User login
Children and COVID: ED visits and new admissions change course
New child cases of COVID-19 made at least a temporary transition from slow increase to decrease, and emergency department visits and new admissions seem to be following a downward trend.
, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association. For some historical perspective, the latest weekly count falls below last year’s Delta surge figure of 121,000 (Aug. 6-12) but above the summer 2020 total of 26,000 (Aug. 7-13).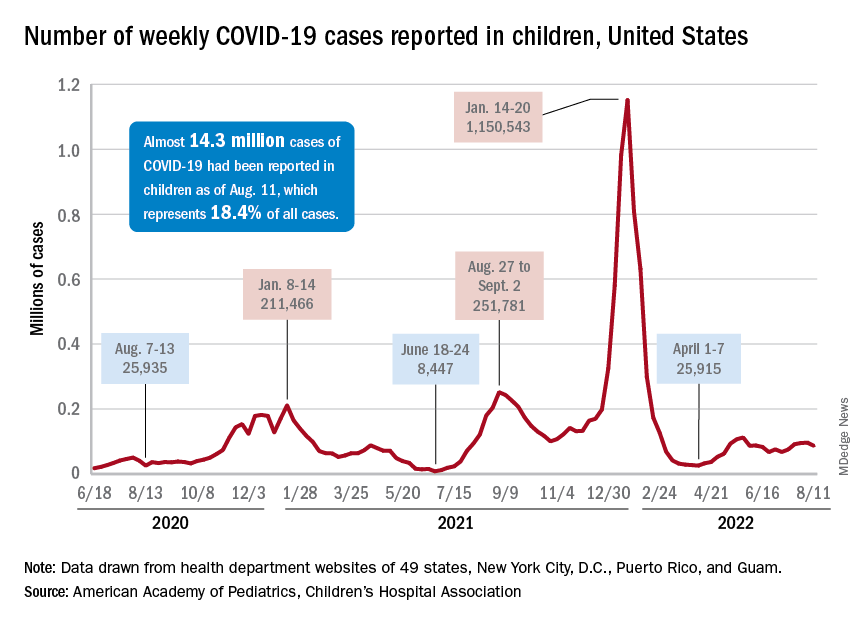
Measures of serious illness finally head downward
The prolonged rise in ED visits and new admissions over the last 5 months, which continued even through late spring when cases were declining, seems to have peaked, CDC data suggest.
That upward trend, driven largely by continued increases among younger children, peaked in late July, when 6.7% of all ED visits for children aged 0-11 years involved diagnosed COVID-19. The corresponding peaks for older children occurred around the same time but were only about half as high: 3.4% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 3.6% for those aged 16-17, the CDC reported.
The data for new admissions present a similar scenario: an increase starting in mid-April that continued unabated into late July despite the decline in new cases. By the time admissions among children aged 0-17 years peaked at 0.46 per 100,000 population in late July, they had reached the same level seen during the Delta surge. By Aug. 7, the rate of new hospitalizations was down to 0.42 per 100,000, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The vaccine is ready for all students, but …
As children all over the country start or get ready to start a new school year, the only large-scale student vaccine mandate belongs to the District of Columbia. California has a mandate pending, but it will not go into effect until after July 1, 2023. There are, however, 20 states that have banned vaccine mandates for students, according to the National Academy for State Health Policy.
Nonmandated vaccination of the youngest children against COVID-19 continues to be slow. In the approximately 7 weeks (June 19 to Aug. 9) since the vaccine was approved for use in children younger than 5 years, just 4.4% of that age group has received at least one dose and 0.7% are fully vaccinated. Among those aged 5-11 years, who have been vaccine-eligible since early November of last year, 37.6% have received at least one dose and 30.2% are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
New child cases of COVID-19 made at least a temporary transition from slow increase to decrease, and emergency department visits and new admissions seem to be following a downward trend.
, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association. For some historical perspective, the latest weekly count falls below last year’s Delta surge figure of 121,000 (Aug. 6-12) but above the summer 2020 total of 26,000 (Aug. 7-13).
Measures of serious illness finally head downward
The prolonged rise in ED visits and new admissions over the last 5 months, which continued even through late spring when cases were declining, seems to have peaked, CDC data suggest.
That upward trend, driven largely by continued increases among younger children, peaked in late July, when 6.7% of all ED visits for children aged 0-11 years involved diagnosed COVID-19. The corresponding peaks for older children occurred around the same time but were only about half as high: 3.4% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 3.6% for those aged 16-17, the CDC reported.
The data for new admissions present a similar scenario: an increase starting in mid-April that continued unabated into late July despite the decline in new cases. By the time admissions among children aged 0-17 years peaked at 0.46 per 100,000 population in late July, they had reached the same level seen during the Delta surge. By Aug. 7, the rate of new hospitalizations was down to 0.42 per 100,000, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The vaccine is ready for all students, but …
As children all over the country start or get ready to start a new school year, the only large-scale student vaccine mandate belongs to the District of Columbia. California has a mandate pending, but it will not go into effect until after July 1, 2023. There are, however, 20 states that have banned vaccine mandates for students, according to the National Academy for State Health Policy.
Nonmandated vaccination of the youngest children against COVID-19 continues to be slow. In the approximately 7 weeks (June 19 to Aug. 9) since the vaccine was approved for use in children younger than 5 years, just 4.4% of that age group has received at least one dose and 0.7% are fully vaccinated. Among those aged 5-11 years, who have been vaccine-eligible since early November of last year, 37.6% have received at least one dose and 30.2% are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
New child cases of COVID-19 made at least a temporary transition from slow increase to decrease, and emergency department visits and new admissions seem to be following a downward trend.
, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association. For some historical perspective, the latest weekly count falls below last year’s Delta surge figure of 121,000 (Aug. 6-12) but above the summer 2020 total of 26,000 (Aug. 7-13).
Measures of serious illness finally head downward
The prolonged rise in ED visits and new admissions over the last 5 months, which continued even through late spring when cases were declining, seems to have peaked, CDC data suggest.
That upward trend, driven largely by continued increases among younger children, peaked in late July, when 6.7% of all ED visits for children aged 0-11 years involved diagnosed COVID-19. The corresponding peaks for older children occurred around the same time but were only about half as high: 3.4% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 3.6% for those aged 16-17, the CDC reported.
The data for new admissions present a similar scenario: an increase starting in mid-April that continued unabated into late July despite the decline in new cases. By the time admissions among children aged 0-17 years peaked at 0.46 per 100,000 population in late July, they had reached the same level seen during the Delta surge. By Aug. 7, the rate of new hospitalizations was down to 0.42 per 100,000, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The vaccine is ready for all students, but …
As children all over the country start or get ready to start a new school year, the only large-scale student vaccine mandate belongs to the District of Columbia. California has a mandate pending, but it will not go into effect until after July 1, 2023. There are, however, 20 states that have banned vaccine mandates for students, according to the National Academy for State Health Policy.
Nonmandated vaccination of the youngest children against COVID-19 continues to be slow. In the approximately 7 weeks (June 19 to Aug. 9) since the vaccine was approved for use in children younger than 5 years, just 4.4% of that age group has received at least one dose and 0.7% are fully vaccinated. Among those aged 5-11 years, who have been vaccine-eligible since early November of last year, 37.6% have received at least one dose and 30.2% are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
U.S. tops 10,000 confirmed monkeypox cases: CDC
The United States passed the 10,000 mark on Aug. 10, with the number climbing to 10,768 by the morning of Aug. 12, according to the latest CDC data. Monkeypox cases have been found in every state except Wyoming. New York (2,187), California (1,892), and Florida (1,053) have reported the most cases. So far, no monkeypox deaths have been reported in the United States.
The numbers are increasing, with 1,391 cases reported in the United States on Aug. 12 alone, by far the most in 1 day since the current outbreak began.
“We are still operating under a containment goal, although I know many states are starting to wonder if we’re shifting to more of a mitigation phase right now, given that our case counts are still rising rapidly,” Jennifer McQuiston, DVM, the CDC’s top monkeypox official, told a group of the agency’s advisers on Aug. 9, according to CBS News.
Since late July, the United States has reported more monkeypox cases than any other nation. After the United States, Spain has reported 5,162 cases, the United Kingdom 3,017, and France 2,423, according to the World Health Organization.
Globally, 31,655 cases have been recorded, with 5,108 of those cases coming in the last 7 days, according to the WHO. There have been 12 deaths attributed to monkeypox, with one coming in the last week.
The smallpox-like disease was first found in humans in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 1970 and has become more common in West and Central Africa. It began spreading to European and other Western nations in May 2022.
The WHO declared it a global public health emergency in late July, and the Biden administration declared it a national health emergency Aug. 4.
To fight the spread of monkeypox, the Biden administration is buying $26 million worth of SIGA Technologies Inc.’s IV version of the antiviral drug TPOXX, the company announced on Aug. 9.
U.S. health officials also modified monkeypox vaccine dosing instructions to stretch the supply of vaccine. Instead of sticking with a standard shot that would enter deep into tissue, the FDA now encourages a new way: just under the skin at one-fifth the usual dose.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The United States passed the 10,000 mark on Aug. 10, with the number climbing to 10,768 by the morning of Aug. 12, according to the latest CDC data. Monkeypox cases have been found in every state except Wyoming. New York (2,187), California (1,892), and Florida (1,053) have reported the most cases. So far, no monkeypox deaths have been reported in the United States.
The numbers are increasing, with 1,391 cases reported in the United States on Aug. 12 alone, by far the most in 1 day since the current outbreak began.
“We are still operating under a containment goal, although I know many states are starting to wonder if we’re shifting to more of a mitigation phase right now, given that our case counts are still rising rapidly,” Jennifer McQuiston, DVM, the CDC’s top monkeypox official, told a group of the agency’s advisers on Aug. 9, according to CBS News.
Since late July, the United States has reported more monkeypox cases than any other nation. After the United States, Spain has reported 5,162 cases, the United Kingdom 3,017, and France 2,423, according to the World Health Organization.
Globally, 31,655 cases have been recorded, with 5,108 of those cases coming in the last 7 days, according to the WHO. There have been 12 deaths attributed to monkeypox, with one coming in the last week.
The smallpox-like disease was first found in humans in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 1970 and has become more common in West and Central Africa. It began spreading to European and other Western nations in May 2022.
The WHO declared it a global public health emergency in late July, and the Biden administration declared it a national health emergency Aug. 4.
To fight the spread of monkeypox, the Biden administration is buying $26 million worth of SIGA Technologies Inc.’s IV version of the antiviral drug TPOXX, the company announced on Aug. 9.
U.S. health officials also modified monkeypox vaccine dosing instructions to stretch the supply of vaccine. Instead of sticking with a standard shot that would enter deep into tissue, the FDA now encourages a new way: just under the skin at one-fifth the usual dose.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The United States passed the 10,000 mark on Aug. 10, with the number climbing to 10,768 by the morning of Aug. 12, according to the latest CDC data. Monkeypox cases have been found in every state except Wyoming. New York (2,187), California (1,892), and Florida (1,053) have reported the most cases. So far, no monkeypox deaths have been reported in the United States.
The numbers are increasing, with 1,391 cases reported in the United States on Aug. 12 alone, by far the most in 1 day since the current outbreak began.
“We are still operating under a containment goal, although I know many states are starting to wonder if we’re shifting to more of a mitigation phase right now, given that our case counts are still rising rapidly,” Jennifer McQuiston, DVM, the CDC’s top monkeypox official, told a group of the agency’s advisers on Aug. 9, according to CBS News.
Since late July, the United States has reported more monkeypox cases than any other nation. After the United States, Spain has reported 5,162 cases, the United Kingdom 3,017, and France 2,423, according to the World Health Organization.
Globally, 31,655 cases have been recorded, with 5,108 of those cases coming in the last 7 days, according to the WHO. There have been 12 deaths attributed to monkeypox, with one coming in the last week.
The smallpox-like disease was first found in humans in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 1970 and has become more common in West and Central Africa. It began spreading to European and other Western nations in May 2022.
The WHO declared it a global public health emergency in late July, and the Biden administration declared it a national health emergency Aug. 4.
To fight the spread of monkeypox, the Biden administration is buying $26 million worth of SIGA Technologies Inc.’s IV version of the antiviral drug TPOXX, the company announced on Aug. 9.
U.S. health officials also modified monkeypox vaccine dosing instructions to stretch the supply of vaccine. Instead of sticking with a standard shot that would enter deep into tissue, the FDA now encourages a new way: just under the skin at one-fifth the usual dose.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA approves Enhertu (trastuzumab deruxtecan) for HER2 lung cancer
Patients with lung cancer now have another treatment option: If their tumors are found to carry HER2 mutations, they can now be treated with trastuzumab deruxtecan (Enhertu), a drug that specifically targets that defect.
This product is already approved for used in HER2-positive breast cancer and gastric cancer.
The FDA also approved companion diagnostic tests to detect HER2 mutations: Life Technologies Corporation’s Oncomine Dx Target Test for use in lung tissue and Guardant Health’s Guardant360 CDx for use on plasma samples. The agency notes that if no mutation is detected in a plasma specimen, the tumor tissue should be tested.
Specifically, the new indication is used in patients with unresectable or metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have activating HER2 (ERBB2) mutations, as detected by an FDA-approved test, and who have already received a prior systemic therapy.
About 3% of nonsquamous NSCLC tumors carry mutations in the HER2 gene, and they are associated with female sex, never-smokers, and a poor prognosis.
“HER2 mutant non–small cell lung cancer is an aggressive form of disease, which commonly affects young patients who have faced limited treatment options and a poor prognosis to date,” said Dave Fredrickson, executive vice-president of the oncology business unit at AstraZeneca.
The new approval “provides these patients with the opportunity to benefit from a targeted therapy and highlights the importance of testing for predictive markers, including HER2 in lung cancer, at the time of diagnosis to ensure patients receive the most appropriate treatment for their specific disease,” he commented in a company press release.
This is an accelerated approval, based on overall response rate data from the DESTINY-Lung02 phase 2 trial, the company noted. An interim efficacy analysis in a prespecified patient cohort showed that trastuzumab deruxtecan (at 5.4 mg/kg) demonstrated a confirmed overall response rate of 57.7% (n = 52; 95% confidence interval, 43.2%-71.3%) in patients with HER2-mutant unresectable or metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC who had received one prior systemic therapy as assessed by blinded independent central review. Complete responses were seen in 1.9% of patients (n = 1) and partial responses in 55.8% of patients (n = 29), with a median duration of response of 8.7 months (95% CI, 7.1-NE).
The FDA noted that for the 52 patients in the primary efficacy population of the DESTINY-Lung02 trial, the median age was 58 years (range, 30-78 years); 69% were female; and 79% were Asian, 12% were White, and 10% were of other races.
Clinical data welcomed by experts
Clinical data are already available from the DESTINY-Lung 01 trial, and the results were welcomed enthusiastically by experts when they were published in the New England Journal of Medicine earlier this year.
“These results establish the new standard of care for patients with NSCLC harboring HER2 mutations,” Antonio Passaro, MD, PhD, from the European Institute of Oncology IRCCS, Milan, and Solange Peters, MD, PhD, from Lausanne (Switzerland) University Hospital, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
This trial involved 91 patients, all treated with trastuzumab deruxtecan (at 6.4 mg/kg of body weight every 3 weeks). The median duration of treatment was 6.9 months, and the median follow-up was 13.1 months.
The results showed a 55% centrally confirmed objective response, and median duration of response was 9.3 months.
In addition, the investigators reported a median progression-free survival of 8.2 months and a median overall survival of almost 18 months, both of which they described as “encouraging” in this patient population.
However, the results also highlighted a problem with the drug in this patient population. Notably, 26% of patients experienced interstitial lung disease, which resulted in death in two patients. The drug was also withdrawn in 16 patients and interrupted in 8 patients because of this adverse event.
Editorialists Dr. Passaro and Dr. Peters described this finding as “a concern” and note that “the incidence of interstitial lung disease is significantly higher among patients with lung cancer than among those with breast or gastric cancers, which may indicate a role of smoking-related damage.”
They also highlighted the need for an “investigation of the clinical efficacy of a reduced dose of trastuzumab deruxtecan,” and so the dose was reduced for the DESTINY-Lung02 trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with lung cancer now have another treatment option: If their tumors are found to carry HER2 mutations, they can now be treated with trastuzumab deruxtecan (Enhertu), a drug that specifically targets that defect.
This product is already approved for used in HER2-positive breast cancer and gastric cancer.
The FDA also approved companion diagnostic tests to detect HER2 mutations: Life Technologies Corporation’s Oncomine Dx Target Test for use in lung tissue and Guardant Health’s Guardant360 CDx for use on plasma samples. The agency notes that if no mutation is detected in a plasma specimen, the tumor tissue should be tested.
Specifically, the new indication is used in patients with unresectable or metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have activating HER2 (ERBB2) mutations, as detected by an FDA-approved test, and who have already received a prior systemic therapy.
About 3% of nonsquamous NSCLC tumors carry mutations in the HER2 gene, and they are associated with female sex, never-smokers, and a poor prognosis.
“HER2 mutant non–small cell lung cancer is an aggressive form of disease, which commonly affects young patients who have faced limited treatment options and a poor prognosis to date,” said Dave Fredrickson, executive vice-president of the oncology business unit at AstraZeneca.
The new approval “provides these patients with the opportunity to benefit from a targeted therapy and highlights the importance of testing for predictive markers, including HER2 in lung cancer, at the time of diagnosis to ensure patients receive the most appropriate treatment for their specific disease,” he commented in a company press release.
This is an accelerated approval, based on overall response rate data from the DESTINY-Lung02 phase 2 trial, the company noted. An interim efficacy analysis in a prespecified patient cohort showed that trastuzumab deruxtecan (at 5.4 mg/kg) demonstrated a confirmed overall response rate of 57.7% (n = 52; 95% confidence interval, 43.2%-71.3%) in patients with HER2-mutant unresectable or metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC who had received one prior systemic therapy as assessed by blinded independent central review. Complete responses were seen in 1.9% of patients (n = 1) and partial responses in 55.8% of patients (n = 29), with a median duration of response of 8.7 months (95% CI, 7.1-NE).
The FDA noted that for the 52 patients in the primary efficacy population of the DESTINY-Lung02 trial, the median age was 58 years (range, 30-78 years); 69% were female; and 79% were Asian, 12% were White, and 10% were of other races.
Clinical data welcomed by experts
Clinical data are already available from the DESTINY-Lung 01 trial, and the results were welcomed enthusiastically by experts when they were published in the New England Journal of Medicine earlier this year.
“These results establish the new standard of care for patients with NSCLC harboring HER2 mutations,” Antonio Passaro, MD, PhD, from the European Institute of Oncology IRCCS, Milan, and Solange Peters, MD, PhD, from Lausanne (Switzerland) University Hospital, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
This trial involved 91 patients, all treated with trastuzumab deruxtecan (at 6.4 mg/kg of body weight every 3 weeks). The median duration of treatment was 6.9 months, and the median follow-up was 13.1 months.
The results showed a 55% centrally confirmed objective response, and median duration of response was 9.3 months.
In addition, the investigators reported a median progression-free survival of 8.2 months and a median overall survival of almost 18 months, both of which they described as “encouraging” in this patient population.
However, the results also highlighted a problem with the drug in this patient population. Notably, 26% of patients experienced interstitial lung disease, which resulted in death in two patients. The drug was also withdrawn in 16 patients and interrupted in 8 patients because of this adverse event.
Editorialists Dr. Passaro and Dr. Peters described this finding as “a concern” and note that “the incidence of interstitial lung disease is significantly higher among patients with lung cancer than among those with breast or gastric cancers, which may indicate a role of smoking-related damage.”
They also highlighted the need for an “investigation of the clinical efficacy of a reduced dose of trastuzumab deruxtecan,” and so the dose was reduced for the DESTINY-Lung02 trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with lung cancer now have another treatment option: If their tumors are found to carry HER2 mutations, they can now be treated with trastuzumab deruxtecan (Enhertu), a drug that specifically targets that defect.
This product is already approved for used in HER2-positive breast cancer and gastric cancer.
The FDA also approved companion diagnostic tests to detect HER2 mutations: Life Technologies Corporation’s Oncomine Dx Target Test for use in lung tissue and Guardant Health’s Guardant360 CDx for use on plasma samples. The agency notes that if no mutation is detected in a plasma specimen, the tumor tissue should be tested.
Specifically, the new indication is used in patients with unresectable or metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have activating HER2 (ERBB2) mutations, as detected by an FDA-approved test, and who have already received a prior systemic therapy.
About 3% of nonsquamous NSCLC tumors carry mutations in the HER2 gene, and they are associated with female sex, never-smokers, and a poor prognosis.
“HER2 mutant non–small cell lung cancer is an aggressive form of disease, which commonly affects young patients who have faced limited treatment options and a poor prognosis to date,” said Dave Fredrickson, executive vice-president of the oncology business unit at AstraZeneca.
The new approval “provides these patients with the opportunity to benefit from a targeted therapy and highlights the importance of testing for predictive markers, including HER2 in lung cancer, at the time of diagnosis to ensure patients receive the most appropriate treatment for their specific disease,” he commented in a company press release.
This is an accelerated approval, based on overall response rate data from the DESTINY-Lung02 phase 2 trial, the company noted. An interim efficacy analysis in a prespecified patient cohort showed that trastuzumab deruxtecan (at 5.4 mg/kg) demonstrated a confirmed overall response rate of 57.7% (n = 52; 95% confidence interval, 43.2%-71.3%) in patients with HER2-mutant unresectable or metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC who had received one prior systemic therapy as assessed by blinded independent central review. Complete responses were seen in 1.9% of patients (n = 1) and partial responses in 55.8% of patients (n = 29), with a median duration of response of 8.7 months (95% CI, 7.1-NE).
The FDA noted that for the 52 patients in the primary efficacy population of the DESTINY-Lung02 trial, the median age was 58 years (range, 30-78 years); 69% were female; and 79% were Asian, 12% were White, and 10% were of other races.
Clinical data welcomed by experts
Clinical data are already available from the DESTINY-Lung 01 trial, and the results were welcomed enthusiastically by experts when they were published in the New England Journal of Medicine earlier this year.
“These results establish the new standard of care for patients with NSCLC harboring HER2 mutations,” Antonio Passaro, MD, PhD, from the European Institute of Oncology IRCCS, Milan, and Solange Peters, MD, PhD, from Lausanne (Switzerland) University Hospital, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
This trial involved 91 patients, all treated with trastuzumab deruxtecan (at 6.4 mg/kg of body weight every 3 weeks). The median duration of treatment was 6.9 months, and the median follow-up was 13.1 months.
The results showed a 55% centrally confirmed objective response, and median duration of response was 9.3 months.
In addition, the investigators reported a median progression-free survival of 8.2 months and a median overall survival of almost 18 months, both of which they described as “encouraging” in this patient population.
However, the results also highlighted a problem with the drug in this patient population. Notably, 26% of patients experienced interstitial lung disease, which resulted in death in two patients. The drug was also withdrawn in 16 patients and interrupted in 8 patients because of this adverse event.
Editorialists Dr. Passaro and Dr. Peters described this finding as “a concern” and note that “the incidence of interstitial lung disease is significantly higher among patients with lung cancer than among those with breast or gastric cancers, which may indicate a role of smoking-related damage.”
They also highlighted the need for an “investigation of the clinical efficacy of a reduced dose of trastuzumab deruxtecan,” and so the dose was reduced for the DESTINY-Lung02 trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA authorizes intradermal use of Jynneos vaccine for monkeypox
The Food and Drug Administration on Aug. 9 authorized intradermal administration of the Jynneos vaccine for the treatment of monkeypox. The process, approved specifically for high-risk patients, was passed under the administration’s Emergency Use Authorization. It follows the decision on Aug. 4 by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services to declare monkeypox a public health emergency. Intradermal administration will allow providers to get five doses out of a one-dose vial.
This news organization will update this article as more information becomes available.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration on Aug. 9 authorized intradermal administration of the Jynneos vaccine for the treatment of monkeypox. The process, approved specifically for high-risk patients, was passed under the administration’s Emergency Use Authorization. It follows the decision on Aug. 4 by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services to declare monkeypox a public health emergency. Intradermal administration will allow providers to get five doses out of a one-dose vial.
This news organization will update this article as more information becomes available.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration on Aug. 9 authorized intradermal administration of the Jynneos vaccine for the treatment of monkeypox. The process, approved specifically for high-risk patients, was passed under the administration’s Emergency Use Authorization. It follows the decision on Aug. 4 by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services to declare monkeypox a public health emergency. Intradermal administration will allow providers to get five doses out of a one-dose vial.
This news organization will update this article as more information becomes available.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: Severe illness rising as vaccination effort stalls
, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
After new child cases jumped by 22% during the week of July 15-21, the two successive weeks have produced increases of 3.9% (July 22-29) and 1.2% (July 30-Aug. 4). The latest weekly count from all states and territories still reporting was 96,599, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report, noting that several states have stopped reporting child cases and that others are reporting every other week.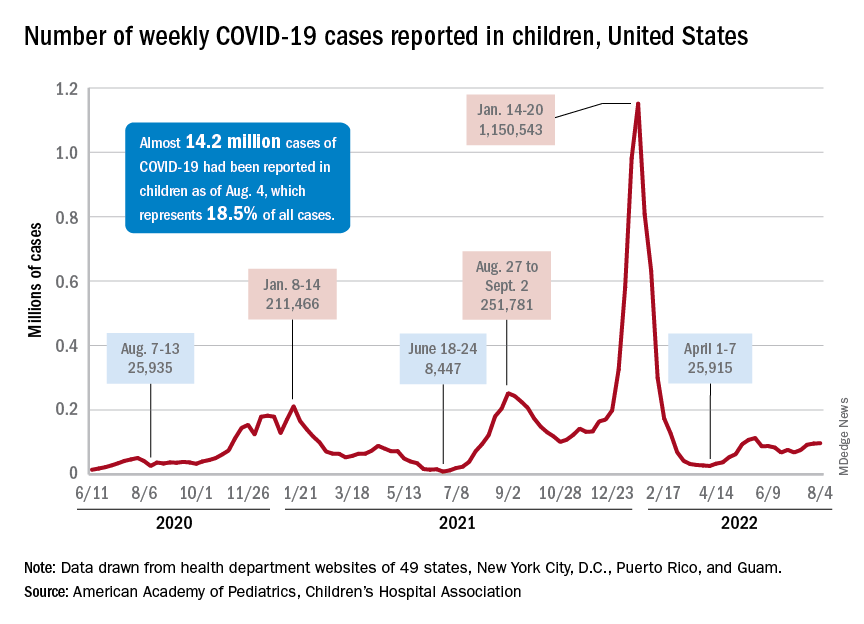
The deceleration in new cases, however, does not apply to emergency department visits and hospital admissions. The proportion of ED visits with diagnosed COVID rose steadily throughout June and July, as 7-day averages went from 2.6% on June 1 to 6.3% on July 31 for children aged 0-11 years, from 2.1% to 3.1% for children aged 12-15, and from 2.4% to 3.5% for 16- to 17-year-olds, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The rate of new admissions with confirmed COVID, which reached 0.46 per 100,000 population for children aged 0-17 years on July 30, has more than tripled since early April, when it had fallen to 0.13 per 100,000 in the wake of the Omicron surge, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
A smaller but more detailed sample of children from the COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Network (COVID-NET), which covers nearly 100 counties in 14 states, indicates that the increase in new admissions is occurring almost entirely among children aged 0-4 years, who had a rate of 5.6 per 100,000 for the week of July 17-23, compared with 0.8 per 100,000 for 5- to 11-year-olds and 1.5 per 100,000 for those aged 12-17, the CDC said.
Vaccine’s summer rollout gets lukewarm reception
As a group, children aged 0-4 years have not exactly flocked to the COVID-19 vaccine. As of Aug. 2 – about 6 weeks since the vaccine was authorized for children aged 6 months to 4 years – just 3.8% of those eligible had received at least one dose. Among children aged 5-11 the corresponding number on Aug. 2 was 37.4%, and for those aged 12-17 years it was 70.3%, the CDC data show.
That 3.8% of children aged less than 5 years represents almost 756,000 initial doses. That compares with over 6 million children aged 5-11 years who had received at least one dose through the first 6 weeks of their vaccination experience and over 5 million children aged 12-15, according to the COVID Data Tracker.
, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
After new child cases jumped by 22% during the week of July 15-21, the two successive weeks have produced increases of 3.9% (July 22-29) and 1.2% (July 30-Aug. 4). The latest weekly count from all states and territories still reporting was 96,599, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report, noting that several states have stopped reporting child cases and that others are reporting every other week.
The deceleration in new cases, however, does not apply to emergency department visits and hospital admissions. The proportion of ED visits with diagnosed COVID rose steadily throughout June and July, as 7-day averages went from 2.6% on June 1 to 6.3% on July 31 for children aged 0-11 years, from 2.1% to 3.1% for children aged 12-15, and from 2.4% to 3.5% for 16- to 17-year-olds, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The rate of new admissions with confirmed COVID, which reached 0.46 per 100,000 population for children aged 0-17 years on July 30, has more than tripled since early April, when it had fallen to 0.13 per 100,000 in the wake of the Omicron surge, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
A smaller but more detailed sample of children from the COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Network (COVID-NET), which covers nearly 100 counties in 14 states, indicates that the increase in new admissions is occurring almost entirely among children aged 0-4 years, who had a rate of 5.6 per 100,000 for the week of July 17-23, compared with 0.8 per 100,000 for 5- to 11-year-olds and 1.5 per 100,000 for those aged 12-17, the CDC said.
Vaccine’s summer rollout gets lukewarm reception
As a group, children aged 0-4 years have not exactly flocked to the COVID-19 vaccine. As of Aug. 2 – about 6 weeks since the vaccine was authorized for children aged 6 months to 4 years – just 3.8% of those eligible had received at least one dose. Among children aged 5-11 the corresponding number on Aug. 2 was 37.4%, and for those aged 12-17 years it was 70.3%, the CDC data show.
That 3.8% of children aged less than 5 years represents almost 756,000 initial doses. That compares with over 6 million children aged 5-11 years who had received at least one dose through the first 6 weeks of their vaccination experience and over 5 million children aged 12-15, according to the COVID Data Tracker.
, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
After new child cases jumped by 22% during the week of July 15-21, the two successive weeks have produced increases of 3.9% (July 22-29) and 1.2% (July 30-Aug. 4). The latest weekly count from all states and territories still reporting was 96,599, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report, noting that several states have stopped reporting child cases and that others are reporting every other week.
The deceleration in new cases, however, does not apply to emergency department visits and hospital admissions. The proportion of ED visits with diagnosed COVID rose steadily throughout June and July, as 7-day averages went from 2.6% on June 1 to 6.3% on July 31 for children aged 0-11 years, from 2.1% to 3.1% for children aged 12-15, and from 2.4% to 3.5% for 16- to 17-year-olds, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The rate of new admissions with confirmed COVID, which reached 0.46 per 100,000 population for children aged 0-17 years on July 30, has more than tripled since early April, when it had fallen to 0.13 per 100,000 in the wake of the Omicron surge, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
A smaller but more detailed sample of children from the COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Network (COVID-NET), which covers nearly 100 counties in 14 states, indicates that the increase in new admissions is occurring almost entirely among children aged 0-4 years, who had a rate of 5.6 per 100,000 for the week of July 17-23, compared with 0.8 per 100,000 for 5- to 11-year-olds and 1.5 per 100,000 for those aged 12-17, the CDC said.
Vaccine’s summer rollout gets lukewarm reception
As a group, children aged 0-4 years have not exactly flocked to the COVID-19 vaccine. As of Aug. 2 – about 6 weeks since the vaccine was authorized for children aged 6 months to 4 years – just 3.8% of those eligible had received at least one dose. Among children aged 5-11 the corresponding number on Aug. 2 was 37.4%, and for those aged 12-17 years it was 70.3%, the CDC data show.
That 3.8% of children aged less than 5 years represents almost 756,000 initial doses. That compares with over 6 million children aged 5-11 years who had received at least one dose through the first 6 weeks of their vaccination experience and over 5 million children aged 12-15, according to the COVID Data Tracker.
Long COVID doubles risk of some serious outcomes in children, teens
Researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that
Heart inflammation; a blood clot in the lung; or a blood clot in the lower leg, thigh, or pelvis were the most common bad outcomes in a new study. Even though the risk was higher for these and some other serious events, the overall numbers were small.
“Many of these conditions were rare or uncommon among children in this analysis, but even a small increase in these conditions is notable,” a CDC new release stated.
The investigators said their findings stress the importance of COVID-19 vaccination in Americans under the age of 18.
The study was published online in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Less is known about long COVID in children
Lyudmyla Kompaniyets, PhD, and colleagues noted that most research on long COVID to date has been done in adults, so little information is available about the risks to Americans ages 17 and younger.
To learn more, they compared post–COVID-19 symptoms and conditions between 781,419 children and teenagers with confirmed COVID-19 to another 2,344,257 without COVID-19. They looked at medical claims and laboratory data for these children and teenagers from March 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2022, to see who got any of 15 specific outcomes linked to long COVID-19.
Long COVID was defined as a condition where symptoms that last for or begin at least 4 weeks after a COVID-19 diagnosis.
Compared to children with no history of a COVID-19 diagnosis, the long COVID-19 group was 101% more likely to have an acute pulmonary embolism, 99% more likely to have myocarditis or cardiomyopathy, 87% more likely to have a venous thromboembolic event, 32% more likely to have acute and unspecified renal failure, and 23% more likely to have type 1 diabetes.
“This report points to the fact that the risks of COVID infection itself, both in terms of the acute effects, MIS-C [multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children], as well as the long-term effects, are real, are concerning, and are potentially very serious,” said Stuart Berger, MD, chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery.
“The message that we should take away from this is that we should be very keen on all the methods of prevention for COVID, especially the vaccine,” said Dr. Berger, chief of cardiology in the department of pediatrics at Northwestern University in Chicago.
A ‘wake-up call’
The study findings are “sobering” and are “a reminder of the seriousness of COVID infection,” says Gregory Poland, MD, an infectious disease expert at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
“When you look in particular at the more serious complications from COVID in this young age group, those are life-altering complications that will have consequences and ramifications throughout their lives,” he said.
“I would take this as a serious wake-up call to parents [at a time when] the immunization rates in younger children are so pitifully low,” Dr. Poland said.
Still early days
The study is suggestive but not definitive, said Peter Katona, MD, professor of medicine and infectious diseases expert at the UCLA Fielding School of Public Health.
It’s still too early to draw conclusions about long COVID, including in children, because many questions remain, he said: Should long COVID be defined as symptoms at 1 month or 3 months after infection? How do you define brain fog?
Dr. Katona and colleagues are studying long COVID intervention among students at UCLA to answer some of these questions, including the incidence and effect of early intervention.
The study had “at least seven limitations,” the researchers noted. Among them was the use of medical claims data that noted long COVID outcomes but not how severe they were; some people in the no COVID group might have had the illness but not been diagnosed; and the researchers did not adjust for vaccination status.
Dr. Poland noted that the study was done during surges in COVID variants including Delta and Omicron. In other words, any long COVID effects linked to more recent variants such as BA.5 or BA.2.75 are unknown.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that
Heart inflammation; a blood clot in the lung; or a blood clot in the lower leg, thigh, or pelvis were the most common bad outcomes in a new study. Even though the risk was higher for these and some other serious events, the overall numbers were small.
“Many of these conditions were rare or uncommon among children in this analysis, but even a small increase in these conditions is notable,” a CDC new release stated.
The investigators said their findings stress the importance of COVID-19 vaccination in Americans under the age of 18.
The study was published online in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Less is known about long COVID in children
Lyudmyla Kompaniyets, PhD, and colleagues noted that most research on long COVID to date has been done in adults, so little information is available about the risks to Americans ages 17 and younger.
To learn more, they compared post–COVID-19 symptoms and conditions between 781,419 children and teenagers with confirmed COVID-19 to another 2,344,257 without COVID-19. They looked at medical claims and laboratory data for these children and teenagers from March 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2022, to see who got any of 15 specific outcomes linked to long COVID-19.
Long COVID was defined as a condition where symptoms that last for or begin at least 4 weeks after a COVID-19 diagnosis.
Compared to children with no history of a COVID-19 diagnosis, the long COVID-19 group was 101% more likely to have an acute pulmonary embolism, 99% more likely to have myocarditis or cardiomyopathy, 87% more likely to have a venous thromboembolic event, 32% more likely to have acute and unspecified renal failure, and 23% more likely to have type 1 diabetes.
“This report points to the fact that the risks of COVID infection itself, both in terms of the acute effects, MIS-C [multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children], as well as the long-term effects, are real, are concerning, and are potentially very serious,” said Stuart Berger, MD, chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery.
“The message that we should take away from this is that we should be very keen on all the methods of prevention for COVID, especially the vaccine,” said Dr. Berger, chief of cardiology in the department of pediatrics at Northwestern University in Chicago.
A ‘wake-up call’
The study findings are “sobering” and are “a reminder of the seriousness of COVID infection,” says Gregory Poland, MD, an infectious disease expert at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
“When you look in particular at the more serious complications from COVID in this young age group, those are life-altering complications that will have consequences and ramifications throughout their lives,” he said.
“I would take this as a serious wake-up call to parents [at a time when] the immunization rates in younger children are so pitifully low,” Dr. Poland said.
Still early days
The study is suggestive but not definitive, said Peter Katona, MD, professor of medicine and infectious diseases expert at the UCLA Fielding School of Public Health.
It’s still too early to draw conclusions about long COVID, including in children, because many questions remain, he said: Should long COVID be defined as symptoms at 1 month or 3 months after infection? How do you define brain fog?
Dr. Katona and colleagues are studying long COVID intervention among students at UCLA to answer some of these questions, including the incidence and effect of early intervention.
The study had “at least seven limitations,” the researchers noted. Among them was the use of medical claims data that noted long COVID outcomes but not how severe they were; some people in the no COVID group might have had the illness but not been diagnosed; and the researchers did not adjust for vaccination status.
Dr. Poland noted that the study was done during surges in COVID variants including Delta and Omicron. In other words, any long COVID effects linked to more recent variants such as BA.5 or BA.2.75 are unknown.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that
Heart inflammation; a blood clot in the lung; or a blood clot in the lower leg, thigh, or pelvis were the most common bad outcomes in a new study. Even though the risk was higher for these and some other serious events, the overall numbers were small.
“Many of these conditions were rare or uncommon among children in this analysis, but even a small increase in these conditions is notable,” a CDC new release stated.
The investigators said their findings stress the importance of COVID-19 vaccination in Americans under the age of 18.
The study was published online in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Less is known about long COVID in children
Lyudmyla Kompaniyets, PhD, and colleagues noted that most research on long COVID to date has been done in adults, so little information is available about the risks to Americans ages 17 and younger.
To learn more, they compared post–COVID-19 symptoms and conditions between 781,419 children and teenagers with confirmed COVID-19 to another 2,344,257 without COVID-19. They looked at medical claims and laboratory data for these children and teenagers from March 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2022, to see who got any of 15 specific outcomes linked to long COVID-19.
Long COVID was defined as a condition where symptoms that last for or begin at least 4 weeks after a COVID-19 diagnosis.
Compared to children with no history of a COVID-19 diagnosis, the long COVID-19 group was 101% more likely to have an acute pulmonary embolism, 99% more likely to have myocarditis or cardiomyopathy, 87% more likely to have a venous thromboembolic event, 32% more likely to have acute and unspecified renal failure, and 23% more likely to have type 1 diabetes.
“This report points to the fact that the risks of COVID infection itself, both in terms of the acute effects, MIS-C [multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children], as well as the long-term effects, are real, are concerning, and are potentially very serious,” said Stuart Berger, MD, chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery.
“The message that we should take away from this is that we should be very keen on all the methods of prevention for COVID, especially the vaccine,” said Dr. Berger, chief of cardiology in the department of pediatrics at Northwestern University in Chicago.
A ‘wake-up call’
The study findings are “sobering” and are “a reminder of the seriousness of COVID infection,” says Gregory Poland, MD, an infectious disease expert at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
“When you look in particular at the more serious complications from COVID in this young age group, those are life-altering complications that will have consequences and ramifications throughout their lives,” he said.
“I would take this as a serious wake-up call to parents [at a time when] the immunization rates in younger children are so pitifully low,” Dr. Poland said.
Still early days
The study is suggestive but not definitive, said Peter Katona, MD, professor of medicine and infectious diseases expert at the UCLA Fielding School of Public Health.
It’s still too early to draw conclusions about long COVID, including in children, because many questions remain, he said: Should long COVID be defined as symptoms at 1 month or 3 months after infection? How do you define brain fog?
Dr. Katona and colleagues are studying long COVID intervention among students at UCLA to answer some of these questions, including the incidence and effect of early intervention.
The study had “at least seven limitations,” the researchers noted. Among them was the use of medical claims data that noted long COVID outcomes but not how severe they were; some people in the no COVID group might have had the illness but not been diagnosed; and the researchers did not adjust for vaccination status.
Dr. Poland noted that the study was done during surges in COVID variants including Delta and Omicron. In other words, any long COVID effects linked to more recent variants such as BA.5 or BA.2.75 are unknown.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM THE MMWR
Ustekinumab becomes second biologic approved for PsA in kids
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the dual interleukin-12 and IL-23 inhibitor ustekinumab (Stelara) for the treatment of juvenile psoriatic arthritis (jPsA) in patients aged 6 years and older, according to an Aug. 1 announcement from its manufacturer, Janssen.
The approval makes jPsA the sixth approved indication for ustekinumab, which include active psoriatic arthritis in adults, moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in both adults and children aged 6 years or older who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy, moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in adults, and moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adults.
In addition, ustekinumab is now the second biologic to be approved for jPsA, following the agency’s December 2021 approval of secukinumab (Cosentyx) to treat jPsA in children and adolescents aged 2 years and older as well as enthesitis-related arthritis in children and adolescents aged 4 years and older.
In pediatric patients, ustekinumab is administered as a subcutaneous injection dosed four times per year after two starter doses.
Ustekinumab’s approval is based on “an extrapolation of the established data and existing safety profile” of ustekinumab in multiple phase 3 studies in adult and pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and adult patients with active PsA, according to Janssen.
“With the limited availability of pediatric patients for clinical trial inclusion, researchers can extrapolate data from trials with adults to determine the potential efficacy and tolerability of a treatment for a pediatric population,” according to the October 2021 announcement from the company that the Biologics License Application had been submitted to the FDA.
Juvenile arthritis occurs in an estimated 20-45 children per 100,000 in the United States, with about 5% of those children having jPsA, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation.
The prescribing information for ustekinumab includes specific warnings and areas of concern. The drug should not be administered to individuals with known hypersensitivity to ustekinumab. The drug may lower the ability of the immune system to fight infections and may increase risk of infections, sometimes serious, and a test for tuberculosis infection should be given before administration.
Patients taking ustekinumab should not be given a live vaccine, and their doctors should be informed if anyone in their household needs a live vaccine. They also should not receive the BCG vaccine during the 1 year before receiving the drug or 1 year after they stop taking it, according to Johnson & Johnson.
The most common adverse effects include nasal congestion, sore throat, runny nose, upper respiratory infections, fever, headache, tiredness, itching, nausea and vomiting, redness at the injection site, vaginal yeast infections, urinary tract infections, sinus infection, bronchitis, diarrhea, stomach pain, and joint pain.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the dual interleukin-12 and IL-23 inhibitor ustekinumab (Stelara) for the treatment of juvenile psoriatic arthritis (jPsA) in patients aged 6 years and older, according to an Aug. 1 announcement from its manufacturer, Janssen.
The approval makes jPsA the sixth approved indication for ustekinumab, which include active psoriatic arthritis in adults, moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in both adults and children aged 6 years or older who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy, moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in adults, and moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adults.
In addition, ustekinumab is now the second biologic to be approved for jPsA, following the agency’s December 2021 approval of secukinumab (Cosentyx) to treat jPsA in children and adolescents aged 2 years and older as well as enthesitis-related arthritis in children and adolescents aged 4 years and older.
In pediatric patients, ustekinumab is administered as a subcutaneous injection dosed four times per year after two starter doses.
Ustekinumab’s approval is based on “an extrapolation of the established data and existing safety profile” of ustekinumab in multiple phase 3 studies in adult and pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and adult patients with active PsA, according to Janssen.
“With the limited availability of pediatric patients for clinical trial inclusion, researchers can extrapolate data from trials with adults to determine the potential efficacy and tolerability of a treatment for a pediatric population,” according to the October 2021 announcement from the company that the Biologics License Application had been submitted to the FDA.
Juvenile arthritis occurs in an estimated 20-45 children per 100,000 in the United States, with about 5% of those children having jPsA, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation.
The prescribing information for ustekinumab includes specific warnings and areas of concern. The drug should not be administered to individuals with known hypersensitivity to ustekinumab. The drug may lower the ability of the immune system to fight infections and may increase risk of infections, sometimes serious, and a test for tuberculosis infection should be given before administration.
Patients taking ustekinumab should not be given a live vaccine, and their doctors should be informed if anyone in their household needs a live vaccine. They also should not receive the BCG vaccine during the 1 year before receiving the drug or 1 year after they stop taking it, according to Johnson & Johnson.
The most common adverse effects include nasal congestion, sore throat, runny nose, upper respiratory infections, fever, headache, tiredness, itching, nausea and vomiting, redness at the injection site, vaginal yeast infections, urinary tract infections, sinus infection, bronchitis, diarrhea, stomach pain, and joint pain.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the dual interleukin-12 and IL-23 inhibitor ustekinumab (Stelara) for the treatment of juvenile psoriatic arthritis (jPsA) in patients aged 6 years and older, according to an Aug. 1 announcement from its manufacturer, Janssen.
The approval makes jPsA the sixth approved indication for ustekinumab, which include active psoriatic arthritis in adults, moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in both adults and children aged 6 years or older who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy, moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in adults, and moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adults.
In addition, ustekinumab is now the second biologic to be approved for jPsA, following the agency’s December 2021 approval of secukinumab (Cosentyx) to treat jPsA in children and adolescents aged 2 years and older as well as enthesitis-related arthritis in children and adolescents aged 4 years and older.
In pediatric patients, ustekinumab is administered as a subcutaneous injection dosed four times per year after two starter doses.
Ustekinumab’s approval is based on “an extrapolation of the established data and existing safety profile” of ustekinumab in multiple phase 3 studies in adult and pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and adult patients with active PsA, according to Janssen.
“With the limited availability of pediatric patients for clinical trial inclusion, researchers can extrapolate data from trials with adults to determine the potential efficacy and tolerability of a treatment for a pediatric population,” according to the October 2021 announcement from the company that the Biologics License Application had been submitted to the FDA.
Juvenile arthritis occurs in an estimated 20-45 children per 100,000 in the United States, with about 5% of those children having jPsA, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation.
The prescribing information for ustekinumab includes specific warnings and areas of concern. The drug should not be administered to individuals with known hypersensitivity to ustekinumab. The drug may lower the ability of the immune system to fight infections and may increase risk of infections, sometimes serious, and a test for tuberculosis infection should be given before administration.
Patients taking ustekinumab should not be given a live vaccine, and their doctors should be informed if anyone in their household needs a live vaccine. They also should not receive the BCG vaccine during the 1 year before receiving the drug or 1 year after they stop taking it, according to Johnson & Johnson.
The most common adverse effects include nasal congestion, sore throat, runny nose, upper respiratory infections, fever, headache, tiredness, itching, nausea and vomiting, redness at the injection site, vaginal yeast infections, urinary tract infections, sinus infection, bronchitis, diarrhea, stomach pain, and joint pain.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: Weekly cases top 95,000, admissions continue to rise
New pediatric COVID-19 cases increased for the third straight week as a substantial number of children under age 5 years started to receive their second doses of the vaccine.
Despite the 3-week trend, however, there are some positive signs. The new-case count for the latest reporting week (July 22-28) was over 95,000, but the 3.9% increase over the previous week’s 92,000 cases is much smaller than that week’s (July 15-21) corresponding jump of almost 22% over the July 8-14 total (75,000), according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.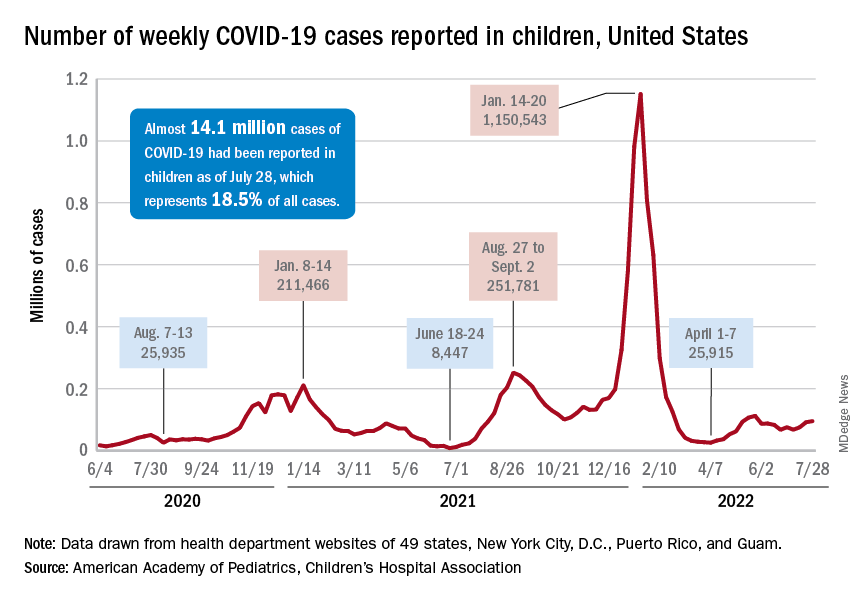
On the not-so-positive side is the trend in admissions among children aged 0-17 years, which continue to climb steadily and have nearly equaled the highest rate seen during the Delta surge in 2021. The rate on July 29 was 0.46 admissions per 100,000 population, and the highest rate over the course of the Delta surge was 0.47 per 100,000, but the all-time high from the Omicron surge – 1.25 per 100,000 in mid-January – is still a long way off, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A similar situation is occurring with emergency department visits, but there is differentiation by age group. Among those aged 0-11 years, visits with diagnosed COVID made up 6.5% of all their ED visits on July 25, which was well above the high (4.0%) during the Delta surge, the CDC said.
That is not the case, however, for the older children, for whom rates are rising more slowly. Those aged 12-15 have reached 3.4% so far this summer, as have the 16- to 17-years-olds, versus Delta highs last year of around 7%, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. As with admissions, though, current rates are well below the all-time Omicron high points, the CDC data show.
Joining the ranks of the fully vaccinated
Over the last 2 weeks, the first children to receive the COVID vaccine after its approval for those under age 5 years have been coming back for their second doses. Almost 50,000, about 0.3% of all those in that age group, had done so by July 27. Just over 662,000, about 3.4% of the total under-5 population, have received at least one dose, the CDC said.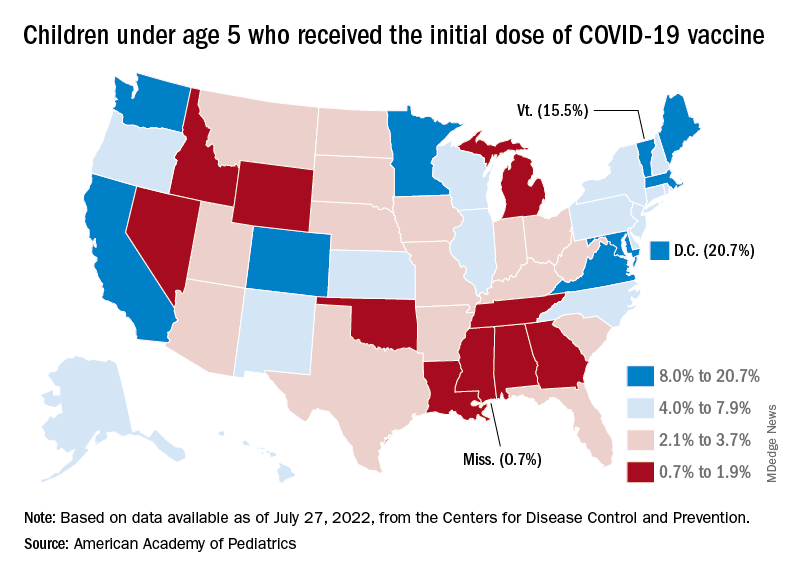
Meanwhile, analysis of “data from the first several weeks following availability of the vaccine in this age group indicate high variability across states,” the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. In the District of Columbia, 20.7% of all children under age 5 have received an initial dose as of July 27, as have 15.5% of those in Vermont and 12.5% in Massachusetts. No other state was above 10%, but Mississippi, at 0.7%, was the only one below 1%.
The older children, obviously, have a head start, so their numbers are much higher. At the state level, Vermont has the highest initial dose rate, 69%, for those aged 5-11 years, while Alabama, Mississippi, and Wyoming, at 17%, are looking up at everyone else in the country. Among children aged 12-17 years, D.C. is the highest with 100% vaccination – Massachusetts and Rhode Island are at 98% – and Wyoming is the lowest with 40%, the AAP said.
New pediatric COVID-19 cases increased for the third straight week as a substantial number of children under age 5 years started to receive their second doses of the vaccine.
Despite the 3-week trend, however, there are some positive signs. The new-case count for the latest reporting week (July 22-28) was over 95,000, but the 3.9% increase over the previous week’s 92,000 cases is much smaller than that week’s (July 15-21) corresponding jump of almost 22% over the July 8-14 total (75,000), according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
On the not-so-positive side is the trend in admissions among children aged 0-17 years, which continue to climb steadily and have nearly equaled the highest rate seen during the Delta surge in 2021. The rate on July 29 was 0.46 admissions per 100,000 population, and the highest rate over the course of the Delta surge was 0.47 per 100,000, but the all-time high from the Omicron surge – 1.25 per 100,000 in mid-January – is still a long way off, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A similar situation is occurring with emergency department visits, but there is differentiation by age group. Among those aged 0-11 years, visits with diagnosed COVID made up 6.5% of all their ED visits on July 25, which was well above the high (4.0%) during the Delta surge, the CDC said.
That is not the case, however, for the older children, for whom rates are rising more slowly. Those aged 12-15 have reached 3.4% so far this summer, as have the 16- to 17-years-olds, versus Delta highs last year of around 7%, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. As with admissions, though, current rates are well below the all-time Omicron high points, the CDC data show.
Joining the ranks of the fully vaccinated
Over the last 2 weeks, the first children to receive the COVID vaccine after its approval for those under age 5 years have been coming back for their second doses. Almost 50,000, about 0.3% of all those in that age group, had done so by July 27. Just over 662,000, about 3.4% of the total under-5 population, have received at least one dose, the CDC said.
Meanwhile, analysis of “data from the first several weeks following availability of the vaccine in this age group indicate high variability across states,” the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. In the District of Columbia, 20.7% of all children under age 5 have received an initial dose as of July 27, as have 15.5% of those in Vermont and 12.5% in Massachusetts. No other state was above 10%, but Mississippi, at 0.7%, was the only one below 1%.
The older children, obviously, have a head start, so their numbers are much higher. At the state level, Vermont has the highest initial dose rate, 69%, for those aged 5-11 years, while Alabama, Mississippi, and Wyoming, at 17%, are looking up at everyone else in the country. Among children aged 12-17 years, D.C. is the highest with 100% vaccination – Massachusetts and Rhode Island are at 98% – and Wyoming is the lowest with 40%, the AAP said.
New pediatric COVID-19 cases increased for the third straight week as a substantial number of children under age 5 years started to receive their second doses of the vaccine.
Despite the 3-week trend, however, there are some positive signs. The new-case count for the latest reporting week (July 22-28) was over 95,000, but the 3.9% increase over the previous week’s 92,000 cases is much smaller than that week’s (July 15-21) corresponding jump of almost 22% over the July 8-14 total (75,000), according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
On the not-so-positive side is the trend in admissions among children aged 0-17 years, which continue to climb steadily and have nearly equaled the highest rate seen during the Delta surge in 2021. The rate on July 29 was 0.46 admissions per 100,000 population, and the highest rate over the course of the Delta surge was 0.47 per 100,000, but the all-time high from the Omicron surge – 1.25 per 100,000 in mid-January – is still a long way off, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A similar situation is occurring with emergency department visits, but there is differentiation by age group. Among those aged 0-11 years, visits with diagnosed COVID made up 6.5% of all their ED visits on July 25, which was well above the high (4.0%) during the Delta surge, the CDC said.
That is not the case, however, for the older children, for whom rates are rising more slowly. Those aged 12-15 have reached 3.4% so far this summer, as have the 16- to 17-years-olds, versus Delta highs last year of around 7%, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. As with admissions, though, current rates are well below the all-time Omicron high points, the CDC data show.
Joining the ranks of the fully vaccinated
Over the last 2 weeks, the first children to receive the COVID vaccine after its approval for those under age 5 years have been coming back for their second doses. Almost 50,000, about 0.3% of all those in that age group, had done so by July 27. Just over 662,000, about 3.4% of the total under-5 population, have received at least one dose, the CDC said.
Meanwhile, analysis of “data from the first several weeks following availability of the vaccine in this age group indicate high variability across states,” the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. In the District of Columbia, 20.7% of all children under age 5 have received an initial dose as of July 27, as have 15.5% of those in Vermont and 12.5% in Massachusetts. No other state was above 10%, but Mississippi, at 0.7%, was the only one below 1%.
The older children, obviously, have a head start, so their numbers are much higher. At the state level, Vermont has the highest initial dose rate, 69%, for those aged 5-11 years, while Alabama, Mississippi, and Wyoming, at 17%, are looking up at everyone else in the country. Among children aged 12-17 years, D.C. is the highest with 100% vaccination – Massachusetts and Rhode Island are at 98% – and Wyoming is the lowest with 40%, the AAP said.
Potentially deadly bacteria detected in U.S. soil
, according to a new alert from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The bacteria, Burkholderia pseudomallei, was found along the Gulf Coast region in southern Mississippi. Typically, the bacteria are in tropical and subtropical climates, especially in parts of Southeast Asia, northern Australia, Central America, South America, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
The bacteria can cause melioidosis, a rare and serious infectious disease that spreads to animals and humans through contact with contaminated soil and water via cuts, wounds, mucous membranes, breathing the bacteria in, or eating or drinking it. Worldwide, the disease is fatal in 10%-50% of those who become infected.
CDC and state officials are investigating the samples to find out how widespread the bacteria are within the United States. So far, modeling suggests that the environmental conditions on the Gulf Coast support the growth of B. pseudomallei.
“It is unclear how long the bacteria has been in the environment and where else it might be found in the U.S.,” according to the CDC statement. “CDC is alerting clinicians throughout the country of this discovery through a national health advisory, reminding them to be aware of the signs and symptoms of melioidosis and to consider melioidosis in patients that present with symptoms of the disease.”
Two unrelated people who live near the Gulf Coast region of Mississippi became sick with melioidosis recently – one in July 2020 and one in May 2022. Neither had traveled outside of the United States. The cases led the CDC and the Mississippi State Department of Health to collect environmental samples and test household products at the patients’ homes in June 2022. Three of the samples taken from soil and puddle water in the 2020 case tested positive for the bacteria.
Genomic sequencing revealed that both patients were infected with the same strain of the bacteria from the Western Hemisphere. They were hospitalized with sepsis due to pneumonia and had known risk factors for melioidosis. Both patients recovered after they were treated with antibiotics.
An average of 12 melioidosis cases are diagnosed in the United States each year, with most in people with recent travel to a country where the bacteria is endemic, or regularly found. Cases have also been linked to contaminated products imported from endemic countries. In late 2021, four cases in four states – Georgia, Kansas, Minnesota, and Texas – were linked to a contaminated aromatherapy spray that was imported, and Walmart issued a recall in November of that year, according to a CDC announcement. Two of the four people died.
Given the small number of cases found in the United States, the CDC believes the risk of melioidosis for the general population continues to be “very low,” and the risk of person-to-person spread is considered “extremely low.” But people who live on the Gulf Coast of Mississippi and who have health conditions that may put them at a higher risk, such as diabetes, chronic kidney disease, chronic lung disease, excessive alcohol use, and immunosuppressive conditions, should protect themselves.
The CDC recommends avoiding contact with soil or muddy water, particularly after heavy rains, and protecting open wounds with waterproof bandages. People should also wear waterproof boots when gardening, working in the yard, or doing agricultural work, which can prevent infection through the feet and lower legs, especially after flooding or storms. People should also wear gloves to protect their hands when working directly with soil.
Melioidosis has a wide range of symptoms, including fever, joint pain, headaches, coughing, chest pain, and belly pain. It can also cause conditions such as pneumonia, abscesses, and blood infections. The disease can infect any organ, including the brain. In most cases, symptoms appear within 1-21 days after exposure, with an average of 7 days after exposure.
The CDC’s health advisory for health professionals and public health officials shows that melioidosis is now considered to be locally endemic in areas of the Gulf Coast region in Mississippi.
“Once well-established in the soil, B. pseudomallei cannot feasibly be removed from the soil,” according to the advisory. “Public health efforts should focus primarily on improving identification of cases so that appropriate treatment can be administered.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new alert from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The bacteria, Burkholderia pseudomallei, was found along the Gulf Coast region in southern Mississippi. Typically, the bacteria are in tropical and subtropical climates, especially in parts of Southeast Asia, northern Australia, Central America, South America, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
The bacteria can cause melioidosis, a rare and serious infectious disease that spreads to animals and humans through contact with contaminated soil and water via cuts, wounds, mucous membranes, breathing the bacteria in, or eating or drinking it. Worldwide, the disease is fatal in 10%-50% of those who become infected.
CDC and state officials are investigating the samples to find out how widespread the bacteria are within the United States. So far, modeling suggests that the environmental conditions on the Gulf Coast support the growth of B. pseudomallei.
“It is unclear how long the bacteria has been in the environment and where else it might be found in the U.S.,” according to the CDC statement. “CDC is alerting clinicians throughout the country of this discovery through a national health advisory, reminding them to be aware of the signs and symptoms of melioidosis and to consider melioidosis in patients that present with symptoms of the disease.”
Two unrelated people who live near the Gulf Coast region of Mississippi became sick with melioidosis recently – one in July 2020 and one in May 2022. Neither had traveled outside of the United States. The cases led the CDC and the Mississippi State Department of Health to collect environmental samples and test household products at the patients’ homes in June 2022. Three of the samples taken from soil and puddle water in the 2020 case tested positive for the bacteria.
Genomic sequencing revealed that both patients were infected with the same strain of the bacteria from the Western Hemisphere. They were hospitalized with sepsis due to pneumonia and had known risk factors for melioidosis. Both patients recovered after they were treated with antibiotics.
An average of 12 melioidosis cases are diagnosed in the United States each year, with most in people with recent travel to a country where the bacteria is endemic, or regularly found. Cases have also been linked to contaminated products imported from endemic countries. In late 2021, four cases in four states – Georgia, Kansas, Minnesota, and Texas – were linked to a contaminated aromatherapy spray that was imported, and Walmart issued a recall in November of that year, according to a CDC announcement. Two of the four people died.
Given the small number of cases found in the United States, the CDC believes the risk of melioidosis for the general population continues to be “very low,” and the risk of person-to-person spread is considered “extremely low.” But people who live on the Gulf Coast of Mississippi and who have health conditions that may put them at a higher risk, such as diabetes, chronic kidney disease, chronic lung disease, excessive alcohol use, and immunosuppressive conditions, should protect themselves.
The CDC recommends avoiding contact with soil or muddy water, particularly after heavy rains, and protecting open wounds with waterproof bandages. People should also wear waterproof boots when gardening, working in the yard, or doing agricultural work, which can prevent infection through the feet and lower legs, especially after flooding or storms. People should also wear gloves to protect their hands when working directly with soil.
Melioidosis has a wide range of symptoms, including fever, joint pain, headaches, coughing, chest pain, and belly pain. It can also cause conditions such as pneumonia, abscesses, and blood infections. The disease can infect any organ, including the brain. In most cases, symptoms appear within 1-21 days after exposure, with an average of 7 days after exposure.
The CDC’s health advisory for health professionals and public health officials shows that melioidosis is now considered to be locally endemic in areas of the Gulf Coast region in Mississippi.
“Once well-established in the soil, B. pseudomallei cannot feasibly be removed from the soil,” according to the advisory. “Public health efforts should focus primarily on improving identification of cases so that appropriate treatment can be administered.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new alert from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The bacteria, Burkholderia pseudomallei, was found along the Gulf Coast region in southern Mississippi. Typically, the bacteria are in tropical and subtropical climates, especially in parts of Southeast Asia, northern Australia, Central America, South America, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
The bacteria can cause melioidosis, a rare and serious infectious disease that spreads to animals and humans through contact with contaminated soil and water via cuts, wounds, mucous membranes, breathing the bacteria in, or eating or drinking it. Worldwide, the disease is fatal in 10%-50% of those who become infected.
CDC and state officials are investigating the samples to find out how widespread the bacteria are within the United States. So far, modeling suggests that the environmental conditions on the Gulf Coast support the growth of B. pseudomallei.
“It is unclear how long the bacteria has been in the environment and where else it might be found in the U.S.,” according to the CDC statement. “CDC is alerting clinicians throughout the country of this discovery through a national health advisory, reminding them to be aware of the signs and symptoms of melioidosis and to consider melioidosis in patients that present with symptoms of the disease.”
Two unrelated people who live near the Gulf Coast region of Mississippi became sick with melioidosis recently – one in July 2020 and one in May 2022. Neither had traveled outside of the United States. The cases led the CDC and the Mississippi State Department of Health to collect environmental samples and test household products at the patients’ homes in June 2022. Three of the samples taken from soil and puddle water in the 2020 case tested positive for the bacteria.
Genomic sequencing revealed that both patients were infected with the same strain of the bacteria from the Western Hemisphere. They were hospitalized with sepsis due to pneumonia and had known risk factors for melioidosis. Both patients recovered after they were treated with antibiotics.
An average of 12 melioidosis cases are diagnosed in the United States each year, with most in people with recent travel to a country where the bacteria is endemic, or regularly found. Cases have also been linked to contaminated products imported from endemic countries. In late 2021, four cases in four states – Georgia, Kansas, Minnesota, and Texas – were linked to a contaminated aromatherapy spray that was imported, and Walmart issued a recall in November of that year, according to a CDC announcement. Two of the four people died.
Given the small number of cases found in the United States, the CDC believes the risk of melioidosis for the general population continues to be “very low,” and the risk of person-to-person spread is considered “extremely low.” But people who live on the Gulf Coast of Mississippi and who have health conditions that may put them at a higher risk, such as diabetes, chronic kidney disease, chronic lung disease, excessive alcohol use, and immunosuppressive conditions, should protect themselves.
The CDC recommends avoiding contact with soil or muddy water, particularly after heavy rains, and protecting open wounds with waterproof bandages. People should also wear waterproof boots when gardening, working in the yard, or doing agricultural work, which can prevent infection through the feet and lower legs, especially after flooding or storms. People should also wear gloves to protect their hands when working directly with soil.
Melioidosis has a wide range of symptoms, including fever, joint pain, headaches, coughing, chest pain, and belly pain. It can also cause conditions such as pneumonia, abscesses, and blood infections. The disease can infect any organ, including the brain. In most cases, symptoms appear within 1-21 days after exposure, with an average of 7 days after exposure.
The CDC’s health advisory for health professionals and public health officials shows that melioidosis is now considered to be locally endemic in areas of the Gulf Coast region in Mississippi.
“Once well-established in the soil, B. pseudomallei cannot feasibly be removed from the soil,” according to the advisory. “Public health efforts should focus primarily on improving identification of cases so that appropriate treatment can be administered.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA approves belimumab for children with lupus nephritis
The Food and Drug Administration has approved belimumab (Benlysta) for treating active lupus nephritis (LN) in children aged 5-17 years. The drug can now be used to treat adult and pediatric patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and LN. The decision expands therapeutic options for the estimated 1.5 million Americans currently living with lupus.
“This approval marks a significant step forward in providing treatment options to these children at risk of incurring kidney damage early on in life,” Stevan W. Gibson, president and CEO of the Lupus Foundation of America, said in a press release issued by the manufacturer, GlaxoSmithKline. LN is a condition that sometimes develops in people with lupus. In LN, the autoimmune cells produced by the disease attack the kidney. Roughly 40% of people with SLE experience LN.
Damage to the kidneys causes the body to have difficulty processing waste and toxins. This can create a host of problems, including end-stage kidney disease, which may be treated only with dialysis or kidney transplant. These situations significantly increase mortality among people with lupus, especially children.
Prior to the approval, the only treatment pathway for children with active LN included immunosuppressants and corticosteroids. While they may be effective, use of these classes of drugs may come with many side effects, including susceptibility to other diseases and infections. Belimumab, by contrast, is a B-lymphocyte stimulator protein inhibitor. It inhibits the survival of B cells, which are thought to play a role in the disease’s pathophysiology.
Belimumab was first approved to treat patients with SLE in 2011. It was approved for children with SLE 8 years later. The drug’s indications were expanded to include adults with LN in 2020.
Organizations within the lupus research community have communicated their support of the FDA’s decision. “Our community has much to celebrate with the approval of the first and much-needed treatment for children with lupus nephritis,” Lupus Research Alliance President and CEO Kenneth M. Farber said in a release from the organization.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved belimumab (Benlysta) for treating active lupus nephritis (LN) in children aged 5-17 years. The drug can now be used to treat adult and pediatric patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and LN. The decision expands therapeutic options for the estimated 1.5 million Americans currently living with lupus.
“This approval marks a significant step forward in providing treatment options to these children at risk of incurring kidney damage early on in life,” Stevan W. Gibson, president and CEO of the Lupus Foundation of America, said in a press release issued by the manufacturer, GlaxoSmithKline. LN is a condition that sometimes develops in people with lupus. In LN, the autoimmune cells produced by the disease attack the kidney. Roughly 40% of people with SLE experience LN.
Damage to the kidneys causes the body to have difficulty processing waste and toxins. This can create a host of problems, including end-stage kidney disease, which may be treated only with dialysis or kidney transplant. These situations significantly increase mortality among people with lupus, especially children.
Prior to the approval, the only treatment pathway for children with active LN included immunosuppressants and corticosteroids. While they may be effective, use of these classes of drugs may come with many side effects, including susceptibility to other diseases and infections. Belimumab, by contrast, is a B-lymphocyte stimulator protein inhibitor. It inhibits the survival of B cells, which are thought to play a role in the disease’s pathophysiology.
Belimumab was first approved to treat patients with SLE in 2011. It was approved for children with SLE 8 years later. The drug’s indications were expanded to include adults with LN in 2020.
Organizations within the lupus research community have communicated their support of the FDA’s decision. “Our community has much to celebrate with the approval of the first and much-needed treatment for children with lupus nephritis,” Lupus Research Alliance President and CEO Kenneth M. Farber said in a release from the organization.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved belimumab (Benlysta) for treating active lupus nephritis (LN) in children aged 5-17 years. The drug can now be used to treat adult and pediatric patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and LN. The decision expands therapeutic options for the estimated 1.5 million Americans currently living with lupus.
“This approval marks a significant step forward in providing treatment options to these children at risk of incurring kidney damage early on in life,” Stevan W. Gibson, president and CEO of the Lupus Foundation of America, said in a press release issued by the manufacturer, GlaxoSmithKline. LN is a condition that sometimes develops in people with lupus. In LN, the autoimmune cells produced by the disease attack the kidney. Roughly 40% of people with SLE experience LN.
Damage to the kidneys causes the body to have difficulty processing waste and toxins. This can create a host of problems, including end-stage kidney disease, which may be treated only with dialysis or kidney transplant. These situations significantly increase mortality among people with lupus, especially children.
Prior to the approval, the only treatment pathway for children with active LN included immunosuppressants and corticosteroids. While they may be effective, use of these classes of drugs may come with many side effects, including susceptibility to other diseases and infections. Belimumab, by contrast, is a B-lymphocyte stimulator protein inhibitor. It inhibits the survival of B cells, which are thought to play a role in the disease’s pathophysiology.
Belimumab was first approved to treat patients with SLE in 2011. It was approved for children with SLE 8 years later. The drug’s indications were expanded to include adults with LN in 2020.
Organizations within the lupus research community have communicated their support of the FDA’s decision. “Our community has much to celebrate with the approval of the first and much-needed treatment for children with lupus nephritis,” Lupus Research Alliance President and CEO Kenneth M. Farber said in a release from the organization.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.

