User login
FDA approves frontline immunotherapy for gastric cancers
This is the first immunotherapy approved for the frontline treatment of gastric cancers, the agency says in a press release.
The approval comes after nivolumab received Priority Review and Orphan Drug designations for this indication. There are approximately 28,000 new diagnoses of gastric cancer annually in the United States, and overall survival is generally poor with currently available therapy, points out the FDA.
“Today’s approval is the first treatment in more than a decade to show a survival benefit for patients with advanced or metastatic gastric cancer who are being treated for the first time,” Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence and acting director of the Office of Oncologic Diseases in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, states in an FDA press release.
Efficacy in the gastric cancer setting was demonstrated in the randomized, phase 3, open-label CheckMate 649 study of 1,518 untreated patients. Median survival was 13.8 months among those treated with nivolumab, compared with 11.6 months with chemotherapy alone (hazard ratio, 0.80; P = .0002).
Common side effects experienced by patients in the nivolumab group included peripheral neuropathy, nausea, fatigue, diarrhea, vomiting, decreased appetite, abdominal pain, constipation, and musculoskeletal pain.
Nivolumab is also approved for numerous other cancers. Other known adverse effects include immune-mediated inflammation of the lungs, colon, liver, endocrine glands, and kidneys.
“Patients should tell their health care providers if they have immune system problems, lung or breathing problems, liver problems, have had an organ transplant, or are pregnant or plan to become pregnant before starting treatment,” the FDA states.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This is the first immunotherapy approved for the frontline treatment of gastric cancers, the agency says in a press release.
The approval comes after nivolumab received Priority Review and Orphan Drug designations for this indication. There are approximately 28,000 new diagnoses of gastric cancer annually in the United States, and overall survival is generally poor with currently available therapy, points out the FDA.
“Today’s approval is the first treatment in more than a decade to show a survival benefit for patients with advanced or metastatic gastric cancer who are being treated for the first time,” Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence and acting director of the Office of Oncologic Diseases in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, states in an FDA press release.
Efficacy in the gastric cancer setting was demonstrated in the randomized, phase 3, open-label CheckMate 649 study of 1,518 untreated patients. Median survival was 13.8 months among those treated with nivolumab, compared with 11.6 months with chemotherapy alone (hazard ratio, 0.80; P = .0002).
Common side effects experienced by patients in the nivolumab group included peripheral neuropathy, nausea, fatigue, diarrhea, vomiting, decreased appetite, abdominal pain, constipation, and musculoskeletal pain.
Nivolumab is also approved for numerous other cancers. Other known adverse effects include immune-mediated inflammation of the lungs, colon, liver, endocrine glands, and kidneys.
“Patients should tell their health care providers if they have immune system problems, lung or breathing problems, liver problems, have had an organ transplant, or are pregnant or plan to become pregnant before starting treatment,” the FDA states.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This is the first immunotherapy approved for the frontline treatment of gastric cancers, the agency says in a press release.
The approval comes after nivolumab received Priority Review and Orphan Drug designations for this indication. There are approximately 28,000 new diagnoses of gastric cancer annually in the United States, and overall survival is generally poor with currently available therapy, points out the FDA.
“Today’s approval is the first treatment in more than a decade to show a survival benefit for patients with advanced or metastatic gastric cancer who are being treated for the first time,” Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence and acting director of the Office of Oncologic Diseases in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, states in an FDA press release.
Efficacy in the gastric cancer setting was demonstrated in the randomized, phase 3, open-label CheckMate 649 study of 1,518 untreated patients. Median survival was 13.8 months among those treated with nivolumab, compared with 11.6 months with chemotherapy alone (hazard ratio, 0.80; P = .0002).
Common side effects experienced by patients in the nivolumab group included peripheral neuropathy, nausea, fatigue, diarrhea, vomiting, decreased appetite, abdominal pain, constipation, and musculoskeletal pain.
Nivolumab is also approved for numerous other cancers. Other known adverse effects include immune-mediated inflammation of the lungs, colon, liver, endocrine glands, and kidneys.
“Patients should tell their health care providers if they have immune system problems, lung or breathing problems, liver problems, have had an organ transplant, or are pregnant or plan to become pregnant before starting treatment,” the FDA states.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
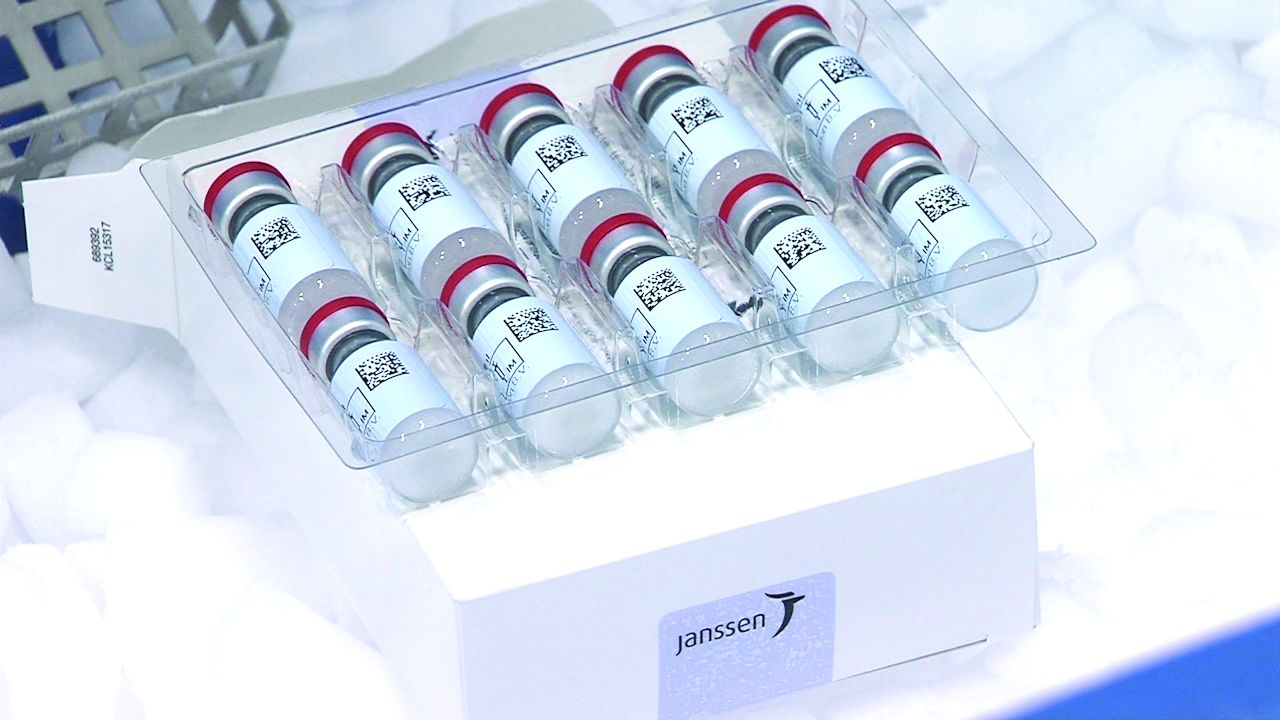
CDC panel: Pause of J&J COVID-19 vaccine to remain for now
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices decided there was not adequate information to change again recommend use of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
The committee’s decision comes the day after the CDC and Food and Drug Administration recommended that J&J injections be paused after reports of rare, but serious types of blood clots in six patients among the 6.8 million people who had received the J&J vaccine in the United States.
A member of the committee, Beth Bell, MD, said: “I do not want to be sending a message that there is some huge concern here on a different order of magnitude than any other vaccine safety signals that we evaluate. And I don’t want to send a message that there is something fundamentally wrong with the vaccine because that also I don’t agree with.”
At the end of the 4-hour meeting, ACIP members decided to call a meeting in 1 or 2 weeks and evaluate more safety data, specifically reports of people who have received the J&J vaccine in the past 2 weeks.
Some, however, pointed out that delaying a decision could have substantial consequences as well in terms of unused vaccine doses and public confidence.
Committee member Camiile Kotton, MD, described the pause as “devastating.”
“Putting this vaccine on pause for those of us that are frontline health care workers has really been devastating,” she said. “I agree in general that we don’t have enough data to make a decision at this time but we were planning on using this vaccine in the state of Massachusetts for people who were homebound and otherwise not able to get a vaccine. We were planning on using it for our vulnerable inpatient population often with many comorbidities and at high risk for disease but haven’t been able to get vaccinated otherwise.”
Pausing the one-and-done vaccine that doesn’t have the significant refrigeration requirements of the others “is a significant loss,” she said.
What is known, not known
Sara Oliver, MD, who leads the COVID-19 Vaccines ACIP Work Group, summarized what is known and unknown about the blood clots.
Among the six cases of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System after the J&J shot, all were women aged 18-48 years and all developed the clots 6-13 days after receiving the vaccine.
No cases of these clots have been reported from either the Pfizer or Moderna shots, she noted.
In the United States, the two mRNA vaccine alternatives – the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines – are available “and based on current projections supply of both vaccines are expected to be relatively stable in the near future,” she said.
She said 14 million doses of Pfizer and Moderna are expected each week in the United States and J&J vaccines makes up less than 5% of vaccines administered in the country.
Approximately 13 million J&J doses are available to order or are already at administration sites, she said.
But much more is unknown, she said.
“There may be more cases identified in the coming days to weeks,” Dr. Oliver said, referring back to the average time from vaccination to symptom onset.
Scott Ratzan, MD, editor-in-chief of the Journal of Health Communication: International Perspectives and executive director of Business Partners to CONVINCE (BP2C), a global network of employers that promotes COVID-19 vaccination among employees, suppliers, and customers, applauded ACIP’s delay on making a decision.
Dr. Ratzan, who watched the deliberations online, said in an interview the decision “shows an admirable abundance of caution in the distribution of COVID-19 vaccines.”
“Unfortunately,” he said, “the pause also worsens the existing and pervasive vaccine hesitancy issue.
“We need a rational strategy regarding who should or should not get the J&J/Janssen vaccine since these rare adverse events appear to affect a particular group of people, females aged 18-48. It is essential that we build vaccine confidence and retain the option of using this vaccine for people who are not in this risk group.”
He pointed out there are safety red flags with the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines.
“We should feel reassured about the process of ensuring vaccine safety as the FDA and CDC have quickly addressed risk and shared the data transparently of the J&J vaccine and taken appropriate action,” he said.
ACIP’s executive secretary, Amanda Cohn, MD, said the date for the next meeting would be set by April 16.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices decided there was not adequate information to change again recommend use of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
The committee’s decision comes the day after the CDC and Food and Drug Administration recommended that J&J injections be paused after reports of rare, but serious types of blood clots in six patients among the 6.8 million people who had received the J&J vaccine in the United States.
A member of the committee, Beth Bell, MD, said: “I do not want to be sending a message that there is some huge concern here on a different order of magnitude than any other vaccine safety signals that we evaluate. And I don’t want to send a message that there is something fundamentally wrong with the vaccine because that also I don’t agree with.”
At the end of the 4-hour meeting, ACIP members decided to call a meeting in 1 or 2 weeks and evaluate more safety data, specifically reports of people who have received the J&J vaccine in the past 2 weeks.
Some, however, pointed out that delaying a decision could have substantial consequences as well in terms of unused vaccine doses and public confidence.
Committee member Camiile Kotton, MD, described the pause as “devastating.”
“Putting this vaccine on pause for those of us that are frontline health care workers has really been devastating,” she said. “I agree in general that we don’t have enough data to make a decision at this time but we were planning on using this vaccine in the state of Massachusetts for people who were homebound and otherwise not able to get a vaccine. We were planning on using it for our vulnerable inpatient population often with many comorbidities and at high risk for disease but haven’t been able to get vaccinated otherwise.”
Pausing the one-and-done vaccine that doesn’t have the significant refrigeration requirements of the others “is a significant loss,” she said.
What is known, not known
Sara Oliver, MD, who leads the COVID-19 Vaccines ACIP Work Group, summarized what is known and unknown about the blood clots.
Among the six cases of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System after the J&J shot, all were women aged 18-48 years and all developed the clots 6-13 days after receiving the vaccine.
No cases of these clots have been reported from either the Pfizer or Moderna shots, she noted.
In the United States, the two mRNA vaccine alternatives – the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines – are available “and based on current projections supply of both vaccines are expected to be relatively stable in the near future,” she said.
She said 14 million doses of Pfizer and Moderna are expected each week in the United States and J&J vaccines makes up less than 5% of vaccines administered in the country.
Approximately 13 million J&J doses are available to order or are already at administration sites, she said.
But much more is unknown, she said.
“There may be more cases identified in the coming days to weeks,” Dr. Oliver said, referring back to the average time from vaccination to symptom onset.
Scott Ratzan, MD, editor-in-chief of the Journal of Health Communication: International Perspectives and executive director of Business Partners to CONVINCE (BP2C), a global network of employers that promotes COVID-19 vaccination among employees, suppliers, and customers, applauded ACIP’s delay on making a decision.
Dr. Ratzan, who watched the deliberations online, said in an interview the decision “shows an admirable abundance of caution in the distribution of COVID-19 vaccines.”
“Unfortunately,” he said, “the pause also worsens the existing and pervasive vaccine hesitancy issue.
“We need a rational strategy regarding who should or should not get the J&J/Janssen vaccine since these rare adverse events appear to affect a particular group of people, females aged 18-48. It is essential that we build vaccine confidence and retain the option of using this vaccine for people who are not in this risk group.”
He pointed out there are safety red flags with the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines.
“We should feel reassured about the process of ensuring vaccine safety as the FDA and CDC have quickly addressed risk and shared the data transparently of the J&J vaccine and taken appropriate action,” he said.
ACIP’s executive secretary, Amanda Cohn, MD, said the date for the next meeting would be set by April 16.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices decided there was not adequate information to change again recommend use of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
The committee’s decision comes the day after the CDC and Food and Drug Administration recommended that J&J injections be paused after reports of rare, but serious types of blood clots in six patients among the 6.8 million people who had received the J&J vaccine in the United States.
A member of the committee, Beth Bell, MD, said: “I do not want to be sending a message that there is some huge concern here on a different order of magnitude than any other vaccine safety signals that we evaluate. And I don’t want to send a message that there is something fundamentally wrong with the vaccine because that also I don’t agree with.”
At the end of the 4-hour meeting, ACIP members decided to call a meeting in 1 or 2 weeks and evaluate more safety data, specifically reports of people who have received the J&J vaccine in the past 2 weeks.
Some, however, pointed out that delaying a decision could have substantial consequences as well in terms of unused vaccine doses and public confidence.
Committee member Camiile Kotton, MD, described the pause as “devastating.”
“Putting this vaccine on pause for those of us that are frontline health care workers has really been devastating,” she said. “I agree in general that we don’t have enough data to make a decision at this time but we were planning on using this vaccine in the state of Massachusetts for people who were homebound and otherwise not able to get a vaccine. We were planning on using it for our vulnerable inpatient population often with many comorbidities and at high risk for disease but haven’t been able to get vaccinated otherwise.”
Pausing the one-and-done vaccine that doesn’t have the significant refrigeration requirements of the others “is a significant loss,” she said.
What is known, not known
Sara Oliver, MD, who leads the COVID-19 Vaccines ACIP Work Group, summarized what is known and unknown about the blood clots.
Among the six cases of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System after the J&J shot, all were women aged 18-48 years and all developed the clots 6-13 days after receiving the vaccine.
No cases of these clots have been reported from either the Pfizer or Moderna shots, she noted.
In the United States, the two mRNA vaccine alternatives – the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines – are available “and based on current projections supply of both vaccines are expected to be relatively stable in the near future,” she said.
She said 14 million doses of Pfizer and Moderna are expected each week in the United States and J&J vaccines makes up less than 5% of vaccines administered in the country.
Approximately 13 million J&J doses are available to order or are already at administration sites, she said.
But much more is unknown, she said.
“There may be more cases identified in the coming days to weeks,” Dr. Oliver said, referring back to the average time from vaccination to symptom onset.
Scott Ratzan, MD, editor-in-chief of the Journal of Health Communication: International Perspectives and executive director of Business Partners to CONVINCE (BP2C), a global network of employers that promotes COVID-19 vaccination among employees, suppliers, and customers, applauded ACIP’s delay on making a decision.
Dr. Ratzan, who watched the deliberations online, said in an interview the decision “shows an admirable abundance of caution in the distribution of COVID-19 vaccines.”
“Unfortunately,” he said, “the pause also worsens the existing and pervasive vaccine hesitancy issue.
“We need a rational strategy regarding who should or should not get the J&J/Janssen vaccine since these rare adverse events appear to affect a particular group of people, females aged 18-48. It is essential that we build vaccine confidence and retain the option of using this vaccine for people who are not in this risk group.”
He pointed out there are safety red flags with the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines.
“We should feel reassured about the process of ensuring vaccine safety as the FDA and CDC have quickly addressed risk and shared the data transparently of the J&J vaccine and taken appropriate action,” he said.
ACIP’s executive secretary, Amanda Cohn, MD, said the date for the next meeting would be set by April 16.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA approves first AI device to detect colon lesions
The GI Genius (Cosmo Artificial Intelligence) identifies areas of the colon where a colorectal polyp or tumor might be located. Clinicians then follow up with a closer examination and possible treatment.
“With the FDA’s authorization of this device today, clinicians now have a tool that could help improve their ability to detect gastrointestinal lesions they may have missed otherwise,” said Courtney H. Lias, PhD, acting director of the FDA’s gastrorenal, ob.gyn., general hospital, and urology devices office, in a media release.
The GI Genius consists of both hardware and software designed to work with an endoscope. It uses machine learning to recognize possible polyps during a colonoscopy. It marks these areas with green squares on the video generated by the endoscope’s camera and emits a short, low-volume sound. Clinicians decide if a lesion is truly present and whether to sample or remove such a lesion.
The device does not diagnose the lesions or recommend treatments and is not intended to take the place of laboratory sampling
The FDA based its approval on a trial in which 700 people aged 40-80 years underwent colonoscopies for colorectal cancer screening, surveillance, follow-up from positive results of a fecal occult blood test, or gastrointestinal symptoms of possible colon cancer.
Of these participants, 263 were being screened or surveilled every 3 years or more. The researchers randomly divided patients into a group of 136 who underwent white-light standard colonoscopy with the GI Genius, and 127 who underwent white-light standard colonoscopy without the GI Genius.
Using the GI Genius, clinicians identified adenomas or carcinomas that were later confirmed through lab results in 55.1% of patients. Without the GI Genius, the clinicians identified such lesions in 42.0% of patients.
The patients examined with the GI Genius received more biopsies, including slightly more that were not adenomas. But the biopsies did not lead to any adverse events such as perforations, infections, bleeding, or further biopsies.
More information on the GI Genius is available on the FDA website.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com .
The GI Genius (Cosmo Artificial Intelligence) identifies areas of the colon where a colorectal polyp or tumor might be located. Clinicians then follow up with a closer examination and possible treatment.
“With the FDA’s authorization of this device today, clinicians now have a tool that could help improve their ability to detect gastrointestinal lesions they may have missed otherwise,” said Courtney H. Lias, PhD, acting director of the FDA’s gastrorenal, ob.gyn., general hospital, and urology devices office, in a media release.
The GI Genius consists of both hardware and software designed to work with an endoscope. It uses machine learning to recognize possible polyps during a colonoscopy. It marks these areas with green squares on the video generated by the endoscope’s camera and emits a short, low-volume sound. Clinicians decide if a lesion is truly present and whether to sample or remove such a lesion.
The device does not diagnose the lesions or recommend treatments and is not intended to take the place of laboratory sampling
The FDA based its approval on a trial in which 700 people aged 40-80 years underwent colonoscopies for colorectal cancer screening, surveillance, follow-up from positive results of a fecal occult blood test, or gastrointestinal symptoms of possible colon cancer.
Of these participants, 263 were being screened or surveilled every 3 years or more. The researchers randomly divided patients into a group of 136 who underwent white-light standard colonoscopy with the GI Genius, and 127 who underwent white-light standard colonoscopy without the GI Genius.
Using the GI Genius, clinicians identified adenomas or carcinomas that were later confirmed through lab results in 55.1% of patients. Without the GI Genius, the clinicians identified such lesions in 42.0% of patients.
The patients examined with the GI Genius received more biopsies, including slightly more that were not adenomas. But the biopsies did not lead to any adverse events such as perforations, infections, bleeding, or further biopsies.
More information on the GI Genius is available on the FDA website.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com .
The GI Genius (Cosmo Artificial Intelligence) identifies areas of the colon where a colorectal polyp or tumor might be located. Clinicians then follow up with a closer examination and possible treatment.
“With the FDA’s authorization of this device today, clinicians now have a tool that could help improve their ability to detect gastrointestinal lesions they may have missed otherwise,” said Courtney H. Lias, PhD, acting director of the FDA’s gastrorenal, ob.gyn., general hospital, and urology devices office, in a media release.
The GI Genius consists of both hardware and software designed to work with an endoscope. It uses machine learning to recognize possible polyps during a colonoscopy. It marks these areas with green squares on the video generated by the endoscope’s camera and emits a short, low-volume sound. Clinicians decide if a lesion is truly present and whether to sample or remove such a lesion.
The device does not diagnose the lesions or recommend treatments and is not intended to take the place of laboratory sampling
The FDA based its approval on a trial in which 700 people aged 40-80 years underwent colonoscopies for colorectal cancer screening, surveillance, follow-up from positive results of a fecal occult blood test, or gastrointestinal symptoms of possible colon cancer.
Of these participants, 263 were being screened or surveilled every 3 years or more. The researchers randomly divided patients into a group of 136 who underwent white-light standard colonoscopy with the GI Genius, and 127 who underwent white-light standard colonoscopy without the GI Genius.
Using the GI Genius, clinicians identified adenomas or carcinomas that were later confirmed through lab results in 55.1% of patients. Without the GI Genius, the clinicians identified such lesions in 42.0% of patients.
The patients examined with the GI Genius received more biopsies, including slightly more that were not adenomas. But the biopsies did not lead to any adverse events such as perforations, infections, bleeding, or further biopsies.
More information on the GI Genius is available on the FDA website.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com .
List of COVID-19 high-risk comorbidities expanded
The list of medical according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
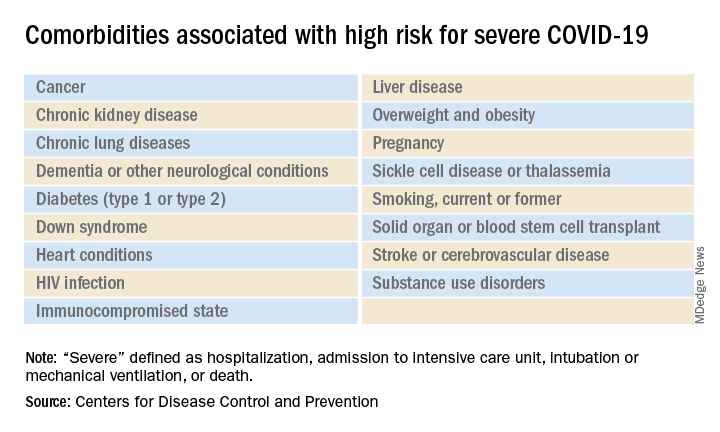
The CDC’s latest list consists of 17 conditions or groups of related conditions that may increase patients’ risk of developing severe outcomes of COVID-19, the CDC said on a web page intended for the general public.
On a separate page, the CDC defines severe outcomes “as hospitalization, admission to the intensive care unit, intubation or mechanical ventilation, or death.”
Asthma is included in the newly expanded list with other chronic lung diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cystic fibrosis; the list’s heart disease entry covers coronary artery disease, heart failure, cardiomyopathies, and hypertension, the CDC said.
The list of medical according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The CDC’s latest list consists of 17 conditions or groups of related conditions that may increase patients’ risk of developing severe outcomes of COVID-19, the CDC said on a web page intended for the general public.
On a separate page, the CDC defines severe outcomes “as hospitalization, admission to the intensive care unit, intubation or mechanical ventilation, or death.”
Asthma is included in the newly expanded list with other chronic lung diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cystic fibrosis; the list’s heart disease entry covers coronary artery disease, heart failure, cardiomyopathies, and hypertension, the CDC said.
The list of medical according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The CDC’s latest list consists of 17 conditions or groups of related conditions that may increase patients’ risk of developing severe outcomes of COVID-19, the CDC said on a web page intended for the general public.
On a separate page, the CDC defines severe outcomes “as hospitalization, admission to the intensive care unit, intubation or mechanical ventilation, or death.”
Asthma is included in the newly expanded list with other chronic lung diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cystic fibrosis; the list’s heart disease entry covers coronary artery disease, heart failure, cardiomyopathies, and hypertension, the CDC said.
FDA approves new ready-to-inject glucagon product
The Food and Drug Administration has approved dasiglucagon (Zegalogue 0.6 mg/0.6 mL, Zealand Pharma) autoinjector and prefilled syringe for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia in people with diabetes aged 6 years and older.
The product has a shelf-life of 36 months at refrigerated temperatures and is stable for up to 12 months at room temperature.
“This approval will help enable appropriate children and adults with diabetes to be able to address sudden and severe hypoglycemia, which can quickly progress from a mild event to an emergency,” Jeremy Pettus, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego, said in a company statement.
The approval marks the latest step in the development of newer glucagon formulations that are easier to use in hypoglycemic emergencies than the traditional formulation that requires several steps for reconstitution.
The first intranasal glucagon (Baqsimi, Eli Lilly) was approved in the United States in July 2019 for people with diabetes age 4 years and older.
In September 2019, the FDA approved another prefilled glucagon rescue pen (Gvoke HypoPen, Xeris Pharmaceuticals) for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia in adult and pediatric patients age 2 years and older with diabetes.
Dasiglucagon is currently in phase 3 trials as a subcutaneous infusion for treating congenital hyperinsulinemia, and in phase 2 trials as part of a bihormonal artificial pancreas pump system.
The FDA approval was based on results from three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 studies of dasiglucagon in children age 6-17 years and adults with type 1 diabetes.
The primary endpoint was time to achieving an increase in blood glucose of 20 mg/dL or greater from time of administration without additional intervention within 45 minutes. That endpoint was achieved in all three studies, with a median time to blood glucose recovery of 10 minutes overall, with 99% of adults recovering within 15 minutes.
The most common adverse events reported in 2% or more of study participants were nausea, vomiting, headache, and injection-site pain in both children and adults. Diarrhea was also reported in adults.
Full launch is expected in late June 2021.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved dasiglucagon (Zegalogue 0.6 mg/0.6 mL, Zealand Pharma) autoinjector and prefilled syringe for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia in people with diabetes aged 6 years and older.
The product has a shelf-life of 36 months at refrigerated temperatures and is stable for up to 12 months at room temperature.
“This approval will help enable appropriate children and adults with diabetes to be able to address sudden and severe hypoglycemia, which can quickly progress from a mild event to an emergency,” Jeremy Pettus, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego, said in a company statement.
The approval marks the latest step in the development of newer glucagon formulations that are easier to use in hypoglycemic emergencies than the traditional formulation that requires several steps for reconstitution.
The first intranasal glucagon (Baqsimi, Eli Lilly) was approved in the United States in July 2019 for people with diabetes age 4 years and older.
In September 2019, the FDA approved another prefilled glucagon rescue pen (Gvoke HypoPen, Xeris Pharmaceuticals) for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia in adult and pediatric patients age 2 years and older with diabetes.
Dasiglucagon is currently in phase 3 trials as a subcutaneous infusion for treating congenital hyperinsulinemia, and in phase 2 trials as part of a bihormonal artificial pancreas pump system.
The FDA approval was based on results from three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 studies of dasiglucagon in children age 6-17 years and adults with type 1 diabetes.
The primary endpoint was time to achieving an increase in blood glucose of 20 mg/dL or greater from time of administration without additional intervention within 45 minutes. That endpoint was achieved in all three studies, with a median time to blood glucose recovery of 10 minutes overall, with 99% of adults recovering within 15 minutes.
The most common adverse events reported in 2% or more of study participants were nausea, vomiting, headache, and injection-site pain in both children and adults. Diarrhea was also reported in adults.
Full launch is expected in late June 2021.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved dasiglucagon (Zegalogue 0.6 mg/0.6 mL, Zealand Pharma) autoinjector and prefilled syringe for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia in people with diabetes aged 6 years and older.
The product has a shelf-life of 36 months at refrigerated temperatures and is stable for up to 12 months at room temperature.
“This approval will help enable appropriate children and adults with diabetes to be able to address sudden and severe hypoglycemia, which can quickly progress from a mild event to an emergency,” Jeremy Pettus, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego, said in a company statement.
The approval marks the latest step in the development of newer glucagon formulations that are easier to use in hypoglycemic emergencies than the traditional formulation that requires several steps for reconstitution.
The first intranasal glucagon (Baqsimi, Eli Lilly) was approved in the United States in July 2019 for people with diabetes age 4 years and older.
In September 2019, the FDA approved another prefilled glucagon rescue pen (Gvoke HypoPen, Xeris Pharmaceuticals) for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia in adult and pediatric patients age 2 years and older with diabetes.
Dasiglucagon is currently in phase 3 trials as a subcutaneous infusion for treating congenital hyperinsulinemia, and in phase 2 trials as part of a bihormonal artificial pancreas pump system.
The FDA approval was based on results from three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 studies of dasiglucagon in children age 6-17 years and adults with type 1 diabetes.
The primary endpoint was time to achieving an increase in blood glucose of 20 mg/dL or greater from time of administration without additional intervention within 45 minutes. That endpoint was achieved in all three studies, with a median time to blood glucose recovery of 10 minutes overall, with 99% of adults recovering within 15 minutes.
The most common adverse events reported in 2% or more of study participants were nausea, vomiting, headache, and injection-site pain in both children and adults. Diarrhea was also reported in adults.
Full launch is expected in late June 2021.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 in 2020: Deaths and disparities
COVID-19 was the third-leading cause of death in the United States in 2020, but that mortality burden did not fall evenly along racial/ethnic lines, according to a provisional report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
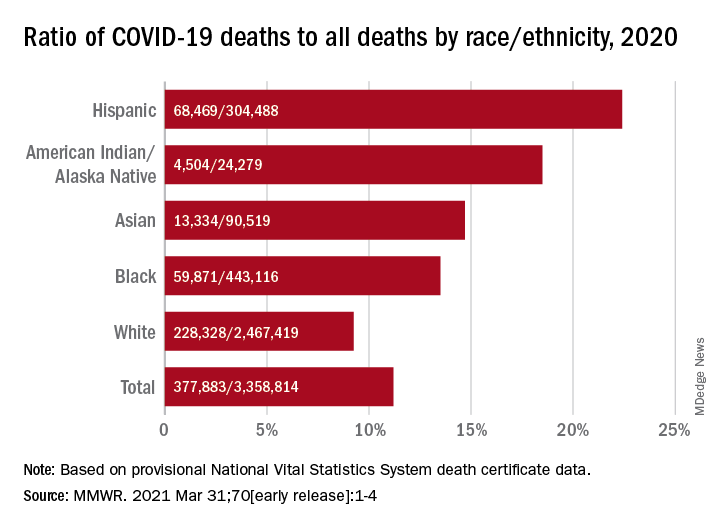
Only heart disease and cancer caused more deaths than SARS-CoV-2, which took the lives of almost 378,000 Americans last year, Farida B. Ahmad, MPH, and associates at the National Center for Health Statistics noted March 31 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
That represents 11.2% of the almost 3.36 million total deaths recorded in 2020. The racial/ethnics demographics, however, show that 22.4% of all deaths among Hispanic Americans were COVID-19–related, as were 18.6% of deaths in American Indians/Alaska Natives. Deaths among Asian persons, at 14.7%, and African Americans, at 13.5%, were closer but still above the national figure, while Whites (9.3%) were the only major subgroup below it, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
Age-adjusted death rates tell a somewhat different story: American Indian/Alaska native persons were highest with a rate of 187.8 COVID-19–associated deaths per 100,000 standard population, with Hispanic persons second at 164.3 per 100,000. Blacks were next at 151.1 deaths per 100,000, but Whites had a higher rate (72.5) than did Asian Americans (66.7), the CDC investigators reported.
“During January-December 2020, the estimated 2020 age-adjusted death rate increased for the first time since 2017, with an increase of 15.9% compared with 2019, from 715.2 to 828.7 deaths per 100,000 population,” they wrote, noting that “certain categories of race (i.e., AI/AN and Asian) and Hispanic ethnicity reported on death certificates might have been misclassified, possibly resulting in underestimates of death rates for some groups.”
COVID-19 was the third-leading cause of death in the United States in 2020, but that mortality burden did not fall evenly along racial/ethnic lines, according to a provisional report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Only heart disease and cancer caused more deaths than SARS-CoV-2, which took the lives of almost 378,000 Americans last year, Farida B. Ahmad, MPH, and associates at the National Center for Health Statistics noted March 31 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
That represents 11.2% of the almost 3.36 million total deaths recorded in 2020. The racial/ethnics demographics, however, show that 22.4% of all deaths among Hispanic Americans were COVID-19–related, as were 18.6% of deaths in American Indians/Alaska Natives. Deaths among Asian persons, at 14.7%, and African Americans, at 13.5%, were closer but still above the national figure, while Whites (9.3%) were the only major subgroup below it, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
Age-adjusted death rates tell a somewhat different story: American Indian/Alaska native persons were highest with a rate of 187.8 COVID-19–associated deaths per 100,000 standard population, with Hispanic persons second at 164.3 per 100,000. Blacks were next at 151.1 deaths per 100,000, but Whites had a higher rate (72.5) than did Asian Americans (66.7), the CDC investigators reported.
“During January-December 2020, the estimated 2020 age-adjusted death rate increased for the first time since 2017, with an increase of 15.9% compared with 2019, from 715.2 to 828.7 deaths per 100,000 population,” they wrote, noting that “certain categories of race (i.e., AI/AN and Asian) and Hispanic ethnicity reported on death certificates might have been misclassified, possibly resulting in underestimates of death rates for some groups.”
COVID-19 was the third-leading cause of death in the United States in 2020, but that mortality burden did not fall evenly along racial/ethnic lines, according to a provisional report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Only heart disease and cancer caused more deaths than SARS-CoV-2, which took the lives of almost 378,000 Americans last year, Farida B. Ahmad, MPH, and associates at the National Center for Health Statistics noted March 31 in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
That represents 11.2% of the almost 3.36 million total deaths recorded in 2020. The racial/ethnics demographics, however, show that 22.4% of all deaths among Hispanic Americans were COVID-19–related, as were 18.6% of deaths in American Indians/Alaska Natives. Deaths among Asian persons, at 14.7%, and African Americans, at 13.5%, were closer but still above the national figure, while Whites (9.3%) were the only major subgroup below it, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
Age-adjusted death rates tell a somewhat different story: American Indian/Alaska native persons were highest with a rate of 187.8 COVID-19–associated deaths per 100,000 standard population, with Hispanic persons second at 164.3 per 100,000. Blacks were next at 151.1 deaths per 100,000, but Whites had a higher rate (72.5) than did Asian Americans (66.7), the CDC investigators reported.
“During January-December 2020, the estimated 2020 age-adjusted death rate increased for the first time since 2017, with an increase of 15.9% compared with 2019, from 715.2 to 828.7 deaths per 100,000 population,” they wrote, noting that “certain categories of race (i.e., AI/AN and Asian) and Hispanic ethnicity reported on death certificates might have been misclassified, possibly resulting in underestimates of death rates for some groups.”
FROM MMWR
CDC adds new medical conditions to COVID-19 high-risk list
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has added several new medical conditions to its list of those that predispose adults to more severe COVID-19 illness.
Conditions that had previously been categorized as “might be” placing individuals at increased risk – but now are listed as high risk – include type 1 diabetes (in addition to type 2), moderate-to-severe asthma, liver disease, dementia or other neurologic conditions, stroke/cerebrovascular disease, HIV infection, cystic fibrosis, and overweight (in addition to obesity).
Substance use disorders, which hadn’t been previously listed, are now also considered high risk.
The new list groups together certain categories, such as chronic lung diseases (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, cystic fibrosis, etc) and heart conditions (heart failure, coronary artery disease, hypertension, etc).
Both diabetes types are now grouped under “diabetes.”
The added medical conditions were posted on the CDC website’s COVID-19 page on March 29.
Type 1 diabetes and other conditions now priority for vaccination
The CDC refers to the medical conditions list as phase 1c in regard to COVID-19 vaccine prioritization, which means that anyone with any of these conditions can now be prioritized for vaccination, following those in groups 1a (frontline essential workers and those in long-term care facilities) and 1b (people aged 65-74 years; other essential workers; and people aged 16-64 years with underlying conditions that increase the risk of serious, life-threatening complications from COVID-19).
But in many cases, multiple states have already either fully opened up vaccine eligibility to all adults or have created their own lists of underlying high-risk medical conditions, CDC spokeswoman Kristen Nordlund told this news organization.
No conditions have been removed from the list.
In January, the American Diabetes Association and 18 other organizations sent a letter to the CDC requesting that type 1 diabetes be prioritized along with type 2, based on data from studies showing people with both types to be at high risk for severe COVID-19 illness.
Now, ADA says, “this updated guidance will help to address the fact that in many states, millions of people with type 1 diabetes have not been prioritized equally, slowing their access to critical vaccines.”
While awaiting this latest CDC move, ADA had been urging state governors to prioritize type 1 and type 2 diabetes equally. As of now, 38 states and the District of Columbia had either done so or announced that they would.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has added several new medical conditions to its list of those that predispose adults to more severe COVID-19 illness.
Conditions that had previously been categorized as “might be” placing individuals at increased risk – but now are listed as high risk – include type 1 diabetes (in addition to type 2), moderate-to-severe asthma, liver disease, dementia or other neurologic conditions, stroke/cerebrovascular disease, HIV infection, cystic fibrosis, and overweight (in addition to obesity).
Substance use disorders, which hadn’t been previously listed, are now also considered high risk.
The new list groups together certain categories, such as chronic lung diseases (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, cystic fibrosis, etc) and heart conditions (heart failure, coronary artery disease, hypertension, etc).
Both diabetes types are now grouped under “diabetes.”
The added medical conditions were posted on the CDC website’s COVID-19 page on March 29.
Type 1 diabetes and other conditions now priority for vaccination
The CDC refers to the medical conditions list as phase 1c in regard to COVID-19 vaccine prioritization, which means that anyone with any of these conditions can now be prioritized for vaccination, following those in groups 1a (frontline essential workers and those in long-term care facilities) and 1b (people aged 65-74 years; other essential workers; and people aged 16-64 years with underlying conditions that increase the risk of serious, life-threatening complications from COVID-19).
But in many cases, multiple states have already either fully opened up vaccine eligibility to all adults or have created their own lists of underlying high-risk medical conditions, CDC spokeswoman Kristen Nordlund told this news organization.
No conditions have been removed from the list.
In January, the American Diabetes Association and 18 other organizations sent a letter to the CDC requesting that type 1 diabetes be prioritized along with type 2, based on data from studies showing people with both types to be at high risk for severe COVID-19 illness.
Now, ADA says, “this updated guidance will help to address the fact that in many states, millions of people with type 1 diabetes have not been prioritized equally, slowing their access to critical vaccines.”
While awaiting this latest CDC move, ADA had been urging state governors to prioritize type 1 and type 2 diabetes equally. As of now, 38 states and the District of Columbia had either done so or announced that they would.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has added several new medical conditions to its list of those that predispose adults to more severe COVID-19 illness.
Conditions that had previously been categorized as “might be” placing individuals at increased risk – but now are listed as high risk – include type 1 diabetes (in addition to type 2), moderate-to-severe asthma, liver disease, dementia or other neurologic conditions, stroke/cerebrovascular disease, HIV infection, cystic fibrosis, and overweight (in addition to obesity).
Substance use disorders, which hadn’t been previously listed, are now also considered high risk.
The new list groups together certain categories, such as chronic lung diseases (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, cystic fibrosis, etc) and heart conditions (heart failure, coronary artery disease, hypertension, etc).
Both diabetes types are now grouped under “diabetes.”
The added medical conditions were posted on the CDC website’s COVID-19 page on March 29.
Type 1 diabetes and other conditions now priority for vaccination
The CDC refers to the medical conditions list as phase 1c in regard to COVID-19 vaccine prioritization, which means that anyone with any of these conditions can now be prioritized for vaccination, following those in groups 1a (frontline essential workers and those in long-term care facilities) and 1b (people aged 65-74 years; other essential workers; and people aged 16-64 years with underlying conditions that increase the risk of serious, life-threatening complications from COVID-19).
But in many cases, multiple states have already either fully opened up vaccine eligibility to all adults or have created their own lists of underlying high-risk medical conditions, CDC spokeswoman Kristen Nordlund told this news organization.
No conditions have been removed from the list.
In January, the American Diabetes Association and 18 other organizations sent a letter to the CDC requesting that type 1 diabetes be prioritized along with type 2, based on data from studies showing people with both types to be at high risk for severe COVID-19 illness.
Now, ADA says, “this updated guidance will help to address the fact that in many states, millions of people with type 1 diabetes have not been prioritized equally, slowing their access to critical vaccines.”
While awaiting this latest CDC move, ADA had been urging state governors to prioritize type 1 and type 2 diabetes equally. As of now, 38 states and the District of Columbia had either done so or announced that they would.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
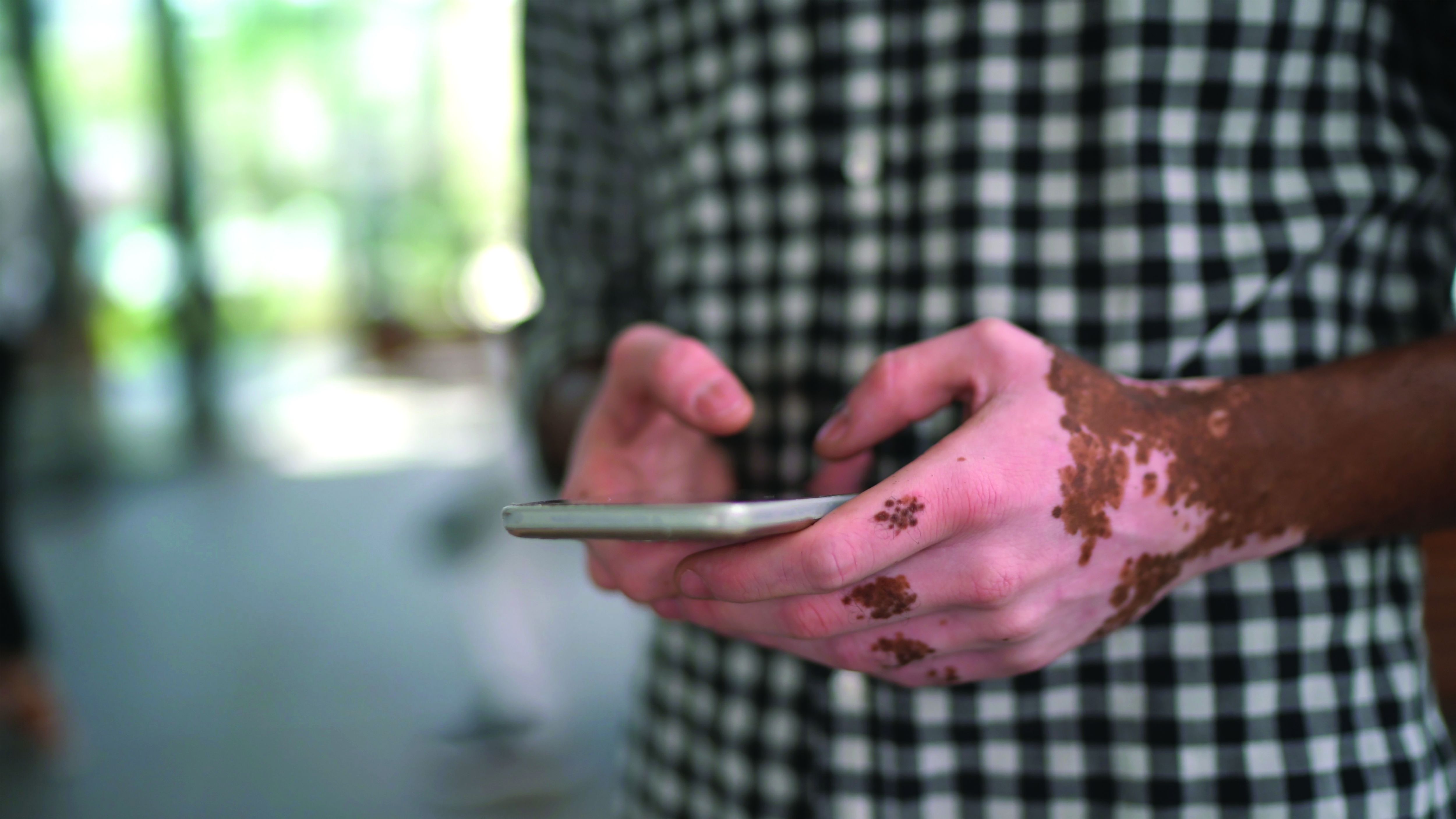
Vitiligo patients share their experiences, frustrations with treatment options with FDA
Patients with vitiligo have faced significant impacts psychosocially and in many cases, profound losses of identity – and they’ve had only minimal success with treatment, according to participants who spoke at and provided input at a public meeting on patient-focused drug development for the disease.
The virtual meeting, held in March, was part of the Food and Drug Administration’s Patient-Focused Drug Development (PFDD) initiative, which began in 2012 and aims to provide a systematic way for patients’ experiences, needs and priorities to be “captured and meaningfully incorporated” into drug development and evaluation.
Seemal Desai, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Texas, Dallas, who attended the meeting as an observer, said in a later interview that while “all skin diseases have a psychosocial component … vitiligo is a really unique one, because it really relates to the patient’s own identity.
“What I heard loud and clear from the FDA [leaders who ran and attended the meeting] is recognition that patients are suffering. They needed to hear about the emotional devastation of the disease and how it is a medical condition,” Dr. Desai said.
The meeting was the “first-ever vitiligo meeting at the FDA” and was a “historic moment for the vitiligo community,” he added.
The pigmentation disorder affects 1% of the world’s population. Nearly 50% have an onset before age 20, and onset before age 12 is common, Brenda Carr, MD, medical officer with the FDA’s Division of Dermatology and Dentistry in the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in an introductory overview.
The only FDA-approved treatment for vitiligo is monobenzone cream, but this is indicated for final depigmentation in extensive vitiligo and is no longer marketed. Treatment options include corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, vitamin D analogues, phototherapy, surgical treatments (tissue grafts and cellular grafts), and camouflage (make-up, tattoos, self-tanning products), Dr. Carr said.
Patients participated in one of two panels – one about the health effects and daily impacts of vitiligo and the other about treatments – or submitted input electronically. All patients were invited to answer poll questions and open-ended queries, including questions about how they would assess new treatments.
Several panel members who are Black shared series of photos that showed the evolution of defined white patches into widespread, generalized depigmentation. One man with skin of color who lives in the Netherlands said he has had vitiligo since the age of 12, but that when he became older, over a 4-year period, he was “transformed from a man of Indonesian roots to a totally white man.”
Experiencing only minimal benefit from treatment and the short-term effectiveness of treatments were the top two answers to a poll question asking participants about the most burdensome impacts of the medical products and interventions they have used. Difficulty in accessing treatment, concern about serious risks of treatment, and uncertainty about long-term effects of treatment were other frequently chosen answers.
Patients described the onerous nature of phototherapy (treatments repeated several times a week over long periods) and other treatments, and several described feeling that some physicians did not take the condition seriously or fully know of treatment options.
In her closing remarks, Kendall Marcus, MD, director of the Division of Dermatology and Dentistry at the FDA, acknowledged the input. “Some of you have had difficulty having your disease taken seriously by physicians who view it as a cosmetic condition and are reluctant to treat because they believe your expectations will not be met, that it will be an exercise in frustration,” she said.
Regarding the impacts of treatments that have been utilized, “some of the treatments make it impossible to do other activities such as work or care for yourself in other ways,” Dr. Marcus said. “Certainly that’s not the kind of treatment … that anybody wants to have.”
Dr. Desai, who utilizes an array of oral and topical treatments and phototherapies in his practice, said he was surprised and disheartened to hear the level of concern about side effects of treatment. Most of those who expressed concerns alluded to phototherapy. “I think light treatments are very safe and effective,” he said in the interview. “I might equate [such concerns] to the older PUVA [psoralen plus UVA ultraviolet light] therapy, but not so much the newer therapies.”
The FDA participants probed patients for their perspective on a meaningful level of repigmentation and an acceptable level of risk for any new hypothetical treatment. Specifically, they asked whether patients would use a new topical cream approved for vitiligo if the cream needed to be applied once a day, would have up to 50% efficacy in some people, and would have common side effects of redness and irritation at the application site, mild acne, and burning, as well as several rarer but more serious side effects.
Only 36% answered yes; 24% said no, and 40% answered maybe. Some patients said during the meeting that they had accepted their condition and were not pursuing any treatment. Others said they were very interested in treatment but only if the level of repigmentation were significantly higher than 50%. Some described their fear that positive treatment effects would be short term only.
Meri Izrail Kohen, who lives in France and has lost half of her skin’s pigmentation, said that treatment efficacy is “not only about how much recovery of pigment it allows, but how long the recovery will last.” Some treatments will work for some patients, she said, “but even in these cases when we stop the treatment, it will come back somehow.”
Lee Thomas, a TV anchor in Detroit, and a reporter and author of the book “Turning White,” described how he tried “every treatment he could afford” but stopped trying 10 years ago. A treatment in Germany “gave me 80% of my pigment back, but it has gone again,” he said. “I would love to have my face back again. I was born a Black child, and I’d like to die a Black man.”
Patients also spoke of their skin burning easily outdoors; skin sensitivity, itchiness, and burning with the spread of disease; treatment expenses and not being able to afford treatment; and worsening of their vitiligo with the stress of the pandemic. Parents expressed having fear that their children would develop vitiligo and experience bullying, isolation, or other emotional or psychosocial impacts that they had experienced; one described having an almost-paralyzing anxiety when he saw patchy white spots on his 20-month-old daughter (it was not diagnosed as vitiligo).
Calls for further advancement with home phototherapy – which Dr. Desai said is a growing market but not yet adequately covered by insurance plans – were also made, as were pleas for research on the root causes of the disease.
Patients clearly indicated “that they need more efficacious treatments, and more comprehensive treatments,” said Dr. Desai, who chairs the advisory committee of the Global Vitiligo Foundation. “It’s disappointing to me that patients come in with a not fully optimistic viewpoint, with a lot of anxiety and angst that treatments are not going to work. … But the Agency needs to hear that. This means that there haven’t been good treatments and we need more.”
The FDA will accept public comments until May 10, 2021, at which time comments will be compiled into a summary report. FDA officials assured patients that the report would be visible and circulated not only within the FDA but among drug companies, researchers, and other product developers.
Patients with vitiligo have faced significant impacts psychosocially and in many cases, profound losses of identity – and they’ve had only minimal success with treatment, according to participants who spoke at and provided input at a public meeting on patient-focused drug development for the disease.
The virtual meeting, held in March, was part of the Food and Drug Administration’s Patient-Focused Drug Development (PFDD) initiative, which began in 2012 and aims to provide a systematic way for patients’ experiences, needs and priorities to be “captured and meaningfully incorporated” into drug development and evaluation.
Seemal Desai, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Texas, Dallas, who attended the meeting as an observer, said in a later interview that while “all skin diseases have a psychosocial component … vitiligo is a really unique one, because it really relates to the patient’s own identity.
“What I heard loud and clear from the FDA [leaders who ran and attended the meeting] is recognition that patients are suffering. They needed to hear about the emotional devastation of the disease and how it is a medical condition,” Dr. Desai said.
The meeting was the “first-ever vitiligo meeting at the FDA” and was a “historic moment for the vitiligo community,” he added.
The pigmentation disorder affects 1% of the world’s population. Nearly 50% have an onset before age 20, and onset before age 12 is common, Brenda Carr, MD, medical officer with the FDA’s Division of Dermatology and Dentistry in the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in an introductory overview.
The only FDA-approved treatment for vitiligo is monobenzone cream, but this is indicated for final depigmentation in extensive vitiligo and is no longer marketed. Treatment options include corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, vitamin D analogues, phototherapy, surgical treatments (tissue grafts and cellular grafts), and camouflage (make-up, tattoos, self-tanning products), Dr. Carr said.
Patients participated in one of two panels – one about the health effects and daily impacts of vitiligo and the other about treatments – or submitted input electronically. All patients were invited to answer poll questions and open-ended queries, including questions about how they would assess new treatments.
Several panel members who are Black shared series of photos that showed the evolution of defined white patches into widespread, generalized depigmentation. One man with skin of color who lives in the Netherlands said he has had vitiligo since the age of 12, but that when he became older, over a 4-year period, he was “transformed from a man of Indonesian roots to a totally white man.”
Experiencing only minimal benefit from treatment and the short-term effectiveness of treatments were the top two answers to a poll question asking participants about the most burdensome impacts of the medical products and interventions they have used. Difficulty in accessing treatment, concern about serious risks of treatment, and uncertainty about long-term effects of treatment were other frequently chosen answers.
Patients described the onerous nature of phototherapy (treatments repeated several times a week over long periods) and other treatments, and several described feeling that some physicians did not take the condition seriously or fully know of treatment options.
In her closing remarks, Kendall Marcus, MD, director of the Division of Dermatology and Dentistry at the FDA, acknowledged the input. “Some of you have had difficulty having your disease taken seriously by physicians who view it as a cosmetic condition and are reluctant to treat because they believe your expectations will not be met, that it will be an exercise in frustration,” she said.
Regarding the impacts of treatments that have been utilized, “some of the treatments make it impossible to do other activities such as work or care for yourself in other ways,” Dr. Marcus said. “Certainly that’s not the kind of treatment … that anybody wants to have.”
Dr. Desai, who utilizes an array of oral and topical treatments and phototherapies in his practice, said he was surprised and disheartened to hear the level of concern about side effects of treatment. Most of those who expressed concerns alluded to phototherapy. “I think light treatments are very safe and effective,” he said in the interview. “I might equate [such concerns] to the older PUVA [psoralen plus UVA ultraviolet light] therapy, but not so much the newer therapies.”
The FDA participants probed patients for their perspective on a meaningful level of repigmentation and an acceptable level of risk for any new hypothetical treatment. Specifically, they asked whether patients would use a new topical cream approved for vitiligo if the cream needed to be applied once a day, would have up to 50% efficacy in some people, and would have common side effects of redness and irritation at the application site, mild acne, and burning, as well as several rarer but more serious side effects.
Only 36% answered yes; 24% said no, and 40% answered maybe. Some patients said during the meeting that they had accepted their condition and were not pursuing any treatment. Others said they were very interested in treatment but only if the level of repigmentation were significantly higher than 50%. Some described their fear that positive treatment effects would be short term only.
Meri Izrail Kohen, who lives in France and has lost half of her skin’s pigmentation, said that treatment efficacy is “not only about how much recovery of pigment it allows, but how long the recovery will last.” Some treatments will work for some patients, she said, “but even in these cases when we stop the treatment, it will come back somehow.”
Lee Thomas, a TV anchor in Detroit, and a reporter and author of the book “Turning White,” described how he tried “every treatment he could afford” but stopped trying 10 years ago. A treatment in Germany “gave me 80% of my pigment back, but it has gone again,” he said. “I would love to have my face back again. I was born a Black child, and I’d like to die a Black man.”
Patients also spoke of their skin burning easily outdoors; skin sensitivity, itchiness, and burning with the spread of disease; treatment expenses and not being able to afford treatment; and worsening of their vitiligo with the stress of the pandemic. Parents expressed having fear that their children would develop vitiligo and experience bullying, isolation, or other emotional or psychosocial impacts that they had experienced; one described having an almost-paralyzing anxiety when he saw patchy white spots on his 20-month-old daughter (it was not diagnosed as vitiligo).
Calls for further advancement with home phototherapy – which Dr. Desai said is a growing market but not yet adequately covered by insurance plans – were also made, as were pleas for research on the root causes of the disease.
Patients clearly indicated “that they need more efficacious treatments, and more comprehensive treatments,” said Dr. Desai, who chairs the advisory committee of the Global Vitiligo Foundation. “It’s disappointing to me that patients come in with a not fully optimistic viewpoint, with a lot of anxiety and angst that treatments are not going to work. … But the Agency needs to hear that. This means that there haven’t been good treatments and we need more.”
The FDA will accept public comments until May 10, 2021, at which time comments will be compiled into a summary report. FDA officials assured patients that the report would be visible and circulated not only within the FDA but among drug companies, researchers, and other product developers.
Patients with vitiligo have faced significant impacts psychosocially and in many cases, profound losses of identity – and they’ve had only minimal success with treatment, according to participants who spoke at and provided input at a public meeting on patient-focused drug development for the disease.
The virtual meeting, held in March, was part of the Food and Drug Administration’s Patient-Focused Drug Development (PFDD) initiative, which began in 2012 and aims to provide a systematic way for patients’ experiences, needs and priorities to be “captured and meaningfully incorporated” into drug development and evaluation.
Seemal Desai, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Texas, Dallas, who attended the meeting as an observer, said in a later interview that while “all skin diseases have a psychosocial component … vitiligo is a really unique one, because it really relates to the patient’s own identity.
“What I heard loud and clear from the FDA [leaders who ran and attended the meeting] is recognition that patients are suffering. They needed to hear about the emotional devastation of the disease and how it is a medical condition,” Dr. Desai said.
The meeting was the “first-ever vitiligo meeting at the FDA” and was a “historic moment for the vitiligo community,” he added.
The pigmentation disorder affects 1% of the world’s population. Nearly 50% have an onset before age 20, and onset before age 12 is common, Brenda Carr, MD, medical officer with the FDA’s Division of Dermatology and Dentistry in the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in an introductory overview.
The only FDA-approved treatment for vitiligo is monobenzone cream, but this is indicated for final depigmentation in extensive vitiligo and is no longer marketed. Treatment options include corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, vitamin D analogues, phototherapy, surgical treatments (tissue grafts and cellular grafts), and camouflage (make-up, tattoos, self-tanning products), Dr. Carr said.
Patients participated in one of two panels – one about the health effects and daily impacts of vitiligo and the other about treatments – or submitted input electronically. All patients were invited to answer poll questions and open-ended queries, including questions about how they would assess new treatments.
Several panel members who are Black shared series of photos that showed the evolution of defined white patches into widespread, generalized depigmentation. One man with skin of color who lives in the Netherlands said he has had vitiligo since the age of 12, but that when he became older, over a 4-year period, he was “transformed from a man of Indonesian roots to a totally white man.”
Experiencing only minimal benefit from treatment and the short-term effectiveness of treatments were the top two answers to a poll question asking participants about the most burdensome impacts of the medical products and interventions they have used. Difficulty in accessing treatment, concern about serious risks of treatment, and uncertainty about long-term effects of treatment were other frequently chosen answers.
Patients described the onerous nature of phototherapy (treatments repeated several times a week over long periods) and other treatments, and several described feeling that some physicians did not take the condition seriously or fully know of treatment options.
In her closing remarks, Kendall Marcus, MD, director of the Division of Dermatology and Dentistry at the FDA, acknowledged the input. “Some of you have had difficulty having your disease taken seriously by physicians who view it as a cosmetic condition and are reluctant to treat because they believe your expectations will not be met, that it will be an exercise in frustration,” she said.
Regarding the impacts of treatments that have been utilized, “some of the treatments make it impossible to do other activities such as work or care for yourself in other ways,” Dr. Marcus said. “Certainly that’s not the kind of treatment … that anybody wants to have.”
Dr. Desai, who utilizes an array of oral and topical treatments and phototherapies in his practice, said he was surprised and disheartened to hear the level of concern about side effects of treatment. Most of those who expressed concerns alluded to phototherapy. “I think light treatments are very safe and effective,” he said in the interview. “I might equate [such concerns] to the older PUVA [psoralen plus UVA ultraviolet light] therapy, but not so much the newer therapies.”
The FDA participants probed patients for their perspective on a meaningful level of repigmentation and an acceptable level of risk for any new hypothetical treatment. Specifically, they asked whether patients would use a new topical cream approved for vitiligo if the cream needed to be applied once a day, would have up to 50% efficacy in some people, and would have common side effects of redness and irritation at the application site, mild acne, and burning, as well as several rarer but more serious side effects.
Only 36% answered yes; 24% said no, and 40% answered maybe. Some patients said during the meeting that they had accepted their condition and were not pursuing any treatment. Others said they were very interested in treatment but only if the level of repigmentation were significantly higher than 50%. Some described their fear that positive treatment effects would be short term only.
Meri Izrail Kohen, who lives in France and has lost half of her skin’s pigmentation, said that treatment efficacy is “not only about how much recovery of pigment it allows, but how long the recovery will last.” Some treatments will work for some patients, she said, “but even in these cases when we stop the treatment, it will come back somehow.”
Lee Thomas, a TV anchor in Detroit, and a reporter and author of the book “Turning White,” described how he tried “every treatment he could afford” but stopped trying 10 years ago. A treatment in Germany “gave me 80% of my pigment back, but it has gone again,” he said. “I would love to have my face back again. I was born a Black child, and I’d like to die a Black man.”
Patients also spoke of their skin burning easily outdoors; skin sensitivity, itchiness, and burning with the spread of disease; treatment expenses and not being able to afford treatment; and worsening of their vitiligo with the stress of the pandemic. Parents expressed having fear that their children would develop vitiligo and experience bullying, isolation, or other emotional or psychosocial impacts that they had experienced; one described having an almost-paralyzing anxiety when he saw patchy white spots on his 20-month-old daughter (it was not diagnosed as vitiligo).
Calls for further advancement with home phototherapy – which Dr. Desai said is a growing market but not yet adequately covered by insurance plans – were also made, as were pleas for research on the root causes of the disease.
Patients clearly indicated “that they need more efficacious treatments, and more comprehensive treatments,” said Dr. Desai, who chairs the advisory committee of the Global Vitiligo Foundation. “It’s disappointing to me that patients come in with a not fully optimistic viewpoint, with a lot of anxiety and angst that treatments are not going to work. … But the Agency needs to hear that. This means that there haven’t been good treatments and we need more.”
The FDA will accept public comments until May 10, 2021, at which time comments will be compiled into a summary report. FDA officials assured patients that the report would be visible and circulated not only within the FDA but among drug companies, researchers, and other product developers.
FROM AN FDA PATIENT-FOCUSED DRUG DEVELOPMENT MEETING
Arcalyst gets FDA nod as first therapy for recurrent pericarditis
The Food and Drug Administration has approved rilonacept (Arcalyst) to treat recurrent pericarditis and reduce the risk for recurrence in adults and children 12 years and older.
Approval of the weekly subcutaneous injection offers patients the first and only FDA-approved therapy for recurrent pericarditis, the agency said in a release.
Recurrent pericarditis is characterized by a remitting relapsing inflammation of the pericardium, and therapeutic options have been limited to NSAIDs, colchicine, and corticosteroids.
Rilonacept is a recombinant fusion protein that blocks interleukin-1 alpha and interleukin-1 beta signaling. It is already approved by the FDA to treat a group of rare inherited inflammatory diseases called cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes.
The new indication is based on the pivotal phase 3 RHAPSODY trial in 86 patients with acute symptoms of recurrent pericarditis and systemic inflammation. After randomization, pericarditis recurred in 2 of 30 patients (7%) treated with rilonacept and in 23 of 31 patients (74%) treated with placebo, representing a 96% reduction in the relative risk for recurrence with rilonacept.
Patients who received rilonacept were also pain free or had minimal pain on 98% of trial days, whereas those who received placebo had minimal or no pain on 46% of trial days.
The most common adverse effects of rilonacept are injection-site reactions and upper-respiratory tract infections.
Serious, life-threatening infections have been reported in patients taking rilonacept, according to the FDA. Patients with active or chronic infections should not take the drug.
The FDA label also advises that patients should avoid live vaccines while taking rilonacept and that it should be discontinued if a hypersensitivity reaction occurs.
The commercial launch is expected in April, according to the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved rilonacept (Arcalyst) to treat recurrent pericarditis and reduce the risk for recurrence in adults and children 12 years and older.
Approval of the weekly subcutaneous injection offers patients the first and only FDA-approved therapy for recurrent pericarditis, the agency said in a release.
Recurrent pericarditis is characterized by a remitting relapsing inflammation of the pericardium, and therapeutic options have been limited to NSAIDs, colchicine, and corticosteroids.
Rilonacept is a recombinant fusion protein that blocks interleukin-1 alpha and interleukin-1 beta signaling. It is already approved by the FDA to treat a group of rare inherited inflammatory diseases called cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes.
The new indication is based on the pivotal phase 3 RHAPSODY trial in 86 patients with acute symptoms of recurrent pericarditis and systemic inflammation. After randomization, pericarditis recurred in 2 of 30 patients (7%) treated with rilonacept and in 23 of 31 patients (74%) treated with placebo, representing a 96% reduction in the relative risk for recurrence with rilonacept.
Patients who received rilonacept were also pain free or had minimal pain on 98% of trial days, whereas those who received placebo had minimal or no pain on 46% of trial days.
The most common adverse effects of rilonacept are injection-site reactions and upper-respiratory tract infections.
Serious, life-threatening infections have been reported in patients taking rilonacept, according to the FDA. Patients with active or chronic infections should not take the drug.
The FDA label also advises that patients should avoid live vaccines while taking rilonacept and that it should be discontinued if a hypersensitivity reaction occurs.
The commercial launch is expected in April, according to the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved rilonacept (Arcalyst) to treat recurrent pericarditis and reduce the risk for recurrence in adults and children 12 years and older.
Approval of the weekly subcutaneous injection offers patients the first and only FDA-approved therapy for recurrent pericarditis, the agency said in a release.
Recurrent pericarditis is characterized by a remitting relapsing inflammation of the pericardium, and therapeutic options have been limited to NSAIDs, colchicine, and corticosteroids.
Rilonacept is a recombinant fusion protein that blocks interleukin-1 alpha and interleukin-1 beta signaling. It is already approved by the FDA to treat a group of rare inherited inflammatory diseases called cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes.
The new indication is based on the pivotal phase 3 RHAPSODY trial in 86 patients with acute symptoms of recurrent pericarditis and systemic inflammation. After randomization, pericarditis recurred in 2 of 30 patients (7%) treated with rilonacept and in 23 of 31 patients (74%) treated with placebo, representing a 96% reduction in the relative risk for recurrence with rilonacept.
Patients who received rilonacept were also pain free or had minimal pain on 98% of trial days, whereas those who received placebo had minimal or no pain on 46% of trial days.
The most common adverse effects of rilonacept are injection-site reactions and upper-respiratory tract infections.
Serious, life-threatening infections have been reported in patients taking rilonacept, according to the FDA. Patients with active or chronic infections should not take the drug.
The FDA label also advises that patients should avoid live vaccines while taking rilonacept and that it should be discontinued if a hypersensitivity reaction occurs.
The commercial launch is expected in April, according to the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA warning letters target OTC cannabidiol product claims for pain relief
The Food and Drug Administration has warned two manufacturers about illegal marketing of drugs containing cannabidiol (CBD) for over-the-counter use without an approved new drug application, for using substandard manufacturing processes, and for failure to comply with current good manufacturing practices. These warnings add to 51 previous warning letters issued by the FDA since 2015 to other manufacturers of products containing CBD who were violating the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act.
In a news release, the agency explained that its two most recent letters, sent to Honest Globe Inc. on March 15 and BioLyte Laboratories LLC on March 18, were issued because CBD has “known pharmacologic effects on humans, with demonstrated risks, it cannot be legally marketed as an inactive ingredient in OTC drug products that are not reviewed and approved by the FDA.” They also describe the companies’ failures to comply with current good manufacturing practices.
“The FDA continues to alert the public to potential safety and efficacy concerns with unapproved CBD products sold online and in stores across the country,” FDA Principal Deputy Commissioner Amy P. Abernethy, MD, PhD, said in the release. “It’s important that consumers understand that the FDA has only approved one drug containing CBD as an ingredient [Epidiolex]. These other, unapproved, CBD products may have dangerous health impacts and side effects. We remain focused on exploring potential pathways for CBD products to be lawfully marketed while also educating the public about these outstanding questions of CBD’s safety. Meanwhile, we will continue to monitor and take action, as needed, against companies that unlawfully market their products – prioritizing those that pose a risk to public health.”
The specific products from Santa Ana, Calif.–based Honest Globe that the FDA called unapproved new drugs and misbranded under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act included Elixicure Original Pain Relief and Elixicure Lavender Pain Relief, both of which were described as containing CBD. Products from Grand Rapids, Mich.–based BioLyte Laboratories LLC that the FDA similarly cited for violations included Silver Gel, Silver Gel with Aloe, Silver Liquid Supplement, Therapeutic Pain Gel, Pain Relief Cream, and Magnesium Oil Spray.
The agency has asked the two companies to respond to its letters within 15 working days, “stating how they will address these violations or providing their reasoning and supporting information as to why they believe these products are not in violation of the law. Failure to adequately address the violations promptly may result in legal action, including product seizure and/or injunction.”
The Food and Drug Administration has warned two manufacturers about illegal marketing of drugs containing cannabidiol (CBD) for over-the-counter use without an approved new drug application, for using substandard manufacturing processes, and for failure to comply with current good manufacturing practices. These warnings add to 51 previous warning letters issued by the FDA since 2015 to other manufacturers of products containing CBD who were violating the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act.
In a news release, the agency explained that its two most recent letters, sent to Honest Globe Inc. on March 15 and BioLyte Laboratories LLC on March 18, were issued because CBD has “known pharmacologic effects on humans, with demonstrated risks, it cannot be legally marketed as an inactive ingredient in OTC drug products that are not reviewed and approved by the FDA.” They also describe the companies’ failures to comply with current good manufacturing practices.
“The FDA continues to alert the public to potential safety and efficacy concerns with unapproved CBD products sold online and in stores across the country,” FDA Principal Deputy Commissioner Amy P. Abernethy, MD, PhD, said in the release. “It’s important that consumers understand that the FDA has only approved one drug containing CBD as an ingredient [Epidiolex]. These other, unapproved, CBD products may have dangerous health impacts and side effects. We remain focused on exploring potential pathways for CBD products to be lawfully marketed while also educating the public about these outstanding questions of CBD’s safety. Meanwhile, we will continue to monitor and take action, as needed, against companies that unlawfully market their products – prioritizing those that pose a risk to public health.”
The specific products from Santa Ana, Calif.–based Honest Globe that the FDA called unapproved new drugs and misbranded under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act included Elixicure Original Pain Relief and Elixicure Lavender Pain Relief, both of which were described as containing CBD. Products from Grand Rapids, Mich.–based BioLyte Laboratories LLC that the FDA similarly cited for violations included Silver Gel, Silver Gel with Aloe, Silver Liquid Supplement, Therapeutic Pain Gel, Pain Relief Cream, and Magnesium Oil Spray.
The agency has asked the two companies to respond to its letters within 15 working days, “stating how they will address these violations or providing their reasoning and supporting information as to why they believe these products are not in violation of the law. Failure to adequately address the violations promptly may result in legal action, including product seizure and/or injunction.”
The Food and Drug Administration has warned two manufacturers about illegal marketing of drugs containing cannabidiol (CBD) for over-the-counter use without an approved new drug application, for using substandard manufacturing processes, and for failure to comply with current good manufacturing practices. These warnings add to 51 previous warning letters issued by the FDA since 2015 to other manufacturers of products containing CBD who were violating the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act.
In a news release, the agency explained that its two most recent letters, sent to Honest Globe Inc. on March 15 and BioLyte Laboratories LLC on March 18, were issued because CBD has “known pharmacologic effects on humans, with demonstrated risks, it cannot be legally marketed as an inactive ingredient in OTC drug products that are not reviewed and approved by the FDA.” They also describe the companies’ failures to comply with current good manufacturing practices.
“The FDA continues to alert the public to potential safety and efficacy concerns with unapproved CBD products sold online and in stores across the country,” FDA Principal Deputy Commissioner Amy P. Abernethy, MD, PhD, said in the release. “It’s important that consumers understand that the FDA has only approved one drug containing CBD as an ingredient [Epidiolex]. These other, unapproved, CBD products may have dangerous health impacts and side effects. We remain focused on exploring potential pathways for CBD products to be lawfully marketed while also educating the public about these outstanding questions of CBD’s safety. Meanwhile, we will continue to monitor and take action, as needed, against companies that unlawfully market their products – prioritizing those that pose a risk to public health.”
The specific products from Santa Ana, Calif.–based Honest Globe that the FDA called unapproved new drugs and misbranded under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act included Elixicure Original Pain Relief and Elixicure Lavender Pain Relief, both of which were described as containing CBD. Products from Grand Rapids, Mich.–based BioLyte Laboratories LLC that the FDA similarly cited for violations included Silver Gel, Silver Gel with Aloe, Silver Liquid Supplement, Therapeutic Pain Gel, Pain Relief Cream, and Magnesium Oil Spray.
The agency has asked the two companies to respond to its letters within 15 working days, “stating how they will address these violations or providing their reasoning and supporting information as to why they believe these products are not in violation of the law. Failure to adequately address the violations promptly may result in legal action, including product seizure and/or injunction.”






