User login
Children and COVID: Weekly cases top 200,000, vaccinations down
Weekly pediatric cases of COVID-19 exceeded 200,000 for just the second time during the pandemic, while new vaccinations in children continued to decline.
The weekly count has now increased for 9 consecutive weeks, during which time it has risen by over 2,300%, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report. Total cases in children number almost 4.8 million since the pandemic started.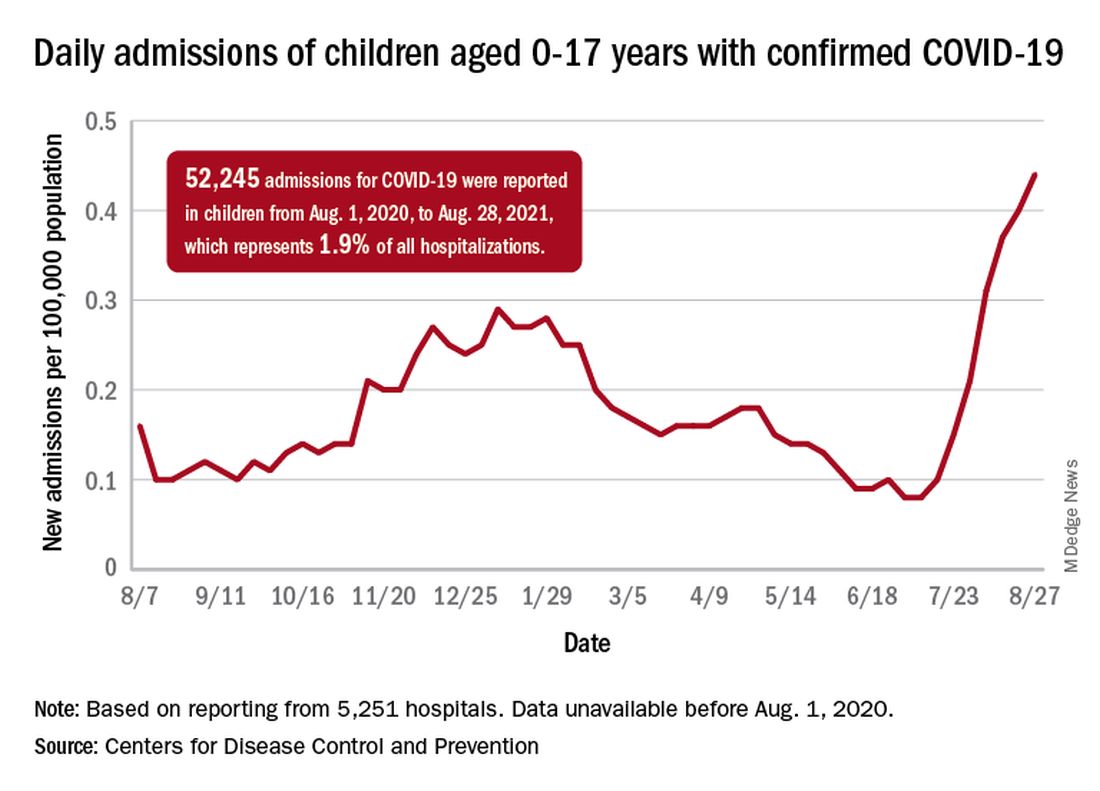
Vaccinations in children are following a different trend. Vaccine initiation has dropped 3 weeks in a row for both of the eligible age groups: First doses administered were down by 29% among 12- to 15-year-olds over that span and by 32% in 16- to 17-year-olds, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Since vaccination for children aged 12-15 years started in May, 49% had received at least one dose, and just over 36% were fully vaccinated as of Aug. 30. Among children aged 16-17 years, who have been eligible since December, 57.5% had gotten at least one dose of the vaccine and 46% have completed the two-dose regimen. The total number of children with at least one dose, including those under age 12 who are involved in clinical trials, was about 12 million, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Hospitalizations are higher than ever
The recent rise in new child cases has been accompanied by an unprecedented increase in hospitalizations. The daily rate in children aged 0-17 years, which did not surpass 0.30 new admissions per 100,000 population during the worst of the winter surge, had risen to 0.45 per 100,000 by Aug. 26. Since July 4, when the new-admission rate was at its low point of 0.07 per 100,000, hospitalizations in children have jumped by 543%, based on data reported to the CDC by 5,251 hospitals.
A total of 52,245 children were admitted with confirmed COVID-19 from Aug. 1, 2020, when the CDC dataset begins, to Aug. 28, 2021. Those children represent 1.9% of all COVID admissions (2.7 million) in the United States over that period, the CDC said.
Total COVID-related deaths in children are up to 425 in the 48 jurisdictions (45 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam) that provide mortality data by age, the AAP and the CHA said.
Record-high numbers for the previous 2 reporting weeks – 23 deaths during Aug. 20-26 and 24 deaths during Aug. 13-19, when the previous weekly high was 16 – at least partially reflect the recent addition of South Carolina and New Mexico to the AAP/CHA database, as the two states just started reporting age-related data.
Weekly pediatric cases of COVID-19 exceeded 200,000 for just the second time during the pandemic, while new vaccinations in children continued to decline.
The weekly count has now increased for 9 consecutive weeks, during which time it has risen by over 2,300%, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report. Total cases in children number almost 4.8 million since the pandemic started.
Vaccinations in children are following a different trend. Vaccine initiation has dropped 3 weeks in a row for both of the eligible age groups: First doses administered were down by 29% among 12- to 15-year-olds over that span and by 32% in 16- to 17-year-olds, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Since vaccination for children aged 12-15 years started in May, 49% had received at least one dose, and just over 36% were fully vaccinated as of Aug. 30. Among children aged 16-17 years, who have been eligible since December, 57.5% had gotten at least one dose of the vaccine and 46% have completed the two-dose regimen. The total number of children with at least one dose, including those under age 12 who are involved in clinical trials, was about 12 million, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Hospitalizations are higher than ever
The recent rise in new child cases has been accompanied by an unprecedented increase in hospitalizations. The daily rate in children aged 0-17 years, which did not surpass 0.30 new admissions per 100,000 population during the worst of the winter surge, had risen to 0.45 per 100,000 by Aug. 26. Since July 4, when the new-admission rate was at its low point of 0.07 per 100,000, hospitalizations in children have jumped by 543%, based on data reported to the CDC by 5,251 hospitals.
A total of 52,245 children were admitted with confirmed COVID-19 from Aug. 1, 2020, when the CDC dataset begins, to Aug. 28, 2021. Those children represent 1.9% of all COVID admissions (2.7 million) in the United States over that period, the CDC said.
Total COVID-related deaths in children are up to 425 in the 48 jurisdictions (45 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam) that provide mortality data by age, the AAP and the CHA said.
Record-high numbers for the previous 2 reporting weeks – 23 deaths during Aug. 20-26 and 24 deaths during Aug. 13-19, when the previous weekly high was 16 – at least partially reflect the recent addition of South Carolina and New Mexico to the AAP/CHA database, as the two states just started reporting age-related data.
Weekly pediatric cases of COVID-19 exceeded 200,000 for just the second time during the pandemic, while new vaccinations in children continued to decline.
The weekly count has now increased for 9 consecutive weeks, during which time it has risen by over 2,300%, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report. Total cases in children number almost 4.8 million since the pandemic started.
Vaccinations in children are following a different trend. Vaccine initiation has dropped 3 weeks in a row for both of the eligible age groups: First doses administered were down by 29% among 12- to 15-year-olds over that span and by 32% in 16- to 17-year-olds, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Since vaccination for children aged 12-15 years started in May, 49% had received at least one dose, and just over 36% were fully vaccinated as of Aug. 30. Among children aged 16-17 years, who have been eligible since December, 57.5% had gotten at least one dose of the vaccine and 46% have completed the two-dose regimen. The total number of children with at least one dose, including those under age 12 who are involved in clinical trials, was about 12 million, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Hospitalizations are higher than ever
The recent rise in new child cases has been accompanied by an unprecedented increase in hospitalizations. The daily rate in children aged 0-17 years, which did not surpass 0.30 new admissions per 100,000 population during the worst of the winter surge, had risen to 0.45 per 100,000 by Aug. 26. Since July 4, when the new-admission rate was at its low point of 0.07 per 100,000, hospitalizations in children have jumped by 543%, based on data reported to the CDC by 5,251 hospitals.
A total of 52,245 children were admitted with confirmed COVID-19 from Aug. 1, 2020, when the CDC dataset begins, to Aug. 28, 2021. Those children represent 1.9% of all COVID admissions (2.7 million) in the United States over that period, the CDC said.
Total COVID-related deaths in children are up to 425 in the 48 jurisdictions (45 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam) that provide mortality data by age, the AAP and the CHA said.
Record-high numbers for the previous 2 reporting weeks – 23 deaths during Aug. 20-26 and 24 deaths during Aug. 13-19, when the previous weekly high was 16 – at least partially reflect the recent addition of South Carolina and New Mexico to the AAP/CHA database, as the two states just started reporting age-related data.
EDs saw more benzodiazepine overdoses, but fewer patients overall, in 2020
In a year when emergency department visits dropped by almost 18%, visits for benzodiazepine overdoses did the opposite, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
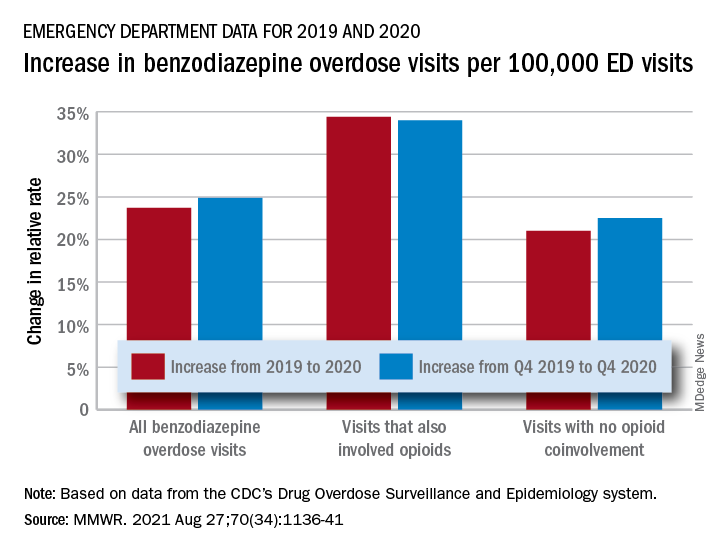
The actual increase in the number of overdose visits for benzodiazepine overdoses was quite small – from 15,547 in 2019 to 15,830 in 2020 (1.8%) – but the 11 million fewer ED visits magnified its effect, Stephen Liu, PhD, and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The rate of benzodiazepine overdose visits to all visits increased by 23.7% from 2019 (24.22 per 100,000 ED visits) to 2020 (29.97 per 100,000), with the larger share going to those involving opioids, which were up by 34.4%, compared with overdose visits not involving opioids (21.0%), the investigators said, based on data reported by 32 states and the District of Columbia to the CDC’s Drug Overdose Surveillance and Epidemiology system. All of the rate changes are statistically significant.
The number of overdose visits without opioid coinvolvement actually dropped, from 2019 (12,276) to 2020 (12,218), but not by enough to offset the decline in total visits, noted Dr. Liu, of the CDC’s National Center for Injury Prevention and Control and associates.
The number of deaths from benzodiazepine overdose, on the other hand, did not drop in 2020. Those data, coming from 23 states participating in the CDC’s State Unintentional Drug Overdose Reporting System, were available only for the first half of the year.
In those 6 months, The first quarter of 2020 also showed an increase, but exact numbers were not provided in the report. Overdose deaths rose by 22% for prescription forms of benzodiazepine and 520% for illicit forms in Q2 of 2020, compared with 2019, the researchers said.
Almost all of the benzodiazepine deaths (93%) in the first half of 2020 also involved opioids, mostly in the form of illicitly manufactured fentanyls (67% of all deaths). Between Q2 of 2019 and Q2 of 2020, involvement of illicit fentanyls in benzodiazepine overdose deaths increased from almost 57% to 71%, Dr. Liu and associates reported.
“Despite progress in reducing coprescribing [of opioids and benzodiazepines] before 2019, this study suggests a reversal in the decline in benzodiazepine deaths from 2017 to 2019, driven in part by increasing involvement of [illicitly manufactured fentanyls] in benzodiazepine deaths and influxes of illicit benzodiazepines,” they wrote.
In a year when emergency department visits dropped by almost 18%, visits for benzodiazepine overdoses did the opposite, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The actual increase in the number of overdose visits for benzodiazepine overdoses was quite small – from 15,547 in 2019 to 15,830 in 2020 (1.8%) – but the 11 million fewer ED visits magnified its effect, Stephen Liu, PhD, and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The rate of benzodiazepine overdose visits to all visits increased by 23.7% from 2019 (24.22 per 100,000 ED visits) to 2020 (29.97 per 100,000), with the larger share going to those involving opioids, which were up by 34.4%, compared with overdose visits not involving opioids (21.0%), the investigators said, based on data reported by 32 states and the District of Columbia to the CDC’s Drug Overdose Surveillance and Epidemiology system. All of the rate changes are statistically significant.
The number of overdose visits without opioid coinvolvement actually dropped, from 2019 (12,276) to 2020 (12,218), but not by enough to offset the decline in total visits, noted Dr. Liu, of the CDC’s National Center for Injury Prevention and Control and associates.
The number of deaths from benzodiazepine overdose, on the other hand, did not drop in 2020. Those data, coming from 23 states participating in the CDC’s State Unintentional Drug Overdose Reporting System, were available only for the first half of the year.
In those 6 months, The first quarter of 2020 also showed an increase, but exact numbers were not provided in the report. Overdose deaths rose by 22% for prescription forms of benzodiazepine and 520% for illicit forms in Q2 of 2020, compared with 2019, the researchers said.
Almost all of the benzodiazepine deaths (93%) in the first half of 2020 also involved opioids, mostly in the form of illicitly manufactured fentanyls (67% of all deaths). Between Q2 of 2019 and Q2 of 2020, involvement of illicit fentanyls in benzodiazepine overdose deaths increased from almost 57% to 71%, Dr. Liu and associates reported.
“Despite progress in reducing coprescribing [of opioids and benzodiazepines] before 2019, this study suggests a reversal in the decline in benzodiazepine deaths from 2017 to 2019, driven in part by increasing involvement of [illicitly manufactured fentanyls] in benzodiazepine deaths and influxes of illicit benzodiazepines,” they wrote.
In a year when emergency department visits dropped by almost 18%, visits for benzodiazepine overdoses did the opposite, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The actual increase in the number of overdose visits for benzodiazepine overdoses was quite small – from 15,547 in 2019 to 15,830 in 2020 (1.8%) – but the 11 million fewer ED visits magnified its effect, Stephen Liu, PhD, and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The rate of benzodiazepine overdose visits to all visits increased by 23.7% from 2019 (24.22 per 100,000 ED visits) to 2020 (29.97 per 100,000), with the larger share going to those involving opioids, which were up by 34.4%, compared with overdose visits not involving opioids (21.0%), the investigators said, based on data reported by 32 states and the District of Columbia to the CDC’s Drug Overdose Surveillance and Epidemiology system. All of the rate changes are statistically significant.
The number of overdose visits without opioid coinvolvement actually dropped, from 2019 (12,276) to 2020 (12,218), but not by enough to offset the decline in total visits, noted Dr. Liu, of the CDC’s National Center for Injury Prevention and Control and associates.
The number of deaths from benzodiazepine overdose, on the other hand, did not drop in 2020. Those data, coming from 23 states participating in the CDC’s State Unintentional Drug Overdose Reporting System, were available only for the first half of the year.
In those 6 months, The first quarter of 2020 also showed an increase, but exact numbers were not provided in the report. Overdose deaths rose by 22% for prescription forms of benzodiazepine and 520% for illicit forms in Q2 of 2020, compared with 2019, the researchers said.
Almost all of the benzodiazepine deaths (93%) in the first half of 2020 also involved opioids, mostly in the form of illicitly manufactured fentanyls (67% of all deaths). Between Q2 of 2019 and Q2 of 2020, involvement of illicit fentanyls in benzodiazepine overdose deaths increased from almost 57% to 71%, Dr. Liu and associates reported.
“Despite progress in reducing coprescribing [of opioids and benzodiazepines] before 2019, this study suggests a reversal in the decline in benzodiazepine deaths from 2017 to 2019, driven in part by increasing involvement of [illicitly manufactured fentanyls] in benzodiazepine deaths and influxes of illicit benzodiazepines,” they wrote.
FROM MMWR
Reassuring data on long-term outcomes among kids with MIS-C
Most children who develop multisystemic inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) after infection with SARS-CoV-2 recover relatively quickly and without significant sequelae, according to a research letter published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
“The results of this research letter offer some reassurance as has been the case with other longitudinal reports, that children with MIS-C largely recover from the illness with minimal sequelae,” said Kanwal M. Farooqi, MD, a pediatric cardiologist from Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York.
“This is despite the severity of the initial clinical presentation, which can be quite significant with signs of systemic inflammation, hypotension, and need for ICU-level care,” continued Dr. Farooqi, who was not involved in the study.
Given that little is known about the medium- and long-term effects of MIS-C following infection with COVID-19, Patrick Davies, MRCPCH, Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust, and colleagues reviewed data from one of the earliest multicenter national cohorts of children in the United Kingdom. The cohort included children admitted to the hospital prior to May 10, 2020, and the analysis was based on data from 68 of 76 (89%) patients of the initial surviving cohort. Information regarding critical care readmissions and outpatient follow-up visits up to April 1, 2021 (1-year post admission), was included in the analysis.
Overall laboratory results appeared normal for most children at 50 days post admission, including neutrophils, platelets, ferritin, creatinine, and alanine transaminase. Just 3% (2/65 test results) of children showed elevated levels of C-reactive protein, 3% (2/59 test results) for D-dimer, and 2% (1/60 test results) for troponin.
Based on echocardiographic data, 14 of the 19 patients who presented with aneurysms had resolution. Nine of 10 patients who presented with “bright” coronary arteries had resolution and only one progressed to having unresolved coronary artery aneurysms with the latest follow-up at 86 days post admission. All of the 38 patients who presented with impaired function without aneurysm had recovered by day 74.
Of the six patients with ongoing echocardiographic abnormalities, all had aneurysmal changes noted on echocardiograms performed between 86 and 336 days post admission. The authors were surprised to find that troponin levels in this group were lower when compared with others in the cohort (0.06 ng/mL [interquartile range, 0.02-0.418 ng/mL] vs. 0.157 ng/mL [0.033-0.81 ng/mL]; P = .02).
These six patients ranged in age from 0 to 13 years (median age, 8.75 years); five were Afro Caribbean boys and one was a White girl.
The researchers acknowledged that, despite coming from a nationwide data set, the interpretation of this data is limited given the small size of the cohort and the lack of standardized follow-up protocol available at the time.
When asked how this data might inform follow-up guidance for children post COVID infection, Dr. Farooqi said, “although it appears from the data that we have seen in the last few months that the patients recover relatively quickly from MIS-C, I believe it is reasonable to evaluate them at 6-month intervals for the second year until we have more information regarding longer-term outcomes.”
The study authors and Dr. Farooqi disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most children who develop multisystemic inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) after infection with SARS-CoV-2 recover relatively quickly and without significant sequelae, according to a research letter published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
“The results of this research letter offer some reassurance as has been the case with other longitudinal reports, that children with MIS-C largely recover from the illness with minimal sequelae,” said Kanwal M. Farooqi, MD, a pediatric cardiologist from Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York.
“This is despite the severity of the initial clinical presentation, which can be quite significant with signs of systemic inflammation, hypotension, and need for ICU-level care,” continued Dr. Farooqi, who was not involved in the study.
Given that little is known about the medium- and long-term effects of MIS-C following infection with COVID-19, Patrick Davies, MRCPCH, Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust, and colleagues reviewed data from one of the earliest multicenter national cohorts of children in the United Kingdom. The cohort included children admitted to the hospital prior to May 10, 2020, and the analysis was based on data from 68 of 76 (89%) patients of the initial surviving cohort. Information regarding critical care readmissions and outpatient follow-up visits up to April 1, 2021 (1-year post admission), was included in the analysis.
Overall laboratory results appeared normal for most children at 50 days post admission, including neutrophils, platelets, ferritin, creatinine, and alanine transaminase. Just 3% (2/65 test results) of children showed elevated levels of C-reactive protein, 3% (2/59 test results) for D-dimer, and 2% (1/60 test results) for troponin.
Based on echocardiographic data, 14 of the 19 patients who presented with aneurysms had resolution. Nine of 10 patients who presented with “bright” coronary arteries had resolution and only one progressed to having unresolved coronary artery aneurysms with the latest follow-up at 86 days post admission. All of the 38 patients who presented with impaired function without aneurysm had recovered by day 74.
Of the six patients with ongoing echocardiographic abnormalities, all had aneurysmal changes noted on echocardiograms performed between 86 and 336 days post admission. The authors were surprised to find that troponin levels in this group were lower when compared with others in the cohort (0.06 ng/mL [interquartile range, 0.02-0.418 ng/mL] vs. 0.157 ng/mL [0.033-0.81 ng/mL]; P = .02).
These six patients ranged in age from 0 to 13 years (median age, 8.75 years); five were Afro Caribbean boys and one was a White girl.
The researchers acknowledged that, despite coming from a nationwide data set, the interpretation of this data is limited given the small size of the cohort and the lack of standardized follow-up protocol available at the time.
When asked how this data might inform follow-up guidance for children post COVID infection, Dr. Farooqi said, “although it appears from the data that we have seen in the last few months that the patients recover relatively quickly from MIS-C, I believe it is reasonable to evaluate them at 6-month intervals for the second year until we have more information regarding longer-term outcomes.”
The study authors and Dr. Farooqi disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most children who develop multisystemic inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) after infection with SARS-CoV-2 recover relatively quickly and without significant sequelae, according to a research letter published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
“The results of this research letter offer some reassurance as has been the case with other longitudinal reports, that children with MIS-C largely recover from the illness with minimal sequelae,” said Kanwal M. Farooqi, MD, a pediatric cardiologist from Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York.
“This is despite the severity of the initial clinical presentation, which can be quite significant with signs of systemic inflammation, hypotension, and need for ICU-level care,” continued Dr. Farooqi, who was not involved in the study.
Given that little is known about the medium- and long-term effects of MIS-C following infection with COVID-19, Patrick Davies, MRCPCH, Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust, and colleagues reviewed data from one of the earliest multicenter national cohorts of children in the United Kingdom. The cohort included children admitted to the hospital prior to May 10, 2020, and the analysis was based on data from 68 of 76 (89%) patients of the initial surviving cohort. Information regarding critical care readmissions and outpatient follow-up visits up to April 1, 2021 (1-year post admission), was included in the analysis.
Overall laboratory results appeared normal for most children at 50 days post admission, including neutrophils, platelets, ferritin, creatinine, and alanine transaminase. Just 3% (2/65 test results) of children showed elevated levels of C-reactive protein, 3% (2/59 test results) for D-dimer, and 2% (1/60 test results) for troponin.
Based on echocardiographic data, 14 of the 19 patients who presented with aneurysms had resolution. Nine of 10 patients who presented with “bright” coronary arteries had resolution and only one progressed to having unresolved coronary artery aneurysms with the latest follow-up at 86 days post admission. All of the 38 patients who presented with impaired function without aneurysm had recovered by day 74.
Of the six patients with ongoing echocardiographic abnormalities, all had aneurysmal changes noted on echocardiograms performed between 86 and 336 days post admission. The authors were surprised to find that troponin levels in this group were lower when compared with others in the cohort (0.06 ng/mL [interquartile range, 0.02-0.418 ng/mL] vs. 0.157 ng/mL [0.033-0.81 ng/mL]; P = .02).
These six patients ranged in age from 0 to 13 years (median age, 8.75 years); five were Afro Caribbean boys and one was a White girl.
The researchers acknowledged that, despite coming from a nationwide data set, the interpretation of this data is limited given the small size of the cohort and the lack of standardized follow-up protocol available at the time.
When asked how this data might inform follow-up guidance for children post COVID infection, Dr. Farooqi said, “although it appears from the data that we have seen in the last few months that the patients recover relatively quickly from MIS-C, I believe it is reasonable to evaluate them at 6-month intervals for the second year until we have more information regarding longer-term outcomes.”
The study authors and Dr. Farooqi disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long COVID symptoms can persist for more than 1 year, study shows
Nearly half of people who are hospitalized with COVID-19 suffer at least one lingering symptom 1 year after discharge, according to the largest study yet to assess the dynamic recovery of a group of COVID-19 survivors 12 months after the illness.
The most common lingering symptoms are fatigue and muscle weakness. One-third continue to have shortness of breath.
Overall, at 12 months, COVID-19 survivors had more problems with mobility, pain or discomfort, and anxiety or depression, and had lower self-assessment scores of quality of life than matched COVID-free peers, the investigators report.
The study was published online Aug. 28 in The Lancet.
“While most had made a good recovery, health problems persisted in some patients, especially those who had been critically ill during their hospital stay,” Bin Cao, MD, from the National Center for Respiratory Medicine at the China-Japan Friendship Hospital and Capital Medical University, both in Beijing, said in a Lancet news release.
“Our findings suggest that recovery for some patients will take longer than 1 year, and this should be taken into account when planning delivery of health care services post pandemic,” Dr. Cao said.
“As the COVID-19 pandemic continues, the need to understand and respond to long COVID is increasingly pressing,” says a Lancet editorial.
“Symptoms such as persistent fatigue, breathlessness, brain fog, and depression could debilitate many millions of people globally. Long COVID is a modern medical challenge of the first order,” it reads.
Study details
Dr. Cao and colleagues studied 1,276 COVID-19 patients (median age 59; 53% men) discharged from a hospital in Wuhan, China, between Jan. 7 and May 29, 2020. The patients were assessed at 6 and 12 months from the date they first experienced COVID-19 symptoms.
Many symptoms resolved over time, regardless of the severity of illness. Yet 49% of patients still had at least one symptom 12 months after their acute illness, down from 68% at the 6-month mark, the authors report.
Fatigue and muscle weakness were the most commonly reported symptoms seen in 52% of patients at 6 months and 20% at 12 months. Compared with men, women were 1.4 times more likely to report fatigue or muscle weakness.
Patients treated with corticosteroids during the acute phase of COVID-19 were 1.5 times as likely to experience fatigue or muscle weakness after 12 months, compared with those who had not received corticosteroids.
Thirty percent of patients reported dyspnea at 12 months, slightly more than at 6 months (26%). Dyspnea was more common in the most severely ill patients needing a ventilator during their hospital stay (39%), compared with those who did not need oxygen treatment (25%).
At the 6-month check, 349 study participants underwent pulmonary function tests and 244 of those patients completed the same test at 12 months.
Spirometric and lung volume parameters of most of these patients were within normal limits at 12 months. But lung diffusion impairment was observed in about 20%-30% of patients who had been moderately ill with COVID-19 and as high as 54% in critically ill patients.
Compared with men, women were almost three times as likely to have lung diffusion impairment after 12 months.
Of 186 patients with abnormal lung CT scan at 6 months, 118 patients had a repeat CT scan at 12 months. The lung imaging abnormality gradually recovered during follow-up, yet 76% of the most critically ill patients still had ground glass opacity at 12 months.
Mental health hit
Among those patients who had been employed full- or part-time before catching COVID, the majority had returned to their original job (88%) and most had returned to their pre-COVID-19 level of work (76%) within 12 months.
Among those who did not return to their original work, 32% cited decreased physical function, 25% were unwilling to do their previous job, and 18% were unemployed.
As shown in multiple other studies, COVID-19 can take a toll on mental health. In this cohort, slightly more patients reported anxiety or depression at 12 months than at 6 months (23% vs. 26%), and the proportion was much greater than in matched community-dwelling adults without COVID-19 (5%).
Compared with men, women were twice as likely to report anxiety or depression.
“We do not yet fully understand why psychiatric symptoms are slightly more common at 1 year than at 6 months in COVID-19 survivors,” study author Xiaoying Gu, PhD, from the Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, said in the news release.
“These could be caused by a biological process linked to the virus infection itself, or the body’s immune response to it. Or they could be linked to reduced social contact, loneliness, incomplete recovery of physical health, or loss of employment associated with illness. Large, long-term studies of COVID-19 survivors are needed so that we can better understand the long-term physical and mental health consequences of COVID-19,” Dr. Gu said.
The authors caution that the findings represent a group of patients from a single hospital in China and the cohort included only a small number of patients who had been admitted to intensive care (94 of 1,276; 7.4%).
The Lancet editorial urges the scientific and medical community to “collaborate to explore the mechanism and pathogenesis of long COVID, estimate the global and regional disease burdens, better delineate who is most at risk, understand how vaccines might affect the condition, and find effective treatments via randomized controlled trials.”
“At the same time, health care providers must acknowledge and validate the toll of the persistent symptoms of long COVID on patients, and health systems need to be prepared to meet individualized, patient-oriented goals, with an appropriately trained workforce involving physical, cognitive, social, and occupational elements,” the editorial states.
“Answering these research questions while providing compassionate and multidisciplinary care will require the full breadth of scientific and medical ingenuity. It is a challenge to which the whole health community must rise,” the editorialists conclude.
The study was funded by the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program of China, Major Projects of National Science and Technology on New Drug Creation and Development of Pulmonary Tuberculosis, the China Evergrande Group, the Jack Ma Foundation, Sino Biopharmaceutical, the Ping An Insurance (Group), and the New Sunshine Charity Foundation. The full list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nearly half of people who are hospitalized with COVID-19 suffer at least one lingering symptom 1 year after discharge, according to the largest study yet to assess the dynamic recovery of a group of COVID-19 survivors 12 months after the illness.
The most common lingering symptoms are fatigue and muscle weakness. One-third continue to have shortness of breath.
Overall, at 12 months, COVID-19 survivors had more problems with mobility, pain or discomfort, and anxiety or depression, and had lower self-assessment scores of quality of life than matched COVID-free peers, the investigators report.
The study was published online Aug. 28 in The Lancet.
“While most had made a good recovery, health problems persisted in some patients, especially those who had been critically ill during their hospital stay,” Bin Cao, MD, from the National Center for Respiratory Medicine at the China-Japan Friendship Hospital and Capital Medical University, both in Beijing, said in a Lancet news release.
“Our findings suggest that recovery for some patients will take longer than 1 year, and this should be taken into account when planning delivery of health care services post pandemic,” Dr. Cao said.
“As the COVID-19 pandemic continues, the need to understand and respond to long COVID is increasingly pressing,” says a Lancet editorial.
“Symptoms such as persistent fatigue, breathlessness, brain fog, and depression could debilitate many millions of people globally. Long COVID is a modern medical challenge of the first order,” it reads.
Study details
Dr. Cao and colleagues studied 1,276 COVID-19 patients (median age 59; 53% men) discharged from a hospital in Wuhan, China, between Jan. 7 and May 29, 2020. The patients were assessed at 6 and 12 months from the date they first experienced COVID-19 symptoms.
Many symptoms resolved over time, regardless of the severity of illness. Yet 49% of patients still had at least one symptom 12 months after their acute illness, down from 68% at the 6-month mark, the authors report.
Fatigue and muscle weakness were the most commonly reported symptoms seen in 52% of patients at 6 months and 20% at 12 months. Compared with men, women were 1.4 times more likely to report fatigue or muscle weakness.
Patients treated with corticosteroids during the acute phase of COVID-19 were 1.5 times as likely to experience fatigue or muscle weakness after 12 months, compared with those who had not received corticosteroids.
Thirty percent of patients reported dyspnea at 12 months, slightly more than at 6 months (26%). Dyspnea was more common in the most severely ill patients needing a ventilator during their hospital stay (39%), compared with those who did not need oxygen treatment (25%).
At the 6-month check, 349 study participants underwent pulmonary function tests and 244 of those patients completed the same test at 12 months.
Spirometric and lung volume parameters of most of these patients were within normal limits at 12 months. But lung diffusion impairment was observed in about 20%-30% of patients who had been moderately ill with COVID-19 and as high as 54% in critically ill patients.
Compared with men, women were almost three times as likely to have lung diffusion impairment after 12 months.
Of 186 patients with abnormal lung CT scan at 6 months, 118 patients had a repeat CT scan at 12 months. The lung imaging abnormality gradually recovered during follow-up, yet 76% of the most critically ill patients still had ground glass opacity at 12 months.
Mental health hit
Among those patients who had been employed full- or part-time before catching COVID, the majority had returned to their original job (88%) and most had returned to their pre-COVID-19 level of work (76%) within 12 months.
Among those who did not return to their original work, 32% cited decreased physical function, 25% were unwilling to do their previous job, and 18% were unemployed.
As shown in multiple other studies, COVID-19 can take a toll on mental health. In this cohort, slightly more patients reported anxiety or depression at 12 months than at 6 months (23% vs. 26%), and the proportion was much greater than in matched community-dwelling adults without COVID-19 (5%).
Compared with men, women were twice as likely to report anxiety or depression.
“We do not yet fully understand why psychiatric symptoms are slightly more common at 1 year than at 6 months in COVID-19 survivors,” study author Xiaoying Gu, PhD, from the Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, said in the news release.
“These could be caused by a biological process linked to the virus infection itself, or the body’s immune response to it. Or they could be linked to reduced social contact, loneliness, incomplete recovery of physical health, or loss of employment associated with illness. Large, long-term studies of COVID-19 survivors are needed so that we can better understand the long-term physical and mental health consequences of COVID-19,” Dr. Gu said.
The authors caution that the findings represent a group of patients from a single hospital in China and the cohort included only a small number of patients who had been admitted to intensive care (94 of 1,276; 7.4%).
The Lancet editorial urges the scientific and medical community to “collaborate to explore the mechanism and pathogenesis of long COVID, estimate the global and regional disease burdens, better delineate who is most at risk, understand how vaccines might affect the condition, and find effective treatments via randomized controlled trials.”
“At the same time, health care providers must acknowledge and validate the toll of the persistent symptoms of long COVID on patients, and health systems need to be prepared to meet individualized, patient-oriented goals, with an appropriately trained workforce involving physical, cognitive, social, and occupational elements,” the editorial states.
“Answering these research questions while providing compassionate and multidisciplinary care will require the full breadth of scientific and medical ingenuity. It is a challenge to which the whole health community must rise,” the editorialists conclude.
The study was funded by the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program of China, Major Projects of National Science and Technology on New Drug Creation and Development of Pulmonary Tuberculosis, the China Evergrande Group, the Jack Ma Foundation, Sino Biopharmaceutical, the Ping An Insurance (Group), and the New Sunshine Charity Foundation. The full list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nearly half of people who are hospitalized with COVID-19 suffer at least one lingering symptom 1 year after discharge, according to the largest study yet to assess the dynamic recovery of a group of COVID-19 survivors 12 months after the illness.
The most common lingering symptoms are fatigue and muscle weakness. One-third continue to have shortness of breath.
Overall, at 12 months, COVID-19 survivors had more problems with mobility, pain or discomfort, and anxiety or depression, and had lower self-assessment scores of quality of life than matched COVID-free peers, the investigators report.
The study was published online Aug. 28 in The Lancet.
“While most had made a good recovery, health problems persisted in some patients, especially those who had been critically ill during their hospital stay,” Bin Cao, MD, from the National Center for Respiratory Medicine at the China-Japan Friendship Hospital and Capital Medical University, both in Beijing, said in a Lancet news release.
“Our findings suggest that recovery for some patients will take longer than 1 year, and this should be taken into account when planning delivery of health care services post pandemic,” Dr. Cao said.
“As the COVID-19 pandemic continues, the need to understand and respond to long COVID is increasingly pressing,” says a Lancet editorial.
“Symptoms such as persistent fatigue, breathlessness, brain fog, and depression could debilitate many millions of people globally. Long COVID is a modern medical challenge of the first order,” it reads.
Study details
Dr. Cao and colleagues studied 1,276 COVID-19 patients (median age 59; 53% men) discharged from a hospital in Wuhan, China, between Jan. 7 and May 29, 2020. The patients were assessed at 6 and 12 months from the date they first experienced COVID-19 symptoms.
Many symptoms resolved over time, regardless of the severity of illness. Yet 49% of patients still had at least one symptom 12 months after their acute illness, down from 68% at the 6-month mark, the authors report.
Fatigue and muscle weakness were the most commonly reported symptoms seen in 52% of patients at 6 months and 20% at 12 months. Compared with men, women were 1.4 times more likely to report fatigue or muscle weakness.
Patients treated with corticosteroids during the acute phase of COVID-19 were 1.5 times as likely to experience fatigue or muscle weakness after 12 months, compared with those who had not received corticosteroids.
Thirty percent of patients reported dyspnea at 12 months, slightly more than at 6 months (26%). Dyspnea was more common in the most severely ill patients needing a ventilator during their hospital stay (39%), compared with those who did not need oxygen treatment (25%).
At the 6-month check, 349 study participants underwent pulmonary function tests and 244 of those patients completed the same test at 12 months.
Spirometric and lung volume parameters of most of these patients were within normal limits at 12 months. But lung diffusion impairment was observed in about 20%-30% of patients who had been moderately ill with COVID-19 and as high as 54% in critically ill patients.
Compared with men, women were almost three times as likely to have lung diffusion impairment after 12 months.
Of 186 patients with abnormal lung CT scan at 6 months, 118 patients had a repeat CT scan at 12 months. The lung imaging abnormality gradually recovered during follow-up, yet 76% of the most critically ill patients still had ground glass opacity at 12 months.
Mental health hit
Among those patients who had been employed full- or part-time before catching COVID, the majority had returned to their original job (88%) and most had returned to their pre-COVID-19 level of work (76%) within 12 months.
Among those who did not return to their original work, 32% cited decreased physical function, 25% were unwilling to do their previous job, and 18% were unemployed.
As shown in multiple other studies, COVID-19 can take a toll on mental health. In this cohort, slightly more patients reported anxiety or depression at 12 months than at 6 months (23% vs. 26%), and the proportion was much greater than in matched community-dwelling adults without COVID-19 (5%).
Compared with men, women were twice as likely to report anxiety or depression.
“We do not yet fully understand why psychiatric symptoms are slightly more common at 1 year than at 6 months in COVID-19 survivors,” study author Xiaoying Gu, PhD, from the Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, said in the news release.
“These could be caused by a biological process linked to the virus infection itself, or the body’s immune response to it. Or they could be linked to reduced social contact, loneliness, incomplete recovery of physical health, or loss of employment associated with illness. Large, long-term studies of COVID-19 survivors are needed so that we can better understand the long-term physical and mental health consequences of COVID-19,” Dr. Gu said.
The authors caution that the findings represent a group of patients from a single hospital in China and the cohort included only a small number of patients who had been admitted to intensive care (94 of 1,276; 7.4%).
The Lancet editorial urges the scientific and medical community to “collaborate to explore the mechanism and pathogenesis of long COVID, estimate the global and regional disease burdens, better delineate who is most at risk, understand how vaccines might affect the condition, and find effective treatments via randomized controlled trials.”
“At the same time, health care providers must acknowledge and validate the toll of the persistent symptoms of long COVID on patients, and health systems need to be prepared to meet individualized, patient-oriented goals, with an appropriately trained workforce involving physical, cognitive, social, and occupational elements,” the editorial states.
“Answering these research questions while providing compassionate and multidisciplinary care will require the full breadth of scientific and medical ingenuity. It is a challenge to which the whole health community must rise,” the editorialists conclude.
The study was funded by the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program of China, Major Projects of National Science and Technology on New Drug Creation and Development of Pulmonary Tuberculosis, the China Evergrande Group, the Jack Ma Foundation, Sino Biopharmaceutical, the Ping An Insurance (Group), and the New Sunshine Charity Foundation. The full list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
EMPEROR-Preserved spouts torrent of reports on empagliflozin treatment of HFpEF
The featured report from the 6,000-patient EMPEROR-Preserved trial at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology drew lots of attention for its headline finding: the first unequivocal demonstration that a medication, empagliflozin, can significantly reduce the rate of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF, a left ventricular ejection fraction of more than 40%), with the details simultaneously published online.
But at the same time, the EMPEROR-Preserved investigators released four additional reports with a lot more outcome analyses that also deserve some attention.
The puzzling neutral effect on renal events
Perhaps the most surprising and complicated set of findings among the main EMPEROR-Preserved outcomes involved renal outcomes.
The trial’s primary outcome was the combined rate of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure (HHF), and the results showed that treatment with empagliflozin (Jardiance) for a median of 26 months on top of standard treatment for patients with HFpEF led to a significant 21% relative risk reduction, compared with placebo-treated patients.
The trial had two prespecified secondary outcomes. One was the total number of HHF, which dropped by a significant 27%, compared with placebo. The second was the mean change in slope of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) on an annualized basis, and the empagliflozin regimen reduced the cumulative annual deficit, compared with placebo by an average of 1.36 mL/min per 1.73 m2, a significant difference.
This preservation of renal function was consistent with results from many prior studies of empagliflozin and all of the other U.S.-approved agents from the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor class. Preservation of renal function and a reduction in renal events has become a hallmark property of all agents in the SGLT2 inhibitor class both in patients with type 2 diabetes, as well as in those without diabetes but with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) or with chronic kidney disease.
EMPEROR-Preserved threw a wrench into what had been an unbroken history of renal protection by SGLT2 inhibitors. That happened when a prespecified endpoint of the study – a composite renal outcome defined as time to first occurrence of chronic dialysis, renal transplantation, a sustained reduction of at least 40% in eGFR, or a sustained drop in eGFR of more than 10 or 15 mL/min per 1.73 m2 from baseline – yielded an unexpected neutral finding.
For this composite renal outcome, EMPEROR-Preserved showed a nonsignificant 5% reduction, compared with placebo, a result that both differed from what had been seen in essentially all the other SGLT2 inhibitor trials that had looked at this, but which also seemed at odds with the observed significant preservation of renal function that seemed substantial enough to produce a clinically meaningful benefit.
Renal effects blunted in HFpEF
The immediate upshot was a letter published by several EMPEROR-Preserved investigators that spelled out this discrepancy and came to the jolting conclusion that “eGFR slope analysis has limitations as a surrogate for predicting the effect of drugs on renal outcomes in patients with heart failure.”
The same authors, along with some additional associates, also published a second letter that noted a further unexpected twist with the renal outcome: “In prior large-scale clinical trials, the effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on heart failure and renal outcomes had consistently tracked together,” they noted, but in this case it didn’t, a discordance they said was “extraordinarily puzzling”.
This led the study’s leaders to reanalyze the renal outcomes using a different definition, one that Milton Packer, MD, who helped design the trial and oversaw several of its analyses, called “a more conventional definition of renal events,” during his presentation of these findings at the congress. The researchers swapped out a 40% drop from baseline eGFR as an event and replaced it with a 50% decline, a change designed to screen out less severe, and often transient, reductions in kidney function that have less lasting impact on health. They also added an additional component to the composite endpoint, renal death. A revised analysis using this new renal composite outcome appeared in the European Journal of Heart Failure letter.
This change cut the total number of renal events tallied in the trial nearly in half, down to 112, and showed a more robust decline in renal events with empagliflozin treatment compared with the initial analysis, although the drop remained nonsignificant. The revised analysis also showed that the overall, nonsignificant 22% relative reduction in renal events in patients on empagliflozin, compared with placebo, dwindled down to completely nonexistent in the tertile of patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction of 60% or greater. In this tertile the hazard ratio actually showed a nonsignificant point estimate of a 24% increased rate of renal events on empagliflozin, with the caveat that this subgroup now included a total of just 40 total events between the two treatment arms. (Each of the two other tertiles also had roughly the same number of total events.)
The biggest effect on renal-event reduction was in the tertile of patients with an ejection fraction of 41%-49%, in which empagliflozin treatment was linked with a significant 59% cut in renal events, compared with placebo. The analysis also showed significant heterogeneity in thus outcome between this subgroup and the other two tertiles that had higher ejection fractions and showed reduced rates of protection by empagliflozin against renal events.
This apparent blunting of a renal effect despite preservation of renal function seemed to mimic the blunting of the primary cardiovascular outcome effect that also appeared in patients with ejection fractions in the 60%-65% range or above.
“If we knew what blunted the effect of empagliflozin on heart failure outcomes at higher ejection fraction levels, we think the same explanation may also apply to the blunting of effect on renal outcomes, but right now we do not know the answer to either question,” Dr. Packer said in an interview. He’s suggested that one possibility is that many of the enrolled patients identified as having HFpEF, but with these high ejection fractions may have not actually had HFpEF, and their signs and symptoms may have instead resulted from atrial fibrillation.
“Many patients with an ejection fraction of 60%-65% and above had atrial fibrillation,” he noted, with a prevalence at enrollment in this subgroup of about 50%. Atrial fibrillation can cause dyspnea, a hallmark symptom leading to diagnosis of heart failure, and it also increases levels of N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide, a metric that served as a gatekeeper for entry into the trial. “Essentially, we are saying that many of the criteria that we specified to ensure that patients had heart failure probably did not work very well in patients with an ejection fraction of 65% or greater,” said Dr. Packer, a cardiologist at Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas. “We need to figure out who these patients are.”
Some experts not involved with the study voiced skepticism that the renal findings reflected a real issue.
“I’m quite optimistic that in the long-term the effect on eGFR will translate into renal protection,” said Rudolf A. de Boer, MD, PhD, a professor of translational cardiology at University Medical Center Groningen (the Netherlands), and designated discussant at the congress for the presentation by Dr. Packer.
John J.V. McMurray, MD, a professor of cardiology and a heart failure specialist at Glasgow University, speculated that the unexpected renal outcomes data may relate to the initial decline in renal function produced by treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors despite their longer-term enhancement of renal protection.
“If you use a treatment that protects the kidneys in the long-term but causes an initial dip in eGFR, more patients receiving that treatment will have an early ‘event,’ ” he noted in an interview. He also cautioned about the dangers of subgroup analyses that dice the study population into small cohorts.
“Trials are powered to look at the effect of treatment in the overall population. Everything else is exploratory, underpowered, and subject to the play of chance,” Dr. McMurray stressed.
Counting additional cardiovascular disease events allows more analyses
A third auxiliary report from the EMPEROR-Preserved investigators performed several prespecified analyses that depended on adding additional cardiovascular disease endpoints to the core tallies of cardiovascular death or HHF – such as emergent, urgent, and outpatient events that reflected worsening heart failure – and also included information on diuretic and vasopressor use because of worsening heart failure. The increased event numbers allowed the researchers to perform 30 additional analyses included in this report, according to the count kept by Dr. Packer who was the lead author.
He highlighted several of the additional results in this paper that documented benefits from empagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo:
- A significant 29% reduction in the need for admission to a cardiac care unit or intensive care unit during an HHF.
- A nonsignificant 33% reduction in the need for intravenous vasopressors or positive inotropic drugs during HHF.
- A significantly increased rate of patients achieving a higher New York Heart Association functional class. For example, after the first year of treatment patients who received empagliflozin had a 37% higher rate of functional class improvement, compared with patients who received placebo.
Dr. McMurray had his own list of key takeaways from this paper, including:
- Among patients who needed hospitalization, “those treated with empagliflozin were less sick than those in the placebo group.”
- In addition to reducing HHF empagliflozin treatment also reduced episodes of outpatient worsening as reflected by their receipt of intensified diuretic treatment, which occurred a significant 27% less often, compared with patients on placebo.
- Treatment with empagliflozin also linked with a significant 39% relative reduction in emergency or urgent-care visits that required intravenous therapy.
Empagliflozin’s performance relative to sacubitril/valsartan
The fourth additional report focused on a post hoc, cross-trial comparison of the results from EMPEROR-Preserved and from another recent trial that, like EMPEROR-Preserved, assessed in patients with HFpEF a drug previously proven to work quite well in patients with HFrEF. The comparator drug was sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto), which underwent testing in patients with HFpEF in the PARAGON-HF trial.
The primary outcome of PARAGON-HF, which randomized 4,822 patients, was reduction in cardiovascular death and in total HHF. This dropped by a relative 13%, compared with placebo, during a median of 35 months, a between-group difference that came close to but did not achieve significance (P = .06). Despite this limitation, the Food and Drug Administration in February 2021 loosened the indication for using sacubitril/valsartan in patients with heart failure and a “below normal” ejection fraction, a category that can include many patients considered to have HFpEF.
Although the researchers who ran this analysis, including Dr. Packer, who was the first author, admitted that “comparison of effect sizes across trials is fraught with difficulties,” they nonetheless concluded from their analysis that “for all outcomes that included HHF the effect size was larger for empagliflozin than for sacubitril/valsartan.”
Dr. McMurray, a lead instigator for PARAGON-HF, said there was little to take away from this analysis.
“The patient populations were different, and sacubitril/valsartan was compared against an active therapy, valsartan,” while in EMPEROR-Preserved empagliflozin compared against placebo. “Most of us believe that sacubitril/valsartan and SGLT2 inhibitors work in different but complementary ways, and their benefits are additive. You would want patients with HFpEF or HFrEF to take both,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Packer agreed with that approach and added that he would probably also prescribe a third agent, spironolactone, to many patients with HFpEF.
EMPEROR-Preserved was sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly, which jointly market empagliflozin (Jardiance). PARAGON-HF was sponsored by Novartis, which markets sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto). Dr. Packer has received consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and from numerous other companies. Dr. de Boer has research contracts with Boehringer Ingelheim as well as from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Cardior, Ionis, Novo Nordisk, and Roche, and he has been a consultant to Novartis as well as to Abbott, AstraZeneca, Gayer, and Roche. Dr. McMurray led trials of sacubitril/valsartan sponsored by Novartis, and his institution has received compensation for his participation in studies sponsored by Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Cardurion, DalCor, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, and Theracos.
The featured report from the 6,000-patient EMPEROR-Preserved trial at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology drew lots of attention for its headline finding: the first unequivocal demonstration that a medication, empagliflozin, can significantly reduce the rate of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF, a left ventricular ejection fraction of more than 40%), with the details simultaneously published online.
But at the same time, the EMPEROR-Preserved investigators released four additional reports with a lot more outcome analyses that also deserve some attention.
The puzzling neutral effect on renal events
Perhaps the most surprising and complicated set of findings among the main EMPEROR-Preserved outcomes involved renal outcomes.
The trial’s primary outcome was the combined rate of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure (HHF), and the results showed that treatment with empagliflozin (Jardiance) for a median of 26 months on top of standard treatment for patients with HFpEF led to a significant 21% relative risk reduction, compared with placebo-treated patients.
The trial had two prespecified secondary outcomes. One was the total number of HHF, which dropped by a significant 27%, compared with placebo. The second was the mean change in slope of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) on an annualized basis, and the empagliflozin regimen reduced the cumulative annual deficit, compared with placebo by an average of 1.36 mL/min per 1.73 m2, a significant difference.
This preservation of renal function was consistent with results from many prior studies of empagliflozin and all of the other U.S.-approved agents from the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor class. Preservation of renal function and a reduction in renal events has become a hallmark property of all agents in the SGLT2 inhibitor class both in patients with type 2 diabetes, as well as in those without diabetes but with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) or with chronic kidney disease.
EMPEROR-Preserved threw a wrench into what had been an unbroken history of renal protection by SGLT2 inhibitors. That happened when a prespecified endpoint of the study – a composite renal outcome defined as time to first occurrence of chronic dialysis, renal transplantation, a sustained reduction of at least 40% in eGFR, or a sustained drop in eGFR of more than 10 or 15 mL/min per 1.73 m2 from baseline – yielded an unexpected neutral finding.
For this composite renal outcome, EMPEROR-Preserved showed a nonsignificant 5% reduction, compared with placebo, a result that both differed from what had been seen in essentially all the other SGLT2 inhibitor trials that had looked at this, but which also seemed at odds with the observed significant preservation of renal function that seemed substantial enough to produce a clinically meaningful benefit.
Renal effects blunted in HFpEF
The immediate upshot was a letter published by several EMPEROR-Preserved investigators that spelled out this discrepancy and came to the jolting conclusion that “eGFR slope analysis has limitations as a surrogate for predicting the effect of drugs on renal outcomes in patients with heart failure.”
The same authors, along with some additional associates, also published a second letter that noted a further unexpected twist with the renal outcome: “In prior large-scale clinical trials, the effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on heart failure and renal outcomes had consistently tracked together,” they noted, but in this case it didn’t, a discordance they said was “extraordinarily puzzling”.
This led the study’s leaders to reanalyze the renal outcomes using a different definition, one that Milton Packer, MD, who helped design the trial and oversaw several of its analyses, called “a more conventional definition of renal events,” during his presentation of these findings at the congress. The researchers swapped out a 40% drop from baseline eGFR as an event and replaced it with a 50% decline, a change designed to screen out less severe, and often transient, reductions in kidney function that have less lasting impact on health. They also added an additional component to the composite endpoint, renal death. A revised analysis using this new renal composite outcome appeared in the European Journal of Heart Failure letter.
This change cut the total number of renal events tallied in the trial nearly in half, down to 112, and showed a more robust decline in renal events with empagliflozin treatment compared with the initial analysis, although the drop remained nonsignificant. The revised analysis also showed that the overall, nonsignificant 22% relative reduction in renal events in patients on empagliflozin, compared with placebo, dwindled down to completely nonexistent in the tertile of patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction of 60% or greater. In this tertile the hazard ratio actually showed a nonsignificant point estimate of a 24% increased rate of renal events on empagliflozin, with the caveat that this subgroup now included a total of just 40 total events between the two treatment arms. (Each of the two other tertiles also had roughly the same number of total events.)
The biggest effect on renal-event reduction was in the tertile of patients with an ejection fraction of 41%-49%, in which empagliflozin treatment was linked with a significant 59% cut in renal events, compared with placebo. The analysis also showed significant heterogeneity in thus outcome between this subgroup and the other two tertiles that had higher ejection fractions and showed reduced rates of protection by empagliflozin against renal events.
This apparent blunting of a renal effect despite preservation of renal function seemed to mimic the blunting of the primary cardiovascular outcome effect that also appeared in patients with ejection fractions in the 60%-65% range or above.
“If we knew what blunted the effect of empagliflozin on heart failure outcomes at higher ejection fraction levels, we think the same explanation may also apply to the blunting of effect on renal outcomes, but right now we do not know the answer to either question,” Dr. Packer said in an interview. He’s suggested that one possibility is that many of the enrolled patients identified as having HFpEF, but with these high ejection fractions may have not actually had HFpEF, and their signs and symptoms may have instead resulted from atrial fibrillation.
“Many patients with an ejection fraction of 60%-65% and above had atrial fibrillation,” he noted, with a prevalence at enrollment in this subgroup of about 50%. Atrial fibrillation can cause dyspnea, a hallmark symptom leading to diagnosis of heart failure, and it also increases levels of N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide, a metric that served as a gatekeeper for entry into the trial. “Essentially, we are saying that many of the criteria that we specified to ensure that patients had heart failure probably did not work very well in patients with an ejection fraction of 65% or greater,” said Dr. Packer, a cardiologist at Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas. “We need to figure out who these patients are.”
Some experts not involved with the study voiced skepticism that the renal findings reflected a real issue.
“I’m quite optimistic that in the long-term the effect on eGFR will translate into renal protection,” said Rudolf A. de Boer, MD, PhD, a professor of translational cardiology at University Medical Center Groningen (the Netherlands), and designated discussant at the congress for the presentation by Dr. Packer.
John J.V. McMurray, MD, a professor of cardiology and a heart failure specialist at Glasgow University, speculated that the unexpected renal outcomes data may relate to the initial decline in renal function produced by treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors despite their longer-term enhancement of renal protection.
“If you use a treatment that protects the kidneys in the long-term but causes an initial dip in eGFR, more patients receiving that treatment will have an early ‘event,’ ” he noted in an interview. He also cautioned about the dangers of subgroup analyses that dice the study population into small cohorts.
“Trials are powered to look at the effect of treatment in the overall population. Everything else is exploratory, underpowered, and subject to the play of chance,” Dr. McMurray stressed.
Counting additional cardiovascular disease events allows more analyses
A third auxiliary report from the EMPEROR-Preserved investigators performed several prespecified analyses that depended on adding additional cardiovascular disease endpoints to the core tallies of cardiovascular death or HHF – such as emergent, urgent, and outpatient events that reflected worsening heart failure – and also included information on diuretic and vasopressor use because of worsening heart failure. The increased event numbers allowed the researchers to perform 30 additional analyses included in this report, according to the count kept by Dr. Packer who was the lead author.
He highlighted several of the additional results in this paper that documented benefits from empagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo:
- A significant 29% reduction in the need for admission to a cardiac care unit or intensive care unit during an HHF.
- A nonsignificant 33% reduction in the need for intravenous vasopressors or positive inotropic drugs during HHF.
- A significantly increased rate of patients achieving a higher New York Heart Association functional class. For example, after the first year of treatment patients who received empagliflozin had a 37% higher rate of functional class improvement, compared with patients who received placebo.
Dr. McMurray had his own list of key takeaways from this paper, including:
- Among patients who needed hospitalization, “those treated with empagliflozin were less sick than those in the placebo group.”
- In addition to reducing HHF empagliflozin treatment also reduced episodes of outpatient worsening as reflected by their receipt of intensified diuretic treatment, which occurred a significant 27% less often, compared with patients on placebo.
- Treatment with empagliflozin also linked with a significant 39% relative reduction in emergency or urgent-care visits that required intravenous therapy.
Empagliflozin’s performance relative to sacubitril/valsartan
The fourth additional report focused on a post hoc, cross-trial comparison of the results from EMPEROR-Preserved and from another recent trial that, like EMPEROR-Preserved, assessed in patients with HFpEF a drug previously proven to work quite well in patients with HFrEF. The comparator drug was sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto), which underwent testing in patients with HFpEF in the PARAGON-HF trial.
The primary outcome of PARAGON-HF, which randomized 4,822 patients, was reduction in cardiovascular death and in total HHF. This dropped by a relative 13%, compared with placebo, during a median of 35 months, a between-group difference that came close to but did not achieve significance (P = .06). Despite this limitation, the Food and Drug Administration in February 2021 loosened the indication for using sacubitril/valsartan in patients with heart failure and a “below normal” ejection fraction, a category that can include many patients considered to have HFpEF.
Although the researchers who ran this analysis, including Dr. Packer, who was the first author, admitted that “comparison of effect sizes across trials is fraught with difficulties,” they nonetheless concluded from their analysis that “for all outcomes that included HHF the effect size was larger for empagliflozin than for sacubitril/valsartan.”
Dr. McMurray, a lead instigator for PARAGON-HF, said there was little to take away from this analysis.
“The patient populations were different, and sacubitril/valsartan was compared against an active therapy, valsartan,” while in EMPEROR-Preserved empagliflozin compared against placebo. “Most of us believe that sacubitril/valsartan and SGLT2 inhibitors work in different but complementary ways, and their benefits are additive. You would want patients with HFpEF or HFrEF to take both,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Packer agreed with that approach and added that he would probably also prescribe a third agent, spironolactone, to many patients with HFpEF.
EMPEROR-Preserved was sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly, which jointly market empagliflozin (Jardiance). PARAGON-HF was sponsored by Novartis, which markets sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto). Dr. Packer has received consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and from numerous other companies. Dr. de Boer has research contracts with Boehringer Ingelheim as well as from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Cardior, Ionis, Novo Nordisk, and Roche, and he has been a consultant to Novartis as well as to Abbott, AstraZeneca, Gayer, and Roche. Dr. McMurray led trials of sacubitril/valsartan sponsored by Novartis, and his institution has received compensation for his participation in studies sponsored by Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Cardurion, DalCor, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, and Theracos.
The featured report from the 6,000-patient EMPEROR-Preserved trial at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology drew lots of attention for its headline finding: the first unequivocal demonstration that a medication, empagliflozin, can significantly reduce the rate of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF, a left ventricular ejection fraction of more than 40%), with the details simultaneously published online.
But at the same time, the EMPEROR-Preserved investigators released four additional reports with a lot more outcome analyses that also deserve some attention.
The puzzling neutral effect on renal events
Perhaps the most surprising and complicated set of findings among the main EMPEROR-Preserved outcomes involved renal outcomes.
The trial’s primary outcome was the combined rate of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure (HHF), and the results showed that treatment with empagliflozin (Jardiance) for a median of 26 months on top of standard treatment for patients with HFpEF led to a significant 21% relative risk reduction, compared with placebo-treated patients.
The trial had two prespecified secondary outcomes. One was the total number of HHF, which dropped by a significant 27%, compared with placebo. The second was the mean change in slope of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) on an annualized basis, and the empagliflozin regimen reduced the cumulative annual deficit, compared with placebo by an average of 1.36 mL/min per 1.73 m2, a significant difference.
This preservation of renal function was consistent with results from many prior studies of empagliflozin and all of the other U.S.-approved agents from the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor class. Preservation of renal function and a reduction in renal events has become a hallmark property of all agents in the SGLT2 inhibitor class both in patients with type 2 diabetes, as well as in those without diabetes but with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) or with chronic kidney disease.
EMPEROR-Preserved threw a wrench into what had been an unbroken history of renal protection by SGLT2 inhibitors. That happened when a prespecified endpoint of the study – a composite renal outcome defined as time to first occurrence of chronic dialysis, renal transplantation, a sustained reduction of at least 40% in eGFR, or a sustained drop in eGFR of more than 10 or 15 mL/min per 1.73 m2 from baseline – yielded an unexpected neutral finding.
For this composite renal outcome, EMPEROR-Preserved showed a nonsignificant 5% reduction, compared with placebo, a result that both differed from what had been seen in essentially all the other SGLT2 inhibitor trials that had looked at this, but which also seemed at odds with the observed significant preservation of renal function that seemed substantial enough to produce a clinically meaningful benefit.
Renal effects blunted in HFpEF
The immediate upshot was a letter published by several EMPEROR-Preserved investigators that spelled out this discrepancy and came to the jolting conclusion that “eGFR slope analysis has limitations as a surrogate for predicting the effect of drugs on renal outcomes in patients with heart failure.”
The same authors, along with some additional associates, also published a second letter that noted a further unexpected twist with the renal outcome: “In prior large-scale clinical trials, the effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on heart failure and renal outcomes had consistently tracked together,” they noted, but in this case it didn’t, a discordance they said was “extraordinarily puzzling”.
This led the study’s leaders to reanalyze the renal outcomes using a different definition, one that Milton Packer, MD, who helped design the trial and oversaw several of its analyses, called “a more conventional definition of renal events,” during his presentation of these findings at the congress. The researchers swapped out a 40% drop from baseline eGFR as an event and replaced it with a 50% decline, a change designed to screen out less severe, and often transient, reductions in kidney function that have less lasting impact on health. They also added an additional component to the composite endpoint, renal death. A revised analysis using this new renal composite outcome appeared in the European Journal of Heart Failure letter.
This change cut the total number of renal events tallied in the trial nearly in half, down to 112, and showed a more robust decline in renal events with empagliflozin treatment compared with the initial analysis, although the drop remained nonsignificant. The revised analysis also showed that the overall, nonsignificant 22% relative reduction in renal events in patients on empagliflozin, compared with placebo, dwindled down to completely nonexistent in the tertile of patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction of 60% or greater. In this tertile the hazard ratio actually showed a nonsignificant point estimate of a 24% increased rate of renal events on empagliflozin, with the caveat that this subgroup now included a total of just 40 total events between the two treatment arms. (Each of the two other tertiles also had roughly the same number of total events.)
The biggest effect on renal-event reduction was in the tertile of patients with an ejection fraction of 41%-49%, in which empagliflozin treatment was linked with a significant 59% cut in renal events, compared with placebo. The analysis also showed significant heterogeneity in thus outcome between this subgroup and the other two tertiles that had higher ejection fractions and showed reduced rates of protection by empagliflozin against renal events.
This apparent blunting of a renal effect despite preservation of renal function seemed to mimic the blunting of the primary cardiovascular outcome effect that also appeared in patients with ejection fractions in the 60%-65% range or above.
“If we knew what blunted the effect of empagliflozin on heart failure outcomes at higher ejection fraction levels, we think the same explanation may also apply to the blunting of effect on renal outcomes, but right now we do not know the answer to either question,” Dr. Packer said in an interview. He’s suggested that one possibility is that many of the enrolled patients identified as having HFpEF, but with these high ejection fractions may have not actually had HFpEF, and their signs and symptoms may have instead resulted from atrial fibrillation.
“Many patients with an ejection fraction of 60%-65% and above had atrial fibrillation,” he noted, with a prevalence at enrollment in this subgroup of about 50%. Atrial fibrillation can cause dyspnea, a hallmark symptom leading to diagnosis of heart failure, and it also increases levels of N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide, a metric that served as a gatekeeper for entry into the trial. “Essentially, we are saying that many of the criteria that we specified to ensure that patients had heart failure probably did not work very well in patients with an ejection fraction of 65% or greater,” said Dr. Packer, a cardiologist at Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas. “We need to figure out who these patients are.”
Some experts not involved with the study voiced skepticism that the renal findings reflected a real issue.
“I’m quite optimistic that in the long-term the effect on eGFR will translate into renal protection,” said Rudolf A. de Boer, MD, PhD, a professor of translational cardiology at University Medical Center Groningen (the Netherlands), and designated discussant at the congress for the presentation by Dr. Packer.
John J.V. McMurray, MD, a professor of cardiology and a heart failure specialist at Glasgow University, speculated that the unexpected renal outcomes data may relate to the initial decline in renal function produced by treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors despite their longer-term enhancement of renal protection.
“If you use a treatment that protects the kidneys in the long-term but causes an initial dip in eGFR, more patients receiving that treatment will have an early ‘event,’ ” he noted in an interview. He also cautioned about the dangers of subgroup analyses that dice the study population into small cohorts.
“Trials are powered to look at the effect of treatment in the overall population. Everything else is exploratory, underpowered, and subject to the play of chance,” Dr. McMurray stressed.
Counting additional cardiovascular disease events allows more analyses
A third auxiliary report from the EMPEROR-Preserved investigators performed several prespecified analyses that depended on adding additional cardiovascular disease endpoints to the core tallies of cardiovascular death or HHF – such as emergent, urgent, and outpatient events that reflected worsening heart failure – and also included information on diuretic and vasopressor use because of worsening heart failure. The increased event numbers allowed the researchers to perform 30 additional analyses included in this report, according to the count kept by Dr. Packer who was the lead author.
He highlighted several of the additional results in this paper that documented benefits from empagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo:
- A significant 29% reduction in the need for admission to a cardiac care unit or intensive care unit during an HHF.
- A nonsignificant 33% reduction in the need for intravenous vasopressors or positive inotropic drugs during HHF.
- A significantly increased rate of patients achieving a higher New York Heart Association functional class. For example, after the first year of treatment patients who received empagliflozin had a 37% higher rate of functional class improvement, compared with patients who received placebo.
Dr. McMurray had his own list of key takeaways from this paper, including:
- Among patients who needed hospitalization, “those treated with empagliflozin were less sick than those in the placebo group.”
- In addition to reducing HHF empagliflozin treatment also reduced episodes of outpatient worsening as reflected by their receipt of intensified diuretic treatment, which occurred a significant 27% less often, compared with patients on placebo.
- Treatment with empagliflozin also linked with a significant 39% relative reduction in emergency or urgent-care visits that required intravenous therapy.
Empagliflozin’s performance relative to sacubitril/valsartan
The fourth additional report focused on a post hoc, cross-trial comparison of the results from EMPEROR-Preserved and from another recent trial that, like EMPEROR-Preserved, assessed in patients with HFpEF a drug previously proven to work quite well in patients with HFrEF. The comparator drug was sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto), which underwent testing in patients with HFpEF in the PARAGON-HF trial.
The primary outcome of PARAGON-HF, which randomized 4,822 patients, was reduction in cardiovascular death and in total HHF. This dropped by a relative 13%, compared with placebo, during a median of 35 months, a between-group difference that came close to but did not achieve significance (P = .06). Despite this limitation, the Food and Drug Administration in February 2021 loosened the indication for using sacubitril/valsartan in patients with heart failure and a “below normal” ejection fraction, a category that can include many patients considered to have HFpEF.
Although the researchers who ran this analysis, including Dr. Packer, who was the first author, admitted that “comparison of effect sizes across trials is fraught with difficulties,” they nonetheless concluded from their analysis that “for all outcomes that included HHF the effect size was larger for empagliflozin than for sacubitril/valsartan.”
Dr. McMurray, a lead instigator for PARAGON-HF, said there was little to take away from this analysis.
“The patient populations were different, and sacubitril/valsartan was compared against an active therapy, valsartan,” while in EMPEROR-Preserved empagliflozin compared against placebo. “Most of us believe that sacubitril/valsartan and SGLT2 inhibitors work in different but complementary ways, and their benefits are additive. You would want patients with HFpEF or HFrEF to take both,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Packer agreed with that approach and added that he would probably also prescribe a third agent, spironolactone, to many patients with HFpEF.
EMPEROR-Preserved was sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly, which jointly market empagliflozin (Jardiance). PARAGON-HF was sponsored by Novartis, which markets sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto). Dr. Packer has received consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and from numerous other companies. Dr. de Boer has research contracts with Boehringer Ingelheim as well as from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Cardior, Ionis, Novo Nordisk, and Roche, and he has been a consultant to Novartis as well as to Abbott, AstraZeneca, Gayer, and Roche. Dr. McMurray led trials of sacubitril/valsartan sponsored by Novartis, and his institution has received compensation for his participation in studies sponsored by Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Cardurion, DalCor, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, and Theracos.
FROM ESC 2021
Early end for trial of experimental oxygenation strategies in ARDS
Background: Both observational studies and clinical trials have found that a liberal oxygenation strategy in multiple inpatient settings may be harmful. Furthermore, a conservative strategy is what has been recommended in guidelines. Conversely, the relevance of this recent concept has been challenged in a large trial of a critically ill population (ICU-ROX).
Study design: Randomized clinical trial, unblinded.
Setting: Thirteen sites in France.
Synopsis: In a multicenter randomized clinical trial, investigators enrolled patients with ARDS to either a liberal oxygenation group (PaO2 target 90-105 mm Hg or SpO2 of 96% or greater) or a conservative oxygenation group (PaO2 target 55-70 mm Hg or SpO2 88%-92%). The trial was planned for inclusion of 850 patients, but the data and safety monitoring board decided to stop the trial after inclusion of 205 patients. Although the primary outcome (28-day all-cause mortality) was not significantly different between groups (34.3% vs 26.5%; absolute difference, 7.8%; 95% confidence interval, –4.8 to 20.6), the direction was signaling possible harm and there were five episodes of mesenteric ischemia in the conservative oxygenation group (none in the liberal oxygenation group).
Bottom line: A conservative oxygenation strategy cannot be currently recommended to patients with ARDS in the ICU. A minimum SpO2 of 90% was suggested in an accompanying editorial.
Editorial commentary: Interestingly, the supplemental results of the article show that prone positioning was used much less frequently in the conservative oxygenation group (34.3 vs 51.0%). If the impressive results of Guerin (2013) would be repeated in this population, this difference could help explain the higher observed mortality in the conservative oxygenation group. It is possible that, by aiming to be less aggressive in improving the PaO2, clinicians inadvertently withheld effective treatments for ARDS. The results of this trial bring up several interesting questions, but provide the bedside clinician with few answers. The complex interplay of treatment factors needs to be dissected in future trials.
Citation: Barrot L et al. Liberal or conservative oxygen therapy for acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Eng J Med. 2020;382:999-1008.
Dr. Saraiva is a hospitalist and assistant professor of medicine at UK HealthCare, Lexington, Ky.
Background: Both observational studies and clinical trials have found that a liberal oxygenation strategy in multiple inpatient settings may be harmful. Furthermore, a conservative strategy is what has been recommended in guidelines. Conversely, the relevance of this recent concept has been challenged in a large trial of a critically ill population (ICU-ROX).
Study design: Randomized clinical trial, unblinded.
Setting: Thirteen sites in France.
Synopsis: In a multicenter randomized clinical trial, investigators enrolled patients with ARDS to either a liberal oxygenation group (PaO2 target 90-105 mm Hg or SpO2 of 96% or greater) or a conservative oxygenation group (PaO2 target 55-70 mm Hg or SpO2 88%-92%). The trial was planned for inclusion of 850 patients, but the data and safety monitoring board decided to stop the trial after inclusion of 205 patients. Although the primary outcome (28-day all-cause mortality) was not significantly different between groups (34.3% vs 26.5%; absolute difference, 7.8%; 95% confidence interval, –4.8 to 20.6), the direction was signaling possible harm and there were five episodes of mesenteric ischemia in the conservative oxygenation group (none in the liberal oxygenation group).
Bottom line: A conservative oxygenation strategy cannot be currently recommended to patients with ARDS in the ICU. A minimum SpO2 of 90% was suggested in an accompanying editorial.
Editorial commentary: Interestingly, the supplemental results of the article show that prone positioning was used much less frequently in the conservative oxygenation group (34.3 vs 51.0%). If the impressive results of Guerin (2013) would be repeated in this population, this difference could help explain the higher observed mortality in the conservative oxygenation group. It is possible that, by aiming to be less aggressive in improving the PaO2, clinicians inadvertently withheld effective treatments for ARDS. The results of this trial bring up several interesting questions, but provide the bedside clinician with few answers. The complex interplay of treatment factors needs to be dissected in future trials.
Citation: Barrot L et al. Liberal or conservative oxygen therapy for acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Eng J Med. 2020;382:999-1008.
Dr. Saraiva is a hospitalist and assistant professor of medicine at UK HealthCare, Lexington, Ky.
Background: Both observational studies and clinical trials have found that a liberal oxygenation strategy in multiple inpatient settings may be harmful. Furthermore, a conservative strategy is what has been recommended in guidelines. Conversely, the relevance of this recent concept has been challenged in a large trial of a critically ill population (ICU-ROX).
Study design: Randomized clinical trial, unblinded.
Setting: Thirteen sites in France.
Synopsis: In a multicenter randomized clinical trial, investigators enrolled patients with ARDS to either a liberal oxygenation group (PaO2 target 90-105 mm Hg or SpO2 of 96% or greater) or a conservative oxygenation group (PaO2 target 55-70 mm Hg or SpO2 88%-92%). The trial was planned for inclusion of 850 patients, but the data and safety monitoring board decided to stop the trial after inclusion of 205 patients. Although the primary outcome (28-day all-cause mortality) was not significantly different between groups (34.3% vs 26.5%; absolute difference, 7.8%; 95% confidence interval, –4.8 to 20.6), the direction was signaling possible harm and there were five episodes of mesenteric ischemia in the conservative oxygenation group (none in the liberal oxygenation group).
Bottom line: A conservative oxygenation strategy cannot be currently recommended to patients with ARDS in the ICU. A minimum SpO2 of 90% was suggested in an accompanying editorial.
Editorial commentary: Interestingly, the supplemental results of the article show that prone positioning was used much less frequently in the conservative oxygenation group (34.3 vs 51.0%). If the impressive results of Guerin (2013) would be repeated in this population, this difference could help explain the higher observed mortality in the conservative oxygenation group. It is possible that, by aiming to be less aggressive in improving the PaO2, clinicians inadvertently withheld effective treatments for ARDS. The results of this trial bring up several interesting questions, but provide the bedside clinician with few answers. The complex interplay of treatment factors needs to be dissected in future trials.
Citation: Barrot L et al. Liberal or conservative oxygen therapy for acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Eng J Med. 2020;382:999-1008.
Dr. Saraiva is a hospitalist and assistant professor of medicine at UK HealthCare, Lexington, Ky.
Report urges complete residency overhaul
from the Graduate Medical Education Review Committee (UGRC) of the Coalition for Physician Accountability.
The 275-page report presents preliminary findings that were released in April 2021 and a long list of stakeholder comments. According to the report, the coalition will meet soon to discuss the final recommendations and consider next steps toward implementation.
The UGRC includes representatives of national medical organizations, medical schools, and residency programs. Among the organizations that participated in the report’s creation are the American Medical Association, the National Board of Medical Examiners, the American Osteopathic Association, the National Board of Osteopathic Medical Examiners, the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates, and the Association of American Medical Colleges.
The report identifies a list of challenges that affect the transition of medical students into residency programs and beyond. They include:
- Too much focus on finding and filling residency positions instead of “assuring learner competence and readiness for residency training”
- Inattention to assuring congruence between applicant goals and program missions
- Overreliance on licensure exam scores rather than “valid, trustworthy measures of students’ competence and clinical abilities”
- Increasing financial costs to students
- Individual and systemic biases in the UME-GME transition, as well as inequities related to international medical graduates
Seeking a common framework for competence
Overall, the report calls for increased standardization of how students are evaluated in medical school and how residency programs evaluate students. Less reliance should be placed on the numerical scores of the U.S. Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE), the report says, and more attention should be paid to the direct observation of student performance in clinical situations. In addition, the various organizations involved in the UME-GME transition process are asked to work better together.
To develop better methods of evaluating medical students and residents, UME and GME educators should jointly define and implement a common framework and set of competencies to apply to learners across the UME-GME transition, the report suggests.
While emphasizing the need for a broader student assessment framework, the report says, USMLE scores should also continue to be used in judging residency applicants. “Assessment information should be shared in residency applications and a postmatch learner handover. Licensing examinations should be used for their intended purpose to ensure requisite competence.”
Among the committee’s three dozen recommendations are the following:
- The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services should change the GME funding structure so that the initial residency period is calculated starting with the second year of postgraduate training. This change would allow residents to reconsider their career choices. Currently, if a resident decides to switch to another program or specialty after beginning training, the hospital may not receive full GME funding, so may be less likely to approve the change.
- Residency programs should improve recruitment practices to increase specialty-specific diversity of residents. Medical educators should also receive additional training regarding antiracism, avoiding bias, and ensuring equity.
- The self-reported demographic information of applicants to residency programs should be measured and shared with stakeholders, including the programs and medical schools, to promote equity. “A residency program that finds bias in its selection process could go back in real time to find qualified applicants who may have been missed, potentially improving outcomes,” the report notes.
- An interactive database of GME program and specialty track information should be created and made available to all applicants, medical schools, and residency programs at no cost to applicants. “Applicants and their advisors should be able to sort the information according to demographic and educational features that may significantly impact the likelihood of matching at a program.”
Less than half of applicants get in-depth reviews
The 2020 National Resident Matching Program Program Director Survey found that only 49% of applications received in-depth review. In light of this, the report suggests that the application system be updated to use modern information technology, including discrete fields for key data to expedite application reviews.
Many applications have been discarded because of various filters used to block consideration of certain applications. The report suggests that new filters be designed to ensure that each detects meaningful differences among applicants and promotes review based on mission alignment and likelihood of success in a program. Filters should be improved to decrease the likelihood of random exclusions of qualified applicants.
Specialty-specific, just-in-time training for all incoming first-year residents is also suggested to support the transition from the role of student to a physician ready to assume increased responsibility for patient care. In addition, the report urges adequate time be allowed between medical school graduation and residency to enable new residents to relocate and find homes.
The report also calls for a standardized process in the United States for initial licensing of doctors at entrance to residency in order to streamline the process of credentialing for both residency training and continuing practice.
Osteopathic students’ dilemma
To promote equitable treatment of applicants regardless of licensure examination requirements, comparable exams with different scales (COMLEX-USA and USMLE) should be reported within the electronic application system in a single field, the report said.
Osteopathic students, who make up 25% of U.S. medical students, must take the COMLEX-USA exam, but residency programs may filter them out if they don’t also take the USMLE exam. Thus, many osteopathic students take both exams, incurring extra time, cost, and stress.
The UGRC recommends creating a combined field in the electronic residency application service that normalizes the scores between the two exams. Residency programs could then filter applications based only on the single normalized score.
This approach makes sense from the viewpoint that it would reduce the pressure on osteopathic students to take the USMLE, Bryan Carmody, MD, an outspoken critic of various current training policies, said in an interview. But it could also have serious disadvantages.
For one thing, only osteopathic students can take the COMLEX-USA exam, he noted. If they don’t like their score, they can then take the USMLE test to get a higher score – an option that allopathic students don’t have. It’s not clear that they’d be prevented from doing this under the UGRC recommendation.
Second, he said, osteopathic students, on average, don’t do as well as allopathic students on the UMSLE exam. If they only take the COMLEX-USA test, they’re competing against other students who don’t do as well on tests as allopathic students do. If their scores were normalized with those of the USMLE test takers, they’d gain an unfair advantage against students who can only take the USMLE, including international medical graduates.
Although Dr. Carmody admitted that osteopathic students face a harder challenge than allopathic students in matching to residency programs, he said that the UGRC approach to the licensing exams might actually penalize them further. As a result of the scores of the two exams being averaged, residency program directors might discount the scores of all osteopathic students.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
from the Graduate Medical Education Review Committee (UGRC) of the Coalition for Physician Accountability.
The 275-page report presents preliminary findings that were released in April 2021 and a long list of stakeholder comments. According to the report, the coalition will meet soon to discuss the final recommendations and consider next steps toward implementation.
The UGRC includes representatives of national medical organizations, medical schools, and residency programs. Among the organizations that participated in the report’s creation are the American Medical Association, the National Board of Medical Examiners, the American Osteopathic Association, the National Board of Osteopathic Medical Examiners, the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates, and the Association of American Medical Colleges.
The report identifies a list of challenges that affect the transition of medical students into residency programs and beyond. They include:
- Too much focus on finding and filling residency positions instead of “assuring learner competence and readiness for residency training”
- Inattention to assuring congruence between applicant goals and program missions
- Overreliance on licensure exam scores rather than “valid, trustworthy measures of students’ competence and clinical abilities”
- Increasing financial costs to students
- Individual and systemic biases in the UME-GME transition, as well as inequities related to international medical graduates
Seeking a common framework for competence
Overall, the report calls for increased standardization of how students are evaluated in medical school and how residency programs evaluate students. Less reliance should be placed on the numerical scores of the U.S. Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE), the report says, and more attention should be paid to the direct observation of student performance in clinical situations. In addition, the various organizations involved in the UME-GME transition process are asked to work better together.
To develop better methods of evaluating medical students and residents, UME and GME educators should jointly define and implement a common framework and set of competencies to apply to learners across the UME-GME transition, the report suggests.
While emphasizing the need for a broader student assessment framework, the report says, USMLE scores should also continue to be used in judging residency applicants. “Assessment information should be shared in residency applications and a postmatch learner handover. Licensing examinations should be used for their intended purpose to ensure requisite competence.”
Among the committee’s three dozen recommendations are the following:
- The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services should change the GME funding structure so that the initial residency period is calculated starting with the second year of postgraduate training. This change would allow residents to reconsider their career choices. Currently, if a resident decides to switch to another program or specialty after beginning training, the hospital may not receive full GME funding, so may be less likely to approve the change.
- Residency programs should improve recruitment practices to increase specialty-specific diversity of residents. Medical educators should also receive additional training regarding antiracism, avoiding bias, and ensuring equity.
- The self-reported demographic information of applicants to residency programs should be measured and shared with stakeholders, including the programs and medical schools, to promote equity. “A residency program that finds bias in its selection process could go back in real time to find qualified applicants who may have been missed, potentially improving outcomes,” the report notes.
- An interactive database of GME program and specialty track information should be created and made available to all applicants, medical schools, and residency programs at no cost to applicants. “Applicants and their advisors should be able to sort the information according to demographic and educational features that may significantly impact the likelihood of matching at a program.”
Less than half of applicants get in-depth reviews
The 2020 National Resident Matching Program Program Director Survey found that only 49% of applications received in-depth review. In light of this, the report suggests that the application system be updated to use modern information technology, including discrete fields for key data to expedite application reviews.
Many applications have been discarded because of various filters used to block consideration of certain applications. The report suggests that new filters be designed to ensure that each detects meaningful differences among applicants and promotes review based on mission alignment and likelihood of success in a program. Filters should be improved to decrease the likelihood of random exclusions of qualified applicants.
Specialty-specific, just-in-time training for all incoming first-year residents is also suggested to support the transition from the role of student to a physician ready to assume increased responsibility for patient care. In addition, the report urges adequate time be allowed between medical school graduation and residency to enable new residents to relocate and find homes.
The report also calls for a standardized process in the United States for initial licensing of doctors at entrance to residency in order to streamline the process of credentialing for both residency training and continuing practice.
Osteopathic students’ dilemma
To promote equitable treatment of applicants regardless of licensure examination requirements, comparable exams with different scales (COMLEX-USA and USMLE) should be reported within the electronic application system in a single field, the report said.
Osteopathic students, who make up 25% of U.S. medical students, must take the COMLEX-USA exam, but residency programs may filter them out if they don’t also take the USMLE exam. Thus, many osteopathic students take both exams, incurring extra time, cost, and stress.
The UGRC recommends creating a combined field in the electronic residency application service that normalizes the scores between the two exams. Residency programs could then filter applications based only on the single normalized score.
This approach makes sense from the viewpoint that it would reduce the pressure on osteopathic students to take the USMLE, Bryan Carmody, MD, an outspoken critic of various current training policies, said in an interview. But it could also have serious disadvantages.
For one thing, only osteopathic students can take the COMLEX-USA exam, he noted. If they don’t like their score, they can then take the USMLE test to get a higher score – an option that allopathic students don’t have. It’s not clear that they’d be prevented from doing this under the UGRC recommendation.
Second, he said, osteopathic students, on average, don’t do as well as allopathic students on the UMSLE exam. If they only take the COMLEX-USA test, they’re competing against other students who don’t do as well on tests as allopathic students do. If their scores were normalized with those of the USMLE test takers, they’d gain an unfair advantage against students who can only take the USMLE, including international medical graduates.
Although Dr. Carmody admitted that osteopathic students face a harder challenge than allopathic students in matching to residency programs, he said that the UGRC approach to the licensing exams might actually penalize them further. As a result of the scores of the two exams being averaged, residency program directors might discount the scores of all osteopathic students.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
from the Graduate Medical Education Review Committee (UGRC) of the Coalition for Physician Accountability.
The 275-page report presents preliminary findings that were released in April 2021 and a long list of stakeholder comments. According to the report, the coalition will meet soon to discuss the final recommendations and consider next steps toward implementation.
The UGRC includes representatives of national medical organizations, medical schools, and residency programs. Among the organizations that participated in the report’s creation are the American Medical Association, the National Board of Medical Examiners, the American Osteopathic Association, the National Board of Osteopathic Medical Examiners, the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates, and the Association of American Medical Colleges.
The report identifies a list of challenges that affect the transition of medical students into residency programs and beyond. They include:
- Too much focus on finding and filling residency positions instead of “assuring learner competence and readiness for residency training”
- Inattention to assuring congruence between applicant goals and program missions
- Overreliance on licensure exam scores rather than “valid, trustworthy measures of students’ competence and clinical abilities”
- Increasing financial costs to students
- Individual and systemic biases in the UME-GME transition, as well as inequities related to international medical graduates
Seeking a common framework for competence
Overall, the report calls for increased standardization of how students are evaluated in medical school and how residency programs evaluate students. Less reliance should be placed on the numerical scores of the U.S. Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE), the report says, and more attention should be paid to the direct observation of student performance in clinical situations. In addition, the various organizations involved in the UME-GME transition process are asked to work better together.
To develop better methods of evaluating medical students and residents, UME and GME educators should jointly define and implement a common framework and set of competencies to apply to learners across the UME-GME transition, the report suggests.
While emphasizing the need for a broader student assessment framework, the report says, USMLE scores should also continue to be used in judging residency applicants. “Assessment information should be shared in residency applications and a postmatch learner handover. Licensing examinations should be used for their intended purpose to ensure requisite competence.”
Among the committee’s three dozen recommendations are the following:
- The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services should change the GME funding structure so that the initial residency period is calculated starting with the second year of postgraduate training. This change would allow residents to reconsider their career choices. Currently, if a resident decides to switch to another program or specialty after beginning training, the hospital may not receive full GME funding, so may be less likely to approve the change.
- Residency programs should improve recruitment practices to increase specialty-specific diversity of residents. Medical educators should also receive additional training regarding antiracism, avoiding bias, and ensuring equity.
- The self-reported demographic information of applicants to residency programs should be measured and shared with stakeholders, including the programs and medical schools, to promote equity. “A residency program that finds bias in its selection process could go back in real time to find qualified applicants who may have been missed, potentially improving outcomes,” the report notes.
- An interactive database of GME program and specialty track information should be created and made available to all applicants, medical schools, and residency programs at no cost to applicants. “Applicants and their advisors should be able to sort the information according to demographic and educational features that may significantly impact the likelihood of matching at a program.”
Less than half of applicants get in-depth reviews
The 2020 National Resident Matching Program Program Director Survey found that only 49% of applications received in-depth review. In light of this, the report suggests that the application system be updated to use modern information technology, including discrete fields for key data to expedite application reviews.
Many applications have been discarded because of various filters used to block consideration of certain applications. The report suggests that new filters be designed to ensure that each detects meaningful differences among applicants and promotes review based on mission alignment and likelihood of success in a program. Filters should be improved to decrease the likelihood of random exclusions of qualified applicants.
Specialty-specific, just-in-time training for all incoming first-year residents is also suggested to support the transition from the role of student to a physician ready to assume increased responsibility for patient care. In addition, the report urges adequate time be allowed between medical school graduation and residency to enable new residents to relocate and find homes.
The report also calls for a standardized process in the United States for initial licensing of doctors at entrance to residency in order to streamline the process of credentialing for both residency training and continuing practice.
Osteopathic students’ dilemma
To promote equitable treatment of applicants regardless of licensure examination requirements, comparable exams with different scales (COMLEX-USA and USMLE) should be reported within the electronic application system in a single field, the report said.
Osteopathic students, who make up 25% of U.S. medical students, must take the COMLEX-USA exam, but residency programs may filter them out if they don’t also take the USMLE exam. Thus, many osteopathic students take both exams, incurring extra time, cost, and stress.
The UGRC recommends creating a combined field in the electronic residency application service that normalizes the scores between the two exams. Residency programs could then filter applications based only on the single normalized score.
This approach makes sense from the viewpoint that it would reduce the pressure on osteopathic students to take the USMLE, Bryan Carmody, MD, an outspoken critic of various current training policies, said in an interview. But it could also have serious disadvantages.
For one thing, only osteopathic students can take the COMLEX-USA exam, he noted. If they don’t like their score, they can then take the USMLE test to get a higher score – an option that allopathic students don’t have. It’s not clear that they’d be prevented from doing this under the UGRC recommendation.
Second, he said, osteopathic students, on average, don’t do as well as allopathic students on the UMSLE exam. If they only take the COMLEX-USA test, they’re competing against other students who don’t do as well on tests as allopathic students do. If their scores were normalized with those of the USMLE test takers, they’d gain an unfair advantage against students who can only take the USMLE, including international medical graduates.
Although Dr. Carmody admitted that osteopathic students face a harder challenge than allopathic students in matching to residency programs, he said that the UGRC approach to the licensing exams might actually penalize them further. As a result of the scores of the two exams being averaged, residency program directors might discount the scores of all osteopathic students.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CDC panel unanimously backs Pfizer vax, fortifying FDA approval
An independent expert panel within the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has studied the potential benefits and risks of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine and voted unanimously to recommend the shots for all Americans ages 16 and older.
The vaccine was fully approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) last week.
The inoculation is still available to teens ages 12 to 15 under an emergency use authorization from the FDA.
ACIP now sends its recommendation to the CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, for her sign off.
After reviewing the evidence behind the vaccine, panel member Sarah Long, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia, said she couldn’t recall another instance where panelists had so much data on which to base their recommendation.
“This vaccine is worthy of the trust of the American people,” she said.
Doctors across the country use vaccines in line with the recommendations made by the ACIP. Their approval typically means that private and government insurers will cover the cost of the shots. In the case of the COVID-19 vaccines, the government is already picking up the tab.
Few surprises
The panel’s independent review of the vaccine’s effectiveness from nine studies held few surprises.
They found the Pfizer vaccine prevented a COVID infection with symptoms about 90%–92% of the time, at least for the first 4 months after the second shot. Protection against hospitalization and death was even higher.
The vaccine was about 89% effective at preventing a COVID infection without symptoms, according to a pooled estimate of five studies.
The data included in the review was updated only through March 13 of this year, however, and does not reflect the impact of further waning of immunity or the impact of the Delta variant.
In making their recommendation, the panel got an update on the safety of the vaccines, which have now been used in the United States for about 9 months.
The rate of anaphylaxis has settled at around five cases for every million shots given, according to the ACIP’s review of the evidence.
Cases of myocarditis and pericarditis were more common after getting a Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine than would be expected to happen naturally in the general population, but the risk was still very rare, and elevated primarily for men younger than age 30.
Out of 17 million second doses of Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines in the United States, there have been 327 confirmed cases of myocarditis reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System in people who are younger than age 30. The average hospital stay for a myocarditis cases is 1 to 2 days.
So far, no one in the United States diagnosed with myocarditis after vaccination has died.
What’s more, the risk of myocarditis after vaccination was dwarfed by the risk of myocarditis after a COVID infection. The risk of myocarditis after a COVID infection was 6 to 34 times higher than the risk after receiving an mRNA vaccine.
About 11% of people who get the vaccine experience a serious reaction to the shot, compared with about 3% in the placebo group. Serious reactions were defined as pain; swelling or redness at the injection site that interferes with activity; needing to visit the hospital or ER for pain; tissue necrosis, or having skin slough off; high fever; vomiting that requires hydration; persistent diarrhea; severe headache; or muscle pain/severe joint pain.
“Safe and effective”
After hearing a presentation on the state of the pandemic in the US, some panel members were struck and shaken that 38% of Americans who are eligible are still not fully vaccinated.
Pablo Sanchez, MD, a pediatrician at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, said, “We’re doing an abysmal job vaccinating the American people. The message has to go out that the vaccines are safe and effective.”
A version of this story first appeared on Medscape.com.
An independent expert panel within the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has studied the potential benefits and risks of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine and voted unanimously to recommend the shots for all Americans ages 16 and older.
The vaccine was fully approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) last week.
The inoculation is still available to teens ages 12 to 15 under an emergency use authorization from the FDA.
ACIP now sends its recommendation to the CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, for her sign off.
After reviewing the evidence behind the vaccine, panel member Sarah Long, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia, said she couldn’t recall another instance where panelists had so much data on which to base their recommendation.
“This vaccine is worthy of the trust of the American people,” she said.
Doctors across the country use vaccines in line with the recommendations made by the ACIP. Their approval typically means that private and government insurers will cover the cost of the shots. In the case of the COVID-19 vaccines, the government is already picking up the tab.
Few surprises
The panel’s independent review of the vaccine’s effectiveness from nine studies held few surprises.
They found the Pfizer vaccine prevented a COVID infection with symptoms about 90%–92% of the time, at least for the first 4 months after the second shot. Protection against hospitalization and death was even higher.
The vaccine was about 89% effective at preventing a COVID infection without symptoms, according to a pooled estimate of five studies.
The data included in the review was updated only through March 13 of this year, however, and does not reflect the impact of further waning of immunity or the impact of the Delta variant.
In making their recommendation, the panel got an update on the safety of the vaccines, which have now been used in the United States for about 9 months.
The rate of anaphylaxis has settled at around five cases for every million shots given, according to the ACIP’s review of the evidence.
Cases of myocarditis and pericarditis were more common after getting a Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine than would be expected to happen naturally in the general population, but the risk was still very rare, and elevated primarily for men younger than age 30.
Out of 17 million second doses of Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines in the United States, there have been 327 confirmed cases of myocarditis reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System in people who are younger than age 30. The average hospital stay for a myocarditis cases is 1 to 2 days.
So far, no one in the United States diagnosed with myocarditis after vaccination has died.
What’s more, the risk of myocarditis after vaccination was dwarfed by the risk of myocarditis after a COVID infection. The risk of myocarditis after a COVID infection was 6 to 34 times higher than the risk after receiving an mRNA vaccine.
About 11% of people who get the vaccine experience a serious reaction to the shot, compared with about 3% in the placebo group. Serious reactions were defined as pain; swelling or redness at the injection site that interferes with activity; needing to visit the hospital or ER for pain; tissue necrosis, or having skin slough off; high fever; vomiting that requires hydration; persistent diarrhea; severe headache; or muscle pain/severe joint pain.
“Safe and effective”
After hearing a presentation on the state of the pandemic in the US, some panel members were struck and shaken that 38% of Americans who are eligible are still not fully vaccinated.
Pablo Sanchez, MD, a pediatrician at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, said, “We’re doing an abysmal job vaccinating the American people. The message has to go out that the vaccines are safe and effective.”
A version of this story first appeared on Medscape.com.
An independent expert panel within the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has studied the potential benefits and risks of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine and voted unanimously to recommend the shots for all Americans ages 16 and older.
The vaccine was fully approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) last week.
The inoculation is still available to teens ages 12 to 15 under an emergency use authorization from the FDA.
ACIP now sends its recommendation to the CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, for her sign off.
After reviewing the evidence behind the vaccine, panel member Sarah Long, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia, said she couldn’t recall another instance where panelists had so much data on which to base their recommendation.
“This vaccine is worthy of the trust of the American people,” she said.
Doctors across the country use vaccines in line with the recommendations made by the ACIP. Their approval typically means that private and government insurers will cover the cost of the shots. In the case of the COVID-19 vaccines, the government is already picking up the tab.
Few surprises
The panel’s independent review of the vaccine’s effectiveness from nine studies held few surprises.
They found the Pfizer vaccine prevented a COVID infection with symptoms about 90%–92% of the time, at least for the first 4 months after the second shot. Protection against hospitalization and death was even higher.
The vaccine was about 89% effective at preventing a COVID infection without symptoms, according to a pooled estimate of five studies.
The data included in the review was updated only through March 13 of this year, however, and does not reflect the impact of further waning of immunity or the impact of the Delta variant.
In making their recommendation, the panel got an update on the safety of the vaccines, which have now been used in the United States for about 9 months.
The rate of anaphylaxis has settled at around five cases for every million shots given, according to the ACIP’s review of the evidence.
Cases of myocarditis and pericarditis were more common after getting a Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine than would be expected to happen naturally in the general population, but the risk was still very rare, and elevated primarily for men younger than age 30.
Out of 17 million second doses of Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines in the United States, there have been 327 confirmed cases of myocarditis reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System in people who are younger than age 30. The average hospital stay for a myocarditis cases is 1 to 2 days.
So far, no one in the United States diagnosed with myocarditis after vaccination has died.
What’s more, the risk of myocarditis after vaccination was dwarfed by the risk of myocarditis after a COVID infection. The risk of myocarditis after a COVID infection was 6 to 34 times higher than the risk after receiving an mRNA vaccine.
About 11% of people who get the vaccine experience a serious reaction to the shot, compared with about 3% in the placebo group. Serious reactions were defined as pain; swelling or redness at the injection site that interferes with activity; needing to visit the hospital or ER for pain; tissue necrosis, or having skin slough off; high fever; vomiting that requires hydration; persistent diarrhea; severe headache; or muscle pain/severe joint pain.
“Safe and effective”
After hearing a presentation on the state of the pandemic in the US, some panel members were struck and shaken that 38% of Americans who are eligible are still not fully vaccinated.
Pablo Sanchez, MD, a pediatrician at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, said, “We’re doing an abysmal job vaccinating the American people. The message has to go out that the vaccines are safe and effective.”
A version of this story first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children’s upper airways primed to combat SARS-CoV-2 infection
Epithelial and immune cells of the upper airways of children are preactivated and primed to detect SARS-CoV-2 infection, which may contribute to stronger early immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection than adults, new research suggests.
The findings may help to explain why children have a lower risk of developing severe COVID-19 illness or becoming infected with SARS-CoV-2 in the first place, the researchers say.
The study was published online Aug. 18 in Nature Biotechnology.
Primed for action
Children appear to be better able than adults to control SARS-CoV-2 infection, but, until now, the exact molecular mechanisms have been unclear.
A team of investigators from Germany did an in-depth analysis of nasal swab samples obtained from 24 children and 21 adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, as well as a control group of 18 children and 23 adults who tested negative for SARS-CoV-2.
“We wanted to understand why viral defense appears to work so much better in children than in adults,” Irina Lehmann, PhD, head of the molecular epidemiology unit at the Berlin Institute of Health Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, explained in a news release.
Single-cell sequencing showed that children had higher baseline levels of certain RNA-sensing receptors that are relevant to SARS-CoV-2 detection, such as MDA5 and RIG-I, in the epithelial and immune cells of their noses.
This differential expression led to stronger early immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection in children than in adults.
Children were also more likely than adults to have distinct immune cell subpopulations, including KLRC1+ cytotoxic T cells, involved in fighting infection, and memory CD8+ T cells, associated with the development of long-lasting immunity.
‘Clear evidence’
The study provides “clear evidence” that upper-airway immune cells of children are “primed for virus sensing, resulting in a stronger early innate antiviral response to SARS-CoV-2 infection than in adults,” the investigators say.
Primed virus sensing and a preactivated innate immune response in children leads to efficient early production of interferons (IFNs) in the infected airways, likely mediating substantial antiviral effects, they note.
Ultimately, this may lead to lower viral replication and faster clearance in children. In fact, several studies have already shown that children eliminate the virus more quickly than adults, consistent with the concept that they shut down viral replication earlier, the study team says.
Weighing in on the findings for this news organization, John Wherry, PhD, director of the Institute for Immunology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said this “interesting study highlights potential differences in innate immunity and possibly geographic immunity in the upper respiratory tract in children versus adults.”
“We know there are differences in innate immunity over a lifespan, but exactly how these differences might relate to viral infection remains unclear,” said Dr. Wherry, who was not involved in the study.
“Children, of course, often have more respiratory infections than adults [but] whether this is due to exposure [i.e., daycare, schools, etc.] or susceptibility [lack of accumulated adaptive immunity over a greater number of years of exposure] is unclear,” Dr. Wherry noted.
“These data may help reveal what kinds of innate immune responses in the upper respiratory tract might help restrain SARS-CoV-2 and [perhaps partially] explain why children typically have milder COVID-19 disease,” he added.
The study was supported by the Berlin Institute of Health COVID-19 research program and fightCOVID@DKFZ initiative, European Commission, German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF), and German Research Foundation. Dr. Lehmann and Dr. Wherry have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Epithelial and immune cells of the upper airways of children are preactivated and primed to detect SARS-CoV-2 infection, which may contribute to stronger early immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection than adults, new research suggests.
The findings may help to explain why children have a lower risk of developing severe COVID-19 illness or becoming infected with SARS-CoV-2 in the first place, the researchers say.
The study was published online Aug. 18 in Nature Biotechnology.
Primed for action
Children appear to be better able than adults to control SARS-CoV-2 infection, but, until now, the exact molecular mechanisms have been unclear.
A team of investigators from Germany did an in-depth analysis of nasal swab samples obtained from 24 children and 21 adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, as well as a control group of 18 children and 23 adults who tested negative for SARS-CoV-2.
“We wanted to understand why viral defense appears to work so much better in children than in adults,” Irina Lehmann, PhD, head of the molecular epidemiology unit at the Berlin Institute of Health Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, explained in a news release.
Single-cell sequencing showed that children had higher baseline levels of certain RNA-sensing receptors that are relevant to SARS-CoV-2 detection, such as MDA5 and RIG-I, in the epithelial and immune cells of their noses.
This differential expression led to stronger early immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection in children than in adults.
Children were also more likely than adults to have distinct immune cell subpopulations, including KLRC1+ cytotoxic T cells, involved in fighting infection, and memory CD8+ T cells, associated with the development of long-lasting immunity.
‘Clear evidence’
The study provides “clear evidence” that upper-airway immune cells of children are “primed for virus sensing, resulting in a stronger early innate antiviral response to SARS-CoV-2 infection than in adults,” the investigators say.
Primed virus sensing and a preactivated innate immune response in children leads to efficient early production of interferons (IFNs) in the infected airways, likely mediating substantial antiviral effects, they note.
Ultimately, this may lead to lower viral replication and faster clearance in children. In fact, several studies have already shown that children eliminate the virus more quickly than adults, consistent with the concept that they shut down viral replication earlier, the study team says.
Weighing in on the findings for this news organization, John Wherry, PhD, director of the Institute for Immunology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said this “interesting study highlights potential differences in innate immunity and possibly geographic immunity in the upper respiratory tract in children versus adults.”
“We know there are differences in innate immunity over a lifespan, but exactly how these differences might relate to viral infection remains unclear,” said Dr. Wherry, who was not involved in the study.
“Children, of course, often have more respiratory infections than adults [but] whether this is due to exposure [i.e., daycare, schools, etc.] or susceptibility [lack of accumulated adaptive immunity over a greater number of years of exposure] is unclear,” Dr. Wherry noted.
“These data may help reveal what kinds of innate immune responses in the upper respiratory tract might help restrain SARS-CoV-2 and [perhaps partially] explain why children typically have milder COVID-19 disease,” he added.
The study was supported by the Berlin Institute of Health COVID-19 research program and fightCOVID@DKFZ initiative, European Commission, German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF), and German Research Foundation. Dr. Lehmann and Dr. Wherry have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Epithelial and immune cells of the upper airways of children are preactivated and primed to detect SARS-CoV-2 infection, which may contribute to stronger early immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection than adults, new research suggests.
The findings may help to explain why children have a lower risk of developing severe COVID-19 illness or becoming infected with SARS-CoV-2 in the first place, the researchers say.
The study was published online Aug. 18 in Nature Biotechnology.
Primed for action
Children appear to be better able than adults to control SARS-CoV-2 infection, but, until now, the exact molecular mechanisms have been unclear.
A team of investigators from Germany did an in-depth analysis of nasal swab samples obtained from 24 children and 21 adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, as well as a control group of 18 children and 23 adults who tested negative for SARS-CoV-2.
“We wanted to understand why viral defense appears to work so much better in children than in adults,” Irina Lehmann, PhD, head of the molecular epidemiology unit at the Berlin Institute of Health Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, explained in a news release.
Single-cell sequencing showed that children had higher baseline levels of certain RNA-sensing receptors that are relevant to SARS-CoV-2 detection, such as MDA5 and RIG-I, in the epithelial and immune cells of their noses.
This differential expression led to stronger early immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection in children than in adults.
Children were also more likely than adults to have distinct immune cell subpopulations, including KLRC1+ cytotoxic T cells, involved in fighting infection, and memory CD8+ T cells, associated with the development of long-lasting immunity.
‘Clear evidence’
The study provides “clear evidence” that upper-airway immune cells of children are “primed for virus sensing, resulting in a stronger early innate antiviral response to SARS-CoV-2 infection than in adults,” the investigators say.
Primed virus sensing and a preactivated innate immune response in children leads to efficient early production of interferons (IFNs) in the infected airways, likely mediating substantial antiviral effects, they note.
Ultimately, this may lead to lower viral replication and faster clearance in children. In fact, several studies have already shown that children eliminate the virus more quickly than adults, consistent with the concept that they shut down viral replication earlier, the study team says.
Weighing in on the findings for this news organization, John Wherry, PhD, director of the Institute for Immunology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said this “interesting study highlights potential differences in innate immunity and possibly geographic immunity in the upper respiratory tract in children versus adults.”
“We know there are differences in innate immunity over a lifespan, but exactly how these differences might relate to viral infection remains unclear,” said Dr. Wherry, who was not involved in the study.
“Children, of course, often have more respiratory infections than adults [but] whether this is due to exposure [i.e., daycare, schools, etc.] or susceptibility [lack of accumulated adaptive immunity over a greater number of years of exposure] is unclear,” Dr. Wherry noted.
“These data may help reveal what kinds of innate immune responses in the upper respiratory tract might help restrain SARS-CoV-2 and [perhaps partially] explain why children typically have milder COVID-19 disease,” he added.
The study was supported by the Berlin Institute of Health COVID-19 research program and fightCOVID@DKFZ initiative, European Commission, German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF), and German Research Foundation. Dr. Lehmann and Dr. Wherry have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ICU infections and all-cause hospital mortality rate
Background: Many articles have been published on sepsis and mortality in ICUs, but there are not many analyzing outcomes in patients with infections, nor types of infections. More information on the infection rate, types of infection, and possible impact on mortality should heighten awareness of infection effects, as well as guide resource allocation and help direct policy development for diagnosis and treatment.
Study design: 24-hour point-prevalence study with longitudinal follow-up.
Setting: ICUs in 1,150 centers in 88 countries.
Synopsis: The study included 15,202 patients who were aged 18 or older (mean, 61.6) within a 24-hour time period on Sept. 13, 2017, who were admitted to the ICU in participating centers and had documented, confirmed, or suspected infection. The investigators looked at prevalence of infection and antibiotic exposure on the study day and the main outcome measure was all cause in-hospital mortality, which was compiled 60 days later. The prevalence of suspected or proven infection in ICUs was 54% (8,135) and that of ICU-acquired infection was 22%. Of confirmed or suspected infection, 65% (5,259) had at least one positive microbiology culture. Of those cultures, 67% were gram-negative and 37% gram-positive bacteria, and 16% were fungal. 70% of ICU patients received at least one antibiotic. The in-hospital mortality rate with proven or suspected infection was 30% (2,404 of 7,936). Multilevel analysis disclosed two independent risk factors for mortality, which were ICU-acquired infections and antibiotic-resistant organisms, specifically, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus, Klebsiella resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics, and carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter.
Despite limitations related to being an observational study, 24-hour point evaluation, a centrally controlled database, and different geographic locations, this study elucidated the world-wide prevalence of ICU infection and high hospital-in mortality in those patients.
Bottom line: There is a high prevalence of infection in ICUs: 43%-60% depending on location. This is associated with 30% in-hospital mortality.
Citation: Vincent J-L et al. Prevalance and outcomes of infection among patients in intensive care units in 2017. JAMA. 2020 Mar 24;323(15):1478-87.
Dr. Rogozinska is a hospitalist and assistant professor of medicine at UK HealthCare, Lexington, Ky.
Background: Many articles have been published on sepsis and mortality in ICUs, but there are not many analyzing outcomes in patients with infections, nor types of infections. More information on the infection rate, types of infection, and possible impact on mortality should heighten awareness of infection effects, as well as guide resource allocation and help direct policy development for diagnosis and treatment.
Study design: 24-hour point-prevalence study with longitudinal follow-up.
Setting: ICUs in 1,150 centers in 88 countries.
Synopsis: The study included 15,202 patients who were aged 18 or older (mean, 61.6) within a 24-hour time period on Sept. 13, 2017, who were admitted to the ICU in participating centers and had documented, confirmed, or suspected infection. The investigators looked at prevalence of infection and antibiotic exposure on the study day and the main outcome measure was all cause in-hospital mortality, which was compiled 60 days later. The prevalence of suspected or proven infection in ICUs was 54% (8,135) and that of ICU-acquired infection was 22%. Of confirmed or suspected infection, 65% (5,259) had at least one positive microbiology culture. Of those cultures, 67% were gram-negative and 37% gram-positive bacteria, and 16% were fungal. 70% of ICU patients received at least one antibiotic. The in-hospital mortality rate with proven or suspected infection was 30% (2,404 of 7,936). Multilevel analysis disclosed two independent risk factors for mortality, which were ICU-acquired infections and antibiotic-resistant organisms, specifically, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus, Klebsiella resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics, and carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter.
Despite limitations related to being an observational study, 24-hour point evaluation, a centrally controlled database, and different geographic locations, this study elucidated the world-wide prevalence of ICU infection and high hospital-in mortality in those patients.
Bottom line: There is a high prevalence of infection in ICUs: 43%-60% depending on location. This is associated with 30% in-hospital mortality.
Citation: Vincent J-L et al. Prevalance and outcomes of infection among patients in intensive care units in 2017. JAMA. 2020 Mar 24;323(15):1478-87.
Dr. Rogozinska is a hospitalist and assistant professor of medicine at UK HealthCare, Lexington, Ky.
Background: Many articles have been published on sepsis and mortality in ICUs, but there are not many analyzing outcomes in patients with infections, nor types of infections. More information on the infection rate, types of infection, and possible impact on mortality should heighten awareness of infection effects, as well as guide resource allocation and help direct policy development for diagnosis and treatment.
Study design: 24-hour point-prevalence study with longitudinal follow-up.
Setting: ICUs in 1,150 centers in 88 countries.
Synopsis: The study included 15,202 patients who were aged 18 or older (mean, 61.6) within a 24-hour time period on Sept. 13, 2017, who were admitted to the ICU in participating centers and had documented, confirmed, or suspected infection. The investigators looked at prevalence of infection and antibiotic exposure on the study day and the main outcome measure was all cause in-hospital mortality, which was compiled 60 days later. The prevalence of suspected or proven infection in ICUs was 54% (8,135) and that of ICU-acquired infection was 22%. Of confirmed or suspected infection, 65% (5,259) had at least one positive microbiology culture. Of those cultures, 67% were gram-negative and 37% gram-positive bacteria, and 16% were fungal. 70% of ICU patients received at least one antibiotic. The in-hospital mortality rate with proven or suspected infection was 30% (2,404 of 7,936). Multilevel analysis disclosed two independent risk factors for mortality, which were ICU-acquired infections and antibiotic-resistant organisms, specifically, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus, Klebsiella resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics, and carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter.
Despite limitations related to being an observational study, 24-hour point evaluation, a centrally controlled database, and different geographic locations, this study elucidated the world-wide prevalence of ICU infection and high hospital-in mortality in those patients.
Bottom line: There is a high prevalence of infection in ICUs: 43%-60% depending on location. This is associated with 30% in-hospital mortality.
Citation: Vincent J-L et al. Prevalance and outcomes of infection among patients in intensive care units in 2017. JAMA. 2020 Mar 24;323(15):1478-87.
Dr. Rogozinska is a hospitalist and assistant professor of medicine at UK HealthCare, Lexington, Ky.






