User login
'The whitest specialty,' revisited
A recent STAT article by Usha Lee McFarling identified orthopedic surgery as “the whitest specialty.” That’s a problem many, perhaps most, orthopedic surgeons are aware of. But seeing it stated so bluntly is jolting. It’s disconcerting to think that the orthopedic community is making so little progress toward achieving the principal ideal articulated in our country’s fundamental declaration of moral values: that all people are created equal and that they have inalienable rights – in our case, that everyone, Black, brown, as well as White, has the right to the same high level of medical care.
Unfortunately, as study after study has shown, minorities do not enjoy the right to equitable care. Instead, they are subject to disparities in treatment and outcomes that speak to the prejudices that are built into the health care system and are present – sometimes consciously, but most often subconsciously – in the minds of physicians. One important contributing element to these disparities is the paucity of minority practitioners. Studies have also shown that Black patients, for example, respond better to Black physicians, who so often share a psychological and cultural sympathy unavailable to most White physicians. It’s for that reason that being identified as “the whitest specialty” is so immensely troubling.
In researching her STAT article, Ms. McFarling spoke with American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons leaders, practicing surgeons, residents, and med students about the dearth of minority and female orthopedic surgeons. What she heard was perplexity and frustration about why better progress hasn’t been made toward correcting the gross underrepresentation of everyone other than White men. The AAOS, she noted, was one of the first specialties to recognize the lack of diversity and over the years has put in great effort to address the problem, creating task forces, committees, and diversity awards and sponsoring conferences and discussions. Yet progress has been glacial, at best.
From her respondents, Ms. McFarling heard an array of reasons for this. Black, Hispanic, and Native American persons are underrepresented in medical schools, so the pool of potential applicants for orthopedic residencies is shallow to begin with. STEM studies are notoriously inadequate in poorer primary and secondary schools, in which so many minority students are educated. The MCAT and USMLE Step 1 test, which play a role in acceptance to residencies, have been shown to be biased. The specialty has few Black or brown role models and, consequently, few advocates and a lack of mentorship. Overt bias may be fairly rare (though microaggressions are still a common and ongoing problem), but most minority and female orthopedic surgeons feel strongly that implicit or subconscious bias is entrenched and works against acceptance to residencies, success in residencies, and advancement in the field.
One of this article’s authors (AW) saw all these factors at work as a resident, then as an admissions committee member at both Yale and Harvard. But the fact is that other medical specialties face exactly these problems and barriers, and yet have been substantially more successful in overcoming them.
What seems to be distinctive about orthopedics is that the mindset which perpetuated (and still perpetuates) In this regard, Kristy Weber, MD, the first female president of the AAOS, told Ms. McFarling that the critical first step to bringing in more women or people of color is changing the culture. There seems to be a consensus about that.
So, what does that mean, given that the AAOS has made serious efforts in that regard that have clearly been less than effective?
The answer, as we see it, is first – to not give in to frustration. The time frames involved in changing customary states of mind are typically elongated, and the deeper the habituation, the longer transformation takes. Deep changes always mean a long, hard slog. For transformations of this sort to take place, the requirements are a general agreement on the value of the transformation, exposure to the destructive consequences of the customary modus operandi, and persuasion for why change needs to happen.
In orthopedics, the first requirement has been met. The AAOS espouses diversity and inclusion as a high-level value. In terms of the second two requirements – exposure and persuasion – orthopedic surgeons have been witness to events, campaigns, conferences, et cetera. But these have not been enough, which means that efforts need to be focused, enlarged, sustained, determined, and innovative.
Does the orthopedic surgery community have the ability to do that?
The answer is: Yes, it does.
Currently the orthopedic surgeon community boasts a number of organizations, groups, and individuals pushing for change, in addition to the AAOS’s Diversity Advisory Board. The predominantly African American J. Robert Gladden Orthopaedic Society, the Ruth Jackson Orthopaedic Society of female orthopedic physicians, and the Association of Latino Orthopaedic Surgeons are all energetic advocates, as is Nth Dimensions, the Perry Initiative, and various ad hoc and individual endeavors.
These are all strong proponents for their own groups in their own way. But history has shown in so many cases that concerted rather than individual action empowers advocacy, and what orthopedic surgery needs in its current situation of gross underrepresentation of minorities and women is an enhanced campaign to raise awareness and redouble persuasion.
One of many examples of the power of collective action is the Association of Minority Health Professions Schools founded by Dr. Louis Sullivan in 1977.* Dr. Sullivan (later secretary of the Department of Health & Human Services) was at that time the founding dean of Morehouse School of Medicine. Morehouse had been launched on a shoestring and needed funding urgently. Other Black health schools, such as Meharry Medical College and Tuskegee College of Veterinary Medicine, were in even more pressing financial need. The coalition of schools that Dr. Sullivan organized became a powerful force in Congress and the National Institutes of Health, magnitudes more effective in raising funds from government and other sources than the best individual efforts of the separate institutions.
Dr. Sullivan’s association is only one of a multitude of historical examples of the effectiveness of unified action. AAOS currently has no single officer charged with bringing together the efforts of the change assets that already exist. It could, perhaps should, have someone in that position. AAOS could invest that same office with a mandate to survey the other medical specialties and bring to bear the most effective diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) practices in their arsenals.
Finally, despite the attention AAOS has brought to DEI needs, a look at the organization’s strategic goals, its core values, and its “key enablers” finds not a single mention of diversity or inclusion. Given the country’s current focus on the need for equality, given the poor performance of the orthopedic surgery specialty in terms of inclusion, the obvious question is: Should there not be an official declaration positing diversity as a primary AAOS desideratum?
There is recent precedent for this in the American College of Physicians/American Board of Internal Medicine’s Physician Charter on Professionalism, which includes “social justice” as a primary goal of medical practice. This highlights and reinforces the humanitarian strivings of the profession. In light of the paralysis illuminated by Ms. McFarling’s STAT article, a clear, concise declaration by the AAOS of the value and need for DEI as a central component of the organization’s values should be high on the AAOS order of business. A commitment in that form would serve as a powerful catalyst for bringing orthopedic surgery into step with its sister specialties, as well as affirming the core egalitarian principle that underlies all of medical care.
Dr. White is the Ellen and Melvin Gordon Distinguished Professor of Medical Education and Professor of Orthopedic Surgery at Harvard Medical School, Boston. Dr. Chanoff is a founding board member of the Augustus A. White III Institute for Healthcare Equity. Neither Dr. White nor Dr. Chanoff reported any conflicts of interest. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Correction, 2/1/22: An earlier version of this article omitted the title of "Dr." before Dr. Louis Sullivan's name.
A recent STAT article by Usha Lee McFarling identified orthopedic surgery as “the whitest specialty.” That’s a problem many, perhaps most, orthopedic surgeons are aware of. But seeing it stated so bluntly is jolting. It’s disconcerting to think that the orthopedic community is making so little progress toward achieving the principal ideal articulated in our country’s fundamental declaration of moral values: that all people are created equal and that they have inalienable rights – in our case, that everyone, Black, brown, as well as White, has the right to the same high level of medical care.
Unfortunately, as study after study has shown, minorities do not enjoy the right to equitable care. Instead, they are subject to disparities in treatment and outcomes that speak to the prejudices that are built into the health care system and are present – sometimes consciously, but most often subconsciously – in the minds of physicians. One important contributing element to these disparities is the paucity of minority practitioners. Studies have also shown that Black patients, for example, respond better to Black physicians, who so often share a psychological and cultural sympathy unavailable to most White physicians. It’s for that reason that being identified as “the whitest specialty” is so immensely troubling.
In researching her STAT article, Ms. McFarling spoke with American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons leaders, practicing surgeons, residents, and med students about the dearth of minority and female orthopedic surgeons. What she heard was perplexity and frustration about why better progress hasn’t been made toward correcting the gross underrepresentation of everyone other than White men. The AAOS, she noted, was one of the first specialties to recognize the lack of diversity and over the years has put in great effort to address the problem, creating task forces, committees, and diversity awards and sponsoring conferences and discussions. Yet progress has been glacial, at best.
From her respondents, Ms. McFarling heard an array of reasons for this. Black, Hispanic, and Native American persons are underrepresented in medical schools, so the pool of potential applicants for orthopedic residencies is shallow to begin with. STEM studies are notoriously inadequate in poorer primary and secondary schools, in which so many minority students are educated. The MCAT and USMLE Step 1 test, which play a role in acceptance to residencies, have been shown to be biased. The specialty has few Black or brown role models and, consequently, few advocates and a lack of mentorship. Overt bias may be fairly rare (though microaggressions are still a common and ongoing problem), but most minority and female orthopedic surgeons feel strongly that implicit or subconscious bias is entrenched and works against acceptance to residencies, success in residencies, and advancement in the field.
One of this article’s authors (AW) saw all these factors at work as a resident, then as an admissions committee member at both Yale and Harvard. But the fact is that other medical specialties face exactly these problems and barriers, and yet have been substantially more successful in overcoming them.
What seems to be distinctive about orthopedics is that the mindset which perpetuated (and still perpetuates) In this regard, Kristy Weber, MD, the first female president of the AAOS, told Ms. McFarling that the critical first step to bringing in more women or people of color is changing the culture. There seems to be a consensus about that.
So, what does that mean, given that the AAOS has made serious efforts in that regard that have clearly been less than effective?
The answer, as we see it, is first – to not give in to frustration. The time frames involved in changing customary states of mind are typically elongated, and the deeper the habituation, the longer transformation takes. Deep changes always mean a long, hard slog. For transformations of this sort to take place, the requirements are a general agreement on the value of the transformation, exposure to the destructive consequences of the customary modus operandi, and persuasion for why change needs to happen.
In orthopedics, the first requirement has been met. The AAOS espouses diversity and inclusion as a high-level value. In terms of the second two requirements – exposure and persuasion – orthopedic surgeons have been witness to events, campaigns, conferences, et cetera. But these have not been enough, which means that efforts need to be focused, enlarged, sustained, determined, and innovative.
Does the orthopedic surgery community have the ability to do that?
The answer is: Yes, it does.
Currently the orthopedic surgeon community boasts a number of organizations, groups, and individuals pushing for change, in addition to the AAOS’s Diversity Advisory Board. The predominantly African American J. Robert Gladden Orthopaedic Society, the Ruth Jackson Orthopaedic Society of female orthopedic physicians, and the Association of Latino Orthopaedic Surgeons are all energetic advocates, as is Nth Dimensions, the Perry Initiative, and various ad hoc and individual endeavors.
These are all strong proponents for their own groups in their own way. But history has shown in so many cases that concerted rather than individual action empowers advocacy, and what orthopedic surgery needs in its current situation of gross underrepresentation of minorities and women is an enhanced campaign to raise awareness and redouble persuasion.
One of many examples of the power of collective action is the Association of Minority Health Professions Schools founded by Dr. Louis Sullivan in 1977.* Dr. Sullivan (later secretary of the Department of Health & Human Services) was at that time the founding dean of Morehouse School of Medicine. Morehouse had been launched on a shoestring and needed funding urgently. Other Black health schools, such as Meharry Medical College and Tuskegee College of Veterinary Medicine, were in even more pressing financial need. The coalition of schools that Dr. Sullivan organized became a powerful force in Congress and the National Institutes of Health, magnitudes more effective in raising funds from government and other sources than the best individual efforts of the separate institutions.
Dr. Sullivan’s association is only one of a multitude of historical examples of the effectiveness of unified action. AAOS currently has no single officer charged with bringing together the efforts of the change assets that already exist. It could, perhaps should, have someone in that position. AAOS could invest that same office with a mandate to survey the other medical specialties and bring to bear the most effective diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) practices in their arsenals.
Finally, despite the attention AAOS has brought to DEI needs, a look at the organization’s strategic goals, its core values, and its “key enablers” finds not a single mention of diversity or inclusion. Given the country’s current focus on the need for equality, given the poor performance of the orthopedic surgery specialty in terms of inclusion, the obvious question is: Should there not be an official declaration positing diversity as a primary AAOS desideratum?
There is recent precedent for this in the American College of Physicians/American Board of Internal Medicine’s Physician Charter on Professionalism, which includes “social justice” as a primary goal of medical practice. This highlights and reinforces the humanitarian strivings of the profession. In light of the paralysis illuminated by Ms. McFarling’s STAT article, a clear, concise declaration by the AAOS of the value and need for DEI as a central component of the organization’s values should be high on the AAOS order of business. A commitment in that form would serve as a powerful catalyst for bringing orthopedic surgery into step with its sister specialties, as well as affirming the core egalitarian principle that underlies all of medical care.
Dr. White is the Ellen and Melvin Gordon Distinguished Professor of Medical Education and Professor of Orthopedic Surgery at Harvard Medical School, Boston. Dr. Chanoff is a founding board member of the Augustus A. White III Institute for Healthcare Equity. Neither Dr. White nor Dr. Chanoff reported any conflicts of interest. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Correction, 2/1/22: An earlier version of this article omitted the title of "Dr." before Dr. Louis Sullivan's name.
A recent STAT article by Usha Lee McFarling identified orthopedic surgery as “the whitest specialty.” That’s a problem many, perhaps most, orthopedic surgeons are aware of. But seeing it stated so bluntly is jolting. It’s disconcerting to think that the orthopedic community is making so little progress toward achieving the principal ideal articulated in our country’s fundamental declaration of moral values: that all people are created equal and that they have inalienable rights – in our case, that everyone, Black, brown, as well as White, has the right to the same high level of medical care.
Unfortunately, as study after study has shown, minorities do not enjoy the right to equitable care. Instead, they are subject to disparities in treatment and outcomes that speak to the prejudices that are built into the health care system and are present – sometimes consciously, but most often subconsciously – in the minds of physicians. One important contributing element to these disparities is the paucity of minority practitioners. Studies have also shown that Black patients, for example, respond better to Black physicians, who so often share a psychological and cultural sympathy unavailable to most White physicians. It’s for that reason that being identified as “the whitest specialty” is so immensely troubling.
In researching her STAT article, Ms. McFarling spoke with American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons leaders, practicing surgeons, residents, and med students about the dearth of minority and female orthopedic surgeons. What she heard was perplexity and frustration about why better progress hasn’t been made toward correcting the gross underrepresentation of everyone other than White men. The AAOS, she noted, was one of the first specialties to recognize the lack of diversity and over the years has put in great effort to address the problem, creating task forces, committees, and diversity awards and sponsoring conferences and discussions. Yet progress has been glacial, at best.
From her respondents, Ms. McFarling heard an array of reasons for this. Black, Hispanic, and Native American persons are underrepresented in medical schools, so the pool of potential applicants for orthopedic residencies is shallow to begin with. STEM studies are notoriously inadequate in poorer primary and secondary schools, in which so many minority students are educated. The MCAT and USMLE Step 1 test, which play a role in acceptance to residencies, have been shown to be biased. The specialty has few Black or brown role models and, consequently, few advocates and a lack of mentorship. Overt bias may be fairly rare (though microaggressions are still a common and ongoing problem), but most minority and female orthopedic surgeons feel strongly that implicit or subconscious bias is entrenched and works against acceptance to residencies, success in residencies, and advancement in the field.
One of this article’s authors (AW) saw all these factors at work as a resident, then as an admissions committee member at both Yale and Harvard. But the fact is that other medical specialties face exactly these problems and barriers, and yet have been substantially more successful in overcoming them.
What seems to be distinctive about orthopedics is that the mindset which perpetuated (and still perpetuates) In this regard, Kristy Weber, MD, the first female president of the AAOS, told Ms. McFarling that the critical first step to bringing in more women or people of color is changing the culture. There seems to be a consensus about that.
So, what does that mean, given that the AAOS has made serious efforts in that regard that have clearly been less than effective?
The answer, as we see it, is first – to not give in to frustration. The time frames involved in changing customary states of mind are typically elongated, and the deeper the habituation, the longer transformation takes. Deep changes always mean a long, hard slog. For transformations of this sort to take place, the requirements are a general agreement on the value of the transformation, exposure to the destructive consequences of the customary modus operandi, and persuasion for why change needs to happen.
In orthopedics, the first requirement has been met. The AAOS espouses diversity and inclusion as a high-level value. In terms of the second two requirements – exposure and persuasion – orthopedic surgeons have been witness to events, campaigns, conferences, et cetera. But these have not been enough, which means that efforts need to be focused, enlarged, sustained, determined, and innovative.
Does the orthopedic surgery community have the ability to do that?
The answer is: Yes, it does.
Currently the orthopedic surgeon community boasts a number of organizations, groups, and individuals pushing for change, in addition to the AAOS’s Diversity Advisory Board. The predominantly African American J. Robert Gladden Orthopaedic Society, the Ruth Jackson Orthopaedic Society of female orthopedic physicians, and the Association of Latino Orthopaedic Surgeons are all energetic advocates, as is Nth Dimensions, the Perry Initiative, and various ad hoc and individual endeavors.
These are all strong proponents for their own groups in their own way. But history has shown in so many cases that concerted rather than individual action empowers advocacy, and what orthopedic surgery needs in its current situation of gross underrepresentation of minorities and women is an enhanced campaign to raise awareness and redouble persuasion.
One of many examples of the power of collective action is the Association of Minority Health Professions Schools founded by Dr. Louis Sullivan in 1977.* Dr. Sullivan (later secretary of the Department of Health & Human Services) was at that time the founding dean of Morehouse School of Medicine. Morehouse had been launched on a shoestring and needed funding urgently. Other Black health schools, such as Meharry Medical College and Tuskegee College of Veterinary Medicine, were in even more pressing financial need. The coalition of schools that Dr. Sullivan organized became a powerful force in Congress and the National Institutes of Health, magnitudes more effective in raising funds from government and other sources than the best individual efforts of the separate institutions.
Dr. Sullivan’s association is only one of a multitude of historical examples of the effectiveness of unified action. AAOS currently has no single officer charged with bringing together the efforts of the change assets that already exist. It could, perhaps should, have someone in that position. AAOS could invest that same office with a mandate to survey the other medical specialties and bring to bear the most effective diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) practices in their arsenals.
Finally, despite the attention AAOS has brought to DEI needs, a look at the organization’s strategic goals, its core values, and its “key enablers” finds not a single mention of diversity or inclusion. Given the country’s current focus on the need for equality, given the poor performance of the orthopedic surgery specialty in terms of inclusion, the obvious question is: Should there not be an official declaration positing diversity as a primary AAOS desideratum?
There is recent precedent for this in the American College of Physicians/American Board of Internal Medicine’s Physician Charter on Professionalism, which includes “social justice” as a primary goal of medical practice. This highlights and reinforces the humanitarian strivings of the profession. In light of the paralysis illuminated by Ms. McFarling’s STAT article, a clear, concise declaration by the AAOS of the value and need for DEI as a central component of the organization’s values should be high on the AAOS order of business. A commitment in that form would serve as a powerful catalyst for bringing orthopedic surgery into step with its sister specialties, as well as affirming the core egalitarian principle that underlies all of medical care.
Dr. White is the Ellen and Melvin Gordon Distinguished Professor of Medical Education and Professor of Orthopedic Surgery at Harvard Medical School, Boston. Dr. Chanoff is a founding board member of the Augustus A. White III Institute for Healthcare Equity. Neither Dr. White nor Dr. Chanoff reported any conflicts of interest. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Correction, 2/1/22: An earlier version of this article omitted the title of "Dr." before Dr. Louis Sullivan's name.
FDA approves risankizumab (Skyrizi) for psoriatic arthritis
The Food and Drug Administration on Jan. 21 approved risankizumab-rzaa (Skyrizi) for a second indication – treating adults with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) – making it the second anti–interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody available to treat PsA, according to an announcement from manufacturer AbbVie.
The agency previously approved risankizumab in April 2019 for adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
The dosing regimen for PsA is the same as it is for patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: a single 150-mg subcutaneous injection four times a year (after two starter doses at weeks 0 and 4), and it can be administered alone or in combination with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
Two phase 3 trials, KEEPsAKE 1 and KEEPsAKE 2, were the basis for the approval. These two trials tested the biologic agent in adults with active PsA, including those who had responded inadequately or were intolerant to biologic therapy and/or nonbiologic DMARDs. Fulfillment of the trials’ primary endpoint of at least a 20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria at 24 weeks occurred in 51.3%-57.3% of patients, compared with 26.5%-33.5% of placebo-treated patients.
Those on risankizumab also achieved significantly higher rates of ACR50 and ACR70 responses than those on placebo. In addition, patients with preexisting dactylitis and enthesitis experienced improvements in these PsA manifestations. Risankizumab was also associated with an improvement in physical function at 24 weeks on the Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index, bettering placebo by a mean difference of 0.16-0.20 points in the two trials. A significantly higher percentage of patients who had psoriatic skin lesions experienced at least 90% improvement with risankizumab on the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index, compared with placebo.
AbbVie said that the safety profile of risankizumab in patients with PsA has been generally consistent with its effects in patients with plaque psoriasis.
The KEEPsAKE 1 and KEEPsAKE 2 studies are ongoing, and patients in the long-term extensions of the trials remain blinded to the original randomized allocation for the duration of the studies.
Phase 3 trials of risankizumab are also ongoing in patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration on Jan. 21 approved risankizumab-rzaa (Skyrizi) for a second indication – treating adults with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) – making it the second anti–interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody available to treat PsA, according to an announcement from manufacturer AbbVie.
The agency previously approved risankizumab in April 2019 for adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
The dosing regimen for PsA is the same as it is for patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: a single 150-mg subcutaneous injection four times a year (after two starter doses at weeks 0 and 4), and it can be administered alone or in combination with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
Two phase 3 trials, KEEPsAKE 1 and KEEPsAKE 2, were the basis for the approval. These two trials tested the biologic agent in adults with active PsA, including those who had responded inadequately or were intolerant to biologic therapy and/or nonbiologic DMARDs. Fulfillment of the trials’ primary endpoint of at least a 20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria at 24 weeks occurred in 51.3%-57.3% of patients, compared with 26.5%-33.5% of placebo-treated patients.
Those on risankizumab also achieved significantly higher rates of ACR50 and ACR70 responses than those on placebo. In addition, patients with preexisting dactylitis and enthesitis experienced improvements in these PsA manifestations. Risankizumab was also associated with an improvement in physical function at 24 weeks on the Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index, bettering placebo by a mean difference of 0.16-0.20 points in the two trials. A significantly higher percentage of patients who had psoriatic skin lesions experienced at least 90% improvement with risankizumab on the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index, compared with placebo.
AbbVie said that the safety profile of risankizumab in patients with PsA has been generally consistent with its effects in patients with plaque psoriasis.
The KEEPsAKE 1 and KEEPsAKE 2 studies are ongoing, and patients in the long-term extensions of the trials remain blinded to the original randomized allocation for the duration of the studies.
Phase 3 trials of risankizumab are also ongoing in patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration on Jan. 21 approved risankizumab-rzaa (Skyrizi) for a second indication – treating adults with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) – making it the second anti–interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody available to treat PsA, according to an announcement from manufacturer AbbVie.
The agency previously approved risankizumab in April 2019 for adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
The dosing regimen for PsA is the same as it is for patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: a single 150-mg subcutaneous injection four times a year (after two starter doses at weeks 0 and 4), and it can be administered alone or in combination with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
Two phase 3 trials, KEEPsAKE 1 and KEEPsAKE 2, were the basis for the approval. These two trials tested the biologic agent in adults with active PsA, including those who had responded inadequately or were intolerant to biologic therapy and/or nonbiologic DMARDs. Fulfillment of the trials’ primary endpoint of at least a 20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria at 24 weeks occurred in 51.3%-57.3% of patients, compared with 26.5%-33.5% of placebo-treated patients.
Those on risankizumab also achieved significantly higher rates of ACR50 and ACR70 responses than those on placebo. In addition, patients with preexisting dactylitis and enthesitis experienced improvements in these PsA manifestations. Risankizumab was also associated with an improvement in physical function at 24 weeks on the Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index, bettering placebo by a mean difference of 0.16-0.20 points in the two trials. A significantly higher percentage of patients who had psoriatic skin lesions experienced at least 90% improvement with risankizumab on the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index, compared with placebo.
AbbVie said that the safety profile of risankizumab in patients with PsA has been generally consistent with its effects in patients with plaque psoriasis.
The KEEPsAKE 1 and KEEPsAKE 2 studies are ongoing, and patients in the long-term extensions of the trials remain blinded to the original randomized allocation for the duration of the studies.
Phase 3 trials of risankizumab are also ongoing in patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Steroid-free remission doesn’t decrease risk of Crohn’s disease progression
Achieving steroid-free clinical and endoscopic remission does not decrease the risk of Crohn’s disease progression measured by surgery, hospitalization, or initiation of new treatments, according to a post hoc analysis of data from a prospective RCT.
The therapeutic goals of Crohn’s disease have evolved from controlling symptoms to blocking disease progression and reducing complications, wrote David Laharie, MD, of Hôpital Haut-Lévêque, Pessac, France, and colleagues. The goal of steroid-free remission has been used as an endpoint of treatment, but data on the impact of such remission on long-term disease are limited, the researchers noted in a retrospective study published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
In the study, the researchers reviewed data from 95 adults with early Crohn’s disease (CD) who participated in the TAILORIX trial involving treatment with infliximab and immunomodulators. The primary endpoint of the TAILORIX trial was sustained corticosteroid-free remission from week 22 to 54. In the current study, the primary endpoint was progression-free survival at 1, 3, and 5 years in patients who did or did not meet the TAILORIX primary endpoint. The median disease duration was 4.5 months, and the median follow-up was 64.2 months.
Progression-free survival was defined as a composite of luminal surgery, anal surgery, hospitalization, and the need for a new CD treatment during the follow-up period.
In the study population, 45 patients achieved corticosteroid-free remission and 50 did not. At 54 weeks, 17 patients with corticosteroid-free remission (38%) and 28 patients without remission (56%) achieved complete mucosal healing, and progression-free survival rates were similar between these groups.
Overall, the rates of progression-free survival at 1, 3, and 5 years were not significantly different between the remission and nonremission groups: 86% versus 91%, respectively, at 1 year; 70% for both groups at 3 years; and 64% and 61%, respectively, at 5 years.
The researchers also compared individual components of the primary endpoint (luminal surgery, anal surgery, hospitalization, and the need for a new CD treatment), and found no significant differences in survival rates in patients who had and had not achieved steroid-free remission.
Survival rates without luminal surgery at 1, 3, and 5 years were 97% versus 96%, 93% versus 90%, and 87% versus 82%, respectively, for remission and nonremission groups. Similarly, survival rates without anal surgery were 93%, 86%, and 86% versus 96%, 88%, and 85%, respectively, for the two groups. Rates of hospitalization-free survival at 1, 3, and 5 years were 90% versus 92%, 81% versus 81%, and 78% versus 69%, respectively, in the remission and nonremission groups. Survival rates without a new systemic CD treatment also were similar at 1, 3, and 5 years: 93% versus 95%, 71% versus 93%, and 60% versus 51%, respectively, for the remission and nonremission groups.
CD progression was not associated with not achieving corticosteroid-free remission (hazard ratio, 0.861). Other factors that were not associated with disease progression in this study included CRP greater than 5 mg/L, age older than 30 years, active smoking, and B1 phenotype.
The researchers noted that, although endoscopic and clinical remission is currently recommended for CD, “there is no validated or standardized definition of this endoscopic goal.” The high rates of survival without major abdominal surgery, regardless of remission status, suggest a significant impact of early combination therapy for CD patients who were biologic naive. Other studies have shown similar improved outcomes for CD patients with early treatment.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design and lack of power to compare long-term progression-free survival, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the robust data on hospitalizations and surgeries from the TAILORIX trial.
The results support a more flexible strategy for CD, “recommending endoscopic and clinical remission in early diagnosed patients and less stringent objectives in those with more refractory or advanced disease,” they concluded.
Findings may guide patient management
The current study is important to help clinicians know whether CD patients who achieve a short-term, steroid-free clinical and endoscopic remission go on to experience better long-term disease outcomes than those who do not achieve this short-term remission, Atsushi Sakuraba, MD, of the University of Chicago said in an interview.
Dr. Sakuraba said that he was surprised by the study findings. “Achieving a clinical remission off steroids with complete endoscopic remission, i.e., deep remission, is considered a treatment goal, but the fact that it did not result in less disease progression was surprising.”
The take-home message for clinicians from the study is that CD patients may still experience disease progression after achieving a single time of clinical and endoscopic remission “mainly due to loss of response to infliximab, so continued long-term disease monitoring and control are required,” Dr. Sakuraba said.
The current study was a post hoc follow-up analysis of a previous trial, Dr. Sakuraba noted. Therefore, studies primarily focused on changing the disease progression and natural course of CD are warranted.
Dr. Laharie disclosed counseling, boards, transportation, or fees from AbbVie, Biogaran, Biogen, Ferring, HAC-pharma, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Prometheus, Roche, Takeda, Theradiag, and Tillots. Dr. Sakuraba had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
This article was updated Feb. 10, 2022.
Achieving steroid-free clinical and endoscopic remission does not decrease the risk of Crohn’s disease progression measured by surgery, hospitalization, or initiation of new treatments, according to a post hoc analysis of data from a prospective RCT.
The therapeutic goals of Crohn’s disease have evolved from controlling symptoms to blocking disease progression and reducing complications, wrote David Laharie, MD, of Hôpital Haut-Lévêque, Pessac, France, and colleagues. The goal of steroid-free remission has been used as an endpoint of treatment, but data on the impact of such remission on long-term disease are limited, the researchers noted in a retrospective study published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
In the study, the researchers reviewed data from 95 adults with early Crohn’s disease (CD) who participated in the TAILORIX trial involving treatment with infliximab and immunomodulators. The primary endpoint of the TAILORIX trial was sustained corticosteroid-free remission from week 22 to 54. In the current study, the primary endpoint was progression-free survival at 1, 3, and 5 years in patients who did or did not meet the TAILORIX primary endpoint. The median disease duration was 4.5 months, and the median follow-up was 64.2 months.
Progression-free survival was defined as a composite of luminal surgery, anal surgery, hospitalization, and the need for a new CD treatment during the follow-up period.
In the study population, 45 patients achieved corticosteroid-free remission and 50 did not. At 54 weeks, 17 patients with corticosteroid-free remission (38%) and 28 patients without remission (56%) achieved complete mucosal healing, and progression-free survival rates were similar between these groups.
Overall, the rates of progression-free survival at 1, 3, and 5 years were not significantly different between the remission and nonremission groups: 86% versus 91%, respectively, at 1 year; 70% for both groups at 3 years; and 64% and 61%, respectively, at 5 years.
The researchers also compared individual components of the primary endpoint (luminal surgery, anal surgery, hospitalization, and the need for a new CD treatment), and found no significant differences in survival rates in patients who had and had not achieved steroid-free remission.
Survival rates without luminal surgery at 1, 3, and 5 years were 97% versus 96%, 93% versus 90%, and 87% versus 82%, respectively, for remission and nonremission groups. Similarly, survival rates without anal surgery were 93%, 86%, and 86% versus 96%, 88%, and 85%, respectively, for the two groups. Rates of hospitalization-free survival at 1, 3, and 5 years were 90% versus 92%, 81% versus 81%, and 78% versus 69%, respectively, in the remission and nonremission groups. Survival rates without a new systemic CD treatment also were similar at 1, 3, and 5 years: 93% versus 95%, 71% versus 93%, and 60% versus 51%, respectively, for the remission and nonremission groups.
CD progression was not associated with not achieving corticosteroid-free remission (hazard ratio, 0.861). Other factors that were not associated with disease progression in this study included CRP greater than 5 mg/L, age older than 30 years, active smoking, and B1 phenotype.
The researchers noted that, although endoscopic and clinical remission is currently recommended for CD, “there is no validated or standardized definition of this endoscopic goal.” The high rates of survival without major abdominal surgery, regardless of remission status, suggest a significant impact of early combination therapy for CD patients who were biologic naive. Other studies have shown similar improved outcomes for CD patients with early treatment.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design and lack of power to compare long-term progression-free survival, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the robust data on hospitalizations and surgeries from the TAILORIX trial.
The results support a more flexible strategy for CD, “recommending endoscopic and clinical remission in early diagnosed patients and less stringent objectives in those with more refractory or advanced disease,” they concluded.
Findings may guide patient management
The current study is important to help clinicians know whether CD patients who achieve a short-term, steroid-free clinical and endoscopic remission go on to experience better long-term disease outcomes than those who do not achieve this short-term remission, Atsushi Sakuraba, MD, of the University of Chicago said in an interview.
Dr. Sakuraba said that he was surprised by the study findings. “Achieving a clinical remission off steroids with complete endoscopic remission, i.e., deep remission, is considered a treatment goal, but the fact that it did not result in less disease progression was surprising.”
The take-home message for clinicians from the study is that CD patients may still experience disease progression after achieving a single time of clinical and endoscopic remission “mainly due to loss of response to infliximab, so continued long-term disease monitoring and control are required,” Dr. Sakuraba said.
The current study was a post hoc follow-up analysis of a previous trial, Dr. Sakuraba noted. Therefore, studies primarily focused on changing the disease progression and natural course of CD are warranted.
Dr. Laharie disclosed counseling, boards, transportation, or fees from AbbVie, Biogaran, Biogen, Ferring, HAC-pharma, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Prometheus, Roche, Takeda, Theradiag, and Tillots. Dr. Sakuraba had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
This article was updated Feb. 10, 2022.
Achieving steroid-free clinical and endoscopic remission does not decrease the risk of Crohn’s disease progression measured by surgery, hospitalization, or initiation of new treatments, according to a post hoc analysis of data from a prospective RCT.
The therapeutic goals of Crohn’s disease have evolved from controlling symptoms to blocking disease progression and reducing complications, wrote David Laharie, MD, of Hôpital Haut-Lévêque, Pessac, France, and colleagues. The goal of steroid-free remission has been used as an endpoint of treatment, but data on the impact of such remission on long-term disease are limited, the researchers noted in a retrospective study published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
In the study, the researchers reviewed data from 95 adults with early Crohn’s disease (CD) who participated in the TAILORIX trial involving treatment with infliximab and immunomodulators. The primary endpoint of the TAILORIX trial was sustained corticosteroid-free remission from week 22 to 54. In the current study, the primary endpoint was progression-free survival at 1, 3, and 5 years in patients who did or did not meet the TAILORIX primary endpoint. The median disease duration was 4.5 months, and the median follow-up was 64.2 months.
Progression-free survival was defined as a composite of luminal surgery, anal surgery, hospitalization, and the need for a new CD treatment during the follow-up period.
In the study population, 45 patients achieved corticosteroid-free remission and 50 did not. At 54 weeks, 17 patients with corticosteroid-free remission (38%) and 28 patients without remission (56%) achieved complete mucosal healing, and progression-free survival rates were similar between these groups.
Overall, the rates of progression-free survival at 1, 3, and 5 years were not significantly different between the remission and nonremission groups: 86% versus 91%, respectively, at 1 year; 70% for both groups at 3 years; and 64% and 61%, respectively, at 5 years.
The researchers also compared individual components of the primary endpoint (luminal surgery, anal surgery, hospitalization, and the need for a new CD treatment), and found no significant differences in survival rates in patients who had and had not achieved steroid-free remission.
Survival rates without luminal surgery at 1, 3, and 5 years were 97% versus 96%, 93% versus 90%, and 87% versus 82%, respectively, for remission and nonremission groups. Similarly, survival rates without anal surgery were 93%, 86%, and 86% versus 96%, 88%, and 85%, respectively, for the two groups. Rates of hospitalization-free survival at 1, 3, and 5 years were 90% versus 92%, 81% versus 81%, and 78% versus 69%, respectively, in the remission and nonremission groups. Survival rates without a new systemic CD treatment also were similar at 1, 3, and 5 years: 93% versus 95%, 71% versus 93%, and 60% versus 51%, respectively, for the remission and nonremission groups.
CD progression was not associated with not achieving corticosteroid-free remission (hazard ratio, 0.861). Other factors that were not associated with disease progression in this study included CRP greater than 5 mg/L, age older than 30 years, active smoking, and B1 phenotype.
The researchers noted that, although endoscopic and clinical remission is currently recommended for CD, “there is no validated or standardized definition of this endoscopic goal.” The high rates of survival without major abdominal surgery, regardless of remission status, suggest a significant impact of early combination therapy for CD patients who were biologic naive. Other studies have shown similar improved outcomes for CD patients with early treatment.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design and lack of power to compare long-term progression-free survival, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the robust data on hospitalizations and surgeries from the TAILORIX trial.
The results support a more flexible strategy for CD, “recommending endoscopic and clinical remission in early diagnosed patients and less stringent objectives in those with more refractory or advanced disease,” they concluded.
Findings may guide patient management
The current study is important to help clinicians know whether CD patients who achieve a short-term, steroid-free clinical and endoscopic remission go on to experience better long-term disease outcomes than those who do not achieve this short-term remission, Atsushi Sakuraba, MD, of the University of Chicago said in an interview.
Dr. Sakuraba said that he was surprised by the study findings. “Achieving a clinical remission off steroids with complete endoscopic remission, i.e., deep remission, is considered a treatment goal, but the fact that it did not result in less disease progression was surprising.”
The take-home message for clinicians from the study is that CD patients may still experience disease progression after achieving a single time of clinical and endoscopic remission “mainly due to loss of response to infliximab, so continued long-term disease monitoring and control are required,” Dr. Sakuraba said.
The current study was a post hoc follow-up analysis of a previous trial, Dr. Sakuraba noted. Therefore, studies primarily focused on changing the disease progression and natural course of CD are warranted.
Dr. Laharie disclosed counseling, boards, transportation, or fees from AbbVie, Biogaran, Biogen, Ferring, HAC-pharma, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Prometheus, Roche, Takeda, Theradiag, and Tillots. Dr. Sakuraba had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
This article was updated Feb. 10, 2022.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
We’re dying to tell you about fatigability
Are you tired? Or are you death tired?
When we’re feeling that burnout monster creep in we sometimes say that we’re being worked to death or that we’re dead tired, but what if that feeling could predict when it’s your actual time to go?
In a recent study published in the Journals of Gerontology: Series A, epidemiologists from the University of Pittsburgh were able to associate a level of “physical fatigability” with mortality.
The researchers administered the Pittsburgh Fatigability Scale to almost 3,000 participants aged ≥ 60 years, who ranked from 0 to 5 on how tired they thought they would be after doing activities like light housework or a leisurely 30-minute walk. After accounting for factors such as preexisting conditions and mental health, the researchers found that people who scored 25 or more points were 2.3 times more likely to die in the next 2.7 years, compared with those who scored under 25.
So what does that tell us about the importance of being continuously active? It’s pretty important.
“Previous research indicates that getting more physical activity can reduce a person’s fatigability. Our study is the first to link more severe physical fatigability to an earlier death,” lead author Nancy W. Glynn, PhD, said in a separate statement. The best way to keep physically active, she suggested, is to set manageable goals and a routine.
A nice walk around the neighborhood during golden hour or a little bit of yoga before breakfast could be a great way to keep the body moving, because you know what they say: Use it or lose it.
This work is NFT protected: Do not screenshot
If you’ve been following the nonmedical news, you’ve likely heard the term “NFT” explode in the past few months. Standing for nonfungible token, NFTs are, at least theoretically, a proof of ownership for digital creations that prevents anyone other than the buyer from reselling the artwork. Sounds like a great idea: It protects artists and buyers alike.
Much like its cousin cryptocurrency, however, the NFT world is rife with speculation, scams, misunderstanding, and drawings of bored monkeys. It’s the Wild West out there in the digital art universe: One poor unfortunate accidentally sold a $300k NFT image for $3,000, a group of investors spent $3 million buying an NFT for a rare version of Dune believing it gave them the copyright (it did not), and an Indonesian engineering student’s 5-year series of expressionless selfies is now worth a million dollars.
This is a column detailing weird medical news, however, so with our setup complete (though our understanding of NFTs is very much not), we move to France and meet our hero (?), Emmanuel Masmejean, an orthopedic surgeon who apparently wasn’t making enough money in his lucrative medical career.
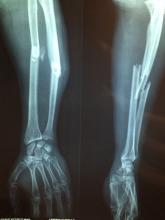
In a move of apocalyptic madness, he threw ethics out the window, delved into his archive, and found an x-ray of a young woman with a bullet lodged in her arm. The woman was a survivor of the Bataclan mass shooting and bombing in 2015, and don’t you worry, our intrepid entrepreneur made sure to identify her as such when he tried selling the x-ray as an NFT on an online art website for $2,776. Yes, this is very much a violation of doctor-patient confidentiality, and no, that’s not a lot of money to risk your medical career on.
Naturally, the woman was horrified and shocked to learn that the image was being sold, her lawyer told the Guardian. When the doctor called her, he merely attempted to justify his action, rather than apologizing or showing any remorse. Dr. Masmejean is now facing legal action and a disciplinary charge for his attempted entry into the NFT world for publishing the image without permission, and the NFT has been removed from the website. Should have stuck with the bored monkeys.
Avatars could be the future
Zoom, FaceTime, and Skype are great when people can’t be together in the same room, state, or country. Not the same as being somewhere in person, but a pretty good replacement during a global pandemic. But what if you had a robot that could be present for you?
Seven-year-old Joshua Martinangeli of Berlin has a severe lung disease and needs to wear a tube in his neck, so he cannot attend school. A robot avatar, donated to Joshua through a private initiative, sits in his seat in the classroom and is able to interact with the students and teacher, according to Reuters. A light on the avatar blinks when Joshua wants to speak and the children can talk with him too. Joshua and his classmates agree that it’s not the same as him really being there to talk and learn, but it’s a great way to keep him included.
“We are the only district in Berlin that has bought four avatars for its schools. The impetus was COVID-19, but I think this will be the future well beyond the pandemic,” Torsten Kuehne, district education councilor, told Reuters.
So where do we get an avatar to go out and run errands? Can we send it to the office instead of Zooming the next meeting? Or maybe our avatar could go to the gym for us. But how do we get the results to show up on our bodies? C’mon science, figure this out.
Futility, thy name is Kiribati
Before we get to the rest of our regularly scheduled hilarity, a brief geography lesson is in order: Kiribati is an island nation – actually 32 atolls and one coral island – in the central Pacific Ocean. Those atolls are spread out across 1.4 million square miles around the intersection of the equator and the International Date Line, so Kiribati is the only country in the world located in all four hemispheres.
Now, back to the news.
Kiribati closed its borders early in the COVID-19 pandemic and recorded only two cases in almost 2 years. Things were going so well that the authorities recently decided to reopen the country to international travelers. Silly authorities.
The first plane was set to arrive on Jan. 14 from Fiji. This being the age of COVID, plans were made and precautions were taken. All 54 passengers quarantined for 2 weeks before the flight and underwent regular testing, the Guardian noted, and “they were only allowed on the flight after returning negative tests.”
You guessed it. Two-thirds of those 54 people tested positive for COVID-19 after landing in Kiribati.
All of the passengers were quarantined, but since then a security guard at the quarantine center has tested positive, as has someone who was not involved in the quarantine. According to NPR, the government said that “there is now an assumption that COVID-19 is now spreading in the community on South Tarawa and Betio.”
Moral of the story? You can’t beat COVID, so never try.
[EDITOR: Is that really the message we want to send to our readers?]
If you can’t beat them, join them.
[EDITOR: Nope. Try again.]
Resistance is futile?
[EDITOR: Sigh. Close enough.]
Are you tired? Or are you death tired?
When we’re feeling that burnout monster creep in we sometimes say that we’re being worked to death or that we’re dead tired, but what if that feeling could predict when it’s your actual time to go?
In a recent study published in the Journals of Gerontology: Series A, epidemiologists from the University of Pittsburgh were able to associate a level of “physical fatigability” with mortality.
The researchers administered the Pittsburgh Fatigability Scale to almost 3,000 participants aged ≥ 60 years, who ranked from 0 to 5 on how tired they thought they would be after doing activities like light housework or a leisurely 30-minute walk. After accounting for factors such as preexisting conditions and mental health, the researchers found that people who scored 25 or more points were 2.3 times more likely to die in the next 2.7 years, compared with those who scored under 25.
So what does that tell us about the importance of being continuously active? It’s pretty important.
“Previous research indicates that getting more physical activity can reduce a person’s fatigability. Our study is the first to link more severe physical fatigability to an earlier death,” lead author Nancy W. Glynn, PhD, said in a separate statement. The best way to keep physically active, she suggested, is to set manageable goals and a routine.
A nice walk around the neighborhood during golden hour or a little bit of yoga before breakfast could be a great way to keep the body moving, because you know what they say: Use it or lose it.
This work is NFT protected: Do not screenshot
If you’ve been following the nonmedical news, you’ve likely heard the term “NFT” explode in the past few months. Standing for nonfungible token, NFTs are, at least theoretically, a proof of ownership for digital creations that prevents anyone other than the buyer from reselling the artwork. Sounds like a great idea: It protects artists and buyers alike.
Much like its cousin cryptocurrency, however, the NFT world is rife with speculation, scams, misunderstanding, and drawings of bored monkeys. It’s the Wild West out there in the digital art universe: One poor unfortunate accidentally sold a $300k NFT image for $3,000, a group of investors spent $3 million buying an NFT for a rare version of Dune believing it gave them the copyright (it did not), and an Indonesian engineering student’s 5-year series of expressionless selfies is now worth a million dollars.
This is a column detailing weird medical news, however, so with our setup complete (though our understanding of NFTs is very much not), we move to France and meet our hero (?), Emmanuel Masmejean, an orthopedic surgeon who apparently wasn’t making enough money in his lucrative medical career.
In a move of apocalyptic madness, he threw ethics out the window, delved into his archive, and found an x-ray of a young woman with a bullet lodged in her arm. The woman was a survivor of the Bataclan mass shooting and bombing in 2015, and don’t you worry, our intrepid entrepreneur made sure to identify her as such when he tried selling the x-ray as an NFT on an online art website for $2,776. Yes, this is very much a violation of doctor-patient confidentiality, and no, that’s not a lot of money to risk your medical career on.
Naturally, the woman was horrified and shocked to learn that the image was being sold, her lawyer told the Guardian. When the doctor called her, he merely attempted to justify his action, rather than apologizing or showing any remorse. Dr. Masmejean is now facing legal action and a disciplinary charge for his attempted entry into the NFT world for publishing the image without permission, and the NFT has been removed from the website. Should have stuck with the bored monkeys.
Avatars could be the future
Zoom, FaceTime, and Skype are great when people can’t be together in the same room, state, or country. Not the same as being somewhere in person, but a pretty good replacement during a global pandemic. But what if you had a robot that could be present for you?
Seven-year-old Joshua Martinangeli of Berlin has a severe lung disease and needs to wear a tube in his neck, so he cannot attend school. A robot avatar, donated to Joshua through a private initiative, sits in his seat in the classroom and is able to interact with the students and teacher, according to Reuters. A light on the avatar blinks when Joshua wants to speak and the children can talk with him too. Joshua and his classmates agree that it’s not the same as him really being there to talk and learn, but it’s a great way to keep him included.
“We are the only district in Berlin that has bought four avatars for its schools. The impetus was COVID-19, but I think this will be the future well beyond the pandemic,” Torsten Kuehne, district education councilor, told Reuters.
So where do we get an avatar to go out and run errands? Can we send it to the office instead of Zooming the next meeting? Or maybe our avatar could go to the gym for us. But how do we get the results to show up on our bodies? C’mon science, figure this out.
Futility, thy name is Kiribati
Before we get to the rest of our regularly scheduled hilarity, a brief geography lesson is in order: Kiribati is an island nation – actually 32 atolls and one coral island – in the central Pacific Ocean. Those atolls are spread out across 1.4 million square miles around the intersection of the equator and the International Date Line, so Kiribati is the only country in the world located in all four hemispheres.
Now, back to the news.
Kiribati closed its borders early in the COVID-19 pandemic and recorded only two cases in almost 2 years. Things were going so well that the authorities recently decided to reopen the country to international travelers. Silly authorities.
The first plane was set to arrive on Jan. 14 from Fiji. This being the age of COVID, plans were made and precautions were taken. All 54 passengers quarantined for 2 weeks before the flight and underwent regular testing, the Guardian noted, and “they were only allowed on the flight after returning negative tests.”
You guessed it. Two-thirds of those 54 people tested positive for COVID-19 after landing in Kiribati.
All of the passengers were quarantined, but since then a security guard at the quarantine center has tested positive, as has someone who was not involved in the quarantine. According to NPR, the government said that “there is now an assumption that COVID-19 is now spreading in the community on South Tarawa and Betio.”
Moral of the story? You can’t beat COVID, so never try.
[EDITOR: Is that really the message we want to send to our readers?]
If you can’t beat them, join them.
[EDITOR: Nope. Try again.]
Resistance is futile?
[EDITOR: Sigh. Close enough.]
Are you tired? Or are you death tired?
When we’re feeling that burnout monster creep in we sometimes say that we’re being worked to death or that we’re dead tired, but what if that feeling could predict when it’s your actual time to go?
In a recent study published in the Journals of Gerontology: Series A, epidemiologists from the University of Pittsburgh were able to associate a level of “physical fatigability” with mortality.
The researchers administered the Pittsburgh Fatigability Scale to almost 3,000 participants aged ≥ 60 years, who ranked from 0 to 5 on how tired they thought they would be after doing activities like light housework or a leisurely 30-minute walk. After accounting for factors such as preexisting conditions and mental health, the researchers found that people who scored 25 or more points were 2.3 times more likely to die in the next 2.7 years, compared with those who scored under 25.
So what does that tell us about the importance of being continuously active? It’s pretty important.
“Previous research indicates that getting more physical activity can reduce a person’s fatigability. Our study is the first to link more severe physical fatigability to an earlier death,” lead author Nancy W. Glynn, PhD, said in a separate statement. The best way to keep physically active, she suggested, is to set manageable goals and a routine.
A nice walk around the neighborhood during golden hour or a little bit of yoga before breakfast could be a great way to keep the body moving, because you know what they say: Use it or lose it.
This work is NFT protected: Do not screenshot
If you’ve been following the nonmedical news, you’ve likely heard the term “NFT” explode in the past few months. Standing for nonfungible token, NFTs are, at least theoretically, a proof of ownership for digital creations that prevents anyone other than the buyer from reselling the artwork. Sounds like a great idea: It protects artists and buyers alike.
Much like its cousin cryptocurrency, however, the NFT world is rife with speculation, scams, misunderstanding, and drawings of bored monkeys. It’s the Wild West out there in the digital art universe: One poor unfortunate accidentally sold a $300k NFT image for $3,000, a group of investors spent $3 million buying an NFT for a rare version of Dune believing it gave them the copyright (it did not), and an Indonesian engineering student’s 5-year series of expressionless selfies is now worth a million dollars.
This is a column detailing weird medical news, however, so with our setup complete (though our understanding of NFTs is very much not), we move to France and meet our hero (?), Emmanuel Masmejean, an orthopedic surgeon who apparently wasn’t making enough money in his lucrative medical career.
In a move of apocalyptic madness, he threw ethics out the window, delved into his archive, and found an x-ray of a young woman with a bullet lodged in her arm. The woman was a survivor of the Bataclan mass shooting and bombing in 2015, and don’t you worry, our intrepid entrepreneur made sure to identify her as such when he tried selling the x-ray as an NFT on an online art website for $2,776. Yes, this is very much a violation of doctor-patient confidentiality, and no, that’s not a lot of money to risk your medical career on.
Naturally, the woman was horrified and shocked to learn that the image was being sold, her lawyer told the Guardian. When the doctor called her, he merely attempted to justify his action, rather than apologizing or showing any remorse. Dr. Masmejean is now facing legal action and a disciplinary charge for his attempted entry into the NFT world for publishing the image without permission, and the NFT has been removed from the website. Should have stuck with the bored monkeys.
Avatars could be the future
Zoom, FaceTime, and Skype are great when people can’t be together in the same room, state, or country. Not the same as being somewhere in person, but a pretty good replacement during a global pandemic. But what if you had a robot that could be present for you?
Seven-year-old Joshua Martinangeli of Berlin has a severe lung disease and needs to wear a tube in his neck, so he cannot attend school. A robot avatar, donated to Joshua through a private initiative, sits in his seat in the classroom and is able to interact with the students and teacher, according to Reuters. A light on the avatar blinks when Joshua wants to speak and the children can talk with him too. Joshua and his classmates agree that it’s not the same as him really being there to talk and learn, but it’s a great way to keep him included.
“We are the only district in Berlin that has bought four avatars for its schools. The impetus was COVID-19, but I think this will be the future well beyond the pandemic,” Torsten Kuehne, district education councilor, told Reuters.
So where do we get an avatar to go out and run errands? Can we send it to the office instead of Zooming the next meeting? Or maybe our avatar could go to the gym for us. But how do we get the results to show up on our bodies? C’mon science, figure this out.
Futility, thy name is Kiribati
Before we get to the rest of our regularly scheduled hilarity, a brief geography lesson is in order: Kiribati is an island nation – actually 32 atolls and one coral island – in the central Pacific Ocean. Those atolls are spread out across 1.4 million square miles around the intersection of the equator and the International Date Line, so Kiribati is the only country in the world located in all four hemispheres.
Now, back to the news.
Kiribati closed its borders early in the COVID-19 pandemic and recorded only two cases in almost 2 years. Things were going so well that the authorities recently decided to reopen the country to international travelers. Silly authorities.
The first plane was set to arrive on Jan. 14 from Fiji. This being the age of COVID, plans were made and precautions were taken. All 54 passengers quarantined for 2 weeks before the flight and underwent regular testing, the Guardian noted, and “they were only allowed on the flight after returning negative tests.”
You guessed it. Two-thirds of those 54 people tested positive for COVID-19 after landing in Kiribati.
All of the passengers were quarantined, but since then a security guard at the quarantine center has tested positive, as has someone who was not involved in the quarantine. According to NPR, the government said that “there is now an assumption that COVID-19 is now spreading in the community on South Tarawa and Betio.”
Moral of the story? You can’t beat COVID, so never try.
[EDITOR: Is that really the message we want to send to our readers?]
If you can’t beat them, join them.
[EDITOR: Nope. Try again.]
Resistance is futile?
[EDITOR: Sigh. Close enough.]
Monotherapy or one-two punch against EGFR-mutant NSCLC?
It is indisputable that patients with newly diagnosed advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) bearing mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathway may benefit from targeted therapy with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) directed against EGFR.
What’s less clear is whether monotherapy with an EGFR TKI or combination therapy with a TKI and chemotherapy, immunotherapy, monoclonal antibodies or other targeted agents is the preferred frontline strategy.
NSCLC guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, for example, recommend that patients with EFGR mutations such as exon 19 deletion, discovered prior to first-line systemic therapy, should preferably received osimertinib (Tagrisso) or another TKI, such as erlotinib (Tarceva), afatinib (Gilotrif), gefitinib (Iressa) or dacomitinib (Vizimpro), or erlotinib with a VEGF inhibitor. For patients with EGFR mutations identified during first-line systemic therapy, NCCN recommends complete systemic therapy or interrupting it, followed by osimertinib as the preferred agent, or another TKI with or without a VEGF inhibitors.
Similarly, guidelines from the American Society of Clinical Oncology and Ontario Health recommend osimertinib monotherapy as a preferred first-line option for patients with L858R/exon 19 deletion EGFR mutations. Alternatives for patients for whom osimertinib is not available include gefitinib plus platinum/pemetrexed chemotherapy with maintenance pemetrexed, monotherapy with dacomitinib, or other targeted agents with or without VEGF inhibitors.
Combination or go it alone?
The guidelines are largely mute on the question of chemotherapy in this population, primarily because they have not caught up to clinical trial evidence, said Paul Wheatley-Price, MBChB, FRCP, MD, from the University of Ottawa Hospital Research Institute.
“There is recent data that looks quite promising on combining EGFR inhibitors with either chemotherapy or antiangiogenic drugs, but it’s too soon, I think, and while the trials are promising, there are still too many question marks over it to make it into the guidelines,” he said in an interview.
The question of frontline combinations vs. monotherapy in patients with advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC was the subject of a recent “controversies in thoracic oncology” feature in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, with Dr. Wheatley-Price and University of Ottawa colleague Sara Moore, MD, FRCPC, arguing that combining EGFR TKIs with either cytotoxic chemotherapy or antiangiogenic monoclonal antibodies targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor has been shown consistently to improve progression-free survival (PFS) and in some cases overall survival (OS).
“There is a consistent drop-off in patients who receive second-line therapy, highlighting the importance of using combination therapy in the first-line setting to ensure patients will be exposed to multiple available therapies that may prolong survival. Chemotherapy-based combinations lead to improved response rates which may be especially helpful in patients with a significant burden of disease,” they wrote.
The authors noted that, compared with patients with wild-type EGFR, patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC had a doubling of response rates to chemotherapy with a platinum-based doublet in the IPASS trial, suggesting that EGFR-mutated tumors may be more chemosensitive.
Promising trials, old drug
“Chemotherapy and EGFR TKIs may have a synergistic effect through combined reduction in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)–mediated angiogenesis, and with EGFR TKIs counteracting chemotherapy-induced up-regulation of downstream EGFR signaling,” they wrote.
The authors cited two studies, one from Japan, and one from India, both of which showed significant improvements in response rates, PFS, and OS with the combination of gefitinib plus carboplatin and pemetrexed chemotherapy with pemetrexed maintenance vs. carboplatin alone,
“Now of course we don’t use gefitinib as our first-line treatment. In Canada and the United States, we use osimertinib, so certainly the chemotherapy/TKI combination, while it looks quite promising, was compared to an old control arm,” Dr. Wheatley-Price said.
He noted that the phase 3 FLAURA2 trial, currently underway, will address the question of whether adding osimertinib to a chemotherapy doublet with pemetrexed plus either carboplatin or cisplatin can improve PFS in patients with EGFR-positive locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC, compared with osimertinib alone.
The authors acknowledged that chemotherapy adds toxicities, compared with the use of TKI monotherapy, but added that, “even with the use of first-line osimertinib monotherapy, patients may still be exposed to chemotherapy with later lines of treatment. Therefore, combination therapy does not expose patients to new toxicity, it simply changes when they will be exposed to that toxicity during their treatment course.”
VEGF plus EGFR
Adding a VEGF-targeted monoclonal antibody or TKI to and EGFR TKI has shown consistent PFS benefits in the NEJ026, ARTEMIS, RELAY, and ACTIVE trials, Dr. Moore and Dr. Wheatley-Price noted.
“In all four trials, resistance testing at the time of progression revealed similar rates of T790M mutation in both arms, highlighting the potential role of optimizing the sequence of therapy with use of second-line osimertinib among those with a T790M resistance mutation,” they wrote.
All four trials also showed higher rates of adverse events in the combination arms, but most, except for hypertension, were low grade, and in the RELAY trial the added toxicities did not significantly affect patient quality of life, they said.
Monotherapy advocated
Although in agreement that the combination of gefitinib and chemotherapy has both PFS and OS benefits compared with monotherapy alone, “these combinations are not applicable to real-life practice given their use of first-generation EGFR TKIs rather than third-generation EGFR TKI osimertinib,” wrote Sophie Stock-Martineau, MD, FRCPC from Hôpital Maisonneuve-Rosemont and the University of Montreal, and Frances A. Shepherd, MD, FRCPC from the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre in Toronto, in an article touting EGFR monotherapy.
They stated that until the results of FLAURA2 are available “osimertinib alone remains the current standard first-line therapy in metastatic EGFRm+ NSCLC.”
“The addition of an antiangiogenic agent to an EGFR TKI mildly prolongs PFS; however, it does not yet translate into survival benefit. Not only does it add more toxicity to patients, but it also adds cost, which is far from negligible,” they wrote.
Dr. Stock-Martineau and Dr. Shepherd also noted that two phase 2 trials comparing afatinib with the EGFR monoclonal antibody cetuximab (Erbitux) showed no PFS or OS benefits in patients with untreated EGFR-mutated NSCLC and were terminated for lack of efficacy.
In addition, clinical trials of combinations of EGFR TKIs with immune checkpoint inhibitors or MET inhibitors have failed to date to demonstrate survival benefits, the authors said.
“No trials have yet revealed PFS or OS benefit with osimertinib combinations. Adding virtually all agents to EGFR TKIs has been associated with more toxicity to patients and a significant financial burden to the health care system. Combinations could potentially also worsen quality of life given their heightened toxicity profiles. Therefore, single-agent EGFR TKI, such as osimertinib, remains for now the standard of care in the first-line setting for advanced EGFRm+ NSCLC,” they concluded.
No funding sources for the articles were reported. All authors declared no conflicts of interest to disclose.
It is indisputable that patients with newly diagnosed advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) bearing mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathway may benefit from targeted therapy with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) directed against EGFR.
What’s less clear is whether monotherapy with an EGFR TKI or combination therapy with a TKI and chemotherapy, immunotherapy, monoclonal antibodies or other targeted agents is the preferred frontline strategy.
NSCLC guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, for example, recommend that patients with EFGR mutations such as exon 19 deletion, discovered prior to first-line systemic therapy, should preferably received osimertinib (Tagrisso) or another TKI, such as erlotinib (Tarceva), afatinib (Gilotrif), gefitinib (Iressa) or dacomitinib (Vizimpro), or erlotinib with a VEGF inhibitor. For patients with EGFR mutations identified during first-line systemic therapy, NCCN recommends complete systemic therapy or interrupting it, followed by osimertinib as the preferred agent, or another TKI with or without a VEGF inhibitors.
Similarly, guidelines from the American Society of Clinical Oncology and Ontario Health recommend osimertinib monotherapy as a preferred first-line option for patients with L858R/exon 19 deletion EGFR mutations. Alternatives for patients for whom osimertinib is not available include gefitinib plus platinum/pemetrexed chemotherapy with maintenance pemetrexed, monotherapy with dacomitinib, or other targeted agents with or without VEGF inhibitors.
Combination or go it alone?
The guidelines are largely mute on the question of chemotherapy in this population, primarily because they have not caught up to clinical trial evidence, said Paul Wheatley-Price, MBChB, FRCP, MD, from the University of Ottawa Hospital Research Institute.
“There is recent data that looks quite promising on combining EGFR inhibitors with either chemotherapy or antiangiogenic drugs, but it’s too soon, I think, and while the trials are promising, there are still too many question marks over it to make it into the guidelines,” he said in an interview.
The question of frontline combinations vs. monotherapy in patients with advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC was the subject of a recent “controversies in thoracic oncology” feature in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, with Dr. Wheatley-Price and University of Ottawa colleague Sara Moore, MD, FRCPC, arguing that combining EGFR TKIs with either cytotoxic chemotherapy or antiangiogenic monoclonal antibodies targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor has been shown consistently to improve progression-free survival (PFS) and in some cases overall survival (OS).
“There is a consistent drop-off in patients who receive second-line therapy, highlighting the importance of using combination therapy in the first-line setting to ensure patients will be exposed to multiple available therapies that may prolong survival. Chemotherapy-based combinations lead to improved response rates which may be especially helpful in patients with a significant burden of disease,” they wrote.
The authors noted that, compared with patients with wild-type EGFR, patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC had a doubling of response rates to chemotherapy with a platinum-based doublet in the IPASS trial, suggesting that EGFR-mutated tumors may be more chemosensitive.
Promising trials, old drug
“Chemotherapy and EGFR TKIs may have a synergistic effect through combined reduction in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)–mediated angiogenesis, and with EGFR TKIs counteracting chemotherapy-induced up-regulation of downstream EGFR signaling,” they wrote.
The authors cited two studies, one from Japan, and one from India, both of which showed significant improvements in response rates, PFS, and OS with the combination of gefitinib plus carboplatin and pemetrexed chemotherapy with pemetrexed maintenance vs. carboplatin alone,
“Now of course we don’t use gefitinib as our first-line treatment. In Canada and the United States, we use osimertinib, so certainly the chemotherapy/TKI combination, while it looks quite promising, was compared to an old control arm,” Dr. Wheatley-Price said.
He noted that the phase 3 FLAURA2 trial, currently underway, will address the question of whether adding osimertinib to a chemotherapy doublet with pemetrexed plus either carboplatin or cisplatin can improve PFS in patients with EGFR-positive locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC, compared with osimertinib alone.
The authors acknowledged that chemotherapy adds toxicities, compared with the use of TKI monotherapy, but added that, “even with the use of first-line osimertinib monotherapy, patients may still be exposed to chemotherapy with later lines of treatment. Therefore, combination therapy does not expose patients to new toxicity, it simply changes when they will be exposed to that toxicity during their treatment course.”
VEGF plus EGFR
Adding a VEGF-targeted monoclonal antibody or TKI to and EGFR TKI has shown consistent PFS benefits in the NEJ026, ARTEMIS, RELAY, and ACTIVE trials, Dr. Moore and Dr. Wheatley-Price noted.
“In all four trials, resistance testing at the time of progression revealed similar rates of T790M mutation in both arms, highlighting the potential role of optimizing the sequence of therapy with use of second-line osimertinib among those with a T790M resistance mutation,” they wrote.
All four trials also showed higher rates of adverse events in the combination arms, but most, except for hypertension, were low grade, and in the RELAY trial the added toxicities did not significantly affect patient quality of life, they said.
Monotherapy advocated
Although in agreement that the combination of gefitinib and chemotherapy has both PFS and OS benefits compared with monotherapy alone, “these combinations are not applicable to real-life practice given their use of first-generation EGFR TKIs rather than third-generation EGFR TKI osimertinib,” wrote Sophie Stock-Martineau, MD, FRCPC from Hôpital Maisonneuve-Rosemont and the University of Montreal, and Frances A. Shepherd, MD, FRCPC from the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre in Toronto, in an article touting EGFR monotherapy.
They stated that until the results of FLAURA2 are available “osimertinib alone remains the current standard first-line therapy in metastatic EGFRm+ NSCLC.”
“The addition of an antiangiogenic agent to an EGFR TKI mildly prolongs PFS; however, it does not yet translate into survival benefit. Not only does it add more toxicity to patients, but it also adds cost, which is far from negligible,” they wrote.
Dr. Stock-Martineau and Dr. Shepherd also noted that two phase 2 trials comparing afatinib with the EGFR monoclonal antibody cetuximab (Erbitux) showed no PFS or OS benefits in patients with untreated EGFR-mutated NSCLC and were terminated for lack of efficacy.
In addition, clinical trials of combinations of EGFR TKIs with immune checkpoint inhibitors or MET inhibitors have failed to date to demonstrate survival benefits, the authors said.
“No trials have yet revealed PFS or OS benefit with osimertinib combinations. Adding virtually all agents to EGFR TKIs has been associated with more toxicity to patients and a significant financial burden to the health care system. Combinations could potentially also worsen quality of life given their heightened toxicity profiles. Therefore, single-agent EGFR TKI, such as osimertinib, remains for now the standard of care in the first-line setting for advanced EGFRm+ NSCLC,” they concluded.
No funding sources for the articles were reported. All authors declared no conflicts of interest to disclose.
It is indisputable that patients with newly diagnosed advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) bearing mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathway may benefit from targeted therapy with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) directed against EGFR.
What’s less clear is whether monotherapy with an EGFR TKI or combination therapy with a TKI and chemotherapy, immunotherapy, monoclonal antibodies or other targeted agents is the preferred frontline strategy.
NSCLC guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, for example, recommend that patients with EFGR mutations such as exon 19 deletion, discovered prior to first-line systemic therapy, should preferably received osimertinib (Tagrisso) or another TKI, such as erlotinib (Tarceva), afatinib (Gilotrif), gefitinib (Iressa) or dacomitinib (Vizimpro), or erlotinib with a VEGF inhibitor. For patients with EGFR mutations identified during first-line systemic therapy, NCCN recommends complete systemic therapy or interrupting it, followed by osimertinib as the preferred agent, or another TKI with or without a VEGF inhibitors.
Similarly, guidelines from the American Society of Clinical Oncology and Ontario Health recommend osimertinib monotherapy as a preferred first-line option for patients with L858R/exon 19 deletion EGFR mutations. Alternatives for patients for whom osimertinib is not available include gefitinib plus platinum/pemetrexed chemotherapy with maintenance pemetrexed, monotherapy with dacomitinib, or other targeted agents with or without VEGF inhibitors.
Combination or go it alone?
The guidelines are largely mute on the question of chemotherapy in this population, primarily because they have not caught up to clinical trial evidence, said Paul Wheatley-Price, MBChB, FRCP, MD, from the University of Ottawa Hospital Research Institute.
“There is recent data that looks quite promising on combining EGFR inhibitors with either chemotherapy or antiangiogenic drugs, but it’s too soon, I think, and while the trials are promising, there are still too many question marks over it to make it into the guidelines,” he said in an interview.
The question of frontline combinations vs. monotherapy in patients with advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC was the subject of a recent “controversies in thoracic oncology” feature in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, with Dr. Wheatley-Price and University of Ottawa colleague Sara Moore, MD, FRCPC, arguing that combining EGFR TKIs with either cytotoxic chemotherapy or antiangiogenic monoclonal antibodies targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor has been shown consistently to improve progression-free survival (PFS) and in some cases overall survival (OS).
“There is a consistent drop-off in patients who receive second-line therapy, highlighting the importance of using combination therapy in the first-line setting to ensure patients will be exposed to multiple available therapies that may prolong survival. Chemotherapy-based combinations lead to improved response rates which may be especially helpful in patients with a significant burden of disease,” they wrote.
The authors noted that, compared with patients with wild-type EGFR, patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC had a doubling of response rates to chemotherapy with a platinum-based doublet in the IPASS trial, suggesting that EGFR-mutated tumors may be more chemosensitive.
Promising trials, old drug
“Chemotherapy and EGFR TKIs may have a synergistic effect through combined reduction in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)–mediated angiogenesis, and with EGFR TKIs counteracting chemotherapy-induced up-regulation of downstream EGFR signaling,” they wrote.
The authors cited two studies, one from Japan, and one from India, both of which showed significant improvements in response rates, PFS, and OS with the combination of gefitinib plus carboplatin and pemetrexed chemotherapy with pemetrexed maintenance vs. carboplatin alone,
“Now of course we don’t use gefitinib as our first-line treatment. In Canada and the United States, we use osimertinib, so certainly the chemotherapy/TKI combination, while it looks quite promising, was compared to an old control arm,” Dr. Wheatley-Price said.
He noted that the phase 3 FLAURA2 trial, currently underway, will address the question of whether adding osimertinib to a chemotherapy doublet with pemetrexed plus either carboplatin or cisplatin can improve PFS in patients with EGFR-positive locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC, compared with osimertinib alone.
The authors acknowledged that chemotherapy adds toxicities, compared with the use of TKI monotherapy, but added that, “even with the use of first-line osimertinib monotherapy, patients may still be exposed to chemotherapy with later lines of treatment. Therefore, combination therapy does not expose patients to new toxicity, it simply changes when they will be exposed to that toxicity during their treatment course.”
VEGF plus EGFR
Adding a VEGF-targeted monoclonal antibody or TKI to and EGFR TKI has shown consistent PFS benefits in the NEJ026, ARTEMIS, RELAY, and ACTIVE trials, Dr. Moore and Dr. Wheatley-Price noted.
“In all four trials, resistance testing at the time of progression revealed similar rates of T790M mutation in both arms, highlighting the potential role of optimizing the sequence of therapy with use of second-line osimertinib among those with a T790M resistance mutation,” they wrote.
All four trials also showed higher rates of adverse events in the combination arms, but most, except for hypertension, were low grade, and in the RELAY trial the added toxicities did not significantly affect patient quality of life, they said.
Monotherapy advocated
Although in agreement that the combination of gefitinib and chemotherapy has both PFS and OS benefits compared with monotherapy alone, “these combinations are not applicable to real-life practice given their use of first-generation EGFR TKIs rather than third-generation EGFR TKI osimertinib,” wrote Sophie Stock-Martineau, MD, FRCPC from Hôpital Maisonneuve-Rosemont and the University of Montreal, and Frances A. Shepherd, MD, FRCPC from the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre in Toronto, in an article touting EGFR monotherapy.
They stated that until the results of FLAURA2 are available “osimertinib alone remains the current standard first-line therapy in metastatic EGFRm+ NSCLC.”
“The addition of an antiangiogenic agent to an EGFR TKI mildly prolongs PFS; however, it does not yet translate into survival benefit. Not only does it add more toxicity to patients, but it also adds cost, which is far from negligible,” they wrote.
Dr. Stock-Martineau and Dr. Shepherd also noted that two phase 2 trials comparing afatinib with the EGFR monoclonal antibody cetuximab (Erbitux) showed no PFS or OS benefits in patients with untreated EGFR-mutated NSCLC and were terminated for lack of efficacy.
In addition, clinical trials of combinations of EGFR TKIs with immune checkpoint inhibitors or MET inhibitors have failed to date to demonstrate survival benefits, the authors said.
“No trials have yet revealed PFS or OS benefit with osimertinib combinations. Adding virtually all agents to EGFR TKIs has been associated with more toxicity to patients and a significant financial burden to the health care system. Combinations could potentially also worsen quality of life given their heightened toxicity profiles. Therefore, single-agent EGFR TKI, such as osimertinib, remains for now the standard of care in the first-line setting for advanced EGFRm+ NSCLC,” they concluded.
No funding sources for the articles were reported. All authors declared no conflicts of interest to disclose.
FROM JOURNAL OF THORACIC ONCOLOGY
Levator ani
Berries, red wine linked to lower mortality in Parkinson’s disease
(PD), new research suggests.
In a prospective analysis of more than 1,200 participants with an eventual PD diagnosis, those who ate three or more servings of flavonoid-rich foods a week had a 70% lower mortality versus those consuming one or fewer servings of such foods per month.
“Adopting a healthy dietary pattern that is high in colorful fruits and veggies like berries, even after a Parkinson diagnosis, could slow disease progression and improve survival rate,” study investigator Xiang Gao, MD, PhD, professor and director, Nutritional Epidemiology Lab, department of nutritional sciences, Penn State University, University Park, said in an interview.
The findings were published online Jan. 26, 2022, in Neurology.
First evidence of survival advantage
Flavonoids are plant-derived polyphenolic molecules found in fruits such as berries, apples, and oranges; vegetables such as kale and broccoli; and beverages, including tea and red wine. They are the dietary components that give many foods their vibrant color.
Certain flavonoids have been shown previously to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
A previous study by Dr. Gao and colleagues showed that flavonoids were associated with a lower future risk for developing PD. However, it did not provide evidence these nutrients improved survival rates among PD patients.
The new analysis included participants from the ongoing Nurses’ Health Study (NHS) of female registered nurses, which began in 1976, and male participants from the ongoing Health Professionals Follow-up Study (HPFS), which began in 1986.
All participants answered questionnaires at baseline and then biennially to update information on demographics, lifestyle, medical history, and occurrence of chronic disease.
Using validated food-frequency questionnaires completed every 4 years, researchers assessed dietary intakes of total flavonoid, six flavonoid subclasses, and flavonoid-rich foods such as tea, apples, berries, oranges and orange juice, and red wine.
They examined flavonoid intake both before and after a PD diagnosis to minimize the potential for reverse causality. The investigators noted that patients with PD have difficulty swallowing and handling food and cutlery, which could impact their consumption of flavonoid-rich foods.
Frequency of consumption of flavonoid-rich foods was categorized into four groups: one or less servings per month (the reference group), one to three servings per month, one to two servings per week, and three or more servings per week.
The analysis included 599 women and 652 men who were newly diagnosed with PD. The mean age at PD diagnosis was 72 years, and the mean time between the last prediagnosis dietary assessment and PD diagnosis was 32 months.
The primary outcome measure was all-cause mortality. There were 528 deaths in men and 416 deaths in women during an average of 33 years of follow-up.
Neuroprotective pathway?
After controlling for age, lifestyle behaviors, medical history, and total energy and caffeine intake, results showed that higher total flavonoid intake before PD diagnosis was associated with a lower risk for all-cause mortality after diagnosis in men, with a hazard ratio of 0.53 (95% confidence interval, 0.39-0.71) when comparing the highest and lowest quartiles (P for trend < .001).
However, this association was not found in women (HR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.68-1.28; P for trend = .69).
The pooled HR was 0.70 (95% CI, 0.40-1.22; P for trend = .25) with significant heterogeneity (P = .01).
There were significant associations between a higher prediagnosis intake of certain flavonoids and lower mortality risk. The pooled HR comparing the highest versus lowest intake quartiles was 0.66 for anthocyanin, 0.78 for flavones, and 0.69 for flavan-3-ols (P < .05 for all).
Compared with participants who consumed less than one serving a month, those consuming more than three servings a week prediagnosis of berries or red wine had a lower mortality risk (pooled HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.58-1.02 for berries and HR, 0.68; 95% CI, 0.51-0.91 for red wine).
After PD diagnosis, higher flavonoid consumption was associated with better survival rates in both men and women.
It’s unclear why there was a gender difference in the association between prediagnosis flavonoid intake and mortality but not for postdiagnosis flavonoid intakes, Dr. Gao said.
A potential neuroprotective pathway by which flavonoids reduce mortality in PD involves direct radical scavenging, which lowers oxidative stress and chronic neuroinflammation levels, he noted.
“Certain flavonoids, for example, anthocyanins, have been shown to exert antiapoptosis effects and protect cognition and motor functions. They could also increase dopamine release,” Dr. Gao added.
Study limitations included not having detailed information on participants’ PD disease severity and that both the NHS and HPFS include predominantly White health care professionals, which limits the generalizability of the results, the investigators noted.
No direct link
Commenting on the findings, Michael S. Okun, MD, medical advisor at the Parkinson’s Foundation and director of the Norman Fixel Institute for Neurological Diseases, University of Florida Health, Gainesville, said the study adds to growing evidence suggesting “subsets of flavonoids and especially berries and wine will have benefits pre- and post–Parkinson’s disease diagnosis.”
However, he emphasized that patients should not take up drinking red wine just to improve survival.
“We don’t recommend that folks who are already diagnosed with Parkinson’s drink alcohol, especially without physician supervision,” said Dr. Okun, who was not involved with the research.
Also commenting for this article, Gunter Kuhnle, PhD, professor of nutrition and food science, University of Reading (England), said because the study doesn’t appear to adjust for socioeconomic status, the results may be driven by factors such as income and education and not food intake.
The study found a beneficial association with anthocyanins, which are mainly found in expensive berries, and with flavan-3-ols found mainly in tea, which in the United States is often a marker of higher income, said Dr. Kuhnle.
The advantage of assessing dietary intake of flavonoids using a food-frequency questionnaire, as was done in this study, is that it captures long-term patterns. However, the disadvantage is a loss in “resolution” by combining similar foods, Dr. Kuhnle noted.
Since flavonoids are found in most fruits and vegetables, high flavonoid intake “might simply be a marker of fruit and vegetable intake and therefore a ‘healthy’ dietary pattern,” he concluded.
The study received funding from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Gao and Dr. Okun reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kuhnle has conducted research into the associations between flavanol and health, some of which has been funded by Mars.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(PD), new research suggests.
In a prospective analysis of more than 1,200 participants with an eventual PD diagnosis, those who ate three or more servings of flavonoid-rich foods a week had a 70% lower mortality versus those consuming one or fewer servings of such foods per month.
“Adopting a healthy dietary pattern that is high in colorful fruits and veggies like berries, even after a Parkinson diagnosis, could slow disease progression and improve survival rate,” study investigator Xiang Gao, MD, PhD, professor and director, Nutritional Epidemiology Lab, department of nutritional sciences, Penn State University, University Park, said in an interview.
The findings were published online Jan. 26, 2022, in Neurology.
First evidence of survival advantage
Flavonoids are plant-derived polyphenolic molecules found in fruits such as berries, apples, and oranges; vegetables such as kale and broccoli; and beverages, including tea and red wine. They are the dietary components that give many foods their vibrant color.
Certain flavonoids have been shown previously to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
A previous study by Dr. Gao and colleagues showed that flavonoids were associated with a lower future risk for developing PD. However, it did not provide evidence these nutrients improved survival rates among PD patients.
The new analysis included participants from the ongoing Nurses’ Health Study (NHS) of female registered nurses, which began in 1976, and male participants from the ongoing Health Professionals Follow-up Study (HPFS), which began in 1986.
All participants answered questionnaires at baseline and then biennially to update information on demographics, lifestyle, medical history, and occurrence of chronic disease.
Using validated food-frequency questionnaires completed every 4 years, researchers assessed dietary intakes of total flavonoid, six flavonoid subclasses, and flavonoid-rich foods such as tea, apples, berries, oranges and orange juice, and red wine.
They examined flavonoid intake both before and after a PD diagnosis to minimize the potential for reverse causality. The investigators noted that patients with PD have difficulty swallowing and handling food and cutlery, which could impact their consumption of flavonoid-rich foods.
Frequency of consumption of flavonoid-rich foods was categorized into four groups: one or less servings per month (the reference group), one to three servings per month, one to two servings per week, and three or more servings per week.
The analysis included 599 women and 652 men who were newly diagnosed with PD. The mean age at PD diagnosis was 72 years, and the mean time between the last prediagnosis dietary assessment and PD diagnosis was 32 months.
The primary outcome measure was all-cause mortality. There were 528 deaths in men and 416 deaths in women during an average of 33 years of follow-up.
Neuroprotective pathway?
After controlling for age, lifestyle behaviors, medical history, and total energy and caffeine intake, results showed that higher total flavonoid intake before PD diagnosis was associated with a lower risk for all-cause mortality after diagnosis in men, with a hazard ratio of 0.53 (95% confidence interval, 0.39-0.71) when comparing the highest and lowest quartiles (P for trend < .001).
However, this association was not found in women (HR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.68-1.28; P for trend = .69).
The pooled HR was 0.70 (95% CI, 0.40-1.22; P for trend = .25) with significant heterogeneity (P = .01).
There were significant associations between a higher prediagnosis intake of certain flavonoids and lower mortality risk. The pooled HR comparing the highest versus lowest intake quartiles was 0.66 for anthocyanin, 0.78 for flavones, and 0.69 for flavan-3-ols (P < .05 for all).
Compared with participants who consumed less than one serving a month, those consuming more than three servings a week prediagnosis of berries or red wine had a lower mortality risk (pooled HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.58-1.02 for berries and HR, 0.68; 95% CI, 0.51-0.91 for red wine).
After PD diagnosis, higher flavonoid consumption was associated with better survival rates in both men and women.
It’s unclear why there was a gender difference in the association between prediagnosis flavonoid intake and mortality but not for postdiagnosis flavonoid intakes, Dr. Gao said.
A potential neuroprotective pathway by which flavonoids reduce mortality in PD involves direct radical scavenging, which lowers oxidative stress and chronic neuroinflammation levels, he noted.
“Certain flavonoids, for example, anthocyanins, have been shown to exert antiapoptosis effects and protect cognition and motor functions. They could also increase dopamine release,” Dr. Gao added.
Study limitations included not having detailed information on participants’ PD disease severity and that both the NHS and HPFS include predominantly White health care professionals, which limits the generalizability of the results, the investigators noted.
No direct link
Commenting on the findings, Michael S. Okun, MD, medical advisor at the Parkinson’s Foundation and director of the Norman Fixel Institute for Neurological Diseases, University of Florida Health, Gainesville, said the study adds to growing evidence suggesting “subsets of flavonoids and especially berries and wine will have benefits pre- and post–Parkinson’s disease diagnosis.”
However, he emphasized that patients should not take up drinking red wine just to improve survival.
“We don’t recommend that folks who are already diagnosed with Parkinson’s drink alcohol, especially without physician supervision,” said Dr. Okun, who was not involved with the research.
Also commenting for this article, Gunter Kuhnle, PhD, professor of nutrition and food science, University of Reading (England), said because the study doesn’t appear to adjust for socioeconomic status, the results may be driven by factors such as income and education and not food intake.
The study found a beneficial association with anthocyanins, which are mainly found in expensive berries, and with flavan-3-ols found mainly in tea, which in the United States is often a marker of higher income, said Dr. Kuhnle.
The advantage of assessing dietary intake of flavonoids using a food-frequency questionnaire, as was done in this study, is that it captures long-term patterns. However, the disadvantage is a loss in “resolution” by combining similar foods, Dr. Kuhnle noted.
Since flavonoids are found in most fruits and vegetables, high flavonoid intake “might simply be a marker of fruit and vegetable intake and therefore a ‘healthy’ dietary pattern,” he concluded.
The study received funding from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Gao and Dr. Okun reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kuhnle has conducted research into the associations between flavanol and health, some of which has been funded by Mars.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(PD), new research suggests.
In a prospective analysis of more than 1,200 participants with an eventual PD diagnosis, those who ate three or more servings of flavonoid-rich foods a week had a 70% lower mortality versus those consuming one or fewer servings of such foods per month.
“Adopting a healthy dietary pattern that is high in colorful fruits and veggies like berries, even after a Parkinson diagnosis, could slow disease progression and improve survival rate,” study investigator Xiang Gao, MD, PhD, professor and director, Nutritional Epidemiology Lab, department of nutritional sciences, Penn State University, University Park, said in an interview.
The findings were published online Jan. 26, 2022, in Neurology.
First evidence of survival advantage
Flavonoids are plant-derived polyphenolic molecules found in fruits such as berries, apples, and oranges; vegetables such as kale and broccoli; and beverages, including tea and red wine. They are the dietary components that give many foods their vibrant color.
Certain flavonoids have been shown previously to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
A previous study by Dr. Gao and colleagues showed that flavonoids were associated with a lower future risk for developing PD. However, it did not provide evidence these nutrients improved survival rates among PD patients.
The new analysis included participants from the ongoing Nurses’ Health Study (NHS) of female registered nurses, which began in 1976, and male participants from the ongoing Health Professionals Follow-up Study (HPFS), which began in 1986.
All participants answered questionnaires at baseline and then biennially to update information on demographics, lifestyle, medical history, and occurrence of chronic disease.
Using validated food-frequency questionnaires completed every 4 years, researchers assessed dietary intakes of total flavonoid, six flavonoid subclasses, and flavonoid-rich foods such as tea, apples, berries, oranges and orange juice, and red wine.
They examined flavonoid intake both before and after a PD diagnosis to minimize the potential for reverse causality. The investigators noted that patients with PD have difficulty swallowing and handling food and cutlery, which could impact their consumption of flavonoid-rich foods.
Frequency of consumption of flavonoid-rich foods was categorized into four groups: one or less servings per month (the reference group), one to three servings per month, one to two servings per week, and three or more servings per week.
The analysis included 599 women and 652 men who were newly diagnosed with PD. The mean age at PD diagnosis was 72 years, and the mean time between the last prediagnosis dietary assessment and PD diagnosis was 32 months.
The primary outcome measure was all-cause mortality. There were 528 deaths in men and 416 deaths in women during an average of 33 years of follow-up.
Neuroprotective pathway?
After controlling for age, lifestyle behaviors, medical history, and total energy and caffeine intake, results showed that higher total flavonoid intake before PD diagnosis was associated with a lower risk for all-cause mortality after diagnosis in men, with a hazard ratio of 0.53 (95% confidence interval, 0.39-0.71) when comparing the highest and lowest quartiles (P for trend < .001).
However, this association was not found in women (HR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.68-1.28; P for trend = .69).
The pooled HR was 0.70 (95% CI, 0.40-1.22; P for trend = .25) with significant heterogeneity (P = .01).
There were significant associations between a higher prediagnosis intake of certain flavonoids and lower mortality risk. The pooled HR comparing the highest versus lowest intake quartiles was 0.66 for anthocyanin, 0.78 for flavones, and 0.69 for flavan-3-ols (P < .05 for all).
Compared with participants who consumed less than one serving a month, those consuming more than three servings a week prediagnosis of berries or red wine had a lower mortality risk (pooled HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.58-1.02 for berries and HR, 0.68; 95% CI, 0.51-0.91 for red wine).
After PD diagnosis, higher flavonoid consumption was associated with better survival rates in both men and women.
It’s unclear why there was a gender difference in the association between prediagnosis flavonoid intake and mortality but not for postdiagnosis flavonoid intakes, Dr. Gao said.
A potential neuroprotective pathway by which flavonoids reduce mortality in PD involves direct radical scavenging, which lowers oxidative stress and chronic neuroinflammation levels, he noted.
“Certain flavonoids, for example, anthocyanins, have been shown to exert antiapoptosis effects and protect cognition and motor functions. They could also increase dopamine release,” Dr. Gao added.
Study limitations included not having detailed information on participants’ PD disease severity and that both the NHS and HPFS include predominantly White health care professionals, which limits the generalizability of the results, the investigators noted.
No direct link
Commenting on the findings, Michael S. Okun, MD, medical advisor at the Parkinson’s Foundation and director of the Norman Fixel Institute for Neurological Diseases, University of Florida Health, Gainesville, said the study adds to growing evidence suggesting “subsets of flavonoids and especially berries and wine will have benefits pre- and post–Parkinson’s disease diagnosis.”
However, he emphasized that patients should not take up drinking red wine just to improve survival.
“We don’t recommend that folks who are already diagnosed with Parkinson’s drink alcohol, especially without physician supervision,” said Dr. Okun, who was not involved with the research.
Also commenting for this article, Gunter Kuhnle, PhD, professor of nutrition and food science, University of Reading (England), said because the study doesn’t appear to adjust for socioeconomic status, the results may be driven by factors such as income and education and not food intake.
The study found a beneficial association with anthocyanins, which are mainly found in expensive berries, and with flavan-3-ols found mainly in tea, which in the United States is often a marker of higher income, said Dr. Kuhnle.
The advantage of assessing dietary intake of flavonoids using a food-frequency questionnaire, as was done in this study, is that it captures long-term patterns. However, the disadvantage is a loss in “resolution” by combining similar foods, Dr. Kuhnle noted.
Since flavonoids are found in most fruits and vegetables, high flavonoid intake “might simply be a marker of fruit and vegetable intake and therefore a ‘healthy’ dietary pattern,” he concluded.
The study received funding from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Gao and Dr. Okun reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kuhnle has conducted research into the associations between flavanol and health, some of which has been funded by Mars.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY
35% of employers to proceed with vaccine mandate, poll shows
despite a recent U.S. Supreme Court ruling that blocked the Biden administration’s vaccine-or-test rule for big businesses.
But the poll by Gartner Inc. showed no consensus among employers. About 4% of polled executives said they’re dropping their vaccine mandate, 29% are in a wait-and-see position, and 12% are less likely to impose a mandate now, Bloomberg reported.
Executives were divided on how a vaccine mandate would affect absenteeism and employee morale. Almost 40% of polled employers said they thought a mandate would attract workers, but about 25% said it would do the opposite, Bloomberg said.
“What is more attractive -- to have a mandate or not?” Brian Kropp, PhD, Gartner’s chief of human resources research, said in an interview with Bloomberg. “Most are not exactly sure what to do.”
Big companies have reacted differently since the court’s ruling.
Starbucks announced it was dropping its vaccine-or-test rule for the company’s approximately 228,000 employees. General Electric dropped its mandate after the ruling, but Honeywell International Inc. announced it was staying with its vaccination policy, Bloomberg said.
The Supreme Court ruled Jan. 13 against the Biden administration’s mandate for businesses. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration had proposed that every company with more than 100 employees would be required to ensure workers were either vaccinated or tested weekly for COVID-19.
State governments and business groups immediately appealed, and the court ruled 6-3 against the mandate. The Biden administration officially dropped its rule on Wednesday.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
despite a recent U.S. Supreme Court ruling that blocked the Biden administration’s vaccine-or-test rule for big businesses.
But the poll by Gartner Inc. showed no consensus among employers. About 4% of polled executives said they’re dropping their vaccine mandate, 29% are in a wait-and-see position, and 12% are less likely to impose a mandate now, Bloomberg reported.
Executives were divided on how a vaccine mandate would affect absenteeism and employee morale. Almost 40% of polled employers said they thought a mandate would attract workers, but about 25% said it would do the opposite, Bloomberg said.
“What is more attractive -- to have a mandate or not?” Brian Kropp, PhD, Gartner’s chief of human resources research, said in an interview with Bloomberg. “Most are not exactly sure what to do.”
Big companies have reacted differently since the court’s ruling.
Starbucks announced it was dropping its vaccine-or-test rule for the company’s approximately 228,000 employees. General Electric dropped its mandate after the ruling, but Honeywell International Inc. announced it was staying with its vaccination policy, Bloomberg said.
The Supreme Court ruled Jan. 13 against the Biden administration’s mandate for businesses. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration had proposed that every company with more than 100 employees would be required to ensure workers were either vaccinated or tested weekly for COVID-19.
State governments and business groups immediately appealed, and the court ruled 6-3 against the mandate. The Biden administration officially dropped its rule on Wednesday.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
despite a recent U.S. Supreme Court ruling that blocked the Biden administration’s vaccine-or-test rule for big businesses.
But the poll by Gartner Inc. showed no consensus among employers. About 4% of polled executives said they’re dropping their vaccine mandate, 29% are in a wait-and-see position, and 12% are less likely to impose a mandate now, Bloomberg reported.
Executives were divided on how a vaccine mandate would affect absenteeism and employee morale. Almost 40% of polled employers said they thought a mandate would attract workers, but about 25% said it would do the opposite, Bloomberg said.
“What is more attractive -- to have a mandate or not?” Brian Kropp, PhD, Gartner’s chief of human resources research, said in an interview with Bloomberg. “Most are not exactly sure what to do.”
Big companies have reacted differently since the court’s ruling.
Starbucks announced it was dropping its vaccine-or-test rule for the company’s approximately 228,000 employees. General Electric dropped its mandate after the ruling, but Honeywell International Inc. announced it was staying with its vaccination policy, Bloomberg said.
The Supreme Court ruled Jan. 13 against the Biden administration’s mandate for businesses. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration had proposed that every company with more than 100 employees would be required to ensure workers were either vaccinated or tested weekly for COVID-19.
State governments and business groups immediately appealed, and the court ruled 6-3 against the mandate. The Biden administration officially dropped its rule on Wednesday.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
More than 1 in 10 people in U.S. have diabetes, CDC says
More than 1 in 10 Americans have diabetes and over a third have prediabetes, according to updated statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The National Diabetes Statistics Report includes data for 2017-2020 from several nationally representative sources on prevalence and incidence of diabetes and prediabetes, risk factors for complications, acute and long-term complications, and costs.
According to the new report, published on Jan. 25, a total of 37.3 million people in the United States have diabetes, or about 11.3% of the population. Of those, 28.7 million are diagnosed (including 28.5 million adults), while 8.5 million, or 23% of those with diabetes, are undiagnosed.
Another 96 million adults have prediabetes, comprising 38.0% of the adult U.S. population, of whom only 19% are aware of their prediabetes status.
In a statement, the American Diabetes Association said the new CDC data “show an alarming increase of diabetes in our nation among adults,” while the high number with prediabetes who don’t know that they have it “is fueling the diabetes epidemic.”
Regarding the total estimated 1.84 million with type 1 diabetes, the advocacy organization JDRF said in a statement: “These data and additional statistical research reinforces the urgency to accelerate life-changing breakthroughs to cure, prevent, and treat [type 1 diabetes] and its complications.”
Overall, the ADA said, “the National Diabetes Statistics Report reaffirms why the ADA is dedicated to innovative research to find a cure for diabetes once and for all.”
Notable increases since 2019
These new data represent notable increases since the CDC’s 2019 Report Card, which gave the U.S. population with diabetes in 2018 as 34.2 million, or 10.5% of the population, including 7.3 million undiagnosed. The prediabetes prevalence that year was 88 million.
Among children and adolescents younger than 20 years, 283,000, or 35 per 10,000 U.S. youths, had diagnosed diabetes in 2019. Of those, 244,000 had type 1 diabetes. Another 1.6 million adults aged 20 and older also reported having type 1 diabetes, comprising 5.7% of U.S. adults with diagnosed diabetes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More than 1 in 10 Americans have diabetes and over a third have prediabetes, according to updated statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The National Diabetes Statistics Report includes data for 2017-2020 from several nationally representative sources on prevalence and incidence of diabetes and prediabetes, risk factors for complications, acute and long-term complications, and costs.
According to the new report, published on Jan. 25, a total of 37.3 million people in the United States have diabetes, or about 11.3% of the population. Of those, 28.7 million are diagnosed (including 28.5 million adults), while 8.5 million, or 23% of those with diabetes, are undiagnosed.
Another 96 million adults have prediabetes, comprising 38.0% of the adult U.S. population, of whom only 19% are aware of their prediabetes status.
In a statement, the American Diabetes Association said the new CDC data “show an alarming increase of diabetes in our nation among adults,” while the high number with prediabetes who don’t know that they have it “is fueling the diabetes epidemic.”
Regarding the total estimated 1.84 million with type 1 diabetes, the advocacy organization JDRF said in a statement: “These data and additional statistical research reinforces the urgency to accelerate life-changing breakthroughs to cure, prevent, and treat [type 1 diabetes] and its complications.”
Overall, the ADA said, “the National Diabetes Statistics Report reaffirms why the ADA is dedicated to innovative research to find a cure for diabetes once and for all.”
Notable increases since 2019
These new data represent notable increases since the CDC’s 2019 Report Card, which gave the U.S. population with diabetes in 2018 as 34.2 million, or 10.5% of the population, including 7.3 million undiagnosed. The prediabetes prevalence that year was 88 million.
Among children and adolescents younger than 20 years, 283,000, or 35 per 10,000 U.S. youths, had diagnosed diabetes in 2019. Of those, 244,000 had type 1 diabetes. Another 1.6 million adults aged 20 and older also reported having type 1 diabetes, comprising 5.7% of U.S. adults with diagnosed diabetes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More than 1 in 10 Americans have diabetes and over a third have prediabetes, according to updated statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The National Diabetes Statistics Report includes data for 2017-2020 from several nationally representative sources on prevalence and incidence of diabetes and prediabetes, risk factors for complications, acute and long-term complications, and costs.
According to the new report, published on Jan. 25, a total of 37.3 million people in the United States have diabetes, or about 11.3% of the population. Of those, 28.7 million are diagnosed (including 28.5 million adults), while 8.5 million, or 23% of those with diabetes, are undiagnosed.
Another 96 million adults have prediabetes, comprising 38.0% of the adult U.S. population, of whom only 19% are aware of their prediabetes status.
In a statement, the American Diabetes Association said the new CDC data “show an alarming increase of diabetes in our nation among adults,” while the high number with prediabetes who don’t know that they have it “is fueling the diabetes epidemic.”
Regarding the total estimated 1.84 million with type 1 diabetes, the advocacy organization JDRF said in a statement: “These data and additional statistical research reinforces the urgency to accelerate life-changing breakthroughs to cure, prevent, and treat [type 1 diabetes] and its complications.”
Overall, the ADA said, “the National Diabetes Statistics Report reaffirms why the ADA is dedicated to innovative research to find a cure for diabetes once and for all.”
Notable increases since 2019
These new data represent notable increases since the CDC’s 2019 Report Card, which gave the U.S. population with diabetes in 2018 as 34.2 million, or 10.5% of the population, including 7.3 million undiagnosed. The prediabetes prevalence that year was 88 million.
Among children and adolescents younger than 20 years, 283,000, or 35 per 10,000 U.S. youths, had diagnosed diabetes in 2019. Of those, 244,000 had type 1 diabetes. Another 1.6 million adults aged 20 and older also reported having type 1 diabetes, comprising 5.7% of U.S. adults with diagnosed diabetes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary care docs have role to play in hypertension prevention and treatment for women of reproductive age
The American Heart Association recently released a scientific statement concerning hypertension in pregnancy, which laid out the variety of disorders, the epidemiology, the future impact of pregnant persons, and the current debates regarding treatment and diagnosis.
This statement addresses all stages from preconception through post pregnancy and outlines the many prevention and treatment options available. Although family physicians were not specifically called out to be partners in the statement, we have a large role to play for both our pregnant patients and those of reproductive age who are not pregnant.
Preconception health
One of the first things pointed out was preconception health. Regardless of whether each individual family physician provides prenatal care, we can all focus on preconception health for those of reproductive age.
The statement from the AHA points out that “lifestyle changes before and during pregnancy may ameliorate both maternal and fetal risks.”
As many already do, family physicians should focus on encouraging their patients to practice healthy eating and exercise prior to pregnancy to help establish routines that will decrease the risk of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy.
Focusing on care prior to pregnancy also allows the primary care provider to be involved in quickly linking patients to prenatal care, as it is well established that early and complete prenatal care is important for improving outcomes.
Later-in-life pregnancy
The AHA also highlights that many are choosing to have pregnancies at older ages and with greater comorbidities than in past years. This is another area in which family physicians can provide important care.
We can help by first identifying the chronic conditions, such as hypertension and diabetes, that make the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy more likely. We should then focus on the treatment of these conditions during the preconception time so that they are well controlled prior to pregnancy.
We should also preferentially choose medications that our patients will be able to continue in pregnancy, so that control may be maintained throughout pregnancy.
The statement particularly highlights the avoidance of antihypertensives that are renin-angiotensin system blockers.
We can also help prepare our patients for the additional medications, testing, and precautions they will likely require during their pregnancy so that they know what to expect.
Family physicians are also already starting to utilize home blood pressure monitoring and can introduce this method so that patients may continue to monitor their blood pressures during pregnancy.
Throughout pregnancy, the new statement calls in the current debates of when prenatal care providers should be diagnosing hypertensive disorders and the goals of treatment.
Prenatal care providers can use shared decision-making for medication choices and blood pressure goals. They can also continue to encourage the healthy lifestyle choices such as diet and exercise to reduce the risk of poor outcomes.
This AHA also indicates that prenatal care providers can integrate the use of home blood pressure monitoring as they monitor the blood pressure for patients with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.
Postpartum care
The postpartum period is another crucial time for family physicians and other primary care providers to greatly impact their patients with hypertensive diseases of pregnancy.
They can work to ensure that blood pressure is closely monitored and controlled, including by prescribing diuretics, which are typically not used during pregnancy.
If a patient’s blood pressure does not go down on its own, the primary care provider can begin treatment for hypertension outside of pregnancy. This can decrease their long-term cardiac risk factors and provide control prior to any future potential pregnancies.
Providing care during this postpartum time also offers a great opportunity to again encourage lifestyle options that may decrease risk.
Family physicians and other primary care providers can also encourage their patient to be involved in registries that gather data on hypertensive disorders in pregnancy.
In the new statement, the AHA acknowledges the great number of things that are not yet known or fully understood and the health inequities that many face.
Family physicians are positioned to help advocate for their patients and utilize a team-based approach to help provide resources to patients. We must continue to be there for our patients at every stage of their lives to help them live their healthiest lives possible.
The statement also indicates that there may be genetic factors at play more than social determinants of health. It is important to identify what those are for the best care of our patients while ensuring we are doing our best to provide our patients with the resources they need.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center and program director of Northwestern University’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program, both in Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
The American Heart Association recently released a scientific statement concerning hypertension in pregnancy, which laid out the variety of disorders, the epidemiology, the future impact of pregnant persons, and the current debates regarding treatment and diagnosis.
This statement addresses all stages from preconception through post pregnancy and outlines the many prevention and treatment options available. Although family physicians were not specifically called out to be partners in the statement, we have a large role to play for both our pregnant patients and those of reproductive age who are not pregnant.
Preconception health
One of the first things pointed out was preconception health. Regardless of whether each individual family physician provides prenatal care, we can all focus on preconception health for those of reproductive age.
The statement from the AHA points out that “lifestyle changes before and during pregnancy may ameliorate both maternal and fetal risks.”
As many already do, family physicians should focus on encouraging their patients to practice healthy eating and exercise prior to pregnancy to help establish routines that will decrease the risk of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy.
Focusing on care prior to pregnancy also allows the primary care provider to be involved in quickly linking patients to prenatal care, as it is well established that early and complete prenatal care is important for improving outcomes.
Later-in-life pregnancy
The AHA also highlights that many are choosing to have pregnancies at older ages and with greater comorbidities than in past years. This is another area in which family physicians can provide important care.
We can help by first identifying the chronic conditions, such as hypertension and diabetes, that make the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy more likely. We should then focus on the treatment of these conditions during the preconception time so that they are well controlled prior to pregnancy.
We should also preferentially choose medications that our patients will be able to continue in pregnancy, so that control may be maintained throughout pregnancy.
The statement particularly highlights the avoidance of antihypertensives that are renin-angiotensin system blockers.
We can also help prepare our patients for the additional medications, testing, and precautions they will likely require during their pregnancy so that they know what to expect.
Family physicians are also already starting to utilize home blood pressure monitoring and can introduce this method so that patients may continue to monitor their blood pressures during pregnancy.
Throughout pregnancy, the new statement calls in the current debates of when prenatal care providers should be diagnosing hypertensive disorders and the goals of treatment.
Prenatal care providers can use shared decision-making for medication choices and blood pressure goals. They can also continue to encourage the healthy lifestyle choices such as diet and exercise to reduce the risk of poor outcomes.
This AHA also indicates that prenatal care providers can integrate the use of home blood pressure monitoring as they monitor the blood pressure for patients with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.
Postpartum care
The postpartum period is another crucial time for family physicians and other primary care providers to greatly impact their patients with hypertensive diseases of pregnancy.
They can work to ensure that blood pressure is closely monitored and controlled, including by prescribing diuretics, which are typically not used during pregnancy.
If a patient’s blood pressure does not go down on its own, the primary care provider can begin treatment for hypertension outside of pregnancy. This can decrease their long-term cardiac risk factors and provide control prior to any future potential pregnancies.
Providing care during this postpartum time also offers a great opportunity to again encourage lifestyle options that may decrease risk.
Family physicians and other primary care providers can also encourage their patient to be involved in registries that gather data on hypertensive disorders in pregnancy.
In the new statement, the AHA acknowledges the great number of things that are not yet known or fully understood and the health inequities that many face.
Family physicians are positioned to help advocate for their patients and utilize a team-based approach to help provide resources to patients. We must continue to be there for our patients at every stage of their lives to help them live their healthiest lives possible.
The statement also indicates that there may be genetic factors at play more than social determinants of health. It is important to identify what those are for the best care of our patients while ensuring we are doing our best to provide our patients with the resources they need.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center and program director of Northwestern University’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program, both in Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
The American Heart Association recently released a scientific statement concerning hypertension in pregnancy, which laid out the variety of disorders, the epidemiology, the future impact of pregnant persons, and the current debates regarding treatment and diagnosis.
This statement addresses all stages from preconception through post pregnancy and outlines the many prevention and treatment options available. Although family physicians were not specifically called out to be partners in the statement, we have a large role to play for both our pregnant patients and those of reproductive age who are not pregnant.
Preconception health
One of the first things pointed out was preconception health. Regardless of whether each individual family physician provides prenatal care, we can all focus on preconception health for those of reproductive age.
The statement from the AHA points out that “lifestyle changes before and during pregnancy may ameliorate both maternal and fetal risks.”
As many already do, family physicians should focus on encouraging their patients to practice healthy eating and exercise prior to pregnancy to help establish routines that will decrease the risk of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy.
Focusing on care prior to pregnancy also allows the primary care provider to be involved in quickly linking patients to prenatal care, as it is well established that early and complete prenatal care is important for improving outcomes.
Later-in-life pregnancy
The AHA also highlights that many are choosing to have pregnancies at older ages and with greater comorbidities than in past years. This is another area in which family physicians can provide important care.
We can help by first identifying the chronic conditions, such as hypertension and diabetes, that make the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy more likely. We should then focus on the treatment of these conditions during the preconception time so that they are well controlled prior to pregnancy.
We should also preferentially choose medications that our patients will be able to continue in pregnancy, so that control may be maintained throughout pregnancy.
The statement particularly highlights the avoidance of antihypertensives that are renin-angiotensin system blockers.
We can also help prepare our patients for the additional medications, testing, and precautions they will likely require during their pregnancy so that they know what to expect.
Family physicians are also already starting to utilize home blood pressure monitoring and can introduce this method so that patients may continue to monitor their blood pressures during pregnancy.
Throughout pregnancy, the new statement calls in the current debates of when prenatal care providers should be diagnosing hypertensive disorders and the goals of treatment.
Prenatal care providers can use shared decision-making for medication choices and blood pressure goals. They can also continue to encourage the healthy lifestyle choices such as diet and exercise to reduce the risk of poor outcomes.
This AHA also indicates that prenatal care providers can integrate the use of home blood pressure monitoring as they monitor the blood pressure for patients with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.
Postpartum care
The postpartum period is another crucial time for family physicians and other primary care providers to greatly impact their patients with hypertensive diseases of pregnancy.
They can work to ensure that blood pressure is closely monitored and controlled, including by prescribing diuretics, which are typically not used during pregnancy.
If a patient’s blood pressure does not go down on its own, the primary care provider can begin treatment for hypertension outside of pregnancy. This can decrease their long-term cardiac risk factors and provide control prior to any future potential pregnancies.
Providing care during this postpartum time also offers a great opportunity to again encourage lifestyle options that may decrease risk.
Family physicians and other primary care providers can also encourage their patient to be involved in registries that gather data on hypertensive disorders in pregnancy.
In the new statement, the AHA acknowledges the great number of things that are not yet known or fully understood and the health inequities that many face.
Family physicians are positioned to help advocate for their patients and utilize a team-based approach to help provide resources to patients. We must continue to be there for our patients at every stage of their lives to help them live their healthiest lives possible.
The statement also indicates that there may be genetic factors at play more than social determinants of health. It is important to identify what those are for the best care of our patients while ensuring we are doing our best to provide our patients with the resources they need.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center and program director of Northwestern University’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program, both in Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].