involves the application of exogenous aminolevulinic acid (ALA), which is metabolized to the endogenous photosensitizer protoporphyrin IX (PpIX) in skin cells by enzymes in the heme biosynthetic pathway.3 The preferential uptake of ALA and conversion to PpIX is due to the altered and increased permeability of abnormal keratin layers of aging, sun-damaged cells, and skin tumors. Selectivity of ALA also occurs due to the preferential intracellular accumulation of PpIX in proliferating, relatively iron–deficient, precancerous and cancerous cells. The therapeutic effect is achieved with light exposure to blue light wavelength at 417 nm and corresponds to the excitation peak of PpIX,4 which activates PpIX and forms reactive oxygen species in the presence of oxygen that ultimately cause cell necrosis and apoptosis.5 Because it takes approximately 24 hours for PpIX to be completely metabolized from the skin, patients are counseled to avoid sun or artificial light exposure in the first 24 hours post-PDT, regardless of the indication, to avoid a severe phototoxic reaction.3,6,7 Although it is normal and desirable for patients to experience some form of a phototoxic reaction, which may include erythema, edema, crusting, vesiculation, or erosion in most patients, these types of reactions most often are secondary to the intended exposure and incidental natural or artificial light exposures.6 We report a case of a severe phototoxic reaction in which a patient experienced painful erythema and purulence on the left side of the chin after being within an arm’s length of a flame in a fireplace following PDT treatment.
A 59-year-old man presented to our dermatology clinic for his second of 3 PDT sessions to treat AKs on the face. He had a history of a basal cell carcinoma on the left nasolabial fold that previously was treated with Mohs micrographic surgery and melanoma on the left ear that was previously treated with excision. The patient received the initial PDT session 1 month prior and experienced a mild reaction with minimal redness and peeling that resolved in 4 to 5 days. For the second treatment, per standard protocol at our clinic, ALA was applied to the face, after which the patient incubated for 1 hour prior to blue light exposure (mean [SD] peak output of 417 [5] nm for 1000 seconds and 10 J/cm2).
After blue light exposure, broad-spectrum sunscreen (sun protection factor 47) was applied to our patient’s face, and he wore a wide-brimmed hat upon leaving the clinic and walking to his car. Similar to the first PDT session 1 month prior, he experienced minimal pain immediately after treatment. Once home and approximately 4 to 5 hours after PDT, he tended to a fire using his left hand and leaned into the fireplace with the left side of his face, which was within an arm’s length of the flames. Although his skin did not come in direct contact with the flames, the brief 2- to 3-minute exposure to the flame’s light and heat produced an immediate intense burning pain that the patient likened to the pain of blue light exposure. Within 24 hours, he developed a severe inflammatory reaction that included erythema, edema, desquamation, and pustules on the left side of the chin and cheek that produced a purulent discharge (Figure). The purulence resolved the next day; however, the other clinical manifestations persisted for 1 week. Despite the discomfort and symptoms, our patient did not seek medical attention and instead managed his symptoms conservatively with cold compresses. Although he noticed an overall subjective improvement in the appearance of his face after this second treatment, he received a third treatment with PDT approximately 1 month later, which resulted in a response that was similar to his first visit.

Photodynamic therapy is an increasingly accepted treatment modality for a plethora of benign and malignant dermatologic conditions. Although blue and red light are the most common light sources utilized with PDT because their wavelengths (404–420 nm and 635 nm, respectively) correspond to the excitation peaks of photosensitizers, alternative light sources increasingly are being explored. There is increasing interest in utilizing infrared (IR) light sources (700–1,000,000 nm) to penetrate deeper into the skin in the treatment of precancerous and cancerous lesions. Exposure to IR radiation is known to raise skin temperature via inside-out dermal water absorption and is thought to be useful in PDT-ALA by promoting ALA penetration and its conversion to PpIX.8 In a randomized controlled trial by Giehl et al,9 visible light plus water-filtered IR-A light was shown to produce considerably less pain in ALA-PDT compared to placebo, though efficacy was not statistically affected. There are burgeoning trials examining the role of IR in treating dermatologic conditions such as acne, but research is still needed on ALA-PDT activated by IR radiation to target AKs.
Although the PDT side-effect profile of phototoxicity, dyspigmentation, and hypersensitivity is well documented, phototoxicity secondary to flame exposure is rare. In our patient, the synergistic effect of light and heat produced an exuberant phototoxic reaction. As the applications for PDT continue to broaden, this case may represent the importance of addressing additional precautions, such as avoiding open flames in the house or while camping, in the PDT aftercare instructions to maximize patient safety.
- Fritsch C, Ruzicka T. Fluorescence diagnosis and photodynamic therapy in dermatology from experimental state to clinic standard methods. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2006;25:425-439.
- Lang K, Schulte KW, Ruzicka T, et al. Aminolevulinic acid (Levulan)in photodynamic therapy of actinic keratoses. Skin Therapy Lett. 2001;6:1-2, 5.
- Kennedy JC, Pottier RH. Endogenous protoporphyrin IX, a clinically useful photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy. J Photochem Photobiol B. 1992;14:275-292.
- Wan MT, Lin JY. Current evidence and applications of photodynamic therapy in dermatology. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2014;7:145-163.
- Gad F, Viau G, Boushira M, et al. Photodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid induces apoptosis and caspase activation in malignant T cells. J Cutan Med Surg. 2001;5:8-13.
- Piacquadio DJ, Chen DM, Farber HF, et al. Photodynamic therapy with aminolevulinic acid topical solution and visible blue light in the treatment of multiple actinic keratoses of the face and scalp: investigator-blinded, phase 3, multicenter trials. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:41-46.
- Rhodes LE, Tsoukas MM, Anderson RR, et al. Iontophoretic delivery of ALA provides a quantitative model for ALA pharmacokinetics and PpIX phototoxicity in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1997;108:87-91.
- Dover JS, Phillips TJ, Arndt KA. Cutaneous effects and therapeutic uses of heat with emphasis on infrared radiation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20(2, pt 1):278-286.
- Giehl KA, Kriz M, Grahovac M, et al. A controlled trial of photodynamic therapy of actinic keratosis comparing different red light sources. Eur J Dermatol. 2014;24:335-341.
- Fritsch C, Ruzicka T. Fluorescence diagnosis and photodynamic therapy in dermatology from experimental state to clinic standard methods. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2006;25:425-439.
- Lang K, Schulte KW, Ruzicka T, et al. Aminolevulinic acid (Levulan)in photodynamic therapy of actinic keratoses. Skin Therapy Lett. 2001;6:1-2, 5.
- Kennedy JC, Pottier RH. Endogenous protoporphyrin IX, a clinically useful photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy. J Photochem Photobiol B. 1992;14:275-292.
- Wan MT, Lin JY. Current evidence and applications of photodynamic therapy in dermatology. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2014;7:145-163.
- Gad F, Viau G, Boushira M, et al. Photodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid induces apoptosis and caspase activation in malignant T cells. J Cutan Med Surg. 2001;5:8-13.
- Piacquadio DJ, Chen DM, Farber HF, et al. Photodynamic therapy with aminolevulinic acid topical solution and visible blue light in the treatment of multiple actinic keratoses of the face and scalp: investigator-blinded, phase 3, multicenter trials. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:41-46.
- Rhodes LE, Tsoukas MM, Anderson RR, et al. Iontophoretic delivery of ALA provides a quantitative model for ALA pharmacokinetics and PpIX phototoxicity in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1997;108:87-91.
- Dover JS, Phillips TJ, Arndt KA. Cutaneous effects and therapeutic uses of heat with emphasis on infrared radiation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20(2, pt 1):278-286.
- Giehl KA, Kriz M, Grahovac M, et al. A controlled trial of photodynamic therapy of actinic keratosis comparing different red light sources. Eur J Dermatol. 2014;24:335-341.
Practice Points
- As the applications of photodynamic therapy (PDT) in dermatology continue to expand, it is imperative for providers and patients alike to be knowledgeable with aftercare instructions and potential adverse effects.
- Avoid open flames in the house or while camping following PDT to maximize patient safety and prevent phototoxicity.
Early Pilomatrix Carcinoma: A Case Report With Emphasis on Molecular Pathology and Review of the Literature
Pilomatrix carcinoma is a rare adnexal tumor with origin from the germinative matrical cells of the hair follicle. Clinically, it presents as a solitary lesion commonly found in the head and neck region as well as the upper back. The tumors cannot be distinguished by their clinical appearance only and frequently are mistaken for cysts. Histopathologic examination provides the definitive diagnosis in most cases. These carcinomas are aggressive neoplasms with a high probability of local recurrence and distant metastasis. Assessment of the Wnt signaling pathway components such as β-catenin, lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (LEF-1), and caudal-related homeobox transcription factor 2 (CDX-2) potentially can be used for diagnostic purposes and targeted therapy.
We report a rare and unique case of early pilomatrix carcinoma with intralesional melanocytes. We review the molecular pathology and pathogenesis of these carcinomas as well as the significance of early diagnosis.
Case Report
A 73-year-old man with a history of extensive sun exposure presented with a 1-cm, raised, rapidly growing, slightly irregular, purple lesion on the right forearm of 3 months’ duration with tendency to bleed. He did not have a history of skin cancers and was otherwise healthy. Excision was recommended due to the progressive and rapid growth of the lesion.
Histopathologic Findings—Gross examination revealed a 0.9×0.7-cm, raised, slightly irregular lesion located 1 mm away from the closest peripheral margin. Histologically, the lesion was a relatively circumscribed, dermal-based basaloid neoplasm with slightly ill-defined edges involving the superficial and deep dermis (Figure 1A). The neoplasm was formed predominantly of sheets of basaloid cells and small nests of ghost cells, in addition to some squamoid and transitional cells (Figure 1B). The basaloid cells exhibited severe nuclear atypia, pleomorphism, increased nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio (Figure 1C), minimal to moderate amounts of eosinophilic cytoplasm, enlarged nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and coarse chromatin pattern. Abundant mitotic activity and apoptotic bodies were present as well as focal area of central necrosis (Figure 1C). Also, melanophages and a multinucleated giant cell reaction was noted. Elastic trichrome special stain highlighted focal infiltration of the neoplastic cells into the adjacent desmoplastic stroma. Melanin stain was negative for melanin pigment within the neoplasm. Given the presence of severely atypical basaloid cells along with ghost cells indicating matrical differentiation, a diagnosis of pilomatrix carcinoma was rendered.
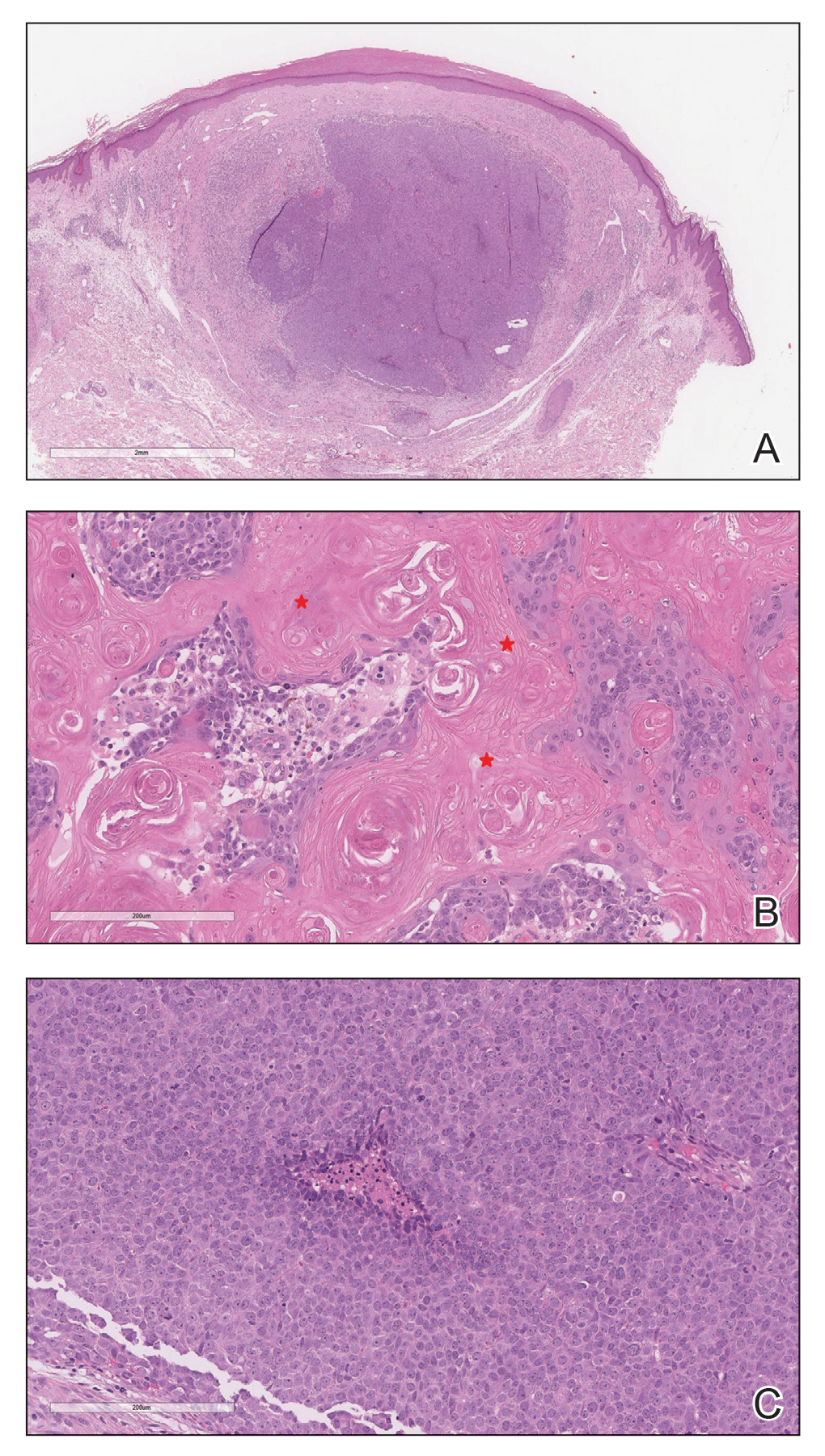
Immunohistochemistry—The neoplastic cells were diffusely positive for p63, CDX-2 (Figure 2A), β-catenin (Figure 2B), and CD10 (Figure 2C), and focally and weakly positive for cytokeratin (CK) 5, BerEP4 (staining the tumor periphery), androgen receptor, and CK18 (a low-molecular-weight keratin). They were negative for monoclonal carcinoembryonic antigen, epithelial membrane antigen, CK7, CK20, CD34, SOX-10, CD56, synaptophysin, and chromogranin. Cytokeratin 14 was positive in the squamoid cells but negative in the basaloid cells. SOX-10 and melanoma cocktail immunostains demonstrated few intralesional dendritic melanocytes.

Comment
Pilomatrix carcinoma is a rare malignant cutaneous adnexal neoplasm with origin from the germinative matrix of the hair bulb region of hair follicles. Pilomatrix carcinoma was first reported in 1980.1,2 These tumors are characterized by rapid growth and aggressive behavior. Their benign counterpart, pilomatrixoma, is a slow-growing, dermal or subcutaneous tumor that rarely recurs after complete excision.
As with pilomatrixoma, pilomatrix carcinomas are asymptomatic and present as solitary dermal or subcutaneous masses3,4 that most commonly are found in the posterior neck, upper back, and preauricular regions of middle-aged or elderly adults with male predominance.5 They range in size from 0.5 to 20 cm with a mean of 4 cm that is slightly larger than pilomatrixoma. Pilomatrix carcinomas predominantly are firm tumors with or without cystic components, and they exhibit a high probability of recurrence and have risk for distant metastasis.6-15
The differential diagnosis includes epidermal cysts, pilomatrixoma, basal cell carcinoma with matrical differentiation, trichoblastoma/trichoblastic carcinoma, and trichilemmal carcinoma. Pilomatrix carcinomas frequently are mistaken for epidermal cysts on clinical examination. Such a distinction can be easily resolved by histopathologic evaluation. The more challenging differential diagnosis is with pilomatrixoma. Histologically, pilomatrixomas consist of a distinct population of cells including basaloid, squamoid, transitional, and shadow cells in variable proportions. The basaloid cells transition to shadow cells in an organized zonal fashion.16 Compared to pilomatrixomas, pilomatrix carcinomas often show predominance of the basaloid cells; marked cytologic atypia and pleomorphism; numerous mitotic figures; deep infiltrative pattern into subcutaneous fat, fascia, and skeletal muscle; stromal desmoplasia; necrosis; and neurovascular invasion (Tables 1 and 2). Furthermore, the shadow cells tend to form a small nested pattern in pilomatrix carcinoma instead of the flat sheetlike pattern usually observed in pilomatrixoma.16 Basal cell carcinoma with matrical differentiation can pose a diagnostic challenge in the differential diagnosis; basal cell carcinoma usually exhibits a peripheral palisade of the basaloid cells accompanied by retraction spaces separating the tumor from the stroma. Trichoblastoma/trichoblastic carcinoma with matrical differentiation can be distinguished by its exuberant stroma, prominent primitive hair follicles, and papillary mesenchymal bodies. Trichilemmal carcinomas are recognized by their connection to the overlying epidermis, peripheral palisading, and presence of clear cells, while pilomatrix carcinoma lacks connection to the surface epithelium.

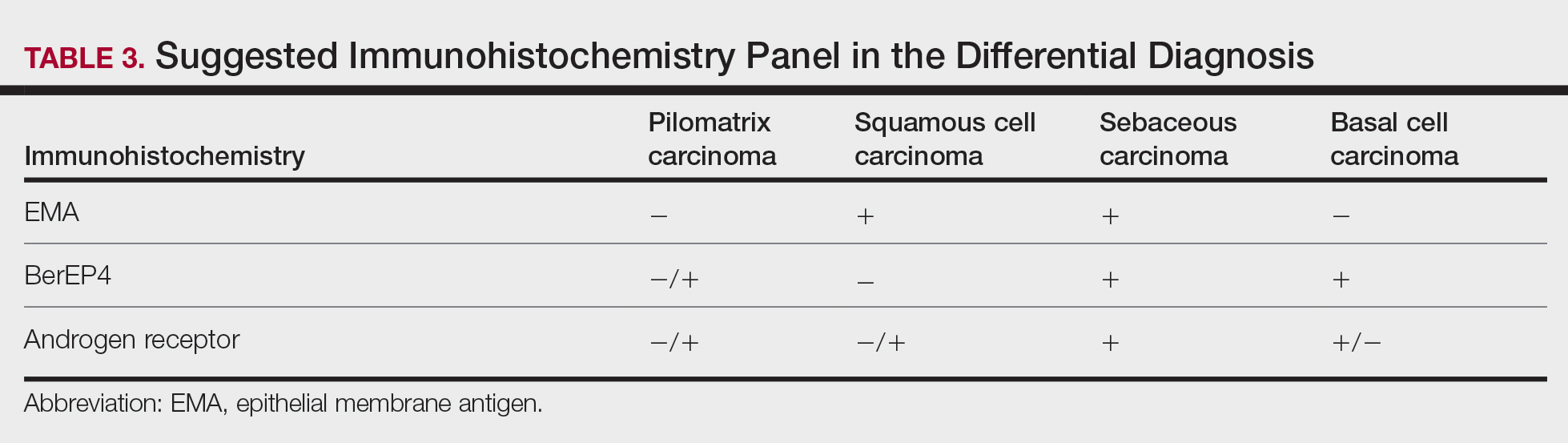
Immunohistochemical stains have little to no role in the differential diagnosis, and morphology is the mainstay in making the diagnosis. Rarely, pilomatrix carcinoma can be confused with poorly differentiated sebaceous carcinoma and poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma. Although careful scrutiny of the histologic features may help identify mature sebocytes in sebaceous carcinoma, evidence of keratinization in squamous cell carcinoma and ghost cells in pilomatrix carcinoma, using a panel of immunohistochemical stains can be helpful in reaching the final diagnosis (Table 3).

The development of hair matrix tumors have been known to harbor mutations in exon 3 of the catenin beta-1 gene, CTNNB1, that encodes for β-catenin, a downstream effector in the Wnt signaling pathway responsible for differentiation, proliferation, and adhesion of epithelial stem cells.17-21 In a study conducted by Kazakov et al,22 DNA was extracted from 86 lesions: 4 were pilomatrixomas and 1 was a pilomatrix carcinoma. A polymerase chain reaction assay revealed 8 pathogenic variants of the β-catenin gene. D32Y (CTNNB1):c.94G>T (p.Asp32Tyr) and G34R (CTNNB1):c.100G>C (p.Gly34Arg) were the mutations present in pilomatrixoma and pilomatrix carcinoma, respectively.22 In addition, there are several proteins that are part of the Wnt pathway in addition to β-catenin—LEF-1 and CDX-2.
Tumminello and Hosler23 found that pilomatrixomas and pilomatrix carcinomas were positive for CDX-2, β-catenin, and LEF-1 by immunohistochemistry. These downstream molecules in the Wnt signaling pathway could have the potential to be used as diagnostic and prognostic markers.2,13,15,23
Although the pathogenesis is unclear, there are 2 possible mechanisms by which pilomatrix carcinomas develop. They can either arise as de novo tumors, or it is possible that initial mutations in β-catenin result in the formation of pilomatrixomas at an early age that may undergo malignant transformation in elderly patients over time with additional mutations.2
Our case was strongly and diffusely positive for β-catenin in a nuclear and cytoplasmic pattern and CDX-2 in a nuclear pattern, supporting the role of the Wnt signaling pathway in such tumors. Furthermore, our case demonstrated the presence of few intralesional normal dendritic melanocytes, a rare finding1,24,25 but not unexpected, as melanocytes normally are present within the hair follicle matrix.
Pilomatrix carcinomas are aggressive tumors with a high risk for local recurrence and tendency for metastasis. In a study of 13 cases of pilomatrix carcinomas, Herrmann et al13 found that metastasis was significantly associated with local tumor recurrence (P<.0413). They concluded that the combination of overall high local recurrence and metastatic rates of pilomatrix carcinoma as well as documented tumor-related deaths would warrant continued patient follow-up, especially for recurrent tumors.13 Rapid growth of a tumor, either de novo or following several months of stable size, should alert physicians to perform a diagnostic biopsy.
Management options of pilomatrix carcinoma include surgery or radiation with close follow-up. The most widely reported treatment of pilomatrix carcinoma is wide local excision with histologically confirmed clear margins. Mohs micrographic surgery is an excellent treatment option.2,13-15 Adjuvant radiation therapy may be necessary following excision. Currently there is no consensus on surgical management, and standard excisional margins have not been defined.26 Jones et al2 concluded that complete excision with wide margins likely is curative, with decreased rates of recurrence, and better awareness of this carcinoma would lead to appropriate treatment while avoiding unnecessary diagnostic tests.2
Conclusion
We report an exceptionally unique case of early pilomatrix carcinoma with a discussion on the pathogenesis and molecular pathology of hair matrix tumors. A large cohort of patients with longer follow-up periods and better molecular characterization is essential in drawing accurate information about their prognosis, identifying molecular markers that can be used as therapeutic targets, and determining ideal management strategy.
- Jani P, Chetty R, Ghazarian DM. An unusual composite pilomatrix carcinoma with intralesional melanocytes: differential diagnosis, immunohistochemical evaluation, and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2008;30:174-177.
- Jones C, Twoon M, Ho W, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: 12-year experience and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:33-38.
- Forbis R, Helwig EB. Pilomatrixoma (calcifying epithelioma). Arch Dermatol. 1961;83:606.
- Elder D, Elenitsas R, Ragsdale BD. Tumors of epidermal appendages. In: Elder D, Elenitsas R, Jaworsky C, eds. Lever’s Histopathology of the Skin. 8th ed. Lippincott Raven; 1997:757-759.
- Aherne NJ, Fitzpatrick DA, Gibbons D, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma presenting as an extra axial mass: clinicopathological features. Diagn Pathol. 2008;3:47.
- Papadakis M, de Bree E, Floros N, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: more malignant biological behavior than was considered in the past. Mol Clin Oncol. 2017;6:415-418.
- LeBoit PE, Parslow TG, Choy SH. Hair matrix differentiation: occurrence in lesions other than pilomatricoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1987;9:399-405.
- Campoy F, Stiefel P, Stiefel E, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: role played by MR imaging. Neuroradiology. 1989;31:196-198.
- Tateyama H, Eimoto T, Tada T, et al. Malignant pilomatricoma: an immunohistochemical study with antihair keratin antibody. Cancer. 1992;69:127-132.
- O’Donovan DG, Freemont AJ, Adams JE, et al. Malignant pilomatrixoma with bone metastasis. Histopathology. 1993;23:385-386.
- Cross P, Richmond I, Wells S, et al. Malignant pilomatrixoma with bone metastasis. Histopathology. 1994;24:499-500.
- Niedermeyer HP, Peris K, Höfler H. Pilomatrix carcinoma with multiple visceral metastases: report of a case. Cancer. 1996;77:1311-1314.
- Herrmann JL, Allan A, Trapp KM, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: 13 new cases and review of the literature with emphasis on predictors of metastasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:38-43.
- Xing L, Marzolf SA, Vandergriff T, et al. Facial pilomatrix carcinomas treated with Mohs micrographic surgery. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:253-255.
- Fernandez-Flores A, Cassarino DS. Sarcomatoid pilomatrix carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:508-514.
- Sau P, Lupton GP, Graham JH. Pilomatrix carcinoma. Cancer. 1993;71:2491-2498.
- Chan E, Gat U, McNiff JM, et al. A common human skin tumour is caused by activating mutations in β-catenin. Nat Genet. 1999;21:410-413.
- Huelsken J, Vogel R, Erdmann B, et al. β-catenin controls hair follicle morphogenesis and stem cell differentiation in the skin. Cell. 2001;105:533-545.
- Kikuchi A. Tumor formation by genetic mutations in the components of the Wnt signaling pathway. Cancer Sci. 2003;94:225-229.
- Durand M, Moles J. Beta-catenin mutations in a common skin cancer: pilomatricoma. Bull Cancer. 1999;86:725-726.
- Lazar AJF, Calonje E, Grayson W, et al. Pilomatrix carcinomas contain mutations in CTNNB1, the gene encoding beta-catenin. J Cutan Pathol. 2005;32:148-157.
- Kazakov DV, Sima R, Vanecek T, et al. Mutations in exon 3 of the CTNNB1 gene (β-catenin gene) in cutaneous adnexal tumors. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009;31:248-255.
- Tumminello K, Hosler GA. CDX2 and LEF-1 expression in pilomatrical tumors and their utility in the diagnosis of pilomatrical carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:318-324.
- Rodic´ N, Taube JM, Manson P, et al Locally invasive dermal squamomelanocytic tumor with matrical differentiation: a peculiar case with review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35:E72-E76.
- Perez C, Debbaneh M, Cassarino D. Preference for the term pilomatrical carcinoma with melanocytic hyperplasia: letter to the editor. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:655-657.
- Herrmann JL, Allan A, Trapp KM, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: 13 new cases and review of the literature with emphasis on predictors of metastasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:38-43.
Pilomatrix carcinoma is a rare adnexal tumor with origin from the germinative matrical cells of the hair follicle. Clinically, it presents as a solitary lesion commonly found in the head and neck region as well as the upper back. The tumors cannot be distinguished by their clinical appearance only and frequently are mistaken for cysts. Histopathologic examination provides the definitive diagnosis in most cases. These carcinomas are aggressive neoplasms with a high probability of local recurrence and distant metastasis. Assessment of the Wnt signaling pathway components such as β-catenin, lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (LEF-1), and caudal-related homeobox transcription factor 2 (CDX-2) potentially can be used for diagnostic purposes and targeted therapy.
We report a rare and unique case of early pilomatrix carcinoma with intralesional melanocytes. We review the molecular pathology and pathogenesis of these carcinomas as well as the significance of early diagnosis.
Case Report
A 73-year-old man with a history of extensive sun exposure presented with a 1-cm, raised, rapidly growing, slightly irregular, purple lesion on the right forearm of 3 months’ duration with tendency to bleed. He did not have a history of skin cancers and was otherwise healthy. Excision was recommended due to the progressive and rapid growth of the lesion.
Histopathologic Findings—Gross examination revealed a 0.9×0.7-cm, raised, slightly irregular lesion located 1 mm away from the closest peripheral margin. Histologically, the lesion was a relatively circumscribed, dermal-based basaloid neoplasm with slightly ill-defined edges involving the superficial and deep dermis (Figure 1A). The neoplasm was formed predominantly of sheets of basaloid cells and small nests of ghost cells, in addition to some squamoid and transitional cells (Figure 1B). The basaloid cells exhibited severe nuclear atypia, pleomorphism, increased nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio (Figure 1C), minimal to moderate amounts of eosinophilic cytoplasm, enlarged nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and coarse chromatin pattern. Abundant mitotic activity and apoptotic bodies were present as well as focal area of central necrosis (Figure 1C). Also, melanophages and a multinucleated giant cell reaction was noted. Elastic trichrome special stain highlighted focal infiltration of the neoplastic cells into the adjacent desmoplastic stroma. Melanin stain was negative for melanin pigment within the neoplasm. Given the presence of severely atypical basaloid cells along with ghost cells indicating matrical differentiation, a diagnosis of pilomatrix carcinoma was rendered.

Immunohistochemistry—The neoplastic cells were diffusely positive for p63, CDX-2 (Figure 2A), β-catenin (Figure 2B), and CD10 (Figure 2C), and focally and weakly positive for cytokeratin (CK) 5, BerEP4 (staining the tumor periphery), androgen receptor, and CK18 (a low-molecular-weight keratin). They were negative for monoclonal carcinoembryonic antigen, epithelial membrane antigen, CK7, CK20, CD34, SOX-10, CD56, synaptophysin, and chromogranin. Cytokeratin 14 was positive in the squamoid cells but negative in the basaloid cells. SOX-10 and melanoma cocktail immunostains demonstrated few intralesional dendritic melanocytes.

Comment
Pilomatrix carcinoma is a rare malignant cutaneous adnexal neoplasm with origin from the germinative matrix of the hair bulb region of hair follicles. Pilomatrix carcinoma was first reported in 1980.1,2 These tumors are characterized by rapid growth and aggressive behavior. Their benign counterpart, pilomatrixoma, is a slow-growing, dermal or subcutaneous tumor that rarely recurs after complete excision.
As with pilomatrixoma, pilomatrix carcinomas are asymptomatic and present as solitary dermal or subcutaneous masses3,4 that most commonly are found in the posterior neck, upper back, and preauricular regions of middle-aged or elderly adults with male predominance.5 They range in size from 0.5 to 20 cm with a mean of 4 cm that is slightly larger than pilomatrixoma. Pilomatrix carcinomas predominantly are firm tumors with or without cystic components, and they exhibit a high probability of recurrence and have risk for distant metastasis.6-15
The differential diagnosis includes epidermal cysts, pilomatrixoma, basal cell carcinoma with matrical differentiation, trichoblastoma/trichoblastic carcinoma, and trichilemmal carcinoma. Pilomatrix carcinomas frequently are mistaken for epidermal cysts on clinical examination. Such a distinction can be easily resolved by histopathologic evaluation. The more challenging differential diagnosis is with pilomatrixoma. Histologically, pilomatrixomas consist of a distinct population of cells including basaloid, squamoid, transitional, and shadow cells in variable proportions. The basaloid cells transition to shadow cells in an organized zonal fashion.16 Compared to pilomatrixomas, pilomatrix carcinomas often show predominance of the basaloid cells; marked cytologic atypia and pleomorphism; numerous mitotic figures; deep infiltrative pattern into subcutaneous fat, fascia, and skeletal muscle; stromal desmoplasia; necrosis; and neurovascular invasion (Tables 1 and 2). Furthermore, the shadow cells tend to form a small nested pattern in pilomatrix carcinoma instead of the flat sheetlike pattern usually observed in pilomatrixoma.16 Basal cell carcinoma with matrical differentiation can pose a diagnostic challenge in the differential diagnosis; basal cell carcinoma usually exhibits a peripheral palisade of the basaloid cells accompanied by retraction spaces separating the tumor from the stroma. Trichoblastoma/trichoblastic carcinoma with matrical differentiation can be distinguished by its exuberant stroma, prominent primitive hair follicles, and papillary mesenchymal bodies. Trichilemmal carcinomas are recognized by their connection to the overlying epidermis, peripheral palisading, and presence of clear cells, while pilomatrix carcinoma lacks connection to the surface epithelium.

Immunohistochemical stains have little to no role in the differential diagnosis, and morphology is the mainstay in making the diagnosis. Rarely, pilomatrix carcinoma can be confused with poorly differentiated sebaceous carcinoma and poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma. Although careful scrutiny of the histologic features may help identify mature sebocytes in sebaceous carcinoma, evidence of keratinization in squamous cell carcinoma and ghost cells in pilomatrix carcinoma, using a panel of immunohistochemical stains can be helpful in reaching the final diagnosis (Table 3).

The development of hair matrix tumors have been known to harbor mutations in exon 3 of the catenin beta-1 gene, CTNNB1, that encodes for β-catenin, a downstream effector in the Wnt signaling pathway responsible for differentiation, proliferation, and adhesion of epithelial stem cells.17-21 In a study conducted by Kazakov et al,22 DNA was extracted from 86 lesions: 4 were pilomatrixomas and 1 was a pilomatrix carcinoma. A polymerase chain reaction assay revealed 8 pathogenic variants of the β-catenin gene. D32Y (CTNNB1):c.94G>T (p.Asp32Tyr) and G34R (CTNNB1):c.100G>C (p.Gly34Arg) were the mutations present in pilomatrixoma and pilomatrix carcinoma, respectively.22 In addition, there are several proteins that are part of the Wnt pathway in addition to β-catenin—LEF-1 and CDX-2.

Tumminello and Hosler23 found that pilomatrixomas and pilomatrix carcinomas were positive for CDX-2, β-catenin, and LEF-1 by immunohistochemistry. These downstream molecules in the Wnt signaling pathway could have the potential to be used as diagnostic and prognostic markers.2,13,15,23
Although the pathogenesis is unclear, there are 2 possible mechanisms by which pilomatrix carcinomas develop. They can either arise as de novo tumors, or it is possible that initial mutations in β-catenin result in the formation of pilomatrixomas at an early age that may undergo malignant transformation in elderly patients over time with additional mutations.2
Our case was strongly and diffusely positive for β-catenin in a nuclear and cytoplasmic pattern and CDX-2 in a nuclear pattern, supporting the role of the Wnt signaling pathway in such tumors. Furthermore, our case demonstrated the presence of few intralesional normal dendritic melanocytes, a rare finding1,24,25 but not unexpected, as melanocytes normally are present within the hair follicle matrix.
Pilomatrix carcinomas are aggressive tumors with a high risk for local recurrence and tendency for metastasis. In a study of 13 cases of pilomatrix carcinomas, Herrmann et al13 found that metastasis was significantly associated with local tumor recurrence (P<.0413). They concluded that the combination of overall high local recurrence and metastatic rates of pilomatrix carcinoma as well as documented tumor-related deaths would warrant continued patient follow-up, especially for recurrent tumors.13 Rapid growth of a tumor, either de novo or following several months of stable size, should alert physicians to perform a diagnostic biopsy.
Management options of pilomatrix carcinoma include surgery or radiation with close follow-up. The most widely reported treatment of pilomatrix carcinoma is wide local excision with histologically confirmed clear margins. Mohs micrographic surgery is an excellent treatment option.2,13-15 Adjuvant radiation therapy may be necessary following excision. Currently there is no consensus on surgical management, and standard excisional margins have not been defined.26 Jones et al2 concluded that complete excision with wide margins likely is curative, with decreased rates of recurrence, and better awareness of this carcinoma would lead to appropriate treatment while avoiding unnecessary diagnostic tests.2
Conclusion
We report an exceptionally unique case of early pilomatrix carcinoma with a discussion on the pathogenesis and molecular pathology of hair matrix tumors. A large cohort of patients with longer follow-up periods and better molecular characterization is essential in drawing accurate information about their prognosis, identifying molecular markers that can be used as therapeutic targets, and determining ideal management strategy.
Pilomatrix carcinoma is a rare adnexal tumor with origin from the germinative matrical cells of the hair follicle. Clinically, it presents as a solitary lesion commonly found in the head and neck region as well as the upper back. The tumors cannot be distinguished by their clinical appearance only and frequently are mistaken for cysts. Histopathologic examination provides the definitive diagnosis in most cases. These carcinomas are aggressive neoplasms with a high probability of local recurrence and distant metastasis. Assessment of the Wnt signaling pathway components such as β-catenin, lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (LEF-1), and caudal-related homeobox transcription factor 2 (CDX-2) potentially can be used for diagnostic purposes and targeted therapy.
We report a rare and unique case of early pilomatrix carcinoma with intralesional melanocytes. We review the molecular pathology and pathogenesis of these carcinomas as well as the significance of early diagnosis.
Case Report
A 73-year-old man with a history of extensive sun exposure presented with a 1-cm, raised, rapidly growing, slightly irregular, purple lesion on the right forearm of 3 months’ duration with tendency to bleed. He did not have a history of skin cancers and was otherwise healthy. Excision was recommended due to the progressive and rapid growth of the lesion.
Histopathologic Findings—Gross examination revealed a 0.9×0.7-cm, raised, slightly irregular lesion located 1 mm away from the closest peripheral margin. Histologically, the lesion was a relatively circumscribed, dermal-based basaloid neoplasm with slightly ill-defined edges involving the superficial and deep dermis (Figure 1A). The neoplasm was formed predominantly of sheets of basaloid cells and small nests of ghost cells, in addition to some squamoid and transitional cells (Figure 1B). The basaloid cells exhibited severe nuclear atypia, pleomorphism, increased nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio (Figure 1C), minimal to moderate amounts of eosinophilic cytoplasm, enlarged nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and coarse chromatin pattern. Abundant mitotic activity and apoptotic bodies were present as well as focal area of central necrosis (Figure 1C). Also, melanophages and a multinucleated giant cell reaction was noted. Elastic trichrome special stain highlighted focal infiltration of the neoplastic cells into the adjacent desmoplastic stroma. Melanin stain was negative for melanin pigment within the neoplasm. Given the presence of severely atypical basaloid cells along with ghost cells indicating matrical differentiation, a diagnosis of pilomatrix carcinoma was rendered.

Immunohistochemistry—The neoplastic cells were diffusely positive for p63, CDX-2 (Figure 2A), β-catenin (Figure 2B), and CD10 (Figure 2C), and focally and weakly positive for cytokeratin (CK) 5, BerEP4 (staining the tumor periphery), androgen receptor, and CK18 (a low-molecular-weight keratin). They were negative for monoclonal carcinoembryonic antigen, epithelial membrane antigen, CK7, CK20, CD34, SOX-10, CD56, synaptophysin, and chromogranin. Cytokeratin 14 was positive in the squamoid cells but negative in the basaloid cells. SOX-10 and melanoma cocktail immunostains demonstrated few intralesional dendritic melanocytes.

Comment
Pilomatrix carcinoma is a rare malignant cutaneous adnexal neoplasm with origin from the germinative matrix of the hair bulb region of hair follicles. Pilomatrix carcinoma was first reported in 1980.1,2 These tumors are characterized by rapid growth and aggressive behavior. Their benign counterpart, pilomatrixoma, is a slow-growing, dermal or subcutaneous tumor that rarely recurs after complete excision.
As with pilomatrixoma, pilomatrix carcinomas are asymptomatic and present as solitary dermal or subcutaneous masses3,4 that most commonly are found in the posterior neck, upper back, and preauricular regions of middle-aged or elderly adults with male predominance.5 They range in size from 0.5 to 20 cm with a mean of 4 cm that is slightly larger than pilomatrixoma. Pilomatrix carcinomas predominantly are firm tumors with or without cystic components, and they exhibit a high probability of recurrence and have risk for distant metastasis.6-15
The differential diagnosis includes epidermal cysts, pilomatrixoma, basal cell carcinoma with matrical differentiation, trichoblastoma/trichoblastic carcinoma, and trichilemmal carcinoma. Pilomatrix carcinomas frequently are mistaken for epidermal cysts on clinical examination. Such a distinction can be easily resolved by histopathologic evaluation. The more challenging differential diagnosis is with pilomatrixoma. Histologically, pilomatrixomas consist of a distinct population of cells including basaloid, squamoid, transitional, and shadow cells in variable proportions. The basaloid cells transition to shadow cells in an organized zonal fashion.16 Compared to pilomatrixomas, pilomatrix carcinomas often show predominance of the basaloid cells; marked cytologic atypia and pleomorphism; numerous mitotic figures; deep infiltrative pattern into subcutaneous fat, fascia, and skeletal muscle; stromal desmoplasia; necrosis; and neurovascular invasion (Tables 1 and 2). Furthermore, the shadow cells tend to form a small nested pattern in pilomatrix carcinoma instead of the flat sheetlike pattern usually observed in pilomatrixoma.16 Basal cell carcinoma with matrical differentiation can pose a diagnostic challenge in the differential diagnosis; basal cell carcinoma usually exhibits a peripheral palisade of the basaloid cells accompanied by retraction spaces separating the tumor from the stroma. Trichoblastoma/trichoblastic carcinoma with matrical differentiation can be distinguished by its exuberant stroma, prominent primitive hair follicles, and papillary mesenchymal bodies. Trichilemmal carcinomas are recognized by their connection to the overlying epidermis, peripheral palisading, and presence of clear cells, while pilomatrix carcinoma lacks connection to the surface epithelium.

Immunohistochemical stains have little to no role in the differential diagnosis, and morphology is the mainstay in making the diagnosis. Rarely, pilomatrix carcinoma can be confused with poorly differentiated sebaceous carcinoma and poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma. Although careful scrutiny of the histologic features may help identify mature sebocytes in sebaceous carcinoma, evidence of keratinization in squamous cell carcinoma and ghost cells in pilomatrix carcinoma, using a panel of immunohistochemical stains can be helpful in reaching the final diagnosis (Table 3).

The development of hair matrix tumors have been known to harbor mutations in exon 3 of the catenin beta-1 gene, CTNNB1, that encodes for β-catenin, a downstream effector in the Wnt signaling pathway responsible for differentiation, proliferation, and adhesion of epithelial stem cells.17-21 In a study conducted by Kazakov et al,22 DNA was extracted from 86 lesions: 4 were pilomatrixomas and 1 was a pilomatrix carcinoma. A polymerase chain reaction assay revealed 8 pathogenic variants of the β-catenin gene. D32Y (CTNNB1):c.94G>T (p.Asp32Tyr) and G34R (CTNNB1):c.100G>C (p.Gly34Arg) were the mutations present in pilomatrixoma and pilomatrix carcinoma, respectively.22 In addition, there are several proteins that are part of the Wnt pathway in addition to β-catenin—LEF-1 and CDX-2.

Tumminello and Hosler23 found that pilomatrixomas and pilomatrix carcinomas were positive for CDX-2, β-catenin, and LEF-1 by immunohistochemistry. These downstream molecules in the Wnt signaling pathway could have the potential to be used as diagnostic and prognostic markers.2,13,15,23
Although the pathogenesis is unclear, there are 2 possible mechanisms by which pilomatrix carcinomas develop. They can either arise as de novo tumors, or it is possible that initial mutations in β-catenin result in the formation of pilomatrixomas at an early age that may undergo malignant transformation in elderly patients over time with additional mutations.2
Our case was strongly and diffusely positive for β-catenin in a nuclear and cytoplasmic pattern and CDX-2 in a nuclear pattern, supporting the role of the Wnt signaling pathway in such tumors. Furthermore, our case demonstrated the presence of few intralesional normal dendritic melanocytes, a rare finding1,24,25 but not unexpected, as melanocytes normally are present within the hair follicle matrix.
Pilomatrix carcinomas are aggressive tumors with a high risk for local recurrence and tendency for metastasis. In a study of 13 cases of pilomatrix carcinomas, Herrmann et al13 found that metastasis was significantly associated with local tumor recurrence (P<.0413). They concluded that the combination of overall high local recurrence and metastatic rates of pilomatrix carcinoma as well as documented tumor-related deaths would warrant continued patient follow-up, especially for recurrent tumors.13 Rapid growth of a tumor, either de novo or following several months of stable size, should alert physicians to perform a diagnostic biopsy.
Management options of pilomatrix carcinoma include surgery or radiation with close follow-up. The most widely reported treatment of pilomatrix carcinoma is wide local excision with histologically confirmed clear margins. Mohs micrographic surgery is an excellent treatment option.2,13-15 Adjuvant radiation therapy may be necessary following excision. Currently there is no consensus on surgical management, and standard excisional margins have not been defined.26 Jones et al2 concluded that complete excision with wide margins likely is curative, with decreased rates of recurrence, and better awareness of this carcinoma would lead to appropriate treatment while avoiding unnecessary diagnostic tests.2
Conclusion
We report an exceptionally unique case of early pilomatrix carcinoma with a discussion on the pathogenesis and molecular pathology of hair matrix tumors. A large cohort of patients with longer follow-up periods and better molecular characterization is essential in drawing accurate information about their prognosis, identifying molecular markers that can be used as therapeutic targets, and determining ideal management strategy.
- Jani P, Chetty R, Ghazarian DM. An unusual composite pilomatrix carcinoma with intralesional melanocytes: differential diagnosis, immunohistochemical evaluation, and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2008;30:174-177.
- Jones C, Twoon M, Ho W, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: 12-year experience and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:33-38.
- Forbis R, Helwig EB. Pilomatrixoma (calcifying epithelioma). Arch Dermatol. 1961;83:606.
- Elder D, Elenitsas R, Ragsdale BD. Tumors of epidermal appendages. In: Elder D, Elenitsas R, Jaworsky C, eds. Lever’s Histopathology of the Skin. 8th ed. Lippincott Raven; 1997:757-759.
- Aherne NJ, Fitzpatrick DA, Gibbons D, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma presenting as an extra axial mass: clinicopathological features. Diagn Pathol. 2008;3:47.
- Papadakis M, de Bree E, Floros N, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: more malignant biological behavior than was considered in the past. Mol Clin Oncol. 2017;6:415-418.
- LeBoit PE, Parslow TG, Choy SH. Hair matrix differentiation: occurrence in lesions other than pilomatricoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1987;9:399-405.
- Campoy F, Stiefel P, Stiefel E, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: role played by MR imaging. Neuroradiology. 1989;31:196-198.
- Tateyama H, Eimoto T, Tada T, et al. Malignant pilomatricoma: an immunohistochemical study with antihair keratin antibody. Cancer. 1992;69:127-132.
- O’Donovan DG, Freemont AJ, Adams JE, et al. Malignant pilomatrixoma with bone metastasis. Histopathology. 1993;23:385-386.
- Cross P, Richmond I, Wells S, et al. Malignant pilomatrixoma with bone metastasis. Histopathology. 1994;24:499-500.
- Niedermeyer HP, Peris K, Höfler H. Pilomatrix carcinoma with multiple visceral metastases: report of a case. Cancer. 1996;77:1311-1314.
- Herrmann JL, Allan A, Trapp KM, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: 13 new cases and review of the literature with emphasis on predictors of metastasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:38-43.
- Xing L, Marzolf SA, Vandergriff T, et al. Facial pilomatrix carcinomas treated with Mohs micrographic surgery. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:253-255.
- Fernandez-Flores A, Cassarino DS. Sarcomatoid pilomatrix carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:508-514.
- Sau P, Lupton GP, Graham JH. Pilomatrix carcinoma. Cancer. 1993;71:2491-2498.
- Chan E, Gat U, McNiff JM, et al. A common human skin tumour is caused by activating mutations in β-catenin. Nat Genet. 1999;21:410-413.
- Huelsken J, Vogel R, Erdmann B, et al. β-catenin controls hair follicle morphogenesis and stem cell differentiation in the skin. Cell. 2001;105:533-545.
- Kikuchi A. Tumor formation by genetic mutations in the components of the Wnt signaling pathway. Cancer Sci. 2003;94:225-229.
- Durand M, Moles J. Beta-catenin mutations in a common skin cancer: pilomatricoma. Bull Cancer. 1999;86:725-726.
- Lazar AJF, Calonje E, Grayson W, et al. Pilomatrix carcinomas contain mutations in CTNNB1, the gene encoding beta-catenin. J Cutan Pathol. 2005;32:148-157.
- Kazakov DV, Sima R, Vanecek T, et al. Mutations in exon 3 of the CTNNB1 gene (β-catenin gene) in cutaneous adnexal tumors. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009;31:248-255.
- Tumminello K, Hosler GA. CDX2 and LEF-1 expression in pilomatrical tumors and their utility in the diagnosis of pilomatrical carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:318-324.
- Rodic´ N, Taube JM, Manson P, et al Locally invasive dermal squamomelanocytic tumor with matrical differentiation: a peculiar case with review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35:E72-E76.
- Perez C, Debbaneh M, Cassarino D. Preference for the term pilomatrical carcinoma with melanocytic hyperplasia: letter to the editor. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:655-657.
- Herrmann JL, Allan A, Trapp KM, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: 13 new cases and review of the literature with emphasis on predictors of metastasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:38-43.
- Jani P, Chetty R, Ghazarian DM. An unusual composite pilomatrix carcinoma with intralesional melanocytes: differential diagnosis, immunohistochemical evaluation, and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2008;30:174-177.
- Jones C, Twoon M, Ho W, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: 12-year experience and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:33-38.
- Forbis R, Helwig EB. Pilomatrixoma (calcifying epithelioma). Arch Dermatol. 1961;83:606.
- Elder D, Elenitsas R, Ragsdale BD. Tumors of epidermal appendages. In: Elder D, Elenitsas R, Jaworsky C, eds. Lever’s Histopathology of the Skin. 8th ed. Lippincott Raven; 1997:757-759.
- Aherne NJ, Fitzpatrick DA, Gibbons D, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma presenting as an extra axial mass: clinicopathological features. Diagn Pathol. 2008;3:47.
- Papadakis M, de Bree E, Floros N, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: more malignant biological behavior than was considered in the past. Mol Clin Oncol. 2017;6:415-418.
- LeBoit PE, Parslow TG, Choy SH. Hair matrix differentiation: occurrence in lesions other than pilomatricoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1987;9:399-405.
- Campoy F, Stiefel P, Stiefel E, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: role played by MR imaging. Neuroradiology. 1989;31:196-198.
- Tateyama H, Eimoto T, Tada T, et al. Malignant pilomatricoma: an immunohistochemical study with antihair keratin antibody. Cancer. 1992;69:127-132.
- O’Donovan DG, Freemont AJ, Adams JE, et al. Malignant pilomatrixoma with bone metastasis. Histopathology. 1993;23:385-386.
- Cross P, Richmond I, Wells S, et al. Malignant pilomatrixoma with bone metastasis. Histopathology. 1994;24:499-500.
- Niedermeyer HP, Peris K, Höfler H. Pilomatrix carcinoma with multiple visceral metastases: report of a case. Cancer. 1996;77:1311-1314.
- Herrmann JL, Allan A, Trapp KM, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: 13 new cases and review of the literature with emphasis on predictors of metastasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:38-43.
- Xing L, Marzolf SA, Vandergriff T, et al. Facial pilomatrix carcinomas treated with Mohs micrographic surgery. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:253-255.
- Fernandez-Flores A, Cassarino DS. Sarcomatoid pilomatrix carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:508-514.
- Sau P, Lupton GP, Graham JH. Pilomatrix carcinoma. Cancer. 1993;71:2491-2498.
- Chan E, Gat U, McNiff JM, et al. A common human skin tumour is caused by activating mutations in β-catenin. Nat Genet. 1999;21:410-413.
- Huelsken J, Vogel R, Erdmann B, et al. β-catenin controls hair follicle morphogenesis and stem cell differentiation in the skin. Cell. 2001;105:533-545.
- Kikuchi A. Tumor formation by genetic mutations in the components of the Wnt signaling pathway. Cancer Sci. 2003;94:225-229.
- Durand M, Moles J. Beta-catenin mutations in a common skin cancer: pilomatricoma. Bull Cancer. 1999;86:725-726.
- Lazar AJF, Calonje E, Grayson W, et al. Pilomatrix carcinomas contain mutations in CTNNB1, the gene encoding beta-catenin. J Cutan Pathol. 2005;32:148-157.
- Kazakov DV, Sima R, Vanecek T, et al. Mutations in exon 3 of the CTNNB1 gene (β-catenin gene) in cutaneous adnexal tumors. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009;31:248-255.
- Tumminello K, Hosler GA. CDX2 and LEF-1 expression in pilomatrical tumors and their utility in the diagnosis of pilomatrical carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:318-324.
- Rodic´ N, Taube JM, Manson P, et al Locally invasive dermal squamomelanocytic tumor with matrical differentiation: a peculiar case with review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35:E72-E76.
- Perez C, Debbaneh M, Cassarino D. Preference for the term pilomatrical carcinoma with melanocytic hyperplasia: letter to the editor. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:655-657.
- Herrmann JL, Allan A, Trapp KM, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: 13 new cases and review of the literature with emphasis on predictors of metastasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:38-43.
Practice Points
- Clinicians and pathologists should be aware of pilomatrix carcinoma to facilitate early detection.
- Early diagnosis and prompt treatment of pilomatrix carcinoma is crucial in lowering recurrence rate and avoiding a poor outcome.
- Caudal-related homeobox transcription factor 2 and β-catenin components of the Wnt signaling pathway play an important role in the pathogenesis of pilomatrix carcinoma.
- Although controversial, wide local excision is the treatment of choice for pilomatrix carcinoma.
TANS Syndrome: Tanorexia, Anorexia, and Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer
The term tanorexia describes compulsive use of a tanning bed, a disorder often identified in White patients. This compulsion is driven by underlying psychological distress that typically correlates with another psychiatric disorder, such as anxiety, body dysmorphic disorder, or an eating disorder. 1 Severe anorexia combined with excessive indoor tanning led to a notable burden of cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) and keratoacanthomas in one of our patients. We discuss the management and approach to patient care in this difficult situation, which we have coined TANS syndrome (for T anorexia, A norexia, and N onmelanoma s kin cancer).
A Patient With TANS Syndrome
A 35-year-old cachectic woman, who appeared much older than her chronologic age, presented for management of numerous painful bleeding skin lesions. Diffuse, erythematous, tender nodules with central keratotic cores, some several centimeters in diameter, were scattered on the abdomen, chest, and extremities (Figure 1); similar lesions were noted on the neck (Figure 2). Numerous erythematous scaly papules and plaques consistent with actinic keratoses were noted throughout the body.
The patient reported that the cutaneous SCCs presented over the last few years, whereas her eating disorder began in adolescence and persisted despite multiple intensive outpatient and inpatient programs. The patient adamantly refused repeat hospitalization, against repeated suggestions by health care providers and her family. Comorbidities related to her anorexia included severe renal insufficiency, iron deficiency anemia, hypertriglyceridemia, kwashiorkor, and pellagra.
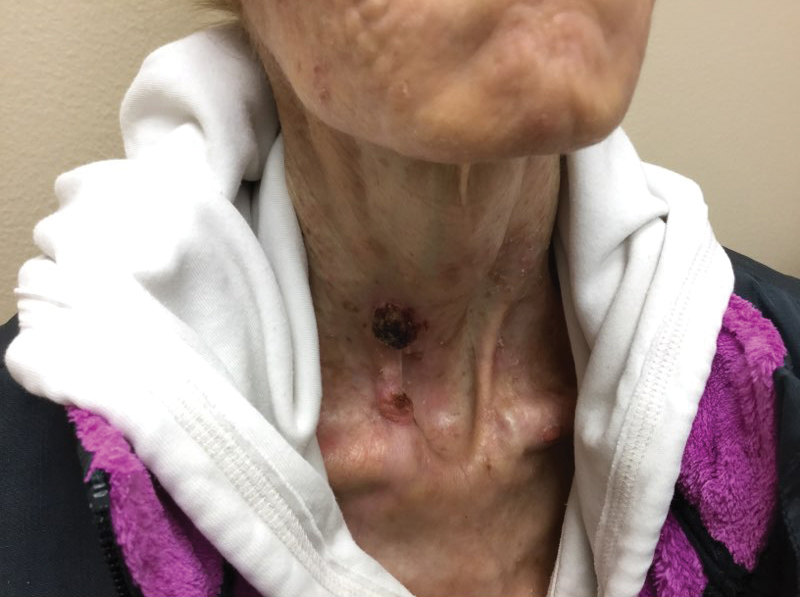
Within the last year, the patient had several biopsies showing SCC, keratoacanthoma type. The largest tumors had been treated by Mohs micrographic surgery, excision, and electrodesiccation or curettage. Adjuvant therapy over the last 2 years consisted of tazarotene cream 0.1%, imiquimod cream 5%, oral nicotinamide 500 mg twice daily, and acitretin 10 to 20 mg daily. Human papillomavirus 9-valent vaccine, recombinant, also had been tried as a chemopreventive and treatment, based on a published report of 2 patients in whom keratinocytic carcinomas decreased after such vaccination.2 The dose of acitretin was kept low because of the patient’s severe renal insufficiency and lack of supporting data for its use in this setting. Despite these modalities, our patient continued to develop new cutaneous SCCs.
We considered starting intralesional methotrexate but deferred this course of action, given the patient’s deteriorating renal function. Our plan was to initiate intralesional 5-fluorouracil; however, the patient was admitted to the hospital and subsequently died due to cardiovascular complications of anorexia.
UV Radiation in the Setting of Immune Compromise
Habitual tanning bed use has been recognized as a psychologic addiction.3,4 After exposure to UV radiation, damaged DNA upregulates pro-opiomelanocortin, which posttranslationally generates β-endorphins to elevate mood.3,5
Tanning beds deliver a higher dose of UVA radiation than UVB radiation and cause darkening of pigmentation by oxidation of preformed melanin and redistribution of melanosomes.3 UVA radiation (320–400 nm) emitted from a tanning bed is 10- to 15-times higher than the radiation emitted by the midday sun and causes DNA damage through generation of reactive oxygen species. UVA penetrates the dermis; its harmful effect on DNA contributes to the pathogenesis of melanoma.
UVB radiation (290–320 nm) is mainly restricted to the epidermis and is largely responsible for erythema of the skin. UVB specifically causes direct damage to DNA by forming pyrimidine dimers, superficially causing sunburn. Excessive exposure to UVB radiation increases the risk for nonmelanoma skin cancer.6
Severe starvation and chronic malnutrition, as seen in anorexia nervosa, also are known to lead to immunosuppression.7 Exposure to UV radiation has been shown to impair the function of antigen-presenting cells, cytokines, and suppressor T cells, and is classified as a Group 1 carcinogen by the World Health Organization.3,8 Combining a compromised immune system in anorexia with DNA damage from frequent indoor tanning provides a dangerous milieu for carcinogenesis.8 Without immune surveillance, as occurs with adequate nutrition, treatment of cutaneous SCC is, at best, challenging.
Primary care physicians, dermatologists, psychiatrists, nutritionists, and public health officials should educate high-risk patients to prevent TANS syndrome.
- Petit A, Karila L, Chalmin F, et al. Phenomenology and psychopathology of excessive indoor tanning. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:664-672. doi:10.1111/ijd.12336
- Nichols AJ, Allen AH, Shareef S, et al. Association of human papillomavirus vaccine with the development of keratinocyte carcinomas. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:571-574. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.5703
- Madigan LM, Lim HW. Tanning beds: impact on health, and recent regulations. Clin Dermatol. 2016;34:640-648. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2016.05.016
- Schwebel DC. Adolescent tanning, disordered eating, and risk taking. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2014;35:225-227. doi:10.1097/DBP.0000000000000045
- Friedman B, English JC 3rd, Ferris LK. Indoor tanning, skin cancer and the young female patient: a review of the literature. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2015;28:275-283. doi:10.1016/j.jpag.2014.07.015
- Armstrong BK, Kricker A. Epidemiology of UV induced skin cancer. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2001;63:8-18. doi:10.1016/s1011-1344(01)00198-1
- Hanachi M, Bohem V, Bemer P, et al. Negative role of malnutrition in cell-mediated immune response: Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) in a severely malnourished, HIV-negative patient with anorexia nervosa. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2018;25:163-165. doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2018.03.121
- Schwarz T, Beissert S. Milestones in photoimmunology. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:E7-E10. doi:10.1038/skinbio.2013.177
The term tanorexia describes compulsive use of a tanning bed, a disorder often identified in White patients. This compulsion is driven by underlying psychological distress that typically correlates with another psychiatric disorder, such as anxiety, body dysmorphic disorder, or an eating disorder. 1 Severe anorexia combined with excessive indoor tanning led to a notable burden of cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) and keratoacanthomas in one of our patients. We discuss the management and approach to patient care in this difficult situation, which we have coined TANS syndrome (for T anorexia, A norexia, and N onmelanoma s kin cancer).
A Patient With TANS Syndrome
A 35-year-old cachectic woman, who appeared much older than her chronologic age, presented for management of numerous painful bleeding skin lesions. Diffuse, erythematous, tender nodules with central keratotic cores, some several centimeters in diameter, were scattered on the abdomen, chest, and extremities (Figure 1); similar lesions were noted on the neck (Figure 2). Numerous erythematous scaly papules and plaques consistent with actinic keratoses were noted throughout the body.

The patient reported that the cutaneous SCCs presented over the last few years, whereas her eating disorder began in adolescence and persisted despite multiple intensive outpatient and inpatient programs. The patient adamantly refused repeat hospitalization, against repeated suggestions by health care providers and her family. Comorbidities related to her anorexia included severe renal insufficiency, iron deficiency anemia, hypertriglyceridemia, kwashiorkor, and pellagra.

Within the last year, the patient had several biopsies showing SCC, keratoacanthoma type. The largest tumors had been treated by Mohs micrographic surgery, excision, and electrodesiccation or curettage. Adjuvant therapy over the last 2 years consisted of tazarotene cream 0.1%, imiquimod cream 5%, oral nicotinamide 500 mg twice daily, and acitretin 10 to 20 mg daily. Human papillomavirus 9-valent vaccine, recombinant, also had been tried as a chemopreventive and treatment, based on a published report of 2 patients in whom keratinocytic carcinomas decreased after such vaccination.2 The dose of acitretin was kept low because of the patient’s severe renal insufficiency and lack of supporting data for its use in this setting. Despite these modalities, our patient continued to develop new cutaneous SCCs.
We considered starting intralesional methotrexate but deferred this course of action, given the patient’s deteriorating renal function. Our plan was to initiate intralesional 5-fluorouracil; however, the patient was admitted to the hospital and subsequently died due to cardiovascular complications of anorexia.
UV Radiation in the Setting of Immune Compromise
Habitual tanning bed use has been recognized as a psychologic addiction.3,4 After exposure to UV radiation, damaged DNA upregulates pro-opiomelanocortin, which posttranslationally generates β-endorphins to elevate mood.3,5
Tanning beds deliver a higher dose of UVA radiation than UVB radiation and cause darkening of pigmentation by oxidation of preformed melanin and redistribution of melanosomes.3 UVA radiation (320–400 nm) emitted from a tanning bed is 10- to 15-times higher than the radiation emitted by the midday sun and causes DNA damage through generation of reactive oxygen species. UVA penetrates the dermis; its harmful effect on DNA contributes to the pathogenesis of melanoma.
UVB radiation (290–320 nm) is mainly restricted to the epidermis and is largely responsible for erythema of the skin. UVB specifically causes direct damage to DNA by forming pyrimidine dimers, superficially causing sunburn. Excessive exposure to UVB radiation increases the risk for nonmelanoma skin cancer.6
Severe starvation and chronic malnutrition, as seen in anorexia nervosa, also are known to lead to immunosuppression.7 Exposure to UV radiation has been shown to impair the function of antigen-presenting cells, cytokines, and suppressor T cells, and is classified as a Group 1 carcinogen by the World Health Organization.3,8 Combining a compromised immune system in anorexia with DNA damage from frequent indoor tanning provides a dangerous milieu for carcinogenesis.8 Without immune surveillance, as occurs with adequate nutrition, treatment of cutaneous SCC is, at best, challenging.
Primary care physicians, dermatologists, psychiatrists, nutritionists, and public health officials should educate high-risk patients to prevent TANS syndrome.
The term tanorexia describes compulsive use of a tanning bed, a disorder often identified in White patients. This compulsion is driven by underlying psychological distress that typically correlates with another psychiatric disorder, such as anxiety, body dysmorphic disorder, or an eating disorder. 1 Severe anorexia combined with excessive indoor tanning led to a notable burden of cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) and keratoacanthomas in one of our patients. We discuss the management and approach to patient care in this difficult situation, which we have coined TANS syndrome (for T anorexia, A norexia, and N onmelanoma s kin cancer).
A Patient With TANS Syndrome
A 35-year-old cachectic woman, who appeared much older than her chronologic age, presented for management of numerous painful bleeding skin lesions. Diffuse, erythematous, tender nodules with central keratotic cores, some several centimeters in diameter, were scattered on the abdomen, chest, and extremities (Figure 1); similar lesions were noted on the neck (Figure 2). Numerous erythematous scaly papules and plaques consistent with actinic keratoses were noted throughout the body.

The patient reported that the cutaneous SCCs presented over the last few years, whereas her eating disorder began in adolescence and persisted despite multiple intensive outpatient and inpatient programs. The patient adamantly refused repeat hospitalization, against repeated suggestions by health care providers and her family. Comorbidities related to her anorexia included severe renal insufficiency, iron deficiency anemia, hypertriglyceridemia, kwashiorkor, and pellagra.

Within the last year, the patient had several biopsies showing SCC, keratoacanthoma type. The largest tumors had been treated by Mohs micrographic surgery, excision, and electrodesiccation or curettage. Adjuvant therapy over the last 2 years consisted of tazarotene cream 0.1%, imiquimod cream 5%, oral nicotinamide 500 mg twice daily, and acitretin 10 to 20 mg daily. Human papillomavirus 9-valent vaccine, recombinant, also had been tried as a chemopreventive and treatment, based on a published report of 2 patients in whom keratinocytic carcinomas decreased after such vaccination.2 The dose of acitretin was kept low because of the patient’s severe renal insufficiency and lack of supporting data for its use in this setting. Despite these modalities, our patient continued to develop new cutaneous SCCs.
We considered starting intralesional methotrexate but deferred this course of action, given the patient’s deteriorating renal function. Our plan was to initiate intralesional 5-fluorouracil; however, the patient was admitted to the hospital and subsequently died due to cardiovascular complications of anorexia.
UV Radiation in the Setting of Immune Compromise
Habitual tanning bed use has been recognized as a psychologic addiction.3,4 After exposure to UV radiation, damaged DNA upregulates pro-opiomelanocortin, which posttranslationally generates β-endorphins to elevate mood.3,5
Tanning beds deliver a higher dose of UVA radiation than UVB radiation and cause darkening of pigmentation by oxidation of preformed melanin and redistribution of melanosomes.3 UVA radiation (320–400 nm) emitted from a tanning bed is 10- to 15-times higher than the radiation emitted by the midday sun and causes DNA damage through generation of reactive oxygen species. UVA penetrates the dermis; its harmful effect on DNA contributes to the pathogenesis of melanoma.
UVB radiation (290–320 nm) is mainly restricted to the epidermis and is largely responsible for erythema of the skin. UVB specifically causes direct damage to DNA by forming pyrimidine dimers, superficially causing sunburn. Excessive exposure to UVB radiation increases the risk for nonmelanoma skin cancer.6
Severe starvation and chronic malnutrition, as seen in anorexia nervosa, also are known to lead to immunosuppression.7 Exposure to UV radiation has been shown to impair the function of antigen-presenting cells, cytokines, and suppressor T cells, and is classified as a Group 1 carcinogen by the World Health Organization.3,8 Combining a compromised immune system in anorexia with DNA damage from frequent indoor tanning provides a dangerous milieu for carcinogenesis.8 Without immune surveillance, as occurs with adequate nutrition, treatment of cutaneous SCC is, at best, challenging.
Primary care physicians, dermatologists, psychiatrists, nutritionists, and public health officials should educate high-risk patients to prevent TANS syndrome.
- Petit A, Karila L, Chalmin F, et al. Phenomenology and psychopathology of excessive indoor tanning. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:664-672. doi:10.1111/ijd.12336
- Nichols AJ, Allen AH, Shareef S, et al. Association of human papillomavirus vaccine with the development of keratinocyte carcinomas. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:571-574. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.5703
- Madigan LM, Lim HW. Tanning beds: impact on health, and recent regulations. Clin Dermatol. 2016;34:640-648. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2016.05.016
- Schwebel DC. Adolescent tanning, disordered eating, and risk taking. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2014;35:225-227. doi:10.1097/DBP.0000000000000045
- Friedman B, English JC 3rd, Ferris LK. Indoor tanning, skin cancer and the young female patient: a review of the literature. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2015;28:275-283. doi:10.1016/j.jpag.2014.07.015
- Armstrong BK, Kricker A. Epidemiology of UV induced skin cancer. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2001;63:8-18. doi:10.1016/s1011-1344(01)00198-1
- Hanachi M, Bohem V, Bemer P, et al. Negative role of malnutrition in cell-mediated immune response: Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) in a severely malnourished, HIV-negative patient with anorexia nervosa. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2018;25:163-165. doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2018.03.121
- Schwarz T, Beissert S. Milestones in photoimmunology. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:E7-E10. doi:10.1038/skinbio.2013.177
- Petit A, Karila L, Chalmin F, et al. Phenomenology and psychopathology of excessive indoor tanning. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:664-672. doi:10.1111/ijd.12336
- Nichols AJ, Allen AH, Shareef S, et al. Association of human papillomavirus vaccine with the development of keratinocyte carcinomas. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:571-574. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.5703
- Madigan LM, Lim HW. Tanning beds: impact on health, and recent regulations. Clin Dermatol. 2016;34:640-648. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2016.05.016
- Schwebel DC. Adolescent tanning, disordered eating, and risk taking. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2014;35:225-227. doi:10.1097/DBP.0000000000000045
- Friedman B, English JC 3rd, Ferris LK. Indoor tanning, skin cancer and the young female patient: a review of the literature. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2015;28:275-283. doi:10.1016/j.jpag.2014.07.015
- Armstrong BK, Kricker A. Epidemiology of UV induced skin cancer. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2001;63:8-18. doi:10.1016/s1011-1344(01)00198-1
- Hanachi M, Bohem V, Bemer P, et al. Negative role of malnutrition in cell-mediated immune response: Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) in a severely malnourished, HIV-negative patient with anorexia nervosa. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2018;25:163-165. doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2018.03.121
- Schwarz T, Beissert S. Milestones in photoimmunology. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:E7-E10. doi:10.1038/skinbio.2013.177
Practice Points
- Primary care physicians, dermatologists, psychiatrists, nutritionists, and public health officials should educate high-risk patients to prevent TANS syndrome.
- Combining a compromised immune system in anorexia with DNA damage from frequent indoor tanning provides a dangerous milieu for carcinogenesis.
- Comorbidities related to TANS syndrome make it challenging to effectively treat cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.
Skin checks reduce all-cause but not melanoma-specific deaths
In Australia, where they know a thing or two about skin cancer, authors of .
Among patients in New South Wales diagnosed with melanoma in 2006 or 2007 and followed for nearly 12 years, there was no significant difference in the rate of melanoma-specific death associated with either patient-detected or clinician-detected melanomas in an analysis adjusted for prognostic factors.
Although melanomas found through routine clinician-performed skin checks were associated with a 25% reduction in all-cause mortality compared with patient-detected lesions (P = .006), this difference may have been due to the tendency of health-oriented patients to participate in screening programs.
The study – one of the largest to date and performed in an area of the world where there is a high incidence of skin cancer and high degree of public awareness of the risks of too much sun exposure – could not fully answer its central question: Can routine skin checks, a proxy for skin cancer screening, significantly decrease the incidence of melanoma-related deaths?
“A large randomized clinical trial is needed to provide definitive evidence that screening for skin cancer reduces melanoma-specific and all-cause mortality among people invited (vs. not invited) to screen, but there are concerns about feasibility. Our findings could be used to estimate the sample size for a future trial,” wrote Caroline G. Watts, PhD, of the University of Sydney, Australia, and colleagues. Their study was published online Nov. 3 in JAMA Dermatology.
In an editorial accompanying the study, dermatologists Allan C. Halpern, MD, and Michael A. Marchetti, MD, of Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York, point out that “there has never been a randomized clinical trial of melanoma screening, nor is there one currently ongoing or planned. Even if one were to be initiated immediately, such a trial would take well over a decade to conduct.
“Thus, for the foreseeable future, our approaches to melanoma secondary prevention need to be based on indirect evidence and our understanding of biology and epidemiology,” they wrote.
A dermatology researcher who was not involved in the study said that while it doesn’t solve the screening conundrum, it does highlight the value of public health campaigns.
“The way that I interpret the data, especially the fact that it’s coming out of Australia, is that if education about self-examination is done properly, that can also be effective in terms of detecting these skin cancers,” said Shawn Demehri, MD, PhD, principal investigator at the Cutaneous Biology Research Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. Dr. Demehri was asked to comment on the study.
“I would argue that the results would probably have been different if the study had been conducted in the U.S. rather than Australia, because the education in terms of self-examination is much more advanced and organized in Australia,” he said in an interview.
Study details
To assess melanoma-specific and all-cause mortality associated with melanoma identified through routine skin checks, Dr. Watts and colleagues followed patients diagnosed with melanoma from October 2006 through October 2007 who were enrolled in the Melanoma Patterns of Care Study. The patients were followed until 2018 (mean follow-up 11.9 years).
Of the 2,452 patients for whom data were available, 291 had an initial diagnosis of primary melanoma in situ (MIS), and 2,161 were diagnosed with invasive cutaneous melanoma.
The median age at diagnosis was 65 years, ranging from 16 to 98 years. Nearly two-thirds of the patients (61%) were men.
Among all patients, 858 (35%) had melanoma detected during a routine skin check, 1,148 (47%) detected the lesions themselves, 293 (12%) had incidentally-detected melanomas, and 153 (6%) had lesions detected by other, unspecified means.
In analyses adjusted for age and sex, the investigators found that compared with patient-detected lesions, melanomas detected during routine skin checks were associated with a 59% lower risk for melanoma-specific mortality (subhazard ratio, 0.41, P < .001) and 36% lower risk for all-cause mortality (hazard ratio, 0.64, P < .001).
But after adjustment for melanoma prognostic factors such as ulceration and mitotic rate, the association of skin check–detected lesions with melanoma-specific mortality was no longer statistically significant. The association with lower all-cause mortality was somewhat attenuated, but remained significant (HR, 0.75, P = .006).
Factors associated with a higher likelihood of melanoma detection during routine skin checks included males vs. females, a history of melanoma, having multiple moles, age 50 or older, and residence in a urban vs. rural areas.
Screen with care
In their editorial, Dr. Halpern and Dr. Marchetti propose methods for screening that find a balance between detection of significant disease and potential harm to patients from unnecessary biopsy or invasive procedures.
“For many lesions, we could use serial photography and dermoscopy in lieu of tissue biopsy to identify those that are truly dynamic outliers and likely to be of greater risk to the patient. An analogous approach is already used for the management of small lung nodules detected incidentally and through screening,” they wrote.
They also raise the issue of potential overdiagnosis and overtreatment of MIS, and recommend an approach similar to that used for some older patients with prostate cancer, for example.
“The consequences of MIS treatment differ greatly based on the type, anatomic location, and size of the tumor; these factors should be considered in shared decision-making with patients. Options such as active surveillance and topical therapy should be discussed, particularly in those with significant comorbidities or advanced age,” they wrote.
The study was supported by grants from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, Cancer Institute New South Wales, and the New South Wales State Government. Dr. Watts, Dr. Halpern, Dr. Marchetti, and Dr. Demehri reported having no conflicts of interest.
In Australia, where they know a thing or two about skin cancer, authors of .
Among patients in New South Wales diagnosed with melanoma in 2006 or 2007 and followed for nearly 12 years, there was no significant difference in the rate of melanoma-specific death associated with either patient-detected or clinician-detected melanomas in an analysis adjusted for prognostic factors.
Although melanomas found through routine clinician-performed skin checks were associated with a 25% reduction in all-cause mortality compared with patient-detected lesions (P = .006), this difference may have been due to the tendency of health-oriented patients to participate in screening programs.
The study – one of the largest to date and performed in an area of the world where there is a high incidence of skin cancer and high degree of public awareness of the risks of too much sun exposure – could not fully answer its central question: Can routine skin checks, a proxy for skin cancer screening, significantly decrease the incidence of melanoma-related deaths?
“A large randomized clinical trial is needed to provide definitive evidence that screening for skin cancer reduces melanoma-specific and all-cause mortality among people invited (vs. not invited) to screen, but there are concerns about feasibility. Our findings could be used to estimate the sample size for a future trial,” wrote Caroline G. Watts, PhD, of the University of Sydney, Australia, and colleagues. Their study was published online Nov. 3 in JAMA Dermatology.
In an editorial accompanying the study, dermatologists Allan C. Halpern, MD, and Michael A. Marchetti, MD, of Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York, point out that “there has never been a randomized clinical trial of melanoma screening, nor is there one currently ongoing or planned. Even if one were to be initiated immediately, such a trial would take well over a decade to conduct.
“Thus, for the foreseeable future, our approaches to melanoma secondary prevention need to be based on indirect evidence and our understanding of biology and epidemiology,” they wrote.
A dermatology researcher who was not involved in the study said that while it doesn’t solve the screening conundrum, it does highlight the value of public health campaigns.
“The way that I interpret the data, especially the fact that it’s coming out of Australia, is that if education about self-examination is done properly, that can also be effective in terms of detecting these skin cancers,” said Shawn Demehri, MD, PhD, principal investigator at the Cutaneous Biology Research Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. Dr. Demehri was asked to comment on the study.
“I would argue that the results would probably have been different if the study had been conducted in the U.S. rather than Australia, because the education in terms of self-examination is much more advanced and organized in Australia,” he said in an interview.
Study details
To assess melanoma-specific and all-cause mortality associated with melanoma identified through routine skin checks, Dr. Watts and colleagues followed patients diagnosed with melanoma from October 2006 through October 2007 who were enrolled in the Melanoma Patterns of Care Study. The patients were followed until 2018 (mean follow-up 11.9 years).
Of the 2,452 patients for whom data were available, 291 had an initial diagnosis of primary melanoma in situ (MIS), and 2,161 were diagnosed with invasive cutaneous melanoma.
The median age at diagnosis was 65 years, ranging from 16 to 98 years. Nearly two-thirds of the patients (61%) were men.
Among all patients, 858 (35%) had melanoma detected during a routine skin check, 1,148 (47%) detected the lesions themselves, 293 (12%) had incidentally-detected melanomas, and 153 (6%) had lesions detected by other, unspecified means.
In analyses adjusted for age and sex, the investigators found that compared with patient-detected lesions, melanomas detected during routine skin checks were associated with a 59% lower risk for melanoma-specific mortality (subhazard ratio, 0.41, P < .001) and 36% lower risk for all-cause mortality (hazard ratio, 0.64, P < .001).
But after adjustment for melanoma prognostic factors such as ulceration and mitotic rate, the association of skin check–detected lesions with melanoma-specific mortality was no longer statistically significant. The association with lower all-cause mortality was somewhat attenuated, but remained significant (HR, 0.75, P = .006).
Factors associated with a higher likelihood of melanoma detection during routine skin checks included males vs. females, a history of melanoma, having multiple moles, age 50 or older, and residence in a urban vs. rural areas.
Screen with care
In their editorial, Dr. Halpern and Dr. Marchetti propose methods for screening that find a balance between detection of significant disease and potential harm to patients from unnecessary biopsy or invasive procedures.
“For many lesions, we could use serial photography and dermoscopy in lieu of tissue biopsy to identify those that are truly dynamic outliers and likely to be of greater risk to the patient. An analogous approach is already used for the management of small lung nodules detected incidentally and through screening,” they wrote.
They also raise the issue of potential overdiagnosis and overtreatment of MIS, and recommend an approach similar to that used for some older patients with prostate cancer, for example.
“The consequences of MIS treatment differ greatly based on the type, anatomic location, and size of the tumor; these factors should be considered in shared decision-making with patients. Options such as active surveillance and topical therapy should be discussed, particularly in those with significant comorbidities or advanced age,” they wrote.
The study was supported by grants from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, Cancer Institute New South Wales, and the New South Wales State Government. Dr. Watts, Dr. Halpern, Dr. Marchetti, and Dr. Demehri reported having no conflicts of interest.
In Australia, where they know a thing or two about skin cancer, authors of .
Among patients in New South Wales diagnosed with melanoma in 2006 or 2007 and followed for nearly 12 years, there was no significant difference in the rate of melanoma-specific death associated with either patient-detected or clinician-detected melanomas in an analysis adjusted for prognostic factors.
Although melanomas found through routine clinician-performed skin checks were associated with a 25% reduction in all-cause mortality compared with patient-detected lesions (P = .006), this difference may have been due to the tendency of health-oriented patients to participate in screening programs.
The study – one of the largest to date and performed in an area of the world where there is a high incidence of skin cancer and high degree of public awareness of the risks of too much sun exposure – could not fully answer its central question: Can routine skin checks, a proxy for skin cancer screening, significantly decrease the incidence of melanoma-related deaths?
“A large randomized clinical trial is needed to provide definitive evidence that screening for skin cancer reduces melanoma-specific and all-cause mortality among people invited (vs. not invited) to screen, but there are concerns about feasibility. Our findings could be used to estimate the sample size for a future trial,” wrote Caroline G. Watts, PhD, of the University of Sydney, Australia, and colleagues. Their study was published online Nov. 3 in JAMA Dermatology.
In an editorial accompanying the study, dermatologists Allan C. Halpern, MD, and Michael A. Marchetti, MD, of Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York, point out that “there has never been a randomized clinical trial of melanoma screening, nor is there one currently ongoing or planned. Even if one were to be initiated immediately, such a trial would take well over a decade to conduct.
“Thus, for the foreseeable future, our approaches to melanoma secondary prevention need to be based on indirect evidence and our understanding of biology and epidemiology,” they wrote.
A dermatology researcher who was not involved in the study said that while it doesn’t solve the screening conundrum, it does highlight the value of public health campaigns.
“The way that I interpret the data, especially the fact that it’s coming out of Australia, is that if education about self-examination is done properly, that can also be effective in terms of detecting these skin cancers,” said Shawn Demehri, MD, PhD, principal investigator at the Cutaneous Biology Research Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. Dr. Demehri was asked to comment on the study.
“I would argue that the results would probably have been different if the study had been conducted in the U.S. rather than Australia, because the education in terms of self-examination is much more advanced and organized in Australia,” he said in an interview.
Study details
To assess melanoma-specific and all-cause mortality associated with melanoma identified through routine skin checks, Dr. Watts and colleagues followed patients diagnosed with melanoma from October 2006 through October 2007 who were enrolled in the Melanoma Patterns of Care Study. The patients were followed until 2018 (mean follow-up 11.9 years).
Of the 2,452 patients for whom data were available, 291 had an initial diagnosis of primary melanoma in situ (MIS), and 2,161 were diagnosed with invasive cutaneous melanoma.
The median age at diagnosis was 65 years, ranging from 16 to 98 years. Nearly two-thirds of the patients (61%) were men.
Among all patients, 858 (35%) had melanoma detected during a routine skin check, 1,148 (47%) detected the lesions themselves, 293 (12%) had incidentally-detected melanomas, and 153 (6%) had lesions detected by other, unspecified means.
In analyses adjusted for age and sex, the investigators found that compared with patient-detected lesions, melanomas detected during routine skin checks were associated with a 59% lower risk for melanoma-specific mortality (subhazard ratio, 0.41, P < .001) and 36% lower risk for all-cause mortality (hazard ratio, 0.64, P < .001).
But after adjustment for melanoma prognostic factors such as ulceration and mitotic rate, the association of skin check–detected lesions with melanoma-specific mortality was no longer statistically significant. The association with lower all-cause mortality was somewhat attenuated, but remained significant (HR, 0.75, P = .006).
Factors associated with a higher likelihood of melanoma detection during routine skin checks included males vs. females, a history of melanoma, having multiple moles, age 50 or older, and residence in a urban vs. rural areas.
Screen with care
In their editorial, Dr. Halpern and Dr. Marchetti propose methods for screening that find a balance between detection of significant disease and potential harm to patients from unnecessary biopsy or invasive procedures.
“For many lesions, we could use serial photography and dermoscopy in lieu of tissue biopsy to identify those that are truly dynamic outliers and likely to be of greater risk to the patient. An analogous approach is already used for the management of small lung nodules detected incidentally and through screening,” they wrote.
They also raise the issue of potential overdiagnosis and overtreatment of MIS, and recommend an approach similar to that used for some older patients with prostate cancer, for example.
“The consequences of MIS treatment differ greatly based on the type, anatomic location, and size of the tumor; these factors should be considered in shared decision-making with patients. Options such as active surveillance and topical therapy should be discussed, particularly in those with significant comorbidities or advanced age,” they wrote.
The study was supported by grants from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, Cancer Institute New South Wales, and the New South Wales State Government. Dr. Watts, Dr. Halpern, Dr. Marchetti, and Dr. Demehri reported having no conflicts of interest.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
My patient is having an affair and has an STI. I’m treating both partners. What would you do?
A psychiatrist was treating a couple individually, one of whom was HIV-positive. During a session, the infected partner revealed he was having sex with other men outside the relationship and not using safe sex practices.
“He was being treated for major depression and anxiety at the time,” explained the anonymous psychiatrist. “I strongly encouraged him to tell his partner, but he was scared of doing so. He stated that they had not been using safe sex practices between the two of them, but he was willing to start at that point.”
At a session with the HIV-negative partner, the psychiatrist inquired about the couple’s current sex practices. The HIV-negative partner reported no changes and said the two continued to have sex without condoms, said the psychiatrist, who shared the experience in Medscape’s Ethics 2020 Survey open-ended questions.
“My dilemma now was whether or not to inform him about his partner’s ‘extracurricular sex behavior,’ the psychiatrist said. “Since he was now at greater risk of contracting HIV, I felt compelled to do something to intervene.”
What would you do in this situation?
according to responses from the Ethics 2020 Report. When asked to share their toughest ethical dilemma, one internist for example, wrote, “I have couples as patients, and it is very challenging if they reveal infidelity or separate/divorce; I cannot reveal info to the spouse, but it makes me very uncomfortable caring for both.” Similarly, an obstetrician-gynecologist wrote about her experience counseling patients who reveal extramarital affairs.
“Women confide deeply with their gynecologist, and although I was not successful in rescuing 100% of them, the majority accepted my counseling and saved their marriages,” the anonymous ob/gyn wrote. “In every case in which my patient was willing to resume her marital relationship, I always ensured that she advised her spouse of the infidelity, and the couple was referred to a qualified provider for marriage counseling.”
When a sexually transmitted infection (STI) comes into play however, physicians describe a deeper level of internal conflict. A family physician wrote her top ethical dilemma was “Cheating spouses and STIs: how do you get the other spouse treated?” An ob-gyn stated that, “disclosure of STI status in couples when this may indicate infidelity,” was a frequent ethical issue in her specialty. Commenters on Medscape’s recent story, “The Secret I’ll Take to my Grave: Doc Reveals,” also raised the uncomfortable topic. One physician recalled a deaf female patient who requested in writing not to test for syphilis and not to discuss the issue with her husband. “Patient knew that she had syphilis, but she did not want her husband to know,” the physician wrote.
It’s not uncommon for physicians to encounter such scenarios when treating long-term couples, especially in the digital era, said Shannon Dowler, MD, chief medical officer for North Carolina Medicaid and a family physician at the Buncombe County STI Clinic.
“This is definitely something I think we see more of in our age of ‘hookup apps’ and easier access to casual sexual connections than we did before,” said Dr. Dowler, who serves on the CDC Advisory Committee on HIV, Viral Hepatitis, and STD Prevention and Treatment.
The topic is particularly timely because of the pandemic’s impact on STI testing and the expected rise in sexually transmitted infection rates over the next year, Dr. Dowler notes.
“People weren’t necessarily coming in for routine screening or testing during the pandemic because they didn’t want to take a chance on being exposed to COVID,” she said. “But also, the reagent used for testing for certain types of transmitted infections was in short supply because they use that same reagent for the COVID test. We had shortages of STI testing in many parts of the country. I expect what we’re going to see over the next year are a lot of diagnoses that were missed during the pandemic and a lot of asymptomatic spread.”
What do the experts suggest?
Caring for spouses or two partners when an STI is discovered can be challenging for physicians, particularly in small towns where many people know each other, said Kenneth Goodman, PhD, founder and director of the Institute for Bioethics and Health Policy at the University of Miami.
“This can be a real challenge for family physicians and others in a small town,” he said. “If you discover one partner is positive for a sexually transmitted infection and the other is negative, then you’ve got a challenge to manage. The way to do that is to start with moral persuasion, namely you tell your patient, ‘You really need to disclose this. Because when he or she gets it, chances are, you’re going to be the prime suspect.’ “
Dr. Dowler, who practices in an STI clinic, said she once diagnosed a sexually transmitted infection in a patient who was married to one of Dowler’s coworkers. The patient would not allow the partner to be notified, she said. In this case, Dr. Dowler practiced expedited partner therapy (EPT), the clinical practice of treating sex partners of patients diagnosed with chlamydia or gonorrhea by giving the patient prescriptions or medications to take to the partner without having first examined the partner. The practice is legal to some extent in all states, Dr. Dowler said, but some states have different rules about how the practice can be utilized.
Physicians are obligated to report communicable diseases to their local health department, Dr. Goodman said. The health department would then do contract tracing and be responsible for conveying the STI diagnosis to any relevant parties. Even so, Dr. Goodman said physicians have a moral obligation to strongly encourage patients to divulge the infection to their partner.
“Doctors should work on being persuasive to change behavior,” he said. “Tell your patients to do the right thing and follow up with them. You should tell patients they have a responsibility to disclose a sexually transmitted infection to any of their partners and a responsibility not to have unprotected sex. Doctors can be very powerful advocates for that.”
Dr. Dowler said if she is treating two partners, and one is diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection, she generally asks the patient for their consent to disclose the diagnosis to the partner. She ensures a witness, usually a nurse, is present when she asks. If consent is refused, Dr. Dowler guides her treatment to be as protective as possible, she said. A helpful resource for patients is Tellyourpartner.org, a website that sends an anonymous text or email about infection exposure and provides guidance on treatment locations and options.
Of course, if the sexually transmitted infection is HIV, another set of rules apply. As of 2021, 35 states have laws that criminalize HIV exposure. Laws vary, but many hold patients criminally liable if they knowingly expose another party to HIV. Many states and some cities also have ‘partner notification’ laws that require health providers to disclose an HIV diagnosis to the patient’s sex partners or to report the names of sex partners to the health department, if known.
However, case law on a physician’s duty to warn is mixed, and doctors’ responsibility for STI reporting and partner notification is determined by individual states. Making matters more complex is the fact that some states have recently changed their HIV control requirements, Dr. Dowler said. In North Carolina for example, patients living with HIV who have been virally suppressed for 6 months and who are adherent to medications, are no longer in violation of the control measure if they do not disclose their HIV diagnosis to sex partners or if they don’t wear a condom.
“This means physicians would not have to report a virally suppressed, adequately treated HIV-positive patient who is having unprotected sex or take measures to inform any known sex partners of the diagnosis,” she said. “The landscape is constantly changing so physicians have to be vigilant about their state public health statutes. It’s a tricky area. It takes an already complicated topic and makes it just a little more complicated.”
Consider drafting a policy
It’s a good idea to have a policy in place at your practice that addresses such ethical dilemmas before they occur, says Michael Heitt, PsyD, a clinical psychologist on the faculty of Loyola University Maryland in Baltimore, and a member of the Maryland Psychological Association’s Ethics Committee. Dr. Heitt developed a model of ethical reasoning called CLEAR Lenses, which stands for Clinical, Legal, Ethical, Administrative, and Risk management. The approach encourages clinicians to identify often competing factors in the decision-making process before choosing a course of action to take.
In the situation of an unfaithful spouse who contracted an STI for example, the physician should consider clinical issues such as the medical likelihood the unaware partner has the STI, and legal issues such as maintaining the confidentiality of all patient information and possible mandated reporting of STI data, Dr. Heitt said. The lenses overlap since confidentiality is also a key ethical issue, and other ethical issues involve the balance of helping the unaware spouse and not harming the infected spouse, he explained. Administrative issues might include how medical records are maintained and whether the physician documents information about patients’ family members in the medical record, while risk management elements may include informed consent, documentation, and consultation.
“So, if the physician has a policy about how such matters are dealt with, and patients are informed about this when they come to the practice, this can guide the physician much more easily through this sticky situation,” Dr. Heitt said. “Documentation of the decision-making process in the medical record demonstrates the physician’s thought process should it ever be challenged in the future, and consultation with peers (while disguising the identity of the patients, of course) sets a foundation of what a ‘reasonable standard’ might be in such situations.”
There is also the conflict-avoidant approach, Dr. Heitt said, in which the physician could perform “routine” STI testing if the unaware spouse was due for an appointment soon.
“But of course, this is far from avoiding any conflict; it just kicks the can down the road as there will surely be conflict — and plenty of confusion — if the wife tests positive for an STI,” he said. “In most situations, it is usually best to be brave, do the hard work upfront, and deal with the tough situation then, rather than trying to avoid the probable inevitable difficult conversation.”
As for the psychiatrist who was treating the cheating HIV-positive partner, the physician ultimately convinced both patients to come in for a couple’s session. The doctor allowed for a 2-hour timeframe to encourage discussion of any conflicts and unresolved issues, the psychiatrist said. After several more couple’s sessions, it was apparent the HIV-positive partner wanted out of the relationship, according to the psychiatrist’s account. The physician referred them to a couples’ therapist for ongoing treatment.
“During that same session, the HIV positive partner disclosed his recent behaviors and, as a result, they decided not to have further sexual contact until they could explore this further in therapy,” the psychiatrist wrote. “At last communication the couple decided to end the relationship, and the HIV negative partner remained negative.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A psychiatrist was treating a couple individually, one of whom was HIV-positive. During a session, the infected partner revealed he was having sex with other men outside the relationship and not using safe sex practices.
“He was being treated for major depression and anxiety at the time,” explained the anonymous psychiatrist. “I strongly encouraged him to tell his partner, but he was scared of doing so. He stated that they had not been using safe sex practices between the two of them, but he was willing to start at that point.”
At a session with the HIV-negative partner, the psychiatrist inquired about the couple’s current sex practices. The HIV-negative partner reported no changes and said the two continued to have sex without condoms, said the psychiatrist, who shared the experience in Medscape’s Ethics 2020 Survey open-ended questions.
“My dilemma now was whether or not to inform him about his partner’s ‘extracurricular sex behavior,’ the psychiatrist said. “Since he was now at greater risk of contracting HIV, I felt compelled to do something to intervene.”
What would you do in this situation?
according to responses from the Ethics 2020 Report. When asked to share their toughest ethical dilemma, one internist for example, wrote, “I have couples as patients, and it is very challenging if they reveal infidelity or separate/divorce; I cannot reveal info to the spouse, but it makes me very uncomfortable caring for both.” Similarly, an obstetrician-gynecologist wrote about her experience counseling patients who reveal extramarital affairs.
“Women confide deeply with their gynecologist, and although I was not successful in rescuing 100% of them, the majority accepted my counseling and saved their marriages,” the anonymous ob/gyn wrote. “In every case in which my patient was willing to resume her marital relationship, I always ensured that she advised her spouse of the infidelity, and the couple was referred to a qualified provider for marriage counseling.”
When a sexually transmitted infection (STI) comes into play however, physicians describe a deeper level of internal conflict. A family physician wrote her top ethical dilemma was “Cheating spouses and STIs: how do you get the other spouse treated?” An ob-gyn stated that, “disclosure of STI status in couples when this may indicate infidelity,” was a frequent ethical issue in her specialty. Commenters on Medscape’s recent story, “The Secret I’ll Take to my Grave: Doc Reveals,” also raised the uncomfortable topic. One physician recalled a deaf female patient who requested in writing not to test for syphilis and not to discuss the issue with her husband. “Patient knew that she had syphilis, but she did not want her husband to know,” the physician wrote.
It’s not uncommon for physicians to encounter such scenarios when treating long-term couples, especially in the digital era, said Shannon Dowler, MD, chief medical officer for North Carolina Medicaid and a family physician at the Buncombe County STI Clinic.
“This is definitely something I think we see more of in our age of ‘hookup apps’ and easier access to casual sexual connections than we did before,” said Dr. Dowler, who serves on the CDC Advisory Committee on HIV, Viral Hepatitis, and STD Prevention and Treatment.
The topic is particularly timely because of the pandemic’s impact on STI testing and the expected rise in sexually transmitted infection rates over the next year, Dr. Dowler notes.
“People weren’t necessarily coming in for routine screening or testing during the pandemic because they didn’t want to take a chance on being exposed to COVID,” she said. “But also, the reagent used for testing for certain types of transmitted infections was in short supply because they use that same reagent for the COVID test. We had shortages of STI testing in many parts of the country. I expect what we’re going to see over the next year are a lot of diagnoses that were missed during the pandemic and a lot of asymptomatic spread.”
What do the experts suggest?
Caring for spouses or two partners when an STI is discovered can be challenging for physicians, particularly in small towns where many people know each other, said Kenneth Goodman, PhD, founder and director of the Institute for Bioethics and Health Policy at the University of Miami.
“This can be a real challenge for family physicians and others in a small town,” he said. “If you discover one partner is positive for a sexually transmitted infection and the other is negative, then you’ve got a challenge to manage. The way to do that is to start with moral persuasion, namely you tell your patient, ‘You really need to disclose this. Because when he or she gets it, chances are, you’re going to be the prime suspect.’ “
Dr. Dowler, who practices in an STI clinic, said she once diagnosed a sexually transmitted infection in a patient who was married to one of Dowler’s coworkers. The patient would not allow the partner to be notified, she said. In this case, Dr. Dowler practiced expedited partner therapy (EPT), the clinical practice of treating sex partners of patients diagnosed with chlamydia or gonorrhea by giving the patient prescriptions or medications to take to the partner without having first examined the partner. The practice is legal to some extent in all states, Dr. Dowler said, but some states have different rules about how the practice can be utilized.
Physicians are obligated to report communicable diseases to their local health department, Dr. Goodman said. The health department would then do contract tracing and be responsible for conveying the STI diagnosis to any relevant parties. Even so, Dr. Goodman said physicians have a moral obligation to strongly encourage patients to divulge the infection to their partner.
“Doctors should work on being persuasive to change behavior,” he said. “Tell your patients to do the right thing and follow up with them. You should tell patients they have a responsibility to disclose a sexually transmitted infection to any of their partners and a responsibility not to have unprotected sex. Doctors can be very powerful advocates for that.”
Dr. Dowler said if she is treating two partners, and one is diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection, she generally asks the patient for their consent to disclose the diagnosis to the partner. She ensures a witness, usually a nurse, is present when she asks. If consent is refused, Dr. Dowler guides her treatment to be as protective as possible, she said. A helpful resource for patients is Tellyourpartner.org, a website that sends an anonymous text or email about infection exposure and provides guidance on treatment locations and options.
Of course, if the sexually transmitted infection is HIV, another set of rules apply. As of 2021, 35 states have laws that criminalize HIV exposure. Laws vary, but many hold patients criminally liable if they knowingly expose another party to HIV. Many states and some cities also have ‘partner notification’ laws that require health providers to disclose an HIV diagnosis to the patient’s sex partners or to report the names of sex partners to the health department, if known.
However, case law on a physician’s duty to warn is mixed, and doctors’ responsibility for STI reporting and partner notification is determined by individual states. Making matters more complex is the fact that some states have recently changed their HIV control requirements, Dr. Dowler said. In North Carolina for example, patients living with HIV who have been virally suppressed for 6 months and who are adherent to medications, are no longer in violation of the control measure if they do not disclose their HIV diagnosis to sex partners or if they don’t wear a condom.
“This means physicians would not have to report a virally suppressed, adequately treated HIV-positive patient who is having unprotected sex or take measures to inform any known sex partners of the diagnosis,” she said. “The landscape is constantly changing so physicians have to be vigilant about their state public health statutes. It’s a tricky area. It takes an already complicated topic and makes it just a little more complicated.”
Consider drafting a policy
It’s a good idea to have a policy in place at your practice that addresses such ethical dilemmas before they occur, says Michael Heitt, PsyD, a clinical psychologist on the faculty of Loyola University Maryland in Baltimore, and a member of the Maryland Psychological Association’s Ethics Committee. Dr. Heitt developed a model of ethical reasoning called CLEAR Lenses, which stands for Clinical, Legal, Ethical, Administrative, and Risk management. The approach encourages clinicians to identify often competing factors in the decision-making process before choosing a course of action to take.
In the situation of an unfaithful spouse who contracted an STI for example, the physician should consider clinical issues such as the medical likelihood the unaware partner has the STI, and legal issues such as maintaining the confidentiality of all patient information and possible mandated reporting of STI data, Dr. Heitt said. The lenses overlap since confidentiality is also a key ethical issue, and other ethical issues involve the balance of helping the unaware spouse and not harming the infected spouse, he explained. Administrative issues might include how medical records are maintained and whether the physician documents information about patients’ family members in the medical record, while risk management elements may include informed consent, documentation, and consultation.
“So, if the physician has a policy about how such matters are dealt with, and patients are informed about this when they come to the practice, this can guide the physician much more easily through this sticky situation,” Dr. Heitt said. “Documentation of the decision-making process in the medical record demonstrates the physician’s thought process should it ever be challenged in the future, and consultation with peers (while disguising the identity of the patients, of course) sets a foundation of what a ‘reasonable standard’ might be in such situations.”
There is also the conflict-avoidant approach, Dr. Heitt said, in which the physician could perform “routine” STI testing if the unaware spouse was due for an appointment soon.
“But of course, this is far from avoiding any conflict; it just kicks the can down the road as there will surely be conflict — and plenty of confusion — if the wife tests positive for an STI,” he said. “In most situations, it is usually best to be brave, do the hard work upfront, and deal with the tough situation then, rather than trying to avoid the probable inevitable difficult conversation.”
As for the psychiatrist who was treating the cheating HIV-positive partner, the physician ultimately convinced both patients to come in for a couple’s session. The doctor allowed for a 2-hour timeframe to encourage discussion of any conflicts and unresolved issues, the psychiatrist said. After several more couple’s sessions, it was apparent the HIV-positive partner wanted out of the relationship, according to the psychiatrist’s account. The physician referred them to a couples’ therapist for ongoing treatment.
“During that same session, the HIV positive partner disclosed his recent behaviors and, as a result, they decided not to have further sexual contact until they could explore this further in therapy,” the psychiatrist wrote. “At last communication the couple decided to end the relationship, and the HIV negative partner remained negative.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A psychiatrist was treating a couple individually, one of whom was HIV-positive. During a session, the infected partner revealed he was having sex with other men outside the relationship and not using safe sex practices.
“He was being treated for major depression and anxiety at the time,” explained the anonymous psychiatrist. “I strongly encouraged him to tell his partner, but he was scared of doing so. He stated that they had not been using safe sex practices between the two of them, but he was willing to start at that point.”
At a session with the HIV-negative partner, the psychiatrist inquired about the couple’s current sex practices. The HIV-negative partner reported no changes and said the two continued to have sex without condoms, said the psychiatrist, who shared the experience in Medscape’s Ethics 2020 Survey open-ended questions.
“My dilemma now was whether or not to inform him about his partner’s ‘extracurricular sex behavior,’ the psychiatrist said. “Since he was now at greater risk of contracting HIV, I felt compelled to do something to intervene.”
What would you do in this situation?
according to responses from the Ethics 2020 Report. When asked to share their toughest ethical dilemma, one internist for example, wrote, “I have couples as patients, and it is very challenging if they reveal infidelity or separate/divorce; I cannot reveal info to the spouse, but it makes me very uncomfortable caring for both.” Similarly, an obstetrician-gynecologist wrote about her experience counseling patients who reveal extramarital affairs.
“Women confide deeply with their gynecologist, and although I was not successful in rescuing 100% of them, the majority accepted my counseling and saved their marriages,” the anonymous ob/gyn wrote. “In every case in which my patient was willing to resume her marital relationship, I always ensured that she advised her spouse of the infidelity, and the couple was referred to a qualified provider for marriage counseling.”
When a sexually transmitted infection (STI) comes into play however, physicians describe a deeper level of internal conflict. A family physician wrote her top ethical dilemma was “Cheating spouses and STIs: how do you get the other spouse treated?” An ob-gyn stated that, “disclosure of STI status in couples when this may indicate infidelity,” was a frequent ethical issue in her specialty. Commenters on Medscape’s recent story, “The Secret I’ll Take to my Grave: Doc Reveals,” also raised the uncomfortable topic. One physician recalled a deaf female patient who requested in writing not to test for syphilis and not to discuss the issue with her husband. “Patient knew that she had syphilis, but she did not want her husband to know,” the physician wrote.
It’s not uncommon for physicians to encounter such scenarios when treating long-term couples, especially in the digital era, said Shannon Dowler, MD, chief medical officer for North Carolina Medicaid and a family physician at the Buncombe County STI Clinic.
“This is definitely something I think we see more of in our age of ‘hookup apps’ and easier access to casual sexual connections than we did before,” said Dr. Dowler, who serves on the CDC Advisory Committee on HIV, Viral Hepatitis, and STD Prevention and Treatment.
The topic is particularly timely because of the pandemic’s impact on STI testing and the expected rise in sexually transmitted infection rates over the next year, Dr. Dowler notes.
“People weren’t necessarily coming in for routine screening or testing during the pandemic because they didn’t want to take a chance on being exposed to COVID,” she said. “But also, the reagent used for testing for certain types of transmitted infections was in short supply because they use that same reagent for the COVID test. We had shortages of STI testing in many parts of the country. I expect what we’re going to see over the next year are a lot of diagnoses that were missed during the pandemic and a lot of asymptomatic spread.”
What do the experts suggest?
Caring for spouses or two partners when an STI is discovered can be challenging for physicians, particularly in small towns where many people know each other, said Kenneth Goodman, PhD, founder and director of the Institute for Bioethics and Health Policy at the University of Miami.
“This can be a real challenge for family physicians and others in a small town,” he said. “If you discover one partner is positive for a sexually transmitted infection and the other is negative, then you’ve got a challenge to manage. The way to do that is to start with moral persuasion, namely you tell your patient, ‘You really need to disclose this. Because when he or she gets it, chances are, you’re going to be the prime suspect.’ “
Dr. Dowler, who practices in an STI clinic, said she once diagnosed a sexually transmitted infection in a patient who was married to one of Dowler’s coworkers. The patient would not allow the partner to be notified, she said. In this case, Dr. Dowler practiced expedited partner therapy (EPT), the clinical practice of treating sex partners of patients diagnosed with chlamydia or gonorrhea by giving the patient prescriptions or medications to take to the partner without having first examined the partner. The practice is legal to some extent in all states, Dr. Dowler said, but some states have different rules about how the practice can be utilized.
Physicians are obligated to report communicable diseases to their local health department, Dr. Goodman said. The health department would then do contract tracing and be responsible for conveying the STI diagnosis to any relevant parties. Even so, Dr. Goodman said physicians have a moral obligation to strongly encourage patients to divulge the infection to their partner.
“Doctors should work on being persuasive to change behavior,” he said. “Tell your patients to do the right thing and follow up with them. You should tell patients they have a responsibility to disclose a sexually transmitted infection to any of their partners and a responsibility not to have unprotected sex. Doctors can be very powerful advocates for that.”
Dr. Dowler said if she is treating two partners, and one is diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection, she generally asks the patient for their consent to disclose the diagnosis to the partner. She ensures a witness, usually a nurse, is present when she asks. If consent is refused, Dr. Dowler guides her treatment to be as protective as possible, she said. A helpful resource for patients is Tellyourpartner.org, a website that sends an anonymous text or email about infection exposure and provides guidance on treatment locations and options.
Of course, if the sexually transmitted infection is HIV, another set of rules apply. As of 2021, 35 states have laws that criminalize HIV exposure. Laws vary, but many hold patients criminally liable if they knowingly expose another party to HIV. Many states and some cities also have ‘partner notification’ laws that require health providers to disclose an HIV diagnosis to the patient’s sex partners or to report the names of sex partners to the health department, if known.
However, case law on a physician’s duty to warn is mixed, and doctors’ responsibility for STI reporting and partner notification is determined by individual states. Making matters more complex is the fact that some states have recently changed their HIV control requirements, Dr. Dowler said. In North Carolina for example, patients living with HIV who have been virally suppressed for 6 months and who are adherent to medications, are no longer in violation of the control measure if they do not disclose their HIV diagnosis to sex partners or if they don’t wear a condom.
“This means physicians would not have to report a virally suppressed, adequately treated HIV-positive patient who is having unprotected sex or take measures to inform any known sex partners of the diagnosis,” she said. “The landscape is constantly changing so physicians have to be vigilant about their state public health statutes. It’s a tricky area. It takes an already complicated topic and makes it just a little more complicated.”
Consider drafting a policy
It’s a good idea to have a policy in place at your practice that addresses such ethical dilemmas before they occur, says Michael Heitt, PsyD, a clinical psychologist on the faculty of Loyola University Maryland in Baltimore, and a member of the Maryland Psychological Association’s Ethics Committee. Dr. Heitt developed a model of ethical reasoning called CLEAR Lenses, which stands for Clinical, Legal, Ethical, Administrative, and Risk management. The approach encourages clinicians to identify often competing factors in the decision-making process before choosing a course of action to take.
In the situation of an unfaithful spouse who contracted an STI for example, the physician should consider clinical issues such as the medical likelihood the unaware partner has the STI, and legal issues such as maintaining the confidentiality of all patient information and possible mandated reporting of STI data, Dr. Heitt said. The lenses overlap since confidentiality is also a key ethical issue, and other ethical issues involve the balance of helping the unaware spouse and not harming the infected spouse, he explained. Administrative issues might include how medical records are maintained and whether the physician documents information about patients’ family members in the medical record, while risk management elements may include informed consent, documentation, and consultation.
“So, if the physician has a policy about how such matters are dealt with, and patients are informed about this when they come to the practice, this can guide the physician much more easily through this sticky situation,” Dr. Heitt said. “Documentation of the decision-making process in the medical record demonstrates the physician’s thought process should it ever be challenged in the future, and consultation with peers (while disguising the identity of the patients, of course) sets a foundation of what a ‘reasonable standard’ might be in such situations.”
There is also the conflict-avoidant approach, Dr. Heitt said, in which the physician could perform “routine” STI testing if the unaware spouse was due for an appointment soon.
“But of course, this is far from avoiding any conflict; it just kicks the can down the road as there will surely be conflict — and plenty of confusion — if the wife tests positive for an STI,” he said. “In most situations, it is usually best to be brave, do the hard work upfront, and deal with the tough situation then, rather than trying to avoid the probable inevitable difficult conversation.”
As for the psychiatrist who was treating the cheating HIV-positive partner, the physician ultimately convinced both patients to come in for a couple’s session. The doctor allowed for a 2-hour timeframe to encourage discussion of any conflicts and unresolved issues, the psychiatrist said. After several more couple’s sessions, it was apparent the HIV-positive partner wanted out of the relationship, according to the psychiatrist’s account. The physician referred them to a couples’ therapist for ongoing treatment.
“During that same session, the HIV positive partner disclosed his recent behaviors and, as a result, they decided not to have further sexual contact until they could explore this further in therapy,” the psychiatrist wrote. “At last communication the couple decided to end the relationship, and the HIV negative partner remained negative.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
What are the legal risks of practicing laser cutaneous surgery?
The physician-patient relationship is a key factor in preventing litigation following cutaneous laser surgery, according to Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD.
“Numerous studies indicate that good communication and rapport are the most important means to avoid a lawsuit,” Dr. Avram, director of laser, cosmetics, and dermatologic surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “It is helpful to say that the outcome was not optimal or what you were anticipating. Communicate your plan [for the complication] clearly and honestly to your patient. The patient may not understand the severity of the complication. If they don’t, they will either leave it alone or they will go elsewhere and may receive poor care.” He added that in New England, “we have some stoic patients who may say ‘I don’t want to bother the doctor’ or ‘It’s my fault for having the procedure done.’ ”
Establishing effective communication with patients from the outset is good practice, he continued, because 75% of physicians in low-risk specialties will face a malpractice claim by age 65. Nearly a decade ago Dr. Avram, H. Ray Jalian, MD, and Chris Jalian, JD, published results from a national legal database analysis identifying common errors and risk factors for litigation in cutaneous surgery. Their search yielded 1,807 documents with 174 unique legal claims involving injury from a cutaneous laser treatment, from 1985 to 2012. The most common litigated procedures were laser hair removal, rejuvenation (mostly related to intense pulsed-light treatments), and laser treatment of leg veins, while the most common injuries sustained were burns, scars, and pigmentary changes. The most common causes of legal action were lack of informed consent and fraud.
Among the 120 cases with public decisions, cases favored the plaintiff 51% of the time. “That’s unusual,” said Dr. Avram, president of American Society for Dermatologic Surgery. “Usually, physicians do better, but I think the fact that they’re cosmetic cases probably shades things a little bit.” The median monetary award was $350,000 and ranged from $5,000 to $2,145,000. The two largest judgments were for improper use of topical anesthesia that led to deaths of patients in laser hair removal cases.
In a separate analysis, the same authors searched an online national database to identify the incidence of medical professional liability claims resulting from cutaneous laser surgery performed by nonphysician operators (NPOs) from 1999 to 2012. Among the 175 cases identified, 43% involved an NPO. “In fact, the cases involving NPOs exploded over a 4-year period; they grew from 36% in 2008 of cases to 78% in 2011,” Dr. Avram said. “This was even more true for laser hair removal.”
The practice setting turned out to be a factor. Only 23% of NPO litigation involving laser procedures arose in medical office settings, while 77% of cases involving NPOs were performed outside of traditional medical settings such as in salons and medical spas – mostly for laser hair removal. “We updated this information by examining the setting for nonphysician operator litigation between 2012 and 2017 and found that 66% of cases involving NPOs were performed outside of a traditional medical setting, while 34% of NPO litigation arose in medical office settings,” Dr. Avram said during the meeting, which was named What’s the Truth? and sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “That’s close to a 2 to 1 ratio.”
In an analysis of medical professional liability claims involving Mohs surgery from 1989 to 2011, 26 of the 42 cases identified involved a primary defendant who was not a Mohs surgeon. In the 26 cases, the most common reasons for lawsuits were failure or delay of diagnosis of a skin cancer, cosmetic outcome issues, lack of informed consent, and delay or failure to refer to a Mohs surgeon. Of the cases that involved Mohs surgeons, the most common causes were lack of proper informed consent and cosmetic outcome issues, but “these cases were overwhelmingly decided in favor of the surgeons,” said Dr. Avram, one of the study authors.
On a related note, Dr. Avram underscored the importance of biopsy-site photography, “because patients and physicians misidentify biopsy sites too commonly,” he said. In a single-center study of 34 biopsy sites of cutaneous head and neck malignancies, patients misidentified the biopsy site 4-7 weeks out in 29% of the cases. Blinded dermatologists and the patient misidentified the biopsy site in 12% of the cases. “Good biopsy site photography should be mandatory in your practice,” he advised.
Clinicians can avoid cutaneous laser surgery complications only by not treating patients. “Complications and side effects are inevitable; you need to know your limits,” he said. “Even in skilled hands, if you treat enough patients, you will encounter challenging side effects. Do not perform a procedure that might produce a side effect that you cannot recognize and treat.”
The best way to avoid complications is to trust your eyes – not the laser – since the same device made by the same manufacturer may produce highly different outputs at the same setting (see J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74[5]:807-19).
“Moreover, lasers can produce much different energies after they have been serviced,” Dr. Avram said. “Do not memorize settings. Do not blindly replicate recommended settings from a colleague or a device manufacturer,” he advised. “Some devices are not externally calibrated. Therefore, the settings on one device may not translate the same way to yours. Often, device manufacturers underplay the settings. Safe and unsafe laser endpoints and close observation are the best means to avoiding clinical complications. That means you follow clinical endpoints, not fluences. The key clinical finding is the endpoint, not the energy setting.”
Temporary and expected side effects include erythema, edema, and purpura. “With these it’s just handholding and unlikely to lead to any legal consequences,” he continued. “With temporary hyperpigmentation that can occur with laser hair removal, time is one your side, because typically this will resolve before any litigation progresses. Permanent side effects from lasers and light sources and injectables are a different issue, things like permanent hypopigmentation, depigmentation, and scarring. These are most likely to produce liability.”
In Dr. Avram’s opinion, complications are best handled with widespread communication. “There is a temptation to avoid a patient with a poor outcome or side effect,” he said. “This is bad medicine and rightfully angers your patient and increases the risk of a lawsuit. [Resist] the temptation to avoid showing a poor outcome to a colleague. Many complications can be significantly improved or cleared with timely and appropriate interventions. You should always document your efforts.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan and Galderma. He is a member of the scientific advisory board for Allergan and Soliton, is an investigator for Endo, and holds stock options in La Jolla NanoMedical Inc.
The physician-patient relationship is a key factor in preventing litigation following cutaneous laser surgery, according to Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD.
“Numerous studies indicate that good communication and rapport are the most important means to avoid a lawsuit,” Dr. Avram, director of laser, cosmetics, and dermatologic surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “It is helpful to say that the outcome was not optimal or what you were anticipating. Communicate your plan [for the complication] clearly and honestly to your patient. The patient may not understand the severity of the complication. If they don’t, they will either leave it alone or they will go elsewhere and may receive poor care.” He added that in New England, “we have some stoic patients who may say ‘I don’t want to bother the doctor’ or ‘It’s my fault for having the procedure done.’ ”
Establishing effective communication with patients from the outset is good practice, he continued, because 75% of physicians in low-risk specialties will face a malpractice claim by age 65. Nearly a decade ago Dr. Avram, H. Ray Jalian, MD, and Chris Jalian, JD, published results from a national legal database analysis identifying common errors and risk factors for litigation in cutaneous surgery. Their search yielded 1,807 documents with 174 unique legal claims involving injury from a cutaneous laser treatment, from 1985 to 2012. The most common litigated procedures were laser hair removal, rejuvenation (mostly related to intense pulsed-light treatments), and laser treatment of leg veins, while the most common injuries sustained were burns, scars, and pigmentary changes. The most common causes of legal action were lack of informed consent and fraud.
Among the 120 cases with public decisions, cases favored the plaintiff 51% of the time. “That’s unusual,” said Dr. Avram, president of American Society for Dermatologic Surgery. “Usually, physicians do better, but I think the fact that they’re cosmetic cases probably shades things a little bit.” The median monetary award was $350,000 and ranged from $5,000 to $2,145,000. The two largest judgments were for improper use of topical anesthesia that led to deaths of patients in laser hair removal cases.
In a separate analysis, the same authors searched an online national database to identify the incidence of medical professional liability claims resulting from cutaneous laser surgery performed by nonphysician operators (NPOs) from 1999 to 2012. Among the 175 cases identified, 43% involved an NPO. “In fact, the cases involving NPOs exploded over a 4-year period; they grew from 36% in 2008 of cases to 78% in 2011,” Dr. Avram said. “This was even more true for laser hair removal.”
The practice setting turned out to be a factor. Only 23% of NPO litigation involving laser procedures arose in medical office settings, while 77% of cases involving NPOs were performed outside of traditional medical settings such as in salons and medical spas – mostly for laser hair removal. “We updated this information by examining the setting for nonphysician operator litigation between 2012 and 2017 and found that 66% of cases involving NPOs were performed outside of a traditional medical setting, while 34% of NPO litigation arose in medical office settings,” Dr. Avram said during the meeting, which was named What’s the Truth? and sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “That’s close to a 2 to 1 ratio.”
In an analysis of medical professional liability claims involving Mohs surgery from 1989 to 2011, 26 of the 42 cases identified involved a primary defendant who was not a Mohs surgeon. In the 26 cases, the most common reasons for lawsuits were failure or delay of diagnosis of a skin cancer, cosmetic outcome issues, lack of informed consent, and delay or failure to refer to a Mohs surgeon. Of the cases that involved Mohs surgeons, the most common causes were lack of proper informed consent and cosmetic outcome issues, but “these cases were overwhelmingly decided in favor of the surgeons,” said Dr. Avram, one of the study authors.
On a related note, Dr. Avram underscored the importance of biopsy-site photography, “because patients and physicians misidentify biopsy sites too commonly,” he said. In a single-center study of 34 biopsy sites of cutaneous head and neck malignancies, patients misidentified the biopsy site 4-7 weeks out in 29% of the cases. Blinded dermatologists and the patient misidentified the biopsy site in 12% of the cases. “Good biopsy site photography should be mandatory in your practice,” he advised.
Clinicians can avoid cutaneous laser surgery complications only by not treating patients. “Complications and side effects are inevitable; you need to know your limits,” he said. “Even in skilled hands, if you treat enough patients, you will encounter challenging side effects. Do not perform a procedure that might produce a side effect that you cannot recognize and treat.”
The best way to avoid complications is to trust your eyes – not the laser – since the same device made by the same manufacturer may produce highly different outputs at the same setting (see J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74[5]:807-19).
“Moreover, lasers can produce much different energies after they have been serviced,” Dr. Avram said. “Do not memorize settings. Do not blindly replicate recommended settings from a colleague or a device manufacturer,” he advised. “Some devices are not externally calibrated. Therefore, the settings on one device may not translate the same way to yours. Often, device manufacturers underplay the settings. Safe and unsafe laser endpoints and close observation are the best means to avoiding clinical complications. That means you follow clinical endpoints, not fluences. The key clinical finding is the endpoint, not the energy setting.”
Temporary and expected side effects include erythema, edema, and purpura. “With these it’s just handholding and unlikely to lead to any legal consequences,” he continued. “With temporary hyperpigmentation that can occur with laser hair removal, time is one your side, because typically this will resolve before any litigation progresses. Permanent side effects from lasers and light sources and injectables are a different issue, things like permanent hypopigmentation, depigmentation, and scarring. These are most likely to produce liability.”
In Dr. Avram’s opinion, complications are best handled with widespread communication. “There is a temptation to avoid a patient with a poor outcome or side effect,” he said. “This is bad medicine and rightfully angers your patient and increases the risk of a lawsuit. [Resist] the temptation to avoid showing a poor outcome to a colleague. Many complications can be significantly improved or cleared with timely and appropriate interventions. You should always document your efforts.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan and Galderma. He is a member of the scientific advisory board for Allergan and Soliton, is an investigator for Endo, and holds stock options in La Jolla NanoMedical Inc.
The physician-patient relationship is a key factor in preventing litigation following cutaneous laser surgery, according to Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD.
“Numerous studies indicate that good communication and rapport are the most important means to avoid a lawsuit,” Dr. Avram, director of laser, cosmetics, and dermatologic surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “It is helpful to say that the outcome was not optimal or what you were anticipating. Communicate your plan [for the complication] clearly and honestly to your patient. The patient may not understand the severity of the complication. If they don’t, they will either leave it alone or they will go elsewhere and may receive poor care.” He added that in New England, “we have some stoic patients who may say ‘I don’t want to bother the doctor’ or ‘It’s my fault for having the procedure done.’ ”
Establishing effective communication with patients from the outset is good practice, he continued, because 75% of physicians in low-risk specialties will face a malpractice claim by age 65. Nearly a decade ago Dr. Avram, H. Ray Jalian, MD, and Chris Jalian, JD, published results from a national legal database analysis identifying common errors and risk factors for litigation in cutaneous surgery. Their search yielded 1,807 documents with 174 unique legal claims involving injury from a cutaneous laser treatment, from 1985 to 2012. The most common litigated procedures were laser hair removal, rejuvenation (mostly related to intense pulsed-light treatments), and laser treatment of leg veins, while the most common injuries sustained were burns, scars, and pigmentary changes. The most common causes of legal action were lack of informed consent and fraud.
Among the 120 cases with public decisions, cases favored the plaintiff 51% of the time. “That’s unusual,” said Dr. Avram, president of American Society for Dermatologic Surgery. “Usually, physicians do better, but I think the fact that they’re cosmetic cases probably shades things a little bit.” The median monetary award was $350,000 and ranged from $5,000 to $2,145,000. The two largest judgments were for improper use of topical anesthesia that led to deaths of patients in laser hair removal cases.
In a separate analysis, the same authors searched an online national database to identify the incidence of medical professional liability claims resulting from cutaneous laser surgery performed by nonphysician operators (NPOs) from 1999 to 2012. Among the 175 cases identified, 43% involved an NPO. “In fact, the cases involving NPOs exploded over a 4-year period; they grew from 36% in 2008 of cases to 78% in 2011,” Dr. Avram said. “This was even more true for laser hair removal.”
The practice setting turned out to be a factor. Only 23% of NPO litigation involving laser procedures arose in medical office settings, while 77% of cases involving NPOs were performed outside of traditional medical settings such as in salons and medical spas – mostly for laser hair removal. “We updated this information by examining the setting for nonphysician operator litigation between 2012 and 2017 and found that 66% of cases involving NPOs were performed outside of a traditional medical setting, while 34% of NPO litigation arose in medical office settings,” Dr. Avram said during the meeting, which was named What’s the Truth? and sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “That’s close to a 2 to 1 ratio.”
In an analysis of medical professional liability claims involving Mohs surgery from 1989 to 2011, 26 of the 42 cases identified involved a primary defendant who was not a Mohs surgeon. In the 26 cases, the most common reasons for lawsuits were failure or delay of diagnosis of a skin cancer, cosmetic outcome issues, lack of informed consent, and delay or failure to refer to a Mohs surgeon. Of the cases that involved Mohs surgeons, the most common causes were lack of proper informed consent and cosmetic outcome issues, but “these cases were overwhelmingly decided in favor of the surgeons,” said Dr. Avram, one of the study authors.
On a related note, Dr. Avram underscored the importance of biopsy-site photography, “because patients and physicians misidentify biopsy sites too commonly,” he said. In a single-center study of 34 biopsy sites of cutaneous head and neck malignancies, patients misidentified the biopsy site 4-7 weeks out in 29% of the cases. Blinded dermatologists and the patient misidentified the biopsy site in 12% of the cases. “Good biopsy site photography should be mandatory in your practice,” he advised.
Clinicians can avoid cutaneous laser surgery complications only by not treating patients. “Complications and side effects are inevitable; you need to know your limits,” he said. “Even in skilled hands, if you treat enough patients, you will encounter challenging side effects. Do not perform a procedure that might produce a side effect that you cannot recognize and treat.”
The best way to avoid complications is to trust your eyes – not the laser – since the same device made by the same manufacturer may produce highly different outputs at the same setting (see J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74[5]:807-19).
“Moreover, lasers can produce much different energies after they have been serviced,” Dr. Avram said. “Do not memorize settings. Do not blindly replicate recommended settings from a colleague or a device manufacturer,” he advised. “Some devices are not externally calibrated. Therefore, the settings on one device may not translate the same way to yours. Often, device manufacturers underplay the settings. Safe and unsafe laser endpoints and close observation are the best means to avoiding clinical complications. That means you follow clinical endpoints, not fluences. The key clinical finding is the endpoint, not the energy setting.”
Temporary and expected side effects include erythema, edema, and purpura. “With these it’s just handholding and unlikely to lead to any legal consequences,” he continued. “With temporary hyperpigmentation that can occur with laser hair removal, time is one your side, because typically this will resolve before any litigation progresses. Permanent side effects from lasers and light sources and injectables are a different issue, things like permanent hypopigmentation, depigmentation, and scarring. These are most likely to produce liability.”
In Dr. Avram’s opinion, complications are best handled with widespread communication. “There is a temptation to avoid a patient with a poor outcome or side effect,” he said. “This is bad medicine and rightfully angers your patient and increases the risk of a lawsuit. [Resist] the temptation to avoid showing a poor outcome to a colleague. Many complications can be significantly improved or cleared with timely and appropriate interventions. You should always document your efforts.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan and Galderma. He is a member of the scientific advisory board for Allergan and Soliton, is an investigator for Endo, and holds stock options in La Jolla NanoMedical Inc.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE
Ulcer on the Leg
The Diagnosis: Calcinosis Cutis Due to Systemic Sclerosis Sine Scleroderma
Laboratory evaluation was notable for high titers of antinuclear antibodies (>1/320; reference range, 0–1/80) and positive anticentromere antibodies. There were no other relevant laboratory findings; phosphocalcic metabolism was within normal limits, and urinary sediment was normal. Biopsy of the edge of the ulcer revealed basophilic material compatible with calcium deposits. In a 3D volume rendering reconstruction from the lower limb scanner, grouped calcifications were observed in subcutaneous cellular tissue near the ulcer (Figure). The patient had a restrictive ventilatory pattern observed in a pulmonary function test. An esophageal motility study was normal.
The patient was diagnosed with systemic sclerosis sine scleroderma (ssSSc) type II because she met the 4 criteria established by Poormoghim et al1 : (1) Raynaud phenomenon or a peripheral vascular equivalent (ie, digital pitting scars, digital-tip ulcers, digital-tip gangrene, abnormal nail fold capillaries); (2) positive antinuclear antibodies; (3) distal esophageal hypomotility, small bowel hypomotility, pulmonary interstitial fibrosis, primary pulmonary arterial hypertension (without fibrosis), cardiac involvement typical of scleroderma, or renal failure; and (4) no other defined connective tissue or other disease as a cause of the prior conditions.
Systemic sclerosis is a chronic disease characterized by progressive fibrosis of the skin and other internal organs—especially the lungs, kidneys, digestive tract, and heart—as well as generalized vascular dysfunction. Cutaneous induration is its hallmark; however, up to 10% of affected patients have ssSSc.2 This entity is characterized by the total or partial absence of cutaneous manifestations of systemic sclerosis with the occurrence of internal organ involvement and serologic abnormalities. There are 3 types of ssSSc depending on the grade of skin involvement. Type I is characterized by the lack of any typical cutaneous stigmata of the disease. Type II is without sclerodactyly but can coexist with other cutaneous findings such as calcifications, telangiectases, or pitting scars. Type III is characterized clinically by internal organ involvement, typical of systemic sclerosis, that has appeared before skin changes.2
An abnormal deposit of calcium in the cutaneous and subcutaneous tissue is called calcinosis cutis. There are 5 subtypes of calcinosis cutis: dystrophic, metastatic, idiopathic, iatrogenic, and calciphylaxis. Dystrophic skin calcifications may appear in patients with connective tissue diseases such as dermatomyositis or systemic sclerosis.3 Up to 25% of patients with systemic sclerosis can develop calcinosis cutis due to local tissue damage, with normal phosphocalcic metabolism.3
Calcinosis cutis is more common in patients with systemic sclerosis and positive anticentromere antibodies.4 The calcifications usually are located in areas that are subject to repeated trauma, such as the fingers or arms, though other locations have been described such as cervical, paraspinal, or on the hips.5,6 Our patient developed calcifications on both legs, which represent atypical areas for this process.
Dermatomyositis also can present with calcinosis cutis. There are 4 patterns of calcification: superficial nodulelike calcified masses; deep calcified masses; deep sheetlike calcifications within the fascial planes; and a rare, diffuse, superficial lacy and reticular calcification that involves almost the entire body surface area.7 Patients with calcinosis cutis secondary to dermatomyositis usually develop proximal muscle weakness, high titers of creatine kinase, heliotrope rash, or interstitial lung disease with specific antibodies.
Calciphylaxis is a serious disorder involving the calcification of dermal and subcutaneous arterioles and capillaries. It presents with painful cutaneous areas of necrosis.
Venous ulcers also can present with secondary dystrophic calcification due to local tissue damage. These patients usually have cutaneous signs of chronic venous insufficiency. Our patient denied prior trauma to the area; therefore, a traumatic ulcer with secondary calcification was ruled out.
The most concerning complication of calcinosis cutis is the development of ulcers, which occurred in 154 of 316 calcinoses (48.7%) in patients with systemic sclerosis and secondary calcifications.8 These ulcers can cause disabling pain or become superinfected, as in our patient.
There currently is no drug capable of removing dystrophic calcifications, but diltiazem, minocycline, or colchicine can reduce their size and prevent their progression. In the event of neurologic compromise or intractable pain, the treatment of choice is surgical removal of the calcification.9 Curettage, intralesional sodium thiosulfate, and intravenous sodium thiosulfate also have been suggested as therapeutic options.10 Antibiotic treatment was carried out in our patient, which controlled the superinfection of the ulcers. Diltiazem also was started, with stabilization of the calcium deposits without a reduction in their size.
There are few studies evaluating the presence of nondigital ulcers in patients with systemic sclerosis. Shanmugam et al11 calculated a 4% (N=249) prevalence of ulcers in the lower limbs of systemic sclerosis patients. In a study by Bohelay et al12 of 45 patients, the estimated prevalence of lower limb ulcers was 12.8%, and the etiologies consisted of 22 cases of venous insufficiency (49%), 21 cases of ischemic causes (47%), and 2 cases of other causes (4%).
We present the case of a woman with ssSSc who developed dystrophic calcinosis cutis in atypical areas with secondary ulceration and superinfection. The skin usually plays a key role in the diagnosis of systemic sclerosis, as sclerodactyly and the characteristic generalized skin induration stand out in affected individuals. Although our patient was diagnosed with ssSSc, her skin manifestations also were crucial for the diagnosis, as she had ulcers on the lower limbs.
- Poormoghim H, Lucas M, Fertig N, et al. Systemic sclerosis sine scleroderma: demographic, clinical, and serologic features and survival in forty-eight patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:444-451.
- Kucharz EJ, Kopec´-Me˛ drek M. Systemic sclerosis sine scleroderma. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017;26:875-880.
- Valenzuela A, Baron M, Herrick AL, et al. Calcinosis is associated with digital ulcers and osteoporosis in patients with systemic sclerosis: a scleroderma clinical trials consortium study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016;46:344-349.
- D’Aoust J, Hudson M, Tatibouet S, et al. Clinical and serologic correlates of antiPM/Scl antibodies in systemic sclerosis: a multicenter study of 763 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2014;66:1608-1615.
- Contreras I, Sallés M, Mínguez S, et al. Hard paracervical tumor in a patient with limited systemic sclerosis. Rheumatol Clin. 2014; 10:336-337.
- Meriglier E, Lafourcade F, Gombert B, et al. Giant calcinosis revealing systemic sclerosis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2019;22:1787-1788.
- Chung CH. Calcinosis universalis in juvenile dermatomyositis [published online September 24, 2020]. Chonnam Med J. 2020;56:212-213.
- Bartoli F, Fiori G, Braschi F, et al. Calcinosis in systemic sclerosis: subsets, distribution and complications [published online May 30, 2016]. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016;55:1610-1614.
- Jung H, Lee D, Cho J, et al. Surgical treatment of extensive tumoral calcinosis associated with systemic sclerosis. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015;48:151-154.
- Badawi AH, Patel V, Warner AE, et al. Dystrophic calcinosis cutis: treatment with intravenous sodium thiosulfate. Cutis. 2020;106:E15-E17.
- Shanmugam V, Price P, Attinger C, et al. Lower extremity ulcers in systemic sclerosis: features and response to therapy [published online August 18, 2010]. Int J Rheumatol. doi:10.1155/2010/747946
- Bohelay G, Blaise S, Levy P, et al. Lower-limb ulcers in systemic sclerosis: a multicentre retrospective case-control study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018;98:677-682.
The Diagnosis: Calcinosis Cutis Due to Systemic Sclerosis Sine Scleroderma
Laboratory evaluation was notable for high titers of antinuclear antibodies (>1/320; reference range, 0–1/80) and positive anticentromere antibodies. There were no other relevant laboratory findings; phosphocalcic metabolism was within normal limits, and urinary sediment was normal. Biopsy of the edge of the ulcer revealed basophilic material compatible with calcium deposits. In a 3D volume rendering reconstruction from the lower limb scanner, grouped calcifications were observed in subcutaneous cellular tissue near the ulcer (Figure). The patient had a restrictive ventilatory pattern observed in a pulmonary function test. An esophageal motility study was normal.
The patient was diagnosed with systemic sclerosis sine scleroderma (ssSSc) type II because she met the 4 criteria established by Poormoghim et al1 : (1) Raynaud phenomenon or a peripheral vascular equivalent (ie, digital pitting scars, digital-tip ulcers, digital-tip gangrene, abnormal nail fold capillaries); (2) positive antinuclear antibodies; (3) distal esophageal hypomotility, small bowel hypomotility, pulmonary interstitial fibrosis, primary pulmonary arterial hypertension (without fibrosis), cardiac involvement typical of scleroderma, or renal failure; and (4) no other defined connective tissue or other disease as a cause of the prior conditions.

Systemic sclerosis is a chronic disease characterized by progressive fibrosis of the skin and other internal organs—especially the lungs, kidneys, digestive tract, and heart—as well as generalized vascular dysfunction. Cutaneous induration is its hallmark; however, up to 10% of affected patients have ssSSc.2 This entity is characterized by the total or partial absence of cutaneous manifestations of systemic sclerosis with the occurrence of internal organ involvement and serologic abnormalities. There are 3 types of ssSSc depending on the grade of skin involvement. Type I is characterized by the lack of any typical cutaneous stigmata of the disease. Type II is without sclerodactyly but can coexist with other cutaneous findings such as calcifications, telangiectases, or pitting scars. Type III is characterized clinically by internal organ involvement, typical of systemic sclerosis, that has appeared before skin changes.2
An abnormal deposit of calcium in the cutaneous and subcutaneous tissue is called calcinosis cutis. There are 5 subtypes of calcinosis cutis: dystrophic, metastatic, idiopathic, iatrogenic, and calciphylaxis. Dystrophic skin calcifications may appear in patients with connective tissue diseases such as dermatomyositis or systemic sclerosis.3 Up to 25% of patients with systemic sclerosis can develop calcinosis cutis due to local tissue damage, with normal phosphocalcic metabolism.3
Calcinosis cutis is more common in patients with systemic sclerosis and positive anticentromere antibodies.4 The calcifications usually are located in areas that are subject to repeated trauma, such as the fingers or arms, though other locations have been described such as cervical, paraspinal, or on the hips.5,6 Our patient developed calcifications on both legs, which represent atypical areas for this process.
Dermatomyositis also can present with calcinosis cutis. There are 4 patterns of calcification: superficial nodulelike calcified masses; deep calcified masses; deep sheetlike calcifications within the fascial planes; and a rare, diffuse, superficial lacy and reticular calcification that involves almost the entire body surface area.7 Patients with calcinosis cutis secondary to dermatomyositis usually develop proximal muscle weakness, high titers of creatine kinase, heliotrope rash, or interstitial lung disease with specific antibodies.
Calciphylaxis is a serious disorder involving the calcification of dermal and subcutaneous arterioles and capillaries. It presents with painful cutaneous areas of necrosis.
Venous ulcers also can present with secondary dystrophic calcification due to local tissue damage. These patients usually have cutaneous signs of chronic venous insufficiency. Our patient denied prior trauma to the area; therefore, a traumatic ulcer with secondary calcification was ruled out.
The most concerning complication of calcinosis cutis is the development of ulcers, which occurred in 154 of 316 calcinoses (48.7%) in patients with systemic sclerosis and secondary calcifications.8 These ulcers can cause disabling pain or become superinfected, as in our patient.
There currently is no drug capable of removing dystrophic calcifications, but diltiazem, minocycline, or colchicine can reduce their size and prevent their progression. In the event of neurologic compromise or intractable pain, the treatment of choice is surgical removal of the calcification.9 Curettage, intralesional sodium thiosulfate, and intravenous sodium thiosulfate also have been suggested as therapeutic options.10 Antibiotic treatment was carried out in our patient, which controlled the superinfection of the ulcers. Diltiazem also was started, with stabilization of the calcium deposits without a reduction in their size.
There are few studies evaluating the presence of nondigital ulcers in patients with systemic sclerosis. Shanmugam et al11 calculated a 4% (N=249) prevalence of ulcers in the lower limbs of systemic sclerosis patients. In a study by Bohelay et al12 of 45 patients, the estimated prevalence of lower limb ulcers was 12.8%, and the etiologies consisted of 22 cases of venous insufficiency (49%), 21 cases of ischemic causes (47%), and 2 cases of other causes (4%).
We present the case of a woman with ssSSc who developed dystrophic calcinosis cutis in atypical areas with secondary ulceration and superinfection. The skin usually plays a key role in the diagnosis of systemic sclerosis, as sclerodactyly and the characteristic generalized skin induration stand out in affected individuals. Although our patient was diagnosed with ssSSc, her skin manifestations also were crucial for the diagnosis, as she had ulcers on the lower limbs.
The Diagnosis: Calcinosis Cutis Due to Systemic Sclerosis Sine Scleroderma
Laboratory evaluation was notable for high titers of antinuclear antibodies (>1/320; reference range, 0–1/80) and positive anticentromere antibodies. There were no other relevant laboratory findings; phosphocalcic metabolism was within normal limits, and urinary sediment was normal. Biopsy of the edge of the ulcer revealed basophilic material compatible with calcium deposits. In a 3D volume rendering reconstruction from the lower limb scanner, grouped calcifications were observed in subcutaneous cellular tissue near the ulcer (Figure). The patient had a restrictive ventilatory pattern observed in a pulmonary function test. An esophageal motility study was normal.
The patient was diagnosed with systemic sclerosis sine scleroderma (ssSSc) type II because she met the 4 criteria established by Poormoghim et al1 : (1) Raynaud phenomenon or a peripheral vascular equivalent (ie, digital pitting scars, digital-tip ulcers, digital-tip gangrene, abnormal nail fold capillaries); (2) positive antinuclear antibodies; (3) distal esophageal hypomotility, small bowel hypomotility, pulmonary interstitial fibrosis, primary pulmonary arterial hypertension (without fibrosis), cardiac involvement typical of scleroderma, or renal failure; and (4) no other defined connective tissue or other disease as a cause of the prior conditions.

Systemic sclerosis is a chronic disease characterized by progressive fibrosis of the skin and other internal organs—especially the lungs, kidneys, digestive tract, and heart—as well as generalized vascular dysfunction. Cutaneous induration is its hallmark; however, up to 10% of affected patients have ssSSc.2 This entity is characterized by the total or partial absence of cutaneous manifestations of systemic sclerosis with the occurrence of internal organ involvement and serologic abnormalities. There are 3 types of ssSSc depending on the grade of skin involvement. Type I is characterized by the lack of any typical cutaneous stigmata of the disease. Type II is without sclerodactyly but can coexist with other cutaneous findings such as calcifications, telangiectases, or pitting scars. Type III is characterized clinically by internal organ involvement, typical of systemic sclerosis, that has appeared before skin changes.2
An abnormal deposit of calcium in the cutaneous and subcutaneous tissue is called calcinosis cutis. There are 5 subtypes of calcinosis cutis: dystrophic, metastatic, idiopathic, iatrogenic, and calciphylaxis. Dystrophic skin calcifications may appear in patients with connective tissue diseases such as dermatomyositis or systemic sclerosis.3 Up to 25% of patients with systemic sclerosis can develop calcinosis cutis due to local tissue damage, with normal phosphocalcic metabolism.3
Calcinosis cutis is more common in patients with systemic sclerosis and positive anticentromere antibodies.4 The calcifications usually are located in areas that are subject to repeated trauma, such as the fingers or arms, though other locations have been described such as cervical, paraspinal, or on the hips.5,6 Our patient developed calcifications on both legs, which represent atypical areas for this process.
Dermatomyositis also can present with calcinosis cutis. There are 4 patterns of calcification: superficial nodulelike calcified masses; deep calcified masses; deep sheetlike calcifications within the fascial planes; and a rare, diffuse, superficial lacy and reticular calcification that involves almost the entire body surface area.7 Patients with calcinosis cutis secondary to dermatomyositis usually develop proximal muscle weakness, high titers of creatine kinase, heliotrope rash, or interstitial lung disease with specific antibodies.
Calciphylaxis is a serious disorder involving the calcification of dermal and subcutaneous arterioles and capillaries. It presents with painful cutaneous areas of necrosis.
Venous ulcers also can present with secondary dystrophic calcification due to local tissue damage. These patients usually have cutaneous signs of chronic venous insufficiency. Our patient denied prior trauma to the area; therefore, a traumatic ulcer with secondary calcification was ruled out.
The most concerning complication of calcinosis cutis is the development of ulcers, which occurred in 154 of 316 calcinoses (48.7%) in patients with systemic sclerosis and secondary calcifications.8 These ulcers can cause disabling pain or become superinfected, as in our patient.
There currently is no drug capable of removing dystrophic calcifications, but diltiazem, minocycline, or colchicine can reduce their size and prevent their progression. In the event of neurologic compromise or intractable pain, the treatment of choice is surgical removal of the calcification.9 Curettage, intralesional sodium thiosulfate, and intravenous sodium thiosulfate also have been suggested as therapeutic options.10 Antibiotic treatment was carried out in our patient, which controlled the superinfection of the ulcers. Diltiazem also was started, with stabilization of the calcium deposits without a reduction in their size.
There are few studies evaluating the presence of nondigital ulcers in patients with systemic sclerosis. Shanmugam et al11 calculated a 4% (N=249) prevalence of ulcers in the lower limbs of systemic sclerosis patients. In a study by Bohelay et al12 of 45 patients, the estimated prevalence of lower limb ulcers was 12.8%, and the etiologies consisted of 22 cases of venous insufficiency (49%), 21 cases of ischemic causes (47%), and 2 cases of other causes (4%).
We present the case of a woman with ssSSc who developed dystrophic calcinosis cutis in atypical areas with secondary ulceration and superinfection. The skin usually plays a key role in the diagnosis of systemic sclerosis, as sclerodactyly and the characteristic generalized skin induration stand out in affected individuals. Although our patient was diagnosed with ssSSc, her skin manifestations also were crucial for the diagnosis, as she had ulcers on the lower limbs.
- Poormoghim H, Lucas M, Fertig N, et al. Systemic sclerosis sine scleroderma: demographic, clinical, and serologic features and survival in forty-eight patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:444-451.
- Kucharz EJ, Kopec´-Me˛ drek M. Systemic sclerosis sine scleroderma. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017;26:875-880.
- Valenzuela A, Baron M, Herrick AL, et al. Calcinosis is associated with digital ulcers and osteoporosis in patients with systemic sclerosis: a scleroderma clinical trials consortium study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016;46:344-349.
- D’Aoust J, Hudson M, Tatibouet S, et al. Clinical and serologic correlates of antiPM/Scl antibodies in systemic sclerosis: a multicenter study of 763 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2014;66:1608-1615.
- Contreras I, Sallés M, Mínguez S, et al. Hard paracervical tumor in a patient with limited systemic sclerosis. Rheumatol Clin. 2014; 10:336-337.
- Meriglier E, Lafourcade F, Gombert B, et al. Giant calcinosis revealing systemic sclerosis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2019;22:1787-1788.
- Chung CH. Calcinosis universalis in juvenile dermatomyositis [published online September 24, 2020]. Chonnam Med J. 2020;56:212-213.
- Bartoli F, Fiori G, Braschi F, et al. Calcinosis in systemic sclerosis: subsets, distribution and complications [published online May 30, 2016]. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016;55:1610-1614.
- Jung H, Lee D, Cho J, et al. Surgical treatment of extensive tumoral calcinosis associated with systemic sclerosis. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015;48:151-154.
- Badawi AH, Patel V, Warner AE, et al. Dystrophic calcinosis cutis: treatment with intravenous sodium thiosulfate. Cutis. 2020;106:E15-E17.
- Shanmugam V, Price P, Attinger C, et al. Lower extremity ulcers in systemic sclerosis: features and response to therapy [published online August 18, 2010]. Int J Rheumatol. doi:10.1155/2010/747946
- Bohelay G, Blaise S, Levy P, et al. Lower-limb ulcers in systemic sclerosis: a multicentre retrospective case-control study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018;98:677-682.
- Poormoghim H, Lucas M, Fertig N, et al. Systemic sclerosis sine scleroderma: demographic, clinical, and serologic features and survival in forty-eight patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:444-451.
- Kucharz EJ, Kopec´-Me˛ drek M. Systemic sclerosis sine scleroderma. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017;26:875-880.
- Valenzuela A, Baron M, Herrick AL, et al. Calcinosis is associated with digital ulcers and osteoporosis in patients with systemic sclerosis: a scleroderma clinical trials consortium study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016;46:344-349.
- D’Aoust J, Hudson M, Tatibouet S, et al. Clinical and serologic correlates of antiPM/Scl antibodies in systemic sclerosis: a multicenter study of 763 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2014;66:1608-1615.
- Contreras I, Sallés M, Mínguez S, et al. Hard paracervical tumor in a patient with limited systemic sclerosis. Rheumatol Clin. 2014; 10:336-337.
- Meriglier E, Lafourcade F, Gombert B, et al. Giant calcinosis revealing systemic sclerosis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2019;22:1787-1788.
- Chung CH. Calcinosis universalis in juvenile dermatomyositis [published online September 24, 2020]. Chonnam Med J. 2020;56:212-213.
- Bartoli F, Fiori G, Braschi F, et al. Calcinosis in systemic sclerosis: subsets, distribution and complications [published online May 30, 2016]. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016;55:1610-1614.
- Jung H, Lee D, Cho J, et al. Surgical treatment of extensive tumoral calcinosis associated with systemic sclerosis. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015;48:151-154.
- Badawi AH, Patel V, Warner AE, et al. Dystrophic calcinosis cutis: treatment with intravenous sodium thiosulfate. Cutis. 2020;106:E15-E17.
- Shanmugam V, Price P, Attinger C, et al. Lower extremity ulcers in systemic sclerosis: features and response to therapy [published online August 18, 2010]. Int J Rheumatol. doi:10.1155/2010/747946
- Bohelay G, Blaise S, Levy P, et al. Lower-limb ulcers in systemic sclerosis: a multicentre retrospective case-control study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018;98:677-682.
A 49-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus, morbid obesity, pulmonary fibrosis, and pulmonary arterial hypertension presented to our hospital with an ulcer on the left leg of unknown etiology that was superinfected by multidrug-resistant Klebsiella according to bacterial culture. She had an axillary temperature of 38.6 °C. She underwent amputation of the second and third toes on the left foot 5 years prior to presentation due to distal necrotic ulcers of ischemic origin. Physical examination revealed an 8×2-cm deep ulcer with abrupt edges on the left leg with fibrin and a purulent exudate. Deep palpation of the perilesional skin revealed indurated subcutaneous nodules. She also had scars on the fingertips of both hands with no induration on the rest of the skin surface. Capillaroscopy showed no pathologic findings. Blood cultures were performed, and she was admitted to the hospital for intravenous antibiotic therapy. During ulcer debridement, some solid whitish material was released.
CDC endorses Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine for young kids
– meaning the shots are now available for immediate use.
The Nov. 2 decision came mere hours after experts that advise the CDC on vaccinations strongly recommended the vaccine for this age group.
“Together, with science leading the charge, we have taken another important step forward in our nation’s fight against the virus that causes COVID-19. We know millions of parents are eager to get their children vaccinated and with this decision, we now have recommended that about 28 million children receive a COVID-19 vaccine. As a mom, I encourage parents with questions to talk to their pediatrician, school nurse, or local pharmacist to learn more about the vaccine and the importance of getting their children vaccinated,” Dr. Walensky said in a prepared statement.
President Joe Biden applauded Dr. Walensky’s endorsement: “Today, we have reached a turning point in our battle against COVID-19: authorization of a safe, effective vaccine for children age 5 to 11. It will allow parents to end months of anxious worrying about their kids, and reduce the extent to which children spread the virus to others. It is a major step forward for our nation in our fight to defeat the virus,” he said in a statement.
The 14 members of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) voted unanimously earlier in the day to recommend the vaccine for kids.
“I feel like I have a responsibility to make this vaccine available to children and their parents,” said committee member Beth Bell, MD, MPH, a clinical professor at the University of Washington in Seattle. Bell noted that all evidence the committee had reviewed pointed to a vaccine that was safe and effective for younger children.
“If I had a grandchild, I would certainly get that grandchild vaccinated as soon as possible,” she said.
Their recommendations follow the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s emergency authorization of Pfizer-BioNTech’s vaccine for this same age group last week.
“I’m voting for this because I think it could have a huge positive impact on [kids’] health and their social and emotional wellbeing,” said Grace Lee, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Stanford University School of Medicine, who chairs the CDC’s ACIP.
She noted that, though masks are available to reduce the risk for kids, they aren’t perfect and transmission still occurs.
“Vaccines are really the only consistent and reliable way to provide that protection,” Lee said.
The vaccine for children is two doses given 3 weeks apart. Each dose is 10 micrograms, which is one-third of the dose used in adults and teens.
To avoid confusion, the smaller dose for kids will come in bottles with orange labels and orange tops. The vaccine for adults is packaged in purple.
The CDC also addressed the question of kids who are close to age 12 when they get their first dose.
In general, pediatricians allow for a 4-day grace period around birthdays to determine which dose is needed. That will be the same with the COVID-19 vaccine.
For kids who are 11 when they start the series, they should get another 10-microgram dose after they turn 12 a few weeks later.
COVID-19 cases in this age group have climbed sharply over the summer and into the fall as schools have fully reopened, sometimes without the benefit of masks.
In the first week of October, roughly 10% of all COVID-19 cases recorded in the United States were among children ages 5 through 11. Since the start of pandemic, about 1.9 million children in this age group have been infected, though that’s almost certainly an undercount. More than 8,300 have been hospitalized, and 94 children have died.
Children of color have been disproportionately impacted. More than two-thirds of hospitalized children have been black or Hispanic.
Weighing benefits and risks
In clinical trials that included more than 4,600 children, the most common adverse events were pain and swelling at the injection site. They could also have side effects like fevers, fatigue, headache, chills, and sometimes swollen lymph nodes.
These kinds of side effects appear to be less common in children ages 5 to 11 than they have been in teens and adults, and they were temporary.
No cases of myocarditis or pericarditis were seen in the studies, but myocarditis is a very rare side effect, and the studies were too small to pick up these cases.
Still, doctors say they’re watching for it. In general, the greatest risk for myocarditis after vaccination has been seen in younger males between the ages of 12 and 30.
Even without COVID-19 or vaccines in the mix, doctors expect to see as many as two cases of myocarditis for every million people over the course of a week. The risk for myocarditis jumps up to about 11 cases for every million doses of mRNA vaccine given to men ages 25 to 30. It’s between 37 and 69 cases per million doses in boys between the ages of 12 and 24.
Still, experts say the possibility of this rare risk shouldn’t deter parents from vaccinating younger children.
Here’s why: The risk for myocarditis is higher after COVID-19 infection than after vaccination. Younger children have a lower risk for myocarditis than teens and young adults, suggesting that this side effect may be less frequent in this age group, although that remains to be seen.
Additionally, the smaller dose authorized for children is expected to minimize the risk for myocarditis even further.
The CDC says parents should call their doctor if a child develops pain in their chest, has trouble breathing, or feels like they have a beating or fluttering heart after vaccination.
What about benefits?
Models looking at the impact of vaccines in this age group predict that, nationally, cases would drop by about 8% if children are vaccinated.
The models also suggested that vaccination of kids this age would slow — but not stop — the emergence of new variants.
For every million doses, the CDC’s modeling predicts that more than 56,000 COVID-19 infections would be prevented in this age group, along with dozens of hospitalizations, and post-COVID conditions like multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children.
CDC experts estimate that just 10 kids would need to be vaccinated over 6 months to prevent a single case of COVID-19.
The CDC pointed out that vaccinating kids may help slow transmission of the virus and would give parents and other caregivers greater confidence in participating in school and extracurricular activities.
CDC experts said they would use a variety of systems, including hospital networks, the open Vaccines and Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) database, the cell-phone based V-SAFE app, and insurance claims databases to keep an eye out for any rare adverse events related to the vaccines in children.
This article, a version of which first appeared on Medscape.com, was updated on Nov. 3, 2021.
– meaning the shots are now available for immediate use.
The Nov. 2 decision came mere hours after experts that advise the CDC on vaccinations strongly recommended the vaccine for this age group.
“Together, with science leading the charge, we have taken another important step forward in our nation’s fight against the virus that causes COVID-19. We know millions of parents are eager to get their children vaccinated and with this decision, we now have recommended that about 28 million children receive a COVID-19 vaccine. As a mom, I encourage parents with questions to talk to their pediatrician, school nurse, or local pharmacist to learn more about the vaccine and the importance of getting their children vaccinated,” Dr. Walensky said in a prepared statement.
President Joe Biden applauded Dr. Walensky’s endorsement: “Today, we have reached a turning point in our battle against COVID-19: authorization of a safe, effective vaccine for children age 5 to 11. It will allow parents to end months of anxious worrying about their kids, and reduce the extent to which children spread the virus to others. It is a major step forward for our nation in our fight to defeat the virus,” he said in a statement.
The 14 members of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) voted unanimously earlier in the day to recommend the vaccine for kids.
“I feel like I have a responsibility to make this vaccine available to children and their parents,” said committee member Beth Bell, MD, MPH, a clinical professor at the University of Washington in Seattle. Bell noted that all evidence the committee had reviewed pointed to a vaccine that was safe and effective for younger children.
“If I had a grandchild, I would certainly get that grandchild vaccinated as soon as possible,” she said.
Their recommendations follow the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s emergency authorization of Pfizer-BioNTech’s vaccine for this same age group last week.
“I’m voting for this because I think it could have a huge positive impact on [kids’] health and their social and emotional wellbeing,” said Grace Lee, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Stanford University School of Medicine, who chairs the CDC’s ACIP.
She noted that, though masks are available to reduce the risk for kids, they aren’t perfect and transmission still occurs.
“Vaccines are really the only consistent and reliable way to provide that protection,” Lee said.
The vaccine for children is two doses given 3 weeks apart. Each dose is 10 micrograms, which is one-third of the dose used in adults and teens.
To avoid confusion, the smaller dose for kids will come in bottles with orange labels and orange tops. The vaccine for adults is packaged in purple.
The CDC also addressed the question of kids who are close to age 12 when they get their first dose.
In general, pediatricians allow for a 4-day grace period around birthdays to determine which dose is needed. That will be the same with the COVID-19 vaccine.
For kids who are 11 when they start the series, they should get another 10-microgram dose after they turn 12 a few weeks later.
COVID-19 cases in this age group have climbed sharply over the summer and into the fall as schools have fully reopened, sometimes without the benefit of masks.
In the first week of October, roughly 10% of all COVID-19 cases recorded in the United States were among children ages 5 through 11. Since the start of pandemic, about 1.9 million children in this age group have been infected, though that’s almost certainly an undercount. More than 8,300 have been hospitalized, and 94 children have died.
Children of color have been disproportionately impacted. More than two-thirds of hospitalized children have been black or Hispanic.
Weighing benefits and risks
In clinical trials that included more than 4,600 children, the most common adverse events were pain and swelling at the injection site. They could also have side effects like fevers, fatigue, headache, chills, and sometimes swollen lymph nodes.
These kinds of side effects appear to be less common in children ages 5 to 11 than they have been in teens and adults, and they were temporary.
No cases of myocarditis or pericarditis were seen in the studies, but myocarditis is a very rare side effect, and the studies were too small to pick up these cases.
Still, doctors say they’re watching for it. In general, the greatest risk for myocarditis after vaccination has been seen in younger males between the ages of 12 and 30.
Even without COVID-19 or vaccines in the mix, doctors expect to see as many as two cases of myocarditis for every million people over the course of a week. The risk for myocarditis jumps up to about 11 cases for every million doses of mRNA vaccine given to men ages 25 to 30. It’s between 37 and 69 cases per million doses in boys between the ages of 12 and 24.
Still, experts say the possibility of this rare risk shouldn’t deter parents from vaccinating younger children.
Here’s why: The risk for myocarditis is higher after COVID-19 infection than after vaccination. Younger children have a lower risk for myocarditis than teens and young adults, suggesting that this side effect may be less frequent in this age group, although that remains to be seen.
Additionally, the smaller dose authorized for children is expected to minimize the risk for myocarditis even further.
The CDC says parents should call their doctor if a child develops pain in their chest, has trouble breathing, or feels like they have a beating or fluttering heart after vaccination.
What about benefits?
Models looking at the impact of vaccines in this age group predict that, nationally, cases would drop by about 8% if children are vaccinated.
The models also suggested that vaccination of kids this age would slow — but not stop — the emergence of new variants.
For every million doses, the CDC’s modeling predicts that more than 56,000 COVID-19 infections would be prevented in this age group, along with dozens of hospitalizations, and post-COVID conditions like multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children.
CDC experts estimate that just 10 kids would need to be vaccinated over 6 months to prevent a single case of COVID-19.
The CDC pointed out that vaccinating kids may help slow transmission of the virus and would give parents and other caregivers greater confidence in participating in school and extracurricular activities.
CDC experts said they would use a variety of systems, including hospital networks, the open Vaccines and Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) database, the cell-phone based V-SAFE app, and insurance claims databases to keep an eye out for any rare adverse events related to the vaccines in children.
This article, a version of which first appeared on Medscape.com, was updated on Nov. 3, 2021.
– meaning the shots are now available for immediate use.
The Nov. 2 decision came mere hours after experts that advise the CDC on vaccinations strongly recommended the vaccine for this age group.
“Together, with science leading the charge, we have taken another important step forward in our nation’s fight against the virus that causes COVID-19. We know millions of parents are eager to get their children vaccinated and with this decision, we now have recommended that about 28 million children receive a COVID-19 vaccine. As a mom, I encourage parents with questions to talk to their pediatrician, school nurse, or local pharmacist to learn more about the vaccine and the importance of getting their children vaccinated,” Dr. Walensky said in a prepared statement.
President Joe Biden applauded Dr. Walensky’s endorsement: “Today, we have reached a turning point in our battle against COVID-19: authorization of a safe, effective vaccine for children age 5 to 11. It will allow parents to end months of anxious worrying about their kids, and reduce the extent to which children spread the virus to others. It is a major step forward for our nation in our fight to defeat the virus,” he said in a statement.
The 14 members of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) voted unanimously earlier in the day to recommend the vaccine for kids.
“I feel like I have a responsibility to make this vaccine available to children and their parents,” said committee member Beth Bell, MD, MPH, a clinical professor at the University of Washington in Seattle. Bell noted that all evidence the committee had reviewed pointed to a vaccine that was safe and effective for younger children.
“If I had a grandchild, I would certainly get that grandchild vaccinated as soon as possible,” she said.
Their recommendations follow the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s emergency authorization of Pfizer-BioNTech’s vaccine for this same age group last week.
“I’m voting for this because I think it could have a huge positive impact on [kids’] health and their social and emotional wellbeing,” said Grace Lee, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Stanford University School of Medicine, who chairs the CDC’s ACIP.
She noted that, though masks are available to reduce the risk for kids, they aren’t perfect and transmission still occurs.
“Vaccines are really the only consistent and reliable way to provide that protection,” Lee said.
The vaccine for children is two doses given 3 weeks apart. Each dose is 10 micrograms, which is one-third of the dose used in adults and teens.
To avoid confusion, the smaller dose for kids will come in bottles with orange labels and orange tops. The vaccine for adults is packaged in purple.
The CDC also addressed the question of kids who are close to age 12 when they get their first dose.
In general, pediatricians allow for a 4-day grace period around birthdays to determine which dose is needed. That will be the same with the COVID-19 vaccine.
For kids who are 11 when they start the series, they should get another 10-microgram dose after they turn 12 a few weeks later.
COVID-19 cases in this age group have climbed sharply over the summer and into the fall as schools have fully reopened, sometimes without the benefit of masks.
In the first week of October, roughly 10% of all COVID-19 cases recorded in the United States were among children ages 5 through 11. Since the start of pandemic, about 1.9 million children in this age group have been infected, though that’s almost certainly an undercount. More than 8,300 have been hospitalized, and 94 children have died.
Children of color have been disproportionately impacted. More than two-thirds of hospitalized children have been black or Hispanic.
Weighing benefits and risks
In clinical trials that included more than 4,600 children, the most common adverse events were pain and swelling at the injection site. They could also have side effects like fevers, fatigue, headache, chills, and sometimes swollen lymph nodes.
These kinds of side effects appear to be less common in children ages 5 to 11 than they have been in teens and adults, and they were temporary.
No cases of myocarditis or pericarditis were seen in the studies, but myocarditis is a very rare side effect, and the studies were too small to pick up these cases.
Still, doctors say they’re watching for it. In general, the greatest risk for myocarditis after vaccination has been seen in younger males between the ages of 12 and 30.
Even without COVID-19 or vaccines in the mix, doctors expect to see as many as two cases of myocarditis for every million people over the course of a week. The risk for myocarditis jumps up to about 11 cases for every million doses of mRNA vaccine given to men ages 25 to 30. It’s between 37 and 69 cases per million doses in boys between the ages of 12 and 24.
Still, experts say the possibility of this rare risk shouldn’t deter parents from vaccinating younger children.
Here’s why: The risk for myocarditis is higher after COVID-19 infection than after vaccination. Younger children have a lower risk for myocarditis than teens and young adults, suggesting that this side effect may be less frequent in this age group, although that remains to be seen.
Additionally, the smaller dose authorized for children is expected to minimize the risk for myocarditis even further.
The CDC says parents should call their doctor if a child develops pain in their chest, has trouble breathing, or feels like they have a beating or fluttering heart after vaccination.
What about benefits?
Models looking at the impact of vaccines in this age group predict that, nationally, cases would drop by about 8% if children are vaccinated.
The models also suggested that vaccination of kids this age would slow — but not stop — the emergence of new variants.
For every million doses, the CDC’s modeling predicts that more than 56,000 COVID-19 infections would be prevented in this age group, along with dozens of hospitalizations, and post-COVID conditions like multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children.
CDC experts estimate that just 10 kids would need to be vaccinated over 6 months to prevent a single case of COVID-19.
The CDC pointed out that vaccinating kids may help slow transmission of the virus and would give parents and other caregivers greater confidence in participating in school and extracurricular activities.
CDC experts said they would use a variety of systems, including hospital networks, the open Vaccines and Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) database, the cell-phone based V-SAFE app, and insurance claims databases to keep an eye out for any rare adverse events related to the vaccines in children.
This article, a version of which first appeared on Medscape.com, was updated on Nov. 3, 2021.