User login
Children and COVID: Many parents see vaccine as the greater risk
New COVID-19 cases rose for the second week in a row as cumulative cases among U.S. children passed the 14-million mark, but a recent survey shows that more than half of parents believe that the vaccine is a greater risk to children under age 5 years than the virus.
In a Kaiser Family Foundation survey conducted July 7-17, 53% of parents with children aged 6 months to 5 years said that the vaccine is “a bigger risk to their child’s health than getting infected with COVID-19, compared to 44% who say getting infected is the bigger risk,” KFF reported July 26.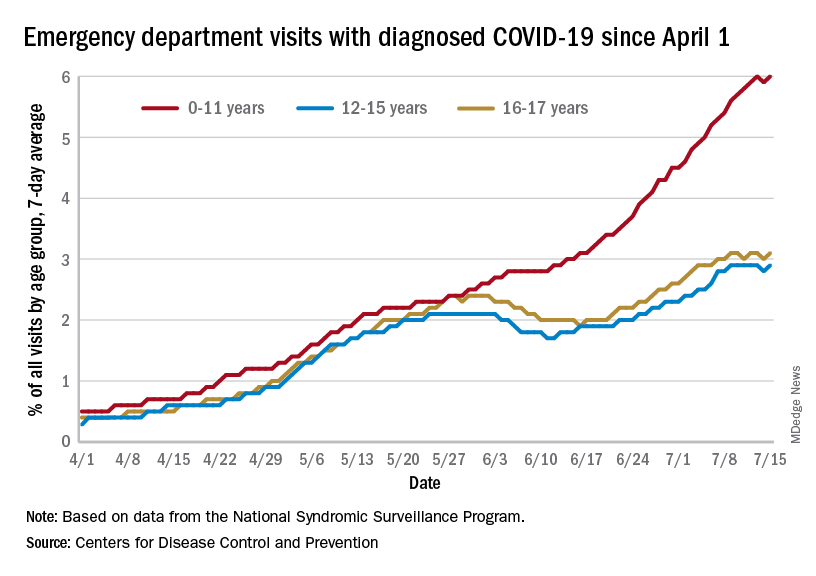
More than 4 out of 10 of respondents (43%) said that they will “definitely not” get their eligible children vaccinated, while only 7% said that their children had already received it and 10% said their children would get it as soon as possible, according to the KFF survey, which had an overall sample size of 1,847 adults, including an oversample of 471 parents of children under age 5.
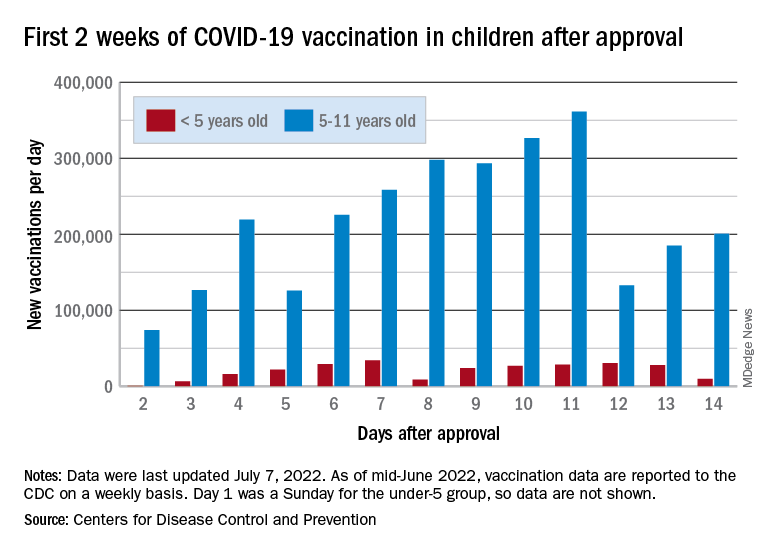
Vaccine initiation has been slow in the first month since it was approved for the youngest children. Just 2.8% of all eligible children under age 5 had received an initial dose as of July 19, compared with first-month uptake figures of more than 18% for the 5- to 11-year-olds and 27% for those aged 12-15, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The current rates for vaccination in those aged 5 and older look like this: 70.2% of 12- to 17-year-olds have received at least one dose, versus 37.1% of those aged 5-11. Just over 60% of the older children were fully vaccinated as of July 19, as were 30.2% of the 5- to 11-year-olds, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
Number of new cases hits 2-month high
Despite the vaccine, SARS-CoV-2 and its various mutations have continued with their summer travels. With 92,000 newly infected children added for the week of July 15-21, there have now been a total of 14,003,497 pediatric cases reported since the start of the pandemic, which works out to 18.6% of cases in all ages, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The 92,000 new cases represent an increase of almost 22% over the previous week and mark the highest 1-week count since May, when the total passed 100,000 for 2 consecutive weeks. More recently the trend had seemed more stable as weekly cases dropped twice and rose twice as the total hovered around 70,000, based on the data collected by the AAP and CHA from state and territorial health departments.
A different scenario has played out for emergency department visits and hospital admissions, which have risen steadily since the beginning of April. The admission rate for children aged 0-17, which was just 0.13 new patients per 100,000 population on April 11, was up to 0.44 per 100,000 on July 21. By comparison, the highest rate reached last year during the Delta surge was 0.47 per 100,000, based on CDC data.
The 7-day average of emergency dept. visits among the youngest age group, 0-11 years, shows the same general increase as hospital admissions, but the older children have diverged form that path (see graph). For those aged 12-15 and 16-17, hospitalizations started dropping in late May and into mid-June before climbing again, although more slowly than for the youngest group, the CDC data show.
The ED visit rate with diagnosed COVID among those aged 0-11, measured at 6.1% of all visits on July 19, is, in fact, considerably higher than at any time during the Delta surge last year, when it never passed 4.0%, although much lower than peak Omicron (14.1%). That 6.1% was also higher than any other age group on that day, adults included, the CDC said.
New COVID-19 cases rose for the second week in a row as cumulative cases among U.S. children passed the 14-million mark, but a recent survey shows that more than half of parents believe that the vaccine is a greater risk to children under age 5 years than the virus.
In a Kaiser Family Foundation survey conducted July 7-17, 53% of parents with children aged 6 months to 5 years said that the vaccine is “a bigger risk to their child’s health than getting infected with COVID-19, compared to 44% who say getting infected is the bigger risk,” KFF reported July 26.
More than 4 out of 10 of respondents (43%) said that they will “definitely not” get their eligible children vaccinated, while only 7% said that their children had already received it and 10% said their children would get it as soon as possible, according to the KFF survey, which had an overall sample size of 1,847 adults, including an oversample of 471 parents of children under age 5.
Vaccine initiation has been slow in the first month since it was approved for the youngest children. Just 2.8% of all eligible children under age 5 had received an initial dose as of July 19, compared with first-month uptake figures of more than 18% for the 5- to 11-year-olds and 27% for those aged 12-15, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The current rates for vaccination in those aged 5 and older look like this: 70.2% of 12- to 17-year-olds have received at least one dose, versus 37.1% of those aged 5-11. Just over 60% of the older children were fully vaccinated as of July 19, as were 30.2% of the 5- to 11-year-olds, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
Number of new cases hits 2-month high
Despite the vaccine, SARS-CoV-2 and its various mutations have continued with their summer travels. With 92,000 newly infected children added for the week of July 15-21, there have now been a total of 14,003,497 pediatric cases reported since the start of the pandemic, which works out to 18.6% of cases in all ages, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The 92,000 new cases represent an increase of almost 22% over the previous week and mark the highest 1-week count since May, when the total passed 100,000 for 2 consecutive weeks. More recently the trend had seemed more stable as weekly cases dropped twice and rose twice as the total hovered around 70,000, based on the data collected by the AAP and CHA from state and territorial health departments.
A different scenario has played out for emergency department visits and hospital admissions, which have risen steadily since the beginning of April. The admission rate for children aged 0-17, which was just 0.13 new patients per 100,000 population on April 11, was up to 0.44 per 100,000 on July 21. By comparison, the highest rate reached last year during the Delta surge was 0.47 per 100,000, based on CDC data.
The 7-day average of emergency dept. visits among the youngest age group, 0-11 years, shows the same general increase as hospital admissions, but the older children have diverged form that path (see graph). For those aged 12-15 and 16-17, hospitalizations started dropping in late May and into mid-June before climbing again, although more slowly than for the youngest group, the CDC data show.
The ED visit rate with diagnosed COVID among those aged 0-11, measured at 6.1% of all visits on July 19, is, in fact, considerably higher than at any time during the Delta surge last year, when it never passed 4.0%, although much lower than peak Omicron (14.1%). That 6.1% was also higher than any other age group on that day, adults included, the CDC said.
New COVID-19 cases rose for the second week in a row as cumulative cases among U.S. children passed the 14-million mark, but a recent survey shows that more than half of parents believe that the vaccine is a greater risk to children under age 5 years than the virus.
In a Kaiser Family Foundation survey conducted July 7-17, 53% of parents with children aged 6 months to 5 years said that the vaccine is “a bigger risk to their child’s health than getting infected with COVID-19, compared to 44% who say getting infected is the bigger risk,” KFF reported July 26.
More than 4 out of 10 of respondents (43%) said that they will “definitely not” get their eligible children vaccinated, while only 7% said that their children had already received it and 10% said their children would get it as soon as possible, according to the KFF survey, which had an overall sample size of 1,847 adults, including an oversample of 471 parents of children under age 5.
Vaccine initiation has been slow in the first month since it was approved for the youngest children. Just 2.8% of all eligible children under age 5 had received an initial dose as of July 19, compared with first-month uptake figures of more than 18% for the 5- to 11-year-olds and 27% for those aged 12-15, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The current rates for vaccination in those aged 5 and older look like this: 70.2% of 12- to 17-year-olds have received at least one dose, versus 37.1% of those aged 5-11. Just over 60% of the older children were fully vaccinated as of July 19, as were 30.2% of the 5- to 11-year-olds, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
Number of new cases hits 2-month high
Despite the vaccine, SARS-CoV-2 and its various mutations have continued with their summer travels. With 92,000 newly infected children added for the week of July 15-21, there have now been a total of 14,003,497 pediatric cases reported since the start of the pandemic, which works out to 18.6% of cases in all ages, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The 92,000 new cases represent an increase of almost 22% over the previous week and mark the highest 1-week count since May, when the total passed 100,000 for 2 consecutive weeks. More recently the trend had seemed more stable as weekly cases dropped twice and rose twice as the total hovered around 70,000, based on the data collected by the AAP and CHA from state and territorial health departments.
A different scenario has played out for emergency department visits and hospital admissions, which have risen steadily since the beginning of April. The admission rate for children aged 0-17, which was just 0.13 new patients per 100,000 population on April 11, was up to 0.44 per 100,000 on July 21. By comparison, the highest rate reached last year during the Delta surge was 0.47 per 100,000, based on CDC data.
The 7-day average of emergency dept. visits among the youngest age group, 0-11 years, shows the same general increase as hospital admissions, but the older children have diverged form that path (see graph). For those aged 12-15 and 16-17, hospitalizations started dropping in late May and into mid-June before climbing again, although more slowly than for the youngest group, the CDC data show.
The ED visit rate with diagnosed COVID among those aged 0-11, measured at 6.1% of all visits on July 19, is, in fact, considerably higher than at any time during the Delta surge last year, when it never passed 4.0%, although much lower than peak Omicron (14.1%). That 6.1% was also higher than any other age group on that day, adults included, the CDC said.
Children and COVID: Does latest rise in new cases point toward stabilization?
New COVID-19 cases rose for the second time in 3 weeks, as the effort to vaccinate the youngest children continued to slow after just 3 full weeks.
Nationally, over 75,000 children under age 5 years received their first dose of COVID-19 vaccine during the week of July 7-13. That number is down from the previous week – 118,000 from June 30 to July 6 – which, in turn, was lower than the 206,000 doses administered through the first 10 days after approval, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That all adds up to just under 400,000 vaccinated children, or 2% of the eligible population under age 5, as of July 13.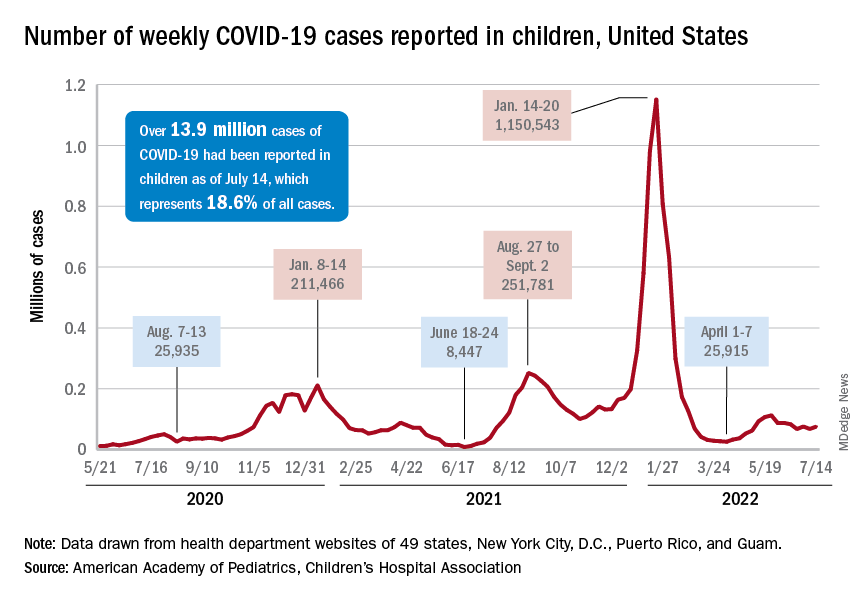
State-level data, meanwhile, show considerable variation, the American Academy of Pediatrics noted in its weekly analysis of the CDC vaccine data. Vermont has already vaccinated 10.0% of children under age 5 years, and Massachusetts is at 9.5%, while Mississippi (0.3%), Alabama (0.5%), and Louisiana (0.8%) are still below 1%, the AAP said.
New cases show signs of steadying
The national count was up by 11.1% for the week of July 8-14, rising to 75,000 new cases, compared with 68,000 the previous week, but the recent trend seems to be leaning toward steadiness. The overall number has been between 67,000 and 76,000 over the past 4 weeks, alternating between rising and falling in that time span, according to data gathered by the AAP and the Children’s Hospital Association from state and territorial health departments.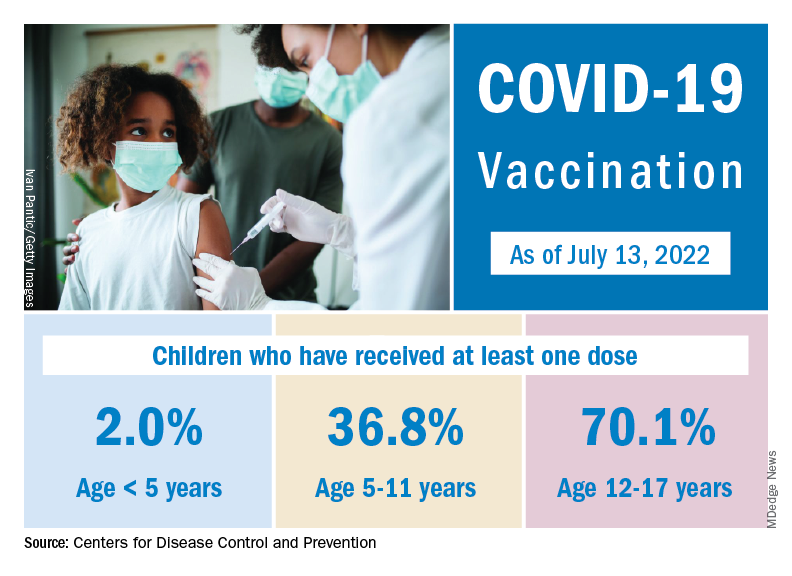
the two groups said, also noting that several states have stopped updating their online dashboards over the past year, making the current total artificially low in comparison.
Taken with that grain of salt, the cumulative number of child cases since the start of the pandemic is just over 13.9 million, which represents 18.6% of all cases in the United States. That proportion has been declining in recent weeks and was as high as 19.0% as late as mid-May. “While COVID-19 cases are likely increasingly underreported for all age groups, this decline indicates that children are disproportionately undercounted in reported COVID-19 cases,” the AAP and CHA said.
New COVID-19 cases rose for the second time in 3 weeks, as the effort to vaccinate the youngest children continued to slow after just 3 full weeks.
Nationally, over 75,000 children under age 5 years received their first dose of COVID-19 vaccine during the week of July 7-13. That number is down from the previous week – 118,000 from June 30 to July 6 – which, in turn, was lower than the 206,000 doses administered through the first 10 days after approval, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That all adds up to just under 400,000 vaccinated children, or 2% of the eligible population under age 5, as of July 13.
State-level data, meanwhile, show considerable variation, the American Academy of Pediatrics noted in its weekly analysis of the CDC vaccine data. Vermont has already vaccinated 10.0% of children under age 5 years, and Massachusetts is at 9.5%, while Mississippi (0.3%), Alabama (0.5%), and Louisiana (0.8%) are still below 1%, the AAP said.
New cases show signs of steadying
The national count was up by 11.1% for the week of July 8-14, rising to 75,000 new cases, compared with 68,000 the previous week, but the recent trend seems to be leaning toward steadiness. The overall number has been between 67,000 and 76,000 over the past 4 weeks, alternating between rising and falling in that time span, according to data gathered by the AAP and the Children’s Hospital Association from state and territorial health departments.
the two groups said, also noting that several states have stopped updating their online dashboards over the past year, making the current total artificially low in comparison.
Taken with that grain of salt, the cumulative number of child cases since the start of the pandemic is just over 13.9 million, which represents 18.6% of all cases in the United States. That proportion has been declining in recent weeks and was as high as 19.0% as late as mid-May. “While COVID-19 cases are likely increasingly underreported for all age groups, this decline indicates that children are disproportionately undercounted in reported COVID-19 cases,” the AAP and CHA said.
New COVID-19 cases rose for the second time in 3 weeks, as the effort to vaccinate the youngest children continued to slow after just 3 full weeks.
Nationally, over 75,000 children under age 5 years received their first dose of COVID-19 vaccine during the week of July 7-13. That number is down from the previous week – 118,000 from June 30 to July 6 – which, in turn, was lower than the 206,000 doses administered through the first 10 days after approval, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That all adds up to just under 400,000 vaccinated children, or 2% of the eligible population under age 5, as of July 13.
State-level data, meanwhile, show considerable variation, the American Academy of Pediatrics noted in its weekly analysis of the CDC vaccine data. Vermont has already vaccinated 10.0% of children under age 5 years, and Massachusetts is at 9.5%, while Mississippi (0.3%), Alabama (0.5%), and Louisiana (0.8%) are still below 1%, the AAP said.
New cases show signs of steadying
The national count was up by 11.1% for the week of July 8-14, rising to 75,000 new cases, compared with 68,000 the previous week, but the recent trend seems to be leaning toward steadiness. The overall number has been between 67,000 and 76,000 over the past 4 weeks, alternating between rising and falling in that time span, according to data gathered by the AAP and the Children’s Hospital Association from state and territorial health departments.
the two groups said, also noting that several states have stopped updating their online dashboards over the past year, making the current total artificially low in comparison.
Taken with that grain of salt, the cumulative number of child cases since the start of the pandemic is just over 13.9 million, which represents 18.6% of all cases in the United States. That proportion has been declining in recent weeks and was as high as 19.0% as late as mid-May. “While COVID-19 cases are likely increasingly underreported for all age groups, this decline indicates that children are disproportionately undercounted in reported COVID-19 cases,” the AAP and CHA said.
FDA grants emergency authorization for Novavax COVID vaccine
on July 13.
The vaccine is authorized for adults only. Should the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention follow suit and approve its use, Novavax would join Moderna, Pfizer and Johnson & Johnson on the U.S. market. A CDC panel of advisors is expected to consider the new entry on July 19.
The Novavax vaccine is only for those who have not yet been vaccinated at all.
“Today’s authorization offers adults in the United States who have not yet received a COVID-19 vaccine another option that meets the FDA’s rigorous standards for safety, effectiveness and manufacturing quality needed to support emergency use authorization,” FDA Commissioner Robert Califf, MD, said in a statement. “COVID-19 vaccines remain the best preventive measure against severe disease caused by COVID-19 and I encourage anyone who is eligible for, but has not yet received a COVID-19 vaccine, to consider doing so.”
The Novavax vaccine is protein-based, making it different than mRNA vaccines from Pfizer and Moderna. It contains harmless elements of actual coronavirus spike protein and an ingredient known as a adjuvant that enhances the patient’s immune response.
Clinical trials found the vaccine to be 90.4% effective in preventing mild, moderate or severe COVID-19. Only 17 patients out of 17,200 developed COVID-19 after receiving both doses.
The FDA said, however, that Novavax’s vaccine did show evidence of increased risk of myocarditis – inflammation of the heart – and pericarditis, inflammation of tissue surrounding the heart. In most people both disorders began within 10 days.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
on July 13.
The vaccine is authorized for adults only. Should the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention follow suit and approve its use, Novavax would join Moderna, Pfizer and Johnson & Johnson on the U.S. market. A CDC panel of advisors is expected to consider the new entry on July 19.
The Novavax vaccine is only for those who have not yet been vaccinated at all.
“Today’s authorization offers adults in the United States who have not yet received a COVID-19 vaccine another option that meets the FDA’s rigorous standards for safety, effectiveness and manufacturing quality needed to support emergency use authorization,” FDA Commissioner Robert Califf, MD, said in a statement. “COVID-19 vaccines remain the best preventive measure against severe disease caused by COVID-19 and I encourage anyone who is eligible for, but has not yet received a COVID-19 vaccine, to consider doing so.”
The Novavax vaccine is protein-based, making it different than mRNA vaccines from Pfizer and Moderna. It contains harmless elements of actual coronavirus spike protein and an ingredient known as a adjuvant that enhances the patient’s immune response.
Clinical trials found the vaccine to be 90.4% effective in preventing mild, moderate or severe COVID-19. Only 17 patients out of 17,200 developed COVID-19 after receiving both doses.
The FDA said, however, that Novavax’s vaccine did show evidence of increased risk of myocarditis – inflammation of the heart – and pericarditis, inflammation of tissue surrounding the heart. In most people both disorders began within 10 days.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
on July 13.
The vaccine is authorized for adults only. Should the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention follow suit and approve its use, Novavax would join Moderna, Pfizer and Johnson & Johnson on the U.S. market. A CDC panel of advisors is expected to consider the new entry on July 19.
The Novavax vaccine is only for those who have not yet been vaccinated at all.
“Today’s authorization offers adults in the United States who have not yet received a COVID-19 vaccine another option that meets the FDA’s rigorous standards for safety, effectiveness and manufacturing quality needed to support emergency use authorization,” FDA Commissioner Robert Califf, MD, said in a statement. “COVID-19 vaccines remain the best preventive measure against severe disease caused by COVID-19 and I encourage anyone who is eligible for, but has not yet received a COVID-19 vaccine, to consider doing so.”
The Novavax vaccine is protein-based, making it different than mRNA vaccines from Pfizer and Moderna. It contains harmless elements of actual coronavirus spike protein and an ingredient known as a adjuvant that enhances the patient’s immune response.
Clinical trials found the vaccine to be 90.4% effective in preventing mild, moderate or severe COVID-19. Only 17 patients out of 17,200 developed COVID-19 after receiving both doses.
The FDA said, however, that Novavax’s vaccine did show evidence of increased risk of myocarditis – inflammation of the heart – and pericarditis, inflammation of tissue surrounding the heart. In most people both disorders began within 10 days.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Children and COVID: Vaccination a harder sell in the summer
The COVID-19 vaccination effort in the youngest children has begun much more slowly than the most recent rollout for older children, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
in early November of 2021, based on CDC data last updated on July 7.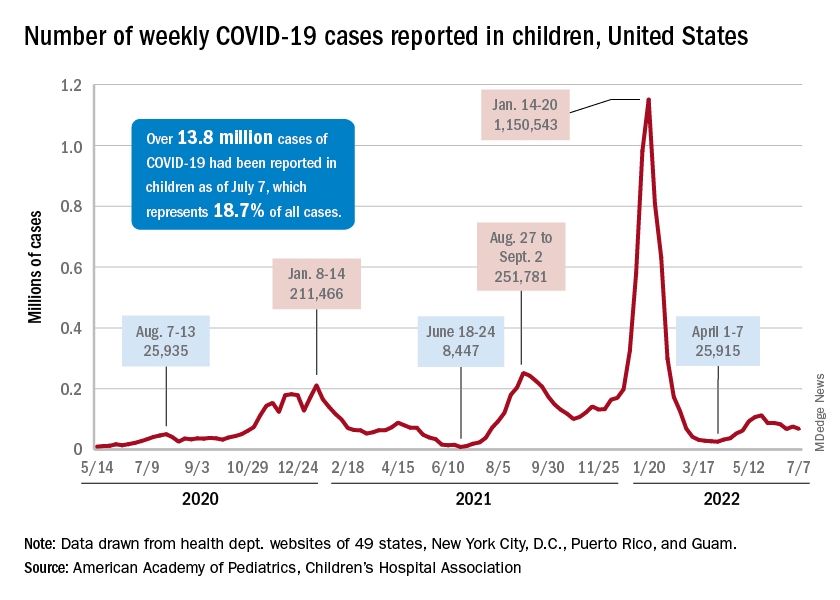
That approval, of course, came between the Delta and Omicron surges, when awareness was higher. The low initial uptake among those under age 5, however, was not unexpected by the Biden administration. “That number in and of itself is very much in line with our expectation, and we’re eager to continue working closely with partners to build on this start,” a senior administration official told ABC News.
With approval of the vaccine occurring after the school year was over, parents’ thoughts have been focused more on vacations and less on vaccinations. “Even before these vaccines officially became available, this was going to be a different rollout; it was going to take more time,” the official explained.
Incidence measures continue on different paths
New COVID-19 cases dropped during the latest reporting week (July 1-7), returning to the downward trend that began in late May and then stopped for 1 week (June 24-30), when cases were up by 12.4%, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Children also represent a smaller share of cases, probably because of underreporting. “There has been a notable decline in the portion of reported weekly COVID-19 cases that are children,” the two groups said in their weekly COVID report. Although “cases are likely increasingly underreported for all age groups, this decline indicates that children are disproportionately undercounted in reported COVID-19 cases.”
Other measures, however, have been rising slowly but steadily since the spring. New admissions of patients aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID, which were down to 0.13 per 100,000 population in early April, had climbed to 0.39 per 100,000 by July 7, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Emergency department visits continue to show the same upward trend, despite a small decline in early June. A COVID diagnosis was involved in just 0.5% of ED visits in children aged 0-11 years on March 26, but by July 6 the rate was 4.7%. Increases were not as high among older children: From 0.3% on March 26 to 2.5% on July 6 for those aged 12-15 and from 0.3% to 2.4% for 16- and 17-year-olds, according to the CDC.
The COVID-19 vaccination effort in the youngest children has begun much more slowly than the most recent rollout for older children, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
in early November of 2021, based on CDC data last updated on July 7.
That approval, of course, came between the Delta and Omicron surges, when awareness was higher. The low initial uptake among those under age 5, however, was not unexpected by the Biden administration. “That number in and of itself is very much in line with our expectation, and we’re eager to continue working closely with partners to build on this start,” a senior administration official told ABC News.
With approval of the vaccine occurring after the school year was over, parents’ thoughts have been focused more on vacations and less on vaccinations. “Even before these vaccines officially became available, this was going to be a different rollout; it was going to take more time,” the official explained.
Incidence measures continue on different paths
New COVID-19 cases dropped during the latest reporting week (July 1-7), returning to the downward trend that began in late May and then stopped for 1 week (June 24-30), when cases were up by 12.4%, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Children also represent a smaller share of cases, probably because of underreporting. “There has been a notable decline in the portion of reported weekly COVID-19 cases that are children,” the two groups said in their weekly COVID report. Although “cases are likely increasingly underreported for all age groups, this decline indicates that children are disproportionately undercounted in reported COVID-19 cases.”
Other measures, however, have been rising slowly but steadily since the spring. New admissions of patients aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID, which were down to 0.13 per 100,000 population in early April, had climbed to 0.39 per 100,000 by July 7, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Emergency department visits continue to show the same upward trend, despite a small decline in early June. A COVID diagnosis was involved in just 0.5% of ED visits in children aged 0-11 years on March 26, but by July 6 the rate was 4.7%. Increases were not as high among older children: From 0.3% on March 26 to 2.5% on July 6 for those aged 12-15 and from 0.3% to 2.4% for 16- and 17-year-olds, according to the CDC.
The COVID-19 vaccination effort in the youngest children has begun much more slowly than the most recent rollout for older children, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
in early November of 2021, based on CDC data last updated on July 7.
That approval, of course, came between the Delta and Omicron surges, when awareness was higher. The low initial uptake among those under age 5, however, was not unexpected by the Biden administration. “That number in and of itself is very much in line with our expectation, and we’re eager to continue working closely with partners to build on this start,” a senior administration official told ABC News.
With approval of the vaccine occurring after the school year was over, parents’ thoughts have been focused more on vacations and less on vaccinations. “Even before these vaccines officially became available, this was going to be a different rollout; it was going to take more time,” the official explained.
Incidence measures continue on different paths
New COVID-19 cases dropped during the latest reporting week (July 1-7), returning to the downward trend that began in late May and then stopped for 1 week (June 24-30), when cases were up by 12.4%, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Children also represent a smaller share of cases, probably because of underreporting. “There has been a notable decline in the portion of reported weekly COVID-19 cases that are children,” the two groups said in their weekly COVID report. Although “cases are likely increasingly underreported for all age groups, this decline indicates that children are disproportionately undercounted in reported COVID-19 cases.”
Other measures, however, have been rising slowly but steadily since the spring. New admissions of patients aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID, which were down to 0.13 per 100,000 population in early April, had climbed to 0.39 per 100,000 by July 7, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Emergency department visits continue to show the same upward trend, despite a small decline in early June. A COVID diagnosis was involved in just 0.5% of ED visits in children aged 0-11 years on March 26, but by July 6 the rate was 4.7%. Increases were not as high among older children: From 0.3% on March 26 to 2.5% on July 6 for those aged 12-15 and from 0.3% to 2.4% for 16- and 17-year-olds, according to the CDC.
U.S. allows pharmacists to prescribe Paxlovid directly
The Food and Drug Administration revised the drug’s emergency use authorization on July 6, letting state-licensed pharmacists screen patients and determine if they are eligible for Paxlovid, according to The Associated Press.
Previously, only doctors could prescribe the antiviral drug, the AP reported. With some limits, pharmacists can now prescribe the medication for patients who face high risks for severe COVID-19.
“The FDA recognizes the important role pharmacists have played and continue to play in combating this pandemic,” Patrizia Cavazzoni, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a statement.
“Since Paxlovid must be taken within 5 days after symptoms begin, authorizing state-licensed pharmacists to prescribe Paxlovid could expand access to timely treatment for some patients who are eligible to receive this drug for the treatment of COVID-19,” she said.
Tom Kraus, the vice president of government relations at the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, said in a statement that the organization was “pleased to see the FDA remove this barrier to patients’ access to this critical treatment.”
“Pharmacists have played a vital role in our pandemic response efforts and are well-positioned to help patients, particularly those in rural and underserved communities, benefit from this medication,” he said.
But some doctor’s groups questioned the FDA’s move. Jack Resneck Jr., MD, the president of the American Medical Association, said in a statement that prescribing Paxlovid “requires knowledge of a patient’s medical history, as well as clinical monitoring for side effects and follow-up care to determine whether a patient is improving” – requirements that are “far beyond a pharmacist’s scope and training.”
“In the fight against a virus that has killed more than a million people in the United States and is still extremely present and transmissible, patients will get the best, most comprehensive care from physician-led teams – teams that include pharmacists. But, whenever possible, prescribing decisions should be made by a physician with knowledge of a patient’s medical history and the ability to follow up. To ensure the best possible care for COVID-19 patients, we urge people who test positive to discuss treatment options with their physician, if they have one,” he said.
After testing positive for COVID-19, patients should first consider seeking care from their regular health care provider or locating a Test-to-Treat site in their area, the FDA said. Although the latest update allows pharmacists to prescribe Paxlovid, community pharmacies that don’t yet take part in the Test-to-Treat program can decide if they will offer the prescription service to patients.
Paxlovid is authorized to treat mild to moderate COVID-19 in adults and in kids ages 12 and older who weigh at least 88 pounds. Patients who report a positive at-home test are eligible for Paxlovid under the FDA authorization.
If patients want to seek a prescription directly from a pharmacist, they should bring electronic or printed health records from the past year, including their most recent reports of blood work, so the pharmacist can review for kidney or liver problems. Pharmacists can also get this information from the patient’s health care provider.
In addition, patients should bring a list of all medications they are taking, including over-the-counter medications, so the pharmacist can screen for drugs that can have serious interactions with Paxlovid.
Under the limits in the updated FDA authorization, pharmacists should refer patients for more screening if Paxlovid isn’t a good option or if there’s not enough information to find out how well their kidneys or liver works, as well as potential drug interactions.
Paxlovid is intended for people with COVID-19 who face the highest risks for serious disease, the AP reported, including older adults and those with health conditions such as heart disease, obesity, cancer, or diabetes. It isn’t recommended for people with severe kidney or liver problems. A course of treatment requires three pills twice a day for 5 days.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Food and Drug Administration revised the drug’s emergency use authorization on July 6, letting state-licensed pharmacists screen patients and determine if they are eligible for Paxlovid, according to The Associated Press.
Previously, only doctors could prescribe the antiviral drug, the AP reported. With some limits, pharmacists can now prescribe the medication for patients who face high risks for severe COVID-19.
“The FDA recognizes the important role pharmacists have played and continue to play in combating this pandemic,” Patrizia Cavazzoni, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a statement.
“Since Paxlovid must be taken within 5 days after symptoms begin, authorizing state-licensed pharmacists to prescribe Paxlovid could expand access to timely treatment for some patients who are eligible to receive this drug for the treatment of COVID-19,” she said.
Tom Kraus, the vice president of government relations at the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, said in a statement that the organization was “pleased to see the FDA remove this barrier to patients’ access to this critical treatment.”
“Pharmacists have played a vital role in our pandemic response efforts and are well-positioned to help patients, particularly those in rural and underserved communities, benefit from this medication,” he said.
But some doctor’s groups questioned the FDA’s move. Jack Resneck Jr., MD, the president of the American Medical Association, said in a statement that prescribing Paxlovid “requires knowledge of a patient’s medical history, as well as clinical monitoring for side effects and follow-up care to determine whether a patient is improving” – requirements that are “far beyond a pharmacist’s scope and training.”
“In the fight against a virus that has killed more than a million people in the United States and is still extremely present and transmissible, patients will get the best, most comprehensive care from physician-led teams – teams that include pharmacists. But, whenever possible, prescribing decisions should be made by a physician with knowledge of a patient’s medical history and the ability to follow up. To ensure the best possible care for COVID-19 patients, we urge people who test positive to discuss treatment options with their physician, if they have one,” he said.
After testing positive for COVID-19, patients should first consider seeking care from their regular health care provider or locating a Test-to-Treat site in their area, the FDA said. Although the latest update allows pharmacists to prescribe Paxlovid, community pharmacies that don’t yet take part in the Test-to-Treat program can decide if they will offer the prescription service to patients.
Paxlovid is authorized to treat mild to moderate COVID-19 in adults and in kids ages 12 and older who weigh at least 88 pounds. Patients who report a positive at-home test are eligible for Paxlovid under the FDA authorization.
If patients want to seek a prescription directly from a pharmacist, they should bring electronic or printed health records from the past year, including their most recent reports of blood work, so the pharmacist can review for kidney or liver problems. Pharmacists can also get this information from the patient’s health care provider.
In addition, patients should bring a list of all medications they are taking, including over-the-counter medications, so the pharmacist can screen for drugs that can have serious interactions with Paxlovid.
Under the limits in the updated FDA authorization, pharmacists should refer patients for more screening if Paxlovid isn’t a good option or if there’s not enough information to find out how well their kidneys or liver works, as well as potential drug interactions.
Paxlovid is intended for people with COVID-19 who face the highest risks for serious disease, the AP reported, including older adults and those with health conditions such as heart disease, obesity, cancer, or diabetes. It isn’t recommended for people with severe kidney or liver problems. A course of treatment requires three pills twice a day for 5 days.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Food and Drug Administration revised the drug’s emergency use authorization on July 6, letting state-licensed pharmacists screen patients and determine if they are eligible for Paxlovid, according to The Associated Press.
Previously, only doctors could prescribe the antiviral drug, the AP reported. With some limits, pharmacists can now prescribe the medication for patients who face high risks for severe COVID-19.
“The FDA recognizes the important role pharmacists have played and continue to play in combating this pandemic,” Patrizia Cavazzoni, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a statement.
“Since Paxlovid must be taken within 5 days after symptoms begin, authorizing state-licensed pharmacists to prescribe Paxlovid could expand access to timely treatment for some patients who are eligible to receive this drug for the treatment of COVID-19,” she said.
Tom Kraus, the vice president of government relations at the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, said in a statement that the organization was “pleased to see the FDA remove this barrier to patients’ access to this critical treatment.”
“Pharmacists have played a vital role in our pandemic response efforts and are well-positioned to help patients, particularly those in rural and underserved communities, benefit from this medication,” he said.
But some doctor’s groups questioned the FDA’s move. Jack Resneck Jr., MD, the president of the American Medical Association, said in a statement that prescribing Paxlovid “requires knowledge of a patient’s medical history, as well as clinical monitoring for side effects and follow-up care to determine whether a patient is improving” – requirements that are “far beyond a pharmacist’s scope and training.”
“In the fight against a virus that has killed more than a million people in the United States and is still extremely present and transmissible, patients will get the best, most comprehensive care from physician-led teams – teams that include pharmacists. But, whenever possible, prescribing decisions should be made by a physician with knowledge of a patient’s medical history and the ability to follow up. To ensure the best possible care for COVID-19 patients, we urge people who test positive to discuss treatment options with their physician, if they have one,” he said.
After testing positive for COVID-19, patients should first consider seeking care from their regular health care provider or locating a Test-to-Treat site in their area, the FDA said. Although the latest update allows pharmacists to prescribe Paxlovid, community pharmacies that don’t yet take part in the Test-to-Treat program can decide if they will offer the prescription service to patients.
Paxlovid is authorized to treat mild to moderate COVID-19 in adults and in kids ages 12 and older who weigh at least 88 pounds. Patients who report a positive at-home test are eligible for Paxlovid under the FDA authorization.
If patients want to seek a prescription directly from a pharmacist, they should bring electronic or printed health records from the past year, including their most recent reports of blood work, so the pharmacist can review for kidney or liver problems. Pharmacists can also get this information from the patient’s health care provider.
In addition, patients should bring a list of all medications they are taking, including over-the-counter medications, so the pharmacist can screen for drugs that can have serious interactions with Paxlovid.
Under the limits in the updated FDA authorization, pharmacists should refer patients for more screening if Paxlovid isn’t a good option or if there’s not enough information to find out how well their kidneys or liver works, as well as potential drug interactions.
Paxlovid is intended for people with COVID-19 who face the highest risks for serious disease, the AP reported, including older adults and those with health conditions such as heart disease, obesity, cancer, or diabetes. It isn’t recommended for people with severe kidney or liver problems. A course of treatment requires three pills twice a day for 5 days.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
CDC recommends high-dose flu vaccines for seniors
In an online statement Fluzone High-Dose Quadrivalent, Flublok Quadrivalent, and Fluad Quadrivalent flu vaccines are among those specified in the release.
The organization says that these higher-dose vaccines may be more effective for the aging population, who often have difficulty mounting a strong enough immune response to protect themselves against the flu virus. People older than 65 years struggle the most during flu season and have the highest proportion of hospitalizations and deaths from flu, according to the release.
But the CDC believes that higher-dose vaccines have the potential to better protect against that danger. One study, from The New England Journal of Medicine, reported that high-dose/adjuvanted vaccines prevented flu in older patients 24% better than did lower-dose/nonadjuvanted vaccines.
These types of vaccines work by creating a larger immune response than a standard vaccine dose. In particular, adjuvanted vaccines contain an extra ingredient within them that helps the immune system produce a stronger reaction to the vaccine. These may be things like aluminum salts, which signal the body to respond faster. Higher-dose vaccines similarly promote a stronger immune response by having more particles of the target virus in their mixture. In theory, this means the body will create an enhanced response to the vaccine. For example, a higher-dose vaccine may quadruple the amount of antigens, compared with the standard dose.
The hope is that this recommendation may increase vaccine use across the board, says José Romero, MD, the director of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases. As quoted in the CDC announcement, Dr. Romero said that this may help reduce racial inequities in access to flu vaccines. A 2019 meta-analysis concluded that Black and Hispanic people are around 30%-40% less likely to get the flu vaccine. So increasing the access to this medication “could help reduce health disparities by making these vaccines more available to racial and ethnic minority groups,” said Dr. Romero.
The decision, spearheaded by CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, follows recommendations from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which presented on this topic during a June 22 meeting. It is now part of official CDC policy and will continue to be developed as the 2022-2023 flu season approaches.
In addition, the organization says they’ll reveal more details for their plan later this summer, in their Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR). For now, seniors should know that they should try to get the recommended high-dose vaccines, but if they can’t, then a standard dose of whatever their provider has on hand will do.
At this point, there is still no specific vaccine recommendation for people aged under 65 years. The CDC historically avoids specifying one type of vaccine over another and says each should still be effective in younger patients.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In an online statement Fluzone High-Dose Quadrivalent, Flublok Quadrivalent, and Fluad Quadrivalent flu vaccines are among those specified in the release.
The organization says that these higher-dose vaccines may be more effective for the aging population, who often have difficulty mounting a strong enough immune response to protect themselves against the flu virus. People older than 65 years struggle the most during flu season and have the highest proportion of hospitalizations and deaths from flu, according to the release.
But the CDC believes that higher-dose vaccines have the potential to better protect against that danger. One study, from The New England Journal of Medicine, reported that high-dose/adjuvanted vaccines prevented flu in older patients 24% better than did lower-dose/nonadjuvanted vaccines.
These types of vaccines work by creating a larger immune response than a standard vaccine dose. In particular, adjuvanted vaccines contain an extra ingredient within them that helps the immune system produce a stronger reaction to the vaccine. These may be things like aluminum salts, which signal the body to respond faster. Higher-dose vaccines similarly promote a stronger immune response by having more particles of the target virus in their mixture. In theory, this means the body will create an enhanced response to the vaccine. For example, a higher-dose vaccine may quadruple the amount of antigens, compared with the standard dose.
The hope is that this recommendation may increase vaccine use across the board, says José Romero, MD, the director of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases. As quoted in the CDC announcement, Dr. Romero said that this may help reduce racial inequities in access to flu vaccines. A 2019 meta-analysis concluded that Black and Hispanic people are around 30%-40% less likely to get the flu vaccine. So increasing the access to this medication “could help reduce health disparities by making these vaccines more available to racial and ethnic minority groups,” said Dr. Romero.
The decision, spearheaded by CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, follows recommendations from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which presented on this topic during a June 22 meeting. It is now part of official CDC policy and will continue to be developed as the 2022-2023 flu season approaches.
In addition, the organization says they’ll reveal more details for their plan later this summer, in their Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR). For now, seniors should know that they should try to get the recommended high-dose vaccines, but if they can’t, then a standard dose of whatever their provider has on hand will do.
At this point, there is still no specific vaccine recommendation for people aged under 65 years. The CDC historically avoids specifying one type of vaccine over another and says each should still be effective in younger patients.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In an online statement Fluzone High-Dose Quadrivalent, Flublok Quadrivalent, and Fluad Quadrivalent flu vaccines are among those specified in the release.
The organization says that these higher-dose vaccines may be more effective for the aging population, who often have difficulty mounting a strong enough immune response to protect themselves against the flu virus. People older than 65 years struggle the most during flu season and have the highest proportion of hospitalizations and deaths from flu, according to the release.
But the CDC believes that higher-dose vaccines have the potential to better protect against that danger. One study, from The New England Journal of Medicine, reported that high-dose/adjuvanted vaccines prevented flu in older patients 24% better than did lower-dose/nonadjuvanted vaccines.
These types of vaccines work by creating a larger immune response than a standard vaccine dose. In particular, adjuvanted vaccines contain an extra ingredient within them that helps the immune system produce a stronger reaction to the vaccine. These may be things like aluminum salts, which signal the body to respond faster. Higher-dose vaccines similarly promote a stronger immune response by having more particles of the target virus in their mixture. In theory, this means the body will create an enhanced response to the vaccine. For example, a higher-dose vaccine may quadruple the amount of antigens, compared with the standard dose.
The hope is that this recommendation may increase vaccine use across the board, says José Romero, MD, the director of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases. As quoted in the CDC announcement, Dr. Romero said that this may help reduce racial inequities in access to flu vaccines. A 2019 meta-analysis concluded that Black and Hispanic people are around 30%-40% less likely to get the flu vaccine. So increasing the access to this medication “could help reduce health disparities by making these vaccines more available to racial and ethnic minority groups,” said Dr. Romero.
The decision, spearheaded by CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, follows recommendations from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which presented on this topic during a June 22 meeting. It is now part of official CDC policy and will continue to be developed as the 2022-2023 flu season approaches.
In addition, the organization says they’ll reveal more details for their plan later this summer, in their Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR). For now, seniors should know that they should try to get the recommended high-dose vaccines, but if they can’t, then a standard dose of whatever their provider has on hand will do.
At this point, there is still no specific vaccine recommendation for people aged under 65 years. The CDC historically avoids specifying one type of vaccine over another and says each should still be effective in younger patients.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA warns of increased risk of death with CLL, lymphoma drug
Duvelisib was approved in 2018 to treat adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) who had received at least two prior therapies that did not work or stopped working.
However, more recent 5-year overall survival results from the randomized phase 3 DUO clinical trial found a possible increased risk of death with duvelisib compared with another drug used to treat leukemia and lymphoma, according to an FDA Drug Safety Communication.
“The trial also found Copiktra was associated with a higher risk of serious side effects, including infections, diarrhea, inflammation of the intestines and lungs, skin reactions, and high liver enzyme levels in the blood,” states the warning, which advises prescribers to weigh the risks and benefits of continued use versus use of other treatments.
More specifically, median 5-year overall survival among 319 patients with CLL or SLL in the DUO trial was 52.3 months with duvelisib versus 63.3 months with the monoclonal antibody ofatumumab (hazard ratio, 1.09 overall and 1.06 among patients who received at least two prior lines of therapy).
Serious adverse events of grade 3 or higher were also more common in those treated with duvelisib.
Of note, in April, the FDA also announced it was withdrawing approval of the relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma indication for duvelisib, following a voluntary request by the drug manufacturer, Secura Bio Inc.
A public meeting will be scheduled to discuss the findings of the trial and whether the drug should continue to be prescribed.
This FDA warning follows the agency’s June 1 withdrawal of approval for umbralisib (Ukoniq), another PI3 kinase inhibitor, following an investigation into a “possible increased risk of death.”
As reported by Medscape, umbralisib had received accelerated approval in February 2021 to treat adults with relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma following at least one prior therapy and those with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma who had received at least three prior therapies.
“These safety findings were similar for other medicines in the same PI3 kinase inhibitor class, which were discussed at an advisory committee meeting of non-FDA experts in April 2022,” according to the FDA warning.
The FDA urges patients and health care professionals to report side effects involving duvelisib or other medicines to the FDA MedWatch program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Duvelisib was approved in 2018 to treat adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) who had received at least two prior therapies that did not work or stopped working.
However, more recent 5-year overall survival results from the randomized phase 3 DUO clinical trial found a possible increased risk of death with duvelisib compared with another drug used to treat leukemia and lymphoma, according to an FDA Drug Safety Communication.
“The trial also found Copiktra was associated with a higher risk of serious side effects, including infections, diarrhea, inflammation of the intestines and lungs, skin reactions, and high liver enzyme levels in the blood,” states the warning, which advises prescribers to weigh the risks and benefits of continued use versus use of other treatments.
More specifically, median 5-year overall survival among 319 patients with CLL or SLL in the DUO trial was 52.3 months with duvelisib versus 63.3 months with the monoclonal antibody ofatumumab (hazard ratio, 1.09 overall and 1.06 among patients who received at least two prior lines of therapy).
Serious adverse events of grade 3 or higher were also more common in those treated with duvelisib.
Of note, in April, the FDA also announced it was withdrawing approval of the relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma indication for duvelisib, following a voluntary request by the drug manufacturer, Secura Bio Inc.
A public meeting will be scheduled to discuss the findings of the trial and whether the drug should continue to be prescribed.
This FDA warning follows the agency’s June 1 withdrawal of approval for umbralisib (Ukoniq), another PI3 kinase inhibitor, following an investigation into a “possible increased risk of death.”
As reported by Medscape, umbralisib had received accelerated approval in February 2021 to treat adults with relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma following at least one prior therapy and those with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma who had received at least three prior therapies.
“These safety findings were similar for other medicines in the same PI3 kinase inhibitor class, which were discussed at an advisory committee meeting of non-FDA experts in April 2022,” according to the FDA warning.
The FDA urges patients and health care professionals to report side effects involving duvelisib or other medicines to the FDA MedWatch program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Duvelisib was approved in 2018 to treat adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) who had received at least two prior therapies that did not work or stopped working.
However, more recent 5-year overall survival results from the randomized phase 3 DUO clinical trial found a possible increased risk of death with duvelisib compared with another drug used to treat leukemia and lymphoma, according to an FDA Drug Safety Communication.
“The trial also found Copiktra was associated with a higher risk of serious side effects, including infections, diarrhea, inflammation of the intestines and lungs, skin reactions, and high liver enzyme levels in the blood,” states the warning, which advises prescribers to weigh the risks and benefits of continued use versus use of other treatments.
More specifically, median 5-year overall survival among 319 patients with CLL or SLL in the DUO trial was 52.3 months with duvelisib versus 63.3 months with the monoclonal antibody ofatumumab (hazard ratio, 1.09 overall and 1.06 among patients who received at least two prior lines of therapy).
Serious adverse events of grade 3 or higher were also more common in those treated with duvelisib.
Of note, in April, the FDA also announced it was withdrawing approval of the relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma indication for duvelisib, following a voluntary request by the drug manufacturer, Secura Bio Inc.
A public meeting will be scheduled to discuss the findings of the trial and whether the drug should continue to be prescribed.
This FDA warning follows the agency’s June 1 withdrawal of approval for umbralisib (Ukoniq), another PI3 kinase inhibitor, following an investigation into a “possible increased risk of death.”
As reported by Medscape, umbralisib had received accelerated approval in February 2021 to treat adults with relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma following at least one prior therapy and those with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma who had received at least three prior therapies.
“These safety findings were similar for other medicines in the same PI3 kinase inhibitor class, which were discussed at an advisory committee meeting of non-FDA experts in April 2022,” according to the FDA warning.
The FDA urges patients and health care professionals to report side effects involving duvelisib or other medicines to the FDA MedWatch program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA Class I recall: Batteries for CARESCAPE 2860 Ventilator
A total of 1,533 complaints allege that the batteries are draining much faster than expected, prompting manufacturer GE Healthcare to initiate the recall. There have been no injuries, and no deaths associated with the use of this device, according to an FDA corrected announcement.
Health care personnel and those patients who receive breathing support with these ventilators should be cautious about using CARESCAPE battery products moving forward, the agency said.
This type of ventilator is primarily powered by plugging into a wall outlet, but it has the capability to operate on backup batteries. These batteries are not solely for emergency situations such as power outages, but are also for routine situations such as transporting a patient within the hospital. GE Healthcare supplies these backup batteries with the ventilator, and sells replacements when they run out.
However, if the ventilator loses power because of battery malfunction, the patient may lose access to oxygen, leading to hypoxia, which can lead to brain injury and death. Therefore, if these batteries drain quicker than anticipated, it may put the patient at risk.
To prevent this danger, GE Healthcare recommends customers perform a battery performance test after they see this notice and every 3 months following. Consumers should take extra precaution and make sure their batteries are charged following a long period of inactivity. If the device is inactive for a while, the company says users should keep it plugged in to avoid draining the battery. Batteries should be replaced at a minimum of every 3 years.
When these devices are still plugged into the wall, they’re safe to use, according to the FDA. But when using the backup power source, clinicians should make sure to have alternative routes for breathing support on hand, such as with a bag-valve mask system.
There are 4,222 of these possibly defective batteries currently on the market. They were distributed from April 2, 2019, through April 18 of this year, when GE Healthcare stopped distributing these products and began the recall process. Any issues with these products should be reported to the FDA’s MedWatch database or by sending a medical device notification acknowledgment response to GE at the email address listed at the bottom of the recall announcement.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 7/6/22.
A total of 1,533 complaints allege that the batteries are draining much faster than expected, prompting manufacturer GE Healthcare to initiate the recall. There have been no injuries, and no deaths associated with the use of this device, according to an FDA corrected announcement.
Health care personnel and those patients who receive breathing support with these ventilators should be cautious about using CARESCAPE battery products moving forward, the agency said.
This type of ventilator is primarily powered by plugging into a wall outlet, but it has the capability to operate on backup batteries. These batteries are not solely for emergency situations such as power outages, but are also for routine situations such as transporting a patient within the hospital. GE Healthcare supplies these backup batteries with the ventilator, and sells replacements when they run out.
However, if the ventilator loses power because of battery malfunction, the patient may lose access to oxygen, leading to hypoxia, which can lead to brain injury and death. Therefore, if these batteries drain quicker than anticipated, it may put the patient at risk.
To prevent this danger, GE Healthcare recommends customers perform a battery performance test after they see this notice and every 3 months following. Consumers should take extra precaution and make sure their batteries are charged following a long period of inactivity. If the device is inactive for a while, the company says users should keep it plugged in to avoid draining the battery. Batteries should be replaced at a minimum of every 3 years.
When these devices are still plugged into the wall, they’re safe to use, according to the FDA. But when using the backup power source, clinicians should make sure to have alternative routes for breathing support on hand, such as with a bag-valve mask system.
There are 4,222 of these possibly defective batteries currently on the market. They were distributed from April 2, 2019, through April 18 of this year, when GE Healthcare stopped distributing these products and began the recall process. Any issues with these products should be reported to the FDA’s MedWatch database or by sending a medical device notification acknowledgment response to GE at the email address listed at the bottom of the recall announcement.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 7/6/22.
A total of 1,533 complaints allege that the batteries are draining much faster than expected, prompting manufacturer GE Healthcare to initiate the recall. There have been no injuries, and no deaths associated with the use of this device, according to an FDA corrected announcement.
Health care personnel and those patients who receive breathing support with these ventilators should be cautious about using CARESCAPE battery products moving forward, the agency said.
This type of ventilator is primarily powered by plugging into a wall outlet, but it has the capability to operate on backup batteries. These batteries are not solely for emergency situations such as power outages, but are also for routine situations such as transporting a patient within the hospital. GE Healthcare supplies these backup batteries with the ventilator, and sells replacements when they run out.
However, if the ventilator loses power because of battery malfunction, the patient may lose access to oxygen, leading to hypoxia, which can lead to brain injury and death. Therefore, if these batteries drain quicker than anticipated, it may put the patient at risk.
To prevent this danger, GE Healthcare recommends customers perform a battery performance test after they see this notice and every 3 months following. Consumers should take extra precaution and make sure their batteries are charged following a long period of inactivity. If the device is inactive for a while, the company says users should keep it plugged in to avoid draining the battery. Batteries should be replaced at a minimum of every 3 years.
When these devices are still plugged into the wall, they’re safe to use, according to the FDA. But when using the backup power source, clinicians should make sure to have alternative routes for breathing support on hand, such as with a bag-valve mask system.
There are 4,222 of these possibly defective batteries currently on the market. They were distributed from April 2, 2019, through April 18 of this year, when GE Healthcare stopped distributing these products and began the recall process. Any issues with these products should be reported to the FDA’s MedWatch database or by sending a medical device notification acknowledgment response to GE at the email address listed at the bottom of the recall announcement.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 7/6/22.
Children and COVID: Vaccination off to slow start for the newly eligible
New cases of COVID-19 continue to drop among children, but the vaccination effort in those under age 5 years began with something less than a bang.
In the first 2 days after their respective approvals, almost 99,000 children aged 5-11 years and over 675,000 children aged 12-15 were vaccinated, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Children aged 0-4 years represent almost 6% of the overall population, compared with 8.7% for the 5- to 11-year-olds and 5.1% for those aged 12-15.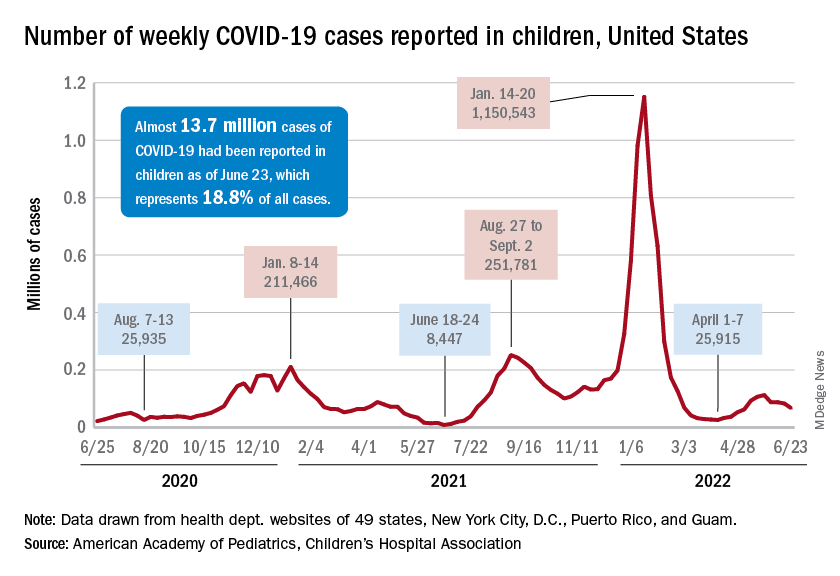
The recent decline in new cases over the past 4 weeks and the substantial decline since the Omicron surge could be a factor in the lack of response, but it is worth noting that the almost 68,000 new child cases reported in the past week, June 17-23, are “far higher than 1 year ago, June 24, 2021, when 8,400 child cases were reported,” the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID report.
That total for June 17-23 was 19% lower than the previous week and down by 40% since new cases hit a spring peak of 112,000 in late May. Regionally, new cases were down in the Midwest, the South, and the West, the AAP/CHA report showed, but the Northeast saw a small increase, which could be a signal of things to come for the summer.
The decline in new cases, however, has not been accompanied by decreases in hospitalizations or emergency department visits. New admissions of children aged 0-17 with confirmed COVID were at 0.31 per 100,000 population on June 24 after reaching that level on June 15, so no drop-off has occurred yet but there are signs of leveling off, based on CDC data.
The ED visit rates have been fairly steady through June, although COVID-related visits were up to 3.4% of all ED visits on June 22 for children aged 0-11 years, after being below 3% for the first 2 weeks of the month. The rate for children aged 12-15 has been between 1.6% and 1.9% for the past 3 weeks and the rate for 16- and 17-year-olds has been hovering between 1.7% and 2.2% for most of June, after going as high as 2.7% in late May, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
New cases of COVID-19 continue to drop among children, but the vaccination effort in those under age 5 years began with something less than a bang.
In the first 2 days after their respective approvals, almost 99,000 children aged 5-11 years and over 675,000 children aged 12-15 were vaccinated, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Children aged 0-4 years represent almost 6% of the overall population, compared with 8.7% for the 5- to 11-year-olds and 5.1% for those aged 12-15.
The recent decline in new cases over the past 4 weeks and the substantial decline since the Omicron surge could be a factor in the lack of response, but it is worth noting that the almost 68,000 new child cases reported in the past week, June 17-23, are “far higher than 1 year ago, June 24, 2021, when 8,400 child cases were reported,” the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID report.
That total for June 17-23 was 19% lower than the previous week and down by 40% since new cases hit a spring peak of 112,000 in late May. Regionally, new cases were down in the Midwest, the South, and the West, the AAP/CHA report showed, but the Northeast saw a small increase, which could be a signal of things to come for the summer.
The decline in new cases, however, has not been accompanied by decreases in hospitalizations or emergency department visits. New admissions of children aged 0-17 with confirmed COVID were at 0.31 per 100,000 population on June 24 after reaching that level on June 15, so no drop-off has occurred yet but there are signs of leveling off, based on CDC data.
The ED visit rates have been fairly steady through June, although COVID-related visits were up to 3.4% of all ED visits on June 22 for children aged 0-11 years, after being below 3% for the first 2 weeks of the month. The rate for children aged 12-15 has been between 1.6% and 1.9% for the past 3 weeks and the rate for 16- and 17-year-olds has been hovering between 1.7% and 2.2% for most of June, after going as high as 2.7% in late May, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
New cases of COVID-19 continue to drop among children, but the vaccination effort in those under age 5 years began with something less than a bang.
In the first 2 days after their respective approvals, almost 99,000 children aged 5-11 years and over 675,000 children aged 12-15 were vaccinated, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Children aged 0-4 years represent almost 6% of the overall population, compared with 8.7% for the 5- to 11-year-olds and 5.1% for those aged 12-15.
The recent decline in new cases over the past 4 weeks and the substantial decline since the Omicron surge could be a factor in the lack of response, but it is worth noting that the almost 68,000 new child cases reported in the past week, June 17-23, are “far higher than 1 year ago, June 24, 2021, when 8,400 child cases were reported,” the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID report.
That total for June 17-23 was 19% lower than the previous week and down by 40% since new cases hit a spring peak of 112,000 in late May. Regionally, new cases were down in the Midwest, the South, and the West, the AAP/CHA report showed, but the Northeast saw a small increase, which could be a signal of things to come for the summer.
The decline in new cases, however, has not been accompanied by decreases in hospitalizations or emergency department visits. New admissions of children aged 0-17 with confirmed COVID were at 0.31 per 100,000 population on June 24 after reaching that level on June 15, so no drop-off has occurred yet but there are signs of leveling off, based on CDC data.
The ED visit rates have been fairly steady through June, although COVID-related visits were up to 3.4% of all ED visits on June 22 for children aged 0-11 years, after being below 3% for the first 2 weeks of the month. The rate for children aged 12-15 has been between 1.6% and 1.9% for the past 3 weeks and the rate for 16- and 17-year-olds has been hovering between 1.7% and 2.2% for most of June, after going as high as 2.7% in late May, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
FDA Volara ventilator warning upgraded to full recall
The Food and Drug Administration has changed the warning about the Volara system to a Class I recall, the most severe level of recall, which is reserved for products that may cause injury or death. At the time of the warning, one injury had been associated with the product; as of June 23, there have been two deaths and one complaint, according to the FDA’s release.
Normally, the Volara system is used for breathing treatments that are administered at home. The medical device company that manufactures it, Baxter International, says the product is designed to help expand the airways and clear mucus for patients who use it. But because of recent product malfunctions, patients are at risk of choking on mucus, developing an infection in their lungs that cuts off their ability to take in oxygen, or in the worst cases, developing brain injury and death.
The risk is especially high because Volara is designed to be used in outpatient settings, not in the hospital under the supervision of a health care professional. It’s supposed to require less supervision than other ventilators. But if there is a problem with the device, or if it’s not connected properly, or if no one is available to assist, people are more likely to be harmed.
People who use the Volara ventilator system at home or people who assist in the use of it should be on alert for these problems. But the FDA advises that patients continue using the therapy if the device has been recommended by a doctor. The device should be used with extra precaution, and patients should be monitored for signs of distress, the release says. Problems while using the device should be reported to the FDA’s Medwatch database.
In addition to these reports, Baxter and its subsidiary company Hillrom say they will update the instructions for the device and will dispatch trainers to make home visits for users. The contact information for the company, as well as additional resources, are listed at the bottom of the release.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has changed the warning about the Volara system to a Class I recall, the most severe level of recall, which is reserved for products that may cause injury or death. At the time of the warning, one injury had been associated with the product; as of June 23, there have been two deaths and one complaint, according to the FDA’s release.
Normally, the Volara system is used for breathing treatments that are administered at home. The medical device company that manufactures it, Baxter International, says the product is designed to help expand the airways and clear mucus for patients who use it. But because of recent product malfunctions, patients are at risk of choking on mucus, developing an infection in their lungs that cuts off their ability to take in oxygen, or in the worst cases, developing brain injury and death.
The risk is especially high because Volara is designed to be used in outpatient settings, not in the hospital under the supervision of a health care professional. It’s supposed to require less supervision than other ventilators. But if there is a problem with the device, or if it’s not connected properly, or if no one is available to assist, people are more likely to be harmed.
People who use the Volara ventilator system at home or people who assist in the use of it should be on alert for these problems. But the FDA advises that patients continue using the therapy if the device has been recommended by a doctor. The device should be used with extra precaution, and patients should be monitored for signs of distress, the release says. Problems while using the device should be reported to the FDA’s Medwatch database.
In addition to these reports, Baxter and its subsidiary company Hillrom say they will update the instructions for the device and will dispatch trainers to make home visits for users. The contact information for the company, as well as additional resources, are listed at the bottom of the release.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has changed the warning about the Volara system to a Class I recall, the most severe level of recall, which is reserved for products that may cause injury or death. At the time of the warning, one injury had been associated with the product; as of June 23, there have been two deaths and one complaint, according to the FDA’s release.
Normally, the Volara system is used for breathing treatments that are administered at home. The medical device company that manufactures it, Baxter International, says the product is designed to help expand the airways and clear mucus for patients who use it. But because of recent product malfunctions, patients are at risk of choking on mucus, developing an infection in their lungs that cuts off their ability to take in oxygen, or in the worst cases, developing brain injury and death.
The risk is especially high because Volara is designed to be used in outpatient settings, not in the hospital under the supervision of a health care professional. It’s supposed to require less supervision than other ventilators. But if there is a problem with the device, or if it’s not connected properly, or if no one is available to assist, people are more likely to be harmed.
People who use the Volara ventilator system at home or people who assist in the use of it should be on alert for these problems. But the FDA advises that patients continue using the therapy if the device has been recommended by a doctor. The device should be used with extra precaution, and patients should be monitored for signs of distress, the release says. Problems while using the device should be reported to the FDA’s Medwatch database.
In addition to these reports, Baxter and its subsidiary company Hillrom say they will update the instructions for the device and will dispatch trainers to make home visits for users. The contact information for the company, as well as additional resources, are listed at the bottom of the release.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.