User login
Enlarging Nodule on the Thigh
The Diagnosis: Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of the Colon
Cutaneous adenocarcinomas are uncommon, whether they present as a primary lesion or metastatic disease. In our patient, the histologic findings and immunohistochemical staining pattern were consistent with metastatic adenocarcinoma of the colon, an uncommon clinical presentation.
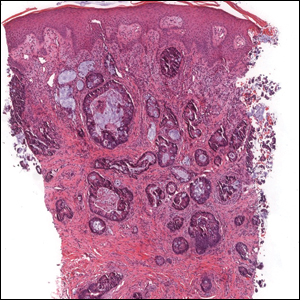
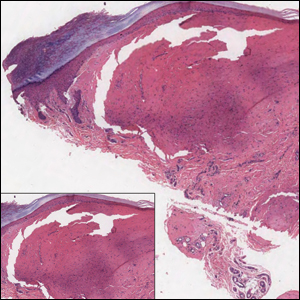
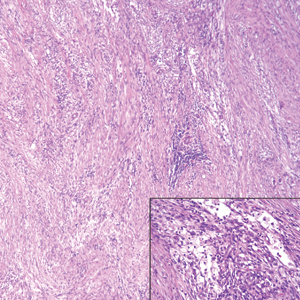
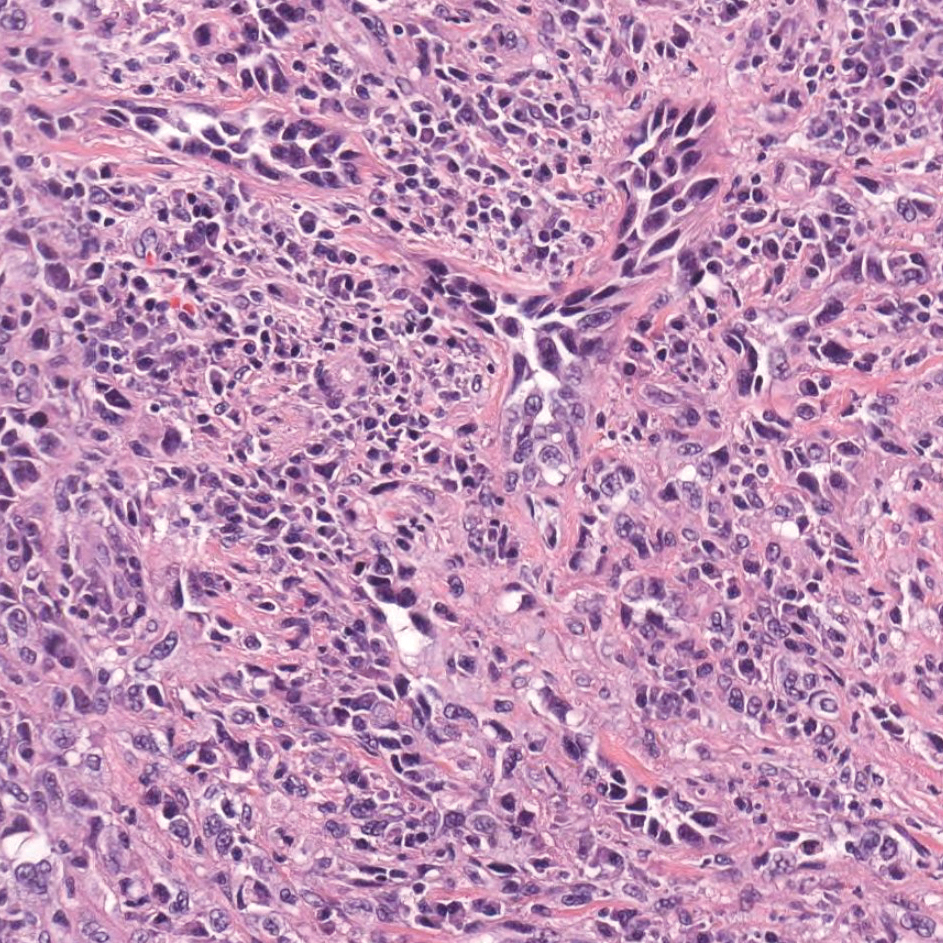
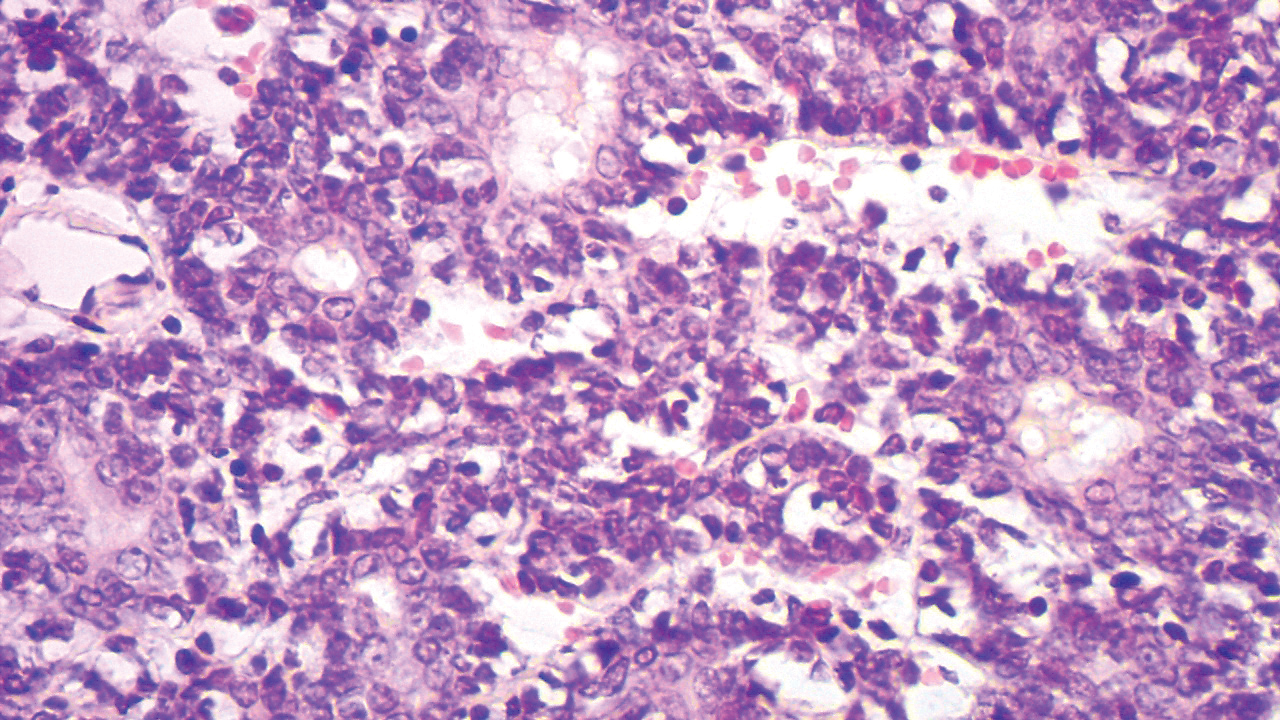
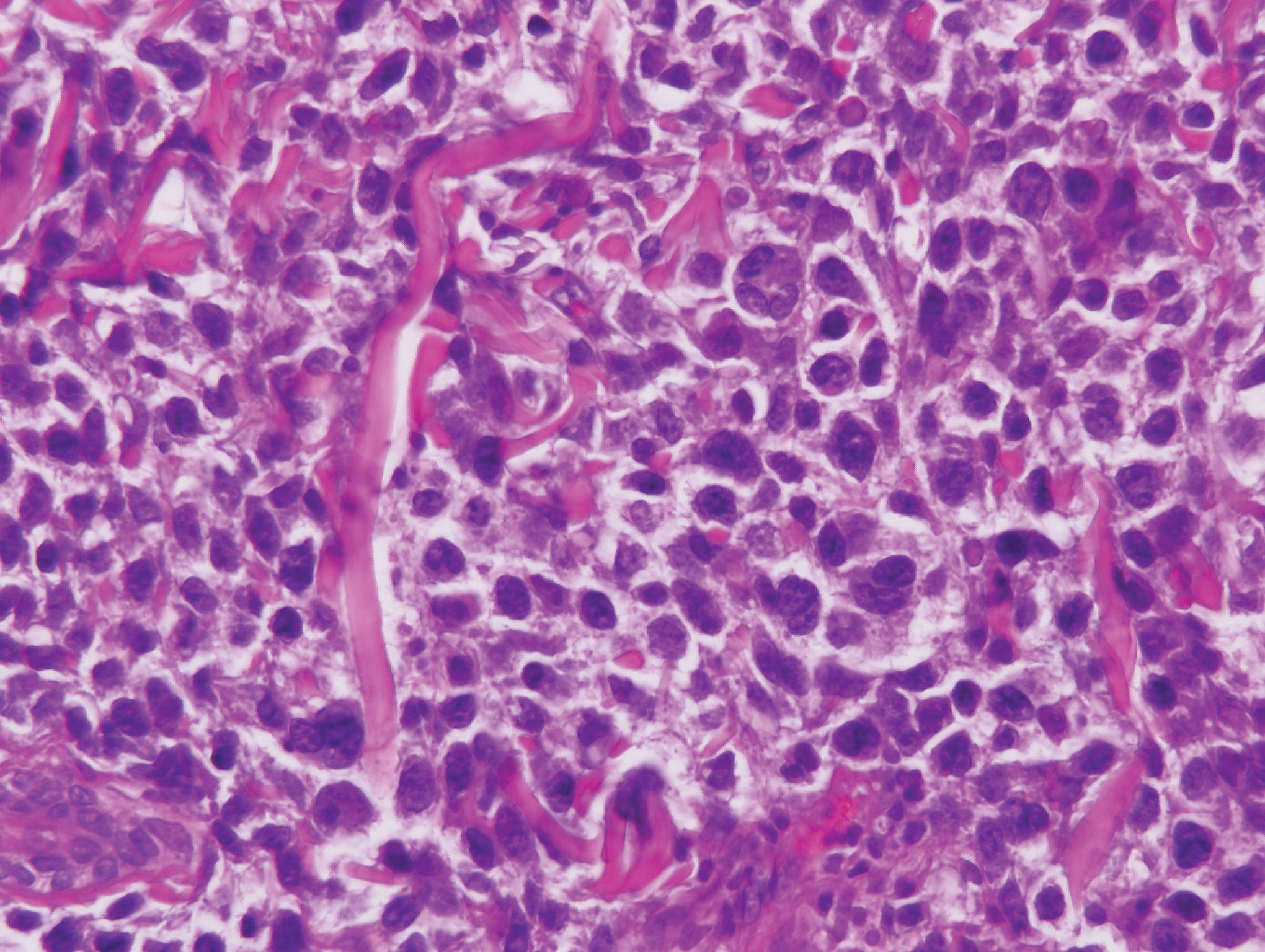
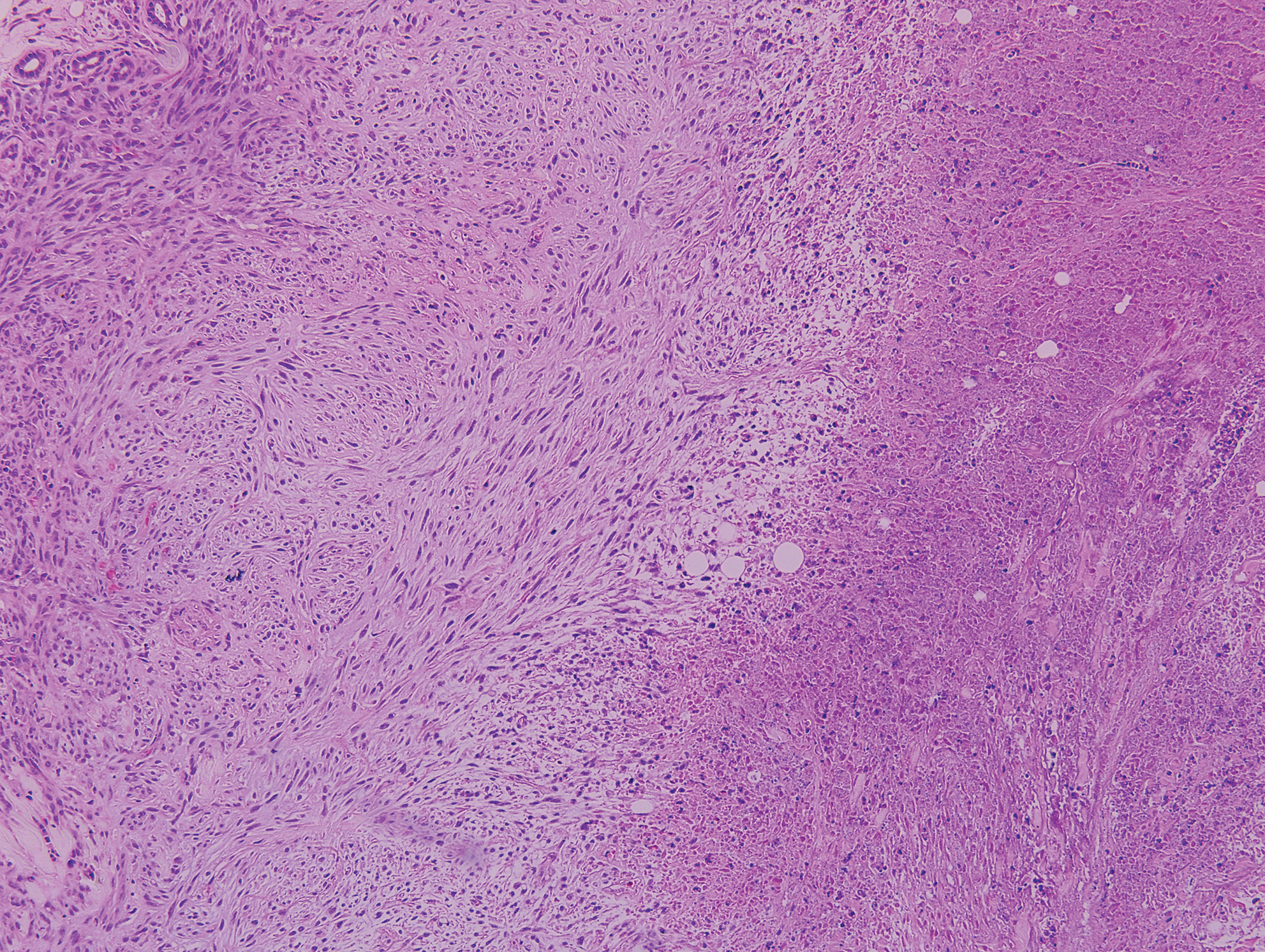
Colonic adenocarcinoma can cause cutaneous metastasis in 3% of cases. The most common sites of metastases include the abdomen, chest, and back.1 On histologic examination, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained sections of cutaneous metastatic adenocarcinoma illustrate a malignant gland-forming neoplasm in the dermis with luminal mucin and necrotic debris (quiz image). The glands are lined by tall columnar epithelial cells with hyperchromatic nuclei. Alternatively, poorly differentiated morphology can be seen with fewer glands and more infiltrating nests of tumor cells.2 Immunohistochemically, colonic adenocarcinoma typically is negative for cytokeratin (CK) 7 and positive for CK20 and caudal type homeobox transcription factor 2 (CDX-2).3
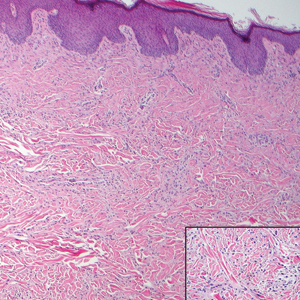
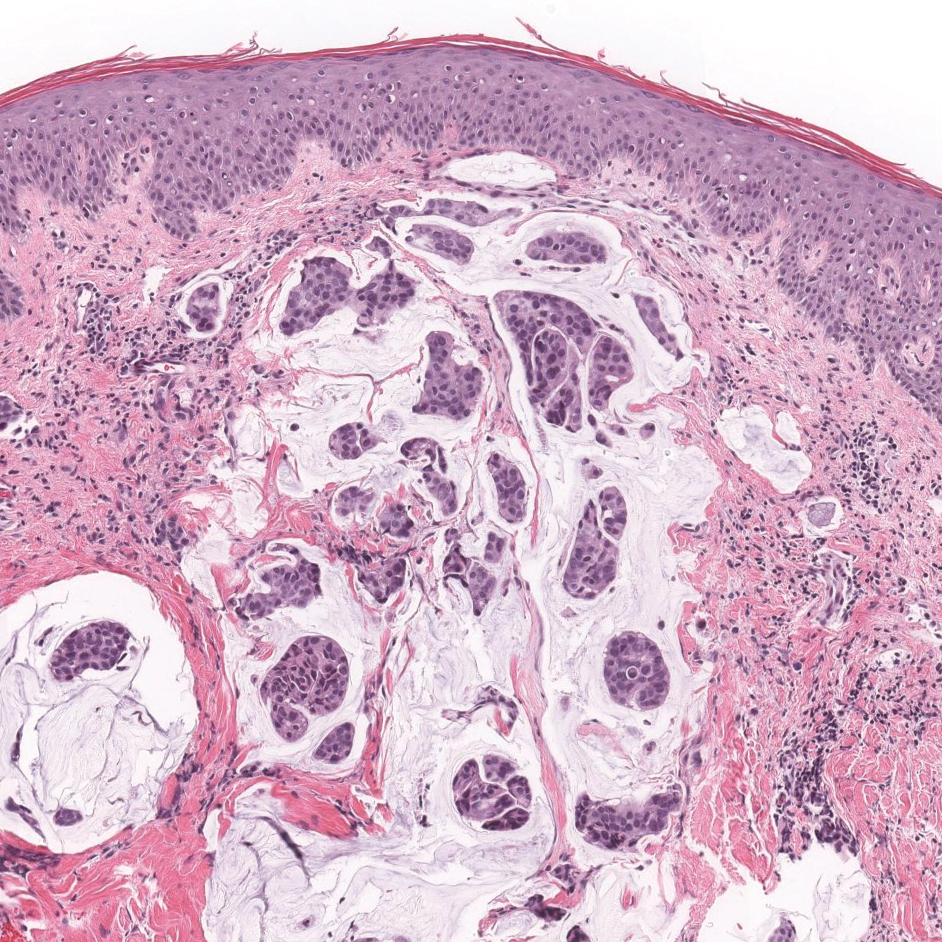
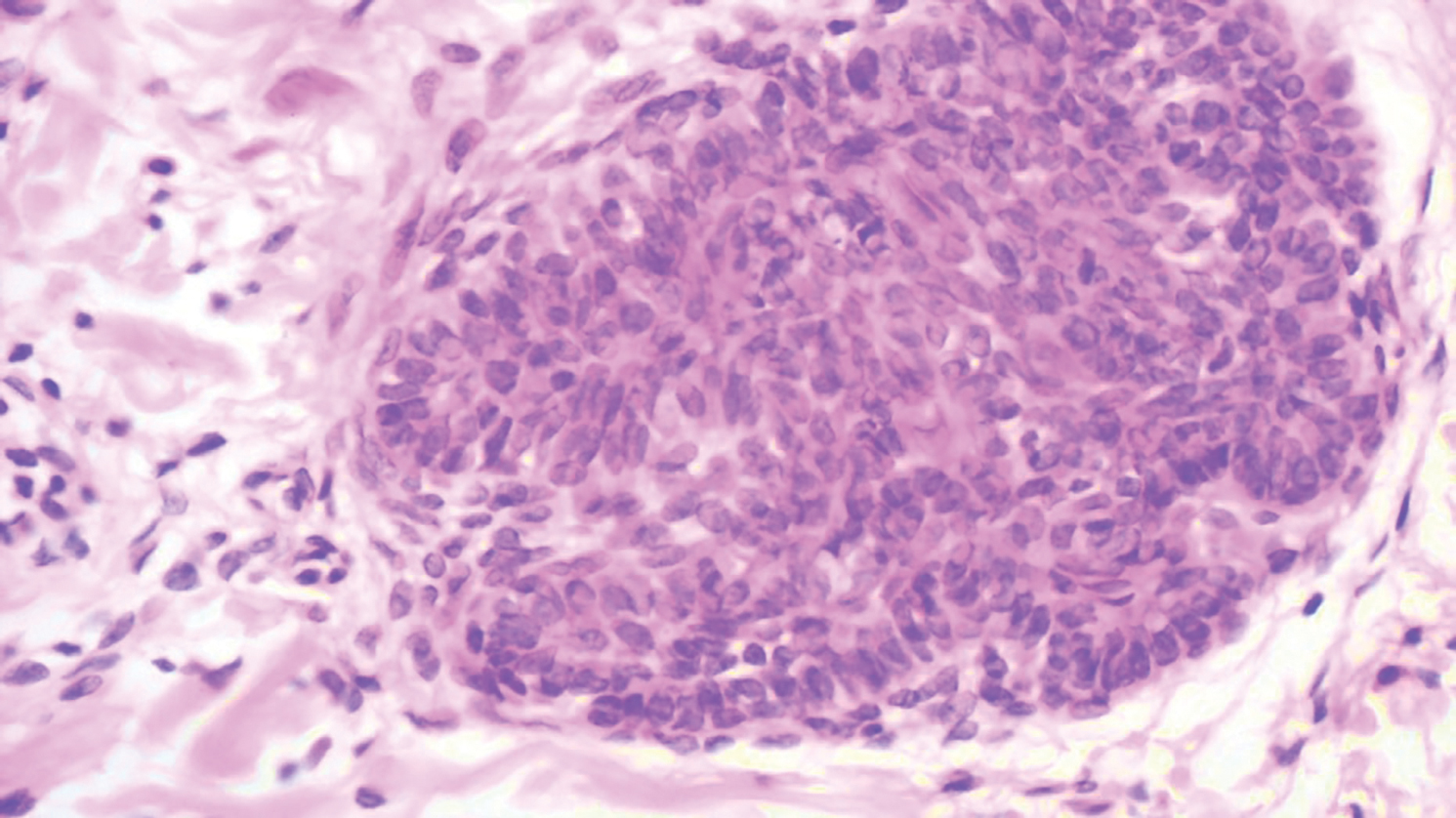
Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma is characterized by islands of neoplastic cells floating in pools of mucin (Figure 1). It may be indistinguishable from metastatic mucinous carcinomas of the colon or breast. Immunohistochemistry can be helpful in differentiating metastatic breast vs colon carcinoma. Cytokeratin 7, GATA binding protein 3, gross cystic disease fluid protein 15, and estrogen receptor will be positive in carcinomas of the breast and will be negative in colonic adenocarcinomas.4-6 Furthermore, lesional cells in metastatic adenocarcinoma of the colon are positive for CDX-2 and CK20, while those in metastatic carcinoma of the breast are negative.2 Immunohistochemistry also can differentiate primary cutaneous carcinoma from metastatic adenocarcinoma. When used in combination, p63 and podoplanin (D2-40) offer a highly sensitive and specific indicator of a primary cutaneous neoplasm, as both demonstrate either focal or diffuse positivity in this setting. In contrast, these stains typically are negative in metastatic adenocarcinomas of the skin.7
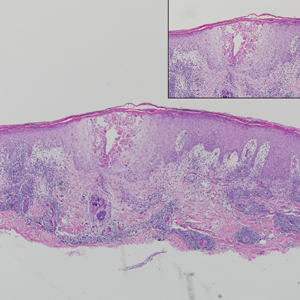
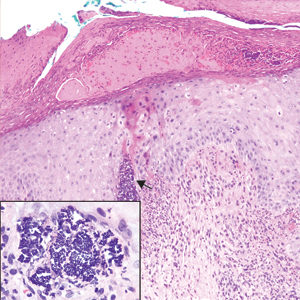
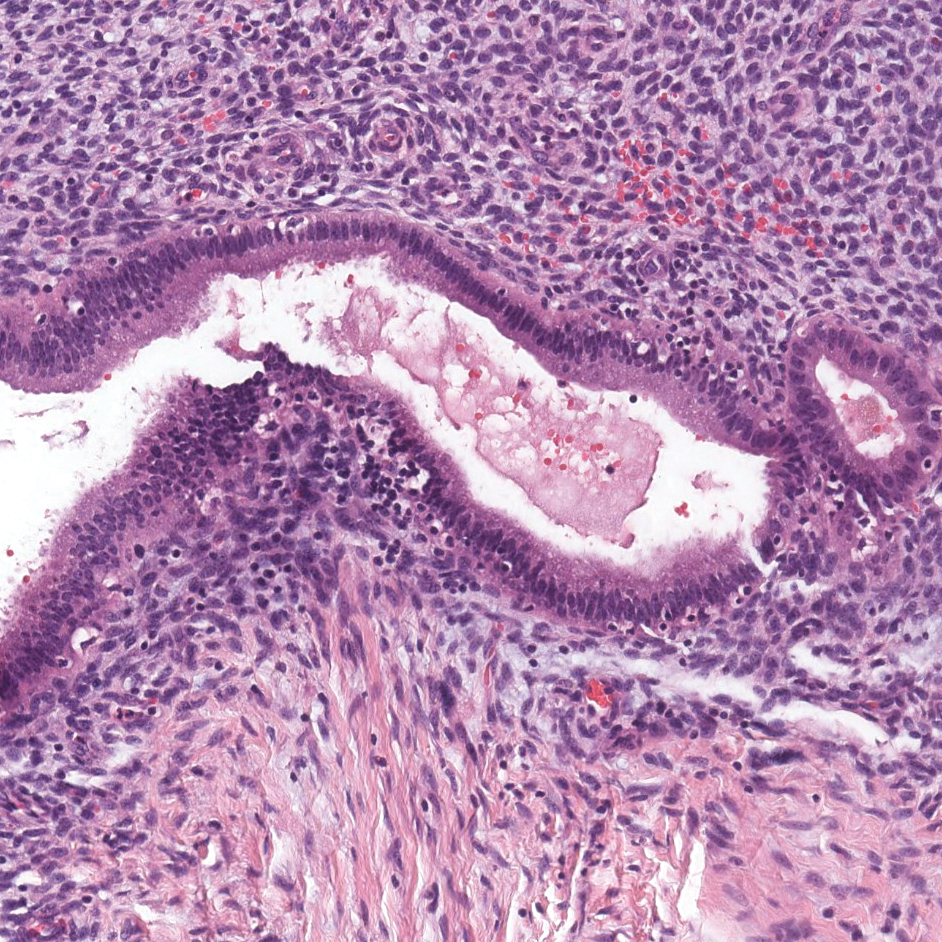
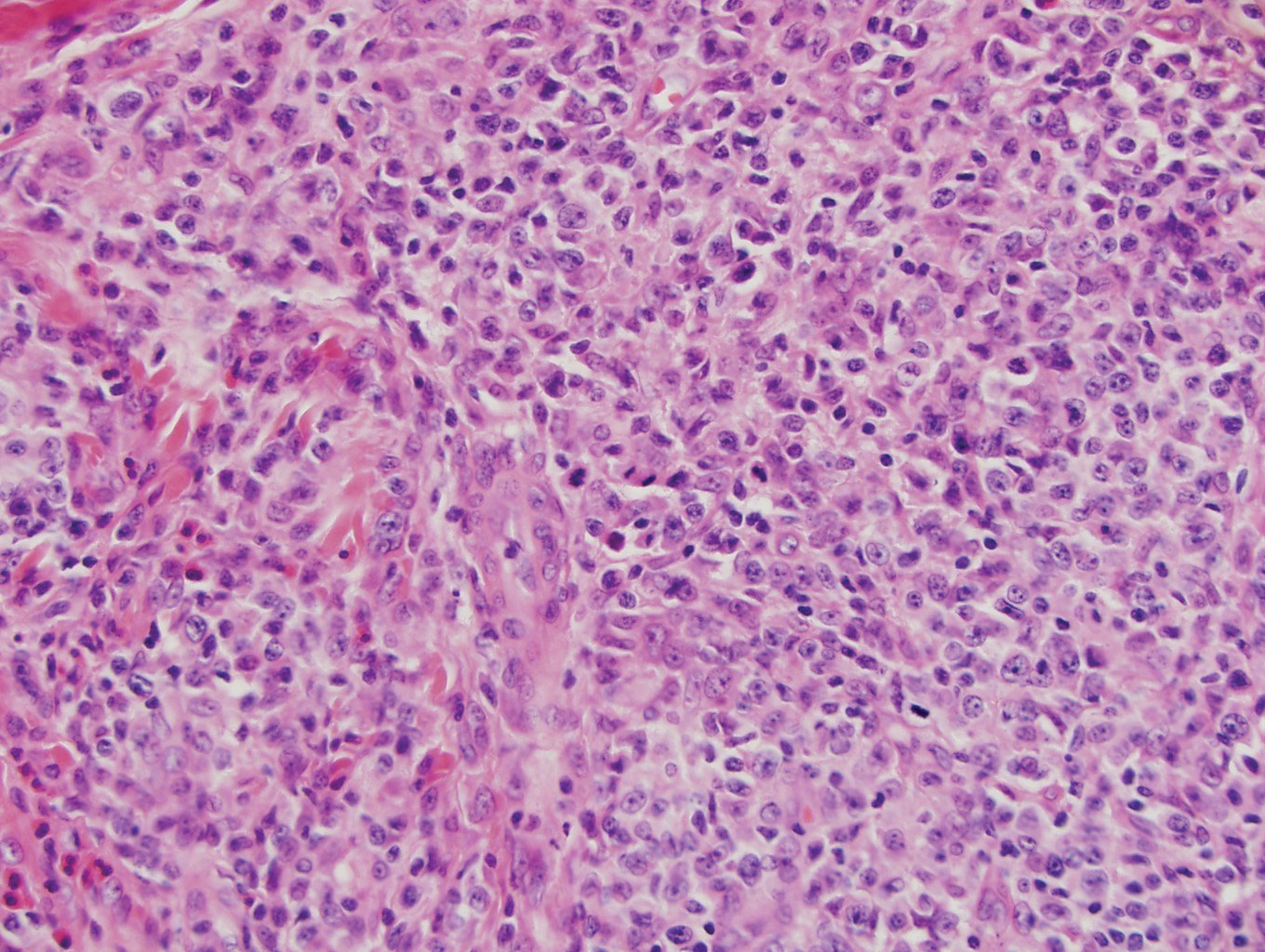
Endometriosis affects 1% to 2% of all reproductive-age females, of which extrapelvic manifestations account for only 0.5% to 1.0% of cases.8 Histologically, extrapelvic endometriosis is characterized by the triad of endometrial-type glands, endometrial stroma, and hemorrhage or hemosiderin deposition (Figure 2). The glands can enlarge and demonstrate architectural distortion with partial lack of polarity. These features initially can be concerning for adenocarcinoma, but on closer examination, nuclear morphology is regular and mitoses are absent.8,9 The diagnosis usually can be rendered with H&E alone; however, immunohistochemical stains for CD10 and estrogen receptor can highlight the endometrial stroma.10 Furthermore, endometrial glands will stain positive for paired box gene 8 (PAX8), a marker that is not expressed within the gastrointestinal tract and associated malignancies.11
cytoplasm (H&E, original magnification ×100).
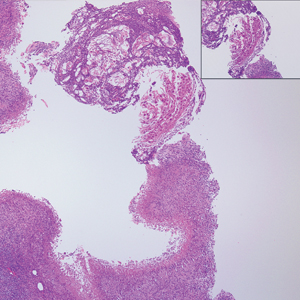
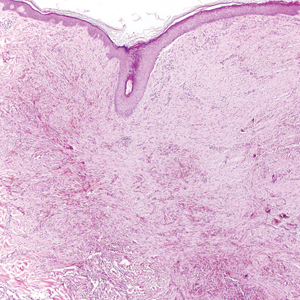
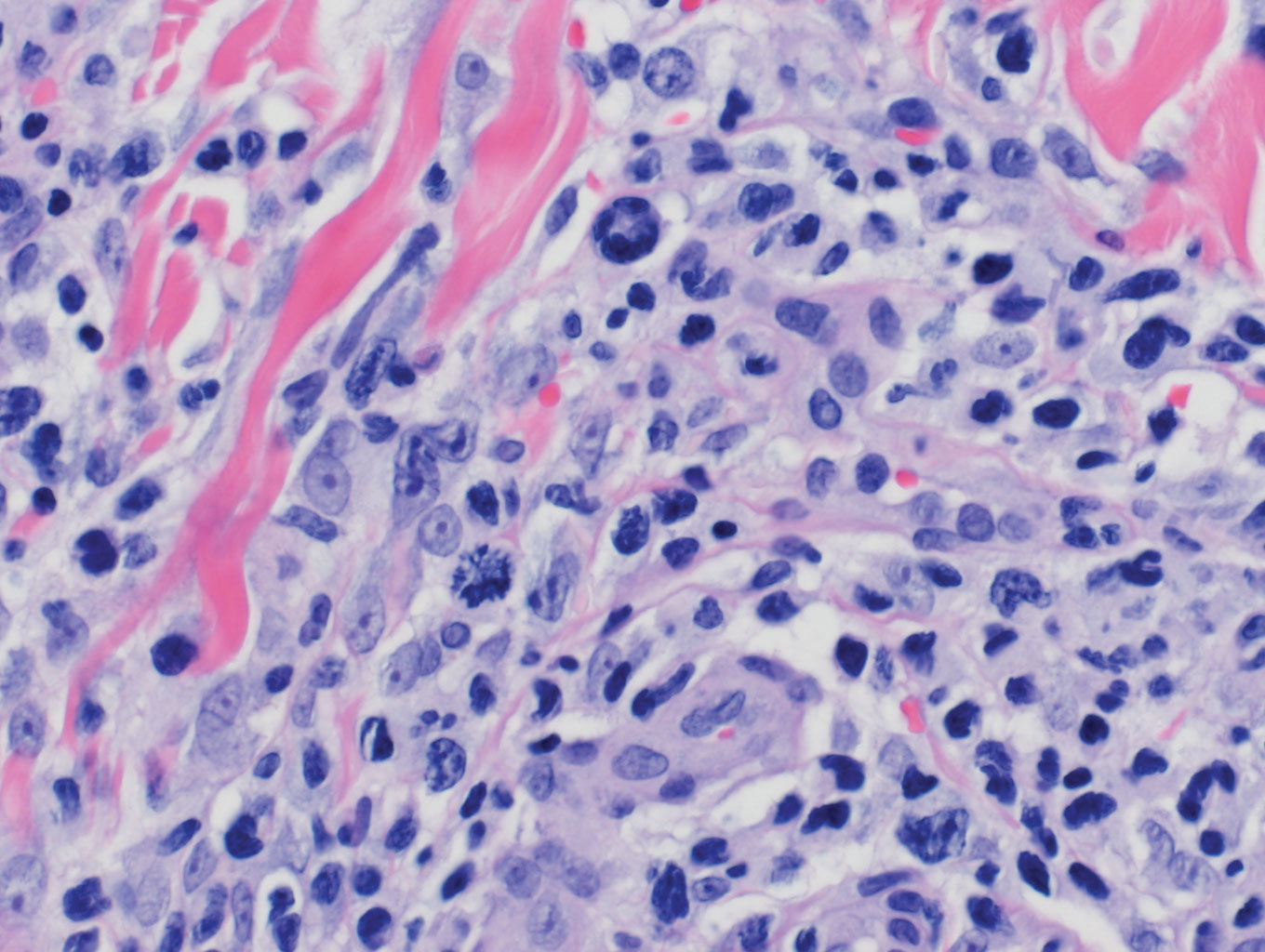
Primary cutaneous angiosarcoma may mimic adenocarcinoma, as the endothelial-lined vessels can be confused as malignant glands (Figure 3). Angiosarcoma often is seen in 1 of 3 clinical presentations: the head and neck of elderly patients, postradiation treatment, and chronic lymphedema.12,13 Regardless of the location, the disease carries a poor prognosis, with a 5-year survival rate of 12% following initial diagnosis.13 Angiosarcoma is characterized by malignant endothelial cells dissecting through the dermis. Although the histology can be deceptively bland in some cases, the neoplasm most commonly demonstrates notable atypia with a multilayered endothelium and occasional intravascular atypical cells ("fish in the creek appearance").13,14 There can be frequent mitoses, and the atypical cells may show intracytoplasmic lumina containing red blood cells. The lesional cells are positive for endothelial markers such as erythroblast transformation specific related gene (ERG), CD31, CD34, and friend leukemia integration factor 1 (FLI-1).15,16
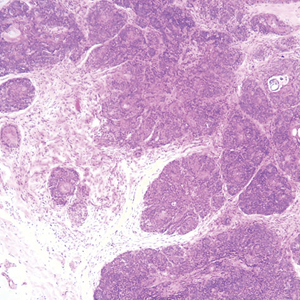
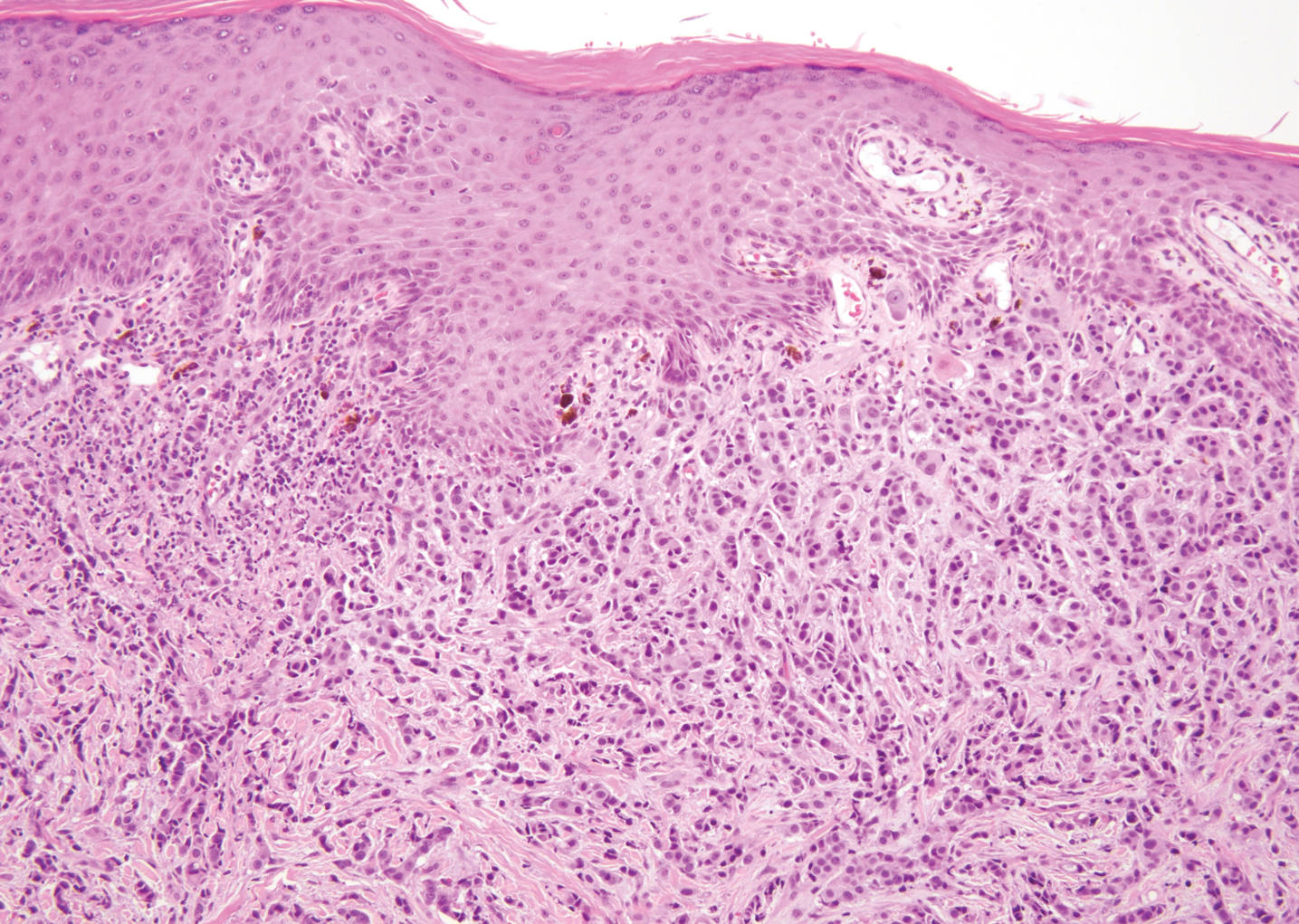
Breast cancer also can cause cutaneous metastases in approximately 20% of cases, with the most common presenting site being the anterior chest wall.17 Macroscopically, these lesions appear most commonly as painless nodules but also as telangiectatic, erysipeloid, fibrotic, and alopecic lesions.17-19 The histologic findings from H&E-stained sections of a cutaneous metastasis of breast cancer are variable and depend on the specific tumor subtype (eg, ductal, lobular, mucinous). However, the classic histologic presentation is that of nests and cords of malignant epithelial cells with variable gland formation. Often, tumor cells infiltrate in a single-file fashion (Figure 4).17 Although inflammatory breast carcinoma is a strictly clinical diagnosis, the presence of tumor cells in the lymphovascular spaces is a histologic clue to this diagnosis. Immunohistochemically, GATA binding protein 3 is helpful in identifying both hormone receptor-positive and -negative breast cancer subtypes that have metastasized.20
Within the histologic differential diagnoses, the most useful tool to diagnose metastatic adenocarcinoma of the colon often is a thorough clinical history. In the absence of a clinical history of adenocarcinoma, immunohistochemistry can be a useful adjunct to aid in the correct characterization and classification of a malignant gland-forming tumor.2,3,6
- Lookingbill DP, Spangler N, Helm KF. Cutaneous metastases in patients with metastatic carcinoma: a retrospective study of 4020 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;29:228-236.
- Kumar V, Robbins SL. Robbins Basic Pathology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders/Elsevier; 2007.
- Taliano RJ, LeGolvan M, Resnick MB. Immunohistochemistry of colorectal carcinoma: current practice and evolving applications. Hum Pathol. 2013;44:151-163.
- Kamalpour L, Brindise RT, Nodzenski M, et al. Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes after surgery. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:380-384.
- Roshan MH, Tambo A, Pace NP. The role of testosterone in colorectal carcinoma: pathomechanisms and open questions. EPMA J. 2016;7:22.
- Mazoujian G, Pinkus GS, Davis S, et al. Immunohistochemistry of a gross cystic disease fluid protein (GCDFP-15) of the breast. a marker of apocrine epithelium and breast carcinomas with apocrine features. Am J Pathol. 1983;110:105-112.
- Plaza JA, Ortega PF, Stockman DL, et al. Value of p63 and podoplanin (D2-40) immunoreactivity in the distinction between primary cutaneous tumors and adenocarcinomas metastatic to the skin: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 79 cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:403-410.
- Machairiotis N, Stylianaki A, Dryllis G, et al. Extrapelvic endometriosis: a rare entity or an under diagnosed condition? Diagn Pathol. 2013;8:194.
- Chen H, Luo Q, Liu S, et al. Rectal mucosal endometriosis primarily misinterpreted as adenocarcinoma: a case report and review of literature. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8:5902-5907.
- Terada S, Miyata Y, Nakazawa H, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of an ectopic endometriosis in the uterine round ligament. Diagn Pathol. 2006;1:27.
- Yemelyanova A, Gown AM, Wu LS, et al. PAX8 expression in uterine adenocarcinomas and mesonephric proliferations. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2014;33:492-499.
- Farid M, Ong WS, Lee MJ, et al. Cutaneous versus non-cutaneous angiosarcoma: clinicopathologic features and treatment outcomes in 60 patients at a single Asian cancer centre. Oncology. 2013;85:182-190.
- Requena C, Sendra E, Llombart B, et al. Cutaneous angiosarcoma: clinical and pathology study of 16 cases. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017;108:457-465.
- Schmidt AP, Tjarks BJ, Lynch DW. Gone fishing: a unique histologic pattern in cutaneous angiosarcoma. Cutis. 2018;101:270-272.
- Sullivan HC, Edgar MA, Cohen C, et al. The utility of ERG, CD31 and CD34 in the cytological diagnosis of angiosarcoma: an analysis of 25 cases. J Clin Pathol. 2015;68:44-50.
- Rossi S, Orvieto E, Furlanetto A, et al. Utility of the immunohistochemical detection of FLI-1 expression in round cell and vascular neoplasm using a monoclonal antibody. Mod Pathol. 2004;17:547-552.
- Tan AR. Cutaneous manifestations of breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 2016;43:331-334.
- Schwartz RA, Wiederkehr M, Lambert WC. Secondary mucinous carcinoma of the skin: metastatic breast cancer. Dermatol Surg. 2004;30(2, pt 1):234-235.
- Mallon E, Dawber RP. Alopecia neoplastica without alopecia: a unique presentation of breast carcinoma scalp metastasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31(2, pt 2):319-321.
- Braxton DR, Cohen C, Siddiqui MT. Utility of GATA3 immunohistochemistry for diagnosis of metastatic breast carcinoma in cytology specimens. Diagn Cytopathol. 2015;43:271-277.
The Diagnosis: Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of the Colon
Cutaneous adenocarcinomas are uncommon, whether they present as a primary lesion or metastatic disease. In our patient, the histologic findings and immunohistochemical staining pattern were consistent with metastatic adenocarcinoma of the colon, an uncommon clinical presentation.
Colonic adenocarcinoma can cause cutaneous metastasis in 3% of cases. The most common sites of metastases include the abdomen, chest, and back.1 On histologic examination, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained sections of cutaneous metastatic adenocarcinoma illustrate a malignant gland-forming neoplasm in the dermis with luminal mucin and necrotic debris (quiz image). The glands are lined by tall columnar epithelial cells with hyperchromatic nuclei. Alternatively, poorly differentiated morphology can be seen with fewer glands and more infiltrating nests of tumor cells.2 Immunohistochemically, colonic adenocarcinoma typically is negative for cytokeratin (CK) 7 and positive for CK20 and caudal type homeobox transcription factor 2 (CDX-2).3
Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma is characterized by islands of neoplastic cells floating in pools of mucin (Figure 1). It may be indistinguishable from metastatic mucinous carcinomas of the colon or breast. Immunohistochemistry can be helpful in differentiating metastatic breast vs colon carcinoma. Cytokeratin 7, GATA binding protein 3, gross cystic disease fluid protein 15, and estrogen receptor will be positive in carcinomas of the breast and will be negative in colonic adenocarcinomas.4-6 Furthermore, lesional cells in metastatic adenocarcinoma of the colon are positive for CDX-2 and CK20, while those in metastatic carcinoma of the breast are negative.2 Immunohistochemistry also can differentiate primary cutaneous carcinoma from metastatic adenocarcinoma. When used in combination, p63 and podoplanin (D2-40) offer a highly sensitive and specific indicator of a primary cutaneous neoplasm, as both demonstrate either focal or diffuse positivity in this setting. In contrast, these stains typically are negative in metastatic adenocarcinomas of the skin.7

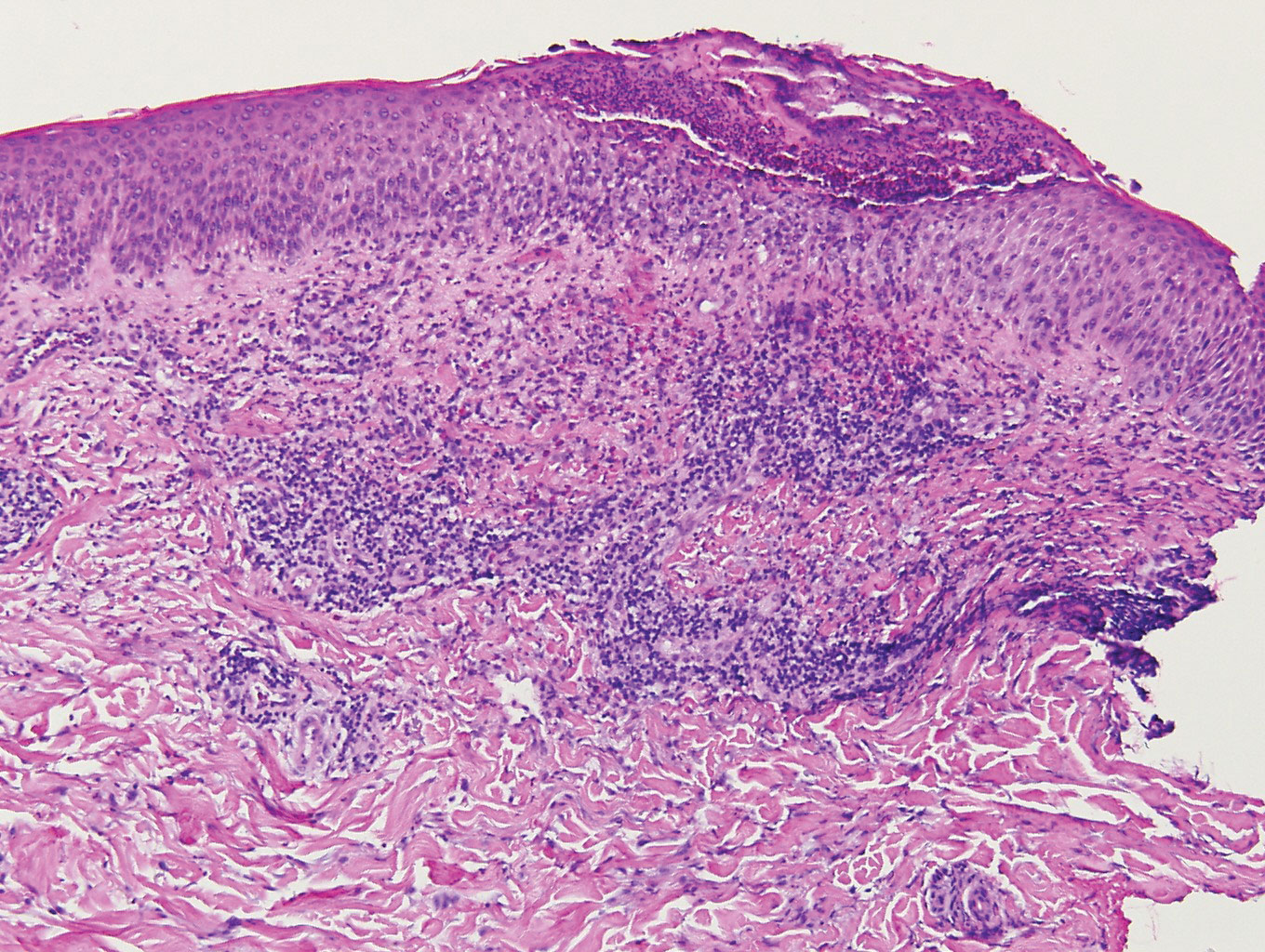
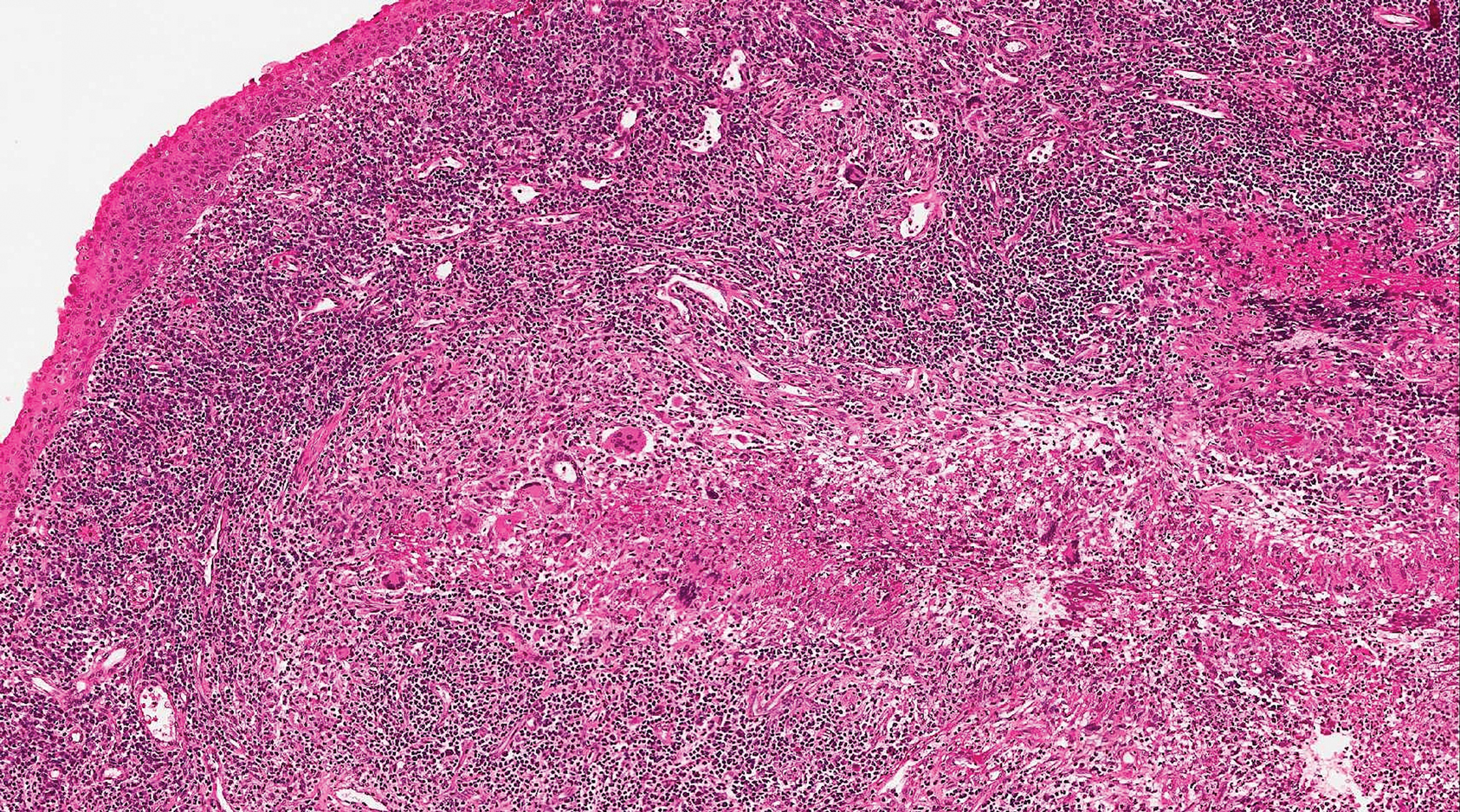
Endometriosis affects 1% to 2% of all reproductive-age females, of which extrapelvic manifestations account for only 0.5% to 1.0% of cases.8 Histologically, extrapelvic endometriosis is characterized by the triad of endometrial-type glands, endometrial stroma, and hemorrhage or hemosiderin deposition (Figure 2). The glands can enlarge and demonstrate architectural distortion with partial lack of polarity. These features initially can be concerning for adenocarcinoma, but on closer examination, nuclear morphology is regular and mitoses are absent.8,9 The diagnosis usually can be rendered with H&E alone; however, immunohistochemical stains for CD10 and estrogen receptor can highlight the endometrial stroma.10 Furthermore, endometrial glands will stain positive for paired box gene 8 (PAX8), a marker that is not expressed within the gastrointestinal tract and associated malignancies.11

cytoplasm (H&E, original magnification ×100).
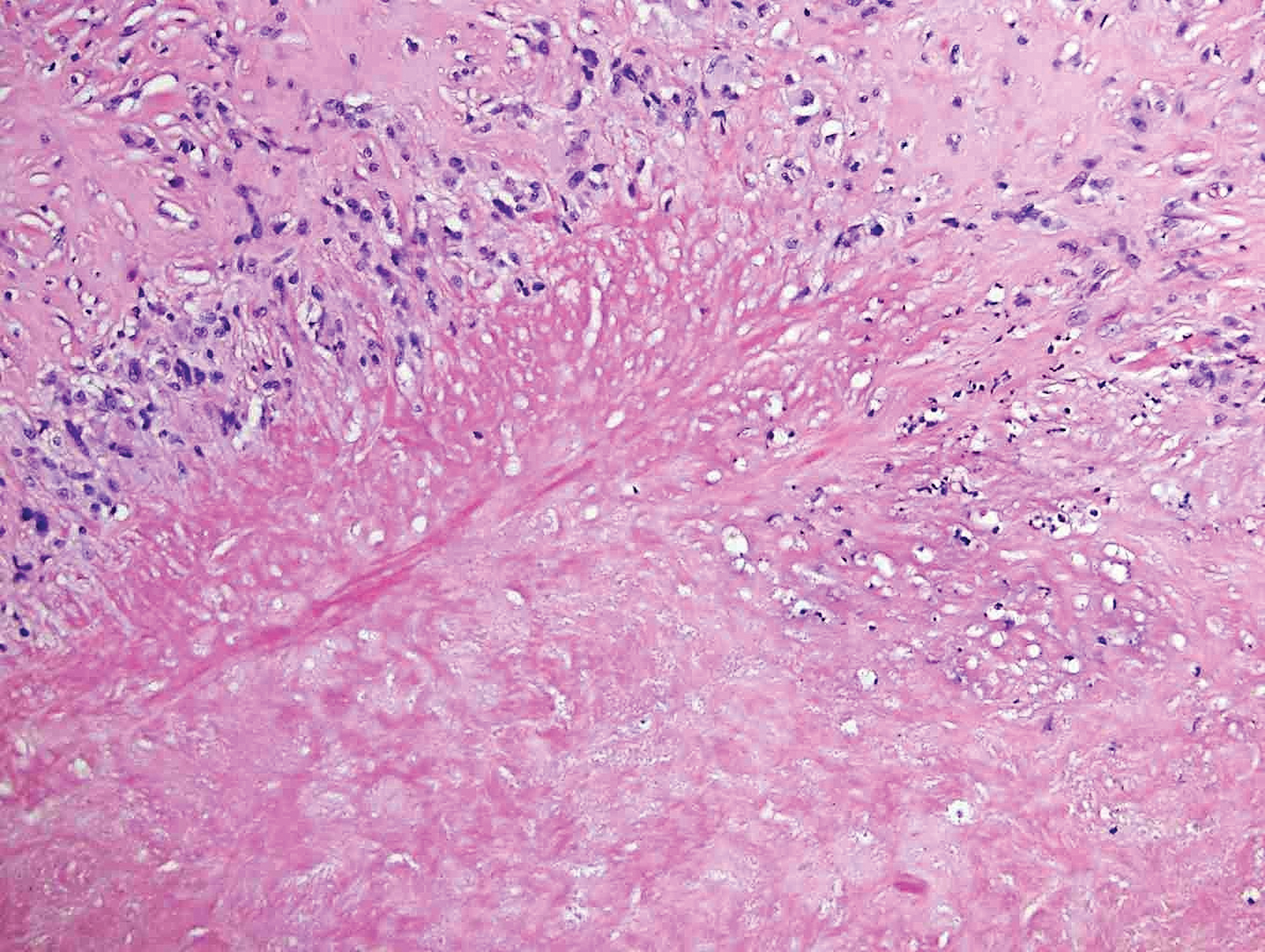
Primary cutaneous angiosarcoma may mimic adenocarcinoma, as the endothelial-lined vessels can be confused as malignant glands (Figure 3). Angiosarcoma often is seen in 1 of 3 clinical presentations: the head and neck of elderly patients, postradiation treatment, and chronic lymphedema.12,13 Regardless of the location, the disease carries a poor prognosis, with a 5-year survival rate of 12% following initial diagnosis.13 Angiosarcoma is characterized by malignant endothelial cells dissecting through the dermis. Although the histology can be deceptively bland in some cases, the neoplasm most commonly demonstrates notable atypia with a multilayered endothelium and occasional intravascular atypical cells ("fish in the creek appearance").13,14 There can be frequent mitoses, and the atypical cells may show intracytoplasmic lumina containing red blood cells. The lesional cells are positive for endothelial markers such as erythroblast transformation specific related gene (ERG), CD31, CD34, and friend leukemia integration factor 1 (FLI-1).15,16

Breast cancer also can cause cutaneous metastases in approximately 20% of cases, with the most common presenting site being the anterior chest wall.17 Macroscopically, these lesions appear most commonly as painless nodules but also as telangiectatic, erysipeloid, fibrotic, and alopecic lesions.17-19 The histologic findings from H&E-stained sections of a cutaneous metastasis of breast cancer are variable and depend on the specific tumor subtype (eg, ductal, lobular, mucinous). However, the classic histologic presentation is that of nests and cords of malignant epithelial cells with variable gland formation. Often, tumor cells infiltrate in a single-file fashion (Figure 4).17 Although inflammatory breast carcinoma is a strictly clinical diagnosis, the presence of tumor cells in the lymphovascular spaces is a histologic clue to this diagnosis. Immunohistochemically, GATA binding protein 3 is helpful in identifying both hormone receptor-positive and -negative breast cancer subtypes that have metastasized.20

Within the histologic differential diagnoses, the most useful tool to diagnose metastatic adenocarcinoma of the colon often is a thorough clinical history. In the absence of a clinical history of adenocarcinoma, immunohistochemistry can be a useful adjunct to aid in the correct characterization and classification of a malignant gland-forming tumor.2,3,6
The Diagnosis: Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of the Colon
Cutaneous adenocarcinomas are uncommon, whether they present as a primary lesion or metastatic disease. In our patient, the histologic findings and immunohistochemical staining pattern were consistent with metastatic adenocarcinoma of the colon, an uncommon clinical presentation.
Colonic adenocarcinoma can cause cutaneous metastasis in 3% of cases. The most common sites of metastases include the abdomen, chest, and back.1 On histologic examination, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained sections of cutaneous metastatic adenocarcinoma illustrate a malignant gland-forming neoplasm in the dermis with luminal mucin and necrotic debris (quiz image). The glands are lined by tall columnar epithelial cells with hyperchromatic nuclei. Alternatively, poorly differentiated morphology can be seen with fewer glands and more infiltrating nests of tumor cells.2 Immunohistochemically, colonic adenocarcinoma typically is negative for cytokeratin (CK) 7 and positive for CK20 and caudal type homeobox transcription factor 2 (CDX-2).3
Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma is characterized by islands of neoplastic cells floating in pools of mucin (Figure 1). It may be indistinguishable from metastatic mucinous carcinomas of the colon or breast. Immunohistochemistry can be helpful in differentiating metastatic breast vs colon carcinoma. Cytokeratin 7, GATA binding protein 3, gross cystic disease fluid protein 15, and estrogen receptor will be positive in carcinomas of the breast and will be negative in colonic adenocarcinomas.4-6 Furthermore, lesional cells in metastatic adenocarcinoma of the colon are positive for CDX-2 and CK20, while those in metastatic carcinoma of the breast are negative.2 Immunohistochemistry also can differentiate primary cutaneous carcinoma from metastatic adenocarcinoma. When used in combination, p63 and podoplanin (D2-40) offer a highly sensitive and specific indicator of a primary cutaneous neoplasm, as both demonstrate either focal or diffuse positivity in this setting. In contrast, these stains typically are negative in metastatic adenocarcinomas of the skin.7

Endometriosis affects 1% to 2% of all reproductive-age females, of which extrapelvic manifestations account for only 0.5% to 1.0% of cases.8 Histologically, extrapelvic endometriosis is characterized by the triad of endometrial-type glands, endometrial stroma, and hemorrhage or hemosiderin deposition (Figure 2). The glands can enlarge and demonstrate architectural distortion with partial lack of polarity. These features initially can be concerning for adenocarcinoma, but on closer examination, nuclear morphology is regular and mitoses are absent.8,9 The diagnosis usually can be rendered with H&E alone; however, immunohistochemical stains for CD10 and estrogen receptor can highlight the endometrial stroma.10 Furthermore, endometrial glands will stain positive for paired box gene 8 (PAX8), a marker that is not expressed within the gastrointestinal tract and associated malignancies.11

cytoplasm (H&E, original magnification ×100).
Primary cutaneous angiosarcoma may mimic adenocarcinoma, as the endothelial-lined vessels can be confused as malignant glands (Figure 3). Angiosarcoma often is seen in 1 of 3 clinical presentations: the head and neck of elderly patients, postradiation treatment, and chronic lymphedema.12,13 Regardless of the location, the disease carries a poor prognosis, with a 5-year survival rate of 12% following initial diagnosis.13 Angiosarcoma is characterized by malignant endothelial cells dissecting through the dermis. Although the histology can be deceptively bland in some cases, the neoplasm most commonly demonstrates notable atypia with a multilayered endothelium and occasional intravascular atypical cells ("fish in the creek appearance").13,14 There can be frequent mitoses, and the atypical cells may show intracytoplasmic lumina containing red blood cells. The lesional cells are positive for endothelial markers such as erythroblast transformation specific related gene (ERG), CD31, CD34, and friend leukemia integration factor 1 (FLI-1).15,16

Breast cancer also can cause cutaneous metastases in approximately 20% of cases, with the most common presenting site being the anterior chest wall.17 Macroscopically, these lesions appear most commonly as painless nodules but also as telangiectatic, erysipeloid, fibrotic, and alopecic lesions.17-19 The histologic findings from H&E-stained sections of a cutaneous metastasis of breast cancer are variable and depend on the specific tumor subtype (eg, ductal, lobular, mucinous). However, the classic histologic presentation is that of nests and cords of malignant epithelial cells with variable gland formation. Often, tumor cells infiltrate in a single-file fashion (Figure 4).17 Although inflammatory breast carcinoma is a strictly clinical diagnosis, the presence of tumor cells in the lymphovascular spaces is a histologic clue to this diagnosis. Immunohistochemically, GATA binding protein 3 is helpful in identifying both hormone receptor-positive and -negative breast cancer subtypes that have metastasized.20

Within the histologic differential diagnoses, the most useful tool to diagnose metastatic adenocarcinoma of the colon often is a thorough clinical history. In the absence of a clinical history of adenocarcinoma, immunohistochemistry can be a useful adjunct to aid in the correct characterization and classification of a malignant gland-forming tumor.2,3,6
- Lookingbill DP, Spangler N, Helm KF. Cutaneous metastases in patients with metastatic carcinoma: a retrospective study of 4020 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;29:228-236.
- Kumar V, Robbins SL. Robbins Basic Pathology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders/Elsevier; 2007.
- Taliano RJ, LeGolvan M, Resnick MB. Immunohistochemistry of colorectal carcinoma: current practice and evolving applications. Hum Pathol. 2013;44:151-163.
- Kamalpour L, Brindise RT, Nodzenski M, et al. Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes after surgery. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:380-384.
- Roshan MH, Tambo A, Pace NP. The role of testosterone in colorectal carcinoma: pathomechanisms and open questions. EPMA J. 2016;7:22.
- Mazoujian G, Pinkus GS, Davis S, et al. Immunohistochemistry of a gross cystic disease fluid protein (GCDFP-15) of the breast. a marker of apocrine epithelium and breast carcinomas with apocrine features. Am J Pathol. 1983;110:105-112.
- Plaza JA, Ortega PF, Stockman DL, et al. Value of p63 and podoplanin (D2-40) immunoreactivity in the distinction between primary cutaneous tumors and adenocarcinomas metastatic to the skin: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 79 cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:403-410.
- Machairiotis N, Stylianaki A, Dryllis G, et al. Extrapelvic endometriosis: a rare entity or an under diagnosed condition? Diagn Pathol. 2013;8:194.
- Chen H, Luo Q, Liu S, et al. Rectal mucosal endometriosis primarily misinterpreted as adenocarcinoma: a case report and review of literature. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8:5902-5907.
- Terada S, Miyata Y, Nakazawa H, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of an ectopic endometriosis in the uterine round ligament. Diagn Pathol. 2006;1:27.
- Yemelyanova A, Gown AM, Wu LS, et al. PAX8 expression in uterine adenocarcinomas and mesonephric proliferations. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2014;33:492-499.
- Farid M, Ong WS, Lee MJ, et al. Cutaneous versus non-cutaneous angiosarcoma: clinicopathologic features and treatment outcomes in 60 patients at a single Asian cancer centre. Oncology. 2013;85:182-190.
- Requena C, Sendra E, Llombart B, et al. Cutaneous angiosarcoma: clinical and pathology study of 16 cases. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017;108:457-465.
- Schmidt AP, Tjarks BJ, Lynch DW. Gone fishing: a unique histologic pattern in cutaneous angiosarcoma. Cutis. 2018;101:270-272.
- Sullivan HC, Edgar MA, Cohen C, et al. The utility of ERG, CD31 and CD34 in the cytological diagnosis of angiosarcoma: an analysis of 25 cases. J Clin Pathol. 2015;68:44-50.
- Rossi S, Orvieto E, Furlanetto A, et al. Utility of the immunohistochemical detection of FLI-1 expression in round cell and vascular neoplasm using a monoclonal antibody. Mod Pathol. 2004;17:547-552.
- Tan AR. Cutaneous manifestations of breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 2016;43:331-334.
- Schwartz RA, Wiederkehr M, Lambert WC. Secondary mucinous carcinoma of the skin: metastatic breast cancer. Dermatol Surg. 2004;30(2, pt 1):234-235.
- Mallon E, Dawber RP. Alopecia neoplastica without alopecia: a unique presentation of breast carcinoma scalp metastasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31(2, pt 2):319-321.
- Braxton DR, Cohen C, Siddiqui MT. Utility of GATA3 immunohistochemistry for diagnosis of metastatic breast carcinoma in cytology specimens. Diagn Cytopathol. 2015;43:271-277.
- Lookingbill DP, Spangler N, Helm KF. Cutaneous metastases in patients with metastatic carcinoma: a retrospective study of 4020 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;29:228-236.
- Kumar V, Robbins SL. Robbins Basic Pathology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders/Elsevier; 2007.
- Taliano RJ, LeGolvan M, Resnick MB. Immunohistochemistry of colorectal carcinoma: current practice and evolving applications. Hum Pathol. 2013;44:151-163.
- Kamalpour L, Brindise RT, Nodzenski M, et al. Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes after surgery. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:380-384.
- Roshan MH, Tambo A, Pace NP. The role of testosterone in colorectal carcinoma: pathomechanisms and open questions. EPMA J. 2016;7:22.
- Mazoujian G, Pinkus GS, Davis S, et al. Immunohistochemistry of a gross cystic disease fluid protein (GCDFP-15) of the breast. a marker of apocrine epithelium and breast carcinomas with apocrine features. Am J Pathol. 1983;110:105-112.
- Plaza JA, Ortega PF, Stockman DL, et al. Value of p63 and podoplanin (D2-40) immunoreactivity in the distinction between primary cutaneous tumors and adenocarcinomas metastatic to the skin: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 79 cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:403-410.
- Machairiotis N, Stylianaki A, Dryllis G, et al. Extrapelvic endometriosis: a rare entity or an under diagnosed condition? Diagn Pathol. 2013;8:194.
- Chen H, Luo Q, Liu S, et al. Rectal mucosal endometriosis primarily misinterpreted as adenocarcinoma: a case report and review of literature. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8:5902-5907.
- Terada S, Miyata Y, Nakazawa H, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of an ectopic endometriosis in the uterine round ligament. Diagn Pathol. 2006;1:27.
- Yemelyanova A, Gown AM, Wu LS, et al. PAX8 expression in uterine adenocarcinomas and mesonephric proliferations. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2014;33:492-499.
- Farid M, Ong WS, Lee MJ, et al. Cutaneous versus non-cutaneous angiosarcoma: clinicopathologic features and treatment outcomes in 60 patients at a single Asian cancer centre. Oncology. 2013;85:182-190.
- Requena C, Sendra E, Llombart B, et al. Cutaneous angiosarcoma: clinical and pathology study of 16 cases. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017;108:457-465.
- Schmidt AP, Tjarks BJ, Lynch DW. Gone fishing: a unique histologic pattern in cutaneous angiosarcoma. Cutis. 2018;101:270-272.
- Sullivan HC, Edgar MA, Cohen C, et al. The utility of ERG, CD31 and CD34 in the cytological diagnosis of angiosarcoma: an analysis of 25 cases. J Clin Pathol. 2015;68:44-50.
- Rossi S, Orvieto E, Furlanetto A, et al. Utility of the immunohistochemical detection of FLI-1 expression in round cell and vascular neoplasm using a monoclonal antibody. Mod Pathol. 2004;17:547-552.
- Tan AR. Cutaneous manifestations of breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 2016;43:331-334.
- Schwartz RA, Wiederkehr M, Lambert WC. Secondary mucinous carcinoma of the skin: metastatic breast cancer. Dermatol Surg. 2004;30(2, pt 1):234-235.
- Mallon E, Dawber RP. Alopecia neoplastica without alopecia: a unique presentation of breast carcinoma scalp metastasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31(2, pt 2):319-321.
- Braxton DR, Cohen C, Siddiqui MT. Utility of GATA3 immunohistochemistry for diagnosis of metastatic breast carcinoma in cytology specimens. Diagn Cytopathol. 2015;43:271-277.
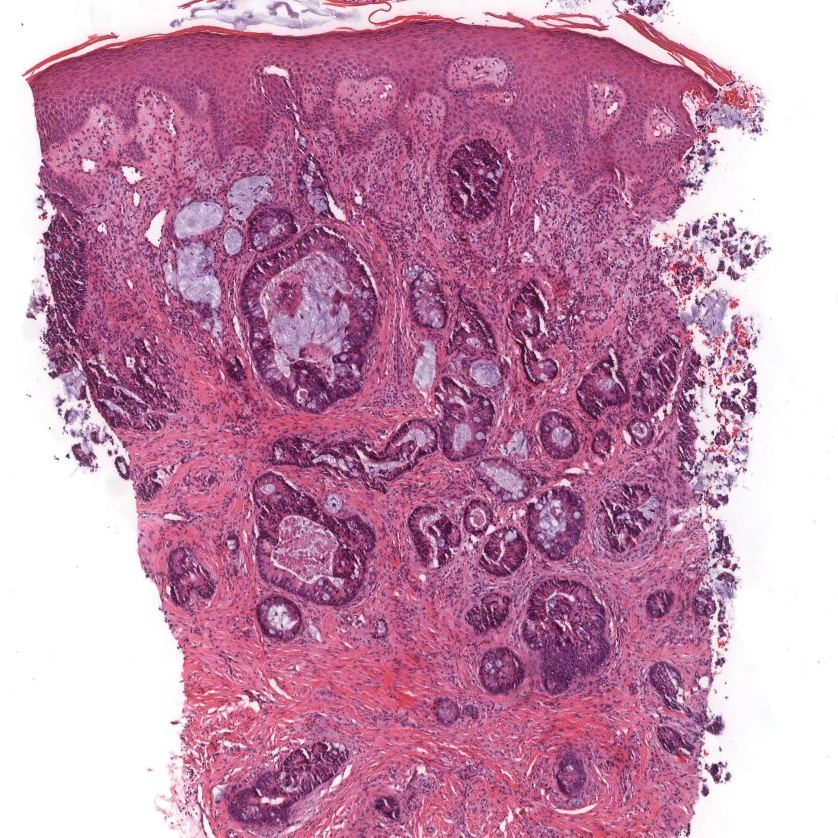
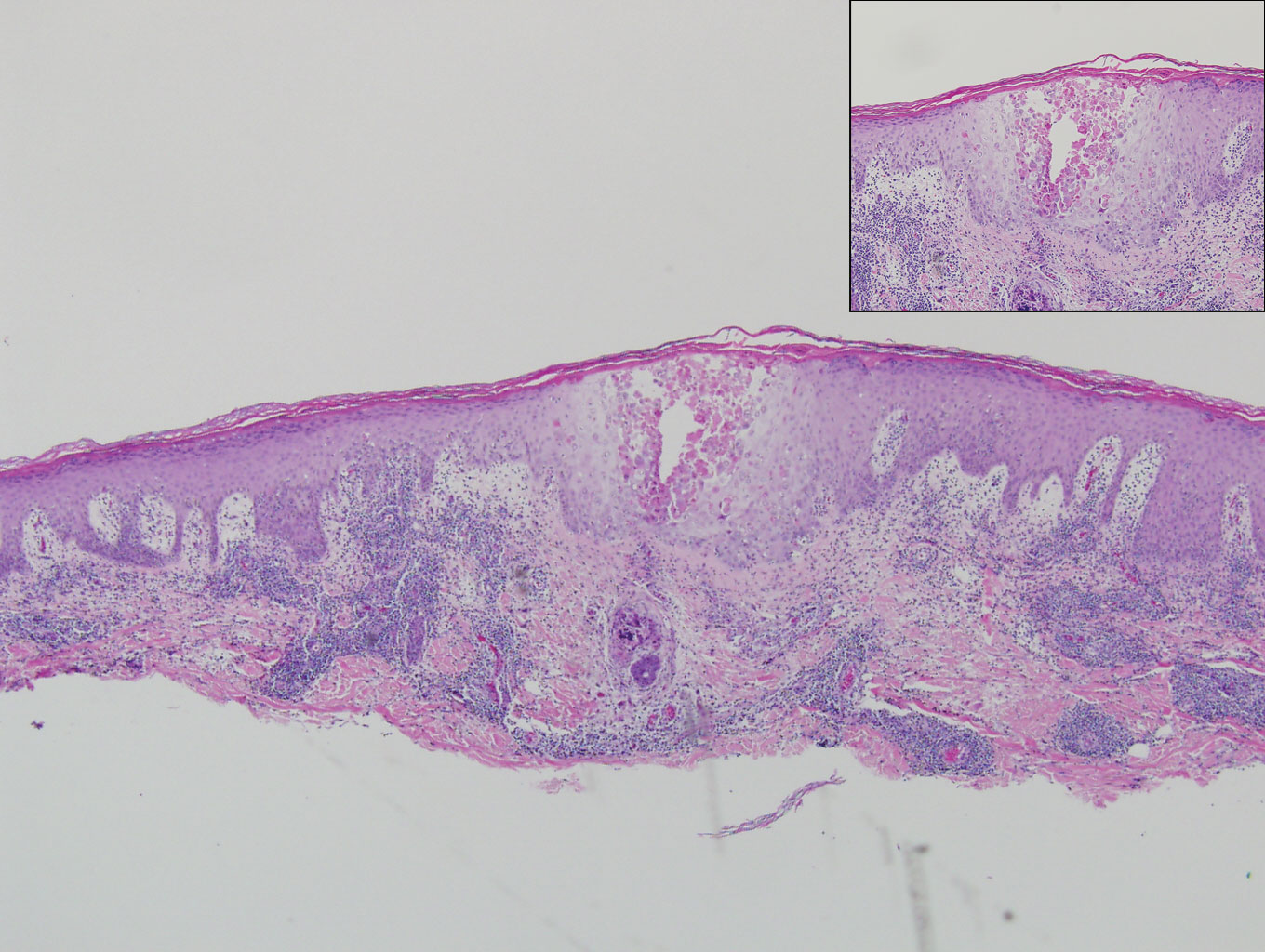
A 68-year-old patient presented with an enlarging flesh-colored nodule on the thigh that was positive for cytokeratin 20 and negative for cytokeratin 7.
Unilateral Facial Papules and Plaques
The Diagnosis: Unilateral Dermatomal Trichoepithelioma
Adnexal lesions presenting with a linear and/or dermatomal pattern rarely have been reported. Bolognia et al1 performed a comprehensive review of Blaschko lines and skin conditions that follow such a pattern. The authors found that adnexal-related lesions included linear nevus comedonicus, linear basal cell nevus with comedones (linear basaloid follicular hamartoma), unilateral nevoid basal cell carcinoma (BCC), linear trichoepithelioma, linear trichodiscoma, linear hamartoma of the follicular infundibulum, nevus sebaceous, syringocystadenoma papilliferum, porokeratotic eccrine ostial and dermal duct nevus, linear eccrine poroma, linear spiradenoma, linear syringoma, and linear eccrine syringofibroadenoma.1
Trichoepithelioma is a hair follicle-related neoplastic lesion presenting most commonly as the autosomal-dominant multiple familial type with lesions mainly centered on the face. Initial genetic studies associated the disease with loss of heterozygosity in the 9p21 region and further studies identified mutations in the CYLD (cylindromatosis [turban tumor syndrome]) gene on chromosome 16q12-q13.2,3 Unilateral, linear, and dermatomal forms of trichoepithelioma rarely are reported. In 1986, Geffner et al4 reported a case of linear and dermatomal trichoepithelioma in a 10-year-old girl. In addition to discrete solitary lesions affecting the face, she developed lesions on the left shoulder, left side of the trunk, and left lower leg following dermatomal distribution. In 2006, 2 cases of dermatomal trichoepitheliomas affecting the face in children, as in our case, were reported.5,6 Another case involving the neck was reported in 2016.7 Although classic multiple familial trichoepithelioma can be part of conditions such as Brooke-Spiegler8 and Rombo syndromes,9 no syndromal association has been reported thus far with the unilateral, linear, or dermatomal variants.
Our case showed typical histopathologic features of trichoepithelioma, including discrete islands of basaloid cells in the dermis set in a conspicuous fibroblastic stroma. Focal connection with the epidermis was present. Most of the islands showed peripheral palisading and horn cysts lined by eosinophilic cells. The fibroblastic component was tightly adherent to the epithelial component, and only stromal clefts were detected. Papillary mesenchymal bodies also were detected as oval aggregates of fibroblastic cells invaginating into epithelial islands to form hair papillae.
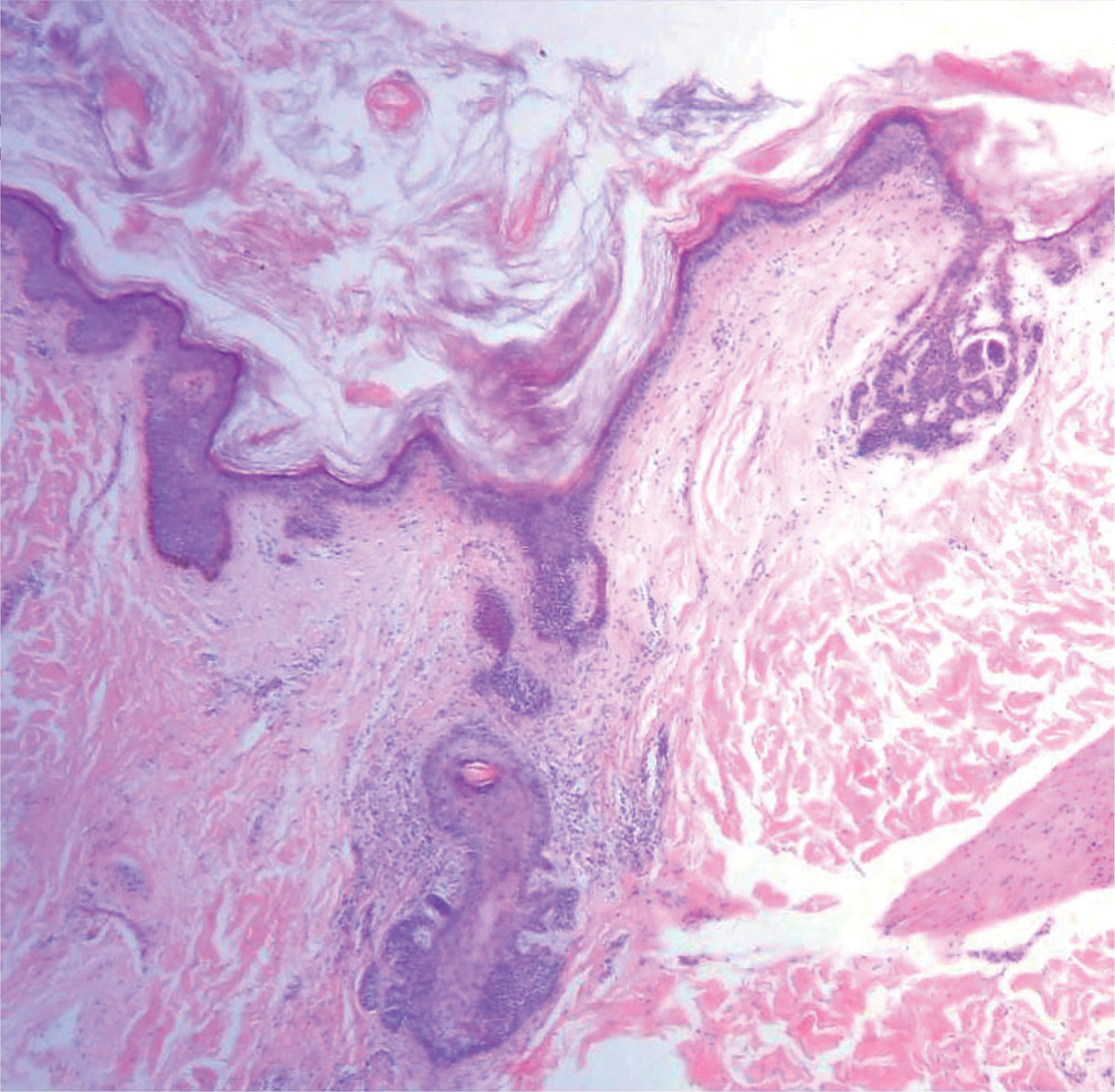
Histopathologically, the 2 most important differential diagnoses of trichoepithelioma include BCC and basaloid follicular hamartoma. In differentiating BCC from trichoepithelioma, the presence of dense fibroblastic stroma and papillary mesenchymal bodies characterize trichoepithelioma, while a fibromucinous stroma with mucinous retraction artifacts and clefting between the basaloid islands and the stroma characterize BCC (Figure 1).10 Immunohistochemical studies using antibodies against Bcl-2, CD34, CD10, androgen receptor, Ki-67, cytokeratin 19, and PHLDA1 (pleckstrin homologylike domain family A member 1) have reportedly been utilized to differentiate trichoepithelioma from BCC.11,12 Basaloid follicular hamartoma is characterized by thin anastomosing strands and branching cords of undifferentiated basaloid cells that replace or associate hair follicles in a latticelike pattern (Figure 2). The strands usually are vertically oriented perpendicular to the epidermis. Peripheral palisading is possible, and the basaloid strands are surrounded with cellular connective tissue stroma.13 Tumor islands in eccrine poroma show broad connections with the epidermis and are composed of poroid cells that show evident ductal differentiation with eosinophilic cuticles (Figure 3).14 Spiradenoma is characterized by capsulated deep-seated tumorous nodules not connected with the epidermis and composed of light and dark cells with ductal differentiation and vascular stroma (Figure 4). Scattered lymphocytes within the tumor lobules and in the stroma also are seen. Eosinophilic hyaline globules rarely can be present.15


Many pathologists consider trichoepithelioma as the superficial variant of trichoblastoma. According to the recent World Health Organization classification of benign tumors with follicular differentiation, trichoepithelioma is considered synonymous with trichoblastoma.16
Trichoepitheliomas are benign tumors, and therapy is mainly directed at removal for cosmetic purposes. Several methods of removal are available including electrocautery, laser therapy, and surgery. Awareness of the possible dermatomal distribution of hair follicle and other adnexal-related conditions is important, and such lesions should be thought of in the differential diagnosis of unilateral and/or dermatomal lesions.
- Bolognia JL, Orlow SJ, Glick SA. Lines of Blaschko. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31(2, pt 1):157-190.
- Harada H, Hashimoto K, Ko MS. The gene for multiple familial trichoepithelioma maps to chromosome 9p21. J Invest Dermatol. 1996;107:41-43.
- Zheng G, Hu L, Huang W, et al. CYLD mutation causes multiple familial trichoepithelioma in three Chinese families. Hum Mutat. 2004;23:400.
- Geffner RE, Goslen JB, Santa Cruz DJ. Linear and dermatomal trichoepitheliomas. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;14(5, pt 2):927-930.
- Chang YC, Colome-Grimmer M, Kelly E. Multiple trichoepitheliomas in the lines of Blaschko. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006;23:149-151.
- Strauss RM, Merchant WJ, Stainforth JM, et al. Unilateral naevoid trichoepitheliomas on the face of a child. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;6:778-780.
- Laska AJ, Belli RA, Kobayashi TT. Linear trichoepithelioma on the neck of a 15-year-old girl. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22. pii:13030/qt87b6h4q8.
- Rasmussen JE. A syndrome of trichoepitheliomas, milia and cylindroma. Arch Dermatol. 1975;111:610-614.
- Michaelson G, Olsson E, Westermark P. The Rombo syndrome. Acta Derm Venereol. 1981;61:497-503.
- Brooke JD, Fitzpatrick JE, Golitz LE. Papillary mesenchymal bodies: a histologic finding useful in differentiating trichoepitheliomas from basal cell carcinomas. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;21(3, pt 1):523-528.
- Mostafa NA, Assaf M, Elhakim S, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of immunohistochemical markers in differentiation between basal cell carcinoma and trichoepithelioma in small biopsy specimens. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:807-816.
- Poniecka AW, Alexis JB. An immunohistochemical study of basal cell carcinoma and trichoepithelioma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1999;21:332-336.
- Abdel-Halim MRE, Fawzy M, Saleh M, et al. Linear unilateral basal cell nevus with comedones (linear nevoid basaloid follicular hamartoma): a case report. J Egypt Womens Dermatol Soc. 2016;13:46-48.
- Hyman AB, Brownstein MH. Eccrine poroma: analysis of 45 new cases. Dermatologica. 1969;138:28-38.
- Mambo NC. Eccrine spiradenoma: clinical and pathologic study of 49 tumors. J Cutan Pathol. 1983;10:312-320.
- Kutzner H, Kaddu S, Kanitakis J, et al. Trichoblastoma. In: Elder D, Massi D, Scolyer RA, et al, eds. WHO Classification of Skin Tumours. 4th ed. Lyon, France: IARC; 2018.
The Diagnosis: Unilateral Dermatomal Trichoepithelioma
Adnexal lesions presenting with a linear and/or dermatomal pattern rarely have been reported. Bolognia et al1 performed a comprehensive review of Blaschko lines and skin conditions that follow such a pattern. The authors found that adnexal-related lesions included linear nevus comedonicus, linear basal cell nevus with comedones (linear basaloid follicular hamartoma), unilateral nevoid basal cell carcinoma (BCC), linear trichoepithelioma, linear trichodiscoma, linear hamartoma of the follicular infundibulum, nevus sebaceous, syringocystadenoma papilliferum, porokeratotic eccrine ostial and dermal duct nevus, linear eccrine poroma, linear spiradenoma, linear syringoma, and linear eccrine syringofibroadenoma.1
Trichoepithelioma is a hair follicle-related neoplastic lesion presenting most commonly as the autosomal-dominant multiple familial type with lesions mainly centered on the face. Initial genetic studies associated the disease with loss of heterozygosity in the 9p21 region and further studies identified mutations in the CYLD (cylindromatosis [turban tumor syndrome]) gene on chromosome 16q12-q13.2,3 Unilateral, linear, and dermatomal forms of trichoepithelioma rarely are reported. In 1986, Geffner et al4 reported a case of linear and dermatomal trichoepithelioma in a 10-year-old girl. In addition to discrete solitary lesions affecting the face, she developed lesions on the left shoulder, left side of the trunk, and left lower leg following dermatomal distribution. In 2006, 2 cases of dermatomal trichoepitheliomas affecting the face in children, as in our case, were reported.5,6 Another case involving the neck was reported in 2016.7 Although classic multiple familial trichoepithelioma can be part of conditions such as Brooke-Spiegler8 and Rombo syndromes,9 no syndromal association has been reported thus far with the unilateral, linear, or dermatomal variants.
Our case showed typical histopathologic features of trichoepithelioma, including discrete islands of basaloid cells in the dermis set in a conspicuous fibroblastic stroma. Focal connection with the epidermis was present. Most of the islands showed peripheral palisading and horn cysts lined by eosinophilic cells. The fibroblastic component was tightly adherent to the epithelial component, and only stromal clefts were detected. Papillary mesenchymal bodies also were detected as oval aggregates of fibroblastic cells invaginating into epithelial islands to form hair papillae.
Histopathologically, the 2 most important differential diagnoses of trichoepithelioma include BCC and basaloid follicular hamartoma. In differentiating BCC from trichoepithelioma, the presence of dense fibroblastic stroma and papillary mesenchymal bodies characterize trichoepithelioma, while a fibromucinous stroma with mucinous retraction artifacts and clefting between the basaloid islands and the stroma characterize BCC (Figure 1).10 Immunohistochemical studies using antibodies against Bcl-2, CD34, CD10, androgen receptor, Ki-67, cytokeratin 19, and PHLDA1 (pleckstrin homologylike domain family A member 1) have reportedly been utilized to differentiate trichoepithelioma from BCC.11,12 Basaloid follicular hamartoma is characterized by thin anastomosing strands and branching cords of undifferentiated basaloid cells that replace or associate hair follicles in a latticelike pattern (Figure 2). The strands usually are vertically oriented perpendicular to the epidermis. Peripheral palisading is possible, and the basaloid strands are surrounded with cellular connective tissue stroma.13 Tumor islands in eccrine poroma show broad connections with the epidermis and are composed of poroid cells that show evident ductal differentiation with eosinophilic cuticles (Figure 3).14 Spiradenoma is characterized by capsulated deep-seated tumorous nodules not connected with the epidermis and composed of light and dark cells with ductal differentiation and vascular stroma (Figure 4). Scattered lymphocytes within the tumor lobules and in the stroma also are seen. Eosinophilic hyaline globules rarely can be present.15




Many pathologists consider trichoepithelioma as the superficial variant of trichoblastoma. According to the recent World Health Organization classification of benign tumors with follicular differentiation, trichoepithelioma is considered synonymous with trichoblastoma.16
Trichoepitheliomas are benign tumors, and therapy is mainly directed at removal for cosmetic purposes. Several methods of removal are available including electrocautery, laser therapy, and surgery. Awareness of the possible dermatomal distribution of hair follicle and other adnexal-related conditions is important, and such lesions should be thought of in the differential diagnosis of unilateral and/or dermatomal lesions.
The Diagnosis: Unilateral Dermatomal Trichoepithelioma
Adnexal lesions presenting with a linear and/or dermatomal pattern rarely have been reported. Bolognia et al1 performed a comprehensive review of Blaschko lines and skin conditions that follow such a pattern. The authors found that adnexal-related lesions included linear nevus comedonicus, linear basal cell nevus with comedones (linear basaloid follicular hamartoma), unilateral nevoid basal cell carcinoma (BCC), linear trichoepithelioma, linear trichodiscoma, linear hamartoma of the follicular infundibulum, nevus sebaceous, syringocystadenoma papilliferum, porokeratotic eccrine ostial and dermal duct nevus, linear eccrine poroma, linear spiradenoma, linear syringoma, and linear eccrine syringofibroadenoma.1
Trichoepithelioma is a hair follicle-related neoplastic lesion presenting most commonly as the autosomal-dominant multiple familial type with lesions mainly centered on the face. Initial genetic studies associated the disease with loss of heterozygosity in the 9p21 region and further studies identified mutations in the CYLD (cylindromatosis [turban tumor syndrome]) gene on chromosome 16q12-q13.2,3 Unilateral, linear, and dermatomal forms of trichoepithelioma rarely are reported. In 1986, Geffner et al4 reported a case of linear and dermatomal trichoepithelioma in a 10-year-old girl. In addition to discrete solitary lesions affecting the face, she developed lesions on the left shoulder, left side of the trunk, and left lower leg following dermatomal distribution. In 2006, 2 cases of dermatomal trichoepitheliomas affecting the face in children, as in our case, were reported.5,6 Another case involving the neck was reported in 2016.7 Although classic multiple familial trichoepithelioma can be part of conditions such as Brooke-Spiegler8 and Rombo syndromes,9 no syndromal association has been reported thus far with the unilateral, linear, or dermatomal variants.
Our case showed typical histopathologic features of trichoepithelioma, including discrete islands of basaloid cells in the dermis set in a conspicuous fibroblastic stroma. Focal connection with the epidermis was present. Most of the islands showed peripheral palisading and horn cysts lined by eosinophilic cells. The fibroblastic component was tightly adherent to the epithelial component, and only stromal clefts were detected. Papillary mesenchymal bodies also were detected as oval aggregates of fibroblastic cells invaginating into epithelial islands to form hair papillae.
Histopathologically, the 2 most important differential diagnoses of trichoepithelioma include BCC and basaloid follicular hamartoma. In differentiating BCC from trichoepithelioma, the presence of dense fibroblastic stroma and papillary mesenchymal bodies characterize trichoepithelioma, while a fibromucinous stroma with mucinous retraction artifacts and clefting between the basaloid islands and the stroma characterize BCC (Figure 1).10 Immunohistochemical studies using antibodies against Bcl-2, CD34, CD10, androgen receptor, Ki-67, cytokeratin 19, and PHLDA1 (pleckstrin homologylike domain family A member 1) have reportedly been utilized to differentiate trichoepithelioma from BCC.11,12 Basaloid follicular hamartoma is characterized by thin anastomosing strands and branching cords of undifferentiated basaloid cells that replace or associate hair follicles in a latticelike pattern (Figure 2). The strands usually are vertically oriented perpendicular to the epidermis. Peripheral palisading is possible, and the basaloid strands are surrounded with cellular connective tissue stroma.13 Tumor islands in eccrine poroma show broad connections with the epidermis and are composed of poroid cells that show evident ductal differentiation with eosinophilic cuticles (Figure 3).14 Spiradenoma is characterized by capsulated deep-seated tumorous nodules not connected with the epidermis and composed of light and dark cells with ductal differentiation and vascular stroma (Figure 4). Scattered lymphocytes within the tumor lobules and in the stroma also are seen. Eosinophilic hyaline globules rarely can be present.15




Many pathologists consider trichoepithelioma as the superficial variant of trichoblastoma. According to the recent World Health Organization classification of benign tumors with follicular differentiation, trichoepithelioma is considered synonymous with trichoblastoma.16
Trichoepitheliomas are benign tumors, and therapy is mainly directed at removal for cosmetic purposes. Several methods of removal are available including electrocautery, laser therapy, and surgery. Awareness of the possible dermatomal distribution of hair follicle and other adnexal-related conditions is important, and such lesions should be thought of in the differential diagnosis of unilateral and/or dermatomal lesions.
- Bolognia JL, Orlow SJ, Glick SA. Lines of Blaschko. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31(2, pt 1):157-190.
- Harada H, Hashimoto K, Ko MS. The gene for multiple familial trichoepithelioma maps to chromosome 9p21. J Invest Dermatol. 1996;107:41-43.
- Zheng G, Hu L, Huang W, et al. CYLD mutation causes multiple familial trichoepithelioma in three Chinese families. Hum Mutat. 2004;23:400.
- Geffner RE, Goslen JB, Santa Cruz DJ. Linear and dermatomal trichoepitheliomas. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;14(5, pt 2):927-930.
- Chang YC, Colome-Grimmer M, Kelly E. Multiple trichoepitheliomas in the lines of Blaschko. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006;23:149-151.
- Strauss RM, Merchant WJ, Stainforth JM, et al. Unilateral naevoid trichoepitheliomas on the face of a child. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;6:778-780.
- Laska AJ, Belli RA, Kobayashi TT. Linear trichoepithelioma on the neck of a 15-year-old girl. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22. pii:13030/qt87b6h4q8.
- Rasmussen JE. A syndrome of trichoepitheliomas, milia and cylindroma. Arch Dermatol. 1975;111:610-614.
- Michaelson G, Olsson E, Westermark P. The Rombo syndrome. Acta Derm Venereol. 1981;61:497-503.
- Brooke JD, Fitzpatrick JE, Golitz LE. Papillary mesenchymal bodies: a histologic finding useful in differentiating trichoepitheliomas from basal cell carcinomas. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;21(3, pt 1):523-528.
- Mostafa NA, Assaf M, Elhakim S, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of immunohistochemical markers in differentiation between basal cell carcinoma and trichoepithelioma in small biopsy specimens. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:807-816.
- Poniecka AW, Alexis JB. An immunohistochemical study of basal cell carcinoma and trichoepithelioma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1999;21:332-336.
- Abdel-Halim MRE, Fawzy M, Saleh M, et al. Linear unilateral basal cell nevus with comedones (linear nevoid basaloid follicular hamartoma): a case report. J Egypt Womens Dermatol Soc. 2016;13:46-48.
- Hyman AB, Brownstein MH. Eccrine poroma: analysis of 45 new cases. Dermatologica. 1969;138:28-38.
- Mambo NC. Eccrine spiradenoma: clinical and pathologic study of 49 tumors. J Cutan Pathol. 1983;10:312-320.
- Kutzner H, Kaddu S, Kanitakis J, et al. Trichoblastoma. In: Elder D, Massi D, Scolyer RA, et al, eds. WHO Classification of Skin Tumours. 4th ed. Lyon, France: IARC; 2018.
- Bolognia JL, Orlow SJ, Glick SA. Lines of Blaschko. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31(2, pt 1):157-190.
- Harada H, Hashimoto K, Ko MS. The gene for multiple familial trichoepithelioma maps to chromosome 9p21. J Invest Dermatol. 1996;107:41-43.
- Zheng G, Hu L, Huang W, et al. CYLD mutation causes multiple familial trichoepithelioma in three Chinese families. Hum Mutat. 2004;23:400.
- Geffner RE, Goslen JB, Santa Cruz DJ. Linear and dermatomal trichoepitheliomas. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;14(5, pt 2):927-930.
- Chang YC, Colome-Grimmer M, Kelly E. Multiple trichoepitheliomas in the lines of Blaschko. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006;23:149-151.
- Strauss RM, Merchant WJ, Stainforth JM, et al. Unilateral naevoid trichoepitheliomas on the face of a child. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;6:778-780.
- Laska AJ, Belli RA, Kobayashi TT. Linear trichoepithelioma on the neck of a 15-year-old girl. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22. pii:13030/qt87b6h4q8.
- Rasmussen JE. A syndrome of trichoepitheliomas, milia and cylindroma. Arch Dermatol. 1975;111:610-614.
- Michaelson G, Olsson E, Westermark P. The Rombo syndrome. Acta Derm Venereol. 1981;61:497-503.
- Brooke JD, Fitzpatrick JE, Golitz LE. Papillary mesenchymal bodies: a histologic finding useful in differentiating trichoepitheliomas from basal cell carcinomas. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;21(3, pt 1):523-528.
- Mostafa NA, Assaf M, Elhakim S, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of immunohistochemical markers in differentiation between basal cell carcinoma and trichoepithelioma in small biopsy specimens. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:807-816.
- Poniecka AW, Alexis JB. An immunohistochemical study of basal cell carcinoma and trichoepithelioma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1999;21:332-336.
- Abdel-Halim MRE, Fawzy M, Saleh M, et al. Linear unilateral basal cell nevus with comedones (linear nevoid basaloid follicular hamartoma): a case report. J Egypt Womens Dermatol Soc. 2016;13:46-48.
- Hyman AB, Brownstein MH. Eccrine poroma: analysis of 45 new cases. Dermatologica. 1969;138:28-38.
- Mambo NC. Eccrine spiradenoma: clinical and pathologic study of 49 tumors. J Cutan Pathol. 1983;10:312-320.
- Kutzner H, Kaddu S, Kanitakis J, et al. Trichoblastoma. In: Elder D, Massi D, Scolyer RA, et al, eds. WHO Classification of Skin Tumours. 4th ed. Lyon, France: IARC; 2018.

A 9-year-old boy presented with a slowly progressive lesion of 5 years’ duration affecting only the left side of the face in a dermatomal pattern. The patient denied any symptoms and had no other anomalies or family history of similar lesions. On physical examination the lesion was found to span a 12×7-cm area of the lateral half of the left cheek and was composed of multiple variable-sized, pinkish to flesh-colored papules that coalesced in some areas to form small plaques. Few milialike cysts were present. One papule was biopsied.
Indurated Plaque on the Shoulder
Herpes zoster (HZ) is a painful skin condition caused by reactivation of latent varicella-zoster virus (VZV) in dorsal root ganglion cells.1 Upon reactivation, VZV replicates in the dorsal root ganglion, which ultimately results in inflammation and necrosis of the neuron and intense neuralgia. Reactivation of latent VZV may occur spontaneously or may be induced by various factors including immunosuppression, stress, illness, and trauma. Prior to the development of skin lesions, many patients experience a prodrome of tingling, pain, or pruritus. Herpes zoster classically presents with grouped vesicles on an erythematous base in a unilateral dermatomal distribution; however, more than one adjacent dermatome may be involved, and the lesions can cross the midline. Furthermore, the development of vesicles may be preceded by the development of edematous papules or plaques.1
On histology, VZV closely resembles herpes simplex virus type 1 and herpes simplex virus type 2 infections.2 Classic histologic findings include ballooning degeneration of keratinocytes, acantholysis, nuclear molding, ground-glass nuclear inclusions, marginated chromatin, and multinucleated keratinocytes, as well as necrosis of follicles and sebaceous glands.2 Varicella-zoster virus polymerase chain reaction or immunostaining can be used to confirm the diagnosis.2
Classic mycosis fungoides (MF) presents with well-circumscribed erythematous patches in non–sun-exposed areas and eventually may progress to plaques and tumors.3 Patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphomas, such as MF, are at a higher risk for skin infections including HZ4,5; however, immunocompromised patients, such as those with cutaneous lymphomas, can have atypical clinical presentations of HZ that may be concerning for cutaneous lymphoma.6 Furthermore, cutaneous malignancies can occur in dermatomal distributions that may mimic HZ.7 Therefore, the threshold for biopsy should be lowered in those patients with dermatomal lesions and history concerning for possible malignancy.
Classically, histologic examination of MF demonstrates an infiltrate of haloed cells at the dermoepidermal junction, which are atypical T cells with hyperchromatic cerebriform nuclei that are larger, darker, and more angulated than the benign recruited lymphocytes in the perivascular infiltrate seen in VZV infection (Figure 1).3 Papillary dermal fibrosis typically is present, and the perivascular infiltrate is denser above the postcapillary venule rather than being symmetrical around the vessel (bare underbelly sign). Clusters of these cells may form within the epidermis, which are called Pautrier microabscesses.3 Mycosis fungoides also can exhibit large cell transformation in which small lymphocytes transform into larger cells, thereby associated with a poorer prognosis.8
Lymphomatoid papulosis is a CD30+-predominant form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma characterized by papules and nodules that spontaneously involute.9 This condition is most commonly associated with MF but can be associated with other lymphomas. This condition may be mistaken for HZ clinically, but histology classically demonstrates large atypical lymphocytes resembling Reed-Sternberg cells in small clusters rather than follicular necrosis (Figure 2).9
Patients with lymphoma may sequentially develop a secondary lymphoma. There have been reports of secondary B-cell lymphomas associated with MF, but this phenomenon is rare.10 The histology depends on the type of B-cell lymphoma present, but follicular necrosis would not be expected (Figure 3).
Unusual hypersensitivity reactions to arthropod attacks have been described in patients with lymphoproliferative disorders and could be mistaken for HZ. Histology may demonstrate a wedge-shaped perivascular and/or interstitial infiltrate containing eosinophils with endothelial swelling (Figure 4), but these findings may vary depending on the type of arthropod involved.11
Our case provided a unique example of HZ in a patient with a known history of MF. Clinically, there was concern for progression of the patient’s underlying disease; however, histology demonstrated ballooning keratinocytes and follicular necrosis, which are classically seen in HZ infection.
- Downing C, Medoza N, Sra K, et al. Human herpesviruses. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. China: Elsevier; 2018:1400-1424.
- Chisholm C, Lopez L. Cutaneous infections caused by Herpesviridae: a review. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135:1357-1362.
- Jawed SI, Myskowski PL, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome): part I. diagnosis: clinical and histopathologic features and new molecular and biologic markers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70: 205.e1-205.e16.
- Vonderheid EC, van Voorst Vader PC. Herpes zoster-varicella in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Arch Dermatol. 1980;116:408-412.
- Lebas E, Arrese JE, Nikkels AF. Risk factors for skin infections in mycosis fungoides. Dermatology. 2016;232:731-737.
- Leinweber B, Kerl H, Cerroni L. Histopathologic features of cutaneous herpes virus infections (herpes simplex, herpes varicella/zoster): a broad spectrum of presentations with common pseudolymphomatous aspects. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30:50-58.
- Niiyama S, Satoh K, Kaneko S, et al. Zosteriform skin involvement of nodal T-cell lymphoma: a review of the published work of cutaneous malignancies mimicking herpes zoster. J Dermatol. 2007;34:68-73.
- Pulitzer M, Myskowski PL, Horwitz SM, et al. Mycosis fungoides with large cell transformation:clinicopathological features and prognostic factors. Pathology. 2014;46:610-616.
- Zackheim HS, Jones C, Leboit PE, et al. Lymphomatoid papulosis associated with mycosis fungoides: a study of 21 patients including analyses for clonality. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:620-623.
- Barzilai A, Trau H, David M, et al. Mycosis fungoides associated with B-cell malignancies. Br J Dermatol. 2006;155:379-386.
- Vassallo C, Passamonti F, Cananzi R, et al. Exaggerated insect bite-like reaction in patients affected by oncohaematological diseases. Acta Derm Venereol. 2005;85:76-77.
Herpes zoster (HZ) is a painful skin condition caused by reactivation of latent varicella-zoster virus (VZV) in dorsal root ganglion cells.1 Upon reactivation, VZV replicates in the dorsal root ganglion, which ultimately results in inflammation and necrosis of the neuron and intense neuralgia. Reactivation of latent VZV may occur spontaneously or may be induced by various factors including immunosuppression, stress, illness, and trauma. Prior to the development of skin lesions, many patients experience a prodrome of tingling, pain, or pruritus. Herpes zoster classically presents with grouped vesicles on an erythematous base in a unilateral dermatomal distribution; however, more than one adjacent dermatome may be involved, and the lesions can cross the midline. Furthermore, the development of vesicles may be preceded by the development of edematous papules or plaques.1
On histology, VZV closely resembles herpes simplex virus type 1 and herpes simplex virus type 2 infections.2 Classic histologic findings include ballooning degeneration of keratinocytes, acantholysis, nuclear molding, ground-glass nuclear inclusions, marginated chromatin, and multinucleated keratinocytes, as well as necrosis of follicles and sebaceous glands.2 Varicella-zoster virus polymerase chain reaction or immunostaining can be used to confirm the diagnosis.2
Classic mycosis fungoides (MF) presents with well-circumscribed erythematous patches in non–sun-exposed areas and eventually may progress to plaques and tumors.3 Patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphomas, such as MF, are at a higher risk for skin infections including HZ4,5; however, immunocompromised patients, such as those with cutaneous lymphomas, can have atypical clinical presentations of HZ that may be concerning for cutaneous lymphoma.6 Furthermore, cutaneous malignancies can occur in dermatomal distributions that may mimic HZ.7 Therefore, the threshold for biopsy should be lowered in those patients with dermatomal lesions and history concerning for possible malignancy.
Classically, histologic examination of MF demonstrates an infiltrate of haloed cells at the dermoepidermal junction, which are atypical T cells with hyperchromatic cerebriform nuclei that are larger, darker, and more angulated than the benign recruited lymphocytes in the perivascular infiltrate seen in VZV infection (Figure 1).3 Papillary dermal fibrosis typically is present, and the perivascular infiltrate is denser above the postcapillary venule rather than being symmetrical around the vessel (bare underbelly sign). Clusters of these cells may form within the epidermis, which are called Pautrier microabscesses.3 Mycosis fungoides also can exhibit large cell transformation in which small lymphocytes transform into larger cells, thereby associated with a poorer prognosis.8

Lymphomatoid papulosis is a CD30+-predominant form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma characterized by papules and nodules that spontaneously involute.9 This condition is most commonly associated with MF but can be associated with other lymphomas. This condition may be mistaken for HZ clinically, but histology classically demonstrates large atypical lymphocytes resembling Reed-Sternberg cells in small clusters rather than follicular necrosis (Figure 2).9

Patients with lymphoma may sequentially develop a secondary lymphoma. There have been reports of secondary B-cell lymphomas associated with MF, but this phenomenon is rare.10 The histology depends on the type of B-cell lymphoma present, but follicular necrosis would not be expected (Figure 3).

Unusual hypersensitivity reactions to arthropod attacks have been described in patients with lymphoproliferative disorders and could be mistaken for HZ. Histology may demonstrate a wedge-shaped perivascular and/or interstitial infiltrate containing eosinophils with endothelial swelling (Figure 4), but these findings may vary depending on the type of arthropod involved.11
Our case provided a unique example of HZ in a patient with a known history of MF. Clinically, there was concern for progression of the patient’s underlying disease; however, histology demonstrated ballooning keratinocytes and follicular necrosis, which are classically seen in HZ infection.

Herpes zoster (HZ) is a painful skin condition caused by reactivation of latent varicella-zoster virus (VZV) in dorsal root ganglion cells.1 Upon reactivation, VZV replicates in the dorsal root ganglion, which ultimately results in inflammation and necrosis of the neuron and intense neuralgia. Reactivation of latent VZV may occur spontaneously or may be induced by various factors including immunosuppression, stress, illness, and trauma. Prior to the development of skin lesions, many patients experience a prodrome of tingling, pain, or pruritus. Herpes zoster classically presents with grouped vesicles on an erythematous base in a unilateral dermatomal distribution; however, more than one adjacent dermatome may be involved, and the lesions can cross the midline. Furthermore, the development of vesicles may be preceded by the development of edematous papules or plaques.1
On histology, VZV closely resembles herpes simplex virus type 1 and herpes simplex virus type 2 infections.2 Classic histologic findings include ballooning degeneration of keratinocytes, acantholysis, nuclear molding, ground-glass nuclear inclusions, marginated chromatin, and multinucleated keratinocytes, as well as necrosis of follicles and sebaceous glands.2 Varicella-zoster virus polymerase chain reaction or immunostaining can be used to confirm the diagnosis.2
Classic mycosis fungoides (MF) presents with well-circumscribed erythematous patches in non–sun-exposed areas and eventually may progress to plaques and tumors.3 Patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphomas, such as MF, are at a higher risk for skin infections including HZ4,5; however, immunocompromised patients, such as those with cutaneous lymphomas, can have atypical clinical presentations of HZ that may be concerning for cutaneous lymphoma.6 Furthermore, cutaneous malignancies can occur in dermatomal distributions that may mimic HZ.7 Therefore, the threshold for biopsy should be lowered in those patients with dermatomal lesions and history concerning for possible malignancy.
Classically, histologic examination of MF demonstrates an infiltrate of haloed cells at the dermoepidermal junction, which are atypical T cells with hyperchromatic cerebriform nuclei that are larger, darker, and more angulated than the benign recruited lymphocytes in the perivascular infiltrate seen in VZV infection (Figure 1).3 Papillary dermal fibrosis typically is present, and the perivascular infiltrate is denser above the postcapillary venule rather than being symmetrical around the vessel (bare underbelly sign). Clusters of these cells may form within the epidermis, which are called Pautrier microabscesses.3 Mycosis fungoides also can exhibit large cell transformation in which small lymphocytes transform into larger cells, thereby associated with a poorer prognosis.8

Lymphomatoid papulosis is a CD30+-predominant form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma characterized by papules and nodules that spontaneously involute.9 This condition is most commonly associated with MF but can be associated with other lymphomas. This condition may be mistaken for HZ clinically, but histology classically demonstrates large atypical lymphocytes resembling Reed-Sternberg cells in small clusters rather than follicular necrosis (Figure 2).9

Patients with lymphoma may sequentially develop a secondary lymphoma. There have been reports of secondary B-cell lymphomas associated with MF, but this phenomenon is rare.10 The histology depends on the type of B-cell lymphoma present, but follicular necrosis would not be expected (Figure 3).

Unusual hypersensitivity reactions to arthropod attacks have been described in patients with lymphoproliferative disorders and could be mistaken for HZ. Histology may demonstrate a wedge-shaped perivascular and/or interstitial infiltrate containing eosinophils with endothelial swelling (Figure 4), but these findings may vary depending on the type of arthropod involved.11
Our case provided a unique example of HZ in a patient with a known history of MF. Clinically, there was concern for progression of the patient’s underlying disease; however, histology demonstrated ballooning keratinocytes and follicular necrosis, which are classically seen in HZ infection.

- Downing C, Medoza N, Sra K, et al. Human herpesviruses. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. China: Elsevier; 2018:1400-1424.
- Chisholm C, Lopez L. Cutaneous infections caused by Herpesviridae: a review. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135:1357-1362.
- Jawed SI, Myskowski PL, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome): part I. diagnosis: clinical and histopathologic features and new molecular and biologic markers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70: 205.e1-205.e16.
- Vonderheid EC, van Voorst Vader PC. Herpes zoster-varicella in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Arch Dermatol. 1980;116:408-412.
- Lebas E, Arrese JE, Nikkels AF. Risk factors for skin infections in mycosis fungoides. Dermatology. 2016;232:731-737.
- Leinweber B, Kerl H, Cerroni L. Histopathologic features of cutaneous herpes virus infections (herpes simplex, herpes varicella/zoster): a broad spectrum of presentations with common pseudolymphomatous aspects. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30:50-58.
- Niiyama S, Satoh K, Kaneko S, et al. Zosteriform skin involvement of nodal T-cell lymphoma: a review of the published work of cutaneous malignancies mimicking herpes zoster. J Dermatol. 2007;34:68-73.
- Pulitzer M, Myskowski PL, Horwitz SM, et al. Mycosis fungoides with large cell transformation:clinicopathological features and prognostic factors. Pathology. 2014;46:610-616.
- Zackheim HS, Jones C, Leboit PE, et al. Lymphomatoid papulosis associated with mycosis fungoides: a study of 21 patients including analyses for clonality. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:620-623.
- Barzilai A, Trau H, David M, et al. Mycosis fungoides associated with B-cell malignancies. Br J Dermatol. 2006;155:379-386.
- Vassallo C, Passamonti F, Cananzi R, et al. Exaggerated insect bite-like reaction in patients affected by oncohaematological diseases. Acta Derm Venereol. 2005;85:76-77.
- Downing C, Medoza N, Sra K, et al. Human herpesviruses. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. China: Elsevier; 2018:1400-1424.
- Chisholm C, Lopez L. Cutaneous infections caused by Herpesviridae: a review. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135:1357-1362.
- Jawed SI, Myskowski PL, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome): part I. diagnosis: clinical and histopathologic features and new molecular and biologic markers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70: 205.e1-205.e16.
- Vonderheid EC, van Voorst Vader PC. Herpes zoster-varicella in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Arch Dermatol. 1980;116:408-412.
- Lebas E, Arrese JE, Nikkels AF. Risk factors for skin infections in mycosis fungoides. Dermatology. 2016;232:731-737.
- Leinweber B, Kerl H, Cerroni L. Histopathologic features of cutaneous herpes virus infections (herpes simplex, herpes varicella/zoster): a broad spectrum of presentations with common pseudolymphomatous aspects. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30:50-58.
- Niiyama S, Satoh K, Kaneko S, et al. Zosteriform skin involvement of nodal T-cell lymphoma: a review of the published work of cutaneous malignancies mimicking herpes zoster. J Dermatol. 2007;34:68-73.
- Pulitzer M, Myskowski PL, Horwitz SM, et al. Mycosis fungoides with large cell transformation:clinicopathological features and prognostic factors. Pathology. 2014;46:610-616.
- Zackheim HS, Jones C, Leboit PE, et al. Lymphomatoid papulosis associated with mycosis fungoides: a study of 21 patients including analyses for clonality. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:620-623.
- Barzilai A, Trau H, David M, et al. Mycosis fungoides associated with B-cell malignancies. Br J Dermatol. 2006;155:379-386.
- Vassallo C, Passamonti F, Cananzi R, et al. Exaggerated insect bite-like reaction in patients affected by oncohaematological diseases. Acta Derm Venereol. 2005;85:76-77.
A 66-year-old man with mycosis fungoides presented with a new indurated plaque on the left shoulder. Biopsies of the left shoulder and back lesions were obtained.
Solitary Nodule on the Thigh
The Diagnosis: Ruptured Molluscum
Molluscum contagiosum (MC) is caused by a DNA virus (MC virus) belonging to the poxvirus family. Molluscum contagiosum is common and predominantly seen in children and young adults. In sexually active adults, the lesions commonly occur in the genital region, abdomen, and inner thighs. In immunocompromised individuals, including those with AIDS, the lesions are more extensive and may cause disfigurement.1 Molluscum contagiosum involving epidermoid cysts has been reported.2
Histopathologically, MC can be classified as noninflammatory or inflammatory. In noninflamed lesions, multiple large, intracytoplasmic, eosinophilic inclusions (Henderson-Paterson bodies) appear within the lobulated endophytic and hyperplastic epidermis. Ultrastructurally, these bodies show membrane-bound collections of MC virus.1 Replicating Henderson-Paterson bodies can result in rupture and inflammation. This case demonstrates a palisading granuloma containing keratin with few Henderson-Paterson bodies (quiz image) due to prior rupture of a molluscum or molluscoid cyst.
Rheumatoid nodules, the most characteristic histopathologic lesions of rheumatoid arthritis, are most commonly found in the subcutis at points of pressure and may occur in connective tissue of numerous organs. Rheumatoid nodules are firm, nontender, and mobile within the subcutaneous tissue but may be fixed to underlying structures including the periosteum, tendons, or bursae.3,4 Occasionally, superficial nodules may perforate the epidermis.5 The inner central necrobiotic zone appears as intensely eosinophilic, amorphous fibrin and other cellular debris. This central area is surrounded by histiocytes in a palisaded configuration (Figure 1). Multinucleated foreign body giant cells also may be present. Occasionally, mast cells, eosinophils, and neutrophils are present.6,7
Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei presents with multiple discrete, smooth, yellow-brown to red, dome-shaped papules. The lesions typically are located on the central and lateral sides of the face and infrequently involve the neck. Other sites including the axillae, arms, hands, legs, and groin occasionally can be involved. Diascopy may reveal an apple jelly color.8,9 The histopathologic hallmark of lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei is an epithelioid cell granuloma with central necrosis (Figure 2).

Epithelioid sarcoma (ES) is a soft tissue tumor with a known propensity for local recurrence, regional lymph node involvement, sporotrichoid spread, and distant metastases.10 The name was coined by Enzinger11 in 1970 during a review of 62 cases of a “peculiar form of sarcoma that has repeatedly been confused with a chronic inflammatory process, a necrotizing granuloma, and a squamous cell carcinoma.” Epithelioid sarcoma tends to grow slowly in a nodular or multinodular manner along fascial structures and tendons, often with central necrosis and ulceration of the overlying skin. Histopathologically, classic ES shows nodular masses of uniform plump epithelioid cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and prominent central necrosis. A biphasic pattern is typical with spindle cells merging with epithelioid cells. Cellular atypia is relatively mild and mitoses are rare (Figure 3). Recurrent or metastatic lesions can show a greater degree of pleomorphism.12 Given the low-grade atypia in early lesions, this sarcoma is easily misdiagnosed as granulomatous dermatitis. Immunohistochemically, the majority of ES cases are positive for cytokeratins and epithelial membrane antigen; SMARCB1/INI-1 expression is characteristically lost.13
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly Wegener granulomatosis) is an autoimmune vasculitis highly associated with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies. Clinical manifestations include systemic necrotizing vasculitis; necrotizing glomerulonephritis; and granulomatous inflammation, which predominantly involves the upper respiratory tract, skin, and mucosa.14,15 Skin involvement may be the initial manifestation of the disease and consists of palpable purpura, papules, ulcerations, vesicles, subcutaneous nodules, necrotizing ulcerations, papulonecrotic lesions, and petechiae. None of the findings are pathognomonic. The cutaneous histopathologic spectrum includes leukocytoclastic vasculitis, extravascular palisading granulomas, and granulomatous vasculitis.16 In the acute lesions of granulomatosis with polyangiitis, the predominant pattern of inflammation is not granulomatous but purulent with the appearance of an abscess. As it evolves, it develops a central zone of necrosis with extensive karyorrhectic debris and palisades of macrophages with scattered multinucleated giant cells (Figure 4).17
1. Nandhini G, Rajkumar K, Kanth KS, et al. Molluscum contagiosum in a 12-year-old child—report of a case and review of literature. J Int Oral Health. 2015;7:63-66.
2. Phelps A, Murphy M, Elaba Z, et al. Molluscum contagiosum virus infection in benign cutaneous epithelial cystic lesions-report of 2 cases with different pathogenesis? Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:740-742.
3. Sayah A, English JC 3rd. Rheumatoid arthritis: a review of the cutaneous manifestations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:191-209; quiz 210-192.
4. Sibbitt WL Jr, Williams RC Jr. Cutaneous manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Dermatol. 1982;21:563-572.
5. Barzilai A, Huszar M, Shpiro D, et al. Pseudorheumatoid nodules in adults: a juxta-articular form of nodular granuloma annulare. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:1-5.
6. Garcia-Patos V. Rheumatoid nodule. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2007;26:100-107.
7. Patterson JW. Rheumatoid nodule and subcutaneous granuloma annulare. a comparative histologic study. Am J Dermatopathol. 1988;10:1-8.
8. Sehgal VN, Srivastava G, Aggarwal AK, et al. Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei part II: an overview. Skinmed. 2005;4:234-238.
9. Cymerman R, Rosenstein R, Shvartsbeyn M, et al. Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21. pii:13030/qt6b83q5gp.
10. Sobanko JF, Meijer L, Nigra TP. Epithelioid sarcoma: a review and update. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2009;2:49-54.
11. Enzinger FM. Epitheloid sarcoma. a sarcoma simulating a granuloma or a carcinoma. Cancer. 1970;26:1029-1041.
12. Fisher C. Epithelioid sarcoma of Enzinger. Adv Anat Pathol. 2006;13:114-121.
13. Miettinen M, Fanburg-Smith JC, Virolainen M, et al. Epithelioid sarcoma: an immunohistochemical analysis of 112 classical and variant cases and a discussion of the differential diagnosis. Hum Pathol. 1999;30:934-942.
14. Lutalo PM, D’Cruz DP. Diagnosis and classification of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (aka Wegener’s granulomatosis)[published online January 29, 2014]. J Autoimmun. 2014;48-49:94-98.
15. Frances C, Du LT, Piette JC, et al. Wegener’s granulomatosis. dermatological manifestations in 75 cases with clinicopathologic correlation. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:861-867.
16. Daoud MS, Gibson LE, DeRemee RA, et al. Cutaneous Wegener’s granulomatosis: clinical, histopathologic, and immunopathologic features of thirty patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31:605-612.
17. Jennette JC. Nomenclature and classification of vasculitis: lessons learned from granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s granulomatosis). Clin Exp Immunol. 2011;164 (suppl 1):7-10.
The Diagnosis: Ruptured Molluscum
Molluscum contagiosum (MC) is caused by a DNA virus (MC virus) belonging to the poxvirus family. Molluscum contagiosum is common and predominantly seen in children and young adults. In sexually active adults, the lesions commonly occur in the genital region, abdomen, and inner thighs. In immunocompromised individuals, including those with AIDS, the lesions are more extensive and may cause disfigurement.1 Molluscum contagiosum involving epidermoid cysts has been reported.2
Histopathologically, MC can be classified as noninflammatory or inflammatory. In noninflamed lesions, multiple large, intracytoplasmic, eosinophilic inclusions (Henderson-Paterson bodies) appear within the lobulated endophytic and hyperplastic epidermis. Ultrastructurally, these bodies show membrane-bound collections of MC virus.1 Replicating Henderson-Paterson bodies can result in rupture and inflammation. This case demonstrates a palisading granuloma containing keratin with few Henderson-Paterson bodies (quiz image) due to prior rupture of a molluscum or molluscoid cyst.
Rheumatoid nodules, the most characteristic histopathologic lesions of rheumatoid arthritis, are most commonly found in the subcutis at points of pressure and may occur in connective tissue of numerous organs. Rheumatoid nodules are firm, nontender, and mobile within the subcutaneous tissue but may be fixed to underlying structures including the periosteum, tendons, or bursae.3,4 Occasionally, superficial nodules may perforate the epidermis.5 The inner central necrobiotic zone appears as intensely eosinophilic, amorphous fibrin and other cellular debris. This central area is surrounded by histiocytes in a palisaded configuration (Figure 1). Multinucleated foreign body giant cells also may be present. Occasionally, mast cells, eosinophils, and neutrophils are present.6,7

Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei presents with multiple discrete, smooth, yellow-brown to red, dome-shaped papules. The lesions typically are located on the central and lateral sides of the face and infrequently involve the neck. Other sites including the axillae, arms, hands, legs, and groin occasionally can be involved. Diascopy may reveal an apple jelly color.8,9 The histopathologic hallmark of lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei is an epithelioid cell granuloma with central necrosis (Figure 2).

Epithelioid sarcoma (ES) is a soft tissue tumor with a known propensity for local recurrence, regional lymph node involvement, sporotrichoid spread, and distant metastases.10 The name was coined by Enzinger11 in 1970 during a review of 62 cases of a “peculiar form of sarcoma that has repeatedly been confused with a chronic inflammatory process, a necrotizing granuloma, and a squamous cell carcinoma.” Epithelioid sarcoma tends to grow slowly in a nodular or multinodular manner along fascial structures and tendons, often with central necrosis and ulceration of the overlying skin. Histopathologically, classic ES shows nodular masses of uniform plump epithelioid cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and prominent central necrosis. A biphasic pattern is typical with spindle cells merging with epithelioid cells. Cellular atypia is relatively mild and mitoses are rare (Figure 3). Recurrent or metastatic lesions can show a greater degree of pleomorphism.12 Given the low-grade atypia in early lesions, this sarcoma is easily misdiagnosed as granulomatous dermatitis. Immunohistochemically, the majority of ES cases are positive for cytokeratins and epithelial membrane antigen; SMARCB1/INI-1 expression is characteristically lost.13

Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly Wegener granulomatosis) is an autoimmune vasculitis highly associated with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies. Clinical manifestations include systemic necrotizing vasculitis; necrotizing glomerulonephritis; and granulomatous inflammation, which predominantly involves the upper respiratory tract, skin, and mucosa.14,15 Skin involvement may be the initial manifestation of the disease and consists of palpable purpura, papules, ulcerations, vesicles, subcutaneous nodules, necrotizing ulcerations, papulonecrotic lesions, and petechiae. None of the findings are pathognomonic. The cutaneous histopathologic spectrum includes leukocytoclastic vasculitis, extravascular palisading granulomas, and granulomatous vasculitis.16 In the acute lesions of granulomatosis with polyangiitis, the predominant pattern of inflammation is not granulomatous but purulent with the appearance of an abscess. As it evolves, it develops a central zone of necrosis with extensive karyorrhectic debris and palisades of macrophages with scattered multinucleated giant cells (Figure 4).17

The Diagnosis: Ruptured Molluscum
Molluscum contagiosum (MC) is caused by a DNA virus (MC virus) belonging to the poxvirus family. Molluscum contagiosum is common and predominantly seen in children and young adults. In sexually active adults, the lesions commonly occur in the genital region, abdomen, and inner thighs. In immunocompromised individuals, including those with AIDS, the lesions are more extensive and may cause disfigurement.1 Molluscum contagiosum involving epidermoid cysts has been reported.2
Histopathologically, MC can be classified as noninflammatory or inflammatory. In noninflamed lesions, multiple large, intracytoplasmic, eosinophilic inclusions (Henderson-Paterson bodies) appear within the lobulated endophytic and hyperplastic epidermis. Ultrastructurally, these bodies show membrane-bound collections of MC virus.1 Replicating Henderson-Paterson bodies can result in rupture and inflammation. This case demonstrates a palisading granuloma containing keratin with few Henderson-Paterson bodies (quiz image) due to prior rupture of a molluscum or molluscoid cyst.
Rheumatoid nodules, the most characteristic histopathologic lesions of rheumatoid arthritis, are most commonly found in the subcutis at points of pressure and may occur in connective tissue of numerous organs. Rheumatoid nodules are firm, nontender, and mobile within the subcutaneous tissue but may be fixed to underlying structures including the periosteum, tendons, or bursae.3,4 Occasionally, superficial nodules may perforate the epidermis.5 The inner central necrobiotic zone appears as intensely eosinophilic, amorphous fibrin and other cellular debris. This central area is surrounded by histiocytes in a palisaded configuration (Figure 1). Multinucleated foreign body giant cells also may be present. Occasionally, mast cells, eosinophils, and neutrophils are present.6,7

Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei presents with multiple discrete, smooth, yellow-brown to red, dome-shaped papules. The lesions typically are located on the central and lateral sides of the face and infrequently involve the neck. Other sites including the axillae, arms, hands, legs, and groin occasionally can be involved. Diascopy may reveal an apple jelly color.8,9 The histopathologic hallmark of lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei is an epithelioid cell granuloma with central necrosis (Figure 2).

Epithelioid sarcoma (ES) is a soft tissue tumor with a known propensity for local recurrence, regional lymph node involvement, sporotrichoid spread, and distant metastases.10 The name was coined by Enzinger11 in 1970 during a review of 62 cases of a “peculiar form of sarcoma that has repeatedly been confused with a chronic inflammatory process, a necrotizing granuloma, and a squamous cell carcinoma.” Epithelioid sarcoma tends to grow slowly in a nodular or multinodular manner along fascial structures and tendons, often with central necrosis and ulceration of the overlying skin. Histopathologically, classic ES shows nodular masses of uniform plump epithelioid cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and prominent central necrosis. A biphasic pattern is typical with spindle cells merging with epithelioid cells. Cellular atypia is relatively mild and mitoses are rare (Figure 3). Recurrent or metastatic lesions can show a greater degree of pleomorphism.12 Given the low-grade atypia in early lesions, this sarcoma is easily misdiagnosed as granulomatous dermatitis. Immunohistochemically, the majority of ES cases are positive for cytokeratins and epithelial membrane antigen; SMARCB1/INI-1 expression is characteristically lost.13

Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly Wegener granulomatosis) is an autoimmune vasculitis highly associated with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies. Clinical manifestations include systemic necrotizing vasculitis; necrotizing glomerulonephritis; and granulomatous inflammation, which predominantly involves the upper respiratory tract, skin, and mucosa.14,15 Skin involvement may be the initial manifestation of the disease and consists of palpable purpura, papules, ulcerations, vesicles, subcutaneous nodules, necrotizing ulcerations, papulonecrotic lesions, and petechiae. None of the findings are pathognomonic. The cutaneous histopathologic spectrum includes leukocytoclastic vasculitis, extravascular palisading granulomas, and granulomatous vasculitis.16 In the acute lesions of granulomatosis with polyangiitis, the predominant pattern of inflammation is not granulomatous but purulent with the appearance of an abscess. As it evolves, it develops a central zone of necrosis with extensive karyorrhectic debris and palisades of macrophages with scattered multinucleated giant cells (Figure 4).17

1. Nandhini G, Rajkumar K, Kanth KS, et al. Molluscum contagiosum in a 12-year-old child—report of a case and review of literature. J Int Oral Health. 2015;7:63-66.
2. Phelps A, Murphy M, Elaba Z, et al. Molluscum contagiosum virus infection in benign cutaneous epithelial cystic lesions-report of 2 cases with different pathogenesis? Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:740-742.
3. Sayah A, English JC 3rd. Rheumatoid arthritis: a review of the cutaneous manifestations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:191-209; quiz 210-192.
4. Sibbitt WL Jr, Williams RC Jr. Cutaneous manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Dermatol. 1982;21:563-572.
5. Barzilai A, Huszar M, Shpiro D, et al. Pseudorheumatoid nodules in adults: a juxta-articular form of nodular granuloma annulare. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:1-5.
6. Garcia-Patos V. Rheumatoid nodule. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2007;26:100-107.
7. Patterson JW. Rheumatoid nodule and subcutaneous granuloma annulare. a comparative histologic study. Am J Dermatopathol. 1988;10:1-8.
8. Sehgal VN, Srivastava G, Aggarwal AK, et al. Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei part II: an overview. Skinmed. 2005;4:234-238.
9. Cymerman R, Rosenstein R, Shvartsbeyn M, et al. Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21. pii:13030/qt6b83q5gp.
10. Sobanko JF, Meijer L, Nigra TP. Epithelioid sarcoma: a review and update. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2009;2:49-54.
11. Enzinger FM. Epitheloid sarcoma. a sarcoma simulating a granuloma or a carcinoma. Cancer. 1970;26:1029-1041.
12. Fisher C. Epithelioid sarcoma of Enzinger. Adv Anat Pathol. 2006;13:114-121.
13. Miettinen M, Fanburg-Smith JC, Virolainen M, et al. Epithelioid sarcoma: an immunohistochemical analysis of 112 classical and variant cases and a discussion of the differential diagnosis. Hum Pathol. 1999;30:934-942.
14. Lutalo PM, D’Cruz DP. Diagnosis and classification of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (aka Wegener’s granulomatosis)[published online January 29, 2014]. J Autoimmun. 2014;48-49:94-98.
15. Frances C, Du LT, Piette JC, et al. Wegener’s granulomatosis. dermatological manifestations in 75 cases with clinicopathologic correlation. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:861-867.
16. Daoud MS, Gibson LE, DeRemee RA, et al. Cutaneous Wegener’s granulomatosis: clinical, histopathologic, and immunopathologic features of thirty patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31:605-612.
17. Jennette JC. Nomenclature and classification of vasculitis: lessons learned from granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s granulomatosis). Clin Exp Immunol. 2011;164 (suppl 1):7-10.
1. Nandhini G, Rajkumar K, Kanth KS, et al. Molluscum contagiosum in a 12-year-old child—report of a case and review of literature. J Int Oral Health. 2015;7:63-66.
2. Phelps A, Murphy M, Elaba Z, et al. Molluscum contagiosum virus infection in benign cutaneous epithelial cystic lesions-report of 2 cases with different pathogenesis? Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:740-742.
3. Sayah A, English JC 3rd. Rheumatoid arthritis: a review of the cutaneous manifestations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:191-209; quiz 210-192.
4. Sibbitt WL Jr, Williams RC Jr. Cutaneous manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Dermatol. 1982;21:563-572.
5. Barzilai A, Huszar M, Shpiro D, et al. Pseudorheumatoid nodules in adults: a juxta-articular form of nodular granuloma annulare. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:1-5.
6. Garcia-Patos V. Rheumatoid nodule. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2007;26:100-107.
7. Patterson JW. Rheumatoid nodule and subcutaneous granuloma annulare. a comparative histologic study. Am J Dermatopathol. 1988;10:1-8.
8. Sehgal VN, Srivastava G, Aggarwal AK, et al. Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei part II: an overview. Skinmed. 2005;4:234-238.
9. Cymerman R, Rosenstein R, Shvartsbeyn M, et al. Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21. pii:13030/qt6b83q5gp.
10. Sobanko JF, Meijer L, Nigra TP. Epithelioid sarcoma: a review and update. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2009;2:49-54.
11. Enzinger FM. Epitheloid sarcoma. a sarcoma simulating a granuloma or a carcinoma. Cancer. 1970;26:1029-1041.
12. Fisher C. Epithelioid sarcoma of Enzinger. Adv Anat Pathol. 2006;13:114-121.
13. Miettinen M, Fanburg-Smith JC, Virolainen M, et al. Epithelioid sarcoma: an immunohistochemical analysis of 112 classical and variant cases and a discussion of the differential diagnosis. Hum Pathol. 1999;30:934-942.
14. Lutalo PM, D’Cruz DP. Diagnosis and classification of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (aka Wegener’s granulomatosis)[published online January 29, 2014]. J Autoimmun. 2014;48-49:94-98.
15. Frances C, Du LT, Piette JC, et al. Wegener’s granulomatosis. dermatological manifestations in 75 cases with clinicopathologic correlation. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:861-867.
16. Daoud MS, Gibson LE, DeRemee RA, et al. Cutaneous Wegener’s granulomatosis: clinical, histopathologic, and immunopathologic features of thirty patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31:605-612.
17. Jennette JC. Nomenclature and classification of vasculitis: lessons learned from granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s granulomatosis). Clin Exp Immunol. 2011;164 (suppl 1):7-10.
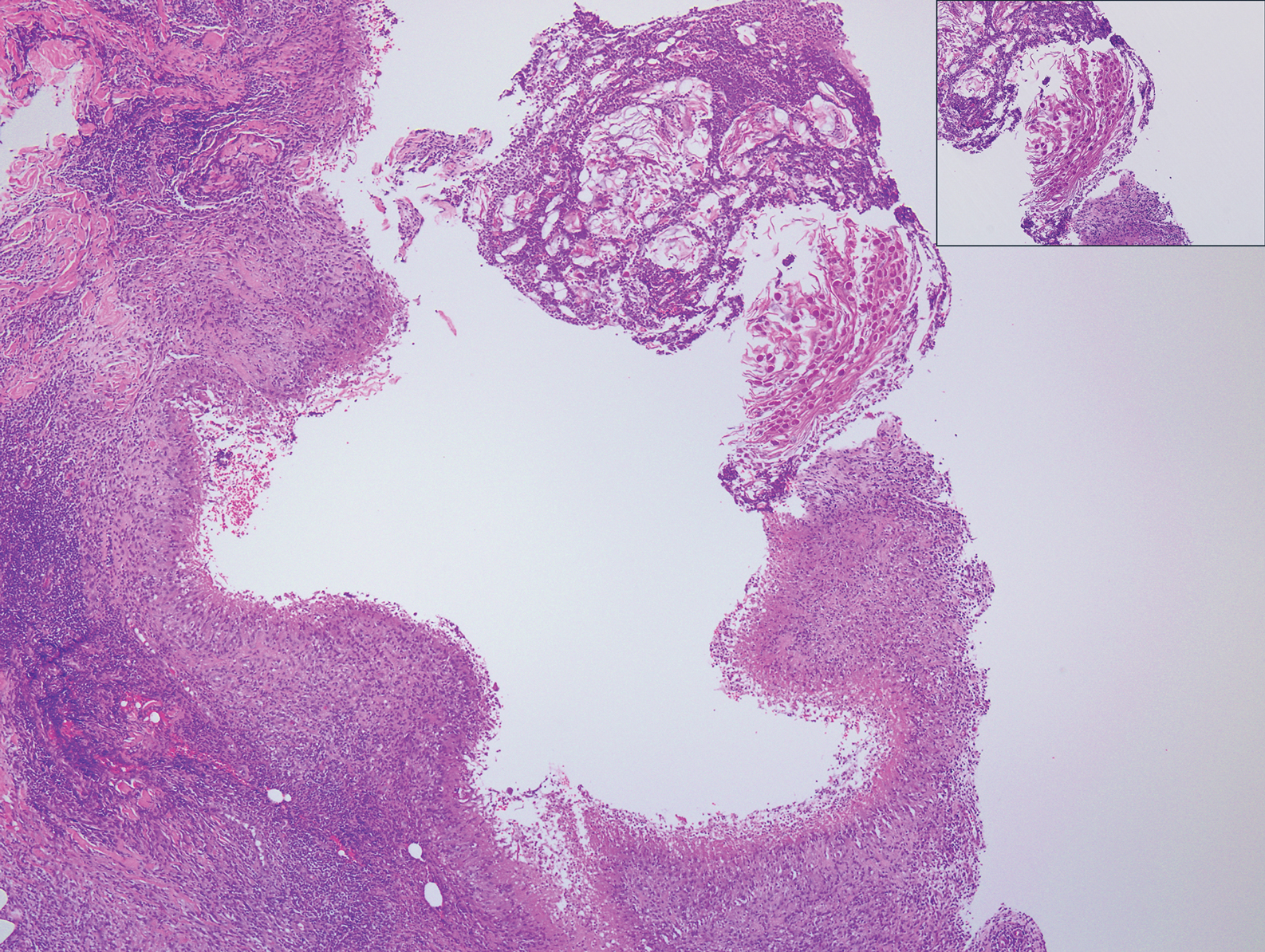
A 17-year-old adolescent girl presented with a discrete nodule on the thigh.
Progressive and Translucent Plaques on the Soles
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Macroglobulinosis
Waldenström macroglobulinemia is a lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma that produces a circulating monoclonal IgM. Incidence in the United States is 1500 patients annually, most commonly men in their 70s.1 The disease process is largely indolent, with early symptoms consisting of generalized weakness, weight loss, and fatigue. Signs of lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and cytopenia may emerge as the disease progresses. Diagnostic criteria include bone marrow biopsy with plasmacytoid/plasmacellular infiltrate; IgM monoclonal gammopathy; and end-organ damage, which may include cutaneous manifestations.2
Cutaneous findings in Waldenström macroglobulinemia are nonspecific and secondary to the disease's hematologic manifestations, presenting as livedo reticularis, purpura, and mucosal bleeding.3 True cutaneous involvement of the disease is rare and was first described in 1978 by Tichenor.4 Specific cutaneous lesions have 2 separate clinical presentations: (1) a primary cutaneous infiltrate of lymphoplasmacytic cells, and (2) deposition of IgM in the dermis.5 Although the primary infiltrate of neoplastic cells appears as erythematous firm papules or plaques on the face and trunk, similar to other manifestations of leukemia cutis, deposition of IgM presents as translucent papules and plaques and is located more distally, particularly on the extensor extremities.6 These depositional plaques are not pruritic but may be tender if located over sites of pressure, as seen with the plantar presentation in our patient.
Histologically, cutaneous macroglobulinosis demonstrates IgM deposition in perieccrine, perivascular, or intravascular tissue that is periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) positive.7 Staining with Congo red and Alcian blue is negative. In our case, biopsy showed a nodular deposition of hypocellular globular material that stained brightly with PAS and PAS diastase. With Masson trichome stain, intensity of staining diminished, suggesting that the deposition was not composed of collagen; rather, this deposition appeared to consist of IgM storage papules on immunohistochemistry (Figure 1). Further workup revealed borderline pancytopenia and elevated globulins with a monoclonal peak on serum protein electrophoresis, confirming the diagnosis of cutaneous macroglobulinosis secondary to Waldenström macroglobulinemia.
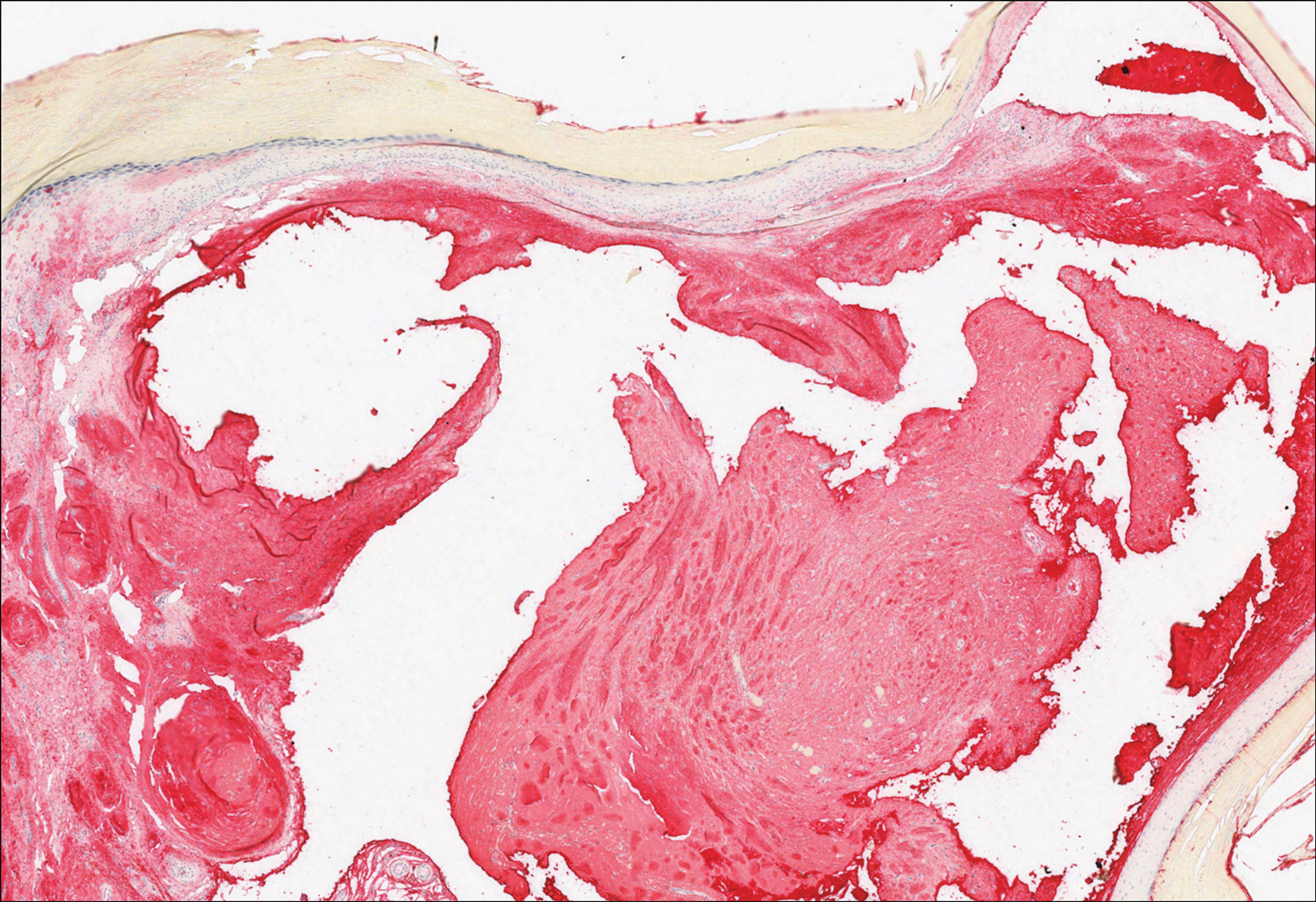
A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms cutaneous, macroglobulinosis, macroglobulinemia, Waldenström's macroglobulinemia, Waldenström's macroglobulinaemia, and macroglobulinemia cutis revealed a total of 19 cases of cutaneous macroglobulinosis (including this case). The average age of presentation in these cases is 60 years (range, 29-83 years) with a predisposition for men (68% [13/19]). The development of cutaneous macroglobulinosis primarily has been noted following diagnosis of Waldenström macroglobulinemia (53% [10/19]), with some cases prior to diagnosis (37% [7/19]) or at the time of diagnosis (11% [2/19]). The presence of cutaneous lesions does not correlate with prognosis of the underlying malignancy.5,8,9
Systemic treatment of the underlying macroglobulinemia has been suggested for symptomatic cases of cutaneous macroglobulinosis.3 Prior therapy has consisted primarily of chlorambucil; however, treatment with rituximab, occasionally in conjunction with the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib, recently has been reported.10 Because of the symptomatic nature of our patient's lesions, she was referred to the oncology department and started on rituximab therapy. The lesions improved with therapy and have remained stable following treatment.
The differential diagnosis for tender pink papules and plaques on the arms and legs includes tophaceous gout, plantar fibromatosis, erythropoietic protoporphyria, and acral fibrokeratoma.
Gouty tophi commonly accumulate as painful, edematous, yellow to whitish nodules and tumors with erythema, often overlying joints or extensor surfaces. Histopathologic examination after formalin fixation shows needle-shaped clefts within feathery amorphous pink areas surrounded by granuloma (Figure 2).11 Yellow, needle-shaped, negatively birefringent crystals can be viewed under polarized microscopy in alcohol-fixed samples.
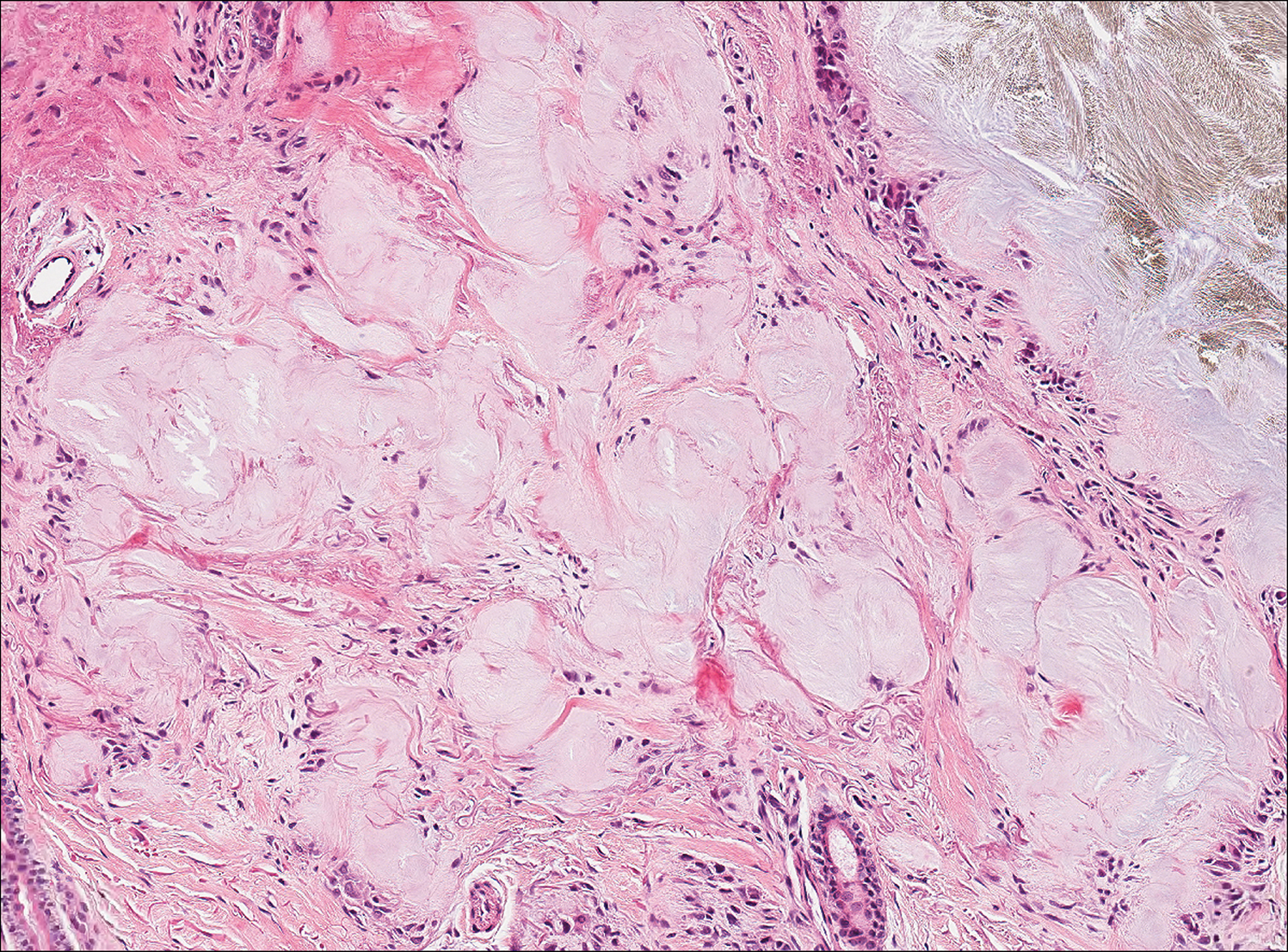
Plantar fibromatosis (Ledderhose disease) is a benign proliferation of the plantar aponeurosis linked to alcohol use; liver disease; and notably epilepsy,12 a component of our patient's medical history. Large nodules appear grossly on the plantar feet and may progress to contractures in more advanced lesions. Biopsy reveals bland hyperproliferation of fibroblasts in a background of fascial fibrous tissue (Figure 3).12 Clinically, this diagnosis is part of the differential diagnosis of plantar nodules but appears histologically different than cutaneous macroglobulinosis because there are no hyaline deposits in plantar fibromatosis.
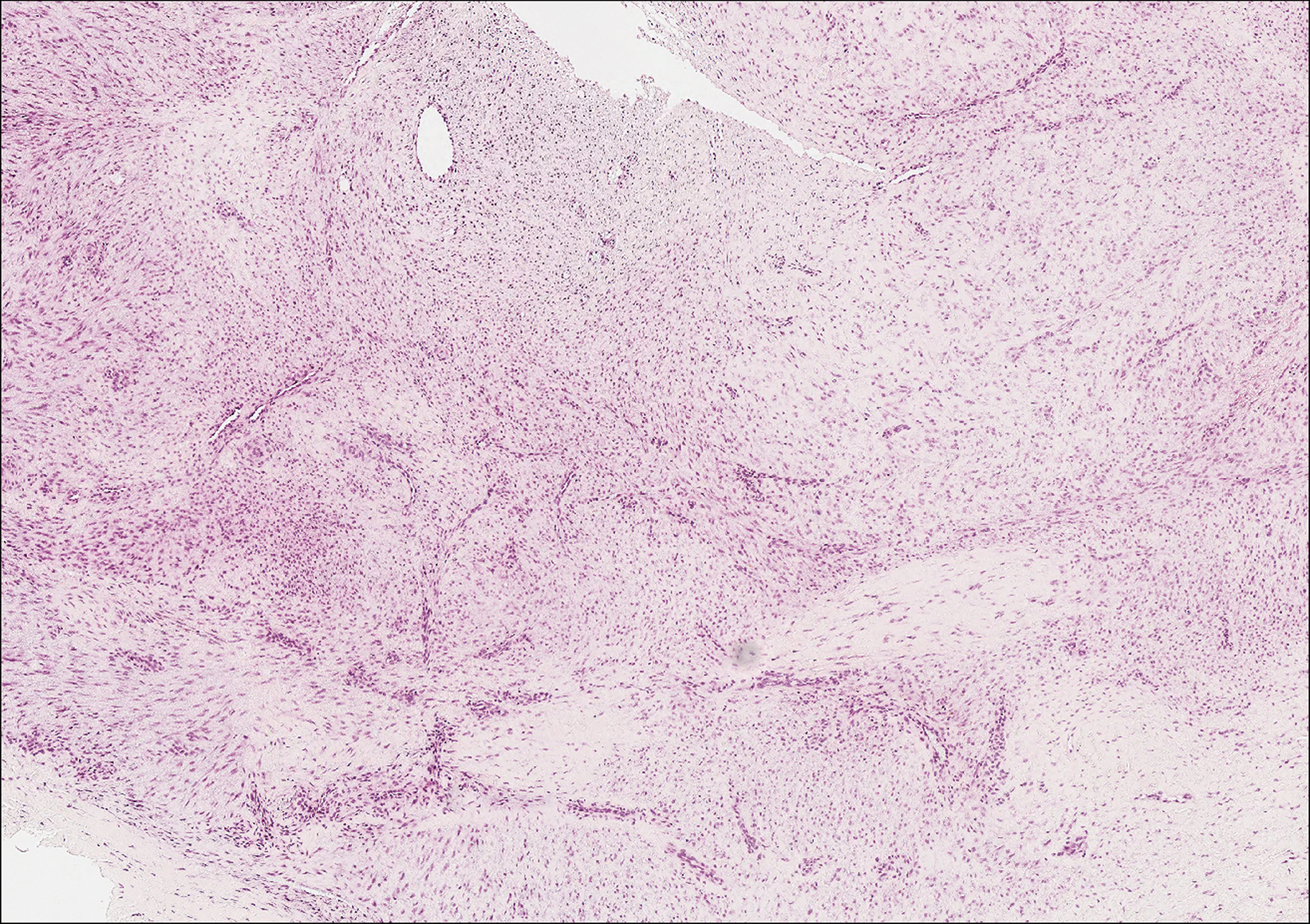
Erythropoietic protoporphyria is a rare disorder that primarily arises due to a congenital deficiency in the ferrochelatase enzyme involved in heme biosynthesis. Erythropoietic protoporphyria is the most common porphyria among children and typically presents in infancy or early childhood as a painful photosensitivity with ensuing cutaneous manifestations and possible hepatobiliary disease. Edema and severe burning pain can be noted within minutes of sun exposure in a dose-response relationship.13 Histologic findings of erythropoietic protoporphyria differ based on acute or chronic skin changes. Acute lesions exhibit a predominantly neutrophilic interstitial dermal infiltrate with vacuoles and intercellular edema. Chronic changes include the accumulation of a PAS-positive, amorphous, hyalinelike substance, similar to the microscopic findings of cutaneous macroglobulinosis (Figure 4).13
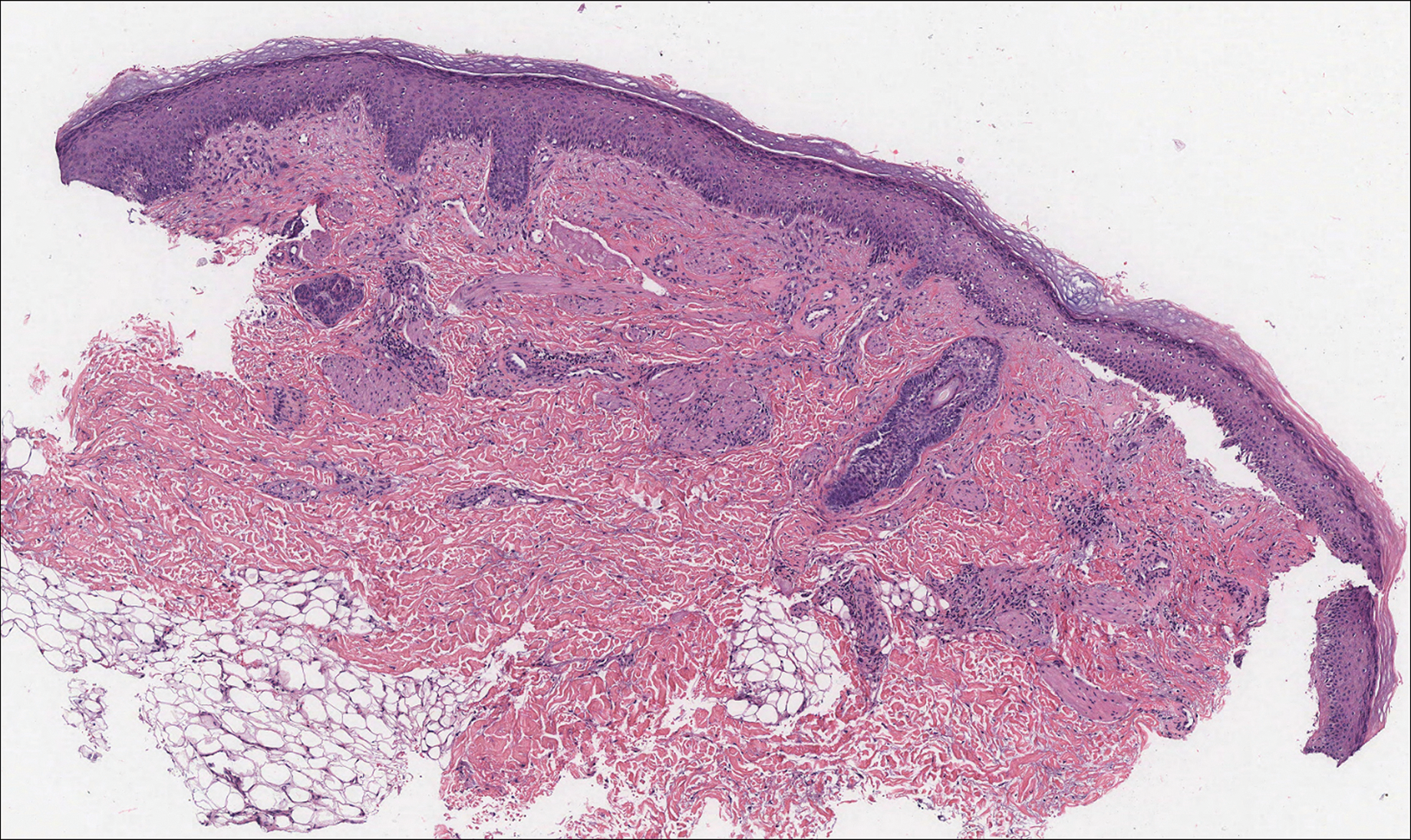
An acral fibrokeratoma is a benign fibroepithelial tumor that clinically appears as a flesh-colored or slightly erythematous exophytic nodule that most commonly is found on the fingers or toes. Thought to arise from trauma to the affected area, it is histologically characterized by interwoven collagenous bundles with overlying epidermal hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and deep thickened rete ridges14 (Figure 5). Although multiple acral fibrokeratomas have been reported (similar to presentations of prurigo nodularis),15 they more commonly appear as solitary lesions as opposed to the numerous translucent papules seen in our patient.
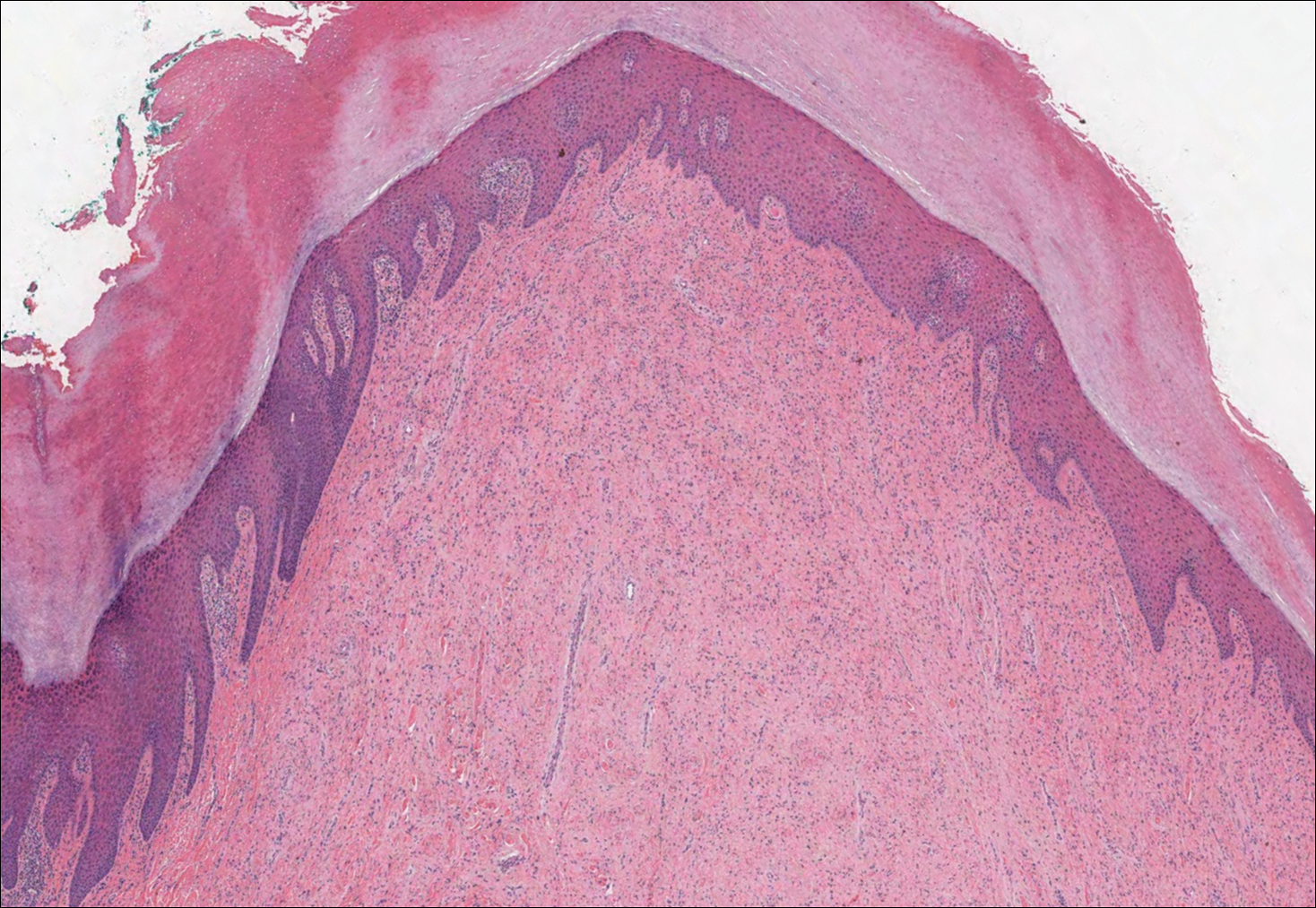
- Camp BJ, Magro CM. Cutaneous macroglobulinosis: a case series. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:962-970.
- Dimopoulos MA, Alexanian R. Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia. Blood. 1994;83:1452-1459.
- D'Acunto C, Nigrisoli E, Liardo EV, et al. Painful plantar nodules: a specific manifestation of cutaneous macroglobulinosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E251-E252.
- Tichenor RE. Macroglobulinemia cutis. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114:280-281.
- Gressier L, Hotz C, Lelièvre JD, et al. Cutaneous macroglobulinosis: a report of 2 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:165-169.
- Spicknall KE, Dubas LE, Mutasim DF. Cutaneous macroglobulinosis with monotypic plasma cells: a specific manifestation of Waldenström macroglobulinemia. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:442-444.
- Lüftl M, Sauter-Jenne B, Gramatzki M, et al. Cutaneous macroglobulinosis deposits in a patient with IgM paraproteinemia/incipient Waldenström macroglobulinemia. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2010;8:1000-1003.
- Mascaro JM, Montserrat E, Estrach T, et al. Specific cutaneous manifestations of Waldenstrom macroglobulinaemia: a report of two cases. Br J Dermatol. 1982;106:217-222.
- Hanke CW, Steck WD, Bergfeld WF, et al. Cutaneous macroglobulinosis. Arch Dermatol. 1980;116:575-577.
- Oshio-Yoshii A, Fujimoto N, Shiba Y, et al. Cutaneous macroglobulinosis: successful treatment with rituximab. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:E30-E31.
- Gupta A, Rai S, Sinha R, et al. Tophi as an initial manifestation of gout. J Cytol. 2009;26:165-166.
- Carroll P, Henshaw RM, Garwood C, et al. Plantar fibromatosis: pathophysiology, surgical and nonsurgical therapies: an evidence-based review. Foot Ankle Spec. 2018;11:168-176.
- Michaels BD, Del Rosso JQ, Mobini N, et al. Erythropoietic protoporphyria: a case report and literature review. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2010;3:44-48.
- Boffeli TJ, Abben KW. Acral fibrokeratoma of the foot treated with excision and trap door flap closure: a case report. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2014;53:449-452.
- Reed RJ. Multiple acral fibrokeratomas (a variant of prurigo nodularis). discussion of classification of acral fibrous nodules and of histogenesis of acral fibrokeratomas. Arch Dermatol. 1971;103:287-297.
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Macroglobulinosis
Waldenström macroglobulinemia is a lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma that produces a circulating monoclonal IgM. Incidence in the United States is 1500 patients annually, most commonly men in their 70s.1 The disease process is largely indolent, with early symptoms consisting of generalized weakness, weight loss, and fatigue. Signs of lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and cytopenia may emerge as the disease progresses. Diagnostic criteria include bone marrow biopsy with plasmacytoid/plasmacellular infiltrate; IgM monoclonal gammopathy; and end-organ damage, which may include cutaneous manifestations.2
Cutaneous findings in Waldenström macroglobulinemia are nonspecific and secondary to the disease's hematologic manifestations, presenting as livedo reticularis, purpura, and mucosal bleeding.3 True cutaneous involvement of the disease is rare and was first described in 1978 by Tichenor.4 Specific cutaneous lesions have 2 separate clinical presentations: (1) a primary cutaneous infiltrate of lymphoplasmacytic cells, and (2) deposition of IgM in the dermis.5 Although the primary infiltrate of neoplastic cells appears as erythematous firm papules or plaques on the face and trunk, similar to other manifestations of leukemia cutis, deposition of IgM presents as translucent papules and plaques and is located more distally, particularly on the extensor extremities.6 These depositional plaques are not pruritic but may be tender if located over sites of pressure, as seen with the plantar presentation in our patient.
Histologically, cutaneous macroglobulinosis demonstrates IgM deposition in perieccrine, perivascular, or intravascular tissue that is periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) positive.7 Staining with Congo red and Alcian blue is negative. In our case, biopsy showed a nodular deposition of hypocellular globular material that stained brightly with PAS and PAS diastase. With Masson trichome stain, intensity of staining diminished, suggesting that the deposition was not composed of collagen; rather, this deposition appeared to consist of IgM storage papules on immunohistochemistry (Figure 1). Further workup revealed borderline pancytopenia and elevated globulins with a monoclonal peak on serum protein electrophoresis, confirming the diagnosis of cutaneous macroglobulinosis secondary to Waldenström macroglobulinemia.

A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms cutaneous, macroglobulinosis, macroglobulinemia, Waldenström's macroglobulinemia, Waldenström's macroglobulinaemia, and macroglobulinemia cutis revealed a total of 19 cases of cutaneous macroglobulinosis (including this case). The average age of presentation in these cases is 60 years (range, 29-83 years) with a predisposition for men (68% [13/19]). The development of cutaneous macroglobulinosis primarily has been noted following diagnosis of Waldenström macroglobulinemia (53% [10/19]), with some cases prior to diagnosis (37% [7/19]) or at the time of diagnosis (11% [2/19]). The presence of cutaneous lesions does not correlate with prognosis of the underlying malignancy.5,8,9
Systemic treatment of the underlying macroglobulinemia has been suggested for symptomatic cases of cutaneous macroglobulinosis.3 Prior therapy has consisted primarily of chlorambucil; however, treatment with rituximab, occasionally in conjunction with the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib, recently has been reported.10 Because of the symptomatic nature of our patient's lesions, she was referred to the oncology department and started on rituximab therapy. The lesions improved with therapy and have remained stable following treatment.
The differential diagnosis for tender pink papules and plaques on the arms and legs includes tophaceous gout, plantar fibromatosis, erythropoietic protoporphyria, and acral fibrokeratoma.
Gouty tophi commonly accumulate as painful, edematous, yellow to whitish nodules and tumors with erythema, often overlying joints or extensor surfaces. Histopathologic examination after formalin fixation shows needle-shaped clefts within feathery amorphous pink areas surrounded by granuloma (Figure 2).11 Yellow, needle-shaped, negatively birefringent crystals can be viewed under polarized microscopy in alcohol-fixed samples.

Plantar fibromatosis (Ledderhose disease) is a benign proliferation of the plantar aponeurosis linked to alcohol use; liver disease; and notably epilepsy,12 a component of our patient's medical history. Large nodules appear grossly on the plantar feet and may progress to contractures in more advanced lesions. Biopsy reveals bland hyperproliferation of fibroblasts in a background of fascial fibrous tissue (Figure 3).12 Clinically, this diagnosis is part of the differential diagnosis of plantar nodules but appears histologically different than cutaneous macroglobulinosis because there are no hyaline deposits in plantar fibromatosis.

Erythropoietic protoporphyria is a rare disorder that primarily arises due to a congenital deficiency in the ferrochelatase enzyme involved in heme biosynthesis. Erythropoietic protoporphyria is the most common porphyria among children and typically presents in infancy or early childhood as a painful photosensitivity with ensuing cutaneous manifestations and possible hepatobiliary disease. Edema and severe burning pain can be noted within minutes of sun exposure in a dose-response relationship.13 Histologic findings of erythropoietic protoporphyria differ based on acute or chronic skin changes. Acute lesions exhibit a predominantly neutrophilic interstitial dermal infiltrate with vacuoles and intercellular edema. Chronic changes include the accumulation of a PAS-positive, amorphous, hyalinelike substance, similar to the microscopic findings of cutaneous macroglobulinosis (Figure 4).13

An acral fibrokeratoma is a benign fibroepithelial tumor that clinically appears as a flesh-colored or slightly erythematous exophytic nodule that most commonly is found on the fingers or toes. Thought to arise from trauma to the affected area, it is histologically characterized by interwoven collagenous bundles with overlying epidermal hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and deep thickened rete ridges14 (Figure 5). Although multiple acral fibrokeratomas have been reported (similar to presentations of prurigo nodularis),15 they more commonly appear as solitary lesions as opposed to the numerous translucent papules seen in our patient.

The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Macroglobulinosis
Waldenström macroglobulinemia is a lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma that produces a circulating monoclonal IgM. Incidence in the United States is 1500 patients annually, most commonly men in their 70s.1 The disease process is largely indolent, with early symptoms consisting of generalized weakness, weight loss, and fatigue. Signs of lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and cytopenia may emerge as the disease progresses. Diagnostic criteria include bone marrow biopsy with plasmacytoid/plasmacellular infiltrate; IgM monoclonal gammopathy; and end-organ damage, which may include cutaneous manifestations.2
Cutaneous findings in Waldenström macroglobulinemia are nonspecific and secondary to the disease's hematologic manifestations, presenting as livedo reticularis, purpura, and mucosal bleeding.3 True cutaneous involvement of the disease is rare and was first described in 1978 by Tichenor.4 Specific cutaneous lesions have 2 separate clinical presentations: (1) a primary cutaneous infiltrate of lymphoplasmacytic cells, and (2) deposition of IgM in the dermis.5 Although the primary infiltrate of neoplastic cells appears as erythematous firm papules or plaques on the face and trunk, similar to other manifestations of leukemia cutis, deposition of IgM presents as translucent papules and plaques and is located more distally, particularly on the extensor extremities.6 These depositional plaques are not pruritic but may be tender if located over sites of pressure, as seen with the plantar presentation in our patient.
Histologically, cutaneous macroglobulinosis demonstrates IgM deposition in perieccrine, perivascular, or intravascular tissue that is periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) positive.7 Staining with Congo red and Alcian blue is negative. In our case, biopsy showed a nodular deposition of hypocellular globular material that stained brightly with PAS and PAS diastase. With Masson trichome stain, intensity of staining diminished, suggesting that the deposition was not composed of collagen; rather, this deposition appeared to consist of IgM storage papules on immunohistochemistry (Figure 1). Further workup revealed borderline pancytopenia and elevated globulins with a monoclonal peak on serum protein electrophoresis, confirming the diagnosis of cutaneous macroglobulinosis secondary to Waldenström macroglobulinemia.

A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms cutaneous, macroglobulinosis, macroglobulinemia, Waldenström's macroglobulinemia, Waldenström's macroglobulinaemia, and macroglobulinemia cutis revealed a total of 19 cases of cutaneous macroglobulinosis (including this case). The average age of presentation in these cases is 60 years (range, 29-83 years) with a predisposition for men (68% [13/19]). The development of cutaneous macroglobulinosis primarily has been noted following diagnosis of Waldenström macroglobulinemia (53% [10/19]), with some cases prior to diagnosis (37% [7/19]) or at the time of diagnosis (11% [2/19]). The presence of cutaneous lesions does not correlate with prognosis of the underlying malignancy.5,8,9
Systemic treatment of the underlying macroglobulinemia has been suggested for symptomatic cases of cutaneous macroglobulinosis.3 Prior therapy has consisted primarily of chlorambucil; however, treatment with rituximab, occasionally in conjunction with the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib, recently has been reported.10 Because of the symptomatic nature of our patient's lesions, she was referred to the oncology department and started on rituximab therapy. The lesions improved with therapy and have remained stable following treatment.
The differential diagnosis for tender pink papules and plaques on the arms and legs includes tophaceous gout, plantar fibromatosis, erythropoietic protoporphyria, and acral fibrokeratoma.
Gouty tophi commonly accumulate as painful, edematous, yellow to whitish nodules and tumors with erythema, often overlying joints or extensor surfaces. Histopathologic examination after formalin fixation shows needle-shaped clefts within feathery amorphous pink areas surrounded by granuloma (Figure 2).11 Yellow, needle-shaped, negatively birefringent crystals can be viewed under polarized microscopy in alcohol-fixed samples.

Plantar fibromatosis (Ledderhose disease) is a benign proliferation of the plantar aponeurosis linked to alcohol use; liver disease; and notably epilepsy,12 a component of our patient's medical history. Large nodules appear grossly on the plantar feet and may progress to contractures in more advanced lesions. Biopsy reveals bland hyperproliferation of fibroblasts in a background of fascial fibrous tissue (Figure 3).12 Clinically, this diagnosis is part of the differential diagnosis of plantar nodules but appears histologically different than cutaneous macroglobulinosis because there are no hyaline deposits in plantar fibromatosis.

Erythropoietic protoporphyria is a rare disorder that primarily arises due to a congenital deficiency in the ferrochelatase enzyme involved in heme biosynthesis. Erythropoietic protoporphyria is the most common porphyria among children and typically presents in infancy or early childhood as a painful photosensitivity with ensuing cutaneous manifestations and possible hepatobiliary disease. Edema and severe burning pain can be noted within minutes of sun exposure in a dose-response relationship.13 Histologic findings of erythropoietic protoporphyria differ based on acute or chronic skin changes. Acute lesions exhibit a predominantly neutrophilic interstitial dermal infiltrate with vacuoles and intercellular edema. Chronic changes include the accumulation of a PAS-positive, amorphous, hyalinelike substance, similar to the microscopic findings of cutaneous macroglobulinosis (Figure 4).13

An acral fibrokeratoma is a benign fibroepithelial tumor that clinically appears as a flesh-colored or slightly erythematous exophytic nodule that most commonly is found on the fingers or toes. Thought to arise from trauma to the affected area, it is histologically characterized by interwoven collagenous bundles with overlying epidermal hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and deep thickened rete ridges14 (Figure 5). Although multiple acral fibrokeratomas have been reported (similar to presentations of prurigo nodularis),15 they more commonly appear as solitary lesions as opposed to the numerous translucent papules seen in our patient.

- Camp BJ, Magro CM. Cutaneous macroglobulinosis: a case series. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:962-970.
- Dimopoulos MA, Alexanian R. Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia. Blood. 1994;83:1452-1459.
- D'Acunto C, Nigrisoli E, Liardo EV, et al. Painful plantar nodules: a specific manifestation of cutaneous macroglobulinosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E251-E252.
- Tichenor RE. Macroglobulinemia cutis. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114:280-281.
- Gressier L, Hotz C, Lelièvre JD, et al. Cutaneous macroglobulinosis: a report of 2 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:165-169.
- Spicknall KE, Dubas LE, Mutasim DF. Cutaneous macroglobulinosis with monotypic plasma cells: a specific manifestation of Waldenström macroglobulinemia. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:442-444.
- Lüftl M, Sauter-Jenne B, Gramatzki M, et al. Cutaneous macroglobulinosis deposits in a patient with IgM paraproteinemia/incipient Waldenström macroglobulinemia. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2010;8:1000-1003.
- Mascaro JM, Montserrat E, Estrach T, et al. Specific cutaneous manifestations of Waldenstrom macroglobulinaemia: a report of two cases. Br J Dermatol. 1982;106:217-222.
- Hanke CW, Steck WD, Bergfeld WF, et al. Cutaneous macroglobulinosis. Arch Dermatol. 1980;116:575-577.
- Oshio-Yoshii A, Fujimoto N, Shiba Y, et al. Cutaneous macroglobulinosis: successful treatment with rituximab. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:E30-E31.
- Gupta A, Rai S, Sinha R, et al. Tophi as an initial manifestation of gout. J Cytol. 2009;26:165-166.
- Carroll P, Henshaw RM, Garwood C, et al. Plantar fibromatosis: pathophysiology, surgical and nonsurgical therapies: an evidence-based review. Foot Ankle Spec. 2018;11:168-176.
- Michaels BD, Del Rosso JQ, Mobini N, et al. Erythropoietic protoporphyria: a case report and literature review. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2010;3:44-48.
- Boffeli TJ, Abben KW. Acral fibrokeratoma of the foot treated with excision and trap door flap closure: a case report. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2014;53:449-452.
- Reed RJ. Multiple acral fibrokeratomas (a variant of prurigo nodularis). discussion of classification of acral fibrous nodules and of histogenesis of acral fibrokeratomas. Arch Dermatol. 1971;103:287-297.
- Camp BJ, Magro CM. Cutaneous macroglobulinosis: a case series. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:962-970.
- Dimopoulos MA, Alexanian R. Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia. Blood. 1994;83:1452-1459.
- D'Acunto C, Nigrisoli E, Liardo EV, et al. Painful plantar nodules: a specific manifestation of cutaneous macroglobulinosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E251-E252.
- Tichenor RE. Macroglobulinemia cutis. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114:280-281.
- Gressier L, Hotz C, Lelièvre JD, et al. Cutaneous macroglobulinosis: a report of 2 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:165-169.
- Spicknall KE, Dubas LE, Mutasim DF. Cutaneous macroglobulinosis with monotypic plasma cells: a specific manifestation of Waldenström macroglobulinemia. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:442-444.
- Lüftl M, Sauter-Jenne B, Gramatzki M, et al. Cutaneous macroglobulinosis deposits in a patient with IgM paraproteinemia/incipient Waldenström macroglobulinemia. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2010;8:1000-1003.
- Mascaro JM, Montserrat E, Estrach T, et al. Specific cutaneous manifestations of Waldenstrom macroglobulinaemia: a report of two cases. Br J Dermatol. 1982;106:217-222.
- Hanke CW, Steck WD, Bergfeld WF, et al. Cutaneous macroglobulinosis. Arch Dermatol. 1980;116:575-577.
- Oshio-Yoshii A, Fujimoto N, Shiba Y, et al. Cutaneous macroglobulinosis: successful treatment with rituximab. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:E30-E31.
- Gupta A, Rai S, Sinha R, et al. Tophi as an initial manifestation of gout. J Cytol. 2009;26:165-166.
- Carroll P, Henshaw RM, Garwood C, et al. Plantar fibromatosis: pathophysiology, surgical and nonsurgical therapies: an evidence-based review. Foot Ankle Spec. 2018;11:168-176.
- Michaels BD, Del Rosso JQ, Mobini N, et al. Erythropoietic protoporphyria: a case report and literature review. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2010;3:44-48.
- Boffeli TJ, Abben KW. Acral fibrokeratoma of the foot treated with excision and trap door flap closure: a case report. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2014;53:449-452.
- Reed RJ. Multiple acral fibrokeratomas (a variant of prurigo nodularis). discussion of classification of acral fibrous nodules and of histogenesis of acral fibrokeratomas. Arch Dermatol. 1971;103:287-297.
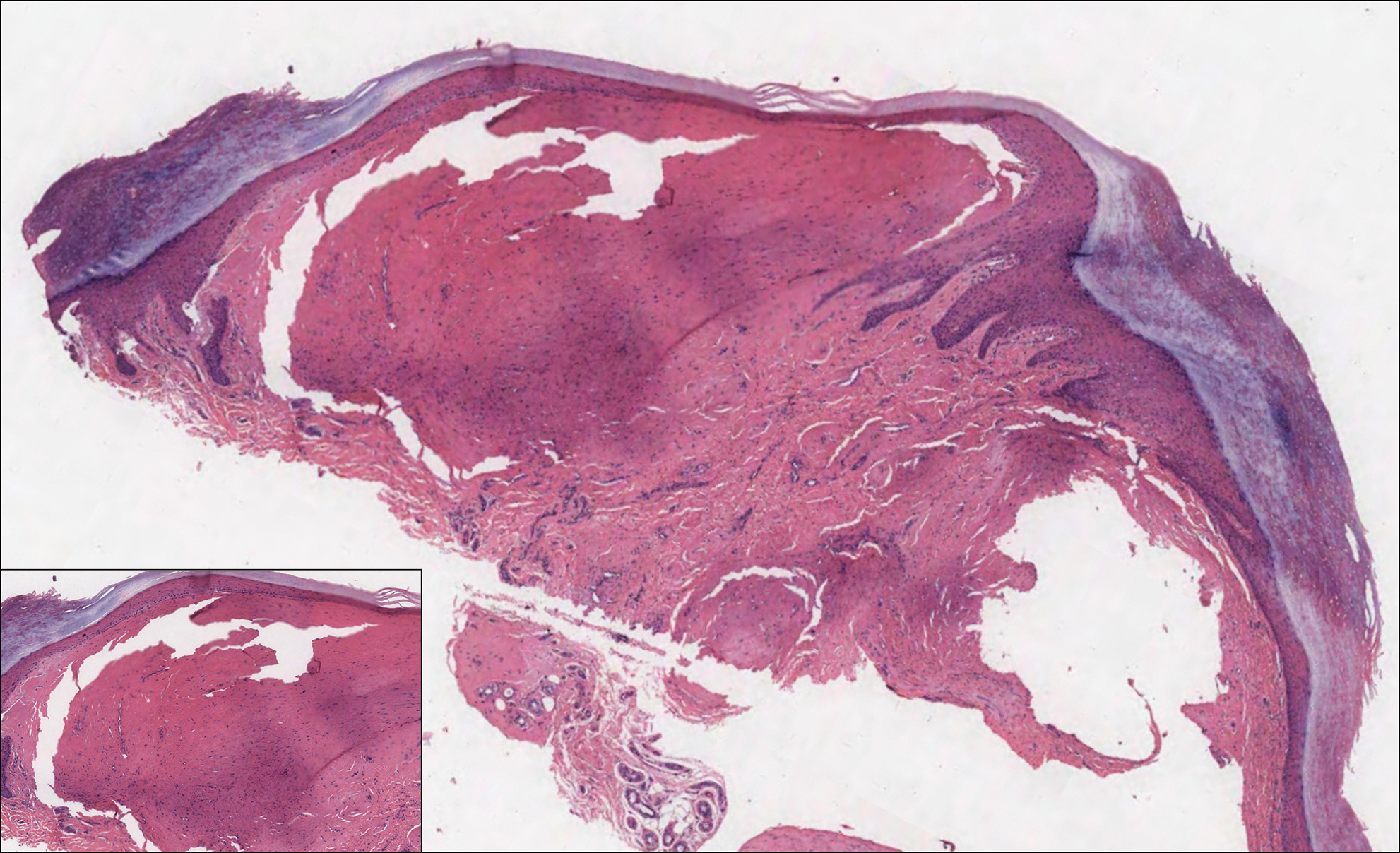
A 64-year-old woman with a medical history of Waldenström macroglobulinemia, multiple sclerosis, and epilepsy presented with slowly growing papules on the plantar feet of 21 months' duration. She was diagnosed with Waldenström macroglobulinemia incidentally on routine blood work 3 years prior and declined treatment because she was asymptomatic. Physical examination revealed a total of 20 firm, variably sized, light pink to purple, partially translucent and telangiectatic papules and plaques bilaterally on the plantar feet. A plaque from the right sole was biopsied.
Multiple Pink Papules on the Chest and Upper Abdomen
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Metastases
Cutaneous metastases (CMs) can present in an otherwise asymptomatic patient as the only sign of an underlying disease process. In women, the most common cause of CM is breast carcinoma.1-3 Cutaneous metastases are found in approximately 25% of all patients with breast carcinoma,1 and breast carcinomas represent approximately 69% of all CMs found in women (Table 1).2 Cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma (CMBC) is associated with a poor prognosis with a mean survival of approximately 6 months at the time of diagnosis.1,3 It commonly presents as a collection of flesh-colored, firm, asymptomatic, and rapidly appearing papules and nodules that can resemble cysts or fibrous tumors.1,3,4 They typically are located on the chest wall or abdomen near the site of the underlying malignancy.1-3 The histologic features of CMBC can include hyperchromatic tumor cells infiltrating between the collagen fibers in a characteristic single file manner,3,5 giving the appearance of a busy dermis, a nonspecific term to describe a focally hypercellular dermis at low-power magnification (Table 2).5,6 Cords and clusters of atypical cells with intracytoplasmic vacuoles or well-developed ducts also can be seen (quiz image [inset]). The carcinoma en cuirasse subtype of CMBC is characterized by a fibrotic scarlike plaque on the chest wall.1,3 If a punch biopsy is obtained, the specimen typically appears rectangular rather than tapered because of the sclerotic dermal collagen.6 In contrast, inflammatory carcinoma (carcinoma erysipelatoides) presents as an erythematous plaque resembling cellulitis due to the lymphatics being congested by tumor cells.3 Immunohistochemistry is a valuable tool in diagnosis. Positive staining is seen with cytokeratin 7, gross cystic disease fluid protein-15, mammaglobin, and GATA-3.1,3,6


Kaposi sarcoma (KS) is a low-grade endothelial malignancy associated with human herpesvirus 8.3,4 Kaposi sarcoma can be divided into 4 main subtypes: classic KS, African KS, AIDS-related KS, and immunosuppression-associated KS that occurs in patients with diseases such as human immunodeficiency virus. The cutaneous lesions are similar between subtypes and present as dark reddish purple macules that may enlarge or become nodular lesions.3,4 Histologically, 3 distinct stages of progression are described: patch, plaque, and tumor. The plaque stage has the appearance of a busy dermis due to the rapid proliferation of vascular structures within the dermis.3,6 A useful histologic feature known as the promontory sign can be seen as the proliferating tumor causes preexisting structures to project into vascular spaces (Figure 1).6 Immunohistochemistry for the endothelial and lymphatic markers CD31 and D2-40, respectively, are positive and may aid in the diagnosis.3 Staining for the latent nuclear antigen-1 of human herpesvirus 8 is a highly specific marker used to diagnose KS and can further distinguish it from the other busy dermis lesions.3
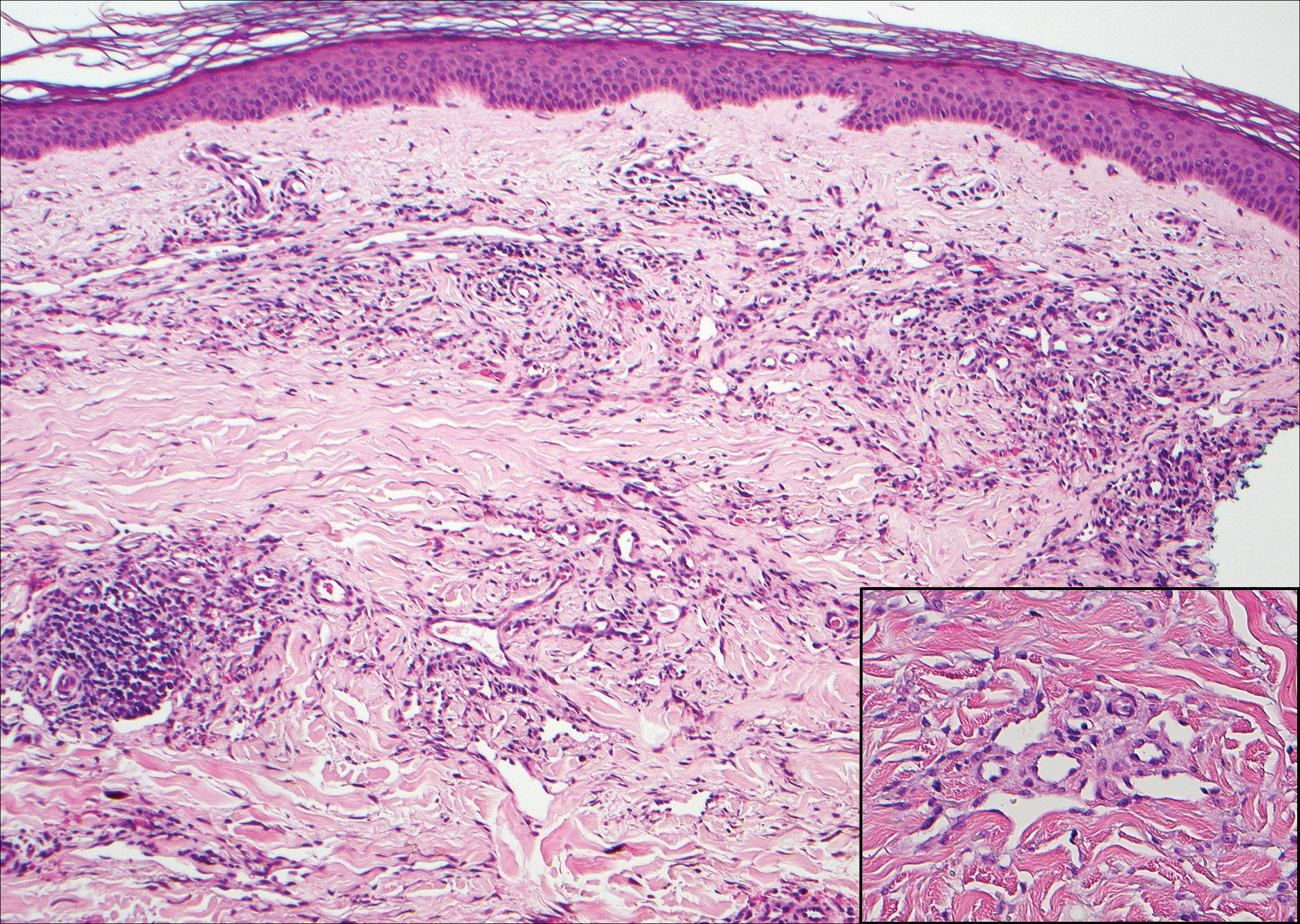
Granuloma annulare (GA) is characterized by rings of small, firm, pink to flesh-colored papules with a variable disease duration.4 Histologically, the interstitial variant of GA is characterized by a scattered inflammatory infiltrate consisting of histiocytes and lymphocytes located between altered collagen fibers in the superficial to mid dermis (Figure 2).3,6 Occasional eosinophils and increased dermal mucin are useful features to distinguish interstitial GA from other entities in the busy dermis differential.7
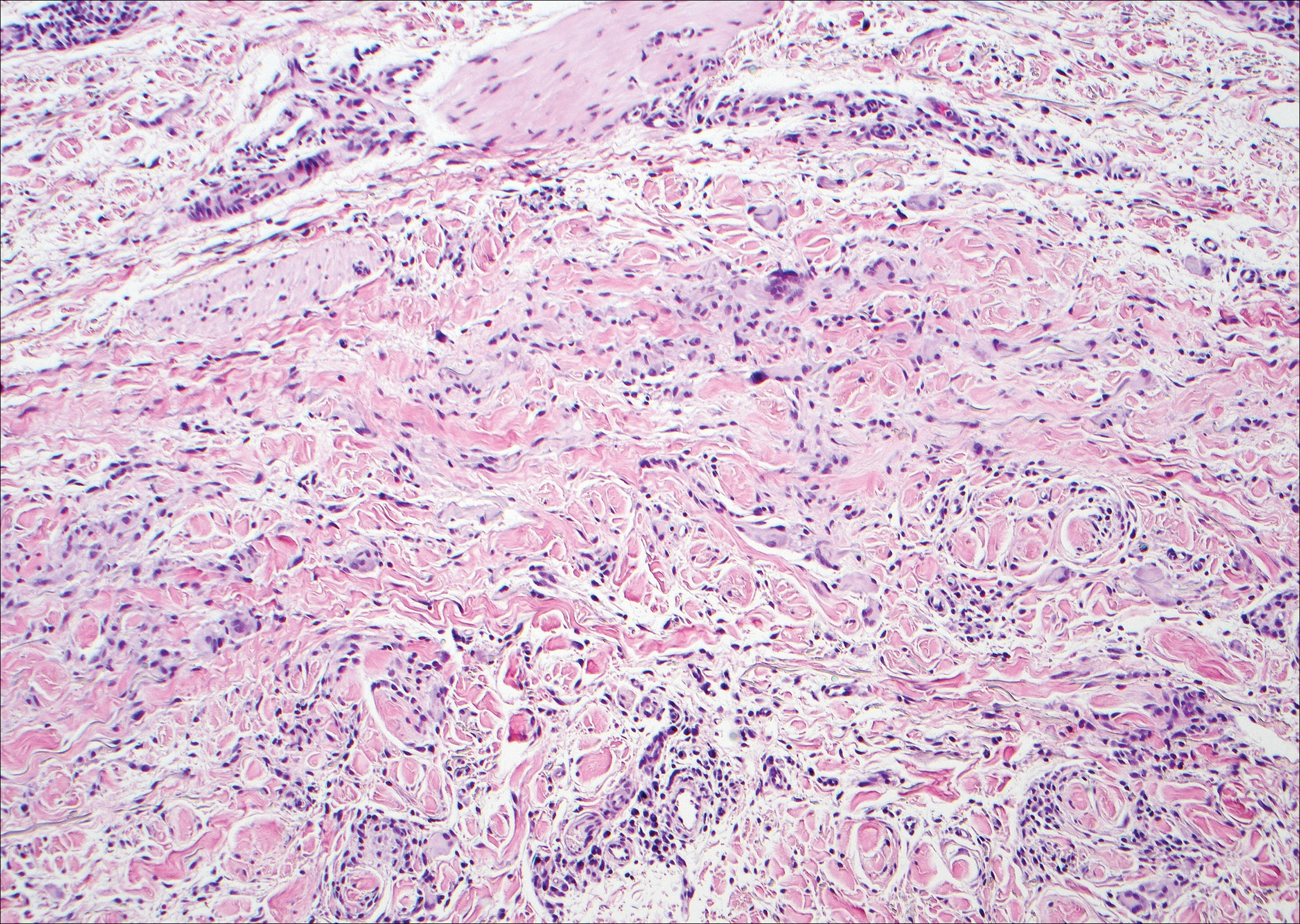
Scleromyxedema, also known as generalized lichen myxedematosus, is a rare mucinosis.3,8 Although its pathogenesis is unknown, it has been suggested that paraproteins related to the underlying gammopathy act to stimulate fibroblast proliferation and mucin overproduction.8 Clinically, characteristic widespread firm, waxy, dome-shaped papules are present over the head, upper trunk, and extremities.3,8 Histologically, scleromyxedema is characterized by increased dermal fibroblasts, mucin, and fibrosis, leading to the appearance of a busy dermis (Figure 3).3,6
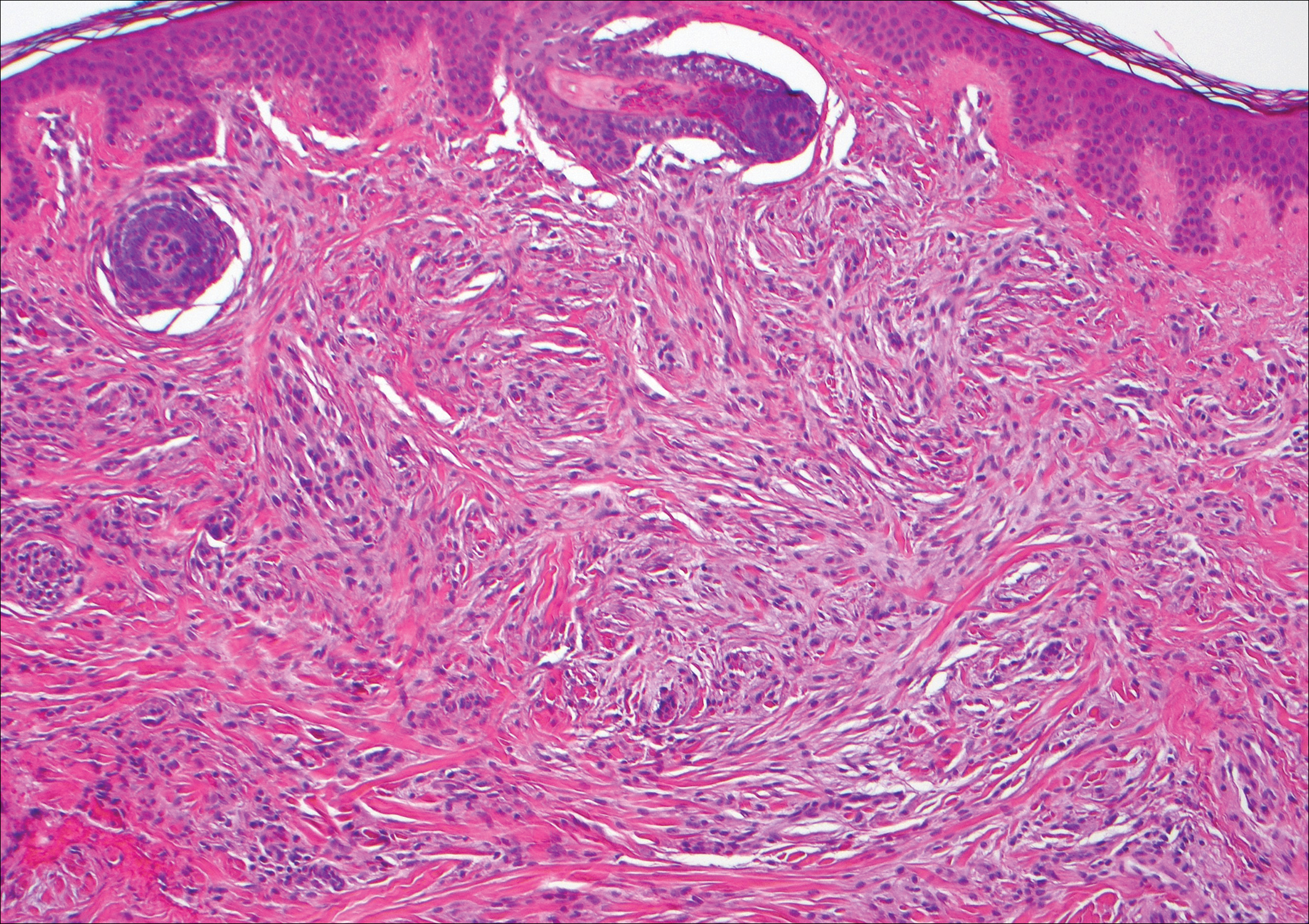
Neurofibromas are common benign peripheral nerve sheath tumors that can occur sporadically or in the setting of neurofibromatosis.3-5 They present as soft, flesh-colored papules or nodules most commonly located on the trunk and limbs.4 Histologically, neurofibromas are nonencapsulated tumors composed of abundant spindle cells with comma-shaped nuclei diffusely arranged in a pale myxoid stroma (Figure 4). Scattered mast cells can be visualized at higher magnification.3,6
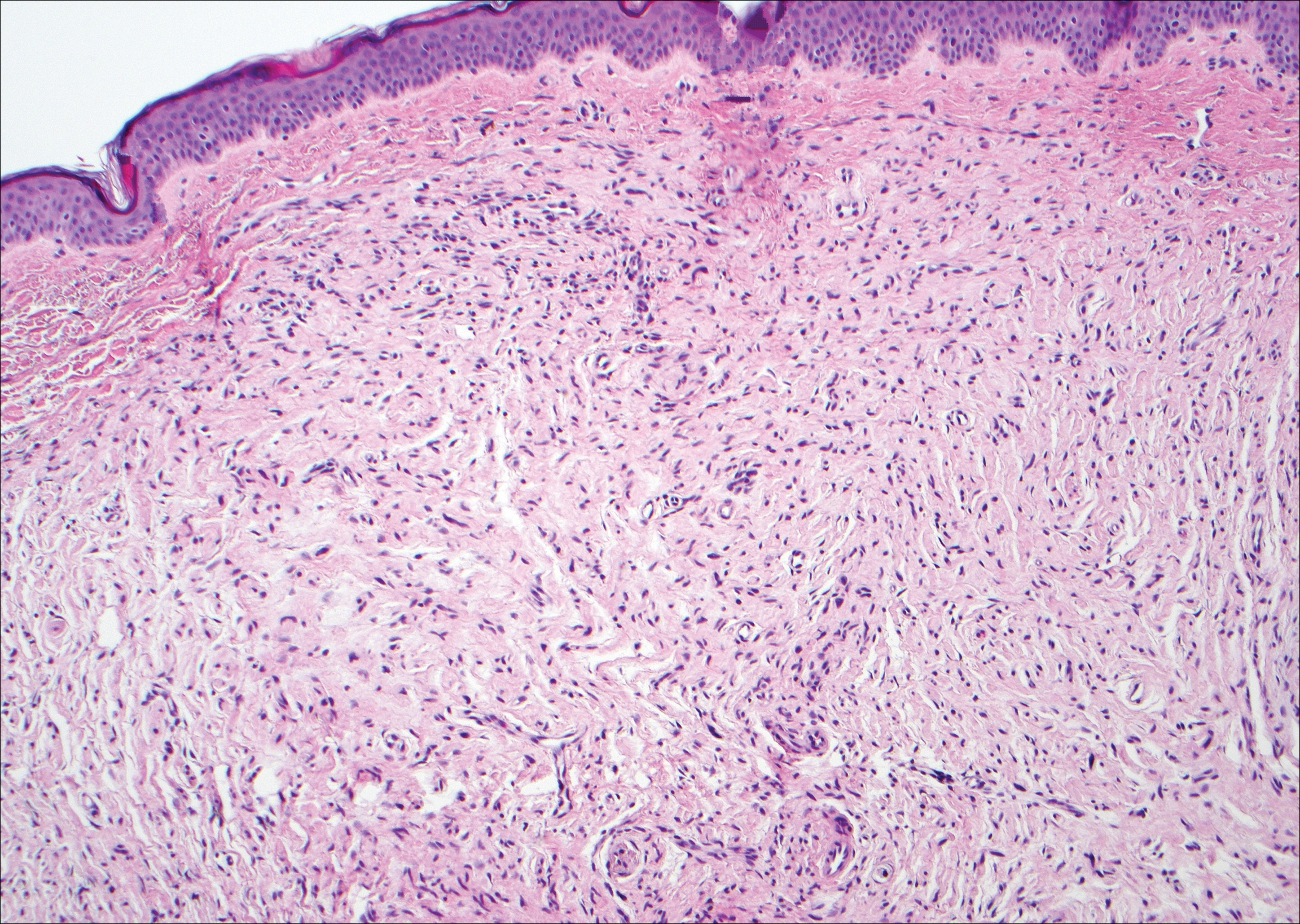
- Alcaraz I, Cerroni L, Rutten A, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34:347-393.
- Habif TP, Dinulos JGH, Chapman MS, et al. Skin Disease: Diagnosis and Treatment. 4th ed. Edinburgh, Scotland: Elsevier; 2017.
- Calonje JE, Brenn T, Lazar AJ, et al, eds. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2012.
- Habif TP. Clinical Dermatology: A Color Guide to Diagnosis and Therapy. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2015.
- Patterson JW, Hosler GA. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; 2016.
- Elston DM, Ferringer T, eds. Dermatopathology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2014.
- Silverman RA, Rabinowitz AD. Eosinophils in the cellular infiltrate of granuloma annulare. J Cutan Pathol. 1985;12:13-17.
- Rongioletti F, Merlo G, Cinotti E, et al. Scleromyxedema: a multicenter study of characteristics, comorbidities, course, and therapy in 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:66-72.
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Metastases
Cutaneous metastases (CMs) can present in an otherwise asymptomatic patient as the only sign of an underlying disease process. In women, the most common cause of CM is breast carcinoma.1-3 Cutaneous metastases are found in approximately 25% of all patients with breast carcinoma,1 and breast carcinomas represent approximately 69% of all CMs found in women (Table 1).2 Cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma (CMBC) is associated with a poor prognosis with a mean survival of approximately 6 months at the time of diagnosis.1,3 It commonly presents as a collection of flesh-colored, firm, asymptomatic, and rapidly appearing papules and nodules that can resemble cysts or fibrous tumors.1,3,4 They typically are located on the chest wall or abdomen near the site of the underlying malignancy.1-3 The histologic features of CMBC can include hyperchromatic tumor cells infiltrating between the collagen fibers in a characteristic single file manner,3,5 giving the appearance of a busy dermis, a nonspecific term to describe a focally hypercellular dermis at low-power magnification (Table 2).5,6 Cords and clusters of atypical cells with intracytoplasmic vacuoles or well-developed ducts also can be seen (quiz image [inset]). The carcinoma en cuirasse subtype of CMBC is characterized by a fibrotic scarlike plaque on the chest wall.1,3 If a punch biopsy is obtained, the specimen typically appears rectangular rather than tapered because of the sclerotic dermal collagen.6 In contrast, inflammatory carcinoma (carcinoma erysipelatoides) presents as an erythematous plaque resembling cellulitis due to the lymphatics being congested by tumor cells.3 Immunohistochemistry is a valuable tool in diagnosis. Positive staining is seen with cytokeratin 7, gross cystic disease fluid protein-15, mammaglobin, and GATA-3.1,3,6


Kaposi sarcoma (KS) is a low-grade endothelial malignancy associated with human herpesvirus 8.3,4 Kaposi sarcoma can be divided into 4 main subtypes: classic KS, African KS, AIDS-related KS, and immunosuppression-associated KS that occurs in patients with diseases such as human immunodeficiency virus. The cutaneous lesions are similar between subtypes and present as dark reddish purple macules that may enlarge or become nodular lesions.3,4 Histologically, 3 distinct stages of progression are described: patch, plaque, and tumor. The plaque stage has the appearance of a busy dermis due to the rapid proliferation of vascular structures within the dermis.3,6 A useful histologic feature known as the promontory sign can be seen as the proliferating tumor causes preexisting structures to project into vascular spaces (Figure 1).6 Immunohistochemistry for the endothelial and lymphatic markers CD31 and D2-40, respectively, are positive and may aid in the diagnosis.3 Staining for the latent nuclear antigen-1 of human herpesvirus 8 is a highly specific marker used to diagnose KS and can further distinguish it from the other busy dermis lesions.3

Granuloma annulare (GA) is characterized by rings of small, firm, pink to flesh-colored papules with a variable disease duration.4 Histologically, the interstitial variant of GA is characterized by a scattered inflammatory infiltrate consisting of histiocytes and lymphocytes located between altered collagen fibers in the superficial to mid dermis (Figure 2).3,6 Occasional eosinophils and increased dermal mucin are useful features to distinguish interstitial GA from other entities in the busy dermis differential.7

Scleromyxedema, also known as generalized lichen myxedematosus, is a rare mucinosis.3,8 Although its pathogenesis is unknown, it has been suggested that paraproteins related to the underlying gammopathy act to stimulate fibroblast proliferation and mucin overproduction.8 Clinically, characteristic widespread firm, waxy, dome-shaped papules are present over the head, upper trunk, and extremities.3,8 Histologically, scleromyxedema is characterized by increased dermal fibroblasts, mucin, and fibrosis, leading to the appearance of a busy dermis (Figure 3).3,6

Neurofibromas are common benign peripheral nerve sheath tumors that can occur sporadically or in the setting of neurofibromatosis.3-5 They present as soft, flesh-colored papules or nodules most commonly located on the trunk and limbs.4 Histologically, neurofibromas are nonencapsulated tumors composed of abundant spindle cells with comma-shaped nuclei diffusely arranged in a pale myxoid stroma (Figure 4). Scattered mast cells can be visualized at higher magnification.3,6

The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Metastases
Cutaneous metastases (CMs) can present in an otherwise asymptomatic patient as the only sign of an underlying disease process. In women, the most common cause of CM is breast carcinoma.1-3 Cutaneous metastases are found in approximately 25% of all patients with breast carcinoma,1 and breast carcinomas represent approximately 69% of all CMs found in women (Table 1).2 Cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma (CMBC) is associated with a poor prognosis with a mean survival of approximately 6 months at the time of diagnosis.1,3 It commonly presents as a collection of flesh-colored, firm, asymptomatic, and rapidly appearing papules and nodules that can resemble cysts or fibrous tumors.1,3,4 They typically are located on the chest wall or abdomen near the site of the underlying malignancy.1-3 The histologic features of CMBC can include hyperchromatic tumor cells infiltrating between the collagen fibers in a characteristic single file manner,3,5 giving the appearance of a busy dermis, a nonspecific term to describe a focally hypercellular dermis at low-power magnification (Table 2).5,6 Cords and clusters of atypical cells with intracytoplasmic vacuoles or well-developed ducts also can be seen (quiz image [inset]). The carcinoma en cuirasse subtype of CMBC is characterized by a fibrotic scarlike plaque on the chest wall.1,3 If a punch biopsy is obtained, the specimen typically appears rectangular rather than tapered because of the sclerotic dermal collagen.6 In contrast, inflammatory carcinoma (carcinoma erysipelatoides) presents as an erythematous plaque resembling cellulitis due to the lymphatics being congested by tumor cells.3 Immunohistochemistry is a valuable tool in diagnosis. Positive staining is seen with cytokeratin 7, gross cystic disease fluid protein-15, mammaglobin, and GATA-3.1,3,6


Kaposi sarcoma (KS) is a low-grade endothelial malignancy associated with human herpesvirus 8.3,4 Kaposi sarcoma can be divided into 4 main subtypes: classic KS, African KS, AIDS-related KS, and immunosuppression-associated KS that occurs in patients with diseases such as human immunodeficiency virus. The cutaneous lesions are similar between subtypes and present as dark reddish purple macules that may enlarge or become nodular lesions.3,4 Histologically, 3 distinct stages of progression are described: patch, plaque, and tumor. The plaque stage has the appearance of a busy dermis due to the rapid proliferation of vascular structures within the dermis.3,6 A useful histologic feature known as the promontory sign can be seen as the proliferating tumor causes preexisting structures to project into vascular spaces (Figure 1).6 Immunohistochemistry for the endothelial and lymphatic markers CD31 and D2-40, respectively, are positive and may aid in the diagnosis.3 Staining for the latent nuclear antigen-1 of human herpesvirus 8 is a highly specific marker used to diagnose KS and can further distinguish it from the other busy dermis lesions.3

Granuloma annulare (GA) is characterized by rings of small, firm, pink to flesh-colored papules with a variable disease duration.4 Histologically, the interstitial variant of GA is characterized by a scattered inflammatory infiltrate consisting of histiocytes and lymphocytes located between altered collagen fibers in the superficial to mid dermis (Figure 2).3,6 Occasional eosinophils and increased dermal mucin are useful features to distinguish interstitial GA from other entities in the busy dermis differential.7

Scleromyxedema, also known as generalized lichen myxedematosus, is a rare mucinosis.3,8 Although its pathogenesis is unknown, it has been suggested that paraproteins related to the underlying gammopathy act to stimulate fibroblast proliferation and mucin overproduction.8 Clinically, characteristic widespread firm, waxy, dome-shaped papules are present over the head, upper trunk, and extremities.3,8 Histologically, scleromyxedema is characterized by increased dermal fibroblasts, mucin, and fibrosis, leading to the appearance of a busy dermis (Figure 3).3,6

Neurofibromas are common benign peripheral nerve sheath tumors that can occur sporadically or in the setting of neurofibromatosis.3-5 They present as soft, flesh-colored papules or nodules most commonly located on the trunk and limbs.4 Histologically, neurofibromas are nonencapsulated tumors composed of abundant spindle cells with comma-shaped nuclei diffusely arranged in a pale myxoid stroma (Figure 4). Scattered mast cells can be visualized at higher magnification.3,6

- Alcaraz I, Cerroni L, Rutten A, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34:347-393.
- Habif TP, Dinulos JGH, Chapman MS, et al. Skin Disease: Diagnosis and Treatment. 4th ed. Edinburgh, Scotland: Elsevier; 2017.
- Calonje JE, Brenn T, Lazar AJ, et al, eds. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2012.
- Habif TP. Clinical Dermatology: A Color Guide to Diagnosis and Therapy. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2015.
- Patterson JW, Hosler GA. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; 2016.
- Elston DM, Ferringer T, eds. Dermatopathology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2014.
- Silverman RA, Rabinowitz AD. Eosinophils in the cellular infiltrate of granuloma annulare. J Cutan Pathol. 1985;12:13-17.
- Rongioletti F, Merlo G, Cinotti E, et al. Scleromyxedema: a multicenter study of characteristics, comorbidities, course, and therapy in 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:66-72.
- Alcaraz I, Cerroni L, Rutten A, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34:347-393.
- Habif TP, Dinulos JGH, Chapman MS, et al. Skin Disease: Diagnosis and Treatment. 4th ed. Edinburgh, Scotland: Elsevier; 2017.
- Calonje JE, Brenn T, Lazar AJ, et al, eds. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2012.
- Habif TP. Clinical Dermatology: A Color Guide to Diagnosis and Therapy. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2015.
- Patterson JW, Hosler GA. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; 2016.
- Elston DM, Ferringer T, eds. Dermatopathology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2014.
- Silverman RA, Rabinowitz AD. Eosinophils in the cellular infiltrate of granuloma annulare. J Cutan Pathol. 1985;12:13-17.
- Rongioletti F, Merlo G, Cinotti E, et al. Scleromyxedema: a multicenter study of characteristics, comorbidities, course, and therapy in 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:66-72.
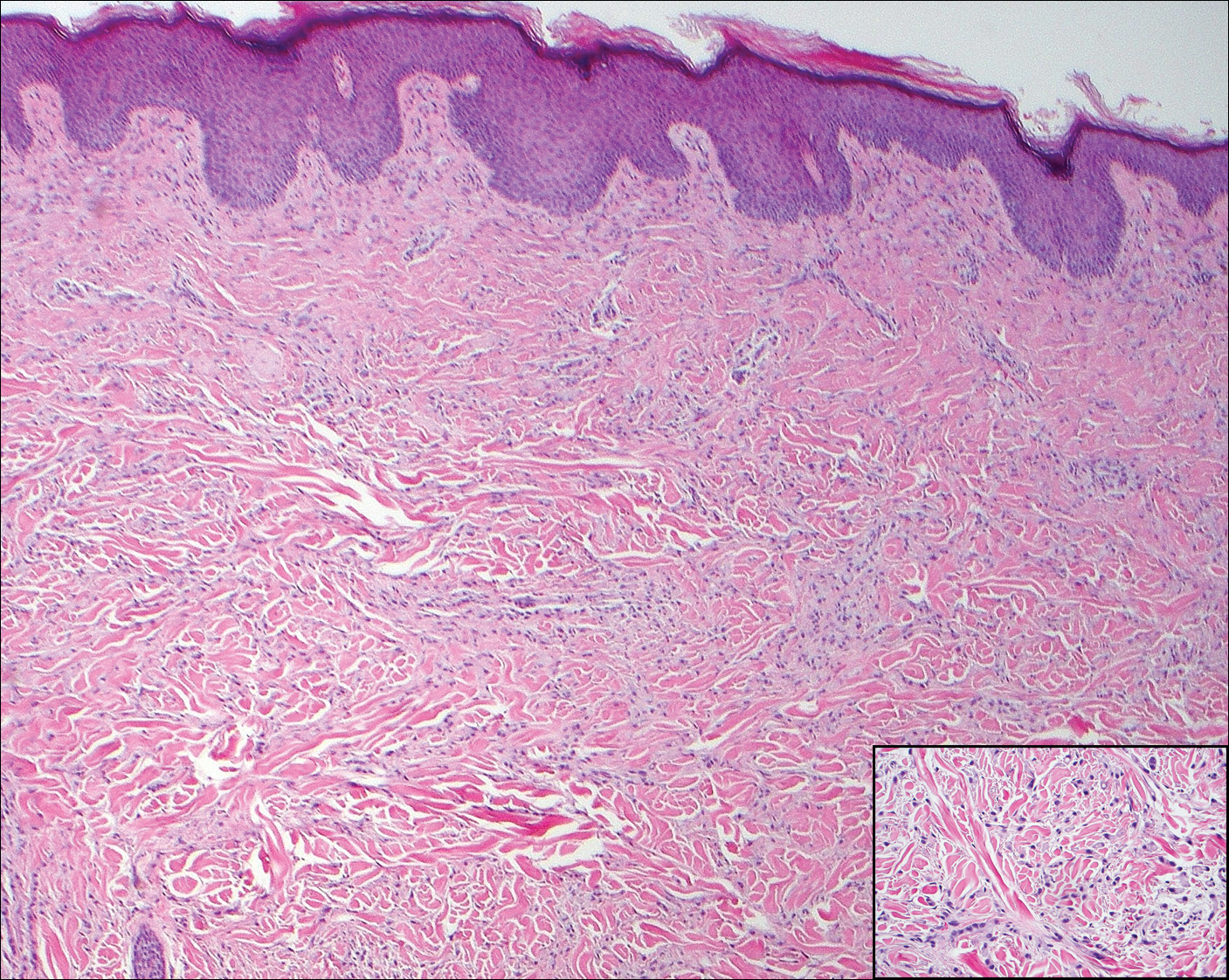
A 56-year-old woman presented with multiple asymptomatic lesions of 2 months' duration. On physical examination firm pink papules were noted dispersed across the upper abdomen, chest, and back. A 5-mm punch biopsy was obtained.
Tetrad Bodies in Skin
The Diagnosis: Bacterial Infection
The tetrad arrangement of organisms seen in this case was classic for Micrococcus and Sarcina species. Both are gram-positive cocci that occur in tetrads, but Micrococcus is aerobic and catalase positive, whereas Sarcina species are anaerobic, catalase negative, acidophilic, and form spores in alkaline pH.1 Although difficult to definitively differentiate on light microscopy, micrococci are smaller in size, ranging from 0.5 to 2.0 μm, and occur in tight clusters, as seen in this case (quiz images), in contrast to Sarcina species, which are relatively larger (1.8-3.0 μm).2 Sarcinae typically are found in soil and air, are considered pathogenic, and are associated with gastric symptoms (Sarcina ventriculi).1 Sarcina species also are reported to colonize the skin of patients with diabetes mellitus, but no pathogenic activity is known in the skin.3 Micrococcus species, with the majority being Micrococcus luteus, are part of the normal flora of the human skin as well as the oral and nasal cavities. Occasional reports of pneumonia, endocarditis, meningitis, arthritis, endophthalmitis, and sepsis have been reported in immunocompromised individuals.4 In the skin, Micrococcus is a commensal organism; however, Micrococcus sedentarius has been associated with pitted keratolysis, and reports of Micrococcus folliculitis in human immunodeficiency virus patients also are described in the literature.5,6 Micrococci are considered opportunistic bacteria and may worsen and prolong a localized cutaneous infection caused by other organisms under favorable conditions.7 Micrococcus luteus is one of the most common bacteria cultured from skin and soft tissue infections caused by fungal organisms.8 Depending on the immune status of an individual, use of broad-spectrum antibiotic and/or elimination of favorable milieu (ie, primary pathogen, breaks in skin) usually treats the infection.
Because of the rarity of infections caused and being part of the normal flora, the clinical implications of subtyping and sensitivity studies via culture or molecular studies may not be important; however, incidental presence of these organisms with unfamiliar morphology may cause confusion for the dermatopathologist. An extremely small size (0.5-2.0 μm) compared to red blood cells (7-8 μm) and white blood cells (10-12 μm) in a tight tetrad arrangement should raise the suspicion for Micrococcus.1 The refractive nature of these organisms from a thick extracellular layer can mimic fungus or plant matter; a negative Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver stain in this case helped in not only differentiating but also ruling out secondary fungal infection. Finally, a Gram stain with violet staining of these organisms reaffirmed the diagnosis of gram-positive bacterial organisms, most consistent with Micrococcus species (Figure 1). Culture studies were not performed because of contamination of the tissue specimen and resolution of the patient's symptoms.
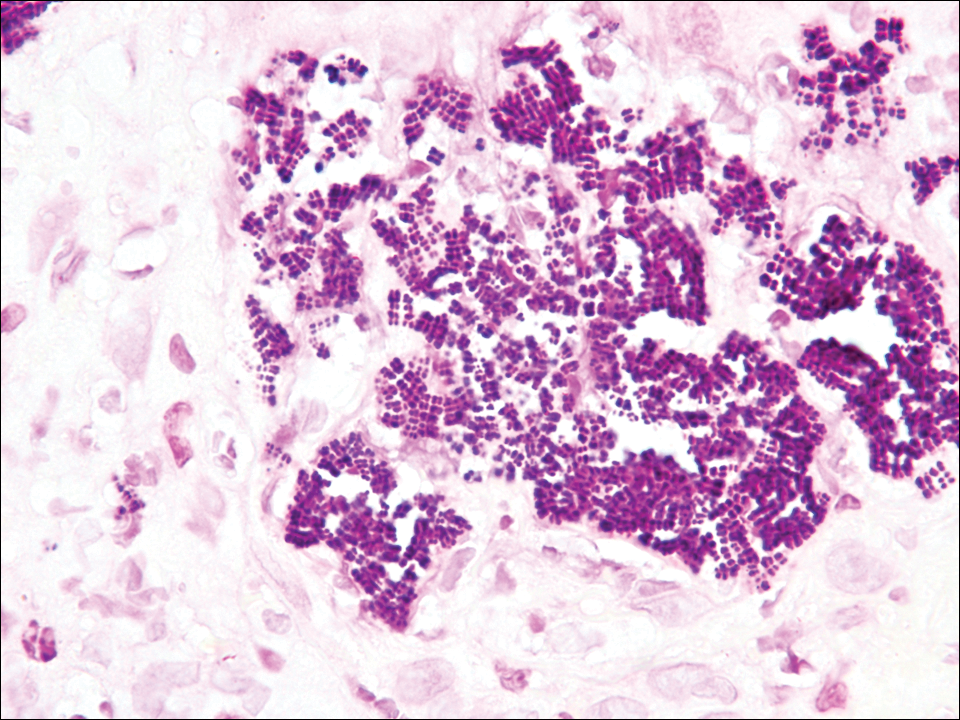
The presence of foreign material in the skin may be traumatic, occupational, cosmetic, iatrogenic, or self-inflicted, including a wide variety of substances that appear in different morphological forms on hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained sections, depending on their structure and physiochemical properties.9 Although not all foreign bodies may polarize, examining the sample under polarized light is considered an important step to narrow down the differential diagnosis. The tissue reaction is primarily dependent on the nature of the substance and duration, consisting of histiocytes, macrophages, plasma cells, lymphocytes, and fibrosis.9 Activated histiocytes, multinucleated giant cells, and granulomas are classic findings that generally are seen surrounding and engulfing the foreign material (Figure 2). In addition to foreign material, substances such as calcium salts, urate crystals, extruded keratin, ruptured cysts, and hair follicles may act as foreign materials and can incite a tissue response.9 Absence of histiocytic response, granuloma formation, and fibrosis in a lesion of 1 month's duration made the tetrad bodies unlikely to be foreign material.
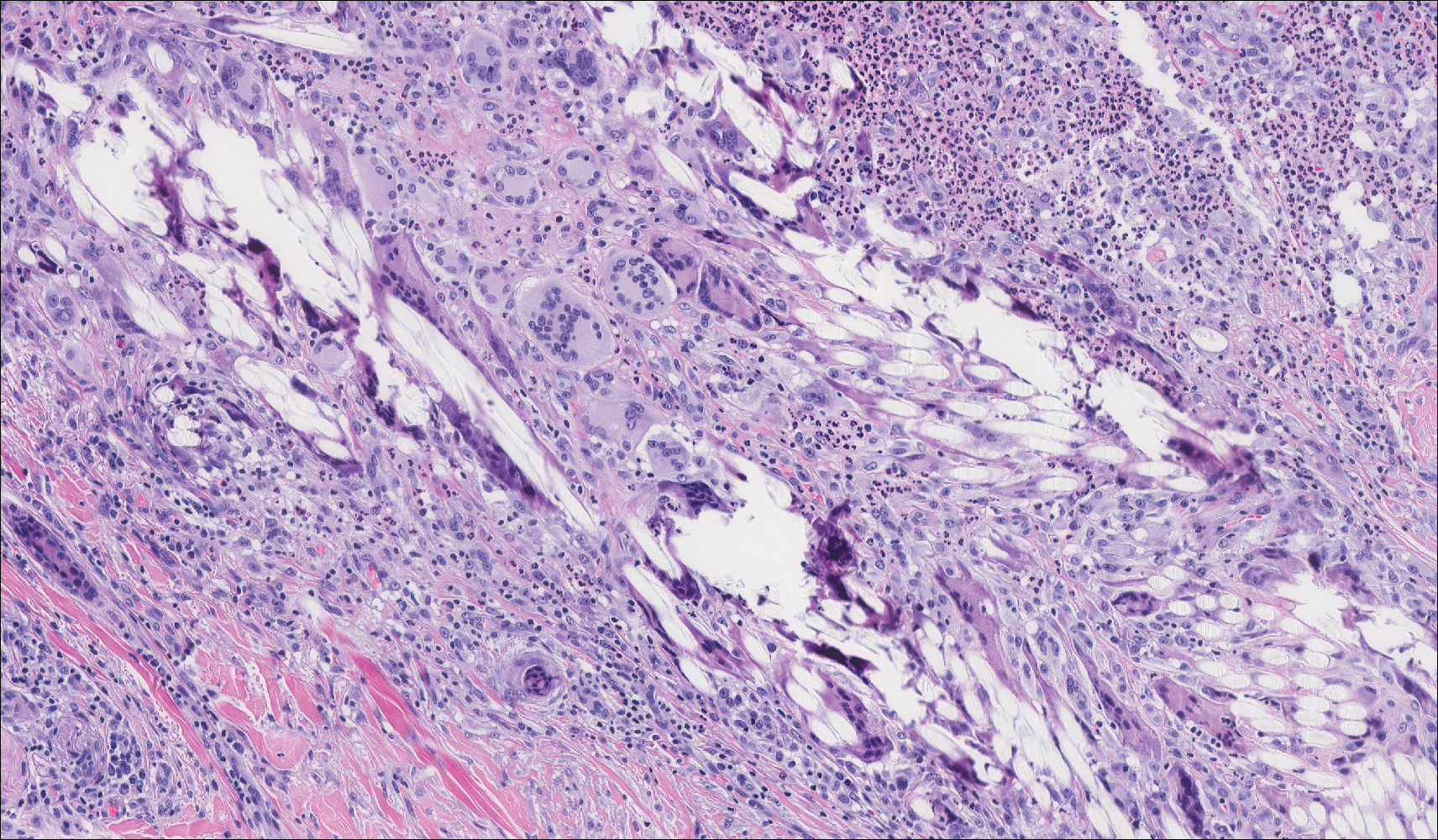
Demodex mites are superficial inhabitants of human skin that are acquired shortly after birth, live in or near pilosebaceous units, and obtain nourishment from skin cells and sebum.10,11 The mites can be recovered on 10% of skin biopsies, most commonly on the face due to high sebum production.10 Adult mites range from 0.1 to 0.4 mm in length and are round to oval in shape. Females lay eggs inside the hair follicle or sebaceous glands.11 They usually are asymptomatic, but their infestation may become pathogenic, especially in immunocompromised individuals.10 The clinical picture may resemble bacterial folliculitis, rosacea, and perioral dermatitis, while histology typically is characterized by spongiosis, lymphohistiocytic inflammation around infested follicles, and mite(s) in follicular infundibula (Figure 3). Sometimes the protrusion of mites and keratin from the follicles is seen as follicular spines on histology and referred to as pityriasis folliculorum.
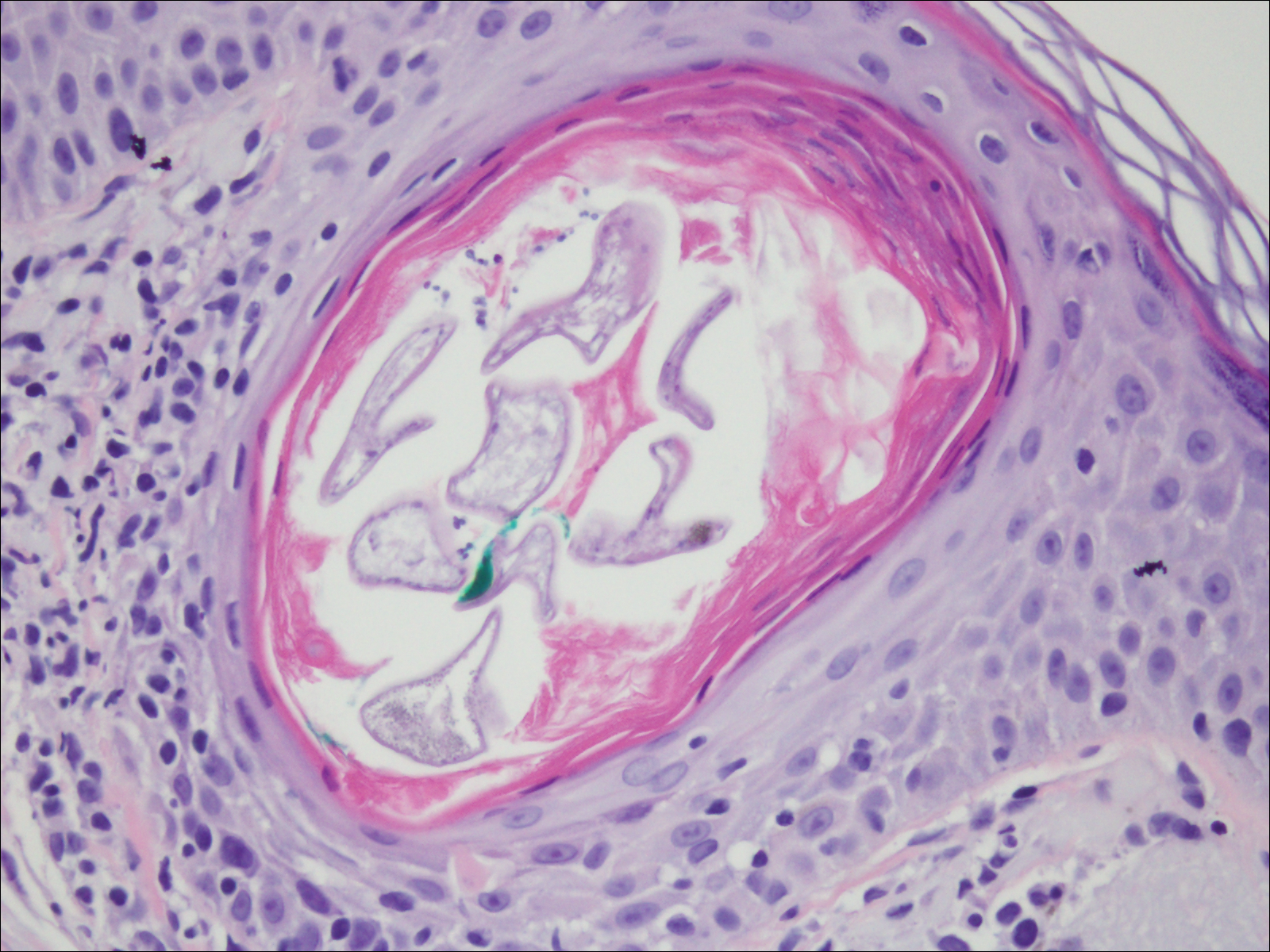
Deposits of urate crystals in skin occur from the elevated serum uric acid levels in gout. The cutaneous deposits are mainly in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue and are extremely painful.12 Urate crystals get dissolved during formalin fixation and leave needlelike clefts in a homogenous, lightly basophilic material on H&E slide (Figure 4). For the same reason, polarized microscopy also is not helpful despite the birefringent nature of urate crystals.12
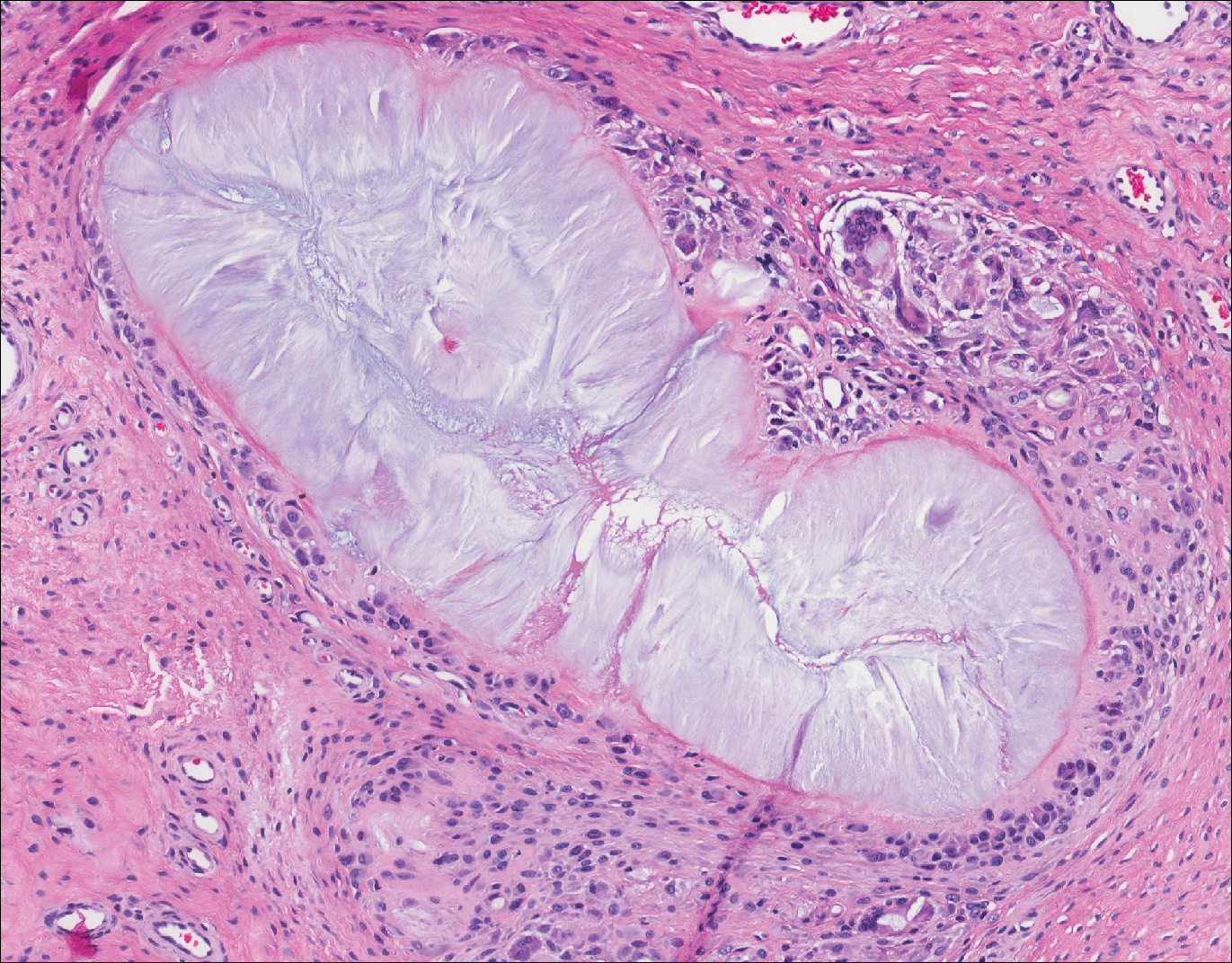
Fungal yeast forms appear round to oval under light microscopy, ranging from 2 to 100 μm in size.13 The common superficial forms involving the epidermis or hair follicles similar to the current case of bacterial infection include Malassezia and dermatophyte infections. Malassezia is part of the normal flora of sebum-rich areas of skin and is associated with superficial infections such as folliculitis, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, and dandruff.14 Malassezia appear as clusters of yeast cells that are pleomorphic and round to oval in shape, ranging from 2 to 6 μm in size. It forms hyphae in its pathogenic form and gives rise to the classic spaghetti and meatball-like appearance that can be highlighted by periodic acid-Schiff (Figure 5) and Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver special stains. Dermatophytes include 3 genera--Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton--with at least 40 species that causes skin infections in humans.14 Fungal spores and hyphae forms are restricted to the stratum corneum. The hyphae forms may not be apparent on H&E stain, and periodic acid-Schiff staining is helpful in visualizing the fungal elements. The presence of neutrophils in the corneal layer, basket weave hyperkeratosis, and presence of fungal hyphae within the corneal layer fissures (sandwich sign) are clues to the dermatophyte infection.15 Other smaller fungi such as Histoplasma capsulatum (2-4 μm), Candida (3-5 μm), and Pneumocystis (2-5 μm) species can be found in skin in disseminated infections, usually affecting immunocompromised individuals.13 Histoplasma is a basophilic yeast that exhibits narrow-based budding and appears clustered within or outside of macrophages. Candida species generally are dimorphic, and yeasts are found intermingled with filamentous forms. Pneumocystis infection in skin is extremely rare, and the fungi appear as spherical or crescent-shaped bodies in a foamy amorphous material.16

- Al Rasheed MR, Senseng CG. Sarcina ventriculi: review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1441-1445.
- Lam-Himlin D, Tsiatis AC, Montgomery E, et al. Sarcina organisms in the gastrointestinal tract: a clinicopathologic and molecular study. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011;35:1700-1705.
- Somerville DA, Lancaster-Smith M. The aerobic cutaneous microflora of diabetic subjects. Br J Dermatol. 1973;89:395-400.
- Hetem DJ, Rooijakkers S, Ekkelenkamp MB. Staphylococci and Micrococci. In: Cohen J, Powderly WG, Opal SM, eds. Infectious Diseases. 4th ed. Vol 2. New York, NY: Elsevier; 2017:1509-1522.
- Nordstrom KM, McGinley KJ, Cappiello L, et al. Pitted keratolysis. the role of Micrococcus sedentarius. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:1320-1325.
- Smith KJ, Neafie R, Yeager J, et al. Micrococcus folliculitis in HIV-1 disease. Br J Dermatol. 1999;141:558-561.
- van Rensburg JJ, Lin H, Gao X, et al. The human skin microbiome associates with the outcome of and is influenced by bacterial infection. mBio. 2015;6:E01315-15. doi:10.1128/mBio.01315-15.
- Chuku A, Nwankiti OO. Association of bacteria with fungal infection of skin and soft tissue lesions in plateau state, Nigeria. Br Microbiol Res J. 2013;3:470-477.
- Molina-Ruiz AM, Requena L. Foreign body granulomas. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:497-523.
- Elston CA, Elston DM. Demodex mites. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:739-743.
- Rather PA, Hassan I. Human Demodex mite: the versatile mite of dermatological importance. Indian J Dermatol. 2014;59:60-66.
- Gaviria JL, Ortega VG, Gaona J, et al. Unusual dermatological manifestations of gout: review of literature and a case report. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2015;3:E445.
- Guarner J, Brandt ME. Histopathologic diagnosis of fungal infections in the 21st century. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011;24:247-280.
- White TC, Findley K, Dawson TL Jr, et al. Fungi on the skin: dermatophytes and Malassezia. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014;4. pii:a019802. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a019802.
- Gottlieb GJ, Ackerman AB. The "sandwich sign" of dermatophytosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1986;8:347.
- Hennessey NP, Parro EL, Cockerell CJ. Cutaneous Pneumocystis carinii infection in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:1699-1701.
The Diagnosis: Bacterial Infection
The tetrad arrangement of organisms seen in this case was classic for Micrococcus and Sarcina species. Both are gram-positive cocci that occur in tetrads, but Micrococcus is aerobic and catalase positive, whereas Sarcina species are anaerobic, catalase negative, acidophilic, and form spores in alkaline pH.1 Although difficult to definitively differentiate on light microscopy, micrococci are smaller in size, ranging from 0.5 to 2.0 μm, and occur in tight clusters, as seen in this case (quiz images), in contrast to Sarcina species, which are relatively larger (1.8-3.0 μm).2 Sarcinae typically are found in soil and air, are considered pathogenic, and are associated with gastric symptoms (Sarcina ventriculi).1 Sarcina species also are reported to colonize the skin of patients with diabetes mellitus, but no pathogenic activity is known in the skin.3 Micrococcus species, with the majority being Micrococcus luteus, are part of the normal flora of the human skin as well as the oral and nasal cavities. Occasional reports of pneumonia, endocarditis, meningitis, arthritis, endophthalmitis, and sepsis have been reported in immunocompromised individuals.4 In the skin, Micrococcus is a commensal organism; however, Micrococcus sedentarius has been associated with pitted keratolysis, and reports of Micrococcus folliculitis in human immunodeficiency virus patients also are described in the literature.5,6 Micrococci are considered opportunistic bacteria and may worsen and prolong a localized cutaneous infection caused by other organisms under favorable conditions.7 Micrococcus luteus is one of the most common bacteria cultured from skin and soft tissue infections caused by fungal organisms.8 Depending on the immune status of an individual, use of broad-spectrum antibiotic and/or elimination of favorable milieu (ie, primary pathogen, breaks in skin) usually treats the infection.
Because of the rarity of infections caused and being part of the normal flora, the clinical implications of subtyping and sensitivity studies via culture or molecular studies may not be important; however, incidental presence of these organisms with unfamiliar morphology may cause confusion for the dermatopathologist. An extremely small size (0.5-2.0 μm) compared to red blood cells (7-8 μm) and white blood cells (10-12 μm) in a tight tetrad arrangement should raise the suspicion for Micrococcus.1 The refractive nature of these organisms from a thick extracellular layer can mimic fungus or plant matter; a negative Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver stain in this case helped in not only differentiating but also ruling out secondary fungal infection. Finally, a Gram stain with violet staining of these organisms reaffirmed the diagnosis of gram-positive bacterial organisms, most consistent with Micrococcus species (Figure 1). Culture studies were not performed because of contamination of the tissue specimen and resolution of the patient's symptoms.

The presence of foreign material in the skin may be traumatic, occupational, cosmetic, iatrogenic, or self-inflicted, including a wide variety of substances that appear in different morphological forms on hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained sections, depending on their structure and physiochemical properties.9 Although not all foreign bodies may polarize, examining the sample under polarized light is considered an important step to narrow down the differential diagnosis. The tissue reaction is primarily dependent on the nature of the substance and duration, consisting of histiocytes, macrophages, plasma cells, lymphocytes, and fibrosis.9 Activated histiocytes, multinucleated giant cells, and granulomas are classic findings that generally are seen surrounding and engulfing the foreign material (Figure 2). In addition to foreign material, substances such as calcium salts, urate crystals, extruded keratin, ruptured cysts, and hair follicles may act as foreign materials and can incite a tissue response.9 Absence of histiocytic response, granuloma formation, and fibrosis in a lesion of 1 month's duration made the tetrad bodies unlikely to be foreign material.

Demodex mites are superficial inhabitants of human skin that are acquired shortly after birth, live in or near pilosebaceous units, and obtain nourishment from skin cells and sebum.10,11 The mites can be recovered on 10% of skin biopsies, most commonly on the face due to high sebum production.10 Adult mites range from 0.1 to 0.4 mm in length and are round to oval in shape. Females lay eggs inside the hair follicle or sebaceous glands.11 They usually are asymptomatic, but their infestation may become pathogenic, especially in immunocompromised individuals.10 The clinical picture may resemble bacterial folliculitis, rosacea, and perioral dermatitis, while histology typically is characterized by spongiosis, lymphohistiocytic inflammation around infested follicles, and mite(s) in follicular infundibula (Figure 3). Sometimes the protrusion of mites and keratin from the follicles is seen as follicular spines on histology and referred to as pityriasis folliculorum.

Deposits of urate crystals in skin occur from the elevated serum uric acid levels in gout. The cutaneous deposits are mainly in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue and are extremely painful.12 Urate crystals get dissolved during formalin fixation and leave needlelike clefts in a homogenous, lightly basophilic material on H&E slide (Figure 4). For the same reason, polarized microscopy also is not helpful despite the birefringent nature of urate crystals.12

Fungal yeast forms appear round to oval under light microscopy, ranging from 2 to 100 μm in size.13 The common superficial forms involving the epidermis or hair follicles similar to the current case of bacterial infection include Malassezia and dermatophyte infections. Malassezia is part of the normal flora of sebum-rich areas of skin and is associated with superficial infections such as folliculitis, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, and dandruff.14 Malassezia appear as clusters of yeast cells that are pleomorphic and round to oval in shape, ranging from 2 to 6 μm in size. It forms hyphae in its pathogenic form and gives rise to the classic spaghetti and meatball-like appearance that can be highlighted by periodic acid-Schiff (Figure 5) and Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver special stains. Dermatophytes include 3 genera--Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton--with at least 40 species that causes skin infections in humans.14 Fungal spores and hyphae forms are restricted to the stratum corneum. The hyphae forms may not be apparent on H&E stain, and periodic acid-Schiff staining is helpful in visualizing the fungal elements. The presence of neutrophils in the corneal layer, basket weave hyperkeratosis, and presence of fungal hyphae within the corneal layer fissures (sandwich sign) are clues to the dermatophyte infection.15 Other smaller fungi such as Histoplasma capsulatum (2-4 μm), Candida (3-5 μm), and Pneumocystis (2-5 μm) species can be found in skin in disseminated infections, usually affecting immunocompromised individuals.13 Histoplasma is a basophilic yeast that exhibits narrow-based budding and appears clustered within or outside of macrophages. Candida species generally are dimorphic, and yeasts are found intermingled with filamentous forms. Pneumocystis infection in skin is extremely rare, and the fungi appear as spherical or crescent-shaped bodies in a foamy amorphous material.16

The Diagnosis: Bacterial Infection
The tetrad arrangement of organisms seen in this case was classic for Micrococcus and Sarcina species. Both are gram-positive cocci that occur in tetrads, but Micrococcus is aerobic and catalase positive, whereas Sarcina species are anaerobic, catalase negative, acidophilic, and form spores in alkaline pH.1 Although difficult to definitively differentiate on light microscopy, micrococci are smaller in size, ranging from 0.5 to 2.0 μm, and occur in tight clusters, as seen in this case (quiz images), in contrast to Sarcina species, which are relatively larger (1.8-3.0 μm).2 Sarcinae typically are found in soil and air, are considered pathogenic, and are associated with gastric symptoms (Sarcina ventriculi).1 Sarcina species also are reported to colonize the skin of patients with diabetes mellitus, but no pathogenic activity is known in the skin.3 Micrococcus species, with the majority being Micrococcus luteus, are part of the normal flora of the human skin as well as the oral and nasal cavities. Occasional reports of pneumonia, endocarditis, meningitis, arthritis, endophthalmitis, and sepsis have been reported in immunocompromised individuals.4 In the skin, Micrococcus is a commensal organism; however, Micrococcus sedentarius has been associated with pitted keratolysis, and reports of Micrococcus folliculitis in human immunodeficiency virus patients also are described in the literature.5,6 Micrococci are considered opportunistic bacteria and may worsen and prolong a localized cutaneous infection caused by other organisms under favorable conditions.7 Micrococcus luteus is one of the most common bacteria cultured from skin and soft tissue infections caused by fungal organisms.8 Depending on the immune status of an individual, use of broad-spectrum antibiotic and/or elimination of favorable milieu (ie, primary pathogen, breaks in skin) usually treats the infection.
Because of the rarity of infections caused and being part of the normal flora, the clinical implications of subtyping and sensitivity studies via culture or molecular studies may not be important; however, incidental presence of these organisms with unfamiliar morphology may cause confusion for the dermatopathologist. An extremely small size (0.5-2.0 μm) compared to red blood cells (7-8 μm) and white blood cells (10-12 μm) in a tight tetrad arrangement should raise the suspicion for Micrococcus.1 The refractive nature of these organisms from a thick extracellular layer can mimic fungus or plant matter; a negative Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver stain in this case helped in not only differentiating but also ruling out secondary fungal infection. Finally, a Gram stain with violet staining of these organisms reaffirmed the diagnosis of gram-positive bacterial organisms, most consistent with Micrococcus species (Figure 1). Culture studies were not performed because of contamination of the tissue specimen and resolution of the patient's symptoms.

The presence of foreign material in the skin may be traumatic, occupational, cosmetic, iatrogenic, or self-inflicted, including a wide variety of substances that appear in different morphological forms on hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained sections, depending on their structure and physiochemical properties.9 Although not all foreign bodies may polarize, examining the sample under polarized light is considered an important step to narrow down the differential diagnosis. The tissue reaction is primarily dependent on the nature of the substance and duration, consisting of histiocytes, macrophages, plasma cells, lymphocytes, and fibrosis.9 Activated histiocytes, multinucleated giant cells, and granulomas are classic findings that generally are seen surrounding and engulfing the foreign material (Figure 2). In addition to foreign material, substances such as calcium salts, urate crystals, extruded keratin, ruptured cysts, and hair follicles may act as foreign materials and can incite a tissue response.9 Absence of histiocytic response, granuloma formation, and fibrosis in a lesion of 1 month's duration made the tetrad bodies unlikely to be foreign material.

Demodex mites are superficial inhabitants of human skin that are acquired shortly after birth, live in or near pilosebaceous units, and obtain nourishment from skin cells and sebum.10,11 The mites can be recovered on 10% of skin biopsies, most commonly on the face due to high sebum production.10 Adult mites range from 0.1 to 0.4 mm in length and are round to oval in shape. Females lay eggs inside the hair follicle or sebaceous glands.11 They usually are asymptomatic, but their infestation may become pathogenic, especially in immunocompromised individuals.10 The clinical picture may resemble bacterial folliculitis, rosacea, and perioral dermatitis, while histology typically is characterized by spongiosis, lymphohistiocytic inflammation around infested follicles, and mite(s) in follicular infundibula (Figure 3). Sometimes the protrusion of mites and keratin from the follicles is seen as follicular spines on histology and referred to as pityriasis folliculorum.

Deposits of urate crystals in skin occur from the elevated serum uric acid levels in gout. The cutaneous deposits are mainly in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue and are extremely painful.12 Urate crystals get dissolved during formalin fixation and leave needlelike clefts in a homogenous, lightly basophilic material on H&E slide (Figure 4). For the same reason, polarized microscopy also is not helpful despite the birefringent nature of urate crystals.12

Fungal yeast forms appear round to oval under light microscopy, ranging from 2 to 100 μm in size.13 The common superficial forms involving the epidermis or hair follicles similar to the current case of bacterial infection include Malassezia and dermatophyte infections. Malassezia is part of the normal flora of sebum-rich areas of skin and is associated with superficial infections such as folliculitis, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, and dandruff.14 Malassezia appear as clusters of yeast cells that are pleomorphic and round to oval in shape, ranging from 2 to 6 μm in size. It forms hyphae in its pathogenic form and gives rise to the classic spaghetti and meatball-like appearance that can be highlighted by periodic acid-Schiff (Figure 5) and Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver special stains. Dermatophytes include 3 genera--Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton--with at least 40 species that causes skin infections in humans.14 Fungal spores and hyphae forms are restricted to the stratum corneum. The hyphae forms may not be apparent on H&E stain, and periodic acid-Schiff staining is helpful in visualizing the fungal elements. The presence of neutrophils in the corneal layer, basket weave hyperkeratosis, and presence of fungal hyphae within the corneal layer fissures (sandwich sign) are clues to the dermatophyte infection.15 Other smaller fungi such as Histoplasma capsulatum (2-4 μm), Candida (3-5 μm), and Pneumocystis (2-5 μm) species can be found in skin in disseminated infections, usually affecting immunocompromised individuals.13 Histoplasma is a basophilic yeast that exhibits narrow-based budding and appears clustered within or outside of macrophages. Candida species generally are dimorphic, and yeasts are found intermingled with filamentous forms. Pneumocystis infection in skin is extremely rare, and the fungi appear as spherical or crescent-shaped bodies in a foamy amorphous material.16

- Al Rasheed MR, Senseng CG. Sarcina ventriculi: review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1441-1445.
- Lam-Himlin D, Tsiatis AC, Montgomery E, et al. Sarcina organisms in the gastrointestinal tract: a clinicopathologic and molecular study. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011;35:1700-1705.
- Somerville DA, Lancaster-Smith M. The aerobic cutaneous microflora of diabetic subjects. Br J Dermatol. 1973;89:395-400.
- Hetem DJ, Rooijakkers S, Ekkelenkamp MB. Staphylococci and Micrococci. In: Cohen J, Powderly WG, Opal SM, eds. Infectious Diseases. 4th ed. Vol 2. New York, NY: Elsevier; 2017:1509-1522.
- Nordstrom KM, McGinley KJ, Cappiello L, et al. Pitted keratolysis. the role of Micrococcus sedentarius. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:1320-1325.
- Smith KJ, Neafie R, Yeager J, et al. Micrococcus folliculitis in HIV-1 disease. Br J Dermatol. 1999;141:558-561.
- van Rensburg JJ, Lin H, Gao X, et al. The human skin microbiome associates with the outcome of and is influenced by bacterial infection. mBio. 2015;6:E01315-15. doi:10.1128/mBio.01315-15.
- Chuku A, Nwankiti OO. Association of bacteria with fungal infection of skin and soft tissue lesions in plateau state, Nigeria. Br Microbiol Res J. 2013;3:470-477.
- Molina-Ruiz AM, Requena L. Foreign body granulomas. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:497-523.
- Elston CA, Elston DM. Demodex mites. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:739-743.
- Rather PA, Hassan I. Human Demodex mite: the versatile mite of dermatological importance. Indian J Dermatol. 2014;59:60-66.
- Gaviria JL, Ortega VG, Gaona J, et al. Unusual dermatological manifestations of gout: review of literature and a case report. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2015;3:E445.
- Guarner J, Brandt ME. Histopathologic diagnosis of fungal infections in the 21st century. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011;24:247-280.
- White TC, Findley K, Dawson TL Jr, et al. Fungi on the skin: dermatophytes and Malassezia. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014;4. pii:a019802. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a019802.
- Gottlieb GJ, Ackerman AB. The "sandwich sign" of dermatophytosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1986;8:347.
- Hennessey NP, Parro EL, Cockerell CJ. Cutaneous Pneumocystis carinii infection in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:1699-1701.
- Al Rasheed MR, Senseng CG. Sarcina ventriculi: review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1441-1445.
- Lam-Himlin D, Tsiatis AC, Montgomery E, et al. Sarcina organisms in the gastrointestinal tract: a clinicopathologic and molecular study. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011;35:1700-1705.
- Somerville DA, Lancaster-Smith M. The aerobic cutaneous microflora of diabetic subjects. Br J Dermatol. 1973;89:395-400.
- Hetem DJ, Rooijakkers S, Ekkelenkamp MB. Staphylococci and Micrococci. In: Cohen J, Powderly WG, Opal SM, eds. Infectious Diseases. 4th ed. Vol 2. New York, NY: Elsevier; 2017:1509-1522.
- Nordstrom KM, McGinley KJ, Cappiello L, et al. Pitted keratolysis. the role of Micrococcus sedentarius. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:1320-1325.
- Smith KJ, Neafie R, Yeager J, et al. Micrococcus folliculitis in HIV-1 disease. Br J Dermatol. 1999;141:558-561.
- van Rensburg JJ, Lin H, Gao X, et al. The human skin microbiome associates with the outcome of and is influenced by bacterial infection. mBio. 2015;6:E01315-15. doi:10.1128/mBio.01315-15.
- Chuku A, Nwankiti OO. Association of bacteria with fungal infection of skin and soft tissue lesions in plateau state, Nigeria. Br Microbiol Res J. 2013;3:470-477.
- Molina-Ruiz AM, Requena L. Foreign body granulomas. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:497-523.
- Elston CA, Elston DM. Demodex mites. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:739-743.
- Rather PA, Hassan I. Human Demodex mite: the versatile mite of dermatological importance. Indian J Dermatol. 2014;59:60-66.
- Gaviria JL, Ortega VG, Gaona J, et al. Unusual dermatological manifestations of gout: review of literature and a case report. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2015;3:E445.
- Guarner J, Brandt ME. Histopathologic diagnosis of fungal infections in the 21st century. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011;24:247-280.
- White TC, Findley K, Dawson TL Jr, et al. Fungi on the skin: dermatophytes and Malassezia. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014;4. pii:a019802. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a019802.
- Gottlieb GJ, Ackerman AB. The "sandwich sign" of dermatophytosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1986;8:347.
- Hennessey NP, Parro EL, Cockerell CJ. Cutaneous Pneumocystis carinii infection in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:1699-1701.
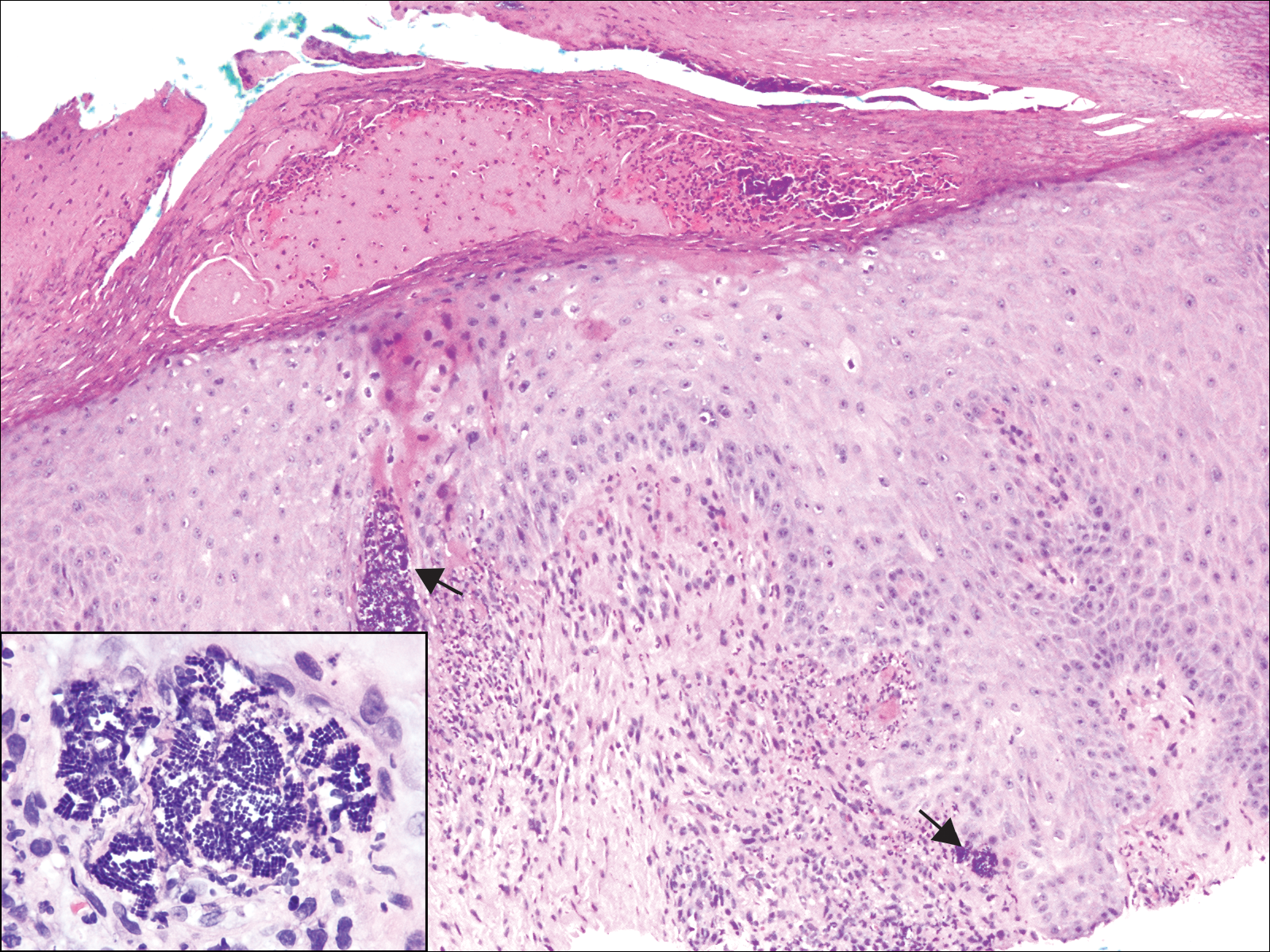
A 72-year-old woman with a medical history notable for multiple sclerosis and intravenous drug abuse presented to the dermatology clinic with a 0.6×0.5-cm, pruritic, wartlike, inflamed, keratotic papule on the palmar aspect of the right finger of more than 1 month's duration. A shave biopsy was performed that showed excoriation with serum crust, parakeratosis, and neutrophilic infiltrate in the papillary dermis. Within the serum crust and at the dermoepidermal junction, clusters of refractive basophilic bodies (arrows) in tetrad arrangement also were noted (inset). The papule resolved after the biopsy without any additional treatment.
Pigmented Lesion on the Forearm
The Diagnosis: Monsel Solution Reaction
Exogenous substances can cause interesting incongruities in cutaneous biopsies of which pathologists and dermatologists should be cognizant. Exogenous lesions are caused by externally introduced foreign bodies, substances, or materials, such as sterile compressed sponges, aluminum chloride hexahydrate and anhydrous ethyl alcohol, silica, paraffin, and Monsel solution. Monsel solution reaction is a florid fibrohistiocytic proliferation stimulated by the application of Monsel solution. Monsel solution is a ferric subsulfate that often is used to achieve hemostasis after shave biopsies. Hemostasis is thought to result from the ability of ferric ions to denature and agglutinate proteins such as fibrinogen.1,2 Application of Monsel solution likely causes ferrugination of fibrin, dermal collagen, and striated muscle fibers. Some ferruginated collagen fibers are eliminated through the epidermis as the epidermis regenerates, while some fibers become calcified. Siderophages (iron-containing macrophages) are present in these areas. The ferrugination of collagen fibers becomes less pronounced as the biopsy sites heal and the iron pigment subsequently is absorbed by macrophages. Ferruginated skeletal muscles can act as foreign bodies and may elicit granulomatous reactions.2
It is currently unclear why fibrohistiocytic responses occur in some instances but not others. Iron stains (eg, Perls Prussian blue stain) make interpretation clear, provided the pathologist is familiar with Monsel solution. The primary differential diagnosis of these lesions centers on heavily pigmented melanocytic proliferations. It is critical to review prior biopsy sections or to have definite knowledge of the prior biopsy diagnosis. Histologically, the epidermis may demonstrate nonspecific reactive changes such as hyperkeratosis with foci of irregular acanthosis. The prominent features are present in the dermis where there is a proliferation of spindle- and polyhedral-shaped cells that may show cytologic atypia and occasional mitotic figures. The cells contain refractile brown pigment scattered in the dermis and deposited on collagen fibers (quiz images). Occasional large black or brown encrustations may be identified. Monsel-containing cells may indiscernibly blend with foci of more blatantly fibrohistiocytic differentiation, in which case iron stains are strongly positive (Figure 1). If the clinician uses Monsel solution for hemostasis during the removal of a nevomelanocytic neoplasm, it might be necessary to use melanin stains or immunohistochemistry on the reexcision specimen to distinguish between residual nevomelanocytic and fibrohistiocytic cells.3
Common blue nevus is a benign, typically intradermal melanocytic lesion. It most frequently occurs in young adults and has a predilection for females. Clinically, it can be found anywhere on the body as a single, asymptomatic, well-circumscribed, blue-black, dome-shaped papule measuring less than 1 cm in diameter. Histologically, it is characterized by pigmented, dendritic, spindle-shaped melanocytes that typically are separated by thick collagen bundles (Figure 2). The melanocytes typically have small nuclei with occasional basophilic nucleolus. Melanocytes typically are diffusely positive for melanocytic markers including human melanoma black (HMB) 45, S-100, Melan-A, and microphthalmia transcription factor 1. In contrast to most other benign melanocytic nevi, HMB-45 strongly stains the entire lesion in blue nevi.4
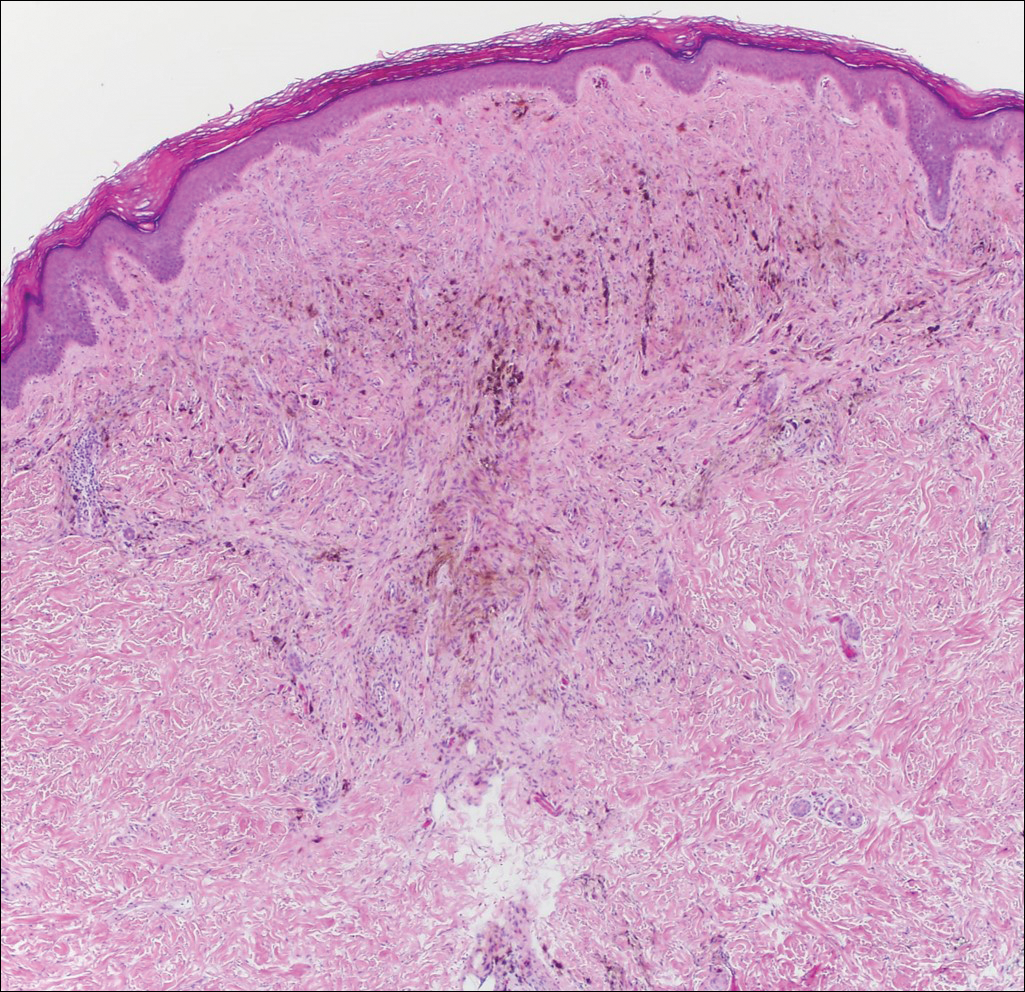
Desmoplastic melanoma accounts for 1% to 4% of all melanomas. The median age at diagnosis is 62 years and, as in other types of melanoma, men are more commonly affected.5 Clinically, desmoplastic melanoma typically presents on the head and neck as a painless indurated plaque, though it can present as a small papule or nodule. Nearly half of desmoplastic melanomas lack obvious pigmentation, which may lead to the misdiagnosis of basal cell carcinoma or a scar. Histologically, desmoplastic melanomas are composed of spindled melanocytes separated by collagen fibers or fibrous stroma (Figure 3). Histology displays variable cytologic atypia and stromal fibrosis. Characteristically there are small islands of lymphocytes and plasma cells within or at the edge of the tumor. The spindle cells stain positive with S-100 and Sry-related HMg-box gene 10, SOX10. Type IV collagen and laminin often are expressed in desmoplastic melanoma. In contrast to many other subtypes of melanoma, HMB-45 and Melan-A usually are negative.6

Animal-type melanoma is a rare neoplasm that differs from other subtypes of melanoma both clinically and histologically. Most frequently, animal-type melanoma affects younger adults (median age, 27 years) and arises on the arms and legs, head and neck, or trunk; men and women are affected equally.7 It most commonly presents with a blue or blue-black nodule with a blue-white veil or irregular white areas. Histologically, animal-type melanoma is a predominantly dermal-based melanocytic proliferation with heavily pigmented epithelioid and spindled melanocytes (Figure 4). The pigmentation pattern ranges widely from fine, granular, light brown deposits to coarse dark brown deposits with malignant cells often arranged in fascicles or sheets. Frequently, there is periadnexal and perieccrine spread. Often, there is epidermal hyperplasia above the dermis. As with conventional melanoma, the immunohistochemistry of animal-type melanoma is positive for S-100 protein, HMB-45, SOX10, and Melan-A.7

Recurrent nevi typically arise within 6 months of a previously biopsied melanocytic nevus. Most recurrent nevi originate from common banal nevi (most often a compound nevus). Recurrent nevi also may arise from congenital, atypical/dysplastic, and Spitz nevi. Most often they are found on the back of women aged 20 to 30 years.8 Clinically, they manifest as a macular area of scar with variegated hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation as well as linear streaking. They may demonstrate variable diffuse, stippled, and halo pigmentation patterns. Classically, recurrent nevi present with a trizonal histologic pattern. Within the epidermis there is a proliferation of melanocytes along the dermoepidermal junction, which may show varying degrees of atypia and pagetoid migration. The melanocytes often are described as epithelioid with round nuclei and even chromatin (Figure 5). The atypical features should be confined to the epidermis overlying the prior biopsy site. Within the dermis there is dense dermal collagen and fibrosis with vertically oriented blood vessels. Finally, features of the original nevus may be seen at the base of the lesion. Although immunohistochemistry may be helpful in some cases, an appropriate clinical history and comparison to the prior biopsy can be invaluable.8
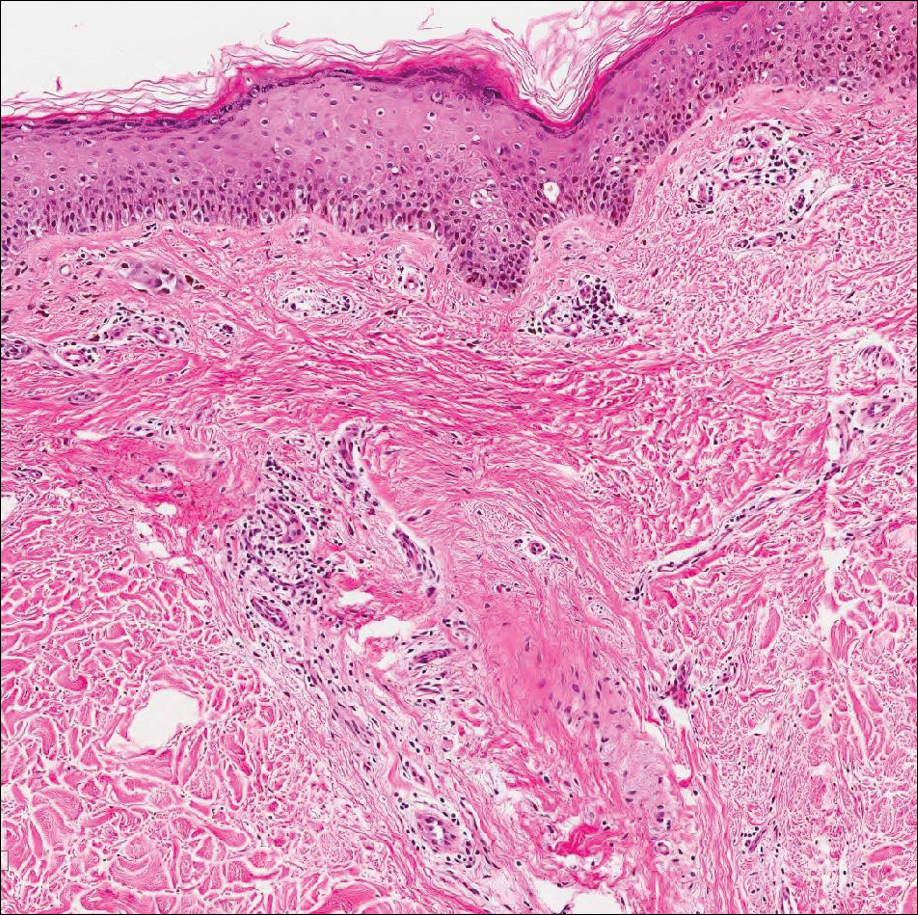
Host tissue reactions resulting in artefactual changes caused by foreign bodies or substances may confound the untrained eye. Monsel solution reaction may be confused for a blue nevus, desmoplastic melanoma, animal-type melanoma, and a residual/recurrent nevus. This confusion could lead to serious diagnostic errors that could cause an unfavorable outcome for the patient. It is critical to know the salient points in the patient's clinical history. Knowledge of the Monsel solution reaction and other exogenous lesions as well as the subsequent unique tissue reaction patterns can aid in facilitating an accurate and prompt pathologic diagnosis.
- Olmstead PM, Lund HZ, Leonard DD. Monsel's solution: a histologic nuisance. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1980;3:492-498.
- Amazon K, Robinson MJ, Rywlin AM. Ferrugination caused by Monsel's solution. clinical observations and experimentations. Am J Dermatopathol. 1980;2:197-205.
- Del Rosario RN, Barr RJ, Graham BS, et al. Exogenous and endogenous cutaneous anomalies and curiosities. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:259-267.
- Calonje E, Blessing K, Glusac E, et al. Blue naevi. In: LeBoit PE, Burg G, Weedon D, et al, eds. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours, Pathology and Genetics of Skin Tumours. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2006:95-99.
- Jain S, Allen PW. Desmoplastic malignant melanoma and its variants. a study of 45 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1989;13:358-373.
- McCarthy SW, Crotty KA, Scolyer RA. Desmoplastic melanoma and desmoplastic neurotropic melanoma. In: LeBoit PE, Burg G, Weedon D, et al, eds. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours, Pathology and Genetics of Skin Tumours. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2006:76-78.
- Vyas R, Keller JJ, Honda K, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of animal-type melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:1031-1039.
- Fox JC, Reed JA, Shea CR. The recurrent nevus phenomenon: a history of challenge, controversy, and discovery. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135:842-846.
The Diagnosis: Monsel Solution Reaction
Exogenous substances can cause interesting incongruities in cutaneous biopsies of which pathologists and dermatologists should be cognizant. Exogenous lesions are caused by externally introduced foreign bodies, substances, or materials, such as sterile compressed sponges, aluminum chloride hexahydrate and anhydrous ethyl alcohol, silica, paraffin, and Monsel solution. Monsel solution reaction is a florid fibrohistiocytic proliferation stimulated by the application of Monsel solution. Monsel solution is a ferric subsulfate that often is used to achieve hemostasis after shave biopsies. Hemostasis is thought to result from the ability of ferric ions to denature and agglutinate proteins such as fibrinogen.1,2 Application of Monsel solution likely causes ferrugination of fibrin, dermal collagen, and striated muscle fibers. Some ferruginated collagen fibers are eliminated through the epidermis as the epidermis regenerates, while some fibers become calcified. Siderophages (iron-containing macrophages) are present in these areas. The ferrugination of collagen fibers becomes less pronounced as the biopsy sites heal and the iron pigment subsequently is absorbed by macrophages. Ferruginated skeletal muscles can act as foreign bodies and may elicit granulomatous reactions.2
It is currently unclear why fibrohistiocytic responses occur in some instances but not others. Iron stains (eg, Perls Prussian blue stain) make interpretation clear, provided the pathologist is familiar with Monsel solution. The primary differential diagnosis of these lesions centers on heavily pigmented melanocytic proliferations. It is critical to review prior biopsy sections or to have definite knowledge of the prior biopsy diagnosis. Histologically, the epidermis may demonstrate nonspecific reactive changes such as hyperkeratosis with foci of irregular acanthosis. The prominent features are present in the dermis where there is a proliferation of spindle- and polyhedral-shaped cells that may show cytologic atypia and occasional mitotic figures. The cells contain refractile brown pigment scattered in the dermis and deposited on collagen fibers (quiz images). Occasional large black or brown encrustations may be identified. Monsel-containing cells may indiscernibly blend with foci of more blatantly fibrohistiocytic differentiation, in which case iron stains are strongly positive (Figure 1). If the clinician uses Monsel solution for hemostasis during the removal of a nevomelanocytic neoplasm, it might be necessary to use melanin stains or immunohistochemistry on the reexcision specimen to distinguish between residual nevomelanocytic and fibrohistiocytic cells.3

Common blue nevus is a benign, typically intradermal melanocytic lesion. It most frequently occurs in young adults and has a predilection for females. Clinically, it can be found anywhere on the body as a single, asymptomatic, well-circumscribed, blue-black, dome-shaped papule measuring less than 1 cm in diameter. Histologically, it is characterized by pigmented, dendritic, spindle-shaped melanocytes that typically are separated by thick collagen bundles (Figure 2). The melanocytes typically have small nuclei with occasional basophilic nucleolus. Melanocytes typically are diffusely positive for melanocytic markers including human melanoma black (HMB) 45, S-100, Melan-A, and microphthalmia transcription factor 1. In contrast to most other benign melanocytic nevi, HMB-45 strongly stains the entire lesion in blue nevi.4

Desmoplastic melanoma accounts for 1% to 4% of all melanomas. The median age at diagnosis is 62 years and, as in other types of melanoma, men are more commonly affected.5 Clinically, desmoplastic melanoma typically presents on the head and neck as a painless indurated plaque, though it can present as a small papule or nodule. Nearly half of desmoplastic melanomas lack obvious pigmentation, which may lead to the misdiagnosis of basal cell carcinoma or a scar. Histologically, desmoplastic melanomas are composed of spindled melanocytes separated by collagen fibers or fibrous stroma (Figure 3). Histology displays variable cytologic atypia and stromal fibrosis. Characteristically there are small islands of lymphocytes and plasma cells within or at the edge of the tumor. The spindle cells stain positive with S-100 and Sry-related HMg-box gene 10, SOX10. Type IV collagen and laminin often are expressed in desmoplastic melanoma. In contrast to many other subtypes of melanoma, HMB-45 and Melan-A usually are negative.6

Animal-type melanoma is a rare neoplasm that differs from other subtypes of melanoma both clinically and histologically. Most frequently, animal-type melanoma affects younger adults (median age, 27 years) and arises on the arms and legs, head and neck, or trunk; men and women are affected equally.7 It most commonly presents with a blue or blue-black nodule with a blue-white veil or irregular white areas. Histologically, animal-type melanoma is a predominantly dermal-based melanocytic proliferation with heavily pigmented epithelioid and spindled melanocytes (Figure 4). The pigmentation pattern ranges widely from fine, granular, light brown deposits to coarse dark brown deposits with malignant cells often arranged in fascicles or sheets. Frequently, there is periadnexal and perieccrine spread. Often, there is epidermal hyperplasia above the dermis. As with conventional melanoma, the immunohistochemistry of animal-type melanoma is positive for S-100 protein, HMB-45, SOX10, and Melan-A.7

Recurrent nevi typically arise within 6 months of a previously biopsied melanocytic nevus. Most recurrent nevi originate from common banal nevi (most often a compound nevus). Recurrent nevi also may arise from congenital, atypical/dysplastic, and Spitz nevi. Most often they are found on the back of women aged 20 to 30 years.8 Clinically, they manifest as a macular area of scar with variegated hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation as well as linear streaking. They may demonstrate variable diffuse, stippled, and halo pigmentation patterns. Classically, recurrent nevi present with a trizonal histologic pattern. Within the epidermis there is a proliferation of melanocytes along the dermoepidermal junction, which may show varying degrees of atypia and pagetoid migration. The melanocytes often are described as epithelioid with round nuclei and even chromatin (Figure 5). The atypical features should be confined to the epidermis overlying the prior biopsy site. Within the dermis there is dense dermal collagen and fibrosis with vertically oriented blood vessels. Finally, features of the original nevus may be seen at the base of the lesion. Although immunohistochemistry may be helpful in some cases, an appropriate clinical history and comparison to the prior biopsy can be invaluable.8

Host tissue reactions resulting in artefactual changes caused by foreign bodies or substances may confound the untrained eye. Monsel solution reaction may be confused for a blue nevus, desmoplastic melanoma, animal-type melanoma, and a residual/recurrent nevus. This confusion could lead to serious diagnostic errors that could cause an unfavorable outcome for the patient. It is critical to know the salient points in the patient's clinical history. Knowledge of the Monsel solution reaction and other exogenous lesions as well as the subsequent unique tissue reaction patterns can aid in facilitating an accurate and prompt pathologic diagnosis.
The Diagnosis: Monsel Solution Reaction
Exogenous substances can cause interesting incongruities in cutaneous biopsies of which pathologists and dermatologists should be cognizant. Exogenous lesions are caused by externally introduced foreign bodies, substances, or materials, such as sterile compressed sponges, aluminum chloride hexahydrate and anhydrous ethyl alcohol, silica, paraffin, and Monsel solution. Monsel solution reaction is a florid fibrohistiocytic proliferation stimulated by the application of Monsel solution. Monsel solution is a ferric subsulfate that often is used to achieve hemostasis after shave biopsies. Hemostasis is thought to result from the ability of ferric ions to denature and agglutinate proteins such as fibrinogen.1,2 Application of Monsel solution likely causes ferrugination of fibrin, dermal collagen, and striated muscle fibers. Some ferruginated collagen fibers are eliminated through the epidermis as the epidermis regenerates, while some fibers become calcified. Siderophages (iron-containing macrophages) are present in these areas. The ferrugination of collagen fibers becomes less pronounced as the biopsy sites heal and the iron pigment subsequently is absorbed by macrophages. Ferruginated skeletal muscles can act as foreign bodies and may elicit granulomatous reactions.2
It is currently unclear why fibrohistiocytic responses occur in some instances but not others. Iron stains (eg, Perls Prussian blue stain) make interpretation clear, provided the pathologist is familiar with Monsel solution. The primary differential diagnosis of these lesions centers on heavily pigmented melanocytic proliferations. It is critical to review prior biopsy sections or to have definite knowledge of the prior biopsy diagnosis. Histologically, the epidermis may demonstrate nonspecific reactive changes such as hyperkeratosis with foci of irregular acanthosis. The prominent features are present in the dermis where there is a proliferation of spindle- and polyhedral-shaped cells that may show cytologic atypia and occasional mitotic figures. The cells contain refractile brown pigment scattered in the dermis and deposited on collagen fibers (quiz images). Occasional large black or brown encrustations may be identified. Monsel-containing cells may indiscernibly blend with foci of more blatantly fibrohistiocytic differentiation, in which case iron stains are strongly positive (Figure 1). If the clinician uses Monsel solution for hemostasis during the removal of a nevomelanocytic neoplasm, it might be necessary to use melanin stains or immunohistochemistry on the reexcision specimen to distinguish between residual nevomelanocytic and fibrohistiocytic cells.3

Common blue nevus is a benign, typically intradermal melanocytic lesion. It most frequently occurs in young adults and has a predilection for females. Clinically, it can be found anywhere on the body as a single, asymptomatic, well-circumscribed, blue-black, dome-shaped papule measuring less than 1 cm in diameter. Histologically, it is characterized by pigmented, dendritic, spindle-shaped melanocytes that typically are separated by thick collagen bundles (Figure 2). The melanocytes typically have small nuclei with occasional basophilic nucleolus. Melanocytes typically are diffusely positive for melanocytic markers including human melanoma black (HMB) 45, S-100, Melan-A, and microphthalmia transcription factor 1. In contrast to most other benign melanocytic nevi, HMB-45 strongly stains the entire lesion in blue nevi.4

Desmoplastic melanoma accounts for 1% to 4% of all melanomas. The median age at diagnosis is 62 years and, as in other types of melanoma, men are more commonly affected.5 Clinically, desmoplastic melanoma typically presents on the head and neck as a painless indurated plaque, though it can present as a small papule or nodule. Nearly half of desmoplastic melanomas lack obvious pigmentation, which may lead to the misdiagnosis of basal cell carcinoma or a scar. Histologically, desmoplastic melanomas are composed of spindled melanocytes separated by collagen fibers or fibrous stroma (Figure 3). Histology displays variable cytologic atypia and stromal fibrosis. Characteristically there are small islands of lymphocytes and plasma cells within or at the edge of the tumor. The spindle cells stain positive with S-100 and Sry-related HMg-box gene 10, SOX10. Type IV collagen and laminin often are expressed in desmoplastic melanoma. In contrast to many other subtypes of melanoma, HMB-45 and Melan-A usually are negative.6

Animal-type melanoma is a rare neoplasm that differs from other subtypes of melanoma both clinically and histologically. Most frequently, animal-type melanoma affects younger adults (median age, 27 years) and arises on the arms and legs, head and neck, or trunk; men and women are affected equally.7 It most commonly presents with a blue or blue-black nodule with a blue-white veil or irregular white areas. Histologically, animal-type melanoma is a predominantly dermal-based melanocytic proliferation with heavily pigmented epithelioid and spindled melanocytes (Figure 4). The pigmentation pattern ranges widely from fine, granular, light brown deposits to coarse dark brown deposits with malignant cells often arranged in fascicles or sheets. Frequently, there is periadnexal and perieccrine spread. Often, there is epidermal hyperplasia above the dermis. As with conventional melanoma, the immunohistochemistry of animal-type melanoma is positive for S-100 protein, HMB-45, SOX10, and Melan-A.7

Recurrent nevi typically arise within 6 months of a previously biopsied melanocytic nevus. Most recurrent nevi originate from common banal nevi (most often a compound nevus). Recurrent nevi also may arise from congenital, atypical/dysplastic, and Spitz nevi. Most often they are found on the back of women aged 20 to 30 years.8 Clinically, they manifest as a macular area of scar with variegated hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation as well as linear streaking. They may demonstrate variable diffuse, stippled, and halo pigmentation patterns. Classically, recurrent nevi present with a trizonal histologic pattern. Within the epidermis there is a proliferation of melanocytes along the dermoepidermal junction, which may show varying degrees of atypia and pagetoid migration. The melanocytes often are described as epithelioid with round nuclei and even chromatin (Figure 5). The atypical features should be confined to the epidermis overlying the prior biopsy site. Within the dermis there is dense dermal collagen and fibrosis with vertically oriented blood vessels. Finally, features of the original nevus may be seen at the base of the lesion. Although immunohistochemistry may be helpful in some cases, an appropriate clinical history and comparison to the prior biopsy can be invaluable.8

Host tissue reactions resulting in artefactual changes caused by foreign bodies or substances may confound the untrained eye. Monsel solution reaction may be confused for a blue nevus, desmoplastic melanoma, animal-type melanoma, and a residual/recurrent nevus. This confusion could lead to serious diagnostic errors that could cause an unfavorable outcome for the patient. It is critical to know the salient points in the patient's clinical history. Knowledge of the Monsel solution reaction and other exogenous lesions as well as the subsequent unique tissue reaction patterns can aid in facilitating an accurate and prompt pathologic diagnosis.
- Olmstead PM, Lund HZ, Leonard DD. Monsel's solution: a histologic nuisance. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1980;3:492-498.
- Amazon K, Robinson MJ, Rywlin AM. Ferrugination caused by Monsel's solution. clinical observations and experimentations. Am J Dermatopathol. 1980;2:197-205.
- Del Rosario RN, Barr RJ, Graham BS, et al. Exogenous and endogenous cutaneous anomalies and curiosities. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:259-267.
- Calonje E, Blessing K, Glusac E, et al. Blue naevi. In: LeBoit PE, Burg G, Weedon D, et al, eds. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours, Pathology and Genetics of Skin Tumours. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2006:95-99.
- Jain S, Allen PW. Desmoplastic malignant melanoma and its variants. a study of 45 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1989;13:358-373.
- McCarthy SW, Crotty KA, Scolyer RA. Desmoplastic melanoma and desmoplastic neurotropic melanoma. In: LeBoit PE, Burg G, Weedon D, et al, eds. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours, Pathology and Genetics of Skin Tumours. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2006:76-78.
- Vyas R, Keller JJ, Honda K, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of animal-type melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:1031-1039.
- Fox JC, Reed JA, Shea CR. The recurrent nevus phenomenon: a history of challenge, controversy, and discovery. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135:842-846.
- Olmstead PM, Lund HZ, Leonard DD. Monsel's solution: a histologic nuisance. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1980;3:492-498.
- Amazon K, Robinson MJ, Rywlin AM. Ferrugination caused by Monsel's solution. clinical observations and experimentations. Am J Dermatopathol. 1980;2:197-205.
- Del Rosario RN, Barr RJ, Graham BS, et al. Exogenous and endogenous cutaneous anomalies and curiosities. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:259-267.
- Calonje E, Blessing K, Glusac E, et al. Blue naevi. In: LeBoit PE, Burg G, Weedon D, et al, eds. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours, Pathology and Genetics of Skin Tumours. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2006:95-99.
- Jain S, Allen PW. Desmoplastic malignant melanoma and its variants. a study of 45 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1989;13:358-373.
- McCarthy SW, Crotty KA, Scolyer RA. Desmoplastic melanoma and desmoplastic neurotropic melanoma. In: LeBoit PE, Burg G, Weedon D, et al, eds. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours, Pathology and Genetics of Skin Tumours. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2006:76-78.
- Vyas R, Keller JJ, Honda K, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of animal-type melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:1031-1039.
- Fox JC, Reed JA, Shea CR. The recurrent nevus phenomenon: a history of challenge, controversy, and discovery. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135:842-846.
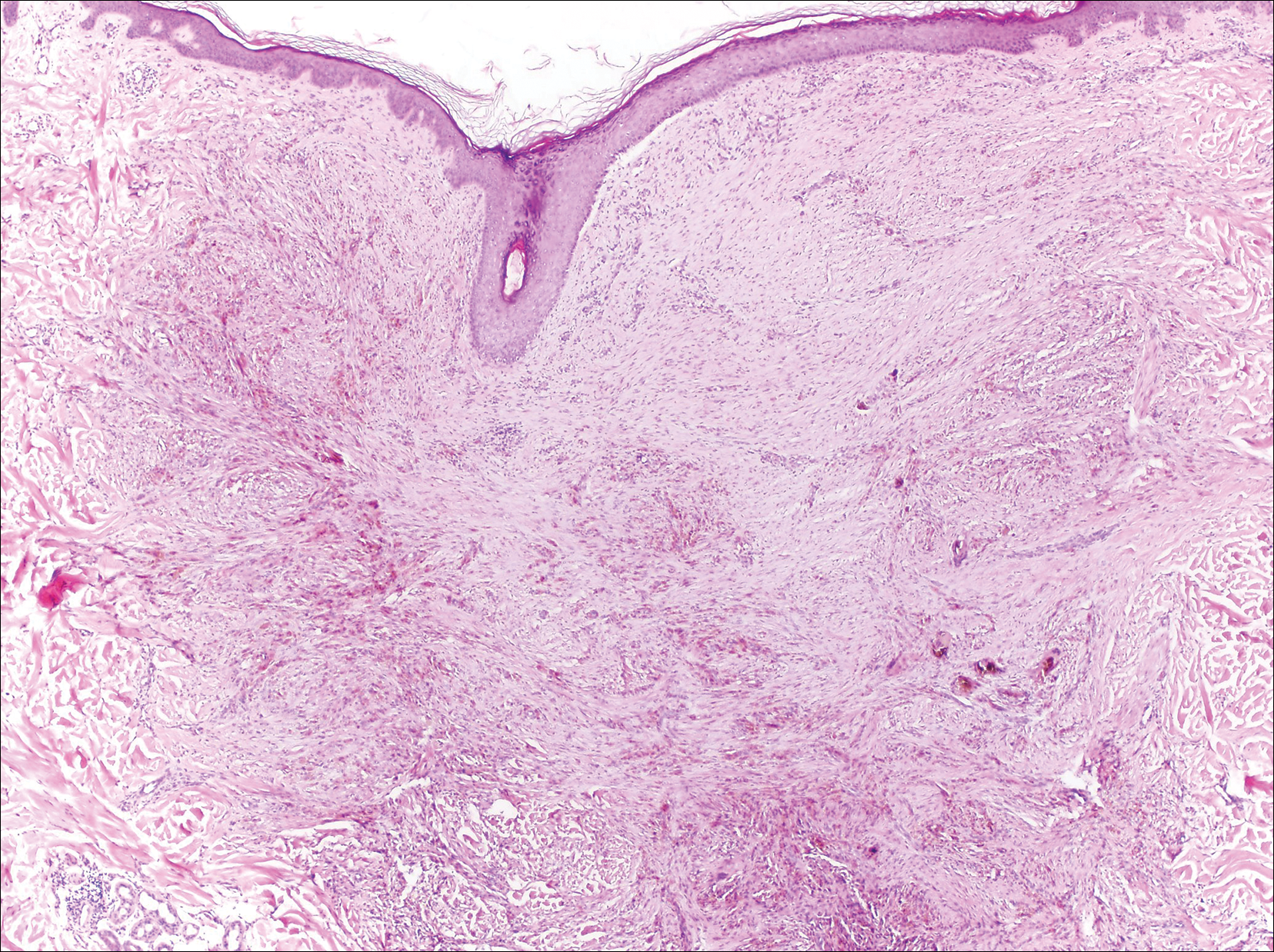
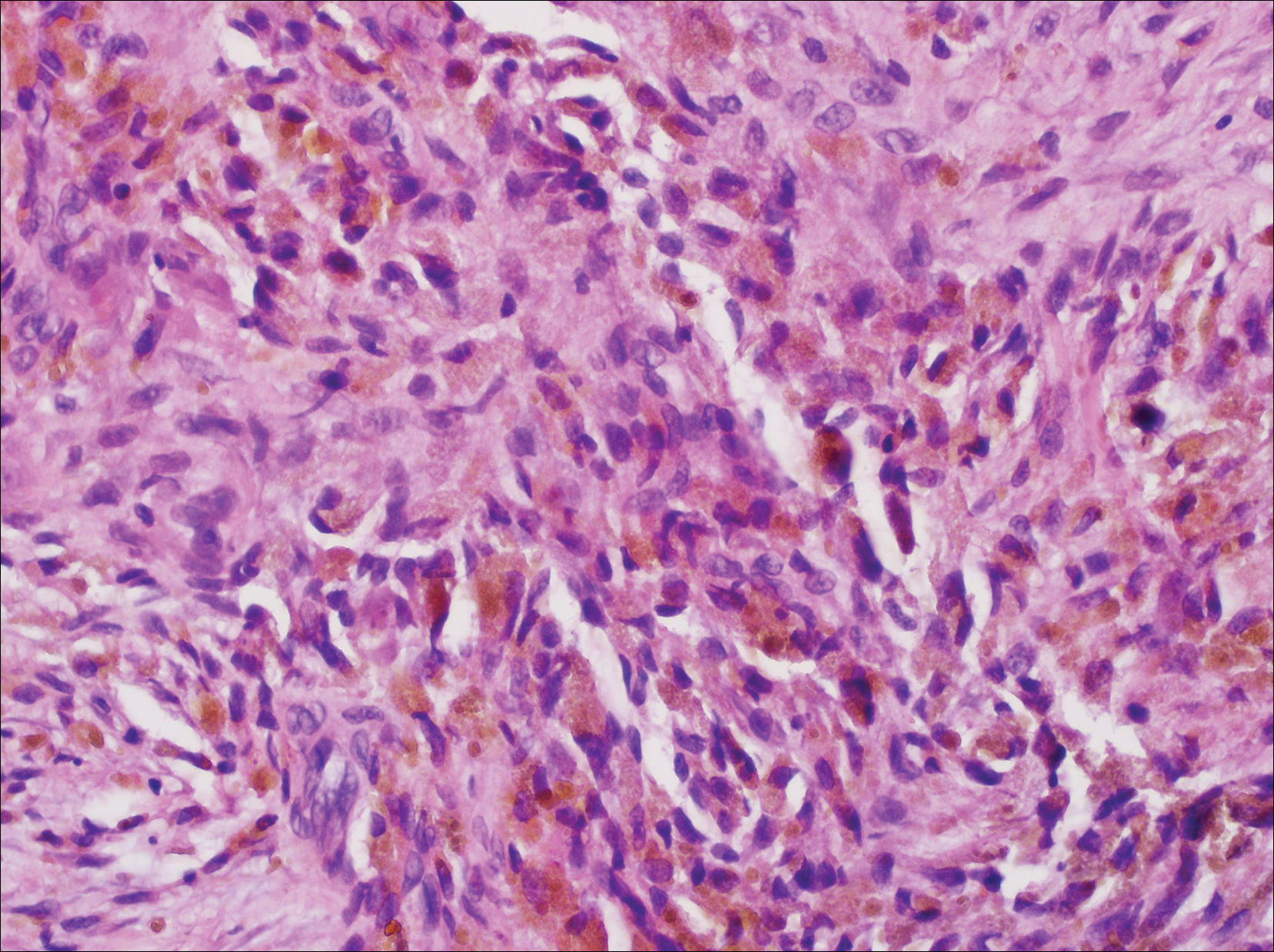
A 67-year-old man presented to the dermatology clinic with a 2-cm pigmented lesion on the forearm. An excisional biopsy was obtained.
Deep Soft Tissue Mass of the Knee
The Diagnosis: Nodular Fasciitis
The diagnosis of spindle cell tumors can be challenging; however, by using a variety of immunoperoxidase stains and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) testing in conjunction with histology, it often is possible to arrive at a definitive diagnosis. For this case, the histologic features in conjunction with the immunoperoxidase stains and FISH were consistent with a diagnosis of nodular fasciitis.
Nodular fasciitis is a benign, self-limiting, myofibroblastic, soft-tissue proliferation typically found in the subcutaneous tissue.1 It can be found anywhere on the body but most commonly on the upper arms and trunk. It most often is seen in young adults, and many cases have been reported in association with a history of trauma to the area.1,2 It typically measures less than 2 cm in diameter.3 The diagnosis of nodular fasciitis is particularly challenging because it mimics sarcoma, both in presentation and in histologic findings with rapid growth, high mitotic activity, and increased cellularity.1,4-7 In contrast to malignancy, nodular fasciitis has no atypical mitoses and little cytologic atypia.8,9 Rather, it contains plump myofibroblasts loosely arranged in a myxoid or fibrous stroma that also may contain lymphocytes, extravasated erythrocytes, and osteoclastlike giant cells distributed throughout.5,10,11 In this case, lymphocytes, extravasated red blood cells, and myxoid change are present, suggesting the diagnosis of nodular fasciitis. In other cases, however, these features may be much more limited, making the diagnosis more challenging. The spindle cells are arranged in poorly defined short fascicles. The tumor cells do not infiltrate between individual adipocytes. There is no notable cytologic atypia.
Because of the difficulty in making the diagnosis, overtreatment of this benign condition can be a problem, causing increased morbidity.1 Erickson-Johnson et al12 identified the role of an ubiquitin-specific peptidase 6, USP6, gene rearrangement on chromosome 17p13 in 92% (44/48) of cases of nodular fasciitis. The USP6 gene most often is rearranged with the myosin heavy chain 9 gene, MYH9, on chromosome 22q12.3. With this rearrangement, the MYH9 promoter leads to the overexpression of USP6, causing tumor formation.2,13 The use of multiple immunoperoxidase stains can be important in the identification of nodular fasciitis. Nodular fasciitis stains negative for S-100, epithelial membrane antigen, CD34, β-catenin, and cytokeratin, but typically stains positive for smooth muscle actin.9
Although dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) was in the differential diagnosis, these tumors tend to have greater cellularity than nodular fasciitis. In addition, the spindle cells of DFSP typically are arranged in a storiform pattern. Another characteristic feature of DFSP is that the tumor cells will infiltrate between adipose cells creating a lacelike or honeycomblike appearance within the subcutaneous tissue (Figure 1). Immunohistochemistry staining and FISH testing may be useful in making a diagnosis of DFSP. These tumors typically are positive for CD34 by immunoperoxidase staining and demonstrate a translocation t(17;22)(q21;q13) between platelet-derived growth factor subunit B gene, PDGFB, and collagen type I alpha 1 chain gene, COL1A1, by FISH.
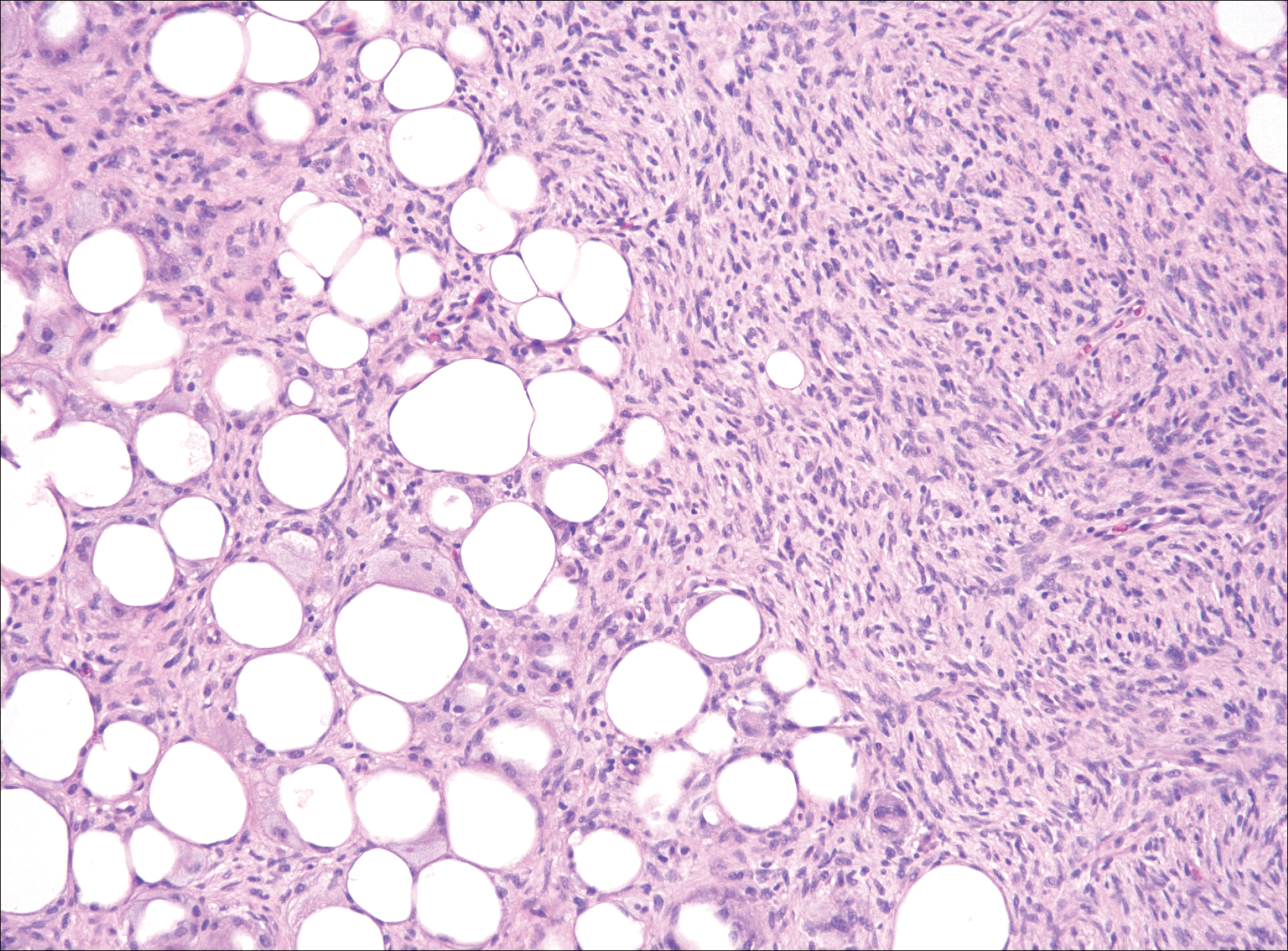
The distinction between the fibrous phase of nodular fasciitis and fibromatosis can be challenging. The size of the lesion may be helpful, with most lesions of nodular fasciitis being less than 3 cm, while lesions of fibromatosis have a mean diameter of 7 cm.5,14 Microscopically, both tumors demonstrate a fascicular growth pattern; however, the fascicles in nodular fasciitis tend to be short and irregular compared to the longer fascicles seen in fibromatosis (Figure 2). Immunohistochemistry staining has limited utility with only 56% (14/25) of superficial fibromatoses having positive nuclear staining for β-catenin.15
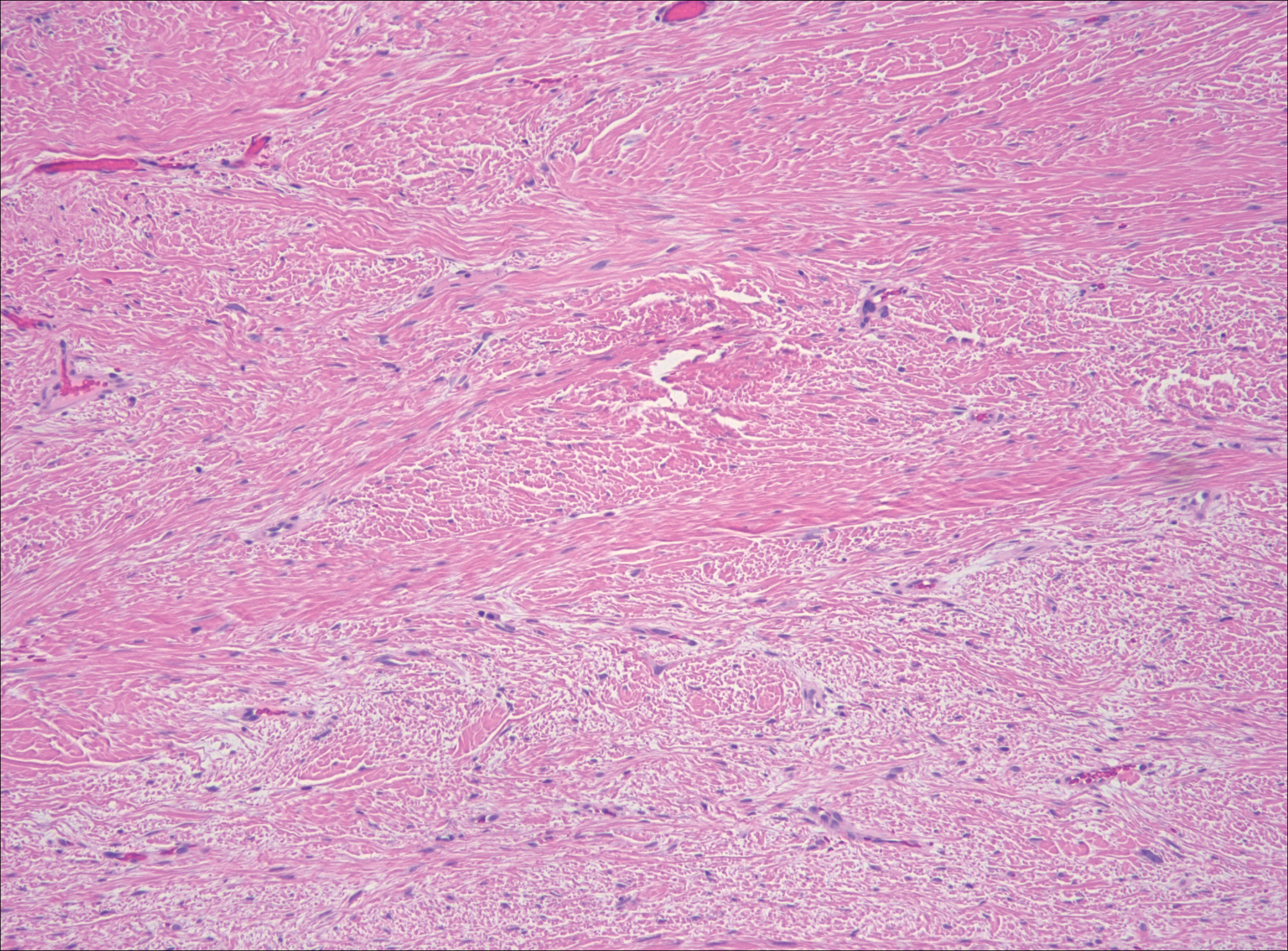
Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (LGFMS) would be unusual in this clinical scenario. Only 13% to 19% of cases present in patients younger than 18 years (mean age, 33 years).16 In LGFMS there are cytologically bland spindle cells that are typically arranged in a patternless or whorled pattern (Figure 3), though fascicular architecture may be seen. There are alternating areas of fibrous and myxoid stroma. A curvilinear vasculature network and lack of lymphocytes and extravasated red blood cells are histologic features favoring LGFMS over nodular fasciitis. Immunohistochemistry staining and FISH testing can be useful in making the diagnosis of LGFMS. These tumors are characterized by a translocation t(7;16)(q34;p11) involving the fusion in sarcoma, FUS, and cAMP responsive element binding protein 3 like 2, CREB3L2, genes.16 Positive immunohistochemistry staining for MUC4 can be seen in up to 100% of LGFMS and is absent in many other spindle cell tumors.16
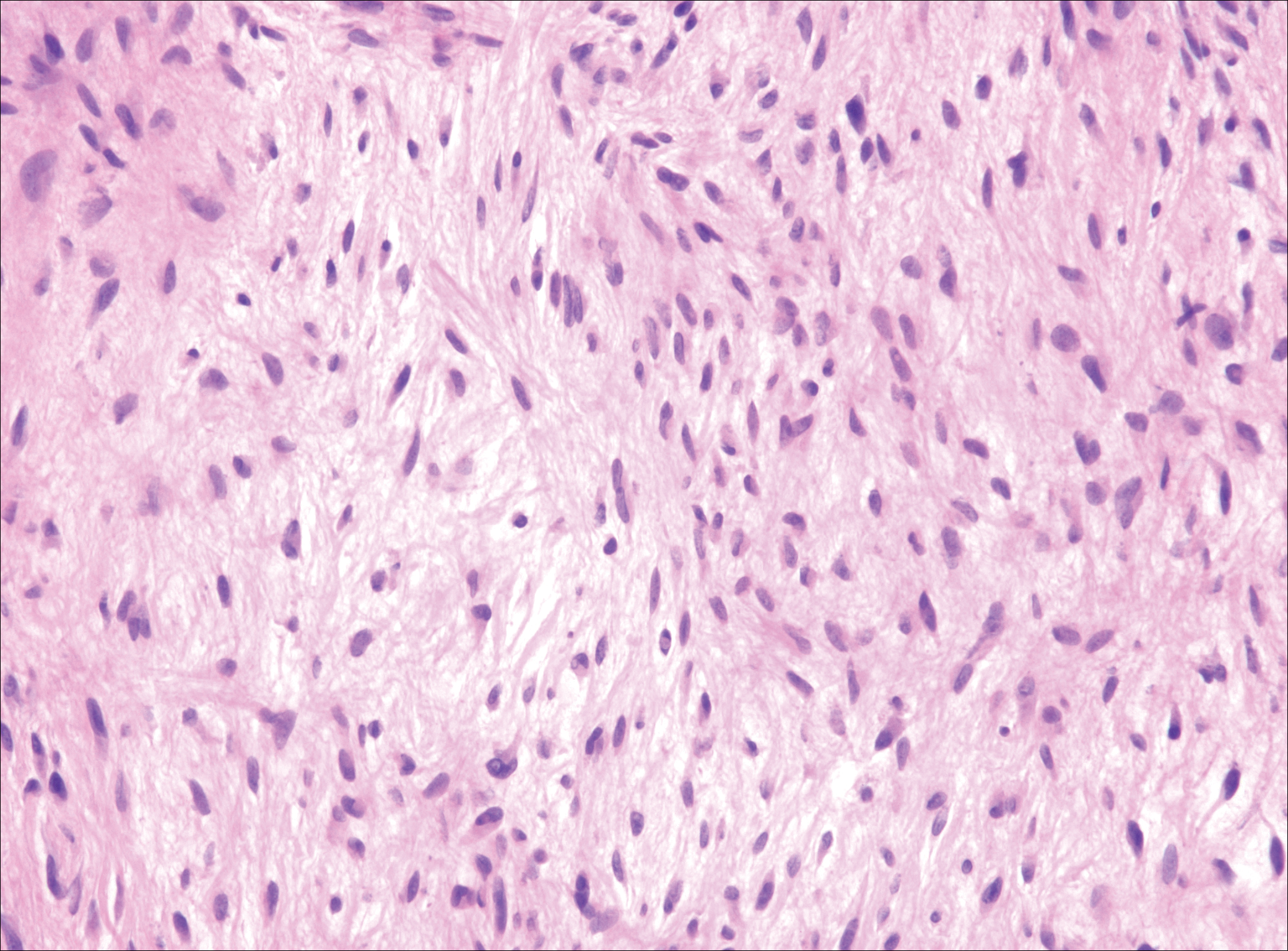
Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor (PFT) is least likely to be confused with nodular fasciitis. Histologically these tumors are characterized by multiple small nodules arranged in a plexiform pattern (Figure 4). Within the nodules, 3 cell types may be noted: spindle fibroblast-like cells, mononuclear histiocyte-like cells, and osteoclastlike cells.17 Either the spindle cells or the mononuclear cells may predominate in cases of PFT. Immunohistochemistry staining of PFT is nonspecific and there are no molecular/FISH studies that can be used to help confirm the diagnosis.
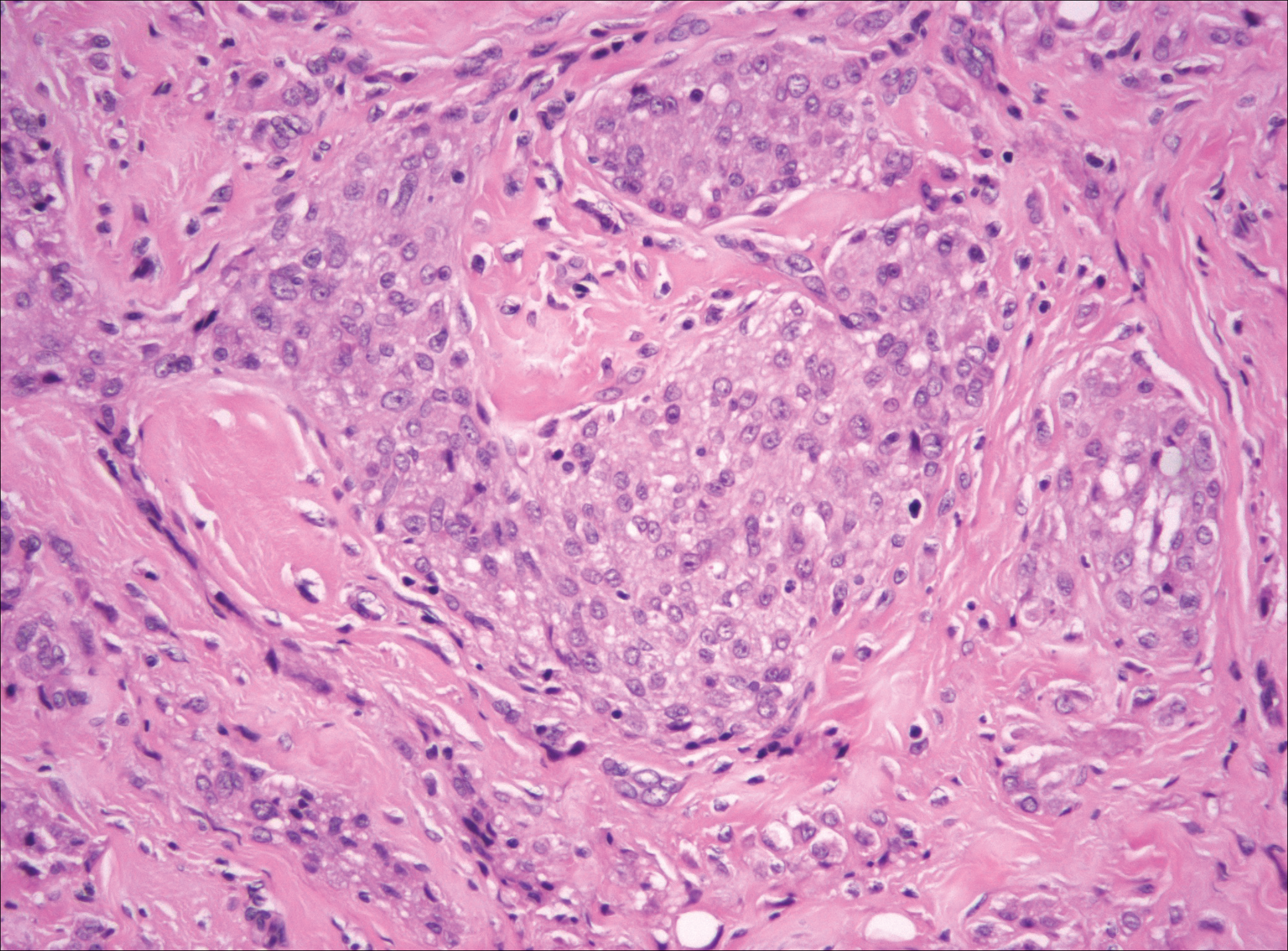
- Shin C, Low I, Ng D, et al. USP6 gene rearrangement in nodular fasciitis and histological mimics. Histopathology. 2016;69:784-791.
- Kumar E, Patel NR, Demicco EG, et al. Cutaneous nodular fasciitis with genetic analysis: a case series. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:1143-1149.
- Nishio J. Updates on the cytogenetics and molecular cytogenetics of benign and intermediate soft tissue tumors. Oncol Lett. 2013;5:12-18.
- Lin X, Wang L, Zhang Y, et al. Variable Ki67 proliferative index in 65 cases of nodular fasciitis, compared with fibrosarcoma and fibromatosis. Diagn Pathol. 2013;8:50.
- Goldstein J, Cates J. Differential diagnostic considerations of desmoid-type fibromatosis. Adv Anat Pathol. 2015;22:260-266.
- Fletcher CDM, Bridge JA, Hogendoorn PCW, et al, eds. WHO Classification of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone. 4th ed. Lyons, France: IARC Press; 2013.
- Bridge JA, Cushman-Vokoun AM. Molecular diagnostics of soft tissue tumors. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135:588-601.
- Anzeljc AJ, Oliveira AM, Grossniklaus HE, et al. Nodular fasciitis of the orbit: a case report confirmed by molecular cytogenetic analysis. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;33(3S suppl 1):S152-S155.
- de Paula SA, Cruz AA, de Alencar VM, et al. Nodular fasciitis presenting as a large mass in the upper eyelid. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;22:494-495.
- Bernstein KE, Lattes R. Nodular (pseudosarcomatous) fasciitis, a nonrecurrent lesion: clinicopathologic study of 134 cases. Cancer. 1982;49:1668-1678.
- Shimizu S, Hashimoto H, Enjoji M. Nodular fasciitis: an analysis of 250 patients. Pathology. 1984;16:161-166.
- Erickson-Johnson MR, Chou MM, Evers BR, et al. Nodular fasciitis: a novel model of transient neoplasia induced by MYH9-USP6 gene fusion. Lab Invest. 2011;91:1427-1433.
- Amary MF, Ye H, Berisha F, et al. Detection of USP6 gene rearrangement in nodular fasciitis: an important diagnostic tool. Virchows Arch. 2013;463:97-98.
- Wirth L, Klein A, Baur-Melnyk A. Desmoid tumors of the extremity and trunk. a retrospective study of 44 patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19:2.
- Carlson JW, Fletcher CD. Immunohistochemistry for beta-catenin in the differential diagnosis of spindle cells lesions: analysis of a series and review of the literature. Histopathology. 2007;51:509-514.
- Mohamed M, Fisher C, Thway K. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma: clinical, morphologic and genetic features. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2017;28:60-67.
- Taher A, Pushpanathan C. Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor: a brief review. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007;131:1135-1138.
The Diagnosis: Nodular Fasciitis
The diagnosis of spindle cell tumors can be challenging; however, by using a variety of immunoperoxidase stains and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) testing in conjunction with histology, it often is possible to arrive at a definitive diagnosis. For this case, the histologic features in conjunction with the immunoperoxidase stains and FISH were consistent with a diagnosis of nodular fasciitis.
Nodular fasciitis is a benign, self-limiting, myofibroblastic, soft-tissue proliferation typically found in the subcutaneous tissue.1 It can be found anywhere on the body but most commonly on the upper arms and trunk. It most often is seen in young adults, and many cases have been reported in association with a history of trauma to the area.1,2 It typically measures less than 2 cm in diameter.3 The diagnosis of nodular fasciitis is particularly challenging because it mimics sarcoma, both in presentation and in histologic findings with rapid growth, high mitotic activity, and increased cellularity.1,4-7 In contrast to malignancy, nodular fasciitis has no atypical mitoses and little cytologic atypia.8,9 Rather, it contains plump myofibroblasts loosely arranged in a myxoid or fibrous stroma that also may contain lymphocytes, extravasated erythrocytes, and osteoclastlike giant cells distributed throughout.5,10,11 In this case, lymphocytes, extravasated red blood cells, and myxoid change are present, suggesting the diagnosis of nodular fasciitis. In other cases, however, these features may be much more limited, making the diagnosis more challenging. The spindle cells are arranged in poorly defined short fascicles. The tumor cells do not infiltrate between individual adipocytes. There is no notable cytologic atypia.
Because of the difficulty in making the diagnosis, overtreatment of this benign condition can be a problem, causing increased morbidity.1 Erickson-Johnson et al12 identified the role of an ubiquitin-specific peptidase 6, USP6, gene rearrangement on chromosome 17p13 in 92% (44/48) of cases of nodular fasciitis. The USP6 gene most often is rearranged with the myosin heavy chain 9 gene, MYH9, on chromosome 22q12.3. With this rearrangement, the MYH9 promoter leads to the overexpression of USP6, causing tumor formation.2,13 The use of multiple immunoperoxidase stains can be important in the identification of nodular fasciitis. Nodular fasciitis stains negative for S-100, epithelial membrane antigen, CD34, β-catenin, and cytokeratin, but typically stains positive for smooth muscle actin.9
Although dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) was in the differential diagnosis, these tumors tend to have greater cellularity than nodular fasciitis. In addition, the spindle cells of DFSP typically are arranged in a storiform pattern. Another characteristic feature of DFSP is that the tumor cells will infiltrate between adipose cells creating a lacelike or honeycomblike appearance within the subcutaneous tissue (Figure 1). Immunohistochemistry staining and FISH testing may be useful in making a diagnosis of DFSP. These tumors typically are positive for CD34 by immunoperoxidase staining and demonstrate a translocation t(17;22)(q21;q13) between platelet-derived growth factor subunit B gene, PDGFB, and collagen type I alpha 1 chain gene, COL1A1, by FISH.

The distinction between the fibrous phase of nodular fasciitis and fibromatosis can be challenging. The size of the lesion may be helpful, with most lesions of nodular fasciitis being less than 3 cm, while lesions of fibromatosis have a mean diameter of 7 cm.5,14 Microscopically, both tumors demonstrate a fascicular growth pattern; however, the fascicles in nodular fasciitis tend to be short and irregular compared to the longer fascicles seen in fibromatosis (Figure 2). Immunohistochemistry staining has limited utility with only 56% (14/25) of superficial fibromatoses having positive nuclear staining for β-catenin.15

Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (LGFMS) would be unusual in this clinical scenario. Only 13% to 19% of cases present in patients younger than 18 years (mean age, 33 years).16 In LGFMS there are cytologically bland spindle cells that are typically arranged in a patternless or whorled pattern (Figure 3), though fascicular architecture may be seen. There are alternating areas of fibrous and myxoid stroma. A curvilinear vasculature network and lack of lymphocytes and extravasated red blood cells are histologic features favoring LGFMS over nodular fasciitis. Immunohistochemistry staining and FISH testing can be useful in making the diagnosis of LGFMS. These tumors are characterized by a translocation t(7;16)(q34;p11) involving the fusion in sarcoma, FUS, and cAMP responsive element binding protein 3 like 2, CREB3L2, genes.16 Positive immunohistochemistry staining for MUC4 can be seen in up to 100% of LGFMS and is absent in many other spindle cell tumors.16

Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor (PFT) is least likely to be confused with nodular fasciitis. Histologically these tumors are characterized by multiple small nodules arranged in a plexiform pattern (Figure 4). Within the nodules, 3 cell types may be noted: spindle fibroblast-like cells, mononuclear histiocyte-like cells, and osteoclastlike cells.17 Either the spindle cells or the mononuclear cells may predominate in cases of PFT. Immunohistochemistry staining of PFT is nonspecific and there are no molecular/FISH studies that can be used to help confirm the diagnosis.

The Diagnosis: Nodular Fasciitis
The diagnosis of spindle cell tumors can be challenging; however, by using a variety of immunoperoxidase stains and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) testing in conjunction with histology, it often is possible to arrive at a definitive diagnosis. For this case, the histologic features in conjunction with the immunoperoxidase stains and FISH were consistent with a diagnosis of nodular fasciitis.
Nodular fasciitis is a benign, self-limiting, myofibroblastic, soft-tissue proliferation typically found in the subcutaneous tissue.1 It can be found anywhere on the body but most commonly on the upper arms and trunk. It most often is seen in young adults, and many cases have been reported in association with a history of trauma to the area.1,2 It typically measures less than 2 cm in diameter.3 The diagnosis of nodular fasciitis is particularly challenging because it mimics sarcoma, both in presentation and in histologic findings with rapid growth, high mitotic activity, and increased cellularity.1,4-7 In contrast to malignancy, nodular fasciitis has no atypical mitoses and little cytologic atypia.8,9 Rather, it contains plump myofibroblasts loosely arranged in a myxoid or fibrous stroma that also may contain lymphocytes, extravasated erythrocytes, and osteoclastlike giant cells distributed throughout.5,10,11 In this case, lymphocytes, extravasated red blood cells, and myxoid change are present, suggesting the diagnosis of nodular fasciitis. In other cases, however, these features may be much more limited, making the diagnosis more challenging. The spindle cells are arranged in poorly defined short fascicles. The tumor cells do not infiltrate between individual adipocytes. There is no notable cytologic atypia.
Because of the difficulty in making the diagnosis, overtreatment of this benign condition can be a problem, causing increased morbidity.1 Erickson-Johnson et al12 identified the role of an ubiquitin-specific peptidase 6, USP6, gene rearrangement on chromosome 17p13 in 92% (44/48) of cases of nodular fasciitis. The USP6 gene most often is rearranged with the myosin heavy chain 9 gene, MYH9, on chromosome 22q12.3. With this rearrangement, the MYH9 promoter leads to the overexpression of USP6, causing tumor formation.2,13 The use of multiple immunoperoxidase stains can be important in the identification of nodular fasciitis. Nodular fasciitis stains negative for S-100, epithelial membrane antigen, CD34, β-catenin, and cytokeratin, but typically stains positive for smooth muscle actin.9
Although dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) was in the differential diagnosis, these tumors tend to have greater cellularity than nodular fasciitis. In addition, the spindle cells of DFSP typically are arranged in a storiform pattern. Another characteristic feature of DFSP is that the tumor cells will infiltrate between adipose cells creating a lacelike or honeycomblike appearance within the subcutaneous tissue (Figure 1). Immunohistochemistry staining and FISH testing may be useful in making a diagnosis of DFSP. These tumors typically are positive for CD34 by immunoperoxidase staining and demonstrate a translocation t(17;22)(q21;q13) between platelet-derived growth factor subunit B gene, PDGFB, and collagen type I alpha 1 chain gene, COL1A1, by FISH.

The distinction between the fibrous phase of nodular fasciitis and fibromatosis can be challenging. The size of the lesion may be helpful, with most lesions of nodular fasciitis being less than 3 cm, while lesions of fibromatosis have a mean diameter of 7 cm.5,14 Microscopically, both tumors demonstrate a fascicular growth pattern; however, the fascicles in nodular fasciitis tend to be short and irregular compared to the longer fascicles seen in fibromatosis (Figure 2). Immunohistochemistry staining has limited utility with only 56% (14/25) of superficial fibromatoses having positive nuclear staining for β-catenin.15

Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (LGFMS) would be unusual in this clinical scenario. Only 13% to 19% of cases present in patients younger than 18 years (mean age, 33 years).16 In LGFMS there are cytologically bland spindle cells that are typically arranged in a patternless or whorled pattern (Figure 3), though fascicular architecture may be seen. There are alternating areas of fibrous and myxoid stroma. A curvilinear vasculature network and lack of lymphocytes and extravasated red blood cells are histologic features favoring LGFMS over nodular fasciitis. Immunohistochemistry staining and FISH testing can be useful in making the diagnosis of LGFMS. These tumors are characterized by a translocation t(7;16)(q34;p11) involving the fusion in sarcoma, FUS, and cAMP responsive element binding protein 3 like 2, CREB3L2, genes.16 Positive immunohistochemistry staining for MUC4 can be seen in up to 100% of LGFMS and is absent in many other spindle cell tumors.16

Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor (PFT) is least likely to be confused with nodular fasciitis. Histologically these tumors are characterized by multiple small nodules arranged in a plexiform pattern (Figure 4). Within the nodules, 3 cell types may be noted: spindle fibroblast-like cells, mononuclear histiocyte-like cells, and osteoclastlike cells.17 Either the spindle cells or the mononuclear cells may predominate in cases of PFT. Immunohistochemistry staining of PFT is nonspecific and there are no molecular/FISH studies that can be used to help confirm the diagnosis.

- Shin C, Low I, Ng D, et al. USP6 gene rearrangement in nodular fasciitis and histological mimics. Histopathology. 2016;69:784-791.
- Kumar E, Patel NR, Demicco EG, et al. Cutaneous nodular fasciitis with genetic analysis: a case series. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:1143-1149.
- Nishio J. Updates on the cytogenetics and molecular cytogenetics of benign and intermediate soft tissue tumors. Oncol Lett. 2013;5:12-18.
- Lin X, Wang L, Zhang Y, et al. Variable Ki67 proliferative index in 65 cases of nodular fasciitis, compared with fibrosarcoma and fibromatosis. Diagn Pathol. 2013;8:50.
- Goldstein J, Cates J. Differential diagnostic considerations of desmoid-type fibromatosis. Adv Anat Pathol. 2015;22:260-266.
- Fletcher CDM, Bridge JA, Hogendoorn PCW, et al, eds. WHO Classification of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone. 4th ed. Lyons, France: IARC Press; 2013.
- Bridge JA, Cushman-Vokoun AM. Molecular diagnostics of soft tissue tumors. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135:588-601.
- Anzeljc AJ, Oliveira AM, Grossniklaus HE, et al. Nodular fasciitis of the orbit: a case report confirmed by molecular cytogenetic analysis. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;33(3S suppl 1):S152-S155.
- de Paula SA, Cruz AA, de Alencar VM, et al. Nodular fasciitis presenting as a large mass in the upper eyelid. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;22:494-495.
- Bernstein KE, Lattes R. Nodular (pseudosarcomatous) fasciitis, a nonrecurrent lesion: clinicopathologic study of 134 cases. Cancer. 1982;49:1668-1678.
- Shimizu S, Hashimoto H, Enjoji M. Nodular fasciitis: an analysis of 250 patients. Pathology. 1984;16:161-166.
- Erickson-Johnson MR, Chou MM, Evers BR, et al. Nodular fasciitis: a novel model of transient neoplasia induced by MYH9-USP6 gene fusion. Lab Invest. 2011;91:1427-1433.
- Amary MF, Ye H, Berisha F, et al. Detection of USP6 gene rearrangement in nodular fasciitis: an important diagnostic tool. Virchows Arch. 2013;463:97-98.
- Wirth L, Klein A, Baur-Melnyk A. Desmoid tumors of the extremity and trunk. a retrospective study of 44 patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19:2.
- Carlson JW, Fletcher CD. Immunohistochemistry for beta-catenin in the differential diagnosis of spindle cells lesions: analysis of a series and review of the literature. Histopathology. 2007;51:509-514.
- Mohamed M, Fisher C, Thway K. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma: clinical, morphologic and genetic features. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2017;28:60-67.
- Taher A, Pushpanathan C. Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor: a brief review. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007;131:1135-1138.
- Shin C, Low I, Ng D, et al. USP6 gene rearrangement in nodular fasciitis and histological mimics. Histopathology. 2016;69:784-791.
- Kumar E, Patel NR, Demicco EG, et al. Cutaneous nodular fasciitis with genetic analysis: a case series. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:1143-1149.
- Nishio J. Updates on the cytogenetics and molecular cytogenetics of benign and intermediate soft tissue tumors. Oncol Lett. 2013;5:12-18.
- Lin X, Wang L, Zhang Y, et al. Variable Ki67 proliferative index in 65 cases of nodular fasciitis, compared with fibrosarcoma and fibromatosis. Diagn Pathol. 2013;8:50.
- Goldstein J, Cates J. Differential diagnostic considerations of desmoid-type fibromatosis. Adv Anat Pathol. 2015;22:260-266.
- Fletcher CDM, Bridge JA, Hogendoorn PCW, et al, eds. WHO Classification of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone. 4th ed. Lyons, France: IARC Press; 2013.
- Bridge JA, Cushman-Vokoun AM. Molecular diagnostics of soft tissue tumors. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135:588-601.
- Anzeljc AJ, Oliveira AM, Grossniklaus HE, et al. Nodular fasciitis of the orbit: a case report confirmed by molecular cytogenetic analysis. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;33(3S suppl 1):S152-S155.
- de Paula SA, Cruz AA, de Alencar VM, et al. Nodular fasciitis presenting as a large mass in the upper eyelid. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;22:494-495.
- Bernstein KE, Lattes R. Nodular (pseudosarcomatous) fasciitis, a nonrecurrent lesion: clinicopathologic study of 134 cases. Cancer. 1982;49:1668-1678.
- Shimizu S, Hashimoto H, Enjoji M. Nodular fasciitis: an analysis of 250 patients. Pathology. 1984;16:161-166.
- Erickson-Johnson MR, Chou MM, Evers BR, et al. Nodular fasciitis: a novel model of transient neoplasia induced by MYH9-USP6 gene fusion. Lab Invest. 2011;91:1427-1433.
- Amary MF, Ye H, Berisha F, et al. Detection of USP6 gene rearrangement in nodular fasciitis: an important diagnostic tool. Virchows Arch. 2013;463:97-98.
- Wirth L, Klein A, Baur-Melnyk A. Desmoid tumors of the extremity and trunk. a retrospective study of 44 patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19:2.
- Carlson JW, Fletcher CD. Immunohistochemistry for beta-catenin in the differential diagnosis of spindle cells lesions: analysis of a series and review of the literature. Histopathology. 2007;51:509-514.
- Mohamed M, Fisher C, Thway K. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma: clinical, morphologic and genetic features. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2017;28:60-67.
- Taher A, Pushpanathan C. Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor: a brief review. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007;131:1135-1138.
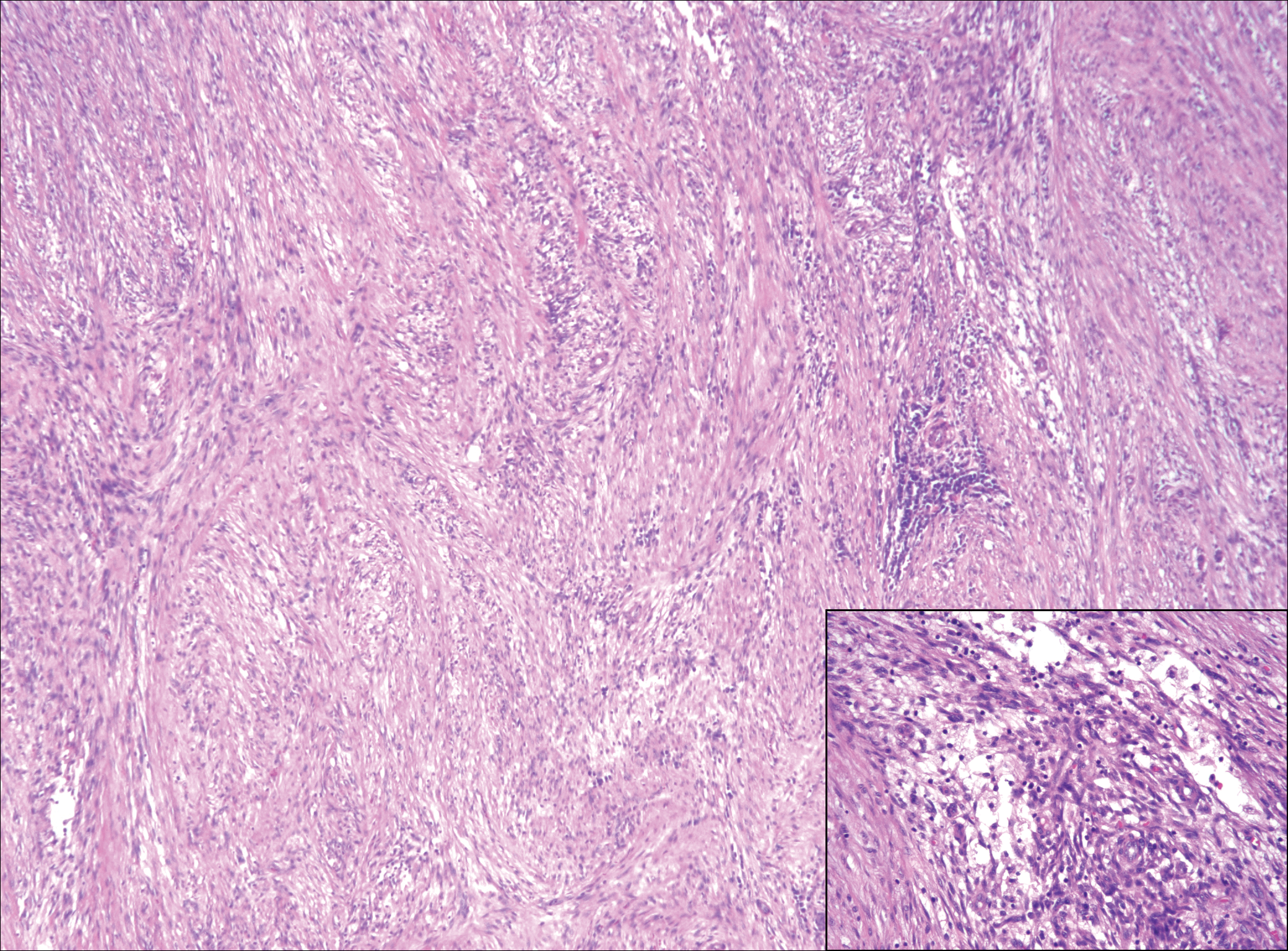
A 16-year-old adolescent girl presented with a bump over the left posterior knee of 1 month's duration. Her medical history was unremarkable. She denied recent trauma or injury to the area. On physical examination there was a visible and palpable tense nontender mass the size of an egg over the left posterior knee. Magnetic resonance imaging showed a lobulated mass-like focus of T2 hyperintensity centered at the subcutaneous tissues and superficial myofascial plane of the gastrocnemius on the posterior knee. Complete excision of the lesion was performed and demonstrated a 2.6.2 ×2.9.2 ×2.1-cm mass within subcutaneous adipose tissue. There was no microscopic involvement of skeletal muscle. Immunohistochemistry staining of the tumor was performed that was positive for smooth muscle actin and negative for desmin, S-100, CD34, pan-cytokeratin, and β-catenin. Fluorescent in situ hybridization testing demonstrated rearrangement of the ubiquitin-specific peptidase 6 gene, USP6, locus (17p13).
Red-Brown Patches in the Groin
The Diagnosis: Erythrasma
Erythrasma usually involves intertriginous areas (eg, axillae, groin, inframammary area). Patients present with well-demarcated, minimally scaly, red-brown patches. The interdigital web space of the toes also can be involved with macerated white plaques, often with coexistent dermatophyte infection. Corynebacterium minutissimum, the bacteria responsible for erythrasma, produces coproporphyrin type III, which emits coral red fluorescence under Wood lamp examination.1 Bathing may result in removal of the porphyrin and result in a false-negative finding. Potassium hydroxide preparation of skin scrapings can show chains of bacilli. Biopsy appears relatively normal at low power but reveals compact orthokeratosis with coccobacilli and filamentous organisms in the superficial stratum corneum (quiz image). When not obvious on hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections, the organisms are Gram-positive and also are seen with periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) and methenamine silver stains. Unlike fungal hyphae, these organisms are thinner and nonrefractile. Inflammation typically is minimal. Due to the subtle histologic findings at low power, erythrasma is considered one of the invisible dermatoses.2 The differential diagnosis of these inconspicuous dermatoses that appear normal at first glance can be approached in a stepwise fashion starting in the stratum corneum, followed by the granular layer, basal layer, dermal papillae, dermal inflammatory cells, dermal connective tissue, and eccrine glands, and should consider each of the following diagnoses: candidiasis, dermatophytosis, ichthyosis vulgaris, vitiligo, macular amyloid, urticaria, telangiectasia macularis eruptiva perstans, connective tissue nevus, and argyria.2
Candidiasis, most commonly caused by Candida albicans, usually involves the oral cavity (eg, thrush, median rhomboid glossitis, angular cheilitis), intertriginous zones, nail fold (paronychia), genital areas (eg, vulvovaginitis, balanitis), and diaper area.3 The web space between the third and fourth fingers (erosio interdigitalis blastomycetica) can be involved in patients whose hands are frequently in water. Intertriginous candidiasis presents with bright red, sometimes erosive patches with satellite lesions. Spores and mycelia (filamentous forms) are noted on potassium hydroxide preparation of skin scrapings. Histologically, the epidermis often is acanthotic, mildly spongiotic, and contains groups of neutrophils in the superficial layers. The mnemonic device for diseases with clusters of neutrophils in the stratum corneum is PTICSS (psoriasis, tinea, impetigo, candida, seborrheic dermatitis, syphilis).2 Yeast, pseudohyphae, and even true hyphae can be seen in the stratum corneum with hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections and PAS. The filamentous forms tend to be vertically oriented in relation to the skin surface (Figure 1) compared to dermatophyte hyphae that tend to be parallel to the surface.2
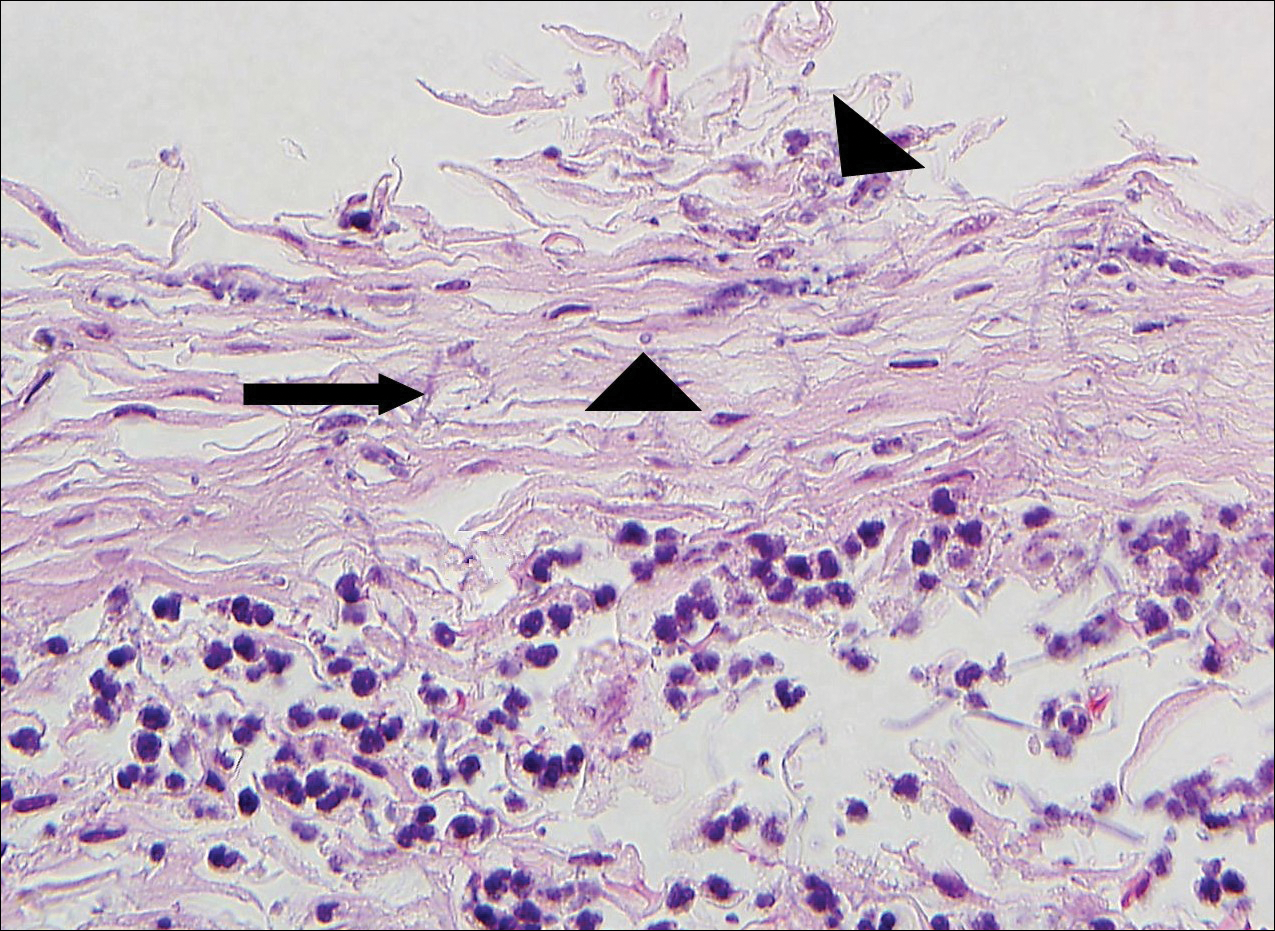
Pitted keratolysis is a superficial bacterial infection involving the soles of the feet. The classic clinical findings are shallow 1- to 2-mm pits in clusters that can coalesce on pressure-bearing areas. Hyperhidrosis, malodor, and maceration commonly are associated. Microscopic examination reveals clusters of small cocci and filamentous bacteria located in the dell or pit of a thick compact orthokeratotic stratum corneum of acral skin with no notable inflammatory infiltrate (Figure 2).2 Special stains such as Gram, methenamine silver, or PAS can assist in visualization of the organisms. Pitted keratolysis is caused by Dermatophilus congolensis and Kytococcus sedentarius (formerly Micrococcus sedentarius), which produce keratinolytic enzymes causing the defect in the stratum corneum.3
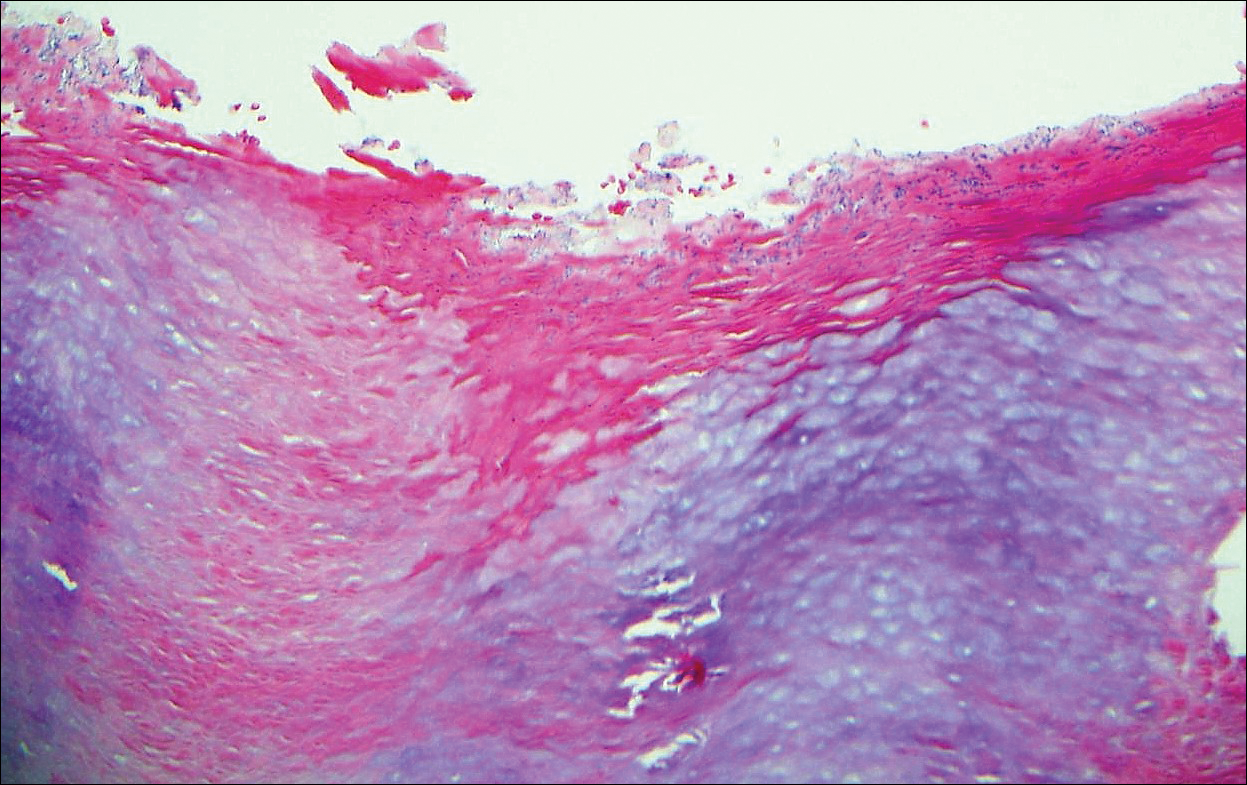
Tinea cruris, also known as jock itch and ringworm of the groin, presents with advancing pruritic, circinate, erythematous, scaling patches with central clearing on the inner thighs and crural folds. Similar to tinea pedis, Trichophyton rubrum is the most common dermatophyte to cause tinea cruris.4 Potassium hydroxide preparation of skin scrapings from the advancing border show fungal hyphae that cross the keratin cell borders. The histopathology of dermatophyte infections can be subtle and resemble normal skin before close inspection of the stratum corneum, which can show compact orthokeratosis, neutrophils, or "sandwich sign" where hyphae are sandwiched between an upper basket weave layer and a lower compact cornified layer (orthokeratotic or parakeratotic)(Figure 3).1 The presence of these patterns in the stratum corneum should result in performance of PAS to highlight obscure hyphae.
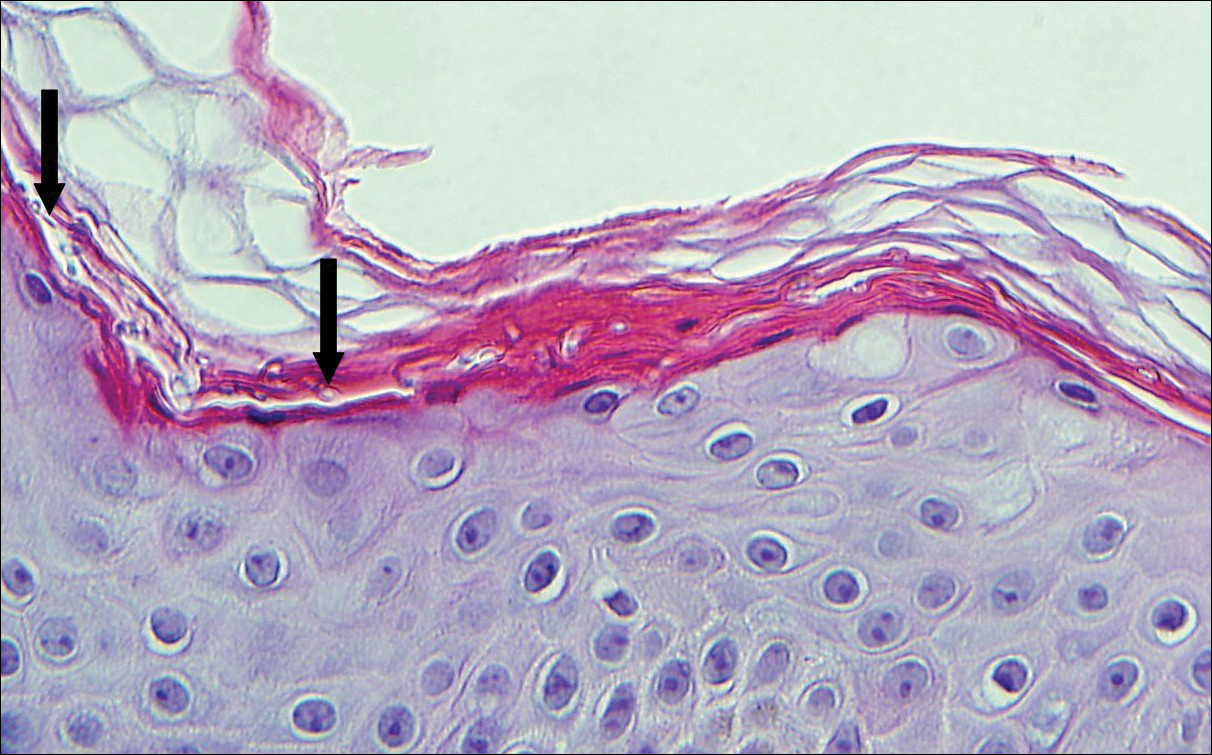
Tinea versicolor, also called pityriasis versicolor, usually presents with hypopigmented or less commonly hyperpigmented circular patches that coalesce on the upper trunk and shoulders. There is a fine fluffy scale that is most notable after scraping the skin for a potassium hydroxide preparation, which shows "spaghetti and meatballs" (hyphae and spores). Tinea versicolor typically is caused by the mycelial phase of the lipophilic yeast Malassezia globosae.3 Histologically, there are yeast and short septate hyphae scattered in a loose basket weave hyperkeratotic stratum corneum with minimal or no inflammation (Figure 4). On occasion, PAS is required for identification.
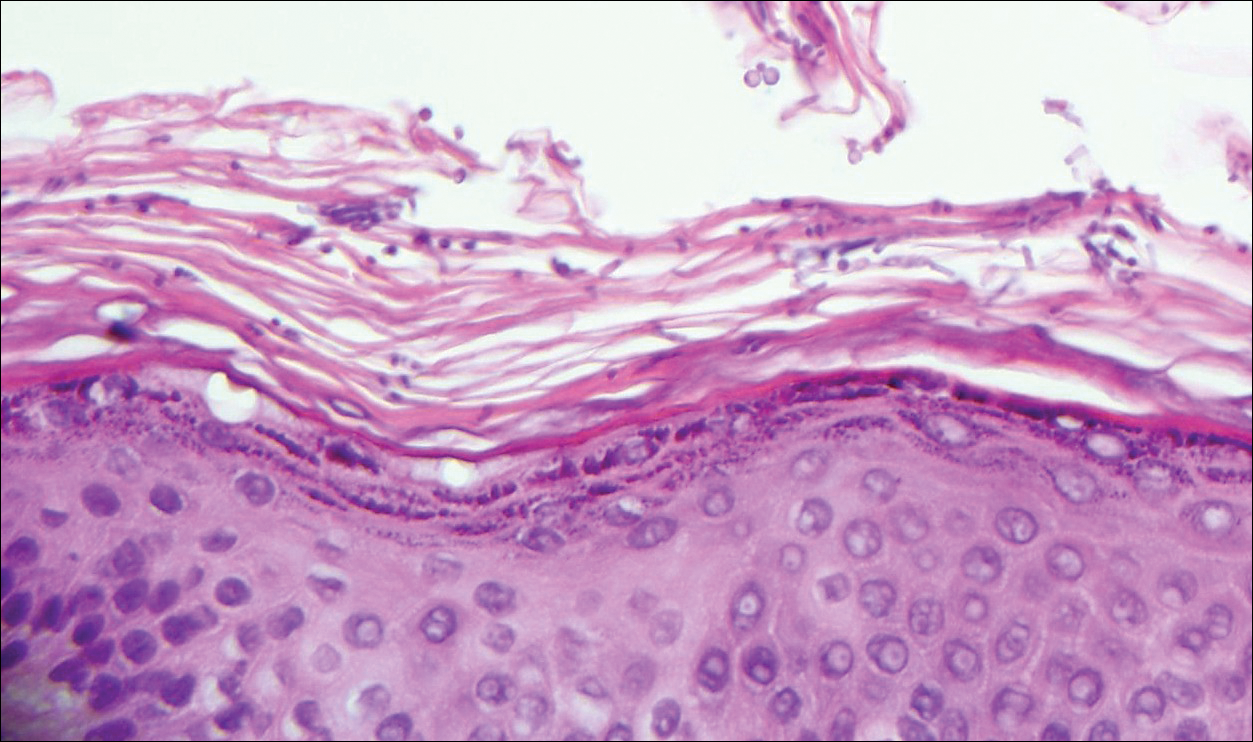
- Patterson JW, Hosler GA. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; 2016.
- Elston DM, Ferringer T, eds. Dermatopathology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2014.
- Calonje E, McKee PH. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. Edinburgh, Scotland: Elsevier/Saunders; 2012.
- Bolognia JL, Shaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatolology. 4th ed. China: Elsevier; 2018.
The Diagnosis: Erythrasma
Erythrasma usually involves intertriginous areas (eg, axillae, groin, inframammary area). Patients present with well-demarcated, minimally scaly, red-brown patches. The interdigital web space of the toes also can be involved with macerated white plaques, often with coexistent dermatophyte infection. Corynebacterium minutissimum, the bacteria responsible for erythrasma, produces coproporphyrin type III, which emits coral red fluorescence under Wood lamp examination.1 Bathing may result in removal of the porphyrin and result in a false-negative finding. Potassium hydroxide preparation of skin scrapings can show chains of bacilli. Biopsy appears relatively normal at low power but reveals compact orthokeratosis with coccobacilli and filamentous organisms in the superficial stratum corneum (quiz image). When not obvious on hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections, the organisms are Gram-positive and also are seen with periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) and methenamine silver stains. Unlike fungal hyphae, these organisms are thinner and nonrefractile. Inflammation typically is minimal. Due to the subtle histologic findings at low power, erythrasma is considered one of the invisible dermatoses.2 The differential diagnosis of these inconspicuous dermatoses that appear normal at first glance can be approached in a stepwise fashion starting in the stratum corneum, followed by the granular layer, basal layer, dermal papillae, dermal inflammatory cells, dermal connective tissue, and eccrine glands, and should consider each of the following diagnoses: candidiasis, dermatophytosis, ichthyosis vulgaris, vitiligo, macular amyloid, urticaria, telangiectasia macularis eruptiva perstans, connective tissue nevus, and argyria.2
Candidiasis, most commonly caused by Candida albicans, usually involves the oral cavity (eg, thrush, median rhomboid glossitis, angular cheilitis), intertriginous zones, nail fold (paronychia), genital areas (eg, vulvovaginitis, balanitis), and diaper area.3 The web space between the third and fourth fingers (erosio interdigitalis blastomycetica) can be involved in patients whose hands are frequently in water. Intertriginous candidiasis presents with bright red, sometimes erosive patches with satellite lesions. Spores and mycelia (filamentous forms) are noted on potassium hydroxide preparation of skin scrapings. Histologically, the epidermis often is acanthotic, mildly spongiotic, and contains groups of neutrophils in the superficial layers. The mnemonic device for diseases with clusters of neutrophils in the stratum corneum is PTICSS (psoriasis, tinea, impetigo, candida, seborrheic dermatitis, syphilis).2 Yeast, pseudohyphae, and even true hyphae can be seen in the stratum corneum with hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections and PAS. The filamentous forms tend to be vertically oriented in relation to the skin surface (Figure 1) compared to dermatophyte hyphae that tend to be parallel to the surface.2

Pitted keratolysis is a superficial bacterial infection involving the soles of the feet. The classic clinical findings are shallow 1- to 2-mm pits in clusters that can coalesce on pressure-bearing areas. Hyperhidrosis, malodor, and maceration commonly are associated. Microscopic examination reveals clusters of small cocci and filamentous bacteria located in the dell or pit of a thick compact orthokeratotic stratum corneum of acral skin with no notable inflammatory infiltrate (Figure 2).2 Special stains such as Gram, methenamine silver, or PAS can assist in visualization of the organisms. Pitted keratolysis is caused by Dermatophilus congolensis and Kytococcus sedentarius (formerly Micrococcus sedentarius), which produce keratinolytic enzymes causing the defect in the stratum corneum.3

Tinea cruris, also known as jock itch and ringworm of the groin, presents with advancing pruritic, circinate, erythematous, scaling patches with central clearing on the inner thighs and crural folds. Similar to tinea pedis, Trichophyton rubrum is the most common dermatophyte to cause tinea cruris.4 Potassium hydroxide preparation of skin scrapings from the advancing border show fungal hyphae that cross the keratin cell borders. The histopathology of dermatophyte infections can be subtle and resemble normal skin before close inspection of the stratum corneum, which can show compact orthokeratosis, neutrophils, or "sandwich sign" where hyphae are sandwiched between an upper basket weave layer and a lower compact cornified layer (orthokeratotic or parakeratotic)(Figure 3).1 The presence of these patterns in the stratum corneum should result in performance of PAS to highlight obscure hyphae.

Tinea versicolor, also called pityriasis versicolor, usually presents with hypopigmented or less commonly hyperpigmented circular patches that coalesce on the upper trunk and shoulders. There is a fine fluffy scale that is most notable after scraping the skin for a potassium hydroxide preparation, which shows "spaghetti and meatballs" (hyphae and spores). Tinea versicolor typically is caused by the mycelial phase of the lipophilic yeast Malassezia globosae.3 Histologically, there are yeast and short septate hyphae scattered in a loose basket weave hyperkeratotic stratum corneum with minimal or no inflammation (Figure 4). On occasion, PAS is required for identification.

The Diagnosis: Erythrasma
Erythrasma usually involves intertriginous areas (eg, axillae, groin, inframammary area). Patients present with well-demarcated, minimally scaly, red-brown patches. The interdigital web space of the toes also can be involved with macerated white plaques, often with coexistent dermatophyte infection. Corynebacterium minutissimum, the bacteria responsible for erythrasma, produces coproporphyrin type III, which emits coral red fluorescence under Wood lamp examination.1 Bathing may result in removal of the porphyrin and result in a false-negative finding. Potassium hydroxide preparation of skin scrapings can show chains of bacilli. Biopsy appears relatively normal at low power but reveals compact orthokeratosis with coccobacilli and filamentous organisms in the superficial stratum corneum (quiz image). When not obvious on hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections, the organisms are Gram-positive and also are seen with periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) and methenamine silver stains. Unlike fungal hyphae, these organisms are thinner and nonrefractile. Inflammation typically is minimal. Due to the subtle histologic findings at low power, erythrasma is considered one of the invisible dermatoses.2 The differential diagnosis of these inconspicuous dermatoses that appear normal at first glance can be approached in a stepwise fashion starting in the stratum corneum, followed by the granular layer, basal layer, dermal papillae, dermal inflammatory cells, dermal connective tissue, and eccrine glands, and should consider each of the following diagnoses: candidiasis, dermatophytosis, ichthyosis vulgaris, vitiligo, macular amyloid, urticaria, telangiectasia macularis eruptiva perstans, connective tissue nevus, and argyria.2
Candidiasis, most commonly caused by Candida albicans, usually involves the oral cavity (eg, thrush, median rhomboid glossitis, angular cheilitis), intertriginous zones, nail fold (paronychia), genital areas (eg, vulvovaginitis, balanitis), and diaper area.3 The web space between the third and fourth fingers (erosio interdigitalis blastomycetica) can be involved in patients whose hands are frequently in water. Intertriginous candidiasis presents with bright red, sometimes erosive patches with satellite lesions. Spores and mycelia (filamentous forms) are noted on potassium hydroxide preparation of skin scrapings. Histologically, the epidermis often is acanthotic, mildly spongiotic, and contains groups of neutrophils in the superficial layers. The mnemonic device for diseases with clusters of neutrophils in the stratum corneum is PTICSS (psoriasis, tinea, impetigo, candida, seborrheic dermatitis, syphilis).2 Yeast, pseudohyphae, and even true hyphae can be seen in the stratum corneum with hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections and PAS. The filamentous forms tend to be vertically oriented in relation to the skin surface (Figure 1) compared to dermatophyte hyphae that tend to be parallel to the surface.2

Pitted keratolysis is a superficial bacterial infection involving the soles of the feet. The classic clinical findings are shallow 1- to 2-mm pits in clusters that can coalesce on pressure-bearing areas. Hyperhidrosis, malodor, and maceration commonly are associated. Microscopic examination reveals clusters of small cocci and filamentous bacteria located in the dell or pit of a thick compact orthokeratotic stratum corneum of acral skin with no notable inflammatory infiltrate (Figure 2).2 Special stains such as Gram, methenamine silver, or PAS can assist in visualization of the organisms. Pitted keratolysis is caused by Dermatophilus congolensis and Kytococcus sedentarius (formerly Micrococcus sedentarius), which produce keratinolytic enzymes causing the defect in the stratum corneum.3

Tinea cruris, also known as jock itch and ringworm of the groin, presents with advancing pruritic, circinate, erythematous, scaling patches with central clearing on the inner thighs and crural folds. Similar to tinea pedis, Trichophyton rubrum is the most common dermatophyte to cause tinea cruris.4 Potassium hydroxide preparation of skin scrapings from the advancing border show fungal hyphae that cross the keratin cell borders. The histopathology of dermatophyte infections can be subtle and resemble normal skin before close inspection of the stratum corneum, which can show compact orthokeratosis, neutrophils, or "sandwich sign" where hyphae are sandwiched between an upper basket weave layer and a lower compact cornified layer (orthokeratotic or parakeratotic)(Figure 3).1 The presence of these patterns in the stratum corneum should result in performance of PAS to highlight obscure hyphae.

Tinea versicolor, also called pityriasis versicolor, usually presents with hypopigmented or less commonly hyperpigmented circular patches that coalesce on the upper trunk and shoulders. There is a fine fluffy scale that is most notable after scraping the skin for a potassium hydroxide preparation, which shows "spaghetti and meatballs" (hyphae and spores). Tinea versicolor typically is caused by the mycelial phase of the lipophilic yeast Malassezia globosae.3 Histologically, there are yeast and short septate hyphae scattered in a loose basket weave hyperkeratotic stratum corneum with minimal or no inflammation (Figure 4). On occasion, PAS is required for identification.

- Patterson JW, Hosler GA. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; 2016.
- Elston DM, Ferringer T, eds. Dermatopathology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2014.
- Calonje E, McKee PH. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. Edinburgh, Scotland: Elsevier/Saunders; 2012.
- Bolognia JL, Shaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatolology. 4th ed. China: Elsevier; 2018.
- Patterson JW, Hosler GA. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; 2016.
- Elston DM, Ferringer T, eds. Dermatopathology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2014.
- Calonje E, McKee PH. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. Edinburgh, Scotland: Elsevier/Saunders; 2012.
- Bolognia JL, Shaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatolology. 4th ed. China: Elsevier; 2018.
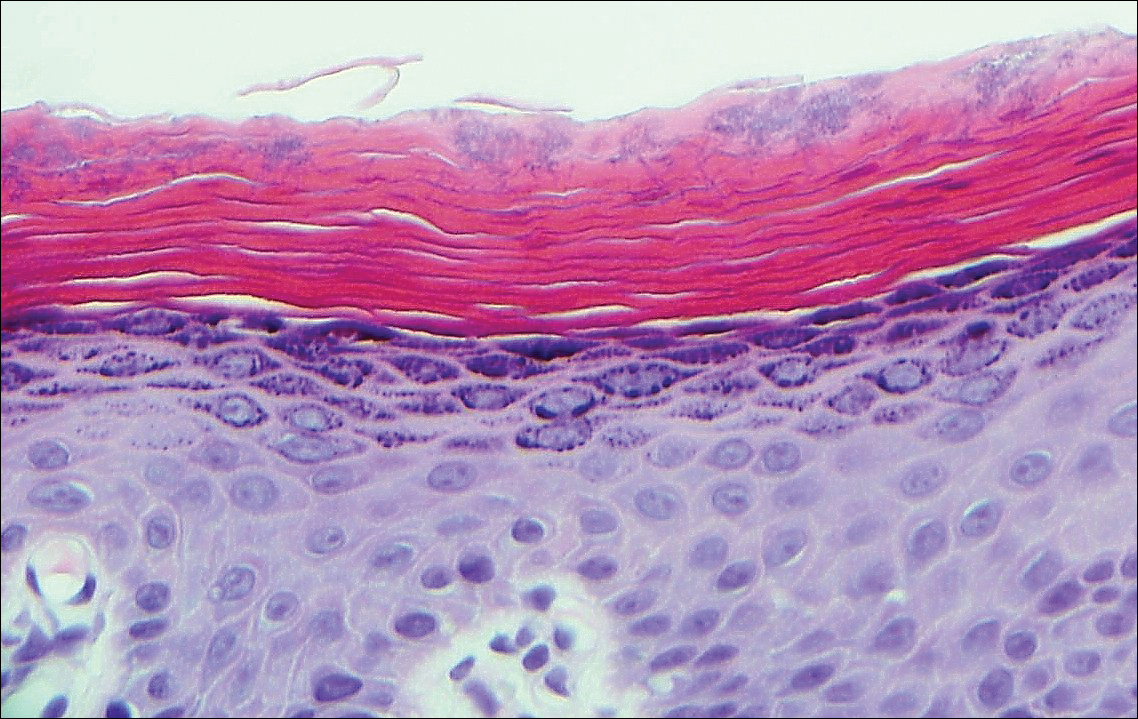
A 66-year-old man presented with reddish arciform patches in the inguinal area.