User login
Physicians: Don’t ignore sexuality in your dying patients
I have a long history of being interested in conversations that others avoid. In medical school, I felt that we didn’t talk enough about death, so I organized a lecture series on end-of-life care for my fellow students. Now, as a sexual medicine specialist, I have other conversations from which many medical providers shy away. So, buckle up!
A key question in palliative care is: How do you want to live the life you have left? And where does the wide range of human pleasures fit in? In her book The Pleasure Zone, sex therapist Stella Resnick describes eight kinds of pleasure:
- pain relief
- play, humor, movement, and sound
- mental
- emotional
- sensual
- spiritual
- primal (just being)
- sexual
At the end of life, both medically and culturally, we pay attention to many of these pleasures. But sexuality is often ignored.
Sexuality – which can be defined as the experience of oneself as a sexual being – may include how sex is experienced in relationships or with oneself, sexual orientation, body image, gender expression and identity, as well as sexual satisfaction and pleasure. People may have different priorities at different times regarding their sexuality, but sexuality is a key aspect of feeling fully alive and human across the lifespan. At the end of life, sexuality, sexual expression, and physical connection may play even more important roles than previously.
‘I just want to be able to have sex with my husband again’
Z was a 75-year-old woman who came to me for help with vaginal stenosis. Her cancer treatments were not going well. I asked her one of my typical questions: “What does sex mean to you?”
Sexual pleasure was “glue” – a critical way for her to connect with her sense of self and with her husband, a man of few words. She described transcendent experiences with partnered sex during her life. Finally, she explained, she was saddened by the idea of not experiencing that again before she died.
As medical providers, we don’t all need to be sex experts, but our patients should be able to have open and shame-free conversations with us about these issues at all stages of life. Up to 86% of palliative care patients want the chance to discuss their sexual concerns with a skilled clinician, and many consider this issue important to their psychological well-being. And yet, 91% reported that sexuality had not been addressed in their care.
In a Canadian study of 10 palliative care patients (and their partners), all but one felt that their medical providers should initiate conversations about sexuality and the effect of illness on sexual experience. They felt that this communication should be an integral component of care. The one person who disagreed said it was appropriate for clinicians to ask patients whether they wanted to talk about sexuality.
Before this study, sexuality had been discussed with only one participant. Here’s the magic part: Several of the patients reported that the study itself was therapeutic. This is my clinical experience as well. More often than not, open and shame-free clinical discussions about sexuality led to patients reflecting: “I’ve never been able to say this to another person, and now I feel so much better.”
One study of palliative care nurses found that while the nurses acknowledged the importance of addressing sexuality, their way of addressing sexuality followed cultural myths and norms or relied on their own experience rather than knowledge-based guidelines. Why? One explanation could be that clinicians raised and educated in North America probably did not get adequate training on this topic. We need to do better.
Second, cultural concepts that equate sexuality with healthy and able bodies who are partnered, young, cisgender, and heterosexual make it hard to conceive of how to relate sexuality to other bodies. We’ve been steeped in the biases of our culture.
Some medical providers avoid the topic because they feel vulnerable, fearful that a conversation about sexuality with a patient will reveal something about themselves. Others may simply deny the possibility that sexual function changes in the face of serious illness or that this could be a priority for their patients. Of course, we have a million other things to talk about – I get it.
Views on sex and sexuality affect how clinicians approach these conversations as well. A study of palliative care professionals described themes among those who did and did not address the topic. The professionals who did not discuss sexuality endorsed a narrow definition of sex based on genital sexual acts between two partners, usually heterosexual. Among these clinicians, when the issue came up, patients had raised the topic. They talked about sex using jokes and euphemisms (“are you still enjoying ‘good moments’ with your partner?”), perhaps to ease their own discomfort.
On the other hand, professionals who more frequently discussed sexuality with their patients endorsed a more holistic concept of sexuality: including genital and nongenital contact as well as nonphysical components like verbal communication and emotions. These clinicians found sexuality applicable to all individuals across the lifespan. They were more likely to initiate discussions about the effect of medications or illness on sexual function and address the need for equipment, such as a larger hospital bed.
I’m hoping that you might one day find yourself in the second group. Our patients at the end of life need our help in accessing the full range of pleasure in their lives. We need better medical education on how to help with sexual concerns when they arise (an article for another day), but we can start right now by simply initiating open, shame-free sexual health conversations. This is often the most important therapeutic intervention.
Dr. Kranz, Clinical Assistant Professor of Obstetrics/Gynecology and Family Medicine, University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
I have a long history of being interested in conversations that others avoid. In medical school, I felt that we didn’t talk enough about death, so I organized a lecture series on end-of-life care for my fellow students. Now, as a sexual medicine specialist, I have other conversations from which many medical providers shy away. So, buckle up!
A key question in palliative care is: How do you want to live the life you have left? And where does the wide range of human pleasures fit in? In her book The Pleasure Zone, sex therapist Stella Resnick describes eight kinds of pleasure:
- pain relief
- play, humor, movement, and sound
- mental
- emotional
- sensual
- spiritual
- primal (just being)
- sexual
At the end of life, both medically and culturally, we pay attention to many of these pleasures. But sexuality is often ignored.
Sexuality – which can be defined as the experience of oneself as a sexual being – may include how sex is experienced in relationships or with oneself, sexual orientation, body image, gender expression and identity, as well as sexual satisfaction and pleasure. People may have different priorities at different times regarding their sexuality, but sexuality is a key aspect of feeling fully alive and human across the lifespan. At the end of life, sexuality, sexual expression, and physical connection may play even more important roles than previously.
‘I just want to be able to have sex with my husband again’
Z was a 75-year-old woman who came to me for help with vaginal stenosis. Her cancer treatments were not going well. I asked her one of my typical questions: “What does sex mean to you?”
Sexual pleasure was “glue” – a critical way for her to connect with her sense of self and with her husband, a man of few words. She described transcendent experiences with partnered sex during her life. Finally, she explained, she was saddened by the idea of not experiencing that again before she died.
As medical providers, we don’t all need to be sex experts, but our patients should be able to have open and shame-free conversations with us about these issues at all stages of life. Up to 86% of palliative care patients want the chance to discuss their sexual concerns with a skilled clinician, and many consider this issue important to their psychological well-being. And yet, 91% reported that sexuality had not been addressed in their care.
In a Canadian study of 10 palliative care patients (and their partners), all but one felt that their medical providers should initiate conversations about sexuality and the effect of illness on sexual experience. They felt that this communication should be an integral component of care. The one person who disagreed said it was appropriate for clinicians to ask patients whether they wanted to talk about sexuality.
Before this study, sexuality had been discussed with only one participant. Here’s the magic part: Several of the patients reported that the study itself was therapeutic. This is my clinical experience as well. More often than not, open and shame-free clinical discussions about sexuality led to patients reflecting: “I’ve never been able to say this to another person, and now I feel so much better.”
One study of palliative care nurses found that while the nurses acknowledged the importance of addressing sexuality, their way of addressing sexuality followed cultural myths and norms or relied on their own experience rather than knowledge-based guidelines. Why? One explanation could be that clinicians raised and educated in North America probably did not get adequate training on this topic. We need to do better.
Second, cultural concepts that equate sexuality with healthy and able bodies who are partnered, young, cisgender, and heterosexual make it hard to conceive of how to relate sexuality to other bodies. We’ve been steeped in the biases of our culture.
Some medical providers avoid the topic because they feel vulnerable, fearful that a conversation about sexuality with a patient will reveal something about themselves. Others may simply deny the possibility that sexual function changes in the face of serious illness or that this could be a priority for their patients. Of course, we have a million other things to talk about – I get it.
Views on sex and sexuality affect how clinicians approach these conversations as well. A study of palliative care professionals described themes among those who did and did not address the topic. The professionals who did not discuss sexuality endorsed a narrow definition of sex based on genital sexual acts between two partners, usually heterosexual. Among these clinicians, when the issue came up, patients had raised the topic. They talked about sex using jokes and euphemisms (“are you still enjoying ‘good moments’ with your partner?”), perhaps to ease their own discomfort.
On the other hand, professionals who more frequently discussed sexuality with their patients endorsed a more holistic concept of sexuality: including genital and nongenital contact as well as nonphysical components like verbal communication and emotions. These clinicians found sexuality applicable to all individuals across the lifespan. They were more likely to initiate discussions about the effect of medications or illness on sexual function and address the need for equipment, such as a larger hospital bed.
I’m hoping that you might one day find yourself in the second group. Our patients at the end of life need our help in accessing the full range of pleasure in their lives. We need better medical education on how to help with sexual concerns when they arise (an article for another day), but we can start right now by simply initiating open, shame-free sexual health conversations. This is often the most important therapeutic intervention.
Dr. Kranz, Clinical Assistant Professor of Obstetrics/Gynecology and Family Medicine, University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
I have a long history of being interested in conversations that others avoid. In medical school, I felt that we didn’t talk enough about death, so I organized a lecture series on end-of-life care for my fellow students. Now, as a sexual medicine specialist, I have other conversations from which many medical providers shy away. So, buckle up!
A key question in palliative care is: How do you want to live the life you have left? And where does the wide range of human pleasures fit in? In her book The Pleasure Zone, sex therapist Stella Resnick describes eight kinds of pleasure:
- pain relief
- play, humor, movement, and sound
- mental
- emotional
- sensual
- spiritual
- primal (just being)
- sexual
At the end of life, both medically and culturally, we pay attention to many of these pleasures. But sexuality is often ignored.
Sexuality – which can be defined as the experience of oneself as a sexual being – may include how sex is experienced in relationships or with oneself, sexual orientation, body image, gender expression and identity, as well as sexual satisfaction and pleasure. People may have different priorities at different times regarding their sexuality, but sexuality is a key aspect of feeling fully alive and human across the lifespan. At the end of life, sexuality, sexual expression, and physical connection may play even more important roles than previously.
‘I just want to be able to have sex with my husband again’
Z was a 75-year-old woman who came to me for help with vaginal stenosis. Her cancer treatments were not going well. I asked her one of my typical questions: “What does sex mean to you?”
Sexual pleasure was “glue” – a critical way for her to connect with her sense of self and with her husband, a man of few words. She described transcendent experiences with partnered sex during her life. Finally, she explained, she was saddened by the idea of not experiencing that again before she died.
As medical providers, we don’t all need to be sex experts, but our patients should be able to have open and shame-free conversations with us about these issues at all stages of life. Up to 86% of palliative care patients want the chance to discuss their sexual concerns with a skilled clinician, and many consider this issue important to their psychological well-being. And yet, 91% reported that sexuality had not been addressed in their care.
In a Canadian study of 10 palliative care patients (and their partners), all but one felt that their medical providers should initiate conversations about sexuality and the effect of illness on sexual experience. They felt that this communication should be an integral component of care. The one person who disagreed said it was appropriate for clinicians to ask patients whether they wanted to talk about sexuality.
Before this study, sexuality had been discussed with only one participant. Here’s the magic part: Several of the patients reported that the study itself was therapeutic. This is my clinical experience as well. More often than not, open and shame-free clinical discussions about sexuality led to patients reflecting: “I’ve never been able to say this to another person, and now I feel so much better.”
One study of palliative care nurses found that while the nurses acknowledged the importance of addressing sexuality, their way of addressing sexuality followed cultural myths and norms or relied on their own experience rather than knowledge-based guidelines. Why? One explanation could be that clinicians raised and educated in North America probably did not get adequate training on this topic. We need to do better.
Second, cultural concepts that equate sexuality with healthy and able bodies who are partnered, young, cisgender, and heterosexual make it hard to conceive of how to relate sexuality to other bodies. We’ve been steeped in the biases of our culture.
Some medical providers avoid the topic because they feel vulnerable, fearful that a conversation about sexuality with a patient will reveal something about themselves. Others may simply deny the possibility that sexual function changes in the face of serious illness or that this could be a priority for their patients. Of course, we have a million other things to talk about – I get it.
Views on sex and sexuality affect how clinicians approach these conversations as well. A study of palliative care professionals described themes among those who did and did not address the topic. The professionals who did not discuss sexuality endorsed a narrow definition of sex based on genital sexual acts between two partners, usually heterosexual. Among these clinicians, when the issue came up, patients had raised the topic. They talked about sex using jokes and euphemisms (“are you still enjoying ‘good moments’ with your partner?”), perhaps to ease their own discomfort.
On the other hand, professionals who more frequently discussed sexuality with their patients endorsed a more holistic concept of sexuality: including genital and nongenital contact as well as nonphysical components like verbal communication and emotions. These clinicians found sexuality applicable to all individuals across the lifespan. They were more likely to initiate discussions about the effect of medications or illness on sexual function and address the need for equipment, such as a larger hospital bed.
I’m hoping that you might one day find yourself in the second group. Our patients at the end of life need our help in accessing the full range of pleasure in their lives. We need better medical education on how to help with sexual concerns when they arise (an article for another day), but we can start right now by simply initiating open, shame-free sexual health conversations. This is often the most important therapeutic intervention.
Dr. Kranz, Clinical Assistant Professor of Obstetrics/Gynecology and Family Medicine, University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is metabolically healthy obesity an ‘illusion’?
I cock my head at my “new” patient, Sherri, who heads into my consultation room at 8:30 on a rainy Monday morning. She looks vaguely familiar but I can’t quite place her face. “Dr. Messer,” she cries, “don’t you remember me? I was one of your very first patients 15 years ago in Westchester. You had just finished training.” Suddenly it all comes back to me.
Meeting Sherri reminded me of the lesson in humility that my mentor, Dr. Alice Levine, taught our crowded lecture hall so many years ago. Once upon a time, she prided herself on being an infinitely important doctor. One day, she met a patient with empty sella syndrome (literally missing his whole pituitary gland – MRI proven). She fully expected to swoop in to save the patient’s life by expertly replacing each absconded pituitary hormone, but to her shock and delight, an invisible little sliver of pituitary left in his brain allowed him to magically eek out completely normal hormone levels.
Sherri walked into my office so many years ago with a body mass index in the mid-40s. In laymen’s terms, she was morbidly obese. I settled in to discuss her hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, fatty liver, polycystic ovary syndrome, etc., but to my shock and delight, her blood pressure and blood work were completely normal. I struggled to keep a neutral face. She was there to discuss hair loss. I had just met my first patient with metabolically healthy obesity (MHO), and I was floored.
Fast-forward 15 years. Sherri sits down across the desk from me and hands me her blood work. Her formerly pristine labs are now peppered with red exclamation points and critically high lab values. Sherri had transitioned from MHO to metabolically unhealthy obesity (MUO).
Early clinical trials concluded that it was possible to have obesity but be metabolically healthy. Approximately 15% of patients living with obesity lack any of the comorbidities typically associated with this phenotype. These findings contributed to the de-emphasis on obesity as a true disease state.
In retrospect, the MHO subtype appears to be much more common in the younger and more active population and is typically quite transient. A new study published in Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism revealed that people with MHO are 1.5 times more likely to develop diabetes vs. metabolically healthy normal-weight individuals. In addition, people living with obesity and no known metabolic complications still had a 50% higher risk for coronary artery disease. The study also showed that over 50% of people initially characterized as MHO eventually became MUO after a 16-year follow-up.
So once again, all roads lead to semaglutide (Wegovy), the most effective U.S. Food and Drug Administration–approved weight loss medication to date. The incretin class of medications not only helps patients lose 15% or more of their body weight, but it also helps reverse insulin resistance, lower the risk for heart disease, melt away fatty liver, and lower cholesterol levels and blood pressures. While an emphasis on lifestyle changes is always important, these medications are critical adjuncts to conventional therapies.
Fifteen years ago, I discussed her hair loss for 45 minutes and never mentioned the looming issue. Of course, back then there was no semaglutide or tirzepatide, which was just approved for obesity.
Sherri left our most recent visit with a prescription for Wegovy as well as appointments with a complimentary trainer and dietitian. Now that we have the tools we need, let’s commit to helping our patients achieve true metabolic health. Unlike the magical pituitary patient, metabolically healthy obesity is an illusion – and we owe it to our patients to treat it as such.
Dr. Messer is a clinical assistant professor at Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, and an associate professor at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y. She disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
I cock my head at my “new” patient, Sherri, who heads into my consultation room at 8:30 on a rainy Monday morning. She looks vaguely familiar but I can’t quite place her face. “Dr. Messer,” she cries, “don’t you remember me? I was one of your very first patients 15 years ago in Westchester. You had just finished training.” Suddenly it all comes back to me.
Meeting Sherri reminded me of the lesson in humility that my mentor, Dr. Alice Levine, taught our crowded lecture hall so many years ago. Once upon a time, she prided herself on being an infinitely important doctor. One day, she met a patient with empty sella syndrome (literally missing his whole pituitary gland – MRI proven). She fully expected to swoop in to save the patient’s life by expertly replacing each absconded pituitary hormone, but to her shock and delight, an invisible little sliver of pituitary left in his brain allowed him to magically eek out completely normal hormone levels.
Sherri walked into my office so many years ago with a body mass index in the mid-40s. In laymen’s terms, she was morbidly obese. I settled in to discuss her hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, fatty liver, polycystic ovary syndrome, etc., but to my shock and delight, her blood pressure and blood work were completely normal. I struggled to keep a neutral face. She was there to discuss hair loss. I had just met my first patient with metabolically healthy obesity (MHO), and I was floored.
Fast-forward 15 years. Sherri sits down across the desk from me and hands me her blood work. Her formerly pristine labs are now peppered with red exclamation points and critically high lab values. Sherri had transitioned from MHO to metabolically unhealthy obesity (MUO).
Early clinical trials concluded that it was possible to have obesity but be metabolically healthy. Approximately 15% of patients living with obesity lack any of the comorbidities typically associated with this phenotype. These findings contributed to the de-emphasis on obesity as a true disease state.
In retrospect, the MHO subtype appears to be much more common in the younger and more active population and is typically quite transient. A new study published in Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism revealed that people with MHO are 1.5 times more likely to develop diabetes vs. metabolically healthy normal-weight individuals. In addition, people living with obesity and no known metabolic complications still had a 50% higher risk for coronary artery disease. The study also showed that over 50% of people initially characterized as MHO eventually became MUO after a 16-year follow-up.
So once again, all roads lead to semaglutide (Wegovy), the most effective U.S. Food and Drug Administration–approved weight loss medication to date. The incretin class of medications not only helps patients lose 15% or more of their body weight, but it also helps reverse insulin resistance, lower the risk for heart disease, melt away fatty liver, and lower cholesterol levels and blood pressures. While an emphasis on lifestyle changes is always important, these medications are critical adjuncts to conventional therapies.
Fifteen years ago, I discussed her hair loss for 45 minutes and never mentioned the looming issue. Of course, back then there was no semaglutide or tirzepatide, which was just approved for obesity.
Sherri left our most recent visit with a prescription for Wegovy as well as appointments with a complimentary trainer and dietitian. Now that we have the tools we need, let’s commit to helping our patients achieve true metabolic health. Unlike the magical pituitary patient, metabolically healthy obesity is an illusion – and we owe it to our patients to treat it as such.
Dr. Messer is a clinical assistant professor at Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, and an associate professor at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y. She disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
I cock my head at my “new” patient, Sherri, who heads into my consultation room at 8:30 on a rainy Monday morning. She looks vaguely familiar but I can’t quite place her face. “Dr. Messer,” she cries, “don’t you remember me? I was one of your very first patients 15 years ago in Westchester. You had just finished training.” Suddenly it all comes back to me.
Meeting Sherri reminded me of the lesson in humility that my mentor, Dr. Alice Levine, taught our crowded lecture hall so many years ago. Once upon a time, she prided herself on being an infinitely important doctor. One day, she met a patient with empty sella syndrome (literally missing his whole pituitary gland – MRI proven). She fully expected to swoop in to save the patient’s life by expertly replacing each absconded pituitary hormone, but to her shock and delight, an invisible little sliver of pituitary left in his brain allowed him to magically eek out completely normal hormone levels.
Sherri walked into my office so many years ago with a body mass index in the mid-40s. In laymen’s terms, she was morbidly obese. I settled in to discuss her hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, fatty liver, polycystic ovary syndrome, etc., but to my shock and delight, her blood pressure and blood work were completely normal. I struggled to keep a neutral face. She was there to discuss hair loss. I had just met my first patient with metabolically healthy obesity (MHO), and I was floored.
Fast-forward 15 years. Sherri sits down across the desk from me and hands me her blood work. Her formerly pristine labs are now peppered with red exclamation points and critically high lab values. Sherri had transitioned from MHO to metabolically unhealthy obesity (MUO).
Early clinical trials concluded that it was possible to have obesity but be metabolically healthy. Approximately 15% of patients living with obesity lack any of the comorbidities typically associated with this phenotype. These findings contributed to the de-emphasis on obesity as a true disease state.
In retrospect, the MHO subtype appears to be much more common in the younger and more active population and is typically quite transient. A new study published in Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism revealed that people with MHO are 1.5 times more likely to develop diabetes vs. metabolically healthy normal-weight individuals. In addition, people living with obesity and no known metabolic complications still had a 50% higher risk for coronary artery disease. The study also showed that over 50% of people initially characterized as MHO eventually became MUO after a 16-year follow-up.
So once again, all roads lead to semaglutide (Wegovy), the most effective U.S. Food and Drug Administration–approved weight loss medication to date. The incretin class of medications not only helps patients lose 15% or more of their body weight, but it also helps reverse insulin resistance, lower the risk for heart disease, melt away fatty liver, and lower cholesterol levels and blood pressures. While an emphasis on lifestyle changes is always important, these medications are critical adjuncts to conventional therapies.
Fifteen years ago, I discussed her hair loss for 45 minutes and never mentioned the looming issue. Of course, back then there was no semaglutide or tirzepatide, which was just approved for obesity.
Sherri left our most recent visit with a prescription for Wegovy as well as appointments with a complimentary trainer and dietitian. Now that we have the tools we need, let’s commit to helping our patients achieve true metabolic health. Unlike the magical pituitary patient, metabolically healthy obesity is an illusion – and we owe it to our patients to treat it as such.
Dr. Messer is a clinical assistant professor at Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, and an associate professor at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y. She disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fatal and nonfatal injuries
I suspect that, like me, you were saddened, but maybe not shocked, to learn that firearm-related fatalities have recently surpassed motor vehicle–related fatalities as the leading cause of death among children. For those of us living in Maine, this revelation came at a particularly difficult time. The body of the presumed shooter in the Lewiston massacre was found less than 10 miles from where I am writing you this letter. There is a good chance he may have been a former patient of mine, but I no longer have access to my records to confirm that.
This reshuffling at the top of the list of mortality causes is just one example of the shifting trends that have occurred in pediatric fatality statistics. In a recent analysis of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention statistics published in Pediatrics investigators discovered that while, in general, fatal injuries have increased over the study period (2011-2021) nonfatal injuries have decreased.
We should no longer be surprised to learn that firearm-related deaths increased more than 87%. Fatal drug poisoning was up 133% and suffocation-related deaths increased 12.5% over that 10-year period. Given this profile of fatalities, it shouldn’t surprise us that nonfatal injuries due to firearms, poisoning, and self-harm also increased.
However, nonfatal injuries in other broad categories decreased: falls were down 52.8%, overexertion 63%, struck by [something or someone] 47.3%, motor vehicle occupant 36.7%, and cut pierce 36.7%. Nonfatal drownings were unchanged.
Diverging trends
What are we to make of these diverging trends? I suspect that when it comes to both firearms and drug poisonings, both fatal and nonfatal, children are now living in an environment in which the sheer volume of guns and drugs have grown the point, and will continue to grow, that contact and its consequences will continue to increase until we reach a saturation point at some unpredictable point in the future. There still may be some opportunities to curb the flow of drugs. But, I am afraid when it comes to firearms, that ship has sailed. We may have a chance to curb assault weapons, but hand guns have become ubiquitous to the point that they will continue to be a threat to children.
The increase in self-harm injuries is clearly a reflection of the increase in pediatric and adolescent mental health disturbances, which in turn is a reflection of the gloom hanging over the population in general.
But, what’s going on with the decrease in nonfatal injuries caused by falls, overexertion, struck by, and cut pierce? Is this a bit of sunshine in an otherwise cloudy picture? The authors of the paper see it as a reflection of our “public health interventions targeting pediatric safety partnered with technological advancement and legislative requirements.” Maybe when we are talking about booster seats and other automotive safety advancements. But I’m not so sure we should be too vigorous as we pat ourselves on the back.
On the other hand, aren’t these decreases in injuries related to activity just more evidence of our increasingly sedentary pediatric population? Falling off the couch seldom creates an injury that generates an ED statistic. Myopia and obesity related to excess screen time doesn’t trigger data points in this study. Overexertion injuries are down. We already know the consequences of underexertion are up.
I’m not sure we need to cut back on our efforts at injury prevention but I worry that we may run the risk of discouraging healthy activity if we aren’t careful with our voices of caution.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I suspect that, like me, you were saddened, but maybe not shocked, to learn that firearm-related fatalities have recently surpassed motor vehicle–related fatalities as the leading cause of death among children. For those of us living in Maine, this revelation came at a particularly difficult time. The body of the presumed shooter in the Lewiston massacre was found less than 10 miles from where I am writing you this letter. There is a good chance he may have been a former patient of mine, but I no longer have access to my records to confirm that.
This reshuffling at the top of the list of mortality causes is just one example of the shifting trends that have occurred in pediatric fatality statistics. In a recent analysis of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention statistics published in Pediatrics investigators discovered that while, in general, fatal injuries have increased over the study period (2011-2021) nonfatal injuries have decreased.
We should no longer be surprised to learn that firearm-related deaths increased more than 87%. Fatal drug poisoning was up 133% and suffocation-related deaths increased 12.5% over that 10-year period. Given this profile of fatalities, it shouldn’t surprise us that nonfatal injuries due to firearms, poisoning, and self-harm also increased.
However, nonfatal injuries in other broad categories decreased: falls were down 52.8%, overexertion 63%, struck by [something or someone] 47.3%, motor vehicle occupant 36.7%, and cut pierce 36.7%. Nonfatal drownings were unchanged.
Diverging trends
What are we to make of these diverging trends? I suspect that when it comes to both firearms and drug poisonings, both fatal and nonfatal, children are now living in an environment in which the sheer volume of guns and drugs have grown the point, and will continue to grow, that contact and its consequences will continue to increase until we reach a saturation point at some unpredictable point in the future. There still may be some opportunities to curb the flow of drugs. But, I am afraid when it comes to firearms, that ship has sailed. We may have a chance to curb assault weapons, but hand guns have become ubiquitous to the point that they will continue to be a threat to children.
The increase in self-harm injuries is clearly a reflection of the increase in pediatric and adolescent mental health disturbances, which in turn is a reflection of the gloom hanging over the population in general.
But, what’s going on with the decrease in nonfatal injuries caused by falls, overexertion, struck by, and cut pierce? Is this a bit of sunshine in an otherwise cloudy picture? The authors of the paper see it as a reflection of our “public health interventions targeting pediatric safety partnered with technological advancement and legislative requirements.” Maybe when we are talking about booster seats and other automotive safety advancements. But I’m not so sure we should be too vigorous as we pat ourselves on the back.
On the other hand, aren’t these decreases in injuries related to activity just more evidence of our increasingly sedentary pediatric population? Falling off the couch seldom creates an injury that generates an ED statistic. Myopia and obesity related to excess screen time doesn’t trigger data points in this study. Overexertion injuries are down. We already know the consequences of underexertion are up.
I’m not sure we need to cut back on our efforts at injury prevention but I worry that we may run the risk of discouraging healthy activity if we aren’t careful with our voices of caution.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I suspect that, like me, you were saddened, but maybe not shocked, to learn that firearm-related fatalities have recently surpassed motor vehicle–related fatalities as the leading cause of death among children. For those of us living in Maine, this revelation came at a particularly difficult time. The body of the presumed shooter in the Lewiston massacre was found less than 10 miles from where I am writing you this letter. There is a good chance he may have been a former patient of mine, but I no longer have access to my records to confirm that.
This reshuffling at the top of the list of mortality causes is just one example of the shifting trends that have occurred in pediatric fatality statistics. In a recent analysis of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention statistics published in Pediatrics investigators discovered that while, in general, fatal injuries have increased over the study period (2011-2021) nonfatal injuries have decreased.
We should no longer be surprised to learn that firearm-related deaths increased more than 87%. Fatal drug poisoning was up 133% and suffocation-related deaths increased 12.5% over that 10-year period. Given this profile of fatalities, it shouldn’t surprise us that nonfatal injuries due to firearms, poisoning, and self-harm also increased.
However, nonfatal injuries in other broad categories decreased: falls were down 52.8%, overexertion 63%, struck by [something or someone] 47.3%, motor vehicle occupant 36.7%, and cut pierce 36.7%. Nonfatal drownings were unchanged.
Diverging trends
What are we to make of these diverging trends? I suspect that when it comes to both firearms and drug poisonings, both fatal and nonfatal, children are now living in an environment in which the sheer volume of guns and drugs have grown the point, and will continue to grow, that contact and its consequences will continue to increase until we reach a saturation point at some unpredictable point in the future. There still may be some opportunities to curb the flow of drugs. But, I am afraid when it comes to firearms, that ship has sailed. We may have a chance to curb assault weapons, but hand guns have become ubiquitous to the point that they will continue to be a threat to children.
The increase in self-harm injuries is clearly a reflection of the increase in pediatric and adolescent mental health disturbances, which in turn is a reflection of the gloom hanging over the population in general.
But, what’s going on with the decrease in nonfatal injuries caused by falls, overexertion, struck by, and cut pierce? Is this a bit of sunshine in an otherwise cloudy picture? The authors of the paper see it as a reflection of our “public health interventions targeting pediatric safety partnered with technological advancement and legislative requirements.” Maybe when we are talking about booster seats and other automotive safety advancements. But I’m not so sure we should be too vigorous as we pat ourselves on the back.
On the other hand, aren’t these decreases in injuries related to activity just more evidence of our increasingly sedentary pediatric population? Falling off the couch seldom creates an injury that generates an ED statistic. Myopia and obesity related to excess screen time doesn’t trigger data points in this study. Overexertion injuries are down. We already know the consequences of underexertion are up.
I’m not sure we need to cut back on our efforts at injury prevention but I worry that we may run the risk of discouraging healthy activity if we aren’t careful with our voices of caution.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Is most Parkinson’s disease man-made and therefore preventable?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Indu Subramanian, MD: It’s my pleasure to have Ray Dorsey on our program today. Ray is a professor of neurology at the University of Rochester and has been doing some amazing advocacy work in largely the space of trying to end Parkinson’s disease.
E. Ray Dorsey, MD: Thanks very much for having me, Indu. I’m delighted to be with you.
Trichloroethylene and PD
Dr. Subramanian: I wanted to first that we talk about as something that is in pretty much everywhere. This paper came out, and you wrote a commentary in JAMA Neurology as well. Perhaps we can summarize the paper and its findings.
Dr. Dorsey: Like most people, I didn’t know what TCE was until about 5 or 6 years ago. TCE is a very simple molecule. It’s got six atoms – two carbon atoms, one hydrogen atom, and three chlorine atoms — hence, its name “trichloroethylene.” There’s a very similar chemical called perchloroethylene, which is widely used in dry cleaning. It’s got one additional chlorine atom, and the prefix “per-” means “four.” I’ll talk about TCE predominantly, but both of these chemicals probably have similar toxicity with respect to Parkinson’s disease.
Research done by Dr. Carlie Tanner and Dr. Sam Goldman about a decade ago showed that in twins who were exposed to this through their work (it’s widely used as a degreasing agent) or hobbies (it’s used in printing and painting, by varnish workers, or by anyone that needs it as a solvent) had a 500% increased risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. Importantly, in that study, they showed that there was a lag time of 10-40 years between exposure to that chemical and the diagnosis of the disease. Because TCE was so widely used, they said that public health implications could be substantial.
What’s Camp Lejeune? Camp Lejeune is a Marine base in North Carolina where many Marines are trained. Between 1953 and 1987 at that Marine base, the drinking water was contaminated with TCE, perchloroethylene, and other toxic chemicals. The reason Camp Lejeune is so infamous is because the Marines knew about the contamination for many years and covered it up.
Indeed, this story only came to the forefront because Jennie Ensminger, the daughter of a Marine drill instructor, developed leukemia at age 6 and died at age 9. Her father, Jerry Ensminger, a retired master sergeant, found out after the fact that these cancer-causing chemicals, including TCE, a known carcinogen, were found at the Marine base and could be an explanation for why his daughter developed and died of leukemia.
Dr. Sam Goldman and Dr. Carlie Tanner and colleagues from UCSF looked at the rates of Parkinson’s among Marines who served at Camp Lejeune during the 1970s and compared that with rates in Marines who served Camp Pendleton on the West Coast. It turned out that the Marines who served at Camp Lejeune had a 70% higher risk of developing Parkinson’s disease than the Marines who served at Camp Pendleton.
Importantly, these Marines, by definition, were healthy. They were young. They were only 20 years old, on average, when they were at Camp Lejeune. They stayed at a Marine base for a short period of time, so on average, they were only there for 2 years. Yet 30 years later, they had a 70% increased risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.
Ending Parkinson’s disease
Dr. Subramanian: Wow, that’s pretty profound. You’ve done a large amount of work, and in fact you, along with some of our colleagues wrote a book about ending Parkinson’s disease. I read that book when it came out a couple of years ago, and I was really struck by a few things. Parkinson’s has doubled in the past 40 years and is going to double again in the next 20 years. Can you tell me a little bit about that statistic and why that is? It’s not just because people are aging. What is the sense of that? How do we interpret that?
Dr. Dorsey: According to the Global Burden of Disease study, which I was fortunate to be part of, the number of people with Parkinson’s disease has more than doubled in the past 25 years. A conservative projection based on aging alone suggests that it’s going to double again unless we change something about it. It’s now the world’s fastest-growing brain disease, and it is growing faster than can be explained by aging alone.
If you look at the map of Parkinson’s disease, if you thought it was purely genetic, you would have a relatively uniform map of rates of Parkinson’s disease. In fact, we don’t see that. Rates of Parkinson’s are five times higher in industrialized parts of the world, like the United States and Canada, than they are in sub-Saharan Africa. Rates of Parkinson’s disease are increasing most rapidly in areas of world that are undergoing the most rapid industrialization, such as India and China, where adjusted for age, the rates of Parkinson’s have more than doubled in the past 25 years.
The thesis of our book is that much of Parkinson’s disease is man-made. Work done by your colleagues at UCLA, including Jeff Bronstein and Beate Ritz, have demonstrated that air pollution and certain pesticides are likely fueling the rise of Parkinson’s disease.
Given that in the United States, rates of Parkinson’s disease are actually higher in urban and suburban areas than they are in rural areas, I think that this dry-cleaning chemical – which was widely used in the 1970s in everything from typewriter correction fluid to decaffeinated coffee and [over] 2 pounds per American [was produced] – could be one of the most important causes or contributing factors to Parkinson’s disease.
What to tell patients
Dr. Subramanian: For the general neurologists or practitioners out there watching this, what can they do? If you have a patient whom you suspect may have been exposed to toxins, what should we tell people who aren’t patients yet who are at risk? What are some things that you think would be helpful?
Dr. Dorsey: I think one of the shortcomings of American medicine is that we often just go from diagnosis to treatment. You’re depressed, you get an antidepressant; you have Parkinson’s disease, you get levodopa; you have seizures, you get put on an antiepileptic medication.
I think we need to spend a couple of minutes at least, maybe at the beginning, to go to the diagnosis of the condition and why you have this disease. If you just do a brief occupational history, after you start the exam – things like finding out what people do for a living or did for a living or how they spend their time – I think you’ll find many of these risk factors are actually present.
It’s pretty easy to identify whether people grew up in a rural area and drank well water, which is prone to be contaminated with pesticides. We know that people who drink [contaminated] well water have about a 75% increased risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. I think you can find for people, especially when they grew up, when they were young, that the most relevant exposure might be that when people were young children.
It’s a little bit harder to identify all exposure to TCE. The Marines at Camp Lejeune didn’t know they were drinking the water that was contaminated with this and only found out about it after the fact because Jerry Ensminger launched a 26-year campaign to bring justice for the Marines and their dependents.
Some people who know that they work with chemicals or with solvents might know about this. In New York City, these chemicals are widely used in dry cleaning. They’re readily volatile. These chemicals can evaporate from dry-cleaning buildings and go into the indoor air of apartments above dry cleaners, for example, in New York City. That can be in toxic levels. These readily dissolve in fat, hence their use in degreasing.
There have been studies, for example, in Germany, that found that supermarkets that are simply near a dry cleaner will have TCE or perchloroethylene in the butter and the cheese that they’re selling.
It gets even worse. For example, you bring your daughter into the dry-cleaning building and she’s eating an ice cream cone. When she leaves, she’s eating perchloroethylene and TCE.
It’s a little bit harder to find it, but I think it’s relevant because some people might be still being exposed and some people might still be drinking well water and they rarely have their well tested. For those people, I recommend they get their well tested and I recommend all my patients to get a carbon filter to decrease exposure to pesticides and chemicals. A carbon filter is just like what Brita and Pure and other brands are.
Because they’re chemicals known to cause cancer, I get a little bit concerned about cancer screening. This is most strongly tied to non-Hodgkin lymphoma, liver cancer, and renal cancer. It’s also linked to multiple myeloma, prostate cancer, probably brain cancer, and probably breast cancer, especially in men.
I tell people to be concerned about those, and then I tell people to avoid pesticides if they have Parkinson’s disease in all its forms, not only in the drinking water but in the produce you buy, the food you eat, what you put on your lawn, what’s on the golf course where you play, and the like.
Dr. Subramanian: I would say, just from the wellness perspective, if people are at risk for degenerative disease in terms of their brain health, things like sleep, mind-body practices, exercise, diet (Mediterranean or organic, if you can), and avoiding pesticides are all important. Social connection is important as well – the things that we think are helpful in general as people age and to prevent Alzheimer’s and other things like that.
Dr. Dorsey: These are fantastic ways to modify disease course. The evidence for them is only increasing. There’s an analogy I like to use. If someone is diagnosed with lung cancer, the first thing we tell them to do is to stop smoking. If someone’s diagnosed with Parkinson’s, we don’t tell them to stop getting exposure to pesticides. We don’t tell them to stop dry cleaning their clothes. We don’t tell them to avoid air pollution. These are all risk factors that are increasingly well established for Parkinson’s disease.
I think Parkinson’s disease, fundamentally for the vast majority of people, is an entirely preventable disease. We’re not taking actions to prevent people from getting this very disabling and very deadly disease.
Advocacy work
Dr. Subramanian: You and I are quite interested in the sense of being advocates as neurologists, and I think it fuels our passion and helps us to wake up every morning feeling like we have something that is meaningful and purposeful in our lives. Could you describe this as your passion and how it may prevent burnout and what it’s given you as a neurologist?
Dr. Dorsey: The credit for much of this is Dr. Carlie Tanner at UC San Francisco. I had the gift of sabbatical and I started reading the literature, I started reading her literature, and I came away with that, over the past 25 years, she detailed these environmental risk factors that are linked to Parkinson’s disease. Pesticides, these dry-cleaning chemicals, and air pollution. When I read it, I just realized that this was the case.
The same time I was reading her work, I read this book called “How to Survive a Plague,” by David France, who was a member of a group called Act Up, which was a group of men in New York City who reacted to the emergence of HIV in the 1980s. If you remember the 1980s, there was no federal response to HIV. People were blamed for the diseases that they were developing. It was only because brave men and women in New York City and in San Francisco banded together and organized that they changed the course of HIV.
They didn’t just do it for themselves. They did it for all of us. You and I and many people may not have HIV because of their courage. They made HIV a treatable condition. It’s actually more treatable than Parkinson’s disease. It’s associated with a near-normal life expectancy. They also made it a preventable disease. Thousands, if not millions, of us don’t have HIV because of their work. It’s an increasingly less common disease. Rates of HIV are actually decreasing, which is something that you or I would never have expected when we were in medical training.
I can’t think of a better outcome for a neurologist or any physician than to make the diseases that they’re caring for nonexistent ... than if we lived in a world that didn’t have HIV, we lived in a world where lung cancer largely didn’t exist. We’ve had worlds in the past where Parkinson’s probably didn’t exist or existed in extremely small numbers. That might be true for diffuse Lewy body disease and others, and if these diseases are preventable, we can take actions as individuals and as a society to lower our risk.
What a wonderful gift for future generations and many generations to come, hopefully, to live in a world that’s largely devoid of Parkinson’s disease. Just like we live in a world free of typhus. We live in a world free of smallpox. We live in a world where polio is extraordinarily uncommon. We don’t even have treatments for polio because we just don’t have polio. I think we can do the same thing for Parkinson’s disease for the vast majority.
Dr. Subramanian: Thank you so much, Ray, for your advocacy. We’re getting to the point in neurology, which is exciting to me, of possibly primary prevention of some of these disorders. I think we have a role in that, which is exciting for the future.
Dr. Dorsey: Absolutely.
Dr. Subramanian is clinical professor, department of neurology, University of California Los Angeles, and director of PADRECC (Parkinson’s Disease Research, Education, and Clinical Centers), West Los Angeles Veterans Association, Los Angeles. She disclosed ties with Acorda Pharma. Dr. Dorsey is the David M. Levy Professor of Neurology, University of Rochester (N.Y.). He disclosed ties to Abbott, AbbVie, Acadia, Acorda Therapeutics, Averitas Pharma, Biogen, BioSensics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Burroughs Wellcome Fund, Caraway Therapeutics, CuraSen, DConsult2, Denali Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, Genentech, Health & Wellness Partners, HMP Education, Included Health, Karger, KOL Groups, Life Sciences, Mediflix, Medrhythms, Merck; MJH Holdings, North American Center for Continuing Medical Education, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, Photopharmics, Praxis Medicine, Roche, Safra Foundation, Sanofi, Seelos Therapeutics, SemCap, Spark Therapeutics, Springer Healthcare, Synapticure, Theravance Biopharmaceuticals, and WebMD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Indu Subramanian, MD: It’s my pleasure to have Ray Dorsey on our program today. Ray is a professor of neurology at the University of Rochester and has been doing some amazing advocacy work in largely the space of trying to end Parkinson’s disease.
E. Ray Dorsey, MD: Thanks very much for having me, Indu. I’m delighted to be with you.
Trichloroethylene and PD
Dr. Subramanian: I wanted to first that we talk about as something that is in pretty much everywhere. This paper came out, and you wrote a commentary in JAMA Neurology as well. Perhaps we can summarize the paper and its findings.
Dr. Dorsey: Like most people, I didn’t know what TCE was until about 5 or 6 years ago. TCE is a very simple molecule. It’s got six atoms – two carbon atoms, one hydrogen atom, and three chlorine atoms — hence, its name “trichloroethylene.” There’s a very similar chemical called perchloroethylene, which is widely used in dry cleaning. It’s got one additional chlorine atom, and the prefix “per-” means “four.” I’ll talk about TCE predominantly, but both of these chemicals probably have similar toxicity with respect to Parkinson’s disease.
Research done by Dr. Carlie Tanner and Dr. Sam Goldman about a decade ago showed that in twins who were exposed to this through their work (it’s widely used as a degreasing agent) or hobbies (it’s used in printing and painting, by varnish workers, or by anyone that needs it as a solvent) had a 500% increased risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. Importantly, in that study, they showed that there was a lag time of 10-40 years between exposure to that chemical and the diagnosis of the disease. Because TCE was so widely used, they said that public health implications could be substantial.
What’s Camp Lejeune? Camp Lejeune is a Marine base in North Carolina where many Marines are trained. Between 1953 and 1987 at that Marine base, the drinking water was contaminated with TCE, perchloroethylene, and other toxic chemicals. The reason Camp Lejeune is so infamous is because the Marines knew about the contamination for many years and covered it up.
Indeed, this story only came to the forefront because Jennie Ensminger, the daughter of a Marine drill instructor, developed leukemia at age 6 and died at age 9. Her father, Jerry Ensminger, a retired master sergeant, found out after the fact that these cancer-causing chemicals, including TCE, a known carcinogen, were found at the Marine base and could be an explanation for why his daughter developed and died of leukemia.
Dr. Sam Goldman and Dr. Carlie Tanner and colleagues from UCSF looked at the rates of Parkinson’s among Marines who served at Camp Lejeune during the 1970s and compared that with rates in Marines who served Camp Pendleton on the West Coast. It turned out that the Marines who served at Camp Lejeune had a 70% higher risk of developing Parkinson’s disease than the Marines who served at Camp Pendleton.
Importantly, these Marines, by definition, were healthy. They were young. They were only 20 years old, on average, when they were at Camp Lejeune. They stayed at a Marine base for a short period of time, so on average, they were only there for 2 years. Yet 30 years later, they had a 70% increased risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.
Ending Parkinson’s disease
Dr. Subramanian: Wow, that’s pretty profound. You’ve done a large amount of work, and in fact you, along with some of our colleagues wrote a book about ending Parkinson’s disease. I read that book when it came out a couple of years ago, and I was really struck by a few things. Parkinson’s has doubled in the past 40 years and is going to double again in the next 20 years. Can you tell me a little bit about that statistic and why that is? It’s not just because people are aging. What is the sense of that? How do we interpret that?
Dr. Dorsey: According to the Global Burden of Disease study, which I was fortunate to be part of, the number of people with Parkinson’s disease has more than doubled in the past 25 years. A conservative projection based on aging alone suggests that it’s going to double again unless we change something about it. It’s now the world’s fastest-growing brain disease, and it is growing faster than can be explained by aging alone.
If you look at the map of Parkinson’s disease, if you thought it was purely genetic, you would have a relatively uniform map of rates of Parkinson’s disease. In fact, we don’t see that. Rates of Parkinson’s are five times higher in industrialized parts of the world, like the United States and Canada, than they are in sub-Saharan Africa. Rates of Parkinson’s disease are increasing most rapidly in areas of world that are undergoing the most rapid industrialization, such as India and China, where adjusted for age, the rates of Parkinson’s have more than doubled in the past 25 years.
The thesis of our book is that much of Parkinson’s disease is man-made. Work done by your colleagues at UCLA, including Jeff Bronstein and Beate Ritz, have demonstrated that air pollution and certain pesticides are likely fueling the rise of Parkinson’s disease.
Given that in the United States, rates of Parkinson’s disease are actually higher in urban and suburban areas than they are in rural areas, I think that this dry-cleaning chemical – which was widely used in the 1970s in everything from typewriter correction fluid to decaffeinated coffee and [over] 2 pounds per American [was produced] – could be one of the most important causes or contributing factors to Parkinson’s disease.
What to tell patients
Dr. Subramanian: For the general neurologists or practitioners out there watching this, what can they do? If you have a patient whom you suspect may have been exposed to toxins, what should we tell people who aren’t patients yet who are at risk? What are some things that you think would be helpful?
Dr. Dorsey: I think one of the shortcomings of American medicine is that we often just go from diagnosis to treatment. You’re depressed, you get an antidepressant; you have Parkinson’s disease, you get levodopa; you have seizures, you get put on an antiepileptic medication.
I think we need to spend a couple of minutes at least, maybe at the beginning, to go to the diagnosis of the condition and why you have this disease. If you just do a brief occupational history, after you start the exam – things like finding out what people do for a living or did for a living or how they spend their time – I think you’ll find many of these risk factors are actually present.
It’s pretty easy to identify whether people grew up in a rural area and drank well water, which is prone to be contaminated with pesticides. We know that people who drink [contaminated] well water have about a 75% increased risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. I think you can find for people, especially when they grew up, when they were young, that the most relevant exposure might be that when people were young children.
It’s a little bit harder to identify all exposure to TCE. The Marines at Camp Lejeune didn’t know they were drinking the water that was contaminated with this and only found out about it after the fact because Jerry Ensminger launched a 26-year campaign to bring justice for the Marines and their dependents.
Some people who know that they work with chemicals or with solvents might know about this. In New York City, these chemicals are widely used in dry cleaning. They’re readily volatile. These chemicals can evaporate from dry-cleaning buildings and go into the indoor air of apartments above dry cleaners, for example, in New York City. That can be in toxic levels. These readily dissolve in fat, hence their use in degreasing.
There have been studies, for example, in Germany, that found that supermarkets that are simply near a dry cleaner will have TCE or perchloroethylene in the butter and the cheese that they’re selling.
It gets even worse. For example, you bring your daughter into the dry-cleaning building and she’s eating an ice cream cone. When she leaves, she’s eating perchloroethylene and TCE.
It’s a little bit harder to find it, but I think it’s relevant because some people might be still being exposed and some people might still be drinking well water and they rarely have their well tested. For those people, I recommend they get their well tested and I recommend all my patients to get a carbon filter to decrease exposure to pesticides and chemicals. A carbon filter is just like what Brita and Pure and other brands are.
Because they’re chemicals known to cause cancer, I get a little bit concerned about cancer screening. This is most strongly tied to non-Hodgkin lymphoma, liver cancer, and renal cancer. It’s also linked to multiple myeloma, prostate cancer, probably brain cancer, and probably breast cancer, especially in men.
I tell people to be concerned about those, and then I tell people to avoid pesticides if they have Parkinson’s disease in all its forms, not only in the drinking water but in the produce you buy, the food you eat, what you put on your lawn, what’s on the golf course where you play, and the like.
Dr. Subramanian: I would say, just from the wellness perspective, if people are at risk for degenerative disease in terms of their brain health, things like sleep, mind-body practices, exercise, diet (Mediterranean or organic, if you can), and avoiding pesticides are all important. Social connection is important as well – the things that we think are helpful in general as people age and to prevent Alzheimer’s and other things like that.
Dr. Dorsey: These are fantastic ways to modify disease course. The evidence for them is only increasing. There’s an analogy I like to use. If someone is diagnosed with lung cancer, the first thing we tell them to do is to stop smoking. If someone’s diagnosed with Parkinson’s, we don’t tell them to stop getting exposure to pesticides. We don’t tell them to stop dry cleaning their clothes. We don’t tell them to avoid air pollution. These are all risk factors that are increasingly well established for Parkinson’s disease.
I think Parkinson’s disease, fundamentally for the vast majority of people, is an entirely preventable disease. We’re not taking actions to prevent people from getting this very disabling and very deadly disease.
Advocacy work
Dr. Subramanian: You and I are quite interested in the sense of being advocates as neurologists, and I think it fuels our passion and helps us to wake up every morning feeling like we have something that is meaningful and purposeful in our lives. Could you describe this as your passion and how it may prevent burnout and what it’s given you as a neurologist?
Dr. Dorsey: The credit for much of this is Dr. Carlie Tanner at UC San Francisco. I had the gift of sabbatical and I started reading the literature, I started reading her literature, and I came away with that, over the past 25 years, she detailed these environmental risk factors that are linked to Parkinson’s disease. Pesticides, these dry-cleaning chemicals, and air pollution. When I read it, I just realized that this was the case.
The same time I was reading her work, I read this book called “How to Survive a Plague,” by David France, who was a member of a group called Act Up, which was a group of men in New York City who reacted to the emergence of HIV in the 1980s. If you remember the 1980s, there was no federal response to HIV. People were blamed for the diseases that they were developing. It was only because brave men and women in New York City and in San Francisco banded together and organized that they changed the course of HIV.
They didn’t just do it for themselves. They did it for all of us. You and I and many people may not have HIV because of their courage. They made HIV a treatable condition. It’s actually more treatable than Parkinson’s disease. It’s associated with a near-normal life expectancy. They also made it a preventable disease. Thousands, if not millions, of us don’t have HIV because of their work. It’s an increasingly less common disease. Rates of HIV are actually decreasing, which is something that you or I would never have expected when we were in medical training.
I can’t think of a better outcome for a neurologist or any physician than to make the diseases that they’re caring for nonexistent ... than if we lived in a world that didn’t have HIV, we lived in a world where lung cancer largely didn’t exist. We’ve had worlds in the past where Parkinson’s probably didn’t exist or existed in extremely small numbers. That might be true for diffuse Lewy body disease and others, and if these diseases are preventable, we can take actions as individuals and as a society to lower our risk.
What a wonderful gift for future generations and many generations to come, hopefully, to live in a world that’s largely devoid of Parkinson’s disease. Just like we live in a world free of typhus. We live in a world free of smallpox. We live in a world where polio is extraordinarily uncommon. We don’t even have treatments for polio because we just don’t have polio. I think we can do the same thing for Parkinson’s disease for the vast majority.
Dr. Subramanian: Thank you so much, Ray, for your advocacy. We’re getting to the point in neurology, which is exciting to me, of possibly primary prevention of some of these disorders. I think we have a role in that, which is exciting for the future.
Dr. Dorsey: Absolutely.
Dr. Subramanian is clinical professor, department of neurology, University of California Los Angeles, and director of PADRECC (Parkinson’s Disease Research, Education, and Clinical Centers), West Los Angeles Veterans Association, Los Angeles. She disclosed ties with Acorda Pharma. Dr. Dorsey is the David M. Levy Professor of Neurology, University of Rochester (N.Y.). He disclosed ties to Abbott, AbbVie, Acadia, Acorda Therapeutics, Averitas Pharma, Biogen, BioSensics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Burroughs Wellcome Fund, Caraway Therapeutics, CuraSen, DConsult2, Denali Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, Genentech, Health & Wellness Partners, HMP Education, Included Health, Karger, KOL Groups, Life Sciences, Mediflix, Medrhythms, Merck; MJH Holdings, North American Center for Continuing Medical Education, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, Photopharmics, Praxis Medicine, Roche, Safra Foundation, Sanofi, Seelos Therapeutics, SemCap, Spark Therapeutics, Springer Healthcare, Synapticure, Theravance Biopharmaceuticals, and WebMD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Indu Subramanian, MD: It’s my pleasure to have Ray Dorsey on our program today. Ray is a professor of neurology at the University of Rochester and has been doing some amazing advocacy work in largely the space of trying to end Parkinson’s disease.
E. Ray Dorsey, MD: Thanks very much for having me, Indu. I’m delighted to be with you.
Trichloroethylene and PD
Dr. Subramanian: I wanted to first that we talk about as something that is in pretty much everywhere. This paper came out, and you wrote a commentary in JAMA Neurology as well. Perhaps we can summarize the paper and its findings.
Dr. Dorsey: Like most people, I didn’t know what TCE was until about 5 or 6 years ago. TCE is a very simple molecule. It’s got six atoms – two carbon atoms, one hydrogen atom, and three chlorine atoms — hence, its name “trichloroethylene.” There’s a very similar chemical called perchloroethylene, which is widely used in dry cleaning. It’s got one additional chlorine atom, and the prefix “per-” means “four.” I’ll talk about TCE predominantly, but both of these chemicals probably have similar toxicity with respect to Parkinson’s disease.
Research done by Dr. Carlie Tanner and Dr. Sam Goldman about a decade ago showed that in twins who were exposed to this through their work (it’s widely used as a degreasing agent) or hobbies (it’s used in printing and painting, by varnish workers, or by anyone that needs it as a solvent) had a 500% increased risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. Importantly, in that study, they showed that there was a lag time of 10-40 years between exposure to that chemical and the diagnosis of the disease. Because TCE was so widely used, they said that public health implications could be substantial.
What’s Camp Lejeune? Camp Lejeune is a Marine base in North Carolina where many Marines are trained. Between 1953 and 1987 at that Marine base, the drinking water was contaminated with TCE, perchloroethylene, and other toxic chemicals. The reason Camp Lejeune is so infamous is because the Marines knew about the contamination for many years and covered it up.
Indeed, this story only came to the forefront because Jennie Ensminger, the daughter of a Marine drill instructor, developed leukemia at age 6 and died at age 9. Her father, Jerry Ensminger, a retired master sergeant, found out after the fact that these cancer-causing chemicals, including TCE, a known carcinogen, were found at the Marine base and could be an explanation for why his daughter developed and died of leukemia.
Dr. Sam Goldman and Dr. Carlie Tanner and colleagues from UCSF looked at the rates of Parkinson’s among Marines who served at Camp Lejeune during the 1970s and compared that with rates in Marines who served Camp Pendleton on the West Coast. It turned out that the Marines who served at Camp Lejeune had a 70% higher risk of developing Parkinson’s disease than the Marines who served at Camp Pendleton.
Importantly, these Marines, by definition, were healthy. They were young. They were only 20 years old, on average, when they were at Camp Lejeune. They stayed at a Marine base for a short period of time, so on average, they were only there for 2 years. Yet 30 years later, they had a 70% increased risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.
Ending Parkinson’s disease
Dr. Subramanian: Wow, that’s pretty profound. You’ve done a large amount of work, and in fact you, along with some of our colleagues wrote a book about ending Parkinson’s disease. I read that book when it came out a couple of years ago, and I was really struck by a few things. Parkinson’s has doubled in the past 40 years and is going to double again in the next 20 years. Can you tell me a little bit about that statistic and why that is? It’s not just because people are aging. What is the sense of that? How do we interpret that?
Dr. Dorsey: According to the Global Burden of Disease study, which I was fortunate to be part of, the number of people with Parkinson’s disease has more than doubled in the past 25 years. A conservative projection based on aging alone suggests that it’s going to double again unless we change something about it. It’s now the world’s fastest-growing brain disease, and it is growing faster than can be explained by aging alone.
If you look at the map of Parkinson’s disease, if you thought it was purely genetic, you would have a relatively uniform map of rates of Parkinson’s disease. In fact, we don’t see that. Rates of Parkinson’s are five times higher in industrialized parts of the world, like the United States and Canada, than they are in sub-Saharan Africa. Rates of Parkinson’s disease are increasing most rapidly in areas of world that are undergoing the most rapid industrialization, such as India and China, where adjusted for age, the rates of Parkinson’s have more than doubled in the past 25 years.
The thesis of our book is that much of Parkinson’s disease is man-made. Work done by your colleagues at UCLA, including Jeff Bronstein and Beate Ritz, have demonstrated that air pollution and certain pesticides are likely fueling the rise of Parkinson’s disease.
Given that in the United States, rates of Parkinson’s disease are actually higher in urban and suburban areas than they are in rural areas, I think that this dry-cleaning chemical – which was widely used in the 1970s in everything from typewriter correction fluid to decaffeinated coffee and [over] 2 pounds per American [was produced] – could be one of the most important causes or contributing factors to Parkinson’s disease.
What to tell patients
Dr. Subramanian: For the general neurologists or practitioners out there watching this, what can they do? If you have a patient whom you suspect may have been exposed to toxins, what should we tell people who aren’t patients yet who are at risk? What are some things that you think would be helpful?
Dr. Dorsey: I think one of the shortcomings of American medicine is that we often just go from diagnosis to treatment. You’re depressed, you get an antidepressant; you have Parkinson’s disease, you get levodopa; you have seizures, you get put on an antiepileptic medication.
I think we need to spend a couple of minutes at least, maybe at the beginning, to go to the diagnosis of the condition and why you have this disease. If you just do a brief occupational history, after you start the exam – things like finding out what people do for a living or did for a living or how they spend their time – I think you’ll find many of these risk factors are actually present.
It’s pretty easy to identify whether people grew up in a rural area and drank well water, which is prone to be contaminated with pesticides. We know that people who drink [contaminated] well water have about a 75% increased risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. I think you can find for people, especially when they grew up, when they were young, that the most relevant exposure might be that when people were young children.
It’s a little bit harder to identify all exposure to TCE. The Marines at Camp Lejeune didn’t know they were drinking the water that was contaminated with this and only found out about it after the fact because Jerry Ensminger launched a 26-year campaign to bring justice for the Marines and their dependents.
Some people who know that they work with chemicals or with solvents might know about this. In New York City, these chemicals are widely used in dry cleaning. They’re readily volatile. These chemicals can evaporate from dry-cleaning buildings and go into the indoor air of apartments above dry cleaners, for example, in New York City. That can be in toxic levels. These readily dissolve in fat, hence their use in degreasing.
There have been studies, for example, in Germany, that found that supermarkets that are simply near a dry cleaner will have TCE or perchloroethylene in the butter and the cheese that they’re selling.
It gets even worse. For example, you bring your daughter into the dry-cleaning building and she’s eating an ice cream cone. When she leaves, she’s eating perchloroethylene and TCE.
It’s a little bit harder to find it, but I think it’s relevant because some people might be still being exposed and some people might still be drinking well water and they rarely have their well tested. For those people, I recommend they get their well tested and I recommend all my patients to get a carbon filter to decrease exposure to pesticides and chemicals. A carbon filter is just like what Brita and Pure and other brands are.
Because they’re chemicals known to cause cancer, I get a little bit concerned about cancer screening. This is most strongly tied to non-Hodgkin lymphoma, liver cancer, and renal cancer. It’s also linked to multiple myeloma, prostate cancer, probably brain cancer, and probably breast cancer, especially in men.
I tell people to be concerned about those, and then I tell people to avoid pesticides if they have Parkinson’s disease in all its forms, not only in the drinking water but in the produce you buy, the food you eat, what you put on your lawn, what’s on the golf course where you play, and the like.
Dr. Subramanian: I would say, just from the wellness perspective, if people are at risk for degenerative disease in terms of their brain health, things like sleep, mind-body practices, exercise, diet (Mediterranean or organic, if you can), and avoiding pesticides are all important. Social connection is important as well – the things that we think are helpful in general as people age and to prevent Alzheimer’s and other things like that.
Dr. Dorsey: These are fantastic ways to modify disease course. The evidence for them is only increasing. There’s an analogy I like to use. If someone is diagnosed with lung cancer, the first thing we tell them to do is to stop smoking. If someone’s diagnosed with Parkinson’s, we don’t tell them to stop getting exposure to pesticides. We don’t tell them to stop dry cleaning their clothes. We don’t tell them to avoid air pollution. These are all risk factors that are increasingly well established for Parkinson’s disease.
I think Parkinson’s disease, fundamentally for the vast majority of people, is an entirely preventable disease. We’re not taking actions to prevent people from getting this very disabling and very deadly disease.
Advocacy work
Dr. Subramanian: You and I are quite interested in the sense of being advocates as neurologists, and I think it fuels our passion and helps us to wake up every morning feeling like we have something that is meaningful and purposeful in our lives. Could you describe this as your passion and how it may prevent burnout and what it’s given you as a neurologist?
Dr. Dorsey: The credit for much of this is Dr. Carlie Tanner at UC San Francisco. I had the gift of sabbatical and I started reading the literature, I started reading her literature, and I came away with that, over the past 25 years, she detailed these environmental risk factors that are linked to Parkinson’s disease. Pesticides, these dry-cleaning chemicals, and air pollution. When I read it, I just realized that this was the case.
The same time I was reading her work, I read this book called “How to Survive a Plague,” by David France, who was a member of a group called Act Up, which was a group of men in New York City who reacted to the emergence of HIV in the 1980s. If you remember the 1980s, there was no federal response to HIV. People were blamed for the diseases that they were developing. It was only because brave men and women in New York City and in San Francisco banded together and organized that they changed the course of HIV.
They didn’t just do it for themselves. They did it for all of us. You and I and many people may not have HIV because of their courage. They made HIV a treatable condition. It’s actually more treatable than Parkinson’s disease. It’s associated with a near-normal life expectancy. They also made it a preventable disease. Thousands, if not millions, of us don’t have HIV because of their work. It’s an increasingly less common disease. Rates of HIV are actually decreasing, which is something that you or I would never have expected when we were in medical training.
I can’t think of a better outcome for a neurologist or any physician than to make the diseases that they’re caring for nonexistent ... than if we lived in a world that didn’t have HIV, we lived in a world where lung cancer largely didn’t exist. We’ve had worlds in the past where Parkinson’s probably didn’t exist or existed in extremely small numbers. That might be true for diffuse Lewy body disease and others, and if these diseases are preventable, we can take actions as individuals and as a society to lower our risk.
What a wonderful gift for future generations and many generations to come, hopefully, to live in a world that’s largely devoid of Parkinson’s disease. Just like we live in a world free of typhus. We live in a world free of smallpox. We live in a world where polio is extraordinarily uncommon. We don’t even have treatments for polio because we just don’t have polio. I think we can do the same thing for Parkinson’s disease for the vast majority.
Dr. Subramanian: Thank you so much, Ray, for your advocacy. We’re getting to the point in neurology, which is exciting to me, of possibly primary prevention of some of these disorders. I think we have a role in that, which is exciting for the future.
Dr. Dorsey: Absolutely.
Dr. Subramanian is clinical professor, department of neurology, University of California Los Angeles, and director of PADRECC (Parkinson’s Disease Research, Education, and Clinical Centers), West Los Angeles Veterans Association, Los Angeles. She disclosed ties with Acorda Pharma. Dr. Dorsey is the David M. Levy Professor of Neurology, University of Rochester (N.Y.). He disclosed ties to Abbott, AbbVie, Acadia, Acorda Therapeutics, Averitas Pharma, Biogen, BioSensics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Burroughs Wellcome Fund, Caraway Therapeutics, CuraSen, DConsult2, Denali Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, Genentech, Health & Wellness Partners, HMP Education, Included Health, Karger, KOL Groups, Life Sciences, Mediflix, Medrhythms, Merck; MJH Holdings, North American Center for Continuing Medical Education, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, Photopharmics, Praxis Medicine, Roche, Safra Foundation, Sanofi, Seelos Therapeutics, SemCap, Spark Therapeutics, Springer Healthcare, Synapticure, Theravance Biopharmaceuticals, and WebMD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
What to tell your patients about anti-amyloids for Alzheimer’s disease
Recorded October 13, 2023. This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Kathrin LaFaver, MD: I’ll be talking today with Dr. Meredith Wicklund, senior associate consultant and behavioral neurologist specialist at Mayo Clinic in Arizona. Welcome, Meredith.
Meredith Wicklund, MD: Thank you.
Lecanemab data
Dr. LaFaver: I’m very excited about our topic. Could you give us a brief overview of why there has been so much research interest in this topic of anti-amyloid antibodies?
Dr. Wicklund: The pathologic component of what defines something as Alzheimer’s disease is, by definition, presence of amyloid plaques and tau tangles. When it was first discovered in the 1980s that the component of the plaques was actually the amyloid protein – beta amyloid specifically – interest went right from there to developing therapies to directly target the pathology that is Alzheimer’s disease.
Dr. LaFaver: Lecanemab is the first FDA-approved disease-modifying antibody in that realm. Could you review the study data, especially as it applies to both of us in daily neurology clinic?
Dr. Wicklund: The study data from a phase 3 trial did show, for the primary outcome, that there was a 27% slowing of decline compared with individuals on placebo. It’s important to point out that this was slowing of decline. It was not stabilizing decline. It was not improving decline.
I think it’s important that we inform our patients that really, even with this therapy, there’s no prospect of stabilizing or restoring cognition or function. We do progress at a slower rate compared with individuals not on this treatment, which, given that this medication is for individuals in mild disease who have relatively preserved functional status, that can be potentially very meaningful to families.
The overall benefit was small. It essentially amounts to half a point on an 18-point scale, which is statistically significant. How much clinical meaningfulness that actually leads to is unclear. Finding clinical meaningfulness cannot be defined by a particular test. It really can only be defined on the individual level, what is meaningful to them.
Recommended tests
Dr. LaFaver: It is my understanding that, to qualify for lecanemab use, one needs to have a biomarker-supported diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease, either via an amyloid PET scan or CSF biomarkers. What would your recommendation be for a neurologist in practice to go about these requirements?
Dr. Wicklund: Since this medication is directly targeting the amyloid pathology, and it does convey a potential risk, we want to make sure that the actual pathology is present in the individuals before we treat them and potentially expose them to risk. The best way of doing that is through either an amyloid PET scan or spinal fluid testing of beta amyloid and tau.
There are several plasma-based biomarkers in development. However, I would avoid using those currently. There are still many unknowns in terms of what exactly is the right species of tau that we should be looking at, the right mechanism of the lab test, how minority status may influence it, and how different comorbidities may influence it.
I would recommend, at this time, sticking with amyloid PET or CSF testing. Given that amyloid PET is not widely available in many community practices, generally only available at academic centers, and is quite costly, many insurances do not cover it – although Medicare has a proposal to potentially start covering it – I generally go with spinal fluid testing, which is more widely available. There are several labs across the country that can process that testing in a reliable way.
Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities
Dr. LaFaver: That’s very helpful to know. There’s been a large amount of buzz just these past couple of weeks about the blood biomarker coming up. I think, as you point out, this wasn’t the marker used in the clinical studies and there are still unknowns. Maybe it’s not quite time for clinical use, unfortunately.
We also have learned that there are significant potential risks involved. One issue that’s really been a focus is ARIA – amyloid-related imaging abnormalities. Could you speak a bit about that and requirements for monitoring?
Dr. Wicklund: ARIA essentially amounts to either vasogenic edema, microhemorrhages, or superficial siderosis that develops as a result of treatment. It relates to activation of the immune system with these passive monoclonal antibodies that’s going to occur with targeting against the plaques. In the parenchyma, it will cause edema. If you have amyloid in the walls of the blood vessels, it can cause microhemorrhages.
While the term “ARIA” implies an imaging-related abnormality, and it largely is purely an imaging finding, it’s not solely an imaging-related finding. It can cause symptoms, including very serious symptoms.
Overall, with lecanemab, the incidence of ARIA within the treatment group in the phase 3 study, combined between both ARIA-E (edema/effusion) and ARIA-H (hemorrhage), was 21.5%, with about 17% being ARIA-H and about 12.5% being ARIA-E. Of course, they can occur at the same time.
Overall, in terms of people in the clinical trials, for most it was purely an imaging-related finding. About 3% developed symptomatic ARIA. Some of those were very serious symptoms, including things like seizures and need to be hospitalized. A couple of deaths have been attributed to ARIA as well.
Patients on anticoagulation
Dr. LaFaver: Along those lines, any additional words to say for people who might be on anticoagulation or might require medications for a stroke, for example?
Dr. Wicklund: While individuals on anticoagulation were allowed in the clinical trials, the current, published appropriate-use guideline is recommending against its use, as several of the serious adverse effects, including the deaths, were for the most part attributed to anticoagulation use.
When it comes to acute stroke treatment, one must carefully consider use of tPA, as two of the three deaths were tPA associated in the clinical trials. It shouldn’t necessarily be an absolute contraindication, but it can make the clinical picture very muddy. If an individual is on lecanemab and comes to the ER with acute stroke-like symptoms, it’s more likely that they’re going to be having an ARIA side effect rather than an acute stroke.
A general recommendation would be to obtain an acute head CT with a CTA, and if there is a large vessel occlusion, proceed to thrombectomy. However, if there isn’t a large vessel occlusion, if you have the ability to get a rapid MRI with diffusion-weighted imaging to screen for acute stroke changes or tissue flair with acute edema changes suggestive of ARIA, that would be preferred before proceeding with thrombolysis. These are all relative contraindications and are going to depend on what’s available near you.
Donanemab approval pending
Dr. LaFaver: This will be an issue because the population we’re talking about is definitely at risk for stroke as well as Alzheimer’s disease. Where do you see this field going as far as amyloid antibody therapy is concerned, with another agent, donanemab, possibly getting FDA approval later this year as well?
Dr. Wicklund: We’re anticipating that donanemab will get FDA approval in the next coming months. Donanemab also targets the amyloid in the brain, although lecanemab and donanemab target different aspects of the production of the amyloid plaque. They were both shown to have roughly equal efficacy in their phase 3 clinical trials. Donanemab has the benefit of being a once-monthly infusion as opposed to twice-monthly infusions with lecanemab. It does have a slightly higher risk for ARIA compared with lecanemab.
Those are just some things to take into consideration when talking with your patients. In terms of where we’re going from here, we’re moving even earlier in terms of disease state. The lecanemab and donanemab phase 3 trials were done in individuals with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease. They should not be used in individuals with moderate or more advanced Alzheimer’s disease.
There are ongoing, large, national, multicenter clinical trials of both lecanemab and donanemab in a preclinical state of Alzheimer’s disease. These individuals have evidence of amyloidosis, either through PET imaging or through CSF, but are clinically asymptomatic and do not yet have any signs of cognitive impairment or functional decline. We look forward to those results in the next few years. Hopefully, they’ll be able to show even greater benefit when moving into these early disease states in terms of delaying or even preventing cognitive decline.
Dr. LaFaver: That’s definitely very interesting to hear about. Where can people go for more information?
Dr. Wicklund: There’s a guideline on the use of lecanemab through the American Academy of Neurology. I encourage you to look at that. Also, look at the appropriate-use recommendations that were published this year in The Journal of Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Dr. LaFaver: Wonderful. With that being said, thank you so much for talking to me. I learned a lot. Thanks, everyone, for listening.
Dr. LaFaver is a neurologist at Saratoga Hospital Medical Group, Saratoga Springs, N.Y. She disclosed having no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Wicklund is senior associate consultant in the department of Neurology at Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, Ariz. She disclosed having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Recorded October 13, 2023. This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Kathrin LaFaver, MD: I’ll be talking today with Dr. Meredith Wicklund, senior associate consultant and behavioral neurologist specialist at Mayo Clinic in Arizona. Welcome, Meredith.
Meredith Wicklund, MD: Thank you.
Lecanemab data
Dr. LaFaver: I’m very excited about our topic. Could you give us a brief overview of why there has been so much research interest in this topic of anti-amyloid antibodies?
Dr. Wicklund: The pathologic component of what defines something as Alzheimer’s disease is, by definition, presence of amyloid plaques and tau tangles. When it was first discovered in the 1980s that the component of the plaques was actually the amyloid protein – beta amyloid specifically – interest went right from there to developing therapies to directly target the pathology that is Alzheimer’s disease.
Dr. LaFaver: Lecanemab is the first FDA-approved disease-modifying antibody in that realm. Could you review the study data, especially as it applies to both of us in daily neurology clinic?
Dr. Wicklund: The study data from a phase 3 trial did show, for the primary outcome, that there was a 27% slowing of decline compared with individuals on placebo. It’s important to point out that this was slowing of decline. It was not stabilizing decline. It was not improving decline.
I think it’s important that we inform our patients that really, even with this therapy, there’s no prospect of stabilizing or restoring cognition or function. We do progress at a slower rate compared with individuals not on this treatment, which, given that this medication is for individuals in mild disease who have relatively preserved functional status, that can be potentially very meaningful to families.
The overall benefit was small. It essentially amounts to half a point on an 18-point scale, which is statistically significant. How much clinical meaningfulness that actually leads to is unclear. Finding clinical meaningfulness cannot be defined by a particular test. It really can only be defined on the individual level, what is meaningful to them.
Recommended tests
Dr. LaFaver: It is my understanding that, to qualify for lecanemab use, one needs to have a biomarker-supported diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease, either via an amyloid PET scan or CSF biomarkers. What would your recommendation be for a neurologist in practice to go about these requirements?
Dr. Wicklund: Since this medication is directly targeting the amyloid pathology, and it does convey a potential risk, we want to make sure that the actual pathology is present in the individuals before we treat them and potentially expose them to risk. The best way of doing that is through either an amyloid PET scan or spinal fluid testing of beta amyloid and tau.
There are several plasma-based biomarkers in development. However, I would avoid using those currently. There are still many unknowns in terms of what exactly is the right species of tau that we should be looking at, the right mechanism of the lab test, how minority status may influence it, and how different comorbidities may influence it.
I would recommend, at this time, sticking with amyloid PET or CSF testing. Given that amyloid PET is not widely available in many community practices, generally only available at academic centers, and is quite costly, many insurances do not cover it – although Medicare has a proposal to potentially start covering it – I generally go with spinal fluid testing, which is more widely available. There are several labs across the country that can process that testing in a reliable way.
Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities
Dr. LaFaver: That’s very helpful to know. There’s been a large amount of buzz just these past couple of weeks about the blood biomarker coming up. I think, as you point out, this wasn’t the marker used in the clinical studies and there are still unknowns. Maybe it’s not quite time for clinical use, unfortunately.
We also have learned that there are significant potential risks involved. One issue that’s really been a focus is ARIA – amyloid-related imaging abnormalities. Could you speak a bit about that and requirements for monitoring?
Dr. Wicklund: ARIA essentially amounts to either vasogenic edema, microhemorrhages, or superficial siderosis that develops as a result of treatment. It relates to activation of the immune system with these passive monoclonal antibodies that’s going to occur with targeting against the plaques. In the parenchyma, it will cause edema. If you have amyloid in the walls of the blood vessels, it can cause microhemorrhages.
While the term “ARIA” implies an imaging-related abnormality, and it largely is purely an imaging finding, it’s not solely an imaging-related finding. It can cause symptoms, including very serious symptoms.
Overall, with lecanemab, the incidence of ARIA within the treatment group in the phase 3 study, combined between both ARIA-E (edema/effusion) and ARIA-H (hemorrhage), was 21.5%, with about 17% being ARIA-H and about 12.5% being ARIA-E. Of course, they can occur at the same time.
Overall, in terms of people in the clinical trials, for most it was purely an imaging-related finding. About 3% developed symptomatic ARIA. Some of those were very serious symptoms, including things like seizures and need to be hospitalized. A couple of deaths have been attributed to ARIA as well.
Patients on anticoagulation
Dr. LaFaver: Along those lines, any additional words to say for people who might be on anticoagulation or might require medications for a stroke, for example?
Dr. Wicklund: While individuals on anticoagulation were allowed in the clinical trials, the current, published appropriate-use guideline is recommending against its use, as several of the serious adverse effects, including the deaths, were for the most part attributed to anticoagulation use.
When it comes to acute stroke treatment, one must carefully consider use of tPA, as two of the three deaths were tPA associated in the clinical trials. It shouldn’t necessarily be an absolute contraindication, but it can make the clinical picture very muddy. If an individual is on lecanemab and comes to the ER with acute stroke-like symptoms, it’s more likely that they’re going to be having an ARIA side effect rather than an acute stroke.
A general recommendation would be to obtain an acute head CT with a CTA, and if there is a large vessel occlusion, proceed to thrombectomy. However, if there isn’t a large vessel occlusion, if you have the ability to get a rapid MRI with diffusion-weighted imaging to screen for acute stroke changes or tissue flair with acute edema changes suggestive of ARIA, that would be preferred before proceeding with thrombolysis. These are all relative contraindications and are going to depend on what’s available near you.
Donanemab approval pending
Dr. LaFaver: This will be an issue because the population we’re talking about is definitely at risk for stroke as well as Alzheimer’s disease. Where do you see this field going as far as amyloid antibody therapy is concerned, with another agent, donanemab, possibly getting FDA approval later this year as well?
Dr. Wicklund: We’re anticipating that donanemab will get FDA approval in the next coming months. Donanemab also targets the amyloid in the brain, although lecanemab and donanemab target different aspects of the production of the amyloid plaque. They were both shown to have roughly equal efficacy in their phase 3 clinical trials. Donanemab has the benefit of being a once-monthly infusion as opposed to twice-monthly infusions with lecanemab. It does have a slightly higher risk for ARIA compared with lecanemab.
Those are just some things to take into consideration when talking with your patients. In terms of where we’re going from here, we’re moving even earlier in terms of disease state. The lecanemab and donanemab phase 3 trials were done in individuals with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease. They should not be used in individuals with moderate or more advanced Alzheimer’s disease.
There are ongoing, large, national, multicenter clinical trials of both lecanemab and donanemab in a preclinical state of Alzheimer’s disease. These individuals have evidence of amyloidosis, either through PET imaging or through CSF, but are clinically asymptomatic and do not yet have any signs of cognitive impairment or functional decline. We look forward to those results in the next few years. Hopefully, they’ll be able to show even greater benefit when moving into these early disease states in terms of delaying or even preventing cognitive decline.
Dr. LaFaver: That’s definitely very interesting to hear about. Where can people go for more information?
Dr. Wicklund: There’s a guideline on the use of lecanemab through the American Academy of Neurology. I encourage you to look at that. Also, look at the appropriate-use recommendations that were published this year in The Journal of Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Dr. LaFaver: Wonderful. With that being said, thank you so much for talking to me. I learned a lot. Thanks, everyone, for listening.
Dr. LaFaver is a neurologist at Saratoga Hospital Medical Group, Saratoga Springs, N.Y. She disclosed having no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Wicklund is senior associate consultant in the department of Neurology at Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, Ariz. She disclosed having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Recorded October 13, 2023. This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Kathrin LaFaver, MD: I’ll be talking today with Dr. Meredith Wicklund, senior associate consultant and behavioral neurologist specialist at Mayo Clinic in Arizona. Welcome, Meredith.
Meredith Wicklund, MD: Thank you.
Lecanemab data
Dr. LaFaver: I’m very excited about our topic. Could you give us a brief overview of why there has been so much research interest in this topic of anti-amyloid antibodies?
Dr. Wicklund: The pathologic component of what defines something as Alzheimer’s disease is, by definition, presence of amyloid plaques and tau tangles. When it was first discovered in the 1980s that the component of the plaques was actually the amyloid protein – beta amyloid specifically – interest went right from there to developing therapies to directly target the pathology that is Alzheimer’s disease.
Dr. LaFaver: Lecanemab is the first FDA-approved disease-modifying antibody in that realm. Could you review the study data, especially as it applies to both of us in daily neurology clinic?
Dr. Wicklund: The study data from a phase 3 trial did show, for the primary outcome, that there was a 27% slowing of decline compared with individuals on placebo. It’s important to point out that this was slowing of decline. It was not stabilizing decline. It was not improving decline.
I think it’s important that we inform our patients that really, even with this therapy, there’s no prospect of stabilizing or restoring cognition or function. We do progress at a slower rate compared with individuals not on this treatment, which, given that this medication is for individuals in mild disease who have relatively preserved functional status, that can be potentially very meaningful to families.
The overall benefit was small. It essentially amounts to half a point on an 18-point scale, which is statistically significant. How much clinical meaningfulness that actually leads to is unclear. Finding clinical meaningfulness cannot be defined by a particular test. It really can only be defined on the individual level, what is meaningful to them.
Recommended tests
Dr. LaFaver: It is my understanding that, to qualify for lecanemab use, one needs to have a biomarker-supported diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease, either via an amyloid PET scan or CSF biomarkers. What would your recommendation be for a neurologist in practice to go about these requirements?
Dr. Wicklund: Since this medication is directly targeting the amyloid pathology, and it does convey a potential risk, we want to make sure that the actual pathology is present in the individuals before we treat them and potentially expose them to risk. The best way of doing that is through either an amyloid PET scan or spinal fluid testing of beta amyloid and tau.
There are several plasma-based biomarkers in development. However, I would avoid using those currently. There are still many unknowns in terms of what exactly is the right species of tau that we should be looking at, the right mechanism of the lab test, how minority status may influence it, and how different comorbidities may influence it.
I would recommend, at this time, sticking with amyloid PET or CSF testing. Given that amyloid PET is not widely available in many community practices, generally only available at academic centers, and is quite costly, many insurances do not cover it – although Medicare has a proposal to potentially start covering it – I generally go with spinal fluid testing, which is more widely available. There are several labs across the country that can process that testing in a reliable way.
Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities
Dr. LaFaver: That’s very helpful to know. There’s been a large amount of buzz just these past couple of weeks about the blood biomarker coming up. I think, as you point out, this wasn’t the marker used in the clinical studies and there are still unknowns. Maybe it’s not quite time for clinical use, unfortunately.
We also have learned that there are significant potential risks involved. One issue that’s really been a focus is ARIA – amyloid-related imaging abnormalities. Could you speak a bit about that and requirements for monitoring?
Dr. Wicklund: ARIA essentially amounts to either vasogenic edema, microhemorrhages, or superficial siderosis that develops as a result of treatment. It relates to activation of the immune system with these passive monoclonal antibodies that’s going to occur with targeting against the plaques. In the parenchyma, it will cause edema. If you have amyloid in the walls of the blood vessels, it can cause microhemorrhages.
While the term “ARIA” implies an imaging-related abnormality, and it largely is purely an imaging finding, it’s not solely an imaging-related finding. It can cause symptoms, including very serious symptoms.
Overall, with lecanemab, the incidence of ARIA within the treatment group in the phase 3 study, combined between both ARIA-E (edema/effusion) and ARIA-H (hemorrhage), was 21.5%, with about 17% being ARIA-H and about 12.5% being ARIA-E. Of course, they can occur at the same time.
Overall, in terms of people in the clinical trials, for most it was purely an imaging-related finding. About 3% developed symptomatic ARIA. Some of those were very serious symptoms, including things like seizures and need to be hospitalized. A couple of deaths have been attributed to ARIA as well.
Patients on anticoagulation
Dr. LaFaver: Along those lines, any additional words to say for people who might be on anticoagulation or might require medications for a stroke, for example?
Dr. Wicklund: While individuals on anticoagulation were allowed in the clinical trials, the current, published appropriate-use guideline is recommending against its use, as several of the serious adverse effects, including the deaths, were for the most part attributed to anticoagulation use.
When it comes to acute stroke treatment, one must carefully consider use of tPA, as two of the three deaths were tPA associated in the clinical trials. It shouldn’t necessarily be an absolute contraindication, but it can make the clinical picture very muddy. If an individual is on lecanemab and comes to the ER with acute stroke-like symptoms, it’s more likely that they’re going to be having an ARIA side effect rather than an acute stroke.
A general recommendation would be to obtain an acute head CT with a CTA, and if there is a large vessel occlusion, proceed to thrombectomy. However, if there isn’t a large vessel occlusion, if you have the ability to get a rapid MRI with diffusion-weighted imaging to screen for acute stroke changes or tissue flair with acute edema changes suggestive of ARIA, that would be preferred before proceeding with thrombolysis. These are all relative contraindications and are going to depend on what’s available near you.
Donanemab approval pending
Dr. LaFaver: This will be an issue because the population we’re talking about is definitely at risk for stroke as well as Alzheimer’s disease. Where do you see this field going as far as amyloid antibody therapy is concerned, with another agent, donanemab, possibly getting FDA approval later this year as well?
Dr. Wicklund: We’re anticipating that donanemab will get FDA approval in the next coming months. Donanemab also targets the amyloid in the brain, although lecanemab and donanemab target different aspects of the production of the amyloid plaque. They were both shown to have roughly equal efficacy in their phase 3 clinical trials. Donanemab has the benefit of being a once-monthly infusion as opposed to twice-monthly infusions with lecanemab. It does have a slightly higher risk for ARIA compared with lecanemab.
Those are just some things to take into consideration when talking with your patients. In terms of where we’re going from here, we’re moving even earlier in terms of disease state. The lecanemab and donanemab phase 3 trials were done in individuals with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease. They should not be used in individuals with moderate or more advanced Alzheimer’s disease.
There are ongoing, large, national, multicenter clinical trials of both lecanemab and donanemab in a preclinical state of Alzheimer’s disease. These individuals have evidence of amyloidosis, either through PET imaging or through CSF, but are clinically asymptomatic and do not yet have any signs of cognitive impairment or functional decline. We look forward to those results in the next few years. Hopefully, they’ll be able to show even greater benefit when moving into these early disease states in terms of delaying or even preventing cognitive decline.
Dr. LaFaver: That’s definitely very interesting to hear about. Where can people go for more information?
Dr. Wicklund: There’s a guideline on the use of lecanemab through the American Academy of Neurology. I encourage you to look at that. Also, look at the appropriate-use recommendations that were published this year in The Journal of Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Dr. LaFaver: Wonderful. With that being said, thank you so much for talking to me. I learned a lot. Thanks, everyone, for listening.
Dr. LaFaver is a neurologist at Saratoga Hospital Medical Group, Saratoga Springs, N.Y. She disclosed having no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Wicklund is senior associate consultant in the department of Neurology at Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, Ariz. She disclosed having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Headache after drinking red wine? This could be why
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert Louis Stevenson famously said, “Wine is bottled poetry.” And I think it works quite well. I’ve had wines that are simple, elegant, and unpretentious like Emily Dickinson, and passionate and mysterious like Pablo Neruda. And I’ve had wines that are more analogous to the limerick you might read scrawled on a rest-stop bathroom wall. Those ones give me headaches.
– and apparently it’s not just the alcohol.
Headaches are common, and headaches after drinking alcohol are particularly common. An interesting epidemiologic phenomenon, not yet adequately explained, is why red wine is associated with more headache than other forms of alcohol. There have been many studies fingering many suspects, from sulfites to tannins to various phenolic compounds, but none have really provided a concrete explanation for what might be going on.
A new hypothesis came to the fore on Nov. 20 in the journal Scientific Reports:
To understand the idea, first a reminder of what happens when you drink alcohol, physiologically.
Alcohol is metabolized by the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase in the gut and then in the liver. That turns it into acetaldehyde, a toxic metabolite. In most of us, aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) quickly metabolizes acetaldehyde to the inert acetate, which can be safely excreted.
I say “most of us” because some populations, particularly those with East Asian ancestry, have a mutation in the ALDH gene which can lead to accumulation of toxic acetaldehyde with alcohol consumption – leading to facial flushing, nausea, and headache.
We can also inhibit the enzyme medically. That’s what the drug disulfiram, also known as Antabuse, does. It doesn’t prevent you from wanting to drink; it makes the consequences of drinking incredibly aversive.
The researchers focused in on the aldehyde dehydrogenase enzyme and conducted a screening study. Are there any compounds in red wine that naturally inhibit ALDH?
The results pointed squarely at quercetin, and particularly its metabolite quercetin glucuronide, which, at 20 micromolar concentrations, inhibited about 80% of ALDH activity.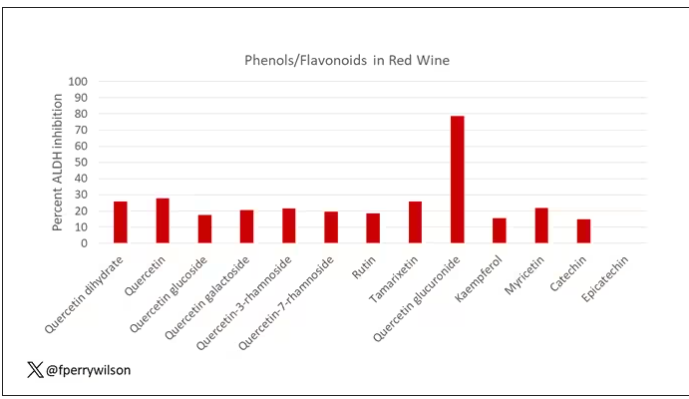
Quercetin is a flavonoid – a compound that gives color to a variety of vegetables and fruits, including grapes. In a test tube, it is an antioxidant, which is enough evidence to spawn a small quercetin-as-supplement industry, but there is no convincing evidence that it is medically useful. The authors then examined the concentration of quercetin glucuronide to achieve various inhibitions of ALDH, as you can see in this graph here.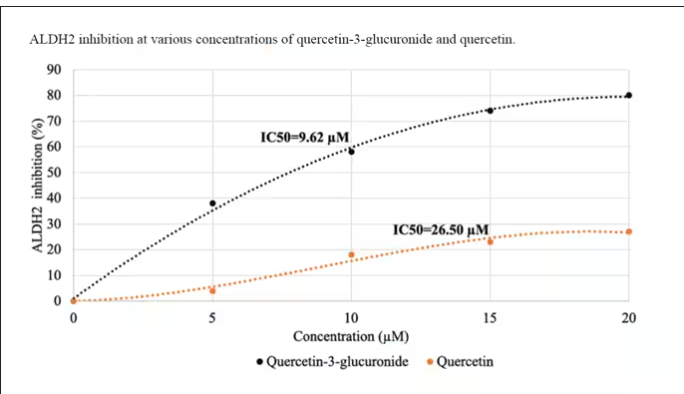
By about 10 micromolar, we see a decent amount of inhibition. Disulfiram is about 10 times more potent than that, but then again, you don’t drink three glasses of disulfiram with Thanksgiving dinner.
This is where this study stops. But it obviously tells us very little about what might be happening in the human body. For that, we need to ask the question: Can we get our quercetin levels to 10 micromolar? Is that remotely achievable?
Let’s start with how much quercetin there is in red wine. Like all things wine, it varies, but this study examining Australian wines found mean concentrations of 11 mg/L. The highest value I saw was close to 50 mg/L.
So let’s do some math. To make the numbers easy, let’s say you drank a liter of Australian wine, taking in 50 mg of quercetin glucuronide.
How much of that gets into your bloodstream? Some studies suggest a bioavailability of less than 1%, which basically means none and should probably put the quercetin hypothesis to bed. But there is some variation here too; it seems to depend on the form of quercetin you ingest.
Let’s say all 50 mg gets into your bloodstream. What blood concentration would that lead to? Well, I’ll keep the stoichiometry in the graphics and just say that if we assume that the volume of distribution of the compound is restricted to plasma alone, then you could achieve similar concentrations to what was done in petri dishes during this study.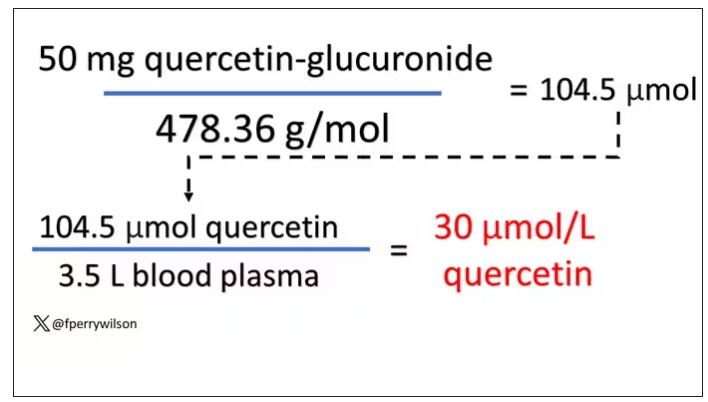
Of course, if quercetin is really the culprit behind red wine headache, I have some questions: Why aren’t the Amazon reviews of quercetin supplements chock full of warnings not to take them with alcohol? And other foods have way higher quercetin concentration than wine, but you don’t hear people warning not to take your red onions with alcohol, or your capers, or lingonberries.
There’s some more work to be done here – most importantly, some human studies. Let’s give people wine with different amounts of quercetin and see what happens. Sign me up. Seriously.
As for Thanksgiving, it’s worth noting that cranberries have a lot of quercetin in them. So between the cranberry sauce, the Beaujolais, and your uncle ranting about the contrails again, the probability of headache is pretty darn high. Stay safe out there, and Happy Thanksgiving.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert Louis Stevenson famously said, “Wine is bottled poetry.” And I think it works quite well. I’ve had wines that are simple, elegant, and unpretentious like Emily Dickinson, and passionate and mysterious like Pablo Neruda. And I’ve had wines that are more analogous to the limerick you might read scrawled on a rest-stop bathroom wall. Those ones give me headaches.
– and apparently it’s not just the alcohol.
Headaches are common, and headaches after drinking alcohol are particularly common. An interesting epidemiologic phenomenon, not yet adequately explained, is why red wine is associated with more headache than other forms of alcohol. There have been many studies fingering many suspects, from sulfites to tannins to various phenolic compounds, but none have really provided a concrete explanation for what might be going on.
A new hypothesis came to the fore on Nov. 20 in the journal Scientific Reports:
To understand the idea, first a reminder of what happens when you drink alcohol, physiologically.
Alcohol is metabolized by the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase in the gut and then in the liver. That turns it into acetaldehyde, a toxic metabolite. In most of us, aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) quickly metabolizes acetaldehyde to the inert acetate, which can be safely excreted.
I say “most of us” because some populations, particularly those with East Asian ancestry, have a mutation in the ALDH gene which can lead to accumulation of toxic acetaldehyde with alcohol consumption – leading to facial flushing, nausea, and headache.
We can also inhibit the enzyme medically. That’s what the drug disulfiram, also known as Antabuse, does. It doesn’t prevent you from wanting to drink; it makes the consequences of drinking incredibly aversive.
The researchers focused in on the aldehyde dehydrogenase enzyme and conducted a screening study. Are there any compounds in red wine that naturally inhibit ALDH?
The results pointed squarely at quercetin, and particularly its metabolite quercetin glucuronide, which, at 20 micromolar concentrations, inhibited about 80% of ALDH activity.
Quercetin is a flavonoid – a compound that gives color to a variety of vegetables and fruits, including grapes. In a test tube, it is an antioxidant, which is enough evidence to spawn a small quercetin-as-supplement industry, but there is no convincing evidence that it is medically useful. The authors then examined the concentration of quercetin glucuronide to achieve various inhibitions of ALDH, as you can see in this graph here.
By about 10 micromolar, we see a decent amount of inhibition. Disulfiram is about 10 times more potent than that, but then again, you don’t drink three glasses of disulfiram with Thanksgiving dinner.
This is where this study stops. But it obviously tells us very little about what might be happening in the human body. For that, we need to ask the question: Can we get our quercetin levels to 10 micromolar? Is that remotely achievable?
Let’s start with how much quercetin there is in red wine. Like all things wine, it varies, but this study examining Australian wines found mean concentrations of 11 mg/L. The highest value I saw was close to 50 mg/L.
So let’s do some math. To make the numbers easy, let’s say you drank a liter of Australian wine, taking in 50 mg of quercetin glucuronide.
How much of that gets into your bloodstream? Some studies suggest a bioavailability of less than 1%, which basically means none and should probably put the quercetin hypothesis to bed. But there is some variation here too; it seems to depend on the form of quercetin you ingest.
Let’s say all 50 mg gets into your bloodstream. What blood concentration would that lead to? Well, I’ll keep the stoichiometry in the graphics and just say that if we assume that the volume of distribution of the compound is restricted to plasma alone, then you could achieve similar concentrations to what was done in petri dishes during this study.
Of course, if quercetin is really the culprit behind red wine headache, I have some questions: Why aren’t the Amazon reviews of quercetin supplements chock full of warnings not to take them with alcohol? And other foods have way higher quercetin concentration than wine, but you don’t hear people warning not to take your red onions with alcohol, or your capers, or lingonberries.
There’s some more work to be done here – most importantly, some human studies. Let’s give people wine with different amounts of quercetin and see what happens. Sign me up. Seriously.
As for Thanksgiving, it’s worth noting that cranberries have a lot of quercetin in them. So between the cranberry sauce, the Beaujolais, and your uncle ranting about the contrails again, the probability of headache is pretty darn high. Stay safe out there, and Happy Thanksgiving.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert Louis Stevenson famously said, “Wine is bottled poetry.” And I think it works quite well. I’ve had wines that are simple, elegant, and unpretentious like Emily Dickinson, and passionate and mysterious like Pablo Neruda. And I’ve had wines that are more analogous to the limerick you might read scrawled on a rest-stop bathroom wall. Those ones give me headaches.
– and apparently it’s not just the alcohol.
Headaches are common, and headaches after drinking alcohol are particularly common. An interesting epidemiologic phenomenon, not yet adequately explained, is why red wine is associated with more headache than other forms of alcohol. There have been many studies fingering many suspects, from sulfites to tannins to various phenolic compounds, but none have really provided a concrete explanation for what might be going on.
A new hypothesis came to the fore on Nov. 20 in the journal Scientific Reports:
To understand the idea, first a reminder of what happens when you drink alcohol, physiologically.
Alcohol is metabolized by the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase in the gut and then in the liver. That turns it into acetaldehyde, a toxic metabolite. In most of us, aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) quickly metabolizes acetaldehyde to the inert acetate, which can be safely excreted.
I say “most of us” because some populations, particularly those with East Asian ancestry, have a mutation in the ALDH gene which can lead to accumulation of toxic acetaldehyde with alcohol consumption – leading to facial flushing, nausea, and headache.
We can also inhibit the enzyme medically. That’s what the drug disulfiram, also known as Antabuse, does. It doesn’t prevent you from wanting to drink; it makes the consequences of drinking incredibly aversive.
The researchers focused in on the aldehyde dehydrogenase enzyme and conducted a screening study. Are there any compounds in red wine that naturally inhibit ALDH?
The results pointed squarely at quercetin, and particularly its metabolite quercetin glucuronide, which, at 20 micromolar concentrations, inhibited about 80% of ALDH activity.
Quercetin is a flavonoid – a compound that gives color to a variety of vegetables and fruits, including grapes. In a test tube, it is an antioxidant, which is enough evidence to spawn a small quercetin-as-supplement industry, but there is no convincing evidence that it is medically useful. The authors then examined the concentration of quercetin glucuronide to achieve various inhibitions of ALDH, as you can see in this graph here.
By about 10 micromolar, we see a decent amount of inhibition. Disulfiram is about 10 times more potent than that, but then again, you don’t drink three glasses of disulfiram with Thanksgiving dinner.
This is where this study stops. But it obviously tells us very little about what might be happening in the human body. For that, we need to ask the question: Can we get our quercetin levels to 10 micromolar? Is that remotely achievable?
Let’s start with how much quercetin there is in red wine. Like all things wine, it varies, but this study examining Australian wines found mean concentrations of 11 mg/L. The highest value I saw was close to 50 mg/L.
So let’s do some math. To make the numbers easy, let’s say you drank a liter of Australian wine, taking in 50 mg of quercetin glucuronide.
How much of that gets into your bloodstream? Some studies suggest a bioavailability of less than 1%, which basically means none and should probably put the quercetin hypothesis to bed. But there is some variation here too; it seems to depend on the form of quercetin you ingest.
Let’s say all 50 mg gets into your bloodstream. What blood concentration would that lead to? Well, I’ll keep the stoichiometry in the graphics and just say that if we assume that the volume of distribution of the compound is restricted to plasma alone, then you could achieve similar concentrations to what was done in petri dishes during this study.
Of course, if quercetin is really the culprit behind red wine headache, I have some questions: Why aren’t the Amazon reviews of quercetin supplements chock full of warnings not to take them with alcohol? And other foods have way higher quercetin concentration than wine, but you don’t hear people warning not to take your red onions with alcohol, or your capers, or lingonberries.
There’s some more work to be done here – most importantly, some human studies. Let’s give people wine with different amounts of quercetin and see what happens. Sign me up. Seriously.
As for Thanksgiving, it’s worth noting that cranberries have a lot of quercetin in them. So between the cranberry sauce, the Beaujolais, and your uncle ranting about the contrails again, the probability of headache is pretty darn high. Stay safe out there, and Happy Thanksgiving.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A better way to control blood pressure
My Bing AI engine, when prompted, tells me that there are about 87 journals, 45 conferences, and 53 workshops presently dedicated exclusively to hypertension. All of that attention, and yet ...
What is going on?
The top killers of Americans remain coronary artery heart disease (26%), cancer (22%), and stroke (6%). The precursors and attributable risk factors for coronary artery heart disease include hypertension (40%), obesity (20%), diabetes (15%), and combustible tobacco use (15%). The key precursors and attributable risk factors for stroke are hypertension (53%), obesity (37%), diabetes (9%), and combustible tobacco use (11%). Obviously, these are estimates, with substantial overlap.
It’s pretty obvious that
We have addressed improving tobacco control and preventing obesity and diabetes on these pages many times, and lamented the medical, public health, and societal failings. Today we turn our attention to the control of hypertension. That is much easier and far less expensive.
All physicians and medical organizations know that hypertension is a major attributable cause of many serious, expensive, and fatal illnesses. As many as 119 million (48%) of American adults have hypertension. The American Heart Association (AHA), American Medical Association (AMA), American College of Cardiology (ACC), and hundreds of other organizations have set a new target of 130/80 (revised from 140/90) for blood pressure control and have launched a major initiative, Target: BP, to reach it.
That is just great. We all wish this massive effort to succeed where few others have. But do AHA, AMA, ACC, and others understand why most efforts to this point have failed? The blame is typically aimed at patients failing to adhere to their instructions. Maybe, but why? And how does Target: BP intend to convert chronic failure into success if it just continues to do everything they have been trying to do that doesn’t work?
At this point, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that fewer than 48% of American patients with hypertension meet even the less stringent historical 140/90 goal.
A group practice in Ohio, PriMed Physicians, has consistently exceeded 90% or even 95% blood pressure control for its patients with hypertension for more than 10 years. Exemplary. How do they do it? This video of the 13th annual Lundberg Institute lecture describes this unique and successful program.
PriMed’s clinicians use the MedsEngine AI tool from MediSync and the NICaS (noninvasive cardiac system with impedance cardiography) to determine each patient’s unique blood pressure pathophysiology. Clinicians and patients understand that the simplest explanation of this pathophysiology encompasses three factors: (1) the volume of “water” (blood) in the system; (2) the strength of the pumping (pulsatile) process; and (3) the tightness (resistance) of the tubes that carry the blood. Patients “get it” when it is explained this way, and they cooperate.
At the first patient encounter, the Food and Drug Administration–approved PhysioFlow is employed to assess those three vital hemodynamic factors. The individual patient’s data are loaded into a tightly programed EHR-based algorithm with 37 clinical factors and five classes of drugs, providing multiple ways to influence the three key pathophysiologic processes. In this way, they arrive at the precise drug(s) and dosages for that patient. During the second visit, most patients are already showing improvement. By the third visit, the blood pressures of most patients have reached target control. After that, it is maintenance and tweaking.
These factors summarize why it works:
- Senior management belief, commitment, and leadership
- Informed buy-in from clinicians and patients
- A test that determines root causes of too much fluid, too strong pump action, or too tight pipes, and their proportionality
- An AI tool that matches those three pathophysiologic factors and 35 other clinical factors with the best drug or drugs (of many, not just a few) and dosages
- Persistent clinician-patient follow-up
- Refusal to accept failure
Since this approach is so successful, why is its use not everywhere?
It is not as if nobody noticed, even if you and many organizations have not. The American Medical Group Association recognized the program’s success by giving its top award to PriMed in 2015.
Klepper and Rodis wrote about this approach for managing multiple chronic conditions in 2021. Here’s a background article and an explainer, Clinical use of impedance cardiography for hemodynamic assessment of early cardiovascular disease and management of hypertension.
I found one pragmatic controlled clinical trial of impedance cardiography with a decision-support system from Beijing that did demonstrate clinical and statistical significance.
Frankly, we do need more rigorous, unbiased, large, controlled clinical trials assessing the MedsEngine and NICaS approach to managing blood pressure to facilitate a massive switch from the old and established (but failing) approach to a starkly better way.
Almost no one ever “completes a database.” All decision makers must act based upon the best data to which they have access. Data are often incomplete. The difference between success and mediocrity is often the ability of an individual or system to decide when enough information is enough and act accordingly.
Cost-effectiveness studies in three countries (United Kingdom, United States, and China) confirm sharply lower lifelong costs when blood pressure is well controlled. Of course.
For the American medical-industrial complex, lowered costs for managing common serious diseases may be an undesired rather than a good thing. In money-driven medicine, lower costs to the payer and purchaser translate to less revenue for the providers. Imagine all of those invasive and noninvasive diagnostic and therapeutic procedures forgone by prevention of hypertension. Is it possible that such an underlying truth is the real reason why American medicine is habitually unsuccessful at controlling blood pressure?
Right now, if my blood pressure were not well controlled (it is), I would find my way to Cincinnati, to give PriMed physicians, MediSync, and MedsEngine a crack at prolonging my useful life.
Dr. Lundberg is editor in chief of Cancer Commons. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
My Bing AI engine, when prompted, tells me that there are about 87 journals, 45 conferences, and 53 workshops presently dedicated exclusively to hypertension. All of that attention, and yet ...
What is going on?
The top killers of Americans remain coronary artery heart disease (26%), cancer (22%), and stroke (6%). The precursors and attributable risk factors for coronary artery heart disease include hypertension (40%), obesity (20%), diabetes (15%), and combustible tobacco use (15%). The key precursors and attributable risk factors for stroke are hypertension (53%), obesity (37%), diabetes (9%), and combustible tobacco use (11%). Obviously, these are estimates, with substantial overlap.
It’s pretty obvious that
We have addressed improving tobacco control and preventing obesity and diabetes on these pages many times, and lamented the medical, public health, and societal failings. Today we turn our attention to the control of hypertension. That is much easier and far less expensive.
All physicians and medical organizations know that hypertension is a major attributable cause of many serious, expensive, and fatal illnesses. As many as 119 million (48%) of American adults have hypertension. The American Heart Association (AHA), American Medical Association (AMA), American College of Cardiology (ACC), and hundreds of other organizations have set a new target of 130/80 (revised from 140/90) for blood pressure control and have launched a major initiative, Target: BP, to reach it.
That is just great. We all wish this massive effort to succeed where few others have. But do AHA, AMA, ACC, and others understand why most efforts to this point have failed? The blame is typically aimed at patients failing to adhere to their instructions. Maybe, but why? And how does Target: BP intend to convert chronic failure into success if it just continues to do everything they have been trying to do that doesn’t work?
At this point, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that fewer than 48% of American patients with hypertension meet even the less stringent historical 140/90 goal.
A group practice in Ohio, PriMed Physicians, has consistently exceeded 90% or even 95% blood pressure control for its patients with hypertension for more than 10 years. Exemplary. How do they do it? This video of the 13th annual Lundberg Institute lecture describes this unique and successful program.
PriMed’s clinicians use the MedsEngine AI tool from MediSync and the NICaS (noninvasive cardiac system with impedance cardiography) to determine each patient’s unique blood pressure pathophysiology. Clinicians and patients understand that the simplest explanation of this pathophysiology encompasses three factors: (1) the volume of “water” (blood) in the system; (2) the strength of the pumping (pulsatile) process; and (3) the tightness (resistance) of the tubes that carry the blood. Patients “get it” when it is explained this way, and they cooperate.
At the first patient encounter, the Food and Drug Administration–approved PhysioFlow is employed to assess those three vital hemodynamic factors. The individual patient’s data are loaded into a tightly programed EHR-based algorithm with 37 clinical factors and five classes of drugs, providing multiple ways to influence the three key pathophysiologic processes. In this way, they arrive at the precise drug(s) and dosages for that patient. During the second visit, most patients are already showing improvement. By the third visit, the blood pressures of most patients have reached target control. After that, it is maintenance and tweaking.
These factors summarize why it works:
- Senior management belief, commitment, and leadership
- Informed buy-in from clinicians and patients
- A test that determines root causes of too much fluid, too strong pump action, or too tight pipes, and their proportionality
- An AI tool that matches those three pathophysiologic factors and 35 other clinical factors with the best drug or drugs (of many, not just a few) and dosages
- Persistent clinician-patient follow-up
- Refusal to accept failure
Since this approach is so successful, why is its use not everywhere?
It is not as if nobody noticed, even if you and many organizations have not. The American Medical Group Association recognized the program’s success by giving its top award to PriMed in 2015.
Klepper and Rodis wrote about this approach for managing multiple chronic conditions in 2021. Here’s a background article and an explainer, Clinical use of impedance cardiography for hemodynamic assessment of early cardiovascular disease and management of hypertension.
I found one pragmatic controlled clinical trial of impedance cardiography with a decision-support system from Beijing that did demonstrate clinical and statistical significance.
Frankly, we do need more rigorous, unbiased, large, controlled clinical trials assessing the MedsEngine and NICaS approach to managing blood pressure to facilitate a massive switch from the old and established (but failing) approach to a starkly better way.
Almost no one ever “completes a database.” All decision makers must act based upon the best data to which they have access. Data are often incomplete. The difference between success and mediocrity is often the ability of an individual or system to decide when enough information is enough and act accordingly.
Cost-effectiveness studies in three countries (United Kingdom, United States, and China) confirm sharply lower lifelong costs when blood pressure is well controlled. Of course.
For the American medical-industrial complex, lowered costs for managing common serious diseases may be an undesired rather than a good thing. In money-driven medicine, lower costs to the payer and purchaser translate to less revenue for the providers. Imagine all of those invasive and noninvasive diagnostic and therapeutic procedures forgone by prevention of hypertension. Is it possible that such an underlying truth is the real reason why American medicine is habitually unsuccessful at controlling blood pressure?
Right now, if my blood pressure were not well controlled (it is), I would find my way to Cincinnati, to give PriMed physicians, MediSync, and MedsEngine a crack at prolonging my useful life.
Dr. Lundberg is editor in chief of Cancer Commons. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
My Bing AI engine, when prompted, tells me that there are about 87 journals, 45 conferences, and 53 workshops presently dedicated exclusively to hypertension. All of that attention, and yet ...
What is going on?
The top killers of Americans remain coronary artery heart disease (26%), cancer (22%), and stroke (6%). The precursors and attributable risk factors for coronary artery heart disease include hypertension (40%), obesity (20%), diabetes (15%), and combustible tobacco use (15%). The key precursors and attributable risk factors for stroke are hypertension (53%), obesity (37%), diabetes (9%), and combustible tobacco use (11%). Obviously, these are estimates, with substantial overlap.
It’s pretty obvious that
We have addressed improving tobacco control and preventing obesity and diabetes on these pages many times, and lamented the medical, public health, and societal failings. Today we turn our attention to the control of hypertension. That is much easier and far less expensive.
All physicians and medical organizations know that hypertension is a major attributable cause of many serious, expensive, and fatal illnesses. As many as 119 million (48%) of American adults have hypertension. The American Heart Association (AHA), American Medical Association (AMA), American College of Cardiology (ACC), and hundreds of other organizations have set a new target of 130/80 (revised from 140/90) for blood pressure control and have launched a major initiative, Target: BP, to reach it.
That is just great. We all wish this massive effort to succeed where few others have. But do AHA, AMA, ACC, and others understand why most efforts to this point have failed? The blame is typically aimed at patients failing to adhere to their instructions. Maybe, but why? And how does Target: BP intend to convert chronic failure into success if it just continues to do everything they have been trying to do that doesn’t work?
At this point, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that fewer than 48% of American patients with hypertension meet even the less stringent historical 140/90 goal.
A group practice in Ohio, PriMed Physicians, has consistently exceeded 90% or even 95% blood pressure control for its patients with hypertension for more than 10 years. Exemplary. How do they do it? This video of the 13th annual Lundberg Institute lecture describes this unique and successful program.
PriMed’s clinicians use the MedsEngine AI tool from MediSync and the NICaS (noninvasive cardiac system with impedance cardiography) to determine each patient’s unique blood pressure pathophysiology. Clinicians and patients understand that the simplest explanation of this pathophysiology encompasses three factors: (1) the volume of “water” (blood) in the system; (2) the strength of the pumping (pulsatile) process; and (3) the tightness (resistance) of the tubes that carry the blood. Patients “get it” when it is explained this way, and they cooperate.
At the first patient encounter, the Food and Drug Administration–approved PhysioFlow is employed to assess those three vital hemodynamic factors. The individual patient’s data are loaded into a tightly programed EHR-based algorithm with 37 clinical factors and five classes of drugs, providing multiple ways to influence the three key pathophysiologic processes. In this way, they arrive at the precise drug(s) and dosages for that patient. During the second visit, most patients are already showing improvement. By the third visit, the blood pressures of most patients have reached target control. After that, it is maintenance and tweaking.
These factors summarize why it works:
- Senior management belief, commitment, and leadership
- Informed buy-in from clinicians and patients
- A test that determines root causes of too much fluid, too strong pump action, or too tight pipes, and their proportionality
- An AI tool that matches those three pathophysiologic factors and 35 other clinical factors with the best drug or drugs (of many, not just a few) and dosages
- Persistent clinician-patient follow-up
- Refusal to accept failure
Since this approach is so successful, why is its use not everywhere?
It is not as if nobody noticed, even if you and many organizations have not. The American Medical Group Association recognized the program’s success by giving its top award to PriMed in 2015.
Klepper and Rodis wrote about this approach for managing multiple chronic conditions in 2021. Here’s a background article and an explainer, Clinical use of impedance cardiography for hemodynamic assessment of early cardiovascular disease and management of hypertension.
I found one pragmatic controlled clinical trial of impedance cardiography with a decision-support system from Beijing that did demonstrate clinical and statistical significance.
Frankly, we do need more rigorous, unbiased, large, controlled clinical trials assessing the MedsEngine and NICaS approach to managing blood pressure to facilitate a massive switch from the old and established (but failing) approach to a starkly better way.
Almost no one ever “completes a database.” All decision makers must act based upon the best data to which they have access. Data are often incomplete. The difference between success and mediocrity is often the ability of an individual or system to decide when enough information is enough and act accordingly.
Cost-effectiveness studies in three countries (United Kingdom, United States, and China) confirm sharply lower lifelong costs when blood pressure is well controlled. Of course.
For the American medical-industrial complex, lowered costs for managing common serious diseases may be an undesired rather than a good thing. In money-driven medicine, lower costs to the payer and purchaser translate to less revenue for the providers. Imagine all of those invasive and noninvasive diagnostic and therapeutic procedures forgone by prevention of hypertension. Is it possible that such an underlying truth is the real reason why American medicine is habitually unsuccessful at controlling blood pressure?
Right now, if my blood pressure were not well controlled (it is), I would find my way to Cincinnati, to give PriMed physicians, MediSync, and MedsEngine a crack at prolonging my useful life.
Dr. Lundberg is editor in chief of Cancer Commons. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A mid-marathon cardiac arrest, an MD’s crisis of confidence
I was running my 25th New York City Marathon. It was 2018, and I almost pulled out of running that year. I wasn’t myself, and maybe that’s an understatement.
A month earlier, I had been involved in a malpractice case. I was found liable for $10 million. My colleagues didn’t think I had done anything wrong, but the jury did. And the local newspapers made me look like a villain.
I was devastated. But my priest, my friends, and my family all told me, “You can’t quit.” So, I decided to run for them.
I started on the Verrazzano-Narrows Bridge that morning with some friends from work. I usually listen to music as I’m running, but I didn’t that year. I was just in my zone, enjoying the crowds. They’re huge. Millions of people on the streets.
I was running well. I did half the race in an hour and 57 minutes. My family always meets me at mile 17, and I was almost there. I had reached 59th Street and was about to make the turn onto First Avenue.
That’s one of the noisiest places in the marathon. There’s a kind of tunnel, and with the crowd and the throng of runners, it’s incredibly loud. But somehow, I heard somebody yell, “Help!”
Now, how I heard that, I don’t know. And if I’d been listening to music like I always do, no way I would’ve heard it. I could swear it was an angel on my shoulder that said, “Turn around, dummy. You’ve got a person that needs your help to your left.”
I turned around and about 30 feet behind me, I saw a woman waving her hands and a runner on the ground. I thought, Somebody fainted. I pushed through the crowd to get to them. The woman was crying, saying, “My friend went down to tie her shoe and she fell back. I think she’s seizing or something.”
I got down and tried to wake the other woman up. I lifted her legs up. But I quickly realized there was more to the story.
Some volunteers and police started coming toward us. The police officers looked at me like, What’s this guy doing? I explained that I was a physician, and one of them began helping me with the CPR. As we did that, someone brought a defibrillator.
Meanwhile, runners were going past, almost over us. The police officers were trying to create a barrier.
The machine gave the woman a shock, but we didn’t get a response, so we resumed CPR. At that point, my legs began to cramp so badly I couldn’t go on. So the police officer took over, and I yelled, “I need an ambu bag!” Somebody brought one, and I started giving her oxygen.
At that point, a paramedic team arrived with a bigger defibrillator. We shocked her again. And again. That time we got results, but she quickly went out again. The fourth time, we got her heart back and she started breathing on her own.
We finally got her into an ambulance. I wanted to go with them, but the woman’s friend needed to get in, so there wasn’t enough room.
And then they were gone, and I was just standing there.
A police officer put his arm around me. He said, “Doc, you’re amazing. What do you need? Where can I take you?”
I said, “Take me? My wife is waiting for me at mile 17.”
I took off and ran. When I got to my wife and kids, they were so worried. We all wear tracking devices, and they could see that I had stopped for more than 20 minutes.
I fell into my wife’s arms and told her what had happened. I was crying. “I don’t know what to do. I need to get to the hospital.”
And she said, “No, you need to go finish the race.”
So, I did. It was painful because of the cramps, but I was numb at that point. I was thinking about the woman the whole way. My time was 5 hours and 20 minutes.
As soon as I finished, I went to every police officer I could find, but nobody knew anything. Suddenly, I remembered my cousin. He had previously been the head of EMS for New York City. I called him. “Abdo, it’s Ted, you’ve got to do me a favor.”
“What?” he said. “Are you delirious from running the marathon?”
I told him what I needed. He called me back 5 minutes later and said, “Ted, what’d you do? Everybody wants to know who you are and where you are! The woman just went out again at New York Cornell. But they got her back, and they’re bringing her up to the cath lab.”
After every marathon that I run, we host a big party at our house. My family and friends and neighbors all celebrate while I’m dying on the couch. That night, my daughter told everyone the story of what happened.
But I was still not right. Still thinking about the malpractice suit.
Yes, I just did something great. But I’d recently been called the worst physician in the world. The distraction of the marathon was gone, and I was back to thinking, What am I going to do with my life? Who’s ever going to want to see me again? I’m a pariah.
Everybody said, “Ted, what happened a month ago isn’t you. What happened today was you.”
I told them to leave it alone, but my daughter and my neighbor started calling people anyway. The next day I got a call from the local newspaper. It was the same journalist who had written about me from the trial. I told him I didn’t want to talk. I was actually pretty nasty.
But my wife said, “Ted, what are you doing? That guy was trying to help you.” So, I called back and apologized.
“Dr. Strange, we knew that story wasn’t right,” he said. “We have to write this story.”
After the article came out, I started getting more calls from the media. Channel 7 News and CBS News did segments. The New York Knicks invited us to a game and presented me with a watch. It was incredible. But I was also really embarrassed by it.
People started calling me a hero. I’m not a hero. I just did what I’m supposed to do, what I’m trained to do. Shame on me if I don’t do that. Good guy and hopefully good physician, sure, but not a hero.
I also give credit to the City of New York Police Department, the FDNY, and the volunteers. Without them, I couldn’t have done what I did. It was a true team effort.
A few weeks later, the woman went home to Minnesota. She’ll never run a marathon again, but she’s still alive to this day. It turned out she had a single lesion called the “widow-maker” lesion. She was in perfect health and had just completed an ultramarathon a few months before; but she had a genetic predisposition. She still calls me every December to thank me for another Christmas.
There’s more.
One year after this whole thing, almost to the date, I got a call from my attorney. “The court just threw out the malpractice verdict,” he said. “You didn’t do anything wrong.”
I’m a man of faith. And I believe all this happened for a reason. Maybe God was sending me a message, and that’s why I heard a call for help on 59th Street in my 25th marathon among millions of people in a crowd.
I ran the marathon the next year. And when I got to that spot, I stopped and reflected. Nobody knew why I was standing there, but I knew. To this day, I could take you to that spot.
I turn 65 next July, and I plan to keep on running the race.
Dr. Strange is chair of medicine at Staten Island University Hospital, associate ambulatory physician executive of the Staten Island Region, and an internal medicine and geriatric medicine physician with Northwell Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
I was running my 25th New York City Marathon. It was 2018, and I almost pulled out of running that year. I wasn’t myself, and maybe that’s an understatement.
A month earlier, I had been involved in a malpractice case. I was found liable for $10 million. My colleagues didn’t think I had done anything wrong, but the jury did. And the local newspapers made me look like a villain.
I was devastated. But my priest, my friends, and my family all told me, “You can’t quit.” So, I decided to run for them.
I started on the Verrazzano-Narrows Bridge that morning with some friends from work. I usually listen to music as I’m running, but I didn’t that year. I was just in my zone, enjoying the crowds. They’re huge. Millions of people on the streets.
I was running well. I did half the race in an hour and 57 minutes. My family always meets me at mile 17, and I was almost there. I had reached 59th Street and was about to make the turn onto First Avenue.
That’s one of the noisiest places in the marathon. There’s a kind of tunnel, and with the crowd and the throng of runners, it’s incredibly loud. But somehow, I heard somebody yell, “Help!”
Now, how I heard that, I don’t know. And if I’d been listening to music like I always do, no way I would’ve heard it. I could swear it was an angel on my shoulder that said, “Turn around, dummy. You’ve got a person that needs your help to your left.”
I turned around and about 30 feet behind me, I saw a woman waving her hands and a runner on the ground. I thought, Somebody fainted. I pushed through the crowd to get to them. The woman was crying, saying, “My friend went down to tie her shoe and she fell back. I think she’s seizing or something.”
I got down and tried to wake the other woman up. I lifted her legs up. But I quickly realized there was more to the story.
Some volunteers and police started coming toward us. The police officers looked at me like, What’s this guy doing? I explained that I was a physician, and one of them began helping me with the CPR. As we did that, someone brought a defibrillator.
Meanwhile, runners were going past, almost over us. The police officers were trying to create a barrier.
The machine gave the woman a shock, but we didn’t get a response, so we resumed CPR. At that point, my legs began to cramp so badly I couldn’t go on. So the police officer took over, and I yelled, “I need an ambu bag!” Somebody brought one, and I started giving her oxygen.
At that point, a paramedic team arrived with a bigger defibrillator. We shocked her again. And again. That time we got results, but she quickly went out again. The fourth time, we got her heart back and she started breathing on her own.
We finally got her into an ambulance. I wanted to go with them, but the woman’s friend needed to get in, so there wasn’t enough room.
And then they were gone, and I was just standing there.
A police officer put his arm around me. He said, “Doc, you’re amazing. What do you need? Where can I take you?”
I said, “Take me? My wife is waiting for me at mile 17.”
I took off and ran. When I got to my wife and kids, they were so worried. We all wear tracking devices, and they could see that I had stopped for more than 20 minutes.
I fell into my wife’s arms and told her what had happened. I was crying. “I don’t know what to do. I need to get to the hospital.”
And she said, “No, you need to go finish the race.”
So, I did. It was painful because of the cramps, but I was numb at that point. I was thinking about the woman the whole way. My time was 5 hours and 20 minutes.
As soon as I finished, I went to every police officer I could find, but nobody knew anything. Suddenly, I remembered my cousin. He had previously been the head of EMS for New York City. I called him. “Abdo, it’s Ted, you’ve got to do me a favor.”
“What?” he said. “Are you delirious from running the marathon?”
I told him what I needed. He called me back 5 minutes later and said, “Ted, what’d you do? Everybody wants to know who you are and where you are! The woman just went out again at New York Cornell. But they got her back, and they’re bringing her up to the cath lab.”
After every marathon that I run, we host a big party at our house. My family and friends and neighbors all celebrate while I’m dying on the couch. That night, my daughter told everyone the story of what happened.
But I was still not right. Still thinking about the malpractice suit.
Yes, I just did something great. But I’d recently been called the worst physician in the world. The distraction of the marathon was gone, and I was back to thinking, What am I going to do with my life? Who’s ever going to want to see me again? I’m a pariah.
Everybody said, “Ted, what happened a month ago isn’t you. What happened today was you.”
I told them to leave it alone, but my daughter and my neighbor started calling people anyway. The next day I got a call from the local newspaper. It was the same journalist who had written about me from the trial. I told him I didn’t want to talk. I was actually pretty nasty.
But my wife said, “Ted, what are you doing? That guy was trying to help you.” So, I called back and apologized.
“Dr. Strange, we knew that story wasn’t right,” he said. “We have to write this story.”
After the article came out, I started getting more calls from the media. Channel 7 News and CBS News did segments. The New York Knicks invited us to a game and presented me with a watch. It was incredible. But I was also really embarrassed by it.
People started calling me a hero. I’m not a hero. I just did what I’m supposed to do, what I’m trained to do. Shame on me if I don’t do that. Good guy and hopefully good physician, sure, but not a hero.
I also give credit to the City of New York Police Department, the FDNY, and the volunteers. Without them, I couldn’t have done what I did. It was a true team effort.
A few weeks later, the woman went home to Minnesota. She’ll never run a marathon again, but she’s still alive to this day. It turned out she had a single lesion called the “widow-maker” lesion. She was in perfect health and had just completed an ultramarathon a few months before; but she had a genetic predisposition. She still calls me every December to thank me for another Christmas.
There’s more.
One year after this whole thing, almost to the date, I got a call from my attorney. “The court just threw out the malpractice verdict,” he said. “You didn’t do anything wrong.”
I’m a man of faith. And I believe all this happened for a reason. Maybe God was sending me a message, and that’s why I heard a call for help on 59th Street in my 25th marathon among millions of people in a crowd.
I ran the marathon the next year. And when I got to that spot, I stopped and reflected. Nobody knew why I was standing there, but I knew. To this day, I could take you to that spot.
I turn 65 next July, and I plan to keep on running the race.
Dr. Strange is chair of medicine at Staten Island University Hospital, associate ambulatory physician executive of the Staten Island Region, and an internal medicine and geriatric medicine physician with Northwell Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
I was running my 25th New York City Marathon. It was 2018, and I almost pulled out of running that year. I wasn’t myself, and maybe that’s an understatement.
A month earlier, I had been involved in a malpractice case. I was found liable for $10 million. My colleagues didn’t think I had done anything wrong, but the jury did. And the local newspapers made me look like a villain.
I was devastated. But my priest, my friends, and my family all told me, “You can’t quit.” So, I decided to run for them.
I started on the Verrazzano-Narrows Bridge that morning with some friends from work. I usually listen to music as I’m running, but I didn’t that year. I was just in my zone, enjoying the crowds. They’re huge. Millions of people on the streets.
I was running well. I did half the race in an hour and 57 minutes. My family always meets me at mile 17, and I was almost there. I had reached 59th Street and was about to make the turn onto First Avenue.
That’s one of the noisiest places in the marathon. There’s a kind of tunnel, and with the crowd and the throng of runners, it’s incredibly loud. But somehow, I heard somebody yell, “Help!”
Now, how I heard that, I don’t know. And if I’d been listening to music like I always do, no way I would’ve heard it. I could swear it was an angel on my shoulder that said, “Turn around, dummy. You’ve got a person that needs your help to your left.”
I turned around and about 30 feet behind me, I saw a woman waving her hands and a runner on the ground. I thought, Somebody fainted. I pushed through the crowd to get to them. The woman was crying, saying, “My friend went down to tie her shoe and she fell back. I think she’s seizing or something.”
I got down and tried to wake the other woman up. I lifted her legs up. But I quickly realized there was more to the story.
Some volunteers and police started coming toward us. The police officers looked at me like, What’s this guy doing? I explained that I was a physician, and one of them began helping me with the CPR. As we did that, someone brought a defibrillator.
Meanwhile, runners were going past, almost over us. The police officers were trying to create a barrier.
The machine gave the woman a shock, but we didn’t get a response, so we resumed CPR. At that point, my legs began to cramp so badly I couldn’t go on. So the police officer took over, and I yelled, “I need an ambu bag!” Somebody brought one, and I started giving her oxygen.
At that point, a paramedic team arrived with a bigger defibrillator. We shocked her again. And again. That time we got results, but she quickly went out again. The fourth time, we got her heart back and she started breathing on her own.
We finally got her into an ambulance. I wanted to go with them, but the woman’s friend needed to get in, so there wasn’t enough room.
And then they were gone, and I was just standing there.
A police officer put his arm around me. He said, “Doc, you’re amazing. What do you need? Where can I take you?”
I said, “Take me? My wife is waiting for me at mile 17.”
I took off and ran. When I got to my wife and kids, they were so worried. We all wear tracking devices, and they could see that I had stopped for more than 20 minutes.
I fell into my wife’s arms and told her what had happened. I was crying. “I don’t know what to do. I need to get to the hospital.”
And she said, “No, you need to go finish the race.”
So, I did. It was painful because of the cramps, but I was numb at that point. I was thinking about the woman the whole way. My time was 5 hours and 20 minutes.
As soon as I finished, I went to every police officer I could find, but nobody knew anything. Suddenly, I remembered my cousin. He had previously been the head of EMS for New York City. I called him. “Abdo, it’s Ted, you’ve got to do me a favor.”
“What?” he said. “Are you delirious from running the marathon?”
I told him what I needed. He called me back 5 minutes later and said, “Ted, what’d you do? Everybody wants to know who you are and where you are! The woman just went out again at New York Cornell. But they got her back, and they’re bringing her up to the cath lab.”
After every marathon that I run, we host a big party at our house. My family and friends and neighbors all celebrate while I’m dying on the couch. That night, my daughter told everyone the story of what happened.
But I was still not right. Still thinking about the malpractice suit.
Yes, I just did something great. But I’d recently been called the worst physician in the world. The distraction of the marathon was gone, and I was back to thinking, What am I going to do with my life? Who’s ever going to want to see me again? I’m a pariah.
Everybody said, “Ted, what happened a month ago isn’t you. What happened today was you.”
I told them to leave it alone, but my daughter and my neighbor started calling people anyway. The next day I got a call from the local newspaper. It was the same journalist who had written about me from the trial. I told him I didn’t want to talk. I was actually pretty nasty.
But my wife said, “Ted, what are you doing? That guy was trying to help you.” So, I called back and apologized.
“Dr. Strange, we knew that story wasn’t right,” he said. “We have to write this story.”
After the article came out, I started getting more calls from the media. Channel 7 News and CBS News did segments. The New York Knicks invited us to a game and presented me with a watch. It was incredible. But I was also really embarrassed by it.
People started calling me a hero. I’m not a hero. I just did what I’m supposed to do, what I’m trained to do. Shame on me if I don’t do that. Good guy and hopefully good physician, sure, but not a hero.
I also give credit to the City of New York Police Department, the FDNY, and the volunteers. Without them, I couldn’t have done what I did. It was a true team effort.
A few weeks later, the woman went home to Minnesota. She’ll never run a marathon again, but she’s still alive to this day. It turned out she had a single lesion called the “widow-maker” lesion. She was in perfect health and had just completed an ultramarathon a few months before; but she had a genetic predisposition. She still calls me every December to thank me for another Christmas.
There’s more.
One year after this whole thing, almost to the date, I got a call from my attorney. “The court just threw out the malpractice verdict,” he said. “You didn’t do anything wrong.”
I’m a man of faith. And I believe all this happened for a reason. Maybe God was sending me a message, and that’s why I heard a call for help on 59th Street in my 25th marathon among millions of people in a crowd.
I ran the marathon the next year. And when I got to that spot, I stopped and reflected. Nobody knew why I was standing there, but I knew. To this day, I could take you to that spot.
I turn 65 next July, and I plan to keep on running the race.
Dr. Strange is chair of medicine at Staten Island University Hospital, associate ambulatory physician executive of the Staten Island Region, and an internal medicine and geriatric medicine physician with Northwell Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Prescription drug affordability boards: Another quick fix with unintended consequences?
Making medications more accessible to those who need them is the focus of attention in the media and in all levels of government. For a drug to be accessible, it must be affordable and available. Something may be affordable, but if it isn’t available, no one will have access to it. Think of toilet paper in the first year of the COVID pandemic. The opposite is also true. An item may be available, but if it isn’t affordable, access is lost. While medication affordability is viewed as the major problem for patients, lack of availability has begun to creep into our drug supply chain. We are now experiencing drug shortages for medications that are very affordable. The perverse incentives, inherent in formulary construction, favor higher-priced medications, which decreases the availability of lower-priced – yet still expensive – drugs, thus increasing patient cost share. Formulary placement and patient cost share, important determinants of accessibility, are controlled by health plans and differ considerably even from the same payer. And yet, the price of drugs remains the target of most approaches to increasing patients’ access. And now price negotiations and drug affordability boards enter into the picture.
What are prescription drug affordability boards?
Both state and federal legislatures have placed the affordability of medications front and center on their agendas. However, neither are considering how formulary construction affects patient’s access to medications. The Inflation Reduction Act is Congress’s foray into price setting/negotiation of expensive drugs. Over the last few years, states are also attempting to make drugs more affordable by creating prescription drug affordability boards (PDABs). Governors (or other state leaders) appoint PDAB members who are charged with the task of evaluating the affordability of certain drugs for both the state and its residents. How to do it, and what the limitations are, vary from state to state. In 2019, Maryland was first state to establish a PDAB, charging its members to study commercial insurance and drug pricing and make recommendations on how to make drugs more affordable for Maryland residents. Other states that have passed PDAB legislation are Colorado, Maine, Minnesota, New Hampshire, Ohio, Oregon, and Washington.
Colorado, Minnesota, and Washington – and soon Maryland and Oregon – hope to make drugs more affordable for patients by allowing their PDABs to set an upper payment limit (UPL). A UPL serves as a cap on the sales price and reimbursement for a drug. The Michigan legislature is actively debating legislation that would establish a PDAB and allow it to set UPLs. On the surface, this may appear to be a potential solution to the affordability issue. However, as always, there are many questions as to how this will work and what are the unintended consequences of price setting and establishing UPLs for medications. UPLs have the potential to harm access to provider-administered drugs. With the help of advocacy from the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations (CSRO), Washington’s PDAB statute potentially has a carve-out for provider-administered drugs.
Possible unintended consequences for provider-administered drugs
CSRO asked for a meeting with the Colorado PDAB after they announced their list of drugs for which UPLs would be set. We spoke with the PDAB in October, hoping to point out some of the unintended consequences that needed to be considered. One of the big questions we have revolves around the “buy and bill” provider-administered drugs. According to the language of the Colorado statute, providers would not be paid any more than the UPL for a drug administered in their office. CSRO is concerned that this would leave providers uncompensated for the service of administering the drug and associated overhead. This is not to mention that providers may not be able to find a group purchasing organization that would even sell the drug at the UPL, much less a lower price than the UPL. And even if a provider could buy it at the UPL, that would mean there would be no margin to cover the overhead for their infusion suite. Interestingly, while Colorado’s rules for the UPL state that pharmacies can be paid an additional reasonable dispensing fee beyond the UPL, no such allowance is made for providers administering one of these medications. In fact, the Colorado PDAB specifically indicated that the goal of the state’s UPL methodology was to ensure that there was no “delta” between what is paid for the drug by the provider and what is reimbursed to a provider for the drug by the payer. This may cause some providers to be unable to “afford” to administer those drugs with UPLs, which ultimately reduces access for residents of Colorado to that particular medication. This is the exact opposite of what the PDAB is supposed to accomplish.
There are still many questions. What impact will UPLs have on a medication’s placement on a formulary? As we know, preferred formulary placement is often given to drugs with the highest price concession from the manufacturers. Will setting a UPL on payment for specialty pharmacy drugs to pharmacy benefit manager-owned specialty pharmacies affect that drug’s ability to be on the formulary? And again, how will the PDAB resolve the issue of compensating the provider for overhead costs associated with administering the medication?
Even more confusing questions remain. How will the UPL be enforced when a “purchase” or “sale” of the drug is made by an out-of-state entity somewhere along the supply chain? When ultimately the drug is purchased and delivered to a Colorado consumer by a Colorado provider/pharmacy, there are multiple points of the supply chain that may be outside of the jurisdiction of Colorado to enforce the UPL. This would create a misalignment in pricing among various supply chain entities.
While the sentiment behind creating PDABs is noble, it may end up having the unintended consequence of patients losing access to these drugs because of the perverse incentives involved in formulary construction or providers’ inability to afford to offer provider-administered drugs with UPLs.
Remember, expensive specialty pharmacy medications are already discounted greatly by manufacturers, often more than 50% to pharmacy benefit managers; and yet those cost savings are not passed on to the patients. Also, there is no oversight of 340B hospital contracted pharmacies to make sure that they pass those savings on to needy patients. Perhaps PDABs should address those issues, as well, if patient access to expensive medications is the goal.
Clearly, there are no easy answers. But with so many variables in the drug supply chain affecting patient access, concentrating only on one aspect may end up causing more harm than good. If your state is thinking of passing a PDAB, please let your legislators know that there are issues with this type of legislation that perhaps should be worked out before the bill is passed.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s Vice President of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate Past President, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. You can reach her at [email protected].
Making medications more accessible to those who need them is the focus of attention in the media and in all levels of government. For a drug to be accessible, it must be affordable and available. Something may be affordable, but if it isn’t available, no one will have access to it. Think of toilet paper in the first year of the COVID pandemic. The opposite is also true. An item may be available, but if it isn’t affordable, access is lost. While medication affordability is viewed as the major problem for patients, lack of availability has begun to creep into our drug supply chain. We are now experiencing drug shortages for medications that are very affordable. The perverse incentives, inherent in formulary construction, favor higher-priced medications, which decreases the availability of lower-priced – yet still expensive – drugs, thus increasing patient cost share. Formulary placement and patient cost share, important determinants of accessibility, are controlled by health plans and differ considerably even from the same payer. And yet, the price of drugs remains the target of most approaches to increasing patients’ access. And now price negotiations and drug affordability boards enter into the picture.
What are prescription drug affordability boards?
Both state and federal legislatures have placed the affordability of medications front and center on their agendas. However, neither are considering how formulary construction affects patient’s access to medications. The Inflation Reduction Act is Congress’s foray into price setting/negotiation of expensive drugs. Over the last few years, states are also attempting to make drugs more affordable by creating prescription drug affordability boards (PDABs). Governors (or other state leaders) appoint PDAB members who are charged with the task of evaluating the affordability of certain drugs for both the state and its residents. How to do it, and what the limitations are, vary from state to state. In 2019, Maryland was first state to establish a PDAB, charging its members to study commercial insurance and drug pricing and make recommendations on how to make drugs more affordable for Maryland residents. Other states that have passed PDAB legislation are Colorado, Maine, Minnesota, New Hampshire, Ohio, Oregon, and Washington.
Colorado, Minnesota, and Washington – and soon Maryland and Oregon – hope to make drugs more affordable for patients by allowing their PDABs to set an upper payment limit (UPL). A UPL serves as a cap on the sales price and reimbursement for a drug. The Michigan legislature is actively debating legislation that would establish a PDAB and allow it to set UPLs. On the surface, this may appear to be a potential solution to the affordability issue. However, as always, there are many questions as to how this will work and what are the unintended consequences of price setting and establishing UPLs for medications. UPLs have the potential to harm access to provider-administered drugs. With the help of advocacy from the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations (CSRO), Washington’s PDAB statute potentially has a carve-out for provider-administered drugs.
Possible unintended consequences for provider-administered drugs
CSRO asked for a meeting with the Colorado PDAB after they announced their list of drugs for which UPLs would be set. We spoke with the PDAB in October, hoping to point out some of the unintended consequences that needed to be considered. One of the big questions we have revolves around the “buy and bill” provider-administered drugs. According to the language of the Colorado statute, providers would not be paid any more than the UPL for a drug administered in their office. CSRO is concerned that this would leave providers uncompensated for the service of administering the drug and associated overhead. This is not to mention that providers may not be able to find a group purchasing organization that would even sell the drug at the UPL, much less a lower price than the UPL. And even if a provider could buy it at the UPL, that would mean there would be no margin to cover the overhead for their infusion suite. Interestingly, while Colorado’s rules for the UPL state that pharmacies can be paid an additional reasonable dispensing fee beyond the UPL, no such allowance is made for providers administering one of these medications. In fact, the Colorado PDAB specifically indicated that the goal of the state’s UPL methodology was to ensure that there was no “delta” between what is paid for the drug by the provider and what is reimbursed to a provider for the drug by the payer. This may cause some providers to be unable to “afford” to administer those drugs with UPLs, which ultimately reduces access for residents of Colorado to that particular medication. This is the exact opposite of what the PDAB is supposed to accomplish.
There are still many questions. What impact will UPLs have on a medication’s placement on a formulary? As we know, preferred formulary placement is often given to drugs with the highest price concession from the manufacturers. Will setting a UPL on payment for specialty pharmacy drugs to pharmacy benefit manager-owned specialty pharmacies affect that drug’s ability to be on the formulary? And again, how will the PDAB resolve the issue of compensating the provider for overhead costs associated with administering the medication?
Even more confusing questions remain. How will the UPL be enforced when a “purchase” or “sale” of the drug is made by an out-of-state entity somewhere along the supply chain? When ultimately the drug is purchased and delivered to a Colorado consumer by a Colorado provider/pharmacy, there are multiple points of the supply chain that may be outside of the jurisdiction of Colorado to enforce the UPL. This would create a misalignment in pricing among various supply chain entities.
While the sentiment behind creating PDABs is noble, it may end up having the unintended consequence of patients losing access to these drugs because of the perverse incentives involved in formulary construction or providers’ inability to afford to offer provider-administered drugs with UPLs.
Remember, expensive specialty pharmacy medications are already discounted greatly by manufacturers, often more than 50% to pharmacy benefit managers; and yet those cost savings are not passed on to the patients. Also, there is no oversight of 340B hospital contracted pharmacies to make sure that they pass those savings on to needy patients. Perhaps PDABs should address those issues, as well, if patient access to expensive medications is the goal.
Clearly, there are no easy answers. But with so many variables in the drug supply chain affecting patient access, concentrating only on one aspect may end up causing more harm than good. If your state is thinking of passing a PDAB, please let your legislators know that there are issues with this type of legislation that perhaps should be worked out before the bill is passed.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s Vice President of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate Past President, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. You can reach her at [email protected].
Making medications more accessible to those who need them is the focus of attention in the media and in all levels of government. For a drug to be accessible, it must be affordable and available. Something may be affordable, but if it isn’t available, no one will have access to it. Think of toilet paper in the first year of the COVID pandemic. The opposite is also true. An item may be available, but if it isn’t affordable, access is lost. While medication affordability is viewed as the major problem for patients, lack of availability has begun to creep into our drug supply chain. We are now experiencing drug shortages for medications that are very affordable. The perverse incentives, inherent in formulary construction, favor higher-priced medications, which decreases the availability of lower-priced – yet still expensive – drugs, thus increasing patient cost share. Formulary placement and patient cost share, important determinants of accessibility, are controlled by health plans and differ considerably even from the same payer. And yet, the price of drugs remains the target of most approaches to increasing patients’ access. And now price negotiations and drug affordability boards enter into the picture.
What are prescription drug affordability boards?
Both state and federal legislatures have placed the affordability of medications front and center on their agendas. However, neither are considering how formulary construction affects patient’s access to medications. The Inflation Reduction Act is Congress’s foray into price setting/negotiation of expensive drugs. Over the last few years, states are also attempting to make drugs more affordable by creating prescription drug affordability boards (PDABs). Governors (or other state leaders) appoint PDAB members who are charged with the task of evaluating the affordability of certain drugs for both the state and its residents. How to do it, and what the limitations are, vary from state to state. In 2019, Maryland was first state to establish a PDAB, charging its members to study commercial insurance and drug pricing and make recommendations on how to make drugs more affordable for Maryland residents. Other states that have passed PDAB legislation are Colorado, Maine, Minnesota, New Hampshire, Ohio, Oregon, and Washington.
Colorado, Minnesota, and Washington – and soon Maryland and Oregon – hope to make drugs more affordable for patients by allowing their PDABs to set an upper payment limit (UPL). A UPL serves as a cap on the sales price and reimbursement for a drug. The Michigan legislature is actively debating legislation that would establish a PDAB and allow it to set UPLs. On the surface, this may appear to be a potential solution to the affordability issue. However, as always, there are many questions as to how this will work and what are the unintended consequences of price setting and establishing UPLs for medications. UPLs have the potential to harm access to provider-administered drugs. With the help of advocacy from the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations (CSRO), Washington’s PDAB statute potentially has a carve-out for provider-administered drugs.
Possible unintended consequences for provider-administered drugs
CSRO asked for a meeting with the Colorado PDAB after they announced their list of drugs for which UPLs would be set. We spoke with the PDAB in October, hoping to point out some of the unintended consequences that needed to be considered. One of the big questions we have revolves around the “buy and bill” provider-administered drugs. According to the language of the Colorado statute, providers would not be paid any more than the UPL for a drug administered in their office. CSRO is concerned that this would leave providers uncompensated for the service of administering the drug and associated overhead. This is not to mention that providers may not be able to find a group purchasing organization that would even sell the drug at the UPL, much less a lower price than the UPL. And even if a provider could buy it at the UPL, that would mean there would be no margin to cover the overhead for their infusion suite. Interestingly, while Colorado’s rules for the UPL state that pharmacies can be paid an additional reasonable dispensing fee beyond the UPL, no such allowance is made for providers administering one of these medications. In fact, the Colorado PDAB specifically indicated that the goal of the state’s UPL methodology was to ensure that there was no “delta” between what is paid for the drug by the provider and what is reimbursed to a provider for the drug by the payer. This may cause some providers to be unable to “afford” to administer those drugs with UPLs, which ultimately reduces access for residents of Colorado to that particular medication. This is the exact opposite of what the PDAB is supposed to accomplish.
There are still many questions. What impact will UPLs have on a medication’s placement on a formulary? As we know, preferred formulary placement is often given to drugs with the highest price concession from the manufacturers. Will setting a UPL on payment for specialty pharmacy drugs to pharmacy benefit manager-owned specialty pharmacies affect that drug’s ability to be on the formulary? And again, how will the PDAB resolve the issue of compensating the provider for overhead costs associated with administering the medication?
Even more confusing questions remain. How will the UPL be enforced when a “purchase” or “sale” of the drug is made by an out-of-state entity somewhere along the supply chain? When ultimately the drug is purchased and delivered to a Colorado consumer by a Colorado provider/pharmacy, there are multiple points of the supply chain that may be outside of the jurisdiction of Colorado to enforce the UPL. This would create a misalignment in pricing among various supply chain entities.
While the sentiment behind creating PDABs is noble, it may end up having the unintended consequence of patients losing access to these drugs because of the perverse incentives involved in formulary construction or providers’ inability to afford to offer provider-administered drugs with UPLs.
Remember, expensive specialty pharmacy medications are already discounted greatly by manufacturers, often more than 50% to pharmacy benefit managers; and yet those cost savings are not passed on to the patients. Also, there is no oversight of 340B hospital contracted pharmacies to make sure that they pass those savings on to needy patients. Perhaps PDABs should address those issues, as well, if patient access to expensive medications is the goal.
Clearly, there are no easy answers. But with so many variables in the drug supply chain affecting patient access, concentrating only on one aspect may end up causing more harm than good. If your state is thinking of passing a PDAB, please let your legislators know that there are issues with this type of legislation that perhaps should be worked out before the bill is passed.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s Vice President of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate Past President, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. You can reach her at [email protected].
Mental health characteristics of refugee children
Since 1983, when I was a child and fled as a boat refugee from Vietnam with my mother, the international plight of displaced people has only worsened. From 1997 to 2022, the number of forcibly displaced people has more than tripled, growing from 34 million to more than 108 million.1
Displaced people are designated as refugees only when they cross international borders and meet the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees’ (UNHCR) definition as “persons outside their countries of origin who are in need of international protection because of a serious threat to their life, physical integrity, or freedom in their country of origin as a result of persecution, armed conflict, violence, or serious public disorder.”2 There is a separate mandate by the United Nations for the aid of Palestinian refugees under the United Nations General Assembly’s United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestinian Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA).3 Of the displaced in 2022, more than 36 million were recognized as refugees under UNHCR and UNRWA mandates.1 Of these, almost 50% were children, at 17.5 million.4 To make matters worse, worldwide children represent less than one-third of the population.4 Since 2022, the increase in refugeeism is mostly driven by Ukraine and Syria, though also significantly Afghanistan, Venezuela, Sudan, Myanmar, Congo, Somalia, and Central African Republic.4 Refugeeism is a growing problem that disproportionately impacts children through sheer number, and one suspects, given their greater overall vulnerabilities compared with adults, physical and mental health consequences.
Traumas of refugees compared with non-refugee immigrants
In terms of mental health, refugees are distinct from non-refugee immigrants in that they likely experience more severe psychosocial adversities from greater poverty, greater risk of family separation, and uncertainty of the asylum process.5-8
From my own experience, this stems from the urgent nature of the refugee’s displacement, where they are often fleeing an immediate danger. My family had fled persecution from Communist forces and the social economic collapse that rendered Vietnam, for a time, one of the poorest in the world.9 Or, as my mother observed, “We had to leave because even doctors were starving.”
Refugees often have little preparation, have little legal protection since they are often criminalized, and are forced to endure dangerous conditions where they are vulnerable to smugglers and criminals who exploit their unprotected status. Once they arrive in their new country, they often do not have other family as social supports or resources. They themselves become the anchor for future legal and orderly immigration of their remaining family, given that they can extend their refugee status to those left behind.10 These non-refugee immigrants, unlike their refugee counterparts, are often flown to their new homes with more preparation, protecting them from dangerous conditions, and have the benefit of family who provide them with resources. As such, refugees tend to experience more traumatic life events than non-refugee immigrants. This was true in my family where those of us who initially escaped became the anchors to legally, and more safely, immigrate most of our family in Vietnam. We became their resources, likely making their acclimation smoother.
The mental health of refugee children and their caregivers
It is important to understand the stressors affecting the caregivers of children, since effective treatment of their mental health conditions can also benefit the children as well.11 In fact, among the greatest protective factors for refugee children is the presence of an adult caregiver, suggesting that the child’s mental health is dependent on the caregivers.
Those children who are separated show much worse mental health sequalae.12 As such, an understanding of the caregiver’s stressors is important. For example, when we were escaping Vietnam, my mom would protect me from our hardships by talking about our goals in America, minimizing our dangers by saying that we would be rewarded with things like a hamburger with its seemingly impossible amount of meat. Physically, my mother would always sleep with her arms around me and a knife hidden in order to ward off any attackers at night. When I was starving in the hull of a boat, having not eaten for days, my mother begged for food and gave me what she could get. And post-escape, my family focused on work and applied for aid for shelter and food, while encouraging us to invest in education, likely preventing involvement in criminal activities or gangs. Though overall, my family shielded me from the worst consequences, they also passed on their fears. One of my uncles had been killed by the police when he tried to escape, and so my family passed down a deep suspicion of authorities, whether they were the police or school principals. My mother had vivid memories of Communist re-education camps, which likely gave her a lasting fear that a Communist would find out our identities in America and re-capture us.
The mental health risk of refugees
Given that refugees tend to experience greater amounts of traumatic life events and a vast array of stressors sustained across years and even decades before, during, and after migration, it is no wonder they have much higher rates of mental health conditions, most predominantly PTSD and affective disorders.13,14 They are at particular risk of developing psychoses because they are more likely to experience a range of physical, psychological, and psychosocial problems associated with adversities such as violence, discrimination, economic stress, and social isolation.13 For example, the period leading up to my escape consisted of decades of prolonged war: the French-Indochina from 1945 to 1954, then the Vietnam War from 1955 to 1975) as well as the persecution and re-education camps afterward. What my family had to endure created a period of fear and loss into which I was born into in 1976. That year, my family had lost its fortune due to the Communist government seizing of our home and business, plunging us from a comfortable middle- to upper-class life to poverty. There was also widespread fear of systematic rape by the Communist victors. So my family endured great stress and the loss of a way of life leading up to our escape.
For the refugees, the escape itself is often a dangerous journey where, given its emergent nature, they are often exposed to the elements. We know about the current situation in Ukraine and Gaza, where children are fleeing from bombs and bullets. In my situation, we endured weeks of starvation crammed in the hull of boat as we forged through the Indian Ocean to the Philippines. One of my aunts, on a separate trip, perished because her boat had capsized, like so many others. Though impossible to verify, it has been estimated that up to 70% of Vietnamese refugees died during their escape.15 After the boat, my mother and I still had to brave Malaysian jungles and prisons, and then refugee camps for a year before we reached safety at an American Embassy in the Philippines. After we gained sponsorship to America, the traumas did not abate, but were only replaced by those of culture shock, poverty, and alienation. Taken by themselves, significant traumas exist in each phase of a refugee child’s escape, whether before, during, or after. These traumas are likely compounded since they are continuously layered and sustained across years, even decades. They affect not only the children, but their parents, and sometimes even a whole nation of people.
Summary
Refugee children and their families experience a variety of traumas, often sustained across years and even decades, because of armed conflict, persecution, or social upheavals. It is known that refugees are at greater risk for PTSD and affective and psychotic disorders, presumably due to increased traumatic life events before, during, and after their migration. The writer uses his own experience as a child refugee from Vietnam to elucidate the stressors evident in various phases of forced displacement.
Dr. Nguyen is a second year resident at UCSF Fresno Psychiatry Residency. He was a public high school English teacher for 15 years previously.
References
1. UNHCR. Global Trends. Forced displacement in 2016. Geneva, Switzerland: The UN Refugee Agency, 2022. https://www.unhcr.org/global-trends.
2. Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. The refugee concept under international law. Global compact for safe, orderly and regular migration. https://www.unhcr.org/sites/
3. United Nations. (2023, November 11). The Question of Palestine. Un.org. https://www.un.org/unispal/document/un-general-assembly-renews-unrwa-mandate-press-release/
4. UNICEF. (2023, November 11). Child displacement. Data.unicef.org. https://data.unicef.org/topic/child-migration-and-displacement/displacement
5. Kinzie JD. Immigrants and refugees: The psychiatric perspective. Transcult Psychiatry. 2006 Dec;43(4):577-91. doi: 10.1177/1363461506070782.
6. Eaton W and Harrison G. Ethnic disadvantage and schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 2000:(407):38-43. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0447.2000.00007.x.
7. Gilliver SC et al. Recent research on the mental health of immigrants to Sweden: a literature review. Eur J Public Health. 2014 Aug:24 Suppl 1:72-9. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/cku101.
8. Rapp MA et al. When local poverty is more important than your income: Mental health in minorities in inner cities. World Psychiatry. 2015 Jun;14(2):249-50. doi: 10.1002/wps.20221.
9. Cima, Ronald, ed. Vietnam: A Country Study. Washington: GPO for the Library of Congress, 1987.
10. United States Citizenship & Immigration Services (2023, November 12). Refugees. Uscis.gov. https://www.uscis.gov/humanitarian/refugees-and-asylum/refugees
11. Fazel M and Betancourt TS. (2018). Preventive mental health interventions for refugee children and adolescents in high-income settings. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2018 Feb;2(2):121-32. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(17)30147-5.
12. Fazel M et al. Mental health of displaced and refugee children resettled in high-income countries: risk and protective factors. Lancet. 2012 Jan 21;379(9812):266-82. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60051-2.
13. Dapunt J et al. Refugees and psychosis: A review of the literature. Transl Psychiatry. 2017 Jun 13;7(6):e1149. doi: 10.1038/tp.2017.119.
14. Fazel M et al. Prevalence of serious mental disorder in 7,000 refugees resettled in western countries: a systematic review. Lancet. 2005 Apr;365(9467):1309-14. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)61027-6.
15. Rummel R. Statistics of Vietnamese Democide, in his Statistics of Democide. 1997. Table 6.1B,lines 730, 749-51.
Since 1983, when I was a child and fled as a boat refugee from Vietnam with my mother, the international plight of displaced people has only worsened. From 1997 to 2022, the number of forcibly displaced people has more than tripled, growing from 34 million to more than 108 million.1
Displaced people are designated as refugees only when they cross international borders and meet the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees’ (UNHCR) definition as “persons outside their countries of origin who are in need of international protection because of a serious threat to their life, physical integrity, or freedom in their country of origin as a result of persecution, armed conflict, violence, or serious public disorder.”2 There is a separate mandate by the United Nations for the aid of Palestinian refugees under the United Nations General Assembly’s United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestinian Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA).3 Of the displaced in 2022, more than 36 million were recognized as refugees under UNHCR and UNRWA mandates.1 Of these, almost 50% were children, at 17.5 million.4 To make matters worse, worldwide children represent less than one-third of the population.4 Since 2022, the increase in refugeeism is mostly driven by Ukraine and Syria, though also significantly Afghanistan, Venezuela, Sudan, Myanmar, Congo, Somalia, and Central African Republic.4 Refugeeism is a growing problem that disproportionately impacts children through sheer number, and one suspects, given their greater overall vulnerabilities compared with adults, physical and mental health consequences.
Traumas of refugees compared with non-refugee immigrants
In terms of mental health, refugees are distinct from non-refugee immigrants in that they likely experience more severe psychosocial adversities from greater poverty, greater risk of family separation, and uncertainty of the asylum process.5-8
From my own experience, this stems from the urgent nature of the refugee’s displacement, where they are often fleeing an immediate danger. My family had fled persecution from Communist forces and the social economic collapse that rendered Vietnam, for a time, one of the poorest in the world.9 Or, as my mother observed, “We had to leave because even doctors were starving.”
Refugees often have little preparation, have little legal protection since they are often criminalized, and are forced to endure dangerous conditions where they are vulnerable to smugglers and criminals who exploit their unprotected status. Once they arrive in their new country, they often do not have other family as social supports or resources. They themselves become the anchor for future legal and orderly immigration of their remaining family, given that they can extend their refugee status to those left behind.10 These non-refugee immigrants, unlike their refugee counterparts, are often flown to their new homes with more preparation, protecting them from dangerous conditions, and have the benefit of family who provide them with resources. As such, refugees tend to experience more traumatic life events than non-refugee immigrants. This was true in my family where those of us who initially escaped became the anchors to legally, and more safely, immigrate most of our family in Vietnam. We became their resources, likely making their acclimation smoother.
The mental health of refugee children and their caregivers
It is important to understand the stressors affecting the caregivers of children, since effective treatment of their mental health conditions can also benefit the children as well.11 In fact, among the greatest protective factors for refugee children is the presence of an adult caregiver, suggesting that the child’s mental health is dependent on the caregivers.
Those children who are separated show much worse mental health sequalae.12 As such, an understanding of the caregiver’s stressors is important. For example, when we were escaping Vietnam, my mom would protect me from our hardships by talking about our goals in America, minimizing our dangers by saying that we would be rewarded with things like a hamburger with its seemingly impossible amount of meat. Physically, my mother would always sleep with her arms around me and a knife hidden in order to ward off any attackers at night. When I was starving in the hull of a boat, having not eaten for days, my mother begged for food and gave me what she could get. And post-escape, my family focused on work and applied for aid for shelter and food, while encouraging us to invest in education, likely preventing involvement in criminal activities or gangs. Though overall, my family shielded me from the worst consequences, they also passed on their fears. One of my uncles had been killed by the police when he tried to escape, and so my family passed down a deep suspicion of authorities, whether they were the police or school principals. My mother had vivid memories of Communist re-education camps, which likely gave her a lasting fear that a Communist would find out our identities in America and re-capture us.
The mental health risk of refugees
Given that refugees tend to experience greater amounts of traumatic life events and a vast array of stressors sustained across years and even decades before, during, and after migration, it is no wonder they have much higher rates of mental health conditions, most predominantly PTSD and affective disorders.13,14 They are at particular risk of developing psychoses because they are more likely to experience a range of physical, psychological, and psychosocial problems associated with adversities such as violence, discrimination, economic stress, and social isolation.13 For example, the period leading up to my escape consisted of decades of prolonged war: the French-Indochina from 1945 to 1954, then the Vietnam War from 1955 to 1975) as well as the persecution and re-education camps afterward. What my family had to endure created a period of fear and loss into which I was born into in 1976. That year, my family had lost its fortune due to the Communist government seizing of our home and business, plunging us from a comfortable middle- to upper-class life to poverty. There was also widespread fear of systematic rape by the Communist victors. So my family endured great stress and the loss of a way of life leading up to our escape.
For the refugees, the escape itself is often a dangerous journey where, given its emergent nature, they are often exposed to the elements. We know about the current situation in Ukraine and Gaza, where children are fleeing from bombs and bullets. In my situation, we endured weeks of starvation crammed in the hull of boat as we forged through the Indian Ocean to the Philippines. One of my aunts, on a separate trip, perished because her boat had capsized, like so many others. Though impossible to verify, it has been estimated that up to 70% of Vietnamese refugees died during their escape.15 After the boat, my mother and I still had to brave Malaysian jungles and prisons, and then refugee camps for a year before we reached safety at an American Embassy in the Philippines. After we gained sponsorship to America, the traumas did not abate, but were only replaced by those of culture shock, poverty, and alienation. Taken by themselves, significant traumas exist in each phase of a refugee child’s escape, whether before, during, or after. These traumas are likely compounded since they are continuously layered and sustained across years, even decades. They affect not only the children, but their parents, and sometimes even a whole nation of people.
Summary
Refugee children and their families experience a variety of traumas, often sustained across years and even decades, because of armed conflict, persecution, or social upheavals. It is known that refugees are at greater risk for PTSD and affective and psychotic disorders, presumably due to increased traumatic life events before, during, and after their migration. The writer uses his own experience as a child refugee from Vietnam to elucidate the stressors evident in various phases of forced displacement.
Dr. Nguyen is a second year resident at UCSF Fresno Psychiatry Residency. He was a public high school English teacher for 15 years previously.
References
1. UNHCR. Global Trends. Forced displacement in 2016. Geneva, Switzerland: The UN Refugee Agency, 2022. https://www.unhcr.org/global-trends.
2. Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. The refugee concept under international law. Global compact for safe, orderly and regular migration. https://www.unhcr.org/sites/
3. United Nations. (2023, November 11). The Question of Palestine. Un.org. https://www.un.org/unispal/document/un-general-assembly-renews-unrwa-mandate-press-release/
4. UNICEF. (2023, November 11). Child displacement. Data.unicef.org. https://data.unicef.org/topic/child-migration-and-displacement/displacement
5. Kinzie JD. Immigrants and refugees: The psychiatric perspective. Transcult Psychiatry. 2006 Dec;43(4):577-91. doi: 10.1177/1363461506070782.
6. Eaton W and Harrison G. Ethnic disadvantage and schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 2000:(407):38-43. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0447.2000.00007.x.
7. Gilliver SC et al. Recent research on the mental health of immigrants to Sweden: a literature review. Eur J Public Health. 2014 Aug:24 Suppl 1:72-9. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/cku101.
8. Rapp MA et al. When local poverty is more important than your income: Mental health in minorities in inner cities. World Psychiatry. 2015 Jun;14(2):249-50. doi: 10.1002/wps.20221.
9. Cima, Ronald, ed. Vietnam: A Country Study. Washington: GPO for the Library of Congress, 1987.
10. United States Citizenship & Immigration Services (2023, November 12). Refugees. Uscis.gov. https://www.uscis.gov/humanitarian/refugees-and-asylum/refugees
11. Fazel M and Betancourt TS. (2018). Preventive mental health interventions for refugee children and adolescents in high-income settings. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2018 Feb;2(2):121-32. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(17)30147-5.
12. Fazel M et al. Mental health of displaced and refugee children resettled in high-income countries: risk and protective factors. Lancet. 2012 Jan 21;379(9812):266-82. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60051-2.
13. Dapunt J et al. Refugees and psychosis: A review of the literature. Transl Psychiatry. 2017 Jun 13;7(6):e1149. doi: 10.1038/tp.2017.119.
14. Fazel M et al. Prevalence of serious mental disorder in 7,000 refugees resettled in western countries: a systematic review. Lancet. 2005 Apr;365(9467):1309-14. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)61027-6.
15. Rummel R. Statistics of Vietnamese Democide, in his Statistics of Democide. 1997. Table 6.1B,lines 730, 749-51.
Since 1983, when I was a child and fled as a boat refugee from Vietnam with my mother, the international plight of displaced people has only worsened. From 1997 to 2022, the number of forcibly displaced people has more than tripled, growing from 34 million to more than 108 million.1
Displaced people are designated as refugees only when they cross international borders and meet the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees’ (UNHCR) definition as “persons outside their countries of origin who are in need of international protection because of a serious threat to their life, physical integrity, or freedom in their country of origin as a result of persecution, armed conflict, violence, or serious public disorder.”2 There is a separate mandate by the United Nations for the aid of Palestinian refugees under the United Nations General Assembly’s United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestinian Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA).3 Of the displaced in 2022, more than 36 million were recognized as refugees under UNHCR and UNRWA mandates.1 Of these, almost 50% were children, at 17.5 million.4 To make matters worse, worldwide children represent less than one-third of the population.4 Since 2022, the increase in refugeeism is mostly driven by Ukraine and Syria, though also significantly Afghanistan, Venezuela, Sudan, Myanmar, Congo, Somalia, and Central African Republic.4 Refugeeism is a growing problem that disproportionately impacts children through sheer number, and one suspects, given their greater overall vulnerabilities compared with adults, physical and mental health consequences.
Traumas of refugees compared with non-refugee immigrants
In terms of mental health, refugees are distinct from non-refugee immigrants in that they likely experience more severe psychosocial adversities from greater poverty, greater risk of family separation, and uncertainty of the asylum process.5-8
From my own experience, this stems from the urgent nature of the refugee’s displacement, where they are often fleeing an immediate danger. My family had fled persecution from Communist forces and the social economic collapse that rendered Vietnam, for a time, one of the poorest in the world.9 Or, as my mother observed, “We had to leave because even doctors were starving.”
Refugees often have little preparation, have little legal protection since they are often criminalized, and are forced to endure dangerous conditions where they are vulnerable to smugglers and criminals who exploit their unprotected status. Once they arrive in their new country, they often do not have other family as social supports or resources. They themselves become the anchor for future legal and orderly immigration of their remaining family, given that they can extend their refugee status to those left behind.10 These non-refugee immigrants, unlike their refugee counterparts, are often flown to their new homes with more preparation, protecting them from dangerous conditions, and have the benefit of family who provide them with resources. As such, refugees tend to experience more traumatic life events than non-refugee immigrants. This was true in my family where those of us who initially escaped became the anchors to legally, and more safely, immigrate most of our family in Vietnam. We became their resources, likely making their acclimation smoother.
The mental health of refugee children and their caregivers
It is important to understand the stressors affecting the caregivers of children, since effective treatment of their mental health conditions can also benefit the children as well.11 In fact, among the greatest protective factors for refugee children is the presence of an adult caregiver, suggesting that the child’s mental health is dependent on the caregivers.
Those children who are separated show much worse mental health sequalae.12 As such, an understanding of the caregiver’s stressors is important. For example, when we were escaping Vietnam, my mom would protect me from our hardships by talking about our goals in America, minimizing our dangers by saying that we would be rewarded with things like a hamburger with its seemingly impossible amount of meat. Physically, my mother would always sleep with her arms around me and a knife hidden in order to ward off any attackers at night. When I was starving in the hull of a boat, having not eaten for days, my mother begged for food and gave me what she could get. And post-escape, my family focused on work and applied for aid for shelter and food, while encouraging us to invest in education, likely preventing involvement in criminal activities or gangs. Though overall, my family shielded me from the worst consequences, they also passed on their fears. One of my uncles had been killed by the police when he tried to escape, and so my family passed down a deep suspicion of authorities, whether they were the police or school principals. My mother had vivid memories of Communist re-education camps, which likely gave her a lasting fear that a Communist would find out our identities in America and re-capture us.
The mental health risk of refugees
Given that refugees tend to experience greater amounts of traumatic life events and a vast array of stressors sustained across years and even decades before, during, and after migration, it is no wonder they have much higher rates of mental health conditions, most predominantly PTSD and affective disorders.13,14 They are at particular risk of developing psychoses because they are more likely to experience a range of physical, psychological, and psychosocial problems associated with adversities such as violence, discrimination, economic stress, and social isolation.13 For example, the period leading up to my escape consisted of decades of prolonged war: the French-Indochina from 1945 to 1954, then the Vietnam War from 1955 to 1975) as well as the persecution and re-education camps afterward. What my family had to endure created a period of fear and loss into which I was born into in 1976. That year, my family had lost its fortune due to the Communist government seizing of our home and business, plunging us from a comfortable middle- to upper-class life to poverty. There was also widespread fear of systematic rape by the Communist victors. So my family endured great stress and the loss of a way of life leading up to our escape.
For the refugees, the escape itself is often a dangerous journey where, given its emergent nature, they are often exposed to the elements. We know about the current situation in Ukraine and Gaza, where children are fleeing from bombs and bullets. In my situation, we endured weeks of starvation crammed in the hull of boat as we forged through the Indian Ocean to the Philippines. One of my aunts, on a separate trip, perished because her boat had capsized, like so many others. Though impossible to verify, it has been estimated that up to 70% of Vietnamese refugees died during their escape.15 After the boat, my mother and I still had to brave Malaysian jungles and prisons, and then refugee camps for a year before we reached safety at an American Embassy in the Philippines. After we gained sponsorship to America, the traumas did not abate, but were only replaced by those of culture shock, poverty, and alienation. Taken by themselves, significant traumas exist in each phase of a refugee child’s escape, whether before, during, or after. These traumas are likely compounded since they are continuously layered and sustained across years, even decades. They affect not only the children, but their parents, and sometimes even a whole nation of people.
Summary
Refugee children and their families experience a variety of traumas, often sustained across years and even decades, because of armed conflict, persecution, or social upheavals. It is known that refugees are at greater risk for PTSD and affective and psychotic disorders, presumably due to increased traumatic life events before, during, and after their migration. The writer uses his own experience as a child refugee from Vietnam to elucidate the stressors evident in various phases of forced displacement.
Dr. Nguyen is a second year resident at UCSF Fresno Psychiatry Residency. He was a public high school English teacher for 15 years previously.
References
1. UNHCR. Global Trends. Forced displacement in 2016. Geneva, Switzerland: The UN Refugee Agency, 2022. https://www.unhcr.org/global-trends.
2. Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. The refugee concept under international law. Global compact for safe, orderly and regular migration. https://www.unhcr.org/sites/
3. United Nations. (2023, November 11). The Question of Palestine. Un.org. https://www.un.org/unispal/document/un-general-assembly-renews-unrwa-mandate-press-release/
4. UNICEF. (2023, November 11). Child displacement. Data.unicef.org. https://data.unicef.org/topic/child-migration-and-displacement/displacement
5. Kinzie JD. Immigrants and refugees: The psychiatric perspective. Transcult Psychiatry. 2006 Dec;43(4):577-91. doi: 10.1177/1363461506070782.
6. Eaton W and Harrison G. Ethnic disadvantage and schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 2000:(407):38-43. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0447.2000.00007.x.
7. Gilliver SC et al. Recent research on the mental health of immigrants to Sweden: a literature review. Eur J Public Health. 2014 Aug:24 Suppl 1:72-9. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/cku101.
8. Rapp MA et al. When local poverty is more important than your income: Mental health in minorities in inner cities. World Psychiatry. 2015 Jun;14(2):249-50. doi: 10.1002/wps.20221.
9. Cima, Ronald, ed. Vietnam: A Country Study. Washington: GPO for the Library of Congress, 1987.
10. United States Citizenship & Immigration Services (2023, November 12). Refugees. Uscis.gov. https://www.uscis.gov/humanitarian/refugees-and-asylum/refugees
11. Fazel M and Betancourt TS. (2018). Preventive mental health interventions for refugee children and adolescents in high-income settings. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2018 Feb;2(2):121-32. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(17)30147-5.
12. Fazel M et al. Mental health of displaced and refugee children resettled in high-income countries: risk and protective factors. Lancet. 2012 Jan 21;379(9812):266-82. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60051-2.
13. Dapunt J et al. Refugees and psychosis: A review of the literature. Transl Psychiatry. 2017 Jun 13;7(6):e1149. doi: 10.1038/tp.2017.119.
14. Fazel M et al. Prevalence of serious mental disorder in 7,000 refugees resettled in western countries: a systematic review. Lancet. 2005 Apr;365(9467):1309-14. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)61027-6.
15. Rummel R. Statistics of Vietnamese Democide, in his Statistics of Democide. 1997. Table 6.1B,lines 730, 749-51.





