User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
Daily Recap: Lifestyle vs. genes in breast cancer showdown; Big pharma sues over insulin affordability law
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Lifestyle choices may reduce breast cancer risk regardless of genetics
A “favorable” lifestyle was associated with a reduced risk of breast cancer even among women at high genetic risk for the disease in a study of more than 90,000 women, researchers reported.
The findings suggest that, regardless of genetic risk, women may be able to reduce their risk of developing breast cancer by getting adequate levels of exercise; maintaining a healthy weight; and limiting or eliminating use of alcohol, oral contraceptives, and hormone replacement therapy.
“These data should empower patients that they can impact on their overall health and reduce the risk of developing breast cancer,” said William Gradishar, MD, who was not invovled with the study. Read more.
Primary care practices may lose $68K per physician this year
Primary care practices stand to lose almost $68,000 per full-time physician this year as COVID-19 causes care delays and cancellations, researchers estimate. And while some outpatient care has started to rebound to near baseline appointment levels, other ambulatory specialties remain dramatically down from prepandemic rates.
Dermatology and rheumatology visits have recovered, but some specialties have cumulative deficits that are particularly concerning. For example, pediatric visits were down by 47% in the 3 months since March 15, and pulmonology visits were down 45% in that time.
This primary care estimate is without a potential second wave of COVID-19, noted Sanjay Basu, MD, director of research and population health at Collective Health in San Francisco, and colleagues.
“We expect ongoing turbulent times, so having a prospective payment could unleash the capacity for primary care practices to be creative in the way they care for their patients,” Daniel Horn, MD, director of population health and quality at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, said in an interview. Read more.
Big pharma sues to block Minnesota insulin affordability law
The Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers Association (PhRMA) is suing the state of Minnesota in an attempt to overturn a law that requires insulin makers to provide an emergency supply to individuals free of charge.
In the July 1 filing, PhRMA’s attorneys said the law is unconstitutional. It “order[s] pharmaceutical manufacturers to give insulin to state residents, on the state’s prescribed terms, at no charge to the recipients and without compensating the manufacturers in any way.”
The state has estimated that as many as 30,000 Minnesotans would be eligible for free insulin in the first year of the program. The drugmakers strenuously objected, noting that would mean they would “be compelled to provide 173,800 monthly supplies of free insulin” just in the first year.
“There is nothing in the U.S. Constitution that prevents states from saving the lives of its citizens who are in imminent danger,” said Mayo Clinic hematologist S. Vincent Rajkumar, MD. “The only motives for this lawsuit in my opinion are greed and the worry that other states may also choose to put lives of patients ahead of pharma profits.” Read more.
Despite guidelines, kids get opioids & steroids for pneumonia, sinusitis
A significant percentage of children receive opioids and systemic corticosteroids for pneumonia and sinusitis despite guidelines, according to an analysis of 2016 Medicaid data from South Carolina.
Prescriptions for these drugs were more likely after visits to EDs than after ambulatory visits, researchers reported in Pediatrics.
“Each of the 828 opioid and 2,737 systemic steroid prescriptions in the data set represent a potentially inappropriate prescription,” wrote Karina G. Phang, MD, MPH, of Geisinger Medical Center in Danville, Pa., and colleagues. “These rates appear excessive given that the use of these medications is not supported by available research or recommended in national guidelines.” Read more.
Study supports changing classification of RCC
The definition of stage IV renal cell carcinoma (RCC) should be expanded to include lymph node–positive stage III disease, according to a population-level cohort study published in Cancer.
While patients with lymph node–negative stage III disease had superior overall survival at 5 years, survival rates were similar between patients with node–positive stage III disease and stage IV disease. This supports reclassifying stage III node-positive RCC to stage IV, according to researchers.
“Prior institutional studies have indicated that, among patients with stage III disease, those with lymph node disease have worse oncologic outcomes and experience survival that is similar to that of patients with American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage IV disease,” wrote Arnav Srivastava, MD, of Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey, New Brunswick, and colleagues. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Lifestyle choices may reduce breast cancer risk regardless of genetics
A “favorable” lifestyle was associated with a reduced risk of breast cancer even among women at high genetic risk for the disease in a study of more than 90,000 women, researchers reported.
The findings suggest that, regardless of genetic risk, women may be able to reduce their risk of developing breast cancer by getting adequate levels of exercise; maintaining a healthy weight; and limiting or eliminating use of alcohol, oral contraceptives, and hormone replacement therapy.
“These data should empower patients that they can impact on their overall health and reduce the risk of developing breast cancer,” said William Gradishar, MD, who was not invovled with the study. Read more.
Primary care practices may lose $68K per physician this year
Primary care practices stand to lose almost $68,000 per full-time physician this year as COVID-19 causes care delays and cancellations, researchers estimate. And while some outpatient care has started to rebound to near baseline appointment levels, other ambulatory specialties remain dramatically down from prepandemic rates.
Dermatology and rheumatology visits have recovered, but some specialties have cumulative deficits that are particularly concerning. For example, pediatric visits were down by 47% in the 3 months since March 15, and pulmonology visits were down 45% in that time.
This primary care estimate is without a potential second wave of COVID-19, noted Sanjay Basu, MD, director of research and population health at Collective Health in San Francisco, and colleagues.
“We expect ongoing turbulent times, so having a prospective payment could unleash the capacity for primary care practices to be creative in the way they care for their patients,” Daniel Horn, MD, director of population health and quality at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, said in an interview. Read more.
Big pharma sues to block Minnesota insulin affordability law
The Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers Association (PhRMA) is suing the state of Minnesota in an attempt to overturn a law that requires insulin makers to provide an emergency supply to individuals free of charge.
In the July 1 filing, PhRMA’s attorneys said the law is unconstitutional. It “order[s] pharmaceutical manufacturers to give insulin to state residents, on the state’s prescribed terms, at no charge to the recipients and without compensating the manufacturers in any way.”
The state has estimated that as many as 30,000 Minnesotans would be eligible for free insulin in the first year of the program. The drugmakers strenuously objected, noting that would mean they would “be compelled to provide 173,800 monthly supplies of free insulin” just in the first year.
“There is nothing in the U.S. Constitution that prevents states from saving the lives of its citizens who are in imminent danger,” said Mayo Clinic hematologist S. Vincent Rajkumar, MD. “The only motives for this lawsuit in my opinion are greed and the worry that other states may also choose to put lives of patients ahead of pharma profits.” Read more.
Despite guidelines, kids get opioids & steroids for pneumonia, sinusitis
A significant percentage of children receive opioids and systemic corticosteroids for pneumonia and sinusitis despite guidelines, according to an analysis of 2016 Medicaid data from South Carolina.
Prescriptions for these drugs were more likely after visits to EDs than after ambulatory visits, researchers reported in Pediatrics.
“Each of the 828 opioid and 2,737 systemic steroid prescriptions in the data set represent a potentially inappropriate prescription,” wrote Karina G. Phang, MD, MPH, of Geisinger Medical Center in Danville, Pa., and colleagues. “These rates appear excessive given that the use of these medications is not supported by available research or recommended in national guidelines.” Read more.
Study supports changing classification of RCC
The definition of stage IV renal cell carcinoma (RCC) should be expanded to include lymph node–positive stage III disease, according to a population-level cohort study published in Cancer.
While patients with lymph node–negative stage III disease had superior overall survival at 5 years, survival rates were similar between patients with node–positive stage III disease and stage IV disease. This supports reclassifying stage III node-positive RCC to stage IV, according to researchers.
“Prior institutional studies have indicated that, among patients with stage III disease, those with lymph node disease have worse oncologic outcomes and experience survival that is similar to that of patients with American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage IV disease,” wrote Arnav Srivastava, MD, of Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey, New Brunswick, and colleagues. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Lifestyle choices may reduce breast cancer risk regardless of genetics
A “favorable” lifestyle was associated with a reduced risk of breast cancer even among women at high genetic risk for the disease in a study of more than 90,000 women, researchers reported.
The findings suggest that, regardless of genetic risk, women may be able to reduce their risk of developing breast cancer by getting adequate levels of exercise; maintaining a healthy weight; and limiting or eliminating use of alcohol, oral contraceptives, and hormone replacement therapy.
“These data should empower patients that they can impact on their overall health and reduce the risk of developing breast cancer,” said William Gradishar, MD, who was not invovled with the study. Read more.
Primary care practices may lose $68K per physician this year
Primary care practices stand to lose almost $68,000 per full-time physician this year as COVID-19 causes care delays and cancellations, researchers estimate. And while some outpatient care has started to rebound to near baseline appointment levels, other ambulatory specialties remain dramatically down from prepandemic rates.
Dermatology and rheumatology visits have recovered, but some specialties have cumulative deficits that are particularly concerning. For example, pediatric visits were down by 47% in the 3 months since March 15, and pulmonology visits were down 45% in that time.
This primary care estimate is without a potential second wave of COVID-19, noted Sanjay Basu, MD, director of research and population health at Collective Health in San Francisco, and colleagues.
“We expect ongoing turbulent times, so having a prospective payment could unleash the capacity for primary care practices to be creative in the way they care for their patients,” Daniel Horn, MD, director of population health and quality at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, said in an interview. Read more.
Big pharma sues to block Minnesota insulin affordability law
The Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers Association (PhRMA) is suing the state of Minnesota in an attempt to overturn a law that requires insulin makers to provide an emergency supply to individuals free of charge.
In the July 1 filing, PhRMA’s attorneys said the law is unconstitutional. It “order[s] pharmaceutical manufacturers to give insulin to state residents, on the state’s prescribed terms, at no charge to the recipients and without compensating the manufacturers in any way.”
The state has estimated that as many as 30,000 Minnesotans would be eligible for free insulin in the first year of the program. The drugmakers strenuously objected, noting that would mean they would “be compelled to provide 173,800 monthly supplies of free insulin” just in the first year.
“There is nothing in the U.S. Constitution that prevents states from saving the lives of its citizens who are in imminent danger,” said Mayo Clinic hematologist S. Vincent Rajkumar, MD. “The only motives for this lawsuit in my opinion are greed and the worry that other states may also choose to put lives of patients ahead of pharma profits.” Read more.
Despite guidelines, kids get opioids & steroids for pneumonia, sinusitis
A significant percentage of children receive opioids and systemic corticosteroids for pneumonia and sinusitis despite guidelines, according to an analysis of 2016 Medicaid data from South Carolina.
Prescriptions for these drugs were more likely after visits to EDs than after ambulatory visits, researchers reported in Pediatrics.
“Each of the 828 opioid and 2,737 systemic steroid prescriptions in the data set represent a potentially inappropriate prescription,” wrote Karina G. Phang, MD, MPH, of Geisinger Medical Center in Danville, Pa., and colleagues. “These rates appear excessive given that the use of these medications is not supported by available research or recommended in national guidelines.” Read more.
Study supports changing classification of RCC
The definition of stage IV renal cell carcinoma (RCC) should be expanded to include lymph node–positive stage III disease, according to a population-level cohort study published in Cancer.
While patients with lymph node–negative stage III disease had superior overall survival at 5 years, survival rates were similar between patients with node–positive stage III disease and stage IV disease. This supports reclassifying stage III node-positive RCC to stage IV, according to researchers.
“Prior institutional studies have indicated that, among patients with stage III disease, those with lymph node disease have worse oncologic outcomes and experience survival that is similar to that of patients with American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage IV disease,” wrote Arnav Srivastava, MD, of Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey, New Brunswick, and colleagues. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Pulmonary function tests can’t substitute for high-resolution CT in early systemic sclerosis ILD screening
Clinicians shouldn’t rely on pulmonary function tests (PFTs) alone to screen for interstitial lung disease (ILD). The tests performed poorly in a retrospective study of 212 patients with systemic sclerosis, reinforcing the findings of previous studies.
Any screening algorithm should include high-resolution CT (HRCT), which is good at prognosticating disease, the investigators wrote in Arthritis & Rheumatology. “I think all newly diagnosed systemic sclerosis patients should have a full set of PFTs (spirometry, lung volumes, and diffusion capacity) and an HRCT at baseline to evaluate for ILD,” the study’s lead author, Elana J. Bernstein, MD, said in an interview.
ILD is a leading cause of death in systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients, affecting 40%-60% of those with the disease. HRCT is currently the preferred option for detection of ILD. PFTs are commonly used to screen for ILD but haven’t performed well in previous studies. “Someone can have abnormalities on HRCT that are consistent with ILD but still have PFTs that are in the ‘normal’ range,” explained Dr. Bernstein of Columbia University, New York. One cross-sectional study of 102 SSc patients found that the test’s sensitivity for the detection of ILD on HRCT was just 37.5% when forced vital capacity (FVC) <80% predicted.
Investigators sought to assess performance characteristics of PFTs in patients with early diffuse cutaneous SSc, a cohort at high risk of developing ILD. The study enlisted patients from the Prospective Registry of Early Systemic Sclerosis (PRESS), a multicenter, prospective cohort study of adults with early diffuse cutaneous SSc. Overall, 212 patients at 11 U.S. academic medical centers participated in the study from April 2012 to January 2019.
All patients had spirometry (PFT) and HRCT chest scans. PFTs were conducted per American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society guidelines. The investigators calculated test characteristics for single PFT and combinations of PFT parameters for the detection of ILD on HRCT. The HRCTs were ordered at the discretion of treating physicians, and scrutinized for ILD features such as reticular changes, honeycombing, traction bronchiectasis, and ground-glass opacities. The investigators defined the lower limit of normal for FVC, total lung capacity, and diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) as 80% predicted.
Overall, Dr. Bernstein and her colleagues found that PFTs lacked sufficient sensitivity and negative predictive value for the detection of ILD on HRCT in these patients.
An FVC <80% predicted performed at only 63% sensitivity and an false negative rate of 37%. Total lung capacity or DLCO <80% predicted had a sensitivity of 46% and 80%, respectively. The combination of FVC or DLCO <80% predicted raised sensitivity to 85%. However, the addition of total lung capacity to this combination did not improve results.
Overall, PFTs had a positive predictive value of 64%-74% and an negative predictive value of 61%-70%. “This means that PFT alone will not accurately predict the presence of ILD in about 35%, and not be correctly negative in about 35%,” observed Daniel E. Furst, MD, professor of medicine (emeritus) at the University of California, Los Angeles, and professor of rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles.
While the combination of FVC <80% predicted or DLCO <80% predicted performed better than the other parameters, the sensitivity “is inadequate for an ILD screening test as it results in an false negative rate of 15%, thereby falsely reassuring 15% of patients that they do not have ILD when in fact they do,” the investigators observed.
“This study reinforces the notion that PFTs alone are ineffective screening tools for ILD in the presence of systemic sclerosis, particularly for patients with early systemic sclerosis,” said Elizabeth Volkmann, MD, MS, assistant professor and codirector of the CTD-ILD program in the division of rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles.
The study’s scope was relatively small, yet the results provide further evidence to show that HRCT should be performed in all SSc patients to screen for the presence of ILD, Dr. Volkmann said in an interview.
Other research has demonstrated the value of baseline HRCT as a prognosticator of ILD outcomes. The method provides useful information about the degree of fibrosis and degree of damage in early-stage disease, said Dr. Furst, also an adjunct professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, and a research professor at the University of Florence (Italy). “If there’s honeycombing, that’s a bad prognosis. If it’s ground glass or reticular changes, the prognosis is better.
“Once there’s a lot of damage, it’s much harder to interpret disease with HRCT,” he added.
HRCT and PFT work well together to assess what’s happening in patients, Dr. Furst explained. HRCT provides an idea of anatomic changes, whereas PFT outlines aspects of functional change to diagnose early ILD in early diffuse SSc. The study results should not apply to patients with later disease who have more developed ILD, he noted.
The investigators acknowledged that they weren’t able to categorize and analyze patients according to disease extent because they didn’t quantify the extent of ILD. Another limitation was that the HRCTs and PFTs were ordered at the discretion of individual physicians, which means that not all participants received the tests.
“Although the tests were done in 90% of the population, there is still a probability of a significant selection bias,” Dr. Furst said.
Dr. Bernstein and several other coauthors in the study received grants from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases to support their work. Dr. Furst disclosed receiving grant/research support from and/or consulting for AbbVie, Actelion, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Corbus, the National Institutes of Health, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche/Genentech. Dr. Volkmann disclosed consulting for and/or receiving grant support from Boehringer Ingelheim, Corbus, and Forbius.
SOURCE: Bernstein EJ et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Jun 25. doi: 10.1002/art.41415.
Clinicians shouldn’t rely on pulmonary function tests (PFTs) alone to screen for interstitial lung disease (ILD). The tests performed poorly in a retrospective study of 212 patients with systemic sclerosis, reinforcing the findings of previous studies.
Any screening algorithm should include high-resolution CT (HRCT), which is good at prognosticating disease, the investigators wrote in Arthritis & Rheumatology. “I think all newly diagnosed systemic sclerosis patients should have a full set of PFTs (spirometry, lung volumes, and diffusion capacity) and an HRCT at baseline to evaluate for ILD,” the study’s lead author, Elana J. Bernstein, MD, said in an interview.
ILD is a leading cause of death in systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients, affecting 40%-60% of those with the disease. HRCT is currently the preferred option for detection of ILD. PFTs are commonly used to screen for ILD but haven’t performed well in previous studies. “Someone can have abnormalities on HRCT that are consistent with ILD but still have PFTs that are in the ‘normal’ range,” explained Dr. Bernstein of Columbia University, New York. One cross-sectional study of 102 SSc patients found that the test’s sensitivity for the detection of ILD on HRCT was just 37.5% when forced vital capacity (FVC) <80% predicted.
Investigators sought to assess performance characteristics of PFTs in patients with early diffuse cutaneous SSc, a cohort at high risk of developing ILD. The study enlisted patients from the Prospective Registry of Early Systemic Sclerosis (PRESS), a multicenter, prospective cohort study of adults with early diffuse cutaneous SSc. Overall, 212 patients at 11 U.S. academic medical centers participated in the study from April 2012 to January 2019.
All patients had spirometry (PFT) and HRCT chest scans. PFTs were conducted per American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society guidelines. The investigators calculated test characteristics for single PFT and combinations of PFT parameters for the detection of ILD on HRCT. The HRCTs were ordered at the discretion of treating physicians, and scrutinized for ILD features such as reticular changes, honeycombing, traction bronchiectasis, and ground-glass opacities. The investigators defined the lower limit of normal for FVC, total lung capacity, and diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) as 80% predicted.
Overall, Dr. Bernstein and her colleagues found that PFTs lacked sufficient sensitivity and negative predictive value for the detection of ILD on HRCT in these patients.
An FVC <80% predicted performed at only 63% sensitivity and an false negative rate of 37%. Total lung capacity or DLCO <80% predicted had a sensitivity of 46% and 80%, respectively. The combination of FVC or DLCO <80% predicted raised sensitivity to 85%. However, the addition of total lung capacity to this combination did not improve results.
Overall, PFTs had a positive predictive value of 64%-74% and an negative predictive value of 61%-70%. “This means that PFT alone will not accurately predict the presence of ILD in about 35%, and not be correctly negative in about 35%,” observed Daniel E. Furst, MD, professor of medicine (emeritus) at the University of California, Los Angeles, and professor of rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles.
While the combination of FVC <80% predicted or DLCO <80% predicted performed better than the other parameters, the sensitivity “is inadequate for an ILD screening test as it results in an false negative rate of 15%, thereby falsely reassuring 15% of patients that they do not have ILD when in fact they do,” the investigators observed.
“This study reinforces the notion that PFTs alone are ineffective screening tools for ILD in the presence of systemic sclerosis, particularly for patients with early systemic sclerosis,” said Elizabeth Volkmann, MD, MS, assistant professor and codirector of the CTD-ILD program in the division of rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles.
The study’s scope was relatively small, yet the results provide further evidence to show that HRCT should be performed in all SSc patients to screen for the presence of ILD, Dr. Volkmann said in an interview.
Other research has demonstrated the value of baseline HRCT as a prognosticator of ILD outcomes. The method provides useful information about the degree of fibrosis and degree of damage in early-stage disease, said Dr. Furst, also an adjunct professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, and a research professor at the University of Florence (Italy). “If there’s honeycombing, that’s a bad prognosis. If it’s ground glass or reticular changes, the prognosis is better.
“Once there’s a lot of damage, it’s much harder to interpret disease with HRCT,” he added.
HRCT and PFT work well together to assess what’s happening in patients, Dr. Furst explained. HRCT provides an idea of anatomic changes, whereas PFT outlines aspects of functional change to diagnose early ILD in early diffuse SSc. The study results should not apply to patients with later disease who have more developed ILD, he noted.
The investigators acknowledged that they weren’t able to categorize and analyze patients according to disease extent because they didn’t quantify the extent of ILD. Another limitation was that the HRCTs and PFTs were ordered at the discretion of individual physicians, which means that not all participants received the tests.
“Although the tests were done in 90% of the population, there is still a probability of a significant selection bias,” Dr. Furst said.
Dr. Bernstein and several other coauthors in the study received grants from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases to support their work. Dr. Furst disclosed receiving grant/research support from and/or consulting for AbbVie, Actelion, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Corbus, the National Institutes of Health, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche/Genentech. Dr. Volkmann disclosed consulting for and/or receiving grant support from Boehringer Ingelheim, Corbus, and Forbius.
SOURCE: Bernstein EJ et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Jun 25. doi: 10.1002/art.41415.
Clinicians shouldn’t rely on pulmonary function tests (PFTs) alone to screen for interstitial lung disease (ILD). The tests performed poorly in a retrospective study of 212 patients with systemic sclerosis, reinforcing the findings of previous studies.
Any screening algorithm should include high-resolution CT (HRCT), which is good at prognosticating disease, the investigators wrote in Arthritis & Rheumatology. “I think all newly diagnosed systemic sclerosis patients should have a full set of PFTs (spirometry, lung volumes, and diffusion capacity) and an HRCT at baseline to evaluate for ILD,” the study’s lead author, Elana J. Bernstein, MD, said in an interview.
ILD is a leading cause of death in systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients, affecting 40%-60% of those with the disease. HRCT is currently the preferred option for detection of ILD. PFTs are commonly used to screen for ILD but haven’t performed well in previous studies. “Someone can have abnormalities on HRCT that are consistent with ILD but still have PFTs that are in the ‘normal’ range,” explained Dr. Bernstein of Columbia University, New York. One cross-sectional study of 102 SSc patients found that the test’s sensitivity for the detection of ILD on HRCT was just 37.5% when forced vital capacity (FVC) <80% predicted.
Investigators sought to assess performance characteristics of PFTs in patients with early diffuse cutaneous SSc, a cohort at high risk of developing ILD. The study enlisted patients from the Prospective Registry of Early Systemic Sclerosis (PRESS), a multicenter, prospective cohort study of adults with early diffuse cutaneous SSc. Overall, 212 patients at 11 U.S. academic medical centers participated in the study from April 2012 to January 2019.
All patients had spirometry (PFT) and HRCT chest scans. PFTs were conducted per American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society guidelines. The investigators calculated test characteristics for single PFT and combinations of PFT parameters for the detection of ILD on HRCT. The HRCTs were ordered at the discretion of treating physicians, and scrutinized for ILD features such as reticular changes, honeycombing, traction bronchiectasis, and ground-glass opacities. The investigators defined the lower limit of normal for FVC, total lung capacity, and diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) as 80% predicted.
Overall, Dr. Bernstein and her colleagues found that PFTs lacked sufficient sensitivity and negative predictive value for the detection of ILD on HRCT in these patients.
An FVC <80% predicted performed at only 63% sensitivity and an false negative rate of 37%. Total lung capacity or DLCO <80% predicted had a sensitivity of 46% and 80%, respectively. The combination of FVC or DLCO <80% predicted raised sensitivity to 85%. However, the addition of total lung capacity to this combination did not improve results.
Overall, PFTs had a positive predictive value of 64%-74% and an negative predictive value of 61%-70%. “This means that PFT alone will not accurately predict the presence of ILD in about 35%, and not be correctly negative in about 35%,” observed Daniel E. Furst, MD, professor of medicine (emeritus) at the University of California, Los Angeles, and professor of rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles.
While the combination of FVC <80% predicted or DLCO <80% predicted performed better than the other parameters, the sensitivity “is inadequate for an ILD screening test as it results in an false negative rate of 15%, thereby falsely reassuring 15% of patients that they do not have ILD when in fact they do,” the investigators observed.
“This study reinforces the notion that PFTs alone are ineffective screening tools for ILD in the presence of systemic sclerosis, particularly for patients with early systemic sclerosis,” said Elizabeth Volkmann, MD, MS, assistant professor and codirector of the CTD-ILD program in the division of rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles.
The study’s scope was relatively small, yet the results provide further evidence to show that HRCT should be performed in all SSc patients to screen for the presence of ILD, Dr. Volkmann said in an interview.
Other research has demonstrated the value of baseline HRCT as a prognosticator of ILD outcomes. The method provides useful information about the degree of fibrosis and degree of damage in early-stage disease, said Dr. Furst, also an adjunct professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, and a research professor at the University of Florence (Italy). “If there’s honeycombing, that’s a bad prognosis. If it’s ground glass or reticular changes, the prognosis is better.
“Once there’s a lot of damage, it’s much harder to interpret disease with HRCT,” he added.
HRCT and PFT work well together to assess what’s happening in patients, Dr. Furst explained. HRCT provides an idea of anatomic changes, whereas PFT outlines aspects of functional change to diagnose early ILD in early diffuse SSc. The study results should not apply to patients with later disease who have more developed ILD, he noted.
The investigators acknowledged that they weren’t able to categorize and analyze patients according to disease extent because they didn’t quantify the extent of ILD. Another limitation was that the HRCTs and PFTs were ordered at the discretion of individual physicians, which means that not all participants received the tests.
“Although the tests were done in 90% of the population, there is still a probability of a significant selection bias,” Dr. Furst said.
Dr. Bernstein and several other coauthors in the study received grants from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases to support their work. Dr. Furst disclosed receiving grant/research support from and/or consulting for AbbVie, Actelion, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Corbus, the National Institutes of Health, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche/Genentech. Dr. Volkmann disclosed consulting for and/or receiving grant support from Boehringer Ingelheim, Corbus, and Forbius.
SOURCE: Bernstein EJ et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Jun 25. doi: 10.1002/art.41415.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Primary care practices may lose about $68k per physician this year
Primary care practices stand to lose almost $68,000 per full-time physician this year as COVID-19 causes care delays and cancellations, researchers estimate. And while some outpatient care has started to rebound to near baseline appointment levels, other ambulatory specialties remain dramatically down from prepandemic rates.
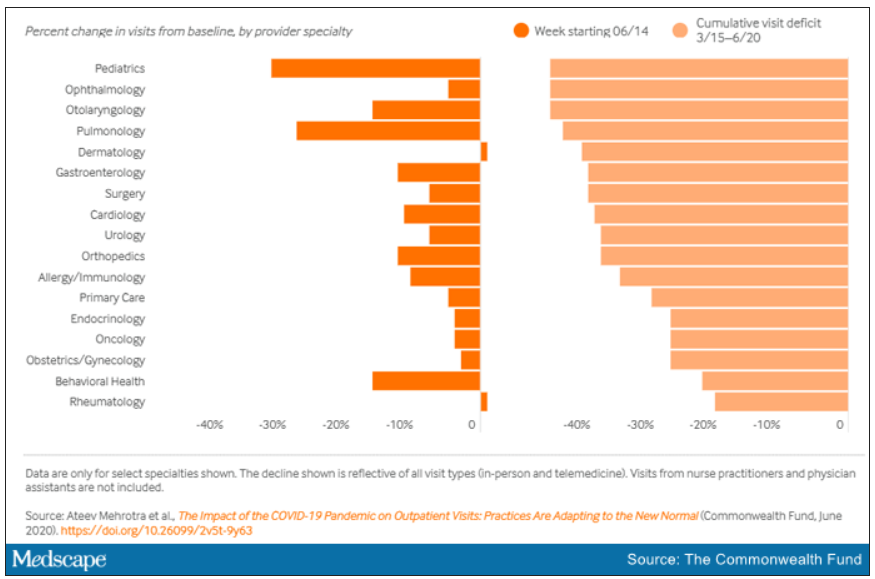
For primary care practices, Sanjay Basu, MD, and colleagues calculated the losses at $67,774 in gross revenue per physician (interquartile range, $80,577-$54,990), with a national toll of $15.1 billion this year.
That’s without a potential second wave of COVID-19, noted Dr. Basu, director of research and population health at Collective Health in San Francisco, and colleagues.
When they added a theoretical stay-at-home order for November and December, the estimated loss climbed to $85,666 in gross revenue per full-time physician, with a loss of $19.1 billion nationally. The findings were published online in Health Affairs.
Meanwhile, clinical losses from canceled outpatient care are piling up as well, according to a study by Ateev Mehrotra, MD, associate professor of health care policy and medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston, and colleagues, which calculated the clinical losses in outpatient care.
“The ‘cumulative deficit’ in visits over the last 3 months (March 15 to June 20) is nearly 40%,” the authors wrote. They reported their findings in an article published online June 25 by the Commonwealth Fund.
When examined by specialty, Dr. Mehrotra and colleagues found that appointment rebound rates have been uneven. Whereas dermatology and rheumatology visits have already recovered, a couple of specialties have cumulative deficits that are particularly concerning. For example, pediatric visits were down by 47% in the 3 months since March 15 and pulmonology visits were down 45% in that time.
Much depends on the future of telehealth
Closing the financial and care gaps will depend largely on changing payment models for outpatient care and assuring adequate and enduring reimbursement for telehealth, according to experts.
COVID-19 has put a spotlight on the fragility of a fee-for-service system that depends on in-person visits for stability, Daniel Horn, MD, director of population health and quality at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, said in an interview.
Several things need to happen to change the outlook for outpatient care, he said.
A need mentioned in both studies is that the COVID-19 waivers that make it possible for telehealth visits to be reimbursed like other visits must continue after the pandemic. Those assurances are critical as practices decide whether to invest in telemedicine.
If U.S. practices revert as of Oct. 1, 2020, to the pre–COVID-19 payment system for telehealth, national losses for the year would be more than double the current estimates.
“Given the number of active primary care physicians (n = 223,125), we estimated that the cost would be $38.7 billion (IQR, $31.1 billion-$48.3 billion) at a national level to neutralize the gross revenue losses caused by COVID-19 among primary care practices, without subjecting staff to furloughs,” Dr. Basu and colleagues wrote.
In addition to stabilizing telehealth payment models, another need to improve the outlook for outpatient care is more effective communication that in-person care is safe again in regions with protocols in place, Dr. Horn said.
However, the most important change, Dr. Horn said, is a switch to prospective lump-sum payments – payments made in advance to physicians to treat each patient in the way they and the patient deem best with the most appropriate appointment type – whether by in-person visit, phone call, text reminders, or video session.
Prospective payments would take multipayer coalitions working in conjunction with leadership on the federal level from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, Dr. Horn said. Commercial payers and states (through Medicaid funds) should already have that money available with the cancellations of nonessential procedures, he said.
“We expect ongoing turbulent times, so having a prospective payment could unleash the capacity for primary care practices to be creative in the way they care for their patients,” Dr. Horn said.
Visit trends still down
Calculations by Dr. Basu, who is also on the faculty at Harvard Medical School’s Center for Primary Care, and colleagues were partially informed by Dr. Mehrotra’s data on how many visits have been lost because of COVID-19.
Dr. Mehrotra said a clear message in their study is that “visit trends are not back to baseline.”
They found that the number of visits to ambulatory practices had dropped nearly 60% by early April. Since then, numbers have rebounded substantially. As of the week of June 14, overall visits, compared with baseline were down 11%. But the drops varied widely across specialties.
Dr. Mehrotra said he found particularly disturbing the drop in pediatric visits and the sharp contrast between those rates and the higher number of visits for adults. While visits for patients aged 75 and older had climbed back to just 3% below baseline, the drop seen among kids aged 3-5 years remains 43% below baseline.
“Even kids 0-2 years old are still down 30% from baseline,” he pointed out.
It’s possible that kids are getting care from other sources or perhaps are not sick as often because they are not in school. However, he added, “I do think there’s a concern that some kids are not getting the care they need for chronic illnesses such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, asthma, eczema, and psoriasis, and vaccination rates have fallen.”
Telemedicine rates dropping
Telemedicine was “supposed to have its shining moment,” Dr. Mehrotra said, but trends show it cannot make up the gaps of in-person care. His team’s data show a decline in telemedicine as a percentage of all visits from a high of 13.8% in mid-April to 7.4% the week of June 14.
He attributes that partially to physicians’ mixed success in getting reimbursed. “While Medicare has done a good job reimbursing, commercial payers and Medicaid plans have been mixed in their coverage.”
Some physicians who don’t get reimbursed or receive delayed or reduced payments are going back to in-person visits, Dr. Mehrotra said.
He said it’s important to remember that, before the pandemic, “telemedicine was making up 0.1% of all visits. Even if now it declines (from the April high of 13.8%) to 5% or 3%, that’s still a 30-fold increase within the course of a couple of months.”
Prospective payments would help expand the possibilities for telemedicine, he said, and could include apps and wearables and texts in addition to or instead of traditional video sessions.
Dr. Mehrotra said change won’t come fast enough for some and many practices won’t survive. “People are worried about their livelihood. This is nothing we’ve ever – at least in my career as a physician – had to focus on. Now we’re really having practices ask whether they can financially sustain themselves.”
For many, he said, the damage will be long term. “That cumulative deficit in visits – I’m not sure if it’s ever coming back. If you’re a primary care practice, you can only work so hard.”
Dr. Basu reported receiving a salary for clinical duties from HealthRIGHT360, a Federally Qualified Health Center, and Collective Health, a care management organization. Dr. Horn and Dr. Mehrotra reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally on Medscape.com.
Primary care practices stand to lose almost $68,000 per full-time physician this year as COVID-19 causes care delays and cancellations, researchers estimate. And while some outpatient care has started to rebound to near baseline appointment levels, other ambulatory specialties remain dramatically down from prepandemic rates.

For primary care practices, Sanjay Basu, MD, and colleagues calculated the losses at $67,774 in gross revenue per physician (interquartile range, $80,577-$54,990), with a national toll of $15.1 billion this year.
That’s without a potential second wave of COVID-19, noted Dr. Basu, director of research and population health at Collective Health in San Francisco, and colleagues.
When they added a theoretical stay-at-home order for November and December, the estimated loss climbed to $85,666 in gross revenue per full-time physician, with a loss of $19.1 billion nationally. The findings were published online in Health Affairs.
Meanwhile, clinical losses from canceled outpatient care are piling up as well, according to a study by Ateev Mehrotra, MD, associate professor of health care policy and medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston, and colleagues, which calculated the clinical losses in outpatient care.
“The ‘cumulative deficit’ in visits over the last 3 months (March 15 to June 20) is nearly 40%,” the authors wrote. They reported their findings in an article published online June 25 by the Commonwealth Fund.
When examined by specialty, Dr. Mehrotra and colleagues found that appointment rebound rates have been uneven. Whereas dermatology and rheumatology visits have already recovered, a couple of specialties have cumulative deficits that are particularly concerning. For example, pediatric visits were down by 47% in the 3 months since March 15 and pulmonology visits were down 45% in that time.
Much depends on the future of telehealth
Closing the financial and care gaps will depend largely on changing payment models for outpatient care and assuring adequate and enduring reimbursement for telehealth, according to experts.
COVID-19 has put a spotlight on the fragility of a fee-for-service system that depends on in-person visits for stability, Daniel Horn, MD, director of population health and quality at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, said in an interview.
Several things need to happen to change the outlook for outpatient care, he said.
A need mentioned in both studies is that the COVID-19 waivers that make it possible for telehealth visits to be reimbursed like other visits must continue after the pandemic. Those assurances are critical as practices decide whether to invest in telemedicine.
If U.S. practices revert as of Oct. 1, 2020, to the pre–COVID-19 payment system for telehealth, national losses for the year would be more than double the current estimates.
“Given the number of active primary care physicians (n = 223,125), we estimated that the cost would be $38.7 billion (IQR, $31.1 billion-$48.3 billion) at a national level to neutralize the gross revenue losses caused by COVID-19 among primary care practices, without subjecting staff to furloughs,” Dr. Basu and colleagues wrote.
In addition to stabilizing telehealth payment models, another need to improve the outlook for outpatient care is more effective communication that in-person care is safe again in regions with protocols in place, Dr. Horn said.
However, the most important change, Dr. Horn said, is a switch to prospective lump-sum payments – payments made in advance to physicians to treat each patient in the way they and the patient deem best with the most appropriate appointment type – whether by in-person visit, phone call, text reminders, or video session.
Prospective payments would take multipayer coalitions working in conjunction with leadership on the federal level from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, Dr. Horn said. Commercial payers and states (through Medicaid funds) should already have that money available with the cancellations of nonessential procedures, he said.
“We expect ongoing turbulent times, so having a prospective payment could unleash the capacity for primary care practices to be creative in the way they care for their patients,” Dr. Horn said.
Visit trends still down
Calculations by Dr. Basu, who is also on the faculty at Harvard Medical School’s Center for Primary Care, and colleagues were partially informed by Dr. Mehrotra’s data on how many visits have been lost because of COVID-19.
Dr. Mehrotra said a clear message in their study is that “visit trends are not back to baseline.”
They found that the number of visits to ambulatory practices had dropped nearly 60% by early April. Since then, numbers have rebounded substantially. As of the week of June 14, overall visits, compared with baseline were down 11%. But the drops varied widely across specialties.
Dr. Mehrotra said he found particularly disturbing the drop in pediatric visits and the sharp contrast between those rates and the higher number of visits for adults. While visits for patients aged 75 and older had climbed back to just 3% below baseline, the drop seen among kids aged 3-5 years remains 43% below baseline.
“Even kids 0-2 years old are still down 30% from baseline,” he pointed out.
It’s possible that kids are getting care from other sources or perhaps are not sick as often because they are not in school. However, he added, “I do think there’s a concern that some kids are not getting the care they need for chronic illnesses such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, asthma, eczema, and psoriasis, and vaccination rates have fallen.”
Telemedicine rates dropping
Telemedicine was “supposed to have its shining moment,” Dr. Mehrotra said, but trends show it cannot make up the gaps of in-person care. His team’s data show a decline in telemedicine as a percentage of all visits from a high of 13.8% in mid-April to 7.4% the week of June 14.
He attributes that partially to physicians’ mixed success in getting reimbursed. “While Medicare has done a good job reimbursing, commercial payers and Medicaid plans have been mixed in their coverage.”
Some physicians who don’t get reimbursed or receive delayed or reduced payments are going back to in-person visits, Dr. Mehrotra said.
He said it’s important to remember that, before the pandemic, “telemedicine was making up 0.1% of all visits. Even if now it declines (from the April high of 13.8%) to 5% or 3%, that’s still a 30-fold increase within the course of a couple of months.”
Prospective payments would help expand the possibilities for telemedicine, he said, and could include apps and wearables and texts in addition to or instead of traditional video sessions.
Dr. Mehrotra said change won’t come fast enough for some and many practices won’t survive. “People are worried about their livelihood. This is nothing we’ve ever – at least in my career as a physician – had to focus on. Now we’re really having practices ask whether they can financially sustain themselves.”
For many, he said, the damage will be long term. “That cumulative deficit in visits – I’m not sure if it’s ever coming back. If you’re a primary care practice, you can only work so hard.”
Dr. Basu reported receiving a salary for clinical duties from HealthRIGHT360, a Federally Qualified Health Center, and Collective Health, a care management organization. Dr. Horn and Dr. Mehrotra reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally on Medscape.com.
Primary care practices stand to lose almost $68,000 per full-time physician this year as COVID-19 causes care delays and cancellations, researchers estimate. And while some outpatient care has started to rebound to near baseline appointment levels, other ambulatory specialties remain dramatically down from prepandemic rates.

For primary care practices, Sanjay Basu, MD, and colleagues calculated the losses at $67,774 in gross revenue per physician (interquartile range, $80,577-$54,990), with a national toll of $15.1 billion this year.
That’s without a potential second wave of COVID-19, noted Dr. Basu, director of research and population health at Collective Health in San Francisco, and colleagues.
When they added a theoretical stay-at-home order for November and December, the estimated loss climbed to $85,666 in gross revenue per full-time physician, with a loss of $19.1 billion nationally. The findings were published online in Health Affairs.
Meanwhile, clinical losses from canceled outpatient care are piling up as well, according to a study by Ateev Mehrotra, MD, associate professor of health care policy and medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston, and colleagues, which calculated the clinical losses in outpatient care.
“The ‘cumulative deficit’ in visits over the last 3 months (March 15 to June 20) is nearly 40%,” the authors wrote. They reported their findings in an article published online June 25 by the Commonwealth Fund.
When examined by specialty, Dr. Mehrotra and colleagues found that appointment rebound rates have been uneven. Whereas dermatology and rheumatology visits have already recovered, a couple of specialties have cumulative deficits that are particularly concerning. For example, pediatric visits were down by 47% in the 3 months since March 15 and pulmonology visits were down 45% in that time.
Much depends on the future of telehealth
Closing the financial and care gaps will depend largely on changing payment models for outpatient care and assuring adequate and enduring reimbursement for telehealth, according to experts.
COVID-19 has put a spotlight on the fragility of a fee-for-service system that depends on in-person visits for stability, Daniel Horn, MD, director of population health and quality at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, said in an interview.
Several things need to happen to change the outlook for outpatient care, he said.
A need mentioned in both studies is that the COVID-19 waivers that make it possible for telehealth visits to be reimbursed like other visits must continue after the pandemic. Those assurances are critical as practices decide whether to invest in telemedicine.
If U.S. practices revert as of Oct. 1, 2020, to the pre–COVID-19 payment system for telehealth, national losses for the year would be more than double the current estimates.
“Given the number of active primary care physicians (n = 223,125), we estimated that the cost would be $38.7 billion (IQR, $31.1 billion-$48.3 billion) at a national level to neutralize the gross revenue losses caused by COVID-19 among primary care practices, without subjecting staff to furloughs,” Dr. Basu and colleagues wrote.
In addition to stabilizing telehealth payment models, another need to improve the outlook for outpatient care is more effective communication that in-person care is safe again in regions with protocols in place, Dr. Horn said.
However, the most important change, Dr. Horn said, is a switch to prospective lump-sum payments – payments made in advance to physicians to treat each patient in the way they and the patient deem best with the most appropriate appointment type – whether by in-person visit, phone call, text reminders, or video session.
Prospective payments would take multipayer coalitions working in conjunction with leadership on the federal level from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, Dr. Horn said. Commercial payers and states (through Medicaid funds) should already have that money available with the cancellations of nonessential procedures, he said.
“We expect ongoing turbulent times, so having a prospective payment could unleash the capacity for primary care practices to be creative in the way they care for their patients,” Dr. Horn said.
Visit trends still down
Calculations by Dr. Basu, who is also on the faculty at Harvard Medical School’s Center for Primary Care, and colleagues were partially informed by Dr. Mehrotra’s data on how many visits have been lost because of COVID-19.
Dr. Mehrotra said a clear message in their study is that “visit trends are not back to baseline.”
They found that the number of visits to ambulatory practices had dropped nearly 60% by early April. Since then, numbers have rebounded substantially. As of the week of June 14, overall visits, compared with baseline were down 11%. But the drops varied widely across specialties.
Dr. Mehrotra said he found particularly disturbing the drop in pediatric visits and the sharp contrast between those rates and the higher number of visits for adults. While visits for patients aged 75 and older had climbed back to just 3% below baseline, the drop seen among kids aged 3-5 years remains 43% below baseline.
“Even kids 0-2 years old are still down 30% from baseline,” he pointed out.
It’s possible that kids are getting care from other sources or perhaps are not sick as often because they are not in school. However, he added, “I do think there’s a concern that some kids are not getting the care they need for chronic illnesses such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, asthma, eczema, and psoriasis, and vaccination rates have fallen.”
Telemedicine rates dropping
Telemedicine was “supposed to have its shining moment,” Dr. Mehrotra said, but trends show it cannot make up the gaps of in-person care. His team’s data show a decline in telemedicine as a percentage of all visits from a high of 13.8% in mid-April to 7.4% the week of June 14.
He attributes that partially to physicians’ mixed success in getting reimbursed. “While Medicare has done a good job reimbursing, commercial payers and Medicaid plans have been mixed in their coverage.”
Some physicians who don’t get reimbursed or receive delayed or reduced payments are going back to in-person visits, Dr. Mehrotra said.
He said it’s important to remember that, before the pandemic, “telemedicine was making up 0.1% of all visits. Even if now it declines (from the April high of 13.8%) to 5% or 3%, that’s still a 30-fold increase within the course of a couple of months.”
Prospective payments would help expand the possibilities for telemedicine, he said, and could include apps and wearables and texts in addition to or instead of traditional video sessions.
Dr. Mehrotra said change won’t come fast enough for some and many practices won’t survive. “People are worried about their livelihood. This is nothing we’ve ever – at least in my career as a physician – had to focus on. Now we’re really having practices ask whether they can financially sustain themselves.”
For many, he said, the damage will be long term. “That cumulative deficit in visits – I’m not sure if it’s ever coming back. If you’re a primary care practice, you can only work so hard.”
Dr. Basu reported receiving a salary for clinical duties from HealthRIGHT360, a Federally Qualified Health Center, and Collective Health, a care management organization. Dr. Horn and Dr. Mehrotra reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally on Medscape.com.
Physician shortage grows in latest projections
Fifteen-year projections for the shortage of primary care and specialty physicians in the United States grew to between 54,000 and 139,000 in the latest annual report by the Association of American Medical Colleges.

Those estimates are up from last year’s projections of a shortfall of 46,900-121,900 by 2032.
The Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projections from 2018 to 2033, was the sixth annual study conducted for the AAMC by the Life Science division of global analytics firm IHS Markit.
This analysis, conducted in 2019, includes supply and demand scenarios but predates the COVID-19 pandemic.
In a telephone press briefing this morning, David J. Skorton, MD, AAMC’s president and CEO, told reporters that the pandemic has highlighted the acute effects of physician shortages.
“We’ve seen in stark detail how fragile and quickly overwhelmed America’s health care system truly is, and we’re nowhere near out of the woods with this public health emergency yet,” he said.
The persistent shortages mean people “will have ongoing difficulty accessing the care that they need, especially as we all age.”
Some of the biggest shortages will be seen in non–primary care specialists. Dr. Skorton notes that, during the pandemic, shortages of specialists in hospital settings, including critical care, emergency medicine, pulmonology, and infectious disease, are an urgent concern.
Population trends continue to be the biggest drivers of the shortage. Report authors found that by 2033, the U.S. population is expected to grow by 10.4% from 327 million to 361 million, with wide differences by age.
The under-18 population is expected to grow by 3.9%, whereas the numbers of those aged 65 and older is expected to balloon by 45.1% in that time, thus stoking demand for specialties focused on care for older Americans.
Physician age is also a large factor in the projections. More than two in five currently active physicians will be 65 or older in the next 10 years, according to the report. A wave of retirements will have a large impact on the supply of physicians.
The report explains that the projected shortages remain under predictable scenarios: an increase in the use of advanced practice nurses (APRNs) and physician assistants (PAs), more care in alternate settings such as retail clinics, and changes in payment and delivery.
According to the report, the supply of APRNs and PAs is on track to double over the next 15 years (with growth rates varying by APRN and PA specialty).
“At current rates of production, by 2033 APRN supply will grow by 276,000 [full-time equivalents (FTEs)] and PA supply by nearly 138,000 FTEs,” the report states.
However, authors acknowledge there is scant evidence on what effect these numbers will have on demand for physicians.
The report points out that if underserved communities were able to access health care in numbers similar to those without barriers imposed by where they live or what insurance they have, demand could rise beyond the projections in this report by an additional 74,000 to 145,000 physicians.
Stemming the shortages
The first step in addressing the shortage, Dr. Skorton said, is assuring a healthy physician pipeline to meet the demand for generations.
“One essential step that we believe Congress must take is to end the freeze that has been in place since 1997 that limits federal support for residency training of new physicians,” Skorton said.
He noted that AAMC supports the bipartisan Resident Physician Shortage Reduction Act, introduced to Congress in 2019, which calls for an increase in Medicare support for 3000 new residency positions each year over the next 5 years.
However, additional steps are needed, including enabling advanced practice providers to play a greater role in increasing the health care workforce, Dr. Skorton said.
Pointing out some of the effects of physician shortages, Janis M. Orlowski, MD, chief health care officer for the AAMC, noted that high rates of maternal morbidity are partially linked to lack of adequate numbers of physicians in the United States, and a lack of behavioral health specialists has exacerbated effects of the opioid epidemic.
Shortages are already evident in the current pandemic, she added, saying, “Today we see governors calling for retired physicians or physicians from other states to come and help battle the pandemic within their states.”
The report explains that long-term effects on physician numbers from the pandemic likely will include workforce exits because of COVID-19 deaths, early retirements from burnout, or a shift in interest in certain specialties.
Karen Fisher, JD, chief public policy officer for AAMC, said telehealth will also play an important role in bridging gaps in access to care, and its importance has already been seen in this first wave of the pandemic.
She noted that temporary federal waivers have made it easier for those enrolled in Medicare, Medicaid, and the Children’s Health Insurance Program to receive telehealth services during the pandemic.
Expanding the access to telehealth permanently will be important in helping to fill gaps, Ms. Fisher said.
Dr. Skorton, Dr. Orlowski, and Ms. Fisher have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Fifteen-year projections for the shortage of primary care and specialty physicians in the United States grew to between 54,000 and 139,000 in the latest annual report by the Association of American Medical Colleges.

Those estimates are up from last year’s projections of a shortfall of 46,900-121,900 by 2032.
The Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projections from 2018 to 2033, was the sixth annual study conducted for the AAMC by the Life Science division of global analytics firm IHS Markit.
This analysis, conducted in 2019, includes supply and demand scenarios but predates the COVID-19 pandemic.
In a telephone press briefing this morning, David J. Skorton, MD, AAMC’s president and CEO, told reporters that the pandemic has highlighted the acute effects of physician shortages.
“We’ve seen in stark detail how fragile and quickly overwhelmed America’s health care system truly is, and we’re nowhere near out of the woods with this public health emergency yet,” he said.
The persistent shortages mean people “will have ongoing difficulty accessing the care that they need, especially as we all age.”
Some of the biggest shortages will be seen in non–primary care specialists. Dr. Skorton notes that, during the pandemic, shortages of specialists in hospital settings, including critical care, emergency medicine, pulmonology, and infectious disease, are an urgent concern.
Population trends continue to be the biggest drivers of the shortage. Report authors found that by 2033, the U.S. population is expected to grow by 10.4% from 327 million to 361 million, with wide differences by age.
The under-18 population is expected to grow by 3.9%, whereas the numbers of those aged 65 and older is expected to balloon by 45.1% in that time, thus stoking demand for specialties focused on care for older Americans.
Physician age is also a large factor in the projections. More than two in five currently active physicians will be 65 or older in the next 10 years, according to the report. A wave of retirements will have a large impact on the supply of physicians.
The report explains that the projected shortages remain under predictable scenarios: an increase in the use of advanced practice nurses (APRNs) and physician assistants (PAs), more care in alternate settings such as retail clinics, and changes in payment and delivery.
According to the report, the supply of APRNs and PAs is on track to double over the next 15 years (with growth rates varying by APRN and PA specialty).
“At current rates of production, by 2033 APRN supply will grow by 276,000 [full-time equivalents (FTEs)] and PA supply by nearly 138,000 FTEs,” the report states.
However, authors acknowledge there is scant evidence on what effect these numbers will have on demand for physicians.
The report points out that if underserved communities were able to access health care in numbers similar to those without barriers imposed by where they live or what insurance they have, demand could rise beyond the projections in this report by an additional 74,000 to 145,000 physicians.
Stemming the shortages
The first step in addressing the shortage, Dr. Skorton said, is assuring a healthy physician pipeline to meet the demand for generations.
“One essential step that we believe Congress must take is to end the freeze that has been in place since 1997 that limits federal support for residency training of new physicians,” Skorton said.
He noted that AAMC supports the bipartisan Resident Physician Shortage Reduction Act, introduced to Congress in 2019, which calls for an increase in Medicare support for 3000 new residency positions each year over the next 5 years.
However, additional steps are needed, including enabling advanced practice providers to play a greater role in increasing the health care workforce, Dr. Skorton said.
Pointing out some of the effects of physician shortages, Janis M. Orlowski, MD, chief health care officer for the AAMC, noted that high rates of maternal morbidity are partially linked to lack of adequate numbers of physicians in the United States, and a lack of behavioral health specialists has exacerbated effects of the opioid epidemic.
Shortages are already evident in the current pandemic, she added, saying, “Today we see governors calling for retired physicians or physicians from other states to come and help battle the pandemic within their states.”
The report explains that long-term effects on physician numbers from the pandemic likely will include workforce exits because of COVID-19 deaths, early retirements from burnout, or a shift in interest in certain specialties.
Karen Fisher, JD, chief public policy officer for AAMC, said telehealth will also play an important role in bridging gaps in access to care, and its importance has already been seen in this first wave of the pandemic.
She noted that temporary federal waivers have made it easier for those enrolled in Medicare, Medicaid, and the Children’s Health Insurance Program to receive telehealth services during the pandemic.
Expanding the access to telehealth permanently will be important in helping to fill gaps, Ms. Fisher said.
Dr. Skorton, Dr. Orlowski, and Ms. Fisher have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Fifteen-year projections for the shortage of primary care and specialty physicians in the United States grew to between 54,000 and 139,000 in the latest annual report by the Association of American Medical Colleges.

Those estimates are up from last year’s projections of a shortfall of 46,900-121,900 by 2032.
The Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projections from 2018 to 2033, was the sixth annual study conducted for the AAMC by the Life Science division of global analytics firm IHS Markit.
This analysis, conducted in 2019, includes supply and demand scenarios but predates the COVID-19 pandemic.
In a telephone press briefing this morning, David J. Skorton, MD, AAMC’s president and CEO, told reporters that the pandemic has highlighted the acute effects of physician shortages.
“We’ve seen in stark detail how fragile and quickly overwhelmed America’s health care system truly is, and we’re nowhere near out of the woods with this public health emergency yet,” he said.
The persistent shortages mean people “will have ongoing difficulty accessing the care that they need, especially as we all age.”
Some of the biggest shortages will be seen in non–primary care specialists. Dr. Skorton notes that, during the pandemic, shortages of specialists in hospital settings, including critical care, emergency medicine, pulmonology, and infectious disease, are an urgent concern.
Population trends continue to be the biggest drivers of the shortage. Report authors found that by 2033, the U.S. population is expected to grow by 10.4% from 327 million to 361 million, with wide differences by age.
The under-18 population is expected to grow by 3.9%, whereas the numbers of those aged 65 and older is expected to balloon by 45.1% in that time, thus stoking demand for specialties focused on care for older Americans.
Physician age is also a large factor in the projections. More than two in five currently active physicians will be 65 or older in the next 10 years, according to the report. A wave of retirements will have a large impact on the supply of physicians.
The report explains that the projected shortages remain under predictable scenarios: an increase in the use of advanced practice nurses (APRNs) and physician assistants (PAs), more care in alternate settings such as retail clinics, and changes in payment and delivery.
According to the report, the supply of APRNs and PAs is on track to double over the next 15 years (with growth rates varying by APRN and PA specialty).
“At current rates of production, by 2033 APRN supply will grow by 276,000 [full-time equivalents (FTEs)] and PA supply by nearly 138,000 FTEs,” the report states.
However, authors acknowledge there is scant evidence on what effect these numbers will have on demand for physicians.
The report points out that if underserved communities were able to access health care in numbers similar to those without barriers imposed by where they live or what insurance they have, demand could rise beyond the projections in this report by an additional 74,000 to 145,000 physicians.
Stemming the shortages
The first step in addressing the shortage, Dr. Skorton said, is assuring a healthy physician pipeline to meet the demand for generations.
“One essential step that we believe Congress must take is to end the freeze that has been in place since 1997 that limits federal support for residency training of new physicians,” Skorton said.
He noted that AAMC supports the bipartisan Resident Physician Shortage Reduction Act, introduced to Congress in 2019, which calls for an increase in Medicare support for 3000 new residency positions each year over the next 5 years.
However, additional steps are needed, including enabling advanced practice providers to play a greater role in increasing the health care workforce, Dr. Skorton said.
Pointing out some of the effects of physician shortages, Janis M. Orlowski, MD, chief health care officer for the AAMC, noted that high rates of maternal morbidity are partially linked to lack of adequate numbers of physicians in the United States, and a lack of behavioral health specialists has exacerbated effects of the opioid epidemic.
Shortages are already evident in the current pandemic, she added, saying, “Today we see governors calling for retired physicians or physicians from other states to come and help battle the pandemic within their states.”
The report explains that long-term effects on physician numbers from the pandemic likely will include workforce exits because of COVID-19 deaths, early retirements from burnout, or a shift in interest in certain specialties.
Karen Fisher, JD, chief public policy officer for AAMC, said telehealth will also play an important role in bridging gaps in access to care, and its importance has already been seen in this first wave of the pandemic.
She noted that temporary federal waivers have made it easier for those enrolled in Medicare, Medicaid, and the Children’s Health Insurance Program to receive telehealth services during the pandemic.
Expanding the access to telehealth permanently will be important in helping to fill gaps, Ms. Fisher said.
Dr. Skorton, Dr. Orlowski, and Ms. Fisher have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Diagnostic criteria may miss some MIS-C cases, experts say
New data from active surveillance of the severe inflammatory condition associated with COVID-19 in previously healthy children provide further insight into the prevalence and course of the rare syndrome, but experts are concerned that current diagnostic criteria may not capture the true scope of the problem.
In separate reports published online June 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine, researchers from the New York State Department of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) describe the epidemiology and clinical features of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) on the basis of information derived from targeted surveillance programs in New York State and across the country.
For the New York study, Elizabeth M. Dufort, MD, from the New York Department of Health in Albany and colleagues analyzed MIS-C surveillance data from 106 hospitals across the state. Of 191 suspected MIS-C cases reported to the Department of Health from March 1 through May 10, 99 met the state’s interim case definition of the condition and were included in the analysis.
The incidence rate for MIS-C was two cases per 100,000 individuals younger than 21 years, whereas the incidence rate of confirmed COVID-19 cases in this age group was 322 per 100,000. Most cases occurred approximately 1 month after the state’s COVID-19 peak.
“Among our patients, predominantly from the New York Metropolitan Region, 40% were black and 36% were Hispanic. This may be a reflection of the well-documented elevated incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among black and Hispanic communities,” the authors report.
All children presented with fever or chills, and most had tachycardia (97%) and gastrointestinal symptoms (80%). Rash (60%), conjunctival infection (56%), hypotension (32%), and mucosal changes (27%) were reported. Among all of the children, levels of inflammatory markers were elevated, including levels of C-reactive protein (100%), D-dimer (91%), and troponin (71%). More than one third of the patients (36%) were diagnosed with myocarditis, and an additional 16% had clinical myocarditis.
Of the full cohort, 80% of the children required intensive care, 62% received vasopressor support, and two children died.
The high prevalence of cardiac dysfunction or depression, coagulopathy, gastrointestinal symptoms, mild respiratory symptoms, and indications for supplemental oxygen in patients with MIS-C stands in contrast to the clinical picture observed in most acute cases of COVID-19 in hospitalized children, the authors write.
“Although most children have mild or no illness from SARS-CoV-2 infection, MIS-C may follow Covid-19 or asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Recognition of the syndrome and early identification of children with MIS-C, including early monitoring of blood pressure and electrocardiographic and echocardiographic evaluation, could inform appropriate supportive care and other potential therapeutic options,” they continue.
The incidence of MIS-C among children infected with SARS-CoV-2 is unclear because children with COVID-19 often have mild or no symptoms and because children are not tested as frequently, the authors state. For this reason, “[i]t is crucial to establish surveillance for MIS-C cases, particularly in communities with higher levels of SARS-CoV-2 transmission.”
Important Differences From Kawasaki Disease
In a separate study, Leora R. Feldstein, MD, of the CDC, and colleagues report 186 cases of MIS-C collected through targeted surveillance of pediatric health centers in 26 US states from March 15 to May 20, 2020. As with the New York cohort, a disproportionate number of children in this cohort were black (25%) and Hispanic or Latino (31%).
Similar to the New York cohort, 80% of the children in this group required intensive care, 48% received vasoactive support, 20% required invasive mechanical ventilation, and four children died. Skin rashes, gastrointestinal symptoms, cardiovascular and hematologic effects, mucous changes, and elevations of inflammatory biomarkers were also similarly observed.
The researchers note that, although many of the features of MIS-C overlap with Kawasaki disease, there are some important differences, particularly with respect to the nature of cardiovascular involvement. “Approximately 5% of children with Kawasaki’s disease in the United States present with cardiovascular shock leading to vasopressor or inotropic support, as compared with 50% of the patients in our series,” the authors write.
In addition, coronary-artery aneurysms affect approximately one quarter of Kawasaki disease patients within 21 days of disease onset. “In our series, a maximum z score of 2.5 or higher in the left anterior descending or right coronary artery was reported in 8% of the patients overall and in 9% of patients with echocardiograms,” they report.
Additional differentiating features include patient age and race/ethnicity. Kawasaki disease occurs most commonly in children younger than 5 years. The median age in the multistate study was 8.3 years, and nearly half of the children in the New York cohort were in the 6- to 12-year age group. Further, Kawasaki disease is disproportionately prevalent in children of Asian descent.
Despite the differences, “until more is known about long-term cardiac sequelae of MIS-C, providers could consider following Kawasaki’s disease guidelines for follow-up, which recommend repeat echocardiographic imaging at 1 to 2 weeks.”
As was the case in the New York series, treatment in the multistate cohort most commonly included intravenous immunoglobulin and systemic glucocorticoids. Optimal management, however, will require a better understanding of the pathogenesis of MIS-C, Feldstein and colleagues write.
Questions Remain
With the accumulating data on this syndrome, the MIS-C picture seems to be getting incrementally clearer, but there is still much uncertainty, according to Michael Levin, FMedSci, PhD, from the Department of Infectious Disease, Imperial College London, United Kingdom.
“The recognition and description of new diseases often resemble the parable of the blind men and the elephant, with each declaring that the part of the beast they have touched fully defines it,” he writes in an accompanying editorial.
“As the coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) pandemic has evolved, case reports have appeared describing children with unusual febrile illnesses that have features of Kawasaki’s disease, toxic shock syndrome, acute abdominal conditions, and encephalopathy, along with other reports of children with fever, elevated inflammatory markers, and multisystem involvement. It is now apparent that these reports were describing different clinical presentations of a new childhood inflammatory disorder.”
Although a consistent clinical picture is emerging, “[t]he published reports have used a variety of hastily developed case definitions based on the most severe cases, possibly missing less serious cases,” Levin writes. In particular, both the CDC and World Health Organization definitions require evidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection or exposure, which might contribute to underrecognition and underreporting because asymptomatic infections are common and antibody testing is not universally available.
“There is concern that children meeting current diagnostic criteria for MIS-C are the ‘tip of the iceberg,’ and a bigger problem may be lurking below the waterline,” Levin states. With approximately 1000 cases of the syndrome reported worldwide, “do we now have a clear picture of the new disorder, or as in the story of the blind men and the elephant, has only part of the beast been described?”
Adrienne Randolph, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital, who is a coauthor of the multistate report, agrees that there is still much to learn about MIS-C before the whole beast can be understood. In an interview with Medscape Medical News, she listed the following key questions that have yet to be answered:
- Why do some children get MIS-C and not others?
- What is the long-term outcome of children with MIS-C?
- How can we differentiate MIS-C from acute COVID-19 infection in children with respiratory failure?
- Does MIS-C occur in young adults?
Randolph said her team is taking the best path forward toward answering these questions, including conducting a second study to identify risk factors for MIS-C and longer-term follow-up studies with the National Institutes of Health. “We are also getting consent to collect blood samples and look at other tests to help distinguish MIS-C from acute COVID-19 infection,” she said. She encouraged heightened awareness among physicians who care for young adults to consider MIS-C in patients aged 21 years and older who present with similar signs and symptoms.
On the basis of the answers to these and additional questions, the case definitions for MIS-C may need refinement to capture the wider spectrum of illness, Levin writes in his editorial. “The challenges of this new condition will now be to understand its pathophysiological mechanisms, to develop diagnostics, and to define the best treatment.”
Kleinman has received grants from the Health Services Resources Administration outside the submitted work. Maddux has received grants from the NIH/NICHD and the Francis Family Foundation outside the submitted work. Randolph has received grants from Genentech and personal fees from La Jolla Pharma outside the submitted work and others from the CDC during the conduct of the study.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data from active surveillance of the severe inflammatory condition associated with COVID-19 in previously healthy children provide further insight into the prevalence and course of the rare syndrome, but experts are concerned that current diagnostic criteria may not capture the true scope of the problem.
In separate reports published online June 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine, researchers from the New York State Department of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) describe the epidemiology and clinical features of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) on the basis of information derived from targeted surveillance programs in New York State and across the country.
For the New York study, Elizabeth M. Dufort, MD, from the New York Department of Health in Albany and colleagues analyzed MIS-C surveillance data from 106 hospitals across the state. Of 191 suspected MIS-C cases reported to the Department of Health from March 1 through May 10, 99 met the state’s interim case definition of the condition and were included in the analysis.
The incidence rate for MIS-C was two cases per 100,000 individuals younger than 21 years, whereas the incidence rate of confirmed COVID-19 cases in this age group was 322 per 100,000. Most cases occurred approximately 1 month after the state’s COVID-19 peak.
“Among our patients, predominantly from the New York Metropolitan Region, 40% were black and 36% were Hispanic. This may be a reflection of the well-documented elevated incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among black and Hispanic communities,” the authors report.
All children presented with fever or chills, and most had tachycardia (97%) and gastrointestinal symptoms (80%). Rash (60%), conjunctival infection (56%), hypotension (32%), and mucosal changes (27%) were reported. Among all of the children, levels of inflammatory markers were elevated, including levels of C-reactive protein (100%), D-dimer (91%), and troponin (71%). More than one third of the patients (36%) were diagnosed with myocarditis, and an additional 16% had clinical myocarditis.
Of the full cohort, 80% of the children required intensive care, 62% received vasopressor support, and two children died.
The high prevalence of cardiac dysfunction or depression, coagulopathy, gastrointestinal symptoms, mild respiratory symptoms, and indications for supplemental oxygen in patients with MIS-C stands in contrast to the clinical picture observed in most acute cases of COVID-19 in hospitalized children, the authors write.
“Although most children have mild or no illness from SARS-CoV-2 infection, MIS-C may follow Covid-19 or asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Recognition of the syndrome and early identification of children with MIS-C, including early monitoring of blood pressure and electrocardiographic and echocardiographic evaluation, could inform appropriate supportive care and other potential therapeutic options,” they continue.
The incidence of MIS-C among children infected with SARS-CoV-2 is unclear because children with COVID-19 often have mild or no symptoms and because children are not tested as frequently, the authors state. For this reason, “[i]t is crucial to establish surveillance for MIS-C cases, particularly in communities with higher levels of SARS-CoV-2 transmission.”
Important Differences From Kawasaki Disease
In a separate study, Leora R. Feldstein, MD, of the CDC, and colleagues report 186 cases of MIS-C collected through targeted surveillance of pediatric health centers in 26 US states from March 15 to May 20, 2020. As with the New York cohort, a disproportionate number of children in this cohort were black (25%) and Hispanic or Latino (31%).
Similar to the New York cohort, 80% of the children in this group required intensive care, 48% received vasoactive support, 20% required invasive mechanical ventilation, and four children died. Skin rashes, gastrointestinal symptoms, cardiovascular and hematologic effects, mucous changes, and elevations of inflammatory biomarkers were also similarly observed.
The researchers note that, although many of the features of MIS-C overlap with Kawasaki disease, there are some important differences, particularly with respect to the nature of cardiovascular involvement. “Approximately 5% of children with Kawasaki’s disease in the United States present with cardiovascular shock leading to vasopressor or inotropic support, as compared with 50% of the patients in our series,” the authors write.
In addition, coronary-artery aneurysms affect approximately one quarter of Kawasaki disease patients within 21 days of disease onset. “In our series, a maximum z score of 2.5 or higher in the left anterior descending or right coronary artery was reported in 8% of the patients overall and in 9% of patients with echocardiograms,” they report.
Additional differentiating features include patient age and race/ethnicity. Kawasaki disease occurs most commonly in children younger than 5 years. The median age in the multistate study was 8.3 years, and nearly half of the children in the New York cohort were in the 6- to 12-year age group. Further, Kawasaki disease is disproportionately prevalent in children of Asian descent.
Despite the differences, “until more is known about long-term cardiac sequelae of MIS-C, providers could consider following Kawasaki’s disease guidelines for follow-up, which recommend repeat echocardiographic imaging at 1 to 2 weeks.”
As was the case in the New York series, treatment in the multistate cohort most commonly included intravenous immunoglobulin and systemic glucocorticoids. Optimal management, however, will require a better understanding of the pathogenesis of MIS-C, Feldstein and colleagues write.
Questions Remain
With the accumulating data on this syndrome, the MIS-C picture seems to be getting incrementally clearer, but there is still much uncertainty, according to Michael Levin, FMedSci, PhD, from the Department of Infectious Disease, Imperial College London, United Kingdom.
“The recognition and description of new diseases often resemble the parable of the blind men and the elephant, with each declaring that the part of the beast they have touched fully defines it,” he writes in an accompanying editorial.
“As the coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) pandemic has evolved, case reports have appeared describing children with unusual febrile illnesses that have features of Kawasaki’s disease, toxic shock syndrome, acute abdominal conditions, and encephalopathy, along with other reports of children with fever, elevated inflammatory markers, and multisystem involvement. It is now apparent that these reports were describing different clinical presentations of a new childhood inflammatory disorder.”
Although a consistent clinical picture is emerging, “[t]he published reports have used a variety of hastily developed case definitions based on the most severe cases, possibly missing less serious cases,” Levin writes. In particular, both the CDC and World Health Organization definitions require evidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection or exposure, which might contribute to underrecognition and underreporting because asymptomatic infections are common and antibody testing is not universally available.
“There is concern that children meeting current diagnostic criteria for MIS-C are the ‘tip of the iceberg,’ and a bigger problem may be lurking below the waterline,” Levin states. With approximately 1000 cases of the syndrome reported worldwide, “do we now have a clear picture of the new disorder, or as in the story of the blind men and the elephant, has only part of the beast been described?”
Adrienne Randolph, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital, who is a coauthor of the multistate report, agrees that there is still much to learn about MIS-C before the whole beast can be understood. In an interview with Medscape Medical News, she listed the following key questions that have yet to be answered:
- Why do some children get MIS-C and not others?
- What is the long-term outcome of children with MIS-C?
- How can we differentiate MIS-C from acute COVID-19 infection in children with respiratory failure?
- Does MIS-C occur in young adults?
Randolph said her team is taking the best path forward toward answering these questions, including conducting a second study to identify risk factors for MIS-C and longer-term follow-up studies with the National Institutes of Health. “We are also getting consent to collect blood samples and look at other tests to help distinguish MIS-C from acute COVID-19 infection,” she said. She encouraged heightened awareness among physicians who care for young adults to consider MIS-C in patients aged 21 years and older who present with similar signs and symptoms.
On the basis of the answers to these and additional questions, the case definitions for MIS-C may need refinement to capture the wider spectrum of illness, Levin writes in his editorial. “The challenges of this new condition will now be to understand its pathophysiological mechanisms, to develop diagnostics, and to define the best treatment.”
Kleinman has received grants from the Health Services Resources Administration outside the submitted work. Maddux has received grants from the NIH/NICHD and the Francis Family Foundation outside the submitted work. Randolph has received grants from Genentech and personal fees from La Jolla Pharma outside the submitted work and others from the CDC during the conduct of the study.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data from active surveillance of the severe inflammatory condition associated with COVID-19 in previously healthy children provide further insight into the prevalence and course of the rare syndrome, but experts are concerned that current diagnostic criteria may not capture the true scope of the problem.
In separate reports published online June 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine, researchers from the New York State Department of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) describe the epidemiology and clinical features of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) on the basis of information derived from targeted surveillance programs in New York State and across the country.
For the New York study, Elizabeth M. Dufort, MD, from the New York Department of Health in Albany and colleagues analyzed MIS-C surveillance data from 106 hospitals across the state. Of 191 suspected MIS-C cases reported to the Department of Health from March 1 through May 10, 99 met the state’s interim case definition of the condition and were included in the analysis.
The incidence rate for MIS-C was two cases per 100,000 individuals younger than 21 years, whereas the incidence rate of confirmed COVID-19 cases in this age group was 322 per 100,000. Most cases occurred approximately 1 month after the state’s COVID-19 peak.
“Among our patients, predominantly from the New York Metropolitan Region, 40% were black and 36% were Hispanic. This may be a reflection of the well-documented elevated incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among black and Hispanic communities,” the authors report.
All children presented with fever or chills, and most had tachycardia (97%) and gastrointestinal symptoms (80%). Rash (60%), conjunctival infection (56%), hypotension (32%), and mucosal changes (27%) were reported. Among all of the children, levels of inflammatory markers were elevated, including levels of C-reactive protein (100%), D-dimer (91%), and troponin (71%). More than one third of the patients (36%) were diagnosed with myocarditis, and an additional 16% had clinical myocarditis.
Of the full cohort, 80% of the children required intensive care, 62% received vasopressor support, and two children died.
The high prevalence of cardiac dysfunction or depression, coagulopathy, gastrointestinal symptoms, mild respiratory symptoms, and indications for supplemental oxygen in patients with MIS-C stands in contrast to the clinical picture observed in most acute cases of COVID-19 in hospitalized children, the authors write.
“Although most children have mild or no illness from SARS-CoV-2 infection, MIS-C may follow Covid-19 or asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Recognition of the syndrome and early identification of children with MIS-C, including early monitoring of blood pressure and electrocardiographic and echocardiographic evaluation, could inform appropriate supportive care and other potential therapeutic options,” they continue.
The incidence of MIS-C among children infected with SARS-CoV-2 is unclear because children with COVID-19 often have mild or no symptoms and because children are not tested as frequently, the authors state. For this reason, “[i]t is crucial to establish surveillance for MIS-C cases, particularly in communities with higher levels of SARS-CoV-2 transmission.”
Important Differences From Kawasaki Disease
In a separate study, Leora R. Feldstein, MD, of the CDC, and colleagues report 186 cases of MIS-C collected through targeted surveillance of pediatric health centers in 26 US states from March 15 to May 20, 2020. As with the New York cohort, a disproportionate number of children in this cohort were black (25%) and Hispanic or Latino (31%).
Similar to the New York cohort, 80% of the children in this group required intensive care, 48% received vasoactive support, 20% required invasive mechanical ventilation, and four children died. Skin rashes, gastrointestinal symptoms, cardiovascular and hematologic effects, mucous changes, and elevations of inflammatory biomarkers were also similarly observed.
The researchers note that, although many of the features of MIS-C overlap with Kawasaki disease, there are some important differences, particularly with respect to the nature of cardiovascular involvement. “Approximately 5% of children with Kawasaki’s disease in the United States present with cardiovascular shock leading to vasopressor or inotropic support, as compared with 50% of the patients in our series,” the authors write.
In addition, coronary-artery aneurysms affect approximately one quarter of Kawasaki disease patients within 21 days of disease onset. “In our series, a maximum z score of 2.5 or higher in the left anterior descending or right coronary artery was reported in 8% of the patients overall and in 9% of patients with echocardiograms,” they report.
Additional differentiating features include patient age and race/ethnicity. Kawasaki disease occurs most commonly in children younger than 5 years. The median age in the multistate study was 8.3 years, and nearly half of the children in the New York cohort were in the 6- to 12-year age group. Further, Kawasaki disease is disproportionately prevalent in children of Asian descent.
Despite the differences, “until more is known about long-term cardiac sequelae of MIS-C, providers could consider following Kawasaki’s disease guidelines for follow-up, which recommend repeat echocardiographic imaging at 1 to 2 weeks.”
As was the case in the New York series, treatment in the multistate cohort most commonly included intravenous immunoglobulin and systemic glucocorticoids. Optimal management, however, will require a better understanding of the pathogenesis of MIS-C, Feldstein and colleagues write.
Questions Remain
With the accumulating data on this syndrome, the MIS-C picture seems to be getting incrementally clearer, but there is still much uncertainty, according to Michael Levin, FMedSci, PhD, from the Department of Infectious Disease, Imperial College London, United Kingdom.
“The recognition and description of new diseases often resemble the parable of the blind men and the elephant, with each declaring that the part of the beast they have touched fully defines it,” he writes in an accompanying editorial.
“As the coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) pandemic has evolved, case reports have appeared describing children with unusual febrile illnesses that have features of Kawasaki’s disease, toxic shock syndrome, acute abdominal conditions, and encephalopathy, along with other reports of children with fever, elevated inflammatory markers, and multisystem involvement. It is now apparent that these reports were describing different clinical presentations of a new childhood inflammatory disorder.”
Although a consistent clinical picture is emerging, “[t]he published reports have used a variety of hastily developed case definitions based on the most severe cases, possibly missing less serious cases,” Levin writes. In particular, both the CDC and World Health Organization definitions require evidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection or exposure, which might contribute to underrecognition and underreporting because asymptomatic infections are common and antibody testing is not universally available.
“There is concern that children meeting current diagnostic criteria for MIS-C are the ‘tip of the iceberg,’ and a bigger problem may be lurking below the waterline,” Levin states. With approximately 1000 cases of the syndrome reported worldwide, “do we now have a clear picture of the new disorder, or as in the story of the blind men and the elephant, has only part of the beast been described?”
Adrienne Randolph, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital, who is a coauthor of the multistate report, agrees that there is still much to learn about MIS-C before the whole beast can be understood. In an interview with Medscape Medical News, she listed the following key questions that have yet to be answered:
- Why do some children get MIS-C and not others?
- What is the long-term outcome of children with MIS-C?
- How can we differentiate MIS-C from acute COVID-19 infection in children with respiratory failure?
- Does MIS-C occur in young adults?
Randolph said her team is taking the best path forward toward answering these questions, including conducting a second study to identify risk factors for MIS-C and longer-term follow-up studies with the National Institutes of Health. “We are also getting consent to collect blood samples and look at other tests to help distinguish MIS-C from acute COVID-19 infection,” she said. She encouraged heightened awareness among physicians who care for young adults to consider MIS-C in patients aged 21 years and older who present with similar signs and symptoms.
On the basis of the answers to these and additional questions, the case definitions for MIS-C may need refinement to capture the wider spectrum of illness, Levin writes in his editorial. “The challenges of this new condition will now be to understand its pathophysiological mechanisms, to develop diagnostics, and to define the best treatment.”
Kleinman has received grants from the Health Services Resources Administration outside the submitted work. Maddux has received grants from the NIH/NICHD and the Francis Family Foundation outside the submitted work. Randolph has received grants from Genentech and personal fees from La Jolla Pharma outside the submitted work and others from the CDC during the conduct of the study.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Daily Recap: Migraine affects pregnancy planning; FDA okays urothelial carcinoma therapy
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Migraine is often a deciding factor in pregnancy planning
Migraine can significantly influence a woman’s decision to have children, new research shows.
Results from a multicenter study of more than 600 women showed that, among participants with migraine, those who were younger, had menstrual migraine, or had chronic migraine were more likely to decide to not become pregnant.
“Women who avoided pregnancy due to migraine were most concerned that migraine would make raising a child difficult, that the migraine medications they take would have a negative impact on their child’s development, and that their migraine pattern would worsen during or just after pregnancy,” said study investigator Ryotaro Ishii, MD, PhD, a visiting scientist at Mayo Clinic in Phoenix.
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American Headache Society. Read more.
FDA approves avelumab as maintenance for urothelial carcinoma
The Food and Drug Administration has approved avelumab (Bavencio) as a maintenance treatment for patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (UC) that has not progressed after first-line platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The new maintenance therapy indication for avelumab is based on efficacy demonstrated in the JAVELIN Bladder 100 trial. Results from this trial were presented as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
The new indication adds to avelumab use in other patient populations, including people with locally advanced or metastatic UC who experience disease progression during or following platinum-containing chemotherapy. The FDA also previously approved avelumab for patients who experienced UC progression within 12 months of neoadjuvant or adjuvant treatment with platinum-containing chemotherapy. The FDA first approved marketing of avelumab in 2017. Other uses include treatment of metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma and first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma in combination with axitinib. Read more.
Lifestyle changes may explain skin lesions in pandemic-era patients
Two European prospective case series found no direct association between skin lesions on the hands and feet and SARS-CoV-2 in young people, which raises questions about other contributing factors, such as lockdown conditions, which may be clarified with additional research. The study appeared in JAMA Dermatology.
Meanwhile, data from the American Academy of Dermatology and a recent paper from the British Journal of Dermatology suggest a real association exists, at in least some patients.
“It’s going to be true that most patients with toe lesions are PCR [polymerase chain reaction]-negative because it tends to be a late phenomenon when patients are no longer shedding virus,” explained Lindy P. Fox, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, who was not an author of either study. Read more.
Take-home test strips allow drug users to detect fentanyl
Illicit drug users seem to overwhelmingly appreciate being able to use take-home test strips to detect the presence of dangerous fentanyl in opioids and other drugs, a new study finds.
More than 95% said they’d use the inexpensive strips again.
“These tests accurately detect fentanyl in the drug supply, and they can be a valuable addition to other drug prevention strategies,” the study’s lead author and addiction medicine specialist Sukhpreet Klaire, MD, of the British Columbia Center on Substance Use in Vancouver, said in an interview.
Dr. Klaire presented the study findings at the virtual annual meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence. Read more.
New data back use of medical cannabis for epilepsy, pain, anxiety
Two new studies offer positive news about medical cannabis, suggesting that marijuana products improve physical and cognitive symptoms, boost quality of life, and rarely produce signs of problematic use.
In one study, patients with epilepsy who used medical cannabis were nearly half as likely to have needed an emergency department visit within the last 30 days as was a control group. In the other study, just 3 of 54 subjects who used medical cannabis showed signs of possible cannabis use disorder (CUD) over 12 months.
The findings show that “there is improvement in a range of outcome variables, and the adverse effects seem to be minimal, compared to what we might have hypothesized based on the bulk of the literature on the negative effects of cannabis on health outcomes,” cannabis researcher Ziva Cooper, PhD, of the University of California at Los Angeles, said in an interview. Dr. Cooper moderated a session about the studies at the virtual annual meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Migraine is often a deciding factor in pregnancy planning
Migraine can significantly influence a woman’s decision to have children, new research shows.
Results from a multicenter study of more than 600 women showed that, among participants with migraine, those who were younger, had menstrual migraine, or had chronic migraine were more likely to decide to not become pregnant.
“Women who avoided pregnancy due to migraine were most concerned that migraine would make raising a child difficult, that the migraine medications they take would have a negative impact on their child’s development, and that their migraine pattern would worsen during or just after pregnancy,” said study investigator Ryotaro Ishii, MD, PhD, a visiting scientist at Mayo Clinic in Phoenix.
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American Headache Society. Read more.
FDA approves avelumab as maintenance for urothelial carcinoma
The Food and Drug Administration has approved avelumab (Bavencio) as a maintenance treatment for patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (UC) that has not progressed after first-line platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The new maintenance therapy indication for avelumab is based on efficacy demonstrated in the JAVELIN Bladder 100 trial. Results from this trial were presented as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
The new indication adds to avelumab use in other patient populations, including people with locally advanced or metastatic UC who experience disease progression during or following platinum-containing chemotherapy. The FDA also previously approved avelumab for patients who experienced UC progression within 12 months of neoadjuvant or adjuvant treatment with platinum-containing chemotherapy. The FDA first approved marketing of avelumab in 2017. Other uses include treatment of metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma and first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma in combination with axitinib. Read more.
Lifestyle changes may explain skin lesions in pandemic-era patients
Two European prospective case series found no direct association between skin lesions on the hands and feet and SARS-CoV-2 in young people, which raises questions about other contributing factors, such as lockdown conditions, which may be clarified with additional research. The study appeared in JAMA Dermatology.
Meanwhile, data from the American Academy of Dermatology and a recent paper from the British Journal of Dermatology suggest a real association exists, at in least some patients.
“It’s going to be true that most patients with toe lesions are PCR [polymerase chain reaction]-negative because it tends to be a late phenomenon when patients are no longer shedding virus,” explained Lindy P. Fox, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, who was not an author of either study. Read more.
Take-home test strips allow drug users to detect fentanyl
Illicit drug users seem to overwhelmingly appreciate being able to use take-home test strips to detect the presence of dangerous fentanyl in opioids and other drugs, a new study finds.
More than 95% said they’d use the inexpensive strips again.
“These tests accurately detect fentanyl in the drug supply, and they can be a valuable addition to other drug prevention strategies,” the study’s lead author and addiction medicine specialist Sukhpreet Klaire, MD, of the British Columbia Center on Substance Use in Vancouver, said in an interview.
Dr. Klaire presented the study findings at the virtual annual meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence. Read more.
New data back use of medical cannabis for epilepsy, pain, anxiety
Two new studies offer positive news about medical cannabis, suggesting that marijuana products improve physical and cognitive symptoms, boost quality of life, and rarely produce signs of problematic use.
In one study, patients with epilepsy who used medical cannabis were nearly half as likely to have needed an emergency department visit within the last 30 days as was a control group. In the other study, just 3 of 54 subjects who used medical cannabis showed signs of possible cannabis use disorder (CUD) over 12 months.
The findings show that “there is improvement in a range of outcome variables, and the adverse effects seem to be minimal, compared to what we might have hypothesized based on the bulk of the literature on the negative effects of cannabis on health outcomes,” cannabis researcher Ziva Cooper, PhD, of the University of California at Los Angeles, said in an interview. Dr. Cooper moderated a session about the studies at the virtual annual meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Migraine is often a deciding factor in pregnancy planning
Migraine can significantly influence a woman’s decision to have children, new research shows.
Results from a multicenter study of more than 600 women showed that, among participants with migraine, those who were younger, had menstrual migraine, or had chronic migraine were more likely to decide to not become pregnant.
“Women who avoided pregnancy due to migraine were most concerned that migraine would make raising a child difficult, that the migraine medications they take would have a negative impact on their child’s development, and that their migraine pattern would worsen during or just after pregnancy,” said study investigator Ryotaro Ishii, MD, PhD, a visiting scientist at Mayo Clinic in Phoenix.
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American Headache Society. Read more.
FDA approves avelumab as maintenance for urothelial carcinoma
The Food and Drug Administration has approved avelumab (Bavencio) as a maintenance treatment for patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (UC) that has not progressed after first-line platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The new maintenance therapy indication for avelumab is based on efficacy demonstrated in the JAVELIN Bladder 100 trial. Results from this trial were presented as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
The new indication adds to avelumab use in other patient populations, including people with locally advanced or metastatic UC who experience disease progression during or following platinum-containing chemotherapy. The FDA also previously approved avelumab for patients who experienced UC progression within 12 months of neoadjuvant or adjuvant treatment with platinum-containing chemotherapy. The FDA first approved marketing of avelumab in 2017. Other uses include treatment of metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma and first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma in combination with axitinib. Read more.
Lifestyle changes may explain skin lesions in pandemic-era patients
Two European prospective case series found no direct association between skin lesions on the hands and feet and SARS-CoV-2 in young people, which raises questions about other contributing factors, such as lockdown conditions, which may be clarified with additional research. The study appeared in JAMA Dermatology.
Meanwhile, data from the American Academy of Dermatology and a recent paper from the British Journal of Dermatology suggest a real association exists, at in least some patients.
“It’s going to be true that most patients with toe lesions are PCR [polymerase chain reaction]-negative because it tends to be a late phenomenon when patients are no longer shedding virus,” explained Lindy P. Fox, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, who was not an author of either study. Read more.
Take-home test strips allow drug users to detect fentanyl
Illicit drug users seem to overwhelmingly appreciate being able to use take-home test strips to detect the presence of dangerous fentanyl in opioids and other drugs, a new study finds.
More than 95% said they’d use the inexpensive strips again.
“These tests accurately detect fentanyl in the drug supply, and they can be a valuable addition to other drug prevention strategies,” the study’s lead author and addiction medicine specialist Sukhpreet Klaire, MD, of the British Columbia Center on Substance Use in Vancouver, said in an interview.
Dr. Klaire presented the study findings at the virtual annual meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence. Read more.
New data back use of medical cannabis for epilepsy, pain, anxiety
Two new studies offer positive news about medical cannabis, suggesting that marijuana products improve physical and cognitive symptoms, boost quality of life, and rarely produce signs of problematic use.
In one study, patients with epilepsy who used medical cannabis were nearly half as likely to have needed an emergency department visit within the last 30 days as was a control group. In the other study, just 3 of 54 subjects who used medical cannabis showed signs of possible cannabis use disorder (CUD) over 12 months.
The findings show that “there is improvement in a range of outcome variables, and the adverse effects seem to be minimal, compared to what we might have hypothesized based on the bulk of the literature on the negative effects of cannabis on health outcomes,” cannabis researcher Ziva Cooper, PhD, of the University of California at Los Angeles, said in an interview. Dr. Cooper moderated a session about the studies at the virtual annual meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Lawmakers question mental health disclosure rules
State medical licensing queries criticized
Several federal lawmakers on June 30 questioned state policies that require disclosure of mental health treatment as part of medical licensing applications and renewals, citing concerns about creating barriers to psychiatric care for clinicians.
Mental health–related questions on state medical boards’ licensing applications are especially worrisome with many clinicians, including ED staff, immersed in the physical and emotional challenges involved in treating waves of people with COVID-19, lawmakers said during a hearing of the House Energy and Commerce Committee’s health panel.
“We must consider the mental health of the providers on the front lines of the pandemic,” said Rep. Morgan Griffith, a Virginia Republican.
The issue of state medical boards’ disclosure rules was not on the official agenda for the House Energy and Commerce health subcommittee’s hearing. And there was no discussion of any specific state medical board’s regulations. The Energy and Commerce health subcommittee is working on more than 20 bills related to mental health, including measures intended to aid first responders, such as firemen and emergency medical personnel, and students.
This hearing marked an early stage in the process for a planned package of mental health legislation, said Rep. Michael C. Burgess, MD, of Texas, who is the top Republican on the Energy and Commerce health subcommittee. There may be opportunities as this legislation advances to add provisions intended to aid physicians, said Dr. Burgess, who practiced for many years as an ob.gyn. before being elected to Congress.
“We knew that suicide was a problem among our colleagues prior to the onset of this coronavirus epidemic and I know it is more pronounced now,” he said.
Dr. Burgess then solicited specific recommendations from the hearing’s witnesses on steps needed to help clinicians’ mental health.
The first suggestion offered in reply by Jeffrey L. Geller, MD, MPH, appearing in his role as president of the American Psychiatric Association, was that Congress should look for ways to encourage states to alter their licensing procedures.
The hearing comes on the heels of the APA, the American Academy of Family Physicians, and more than 40 other groups having jointly signed a statement calling for changes to disclosure rules about mental health.
“Licensing and credentialing applications by covered entities should only employ narrowly focused questions that address current functional impairment,” the statement said. “Additionally, we strongly support The Joint Commission (TJC) statement on Removing Barriers to Mental Health Care for Clinicians and Health Care Staff. TJC ‘supports the removal of any barriers that inhibit clinicians and health care staff from accessing mental health care services.’ ”
Physicians and other clinicians must be able to safely secure treatment for mental or other health issues, just as any other individual,” the groups wrote. “A provider’s history of mental illness or substance use disorder should not be used as any indication of their current or future ability to practice competently and without impairment.”
Also among the signers to this statement was the Federation of State Medical Boards, which has been leading an effort for years to change licensing.
In 2018, the FSMB recommended state medical boards reconsider whether it is necessary to include probing questions about a physician applicant’s mental health, addiction, or substance use on applications for medical licensure or their renewal. While the intent of these questions may be to protect patients, these queries can discourage physicians from getting needed help, the FSMB said.
Several states have since revised or considered revising their license applications and renewals. In May 2020, The Joint Commission urged broader adoption of recommendations from the FSMB and the American Medical Association to limit queries about clinicians’ mental health to “conditions that currently impair the clinicians’ ability to perform their job.”
“We strongly encourage organizations to not ask about past history of mental health conditions or treatment,” said The Joint Commission, which accredits hospitals, in a statement. “It is critical that we ensure health care workers can feel free to access mental health resources.”
Rep. Susan Brooks, an Indiana Republican who is an attorney, suggested there may need to be a broader look at how state officials pose questions about past mental health treatment to people in many professions, including her own.
“It does build on the stigma on accessing services” to know a state or licensing authority may question a professional about receiving treatment for mental health, she said.
Also at the hearing, Rep. Nanette Diaz Barragán, a California Democrat, spoke of her own reaction to seeing a question about mental health treatment while applying for a White House internship. During her college years, Rep. Barragán had to cope with her father’s terminal illness.
“I remember thinking to myself: ‘Jeez, if I end up seeing a mental health expert maybe one day I couldn’t work in government,’ ” she said.
State medical licensing queries criticized
State medical licensing queries criticized
Several federal lawmakers on June 30 questioned state policies that require disclosure of mental health treatment as part of medical licensing applications and renewals, citing concerns about creating barriers to psychiatric care for clinicians.
Mental health–related questions on state medical boards’ licensing applications are especially worrisome with many clinicians, including ED staff, immersed in the physical and emotional challenges involved in treating waves of people with COVID-19, lawmakers said during a hearing of the House Energy and Commerce Committee’s health panel.
“We must consider the mental health of the providers on the front lines of the pandemic,” said Rep. Morgan Griffith, a Virginia Republican.
The issue of state medical boards’ disclosure rules was not on the official agenda for the House Energy and Commerce health subcommittee’s hearing. And there was no discussion of any specific state medical board’s regulations. The Energy and Commerce health subcommittee is working on more than 20 bills related to mental health, including measures intended to aid first responders, such as firemen and emergency medical personnel, and students.
This hearing marked an early stage in the process for a planned package of mental health legislation, said Rep. Michael C. Burgess, MD, of Texas, who is the top Republican on the Energy and Commerce health subcommittee. There may be opportunities as this legislation advances to add provisions intended to aid physicians, said Dr. Burgess, who practiced for many years as an ob.gyn. before being elected to Congress.
“We knew that suicide was a problem among our colleagues prior to the onset of this coronavirus epidemic and I know it is more pronounced now,” he said.
Dr. Burgess then solicited specific recommendations from the hearing’s witnesses on steps needed to help clinicians’ mental health.
The first suggestion offered in reply by Jeffrey L. Geller, MD, MPH, appearing in his role as president of the American Psychiatric Association, was that Congress should look for ways to encourage states to alter their licensing procedures.
The hearing comes on the heels of the APA, the American Academy of Family Physicians, and more than 40 other groups having jointly signed a statement calling for changes to disclosure rules about mental health.
“Licensing and credentialing applications by covered entities should only employ narrowly focused questions that address current functional impairment,” the statement said. “Additionally, we strongly support The Joint Commission (TJC) statement on Removing Barriers to Mental Health Care for Clinicians and Health Care Staff. TJC ‘supports the removal of any barriers that inhibit clinicians and health care staff from accessing mental health care services.’ ”
Physicians and other clinicians must be able to safely secure treatment for mental or other health issues, just as any other individual,” the groups wrote. “A provider’s history of mental illness or substance use disorder should not be used as any indication of their current or future ability to practice competently and without impairment.”
Also among the signers to this statement was the Federation of State Medical Boards, which has been leading an effort for years to change licensing.
In 2018, the FSMB recommended state medical boards reconsider whether it is necessary to include probing questions about a physician applicant’s mental health, addiction, or substance use on applications for medical licensure or their renewal. While the intent of these questions may be to protect patients, these queries can discourage physicians from getting needed help, the FSMB said.
Several states have since revised or considered revising their license applications and renewals. In May 2020, The Joint Commission urged broader adoption of recommendations from the FSMB and the American Medical Association to limit queries about clinicians’ mental health to “conditions that currently impair the clinicians’ ability to perform their job.”
“We strongly encourage organizations to not ask about past history of mental health conditions or treatment,” said The Joint Commission, which accredits hospitals, in a statement. “It is critical that we ensure health care workers can feel free to access mental health resources.”
Rep. Susan Brooks, an Indiana Republican who is an attorney, suggested there may need to be a broader look at how state officials pose questions about past mental health treatment to people in many professions, including her own.
“It does build on the stigma on accessing services” to know a state or licensing authority may question a professional about receiving treatment for mental health, she said.
Also at the hearing, Rep. Nanette Diaz Barragán, a California Democrat, spoke of her own reaction to seeing a question about mental health treatment while applying for a White House internship. During her college years, Rep. Barragán had to cope with her father’s terminal illness.
“I remember thinking to myself: ‘Jeez, if I end up seeing a mental health expert maybe one day I couldn’t work in government,’ ” she said.
Several federal lawmakers on June 30 questioned state policies that require disclosure of mental health treatment as part of medical licensing applications and renewals, citing concerns about creating barriers to psychiatric care for clinicians.
Mental health–related questions on state medical boards’ licensing applications are especially worrisome with many clinicians, including ED staff, immersed in the physical and emotional challenges involved in treating waves of people with COVID-19, lawmakers said during a hearing of the House Energy and Commerce Committee’s health panel.
“We must consider the mental health of the providers on the front lines of the pandemic,” said Rep. Morgan Griffith, a Virginia Republican.
The issue of state medical boards’ disclosure rules was not on the official agenda for the House Energy and Commerce health subcommittee’s hearing. And there was no discussion of any specific state medical board’s regulations. The Energy and Commerce health subcommittee is working on more than 20 bills related to mental health, including measures intended to aid first responders, such as firemen and emergency medical personnel, and students.
This hearing marked an early stage in the process for a planned package of mental health legislation, said Rep. Michael C. Burgess, MD, of Texas, who is the top Republican on the Energy and Commerce health subcommittee. There may be opportunities as this legislation advances to add provisions intended to aid physicians, said Dr. Burgess, who practiced for many years as an ob.gyn. before being elected to Congress.
“We knew that suicide was a problem among our colleagues prior to the onset of this coronavirus epidemic and I know it is more pronounced now,” he said.
Dr. Burgess then solicited specific recommendations from the hearing’s witnesses on steps needed to help clinicians’ mental health.
The first suggestion offered in reply by Jeffrey L. Geller, MD, MPH, appearing in his role as president of the American Psychiatric Association, was that Congress should look for ways to encourage states to alter their licensing procedures.
The hearing comes on the heels of the APA, the American Academy of Family Physicians, and more than 40 other groups having jointly signed a statement calling for changes to disclosure rules about mental health.
“Licensing and credentialing applications by covered entities should only employ narrowly focused questions that address current functional impairment,” the statement said. “Additionally, we strongly support The Joint Commission (TJC) statement on Removing Barriers to Mental Health Care for Clinicians and Health Care Staff. TJC ‘supports the removal of any barriers that inhibit clinicians and health care staff from accessing mental health care services.’ ”
Physicians and other clinicians must be able to safely secure treatment for mental or other health issues, just as any other individual,” the groups wrote. “A provider’s history of mental illness or substance use disorder should not be used as any indication of their current or future ability to practice competently and without impairment.”
Also among the signers to this statement was the Federation of State Medical Boards, which has been leading an effort for years to change licensing.
In 2018, the FSMB recommended state medical boards reconsider whether it is necessary to include probing questions about a physician applicant’s mental health, addiction, or substance use on applications for medical licensure or their renewal. While the intent of these questions may be to protect patients, these queries can discourage physicians from getting needed help, the FSMB said.
Several states have since revised or considered revising their license applications and renewals. In May 2020, The Joint Commission urged broader adoption of recommendations from the FSMB and the American Medical Association to limit queries about clinicians’ mental health to “conditions that currently impair the clinicians’ ability to perform their job.”
“We strongly encourage organizations to not ask about past history of mental health conditions or treatment,” said The Joint Commission, which accredits hospitals, in a statement. “It is critical that we ensure health care workers can feel free to access mental health resources.”
Rep. Susan Brooks, an Indiana Republican who is an attorney, suggested there may need to be a broader look at how state officials pose questions about past mental health treatment to people in many professions, including her own.
“It does build on the stigma on accessing services” to know a state or licensing authority may question a professional about receiving treatment for mental health, she said.
Also at the hearing, Rep. Nanette Diaz Barragán, a California Democrat, spoke of her own reaction to seeing a question about mental health treatment while applying for a White House internship. During her college years, Rep. Barragán had to cope with her father’s terminal illness.
“I remember thinking to myself: ‘Jeez, if I end up seeing a mental health expert maybe one day I couldn’t work in government,’ ” she said.
FROM A HOUSE ENERGY AND COMMERCE’S HEALTH SUBCOMMITTEE HEARING
Lifestyle changes may explain skin lesions in pandemic-era patients
such as lockdown conditions, which may be clarified with additional research.
Lindy P. Fox, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, who was not an author of either study, urged caution in interpreting these results. Data from the American Academy of Dermatology and a recent paper from the British Journal of Dermatology suggest a real association exists, at in least some patients. “It’s going to be true that most patients with toe lesions are PCR [polymerase chain reaction]-negative because it tends to be a late phenomenon when patients are no longer shedding virus,” Dr. Fox said in an interview.
Reports about chickenpox-like vesicles, urticaria, and other skin lesions in SARS-CoV-2 patients have circulated in the clinical literature and the media. Acute acro-ischemia has been cited as a potential sign of infection in adolescents and children.
One of the European studies, which was published in JAMA Dermatology, explored this association in 20 patients aged 1-18 years (mean age, 12.3 years), who presented with new-onset acral inflammatory lesions in their hands and feet at La Fe University Hospital, in Valencia, during the country’s peak quarantine period in April. Investigators conducted blood tests and reverse transcriptase–PCR (RT-PCR) for SARS-CoV-2, and six patients had skin biopsies.
Juncal Roca-Ginés, MD, of the department of dermatology, at the Hospital Universitario y Politécnico in La Fe, and coauthors, identified acral erythema in 6 (30%) of the cases, dactylitis in 4 (20%), purpuric maculopapules in 7 (35%), and a mixed pattern in 3 (15%). Serologic and viral testing yielded no positive results for SARS-CoV-2 or other viruses, and none of the patients exhibited COVID-19 symptoms such as fever, dry cough, sore throat, myalgia, or taste or smell disorders. In other findings, 45% of the patients had a history of vascular reactive disease of the hands, and 75% reported walking barefoot in their homes while staying at home. Only two patients reported taking medications.
In the six patients who had a biopsy, the findings were characteristic of chillblains, “confirming the clinical impression,” the authors wrote. Concluding that they could not show a relationship between acute acral skin changes and COVID-19, they noted that “other studies with improved microbiologic tests or molecular techniques aimed at demonstrating the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in the skin may help to clarify this problem.”
The other case series, which was also published in JAMA Dermatology and included 31 adults at a hospital in Brussels, who had recently developed chillblains, also looked for a connection between SARS-CoV-2 and chilblains, in April. Most of the participants were in their teens or 20s. Lesions had appeared on hands, feet, or on both extremities within 1-30 days of consultation, presenting as erythematous or purplish erythematous macules, occasionally with central vesicular or bullous lesions or necrotic areas. Patients reported pain, burning, and itching.
Skin biopsies were obtained in 22 patients and confirmed the diagnosis of chilblains; of the 15 with immunofluorescence analyses, 7 patients were found to have vasculitis of small-diameter vessels.
Of the 31 patients, 20 (64%) reported mild symptoms consistent with SARS-CoV-2, yet none of the RT-PCR or serologic test results showed signs of the virus in all 31 patients. “Because some patients had experienced chilblains for more than 15 days [under 30 days or less] at the time of inclusion, we can reasonably exclude the possibility that serologic testing was done too soon,” observed the authors. They also didn’t find eosinopenia, lymphopenia, and hyperferritinemia, which have been associated with COVID-19, they added.
Changes in lifestyle conditions during the pandemic may explain the appearance of these lesions, according to the authors of both studies, who mentioned that walking around in socks or bare feet and reduced physical activity could have indirectly led to the development of skin lesions.
It’s also possible that young people have less severe disease and a delayed reaction to the virus, Ignacio Torres-Navarro, MD, a dermatologist with La Fe University and the Spanish study’s corresponding author, said in an interview. Their feet may lack maturity in neurovascular regulation and/or the eccrine glands, which can happen in other diseases such as neutrophilic idiopathic eccrine hidradenitis. “In this context, perhaps there was an observational bias of the parents to the children when this manifestation was reported in the media. However, nothing has been demonstrated,” he said.
In an accompanying editor’s note, Claudia Hernandez, MD, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, and Anna L. Bruckner, MD, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of Colorado, Aurora, wrote that “it is still unclear whether a viral cytopathic process vs a viral reaction pattern or other mechanism is responsible for ‘COVID toes.’ ” Lack of confirmatory testing and reliance on indirect evidence of infection complicates this further, they noted, adding that “dermatologists must be aware of the protean cutaneous findings that are possibly associated with COVID-19, even if our understanding of their origins remains incomplete.”
In an interview, Dr. Fox, a member of the AAD’s’s COVID-19 Registry task force, offered other possible reasons for the negative antibody tests in the studies. The assay might not have been testing the correct antigen, or the timing of the test might not have been optimal. “More studies will help this become less controversial,” she said.
The authors of the two case series acknowledged potential limitations of their studies. Neither was large in scope: Both took place over a week’s time and included small cohorts. The Belgian study had no control group or long-term follow-up. Little is still known about the clinical manifestations and detection methods for SARS-CoV-2, noted the authors of the Spanish study.
The Spanish study received funding La Fe University Hospital’s department of dermatology, and the authors had no disclosures. The Belgian study received support from the Fondation Saint-Luc, which provided academic funding for its lead author, Marie Baeck, MD, PhD. Another author of this study received personal fees from the Fondation Saint-Luc and personal fees and nonfinancial support from Bioderma. The authors of the editor’s note had no disclosures.
SOURCES: Roca-Ginés J et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jun 25. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2340; Herman A et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jun 25. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2368.
such as lockdown conditions, which may be clarified with additional research.
Lindy P. Fox, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, who was not an author of either study, urged caution in interpreting these results. Data from the American Academy of Dermatology and a recent paper from the British Journal of Dermatology suggest a real association exists, at in least some patients. “It’s going to be true that most patients with toe lesions are PCR [polymerase chain reaction]-negative because it tends to be a late phenomenon when patients are no longer shedding virus,” Dr. Fox said in an interview.
Reports about chickenpox-like vesicles, urticaria, and other skin lesions in SARS-CoV-2 patients have circulated in the clinical literature and the media. Acute acro-ischemia has been cited as a potential sign of infection in adolescents and children.
One of the European studies, which was published in JAMA Dermatology, explored this association in 20 patients aged 1-18 years (mean age, 12.3 years), who presented with new-onset acral inflammatory lesions in their hands and feet at La Fe University Hospital, in Valencia, during the country’s peak quarantine period in April. Investigators conducted blood tests and reverse transcriptase–PCR (RT-PCR) for SARS-CoV-2, and six patients had skin biopsies.
Juncal Roca-Ginés, MD, of the department of dermatology, at the Hospital Universitario y Politécnico in La Fe, and coauthors, identified acral erythema in 6 (30%) of the cases, dactylitis in 4 (20%), purpuric maculopapules in 7 (35%), and a mixed pattern in 3 (15%). Serologic and viral testing yielded no positive results for SARS-CoV-2 or other viruses, and none of the patients exhibited COVID-19 symptoms such as fever, dry cough, sore throat, myalgia, or taste or smell disorders. In other findings, 45% of the patients had a history of vascular reactive disease of the hands, and 75% reported walking barefoot in their homes while staying at home. Only two patients reported taking medications.
In the six patients who had a biopsy, the findings were characteristic of chillblains, “confirming the clinical impression,” the authors wrote. Concluding that they could not show a relationship between acute acral skin changes and COVID-19, they noted that “other studies with improved microbiologic tests or molecular techniques aimed at demonstrating the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in the skin may help to clarify this problem.”
The other case series, which was also published in JAMA Dermatology and included 31 adults at a hospital in Brussels, who had recently developed chillblains, also looked for a connection between SARS-CoV-2 and chilblains, in April. Most of the participants were in their teens or 20s. Lesions had appeared on hands, feet, or on both extremities within 1-30 days of consultation, presenting as erythematous or purplish erythematous macules, occasionally with central vesicular or bullous lesions or necrotic areas. Patients reported pain, burning, and itching.
Skin biopsies were obtained in 22 patients and confirmed the diagnosis of chilblains; of the 15 with immunofluorescence analyses, 7 patients were found to have vasculitis of small-diameter vessels.
Of the 31 patients, 20 (64%) reported mild symptoms consistent with SARS-CoV-2, yet none of the RT-PCR or serologic test results showed signs of the virus in all 31 patients. “Because some patients had experienced chilblains for more than 15 days [under 30 days or less] at the time of inclusion, we can reasonably exclude the possibility that serologic testing was done too soon,” observed the authors. They also didn’t find eosinopenia, lymphopenia, and hyperferritinemia, which have been associated with COVID-19, they added.
Changes in lifestyle conditions during the pandemic may explain the appearance of these lesions, according to the authors of both studies, who mentioned that walking around in socks or bare feet and reduced physical activity could have indirectly led to the development of skin lesions.
It’s also possible that young people have less severe disease and a delayed reaction to the virus, Ignacio Torres-Navarro, MD, a dermatologist with La Fe University and the Spanish study’s corresponding author, said in an interview. Their feet may lack maturity in neurovascular regulation and/or the eccrine glands, which can happen in other diseases such as neutrophilic idiopathic eccrine hidradenitis. “In this context, perhaps there was an observational bias of the parents to the children when this manifestation was reported in the media. However, nothing has been demonstrated,” he said.
In an accompanying editor’s note, Claudia Hernandez, MD, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, and Anna L. Bruckner, MD, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of Colorado, Aurora, wrote that “it is still unclear whether a viral cytopathic process vs a viral reaction pattern or other mechanism is responsible for ‘COVID toes.’ ” Lack of confirmatory testing and reliance on indirect evidence of infection complicates this further, they noted, adding that “dermatologists must be aware of the protean cutaneous findings that are possibly associated with COVID-19, even if our understanding of their origins remains incomplete.”
In an interview, Dr. Fox, a member of the AAD’s’s COVID-19 Registry task force, offered other possible reasons for the negative antibody tests in the studies. The assay might not have been testing the correct antigen, or the timing of the test might not have been optimal. “More studies will help this become less controversial,” she said.
The authors of the two case series acknowledged potential limitations of their studies. Neither was large in scope: Both took place over a week’s time and included small cohorts. The Belgian study had no control group or long-term follow-up. Little is still known about the clinical manifestations and detection methods for SARS-CoV-2, noted the authors of the Spanish study.
The Spanish study received funding La Fe University Hospital’s department of dermatology, and the authors had no disclosures. The Belgian study received support from the Fondation Saint-Luc, which provided academic funding for its lead author, Marie Baeck, MD, PhD. Another author of this study received personal fees from the Fondation Saint-Luc and personal fees and nonfinancial support from Bioderma. The authors of the editor’s note had no disclosures.
SOURCES: Roca-Ginés J et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jun 25. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2340; Herman A et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jun 25. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2368.
such as lockdown conditions, which may be clarified with additional research.
Lindy P. Fox, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, who was not an author of either study, urged caution in interpreting these results. Data from the American Academy of Dermatology and a recent paper from the British Journal of Dermatology suggest a real association exists, at in least some patients. “It’s going to be true that most patients with toe lesions are PCR [polymerase chain reaction]-negative because it tends to be a late phenomenon when patients are no longer shedding virus,” Dr. Fox said in an interview.
Reports about chickenpox-like vesicles, urticaria, and other skin lesions in SARS-CoV-2 patients have circulated in the clinical literature and the media. Acute acro-ischemia has been cited as a potential sign of infection in adolescents and children.
One of the European studies, which was published in JAMA Dermatology, explored this association in 20 patients aged 1-18 years (mean age, 12.3 years), who presented with new-onset acral inflammatory lesions in their hands and feet at La Fe University Hospital, in Valencia, during the country’s peak quarantine period in April. Investigators conducted blood tests and reverse transcriptase–PCR (RT-PCR) for SARS-CoV-2, and six patients had skin biopsies.
Juncal Roca-Ginés, MD, of the department of dermatology, at the Hospital Universitario y Politécnico in La Fe, and coauthors, identified acral erythema in 6 (30%) of the cases, dactylitis in 4 (20%), purpuric maculopapules in 7 (35%), and a mixed pattern in 3 (15%). Serologic and viral testing yielded no positive results for SARS-CoV-2 or other viruses, and none of the patients exhibited COVID-19 symptoms such as fever, dry cough, sore throat, myalgia, or taste or smell disorders. In other findings, 45% of the patients had a history of vascular reactive disease of the hands, and 75% reported walking barefoot in their homes while staying at home. Only two patients reported taking medications.
In the six patients who had a biopsy, the findings were characteristic of chillblains, “confirming the clinical impression,” the authors wrote. Concluding that they could not show a relationship between acute acral skin changes and COVID-19, they noted that “other studies with improved microbiologic tests or molecular techniques aimed at demonstrating the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in the skin may help to clarify this problem.”
The other case series, which was also published in JAMA Dermatology and included 31 adults at a hospital in Brussels, who had recently developed chillblains, also looked for a connection between SARS-CoV-2 and chilblains, in April. Most of the participants were in their teens or 20s. Lesions had appeared on hands, feet, or on both extremities within 1-30 days of consultation, presenting as erythematous or purplish erythematous macules, occasionally with central vesicular or bullous lesions or necrotic areas. Patients reported pain, burning, and itching.
Skin biopsies were obtained in 22 patients and confirmed the diagnosis of chilblains; of the 15 with immunofluorescence analyses, 7 patients were found to have vasculitis of small-diameter vessels.
Of the 31 patients, 20 (64%) reported mild symptoms consistent with SARS-CoV-2, yet none of the RT-PCR or serologic test results showed signs of the virus in all 31 patients. “Because some patients had experienced chilblains for more than 15 days [under 30 days or less] at the time of inclusion, we can reasonably exclude the possibility that serologic testing was done too soon,” observed the authors. They also didn’t find eosinopenia, lymphopenia, and hyperferritinemia, which have been associated with COVID-19, they added.
Changes in lifestyle conditions during the pandemic may explain the appearance of these lesions, according to the authors of both studies, who mentioned that walking around in socks or bare feet and reduced physical activity could have indirectly led to the development of skin lesions.
It’s also possible that young people have less severe disease and a delayed reaction to the virus, Ignacio Torres-Navarro, MD, a dermatologist with La Fe University and the Spanish study’s corresponding author, said in an interview. Their feet may lack maturity in neurovascular regulation and/or the eccrine glands, which can happen in other diseases such as neutrophilic idiopathic eccrine hidradenitis. “In this context, perhaps there was an observational bias of the parents to the children when this manifestation was reported in the media. However, nothing has been demonstrated,” he said.
In an accompanying editor’s note, Claudia Hernandez, MD, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, and Anna L. Bruckner, MD, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of Colorado, Aurora, wrote that “it is still unclear whether a viral cytopathic process vs a viral reaction pattern or other mechanism is responsible for ‘COVID toes.’ ” Lack of confirmatory testing and reliance on indirect evidence of infection complicates this further, they noted, adding that “dermatologists must be aware of the protean cutaneous findings that are possibly associated with COVID-19, even if our understanding of their origins remains incomplete.”
In an interview, Dr. Fox, a member of the AAD’s’s COVID-19 Registry task force, offered other possible reasons for the negative antibody tests in the studies. The assay might not have been testing the correct antigen, or the timing of the test might not have been optimal. “More studies will help this become less controversial,” she said.
The authors of the two case series acknowledged potential limitations of their studies. Neither was large in scope: Both took place over a week’s time and included small cohorts. The Belgian study had no control group or long-term follow-up. Little is still known about the clinical manifestations and detection methods for SARS-CoV-2, noted the authors of the Spanish study.
The Spanish study received funding La Fe University Hospital’s department of dermatology, and the authors had no disclosures. The Belgian study received support from the Fondation Saint-Luc, which provided academic funding for its lead author, Marie Baeck, MD, PhD. Another author of this study received personal fees from the Fondation Saint-Luc and personal fees and nonfinancial support from Bioderma. The authors of the editor’s note had no disclosures.
SOURCES: Roca-Ginés J et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jun 25. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2340; Herman A et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jun 25. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2368.
Daily Recap: Hospitalized COVID patients need MRIs; Americans vote for face masks
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Three stages to COVID-19 brain damage, new review suggests
A new review outlined a three-stage classification of the impact of COVID-19 on the central nervous system and recommended all hospitalized patients with the virus undergo MRI to flag potential neurologic damage and inform postdischarge monitoring.
In stage 1, viral damage is limited to epithelial cells of the nose and mouth, and in stage 2 blood clots that form in the lungs may travel to the brain, leading to stroke. In stage 3, the virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain.
“Our major take-home points are that patients with COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath, headache, or dizziness, may have neurological symptoms that, at the time of hospitalization, might not be noticed or prioritized, or whose neurological symptoms may become apparent only after they leave the hospital,” said lead author Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD. The review was published online in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. Read more.
Topline results for novel intranasal med to treat opioid overdose
Topline results show positive results for the experimental intranasal nalmefene product OX125 for opioid overdose reversal, Orexo, the drug’s manufacturer, announced.
A crossover, comparative bioavailability study was conducted in healthy volunteers to assess nalmefene absorption of three development formulations of OX125. Preliminary results showed “extensive and rapid absorption” across all three formulations versus an intramuscular injection of nalmefene, Orexo reported.
“As the U.S. heroin crisis has developed to a fentanyl crisis, the medical need for novel and more powerful opioid rescue medications is vast,” Nikolaj Sørensen, president and CEO of Orexo, said in a press release. Read more.
Republican or Democrat, Americans vote for face masks
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.
Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that such testing was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Read more.
Weight loss failures drive bariatric surgery regrets
Not all weight loss surgery patients “live happily ever after,” according to Daniel B. Jones, MD.
A 2014 study of 22 women who underwent weight loss surgery reported lower energy, worse quality of life, and persistent eating disorders.
Of gastric band patients, “almost 20% did not think they made the right decision,” he said. As for RYGP patients, 13% of patients at 1 year and 4 years reported that weight loss surgery caused “some” or “a lot” of negative effects. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Three stages to COVID-19 brain damage, new review suggests
A new review outlined a three-stage classification of the impact of COVID-19 on the central nervous system and recommended all hospitalized patients with the virus undergo MRI to flag potential neurologic damage and inform postdischarge monitoring.
In stage 1, viral damage is limited to epithelial cells of the nose and mouth, and in stage 2 blood clots that form in the lungs may travel to the brain, leading to stroke. In stage 3, the virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain.
“Our major take-home points are that patients with COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath, headache, or dizziness, may have neurological symptoms that, at the time of hospitalization, might not be noticed or prioritized, or whose neurological symptoms may become apparent only after they leave the hospital,” said lead author Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD. The review was published online in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. Read more.
Topline results for novel intranasal med to treat opioid overdose
Topline results show positive results for the experimental intranasal nalmefene product OX125 for opioid overdose reversal, Orexo, the drug’s manufacturer, announced.
A crossover, comparative bioavailability study was conducted in healthy volunteers to assess nalmefene absorption of three development formulations of OX125. Preliminary results showed “extensive and rapid absorption” across all three formulations versus an intramuscular injection of nalmefene, Orexo reported.
“As the U.S. heroin crisis has developed to a fentanyl crisis, the medical need for novel and more powerful opioid rescue medications is vast,” Nikolaj Sørensen, president and CEO of Orexo, said in a press release. Read more.
Republican or Democrat, Americans vote for face masks
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.
Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that such testing was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Read more.
Weight loss failures drive bariatric surgery regrets
Not all weight loss surgery patients “live happily ever after,” according to Daniel B. Jones, MD.
A 2014 study of 22 women who underwent weight loss surgery reported lower energy, worse quality of life, and persistent eating disorders.
Of gastric band patients, “almost 20% did not think they made the right decision,” he said. As for RYGP patients, 13% of patients at 1 year and 4 years reported that weight loss surgery caused “some” or “a lot” of negative effects. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Three stages to COVID-19 brain damage, new review suggests
A new review outlined a three-stage classification of the impact of COVID-19 on the central nervous system and recommended all hospitalized patients with the virus undergo MRI to flag potential neurologic damage and inform postdischarge monitoring.
In stage 1, viral damage is limited to epithelial cells of the nose and mouth, and in stage 2 blood clots that form in the lungs may travel to the brain, leading to stroke. In stage 3, the virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain.
“Our major take-home points are that patients with COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath, headache, or dizziness, may have neurological symptoms that, at the time of hospitalization, might not be noticed or prioritized, or whose neurological symptoms may become apparent only after they leave the hospital,” said lead author Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD. The review was published online in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. Read more.
Topline results for novel intranasal med to treat opioid overdose
Topline results show positive results for the experimental intranasal nalmefene product OX125 for opioid overdose reversal, Orexo, the drug’s manufacturer, announced.
A crossover, comparative bioavailability study was conducted in healthy volunteers to assess nalmefene absorption of three development formulations of OX125. Preliminary results showed “extensive and rapid absorption” across all three formulations versus an intramuscular injection of nalmefene, Orexo reported.
“As the U.S. heroin crisis has developed to a fentanyl crisis, the medical need for novel and more powerful opioid rescue medications is vast,” Nikolaj Sørensen, president and CEO of Orexo, said in a press release. Read more.
Republican or Democrat, Americans vote for face masks
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.
Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that such testing was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Read more.
Weight loss failures drive bariatric surgery regrets
Not all weight loss surgery patients “live happily ever after,” according to Daniel B. Jones, MD.
A 2014 study of 22 women who underwent weight loss surgery reported lower energy, worse quality of life, and persistent eating disorders.
Of gastric band patients, “almost 20% did not think they made the right decision,” he said. As for RYGP patients, 13% of patients at 1 year and 4 years reported that weight loss surgery caused “some” or “a lot” of negative effects. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Republican or Democrat, Americans vote for face masks
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.
Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
In that survey, conducted from May 13 to June 2, 2020, and involving 2,271 respondents, regular COVID-19 testing for everyone was supported by 81% of the sample as way to ensure a safe work environment until a vaccine is available, the researchers said in the report.
Support on both issues was consistently high across both racial/ethnic and political lines. Mandatory mask use gained 91% support among black respondents, 90% in Hispanics, and 82% in whites. There was greater distance between the political parties, but 70% of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents support mask use, compared with 95% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents, they said.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that it was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Hispanics offered the most support by race/ethnicity, with 90% saying that testing was very/somewhat important, compared with 86% of black respondents and 78% of white respondents, Dr. Collins and associates said.
Two-thirds of Republicans said that it was very/somewhat important for the government to trace the contacts of any person who tested positive for COVID-19, a sentiment shared by 91% of Democrats. That type of tracing was supported by 88% of blacks, 85% of Hispanics, and 79% of whites, based on the polling results.
The survey, conducted for the Commonwealth Fund by the survey and market research firm SSRS, had a margin of error of ± 2.4 percentage points.
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.

Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
In that survey, conducted from May 13 to June 2, 2020, and involving 2,271 respondents, regular COVID-19 testing for everyone was supported by 81% of the sample as way to ensure a safe work environment until a vaccine is available, the researchers said in the report.
Support on both issues was consistently high across both racial/ethnic and political lines. Mandatory mask use gained 91% support among black respondents, 90% in Hispanics, and 82% in whites. There was greater distance between the political parties, but 70% of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents support mask use, compared with 95% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents, they said.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that it was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Hispanics offered the most support by race/ethnicity, with 90% saying that testing was very/somewhat important, compared with 86% of black respondents and 78% of white respondents, Dr. Collins and associates said.
Two-thirds of Republicans said that it was very/somewhat important for the government to trace the contacts of any person who tested positive for COVID-19, a sentiment shared by 91% of Democrats. That type of tracing was supported by 88% of blacks, 85% of Hispanics, and 79% of whites, based on the polling results.
The survey, conducted for the Commonwealth Fund by the survey and market research firm SSRS, had a margin of error of ± 2.4 percentage points.
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.

Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
In that survey, conducted from May 13 to June 2, 2020, and involving 2,271 respondents, regular COVID-19 testing for everyone was supported by 81% of the sample as way to ensure a safe work environment until a vaccine is available, the researchers said in the report.
Support on both issues was consistently high across both racial/ethnic and political lines. Mandatory mask use gained 91% support among black respondents, 90% in Hispanics, and 82% in whites. There was greater distance between the political parties, but 70% of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents support mask use, compared with 95% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents, they said.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that it was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Hispanics offered the most support by race/ethnicity, with 90% saying that testing was very/somewhat important, compared with 86% of black respondents and 78% of white respondents, Dr. Collins and associates said.
Two-thirds of Republicans said that it was very/somewhat important for the government to trace the contacts of any person who tested positive for COVID-19, a sentiment shared by 91% of Democrats. That type of tracing was supported by 88% of blacks, 85% of Hispanics, and 79% of whites, based on the polling results.
The survey, conducted for the Commonwealth Fund by the survey and market research firm SSRS, had a margin of error of ± 2.4 percentage points.






