User login
CML: Biomarkers can predict relapse in patients on treatment-free remission
Key clinical point: Biomarkers can predict relapse in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) who are eligible for a controlled treatment interruption.
Major finding: Predictors of CML relapse after treatment interruptions were low levels of cytotoxic cells such as CD56+ with low expression of CD16 and CD94/NKG2 receptors and CD8± T cells expressing TCRγβ+; low expression of activating receptors on the surface of natural killer (NK) and NK T cells; impaired synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines or proteases from NK cells; and HLA-E*0103 homozygosis and KIR haplotype BX.
Study details: The data come from an observational, cross-sectional study of 93 patients with chronic phase CML and 20 age- and gender-matched controls. Among patients with CML, 45 were on treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), 27 on sustained treatment-free remission (off TKIs), 15 had a relapse, and 6 had newly diagnosed CML.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the Foundation for Biomedical Research of the Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal, the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness, and the Spanish AIDS Research Network. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Vigón L et al. J Clin Med. 2020 Dec 25. doi: 10.3390/jcm10010042.
Key clinical point: Biomarkers can predict relapse in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) who are eligible for a controlled treatment interruption.
Major finding: Predictors of CML relapse after treatment interruptions were low levels of cytotoxic cells such as CD56+ with low expression of CD16 and CD94/NKG2 receptors and CD8± T cells expressing TCRγβ+; low expression of activating receptors on the surface of natural killer (NK) and NK T cells; impaired synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines or proteases from NK cells; and HLA-E*0103 homozygosis and KIR haplotype BX.
Study details: The data come from an observational, cross-sectional study of 93 patients with chronic phase CML and 20 age- and gender-matched controls. Among patients with CML, 45 were on treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), 27 on sustained treatment-free remission (off TKIs), 15 had a relapse, and 6 had newly diagnosed CML.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the Foundation for Biomedical Research of the Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal, the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness, and the Spanish AIDS Research Network. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Vigón L et al. J Clin Med. 2020 Dec 25. doi: 10.3390/jcm10010042.
Key clinical point: Biomarkers can predict relapse in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) who are eligible for a controlled treatment interruption.
Major finding: Predictors of CML relapse after treatment interruptions were low levels of cytotoxic cells such as CD56+ with low expression of CD16 and CD94/NKG2 receptors and CD8± T cells expressing TCRγβ+; low expression of activating receptors on the surface of natural killer (NK) and NK T cells; impaired synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines or proteases from NK cells; and HLA-E*0103 homozygosis and KIR haplotype BX.
Study details: The data come from an observational, cross-sectional study of 93 patients with chronic phase CML and 20 age- and gender-matched controls. Among patients with CML, 45 were on treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), 27 on sustained treatment-free remission (off TKIs), 15 had a relapse, and 6 had newly diagnosed CML.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the Foundation for Biomedical Research of the Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal, the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness, and the Spanish AIDS Research Network. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Vigón L et al. J Clin Med. 2020 Dec 25. doi: 10.3390/jcm10010042.
Risk factors for COVID-19 mortality in patients with CML
Key clinical point: Older age and imatinib therapy were associated with a higher mortality rate in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) who contracted COVID-19. However, imatinib could be a confounding factor.
Major finding: Outcome was favorable and fatal in 86% and 14% of patients, respectively. COVID-19 mortality rate was higher in patients aged 75 years vs. less than 75 years (60% vs. 7%; P less than .001) and in those on imatinib vs. second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) vs. no TKIs (25% vs. 3% vs. 0%; P = .003). However, 25% vs. 0% of patients treated with imatinib vs. second-generation TKIs were more than 75 years old.
Study details: The CANDID study evaluated 110 cases of COVID-19 in patients with CML reported by physicians to the International CML Foundation until July 1, 2020 across 20 countries.
Disclosures: No study sponsor was identified. The lead author reported ties with BMS, Incyte, Novartis, and Pfizer. Some co-authors also reported ties with various pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Rea D et al. ASH 2020. 2020 Dec 7. Abstract 649.
Key clinical point: Older age and imatinib therapy were associated with a higher mortality rate in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) who contracted COVID-19. However, imatinib could be a confounding factor.
Major finding: Outcome was favorable and fatal in 86% and 14% of patients, respectively. COVID-19 mortality rate was higher in patients aged 75 years vs. less than 75 years (60% vs. 7%; P less than .001) and in those on imatinib vs. second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) vs. no TKIs (25% vs. 3% vs. 0%; P = .003). However, 25% vs. 0% of patients treated with imatinib vs. second-generation TKIs were more than 75 years old.
Study details: The CANDID study evaluated 110 cases of COVID-19 in patients with CML reported by physicians to the International CML Foundation until July 1, 2020 across 20 countries.
Disclosures: No study sponsor was identified. The lead author reported ties with BMS, Incyte, Novartis, and Pfizer. Some co-authors also reported ties with various pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Rea D et al. ASH 2020. 2020 Dec 7. Abstract 649.
Key clinical point: Older age and imatinib therapy were associated with a higher mortality rate in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) who contracted COVID-19. However, imatinib could be a confounding factor.
Major finding: Outcome was favorable and fatal in 86% and 14% of patients, respectively. COVID-19 mortality rate was higher in patients aged 75 years vs. less than 75 years (60% vs. 7%; P less than .001) and in those on imatinib vs. second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) vs. no TKIs (25% vs. 3% vs. 0%; P = .003). However, 25% vs. 0% of patients treated with imatinib vs. second-generation TKIs were more than 75 years old.
Study details: The CANDID study evaluated 110 cases of COVID-19 in patients with CML reported by physicians to the International CML Foundation until July 1, 2020 across 20 countries.
Disclosures: No study sponsor was identified. The lead author reported ties with BMS, Incyte, Novartis, and Pfizer. Some co-authors also reported ties with various pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Rea D et al. ASH 2020. 2020 Dec 7. Abstract 649.
TNF inhibitors may slow spinal progression in axial spondyloarthritis
Patients with axial spondyloarthritis showed reduced spinal radiographic progression after treatment with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, based on data from 314 adults in a prospective cohort study.
Evidence of a link between inflammation and axial damage in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) has been reported, and these patients are routinely treated with NSAIDs and TNF inhibitors (TNFi), wrote Alexandre Sepriano, MD, PhD, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center, and colleagues.
“However, and despite significant efforts, it remains to be clarified whether there is also an effect of these drugs on axial damage accrual,” they noted.
In a study published in Arthritis & Rheumatology, the researchers recruited consecutive patients from rheumatology practices in Northern Alberta to enroll in the Follow Up Research Cohort in Ankylosing Spondylitis Treatment (ALBERTA FORCAST) observational cohort study. The average age of the patients was 41 years, 74% were men, 83% were HLA-B27 positive, and the average duration of symptoms was 18 years.
Progression was measured via spine radiographs every 2 years for up to 10 years; the radiographs were scored using the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score (mSASSS). In addition, the researchers assessed the interaction between TNFi exposure and clinical disease activity using the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) and the impact on mSASSS every 2 years. The analysis included 442 2-year intervals.
Overall, the researchers found a significant interaction between ASDAS and TNFi at the start of the interval, followed by gradient effect of ASDAS at the start of the interval on mSASSS 2 years later, which was more than twice as high in patients never treated with TNFi (beta = 0.41), compared with patients who were continuously treated with a TNFi (beta = 0.16).
“Similarly, patients treated with TNFi were 30% less likely to develop a new syndesmophyte 2 years later compared to those not treated,” the researchers said.
TNFi also directly slowed progression, as treated patients averaged 0.85 mSASSS units less 2 years later, compared with untreated patients.
Of note, “treatment with NSAIDs during follow-up was neither associated with the outcome nor did it modify or confound the association between TNFi and mSASSS,” the researchers said. In addition, “the direct effect of TNFi on mSASSS was still present after adjusting for a propensity score,” they wrote.
The study results were limited by several factors including the observational design, lack of data on long-term treatment effects, and inability to assess individual TNFi drugs separately, the researchers noted.
However, “the present study informs the rheumatology community by addressing the question as to whether or not TNFi inhibit radiographic progression in axSpA and if this effect is mediated solely by their effects on inflammation, as measured by the ASDAS, or whether additional mechanisms may be relevant,” they emphasized.
“A better understanding of these mechanisms might open avenues to further treatment strategies that might finally lead to effective disease modification in axial SpA,” they concluded.
The ALBERTA FORCAST study was supported by AbbVie. Several authors disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie and other manufacturers of TNFi.
Patients with axial spondyloarthritis showed reduced spinal radiographic progression after treatment with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, based on data from 314 adults in a prospective cohort study.
Evidence of a link between inflammation and axial damage in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) has been reported, and these patients are routinely treated with NSAIDs and TNF inhibitors (TNFi), wrote Alexandre Sepriano, MD, PhD, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center, and colleagues.
“However, and despite significant efforts, it remains to be clarified whether there is also an effect of these drugs on axial damage accrual,” they noted.
In a study published in Arthritis & Rheumatology, the researchers recruited consecutive patients from rheumatology practices in Northern Alberta to enroll in the Follow Up Research Cohort in Ankylosing Spondylitis Treatment (ALBERTA FORCAST) observational cohort study. The average age of the patients was 41 years, 74% were men, 83% were HLA-B27 positive, and the average duration of symptoms was 18 years.
Progression was measured via spine radiographs every 2 years for up to 10 years; the radiographs were scored using the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score (mSASSS). In addition, the researchers assessed the interaction between TNFi exposure and clinical disease activity using the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) and the impact on mSASSS every 2 years. The analysis included 442 2-year intervals.
Overall, the researchers found a significant interaction between ASDAS and TNFi at the start of the interval, followed by gradient effect of ASDAS at the start of the interval on mSASSS 2 years later, which was more than twice as high in patients never treated with TNFi (beta = 0.41), compared with patients who were continuously treated with a TNFi (beta = 0.16).
“Similarly, patients treated with TNFi were 30% less likely to develop a new syndesmophyte 2 years later compared to those not treated,” the researchers said.
TNFi also directly slowed progression, as treated patients averaged 0.85 mSASSS units less 2 years later, compared with untreated patients.
Of note, “treatment with NSAIDs during follow-up was neither associated with the outcome nor did it modify or confound the association between TNFi and mSASSS,” the researchers said. In addition, “the direct effect of TNFi on mSASSS was still present after adjusting for a propensity score,” they wrote.
The study results were limited by several factors including the observational design, lack of data on long-term treatment effects, and inability to assess individual TNFi drugs separately, the researchers noted.
However, “the present study informs the rheumatology community by addressing the question as to whether or not TNFi inhibit radiographic progression in axSpA and if this effect is mediated solely by their effects on inflammation, as measured by the ASDAS, or whether additional mechanisms may be relevant,” they emphasized.
“A better understanding of these mechanisms might open avenues to further treatment strategies that might finally lead to effective disease modification in axial SpA,” they concluded.
The ALBERTA FORCAST study was supported by AbbVie. Several authors disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie and other manufacturers of TNFi.
Patients with axial spondyloarthritis showed reduced spinal radiographic progression after treatment with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, based on data from 314 adults in a prospective cohort study.
Evidence of a link between inflammation and axial damage in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) has been reported, and these patients are routinely treated with NSAIDs and TNF inhibitors (TNFi), wrote Alexandre Sepriano, MD, PhD, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center, and colleagues.
“However, and despite significant efforts, it remains to be clarified whether there is also an effect of these drugs on axial damage accrual,” they noted.
In a study published in Arthritis & Rheumatology, the researchers recruited consecutive patients from rheumatology practices in Northern Alberta to enroll in the Follow Up Research Cohort in Ankylosing Spondylitis Treatment (ALBERTA FORCAST) observational cohort study. The average age of the patients was 41 years, 74% were men, 83% were HLA-B27 positive, and the average duration of symptoms was 18 years.
Progression was measured via spine radiographs every 2 years for up to 10 years; the radiographs were scored using the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score (mSASSS). In addition, the researchers assessed the interaction between TNFi exposure and clinical disease activity using the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) and the impact on mSASSS every 2 years. The analysis included 442 2-year intervals.
Overall, the researchers found a significant interaction between ASDAS and TNFi at the start of the interval, followed by gradient effect of ASDAS at the start of the interval on mSASSS 2 years later, which was more than twice as high in patients never treated with TNFi (beta = 0.41), compared with patients who were continuously treated with a TNFi (beta = 0.16).
“Similarly, patients treated with TNFi were 30% less likely to develop a new syndesmophyte 2 years later compared to those not treated,” the researchers said.
TNFi also directly slowed progression, as treated patients averaged 0.85 mSASSS units less 2 years later, compared with untreated patients.
Of note, “treatment with NSAIDs during follow-up was neither associated with the outcome nor did it modify or confound the association between TNFi and mSASSS,” the researchers said. In addition, “the direct effect of TNFi on mSASSS was still present after adjusting for a propensity score,” they wrote.
The study results were limited by several factors including the observational design, lack of data on long-term treatment effects, and inability to assess individual TNFi drugs separately, the researchers noted.
However, “the present study informs the rheumatology community by addressing the question as to whether or not TNFi inhibit radiographic progression in axSpA and if this effect is mediated solely by their effects on inflammation, as measured by the ASDAS, or whether additional mechanisms may be relevant,” they emphasized.
“A better understanding of these mechanisms might open avenues to further treatment strategies that might finally lead to effective disease modification in axial SpA,” they concluded.
The ALBERTA FORCAST study was supported by AbbVie. Several authors disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie and other manufacturers of TNFi.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Which behavioral health screening tool should you use—and when?
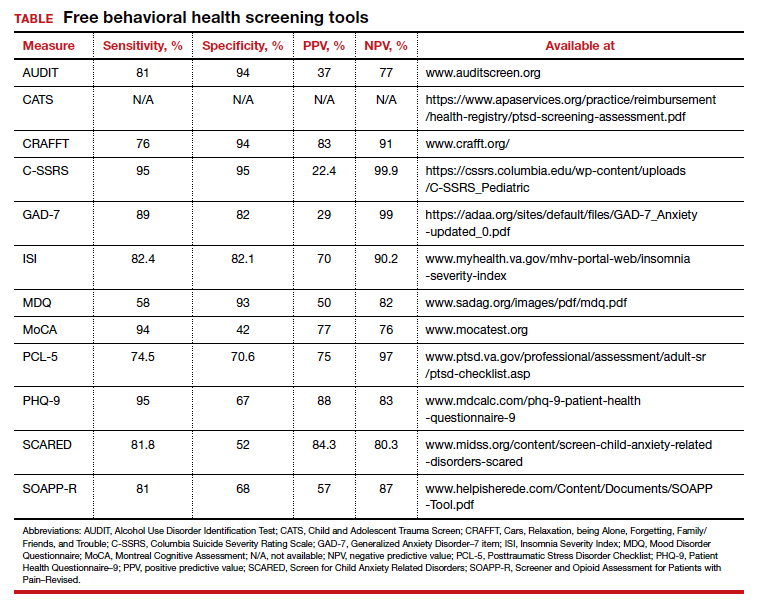
Many screening tools are available in the public domain to assess a variety of symptoms related to impaired mental health. These tools can be used to quickly evaluate for mood, suicidal ideation or behavior, anxiety, sleep, substance use, pain, trauma, memory, and cognition (TABLE). Individuals with poor mental health incur high health care costs. Those suffering from anxiety and posttraumatic stress have more outpatient and emergency department visits and hospitalizations than patients without these disorders,1,2 although use of mental health care services has been related to a decrease in the overutilization of health care services in general.3
Here we review several screening tools that can help you to identify symptoms of mental illnesses and thus, provide prompt early intervention, including referrals to psychological and psychiatric services.
Mood disorders
Most patients with mood disorders are treated in primary care settings.4 Quickly measuring patients’ mood symptoms can expedite treatment for those who need it. Many primary care clinics use the 9-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) to screen for depression.5 The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has recommended screening for depression with adequate systems to ensure accurate diagnoses, effective treatment, and follow-up. Although the USPSTF did not specially endorse screening for bipolar disorder, it followed that recommendation with the qualifying statement, “positive screening results [for depression] should lead to additional assessment that considers severity of depression and comorbid psychological problems, alternate diagnoses, and medical conditions.”6 Thus, following a positive screen result for depression, consider using a screening tool for mood disorders to provide diagnostic clarification.
The Mood Disorder Questionnaire (MDQ) is a validated 15-item, self-administered questionnaire that takes only 5 minutes to use in screening adult patients for bipolar I disorder.7 The MDQ assesses specific behaviors related to bipolar disorder, symptom co-occurrence, and functional impairment. The MDQ has low sensitivity (58%) but good specificity (93%) in a primary care setting.8 However, the MDQ is not a diagnostic instrument. A positive screen result should prompt a more thorough clinical evaluation, if necessary, by a professional trained in psychiatric disorders.
We recommend completing the MDQ prior to prescribing antidepressants. You can also monitor a patient’s response to treatment with serial MDQ testing. The MDQ is useful, too, when a patient has unclear mood symptoms that may have features overlapping with bipolar disorder. Furthermore, we recommend screening for bipolar disorder with every patient who reports symptoms of depression, given that some pharmacologic treatments (predominately selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) can induce mania in patients who actually have unrecognized bipolar disorder.9
Continue to: Suicide...
Suicide
Suicide is the 10th leading cause of death among the general population. All demographic groups are impacted by suicide; however, the most vulnerable are men ages 45 to 64 years.10 Given the imminent risk to individuals who experience suicidal ideation, properly assessing and targeting suicidal risk is paramount.
The Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) can be completed in an interview format or as a patient self-report. Versions of the C-SSRS are available for children, adolescents, and adults. It can be used in practice with any patient who may be at risk for suicide. Specifically, consider using the C-SSRS when a patient scores 1 or greater on the PHQ-9 or when risk is revealed with another brief screening tool that includes suicidal ideation.
The C-SSRS covers 10 categories related to suicidal ideation and behavior that the clinician explores with questions requiring only Yes/No responses. The C-SSRS demonstrates moderate-to-strong internal consistency and reliability, and it has shown a high degree of sensitivity (95%) and specificity (95%) for suicidal ideation.11
Anxiety and physiologic arousal
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is one of the most common anxiety disorders, with an estimated prevalence of 2.8% to 8.5% among primary care patients.12 Brief, validated screening tools such as the Generalized Anxiety Disorder–7 item (GAD-7) scale can be effective in identifying anxiety and other related disorders in primary care settings.
The GAD-7 comprises 7 items inquiring about symptoms experienced in the past 2 weeks. Scores range from 0 to 21, with cutoffs of 5, 10, and 15 indicating mild, moderate, and severe anxiety, respectively. This questionnaire is appropriate for use with adults and has strong specificity, internal consistency, and test-retest reliability.12 Specificity and sensitivity of the GAD-7 are maximized at a cutoff score of 10 or greater, both exceeding 80%.12 The GAD-7 can be used when patients report symptoms of anxiety or when one needs to screen for anxiety with new patients or more clearly understand symptoms among patients who have complex mental health concerns.
The Screen for Child Anxiety Related Disorders (SCARED) is a 41-item self-report measure of anxiety for children ages 8 to 18. The SCARED questionnaire yields an overall anxiety score, as well as subscales for panic disorder or significant somatic symptoms, generalized anxiety disorder, separation anxiety, social anxiety disorder, and significant school avoidance.13 There is also a 5-item version of the SCARED, which can be useful for brief screening in fast-paced settings when no anxiety disorder is suspected, or for children who may have anxiety but exhibit reduced verbal capacity. The SCARED has been found to have moderate sensitivity (81.8%) and specificity (52%) for diagnosing anxiety disorders in a community sample, with an optimal cutoff point of 22 on the total scale.14
Sleep
Sleep concerns are common, with the prevalence of insomnia among adults in the United States estimated to be 19.2%.15 The importance of assessing these concerns cannot be overstated, and primary care providers are the ones patients consult most often.16 The gold standard in assessing sleep disorders is a structured clinical interview, polysomnography, sleep diary, and actigraphy (home-based monitoring of movement through a device, often worn on the wrist).17,18 However, this work-up is expensive, time-intensive, and impractical in integrated care settings; thus the need for a brief, self-report screening tool to guide further assessment and intervention.
The Insomnia Severity Index (ISI) assesses patients’ perceptions of their insomnia. The ISI was developed to aid both in the clinical evaluation of patients with insomnia and to measure treatment outcomes. Administration of the ISI takes approximately 5 minutes, and scoring takes less than 1 minute.
The ISI is composed of 7 items that measure the severity of sleep onset and sleep maintenance difficulties, satisfaction with current sleep, impact on daily functioning, impairment observable to others, and degree of distress caused by the sleep problems. Each item is scored on a 0 to 4 Likert-type scale, and the individual items are summed for a total score of 0 to 28, with higher scores suggesting more severe insomnia. Evidence-based guidelines recommend cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) as the first-line treatment for adults with primary insomnia.19
Several validation studies have found the ISI to be a reliable measure of perceived insomnia severity, and one that is sensitive to changes in patients’ perceptions of treatment outcomes.20,21 An additional validation study confirmed that in primary care settings, a cutoff score of 14 should be used to indicate the likely presence of clinical insomnia22 and to guide further assessment and intervention.
The percentage of insomniac patients correctly identified with the ISI was 82.2%, with moderate sensitivity (82.4%) and specificity (82.1%).22 A positive predictive value of 70% was found, meaning that an insomnia disorder is probable when the ISI total score is 14 or higher; conversely, the negative predictive value was 90.2%.
Continue to: Substance use and pain...
Substance use and pain
The evaluation of alcohol and drug use is an integral part of assessing risky health behaviors. The 10-item Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT) is a self-report tool developed by the World Health Organization.23,24 Validated in medical settings, scores of 8 or higher suggest problematic drinking.25,26 The AUDIT has demonstrated high specificity (94%) and moderate sensitivity (81%) in primary care settings.27 The AUDIT-C (items 1, 2, and 3 of the AUDIT) has also demonstrated comparable sensitivity, although slightly lower specificity, than the full AUDIT, suggesting that this 3-question screen can also be used in primary care settings.27
Opioid medications, frequently prescribed for chronic pain, present serious risks for many patients. The Screener and Opioid Assessment for Patients with Pain–Revised (SOAPP-R) is a 24-item self-reporting scale that can be completed in approximately 10 minutes.28 A score of 18 or higher has identified 81% of patients at high risk for opioid misuse in a clinical setting, with moderate specificity (68%). Although other factors should be considered when assessing risk of opioid misuse, the SOAPP-R is a helpful and quick addition to an opioid risk assessment.
The CRAFFT Screening Tool for Adolescent Substance Use is administered by the clinician for youths ages 14 to 21. The first 3 questions ask about use of alcohol, marijuana, or other substances during the past 12 months. What follows are questions related to the young person’s specific experiences with substances in relation to Cars, Relaxation, being Alone, Forgetting, Family/Friends, and Trouble (CRAFFT). The CRAFFT has shown moderate sensitivity (76%) and good specificity (94%) for identifying any problem with substance use.29 These measures may be administered to clarify or confirm substance use patterns (ie, duration, frequency), or to determine the severity of problems related to substance use (ie, social or legal problems).
Trauma and PTSD
Approximately 7.7 million adults per year will experience posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms, although PTSD can affect individuals of any age.30 Given the impact that trauma can have, assess for PTSD in patients who have a history of trauma or who otherwise seem to be at risk. The Post-traumatic Stress Disorder Checklist (PCL-5) is a 20-item self-report questionnaire that screens for symptoms directly from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5) criteria for PTSD. One limitation is that the questionnaire is only validated for adults ages 18 years or older. Completion of the PCL-5 takes 5 to 10 minutes. The PCL-5 has strong internal consistency reliability (94%) and test-retest reliability (82%).31 With a cutoff score of 33 or higher, the sensitivity and specificity have been shown to be moderately high (74.5% and 70.6%, respectively).32
The Child and Adolescent Trauma Screen (CATS) is used to assess for potentially traumatic events and PTSD symptoms in children and adolescents. These symptoms are based on the DSM-5, and therefore the CATS can act as a useful diagnostic aid. The CATS is also available in Spanish, with both caregiver-report (for children ages 3-6 years or 7-17 years) and self-report (for ages 7-17 years) versions. Practical use of the PCL-5 and the CATS involves screening for PTSD symptoms, supporting a provisional diagnosis of PTSD, and monitoring PTSD symptom changes during and after treatment.
Memory and cognition
Cognitive screening is a first step in evaluating possible dementia and other neuropsychological disorders. The importance of brief cognitive screening in primary care cannot be understated, especially for an aging patient population. Although the Mini Mental Status Exam (MMSE) has been widely used among health care providers and researchers, we recommend the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA).
The MoCA is a simple, standalone cognitive screening tool validated for adults ages 55 to 85 years.33 The MoCA addresses many important cognitive domains, fits on one page, and can be administered by a trained provider in 10 minutes. Research also suggests that it has strong test-retest reliability and positive and negative predictive values for mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer dementia, and it has been found to be more sensitive than the MMSE.34 We additionally recommend the MoCA as it measures several cognitive skills that are not addressed on the MMSE, including verbal fluency and abstraction.34 Scores below 25 are suggestive of cognitive impairment and should lead to a referral for neuropsychological testing.
The MoCA’s sensitivity for detecting cognitive impairment is high (94%), and specificity is low (42%).35 To ensure consistency and accuracy in administering the MoCA, certification is now required via an online training program through www.mocatest.org.
Adapting these screening tools to practice
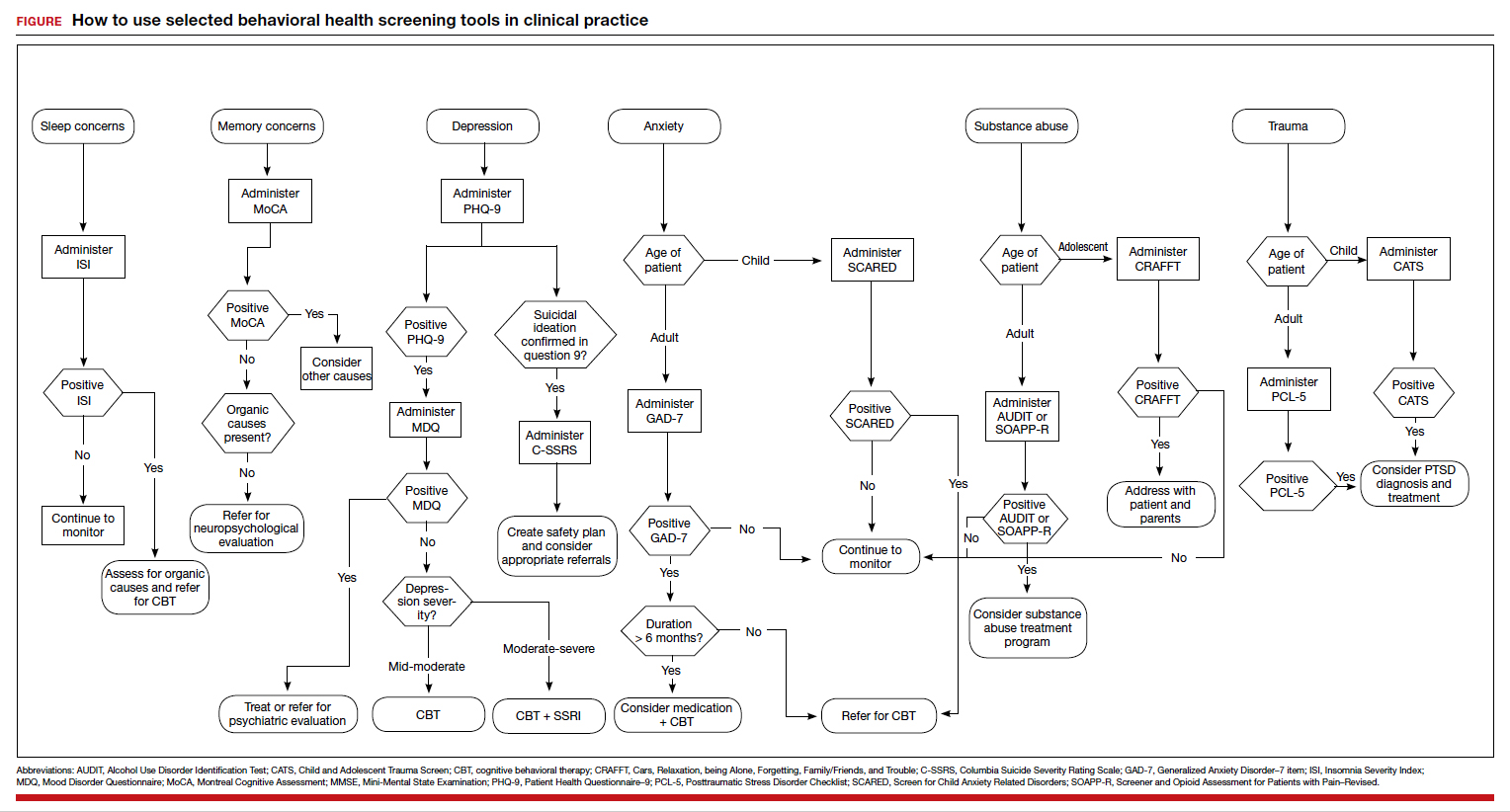
These tools are not meant to be used at every appointment. Every practice is different, and each clinic or physician can tailor the use of these screening tools to the needs of the patient population, as concerns arise, or in collaboration with other providers. Additionally, these screening tools can be used in both integrated care and in private practice, to prompt a more thorough assessment or to aid in—and inform—treatment. Although some physicians choose to administer certain screening tools at each clinic visit, knowing about the availability of other tools can be useful in assessing various issues. The FIGURE can be used to aid in the clinical decision-making process.
- Robinson RL, Grabner M, Palli SR, et al. Covariates of depression and high utilizers of healthcare: impact on resource use and costs. J Psychosom Res. 2016,85:35-43.
- Fogarty CT, Sharma S, Chetty VK, et al. Mental health conditions are associated with increased health care utilization among urban family medicine patients. J Am Board Fam Med. 2008,21:398-407.
- Weissman JD, Russell D, Beasley J, et al. Relationships between adult emotional states and indicators of health care utilization: findings from the National Health Interview Survey 2006–2014. J Psychosom Res. 2016,91:75-81.
- Haddad M, Walters P. Mood disorders in primary care. Psychiatry. 2009,8:71-75.
- Mitchell AJ, Yadegarfar M, Gill J, et al. Case finding and screening clinical utility of the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9 and PHQ-2) for depression in primary care: a diagnostic metaanalysis of 40 studies. BJPsych Open. 2016,2:127-138.
- Siu AL and US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for depression in adults. JAMA. 2016;315:380-387.
- Hirschfeld RM, Williams JB, Spitzer RL, et al. Development and validation of a screening instrument for bipolar spectrum disorder: the Mood Disorder Questionnaire. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157:1873-1875.
- Hirschfeld RM, Cass AR, Holt DC, et al. Screening for bipolar disorder in patients treated for depression in a family medicine clinic. J Am Board Fam Med. 2005;18:233-239.
- Das AK, Olfson M, Gameroff MJ, et al. Screening for bipolar disorder in a primary care practice. JAMA. 2005;293:956-963.
- CDC. Suicide mortality in the United States, 1999-2017. www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db330.htm. Accessed October 23, 2020.
- Viguera AC, Milano N, Ralston L, et al. Comparison of electronic screening for suicidal risk with Patient Health Questionnaire Item 9 and the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale in an outpatient psychiatric clinic. Psychosomatics. 2015;56:460-469.
- Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JBW, et al. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1092-1097.
- Birmaher B, Khetarpal S, Brent D, et al. The Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders (SCARED): scale construction and psychometric characteristics. J Am Acad Chil Adolesc Psychiatry. 1997;36:545-553.
- DeSousa DA, Salum GA, Isolan LR, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders (SCARED): a community-based study. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2013;44:391-399.
- Ford ES, Cunningham TJ, Giles WH, et al. Trends in insomnia and excessive daytime sleepiness among U.S. adults from 2002 to 2012. Sleep Med. 2015;16:372-378.
- Morin CM, LeBlanc M, Daley M, et al. Epidemiology of insomnia: prevalence, self-help treatments, consultations, and determinants of help-seeking behaviors. Sleep Med. 2006;7:123-130.
- Buysse DJ, Ancoli-Israel S, Edinger JD, et al. Recommendations for a standard research assessment of insomnia. Sleep. 2006;29:1155-1173.
- Martin JL, Hakim AD. Wrist actigraphy. Chest. 2011;139:1514-1527.
- Riemann D, Baglioni C, Bassetti C, et al. European guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of insomnia. J Sleep Res. 2017;26:675-700.
- Bastien CH, Vallières A, Morin CM. Validation of the Insomnia Severity Index as an outcome measure for insomnia research. Sleep Med. 2001;2:297-307.
- Wong ML, Lau KNT, Espie CA, et al. Psychometric properties of the Sleep Condition Indicator and Insomnia Severity Index in the evaluation of insomnia disorder. Sleep Med. 2017;33:76-81.
- Gagnon C, Bélanger L, Ivers H, et al. Validation of the Insomnia Severity Index in primary care. J Am Board Fam Med. 2013;26:701-710.
- Saunders JB, Aasland OG, Babor TF, et al. Development of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT): WHO Collaborative Project on Early Detection of Persons with Harmful Alcohol Consumption. Addiction. 1993;88:791-804.
- Selin KH. Test-retest reliability of the Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test in a general population sample. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2003;27:1428-1435.
- Bohn MJ, Babor TF, Kranzler HR. The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT): validation of a screening instrument for use in medical settings. J Stud Alcohol. 1995;56:423-432.
- Conigrave KM, Hall WD, Saunders JB. The AUDIT questionnaire: choosing a cut-off score. Addiction. 1995;90:1349-1356.
- Gomez A, Conde A, Santana JM, et al. Diagnostic usefulness of brief versions of Alcohol Use Identification Test (AUDIT) for detecting hazardous drinkers in primary care settings. J Stud Alcohol. 2005;66:305-308.
- Butler SF, Fernandez K, Benoit C, et al. Validation of the revised Screener and Opioid Assessment for Patients with Pain (SOAPPR). J Pain. 2008;9:360-372.
- Knight JR, Sherritt L, Shrier LA, et al. Validity of the CRAFFT substance abuse screening test among adolescent clinic patients. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2002;156:607-614.
- DHHS. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). https://archives.nih.gov/asites/report/09-09-2019/report.nih.gov/nihfactsheets/ViewFactSheetfdf8.html?csid=58&key=P#P. Accessed October 23,2020.
- Blevins CA, Weathers FW, Davis MT, et al. The Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5): development and initial psychometric evaluation. J Trauma Stress. 2015;28:489-498.
- Verhey R, Chilbanda D, Gibson L, et al. Validation of the Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Checklist- 5 (PCL-5) in a primary care population with high HIV prevalence in Zimbabwe. BMC Psychiatry. 2018;18:109.
- Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bédirian V, et al. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53:695-699.
- Stewart S, O’Riley A, Edelstein B, et al. A preliminary comparison of three cognitive screening instruments in long term care: the MMSE, SLUMS, and MoCA. Clin Gerontol. 2012;35:57-75.
- Godefroy O, Fickl A, Roussel M, et al. Is the Montreal Cognitive Assessment superior to the Mini-Mental State Examination to detect poststroke cognitive impairment? A study with neuropsychological evaluation. Stroke. 2011;42:1712-1716.
Many screening tools are available in the public domain to assess a variety of symptoms related to impaired mental health. These tools can be used to quickly evaluate for mood, suicidal ideation or behavior, anxiety, sleep, substance use, pain, trauma, memory, and cognition (TABLE). Individuals with poor mental health incur high health care costs. Those suffering from anxiety and posttraumatic stress have more outpatient and emergency department visits and hospitalizations than patients without these disorders,1,2 although use of mental health care services has been related to a decrease in the overutilization of health care services in general.3

Here we review several screening tools that can help you to identify symptoms of mental illnesses and thus, provide prompt early intervention, including referrals to psychological and psychiatric services.
Mood disorders
Most patients with mood disorders are treated in primary care settings.4 Quickly measuring patients’ mood symptoms can expedite treatment for those who need it. Many primary care clinics use the 9-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) to screen for depression.5 The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has recommended screening for depression with adequate systems to ensure accurate diagnoses, effective treatment, and follow-up. Although the USPSTF did not specially endorse screening for bipolar disorder, it followed that recommendation with the qualifying statement, “positive screening results [for depression] should lead to additional assessment that considers severity of depression and comorbid psychological problems, alternate diagnoses, and medical conditions.”6 Thus, following a positive screen result for depression, consider using a screening tool for mood disorders to provide diagnostic clarification.
The Mood Disorder Questionnaire (MDQ) is a validated 15-item, self-administered questionnaire that takes only 5 minutes to use in screening adult patients for bipolar I disorder.7 The MDQ assesses specific behaviors related to bipolar disorder, symptom co-occurrence, and functional impairment. The MDQ has low sensitivity (58%) but good specificity (93%) in a primary care setting.8 However, the MDQ is not a diagnostic instrument. A positive screen result should prompt a more thorough clinical evaluation, if necessary, by a professional trained in psychiatric disorders.
We recommend completing the MDQ prior to prescribing antidepressants. You can also monitor a patient’s response to treatment with serial MDQ testing. The MDQ is useful, too, when a patient has unclear mood symptoms that may have features overlapping with bipolar disorder. Furthermore, we recommend screening for bipolar disorder with every patient who reports symptoms of depression, given that some pharmacologic treatments (predominately selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) can induce mania in patients who actually have unrecognized bipolar disorder.9
Continue to: Suicide...
Suicide
Suicide is the 10th leading cause of death among the general population. All demographic groups are impacted by suicide; however, the most vulnerable are men ages 45 to 64 years.10 Given the imminent risk to individuals who experience suicidal ideation, properly assessing and targeting suicidal risk is paramount.
The Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) can be completed in an interview format or as a patient self-report. Versions of the C-SSRS are available for children, adolescents, and adults. It can be used in practice with any patient who may be at risk for suicide. Specifically, consider using the C-SSRS when a patient scores 1 or greater on the PHQ-9 or when risk is revealed with another brief screening tool that includes suicidal ideation.
The C-SSRS covers 10 categories related to suicidal ideation and behavior that the clinician explores with questions requiring only Yes/No responses. The C-SSRS demonstrates moderate-to-strong internal consistency and reliability, and it has shown a high degree of sensitivity (95%) and specificity (95%) for suicidal ideation.11
Anxiety and physiologic arousal
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is one of the most common anxiety disorders, with an estimated prevalence of 2.8% to 8.5% among primary care patients.12 Brief, validated screening tools such as the Generalized Anxiety Disorder–7 item (GAD-7) scale can be effective in identifying anxiety and other related disorders in primary care settings.
The GAD-7 comprises 7 items inquiring about symptoms experienced in the past 2 weeks. Scores range from 0 to 21, with cutoffs of 5, 10, and 15 indicating mild, moderate, and severe anxiety, respectively. This questionnaire is appropriate for use with adults and has strong specificity, internal consistency, and test-retest reliability.12 Specificity and sensitivity of the GAD-7 are maximized at a cutoff score of 10 or greater, both exceeding 80%.12 The GAD-7 can be used when patients report symptoms of anxiety or when one needs to screen for anxiety with new patients or more clearly understand symptoms among patients who have complex mental health concerns.
The Screen for Child Anxiety Related Disorders (SCARED) is a 41-item self-report measure of anxiety for children ages 8 to 18. The SCARED questionnaire yields an overall anxiety score, as well as subscales for panic disorder or significant somatic symptoms, generalized anxiety disorder, separation anxiety, social anxiety disorder, and significant school avoidance.13 There is also a 5-item version of the SCARED, which can be useful for brief screening in fast-paced settings when no anxiety disorder is suspected, or for children who may have anxiety but exhibit reduced verbal capacity. The SCARED has been found to have moderate sensitivity (81.8%) and specificity (52%) for diagnosing anxiety disorders in a community sample, with an optimal cutoff point of 22 on the total scale.14
Sleep
Sleep concerns are common, with the prevalence of insomnia among adults in the United States estimated to be 19.2%.15 The importance of assessing these concerns cannot be overstated, and primary care providers are the ones patients consult most often.16 The gold standard in assessing sleep disorders is a structured clinical interview, polysomnography, sleep diary, and actigraphy (home-based monitoring of movement through a device, often worn on the wrist).17,18 However, this work-up is expensive, time-intensive, and impractical in integrated care settings; thus the need for a brief, self-report screening tool to guide further assessment and intervention.
The Insomnia Severity Index (ISI) assesses patients’ perceptions of their insomnia. The ISI was developed to aid both in the clinical evaluation of patients with insomnia and to measure treatment outcomes. Administration of the ISI takes approximately 5 minutes, and scoring takes less than 1 minute.
The ISI is composed of 7 items that measure the severity of sleep onset and sleep maintenance difficulties, satisfaction with current sleep, impact on daily functioning, impairment observable to others, and degree of distress caused by the sleep problems. Each item is scored on a 0 to 4 Likert-type scale, and the individual items are summed for a total score of 0 to 28, with higher scores suggesting more severe insomnia. Evidence-based guidelines recommend cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) as the first-line treatment for adults with primary insomnia.19
Several validation studies have found the ISI to be a reliable measure of perceived insomnia severity, and one that is sensitive to changes in patients’ perceptions of treatment outcomes.20,21 An additional validation study confirmed that in primary care settings, a cutoff score of 14 should be used to indicate the likely presence of clinical insomnia22 and to guide further assessment and intervention.
The percentage of insomniac patients correctly identified with the ISI was 82.2%, with moderate sensitivity (82.4%) and specificity (82.1%).22 A positive predictive value of 70% was found, meaning that an insomnia disorder is probable when the ISI total score is 14 or higher; conversely, the negative predictive value was 90.2%.
Continue to: Substance use and pain...
Substance use and pain
The evaluation of alcohol and drug use is an integral part of assessing risky health behaviors. The 10-item Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT) is a self-report tool developed by the World Health Organization.23,24 Validated in medical settings, scores of 8 or higher suggest problematic drinking.25,26 The AUDIT has demonstrated high specificity (94%) and moderate sensitivity (81%) in primary care settings.27 The AUDIT-C (items 1, 2, and 3 of the AUDIT) has also demonstrated comparable sensitivity, although slightly lower specificity, than the full AUDIT, suggesting that this 3-question screen can also be used in primary care settings.27
Opioid medications, frequently prescribed for chronic pain, present serious risks for many patients. The Screener and Opioid Assessment for Patients with Pain–Revised (SOAPP-R) is a 24-item self-reporting scale that can be completed in approximately 10 minutes.28 A score of 18 or higher has identified 81% of patients at high risk for opioid misuse in a clinical setting, with moderate specificity (68%). Although other factors should be considered when assessing risk of opioid misuse, the SOAPP-R is a helpful and quick addition to an opioid risk assessment.
The CRAFFT Screening Tool for Adolescent Substance Use is administered by the clinician for youths ages 14 to 21. The first 3 questions ask about use of alcohol, marijuana, or other substances during the past 12 months. What follows are questions related to the young person’s specific experiences with substances in relation to Cars, Relaxation, being Alone, Forgetting, Family/Friends, and Trouble (CRAFFT). The CRAFFT has shown moderate sensitivity (76%) and good specificity (94%) for identifying any problem with substance use.29 These measures may be administered to clarify or confirm substance use patterns (ie, duration, frequency), or to determine the severity of problems related to substance use (ie, social or legal problems).
Trauma and PTSD
Approximately 7.7 million adults per year will experience posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms, although PTSD can affect individuals of any age.30 Given the impact that trauma can have, assess for PTSD in patients who have a history of trauma or who otherwise seem to be at risk. The Post-traumatic Stress Disorder Checklist (PCL-5) is a 20-item self-report questionnaire that screens for symptoms directly from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5) criteria for PTSD. One limitation is that the questionnaire is only validated for adults ages 18 years or older. Completion of the PCL-5 takes 5 to 10 minutes. The PCL-5 has strong internal consistency reliability (94%) and test-retest reliability (82%).31 With a cutoff score of 33 or higher, the sensitivity and specificity have been shown to be moderately high (74.5% and 70.6%, respectively).32
The Child and Adolescent Trauma Screen (CATS) is used to assess for potentially traumatic events and PTSD symptoms in children and adolescents. These symptoms are based on the DSM-5, and therefore the CATS can act as a useful diagnostic aid. The CATS is also available in Spanish, with both caregiver-report (for children ages 3-6 years or 7-17 years) and self-report (for ages 7-17 years) versions. Practical use of the PCL-5 and the CATS involves screening for PTSD symptoms, supporting a provisional diagnosis of PTSD, and monitoring PTSD symptom changes during and after treatment.
Memory and cognition
Cognitive screening is a first step in evaluating possible dementia and other neuropsychological disorders. The importance of brief cognitive screening in primary care cannot be understated, especially for an aging patient population. Although the Mini Mental Status Exam (MMSE) has been widely used among health care providers and researchers, we recommend the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA).
The MoCA is a simple, standalone cognitive screening tool validated for adults ages 55 to 85 years.33 The MoCA addresses many important cognitive domains, fits on one page, and can be administered by a trained provider in 10 minutes. Research also suggests that it has strong test-retest reliability and positive and negative predictive values for mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer dementia, and it has been found to be more sensitive than the MMSE.34 We additionally recommend the MoCA as it measures several cognitive skills that are not addressed on the MMSE, including verbal fluency and abstraction.34 Scores below 25 are suggestive of cognitive impairment and should lead to a referral for neuropsychological testing.
The MoCA’s sensitivity for detecting cognitive impairment is high (94%), and specificity is low (42%).35 To ensure consistency and accuracy in administering the MoCA, certification is now required via an online training program through www.mocatest.org.
Adapting these screening tools to practice
These tools are not meant to be used at every appointment. Every practice is different, and each clinic or physician can tailor the use of these screening tools to the needs of the patient population, as concerns arise, or in collaboration with other providers. Additionally, these screening tools can be used in both integrated care and in private practice, to prompt a more thorough assessment or to aid in—and inform—treatment. Although some physicians choose to administer certain screening tools at each clinic visit, knowing about the availability of other tools can be useful in assessing various issues. The FIGURE can be used to aid in the clinical decision-making process.

Many screening tools are available in the public domain to assess a variety of symptoms related to impaired mental health. These tools can be used to quickly evaluate for mood, suicidal ideation or behavior, anxiety, sleep, substance use, pain, trauma, memory, and cognition (TABLE). Individuals with poor mental health incur high health care costs. Those suffering from anxiety and posttraumatic stress have more outpatient and emergency department visits and hospitalizations than patients without these disorders,1,2 although use of mental health care services has been related to a decrease in the overutilization of health care services in general.3

Here we review several screening tools that can help you to identify symptoms of mental illnesses and thus, provide prompt early intervention, including referrals to psychological and psychiatric services.
Mood disorders
Most patients with mood disorders are treated in primary care settings.4 Quickly measuring patients’ mood symptoms can expedite treatment for those who need it. Many primary care clinics use the 9-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) to screen for depression.5 The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has recommended screening for depression with adequate systems to ensure accurate diagnoses, effective treatment, and follow-up. Although the USPSTF did not specially endorse screening for bipolar disorder, it followed that recommendation with the qualifying statement, “positive screening results [for depression] should lead to additional assessment that considers severity of depression and comorbid psychological problems, alternate diagnoses, and medical conditions.”6 Thus, following a positive screen result for depression, consider using a screening tool for mood disorders to provide diagnostic clarification.
The Mood Disorder Questionnaire (MDQ) is a validated 15-item, self-administered questionnaire that takes only 5 minutes to use in screening adult patients for bipolar I disorder.7 The MDQ assesses specific behaviors related to bipolar disorder, symptom co-occurrence, and functional impairment. The MDQ has low sensitivity (58%) but good specificity (93%) in a primary care setting.8 However, the MDQ is not a diagnostic instrument. A positive screen result should prompt a more thorough clinical evaluation, if necessary, by a professional trained in psychiatric disorders.
We recommend completing the MDQ prior to prescribing antidepressants. You can also monitor a patient’s response to treatment with serial MDQ testing. The MDQ is useful, too, when a patient has unclear mood symptoms that may have features overlapping with bipolar disorder. Furthermore, we recommend screening for bipolar disorder with every patient who reports symptoms of depression, given that some pharmacologic treatments (predominately selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) can induce mania in patients who actually have unrecognized bipolar disorder.9
Continue to: Suicide...
Suicide
Suicide is the 10th leading cause of death among the general population. All demographic groups are impacted by suicide; however, the most vulnerable are men ages 45 to 64 years.10 Given the imminent risk to individuals who experience suicidal ideation, properly assessing and targeting suicidal risk is paramount.
The Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) can be completed in an interview format or as a patient self-report. Versions of the C-SSRS are available for children, adolescents, and adults. It can be used in practice with any patient who may be at risk for suicide. Specifically, consider using the C-SSRS when a patient scores 1 or greater on the PHQ-9 or when risk is revealed with another brief screening tool that includes suicidal ideation.
The C-SSRS covers 10 categories related to suicidal ideation and behavior that the clinician explores with questions requiring only Yes/No responses. The C-SSRS demonstrates moderate-to-strong internal consistency and reliability, and it has shown a high degree of sensitivity (95%) and specificity (95%) for suicidal ideation.11
Anxiety and physiologic arousal
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is one of the most common anxiety disorders, with an estimated prevalence of 2.8% to 8.5% among primary care patients.12 Brief, validated screening tools such as the Generalized Anxiety Disorder–7 item (GAD-7) scale can be effective in identifying anxiety and other related disorders in primary care settings.
The GAD-7 comprises 7 items inquiring about symptoms experienced in the past 2 weeks. Scores range from 0 to 21, with cutoffs of 5, 10, and 15 indicating mild, moderate, and severe anxiety, respectively. This questionnaire is appropriate for use with adults and has strong specificity, internal consistency, and test-retest reliability.12 Specificity and sensitivity of the GAD-7 are maximized at a cutoff score of 10 or greater, both exceeding 80%.12 The GAD-7 can be used when patients report symptoms of anxiety or when one needs to screen for anxiety with new patients or more clearly understand symptoms among patients who have complex mental health concerns.
The Screen for Child Anxiety Related Disorders (SCARED) is a 41-item self-report measure of anxiety for children ages 8 to 18. The SCARED questionnaire yields an overall anxiety score, as well as subscales for panic disorder or significant somatic symptoms, generalized anxiety disorder, separation anxiety, social anxiety disorder, and significant school avoidance.13 There is also a 5-item version of the SCARED, which can be useful for brief screening in fast-paced settings when no anxiety disorder is suspected, or for children who may have anxiety but exhibit reduced verbal capacity. The SCARED has been found to have moderate sensitivity (81.8%) and specificity (52%) for diagnosing anxiety disorders in a community sample, with an optimal cutoff point of 22 on the total scale.14
Sleep
Sleep concerns are common, with the prevalence of insomnia among adults in the United States estimated to be 19.2%.15 The importance of assessing these concerns cannot be overstated, and primary care providers are the ones patients consult most often.16 The gold standard in assessing sleep disorders is a structured clinical interview, polysomnography, sleep diary, and actigraphy (home-based monitoring of movement through a device, often worn on the wrist).17,18 However, this work-up is expensive, time-intensive, and impractical in integrated care settings; thus the need for a brief, self-report screening tool to guide further assessment and intervention.
The Insomnia Severity Index (ISI) assesses patients’ perceptions of their insomnia. The ISI was developed to aid both in the clinical evaluation of patients with insomnia and to measure treatment outcomes. Administration of the ISI takes approximately 5 minutes, and scoring takes less than 1 minute.
The ISI is composed of 7 items that measure the severity of sleep onset and sleep maintenance difficulties, satisfaction with current sleep, impact on daily functioning, impairment observable to others, and degree of distress caused by the sleep problems. Each item is scored on a 0 to 4 Likert-type scale, and the individual items are summed for a total score of 0 to 28, with higher scores suggesting more severe insomnia. Evidence-based guidelines recommend cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) as the first-line treatment for adults with primary insomnia.19
Several validation studies have found the ISI to be a reliable measure of perceived insomnia severity, and one that is sensitive to changes in patients’ perceptions of treatment outcomes.20,21 An additional validation study confirmed that in primary care settings, a cutoff score of 14 should be used to indicate the likely presence of clinical insomnia22 and to guide further assessment and intervention.
The percentage of insomniac patients correctly identified with the ISI was 82.2%, with moderate sensitivity (82.4%) and specificity (82.1%).22 A positive predictive value of 70% was found, meaning that an insomnia disorder is probable when the ISI total score is 14 or higher; conversely, the negative predictive value was 90.2%.
Continue to: Substance use and pain...
Substance use and pain
The evaluation of alcohol and drug use is an integral part of assessing risky health behaviors. The 10-item Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT) is a self-report tool developed by the World Health Organization.23,24 Validated in medical settings, scores of 8 or higher suggest problematic drinking.25,26 The AUDIT has demonstrated high specificity (94%) and moderate sensitivity (81%) in primary care settings.27 The AUDIT-C (items 1, 2, and 3 of the AUDIT) has also demonstrated comparable sensitivity, although slightly lower specificity, than the full AUDIT, suggesting that this 3-question screen can also be used in primary care settings.27
Opioid medications, frequently prescribed for chronic pain, present serious risks for many patients. The Screener and Opioid Assessment for Patients with Pain–Revised (SOAPP-R) is a 24-item self-reporting scale that can be completed in approximately 10 minutes.28 A score of 18 or higher has identified 81% of patients at high risk for opioid misuse in a clinical setting, with moderate specificity (68%). Although other factors should be considered when assessing risk of opioid misuse, the SOAPP-R is a helpful and quick addition to an opioid risk assessment.
The CRAFFT Screening Tool for Adolescent Substance Use is administered by the clinician for youths ages 14 to 21. The first 3 questions ask about use of alcohol, marijuana, or other substances during the past 12 months. What follows are questions related to the young person’s specific experiences with substances in relation to Cars, Relaxation, being Alone, Forgetting, Family/Friends, and Trouble (CRAFFT). The CRAFFT has shown moderate sensitivity (76%) and good specificity (94%) for identifying any problem with substance use.29 These measures may be administered to clarify or confirm substance use patterns (ie, duration, frequency), or to determine the severity of problems related to substance use (ie, social or legal problems).
Trauma and PTSD
Approximately 7.7 million adults per year will experience posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms, although PTSD can affect individuals of any age.30 Given the impact that trauma can have, assess for PTSD in patients who have a history of trauma or who otherwise seem to be at risk. The Post-traumatic Stress Disorder Checklist (PCL-5) is a 20-item self-report questionnaire that screens for symptoms directly from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5) criteria for PTSD. One limitation is that the questionnaire is only validated for adults ages 18 years or older. Completion of the PCL-5 takes 5 to 10 minutes. The PCL-5 has strong internal consistency reliability (94%) and test-retest reliability (82%).31 With a cutoff score of 33 or higher, the sensitivity and specificity have been shown to be moderately high (74.5% and 70.6%, respectively).32
The Child and Adolescent Trauma Screen (CATS) is used to assess for potentially traumatic events and PTSD symptoms in children and adolescents. These symptoms are based on the DSM-5, and therefore the CATS can act as a useful diagnostic aid. The CATS is also available in Spanish, with both caregiver-report (for children ages 3-6 years or 7-17 years) and self-report (for ages 7-17 years) versions. Practical use of the PCL-5 and the CATS involves screening for PTSD symptoms, supporting a provisional diagnosis of PTSD, and monitoring PTSD symptom changes during and after treatment.
Memory and cognition
Cognitive screening is a first step in evaluating possible dementia and other neuropsychological disorders. The importance of brief cognitive screening in primary care cannot be understated, especially for an aging patient population. Although the Mini Mental Status Exam (MMSE) has been widely used among health care providers and researchers, we recommend the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA).
The MoCA is a simple, standalone cognitive screening tool validated for adults ages 55 to 85 years.33 The MoCA addresses many important cognitive domains, fits on one page, and can be administered by a trained provider in 10 minutes. Research also suggests that it has strong test-retest reliability and positive and negative predictive values for mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer dementia, and it has been found to be more sensitive than the MMSE.34 We additionally recommend the MoCA as it measures several cognitive skills that are not addressed on the MMSE, including verbal fluency and abstraction.34 Scores below 25 are suggestive of cognitive impairment and should lead to a referral for neuropsychological testing.
The MoCA’s sensitivity for detecting cognitive impairment is high (94%), and specificity is low (42%).35 To ensure consistency and accuracy in administering the MoCA, certification is now required via an online training program through www.mocatest.org.
Adapting these screening tools to practice
These tools are not meant to be used at every appointment. Every practice is different, and each clinic or physician can tailor the use of these screening tools to the needs of the patient population, as concerns arise, or in collaboration with other providers. Additionally, these screening tools can be used in both integrated care and in private practice, to prompt a more thorough assessment or to aid in—and inform—treatment. Although some physicians choose to administer certain screening tools at each clinic visit, knowing about the availability of other tools can be useful in assessing various issues. The FIGURE can be used to aid in the clinical decision-making process.

- Robinson RL, Grabner M, Palli SR, et al. Covariates of depression and high utilizers of healthcare: impact on resource use and costs. J Psychosom Res. 2016,85:35-43.
- Fogarty CT, Sharma S, Chetty VK, et al. Mental health conditions are associated with increased health care utilization among urban family medicine patients. J Am Board Fam Med. 2008,21:398-407.
- Weissman JD, Russell D, Beasley J, et al. Relationships between adult emotional states and indicators of health care utilization: findings from the National Health Interview Survey 2006–2014. J Psychosom Res. 2016,91:75-81.
- Haddad M, Walters P. Mood disorders in primary care. Psychiatry. 2009,8:71-75.
- Mitchell AJ, Yadegarfar M, Gill J, et al. Case finding and screening clinical utility of the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9 and PHQ-2) for depression in primary care: a diagnostic metaanalysis of 40 studies. BJPsych Open. 2016,2:127-138.
- Siu AL and US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for depression in adults. JAMA. 2016;315:380-387.
- Hirschfeld RM, Williams JB, Spitzer RL, et al. Development and validation of a screening instrument for bipolar spectrum disorder: the Mood Disorder Questionnaire. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157:1873-1875.
- Hirschfeld RM, Cass AR, Holt DC, et al. Screening for bipolar disorder in patients treated for depression in a family medicine clinic. J Am Board Fam Med. 2005;18:233-239.
- Das AK, Olfson M, Gameroff MJ, et al. Screening for bipolar disorder in a primary care practice. JAMA. 2005;293:956-963.
- CDC. Suicide mortality in the United States, 1999-2017. www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db330.htm. Accessed October 23, 2020.
- Viguera AC, Milano N, Ralston L, et al. Comparison of electronic screening for suicidal risk with Patient Health Questionnaire Item 9 and the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale in an outpatient psychiatric clinic. Psychosomatics. 2015;56:460-469.
- Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JBW, et al. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1092-1097.
- Birmaher B, Khetarpal S, Brent D, et al. The Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders (SCARED): scale construction and psychometric characteristics. J Am Acad Chil Adolesc Psychiatry. 1997;36:545-553.
- DeSousa DA, Salum GA, Isolan LR, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders (SCARED): a community-based study. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2013;44:391-399.
- Ford ES, Cunningham TJ, Giles WH, et al. Trends in insomnia and excessive daytime sleepiness among U.S. adults from 2002 to 2012. Sleep Med. 2015;16:372-378.
- Morin CM, LeBlanc M, Daley M, et al. Epidemiology of insomnia: prevalence, self-help treatments, consultations, and determinants of help-seeking behaviors. Sleep Med. 2006;7:123-130.
- Buysse DJ, Ancoli-Israel S, Edinger JD, et al. Recommendations for a standard research assessment of insomnia. Sleep. 2006;29:1155-1173.
- Martin JL, Hakim AD. Wrist actigraphy. Chest. 2011;139:1514-1527.
- Riemann D, Baglioni C, Bassetti C, et al. European guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of insomnia. J Sleep Res. 2017;26:675-700.
- Bastien CH, Vallières A, Morin CM. Validation of the Insomnia Severity Index as an outcome measure for insomnia research. Sleep Med. 2001;2:297-307.
- Wong ML, Lau KNT, Espie CA, et al. Psychometric properties of the Sleep Condition Indicator and Insomnia Severity Index in the evaluation of insomnia disorder. Sleep Med. 2017;33:76-81.
- Gagnon C, Bélanger L, Ivers H, et al. Validation of the Insomnia Severity Index in primary care. J Am Board Fam Med. 2013;26:701-710.
- Saunders JB, Aasland OG, Babor TF, et al. Development of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT): WHO Collaborative Project on Early Detection of Persons with Harmful Alcohol Consumption. Addiction. 1993;88:791-804.
- Selin KH. Test-retest reliability of the Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test in a general population sample. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2003;27:1428-1435.
- Bohn MJ, Babor TF, Kranzler HR. The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT): validation of a screening instrument for use in medical settings. J Stud Alcohol. 1995;56:423-432.
- Conigrave KM, Hall WD, Saunders JB. The AUDIT questionnaire: choosing a cut-off score. Addiction. 1995;90:1349-1356.
- Gomez A, Conde A, Santana JM, et al. Diagnostic usefulness of brief versions of Alcohol Use Identification Test (AUDIT) for detecting hazardous drinkers in primary care settings. J Stud Alcohol. 2005;66:305-308.
- Butler SF, Fernandez K, Benoit C, et al. Validation of the revised Screener and Opioid Assessment for Patients with Pain (SOAPPR). J Pain. 2008;9:360-372.
- Knight JR, Sherritt L, Shrier LA, et al. Validity of the CRAFFT substance abuse screening test among adolescent clinic patients. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2002;156:607-614.
- DHHS. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). https://archives.nih.gov/asites/report/09-09-2019/report.nih.gov/nihfactsheets/ViewFactSheetfdf8.html?csid=58&key=P#P. Accessed October 23,2020.
- Blevins CA, Weathers FW, Davis MT, et al. The Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5): development and initial psychometric evaluation. J Trauma Stress. 2015;28:489-498.
- Verhey R, Chilbanda D, Gibson L, et al. Validation of the Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Checklist- 5 (PCL-5) in a primary care population with high HIV prevalence in Zimbabwe. BMC Psychiatry. 2018;18:109.
- Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bédirian V, et al. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53:695-699.
- Stewart S, O’Riley A, Edelstein B, et al. A preliminary comparison of three cognitive screening instruments in long term care: the MMSE, SLUMS, and MoCA. Clin Gerontol. 2012;35:57-75.
- Godefroy O, Fickl A, Roussel M, et al. Is the Montreal Cognitive Assessment superior to the Mini-Mental State Examination to detect poststroke cognitive impairment? A study with neuropsychological evaluation. Stroke. 2011;42:1712-1716.
- Robinson RL, Grabner M, Palli SR, et al. Covariates of depression and high utilizers of healthcare: impact on resource use and costs. J Psychosom Res. 2016,85:35-43.
- Fogarty CT, Sharma S, Chetty VK, et al. Mental health conditions are associated with increased health care utilization among urban family medicine patients. J Am Board Fam Med. 2008,21:398-407.
- Weissman JD, Russell D, Beasley J, et al. Relationships between adult emotional states and indicators of health care utilization: findings from the National Health Interview Survey 2006–2014. J Psychosom Res. 2016,91:75-81.
- Haddad M, Walters P. Mood disorders in primary care. Psychiatry. 2009,8:71-75.
- Mitchell AJ, Yadegarfar M, Gill J, et al. Case finding and screening clinical utility of the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9 and PHQ-2) for depression in primary care: a diagnostic metaanalysis of 40 studies. BJPsych Open. 2016,2:127-138.
- Siu AL and US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for depression in adults. JAMA. 2016;315:380-387.
- Hirschfeld RM, Williams JB, Spitzer RL, et al. Development and validation of a screening instrument for bipolar spectrum disorder: the Mood Disorder Questionnaire. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157:1873-1875.
- Hirschfeld RM, Cass AR, Holt DC, et al. Screening for bipolar disorder in patients treated for depression in a family medicine clinic. J Am Board Fam Med. 2005;18:233-239.
- Das AK, Olfson M, Gameroff MJ, et al. Screening for bipolar disorder in a primary care practice. JAMA. 2005;293:956-963.
- CDC. Suicide mortality in the United States, 1999-2017. www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db330.htm. Accessed October 23, 2020.
- Viguera AC, Milano N, Ralston L, et al. Comparison of electronic screening for suicidal risk with Patient Health Questionnaire Item 9 and the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale in an outpatient psychiatric clinic. Psychosomatics. 2015;56:460-469.
- Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JBW, et al. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1092-1097.
- Birmaher B, Khetarpal S, Brent D, et al. The Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders (SCARED): scale construction and psychometric characteristics. J Am Acad Chil Adolesc Psychiatry. 1997;36:545-553.
- DeSousa DA, Salum GA, Isolan LR, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders (SCARED): a community-based study. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2013;44:391-399.
- Ford ES, Cunningham TJ, Giles WH, et al. Trends in insomnia and excessive daytime sleepiness among U.S. adults from 2002 to 2012. Sleep Med. 2015;16:372-378.
- Morin CM, LeBlanc M, Daley M, et al. Epidemiology of insomnia: prevalence, self-help treatments, consultations, and determinants of help-seeking behaviors. Sleep Med. 2006;7:123-130.
- Buysse DJ, Ancoli-Israel S, Edinger JD, et al. Recommendations for a standard research assessment of insomnia. Sleep. 2006;29:1155-1173.
- Martin JL, Hakim AD. Wrist actigraphy. Chest. 2011;139:1514-1527.
- Riemann D, Baglioni C, Bassetti C, et al. European guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of insomnia. J Sleep Res. 2017;26:675-700.
- Bastien CH, Vallières A, Morin CM. Validation of the Insomnia Severity Index as an outcome measure for insomnia research. Sleep Med. 2001;2:297-307.
- Wong ML, Lau KNT, Espie CA, et al. Psychometric properties of the Sleep Condition Indicator and Insomnia Severity Index in the evaluation of insomnia disorder. Sleep Med. 2017;33:76-81.
- Gagnon C, Bélanger L, Ivers H, et al. Validation of the Insomnia Severity Index in primary care. J Am Board Fam Med. 2013;26:701-710.
- Saunders JB, Aasland OG, Babor TF, et al. Development of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT): WHO Collaborative Project on Early Detection of Persons with Harmful Alcohol Consumption. Addiction. 1993;88:791-804.
- Selin KH. Test-retest reliability of the Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test in a general population sample. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2003;27:1428-1435.
- Bohn MJ, Babor TF, Kranzler HR. The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT): validation of a screening instrument for use in medical settings. J Stud Alcohol. 1995;56:423-432.
- Conigrave KM, Hall WD, Saunders JB. The AUDIT questionnaire: choosing a cut-off score. Addiction. 1995;90:1349-1356.
- Gomez A, Conde A, Santana JM, et al. Diagnostic usefulness of brief versions of Alcohol Use Identification Test (AUDIT) for detecting hazardous drinkers in primary care settings. J Stud Alcohol. 2005;66:305-308.
- Butler SF, Fernandez K, Benoit C, et al. Validation of the revised Screener and Opioid Assessment for Patients with Pain (SOAPPR). J Pain. 2008;9:360-372.
- Knight JR, Sherritt L, Shrier LA, et al. Validity of the CRAFFT substance abuse screening test among adolescent clinic patients. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2002;156:607-614.
- DHHS. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). https://archives.nih.gov/asites/report/09-09-2019/report.nih.gov/nihfactsheets/ViewFactSheetfdf8.html?csid=58&key=P#P. Accessed October 23,2020.
- Blevins CA, Weathers FW, Davis MT, et al. The Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5): development and initial psychometric evaluation. J Trauma Stress. 2015;28:489-498.
- Verhey R, Chilbanda D, Gibson L, et al. Validation of the Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Checklist- 5 (PCL-5) in a primary care population with high HIV prevalence in Zimbabwe. BMC Psychiatry. 2018;18:109.
- Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bédirian V, et al. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53:695-699.
- Stewart S, O’Riley A, Edelstein B, et al. A preliminary comparison of three cognitive screening instruments in long term care: the MMSE, SLUMS, and MoCA. Clin Gerontol. 2012;35:57-75.
- Godefroy O, Fickl A, Roussel M, et al. Is the Montreal Cognitive Assessment superior to the Mini-Mental State Examination to detect poststroke cognitive impairment? A study with neuropsychological evaluation. Stroke. 2011;42:1712-1716.
Hidden Basal Cell Carcinoma in the Intergluteal Crease
Practice Gap
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common cancer, and its incidence is on the rise.1 The risk of this skin cancer is increased when there is a history of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) or BCC.2 Basal cell carcinoma often is found in sun-exposed areas, most commonly due to a history of intense sunburn.3 Other risk factors include male gender and increased age.4
Eighty percent to 85% of BCCs present on the head and neck5; however, BCC also can occur in unusual locations. When BCC presents in areas such as the perianal region, it is found to be larger than when found in more common areas,6 likely because neoplasms in this sensitive area often are overlooked. Literature on BCC of the intergluteal crease is limited.7 Being educated on the existence of BCC in this sensitive area can aid proper diagnosis.
The Technique and Case
An 83-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic for a suspicious lesion in the intergluteal crease that was tender to palpation with drainage. She first noticed this lesion and reported it to her primary care physician at a visit 6 months prior. The primary care physician did not pursue investigation of the lesion. One month later, the patient was seen by a gastroenterologist for the lesion and was referred to dermatology. The patient’s medical history included SCC and BCC on the face, both treated successfully with Mohs micrographic surgery.
Physical examination revealed a 2.6×1.1-cm, erythematous, nodular plaque in the coccygeal area of the intergluteal crease (Figure 1). A shave biopsy disclosed BCC, nodular type, ulcerated. Microscopically, there were nodular aggregates of basaloid cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and peripheral palisading, separated from mucinous stromal surroundings by artefactual clefts.
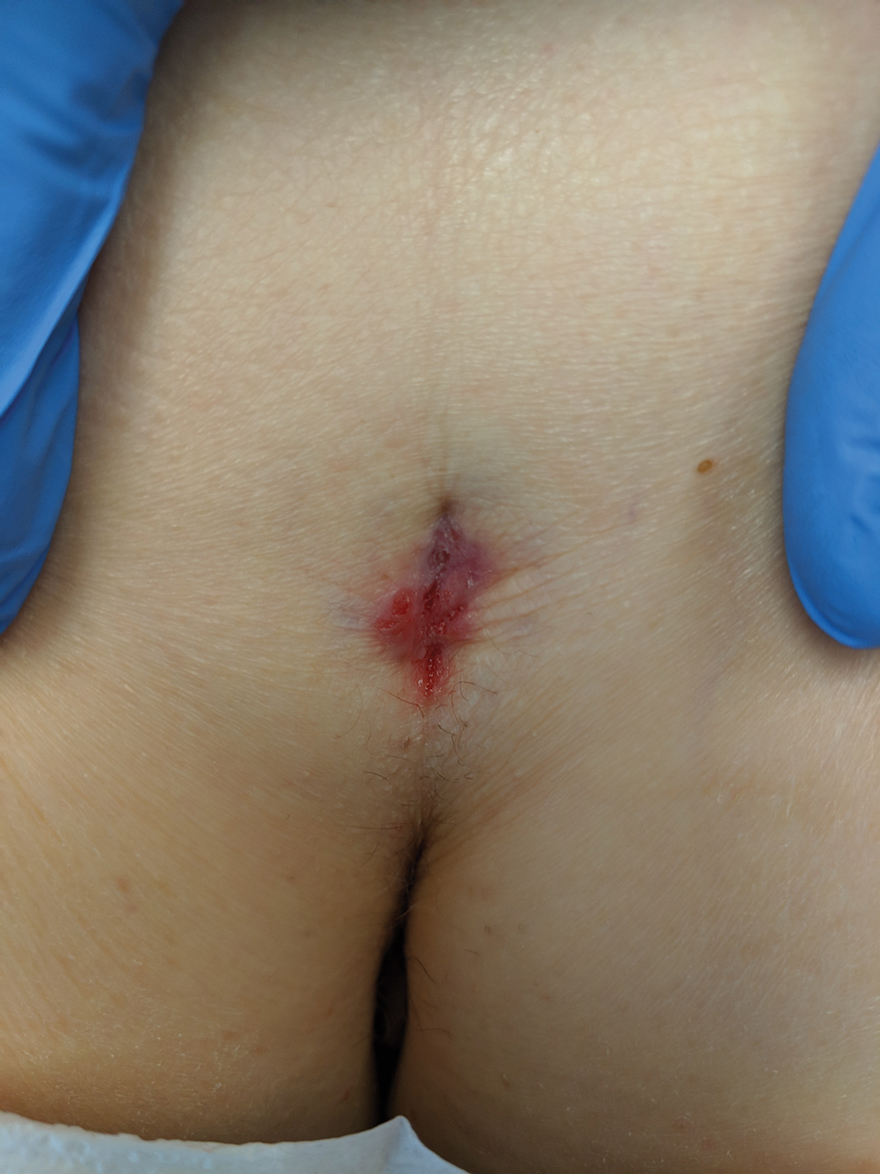
The initial differential diagnosis for this patient’s lesion included an ulcer or SCC. Basal cell carcinoma was not suspected due to the location and appearance of the lesion. The patient was successfully treated with Mohs micrographic surgery.
Practical Implications
Without thorough examination, this cancerous lesion would not have been seen (Figure 2). Therefore, it is important to practice thorough physical examination skills to avoid missing these cancers, particularly when examining a patient with a history of SCC or BCC. Furthermore, biopsy is recommended for suspicious lesions to rule out BCC.
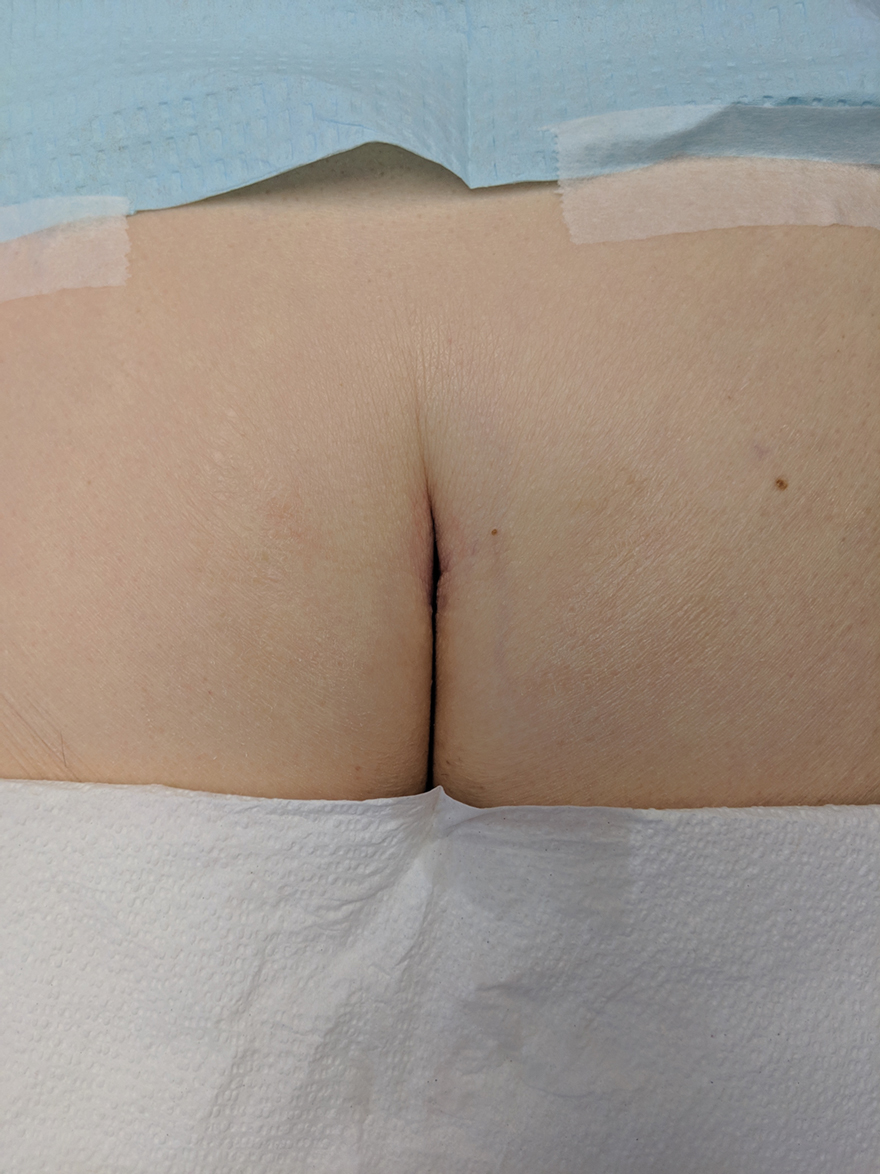
Be careful not to get caught up in epidemiological or demographic considerations when making a diagnosis of this kind or when assessing the severity of a lesion. This patient, for instance, was female, which makes her less likely to present with BCC.8 Moreover, the cancer presented in a highly unlikely location for BCC, where there had not been significant sunburn.9 Patients and physicians should be educated about the incidence of BCC in unexpected areas; without a second and close look, this BCC could have been missed.
Final Thoughts
The literature continuously demonstrates the rarity of BCC in the intergluteal crease.10 However, when perianal BCC is properly identified and treated with local excision, prognosis is good.11 Basal cell carcinoma has been seen to arise in other sensitive locations; vulvar, nipple, and scrotal BCC neoplasms are among the uncommon locations where BCC has appeared.12 These areas are frequently—and easily—ignored. A total-body skin examination should be performed to ensure that these insidious-onset carcinomas are not overlooked to protect patients from the adverse consequences of untreated cancer.13
- Roewert-Huber J, Lange-Asschenfeldt B, Stockfleth E, et al. Epidemiology and aetiology of basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157(suppl 2):47-51.
- Rogers HW, Weinstock MA, Feldman SR, et al. Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinomas) in the US population, 2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1081-1086.
- Zanetti R, Rosso S, Martinez C, et al. Comparison of risk patterns in carcinoma and melanoma of the skin in men: a multi-centre case–case–control study. Br J Cancer. 2006;94:743-751.
- Marzuka AG, Book SE. Basal cell carcinoma: pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. Yale J Biol Med. 2015;88:167-179.
- Lorenzini M, Gatti S, Giannitrapani A. Giant basal cell carcinoma of the thoracic wall: a case report and review of the literature. Br J Plast Surg. 2005;58:1007-1010.
- Lee HS, Kim SK. Basal cell carcinoma presenting as a perianal ulcer and treated with radiotherapy. Ann Dermatol. 2015;27:212-214.
- Salih AM, Kakamad FH, Rauf GM. Basal cell carcinoma mimicking pilonidal sinus: a case report with literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2016;28:121-123.
- Scrivener Y, Grosshans E, Cribier B. Variations of basal cell carcinomas according to gender, age, location and histopathological subtype. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:41-47.
- Park J, Cho Y-S, Song K-H, et al. Basal cell carcinoma on the pubic area: report of a case and review of 19 Korean cases of BCC from non-sun-exposed areas. Ann Dermatol. 2011;23:405-408.
- Damin DC, Rosito MA, Gus P, et al. Perianal basal cell carcinoma. J Cutan Med Surg. 2002;6:26-28.
- Paterson CA, Young-Fadok TM, Dozois RR. Basal cell carcinoma of the perianal region: 20-year experience. Dis Colon Rectum. 1999;42:1200-1202.
- Mulvany NJ, Rayoo M, Allen DG. Basal cell carcinoma of the vulva: a case series. Pathology. 2012;44:528-533.
- Leonard D, Beddy D, Dozois EJ. Neoplasms of anal canal and perianal skin. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2011;24:54-63.
Practice Gap
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common cancer, and its incidence is on the rise.1 The risk of this skin cancer is increased when there is a history of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) or BCC.2 Basal cell carcinoma often is found in sun-exposed areas, most commonly due to a history of intense sunburn.3 Other risk factors include male gender and increased age.4
Eighty percent to 85% of BCCs present on the head and neck5; however, BCC also can occur in unusual locations. When BCC presents in areas such as the perianal region, it is found to be larger than when found in more common areas,6 likely because neoplasms in this sensitive area often are overlooked. Literature on BCC of the intergluteal crease is limited.7 Being educated on the existence of BCC in this sensitive area can aid proper diagnosis.
The Technique and Case
An 83-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic for a suspicious lesion in the intergluteal crease that was tender to palpation with drainage. She first noticed this lesion and reported it to her primary care physician at a visit 6 months prior. The primary care physician did not pursue investigation of the lesion. One month later, the patient was seen by a gastroenterologist for the lesion and was referred to dermatology. The patient’s medical history included SCC and BCC on the face, both treated successfully with Mohs micrographic surgery.
Physical examination revealed a 2.6×1.1-cm, erythematous, nodular plaque in the coccygeal area of the intergluteal crease (Figure 1). A shave biopsy disclosed BCC, nodular type, ulcerated. Microscopically, there were nodular aggregates of basaloid cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and peripheral palisading, separated from mucinous stromal surroundings by artefactual clefts.

The initial differential diagnosis for this patient’s lesion included an ulcer or SCC. Basal cell carcinoma was not suspected due to the location and appearance of the lesion. The patient was successfully treated with Mohs micrographic surgery.
Practical Implications
Without thorough examination, this cancerous lesion would not have been seen (Figure 2). Therefore, it is important to practice thorough physical examination skills to avoid missing these cancers, particularly when examining a patient with a history of SCC or BCC. Furthermore, biopsy is recommended for suspicious lesions to rule out BCC.

Be careful not to get caught up in epidemiological or demographic considerations when making a diagnosis of this kind or when assessing the severity of a lesion. This patient, for instance, was female, which makes her less likely to present with BCC.8 Moreover, the cancer presented in a highly unlikely location for BCC, where there had not been significant sunburn.9 Patients and physicians should be educated about the incidence of BCC in unexpected areas; without a second and close look, this BCC could have been missed.
Final Thoughts
The literature continuously demonstrates the rarity of BCC in the intergluteal crease.10 However, when perianal BCC is properly identified and treated with local excision, prognosis is good.11 Basal cell carcinoma has been seen to arise in other sensitive locations; vulvar, nipple, and scrotal BCC neoplasms are among the uncommon locations where BCC has appeared.12 These areas are frequently—and easily—ignored. A total-body skin examination should be performed to ensure that these insidious-onset carcinomas are not overlooked to protect patients from the adverse consequences of untreated cancer.13
Practice Gap
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common cancer, and its incidence is on the rise.1 The risk of this skin cancer is increased when there is a history of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) or BCC.2 Basal cell carcinoma often is found in sun-exposed areas, most commonly due to a history of intense sunburn.3 Other risk factors include male gender and increased age.4
Eighty percent to 85% of BCCs present on the head and neck5; however, BCC also can occur in unusual locations. When BCC presents in areas such as the perianal region, it is found to be larger than when found in more common areas,6 likely because neoplasms in this sensitive area often are overlooked. Literature on BCC of the intergluteal crease is limited.7 Being educated on the existence of BCC in this sensitive area can aid proper diagnosis.
The Technique and Case
An 83-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic for a suspicious lesion in the intergluteal crease that was tender to palpation with drainage. She first noticed this lesion and reported it to her primary care physician at a visit 6 months prior. The primary care physician did not pursue investigation of the lesion. One month later, the patient was seen by a gastroenterologist for the lesion and was referred to dermatology. The patient’s medical history included SCC and BCC on the face, both treated successfully with Mohs micrographic surgery.
Physical examination revealed a 2.6×1.1-cm, erythematous, nodular plaque in the coccygeal area of the intergluteal crease (Figure 1). A shave biopsy disclosed BCC, nodular type, ulcerated. Microscopically, there were nodular aggregates of basaloid cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and peripheral palisading, separated from mucinous stromal surroundings by artefactual clefts.

The initial differential diagnosis for this patient’s lesion included an ulcer or SCC. Basal cell carcinoma was not suspected due to the location and appearance of the lesion. The patient was successfully treated with Mohs micrographic surgery.
Practical Implications
Without thorough examination, this cancerous lesion would not have been seen (Figure 2). Therefore, it is important to practice thorough physical examination skills to avoid missing these cancers, particularly when examining a patient with a history of SCC or BCC. Furthermore, biopsy is recommended for suspicious lesions to rule out BCC.

Be careful not to get caught up in epidemiological or demographic considerations when making a diagnosis of this kind or when assessing the severity of a lesion. This patient, for instance, was female, which makes her less likely to present with BCC.8 Moreover, the cancer presented in a highly unlikely location for BCC, where there had not been significant sunburn.9 Patients and physicians should be educated about the incidence of BCC in unexpected areas; without a second and close look, this BCC could have been missed.
Final Thoughts
The literature continuously demonstrates the rarity of BCC in the intergluteal crease.10 However, when perianal BCC is properly identified and treated with local excision, prognosis is good.11 Basal cell carcinoma has been seen to arise in other sensitive locations; vulvar, nipple, and scrotal BCC neoplasms are among the uncommon locations where BCC has appeared.12 These areas are frequently—and easily—ignored. A total-body skin examination should be performed to ensure that these insidious-onset carcinomas are not overlooked to protect patients from the adverse consequences of untreated cancer.13
- Roewert-Huber J, Lange-Asschenfeldt B, Stockfleth E, et al. Epidemiology and aetiology of basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157(suppl 2):47-51.
- Rogers HW, Weinstock MA, Feldman SR, et al. Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinomas) in the US population, 2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1081-1086.
- Zanetti R, Rosso S, Martinez C, et al. Comparison of risk patterns in carcinoma and melanoma of the skin in men: a multi-centre case–case–control study. Br J Cancer. 2006;94:743-751.
- Marzuka AG, Book SE. Basal cell carcinoma: pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. Yale J Biol Med. 2015;88:167-179.
- Lorenzini M, Gatti S, Giannitrapani A. Giant basal cell carcinoma of the thoracic wall: a case report and review of the literature. Br J Plast Surg. 2005;58:1007-1010.
- Lee HS, Kim SK. Basal cell carcinoma presenting as a perianal ulcer and treated with radiotherapy. Ann Dermatol. 2015;27:212-214.
- Salih AM, Kakamad FH, Rauf GM. Basal cell carcinoma mimicking pilonidal sinus: a case report with literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2016;28:121-123.
- Scrivener Y, Grosshans E, Cribier B. Variations of basal cell carcinomas according to gender, age, location and histopathological subtype. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:41-47.
- Park J, Cho Y-S, Song K-H, et al. Basal cell carcinoma on the pubic area: report of a case and review of 19 Korean cases of BCC from non-sun-exposed areas. Ann Dermatol. 2011;23:405-408.
- Damin DC, Rosito MA, Gus P, et al. Perianal basal cell carcinoma. J Cutan Med Surg. 2002;6:26-28.
- Paterson CA, Young-Fadok TM, Dozois RR. Basal cell carcinoma of the perianal region: 20-year experience. Dis Colon Rectum. 1999;42:1200-1202.
- Mulvany NJ, Rayoo M, Allen DG. Basal cell carcinoma of the vulva: a case series. Pathology. 2012;44:528-533.
- Leonard D, Beddy D, Dozois EJ. Neoplasms of anal canal and perianal skin. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2011;24:54-63.
- Roewert-Huber J, Lange-Asschenfeldt B, Stockfleth E, et al. Epidemiology and aetiology of basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157(suppl 2):47-51.
- Rogers HW, Weinstock MA, Feldman SR, et al. Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinomas) in the US population, 2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1081-1086.
- Zanetti R, Rosso S, Martinez C, et al. Comparison of risk patterns in carcinoma and melanoma of the skin in men: a multi-centre case–case–control study. Br J Cancer. 2006;94:743-751.
- Marzuka AG, Book SE. Basal cell carcinoma: pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. Yale J Biol Med. 2015;88:167-179.
- Lorenzini M, Gatti S, Giannitrapani A. Giant basal cell carcinoma of the thoracic wall: a case report and review of the literature. Br J Plast Surg. 2005;58:1007-1010.
- Lee HS, Kim SK. Basal cell carcinoma presenting as a perianal ulcer and treated with radiotherapy. Ann Dermatol. 2015;27:212-214.
- Salih AM, Kakamad FH, Rauf GM. Basal cell carcinoma mimicking pilonidal sinus: a case report with literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2016;28:121-123.
- Scrivener Y, Grosshans E, Cribier B. Variations of basal cell carcinomas according to gender, age, location and histopathological subtype. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:41-47.
- Park J, Cho Y-S, Song K-H, et al. Basal cell carcinoma on the pubic area: report of a case and review of 19 Korean cases of BCC from non-sun-exposed areas. Ann Dermatol. 2011;23:405-408.
- Damin DC, Rosito MA, Gus P, et al. Perianal basal cell carcinoma. J Cutan Med Surg. 2002;6:26-28.
- Paterson CA, Young-Fadok TM, Dozois RR. Basal cell carcinoma of the perianal region: 20-year experience. Dis Colon Rectum. 1999;42:1200-1202.
- Mulvany NJ, Rayoo M, Allen DG. Basal cell carcinoma of the vulva: a case series. Pathology. 2012;44:528-533.
- Leonard D, Beddy D, Dozois EJ. Neoplasms of anal canal and perianal skin. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2011;24:54-63.
Low-dose aspirin did not reduce preterm birth rates but don’t rule it out yet
Women at risk of preterm birth who took daily low-dose aspirin did not have significantly lower rates of preterm birth than those who did not take aspirin, according to preliminary findings from a small randomized controlled trial. There was a trend toward lower rates, especially among those with the highest compliance, but the study was underpowered to detect a difference with statistical significance, said Anadeijda Landman, MD, of the Amsterdam University Medical Center. Dr. Landman presented the findings Jan. 28 at a meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
Preterm birth accounts for a third of all neonatal mortality, she told attendees. Among 15 million preterm births worldwide each year, 65% are spontaneous, indicating the need for effective preventive interventions. Dr. Landman reviewed several mechanisms by which aspirin may help reduce preterm birth via different pathways.
The researchers’ multicenter, placebo-controlled trial involved 8 tertiary care and 26 secondary care hospitals in the Netherlands between May 2016 and June 2019. Starting between 8 and 15 weeks’ gestation, women took either 80 mg of aspirin or a placebo daily until 36 weeks’ gestation or delivery. Women also received progesterone, cerclage, or pessary as indicated according to local protocols.
The study enrolled 406 women with singleton pregnancy and a history of preterm birth delivered between 22 and 37 weeks’ gestation. The final analysis, after exclusions for pregnancy termination, congenital anomalies, multiples pregnancy, or similar reasons, included 193 women in the intervention group and 194 in the placebo group. The women had similar baseline characteristics across both groups except a higher number of past mid-trimester fetal deaths in the aspirin group.
“It’s important to realize these women had multiple preterm births, as one of our inclusion criteria was previous spontaneous preterm birth later than 22 weeks’ gestation, so this particular group is very high risk for cervical insufficiency as a probable cause,” Dr. Landman told attendees.
Among women in the aspirin group, 21.2% delivered before 37 weeks, compared with 25.4% in the placebo group (P = .323). The rate of spontaneous birth was 20.1% in the aspirin group and 23.8% in the placebo group (P = .376). Though still not statistically significant, the difference between the groups was larger when the researchers limited their analysis to the 245 women with at least 80% compliance: 18.5% of women in the aspirin group had a preterm birth, compared with 24.8% of women in the placebo group (P = .238).
There were no significant differences between the groups in composite poor neonatal outcomes or in a range of prespecified newborn complications. The aspirin group did have two stillbirths, two mid-trimester fetal losses, and two extremely preterm newborns (at 24+2 weeks and 25+2 weeks). The placebo group had two mid-trimester fetal losses.
“These deaths are inherent to the study population, and it seems unlikely they are related to the use of aspirin,” Dr. Landman said. “Moreover other aspirin studies have not found an increased perinatal mortality rate, and some large studies indicated the neonatal mortality rate is even reduced.”
Although preterm birth only trended lower in the aspirin group, Dr. Landman said the researchers believe they cannot rule out an effect from aspirin.
“It’s also important to note that our study was underpowered as the recurrence risk of preterm birth in our study was lower than expected, so it’s possible a small treatment effect of aspirin could not be demonstrated in our study,” she said. “And, despite the proper randomization procedure, many more women in the aspirin group had a previous mid-trimester fetal loss. This indicates that the aspirin group might be more at risk for preterm birth than the placebo group, and this imbalance could also have diminished a small protective effect of aspirin.”
In response to an audience question, Dr. Landman acknowledged that more recent studies on aspirin have used 100- to 150-mg dosages, but that evidence was not as clear when their study began in 2015. She added that her research team does not advise changing clinical care currently and believes it is too soon to recommend aspirin to this population.
Tracy Manuck, MD, MS, an associate professor of ob.gyn. at the University of North Carolina in Chapel Hill, agreed that it is premature to begin prescribing aspirin for preterm birth prevention, but she noted that most of the patients she cares for clinically already meet criteria for aspirin based on their risk factors for preeclampsia.
“Additional research is needed in the form of a well-designed and large [randomized, controlled trial],” Dr Manuck, who moderated the session, said in an interview. “However, such a trial is becoming increasingly difficult to conduct because so many pregnant women qualify to receive aspirin for the prevention of preeclampsia due to their weight, medical comorbidities, or prior pregnancy history.”
She said she anticipates seeing patient-level data meta-analyses in the coming months as more data on aspirin for preterm birth prevention are published.
“Given that these data are supportive of the overall trends seen in prior publications, I do think that low-dose aspirin will eventually bear out as a helpful preventative measure to prevent recurrent preterm birth. Aspirin is low risk, readily available, and is inexpensive,” Dr. Manuck said. “I hope that meta-analysis data will provide additional information regarding the benefit of low-dose aspirin for prematurity prevention.”
The research was funded by the Dutch Organization for Health Care Research and the Dutch Consortium for Research in Women’s Health. Dr. Landman and Dr. Manuck had no disclosures.
Women at risk of preterm birth who took daily low-dose aspirin did not have significantly lower rates of preterm birth than those who did not take aspirin, according to preliminary findings from a small randomized controlled trial. There was a trend toward lower rates, especially among those with the highest compliance, but the study was underpowered to detect a difference with statistical significance, said Anadeijda Landman, MD, of the Amsterdam University Medical Center. Dr. Landman presented the findings Jan. 28 at a meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
Preterm birth accounts for a third of all neonatal mortality, she told attendees. Among 15 million preterm births worldwide each year, 65% are spontaneous, indicating the need for effective preventive interventions. Dr. Landman reviewed several mechanisms by which aspirin may help reduce preterm birth via different pathways.
The researchers’ multicenter, placebo-controlled trial involved 8 tertiary care and 26 secondary care hospitals in the Netherlands between May 2016 and June 2019. Starting between 8 and 15 weeks’ gestation, women took either 80 mg of aspirin or a placebo daily until 36 weeks’ gestation or delivery. Women also received progesterone, cerclage, or pessary as indicated according to local protocols.
The study enrolled 406 women with singleton pregnancy and a history of preterm birth delivered between 22 and 37 weeks’ gestation. The final analysis, after exclusions for pregnancy termination, congenital anomalies, multiples pregnancy, or similar reasons, included 193 women in the intervention group and 194 in the placebo group. The women had similar baseline characteristics across both groups except a higher number of past mid-trimester fetal deaths in the aspirin group.
“It’s important to realize these women had multiple preterm births, as one of our inclusion criteria was previous spontaneous preterm birth later than 22 weeks’ gestation, so this particular group is very high risk for cervical insufficiency as a probable cause,” Dr. Landman told attendees.
Among women in the aspirin group, 21.2% delivered before 37 weeks, compared with 25.4% in the placebo group (P = .323). The rate of spontaneous birth was 20.1% in the aspirin group and 23.8% in the placebo group (P = .376). Though still not statistically significant, the difference between the groups was larger when the researchers limited their analysis to the 245 women with at least 80% compliance: 18.5% of women in the aspirin group had a preterm birth, compared with 24.8% of women in the placebo group (P = .238).
There were no significant differences between the groups in composite poor neonatal outcomes or in a range of prespecified newborn complications. The aspirin group did have two stillbirths, two mid-trimester fetal losses, and two extremely preterm newborns (at 24+2 weeks and 25+2 weeks). The placebo group had two mid-trimester fetal losses.
“These deaths are inherent to the study population, and it seems unlikely they are related to the use of aspirin,” Dr. Landman said. “Moreover other aspirin studies have not found an increased perinatal mortality rate, and some large studies indicated the neonatal mortality rate is even reduced.”
Although preterm birth only trended lower in the aspirin group, Dr. Landman said the researchers believe they cannot rule out an effect from aspirin.
“It’s also important to note that our study was underpowered as the recurrence risk of preterm birth in our study was lower than expected, so it’s possible a small treatment effect of aspirin could not be demonstrated in our study,” she said. “And, despite the proper randomization procedure, many more women in the aspirin group had a previous mid-trimester fetal loss. This indicates that the aspirin group might be more at risk for preterm birth than the placebo group, and this imbalance could also have diminished a small protective effect of aspirin.”
In response to an audience question, Dr. Landman acknowledged that more recent studies on aspirin have used 100- to 150-mg dosages, but that evidence was not as clear when their study began in 2015. She added that her research team does not advise changing clinical care currently and believes it is too soon to recommend aspirin to this population.
Tracy Manuck, MD, MS, an associate professor of ob.gyn. at the University of North Carolina in Chapel Hill, agreed that it is premature to begin prescribing aspirin for preterm birth prevention, but she noted that most of the patients she cares for clinically already meet criteria for aspirin based on their risk factors for preeclampsia.
“Additional research is needed in the form of a well-designed and large [randomized, controlled trial],” Dr Manuck, who moderated the session, said in an interview. “However, such a trial is becoming increasingly difficult to conduct because so many pregnant women qualify to receive aspirin for the prevention of preeclampsia due to their weight, medical comorbidities, or prior pregnancy history.”
She said she anticipates seeing patient-level data meta-analyses in the coming months as more data on aspirin for preterm birth prevention are published.
“Given that these data are supportive of the overall trends seen in prior publications, I do think that low-dose aspirin will eventually bear out as a helpful preventative measure to prevent recurrent preterm birth. Aspirin is low risk, readily available, and is inexpensive,” Dr. Manuck said. “I hope that meta-analysis data will provide additional information regarding the benefit of low-dose aspirin for prematurity prevention.”
The research was funded by the Dutch Organization for Health Care Research and the Dutch Consortium for Research in Women’s Health. Dr. Landman and Dr. Manuck had no disclosures.
Women at risk of preterm birth who took daily low-dose aspirin did not have significantly lower rates of preterm birth than those who did not take aspirin, according to preliminary findings from a small randomized controlled trial. There was a trend toward lower rates, especially among those with the highest compliance, but the study was underpowered to detect a difference with statistical significance, said Anadeijda Landman, MD, of the Amsterdam University Medical Center. Dr. Landman presented the findings Jan. 28 at a meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
Preterm birth accounts for a third of all neonatal mortality, she told attendees. Among 15 million preterm births worldwide each year, 65% are spontaneous, indicating the need for effective preventive interventions. Dr. Landman reviewed several mechanisms by which aspirin may help reduce preterm birth via different pathways.
The researchers’ multicenter, placebo-controlled trial involved 8 tertiary care and 26 secondary care hospitals in the Netherlands between May 2016 and June 2019. Starting between 8 and 15 weeks’ gestation, women took either 80 mg of aspirin or a placebo daily until 36 weeks’ gestation or delivery. Women also received progesterone, cerclage, or pessary as indicated according to local protocols.
The study enrolled 406 women with singleton pregnancy and a history of preterm birth delivered between 22 and 37 weeks’ gestation. The final analysis, after exclusions for pregnancy termination, congenital anomalies, multiples pregnancy, or similar reasons, included 193 women in the intervention group and 194 in the placebo group. The women had similar baseline characteristics across both groups except a higher number of past mid-trimester fetal deaths in the aspirin group.
“It’s important to realize these women had multiple preterm births, as one of our inclusion criteria was previous spontaneous preterm birth later than 22 weeks’ gestation, so this particular group is very high risk for cervical insufficiency as a probable cause,” Dr. Landman told attendees.
Among women in the aspirin group, 21.2% delivered before 37 weeks, compared with 25.4% in the placebo group (P = .323). The rate of spontaneous birth was 20.1% in the aspirin group and 23.8% in the placebo group (P = .376). Though still not statistically significant, the difference between the groups was larger when the researchers limited their analysis to the 245 women with at least 80% compliance: 18.5% of women in the aspirin group had a preterm birth, compared with 24.8% of women in the placebo group (P = .238).
There were no significant differences between the groups in composite poor neonatal outcomes or in a range of prespecified newborn complications. The aspirin group did have two stillbirths, two mid-trimester fetal losses, and two extremely preterm newborns (at 24+2 weeks and 25+2 weeks). The placebo group had two mid-trimester fetal losses.
“These deaths are inherent to the study population, and it seems unlikely they are related to the use of aspirin,” Dr. Landman said. “Moreover other aspirin studies have not found an increased perinatal mortality rate, and some large studies indicated the neonatal mortality rate is even reduced.”
Although preterm birth only trended lower in the aspirin group, Dr. Landman said the researchers believe they cannot rule out an effect from aspirin.
“It’s also important to note that our study was underpowered as the recurrence risk of preterm birth in our study was lower than expected, so it’s possible a small treatment effect of aspirin could not be demonstrated in our study,” she said. “And, despite the proper randomization procedure, many more women in the aspirin group had a previous mid-trimester fetal loss. This indicates that the aspirin group might be more at risk for preterm birth than the placebo group, and this imbalance could also have diminished a small protective effect of aspirin.”
In response to an audience question, Dr. Landman acknowledged that more recent studies on aspirin have used 100- to 150-mg dosages, but that evidence was not as clear when their study began in 2015. She added that her research team does not advise changing clinical care currently and believes it is too soon to recommend aspirin to this population.
Tracy Manuck, MD, MS, an associate professor of ob.gyn. at the University of North Carolina in Chapel Hill, agreed that it is premature to begin prescribing aspirin for preterm birth prevention, but she noted that most of the patients she cares for clinically already meet criteria for aspirin based on their risk factors for preeclampsia.
“Additional research is needed in the form of a well-designed and large [randomized, controlled trial],” Dr Manuck, who moderated the session, said in an interview. “However, such a trial is becoming increasingly difficult to conduct because so many pregnant women qualify to receive aspirin for the prevention of preeclampsia due to their weight, medical comorbidities, or prior pregnancy history.”
She said she anticipates seeing patient-level data meta-analyses in the coming months as more data on aspirin for preterm birth prevention are published.
“Given that these data are supportive of the overall trends seen in prior publications, I do think that low-dose aspirin will eventually bear out as a helpful preventative measure to prevent recurrent preterm birth. Aspirin is low risk, readily available, and is inexpensive,” Dr. Manuck said. “I hope that meta-analysis data will provide additional information regarding the benefit of low-dose aspirin for prematurity prevention.”
The research was funded by the Dutch Organization for Health Care Research and the Dutch Consortium for Research in Women’s Health. Dr. Landman and Dr. Manuck had no disclosures.
FROM THE PREGNANCY MEETING
Some COVID-19 vaccine reactions could be pseudoallergic, experts say
On Jan. 13, 2 days after a drive-through vaccination “superstation” opened in San Diego, six people were treated for anaphylaxis after they received the Moderna vaccine, leading the California state epidemiologist to recommend pausing the administration of that particular lot.
A group of allergy and immunology experts and public health officials reviewed the cases, as well as an incident that occurred the day before, and concluded that at least some of the responses were angioedema, or swelling — a serious allergic reaction — but none were actually anaphylaxis. No similar clusters had occurred with the same vaccine lot in other states, and California resumed using the doses.
Yet questions remain about the reactions and the mechanisms for them. Some might have been triggered by an allergy to a vaccine component, most likely the polyethylene glycol (PEG) that stabilizes the lipid surrounding the mRNA, the key vaccine component in both the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines. Another possible explanation is that some could be pseudoallergic reactions to a blood protein known as complement, a little-understood process that resembles an antigen-based reaction but doesn’t leave an immune memory and might not recur.
Cases of complement-activation-related pseudoallergy look like a severe allergic reaction but occur through a different mechanism and don’t require previous exposure to an allergen.
“It has the same signs and symptoms and is treated the same way, but it occurs through a different pathway,” explained Neal Halsey, MD, director emeritus of the Institute for Vaccine Safety and emeritus professor at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore.
Pseudoallergies are not well understood, but they have been associated with reactions to the contrast media used in imaging, such as with MRI. “If people have had an anaphylaxis-type reaction following the injection of contrast-dye material, that is a strong signal that it might be a complement-activation-related pseudoallergy,” said Dr. Halsey, a member of the Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Network. “Those are the people who definitely need to consider seeing an allergist before getting the COVID vaccines.”
When Aleena Banerji, MD, clinical director of the allergy and clinical immunology unit at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, talks to patients about vaccine reactions, she addresses the risk for COVID-19 infection. All of the people who developed allergies after the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines recovered, but more than 445,000 Americans have died from COVID-19.
Most people with common allergies, such as to food or oral medications, don’t need to worry about reactions, said Dr. Banerji, lead author of a review that assessed the risk for allergic reactions to the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines.
Investigating reactions
As investigators search for the answers to what causes reactions, transparency is crucial to trust, said Kathryn Edwards, MD, principal investigator of the Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Project, a vaccine safety network funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Unless the public knows that we’re really investigating and we’re taking this seriously, then I think the vaccine hesitancy is going to increase,” said Dr. Edwards, professor of pediatrics at Vanderbilt University Medical Center and scientific director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Research Program in Nashville, Tenn.
First reports of anaphylaxis came quickly after COVID-19 vaccinations began. In the 2 weeks before the holidays, almost 2 million health care workers received the Pfizer vaccine, and 21 of them developed anaphylaxis, according to CDC researchers who reviewed case reports from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). That rate of about 1 in 100,000 is 10 times higher than the occurrence with other vaccines. No deaths from anaphylaxis were reported.
As the vaccinations ramped up, the rate declined. As of Jan. 18, 50 cases of anaphylaxis were reported to VAERS after the administration of 9,943,247 Pfizer doses, for a rate of 5.0 per million, according to data presented at the Jan. 27 meeting of the CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. And 21 cases of anaphylaxis were reported to VAERS after the administration of 7,581,429 Moderna doses, for a rate of 2.8 per million.
The anaphylaxis occurred almost exclusively in women; only three of the VAERS anaphylaxis reports were from men. Only 24% had a history of anaphylaxis.
The earlier CDC report explored the potential link to allergies. One person with anaphylaxis had a history of allergy to iodinated contrast media, and others had allergies to various medications, vaccines, foods, and animals. The researchers reported 86 nonanaphylaxis allergic reactions and 61 nonallergic adverse events among the 175 case reports they reviewed as possible cases of severe allergic reaction.
Of 1,266 reports that VAERS received from Dec. 21 to Jan. 10, the CDC identified 108 possible cases of severe allergic reaction after the Moderna vaccine. Only 10 met the case definition of anaphylaxis put forward by the Brighton Collaboration, a vaccine safety organization. All but one case involved a history of allergies or allergic reactions; only five had a previously experienced anaphylaxis.
There were 47 nonanaphylaxis allergic reactions.
The San Diego cluster also met the Brighton case definition for anaphylaxis, Dr. Edwards reported. This discrepancy highlights the difficulties in characterizing vaccine reactions.
Measuring a pseudoallergic reaction is a challenge. It requires that a blood sample be drawn soon after the incident and then frozen to protect heat-sensitive blood markers, Dr. Edwards explained.
And as vaccinations rise, so do adverse-event reports. But unlike in clinical trials, there is no control group for comparison. That is why vaccine safety experts urge caution when evaluating events and, where possible, advise looking at background rates.
“A major way to determine whether the adverse event is causally related is to assess the incidence of the adverse event in vaccines versus nonvaccines,” said Walter Orenstein, MD, who directed the U.S. Immunization Program from 1988 to 2004 and is now associate director of the Emory Vaccine Center and professor of infectious diseases at Emory University in Atlanta. Public health officials could then identify vaccine risk factors, he said.
When a reaction occurs almost immediately after vaccination, vaccine safety investigators look for probable triggers. If allergy to PEG is the culprit in anaphylactic reactions, then the individuals would have had a previous exposure, perhaps from injectable medications, Dr. Edwards said.
It might be feasible to perform a skin test for allergy to PEG. “If the skin testing is negative, that doesn’t completely rule out allergy, but it can be used in the decision-making about giving the first or second vaccine dose,” Dr. Banerji said.
Other vaccines, such as childhood vaccines, contain polysorbate as a stabilizer, which has a similar chemical structure, and it’s not clear why someone would react to PEG but not to polysorbate, Dr. Edwards said.
Meanwhile, other illnesses and even deaths sometimes occur in the days after vaccination, but that doesn’t mean the vaccine caused them, cautioned Steve Black, MD, emeritus professor of pediatrics at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and cofounder of the Global Vaccine Data Network, an international vaccine safety collaboration.
“Different events and clusters of events will occur by chance alone, as these events can occur without vaccines. We need to not immediately assume that they’re due to the vaccine,” he said. “You don’t want to undermine the whole vaccine program every time something comes up and assume that it’s associated with the vaccine.”
The CDC only has three contraindications for the vaccines:
- Severe allergic reaction (such as anaphylaxis) after a previous dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine or any of its components.
- Immediate allergic reaction of any severity to a previous dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine or any of its components (including PEG).
- Immediate allergic reaction of any severity to polysorbate (due to potential cross-reactive hypersensitivity with PEG).
People who have had an immediate allergic reaction to other vaccines or injectable therapies should consider consulting with an allergist or immunologist before getting the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines, the CDC advises.
The CDC also says that people with a history of anaphylaxis from any cause should be observed for 30 minutes after vaccination. Vaccination protocol calls for everyone else to wait on site for 15 minutes after vaccination.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On Jan. 13, 2 days after a drive-through vaccination “superstation” opened in San Diego, six people were treated for anaphylaxis after they received the Moderna vaccine, leading the California state epidemiologist to recommend pausing the administration of that particular lot.
A group of allergy and immunology experts and public health officials reviewed the cases, as well as an incident that occurred the day before, and concluded that at least some of the responses were angioedema, or swelling — a serious allergic reaction — but none were actually anaphylaxis. No similar clusters had occurred with the same vaccine lot in other states, and California resumed using the doses.
Yet questions remain about the reactions and the mechanisms for them. Some might have been triggered by an allergy to a vaccine component, most likely the polyethylene glycol (PEG) that stabilizes the lipid surrounding the mRNA, the key vaccine component in both the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines. Another possible explanation is that some could be pseudoallergic reactions to a blood protein known as complement, a little-understood process that resembles an antigen-based reaction but doesn’t leave an immune memory and might not recur.
Cases of complement-activation-related pseudoallergy look like a severe allergic reaction but occur through a different mechanism and don’t require previous exposure to an allergen.
“It has the same signs and symptoms and is treated the same way, but it occurs through a different pathway,” explained Neal Halsey, MD, director emeritus of the Institute for Vaccine Safety and emeritus professor at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore.
Pseudoallergies are not well understood, but they have been associated with reactions to the contrast media used in imaging, such as with MRI. “If people have had an anaphylaxis-type reaction following the injection of contrast-dye material, that is a strong signal that it might be a complement-activation-related pseudoallergy,” said Dr. Halsey, a member of the Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Network. “Those are the people who definitely need to consider seeing an allergist before getting the COVID vaccines.”
When Aleena Banerji, MD, clinical director of the allergy and clinical immunology unit at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, talks to patients about vaccine reactions, she addresses the risk for COVID-19 infection. All of the people who developed allergies after the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines recovered, but more than 445,000 Americans have died from COVID-19.
Most people with common allergies, such as to food or oral medications, don’t need to worry about reactions, said Dr. Banerji, lead author of a review that assessed the risk for allergic reactions to the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines.
Investigating reactions
As investigators search for the answers to what causes reactions, transparency is crucial to trust, said Kathryn Edwards, MD, principal investigator of the Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Project, a vaccine safety network funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Unless the public knows that we’re really investigating and we’re taking this seriously, then I think the vaccine hesitancy is going to increase,” said Dr. Edwards, professor of pediatrics at Vanderbilt University Medical Center and scientific director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Research Program in Nashville, Tenn.
First reports of anaphylaxis came quickly after COVID-19 vaccinations began. In the 2 weeks before the holidays, almost 2 million health care workers received the Pfizer vaccine, and 21 of them developed anaphylaxis, according to CDC researchers who reviewed case reports from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). That rate of about 1 in 100,000 is 10 times higher than the occurrence with other vaccines. No deaths from anaphylaxis were reported.
As the vaccinations ramped up, the rate declined. As of Jan. 18, 50 cases of anaphylaxis were reported to VAERS after the administration of 9,943,247 Pfizer doses, for a rate of 5.0 per million, according to data presented at the Jan. 27 meeting of the CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. And 21 cases of anaphylaxis were reported to VAERS after the administration of 7,581,429 Moderna doses, for a rate of 2.8 per million.
The anaphylaxis occurred almost exclusively in women; only three of the VAERS anaphylaxis reports were from men. Only 24% had a history of anaphylaxis.
The earlier CDC report explored the potential link to allergies. One person with anaphylaxis had a history of allergy to iodinated contrast media, and others had allergies to various medications, vaccines, foods, and animals. The researchers reported 86 nonanaphylaxis allergic reactions and 61 nonallergic adverse events among the 175 case reports they reviewed as possible cases of severe allergic reaction.
Of 1,266 reports that VAERS received from Dec. 21 to Jan. 10, the CDC identified 108 possible cases of severe allergic reaction after the Moderna vaccine. Only 10 met the case definition of anaphylaxis put forward by the Brighton Collaboration, a vaccine safety organization. All but one case involved a history of allergies or allergic reactions; only five had a previously experienced anaphylaxis.
There were 47 nonanaphylaxis allergic reactions.
The San Diego cluster also met the Brighton case definition for anaphylaxis, Dr. Edwards reported. This discrepancy highlights the difficulties in characterizing vaccine reactions.
Measuring a pseudoallergic reaction is a challenge. It requires that a blood sample be drawn soon after the incident and then frozen to protect heat-sensitive blood markers, Dr. Edwards explained.
And as vaccinations rise, so do adverse-event reports. But unlike in clinical trials, there is no control group for comparison. That is why vaccine safety experts urge caution when evaluating events and, where possible, advise looking at background rates.
“A major way to determine whether the adverse event is causally related is to assess the incidence of the adverse event in vaccines versus nonvaccines,” said Walter Orenstein, MD, who directed the U.S. Immunization Program from 1988 to 2004 and is now associate director of the Emory Vaccine Center and professor of infectious diseases at Emory University in Atlanta. Public health officials could then identify vaccine risk factors, he said.
When a reaction occurs almost immediately after vaccination, vaccine safety investigators look for probable triggers. If allergy to PEG is the culprit in anaphylactic reactions, then the individuals would have had a previous exposure, perhaps from injectable medications, Dr. Edwards said.
It might be feasible to perform a skin test for allergy to PEG. “If the skin testing is negative, that doesn’t completely rule out allergy, but it can be used in the decision-making about giving the first or second vaccine dose,” Dr. Banerji said.
Other vaccines, such as childhood vaccines, contain polysorbate as a stabilizer, which has a similar chemical structure, and it’s not clear why someone would react to PEG but not to polysorbate, Dr. Edwards said.
Meanwhile, other illnesses and even deaths sometimes occur in the days after vaccination, but that doesn’t mean the vaccine caused them, cautioned Steve Black, MD, emeritus professor of pediatrics at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and cofounder of the Global Vaccine Data Network, an international vaccine safety collaboration.
“Different events and clusters of events will occur by chance alone, as these events can occur without vaccines. We need to not immediately assume that they’re due to the vaccine,” he said. “You don’t want to undermine the whole vaccine program every time something comes up and assume that it’s associated with the vaccine.”
The CDC only has three contraindications for the vaccines:
- Severe allergic reaction (such as anaphylaxis) after a previous dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine or any of its components.
- Immediate allergic reaction of any severity to a previous dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine or any of its components (including PEG).
- Immediate allergic reaction of any severity to polysorbate (due to potential cross-reactive hypersensitivity with PEG).
People who have had an immediate allergic reaction to other vaccines or injectable therapies should consider consulting with an allergist or immunologist before getting the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines, the CDC advises.
The CDC also says that people with a history of anaphylaxis from any cause should be observed for 30 minutes after vaccination. Vaccination protocol calls for everyone else to wait on site for 15 minutes after vaccination.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On Jan. 13, 2 days after a drive-through vaccination “superstation” opened in San Diego, six people were treated for anaphylaxis after they received the Moderna vaccine, leading the California state epidemiologist to recommend pausing the administration of that particular lot.
A group of allergy and immunology experts and public health officials reviewed the cases, as well as an incident that occurred the day before, and concluded that at least some of the responses were angioedema, or swelling — a serious allergic reaction — but none were actually anaphylaxis. No similar clusters had occurred with the same vaccine lot in other states, and California resumed using the doses.
Yet questions remain about the reactions and the mechanisms for them. Some might have been triggered by an allergy to a vaccine component, most likely the polyethylene glycol (PEG) that stabilizes the lipid surrounding the mRNA, the key vaccine component in both the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines. Another possible explanation is that some could be pseudoallergic reactions to a blood protein known as complement, a little-understood process that resembles an antigen-based reaction but doesn’t leave an immune memory and might not recur.
Cases of complement-activation-related pseudoallergy look like a severe allergic reaction but occur through a different mechanism and don’t require previous exposure to an allergen.
“It has the same signs and symptoms and is treated the same way, but it occurs through a different pathway,” explained Neal Halsey, MD, director emeritus of the Institute for Vaccine Safety and emeritus professor at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore.
Pseudoallergies are not well understood, but they have been associated with reactions to the contrast media used in imaging, such as with MRI. “If people have had an anaphylaxis-type reaction following the injection of contrast-dye material, that is a strong signal that it might be a complement-activation-related pseudoallergy,” said Dr. Halsey, a member of the Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Network. “Those are the people who definitely need to consider seeing an allergist before getting the COVID vaccines.”
When Aleena Banerji, MD, clinical director of the allergy and clinical immunology unit at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, talks to patients about vaccine reactions, she addresses the risk for COVID-19 infection. All of the people who developed allergies after the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines recovered, but more than 445,000 Americans have died from COVID-19.
Most people with common allergies, such as to food or oral medications, don’t need to worry about reactions, said Dr. Banerji, lead author of a review that assessed the risk for allergic reactions to the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines.
Investigating reactions
As investigators search for the answers to what causes reactions, transparency is crucial to trust, said Kathryn Edwards, MD, principal investigator of the Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Project, a vaccine safety network funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Unless the public knows that we’re really investigating and we’re taking this seriously, then I think the vaccine hesitancy is going to increase,” said Dr. Edwards, professor of pediatrics at Vanderbilt University Medical Center and scientific director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Research Program in Nashville, Tenn.
First reports of anaphylaxis came quickly after COVID-19 vaccinations began. In the 2 weeks before the holidays, almost 2 million health care workers received the Pfizer vaccine, and 21 of them developed anaphylaxis, according to CDC researchers who reviewed case reports from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). That rate of about 1 in 100,000 is 10 times higher than the occurrence with other vaccines. No deaths from anaphylaxis were reported.
As the vaccinations ramped up, the rate declined. As of Jan. 18, 50 cases of anaphylaxis were reported to VAERS after the administration of 9,943,247 Pfizer doses, for a rate of 5.0 per million, according to data presented at the Jan. 27 meeting of the CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. And 21 cases of anaphylaxis were reported to VAERS after the administration of 7,581,429 Moderna doses, for a rate of 2.8 per million.
The anaphylaxis occurred almost exclusively in women; only three of the VAERS anaphylaxis reports were from men. Only 24% had a history of anaphylaxis.
The earlier CDC report explored the potential link to allergies. One person with anaphylaxis had a history of allergy to iodinated contrast media, and others had allergies to various medications, vaccines, foods, and animals. The researchers reported 86 nonanaphylaxis allergic reactions and 61 nonallergic adverse events among the 175 case reports they reviewed as possible cases of severe allergic reaction.
Of 1,266 reports that VAERS received from Dec. 21 to Jan. 10, the CDC identified 108 possible cases of severe allergic reaction after the Moderna vaccine. Only 10 met the case definition of anaphylaxis put forward by the Brighton Collaboration, a vaccine safety organization. All but one case involved a history of allergies or allergic reactions; only five had a previously experienced anaphylaxis.
There were 47 nonanaphylaxis allergic reactions.
The San Diego cluster also met the Brighton case definition for anaphylaxis, Dr. Edwards reported. This discrepancy highlights the difficulties in characterizing vaccine reactions.
Measuring a pseudoallergic reaction is a challenge. It requires that a blood sample be drawn soon after the incident and then frozen to protect heat-sensitive blood markers, Dr. Edwards explained.
And as vaccinations rise, so do adverse-event reports. But unlike in clinical trials, there is no control group for comparison. That is why vaccine safety experts urge caution when evaluating events and, where possible, advise looking at background rates.
“A major way to determine whether the adverse event is causally related is to assess the incidence of the adverse event in vaccines versus nonvaccines,” said Walter Orenstein, MD, who directed the U.S. Immunization Program from 1988 to 2004 and is now associate director of the Emory Vaccine Center and professor of infectious diseases at Emory University in Atlanta. Public health officials could then identify vaccine risk factors, he said.
When a reaction occurs almost immediately after vaccination, vaccine safety investigators look for probable triggers. If allergy to PEG is the culprit in anaphylactic reactions, then the individuals would have had a previous exposure, perhaps from injectable medications, Dr. Edwards said.
It might be feasible to perform a skin test for allergy to PEG. “If the skin testing is negative, that doesn’t completely rule out allergy, but it can be used in the decision-making about giving the first or second vaccine dose,” Dr. Banerji said.
Other vaccines, such as childhood vaccines, contain polysorbate as a stabilizer, which has a similar chemical structure, and it’s not clear why someone would react to PEG but not to polysorbate, Dr. Edwards said.
Meanwhile, other illnesses and even deaths sometimes occur in the days after vaccination, but that doesn’t mean the vaccine caused them, cautioned Steve Black, MD, emeritus professor of pediatrics at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and cofounder of the Global Vaccine Data Network, an international vaccine safety collaboration.
“Different events and clusters of events will occur by chance alone, as these events can occur without vaccines. We need to not immediately assume that they’re due to the vaccine,” he said. “You don’t want to undermine the whole vaccine program every time something comes up and assume that it’s associated with the vaccine.”
The CDC only has three contraindications for the vaccines:
- Severe allergic reaction (such as anaphylaxis) after a previous dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine or any of its components.
- Immediate allergic reaction of any severity to a previous dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine or any of its components (including PEG).
- Immediate allergic reaction of any severity to polysorbate (due to potential cross-reactive hypersensitivity with PEG).
People who have had an immediate allergic reaction to other vaccines or injectable therapies should consider consulting with an allergist or immunologist before getting the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines, the CDC advises.
The CDC also says that people with a history of anaphylaxis from any cause should be observed for 30 minutes after vaccination. Vaccination protocol calls for everyone else to wait on site for 15 minutes after vaccination.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Inhaled hyaluronan may bring sigh of relief to COPD patients
(COPD), findings of a new study suggest.
HMW-HA was associated with a significantly shorter duration of noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation (NIPPV), lower systemic inflammatory markers, and lower measured peak airway pressure, compared with placebo, reported lead author Flavia Galdi, MD, of Campus Bio-Medico University Hospital, Rome, and colleagues.
“HMW-HA is a naturally occurring sugar that is abundant in the extracellular matrix, including in the lung,” the investigators wrote in Respiratory Research. “[It] has been used routinely, together with hypertonic saline, in cystic fibrosis patients [for several years] with no reported side effects; rather, it improves tolerability and decreases the need for bronchodilators in these patients.”
According to Robert A. Sandhaus, MD, PhD, FCCP, of National Jewish Health, Denver, the role of hyaluronan in lung disease was first recognized decades ago.
“Data stretching back into the 1970s has identified decreases in hyaluronan content in emphysematous lung tissue, protection of lung connective tissue from proteolysis by hyaluronan, and potential therapeutic roles for hyaluronan in a variety of disease, especially of the lungs,” he said in an interview.
For patients with COPD, treatment with HMW-HA may provide benefit by counteracting an imbalance in diseased lung tissue, wrote Dr. Galdi and colleagues.
“Emerging evidence suggests that imbalance between declining HMW-HA levels, and increasing smaller fragments of hyaluronan may contribute to chronic airway disease pathogenesis,” they wrote. “This has led to the hypothesis that exogenous supplementation of HMW-HA may restore hyaluronan homeostasis in favor of undegraded molecules, inhibit inflammation and loss of lung function, and ameliorate COPD progression.”
To test this hypothesis, the investigators screened 44 patients with a history of acute exacerbations of COPD necessitating NIPPV, ultimately excluding 3 patients because of heart failure. Following 1:1 randomization, 20 patients received HMW-HA while 21 received placebo, each twice daily, in conjunction with NIPPV and standard medical therapy. Treatment continued until NIPPV failure or liberation from NIPPV. Most patients received NIPPV in the hospital; however, home/chronic NIPPV was given to four patients in the placebo group and three patients in the HMW-HA group.
The primary outcome was duration of NIPPV. Secondary outcomes included markers of systemic inflammation associated with acute exacerbations of COPD and respiratory physiology parameters. Adverse events were also reported.
Results showed that patients treated with HMW-HA were liberated sooner from NIPPV than were those who received placebo (mean, 5.2 vs 6.4 days; P < .037). Similarly, patients in the HMW-HA group had significantly shorter hospital stay, on average, than those in the placebo group (mean, 7.2 vs 10.2 days; P = .039). Median values followed a similar pattern.
“These data suggest that HMW-HA shortened the duration of acute respiratory failure, need for NIPPV and, consequently, hospital length of stay in these patients,” the investigators wrote.
Secondary outcomes further supported these therapeutic benefits. Compared with placebo, HMW-HA was associated with significantly lower peak pressure and greater improvements in both pCO2/FiO2 ratio and inflammatory markers. No adverse events were reported.
Further analyses involving human bronchial epithelial cell cultures offered some mechanistic insight. Using micro-optical coherence tomography imaging, the investigators found that HMW-HA treatment was associated with “a prominent effect on mucociliary transport” in cell cultures derived from COPD patients and in healthy nonsmoker cell cultures exposed to cigarette smoke extract.
“Our study shows for the first time the therapeutic potential of an extracellular matrix molecule in acute exacerbation of human lung disease,” the investigators concluded, noting a “clinically meaningful salutary effect” on duration of NIPPV.
Dr. Galdi and colleagues went on to predict that benefits in a real-world patient population could be even more meaningful.
“Since the serum samples were collected at the end of NIPPV, HMW-HA–treated patients were on average sampled a day earlier than placebo-treated patients (because they were liberated from NIPPV a day earlier on average),” the investigators wrote. “Thus, HMW-HA treatment effects may have been underestimated in our study.”
According to Dr. Sandhaus, “The current report, while a relatively small single-center study, is well controlled and the results suggest that inhaled hyaluronan decreased time on noninvasive ventilation, decreased hospital stay duration, and decreased some mediators of inflammation.”
He also suggested that HMW-HA may have a role in the prophylactic setting.
“The limitations of this pilot study are appropriately explored by the authors but do not dampen the exciting possibility that this therapeutic approach may hold promise not only in severe exacerbations of COPD but potentially for the prevention of such exacerbations,” Dr. Sandhaus said.
Jerome O. Cantor, MD, FCCP, of St. John’s University, New York, who previously conducted a pilot study for using lower molecular weight hyaluronan in COPD and published a review on the subject, said that more studies are necessary.
“Further clinical trials are needed to better determine the role of hyaluronan as an adjunct to existing therapies for COPD exacerbations,” he said.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The investigators and Dr. Sandhaus declared no conflicts of interest. Dr. Cantor disclosed a relationship with MatRx Therapeutics.
(COPD), findings of a new study suggest.
HMW-HA was associated with a significantly shorter duration of noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation (NIPPV), lower systemic inflammatory markers, and lower measured peak airway pressure, compared with placebo, reported lead author Flavia Galdi, MD, of Campus Bio-Medico University Hospital, Rome, and colleagues.
“HMW-HA is a naturally occurring sugar that is abundant in the extracellular matrix, including in the lung,” the investigators wrote in Respiratory Research. “[It] has been used routinely, together with hypertonic saline, in cystic fibrosis patients [for several years] with no reported side effects; rather, it improves tolerability and decreases the need for bronchodilators in these patients.”
According to Robert A. Sandhaus, MD, PhD, FCCP, of National Jewish Health, Denver, the role of hyaluronan in lung disease was first recognized decades ago.
“Data stretching back into the 1970s has identified decreases in hyaluronan content in emphysematous lung tissue, protection of lung connective tissue from proteolysis by hyaluronan, and potential therapeutic roles for hyaluronan in a variety of disease, especially of the lungs,” he said in an interview.
For patients with COPD, treatment with HMW-HA may provide benefit by counteracting an imbalance in diseased lung tissue, wrote Dr. Galdi and colleagues.
“Emerging evidence suggests that imbalance between declining HMW-HA levels, and increasing smaller fragments of hyaluronan may contribute to chronic airway disease pathogenesis,” they wrote. “This has led to the hypothesis that exogenous supplementation of HMW-HA may restore hyaluronan homeostasis in favor of undegraded molecules, inhibit inflammation and loss of lung function, and ameliorate COPD progression.”
To test this hypothesis, the investigators screened 44 patients with a history of acute exacerbations of COPD necessitating NIPPV, ultimately excluding 3 patients because of heart failure. Following 1:1 randomization, 20 patients received HMW-HA while 21 received placebo, each twice daily, in conjunction with NIPPV and standard medical therapy. Treatment continued until NIPPV failure or liberation from NIPPV. Most patients received NIPPV in the hospital; however, home/chronic NIPPV was given to four patients in the placebo group and three patients in the HMW-HA group.
The primary outcome was duration of NIPPV. Secondary outcomes included markers of systemic inflammation associated with acute exacerbations of COPD and respiratory physiology parameters. Adverse events were also reported.
Results showed that patients treated with HMW-HA were liberated sooner from NIPPV than were those who received placebo (mean, 5.2 vs 6.4 days; P < .037). Similarly, patients in the HMW-HA group had significantly shorter hospital stay, on average, than those in the placebo group (mean, 7.2 vs 10.2 days; P = .039). Median values followed a similar pattern.
“These data suggest that HMW-HA shortened the duration of acute respiratory failure, need for NIPPV and, consequently, hospital length of stay in these patients,” the investigators wrote.
Secondary outcomes further supported these therapeutic benefits. Compared with placebo, HMW-HA was associated with significantly lower peak pressure and greater improvements in both pCO2/FiO2 ratio and inflammatory markers. No adverse events were reported.
Further analyses involving human bronchial epithelial cell cultures offered some mechanistic insight. Using micro-optical coherence tomography imaging, the investigators found that HMW-HA treatment was associated with “a prominent effect on mucociliary transport” in cell cultures derived from COPD patients and in healthy nonsmoker cell cultures exposed to cigarette smoke extract.
“Our study shows for the first time the therapeutic potential of an extracellular matrix molecule in acute exacerbation of human lung disease,” the investigators concluded, noting a “clinically meaningful salutary effect” on duration of NIPPV.
Dr. Galdi and colleagues went on to predict that benefits in a real-world patient population could be even more meaningful.
“Since the serum samples were collected at the end of NIPPV, HMW-HA–treated patients were on average sampled a day earlier than placebo-treated patients (because they were liberated from NIPPV a day earlier on average),” the investigators wrote. “Thus, HMW-HA treatment effects may have been underestimated in our study.”
According to Dr. Sandhaus, “The current report, while a relatively small single-center study, is well controlled and the results suggest that inhaled hyaluronan decreased time on noninvasive ventilation, decreased hospital stay duration, and decreased some mediators of inflammation.”
He also suggested that HMW-HA may have a role in the prophylactic setting.
“The limitations of this pilot study are appropriately explored by the authors but do not dampen the exciting possibility that this therapeutic approach may hold promise not only in severe exacerbations of COPD but potentially for the prevention of such exacerbations,” Dr. Sandhaus said.
Jerome O. Cantor, MD, FCCP, of St. John’s University, New York, who previously conducted a pilot study for using lower molecular weight hyaluronan in COPD and published a review on the subject, said that more studies are necessary.
“Further clinical trials are needed to better determine the role of hyaluronan as an adjunct to existing therapies for COPD exacerbations,” he said.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The investigators and Dr. Sandhaus declared no conflicts of interest. Dr. Cantor disclosed a relationship with MatRx Therapeutics.
(COPD), findings of a new study suggest.
HMW-HA was associated with a significantly shorter duration of noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation (NIPPV), lower systemic inflammatory markers, and lower measured peak airway pressure, compared with placebo, reported lead author Flavia Galdi, MD, of Campus Bio-Medico University Hospital, Rome, and colleagues.
“HMW-HA is a naturally occurring sugar that is abundant in the extracellular matrix, including in the lung,” the investigators wrote in Respiratory Research. “[It] has been used routinely, together with hypertonic saline, in cystic fibrosis patients [for several years] with no reported side effects; rather, it improves tolerability and decreases the need for bronchodilators in these patients.”
According to Robert A. Sandhaus, MD, PhD, FCCP, of National Jewish Health, Denver, the role of hyaluronan in lung disease was first recognized decades ago.
“Data stretching back into the 1970s has identified decreases in hyaluronan content in emphysematous lung tissue, protection of lung connective tissue from proteolysis by hyaluronan, and potential therapeutic roles for hyaluronan in a variety of disease, especially of the lungs,” he said in an interview.
For patients with COPD, treatment with HMW-HA may provide benefit by counteracting an imbalance in diseased lung tissue, wrote Dr. Galdi and colleagues.
“Emerging evidence suggests that imbalance between declining HMW-HA levels, and increasing smaller fragments of hyaluronan may contribute to chronic airway disease pathogenesis,” they wrote. “This has led to the hypothesis that exogenous supplementation of HMW-HA may restore hyaluronan homeostasis in favor of undegraded molecules, inhibit inflammation and loss of lung function, and ameliorate COPD progression.”
To test this hypothesis, the investigators screened 44 patients with a history of acute exacerbations of COPD necessitating NIPPV, ultimately excluding 3 patients because of heart failure. Following 1:1 randomization, 20 patients received HMW-HA while 21 received placebo, each twice daily, in conjunction with NIPPV and standard medical therapy. Treatment continued until NIPPV failure or liberation from NIPPV. Most patients received NIPPV in the hospital; however, home/chronic NIPPV was given to four patients in the placebo group and three patients in the HMW-HA group.
The primary outcome was duration of NIPPV. Secondary outcomes included markers of systemic inflammation associated with acute exacerbations of COPD and respiratory physiology parameters. Adverse events were also reported.
Results showed that patients treated with HMW-HA were liberated sooner from NIPPV than were those who received placebo (mean, 5.2 vs 6.4 days; P < .037). Similarly, patients in the HMW-HA group had significantly shorter hospital stay, on average, than those in the placebo group (mean, 7.2 vs 10.2 days; P = .039). Median values followed a similar pattern.
“These data suggest that HMW-HA shortened the duration of acute respiratory failure, need for NIPPV and, consequently, hospital length of stay in these patients,” the investigators wrote.
Secondary outcomes further supported these therapeutic benefits. Compared with placebo, HMW-HA was associated with significantly lower peak pressure and greater improvements in both pCO2/FiO2 ratio and inflammatory markers. No adverse events were reported.
Further analyses involving human bronchial epithelial cell cultures offered some mechanistic insight. Using micro-optical coherence tomography imaging, the investigators found that HMW-HA treatment was associated with “a prominent effect on mucociliary transport” in cell cultures derived from COPD patients and in healthy nonsmoker cell cultures exposed to cigarette smoke extract.
“Our study shows for the first time the therapeutic potential of an extracellular matrix molecule in acute exacerbation of human lung disease,” the investigators concluded, noting a “clinically meaningful salutary effect” on duration of NIPPV.
Dr. Galdi and colleagues went on to predict that benefits in a real-world patient population could be even more meaningful.
“Since the serum samples were collected at the end of NIPPV, HMW-HA–treated patients were on average sampled a day earlier than placebo-treated patients (because they were liberated from NIPPV a day earlier on average),” the investigators wrote. “Thus, HMW-HA treatment effects may have been underestimated in our study.”
According to Dr. Sandhaus, “The current report, while a relatively small single-center study, is well controlled and the results suggest that inhaled hyaluronan decreased time on noninvasive ventilation, decreased hospital stay duration, and decreased some mediators of inflammation.”
He also suggested that HMW-HA may have a role in the prophylactic setting.
“The limitations of this pilot study are appropriately explored by the authors but do not dampen the exciting possibility that this therapeutic approach may hold promise not only in severe exacerbations of COPD but potentially for the prevention of such exacerbations,” Dr. Sandhaus said.
Jerome O. Cantor, MD, FCCP, of St. John’s University, New York, who previously conducted a pilot study for using lower molecular weight hyaluronan in COPD and published a review on the subject, said that more studies are necessary.
“Further clinical trials are needed to better determine the role of hyaluronan as an adjunct to existing therapies for COPD exacerbations,” he said.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The investigators and Dr. Sandhaus declared no conflicts of interest. Dr. Cantor disclosed a relationship with MatRx Therapeutics.
FROM RESPIRATORY RESEARCH
Women increasingly turn to CBD, with or without doc’s blessing
When 42-year-old Danielle Simone Brand started having hormonal migraines, she first turned to cannabidiol (CBD) oil, eventually adding an occasional pull on a prefilled tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) vape for nighttime use. She was careful to avoid THC during work hours. A parenting and cannabis writer, Ms. Brand had more than a cursory background in cannabinoid medicine and had spent time at her local California dispensary discussing various cannabinoid components that might help alleviate her pain.
A self-professed “do-it-yourselfer,” Ms. Brand continues to use cannabinoids for her monthly headaches, forgoing any other pain medication. “There are times for conventional medicine in partnership with your doctor, but when it comes to health and wellness, women should be empowered to make decisions and self-experiment,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Brand is not alone. Significant numbers of women are replacing or supplementing prescription medications with cannabinoids, often without consulting their primary care physician, ob.gyn., or other specialist. At times, women have tried to have these conversations, only to be met with silence or worse.
Take Linda Fuller, a 58-year-old yoga instructor from Long Island who says that she uses CBD and THC for chronic sacroiliac pain after a car accident and to alleviate stress-triggered eczema flares. “I’ve had doctors turn their backs on me; I’ve had nurse practitioners walk out on me in the middle of a sentence,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Fuller said her conversion to cannabinoid medicine is relatively new; she never used cannabis recreationally before her accident but now considers it a gift. She doesn’t keep aspirin in the house and refused pain medication immediately after she injured her back.
Diana Krach, a 34-year-old writer from Maryland, says she’s encountered roadblocks about her decision to use cannabinoids for endometriosis and for pain from Crohn’s disease. When she tried to discuss her CBD use with a gastroenterologist, he interrupted her: “Whatever pot you’re smoking isn’t going to work, you’re going on biologics.”
Ms. Krach had not been smoking anything but had turned to a CBD tincture for symptom relief after prescription pain medications failed to help.
Ms. Brand, Ms. Fuller, and Ms. Krach are the tip of the iceberg when it comes to women seeking symptom relief outside the medicine cabinet. A recent survey in the Journal of Women’s Health of almost 1,000 women show that 90% (most between the ages of 35 and 44) had used cannabis and would consider using it to treat gynecologic pain. Roughly 80% said they would consider using it for procedure-related pain or other conditions. Additionally, women have reported using cannabinoids for PTSD, sleep disturbances or insomnia, anxiety, and migraine headaches.
Observational survey data have likewise shown that 80% of women with advanced or recurrent gynecologic malignancies who were prescribed cannabis reported that it was equivalent or superior to other medications for relieving pain, neuropathy, nausea, insomnia, decreased appetite, and anxiety.
In another survey, almost half (45%) of women with gynecologic malignancies who used nonprescribed cannabis for the same symptoms reported that they had reduced their use of prescription narcotics after initiating use of cannabis.
The gray zone
There has been a surge in self-reported cannabis use among pregnant women in particular. The National Survey on Drug Use and Health findings for the periods 2002-2003 and 2016-2017 highlight increases in adjusted prevalence rates from 3.4% to 7% in past-month use among pregnant women overall and from 5.7% to 12.1% during the first trimester alone.
“The more that you talk to pregnant women, the more that you realize that a lot are using cannabinoids for something that is basically medicinal, for sleep, for anxiety, or for nausea,” Katrina Mark, MD, an ob.gyn. and associate professor of medicine at the University of Maryland, College Park, said in an interview. “I’m not saying it’s fine to use drugs in pregnancy, but it is a grayer conversation than a lot of colleagues want to believe. Telling women to quit seems foolish since the alternative is to be anxious, don’t sleep, don’t eat, or use a medication that also has risks to it.”
One observational study shows that pregnant women themselves are conflicted. Although the majority believe that cannabis is “natural” and “safe,” compared with prescription drugs, they aren’t entirely in the dark about potential risks. They often express frustration with practitioners’ responses when these topics are broached during office visits. An observational survey among women and practitioners published in 2020 highlights that only half of doctors openly discouraged perinatal cannabis use and that others opted out of the discussion entirely.
This is the experience of many of the women that this news organization spoke with. Ms. Krach pointed out that “there’s a big deficit in listening; the doctor is supposed to be working for our behalf, especially when it comes to reproductive health.”
Dr. Mark believed that a lot of the conversation has been clouded by the illegality of the substance but that cannabinoids deserve as much of a fair chance for discussion and consideration as other medicines, which also carry risks in pregnancy. “There’s literally no evidence that it will work in pregnancy [for these symptoms], but there’s no evidence that it doesn’t, either,” she said in an interview. “When I have this conversation with colleagues who do not share my views, I try to encourage them to look at the actual risks versus the benefits versus the alternatives.”
The ‘entourage effect’
Data supporting cannabinoids have been mostly laboratory based, case based, or observational. However, several well-designed (albeit small) trials have demonstrated efficacy for chronic pain conditions, including neuropathic and headache pain, as well as in Crohn’s disease. Most investigators have concluded that dosage is important and that there is a synergistic interaction between compounds (known as the “entourage effect”) that relates to cannabinoid efficacy or lack thereof, as well as possible adverse effects.
In addition to legality issues, the entourage effect is one of the most important factors related to the medical use of cannabinoids. “There are literally thousands of cultivars of cannabis, each with their own phytocannabinoid and terpenic profiles that may produce distinct therapeutic effects, [so] it is misguided to speak of cannabis in monolithic terms. It is like making broad claims about soup,” wrote coauthor Samoon Ahmad, MD, in Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook.
Additionally, the role that reproductive hormones play is not entirely understood. Reproductive-aged women appear to be more susceptible to a “telescoping” (gender-related progression to dependence) effect in comparison with men. Ziva Cooper, PhD, director of the Cannabis Research Initiative at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview. She explained that research has shown that factors such as the degree of exposure, frequency of use, and menses confound this susceptibility.
It’s the data
Frustration over cannabinoid therapeutics abound, especially when it comes to data, legal issues, and lack of training. “The feedback that I hear from providers is that there isn’t enough information; we just don’t know enough about it,” Dr. Mark said, “but there is information that we do have, and ignoring it is not beneficial.”
Dr. Cooper concurred. Although she readily acknowledges that data from randomized, placebo-controlled trials are mostly lacking, she says, “There are signals in the literature providing evidence for the utility of cannabis and cannabinoids for pain and some other effects.”
Other practitioners said in an interview that some patients admit to using cannabinoids but that they lack the ample information to guide these patients. By and large, many women equate “natural” with “safe,” and some will experiment on their own to see what works.
Those experiments are not without risk, which is why “it’s just as important for physicians to talk to their patients about cannabis use as it is for patients to be forthcoming about that use,” said Dr. Cooper. “It could have implications on their overall health as well as interactions with other drugs that they’re using.”
That balance from a clinical perspective on cannabis is crucial, wrote coauthor Kenneth Hill, MD, in Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook. “Without it,” he wrote, “the window of opportunity for a patient to accept treatment that she needs may not be open very long.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When 42-year-old Danielle Simone Brand started having hormonal migraines, she first turned to cannabidiol (CBD) oil, eventually adding an occasional pull on a prefilled tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) vape for nighttime use. She was careful to avoid THC during work hours. A parenting and cannabis writer, Ms. Brand had more than a cursory background in cannabinoid medicine and had spent time at her local California dispensary discussing various cannabinoid components that might help alleviate her pain.
A self-professed “do-it-yourselfer,” Ms. Brand continues to use cannabinoids for her monthly headaches, forgoing any other pain medication. “There are times for conventional medicine in partnership with your doctor, but when it comes to health and wellness, women should be empowered to make decisions and self-experiment,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Brand is not alone. Significant numbers of women are replacing or supplementing prescription medications with cannabinoids, often without consulting their primary care physician, ob.gyn., or other specialist. At times, women have tried to have these conversations, only to be met with silence or worse.
Take Linda Fuller, a 58-year-old yoga instructor from Long Island who says that she uses CBD and THC for chronic sacroiliac pain after a car accident and to alleviate stress-triggered eczema flares. “I’ve had doctors turn their backs on me; I’ve had nurse practitioners walk out on me in the middle of a sentence,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Fuller said her conversion to cannabinoid medicine is relatively new; she never used cannabis recreationally before her accident but now considers it a gift. She doesn’t keep aspirin in the house and refused pain medication immediately after she injured her back.
Diana Krach, a 34-year-old writer from Maryland, says she’s encountered roadblocks about her decision to use cannabinoids for endometriosis and for pain from Crohn’s disease. When she tried to discuss her CBD use with a gastroenterologist, he interrupted her: “Whatever pot you’re smoking isn’t going to work, you’re going on biologics.”
Ms. Krach had not been smoking anything but had turned to a CBD tincture for symptom relief after prescription pain medications failed to help.
Ms. Brand, Ms. Fuller, and Ms. Krach are the tip of the iceberg when it comes to women seeking symptom relief outside the medicine cabinet. A recent survey in the Journal of Women’s Health of almost 1,000 women show that 90% (most between the ages of 35 and 44) had used cannabis and would consider using it to treat gynecologic pain. Roughly 80% said they would consider using it for procedure-related pain or other conditions. Additionally, women have reported using cannabinoids for PTSD, sleep disturbances or insomnia, anxiety, and migraine headaches.
Observational survey data have likewise shown that 80% of women with advanced or recurrent gynecologic malignancies who were prescribed cannabis reported that it was equivalent or superior to other medications for relieving pain, neuropathy, nausea, insomnia, decreased appetite, and anxiety.
In another survey, almost half (45%) of women with gynecologic malignancies who used nonprescribed cannabis for the same symptoms reported that they had reduced their use of prescription narcotics after initiating use of cannabis.
The gray zone
There has been a surge in self-reported cannabis use among pregnant women in particular. The National Survey on Drug Use and Health findings for the periods 2002-2003 and 2016-2017 highlight increases in adjusted prevalence rates from 3.4% to 7% in past-month use among pregnant women overall and from 5.7% to 12.1% during the first trimester alone.
“The more that you talk to pregnant women, the more that you realize that a lot are using cannabinoids for something that is basically medicinal, for sleep, for anxiety, or for nausea,” Katrina Mark, MD, an ob.gyn. and associate professor of medicine at the University of Maryland, College Park, said in an interview. “I’m not saying it’s fine to use drugs in pregnancy, but it is a grayer conversation than a lot of colleagues want to believe. Telling women to quit seems foolish since the alternative is to be anxious, don’t sleep, don’t eat, or use a medication that also has risks to it.”
One observational study shows that pregnant women themselves are conflicted. Although the majority believe that cannabis is “natural” and “safe,” compared with prescription drugs, they aren’t entirely in the dark about potential risks. They often express frustration with practitioners’ responses when these topics are broached during office visits. An observational survey among women and practitioners published in 2020 highlights that only half of doctors openly discouraged perinatal cannabis use and that others opted out of the discussion entirely.
This is the experience of many of the women that this news organization spoke with. Ms. Krach pointed out that “there’s a big deficit in listening; the doctor is supposed to be working for our behalf, especially when it comes to reproductive health.”
Dr. Mark believed that a lot of the conversation has been clouded by the illegality of the substance but that cannabinoids deserve as much of a fair chance for discussion and consideration as other medicines, which also carry risks in pregnancy. “There’s literally no evidence that it will work in pregnancy [for these symptoms], but there’s no evidence that it doesn’t, either,” she said in an interview. “When I have this conversation with colleagues who do not share my views, I try to encourage them to look at the actual risks versus the benefits versus the alternatives.”
The ‘entourage effect’
Data supporting cannabinoids have been mostly laboratory based, case based, or observational. However, several well-designed (albeit small) trials have demonstrated efficacy for chronic pain conditions, including neuropathic and headache pain, as well as in Crohn’s disease. Most investigators have concluded that dosage is important and that there is a synergistic interaction between compounds (known as the “entourage effect”) that relates to cannabinoid efficacy or lack thereof, as well as possible adverse effects.
In addition to legality issues, the entourage effect is one of the most important factors related to the medical use of cannabinoids. “There are literally thousands of cultivars of cannabis, each with their own phytocannabinoid and terpenic profiles that may produce distinct therapeutic effects, [so] it is misguided to speak of cannabis in monolithic terms. It is like making broad claims about soup,” wrote coauthor Samoon Ahmad, MD, in Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook.
Additionally, the role that reproductive hormones play is not entirely understood. Reproductive-aged women appear to be more susceptible to a “telescoping” (gender-related progression to dependence) effect in comparison with men. Ziva Cooper, PhD, director of the Cannabis Research Initiative at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview. She explained that research has shown that factors such as the degree of exposure, frequency of use, and menses confound this susceptibility.
It’s the data
Frustration over cannabinoid therapeutics abound, especially when it comes to data, legal issues, and lack of training. “The feedback that I hear from providers is that there isn’t enough information; we just don’t know enough about it,” Dr. Mark said, “but there is information that we do have, and ignoring it is not beneficial.”
Dr. Cooper concurred. Although she readily acknowledges that data from randomized, placebo-controlled trials are mostly lacking, she says, “There are signals in the literature providing evidence for the utility of cannabis and cannabinoids for pain and some other effects.”
Other practitioners said in an interview that some patients admit to using cannabinoids but that they lack the ample information to guide these patients. By and large, many women equate “natural” with “safe,” and some will experiment on their own to see what works.
Those experiments are not without risk, which is why “it’s just as important for physicians to talk to their patients about cannabis use as it is for patients to be forthcoming about that use,” said Dr. Cooper. “It could have implications on their overall health as well as interactions with other drugs that they’re using.”
That balance from a clinical perspective on cannabis is crucial, wrote coauthor Kenneth Hill, MD, in Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook. “Without it,” he wrote, “the window of opportunity for a patient to accept treatment that she needs may not be open very long.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When 42-year-old Danielle Simone Brand started having hormonal migraines, she first turned to cannabidiol (CBD) oil, eventually adding an occasional pull on a prefilled tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) vape for nighttime use. She was careful to avoid THC during work hours. A parenting and cannabis writer, Ms. Brand had more than a cursory background in cannabinoid medicine and had spent time at her local California dispensary discussing various cannabinoid components that might help alleviate her pain.
A self-professed “do-it-yourselfer,” Ms. Brand continues to use cannabinoids for her monthly headaches, forgoing any other pain medication. “There are times for conventional medicine in partnership with your doctor, but when it comes to health and wellness, women should be empowered to make decisions and self-experiment,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Brand is not alone. Significant numbers of women are replacing or supplementing prescription medications with cannabinoids, often without consulting their primary care physician, ob.gyn., or other specialist. At times, women have tried to have these conversations, only to be met with silence or worse.
Take Linda Fuller, a 58-year-old yoga instructor from Long Island who says that she uses CBD and THC for chronic sacroiliac pain after a car accident and to alleviate stress-triggered eczema flares. “I’ve had doctors turn their backs on me; I’ve had nurse practitioners walk out on me in the middle of a sentence,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Fuller said her conversion to cannabinoid medicine is relatively new; she never used cannabis recreationally before her accident but now considers it a gift. She doesn’t keep aspirin in the house and refused pain medication immediately after she injured her back.
Diana Krach, a 34-year-old writer from Maryland, says she’s encountered roadblocks about her decision to use cannabinoids for endometriosis and for pain from Crohn’s disease. When she tried to discuss her CBD use with a gastroenterologist, he interrupted her: “Whatever pot you’re smoking isn’t going to work, you’re going on biologics.”
Ms. Krach had not been smoking anything but had turned to a CBD tincture for symptom relief after prescription pain medications failed to help.
Ms. Brand, Ms. Fuller, and Ms. Krach are the tip of the iceberg when it comes to women seeking symptom relief outside the medicine cabinet. A recent survey in the Journal of Women’s Health of almost 1,000 women show that 90% (most between the ages of 35 and 44) had used cannabis and would consider using it to treat gynecologic pain. Roughly 80% said they would consider using it for procedure-related pain or other conditions. Additionally, women have reported using cannabinoids for PTSD, sleep disturbances or insomnia, anxiety, and migraine headaches.
Observational survey data have likewise shown that 80% of women with advanced or recurrent gynecologic malignancies who were prescribed cannabis reported that it was equivalent or superior to other medications for relieving pain, neuropathy, nausea, insomnia, decreased appetite, and anxiety.
In another survey, almost half (45%) of women with gynecologic malignancies who used nonprescribed cannabis for the same symptoms reported that they had reduced their use of prescription narcotics after initiating use of cannabis.
The gray zone
There has been a surge in self-reported cannabis use among pregnant women in particular. The National Survey on Drug Use and Health findings for the periods 2002-2003 and 2016-2017 highlight increases in adjusted prevalence rates from 3.4% to 7% in past-month use among pregnant women overall and from 5.7% to 12.1% during the first trimester alone.
“The more that you talk to pregnant women, the more that you realize that a lot are using cannabinoids for something that is basically medicinal, for sleep, for anxiety, or for nausea,” Katrina Mark, MD, an ob.gyn. and associate professor of medicine at the University of Maryland, College Park, said in an interview. “I’m not saying it’s fine to use drugs in pregnancy, but it is a grayer conversation than a lot of colleagues want to believe. Telling women to quit seems foolish since the alternative is to be anxious, don’t sleep, don’t eat, or use a medication that also has risks to it.”
One observational study shows that pregnant women themselves are conflicted. Although the majority believe that cannabis is “natural” and “safe,” compared with prescription drugs, they aren’t entirely in the dark about potential risks. They often express frustration with practitioners’ responses when these topics are broached during office visits. An observational survey among women and practitioners published in 2020 highlights that only half of doctors openly discouraged perinatal cannabis use and that others opted out of the discussion entirely.
This is the experience of many of the women that this news organization spoke with. Ms. Krach pointed out that “there’s a big deficit in listening; the doctor is supposed to be working for our behalf, especially when it comes to reproductive health.”
Dr. Mark believed that a lot of the conversation has been clouded by the illegality of the substance but that cannabinoids deserve as much of a fair chance for discussion and consideration as other medicines, which also carry risks in pregnancy. “There’s literally no evidence that it will work in pregnancy [for these symptoms], but there’s no evidence that it doesn’t, either,” she said in an interview. “When I have this conversation with colleagues who do not share my views, I try to encourage them to look at the actual risks versus the benefits versus the alternatives.”
The ‘entourage effect’
Data supporting cannabinoids have been mostly laboratory based, case based, or observational. However, several well-designed (albeit small) trials have demonstrated efficacy for chronic pain conditions, including neuropathic and headache pain, as well as in Crohn’s disease. Most investigators have concluded that dosage is important and that there is a synergistic interaction between compounds (known as the “entourage effect”) that relates to cannabinoid efficacy or lack thereof, as well as possible adverse effects.
In addition to legality issues, the entourage effect is one of the most important factors related to the medical use of cannabinoids. “There are literally thousands of cultivars of cannabis, each with their own phytocannabinoid and terpenic profiles that may produce distinct therapeutic effects, [so] it is misguided to speak of cannabis in monolithic terms. It is like making broad claims about soup,” wrote coauthor Samoon Ahmad, MD, in Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook.
Additionally, the role that reproductive hormones play is not entirely understood. Reproductive-aged women appear to be more susceptible to a “telescoping” (gender-related progression to dependence) effect in comparison with men. Ziva Cooper, PhD, director of the Cannabis Research Initiative at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview. She explained that research has shown that factors such as the degree of exposure, frequency of use, and menses confound this susceptibility.
It’s the data
Frustration over cannabinoid therapeutics abound, especially when it comes to data, legal issues, and lack of training. “The feedback that I hear from providers is that there isn’t enough information; we just don’t know enough about it,” Dr. Mark said, “but there is information that we do have, and ignoring it is not beneficial.”
Dr. Cooper concurred. Although she readily acknowledges that data from randomized, placebo-controlled trials are mostly lacking, she says, “There are signals in the literature providing evidence for the utility of cannabis and cannabinoids for pain and some other effects.”
Other practitioners said in an interview that some patients admit to using cannabinoids but that they lack the ample information to guide these patients. By and large, many women equate “natural” with “safe,” and some will experiment on their own to see what works.
Those experiments are not without risk, which is why “it’s just as important for physicians to talk to their patients about cannabis use as it is for patients to be forthcoming about that use,” said Dr. Cooper. “It could have implications on their overall health as well as interactions with other drugs that they’re using.”
That balance from a clinical perspective on cannabis is crucial, wrote coauthor Kenneth Hill, MD, in Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook. “Without it,” he wrote, “the window of opportunity for a patient to accept treatment that she needs may not be open very long.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘We can do better’: COVID-19 vaccination in patients with cancer
Every day, around 1.5 million doses of the COVID-19 vaccine are being delivered across the United States, but oncologists and patient advocates say that patients with cancer are missing out.
While official bodies recommend that patients with cancer are given priority, only 16 states currently prioritize them in the vaccine rollout. The other 34 states have thus far not singled out patients with cancer for earlier vaccination.
This flies in the face of recommendations from heavy hitters such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, and the American Association for Cancer Research.
All are in agreement: Patients on active cancer treatment should be prioritized for available vaccine because of their greater risk of death or complications from SARS-CoV-2 infection.
“All municipalities, states, cities, and even individual hospitals have so far been left to their own devices to try to figure out what the best way to do this is and that often conflicts with other recommendations or guidelines,” said E. John Wherry, PhD, chair of the department of systems pharmacology and translational therapeutics at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Dr. Wherry was on a panel at an AACR conference last week that discussed the failings of vaccine delivery to cancer patients.
During the meeting, lung cancer advocate Jill Feldman commented on the situation in Chicago, one of the jurisdictions that has not prioritized patients with cancer: “People don’t know what to do. ‘Do I need to sign up myself somewhere? Is my doctor’s office going to contact me?’ ”
Ms. Feldman said many people have called their cancer centers, “but cancer centers aren’t really providing updates directly to us. And they aren’t because they don’t have the information [either].”
Even in the 16 states that have ushered patients with cancer to the front of the line, the process for flagging these individuals is often unclear or nonexistent.
“Everyone that registers is basically on the same playing field ... because there’s no verification process. That’s very unfortunate,” said patient advocate Grace Cordovano, PhD, describing the vaccine sign-up process in New Jersey.
“It’s an easy fix,” said Dr. Cordovano. “Adding a few more fields [in the form] could really make a difference.”
COVID-19 fatality rates are twice as high in people with cancer than in people without cancer, according to a review published in December 2020 by the AACR’s COVID-19 and Cancer Task Force in the journal Cancer Discovery. Hematologic malignancies conferred an especially high risk.
“Any delay in vaccine access will result in loss of life that could be prevented with earlier access to vaccination,” AACR President Antoni Ribas, MD, told this news organization at the time.
There are also sound epidemiologic reasons to prioritize high-risk cancer patients for the COVID-19 vaccine, Dr. Wherry said in an interview. “What we do in infectious disease is to think about where your transmission and your risks are highest,” he said, citing cancer treatment centers as examples.
People with hematologic malignancies also tend to be long-term viral shedders, he said, putting caregivers and health care staff at increased risk. “There’s a big, big impact [in vaccinating cancer patients] and the numbers are not small.”
The CDC’s Jan. 1 recommendation is that patients with cancer should be assigned to priority group 1c, along with other “persons aged 16-64 with other high-risk medical conditions.”
However, more recent guidance from the NCCN hastened the urgency, advising that “patients with cancer should be assigned to the [CDC] priority group 1b/c.”
Out of 16 states that currently prioritize patients with cancer, 3 states have exceeded official advice, placing patients with cancer in priority group 1a. They opened their first batches of vaccine to everyone “deemed extremely vulnerable to COVID-19 by hospital providers” (Florida), or to “16-64 years old with a chronic health condition” (Mississippi) and to “persons aged 16-64 with high-risk conditions” (Pennsylvania, some jurisdictions).
However, despite these heroic intentions, no jurisdiction appears to have specifically tackled the thorny issue of subgroups of cancer that are more urgent than others, and this worries oncologists.
“Not all cancer patients are the same,” said Marina Garassino, MD, a medical oncologist at the National Tumor Institute of Milan. She shared registry data with the AACR panelists indicating that COVID-19 mortality in thoracic and hematologic malignancies rises to 30%-40%, compared with 13% for cancer overall.
At the AACR meeting, Dr. Ribas summed up his feelings on the issue: “It’s clear to me that patients with cancer should be prioritized. We have to then start defining this population and it should be the patient with an active cancer diagnosis undergoing treatment, in particular patients with lung cancers or hematologic malignancies.”
Since patients with cancer as a whole have problems getting timely vaccination – let alone someone with lung cancer or leukemia – the AACR meeting panelists grappled with solutions.
Dr. Cordovano said it was a “no brainer” to start with cancer centers. “Patients there are already registered, they have an account in the electronic health record system, they have insurance information, the care team knows them.”
Vaccination referrals sent directly from oncology centers would eliminate the need for the patient to provide verification or any additional documentation, she pointed out.
However, in New Jersey, cancer centers “have been completely excluded from the process,” she said.
Florida and New Hampshire have somewhat adopted the mechanism suggested by Dr. Cordovano. These states require health care providers to verify that a patient is “especially vulnerable” (Florida) or “medically vulnerable” (New Hampshire) in order for the patient to receive priority vaccine access. In New Hampshire, patients must have at least one other medical condition in addition to cancer to get on the list.
Jia Luo, MD, a medical oncology fellow at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, told the meeting that MSKCC has set up a proactive task force that sends “daily emails” to clinic staff highlighting patients eligible for the vaccine. “My sense is, it’s being prioritized to active cancer treatment,” said Dr. Luo. “All of our physicians are currently discussing [it] at each appointment and ... all of our nurses and staff have been talking to our patients on the phone.”
Dr. Cordovano, while advocating hard for cancer patients today, retained optimism about tomorrow: “This isn’t a long-term thing. This is just until things catch up. We knew we were going to have this problem.” Her hope is that, within 6 months, COVID-19 vaccination will become a standard of care in cancer.
Dr. Wherry agreed: “It’s going to take time to catch up with how far behind we are on certain things. ... What we’re seeing is a healthy debate rather than something that we should be concerned about – as long as that debate leads to rapid action.”
“We have to follow the science,” concluded Cordovano. “We can do better than this.”
Dr. Cordovano, Ms. Feldman, and Dr. Wherry have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Luo declared a financial relationship with Targeted Oncology. Dr. Ribas declared financial relationships with 4C Biomed, Advaxis, Agilent, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Arcus, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Kite-Gilead.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Every day, around 1.5 million doses of the COVID-19 vaccine are being delivered across the United States, but oncologists and patient advocates say that patients with cancer are missing out.
While official bodies recommend that patients with cancer are given priority, only 16 states currently prioritize them in the vaccine rollout. The other 34 states have thus far not singled out patients with cancer for earlier vaccination.
This flies in the face of recommendations from heavy hitters such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, and the American Association for Cancer Research.
All are in agreement: Patients on active cancer treatment should be prioritized for available vaccine because of their greater risk of death or complications from SARS-CoV-2 infection.
“All municipalities, states, cities, and even individual hospitals have so far been left to their own devices to try to figure out what the best way to do this is and that often conflicts with other recommendations or guidelines,” said E. John Wherry, PhD, chair of the department of systems pharmacology and translational therapeutics at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Dr. Wherry was on a panel at an AACR conference last week that discussed the failings of vaccine delivery to cancer patients.
During the meeting, lung cancer advocate Jill Feldman commented on the situation in Chicago, one of the jurisdictions that has not prioritized patients with cancer: “People don’t know what to do. ‘Do I need to sign up myself somewhere? Is my doctor’s office going to contact me?’ ”
Ms. Feldman said many people have called their cancer centers, “but cancer centers aren’t really providing updates directly to us. And they aren’t because they don’t have the information [either].”
Even in the 16 states that have ushered patients with cancer to the front of the line, the process for flagging these individuals is often unclear or nonexistent.
“Everyone that registers is basically on the same playing field ... because there’s no verification process. That’s very unfortunate,” said patient advocate Grace Cordovano, PhD, describing the vaccine sign-up process in New Jersey.
“It’s an easy fix,” said Dr. Cordovano. “Adding a few more fields [in the form] could really make a difference.”
COVID-19 fatality rates are twice as high in people with cancer than in people without cancer, according to a review published in December 2020 by the AACR’s COVID-19 and Cancer Task Force in the journal Cancer Discovery. Hematologic malignancies conferred an especially high risk.
“Any delay in vaccine access will result in loss of life that could be prevented with earlier access to vaccination,” AACR President Antoni Ribas, MD, told this news organization at the time.
There are also sound epidemiologic reasons to prioritize high-risk cancer patients for the COVID-19 vaccine, Dr. Wherry said in an interview. “What we do in infectious disease is to think about where your transmission and your risks are highest,” he said, citing cancer treatment centers as examples.
People with hematologic malignancies also tend to be long-term viral shedders, he said, putting caregivers and health care staff at increased risk. “There’s a big, big impact [in vaccinating cancer patients] and the numbers are not small.”
The CDC’s Jan. 1 recommendation is that patients with cancer should be assigned to priority group 1c, along with other “persons aged 16-64 with other high-risk medical conditions.”
However, more recent guidance from the NCCN hastened the urgency, advising that “patients with cancer should be assigned to the [CDC] priority group 1b/c.”
Out of 16 states that currently prioritize patients with cancer, 3 states have exceeded official advice, placing patients with cancer in priority group 1a. They opened their first batches of vaccine to everyone “deemed extremely vulnerable to COVID-19 by hospital providers” (Florida), or to “16-64 years old with a chronic health condition” (Mississippi) and to “persons aged 16-64 with high-risk conditions” (Pennsylvania, some jurisdictions).
However, despite these heroic intentions, no jurisdiction appears to have specifically tackled the thorny issue of subgroups of cancer that are more urgent than others, and this worries oncologists.
“Not all cancer patients are the same,” said Marina Garassino, MD, a medical oncologist at the National Tumor Institute of Milan. She shared registry data with the AACR panelists indicating that COVID-19 mortality in thoracic and hematologic malignancies rises to 30%-40%, compared with 13% for cancer overall.
At the AACR meeting, Dr. Ribas summed up his feelings on the issue: “It’s clear to me that patients with cancer should be prioritized. We have to then start defining this population and it should be the patient with an active cancer diagnosis undergoing treatment, in particular patients with lung cancers or hematologic malignancies.”
Since patients with cancer as a whole have problems getting timely vaccination – let alone someone with lung cancer or leukemia – the AACR meeting panelists grappled with solutions.
Dr. Cordovano said it was a “no brainer” to start with cancer centers. “Patients there are already registered, they have an account in the electronic health record system, they have insurance information, the care team knows them.”
Vaccination referrals sent directly from oncology centers would eliminate the need for the patient to provide verification or any additional documentation, she pointed out.
However, in New Jersey, cancer centers “have been completely excluded from the process,” she said.
Florida and New Hampshire have somewhat adopted the mechanism suggested by Dr. Cordovano. These states require health care providers to verify that a patient is “especially vulnerable” (Florida) or “medically vulnerable” (New Hampshire) in order for the patient to receive priority vaccine access. In New Hampshire, patients must have at least one other medical condition in addition to cancer to get on the list.
Jia Luo, MD, a medical oncology fellow at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, told the meeting that MSKCC has set up a proactive task force that sends “daily emails” to clinic staff highlighting patients eligible for the vaccine. “My sense is, it’s being prioritized to active cancer treatment,” said Dr. Luo. “All of our physicians are currently discussing [it] at each appointment and ... all of our nurses and staff have been talking to our patients on the phone.”
Dr. Cordovano, while advocating hard for cancer patients today, retained optimism about tomorrow: “This isn’t a long-term thing. This is just until things catch up. We knew we were going to have this problem.” Her hope is that, within 6 months, COVID-19 vaccination will become a standard of care in cancer.
Dr. Wherry agreed: “It’s going to take time to catch up with how far behind we are on certain things. ... What we’re seeing is a healthy debate rather than something that we should be concerned about – as long as that debate leads to rapid action.”
“We have to follow the science,” concluded Cordovano. “We can do better than this.”
Dr. Cordovano, Ms. Feldman, and Dr. Wherry have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Luo declared a financial relationship with Targeted Oncology. Dr. Ribas declared financial relationships with 4C Biomed, Advaxis, Agilent, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Arcus, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Kite-Gilead.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Every day, around 1.5 million doses of the COVID-19 vaccine are being delivered across the United States, but oncologists and patient advocates say that patients with cancer are missing out.
While official bodies recommend that patients with cancer are given priority, only 16 states currently prioritize them in the vaccine rollout. The other 34 states have thus far not singled out patients with cancer for earlier vaccination.
This flies in the face of recommendations from heavy hitters such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, and the American Association for Cancer Research.
All are in agreement: Patients on active cancer treatment should be prioritized for available vaccine because of their greater risk of death or complications from SARS-CoV-2 infection.
“All municipalities, states, cities, and even individual hospitals have so far been left to their own devices to try to figure out what the best way to do this is and that often conflicts with other recommendations or guidelines,” said E. John Wherry, PhD, chair of the department of systems pharmacology and translational therapeutics at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Dr. Wherry was on a panel at an AACR conference last week that discussed the failings of vaccine delivery to cancer patients.
During the meeting, lung cancer advocate Jill Feldman commented on the situation in Chicago, one of the jurisdictions that has not prioritized patients with cancer: “People don’t know what to do. ‘Do I need to sign up myself somewhere? Is my doctor’s office going to contact me?’ ”
Ms. Feldman said many people have called their cancer centers, “but cancer centers aren’t really providing updates directly to us. And they aren’t because they don’t have the information [either].”
Even in the 16 states that have ushered patients with cancer to the front of the line, the process for flagging these individuals is often unclear or nonexistent.
“Everyone that registers is basically on the same playing field ... because there’s no verification process. That’s very unfortunate,” said patient advocate Grace Cordovano, PhD, describing the vaccine sign-up process in New Jersey.
“It’s an easy fix,” said Dr. Cordovano. “Adding a few more fields [in the form] could really make a difference.”
COVID-19 fatality rates are twice as high in people with cancer than in people without cancer, according to a review published in December 2020 by the AACR’s COVID-19 and Cancer Task Force in the journal Cancer Discovery. Hematologic malignancies conferred an especially high risk.
“Any delay in vaccine access will result in loss of life that could be prevented with earlier access to vaccination,” AACR President Antoni Ribas, MD, told this news organization at the time.
There are also sound epidemiologic reasons to prioritize high-risk cancer patients for the COVID-19 vaccine, Dr. Wherry said in an interview. “What we do in infectious disease is to think about where your transmission and your risks are highest,” he said, citing cancer treatment centers as examples.
People with hematologic malignancies also tend to be long-term viral shedders, he said, putting caregivers and health care staff at increased risk. “There’s a big, big impact [in vaccinating cancer patients] and the numbers are not small.”
The CDC’s Jan. 1 recommendation is that patients with cancer should be assigned to priority group 1c, along with other “persons aged 16-64 with other high-risk medical conditions.”
However, more recent guidance from the NCCN hastened the urgency, advising that “patients with cancer should be assigned to the [CDC] priority group 1b/c.”
Out of 16 states that currently prioritize patients with cancer, 3 states have exceeded official advice, placing patients with cancer in priority group 1a. They opened their first batches of vaccine to everyone “deemed extremely vulnerable to COVID-19 by hospital providers” (Florida), or to “16-64 years old with a chronic health condition” (Mississippi) and to “persons aged 16-64 with high-risk conditions” (Pennsylvania, some jurisdictions).
However, despite these heroic intentions, no jurisdiction appears to have specifically tackled the thorny issue of subgroups of cancer that are more urgent than others, and this worries oncologists.
“Not all cancer patients are the same,” said Marina Garassino, MD, a medical oncologist at the National Tumor Institute of Milan. She shared registry data with the AACR panelists indicating that COVID-19 mortality in thoracic and hematologic malignancies rises to 30%-40%, compared with 13% for cancer overall.
At the AACR meeting, Dr. Ribas summed up his feelings on the issue: “It’s clear to me that patients with cancer should be prioritized. We have to then start defining this population and it should be the patient with an active cancer diagnosis undergoing treatment, in particular patients with lung cancers or hematologic malignancies.”
Since patients with cancer as a whole have problems getting timely vaccination – let alone someone with lung cancer or leukemia – the AACR meeting panelists grappled with solutions.
Dr. Cordovano said it was a “no brainer” to start with cancer centers. “Patients there are already registered, they have an account in the electronic health record system, they have insurance information, the care team knows them.”
Vaccination referrals sent directly from oncology centers would eliminate the need for the patient to provide verification or any additional documentation, she pointed out.
However, in New Jersey, cancer centers “have been completely excluded from the process,” she said.
Florida and New Hampshire have somewhat adopted the mechanism suggested by Dr. Cordovano. These states require health care providers to verify that a patient is “especially vulnerable” (Florida) or “medically vulnerable” (New Hampshire) in order for the patient to receive priority vaccine access. In New Hampshire, patients must have at least one other medical condition in addition to cancer to get on the list.
Jia Luo, MD, a medical oncology fellow at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, told the meeting that MSKCC has set up a proactive task force that sends “daily emails” to clinic staff highlighting patients eligible for the vaccine. “My sense is, it’s being prioritized to active cancer treatment,” said Dr. Luo. “All of our physicians are currently discussing [it] at each appointment and ... all of our nurses and staff have been talking to our patients on the phone.”
Dr. Cordovano, while advocating hard for cancer patients today, retained optimism about tomorrow: “This isn’t a long-term thing. This is just until things catch up. We knew we were going to have this problem.” Her hope is that, within 6 months, COVID-19 vaccination will become a standard of care in cancer.
Dr. Wherry agreed: “It’s going to take time to catch up with how far behind we are on certain things. ... What we’re seeing is a healthy debate rather than something that we should be concerned about – as long as that debate leads to rapid action.”
“We have to follow the science,” concluded Cordovano. “We can do better than this.”
Dr. Cordovano, Ms. Feldman, and Dr. Wherry have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Luo declared a financial relationship with Targeted Oncology. Dr. Ribas declared financial relationships with 4C Biomed, Advaxis, Agilent, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Arcus, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Kite-Gilead.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.