User login
As demand for mental health care spikes, budget ax set to strike
When the pandemic hit, health officials in Montana’s Beaverhead County had barely begun to fill a hole left by the 2017 closure of the local public assistance office, mental health clinic, chemical dependency center and job placement office after the state’s last budget shortfall.
Now, those health officials worry more cuts are coming, even as they brace for a spike in demand for substance abuse and mental health services. That would be no small challenge in a poor farming and ranching region where stigma often prevents people from admitting they need help, said Katherine Buckley-Patton, who chairs the county’s Mental Health Local Advisory Council.
“I find it very challenging to find the words that will not make one of my hard-nosed cowboys turn around and walk away,” Ms. Buckley-Patton said.
States across the U.S. are still stinging after businesses closed and millions of people lost jobs because of COVID-related shutdowns and restrictions. Meanwhile, the pandemic has led to a dramatic increase in the number of people who say their mental health has suffered, rising from one in three people in March to more than half of people polled by KFF in July. (KHN is an editorially independent program of KFF.)
The full extent of the mental health crisis and the demand for behavioral health services may not be known until after the pandemic is over, mental health experts said. That could add costs that budget writers haven’t anticipated.
“It usually takes a while before people feel comfortable seeking care from a specialty behavioral health organization,” said Chuck Ingoglia, president and CEO of the nonprofit National Council for Behavioral Health in Washington, D.C. “We are not likely to see the results of that either in terms of people seeking care – or suicide rates going up – until we’re on the other side of the pandemic.”
Last year, states slashed agency budgets, froze pay, furloughed workers, borrowed money, and tapped into rainy-day funds to make ends meet. Health programs, often among the most expensive part of a state’s budget, were targeted for cuts in several states even as health officials led efforts to stem the spread of the coronavirus.
This year, the outlook doesn’t seem quite so bleak, partly because of relief packages passed by Congress last spring and in December that buoyed state economies. Another major advantage was that income increased or held steady for people with well-paying jobs and investment income, which boosted states’ tax revenues even as millions of lower-income workers were laid off.
“It has turned out to be not as bad as it might have been in terms of state budgets,” said Mike Leachman, vice president for state fiscal policy for the nonpartisan Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
But many states still face cash shortfalls that will be made worse if additional federal aid doesn’t come, Mr. Leachman said. President Joe Biden has pledged to push through Congress a $1.9 billion relief package that includes aid to states, while congressional Republicans are proposing a package worth about a third of that amount. States are banking on federal help.
New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo, a Democrat, predicted his state would have to plug a $15 billion deficit with spending cuts and tax increases if a fresh round of aid doesn’t materialize. Some states, such as New Jersey, borrowed to make their budgets whole, and they’re going to have to start paying that money back. Tourism states such as Hawaii and energy-producing states such as Alaska and Wyoming continue to face grim economic outlooks with oil, gas, and coal prices down and tourists cutting back on travel, Mr. Leachman said.
Even states with a relatively rosy economic outlook are being cautious. In Colorado, for example, Democratic Gov. Jared Polis proposed a budget that restores the cuts made last year to Medicaid and substance abuse programs. But health providers are doubtful the legislature will approve any significant spending increases in this economy.
“Everybody right now is just trying to protect and make sure we don’t have additional cuts,” said Doyle Forrestal, CEO of the Colorado Behavioral Healthcare Council.
That’s also what Ms. Buckley-Patton wants for Montana’s Beaverhead County, where most of the 9,400 residents live in poverty or earn low incomes.
She led the county’s effort to recover from the loss in 2017 of a wide range of behavioral health services, along with offices to help poor people receive Medicaid health services, plus cash and food assistance.
Through persuasive grant writing and donations coaxed from elected officials, Ms. Buckley-Patton and her team secured office space, equipment, and a part-time employee for a resource center that’s open once a week in the county in the southwestern corner of the state, she said. They also convinced the state health department to send two people every other week on a 120-mile round trip from the Butte office to help county residents with their Medicaid and public assistance applications.
But now Ms. Buckley-Patton worries even those modest gains will be threatened in this year’s budget. Montana is one of the few states with a budget on a 2-year cycle, so this is the first time lawmakers have had to craft a spending plan since the pandemic began.
Revenue forecasts predict healthy tax collections over the next 2 years.
In January, at the start of the legislative session, the panel in charge of building the state health department’s budget proposed starting with nearly $1 billion in cuts. The panel’s chairperson, Republican Rep. Matt Regier, pledged to add back programs and services on their merits during the months-long budget process.
It’s a strategy Ms. Buckley-Patton worries will lead to a net loss of funding for Beaverhead County, which covers more land than Connecticut.
“I have grave concerns about this legislative session,” she said. “We’re not digging out of the hole; we’re only going deeper.”
Republicans, who are in control of the Montana House, Senate, and governor’s office for the first time in 16 years, are considering reducing the income tax level for the state’s top earners. Such a measure that could affect state revenue in an uncertain economy has some observers concerned, particularly when an increased need for health services is expected.
“Are legislators committed to building back up that budget in a way that works for communities and for health providers, or are we going to see tax cuts that reduce revenue that put us yet again in another really tight budget?” asked Heather O’Loughlin, codirector of the Montana Budget and Policy Center.
Mary Windecker, executive director of the Behavioral Health Alliance of Montana, said that health providers across the state are still clawing back from more than $100 million in budget cuts in 2017, and that she worries more cuts are on the horizon.
But one bright spot, she said, is a proposal by new Gov. Greg Gianforte to create a fund that would put $23 million a year toward community substance abuse prevention and treatment programs. It would be partially funded by tax revenue the state will receive from recreational marijuana, which voters approved in November, with sales to begin next year.
Ms. Windecker cautioned, though, that mental health and substance use are linked, and the governor and lawmakers should plan with that in mind.
“In the public’s mind, there’s drug addicts and there’s the mentally ill,” she said. “Quite often, the same people who have a substance use disorder are using it to treat a mental health issue that is underlying that substance use. So, you can never split the two out.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
When the pandemic hit, health officials in Montana’s Beaverhead County had barely begun to fill a hole left by the 2017 closure of the local public assistance office, mental health clinic, chemical dependency center and job placement office after the state’s last budget shortfall.
Now, those health officials worry more cuts are coming, even as they brace for a spike in demand for substance abuse and mental health services. That would be no small challenge in a poor farming and ranching region where stigma often prevents people from admitting they need help, said Katherine Buckley-Patton, who chairs the county’s Mental Health Local Advisory Council.
“I find it very challenging to find the words that will not make one of my hard-nosed cowboys turn around and walk away,” Ms. Buckley-Patton said.
States across the U.S. are still stinging after businesses closed and millions of people lost jobs because of COVID-related shutdowns and restrictions. Meanwhile, the pandemic has led to a dramatic increase in the number of people who say their mental health has suffered, rising from one in three people in March to more than half of people polled by KFF in July. (KHN is an editorially independent program of KFF.)
The full extent of the mental health crisis and the demand for behavioral health services may not be known until after the pandemic is over, mental health experts said. That could add costs that budget writers haven’t anticipated.
“It usually takes a while before people feel comfortable seeking care from a specialty behavioral health organization,” said Chuck Ingoglia, president and CEO of the nonprofit National Council for Behavioral Health in Washington, D.C. “We are not likely to see the results of that either in terms of people seeking care – or suicide rates going up – until we’re on the other side of the pandemic.”
Last year, states slashed agency budgets, froze pay, furloughed workers, borrowed money, and tapped into rainy-day funds to make ends meet. Health programs, often among the most expensive part of a state’s budget, were targeted for cuts in several states even as health officials led efforts to stem the spread of the coronavirus.
This year, the outlook doesn’t seem quite so bleak, partly because of relief packages passed by Congress last spring and in December that buoyed state economies. Another major advantage was that income increased or held steady for people with well-paying jobs and investment income, which boosted states’ tax revenues even as millions of lower-income workers were laid off.
“It has turned out to be not as bad as it might have been in terms of state budgets,” said Mike Leachman, vice president for state fiscal policy for the nonpartisan Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
But many states still face cash shortfalls that will be made worse if additional federal aid doesn’t come, Mr. Leachman said. President Joe Biden has pledged to push through Congress a $1.9 billion relief package that includes aid to states, while congressional Republicans are proposing a package worth about a third of that amount. States are banking on federal help.
New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo, a Democrat, predicted his state would have to plug a $15 billion deficit with spending cuts and tax increases if a fresh round of aid doesn’t materialize. Some states, such as New Jersey, borrowed to make their budgets whole, and they’re going to have to start paying that money back. Tourism states such as Hawaii and energy-producing states such as Alaska and Wyoming continue to face grim economic outlooks with oil, gas, and coal prices down and tourists cutting back on travel, Mr. Leachman said.
Even states with a relatively rosy economic outlook are being cautious. In Colorado, for example, Democratic Gov. Jared Polis proposed a budget that restores the cuts made last year to Medicaid and substance abuse programs. But health providers are doubtful the legislature will approve any significant spending increases in this economy.
“Everybody right now is just trying to protect and make sure we don’t have additional cuts,” said Doyle Forrestal, CEO of the Colorado Behavioral Healthcare Council.
That’s also what Ms. Buckley-Patton wants for Montana’s Beaverhead County, where most of the 9,400 residents live in poverty or earn low incomes.
She led the county’s effort to recover from the loss in 2017 of a wide range of behavioral health services, along with offices to help poor people receive Medicaid health services, plus cash and food assistance.
Through persuasive grant writing and donations coaxed from elected officials, Ms. Buckley-Patton and her team secured office space, equipment, and a part-time employee for a resource center that’s open once a week in the county in the southwestern corner of the state, she said. They also convinced the state health department to send two people every other week on a 120-mile round trip from the Butte office to help county residents with their Medicaid and public assistance applications.
But now Ms. Buckley-Patton worries even those modest gains will be threatened in this year’s budget. Montana is one of the few states with a budget on a 2-year cycle, so this is the first time lawmakers have had to craft a spending plan since the pandemic began.
Revenue forecasts predict healthy tax collections over the next 2 years.
In January, at the start of the legislative session, the panel in charge of building the state health department’s budget proposed starting with nearly $1 billion in cuts. The panel’s chairperson, Republican Rep. Matt Regier, pledged to add back programs and services on their merits during the months-long budget process.
It’s a strategy Ms. Buckley-Patton worries will lead to a net loss of funding for Beaverhead County, which covers more land than Connecticut.
“I have grave concerns about this legislative session,” she said. “We’re not digging out of the hole; we’re only going deeper.”
Republicans, who are in control of the Montana House, Senate, and governor’s office for the first time in 16 years, are considering reducing the income tax level for the state’s top earners. Such a measure that could affect state revenue in an uncertain economy has some observers concerned, particularly when an increased need for health services is expected.
“Are legislators committed to building back up that budget in a way that works for communities and for health providers, or are we going to see tax cuts that reduce revenue that put us yet again in another really tight budget?” asked Heather O’Loughlin, codirector of the Montana Budget and Policy Center.
Mary Windecker, executive director of the Behavioral Health Alliance of Montana, said that health providers across the state are still clawing back from more than $100 million in budget cuts in 2017, and that she worries more cuts are on the horizon.
But one bright spot, she said, is a proposal by new Gov. Greg Gianforte to create a fund that would put $23 million a year toward community substance abuse prevention and treatment programs. It would be partially funded by tax revenue the state will receive from recreational marijuana, which voters approved in November, with sales to begin next year.
Ms. Windecker cautioned, though, that mental health and substance use are linked, and the governor and lawmakers should plan with that in mind.
“In the public’s mind, there’s drug addicts and there’s the mentally ill,” she said. “Quite often, the same people who have a substance use disorder are using it to treat a mental health issue that is underlying that substance use. So, you can never split the two out.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
When the pandemic hit, health officials in Montana’s Beaverhead County had barely begun to fill a hole left by the 2017 closure of the local public assistance office, mental health clinic, chemical dependency center and job placement office after the state’s last budget shortfall.
Now, those health officials worry more cuts are coming, even as they brace for a spike in demand for substance abuse and mental health services. That would be no small challenge in a poor farming and ranching region where stigma often prevents people from admitting they need help, said Katherine Buckley-Patton, who chairs the county’s Mental Health Local Advisory Council.
“I find it very challenging to find the words that will not make one of my hard-nosed cowboys turn around and walk away,” Ms. Buckley-Patton said.
States across the U.S. are still stinging after businesses closed and millions of people lost jobs because of COVID-related shutdowns and restrictions. Meanwhile, the pandemic has led to a dramatic increase in the number of people who say their mental health has suffered, rising from one in three people in March to more than half of people polled by KFF in July. (KHN is an editorially independent program of KFF.)
The full extent of the mental health crisis and the demand for behavioral health services may not be known until after the pandemic is over, mental health experts said. That could add costs that budget writers haven’t anticipated.
“It usually takes a while before people feel comfortable seeking care from a specialty behavioral health organization,” said Chuck Ingoglia, president and CEO of the nonprofit National Council for Behavioral Health in Washington, D.C. “We are not likely to see the results of that either in terms of people seeking care – or suicide rates going up – until we’re on the other side of the pandemic.”
Last year, states slashed agency budgets, froze pay, furloughed workers, borrowed money, and tapped into rainy-day funds to make ends meet. Health programs, often among the most expensive part of a state’s budget, were targeted for cuts in several states even as health officials led efforts to stem the spread of the coronavirus.
This year, the outlook doesn’t seem quite so bleak, partly because of relief packages passed by Congress last spring and in December that buoyed state economies. Another major advantage was that income increased or held steady for people with well-paying jobs and investment income, which boosted states’ tax revenues even as millions of lower-income workers were laid off.
“It has turned out to be not as bad as it might have been in terms of state budgets,” said Mike Leachman, vice president for state fiscal policy for the nonpartisan Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
But many states still face cash shortfalls that will be made worse if additional federal aid doesn’t come, Mr. Leachman said. President Joe Biden has pledged to push through Congress a $1.9 billion relief package that includes aid to states, while congressional Republicans are proposing a package worth about a third of that amount. States are banking on federal help.
New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo, a Democrat, predicted his state would have to plug a $15 billion deficit with spending cuts and tax increases if a fresh round of aid doesn’t materialize. Some states, such as New Jersey, borrowed to make their budgets whole, and they’re going to have to start paying that money back. Tourism states such as Hawaii and energy-producing states such as Alaska and Wyoming continue to face grim economic outlooks with oil, gas, and coal prices down and tourists cutting back on travel, Mr. Leachman said.
Even states with a relatively rosy economic outlook are being cautious. In Colorado, for example, Democratic Gov. Jared Polis proposed a budget that restores the cuts made last year to Medicaid and substance abuse programs. But health providers are doubtful the legislature will approve any significant spending increases in this economy.
“Everybody right now is just trying to protect and make sure we don’t have additional cuts,” said Doyle Forrestal, CEO of the Colorado Behavioral Healthcare Council.
That’s also what Ms. Buckley-Patton wants for Montana’s Beaverhead County, where most of the 9,400 residents live in poverty or earn low incomes.
She led the county’s effort to recover from the loss in 2017 of a wide range of behavioral health services, along with offices to help poor people receive Medicaid health services, plus cash and food assistance.
Through persuasive grant writing and donations coaxed from elected officials, Ms. Buckley-Patton and her team secured office space, equipment, and a part-time employee for a resource center that’s open once a week in the county in the southwestern corner of the state, she said. They also convinced the state health department to send two people every other week on a 120-mile round trip from the Butte office to help county residents with their Medicaid and public assistance applications.
But now Ms. Buckley-Patton worries even those modest gains will be threatened in this year’s budget. Montana is one of the few states with a budget on a 2-year cycle, so this is the first time lawmakers have had to craft a spending plan since the pandemic began.
Revenue forecasts predict healthy tax collections over the next 2 years.
In January, at the start of the legislative session, the panel in charge of building the state health department’s budget proposed starting with nearly $1 billion in cuts. The panel’s chairperson, Republican Rep. Matt Regier, pledged to add back programs and services on their merits during the months-long budget process.
It’s a strategy Ms. Buckley-Patton worries will lead to a net loss of funding for Beaverhead County, which covers more land than Connecticut.
“I have grave concerns about this legislative session,” she said. “We’re not digging out of the hole; we’re only going deeper.”
Republicans, who are in control of the Montana House, Senate, and governor’s office for the first time in 16 years, are considering reducing the income tax level for the state’s top earners. Such a measure that could affect state revenue in an uncertain economy has some observers concerned, particularly when an increased need for health services is expected.
“Are legislators committed to building back up that budget in a way that works for communities and for health providers, or are we going to see tax cuts that reduce revenue that put us yet again in another really tight budget?” asked Heather O’Loughlin, codirector of the Montana Budget and Policy Center.
Mary Windecker, executive director of the Behavioral Health Alliance of Montana, said that health providers across the state are still clawing back from more than $100 million in budget cuts in 2017, and that she worries more cuts are on the horizon.
But one bright spot, she said, is a proposal by new Gov. Greg Gianforte to create a fund that would put $23 million a year toward community substance abuse prevention and treatment programs. It would be partially funded by tax revenue the state will receive from recreational marijuana, which voters approved in November, with sales to begin next year.
Ms. Windecker cautioned, though, that mental health and substance use are linked, and the governor and lawmakers should plan with that in mind.
“In the public’s mind, there’s drug addicts and there’s the mentally ill,” she said. “Quite often, the same people who have a substance use disorder are using it to treat a mental health issue that is underlying that substance use. So, you can never split the two out.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Cemiplimab approved for locally advanced, metastatic basal cell carcinoma
The FDA granted full approval for the locally advanced BCC indication and accelerated approval for the metastatic BCC indication, according to a press release from Regeneron and Sanofi, the companies jointly developing cemiplimab.
Cemiplimab is a programmed death–1 inhibitor that was first FDA approved in 2018 for locally advanced or metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma not eligible for curative surgery or radiation.
The new approval “will change the treatment paradigm for patients with advanced basal cell carcinoma,” according to Karl Lewis, MD, a professor at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and an investigator on the phase 2 trial of cemiplimab.
“While the primary systemic treatment options are hedgehog inhibitors, many patients will eventually progress on or become intolerant to this therapy,” Dr. Lewis said in the press release. “With Libtayo [cemiplimab], these patients now have a new immunotherapy option.”
The approval of cemiplimab in BCC was based on an open-label, phase 2 trial of 132 patients with advanced BCC. Patients could not tolerate, had progressed on, or had not responded to HHIs after 9 months of treatment.
Cemiplimab was given at 350 mg every 3 weeks. The study was not placebo controlled and has not been published, a Regeneron spokesperson said.
There were 112 patients in the efficacy analysis. The overall response rate was 21% (6/28) in metastatic BCC patients, with no complete responders. In locally advanced BCC patients, the objective response rate was 29% (24/84), with five complete responders.
The median duration of response was not reached in either group but was at least 6 months long in all metastatic patients and in 79% (19/84) of the locally advanced BCC patients.
The most common adverse events among the 132 subjects evaluable for safety were fatigue (49%), musculoskeletal pain (33%), diarrhea (25%), rash (22%), pruritus (20%), and upper respiratory tract infection (15%).
Serious adverse events occurred in 32% of patients, including colitis, acute kidney injury, adrenal insufficiency, and anemia. Adverse events led to discontinuation in 13% of patients, most often for colitis and general physical health deterioration.
For more details on cemiplimab, see the full prescribing information.
The FDA granted full approval for the locally advanced BCC indication and accelerated approval for the metastatic BCC indication, according to a press release from Regeneron and Sanofi, the companies jointly developing cemiplimab.
Cemiplimab is a programmed death–1 inhibitor that was first FDA approved in 2018 for locally advanced or metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma not eligible for curative surgery or radiation.
The new approval “will change the treatment paradigm for patients with advanced basal cell carcinoma,” according to Karl Lewis, MD, a professor at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and an investigator on the phase 2 trial of cemiplimab.
“While the primary systemic treatment options are hedgehog inhibitors, many patients will eventually progress on or become intolerant to this therapy,” Dr. Lewis said in the press release. “With Libtayo [cemiplimab], these patients now have a new immunotherapy option.”
The approval of cemiplimab in BCC was based on an open-label, phase 2 trial of 132 patients with advanced BCC. Patients could not tolerate, had progressed on, or had not responded to HHIs after 9 months of treatment.
Cemiplimab was given at 350 mg every 3 weeks. The study was not placebo controlled and has not been published, a Regeneron spokesperson said.
There were 112 patients in the efficacy analysis. The overall response rate was 21% (6/28) in metastatic BCC patients, with no complete responders. In locally advanced BCC patients, the objective response rate was 29% (24/84), with five complete responders.
The median duration of response was not reached in either group but was at least 6 months long in all metastatic patients and in 79% (19/84) of the locally advanced BCC patients.
The most common adverse events among the 132 subjects evaluable for safety were fatigue (49%), musculoskeletal pain (33%), diarrhea (25%), rash (22%), pruritus (20%), and upper respiratory tract infection (15%).
Serious adverse events occurred in 32% of patients, including colitis, acute kidney injury, adrenal insufficiency, and anemia. Adverse events led to discontinuation in 13% of patients, most often for colitis and general physical health deterioration.
For more details on cemiplimab, see the full prescribing information.
The FDA granted full approval for the locally advanced BCC indication and accelerated approval for the metastatic BCC indication, according to a press release from Regeneron and Sanofi, the companies jointly developing cemiplimab.
Cemiplimab is a programmed death–1 inhibitor that was first FDA approved in 2018 for locally advanced or metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma not eligible for curative surgery or radiation.
The new approval “will change the treatment paradigm for patients with advanced basal cell carcinoma,” according to Karl Lewis, MD, a professor at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and an investigator on the phase 2 trial of cemiplimab.
“While the primary systemic treatment options are hedgehog inhibitors, many patients will eventually progress on or become intolerant to this therapy,” Dr. Lewis said in the press release. “With Libtayo [cemiplimab], these patients now have a new immunotherapy option.”
The approval of cemiplimab in BCC was based on an open-label, phase 2 trial of 132 patients with advanced BCC. Patients could not tolerate, had progressed on, or had not responded to HHIs after 9 months of treatment.
Cemiplimab was given at 350 mg every 3 weeks. The study was not placebo controlled and has not been published, a Regeneron spokesperson said.
There were 112 patients in the efficacy analysis. The overall response rate was 21% (6/28) in metastatic BCC patients, with no complete responders. In locally advanced BCC patients, the objective response rate was 29% (24/84), with five complete responders.
The median duration of response was not reached in either group but was at least 6 months long in all metastatic patients and in 79% (19/84) of the locally advanced BCC patients.
The most common adverse events among the 132 subjects evaluable for safety were fatigue (49%), musculoskeletal pain (33%), diarrhea (25%), rash (22%), pruritus (20%), and upper respiratory tract infection (15%).
Serious adverse events occurred in 32% of patients, including colitis, acute kidney injury, adrenal insufficiency, and anemia. Adverse events led to discontinuation in 13% of patients, most often for colitis and general physical health deterioration.
For more details on cemiplimab, see the full prescribing information.
COVID-19 in children: New cases down for third straight week
New COVID-19 cases in children dropped for the third consecutive week, even as children continue to make up a larger share of all cases, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
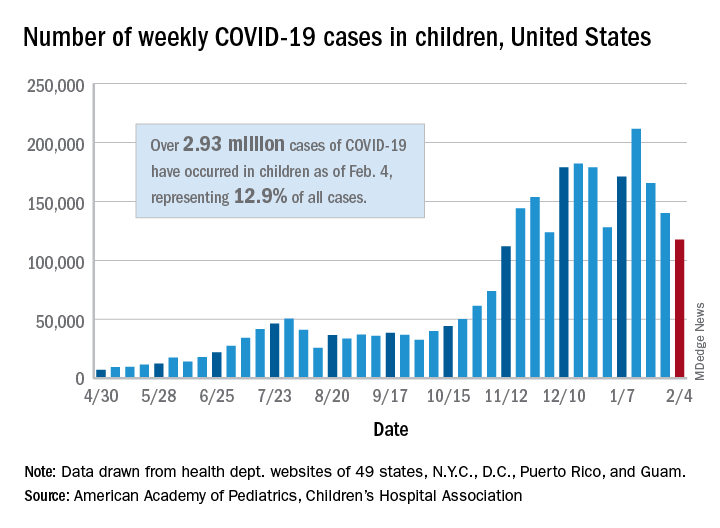
New child cases totaled almost 118,000 for the week of Jan. 29-Feb. 4, continuing the decline that began right after the United States topped 200,000 cases for the only time Jan. 8-14, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
For the latest week, however, children represented 16.0% of all new COVID-19 cases, continuing a 5-week increase that began in early December 2020, after the proportion had dropped to 12.6%, based on data collected from the health departments of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. During the week of Sept. 11-17, children made up 16.9% of all cases, the highest level seen during the pandemic.
The 2.93 million cases that have been reported in children make up 12.9% of all cases since the pandemic began, and the overall rate of pediatric coronavirus infection is 3,899 cases per 100,000 children in the population. Taking a step down from the national level, 30 states are above that rate and 18 are below it, along with D.C., New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam (New York and Texas are excluded), the AAP and CHA reported.
There were 12 new COVID-19–related child deaths in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are reporting such data, bringing the total to 227. Nationally, 0.06% of all deaths have occurred in children, with rates ranging from 0.00% (11 states) to 0.26% (Nebraska) in the 45 jurisdictions, the AAP/CHA report shows.
Child hospitalizations rose to 1.9% of all hospitalizations after holding at 1.8% since mid-November in 25 reporting jurisdictions (24 states and New York City), but the hospitalization rate among children with COVID held at 0.8%, where it has been for the last 4 weeks. Hospitalization rates as high as 3.8% were recorded early in the pandemic, the AAP and CHA noted.
New COVID-19 cases in children dropped for the third consecutive week, even as children continue to make up a larger share of all cases, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

New child cases totaled almost 118,000 for the week of Jan. 29-Feb. 4, continuing the decline that began right after the United States topped 200,000 cases for the only time Jan. 8-14, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
For the latest week, however, children represented 16.0% of all new COVID-19 cases, continuing a 5-week increase that began in early December 2020, after the proportion had dropped to 12.6%, based on data collected from the health departments of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. During the week of Sept. 11-17, children made up 16.9% of all cases, the highest level seen during the pandemic.
The 2.93 million cases that have been reported in children make up 12.9% of all cases since the pandemic began, and the overall rate of pediatric coronavirus infection is 3,899 cases per 100,000 children in the population. Taking a step down from the national level, 30 states are above that rate and 18 are below it, along with D.C., New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam (New York and Texas are excluded), the AAP and CHA reported.
There were 12 new COVID-19–related child deaths in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are reporting such data, bringing the total to 227. Nationally, 0.06% of all deaths have occurred in children, with rates ranging from 0.00% (11 states) to 0.26% (Nebraska) in the 45 jurisdictions, the AAP/CHA report shows.
Child hospitalizations rose to 1.9% of all hospitalizations after holding at 1.8% since mid-November in 25 reporting jurisdictions (24 states and New York City), but the hospitalization rate among children with COVID held at 0.8%, where it has been for the last 4 weeks. Hospitalization rates as high as 3.8% were recorded early in the pandemic, the AAP and CHA noted.
New COVID-19 cases in children dropped for the third consecutive week, even as children continue to make up a larger share of all cases, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

New child cases totaled almost 118,000 for the week of Jan. 29-Feb. 4, continuing the decline that began right after the United States topped 200,000 cases for the only time Jan. 8-14, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
For the latest week, however, children represented 16.0% of all new COVID-19 cases, continuing a 5-week increase that began in early December 2020, after the proportion had dropped to 12.6%, based on data collected from the health departments of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. During the week of Sept. 11-17, children made up 16.9% of all cases, the highest level seen during the pandemic.
The 2.93 million cases that have been reported in children make up 12.9% of all cases since the pandemic began, and the overall rate of pediatric coronavirus infection is 3,899 cases per 100,000 children in the population. Taking a step down from the national level, 30 states are above that rate and 18 are below it, along with D.C., New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam (New York and Texas are excluded), the AAP and CHA reported.
There were 12 new COVID-19–related child deaths in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are reporting such data, bringing the total to 227. Nationally, 0.06% of all deaths have occurred in children, with rates ranging from 0.00% (11 states) to 0.26% (Nebraska) in the 45 jurisdictions, the AAP/CHA report shows.
Child hospitalizations rose to 1.9% of all hospitalizations after holding at 1.8% since mid-November in 25 reporting jurisdictions (24 states and New York City), but the hospitalization rate among children with COVID held at 0.8%, where it has been for the last 4 weeks. Hospitalization rates as high as 3.8% were recorded early in the pandemic, the AAP and CHA noted.
Study tests ways to increase autism screening and referrals
To improve autism screening rates, researchers in Utah tried a range of interventions.
They added automatic reminders to the electronic health record (EHR). They started using a shorter, more sensitive screening instrument. And they trained clinicians to perform autism-specific evaluations in a primary care clinic.
The researchers found that these interventions were associated with increased rates of autism screening and referrals.
At the same time, they looked at screening and referral rates at other community clinics in their health care system. These clinics incorporated EHR reminders but not all of the other changes.
“The community clinics had an increase in screening frequency with only automatic reminders,” the researchers reported. At the two intervention clinics, however, screening rates increased more than they did at the community clinics. Referrals did not significantly increase at the community clinics.
Kathleen Campbell, MD, MHSc, a pediatric resident at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, and colleagues described their research in a study published in Pediatrics.
Three phases
They examined more than 12,000 well-child visits for children aged 16-30 months between July 2017 and June 2019.
In all, 4,155 visits occurred at the 2 intervention clinics, and 8,078 visits occurred at the 27 community clinics in the University of Utah health care system.
From baseline through the interventions, the proportion of visits with screening increased by 51% in the intervention clinics (from 58.6% to 88.8%), and by 21% in the community clinics (from 43.4% to 52.4%). The proportion of referrals increased 1.5-fold in intervention clinics, from 1.3% to 3.3%, the authors said.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) supports screening for autism in all children starting at age 18 months, but “only 44% of children with autism have had a comprehensive autism evaluation before age 36 months,” Dr. Campbell and colleagues wrote.
In their system, about half of the children were being screened for autism, and 0.5% had autism diagnosed.
In an effort to increase the proportion of visits with screening for autism and the proportion of visits with referrals for autism evaluation, Dr. Campbell and colleagues designed a quality improvement study.
Following a baseline period, they implemented interventions in three phases.
Initially, all clinics used the Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers, Revised (M-CHAT-R) for autism screening. For the first phase starting in July 2018, the researchers changed the screening instrument at the two intervention clinics to the Parent’s Observation of Social Interaction (POSI). This instrument “is embedded in a broadband developmental screen, is shorter than the M-CHAT-R, and includes questions about the consistency of the child’s behavior,” the authors said. “The POSI has greater sensitivity than the M-CHAT-R ... and similar, although somewhat lower, specificity.”
In intervention phase 2 starting in November 2018, the researchers “added an automatic reminder for autism screening to the EHR health maintenance screen.” Both the intervention clinics and the community clinics received the automatic reminders.
In intervention phase 3 starting in February 2019, they “added a referral option that clinicians could use for rapid access to autism-specific evaluation ... for children who had a POSI result suggestive of autism and for whom the clinician had sufficient concerns about autism that would indicate the need for referral for autism evaluation,” the researchers said.
“Using an online tutorial, we trained three clinicians in the intervention clinics to administer an observational assessment known as the Screening Tool for Autism in Toddlers (STAT),” which requires a 30-minute visit, they said. “Children who had a STAT result suggestive of autism were referred for expedited autism diagnostic evaluation, which was performed by a multidisciplinary team in our university-based developmental assessment clinic. Children who had a STAT result that did not suggest autism did not receive further autism evaluations unless the clinician felt they still needed further evaluation at the developmental clinic.”
After the switch to POSI, the percentage of visits with a positive screen result increased from 4.7% to 13.5% in the intervention clinics.
Furthermore, referrals were 3.4 times more frequent for visits during phase 3 in the intervention clinics, relative to the baseline period.
Potential to overwhelm
“The change to a more sensitive screening instrument increased the frequency of screening results suggestive of autism and informed our improvement team of the need to implement autism evaluation in primary care to avoid overwhelming our referral system,” Dr. Campbell and coauthors reported.
Future studies may assess whether increased screening and referrals speed the time to diagnosis and treatment and improve long-term functional abilities of children with autism. Some children in the study have received an autism diagnosis, while others have not yet been evaluated.
The use of STAT in primary care may be limited by “the barriers of training providers and purchasing materials,” the authors noted. “However, the time-based billing for lengthier appointments and billing for developmental testing help to cover cost.”
The intervention clinics and community clinics were staffed by pediatric providers, including residents and attendings, said Dr. Campbell.
“The staffing is similar at the community and intervention clinics, with mostly pediatricians and some nurse practitioners,” Dr. Campbell said. “One difference is that there are a few family medicine physicians in the community clinics, but we did not study whether that made a difference in screening. At the beginning of the study the approach to screening was the same.”
From the start, the community clinics were screening for autism and referring for further autism evaluation less often than the intervention clinics. “I don’t know why they were screening less, but they did improve with the automatic reminders,” said Dr. Campbell. “We didn’t examine type of provider or type of practice in this study, but the literature suggests that family physicians do not screen for autism as often as pediatricians.”
Payment and referral challenges
In theory, the approach in the study is a great idea, but it may not be feasible to implement for many private practices, said Herschel Lessin, MD. Dr. Lessin is a senior partner of the Children’s Medical Group in New York.
“We desperately need autism screening in a primary care setting,” Dr. Lessin said. “These authors found that wasn’t being done as recommended by the AAP Bright Futures, which is a problem.”
However, the researchers incorporated the interventions in a health care system with “far more resources than most people in practice would ever have” and substituted a less familiar screening tool.
In addition, the ability to use confirmatory STAT for primary care evaluations may be limited. “Unless you can find pediatricians willing to commit 30 to 45 minutes on one of these evaluations ... few are going to do that,” he said.
“The whole problem is that there are no referrals available or very few referrals available, and that insurance payments so underpay for developmental screening and evaluation that it does not justify the time doing it, so a lot of doctors are unable to do it,” said Dr. Lessin. When a referral is warranted, developmental pediatricians may have 6- to 12-month waiting lists, he said.
“For people in clinical practice, this is not news,” Dr. Lessin said. “We know we should screen for autism. The problem is it’s time consuming. Nobody pays for it. We have no place to send them even when we are suspicious.”
From screening to diagnosis to treatment
“Autism screen approaches vary but with educational efforts on the part of the AAP, CDC, and family organizations the rates for autism screening have dramatically improved,” said Susan L. Hyman, MD, professor of pediatrics at the University of Rochester in New York. “I do not know if screening rates have been impacted by COVID.”
Dr. Hyman and coauthors wrote an AAP clinical report on the identification, evaluation, and management of children with autism spectrum disorder. The report was published in the January 2020 issue of Pediatrics.
After screening and diagnostic testing, patients most importantly need to be able to access “timely and equitable evidence-based intervention,” which should be available, said Dr. Hyman.
Although researchers have proposed training primary care providers in autism diagnostics, “older, more complex patients with co-occurring behavioral health or other developmental disorders may need more specialized diagnostic assessment than could be accomplished in a primary care setting,” Dr. Hyman added.
“However, it is very important to identify children with therapeutic needs as early as possible and move them through the continuum from screening to diagnosis to treatment in a timely fashion. It would be wonderful if symptoms could be addressed without the need for diagnosis in the very youngest children,” Dr. Hyman said. “Early symptoms, even if not autism, are likely to be appropriate for intervention – whether it is speech therapy, attention to food selectivity, sleep problems – things that impact quality of life and potential future symptoms.”
The research was supported by the Utah Stimulating Access to Research in Residency Transition Scholar award, which is funded by the National Institutes of Health.
Dr. Campbell is an inventor on a patent related to screening for autism. The study authors otherwise had no disclosures. Dr. Lessin is on the editorial advisory board for Pediatric News and is on an advisory board for Cognoa, which is developing a medical device to diagnose autism and he is also the co-editor of the AAP's current ADHD Toolkit. Dr. Hyman had no relevant financial disclosures.
*This story was updated on Feb. 11, 2021.
To improve autism screening rates, researchers in Utah tried a range of interventions.
They added automatic reminders to the electronic health record (EHR). They started using a shorter, more sensitive screening instrument. And they trained clinicians to perform autism-specific evaluations in a primary care clinic.
The researchers found that these interventions were associated with increased rates of autism screening and referrals.
At the same time, they looked at screening and referral rates at other community clinics in their health care system. These clinics incorporated EHR reminders but not all of the other changes.
“The community clinics had an increase in screening frequency with only automatic reminders,” the researchers reported. At the two intervention clinics, however, screening rates increased more than they did at the community clinics. Referrals did not significantly increase at the community clinics.
Kathleen Campbell, MD, MHSc, a pediatric resident at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, and colleagues described their research in a study published in Pediatrics.
Three phases
They examined more than 12,000 well-child visits for children aged 16-30 months between July 2017 and June 2019.
In all, 4,155 visits occurred at the 2 intervention clinics, and 8,078 visits occurred at the 27 community clinics in the University of Utah health care system.
From baseline through the interventions, the proportion of visits with screening increased by 51% in the intervention clinics (from 58.6% to 88.8%), and by 21% in the community clinics (from 43.4% to 52.4%). The proportion of referrals increased 1.5-fold in intervention clinics, from 1.3% to 3.3%, the authors said.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) supports screening for autism in all children starting at age 18 months, but “only 44% of children with autism have had a comprehensive autism evaluation before age 36 months,” Dr. Campbell and colleagues wrote.
In their system, about half of the children were being screened for autism, and 0.5% had autism diagnosed.
In an effort to increase the proportion of visits with screening for autism and the proportion of visits with referrals for autism evaluation, Dr. Campbell and colleagues designed a quality improvement study.
Following a baseline period, they implemented interventions in three phases.
Initially, all clinics used the Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers, Revised (M-CHAT-R) for autism screening. For the first phase starting in July 2018, the researchers changed the screening instrument at the two intervention clinics to the Parent’s Observation of Social Interaction (POSI). This instrument “is embedded in a broadband developmental screen, is shorter than the M-CHAT-R, and includes questions about the consistency of the child’s behavior,” the authors said. “The POSI has greater sensitivity than the M-CHAT-R ... and similar, although somewhat lower, specificity.”
In intervention phase 2 starting in November 2018, the researchers “added an automatic reminder for autism screening to the EHR health maintenance screen.” Both the intervention clinics and the community clinics received the automatic reminders.
In intervention phase 3 starting in February 2019, they “added a referral option that clinicians could use for rapid access to autism-specific evaluation ... for children who had a POSI result suggestive of autism and for whom the clinician had sufficient concerns about autism that would indicate the need for referral for autism evaluation,” the researchers said.
“Using an online tutorial, we trained three clinicians in the intervention clinics to administer an observational assessment known as the Screening Tool for Autism in Toddlers (STAT),” which requires a 30-minute visit, they said. “Children who had a STAT result suggestive of autism were referred for expedited autism diagnostic evaluation, which was performed by a multidisciplinary team in our university-based developmental assessment clinic. Children who had a STAT result that did not suggest autism did not receive further autism evaluations unless the clinician felt they still needed further evaluation at the developmental clinic.”
After the switch to POSI, the percentage of visits with a positive screen result increased from 4.7% to 13.5% in the intervention clinics.
Furthermore, referrals were 3.4 times more frequent for visits during phase 3 in the intervention clinics, relative to the baseline period.
Potential to overwhelm
“The change to a more sensitive screening instrument increased the frequency of screening results suggestive of autism and informed our improvement team of the need to implement autism evaluation in primary care to avoid overwhelming our referral system,” Dr. Campbell and coauthors reported.
Future studies may assess whether increased screening and referrals speed the time to diagnosis and treatment and improve long-term functional abilities of children with autism. Some children in the study have received an autism diagnosis, while others have not yet been evaluated.
The use of STAT in primary care may be limited by “the barriers of training providers and purchasing materials,” the authors noted. “However, the time-based billing for lengthier appointments and billing for developmental testing help to cover cost.”
The intervention clinics and community clinics were staffed by pediatric providers, including residents and attendings, said Dr. Campbell.
“The staffing is similar at the community and intervention clinics, with mostly pediatricians and some nurse practitioners,” Dr. Campbell said. “One difference is that there are a few family medicine physicians in the community clinics, but we did not study whether that made a difference in screening. At the beginning of the study the approach to screening was the same.”
From the start, the community clinics were screening for autism and referring for further autism evaluation less often than the intervention clinics. “I don’t know why they were screening less, but they did improve with the automatic reminders,” said Dr. Campbell. “We didn’t examine type of provider or type of practice in this study, but the literature suggests that family physicians do not screen for autism as often as pediatricians.”
Payment and referral challenges
In theory, the approach in the study is a great idea, but it may not be feasible to implement for many private practices, said Herschel Lessin, MD. Dr. Lessin is a senior partner of the Children’s Medical Group in New York.
“We desperately need autism screening in a primary care setting,” Dr. Lessin said. “These authors found that wasn’t being done as recommended by the AAP Bright Futures, which is a problem.”
However, the researchers incorporated the interventions in a health care system with “far more resources than most people in practice would ever have” and substituted a less familiar screening tool.
In addition, the ability to use confirmatory STAT for primary care evaluations may be limited. “Unless you can find pediatricians willing to commit 30 to 45 minutes on one of these evaluations ... few are going to do that,” he said.
“The whole problem is that there are no referrals available or very few referrals available, and that insurance payments so underpay for developmental screening and evaluation that it does not justify the time doing it, so a lot of doctors are unable to do it,” said Dr. Lessin. When a referral is warranted, developmental pediatricians may have 6- to 12-month waiting lists, he said.
“For people in clinical practice, this is not news,” Dr. Lessin said. “We know we should screen for autism. The problem is it’s time consuming. Nobody pays for it. We have no place to send them even when we are suspicious.”
From screening to diagnosis to treatment
“Autism screen approaches vary but with educational efforts on the part of the AAP, CDC, and family organizations the rates for autism screening have dramatically improved,” said Susan L. Hyman, MD, professor of pediatrics at the University of Rochester in New York. “I do not know if screening rates have been impacted by COVID.”
Dr. Hyman and coauthors wrote an AAP clinical report on the identification, evaluation, and management of children with autism spectrum disorder. The report was published in the January 2020 issue of Pediatrics.
After screening and diagnostic testing, patients most importantly need to be able to access “timely and equitable evidence-based intervention,” which should be available, said Dr. Hyman.
Although researchers have proposed training primary care providers in autism diagnostics, “older, more complex patients with co-occurring behavioral health or other developmental disorders may need more specialized diagnostic assessment than could be accomplished in a primary care setting,” Dr. Hyman added.
“However, it is very important to identify children with therapeutic needs as early as possible and move them through the continuum from screening to diagnosis to treatment in a timely fashion. It would be wonderful if symptoms could be addressed without the need for diagnosis in the very youngest children,” Dr. Hyman said. “Early symptoms, even if not autism, are likely to be appropriate for intervention – whether it is speech therapy, attention to food selectivity, sleep problems – things that impact quality of life and potential future symptoms.”
The research was supported by the Utah Stimulating Access to Research in Residency Transition Scholar award, which is funded by the National Institutes of Health.
Dr. Campbell is an inventor on a patent related to screening for autism. The study authors otherwise had no disclosures. Dr. Lessin is on the editorial advisory board for Pediatric News and is on an advisory board for Cognoa, which is developing a medical device to diagnose autism and he is also the co-editor of the AAP's current ADHD Toolkit. Dr. Hyman had no relevant financial disclosures.
*This story was updated on Feb. 11, 2021.
To improve autism screening rates, researchers in Utah tried a range of interventions.
They added automatic reminders to the electronic health record (EHR). They started using a shorter, more sensitive screening instrument. And they trained clinicians to perform autism-specific evaluations in a primary care clinic.
The researchers found that these interventions were associated with increased rates of autism screening and referrals.
At the same time, they looked at screening and referral rates at other community clinics in their health care system. These clinics incorporated EHR reminders but not all of the other changes.
“The community clinics had an increase in screening frequency with only automatic reminders,” the researchers reported. At the two intervention clinics, however, screening rates increased more than they did at the community clinics. Referrals did not significantly increase at the community clinics.
Kathleen Campbell, MD, MHSc, a pediatric resident at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, and colleagues described their research in a study published in Pediatrics.
Three phases
They examined more than 12,000 well-child visits for children aged 16-30 months between July 2017 and June 2019.
In all, 4,155 visits occurred at the 2 intervention clinics, and 8,078 visits occurred at the 27 community clinics in the University of Utah health care system.
From baseline through the interventions, the proportion of visits with screening increased by 51% in the intervention clinics (from 58.6% to 88.8%), and by 21% in the community clinics (from 43.4% to 52.4%). The proportion of referrals increased 1.5-fold in intervention clinics, from 1.3% to 3.3%, the authors said.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) supports screening for autism in all children starting at age 18 months, but “only 44% of children with autism have had a comprehensive autism evaluation before age 36 months,” Dr. Campbell and colleagues wrote.
In their system, about half of the children were being screened for autism, and 0.5% had autism diagnosed.
In an effort to increase the proportion of visits with screening for autism and the proportion of visits with referrals for autism evaluation, Dr. Campbell and colleagues designed a quality improvement study.
Following a baseline period, they implemented interventions in three phases.
Initially, all clinics used the Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers, Revised (M-CHAT-R) for autism screening. For the first phase starting in July 2018, the researchers changed the screening instrument at the two intervention clinics to the Parent’s Observation of Social Interaction (POSI). This instrument “is embedded in a broadband developmental screen, is shorter than the M-CHAT-R, and includes questions about the consistency of the child’s behavior,” the authors said. “The POSI has greater sensitivity than the M-CHAT-R ... and similar, although somewhat lower, specificity.”
In intervention phase 2 starting in November 2018, the researchers “added an automatic reminder for autism screening to the EHR health maintenance screen.” Both the intervention clinics and the community clinics received the automatic reminders.
In intervention phase 3 starting in February 2019, they “added a referral option that clinicians could use for rapid access to autism-specific evaluation ... for children who had a POSI result suggestive of autism and for whom the clinician had sufficient concerns about autism that would indicate the need for referral for autism evaluation,” the researchers said.
“Using an online tutorial, we trained three clinicians in the intervention clinics to administer an observational assessment known as the Screening Tool for Autism in Toddlers (STAT),” which requires a 30-minute visit, they said. “Children who had a STAT result suggestive of autism were referred for expedited autism diagnostic evaluation, which was performed by a multidisciplinary team in our university-based developmental assessment clinic. Children who had a STAT result that did not suggest autism did not receive further autism evaluations unless the clinician felt they still needed further evaluation at the developmental clinic.”
After the switch to POSI, the percentage of visits with a positive screen result increased from 4.7% to 13.5% in the intervention clinics.
Furthermore, referrals were 3.4 times more frequent for visits during phase 3 in the intervention clinics, relative to the baseline period.
Potential to overwhelm
“The change to a more sensitive screening instrument increased the frequency of screening results suggestive of autism and informed our improvement team of the need to implement autism evaluation in primary care to avoid overwhelming our referral system,” Dr. Campbell and coauthors reported.
Future studies may assess whether increased screening and referrals speed the time to diagnosis and treatment and improve long-term functional abilities of children with autism. Some children in the study have received an autism diagnosis, while others have not yet been evaluated.
The use of STAT in primary care may be limited by “the barriers of training providers and purchasing materials,” the authors noted. “However, the time-based billing for lengthier appointments and billing for developmental testing help to cover cost.”
The intervention clinics and community clinics were staffed by pediatric providers, including residents and attendings, said Dr. Campbell.
“The staffing is similar at the community and intervention clinics, with mostly pediatricians and some nurse practitioners,” Dr. Campbell said. “One difference is that there are a few family medicine physicians in the community clinics, but we did not study whether that made a difference in screening. At the beginning of the study the approach to screening was the same.”
From the start, the community clinics were screening for autism and referring for further autism evaluation less often than the intervention clinics. “I don’t know why they were screening less, but they did improve with the automatic reminders,” said Dr. Campbell. “We didn’t examine type of provider or type of practice in this study, but the literature suggests that family physicians do not screen for autism as often as pediatricians.”
Payment and referral challenges
In theory, the approach in the study is a great idea, but it may not be feasible to implement for many private practices, said Herschel Lessin, MD. Dr. Lessin is a senior partner of the Children’s Medical Group in New York.
“We desperately need autism screening in a primary care setting,” Dr. Lessin said. “These authors found that wasn’t being done as recommended by the AAP Bright Futures, which is a problem.”
However, the researchers incorporated the interventions in a health care system with “far more resources than most people in practice would ever have” and substituted a less familiar screening tool.
In addition, the ability to use confirmatory STAT for primary care evaluations may be limited. “Unless you can find pediatricians willing to commit 30 to 45 minutes on one of these evaluations ... few are going to do that,” he said.
“The whole problem is that there are no referrals available or very few referrals available, and that insurance payments so underpay for developmental screening and evaluation that it does not justify the time doing it, so a lot of doctors are unable to do it,” said Dr. Lessin. When a referral is warranted, developmental pediatricians may have 6- to 12-month waiting lists, he said.
“For people in clinical practice, this is not news,” Dr. Lessin said. “We know we should screen for autism. The problem is it’s time consuming. Nobody pays for it. We have no place to send them even when we are suspicious.”
From screening to diagnosis to treatment
“Autism screen approaches vary but with educational efforts on the part of the AAP, CDC, and family organizations the rates for autism screening have dramatically improved,” said Susan L. Hyman, MD, professor of pediatrics at the University of Rochester in New York. “I do not know if screening rates have been impacted by COVID.”
Dr. Hyman and coauthors wrote an AAP clinical report on the identification, evaluation, and management of children with autism spectrum disorder. The report was published in the January 2020 issue of Pediatrics.
After screening and diagnostic testing, patients most importantly need to be able to access “timely and equitable evidence-based intervention,” which should be available, said Dr. Hyman.
Although researchers have proposed training primary care providers in autism diagnostics, “older, more complex patients with co-occurring behavioral health or other developmental disorders may need more specialized diagnostic assessment than could be accomplished in a primary care setting,” Dr. Hyman added.
“However, it is very important to identify children with therapeutic needs as early as possible and move them through the continuum from screening to diagnosis to treatment in a timely fashion. It would be wonderful if symptoms could be addressed without the need for diagnosis in the very youngest children,” Dr. Hyman said. “Early symptoms, even if not autism, are likely to be appropriate for intervention – whether it is speech therapy, attention to food selectivity, sleep problems – things that impact quality of life and potential future symptoms.”
The research was supported by the Utah Stimulating Access to Research in Residency Transition Scholar award, which is funded by the National Institutes of Health.
Dr. Campbell is an inventor on a patent related to screening for autism. The study authors otherwise had no disclosures. Dr. Lessin is on the editorial advisory board for Pediatric News and is on an advisory board for Cognoa, which is developing a medical device to diagnose autism and he is also the co-editor of the AAP's current ADHD Toolkit. Dr. Hyman had no relevant financial disclosures.
*This story was updated on Feb. 11, 2021.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Coffee lowers heart failure risk in unique study
Higher coffee consumption is associated with a lower risk of heart failure, according to a machine learning–based algorithm that analyzed data from three large observational trials.
“Coffee consumption actually was predictive on top of known risk factors originally identified from those three trials.” The study is significant because it underscores the potential of big data for individualizing patient management, lead investigator David Kao, MD, said in an interview. “We in fact adjusted for the scores that are commonly used to predict heart disease, and coffee consumption remained a predictor even on top of that.”
The study used supervised machine learning to analyze data on diet and other variables from three well-known observational studies: Framingham Heart Study (FHS), Cardiovascular Heart Study (CHS), and ARIC (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities). The goal of the study, published online on Feb. 9, 2021*, was to identify potential novel risk factors for incident coronary heart disease, stroke, and heart failure.
“The main difference of the relationship between coffee and heart disease, compared with prior analyses, is that we’re able to find it in these well-known and well-accepted studies that have helped us find risk factors before,” Dr. Kao said
The study included 2,732 FHS participants aged 30-62 years, 3,704 CHS patients aged 65 and older, and 14,925 ARIC subjects aged 45-64, all of whom had no history of cardiovascular disease events when they enrolled. Primary outcomes for the machine-learning study were times to incident coronary heart disease, heart failure, and stroke.
Mathematics, not hypotheses
To compensate for variations in methodologies between the three observational trials, the study used 204 data measurements collected at the first FHS exam, including 16 dietary variables and for which similar data were collected for the other two studies.
The machine-learning model used what’s known as a random forest analysis to identify the leading potential risk factors from among the 204 variables. To confirm findings between studies, the authors used a technique called “data harmonization” to smooth variations in the methodologies of the trials, not only with participant age and duration and date of the trials, but also in how data on coffee consumption were gathered. For example, FHS collected that data as cups per day, whereas CHS and ARIC collected that as monthly, weekly, and daily consumption. The study converted the coffee consumption data from CHS and ARIC to cups per day to conform to FHS data.
Random forest analysis is a type of machine learning that randomly creates a cluster of decision trees – the “forest” – to determine which variables, such as dietary factors, are important in predicting a result. The analysis uses mathematics, not hypotheses, to identify important variables.
Heart failure and risk reduced
In this study, the analysis determined that each cup of caffeinated coffee daily was linked with a 5% reduction in the risk of heart failure (hazard ratio, 0.95; P = .02) and 6% reduction in stroke risk (HR, 0.94; P = .02), but had no significant impact on risk for coronary heart disease or cardiovascular disease.
When the data were adjusted for the FHS CVD risk score, increasing coffee consumption remained significantly associated with an identical lower risk of heart failure (P = .03) but not stroke (P = .33).
While the study supports an association between coffee consumption and heart failure risk, it doesn’t establish causation, noted Alice H. Lichtenstein, DSc, director and senior scientist at the Cardiovascular Nutrition Laboratory at Tufts University, Boston. “The authors could not rule out the possibility that caffeinated coffee intake was a proxy for other heart-healthy lifestyle behaviors,” Dr. Lichtenstein said. “Perhaps the best message from the study is that there appears to be no adverse effects of drinking moderate amounts of caffeinated coffee, and there may be benefits.”
She added a note of caution. “This result does not suggest coffee intake should be increased, nor does it give license to increasing coffee drinks with a lot of added cream and sugar.”
Machine learning mines observational trials
Dr. Kao explained the rationale for applying a machine-learning algorithm to the three observational trials. “When these trials were designed in general, they had an idea of what they were looking for in terms of what might be a risk factor,” said Dr. Kao, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. “What we were interested in doing was to look for risk factors that nobody really thought about ahead of time and let the data show us what might be a predictor without any bias of what we imagined to be true.”
He described the role of machine learning in extracting and “filtering” data from the trials. “Machine learning allows us to look at a very large number of factors or variables and identify the most important ones in predicting a specific outcome,” he said. This study evaluated the 204 variables and focused on dietary factors because they’re modifiable.
“We looked at them in these different studies where we could, and coffee was the one that was reproducible in all of them,” he said. “Machine learning helped filter down these very large numbers of variables in ways you can’t do with traditional statistics. It’s useful in studies like this because they gather thousands and thousands of variables that generally nobody uses, but these methods allow you to actually do something with them – to determine which ones are most important.”
He added: “These methods I think will take us toward personalized medicine where you’re really individualizing a plan for keeping a patient healthy. We still have a lot of work to do, but there’s a lot of promise for really helping each of us to figure out the ways we can become the healthiest that we can be.”
The study was supported with funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the American Heart Association. Dr. Kao and coauthors, as well as Dr. Lichtenstein, had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
*Correction, 2/10/21: An earlier version of this article misstated the study's publication date.
Higher coffee consumption is associated with a lower risk of heart failure, according to a machine learning–based algorithm that analyzed data from three large observational trials.
“Coffee consumption actually was predictive on top of known risk factors originally identified from those three trials.” The study is significant because it underscores the potential of big data for individualizing patient management, lead investigator David Kao, MD, said in an interview. “We in fact adjusted for the scores that are commonly used to predict heart disease, and coffee consumption remained a predictor even on top of that.”
The study used supervised machine learning to analyze data on diet and other variables from three well-known observational studies: Framingham Heart Study (FHS), Cardiovascular Heart Study (CHS), and ARIC (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities). The goal of the study, published online on Feb. 9, 2021*, was to identify potential novel risk factors for incident coronary heart disease, stroke, and heart failure.
“The main difference of the relationship between coffee and heart disease, compared with prior analyses, is that we’re able to find it in these well-known and well-accepted studies that have helped us find risk factors before,” Dr. Kao said
The study included 2,732 FHS participants aged 30-62 years, 3,704 CHS patients aged 65 and older, and 14,925 ARIC subjects aged 45-64, all of whom had no history of cardiovascular disease events when they enrolled. Primary outcomes for the machine-learning study were times to incident coronary heart disease, heart failure, and stroke.
Mathematics, not hypotheses
To compensate for variations in methodologies between the three observational trials, the study used 204 data measurements collected at the first FHS exam, including 16 dietary variables and for which similar data were collected for the other two studies.
The machine-learning model used what’s known as a random forest analysis to identify the leading potential risk factors from among the 204 variables. To confirm findings between studies, the authors used a technique called “data harmonization” to smooth variations in the methodologies of the trials, not only with participant age and duration and date of the trials, but also in how data on coffee consumption were gathered. For example, FHS collected that data as cups per day, whereas CHS and ARIC collected that as monthly, weekly, and daily consumption. The study converted the coffee consumption data from CHS and ARIC to cups per day to conform to FHS data.
Random forest analysis is a type of machine learning that randomly creates a cluster of decision trees – the “forest” – to determine which variables, such as dietary factors, are important in predicting a result. The analysis uses mathematics, not hypotheses, to identify important variables.
Heart failure and risk reduced
In this study, the analysis determined that each cup of caffeinated coffee daily was linked with a 5% reduction in the risk of heart failure (hazard ratio, 0.95; P = .02) and 6% reduction in stroke risk (HR, 0.94; P = .02), but had no significant impact on risk for coronary heart disease or cardiovascular disease.
When the data were adjusted for the FHS CVD risk score, increasing coffee consumption remained significantly associated with an identical lower risk of heart failure (P = .03) but not stroke (P = .33).
While the study supports an association between coffee consumption and heart failure risk, it doesn’t establish causation, noted Alice H. Lichtenstein, DSc, director and senior scientist at the Cardiovascular Nutrition Laboratory at Tufts University, Boston. “The authors could not rule out the possibility that caffeinated coffee intake was a proxy for other heart-healthy lifestyle behaviors,” Dr. Lichtenstein said. “Perhaps the best message from the study is that there appears to be no adverse effects of drinking moderate amounts of caffeinated coffee, and there may be benefits.”
She added a note of caution. “This result does not suggest coffee intake should be increased, nor does it give license to increasing coffee drinks with a lot of added cream and sugar.”
Machine learning mines observational trials
Dr. Kao explained the rationale for applying a machine-learning algorithm to the three observational trials. “When these trials were designed in general, they had an idea of what they were looking for in terms of what might be a risk factor,” said Dr. Kao, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. “What we were interested in doing was to look for risk factors that nobody really thought about ahead of time and let the data show us what might be a predictor without any bias of what we imagined to be true.”
He described the role of machine learning in extracting and “filtering” data from the trials. “Machine learning allows us to look at a very large number of factors or variables and identify the most important ones in predicting a specific outcome,” he said. This study evaluated the 204 variables and focused on dietary factors because they’re modifiable.
“We looked at them in these different studies where we could, and coffee was the one that was reproducible in all of them,” he said. “Machine learning helped filter down these very large numbers of variables in ways you can’t do with traditional statistics. It’s useful in studies like this because they gather thousands and thousands of variables that generally nobody uses, but these methods allow you to actually do something with them – to determine which ones are most important.”
He added: “These methods I think will take us toward personalized medicine where you’re really individualizing a plan for keeping a patient healthy. We still have a lot of work to do, but there’s a lot of promise for really helping each of us to figure out the ways we can become the healthiest that we can be.”
The study was supported with funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the American Heart Association. Dr. Kao and coauthors, as well as Dr. Lichtenstein, had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
*Correction, 2/10/21: An earlier version of this article misstated the study's publication date.
Higher coffee consumption is associated with a lower risk of heart failure, according to a machine learning–based algorithm that analyzed data from three large observational trials.
“Coffee consumption actually was predictive on top of known risk factors originally identified from those three trials.” The study is significant because it underscores the potential of big data for individualizing patient management, lead investigator David Kao, MD, said in an interview. “We in fact adjusted for the scores that are commonly used to predict heart disease, and coffee consumption remained a predictor even on top of that.”
The study used supervised machine learning to analyze data on diet and other variables from three well-known observational studies: Framingham Heart Study (FHS), Cardiovascular Heart Study (CHS), and ARIC (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities). The goal of the study, published online on Feb. 9, 2021*, was to identify potential novel risk factors for incident coronary heart disease, stroke, and heart failure.
“The main difference of the relationship between coffee and heart disease, compared with prior analyses, is that we’re able to find it in these well-known and well-accepted studies that have helped us find risk factors before,” Dr. Kao said
The study included 2,732 FHS participants aged 30-62 years, 3,704 CHS patients aged 65 and older, and 14,925 ARIC subjects aged 45-64, all of whom had no history of cardiovascular disease events when they enrolled. Primary outcomes for the machine-learning study were times to incident coronary heart disease, heart failure, and stroke.
Mathematics, not hypotheses
To compensate for variations in methodologies between the three observational trials, the study used 204 data measurements collected at the first FHS exam, including 16 dietary variables and for which similar data were collected for the other two studies.
The machine-learning model used what’s known as a random forest analysis to identify the leading potential risk factors from among the 204 variables. To confirm findings between studies, the authors used a technique called “data harmonization” to smooth variations in the methodologies of the trials, not only with participant age and duration and date of the trials, but also in how data on coffee consumption were gathered. For example, FHS collected that data as cups per day, whereas CHS and ARIC collected that as monthly, weekly, and daily consumption. The study converted the coffee consumption data from CHS and ARIC to cups per day to conform to FHS data.
Random forest analysis is a type of machine learning that randomly creates a cluster of decision trees – the “forest” – to determine which variables, such as dietary factors, are important in predicting a result. The analysis uses mathematics, not hypotheses, to identify important variables.
Heart failure and risk reduced
In this study, the analysis determined that each cup of caffeinated coffee daily was linked with a 5% reduction in the risk of heart failure (hazard ratio, 0.95; P = .02) and 6% reduction in stroke risk (HR, 0.94; P = .02), but had no significant impact on risk for coronary heart disease or cardiovascular disease.
When the data were adjusted for the FHS CVD risk score, increasing coffee consumption remained significantly associated with an identical lower risk of heart failure (P = .03) but not stroke (P = .33).
While the study supports an association between coffee consumption and heart failure risk, it doesn’t establish causation, noted Alice H. Lichtenstein, DSc, director and senior scientist at the Cardiovascular Nutrition Laboratory at Tufts University, Boston. “The authors could not rule out the possibility that caffeinated coffee intake was a proxy for other heart-healthy lifestyle behaviors,” Dr. Lichtenstein said. “Perhaps the best message from the study is that there appears to be no adverse effects of drinking moderate amounts of caffeinated coffee, and there may be benefits.”
She added a note of caution. “This result does not suggest coffee intake should be increased, nor does it give license to increasing coffee drinks with a lot of added cream and sugar.”
Machine learning mines observational trials
Dr. Kao explained the rationale for applying a machine-learning algorithm to the three observational trials. “When these trials were designed in general, they had an idea of what they were looking for in terms of what might be a risk factor,” said Dr. Kao, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. “What we were interested in doing was to look for risk factors that nobody really thought about ahead of time and let the data show us what might be a predictor without any bias of what we imagined to be true.”
He described the role of machine learning in extracting and “filtering” data from the trials. “Machine learning allows us to look at a very large number of factors or variables and identify the most important ones in predicting a specific outcome,” he said. This study evaluated the 204 variables and focused on dietary factors because they’re modifiable.
“We looked at them in these different studies where we could, and coffee was the one that was reproducible in all of them,” he said. “Machine learning helped filter down these very large numbers of variables in ways you can’t do with traditional statistics. It’s useful in studies like this because they gather thousands and thousands of variables that generally nobody uses, but these methods allow you to actually do something with them – to determine which ones are most important.”
He added: “These methods I think will take us toward personalized medicine where you’re really individualizing a plan for keeping a patient healthy. We still have a lot of work to do, but there’s a lot of promise for really helping each of us to figure out the ways we can become the healthiest that we can be.”
The study was supported with funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the American Heart Association. Dr. Kao and coauthors, as well as Dr. Lichtenstein, had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
*Correction, 2/10/21: An earlier version of this article misstated the study's publication date.
FROM CIRCULATION: HEART FAILURE
Customized chemotherapy did not improve survival in early NSCLC
The patients were randomized to receive investigator’s choice of platinum-based chemotherapy or treatment tailored according to messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of two molecular markers – excision repair cross complementation 1 (ERCC1) and thymidylate synthase (TS).
There was no significant difference in overall survival or recurrence-free survival between the treatment approaches. However, toxicity was less common among patients who received customized treatment.
These results, from the phase 3 ITACA trial, were presented at the 2020 World Conference on Lung Cancer (Abstract 1820), which was rescheduled to January 2021.
“There is a clear need to define patients most likely to derive survival benefit from adjuvant therapy and spare patients who do not need adjuvant chemotherapy due to the toxicity of such therapy,” said presenter Silvia Novello, MD, PhD, of the University of Turin in Italy. “mRNA expression of different genes has been correlated with the sensitivity or resistance to specific anticancer agents.”
With this in mind, Dr. Novello and colleagues conducted the ITACA trial. The researchers’ primary goal was to determine whether an adjuvant pharmacogenomic-driven approach was able to improve overall survival in completely resected NSCLC.
Patients and treatment
The researchers randomized 773 NSCLC patients within 5-8 weeks after radical surgery. Genomic analyses were performed soon after surgery, and patients were randomly assigned to investigator’s choice of platinum-based chemotherapy or to tailored treatments defined by mRNA levels of ERCC1 and TS.
Patients with high ERCC1 mRNA expression who were randomized to tailored treatment received single-agent docetaxel if their TS level was high or pemetrexed monotherapy if their TS level was low.
Patients with low ERCC1 mRNA expression who were randomized to tailored treatment received cisplatin-gemcitabine if their TS level was high or cisplatin-pemetrexed if their TS was low.
The most frequent doublets used in control patients were cisplatin-gemcitabine and cisplatin-vinorelbine.
The demographic characteristics of the 384 patients randomized to tailored therapy and the 389 control subjects were well-balanced, Dr. Novello said. Two-thirds of patients had stage II disease, 11% were never smokers, and the vast majority had a lobectomy as the resection method.
Results
At a median follow-up of 28.2 months, the median overall survival was 96.4 months in the tailored therapy arm and 83.5 months in the control arm. The median recurrence-free survival was 64.4 months and 41.5 months, respectively.
“Adjuvant chemotherapy customization based on the primary tumor tissue mRNA expression of ERCC1 and TS did not significantly improve overall survival or recurrence-free survival,” Dr. Novello said. “There was a non–statistically significant trend for overall survival favoring the customized arm.”
Dr. Novello noted that, when the final analysis was performed, the study was underpowered, as only 46% of expected events were collected. Assuming the same hazard ratio point estimate and that the expected 336 events were collected, the hazard ratio estimate would be 0.76 (P = .012).
Grade 3/4 toxicities occurred in 32.6% of patients in the tailored therapy arm and 45.9% of those in the control arm (P < .001).
“It is important to underline that the treatment customization significantly improved the toxicity profile without compromising the efficacy,” Dr. Novello said.
She added that “more comprehensive and high-throughput diagnostic techniques will be needed in order to tailor adjuvant chemotherapy, with or without immunotherapy, in completely resected NSCLC.”
“The ITACA study is the largest adjuvant study tailored to ERCC1/TS status, and the results have been long-awaited,” said Tetsuya Mitsudomi, MD, a professor at Kindai University in Japan and president of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer.
“This trial should be praised for the mandated genomic analysis that was accomplished within a reasonably short time frame before random assignment. In addition, this trial confirmed that there is no biomarker strong enough to predict the efficacy of cytotoxic chemotherapy. However, the concept of customizing adjuvant therapy according to the genomic status of patients’ tumors is valid, leading to the recent demonstration in the ADAURA study of the superiority of osimertinib in delaying the postoperative recurrence of disease in patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC.”
The ITACA study was funded by University of Turin and Eli Lilly. Dr. Novello disclosed relationships with Eli Lilly, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bohringer Ingelheim, Beigene, Pfizer, Roche, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Takeda, and Sanofi. Dr. Mitsudomi disclosed relationships with Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Chugai, Pfizer, Merck, Ono Pharmaceutical, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, ThermoFisher, Guardant, Eisai, Amgen, and Johnson & Johnson.
The patients were randomized to receive investigator’s choice of platinum-based chemotherapy or treatment tailored according to messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of two molecular markers – excision repair cross complementation 1 (ERCC1) and thymidylate synthase (TS).
There was no significant difference in overall survival or recurrence-free survival between the treatment approaches. However, toxicity was less common among patients who received customized treatment.
These results, from the phase 3 ITACA trial, were presented at the 2020 World Conference on Lung Cancer (Abstract 1820), which was rescheduled to January 2021.
“There is a clear need to define patients most likely to derive survival benefit from adjuvant therapy and spare patients who do not need adjuvant chemotherapy due to the toxicity of such therapy,” said presenter Silvia Novello, MD, PhD, of the University of Turin in Italy. “mRNA expression of different genes has been correlated with the sensitivity or resistance to specific anticancer agents.”
With this in mind, Dr. Novello and colleagues conducted the ITACA trial. The researchers’ primary goal was to determine whether an adjuvant pharmacogenomic-driven approach was able to improve overall survival in completely resected NSCLC.
Patients and treatment
The researchers randomized 773 NSCLC patients within 5-8 weeks after radical surgery. Genomic analyses were performed soon after surgery, and patients were randomly assigned to investigator’s choice of platinum-based chemotherapy or to tailored treatments defined by mRNA levels of ERCC1 and TS.
Patients with high ERCC1 mRNA expression who were randomized to tailored treatment received single-agent docetaxel if their TS level was high or pemetrexed monotherapy if their TS level was low.
Patients with low ERCC1 mRNA expression who were randomized to tailored treatment received cisplatin-gemcitabine if their TS level was high or cisplatin-pemetrexed if their TS was low.
The most frequent doublets used in control patients were cisplatin-gemcitabine and cisplatin-vinorelbine.
The demographic characteristics of the 384 patients randomized to tailored therapy and the 389 control subjects were well-balanced, Dr. Novello said. Two-thirds of patients had stage II disease, 11% were never smokers, and the vast majority had a lobectomy as the resection method.
Results
At a median follow-up of 28.2 months, the median overall survival was 96.4 months in the tailored therapy arm and 83.5 months in the control arm. The median recurrence-free survival was 64.4 months and 41.5 months, respectively.
“Adjuvant chemotherapy customization based on the primary tumor tissue mRNA expression of ERCC1 and TS did not significantly improve overall survival or recurrence-free survival,” Dr. Novello said. “There was a non–statistically significant trend for overall survival favoring the customized arm.”
Dr. Novello noted that, when the final analysis was performed, the study was underpowered, as only 46% of expected events were collected. Assuming the same hazard ratio point estimate and that the expected 336 events were collected, the hazard ratio estimate would be 0.76 (P = .012).
Grade 3/4 toxicities occurred in 32.6% of patients in the tailored therapy arm and 45.9% of those in the control arm (P < .001).
“It is important to underline that the treatment customization significantly improved the toxicity profile without compromising the efficacy,” Dr. Novello said.
She added that “more comprehensive and high-throughput diagnostic techniques will be needed in order to tailor adjuvant chemotherapy, with or without immunotherapy, in completely resected NSCLC.”
“The ITACA study is the largest adjuvant study tailored to ERCC1/TS status, and the results have been long-awaited,” said Tetsuya Mitsudomi, MD, a professor at Kindai University in Japan and president of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer.
“This trial should be praised for the mandated genomic analysis that was accomplished within a reasonably short time frame before random assignment. In addition, this trial confirmed that there is no biomarker strong enough to predict the efficacy of cytotoxic chemotherapy. However, the concept of customizing adjuvant therapy according to the genomic status of patients’ tumors is valid, leading to the recent demonstration in the ADAURA study of the superiority of osimertinib in delaying the postoperative recurrence of disease in patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC.”
The ITACA study was funded by University of Turin and Eli Lilly. Dr. Novello disclosed relationships with Eli Lilly, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bohringer Ingelheim, Beigene, Pfizer, Roche, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Takeda, and Sanofi. Dr. Mitsudomi disclosed relationships with Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Chugai, Pfizer, Merck, Ono Pharmaceutical, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, ThermoFisher, Guardant, Eisai, Amgen, and Johnson & Johnson.
The patients were randomized to receive investigator’s choice of platinum-based chemotherapy or treatment tailored according to messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of two molecular markers – excision repair cross complementation 1 (ERCC1) and thymidylate synthase (TS).
There was no significant difference in overall survival or recurrence-free survival between the treatment approaches. However, toxicity was less common among patients who received customized treatment.
These results, from the phase 3 ITACA trial, were presented at the 2020 World Conference on Lung Cancer (Abstract 1820), which was rescheduled to January 2021.
“There is a clear need to define patients most likely to derive survival benefit from adjuvant therapy and spare patients who do not need adjuvant chemotherapy due to the toxicity of such therapy,” said presenter Silvia Novello, MD, PhD, of the University of Turin in Italy. “mRNA expression of different genes has been correlated with the sensitivity or resistance to specific anticancer agents.”
With this in mind, Dr. Novello and colleagues conducted the ITACA trial. The researchers’ primary goal was to determine whether an adjuvant pharmacogenomic-driven approach was able to improve overall survival in completely resected NSCLC.
Patients and treatment
The researchers randomized 773 NSCLC patients within 5-8 weeks after radical surgery. Genomic analyses were performed soon after surgery, and patients were randomly assigned to investigator’s choice of platinum-based chemotherapy or to tailored treatments defined by mRNA levels of ERCC1 and TS.
Patients with high ERCC1 mRNA expression who were randomized to tailored treatment received single-agent docetaxel if their TS level was high or pemetrexed monotherapy if their TS level was low.
Patients with low ERCC1 mRNA expression who were randomized to tailored treatment received cisplatin-gemcitabine if their TS level was high or cisplatin-pemetrexed if their TS was low.
The most frequent doublets used in control patients were cisplatin-gemcitabine and cisplatin-vinorelbine.
The demographic characteristics of the 384 patients randomized to tailored therapy and the 389 control subjects were well-balanced, Dr. Novello said. Two-thirds of patients had stage II disease, 11% were never smokers, and the vast majority had a lobectomy as the resection method.
Results
At a median follow-up of 28.2 months, the median overall survival was 96.4 months in the tailored therapy arm and 83.5 months in the control arm. The median recurrence-free survival was 64.4 months and 41.5 months, respectively.
“Adjuvant chemotherapy customization based on the primary tumor tissue mRNA expression of ERCC1 and TS did not significantly improve overall survival or recurrence-free survival,” Dr. Novello said. “There was a non–statistically significant trend for overall survival favoring the customized arm.”
Dr. Novello noted that, when the final analysis was performed, the study was underpowered, as only 46% of expected events were collected. Assuming the same hazard ratio point estimate and that the expected 336 events were collected, the hazard ratio estimate would be 0.76 (P = .012).
Grade 3/4 toxicities occurred in 32.6% of patients in the tailored therapy arm and 45.9% of those in the control arm (P < .001).
“It is important to underline that the treatment customization significantly improved the toxicity profile without compromising the efficacy,” Dr. Novello said.
She added that “more comprehensive and high-throughput diagnostic techniques will be needed in order to tailor adjuvant chemotherapy, with or without immunotherapy, in completely resected NSCLC.”
“The ITACA study is the largest adjuvant study tailored to ERCC1/TS status, and the results have been long-awaited,” said Tetsuya Mitsudomi, MD, a professor at Kindai University in Japan and president of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer.
“This trial should be praised for the mandated genomic analysis that was accomplished within a reasonably short time frame before random assignment. In addition, this trial confirmed that there is no biomarker strong enough to predict the efficacy of cytotoxic chemotherapy. However, the concept of customizing adjuvant therapy according to the genomic status of patients’ tumors is valid, leading to the recent demonstration in the ADAURA study of the superiority of osimertinib in delaying the postoperative recurrence of disease in patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC.”
The ITACA study was funded by University of Turin and Eli Lilly. Dr. Novello disclosed relationships with Eli Lilly, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bohringer Ingelheim, Beigene, Pfizer, Roche, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Takeda, and Sanofi. Dr. Mitsudomi disclosed relationships with Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Chugai, Pfizer, Merck, Ono Pharmaceutical, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, ThermoFisher, Guardant, Eisai, Amgen, and Johnson & Johnson.
FROM WCLC 2020
CXR-Net: An AI-based diagnostic tool for COVID-19
The system, called CXR-Net, was trained to differentiate SARS-CoV-2 chest x-rays (CXRs) from CXRs that are either normal or non–COVID-19 lung pathologies, explained Abdulah Haikal, an MD candidate at Wayne State University, Detroit.
Mr. Haikal described CXR-Net at the AACR Virtual Meeting: COVID-19 and Cancer (Abstract S11-04).
CXR-Net is a two-module pipeline, Mr. Haikal explained. Module I is based on Res-CR-Net, a type of neural network originally designed for the semantic segmentation of microscopy images, with the ability to retain the original resolution of the input images in the feature maps of all layers and in the final output.
Module II is a hybrid convolutional neural network in which the first convolutional layer with learned coefficients is replaced by a layer with fixed coefficients provided by the Wavelet Scattering Transform. Module II inputs patients’ CXRs and corresponding lung masks quantified by Module I, and generates as outputs a class assignment (COVID-19 or non–COVID-19) and high-resolution heat maps that detect the severe acute respiratory syndrome–-associated lung regions.
“The system is trained to differentiate COVID and non-COVID pathologies and produces a highly discriminative heat map to point to lung regions where COVID is suspected,” Mr. Haikal said. “The Wavelet Scattering Transform allows for fast determination of COVID versus non-COVID CXRs.”
Preliminary results and implications
CXR-Net was piloted on a small dataset of CXRs from non–COVID-19 and polymerase chain reaction–confirmed COVID-19 patients acquired at a single center in Detroit.
Upon fivefold cross validation of the training set with 2,265 images, 90% accuracy was observed when the training set was tested against the validation set. However, once 1,532 new images were introduced, a 76% accuracy rate was observed.
The F1 scores were 0.81 and 0.70 for the training and test sets, respectively.
“I’m really excited about this new approach, and I think AI will allow us to do more with less, which is exciting,” said Ross L. Levine, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, who led a discussion session with Mr. Haikal about CXR-Net.
One question raised during the discussion was whether the technology will help health care providers be more thoughtful about when and how they image COVID-19 patients.
“The more data you feed into the system, the stronger and more accurate it becomes,” Mr. Haikal said. “However, until we have data sharing from multiple centers, we won’t see improved accuracy results.”
Another question was whether this technology could be integrated with more clinical parameters.
“Some individuals are afraid that AI will replace the job of a professional, but it will only make it better for us,” Mr. Haikal said. “We don’t rely on current imaging techniques to make a definitive diagnosis, but rather have a specificity and sensitivity to establish a diagnosis, and AI can be used in the same way as a diagnostic tool.”
Mr. Haikal and Dr. Levine disclosed no conflicts of interest. No funding sources were reported in the presentation.
The system, called CXR-Net, was trained to differentiate SARS-CoV-2 chest x-rays (CXRs) from CXRs that are either normal or non–COVID-19 lung pathologies, explained Abdulah Haikal, an MD candidate at Wayne State University, Detroit.
Mr. Haikal described CXR-Net at the AACR Virtual Meeting: COVID-19 and Cancer (Abstract S11-04).
CXR-Net is a two-module pipeline, Mr. Haikal explained. Module I is based on Res-CR-Net, a type of neural network originally designed for the semantic segmentation of microscopy images, with the ability to retain the original resolution of the input images in the feature maps of all layers and in the final output.
Module II is a hybrid convolutional neural network in which the first convolutional layer with learned coefficients is replaced by a layer with fixed coefficients provided by the Wavelet Scattering Transform. Module II inputs patients’ CXRs and corresponding lung masks quantified by Module I, and generates as outputs a class assignment (COVID-19 or non–COVID-19) and high-resolution heat maps that detect the severe acute respiratory syndrome–-associated lung regions.
“The system is trained to differentiate COVID and non-COVID pathologies and produces a highly discriminative heat map to point to lung regions where COVID is suspected,” Mr. Haikal said. “The Wavelet Scattering Transform allows for fast determination of COVID versus non-COVID CXRs.”
Preliminary results and implications
CXR-Net was piloted on a small dataset of CXRs from non–COVID-19 and polymerase chain reaction–confirmed COVID-19 patients acquired at a single center in Detroit.
Upon fivefold cross validation of the training set with 2,265 images, 90% accuracy was observed when the training set was tested against the validation set. However, once 1,532 new images were introduced, a 76% accuracy rate was observed.
The F1 scores were 0.81 and 0.70 for the training and test sets, respectively.
“I’m really excited about this new approach, and I think AI will allow us to do more with less, which is exciting,” said Ross L. Levine, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, who led a discussion session with Mr. Haikal about CXR-Net.
One question raised during the discussion was whether the technology will help health care providers be more thoughtful about when and how they image COVID-19 patients.
“The more data you feed into the system, the stronger and more accurate it becomes,” Mr. Haikal said. “However, until we have data sharing from multiple centers, we won’t see improved accuracy results.”
Another question was whether this technology could be integrated with more clinical parameters.
“Some individuals are afraid that AI will replace the job of a professional, but it will only make it better for us,” Mr. Haikal said. “We don’t rely on current imaging techniques to make a definitive diagnosis, but rather have a specificity and sensitivity to establish a diagnosis, and AI can be used in the same way as a diagnostic tool.”
Mr. Haikal and Dr. Levine disclosed no conflicts of interest. No funding sources were reported in the presentation.
The system, called CXR-Net, was trained to differentiate SARS-CoV-2 chest x-rays (CXRs) from CXRs that are either normal or non–COVID-19 lung pathologies, explained Abdulah Haikal, an MD candidate at Wayne State University, Detroit.
Mr. Haikal described CXR-Net at the AACR Virtual Meeting: COVID-19 and Cancer (Abstract S11-04).
CXR-Net is a two-module pipeline, Mr. Haikal explained. Module I is based on Res-CR-Net, a type of neural network originally designed for the semantic segmentation of microscopy images, with the ability to retain the original resolution of the input images in the feature maps of all layers and in the final output.
Module II is a hybrid convolutional neural network in which the first convolutional layer with learned coefficients is replaced by a layer with fixed coefficients provided by the Wavelet Scattering Transform. Module II inputs patients’ CXRs and corresponding lung masks quantified by Module I, and generates as outputs a class assignment (COVID-19 or non–COVID-19) and high-resolution heat maps that detect the severe acute respiratory syndrome–-associated lung regions.
“The system is trained to differentiate COVID and non-COVID pathologies and produces a highly discriminative heat map to point to lung regions where COVID is suspected,” Mr. Haikal said. “The Wavelet Scattering Transform allows for fast determination of COVID versus non-COVID CXRs.”
Preliminary results and implications
CXR-Net was piloted on a small dataset of CXRs from non–COVID-19 and polymerase chain reaction–confirmed COVID-19 patients acquired at a single center in Detroit.
Upon fivefold cross validation of the training set with 2,265 images, 90% accuracy was observed when the training set was tested against the validation set. However, once 1,532 new images were introduced, a 76% accuracy rate was observed.
The F1 scores were 0.81 and 0.70 for the training and test sets, respectively.
“I’m really excited about this new approach, and I think AI will allow us to do more with less, which is exciting,” said Ross L. Levine, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, who led a discussion session with Mr. Haikal about CXR-Net.
One question raised during the discussion was whether the technology will help health care providers be more thoughtful about when and how they image COVID-19 patients.
“The more data you feed into the system, the stronger and more accurate it becomes,” Mr. Haikal said. “However, until we have data sharing from multiple centers, we won’t see improved accuracy results.”
Another question was whether this technology could be integrated with more clinical parameters.
“Some individuals are afraid that AI will replace the job of a professional, but it will only make it better for us,” Mr. Haikal said. “We don’t rely on current imaging techniques to make a definitive diagnosis, but rather have a specificity and sensitivity to establish a diagnosis, and AI can be used in the same way as a diagnostic tool.”
Mr. Haikal and Dr. Levine disclosed no conflicts of interest. No funding sources were reported in the presentation.
FROM AACR: COVID-19 AND CANCER 2021
Cisplatin tops cetuximab for advanced head and neck cancer
Concurrent cisplatin should remain the standard treatment over cetuximab for patients with locoregionally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, according to a large comparative phase 3 trial.
Based on the results of an interim analysis of the ARTSCAN III clinical trial, the independent safety data monitoring committee recommended early closure of the study because the results of the study suggest that cetuximab may be inferior to cisplatin.
“This study supports previous retrospective and prospective studies that suggest that concurrent cisplatin with radiation is superior to regimens with concurrent cetuximab in locally advanced head and neck cancers,” commented Sachin Jhawar, MD, MSCI, assistant professor in the department of radiation oncology at Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus. “While the previous studies De-ESCALaTE HPV and RTOG 1016 were specific to HPV [human papillomavirus]-positive cancers, this study allowed non–virally mediated tumors, though the majority of cases were HPV related.”
The new study also used a lower-dose weekly regimen of cisplatin than the other two studies, noted Dr. Jhawar. Early trials used a cisplatin dose of 100 mg/m2 every 3 weeks, but “the field is moving toward a dose of 40 mg/m2 weekly, the dose use in the Swedish study. This study had an interesting second randomization of radiation dose-escalation for more advanced primary T stage tumors, but because the study ended early it is difficult to fully interpret those results.”
Swedish researchers, led by Maria Gebre-Medhin, MD, PhD, department of hematology, oncology, and radiation physics, Skåne University Hospital, Lund, Sweden, performed an open-label, randomized, controlled, phase 3 study of patients with locoregionally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. The patients received IV cetuximab 400 mg/m2 1 week before the start of radiation therapy followed by 250 mg/m2 per week, or weekly IV cisplatin 40 mg/m2 during radiation therapy.
The study results were published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The study was prematurely closed after an unplanned interim analysis when 298 patients had been randomly assigned. The cumulative incidence of locoregional failures at 3 years was more than twice as high in the cetuximab group (23%), compared with the cisplatin group (9%; P = .0036). At 3 years, overall survival was higher in the cisplatin (88%) group than in the cetuximab group (78%), but the difference was not significant (P = .086). The cumulative incidence of distant failures did not differ between the treatment groups, and the toxicity burden was similar.
“Concurrent cisplatin led to improved locoregional control and event-free survival with a trend toward improved overall survival. The types of toxicity were different, as would be expected with the different drug mechanisms, but the rate of toxicity was not,” said Dr. Dr. Jhawar. “Interestingly, the benefit of cisplatin seemed to be limited to patients with p16-positive oropharyngeal cancer. There was clinical equipoise in the p16-negative oropharyngeal cancer group and in the non–oropharyngeal cancer group. The numbers were small, but this is intriguing and suggests that there is more work to be done in this group of patients to tease out if we can escalate or use alternative therapy.”
Cisplatin has been repeatedly proven to be superior in selected populations. The next steps, said Dr. Jhawar, include defining “optimal regimens in cisplatin-ineligible populations based on age, performance status, kidney function, hearing loss, neuropathy, and HIV/AIDS; improvements with new targeted therapies and immunotherapies; and deescalation of systemic and/or radiation regimens in the best outcome groups, such as low-risk HPV-positive patients. And we are going to see more personalized medicine with genetic testing of tumors.”
When patients are ineligible for cisplatin, no optimal regimens have been defined as yet. At Ohio State, Dr. Jhawar and colleagues use carboplatin therapy.
For practicing oncologists, Dr. Jhawar said the bottom line is “patients who are eligible should receive concurrent cisplatin therapy for locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer.”
The ARTSCAN III study was funded by the Swedish Cancer Society and the Mrs. Berta Kamprad Cancer Foundation. One of the study’s coauthors reported a leadership role in ScandiDos. The other authors reported they had no conflicts. Dr. Jhawar reported he had no conflicts of interest.
Concurrent cisplatin should remain the standard treatment over cetuximab for patients with locoregionally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, according to a large comparative phase 3 trial.
Based on the results of an interim analysis of the ARTSCAN III clinical trial, the independent safety data monitoring committee recommended early closure of the study because the results of the study suggest that cetuximab may be inferior to cisplatin.
“This study supports previous retrospective and prospective studies that suggest that concurrent cisplatin with radiation is superior to regimens with concurrent cetuximab in locally advanced head and neck cancers,” commented Sachin Jhawar, MD, MSCI, assistant professor in the department of radiation oncology at Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus. “While the previous studies De-ESCALaTE HPV and RTOG 1016 were specific to HPV [human papillomavirus]-positive cancers, this study allowed non–virally mediated tumors, though the majority of cases were HPV related.”
The new study also used a lower-dose weekly regimen of cisplatin than the other two studies, noted Dr. Jhawar. Early trials used a cisplatin dose of 100 mg/m2 every 3 weeks, but “the field is moving toward a dose of 40 mg/m2 weekly, the dose use in the Swedish study. This study had an interesting second randomization of radiation dose-escalation for more advanced primary T stage tumors, but because the study ended early it is difficult to fully interpret those results.”
Swedish researchers, led by Maria Gebre-Medhin, MD, PhD, department of hematology, oncology, and radiation physics, Skåne University Hospital, Lund, Sweden, performed an open-label, randomized, controlled, phase 3 study of patients with locoregionally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. The patients received IV cetuximab 400 mg/m2 1 week before the start of radiation therapy followed by 250 mg/m2 per week, or weekly IV cisplatin 40 mg/m2 during radiation therapy.
The study results were published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The study was prematurely closed after an unplanned interim analysis when 298 patients had been randomly assigned. The cumulative incidence of locoregional failures at 3 years was more than twice as high in the cetuximab group (23%), compared with the cisplatin group (9%; P = .0036). At 3 years, overall survival was higher in the cisplatin (88%) group than in the cetuximab group (78%), but the difference was not significant (P = .086). The cumulative incidence of distant failures did not differ between the treatment groups, and the toxicity burden was similar.
“Concurrent cisplatin led to improved locoregional control and event-free survival with a trend toward improved overall survival. The types of toxicity were different, as would be expected with the different drug mechanisms, but the rate of toxicity was not,” said Dr. Dr. Jhawar. “Interestingly, the benefit of cisplatin seemed to be limited to patients with p16-positive oropharyngeal cancer. There was clinical equipoise in the p16-negative oropharyngeal cancer group and in the non–oropharyngeal cancer group. The numbers were small, but this is intriguing and suggests that there is more work to be done in this group of patients to tease out if we can escalate or use alternative therapy.”
Cisplatin has been repeatedly proven to be superior in selected populations. The next steps, said Dr. Jhawar, include defining “optimal regimens in cisplatin-ineligible populations based on age, performance status, kidney function, hearing loss, neuropathy, and HIV/AIDS; improvements with new targeted therapies and immunotherapies; and deescalation of systemic and/or radiation regimens in the best outcome groups, such as low-risk HPV-positive patients. And we are going to see more personalized medicine with genetic testing of tumors.”
When patients are ineligible for cisplatin, no optimal regimens have been defined as yet. At Ohio State, Dr. Jhawar and colleagues use carboplatin therapy.
For practicing oncologists, Dr. Jhawar said the bottom line is “patients who are eligible should receive concurrent cisplatin therapy for locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer.”
The ARTSCAN III study was funded by the Swedish Cancer Society and the Mrs. Berta Kamprad Cancer Foundation. One of the study’s coauthors reported a leadership role in ScandiDos. The other authors reported they had no conflicts. Dr. Jhawar reported he had no conflicts of interest.
Concurrent cisplatin should remain the standard treatment over cetuximab for patients with locoregionally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, according to a large comparative phase 3 trial.
Based on the results of an interim analysis of the ARTSCAN III clinical trial, the independent safety data monitoring committee recommended early closure of the study because the results of the study suggest that cetuximab may be inferior to cisplatin.
“This study supports previous retrospective and prospective studies that suggest that concurrent cisplatin with radiation is superior to regimens with concurrent cetuximab in locally advanced head and neck cancers,” commented Sachin Jhawar, MD, MSCI, assistant professor in the department of radiation oncology at Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus. “While the previous studies De-ESCALaTE HPV and RTOG 1016 were specific to HPV [human papillomavirus]-positive cancers, this study allowed non–virally mediated tumors, though the majority of cases were HPV related.”
The new study also used a lower-dose weekly regimen of cisplatin than the other two studies, noted Dr. Jhawar. Early trials used a cisplatin dose of 100 mg/m2 every 3 weeks, but “the field is moving toward a dose of 40 mg/m2 weekly, the dose use in the Swedish study. This study had an interesting second randomization of radiation dose-escalation for more advanced primary T stage tumors, but because the study ended early it is difficult to fully interpret those results.”
Swedish researchers, led by Maria Gebre-Medhin, MD, PhD, department of hematology, oncology, and radiation physics, Skåne University Hospital, Lund, Sweden, performed an open-label, randomized, controlled, phase 3 study of patients with locoregionally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. The patients received IV cetuximab 400 mg/m2 1 week before the start of radiation therapy followed by 250 mg/m2 per week, or weekly IV cisplatin 40 mg/m2 during radiation therapy.
The study results were published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The study was prematurely closed after an unplanned interim analysis when 298 patients had been randomly assigned. The cumulative incidence of locoregional failures at 3 years was more than twice as high in the cetuximab group (23%), compared with the cisplatin group (9%; P = .0036). At 3 years, overall survival was higher in the cisplatin (88%) group than in the cetuximab group (78%), but the difference was not significant (P = .086). The cumulative incidence of distant failures did not differ between the treatment groups, and the toxicity burden was similar.
“Concurrent cisplatin led to improved locoregional control and event-free survival with a trend toward improved overall survival. The types of toxicity were different, as would be expected with the different drug mechanisms, but the rate of toxicity was not,” said Dr. Dr. Jhawar. “Interestingly, the benefit of cisplatin seemed to be limited to patients with p16-positive oropharyngeal cancer. There was clinical equipoise in the p16-negative oropharyngeal cancer group and in the non–oropharyngeal cancer group. The numbers were small, but this is intriguing and suggests that there is more work to be done in this group of patients to tease out if we can escalate or use alternative therapy.”
Cisplatin has been repeatedly proven to be superior in selected populations. The next steps, said Dr. Jhawar, include defining “optimal regimens in cisplatin-ineligible populations based on age, performance status, kidney function, hearing loss, neuropathy, and HIV/AIDS; improvements with new targeted therapies and immunotherapies; and deescalation of systemic and/or radiation regimens in the best outcome groups, such as low-risk HPV-positive patients. And we are going to see more personalized medicine with genetic testing of tumors.”
When patients are ineligible for cisplatin, no optimal regimens have been defined as yet. At Ohio State, Dr. Jhawar and colleagues use carboplatin therapy.
For practicing oncologists, Dr. Jhawar said the bottom line is “patients who are eligible should receive concurrent cisplatin therapy for locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer.”
The ARTSCAN III study was funded by the Swedish Cancer Society and the Mrs. Berta Kamprad Cancer Foundation. One of the study’s coauthors reported a leadership role in ScandiDos. The other authors reported they had no conflicts. Dr. Jhawar reported he had no conflicts of interest.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY









