User login
ID Practitioner is an independent news source that provides infectious disease specialists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on the infectious disease specialist’s practice. Specialty focus topics include antimicrobial resistance, emerging infections, global ID, hepatitis, HIV, hospital-acquired infections, immunizations and vaccines, influenza, mycoses, pediatric infections, and STIs. Infectious Diseases News is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
sofosbuvir
ritonavir with dasabuvir
discount
support path
program
ritonavir
greedy
ledipasvir
assistance
viekira pak
vpak
advocacy
needy
protest
abbvie
paritaprevir
ombitasvir
direct-acting antivirals
dasabuvir
gilead
fake-ovir
support
v pak
oasis
harvoni
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-idp')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-medstat-latest-articles-articles-section')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-idp')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-idp')]
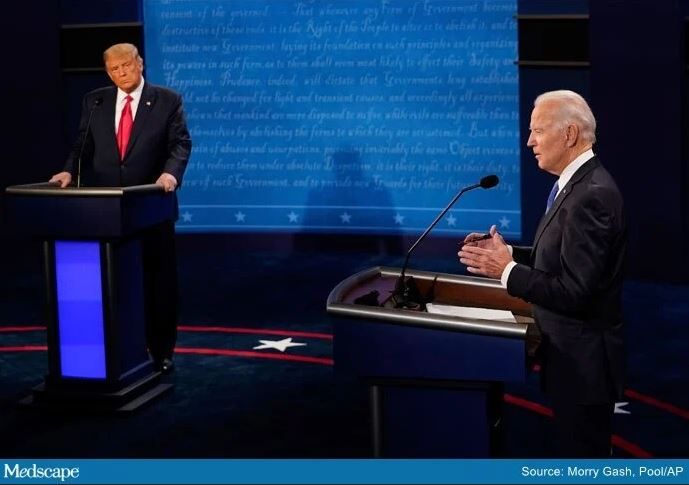
Trump and Biden face off over COVID-19, ACA in final debate
The COVID-19 pandemic figured prominently in the final debate between President Donald Trump and former Vice President Joe Biden when they met on stage for a 90-minute debate in Nashville, Tennessee, Thursday evening.
The adequacy of the COVID-19 response to date, the likely timeline for vaccine availability, and how to reopen businesses while keeping Americans safe were among the points on which the two candidates disagreed. The two candidates also sparred over the value of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the future of healthcare in the United States.
Trump and Biden also differed on whether or not the country is facing a “dark winter” because of the pandemic.
Moderator Kristen Welker, NBC News White House correspondent, asked Trump to comment on the fact that 40,000 people are in the hospital on debate night with COVID-19 and that 16,000 have died since the last presidential debate.
Trump said, “2.2 million people modeled out were expected to die.” He said COVID-19 is a worldwide disease that does not only affect the United States.
“The mortality rate is down 85%, and the excess mortality is also down,” he added. He pointed out that previous spikes in Florida, Texas, and Arizona are now gone, and “spikes and surges in other places will soon be gone.
“It will go away, we are rounding the corner,” Trump said. “From personal experience, I was in the hospital, I had it, and they gave me a therapeutic, some would call it a cure...and now they say I’m immune. Whether it’s for a month or lifetime, nobody has been able to say that, but I’m immune.”
Biden countered by saying that “220,000 people are dead. If you hear nothing else I say tonight, hear this: Anyone who’s responsible for that many deaths should not remain president of the United States of America.”
Biden said there are a thousand deaths a day now and that there are over 70K new cases per day. “The expectation is we will have another 200,000 people down before the end of this year. If we just all wore these masks, we could save 100,000.”
“The New England Journal of Medicine said the way the president has handled this is absolutely tragic,” Biden added.
Vaccine timeline
Welker asked Trump if he could guarantee that there will be a COVID-19 vaccine within weeks.
“I can’t guarantee that, but it will be by end of the year. It will be distributed very quickly,” Trump said. He added that three leading vaccine developers, Johnson & Johnson, Moderna, and Pfizer, “are doing very well.”
“We’re about to go into a dark winter and he has no clear plan,” Biden said. “There is no prospect there will be a vaccine for most Americans by middle of next year.”
“It will not be a dark winter,” Trump responded.
Reopening the economy
Trump and Biden disagreed on how aggressively the economy should be reopened in light of the pandemic.
“I want to open the schools. We can’t keep this country closed,” Trump said. “This is a massive country with a massive economy.” He pointed out that rates of depression and suicide have risen because of the economic shutdown. “The cure cannot be worse than the problem.
“His Democrat governors...shut down so tight, and they’re dying,” the president added, gesturing toward Biden. “We are not going to shut down. We are going to open the schools.” As an example of the resiliency of young people, he mentioned that his son Barron tested positive for COVID-19 and recovered.
“I would shut down the virus, not the country,” Biden said. “It’s his ineptitude that caused so many schools and businesses to close in large part. Instead of being in a sand trap playing golf, he should have been negotiating with Nancy Pelosi.”
“He says we’re learning to live with it,” the former vice president said, but instead, “people are learning to die with it.”
Biden added that reopening the economy and minimizing transmission of COVID-19 are not mutually exclusive. “We can walk and chew gum at the same time.”
Divergence over the ACA
The fate of the ACA also garnered considerable attention. The discussion underlined a vast difference of opinion between the two candidates on the US healthcare system.
The moderator asked Trump what he would do for the 20 million Americans who get their healthcare through the ACA if it’s taken away.
“Through the legislature, I terminated the individual mandate, the worst part of Obamacare,” Trump said. “And now it’s in court because Obamacare is no good.
“Preexisting conditions will stay,” Trump added.
“I want to terminate Obamacare, and I want to come up with a beautiful healthcare [plan],” Trump added, turning the discussion toward private health insurance. “One thing that is very important is we have 180 million out there who have great private healthcare. Joe Biden will terminate all of their healthcare.”
Trump described Biden’s plan as “socialized medicine.” He also emphasized that protections for people with preexisting conditions “will stay.”
The Trump administration is supporting a lawsuit to overturn the ACA. The suit was filed by 18 Republican-led states. Arguments before the US Supreme Court on the constitutionality of the ACA are scheduled for November 10.
The moderator asked what Biden plans to do if the ACA is struck down. “I will pass Obamacare with a public option ― that will be ‘Bidencare.’ “ He said his plan will reduce premiums and drug prices. “I support private insurance. No one lost their private insurance under Obamacare.
“There is no way he can protect preexisting conditions,” Biden said. He added that 10 million people have already lost their private healthcare through unemployment during the pandemic.
Muting the mic
Following what many described as a chaotic first debate at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio on September 29, the Commission on Presidential Debate opted to allow the muting of the microphone during the first 2 minutes of remarks made by each candidate during each debate segment.
The muting of the microphones appeared to prevent crosstalk during the beginning of each segment of the debate. The candidates did manage to talk over and interrupt each other, as well as the moderator, during portions of the debate.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic figured prominently in the final debate between President Donald Trump and former Vice President Joe Biden when they met on stage for a 90-minute debate in Nashville, Tennessee, Thursday evening.
The adequacy of the COVID-19 response to date, the likely timeline for vaccine availability, and how to reopen businesses while keeping Americans safe were among the points on which the two candidates disagreed. The two candidates also sparred over the value of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the future of healthcare in the United States.
Trump and Biden also differed on whether or not the country is facing a “dark winter” because of the pandemic.
Moderator Kristen Welker, NBC News White House correspondent, asked Trump to comment on the fact that 40,000 people are in the hospital on debate night with COVID-19 and that 16,000 have died since the last presidential debate.
Trump said, “2.2 million people modeled out were expected to die.” He said COVID-19 is a worldwide disease that does not only affect the United States.
“The mortality rate is down 85%, and the excess mortality is also down,” he added. He pointed out that previous spikes in Florida, Texas, and Arizona are now gone, and “spikes and surges in other places will soon be gone.
“It will go away, we are rounding the corner,” Trump said. “From personal experience, I was in the hospital, I had it, and they gave me a therapeutic, some would call it a cure...and now they say I’m immune. Whether it’s for a month or lifetime, nobody has been able to say that, but I’m immune.”
Biden countered by saying that “220,000 people are dead. If you hear nothing else I say tonight, hear this: Anyone who’s responsible for that many deaths should not remain president of the United States of America.”
Biden said there are a thousand deaths a day now and that there are over 70K new cases per day. “The expectation is we will have another 200,000 people down before the end of this year. If we just all wore these masks, we could save 100,000.”
“The New England Journal of Medicine said the way the president has handled this is absolutely tragic,” Biden added.
Vaccine timeline
Welker asked Trump if he could guarantee that there will be a COVID-19 vaccine within weeks.
“I can’t guarantee that, but it will be by end of the year. It will be distributed very quickly,” Trump said. He added that three leading vaccine developers, Johnson & Johnson, Moderna, and Pfizer, “are doing very well.”
“We’re about to go into a dark winter and he has no clear plan,” Biden said. “There is no prospect there will be a vaccine for most Americans by middle of next year.”
“It will not be a dark winter,” Trump responded.
Reopening the economy
Trump and Biden disagreed on how aggressively the economy should be reopened in light of the pandemic.
“I want to open the schools. We can’t keep this country closed,” Trump said. “This is a massive country with a massive economy.” He pointed out that rates of depression and suicide have risen because of the economic shutdown. “The cure cannot be worse than the problem.
“His Democrat governors...shut down so tight, and they’re dying,” the president added, gesturing toward Biden. “We are not going to shut down. We are going to open the schools.” As an example of the resiliency of young people, he mentioned that his son Barron tested positive for COVID-19 and recovered.
“I would shut down the virus, not the country,” Biden said. “It’s his ineptitude that caused so many schools and businesses to close in large part. Instead of being in a sand trap playing golf, he should have been negotiating with Nancy Pelosi.”
“He says we’re learning to live with it,” the former vice president said, but instead, “people are learning to die with it.”
Biden added that reopening the economy and minimizing transmission of COVID-19 are not mutually exclusive. “We can walk and chew gum at the same time.”
Divergence over the ACA
The fate of the ACA also garnered considerable attention. The discussion underlined a vast difference of opinion between the two candidates on the US healthcare system.
The moderator asked Trump what he would do for the 20 million Americans who get their healthcare through the ACA if it’s taken away.
“Through the legislature, I terminated the individual mandate, the worst part of Obamacare,” Trump said. “And now it’s in court because Obamacare is no good.
“Preexisting conditions will stay,” Trump added.
“I want to terminate Obamacare, and I want to come up with a beautiful healthcare [plan],” Trump added, turning the discussion toward private health insurance. “One thing that is very important is we have 180 million out there who have great private healthcare. Joe Biden will terminate all of their healthcare.”
Trump described Biden’s plan as “socialized medicine.” He also emphasized that protections for people with preexisting conditions “will stay.”
The Trump administration is supporting a lawsuit to overturn the ACA. The suit was filed by 18 Republican-led states. Arguments before the US Supreme Court on the constitutionality of the ACA are scheduled for November 10.
The moderator asked what Biden plans to do if the ACA is struck down. “I will pass Obamacare with a public option ― that will be ‘Bidencare.’ “ He said his plan will reduce premiums and drug prices. “I support private insurance. No one lost their private insurance under Obamacare.
“There is no way he can protect preexisting conditions,” Biden said. He added that 10 million people have already lost their private healthcare through unemployment during the pandemic.
Muting the mic
Following what many described as a chaotic first debate at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio on September 29, the Commission on Presidential Debate opted to allow the muting of the microphone during the first 2 minutes of remarks made by each candidate during each debate segment.
The muting of the microphones appeared to prevent crosstalk during the beginning of each segment of the debate. The candidates did manage to talk over and interrupt each other, as well as the moderator, during portions of the debate.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic figured prominently in the final debate between President Donald Trump and former Vice President Joe Biden when they met on stage for a 90-minute debate in Nashville, Tennessee, Thursday evening.
The adequacy of the COVID-19 response to date, the likely timeline for vaccine availability, and how to reopen businesses while keeping Americans safe were among the points on which the two candidates disagreed. The two candidates also sparred over the value of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the future of healthcare in the United States.
Trump and Biden also differed on whether or not the country is facing a “dark winter” because of the pandemic.
Moderator Kristen Welker, NBC News White House correspondent, asked Trump to comment on the fact that 40,000 people are in the hospital on debate night with COVID-19 and that 16,000 have died since the last presidential debate.
Trump said, “2.2 million people modeled out were expected to die.” He said COVID-19 is a worldwide disease that does not only affect the United States.
“The mortality rate is down 85%, and the excess mortality is also down,” he added. He pointed out that previous spikes in Florida, Texas, and Arizona are now gone, and “spikes and surges in other places will soon be gone.
“It will go away, we are rounding the corner,” Trump said. “From personal experience, I was in the hospital, I had it, and they gave me a therapeutic, some would call it a cure...and now they say I’m immune. Whether it’s for a month or lifetime, nobody has been able to say that, but I’m immune.”
Biden countered by saying that “220,000 people are dead. If you hear nothing else I say tonight, hear this: Anyone who’s responsible for that many deaths should not remain president of the United States of America.”
Biden said there are a thousand deaths a day now and that there are over 70K new cases per day. “The expectation is we will have another 200,000 people down before the end of this year. If we just all wore these masks, we could save 100,000.”
“The New England Journal of Medicine said the way the president has handled this is absolutely tragic,” Biden added.
Vaccine timeline
Welker asked Trump if he could guarantee that there will be a COVID-19 vaccine within weeks.
“I can’t guarantee that, but it will be by end of the year. It will be distributed very quickly,” Trump said. He added that three leading vaccine developers, Johnson & Johnson, Moderna, and Pfizer, “are doing very well.”
“We’re about to go into a dark winter and he has no clear plan,” Biden said. “There is no prospect there will be a vaccine for most Americans by middle of next year.”
“It will not be a dark winter,” Trump responded.
Reopening the economy
Trump and Biden disagreed on how aggressively the economy should be reopened in light of the pandemic.
“I want to open the schools. We can’t keep this country closed,” Trump said. “This is a massive country with a massive economy.” He pointed out that rates of depression and suicide have risen because of the economic shutdown. “The cure cannot be worse than the problem.
“His Democrat governors...shut down so tight, and they’re dying,” the president added, gesturing toward Biden. “We are not going to shut down. We are going to open the schools.” As an example of the resiliency of young people, he mentioned that his son Barron tested positive for COVID-19 and recovered.
“I would shut down the virus, not the country,” Biden said. “It’s his ineptitude that caused so many schools and businesses to close in large part. Instead of being in a sand trap playing golf, he should have been negotiating with Nancy Pelosi.”
“He says we’re learning to live with it,” the former vice president said, but instead, “people are learning to die with it.”
Biden added that reopening the economy and minimizing transmission of COVID-19 are not mutually exclusive. “We can walk and chew gum at the same time.”
Divergence over the ACA
The fate of the ACA also garnered considerable attention. The discussion underlined a vast difference of opinion between the two candidates on the US healthcare system.
The moderator asked Trump what he would do for the 20 million Americans who get their healthcare through the ACA if it’s taken away.
“Through the legislature, I terminated the individual mandate, the worst part of Obamacare,” Trump said. “And now it’s in court because Obamacare is no good.
“Preexisting conditions will stay,” Trump added.
“I want to terminate Obamacare, and I want to come up with a beautiful healthcare [plan],” Trump added, turning the discussion toward private health insurance. “One thing that is very important is we have 180 million out there who have great private healthcare. Joe Biden will terminate all of their healthcare.”
Trump described Biden’s plan as “socialized medicine.” He also emphasized that protections for people with preexisting conditions “will stay.”
The Trump administration is supporting a lawsuit to overturn the ACA. The suit was filed by 18 Republican-led states. Arguments before the US Supreme Court on the constitutionality of the ACA are scheduled for November 10.
The moderator asked what Biden plans to do if the ACA is struck down. “I will pass Obamacare with a public option ― that will be ‘Bidencare.’ “ He said his plan will reduce premiums and drug prices. “I support private insurance. No one lost their private insurance under Obamacare.
“There is no way he can protect preexisting conditions,” Biden said. He added that 10 million people have already lost their private healthcare through unemployment during the pandemic.
Muting the mic
Following what many described as a chaotic first debate at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio on September 29, the Commission on Presidential Debate opted to allow the muting of the microphone during the first 2 minutes of remarks made by each candidate during each debate segment.
The muting of the microphones appeared to prevent crosstalk during the beginning of each segment of the debate. The candidates did manage to talk over and interrupt each other, as well as the moderator, during portions of the debate.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
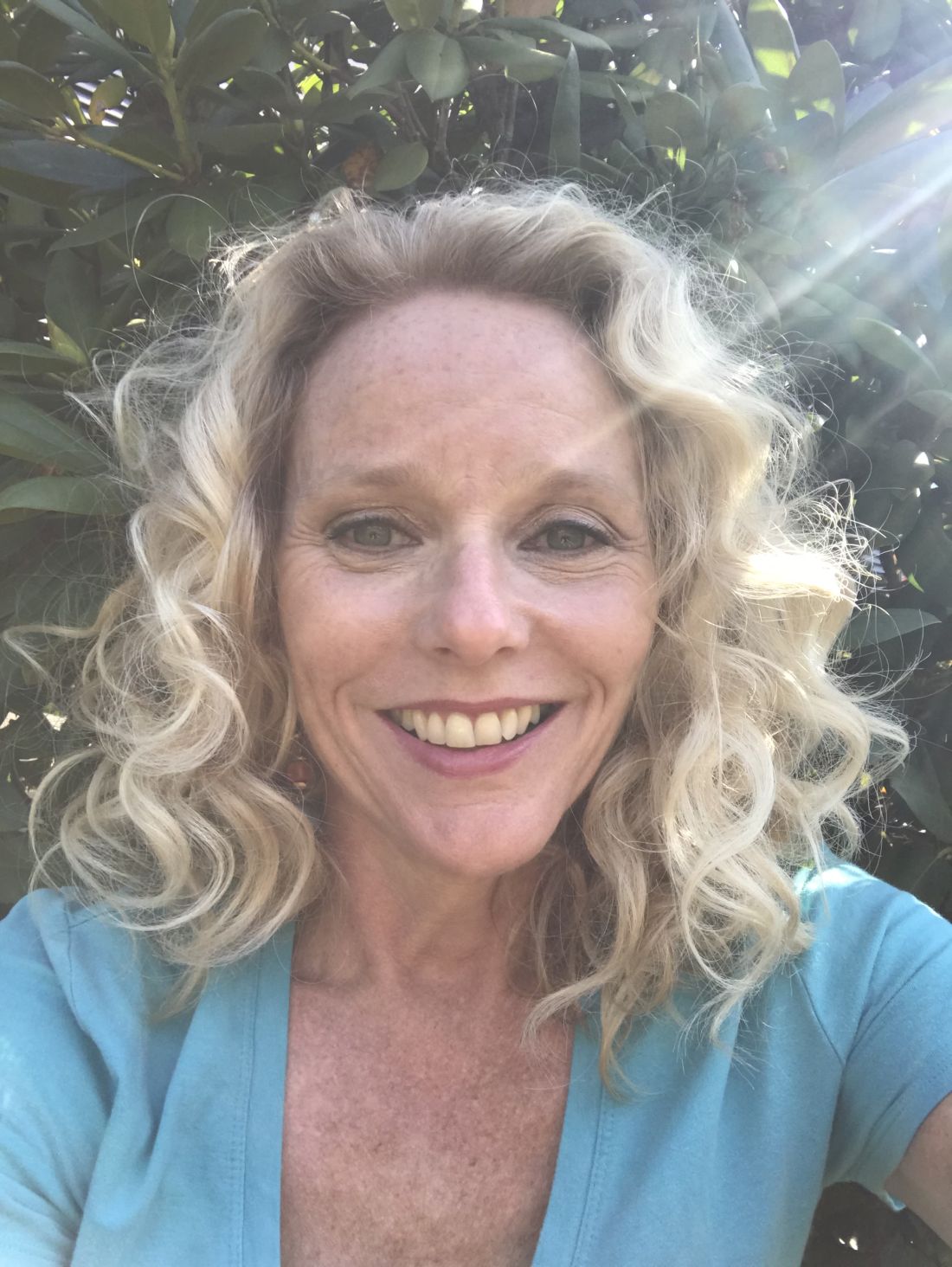
COVID-19 a new opportunity for suicide prevention
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic poses clear threats to mental well-being, but an increase in suicide is not inevitable if appropriate action is taken, one expert says.
“Increases in suicide rates should not be a foregone conclusion, even with the negative effects of the pandemic. If the lessons of suicide prevention research are heeded during and after the pandemic, this potential for increased risk could be substantially mitigated,” writes Christine Moutier, MD, chief medical officer of the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention, in an invited communication in JAMA Psychiatry.
“This is a moment in history when suicide prevention must be prioritized as a serious public health concern,” she writes.
Mitigating suicide risk
Although evidence from the first 6 months of the pandemic reveal specific effects on suicide risk, real-time data on suicide deaths are not available in most regions of the world. From emerging data from several countries, there is no evidence of increased suicide rates during the pandemic thus far, Moutier notes.
Still, a number of pandemic-related risk factors could increase individual and population suicide risk.
They include deterioration or recurrence of serious mental illness; increased isolation, loneliness, and bereavement; increased use of drugs and alcohol; job loss and other financial stressors; and increases in domestic violence.
There are mitigating strategies for each of these “threats to suicide risk.” The science is “very clear,” Moutier told Medscape Medical News.
“Suicide risk is never a situation of inevitability. It’s dynamic, with multiple forces at play in each individual and in the population. Lives can be saved simply by making people feel more connected to each other, that they are part of a larger community,” she added.
The political will
Moutier notes that prior to the pandemic, four countries ― Finland, Norway, Sweden, and Australia ― had fully implemented national suicide prevention plans and had achieved reductions in their national suicide rates. However, in the United States, the suicide rate has been steadily increasing since 1999.
A Centers for Disease Control and Prevention survey released in August 2020 found that 40% of US adults reported symptoms of depression, anxiety, or increased substance use during COVID-19 and that about 11% reported suicidal ideation in the past month, all increases from prior surveys.
COVID-19 presents a “new and urgent opportunity” to focus political will, federal investments, and the global community on suicide prevention, Moutier writes.
“The political will to address suicide has actually moved in the right direction during COVID, as evidenced by a number of pieces of legislation that have suddenly found their way to passing that we’ve been working on for years,” she said in an interview.
One example, she said, is the National Suicide Hotline Designation Act, signed into law earlier this month by President Donald Trump.
As previously reported, under the law, beginning in July 2022, Americans experiencing a mental health crisis will be able to dial 9-8-8 and be connected to the services and counselors at the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline.
Moutier reports no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic poses clear threats to mental well-being, but an increase in suicide is not inevitable if appropriate action is taken, one expert says.
“Increases in suicide rates should not be a foregone conclusion, even with the negative effects of the pandemic. If the lessons of suicide prevention research are heeded during and after the pandemic, this potential for increased risk could be substantially mitigated,” writes Christine Moutier, MD, chief medical officer of the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention, in an invited communication in JAMA Psychiatry.
“This is a moment in history when suicide prevention must be prioritized as a serious public health concern,” she writes.
Mitigating suicide risk
Although evidence from the first 6 months of the pandemic reveal specific effects on suicide risk, real-time data on suicide deaths are not available in most regions of the world. From emerging data from several countries, there is no evidence of increased suicide rates during the pandemic thus far, Moutier notes.
Still, a number of pandemic-related risk factors could increase individual and population suicide risk.
They include deterioration or recurrence of serious mental illness; increased isolation, loneliness, and bereavement; increased use of drugs and alcohol; job loss and other financial stressors; and increases in domestic violence.
There are mitigating strategies for each of these “threats to suicide risk.” The science is “very clear,” Moutier told Medscape Medical News.
“Suicide risk is never a situation of inevitability. It’s dynamic, with multiple forces at play in each individual and in the population. Lives can be saved simply by making people feel more connected to each other, that they are part of a larger community,” she added.
The political will
Moutier notes that prior to the pandemic, four countries ― Finland, Norway, Sweden, and Australia ― had fully implemented national suicide prevention plans and had achieved reductions in their national suicide rates. However, in the United States, the suicide rate has been steadily increasing since 1999.
A Centers for Disease Control and Prevention survey released in August 2020 found that 40% of US adults reported symptoms of depression, anxiety, or increased substance use during COVID-19 and that about 11% reported suicidal ideation in the past month, all increases from prior surveys.
COVID-19 presents a “new and urgent opportunity” to focus political will, federal investments, and the global community on suicide prevention, Moutier writes.
“The political will to address suicide has actually moved in the right direction during COVID, as evidenced by a number of pieces of legislation that have suddenly found their way to passing that we’ve been working on for years,” she said in an interview.
One example, she said, is the National Suicide Hotline Designation Act, signed into law earlier this month by President Donald Trump.
As previously reported, under the law, beginning in July 2022, Americans experiencing a mental health crisis will be able to dial 9-8-8 and be connected to the services and counselors at the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline.
Moutier reports no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic poses clear threats to mental well-being, but an increase in suicide is not inevitable if appropriate action is taken, one expert says.
“Increases in suicide rates should not be a foregone conclusion, even with the negative effects of the pandemic. If the lessons of suicide prevention research are heeded during and after the pandemic, this potential for increased risk could be substantially mitigated,” writes Christine Moutier, MD, chief medical officer of the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention, in an invited communication in JAMA Psychiatry.
“This is a moment in history when suicide prevention must be prioritized as a serious public health concern,” she writes.
Mitigating suicide risk
Although evidence from the first 6 months of the pandemic reveal specific effects on suicide risk, real-time data on suicide deaths are not available in most regions of the world. From emerging data from several countries, there is no evidence of increased suicide rates during the pandemic thus far, Moutier notes.
Still, a number of pandemic-related risk factors could increase individual and population suicide risk.
They include deterioration or recurrence of serious mental illness; increased isolation, loneliness, and bereavement; increased use of drugs and alcohol; job loss and other financial stressors; and increases in domestic violence.
There are mitigating strategies for each of these “threats to suicide risk.” The science is “very clear,” Moutier told Medscape Medical News.
“Suicide risk is never a situation of inevitability. It’s dynamic, with multiple forces at play in each individual and in the population. Lives can be saved simply by making people feel more connected to each other, that they are part of a larger community,” she added.
The political will
Moutier notes that prior to the pandemic, four countries ― Finland, Norway, Sweden, and Australia ― had fully implemented national suicide prevention plans and had achieved reductions in their national suicide rates. However, in the United States, the suicide rate has been steadily increasing since 1999.
A Centers for Disease Control and Prevention survey released in August 2020 found that 40% of US adults reported symptoms of depression, anxiety, or increased substance use during COVID-19 and that about 11% reported suicidal ideation in the past month, all increases from prior surveys.
COVID-19 presents a “new and urgent opportunity” to focus political will, federal investments, and the global community on suicide prevention, Moutier writes.
“The political will to address suicide has actually moved in the right direction during COVID, as evidenced by a number of pieces of legislation that have suddenly found their way to passing that we’ve been working on for years,” she said in an interview.
One example, she said, is the National Suicide Hotline Designation Act, signed into law earlier this month by President Donald Trump.
As previously reported, under the law, beginning in July 2022, Americans experiencing a mental health crisis will be able to dial 9-8-8 and be connected to the services and counselors at the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline.
Moutier reports no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
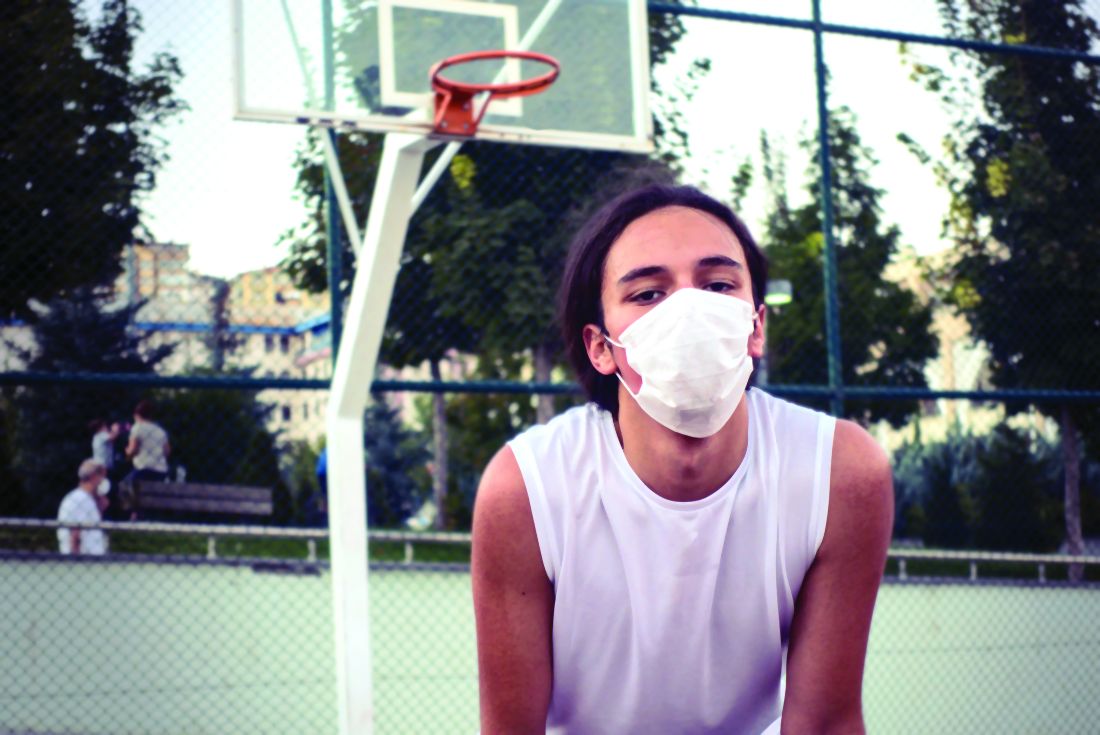
When should students resume sports after a COVID-19 diagnosis?
Many student athletes who test positive for COVID-19 likely can have an uneventful return to their sports after they have rested for 2 weeks in quarantine, doctors suggest.
There are reasons for caution, however, especially when a patient has symptoms that indicate possible cardiac involvement. In these cases, patients should undergo cardiac testing before a physician clears them to return to play, according to guidance from professional associations. Reports of myocarditis in college athletes who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 but were asymptomatic are among the reasons for concern. Myocarditis may increase the risk of sudden death during exercise.
“The thing that you need to keep in mind is that this is not just a respiratory illness,” David T. Bernhardt, MD, professor of pediatrics, orthopedics, and rehabilitation at the University of Wisconsin in Madison, said in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year. High school and college athletes have had cardiac, neurologic, hematologic, and renal problems that “can complicate their recovery and their return to sport.”
Still, children who test positive for COVID-19 tend to have mild illness and often are asymptomatic. “It is more than likely going to be safe for the majority of the student athletes who are in the elementary and middle school age to return to sport,” said Dr. Bernhardt. Given that 18-year-old college freshmen have had cardiac complications, there may be reason for more caution with high school students.
Limited data
The AAP has released interim guidance on returning to sports and recommends that primary care physicians clear all patients with COVID-19 before they resume training. Physicians should screen for cardiac symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, palpitations, or syncope.
Those with severe illness should be restricted from exercise and participation for 3-6 months. Primary care physicians, preferably in consultation with pediatric cardiologists, should clear athletes who experience severe illness.
“Most of the recommendations come from the fact that we simply do not know what we do not know with COVID-19,” Susannah Briskin, MD, a coauthor of the interim guidance, said in an interview. “We have to be cautious in returning individuals to play and closely monitor them as we learn more about the disease process and its effect on kids.”
Patients with severe illness could include those who were hospitalized and experienced hypotension or arrhythmias, required intubation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) support, had kidney or cardiac failure, or developed multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), said Dr. Briskin, a specialist in pediatric sports medicine at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland.
“The majority of COVID-19 cases will not present like this in kids. We have no idea how common myocarditis is in kids post infection. We do know that, if anyone has chest pain, shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, syncope [passing out], or arrhythmia [feeling of their heart skipping beats], they should undergo further evaluation for myocarditis,” Dr. Briskin said.
Patients who are asymptomatic or have mild symptoms should rest for 14 days after their positive test. After their infectious period has passed, a doctor should assess for any concerning cardiac symptoms. “Anyone with prolonged fever or moderate symptoms should see their pediatrician and have an EKG performed, at a minimum, prior to return to sports,” Dr. Briskin said. “Anyone with an abnormal EKG or concerning signs or symptoms should be referred on to pediatric cardiology for a further assessment.”
Most patients who Dr. Briskin has seen have been asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic. “They have done well with a gradual return to physical activity,” she said. “We recommend a gradual return so individuals can be monitored for any signs or symptoms concerning for myocarditis. The far majority of individuals likely have an uneventful return to play.”
Mitigating risk
COVID-19 adds elements of uncertainty and complexity to the usual process of mitigating risk in sports, Dr. Bernhardt noted in his lecture. “You are dealing with an infection that we do not know a lot about,” he said. “And we are trying to mitigate risk not only for the individual who may or may not have underlying health problems, but you are also trying to mitigate risk for anybody else involved with the sport, including athletic trainers and team physicians, coaches, spectators, custodial staff, people working at a snack shack, and all the other people that can be involved in a typical sporting type of atmosphere.”
When patients do return to play after an illness, they should gradually increase the training load to avoid injury. In addition, clinicians should screen for depression and anxiety using tools such as the Four-Item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-4) when they see patients. “The pandemic has been quite stressful for everybody, including our high school student athletes,” Dr. Bernhardt said. “Giving everybody a PHQ-4 when they come into clinic right now probably makes sense in terms of the stress levels that all of us are experiencing.”
If a patient screens positive, take additional history and refer for more in-depth mental health evaluation and treatment if warranted. Sharing breathing and relaxation exercises, promoting healthy behaviors, and paying attention to unhealthy strategies also may help, Dr. Bernhardt suggested.
Ultimately, determining when an athlete with COVID-19 can be medically cleared to return to play may be a challenge. There are limited data on epidemiology and clinical presentations that could help identify cardiac injury related to the disease, Dr. Bernhardt said. Guidance from the American College of Cardiology provides a framework for evaluating athletes for return to play, and pediatric cardiologists have discussed how the guidance relates to a pediatric population. Cardiac assessments may include measures of biomarkers such as troponin, B-type natriuretic peptide, and sedimentation rate, along with electrocardiograms, echocardiograms, and cardiac MRI.
Beyond return-to-play decisions, encourage the use of cloth face coverings on the sidelines and away from the playing field, and stress proper quarantining, Dr. Briskin added. Too often, she hears about children not quarantining properly. “Individuals with a known exposure should be quarantined in their house – ideally in a separate room from everyone else. ... When they come out of their room, they should wash their hands well and wear a cloth face covering. They should not be eating with other people.”
Dr. Bernhardt had no relevant disclosures.
Many student athletes who test positive for COVID-19 likely can have an uneventful return to their sports after they have rested for 2 weeks in quarantine, doctors suggest.
There are reasons for caution, however, especially when a patient has symptoms that indicate possible cardiac involvement. In these cases, patients should undergo cardiac testing before a physician clears them to return to play, according to guidance from professional associations. Reports of myocarditis in college athletes who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 but were asymptomatic are among the reasons for concern. Myocarditis may increase the risk of sudden death during exercise.
“The thing that you need to keep in mind is that this is not just a respiratory illness,” David T. Bernhardt, MD, professor of pediatrics, orthopedics, and rehabilitation at the University of Wisconsin in Madison, said in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year. High school and college athletes have had cardiac, neurologic, hematologic, and renal problems that “can complicate their recovery and their return to sport.”
Still, children who test positive for COVID-19 tend to have mild illness and often are asymptomatic. “It is more than likely going to be safe for the majority of the student athletes who are in the elementary and middle school age to return to sport,” said Dr. Bernhardt. Given that 18-year-old college freshmen have had cardiac complications, there may be reason for more caution with high school students.
Limited data
The AAP has released interim guidance on returning to sports and recommends that primary care physicians clear all patients with COVID-19 before they resume training. Physicians should screen for cardiac symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, palpitations, or syncope.
Those with severe illness should be restricted from exercise and participation for 3-6 months. Primary care physicians, preferably in consultation with pediatric cardiologists, should clear athletes who experience severe illness.
“Most of the recommendations come from the fact that we simply do not know what we do not know with COVID-19,” Susannah Briskin, MD, a coauthor of the interim guidance, said in an interview. “We have to be cautious in returning individuals to play and closely monitor them as we learn more about the disease process and its effect on kids.”
Patients with severe illness could include those who were hospitalized and experienced hypotension or arrhythmias, required intubation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) support, had kidney or cardiac failure, or developed multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), said Dr. Briskin, a specialist in pediatric sports medicine at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland.
“The majority of COVID-19 cases will not present like this in kids. We have no idea how common myocarditis is in kids post infection. We do know that, if anyone has chest pain, shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, syncope [passing out], or arrhythmia [feeling of their heart skipping beats], they should undergo further evaluation for myocarditis,” Dr. Briskin said.
Patients who are asymptomatic or have mild symptoms should rest for 14 days after their positive test. After their infectious period has passed, a doctor should assess for any concerning cardiac symptoms. “Anyone with prolonged fever or moderate symptoms should see their pediatrician and have an EKG performed, at a minimum, prior to return to sports,” Dr. Briskin said. “Anyone with an abnormal EKG or concerning signs or symptoms should be referred on to pediatric cardiology for a further assessment.”
Most patients who Dr. Briskin has seen have been asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic. “They have done well with a gradual return to physical activity,” she said. “We recommend a gradual return so individuals can be monitored for any signs or symptoms concerning for myocarditis. The far majority of individuals likely have an uneventful return to play.”
Mitigating risk
COVID-19 adds elements of uncertainty and complexity to the usual process of mitigating risk in sports, Dr. Bernhardt noted in his lecture. “You are dealing with an infection that we do not know a lot about,” he said. “And we are trying to mitigate risk not only for the individual who may or may not have underlying health problems, but you are also trying to mitigate risk for anybody else involved with the sport, including athletic trainers and team physicians, coaches, spectators, custodial staff, people working at a snack shack, and all the other people that can be involved in a typical sporting type of atmosphere.”
When patients do return to play after an illness, they should gradually increase the training load to avoid injury. In addition, clinicians should screen for depression and anxiety using tools such as the Four-Item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-4) when they see patients. “The pandemic has been quite stressful for everybody, including our high school student athletes,” Dr. Bernhardt said. “Giving everybody a PHQ-4 when they come into clinic right now probably makes sense in terms of the stress levels that all of us are experiencing.”
If a patient screens positive, take additional history and refer for more in-depth mental health evaluation and treatment if warranted. Sharing breathing and relaxation exercises, promoting healthy behaviors, and paying attention to unhealthy strategies also may help, Dr. Bernhardt suggested.
Ultimately, determining when an athlete with COVID-19 can be medically cleared to return to play may be a challenge. There are limited data on epidemiology and clinical presentations that could help identify cardiac injury related to the disease, Dr. Bernhardt said. Guidance from the American College of Cardiology provides a framework for evaluating athletes for return to play, and pediatric cardiologists have discussed how the guidance relates to a pediatric population. Cardiac assessments may include measures of biomarkers such as troponin, B-type natriuretic peptide, and sedimentation rate, along with electrocardiograms, echocardiograms, and cardiac MRI.
Beyond return-to-play decisions, encourage the use of cloth face coverings on the sidelines and away from the playing field, and stress proper quarantining, Dr. Briskin added. Too often, she hears about children not quarantining properly. “Individuals with a known exposure should be quarantined in their house – ideally in a separate room from everyone else. ... When they come out of their room, they should wash their hands well and wear a cloth face covering. They should not be eating with other people.”
Dr. Bernhardt had no relevant disclosures.
Many student athletes who test positive for COVID-19 likely can have an uneventful return to their sports after they have rested for 2 weeks in quarantine, doctors suggest.
There are reasons for caution, however, especially when a patient has symptoms that indicate possible cardiac involvement. In these cases, patients should undergo cardiac testing before a physician clears them to return to play, according to guidance from professional associations. Reports of myocarditis in college athletes who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 but were asymptomatic are among the reasons for concern. Myocarditis may increase the risk of sudden death during exercise.
“The thing that you need to keep in mind is that this is not just a respiratory illness,” David T. Bernhardt, MD, professor of pediatrics, orthopedics, and rehabilitation at the University of Wisconsin in Madison, said in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year. High school and college athletes have had cardiac, neurologic, hematologic, and renal problems that “can complicate their recovery and their return to sport.”
Still, children who test positive for COVID-19 tend to have mild illness and often are asymptomatic. “It is more than likely going to be safe for the majority of the student athletes who are in the elementary and middle school age to return to sport,” said Dr. Bernhardt. Given that 18-year-old college freshmen have had cardiac complications, there may be reason for more caution with high school students.
Limited data
The AAP has released interim guidance on returning to sports and recommends that primary care physicians clear all patients with COVID-19 before they resume training. Physicians should screen for cardiac symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, palpitations, or syncope.
Those with severe illness should be restricted from exercise and participation for 3-6 months. Primary care physicians, preferably in consultation with pediatric cardiologists, should clear athletes who experience severe illness.
“Most of the recommendations come from the fact that we simply do not know what we do not know with COVID-19,” Susannah Briskin, MD, a coauthor of the interim guidance, said in an interview. “We have to be cautious in returning individuals to play and closely monitor them as we learn more about the disease process and its effect on kids.”
Patients with severe illness could include those who were hospitalized and experienced hypotension or arrhythmias, required intubation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) support, had kidney or cardiac failure, or developed multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), said Dr. Briskin, a specialist in pediatric sports medicine at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland.
“The majority of COVID-19 cases will not present like this in kids. We have no idea how common myocarditis is in kids post infection. We do know that, if anyone has chest pain, shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, syncope [passing out], or arrhythmia [feeling of their heart skipping beats], they should undergo further evaluation for myocarditis,” Dr. Briskin said.
Patients who are asymptomatic or have mild symptoms should rest for 14 days after their positive test. After their infectious period has passed, a doctor should assess for any concerning cardiac symptoms. “Anyone with prolonged fever or moderate symptoms should see their pediatrician and have an EKG performed, at a minimum, prior to return to sports,” Dr. Briskin said. “Anyone with an abnormal EKG or concerning signs or symptoms should be referred on to pediatric cardiology for a further assessment.”
Most patients who Dr. Briskin has seen have been asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic. “They have done well with a gradual return to physical activity,” she said. “We recommend a gradual return so individuals can be monitored for any signs or symptoms concerning for myocarditis. The far majority of individuals likely have an uneventful return to play.”
Mitigating risk
COVID-19 adds elements of uncertainty and complexity to the usual process of mitigating risk in sports, Dr. Bernhardt noted in his lecture. “You are dealing with an infection that we do not know a lot about,” he said. “And we are trying to mitigate risk not only for the individual who may or may not have underlying health problems, but you are also trying to mitigate risk for anybody else involved with the sport, including athletic trainers and team physicians, coaches, spectators, custodial staff, people working at a snack shack, and all the other people that can be involved in a typical sporting type of atmosphere.”
When patients do return to play after an illness, they should gradually increase the training load to avoid injury. In addition, clinicians should screen for depression and anxiety using tools such as the Four-Item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-4) when they see patients. “The pandemic has been quite stressful for everybody, including our high school student athletes,” Dr. Bernhardt said. “Giving everybody a PHQ-4 when they come into clinic right now probably makes sense in terms of the stress levels that all of us are experiencing.”
If a patient screens positive, take additional history and refer for more in-depth mental health evaluation and treatment if warranted. Sharing breathing and relaxation exercises, promoting healthy behaviors, and paying attention to unhealthy strategies also may help, Dr. Bernhardt suggested.
Ultimately, determining when an athlete with COVID-19 can be medically cleared to return to play may be a challenge. There are limited data on epidemiology and clinical presentations that could help identify cardiac injury related to the disease, Dr. Bernhardt said. Guidance from the American College of Cardiology provides a framework for evaluating athletes for return to play, and pediatric cardiologists have discussed how the guidance relates to a pediatric population. Cardiac assessments may include measures of biomarkers such as troponin, B-type natriuretic peptide, and sedimentation rate, along with electrocardiograms, echocardiograms, and cardiac MRI.
Beyond return-to-play decisions, encourage the use of cloth face coverings on the sidelines and away from the playing field, and stress proper quarantining, Dr. Briskin added. Too often, she hears about children not quarantining properly. “Individuals with a known exposure should be quarantined in their house – ideally in a separate room from everyone else. ... When they come out of their room, they should wash their hands well and wear a cloth face covering. They should not be eating with other people.”
Dr. Bernhardt had no relevant disclosures.
FROM AAP 2020
COVID-19 vaccine standards questioned at FDA advisory meeting
The FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee met for a wide-ranging discussion beginning around 10 am. The FDA did not ask the panel to weigh in on any particular vaccine. Instead, the FDA asked for the panel’s feedback on a series of questions, including considerations for continuing phase 3 trials if a product were to get an interim clearance known as an emergency use authorization (EUA).
Speakers at the hearing made a variety of requests, including asking for data showing COVID-19 vaccines can prevent serious illness and urging transparency about the agency’s deliberations for each product to be considered.
FDA staff are closely tracking the crop of experimental vaccines that have made it into advanced stages of testing, including products from Pfizer Inc, AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson, and Moderna.
‘Time for a reset’
Among the speakers at the public hearing was Peter Lurie, MD, who served as an FDA associate commissioner from 2014 to 2017. Now the president of the Center for Science in the Public Interest, Lurie was among the speakers who asked the agency to make its independence clear.
President Donald Trump has for months been making predictions about COVID-19 vaccine approvals that have been overly optimistic. In one example, the president, who is seeking re-election on November 3, last month spoke about being able to begin distributing a vaccine in October.
“Until now the process of developing candidate vaccines has been inappropriately politicized with an eye on the election calendar, rather than the deliberate timeframe science requires,” Lurie told the FDA advisory panel. “Now is the time for a reset. This committee has a unique opportunity to set a new tone for vaccine deliberations going forward.”
Lurie asked the panel to press the FDA to commit to hold an advisory committee meeting on requests by drugmakers for EUAs. He also asked the panel to demand that informed consent forms and minutes from institutional review board (IRB) discussions of COVID-19 vaccines trials be made public.
Also among the speakers at the public hearing was Peter Doshi, PhD, an associate professor at the University of Maryland School of Pharmacy, who argued that the current trials won’t answer the right questions about the COVID-19 vaccines.
“We could end up with approved vaccines that reduce the risk of mild infection, but do not decrease the risk of hospitalization, ICU use, or death — either at all or by a clinically relevant amount,” Doshi told the panel.
In his presentation, he reiterated points he had made previously, including in an October 21 article in the BMJ, for which he is an associate editor. Doshi also raised these concerns in a September opinion article in The New York Times, co-authored with Eric Topol, MD, director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute and editor-in-chief of Medscape.
Risks of a ‘rushed vaccine’
Other complaints about the FDA’s approach included criticism of a 2-month follow-up time after vaccination, which was seen as too short. ECRI, a nonprofit organization that seeks to improve the safety, quality, and cost-effectiveness of medicines, has argued that approving a weak COVID-19 vaccine might worsen the pandemic.
In an October 21 statement, ECRI noted the risk of a partially effective vaccine, which could be welcomed as a means of slowing transmission of the virus. But public response and attitudes over the past 9 months in the United States suggest that people would relax their precautions as soon as a vaccine is available.
“Resulting infections may offset the vaccine’s impact and end up increasing the mortality and morbidity burden,” ECRI said in the brief.
“The risks and consequences of a rushed vaccine could be very severe if the review is anything shy of thorough,” ECRI Chief Executive Officer Marcus Schabacker, MD, PhD, said in a statement prepared for the hearing.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee met for a wide-ranging discussion beginning around 10 am. The FDA did not ask the panel to weigh in on any particular vaccine. Instead, the FDA asked for the panel’s feedback on a series of questions, including considerations for continuing phase 3 trials if a product were to get an interim clearance known as an emergency use authorization (EUA).
Speakers at the hearing made a variety of requests, including asking for data showing COVID-19 vaccines can prevent serious illness and urging transparency about the agency’s deliberations for each product to be considered.
FDA staff are closely tracking the crop of experimental vaccines that have made it into advanced stages of testing, including products from Pfizer Inc, AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson, and Moderna.
‘Time for a reset’
Among the speakers at the public hearing was Peter Lurie, MD, who served as an FDA associate commissioner from 2014 to 2017. Now the president of the Center for Science in the Public Interest, Lurie was among the speakers who asked the agency to make its independence clear.
President Donald Trump has for months been making predictions about COVID-19 vaccine approvals that have been overly optimistic. In one example, the president, who is seeking re-election on November 3, last month spoke about being able to begin distributing a vaccine in October.
“Until now the process of developing candidate vaccines has been inappropriately politicized with an eye on the election calendar, rather than the deliberate timeframe science requires,” Lurie told the FDA advisory panel. “Now is the time for a reset. This committee has a unique opportunity to set a new tone for vaccine deliberations going forward.”
Lurie asked the panel to press the FDA to commit to hold an advisory committee meeting on requests by drugmakers for EUAs. He also asked the panel to demand that informed consent forms and minutes from institutional review board (IRB) discussions of COVID-19 vaccines trials be made public.
Also among the speakers at the public hearing was Peter Doshi, PhD, an associate professor at the University of Maryland School of Pharmacy, who argued that the current trials won’t answer the right questions about the COVID-19 vaccines.
“We could end up with approved vaccines that reduce the risk of mild infection, but do not decrease the risk of hospitalization, ICU use, or death — either at all or by a clinically relevant amount,” Doshi told the panel.
In his presentation, he reiterated points he had made previously, including in an October 21 article in the BMJ, for which he is an associate editor. Doshi also raised these concerns in a September opinion article in The New York Times, co-authored with Eric Topol, MD, director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute and editor-in-chief of Medscape.
Risks of a ‘rushed vaccine’
Other complaints about the FDA’s approach included criticism of a 2-month follow-up time after vaccination, which was seen as too short. ECRI, a nonprofit organization that seeks to improve the safety, quality, and cost-effectiveness of medicines, has argued that approving a weak COVID-19 vaccine might worsen the pandemic.
In an October 21 statement, ECRI noted the risk of a partially effective vaccine, which could be welcomed as a means of slowing transmission of the virus. But public response and attitudes over the past 9 months in the United States suggest that people would relax their precautions as soon as a vaccine is available.
“Resulting infections may offset the vaccine’s impact and end up increasing the mortality and morbidity burden,” ECRI said in the brief.
“The risks and consequences of a rushed vaccine could be very severe if the review is anything shy of thorough,” ECRI Chief Executive Officer Marcus Schabacker, MD, PhD, said in a statement prepared for the hearing.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee met for a wide-ranging discussion beginning around 10 am. The FDA did not ask the panel to weigh in on any particular vaccine. Instead, the FDA asked for the panel’s feedback on a series of questions, including considerations for continuing phase 3 trials if a product were to get an interim clearance known as an emergency use authorization (EUA).
Speakers at the hearing made a variety of requests, including asking for data showing COVID-19 vaccines can prevent serious illness and urging transparency about the agency’s deliberations for each product to be considered.
FDA staff are closely tracking the crop of experimental vaccines that have made it into advanced stages of testing, including products from Pfizer Inc, AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson, and Moderna.
‘Time for a reset’
Among the speakers at the public hearing was Peter Lurie, MD, who served as an FDA associate commissioner from 2014 to 2017. Now the president of the Center for Science in the Public Interest, Lurie was among the speakers who asked the agency to make its independence clear.
President Donald Trump has for months been making predictions about COVID-19 vaccine approvals that have been overly optimistic. In one example, the president, who is seeking re-election on November 3, last month spoke about being able to begin distributing a vaccine in October.
“Until now the process of developing candidate vaccines has been inappropriately politicized with an eye on the election calendar, rather than the deliberate timeframe science requires,” Lurie told the FDA advisory panel. “Now is the time for a reset. This committee has a unique opportunity to set a new tone for vaccine deliberations going forward.”
Lurie asked the panel to press the FDA to commit to hold an advisory committee meeting on requests by drugmakers for EUAs. He also asked the panel to demand that informed consent forms and minutes from institutional review board (IRB) discussions of COVID-19 vaccines trials be made public.
Also among the speakers at the public hearing was Peter Doshi, PhD, an associate professor at the University of Maryland School of Pharmacy, who argued that the current trials won’t answer the right questions about the COVID-19 vaccines.
“We could end up with approved vaccines that reduce the risk of mild infection, but do not decrease the risk of hospitalization, ICU use, or death — either at all or by a clinically relevant amount,” Doshi told the panel.
In his presentation, he reiterated points he had made previously, including in an October 21 article in the BMJ, for which he is an associate editor. Doshi also raised these concerns in a September opinion article in The New York Times, co-authored with Eric Topol, MD, director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute and editor-in-chief of Medscape.
Risks of a ‘rushed vaccine’
Other complaints about the FDA’s approach included criticism of a 2-month follow-up time after vaccination, which was seen as too short. ECRI, a nonprofit organization that seeks to improve the safety, quality, and cost-effectiveness of medicines, has argued that approving a weak COVID-19 vaccine might worsen the pandemic.
In an October 21 statement, ECRI noted the risk of a partially effective vaccine, which could be welcomed as a means of slowing transmission of the virus. But public response and attitudes over the past 9 months in the United States suggest that people would relax their precautions as soon as a vaccine is available.
“Resulting infections may offset the vaccine’s impact and end up increasing the mortality and morbidity burden,” ECRI said in the brief.
“The risks and consequences of a rushed vaccine could be very severe if the review is anything shy of thorough,” ECRI Chief Executive Officer Marcus Schabacker, MD, PhD, said in a statement prepared for the hearing.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
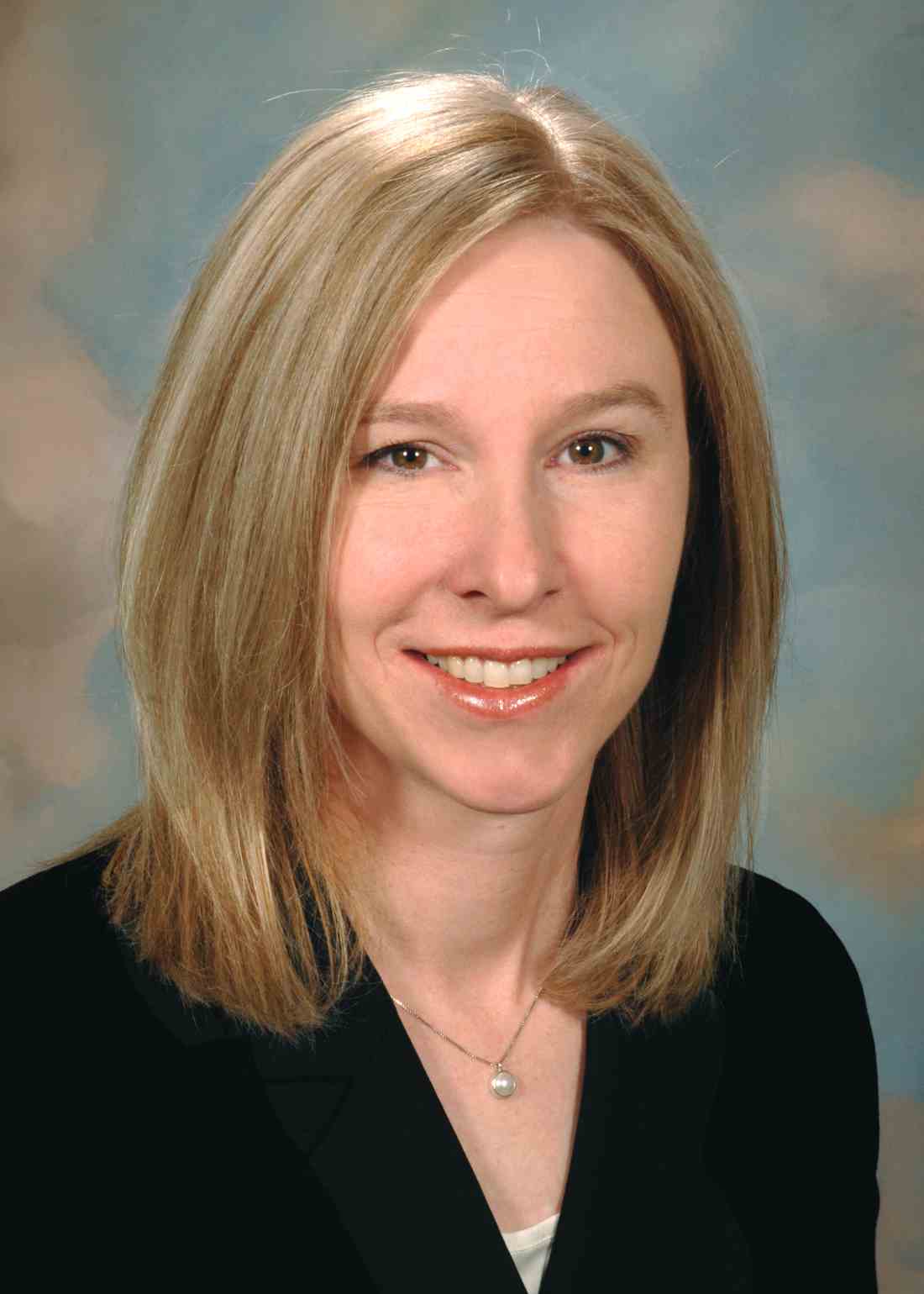
Data on potential risks of COVID-19 in psoriasis patients limited, but reassuring
The available according to a summary of published studies and expert opinions summarized at the annual Coastal Dermatology Symposium, held virtually.
For patients with psoriasis concerned about their outcome if infected with COVID-19, “there is no evidence to support stopping biologics or systemic agents, so I am asking my patients to continue,” Kristina C. Duffin, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, said at the meeting.
The National Psoriasis Foundation, which created a COVID-19 task force and maintains a COVID-19 Resource Center on its website, has provided similar advice. Many statements are phrased cautiously and clinicians are encouraged to practice shared decision-making, but the NPF guidance supports continuing effective therapy – or, in newly diagnosed patients, starting effective therapy – among those who are not infected with SARS-CoV2.
Patients with a new diagnosis of psoriasis “should be aware that untreated psoriatic disease is associated with serious impact on physical and emotional health, and in the case of psoriatic arthritis, can lead to permanent joint damage and disability,” according to the NPF guidance.
Overall, the “existing data generally suggest” that most treatments for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis “do not meaningfully alter the risks of contracting SARS-CoV2 or having a worse course of COVID-19 illness,” the current guidance states. Yet, because of limited data this “is not known with certainty.”
Chronic systemic steroids are an exception. In a review of recently published studies evaluating whether psoriasis or its therapies increase risk of adverse outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection, Dr. Duffin pointed to several that associated systemic steroids with hospitalization or other markers of severe disease.
The NPF guidance also recommends avoiding chronic systemic steroids in patients with psoriasis during the current COVID-19 era “if possible.” In patients with psoriatic arthritis who require systemic steroids, the guidance recommends “the lowest dose necessary to achieve the desired therapeutic effect.”
This is not necessarily true in patients with psoriasis and COVID-19 infection. Based on the potential for systemic steroids to improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients requiring oxygen, steroids “should not be withheld” even when the justification is concern about the potential risk of flares with withdrawal, according to the NPF guidance statement.
The NPF guidance specifically cautions against use of hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine for prevention or treatment of COVID-19. In addition to an uncertain benefit, these antimalarial drugs have been associated previously with flares of psoriasis.
Dr. Duffin agreed and went on to warn that COVID-19 infection itself is a potential trigger for flares. She cited two published case reports of flares associated with psoriasis. Although one patient had also been exposed to hydroxychloroquine, she said the risk of psoriasis-induced flare “makes sense” based on previous associations made between flares and other viral infections and stress.
In patients with psoriasis who contract COVID-19 infection, Dr. Duffin concurred with the NPF guidance that management decisions should be made on a “case-by-case basis.” Although the NPF guidance states that “most patients can restart psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis treatments after complete resolution of COVID-19 symptoms,” no specific advice was offered on the decision to stop treatments.
For protecting psoriasis patients from infection and managing COVID-19 in those who become infected, much of the NPF advice is consistent with that offered to patients without psoriasis. This involves practicing infection control that reduces risk of transmission. Both the NPF guidance and Dr. Duffin suggested telemedicine is appropriate for limiting in-patient visits under pandemic conditions.
Although patients with psoriasis are more likely than the general population to have the comorbidities associated with bad COVID-19 infection outcomes, according to the NPF guidance, Dr. Duffin called the overall data evaluating susceptibility among psoriasis patients “reassuring.” She cautioned that the data are still limited, but the evidence so far suggests that neither psoriasis nor biologics are independent risk factors for acquiring COVID-19 or having a worse outcome if infected.
Yet, more definitive data are needed, and Dr. Duffin advised clinicians and patients to consult the NPF website for updates. “More up-to-date information will certainly be added as we go forward,” she said at the meeting, jointly presented by the University of Louisville and Global Academy for Medical Education.
This NPF task force on COVID-19 is meeting every 2 weeks, according to Joel M. Gelfand, MD, professor of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and cochair of the task force. Dr. Gelfand reported that updates are based on a discussion of the available data.
“We will be releasing additional recommendations as necessary based on the developments,” he said in an interview. Updates are not necessarily required at this frequency but can be if appropriate. The goal is to keep recommendations current and evidence-based.
Dr. Duffin reported financial relationships with Amgen, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Siena, and UCB. Dr. Gelfand reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Lilly, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB.
This publication and Global Academy for Medical Education are owned by the same parent company.
The available according to a summary of published studies and expert opinions summarized at the annual Coastal Dermatology Symposium, held virtually.
For patients with psoriasis concerned about their outcome if infected with COVID-19, “there is no evidence to support stopping biologics or systemic agents, so I am asking my patients to continue,” Kristina C. Duffin, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, said at the meeting.
The National Psoriasis Foundation, which created a COVID-19 task force and maintains a COVID-19 Resource Center on its website, has provided similar advice. Many statements are phrased cautiously and clinicians are encouraged to practice shared decision-making, but the NPF guidance supports continuing effective therapy – or, in newly diagnosed patients, starting effective therapy – among those who are not infected with SARS-CoV2.
Patients with a new diagnosis of psoriasis “should be aware that untreated psoriatic disease is associated with serious impact on physical and emotional health, and in the case of psoriatic arthritis, can lead to permanent joint damage and disability,” according to the NPF guidance.
Overall, the “existing data generally suggest” that most treatments for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis “do not meaningfully alter the risks of contracting SARS-CoV2 or having a worse course of COVID-19 illness,” the current guidance states. Yet, because of limited data this “is not known with certainty.”
Chronic systemic steroids are an exception. In a review of recently published studies evaluating whether psoriasis or its therapies increase risk of adverse outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection, Dr. Duffin pointed to several that associated systemic steroids with hospitalization or other markers of severe disease.
The NPF guidance also recommends avoiding chronic systemic steroids in patients with psoriasis during the current COVID-19 era “if possible.” In patients with psoriatic arthritis who require systemic steroids, the guidance recommends “the lowest dose necessary to achieve the desired therapeutic effect.”
This is not necessarily true in patients with psoriasis and COVID-19 infection. Based on the potential for systemic steroids to improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients requiring oxygen, steroids “should not be withheld” even when the justification is concern about the potential risk of flares with withdrawal, according to the NPF guidance statement.
The NPF guidance specifically cautions against use of hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine for prevention or treatment of COVID-19. In addition to an uncertain benefit, these antimalarial drugs have been associated previously with flares of psoriasis.
Dr. Duffin agreed and went on to warn that COVID-19 infection itself is a potential trigger for flares. She cited two published case reports of flares associated with psoriasis. Although one patient had also been exposed to hydroxychloroquine, she said the risk of psoriasis-induced flare “makes sense” based on previous associations made between flares and other viral infections and stress.
In patients with psoriasis who contract COVID-19 infection, Dr. Duffin concurred with the NPF guidance that management decisions should be made on a “case-by-case basis.” Although the NPF guidance states that “most patients can restart psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis treatments after complete resolution of COVID-19 symptoms,” no specific advice was offered on the decision to stop treatments.
For protecting psoriasis patients from infection and managing COVID-19 in those who become infected, much of the NPF advice is consistent with that offered to patients without psoriasis. This involves practicing infection control that reduces risk of transmission. Both the NPF guidance and Dr. Duffin suggested telemedicine is appropriate for limiting in-patient visits under pandemic conditions.
Although patients with psoriasis are more likely than the general population to have the comorbidities associated with bad COVID-19 infection outcomes, according to the NPF guidance, Dr. Duffin called the overall data evaluating susceptibility among psoriasis patients “reassuring.” She cautioned that the data are still limited, but the evidence so far suggests that neither psoriasis nor biologics are independent risk factors for acquiring COVID-19 or having a worse outcome if infected.
Yet, more definitive data are needed, and Dr. Duffin advised clinicians and patients to consult the NPF website for updates. “More up-to-date information will certainly be added as we go forward,” she said at the meeting, jointly presented by the University of Louisville and Global Academy for Medical Education.
This NPF task force on COVID-19 is meeting every 2 weeks, according to Joel M. Gelfand, MD, professor of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and cochair of the task force. Dr. Gelfand reported that updates are based on a discussion of the available data.
“We will be releasing additional recommendations as necessary based on the developments,” he said in an interview. Updates are not necessarily required at this frequency but can be if appropriate. The goal is to keep recommendations current and evidence-based.
Dr. Duffin reported financial relationships with Amgen, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Siena, and UCB. Dr. Gelfand reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Lilly, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB.
This publication and Global Academy for Medical Education are owned by the same parent company.
The available according to a summary of published studies and expert opinions summarized at the annual Coastal Dermatology Symposium, held virtually.
For patients with psoriasis concerned about their outcome if infected with COVID-19, “there is no evidence to support stopping biologics or systemic agents, so I am asking my patients to continue,” Kristina C. Duffin, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, said at the meeting.
The National Psoriasis Foundation, which created a COVID-19 task force and maintains a COVID-19 Resource Center on its website, has provided similar advice. Many statements are phrased cautiously and clinicians are encouraged to practice shared decision-making, but the NPF guidance supports continuing effective therapy – or, in newly diagnosed patients, starting effective therapy – among those who are not infected with SARS-CoV2.
Patients with a new diagnosis of psoriasis “should be aware that untreated psoriatic disease is associated with serious impact on physical and emotional health, and in the case of psoriatic arthritis, can lead to permanent joint damage and disability,” according to the NPF guidance.
Overall, the “existing data generally suggest” that most treatments for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis “do not meaningfully alter the risks of contracting SARS-CoV2 or having a worse course of COVID-19 illness,” the current guidance states. Yet, because of limited data this “is not known with certainty.”
Chronic systemic steroids are an exception. In a review of recently published studies evaluating whether psoriasis or its therapies increase risk of adverse outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection, Dr. Duffin pointed to several that associated systemic steroids with hospitalization or other markers of severe disease.
The NPF guidance also recommends avoiding chronic systemic steroids in patients with psoriasis during the current COVID-19 era “if possible.” In patients with psoriatic arthritis who require systemic steroids, the guidance recommends “the lowest dose necessary to achieve the desired therapeutic effect.”
This is not necessarily true in patients with psoriasis and COVID-19 infection. Based on the potential for systemic steroids to improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients requiring oxygen, steroids “should not be withheld” even when the justification is concern about the potential risk of flares with withdrawal, according to the NPF guidance statement.
The NPF guidance specifically cautions against use of hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine for prevention or treatment of COVID-19. In addition to an uncertain benefit, these antimalarial drugs have been associated previously with flares of psoriasis.
Dr. Duffin agreed and went on to warn that COVID-19 infection itself is a potential trigger for flares. She cited two published case reports of flares associated with psoriasis. Although one patient had also been exposed to hydroxychloroquine, she said the risk of psoriasis-induced flare “makes sense” based on previous associations made between flares and other viral infections and stress.
In patients with psoriasis who contract COVID-19 infection, Dr. Duffin concurred with the NPF guidance that management decisions should be made on a “case-by-case basis.” Although the NPF guidance states that “most patients can restart psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis treatments after complete resolution of COVID-19 symptoms,” no specific advice was offered on the decision to stop treatments.
For protecting psoriasis patients from infection and managing COVID-19 in those who become infected, much of the NPF advice is consistent with that offered to patients without psoriasis. This involves practicing infection control that reduces risk of transmission. Both the NPF guidance and Dr. Duffin suggested telemedicine is appropriate for limiting in-patient visits under pandemic conditions.
Although patients with psoriasis are more likely than the general population to have the comorbidities associated with bad COVID-19 infection outcomes, according to the NPF guidance, Dr. Duffin called the overall data evaluating susceptibility among psoriasis patients “reassuring.” She cautioned that the data are still limited, but the evidence so far suggests that neither psoriasis nor biologics are independent risk factors for acquiring COVID-19 or having a worse outcome if infected.
Yet, more definitive data are needed, and Dr. Duffin advised clinicians and patients to consult the NPF website for updates. “More up-to-date information will certainly be added as we go forward,” she said at the meeting, jointly presented by the University of Louisville and Global Academy for Medical Education.
This NPF task force on COVID-19 is meeting every 2 weeks, according to Joel M. Gelfand, MD, professor of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and cochair of the task force. Dr. Gelfand reported that updates are based on a discussion of the available data.
“We will be releasing additional recommendations as necessary based on the developments,” he said in an interview. Updates are not necessarily required at this frequency but can be if appropriate. The goal is to keep recommendations current and evidence-based.
Dr. Duffin reported financial relationships with Amgen, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Siena, and UCB. Dr. Gelfand reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Lilly, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB.
This publication and Global Academy for Medical Education are owned by the same parent company.
FROM COASTAL DERM
Direct-acting agents cure hepatitis C in children
Between 23,000 and 46,000 U.S. children live with chronic hepatitis C virus with a prevalence of 0.17% anti–hepatitis C virus (HCV) antibody positivity in those aged 6-11 years and 0.39% among children aged 12-19 years. In the United States, genotype 1 is most frequent, followed by genotypes 2 and 3. About 99% of cases result from vertical transmission; transfusion-related cases have not been observed in recent decades.Only viremic mothers are at risk of transmission as those who have spontaneously cleared HCV viremia or have been treated successfully do not risk transmission. Maternal HCV viral load appears to be a risk factor for HCV transmission, however transmission is reported at all levels of viremia.
In conjunction with the opioid epidemics, the prevalence of HCV infection has increased over the last decade. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that, between 2009 and 2014, the prevalence of HCV infection increased from 1.8 to 3.4 per 1,000 live births. They identified substantial state-to-state variation with the highest rate in West Virginia (22.6 per 1,000 live births), and the lowest in Hawaii (0.7 per 1,000 live births). The implications are clear that increasing numbers of newborns are exposed to HCV and, if transmission rates are between 1% and 5%, 80-400 U.S. infants each year acquire HCV infection.
HCV in children
HCV in children is almost always associated with persistent transaminitis. Chronic infection is defined as the persistence of HCV RNA for at least 6 months, and clearance of HCV infection is determined by the persistent disappearance of HCV RNA. Regardless of infection status, an infant may have detectable maternal anti-HCV antibody in serum until 18 months of age, resulting from passive transfer. In addition, prolonged infection can lead to cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, or decompensated liver disease. Potential extrahepatic manifestations including reduced physical and psychosocial health also are linked to chronic HCV. Autoimmune disease also has been reported in children with HCV. As well, the stigma of HCV elicits fear in school and child care settings that is a result of public misunderstanding regarding routes of hepatitis C transmission. No restriction of regular childhood activities is required in the daily life of HCV-infected children.
Taken together, increasing rates of HCV infection in pregnant women, increasing numbers of exposed and infected infants annually, potential for both short- and long-term morbidity, and curative nontoxic treatment,
Screening for HCV
There is considerable discussion about which strategy for screening of at-risk infants is more appropriate. Some groups advocate for HCV-RNA testing within the first year of life. Proponents argue the use of a highly sensitive RNA assay early in life has potential to increase detection of infected infants while a negative result allows the conclusion the infant is not infected. Advocates hypothesize that early identification has potential to improve continued follow-up.
Opponents argue that early testing does not change the need for repeat testing after 18 months to confirm diagnosis. They also argue that HCV RNA is more expensive than an antibody-based testing; and treatment will not begin prior to age 3 as there is still opportunity for viremia to spontaneously clear.
Direct acting agents licensed
Ledipasvir/sofosbuvir (Harvoni) was initially demonstrated as curative for genotype 1, 4, 5, or 6 infection in a phase 2, multicenter, open-label study of 100 adolescents with genotype 1 treated for 12 weeks. Sustained virologic response (SVR) was documented in 98% of participants.The regimen was safe and well tolerated in this population, and the adult dosage formulation resulted in pharmacokinetic characteristics similar to those observed in adults. Two clinical trials supported the efficacy of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir in the pediatric population aged 3-11 years. This regimen also is recommended for interferon-experienced (± ribavirin, with or without an HCV protease inhibitor) children and adolescents aged 3 years or older with genotype 1 or 4. A 12-week course is recommended for patients without cirrhosis; 24 weeks is recommended for those with compensated cirrhosis. The combination of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir is the only treatment option for children aged 3-6 years with genotype 1, 4, 5, or 6 infection.
The efficacy of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir (Epclusa) once daily for 12 weeks was first evaluated in an open-label trial among children aged 6 years and older with genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, or 6 infection, without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis. Subsequently, the “cocktail” was evaluated in children aged 6-12 years, with 76% genotype 1, 3% genotype 2, 15% genotype 3, and 6% genotype 4. SVR12 rates were 93% (50/54) in children with genotype 1, 91% (10/11) in those with genotype 3, and 100% in participants with genotype 2 (2/2) or genotype 4 (4/4). Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir was approved in March 2020 by the Food and Drug Administration for pediatric patients aged 6 years and older. Given its pangenotypic activity, safety, and efficacy, sofosbuvir/velpatasvir is currently recommended as a first choice for HCV treatment in children and adolescents aged at least 6 years.
The daily fixed-dose combination of glecaprevir/pibrentasvir (Mavyret) was approved in April 2019 for adolescents aged 12-17 years, and weighing at least 45 kg.Treatment is for 8 weeks, and includes treatment-naive patients without cirrhosis or those with compensated cirrhosis. SVR12 rates for Mavyret have ranged from 91% to 100 % across clinic trials. FDA approval and HCV guideline treatment recommendations for direct-acting antiviral (DAA)–experienced adolescents are based on clinical trial data from adults. Given its pangenotypic activity, safety, and efficacy record in adult patients, glecaprevir/pibrentasvir is recommended as a first choice for adolescent HCV treatment. Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir once approved for children less than 3 years of age will be safe and efficacious as a pangenotypic treatment option in children with chronic HCV infection.
Current recommendations
Tools for identifying HCV infected infants as early as a few months of age are available, yet studies demonstrate that a minority of at-risk children are tested for HCV using either an HCV polymerase chain reaction strategy early in life or an anti-HCV antibody strategy after 18 months of age.
Therapy with direct-acting agents is now licensed to those aged 3 years and offers the potential for cure, eliminating concern for possible progression after prolonged infection. Such therapy offers the potential to eliminate the stigma faced by many children as well as the hepatic and extrahepatic manifestations observed in children. Medication formulation and the child’s abilities to take the medication needs to be considered when prescribing DAAs. It is important to assess if the child can successfully swallow pills. Currently, Harvoni is the only medication that comes in both pellet and pill formulations. The dose is based on weight. The pellets need to be given in a small amount of nonacidic food; they cannot be chewed.
All children with chronic HCV infection are candidates for treatment. When significant fibrosis and/or cirrhosis is present treatment should not be delayed once the child is age 3 years; when only transaminitis is present, treatment can be delayed. In our experience, parents are eager to complete treatment before starting kindergarten.
Liver biopsy for obtaining liver tissue for histopathologic examination is not routinely indicated in children with chronic HCV infection but should be evaluated case by case. Noninvasive tests of hepatic fibrosis have been used in children, these include serologic markers (i.e., FibroSure) and radiologic tests such as ultrasound-based transient elastography (i.e., Fibroscan). Validation for pediatric patients is variable for the different serologic tests. Studies have shown that Fibroscan using the M probe is feasible for a wide range of ages, but poor patient cooperation may make measurement difficult.
Further details regarding dosing and choice of formulation is available at https://www.hcvguidelines.org/unique-populations/children.
Dr. Sabharwal is assistant professor of pediatrics at Boston University and attending physician in pediatric infectious diseases at Boston Medical Center. Ms. Moloney is an instructor in pediatrics at Boston University and a pediatric nurse practitioner in pediatric infectious diseases at Boston Medicine Center. Dr. Pelton is professor of pediatrics and epidemiology at Boston University and public health and senior attending physician at Boston Medical Center. Boston Medical Center received funding from AbbVie for study of Harvoni in Children 3 years of age and older. Email them at [email protected].
References
MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017 May 12;66(18):470-3. Hepatol Commun. 2017 March 23. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1028. Hepatology. 2020 Feb;71(2):422-30. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Apr 11. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30046-9. Arch Dis Child. 2006 Sep;91(9):781-5. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010 Feb;50(2):123-31.
Between 23,000 and 46,000 U.S. children live with chronic hepatitis C virus with a prevalence of 0.17% anti–hepatitis C virus (HCV) antibody positivity in those aged 6-11 years and 0.39% among children aged 12-19 years. In the United States, genotype 1 is most frequent, followed by genotypes 2 and 3. About 99% of cases result from vertical transmission; transfusion-related cases have not been observed in recent decades.Only viremic mothers are at risk of transmission as those who have spontaneously cleared HCV viremia or have been treated successfully do not risk transmission. Maternal HCV viral load appears to be a risk factor for HCV transmission, however transmission is reported at all levels of viremia.
In conjunction with the opioid epidemics, the prevalence of HCV infection has increased over the last decade. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that, between 2009 and 2014, the prevalence of HCV infection increased from 1.8 to 3.4 per 1,000 live births. They identified substantial state-to-state variation with the highest rate in West Virginia (22.6 per 1,000 live births), and the lowest in Hawaii (0.7 per 1,000 live births). The implications are clear that increasing numbers of newborns are exposed to HCV and, if transmission rates are between 1% and 5%, 80-400 U.S. infants each year acquire HCV infection.
HCV in children
HCV in children is almost always associated with persistent transaminitis. Chronic infection is defined as the persistence of HCV RNA for at least 6 months, and clearance of HCV infection is determined by the persistent disappearance of HCV RNA. Regardless of infection status, an infant may have detectable maternal anti-HCV antibody in serum until 18 months of age, resulting from passive transfer. In addition, prolonged infection can lead to cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, or decompensated liver disease. Potential extrahepatic manifestations including reduced physical and psychosocial health also are linked to chronic HCV. Autoimmune disease also has been reported in children with HCV. As well, the stigma of HCV elicits fear in school and child care settings that is a result of public misunderstanding regarding routes of hepatitis C transmission. No restriction of regular childhood activities is required in the daily life of HCV-infected children.
Taken together, increasing rates of HCV infection in pregnant women, increasing numbers of exposed and infected infants annually, potential for both short- and long-term morbidity, and curative nontoxic treatment,
Screening for HCV
There is considerable discussion about which strategy for screening of at-risk infants is more appropriate. Some groups advocate for HCV-RNA testing within the first year of life. Proponents argue the use of a highly sensitive RNA assay early in life has potential to increase detection of infected infants while a negative result allows the conclusion the infant is not infected. Advocates hypothesize that early identification has potential to improve continued follow-up.
Opponents argue that early testing does not change the need for repeat testing after 18 months to confirm diagnosis. They also argue that HCV RNA is more expensive than an antibody-based testing; and treatment will not begin prior to age 3 as there is still opportunity for viremia to spontaneously clear.
Direct acting agents licensed
Ledipasvir/sofosbuvir (Harvoni) was initially demonstrated as curative for genotype 1, 4, 5, or 6 infection in a phase 2, multicenter, open-label study of 100 adolescents with genotype 1 treated for 12 weeks. Sustained virologic response (SVR) was documented in 98% of participants.The regimen was safe and well tolerated in this population, and the adult dosage formulation resulted in pharmacokinetic characteristics similar to those observed in adults. Two clinical trials supported the efficacy of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir in the pediatric population aged 3-11 years. This regimen also is recommended for interferon-experienced (± ribavirin, with or without an HCV protease inhibitor) children and adolescents aged 3 years or older with genotype 1 or 4. A 12-week course is recommended for patients without cirrhosis; 24 weeks is recommended for those with compensated cirrhosis. The combination of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir is the only treatment option for children aged 3-6 years with genotype 1, 4, 5, or 6 infection.
The efficacy of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir (Epclusa) once daily for 12 weeks was first evaluated in an open-label trial among children aged 6 years and older with genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, or 6 infection, without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis. Subsequently, the “cocktail” was evaluated in children aged 6-12 years, with 76% genotype 1, 3% genotype 2, 15% genotype 3, and 6% genotype 4. SVR12 rates were 93% (50/54) in children with genotype 1, 91% (10/11) in those with genotype 3, and 100% in participants with genotype 2 (2/2) or genotype 4 (4/4). Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir was approved in March 2020 by the Food and Drug Administration for pediatric patients aged 6 years and older. Given its pangenotypic activity, safety, and efficacy, sofosbuvir/velpatasvir is currently recommended as a first choice for HCV treatment in children and adolescents aged at least 6 years.
The daily fixed-dose combination of glecaprevir/pibrentasvir (Mavyret) was approved in April 2019 for adolescents aged 12-17 years, and weighing at least 45 kg.Treatment is for 8 weeks, and includes treatment-naive patients without cirrhosis or those with compensated cirrhosis. SVR12 rates for Mavyret have ranged from 91% to 100 % across clinic trials. FDA approval and HCV guideline treatment recommendations for direct-acting antiviral (DAA)–experienced adolescents are based on clinical trial data from adults. Given its pangenotypic activity, safety, and efficacy record in adult patients, glecaprevir/pibrentasvir is recommended as a first choice for adolescent HCV treatment. Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir once approved for children less than 3 years of age will be safe and efficacious as a pangenotypic treatment option in children with chronic HCV infection.
Current recommendations
Tools for identifying HCV infected infants as early as a few months of age are available, yet studies demonstrate that a minority of at-risk children are tested for HCV using either an HCV polymerase chain reaction strategy early in life or an anti-HCV antibody strategy after 18 months of age.
Therapy with direct-acting agents is now licensed to those aged 3 years and offers the potential for cure, eliminating concern for possible progression after prolonged infection. Such therapy offers the potential to eliminate the stigma faced by many children as well as the hepatic and extrahepatic manifestations observed in children. Medication formulation and the child’s abilities to take the medication needs to be considered when prescribing DAAs. It is important to assess if the child can successfully swallow pills. Currently, Harvoni is the only medication that comes in both pellet and pill formulations. The dose is based on weight. The pellets need to be given in a small amount of nonacidic food; they cannot be chewed.
All children with chronic HCV infection are candidates for treatment. When significant fibrosis and/or cirrhosis is present treatment should not be delayed once the child is age 3 years; when only transaminitis is present, treatment can be delayed. In our experience, parents are eager to complete treatment before starting kindergarten.
Liver biopsy for obtaining liver tissue for histopathologic examination is not routinely indicated in children with chronic HCV infection but should be evaluated case by case. Noninvasive tests of hepatic fibrosis have been used in children, these include serologic markers (i.e., FibroSure) and radiologic tests such as ultrasound-based transient elastography (i.e., Fibroscan). Validation for pediatric patients is variable for the different serologic tests. Studies have shown that Fibroscan using the M probe is feasible for a wide range of ages, but poor patient cooperation may make measurement difficult.
Further details regarding dosing and choice of formulation is available at https://www.hcvguidelines.org/unique-populations/children.
Dr. Sabharwal is assistant professor of pediatrics at Boston University and attending physician in pediatric infectious diseases at Boston Medical Center. Ms. Moloney is an instructor in pediatrics at Boston University and a pediatric nurse practitioner in pediatric infectious diseases at Boston Medicine Center. Dr. Pelton is professor of pediatrics and epidemiology at Boston University and public health and senior attending physician at Boston Medical Center. Boston Medical Center received funding from AbbVie for study of Harvoni in Children 3 years of age and older. Email them at [email protected].
References
MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017 May 12;66(18):470-3. Hepatol Commun. 2017 March 23. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1028. Hepatology. 2020 Feb;71(2):422-30. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Apr 11. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30046-9. Arch Dis Child. 2006 Sep;91(9):781-5. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010 Feb;50(2):123-31.
Between 23,000 and 46,000 U.S. children live with chronic hepatitis C virus with a prevalence of 0.17% anti–hepatitis C virus (HCV) antibody positivity in those aged 6-11 years and 0.39% among children aged 12-19 years. In the United States, genotype 1 is most frequent, followed by genotypes 2 and 3. About 99% of cases result from vertical transmission; transfusion-related cases have not been observed in recent decades.Only viremic mothers are at risk of transmission as those who have spontaneously cleared HCV viremia or have been treated successfully do not risk transmission. Maternal HCV viral load appears to be a risk factor for HCV transmission, however transmission is reported at all levels of viremia.
In conjunction with the opioid epidemics, the prevalence of HCV infection has increased over the last decade. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that, between 2009 and 2014, the prevalence of HCV infection increased from 1.8 to 3.4 per 1,000 live births. They identified substantial state-to-state variation with the highest rate in West Virginia (22.6 per 1,000 live births), and the lowest in Hawaii (0.7 per 1,000 live births). The implications are clear that increasing numbers of newborns are exposed to HCV and, if transmission rates are between 1% and 5%, 80-400 U.S. infants each year acquire HCV infection.
HCV in children
HCV in children is almost always associated with persistent transaminitis. Chronic infection is defined as the persistence of HCV RNA for at least 6 months, and clearance of HCV infection is determined by the persistent disappearance of HCV RNA. Regardless of infection status, an infant may have detectable maternal anti-HCV antibody in serum until 18 months of age, resulting from passive transfer. In addition, prolonged infection can lead to cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, or decompensated liver disease. Potential extrahepatic manifestations including reduced physical and psychosocial health also are linked to chronic HCV. Autoimmune disease also has been reported in children with HCV. As well, the stigma of HCV elicits fear in school and child care settings that is a result of public misunderstanding regarding routes of hepatitis C transmission. No restriction of regular childhood activities is required in the daily life of HCV-infected children.
Taken together, increasing rates of HCV infection in pregnant women, increasing numbers of exposed and infected infants annually, potential for both short- and long-term morbidity, and curative nontoxic treatment,
Screening for HCV
There is considerable discussion about which strategy for screening of at-risk infants is more appropriate. Some groups advocate for HCV-RNA testing within the first year of life. Proponents argue the use of a highly sensitive RNA assay early in life has potential to increase detection of infected infants while a negative result allows the conclusion the infant is not infected. Advocates hypothesize that early identification has potential to improve continued follow-up.
Opponents argue that early testing does not change the need for repeat testing after 18 months to confirm diagnosis. They also argue that HCV RNA is more expensive than an antibody-based testing; and treatment will not begin prior to age 3 as there is still opportunity for viremia to spontaneously clear.
Direct acting agents licensed
Ledipasvir/sofosbuvir (Harvoni) was initially demonstrated as curative for genotype 1, 4, 5, or 6 infection in a phase 2, multicenter, open-label study of 100 adolescents with genotype 1 treated for 12 weeks. Sustained virologic response (SVR) was documented in 98% of participants.The regimen was safe and well tolerated in this population, and the adult dosage formulation resulted in pharmacokinetic characteristics similar to those observed in adults. Two clinical trials supported the efficacy of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir in the pediatric population aged 3-11 years. This regimen also is recommended for interferon-experienced (± ribavirin, with or without an HCV protease inhibitor) children and adolescents aged 3 years or older with genotype 1 or 4. A 12-week course is recommended for patients without cirrhosis; 24 weeks is recommended for those with compensated cirrhosis. The combination of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir is the only treatment option for children aged 3-6 years with genotype 1, 4, 5, or 6 infection.
The efficacy of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir (Epclusa) once daily for 12 weeks was first evaluated in an open-label trial among children aged 6 years and older with genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, or 6 infection, without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis. Subsequently, the “cocktail” was evaluated in children aged 6-12 years, with 76% genotype 1, 3% genotype 2, 15% genotype 3, and 6% genotype 4. SVR12 rates were 93% (50/54) in children with genotype 1, 91% (10/11) in those with genotype 3, and 100% in participants with genotype 2 (2/2) or genotype 4 (4/4). Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir was approved in March 2020 by the Food and Drug Administration for pediatric patients aged 6 years and older. Given its pangenotypic activity, safety, and efficacy, sofosbuvir/velpatasvir is currently recommended as a first choice for HCV treatment in children and adolescents aged at least 6 years.
The daily fixed-dose combination of glecaprevir/pibrentasvir (Mavyret) was approved in April 2019 for adolescents aged 12-17 years, and weighing at least 45 kg.Treatment is for 8 weeks, and includes treatment-naive patients without cirrhosis or those with compensated cirrhosis. SVR12 rates for Mavyret have ranged from 91% to 100 % across clinic trials. FDA approval and HCV guideline treatment recommendations for direct-acting antiviral (DAA)–experienced adolescents are based on clinical trial data from adults. Given its pangenotypic activity, safety, and efficacy record in adult patients, glecaprevir/pibrentasvir is recommended as a first choice for adolescent HCV treatment. Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir once approved for children less than 3 years of age will be safe and efficacious as a pangenotypic treatment option in children with chronic HCV infection.
Current recommendations
Tools for identifying HCV infected infants as early as a few months of age are available, yet studies demonstrate that a minority of at-risk children are tested for HCV using either an HCV polymerase chain reaction strategy early in life or an anti-HCV antibody strategy after 18 months of age.
Therapy with direct-acting agents is now licensed to those aged 3 years and offers the potential for cure, eliminating concern for possible progression after prolonged infection. Such therapy offers the potential to eliminate the stigma faced by many children as well as the hepatic and extrahepatic manifestations observed in children. Medication formulation and the child’s abilities to take the medication needs to be considered when prescribing DAAs. It is important to assess if the child can successfully swallow pills. Currently, Harvoni is the only medication that comes in both pellet and pill formulations. The dose is based on weight. The pellets need to be given in a small amount of nonacidic food; they cannot be chewed.
All children with chronic HCV infection are candidates for treatment. When significant fibrosis and/or cirrhosis is present treatment should not be delayed once the child is age 3 years; when only transaminitis is present, treatment can be delayed. In our experience, parents are eager to complete treatment before starting kindergarten.
Liver biopsy for obtaining liver tissue for histopathologic examination is not routinely indicated in children with chronic HCV infection but should be evaluated case by case. Noninvasive tests of hepatic fibrosis have been used in children, these include serologic markers (i.e., FibroSure) and radiologic tests such as ultrasound-based transient elastography (i.e., Fibroscan). Validation for pediatric patients is variable for the different serologic tests. Studies have shown that Fibroscan using the M probe is feasible for a wide range of ages, but poor patient cooperation may make measurement difficult.
Further details regarding dosing and choice of formulation is available at https://www.hcvguidelines.org/unique-populations/children.
Dr. Sabharwal is assistant professor of pediatrics at Boston University and attending physician in pediatric infectious diseases at Boston Medical Center. Ms. Moloney is an instructor in pediatrics at Boston University and a pediatric nurse practitioner in pediatric infectious diseases at Boston Medicine Center. Dr. Pelton is professor of pediatrics and epidemiology at Boston University and public health and senior attending physician at Boston Medical Center. Boston Medical Center received funding from AbbVie for study of Harvoni in Children 3 years of age and older. Email them at [email protected].
References
MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017 May 12;66(18):470-3. Hepatol Commun. 2017 March 23. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1028. Hepatology. 2020 Feb;71(2):422-30. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Apr 11. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30046-9. Arch Dis Child. 2006 Sep;91(9):781-5. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010 Feb;50(2):123-31.
CDC expands definition of COVID-19 exposure from ‘close contact’
New data suggest each close encounter – coming within 6 feet of an infected person – can increase the risk for transmission, CDC director Robert Redfield, MD, said during a media briefing.
“As we get more data and understand the science of COVID, we’re going to continue to incorporate that in our recommendations,” Dr. Redfield said in response to a reporter’s question about a recent study.
Previously, the CDC cautioned against spending 15 minutes or longer in close proximity to an infected person, particularly in enclosed indoor spaces.
In a new report published online Oct. 21 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, however, investigators “determined that an individual who had a series of shorter contacts that over time added up to more than 15 minutes became infected.”
Beware of brief encounters?
On July 28, a 20-year-old male correctional officer in Vermont had multiple brief encounters with six transferred incarcerated or detained people while their SARS-CoV-2 test results were pending. The six were asymptomatic at the time and were housed in a quarantine unit, reported CDC researcher Julia Pringle, PhD, and colleagues.
The following day, all six inmates tested polymerase chain reaction (PCR) positive for COVID-19. The correctional officer did not spend 15 minutes or more within 6 feet of any of the inmates, according to video surveillance footage, and he continued to work.
On Aug. 4, however, he developed symptoms that included loss of smell and taste, myalgia, runny nose, cough, shortness of breath, headache, loss of appetite, and gastrointestinal symptoms. He stayed home starting the next day and tested PCR positive for COVID-19 on Aug. 11.
Further review of the surveillance video showed that the officer had numerous brief encounters of approximately 1 minute each that cumulatively exceeded 15 minutes over a 24-hour period, the researchers reported.
During all the interactions with inmates, the correctional officer wore a cloth mask, gown, and eye protection. The inmates wore masks while in their cells but did not have them on during brief cell doorway interactions or in the recreation room, according to the report.
No interaction is 100% safe
“We know that every activity that involves interacting with others has some degree of risk right now,” said Jay Butler, MD, CDC deputy director for infectious diseases.
“Unfortunately, we’re seeing a distressing trend here in the United States with COVID-19 cases increasing in nearly 75% of the country,” he said. “We’ve confirmed 8.1 million cases and, sadly, over 220,000 deaths since January.
“I know these are numbers, but these are also people,” Dr. Butler added.
“The pandemic is not over,” Dr. Redfield said. “Earlier this week, COVID virus cases reached over 40 million globally. Here in the United States we are approaching a critical phase.”
Four factors associated with higher risk for transmission are the proximity of each encounter, its duration, whether an interaction takes place indoors or outdoors, and the number of people encountered, Dr. Butler said.
Dr. Butler acknowledged widespread fatigue with adherence to personal protection measures, but added that social distancing, mask-wearing, and other measures are more important now than ever. He noted that more Americans will be spending time indoors with the onset of cooler weather and the upcoming holidays.
A note of optimism
Dr. Redfield remains optimistic about the limited availability of a vaccine or vaccines by year’s end but added that “it’s important for all of us to remain diligent in our efforts to defeat this virus.”
“There is hope on the way, in the form of safe and effective vaccines in a matter of weeks or months. To bridge to that next phase, we have to take steps to keep ourselves, our families, and our communities safe,” said Alex Azar, secretary of the Department of Health & Human Services.
“I know it’s been a difficult year for Americans, but we are going to come through this on the other side,” Dr. Redfield said.
New data suggest each close encounter – coming within 6 feet of an infected person – can increase the risk for transmission, CDC director Robert Redfield, MD, said during a media briefing.
“As we get more data and understand the science of COVID, we’re going to continue to incorporate that in our recommendations,” Dr. Redfield said in response to a reporter’s question about a recent study.
Previously, the CDC cautioned against spending 15 minutes or longer in close proximity to an infected person, particularly in enclosed indoor spaces.
In a new report published online Oct. 21 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, however, investigators “determined that an individual who had a series of shorter contacts that over time added up to more than 15 minutes became infected.”
Beware of brief encounters?
On July 28, a 20-year-old male correctional officer in Vermont had multiple brief encounters with six transferred incarcerated or detained people while their SARS-CoV-2 test results were pending. The six were asymptomatic at the time and were housed in a quarantine unit, reported CDC researcher Julia Pringle, PhD, and colleagues.
The following day, all six inmates tested polymerase chain reaction (PCR) positive for COVID-19. The correctional officer did not spend 15 minutes or more within 6 feet of any of the inmates, according to video surveillance footage, and he continued to work.
On Aug. 4, however, he developed symptoms that included loss of smell and taste, myalgia, runny nose, cough, shortness of breath, headache, loss of appetite, and gastrointestinal symptoms. He stayed home starting the next day and tested PCR positive for COVID-19 on Aug. 11.
Further review of the surveillance video showed that the officer had numerous brief encounters of approximately 1 minute each that cumulatively exceeded 15 minutes over a 24-hour period, the researchers reported.
During all the interactions with inmates, the correctional officer wore a cloth mask, gown, and eye protection. The inmates wore masks while in their cells but did not have them on during brief cell doorway interactions or in the recreation room, according to the report.
No interaction is 100% safe
“We know that every activity that involves interacting with others has some degree of risk right now,” said Jay Butler, MD, CDC deputy director for infectious diseases.
“Unfortunately, we’re seeing a distressing trend here in the United States with COVID-19 cases increasing in nearly 75% of the country,” he said. “We’ve confirmed 8.1 million cases and, sadly, over 220,000 deaths since January.
“I know these are numbers, but these are also people,” Dr. Butler added.
“The pandemic is not over,” Dr. Redfield said. “Earlier this week, COVID virus cases reached over 40 million globally. Here in the United States we are approaching a critical phase.”
Four factors associated with higher risk for transmission are the proximity of each encounter, its duration, whether an interaction takes place indoors or outdoors, and the number of people encountered, Dr. Butler said.
Dr. Butler acknowledged widespread fatigue with adherence to personal protection measures, but added that social distancing, mask-wearing, and other measures are more important now than ever. He noted that more Americans will be spending time indoors with the onset of cooler weather and the upcoming holidays.
A note of optimism
Dr. Redfield remains optimistic about the limited availability of a vaccine or vaccines by year’s end but added that “it’s important for all of us to remain diligent in our efforts to defeat this virus.”
“There is hope on the way, in the form of safe and effective vaccines in a matter of weeks or months. To bridge to that next phase, we have to take steps to keep ourselves, our families, and our communities safe,” said Alex Azar, secretary of the Department of Health & Human Services.
“I know it’s been a difficult year for Americans, but we are going to come through this on the other side,” Dr. Redfield said.
New data suggest each close encounter – coming within 6 feet of an infected person – can increase the risk for transmission, CDC director Robert Redfield, MD, said during a media briefing.
“As we get more data and understand the science of COVID, we’re going to continue to incorporate that in our recommendations,” Dr. Redfield said in response to a reporter’s question about a recent study.
Previously, the CDC cautioned against spending 15 minutes or longer in close proximity to an infected person, particularly in enclosed indoor spaces.
In a new report published online Oct. 21 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, however, investigators “determined that an individual who had a series of shorter contacts that over time added up to more than 15 minutes became infected.”
Beware of brief encounters?
On July 28, a 20-year-old male correctional officer in Vermont had multiple brief encounters with six transferred incarcerated or detained people while their SARS-CoV-2 test results were pending. The six were asymptomatic at the time and were housed in a quarantine unit, reported CDC researcher Julia Pringle, PhD, and colleagues.
The following day, all six inmates tested polymerase chain reaction (PCR) positive for COVID-19. The correctional officer did not spend 15 minutes or more within 6 feet of any of the inmates, according to video surveillance footage, and he continued to work.
On Aug. 4, however, he developed symptoms that included loss of smell and taste, myalgia, runny nose, cough, shortness of breath, headache, loss of appetite, and gastrointestinal symptoms. He stayed home starting the next day and tested PCR positive for COVID-19 on Aug. 11.
Further review of the surveillance video showed that the officer had numerous brief encounters of approximately 1 minute each that cumulatively exceeded 15 minutes over a 24-hour period, the researchers reported.
During all the interactions with inmates, the correctional officer wore a cloth mask, gown, and eye protection. The inmates wore masks while in their cells but did not have them on during brief cell doorway interactions or in the recreation room, according to the report.
No interaction is 100% safe
“We know that every activity that involves interacting with others has some degree of risk right now,” said Jay Butler, MD, CDC deputy director for infectious diseases.
“Unfortunately, we’re seeing a distressing trend here in the United States with COVID-19 cases increasing in nearly 75% of the country,” he said. “We’ve confirmed 8.1 million cases and, sadly, over 220,000 deaths since January.
“I know these are numbers, but these are also people,” Dr. Butler added.
“The pandemic is not over,” Dr. Redfield said. “Earlier this week, COVID virus cases reached over 40 million globally. Here in the United States we are approaching a critical phase.”
Four factors associated with higher risk for transmission are the proximity of each encounter, its duration, whether an interaction takes place indoors or outdoors, and the number of people encountered, Dr. Butler said.
Dr. Butler acknowledged widespread fatigue with adherence to personal protection measures, but added that social distancing, mask-wearing, and other measures are more important now than ever. He noted that more Americans will be spending time indoors with the onset of cooler weather and the upcoming holidays.
A note of optimism
Dr. Redfield remains optimistic about the limited availability of a vaccine or vaccines by year’s end but added that “it’s important for all of us to remain diligent in our efforts to defeat this virus.”
“There is hope on the way, in the form of safe and effective vaccines in a matter of weeks or months. To bridge to that next phase, we have to take steps to keep ourselves, our families, and our communities safe,” said Alex Azar, secretary of the Department of Health & Human Services.
“I know it’s been a difficult year for Americans, but we are going to come through this on the other side,” Dr. Redfield said.
COVID-19: Convalescent plasma falls short in phase 2 trial
Convalescent plasma may not prevent progression to severe disease or reduce mortality risk in hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19, based on a phase 2 trial involving more than 400 patients in India.
The PLACID trial offers real-world data with “high generalizability,” according to lead author Anup Agarwal, MD, of the Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, and colleagues.
“Evidence suggests that convalescent plasma collected from survivors of COVID-19 contains receptor binding domain specific antibodies with potent antiviral activity,” the investigators wrote in the BMJ. “However, effective titers of antiviral neutralizing antibodies, optimal timing for convalescent plasma treatment, optimal timing for plasma donation, and the severity class of patients who are likely to benefit from convalescent plasma remain unclear.”
According to Dr. Agarwal and colleagues, case series and observational studies have suggested that convalescent plasma may reduce viral load, hospital stay, and mortality, but randomized controlled trials to date have ended prematurely because of issues with enrollment and design, making PLACID the first randomized controlled trial of its kind to reach completion.
The open-label, multicenter study involved 464 hospitalized adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 via reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Enrollment also required a respiratory rate of more than 24 breaths/min with an oxygen saturation (SpO2) of 93% or less on room air, or a partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood/fraction of inspired oxygen (PaO2 /FiO2 ) ratio between 200 and 300 mm Hg.
Patients were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive either best standard of care (control), or best standard of care plus convalescent plasma, which was given in two doses of 200 mL, 24 hours apart. Patients were assessed via clinical examination, chest imaging, and serial laboratory testing, the latter of which included neutralizing antibody titers on days 0, 3, and 7.
The primary outcome was a 28-day composite of progression to severe disease (PaO2/FiO2 ratio < 100 mm Hg) and all-cause mortality. An array of secondary outcomes were also reported, including symptom resolution, total duration of respiratory support, change in oxygen requirement, and others.
In the convalescent plasma group, 19% of patients progressed to severe disease or died within 28 days, compared with 18% of those in the control group (risk ratio, 1.04; 95% confidence interval, 0.71-1.54), suggesting no statistically significant benefit from the intervention. This lack of benefit was also found in a subgroup analysis of patients with detectable titers of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2, and when progression to severe disease and all-cause mortality were analyzed independently across all patients.
Still, at day 7, patients treated with convalescent plasma were significantly more likely to have resolution of fatigue (RR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.02-1.42) and shortness of breath (RR, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.02-1.32). And at the same time point, patients treated with convalescent plasma were 20% more likely to test negative for SARS-CoV-2 RNA (RR, 1.2; 95% CI, 1.04-1.5).
In an accompanying editorial, Elizabeth B. Pathak, PhD, of the Women’s Institute for Independent Social Enquiry, Olney, Md., suggested that the reported symptom improvements need to be viewed with skepticism.
“These results should be interpreted with caution, because the trial was not blinded, so knowledge of treatment status could have influenced the reporting of subjective symptoms by patients who survived to day 7,” Dr. Pathak wrote.
Dr. Pathak noted that convalescent plasma did appear to have an antiviral effect, based on the higher rate of negative RNA test results at day 7. She hypothesized that the lack of major corresponding clinical benefit could be explained by detrimental thrombotic processes.
“The net effect of plasma is prothrombotic,” Dr. Pathak wrote, which should raise safety concerns, since “COVID-19 is a life-threatening thrombotic disorder.”
According to Dr. Pathak, large-scale datasets may be giving a false sense of security. She cited a recent safety analysis of 20,000 U.S. patients who received convalescent plasma, in which the investigators excluded 88.2% of cardiac events and 66.3% of thrombotic events, as these were deemed unrelated to transfusion; but this decision was made by the treating physician, without independent review or a defined protocol.
Michael J. Joyner, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., was the lead author of the above safety study, and is leading the Food and Drug Administration expanded access program for convalescent plasma in patients with COVID-19. He suggested that the study by Dr. Agarwal and colleagues was admirable, but flaws in the treatment protocol cast doubt upon the efficacy findings.
“It is very impressive that these investigators performed a large trial of convalescent plasma in the midst of a pandemic,” Dr. Joyner said. “Unfortunately it is unclear how generalizable the findings are because many of the units of plasma had either very low or no antibody titers and because the plasma was given late in the course of the disease. It has been known since at least the 1930s that antibody therapy works best when enough product is given either prophylactically or early in the course of disease.”
Dr. Joyner had a more positive interpretation of the reported symptom improvements.
“It is also interesting to note that while there was no mortality benefit, that – even with the limitations of the study – there was some evidence of improved patient physiology at 7 days,” he said. “So, at one level, [this is] a negative study, but at least [there are] some hints of efficacy given the suboptimal use case in the patients studied.”
The study was funded by the Indian Council of Medical Research, which employs several of the authors and PLACID Trial Collaborators. Dr. Pathak and Dr. Joyner reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Agarwal A et al. BMJ. 2020 Oct 23. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m3939 .
Convalescent plasma may not prevent progression to severe disease or reduce mortality risk in hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19, based on a phase 2 trial involving more than 400 patients in India.
The PLACID trial offers real-world data with “high generalizability,” according to lead author Anup Agarwal, MD, of the Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, and colleagues.
“Evidence suggests that convalescent plasma collected from survivors of COVID-19 contains receptor binding domain specific antibodies with potent antiviral activity,” the investigators wrote in the BMJ. “However, effective titers of antiviral neutralizing antibodies, optimal timing for convalescent plasma treatment, optimal timing for plasma donation, and the severity class of patients who are likely to benefit from convalescent plasma remain unclear.”
According to Dr. Agarwal and colleagues, case series and observational studies have suggested that convalescent plasma may reduce viral load, hospital stay, and mortality, but randomized controlled trials to date have ended prematurely because of issues with enrollment and design, making PLACID the first randomized controlled trial of its kind to reach completion.
The open-label, multicenter study involved 464 hospitalized adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 via reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Enrollment also required a respiratory rate of more than 24 breaths/min with an oxygen saturation (SpO2) of 93% or less on room air, or a partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood/fraction of inspired oxygen (PaO2 /FiO2 ) ratio between 200 and 300 mm Hg.
Patients were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive either best standard of care (control), or best standard of care plus convalescent plasma, which was given in two doses of 200 mL, 24 hours apart. Patients were assessed via clinical examination, chest imaging, and serial laboratory testing, the latter of which included neutralizing antibody titers on days 0, 3, and 7.
The primary outcome was a 28-day composite of progression to severe disease (PaO2/FiO2 ratio < 100 mm Hg) and all-cause mortality. An array of secondary outcomes were also reported, including symptom resolution, total duration of respiratory support, change in oxygen requirement, and others.
In the convalescent plasma group, 19% of patients progressed to severe disease or died within 28 days, compared with 18% of those in the control group (risk ratio, 1.04; 95% confidence interval, 0.71-1.54), suggesting no statistically significant benefit from the intervention. This lack of benefit was also found in a subgroup analysis of patients with detectable titers of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2, and when progression to severe disease and all-cause mortality were analyzed independently across all patients.
Still, at day 7, patients treated with convalescent plasma were significantly more likely to have resolution of fatigue (RR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.02-1.42) and shortness of breath (RR, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.02-1.32). And at the same time point, patients treated with convalescent plasma were 20% more likely to test negative for SARS-CoV-2 RNA (RR, 1.2; 95% CI, 1.04-1.5).
In an accompanying editorial, Elizabeth B. Pathak, PhD, of the Women’s Institute for Independent Social Enquiry, Olney, Md., suggested that the reported symptom improvements need to be viewed with skepticism.
“These results should be interpreted with caution, because the trial was not blinded, so knowledge of treatment status could have influenced the reporting of subjective symptoms by patients who survived to day 7,” Dr. Pathak wrote.
Dr. Pathak noted that convalescent plasma did appear to have an antiviral effect, based on the higher rate of negative RNA test results at day 7. She hypothesized that the lack of major corresponding clinical benefit could be explained by detrimental thrombotic processes.
“The net effect of plasma is prothrombotic,” Dr. Pathak wrote, which should raise safety concerns, since “COVID-19 is a life-threatening thrombotic disorder.”
According to Dr. Pathak, large-scale datasets may be giving a false sense of security. She cited a recent safety analysis of 20,000 U.S. patients who received convalescent plasma, in which the investigators excluded 88.2% of cardiac events and 66.3% of thrombotic events, as these were deemed unrelated to transfusion; but this decision was made by the treating physician, without independent review or a defined protocol.
Michael J. Joyner, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., was the lead author of the above safety study, and is leading the Food and Drug Administration expanded access program for convalescent plasma in patients with COVID-19. He suggested that the study by Dr. Agarwal and colleagues was admirable, but flaws in the treatment protocol cast doubt upon the efficacy findings.
“It is very impressive that these investigators performed a large trial of convalescent plasma in the midst of a pandemic,” Dr. Joyner said. “Unfortunately it is unclear how generalizable the findings are because many of the units of plasma had either very low or no antibody titers and because the plasma was given late in the course of the disease. It has been known since at least the 1930s that antibody therapy works best when enough product is given either prophylactically or early in the course of disease.”
Dr. Joyner had a more positive interpretation of the reported symptom improvements.
“It is also interesting to note that while there was no mortality benefit, that – even with the limitations of the study – there was some evidence of improved patient physiology at 7 days,” he said. “So, at one level, [this is] a negative study, but at least [there are] some hints of efficacy given the suboptimal use case in the patients studied.”
The study was funded by the Indian Council of Medical Research, which employs several of the authors and PLACID Trial Collaborators. Dr. Pathak and Dr. Joyner reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Agarwal A et al. BMJ. 2020 Oct 23. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m3939 .
Convalescent plasma may not prevent progression to severe disease or reduce mortality risk in hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19, based on a phase 2 trial involving more than 400 patients in India.
The PLACID trial offers real-world data with “high generalizability,” according to lead author Anup Agarwal, MD, of the Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, and colleagues.
“Evidence suggests that convalescent plasma collected from survivors of COVID-19 contains receptor binding domain specific antibodies with potent antiviral activity,” the investigators wrote in the BMJ. “However, effective titers of antiviral neutralizing antibodies, optimal timing for convalescent plasma treatment, optimal timing for plasma donation, and the severity class of patients who are likely to benefit from convalescent plasma remain unclear.”
According to Dr. Agarwal and colleagues, case series and observational studies have suggested that convalescent plasma may reduce viral load, hospital stay, and mortality, but randomized controlled trials to date have ended prematurely because of issues with enrollment and design, making PLACID the first randomized controlled trial of its kind to reach completion.
The open-label, multicenter study involved 464 hospitalized adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 via reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Enrollment also required a respiratory rate of more than 24 breaths/min with an oxygen saturation (SpO2) of 93% or less on room air, or a partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood/fraction of inspired oxygen (PaO2 /FiO2 ) ratio between 200 and 300 mm Hg.
Patients were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive either best standard of care (control), or best standard of care plus convalescent plasma, which was given in two doses of 200 mL, 24 hours apart. Patients were assessed via clinical examination, chest imaging, and serial laboratory testing, the latter of which included neutralizing antibody titers on days 0, 3, and 7.
The primary outcome was a 28-day composite of progression to severe disease (PaO2/FiO2 ratio < 100 mm Hg) and all-cause mortality. An array of secondary outcomes were also reported, including symptom resolution, total duration of respiratory support, change in oxygen requirement, and others.
In the convalescent plasma group, 19% of patients progressed to severe disease or died within 28 days, compared with 18% of those in the control group (risk ratio, 1.04; 95% confidence interval, 0.71-1.54), suggesting no statistically significant benefit from the intervention. This lack of benefit was also found in a subgroup analysis of patients with detectable titers of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2, and when progression to severe disease and all-cause mortality were analyzed independently across all patients.
Still, at day 7, patients treated with convalescent plasma were significantly more likely to have resolution of fatigue (RR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.02-1.42) and shortness of breath (RR, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.02-1.32). And at the same time point, patients treated with convalescent plasma were 20% more likely to test negative for SARS-CoV-2 RNA (RR, 1.2; 95% CI, 1.04-1.5).
In an accompanying editorial, Elizabeth B. Pathak, PhD, of the Women’s Institute for Independent Social Enquiry, Olney, Md., suggested that the reported symptom improvements need to be viewed with skepticism.
“These results should be interpreted with caution, because the trial was not blinded, so knowledge of treatment status could have influenced the reporting of subjective symptoms by patients who survived to day 7,” Dr. Pathak wrote.
Dr. Pathak noted that convalescent plasma did appear to have an antiviral effect, based on the higher rate of negative RNA test results at day 7. She hypothesized that the lack of major corresponding clinical benefit could be explained by detrimental thrombotic processes.
“The net effect of plasma is prothrombotic,” Dr. Pathak wrote, which should raise safety concerns, since “COVID-19 is a life-threatening thrombotic disorder.”
According to Dr. Pathak, large-scale datasets may be giving a false sense of security. She cited a recent safety analysis of 20,000 U.S. patients who received convalescent plasma, in which the investigators excluded 88.2% of cardiac events and 66.3% of thrombotic events, as these were deemed unrelated to transfusion; but this decision was made by the treating physician, without independent review or a defined protocol.
Michael J. Joyner, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., was the lead author of the above safety study, and is leading the Food and Drug Administration expanded access program for convalescent plasma in patients with COVID-19. He suggested that the study by Dr. Agarwal and colleagues was admirable, but flaws in the treatment protocol cast doubt upon the efficacy findings.
“It is very impressive that these investigators performed a large trial of convalescent plasma in the midst of a pandemic,” Dr. Joyner said. “Unfortunately it is unclear how generalizable the findings are because many of the units of plasma had either very low or no antibody titers and because the plasma was given late in the course of the disease. It has been known since at least the 1930s that antibody therapy works best when enough product is given either prophylactically or early in the course of disease.”
Dr. Joyner had a more positive interpretation of the reported symptom improvements.
“It is also interesting to note that while there was no mortality benefit, that – even with the limitations of the study – there was some evidence of improved patient physiology at 7 days,” he said. “So, at one level, [this is] a negative study, but at least [there are] some hints of efficacy given the suboptimal use case in the patients studied.”
The study was funded by the Indian Council of Medical Research, which employs several of the authors and PLACID Trial Collaborators. Dr. Pathak and Dr. Joyner reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Agarwal A et al. BMJ. 2020 Oct 23. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m3939 .
FROM BMJ
FDA approves remdesivir, first treatment for COVID-19
making it the first and only approved treatment for COVID-19, according to a release from drug manufacturer Gilead Sciences.
The FDA’s initial Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) of the antiviral, issued in May, allowed the drug to be used only for patients with severe COVID-19, specifically, COVID-19 patients with low blood oxygen levels or who needed oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation.
An August EUA expanded treatment to include all adult and pediatric hospitalized COVID-19 patients, regardless of the severity of their disease. The FDA also issued a new EUA for remdesivir Oct. 22 allowing treatment of hospitalized pediatric patients younger than 12 weighing at least 3.5 kg.
Today’s approval is based on three randomized controlled trials, according to Gilead.
Final trial results from one of them, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease–funded ACTT-1 trial, published earlier in October, showed that hospitalized patients with COVID-19 who received remdesivir had a shorter median recovery time than those who received a placebo – 10 days versus 15 days.
This difference and some related secondary endpoints were statistically significant in the randomized trial, but there was not a statistically significant difference in mortality between the treatment and placebo groups.
The other two trials used for the approval, the SIMPLE trials, were open-label phase 3 trials conducted in countries with a high prevalence of COVID-19 infections, according to Gilead.
The SIMPLE-Severe trial was a randomized, multicenter study that evaluated the efficacy and safety of 5-day and 10-day dosing plus standard of care in 397 hospitalized adult patients with severe COVID-19. The primary endpoint was clinical status on day 14 assessed on a 7-point ordinal scale, according to Gilead.
The trial found that a 5-day or a 10-day treatment course of Veklury achieved similar clinical outcomes to the ACTT-1 trial (odds ratio, 0.75; 95% confidence interval, 0.51-1.12).
The SIMPLE-Moderate trial was a randomized, controlled, multicenter study that evaluated the efficacy and safety of 5-day and 10-day dosing durations of Veklury plus standard of care, compared with standard of care alone in 600 hospitalized adult patients with moderate COVID-19, Gilead stated in its release.
The primary endpoint was clinical status on day 11 assessed on a 7-point ordinal scale.
The results showed statistically improved clinical outcomes with a 5-day treatment course of Veklury, compared with standard of care (OR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.0-2.48; P = .017), according to Gilead.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
making it the first and only approved treatment for COVID-19, according to a release from drug manufacturer Gilead Sciences.
The FDA’s initial Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) of the antiviral, issued in May, allowed the drug to be used only for patients with severe COVID-19, specifically, COVID-19 patients with low blood oxygen levels or who needed oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation.
An August EUA expanded treatment to include all adult and pediatric hospitalized COVID-19 patients, regardless of the severity of their disease. The FDA also issued a new EUA for remdesivir Oct. 22 allowing treatment of hospitalized pediatric patients younger than 12 weighing at least 3.5 kg.
Today’s approval is based on three randomized controlled trials, according to Gilead.
Final trial results from one of them, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease–funded ACTT-1 trial, published earlier in October, showed that hospitalized patients with COVID-19 who received remdesivir had a shorter median recovery time than those who received a placebo – 10 days versus 15 days.
This difference and some related secondary endpoints were statistically significant in the randomized trial, but there was not a statistically significant difference in mortality between the treatment and placebo groups.
The other two trials used for the approval, the SIMPLE trials, were open-label phase 3 trials conducted in countries with a high prevalence of COVID-19 infections, according to Gilead.
The SIMPLE-Severe trial was a randomized, multicenter study that evaluated the efficacy and safety of 5-day and 10-day dosing plus standard of care in 397 hospitalized adult patients with severe COVID-19. The primary endpoint was clinical status on day 14 assessed on a 7-point ordinal scale, according to Gilead.
The trial found that a 5-day or a 10-day treatment course of Veklury achieved similar clinical outcomes to the ACTT-1 trial (odds ratio, 0.75; 95% confidence interval, 0.51-1.12).
The SIMPLE-Moderate trial was a randomized, controlled, multicenter study that evaluated the efficacy and safety of 5-day and 10-day dosing durations of Veklury plus standard of care, compared with standard of care alone in 600 hospitalized adult patients with moderate COVID-19, Gilead stated in its release.
The primary endpoint was clinical status on day 11 assessed on a 7-point ordinal scale.
The results showed statistically improved clinical outcomes with a 5-day treatment course of Veklury, compared with standard of care (OR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.0-2.48; P = .017), according to Gilead.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
making it the first and only approved treatment for COVID-19, according to a release from drug manufacturer Gilead Sciences.
The FDA’s initial Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) of the antiviral, issued in May, allowed the drug to be used only for patients with severe COVID-19, specifically, COVID-19 patients with low blood oxygen levels or who needed oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation.
An August EUA expanded treatment to include all adult and pediatric hospitalized COVID-19 patients, regardless of the severity of their disease. The FDA also issued a new EUA for remdesivir Oct. 22 allowing treatment of hospitalized pediatric patients younger than 12 weighing at least 3.5 kg.
Today’s approval is based on three randomized controlled trials, according to Gilead.
Final trial results from one of them, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease–funded ACTT-1 trial, published earlier in October, showed that hospitalized patients with COVID-19 who received remdesivir had a shorter median recovery time than those who received a placebo – 10 days versus 15 days.
This difference and some related secondary endpoints were statistically significant in the randomized trial, but there was not a statistically significant difference in mortality between the treatment and placebo groups.
The other two trials used for the approval, the SIMPLE trials, were open-label phase 3 trials conducted in countries with a high prevalence of COVID-19 infections, according to Gilead.
The SIMPLE-Severe trial was a randomized, multicenter study that evaluated the efficacy and safety of 5-day and 10-day dosing plus standard of care in 397 hospitalized adult patients with severe COVID-19. The primary endpoint was clinical status on day 14 assessed on a 7-point ordinal scale, according to Gilead.
The trial found that a 5-day or a 10-day treatment course of Veklury achieved similar clinical outcomes to the ACTT-1 trial (odds ratio, 0.75; 95% confidence interval, 0.51-1.12).
The SIMPLE-Moderate trial was a randomized, controlled, multicenter study that evaluated the efficacy and safety of 5-day and 10-day dosing durations of Veklury plus standard of care, compared with standard of care alone in 600 hospitalized adult patients with moderate COVID-19, Gilead stated in its release.
The primary endpoint was clinical status on day 11 assessed on a 7-point ordinal scale.
The results showed statistically improved clinical outcomes with a 5-day treatment course of Veklury, compared with standard of care (OR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.0-2.48; P = .017), according to Gilead.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rinse and repeat? Mouthwash might mitigate COVID-19 spread
Listerine Antiseptic led the list of most effective mouthwashes for inactivating the coronavirus. Interestingly, a 1% nasal rinse solution of Johnson’s Baby Shampoo also worked, eliminating up to 99.9% of the viral load in the in vitro experiments.
In contrast, use of a neti pot nasal solution yielded no decrease in virus levels.
The study was published in the Journal of Medical Virology.
Because the mouthwash and hydrogen peroxide oral rinses in the study are widely available and easy to use, “I would recommend the use of the rinses on top of wearing mask and social distancing. This could add a layer of protection for yourself and others,” lead study author Craig Meyers, PhD, professor of microbiology and immunology and obstetrics and gynecology, Penn State College of Medicine in Hershey, Pennsylvania, told Medscape Medical News.
Meyers and colleagues found that efficacy aligned with duration of time the cell cultures were exposed to each mouthwash or rinse product. Although it varied, the products required at least 30 seconds to kill most of the virus. Waiting 1 or 2 minutes tended to fortify results.
“This study adds to and further confirms the recently published evidence from virologists in Germany that mouthwashes can inactivate the virus that causes COVID-19 in a test tube,” Valerie O’Donnell, PhD, co-director of the Systems Immunity Research Institute of Cardiff University, Cardiff, Wales, said when asked to comment on the study.
“While this is great to see, what is still lacking is in vivo evidence, since we know the virus will be continually shed in the mouth,” O’Donnell said. “So, the question now becomes, by how much could mouthwashes reduce viral load in the oropharynx of infected people, and if so, then for how long?”
Meyers noted that studies of people positive for COVID-19 using each product would be informative. It remains unknown, for example, if swishing, gargling, and/or spitting out mouthwash would add or decrease the efficacy demonstrated in the lab.
The investigators used the human coronavirus HCoV‐229e as a surrogate for SARS-CoV-2. They noted HCoV-229e is analogous, and SARS-CoV-2 would have been more expensive, less available, and would have required biosafety level 3 laboratory conditions.
Listerine Antiseptic leads the way
“Surprisingly, we found that several of these common products had strong virucidal properties, inactivating from 2 log10 [or 99%] to greater than 4 log10 [or 99.99%] of infectious human coronavirus,” the researchers note.
The researchers added a small amount of organic material (extra protein) to each product to more closely mimic physiologic conditions in the nasopharynx.
Listerine Antiseptic “historically has claimed numerous antimicrobial properties,” the researchers note. Although the label currently only claims to kill germs that cause bad breath, “our tests show that it is highly effective at inactivating human coronavirus in solution. Even at the lowest contact time of 30 seconds, it inactivated greater than 99.99% of human coronavirus.”
Interestingly, the mouthwashes that contained the same active ingredients as Listerine Antiseptic — Listerine Ultra, Equate Antiseptic, and CVS Antiseptic Mouth Wash — were less efficacious. Meyers said the reason remains unclear, but he and colleagues found the same result when they repeated the comparisons.
Timing of the essence?
Meyers and colleagues also tested a nasal rinse solution of 1% baby shampoo because it is sometimes used to treat people with chronic rhinosinusitis. They found 30 seconds led to < 90% to < 99.99% effectiveness, but that, by 2 minutes, efficacy climbed to > 99.9% to > 99.99%.
“Thirty seconds for some products just was not enough time for the efficacy to be observed,” Meyers said. “Whereas, after a minute or two the active ingredient had enough time to work. Thirty seconds may be at the border to see full efficacy.” More research is needed to confirm the timing and determine which active ingredients are driving the findings.
A future trial could test the efficacy of mouthwash products to reduce the viral load in people with COVID-19. “If we are able to get funding to continue, I would like to see a small clinical trial as the next step,” Meyers said.
Meyers and O’Donnell disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Listerine Antiseptic led the list of most effective mouthwashes for inactivating the coronavirus. Interestingly, a 1% nasal rinse solution of Johnson’s Baby Shampoo also worked, eliminating up to 99.9% of the viral load in the in vitro experiments.
In contrast, use of a neti pot nasal solution yielded no decrease in virus levels.
The study was published in the Journal of Medical Virology.
Because the mouthwash and hydrogen peroxide oral rinses in the study are widely available and easy to use, “I would recommend the use of the rinses on top of wearing mask and social distancing. This could add a layer of protection for yourself and others,” lead study author Craig Meyers, PhD, professor of microbiology and immunology and obstetrics and gynecology, Penn State College of Medicine in Hershey, Pennsylvania, told Medscape Medical News.
Meyers and colleagues found that efficacy aligned with duration of time the cell cultures were exposed to each mouthwash or rinse product. Although it varied, the products required at least 30 seconds to kill most of the virus. Waiting 1 or 2 minutes tended to fortify results.
“This study adds to and further confirms the recently published evidence from virologists in Germany that mouthwashes can inactivate the virus that causes COVID-19 in a test tube,” Valerie O’Donnell, PhD, co-director of the Systems Immunity Research Institute of Cardiff University, Cardiff, Wales, said when asked to comment on the study.
“While this is great to see, what is still lacking is in vivo evidence, since we know the virus will be continually shed in the mouth,” O’Donnell said. “So, the question now becomes, by how much could mouthwashes reduce viral load in the oropharynx of infected people, and if so, then for how long?”
Meyers noted that studies of people positive for COVID-19 using each product would be informative. It remains unknown, for example, if swishing, gargling, and/or spitting out mouthwash would add or decrease the efficacy demonstrated in the lab.
The investigators used the human coronavirus HCoV‐229e as a surrogate for SARS-CoV-2. They noted HCoV-229e is analogous, and SARS-CoV-2 would have been more expensive, less available, and would have required biosafety level 3 laboratory conditions.
Listerine Antiseptic leads the way
“Surprisingly, we found that several of these common products had strong virucidal properties, inactivating from 2 log10 [or 99%] to greater than 4 log10 [or 99.99%] of infectious human coronavirus,” the researchers note.
The researchers added a small amount of organic material (extra protein) to each product to more closely mimic physiologic conditions in the nasopharynx.
Listerine Antiseptic “historically has claimed numerous antimicrobial properties,” the researchers note. Although the label currently only claims to kill germs that cause bad breath, “our tests show that it is highly effective at inactivating human coronavirus in solution. Even at the lowest contact time of 30 seconds, it inactivated greater than 99.99% of human coronavirus.”
Interestingly, the mouthwashes that contained the same active ingredients as Listerine Antiseptic — Listerine Ultra, Equate Antiseptic, and CVS Antiseptic Mouth Wash — were less efficacious. Meyers said the reason remains unclear, but he and colleagues found the same result when they repeated the comparisons.
Timing of the essence?
Meyers and colleagues also tested a nasal rinse solution of 1% baby shampoo because it is sometimes used to treat people with chronic rhinosinusitis. They found 30 seconds led to < 90% to < 99.99% effectiveness, but that, by 2 minutes, efficacy climbed to > 99.9% to > 99.99%.
“Thirty seconds for some products just was not enough time for the efficacy to be observed,” Meyers said. “Whereas, after a minute or two the active ingredient had enough time to work. Thirty seconds may be at the border to see full efficacy.” More research is needed to confirm the timing and determine which active ingredients are driving the findings.
A future trial could test the efficacy of mouthwash products to reduce the viral load in people with COVID-19. “If we are able to get funding to continue, I would like to see a small clinical trial as the next step,” Meyers said.
Meyers and O’Donnell disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Listerine Antiseptic led the list of most effective mouthwashes for inactivating the coronavirus. Interestingly, a 1% nasal rinse solution of Johnson’s Baby Shampoo also worked, eliminating up to 99.9% of the viral load in the in vitro experiments.
In contrast, use of a neti pot nasal solution yielded no decrease in virus levels.
The study was published in the Journal of Medical Virology.
Because the mouthwash and hydrogen peroxide oral rinses in the study are widely available and easy to use, “I would recommend the use of the rinses on top of wearing mask and social distancing. This could add a layer of protection for yourself and others,” lead study author Craig Meyers, PhD, professor of microbiology and immunology and obstetrics and gynecology, Penn State College of Medicine in Hershey, Pennsylvania, told Medscape Medical News.
Meyers and colleagues found that efficacy aligned with duration of time the cell cultures were exposed to each mouthwash or rinse product. Although it varied, the products required at least 30 seconds to kill most of the virus. Waiting 1 or 2 minutes tended to fortify results.
“This study adds to and further confirms the recently published evidence from virologists in Germany that mouthwashes can inactivate the virus that causes COVID-19 in a test tube,” Valerie O’Donnell, PhD, co-director of the Systems Immunity Research Institute of Cardiff University, Cardiff, Wales, said when asked to comment on the study.
“While this is great to see, what is still lacking is in vivo evidence, since we know the virus will be continually shed in the mouth,” O’Donnell said. “So, the question now becomes, by how much could mouthwashes reduce viral load in the oropharynx of infected people, and if so, then for how long?”
Meyers noted that studies of people positive for COVID-19 using each product would be informative. It remains unknown, for example, if swishing, gargling, and/or spitting out mouthwash would add or decrease the efficacy demonstrated in the lab.
The investigators used the human coronavirus HCoV‐229e as a surrogate for SARS-CoV-2. They noted HCoV-229e is analogous, and SARS-CoV-2 would have been more expensive, less available, and would have required biosafety level 3 laboratory conditions.
Listerine Antiseptic leads the way
“Surprisingly, we found that several of these common products had strong virucidal properties, inactivating from 2 log10 [or 99%] to greater than 4 log10 [or 99.99%] of infectious human coronavirus,” the researchers note.
The researchers added a small amount of organic material (extra protein) to each product to more closely mimic physiologic conditions in the nasopharynx.
Listerine Antiseptic “historically has claimed numerous antimicrobial properties,” the researchers note. Although the label currently only claims to kill germs that cause bad breath, “our tests show that it is highly effective at inactivating human coronavirus in solution. Even at the lowest contact time of 30 seconds, it inactivated greater than 99.99% of human coronavirus.”
Interestingly, the mouthwashes that contained the same active ingredients as Listerine Antiseptic — Listerine Ultra, Equate Antiseptic, and CVS Antiseptic Mouth Wash — were less efficacious. Meyers said the reason remains unclear, but he and colleagues found the same result when they repeated the comparisons.
Timing of the essence?
Meyers and colleagues also tested a nasal rinse solution of 1% baby shampoo because it is sometimes used to treat people with chronic rhinosinusitis. They found 30 seconds led to < 90% to < 99.99% effectiveness, but that, by 2 minutes, efficacy climbed to > 99.9% to > 99.99%.
“Thirty seconds for some products just was not enough time for the efficacy to be observed,” Meyers said. “Whereas, after a minute or two the active ingredient had enough time to work. Thirty seconds may be at the border to see full efficacy.” More research is needed to confirm the timing and determine which active ingredients are driving the findings.
A future trial could test the efficacy of mouthwash products to reduce the viral load in people with COVID-19. “If we are able to get funding to continue, I would like to see a small clinical trial as the next step,” Meyers said.
Meyers and O’Donnell disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.