User login
FDA okays upfront pembro for advanced HER2+ gastric cancer
The checkpoint inhibitor is to be used in conjunction with trastuzumab (Herceptin) and fluoropyrimidine- and platinum-containing chemotherapy.
Previously, pembrolizumab was approved as a single agent for these cancers for patients whose tumors express PD-L1 and whose disease progressed after two or more lines of treatment that included chemotherapy and HER2-targeted therapy.
The new approval comes about a year after the FDA’s first-ever approval of a checkpoint inhibitor (nivolumab [Opdivo] in combination with chemotherapies) for the frontline treatment of gastric cancers, as reported by this news organization.
The new approval is based on interim data from the first 264 patients of the ongoing KEYNOTE-811 trial, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial involving patients with HER2-positive advanced gastric or GEJ adenocarcinoma who had not previously received systemic therapy for their metastatic disease.
Patients were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive either pembrolizumab at 200 mg or placebo every 3 weeks in combination with trastuzumab and either fluorouracil plus cisplatin or capecitabine plus oxaliplatin.
The overall response rate, which is the primary outcome, was 74% in the pembrolizumab arm and 52% in the placebo arm (one-sided P < .0001).
The median duration of response was 10.6 months in the pembrolizumab arm and 9.5 months in the placebo arm.
The adverse-reaction profile for patients receiving pembrolizumab is consistent with the known pembrolizumab safety profile, the FDA said in a statement.
The recommended pembrolizumab dose in this setting is 200 mg every 3 weeks or 400 mg every 6 weeks.
The FDA’s review, which was granted priority status, used the Real-Time Oncology Review pilot program, which allows streamlined data submission prior to the filing of the full clinical application, and Assessment Aid, a voluntary submission that facilitates the FDA’s assessment.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The checkpoint inhibitor is to be used in conjunction with trastuzumab (Herceptin) and fluoropyrimidine- and platinum-containing chemotherapy.
Previously, pembrolizumab was approved as a single agent for these cancers for patients whose tumors express PD-L1 and whose disease progressed after two or more lines of treatment that included chemotherapy and HER2-targeted therapy.
The new approval comes about a year after the FDA’s first-ever approval of a checkpoint inhibitor (nivolumab [Opdivo] in combination with chemotherapies) for the frontline treatment of gastric cancers, as reported by this news organization.
The new approval is based on interim data from the first 264 patients of the ongoing KEYNOTE-811 trial, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial involving patients with HER2-positive advanced gastric or GEJ adenocarcinoma who had not previously received systemic therapy for their metastatic disease.
Patients were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive either pembrolizumab at 200 mg or placebo every 3 weeks in combination with trastuzumab and either fluorouracil plus cisplatin or capecitabine plus oxaliplatin.
The overall response rate, which is the primary outcome, was 74% in the pembrolizumab arm and 52% in the placebo arm (one-sided P < .0001).
The median duration of response was 10.6 months in the pembrolizumab arm and 9.5 months in the placebo arm.
The adverse-reaction profile for patients receiving pembrolizumab is consistent with the known pembrolizumab safety profile, the FDA said in a statement.
The recommended pembrolizumab dose in this setting is 200 mg every 3 weeks or 400 mg every 6 weeks.
The FDA’s review, which was granted priority status, used the Real-Time Oncology Review pilot program, which allows streamlined data submission prior to the filing of the full clinical application, and Assessment Aid, a voluntary submission that facilitates the FDA’s assessment.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The checkpoint inhibitor is to be used in conjunction with trastuzumab (Herceptin) and fluoropyrimidine- and platinum-containing chemotherapy.
Previously, pembrolizumab was approved as a single agent for these cancers for patients whose tumors express PD-L1 and whose disease progressed after two or more lines of treatment that included chemotherapy and HER2-targeted therapy.
The new approval comes about a year after the FDA’s first-ever approval of a checkpoint inhibitor (nivolumab [Opdivo] in combination with chemotherapies) for the frontline treatment of gastric cancers, as reported by this news organization.
The new approval is based on interim data from the first 264 patients of the ongoing KEYNOTE-811 trial, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial involving patients with HER2-positive advanced gastric or GEJ adenocarcinoma who had not previously received systemic therapy for their metastatic disease.
Patients were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive either pembrolizumab at 200 mg or placebo every 3 weeks in combination with trastuzumab and either fluorouracil plus cisplatin or capecitabine plus oxaliplatin.
The overall response rate, which is the primary outcome, was 74% in the pembrolizumab arm and 52% in the placebo arm (one-sided P < .0001).
The median duration of response was 10.6 months in the pembrolizumab arm and 9.5 months in the placebo arm.
The adverse-reaction profile for patients receiving pembrolizumab is consistent with the known pembrolizumab safety profile, the FDA said in a statement.
The recommended pembrolizumab dose in this setting is 200 mg every 3 weeks or 400 mg every 6 weeks.
The FDA’s review, which was granted priority status, used the Real-Time Oncology Review pilot program, which allows streamlined data submission prior to the filing of the full clinical application, and Assessment Aid, a voluntary submission that facilitates the FDA’s assessment.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA set to okay Pfizer vaccine in younger teens
The Food and Drug Administration could expand the use of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine to teens early next week, The New York Times and CNN reported, both citing unnamed officials familiar with the agency’s plans.
In late March, Pfizer submitted data to the FDA showing its mRNA vaccine was 100% effective at preventing COVID-19 infection in children ages 12 to 15. Their vaccine is already authorized for use teens and adults ages 16 and older.
The move would make about 17 million more Americans eligible for vaccination and would be a major step toward getting both adolescents and teens back into classrooms full time by next fall.
“Across the globe, we are longing for a normal life. This is especially true for our children. The initial results we have seen in the adolescent studies suggest that children are particularly well protected by vaccination, which is very encouraging given the trends we have seen in recent weeks regarding the spread of the B.1.1.7 U.K. variant,” Ugur Sahin, CEO and co-founder of Pfizer partner BioNTech, said in a March 31 press release.
Getting schools fully reopened for in-person learning has been a goal of both the Trump and Biden administrations, but it has been tricky to pull off, as some parents and teachers have been reluctant to return to classrooms with so much uncertainty about the risk and the role of children in spreading the virus.
A recent study of roughly 150,000 school-aged children in Israel found that while kids under age 10 were unlikely to catch or spread the virus as they reentered classrooms. Older children, though, were a different story. The study found that children ages 10-19 had risks of catching the virus that were as high as adults ages 20-60.
The risk for severe illness and death from COVID-19 rises with age.
Children and teens are at relatively low risk from severe outcomes after a COVID-19 infection compared to adults, but they can catch it and some will get really sick with it, especially if they have an underlying health condition, like obesity or asthma that makes them more vulnerable.
Beyond the initial infection, children can get a rare late complication called MIS-C, that while treatable, can be severe and requires hospitalization. Emerging reports also suggest there are some kids that become long haulers in much the same way adults do, dealing with lingering problems for months after they first get sick.
As new variants of the coronavirus circulate in the United States, some states have seen big increases in the number of children and teens with COVID. In Michigan, for example, which recently dealt with a spring surge of cases dominated by the B.1.1.7 variant, cases in children and teens quadrupled in April compared to February.
Beyond individual protection, vaccinating children and teens has been seen as important to achieving strong community protection, or herd immunity, against the new coronavirus.
If the FDA expands the authorization for the Pfizer vaccine, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will likely meet to review data on the safety and efficacy of the vaccine. The committee may then vote on new recommendations for use of the vaccine in the United States.
Not everyone agrees with the idea that American adolescents, who are at relatively low risk of bad outcomes, could get access to COVID vaccines ahead of vulnerable essential workers and seniors in other parts of the world that are still fighting the pandemic with little access to vaccines.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Food and Drug Administration could expand the use of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine to teens early next week, The New York Times and CNN reported, both citing unnamed officials familiar with the agency’s plans.
In late March, Pfizer submitted data to the FDA showing its mRNA vaccine was 100% effective at preventing COVID-19 infection in children ages 12 to 15. Their vaccine is already authorized for use teens and adults ages 16 and older.
The move would make about 17 million more Americans eligible for vaccination and would be a major step toward getting both adolescents and teens back into classrooms full time by next fall.
“Across the globe, we are longing for a normal life. This is especially true for our children. The initial results we have seen in the adolescent studies suggest that children are particularly well protected by vaccination, which is very encouraging given the trends we have seen in recent weeks regarding the spread of the B.1.1.7 U.K. variant,” Ugur Sahin, CEO and co-founder of Pfizer partner BioNTech, said in a March 31 press release.
Getting schools fully reopened for in-person learning has been a goal of both the Trump and Biden administrations, but it has been tricky to pull off, as some parents and teachers have been reluctant to return to classrooms with so much uncertainty about the risk and the role of children in spreading the virus.
A recent study of roughly 150,000 school-aged children in Israel found that while kids under age 10 were unlikely to catch or spread the virus as they reentered classrooms. Older children, though, were a different story. The study found that children ages 10-19 had risks of catching the virus that were as high as adults ages 20-60.
The risk for severe illness and death from COVID-19 rises with age.
Children and teens are at relatively low risk from severe outcomes after a COVID-19 infection compared to adults, but they can catch it and some will get really sick with it, especially if they have an underlying health condition, like obesity or asthma that makes them more vulnerable.
Beyond the initial infection, children can get a rare late complication called MIS-C, that while treatable, can be severe and requires hospitalization. Emerging reports also suggest there are some kids that become long haulers in much the same way adults do, dealing with lingering problems for months after they first get sick.
As new variants of the coronavirus circulate in the United States, some states have seen big increases in the number of children and teens with COVID. In Michigan, for example, which recently dealt with a spring surge of cases dominated by the B.1.1.7 variant, cases in children and teens quadrupled in April compared to February.
Beyond individual protection, vaccinating children and teens has been seen as important to achieving strong community protection, or herd immunity, against the new coronavirus.
If the FDA expands the authorization for the Pfizer vaccine, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will likely meet to review data on the safety and efficacy of the vaccine. The committee may then vote on new recommendations for use of the vaccine in the United States.
Not everyone agrees with the idea that American adolescents, who are at relatively low risk of bad outcomes, could get access to COVID vaccines ahead of vulnerable essential workers and seniors in other parts of the world that are still fighting the pandemic with little access to vaccines.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Food and Drug Administration could expand the use of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine to teens early next week, The New York Times and CNN reported, both citing unnamed officials familiar with the agency’s plans.
In late March, Pfizer submitted data to the FDA showing its mRNA vaccine was 100% effective at preventing COVID-19 infection in children ages 12 to 15. Their vaccine is already authorized for use teens and adults ages 16 and older.
The move would make about 17 million more Americans eligible for vaccination and would be a major step toward getting both adolescents and teens back into classrooms full time by next fall.
“Across the globe, we are longing for a normal life. This is especially true for our children. The initial results we have seen in the adolescent studies suggest that children are particularly well protected by vaccination, which is very encouraging given the trends we have seen in recent weeks regarding the spread of the B.1.1.7 U.K. variant,” Ugur Sahin, CEO and co-founder of Pfizer partner BioNTech, said in a March 31 press release.
Getting schools fully reopened for in-person learning has been a goal of both the Trump and Biden administrations, but it has been tricky to pull off, as some parents and teachers have been reluctant to return to classrooms with so much uncertainty about the risk and the role of children in spreading the virus.
A recent study of roughly 150,000 school-aged children in Israel found that while kids under age 10 were unlikely to catch or spread the virus as they reentered classrooms. Older children, though, were a different story. The study found that children ages 10-19 had risks of catching the virus that were as high as adults ages 20-60.
The risk for severe illness and death from COVID-19 rises with age.
Children and teens are at relatively low risk from severe outcomes after a COVID-19 infection compared to adults, but they can catch it and some will get really sick with it, especially if they have an underlying health condition, like obesity or asthma that makes them more vulnerable.
Beyond the initial infection, children can get a rare late complication called MIS-C, that while treatable, can be severe and requires hospitalization. Emerging reports also suggest there are some kids that become long haulers in much the same way adults do, dealing with lingering problems for months after they first get sick.
As new variants of the coronavirus circulate in the United States, some states have seen big increases in the number of children and teens with COVID. In Michigan, for example, which recently dealt with a spring surge of cases dominated by the B.1.1.7 variant, cases in children and teens quadrupled in April compared to February.
Beyond individual protection, vaccinating children and teens has been seen as important to achieving strong community protection, or herd immunity, against the new coronavirus.
If the FDA expands the authorization for the Pfizer vaccine, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will likely meet to review data on the safety and efficacy of the vaccine. The committee may then vote on new recommendations for use of the vaccine in the United States.
Not everyone agrees with the idea that American adolescents, who are at relatively low risk of bad outcomes, could get access to COVID vaccines ahead of vulnerable essential workers and seniors in other parts of the world that are still fighting the pandemic with little access to vaccines.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA panel votes against 2 cancer indications but backs 4 of 6
Federal advisers have supported the efforts of pharmaceutical companies in four of six cases in which these firms are fighting to maintain cancer indications for approved drugs. The advisers voted against the companies in two cases.
The staff of the Food and Drug Administration will now consider these votes as they decide what to do regarding the six cases of what they have termed “dangling” accelerated approvals.
“One of the reasons I think we’re convening today is to prevent these accelerated approvals from dangling ad infinitum,” commented one of the members of the advisory panel.
In these cases, companies have been unable to prove the expected benefits that led the FDA to grant accelerated approvals for these indications.
These accelerated approvals, which are often based on surrogate endpoints, such as overall response rates, are granted on the condition that further findings show a clinical benefit – such as in progression-free survival or overall survival – in larger trials.
The FDA tasked its Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC) with conducting the review of the six accelerated approvals for cancer indications at a 3-day meeting (April 27-29).
These reviews were only for specific cancer indications and will not lead to the removal of drugs from the market. These drugs have already been approved for several cancer indications. For example, one of the drugs that was reviewed, pembrolizumab (Keytruda), is approved in the United States for 28 indications.
The FDA is facing growing pains in its efforts to manage the rapidly changing landscape for these immune checkpoint inhibitors. This field of medicine has experienced an “unprecedented level of drug development” in recent years, FDA officials said in briefing materials, owing in part to the agency’s willingness to accept surrogate markers for accelerated approvals. Although some companies have struggled with these, others have built strong cases for the use of their checkpoint inhibitors for these indications.
The ODAC panelists, for example, noted the emergence of nivolumab (Opdivo) as an option for patients with gastric cancer as a reason for seeking to withdraw an indication for pembrolizumab (Keytruda) for this disease.
Just weeks before the meeting, on April 16, the FDA approved nivolumab plus chemotherapy as a first-line treatment for advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, gastroesophageal junction cancer, and esophageal adenocarcinoma. This was a full approval based on data showing an overall survival benefit from a phase 3 trial.
Votes by indication
On April 29, the last day of the meeting, the ODAC panel voted 6-2 against maintaining pembrolizumab’s indication as monotherapy for an advanced form of gastric cancer. This was an accelerated approval (granted in 2017) that was based on overall response rates from an open-label trial.
That last day of the meeting also saw another negative vote. On April 29, the ODAC panel voted 5-4 against maintaining an indication for nivolumab in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who were previously treated with sorafenib (Nexavar).
This accelerated approval for nivolumab was granted in 2017. The FDA said it had requested ODAC’s feedback on this indication because of the recent full approval of another checkpoint inhibitor for HCC, atezolizumab (Tecentriq), in combination with bevacizumab (Avastin) for patients with unresectable or metastatic diseases who have not received prior systemic therapy. This full approval (in May 2020) was based on an overall survival benefit.
There was one last vote on the third day of the meeting, and it was positive. The ODAC panel voted 8-0 in favor of maintaining the indication for the use of pembrolizumab as monotherapy for patients with HCC who have previously been treated with sorafenib.
The FDA altered the composition of the ODAC panel during the week, adding members in some cases who had expertise in particular cancers. That led to different totals for the week’s ODAC votes, as shown in the tallies summarized below.
On the first day of the meeting (April 27), the ODAC panel voted 7-2 in favor of maintaining a breast cancer indication for atezolizumab (Tecentriq). This covered use of the immunotherapy in combination with nab-paclitaxel for patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer whose tumors express PD-L1.
The second day of the meeting (April 28) also saw two positive votes. The ODAC panel voted 10-1 for maintaining the indication for atezolizumab for the first-line treatment of cisplatin-ineligible patients with advanced/metastatic urothelial carcinoma, pending final overall survival results from the IMvigor130 trial. The panel also voted 5-3 for maintaining the indication for pembrolizumab in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma who are not eligible for cisplatin-containing chemotherapy and whose tumors express PD-L1.
The FDA is not bound to follow the voting and recommendations of its advisory panels, but it usually does so.
Managing shifts in treatment
In both of the cases in which ODAC voted against maintaining indications, Richard Pazdur, MD, the FDA’s top regulator for cancer medicines, jumped into the debate. Dr. Pazdur countered arguments put forward by representatives of the manufacturers as they sought to maintain indications for their drugs.
Merck officials and representatives argued for pembrolizumab, saying that maintaining the gastric cancer indication might help patients whose disease has progressed despite earlier treatment.
Dr. Pazdur emphasized that the agency would help Merck and physicians to have access to pembrolizumab for these patients even if this one indication were to be withdrawn. But Dr. Pazdur and ODAC members also noted the recent shift in the landscape for gastric cancer, with the recent approval of a new indication for nivolumab.
“I want to emphasize to the patient community out there [that] we firmly believe in the role of checkpoint inhibitors in this disease,” Dr. Pazdur said during the discussion of the indication for pembrolizumab for gastric cancer. “We have to be cognizant of what is the appropriate setting for that, and it currently is in the first line.”
Dr. Pazdur noted that two studies had failed to confirm the expected benefit from pembrolizumab for patients with more advanced disease. Still, if “small numbers” of patients with advanced disease wanted access to Merck’s drug, the FDA and the company could accommodate them. The FDA could delay the removal of the gastric indication to allow patients to continue receiving it. The FDA also could work with physicians on other routes to provide the medicine, such as through single-patient investigational new drug applications or an expanded access program.
“Or Merck can alternatively give the drug gratis to patients,” Dr. Pazdur said.
#ProjectFacilitate for expanded access
One of Merck’s speakers at the ODAC meeting, Peter Enzinger, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, objected to Dr. Pazdur’s plan.
A loss of the gastric indication for pembrolizumab would result in patients with advanced cancer missing out on a chance to try this therapy. Some patients will not have had a chance to try a checkpoint inhibitor earlier in their treatment, and a loss of the indication would cost them that opportunity, he said.
“An expanded-access program sounds very nice, but the reality is that our patients are incredibly sick and that weeks matter,” Dr. Enzinger said, citing administrative hurdles as a barrier to treatment.
“Our patients just don’t have the time for that, and therefore I don’t think an expanded access program is the way to go,” Dr. Enzinger said.
Dr. Pazdur responded to these objections by highlighting an initiative called Project Facilitate at the FDA’s Oncology Center for Excellence. During the meeting, Dr. Pazdur’s division used its @FDAOncology Twitter handle to draw attention to this project.
ODAC panelist Diane Reidy-Lagunes, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, said she had struggled with this vote. She was one of the two panelists to vote in favor of keeping the indication.
“This is also incredibly hard for me. I actually changed it at the last minute,” she said of her vote.
But Dr. Reidy-Lagunes said she was concerned that some patients with advanced disease might not be able to get a checkpoint inhibitor.
“With disparities in healthcare and differences in the way that patients are treated throughout our country, I was nervous that they may not be able to get treated,” she said, noting that she shared her fellow panelists’ doubts about use of pembrolizumab as third-line treatment, owing to negative results in trials.
ODAC member David Mitchell, who served as a consumer representative, also said he found the vote on the gastric indication for pembrolizumab to be a difficult decision.
“As a patient with incurable cancer who’s now being given all three major classes of drugs to treat my disease in combination, these issues really cut close to home,” Mr. Mitchell said.
He said the expectation that the FDA’s expanded access program could help patients with advanced disease try pembrolizumab helped him decide to vote with the 6-2 majority against maintaining this gastric cancer approval.
His vote was based on “the changing treatment landscape.” There is general agreement that the patients in question should receive checkpoint inhibitors as first-line treatment, not third-line treatment, Mr. Mitchell said. The FDA should delay a withdrawal of the approval for pembrolizumab in this case and should allow a transition for those who missed out on treatment with a checkpoint inhibitor earlier in the disease course, he suggested.
“To protect the safety and well-being of patients, we have to base decisions on data,” Mr. Mitchell said. “The data don’t support maintaining the indication” for pembrolizumab.
Close split on nivolumab
In contrast to the 6-2 vote against maintaining the pembrolizumab indication, the ODAC panel split more closely, 5-4, on the question of maintaining an indication for the use as monotherapy of nivolumab in HCC.
ODAC panelist Philip C. Hoffman, MD, of the University of Chicago was among those who supported keeping the indication.
“There’s still an unmet need for second-line immunotherapy because there will always be some patients who are poor candidates for bevacizumab or who are not tolerating or responding to sorafenib,” he said.
ODAC panelist Mark A. Lewis, MD, of Intermountain Healthcare, Salt Lake City, said he voted “no” in part because he doubted that Bristol-Myers Squibb would be able to soon produce data for nivolumab that was needed to support this indication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Federal advisers have supported the efforts of pharmaceutical companies in four of six cases in which these firms are fighting to maintain cancer indications for approved drugs. The advisers voted against the companies in two cases.
The staff of the Food and Drug Administration will now consider these votes as they decide what to do regarding the six cases of what they have termed “dangling” accelerated approvals.
“One of the reasons I think we’re convening today is to prevent these accelerated approvals from dangling ad infinitum,” commented one of the members of the advisory panel.
In these cases, companies have been unable to prove the expected benefits that led the FDA to grant accelerated approvals for these indications.
These accelerated approvals, which are often based on surrogate endpoints, such as overall response rates, are granted on the condition that further findings show a clinical benefit – such as in progression-free survival or overall survival – in larger trials.
The FDA tasked its Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC) with conducting the review of the six accelerated approvals for cancer indications at a 3-day meeting (April 27-29).
These reviews were only for specific cancer indications and will not lead to the removal of drugs from the market. These drugs have already been approved for several cancer indications. For example, one of the drugs that was reviewed, pembrolizumab (Keytruda), is approved in the United States for 28 indications.
The FDA is facing growing pains in its efforts to manage the rapidly changing landscape for these immune checkpoint inhibitors. This field of medicine has experienced an “unprecedented level of drug development” in recent years, FDA officials said in briefing materials, owing in part to the agency’s willingness to accept surrogate markers for accelerated approvals. Although some companies have struggled with these, others have built strong cases for the use of their checkpoint inhibitors for these indications.
The ODAC panelists, for example, noted the emergence of nivolumab (Opdivo) as an option for patients with gastric cancer as a reason for seeking to withdraw an indication for pembrolizumab (Keytruda) for this disease.
Just weeks before the meeting, on April 16, the FDA approved nivolumab plus chemotherapy as a first-line treatment for advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, gastroesophageal junction cancer, and esophageal adenocarcinoma. This was a full approval based on data showing an overall survival benefit from a phase 3 trial.
Votes by indication
On April 29, the last day of the meeting, the ODAC panel voted 6-2 against maintaining pembrolizumab’s indication as monotherapy for an advanced form of gastric cancer. This was an accelerated approval (granted in 2017) that was based on overall response rates from an open-label trial.
That last day of the meeting also saw another negative vote. On April 29, the ODAC panel voted 5-4 against maintaining an indication for nivolumab in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who were previously treated with sorafenib (Nexavar).
This accelerated approval for nivolumab was granted in 2017. The FDA said it had requested ODAC’s feedback on this indication because of the recent full approval of another checkpoint inhibitor for HCC, atezolizumab (Tecentriq), in combination with bevacizumab (Avastin) for patients with unresectable or metastatic diseases who have not received prior systemic therapy. This full approval (in May 2020) was based on an overall survival benefit.
There was one last vote on the third day of the meeting, and it was positive. The ODAC panel voted 8-0 in favor of maintaining the indication for the use of pembrolizumab as monotherapy for patients with HCC who have previously been treated with sorafenib.
The FDA altered the composition of the ODAC panel during the week, adding members in some cases who had expertise in particular cancers. That led to different totals for the week’s ODAC votes, as shown in the tallies summarized below.
On the first day of the meeting (April 27), the ODAC panel voted 7-2 in favor of maintaining a breast cancer indication for atezolizumab (Tecentriq). This covered use of the immunotherapy in combination with nab-paclitaxel for patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer whose tumors express PD-L1.
The second day of the meeting (April 28) also saw two positive votes. The ODAC panel voted 10-1 for maintaining the indication for atezolizumab for the first-line treatment of cisplatin-ineligible patients with advanced/metastatic urothelial carcinoma, pending final overall survival results from the IMvigor130 trial. The panel also voted 5-3 for maintaining the indication for pembrolizumab in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma who are not eligible for cisplatin-containing chemotherapy and whose tumors express PD-L1.
The FDA is not bound to follow the voting and recommendations of its advisory panels, but it usually does so.
Managing shifts in treatment
In both of the cases in which ODAC voted against maintaining indications, Richard Pazdur, MD, the FDA’s top regulator for cancer medicines, jumped into the debate. Dr. Pazdur countered arguments put forward by representatives of the manufacturers as they sought to maintain indications for their drugs.
Merck officials and representatives argued for pembrolizumab, saying that maintaining the gastric cancer indication might help patients whose disease has progressed despite earlier treatment.
Dr. Pazdur emphasized that the agency would help Merck and physicians to have access to pembrolizumab for these patients even if this one indication were to be withdrawn. But Dr. Pazdur and ODAC members also noted the recent shift in the landscape for gastric cancer, with the recent approval of a new indication for nivolumab.
“I want to emphasize to the patient community out there [that] we firmly believe in the role of checkpoint inhibitors in this disease,” Dr. Pazdur said during the discussion of the indication for pembrolizumab for gastric cancer. “We have to be cognizant of what is the appropriate setting for that, and it currently is in the first line.”
Dr. Pazdur noted that two studies had failed to confirm the expected benefit from pembrolizumab for patients with more advanced disease. Still, if “small numbers” of patients with advanced disease wanted access to Merck’s drug, the FDA and the company could accommodate them. The FDA could delay the removal of the gastric indication to allow patients to continue receiving it. The FDA also could work with physicians on other routes to provide the medicine, such as through single-patient investigational new drug applications or an expanded access program.
“Or Merck can alternatively give the drug gratis to patients,” Dr. Pazdur said.
#ProjectFacilitate for expanded access
One of Merck’s speakers at the ODAC meeting, Peter Enzinger, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, objected to Dr. Pazdur’s plan.
A loss of the gastric indication for pembrolizumab would result in patients with advanced cancer missing out on a chance to try this therapy. Some patients will not have had a chance to try a checkpoint inhibitor earlier in their treatment, and a loss of the indication would cost them that opportunity, he said.
“An expanded-access program sounds very nice, but the reality is that our patients are incredibly sick and that weeks matter,” Dr. Enzinger said, citing administrative hurdles as a barrier to treatment.
“Our patients just don’t have the time for that, and therefore I don’t think an expanded access program is the way to go,” Dr. Enzinger said.
Dr. Pazdur responded to these objections by highlighting an initiative called Project Facilitate at the FDA’s Oncology Center for Excellence. During the meeting, Dr. Pazdur’s division used its @FDAOncology Twitter handle to draw attention to this project.
ODAC panelist Diane Reidy-Lagunes, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, said she had struggled with this vote. She was one of the two panelists to vote in favor of keeping the indication.
“This is also incredibly hard for me. I actually changed it at the last minute,” she said of her vote.
But Dr. Reidy-Lagunes said she was concerned that some patients with advanced disease might not be able to get a checkpoint inhibitor.
“With disparities in healthcare and differences in the way that patients are treated throughout our country, I was nervous that they may not be able to get treated,” she said, noting that she shared her fellow panelists’ doubts about use of pembrolizumab as third-line treatment, owing to negative results in trials.
ODAC member David Mitchell, who served as a consumer representative, also said he found the vote on the gastric indication for pembrolizumab to be a difficult decision.
“As a patient with incurable cancer who’s now being given all three major classes of drugs to treat my disease in combination, these issues really cut close to home,” Mr. Mitchell said.
He said the expectation that the FDA’s expanded access program could help patients with advanced disease try pembrolizumab helped him decide to vote with the 6-2 majority against maintaining this gastric cancer approval.
His vote was based on “the changing treatment landscape.” There is general agreement that the patients in question should receive checkpoint inhibitors as first-line treatment, not third-line treatment, Mr. Mitchell said. The FDA should delay a withdrawal of the approval for pembrolizumab in this case and should allow a transition for those who missed out on treatment with a checkpoint inhibitor earlier in the disease course, he suggested.
“To protect the safety and well-being of patients, we have to base decisions on data,” Mr. Mitchell said. “The data don’t support maintaining the indication” for pembrolizumab.
Close split on nivolumab
In contrast to the 6-2 vote against maintaining the pembrolizumab indication, the ODAC panel split more closely, 5-4, on the question of maintaining an indication for the use as monotherapy of nivolumab in HCC.
ODAC panelist Philip C. Hoffman, MD, of the University of Chicago was among those who supported keeping the indication.
“There’s still an unmet need for second-line immunotherapy because there will always be some patients who are poor candidates for bevacizumab or who are not tolerating or responding to sorafenib,” he said.
ODAC panelist Mark A. Lewis, MD, of Intermountain Healthcare, Salt Lake City, said he voted “no” in part because he doubted that Bristol-Myers Squibb would be able to soon produce data for nivolumab that was needed to support this indication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Federal advisers have supported the efforts of pharmaceutical companies in four of six cases in which these firms are fighting to maintain cancer indications for approved drugs. The advisers voted against the companies in two cases.
The staff of the Food and Drug Administration will now consider these votes as they decide what to do regarding the six cases of what they have termed “dangling” accelerated approvals.
“One of the reasons I think we’re convening today is to prevent these accelerated approvals from dangling ad infinitum,” commented one of the members of the advisory panel.
In these cases, companies have been unable to prove the expected benefits that led the FDA to grant accelerated approvals for these indications.
These accelerated approvals, which are often based on surrogate endpoints, such as overall response rates, are granted on the condition that further findings show a clinical benefit – such as in progression-free survival or overall survival – in larger trials.
The FDA tasked its Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC) with conducting the review of the six accelerated approvals for cancer indications at a 3-day meeting (April 27-29).
These reviews were only for specific cancer indications and will not lead to the removal of drugs from the market. These drugs have already been approved for several cancer indications. For example, one of the drugs that was reviewed, pembrolizumab (Keytruda), is approved in the United States for 28 indications.
The FDA is facing growing pains in its efforts to manage the rapidly changing landscape for these immune checkpoint inhibitors. This field of medicine has experienced an “unprecedented level of drug development” in recent years, FDA officials said in briefing materials, owing in part to the agency’s willingness to accept surrogate markers for accelerated approvals. Although some companies have struggled with these, others have built strong cases for the use of their checkpoint inhibitors for these indications.
The ODAC panelists, for example, noted the emergence of nivolumab (Opdivo) as an option for patients with gastric cancer as a reason for seeking to withdraw an indication for pembrolizumab (Keytruda) for this disease.
Just weeks before the meeting, on April 16, the FDA approved nivolumab plus chemotherapy as a first-line treatment for advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, gastroesophageal junction cancer, and esophageal adenocarcinoma. This was a full approval based on data showing an overall survival benefit from a phase 3 trial.
Votes by indication
On April 29, the last day of the meeting, the ODAC panel voted 6-2 against maintaining pembrolizumab’s indication as monotherapy for an advanced form of gastric cancer. This was an accelerated approval (granted in 2017) that was based on overall response rates from an open-label trial.
That last day of the meeting also saw another negative vote. On April 29, the ODAC panel voted 5-4 against maintaining an indication for nivolumab in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who were previously treated with sorafenib (Nexavar).
This accelerated approval for nivolumab was granted in 2017. The FDA said it had requested ODAC’s feedback on this indication because of the recent full approval of another checkpoint inhibitor for HCC, atezolizumab (Tecentriq), in combination with bevacizumab (Avastin) for patients with unresectable or metastatic diseases who have not received prior systemic therapy. This full approval (in May 2020) was based on an overall survival benefit.
There was one last vote on the third day of the meeting, and it was positive. The ODAC panel voted 8-0 in favor of maintaining the indication for the use of pembrolizumab as monotherapy for patients with HCC who have previously been treated with sorafenib.
The FDA altered the composition of the ODAC panel during the week, adding members in some cases who had expertise in particular cancers. That led to different totals for the week’s ODAC votes, as shown in the tallies summarized below.
On the first day of the meeting (April 27), the ODAC panel voted 7-2 in favor of maintaining a breast cancer indication for atezolizumab (Tecentriq). This covered use of the immunotherapy in combination with nab-paclitaxel for patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer whose tumors express PD-L1.
The second day of the meeting (April 28) also saw two positive votes. The ODAC panel voted 10-1 for maintaining the indication for atezolizumab for the first-line treatment of cisplatin-ineligible patients with advanced/metastatic urothelial carcinoma, pending final overall survival results from the IMvigor130 trial. The panel also voted 5-3 for maintaining the indication for pembrolizumab in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma who are not eligible for cisplatin-containing chemotherapy and whose tumors express PD-L1.
The FDA is not bound to follow the voting and recommendations of its advisory panels, but it usually does so.
Managing shifts in treatment
In both of the cases in which ODAC voted against maintaining indications, Richard Pazdur, MD, the FDA’s top regulator for cancer medicines, jumped into the debate. Dr. Pazdur countered arguments put forward by representatives of the manufacturers as they sought to maintain indications for their drugs.
Merck officials and representatives argued for pembrolizumab, saying that maintaining the gastric cancer indication might help patients whose disease has progressed despite earlier treatment.
Dr. Pazdur emphasized that the agency would help Merck and physicians to have access to pembrolizumab for these patients even if this one indication were to be withdrawn. But Dr. Pazdur and ODAC members also noted the recent shift in the landscape for gastric cancer, with the recent approval of a new indication for nivolumab.
“I want to emphasize to the patient community out there [that] we firmly believe in the role of checkpoint inhibitors in this disease,” Dr. Pazdur said during the discussion of the indication for pembrolizumab for gastric cancer. “We have to be cognizant of what is the appropriate setting for that, and it currently is in the first line.”
Dr. Pazdur noted that two studies had failed to confirm the expected benefit from pembrolizumab for patients with more advanced disease. Still, if “small numbers” of patients with advanced disease wanted access to Merck’s drug, the FDA and the company could accommodate them. The FDA could delay the removal of the gastric indication to allow patients to continue receiving it. The FDA also could work with physicians on other routes to provide the medicine, such as through single-patient investigational new drug applications or an expanded access program.
“Or Merck can alternatively give the drug gratis to patients,” Dr. Pazdur said.
#ProjectFacilitate for expanded access
One of Merck’s speakers at the ODAC meeting, Peter Enzinger, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, objected to Dr. Pazdur’s plan.
A loss of the gastric indication for pembrolizumab would result in patients with advanced cancer missing out on a chance to try this therapy. Some patients will not have had a chance to try a checkpoint inhibitor earlier in their treatment, and a loss of the indication would cost them that opportunity, he said.
“An expanded-access program sounds very nice, but the reality is that our patients are incredibly sick and that weeks matter,” Dr. Enzinger said, citing administrative hurdles as a barrier to treatment.
“Our patients just don’t have the time for that, and therefore I don’t think an expanded access program is the way to go,” Dr. Enzinger said.
Dr. Pazdur responded to these objections by highlighting an initiative called Project Facilitate at the FDA’s Oncology Center for Excellence. During the meeting, Dr. Pazdur’s division used its @FDAOncology Twitter handle to draw attention to this project.
ODAC panelist Diane Reidy-Lagunes, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, said she had struggled with this vote. She was one of the two panelists to vote in favor of keeping the indication.
“This is also incredibly hard for me. I actually changed it at the last minute,” she said of her vote.
But Dr. Reidy-Lagunes said she was concerned that some patients with advanced disease might not be able to get a checkpoint inhibitor.
“With disparities in healthcare and differences in the way that patients are treated throughout our country, I was nervous that they may not be able to get treated,” she said, noting that she shared her fellow panelists’ doubts about use of pembrolizumab as third-line treatment, owing to negative results in trials.
ODAC member David Mitchell, who served as a consumer representative, also said he found the vote on the gastric indication for pembrolizumab to be a difficult decision.
“As a patient with incurable cancer who’s now being given all three major classes of drugs to treat my disease in combination, these issues really cut close to home,” Mr. Mitchell said.
He said the expectation that the FDA’s expanded access program could help patients with advanced disease try pembrolizumab helped him decide to vote with the 6-2 majority against maintaining this gastric cancer approval.
His vote was based on “the changing treatment landscape.” There is general agreement that the patients in question should receive checkpoint inhibitors as first-line treatment, not third-line treatment, Mr. Mitchell said. The FDA should delay a withdrawal of the approval for pembrolizumab in this case and should allow a transition for those who missed out on treatment with a checkpoint inhibitor earlier in the disease course, he suggested.
“To protect the safety and well-being of patients, we have to base decisions on data,” Mr. Mitchell said. “The data don’t support maintaining the indication” for pembrolizumab.
Close split on nivolumab
In contrast to the 6-2 vote against maintaining the pembrolizumab indication, the ODAC panel split more closely, 5-4, on the question of maintaining an indication for the use as monotherapy of nivolumab in HCC.
ODAC panelist Philip C. Hoffman, MD, of the University of Chicago was among those who supported keeping the indication.
“There’s still an unmet need for second-line immunotherapy because there will always be some patients who are poor candidates for bevacizumab or who are not tolerating or responding to sorafenib,” he said.
ODAC panelist Mark A. Lewis, MD, of Intermountain Healthcare, Salt Lake City, said he voted “no” in part because he doubted that Bristol-Myers Squibb would be able to soon produce data for nivolumab that was needed to support this indication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA moves to ban menthol in cigarettes
The Food and Drug Administration said that within a year it will ban menthol in cigarettes and ban all flavors including menthol in cigars.
Menthol makes it easier to start smoking, and also enhances the effects of nicotine, making it more addictive and harder to quit, the FDA said in announcing its actions on Thursday.
Nineteen organizations – including the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Cancer Society, American College of Chest Physicians, American Medical Association, American Heart Association, and the National Medical Association – have pushed the FDA to ban menthol for years. The agency banned all flavors in cigarettes in 2009 but did not take any action against menthol. In 2013, the groups filed a petition demanding that the FDA ban menthol, too. The agency responded months later with a notice that it would start the process.
But it never took any action. Action on Smoking and Health and the African American Tobacco Control Leadership Council, later joined by the AMA and the NMA, sued in 2020 to compel the agency to do something. Now it has finally agreed to act.
The African American Tobacco Control Leadership Council welcomed the move but said the fight is not over and encouraged tobacco control activists to fight to ban menthol tobacco products at the local, state and federal level. “We know that this rule-making process could take years and we know that the tobacco industry will continue to do everything in their power to derail any attempt to remove their deadly products from the market,” Phillip Gardiner, MD, council cochair, said in a statement.
The AMA is urging the FDA to quickly implement the ban and remove the products “without further delay,” AMA President Susan R. Bailey, MD, said in a statement.
“FDA’s long-awaited decision to take action to eliminate menthol flavoring in cigarettes and all flavors in cigars ends a decades-long deference to the tobacco industry, which has repeatedly demonstrated its willingness to profit from products that result in death,” Lisa Lacasse, president of the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network, said in her own statement.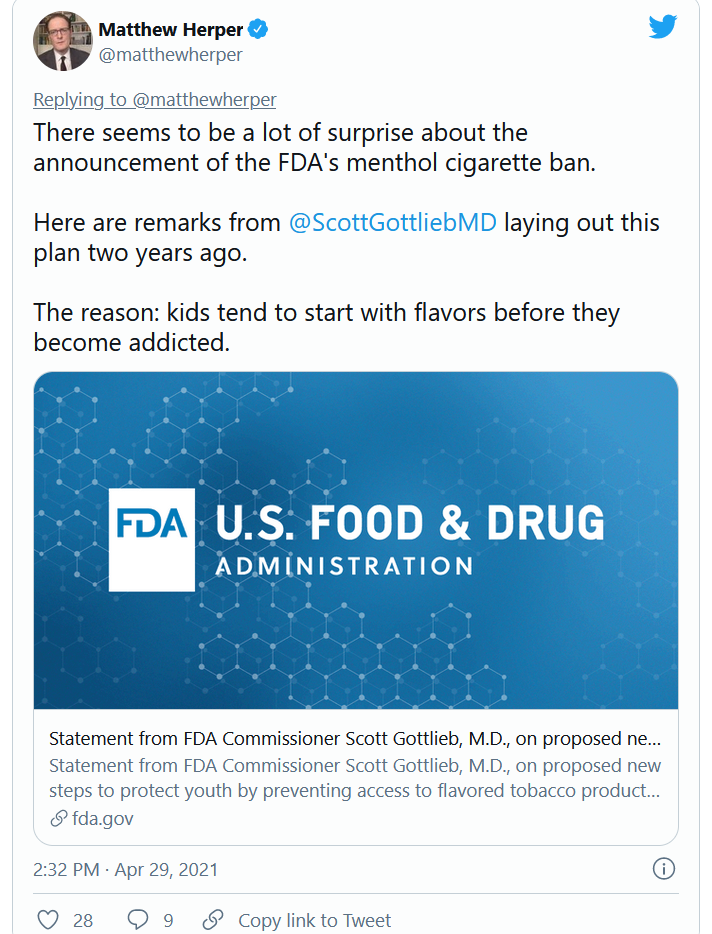
Ms. Lacasse said banning menthol will help eliminate health disparities. She said 86% of Black people who smoke use menthol cigarettes, compared with 46% of Hispanic people who smoke, 39% of Asian people who smoke, and 29% of White people who smoke. “FDA’s actions today send a clear message that Big Tobacco’s strategy to profit off addicting Black communities will no longer be tolerated,” she said.
Not all groups are on board, however. The American Civil Liberties Union and several other organizations wrote to the country’s top health officials urging them to reconsider.
“Such a ban will trigger criminal penalties which will disproportionately impact people of color, as well as prioritize criminalization over public health and harm reduction,” the letter says. “A ban will also lead to unconstitutional policing and other negative interactions with local law enforcement.”
The letter calls the proposed ban “well intentioned,” but said any effort to reduce death and disease from tobacco “must avoid solutions that will create yet another reason for armed police to engage citizens on the street based on pretext or conduct that does not pose a threat to public safety.”
Instead of a ban, the organizations said, policy makers should consider increased education for adults and minors, stop-smoking programs, and increased funding for health centers in communities of color.
The Biden administration, however, pressed the point that banning menthol will bring many positives. Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD said in a statement that banning menthol “will help significantly reduce youth initiation, increase the chances of smoking cessation among current smokers, and address health disparities experienced by communities of color, low-income populations, and LGBTQ-plus individuals, all of whom are far more likely to use these tobacco products.”
The FDA cited data showing that, in the first year or so after a ban goes into effect, an additional 923,000 smokers would quit, including 230,000 African Americans. Another study suggests that 633,000 deaths would be averted, including 237,000 Black Americans.
Dr. Woodcock added that, “armed with strong scientific evidence, and with full support from the [Biden] administration, we believe these actions will launch us on a trajectory toward ending tobacco-related disease and death in the U.S.”
The FDA estimates that 18.6 million Americans who are current smokers use menthol cigarettes, with a disproportionately high number being Black people. Menthol cigarette use among Black and Hispanic youth increased from 2011 to 2018, but declined for non-Hispanic White youth.
Flavored mass-produced cigars and cigarillos are disproportionately popular among youth, especially non-Hispanic Black high school students, who in 2020 reported past 30-day cigar smoking at levels twice as high as their White counterparts, said the FDA. Three-quarters of 12- to 17-year-olds reported they smoke cigars because they like the flavors. In 2020, more young people tried a cigar every day than tried a cigarette, reports the agency.
“This long-overdue decision will protect future generations of young people from nicotine addiction, especially Black children and communities, which have disproportionately suffered from menthol tobacco use due to targeted efforts from the tobacco industry,” Lee Savio Beers, MD, president of the American Academy of Pediatrics, said in a statement.
The FDA’s announcement “is only a first step that must be followed with urgent, comprehensive action to remove these flavored products from the market,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Food and Drug Administration said that within a year it will ban menthol in cigarettes and ban all flavors including menthol in cigars.
Menthol makes it easier to start smoking, and also enhances the effects of nicotine, making it more addictive and harder to quit, the FDA said in announcing its actions on Thursday.
Nineteen organizations – including the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Cancer Society, American College of Chest Physicians, American Medical Association, American Heart Association, and the National Medical Association – have pushed the FDA to ban menthol for years. The agency banned all flavors in cigarettes in 2009 but did not take any action against menthol. In 2013, the groups filed a petition demanding that the FDA ban menthol, too. The agency responded months later with a notice that it would start the process.
But it never took any action. Action on Smoking and Health and the African American Tobacco Control Leadership Council, later joined by the AMA and the NMA, sued in 2020 to compel the agency to do something. Now it has finally agreed to act.
The African American Tobacco Control Leadership Council welcomed the move but said the fight is not over and encouraged tobacco control activists to fight to ban menthol tobacco products at the local, state and federal level. “We know that this rule-making process could take years and we know that the tobacco industry will continue to do everything in their power to derail any attempt to remove their deadly products from the market,” Phillip Gardiner, MD, council cochair, said in a statement.
The AMA is urging the FDA to quickly implement the ban and remove the products “without further delay,” AMA President Susan R. Bailey, MD, said in a statement.
“FDA’s long-awaited decision to take action to eliminate menthol flavoring in cigarettes and all flavors in cigars ends a decades-long deference to the tobacco industry, which has repeatedly demonstrated its willingness to profit from products that result in death,” Lisa Lacasse, president of the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network, said in her own statement.
Ms. Lacasse said banning menthol will help eliminate health disparities. She said 86% of Black people who smoke use menthol cigarettes, compared with 46% of Hispanic people who smoke, 39% of Asian people who smoke, and 29% of White people who smoke. “FDA’s actions today send a clear message that Big Tobacco’s strategy to profit off addicting Black communities will no longer be tolerated,” she said.
Not all groups are on board, however. The American Civil Liberties Union and several other organizations wrote to the country’s top health officials urging them to reconsider.
“Such a ban will trigger criminal penalties which will disproportionately impact people of color, as well as prioritize criminalization over public health and harm reduction,” the letter says. “A ban will also lead to unconstitutional policing and other negative interactions with local law enforcement.”
The letter calls the proposed ban “well intentioned,” but said any effort to reduce death and disease from tobacco “must avoid solutions that will create yet another reason for armed police to engage citizens on the street based on pretext or conduct that does not pose a threat to public safety.”
Instead of a ban, the organizations said, policy makers should consider increased education for adults and minors, stop-smoking programs, and increased funding for health centers in communities of color.
The Biden administration, however, pressed the point that banning menthol will bring many positives. Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD said in a statement that banning menthol “will help significantly reduce youth initiation, increase the chances of smoking cessation among current smokers, and address health disparities experienced by communities of color, low-income populations, and LGBTQ-plus individuals, all of whom are far more likely to use these tobacco products.”
The FDA cited data showing that, in the first year or so after a ban goes into effect, an additional 923,000 smokers would quit, including 230,000 African Americans. Another study suggests that 633,000 deaths would be averted, including 237,000 Black Americans.
Dr. Woodcock added that, “armed with strong scientific evidence, and with full support from the [Biden] administration, we believe these actions will launch us on a trajectory toward ending tobacco-related disease and death in the U.S.”
The FDA estimates that 18.6 million Americans who are current smokers use menthol cigarettes, with a disproportionately high number being Black people. Menthol cigarette use among Black and Hispanic youth increased from 2011 to 2018, but declined for non-Hispanic White youth.
Flavored mass-produced cigars and cigarillos are disproportionately popular among youth, especially non-Hispanic Black high school students, who in 2020 reported past 30-day cigar smoking at levels twice as high as their White counterparts, said the FDA. Three-quarters of 12- to 17-year-olds reported they smoke cigars because they like the flavors. In 2020, more young people tried a cigar every day than tried a cigarette, reports the agency.
“This long-overdue decision will protect future generations of young people from nicotine addiction, especially Black children and communities, which have disproportionately suffered from menthol tobacco use due to targeted efforts from the tobacco industry,” Lee Savio Beers, MD, president of the American Academy of Pediatrics, said in a statement.
The FDA’s announcement “is only a first step that must be followed with urgent, comprehensive action to remove these flavored products from the market,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Food and Drug Administration said that within a year it will ban menthol in cigarettes and ban all flavors including menthol in cigars.
Menthol makes it easier to start smoking, and also enhances the effects of nicotine, making it more addictive and harder to quit, the FDA said in announcing its actions on Thursday.
Nineteen organizations – including the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Cancer Society, American College of Chest Physicians, American Medical Association, American Heart Association, and the National Medical Association – have pushed the FDA to ban menthol for years. The agency banned all flavors in cigarettes in 2009 but did not take any action against menthol. In 2013, the groups filed a petition demanding that the FDA ban menthol, too. The agency responded months later with a notice that it would start the process.
But it never took any action. Action on Smoking and Health and the African American Tobacco Control Leadership Council, later joined by the AMA and the NMA, sued in 2020 to compel the agency to do something. Now it has finally agreed to act.
The African American Tobacco Control Leadership Council welcomed the move but said the fight is not over and encouraged tobacco control activists to fight to ban menthol tobacco products at the local, state and federal level. “We know that this rule-making process could take years and we know that the tobacco industry will continue to do everything in their power to derail any attempt to remove their deadly products from the market,” Phillip Gardiner, MD, council cochair, said in a statement.
The AMA is urging the FDA to quickly implement the ban and remove the products “without further delay,” AMA President Susan R. Bailey, MD, said in a statement.
“FDA’s long-awaited decision to take action to eliminate menthol flavoring in cigarettes and all flavors in cigars ends a decades-long deference to the tobacco industry, which has repeatedly demonstrated its willingness to profit from products that result in death,” Lisa Lacasse, president of the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network, said in her own statement.
Ms. Lacasse said banning menthol will help eliminate health disparities. She said 86% of Black people who smoke use menthol cigarettes, compared with 46% of Hispanic people who smoke, 39% of Asian people who smoke, and 29% of White people who smoke. “FDA’s actions today send a clear message that Big Tobacco’s strategy to profit off addicting Black communities will no longer be tolerated,” she said.
Not all groups are on board, however. The American Civil Liberties Union and several other organizations wrote to the country’s top health officials urging them to reconsider.
“Such a ban will trigger criminal penalties which will disproportionately impact people of color, as well as prioritize criminalization over public health and harm reduction,” the letter says. “A ban will also lead to unconstitutional policing and other negative interactions with local law enforcement.”
The letter calls the proposed ban “well intentioned,” but said any effort to reduce death and disease from tobacco “must avoid solutions that will create yet another reason for armed police to engage citizens on the street based on pretext or conduct that does not pose a threat to public safety.”
Instead of a ban, the organizations said, policy makers should consider increased education for adults and minors, stop-smoking programs, and increased funding for health centers in communities of color.
The Biden administration, however, pressed the point that banning menthol will bring many positives. Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD said in a statement that banning menthol “will help significantly reduce youth initiation, increase the chances of smoking cessation among current smokers, and address health disparities experienced by communities of color, low-income populations, and LGBTQ-plus individuals, all of whom are far more likely to use these tobacco products.”
The FDA cited data showing that, in the first year or so after a ban goes into effect, an additional 923,000 smokers would quit, including 230,000 African Americans. Another study suggests that 633,000 deaths would be averted, including 237,000 Black Americans.
Dr. Woodcock added that, “armed with strong scientific evidence, and with full support from the [Biden] administration, we believe these actions will launch us on a trajectory toward ending tobacco-related disease and death in the U.S.”
The FDA estimates that 18.6 million Americans who are current smokers use menthol cigarettes, with a disproportionately high number being Black people. Menthol cigarette use among Black and Hispanic youth increased from 2011 to 2018, but declined for non-Hispanic White youth.
Flavored mass-produced cigars and cigarillos are disproportionately popular among youth, especially non-Hispanic Black high school students, who in 2020 reported past 30-day cigar smoking at levels twice as high as their White counterparts, said the FDA. Three-quarters of 12- to 17-year-olds reported they smoke cigars because they like the flavors. In 2020, more young people tried a cigar every day than tried a cigarette, reports the agency.
“This long-overdue decision will protect future generations of young people from nicotine addiction, especially Black children and communities, which have disproportionately suffered from menthol tobacco use due to targeted efforts from the tobacco industry,” Lee Savio Beers, MD, president of the American Academy of Pediatrics, said in a statement.
The FDA’s announcement “is only a first step that must be followed with urgent, comprehensive action to remove these flavored products from the market,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
CDC guidelines coming on long COVID
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is finalizing new guidelines to help clinicians diagnose and manage long COVID, or postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
In a day-long congressional hearing on April 28, John Brooks, MD, a medical epidemiologist at the CDC’s division of HIV/AIDS prevention, testified that the guidelines were going through the clearance process at the agency, but would be forthcoming.
“They should be coming out very shortly,” Dr. Brooks said.
The guidelines, which were developed in collaboration with newly established long-COVID clinics and patient advocacy groups, will “illustrate how to diagnose and begin to pull together what we know about management,” of the complex condition, he said.
For many doctors and patients who are struggling to understand symptoms that persist for months after the initial viral infection, the guidelines can’t come soon enough.
National Institutes of Health Director Francis Collins, MD, PhD, who also testified at the hearing, estimated that as many as 3 million people could be left with chronic health problems after even mild COVID infections.
“I can’t overstate how serious this issue is for the health of our nation,” he said.
Dr. Collins said his estimate was based on studies showing that roughly 10% of people who get COVID could be affected by this and whose “long-term course is uncertain,” he said. So far, more than 32 million Americans are known to have been infected with the new coronavirus.
“We need to make sure we put our arms around them and bring answers and care to them,” said Rep. Anna Eshoo (D-Calif.), chairwoman of the Subcommittee on Health.
Jennifer Possick, MD, who directs the post-COVID recovery program at Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital, testified that the tidal wave of patients she and her colleagues were seeing was overwhelming.
“We are a well-resourced program at an academic medical center, but we are swamped by the need in our community. This year, we have seen more patients with post COVID-19 conditions in our clinic alone than we have new cases of asthma and COPD combined,” she said. “The magnitude of the challenge is daunting.”
Dr. Possick estimated that there are “over 60” clinics in the United States that have started to treat long-COVID patients, but said they are grassroots efforts and all very different from each other.
“Whoever had the resources, had the time, [and] was able to take the initiative and forge to the relationships because most of them are multidisciplinary, did so,” she said.
Patients testify
Several representatives shared moving personal stories of loved ones or staffers who remained ill months after a COVID diagnosis.
Rep. Ann Kuster, from New Hampshire, talked about her 34-year-old niece, a member of the U.S. Ski Team, who had COVID just over a year ago and “continues to struggle with everything, even the simplest activities of daily living” she said. “She has to choose between taking a shower or making dinner. I’m so proud of her for hanging in there.”
Long-COVID patients invited to testify by the subcommittee described months of disability that left them with soaring medical bills and no ability to work to pay them.
“I am now a poor, Black, disabled woman, living with long COVID,” said Chimere Smith, who said she had been a school teacher in Baltimore. “Saying it aloud makes it no more easy to accept.”
She said COVID had affected her ability to think clearly and caused debilitating fatigue, which prevented her from working. She said she lost her vision for almost 5 months because doctors misdiagnosed a cataract caused by long COVID as dry eye.
“If I did not have a loving family, I [would] be speaking to you today [from] my car, the only property I now own.”
Ms. Smith said that long-COVID clinics, which are mostly housed within academic medical centers, were not going to be accessible for all long-haulers, who are disproportionately women of color. She has started a clinic, based out of her church, to help other patients from her community.
“No one wants to hear that long COVID has decimated my life or the lives of other black women in less than a year,” Ms. Smith said. “We’ve just been waiting and hoping for compassionate doctors and politicians who would acknowledge us.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is finalizing new guidelines to help clinicians diagnose and manage long COVID, or postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
In a day-long congressional hearing on April 28, John Brooks, MD, a medical epidemiologist at the CDC’s division of HIV/AIDS prevention, testified that the guidelines were going through the clearance process at the agency, but would be forthcoming.
“They should be coming out very shortly,” Dr. Brooks said.
The guidelines, which were developed in collaboration with newly established long-COVID clinics and patient advocacy groups, will “illustrate how to diagnose and begin to pull together what we know about management,” of the complex condition, he said.
For many doctors and patients who are struggling to understand symptoms that persist for months after the initial viral infection, the guidelines can’t come soon enough.
National Institutes of Health Director Francis Collins, MD, PhD, who also testified at the hearing, estimated that as many as 3 million people could be left with chronic health problems after even mild COVID infections.
“I can’t overstate how serious this issue is for the health of our nation,” he said.
Dr. Collins said his estimate was based on studies showing that roughly 10% of people who get COVID could be affected by this and whose “long-term course is uncertain,” he said. So far, more than 32 million Americans are known to have been infected with the new coronavirus.
“We need to make sure we put our arms around them and bring answers and care to them,” said Rep. Anna Eshoo (D-Calif.), chairwoman of the Subcommittee on Health.
Jennifer Possick, MD, who directs the post-COVID recovery program at Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital, testified that the tidal wave of patients she and her colleagues were seeing was overwhelming.
“We are a well-resourced program at an academic medical center, but we are swamped by the need in our community. This year, we have seen more patients with post COVID-19 conditions in our clinic alone than we have new cases of asthma and COPD combined,” she said. “The magnitude of the challenge is daunting.”
Dr. Possick estimated that there are “over 60” clinics in the United States that have started to treat long-COVID patients, but said they are grassroots efforts and all very different from each other.
“Whoever had the resources, had the time, [and] was able to take the initiative and forge to the relationships because most of them are multidisciplinary, did so,” she said.
Patients testify
Several representatives shared moving personal stories of loved ones or staffers who remained ill months after a COVID diagnosis.
Rep. Ann Kuster, from New Hampshire, talked about her 34-year-old niece, a member of the U.S. Ski Team, who had COVID just over a year ago and “continues to struggle with everything, even the simplest activities of daily living” she said. “She has to choose between taking a shower or making dinner. I’m so proud of her for hanging in there.”
Long-COVID patients invited to testify by the subcommittee described months of disability that left them with soaring medical bills and no ability to work to pay them.
“I am now a poor, Black, disabled woman, living with long COVID,” said Chimere Smith, who said she had been a school teacher in Baltimore. “Saying it aloud makes it no more easy to accept.”
She said COVID had affected her ability to think clearly and caused debilitating fatigue, which prevented her from working. She said she lost her vision for almost 5 months because doctors misdiagnosed a cataract caused by long COVID as dry eye.
“If I did not have a loving family, I [would] be speaking to you today [from] my car, the only property I now own.”
Ms. Smith said that long-COVID clinics, which are mostly housed within academic medical centers, were not going to be accessible for all long-haulers, who are disproportionately women of color. She has started a clinic, based out of her church, to help other patients from her community.
“No one wants to hear that long COVID has decimated my life or the lives of other black women in less than a year,” Ms. Smith said. “We’ve just been waiting and hoping for compassionate doctors and politicians who would acknowledge us.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is finalizing new guidelines to help clinicians diagnose and manage long COVID, or postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
In a day-long congressional hearing on April 28, John Brooks, MD, a medical epidemiologist at the CDC’s division of HIV/AIDS prevention, testified that the guidelines were going through the clearance process at the agency, but would be forthcoming.
“They should be coming out very shortly,” Dr. Brooks said.
The guidelines, which were developed in collaboration with newly established long-COVID clinics and patient advocacy groups, will “illustrate how to diagnose and begin to pull together what we know about management,” of the complex condition, he said.
For many doctors and patients who are struggling to understand symptoms that persist for months after the initial viral infection, the guidelines can’t come soon enough.
National Institutes of Health Director Francis Collins, MD, PhD, who also testified at the hearing, estimated that as many as 3 million people could be left with chronic health problems after even mild COVID infections.
“I can’t overstate how serious this issue is for the health of our nation,” he said.
Dr. Collins said his estimate was based on studies showing that roughly 10% of people who get COVID could be affected by this and whose “long-term course is uncertain,” he said. So far, more than 32 million Americans are known to have been infected with the new coronavirus.
“We need to make sure we put our arms around them and bring answers and care to them,” said Rep. Anna Eshoo (D-Calif.), chairwoman of the Subcommittee on Health.
Jennifer Possick, MD, who directs the post-COVID recovery program at Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital, testified that the tidal wave of patients she and her colleagues were seeing was overwhelming.
“We are a well-resourced program at an academic medical center, but we are swamped by the need in our community. This year, we have seen more patients with post COVID-19 conditions in our clinic alone than we have new cases of asthma and COPD combined,” she said. “The magnitude of the challenge is daunting.”
Dr. Possick estimated that there are “over 60” clinics in the United States that have started to treat long-COVID patients, but said they are grassroots efforts and all very different from each other.
“Whoever had the resources, had the time, [and] was able to take the initiative and forge to the relationships because most of them are multidisciplinary, did so,” she said.
Patients testify
Several representatives shared moving personal stories of loved ones or staffers who remained ill months after a COVID diagnosis.
Rep. Ann Kuster, from New Hampshire, talked about her 34-year-old niece, a member of the U.S. Ski Team, who had COVID just over a year ago and “continues to struggle with everything, even the simplest activities of daily living” she said. “She has to choose between taking a shower or making dinner. I’m so proud of her for hanging in there.”
Long-COVID patients invited to testify by the subcommittee described months of disability that left them with soaring medical bills and no ability to work to pay them.
“I am now a poor, Black, disabled woman, living with long COVID,” said Chimere Smith, who said she had been a school teacher in Baltimore. “Saying it aloud makes it no more easy to accept.”
She said COVID had affected her ability to think clearly and caused debilitating fatigue, which prevented her from working. She said she lost her vision for almost 5 months because doctors misdiagnosed a cataract caused by long COVID as dry eye.
“If I did not have a loving family, I [would] be speaking to you today [from] my car, the only property I now own.”
Ms. Smith said that long-COVID clinics, which are mostly housed within academic medical centers, were not going to be accessible for all long-haulers, who are disproportionately women of color. She has started a clinic, based out of her church, to help other patients from her community.
“No one wants to hear that long COVID has decimated my life or the lives of other black women in less than a year,” Ms. Smith said. “We’ve just been waiting and hoping for compassionate doctors and politicians who would acknowledge us.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To stay: Two more cancer indications with ‘dangling approvals’
Two more cancer indications that had been granted accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration are going to stay in place, at least for now. This was the verdict after the second day of a historic 3-day meeting (April 27-29) and follows a similar verdict from day 1.
Federal advisers so far have supported the idea of maintaining conditional approvals of some cancer indications for a number of immune checkpoint inhibitors, despite poor results in studies that were meant to confirm the benefit of these medicines for certain patients.
On the second day (April 28) of the FDA meeting, the Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC) supported the views of pharmaceutical companies in two more cases of what top agency staff call “dangling accelerated approvals.”
ODAC voted 10-1 in favor of maintaining the indication for atezolizumab (Tecentriq) for the first-line treatment of cisplatin-ineligible patients with advanced/metastatic urothelial carcinoma, pending final overall survival results from the IMvigor130 trial.
ODAC also voted 5-3 that day in favor of maintaining accelerated approval for pembrolizumab (Keytruda) for first-line cisplatin- and carboplatin-ineligible patients with advanced/metastatic urothelial carcinoma.
The FDA often follows the advice of its panels, but it is not bound to do so. If the FDA were to decide to strip the indications in question from these PD-1 medicines, such decisions would not remove these drugs from the market. The three drugs have already been approved for a number of other cancer indications.
Off-label prescribing is not uncommon in oncology, but a loss of an approved indication would affect reimbursement for these medicines, Scot Ebbinghaus, MD, vice president of oncology clinical research at Merck (the manufacturer of pembrolizumab), told ODAC members during a discussion of the possible consequences of removing the indications in question.
“Access to those treatments may end up being substantially limited, and really the best way to ensure that there’s access is to maintain FDA approval,” Dr. Ebbinghaus said.
Another participant at the meeting asked the panel and the FDA to consider the burden on patients in paying for medicines that have not yet proved to be beneficial.
Diana Zuckerman, PhD, of the nonprofit National Center for Health Research, noted that the ODAC panel included physicians who see cancer patients.
“You’re used to trying different types of treatments in hopes that something will work,” she said. “Shouldn’t cancer patients be eligible for free treatment in clinical trials instead of paying for treatment that isn’t proven to work?”
Rapid development of PD-1 drugs
Top officials at the FDA framed the challenges with accelerated approvals for immunotherapy drugs in an April 21 article in The New England Journal of Medicine. Over the course of about 6 years, the FDA approved six of these PD-1 or PD-L1 drugs for more than 75 indications in oncology, wrote Richard Pazdur, MD, and Julia A. Beaver, MD, of the FDA.
“Development of drugs in this class occurred more rapidly than that in any other therapeutic area in history,” they wrote.
In 10 cases, the required follow-up trials did not confirm the expected benefit, and yet marketing authorization for these drugs continued, leading Dr. Pazdur and Dr. Beaver to dub these “dangling” accelerated approvals. Four of these indications were voluntarily withdrawn. For the other six indications, the FDA sought feedback from ODAC during the 3-day meeting. Over the first 2 days of the meeting, ODAC recommended that three of these cancer indications remain. Three more will be considered on the last day of the meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two more cancer indications that had been granted accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration are going to stay in place, at least for now. This was the verdict after the second day of a historic 3-day meeting (April 27-29) and follows a similar verdict from day 1.
Federal advisers so far have supported the idea of maintaining conditional approvals of some cancer indications for a number of immune checkpoint inhibitors, despite poor results in studies that were meant to confirm the benefit of these medicines for certain patients.
On the second day (April 28) of the FDA meeting, the Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC) supported the views of pharmaceutical companies in two more cases of what top agency staff call “dangling accelerated approvals.”
ODAC voted 10-1 in favor of maintaining the indication for atezolizumab (Tecentriq) for the first-line treatment of cisplatin-ineligible patients with advanced/metastatic urothelial carcinoma, pending final overall survival results from the IMvigor130 trial.
ODAC also voted 5-3 that day in favor of maintaining accelerated approval for pembrolizumab (Keytruda) for first-line cisplatin- and carboplatin-ineligible patients with advanced/metastatic urothelial carcinoma.
The FDA often follows the advice of its panels, but it is not bound to do so. If the FDA were to decide to strip the indications in question from these PD-1 medicines, such decisions would not remove these drugs from the market. The three drugs have already been approved for a number of other cancer indications.
Off-label prescribing is not uncommon in oncology, but a loss of an approved indication would affect reimbursement for these medicines, Scot Ebbinghaus, MD, vice president of oncology clinical research at Merck (the manufacturer of pembrolizumab), told ODAC members during a discussion of the possible consequences of removing the indications in question.
“Access to those treatments may end up being substantially limited, and really the best way to ensure that there’s access is to maintain FDA approval,” Dr. Ebbinghaus said.
Another participant at the meeting asked the panel and the FDA to consider the burden on patients in paying for medicines that have not yet proved to be beneficial.
Diana Zuckerman, PhD, of the nonprofit National Center for Health Research, noted that the ODAC panel included physicians who see cancer patients.
“You’re used to trying different types of treatments in hopes that something will work,” she said. “Shouldn’t cancer patients be eligible for free treatment in clinical trials instead of paying for treatment that isn’t proven to work?”
Rapid development of PD-1 drugs
Top officials at the FDA framed the challenges with accelerated approvals for immunotherapy drugs in an April 21 article in The New England Journal of Medicine. Over the course of about 6 years, the FDA approved six of these PD-1 or PD-L1 drugs for more than 75 indications in oncology, wrote Richard Pazdur, MD, and Julia A. Beaver, MD, of the FDA.
“Development of drugs in this class occurred more rapidly than that in any other therapeutic area in history,” they wrote.
In 10 cases, the required follow-up trials did not confirm the expected benefit, and yet marketing authorization for these drugs continued, leading Dr. Pazdur and Dr. Beaver to dub these “dangling” accelerated approvals. Four of these indications were voluntarily withdrawn. For the other six indications, the FDA sought feedback from ODAC during the 3-day meeting. Over the first 2 days of the meeting, ODAC recommended that three of these cancer indications remain. Three more will be considered on the last day of the meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two more cancer indications that had been granted accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration are going to stay in place, at least for now. This was the verdict after the second day of a historic 3-day meeting (April 27-29) and follows a similar verdict from day 1.
Federal advisers so far have supported the idea of maintaining conditional approvals of some cancer indications for a number of immune checkpoint inhibitors, despite poor results in studies that were meant to confirm the benefit of these medicines for certain patients.
On the second day (April 28) of the FDA meeting, the Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC) supported the views of pharmaceutical companies in two more cases of what top agency staff call “dangling accelerated approvals.”
ODAC voted 10-1 in favor of maintaining the indication for atezolizumab (Tecentriq) for the first-line treatment of cisplatin-ineligible patients with advanced/metastatic urothelial carcinoma, pending final overall survival results from the IMvigor130 trial.
ODAC also voted 5-3 that day in favor of maintaining accelerated approval for pembrolizumab (Keytruda) for first-line cisplatin- and carboplatin-ineligible patients with advanced/metastatic urothelial carcinoma.
The FDA often follows the advice of its panels, but it is not bound to do so. If the FDA were to decide to strip the indications in question from these PD-1 medicines, such decisions would not remove these drugs from the market. The three drugs have already been approved for a number of other cancer indications.
Off-label prescribing is not uncommon in oncology, but a loss of an approved indication would affect reimbursement for these medicines, Scot Ebbinghaus, MD, vice president of oncology clinical research at Merck (the manufacturer of pembrolizumab), told ODAC members during a discussion of the possible consequences of removing the indications in question.
“Access to those treatments may end up being substantially limited, and really the best way to ensure that there’s access is to maintain FDA approval,” Dr. Ebbinghaus said.
Another participant at the meeting asked the panel and the FDA to consider the burden on patients in paying for medicines that have not yet proved to be beneficial.
Diana Zuckerman, PhD, of the nonprofit National Center for Health Research, noted that the ODAC panel included physicians who see cancer patients.
“You’re used to trying different types of treatments in hopes that something will work,” she said. “Shouldn’t cancer patients be eligible for free treatment in clinical trials instead of paying for treatment that isn’t proven to work?”
Rapid development of PD-1 drugs
Top officials at the FDA framed the challenges with accelerated approvals for immunotherapy drugs in an April 21 article in The New England Journal of Medicine. Over the course of about 6 years, the FDA approved six of these PD-1 or PD-L1 drugs for more than 75 indications in oncology, wrote Richard Pazdur, MD, and Julia A. Beaver, MD, of the FDA.
“Development of drugs in this class occurred more rapidly than that in any other therapeutic area in history,” they wrote.
In 10 cases, the required follow-up trials did not confirm the expected benefit, and yet marketing authorization for these drugs continued, leading Dr. Pazdur and Dr. Beaver to dub these “dangling” accelerated approvals. Four of these indications were voluntarily withdrawn. For the other six indications, the FDA sought feedback from ODAC during the 3-day meeting. Over the first 2 days of the meeting, ODAC recommended that three of these cancer indications remain. Three more will be considered on the last day of the meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA panel backs atezolizumab for mTNBC – at least for now
On the first day of a historic 3-day meeting about drugs that were granted an accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration for cancer indications, the first approval to come under discussion is staying in place, at least for now.
Members of the FDA’s Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee voted 7-2 in favor of keeping in place the indication for atezolizumab (Tecentriq) for use in a certain form of breast cancer. At the same time, the committee urged the manufacturer, Genentech, to do the research needed to prove the medicine works for these patients.
The specific indication is for atezolizumab as part of a combination with nab-paclitaxel for patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (mTNBC) whose tumors are PD-L1 positive.
The FDA granted accelerated approval in 2019 for this use of atezolizumab, expecting Genentech to produce more extensive evidence of this benefit. But so far, Genentech has not produced the data proving to the FDA that atezolizumab provides the expected benefit.
The drug was already available for use in bladder cancer, having been granted a full approval for this indication in 2016.
Other accelerated approvals withdrawn
This week’s 3-day ODAC meeting is part of the FDA’s broader reconsideration of what it has described as “dangling accelerated approvals.”
Earlier discussions between the FDA and drugmakers have already triggered four voluntary withdrawals of cancer indications with these accelerated approvals, noted Julia A. Beaver, MD, and Richard Pazdur, MD, two of the FDA’s top regulators of oncology medicine, in an April 21 perspective article in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“The small percentage of drugs whose clinical benefit is ultimately not confirmed should be viewed not as a failure of accelerated approval but rather as an expected trade-off in expediting drug development that benefits patients with severe or life-threatening diseases,” Dr. Beaver and Dr. Pazdur wrote.
But making these calls can be tough. On the first day of the meeting, even ODAC panelists who backed Genentech’s bid to maintain an mTNBC indication for atezolizumab expressed discomfort with this choice.
The FDA granted the accelerated approval for use of this drug in March 2019 based on improved progression-free survival from the IMpassion130 trial. But the drug fell short in subsequent efforts to confirm the results seen in that study. The confirmatory IMpassion131 trial failed to meet the primary endpoint, the FDA staff noted in briefing materials for the ODAC meeting.
ODAC panelist Stan Lipkowitz, MD, PhD, of the National Cancer Institute, said he expected this vote had been a tough one for all members serving on ODAC that day.
“In some ways, the purist in me said I should have voted no. But when I looked at the data, there are a couple of things that struck me,” said Dr. Lipkowitz, who is the chief of the Women’s Malignancies Branch at NCI’s Center for Cancer Research. “First of all, the landscape hasn’t changed. There’s really no therapy in the first line for triple-negative metastatic that is shown to improve survival.”
Dr. Lipkowitz emphasized that Genentech needs to continue to try to prove atezolizumab works in this setting.
“There needs to be confirmatory study,” Dr. Lipkowitz concluded.
ODAC panelist Matthew Ellis, MD, PhD, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said he also understood the difficult outlook for women fighting this cancer, but he voted against maintaining the approval.
“It’s not that I don’t feel the tragedy of these women,” said Dr. Ellis, citing his own decades of clinical experience.
“I just think that the data are the data,” Dr. Ellis said, adding that, in his view, “the only correct interpretation” of the evidence supported a vote against allowing the indication to stay.
The FDA considers the recommendations of its advisory committees but is not bound by them.
In a statement issued after the vote, Genentech said it intends to work with the FDA to determine the next steps for this indication of atezolizumab because “the clinically meaningful benefit demonstrated in the IMpassion130 study remains.”
The ODAC meeting continues for 2 more days, and will consider five more cancer indications that have been granted an accelerated approval.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On the first day of a historic 3-day meeting about drugs that were granted an accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration for cancer indications, the first approval to come under discussion is staying in place, at least for now.
Members of the FDA’s Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee voted 7-2 in favor of keeping in place the indication for atezolizumab (Tecentriq) for use in a certain form of breast cancer. At the same time, the committee urged the manufacturer, Genentech, to do the research needed to prove the medicine works for these patients.
The specific indication is for atezolizumab as part of a combination with nab-paclitaxel for patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (mTNBC) whose tumors are PD-L1 positive.
The FDA granted accelerated approval in 2019 for this use of atezolizumab, expecting Genentech to produce more extensive evidence of this benefit. But so far, Genentech has not produced the data proving to the FDA that atezolizumab provides the expected benefit.
The drug was already available for use in bladder cancer, having been granted a full approval for this indication in 2016.
Other accelerated approvals withdrawn
This week’s 3-day ODAC meeting is part of the FDA’s broader reconsideration of what it has described as “dangling accelerated approvals.”
Earlier discussions between the FDA and drugmakers have already triggered four voluntary withdrawals of cancer indications with these accelerated approvals, noted Julia A. Beaver, MD, and Richard Pazdur, MD, two of the FDA’s top regulators of oncology medicine, in an April 21 perspective article in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“The small percentage of drugs whose clinical benefit is ultimately not confirmed should be viewed not as a failure of accelerated approval but rather as an expected trade-off in expediting drug development that benefits patients with severe or life-threatening diseases,” Dr. Beaver and Dr. Pazdur wrote.
But making these calls can be tough. On the first day of the meeting, even ODAC panelists who backed Genentech’s bid to maintain an mTNBC indication for atezolizumab expressed discomfort with this choice.
The FDA granted the accelerated approval for use of this drug in March 2019 based on improved progression-free survival from the IMpassion130 trial. But the drug fell short in subsequent efforts to confirm the results seen in that study. The confirmatory IMpassion131 trial failed to meet the primary endpoint, the FDA staff noted in briefing materials for the ODAC meeting.
ODAC panelist Stan Lipkowitz, MD, PhD, of the National Cancer Institute, said he expected this vote had been a tough one for all members serving on ODAC that day.
“In some ways, the purist in me said I should have voted no. But when I looked at the data, there are a couple of things that struck me,” said Dr. Lipkowitz, who is the chief of the Women’s Malignancies Branch at NCI’s Center for Cancer Research. “First of all, the landscape hasn’t changed. There’s really no therapy in the first line for triple-negative metastatic that is shown to improve survival.”
Dr. Lipkowitz emphasized that Genentech needs to continue to try to prove atezolizumab works in this setting.
“There needs to be confirmatory study,” Dr. Lipkowitz concluded.
ODAC panelist Matthew Ellis, MD, PhD, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said he also understood the difficult outlook for women fighting this cancer, but he voted against maintaining the approval.
“It’s not that I don’t feel the tragedy of these women,” said Dr. Ellis, citing his own decades of clinical experience.
“I just think that the data are the data,” Dr. Ellis said, adding that, in his view, “the only correct interpretation” of the evidence supported a vote against allowing the indication to stay.
The FDA considers the recommendations of its advisory committees but is not bound by them.
In a statement issued after the vote, Genentech said it intends to work with the FDA to determine the next steps for this indication of atezolizumab because “the clinically meaningful benefit demonstrated in the IMpassion130 study remains.”
The ODAC meeting continues for 2 more days, and will consider five more cancer indications that have been granted an accelerated approval.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On the first day of a historic 3-day meeting about drugs that were granted an accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration for cancer indications, the first approval to come under discussion is staying in place, at least for now.
Members of the FDA’s Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee voted 7-2 in favor of keeping in place the indication for atezolizumab (Tecentriq) for use in a certain form of breast cancer. At the same time, the committee urged the manufacturer, Genentech, to do the research needed to prove the medicine works for these patients.
The specific indication is for atezolizumab as part of a combination with nab-paclitaxel for patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (mTNBC) whose tumors are PD-L1 positive.
The FDA granted accelerated approval in 2019 for this use of atezolizumab, expecting Genentech to produce more extensive evidence of this benefit. But so far, Genentech has not produced the data proving to the FDA that atezolizumab provides the expected benefit.
The drug was already available for use in bladder cancer, having been granted a full approval for this indication in 2016.
Other accelerated approvals withdrawn
This week’s 3-day ODAC meeting is part of the FDA’s broader reconsideration of what it has described as “dangling accelerated approvals.”
Earlier discussions between the FDA and drugmakers have already triggered four voluntary withdrawals of cancer indications with these accelerated approvals, noted Julia A. Beaver, MD, and Richard Pazdur, MD, two of the FDA’s top regulators of oncology medicine, in an April 21 perspective article in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“The small percentage of drugs whose clinical benefit is ultimately not confirmed should be viewed not as a failure of accelerated approval but rather as an expected trade-off in expediting drug development that benefits patients with severe or life-threatening diseases,” Dr. Beaver and Dr. Pazdur wrote.
But making these calls can be tough. On the first day of the meeting, even ODAC panelists who backed Genentech’s bid to maintain an mTNBC indication for atezolizumab expressed discomfort with this choice.
The FDA granted the accelerated approval for use of this drug in March 2019 based on improved progression-free survival from the IMpassion130 trial. But the drug fell short in subsequent efforts to confirm the results seen in that study. The confirmatory IMpassion131 trial failed to meet the primary endpoint, the FDA staff noted in briefing materials for the ODAC meeting.
ODAC panelist Stan Lipkowitz, MD, PhD, of the National Cancer Institute, said he expected this vote had been a tough one for all members serving on ODAC that day.
“In some ways, the purist in me said I should have voted no. But when I looked at the data, there are a couple of things that struck me,” said Dr. Lipkowitz, who is the chief of the Women’s Malignancies Branch at NCI’s Center for Cancer Research. “First of all, the landscape hasn’t changed. There’s really no therapy in the first line for triple-negative metastatic that is shown to improve survival.”
Dr. Lipkowitz emphasized that Genentech needs to continue to try to prove atezolizumab works in this setting.
“There needs to be confirmatory study,” Dr. Lipkowitz concluded.
ODAC panelist Matthew Ellis, MD, PhD, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said he also understood the difficult outlook for women fighting this cancer, but he voted against maintaining the approval.
“It’s not that I don’t feel the tragedy of these women,” said Dr. Ellis, citing his own decades of clinical experience.
“I just think that the data are the data,” Dr. Ellis said, adding that, in his view, “the only correct interpretation” of the evidence supported a vote against allowing the indication to stay.
The FDA considers the recommendations of its advisory committees but is not bound by them.
In a statement issued after the vote, Genentech said it intends to work with the FDA to determine the next steps for this indication of atezolizumab because “the clinically meaningful benefit demonstrated in the IMpassion130 study remains.”
The ODAC meeting continues for 2 more days, and will consider five more cancer indications that have been granted an accelerated approval.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Feds lift pause of J&J COVID vaccine, add new warning
Use of the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine should resume in the United States for all adults, the Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Disease Contol and Prevention said April 23, although health care providers should warn patients of the risk of developing the rare and serious blood clots that caused the agencies to pause the vaccine’s distribution earlier this month.
“What we are seeing is the overall rate of events was 1.9 cases per million people. In women 18 to 29 years there was an approximate 7 cases per million. The risk is even lower in women over the age of 50 at .9 cases per million,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said in a news briefing the same day.
In the end, the potential benefits of the vaccine far outweighed its risks.
“In terms of benefits, we found that for every 1 million doses of this vaccine, the J&J vaccine could prevent over 650 hospitalizations and 12 deaths among women ages 18-49,” Dr. Walensky said. The potential benefits to women over 50 were even greater: It could prevent 4,700 hospitalizations and 650 deaths.
“In the end, this vaccine was shown to be safe and effective for the vast majority of people,” Dr. Walensky said.
The recommendation to continue the vaccine’s rollout came barely 2 hours after a CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted to recommend the pause be lifted. The vote was 10-4 with one abstention.
The decision also includes instructions for the warning directed at women under 50 who have an increased risk of a rare but serious blood clot disorder called thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS).
As of April 21, 15 cases of TTS, all in women and 13 of them in women under 50, have been confirmed among 7.98 million doses of the J&J vaccine administered in the United States. Three women have died.
The FDA and CDC recommended the pause on April 13 after reports that 6 women developed a blood clotting disorder 6 to 13 days after they received the J&J vaccine.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, and a non-voting ACIP member, said in an interview the panel made the right recommendation.
He applauded both the decision to restart the vaccine and the updated warning information that “will explain [TTS] more fully to people, particularly women, who are coming to be vaccinated.”
As to women in the risk group needing to have a choice of vaccines, Dr. Schaffner said that will be addressed differently across the country.
“Every provider will not have alternative vaccines in their location so there will be many different ways to do this. You may have to get this information and select which site you’re going to depending on which vaccine is available if this matter is important to you,” he noted.
ACIP made the decision after a 6-hour emergency meeting to hear evidence on the Johnson & Johnson vaccine's protective benefits against COVID-19 vs. risk of TTS.
In the CDC-FDA press briefing, Dr. Walensky pointed out that over the past few days, as regulators have reviewed the rare events, newly identified patients had been treated appropriately, without the use of heparin, which is not advised for treating TTS.
As a result, regulators felt as if their messages had gotten out to doctors who now knew how to take special precautions when treating patients with the disorder.
She said the Johnson & Johnson shot remained an important option because it was convenient to give and easier to store than the other vaccines currently authorized in the United States.
Peter Marks, MD, the director of FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said the agency had already added information describing the risk of the rare clotting disorder to its fact sheets for patients and doctors.
Janet Woodcock, MD, acting commissioner of the FDA, said vaccination centers could resume giving the “one and done” shots as early as April 24.
This article was updated April 24, 2021, and first appeared on WebMD.com.
Use of the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine should resume in the United States for all adults, the Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Disease Contol and Prevention said April 23, although health care providers should warn patients of the risk of developing the rare and serious blood clots that caused the agencies to pause the vaccine’s distribution earlier this month.
“What we are seeing is the overall rate of events was 1.9 cases per million people. In women 18 to 29 years there was an approximate 7 cases per million. The risk is even lower in women over the age of 50 at .9 cases per million,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said in a news briefing the same day.
In the end, the potential benefits of the vaccine far outweighed its risks.
“In terms of benefits, we found that for every 1 million doses of this vaccine, the J&J vaccine could prevent over 650 hospitalizations and 12 deaths among women ages 18-49,” Dr. Walensky said. The potential benefits to women over 50 were even greater: It could prevent 4,700 hospitalizations and 650 deaths.
“In the end, this vaccine was shown to be safe and effective for the vast majority of people,” Dr. Walensky said.
The recommendation to continue the vaccine’s rollout came barely 2 hours after a CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted to recommend the pause be lifted. The vote was 10-4 with one abstention.
The decision also includes instructions for the warning directed at women under 50 who have an increased risk of a rare but serious blood clot disorder called thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS).
As of April 21, 15 cases of TTS, all in women and 13 of them in women under 50, have been confirmed among 7.98 million doses of the J&J vaccine administered in the United States. Three women have died.
The FDA and CDC recommended the pause on April 13 after reports that 6 women developed a blood clotting disorder 6 to 13 days after they received the J&J vaccine.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, and a non-voting ACIP member, said in an interview the panel made the right recommendation.
He applauded both the decision to restart the vaccine and the updated warning information that “will explain [TTS] more fully to people, particularly women, who are coming to be vaccinated.”
As to women in the risk group needing to have a choice of vaccines, Dr. Schaffner said that will be addressed differently across the country.
“Every provider will not have alternative vaccines in their location so there will be many different ways to do this. You may have to get this information and select which site you’re going to depending on which vaccine is available if this matter is important to you,” he noted.
ACIP made the decision after a 6-hour emergency meeting to hear evidence on the Johnson & Johnson vaccine's protective benefits against COVID-19 vs. risk of TTS.
In the CDC-FDA press briefing, Dr. Walensky pointed out that over the past few days, as regulators have reviewed the rare events, newly identified patients had been treated appropriately, without the use of heparin, which is not advised for treating TTS.
As a result, regulators felt as if their messages had gotten out to doctors who now knew how to take special precautions when treating patients with the disorder.
She said the Johnson & Johnson shot remained an important option because it was convenient to give and easier to store than the other vaccines currently authorized in the United States.
Peter Marks, MD, the director of FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said the agency had already added information describing the risk of the rare clotting disorder to its fact sheets for patients and doctors.
Janet Woodcock, MD, acting commissioner of the FDA, said vaccination centers could resume giving the “one and done” shots as early as April 24.
This article was updated April 24, 2021, and first appeared on WebMD.com.
Use of the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine should resume in the United States for all adults, the Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Disease Contol and Prevention said April 23, although health care providers should warn patients of the risk of developing the rare and serious blood clots that caused the agencies to pause the vaccine’s distribution earlier this month.
“What we are seeing is the overall rate of events was 1.9 cases per million people. In women 18 to 29 years there was an approximate 7 cases per million. The risk is even lower in women over the age of 50 at .9 cases per million,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said in a news briefing the same day.
In the end, the potential benefits of the vaccine far outweighed its risks.
“In terms of benefits, we found that for every 1 million doses of this vaccine, the J&J vaccine could prevent over 650 hospitalizations and 12 deaths among women ages 18-49,” Dr. Walensky said. The potential benefits to women over 50 were even greater: It could prevent 4,700 hospitalizations and 650 deaths.
“In the end, this vaccine was shown to be safe and effective for the vast majority of people,” Dr. Walensky said.
The recommendation to continue the vaccine’s rollout came barely 2 hours after a CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted to recommend the pause be lifted. The vote was 10-4 with one abstention.
The decision also includes instructions for the warning directed at women under 50 who have an increased risk of a rare but serious blood clot disorder called thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS).
As of April 21, 15 cases of TTS, all in women and 13 of them in women under 50, have been confirmed among 7.98 million doses of the J&J vaccine administered in the United States. Three women have died.
The FDA and CDC recommended the pause on April 13 after reports that 6 women developed a blood clotting disorder 6 to 13 days after they received the J&J vaccine.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, and a non-voting ACIP member, said in an interview the panel made the right recommendation.
He applauded both the decision to restart the vaccine and the updated warning information that “will explain [TTS] more fully to people, particularly women, who are coming to be vaccinated.”
As to women in the risk group needing to have a choice of vaccines, Dr. Schaffner said that will be addressed differently across the country.
“Every provider will not have alternative vaccines in their location so there will be many different ways to do this. You may have to get this information and select which site you’re going to depending on which vaccine is available if this matter is important to you,” he noted.
ACIP made the decision after a 6-hour emergency meeting to hear evidence on the Johnson & Johnson vaccine's protective benefits against COVID-19 vs. risk of TTS.
In the CDC-FDA press briefing, Dr. Walensky pointed out that over the past few days, as regulators have reviewed the rare events, newly identified patients had been treated appropriately, without the use of heparin, which is not advised for treating TTS.
As a result, regulators felt as if their messages had gotten out to doctors who now knew how to take special precautions when treating patients with the disorder.
She said the Johnson & Johnson shot remained an important option because it was convenient to give and easier to store than the other vaccines currently authorized in the United States.
Peter Marks, MD, the director of FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said the agency had already added information describing the risk of the rare clotting disorder to its fact sheets for patients and doctors.
Janet Woodcock, MD, acting commissioner of the FDA, said vaccination centers could resume giving the “one and done” shots as early as April 24.
This article was updated April 24, 2021, and first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA expands use of SLIT pollen allergy treatment to children
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a new indication for ALK’s under-the-tongue immunotherapy tablet Ragwitek (Ambrosia artemisiifolia) to treat ragweed pollen–induced hay fever in children aged 5-17 years.
Ragwitek received FDA approval in 2014 to treat short ragweed pollen–induced hay fever, with or without allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, in adults aged 18-65 years.
The approval for Ragwitek comes with a boxed warning regarding a risk for life-threatening allergic reactions associated with the immunotherapy treatment, including anaphylaxis and severe laryngopharyngeal restriction. The package insert specifies that physicians should prescribe autoinjectable epinephrine with the drug.
“Ragwitek tablets provide a new immunotherapy treatment option for children and adolescents with seasonal ragweed allergies which often causes uncomfortable nasal symptoms and red, itchy eyes during the late summer and early fall,” David I. Bernstein, MD, University of Cincinnati, Bernstein Clinical Research, said in a company press release.
Short ragweed pollen is one of the most common weed allergies. Allergic rhinitis, or hay fever, affects 10%-30% of the population worldwide, according to the American Academy of Allergy Asthma & Immunology. In the United States, approximately 7.7% of adults and 7.2% of children were diagnosed with it annually, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The new indication was based partly on data from a phase 3 clinical trial in children with short ragweed–induced allergic rhinitis, or hay fever, published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. In the study, researchers evaluated the efficacy and safety of the treatment in 1,022 participants aged 5-17 years with a history of ragweed-induced rhinoconjunctivitis and sensitivity to ragweed over a 20- to 28-week treatment period.
Researchers found that Ragwitek improved symptoms in children and adolescents and decreased their use of symptom-relieving medication, compared with placebo.
Among children and adolescents aged 5-17 years, the most common adverse reactions reported were throat irritation/tickle (48.3% in the Ragwitek group vs. 17.7% in the placebo group), itching in the mouth (47.8% vs. 11.2%), itching in the ear (33.9% vs. 6.3%), mouth pain (18.9% vs. 4.5%), swelling of the lips (13.8% vs. 1.2%), nausea (11.5% vs. 3.3%), swelling of the tongue (11.3% vs. 0.8%), throat swelling (10.7% vs. 1.6%), and stomach pain (10.1% vs. 4.5%).
The FDA also recommends that Ragwitek not be prescribed to people with severe, unstable, or uncontrolled asthma, those with a history of severe systemic allergic reactions, and those with a history of eosinophilic esophagitis. The immunotherapy treatment also may not be suitable for people who are unresponsive to epinephrine or inhaled bronchodilators.
In addition, the treatment is not approved for the immediate relief of allergic symptoms in children or adults. The once-daily treatment, which contains an extract from short ragweed pollen, should begin 12 weeks before the start of ragweed pollen season and continue throughout the season, according to the FDA.
Dr. Bernstein said that the under-the-tongue immunotherapy works by targeting the specific allergy trigger and reducing allergy symptoms by “stimulating the immune system.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a new indication for ALK’s under-the-tongue immunotherapy tablet Ragwitek (Ambrosia artemisiifolia) to treat ragweed pollen–induced hay fever in children aged 5-17 years.
Ragwitek received FDA approval in 2014 to treat short ragweed pollen–induced hay fever, with or without allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, in adults aged 18-65 years.
The approval for Ragwitek comes with a boxed warning regarding a risk for life-threatening allergic reactions associated with the immunotherapy treatment, including anaphylaxis and severe laryngopharyngeal restriction. The package insert specifies that physicians should prescribe autoinjectable epinephrine with the drug.
“Ragwitek tablets provide a new immunotherapy treatment option for children and adolescents with seasonal ragweed allergies which often causes uncomfortable nasal symptoms and red, itchy eyes during the late summer and early fall,” David I. Bernstein, MD, University of Cincinnati, Bernstein Clinical Research, said in a company press release.
Short ragweed pollen is one of the most common weed allergies. Allergic rhinitis, or hay fever, affects 10%-30% of the population worldwide, according to the American Academy of Allergy Asthma & Immunology. In the United States, approximately 7.7% of adults and 7.2% of children were diagnosed with it annually, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The new indication was based partly on data from a phase 3 clinical trial in children with short ragweed–induced allergic rhinitis, or hay fever, published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. In the study, researchers evaluated the efficacy and safety of the treatment in 1,022 participants aged 5-17 years with a history of ragweed-induced rhinoconjunctivitis and sensitivity to ragweed over a 20- to 28-week treatment period.
Researchers found that Ragwitek improved symptoms in children and adolescents and decreased their use of symptom-relieving medication, compared with placebo.
Among children and adolescents aged 5-17 years, the most common adverse reactions reported were throat irritation/tickle (48.3% in the Ragwitek group vs. 17.7% in the placebo group), itching in the mouth (47.8% vs. 11.2%), itching in the ear (33.9% vs. 6.3%), mouth pain (18.9% vs. 4.5%), swelling of the lips (13.8% vs. 1.2%), nausea (11.5% vs. 3.3%), swelling of the tongue (11.3% vs. 0.8%), throat swelling (10.7% vs. 1.6%), and stomach pain (10.1% vs. 4.5%).
The FDA also recommends that Ragwitek not be prescribed to people with severe, unstable, or uncontrolled asthma, those with a history of severe systemic allergic reactions, and those with a history of eosinophilic esophagitis. The immunotherapy treatment also may not be suitable for people who are unresponsive to epinephrine or inhaled bronchodilators.
In addition, the treatment is not approved for the immediate relief of allergic symptoms in children or adults. The once-daily treatment, which contains an extract from short ragweed pollen, should begin 12 weeks before the start of ragweed pollen season and continue throughout the season, according to the FDA.
Dr. Bernstein said that the under-the-tongue immunotherapy works by targeting the specific allergy trigger and reducing allergy symptoms by “stimulating the immune system.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a new indication for ALK’s under-the-tongue immunotherapy tablet Ragwitek (Ambrosia artemisiifolia) to treat ragweed pollen–induced hay fever in children aged 5-17 years.
Ragwitek received FDA approval in 2014 to treat short ragweed pollen–induced hay fever, with or without allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, in adults aged 18-65 years.
The approval for Ragwitek comes with a boxed warning regarding a risk for life-threatening allergic reactions associated with the immunotherapy treatment, including anaphylaxis and severe laryngopharyngeal restriction. The package insert specifies that physicians should prescribe autoinjectable epinephrine with the drug.
“Ragwitek tablets provide a new immunotherapy treatment option for children and adolescents with seasonal ragweed allergies which often causes uncomfortable nasal symptoms and red, itchy eyes during the late summer and early fall,” David I. Bernstein, MD, University of Cincinnati, Bernstein Clinical Research, said in a company press release.
Short ragweed pollen is one of the most common weed allergies. Allergic rhinitis, or hay fever, affects 10%-30% of the population worldwide, according to the American Academy of Allergy Asthma & Immunology. In the United States, approximately 7.7% of adults and 7.2% of children were diagnosed with it annually, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The new indication was based partly on data from a phase 3 clinical trial in children with short ragweed–induced allergic rhinitis, or hay fever, published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. In the study, researchers evaluated the efficacy and safety of the treatment in 1,022 participants aged 5-17 years with a history of ragweed-induced rhinoconjunctivitis and sensitivity to ragweed over a 20- to 28-week treatment period.
Researchers found that Ragwitek improved symptoms in children and adolescents and decreased their use of symptom-relieving medication, compared with placebo.
Among children and adolescents aged 5-17 years, the most common adverse reactions reported were throat irritation/tickle (48.3% in the Ragwitek group vs. 17.7% in the placebo group), itching in the mouth (47.8% vs. 11.2%), itching in the ear (33.9% vs. 6.3%), mouth pain (18.9% vs. 4.5%), swelling of the lips (13.8% vs. 1.2%), nausea (11.5% vs. 3.3%), swelling of the tongue (11.3% vs. 0.8%), throat swelling (10.7% vs. 1.6%), and stomach pain (10.1% vs. 4.5%).
The FDA also recommends that Ragwitek not be prescribed to people with severe, unstable, or uncontrolled asthma, those with a history of severe systemic allergic reactions, and those with a history of eosinophilic esophagitis. The immunotherapy treatment also may not be suitable for people who are unresponsive to epinephrine or inhaled bronchodilators.
In addition, the treatment is not approved for the immediate relief of allergic symptoms in children or adults. The once-daily treatment, which contains an extract from short ragweed pollen, should begin 12 weeks before the start of ragweed pollen season and continue throughout the season, according to the FDA.
Dr. Bernstein said that the under-the-tongue immunotherapy works by targeting the specific allergy trigger and reducing allergy symptoms by “stimulating the immune system.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves new immunotherapy for endometrial cancer
Use limited to patients with biomarker
Usage of the new checkpoint inhibitor is limited to patients who have progressed on or following prior treatment with a platinum-containing chemotherapy. Eligibility must also be determined by an FDA-approved test for the dMMR biomarker. Approximately 25%-30% of patients with advanced endometrial cancer have dMMR tumors, according to the FDA.
The approval is “evidence of the FDA’s progress in applying precision medicine to expand treatment options for patients with cancer,” said Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence and acting director of the Office of Oncologic Diseases in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
He explained that the immunotherapy was “specifically studied to target dMMR endometrial cancer and leverages scientific knowledge surrounding the mechanism of immunotherapy response.”
The new drug also addresses an unmet medical need, as there are limited therapeutic options in this setting following frontline standard treatment with a platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The approval is based on safety and efficacy data from a single-arm, multicohort clinical trial. Of the 71 patients with dMMR recurrent or advanced endometrial cancer who received dostarlimab, 42.3% had a response. For 93% of that group, the response lasted 6 months or longer.
The drug’s maker, GlaxoSmithKline, is currently conducting additional, larger trials in more patients with dMMR endometrial tumors to verify and further describe clinical benefits.
Common side effects of dostarlimab include fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, anemia, and constipation. Like other checkpoint inhibitors, the new drug can cause immune-mediated side effects such as pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, and nephritis.
Dostarlimab is contraindicated in women who are pregnant or breastfeeding because it may cause harm to a developing fetus or newborn baby.
The FDA approval comes a month after the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use of the European Medicines Agency recommended granting conditional marketing authorization for dostarlimab for use as monotherapy in this same patient group.
In the United States, dostarlimab received Priority Review designation and Breakthrough Therapy designation for this indication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Use limited to patients with biomarker
Use limited to patients with biomarker
Usage of the new checkpoint inhibitor is limited to patients who have progressed on or following prior treatment with a platinum-containing chemotherapy. Eligibility must also be determined by an FDA-approved test for the dMMR biomarker. Approximately 25%-30% of patients with advanced endometrial cancer have dMMR tumors, according to the FDA.
The approval is “evidence of the FDA’s progress in applying precision medicine to expand treatment options for patients with cancer,” said Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence and acting director of the Office of Oncologic Diseases in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
He explained that the immunotherapy was “specifically studied to target dMMR endometrial cancer and leverages scientific knowledge surrounding the mechanism of immunotherapy response.”
The new drug also addresses an unmet medical need, as there are limited therapeutic options in this setting following frontline standard treatment with a platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The approval is based on safety and efficacy data from a single-arm, multicohort clinical trial. Of the 71 patients with dMMR recurrent or advanced endometrial cancer who received dostarlimab, 42.3% had a response. For 93% of that group, the response lasted 6 months or longer.
The drug’s maker, GlaxoSmithKline, is currently conducting additional, larger trials in more patients with dMMR endometrial tumors to verify and further describe clinical benefits.
Common side effects of dostarlimab include fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, anemia, and constipation. Like other checkpoint inhibitors, the new drug can cause immune-mediated side effects such as pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, and nephritis.
Dostarlimab is contraindicated in women who are pregnant or breastfeeding because it may cause harm to a developing fetus or newborn baby.
The FDA approval comes a month after the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use of the European Medicines Agency recommended granting conditional marketing authorization for dostarlimab for use as monotherapy in this same patient group.
In the United States, dostarlimab received Priority Review designation and Breakthrough Therapy designation for this indication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Usage of the new checkpoint inhibitor is limited to patients who have progressed on or following prior treatment with a platinum-containing chemotherapy. Eligibility must also be determined by an FDA-approved test for the dMMR biomarker. Approximately 25%-30% of patients with advanced endometrial cancer have dMMR tumors, according to the FDA.
The approval is “evidence of the FDA’s progress in applying precision medicine to expand treatment options for patients with cancer,” said Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence and acting director of the Office of Oncologic Diseases in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
He explained that the immunotherapy was “specifically studied to target dMMR endometrial cancer and leverages scientific knowledge surrounding the mechanism of immunotherapy response.”
The new drug also addresses an unmet medical need, as there are limited therapeutic options in this setting following frontline standard treatment with a platinum-containing chemotherapy.
The approval is based on safety and efficacy data from a single-arm, multicohort clinical trial. Of the 71 patients with dMMR recurrent or advanced endometrial cancer who received dostarlimab, 42.3% had a response. For 93% of that group, the response lasted 6 months or longer.
The drug’s maker, GlaxoSmithKline, is currently conducting additional, larger trials in more patients with dMMR endometrial tumors to verify and further describe clinical benefits.
Common side effects of dostarlimab include fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, anemia, and constipation. Like other checkpoint inhibitors, the new drug can cause immune-mediated side effects such as pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, and nephritis.
Dostarlimab is contraindicated in women who are pregnant or breastfeeding because it may cause harm to a developing fetus or newborn baby.
The FDA approval comes a month after the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use of the European Medicines Agency recommended granting conditional marketing authorization for dostarlimab for use as monotherapy in this same patient group.
In the United States, dostarlimab received Priority Review designation and Breakthrough Therapy designation for this indication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.



