User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
div[contains(@class, 'medstat-accordion-set article-series')]
No Benefit to High-Dose IV Vs Oral Steroids in Giant Cell Arteritis
TOPLINE:
In patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA), intravenous methylprednisolone compared with oral glucocorticoids alone does not improve visual acuity and increases the risk for diabetes within the first year. Survival rates do not differ with these two treatments.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a population-based retrospective study at three centers in Sweden to assess the clinical characteristics, treatment-related toxicity, and mortality in patients with GCA who were receiving high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone.
- A total of 419 patients with biopsy-confirmed GCA (mean age at diagnosis, 75 years; 69% women) diagnosed from 2004 to 2019 were included.
- Patients were treated with either intravenous methylprednisolone (n = 111) at a dose of 500-1000 mg per day for 3 consecutive days or oral glucocorticoids alone (n = 308).
- Ischemic visual complications considered to indicate visual involvement were confirmed by an ophthalmologist, and data on visual acuity were collected from ophthalmologic clinic records at initial consultations and follow-up at 3-18 months.
TAKEAWAY:
- Despite a tendency toward improvement, no significant difference in visual acuity was observed with intravenous methylprednisolone compared with oral glucocorticoids.
- Patients treated with intravenous methylprednisolone had a higher risk for newly diagnosed diabetes within a year of GCA diagnosis (odds ratio [OR], 2.59; P = .01).
- The risk for diabetes remained elevated even after adjustment for the cumulative oral glucocorticoid dose at 3 months (adjusted OR, 3.30; P = .01).
- Survival rates did not significantly differ between the treatment groups over a mean follow-up of 6.6 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“In this study on the use of intravenous methylprednisolone treatment in GCA, we found no evidence of a beneficial effect in improving visual acuity or enabling more rapid tapering of the oral glucocorticoid dose,” the authors wrote. “The use of IVMP [intravenous methylprednisolone] was associated with an increased risk of diabetes during the first year compared with oral GC [glucocorticoid], raising questions about the value of IVMP in GCA treatment.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Hampus Henningson, Department of Clinical Sciences, Rheumatology, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, was published online in Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective nature of the study may have resulted in missing data and difficulty in accurately quantifying the cumulative glucocorticoid doses. The study did not validate the diagnoses of comorbidities but relied solely on diagnostic codes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the Swedish Research Council, Swedish Rheumatism Association, Swedish Medical Society, Alfred Österlund’s Foundation, and King Gustaf V’s 80-year foundation. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA), intravenous methylprednisolone compared with oral glucocorticoids alone does not improve visual acuity and increases the risk for diabetes within the first year. Survival rates do not differ with these two treatments.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a population-based retrospective study at three centers in Sweden to assess the clinical characteristics, treatment-related toxicity, and mortality in patients with GCA who were receiving high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone.
- A total of 419 patients with biopsy-confirmed GCA (mean age at diagnosis, 75 years; 69% women) diagnosed from 2004 to 2019 were included.
- Patients were treated with either intravenous methylprednisolone (n = 111) at a dose of 500-1000 mg per day for 3 consecutive days or oral glucocorticoids alone (n = 308).
- Ischemic visual complications considered to indicate visual involvement were confirmed by an ophthalmologist, and data on visual acuity were collected from ophthalmologic clinic records at initial consultations and follow-up at 3-18 months.
TAKEAWAY:
- Despite a tendency toward improvement, no significant difference in visual acuity was observed with intravenous methylprednisolone compared with oral glucocorticoids.
- Patients treated with intravenous methylprednisolone had a higher risk for newly diagnosed diabetes within a year of GCA diagnosis (odds ratio [OR], 2.59; P = .01).
- The risk for diabetes remained elevated even after adjustment for the cumulative oral glucocorticoid dose at 3 months (adjusted OR, 3.30; P = .01).
- Survival rates did not significantly differ between the treatment groups over a mean follow-up of 6.6 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“In this study on the use of intravenous methylprednisolone treatment in GCA, we found no evidence of a beneficial effect in improving visual acuity or enabling more rapid tapering of the oral glucocorticoid dose,” the authors wrote. “The use of IVMP [intravenous methylprednisolone] was associated with an increased risk of diabetes during the first year compared with oral GC [glucocorticoid], raising questions about the value of IVMP in GCA treatment.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Hampus Henningson, Department of Clinical Sciences, Rheumatology, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, was published online in Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective nature of the study may have resulted in missing data and difficulty in accurately quantifying the cumulative glucocorticoid doses. The study did not validate the diagnoses of comorbidities but relied solely on diagnostic codes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the Swedish Research Council, Swedish Rheumatism Association, Swedish Medical Society, Alfred Österlund’s Foundation, and King Gustaf V’s 80-year foundation. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA), intravenous methylprednisolone compared with oral glucocorticoids alone does not improve visual acuity and increases the risk for diabetes within the first year. Survival rates do not differ with these two treatments.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a population-based retrospective study at three centers in Sweden to assess the clinical characteristics, treatment-related toxicity, and mortality in patients with GCA who were receiving high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone.
- A total of 419 patients with biopsy-confirmed GCA (mean age at diagnosis, 75 years; 69% women) diagnosed from 2004 to 2019 were included.
- Patients were treated with either intravenous methylprednisolone (n = 111) at a dose of 500-1000 mg per day for 3 consecutive days or oral glucocorticoids alone (n = 308).
- Ischemic visual complications considered to indicate visual involvement were confirmed by an ophthalmologist, and data on visual acuity were collected from ophthalmologic clinic records at initial consultations and follow-up at 3-18 months.
TAKEAWAY:
- Despite a tendency toward improvement, no significant difference in visual acuity was observed with intravenous methylprednisolone compared with oral glucocorticoids.
- Patients treated with intravenous methylprednisolone had a higher risk for newly diagnosed diabetes within a year of GCA diagnosis (odds ratio [OR], 2.59; P = .01).
- The risk for diabetes remained elevated even after adjustment for the cumulative oral glucocorticoid dose at 3 months (adjusted OR, 3.30; P = .01).
- Survival rates did not significantly differ between the treatment groups over a mean follow-up of 6.6 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“In this study on the use of intravenous methylprednisolone treatment in GCA, we found no evidence of a beneficial effect in improving visual acuity or enabling more rapid tapering of the oral glucocorticoid dose,” the authors wrote. “The use of IVMP [intravenous methylprednisolone] was associated with an increased risk of diabetes during the first year compared with oral GC [glucocorticoid], raising questions about the value of IVMP in GCA treatment.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Hampus Henningson, Department of Clinical Sciences, Rheumatology, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, was published online in Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective nature of the study may have resulted in missing data and difficulty in accurately quantifying the cumulative glucocorticoid doses. The study did not validate the diagnoses of comorbidities but relied solely on diagnostic codes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the Swedish Research Council, Swedish Rheumatism Association, Swedish Medical Society, Alfred Österlund’s Foundation, and King Gustaf V’s 80-year foundation. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Minor Progress in Gender Pay Equity, But a Big Gap Persists
Despite some recent progress in compensation equity, women in medicine continue to be paid significantly lower salaries than men.
According to the Female Compensation Report 2024 by Medscape, male doctors of any kind earned an average salary of about $400,000, whereas female doctors earned approximately $309,000 — a 29% gap.
The report analyzed survey data from 7000 practicing physicians who were recruited over a 4-month period starting in October 2023. The respondents comprised roughly 60% women representing over 29 specialties.
In the 2022 report, the pay gap between the genders was 32%. But some women in the field argued substantial headway is still needed.
“You can try and pick apart the data, but I’d say we’re not really making progress,” said Susan T. Hingle, MD, an internist in Illinois and president of the American Medical Women’s Association. “A decline by a couple of percentage points is not significantly addressing this pay gap that over a lifetime is huge, can be millions of dollars.”
The gender gap was narrower among female primary care physicians (PCPs) vs medical specialists. Female PCPs earned around $253,000 per year, whereas male PCPs earned about $295,000 per year. Hingle suggested that female PCPs may enjoy more pay equity because health systems have a harder time filling these positions.
On the other hand, the gap for specialists rose from 27% in 2022 to 31% in 2023. Differences in how aggressively women and men negotiate compensation packages may play a role, said Hingle.
“Taking negotiation out of the equation would be progress to me,” said Hingle.
Pay disparity did not appear to be the result of time spent on the job — female doctors reported an average of 49 work hours per week, whereas their male counterparts reported 50 work hours per week.
Meanwhile, the pay gap progressively worsened over time. Among doctors aged 28-34 years, men earned an average of $53,000 more than women. By ages 46-49, men earned an average of $157,000 more than women.
“I had to take my employer to court to get equal compensation, sad as it is to say,” said a hospitalist in North Carolina.
Nearly 60% of women surveyed felt they were not being paid fairly for their efforts, up from less than half reported in Medscape’s 2021 report. Hingle said that this figure may not only reflect sentiments about the compensation gap, but also less support on the job, including fewer physician assistants (PAs), nurses, and administrative staff.
“At my job, I do the work of multiple people,” said a survey respondent. “Junior resident, senior resident, social worker, nurse practitioner, PA — as well as try to be a teacher, researcher, [and] an excellent doctor and have the time to make patients feel as if they are not in a rush.”
Roughly 30% of women physicians said they would not choose to go into medicine again if given the chance compared with 26% of male physicians.
“Gender inequities in our profession have a direct impact,” said Shikha Jain, MD, an oncologist in Chicago and founder of the Women in Medicine nonprofit. “I think women in general don’t feel valued in the care they’re providing.”
Jain cited bullying, harassment, and fewer opportunities for leadership and recognition as factors beyond pay that affect female physicians’ feelings of being valued.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite some recent progress in compensation equity, women in medicine continue to be paid significantly lower salaries than men.
According to the Female Compensation Report 2024 by Medscape, male doctors of any kind earned an average salary of about $400,000, whereas female doctors earned approximately $309,000 — a 29% gap.
The report analyzed survey data from 7000 practicing physicians who were recruited over a 4-month period starting in October 2023. The respondents comprised roughly 60% women representing over 29 specialties.
In the 2022 report, the pay gap between the genders was 32%. But some women in the field argued substantial headway is still needed.
“You can try and pick apart the data, but I’d say we’re not really making progress,” said Susan T. Hingle, MD, an internist in Illinois and president of the American Medical Women’s Association. “A decline by a couple of percentage points is not significantly addressing this pay gap that over a lifetime is huge, can be millions of dollars.”
The gender gap was narrower among female primary care physicians (PCPs) vs medical specialists. Female PCPs earned around $253,000 per year, whereas male PCPs earned about $295,000 per year. Hingle suggested that female PCPs may enjoy more pay equity because health systems have a harder time filling these positions.
On the other hand, the gap for specialists rose from 27% in 2022 to 31% in 2023. Differences in how aggressively women and men negotiate compensation packages may play a role, said Hingle.
“Taking negotiation out of the equation would be progress to me,” said Hingle.
Pay disparity did not appear to be the result of time spent on the job — female doctors reported an average of 49 work hours per week, whereas their male counterparts reported 50 work hours per week.
Meanwhile, the pay gap progressively worsened over time. Among doctors aged 28-34 years, men earned an average of $53,000 more than women. By ages 46-49, men earned an average of $157,000 more than women.
“I had to take my employer to court to get equal compensation, sad as it is to say,” said a hospitalist in North Carolina.
Nearly 60% of women surveyed felt they were not being paid fairly for their efforts, up from less than half reported in Medscape’s 2021 report. Hingle said that this figure may not only reflect sentiments about the compensation gap, but also less support on the job, including fewer physician assistants (PAs), nurses, and administrative staff.
“At my job, I do the work of multiple people,” said a survey respondent. “Junior resident, senior resident, social worker, nurse practitioner, PA — as well as try to be a teacher, researcher, [and] an excellent doctor and have the time to make patients feel as if they are not in a rush.”
Roughly 30% of women physicians said they would not choose to go into medicine again if given the chance compared with 26% of male physicians.
“Gender inequities in our profession have a direct impact,” said Shikha Jain, MD, an oncologist in Chicago and founder of the Women in Medicine nonprofit. “I think women in general don’t feel valued in the care they’re providing.”
Jain cited bullying, harassment, and fewer opportunities for leadership and recognition as factors beyond pay that affect female physicians’ feelings of being valued.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite some recent progress in compensation equity, women in medicine continue to be paid significantly lower salaries than men.
According to the Female Compensation Report 2024 by Medscape, male doctors of any kind earned an average salary of about $400,000, whereas female doctors earned approximately $309,000 — a 29% gap.
The report analyzed survey data from 7000 practicing physicians who were recruited over a 4-month period starting in October 2023. The respondents comprised roughly 60% women representing over 29 specialties.
In the 2022 report, the pay gap between the genders was 32%. But some women in the field argued substantial headway is still needed.
“You can try and pick apart the data, but I’d say we’re not really making progress,” said Susan T. Hingle, MD, an internist in Illinois and president of the American Medical Women’s Association. “A decline by a couple of percentage points is not significantly addressing this pay gap that over a lifetime is huge, can be millions of dollars.”
The gender gap was narrower among female primary care physicians (PCPs) vs medical specialists. Female PCPs earned around $253,000 per year, whereas male PCPs earned about $295,000 per year. Hingle suggested that female PCPs may enjoy more pay equity because health systems have a harder time filling these positions.
On the other hand, the gap for specialists rose from 27% in 2022 to 31% in 2023. Differences in how aggressively women and men negotiate compensation packages may play a role, said Hingle.
“Taking negotiation out of the equation would be progress to me,” said Hingle.
Pay disparity did not appear to be the result of time spent on the job — female doctors reported an average of 49 work hours per week, whereas their male counterparts reported 50 work hours per week.
Meanwhile, the pay gap progressively worsened over time. Among doctors aged 28-34 years, men earned an average of $53,000 more than women. By ages 46-49, men earned an average of $157,000 more than women.
“I had to take my employer to court to get equal compensation, sad as it is to say,” said a hospitalist in North Carolina.
Nearly 60% of women surveyed felt they were not being paid fairly for their efforts, up from less than half reported in Medscape’s 2021 report. Hingle said that this figure may not only reflect sentiments about the compensation gap, but also less support on the job, including fewer physician assistants (PAs), nurses, and administrative staff.
“At my job, I do the work of multiple people,” said a survey respondent. “Junior resident, senior resident, social worker, nurse practitioner, PA — as well as try to be a teacher, researcher, [and] an excellent doctor and have the time to make patients feel as if they are not in a rush.”
Roughly 30% of women physicians said they would not choose to go into medicine again if given the chance compared with 26% of male physicians.
“Gender inequities in our profession have a direct impact,” said Shikha Jain, MD, an oncologist in Chicago and founder of the Women in Medicine nonprofit. “I think women in general don’t feel valued in the care they’re providing.”
Jain cited bullying, harassment, and fewer opportunities for leadership and recognition as factors beyond pay that affect female physicians’ feelings of being valued.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cannabis Often Used as a Substitute for Traditional Medications
Nearly two thirds of patients with rheumatic conditions switched to medical cannabis from medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and opioids, with the substitution being associated with greater self-reported improvement in symptoms than nonsubstitution.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a cross-sectional survey to investigate the prevalence of switching to medical cannabis from traditional medications in patients with rheumatic conditions from the United States and Canada.
- The survey included questions on current and past medical cannabis use, sociodemographic characteristics, medication taken and substituted, substance use, and patient-reported outcomes.
- Of the 1727 patients who completed the survey, 763 patients (mean age, 59 years; 84.1% women) reported current use of cannabis and were included in this analysis.
- Participants were asked if they had substituted any medications with medical cannabis and were sub-grouped accordingly.
- They also reported any changes in symptoms after initiating cannabis, the current and anticipated duration of medical cannabis use, methods of ingestion, cannabinoid content, and frequency of use.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 62.5% reported substituting medical cannabis for certain medications, including NSAIDs (54.7%), opioids (48.6%), sleep aids (29.6%), muscle relaxants (25.2%), benzodiazepines (15.5%), and gabapentinoids (10.5%).
- The most common reasons given for substituting medical cannabis were fewer side effects (39%), better symptom control (27%), and fewer adverse effects (12%).
- Participants who substituted medical cannabis reported significant improvements in symptoms such as pain, sleep, joint stiffness, muscle spasms, and inflammation, and in overall health, compared with those who did not substitute it for medications.
- The substitution group was more likely to use inhalation methods (smoking and vaporizing) than the nonsubstitution group; they also used medical cannabis more frequently and preferred products containing delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol.
IN PRACTICE:
“The changing legal status of cannabis has allowed a greater openness with more people willing to try cannabis for symptom relief. These encouraging results of medication reduction and favorable effect of [medical cannabis] require confirmation with more rigorous methods. At this time, survey information may be seen as a signal for effect, rather than sound evidence that could be applicable to those with musculoskeletal complaints in general,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Kevin F. Boehnke, PhD, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, and was published online in ACR Open Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional nature of the study limited the determination of causality between medical cannabis use and symptom improvement. Moreover, the anonymous and self-reported nature of the survey at a single timepoint may have introduced recall bias. The sample predominantly consisted of older, White females, which may have limited the generalizability of the findings to other demographic groups.
DISCLOSURES:
Some authors received grant support from the National Institute on Drug Abuse and the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Some others received payments, honoraria, grant funding, consulting fees, and travel support, and reported other ties with pharmaceutical companies and other institutions.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nearly two thirds of patients with rheumatic conditions switched to medical cannabis from medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and opioids, with the substitution being associated with greater self-reported improvement in symptoms than nonsubstitution.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a cross-sectional survey to investigate the prevalence of switching to medical cannabis from traditional medications in patients with rheumatic conditions from the United States and Canada.
- The survey included questions on current and past medical cannabis use, sociodemographic characteristics, medication taken and substituted, substance use, and patient-reported outcomes.
- Of the 1727 patients who completed the survey, 763 patients (mean age, 59 years; 84.1% women) reported current use of cannabis and were included in this analysis.
- Participants were asked if they had substituted any medications with medical cannabis and were sub-grouped accordingly.
- They also reported any changes in symptoms after initiating cannabis, the current and anticipated duration of medical cannabis use, methods of ingestion, cannabinoid content, and frequency of use.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 62.5% reported substituting medical cannabis for certain medications, including NSAIDs (54.7%), opioids (48.6%), sleep aids (29.6%), muscle relaxants (25.2%), benzodiazepines (15.5%), and gabapentinoids (10.5%).
- The most common reasons given for substituting medical cannabis were fewer side effects (39%), better symptom control (27%), and fewer adverse effects (12%).
- Participants who substituted medical cannabis reported significant improvements in symptoms such as pain, sleep, joint stiffness, muscle spasms, and inflammation, and in overall health, compared with those who did not substitute it for medications.
- The substitution group was more likely to use inhalation methods (smoking and vaporizing) than the nonsubstitution group; they also used medical cannabis more frequently and preferred products containing delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol.
IN PRACTICE:
“The changing legal status of cannabis has allowed a greater openness with more people willing to try cannabis for symptom relief. These encouraging results of medication reduction and favorable effect of [medical cannabis] require confirmation with more rigorous methods. At this time, survey information may be seen as a signal for effect, rather than sound evidence that could be applicable to those with musculoskeletal complaints in general,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Kevin F. Boehnke, PhD, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, and was published online in ACR Open Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional nature of the study limited the determination of causality between medical cannabis use and symptom improvement. Moreover, the anonymous and self-reported nature of the survey at a single timepoint may have introduced recall bias. The sample predominantly consisted of older, White females, which may have limited the generalizability of the findings to other demographic groups.
DISCLOSURES:
Some authors received grant support from the National Institute on Drug Abuse and the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Some others received payments, honoraria, grant funding, consulting fees, and travel support, and reported other ties with pharmaceutical companies and other institutions.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nearly two thirds of patients with rheumatic conditions switched to medical cannabis from medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and opioids, with the substitution being associated with greater self-reported improvement in symptoms than nonsubstitution.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a cross-sectional survey to investigate the prevalence of switching to medical cannabis from traditional medications in patients with rheumatic conditions from the United States and Canada.
- The survey included questions on current and past medical cannabis use, sociodemographic characteristics, medication taken and substituted, substance use, and patient-reported outcomes.
- Of the 1727 patients who completed the survey, 763 patients (mean age, 59 years; 84.1% women) reported current use of cannabis and were included in this analysis.
- Participants were asked if they had substituted any medications with medical cannabis and were sub-grouped accordingly.
- They also reported any changes in symptoms after initiating cannabis, the current and anticipated duration of medical cannabis use, methods of ingestion, cannabinoid content, and frequency of use.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 62.5% reported substituting medical cannabis for certain medications, including NSAIDs (54.7%), opioids (48.6%), sleep aids (29.6%), muscle relaxants (25.2%), benzodiazepines (15.5%), and gabapentinoids (10.5%).
- The most common reasons given for substituting medical cannabis were fewer side effects (39%), better symptom control (27%), and fewer adverse effects (12%).
- Participants who substituted medical cannabis reported significant improvements in symptoms such as pain, sleep, joint stiffness, muscle spasms, and inflammation, and in overall health, compared with those who did not substitute it for medications.
- The substitution group was more likely to use inhalation methods (smoking and vaporizing) than the nonsubstitution group; they also used medical cannabis more frequently and preferred products containing delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol.
IN PRACTICE:
“The changing legal status of cannabis has allowed a greater openness with more people willing to try cannabis for symptom relief. These encouraging results of medication reduction and favorable effect of [medical cannabis] require confirmation with more rigorous methods. At this time, survey information may be seen as a signal for effect, rather than sound evidence that could be applicable to those with musculoskeletal complaints in general,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Kevin F. Boehnke, PhD, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, and was published online in ACR Open Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional nature of the study limited the determination of causality between medical cannabis use and symptom improvement. Moreover, the anonymous and self-reported nature of the survey at a single timepoint may have introduced recall bias. The sample predominantly consisted of older, White females, which may have limited the generalizability of the findings to other demographic groups.
DISCLOSURES:
Some authors received grant support from the National Institute on Drug Abuse and the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Some others received payments, honoraria, grant funding, consulting fees, and travel support, and reported other ties with pharmaceutical companies and other institutions.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is This Methadone’s Moment?
Methadone has been shown to be highly effective for opioid use disorder. So why is it still so difficult to prescribe in the United States and is that about to change?
This paper included more than 30,000 patients with opioid use disorder and showed those on methadone were almost 60% significantly less likely to stop treatment at 24 months than their peers assigned to buprenorphine/naloxone (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.58), with no difference in mortality risk (aHR, 0.57).
“In Canada, unlike the US, methadone and buprenorphine/naloxone are both available in office-based settings. Methadone really outperforms buprenorphine/naloxone in being able to retain people in treatment, which is our main goal and comes with a host of benefits,” Bohdan Nosyk, PhD, with Simon Fraser University in Burnaby, British Columbia, Canada, who worked on the study, said in an interview.
In addition, a recent systematic review and meta-analysis of relevant research involving more than 1 million patients with opioid use disorder also showed better treatment retention with methadone than with buprenorphine.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, relaxed methadone regulations, that included take-home medications, did not lead to an increase in overdoses. Instead, these changes improved treatment retention and patient experiences, highlighting the potential benefits of further deregulation.
‘Atrocious’ Outdated Policies
However, despite methadone’s proven efficacy and safety for opioid use disorder, it remains vastly underutilized because of outdated US policies restricting its use to opioid treatment programs (OTPs).
“It’s absolutely atrocious that methadone policies have not kept up with the evidence. If you look at other countries that have expanded their access to methadone, their overdose rates have fallen dramatically,” said Leslie Suen, MD, with the University of California, San Francisco, and coauthor of a recent JAMA Viewpoint on this topic.
“Methadone is a very good medication that’s been shown over and over to be very effective and safe,” Alan Leshner, PhD, past director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, said in an interview.
“There is no reason why it couldn’t be administered through pharmacies or through physicians’ offices as long as it’s done in a controlled and careful way,” said Leshner.
Leshner chaired the committee that produced the 2019 report Medications for Opioid Use Disorder Save Lives.
“We learned during COVID that increasing the amount of take-home methadone and increasing access does not lead to an increase in deaths or an increase in overdose, so it’s hard to find a reason not to do it,” he said.
Change Finally on the Horizon?
Several recent and proposed policy changes could revolutionize methadone delivery in the United States.
In March 2022, in response to the pandemic, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) allowed hospitals to dispense up to a 3-day supply of methadone (known as the 72-hour rule) to bridge care transitions without needing OTPs.
In April 2024, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration and DEA codified many methadone and buprenorphine delivery flexibilities granted temporarily during the pandemic, including increased use of telehealth assessments and earlier access to take-home methadone doses.
Another contemporary policy change is expansion of the Americans with Disabilities Act mandating that patients taking medications for opioid use disorder, such as methadone, be able to continue treatment when transitioning to settings such as hospitals, jails, and skilled nursing facilities.
At the state level, California Governor Gavin Newsom recently signed a bill, effective immediately, that expands access to methadone treatment in his state.
On the horizon at the federal level is the Modernizing Opioid Treatment Access Act (MOTAA) — the bipartisan and bicameral bill introduced by Sen. Ed Markey (D-MA) and Sen. Rand Paul (R-KY), along with Rep. Donald Norcross (D-NJ) and Rep. Don Bacon, (R-NE) — that would allow methadone to be prescribed by addiction specialists and dispensed in community pharmacies.
An Ethical Imperative
“With only about 2000 OTP clinics clustered in urban areas, less than 25% of people who are diagnosed with opioid use disorder are actually able to access methadone,” Caty Simon, with the National Survivors Union, Greensboro, North Carolina, and coauthor of the JAMA Viewpoint, said in an interview.
While MOTAA represents a major step forward, limiting methadone prescribing to addiction specialists may not fully address the treatment gap, particularly in rural and underserved areas, Simon said.
To optimize methadone’s potential, she’d like to see further expansion of prescribing privileges to general healthcare providers.
“As someone with lived and living experience of opioid use and treatment, and somebody who works nationally and locally in organizations of people impacted by drug use, I know people in my area right now — marginalized people of color — who would have much better chances of survival if they were able to access methadone. If MOTAA passed tomorrow, we could save so many lives. There is an ethical imperative to pass it,” Simon said.
Leshner said he is “always very concerned about access, particularly for underserved populations, poor people, people living in rural areas. If you can access the medications you need, you’re in big trouble.”
Is this methadone’s moment? “I’m a little optimistic, but I haven’t seen the progress I would like to see,” Leshner said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Methadone has been shown to be highly effective for opioid use disorder. So why is it still so difficult to prescribe in the United States and is that about to change?
This paper included more than 30,000 patients with opioid use disorder and showed those on methadone were almost 60% significantly less likely to stop treatment at 24 months than their peers assigned to buprenorphine/naloxone (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.58), with no difference in mortality risk (aHR, 0.57).
“In Canada, unlike the US, methadone and buprenorphine/naloxone are both available in office-based settings. Methadone really outperforms buprenorphine/naloxone in being able to retain people in treatment, which is our main goal and comes with a host of benefits,” Bohdan Nosyk, PhD, with Simon Fraser University in Burnaby, British Columbia, Canada, who worked on the study, said in an interview.
In addition, a recent systematic review and meta-analysis of relevant research involving more than 1 million patients with opioid use disorder also showed better treatment retention with methadone than with buprenorphine.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, relaxed methadone regulations, that included take-home medications, did not lead to an increase in overdoses. Instead, these changes improved treatment retention and patient experiences, highlighting the potential benefits of further deregulation.
‘Atrocious’ Outdated Policies
However, despite methadone’s proven efficacy and safety for opioid use disorder, it remains vastly underutilized because of outdated US policies restricting its use to opioid treatment programs (OTPs).
“It’s absolutely atrocious that methadone policies have not kept up with the evidence. If you look at other countries that have expanded their access to methadone, their overdose rates have fallen dramatically,” said Leslie Suen, MD, with the University of California, San Francisco, and coauthor of a recent JAMA Viewpoint on this topic.
“Methadone is a very good medication that’s been shown over and over to be very effective and safe,” Alan Leshner, PhD, past director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, said in an interview.
“There is no reason why it couldn’t be administered through pharmacies or through physicians’ offices as long as it’s done in a controlled and careful way,” said Leshner.
Leshner chaired the committee that produced the 2019 report Medications for Opioid Use Disorder Save Lives.
“We learned during COVID that increasing the amount of take-home methadone and increasing access does not lead to an increase in deaths or an increase in overdose, so it’s hard to find a reason not to do it,” he said.
Change Finally on the Horizon?
Several recent and proposed policy changes could revolutionize methadone delivery in the United States.
In March 2022, in response to the pandemic, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) allowed hospitals to dispense up to a 3-day supply of methadone (known as the 72-hour rule) to bridge care transitions without needing OTPs.
In April 2024, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration and DEA codified many methadone and buprenorphine delivery flexibilities granted temporarily during the pandemic, including increased use of telehealth assessments and earlier access to take-home methadone doses.
Another contemporary policy change is expansion of the Americans with Disabilities Act mandating that patients taking medications for opioid use disorder, such as methadone, be able to continue treatment when transitioning to settings such as hospitals, jails, and skilled nursing facilities.
At the state level, California Governor Gavin Newsom recently signed a bill, effective immediately, that expands access to methadone treatment in his state.
On the horizon at the federal level is the Modernizing Opioid Treatment Access Act (MOTAA) — the bipartisan and bicameral bill introduced by Sen. Ed Markey (D-MA) and Sen. Rand Paul (R-KY), along with Rep. Donald Norcross (D-NJ) and Rep. Don Bacon, (R-NE) — that would allow methadone to be prescribed by addiction specialists and dispensed in community pharmacies.
An Ethical Imperative
“With only about 2000 OTP clinics clustered in urban areas, less than 25% of people who are diagnosed with opioid use disorder are actually able to access methadone,” Caty Simon, with the National Survivors Union, Greensboro, North Carolina, and coauthor of the JAMA Viewpoint, said in an interview.
While MOTAA represents a major step forward, limiting methadone prescribing to addiction specialists may not fully address the treatment gap, particularly in rural and underserved areas, Simon said.
To optimize methadone’s potential, she’d like to see further expansion of prescribing privileges to general healthcare providers.
“As someone with lived and living experience of opioid use and treatment, and somebody who works nationally and locally in organizations of people impacted by drug use, I know people in my area right now — marginalized people of color — who would have much better chances of survival if they were able to access methadone. If MOTAA passed tomorrow, we could save so many lives. There is an ethical imperative to pass it,” Simon said.
Leshner said he is “always very concerned about access, particularly for underserved populations, poor people, people living in rural areas. If you can access the medications you need, you’re in big trouble.”
Is this methadone’s moment? “I’m a little optimistic, but I haven’t seen the progress I would like to see,” Leshner said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Methadone has been shown to be highly effective for opioid use disorder. So why is it still so difficult to prescribe in the United States and is that about to change?
This paper included more than 30,000 patients with opioid use disorder and showed those on methadone were almost 60% significantly less likely to stop treatment at 24 months than their peers assigned to buprenorphine/naloxone (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.58), with no difference in mortality risk (aHR, 0.57).
“In Canada, unlike the US, methadone and buprenorphine/naloxone are both available in office-based settings. Methadone really outperforms buprenorphine/naloxone in being able to retain people in treatment, which is our main goal and comes with a host of benefits,” Bohdan Nosyk, PhD, with Simon Fraser University in Burnaby, British Columbia, Canada, who worked on the study, said in an interview.
In addition, a recent systematic review and meta-analysis of relevant research involving more than 1 million patients with opioid use disorder also showed better treatment retention with methadone than with buprenorphine.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, relaxed methadone regulations, that included take-home medications, did not lead to an increase in overdoses. Instead, these changes improved treatment retention and patient experiences, highlighting the potential benefits of further deregulation.
‘Atrocious’ Outdated Policies
However, despite methadone’s proven efficacy and safety for opioid use disorder, it remains vastly underutilized because of outdated US policies restricting its use to opioid treatment programs (OTPs).
“It’s absolutely atrocious that methadone policies have not kept up with the evidence. If you look at other countries that have expanded their access to methadone, their overdose rates have fallen dramatically,” said Leslie Suen, MD, with the University of California, San Francisco, and coauthor of a recent JAMA Viewpoint on this topic.
“Methadone is a very good medication that’s been shown over and over to be very effective and safe,” Alan Leshner, PhD, past director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, said in an interview.
“There is no reason why it couldn’t be administered through pharmacies or through physicians’ offices as long as it’s done in a controlled and careful way,” said Leshner.
Leshner chaired the committee that produced the 2019 report Medications for Opioid Use Disorder Save Lives.
“We learned during COVID that increasing the amount of take-home methadone and increasing access does not lead to an increase in deaths or an increase in overdose, so it’s hard to find a reason not to do it,” he said.
Change Finally on the Horizon?
Several recent and proposed policy changes could revolutionize methadone delivery in the United States.
In March 2022, in response to the pandemic, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) allowed hospitals to dispense up to a 3-day supply of methadone (known as the 72-hour rule) to bridge care transitions without needing OTPs.
In April 2024, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration and DEA codified many methadone and buprenorphine delivery flexibilities granted temporarily during the pandemic, including increased use of telehealth assessments and earlier access to take-home methadone doses.
Another contemporary policy change is expansion of the Americans with Disabilities Act mandating that patients taking medications for opioid use disorder, such as methadone, be able to continue treatment when transitioning to settings such as hospitals, jails, and skilled nursing facilities.
At the state level, California Governor Gavin Newsom recently signed a bill, effective immediately, that expands access to methadone treatment in his state.
On the horizon at the federal level is the Modernizing Opioid Treatment Access Act (MOTAA) — the bipartisan and bicameral bill introduced by Sen. Ed Markey (D-MA) and Sen. Rand Paul (R-KY), along with Rep. Donald Norcross (D-NJ) and Rep. Don Bacon, (R-NE) — that would allow methadone to be prescribed by addiction specialists and dispensed in community pharmacies.
An Ethical Imperative
“With only about 2000 OTP clinics clustered in urban areas, less than 25% of people who are diagnosed with opioid use disorder are actually able to access methadone,” Caty Simon, with the National Survivors Union, Greensboro, North Carolina, and coauthor of the JAMA Viewpoint, said in an interview.
While MOTAA represents a major step forward, limiting methadone prescribing to addiction specialists may not fully address the treatment gap, particularly in rural and underserved areas, Simon said.
To optimize methadone’s potential, she’d like to see further expansion of prescribing privileges to general healthcare providers.
“As someone with lived and living experience of opioid use and treatment, and somebody who works nationally and locally in organizations of people impacted by drug use, I know people in my area right now — marginalized people of color — who would have much better chances of survival if they were able to access methadone. If MOTAA passed tomorrow, we could save so many lives. There is an ethical imperative to pass it,” Simon said.
Leshner said he is “always very concerned about access, particularly for underserved populations, poor people, people living in rural areas. If you can access the medications you need, you’re in big trouble.”
Is this methadone’s moment? “I’m a little optimistic, but I haven’t seen the progress I would like to see,” Leshner said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA Okays Abuse-Deterrent Opioid for Severe Pain
Roxybond, an immediate-release (IR) formulation of oxycodone hydrochloride, is made with Protega’s SentryBond technology, which makes it harder for people to crush, inject, or snort, according to the company.
In a statement from Protega, Paul Howe, the company’s chief commercial officer, said the drug meets an “unmet need for an IR opioid with abuse-deterrent technology that may reduce misuse and abuse while providing pain relief to medically appropriate patients when used as indicated.”
To determine the tablet’s ability to withstand manipulation, more than 2000 in vitro tests were conducted, according to the release. The findings indicate Roxybond reduces — but does not entirely negate — the potential for intranasal and intravenous abuse.
Roxybond was previously approved in 5-, 15-, and 30-mg doses. The 10 mg option provides clinicians with the ability to better modify side effects, manage titration, and provide precision care for patients on opioid therapy, according to Protega.
“For patients, the range of doses can provide better pain control, reduce the risk of side effects, and provide a smoother transition during dosing transitions,” the company stated.
Roxybond is contraindicated in patients with significant respiratory depression, acute or severe bronchial asthma, gastrointestinal obstruction, or hypersensitivity to oxycodone. The drug is not intended for long-term use unless otherwise determined by a clinician. Roxybond also is subject to the FDA’s Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies for opioids.
“The development of Roxybond with SentryBond is a step forward in fighting the national epidemic of prescription opioid overdose,” said Eric Kinzler, PhD, vice president of medical and regulatory affairs for Protega, in a release. “Protega is dedicated to our mission to block the path to abuse and work with healthcare professionals across the continuum of care to reduce misuse and abuse.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Roxybond, an immediate-release (IR) formulation of oxycodone hydrochloride, is made with Protega’s SentryBond technology, which makes it harder for people to crush, inject, or snort, according to the company.
In a statement from Protega, Paul Howe, the company’s chief commercial officer, said the drug meets an “unmet need for an IR opioid with abuse-deterrent technology that may reduce misuse and abuse while providing pain relief to medically appropriate patients when used as indicated.”
To determine the tablet’s ability to withstand manipulation, more than 2000 in vitro tests were conducted, according to the release. The findings indicate Roxybond reduces — but does not entirely negate — the potential for intranasal and intravenous abuse.
Roxybond was previously approved in 5-, 15-, and 30-mg doses. The 10 mg option provides clinicians with the ability to better modify side effects, manage titration, and provide precision care for patients on opioid therapy, according to Protega.
“For patients, the range of doses can provide better pain control, reduce the risk of side effects, and provide a smoother transition during dosing transitions,” the company stated.
Roxybond is contraindicated in patients with significant respiratory depression, acute or severe bronchial asthma, gastrointestinal obstruction, or hypersensitivity to oxycodone. The drug is not intended for long-term use unless otherwise determined by a clinician. Roxybond also is subject to the FDA’s Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies for opioids.
“The development of Roxybond with SentryBond is a step forward in fighting the national epidemic of prescription opioid overdose,” said Eric Kinzler, PhD, vice president of medical and regulatory affairs for Protega, in a release. “Protega is dedicated to our mission to block the path to abuse and work with healthcare professionals across the continuum of care to reduce misuse and abuse.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Roxybond, an immediate-release (IR) formulation of oxycodone hydrochloride, is made with Protega’s SentryBond technology, which makes it harder for people to crush, inject, or snort, according to the company.
In a statement from Protega, Paul Howe, the company’s chief commercial officer, said the drug meets an “unmet need for an IR opioid with abuse-deterrent technology that may reduce misuse and abuse while providing pain relief to medically appropriate patients when used as indicated.”
To determine the tablet’s ability to withstand manipulation, more than 2000 in vitro tests were conducted, according to the release. The findings indicate Roxybond reduces — but does not entirely negate — the potential for intranasal and intravenous abuse.
Roxybond was previously approved in 5-, 15-, and 30-mg doses. The 10 mg option provides clinicians with the ability to better modify side effects, manage titration, and provide precision care for patients on opioid therapy, according to Protega.
“For patients, the range of doses can provide better pain control, reduce the risk of side effects, and provide a smoother transition during dosing transitions,” the company stated.
Roxybond is contraindicated in patients with significant respiratory depression, acute or severe bronchial asthma, gastrointestinal obstruction, or hypersensitivity to oxycodone. The drug is not intended for long-term use unless otherwise determined by a clinician. Roxybond also is subject to the FDA’s Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies for opioids.
“The development of Roxybond with SentryBond is a step forward in fighting the national epidemic of prescription opioid overdose,” said Eric Kinzler, PhD, vice president of medical and regulatory affairs for Protega, in a release. “Protega is dedicated to our mission to block the path to abuse and work with healthcare professionals across the continuum of care to reduce misuse and abuse.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Total Hip Replacement Superior to Exercise Therapy for Improving Hip Osteoarthritis Pain and Function
For people with severe symptomatic hip osteoarthritis, total hip replacement (THR) alleviates hip pain and improves function much more effectively than a resistance training program supervised by a physiotherapist, according to the results of a randomized controlled clinical trial.
In the PROHIP study, the mean increases in Oxford Hip Scores from baseline to 6 months were 15.9 points for THR and 4.5 points for resistance training. The 11.4-point difference in scores was both statistically and clinically significant, the study’s investigators reported in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“Our results are clear: Surgery is superior to exercise in patients who have hip osteoarthritis and indication for surgery, and now we have finally proven that with the highest level of evidence,” corresponding author Thomas Frydendal, PT, PhD, MSc, told this news organization.
Frydendal, who was involved in the study while working on his PhD at University Hospital of Southern Denmark – Lillebaelt Hospital, Vejle, Denmark, the primary center for the trial, is now a postdoctoral researcher at the Department of Clinical Medicine, Aarhus University, and Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Aarhus University Hospital.
“We believe that our findings are pretty robust,” Frydendal added. “I think if someone in the world conducts a trial similar to ours, they will find fairly close or consistent findings, no matter what type of exercise they choose.”
The PROHIP Study
THR is routinely recommended for the management of severe hip osteoarthritis, but since there are no clinical trial data on the effectiveness of this procedure as compared with first-line treatment such as resistance training, the PROHIP study was conceived.
The trial was conducted at four Danish orthopedic centers and designed as a superiority study, the hypothesis being that THR would be better at alleviating self-reported hip pain and improving hip function than resistance training.
Of a possible 1474 individuals with a clinical suspicion of hip osteoarthritis, 791 were deemed eligible for inclusion in the trial. Inclusion criteria were being aged 50 years or older and having an indication for THR based on the presence of hip pain and clinical and radiographic findings.
However, the majority (86%) declined to enter the study, with almost half (43%) deciding to have a THR and enroll in a parallel observational cohort. This meant that only 110 (14%) individuals agreed to participate and underwent randomization, which does limit the study’s generalizability, the PROHIP investigators acknowledged.
Design and Study Population
The change in Oxford Hip Score from baseline to 6 months was selected as the primary outcome measure based on the findings of a prior qualitative study. This 12-item, patient-reported outcome measure gives a score ranging from 0 to 48, with higher scores indicating less hip pain and better hip function. The estimated minimal clinically important difference is a change of 5 points.
After a baseline assessment, 53 of 109 individuals were randomly assigned to undergo THR and 56 to participate in the resistance training program. Overall, the mean age of participants was 67.6 years, and half were women. The average duration of hip pain was a median of 1.7 years.
The median time to receipt of the allocated treatment was 2.8 months in the THR group and 0.5 months in the resistance training group.
Those allocated to the THR group also underwent a “fast track” program that involved patient education, pain management, and early mobilization.
The resistance training group received 12 weeks of exercise supervised by a physiotherapist and then offered 12 weeks of additional exercise conducted on their own. The physiotherapist-supervised exercise sessions were held twice weekly and lasted for 1 hour. These started with a 10-minute warm-up on a stationary bike, followed by a standard set of resistance-based exercises that included a leg press, hip extension, hip flexion, and hip abduction.
‘Reassuring’ Results
In a comment, consultant orthopedic surgeon Antony Palmer, MA, BMBCh, DPhil, said: “It’s reassuring that patients with advanced symptomatic osteoarthritis do well with hip replacements.”
THR does of course come with the potential risk for complications, but “the rate of these is what you’d expect for that procedure,” Palmer said, who works for the Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre, Oxford University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, and is a senior clinical research fellow at Oxford University in England.
In the THR arm, there was one case of prosthetic joint infection, one hip dislocation, two revision surgeries, one instance of foot drop, and one case of gastroesophageal reflux. Meanwhile, in the resistance training group, there was one hip dislocation, one pelvic fracture, one case of atrial fibrillation, and one urinary tract and renal infection.
Overall, any serious adverse event was reported in six (12%) of 48 patients in the THR arm vs five (9%) of 55 participants in the resistance training group, of which only one, occurring in the resistance training group, resulted in discontinuation of the program.
Resistance Training Role
A notable finding was that, at 6 months, five (9%) people assigned to the THR arm had not undergone surgery, and 12 (21%) people in the resistance training group had undergone a THR.
This could suggest two things, Palmer suggested in the interview. The first is that there could be a small proportion of people assigned to THR who may not need the operation and do well with exercise therapy. And, conversely, there may be those who would do well having the surgery without first going through the intermediate stage of physical therapy.
It’s a suggestion that “maybe we’ve got to refine that a bit better and identify the patients that really do benefit from physiotherapy and who might not need hip replacement as a result,” Palmer said.
Or in other words, “should all patients undergo a program of physiotherapy before considering surgery?” he added.
Authors’ View
The PROHIP investigators conclude: “These results support current recommendations for the management of hip osteoarthritis and may be used to inform and guide shared decision making in clinical practice.”
Moreover, the results “do not oppose the use of resistance training as initial treatment,” says the authors.
Frydendal highlighted in his interview that nearly three out of four of the patients reported not to have undertaken any type of supervised exercise before entry into the study, which is a first-line, guideline-recommended option.
“If a patient tells me, ‘I haven’t done any exercise previously,’ I’d recommend starting with completing a 6- to 12-week exercise program that is tailored to your individual needs and evaluate your symptoms afterward,” he said.
“But we should refer the patient if our first-line treatment does not offer any improvements in the patient’s symptoms, as surgery with total hip replacement is clearly a really good treatment option,” Frydendal said.
The study was funded by the Danish Rheumatism Association, among other independent bodies. Frydendal and Palmer reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For people with severe symptomatic hip osteoarthritis, total hip replacement (THR) alleviates hip pain and improves function much more effectively than a resistance training program supervised by a physiotherapist, according to the results of a randomized controlled clinical trial.
In the PROHIP study, the mean increases in Oxford Hip Scores from baseline to 6 months were 15.9 points for THR and 4.5 points for resistance training. The 11.4-point difference in scores was both statistically and clinically significant, the study’s investigators reported in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“Our results are clear: Surgery is superior to exercise in patients who have hip osteoarthritis and indication for surgery, and now we have finally proven that with the highest level of evidence,” corresponding author Thomas Frydendal, PT, PhD, MSc, told this news organization.
Frydendal, who was involved in the study while working on his PhD at University Hospital of Southern Denmark – Lillebaelt Hospital, Vejle, Denmark, the primary center for the trial, is now a postdoctoral researcher at the Department of Clinical Medicine, Aarhus University, and Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Aarhus University Hospital.
“We believe that our findings are pretty robust,” Frydendal added. “I think if someone in the world conducts a trial similar to ours, they will find fairly close or consistent findings, no matter what type of exercise they choose.”
The PROHIP Study
THR is routinely recommended for the management of severe hip osteoarthritis, but since there are no clinical trial data on the effectiveness of this procedure as compared with first-line treatment such as resistance training, the PROHIP study was conceived.
The trial was conducted at four Danish orthopedic centers and designed as a superiority study, the hypothesis being that THR would be better at alleviating self-reported hip pain and improving hip function than resistance training.
Of a possible 1474 individuals with a clinical suspicion of hip osteoarthritis, 791 were deemed eligible for inclusion in the trial. Inclusion criteria were being aged 50 years or older and having an indication for THR based on the presence of hip pain and clinical and radiographic findings.
However, the majority (86%) declined to enter the study, with almost half (43%) deciding to have a THR and enroll in a parallel observational cohort. This meant that only 110 (14%) individuals agreed to participate and underwent randomization, which does limit the study’s generalizability, the PROHIP investigators acknowledged.
Design and Study Population
The change in Oxford Hip Score from baseline to 6 months was selected as the primary outcome measure based on the findings of a prior qualitative study. This 12-item, patient-reported outcome measure gives a score ranging from 0 to 48, with higher scores indicating less hip pain and better hip function. The estimated minimal clinically important difference is a change of 5 points.
After a baseline assessment, 53 of 109 individuals were randomly assigned to undergo THR and 56 to participate in the resistance training program. Overall, the mean age of participants was 67.6 years, and half were women. The average duration of hip pain was a median of 1.7 years.
The median time to receipt of the allocated treatment was 2.8 months in the THR group and 0.5 months in the resistance training group.
Those allocated to the THR group also underwent a “fast track” program that involved patient education, pain management, and early mobilization.
The resistance training group received 12 weeks of exercise supervised by a physiotherapist and then offered 12 weeks of additional exercise conducted on their own. The physiotherapist-supervised exercise sessions were held twice weekly and lasted for 1 hour. These started with a 10-minute warm-up on a stationary bike, followed by a standard set of resistance-based exercises that included a leg press, hip extension, hip flexion, and hip abduction.
‘Reassuring’ Results
In a comment, consultant orthopedic surgeon Antony Palmer, MA, BMBCh, DPhil, said: “It’s reassuring that patients with advanced symptomatic osteoarthritis do well with hip replacements.”
THR does of course come with the potential risk for complications, but “the rate of these is what you’d expect for that procedure,” Palmer said, who works for the Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre, Oxford University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, and is a senior clinical research fellow at Oxford University in England.
In the THR arm, there was one case of prosthetic joint infection, one hip dislocation, two revision surgeries, one instance of foot drop, and one case of gastroesophageal reflux. Meanwhile, in the resistance training group, there was one hip dislocation, one pelvic fracture, one case of atrial fibrillation, and one urinary tract and renal infection.
Overall, any serious adverse event was reported in six (12%) of 48 patients in the THR arm vs five (9%) of 55 participants in the resistance training group, of which only one, occurring in the resistance training group, resulted in discontinuation of the program.
Resistance Training Role
A notable finding was that, at 6 months, five (9%) people assigned to the THR arm had not undergone surgery, and 12 (21%) people in the resistance training group had undergone a THR.
This could suggest two things, Palmer suggested in the interview. The first is that there could be a small proportion of people assigned to THR who may not need the operation and do well with exercise therapy. And, conversely, there may be those who would do well having the surgery without first going through the intermediate stage of physical therapy.
It’s a suggestion that “maybe we’ve got to refine that a bit better and identify the patients that really do benefit from physiotherapy and who might not need hip replacement as a result,” Palmer said.
Or in other words, “should all patients undergo a program of physiotherapy before considering surgery?” he added.
Authors’ View
The PROHIP investigators conclude: “These results support current recommendations for the management of hip osteoarthritis and may be used to inform and guide shared decision making in clinical practice.”
Moreover, the results “do not oppose the use of resistance training as initial treatment,” says the authors.
Frydendal highlighted in his interview that nearly three out of four of the patients reported not to have undertaken any type of supervised exercise before entry into the study, which is a first-line, guideline-recommended option.
“If a patient tells me, ‘I haven’t done any exercise previously,’ I’d recommend starting with completing a 6- to 12-week exercise program that is tailored to your individual needs and evaluate your symptoms afterward,” he said.
“But we should refer the patient if our first-line treatment does not offer any improvements in the patient’s symptoms, as surgery with total hip replacement is clearly a really good treatment option,” Frydendal said.
The study was funded by the Danish Rheumatism Association, among other independent bodies. Frydendal and Palmer reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For people with severe symptomatic hip osteoarthritis, total hip replacement (THR) alleviates hip pain and improves function much more effectively than a resistance training program supervised by a physiotherapist, according to the results of a randomized controlled clinical trial.
In the PROHIP study, the mean increases in Oxford Hip Scores from baseline to 6 months were 15.9 points for THR and 4.5 points for resistance training. The 11.4-point difference in scores was both statistically and clinically significant, the study’s investigators reported in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“Our results are clear: Surgery is superior to exercise in patients who have hip osteoarthritis and indication for surgery, and now we have finally proven that with the highest level of evidence,” corresponding author Thomas Frydendal, PT, PhD, MSc, told this news organization.
Frydendal, who was involved in the study while working on his PhD at University Hospital of Southern Denmark – Lillebaelt Hospital, Vejle, Denmark, the primary center for the trial, is now a postdoctoral researcher at the Department of Clinical Medicine, Aarhus University, and Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Aarhus University Hospital.
“We believe that our findings are pretty robust,” Frydendal added. “I think if someone in the world conducts a trial similar to ours, they will find fairly close or consistent findings, no matter what type of exercise they choose.”
The PROHIP Study
THR is routinely recommended for the management of severe hip osteoarthritis, but since there are no clinical trial data on the effectiveness of this procedure as compared with first-line treatment such as resistance training, the PROHIP study was conceived.
The trial was conducted at four Danish orthopedic centers and designed as a superiority study, the hypothesis being that THR would be better at alleviating self-reported hip pain and improving hip function than resistance training.
Of a possible 1474 individuals with a clinical suspicion of hip osteoarthritis, 791 were deemed eligible for inclusion in the trial. Inclusion criteria were being aged 50 years or older and having an indication for THR based on the presence of hip pain and clinical and radiographic findings.
However, the majority (86%) declined to enter the study, with almost half (43%) deciding to have a THR and enroll in a parallel observational cohort. This meant that only 110 (14%) individuals agreed to participate and underwent randomization, which does limit the study’s generalizability, the PROHIP investigators acknowledged.
Design and Study Population
The change in Oxford Hip Score from baseline to 6 months was selected as the primary outcome measure based on the findings of a prior qualitative study. This 12-item, patient-reported outcome measure gives a score ranging from 0 to 48, with higher scores indicating less hip pain and better hip function. The estimated minimal clinically important difference is a change of 5 points.
After a baseline assessment, 53 of 109 individuals were randomly assigned to undergo THR and 56 to participate in the resistance training program. Overall, the mean age of participants was 67.6 years, and half were women. The average duration of hip pain was a median of 1.7 years.
The median time to receipt of the allocated treatment was 2.8 months in the THR group and 0.5 months in the resistance training group.
Those allocated to the THR group also underwent a “fast track” program that involved patient education, pain management, and early mobilization.
The resistance training group received 12 weeks of exercise supervised by a physiotherapist and then offered 12 weeks of additional exercise conducted on their own. The physiotherapist-supervised exercise sessions were held twice weekly and lasted for 1 hour. These started with a 10-minute warm-up on a stationary bike, followed by a standard set of resistance-based exercises that included a leg press, hip extension, hip flexion, and hip abduction.
‘Reassuring’ Results
In a comment, consultant orthopedic surgeon Antony Palmer, MA, BMBCh, DPhil, said: “It’s reassuring that patients with advanced symptomatic osteoarthritis do well with hip replacements.”
THR does of course come with the potential risk for complications, but “the rate of these is what you’d expect for that procedure,” Palmer said, who works for the Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre, Oxford University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, and is a senior clinical research fellow at Oxford University in England.
In the THR arm, there was one case of prosthetic joint infection, one hip dislocation, two revision surgeries, one instance of foot drop, and one case of gastroesophageal reflux. Meanwhile, in the resistance training group, there was one hip dislocation, one pelvic fracture, one case of atrial fibrillation, and one urinary tract and renal infection.
Overall, any serious adverse event was reported in six (12%) of 48 patients in the THR arm vs five (9%) of 55 participants in the resistance training group, of which only one, occurring in the resistance training group, resulted in discontinuation of the program.
Resistance Training Role
A notable finding was that, at 6 months, five (9%) people assigned to the THR arm had not undergone surgery, and 12 (21%) people in the resistance training group had undergone a THR.
This could suggest two things, Palmer suggested in the interview. The first is that there could be a small proportion of people assigned to THR who may not need the operation and do well with exercise therapy. And, conversely, there may be those who would do well having the surgery without first going through the intermediate stage of physical therapy.
It’s a suggestion that “maybe we’ve got to refine that a bit better and identify the patients that really do benefit from physiotherapy and who might not need hip replacement as a result,” Palmer said.
Or in other words, “should all patients undergo a program of physiotherapy before considering surgery?” he added.
Authors’ View
The PROHIP investigators conclude: “These results support current recommendations for the management of hip osteoarthritis and may be used to inform and guide shared decision making in clinical practice.”
Moreover, the results “do not oppose the use of resistance training as initial treatment,” says the authors.
Frydendal highlighted in his interview that nearly three out of four of the patients reported not to have undertaken any type of supervised exercise before entry into the study, which is a first-line, guideline-recommended option.
“If a patient tells me, ‘I haven’t done any exercise previously,’ I’d recommend starting with completing a 6- to 12-week exercise program that is tailored to your individual needs and evaluate your symptoms afterward,” he said.
“But we should refer the patient if our first-line treatment does not offer any improvements in the patient’s symptoms, as surgery with total hip replacement is clearly a really good treatment option,” Frydendal said.
The study was funded by the Danish Rheumatism Association, among other independent bodies. Frydendal and Palmer reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Is Being ‘Manly’ a Threat to a Man’s Health?
When my normally adorable cat Biscuit bit my ankle in a playful stalking exercise gone wrong, I washed it with soap and some rubbing alcohol, slapped on a Band-Aid, and went about my day.
The next morning, when it was swollen, I told myself it was probably just a hematoma and went about my day.
The next day, when the swelling had increased and red lines started creeping up my leg, I called my doctor. Long story short, I ended up hospitalized for intravenous antibiotics.
This is all to say that, yes, I’m sort of an idiot, but also to introduce the idea that maybe I minimized my very obvious lymphangitis because I am a man.
This week, we have empirical evidence that men downplay their medical symptoms — and that manlier men downplay them even more.
I’m going to talk about a study that links manliness (or, scientifically speaking, “male gender expressivity”) to medical diagnoses that are based on hard evidence and medical diagnoses that are based on self-report. You see where this is going but I want to walk you through the methods here because they are fairly interesting.
This study used data from the US National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health. This study enrolled 20,000 adolescents who were in grades 7-12 in the 1994-1995 school year and has been following them ever since — about 30 years so far.
The authors wanted to link early gender roles to long-term outcomes, so they cut that 20,000 number down to the 4230 males in the group who had complete follow-up.
Now comes the first interesting question. How do you quantify the “male gender expressivity” of boys in 7th-12th grade? There was no survey item that asked them how masculine or manly they felt. What the authors did was look at the surveys that were administered and identify the questions on those surveys where boys and girls gave the most disparate answers. I have some examples here. 
Some of these questions make sense when it comes to gender expressivity: “How often do you cry?” for example, has a lot of validity for the social construct that is gender. But some questions where boys and girls gave very different answers — like “How often do you exercise?” — don’t quite fit that mold. Regardless, this structure allowed the researchers to take individual kids’ responses to these questions and combine them into what amounts to a manliness score — how much their answers aligned with the typical male answer.
The score was established in adolescence — which is interesting because I’m sure some of this stuff may change over time — but notable because adolescence is where many gender roles develop.
Now we can fast-forward 30 years and see how these manliness scores link to various outcomes. The authors were interested in fairly common diseases: diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
Let’s start simply. Are males with higher gender expressivity in adolescence more or less likely to have these diseases in the future?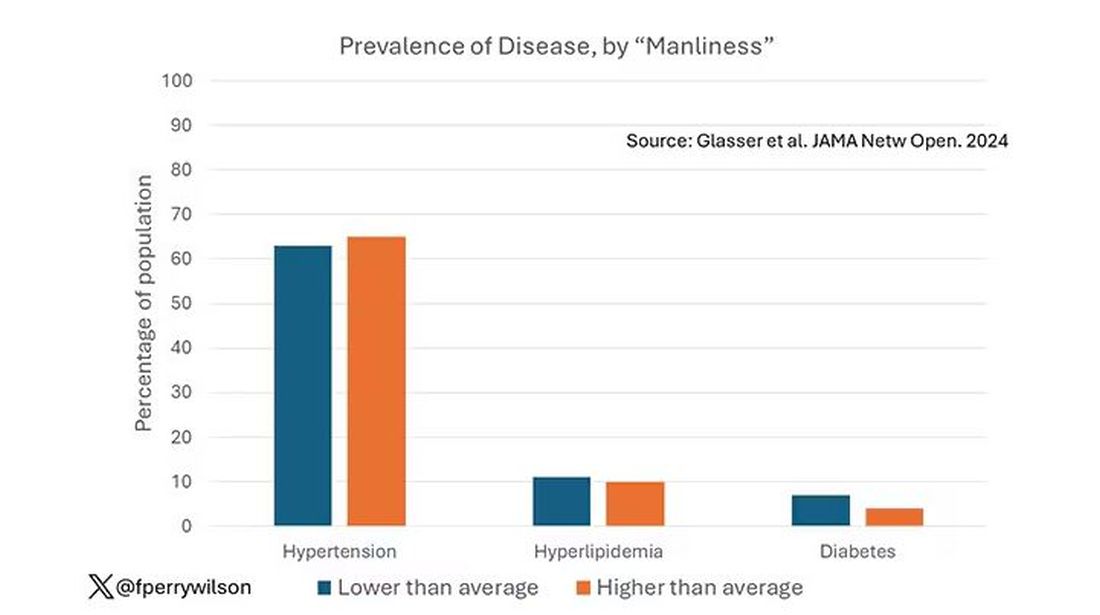
Not really. Those above the average in male gender expressivity had similar rates of hypertension and hyperlipidemia as those below the median. They were actually a bit less likely to have diabetes.
But that’s not what’s really interesting here.
I told you that there was no difference in the rate of hypertension among those with high vs low male gender expressivity. But there was a significant difference in their answer to the question “Do you have hypertension?” The same was seen for hyperlipidemia. In other words, those with higher manliness scores are less likely to admit (or perhaps know) that they have a particular disease.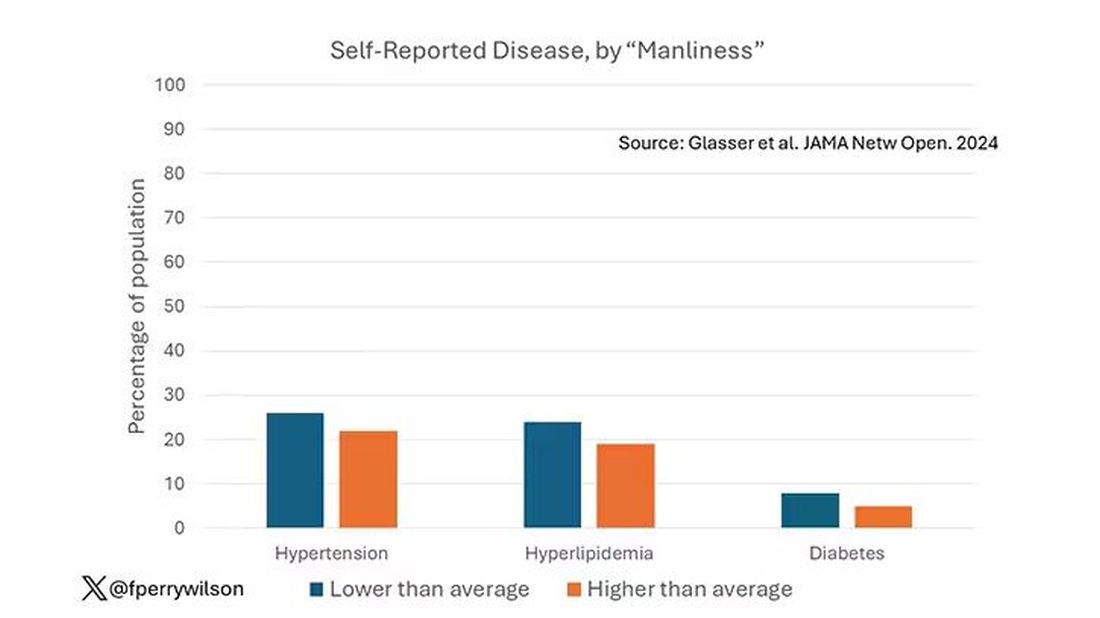
You can see the relationship across the manliness spectrum here in a series of adjusted models. The x-axis is the male gender expressivity score, and the y-axis is the percentage of people who report having the disease that we know they have based on the actual laboratory tests or vital sign measurements. As manliness increases, the self-report of a given disease decreases.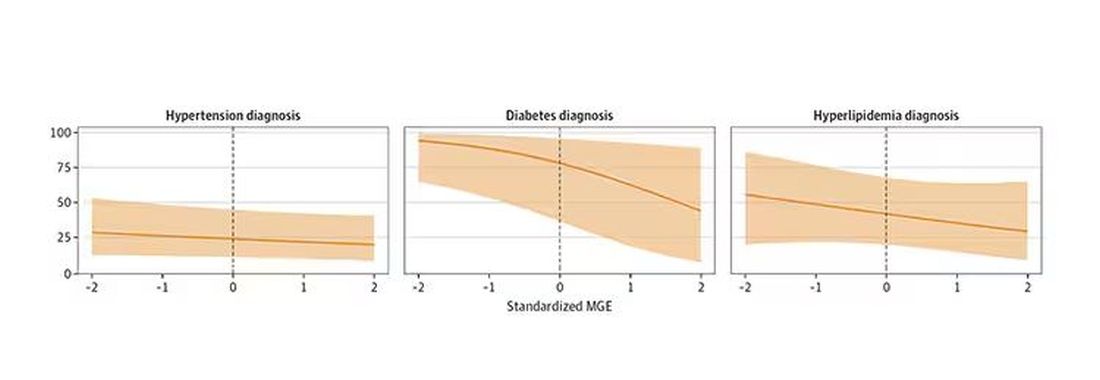
There are some important consequences of this systematic denial. Specifically, men with the diseases of interest who have higher male gender expressivity are less likely to get treatment. And, as we all know, the lack of treatment of something like hypertension puts people at risk for bad downstream outcomes.
Putting this all together, I’m not that surprised. Society trains boys from a young age to behave in certain ways: to hide emotions, to eschew vulnerability, to not complain when we are hurt. And those lessons can persist into later life. Whether the disease that strikes is hypertension or Pasteurella multocida from a slightly psychotic house cat, men are more likely to ignore it, to their detriment.
So, gents, be brave. Get your blood tests and check your blood pressure. If there’s something wrong, admit it, and fix it. After all, fixing problems — that’s a manly thing, right?
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When my normally adorable cat Biscuit bit my ankle in a playful stalking exercise gone wrong, I washed it with soap and some rubbing alcohol, slapped on a Band-Aid, and went about my day.
The next morning, when it was swollen, I told myself it was probably just a hematoma and went about my day.
The next day, when the swelling had increased and red lines started creeping up my leg, I called my doctor. Long story short, I ended up hospitalized for intravenous antibiotics.
This is all to say that, yes, I’m sort of an idiot, but also to introduce the idea that maybe I minimized my very obvious lymphangitis because I am a man.
This week, we have empirical evidence that men downplay their medical symptoms — and that manlier men downplay them even more.
I’m going to talk about a study that links manliness (or, scientifically speaking, “male gender expressivity”) to medical diagnoses that are based on hard evidence and medical diagnoses that are based on self-report. You see where this is going but I want to walk you through the methods here because they are fairly interesting.
This study used data from the US National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health. This study enrolled 20,000 adolescents who were in grades 7-12 in the 1994-1995 school year and has been following them ever since — about 30 years so far.
The authors wanted to link early gender roles to long-term outcomes, so they cut that 20,000 number down to the 4230 males in the group who had complete follow-up.
Now comes the first interesting question. How do you quantify the “male gender expressivity” of boys in 7th-12th grade? There was no survey item that asked them how masculine or manly they felt. What the authors did was look at the surveys that were administered and identify the questions on those surveys where boys and girls gave the most disparate answers. I have some examples here. 
Some of these questions make sense when it comes to gender expressivity: “How often do you cry?” for example, has a lot of validity for the social construct that is gender. But some questions where boys and girls gave very different answers — like “How often do you exercise?” — don’t quite fit that mold. Regardless, this structure allowed the researchers to take individual kids’ responses to these questions and combine them into what amounts to a manliness score — how much their answers aligned with the typical male answer.
The score was established in adolescence — which is interesting because I’m sure some of this stuff may change over time — but notable because adolescence is where many gender roles develop.
Now we can fast-forward 30 years and see how these manliness scores link to various outcomes. The authors were interested in fairly common diseases: diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
Let’s start simply. Are males with higher gender expressivity in adolescence more or less likely to have these diseases in the future?
Not really. Those above the average in male gender expressivity had similar rates of hypertension and hyperlipidemia as those below the median. They were actually a bit less likely to have diabetes.
But that’s not what’s really interesting here.
I told you that there was no difference in the rate of hypertension among those with high vs low male gender expressivity. But there was a significant difference in their answer to the question “Do you have hypertension?” The same was seen for hyperlipidemia. In other words, those with higher manliness scores are less likely to admit (or perhaps know) that they have a particular disease.
You can see the relationship across the manliness spectrum here in a series of adjusted models. The x-axis is the male gender expressivity score, and the y-axis is the percentage of people who report having the disease that we know they have based on the actual laboratory tests or vital sign measurements. As manliness increases, the self-report of a given disease decreases.
There are some important consequences of this systematic denial. Specifically, men with the diseases of interest who have higher male gender expressivity are less likely to get treatment. And, as we all know, the lack of treatment of something like hypertension puts people at risk for bad downstream outcomes.
Putting this all together, I’m not that surprised. Society trains boys from a young age to behave in certain ways: to hide emotions, to eschew vulnerability, to not complain when we are hurt. And those lessons can persist into later life. Whether the disease that strikes is hypertension or Pasteurella multocida from a slightly psychotic house cat, men are more likely to ignore it, to their detriment.
So, gents, be brave. Get your blood tests and check your blood pressure. If there’s something wrong, admit it, and fix it. After all, fixing problems — that’s a manly thing, right?
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When my normally adorable cat Biscuit bit my ankle in a playful stalking exercise gone wrong, I washed it with soap and some rubbing alcohol, slapped on a Band-Aid, and went about my day.
The next morning, when it was swollen, I told myself it was probably just a hematoma and went about my day.
The next day, when the swelling had increased and red lines started creeping up my leg, I called my doctor. Long story short, I ended up hospitalized for intravenous antibiotics.
This is all to say that, yes, I’m sort of an idiot, but also to introduce the idea that maybe I minimized my very obvious lymphangitis because I am a man.
This week, we have empirical evidence that men downplay their medical symptoms — and that manlier men downplay them even more.
I’m going to talk about a study that links manliness (or, scientifically speaking, “male gender expressivity”) to medical diagnoses that are based on hard evidence and medical diagnoses that are based on self-report. You see where this is going but I want to walk you through the methods here because they are fairly interesting.
This study used data from the US National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health. This study enrolled 20,000 adolescents who were in grades 7-12 in the 1994-1995 school year and has been following them ever since — about 30 years so far.
The authors wanted to link early gender roles to long-term outcomes, so they cut that 20,000 number down to the 4230 males in the group who had complete follow-up.
Now comes the first interesting question. How do you quantify the “male gender expressivity” of boys in 7th-12th grade? There was no survey item that asked them how masculine or manly they felt. What the authors did was look at the surveys that were administered and identify the questions on those surveys where boys and girls gave the most disparate answers. I have some examples here. 
Some of these questions make sense when it comes to gender expressivity: “How often do you cry?” for example, has a lot of validity for the social construct that is gender. But some questions where boys and girls gave very different answers — like “How often do you exercise?” — don’t quite fit that mold. Regardless, this structure allowed the researchers to take individual kids’ responses to these questions and combine them into what amounts to a manliness score — how much their answers aligned with the typical male answer.
The score was established in adolescence — which is interesting because I’m sure some of this stuff may change over time — but notable because adolescence is where many gender roles develop.
Now we can fast-forward 30 years and see how these manliness scores link to various outcomes. The authors were interested in fairly common diseases: diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
Let’s start simply. Are males with higher gender expressivity in adolescence more or less likely to have these diseases in the future?
Not really. Those above the average in male gender expressivity had similar rates of hypertension and hyperlipidemia as those below the median. They were actually a bit less likely to have diabetes.
But that’s not what’s really interesting here.
I told you that there was no difference in the rate of hypertension among those with high vs low male gender expressivity. But there was a significant difference in their answer to the question “Do you have hypertension?” The same was seen for hyperlipidemia. In other words, those with higher manliness scores are less likely to admit (or perhaps know) that they have a particular disease.
You can see the relationship across the manliness spectrum here in a series of adjusted models. The x-axis is the male gender expressivity score, and the y-axis is the percentage of people who report having the disease that we know they have based on the actual laboratory tests or vital sign measurements. As manliness increases, the self-report of a given disease decreases.
There are some important consequences of this systematic denial. Specifically, men with the diseases of interest who have higher male gender expressivity are less likely to get treatment. And, as we all know, the lack of treatment of something like hypertension puts people at risk for bad downstream outcomes.
Putting this all together, I’m not that surprised. Society trains boys from a young age to behave in certain ways: to hide emotions, to eschew vulnerability, to not complain when we are hurt. And those lessons can persist into later life. Whether the disease that strikes is hypertension or Pasteurella multocida from a slightly psychotic house cat, men are more likely to ignore it, to their detriment.
So, gents, be brave. Get your blood tests and check your blood pressure. If there’s something wrong, admit it, and fix it. After all, fixing problems — that’s a manly thing, right?
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Commentary: Factors Affecting PsA and Updated Therapy Efficacy Data, November 2024
Smoking is another important modifiable environmental factor. Smoking generally has an adverse impact on treatment. In a post hoc analysis of pooled data from phase 2 and 3 trials and a long-term extension study involving 914 patients with PsA and 372 patients with ankylosing spondylitis who received tofacitinib (a Janus kinase inhibitor) or placebo, Ogdie and coworkers assessed the impact of smoking on treatment efficacy and safety. The efficacy rates were generally similar in current/past smokers and never-smokers. The incidence rates of treatment-emergent adverse events were higher in current/past smokers compared with never-smokers. Thus, in contrast to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, smoking status may not have an impact on tofacitinib efficacy. However, current/past smokers experienced increased rates of adverse events.
Secukinumab, an anti-interleukin (IL)-17A antibody, is an established treatment for PsA and is approved for use as fixed-dose (150/300 mg) subcutaneous injections. The efficacy and safety of weight-based intravenous (IV) therapy is unknown. Kivitz and colleagues recently reported the results of the phase 3 INVIGORATE-2 trial, in which 381 patients with active PsA and either plaque psoriasis or nail psoriasis were randomly assigned to receive IV secukinumab or placebo with crossover to IV secukinumab at week 16. They demonstrated that at week 16, IV secukinumab significantly improved the American College of Rheumatology 50 response rate (ACR50) compared with placebo (31.4% vs 6.3%; adjusted P < .0001). Improvements were observed as early as week 4 and were sustained through week 52. No new safety signals were reported. Thus, IV secukinumab is a safe and efficacious treatment for PsA. This mode of administration of secukinumab is a welcome addition to the PsA therapeutic armamentarium.
There are many targeted therapies available for PsA. However, data on comparative effectiveness is lacking. Kristensen and associates reported the results of an interim analysis of the PRO-SPIRIT real-world study that included 1192 patients with PsA across six countries who initiated or switched to a new biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug. They showed that at 3 months, ixekizumab significantly improved clinical disease activity in patients with PsA compared with IL-12/23 inhibitors and IL-23 inhibitors. The improvements in the joints were similar to those with TNF inhibitors and JAK inhibitors, but the improvement in psoriasis was higher. Thus, ixekizumab leads to rapid response to active skin and musculoskeletal disease activity in PsA. Comparative data on treatment persistence as well as adverse events are required.
Smoking is another important modifiable environmental factor. Smoking generally has an adverse impact on treatment. In a post hoc analysis of pooled data from phase 2 and 3 trials and a long-term extension study involving 914 patients with PsA and 372 patients with ankylosing spondylitis who received tofacitinib (a Janus kinase inhibitor) or placebo, Ogdie and coworkers assessed the impact of smoking on treatment efficacy and safety. The efficacy rates were generally similar in current/past smokers and never-smokers. The incidence rates of treatment-emergent adverse events were higher in current/past smokers compared with never-smokers. Thus, in contrast to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, smoking status may not have an impact on tofacitinib efficacy. However, current/past smokers experienced increased rates of adverse events.
Secukinumab, an anti-interleukin (IL)-17A antibody, is an established treatment for PsA and is approved for use as fixed-dose (150/300 mg) subcutaneous injections. The efficacy and safety of weight-based intravenous (IV) therapy is unknown. Kivitz and colleagues recently reported the results of the phase 3 INVIGORATE-2 trial, in which 381 patients with active PsA and either plaque psoriasis or nail psoriasis were randomly assigned to receive IV secukinumab or placebo with crossover to IV secukinumab at week 16. They demonstrated that at week 16, IV secukinumab significantly improved the American College of Rheumatology 50 response rate (ACR50) compared with placebo (31.4% vs 6.3%; adjusted P < .0001). Improvements were observed as early as week 4 and were sustained through week 52. No new safety signals were reported. Thus, IV secukinumab is a safe and efficacious treatment for PsA. This mode of administration of secukinumab is a welcome addition to the PsA therapeutic armamentarium.
There are many targeted therapies available for PsA. However, data on comparative effectiveness is lacking. Kristensen and associates reported the results of an interim analysis of the PRO-SPIRIT real-world study that included 1192 patients with PsA across six countries who initiated or switched to a new biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug. They showed that at 3 months, ixekizumab significantly improved clinical disease activity in patients with PsA compared with IL-12/23 inhibitors and IL-23 inhibitors. The improvements in the joints were similar to those with TNF inhibitors and JAK inhibitors, but the improvement in psoriasis was higher. Thus, ixekizumab leads to rapid response to active skin and musculoskeletal disease activity in PsA. Comparative data on treatment persistence as well as adverse events are required.
Smoking is another important modifiable environmental factor. Smoking generally has an adverse impact on treatment. In a post hoc analysis of pooled data from phase 2 and 3 trials and a long-term extension study involving 914 patients with PsA and 372 patients with ankylosing spondylitis who received tofacitinib (a Janus kinase inhibitor) or placebo, Ogdie and coworkers assessed the impact of smoking on treatment efficacy and safety. The efficacy rates were generally similar in current/past smokers and never-smokers. The incidence rates of treatment-emergent adverse events were higher in current/past smokers compared with never-smokers. Thus, in contrast to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, smoking status may not have an impact on tofacitinib efficacy. However, current/past smokers experienced increased rates of adverse events.
Secukinumab, an anti-interleukin (IL)-17A antibody, is an established treatment for PsA and is approved for use as fixed-dose (150/300 mg) subcutaneous injections. The efficacy and safety of weight-based intravenous (IV) therapy is unknown. Kivitz and colleagues recently reported the results of the phase 3 INVIGORATE-2 trial, in which 381 patients with active PsA and either plaque psoriasis or nail psoriasis were randomly assigned to receive IV secukinumab or placebo with crossover to IV secukinumab at week 16. They demonstrated that at week 16, IV secukinumab significantly improved the American College of Rheumatology 50 response rate (ACR50) compared with placebo (31.4% vs 6.3%; adjusted P < .0001). Improvements were observed as early as week 4 and were sustained through week 52. No new safety signals were reported. Thus, IV secukinumab is a safe and efficacious treatment for PsA. This mode of administration of secukinumab is a welcome addition to the PsA therapeutic armamentarium.
There are many targeted therapies available for PsA. However, data on comparative effectiveness is lacking. Kristensen and associates reported the results of an interim analysis of the PRO-SPIRIT real-world study that included 1192 patients with PsA across six countries who initiated or switched to a new biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug. They showed that at 3 months, ixekizumab significantly improved clinical disease activity in patients with PsA compared with IL-12/23 inhibitors and IL-23 inhibitors. The improvements in the joints were similar to those with TNF inhibitors and JAK inhibitors, but the improvement in psoriasis was higher. Thus, ixekizumab leads to rapid response to active skin and musculoskeletal disease activity in PsA. Comparative data on treatment persistence as well as adverse events are required.
Expanding Treatment Options for Psoriatic Arthritis in Adults
Over the past two decades, the treatment of active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) has been transformed by targeted biologic therapies. In this ReCAP, Dr Eric Ruderman, from the Feinberg School of Medicine at Northwestern University, reports on the safety and efficacy of several approved therapies.
Dr Ruderman first discusses different treatment options, including TNF inhibitors, which have been the standard first-line therapy for nearly two decades. He also reports that other agents, including Il-12/23 inhibitors abatacept, apremilast, and a number of JAK inhibitors, have shown efficacy for patients who don’t respond well or are intolerant to TNF inhibitors.
In recent years, various specific IL-23 inhibitors have been approved to treat psoriasis and, most recently, psoriatic arthritis in psoriasis. Guselkumab, risankizumab, and tildrakizumab were approved to treat the skin disease.
In psoriatic arthritis, guselkumab and risankizumab have also been approved. These drugs have shown more efficacy than the IL-12/23 inhibitor, according to Ruderman, and show a lower risk for infection compared with some of the other agents.
--
Eric M. Ruderman, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, Division of Rheumatology, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine; Associate Division Chief, Clinical Affairs, Department of Rheumatology, Northwestern Medical Group, Chicago, Illinois
Eric M. Ruderman, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; Amgen; Bristol Myers Squibb; Janssen; Lilly; Merck; Novartis; NS Pharma; UCB
Over the past two decades, the treatment of active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) has been transformed by targeted biologic therapies. In this ReCAP, Dr Eric Ruderman, from the Feinberg School of Medicine at Northwestern University, reports on the safety and efficacy of several approved therapies.
Dr Ruderman first discusses different treatment options, including TNF inhibitors, which have been the standard first-line therapy for nearly two decades. He also reports that other agents, including Il-12/23 inhibitors abatacept, apremilast, and a number of JAK inhibitors, have shown efficacy for patients who don’t respond well or are intolerant to TNF inhibitors.
In recent years, various specific IL-23 inhibitors have been approved to treat psoriasis and, most recently, psoriatic arthritis in psoriasis. Guselkumab, risankizumab, and tildrakizumab were approved to treat the skin disease.
In psoriatic arthritis, guselkumab and risankizumab have also been approved. These drugs have shown more efficacy than the IL-12/23 inhibitor, according to Ruderman, and show a lower risk for infection compared with some of the other agents.
--
Eric M. Ruderman, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, Division of Rheumatology, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine; Associate Division Chief, Clinical Affairs, Department of Rheumatology, Northwestern Medical Group, Chicago, Illinois
Eric M. Ruderman, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; Amgen; Bristol Myers Squibb; Janssen; Lilly; Merck; Novartis; NS Pharma; UCB
Over the past two decades, the treatment of active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) has been transformed by targeted biologic therapies. In this ReCAP, Dr Eric Ruderman, from the Feinberg School of Medicine at Northwestern University, reports on the safety and efficacy of several approved therapies.
Dr Ruderman first discusses different treatment options, including TNF inhibitors, which have been the standard first-line therapy for nearly two decades. He also reports that other agents, including Il-12/23 inhibitors abatacept, apremilast, and a number of JAK inhibitors, have shown efficacy for patients who don’t respond well or are intolerant to TNF inhibitors.
In recent years, various specific IL-23 inhibitors have been approved to treat psoriasis and, most recently, psoriatic arthritis in psoriasis. Guselkumab, risankizumab, and tildrakizumab were approved to treat the skin disease.
In psoriatic arthritis, guselkumab and risankizumab have also been approved. These drugs have shown more efficacy than the IL-12/23 inhibitor, according to Ruderman, and show a lower risk for infection compared with some of the other agents.
--
Eric M. Ruderman, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, Division of Rheumatology, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine; Associate Division Chief, Clinical Affairs, Department of Rheumatology, Northwestern Medical Group, Chicago, Illinois
Eric M. Ruderman, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; Amgen; Bristol Myers Squibb; Janssen; Lilly; Merck; Novartis; NS Pharma; UCB

AI in Medicine: Are Large Language Models Ready for the Exam Room?
In seconds, Ravi Parikh, MD, an oncologist at the Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, had a summary of his patient’s entire medical history. Normally, Parikh skimmed the cumbersome files before seeing a patient. However, the artificial intelligence (AI) tool his institution was testing could list the highlights he needed in a fraction of the time.
“On the whole, I like it ... it saves me time,” Parikh said of the tool. “But I’d be lying if I told you it was perfect all the time. It’s interpreting the [patient] history in some ways that may be inaccurate,” he said.
Within the first week of testing the tool, Parikh started to notice that the large language model (LLM) made a particular mistake in his patients with prostate cancer. If their prostate-specific antigen test results came back slightly elevated — which is part of normal variation — the LLM recorded it as disease progression. Because Parikh reviews all his notes — with or without using an AI tool — after a visit, he easily caught the mistake before it was added to the chart. “The problem, I think, is if these mistakes go under the hood,” he said.
In the data science world, these mistakes are called hallucinations. And a growing body of research suggests they’re happening more frequently than is safe for healthcare. The industry promised LLMs would alleviate administrative burden and reduce physician burnout. But so far, studies show these AI-tool mistakes often create more work for doctors, not less. To truly help physicians and be safe for patients, some experts say healthcare needs to build its own LLMs from the ground up. And all agree that the field desperately needs a way to vet these algorithms more thoroughly.
Prone to Error
Right now, “I think the industry is focused on taking existing LLMs and forcing them into usage for healthcare,” said Nigam H. Shah, MBBS, PhD, chief data scientist for Stanford Health. However, the value of deploying general LLMs in the healthcare space is questionable. “People are starting to wonder if we’re using these tools wrong,” he told this news organization.
In 2023, Shah and his colleagues evaluated seven LLMs on their ability to answer electronic health record–based questions. For realistic tasks, the error rate in the best cases was about 35%, he said. “To me, that rate seems a bit high ... to adopt for routine use.”
A study earlier this year by the UC San Diego School of Medicine showed that using LLMs to respond to patient messages increased the time doctors spent on messages. And this summer, a study by the clinical AI firm Mendel found that when GPT-4o or Llama-3 were used to summarize patient medical records, almost every summary contained at least one type of hallucination.
“We’ve seen cases where a patient does have drug allergies, but the system says ‘no known drug allergies’ ” in the medical history summary, said Wael Salloum, PhD, cofounder and chief science officer at Mendel. “That’s a serious hallucination.” And if physicians have to constantly verify what the system is telling them, that “defeats the purpose [of summarization],” he said.
A Higher Quality Diet
Part of the trouble with LLMs is that there’s just not enough high-quality information to feed them. The algorithms are insatiable, requiring vast swaths of data for training. GPT-3.5, for instance, was trained on 570 GB of data from the internet, more than 300 billion words. And to train GPT-4o, OpenAI reportedly transcribed more than 1 million hours of YouTube content.
However, the strategies that built these general LLMs don’t always translate well to healthcare. The internet is full of low-quality or misleading health information from wellness sites and supplement advertisements. And even data that are trustworthy, like the millions of clinical studies and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) statements, can be outdated, Salloum said. And “an LLM in training can’t distinguish good from bad,” he added.
The good news is that clinicians don’t rely on controversial information in the real world. Medical knowledge is standardized. “Healthcare is a domain rich with explicit knowledge,” Salloum said. So there’s potential to build a more reliable LLM that is guided by robust medical standards and guidelines.
It’s possible that healthcare could use small language models, which are LLM’s pocket-sized cousins, and perform tasks needing only bite-sized datasets requiring fewer resources and easier fine-tuning, according to Microsoft’s website. Shah said training these smaller models on real medical data might be an option, like an LLM meant to respond to patient messages that could be trained with real messages sent by physicians.
Several groups are already working on databases of standardized human medical knowledge or real physician responses. “Perhaps that will work better than using LLMs trained on the general internet. Those studies need to be done,” Shah said.
Jon Tamir, assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering and co-lead of the AI Health Lab at The University of Texas at Austin, said, “The community has recognized that we are entering a new era of AI where the dataset itself is the most important aspect. We need training sets that are highly curated and highly specialized.
“If the dataset is highly specialized, it will definitely help reduce hallucinations,” he said.
Cutting Overconfidence
A major problem with LLM mistakes is that they are often hard to detect. Hallucinations can be highly convincing even if they’re highly inaccurate, according to Tamir.
When Shah, for instance, was recently testing an LLM on de-identified patient data, he asked the LLM which blood test the patient last had. The model responded with “complete blood count [CBC].” But when he asked for the results, the model gave him white blood count and other values. “Turns out that record did not have a CBC done at all! The result was entirely made up,” he said.
Making healthcare LLMs safer and more reliable will mean training AI to acknowledge potential mistakes and uncertainty. Existing LLMs are trained to project confidence and produce a lot of answers, even when there isn’t one, Salloum said. They rarely respond with “I don’t know” even when their prediction has low confidence, he added.
Healthcare stands to benefit from a system that highlights uncertainty and potential errors. For instance, if a patient’s history shows they have smoked, stopped smoking, vaped, and started smoking again. The LLM might call them a smoker but flag the comment as uncertain because the chronology is complicated, Salloum said.
Tamir added that this strategy could improve LLM and doctor collaboration by honing in on where human expertise is needed most.
Too Little Evaluation
For any improvement strategy to work, LLMs — and all AI-assisted healthcare tools — first need a better evaluation framework. So far, LLMs have “been used in really exciting ways but not really well-vetted ways,” Tamir said.
While some AI-assisted tools, particularly in medical imaging, have undergone rigorous FDA evaluations and earned approval, most haven’t. And because the FDA only regulates algorithms that are considered medical devices, Parikh said that most LLMs used for administrative tasks and efficiency don’t fall under the regulatory agency’s purview.
But these algorithms still have access to patient information and can directly influence patient and doctor decisions. Third-party regulatory agencies are expected to emerge, but it’s still unclear who those will be. Before developers can build a safer and more efficient LLM for healthcare, they’ll need better guidelines and guardrails. “Unless we figure out evaluation, how would we know whether the healthcare-appropriate large language models are better or worse?” Shah asked.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In seconds, Ravi Parikh, MD, an oncologist at the Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, had a summary of his patient’s entire medical history. Normally, Parikh skimmed the cumbersome files before seeing a patient. However, the artificial intelligence (AI) tool his institution was testing could list the highlights he needed in a fraction of the time.
“On the whole, I like it ... it saves me time,” Parikh said of the tool. “But I’d be lying if I told you it was perfect all the time. It’s interpreting the [patient] history in some ways that may be inaccurate,” he said.
Within the first week of testing the tool, Parikh started to notice that the large language model (LLM) made a particular mistake in his patients with prostate cancer. If their prostate-specific antigen test results came back slightly elevated — which is part of normal variation — the LLM recorded it as disease progression. Because Parikh reviews all his notes — with or without using an AI tool — after a visit, he easily caught the mistake before it was added to the chart. “The problem, I think, is if these mistakes go under the hood,” he said.
In the data science world, these mistakes are called hallucinations. And a growing body of research suggests they’re happening more frequently than is safe for healthcare. The industry promised LLMs would alleviate administrative burden and reduce physician burnout. But so far, studies show these AI-tool mistakes often create more work for doctors, not less. To truly help physicians and be safe for patients, some experts say healthcare needs to build its own LLMs from the ground up. And all agree that the field desperately needs a way to vet these algorithms more thoroughly.
Prone to Error
Right now, “I think the industry is focused on taking existing LLMs and forcing them into usage for healthcare,” said Nigam H. Shah, MBBS, PhD, chief data scientist for Stanford Health. However, the value of deploying general LLMs in the healthcare space is questionable. “People are starting to wonder if we’re using these tools wrong,” he told this news organization.
In 2023, Shah and his colleagues evaluated seven LLMs on their ability to answer electronic health record–based questions. For realistic tasks, the error rate in the best cases was about 35%, he said. “To me, that rate seems a bit high ... to adopt for routine use.”
A study earlier this year by the UC San Diego School of Medicine showed that using LLMs to respond to patient messages increased the time doctors spent on messages. And this summer, a study by the clinical AI firm Mendel found that when GPT-4o or Llama-3 were used to summarize patient medical records, almost every summary contained at least one type of hallucination.
“We’ve seen cases where a patient does have drug allergies, but the system says ‘no known drug allergies’ ” in the medical history summary, said Wael Salloum, PhD, cofounder and chief science officer at Mendel. “That’s a serious hallucination.” And if physicians have to constantly verify what the system is telling them, that “defeats the purpose [of summarization],” he said.
A Higher Quality Diet
Part of the trouble with LLMs is that there’s just not enough high-quality information to feed them. The algorithms are insatiable, requiring vast swaths of data for training. GPT-3.5, for instance, was trained on 570 GB of data from the internet, more than 300 billion words. And to train GPT-4o, OpenAI reportedly transcribed more than 1 million hours of YouTube content.
However, the strategies that built these general LLMs don’t always translate well to healthcare. The internet is full of low-quality or misleading health information from wellness sites and supplement advertisements. And even data that are trustworthy, like the millions of clinical studies and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) statements, can be outdated, Salloum said. And “an LLM in training can’t distinguish good from bad,” he added.
The good news is that clinicians don’t rely on controversial information in the real world. Medical knowledge is standardized. “Healthcare is a domain rich with explicit knowledge,” Salloum said. So there’s potential to build a more reliable LLM that is guided by robust medical standards and guidelines.
It’s possible that healthcare could use small language models, which are LLM’s pocket-sized cousins, and perform tasks needing only bite-sized datasets requiring fewer resources and easier fine-tuning, according to Microsoft’s website. Shah said training these smaller models on real medical data might be an option, like an LLM meant to respond to patient messages that could be trained with real messages sent by physicians.
Several groups are already working on databases of standardized human medical knowledge or real physician responses. “Perhaps that will work better than using LLMs trained on the general internet. Those studies need to be done,” Shah said.
Jon Tamir, assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering and co-lead of the AI Health Lab at The University of Texas at Austin, said, “The community has recognized that we are entering a new era of AI where the dataset itself is the most important aspect. We need training sets that are highly curated and highly specialized.
“If the dataset is highly specialized, it will definitely help reduce hallucinations,” he said.
Cutting Overconfidence
A major problem with LLM mistakes is that they are often hard to detect. Hallucinations can be highly convincing even if they’re highly inaccurate, according to Tamir.
When Shah, for instance, was recently testing an LLM on de-identified patient data, he asked the LLM which blood test the patient last had. The model responded with “complete blood count [CBC].” But when he asked for the results, the model gave him white blood count and other values. “Turns out that record did not have a CBC done at all! The result was entirely made up,” he said.
Making healthcare LLMs safer and more reliable will mean training AI to acknowledge potential mistakes and uncertainty. Existing LLMs are trained to project confidence and produce a lot of answers, even when there isn’t one, Salloum said. They rarely respond with “I don’t know” even when their prediction has low confidence, he added.
Healthcare stands to benefit from a system that highlights uncertainty and potential errors. For instance, if a patient’s history shows they have smoked, stopped smoking, vaped, and started smoking again. The LLM might call them a smoker but flag the comment as uncertain because the chronology is complicated, Salloum said.
Tamir added that this strategy could improve LLM and doctor collaboration by honing in on where human expertise is needed most.
Too Little Evaluation
For any improvement strategy to work, LLMs — and all AI-assisted healthcare tools — first need a better evaluation framework. So far, LLMs have “been used in really exciting ways but not really well-vetted ways,” Tamir said.
While some AI-assisted tools, particularly in medical imaging, have undergone rigorous FDA evaluations and earned approval, most haven’t. And because the FDA only regulates algorithms that are considered medical devices, Parikh said that most LLMs used for administrative tasks and efficiency don’t fall under the regulatory agency’s purview.
But these algorithms still have access to patient information and can directly influence patient and doctor decisions. Third-party regulatory agencies are expected to emerge, but it’s still unclear who those will be. Before developers can build a safer and more efficient LLM for healthcare, they’ll need better guidelines and guardrails. “Unless we figure out evaluation, how would we know whether the healthcare-appropriate large language models are better or worse?” Shah asked.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In seconds, Ravi Parikh, MD, an oncologist at the Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, had a summary of his patient’s entire medical history. Normally, Parikh skimmed the cumbersome files before seeing a patient. However, the artificial intelligence (AI) tool his institution was testing could list the highlights he needed in a fraction of the time.
“On the whole, I like it ... it saves me time,” Parikh said of the tool. “But I’d be lying if I told you it was perfect all the time. It’s interpreting the [patient] history in some ways that may be inaccurate,” he said.
Within the first week of testing the tool, Parikh started to notice that the large language model (LLM) made a particular mistake in his patients with prostate cancer. If their prostate-specific antigen test results came back slightly elevated — which is part of normal variation — the LLM recorded it as disease progression. Because Parikh reviews all his notes — with or without using an AI tool — after a visit, he easily caught the mistake before it was added to the chart. “The problem, I think, is if these mistakes go under the hood,” he said.
In the data science world, these mistakes are called hallucinations. And a growing body of research suggests they’re happening more frequently than is safe for healthcare. The industry promised LLMs would alleviate administrative burden and reduce physician burnout. But so far, studies show these AI-tool mistakes often create more work for doctors, not less. To truly help physicians and be safe for patients, some experts say healthcare needs to build its own LLMs from the ground up. And all agree that the field desperately needs a way to vet these algorithms more thoroughly.
Prone to Error
Right now, “I think the industry is focused on taking existing LLMs and forcing them into usage for healthcare,” said Nigam H. Shah, MBBS, PhD, chief data scientist for Stanford Health. However, the value of deploying general LLMs in the healthcare space is questionable. “People are starting to wonder if we’re using these tools wrong,” he told this news organization.
In 2023, Shah and his colleagues evaluated seven LLMs on their ability to answer electronic health record–based questions. For realistic tasks, the error rate in the best cases was about 35%, he said. “To me, that rate seems a bit high ... to adopt for routine use.”
A study earlier this year by the UC San Diego School of Medicine showed that using LLMs to respond to patient messages increased the time doctors spent on messages. And this summer, a study by the clinical AI firm Mendel found that when GPT-4o or Llama-3 were used to summarize patient medical records, almost every summary contained at least one type of hallucination.
“We’ve seen cases where a patient does have drug allergies, but the system says ‘no known drug allergies’ ” in the medical history summary, said Wael Salloum, PhD, cofounder and chief science officer at Mendel. “That’s a serious hallucination.” And if physicians have to constantly verify what the system is telling them, that “defeats the purpose [of summarization],” he said.
A Higher Quality Diet
Part of the trouble with LLMs is that there’s just not enough high-quality information to feed them. The algorithms are insatiable, requiring vast swaths of data for training. GPT-3.5, for instance, was trained on 570 GB of data from the internet, more than 300 billion words. And to train GPT-4o, OpenAI reportedly transcribed more than 1 million hours of YouTube content.
However, the strategies that built these general LLMs don’t always translate well to healthcare. The internet is full of low-quality or misleading health information from wellness sites and supplement advertisements. And even data that are trustworthy, like the millions of clinical studies and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) statements, can be outdated, Salloum said. And “an LLM in training can’t distinguish good from bad,” he added.
The good news is that clinicians don’t rely on controversial information in the real world. Medical knowledge is standardized. “Healthcare is a domain rich with explicit knowledge,” Salloum said. So there’s potential to build a more reliable LLM that is guided by robust medical standards and guidelines.
It’s possible that healthcare could use small language models, which are LLM’s pocket-sized cousins, and perform tasks needing only bite-sized datasets requiring fewer resources and easier fine-tuning, according to Microsoft’s website. Shah said training these smaller models on real medical data might be an option, like an LLM meant to respond to patient messages that could be trained with real messages sent by physicians.
Several groups are already working on databases of standardized human medical knowledge or real physician responses. “Perhaps that will work better than using LLMs trained on the general internet. Those studies need to be done,” Shah said.
Jon Tamir, assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering and co-lead of the AI Health Lab at The University of Texas at Austin, said, “The community has recognized that we are entering a new era of AI where the dataset itself is the most important aspect. We need training sets that are highly curated and highly specialized.
“If the dataset is highly specialized, it will definitely help reduce hallucinations,” he said.
Cutting Overconfidence
A major problem with LLM mistakes is that they are often hard to detect. Hallucinations can be highly convincing even if they’re highly inaccurate, according to Tamir.
When Shah, for instance, was recently testing an LLM on de-identified patient data, he asked the LLM which blood test the patient last had. The model responded with “complete blood count [CBC].” But when he asked for the results, the model gave him white blood count and other values. “Turns out that record did not have a CBC done at all! The result was entirely made up,” he said.
Making healthcare LLMs safer and more reliable will mean training AI to acknowledge potential mistakes and uncertainty. Existing LLMs are trained to project confidence and produce a lot of answers, even when there isn’t one, Salloum said. They rarely respond with “I don’t know” even when their prediction has low confidence, he added.
Healthcare stands to benefit from a system that highlights uncertainty and potential errors. For instance, if a patient’s history shows they have smoked, stopped smoking, vaped, and started smoking again. The LLM might call them a smoker but flag the comment as uncertain because the chronology is complicated, Salloum said.
Tamir added that this strategy could improve LLM and doctor collaboration by honing in on where human expertise is needed most.
Too Little Evaluation
For any improvement strategy to work, LLMs — and all AI-assisted healthcare tools — first need a better evaluation framework. So far, LLMs have “been used in really exciting ways but not really well-vetted ways,” Tamir said.
While some AI-assisted tools, particularly in medical imaging, have undergone rigorous FDA evaluations and earned approval, most haven’t. And because the FDA only regulates algorithms that are considered medical devices, Parikh said that most LLMs used for administrative tasks and efficiency don’t fall under the regulatory agency’s purview.
But these algorithms still have access to patient information and can directly influence patient and doctor decisions. Third-party regulatory agencies are expected to emerge, but it’s still unclear who those will be. Before developers can build a safer and more efficient LLM for healthcare, they’ll need better guidelines and guardrails. “Unless we figure out evaluation, how would we know whether the healthcare-appropriate large language models are better or worse?” Shah asked.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.