User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
States allow doctors to practice across state lines during COVID-19 crisis
Legal orders and waivers of licensing requirements could change the way many doctors see patients during the COVID-19 crisis.
A number of states have already taken steps to waive their requirement that a physician be licensed in the state in order to provide care to patients. California and Florida are among the states that have done so – through their respective declarations of statewide emergency. More states are sure to follow.
Another route around traditional medical licensing requirements is the Uniform Emergency Volunteer Health Practitioner Act (UEVHPA), which – in the 20 or so states that have adopted it – can take effect once a statewide emergency is declared. This law lets volunteer health practitioners who are licensed in another state practice in the state where the emergency was declared, without first needing to obtain a license there. The practitioner need only be in good standing with any state in which he or she is currently licensed and be registered as a volunteer in the system. The Washington State Department of Health was one of the first such departments to invoke the UEVHPA in response to the coronavirus.
“The waiving of state licensure requirements should help ease a number of stress points of the current crisis in ways that benefit society,” said Gregory A. Hood, MD, an internist in Lexington, Ky., who is on the advisory board of Medscape Business of Medicine.
“As many have chosen to shelter in place, hoping to ride out the end of winter and, optimistically, the COVID-19 pandemic, there are physicians with second homes in South Carolina, Florida, and elsewhere who could be envisioned being brought into service to ease staffing shortfalls should the crisis exceed available resources.
“However, likely the most novel, necessary, and widespread impact of the waiving of licensure requirements will be aiding physicians in practicing telehealth video visits, as now authorized by Medicare and (hopefully) commercial insurers,” said Dr. Hood.
“Historically, there has been concern regarding the fact that most state medical boards require the physician to be licensed in the state where the patient resides or is located,” he said. “[Recently] I was able to conduct a video visit with a patient in Florida, at her initiation, over the potential of a broken bone. The case should be expected to have fallen under an emergency, but this waiver provides reassuring clarity.
“With the assistance of her boyfriend performing elements of the physical examination under my direction, we were able to establish a probable diagnosis, as well as a treatment plan – all while avoiding her exposing herself by leaving voluntary self-isolation or consuming resources in the emergency room,” Dr. Hood said.
Elsewhere, in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the Federation of State Medical Boards has announced that it will act to verify licenses and credentials for doctors wishing to practice across state lines.
The “emergency exception” to in-state licensing requirements
Most state medical boards recognize some version of an exception to the in-state licensing requirement if a doctor or other healthcare professional is providing emergency care to a patient. But these exceptions rarely define what qualifies as an emergency. So, whether treatment of a COVID-19 patient or treatment of a non-COVID-19 patient who requires care in a triage setting constitutes an emergency – so that the exception to the licensing requirement applies—has been something of an open question.
What’s more, many states have laid out various exceptions to the exception. For example, in some states, the person providing the emergency treatment cannot be doing so in exchange for monetary compensation. Elsewhere, the emergency treatment must be provided outside of a traditional health care setting (not in a hospital or doctor’s office) to qualify under the exception.
Is expedited medical licensing an option?
There are ways for a care provider to obtain a medical license in some states without relying on the traditional (and often time-intensive) process. In Ohio, for example, the state’s medical board can issue an expedited license to practice medicine, although the care provider still needs to submit an application – in other words, expedited licensing can’t be granted retroactively. And in many states – including California, where medical board staff is required to complete initial review of an application within 60 working days – an expedited application isn’t an option (at least not yet).
Around 30 states have joined the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact, which makes it easier for doctors to get licensed in multiple states through an expedited application process. According to the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact Commission, around 80% of doctors meet the criteria for licensing through the Compact.
Why licensing matters
State medical boards and other licensing agencies protect patients by making sure that an individual who practices medicine in the state is qualified to do so. That means scrutinizing applications to practice medicine in the state, reviewing credentials, and ensuring fitness to practice.
The practice of medicine without a license is typically considered a criminal act and is punishable by a variety of different sanctions (criminal, administrative, and professional). What’s more, the fact that a care provider was practicing medicine without a license could set the table for allegations of medical malpractice.
From a liability standpoint, if a doctor or other clinician treats a patient in a state where the clinician is unlicensed, then it’s a near certainty that any medical liability insurance the doctor carries will not apply to the treatment scenario. Suppose a patient is given substandard care and suffers harm at some point within the unlicensed treatment setting, and the patient files a malpractice lawsuit. In that situation, the doctor (and not an insurance company with so-called “deep pockets”) will be on the financial hook for the patient’s harm.
Doctors and other health care providers continue to serve the most critical of roles in our nation’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Like most things related to COVID-19, the information presented here is sure to change.
David Goguen is a legal editor at Nolo whose work focuses on claimants’ rights in personal injury cases. He is a member of the California State Bar and has more than a decade of experience in litigation and legal publishing. He is a graduate of the University of San Francisco School of Law.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Legal orders and waivers of licensing requirements could change the way many doctors see patients during the COVID-19 crisis.
A number of states have already taken steps to waive their requirement that a physician be licensed in the state in order to provide care to patients. California and Florida are among the states that have done so – through their respective declarations of statewide emergency. More states are sure to follow.
Another route around traditional medical licensing requirements is the Uniform Emergency Volunteer Health Practitioner Act (UEVHPA), which – in the 20 or so states that have adopted it – can take effect once a statewide emergency is declared. This law lets volunteer health practitioners who are licensed in another state practice in the state where the emergency was declared, without first needing to obtain a license there. The practitioner need only be in good standing with any state in which he or she is currently licensed and be registered as a volunteer in the system. The Washington State Department of Health was one of the first such departments to invoke the UEVHPA in response to the coronavirus.
“The waiving of state licensure requirements should help ease a number of stress points of the current crisis in ways that benefit society,” said Gregory A. Hood, MD, an internist in Lexington, Ky., who is on the advisory board of Medscape Business of Medicine.
“As many have chosen to shelter in place, hoping to ride out the end of winter and, optimistically, the COVID-19 pandemic, there are physicians with second homes in South Carolina, Florida, and elsewhere who could be envisioned being brought into service to ease staffing shortfalls should the crisis exceed available resources.
“However, likely the most novel, necessary, and widespread impact of the waiving of licensure requirements will be aiding physicians in practicing telehealth video visits, as now authorized by Medicare and (hopefully) commercial insurers,” said Dr. Hood.
“Historically, there has been concern regarding the fact that most state medical boards require the physician to be licensed in the state where the patient resides or is located,” he said. “[Recently] I was able to conduct a video visit with a patient in Florida, at her initiation, over the potential of a broken bone. The case should be expected to have fallen under an emergency, but this waiver provides reassuring clarity.
“With the assistance of her boyfriend performing elements of the physical examination under my direction, we were able to establish a probable diagnosis, as well as a treatment plan – all while avoiding her exposing herself by leaving voluntary self-isolation or consuming resources in the emergency room,” Dr. Hood said.
Elsewhere, in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the Federation of State Medical Boards has announced that it will act to verify licenses and credentials for doctors wishing to practice across state lines.
The “emergency exception” to in-state licensing requirements
Most state medical boards recognize some version of an exception to the in-state licensing requirement if a doctor or other healthcare professional is providing emergency care to a patient. But these exceptions rarely define what qualifies as an emergency. So, whether treatment of a COVID-19 patient or treatment of a non-COVID-19 patient who requires care in a triage setting constitutes an emergency – so that the exception to the licensing requirement applies—has been something of an open question.
What’s more, many states have laid out various exceptions to the exception. For example, in some states, the person providing the emergency treatment cannot be doing so in exchange for monetary compensation. Elsewhere, the emergency treatment must be provided outside of a traditional health care setting (not in a hospital or doctor’s office) to qualify under the exception.
Is expedited medical licensing an option?
There are ways for a care provider to obtain a medical license in some states without relying on the traditional (and often time-intensive) process. In Ohio, for example, the state’s medical board can issue an expedited license to practice medicine, although the care provider still needs to submit an application – in other words, expedited licensing can’t be granted retroactively. And in many states – including California, where medical board staff is required to complete initial review of an application within 60 working days – an expedited application isn’t an option (at least not yet).
Around 30 states have joined the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact, which makes it easier for doctors to get licensed in multiple states through an expedited application process. According to the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact Commission, around 80% of doctors meet the criteria for licensing through the Compact.
Why licensing matters
State medical boards and other licensing agencies protect patients by making sure that an individual who practices medicine in the state is qualified to do so. That means scrutinizing applications to practice medicine in the state, reviewing credentials, and ensuring fitness to practice.
The practice of medicine without a license is typically considered a criminal act and is punishable by a variety of different sanctions (criminal, administrative, and professional). What’s more, the fact that a care provider was practicing medicine without a license could set the table for allegations of medical malpractice.
From a liability standpoint, if a doctor or other clinician treats a patient in a state where the clinician is unlicensed, then it’s a near certainty that any medical liability insurance the doctor carries will not apply to the treatment scenario. Suppose a patient is given substandard care and suffers harm at some point within the unlicensed treatment setting, and the patient files a malpractice lawsuit. In that situation, the doctor (and not an insurance company with so-called “deep pockets”) will be on the financial hook for the patient’s harm.
Doctors and other health care providers continue to serve the most critical of roles in our nation’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Like most things related to COVID-19, the information presented here is sure to change.
David Goguen is a legal editor at Nolo whose work focuses on claimants’ rights in personal injury cases. He is a member of the California State Bar and has more than a decade of experience in litigation and legal publishing. He is a graduate of the University of San Francisco School of Law.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Legal orders and waivers of licensing requirements could change the way many doctors see patients during the COVID-19 crisis.
A number of states have already taken steps to waive their requirement that a physician be licensed in the state in order to provide care to patients. California and Florida are among the states that have done so – through their respective declarations of statewide emergency. More states are sure to follow.
Another route around traditional medical licensing requirements is the Uniform Emergency Volunteer Health Practitioner Act (UEVHPA), which – in the 20 or so states that have adopted it – can take effect once a statewide emergency is declared. This law lets volunteer health practitioners who are licensed in another state practice in the state where the emergency was declared, without first needing to obtain a license there. The practitioner need only be in good standing with any state in which he or she is currently licensed and be registered as a volunteer in the system. The Washington State Department of Health was one of the first such departments to invoke the UEVHPA in response to the coronavirus.
“The waiving of state licensure requirements should help ease a number of stress points of the current crisis in ways that benefit society,” said Gregory A. Hood, MD, an internist in Lexington, Ky., who is on the advisory board of Medscape Business of Medicine.
“As many have chosen to shelter in place, hoping to ride out the end of winter and, optimistically, the COVID-19 pandemic, there are physicians with second homes in South Carolina, Florida, and elsewhere who could be envisioned being brought into service to ease staffing shortfalls should the crisis exceed available resources.
“However, likely the most novel, necessary, and widespread impact of the waiving of licensure requirements will be aiding physicians in practicing telehealth video visits, as now authorized by Medicare and (hopefully) commercial insurers,” said Dr. Hood.
“Historically, there has been concern regarding the fact that most state medical boards require the physician to be licensed in the state where the patient resides or is located,” he said. “[Recently] I was able to conduct a video visit with a patient in Florida, at her initiation, over the potential of a broken bone. The case should be expected to have fallen under an emergency, but this waiver provides reassuring clarity.
“With the assistance of her boyfriend performing elements of the physical examination under my direction, we were able to establish a probable diagnosis, as well as a treatment plan – all while avoiding her exposing herself by leaving voluntary self-isolation or consuming resources in the emergency room,” Dr. Hood said.
Elsewhere, in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the Federation of State Medical Boards has announced that it will act to verify licenses and credentials for doctors wishing to practice across state lines.
The “emergency exception” to in-state licensing requirements
Most state medical boards recognize some version of an exception to the in-state licensing requirement if a doctor or other healthcare professional is providing emergency care to a patient. But these exceptions rarely define what qualifies as an emergency. So, whether treatment of a COVID-19 patient or treatment of a non-COVID-19 patient who requires care in a triage setting constitutes an emergency – so that the exception to the licensing requirement applies—has been something of an open question.
What’s more, many states have laid out various exceptions to the exception. For example, in some states, the person providing the emergency treatment cannot be doing so in exchange for monetary compensation. Elsewhere, the emergency treatment must be provided outside of a traditional health care setting (not in a hospital or doctor’s office) to qualify under the exception.
Is expedited medical licensing an option?
There are ways for a care provider to obtain a medical license in some states without relying on the traditional (and often time-intensive) process. In Ohio, for example, the state’s medical board can issue an expedited license to practice medicine, although the care provider still needs to submit an application – in other words, expedited licensing can’t be granted retroactively. And in many states – including California, where medical board staff is required to complete initial review of an application within 60 working days – an expedited application isn’t an option (at least not yet).
Around 30 states have joined the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact, which makes it easier for doctors to get licensed in multiple states through an expedited application process. According to the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact Commission, around 80% of doctors meet the criteria for licensing through the Compact.
Why licensing matters
State medical boards and other licensing agencies protect patients by making sure that an individual who practices medicine in the state is qualified to do so. That means scrutinizing applications to practice medicine in the state, reviewing credentials, and ensuring fitness to practice.
The practice of medicine without a license is typically considered a criminal act and is punishable by a variety of different sanctions (criminal, administrative, and professional). What’s more, the fact that a care provider was practicing medicine without a license could set the table for allegations of medical malpractice.
From a liability standpoint, if a doctor or other clinician treats a patient in a state where the clinician is unlicensed, then it’s a near certainty that any medical liability insurance the doctor carries will not apply to the treatment scenario. Suppose a patient is given substandard care and suffers harm at some point within the unlicensed treatment setting, and the patient files a malpractice lawsuit. In that situation, the doctor (and not an insurance company with so-called “deep pockets”) will be on the financial hook for the patient’s harm.
Doctors and other health care providers continue to serve the most critical of roles in our nation’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Like most things related to COVID-19, the information presented here is sure to change.
David Goguen is a legal editor at Nolo whose work focuses on claimants’ rights in personal injury cases. He is a member of the California State Bar and has more than a decade of experience in litigation and legal publishing. He is a graduate of the University of San Francisco School of Law.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Firings, furloughs, and pay cuts in advance of COVID-19 surge
Doctors at a Boston-area hospital learned via video conferencing that they would be receiving a 20% pay cut – a slap in the face at the precise moment that those on the front lines of the COVID-19 pandemic need a pat on the back (and more N95 respirators).
But Steward Health Care System*, which runs the hospital and dozens of others around the country, did the math and decided that the pay cuts were necessary to survive what they called “a seismic shock to our system.” They also announced furloughs for a large number of their nonclinical staff.
Spirits sank after the announcement. “It was devastating,” said one Boston doctor, who works for Steward and asked not to be identified for fear of retribution. “I didn’t say much during the call because I was so panicked, and I didn’t want to be crying on the call.”
Someone else did speak up, a senior colleague who warned that such a cut would kill morale at a time when physicians were already feeling vulnerable because of other shortages, including personal protective equipment. (Requests for interviews with Steward Health Care System executives were declined.)
Furloughs, layoffs, and even firings are happening elsewhere too. Hospitals in virus hotspots have already come up short on beds and face masks. Now a shortage of cash is prompting many to fire some of their health care workers, furlough them temporarily, or – like Steward Health Care System – slash their pay checks.
Despite almost $200 billion earmarked for hospital systems in the recently passed federal stimulus package, many hospitals are still in dire financial straits. Most make the majority of their money through so-called elective procedures, such as knee replacements and cataract surgeries, almost all of which have been postponed in order to conserve personal protective equipment and minimize spread of the virus. Those cancellations translate to a significant financial hit.
On top of that, hospitals will lose an average of $1,800 on every COVID-19 case, according to projections by Strata Decision Technology, a health care financial planning and analytic company. Some, they estimate, may lose much more, between $6,000 and $8,000 per patient. And hospitals were already hurting. According to a report from Bloomberg, at least 30 hospitals entered bankruptcy in 2019.
“This pressure on institutions to control costs has been around for several years,” said Steve Lefar, executive director of the data science division of Strata Decision Technology and lead author of the study. “This is just making it incredibly acute for them.”
Many hospital executives are bracing for months of hardship, leading to wrenching decisions to furlough or lay off staff, suspend bonuses, or cut pay – even as some short-staffed hospitals in COVID-19 hotspots are issuing pleas for doctors to come out of retirement.
Forward thinking?
While most furloughs and layoffs so far have affected people who don’t work directly with patients, many on the front lines have been hit with pay cuts or withheld bonuses or retirement contributions. In Massachusetts, the state’s medical society has asked Governor Charlie Baker for financial relief for health care workers in the form of grants, no-interest or forgivable small-business loans for physician practices, and deferment of medical student loan payments.
At St. Alexius Hospital in St. Louis, Sonny Saggar, MD, was fired as CEO after he clashed with a bankruptcy trustee. Dr. Saggar had proposed offering open beds to other hospital systems during the pandemic – an idea that, he said, was turned down out of concern for the bottom line.
“This is one of those times where we need to put down our search for profit and money and just look after people’s lives. We’re supposed to have that calling in health care,” said Dr. Saggar, who has since been reinstated as chief strategy officer and director of the COVID task force and ED. He noted that he and the trustee have resolved differences over funding.
At St. Claire HealthCare in Morehead, Ky., 300 employees who were not involved in direct patient care – a quarter of the hospital’s staff – have been furloughed, something Donald Lloyd II, St. Claire HealthCare’s CEO as of May 1, described as forward thinking.
To prepare for the influx of COVID-19 patients, the hospital shut down elective procedures early. “Prudence dictates the need to be extremely proactive,” Mr. Lloyd said. “We need to devote our limited resources to frontline clinical teams.”
Other hospitals are making similar moves, although many are not doing so publicly. Mr. Lloyd decided to put out a press release because he found it offensive that the federal government was “bailing out airlines and cruise lines before our frontline men and women caring for patients.”
Massachusetts-based Atrius Health, for instance, placed many staffers on a 1-month furlough, while simultaneously withholding a percentage of working physicians’ paychecks, saying that they plan to pay them back at a later date. TriHealth, in Cincinnati, looked elsewhere for ways to save money. Instead of cutting physician salaries, 11 executives took a 20% pay cut.
There are both better and worse ways to go about such staff reductions, according to Mr. Lefar. If reductions have to be made, it would be best if CEOs keep cuts as far away as possible from the front lines of patient care.
“My bias is to start with pay reductions for high-paid executives, then furloughs, and beyond that layoffs,” he said. (Furloughs allow employees to be brought back and receive unemployment benefits while not working.) “Anyone related to patient care – these are the people who are getting the country through this, these are the heroes.”
After the pandemic
Large hospital systems that can designate separate buildings for COVID-19 care may fare best financially, Mr. Lefar said. By retaining a clean, noninfectious facility, such setups could allow for an earlier return to regular procedures – as long as rapid COVID-19 testing becomes available.
Smaller hospitals, nearly half of which run at a financial loss, according to the Chartis Center for Rural Health, face the additional burdens of both limited capacity and a limited ability to separate COVID-19 care.
Mostly, Mr. Lefar said, it’s a matter of doing whatever is necessary to get through the worst of it. “A lot of what is deemed elective or scheduled will come back,” he said. “Right now it’s crisis mode. ... I think it’s going to be a rough 6-9 months, but we will get back to it.”
*Correction, 4/7/20: An earlier version of this article misstated the name of a hospital in the Boston area run by Steward Health Care System.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctors at a Boston-area hospital learned via video conferencing that they would be receiving a 20% pay cut – a slap in the face at the precise moment that those on the front lines of the COVID-19 pandemic need a pat on the back (and more N95 respirators).
But Steward Health Care System*, which runs the hospital and dozens of others around the country, did the math and decided that the pay cuts were necessary to survive what they called “a seismic shock to our system.” They also announced furloughs for a large number of their nonclinical staff.
Spirits sank after the announcement. “It was devastating,” said one Boston doctor, who works for Steward and asked not to be identified for fear of retribution. “I didn’t say much during the call because I was so panicked, and I didn’t want to be crying on the call.”
Someone else did speak up, a senior colleague who warned that such a cut would kill morale at a time when physicians were already feeling vulnerable because of other shortages, including personal protective equipment. (Requests for interviews with Steward Health Care System executives were declined.)
Furloughs, layoffs, and even firings are happening elsewhere too. Hospitals in virus hotspots have already come up short on beds and face masks. Now a shortage of cash is prompting many to fire some of their health care workers, furlough them temporarily, or – like Steward Health Care System – slash their pay checks.
Despite almost $200 billion earmarked for hospital systems in the recently passed federal stimulus package, many hospitals are still in dire financial straits. Most make the majority of their money through so-called elective procedures, such as knee replacements and cataract surgeries, almost all of which have been postponed in order to conserve personal protective equipment and minimize spread of the virus. Those cancellations translate to a significant financial hit.
On top of that, hospitals will lose an average of $1,800 on every COVID-19 case, according to projections by Strata Decision Technology, a health care financial planning and analytic company. Some, they estimate, may lose much more, between $6,000 and $8,000 per patient. And hospitals were already hurting. According to a report from Bloomberg, at least 30 hospitals entered bankruptcy in 2019.
“This pressure on institutions to control costs has been around for several years,” said Steve Lefar, executive director of the data science division of Strata Decision Technology and lead author of the study. “This is just making it incredibly acute for them.”
Many hospital executives are bracing for months of hardship, leading to wrenching decisions to furlough or lay off staff, suspend bonuses, or cut pay – even as some short-staffed hospitals in COVID-19 hotspots are issuing pleas for doctors to come out of retirement.
Forward thinking?
While most furloughs and layoffs so far have affected people who don’t work directly with patients, many on the front lines have been hit with pay cuts or withheld bonuses or retirement contributions. In Massachusetts, the state’s medical society has asked Governor Charlie Baker for financial relief for health care workers in the form of grants, no-interest or forgivable small-business loans for physician practices, and deferment of medical student loan payments.
At St. Alexius Hospital in St. Louis, Sonny Saggar, MD, was fired as CEO after he clashed with a bankruptcy trustee. Dr. Saggar had proposed offering open beds to other hospital systems during the pandemic – an idea that, he said, was turned down out of concern for the bottom line.
“This is one of those times where we need to put down our search for profit and money and just look after people’s lives. We’re supposed to have that calling in health care,” said Dr. Saggar, who has since been reinstated as chief strategy officer and director of the COVID task force and ED. He noted that he and the trustee have resolved differences over funding.
At St. Claire HealthCare in Morehead, Ky., 300 employees who were not involved in direct patient care – a quarter of the hospital’s staff – have been furloughed, something Donald Lloyd II, St. Claire HealthCare’s CEO as of May 1, described as forward thinking.
To prepare for the influx of COVID-19 patients, the hospital shut down elective procedures early. “Prudence dictates the need to be extremely proactive,” Mr. Lloyd said. “We need to devote our limited resources to frontline clinical teams.”
Other hospitals are making similar moves, although many are not doing so publicly. Mr. Lloyd decided to put out a press release because he found it offensive that the federal government was “bailing out airlines and cruise lines before our frontline men and women caring for patients.”
Massachusetts-based Atrius Health, for instance, placed many staffers on a 1-month furlough, while simultaneously withholding a percentage of working physicians’ paychecks, saying that they plan to pay them back at a later date. TriHealth, in Cincinnati, looked elsewhere for ways to save money. Instead of cutting physician salaries, 11 executives took a 20% pay cut.
There are both better and worse ways to go about such staff reductions, according to Mr. Lefar. If reductions have to be made, it would be best if CEOs keep cuts as far away as possible from the front lines of patient care.
“My bias is to start with pay reductions for high-paid executives, then furloughs, and beyond that layoffs,” he said. (Furloughs allow employees to be brought back and receive unemployment benefits while not working.) “Anyone related to patient care – these are the people who are getting the country through this, these are the heroes.”
After the pandemic
Large hospital systems that can designate separate buildings for COVID-19 care may fare best financially, Mr. Lefar said. By retaining a clean, noninfectious facility, such setups could allow for an earlier return to regular procedures – as long as rapid COVID-19 testing becomes available.
Smaller hospitals, nearly half of which run at a financial loss, according to the Chartis Center for Rural Health, face the additional burdens of both limited capacity and a limited ability to separate COVID-19 care.
Mostly, Mr. Lefar said, it’s a matter of doing whatever is necessary to get through the worst of it. “A lot of what is deemed elective or scheduled will come back,” he said. “Right now it’s crisis mode. ... I think it’s going to be a rough 6-9 months, but we will get back to it.”
*Correction, 4/7/20: An earlier version of this article misstated the name of a hospital in the Boston area run by Steward Health Care System.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctors at a Boston-area hospital learned via video conferencing that they would be receiving a 20% pay cut – a slap in the face at the precise moment that those on the front lines of the COVID-19 pandemic need a pat on the back (and more N95 respirators).
But Steward Health Care System*, which runs the hospital and dozens of others around the country, did the math and decided that the pay cuts were necessary to survive what they called “a seismic shock to our system.” They also announced furloughs for a large number of their nonclinical staff.
Spirits sank after the announcement. “It was devastating,” said one Boston doctor, who works for Steward and asked not to be identified for fear of retribution. “I didn’t say much during the call because I was so panicked, and I didn’t want to be crying on the call.”
Someone else did speak up, a senior colleague who warned that such a cut would kill morale at a time when physicians were already feeling vulnerable because of other shortages, including personal protective equipment. (Requests for interviews with Steward Health Care System executives were declined.)
Furloughs, layoffs, and even firings are happening elsewhere too. Hospitals in virus hotspots have already come up short on beds and face masks. Now a shortage of cash is prompting many to fire some of their health care workers, furlough them temporarily, or – like Steward Health Care System – slash their pay checks.
Despite almost $200 billion earmarked for hospital systems in the recently passed federal stimulus package, many hospitals are still in dire financial straits. Most make the majority of their money through so-called elective procedures, such as knee replacements and cataract surgeries, almost all of which have been postponed in order to conserve personal protective equipment and minimize spread of the virus. Those cancellations translate to a significant financial hit.
On top of that, hospitals will lose an average of $1,800 on every COVID-19 case, according to projections by Strata Decision Technology, a health care financial planning and analytic company. Some, they estimate, may lose much more, between $6,000 and $8,000 per patient. And hospitals were already hurting. According to a report from Bloomberg, at least 30 hospitals entered bankruptcy in 2019.
“This pressure on institutions to control costs has been around for several years,” said Steve Lefar, executive director of the data science division of Strata Decision Technology and lead author of the study. “This is just making it incredibly acute for them.”
Many hospital executives are bracing for months of hardship, leading to wrenching decisions to furlough or lay off staff, suspend bonuses, or cut pay – even as some short-staffed hospitals in COVID-19 hotspots are issuing pleas for doctors to come out of retirement.
Forward thinking?
While most furloughs and layoffs so far have affected people who don’t work directly with patients, many on the front lines have been hit with pay cuts or withheld bonuses or retirement contributions. In Massachusetts, the state’s medical society has asked Governor Charlie Baker for financial relief for health care workers in the form of grants, no-interest or forgivable small-business loans for physician practices, and deferment of medical student loan payments.
At St. Alexius Hospital in St. Louis, Sonny Saggar, MD, was fired as CEO after he clashed with a bankruptcy trustee. Dr. Saggar had proposed offering open beds to other hospital systems during the pandemic – an idea that, he said, was turned down out of concern for the bottom line.
“This is one of those times where we need to put down our search for profit and money and just look after people’s lives. We’re supposed to have that calling in health care,” said Dr. Saggar, who has since been reinstated as chief strategy officer and director of the COVID task force and ED. He noted that he and the trustee have resolved differences over funding.
At St. Claire HealthCare in Morehead, Ky., 300 employees who were not involved in direct patient care – a quarter of the hospital’s staff – have been furloughed, something Donald Lloyd II, St. Claire HealthCare’s CEO as of May 1, described as forward thinking.
To prepare for the influx of COVID-19 patients, the hospital shut down elective procedures early. “Prudence dictates the need to be extremely proactive,” Mr. Lloyd said. “We need to devote our limited resources to frontline clinical teams.”
Other hospitals are making similar moves, although many are not doing so publicly. Mr. Lloyd decided to put out a press release because he found it offensive that the federal government was “bailing out airlines and cruise lines before our frontline men and women caring for patients.”
Massachusetts-based Atrius Health, for instance, placed many staffers on a 1-month furlough, while simultaneously withholding a percentage of working physicians’ paychecks, saying that they plan to pay them back at a later date. TriHealth, in Cincinnati, looked elsewhere for ways to save money. Instead of cutting physician salaries, 11 executives took a 20% pay cut.
There are both better and worse ways to go about such staff reductions, according to Mr. Lefar. If reductions have to be made, it would be best if CEOs keep cuts as far away as possible from the front lines of patient care.
“My bias is to start with pay reductions for high-paid executives, then furloughs, and beyond that layoffs,” he said. (Furloughs allow employees to be brought back and receive unemployment benefits while not working.) “Anyone related to patient care – these are the people who are getting the country through this, these are the heroes.”
After the pandemic
Large hospital systems that can designate separate buildings for COVID-19 care may fare best financially, Mr. Lefar said. By retaining a clean, noninfectious facility, such setups could allow for an earlier return to regular procedures – as long as rapid COVID-19 testing becomes available.
Smaller hospitals, nearly half of which run at a financial loss, according to the Chartis Center for Rural Health, face the additional burdens of both limited capacity and a limited ability to separate COVID-19 care.
Mostly, Mr. Lefar said, it’s a matter of doing whatever is necessary to get through the worst of it. “A lot of what is deemed elective or scheduled will come back,” he said. “Right now it’s crisis mode. ... I think it’s going to be a rough 6-9 months, but we will get back to it.”
*Correction, 4/7/20: An earlier version of this article misstated the name of a hospital in the Boston area run by Steward Health Care System.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Rise in autism prevalence indicates earlier diagnosis
The prevalence of autism spectrum disorder in 4-year-olds rose from 2014 to 2016, indicating more early identification of ASD among the children born in 2012, compared with 2008, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
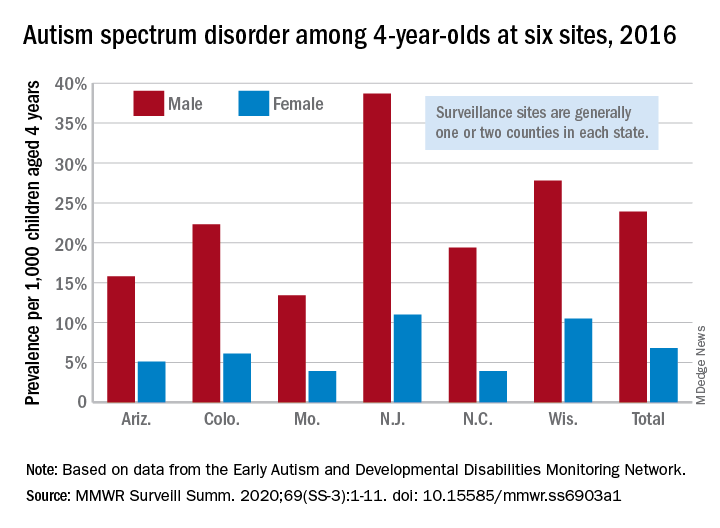
Data from individual surveillance sites in the CDC’s Early Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (Early ADDM) Network, however, show “wide variability in estimates [that] could reflect variable success in improving community identification,” Kelly A. Shaw, PhD, and associates wrote in MMWR Surveillance Summaries.
they reported.
“In addition, the cumulative incidence of ASD diagnoses at age 48 months was higher for children born in 2012 than for children born in 2008, which indicates a higher rate of diagnosis for the younger cohort,” wrote Dr. Shaw of the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, Atlanta, and associates.
A closer look at the six Early ADDM Network sites shows considerable variation in prevalence. The New Jersey site, consisting of one full county and part of another that includes metropolitan Newark, reported a rate of 25.3 per 1,000 – 38.7 for males and 11.0 for females – while the rates for Missouri – one county in metropolitan St. Louis – were 13.4 (male), 3.9 (female), and 8.8 (combined), the investigators wrote.
ASD prevalence across the six sites was 3.5 times higher among males (23.9 per 1,000) than females (6.8). “Cumulative incidence patterns also differed by sex, with a steady increase in diagnoses with age for boys but an apparent plateau for girls at approximately age 36 months,” they noted.
The median age at earliest diagnosis was 33 months for all sites, with North Carolina lowest at 29 months and Wisconsin highest at 36 months.
The overall median, Dr. Shaw and associates pointed out, is “well above the youngest age at which ASD can be identified, [so] work remains to improve early diagnosis so children can receive timely services.”
SOURCE: Shaw KA et al. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2020;69(SS-3):1-11. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss6903a1.
The prevalence of autism spectrum disorder in 4-year-olds rose from 2014 to 2016, indicating more early identification of ASD among the children born in 2012, compared with 2008, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Data from individual surveillance sites in the CDC’s Early Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (Early ADDM) Network, however, show “wide variability in estimates [that] could reflect variable success in improving community identification,” Kelly A. Shaw, PhD, and associates wrote in MMWR Surveillance Summaries.
they reported.
“In addition, the cumulative incidence of ASD diagnoses at age 48 months was higher for children born in 2012 than for children born in 2008, which indicates a higher rate of diagnosis for the younger cohort,” wrote Dr. Shaw of the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, Atlanta, and associates.
A closer look at the six Early ADDM Network sites shows considerable variation in prevalence. The New Jersey site, consisting of one full county and part of another that includes metropolitan Newark, reported a rate of 25.3 per 1,000 – 38.7 for males and 11.0 for females – while the rates for Missouri – one county in metropolitan St. Louis – were 13.4 (male), 3.9 (female), and 8.8 (combined), the investigators wrote.
ASD prevalence across the six sites was 3.5 times higher among males (23.9 per 1,000) than females (6.8). “Cumulative incidence patterns also differed by sex, with a steady increase in diagnoses with age for boys but an apparent plateau for girls at approximately age 36 months,” they noted.
The median age at earliest diagnosis was 33 months for all sites, with North Carolina lowest at 29 months and Wisconsin highest at 36 months.
The overall median, Dr. Shaw and associates pointed out, is “well above the youngest age at which ASD can be identified, [so] work remains to improve early diagnosis so children can receive timely services.”
SOURCE: Shaw KA et al. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2020;69(SS-3):1-11. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss6903a1.
The prevalence of autism spectrum disorder in 4-year-olds rose from 2014 to 2016, indicating more early identification of ASD among the children born in 2012, compared with 2008, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Data from individual surveillance sites in the CDC’s Early Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (Early ADDM) Network, however, show “wide variability in estimates [that] could reflect variable success in improving community identification,” Kelly A. Shaw, PhD, and associates wrote in MMWR Surveillance Summaries.
they reported.
“In addition, the cumulative incidence of ASD diagnoses at age 48 months was higher for children born in 2012 than for children born in 2008, which indicates a higher rate of diagnosis for the younger cohort,” wrote Dr. Shaw of the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, Atlanta, and associates.
A closer look at the six Early ADDM Network sites shows considerable variation in prevalence. The New Jersey site, consisting of one full county and part of another that includes metropolitan Newark, reported a rate of 25.3 per 1,000 – 38.7 for males and 11.0 for females – while the rates for Missouri – one county in metropolitan St. Louis – were 13.4 (male), 3.9 (female), and 8.8 (combined), the investigators wrote.
ASD prevalence across the six sites was 3.5 times higher among males (23.9 per 1,000) than females (6.8). “Cumulative incidence patterns also differed by sex, with a steady increase in diagnoses with age for boys but an apparent plateau for girls at approximately age 36 months,” they noted.
The median age at earliest diagnosis was 33 months for all sites, with North Carolina lowest at 29 months and Wisconsin highest at 36 months.
The overall median, Dr. Shaw and associates pointed out, is “well above the youngest age at which ASD can be identified, [so] work remains to improve early diagnosis so children can receive timely services.”
SOURCE: Shaw KA et al. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2020;69(SS-3):1-11. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss6903a1.
FROM MMWR SURVEILLANCE SUMMARIES
Behavior, family traits impact kids’ vulnerability as bullying targets
according to data from a large, cohort study of 1,760 children in Canada.
“Peer victimization is characterized by substantial individual variability in its timing, duration, and intensity,” but the specific variations in victimization patterns have not been well studied, wrote Sinziana I. Oncioiu, MPH, of the University of Bordeaux (France) and colleagues.
To better describe the trajectories of peer victimization and identify factors associated with them, the researchers used data from the Quebec Longitudinal Study of Child Development of children born in Quebec in 1997-1998 and followed from 5 months to 17 years of age. Participants reported being the target of a bully at least once in ages 6-17 years. The study included 862 boys and 898 girls; 59% provided data on being bullied seven or eight times out of a possible eight assessments in the study published in Pediatrics.
The researchers identified four trajectories of peer victimization for ages 6-17 years: low (33%), moderate emerging (30%), childhood limited (26%), and high chronic (11%). Low victimization was defined as low victimization throughout the follow-up period. Moderate-emerging victimization was defined as steady levels from 6-12 years, followed by adolescent victimization. Childhood-limited peer victimization was defined as a high level of bullying at 6 years of age, followed by a sharp decline from 6 to 17 years. High-chronic victimization was defined as persistently high victimization compared, with the other groups, although levels declined from 6 to 17 years.
Overall, in a multivariate analysis, children in the moderate-emerging, childhood-limited, and high-chronic groups were more likely than those in the low victimization group to demonstrate externalizing behavior problems in early childhood. In addition, children with a paternal history of antisocial behavior were significantly more likely to be in moderate-emerging and high-chronic groups, compared with the low group (odds ratios 1.54 and 1.93, respectively). Children living in a nonintact family in early childhood were significantly more likely to fall into the childhood-limited and high-chronic groups, compared with the low group.
The study findings were limited by several factors including lack of assessment of power imbalances between bullies and victims and a lack of differentiation between children who were both bullies and victims and those who were victims only, the researchers noted. The use of self-reports and some attrition of the study population also limited the results, they said.
However, the study’s large size and long-term follow-up strengthen the results, which support the need for targeted interventions to address individual and family vulnerabilities and prevent persistent victimization during children’s school years, the researchers concluded.
Pediatricians have an important role to play in reducing potential vulnerability to being bullied among their patients, Stephen S. Leff, PhD; Brooke S. Paskewich, PsyD; and Nathan J. Blum, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“Given that nearly two-thirds of school-aged youth in the current study report peer victimization during elementary and/or middle school, this is an important period in which pediatricians can screen for victimization during well-child visits,” they said. It also is important to have resources and referral information available, whether it is in the practice, the community, or online. Anticipatory guidance also is valuable by defining bullying (“aggressive or mean behavior that happens repeatedly in the context of a power imbalance,”) forms of bullying (physical, verbal, using gossip, and social exclusion in real time or online), and the impact of bullying on children and families.
In addition, pediatricians should “recognize externalizing behaviors as risk factors for adverse outcomes and assist families in accessing evidence-based interventions such as family behavioral counseling or parent training,” the editorialists said. “There may also be value in pediatricians being more attuned to indicators of parental psychopathology so that they can make recommendations to address the parents’ mental health needs and better prepare parents to support their child’s social-emotional development.”
The study was supported by the Quebec Government Ministry of Health, Canadian Institute of Health Research, Quebec’s Health Research Fund, and other Canadian organizations and universities. The editorial was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health and the Department of Health and Human Services. The researchers and editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCEs: Oncioiu SI et al. Pediatrics. 2020. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2654.
according to data from a large, cohort study of 1,760 children in Canada.
“Peer victimization is characterized by substantial individual variability in its timing, duration, and intensity,” but the specific variations in victimization patterns have not been well studied, wrote Sinziana I. Oncioiu, MPH, of the University of Bordeaux (France) and colleagues.
To better describe the trajectories of peer victimization and identify factors associated with them, the researchers used data from the Quebec Longitudinal Study of Child Development of children born in Quebec in 1997-1998 and followed from 5 months to 17 years of age. Participants reported being the target of a bully at least once in ages 6-17 years. The study included 862 boys and 898 girls; 59% provided data on being bullied seven or eight times out of a possible eight assessments in the study published in Pediatrics.
The researchers identified four trajectories of peer victimization for ages 6-17 years: low (33%), moderate emerging (30%), childhood limited (26%), and high chronic (11%). Low victimization was defined as low victimization throughout the follow-up period. Moderate-emerging victimization was defined as steady levels from 6-12 years, followed by adolescent victimization. Childhood-limited peer victimization was defined as a high level of bullying at 6 years of age, followed by a sharp decline from 6 to 17 years. High-chronic victimization was defined as persistently high victimization compared, with the other groups, although levels declined from 6 to 17 years.
Overall, in a multivariate analysis, children in the moderate-emerging, childhood-limited, and high-chronic groups were more likely than those in the low victimization group to demonstrate externalizing behavior problems in early childhood. In addition, children with a paternal history of antisocial behavior were significantly more likely to be in moderate-emerging and high-chronic groups, compared with the low group (odds ratios 1.54 and 1.93, respectively). Children living in a nonintact family in early childhood were significantly more likely to fall into the childhood-limited and high-chronic groups, compared with the low group.
The study findings were limited by several factors including lack of assessment of power imbalances between bullies and victims and a lack of differentiation between children who were both bullies and victims and those who were victims only, the researchers noted. The use of self-reports and some attrition of the study population also limited the results, they said.
However, the study’s large size and long-term follow-up strengthen the results, which support the need for targeted interventions to address individual and family vulnerabilities and prevent persistent victimization during children’s school years, the researchers concluded.
Pediatricians have an important role to play in reducing potential vulnerability to being bullied among their patients, Stephen S. Leff, PhD; Brooke S. Paskewich, PsyD; and Nathan J. Blum, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“Given that nearly two-thirds of school-aged youth in the current study report peer victimization during elementary and/or middle school, this is an important period in which pediatricians can screen for victimization during well-child visits,” they said. It also is important to have resources and referral information available, whether it is in the practice, the community, or online. Anticipatory guidance also is valuable by defining bullying (“aggressive or mean behavior that happens repeatedly in the context of a power imbalance,”) forms of bullying (physical, verbal, using gossip, and social exclusion in real time or online), and the impact of bullying on children and families.
In addition, pediatricians should “recognize externalizing behaviors as risk factors for adverse outcomes and assist families in accessing evidence-based interventions such as family behavioral counseling or parent training,” the editorialists said. “There may also be value in pediatricians being more attuned to indicators of parental psychopathology so that they can make recommendations to address the parents’ mental health needs and better prepare parents to support their child’s social-emotional development.”
The study was supported by the Quebec Government Ministry of Health, Canadian Institute of Health Research, Quebec’s Health Research Fund, and other Canadian organizations and universities. The editorial was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health and the Department of Health and Human Services. The researchers and editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCEs: Oncioiu SI et al. Pediatrics. 2020. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2654.
according to data from a large, cohort study of 1,760 children in Canada.
“Peer victimization is characterized by substantial individual variability in its timing, duration, and intensity,” but the specific variations in victimization patterns have not been well studied, wrote Sinziana I. Oncioiu, MPH, of the University of Bordeaux (France) and colleagues.
To better describe the trajectories of peer victimization and identify factors associated with them, the researchers used data from the Quebec Longitudinal Study of Child Development of children born in Quebec in 1997-1998 and followed from 5 months to 17 years of age. Participants reported being the target of a bully at least once in ages 6-17 years. The study included 862 boys and 898 girls; 59% provided data on being bullied seven or eight times out of a possible eight assessments in the study published in Pediatrics.
The researchers identified four trajectories of peer victimization for ages 6-17 years: low (33%), moderate emerging (30%), childhood limited (26%), and high chronic (11%). Low victimization was defined as low victimization throughout the follow-up period. Moderate-emerging victimization was defined as steady levels from 6-12 years, followed by adolescent victimization. Childhood-limited peer victimization was defined as a high level of bullying at 6 years of age, followed by a sharp decline from 6 to 17 years. High-chronic victimization was defined as persistently high victimization compared, with the other groups, although levels declined from 6 to 17 years.
Overall, in a multivariate analysis, children in the moderate-emerging, childhood-limited, and high-chronic groups were more likely than those in the low victimization group to demonstrate externalizing behavior problems in early childhood. In addition, children with a paternal history of antisocial behavior were significantly more likely to be in moderate-emerging and high-chronic groups, compared with the low group (odds ratios 1.54 and 1.93, respectively). Children living in a nonintact family in early childhood were significantly more likely to fall into the childhood-limited and high-chronic groups, compared with the low group.
The study findings were limited by several factors including lack of assessment of power imbalances between bullies and victims and a lack of differentiation between children who were both bullies and victims and those who were victims only, the researchers noted. The use of self-reports and some attrition of the study population also limited the results, they said.
However, the study’s large size and long-term follow-up strengthen the results, which support the need for targeted interventions to address individual and family vulnerabilities and prevent persistent victimization during children’s school years, the researchers concluded.
Pediatricians have an important role to play in reducing potential vulnerability to being bullied among their patients, Stephen S. Leff, PhD; Brooke S. Paskewich, PsyD; and Nathan J. Blum, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“Given that nearly two-thirds of school-aged youth in the current study report peer victimization during elementary and/or middle school, this is an important period in which pediatricians can screen for victimization during well-child visits,” they said. It also is important to have resources and referral information available, whether it is in the practice, the community, or online. Anticipatory guidance also is valuable by defining bullying (“aggressive or mean behavior that happens repeatedly in the context of a power imbalance,”) forms of bullying (physical, verbal, using gossip, and social exclusion in real time or online), and the impact of bullying on children and families.
In addition, pediatricians should “recognize externalizing behaviors as risk factors for adverse outcomes and assist families in accessing evidence-based interventions such as family behavioral counseling or parent training,” the editorialists said. “There may also be value in pediatricians being more attuned to indicators of parental psychopathology so that they can make recommendations to address the parents’ mental health needs and better prepare parents to support their child’s social-emotional development.”
The study was supported by the Quebec Government Ministry of Health, Canadian Institute of Health Research, Quebec’s Health Research Fund, and other Canadian organizations and universities. The editorial was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health and the Department of Health and Human Services. The researchers and editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCEs: Oncioiu SI et al. Pediatrics. 2020. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2654.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Key clinical point: Being targeted by bullies as children and adolescents may be affected in part by early childhood externalizing behavior and family vulnerability
Major finding: The researchers identified four distinct trajectories of peer victimization in the study population: low (33%), moderate emerging (30%), childhood limited (26%), and high chronic (11%).
Study details: The data come from a population-based cohort study of 1,760 Canadian children.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the Quebec Government Ministry of Health, Canadian Institute of Health Research, Quebec’s Health Research Fund, and other Canadian organizations and universities. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Sources: Oncioiu SI et al. Pediatrics. 2020. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2654.
CMS implements temporary regulatory changes to aid COVID-19 response
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services has announced a wide range of temporary regulatory moves aimed at helping hospitals and health systems handle the surge of COVID-19 patients.
“We are waiving a wide and unprecedented range of regulatory requirements to equip the American health care system with maximum flexibility to deal with an influx of cases,” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said during a March 30 conference call with reporters. “Many health care systems may not need these waivers and they shouldn’t use them if the situation doesn’t warrant it. But the flexibilities are there if it does. At a time of crisis, no regulatory barriers should stand in the way of patient care.”
Among the changes is an expansion of the venues in which health care systems and hospitals can provide services.
Federal regulations call for hospitals to provide services within their own buildings, raising concerns as to whether there will be enough capacity to handle the anticipated COVID-19 caseload.
“Under CMS’s temporary new rules, hospitals will be able to transfer patients to outside facilities, such as ambulatory surgery centers, inpatient rehabilitation hospitals, hotels, and dormitories, while still receiving hospital payments under Medicare,” CMS stated in a fact sheet highlighting the regulatory changes. “For example, a health care system can use a hotel to take care of patients needing less intensive care while using inpatient beds for COVID-19 patients.”
With these waivers, hospital systems will not have to rely on the Federal Emergency Management Agency to set up temporary hospitals and can move ahead using available community resources to help deal with the expected surge, Ms. Verma said.
These regulatory changes will be effect for the duration of the public health emergency, according to Ms. Verma.
Ambulatory surgery centers will have the option to contract with local health care systems to provide hospital services or they can enroll and bill as hospitals during the emergency, the fact sheet noted. They will be able to perform hospital services such as cancer procedures, trauma surgeries, and other essential surgeries.
CMS also is waiving the limit on the number of beds a doctor-owned hospital can have.
Additionally, for Medicare patients who may be homebound, CMS will now pay for a laboratory technician to make a home visit to collect a specimen for COVID-19 testing, and hospitals will be able to conduct testing in homes or other community-based settings under certain circumstances.
CMS also is taking actions aimed at expanding the health care workforce.
For instance, the agency is issuing a “blanket waiver” that allows hospitals to provide benefits to medical staff, including multiple daily meals, laundry service for personal clothing, or child care services while the staff is at the hospital providing patient care, according to the fact sheet.
Teaching hospitals will also receive more flexibility in using residents to provide health care services under the virtual direction of a teaching physician, who may be available through audio/video technology.
CMS also is temporarily eliminating paperwork requirements, and allowed greater use of verbal orders, to allow clinicians to spend more time on direct patient care.
On the device/equipment side, Medicare will cover respiratory-related devices and equipment “for any medical reason determined by clinicians,” according to the fact sheet, rather than only under certain circumstances.
And on the telehealth side, CMS is expanding the number of services that it will pay for via telehealth by more than 80, including emergency department visits, initial nursing facility and discharge visits, and home visits, which must be provided by a clinician that is allowed to provide telehealth. CMS will allow the use of commonly available interactive apps with audio and video, as well as audio-only phones.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services has announced a wide range of temporary regulatory moves aimed at helping hospitals and health systems handle the surge of COVID-19 patients.
“We are waiving a wide and unprecedented range of regulatory requirements to equip the American health care system with maximum flexibility to deal with an influx of cases,” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said during a March 30 conference call with reporters. “Many health care systems may not need these waivers and they shouldn’t use them if the situation doesn’t warrant it. But the flexibilities are there if it does. At a time of crisis, no regulatory barriers should stand in the way of patient care.”
Among the changes is an expansion of the venues in which health care systems and hospitals can provide services.
Federal regulations call for hospitals to provide services within their own buildings, raising concerns as to whether there will be enough capacity to handle the anticipated COVID-19 caseload.
“Under CMS’s temporary new rules, hospitals will be able to transfer patients to outside facilities, such as ambulatory surgery centers, inpatient rehabilitation hospitals, hotels, and dormitories, while still receiving hospital payments under Medicare,” CMS stated in a fact sheet highlighting the regulatory changes. “For example, a health care system can use a hotel to take care of patients needing less intensive care while using inpatient beds for COVID-19 patients.”
With these waivers, hospital systems will not have to rely on the Federal Emergency Management Agency to set up temporary hospitals and can move ahead using available community resources to help deal with the expected surge, Ms. Verma said.
These regulatory changes will be effect for the duration of the public health emergency, according to Ms. Verma.
Ambulatory surgery centers will have the option to contract with local health care systems to provide hospital services or they can enroll and bill as hospitals during the emergency, the fact sheet noted. They will be able to perform hospital services such as cancer procedures, trauma surgeries, and other essential surgeries.
CMS also is waiving the limit on the number of beds a doctor-owned hospital can have.
Additionally, for Medicare patients who may be homebound, CMS will now pay for a laboratory technician to make a home visit to collect a specimen for COVID-19 testing, and hospitals will be able to conduct testing in homes or other community-based settings under certain circumstances.
CMS also is taking actions aimed at expanding the health care workforce.
For instance, the agency is issuing a “blanket waiver” that allows hospitals to provide benefits to medical staff, including multiple daily meals, laundry service for personal clothing, or child care services while the staff is at the hospital providing patient care, according to the fact sheet.
Teaching hospitals will also receive more flexibility in using residents to provide health care services under the virtual direction of a teaching physician, who may be available through audio/video technology.
CMS also is temporarily eliminating paperwork requirements, and allowed greater use of verbal orders, to allow clinicians to spend more time on direct patient care.
On the device/equipment side, Medicare will cover respiratory-related devices and equipment “for any medical reason determined by clinicians,” according to the fact sheet, rather than only under certain circumstances.
And on the telehealth side, CMS is expanding the number of services that it will pay for via telehealth by more than 80, including emergency department visits, initial nursing facility and discharge visits, and home visits, which must be provided by a clinician that is allowed to provide telehealth. CMS will allow the use of commonly available interactive apps with audio and video, as well as audio-only phones.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services has announced a wide range of temporary regulatory moves aimed at helping hospitals and health systems handle the surge of COVID-19 patients.
“We are waiving a wide and unprecedented range of regulatory requirements to equip the American health care system with maximum flexibility to deal with an influx of cases,” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said during a March 30 conference call with reporters. “Many health care systems may not need these waivers and they shouldn’t use them if the situation doesn’t warrant it. But the flexibilities are there if it does. At a time of crisis, no regulatory barriers should stand in the way of patient care.”
Among the changes is an expansion of the venues in which health care systems and hospitals can provide services.
Federal regulations call for hospitals to provide services within their own buildings, raising concerns as to whether there will be enough capacity to handle the anticipated COVID-19 caseload.
“Under CMS’s temporary new rules, hospitals will be able to transfer patients to outside facilities, such as ambulatory surgery centers, inpatient rehabilitation hospitals, hotels, and dormitories, while still receiving hospital payments under Medicare,” CMS stated in a fact sheet highlighting the regulatory changes. “For example, a health care system can use a hotel to take care of patients needing less intensive care while using inpatient beds for COVID-19 patients.”
With these waivers, hospital systems will not have to rely on the Federal Emergency Management Agency to set up temporary hospitals and can move ahead using available community resources to help deal with the expected surge, Ms. Verma said.
These regulatory changes will be effect for the duration of the public health emergency, according to Ms. Verma.
Ambulatory surgery centers will have the option to contract with local health care systems to provide hospital services or they can enroll and bill as hospitals during the emergency, the fact sheet noted. They will be able to perform hospital services such as cancer procedures, trauma surgeries, and other essential surgeries.
CMS also is waiving the limit on the number of beds a doctor-owned hospital can have.
Additionally, for Medicare patients who may be homebound, CMS will now pay for a laboratory technician to make a home visit to collect a specimen for COVID-19 testing, and hospitals will be able to conduct testing in homes or other community-based settings under certain circumstances.
CMS also is taking actions aimed at expanding the health care workforce.
For instance, the agency is issuing a “blanket waiver” that allows hospitals to provide benefits to medical staff, including multiple daily meals, laundry service for personal clothing, or child care services while the staff is at the hospital providing patient care, according to the fact sheet.
Teaching hospitals will also receive more flexibility in using residents to provide health care services under the virtual direction of a teaching physician, who may be available through audio/video technology.
CMS also is temporarily eliminating paperwork requirements, and allowed greater use of verbal orders, to allow clinicians to spend more time on direct patient care.
On the device/equipment side, Medicare will cover respiratory-related devices and equipment “for any medical reason determined by clinicians,” according to the fact sheet, rather than only under certain circumstances.
And on the telehealth side, CMS is expanding the number of services that it will pay for via telehealth by more than 80, including emergency department visits, initial nursing facility and discharge visits, and home visits, which must be provided by a clinician that is allowed to provide telehealth. CMS will allow the use of commonly available interactive apps with audio and video, as well as audio-only phones.
Top 10 must-dos in ICU in COVID-19 include prone ventilation
As the first international guidelines on the management of critically ill patients with COVID-19 are understandably comprehensive, one expert involved in their development highlights the essential recommendations and explains the rationale behind prone ventilation.
A panel of 39 experts from 12 countries from across the globe developed the 50 recommendations within four domains, under the auspices of the Surviving Sepsis Campaign. They are issued by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM), and will subsequently be published in the journal Intensive Care Medicine.
A central aspect of the guidance is what works, and what does not, in treating critically ill patients with COVID-19 in intensive care.
Ten of the recommendations cover potential pharmacotherapies, most of which have only weak or no evidence of benefit, as discussed in a recent perspective on Medscape. All 50 recommendations, along with the associated level of evidence, are detailed in table 2 in the paper.
There is also an algorithm for the management of patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure secondary to COVID-19 (figure 2) and a summary of clinical practice recommendations (figure 3).
In an editorial in the Journal of the American Medical Association issued just days after these new guidelines, Francois Lamontagne, MD, MSc, and Derek C. Angus, MD, MPH, say they “represent an excellent first step toward optimal, evidence-informed care for patients with COVID-19.” Lamontagne is from Universitaire de Sherbrooke, Canada, and Angus is from University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pennsylvania, and is an associate editor with JAMA.
Dealing With Tide of COVID-19 Patients, Protecting Healthcare Workers
Editor in chief of Intensive Care Medicine Giuseppe Citerio, MD, from University of Milano-Bicocca, Monza, Italy, said: “COVID-19 cases are rising rapidly worldwide, and so we are increasingly seeing that intensive care units [ICUs] have difficulty in dealing with the tide of patients.”
“We need more resource in ICUs, and quickly. This means more ventilators and more trained personnel. In the meantime, this guidance aims to rationalize our approach and to avoid unproven strategies,” he explains in a press release from ESICM.
“This is the first guidance to lay out what works and what doesn’t in treating coronavirus-infected patients in intensive care. It’s based on decades of research on acute respiratory infection being applied to COVID-19 patients,” added ESICM President-Elect Maurizio Cecconi, MD, from Humanitas University, Milan, Italy.
“At the same time as caring for patients, we need to make sure that health workers are following procedures which will allow themselves to be protected against infection,” he stressed.
“We must protect them, they are in the frontline. We cannot allow our healthcare workers to be at risk. On top of that, if they get infected they could also spread the disease further.”
Top-10 Recommendations
While all 50 recommendations are key to the successful management of COVID-19 patients, busy clinicians on the frontline need to zone in on those indispensable practical recommendations that they should implement immediately.
Medscape Medical News therefore asked lead author Waleed Alhazzani, MD, MSc, from the Division of Critical Care, McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada, to give his personal top 10, the first three of which are focused on limiting the spread of infection.
1. For healthcare workers performing aerosol-generating procedures1 on patients with COVID-19 in the ICU, we recommend using fitted respirator masks (N95 respirators, FFP2, or equivalent), as compared to surgical/medical masks, in addition to other personal protective equipment (eg, gloves, gown, and eye protection such as a face shield or safety goggles.
2. We recommend performing aerosol-generating procedures on ICU patients with COVID-19 in a negative-pressure room.
3. For healthcare workers providing usual care for nonventilated COVID-19 patients, we suggest using surgical/medical masks, as compared to respirator masks in addition to other personal protective equipment.
4. For healthcare workers performing endotracheal intubation on patients with COVID-19, we suggest using video guided laryngoscopy, over direct laryngoscopy, if available.
5. We recommend endotracheal intubation in patients with COVID-19, performed by healthcare workers experienced with airway management, to minimize the number of attempts and risk of transmission.
6. For intubated and mechanically ventilated adults with suspicion of COVID-19, we suggest obtaining endotracheal aspirates, over bronchial wash or bronchoalveolar lavage samples.
7. For adults with COVID-19 and acute hypoxemic respiratory failure, we suggest using high-flow nasal cannula [HFNC] over noninvasive positive pressure ventilation [NIPPV].
8. For adults with COVID-19 receiving NIPPV or HFNC, we recommend close monitoring for worsening of respiratory status and early intubation in a controlled setting if worsening occurs.
9. For mechanically ventilated adults with COVID-19 and moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome [ARDS], we suggest prone ventilation for 12 to 16 hours over no prone ventilation.
10. For mechanically ventilated adults with COVID-19 and respiratory failure (without ARDS), we don’t recommend routine use of systemic corticosteroids.
1 This includes endotracheal intubation, bronchoscopy, open suctioning, administration of nebulized treatment, manual ventilation before intubation, physical proning of the patient, disconnecting the patient from the ventilator, noninvasive positive pressure ventilation, tracheostomy, and cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
These choices are in broad agreement with those selected by Jason T. Poston, MD, University of Chicago, Illinois, and colleagues in their synopsis of these guidelines, published online March 26 in JAMA, although they also highlight another recommendation on infection control:
- For healthcare workers who are performing non-aerosol-generating procedures on mechanically ventilated (closed circuit) patients with COVID-19, we suggest using surgical/medical masks, as opposed to respirator masks, in addition to other personal protective equipment.
Importance of Prone Ventilation, Perhaps for Many Days
One recommendation singled out by both Alhazzani and coauthors, and Poston and colleagues, relates to prone ventilation for 12 to 16 hours in adults with moderate to severe ARDS receiving mechanical ventilation.
Michelle N. Gong, MD, MS, chief of critical care medicine at Montefiore Medical Center, New York City, also highlighted this practice in a live-stream interview with JAMA editor in chief Howard Bauchner, MD.
She explained that, in her institution, they have been “very aggressive about proning these patients as early as possible, but unlike some of the past ARDS patients…they tend to require many, many days of proning in order to get a response”.
Gong added that patients “may improve very rapidly when they are proned, but when we supinate them, they lose [the improvement] and then they get proned for upwards of 10 days or more, if need be.”
Alhazzani told Medscape Medical News that prone ventilation “is a simple intervention that requires training of healthcare providers but can be applied in most contexts.”
He explained that the recommendation “is driven by indirect evidence from ARDS,” not specifically those in COVID-19, with recent studies having shown that COVID-19 “can affect lung bases and may cause significant atelectasis and reduced lung compliance in the context of ARDS.”
“Prone ventilation has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with moderate to severe ARDS. Therefore, we issued a suggestion for clinicians to consider prone ventilation in this population.”
‘Impressively Thorough’ Recommendations, With Some Caveats
In their JAMA editorial, Lamontagne and Angus describe the recommendations as “impressively thorough and expansive.”
They note that they address resource scarcity, which “is likely to be a critical issue in low- and middle-income countries experiencing any reasonably large number of cases and in high-income countries experiencing a surge in the demand for critical care.”
The authors say, however, that a “weakness” of the guidelines is that they make recommendations for interventions that “lack supporting evidence.”
Consequently, “when prioritizing scarce resources, clinicians and healthcare systems will have to choose among options that have limited evidence to support them.”
“In future iterations of the guidelines, there should be more detailed recommendations for how clinicians should prioritize scarce resources, or include more recommendations against the use of unproven therapies.”
“The tasks ahead for the dissemination and uptake of optimal critical care are herculean,” Lamontagne and Angus say.
They include “a need to generate more robust evidence, consider carefully the application of that evidence across a wide variety of clinical circumstances, and generate supporting materials to ensure effective implementation of the guideline recommendations,” they conclude.
ESICM recommendations coauthor Yaseen Arabi is the principal investigator on a clinical trial for lopinavir/ritonavir and interferon in Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) and he was a nonpaid consultant on antiviral active for MERS- coronavirus (CoV) for Gilead Sciences and SAB Biotherapeutics. He is an investigator on REMAP-CAP trial and is a Board Members of the International Severe Acute Respiratory and Emerging Infection Consortium (ISARIC). Coauthor Eddy Fan declared receiving consultancy fees from ALung Technologies and MC3 Cardiopulmonary. Coauthor Maurizio Cecconi declared consultancy work with Edwards Lifesciences, Directed Systems, and Cheetah Medical.
JAMA Clinical Guidelines Synopsis coauthor Poston declares receiving honoraria for the CHEST Critical Care Board Review Course.
Editorialist Lamontagne reported receiving grants from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), Fonds de recherche du Québec-Santé, and the Lotte & John Hecht Foundation, unrelated to this work. Editorialist Angus participated in the development of Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines for sepsis, but had no role in the creation of the current COVID-19 guidelines, nor the decision to create these guidelines.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As the first international guidelines on the management of critically ill patients with COVID-19 are understandably comprehensive, one expert involved in their development highlights the essential recommendations and explains the rationale behind prone ventilation.
A panel of 39 experts from 12 countries from across the globe developed the 50 recommendations within four domains, under the auspices of the Surviving Sepsis Campaign. They are issued by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM), and will subsequently be published in the journal Intensive Care Medicine.
A central aspect of the guidance is what works, and what does not, in treating critically ill patients with COVID-19 in intensive care.
Ten of the recommendations cover potential pharmacotherapies, most of which have only weak or no evidence of benefit, as discussed in a recent perspective on Medscape. All 50 recommendations, along with the associated level of evidence, are detailed in table 2 in the paper.
There is also an algorithm for the management of patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure secondary to COVID-19 (figure 2) and a summary of clinical practice recommendations (figure 3).
In an editorial in the Journal of the American Medical Association issued just days after these new guidelines, Francois Lamontagne, MD, MSc, and Derek C. Angus, MD, MPH, say they “represent an excellent first step toward optimal, evidence-informed care for patients with COVID-19.” Lamontagne is from Universitaire de Sherbrooke, Canada, and Angus is from University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pennsylvania, and is an associate editor with JAMA.
Dealing With Tide of COVID-19 Patients, Protecting Healthcare Workers
Editor in chief of Intensive Care Medicine Giuseppe Citerio, MD, from University of Milano-Bicocca, Monza, Italy, said: “COVID-19 cases are rising rapidly worldwide, and so we are increasingly seeing that intensive care units [ICUs] have difficulty in dealing with the tide of patients.”
“We need more resource in ICUs, and quickly. This means more ventilators and more trained personnel. In the meantime, this guidance aims to rationalize our approach and to avoid unproven strategies,” he explains in a press release from ESICM.
“This is the first guidance to lay out what works and what doesn’t in treating coronavirus-infected patients in intensive care. It’s based on decades of research on acute respiratory infection being applied to COVID-19 patients,” added ESICM President-Elect Maurizio Cecconi, MD, from Humanitas University, Milan, Italy.
“At the same time as caring for patients, we need to make sure that health workers are following procedures which will allow themselves to be protected against infection,” he stressed.
“We must protect them, they are in the frontline. We cannot allow our healthcare workers to be at risk. On top of that, if they get infected they could also spread the disease further.”
Top-10 Recommendations
While all 50 recommendations are key to the successful management of COVID-19 patients, busy clinicians on the frontline need to zone in on those indispensable practical recommendations that they should implement immediately.
Medscape Medical News therefore asked lead author Waleed Alhazzani, MD, MSc, from the Division of Critical Care, McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada, to give his personal top 10, the first three of which are focused on limiting the spread of infection.
1. For healthcare workers performing aerosol-generating procedures1 on patients with COVID-19 in the ICU, we recommend using fitted respirator masks (N95 respirators, FFP2, or equivalent), as compared to surgical/medical masks, in addition to other personal protective equipment (eg, gloves, gown, and eye protection such as a face shield or safety goggles.
2. We recommend performing aerosol-generating procedures on ICU patients with COVID-19 in a negative-pressure room.
3. For healthcare workers providing usual care for nonventilated COVID-19 patients, we suggest using surgical/medical masks, as compared to respirator masks in addition to other personal protective equipment.
4. For healthcare workers performing endotracheal intubation on patients with COVID-19, we suggest using video guided laryngoscopy, over direct laryngoscopy, if available.
5. We recommend endotracheal intubation in patients with COVID-19, performed by healthcare workers experienced with airway management, to minimize the number of attempts and risk of transmission.
6. For intubated and mechanically ventilated adults with suspicion of COVID-19, we suggest obtaining endotracheal aspirates, over bronchial wash or bronchoalveolar lavage samples.
7. For adults with COVID-19 and acute hypoxemic respiratory failure, we suggest using high-flow nasal cannula [HFNC] over noninvasive positive pressure ventilation [NIPPV].
8. For adults with COVID-19 receiving NIPPV or HFNC, we recommend close monitoring for worsening of respiratory status and early intubation in a controlled setting if worsening occurs.
9. For mechanically ventilated adults with COVID-19 and moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome [ARDS], we suggest prone ventilation for 12 to 16 hours over no prone ventilation.
10. For mechanically ventilated adults with COVID-19 and respiratory failure (without ARDS), we don’t recommend routine use of systemic corticosteroids.
1 This includes endotracheal intubation, bronchoscopy, open suctioning, administration of nebulized treatment, manual ventilation before intubation, physical proning of the patient, disconnecting the patient from the ventilator, noninvasive positive pressure ventilation, tracheostomy, and cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
These choices are in broad agreement with those selected by Jason T. Poston, MD, University of Chicago, Illinois, and colleagues in their synopsis of these guidelines, published online March 26 in JAMA, although they also highlight another recommendation on infection control:
- For healthcare workers who are performing non-aerosol-generating procedures on mechanically ventilated (closed circuit) patients with COVID-19, we suggest using surgical/medical masks, as opposed to respirator masks, in addition to other personal protective equipment.
Importance of Prone Ventilation, Perhaps for Many Days
One recommendation singled out by both Alhazzani and coauthors, and Poston and colleagues, relates to prone ventilation for 12 to 16 hours in adults with moderate to severe ARDS receiving mechanical ventilation.
Michelle N. Gong, MD, MS, chief of critical care medicine at Montefiore Medical Center, New York City, also highlighted this practice in a live-stream interview with JAMA editor in chief Howard Bauchner, MD.
She explained that, in her institution, they have been “very aggressive about proning these patients as early as possible, but unlike some of the past ARDS patients…they tend to require many, many days of proning in order to get a response”.
Gong added that patients “may improve very rapidly when they are proned, but when we supinate them, they lose [the improvement] and then they get proned for upwards of 10 days or more, if need be.”
Alhazzani told Medscape Medical News that prone ventilation “is a simple intervention that requires training of healthcare providers but can be applied in most contexts.”
He explained that the recommendation “is driven by indirect evidence from ARDS,” not specifically those in COVID-19, with recent studies having shown that COVID-19 “can affect lung bases and may cause significant atelectasis and reduced lung compliance in the context of ARDS.”
“Prone ventilation has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with moderate to severe ARDS. Therefore, we issued a suggestion for clinicians to consider prone ventilation in this population.”
‘Impressively Thorough’ Recommendations, With Some Caveats
In their JAMA editorial, Lamontagne and Angus describe the recommendations as “impressively thorough and expansive.”
They note that they address resource scarcity, which “is likely to be a critical issue in low- and middle-income countries experiencing any reasonably large number of cases and in high-income countries experiencing a surge in the demand for critical care.”
The authors say, however, that a “weakness” of the guidelines is that they make recommendations for interventions that “lack supporting evidence.”
Consequently, “when prioritizing scarce resources, clinicians and healthcare systems will have to choose among options that have limited evidence to support them.”
“In future iterations of the guidelines, there should be more detailed recommendations for how clinicians should prioritize scarce resources, or include more recommendations against the use of unproven therapies.”
“The tasks ahead for the dissemination and uptake of optimal critical care are herculean,” Lamontagne and Angus say.
They include “a need to generate more robust evidence, consider carefully the application of that evidence across a wide variety of clinical circumstances, and generate supporting materials to ensure effective implementation of the guideline recommendations,” they conclude.
ESICM recommendations coauthor Yaseen Arabi is the principal investigator on a clinical trial for lopinavir/ritonavir and interferon in Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) and he was a nonpaid consultant on antiviral active for MERS- coronavirus (CoV) for Gilead Sciences and SAB Biotherapeutics. He is an investigator on REMAP-CAP trial and is a Board Members of the International Severe Acute Respiratory and Emerging Infection Consortium (ISARIC). Coauthor Eddy Fan declared receiving consultancy fees from ALung Technologies and MC3 Cardiopulmonary. Coauthor Maurizio Cecconi declared consultancy work with Edwards Lifesciences, Directed Systems, and Cheetah Medical.
JAMA Clinical Guidelines Synopsis coauthor Poston declares receiving honoraria for the CHEST Critical Care Board Review Course.
Editorialist Lamontagne reported receiving grants from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), Fonds de recherche du Québec-Santé, and the Lotte & John Hecht Foundation, unrelated to this work. Editorialist Angus participated in the development of Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines for sepsis, but had no role in the creation of the current COVID-19 guidelines, nor the decision to create these guidelines.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As the first international guidelines on the management of critically ill patients with COVID-19 are understandably comprehensive, one expert involved in their development highlights the essential recommendations and explains the rationale behind prone ventilation.
A panel of 39 experts from 12 countries from across the globe developed the 50 recommendations within four domains, under the auspices of the Surviving Sepsis Campaign. They are issued by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM), and will subsequently be published in the journal Intensive Care Medicine.
A central aspect of the guidance is what works, and what does not, in treating critically ill patients with COVID-19 in intensive care.
Ten of the recommendations cover potential pharmacotherapies, most of which have only weak or no evidence of benefit, as discussed in a recent perspective on Medscape. All 50 recommendations, along with the associated level of evidence, are detailed in table 2 in the paper.
There is also an algorithm for the management of patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure secondary to COVID-19 (figure 2) and a summary of clinical practice recommendations (figure 3).
In an editorial in the Journal of the American Medical Association issued just days after these new guidelines, Francois Lamontagne, MD, MSc, and Derek C. Angus, MD, MPH, say they “represent an excellent first step toward optimal, evidence-informed care for patients with COVID-19.” Lamontagne is from Universitaire de Sherbrooke, Canada, and Angus is from University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pennsylvania, and is an associate editor with JAMA.
Dealing With Tide of COVID-19 Patients, Protecting Healthcare Workers
Editor in chief of Intensive Care Medicine Giuseppe Citerio, MD, from University of Milano-Bicocca, Monza, Italy, said: “COVID-19 cases are rising rapidly worldwide, and so we are increasingly seeing that intensive care units [ICUs] have difficulty in dealing with the tide of patients.”
“We need more resource in ICUs, and quickly. This means more ventilators and more trained personnel. In the meantime, this guidance aims to rationalize our approach and to avoid unproven strategies,” he explains in a press release from ESICM.
“This is the first guidance to lay out what works and what doesn’t in treating coronavirus-infected patients in intensive care. It’s based on decades of research on acute respiratory infection being applied to COVID-19 patients,” added ESICM President-Elect Maurizio Cecconi, MD, from Humanitas University, Milan, Italy.
“At the same time as caring for patients, we need to make sure that health workers are following procedures which will allow themselves to be protected against infection,” he stressed.
“We must protect them, they are in the frontline. We cannot allow our healthcare workers to be at risk. On top of that, if they get infected they could also spread the disease further.”
Top-10 Recommendations
While all 50 recommendations are key to the successful management of COVID-19 patients, busy clinicians on the frontline need to zone in on those indispensable practical recommendations that they should implement immediately.
Medscape Medical News therefore asked lead author Waleed Alhazzani, MD, MSc, from the Division of Critical Care, McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada, to give his personal top 10, the first three of which are focused on limiting the spread of infection.
1. For healthcare workers performing aerosol-generating procedures1 on patients with COVID-19 in the ICU, we recommend using fitted respirator masks (N95 respirators, FFP2, or equivalent), as compared to surgical/medical masks, in addition to other personal protective equipment (eg, gloves, gown, and eye protection such as a face shield or safety goggles.
2. We recommend performing aerosol-generating procedures on ICU patients with COVID-19 in a negative-pressure room.
3. For healthcare workers providing usual care for nonventilated COVID-19 patients, we suggest using surgical/medical masks, as compared to respirator masks in addition to other personal protective equipment.
4. For healthcare workers performing endotracheal intubation on patients with COVID-19, we suggest using video guided laryngoscopy, over direct laryngoscopy, if available.
5. We recommend endotracheal intubation in patients with COVID-19, performed by healthcare workers experienced with airway management, to minimize the number of attempts and risk of transmission.
6. For intubated and mechanically ventilated adults with suspicion of COVID-19, we suggest obtaining endotracheal aspirates, over bronchial wash or bronchoalveolar lavage samples.
7. For adults with COVID-19 and acute hypoxemic respiratory failure, we suggest using high-flow nasal cannula [HFNC] over noninvasive positive pressure ventilation [NIPPV].
8. For adults with COVID-19 receiving NIPPV or HFNC, we recommend close monitoring for worsening of respiratory status and early intubation in a controlled setting if worsening occurs.
9. For mechanically ventilated adults with COVID-19 and moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome [ARDS], we suggest prone ventilation for 12 to 16 hours over no prone ventilation.
10. For mechanically ventilated adults with COVID-19 and respiratory failure (without ARDS), we don’t recommend routine use of systemic corticosteroids.
1 This includes endotracheal intubation, bronchoscopy, open suctioning, administration of nebulized treatment, manual ventilation before intubation, physical proning of the patient, disconnecting the patient from the ventilator, noninvasive positive pressure ventilation, tracheostomy, and cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
These choices are in broad agreement with those selected by Jason T. Poston, MD, University of Chicago, Illinois, and colleagues in their synopsis of these guidelines, published online March 26 in JAMA, although they also highlight another recommendation on infection control:
- For healthcare workers who are performing non-aerosol-generating procedures on mechanically ventilated (closed circuit) patients with COVID-19, we suggest using surgical/medical masks, as opposed to respirator masks, in addition to other personal protective equipment.
Importance of Prone Ventilation, Perhaps for Many Days
One recommendation singled out by both Alhazzani and coauthors, and Poston and colleagues, relates to prone ventilation for 12 to 16 hours in adults with moderate to severe ARDS receiving mechanical ventilation.
Michelle N. Gong, MD, MS, chief of critical care medicine at Montefiore Medical Center, New York City, also highlighted this practice in a live-stream interview with JAMA editor in chief Howard Bauchner, MD.
She explained that, in her institution, they have been “very aggressive about proning these patients as early as possible, but unlike some of the past ARDS patients…they tend to require many, many days of proning in order to get a response”.
Gong added that patients “may improve very rapidly when they are proned, but when we supinate them, they lose [the improvement] and then they get proned for upwards of 10 days or more, if need be.”
Alhazzani told Medscape Medical News that prone ventilation “is a simple intervention that requires training of healthcare providers but can be applied in most contexts.”
He explained that the recommendation “is driven by indirect evidence from ARDS,” not specifically those in COVID-19, with recent studies having shown that COVID-19 “can affect lung bases and may cause significant atelectasis and reduced lung compliance in the context of ARDS.”
“Prone ventilation has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with moderate to severe ARDS. Therefore, we issued a suggestion for clinicians to consider prone ventilation in this population.”
‘Impressively Thorough’ Recommendations, With Some Caveats
In their JAMA editorial, Lamontagne and Angus describe the recommendations as “impressively thorough and expansive.”
They note that they address resource scarcity, which “is likely to be a critical issue in low- and middle-income countries experiencing any reasonably large number of cases and in high-income countries experiencing a surge in the demand for critical care.”
The authors say, however, that a “weakness” of the guidelines is that they make recommendations for interventions that “lack supporting evidence.”
Consequently, “when prioritizing scarce resources, clinicians and healthcare systems will have to choose among options that have limited evidence to support them.”
“In future iterations of the guidelines, there should be more detailed recommendations for how clinicians should prioritize scarce resources, or include more recommendations against the use of unproven therapies.”
“The tasks ahead for the dissemination and uptake of optimal critical care are herculean,” Lamontagne and Angus say.
They include “a need to generate more robust evidence, consider carefully the application of that evidence across a wide variety of clinical circumstances, and generate supporting materials to ensure effective implementation of the guideline recommendations,” they conclude.
ESICM recommendations coauthor Yaseen Arabi is the principal investigator on a clinical trial for lopinavir/ritonavir and interferon in Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) and he was a nonpaid consultant on antiviral active for MERS- coronavirus (CoV) for Gilead Sciences and SAB Biotherapeutics. He is an investigator on REMAP-CAP trial and is a Board Members of the International Severe Acute Respiratory and Emerging Infection Consortium (ISARIC). Coauthor Eddy Fan declared receiving consultancy fees from ALung Technologies and MC3 Cardiopulmonary. Coauthor Maurizio Cecconi declared consultancy work with Edwards Lifesciences, Directed Systems, and Cheetah Medical.
JAMA Clinical Guidelines Synopsis coauthor Poston declares receiving honoraria for the CHEST Critical Care Board Review Course.
Editorialist Lamontagne reported receiving grants from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), Fonds de recherche du Québec-Santé, and the Lotte & John Hecht Foundation, unrelated to this work. Editorialist Angus participated in the development of Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines for sepsis, but had no role in the creation of the current COVID-19 guidelines, nor the decision to create these guidelines.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘We will get through this’: Advice for lessening your pandemic anxiety
The COVID-19 pandemic is an experience that is unprecedented in our lifetime. It is having a pervasive effect due to how mysterious, potentially dangerous, and sustained it is. We don’t know how bad it’s going to get or how long it’s going to last. We have natural disasters like hurricanes and earthquakes, but they are limited in time and scope. But this global pandemic is something we can’t put our arms around just yet, breeding uncertainty, worry, and fear. This is where mental health professionals need to come in.
The populations being affected by this pandemic can be placed into different groups on the basis of their mental health consequences and needs. First you have, for lack of a better term, “the worried well.” These are people with no preexisting mental disorder who are naturally worried by this and are trying to take appropriate actions to protect themselves and prepare. For such individuals, the equivalent of mental health first-aid should be useful (we’ll come back to that in a moment). Given the proper guidance and sources of information, most such people should be able to manage the anxiety, worry, and dysphoria associated with this critical pandemic.
Then there are those who have preexisting mental conditions related to mood, anxiety, stress, or obsessive tendencies. They are probably going to have an increase in their symptoms, and as such, a corresponding need for adjusting treatment. This may require an increase in their existing medications or the addition of an ad hoc medication, or perhaps more frequent contact with their doctor or therapist.
Because travel and direct visitation is discouraged at the moment, virtual methods of communication should be used to speak with these patients. Such methods have long existed but haven’t been adopted in large numbers; this may be the impetus to finally make it happen. Using the telephone, FaceTime, Skype, WebEx, Zoom, and other means of videoconferencing should be feasible. As billing procedures are being adapted for this moment, there’s no reason why individuals shouldn’t be able to contact their mental health provider.
Substance abuse is also a condition vulnerable to the stress effects of this pandemic. This will prompt or tempt those to use substances that they’ve abused or turned to in the past as a way of self-medicating and assuaging their anxiety and worry.
It’s possible that the pandemic could find its way into delusions or exacerbate symptoms, but somewhat paradoxically, people with serious mental illnesses often respond more calmly to crises than do individuals without them. As a result, the number of these patients requiring emergency room admission for possible exacerbation of symptoms is probably not going to be that much greater than normal.
How to Cope With an Unprecedented Situation
For the worried well and for the clinicians who have understandable fears about exposure, there are several things you can try to manage your anxiety. There are concentric circles of concern that you have to maintain. Think of it like the instructions on an airplane when, if there’s a drop in cabin pressure, you’re asked to apply your own oxygen mask first before placing one on your child. In the same way, you must first think about protecting yourself by limiting your exposure and monitoring your own physical state for any symptoms. But then you must be concerned about your family, your friends, and also society. This is a situation where the impulse and the ethos of worrying about your fellow persons—being your brother’s keeper—is imperative.
The epidemic has been successfully managed in some countries, like Singapore and China, which, once they got on top of it, were able to limit contagion in a very dramatic way. But these are authoritarian governments. The United States doesn’t work that way, which is what makes appealing to the principle of caring for others so crucial. You can protect yourself, but if other people aren’t also protected, it may not matter. You have to worry not just about yourself but about everyone else.
When it comes to stress management, I recommend not catastrophizing or watching the news media 24/7. Distract yourself with other work or recreational activities. Reach out and communicate—virtually, of course—with friends, family, and healthcare providers as needed. Staying in touch acts not just as a diversion but also as an outlet for assuaging your feelings, your sense of being in this alone, feeling isolated.
There are also cognitive reframing mechanisms you can employ. Consider that although this is bad, some countries have already gone through it. And we’ll get through it too. You’ll understandably ask yourself what it would mean if you were to be exposed. In most cases you can say, “I’m going to have the flu and symptoms that are not going to be pleasant, but I’ve had the flu or serious sickness before.”
Remember that there are already antiretroviral treatments being tested in clinical trials and showing efficacy. It’s good to know that before this pandemic ends, some of these treatments will probably be clinically applied, mostly to those who are severely affected and in intensive care.
Diagnose yourself. Monitor your state. Determine whether the stress is really having an impact on you. Is it affecting your sleep, appetite, concentration, mood? And if you do have a preexisting psychiatric condition, don’t feel afraid to reach out to your mental health provider. Understand that you’re going to be anxious, which may aggravate your symptoms and require an adjustment in your treatment. That’s okay. It’s to be expected and your provider should be available to help you.
Controlling this outbreak via the same epidemiologic infectious disease prevention guidance that works in authoritarian societies is not going to be applicable here because of the liberties that we experience in American society. What will determine our success is the belief that we’re in this together, that we’re going to help each other. We should be proud of that, as it shows how Americans and people around the world stand up in situations like this.
Let’s also note that even though everybody is affected and undergoing previously unimaginable levels of anticipated stress and dislocation, it’s the healthcare providers who are really on the frontlines. They’re under tremendous pressure to continue to perform heroically, at great risk to themselves. They deserve a real debt of gratitude.
We will get through this, but as we do, it will not end until we’ve undergone an extreme test of our character. I certainly hope and trust that we will be up to it.
Dr. Jeffrey A. Lieberman is chairman of the Department of Psychiatry at Columbia University. He is a former president of the American Psychiatric Association.
Disclosure: Jeffrey A. Lieberman, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Clintara; Intracellular Therapies. Received research grant from Alkermes; Biomarin; EnVivo/Forum; Genentech; Novartis/Novation; Sunovion. Patent: Repligen.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic is an experience that is unprecedented in our lifetime. It is having a pervasive effect due to how mysterious, potentially dangerous, and sustained it is. We don’t know how bad it’s going to get or how long it’s going to last. We have natural disasters like hurricanes and earthquakes, but they are limited in time and scope. But this global pandemic is something we can’t put our arms around just yet, breeding uncertainty, worry, and fear. This is where mental health professionals need to come in.
The populations being affected by this pandemic can be placed into different groups on the basis of their mental health consequences and needs. First you have, for lack of a better term, “the worried well.” These are people with no preexisting mental disorder who are naturally worried by this and are trying to take appropriate actions to protect themselves and prepare. For such individuals, the equivalent of mental health first-aid should be useful (we’ll come back to that in a moment). Given the proper guidance and sources of information, most such people should be able to manage the anxiety, worry, and dysphoria associated with this critical pandemic.
Then there are those who have preexisting mental conditions related to mood, anxiety, stress, or obsessive tendencies. They are probably going to have an increase in their symptoms, and as such, a corresponding need for adjusting treatment. This may require an increase in their existing medications or the addition of an ad hoc medication, or perhaps more frequent contact with their doctor or therapist.
Because travel and direct visitation is discouraged at the moment, virtual methods of communication should be used to speak with these patients. Such methods have long existed but haven’t been adopted in large numbers; this may be the impetus to finally make it happen. Using the telephone, FaceTime, Skype, WebEx, Zoom, and other means of videoconferencing should be feasible. As billing procedures are being adapted for this moment, there’s no reason why individuals shouldn’t be able to contact their mental health provider.
Substance abuse is also a condition vulnerable to the stress effects of this pandemic. This will prompt or tempt those to use substances that they’ve abused or turned to in the past as a way of self-medicating and assuaging their anxiety and worry.
It’s possible that the pandemic could find its way into delusions or exacerbate symptoms, but somewhat paradoxically, people with serious mental illnesses often respond more calmly to crises than do individuals without them. As a result, the number of these patients requiring emergency room admission for possible exacerbation of symptoms is probably not going to be that much greater than normal.
How to Cope With an Unprecedented Situation
For the worried well and for the clinicians who have understandable fears about exposure, there are several things you can try to manage your anxiety. There are concentric circles of concern that you have to maintain. Think of it like the instructions on an airplane when, if there’s a drop in cabin pressure, you’re asked to apply your own oxygen mask first before placing one on your child. In the same way, you must first think about protecting yourself by limiting your exposure and monitoring your own physical state for any symptoms. But then you must be concerned about your family, your friends, and also society. This is a situation where the impulse and the ethos of worrying about your fellow persons—being your brother’s keeper—is imperative.
The epidemic has been successfully managed in some countries, like Singapore and China, which, once they got on top of it, were able to limit contagion in a very dramatic way. But these are authoritarian governments. The United States doesn’t work that way, which is what makes appealing to the principle of caring for others so crucial. You can protect yourself, but if other people aren’t also protected, it may not matter. You have to worry not just about yourself but about everyone else.
When it comes to stress management, I recommend not catastrophizing or watching the news media 24/7. Distract yourself with other work or recreational activities. Reach out and communicate—virtually, of course—with friends, family, and healthcare providers as needed. Staying in touch acts not just as a diversion but also as an outlet for assuaging your feelings, your sense of being in this alone, feeling isolated.
There are also cognitive reframing mechanisms you can employ. Consider that although this is bad, some countries have already gone through it. And we’ll get through it too. You’ll understandably ask yourself what it would mean if you were to be exposed. In most cases you can say, “I’m going to have the flu and symptoms that are not going to be pleasant, but I’ve had the flu or serious sickness before.”
Remember that there are already antiretroviral treatments being tested in clinical trials and showing efficacy. It’s good to know that before this pandemic ends, some of these treatments will probably be clinically applied, mostly to those who are severely affected and in intensive care.
Diagnose yourself. Monitor your state. Determine whether the stress is really having an impact on you. Is it affecting your sleep, appetite, concentration, mood? And if you do have a preexisting psychiatric condition, don’t feel afraid to reach out to your mental health provider. Understand that you’re going to be anxious, which may aggravate your symptoms and require an adjustment in your treatment. That’s okay. It’s to be expected and your provider should be available to help you.
Controlling this outbreak via the same epidemiologic infectious disease prevention guidance that works in authoritarian societies is not going to be applicable here because of the liberties that we experience in American society. What will determine our success is the belief that we’re in this together, that we’re going to help each other. We should be proud of that, as it shows how Americans and people around the world stand up in situations like this.
Let’s also note that even though everybody is affected and undergoing previously unimaginable levels of anticipated stress and dislocation, it’s the healthcare providers who are really on the frontlines. They’re under tremendous pressure to continue to perform heroically, at great risk to themselves. They deserve a real debt of gratitude.
We will get through this, but as we do, it will not end until we’ve undergone an extreme test of our character. I certainly hope and trust that we will be up to it.
Dr. Jeffrey A. Lieberman is chairman of the Department of Psychiatry at Columbia University. He is a former president of the American Psychiatric Association.
Disclosure: Jeffrey A. Lieberman, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Clintara; Intracellular Therapies. Received research grant from Alkermes; Biomarin; EnVivo/Forum; Genentech; Novartis/Novation; Sunovion. Patent: Repligen.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic is an experience that is unprecedented in our lifetime. It is having a pervasive effect due to how mysterious, potentially dangerous, and sustained it is. We don’t know how bad it’s going to get or how long it’s going to last. We have natural disasters like hurricanes and earthquakes, but they are limited in time and scope. But this global pandemic is something we can’t put our arms around just yet, breeding uncertainty, worry, and fear. This is where mental health professionals need to come in.
The populations being affected by this pandemic can be placed into different groups on the basis of their mental health consequences and needs. First you have, for lack of a better term, “the worried well.” These are people with no preexisting mental disorder who are naturally worried by this and are trying to take appropriate actions to protect themselves and prepare. For such individuals, the equivalent of mental health first-aid should be useful (we’ll come back to that in a moment). Given the proper guidance and sources of information, most such people should be able to manage the anxiety, worry, and dysphoria associated with this critical pandemic.
Then there are those who have preexisting mental conditions related to mood, anxiety, stress, or obsessive tendencies. They are probably going to have an increase in their symptoms, and as such, a corresponding need for adjusting treatment. This may require an increase in their existing medications or the addition of an ad hoc medication, or perhaps more frequent contact with their doctor or therapist.
Because travel and direct visitation is discouraged at the moment, virtual methods of communication should be used to speak with these patients. Such methods have long existed but haven’t been adopted in large numbers; this may be the impetus to finally make it happen. Using the telephone, FaceTime, Skype, WebEx, Zoom, and other means of videoconferencing should be feasible. As billing procedures are being adapted for this moment, there’s no reason why individuals shouldn’t be able to contact their mental health provider.
Substance abuse is also a condition vulnerable to the stress effects of this pandemic. This will prompt or tempt those to use substances that they’ve abused or turned to in the past as a way of self-medicating and assuaging their anxiety and worry.
It’s possible that the pandemic could find its way into delusions or exacerbate symptoms, but somewhat paradoxically, people with serious mental illnesses often respond more calmly to crises than do individuals without them. As a result, the number of these patients requiring emergency room admission for possible exacerbation of symptoms is probably not going to be that much greater than normal.
How to Cope With an Unprecedented Situation
For the worried well and for the clinicians who have understandable fears about exposure, there are several things you can try to manage your anxiety. There are concentric circles of concern that you have to maintain. Think of it like the instructions on an airplane when, if there’s a drop in cabin pressure, you’re asked to apply your own oxygen mask first before placing one on your child. In the same way, you must first think about protecting yourself by limiting your exposure and monitoring your own physical state for any symptoms. But then you must be concerned about your family, your friends, and also society. This is a situation where the impulse and the ethos of worrying about your fellow persons—being your brother’s keeper—is imperative.
The epidemic has been successfully managed in some countries, like Singapore and China, which, once they got on top of it, were able to limit contagion in a very dramatic way. But these are authoritarian governments. The United States doesn’t work that way, which is what makes appealing to the principle of caring for others so crucial. You can protect yourself, but if other people aren’t also protected, it may not matter. You have to worry not just about yourself but about everyone else.
When it comes to stress management, I recommend not catastrophizing or watching the news media 24/7. Distract yourself with other work or recreational activities. Reach out and communicate—virtually, of course—with friends, family, and healthcare providers as needed. Staying in touch acts not just as a diversion but also as an outlet for assuaging your feelings, your sense of being in this alone, feeling isolated.
There are also cognitive reframing mechanisms you can employ. Consider that although this is bad, some countries have already gone through it. And we’ll get through it too. You’ll understandably ask yourself what it would mean if you were to be exposed. In most cases you can say, “I’m going to have the flu and symptoms that are not going to be pleasant, but I’ve had the flu or serious sickness before.”
Remember that there are already antiretroviral treatments being tested in clinical trials and showing efficacy. It’s good to know that before this pandemic ends, some of these treatments will probably be clinically applied, mostly to those who are severely affected and in intensive care.
Diagnose yourself. Monitor your state. Determine whether the stress is really having an impact on you. Is it affecting your sleep, appetite, concentration, mood? And if you do have a preexisting psychiatric condition, don’t feel afraid to reach out to your mental health provider. Understand that you’re going to be anxious, which may aggravate your symptoms and require an adjustment in your treatment. That’s okay. It’s to be expected and your provider should be available to help you.
Controlling this outbreak via the same epidemiologic infectious disease prevention guidance that works in authoritarian societies is not going to be applicable here because of the liberties that we experience in American society. What will determine our success is the belief that we’re in this together, that we’re going to help each other. We should be proud of that, as it shows how Americans and people around the world stand up in situations like this.
Let’s also note that even though everybody is affected and undergoing previously unimaginable levels of anticipated stress and dislocation, it’s the healthcare providers who are really on the frontlines. They’re under tremendous pressure to continue to perform heroically, at great risk to themselves. They deserve a real debt of gratitude.
We will get through this, but as we do, it will not end until we’ve undergone an extreme test of our character. I certainly hope and trust that we will be up to it.
Dr. Jeffrey A. Lieberman is chairman of the Department of Psychiatry at Columbia University. He is a former president of the American Psychiatric Association.
Disclosure: Jeffrey A. Lieberman, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Clintara; Intracellular Therapies. Received research grant from Alkermes; Biomarin; EnVivo/Forum; Genentech; Novartis/Novation; Sunovion. Patent: Repligen.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
U.S. lifts visa halt to boost COVID-19 physician workforce
New information from the US State Department indicates that it is lifting the suspension on visas for foreign-trained medical professionals, a move that has promise for boosting the US physician workforce battling COVID-19.
The move may also help physicians extend their visas.
The communication late last week follows a March 18 announcement that, because of COVID-19, the United States was suspending routine processing of immigrant and nonimmigrant visas, including the J and H visas, at embassies and consulates worldwide.
As reported by Medscape Medical News, the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates (ECFMG) appealed to the State Department to lift the suspension, noting that 4222 graduates of medical schools outside the United States who had matched into residencies in the United States and were ready to start on July 1 would not get the visas most of them need to begin training.
The State Department lifted the suspensions and issued this update:
“We encourage medical professionals with an approved US non-immigrant or immigrant visa petition (I-129, I-140, or similar) or a certificate of eligibility in an approved exchange visitor program (DS-2019), particularly those working to treat or mitigate the effects of COVID-19, to review the website of their nearest embassy or consulate for procedures to request a visa appointment.”
The State Department also issued guidance for foreign medical professionals already in the United States:
“J-1 Alien Physicians (medical residents) may consult with their program sponsor, ECFMG, to extend their programs in the United States. Generally, a J-1 program for a foreign medical resident can be extended one year at a time for up to seven years.
“Note that the expiration date on a US visa does not determine how long one can be in the United States. The way to confirm one’s required departure date is here : https://i94.cbp.dhs.gov/I94/#/home.
“Those who need to extend their stay or adjust their visa status must apply with USCIS (US Citizenship and Immigration Services).”
Complications Still Exist
ECFMG’s CEO, William W. Pinsky, MD, told Medscape Medical News that, although they welcomed the news from the State Department, there are still unanswered questions.
ECFMG explained that J-1 visas are currently granted only 30 days before the residency program begins.
However, travel to the United States may still be difficult in June, Pinsky said, and physicians may need to be quarantined for 2 weeks upon arrival.
“We’re still having some discussion with the Department of State on whether that regulation could be relaxed and they could come in earlier,” he said.
He cautioned that even after a J-1 visa application is made, the physician’s home country has to endorse the application.
Pinsky said he did not yet know whether that would be a problem.
He also said that, in response to New York’s plea for more healthcare workers, ECFMG is offering to verify education and licensing credentials for physicians educated outside the United States at no cost.
Individual hospitals and regulatory authorities can decide whether there may be roles in some capacity for physicians who have graduated from medical school, even if they have not completed residency or have not been licensed, he said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New information from the US State Department indicates that it is lifting the suspension on visas for foreign-trained medical professionals, a move that has promise for boosting the US physician workforce battling COVID-19.
The move may also help physicians extend their visas.
The communication late last week follows a March 18 announcement that, because of COVID-19, the United States was suspending routine processing of immigrant and nonimmigrant visas, including the J and H visas, at embassies and consulates worldwide.
As reported by Medscape Medical News, the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates (ECFMG) appealed to the State Department to lift the suspension, noting that 4222 graduates of medical schools outside the United States who had matched into residencies in the United States and were ready to start on July 1 would not get the visas most of them need to begin training.
The State Department lifted the suspensions and issued this update:
“We encourage medical professionals with an approved US non-immigrant or immigrant visa petition (I-129, I-140, or similar) or a certificate of eligibility in an approved exchange visitor program (DS-2019), particularly those working to treat or mitigate the effects of COVID-19, to review the website of their nearest embassy or consulate for procedures to request a visa appointment.”
The State Department also issued guidance for foreign medical professionals already in the United States:
“J-1 Alien Physicians (medical residents) may consult with their program sponsor, ECFMG, to extend their programs in the United States. Generally, a J-1 program for a foreign medical resident can be extended one year at a time for up to seven years.
“Note that the expiration date on a US visa does not determine how long one can be in the United States. The way to confirm one’s required departure date is here : https://i94.cbp.dhs.gov/I94/#/home.
“Those who need to extend their stay or adjust their visa status must apply with USCIS (US Citizenship and Immigration Services).”
Complications Still Exist
ECFMG’s CEO, William W. Pinsky, MD, told Medscape Medical News that, although they welcomed the news from the State Department, there are still unanswered questions.
ECFMG explained that J-1 visas are currently granted only 30 days before the residency program begins.
However, travel to the United States may still be difficult in June, Pinsky said, and physicians may need to be quarantined for 2 weeks upon arrival.
“We’re still having some discussion with the Department of State on whether that regulation could be relaxed and they could come in earlier,” he said.
He cautioned that even after a J-1 visa application is made, the physician’s home country has to endorse the application.
Pinsky said he did not yet know whether that would be a problem.
He also said that, in response to New York’s plea for more healthcare workers, ECFMG is offering to verify education and licensing credentials for physicians educated outside the United States at no cost.
Individual hospitals and regulatory authorities can decide whether there may be roles in some capacity for physicians who have graduated from medical school, even if they have not completed residency or have not been licensed, he said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New information from the US State Department indicates that it is lifting the suspension on visas for foreign-trained medical professionals, a move that has promise for boosting the US physician workforce battling COVID-19.
The move may also help physicians extend their visas.
The communication late last week follows a March 18 announcement that, because of COVID-19, the United States was suspending routine processing of immigrant and nonimmigrant visas, including the J and H visas, at embassies and consulates worldwide.
As reported by Medscape Medical News, the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates (ECFMG) appealed to the State Department to lift the suspension, noting that 4222 graduates of medical schools outside the United States who had matched into residencies in the United States and were ready to start on July 1 would not get the visas most of them need to begin training.
The State Department lifted the suspensions and issued this update:
“We encourage medical professionals with an approved US non-immigrant or immigrant visa petition (I-129, I-140, or similar) or a certificate of eligibility in an approved exchange visitor program (DS-2019), particularly those working to treat or mitigate the effects of COVID-19, to review the website of their nearest embassy or consulate for procedures to request a visa appointment.”
The State Department also issued guidance for foreign medical professionals already in the United States:
“J-1 Alien Physicians (medical residents) may consult with their program sponsor, ECFMG, to extend their programs in the United States. Generally, a J-1 program for a foreign medical resident can be extended one year at a time for up to seven years.
“Note that the expiration date on a US visa does not determine how long one can be in the United States. The way to confirm one’s required departure date is here : https://i94.cbp.dhs.gov/I94/#/home.
“Those who need to extend their stay or adjust their visa status must apply with USCIS (US Citizenship and Immigration Services).”
Complications Still Exist
ECFMG’s CEO, William W. Pinsky, MD, told Medscape Medical News that, although they welcomed the news from the State Department, there are still unanswered questions.
ECFMG explained that J-1 visas are currently granted only 30 days before the residency program begins.
However, travel to the United States may still be difficult in June, Pinsky said, and physicians may need to be quarantined for 2 weeks upon arrival.
“We’re still having some discussion with the Department of State on whether that regulation could be relaxed and they could come in earlier,” he said.
He cautioned that even after a J-1 visa application is made, the physician’s home country has to endorse the application.
Pinsky said he did not yet know whether that would be a problem.
He also said that, in response to New York’s plea for more healthcare workers, ECFMG is offering to verify education and licensing credentials for physicians educated outside the United States at no cost.
Individual hospitals and regulatory authorities can decide whether there may be roles in some capacity for physicians who have graduated from medical school, even if they have not completed residency or have not been licensed, he said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sunshine on my shoulders
On March 26, 2020, it’s hard to write or think of anything beyond the COVID-19 pandemic. Those of you who are on the front lines of the battle may find it strange that I am just a bit envious. Having stepped back from clinical medicine nearly a decade ago, it is frustrating to feel that there is little I can do to help other than offering to venture into the grocery store to shop for friends and neighbors who feel more vulnerable than I do.
Here in Maine, we are blessed by geographic isolation that for the moment seems to have damped the surge from the metropolitan centers to our south. But, the virus is here and, as the state with the oldest population, we are beginning to be affected.
For nearly a century, we could count on the outhouses here in Maine would be stocked with outdated Sears Roebucks catalogs when toilet paper was in short supply. Many outhouses remain but Sears Roebucks and its catalogs have disappeared from the landscape. I take a little comfort in the learning that I’m not the only human on the planet who can envision the horror of a week or even a day without toilet paper.
So I am left to sit on the sidelines and watch how my fellow Mainers are coping with the anxiety, depression, and loneliness that come with the forced social isolation. It is pretty clear that walking outside has become the coping strategy of choice. On a usual March day the walkers comprise a skimpy mix of dog walkers and wannabe arctic explorers testing the weather-defying capabilities of their high-tech outerwear. But, to say the least, this is not a usual March and the number of walkers has surged bolstered by gym rats forced off their sweat-drenched ellipticals and treadmills.
This increase in outdoor activity is clearly perceptible even on an overcast day, but it is far less than one would expect given the magnitude of the disruption to everyone’s routines. But, when the sun comes out! The doors fly open and onto the sidewalks and quiet rural roads spill scores of people I haven’t seen for months and in some cases decades. One can almost hear John Denver singing “sunshine on my shoulders makes me happy.” Everyone is smiling and waving to each other. It feels as though the community has, at least for a few hours, been able to throw off the burden of angst that the pandemic laid on us.
There has been a good bit of research about seasonal affective disorder, and I suspect that almost everyone has heard about the value of sunshine for depression. But it is unfortunate that the psychological benefits of just being outdoors – even on an overcast day – has gone pretty much unpublicized. As part of their marketing strategy, a local company that specializes in recreational clothing and gear is encouraging its customers to become “outsiders.” It may be that the pandemic will make more people realize the psychological benefits of being active outside. As physicians we should continue to encourage our patients to be more active and remind them that they don’t need to wait for a sunny day to do so.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
On March 26, 2020, it’s hard to write or think of anything beyond the COVID-19 pandemic. Those of you who are on the front lines of the battle may find it strange that I am just a bit envious. Having stepped back from clinical medicine nearly a decade ago, it is frustrating to feel that there is little I can do to help other than offering to venture into the grocery store to shop for friends and neighbors who feel more vulnerable than I do.
Here in Maine, we are blessed by geographic isolation that for the moment seems to have damped the surge from the metropolitan centers to our south. But, the virus is here and, as the state with the oldest population, we are beginning to be affected.
For nearly a century, we could count on the outhouses here in Maine would be stocked with outdated Sears Roebucks catalogs when toilet paper was in short supply. Many outhouses remain but Sears Roebucks and its catalogs have disappeared from the landscape. I take a little comfort in the learning that I’m not the only human on the planet who can envision the horror of a week or even a day without toilet paper.
So I am left to sit on the sidelines and watch how my fellow Mainers are coping with the anxiety, depression, and loneliness that come with the forced social isolation. It is pretty clear that walking outside has become the coping strategy of choice. On a usual March day the walkers comprise a skimpy mix of dog walkers and wannabe arctic explorers testing the weather-defying capabilities of their high-tech outerwear. But, to say the least, this is not a usual March and the number of walkers has surged bolstered by gym rats forced off their sweat-drenched ellipticals and treadmills.
This increase in outdoor activity is clearly perceptible even on an overcast day, but it is far less than one would expect given the magnitude of the disruption to everyone’s routines. But, when the sun comes out! The doors fly open and onto the sidewalks and quiet rural roads spill scores of people I haven’t seen for months and in some cases decades. One can almost hear John Denver singing “sunshine on my shoulders makes me happy.” Everyone is smiling and waving to each other. It feels as though the community has, at least for a few hours, been able to throw off the burden of angst that the pandemic laid on us.
There has been a good bit of research about seasonal affective disorder, and I suspect that almost everyone has heard about the value of sunshine for depression. But it is unfortunate that the psychological benefits of just being outdoors – even on an overcast day – has gone pretty much unpublicized. As part of their marketing strategy, a local company that specializes in recreational clothing and gear is encouraging its customers to become “outsiders.” It may be that the pandemic will make more people realize the psychological benefits of being active outside. As physicians we should continue to encourage our patients to be more active and remind them that they don’t need to wait for a sunny day to do so.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
On March 26, 2020, it’s hard to write or think of anything beyond the COVID-19 pandemic. Those of you who are on the front lines of the battle may find it strange that I am just a bit envious. Having stepped back from clinical medicine nearly a decade ago, it is frustrating to feel that there is little I can do to help other than offering to venture into the grocery store to shop for friends and neighbors who feel more vulnerable than I do.
Here in Maine, we are blessed by geographic isolation that for the moment seems to have damped the surge from the metropolitan centers to our south. But, the virus is here and, as the state with the oldest population, we are beginning to be affected.
For nearly a century, we could count on the outhouses here in Maine would be stocked with outdated Sears Roebucks catalogs when toilet paper was in short supply. Many outhouses remain but Sears Roebucks and its catalogs have disappeared from the landscape. I take a little comfort in the learning that I’m not the only human on the planet who can envision the horror of a week or even a day without toilet paper.
So I am left to sit on the sidelines and watch how my fellow Mainers are coping with the anxiety, depression, and loneliness that come with the forced social isolation. It is pretty clear that walking outside has become the coping strategy of choice. On a usual March day the walkers comprise a skimpy mix of dog walkers and wannabe arctic explorers testing the weather-defying capabilities of their high-tech outerwear. But, to say the least, this is not a usual March and the number of walkers has surged bolstered by gym rats forced off their sweat-drenched ellipticals and treadmills.
This increase in outdoor activity is clearly perceptible even on an overcast day, but it is far less than one would expect given the magnitude of the disruption to everyone’s routines. But, when the sun comes out! The doors fly open and onto the sidewalks and quiet rural roads spill scores of people I haven’t seen for months and in some cases decades. One can almost hear John Denver singing “sunshine on my shoulders makes me happy.” Everyone is smiling and waving to each other. It feels as though the community has, at least for a few hours, been able to throw off the burden of angst that the pandemic laid on us.
There has been a good bit of research about seasonal affective disorder, and I suspect that almost everyone has heard about the value of sunshine for depression. But it is unfortunate that the psychological benefits of just being outdoors – even on an overcast day – has gone pretty much unpublicized. As part of their marketing strategy, a local company that specializes in recreational clothing and gear is encouraging its customers to become “outsiders.” It may be that the pandemic will make more people realize the psychological benefits of being active outside. As physicians we should continue to encourage our patients to be more active and remind them that they don’t need to wait for a sunny day to do so.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
Mental Health Support for Self-Isolated Veterans
The message everywhere is “stay home!” But what if staying home threatens your mental health? Veterans are a doubly vulnerable group these days—vulnerable both to the COVID-19 infection and to the mental stress that self-isolation can inflict. To help relieve that pressure and, in particular, to reach veterans who might not otherwise seek counseling and mental health support, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has been shifting some outpatient care to telehealth and deploying Mobile Vet Center units to coronavirus-crisis areas.
The VA received some money to beef up its telehealth system from the $2 trillion CARES (Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security) Act relief package passed and signed last week: $14.4 billion to expand telehealth services and another $2.15 billion to expand coronavirus-related services, including the purchase of mHealth devices.
Several of the provisions in the CARES Act directly address the needs of rural and underserved veterans. For instance, the Act authorizes the VA to expand telemental health services and enter into short-term agreements with telecommunications companies to provide temporary broadband services to veterans, a critical need among rural residents who may be physically isolated from mental healthcare. The act also allows federally qualified health centers and rural health clinics, 2 types of facilities that serve rural and underserved populations, to be designated as distant sites for telehealth.
Between 2002, when telemental health services were launched, and 2019, veterans have worked with a counselor nearly 3 million times. In 2017, the VA says, psychiatric hospitalizations dropped 31%. Veterans have said they prefer videoconferencing over in-person therapy because they can are more at ease at home.
Using video telehealth, veterans can connect with care teams from anywhere—a safer alternative to traveling to appointments—using the camera on a phone, computer, or Apple or Android devices. Veterans also can use My HealtheVet’s secure messaging feature for non-urgent health questions. VA mental health professionals use both synchronous and asynchronous care: The first to connect patients to providers through a communication link, usually videoconferencing, the second to send data to specialists.
The current pandemic puts a strain on both patients and providers, but the Mobile Vet Centers may help relieve some of that strain. An extension of the VA’s brick-and-mortar Vet Centers, the mobile units provide a range of services, including individual, group, marriage, and family counseling. They also can refer active duty service members, veterans, and their families to VA care or other care facilities.
The mobile units are staffed by Vet Center employees who volunteer to deploy in emergencies, such as hurricanes and wildfires. The first units responding to the COVID-19 pandemic were dispatched to New York City, San Francisco, New Orleans, and Los Angeles.
“In times like this, it’s important to stand shoulder to shoulder with our local communities, support their local needs, and [assure] them they are not alone in navigating this crisis,” said Brooklyn Vet Center Director Gabe Botero.
Although the VA’s top priority remains keeping veterans safe while also making sure they receive the mental and physical healthcare they need , it has been criticized recently for “pausing” the Mission Act, which allows some veterans to get healthcare outside VA centers. The concern was that seeking outside care could expose veterans to the virus and potentially tax private health resources.
Government spokespeople have said the VA is not stopping or pausing the law, but “ensuring the best medical interests of America’s veterans are met.”
The message everywhere is “stay home!” But what if staying home threatens your mental health? Veterans are a doubly vulnerable group these days—vulnerable both to the COVID-19 infection and to the mental stress that self-isolation can inflict. To help relieve that pressure and, in particular, to reach veterans who might not otherwise seek counseling and mental health support, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has been shifting some outpatient care to telehealth and deploying Mobile Vet Center units to coronavirus-crisis areas.
The VA received some money to beef up its telehealth system from the $2 trillion CARES (Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security) Act relief package passed and signed last week: $14.4 billion to expand telehealth services and another $2.15 billion to expand coronavirus-related services, including the purchase of mHealth devices.
Several of the provisions in the CARES Act directly address the needs of rural and underserved veterans. For instance, the Act authorizes the VA to expand telemental health services and enter into short-term agreements with telecommunications companies to provide temporary broadband services to veterans, a critical need among rural residents who may be physically isolated from mental healthcare. The act also allows federally qualified health centers and rural health clinics, 2 types of facilities that serve rural and underserved populations, to be designated as distant sites for telehealth.
Between 2002, when telemental health services were launched, and 2019, veterans have worked with a counselor nearly 3 million times. In 2017, the VA says, psychiatric hospitalizations dropped 31%. Veterans have said they prefer videoconferencing over in-person therapy because they can are more at ease at home.
Using video telehealth, veterans can connect with care teams from anywhere—a safer alternative to traveling to appointments—using the camera on a phone, computer, or Apple or Android devices. Veterans also can use My HealtheVet’s secure messaging feature for non-urgent health questions. VA mental health professionals use both synchronous and asynchronous care: The first to connect patients to providers through a communication link, usually videoconferencing, the second to send data to specialists.
The current pandemic puts a strain on both patients and providers, but the Mobile Vet Centers may help relieve some of that strain. An extension of the VA’s brick-and-mortar Vet Centers, the mobile units provide a range of services, including individual, group, marriage, and family counseling. They also can refer active duty service members, veterans, and their families to VA care or other care facilities.
The mobile units are staffed by Vet Center employees who volunteer to deploy in emergencies, such as hurricanes and wildfires. The first units responding to the COVID-19 pandemic were dispatched to New York City, San Francisco, New Orleans, and Los Angeles.
“In times like this, it’s important to stand shoulder to shoulder with our local communities, support their local needs, and [assure] them they are not alone in navigating this crisis,” said Brooklyn Vet Center Director Gabe Botero.
Although the VA’s top priority remains keeping veterans safe while also making sure they receive the mental and physical healthcare they need , it has been criticized recently for “pausing” the Mission Act, which allows some veterans to get healthcare outside VA centers. The concern was that seeking outside care could expose veterans to the virus and potentially tax private health resources.
Government spokespeople have said the VA is not stopping or pausing the law, but “ensuring the best medical interests of America’s veterans are met.”
The message everywhere is “stay home!” But what if staying home threatens your mental health? Veterans are a doubly vulnerable group these days—vulnerable both to the COVID-19 infection and to the mental stress that self-isolation can inflict. To help relieve that pressure and, in particular, to reach veterans who might not otherwise seek counseling and mental health support, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has been shifting some outpatient care to telehealth and deploying Mobile Vet Center units to coronavirus-crisis areas.
The VA received some money to beef up its telehealth system from the $2 trillion CARES (Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security) Act relief package passed and signed last week: $14.4 billion to expand telehealth services and another $2.15 billion to expand coronavirus-related services, including the purchase of mHealth devices.
Several of the provisions in the CARES Act directly address the needs of rural and underserved veterans. For instance, the Act authorizes the VA to expand telemental health services and enter into short-term agreements with telecommunications companies to provide temporary broadband services to veterans, a critical need among rural residents who may be physically isolated from mental healthcare. The act also allows federally qualified health centers and rural health clinics, 2 types of facilities that serve rural and underserved populations, to be designated as distant sites for telehealth.
Between 2002, when telemental health services were launched, and 2019, veterans have worked with a counselor nearly 3 million times. In 2017, the VA says, psychiatric hospitalizations dropped 31%. Veterans have said they prefer videoconferencing over in-person therapy because they can are more at ease at home.
Using video telehealth, veterans can connect with care teams from anywhere—a safer alternative to traveling to appointments—using the camera on a phone, computer, or Apple or Android devices. Veterans also can use My HealtheVet’s secure messaging feature for non-urgent health questions. VA mental health professionals use both synchronous and asynchronous care: The first to connect patients to providers through a communication link, usually videoconferencing, the second to send data to specialists.
The current pandemic puts a strain on both patients and providers, but the Mobile Vet Centers may help relieve some of that strain. An extension of the VA’s brick-and-mortar Vet Centers, the mobile units provide a range of services, including individual, group, marriage, and family counseling. They also can refer active duty service members, veterans, and their families to VA care or other care facilities.
The mobile units are staffed by Vet Center employees who volunteer to deploy in emergencies, such as hurricanes and wildfires. The first units responding to the COVID-19 pandemic were dispatched to New York City, San Francisco, New Orleans, and Los Angeles.
“In times like this, it’s important to stand shoulder to shoulder with our local communities, support their local needs, and [assure] them they are not alone in navigating this crisis,” said Brooklyn Vet Center Director Gabe Botero.
Although the VA’s top priority remains keeping veterans safe while also making sure they receive the mental and physical healthcare they need , it has been criticized recently for “pausing” the Mission Act, which allows some veterans to get healthcare outside VA centers. The concern was that seeking outside care could expose veterans to the virus and potentially tax private health resources.
Government spokespeople have said the VA is not stopping or pausing the law, but “ensuring the best medical interests of America’s veterans are met.”










