User login
Targeted agents vs. chemoimmunotherapy as first-line treatment of CLL
SAN FRANCISCO – Should targeted agents replace chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) as first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)? A recent debate suggests there’s no consensus.
William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and Jennifer R. Brown, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, debated the topic at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Wierda argued that CLL patients should receive a BTK inhibitor or BCL2 inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab, as first-line therapy because these targeted agents have been shown to provide better progression-free survival (PFS) than CIT, and the targeted therapies may prolong overall survival (OS) as well.
Dr. Brown countered that targeted agents don’t improve PFS for all CLL patients, improved PFS doesn’t always translate to improved OS, and targeted agents cost more than CIT.
No role for CIT as first-line treatment
“We have two approaches right now, with nonchemoimmunotherapy-based treatment,” Dr. Wierda said. “One approach, with small-molecule inhibitors, is to have a sustained and durable period of disease control, particularly with BTK inhibitors. The other strategy that has emerged is deep remissions with fixed-duration treatment with BCL2 small-molecule inhibitor-based therapy, which, I would argue, is better than being exposed to genotoxic chemoimmunotherapy.”
Dr. Wierda went on to explain that the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib has been shown to improve PFS, compared with CIT, in phase 3 trials.
In the iLLUMINATE trial, researchers compared ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab as first-line treatment in CLL. At a median follow-up of 31.3 months, the median PFS was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 19 months in the chlorambucil arm (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56).
In the A041202 study, researchers compared ibrutinib alone (Ib) or in combination with rituximab (Ib-R) to bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) in untreated, older patients with CLL. The 2-year PFS estimates were 74% in the BR arm, 87% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (P less than .001 for BR vs. Ib or Ib-R; N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the E1912 trial, researchers compared Ib-R to fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) in younger, untreated CLL patients. The 3-year PFS was 89.4% with Ib-R and 72.9% with FCR (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43).
Dr. Wierda noted that the E1912 trial also showed superior OS with Ib-R. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% with Ib-R and 91.5% with FCR (P less than .001). However, there was no significant difference in OS between the treatment arms in the A041202 trial or the iLLUMINATE trial.
“But I would argue that is, in part, because of short follow-up,” Dr. Wierda said. “The trials were all designed to look at progression-free survival, not overall survival. With longer follow-up, we may see differences in overall survival emerging.”
Dr. Wierda went on to say that fixed‐duration treatment with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax can improve PFS over CIT.
In the phase 3 CLL14 trial, researchers compared fixed-duration treatment with venetoclax plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated CLL patients with comorbidities. The estimated PFS at 2 years was 88.2% in the venetoclax group and 64.1% in the chlorambucil group (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
“[There was] no difference in overall survival,” Dr. Wierda noted. “But, again, I would argue ... that follow-up is relatively limited. We may ultimately see a difference in overall survival.”
Based on these findings, Dr. Wierda made the following treatment recommendations:
- Any CLL patient with del(17p) or TP53 mutation, and older, unfit patients with unmutated IGHV should receive a BTK inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab.
- All young, fit patients, and older, unfit patients with mutated IGHV should receive a BCL2 inhibitor plus obinutuzumab.
Dr. Wierda also noted that ibrutinib and venetoclax in combination have shown early promise for patients with previously untreated CLL (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2095-2103).
CIT still has a role as first-line treatment
Dr. Brown suggested that a PFS benefit may not be enough to recommend targeted agents over CIT. For one thing, the PFS benefit doesn’t apply to all patients, as the IGHV-mutated subgroup does equally well with CIT and targeted agents.
In the IGHV-mutated group from the E1912 trial, the 3-year PFS was 88% for patients who received Ib-R and those who received FCR (N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). In the A041202 study, the 2-year PFS among IGHV-mutated patients was 87% in the BR arm, 86% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the CLL14 trial, PFS rates were similar among IGHV-mutated patients who received chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab and IGHV-mutated or unmutated patients who received venetoclax and obinutuzumab (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
Dr. Brown also noted that the overall improvement in PFS observed with ibrutinib and venetoclax doesn’t always translate to improved OS.
In the A041202 study, there was no significant difference in OS between the Ib, Ib-R, and BR arms (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28). There was no significant difference in OS between the ibrutinib and chlorambucil arms in the iLLUMINATE trial (Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56). And there was no significant difference in OS between the venetoclax and chlorambucil arms in the CLL14 trial (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
However, in the RESONATE-2 trial, ibrutinib provided an OS benefit over chlorambucil. The 2-year OS was 95% and 84%, respectively (P = .0145; Haematologica. Sept 2018;103:1502-10). Dr. Brown said the OS advantage in this study was due to the “very poor comparator of chlorambucil and very limited crossover.”
As Dr. Wierda mentioned, the OS rate was higher with Ib-R than with FCR in the E1912 trial. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% and 91.5%, respectively (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). Dr. Brown noted, however, that there were few deaths in this study, and many of them “were not clearly related to the disease or its treatment.”
Dr. Brown also pointed out that FCR has been shown to have curative potential in IGHV-mutated CLL in both the FCR300 trial (Blood. 2016 127:303-9) and the CLL8 trial (Blood. 2016 127:208-15).
Another factor to consider is the greater cost of targeted agents. One analysis suggested the per-patient lifetime cost of CLL treatment in the United States will increase from $147,000 to $604,000 as targeted therapies overtake CIT as first-line treatment (J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jan 10;35[2]:166-174).
“Given all of the above, chemoimmunotherapy is going to remain part of the treatment repertoire for CLL,” Dr. Brown said. “It’s our only known potential cure for the fit, mutated patients ... and can also result in prolonged treatment-free intervals for patients who are older. As we manage CLL as a chronic disease over a lifetime, we need to continue to have this in our armamentarium.”
Specifically, Dr. Brown said CIT is appropriate for patients who don’t have del(17p) or mutated TP53. FCR should be given to young, fit patients with IGHV-mutated CLL, and FCR or BR should be given to older patients and young, fit patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL.
Dr. Brown and Dr. Wierda reported financial ties to multiple pharmaceutical companies, including makers of CLL treatments.
SAN FRANCISCO – Should targeted agents replace chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) as first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)? A recent debate suggests there’s no consensus.
William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and Jennifer R. Brown, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, debated the topic at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Wierda argued that CLL patients should receive a BTK inhibitor or BCL2 inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab, as first-line therapy because these targeted agents have been shown to provide better progression-free survival (PFS) than CIT, and the targeted therapies may prolong overall survival (OS) as well.
Dr. Brown countered that targeted agents don’t improve PFS for all CLL patients, improved PFS doesn’t always translate to improved OS, and targeted agents cost more than CIT.
No role for CIT as first-line treatment
“We have two approaches right now, with nonchemoimmunotherapy-based treatment,” Dr. Wierda said. “One approach, with small-molecule inhibitors, is to have a sustained and durable period of disease control, particularly with BTK inhibitors. The other strategy that has emerged is deep remissions with fixed-duration treatment with BCL2 small-molecule inhibitor-based therapy, which, I would argue, is better than being exposed to genotoxic chemoimmunotherapy.”
Dr. Wierda went on to explain that the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib has been shown to improve PFS, compared with CIT, in phase 3 trials.
In the iLLUMINATE trial, researchers compared ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab as first-line treatment in CLL. At a median follow-up of 31.3 months, the median PFS was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 19 months in the chlorambucil arm (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56).
In the A041202 study, researchers compared ibrutinib alone (Ib) or in combination with rituximab (Ib-R) to bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) in untreated, older patients with CLL. The 2-year PFS estimates were 74% in the BR arm, 87% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (P less than .001 for BR vs. Ib or Ib-R; N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the E1912 trial, researchers compared Ib-R to fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) in younger, untreated CLL patients. The 3-year PFS was 89.4% with Ib-R and 72.9% with FCR (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43).
Dr. Wierda noted that the E1912 trial also showed superior OS with Ib-R. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% with Ib-R and 91.5% with FCR (P less than .001). However, there was no significant difference in OS between the treatment arms in the A041202 trial or the iLLUMINATE trial.
“But I would argue that is, in part, because of short follow-up,” Dr. Wierda said. “The trials were all designed to look at progression-free survival, not overall survival. With longer follow-up, we may see differences in overall survival emerging.”
Dr. Wierda went on to say that fixed‐duration treatment with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax can improve PFS over CIT.
In the phase 3 CLL14 trial, researchers compared fixed-duration treatment with venetoclax plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated CLL patients with comorbidities. The estimated PFS at 2 years was 88.2% in the venetoclax group and 64.1% in the chlorambucil group (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
“[There was] no difference in overall survival,” Dr. Wierda noted. “But, again, I would argue ... that follow-up is relatively limited. We may ultimately see a difference in overall survival.”
Based on these findings, Dr. Wierda made the following treatment recommendations:
- Any CLL patient with del(17p) or TP53 mutation, and older, unfit patients with unmutated IGHV should receive a BTK inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab.
- All young, fit patients, and older, unfit patients with mutated IGHV should receive a BCL2 inhibitor plus obinutuzumab.
Dr. Wierda also noted that ibrutinib and venetoclax in combination have shown early promise for patients with previously untreated CLL (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2095-2103).
CIT still has a role as first-line treatment
Dr. Brown suggested that a PFS benefit may not be enough to recommend targeted agents over CIT. For one thing, the PFS benefit doesn’t apply to all patients, as the IGHV-mutated subgroup does equally well with CIT and targeted agents.
In the IGHV-mutated group from the E1912 trial, the 3-year PFS was 88% for patients who received Ib-R and those who received FCR (N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). In the A041202 study, the 2-year PFS among IGHV-mutated patients was 87% in the BR arm, 86% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the CLL14 trial, PFS rates were similar among IGHV-mutated patients who received chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab and IGHV-mutated or unmutated patients who received venetoclax and obinutuzumab (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
Dr. Brown also noted that the overall improvement in PFS observed with ibrutinib and venetoclax doesn’t always translate to improved OS.
In the A041202 study, there was no significant difference in OS between the Ib, Ib-R, and BR arms (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28). There was no significant difference in OS between the ibrutinib and chlorambucil arms in the iLLUMINATE trial (Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56). And there was no significant difference in OS between the venetoclax and chlorambucil arms in the CLL14 trial (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
However, in the RESONATE-2 trial, ibrutinib provided an OS benefit over chlorambucil. The 2-year OS was 95% and 84%, respectively (P = .0145; Haematologica. Sept 2018;103:1502-10). Dr. Brown said the OS advantage in this study was due to the “very poor comparator of chlorambucil and very limited crossover.”
As Dr. Wierda mentioned, the OS rate was higher with Ib-R than with FCR in the E1912 trial. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% and 91.5%, respectively (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). Dr. Brown noted, however, that there were few deaths in this study, and many of them “were not clearly related to the disease or its treatment.”
Dr. Brown also pointed out that FCR has been shown to have curative potential in IGHV-mutated CLL in both the FCR300 trial (Blood. 2016 127:303-9) and the CLL8 trial (Blood. 2016 127:208-15).
Another factor to consider is the greater cost of targeted agents. One analysis suggested the per-patient lifetime cost of CLL treatment in the United States will increase from $147,000 to $604,000 as targeted therapies overtake CIT as first-line treatment (J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jan 10;35[2]:166-174).
“Given all of the above, chemoimmunotherapy is going to remain part of the treatment repertoire for CLL,” Dr. Brown said. “It’s our only known potential cure for the fit, mutated patients ... and can also result in prolonged treatment-free intervals for patients who are older. As we manage CLL as a chronic disease over a lifetime, we need to continue to have this in our armamentarium.”
Specifically, Dr. Brown said CIT is appropriate for patients who don’t have del(17p) or mutated TP53. FCR should be given to young, fit patients with IGHV-mutated CLL, and FCR or BR should be given to older patients and young, fit patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL.
Dr. Brown and Dr. Wierda reported financial ties to multiple pharmaceutical companies, including makers of CLL treatments.
SAN FRANCISCO – Should targeted agents replace chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) as first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)? A recent debate suggests there’s no consensus.
William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and Jennifer R. Brown, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, debated the topic at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Wierda argued that CLL patients should receive a BTK inhibitor or BCL2 inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab, as first-line therapy because these targeted agents have been shown to provide better progression-free survival (PFS) than CIT, and the targeted therapies may prolong overall survival (OS) as well.
Dr. Brown countered that targeted agents don’t improve PFS for all CLL patients, improved PFS doesn’t always translate to improved OS, and targeted agents cost more than CIT.
No role for CIT as first-line treatment
“We have two approaches right now, with nonchemoimmunotherapy-based treatment,” Dr. Wierda said. “One approach, with small-molecule inhibitors, is to have a sustained and durable period of disease control, particularly with BTK inhibitors. The other strategy that has emerged is deep remissions with fixed-duration treatment with BCL2 small-molecule inhibitor-based therapy, which, I would argue, is better than being exposed to genotoxic chemoimmunotherapy.”
Dr. Wierda went on to explain that the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib has been shown to improve PFS, compared with CIT, in phase 3 trials.
In the iLLUMINATE trial, researchers compared ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab as first-line treatment in CLL. At a median follow-up of 31.3 months, the median PFS was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 19 months in the chlorambucil arm (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56).
In the A041202 study, researchers compared ibrutinib alone (Ib) or in combination with rituximab (Ib-R) to bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) in untreated, older patients with CLL. The 2-year PFS estimates were 74% in the BR arm, 87% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (P less than .001 for BR vs. Ib or Ib-R; N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the E1912 trial, researchers compared Ib-R to fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) in younger, untreated CLL patients. The 3-year PFS was 89.4% with Ib-R and 72.9% with FCR (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43).
Dr. Wierda noted that the E1912 trial also showed superior OS with Ib-R. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% with Ib-R and 91.5% with FCR (P less than .001). However, there was no significant difference in OS between the treatment arms in the A041202 trial or the iLLUMINATE trial.
“But I would argue that is, in part, because of short follow-up,” Dr. Wierda said. “The trials were all designed to look at progression-free survival, not overall survival. With longer follow-up, we may see differences in overall survival emerging.”
Dr. Wierda went on to say that fixed‐duration treatment with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax can improve PFS over CIT.
In the phase 3 CLL14 trial, researchers compared fixed-duration treatment with venetoclax plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated CLL patients with comorbidities. The estimated PFS at 2 years was 88.2% in the venetoclax group and 64.1% in the chlorambucil group (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
“[There was] no difference in overall survival,” Dr. Wierda noted. “But, again, I would argue ... that follow-up is relatively limited. We may ultimately see a difference in overall survival.”
Based on these findings, Dr. Wierda made the following treatment recommendations:
- Any CLL patient with del(17p) or TP53 mutation, and older, unfit patients with unmutated IGHV should receive a BTK inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab.
- All young, fit patients, and older, unfit patients with mutated IGHV should receive a BCL2 inhibitor plus obinutuzumab.
Dr. Wierda also noted that ibrutinib and venetoclax in combination have shown early promise for patients with previously untreated CLL (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2095-2103).
CIT still has a role as first-line treatment
Dr. Brown suggested that a PFS benefit may not be enough to recommend targeted agents over CIT. For one thing, the PFS benefit doesn’t apply to all patients, as the IGHV-mutated subgroup does equally well with CIT and targeted agents.
In the IGHV-mutated group from the E1912 trial, the 3-year PFS was 88% for patients who received Ib-R and those who received FCR (N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). In the A041202 study, the 2-year PFS among IGHV-mutated patients was 87% in the BR arm, 86% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the CLL14 trial, PFS rates were similar among IGHV-mutated patients who received chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab and IGHV-mutated or unmutated patients who received venetoclax and obinutuzumab (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
Dr. Brown also noted that the overall improvement in PFS observed with ibrutinib and venetoclax doesn’t always translate to improved OS.
In the A041202 study, there was no significant difference in OS between the Ib, Ib-R, and BR arms (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28). There was no significant difference in OS between the ibrutinib and chlorambucil arms in the iLLUMINATE trial (Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56). And there was no significant difference in OS between the venetoclax and chlorambucil arms in the CLL14 trial (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
However, in the RESONATE-2 trial, ibrutinib provided an OS benefit over chlorambucil. The 2-year OS was 95% and 84%, respectively (P = .0145; Haematologica. Sept 2018;103:1502-10). Dr. Brown said the OS advantage in this study was due to the “very poor comparator of chlorambucil and very limited crossover.”
As Dr. Wierda mentioned, the OS rate was higher with Ib-R than with FCR in the E1912 trial. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% and 91.5%, respectively (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). Dr. Brown noted, however, that there were few deaths in this study, and many of them “were not clearly related to the disease or its treatment.”
Dr. Brown also pointed out that FCR has been shown to have curative potential in IGHV-mutated CLL in both the FCR300 trial (Blood. 2016 127:303-9) and the CLL8 trial (Blood. 2016 127:208-15).
Another factor to consider is the greater cost of targeted agents. One analysis suggested the per-patient lifetime cost of CLL treatment in the United States will increase from $147,000 to $604,000 as targeted therapies overtake CIT as first-line treatment (J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jan 10;35[2]:166-174).
“Given all of the above, chemoimmunotherapy is going to remain part of the treatment repertoire for CLL,” Dr. Brown said. “It’s our only known potential cure for the fit, mutated patients ... and can also result in prolonged treatment-free intervals for patients who are older. As we manage CLL as a chronic disease over a lifetime, we need to continue to have this in our armamentarium.”
Specifically, Dr. Brown said CIT is appropriate for patients who don’t have del(17p) or mutated TP53. FCR should be given to young, fit patients with IGHV-mutated CLL, and FCR or BR should be given to older patients and young, fit patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL.
Dr. Brown and Dr. Wierda reported financial ties to multiple pharmaceutical companies, including makers of CLL treatments.
REPORTING FROM NCCN HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
Clinical Pharmacists Improve Patient Outcomes and Expand Access to Care
The US is in the midst of a chronic disease crisis. According to the latest published data available, 60% of Americans have at least 1 chronic condition, and 42% have ≥ 2 chronic conditions.1 Estimates by the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) indicate a current shortfall of 13 800 primary care physicians and a projected escalation of that shortage to be between 14 800 and 49 300 physicians by the year 2030.2
The US Public Health Service (USPHS) has used pharmacists since 1930 to provide direct patient care to underserved and vulnerable populations. Clinical pharmacists currently serve in direct patient care roles within the Indian Health Service (IHS), Federal Bureau of Prisons (BOP), Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), and the United States Coast Guard (USCG) in many states (Figure). These pharmacists play a vital role in improving access to care and delivering quality care by managing acute and chronic diseases in collaborative practice settings and pharmacist-managed clinics.
It has previously been reported that in the face of physician shortages and growing demand for primary health care providers, pharmacists are well-equipped and motivated to meet this demand.3 A review of the previous 2 years of outcomes reported by clinical pharmacists certified through the USPHS National Clinical Pharmacy Specialist (NCPS) Committee are presented to demonstrate the impact of pharmacists in advancing the health of the populations they serve and to showcase a model for ameliorating the ongoing physician shortage.
Background
The USPHS NCPS Committee serves to promote uniform competency among clinical pharmacists by establishing national standards for protocols, collaborative practice agreements (CPAs), credentialing and privileging of pharmacists, and by collecting, reviewing, and publishing health care outcomes. The committee, whose constituents include pharmacist and physician subject matter experts from across USPHS agencies, reviews applications and protocols and certifies pharmacists (civilian and uniformed) to recognize an advanced scope of practice in managing various diseases and optimizing medication therapy. NCPScertified pharmacists manage a wide spectrum of diseases, including coagulopathy, asthma, diabetes mellitus (DM), hepatitis C, HIV, hypertension, pain, seizure disorders, and tobacco use disorders.
Clinical pharmacists practicing chronic disease management establish a clinical service in collaboration with 1 or more physicians, physician assistants, or nurse practitioners. In this collaborative practice, the health care practitioner(s) refer patients to be managed by a pharmacist for specific medical needs, such as anticoagulation management, or for holistic medication- focused care (eg, cardiovascular risk reduction, DM management, HIV, hepatitis, or mental health). The pharmacist may order and interpret laboratory tests, check vital signs, perform a limited physical examination, and gather other pertinent information from the patient and the medical record in order to provide the best possible care to the patient.
Medications may be started, stopped, or adjusted, education is provided, and therapeutic lifestyle interventions may be recommended. The pharmacist-run clinic provides the patient more frequent interaction with a health care professional (pharmacist) and focused disease management. As a result, pharmacists increase access to care and allow the medical team to handle a larger panel of patients as the practitioner delegates specified diseases to the pharmacist- managed clinic(s). The number of NCPS-certified pharmacists grew 46% from 2012 (n = 230) to 2017 (n = 336), reflecting an evolution of pharmacists’ practice to better meet the need of patients across the nation.
Methods
The NCPS Committee requires NCPS pharmacists to report data annually from all patients referred for pharmacist management for specific diseases in which they have been certified. The data reflect the patient’s clinical outcome goal status at the time of referral as well as the same status at the end of the reporting period or on release from the pharmacist-run clinic. These data describe the impact prescribing pharmacists have on patients reaching clinical outcome goals acting as the team member specializing in the medication selection and dosing aspect of care.
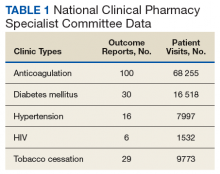
These records were reviewed for the fiscal year (FY) periods of October 1, 2015 to September 30, 2016 (FY 2016) and October 1, 2016 to September 30, 2017 (FY 2017). A systematic review of submitted reports resulted in 181 reports that included all requested data points for the disease as published here for FYs 2016 and 2017. These include 66 reports from FY 2016 and 115 reports from FY 2017; they cover 76 BOP and IHS facilities located across 24 states. Table 1 shows the number of outcome reports collected from 104 075 patient visits in pharmacist-run clinics in FYs 2016 and 2017.
Results
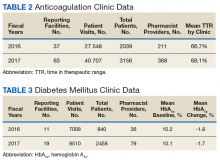
The following tables represent the standardized outcomes collected by NCPS-certified pharmacists providing direct patient care. Patients on anticoagulants (eg, warfarin) require special monitoring and education for drug interactions and adverse effects. NCPS-certified pharmacists were able to achieve a mean patient time in therapeutic range (TTR) of 67.6% (regardless of indication) over the 2 years (calculated per each facility by Rosendaal method of linear interpolation then combined in a weighted average per visit). The TTR produced by NCPS-certified pharmacists are consistent with Chest Guidelines and Expert Panel Report suggesting that TTR should be between 65% and 70%.4 Table 2 shows data from 100 reports with 68 255 patient visits for anticoagulation management.
DM management can be complex and time-intensive. NCPS data indicate pharmacist intervention resulted in a mean decrease in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) of 1.8% from a baseline of 10.2% (decrease calculated per each facility then combined by weighted average per visit). Table 3 shows data from 30 reports with 16 518 patient visits for DM care.
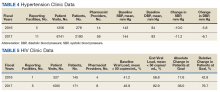
In addition to diet and exercise, medication management plays a vital role in managing hypertension. Patients managed by an NCPS-certified pharmacist experienced a mean decrease in blood pressure from 144/83 to 133/77, putting them in goal for both systolic and diastolic ranges (decrease calculated per each facility then combined by weighted average per visit). Table 4 shows data from 16 reports and 7997 patient visits for treatment of hypertension.
HIV viral suppression is vital in order to best manage patients with HIV and reduce the risk of transmission. Pharmacistled clinics have shown a 32.9% absolute improvement in patients at goal (viral load < 50 copies/mL), from a mean baseline of 46.0% to a mean final assessment of 71.6% of patients at goal (combined by weighted average visits). Table 5 shows data from 6 reports covering 1532 patient encounters for management of HIV.
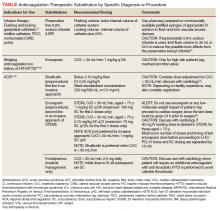
Nicotine dependence includes the use of cigarettes, cigars, pipe tobacco, chewing tobacco, and vaping products containing nicotine. NCPS-certified pharmacists have successfully helped patients improve their chance of quitting, with a 6-month quit rate of 22.2% (quit rate calculated per each facility then combined by weighted average by visits), which is higher than the national average of 9.4% as reported by the Centers for Disease and Control and Prevention. 5 Table 6 shows 29 reports covering 9773 patient visits for treatment of nicotine dependence.
Discussion
These data demonstrate the ability of advanced practice pharmacists in multiple locations within the federal sector to improve targeted clinical outcomes in patients with varying diseases. These results are strengthened by their varied origins as well as the improvements observed across the board. Limitations include the general lack of a comparable dataset, manual method of selfreporting by the individual facilities, and the relatively limited array of diseases reported. Although NCPS-certified pharmacists are currently providing care for patients with hepatitis C, asthma, seizure, pain and other diseases not reported here, there are insufficient data collected for FYs 2016 and 2017 to merit inclusion within this report.
Pharmacists are trusted, readily available medication experts. In a clinical role, NCPS-certified pharmacists have increased access to primary care services and demonstrated beneficial impact on important health outcomes as exhibited by the data reported above. Clinical pharmacy is a growing field, and NCPS has displayed continual growth in both the number of NCPS-certified pharmacists and the number of patient encounters performed by these providers. As more pharmacists in all settings collaborate with medical providers to offer high-quality clinical care, these providers will have more opportunity to delegate disease management. Continued reporting of clinical pharmacy outcomes is expected to increase confidence in pharmacists as primary care providers, increase utilization of pharmacy clinical services, and assist in easing the burden of primary care provider shortages across our nation.
Although these outcomes indicate demonstrable benefit in patient-centered outcomes, the need for ongoing assessment and continued improvement is not obviated. Future efforts may benefit from a comparison of alternative approaches to better facilitate the establishment of best practices. Alignment of clinical outcomes with the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Electronic Clinical Quality Measures, where applicable, also may prove beneficial by automating the reporting process and thereby decreasing the burden of reporting as well as providing an avenue for standard comparison across multiple populations. Clinical pharmacy interventions have positive outcomes based on the NCPS model, and the NCPS Committee invites other clinical settings to report outcomes data with which to compare.
Conclusion
The NCPS Committee has documented positive outcomes of clinical pharmacy intervention and anticipates growth of the pharmacy profession as additional states and health systems recognize the capacity of the pharmacist to provide high-quality, multidisciplinary patient care. Clinical pharmacists are prepared to address critical health care needs as the US continues to face a PCP shortage.2 The NCPS Committee challenges those participating in clinical pharmacy practice to report outcomes to amplify this body of evidence.
Acknowledgments
NCPS-certified pharmacists provided the outcomes detailed in this report. For document review and edits: Federal Bureau of Prison Publication Review Workgroup; RADM Ty Bingham, USPHS; CAPT Cindy Gunderson, USPHS; CAPT Kevin Brooks, USPHS.
1. Buttorff C, Ruder T, Bauman M. Multiple Chronic Conditions in the United States. Santa Monica, CA: Rand Corp; 2017.
2. Dall T, West T, Chakrabarti R, Reynolds R, Iacobucci W. The complexities of physician supply and demand: projections from 2016 to 2030, 2018 update. Association of American Medical Colleges. March 2018.
3. Giberson S, Yoder S, Lee MP. Improving patient and health system outcomes through advanced pharmacy practice. A report to the U.S. Surgeon General 2011. https://www .accp.com/docs/positions/misc/improving_patient_and _health_system_outcomes.pdf. Updated December 2011. Accessed September 11, 2019.
4. Lip G, Banerjee A, Boriani G, et al. Antithrombotic therapy for atrial fibrillation. CHEST guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest. 2018;154(5):1121-1201.
5. Babb S, Marlarcher A, Schauer G, Asman K, Jamal A. Quitting smoking among adults—United States, 2000-2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;65(52):1457-1464.
The US is in the midst of a chronic disease crisis. According to the latest published data available, 60% of Americans have at least 1 chronic condition, and 42% have ≥ 2 chronic conditions.1 Estimates by the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) indicate a current shortfall of 13 800 primary care physicians and a projected escalation of that shortage to be between 14 800 and 49 300 physicians by the year 2030.2
The US Public Health Service (USPHS) has used pharmacists since 1930 to provide direct patient care to underserved and vulnerable populations. Clinical pharmacists currently serve in direct patient care roles within the Indian Health Service (IHS), Federal Bureau of Prisons (BOP), Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), and the United States Coast Guard (USCG) in many states (Figure). These pharmacists play a vital role in improving access to care and delivering quality care by managing acute and chronic diseases in collaborative practice settings and pharmacist-managed clinics.
It has previously been reported that in the face of physician shortages and growing demand for primary health care providers, pharmacists are well-equipped and motivated to meet this demand.3 A review of the previous 2 years of outcomes reported by clinical pharmacists certified through the USPHS National Clinical Pharmacy Specialist (NCPS) Committee are presented to demonstrate the impact of pharmacists in advancing the health of the populations they serve and to showcase a model for ameliorating the ongoing physician shortage.
Background
The USPHS NCPS Committee serves to promote uniform competency among clinical pharmacists by establishing national standards for protocols, collaborative practice agreements (CPAs), credentialing and privileging of pharmacists, and by collecting, reviewing, and publishing health care outcomes. The committee, whose constituents include pharmacist and physician subject matter experts from across USPHS agencies, reviews applications and protocols and certifies pharmacists (civilian and uniformed) to recognize an advanced scope of practice in managing various diseases and optimizing medication therapy. NCPScertified pharmacists manage a wide spectrum of diseases, including coagulopathy, asthma, diabetes mellitus (DM), hepatitis C, HIV, hypertension, pain, seizure disorders, and tobacco use disorders.
Clinical pharmacists practicing chronic disease management establish a clinical service in collaboration with 1 or more physicians, physician assistants, or nurse practitioners. In this collaborative practice, the health care practitioner(s) refer patients to be managed by a pharmacist for specific medical needs, such as anticoagulation management, or for holistic medication- focused care (eg, cardiovascular risk reduction, DM management, HIV, hepatitis, or mental health). The pharmacist may order and interpret laboratory tests, check vital signs, perform a limited physical examination, and gather other pertinent information from the patient and the medical record in order to provide the best possible care to the patient.
Medications may be started, stopped, or adjusted, education is provided, and therapeutic lifestyle interventions may be recommended. The pharmacist-run clinic provides the patient more frequent interaction with a health care professional (pharmacist) and focused disease management. As a result, pharmacists increase access to care and allow the medical team to handle a larger panel of patients as the practitioner delegates specified diseases to the pharmacist- managed clinic(s). The number of NCPS-certified pharmacists grew 46% from 2012 (n = 230) to 2017 (n = 336), reflecting an evolution of pharmacists’ practice to better meet the need of patients across the nation.
Methods
The NCPS Committee requires NCPS pharmacists to report data annually from all patients referred for pharmacist management for specific diseases in which they have been certified. The data reflect the patient’s clinical outcome goal status at the time of referral as well as the same status at the end of the reporting period or on release from the pharmacist-run clinic. These data describe the impact prescribing pharmacists have on patients reaching clinical outcome goals acting as the team member specializing in the medication selection and dosing aspect of care.
These records were reviewed for the fiscal year (FY) periods of October 1, 2015 to September 30, 2016 (FY 2016) and October 1, 2016 to September 30, 2017 (FY 2017). A systematic review of submitted reports resulted in 181 reports that included all requested data points for the disease as published here for FYs 2016 and 2017. These include 66 reports from FY 2016 and 115 reports from FY 2017; they cover 76 BOP and IHS facilities located across 24 states. Table 1 shows the number of outcome reports collected from 104 075 patient visits in pharmacist-run clinics in FYs 2016 and 2017.
Results
The following tables represent the standardized outcomes collected by NCPS-certified pharmacists providing direct patient care. Patients on anticoagulants (eg, warfarin) require special monitoring and education for drug interactions and adverse effects. NCPS-certified pharmacists were able to achieve a mean patient time in therapeutic range (TTR) of 67.6% (regardless of indication) over the 2 years (calculated per each facility by Rosendaal method of linear interpolation then combined in a weighted average per visit). The TTR produced by NCPS-certified pharmacists are consistent with Chest Guidelines and Expert Panel Report suggesting that TTR should be between 65% and 70%.4 Table 2 shows data from 100 reports with 68 255 patient visits for anticoagulation management.
DM management can be complex and time-intensive. NCPS data indicate pharmacist intervention resulted in a mean decrease in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) of 1.8% from a baseline of 10.2% (decrease calculated per each facility then combined by weighted average per visit). Table 3 shows data from 30 reports with 16 518 patient visits for DM care.
In addition to diet and exercise, medication management plays a vital role in managing hypertension. Patients managed by an NCPS-certified pharmacist experienced a mean decrease in blood pressure from 144/83 to 133/77, putting them in goal for both systolic and diastolic ranges (decrease calculated per each facility then combined by weighted average per visit). Table 4 shows data from 16 reports and 7997 patient visits for treatment of hypertension.
HIV viral suppression is vital in order to best manage patients with HIV and reduce the risk of transmission. Pharmacistled clinics have shown a 32.9% absolute improvement in patients at goal (viral load < 50 copies/mL), from a mean baseline of 46.0% to a mean final assessment of 71.6% of patients at goal (combined by weighted average visits). Table 5 shows data from 6 reports covering 1532 patient encounters for management of HIV.
Nicotine dependence includes the use of cigarettes, cigars, pipe tobacco, chewing tobacco, and vaping products containing nicotine. NCPS-certified pharmacists have successfully helped patients improve their chance of quitting, with a 6-month quit rate of 22.2% (quit rate calculated per each facility then combined by weighted average by visits), which is higher than the national average of 9.4% as reported by the Centers for Disease and Control and Prevention. 5 Table 6 shows 29 reports covering 9773 patient visits for treatment of nicotine dependence.
Discussion
These data demonstrate the ability of advanced practice pharmacists in multiple locations within the federal sector to improve targeted clinical outcomes in patients with varying diseases. These results are strengthened by their varied origins as well as the improvements observed across the board. Limitations include the general lack of a comparable dataset, manual method of selfreporting by the individual facilities, and the relatively limited array of diseases reported. Although NCPS-certified pharmacists are currently providing care for patients with hepatitis C, asthma, seizure, pain and other diseases not reported here, there are insufficient data collected for FYs 2016 and 2017 to merit inclusion within this report.
Pharmacists are trusted, readily available medication experts. In a clinical role, NCPS-certified pharmacists have increased access to primary care services and demonstrated beneficial impact on important health outcomes as exhibited by the data reported above. Clinical pharmacy is a growing field, and NCPS has displayed continual growth in both the number of NCPS-certified pharmacists and the number of patient encounters performed by these providers. As more pharmacists in all settings collaborate with medical providers to offer high-quality clinical care, these providers will have more opportunity to delegate disease management. Continued reporting of clinical pharmacy outcomes is expected to increase confidence in pharmacists as primary care providers, increase utilization of pharmacy clinical services, and assist in easing the burden of primary care provider shortages across our nation.
Although these outcomes indicate demonstrable benefit in patient-centered outcomes, the need for ongoing assessment and continued improvement is not obviated. Future efforts may benefit from a comparison of alternative approaches to better facilitate the establishment of best practices. Alignment of clinical outcomes with the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Electronic Clinical Quality Measures, where applicable, also may prove beneficial by automating the reporting process and thereby decreasing the burden of reporting as well as providing an avenue for standard comparison across multiple populations. Clinical pharmacy interventions have positive outcomes based on the NCPS model, and the NCPS Committee invites other clinical settings to report outcomes data with which to compare.
Conclusion
The NCPS Committee has documented positive outcomes of clinical pharmacy intervention and anticipates growth of the pharmacy profession as additional states and health systems recognize the capacity of the pharmacist to provide high-quality, multidisciplinary patient care. Clinical pharmacists are prepared to address critical health care needs as the US continues to face a PCP shortage.2 The NCPS Committee challenges those participating in clinical pharmacy practice to report outcomes to amplify this body of evidence.
Acknowledgments
NCPS-certified pharmacists provided the outcomes detailed in this report. For document review and edits: Federal Bureau of Prison Publication Review Workgroup; RADM Ty Bingham, USPHS; CAPT Cindy Gunderson, USPHS; CAPT Kevin Brooks, USPHS.
The US is in the midst of a chronic disease crisis. According to the latest published data available, 60% of Americans have at least 1 chronic condition, and 42% have ≥ 2 chronic conditions.1 Estimates by the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) indicate a current shortfall of 13 800 primary care physicians and a projected escalation of that shortage to be between 14 800 and 49 300 physicians by the year 2030.2
The US Public Health Service (USPHS) has used pharmacists since 1930 to provide direct patient care to underserved and vulnerable populations. Clinical pharmacists currently serve in direct patient care roles within the Indian Health Service (IHS), Federal Bureau of Prisons (BOP), Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), and the United States Coast Guard (USCG) in many states (Figure). These pharmacists play a vital role in improving access to care and delivering quality care by managing acute and chronic diseases in collaborative practice settings and pharmacist-managed clinics.
It has previously been reported that in the face of physician shortages and growing demand for primary health care providers, pharmacists are well-equipped and motivated to meet this demand.3 A review of the previous 2 years of outcomes reported by clinical pharmacists certified through the USPHS National Clinical Pharmacy Specialist (NCPS) Committee are presented to demonstrate the impact of pharmacists in advancing the health of the populations they serve and to showcase a model for ameliorating the ongoing physician shortage.
Background
The USPHS NCPS Committee serves to promote uniform competency among clinical pharmacists by establishing national standards for protocols, collaborative practice agreements (CPAs), credentialing and privileging of pharmacists, and by collecting, reviewing, and publishing health care outcomes. The committee, whose constituents include pharmacist and physician subject matter experts from across USPHS agencies, reviews applications and protocols and certifies pharmacists (civilian and uniformed) to recognize an advanced scope of practice in managing various diseases and optimizing medication therapy. NCPScertified pharmacists manage a wide spectrum of diseases, including coagulopathy, asthma, diabetes mellitus (DM), hepatitis C, HIV, hypertension, pain, seizure disorders, and tobacco use disorders.
Clinical pharmacists practicing chronic disease management establish a clinical service in collaboration with 1 or more physicians, physician assistants, or nurse practitioners. In this collaborative practice, the health care practitioner(s) refer patients to be managed by a pharmacist for specific medical needs, such as anticoagulation management, or for holistic medication- focused care (eg, cardiovascular risk reduction, DM management, HIV, hepatitis, or mental health). The pharmacist may order and interpret laboratory tests, check vital signs, perform a limited physical examination, and gather other pertinent information from the patient and the medical record in order to provide the best possible care to the patient.
Medications may be started, stopped, or adjusted, education is provided, and therapeutic lifestyle interventions may be recommended. The pharmacist-run clinic provides the patient more frequent interaction with a health care professional (pharmacist) and focused disease management. As a result, pharmacists increase access to care and allow the medical team to handle a larger panel of patients as the practitioner delegates specified diseases to the pharmacist- managed clinic(s). The number of NCPS-certified pharmacists grew 46% from 2012 (n = 230) to 2017 (n = 336), reflecting an evolution of pharmacists’ practice to better meet the need of patients across the nation.
Methods
The NCPS Committee requires NCPS pharmacists to report data annually from all patients referred for pharmacist management for specific diseases in which they have been certified. The data reflect the patient’s clinical outcome goal status at the time of referral as well as the same status at the end of the reporting period or on release from the pharmacist-run clinic. These data describe the impact prescribing pharmacists have on patients reaching clinical outcome goals acting as the team member specializing in the medication selection and dosing aspect of care.
These records were reviewed for the fiscal year (FY) periods of October 1, 2015 to September 30, 2016 (FY 2016) and October 1, 2016 to September 30, 2017 (FY 2017). A systematic review of submitted reports resulted in 181 reports that included all requested data points for the disease as published here for FYs 2016 and 2017. These include 66 reports from FY 2016 and 115 reports from FY 2017; they cover 76 BOP and IHS facilities located across 24 states. Table 1 shows the number of outcome reports collected from 104 075 patient visits in pharmacist-run clinics in FYs 2016 and 2017.
Results
The following tables represent the standardized outcomes collected by NCPS-certified pharmacists providing direct patient care. Patients on anticoagulants (eg, warfarin) require special monitoring and education for drug interactions and adverse effects. NCPS-certified pharmacists were able to achieve a mean patient time in therapeutic range (TTR) of 67.6% (regardless of indication) over the 2 years (calculated per each facility by Rosendaal method of linear interpolation then combined in a weighted average per visit). The TTR produced by NCPS-certified pharmacists are consistent with Chest Guidelines and Expert Panel Report suggesting that TTR should be between 65% and 70%.4 Table 2 shows data from 100 reports with 68 255 patient visits for anticoagulation management.
DM management can be complex and time-intensive. NCPS data indicate pharmacist intervention resulted in a mean decrease in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) of 1.8% from a baseline of 10.2% (decrease calculated per each facility then combined by weighted average per visit). Table 3 shows data from 30 reports with 16 518 patient visits for DM care.
In addition to diet and exercise, medication management plays a vital role in managing hypertension. Patients managed by an NCPS-certified pharmacist experienced a mean decrease in blood pressure from 144/83 to 133/77, putting them in goal for both systolic and diastolic ranges (decrease calculated per each facility then combined by weighted average per visit). Table 4 shows data from 16 reports and 7997 patient visits for treatment of hypertension.
HIV viral suppression is vital in order to best manage patients with HIV and reduce the risk of transmission. Pharmacistled clinics have shown a 32.9% absolute improvement in patients at goal (viral load < 50 copies/mL), from a mean baseline of 46.0% to a mean final assessment of 71.6% of patients at goal (combined by weighted average visits). Table 5 shows data from 6 reports covering 1532 patient encounters for management of HIV.
Nicotine dependence includes the use of cigarettes, cigars, pipe tobacco, chewing tobacco, and vaping products containing nicotine. NCPS-certified pharmacists have successfully helped patients improve their chance of quitting, with a 6-month quit rate of 22.2% (quit rate calculated per each facility then combined by weighted average by visits), which is higher than the national average of 9.4% as reported by the Centers for Disease and Control and Prevention. 5 Table 6 shows 29 reports covering 9773 patient visits for treatment of nicotine dependence.
Discussion
These data demonstrate the ability of advanced practice pharmacists in multiple locations within the federal sector to improve targeted clinical outcomes in patients with varying diseases. These results are strengthened by their varied origins as well as the improvements observed across the board. Limitations include the general lack of a comparable dataset, manual method of selfreporting by the individual facilities, and the relatively limited array of diseases reported. Although NCPS-certified pharmacists are currently providing care for patients with hepatitis C, asthma, seizure, pain and other diseases not reported here, there are insufficient data collected for FYs 2016 and 2017 to merit inclusion within this report.
Pharmacists are trusted, readily available medication experts. In a clinical role, NCPS-certified pharmacists have increased access to primary care services and demonstrated beneficial impact on important health outcomes as exhibited by the data reported above. Clinical pharmacy is a growing field, and NCPS has displayed continual growth in both the number of NCPS-certified pharmacists and the number of patient encounters performed by these providers. As more pharmacists in all settings collaborate with medical providers to offer high-quality clinical care, these providers will have more opportunity to delegate disease management. Continued reporting of clinical pharmacy outcomes is expected to increase confidence in pharmacists as primary care providers, increase utilization of pharmacy clinical services, and assist in easing the burden of primary care provider shortages across our nation.
Although these outcomes indicate demonstrable benefit in patient-centered outcomes, the need for ongoing assessment and continued improvement is not obviated. Future efforts may benefit from a comparison of alternative approaches to better facilitate the establishment of best practices. Alignment of clinical outcomes with the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Electronic Clinical Quality Measures, where applicable, also may prove beneficial by automating the reporting process and thereby decreasing the burden of reporting as well as providing an avenue for standard comparison across multiple populations. Clinical pharmacy interventions have positive outcomes based on the NCPS model, and the NCPS Committee invites other clinical settings to report outcomes data with which to compare.
Conclusion
The NCPS Committee has documented positive outcomes of clinical pharmacy intervention and anticipates growth of the pharmacy profession as additional states and health systems recognize the capacity of the pharmacist to provide high-quality, multidisciplinary patient care. Clinical pharmacists are prepared to address critical health care needs as the US continues to face a PCP shortage.2 The NCPS Committee challenges those participating in clinical pharmacy practice to report outcomes to amplify this body of evidence.
Acknowledgments
NCPS-certified pharmacists provided the outcomes detailed in this report. For document review and edits: Federal Bureau of Prison Publication Review Workgroup; RADM Ty Bingham, USPHS; CAPT Cindy Gunderson, USPHS; CAPT Kevin Brooks, USPHS.
1. Buttorff C, Ruder T, Bauman M. Multiple Chronic Conditions in the United States. Santa Monica, CA: Rand Corp; 2017.
2. Dall T, West T, Chakrabarti R, Reynolds R, Iacobucci W. The complexities of physician supply and demand: projections from 2016 to 2030, 2018 update. Association of American Medical Colleges. March 2018.
3. Giberson S, Yoder S, Lee MP. Improving patient and health system outcomes through advanced pharmacy practice. A report to the U.S. Surgeon General 2011. https://www .accp.com/docs/positions/misc/improving_patient_and _health_system_outcomes.pdf. Updated December 2011. Accessed September 11, 2019.
4. Lip G, Banerjee A, Boriani G, et al. Antithrombotic therapy for atrial fibrillation. CHEST guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest. 2018;154(5):1121-1201.
5. Babb S, Marlarcher A, Schauer G, Asman K, Jamal A. Quitting smoking among adults—United States, 2000-2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;65(52):1457-1464.
1. Buttorff C, Ruder T, Bauman M. Multiple Chronic Conditions in the United States. Santa Monica, CA: Rand Corp; 2017.
2. Dall T, West T, Chakrabarti R, Reynolds R, Iacobucci W. The complexities of physician supply and demand: projections from 2016 to 2030, 2018 update. Association of American Medical Colleges. March 2018.
3. Giberson S, Yoder S, Lee MP. Improving patient and health system outcomes through advanced pharmacy practice. A report to the U.S. Surgeon General 2011. https://www .accp.com/docs/positions/misc/improving_patient_and _health_system_outcomes.pdf. Updated December 2011. Accessed September 11, 2019.
4. Lip G, Banerjee A, Boriani G, et al. Antithrombotic therapy for atrial fibrillation. CHEST guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest. 2018;154(5):1121-1201.
5. Babb S, Marlarcher A, Schauer G, Asman K, Jamal A. Quitting smoking among adults—United States, 2000-2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;65(52):1457-1464.
Few antidepressant adverse effects backed by convincing evidence
Relatively few of the adverse health outcomes attributed to antidepressants are supported by convincing evidence, reported the authors of a systematic review of 45 meta-analyses.
The authors did find convincing evidence linking the use of antidepressants and suicide attempt or completion among people under age 19 years and use of the medication and autism risk among offspring. “However, the few [studies] with convincing evidence associations did not reflect causality, and none of them remained at the convincing evidence level after accounting for confounding by indication,” wrote Elena Dragioti, PhD, of the Pain and Rehabilitation Centre at Linköping (Sweden) University and coauthors. The study was published in JAMA Psychiatry.
Dr. Dragioti and coauthors undertook a systematic “umbrella review” grading the evidence from the 45 meta-analyses of 695 observational studies into the association between antidepressant use and the risk of adverse health outcomes. All the meta-analyses included a control group not exposed to antidepressants, with the exception of one that compared the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding between two classes of antidepressants.
They found 120 possible adverse health associations described in the meta-analyses, 61.7% of which related to maternal and pregnancy-related adverse health outcomes. Two-thirds of the adverse health outcome associations involved selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs).
However, among the 120 adverse health associations, only three (2.5%) were supported by “convincing” evidence. One was the association between SSRIs and increased risk of suicide attempts and completion in children and adolescents. Convincing evidence also was found between any antidepressant use before pregnancy and autism spectrum disorder and between SSRI use during pregnancy and autism spectrum disorder. The evidence for the association with suicide risk was deemed high quality, but the two associations with autism spectrum disorder were only of moderate quality.
The authors commented that these findings needed to be considered when prescribing antidepressants in adolescents and children, particularly as another networked meta-analysis had found fluoxetine was the only antidepressant that worked better than placebo in children and adolescents. “In addition, they wrote.
The review found that 11 adverse health outcomes (9.2%) had “highly suggestive” evidence linking them to antidepressant use. These were ADHD in children, cataract development, severe bleeding at any site, upper gastrointestinal tract bleeding, postpartum hemorrhage, preterm birth, lower Apgar score at 5 minutes, osteoporotic fracture, and hip fracture.
Seven of those – ADHD in children, lower Apgar score, severe bleeding at any site, cataract development, osteoporotic features, preterm birth, and upper GI bleeding – had moderate-quality evidence. However, the authors noted that the effect sizes were small and had low prevalence.
The study also found highly suggestive evidence linking antidepressant use to a decreased risk of suicide attempts or completion in adults.
The authors said several of those adverse events in adults, such as GI bleeding and osteoporotic fractures, could be prevented with medication, so the advantages of antidepressant use in adults could outweigh the disadvantage of those preventable safety issues.
Twenty-one adverse health outcomes showed either suggestive, weak, or no evidence for their association with antidepressant use.
They also conducted a sensitivity analysis that limited the analysis to cohort studies, prospective cohort studies, studies that controlled for confounding by the treatment indication, and studies from North America. This showed that none of the associations for which there was originally deemed to be convincing evidence retained that same rank.
“Overall, the results showed that the association between antidepressant use and adverse health outcomes was not supported by robust evidence and that the underlying disease likely inflated the findings in a relevant way,” the authors wrote.
However, when they looked solely at prospective cohort studies, the association between preterm birth and use of any antidepressant was upgraded to having convincing evidence.
When the analysis focused on SSRIs only, the association with lower Apgar scores at 5 minutes also was upgraded to having convincing evidence. Similarly, the evidence for an association with preterm birth also was found to be convincing when the analysis was limited to other or mixed antidepressants.
Dr. Dragioti and coauthors cited several limitations, including the inability of some randomized, controlled trials to address adverse outcomes.
“Antidepressant use appears to be safe for the treatment of psychiatric disorders, but more studies matching for underlying disease are needed to clarify the degree of confounding by indication and other biases,” the authors wrote.
The study was funded by several entities, including the National Institute for Health Research’s Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust. Dr. Dragioti reported no disclosures. Four authors declared funding, consultancies, personal fees, royalties, or shares in the pharmaceutical sector. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Dragioti E et al. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019 Oct 2. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.2859.
Relatively few of the adverse health outcomes attributed to antidepressants are supported by convincing evidence, reported the authors of a systematic review of 45 meta-analyses.
The authors did find convincing evidence linking the use of antidepressants and suicide attempt or completion among people under age 19 years and use of the medication and autism risk among offspring. “However, the few [studies] with convincing evidence associations did not reflect causality, and none of them remained at the convincing evidence level after accounting for confounding by indication,” wrote Elena Dragioti, PhD, of the Pain and Rehabilitation Centre at Linköping (Sweden) University and coauthors. The study was published in JAMA Psychiatry.
Dr. Dragioti and coauthors undertook a systematic “umbrella review” grading the evidence from the 45 meta-analyses of 695 observational studies into the association between antidepressant use and the risk of adverse health outcomes. All the meta-analyses included a control group not exposed to antidepressants, with the exception of one that compared the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding between two classes of antidepressants.
They found 120 possible adverse health associations described in the meta-analyses, 61.7% of which related to maternal and pregnancy-related adverse health outcomes. Two-thirds of the adverse health outcome associations involved selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs).
However, among the 120 adverse health associations, only three (2.5%) were supported by “convincing” evidence. One was the association between SSRIs and increased risk of suicide attempts and completion in children and adolescents. Convincing evidence also was found between any antidepressant use before pregnancy and autism spectrum disorder and between SSRI use during pregnancy and autism spectrum disorder. The evidence for the association with suicide risk was deemed high quality, but the two associations with autism spectrum disorder were only of moderate quality.
The authors commented that these findings needed to be considered when prescribing antidepressants in adolescents and children, particularly as another networked meta-analysis had found fluoxetine was the only antidepressant that worked better than placebo in children and adolescents. “In addition, they wrote.
The review found that 11 adverse health outcomes (9.2%) had “highly suggestive” evidence linking them to antidepressant use. These were ADHD in children, cataract development, severe bleeding at any site, upper gastrointestinal tract bleeding, postpartum hemorrhage, preterm birth, lower Apgar score at 5 minutes, osteoporotic fracture, and hip fracture.
Seven of those – ADHD in children, lower Apgar score, severe bleeding at any site, cataract development, osteoporotic features, preterm birth, and upper GI bleeding – had moderate-quality evidence. However, the authors noted that the effect sizes were small and had low prevalence.
The study also found highly suggestive evidence linking antidepressant use to a decreased risk of suicide attempts or completion in adults.
The authors said several of those adverse events in adults, such as GI bleeding and osteoporotic fractures, could be prevented with medication, so the advantages of antidepressant use in adults could outweigh the disadvantage of those preventable safety issues.
Twenty-one adverse health outcomes showed either suggestive, weak, or no evidence for their association with antidepressant use.
They also conducted a sensitivity analysis that limited the analysis to cohort studies, prospective cohort studies, studies that controlled for confounding by the treatment indication, and studies from North America. This showed that none of the associations for which there was originally deemed to be convincing evidence retained that same rank.
“Overall, the results showed that the association between antidepressant use and adverse health outcomes was not supported by robust evidence and that the underlying disease likely inflated the findings in a relevant way,” the authors wrote.
However, when they looked solely at prospective cohort studies, the association between preterm birth and use of any antidepressant was upgraded to having convincing evidence.
When the analysis focused on SSRIs only, the association with lower Apgar scores at 5 minutes also was upgraded to having convincing evidence. Similarly, the evidence for an association with preterm birth also was found to be convincing when the analysis was limited to other or mixed antidepressants.
Dr. Dragioti and coauthors cited several limitations, including the inability of some randomized, controlled trials to address adverse outcomes.
“Antidepressant use appears to be safe for the treatment of psychiatric disorders, but more studies matching for underlying disease are needed to clarify the degree of confounding by indication and other biases,” the authors wrote.
The study was funded by several entities, including the National Institute for Health Research’s Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust. Dr. Dragioti reported no disclosures. Four authors declared funding, consultancies, personal fees, royalties, or shares in the pharmaceutical sector. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Dragioti E et al. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019 Oct 2. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.2859.
Relatively few of the adverse health outcomes attributed to antidepressants are supported by convincing evidence, reported the authors of a systematic review of 45 meta-analyses.
The authors did find convincing evidence linking the use of antidepressants and suicide attempt or completion among people under age 19 years and use of the medication and autism risk among offspring. “However, the few [studies] with convincing evidence associations did not reflect causality, and none of them remained at the convincing evidence level after accounting for confounding by indication,” wrote Elena Dragioti, PhD, of the Pain and Rehabilitation Centre at Linköping (Sweden) University and coauthors. The study was published in JAMA Psychiatry.
Dr. Dragioti and coauthors undertook a systematic “umbrella review” grading the evidence from the 45 meta-analyses of 695 observational studies into the association between antidepressant use and the risk of adverse health outcomes. All the meta-analyses included a control group not exposed to antidepressants, with the exception of one that compared the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding between two classes of antidepressants.
They found 120 possible adverse health associations described in the meta-analyses, 61.7% of which related to maternal and pregnancy-related adverse health outcomes. Two-thirds of the adverse health outcome associations involved selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs).
However, among the 120 adverse health associations, only three (2.5%) were supported by “convincing” evidence. One was the association between SSRIs and increased risk of suicide attempts and completion in children and adolescents. Convincing evidence also was found between any antidepressant use before pregnancy and autism spectrum disorder and between SSRI use during pregnancy and autism spectrum disorder. The evidence for the association with suicide risk was deemed high quality, but the two associations with autism spectrum disorder were only of moderate quality.
The authors commented that these findings needed to be considered when prescribing antidepressants in adolescents and children, particularly as another networked meta-analysis had found fluoxetine was the only antidepressant that worked better than placebo in children and adolescents. “In addition, they wrote.
The review found that 11 adverse health outcomes (9.2%) had “highly suggestive” evidence linking them to antidepressant use. These were ADHD in children, cataract development, severe bleeding at any site, upper gastrointestinal tract bleeding, postpartum hemorrhage, preterm birth, lower Apgar score at 5 minutes, osteoporotic fracture, and hip fracture.
Seven of those – ADHD in children, lower Apgar score, severe bleeding at any site, cataract development, osteoporotic features, preterm birth, and upper GI bleeding – had moderate-quality evidence. However, the authors noted that the effect sizes were small and had low prevalence.
The study also found highly suggestive evidence linking antidepressant use to a decreased risk of suicide attempts or completion in adults.
The authors said several of those adverse events in adults, such as GI bleeding and osteoporotic fractures, could be prevented with medication, so the advantages of antidepressant use in adults could outweigh the disadvantage of those preventable safety issues.
Twenty-one adverse health outcomes showed either suggestive, weak, or no evidence for their association with antidepressant use.
They also conducted a sensitivity analysis that limited the analysis to cohort studies, prospective cohort studies, studies that controlled for confounding by the treatment indication, and studies from North America. This showed that none of the associations for which there was originally deemed to be convincing evidence retained that same rank.
“Overall, the results showed that the association between antidepressant use and adverse health outcomes was not supported by robust evidence and that the underlying disease likely inflated the findings in a relevant way,” the authors wrote.
However, when they looked solely at prospective cohort studies, the association between preterm birth and use of any antidepressant was upgraded to having convincing evidence.
When the analysis focused on SSRIs only, the association with lower Apgar scores at 5 minutes also was upgraded to having convincing evidence. Similarly, the evidence for an association with preterm birth also was found to be convincing when the analysis was limited to other or mixed antidepressants.
Dr. Dragioti and coauthors cited several limitations, including the inability of some randomized, controlled trials to address adverse outcomes.
“Antidepressant use appears to be safe for the treatment of psychiatric disorders, but more studies matching for underlying disease are needed to clarify the degree of confounding by indication and other biases,” the authors wrote.
The study was funded by several entities, including the National Institute for Health Research’s Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust. Dr. Dragioti reported no disclosures. Four authors declared funding, consultancies, personal fees, royalties, or shares in the pharmaceutical sector. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Dragioti E et al. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019 Oct 2. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.2859.
FROM JAMA PSYCHIATRY
Key clinical point: “More studies [of antidepressants] matching for underlying disease are needed to clarify the degree of confounding by indication and other biases.”
Major finding: Increased suicide risk in children and adolescents is one of the few adverse health outcomes of antidepressants that is backed by evidence.
Study details: Systematic umbrella review of 45 meta-analyses of 695 observational studies.
Disclosures: The study was funded by several entities, including the National Institute for Health Research’s Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust. Dr. Dragioti reported no disclosures. Four authors declared funding, consultancies, personal fees, royalties, or shares in the pharmaceutical sector. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
Source: Dragioti E et al. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019 Oct 2. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.2859.
Heparin Drug Shortage Conservation Strategies
Heparin is the anticoagulant of choice when a rapid anticoagulant is indicated: Onset of action is immediate when administered IV as a bolus.1 The major anticoagulant effect of heparin is mediated by heparin/antithrombin (AT) interaction. Heparin/AT inactivates factor IIa (thrombin) and factors Xa, IXa, XIa, and XIIa. Heparin is approved for multiple indications, such as venous thromboembolism (VTE) treatment and prophylaxis of medical and surgical patients; stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation (AF); acute coronary syndrome (ACS); vascular and cardiac surgeries; and various interventional procedures (eg, diagnostic angiography and percutaneous coronary intervention [PCI]). It also is used as an anticoagulant in blood transfusions, extracorporeal circulation, and for maintaining patency of central vascular access devices (CVADs).
About 60% of the crude heparin used to manufacture heparin in the US originates in China, derived from porcine mucosa. African swine fever, a contagious virus with no cure, has eliminated about 25% to 35% of China’s pig population, or about 150 million pigs. In July 2019, members of the US House of Representatives Committee on Energy and Commerce sent a letter to the US Food and Drug Administration asking for details on the potential impact of African swine fever on the supply of heparin.2
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) heath care system is currently experiencing a shortage of heparin vials and syringes. It is unclear when resolution of this shortage will occur as it could resolve within several weeks or as late as January 2020.3 Although vials and syringes are the current products that are affected, it is possible the shortage may eventually include IV heparin bags as well.
Since the foremost objective of VA health care providers is to provide timely access to medications for veterans, strategies to conserve unfractionated heparin (UfH) must be used since it is a first-line therapy where few evidence-based alternatives exist. Conservation strategies may include drug rationing, therapeutic substitution, and compounding of needed products using the limited stock available in the pharmacy.4 It is important that all staff are educated on facility strategies in order to be familiar with alternatives and limit the potential for near misses, adverse events, and provider frustration.
In shortage situations, the VA-Pharmacy Benefits Management (PBM) defers decisions regarding drug preservation, processes to shift to viable alternatives, and the best practice for safe transitions to local facilities and their subject matter experts.5 At the VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System, a 1A, tertiary, dual campus health care system, a pharmacy task force has formed to track drug shortages impacting the facility’s efficiencies and budgets. This group communicates with the Pharmacy and Therapeutics committee about potential risks to patient care and develops shortage briefs (following an SBAR [situation, background, assessment, recommendation] design) generally authored and championed by at least 1 clinical pharmacy specialist and supervising physicians who are field experts. Prior to dissemination, the SBAR undergoes a rapid peer-review process.
To date, VA PBM has not issued specific guidance on how pharmacists should proceed in case of a shortage. However, we recommend strategies that may be considered for implementation during a potential UfH shortage. For example, pharmacists can use therapeutic alternatives for which best available evidence suggests no disadvantage.4 The Table lists alternative agents according to indication and patient-specific considerations that may preclude use. Existing UfH products may also be used for drug compounding (eg, use current stock to provide an indicated aliquot) to meet the need of prioritized patients.4 In addition, we suggest prioritizing current UfH/heparinized saline for use for the following groups of patients4:
- Emergent/urgent cardiac surgery1,6;
- Hemodialysis patients1,7-9 for which the low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) dalteparin is deemed inappropriate or the patient is not monitored in the intensive care unit for regional citrate administration;
- VTE prophylaxis for patients with epidurals or chest tubes for which urgent invasive management may occur, recent cardiac or neurosurgery, or for patients with a creatine clearance < 15 mL/min or receiving hemodialysis10-12;
- Vascular surgery (eg, limb ischemia) and interventions (eg, carotid stenting, endarterectomy)13,14;
- Mesenteric ischemia (venous thrombosis) with a potential to proceed to laparotomy15;
- Critically ill patients with arterial lines for which normal saline is deemed inappropriate for line flushing16;
- Electrophysiology procedures (eg, AF ablation)17; and
- Contraindication to use of a long-acting alternative listed in the table or a medical necessity exists for using a rapidly reversible agent. Examples for this category include but are not limited to recent gastrointestinal bleeding, central nervous system lesion, and select neurologic diagnoses (eg, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis with hemorrhage, thrombus in vertebral basilar system or anterior circulation, intraparenchymal hemorrhage plus mechanical valve, medium to large cardioembolic stroke with intracardiac thrombus).
Conclusion
The UfH drug shortage represents a significant threat to public health and is a major challenge for US health care systems, including the Veterans Health Administration. Overreliance on a predominant source of crude heparin has affected multiple UfH manufacturers and products. Current alternatives to UfH include low-molecular-weight heparins, IV direct thrombin inhibitors, and SC fondaparinux, with selection supported by guidelines or evolving literature. However, the shortage has the potential to expand to other injectables, such as dalteparin and enoxaparin, and severely limit care for veterans. It is vital that clinicians rapidly address the current shortage by creating a plan to develop efficient and equitable access to UfH, continue to assess supply and update stakeholders, and select evidence-based alternatives while maintaining focus on efficacy and safety.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ashley Yost, PharmD, for her coordination of the multidisciplinary task force assigned to efficiently manage the heparin drug shortage. This material is the result of work supported with resources and the use of facilities at the VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System in Nashville, Tennessee.
1. Hirsh J, Warkentin TE, Shaughnessy SG, et al. Heparin and low-molecular-weight heparin mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, dosing, monitoring, efficacy, and safety. Chest. 2001;119(1):64S-94S.
2. Bipartisan E&C leaders request FDA briefing on threat to U.S. heparin supply [press release]. Washington, DC: House Committee on Energy and Commerce; July 30, 2019. https://energycommerce.house.gov/newsroom/press-releases/bipartisan-ec-leaders-request-fda-briefing-on-threat-to-us-heparin-supply. Accessed September 19, 2019.
3. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Drug Shortages. Heparin injection. https://www.ashp.org/Drug-Shortages/Current-Shortages/Drug-Shortages-List?page=CurrentShortages. Accessed September 19, 2019.
4. Reed BN, Fox ER, Konig M, et al. The impact of drug shortages on patients with cardiovascular disease: causes, consequences, and a call to action. Am Heart J. 2016;175:130-141.
5. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Pharmacy Benefits Management Services, Medical Advisory Panel, VISN Pharmacist Executives, The Center For Medication Safety. Heparin supply status: frequently asked questions. PBM-2018-02. https://www.pbm.va.gov/PBM/vacenterformedicationsafety/HeparinandSalineSyringeRecallDuetoContamination_NationalPBMPati.pdf. Published May 3, 2018. Accessed September 11, 2019.
6. Shore-Lesserson I, Baker RA, Ferraris VA, et al. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons, The Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, and the American Society of ExtraCorporeal Technology: Clinical Practice Guidelines-anticoagulation during cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann Thorac Surg. 2018;105(2):650-662.
7. Soroka S, Agharazii M, Donnelly S, et al. An adjustable dalteparin sodium dose regimen for the prevention of clotting in the extracorporeal circuit in hemodialysis: a clinical trial of safety and efficacy (the PARROT Study). Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2018;5:1-12.
8. Shantha GPS, Kumar AA, Sethi M, Khanna RC, Pancholy SB. Efficacy and safety of low molecular weight heparin compared to unfractionated heparin for chronic outpatient hemodialysis in end stage renal disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Peer J. 2015;3:e835.
9. Kessler M, Moureau F, and Nguyen P. Anticoagulation in chronic hemodialysis: progress toward an optimal approach. Semin Dial. 2015;28(5):474-489.
10. Gould MK, Garcia DA, Wren SM, et al. Prevention of VTE in nonorthopedic surgical patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2)(suppl):e227s-e277S.
11. Kaye AD, Brunk AJ, Kaye AJ, et al. Regional anesthesia in patients on anticoagulation therapies—evidence-based recommendations. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2019;23(9):67.
12. Kahn SR, Lim W, Dunn AS, et al. Prevention of VTE in nonsurgical patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2)(suppl):e195S-e226S.
13. Naylor AR, Ricco JB, de Borst GJ, et al. Management of atherosclerotic carotid and vertebral artery disease: 2017 clinical practice guidelines of the European Society for Vascular Surgery. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2018;55:3-81.
14. Gerhard-Herman MD, Gornik HL, Barrett C, et al. 2016 AHA/ACC Guideline on the Management of Patients With Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. JACC. 2017;69(11): e71-e126.
15. Bjorck M, Koelemaya M, Acosta S, et al. Management of diseases of mesenteric arteries and veins. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2017;53(4):460-510.
16. Gorski L, Hadaway L, Hagle ME, McGoldrick M, Orr M, Doellman D. Infusion therapy standards of practice. J Infusion Nurs. 2016;39:S1-S156.
17. Calkins H, Hindricks G, Cappato R, et al. 2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2017;14(10):e275-e444.
18. Spyropoulos AC, Al-Badri A, Sherwood MW, Douketis JD. Periprocedural management of patients receiving a vitamin K antagonist or a direct oral anticoagulant requiring an elective procedure or surgery. J Thromb Haemost. 2016;14(5):875-885.
, . Periprocedural bridging management of anticoagulation. Circulation. 2012;126(4):486-490.
20. Douketis JD, Spyropoulos AC, Spencer FA, et al. Perioperative management of antithrombotic therapy: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2)(suppl):e326S-e350S.
21. Sousa-Uva M, Neumann F-J, Ahlsson A, et al; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2018 ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization. The Task Force on myocardial revascularization of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Developed with a special contribution of the European Association for Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI). Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019;55(1):4-90.
22. Amsterdam EA, Wenger NK, Brindis RG, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes. JACC. 2014;64(24):e139-e228.
23. O’Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction. JACC. 2013;61(4):e78-e140.
24. Angiomax [package insert]. Parsippany, NJ: The Medicines Company; March 2016.
25. Sousa-Uva, Head SJ, Milojevic M, et al. 2017 EACTS guidelines on perioperative medication in adult cardiac surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018;53(1):5-33.
26. Witt DM, Nieuwlaat R, Clark NP, et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for the management of venous thromboembolism: optimal management of anticoagulation therapy. Blood Adv. 2018: 2(22):3257-3291
27. Kearon C, Akl EA, Blaivas A, et al. Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: Chest guideline and expert panel report. Chest. 2016;149(2):315-352.
28. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Pharmacy Benefits Manager Service. Direct oral anticoagulants criteria for use and algorithm for venous thromboembolism treatment. https://www.pbm.va.gov/PBM/clinicalguidance/criteriaforuse.asp. Updated December 2016. [Source not verified]
29. Falck-Ytter Y, Francis CW, Johanson NA, et al. Prevention of VTE in orthopedic surgery patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2)(suppl):e278S-e325S.
30. Raja S, Idrees JJ, Blackstone EH, et al. Routine venous thromboembolism screening after pneumonectomy: the more you look, the more you see. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;152(2):524-532.e2.
31. Schünemann HJ, Cushman M, Burnett AE, et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: prophylaxis for hospitalized and nonhospitalized patients. Blood Adv. 2018;2(22):3198-3225.
32. Naidu SS, Aronow HD, Box LC, et al. SCAI expert consensus statement: 2016 best practices in the cardiac catheterization laboratory:(endorsed by the Cardiological Society of India, and Sociedad Latino Americana de Cardiologia Intervencionista; affirmation of value by the Canadian Association of Interventional Cardiology-Association Canadienne de Cardiologie d’intervention). Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2016;88(3):407-423.
33. Levine GN, Bates ER, Blankenship JC, et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA/SCAI guideline for percutaneous coronary intervention. A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions. JACC. 2011;58(24):e44-e122.
34. Mason PJ, Shah B, Tamis-Holland JE, et al; American Heart Association Interventional Cardiovascular Care Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology; Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease; and Council on Genomic and Precision Medicine. AHA scientific statement: an update on radial artery access and best practices for transradial coronary angiography and intervention in acute coronary syndrome. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2018;11(9):e000035.
35. Rao SV, Tremmel JA, Gilchrist IC, et al; Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Intervention’s Transradial Working Group. Best practices for transradial angiography and intervention: a consensus statement from the society for cardiovascular angiography and interventions’ transradial working group. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;83(2):228-236. 36. Moran JE, Ash SR. Locking solutions for hemodialysis catheters; heparin and citrate: a position paper by ASDIN. Semin Dial. 2008;21(5):490-492.
Heparin is the anticoagulant of choice when a rapid anticoagulant is indicated: Onset of action is immediate when administered IV as a bolus.1 The major anticoagulant effect of heparin is mediated by heparin/antithrombin (AT) interaction. Heparin/AT inactivates factor IIa (thrombin) and factors Xa, IXa, XIa, and XIIa. Heparin is approved for multiple indications, such as venous thromboembolism (VTE) treatment and prophylaxis of medical and surgical patients; stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation (AF); acute coronary syndrome (ACS); vascular and cardiac surgeries; and various interventional procedures (eg, diagnostic angiography and percutaneous coronary intervention [PCI]). It also is used as an anticoagulant in blood transfusions, extracorporeal circulation, and for maintaining patency of central vascular access devices (CVADs).
About 60% of the crude heparin used to manufacture heparin in the US originates in China, derived from porcine mucosa. African swine fever, a contagious virus with no cure, has eliminated about 25% to 35% of China’s pig population, or about 150 million pigs. In July 2019, members of the US House of Representatives Committee on Energy and Commerce sent a letter to the US Food and Drug Administration asking for details on the potential impact of African swine fever on the supply of heparin.2
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) heath care system is currently experiencing a shortage of heparin vials and syringes. It is unclear when resolution of this shortage will occur as it could resolve within several weeks or as late as January 2020.3 Although vials and syringes are the current products that are affected, it is possible the shortage may eventually include IV heparin bags as well.
Since the foremost objective of VA health care providers is to provide timely access to medications for veterans, strategies to conserve unfractionated heparin (UfH) must be used since it is a first-line therapy where few evidence-based alternatives exist. Conservation strategies may include drug rationing, therapeutic substitution, and compounding of needed products using the limited stock available in the pharmacy.4 It is important that all staff are educated on facility strategies in order to be familiar with alternatives and limit the potential for near misses, adverse events, and provider frustration.
In shortage situations, the VA-Pharmacy Benefits Management (PBM) defers decisions regarding drug preservation, processes to shift to viable alternatives, and the best practice for safe transitions to local facilities and their subject matter experts.5 At the VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System, a 1A, tertiary, dual campus health care system, a pharmacy task force has formed to track drug shortages impacting the facility’s efficiencies and budgets. This group communicates with the Pharmacy and Therapeutics committee about potential risks to patient care and develops shortage briefs (following an SBAR [situation, background, assessment, recommendation] design) generally authored and championed by at least 1 clinical pharmacy specialist and supervising physicians who are field experts. Prior to dissemination, the SBAR undergoes a rapid peer-review process.
To date, VA PBM has not issued specific guidance on how pharmacists should proceed in case of a shortage. However, we recommend strategies that may be considered for implementation during a potential UfH shortage. For example, pharmacists can use therapeutic alternatives for which best available evidence suggests no disadvantage.4 The Table lists alternative agents according to indication and patient-specific considerations that may preclude use. Existing UfH products may also be used for drug compounding (eg, use current stock to provide an indicated aliquot) to meet the need of prioritized patients.4 In addition, we suggest prioritizing current UfH/heparinized saline for use for the following groups of patients4:
- Emergent/urgent cardiac surgery1,6;
- Hemodialysis patients1,7-9 for which the low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) dalteparin is deemed inappropriate or the patient is not monitored in the intensive care unit for regional citrate administration;
- VTE prophylaxis for patients with epidurals or chest tubes for which urgent invasive management may occur, recent cardiac or neurosurgery, or for patients with a creatine clearance < 15 mL/min or receiving hemodialysis10-12;
- Vascular surgery (eg, limb ischemia) and interventions (eg, carotid stenting, endarterectomy)13,14;
- Mesenteric ischemia (venous thrombosis) with a potential to proceed to laparotomy15;
- Critically ill patients with arterial lines for which normal saline is deemed inappropriate for line flushing16;
- Electrophysiology procedures (eg, AF ablation)17; and
- Contraindication to use of a long-acting alternative listed in the table or a medical necessity exists for using a rapidly reversible agent. Examples for this category include but are not limited to recent gastrointestinal bleeding, central nervous system lesion, and select neurologic diagnoses (eg, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis with hemorrhage, thrombus in vertebral basilar system or anterior circulation, intraparenchymal hemorrhage plus mechanical valve, medium to large cardioembolic stroke with intracardiac thrombus).
Conclusion
The UfH drug shortage represents a significant threat to public health and is a major challenge for US health care systems, including the Veterans Health Administration. Overreliance on a predominant source of crude heparin has affected multiple UfH manufacturers and products. Current alternatives to UfH include low-molecular-weight heparins, IV direct thrombin inhibitors, and SC fondaparinux, with selection supported by guidelines or evolving literature. However, the shortage has the potential to expand to other injectables, such as dalteparin and enoxaparin, and severely limit care for veterans. It is vital that clinicians rapidly address the current shortage by creating a plan to develop efficient and equitable access to UfH, continue to assess supply and update stakeholders, and select evidence-based alternatives while maintaining focus on efficacy and safety.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ashley Yost, PharmD, for her coordination of the multidisciplinary task force assigned to efficiently manage the heparin drug shortage. This material is the result of work supported with resources and the use of facilities at the VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System in Nashville, Tennessee.
Heparin is the anticoagulant of choice when a rapid anticoagulant is indicated: Onset of action is immediate when administered IV as a bolus.1 The major anticoagulant effect of heparin is mediated by heparin/antithrombin (AT) interaction. Heparin/AT inactivates factor IIa (thrombin) and factors Xa, IXa, XIa, and XIIa. Heparin is approved for multiple indications, such as venous thromboembolism (VTE) treatment and prophylaxis of medical and surgical patients; stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation (AF); acute coronary syndrome (ACS); vascular and cardiac surgeries; and various interventional procedures (eg, diagnostic angiography and percutaneous coronary intervention [PCI]). It also is used as an anticoagulant in blood transfusions, extracorporeal circulation, and for maintaining patency of central vascular access devices (CVADs).
About 60% of the crude heparin used to manufacture heparin in the US originates in China, derived from porcine mucosa. African swine fever, a contagious virus with no cure, has eliminated about 25% to 35% of China’s pig population, or about 150 million pigs. In July 2019, members of the US House of Representatives Committee on Energy and Commerce sent a letter to the US Food and Drug Administration asking for details on the potential impact of African swine fever on the supply of heparin.2
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) heath care system is currently experiencing a shortage of heparin vials and syringes. It is unclear when resolution of this shortage will occur as it could resolve within several weeks or as late as January 2020.3 Although vials and syringes are the current products that are affected, it is possible the shortage may eventually include IV heparin bags as well.
Since the foremost objective of VA health care providers is to provide timely access to medications for veterans, strategies to conserve unfractionated heparin (UfH) must be used since it is a first-line therapy where few evidence-based alternatives exist. Conservation strategies may include drug rationing, therapeutic substitution, and compounding of needed products using the limited stock available in the pharmacy.4 It is important that all staff are educated on facility strategies in order to be familiar with alternatives and limit the potential for near misses, adverse events, and provider frustration.
In shortage situations, the VA-Pharmacy Benefits Management (PBM) defers decisions regarding drug preservation, processes to shift to viable alternatives, and the best practice for safe transitions to local facilities and their subject matter experts.5 At the VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System, a 1A, tertiary, dual campus health care system, a pharmacy task force has formed to track drug shortages impacting the facility’s efficiencies and budgets. This group communicates with the Pharmacy and Therapeutics committee about potential risks to patient care and develops shortage briefs (following an SBAR [situation, background, assessment, recommendation] design) generally authored and championed by at least 1 clinical pharmacy specialist and supervising physicians who are field experts. Prior to dissemination, the SBAR undergoes a rapid peer-review process.
To date, VA PBM has not issued specific guidance on how pharmacists should proceed in case of a shortage. However, we recommend strategies that may be considered for implementation during a potential UfH shortage. For example, pharmacists can use therapeutic alternatives for which best available evidence suggests no disadvantage.4 The Table lists alternative agents according to indication and patient-specific considerations that may preclude use. Existing UfH products may also be used for drug compounding (eg, use current stock to provide an indicated aliquot) to meet the need of prioritized patients.4 In addition, we suggest prioritizing current UfH/heparinized saline for use for the following groups of patients4:
- Emergent/urgent cardiac surgery1,6;
- Hemodialysis patients1,7-9 for which the low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) dalteparin is deemed inappropriate or the patient is not monitored in the intensive care unit for regional citrate administration;
- VTE prophylaxis for patients with epidurals or chest tubes for which urgent invasive management may occur, recent cardiac or neurosurgery, or for patients with a creatine clearance < 15 mL/min or receiving hemodialysis10-12;
- Vascular surgery (eg, limb ischemia) and interventions (eg, carotid stenting, endarterectomy)13,14;
- Mesenteric ischemia (venous thrombosis) with a potential to proceed to laparotomy15;
- Critically ill patients with arterial lines for which normal saline is deemed inappropriate for line flushing16;
- Electrophysiology procedures (eg, AF ablation)17; and
- Contraindication to use of a long-acting alternative listed in the table or a medical necessity exists for using a rapidly reversible agent. Examples for this category include but are not limited to recent gastrointestinal bleeding, central nervous system lesion, and select neurologic diagnoses (eg, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis with hemorrhage, thrombus in vertebral basilar system or anterior circulation, intraparenchymal hemorrhage plus mechanical valve, medium to large cardioembolic stroke with intracardiac thrombus).
Conclusion
The UfH drug shortage represents a significant threat to public health and is a major challenge for US health care systems, including the Veterans Health Administration. Overreliance on a predominant source of crude heparin has affected multiple UfH manufacturers and products. Current alternatives to UfH include low-molecular-weight heparins, IV direct thrombin inhibitors, and SC fondaparinux, with selection supported by guidelines or evolving literature. However, the shortage has the potential to expand to other injectables, such as dalteparin and enoxaparin, and severely limit care for veterans. It is vital that clinicians rapidly address the current shortage by creating a plan to develop efficient and equitable access to UfH, continue to assess supply and update stakeholders, and select evidence-based alternatives while maintaining focus on efficacy and safety.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ashley Yost, PharmD, for her coordination of the multidisciplinary task force assigned to efficiently manage the heparin drug shortage. This material is the result of work supported with resources and the use of facilities at the VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System in Nashville, Tennessee.
1. Hirsh J, Warkentin TE, Shaughnessy SG, et al. Heparin and low-molecular-weight heparin mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, dosing, monitoring, efficacy, and safety. Chest. 2001;119(1):64S-94S.
2. Bipartisan E&C leaders request FDA briefing on threat to U.S. heparin supply [press release]. Washington, DC: House Committee on Energy and Commerce; July 30, 2019. https://energycommerce.house.gov/newsroom/press-releases/bipartisan-ec-leaders-request-fda-briefing-on-threat-to-us-heparin-supply. Accessed September 19, 2019.
3. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Drug Shortages. Heparin injection. https://www.ashp.org/Drug-Shortages/Current-Shortages/Drug-Shortages-List?page=CurrentShortages. Accessed September 19, 2019.
4. Reed BN, Fox ER, Konig M, et al. The impact of drug shortages on patients with cardiovascular disease: causes, consequences, and a call to action. Am Heart J. 2016;175:130-141.
5. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Pharmacy Benefits Management Services, Medical Advisory Panel, VISN Pharmacist Executives, The Center For Medication Safety. Heparin supply status: frequently asked questions. PBM-2018-02. https://www.pbm.va.gov/PBM/vacenterformedicationsafety/HeparinandSalineSyringeRecallDuetoContamination_NationalPBMPati.pdf. Published May 3, 2018. Accessed September 11, 2019.
6. Shore-Lesserson I, Baker RA, Ferraris VA, et al. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons, The Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, and the American Society of ExtraCorporeal Technology: Clinical Practice Guidelines-anticoagulation during cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann Thorac Surg. 2018;105(2):650-662.
7. Soroka S, Agharazii M, Donnelly S, et al. An adjustable dalteparin sodium dose regimen for the prevention of clotting in the extracorporeal circuit in hemodialysis: a clinical trial of safety and efficacy (the PARROT Study). Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2018;5:1-12.
8. Shantha GPS, Kumar AA, Sethi M, Khanna RC, Pancholy SB. Efficacy and safety of low molecular weight heparin compared to unfractionated heparin for chronic outpatient hemodialysis in end stage renal disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Peer J. 2015;3:e835.
9. Kessler M, Moureau F, and Nguyen P. Anticoagulation in chronic hemodialysis: progress toward an optimal approach. Semin Dial. 2015;28(5):474-489.
10. Gould MK, Garcia DA, Wren SM, et al. Prevention of VTE in nonorthopedic surgical patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2)(suppl):e227s-e277S.
11. Kaye AD, Brunk AJ, Kaye AJ, et al. Regional anesthesia in patients on anticoagulation therapies—evidence-based recommendations. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2019;23(9):67.
12. Kahn SR, Lim W, Dunn AS, et al. Prevention of VTE in nonsurgical patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2)(suppl):e195S-e226S.
13. Naylor AR, Ricco JB, de Borst GJ, et al. Management of atherosclerotic carotid and vertebral artery disease: 2017 clinical practice guidelines of the European Society for Vascular Surgery. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2018;55:3-81.
14. Gerhard-Herman MD, Gornik HL, Barrett C, et al. 2016 AHA/ACC Guideline on the Management of Patients With Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. JACC. 2017;69(11): e71-e126.
15. Bjorck M, Koelemaya M, Acosta S, et al. Management of diseases of mesenteric arteries and veins. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2017;53(4):460-510.
16. Gorski L, Hadaway L, Hagle ME, McGoldrick M, Orr M, Doellman D. Infusion therapy standards of practice. J Infusion Nurs. 2016;39:S1-S156.
17. Calkins H, Hindricks G, Cappato R, et al. 2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2017;14(10):e275-e444.
18. Spyropoulos AC, Al-Badri A, Sherwood MW, Douketis JD. Periprocedural management of patients receiving a vitamin K antagonist or a direct oral anticoagulant requiring an elective procedure or surgery. J Thromb Haemost. 2016;14(5):875-885.
, . Periprocedural bridging management of anticoagulation. Circulation. 2012;126(4):486-490.
20. Douketis JD, Spyropoulos AC, Spencer FA, et al. Perioperative management of antithrombotic therapy: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2)(suppl):e326S-e350S.
21. Sousa-Uva M, Neumann F-J, Ahlsson A, et al; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2018 ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization. The Task Force on myocardial revascularization of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Developed with a special contribution of the European Association for Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI). Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019;55(1):4-90.
22. Amsterdam EA, Wenger NK, Brindis RG, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes. JACC. 2014;64(24):e139-e228.
23. O’Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction. JACC. 2013;61(4):e78-e140.
24. Angiomax [package insert]. Parsippany, NJ: The Medicines Company; March 2016.
25. Sousa-Uva, Head SJ, Milojevic M, et al. 2017 EACTS guidelines on perioperative medication in adult cardiac surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018;53(1):5-33.
26. Witt DM, Nieuwlaat R, Clark NP, et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for the management of venous thromboembolism: optimal management of anticoagulation therapy. Blood Adv. 2018: 2(22):3257-3291
27. Kearon C, Akl EA, Blaivas A, et al. Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: Chest guideline and expert panel report. Chest. 2016;149(2):315-352.
28. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Pharmacy Benefits Manager Service. Direct oral anticoagulants criteria for use and algorithm for venous thromboembolism treatment. https://www.pbm.va.gov/PBM/clinicalguidance/criteriaforuse.asp. Updated December 2016. [Source not verified]
29. Falck-Ytter Y, Francis CW, Johanson NA, et al. Prevention of VTE in orthopedic surgery patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2)(suppl):e278S-e325S.
30. Raja S, Idrees JJ, Blackstone EH, et al. Routine venous thromboembolism screening after pneumonectomy: the more you look, the more you see. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;152(2):524-532.e2.
31. Schünemann HJ, Cushman M, Burnett AE, et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: prophylaxis for hospitalized and nonhospitalized patients. Blood Adv. 2018;2(22):3198-3225.
32. Naidu SS, Aronow HD, Box LC, et al. SCAI expert consensus statement: 2016 best practices in the cardiac catheterization laboratory:(endorsed by the Cardiological Society of India, and Sociedad Latino Americana de Cardiologia Intervencionista; affirmation of value by the Canadian Association of Interventional Cardiology-Association Canadienne de Cardiologie d’intervention). Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2016;88(3):407-423.
33. Levine GN, Bates ER, Blankenship JC, et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA/SCAI guideline for percutaneous coronary intervention. A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions. JACC. 2011;58(24):e44-e122.
34. Mason PJ, Shah B, Tamis-Holland JE, et al; American Heart Association Interventional Cardiovascular Care Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology; Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease; and Council on Genomic and Precision Medicine. AHA scientific statement: an update on radial artery access and best practices for transradial coronary angiography and intervention in acute coronary syndrome. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2018;11(9):e000035.
35. Rao SV, Tremmel JA, Gilchrist IC, et al; Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Intervention’s Transradial Working Group. Best practices for transradial angiography and intervention: a consensus statement from the society for cardiovascular angiography and interventions’ transradial working group. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;83(2):228-236. 36. Moran JE, Ash SR. Locking solutions for hemodialysis catheters; heparin and citrate: a position paper by ASDIN. Semin Dial. 2008;21(5):490-492.
1. Hirsh J, Warkentin TE, Shaughnessy SG, et al. Heparin and low-molecular-weight heparin mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, dosing, monitoring, efficacy, and safety. Chest. 2001;119(1):64S-94S.
2. Bipartisan E&C leaders request FDA briefing on threat to U.S. heparin supply [press release]. Washington, DC: House Committee on Energy and Commerce; July 30, 2019. https://energycommerce.house.gov/newsroom/press-releases/bipartisan-ec-leaders-request-fda-briefing-on-threat-to-us-heparin-supply. Accessed September 19, 2019.
3. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Drug Shortages. Heparin injection. https://www.ashp.org/Drug-Shortages/Current-Shortages/Drug-Shortages-List?page=CurrentShortages. Accessed September 19, 2019.
4. Reed BN, Fox ER, Konig M, et al. The impact of drug shortages on patients with cardiovascular disease: causes, consequences, and a call to action. Am Heart J. 2016;175:130-141.
5. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Pharmacy Benefits Management Services, Medical Advisory Panel, VISN Pharmacist Executives, The Center For Medication Safety. Heparin supply status: frequently asked questions. PBM-2018-02. https://www.pbm.va.gov/PBM/vacenterformedicationsafety/HeparinandSalineSyringeRecallDuetoContamination_NationalPBMPati.pdf. Published May 3, 2018. Accessed September 11, 2019.
6. Shore-Lesserson I, Baker RA, Ferraris VA, et al. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons, The Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, and the American Society of ExtraCorporeal Technology: Clinical Practice Guidelines-anticoagulation during cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann Thorac Surg. 2018;105(2):650-662.
7. Soroka S, Agharazii M, Donnelly S, et al. An adjustable dalteparin sodium dose regimen for the prevention of clotting in the extracorporeal circuit in hemodialysis: a clinical trial of safety and efficacy (the PARROT Study). Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2018;5:1-12.
8. Shantha GPS, Kumar AA, Sethi M, Khanna RC, Pancholy SB. Efficacy and safety of low molecular weight heparin compared to unfractionated heparin for chronic outpatient hemodialysis in end stage renal disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Peer J. 2015;3:e835.
9. Kessler M, Moureau F, and Nguyen P. Anticoagulation in chronic hemodialysis: progress toward an optimal approach. Semin Dial. 2015;28(5):474-489.
10. Gould MK, Garcia DA, Wren SM, et al. Prevention of VTE in nonorthopedic surgical patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2)(suppl):e227s-e277S.
11. Kaye AD, Brunk AJ, Kaye AJ, et al. Regional anesthesia in patients on anticoagulation therapies—evidence-based recommendations. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2019;23(9):67.
12. Kahn SR, Lim W, Dunn AS, et al. Prevention of VTE in nonsurgical patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2)(suppl):e195S-e226S.
13. Naylor AR, Ricco JB, de Borst GJ, et al. Management of atherosclerotic carotid and vertebral artery disease: 2017 clinical practice guidelines of the European Society for Vascular Surgery. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2018;55:3-81.
14. Gerhard-Herman MD, Gornik HL, Barrett C, et al. 2016 AHA/ACC Guideline on the Management of Patients With Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. JACC. 2017;69(11): e71-e126.
15. Bjorck M, Koelemaya M, Acosta S, et al. Management of diseases of mesenteric arteries and veins. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2017;53(4):460-510.
16. Gorski L, Hadaway L, Hagle ME, McGoldrick M, Orr M, Doellman D. Infusion therapy standards of practice. J Infusion Nurs. 2016;39:S1-S156.
17. Calkins H, Hindricks G, Cappato R, et al. 2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2017;14(10):e275-e444.
18. Spyropoulos AC, Al-Badri A, Sherwood MW, Douketis JD. Periprocedural management of patients receiving a vitamin K antagonist or a direct oral anticoagulant requiring an elective procedure or surgery. J Thromb Haemost. 2016;14(5):875-885.
, . Periprocedural bridging management of anticoagulation. Circulation. 2012;126(4):486-490.
20. Douketis JD, Spyropoulos AC, Spencer FA, et al. Perioperative management of antithrombotic therapy: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2)(suppl):e326S-e350S.
21. Sousa-Uva M, Neumann F-J, Ahlsson A, et al; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2018 ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization. The Task Force on myocardial revascularization of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Developed with a special contribution of the European Association for Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI). Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019;55(1):4-90.
22. Amsterdam EA, Wenger NK, Brindis RG, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes. JACC. 2014;64(24):e139-e228.
23. O’Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction. JACC. 2013;61(4):e78-e140.
24. Angiomax [package insert]. Parsippany, NJ: The Medicines Company; March 2016.
25. Sousa-Uva, Head SJ, Milojevic M, et al. 2017 EACTS guidelines on perioperative medication in adult cardiac surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018;53(1):5-33.
26. Witt DM, Nieuwlaat R, Clark NP, et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for the management of venous thromboembolism: optimal management of anticoagulation therapy. Blood Adv. 2018: 2(22):3257-3291
27. Kearon C, Akl EA, Blaivas A, et al. Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: Chest guideline and expert panel report. Chest. 2016;149(2):315-352.
28. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Pharmacy Benefits Manager Service. Direct oral anticoagulants criteria for use and algorithm for venous thromboembolism treatment. https://www.pbm.va.gov/PBM/clinicalguidance/criteriaforuse.asp. Updated December 2016. [Source not verified]
29. Falck-Ytter Y, Francis CW, Johanson NA, et al. Prevention of VTE in orthopedic surgery patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2)(suppl):e278S-e325S.
30. Raja S, Idrees JJ, Blackstone EH, et al. Routine venous thromboembolism screening after pneumonectomy: the more you look, the more you see. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;152(2):524-532.e2.
31. Schünemann HJ, Cushman M, Burnett AE, et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: prophylaxis for hospitalized and nonhospitalized patients. Blood Adv. 2018;2(22):3198-3225.
32. Naidu SS, Aronow HD, Box LC, et al. SCAI expert consensus statement: 2016 best practices in the cardiac catheterization laboratory:(endorsed by the Cardiological Society of India, and Sociedad Latino Americana de Cardiologia Intervencionista; affirmation of value by the Canadian Association of Interventional Cardiology-Association Canadienne de Cardiologie d’intervention). Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2016;88(3):407-423.
33. Levine GN, Bates ER, Blankenship JC, et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA/SCAI guideline for percutaneous coronary intervention. A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions. JACC. 2011;58(24):e44-e122.
34. Mason PJ, Shah B, Tamis-Holland JE, et al; American Heart Association Interventional Cardiovascular Care Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology; Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease; and Council on Genomic and Precision Medicine. AHA scientific statement: an update on radial artery access and best practices for transradial coronary angiography and intervention in acute coronary syndrome. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2018;11(9):e000035.
35. Rao SV, Tremmel JA, Gilchrist IC, et al; Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Intervention’s Transradial Working Group. Best practices for transradial angiography and intervention: a consensus statement from the society for cardiovascular angiography and interventions’ transradial working group. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;83(2):228-236. 36. Moran JE, Ash SR. Locking solutions for hemodialysis catheters; heparin and citrate: a position paper by ASDIN. Semin Dial. 2008;21(5):490-492.
Vitamin C infusion falls short for sepsis and ARDS patients
Vitamin C infusion did not improve outcomes related to organ failure, inflammation, or vascular injury for patients with sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome, based on data from 167 adults.
“Previous research found that vitamin C attenuates systemic inflammation, corrects sepsis-induced coagulopathy, and attenuates vascular injury,” wrote Alpha A. Fowler III, MD, of Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, and colleagues.
To examine the impact of vitamin C infusion on patients with sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), the researchers designed the CITRIS-ALI trial, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study conducted at 7 medical intensive care units in the United States.
In the study, published in JAMA, the researchers randomized 167 adults with sepsis and ARDS to receive high-dose intravenous vitamin C (50 mg/kg in 5% dextrose in water) or placebo (5% dextrose in water only) every 6 hours for 96 hours. The primary outcomes were measures of organ failure based on changes in the modified Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score (mSOFA), inflammation (based on changes in C-reactive protein), and vascular injury based on thrombomodulin.
Overall, no significant differences appeared between the vitamin C and placebo groups, respectively in the three primary outcome measures: change in average SOFA score (3-point change vs. a 3.5-point change) at 96 hours; change in C-reactive protein levels (change of 54.1 mcg/mL vs. 46.1 mcg/mL) at 168 hours; and change in thrombomodulin levels (14.5 ng/mL vs. 13.8 ng/mL) at 168 hours.
The average age of the patients was 55 years, and 54% were men.
The researchers also assessed 46 secondary outcomes. Most of these showed no significant differences between the groups, but 28-day all-cause mortality was significantly lower in the vitamin C group, compared with the placebo group (46.3% vs. 29.8%), the researchers said. Vitamin C also was significantly associated with increased ICU-free days to day 28 and hospital-free days to day 60, compared with placebo.
No significant differences were seen between the groups on 43 other secondary outcomes including ventilator-free days and vasopressor use. However, “these findings were based on analyses that did not account for multiple comparisons and therefore must be considered exploratory,” they said.
“The inability of vitamin C to affect C-reactive protein and thrombomodulin levels in this trial possibly resulted from the advanced stages of sepsis that were present before the development of ARDS,” the researchers noted.
The findings were limited by several factors including the variability in the timing of vitamin C administration and the use of a single high dose of vitamin C, they emphasized. However, the results suggest that further research may be needed to determine the potential of vitamin C for improving outcomes in patients with sepsis and ARDS, they said.
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, VCU Wright Center for Translational Science Award, VCU Investigational Drug Services, and McGuff Pharmaceuticals, who supplied the vitamin C free of charge. Dr. Fowler disclosed funding from Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Richmond; the NHLBI; and study materials from McGuff Pharmaceuticals.
SOURCE: Fowler AA et al. JAMA. 2019 Oct 1;322:1261-70. doi:10.1001/jama.2019.11825.
Although none of the primary outcomes was significant, “the difference in mortality is tantalizing and likely to spur much debate,” wrote Emily B. Brant, MD, and Derek C. Angus, MD, in an accompanying editorial.
“However, this outcome was one of many secondary outcomes, and although reported as statistically significant, that finding was without adjustment for multiple comparisons,” they said.
The study was well-designed, and resulted in the collection of considerable patient data, they said. Previous studies have suggested that approximately 40% of sepsis patients are vitamin C deficient, and vitamin C is considered safe and inexpensive, which may be reason to pursue research in this area, they added.
Study design for addition research should keep in mind the timing and dosage that were limitations in the current study; the lack of effect on organ dysfunction may have occurred because vitamin C was given too late, they said.
Researchers planning further evaluation might “reconsider optimal dosing and timing, as well as the likelihood that any potential benefits may only accrue to subsets of patients, given the underlying heterogeneity of sepsis,” they concluded (JAMA. 2019 Oct 1; 322:1257-8).
Dr. Brant and Dr. Angus are affiliated with the department of critical care medicine, University of Pittsburgh. Dr. Angus serves as a associate editor for JAMA and disclosed receiving consulting fees from Ferring, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Beckman Coulter; holding stock in Alung Technologies; and holding pending patents for selepressin and for proteomic biomarkers of sepsis in elderly patients. Dr. Brant had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Although none of the primary outcomes was significant, “the difference in mortality is tantalizing and likely to spur much debate,” wrote Emily B. Brant, MD, and Derek C. Angus, MD, in an accompanying editorial.
“However, this outcome was one of many secondary outcomes, and although reported as statistically significant, that finding was without adjustment for multiple comparisons,” they said.
The study was well-designed, and resulted in the collection of considerable patient data, they said. Previous studies have suggested that approximately 40% of sepsis patients are vitamin C deficient, and vitamin C is considered safe and inexpensive, which may be reason to pursue research in this area, they added.
Study design for addition research should keep in mind the timing and dosage that were limitations in the current study; the lack of effect on organ dysfunction may have occurred because vitamin C was given too late, they said.
Researchers planning further evaluation might “reconsider optimal dosing and timing, as well as the likelihood that any potential benefits may only accrue to subsets of patients, given the underlying heterogeneity of sepsis,” they concluded (JAMA. 2019 Oct 1; 322:1257-8).
Dr. Brant and Dr. Angus are affiliated with the department of critical care medicine, University of Pittsburgh. Dr. Angus serves as a associate editor for JAMA and disclosed receiving consulting fees from Ferring, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Beckman Coulter; holding stock in Alung Technologies; and holding pending patents for selepressin and for proteomic biomarkers of sepsis in elderly patients. Dr. Brant had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Although none of the primary outcomes was significant, “the difference in mortality is tantalizing and likely to spur much debate,” wrote Emily B. Brant, MD, and Derek C. Angus, MD, in an accompanying editorial.
“However, this outcome was one of many secondary outcomes, and although reported as statistically significant, that finding was without adjustment for multiple comparisons,” they said.
The study was well-designed, and resulted in the collection of considerable patient data, they said. Previous studies have suggested that approximately 40% of sepsis patients are vitamin C deficient, and vitamin C is considered safe and inexpensive, which may be reason to pursue research in this area, they added.
Study design for addition research should keep in mind the timing and dosage that were limitations in the current study; the lack of effect on organ dysfunction may have occurred because vitamin C was given too late, they said.
Researchers planning further evaluation might “reconsider optimal dosing and timing, as well as the likelihood that any potential benefits may only accrue to subsets of patients, given the underlying heterogeneity of sepsis,” they concluded (JAMA. 2019 Oct 1; 322:1257-8).
Dr. Brant and Dr. Angus are affiliated with the department of critical care medicine, University of Pittsburgh. Dr. Angus serves as a associate editor for JAMA and disclosed receiving consulting fees from Ferring, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Beckman Coulter; holding stock in Alung Technologies; and holding pending patents for selepressin and for proteomic biomarkers of sepsis in elderly patients. Dr. Brant had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Vitamin C infusion did not improve outcomes related to organ failure, inflammation, or vascular injury for patients with sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome, based on data from 167 adults.
“Previous research found that vitamin C attenuates systemic inflammation, corrects sepsis-induced coagulopathy, and attenuates vascular injury,” wrote Alpha A. Fowler III, MD, of Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, and colleagues.
To examine the impact of vitamin C infusion on patients with sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), the researchers designed the CITRIS-ALI trial, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study conducted at 7 medical intensive care units in the United States.
In the study, published in JAMA, the researchers randomized 167 adults with sepsis and ARDS to receive high-dose intravenous vitamin C (50 mg/kg in 5% dextrose in water) or placebo (5% dextrose in water only) every 6 hours for 96 hours. The primary outcomes were measures of organ failure based on changes in the modified Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score (mSOFA), inflammation (based on changes in C-reactive protein), and vascular injury based on thrombomodulin.
Overall, no significant differences appeared between the vitamin C and placebo groups, respectively in the three primary outcome measures: change in average SOFA score (3-point change vs. a 3.5-point change) at 96 hours; change in C-reactive protein levels (change of 54.1 mcg/mL vs. 46.1 mcg/mL) at 168 hours; and change in thrombomodulin levels (14.5 ng/mL vs. 13.8 ng/mL) at 168 hours.
The average age of the patients was 55 years, and 54% were men.
The researchers also assessed 46 secondary outcomes. Most of these showed no significant differences between the groups, but 28-day all-cause mortality was significantly lower in the vitamin C group, compared with the placebo group (46.3% vs. 29.8%), the researchers said. Vitamin C also was significantly associated with increased ICU-free days to day 28 and hospital-free days to day 60, compared with placebo.
No significant differences were seen between the groups on 43 other secondary outcomes including ventilator-free days and vasopressor use. However, “these findings were based on analyses that did not account for multiple comparisons and therefore must be considered exploratory,” they said.
“The inability of vitamin C to affect C-reactive protein and thrombomodulin levels in this trial possibly resulted from the advanced stages of sepsis that were present before the development of ARDS,” the researchers noted.
The findings were limited by several factors including the variability in the timing of vitamin C administration and the use of a single high dose of vitamin C, they emphasized. However, the results suggest that further research may be needed to determine the potential of vitamin C for improving outcomes in patients with sepsis and ARDS, they said.
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, VCU Wright Center for Translational Science Award, VCU Investigational Drug Services, and McGuff Pharmaceuticals, who supplied the vitamin C free of charge. Dr. Fowler disclosed funding from Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Richmond; the NHLBI; and study materials from McGuff Pharmaceuticals.
SOURCE: Fowler AA et al. JAMA. 2019 Oct 1;322:1261-70. doi:10.1001/jama.2019.11825.
Vitamin C infusion did not improve outcomes related to organ failure, inflammation, or vascular injury for patients with sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome, based on data from 167 adults.
“Previous research found that vitamin C attenuates systemic inflammation, corrects sepsis-induced coagulopathy, and attenuates vascular injury,” wrote Alpha A. Fowler III, MD, of Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, and colleagues.
To examine the impact of vitamin C infusion on patients with sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), the researchers designed the CITRIS-ALI trial, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study conducted at 7 medical intensive care units in the United States.
In the study, published in JAMA, the researchers randomized 167 adults with sepsis and ARDS to receive high-dose intravenous vitamin C (50 mg/kg in 5% dextrose in water) or placebo (5% dextrose in water only) every 6 hours for 96 hours. The primary outcomes were measures of organ failure based on changes in the modified Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score (mSOFA), inflammation (based on changes in C-reactive protein), and vascular injury based on thrombomodulin.
Overall, no significant differences appeared between the vitamin C and placebo groups, respectively in the three primary outcome measures: change in average SOFA score (3-point change vs. a 3.5-point change) at 96 hours; change in C-reactive protein levels (change of 54.1 mcg/mL vs. 46.1 mcg/mL) at 168 hours; and change in thrombomodulin levels (14.5 ng/mL vs. 13.8 ng/mL) at 168 hours.
The average age of the patients was 55 years, and 54% were men.
The researchers also assessed 46 secondary outcomes. Most of these showed no significant differences between the groups, but 28-day all-cause mortality was significantly lower in the vitamin C group, compared with the placebo group (46.3% vs. 29.8%), the researchers said. Vitamin C also was significantly associated with increased ICU-free days to day 28 and hospital-free days to day 60, compared with placebo.
No significant differences were seen between the groups on 43 other secondary outcomes including ventilator-free days and vasopressor use. However, “these findings were based on analyses that did not account for multiple comparisons and therefore must be considered exploratory,” they said.
“The inability of vitamin C to affect C-reactive protein and thrombomodulin levels in this trial possibly resulted from the advanced stages of sepsis that were present before the development of ARDS,” the researchers noted.
The findings were limited by several factors including the variability in the timing of vitamin C administration and the use of a single high dose of vitamin C, they emphasized. However, the results suggest that further research may be needed to determine the potential of vitamin C for improving outcomes in patients with sepsis and ARDS, they said.
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, VCU Wright Center for Translational Science Award, VCU Investigational Drug Services, and McGuff Pharmaceuticals, who supplied the vitamin C free of charge. Dr. Fowler disclosed funding from Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Richmond; the NHLBI; and study materials from McGuff Pharmaceuticals.
SOURCE: Fowler AA et al. JAMA. 2019 Oct 1;322:1261-70. doi:10.1001/jama.2019.11825.
FROM JAMA
Key clinical point: Vitamin C infusion failed to improve outcomes for patients with ARDS and sepsis.
Major finding: The average SOFA score to measure organ failure changed by 3 points in the vitamin C group vs. 3.5 points in the placebo group.
Study details: The data come from a randomized trial of 167 adults with ARDS and sepsis.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, VCU Wright Center for Translational Science Award, VCU Investigational Drug Services, and McGuff Pharmaceuticals, who supplied the vitamin C free of charge. Dr. Fowler disclosed funding from Virginia Tech School of Medicine, the NHLBI, and study materials from McGuff Pharmaceuticals.
Source: Fowler AA et al. JAMA. 2019 Oct 1;322:1261-70. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.11825.
Osimertinib improves survival in advanced NSCLC
BARCELONA – In patients with , compared with other agents targeted against NSCLC with epidermal growth factor–receptor (EGFR) mutations, investigators for the FLAURA trial reported.
After median follow-up ranging from 27 to 35.8 months, the median overall survival was 38.6 months for patients randomized to osimertinib, compared with 31.8 months for patients assigned to either of two comparator tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), gefitinib (Iressa) or erlotinib (Tarceva).
The hazard ratio for death with osimertinib was 0.799 (P = .0462), reported Suresh Ramalingam, MD, director of the lung cancer program at Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University, Atlanta.
“I’m excited that the new milestone accomplished with osimertinib in this trial will serve as the platform to build on in our efforts to improve the lives of patients with lung cancer,” he said at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
Osimertinib is the first TKI to show improvement in overall survival over another TKI in the treatment of advanced stage cancers, he noted.
Overall survival was a secondary endpoint of the FLAURA trial. As previously reported, FLAURA met its primary endpoint of improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) in an interim analysis presented at ESMO 2017. In that analysis, osimertinib cut the risk of disease progression by 54%, compared with gefitinib or erlotinib.
Among 279 patients with EGFR-mutated locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC treated with osimertinib, the median PFS was 18.9 months, compared with 10.2 months for 277 patients treated with the standard of care, which translated into a HR of 0.46 (P less than .0001).
The FLAURA results supported Food and Drug Administration approval of osimertinib in April 2018 for first-line treatment of patients with metastatic NSCLC with EGFR mutations as detected by an FDA-approved test.
The current overall survival analysis, although not powered to show differences among patient subgroups, showed trends favoring osimertinib over a comparator TKI among both men and women, older and younger patients, patients with central nervous system metastases at trial entry, and patients with the EGFR exon 19 deletion at randomization.
The 31.8 month median overall survival for the control (comparator-TKI) arm is among the highest reported for patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC, Dr. Ramalingam noted.
“That is because a lot of patients crossed over from the control group to receive osimertinib on progression,” he said, adding that the magnitude of benefit from osimertinib was greater among non-Asian patients, compared with Asians.
FLAURA details
In the phase 3 FLAURA trial, investigators stratified patients with previously untreated NSCLC positive for EGFR resistance mutations according to mutation status (exon 19 deletion or the L858R amino acid substitution in exon 21) and race (Asian or non-Asian).
Patients were randomly assigned to treatment with either oral osimertinib 80 mg daily or an EGFR TKI, either oral gefitinib 250 mg or erlotinib 150 mg daily.
The patients were assessed by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) every 6 weeks until objective disease progression.
Patients assigned to the standard-of-care arm who had central confirmation of progression and T790M positivity were allowed to cross over to open-label osimertinib.
PFS, the primary endpoint, was also significantly better with osimertinib than with either of the comparator TKIs in patients with and without central nervous system metastases at study entry (HR, 0.47; P = .0009 for patients with CNS metastases; HR, 0.46; P less than .0001 for patients with no CNS metastases).
“For clinicians, for patients, and also for our health authorities, the results in terms of overall survival are really relevant, and this is why this study is so important, knowing this secondary endpoint from a statistical point of view. The study is statistically significant and clinically relevant,” commented Pilar Garrido, MD, from the department of medical oncology, Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal in Madrid, the invited discussant at a briefing where Dr. Ramalingam outlined the study findings prior to his presentation of the data in a symposium.
“What’s the future of EGFR mutant lung cancer? Well, I think we should be done with single-agent EGFR-TKI comparisons: We have a clear agent that’s associated with an improvement in survival. I think our focus needs to shift to building on or adding to osimertinib,” commented Pasi A Jänne, MD, PhD, director of the Lowe Center for Thoracic Oncology at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, the invited discussant at the symposium.
He said that the challenge for clinicians will be to identify high- and low-risk EGFR-mutant NSCLC, and to determine which patients could be treated with a single agent, and which may require a combination therapy approach.
FLAURA was sponsored by AstraZeneca. Dr. Ramalingam disclosed honoraria, an advisory or consulting role, and research funding from that company and others. Dr. Garrido disclosed a speaker and advisory role for AstraZeneca and others. Dr. Jänne disclosed prior consulting for AstraZeneca.
SOURCE: Ramalingam S et al. ESMO 2019. Abstract LBA5_PR.
BARCELONA – In patients with , compared with other agents targeted against NSCLC with epidermal growth factor–receptor (EGFR) mutations, investigators for the FLAURA trial reported.
After median follow-up ranging from 27 to 35.8 months, the median overall survival was 38.6 months for patients randomized to osimertinib, compared with 31.8 months for patients assigned to either of two comparator tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), gefitinib (Iressa) or erlotinib (Tarceva).
The hazard ratio for death with osimertinib was 0.799 (P = .0462), reported Suresh Ramalingam, MD, director of the lung cancer program at Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University, Atlanta.
“I’m excited that the new milestone accomplished with osimertinib in this trial will serve as the platform to build on in our efforts to improve the lives of patients with lung cancer,” he said at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
Osimertinib is the first TKI to show improvement in overall survival over another TKI in the treatment of advanced stage cancers, he noted.
Overall survival was a secondary endpoint of the FLAURA trial. As previously reported, FLAURA met its primary endpoint of improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) in an interim analysis presented at ESMO 2017. In that analysis, osimertinib cut the risk of disease progression by 54%, compared with gefitinib or erlotinib.
Among 279 patients with EGFR-mutated locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC treated with osimertinib, the median PFS was 18.9 months, compared with 10.2 months for 277 patients treated with the standard of care, which translated into a HR of 0.46 (P less than .0001).
The FLAURA results supported Food and Drug Administration approval of osimertinib in April 2018 for first-line treatment of patients with metastatic NSCLC with EGFR mutations as detected by an FDA-approved test.
The current overall survival analysis, although not powered to show differences among patient subgroups, showed trends favoring osimertinib over a comparator TKI among both men and women, older and younger patients, patients with central nervous system metastases at trial entry, and patients with the EGFR exon 19 deletion at randomization.
The 31.8 month median overall survival for the control (comparator-TKI) arm is among the highest reported for patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC, Dr. Ramalingam noted.
“That is because a lot of patients crossed over from the control group to receive osimertinib on progression,” he said, adding that the magnitude of benefit from osimertinib was greater among non-Asian patients, compared with Asians.
FLAURA details
In the phase 3 FLAURA trial, investigators stratified patients with previously untreated NSCLC positive for EGFR resistance mutations according to mutation status (exon 19 deletion or the L858R amino acid substitution in exon 21) and race (Asian or non-Asian).
Patients were randomly assigned to treatment with either oral osimertinib 80 mg daily or an EGFR TKI, either oral gefitinib 250 mg or erlotinib 150 mg daily.
The patients were assessed by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) every 6 weeks until objective disease progression.
Patients assigned to the standard-of-care arm who had central confirmation of progression and T790M positivity were allowed to cross over to open-label osimertinib.
PFS, the primary endpoint, was also significantly better with osimertinib than with either of the comparator TKIs in patients with and without central nervous system metastases at study entry (HR, 0.47; P = .0009 for patients with CNS metastases; HR, 0.46; P less than .0001 for patients with no CNS metastases).
“For clinicians, for patients, and also for our health authorities, the results in terms of overall survival are really relevant, and this is why this study is so important, knowing this secondary endpoint from a statistical point of view. The study is statistically significant and clinically relevant,” commented Pilar Garrido, MD, from the department of medical oncology, Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal in Madrid, the invited discussant at a briefing where Dr. Ramalingam outlined the study findings prior to his presentation of the data in a symposium.
“What’s the future of EGFR mutant lung cancer? Well, I think we should be done with single-agent EGFR-TKI comparisons: We have a clear agent that’s associated with an improvement in survival. I think our focus needs to shift to building on or adding to osimertinib,” commented Pasi A Jänne, MD, PhD, director of the Lowe Center for Thoracic Oncology at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, the invited discussant at the symposium.
He said that the challenge for clinicians will be to identify high- and low-risk EGFR-mutant NSCLC, and to determine which patients could be treated with a single agent, and which may require a combination therapy approach.
FLAURA was sponsored by AstraZeneca. Dr. Ramalingam disclosed honoraria, an advisory or consulting role, and research funding from that company and others. Dr. Garrido disclosed a speaker and advisory role for AstraZeneca and others. Dr. Jänne disclosed prior consulting for AstraZeneca.
SOURCE: Ramalingam S et al. ESMO 2019. Abstract LBA5_PR.
BARCELONA – In patients with , compared with other agents targeted against NSCLC with epidermal growth factor–receptor (EGFR) mutations, investigators for the FLAURA trial reported.
After median follow-up ranging from 27 to 35.8 months, the median overall survival was 38.6 months for patients randomized to osimertinib, compared with 31.8 months for patients assigned to either of two comparator tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), gefitinib (Iressa) or erlotinib (Tarceva).
The hazard ratio for death with osimertinib was 0.799 (P = .0462), reported Suresh Ramalingam, MD, director of the lung cancer program at Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University, Atlanta.
“I’m excited that the new milestone accomplished with osimertinib in this trial will serve as the platform to build on in our efforts to improve the lives of patients with lung cancer,” he said at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
Osimertinib is the first TKI to show improvement in overall survival over another TKI in the treatment of advanced stage cancers, he noted.
Overall survival was a secondary endpoint of the FLAURA trial. As previously reported, FLAURA met its primary endpoint of improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) in an interim analysis presented at ESMO 2017. In that analysis, osimertinib cut the risk of disease progression by 54%, compared with gefitinib or erlotinib.
Among 279 patients with EGFR-mutated locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC treated with osimertinib, the median PFS was 18.9 months, compared with 10.2 months for 277 patients treated with the standard of care, which translated into a HR of 0.46 (P less than .0001).
The FLAURA results supported Food and Drug Administration approval of osimertinib in April 2018 for first-line treatment of patients with metastatic NSCLC with EGFR mutations as detected by an FDA-approved test.
The current overall survival analysis, although not powered to show differences among patient subgroups, showed trends favoring osimertinib over a comparator TKI among both men and women, older and younger patients, patients with central nervous system metastases at trial entry, and patients with the EGFR exon 19 deletion at randomization.
The 31.8 month median overall survival for the control (comparator-TKI) arm is among the highest reported for patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC, Dr. Ramalingam noted.
“That is because a lot of patients crossed over from the control group to receive osimertinib on progression,” he said, adding that the magnitude of benefit from osimertinib was greater among non-Asian patients, compared with Asians.
FLAURA details
In the phase 3 FLAURA trial, investigators stratified patients with previously untreated NSCLC positive for EGFR resistance mutations according to mutation status (exon 19 deletion or the L858R amino acid substitution in exon 21) and race (Asian or non-Asian).
Patients were randomly assigned to treatment with either oral osimertinib 80 mg daily or an EGFR TKI, either oral gefitinib 250 mg or erlotinib 150 mg daily.
The patients were assessed by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) every 6 weeks until objective disease progression.
Patients assigned to the standard-of-care arm who had central confirmation of progression and T790M positivity were allowed to cross over to open-label osimertinib.
PFS, the primary endpoint, was also significantly better with osimertinib than with either of the comparator TKIs in patients with and without central nervous system metastases at study entry (HR, 0.47; P = .0009 for patients with CNS metastases; HR, 0.46; P less than .0001 for patients with no CNS metastases).
“For clinicians, for patients, and also for our health authorities, the results in terms of overall survival are really relevant, and this is why this study is so important, knowing this secondary endpoint from a statistical point of view. The study is statistically significant and clinically relevant,” commented Pilar Garrido, MD, from the department of medical oncology, Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal in Madrid, the invited discussant at a briefing where Dr. Ramalingam outlined the study findings prior to his presentation of the data in a symposium.
“What’s the future of EGFR mutant lung cancer? Well, I think we should be done with single-agent EGFR-TKI comparisons: We have a clear agent that’s associated with an improvement in survival. I think our focus needs to shift to building on or adding to osimertinib,” commented Pasi A Jänne, MD, PhD, director of the Lowe Center for Thoracic Oncology at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, the invited discussant at the symposium.
He said that the challenge for clinicians will be to identify high- and low-risk EGFR-mutant NSCLC, and to determine which patients could be treated with a single agent, and which may require a combination therapy approach.
FLAURA was sponsored by AstraZeneca. Dr. Ramalingam disclosed honoraria, an advisory or consulting role, and research funding from that company and others. Dr. Garrido disclosed a speaker and advisory role for AstraZeneca and others. Dr. Jänne disclosed prior consulting for AstraZeneca.
SOURCE: Ramalingam S et al. ESMO 2019. Abstract LBA5_PR.
REPORTING FROM ESMO 2019
CONCLUDE data inconclusive on hypoglycemia risk for degludec vs. glargine
BARCELONA – data presented at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
During a 36-week maintenance treatment period, the rate ratio (RR) for the primary endpoint of the study – severe or confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia, defined as a blood-glucose level of less than 3.1 mmol/L (56 mg/dL) – was 0.88 (95% confidence interval, 0.73-1.06; P = .17) in a comparison the two long-acting insulins.
There were some differences that favored insulin degludec over insulin glargine when other endpoints were considered, but because a statistical testing hierarchy was used, “no confirmatory results can be made from CONCLUDE,” one of the study investigators, Athena Philis-Tsimikas, MD, of Scripps Whittier Diabetes Institute, San Diego, said during a special symposium at the meeting.
“If the primary endpoint was not achieved, the testing hierarchy stopped after the first occurrence of nonsignificance,” she explained. Although that occurred, the other endpoints could still be analyzed as they were all prespecified, she argued. These showed that during the maintenance treatment period, there were lower rates of nocturnal symptomatic hypoglycemic episodes (RR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.48-0.84; P = .0014) and severe episodes (those requiring third-party assistance; RR, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.07-0.57; P = .0027) with insulin degludec, compared with insulin glargine.
The trial came under fire, however, from Stefano Del Prato, MD, professor of endocrinology in the department of endocrinology metabolism and chief of the section of diabetes at the University of Pisa, Italy, who provided the EASD-invited independent commentary on the study’s findings. “This is the CONCLUDE trial. You’d could expect a CONCLUDE trial to be conclusive in its conclusions!” he said, noting that there were “too many uncertainties” in the trial.
CONCLUDE was a randomized, open-label, head-to-head study of insulin degludec versus insulin glargine in 1,609 adult patients with type 2 diabetes who were inadequately treated with basal insulin with or without oral antidiabetic drugs. The aim of the trial was to evaluate the risk of hypoglycemia associated with the two long-acting insulins.
“Hypoglycemia is a very common event in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes,” Thomas Pieber, MD, Medical University Graz, Austria, reminded the audience. Severe hypoglycemia is associated with insulin use, and data show that patients with type 2 diabetes are at as much risk as are those with type 1 diabetes in the longer term (Diabetologia. 2007;50:1140-7).
The rationale for the CONCLUDE study comes from evidence from other trials, he said. Specifically, there was a pharmacodynamic/pharmacokinetic study comparing insulin degludec U200 with insulin glargine U300 that showed four times lower day-to-day variability in favor of insulin degludec (Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19:1032-9). Dr. Pieber noted that there was also a 30% lower potency of insulin glargine U300 versus insulin degludec U200. Those findings, together with findings from the SWITCH 2 (JAMA. 2017;318:45-56) and EDITION II (Diabetes Care. 2014;37:3235-43) trials, led to the hypothesis that there might be lower rates of hypoglycemia with insulin degludec U200 than with insulin glargine U300.
Dr. Pieber noted that one early issue with the trial was how patients’ blood glucose had been initially measured, because the blood glucose monitoring system that patients were first using seemed to display falsely higher values than what was actually expected, potentially putting patients’ safety at risk. This called for a protocol amendment (J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2019;13:498-506) and a new blood glucose monitoring system being used.
A similar proportion of patients in each group discontinued treatment during the study – 12.3% in the insulin degludec arm, and 11.4% in the insulin glargine arm – for reasons including adverse events (2.9% vs. 2.1%, respectively) and lack of efficacy (1.0% vs. 1.6%), he said.
Post hoc analyses hinted at slight benefits of insulin degludec over insulin glargine in terms of end of treatment hemoglobin A1c and the daily observed insulin dose, but less weight gain for insulin glargine.
Commenting further on the study, Dr. Del Prato said there was much debate around the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic differences between insulin degludec and insulin glargine, and that the data should be interpreted “with a lot of caution.”
He said that it was not clear from the findings why there might be a lower risk of hypoglycemia with insulin degludec. He noted that the rate of diurnal hypoglycemia should be considered, and that the statistical interpretation of the data may be “a matter of uncertainty as well.”
Dr. Del Prato agreed that “prevention of hypoglycemia remained a major task in treating type 2 diabetic patients, particularly those on insulin therapy.” He proposed that differentiating between new basal insulin analogs may need “better tools for characterization of PK/PD, rigorous interpretation of the results, careful assessment of the generalizability of results from randomized controlled trials performed in selected study populations, and independent research and careful real-world studies to be performed.”
Furthermore, he said translating the potential benefit of new insulin analogs “cannot just rely on their properties, rather it requires validation over the time of the accuracy of glucose meters, and adequate patient education, and even more, education reinforcement.”
All of the speakers disclosed ties with Novo Nordisk, which funded the study, as well as other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCES: Philis-Tsimikas A. EASD 2019, Oral Presentation 90; Pieber T. EASD 2019, Oral Presentation S38.1; Philis-Tsimikas A. EASD 2019, Oral Presentation S38.2; Del Prato S. EASD 2019. Oral Presentation S38.3.
BARCELONA – data presented at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
During a 36-week maintenance treatment period, the rate ratio (RR) for the primary endpoint of the study – severe or confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia, defined as a blood-glucose level of less than 3.1 mmol/L (56 mg/dL) – was 0.88 (95% confidence interval, 0.73-1.06; P = .17) in a comparison the two long-acting insulins.
There were some differences that favored insulin degludec over insulin glargine when other endpoints were considered, but because a statistical testing hierarchy was used, “no confirmatory results can be made from CONCLUDE,” one of the study investigators, Athena Philis-Tsimikas, MD, of Scripps Whittier Diabetes Institute, San Diego, said during a special symposium at the meeting.
“If the primary endpoint was not achieved, the testing hierarchy stopped after the first occurrence of nonsignificance,” she explained. Although that occurred, the other endpoints could still be analyzed as they were all prespecified, she argued. These showed that during the maintenance treatment period, there were lower rates of nocturnal symptomatic hypoglycemic episodes (RR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.48-0.84; P = .0014) and severe episodes (those requiring third-party assistance; RR, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.07-0.57; P = .0027) with insulin degludec, compared with insulin glargine.
The trial came under fire, however, from Stefano Del Prato, MD, professor of endocrinology in the department of endocrinology metabolism and chief of the section of diabetes at the University of Pisa, Italy, who provided the EASD-invited independent commentary on the study’s findings. “This is the CONCLUDE trial. You’d could expect a CONCLUDE trial to be conclusive in its conclusions!” he said, noting that there were “too many uncertainties” in the trial.
CONCLUDE was a randomized, open-label, head-to-head study of insulin degludec versus insulin glargine in 1,609 adult patients with type 2 diabetes who were inadequately treated with basal insulin with or without oral antidiabetic drugs. The aim of the trial was to evaluate the risk of hypoglycemia associated with the two long-acting insulins.
“Hypoglycemia is a very common event in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes,” Thomas Pieber, MD, Medical University Graz, Austria, reminded the audience. Severe hypoglycemia is associated with insulin use, and data show that patients with type 2 diabetes are at as much risk as are those with type 1 diabetes in the longer term (Diabetologia. 2007;50:1140-7).
The rationale for the CONCLUDE study comes from evidence from other trials, he said. Specifically, there was a pharmacodynamic/pharmacokinetic study comparing insulin degludec U200 with insulin glargine U300 that showed four times lower day-to-day variability in favor of insulin degludec (Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19:1032-9). Dr. Pieber noted that there was also a 30% lower potency of insulin glargine U300 versus insulin degludec U200. Those findings, together with findings from the SWITCH 2 (JAMA. 2017;318:45-56) and EDITION II (Diabetes Care. 2014;37:3235-43) trials, led to the hypothesis that there might be lower rates of hypoglycemia with insulin degludec U200 than with insulin glargine U300.
Dr. Pieber noted that one early issue with the trial was how patients’ blood glucose had been initially measured, because the blood glucose monitoring system that patients were first using seemed to display falsely higher values than what was actually expected, potentially putting patients’ safety at risk. This called for a protocol amendment (J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2019;13:498-506) and a new blood glucose monitoring system being used.
A similar proportion of patients in each group discontinued treatment during the study – 12.3% in the insulin degludec arm, and 11.4% in the insulin glargine arm – for reasons including adverse events (2.9% vs. 2.1%, respectively) and lack of efficacy (1.0% vs. 1.6%), he said.
Post hoc analyses hinted at slight benefits of insulin degludec over insulin glargine in terms of end of treatment hemoglobin A1c and the daily observed insulin dose, but less weight gain for insulin glargine.
Commenting further on the study, Dr. Del Prato said there was much debate around the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic differences between insulin degludec and insulin glargine, and that the data should be interpreted “with a lot of caution.”
He said that it was not clear from the findings why there might be a lower risk of hypoglycemia with insulin degludec. He noted that the rate of diurnal hypoglycemia should be considered, and that the statistical interpretation of the data may be “a matter of uncertainty as well.”
Dr. Del Prato agreed that “prevention of hypoglycemia remained a major task in treating type 2 diabetic patients, particularly those on insulin therapy.” He proposed that differentiating between new basal insulin analogs may need “better tools for characterization of PK/PD, rigorous interpretation of the results, careful assessment of the generalizability of results from randomized controlled trials performed in selected study populations, and independent research and careful real-world studies to be performed.”
Furthermore, he said translating the potential benefit of new insulin analogs “cannot just rely on their properties, rather it requires validation over the time of the accuracy of glucose meters, and adequate patient education, and even more, education reinforcement.”
All of the speakers disclosed ties with Novo Nordisk, which funded the study, as well as other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCES: Philis-Tsimikas A. EASD 2019, Oral Presentation 90; Pieber T. EASD 2019, Oral Presentation S38.1; Philis-Tsimikas A. EASD 2019, Oral Presentation S38.2; Del Prato S. EASD 2019. Oral Presentation S38.3.
BARCELONA – data presented at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
During a 36-week maintenance treatment period, the rate ratio (RR) for the primary endpoint of the study – severe or confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia, defined as a blood-glucose level of less than 3.1 mmol/L (56 mg/dL) – was 0.88 (95% confidence interval, 0.73-1.06; P = .17) in a comparison the two long-acting insulins.
There were some differences that favored insulin degludec over insulin glargine when other endpoints were considered, but because a statistical testing hierarchy was used, “no confirmatory results can be made from CONCLUDE,” one of the study investigators, Athena Philis-Tsimikas, MD, of Scripps Whittier Diabetes Institute, San Diego, said during a special symposium at the meeting.
“If the primary endpoint was not achieved, the testing hierarchy stopped after the first occurrence of nonsignificance,” she explained. Although that occurred, the other endpoints could still be analyzed as they were all prespecified, she argued. These showed that during the maintenance treatment period, there were lower rates of nocturnal symptomatic hypoglycemic episodes (RR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.48-0.84; P = .0014) and severe episodes (those requiring third-party assistance; RR, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.07-0.57; P = .0027) with insulin degludec, compared with insulin glargine.
The trial came under fire, however, from Stefano Del Prato, MD, professor of endocrinology in the department of endocrinology metabolism and chief of the section of diabetes at the University of Pisa, Italy, who provided the EASD-invited independent commentary on the study’s findings. “This is the CONCLUDE trial. You’d could expect a CONCLUDE trial to be conclusive in its conclusions!” he said, noting that there were “too many uncertainties” in the trial.
CONCLUDE was a randomized, open-label, head-to-head study of insulin degludec versus insulin glargine in 1,609 adult patients with type 2 diabetes who were inadequately treated with basal insulin with or without oral antidiabetic drugs. The aim of the trial was to evaluate the risk of hypoglycemia associated with the two long-acting insulins.
“Hypoglycemia is a very common event in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes,” Thomas Pieber, MD, Medical University Graz, Austria, reminded the audience. Severe hypoglycemia is associated with insulin use, and data show that patients with type 2 diabetes are at as much risk as are those with type 1 diabetes in the longer term (Diabetologia. 2007;50:1140-7).
The rationale for the CONCLUDE study comes from evidence from other trials, he said. Specifically, there was a pharmacodynamic/pharmacokinetic study comparing insulin degludec U200 with insulin glargine U300 that showed four times lower day-to-day variability in favor of insulin degludec (Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19:1032-9). Dr. Pieber noted that there was also a 30% lower potency of insulin glargine U300 versus insulin degludec U200. Those findings, together with findings from the SWITCH 2 (JAMA. 2017;318:45-56) and EDITION II (Diabetes Care. 2014;37:3235-43) trials, led to the hypothesis that there might be lower rates of hypoglycemia with insulin degludec U200 than with insulin glargine U300.
Dr. Pieber noted that one early issue with the trial was how patients’ blood glucose had been initially measured, because the blood glucose monitoring system that patients were first using seemed to display falsely higher values than what was actually expected, potentially putting patients’ safety at risk. This called for a protocol amendment (J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2019;13:498-506) and a new blood glucose monitoring system being used.
A similar proportion of patients in each group discontinued treatment during the study – 12.3% in the insulin degludec arm, and 11.4% in the insulin glargine arm – for reasons including adverse events (2.9% vs. 2.1%, respectively) and lack of efficacy (1.0% vs. 1.6%), he said.
Post hoc analyses hinted at slight benefits of insulin degludec over insulin glargine in terms of end of treatment hemoglobin A1c and the daily observed insulin dose, but less weight gain for insulin glargine.
Commenting further on the study, Dr. Del Prato said there was much debate around the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic differences between insulin degludec and insulin glargine, and that the data should be interpreted “with a lot of caution.”
He said that it was not clear from the findings why there might be a lower risk of hypoglycemia with insulin degludec. He noted that the rate of diurnal hypoglycemia should be considered, and that the statistical interpretation of the data may be “a matter of uncertainty as well.”
Dr. Del Prato agreed that “prevention of hypoglycemia remained a major task in treating type 2 diabetic patients, particularly those on insulin therapy.” He proposed that differentiating between new basal insulin analogs may need “better tools for characterization of PK/PD, rigorous interpretation of the results, careful assessment of the generalizability of results from randomized controlled trials performed in selected study populations, and independent research and careful real-world studies to be performed.”
Furthermore, he said translating the potential benefit of new insulin analogs “cannot just rely on their properties, rather it requires validation over the time of the accuracy of glucose meters, and adequate patient education, and even more, education reinforcement.”
All of the speakers disclosed ties with Novo Nordisk, which funded the study, as well as other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCES: Philis-Tsimikas A. EASD 2019, Oral Presentation 90; Pieber T. EASD 2019, Oral Presentation S38.1; Philis-Tsimikas A. EASD 2019, Oral Presentation S38.2; Del Prato S. EASD 2019. Oral Presentation S38.3.
REPORTING FROM EASD 2019
Vitamin D does not improve bone density, structure in healthy patients
ORLANDO – after 2 years of daily use, according to data presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
“Participants may have already reached the vitamin D level needed for bone health,” Meryl S. LeBoff, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, said in her presentation.
Dr. LeBoff presented results from 771 patients (mean age, 63.8 years) in the Bone Health Subcohort of VITAL (Vitamin D and OmegA-3 TriaL) who were not on any bone active medications and were randomized to receive daily vitamin D3 at a dose of 2,000 IU or placebo. Patients received bone imaging at baseline and at 2 years; areal bone mineral density (aBMD) of the whole body, femoral neck, total hip, and spine was assessed via dual x-ray absorptiometry scan. Total 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels were measured via liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry, and free 25(OH)D levels were measured via the ELISA assay. The baseline characteristics of the vitamin D3 supplementation and placebo groups were similar. Overall, 52% of patients had osteopenia and 10.4% had osteoporosis.
Between baseline and 2 years, the vitamin D group’s total 25(OH)D levels increased from a mean 27.0 ng/mL to 39.5 ng/mL (46%) and the free 25(OH)D levels increased from 5.8 pg/mL to 9.0 pg/mL (55%), whereas levels in the placebo stayed the same. The researchers found no significant absolute percentage changes over 2 years in aBMD of the whole body (P = .60), femoral neck (P = .16), total hip (P = .23) and spine (P = .55), compared with patients in the placebo group.
In a secondary analysis, Dr. LeBoff and colleagues found no benefit to volumetric BMD (vBMD) of the radius and the tibia at 2 years, and the results persisted after they performed a sensitivity analysis. Adverse events, such as hypercalciuria, kidney stones, and gastrointestinal symptoms, were not significantly different in the vitamin D group, compared with the placebo group.
Dr. LeBoff noted among the limitations of the study that it evaluated one dose level of vitamin D and was not designed to determine whether vitamin D supplementation was effective in people with vitamin D insufficiency, and the results are not generalizable to patients with osteoporosis or osteomalacia. Future studies should also examine whether free 25(OH)D levels can be used to detect which patients can benefit from vitamin D supplementation, she added.
Risk of falls
In a separate abstract, which Dr. LeBoff presented in a different session, 12,927 patients who received vitamin D supplementation for 5 years, were studied for risk of falls, compared with 12,994 individuals in a placebo group. At baseline, 33.3% of patients had fallen at least once in the previous year, and overall 6,605 patients reported 13,235 falls. At 5.3 years of follow-up, there were no significant differences in number of falls between groups, falls leading to injury, and falls leading to a doctor or a hospital visit.
There are ongoing parallel studies examining the incidence of fractures between groups in the total population of the VITAL study (25,871 participants); bone turnover markers; bone microarchitecture measurements through high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography; and examining the connection between free 25(OH)D, parathyroid hormone, and vitamin D binding protein, said Dr. LeBoff.
The study was funded in part by grants from the National Cancer Institute, the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, the Office of Dietary Supplements, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, and the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. Dr. LeBoff reported receiving grants from the National Institute of Arthritis Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Two authors reported nonfinancial support Pharmavite LLC of Northridge, Calif., Pronova BioPharma of Norway and BASF, and Quest Diagnostics. The remaining authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: LeBoff M et al. ASBMR 2019, Abstracts 1046 and 1057.
ORLANDO – after 2 years of daily use, according to data presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
“Participants may have already reached the vitamin D level needed for bone health,” Meryl S. LeBoff, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, said in her presentation.
Dr. LeBoff presented results from 771 patients (mean age, 63.8 years) in the Bone Health Subcohort of VITAL (Vitamin D and OmegA-3 TriaL) who were not on any bone active medications and were randomized to receive daily vitamin D3 at a dose of 2,000 IU or placebo. Patients received bone imaging at baseline and at 2 years; areal bone mineral density (aBMD) of the whole body, femoral neck, total hip, and spine was assessed via dual x-ray absorptiometry scan. Total 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels were measured via liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry, and free 25(OH)D levels were measured via the ELISA assay. The baseline characteristics of the vitamin D3 supplementation and placebo groups were similar. Overall, 52% of patients had osteopenia and 10.4% had osteoporosis.
Between baseline and 2 years, the vitamin D group’s total 25(OH)D levels increased from a mean 27.0 ng/mL to 39.5 ng/mL (46%) and the free 25(OH)D levels increased from 5.8 pg/mL to 9.0 pg/mL (55%), whereas levels in the placebo stayed the same. The researchers found no significant absolute percentage changes over 2 years in aBMD of the whole body (P = .60), femoral neck (P = .16), total hip (P = .23) and spine (P = .55), compared with patients in the placebo group.
In a secondary analysis, Dr. LeBoff and colleagues found no benefit to volumetric BMD (vBMD) of the radius and the tibia at 2 years, and the results persisted after they performed a sensitivity analysis. Adverse events, such as hypercalciuria, kidney stones, and gastrointestinal symptoms, were not significantly different in the vitamin D group, compared with the placebo group.
Dr. LeBoff noted among the limitations of the study that it evaluated one dose level of vitamin D and was not designed to determine whether vitamin D supplementation was effective in people with vitamin D insufficiency, and the results are not generalizable to patients with osteoporosis or osteomalacia. Future studies should also examine whether free 25(OH)D levels can be used to detect which patients can benefit from vitamin D supplementation, she added.
Risk of falls
In a separate abstract, which Dr. LeBoff presented in a different session, 12,927 patients who received vitamin D supplementation for 5 years, were studied for risk of falls, compared with 12,994 individuals in a placebo group. At baseline, 33.3% of patients had fallen at least once in the previous year, and overall 6,605 patients reported 13,235 falls. At 5.3 years of follow-up, there were no significant differences in number of falls between groups, falls leading to injury, and falls leading to a doctor or a hospital visit.
There are ongoing parallel studies examining the incidence of fractures between groups in the total population of the VITAL study (25,871 participants); bone turnover markers; bone microarchitecture measurements through high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography; and examining the connection between free 25(OH)D, parathyroid hormone, and vitamin D binding protein, said Dr. LeBoff.
The study was funded in part by grants from the National Cancer Institute, the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, the Office of Dietary Supplements, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, and the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. Dr. LeBoff reported receiving grants from the National Institute of Arthritis Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Two authors reported nonfinancial support Pharmavite LLC of Northridge, Calif., Pronova BioPharma of Norway and BASF, and Quest Diagnostics. The remaining authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: LeBoff M et al. ASBMR 2019, Abstracts 1046 and 1057.
ORLANDO – after 2 years of daily use, according to data presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
“Participants may have already reached the vitamin D level needed for bone health,” Meryl S. LeBoff, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, said in her presentation.
Dr. LeBoff presented results from 771 patients (mean age, 63.8 years) in the Bone Health Subcohort of VITAL (Vitamin D and OmegA-3 TriaL) who were not on any bone active medications and were randomized to receive daily vitamin D3 at a dose of 2,000 IU or placebo. Patients received bone imaging at baseline and at 2 years; areal bone mineral density (aBMD) of the whole body, femoral neck, total hip, and spine was assessed via dual x-ray absorptiometry scan. Total 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels were measured via liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry, and free 25(OH)D levels were measured via the ELISA assay. The baseline characteristics of the vitamin D3 supplementation and placebo groups were similar. Overall, 52% of patients had osteopenia and 10.4% had osteoporosis.
Between baseline and 2 years, the vitamin D group’s total 25(OH)D levels increased from a mean 27.0 ng/mL to 39.5 ng/mL (46%) and the free 25(OH)D levels increased from 5.8 pg/mL to 9.0 pg/mL (55%), whereas levels in the placebo stayed the same. The researchers found no significant absolute percentage changes over 2 years in aBMD of the whole body (P = .60), femoral neck (P = .16), total hip (P = .23) and spine (P = .55), compared with patients in the placebo group.
In a secondary analysis, Dr. LeBoff and colleagues found no benefit to volumetric BMD (vBMD) of the radius and the tibia at 2 years, and the results persisted after they performed a sensitivity analysis. Adverse events, such as hypercalciuria, kidney stones, and gastrointestinal symptoms, were not significantly different in the vitamin D group, compared with the placebo group.
Dr. LeBoff noted among the limitations of the study that it evaluated one dose level of vitamin D and was not designed to determine whether vitamin D supplementation was effective in people with vitamin D insufficiency, and the results are not generalizable to patients with osteoporosis or osteomalacia. Future studies should also examine whether free 25(OH)D levels can be used to detect which patients can benefit from vitamin D supplementation, she added.
Risk of falls
In a separate abstract, which Dr. LeBoff presented in a different session, 12,927 patients who received vitamin D supplementation for 5 years, were studied for risk of falls, compared with 12,994 individuals in a placebo group. At baseline, 33.3% of patients had fallen at least once in the previous year, and overall 6,605 patients reported 13,235 falls. At 5.3 years of follow-up, there were no significant differences in number of falls between groups, falls leading to injury, and falls leading to a doctor or a hospital visit.
There are ongoing parallel studies examining the incidence of fractures between groups in the total population of the VITAL study (25,871 participants); bone turnover markers; bone microarchitecture measurements through high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography; and examining the connection between free 25(OH)D, parathyroid hormone, and vitamin D binding protein, said Dr. LeBoff.
The study was funded in part by grants from the National Cancer Institute, the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, the Office of Dietary Supplements, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, and the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. Dr. LeBoff reported receiving grants from the National Institute of Arthritis Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Two authors reported nonfinancial support Pharmavite LLC of Northridge, Calif., Pronova BioPharma of Norway and BASF, and Quest Diagnostics. The remaining authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: LeBoff M et al. ASBMR 2019, Abstracts 1046 and 1057.
REPORTING FROM ASBMR 2019
Milrinone beats dobutamine in extending survival in HF
PHILADELPHIA – Milrinone was associated with a 50% reduction in mortality, compared with dobutamine, in patients with heart failure who were receiving home inotropes as a bridge to advanced therapies, according to results of a large U.S. registry study.
The survival profile for milrinone was more favorable than that for dobutamine across various indications for use, including bridge to transplant, bridge to mechanical support, and palliation.
The findings illustrate an “urgent need” for randomized trials that compare inotropic therapy strategies in patients with end-stage heart failure, said investigator Behram P. Mody, MD, of the division of cardiology at the University of California, San Diego, La Jolla.
“Although [there is] the possibility of selection bias and there are confounding variables, this consistent finding may reflect a true benefit of milrinone,” Dr. Mody said in a presentation at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America
The evidence to support use of continuous outpatient intravenous inotropic therapy in stage D heart failure is limited and comes mainly from case series, and small, randomized trials demonstrating poor outcomes, Dr. Mody explained.
“Long-term survival associated with home inotropes in the modern era of guideline-directed medical and device therapy is poorly defined,” he said.
The retrospective study Dr. Mody presented at the meeting included 1,149 patients (mean age, 60 years; 29.9% women) who received continuous intravenous outpatient inotropic therapy (milrinone or dobutamine) from 2015 to 2017. This is possibly the largest body of data reported to date of patients receiving home inotropes, he said.
For the overall population, the estimated 1-year survival rate was 71% with milrinone, compared with 46% for dobutamine (P less than .0001), Dr. Mody reported. After adjusting for age, gender, weight, and indication, milrinone use was still significantly associated with lower mortality, compared with dobutamine (hazard ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.39-0.64; P less than .0001).
The survival benefit of milrinone over dobutamine was also significant in subsets of patients receiving home inotropes as bridge to transplant, bridge to mechanical support, or palliation. A similar trend, though not statistically significant, was seen for inotropes used as a bridge to decision, he added.
Mortality was generally higher in patients receiving inotropes as palliation, as opposed to bridge therapy, with 1-year survival of 55.0% and 65.6%, respectively, and median survival of 461 days and 584 days.
These findings suggest home inotropes can be “beneficial” in patients with end-stage heart failure in an era of guideline-directed medical therapy and greater defibrillator use, Dr. Mody said.
“I’m not saying that it should replace left ventricular assist devices as the bridge to transplant,” he added, “but it could be an alternative strategy for our patients.”
No funding source was given. Dr. Mody had no disclosures related to the study.
SOURCE: Mody BP et al. J Card Fail. 2019 Sep 14. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2019.07.021.
PHILADELPHIA – Milrinone was associated with a 50% reduction in mortality, compared with dobutamine, in patients with heart failure who were receiving home inotropes as a bridge to advanced therapies, according to results of a large U.S. registry study.
The survival profile for milrinone was more favorable than that for dobutamine across various indications for use, including bridge to transplant, bridge to mechanical support, and palliation.
The findings illustrate an “urgent need” for randomized trials that compare inotropic therapy strategies in patients with end-stage heart failure, said investigator Behram P. Mody, MD, of the division of cardiology at the University of California, San Diego, La Jolla.
“Although [there is] the possibility of selection bias and there are confounding variables, this consistent finding may reflect a true benefit of milrinone,” Dr. Mody said in a presentation at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America
The evidence to support use of continuous outpatient intravenous inotropic therapy in stage D heart failure is limited and comes mainly from case series, and small, randomized trials demonstrating poor outcomes, Dr. Mody explained.
“Long-term survival associated with home inotropes in the modern era of guideline-directed medical and device therapy is poorly defined,” he said.
The retrospective study Dr. Mody presented at the meeting included 1,149 patients (mean age, 60 years; 29.9% women) who received continuous intravenous outpatient inotropic therapy (milrinone or dobutamine) from 2015 to 2017. This is possibly the largest body of data reported to date of patients receiving home inotropes, he said.
For the overall population, the estimated 1-year survival rate was 71% with milrinone, compared with 46% for dobutamine (P less than .0001), Dr. Mody reported. After adjusting for age, gender, weight, and indication, milrinone use was still significantly associated with lower mortality, compared with dobutamine (hazard ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.39-0.64; P less than .0001).
The survival benefit of milrinone over dobutamine was also significant in subsets of patients receiving home inotropes as bridge to transplant, bridge to mechanical support, or palliation. A similar trend, though not statistically significant, was seen for inotropes used as a bridge to decision, he added.
Mortality was generally higher in patients receiving inotropes as palliation, as opposed to bridge therapy, with 1-year survival of 55.0% and 65.6%, respectively, and median survival of 461 days and 584 days.
These findings suggest home inotropes can be “beneficial” in patients with end-stage heart failure in an era of guideline-directed medical therapy and greater defibrillator use, Dr. Mody said.
“I’m not saying that it should replace left ventricular assist devices as the bridge to transplant,” he added, “but it could be an alternative strategy for our patients.”
No funding source was given. Dr. Mody had no disclosures related to the study.
SOURCE: Mody BP et al. J Card Fail. 2019 Sep 14. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2019.07.021.
PHILADELPHIA – Milrinone was associated with a 50% reduction in mortality, compared with dobutamine, in patients with heart failure who were receiving home inotropes as a bridge to advanced therapies, according to results of a large U.S. registry study.
The survival profile for milrinone was more favorable than that for dobutamine across various indications for use, including bridge to transplant, bridge to mechanical support, and palliation.
The findings illustrate an “urgent need” for randomized trials that compare inotropic therapy strategies in patients with end-stage heart failure, said investigator Behram P. Mody, MD, of the division of cardiology at the University of California, San Diego, La Jolla.
“Although [there is] the possibility of selection bias and there are confounding variables, this consistent finding may reflect a true benefit of milrinone,” Dr. Mody said in a presentation at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America
The evidence to support use of continuous outpatient intravenous inotropic therapy in stage D heart failure is limited and comes mainly from case series, and small, randomized trials demonstrating poor outcomes, Dr. Mody explained.
“Long-term survival associated with home inotropes in the modern era of guideline-directed medical and device therapy is poorly defined,” he said.
The retrospective study Dr. Mody presented at the meeting included 1,149 patients (mean age, 60 years; 29.9% women) who received continuous intravenous outpatient inotropic therapy (milrinone or dobutamine) from 2015 to 2017. This is possibly the largest body of data reported to date of patients receiving home inotropes, he said.
For the overall population, the estimated 1-year survival rate was 71% with milrinone, compared with 46% for dobutamine (P less than .0001), Dr. Mody reported. After adjusting for age, gender, weight, and indication, milrinone use was still significantly associated with lower mortality, compared with dobutamine (hazard ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.39-0.64; P less than .0001).
The survival benefit of milrinone over dobutamine was also significant in subsets of patients receiving home inotropes as bridge to transplant, bridge to mechanical support, or palliation. A similar trend, though not statistically significant, was seen for inotropes used as a bridge to decision, he added.
Mortality was generally higher in patients receiving inotropes as palliation, as opposed to bridge therapy, with 1-year survival of 55.0% and 65.6%, respectively, and median survival of 461 days and 584 days.
These findings suggest home inotropes can be “beneficial” in patients with end-stage heart failure in an era of guideline-directed medical therapy and greater defibrillator use, Dr. Mody said.
“I’m not saying that it should replace left ventricular assist devices as the bridge to transplant,” he added, “but it could be an alternative strategy for our patients.”
No funding source was given. Dr. Mody had no disclosures related to the study.
SOURCE: Mody BP et al. J Card Fail. 2019 Sep 14. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2019.07.021.
REPORTING FROM HFSA 2019
Hospital-acquired C. diff. tied to four ‘high-risk’ antibiotic classes
The use of four antibiotic classes designated “high risk” was found to be an independent predictor of hospital-acquired Clostridioides difficile (CDI), based upon an analysis of microbiologic and pharmacy data from 171 hospitals in the United States.
The high-risk antibiotic classes were second-, third-, and fourth-generation cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, carbapenems, and lincosamides, according to a report by Ying P. Tabak, PhD, of Becton Dickinson in Franklin Lakes, N.J., and colleagues published in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology.
Of the 171 study sites studied, 66 (39%) were teaching hospitals and 105 (61%) were nonteaching hospitals. The high-risk antibiotics most frequently used were cephalosporins (47.9%), fluoroquinolones (31.6%), carbapenems (13.0%), and lincosamides (7.6%). The sites were distributed across various regions of the United States. The hospital-level antibiotic use was measured as days of therapy (DOT) per 1,000 days present (DP).
The study was not able to determine specific links to individual antibiotic classes but to the use of high-risk antibiotics as a whole, except for cephalosporins, which were significantly correlated with hospital-acquired CDI (r = 0.23; P less than .01).
The overall correlation of high-risk antibiotic use and hospital-acquired CDI was 0.22 (P = .003). Higher correlation was observed in teaching hospitals (r = 0.38; P = .002) versus nonteaching hospitals (r = 0.19; P = .055), according to the researchers. The authors attributed this to the possibility of teaching hospitals dealing with more elderly and sicker patients.
After adjusting for significant confounders, the use of high-risk antibiotics was still independently associated with significant risk for hospital-acquired CDI. “For every 100-day increase of DOT per 1,000 DP in high-risk antibiotic use, there was a 12% increase in [hospital-acquired] CDI (RR, 1.12; 95% [confidence interval], 1.04-1.21; P = .002),” according to the authors. This translated to four additional hospital-acquired CDI cases with every 100 DOT increase per 1,000 DP.
“Using a large and current dataset, we found an independent impact of hospital-level high-risk antibiotic use on [hospital-acquired] CDI even after adjusting for confounding factors such as community CDI pressure, proportion of patients aged 65 years or older, average length of stay, and hospital teaching status,” the researchers concluded.
Funding was provided by Nabriva Therapeutics, an antibiotic development company. Four of the authors are full-time employees of Becton Dickinson, which sells diagnostics for infectious diseases, including CDI, and one author was an employee of Nabriva Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Tabak YP et al. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2019 Sep 16. doi: 10.1017/ice.2019.236.
The use of four antibiotic classes designated “high risk” was found to be an independent predictor of hospital-acquired Clostridioides difficile (CDI), based upon an analysis of microbiologic and pharmacy data from 171 hospitals in the United States.
The high-risk antibiotic classes were second-, third-, and fourth-generation cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, carbapenems, and lincosamides, according to a report by Ying P. Tabak, PhD, of Becton Dickinson in Franklin Lakes, N.J., and colleagues published in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology.
Of the 171 study sites studied, 66 (39%) were teaching hospitals and 105 (61%) were nonteaching hospitals. The high-risk antibiotics most frequently used were cephalosporins (47.9%), fluoroquinolones (31.6%), carbapenems (13.0%), and lincosamides (7.6%). The sites were distributed across various regions of the United States. The hospital-level antibiotic use was measured as days of therapy (DOT) per 1,000 days present (DP).
The study was not able to determine specific links to individual antibiotic classes but to the use of high-risk antibiotics as a whole, except for cephalosporins, which were significantly correlated with hospital-acquired CDI (r = 0.23; P less than .01).
The overall correlation of high-risk antibiotic use and hospital-acquired CDI was 0.22 (P = .003). Higher correlation was observed in teaching hospitals (r = 0.38; P = .002) versus nonteaching hospitals (r = 0.19; P = .055), according to the researchers. The authors attributed this to the possibility of teaching hospitals dealing with more elderly and sicker patients.
After adjusting for significant confounders, the use of high-risk antibiotics was still independently associated with significant risk for hospital-acquired CDI. “For every 100-day increase of DOT per 1,000 DP in high-risk antibiotic use, there was a 12% increase in [hospital-acquired] CDI (RR, 1.12; 95% [confidence interval], 1.04-1.21; P = .002),” according to the authors. This translated to four additional hospital-acquired CDI cases with every 100 DOT increase per 1,000 DP.
“Using a large and current dataset, we found an independent impact of hospital-level high-risk antibiotic use on [hospital-acquired] CDI even after adjusting for confounding factors such as community CDI pressure, proportion of patients aged 65 years or older, average length of stay, and hospital teaching status,” the researchers concluded.
Funding was provided by Nabriva Therapeutics, an antibiotic development company. Four of the authors are full-time employees of Becton Dickinson, which sells diagnostics for infectious diseases, including CDI, and one author was an employee of Nabriva Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Tabak YP et al. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2019 Sep 16. doi: 10.1017/ice.2019.236.
The use of four antibiotic classes designated “high risk” was found to be an independent predictor of hospital-acquired Clostridioides difficile (CDI), based upon an analysis of microbiologic and pharmacy data from 171 hospitals in the United States.
The high-risk antibiotic classes were second-, third-, and fourth-generation cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, carbapenems, and lincosamides, according to a report by Ying P. Tabak, PhD, of Becton Dickinson in Franklin Lakes, N.J., and colleagues published in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology.
Of the 171 study sites studied, 66 (39%) were teaching hospitals and 105 (61%) were nonteaching hospitals. The high-risk antibiotics most frequently used were cephalosporins (47.9%), fluoroquinolones (31.6%), carbapenems (13.0%), and lincosamides (7.6%). The sites were distributed across various regions of the United States. The hospital-level antibiotic use was measured as days of therapy (DOT) per 1,000 days present (DP).
The study was not able to determine specific links to individual antibiotic classes but to the use of high-risk antibiotics as a whole, except for cephalosporins, which were significantly correlated with hospital-acquired CDI (r = 0.23; P less than .01).
The overall correlation of high-risk antibiotic use and hospital-acquired CDI was 0.22 (P = .003). Higher correlation was observed in teaching hospitals (r = 0.38; P = .002) versus nonteaching hospitals (r = 0.19; P = .055), according to the researchers. The authors attributed this to the possibility of teaching hospitals dealing with more elderly and sicker patients.
After adjusting for significant confounders, the use of high-risk antibiotics was still independently associated with significant risk for hospital-acquired CDI. “For every 100-day increase of DOT per 1,000 DP in high-risk antibiotic use, there was a 12% increase in [hospital-acquired] CDI (RR, 1.12; 95% [confidence interval], 1.04-1.21; P = .002),” according to the authors. This translated to four additional hospital-acquired CDI cases with every 100 DOT increase per 1,000 DP.
“Using a large and current dataset, we found an independent impact of hospital-level high-risk antibiotic use on [hospital-acquired] CDI even after adjusting for confounding factors such as community CDI pressure, proportion of patients aged 65 years or older, average length of stay, and hospital teaching status,” the researchers concluded.
Funding was provided by Nabriva Therapeutics, an antibiotic development company. Four of the authors are full-time employees of Becton Dickinson, which sells diagnostics for infectious diseases, including CDI, and one author was an employee of Nabriva Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Tabak YP et al. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2019 Sep 16. doi: 10.1017/ice.2019.236.
FROM INFECTION CONTROL & HOSPITAL EPIDEMIOLOGY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: For every 100-day increase in high-risk antibiotic therapy, there was a 12% increase in hospital-acquired C. difficile.
Study details: Microbiological and pharmacy data from 171 hospitals comparing hospitalwide use of four antibiotics classes on hospital-acquired C. difficile.
Disclosures: Funding was provided Nabriva Therapeutics, an antibiotic development company. Four of the authors are full-time employees of Becton Dickinson, which sells diagnostics for infectious diseases, including C. difficile, and one author was an employee of Nabriva Therapeutics.
Source: Tabak YP et al. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2019 Sep 16. doi: 10.1017/ice.2019.236.