User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
1 in 15 patients who start dupilumab may develop conjunctivitis, large analysis finds
showed.
“About 4 years after dupilumab’s approval, we’re interested in how conjunctivitis has played out in our daily clinical practice,” lead study investigator Maria C. Schneeweiss, MD, said during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis symposium.
Drawing from two nationwide U.S. databases, MarketScan and Optum, Dr. Schneeweiss, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and colleagues sought to characterize the incidence of bacterial and nonbacterial conjunctivitis among 6,730 patients with AD who started treatment with either dupilumab, methotrexate, mycophenolate, or cyclosporine between March 2017 and January 2020. They also wanted to identify patient subgroups at increased or decreased risk of dupilumab-related conjunctivitis in clinical practice.
Of the 6,730 patients, 3,755 started treatment with dupilumab, while 2,010 started with methotrexate, 536 started with mycophenolate, and 429 started with cyclosporine. Using a new-user, active-comparator study design, the researchers identified patients with AD from both databases and selected three dupilumab cohorts: dupilumab versus methotrexate (MTX), dupilumab versus mycophenolate (MMF), and dupilumab versus cyclosporine (CsA). Follow-up lasted 6 months and 1:1 propensity score matching was used to account for conjunctivitis risk factor differences. Patients with a history of conjunctivitis were excluded from the study, except one subgroup limited to those with prior conjunctivitis.
Dr. Schneeweiss reported that the overall incidence rate of conjunctivitis within 6 months of treatment initiation was 6.6% in dupilumab users, or 1 in 15 patients, compared with 3.3% in MTX users, 4.2% in MMF users, and 2.8% in CsA users. The incidence rates for the different types of conjunctivitis were as follows:
- Bacterial conjunctivitis: 1.5% in dupilumab users versus 0.95% in MTX, 0.4% in MMF, and 0.7% in CsA users.
- Allergic conjunctivitis: 2.2% in dupilumab users versus 0.8% in MTX, 0.2% in MMF, and 1.6% in CsA users.
- Keratoconjunctivitis: 0.8% in dupilumab users versus 1.1% in MTX, 1.5% in MMF, and 0.5% in CsA users.
In addition, the rate of conjunctivitis requiring ophthalmic medication was 2.6% in dupilumab users versus 0.7% in MTX, 1% in MMF, and 0.5% in CsA users.
After the researchers applied 1:1 propensity score matching, they observed that the risk of conjunctivitis within 6 months of starting treatment was increased in dupilumab users versus MTX users (relative risk, 2.12), dupilumab versus MMF users (RR, 2.43), and dupilumab versus CsA users (RR, 1.83). Among dupilumab users, the risk of conjunctivitis requiring ophthalmic medication was increased six to eightfold, compared with those who used MTX, MMF or CsA. In addition, bacterial conjunctivitis was increased 1.6- to 4.0-fold, compared with those who used MTX, MMF or CsA, but the confidence intervals were wide and included the null, while allergic conjunctivitis was increased 2.7- to 7-fold when compared with those who used MTX and MMF.
In other findings, the risk of allergic conjunctivitis was similar between dupilumab and CsA users (RR, 1.14), and there was no increased risk of keratoconjunctivitis in dupilumab users, compared with those who used MTX, MMF, or CsA. The relative risk of conjunctivitis in those who used dupilumab was further increased when the analysis was limited to AD patients with comorbid asthma (RR, 2.86), those who used systemic glucocorticoids fewer than 30 days prior (RR, 2.88), and those age 65 and older (RR, 2.57), compared with those who used methotrexate.
“Compared to AD patients who received treatment with other systemic agents, dupilumab treatment doubled the risk of conjunctivitis in clinical practice,” Dr. Schneeweiss concluded. “Risk factors that further increase the risk include comorbid asthma, use of systemic corticosteroids, and older age. It should be noted that conjunctivitis does not require treatment discontinuation and is manageable with ophthalmic medications.”
Lawrence J. Green, MD, clinical professor of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study, said that the work “verifies what we see clinically: that conjunctivitis is increased among dupilumab users even when it is compared to immunosuppressive agents used to treat other conditions. Because the study is retrospective, one cannot assume all diagnosis of types of conjunctivitis or even of skin disease is entirely accurate. But, with the large numbers of claims looked at and compared, one would think its conclusions are accurate.”
Dr. Schneeweiss reported having no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Green disclosed that he is a speaker, consultant, or investigator for Amgen, AbbVie, Arcutis, Brickell, Candescent, Cassiopeia, Dermavant, Galderma, Janssen, Forte, Incyte, MC-2, Lilly, Novartis, Novan, Ortho Dermatologics, Revance, Sun Pharma, UCB, and Vyne.
showed.
“About 4 years after dupilumab’s approval, we’re interested in how conjunctivitis has played out in our daily clinical practice,” lead study investigator Maria C. Schneeweiss, MD, said during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis symposium.
Drawing from two nationwide U.S. databases, MarketScan and Optum, Dr. Schneeweiss, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and colleagues sought to characterize the incidence of bacterial and nonbacterial conjunctivitis among 6,730 patients with AD who started treatment with either dupilumab, methotrexate, mycophenolate, or cyclosporine between March 2017 and January 2020. They also wanted to identify patient subgroups at increased or decreased risk of dupilumab-related conjunctivitis in clinical practice.
Of the 6,730 patients, 3,755 started treatment with dupilumab, while 2,010 started with methotrexate, 536 started with mycophenolate, and 429 started with cyclosporine. Using a new-user, active-comparator study design, the researchers identified patients with AD from both databases and selected three dupilumab cohorts: dupilumab versus methotrexate (MTX), dupilumab versus mycophenolate (MMF), and dupilumab versus cyclosporine (CsA). Follow-up lasted 6 months and 1:1 propensity score matching was used to account for conjunctivitis risk factor differences. Patients with a history of conjunctivitis were excluded from the study, except one subgroup limited to those with prior conjunctivitis.
Dr. Schneeweiss reported that the overall incidence rate of conjunctivitis within 6 months of treatment initiation was 6.6% in dupilumab users, or 1 in 15 patients, compared with 3.3% in MTX users, 4.2% in MMF users, and 2.8% in CsA users. The incidence rates for the different types of conjunctivitis were as follows:
- Bacterial conjunctivitis: 1.5% in dupilumab users versus 0.95% in MTX, 0.4% in MMF, and 0.7% in CsA users.
- Allergic conjunctivitis: 2.2% in dupilumab users versus 0.8% in MTX, 0.2% in MMF, and 1.6% in CsA users.
- Keratoconjunctivitis: 0.8% in dupilumab users versus 1.1% in MTX, 1.5% in MMF, and 0.5% in CsA users.
In addition, the rate of conjunctivitis requiring ophthalmic medication was 2.6% in dupilumab users versus 0.7% in MTX, 1% in MMF, and 0.5% in CsA users.
After the researchers applied 1:1 propensity score matching, they observed that the risk of conjunctivitis within 6 months of starting treatment was increased in dupilumab users versus MTX users (relative risk, 2.12), dupilumab versus MMF users (RR, 2.43), and dupilumab versus CsA users (RR, 1.83). Among dupilumab users, the risk of conjunctivitis requiring ophthalmic medication was increased six to eightfold, compared with those who used MTX, MMF or CsA. In addition, bacterial conjunctivitis was increased 1.6- to 4.0-fold, compared with those who used MTX, MMF or CsA, but the confidence intervals were wide and included the null, while allergic conjunctivitis was increased 2.7- to 7-fold when compared with those who used MTX and MMF.
In other findings, the risk of allergic conjunctivitis was similar between dupilumab and CsA users (RR, 1.14), and there was no increased risk of keratoconjunctivitis in dupilumab users, compared with those who used MTX, MMF, or CsA. The relative risk of conjunctivitis in those who used dupilumab was further increased when the analysis was limited to AD patients with comorbid asthma (RR, 2.86), those who used systemic glucocorticoids fewer than 30 days prior (RR, 2.88), and those age 65 and older (RR, 2.57), compared with those who used methotrexate.
“Compared to AD patients who received treatment with other systemic agents, dupilumab treatment doubled the risk of conjunctivitis in clinical practice,” Dr. Schneeweiss concluded. “Risk factors that further increase the risk include comorbid asthma, use of systemic corticosteroids, and older age. It should be noted that conjunctivitis does not require treatment discontinuation and is manageable with ophthalmic medications.”
Lawrence J. Green, MD, clinical professor of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study, said that the work “verifies what we see clinically: that conjunctivitis is increased among dupilumab users even when it is compared to immunosuppressive agents used to treat other conditions. Because the study is retrospective, one cannot assume all diagnosis of types of conjunctivitis or even of skin disease is entirely accurate. But, with the large numbers of claims looked at and compared, one would think its conclusions are accurate.”
Dr. Schneeweiss reported having no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Green disclosed that he is a speaker, consultant, or investigator for Amgen, AbbVie, Arcutis, Brickell, Candescent, Cassiopeia, Dermavant, Galderma, Janssen, Forte, Incyte, MC-2, Lilly, Novartis, Novan, Ortho Dermatologics, Revance, Sun Pharma, UCB, and Vyne.
showed.
“About 4 years after dupilumab’s approval, we’re interested in how conjunctivitis has played out in our daily clinical practice,” lead study investigator Maria C. Schneeweiss, MD, said during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis symposium.
Drawing from two nationwide U.S. databases, MarketScan and Optum, Dr. Schneeweiss, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and colleagues sought to characterize the incidence of bacterial and nonbacterial conjunctivitis among 6,730 patients with AD who started treatment with either dupilumab, methotrexate, mycophenolate, or cyclosporine between March 2017 and January 2020. They also wanted to identify patient subgroups at increased or decreased risk of dupilumab-related conjunctivitis in clinical practice.
Of the 6,730 patients, 3,755 started treatment with dupilumab, while 2,010 started with methotrexate, 536 started with mycophenolate, and 429 started with cyclosporine. Using a new-user, active-comparator study design, the researchers identified patients with AD from both databases and selected three dupilumab cohorts: dupilumab versus methotrexate (MTX), dupilumab versus mycophenolate (MMF), and dupilumab versus cyclosporine (CsA). Follow-up lasted 6 months and 1:1 propensity score matching was used to account for conjunctivitis risk factor differences. Patients with a history of conjunctivitis were excluded from the study, except one subgroup limited to those with prior conjunctivitis.
Dr. Schneeweiss reported that the overall incidence rate of conjunctivitis within 6 months of treatment initiation was 6.6% in dupilumab users, or 1 in 15 patients, compared with 3.3% in MTX users, 4.2% in MMF users, and 2.8% in CsA users. The incidence rates for the different types of conjunctivitis were as follows:
- Bacterial conjunctivitis: 1.5% in dupilumab users versus 0.95% in MTX, 0.4% in MMF, and 0.7% in CsA users.
- Allergic conjunctivitis: 2.2% in dupilumab users versus 0.8% in MTX, 0.2% in MMF, and 1.6% in CsA users.
- Keratoconjunctivitis: 0.8% in dupilumab users versus 1.1% in MTX, 1.5% in MMF, and 0.5% in CsA users.
In addition, the rate of conjunctivitis requiring ophthalmic medication was 2.6% in dupilumab users versus 0.7% in MTX, 1% in MMF, and 0.5% in CsA users.
After the researchers applied 1:1 propensity score matching, they observed that the risk of conjunctivitis within 6 months of starting treatment was increased in dupilumab users versus MTX users (relative risk, 2.12), dupilumab versus MMF users (RR, 2.43), and dupilumab versus CsA users (RR, 1.83). Among dupilumab users, the risk of conjunctivitis requiring ophthalmic medication was increased six to eightfold, compared with those who used MTX, MMF or CsA. In addition, bacterial conjunctivitis was increased 1.6- to 4.0-fold, compared with those who used MTX, MMF or CsA, but the confidence intervals were wide and included the null, while allergic conjunctivitis was increased 2.7- to 7-fold when compared with those who used MTX and MMF.
In other findings, the risk of allergic conjunctivitis was similar between dupilumab and CsA users (RR, 1.14), and there was no increased risk of keratoconjunctivitis in dupilumab users, compared with those who used MTX, MMF, or CsA. The relative risk of conjunctivitis in those who used dupilumab was further increased when the analysis was limited to AD patients with comorbid asthma (RR, 2.86), those who used systemic glucocorticoids fewer than 30 days prior (RR, 2.88), and those age 65 and older (RR, 2.57), compared with those who used methotrexate.
“Compared to AD patients who received treatment with other systemic agents, dupilumab treatment doubled the risk of conjunctivitis in clinical practice,” Dr. Schneeweiss concluded. “Risk factors that further increase the risk include comorbid asthma, use of systemic corticosteroids, and older age. It should be noted that conjunctivitis does not require treatment discontinuation and is manageable with ophthalmic medications.”
Lawrence J. Green, MD, clinical professor of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study, said that the work “verifies what we see clinically: that conjunctivitis is increased among dupilumab users even when it is compared to immunosuppressive agents used to treat other conditions. Because the study is retrospective, one cannot assume all diagnosis of types of conjunctivitis or even of skin disease is entirely accurate. But, with the large numbers of claims looked at and compared, one would think its conclusions are accurate.”
Dr. Schneeweiss reported having no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Green disclosed that he is a speaker, consultant, or investigator for Amgen, AbbVie, Arcutis, Brickell, Candescent, Cassiopeia, Dermavant, Galderma, Janssen, Forte, Incyte, MC-2, Lilly, Novartis, Novan, Ortho Dermatologics, Revance, Sun Pharma, UCB, and Vyne.
FROM REVOLUTIONIZING AD 2021
Trial offers first look at how tralokinumab-treated patients weather COVID-19
and all patients continued tralokinumab treatment following their diagnosis.
“This is a great first look at COVID-19 outcomes in this population,” lead study investigator Andrew Blauvelt, MD, MBA, said during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis symposium. “This suggests that tralokinumab does not significantly impact the ability to respond to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. It’s encouraging and promising.”
Tralokinumab is a fully human IgG4 monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to interleukin-13, which is a key driver of underlying inflammation in AD. An ongoing, open-label extension trial called ECZTEND is investigating the long-term safety and efficacy of tralokinumab in patients with AD who participated in previous tralokinumab trials. The purpose of the current case series is to describe the outcomes of patients diagnosed with COVID-19 while participating in ECZTEND, which is a 5-year study.
“Patients are receiving tralokinumab 300 mg every 2 weeks,” said Dr. Blauvelt, a dermatologist who is president of Oregon Medical Research Center, Portland. “They’re allowed to use topical steroids, but they’re not allowed to use other AD treatments. We do regular clinical and safety assessments throughout the study.”
As of Feb. 26, 2021, there were 51 adults with moderate to severe AD who had confirmed COVID-19 infection during treatment with tralokinumab every 2 weeks. “Patients were not required to discontinue tralokinumab treatment following a COVID-19 diagnosis, if continuation was deemed appropriate by the investigator,” Dr. Blauvelt said. Of the 51 patients, 22 were male, 29 were female, their mean age was 38 years, and their baseline body mass index was 27.6 kg/m2. Most of the patients (36, or 71%) were from Europe, 15 (29%) were from North America, and 30 (59%) had a history of asthma.
The average duration of COVID-19 infection was 15 days and severity of disease was mild in 35 patients (69%), moderate in 14 (27%), and severe in 2 (4%). According to the study abstract, those two patients had multiple risk factors and comorbidities, including obesity, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and cardiovascular disease. They were hospitalized for a mean of 7 days, but subsequently recovered – one with sequelae. None of the patients died.
Of the 51 COVID-19 cases, 2 were deemed to be possibly related to tralokinumab treatment by the investigator, Dr. Blauvelt said. Both were mild or moderate cases that occurred in patients younger than age 30. “Interestingly, 75% of the COVID-19 patients had no dose interruption; they continued dosing their tralokinumab every 2 weeks during and around the time they had COVID-19,” he said. “However, 25% of patients did interrupt their dosing during COVID-19 infection. That means that they either delayed or stopped dosing while they were sick.”
Of the 51 patients, 19 (37%) had received their first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine and 6 (12%) had received their second dose. “So, 12% of patients were fully vaccinated,” Dr. Blauvelt said. “We do know that the mRNA vaccines are about 95% effective in preventing COVID-19. Currently in Oregon, about 98% of our cases are in unvaccinated patients and about 2% of COVID-19 patients are fully vaccinated.”
In addition, the recently published ECZTRA5 vaccine study showed that nonlive vaccines (tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis; and meningococcal vaccines) could be safely administered and can elicit normal immune responses in patients treated with tralokinumab.
“We sorely need COVID-19–related safety data for all of our current and emerging systemic and biologic therapies used to treat atopic dermatitis,” said Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH, director of clinical research in the division of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment about these results. “This study is important because it shows that tralokinumab was not associated with any obvious safety signals with respect to COVID-19 infections. The major limitation is that it is not a prospective study designed to assess tralokinumab efficacy in COVID-19 patients per se. However, this post hoc study provides reassuring data. We need similar or even more robust studies for other systemic therapies in AD.”
Dr. Blauvelt reported that he is an investigator and a scientific advisor for LEO Pharma, which is developing tralokinumab, and for several other pharmaceutical companies developing treatments for AD. Dr. Silverberg reported that he is a consultant to and/or an advisory board member for several pharmaceutical companies, including LEO Pharma.
and all patients continued tralokinumab treatment following their diagnosis.
“This is a great first look at COVID-19 outcomes in this population,” lead study investigator Andrew Blauvelt, MD, MBA, said during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis symposium. “This suggests that tralokinumab does not significantly impact the ability to respond to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. It’s encouraging and promising.”
Tralokinumab is a fully human IgG4 monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to interleukin-13, which is a key driver of underlying inflammation in AD. An ongoing, open-label extension trial called ECZTEND is investigating the long-term safety and efficacy of tralokinumab in patients with AD who participated in previous tralokinumab trials. The purpose of the current case series is to describe the outcomes of patients diagnosed with COVID-19 while participating in ECZTEND, which is a 5-year study.
“Patients are receiving tralokinumab 300 mg every 2 weeks,” said Dr. Blauvelt, a dermatologist who is president of Oregon Medical Research Center, Portland. “They’re allowed to use topical steroids, but they’re not allowed to use other AD treatments. We do regular clinical and safety assessments throughout the study.”
As of Feb. 26, 2021, there were 51 adults with moderate to severe AD who had confirmed COVID-19 infection during treatment with tralokinumab every 2 weeks. “Patients were not required to discontinue tralokinumab treatment following a COVID-19 diagnosis, if continuation was deemed appropriate by the investigator,” Dr. Blauvelt said. Of the 51 patients, 22 were male, 29 were female, their mean age was 38 years, and their baseline body mass index was 27.6 kg/m2. Most of the patients (36, or 71%) were from Europe, 15 (29%) were from North America, and 30 (59%) had a history of asthma.
The average duration of COVID-19 infection was 15 days and severity of disease was mild in 35 patients (69%), moderate in 14 (27%), and severe in 2 (4%). According to the study abstract, those two patients had multiple risk factors and comorbidities, including obesity, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and cardiovascular disease. They were hospitalized for a mean of 7 days, but subsequently recovered – one with sequelae. None of the patients died.
Of the 51 COVID-19 cases, 2 were deemed to be possibly related to tralokinumab treatment by the investigator, Dr. Blauvelt said. Both were mild or moderate cases that occurred in patients younger than age 30. “Interestingly, 75% of the COVID-19 patients had no dose interruption; they continued dosing their tralokinumab every 2 weeks during and around the time they had COVID-19,” he said. “However, 25% of patients did interrupt their dosing during COVID-19 infection. That means that they either delayed or stopped dosing while they were sick.”
Of the 51 patients, 19 (37%) had received their first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine and 6 (12%) had received their second dose. “So, 12% of patients were fully vaccinated,” Dr. Blauvelt said. “We do know that the mRNA vaccines are about 95% effective in preventing COVID-19. Currently in Oregon, about 98% of our cases are in unvaccinated patients and about 2% of COVID-19 patients are fully vaccinated.”
In addition, the recently published ECZTRA5 vaccine study showed that nonlive vaccines (tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis; and meningococcal vaccines) could be safely administered and can elicit normal immune responses in patients treated with tralokinumab.
“We sorely need COVID-19–related safety data for all of our current and emerging systemic and biologic therapies used to treat atopic dermatitis,” said Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH, director of clinical research in the division of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment about these results. “This study is important because it shows that tralokinumab was not associated with any obvious safety signals with respect to COVID-19 infections. The major limitation is that it is not a prospective study designed to assess tralokinumab efficacy in COVID-19 patients per se. However, this post hoc study provides reassuring data. We need similar or even more robust studies for other systemic therapies in AD.”
Dr. Blauvelt reported that he is an investigator and a scientific advisor for LEO Pharma, which is developing tralokinumab, and for several other pharmaceutical companies developing treatments for AD. Dr. Silverberg reported that he is a consultant to and/or an advisory board member for several pharmaceutical companies, including LEO Pharma.
and all patients continued tralokinumab treatment following their diagnosis.
“This is a great first look at COVID-19 outcomes in this population,” lead study investigator Andrew Blauvelt, MD, MBA, said during the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis symposium. “This suggests that tralokinumab does not significantly impact the ability to respond to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. It’s encouraging and promising.”
Tralokinumab is a fully human IgG4 monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to interleukin-13, which is a key driver of underlying inflammation in AD. An ongoing, open-label extension trial called ECZTEND is investigating the long-term safety and efficacy of tralokinumab in patients with AD who participated in previous tralokinumab trials. The purpose of the current case series is to describe the outcomes of patients diagnosed with COVID-19 while participating in ECZTEND, which is a 5-year study.
“Patients are receiving tralokinumab 300 mg every 2 weeks,” said Dr. Blauvelt, a dermatologist who is president of Oregon Medical Research Center, Portland. “They’re allowed to use topical steroids, but they’re not allowed to use other AD treatments. We do regular clinical and safety assessments throughout the study.”
As of Feb. 26, 2021, there were 51 adults with moderate to severe AD who had confirmed COVID-19 infection during treatment with tralokinumab every 2 weeks. “Patients were not required to discontinue tralokinumab treatment following a COVID-19 diagnosis, if continuation was deemed appropriate by the investigator,” Dr. Blauvelt said. Of the 51 patients, 22 were male, 29 were female, their mean age was 38 years, and their baseline body mass index was 27.6 kg/m2. Most of the patients (36, or 71%) were from Europe, 15 (29%) were from North America, and 30 (59%) had a history of asthma.
The average duration of COVID-19 infection was 15 days and severity of disease was mild in 35 patients (69%), moderate in 14 (27%), and severe in 2 (4%). According to the study abstract, those two patients had multiple risk factors and comorbidities, including obesity, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and cardiovascular disease. They were hospitalized for a mean of 7 days, but subsequently recovered – one with sequelae. None of the patients died.
Of the 51 COVID-19 cases, 2 were deemed to be possibly related to tralokinumab treatment by the investigator, Dr. Blauvelt said. Both were mild or moderate cases that occurred in patients younger than age 30. “Interestingly, 75% of the COVID-19 patients had no dose interruption; they continued dosing their tralokinumab every 2 weeks during and around the time they had COVID-19,” he said. “However, 25% of patients did interrupt their dosing during COVID-19 infection. That means that they either delayed or stopped dosing while they were sick.”
Of the 51 patients, 19 (37%) had received their first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine and 6 (12%) had received their second dose. “So, 12% of patients were fully vaccinated,” Dr. Blauvelt said. “We do know that the mRNA vaccines are about 95% effective in preventing COVID-19. Currently in Oregon, about 98% of our cases are in unvaccinated patients and about 2% of COVID-19 patients are fully vaccinated.”
In addition, the recently published ECZTRA5 vaccine study showed that nonlive vaccines (tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis; and meningococcal vaccines) could be safely administered and can elicit normal immune responses in patients treated with tralokinumab.
“We sorely need COVID-19–related safety data for all of our current and emerging systemic and biologic therapies used to treat atopic dermatitis,” said Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH, director of clinical research in the division of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment about these results. “This study is important because it shows that tralokinumab was not associated with any obvious safety signals with respect to COVID-19 infections. The major limitation is that it is not a prospective study designed to assess tralokinumab efficacy in COVID-19 patients per se. However, this post hoc study provides reassuring data. We need similar or even more robust studies for other systemic therapies in AD.”
Dr. Blauvelt reported that he is an investigator and a scientific advisor for LEO Pharma, which is developing tralokinumab, and for several other pharmaceutical companies developing treatments for AD. Dr. Silverberg reported that he is a consultant to and/or an advisory board member for several pharmaceutical companies, including LEO Pharma.
FROM REVOLUTIONIZING AD 2021
Complying with the Americans With Disabilities Act
. And 7 years ago, the government raised the penalties for failing to do so. So it might be time to re-educate yourself on what the ADA requires.
ADA compliance is not an issue that we talk about or provide training for in medical schools or with our professional organizations. Since fines for small businesses are now $75,000 for a first offense and $150,000 for each subsequent violation, this could be an expensive oversight that malpractice and other liability policies will not cover.
A 2019 study in Boston examined physicians’ knowledge of legal obligations when caring for patients with disabilities. Researchers concluded that most physicians interviewed “exhibited a superficial or incorrect understanding of their legal responsibilities to patients with a disability.” If you feel you’re in that boat, you might want to consult federal guidance with information and common questions physicians ask about their ADA obligations.
The ADA defines a person with a disability as someone with “a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more life activities”; someone with a record of such an impairment; or someone who is “regarded as having such an impairment.” Among the ADA standards required for accessible exam rooms, according to the guidance:
- The entry door to the exam room should be a minimum width of 32 inches when the door is opened at a 90-degree angle.
- There should be a minimum of 30 by 48 inches of clear floor space next to the exam table.
- An accessible exam table should be able to be lowered to the height of the patient’s wheelchair seat, 17 to 19 inches from the floor.
This does not mean that all of your exam rooms must meet these standards, of course; but if you see any patients with disabilities – and who doesn’t? – you need at least one room that meets the criteria.
Federal guidance also includes requirements on removal of architectural barriers, accessible parking, and entrance and maneuvering spaces – which apply to both for-profit and nonprofit organizations. Among them:
- Designated accessible parking spaces must be included among any parking the business provides for the public “if doing so is readily achievable.” Those parking spaces should be the closest to the accessible entrance, on level ground. The spaces should be at least eight feet wide, with an access aisle on either side.
- For accessible spaces for cars, the adjacent access aisle must be at least five feet wide; for van spaces, eight feet wide.
- “If achievable,” an accessible service counter must have a maximum height of 36 inches, with a clear floor space of 30 by 48 inches to permit the use of a wheelchair.
A common misconception is that only new construction and alterations need to be accessible, and that older facilities are “grandfathered,” but that’s not true. Because the ADA is a civil rights law and not a building code, ADA rules apply equally to all facilities, young and old. This is particularly important to remember in light of the long-standing cottage industry of attorneys who sue small businesses for alleged ADA violations.
Another common mistake made by physicians who lease their office space is to assume that their landlord is responsible for meeting all ADA obligations. In fact, The ADA places the legal obligation on both the landlord and the tenant. The landlord and the tenant may decide among themselves who will actually make the changes and provide the aids and services, but both remain legally responsible.
Another aspect that you might not have thought of is access to your website. While ADA applicability to online services remains vague, lawsuits have been filed, and are likely to increase. Online accessibility issues that have been identified include:
- Ability to find and process information on a website (e.g., providing audio descriptions for video content, for the sight-impaired).
- Ability to navigate and use a website (e.g., ensuring that all site functions are easily accessible with only a keyboard).
- Ability to comprehend all information (including clearly understandable error messages).
Hearing-impaired patients present their own considerations for delivering adequate care, which I will discuss in my next column.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
. And 7 years ago, the government raised the penalties for failing to do so. So it might be time to re-educate yourself on what the ADA requires.
ADA compliance is not an issue that we talk about or provide training for in medical schools or with our professional organizations. Since fines for small businesses are now $75,000 for a first offense and $150,000 for each subsequent violation, this could be an expensive oversight that malpractice and other liability policies will not cover.
A 2019 study in Boston examined physicians’ knowledge of legal obligations when caring for patients with disabilities. Researchers concluded that most physicians interviewed “exhibited a superficial or incorrect understanding of their legal responsibilities to patients with a disability.” If you feel you’re in that boat, you might want to consult federal guidance with information and common questions physicians ask about their ADA obligations.
The ADA defines a person with a disability as someone with “a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more life activities”; someone with a record of such an impairment; or someone who is “regarded as having such an impairment.” Among the ADA standards required for accessible exam rooms, according to the guidance:
- The entry door to the exam room should be a minimum width of 32 inches when the door is opened at a 90-degree angle.
- There should be a minimum of 30 by 48 inches of clear floor space next to the exam table.
- An accessible exam table should be able to be lowered to the height of the patient’s wheelchair seat, 17 to 19 inches from the floor.
This does not mean that all of your exam rooms must meet these standards, of course; but if you see any patients with disabilities – and who doesn’t? – you need at least one room that meets the criteria.
Federal guidance also includes requirements on removal of architectural barriers, accessible parking, and entrance and maneuvering spaces – which apply to both for-profit and nonprofit organizations. Among them:
- Designated accessible parking spaces must be included among any parking the business provides for the public “if doing so is readily achievable.” Those parking spaces should be the closest to the accessible entrance, on level ground. The spaces should be at least eight feet wide, with an access aisle on either side.
- For accessible spaces for cars, the adjacent access aisle must be at least five feet wide; for van spaces, eight feet wide.
- “If achievable,” an accessible service counter must have a maximum height of 36 inches, with a clear floor space of 30 by 48 inches to permit the use of a wheelchair.
A common misconception is that only new construction and alterations need to be accessible, and that older facilities are “grandfathered,” but that’s not true. Because the ADA is a civil rights law and not a building code, ADA rules apply equally to all facilities, young and old. This is particularly important to remember in light of the long-standing cottage industry of attorneys who sue small businesses for alleged ADA violations.
Another common mistake made by physicians who lease their office space is to assume that their landlord is responsible for meeting all ADA obligations. In fact, The ADA places the legal obligation on both the landlord and the tenant. The landlord and the tenant may decide among themselves who will actually make the changes and provide the aids and services, but both remain legally responsible.
Another aspect that you might not have thought of is access to your website. While ADA applicability to online services remains vague, lawsuits have been filed, and are likely to increase. Online accessibility issues that have been identified include:
- Ability to find and process information on a website (e.g., providing audio descriptions for video content, for the sight-impaired).
- Ability to navigate and use a website (e.g., ensuring that all site functions are easily accessible with only a keyboard).
- Ability to comprehend all information (including clearly understandable error messages).
Hearing-impaired patients present their own considerations for delivering adequate care, which I will discuss in my next column.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
. And 7 years ago, the government raised the penalties for failing to do so. So it might be time to re-educate yourself on what the ADA requires.
ADA compliance is not an issue that we talk about or provide training for in medical schools or with our professional organizations. Since fines for small businesses are now $75,000 for a first offense and $150,000 for each subsequent violation, this could be an expensive oversight that malpractice and other liability policies will not cover.
A 2019 study in Boston examined physicians’ knowledge of legal obligations when caring for patients with disabilities. Researchers concluded that most physicians interviewed “exhibited a superficial or incorrect understanding of their legal responsibilities to patients with a disability.” If you feel you’re in that boat, you might want to consult federal guidance with information and common questions physicians ask about their ADA obligations.
The ADA defines a person with a disability as someone with “a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more life activities”; someone with a record of such an impairment; or someone who is “regarded as having such an impairment.” Among the ADA standards required for accessible exam rooms, according to the guidance:
- The entry door to the exam room should be a minimum width of 32 inches when the door is opened at a 90-degree angle.
- There should be a minimum of 30 by 48 inches of clear floor space next to the exam table.
- An accessible exam table should be able to be lowered to the height of the patient’s wheelchair seat, 17 to 19 inches from the floor.
This does not mean that all of your exam rooms must meet these standards, of course; but if you see any patients with disabilities – and who doesn’t? – you need at least one room that meets the criteria.
Federal guidance also includes requirements on removal of architectural barriers, accessible parking, and entrance and maneuvering spaces – which apply to both for-profit and nonprofit organizations. Among them:
- Designated accessible parking spaces must be included among any parking the business provides for the public “if doing so is readily achievable.” Those parking spaces should be the closest to the accessible entrance, on level ground. The spaces should be at least eight feet wide, with an access aisle on either side.
- For accessible spaces for cars, the adjacent access aisle must be at least five feet wide; for van spaces, eight feet wide.
- “If achievable,” an accessible service counter must have a maximum height of 36 inches, with a clear floor space of 30 by 48 inches to permit the use of a wheelchair.
A common misconception is that only new construction and alterations need to be accessible, and that older facilities are “grandfathered,” but that’s not true. Because the ADA is a civil rights law and not a building code, ADA rules apply equally to all facilities, young and old. This is particularly important to remember in light of the long-standing cottage industry of attorneys who sue small businesses for alleged ADA violations.
Another common mistake made by physicians who lease their office space is to assume that their landlord is responsible for meeting all ADA obligations. In fact, The ADA places the legal obligation on both the landlord and the tenant. The landlord and the tenant may decide among themselves who will actually make the changes and provide the aids and services, but both remain legally responsible.
Another aspect that you might not have thought of is access to your website. While ADA applicability to online services remains vague, lawsuits have been filed, and are likely to increase. Online accessibility issues that have been identified include:
- Ability to find and process information on a website (e.g., providing audio descriptions for video content, for the sight-impaired).
- Ability to navigate and use a website (e.g., ensuring that all site functions are easily accessible with only a keyboard).
- Ability to comprehend all information (including clearly understandable error messages).
Hearing-impaired patients present their own considerations for delivering adequate care, which I will discuss in my next column.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
New AMA president discusses pandemic during inaugural address
He has encountered “all manner of unexpected situations” and feels “more than prepared” to serve as president of the American Medical Association, he said.
At the same time, “I still find myself a little nervous about it,” Dr. Harmon said in an interview the day after he was sworn in as president. “I would be less than candid if I didn’t tell you that. I don’t mean intimidated. ... It’s almost like before an athletic event.”
Dr. Harmon was sworn in June 15 as the 176th president of the AMA during the virtual Special Meeting of the AMA House of Delegates. He follows Susan R. Bailey, MD, an allergist from Fort Worth, Tex., in leading the organization, which has more than 270,000 members.
Advancing health equity
During his inaugural address, Dr. Harmon discussed the pandemic and the AMA’s plan to advance health equity.
COVID-19 “has revealed enormous gaps in how we care for people and communities in America, demonstrated in the disproportionate impact of this pandemic on communities of color and in the weaknesses of our underfunded and underresourced public health infrastructure,” Dr. Harmon said.
He described medical professionals as being “at war against seemingly formidable adversaries,” including the pandemic, the effects of prolonged isolation on emotional and behavioral health, and political and racial tension. There is an “immense battle to rid our health system – and society – of health disparities and racism,” he said. “As we face these battles, we must remember that our actions as physicians and as leaders will have far-reaching consequences.”
Other challenges before the AMA include vaccinating patients, recovering from the ongoing pandemic, removing unnecessary obstacles to care, ending an epidemic of drug overdoses, improving outcomes for patients with chronic disease, incorporating technology in ways that benefit doctors and patients, and preparing future physicians, Dr. Harmon noted.
“We are going to embed the principles of equity and racial justice within the AMA and throughout our health system,” added Dr. Harmon, who has been an AMA board member since 2013 and served as board chair from 2017 to 2018. He highlighted the AMA’s strategic plan, released in May 2021, to advance health equity and justice and improve the quality of care for people who have been marginalized.
“Meaningful progress won’t happen until we, as doctors, recognize how profoundly systemic racism influences the health of our patients, and until we commit to taking action within our own spheres of influence,” Dr. Harmon said. “As a family doctor in a very diverse state, I have treated people from all backgrounds, and have seen inequities up close, inequities that understandably lead to distrust.”
Commenting in an interview on JAMA’s controversial tweet and podcast related to structural racism from earlier this year that have been deleted and removed from JAMA’s website, Dr. Harmon said, JAMA maintains editorial independence from the AMA, but that direction from a journal oversight committee could lead to changes at the journal that could help prevent similar incidents.
“We’ll support whatever the journal oversight committee suggests,” Dr. Harmon said.
“We had public statements about [the podcast]. I do think that we’ll be able to move very quickly in a stronger direction to address the issue of systemic racism,” Dr. Harmon said. “The AMA has acknowledged that it is a public health threat. We have acknowledged that it is ... a political description versus a biologic construct. So, I would anticipate that you’ll find changes.”
The AMA began developing its strategic plan to advance equity several years ago, Dr. Harmon noted. “I think we are very well poised to move forward and attack this enemy of health disparity.”
AAFP president supporting Dr. Harmon’s inauguration
Among those congratulating Dr. Harmon on his inauguration was Ada Stewart, MD, a fellow family physician and South Carolina resident who is the president of the American Academy of Family Physicians.
“We are very excited that family physician Dr. Gerald Harmon will serve as president of the AMA this coming year,” Dr. Stewart said. “Family medicine encompasses the very essence of medicine – treating the whole person, in the context of family, community, and each individual’s unique circumstances. As a family physician, Dr. Harmon brings important perspectives from the front lines of primary care. His commitment to health equity and evidence-based care, as well as his concern for practice sustainability and physician well-being, will serve him well as he leads the house of medicine into the future.”
Dr. Harmon has practiced as a family medicine specialist in Georgetown, S.C., for more than 30 years. He is a member of the clinical faculty for the Tidelands Health Medical University of South Carolina family medicine residency program, advises a community health system, and is vice president of a multispecialty physician practice. In addition, Dr. Harmon is the medical director of a nonprofit hospice and volunteers as medical supervisor for his local school district.
Dr. Harmon received his undergraduate degree in physics and mathematics from the University of South Carolina, Columbia, and received his medical degree from the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston. He completed a residency training program in family medicine with the U.S. Air Force at Eglin (Fla.) AFB, Florida.
During a 35-year military career, Dr. Harmon served as chief surgeon for the National Guard Bureau and assistant surgeon general for the U.S. Air Force. He retired from the military as a major general.
Dr. Harmon and his wife, Linda, have three married children and eight grandchildren.
Every now and then, a bucket of tomatoes or even a half bushel of corn shows up in the back of Dr. Harmon’s pickup truck, with a note on the window thanking him. “That really touches you deeply,” Dr. Harmon said. “I practice that type of medicine and I’m honored to be able to do that every day.”
He has encountered “all manner of unexpected situations” and feels “more than prepared” to serve as president of the American Medical Association, he said.
At the same time, “I still find myself a little nervous about it,” Dr. Harmon said in an interview the day after he was sworn in as president. “I would be less than candid if I didn’t tell you that. I don’t mean intimidated. ... It’s almost like before an athletic event.”
Dr. Harmon was sworn in June 15 as the 176th president of the AMA during the virtual Special Meeting of the AMA House of Delegates. He follows Susan R. Bailey, MD, an allergist from Fort Worth, Tex., in leading the organization, which has more than 270,000 members.
Advancing health equity
During his inaugural address, Dr. Harmon discussed the pandemic and the AMA’s plan to advance health equity.
COVID-19 “has revealed enormous gaps in how we care for people and communities in America, demonstrated in the disproportionate impact of this pandemic on communities of color and in the weaknesses of our underfunded and underresourced public health infrastructure,” Dr. Harmon said.
He described medical professionals as being “at war against seemingly formidable adversaries,” including the pandemic, the effects of prolonged isolation on emotional and behavioral health, and political and racial tension. There is an “immense battle to rid our health system – and society – of health disparities and racism,” he said. “As we face these battles, we must remember that our actions as physicians and as leaders will have far-reaching consequences.”
Other challenges before the AMA include vaccinating patients, recovering from the ongoing pandemic, removing unnecessary obstacles to care, ending an epidemic of drug overdoses, improving outcomes for patients with chronic disease, incorporating technology in ways that benefit doctors and patients, and preparing future physicians, Dr. Harmon noted.
“We are going to embed the principles of equity and racial justice within the AMA and throughout our health system,” added Dr. Harmon, who has been an AMA board member since 2013 and served as board chair from 2017 to 2018. He highlighted the AMA’s strategic plan, released in May 2021, to advance health equity and justice and improve the quality of care for people who have been marginalized.
“Meaningful progress won’t happen until we, as doctors, recognize how profoundly systemic racism influences the health of our patients, and until we commit to taking action within our own spheres of influence,” Dr. Harmon said. “As a family doctor in a very diverse state, I have treated people from all backgrounds, and have seen inequities up close, inequities that understandably lead to distrust.”
Commenting in an interview on JAMA’s controversial tweet and podcast related to structural racism from earlier this year that have been deleted and removed from JAMA’s website, Dr. Harmon said, JAMA maintains editorial independence from the AMA, but that direction from a journal oversight committee could lead to changes at the journal that could help prevent similar incidents.
“We’ll support whatever the journal oversight committee suggests,” Dr. Harmon said.
“We had public statements about [the podcast]. I do think that we’ll be able to move very quickly in a stronger direction to address the issue of systemic racism,” Dr. Harmon said. “The AMA has acknowledged that it is a public health threat. We have acknowledged that it is ... a political description versus a biologic construct. So, I would anticipate that you’ll find changes.”
The AMA began developing its strategic plan to advance equity several years ago, Dr. Harmon noted. “I think we are very well poised to move forward and attack this enemy of health disparity.”
AAFP president supporting Dr. Harmon’s inauguration
Among those congratulating Dr. Harmon on his inauguration was Ada Stewart, MD, a fellow family physician and South Carolina resident who is the president of the American Academy of Family Physicians.
“We are very excited that family physician Dr. Gerald Harmon will serve as president of the AMA this coming year,” Dr. Stewart said. “Family medicine encompasses the very essence of medicine – treating the whole person, in the context of family, community, and each individual’s unique circumstances. As a family physician, Dr. Harmon brings important perspectives from the front lines of primary care. His commitment to health equity and evidence-based care, as well as his concern for practice sustainability and physician well-being, will serve him well as he leads the house of medicine into the future.”
Dr. Harmon has practiced as a family medicine specialist in Georgetown, S.C., for more than 30 years. He is a member of the clinical faculty for the Tidelands Health Medical University of South Carolina family medicine residency program, advises a community health system, and is vice president of a multispecialty physician practice. In addition, Dr. Harmon is the medical director of a nonprofit hospice and volunteers as medical supervisor for his local school district.
Dr. Harmon received his undergraduate degree in physics and mathematics from the University of South Carolina, Columbia, and received his medical degree from the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston. He completed a residency training program in family medicine with the U.S. Air Force at Eglin (Fla.) AFB, Florida.
During a 35-year military career, Dr. Harmon served as chief surgeon for the National Guard Bureau and assistant surgeon general for the U.S. Air Force. He retired from the military as a major general.
Dr. Harmon and his wife, Linda, have three married children and eight grandchildren.
Every now and then, a bucket of tomatoes or even a half bushel of corn shows up in the back of Dr. Harmon’s pickup truck, with a note on the window thanking him. “That really touches you deeply,” Dr. Harmon said. “I practice that type of medicine and I’m honored to be able to do that every day.”
He has encountered “all manner of unexpected situations” and feels “more than prepared” to serve as president of the American Medical Association, he said.
At the same time, “I still find myself a little nervous about it,” Dr. Harmon said in an interview the day after he was sworn in as president. “I would be less than candid if I didn’t tell you that. I don’t mean intimidated. ... It’s almost like before an athletic event.”
Dr. Harmon was sworn in June 15 as the 176th president of the AMA during the virtual Special Meeting of the AMA House of Delegates. He follows Susan R. Bailey, MD, an allergist from Fort Worth, Tex., in leading the organization, which has more than 270,000 members.
Advancing health equity
During his inaugural address, Dr. Harmon discussed the pandemic and the AMA’s plan to advance health equity.
COVID-19 “has revealed enormous gaps in how we care for people and communities in America, demonstrated in the disproportionate impact of this pandemic on communities of color and in the weaknesses of our underfunded and underresourced public health infrastructure,” Dr. Harmon said.
He described medical professionals as being “at war against seemingly formidable adversaries,” including the pandemic, the effects of prolonged isolation on emotional and behavioral health, and political and racial tension. There is an “immense battle to rid our health system – and society – of health disparities and racism,” he said. “As we face these battles, we must remember that our actions as physicians and as leaders will have far-reaching consequences.”
Other challenges before the AMA include vaccinating patients, recovering from the ongoing pandemic, removing unnecessary obstacles to care, ending an epidemic of drug overdoses, improving outcomes for patients with chronic disease, incorporating technology in ways that benefit doctors and patients, and preparing future physicians, Dr. Harmon noted.
“We are going to embed the principles of equity and racial justice within the AMA and throughout our health system,” added Dr. Harmon, who has been an AMA board member since 2013 and served as board chair from 2017 to 2018. He highlighted the AMA’s strategic plan, released in May 2021, to advance health equity and justice and improve the quality of care for people who have been marginalized.
“Meaningful progress won’t happen until we, as doctors, recognize how profoundly systemic racism influences the health of our patients, and until we commit to taking action within our own spheres of influence,” Dr. Harmon said. “As a family doctor in a very diverse state, I have treated people from all backgrounds, and have seen inequities up close, inequities that understandably lead to distrust.”
Commenting in an interview on JAMA’s controversial tweet and podcast related to structural racism from earlier this year that have been deleted and removed from JAMA’s website, Dr. Harmon said, JAMA maintains editorial independence from the AMA, but that direction from a journal oversight committee could lead to changes at the journal that could help prevent similar incidents.
“We’ll support whatever the journal oversight committee suggests,” Dr. Harmon said.
“We had public statements about [the podcast]. I do think that we’ll be able to move very quickly in a stronger direction to address the issue of systemic racism,” Dr. Harmon said. “The AMA has acknowledged that it is a public health threat. We have acknowledged that it is ... a political description versus a biologic construct. So, I would anticipate that you’ll find changes.”
The AMA began developing its strategic plan to advance equity several years ago, Dr. Harmon noted. “I think we are very well poised to move forward and attack this enemy of health disparity.”
AAFP president supporting Dr. Harmon’s inauguration
Among those congratulating Dr. Harmon on his inauguration was Ada Stewart, MD, a fellow family physician and South Carolina resident who is the president of the American Academy of Family Physicians.
“We are very excited that family physician Dr. Gerald Harmon will serve as president of the AMA this coming year,” Dr. Stewart said. “Family medicine encompasses the very essence of medicine – treating the whole person, in the context of family, community, and each individual’s unique circumstances. As a family physician, Dr. Harmon brings important perspectives from the front lines of primary care. His commitment to health equity and evidence-based care, as well as his concern for practice sustainability and physician well-being, will serve him well as he leads the house of medicine into the future.”
Dr. Harmon has practiced as a family medicine specialist in Georgetown, S.C., for more than 30 years. He is a member of the clinical faculty for the Tidelands Health Medical University of South Carolina family medicine residency program, advises a community health system, and is vice president of a multispecialty physician practice. In addition, Dr. Harmon is the medical director of a nonprofit hospice and volunteers as medical supervisor for his local school district.
Dr. Harmon received his undergraduate degree in physics and mathematics from the University of South Carolina, Columbia, and received his medical degree from the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston. He completed a residency training program in family medicine with the U.S. Air Force at Eglin (Fla.) AFB, Florida.
During a 35-year military career, Dr. Harmon served as chief surgeon for the National Guard Bureau and assistant surgeon general for the U.S. Air Force. He retired from the military as a major general.
Dr. Harmon and his wife, Linda, have three married children and eight grandchildren.
Every now and then, a bucket of tomatoes or even a half bushel of corn shows up in the back of Dr. Harmon’s pickup truck, with a note on the window thanking him. “That really touches you deeply,” Dr. Harmon said. “I practice that type of medicine and I’m honored to be able to do that every day.”
Supreme Court upholds Affordable Care Act
The challengers were comprised of 18 GOP-dominated states, led by Texas, that took issue with the ACA’s individual mandate – which required most Americans to have health insurance or pay a tax penalty.
But Congress reduced the penalty to zero in 2017. Challengers argued that without the mandate, the rest of the law should be scrapped, too. The court ruled that eliminated the harm the states were claiming.
“To have standing, a plaintiff must ‘allege personal injury fairly traceable to the defendant’s allegedly unlawful conduct and likely to be redressed by the requested relief,’” the majority wrote. “No plaintiff has shown such an injury ‘fairly traceable’ to the ‘allegedly unlawful conduct’ challenged here.”
Justice Stephen Breyer authored the opinion. Justices Samuel Alito and Neil Gorsuch dissented.
The decision said that the mandate in question did not require the 18 states that brought the complaint to pay anything, and therefore they had no standing.
President Joe Biden has said he plans to build on the ACA – which was enacted while he was vice president – to offer coverage to more Americans.
This marks the third time the Supreme Court spared the Obama-era law from GOP attacks. The mandate was also upheld in 2012 in a 5 to 4 ruling.
American Medical Association president Gerald Harmon, MD, also called for building on the ruling to expand the law.
“With yet another court decision upholding the ACA now behind us, we remain committed to strengthening the current law and look forward to policymakers advancing solutions to improve the ACA,” Dr. Harmon said in a statement. “The AMA will continue working to expand access to health care and ensure that all Americans have meaningful, comprehensive, and affordable health coverage to improve the health of the nation.”
House Speaker Nancy Pelosi (D-Calif.), a longtime advocate for the ACA, called the decision a “landmark victory for Democrats.”
“Thanks to the tireless advocacy of Americans across the country and Democrats in Congress, the Affordable Care Act endures as a pillar of American health and economic security alongside Medicare, Medicaid and Social Security,” she said in a statement.
Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer (D-N.Y.) also celebrated the ruling.
“The Affordable Care Act has won. The Supreme Court has just ruled: the ACA is here to stay and now we’re going to try to make it bigger and better,” he said, according to CNN. “For more than a decade, the assault on our health care law was relentless from Republicans in Congress, from the executive branch itself and from Republican attorneys general in the courts. Each time in each arena, the ACA has prevailed.”
This article was updated June 17, 2021.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The challengers were comprised of 18 GOP-dominated states, led by Texas, that took issue with the ACA’s individual mandate – which required most Americans to have health insurance or pay a tax penalty.
But Congress reduced the penalty to zero in 2017. Challengers argued that without the mandate, the rest of the law should be scrapped, too. The court ruled that eliminated the harm the states were claiming.
“To have standing, a plaintiff must ‘allege personal injury fairly traceable to the defendant’s allegedly unlawful conduct and likely to be redressed by the requested relief,’” the majority wrote. “No plaintiff has shown such an injury ‘fairly traceable’ to the ‘allegedly unlawful conduct’ challenged here.”
Justice Stephen Breyer authored the opinion. Justices Samuel Alito and Neil Gorsuch dissented.
The decision said that the mandate in question did not require the 18 states that brought the complaint to pay anything, and therefore they had no standing.
President Joe Biden has said he plans to build on the ACA – which was enacted while he was vice president – to offer coverage to more Americans.
This marks the third time the Supreme Court spared the Obama-era law from GOP attacks. The mandate was also upheld in 2012 in a 5 to 4 ruling.
American Medical Association president Gerald Harmon, MD, also called for building on the ruling to expand the law.
“With yet another court decision upholding the ACA now behind us, we remain committed to strengthening the current law and look forward to policymakers advancing solutions to improve the ACA,” Dr. Harmon said in a statement. “The AMA will continue working to expand access to health care and ensure that all Americans have meaningful, comprehensive, and affordable health coverage to improve the health of the nation.”
House Speaker Nancy Pelosi (D-Calif.), a longtime advocate for the ACA, called the decision a “landmark victory for Democrats.”
“Thanks to the tireless advocacy of Americans across the country and Democrats in Congress, the Affordable Care Act endures as a pillar of American health and economic security alongside Medicare, Medicaid and Social Security,” she said in a statement.
Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer (D-N.Y.) also celebrated the ruling.
“The Affordable Care Act has won. The Supreme Court has just ruled: the ACA is here to stay and now we’re going to try to make it bigger and better,” he said, according to CNN. “For more than a decade, the assault on our health care law was relentless from Republicans in Congress, from the executive branch itself and from Republican attorneys general in the courts. Each time in each arena, the ACA has prevailed.”
This article was updated June 17, 2021.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The challengers were comprised of 18 GOP-dominated states, led by Texas, that took issue with the ACA’s individual mandate – which required most Americans to have health insurance or pay a tax penalty.
But Congress reduced the penalty to zero in 2017. Challengers argued that without the mandate, the rest of the law should be scrapped, too. The court ruled that eliminated the harm the states were claiming.
“To have standing, a plaintiff must ‘allege personal injury fairly traceable to the defendant’s allegedly unlawful conduct and likely to be redressed by the requested relief,’” the majority wrote. “No plaintiff has shown such an injury ‘fairly traceable’ to the ‘allegedly unlawful conduct’ challenged here.”
Justice Stephen Breyer authored the opinion. Justices Samuel Alito and Neil Gorsuch dissented.
The decision said that the mandate in question did not require the 18 states that brought the complaint to pay anything, and therefore they had no standing.
President Joe Biden has said he plans to build on the ACA – which was enacted while he was vice president – to offer coverage to more Americans.
This marks the third time the Supreme Court spared the Obama-era law from GOP attacks. The mandate was also upheld in 2012 in a 5 to 4 ruling.
American Medical Association president Gerald Harmon, MD, also called for building on the ruling to expand the law.
“With yet another court decision upholding the ACA now behind us, we remain committed to strengthening the current law and look forward to policymakers advancing solutions to improve the ACA,” Dr. Harmon said in a statement. “The AMA will continue working to expand access to health care and ensure that all Americans have meaningful, comprehensive, and affordable health coverage to improve the health of the nation.”
House Speaker Nancy Pelosi (D-Calif.), a longtime advocate for the ACA, called the decision a “landmark victory for Democrats.”
“Thanks to the tireless advocacy of Americans across the country and Democrats in Congress, the Affordable Care Act endures as a pillar of American health and economic security alongside Medicare, Medicaid and Social Security,” she said in a statement.
Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer (D-N.Y.) also celebrated the ruling.
“The Affordable Care Act has won. The Supreme Court has just ruled: the ACA is here to stay and now we’re going to try to make it bigger and better,” he said, according to CNN. “For more than a decade, the assault on our health care law was relentless from Republicans in Congress, from the executive branch itself and from Republican attorneys general in the courts. Each time in each arena, the ACA has prevailed.”
This article was updated June 17, 2021.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
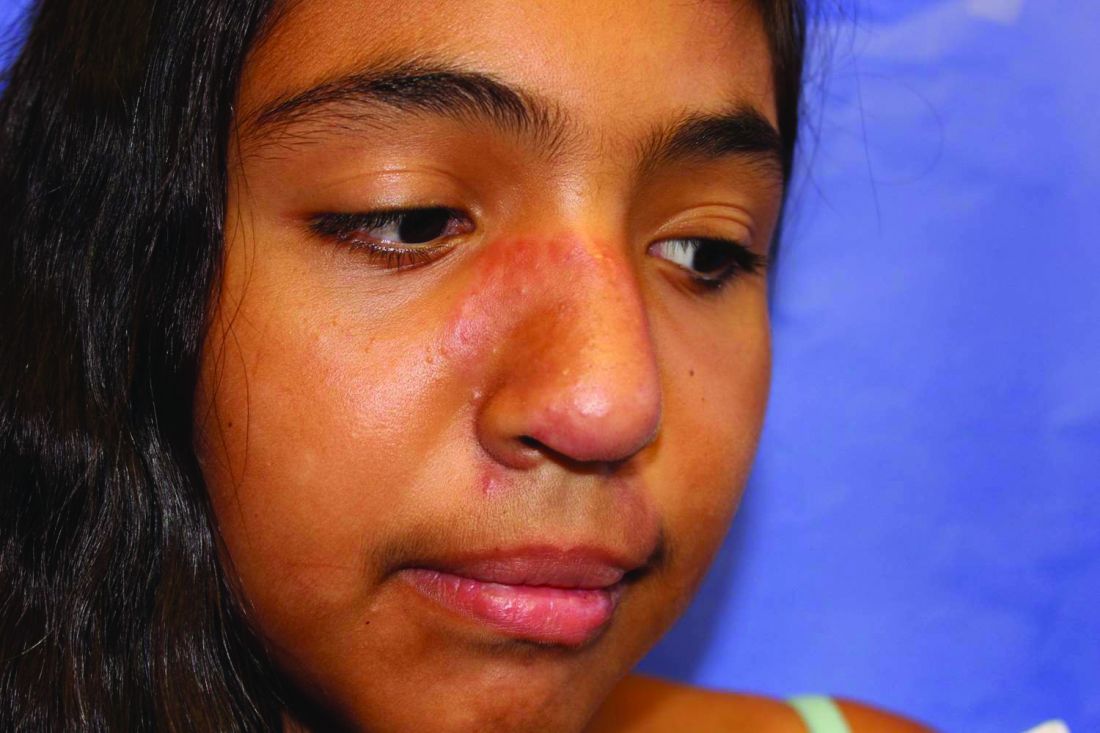
Lupus images fall short on diverse examples
Lupus images in medical resource materials underrepresent patients with skin of color, based on data from a review of more than 1,400 images published between 2014 and 2019 in materials from a university’s online medical library.
Patients with skin of color who develop lupus tend to present earlier and with more severe cases, and often experience worse outcomes, compared with other populations, wrote Amaad Rana, MD, of Washington University, St. Louis, and colleagues. Medical resources in general have historically underrepresented patients of color, and the researchers reviewed lupus materials for a similar publication bias.
In a study published in Arthritis Care & Research, the investigators identified 1,417 images in rheumatology, dermatology, and internal medicine resources, including 119 medical textbooks, 15 medical journals, 2 online image libraries, and the online image collections of Google and UpToDate. An additional 24 images came from skin of color atlases.
Excluding the skin of color atlases, 56.4% of the images represented light skin, 35.1% showed medium skin, and 8.5% showed dark skin. Overall, publishers were more than twice as likely to portray light skin tones and were significantly less likely to portray dark skin tones (odds ratios, 2.59 and 0.19, respectively), compared with an equal representation of skin tones; however, the difference was not significant for portrayal of medium skin tones (OR, 1.08).
By specialty, dermatology was more inclusive of skin of color images than rheumatology or internal medicine, although the internal medicine sample size was too small for comparable analysis, the researchers noted. Dermatology textbooks were 2.42 times more likely and rheumatology textbooks were 4.87 times more likely to depict light skin tones than an equal representation of light, medium, and dark skin tones.
The researchers rated the skin color in the images using the New Immigrant Survey Skin Color Scale and categorized the images as representing light (NISSCS scores, 1-2), medium (NISSCS scores, 3-5), or dark skin (NISSCS scores, 6-10). Medical journals had the most images of dark skin, excluding skin of color atlases. In a comparison of specialties, dermatology materials included the most images of medium and darker skin tones.
The underrepresentation of skin of color patients can contribute to a limited knowledge of lupus presentation that could lead to disparate health outcomes, the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the review of only the online textbooks and journals available through the medical library of a single university, the researchers noted. In addition, definitions of light, medium, and dark skin tones were variable among studies, and the researchers did not distinguish among lupus pathologies.
“Further research is needed to quantitatively assess the influence these materials have on healthcare providers’ ability to care for patients with lupus and SOC, and new material and strategies will be required to correct this disparity and promote equitable representation,” the researchers emphasized. “Ultimately, this will arm practitioners with the resources to competently treat patients with any skin color and work towards reducing disparities in health outcomes.”
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Lupus images in medical resource materials underrepresent patients with skin of color, based on data from a review of more than 1,400 images published between 2014 and 2019 in materials from a university’s online medical library.
Patients with skin of color who develop lupus tend to present earlier and with more severe cases, and often experience worse outcomes, compared with other populations, wrote Amaad Rana, MD, of Washington University, St. Louis, and colleagues. Medical resources in general have historically underrepresented patients of color, and the researchers reviewed lupus materials for a similar publication bias.
In a study published in Arthritis Care & Research, the investigators identified 1,417 images in rheumatology, dermatology, and internal medicine resources, including 119 medical textbooks, 15 medical journals, 2 online image libraries, and the online image collections of Google and UpToDate. An additional 24 images came from skin of color atlases.
Excluding the skin of color atlases, 56.4% of the images represented light skin, 35.1% showed medium skin, and 8.5% showed dark skin. Overall, publishers were more than twice as likely to portray light skin tones and were significantly less likely to portray dark skin tones (odds ratios, 2.59 and 0.19, respectively), compared with an equal representation of skin tones; however, the difference was not significant for portrayal of medium skin tones (OR, 1.08).
By specialty, dermatology was more inclusive of skin of color images than rheumatology or internal medicine, although the internal medicine sample size was too small for comparable analysis, the researchers noted. Dermatology textbooks were 2.42 times more likely and rheumatology textbooks were 4.87 times more likely to depict light skin tones than an equal representation of light, medium, and dark skin tones.
The researchers rated the skin color in the images using the New Immigrant Survey Skin Color Scale and categorized the images as representing light (NISSCS scores, 1-2), medium (NISSCS scores, 3-5), or dark skin (NISSCS scores, 6-10). Medical journals had the most images of dark skin, excluding skin of color atlases. In a comparison of specialties, dermatology materials included the most images of medium and darker skin tones.
The underrepresentation of skin of color patients can contribute to a limited knowledge of lupus presentation that could lead to disparate health outcomes, the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the review of only the online textbooks and journals available through the medical library of a single university, the researchers noted. In addition, definitions of light, medium, and dark skin tones were variable among studies, and the researchers did not distinguish among lupus pathologies.
“Further research is needed to quantitatively assess the influence these materials have on healthcare providers’ ability to care for patients with lupus and SOC, and new material and strategies will be required to correct this disparity and promote equitable representation,” the researchers emphasized. “Ultimately, this will arm practitioners with the resources to competently treat patients with any skin color and work towards reducing disparities in health outcomes.”
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Lupus images in medical resource materials underrepresent patients with skin of color, based on data from a review of more than 1,400 images published between 2014 and 2019 in materials from a university’s online medical library.
Patients with skin of color who develop lupus tend to present earlier and with more severe cases, and often experience worse outcomes, compared with other populations, wrote Amaad Rana, MD, of Washington University, St. Louis, and colleagues. Medical resources in general have historically underrepresented patients of color, and the researchers reviewed lupus materials for a similar publication bias.
In a study published in Arthritis Care & Research, the investigators identified 1,417 images in rheumatology, dermatology, and internal medicine resources, including 119 medical textbooks, 15 medical journals, 2 online image libraries, and the online image collections of Google and UpToDate. An additional 24 images came from skin of color atlases.
Excluding the skin of color atlases, 56.4% of the images represented light skin, 35.1% showed medium skin, and 8.5% showed dark skin. Overall, publishers were more than twice as likely to portray light skin tones and were significantly less likely to portray dark skin tones (odds ratios, 2.59 and 0.19, respectively), compared with an equal representation of skin tones; however, the difference was not significant for portrayal of medium skin tones (OR, 1.08).
By specialty, dermatology was more inclusive of skin of color images than rheumatology or internal medicine, although the internal medicine sample size was too small for comparable analysis, the researchers noted. Dermatology textbooks were 2.42 times more likely and rheumatology textbooks were 4.87 times more likely to depict light skin tones than an equal representation of light, medium, and dark skin tones.
The researchers rated the skin color in the images using the New Immigrant Survey Skin Color Scale and categorized the images as representing light (NISSCS scores, 1-2), medium (NISSCS scores, 3-5), or dark skin (NISSCS scores, 6-10). Medical journals had the most images of dark skin, excluding skin of color atlases. In a comparison of specialties, dermatology materials included the most images of medium and darker skin tones.
The underrepresentation of skin of color patients can contribute to a limited knowledge of lupus presentation that could lead to disparate health outcomes, the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the review of only the online textbooks and journals available through the medical library of a single university, the researchers noted. In addition, definitions of light, medium, and dark skin tones were variable among studies, and the researchers did not distinguish among lupus pathologies.
“Further research is needed to quantitatively assess the influence these materials have on healthcare providers’ ability to care for patients with lupus and SOC, and new material and strategies will be required to correct this disparity and promote equitable representation,” the researchers emphasized. “Ultimately, this will arm practitioners with the resources to competently treat patients with any skin color and work towards reducing disparities in health outcomes.”
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM ARTHRITIS CARE & RESEARCH
The good old days
“It’s good to be in something from the ground floor. I came too late for that. ... But lately, I’m getting the feeling that I came in at the end. The best is over.” –Tony Soprano
For me, I’m unsure. Sometimes it feels like our best days are behind us. When I was a kid, we explored life in pond water, watching water fleas and hydra swim under our Child World toy microscopes. Today, kids learn to eat Tide Pods from TikTok. Back when I was young, a doctor’s appointment was a special occasion! My brothers and I had a bath and got dressed in our Sunday best for our appointment with Dr. Bellin, a genteel, gray-haired pediatrician who worked out of his Victorian office with wooden floors and crystal door handles. Contrast that with the appointment I had with a patient the other day, done by telephone while she was in line ordering at Starbucks. I waited patiently for her to give her order.
This ache I feel for the past is called nostalgia. At one time, it was a diagnosable condition. It was first used by Dr. Johannes Hofer in the 17th century to describe Swiss soldiers fighting in foreign lands. From the Greek, it means “homecoming pain.” Although over time nostalgia has lost its clinical meaning, the feeling of yearning for the past has dramatically gained in prevalence. The word “nostalgia” appears more in print now than at any point since 1800. We are most nostalgic during times of duress, it seems. This, no doubt, is because it’s comforting to think we’d be better off back in pastoral, idyll times, back when work ended at 5 p.m. and cotton balls were soaked in alcohol and office visits ended with a lollipop on a loop.
Of course, the good old days weren’t really better. We have a selective view of history – as many things were contemptible or bad then as now. Yes, Dr. Bellin was the consummate professional, but thank goodness, I didn’t have acute lymphocytic leukemia or Haemophilus influenzae type B or even suffocate under a pile of blankets while sleeping on my stomach. Without doubt, clinically we’re much better today. Also back then, there was hardly a consideration for atrocious racial disparities in care. We’ve not come far, but we are at least better off today than a few decades ago. And what about medicine as a profession? Although he had loads of autonomy and respect, Dr. Bellin also started every day of his 50-year career at 6 a.m. rounding in the newborn nursery before seeing patients in the office 6 days a week. Not many of us would trade our practice for his.
Yet, there’s reasons to be nostalgic. Chart notes might have been barely legible, but at least they served a purpose. The problem-oriented medical record was intended to logically capture and organize data. SOAP notes were invented to help us think better, to get diagnoses correct, to succinctly see progress. Today, notes are written for administrators and payers and patients. As a result, they’re often useless to us.
And although it may have been inconvenient to sit in the waiting room reading Highlights magazine, I’m unsure it was a worse user experience, compared with a chain pharmacy “virtual” doctor visit. (Particularly because you could always drop pennies down the large hot-air iron floor grate in the corner).
The thrumming undercurrent of progress promises artificial intelligence and genomics and wearable diagnostics in our future. But the assumption is the new things will be better suited to our needs than the old. Sometimes, they are not. Sometimes technology diminishes us instead of enhancing us.
I cannot count how many times I’ve hit my head or whacked my shin because our Tesla Model X doors open by magic and of their own accord. Back when I was young, we opened car doors by pulling on the door handle. I sometimes miss those days.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
“It’s good to be in something from the ground floor. I came too late for that. ... But lately, I’m getting the feeling that I came in at the end. The best is over.” –Tony Soprano
For me, I’m unsure. Sometimes it feels like our best days are behind us. When I was a kid, we explored life in pond water, watching water fleas and hydra swim under our Child World toy microscopes. Today, kids learn to eat Tide Pods from TikTok. Back when I was young, a doctor’s appointment was a special occasion! My brothers and I had a bath and got dressed in our Sunday best for our appointment with Dr. Bellin, a genteel, gray-haired pediatrician who worked out of his Victorian office with wooden floors and crystal door handles. Contrast that with the appointment I had with a patient the other day, done by telephone while she was in line ordering at Starbucks. I waited patiently for her to give her order.
This ache I feel for the past is called nostalgia. At one time, it was a diagnosable condition. It was first used by Dr. Johannes Hofer in the 17th century to describe Swiss soldiers fighting in foreign lands. From the Greek, it means “homecoming pain.” Although over time nostalgia has lost its clinical meaning, the feeling of yearning for the past has dramatically gained in prevalence. The word “nostalgia” appears more in print now than at any point since 1800. We are most nostalgic during times of duress, it seems. This, no doubt, is because it’s comforting to think we’d be better off back in pastoral, idyll times, back when work ended at 5 p.m. and cotton balls were soaked in alcohol and office visits ended with a lollipop on a loop.
Of course, the good old days weren’t really better. We have a selective view of history – as many things were contemptible or bad then as now. Yes, Dr. Bellin was the consummate professional, but thank goodness, I didn’t have acute lymphocytic leukemia or Haemophilus influenzae type B or even suffocate under a pile of blankets while sleeping on my stomach. Without doubt, clinically we’re much better today. Also back then, there was hardly a consideration for atrocious racial disparities in care. We’ve not come far, but we are at least better off today than a few decades ago. And what about medicine as a profession? Although he had loads of autonomy and respect, Dr. Bellin also started every day of his 50-year career at 6 a.m. rounding in the newborn nursery before seeing patients in the office 6 days a week. Not many of us would trade our practice for his.
Yet, there’s reasons to be nostalgic. Chart notes might have been barely legible, but at least they served a purpose. The problem-oriented medical record was intended to logically capture and organize data. SOAP notes were invented to help us think better, to get diagnoses correct, to succinctly see progress. Today, notes are written for administrators and payers and patients. As a result, they’re often useless to us.
And although it may have been inconvenient to sit in the waiting room reading Highlights magazine, I’m unsure it was a worse user experience, compared with a chain pharmacy “virtual” doctor visit. (Particularly because you could always drop pennies down the large hot-air iron floor grate in the corner).
The thrumming undercurrent of progress promises artificial intelligence and genomics and wearable diagnostics in our future. But the assumption is the new things will be better suited to our needs than the old. Sometimes, they are not. Sometimes technology diminishes us instead of enhancing us.
I cannot count how many times I’ve hit my head or whacked my shin because our Tesla Model X doors open by magic and of their own accord. Back when I was young, we opened car doors by pulling on the door handle. I sometimes miss those days.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
“It’s good to be in something from the ground floor. I came too late for that. ... But lately, I’m getting the feeling that I came in at the end. The best is over.” –Tony Soprano
For me, I’m unsure. Sometimes it feels like our best days are behind us. When I was a kid, we explored life in pond water, watching water fleas and hydra swim under our Child World toy microscopes. Today, kids learn to eat Tide Pods from TikTok. Back when I was young, a doctor’s appointment was a special occasion! My brothers and I had a bath and got dressed in our Sunday best for our appointment with Dr. Bellin, a genteel, gray-haired pediatrician who worked out of his Victorian office with wooden floors and crystal door handles. Contrast that with the appointment I had with a patient the other day, done by telephone while she was in line ordering at Starbucks. I waited patiently for her to give her order.
This ache I feel for the past is called nostalgia. At one time, it was a diagnosable condition. It was first used by Dr. Johannes Hofer in the 17th century to describe Swiss soldiers fighting in foreign lands. From the Greek, it means “homecoming pain.” Although over time nostalgia has lost its clinical meaning, the feeling of yearning for the past has dramatically gained in prevalence. The word “nostalgia” appears more in print now than at any point since 1800. We are most nostalgic during times of duress, it seems. This, no doubt, is because it’s comforting to think we’d be better off back in pastoral, idyll times, back when work ended at 5 p.m. and cotton balls were soaked in alcohol and office visits ended with a lollipop on a loop.
Of course, the good old days weren’t really better. We have a selective view of history – as many things were contemptible or bad then as now. Yes, Dr. Bellin was the consummate professional, but thank goodness, I didn’t have acute lymphocytic leukemia or Haemophilus influenzae type B or even suffocate under a pile of blankets while sleeping on my stomach. Without doubt, clinically we’re much better today. Also back then, there was hardly a consideration for atrocious racial disparities in care. We’ve not come far, but we are at least better off today than a few decades ago. And what about medicine as a profession? Although he had loads of autonomy and respect, Dr. Bellin also started every day of his 50-year career at 6 a.m. rounding in the newborn nursery before seeing patients in the office 6 days a week. Not many of us would trade our practice for his.
Yet, there’s reasons to be nostalgic. Chart notes might have been barely legible, but at least they served a purpose. The problem-oriented medical record was intended to logically capture and organize data. SOAP notes were invented to help us think better, to get diagnoses correct, to succinctly see progress. Today, notes are written for administrators and payers and patients. As a result, they’re often useless to us.
And although it may have been inconvenient to sit in the waiting room reading Highlights magazine, I’m unsure it was a worse user experience, compared with a chain pharmacy “virtual” doctor visit. (Particularly because you could always drop pennies down the large hot-air iron floor grate in the corner).
The thrumming undercurrent of progress promises artificial intelligence and genomics and wearable diagnostics in our future. But the assumption is the new things will be better suited to our needs than the old. Sometimes, they are not. Sometimes technology diminishes us instead of enhancing us.
I cannot count how many times I’ve hit my head or whacked my shin because our Tesla Model X doors open by magic and of their own accord. Back when I was young, we opened car doors by pulling on the door handle. I sometimes miss those days.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
Toxic chemicals found in many cosmetics
People may be absorbing and ingesting potentially toxic chemicals from their cosmetic products, a new study suggests.
– per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Many of these chemicals were not included on the product labels, making it difficult for consumers to consciously avoid them.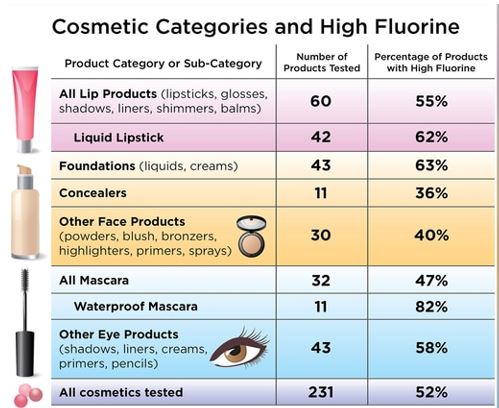
“This study is very helpful for elucidating the PFAS content of different types of cosmetics in the U.S. and Canadian markets,” said Elsie Sunderland, PhD, an environmental scientist who was not involved with the study.
“Previously, all the data had been collected in Europe, and this study shows we are dealing with similar problems in the North American marketplace,” said Dr. Sunderland, a professor of environmental chemistry at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston.
PFAS are a class of chemicals used in a variety of consumer products, such as nonstick cookware, stain-resistant carpeting, and water-repellent clothing, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. They are added to cosmetics to make the products more durable and spreadable, researchers said in the study.
“[PFAS] are added to change the properties of surfaces, to make them nonstick or resistant to stay in water or oils,” said study coauthor Tom Bruton, PhD, senior scientist at the Green Science Policy Institute in Berkeley, Calif. “The concerning thing about cosmetics is that these are products that you’re applying to your skin and face every day, so there’s the skin absorption route that’s of concern, but also incidental ingestion of cosmetics is also a concern as well.”
The CDC says some of the potential health effects of PFAS exposure includes increased cholesterol levels, increased risk of kidney and testicular cancer, changes in liver enzymes, decreased vaccine response in children, and a higher risk of high blood pressure or preeclampsia in pregnant women.
“PFAS are a large class of chemicals. In humans, exposure to some of these chemicals has been associated with impaired immune function, certain cancers, increased risks of diabetes, obesity and endocrine disruption,” Dr. Sunderland said. “They appear to be harmful to every major organ system in the human body.”
For the current study, published online in Environmental Science & Technology Letters, Dr. Bruton and colleagues purchased 231 cosmetic products in the United States and Canada from retailers such as Ulta Beauty, Sephora, Target, and Bed Bath & Beyond. They then screened them for fluorine.Three-quarters of waterproof mascara samples contained high fluorine concentrations, as did nearly two-thirds of foundations and liquid lipsticks, and more than half of the eye and lip products tested.
The authors found that different categories of makeup tended to have higher or lower fluorine concentrations. “High fluorine levels were found in products commonly advertised as ‘wear-resistant’ to water and oils or ‘long-lasting,’ including foundations, liquid lipsticks, and waterproof mascaras,” Dr. Bruton and colleagues wrote.
When they further analyzed a subset of 29 products to determine what types of chemicals were present, they found that each cosmetic product contained at least 4 PFAS, with one product containing 13.The PFAS substances found included some that break down into other chemicals that are known to be highly toxic and environmentally harmful.
“It’s concerning that some of the products we tested appear to be intentionally using PFAS, but not listing those ingredients on the label,” Dr. Bruton said. “I do think that it is helpful for consumers to read labels, but beyond that, there’s not a lot of ways that consumers themselves can solve this problem. ... We think that the industry needs to be more proactive about moving away from this group of chemicals.”
Dr. Sunderland said a resource people can use when trying to avoid PFAS is the Environmental Working Group, a nonprofit organization that maintains an extensive database of cosmetics and personal care products.
“At this point, there is very little regulatory activity related to PFAS in cosmetics,” Dr. Sunderland said. “The best thing to happen now would be for consumers to indicate that they prefer products without PFAS and to demand better transparency in product ingredient lists.”
A similar study done in 2018 by the Danish Environmental Protection Agency found high levels of PFAS in nearly one-third of the cosmetics products it tested.
People can also be exposed to PFAS by eating or drinking contaminated food or water and through food packaging. Dr. Sunderland said some wild foods like seafood are known to accumulate these compounds in the environment.
“There are examples of contaminated biosolids leading to accumulation of PFAS in vegetables and milk,” Dr. Sunderland explained. “Food packaging is another concern because it can also result in PFAS accumulation in the foods we eat.”
Although it’s difficult to avoid PFAS altogether, the CDC suggests lowering exposure rates by avoiding contaminated water and food. If you’re not sure if your water is contaminated, you should ask your local or state health and environmental quality departments for fish or water advisories in your area.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
People may be absorbing and ingesting potentially toxic chemicals from their cosmetic products, a new study suggests.
– per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Many of these chemicals were not included on the product labels, making it difficult for consumers to consciously avoid them.
“This study is very helpful for elucidating the PFAS content of different types of cosmetics in the U.S. and Canadian markets,” said Elsie Sunderland, PhD, an environmental scientist who was not involved with the study.
“Previously, all the data had been collected in Europe, and this study shows we are dealing with similar problems in the North American marketplace,” said Dr. Sunderland, a professor of environmental chemistry at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston.
PFAS are a class of chemicals used in a variety of consumer products, such as nonstick cookware, stain-resistant carpeting, and water-repellent clothing, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. They are added to cosmetics to make the products more durable and spreadable, researchers said in the study.
“[PFAS] are added to change the properties of surfaces, to make them nonstick or resistant to stay in water or oils,” said study coauthor Tom Bruton, PhD, senior scientist at the Green Science Policy Institute in Berkeley, Calif. “The concerning thing about cosmetics is that these are products that you’re applying to your skin and face every day, so there’s the skin absorption route that’s of concern, but also incidental ingestion of cosmetics is also a concern as well.”
The CDC says some of the potential health effects of PFAS exposure includes increased cholesterol levels, increased risk of kidney and testicular cancer, changes in liver enzymes, decreased vaccine response in children, and a higher risk of high blood pressure or preeclampsia in pregnant women.
“PFAS are a large class of chemicals. In humans, exposure to some of these chemicals has been associated with impaired immune function, certain cancers, increased risks of diabetes, obesity and endocrine disruption,” Dr. Sunderland said. “They appear to be harmful to every major organ system in the human body.”
For the current study, published online in Environmental Science & Technology Letters, Dr. Bruton and colleagues purchased 231 cosmetic products in the United States and Canada from retailers such as Ulta Beauty, Sephora, Target, and Bed Bath & Beyond. They then screened them for fluorine.Three-quarters of waterproof mascara samples contained high fluorine concentrations, as did nearly two-thirds of foundations and liquid lipsticks, and more than half of the eye and lip products tested.
The authors found that different categories of makeup tended to have higher or lower fluorine concentrations. “High fluorine levels were found in products commonly advertised as ‘wear-resistant’ to water and oils or ‘long-lasting,’ including foundations, liquid lipsticks, and waterproof mascaras,” Dr. Bruton and colleagues wrote.
When they further analyzed a subset of 29 products to determine what types of chemicals were present, they found that each cosmetic product contained at least 4 PFAS, with one product containing 13.The PFAS substances found included some that break down into other chemicals that are known to be highly toxic and environmentally harmful.
“It’s concerning that some of the products we tested appear to be intentionally using PFAS, but not listing those ingredients on the label,” Dr. Bruton said. “I do think that it is helpful for consumers to read labels, but beyond that, there’s not a lot of ways that consumers themselves can solve this problem. ... We think that the industry needs to be more proactive about moving away from this group of chemicals.”
Dr. Sunderland said a resource people can use when trying to avoid PFAS is the Environmental Working Group, a nonprofit organization that maintains an extensive database of cosmetics and personal care products.
“At this point, there is very little regulatory activity related to PFAS in cosmetics,” Dr. Sunderland said. “The best thing to happen now would be for consumers to indicate that they prefer products without PFAS and to demand better transparency in product ingredient lists.”
A similar study done in 2018 by the Danish Environmental Protection Agency found high levels of PFAS in nearly one-third of the cosmetics products it tested.
People can also be exposed to PFAS by eating or drinking contaminated food or water and through food packaging. Dr. Sunderland said some wild foods like seafood are known to accumulate these compounds in the environment.
“There are examples of contaminated biosolids leading to accumulation of PFAS in vegetables and milk,” Dr. Sunderland explained. “Food packaging is another concern because it can also result in PFAS accumulation in the foods we eat.”
Although it’s difficult to avoid PFAS altogether, the CDC suggests lowering exposure rates by avoiding contaminated water and food. If you’re not sure if your water is contaminated, you should ask your local or state health and environmental quality departments for fish or water advisories in your area.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
People may be absorbing and ingesting potentially toxic chemicals from their cosmetic products, a new study suggests.
– per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Many of these chemicals were not included on the product labels, making it difficult for consumers to consciously avoid them.
“This study is very helpful for elucidating the PFAS content of different types of cosmetics in the U.S. and Canadian markets,” said Elsie Sunderland, PhD, an environmental scientist who was not involved with the study.
“Previously, all the data had been collected in Europe, and this study shows we are dealing with similar problems in the North American marketplace,” said Dr. Sunderland, a professor of environmental chemistry at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston.
PFAS are a class of chemicals used in a variety of consumer products, such as nonstick cookware, stain-resistant carpeting, and water-repellent clothing, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. They are added to cosmetics to make the products more durable and spreadable, researchers said in the study.
“[PFAS] are added to change the properties of surfaces, to make them nonstick or resistant to stay in water or oils,” said study coauthor Tom Bruton, PhD, senior scientist at the Green Science Policy Institute in Berkeley, Calif. “The concerning thing about cosmetics is that these are products that you’re applying to your skin and face every day, so there’s the skin absorption route that’s of concern, but also incidental ingestion of cosmetics is also a concern as well.”
The CDC says some of the potential health effects of PFAS exposure includes increased cholesterol levels, increased risk of kidney and testicular cancer, changes in liver enzymes, decreased vaccine response in children, and a higher risk of high blood pressure or preeclampsia in pregnant women.
“PFAS are a large class of chemicals. In humans, exposure to some of these chemicals has been associated with impaired immune function, certain cancers, increased risks of diabetes, obesity and endocrine disruption,” Dr. Sunderland said. “They appear to be harmful to every major organ system in the human body.”
For the current study, published online in Environmental Science & Technology Letters, Dr. Bruton and colleagues purchased 231 cosmetic products in the United States and Canada from retailers such as Ulta Beauty, Sephora, Target, and Bed Bath & Beyond. They then screened them for fluorine.Three-quarters of waterproof mascara samples contained high fluorine concentrations, as did nearly two-thirds of foundations and liquid lipsticks, and more than half of the eye and lip products tested.
The authors found that different categories of makeup tended to have higher or lower fluorine concentrations. “High fluorine levels were found in products commonly advertised as ‘wear-resistant’ to water and oils or ‘long-lasting,’ including foundations, liquid lipsticks, and waterproof mascaras,” Dr. Bruton and colleagues wrote.
When they further analyzed a subset of 29 products to determine what types of chemicals were present, they found that each cosmetic product contained at least 4 PFAS, with one product containing 13.The PFAS substances found included some that break down into other chemicals that are known to be highly toxic and environmentally harmful.
“It’s concerning that some of the products we tested appear to be intentionally using PFAS, but not listing those ingredients on the label,” Dr. Bruton said. “I do think that it is helpful for consumers to read labels, but beyond that, there’s not a lot of ways that consumers themselves can solve this problem. ... We think that the industry needs to be more proactive about moving away from this group of chemicals.”
Dr. Sunderland said a resource people can use when trying to avoid PFAS is the Environmental Working Group, a nonprofit organization that maintains an extensive database of cosmetics and personal care products.
“At this point, there is very little regulatory activity related to PFAS in cosmetics,” Dr. Sunderland said. “The best thing to happen now would be for consumers to indicate that they prefer products without PFAS and to demand better transparency in product ingredient lists.”
A similar study done in 2018 by the Danish Environmental Protection Agency found high levels of PFAS in nearly one-third of the cosmetics products it tested.
People can also be exposed to PFAS by eating or drinking contaminated food or water and through food packaging. Dr. Sunderland said some wild foods like seafood are known to accumulate these compounds in the environment.
“There are examples of contaminated biosolids leading to accumulation of PFAS in vegetables and milk,” Dr. Sunderland explained. “Food packaging is another concern because it can also result in PFAS accumulation in the foods we eat.”
Although it’s difficult to avoid PFAS altogether, the CDC suggests lowering exposure rates by avoiding contaminated water and food. If you’re not sure if your water is contaminated, you should ask your local or state health and environmental quality departments for fish or water advisories in your area.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Incorporating self-care, wellness into routines can prevent doctors’ burnout
Gradually, we are emerging from the chaos, isolation, and anxiety of COVID-19. As the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention adjusts its recommendations and vaccinations become more widely available, our communities are beginning to return to normalcy. We are encouraged to put aside our masks if vaccinated and rejoin society, to venture out with less hesitancy and anxiety. As family and friends reunite, memories of confusion, frustration, and fear are beginning to fade to black. Despite the prevailing belief that we should move on, look forward, and remember the past to safeguard our future, remnants of the pandemic remain.
Unvaccinated individuals, notably children under the age of 12, are quite significant in number. The use of telehealth is now standard practice.
For several years, we were warned about the looming “mental health crisis.” The past year has demonstrated that a crisis no longer looms – it has arrived. Our patients can reveal the vulnerability COVID-19 has wrought – from the devastation of lives lost, supply shortages, loss of employment and financial stability – to a lack of access to computers and thereby, the risk of educational decline. Those factors, coupled with isolation and uncertainty about the future, have led to an influx of individuals with anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders seeking mental health treatment.
Doctors, others suffering
As result of a medical culture guided by the sacred oath to which care, compassion, and dedication held as true in ancient Greece as it does today, the focus centers on those around us – while signs of our own weariness are waved away as “a bad day.” Even though several support groups are readily available to offer a listening ear and mental health physicians who focus on the treatment of health care professionals are becoming more ubiquitous, the vestiges of past doctrine remain.
In this modern age of medical training, there is often as much sacrifice as there is attainment of knowledge. This philosophy is so ingrained that throughout training and practice one may come across colleagues experiencing an abundance of guilt when leave is needed for personal reasons. We are quick to recommend such steps for our patients, family, and friends, but hesitant to consider such for ourselves. Yet, of all the lessons this past year has wrought, the importance of mental health and self-care cannot be overstated. This raises the question:
It is vital to accept our humanity as something not to repair, treat, or overcome but to understand. There is strength and power in vulnerability. If we do not perceive and validate this process within ourselves, how can we do so for others? In other words, the oxygen mask must be placed on us first before we can place it on anyone else – patients or otherwise.
Chiefly and above all else, the importance of identifying individual signs of stress is essential. Where do you hold tension? Are you prone to GI distress or headaches when taxed? Do you tend toward irritability, apathy, or exhaustion?
Once this is determined, it is important to assess your stress on a numerical scale, such as those used for pain. Are you a 5 or an 8? Finally, are there identifiable triggers or reliable alleviators? Is there a time of day or day of the week that is most difficult to manage? Can you anticipate potential stressors? Understanding your triggers, listening to your body, and practicing the language of self is the first step toward wellness.
Following introspection and observation, the next step is inventory. Take stock of your reserves. What replenishes? What depletes? What brings joy? What brings dread? Are there certain activities that mitigate stress? If so, how much time do they entail? Identify your number on a scale and associate that number with specific strategies or techniques. Remember that decompression for a 6 might be excessive for a 4. Furthermore, what is the duration of these feelings? Chronic stressors may incur gradual change verses sudden impact if acute. Through identifying personal signs, devising and using a scale, as well as escalating or de-escalating factors, individuals become more in tune with their bodies and therefore, more likely to intervene before burnout takes hold.
With this process well integrated, one can now consider stylized approaches for stress management. For example, those inclined toward mindfulness practices may find yoga, meditation, and relaxation exercises beneficial. Others may thrive on positive affirmations, gratitude, and thankfulness. While some might find relief in physical activity, be it strenuous or casual, the creative arts might appeal to those who find joy in painting, writing, or doing crafts. In addition, baking, reading, dancing, and/or listening to music might help lift stress.
Along with those discoveries, or in some cases, rediscoveries, basic needs such as dietary habits and nutrition, hydration, and sleep are vital toward emotional regulation, physiological homeostasis, and stress modulation. Remember HALT: Hungry, Angry, Lonely, Tired, Too hot, Too cold, Sad or Stressed. Those strategies are meant to guide self-care and highlight the importance of allowing time for self-awareness. Imagine yourself as if you are meeting a new patient. Establish rapport, identify symptoms, and explore options for treatment. When we give time to ourselves, we can give time more freely to others. With this in mind, try following the 5-minute wellness check that I formulated:
1. How am I feeling? What am I feeling?
2. Assess HALTS.
3. Identify the number on your scale.
4. Methods of quick de-escalation:
- Designate and schedule personal time.
- Write down daily goals.
- Repeat positive affirmations or write down words of gratitude.
- Use deep breathing exercises.
- Stretch or take a brief walk.
- Engage in mindfulness practices, such as meditation.
Once we develop a habit of monitoring, assessing, and practicing self-care, the process becomes more efficient and effective. Think of the way a seasoned attending can manage workflow with ease, compared with an intern. Recognizing signs and using these strategies routinely can become a quick daily measure of well-being.
Dr. Thomas is a board-certified adult psychiatrist with interests in chronic illness, women’s behavioral health, and minority mental health. She currently practices in North Kingstown and East Providence, R.I. Dr. Thomas has no conflicts of interest.
Gradually, we are emerging from the chaos, isolation, and anxiety of COVID-19. As the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention adjusts its recommendations and vaccinations become more widely available, our communities are beginning to return to normalcy. We are encouraged to put aside our masks if vaccinated and rejoin society, to venture out with less hesitancy and anxiety. As family and friends reunite, memories of confusion, frustration, and fear are beginning to fade to black. Despite the prevailing belief that we should move on, look forward, and remember the past to safeguard our future, remnants of the pandemic remain.
Unvaccinated individuals, notably children under the age of 12, are quite significant in number. The use of telehealth is now standard practice.
For several years, we were warned about the looming “mental health crisis.” The past year has demonstrated that a crisis no longer looms – it has arrived. Our patients can reveal the vulnerability COVID-19 has wrought – from the devastation of lives lost, supply shortages, loss of employment and financial stability – to a lack of access to computers and thereby, the risk of educational decline. Those factors, coupled with isolation and uncertainty about the future, have led to an influx of individuals with anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders seeking mental health treatment.
Doctors, others suffering
As result of a medical culture guided by the sacred oath to which care, compassion, and dedication held as true in ancient Greece as it does today, the focus centers on those around us – while signs of our own weariness are waved away as “a bad day.” Even though several support groups are readily available to offer a listening ear and mental health physicians who focus on the treatment of health care professionals are becoming more ubiquitous, the vestiges of past doctrine remain.
In this modern age of medical training, there is often as much sacrifice as there is attainment of knowledge. This philosophy is so ingrained that throughout training and practice one may come across colleagues experiencing an abundance of guilt when leave is needed for personal reasons. We are quick to recommend such steps for our patients, family, and friends, but hesitant to consider such for ourselves. Yet, of all the lessons this past year has wrought, the importance of mental health and self-care cannot be overstated. This raises the question:
It is vital to accept our humanity as something not to repair, treat, or overcome but to understand. There is strength and power in vulnerability. If we do not perceive and validate this process within ourselves, how can we do so for others? In other words, the oxygen mask must be placed on us first before we can place it on anyone else – patients or otherwise.
Chiefly and above all else, the importance of identifying individual signs of stress is essential. Where do you hold tension? Are you prone to GI distress or headaches when taxed? Do you tend toward irritability, apathy, or exhaustion?
Once this is determined, it is important to assess your stress on a numerical scale, such as those used for pain. Are you a 5 or an 8? Finally, are there identifiable triggers or reliable alleviators? Is there a time of day or day of the week that is most difficult to manage? Can you anticipate potential stressors? Understanding your triggers, listening to your body, and practicing the language of self is the first step toward wellness.
Following introspection and observation, the next step is inventory. Take stock of your reserves. What replenishes? What depletes? What brings joy? What brings dread? Are there certain activities that mitigate stress? If so, how much time do they entail? Identify your number on a scale and associate that number with specific strategies or techniques. Remember that decompression for a 6 might be excessive for a 4. Furthermore, what is the duration of these feelings? Chronic stressors may incur gradual change verses sudden impact if acute. Through identifying personal signs, devising and using a scale, as well as escalating or de-escalating factors, individuals become more in tune with their bodies and therefore, more likely to intervene before burnout takes hold.
With this process well integrated, one can now consider stylized approaches for stress management. For example, those inclined toward mindfulness practices may find yoga, meditation, and relaxation exercises beneficial. Others may thrive on positive affirmations, gratitude, and thankfulness. While some might find relief in physical activity, be it strenuous or casual, the creative arts might appeal to those who find joy in painting, writing, or doing crafts. In addition, baking, reading, dancing, and/or listening to music might help lift stress.
Along with those discoveries, or in some cases, rediscoveries, basic needs such as dietary habits and nutrition, hydration, and sleep are vital toward emotional regulation, physiological homeostasis, and stress modulation. Remember HALT: Hungry, Angry, Lonely, Tired, Too hot, Too cold, Sad or Stressed. Those strategies are meant to guide self-care and highlight the importance of allowing time for self-awareness. Imagine yourself as if you are meeting a new patient. Establish rapport, identify symptoms, and explore options for treatment. When we give time to ourselves, we can give time more freely to others. With this in mind, try following the 5-minute wellness check that I formulated:
1. How am I feeling? What am I feeling?
2. Assess HALTS.
3. Identify the number on your scale.
4. Methods of quick de-escalation:
- Designate and schedule personal time.
- Write down daily goals.
- Repeat positive affirmations or write down words of gratitude.
- Use deep breathing exercises.
- Stretch or take a brief walk.
- Engage in mindfulness practices, such as meditation.
Once we develop a habit of monitoring, assessing, and practicing self-care, the process becomes more efficient and effective. Think of the way a seasoned attending can manage workflow with ease, compared with an intern. Recognizing signs and using these strategies routinely can become a quick daily measure of well-being.
Dr. Thomas is a board-certified adult psychiatrist with interests in chronic illness, women’s behavioral health, and minority mental health. She currently practices in North Kingstown and East Providence, R.I. Dr. Thomas has no conflicts of interest.
Gradually, we are emerging from the chaos, isolation, and anxiety of COVID-19. As the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention adjusts its recommendations and vaccinations become more widely available, our communities are beginning to return to normalcy. We are encouraged to put aside our masks if vaccinated and rejoin society, to venture out with less hesitancy and anxiety. As family and friends reunite, memories of confusion, frustration, and fear are beginning to fade to black. Despite the prevailing belief that we should move on, look forward, and remember the past to safeguard our future, remnants of the pandemic remain.
Unvaccinated individuals, notably children under the age of 12, are quite significant in number. The use of telehealth is now standard practice.
For several years, we were warned about the looming “mental health crisis.” The past year has demonstrated that a crisis no longer looms – it has arrived. Our patients can reveal the vulnerability COVID-19 has wrought – from the devastation of lives lost, supply shortages, loss of employment and financial stability – to a lack of access to computers and thereby, the risk of educational decline. Those factors, coupled with isolation and uncertainty about the future, have led to an influx of individuals with anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders seeking mental health treatment.
Doctors, others suffering
As result of a medical culture guided by the sacred oath to which care, compassion, and dedication held as true in ancient Greece as it does today, the focus centers on those around us – while signs of our own weariness are waved away as “a bad day.” Even though several support groups are readily available to offer a listening ear and mental health physicians who focus on the treatment of health care professionals are becoming more ubiquitous, the vestiges of past doctrine remain.
In this modern age of medical training, there is often as much sacrifice as there is attainment of knowledge. This philosophy is so ingrained that throughout training and practice one may come across colleagues experiencing an abundance of guilt when leave is needed for personal reasons. We are quick to recommend such steps for our patients, family, and friends, but hesitant to consider such for ourselves. Yet, of all the lessons this past year has wrought, the importance of mental health and self-care cannot be overstated. This raises the question:
It is vital to accept our humanity as something not to repair, treat, or overcome but to understand. There is strength and power in vulnerability. If we do not perceive and validate this process within ourselves, how can we do so for others? In other words, the oxygen mask must be placed on us first before we can place it on anyone else – patients or otherwise.
Chiefly and above all else, the importance of identifying individual signs of stress is essential. Where do you hold tension? Are you prone to GI distress or headaches when taxed? Do you tend toward irritability, apathy, or exhaustion?
Once this is determined, it is important to assess your stress on a numerical scale, such as those used for pain. Are you a 5 or an 8? Finally, are there identifiable triggers or reliable alleviators? Is there a time of day or day of the week that is most difficult to manage? Can you anticipate potential stressors? Understanding your triggers, listening to your body, and practicing the language of self is the first step toward wellness.
Following introspection and observation, the next step is inventory. Take stock of your reserves. What replenishes? What depletes? What brings joy? What brings dread? Are there certain activities that mitigate stress? If so, how much time do they entail? Identify your number on a scale and associate that number with specific strategies or techniques. Remember that decompression for a 6 might be excessive for a 4. Furthermore, what is the duration of these feelings? Chronic stressors may incur gradual change verses sudden impact if acute. Through identifying personal signs, devising and using a scale, as well as escalating or de-escalating factors, individuals become more in tune with their bodies and therefore, more likely to intervene before burnout takes hold.
With this process well integrated, one can now consider stylized approaches for stress management. For example, those inclined toward mindfulness practices may find yoga, meditation, and relaxation exercises beneficial. Others may thrive on positive affirmations, gratitude, and thankfulness. While some might find relief in physical activity, be it strenuous or casual, the creative arts might appeal to those who find joy in painting, writing, or doing crafts. In addition, baking, reading, dancing, and/or listening to music might help lift stress.
Along with those discoveries, or in some cases, rediscoveries, basic needs such as dietary habits and nutrition, hydration, and sleep are vital toward emotional regulation, physiological homeostasis, and stress modulation. Remember HALT: Hungry, Angry, Lonely, Tired, Too hot, Too cold, Sad or Stressed. Those strategies are meant to guide self-care and highlight the importance of allowing time for self-awareness. Imagine yourself as if you are meeting a new patient. Establish rapport, identify symptoms, and explore options for treatment. When we give time to ourselves, we can give time more freely to others. With this in mind, try following the 5-minute wellness check that I formulated:
1. How am I feeling? What am I feeling?
2. Assess HALTS.
3. Identify the number on your scale.
4. Methods of quick de-escalation:
- Designate and schedule personal time.
- Write down daily goals.
- Repeat positive affirmations or write down words of gratitude.
- Use deep breathing exercises.
- Stretch or take a brief walk.
- Engage in mindfulness practices, such as meditation.
Once we develop a habit of monitoring, assessing, and practicing self-care, the process becomes more efficient and effective. Think of the way a seasoned attending can manage workflow with ease, compared with an intern. Recognizing signs and using these strategies routinely can become a quick daily measure of well-being.
Dr. Thomas is a board-certified adult psychiatrist with interests in chronic illness, women’s behavioral health, and minority mental health. She currently practices in North Kingstown and East Providence, R.I. Dr. Thomas has no conflicts of interest.
AMA acknowledges medical education racism of past, vows better future
The report received overwhelming support at the House of Delegates, the AMA’s legislative policy making body, during an online meeting held June 13.
The Council on Medical Education’s report recommends that the AMA acknowledge the harm caused by the Flexner Report, which was issued in 1910 and has since shaped medical education. The Flexner Report caused harm not only to historically Black medical schools, but also to physician workforce diversity and to the clinical outcomes of minority and marginalized patients, according to the medical education advisory body.
The council also recommended conducting a study on medical education with a focus on health equity and racial justice, improving diversity among healthcare workers, and fixing inequitable outcomes from minorities and marginalized patient populations.
The report comes on the heels of the resignation of JAMA editor-in-chief Howard Bauchner, MD, and another high-ranking editor following a February podcast on systemic racism in medicine. The AMA has since released a strategic plan addressing racism and health inequity that has divided membership.
Flexner Report’s effect on physician diversity
The Council on Medical Education’s report observed that as a result of the Flexner Report’s recommendations, 89 medical schools, including 5 of the 7 existing medical schools training Black physicians, were closed because they didn’t meet the report’s standards. In addition, the report created a limited role for Black physicians while “hint[ing] that Black physicians possessed less potential and ability than their White counterparts,” read the Council’s report.
In addition to consigning the role of the Black physician to “educating the [Black] race to know and to practice fundamental hygienic principles,” the Flexner Report also observed that “a well-taught negro sanitarian will be immensely useful,” per the Council’s report.
The impact of the closure of medical schools training Black physicians was dramatic. According to the Council’s report, in 1964, 93% of medical students in the United States were men and 97% of those students were non-Hispanic White.
Today, 56% of physicians identify as White, 17% as Asian, 6% as Hispanic, and 5% as Black or African American, per the Association of American Medical Colleges; nearly 14% of active physicians didn’t report their race in the survey. By means of contrast, the U.S. population in 2019 was 60% White, 19% Latino/Hispanic, 13% Black or African American, and 6% Asian American, according to the Brookings Institute.
Abraham Flexner, who wrote the Flexner Report, is often referred to as the “father of modern medical education,” according to the AAMC. In November, the AAMC observed that the Flexner Report contained racist and sexist ideas and that his work contributed to the closure of historically Black medical schools. Both statements were included in AAMC’s announcement about the removal of Flexner’s name from its most prestigious award. As of January, the award is now called the AAMC Award for Excellence in Medical Education.
Pathway programs can increase diversity
Pathway programs, which leverage targeted milestones along the journey to becoming a physician in order to increase diversity, were an area of focus in the council’s report. These programs “can exert a meaningful, positive effect on student outcomes and increase diversity across various levels of educational settings,” according to its report.
Centers of Excellence, which provides grants for mentorship and training programs, is one of many pathway programs. During the 2018-2019 academic year, Centers of Excellence supported more than 1,300 trainees – 99% of them were underrepresented minorities and 64% came from financially or educationally disadvantaged backgrounds. In 2006, federal funding was cut to these programs and the number of Centers of Excellence fell.
Still, the report cites the passage of federal funding in 2020 of $50 million for public institutions of higher education that train physicians; educational institutions in states with a projected primary care shortage in 2025 are given priority in the grant-funding process.
AMA council’s report garners support from delegates
Delegates voiced overwhelming support of the council’s report during the June 13 meeting. Lou Edje, MD, a Perrysburgh, Ohio–based family physician, voiced strong support for the council’s report, in particular its recommendations that recognize the harm caused by the Flexner Report. Dr. Edje observed that the Flexner Report, with its elimination of five of seven Black medical schools, “[set] back admissions of Black students into medicine by 50 years.”
“Empathy is what we are called to have as physicians. I implore you to simply substitute your ethnicity into these quotes to help understand the historic need for health equity in medicine today. This CME report is part of the antidote to Flexner. We support [it] fully,” concluded Dr. Edje, who spoke for the Great Lakes States Coalition of the AMA.
Rohan Khazanchi, a medical student at the University of Nebraska, Omaha, and a member of the council, said, “Our broad attempt with this report was twofold: to fill gaps in AMA policy with evidence-based recommendations which could improve diversity in our health workforce and, second, to enhance our organization’s vision for truth, reconciliation, and healing to redress the historic marginalization of minoritized physicians in medicine.”
According to an AMA spokesperson, the House of Delegates will vote on this and other policies this week, after which the policies are considered final.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The report received overwhelming support at the House of Delegates, the AMA’s legislative policy making body, during an online meeting held June 13.
The Council on Medical Education’s report recommends that the AMA acknowledge the harm caused by the Flexner Report, which was issued in 1910 and has since shaped medical education. The Flexner Report caused harm not only to historically Black medical schools, but also to physician workforce diversity and to the clinical outcomes of minority and marginalized patients, according to the medical education advisory body.
The council also recommended conducting a study on medical education with a focus on health equity and racial justice, improving diversity among healthcare workers, and fixing inequitable outcomes from minorities and marginalized patient populations.
The report comes on the heels of the resignation of JAMA editor-in-chief Howard Bauchner, MD, and another high-ranking editor following a February podcast on systemic racism in medicine. The AMA has since released a strategic plan addressing racism and health inequity that has divided membership.
Flexner Report’s effect on physician diversity
The Council on Medical Education’s report observed that as a result of the Flexner Report’s recommendations, 89 medical schools, including 5 of the 7 existing medical schools training Black physicians, were closed because they didn’t meet the report’s standards. In addition, the report created a limited role for Black physicians while “hint[ing] that Black physicians possessed less potential and ability than their White counterparts,” read the Council’s report.
In addition to consigning the role of the Black physician to “educating the [Black] race to know and to practice fundamental hygienic principles,” the Flexner Report also observed that “a well-taught negro sanitarian will be immensely useful,” per the Council’s report.
The impact of the closure of medical schools training Black physicians was dramatic. According to the Council’s report, in 1964, 93% of medical students in the United States were men and 97% of those students were non-Hispanic White.
Today, 56% of physicians identify as White, 17% as Asian, 6% as Hispanic, and 5% as Black or African American, per the Association of American Medical Colleges; nearly 14% of active physicians didn’t report their race in the survey. By means of contrast, the U.S. population in 2019 was 60% White, 19% Latino/Hispanic, 13% Black or African American, and 6% Asian American, according to the Brookings Institute.
Abraham Flexner, who wrote the Flexner Report, is often referred to as the “father of modern medical education,” according to the AAMC. In November, the AAMC observed that the Flexner Report contained racist and sexist ideas and that his work contributed to the closure of historically Black medical schools. Both statements were included in AAMC’s announcement about the removal of Flexner’s name from its most prestigious award. As of January, the award is now called the AAMC Award for Excellence in Medical Education.
Pathway programs can increase diversity
Pathway programs, which leverage targeted milestones along the journey to becoming a physician in order to increase diversity, were an area of focus in the council’s report. These programs “can exert a meaningful, positive effect on student outcomes and increase diversity across various levels of educational settings,” according to its report.
Centers of Excellence, which provides grants for mentorship and training programs, is one of many pathway programs. During the 2018-2019 academic year, Centers of Excellence supported more than 1,300 trainees – 99% of them were underrepresented minorities and 64% came from financially or educationally disadvantaged backgrounds. In 2006, federal funding was cut to these programs and the number of Centers of Excellence fell.
Still, the report cites the passage of federal funding in 2020 of $50 million for public institutions of higher education that train physicians; educational institutions in states with a projected primary care shortage in 2025 are given priority in the grant-funding process.
AMA council’s report garners support from delegates
Delegates voiced overwhelming support of the council’s report during the June 13 meeting. Lou Edje, MD, a Perrysburgh, Ohio–based family physician, voiced strong support for the council’s report, in particular its recommendations that recognize the harm caused by the Flexner Report. Dr. Edje observed that the Flexner Report, with its elimination of five of seven Black medical schools, “[set] back admissions of Black students into medicine by 50 years.”
“Empathy is what we are called to have as physicians. I implore you to simply substitute your ethnicity into these quotes to help understand the historic need for health equity in medicine today. This CME report is part of the antidote to Flexner. We support [it] fully,” concluded Dr. Edje, who spoke for the Great Lakes States Coalition of the AMA.
Rohan Khazanchi, a medical student at the University of Nebraska, Omaha, and a member of the council, said, “Our broad attempt with this report was twofold: to fill gaps in AMA policy with evidence-based recommendations which could improve diversity in our health workforce and, second, to enhance our organization’s vision for truth, reconciliation, and healing to redress the historic marginalization of minoritized physicians in medicine.”
According to an AMA spokesperson, the House of Delegates will vote on this and other policies this week, after which the policies are considered final.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The report received overwhelming support at the House of Delegates, the AMA’s legislative policy making body, during an online meeting held June 13.
The Council on Medical Education’s report recommends that the AMA acknowledge the harm caused by the Flexner Report, which was issued in 1910 and has since shaped medical education. The Flexner Report caused harm not only to historically Black medical schools, but also to physician workforce diversity and to the clinical outcomes of minority and marginalized patients, according to the medical education advisory body.
The council also recommended conducting a study on medical education with a focus on health equity and racial justice, improving diversity among healthcare workers, and fixing inequitable outcomes from minorities and marginalized patient populations.
The report comes on the heels of the resignation of JAMA editor-in-chief Howard Bauchner, MD, and another high-ranking editor following a February podcast on systemic racism in medicine. The AMA has since released a strategic plan addressing racism and health inequity that has divided membership.
Flexner Report’s effect on physician diversity
The Council on Medical Education’s report observed that as a result of the Flexner Report’s recommendations, 89 medical schools, including 5 of the 7 existing medical schools training Black physicians, were closed because they didn’t meet the report’s standards. In addition, the report created a limited role for Black physicians while “hint[ing] that Black physicians possessed less potential and ability than their White counterparts,” read the Council’s report.
In addition to consigning the role of the Black physician to “educating the [Black] race to know and to practice fundamental hygienic principles,” the Flexner Report also observed that “a well-taught negro sanitarian will be immensely useful,” per the Council’s report.
The impact of the closure of medical schools training Black physicians was dramatic. According to the Council’s report, in 1964, 93% of medical students in the United States were men and 97% of those students were non-Hispanic White.
Today, 56% of physicians identify as White, 17% as Asian, 6% as Hispanic, and 5% as Black or African American, per the Association of American Medical Colleges; nearly 14% of active physicians didn’t report their race in the survey. By means of contrast, the U.S. population in 2019 was 60% White, 19% Latino/Hispanic, 13% Black or African American, and 6% Asian American, according to the Brookings Institute.
Abraham Flexner, who wrote the Flexner Report, is often referred to as the “father of modern medical education,” according to the AAMC. In November, the AAMC observed that the Flexner Report contained racist and sexist ideas and that his work contributed to the closure of historically Black medical schools. Both statements were included in AAMC’s announcement about the removal of Flexner’s name from its most prestigious award. As of January, the award is now called the AAMC Award for Excellence in Medical Education.
Pathway programs can increase diversity
Pathway programs, which leverage targeted milestones along the journey to becoming a physician in order to increase diversity, were an area of focus in the council’s report. These programs “can exert a meaningful, positive effect on student outcomes and increase diversity across various levels of educational settings,” according to its report.
Centers of Excellence, which provides grants for mentorship and training programs, is one of many pathway programs. During the 2018-2019 academic year, Centers of Excellence supported more than 1,300 trainees – 99% of them were underrepresented minorities and 64% came from financially or educationally disadvantaged backgrounds. In 2006, federal funding was cut to these programs and the number of Centers of Excellence fell.
Still, the report cites the passage of federal funding in 2020 of $50 million for public institutions of higher education that train physicians; educational institutions in states with a projected primary care shortage in 2025 are given priority in the grant-funding process.
AMA council’s report garners support from delegates
Delegates voiced overwhelming support of the council’s report during the June 13 meeting. Lou Edje, MD, a Perrysburgh, Ohio–based family physician, voiced strong support for the council’s report, in particular its recommendations that recognize the harm caused by the Flexner Report. Dr. Edje observed that the Flexner Report, with its elimination of five of seven Black medical schools, “[set] back admissions of Black students into medicine by 50 years.”
“Empathy is what we are called to have as physicians. I implore you to simply substitute your ethnicity into these quotes to help understand the historic need for health equity in medicine today. This CME report is part of the antidote to Flexner. We support [it] fully,” concluded Dr. Edje, who spoke for the Great Lakes States Coalition of the AMA.
Rohan Khazanchi, a medical student at the University of Nebraska, Omaha, and a member of the council, said, “Our broad attempt with this report was twofold: to fill gaps in AMA policy with evidence-based recommendations which could improve diversity in our health workforce and, second, to enhance our organization’s vision for truth, reconciliation, and healing to redress the historic marginalization of minoritized physicians in medicine.”
According to an AMA spokesperson, the House of Delegates will vote on this and other policies this week, after which the policies are considered final.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.