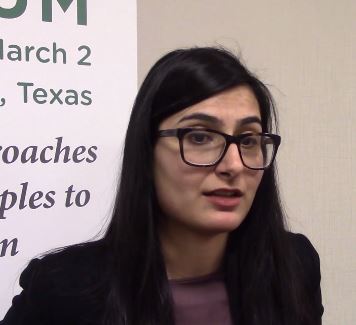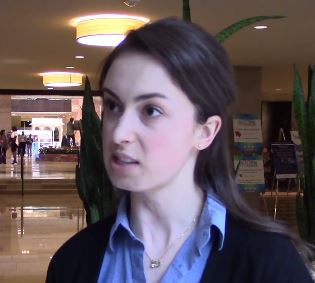User login
DDNA 2019 - Heartburn: Modern Diagnosis of GERD
AT DIGESTIVE DISEASES: NEW ADVANCES
Immunomodulators for pediatric skin diseases
WASHINGTON – At the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, colleagues A. Yasmine Kirkorian, MD, a pediatric dermatologist at George Washington University, Washington, and interim chief of pediatric dermatology at Children’s National Health System, and Adam Friedman, MD, professor and interim chair of dermatology at the university, sat down with Dermatology News and discussed their presentations at a session on the use of immunomodulators for inflammatory and neoplastic skin diseases.
In this video, , with her clinical pearls and practical considerations for treating atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and hidradenitis suppurativa in pediatric patients, covering both on- and off-label treatments.
“Children sometimes require systemic treatment and we shouldn’t hold it back from them because of their age; if they’re severely ill ... they need to be treated,” she said, summing up one of her main points.
During the interview immediately after the AAD meeting, she mentioned dupilumab, which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of moderate to severe AD in patients aged 12-17 years.
Dr. Friedman and Dr. Kirkorian reported having no financial disclosures.
WASHINGTON – At the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, colleagues A. Yasmine Kirkorian, MD, a pediatric dermatologist at George Washington University, Washington, and interim chief of pediatric dermatology at Children’s National Health System, and Adam Friedman, MD, professor and interim chair of dermatology at the university, sat down with Dermatology News and discussed their presentations at a session on the use of immunomodulators for inflammatory and neoplastic skin diseases.
In this video, , with her clinical pearls and practical considerations for treating atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and hidradenitis suppurativa in pediatric patients, covering both on- and off-label treatments.
“Children sometimes require systemic treatment and we shouldn’t hold it back from them because of their age; if they’re severely ill ... they need to be treated,” she said, summing up one of her main points.
During the interview immediately after the AAD meeting, she mentioned dupilumab, which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of moderate to severe AD in patients aged 12-17 years.
Dr. Friedman and Dr. Kirkorian reported having no financial disclosures.
WASHINGTON – At the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, colleagues A. Yasmine Kirkorian, MD, a pediatric dermatologist at George Washington University, Washington, and interim chief of pediatric dermatology at Children’s National Health System, and Adam Friedman, MD, professor and interim chair of dermatology at the university, sat down with Dermatology News and discussed their presentations at a session on the use of immunomodulators for inflammatory and neoplastic skin diseases.
In this video, , with her clinical pearls and practical considerations for treating atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and hidradenitis suppurativa in pediatric patients, covering both on- and off-label treatments.
“Children sometimes require systemic treatment and we shouldn’t hold it back from them because of their age; if they’re severely ill ... they need to be treated,” she said, summing up one of her main points.
During the interview immediately after the AAD meeting, she mentioned dupilumab, which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of moderate to severe AD in patients aged 12-17 years.
Dr. Friedman and Dr. Kirkorian reported having no financial disclosures.
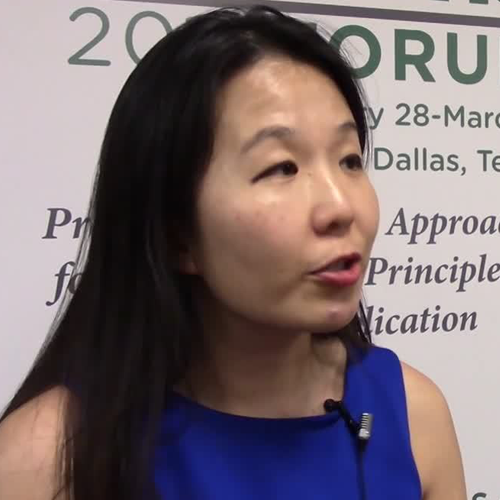
MRI is a critical part of the MS precision medicine toolkit
DALLAS – MRI has long been important in both diagnosis and management of multiple sclerosis (MS). It’s more important than ever though, as perivenular demyelinating lesions emerge as a potential biomarker of the disease, and a key tool in precision medicine initiatives that target MS.
“The central vein sign is at the current time still a research tool that is being touted as an imaging finding that may be a very useful biomarker for diagnosis in MS,” said Jiwon Oh, MD, PhD, in an interview at the meeting presented by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis.
It’s almost ready for “prime time,” she said, “because it can easily be acquired on most conventional 3 Tesla MRI scanners, the sequences that you use don’t require an inordinate amount of time [and] it doesn’t take too much training to be able to easily identify the sign.”
A number of groups have evaluated the central vein sign and are finding it “a very specific biomarker” for MS, Dr. Oh said.
“It would be very useful in very early stages of diagnosis because it would prevent people from being misdiagnosed” and being treated unnecessarily, she said.
In her own work, Dr. Oh and her collaborators are following a cohort of people with radiologically isolated syndrome (RIS) discovered incidentally on brain imaging. “It’s a very valuable patient population to study because it may give us insight into the very earliest stages of MS,” as the lesions were not accompanied by any symptoms when they were first noticed.
Dr. Oh and her colleagues are finding that, among RIS patients, “the vast, vast majority of people have lesions with central veins; in our cohort, over 90% of patients met the 40% threshold that has been proposed to distinguish MS from other white matter changes.”
Dr. Oh said that the central vein sign may prove to be prognostic among RIS patients; they continue to follow the cohort being studied at the University of Toronto, where Dr. Oh is a neurologist.
DALLAS – MRI has long been important in both diagnosis and management of multiple sclerosis (MS). It’s more important than ever though, as perivenular demyelinating lesions emerge as a potential biomarker of the disease, and a key tool in precision medicine initiatives that target MS.
“The central vein sign is at the current time still a research tool that is being touted as an imaging finding that may be a very useful biomarker for diagnosis in MS,” said Jiwon Oh, MD, PhD, in an interview at the meeting presented by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis.
It’s almost ready for “prime time,” she said, “because it can easily be acquired on most conventional 3 Tesla MRI scanners, the sequences that you use don’t require an inordinate amount of time [and] it doesn’t take too much training to be able to easily identify the sign.”
A number of groups have evaluated the central vein sign and are finding it “a very specific biomarker” for MS, Dr. Oh said.
“It would be very useful in very early stages of diagnosis because it would prevent people from being misdiagnosed” and being treated unnecessarily, she said.
In her own work, Dr. Oh and her collaborators are following a cohort of people with radiologically isolated syndrome (RIS) discovered incidentally on brain imaging. “It’s a very valuable patient population to study because it may give us insight into the very earliest stages of MS,” as the lesions were not accompanied by any symptoms when they were first noticed.
Dr. Oh and her colleagues are finding that, among RIS patients, “the vast, vast majority of people have lesions with central veins; in our cohort, over 90% of patients met the 40% threshold that has been proposed to distinguish MS from other white matter changes.”
Dr. Oh said that the central vein sign may prove to be prognostic among RIS patients; they continue to follow the cohort being studied at the University of Toronto, where Dr. Oh is a neurologist.
DALLAS – MRI has long been important in both diagnosis and management of multiple sclerosis (MS). It’s more important than ever though, as perivenular demyelinating lesions emerge as a potential biomarker of the disease, and a key tool in precision medicine initiatives that target MS.
“The central vein sign is at the current time still a research tool that is being touted as an imaging finding that may be a very useful biomarker for diagnosis in MS,” said Jiwon Oh, MD, PhD, in an interview at the meeting presented by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis.
It’s almost ready for “prime time,” she said, “because it can easily be acquired on most conventional 3 Tesla MRI scanners, the sequences that you use don’t require an inordinate amount of time [and] it doesn’t take too much training to be able to easily identify the sign.”
A number of groups have evaluated the central vein sign and are finding it “a very specific biomarker” for MS, Dr. Oh said.
“It would be very useful in very early stages of diagnosis because it would prevent people from being misdiagnosed” and being treated unnecessarily, she said.
In her own work, Dr. Oh and her collaborators are following a cohort of people with radiologically isolated syndrome (RIS) discovered incidentally on brain imaging. “It’s a very valuable patient population to study because it may give us insight into the very earliest stages of MS,” as the lesions were not accompanied by any symptoms when they were first noticed.
Dr. Oh and her colleagues are finding that, among RIS patients, “the vast, vast majority of people have lesions with central veins; in our cohort, over 90% of patients met the 40% threshold that has been proposed to distinguish MS from other white matter changes.”
Dr. Oh said that the central vein sign may prove to be prognostic among RIS patients; they continue to follow the cohort being studied at the University of Toronto, where Dr. Oh is a neurologist.
REPORTING FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2019
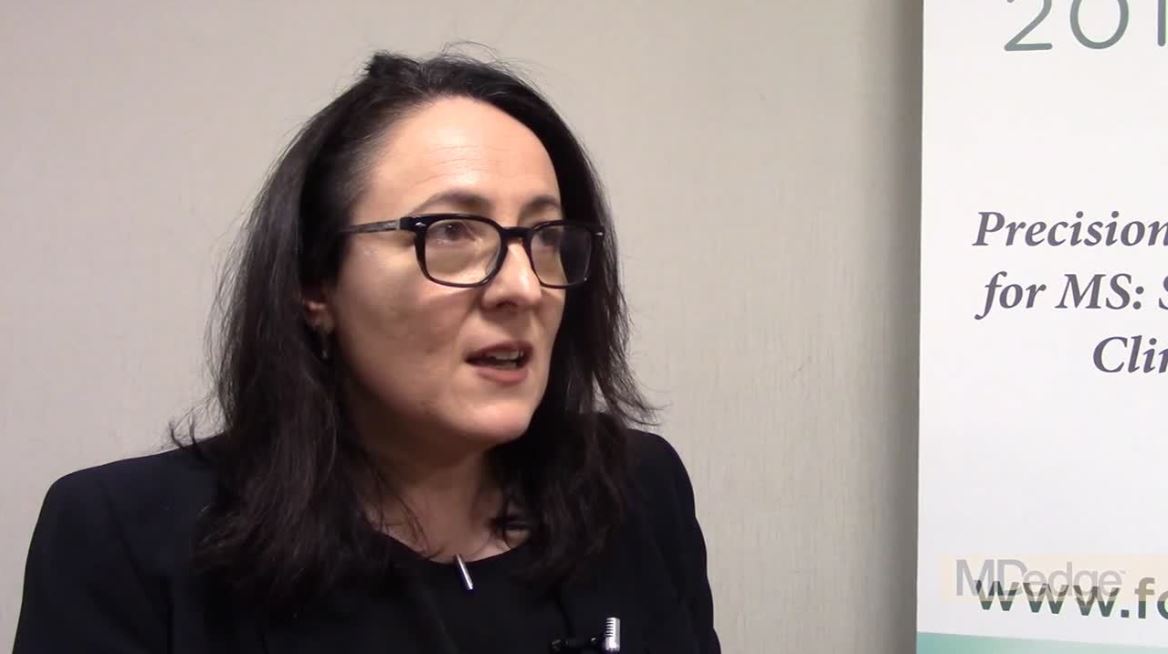
Barancik award winner probes role of fibrinogen in MS
DALLAS – The National Multiple Sclerosis society has awarded the 2018 Barancik Prize for Innovation in Multiple Sclerosis Research to Katerina Akassoglou, PhD.
Dr. Akassoglou laid out the course of research into the role of fibrinogen in multiple sclerosis and other neurodegenerative disorders during her talk at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis.
Dr. Akassoglou and her collaborators questioned the received wisdom about what happens when the brain’s vasculature is disrupted, she said in a video interview. “Fibrinogen was studied for several decades as only a marker of blood-brain barrier disruption. We asked the question, ‘Is it possible that it’s not only a marker, but it also plays a role in disease pathogenesis?’ ”
Over the years, said Dr. Akassoglou, she and her collaborators have developed tools “to dissect this chicken-and-egg question.” A key answer came when the researchers found that when fibrinogen leaks through the vasculature into brain tissue, it can promote inflammatory processes. “At the same time, it induced pathogenic responses in brain immune cells, causing them to be toxic to neuronal cells.”
“Using genetic models of depleting fibrinogen, or blocking its interactions with immune receptors, provided compelling data that this could be an important target for neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation,” said Dr. Akassoglou, professor of neurology at the University of California, San Francisco.
The problem came in trying to find a way to block or deplete fibrinogen inside central nervous system tissue without inactivating it throughout the circulation, since it’s essential for hemostasis.
A promising answer to this problem lies in an investigational monoclonal antibody that binds selectively to sites on fibrinogen that are activated in the brain but are not involved with fibrinogen’s usual role in the clotting cascade in the peripheral circulation, she said.
DALLAS – The National Multiple Sclerosis society has awarded the 2018 Barancik Prize for Innovation in Multiple Sclerosis Research to Katerina Akassoglou, PhD.
Dr. Akassoglou laid out the course of research into the role of fibrinogen in multiple sclerosis and other neurodegenerative disorders during her talk at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis.
Dr. Akassoglou and her collaborators questioned the received wisdom about what happens when the brain’s vasculature is disrupted, she said in a video interview. “Fibrinogen was studied for several decades as only a marker of blood-brain barrier disruption. We asked the question, ‘Is it possible that it’s not only a marker, but it also plays a role in disease pathogenesis?’ ”
Over the years, said Dr. Akassoglou, she and her collaborators have developed tools “to dissect this chicken-and-egg question.” A key answer came when the researchers found that when fibrinogen leaks through the vasculature into brain tissue, it can promote inflammatory processes. “At the same time, it induced pathogenic responses in brain immune cells, causing them to be toxic to neuronal cells.”
“Using genetic models of depleting fibrinogen, or blocking its interactions with immune receptors, provided compelling data that this could be an important target for neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation,” said Dr. Akassoglou, professor of neurology at the University of California, San Francisco.
The problem came in trying to find a way to block or deplete fibrinogen inside central nervous system tissue without inactivating it throughout the circulation, since it’s essential for hemostasis.
A promising answer to this problem lies in an investigational monoclonal antibody that binds selectively to sites on fibrinogen that are activated in the brain but are not involved with fibrinogen’s usual role in the clotting cascade in the peripheral circulation, she said.
DALLAS – The National Multiple Sclerosis society has awarded the 2018 Barancik Prize for Innovation in Multiple Sclerosis Research to Katerina Akassoglou, PhD.
Dr. Akassoglou laid out the course of research into the role of fibrinogen in multiple sclerosis and other neurodegenerative disorders during her talk at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis.
Dr. Akassoglou and her collaborators questioned the received wisdom about what happens when the brain’s vasculature is disrupted, she said in a video interview. “Fibrinogen was studied for several decades as only a marker of blood-brain barrier disruption. We asked the question, ‘Is it possible that it’s not only a marker, but it also plays a role in disease pathogenesis?’ ”
Over the years, said Dr. Akassoglou, she and her collaborators have developed tools “to dissect this chicken-and-egg question.” A key answer came when the researchers found that when fibrinogen leaks through the vasculature into brain tissue, it can promote inflammatory processes. “At the same time, it induced pathogenic responses in brain immune cells, causing them to be toxic to neuronal cells.”
“Using genetic models of depleting fibrinogen, or blocking its interactions with immune receptors, provided compelling data that this could be an important target for neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation,” said Dr. Akassoglou, professor of neurology at the University of California, San Francisco.
The problem came in trying to find a way to block or deplete fibrinogen inside central nervous system tissue without inactivating it throughout the circulation, since it’s essential for hemostasis.
A promising answer to this problem lies in an investigational monoclonal antibody that binds selectively to sites on fibrinogen that are activated in the brain but are not involved with fibrinogen’s usual role in the clotting cascade in the peripheral circulation, she said.
REPORTING FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2019
From bedside to bench to bedside: Derisking MS research
DALLAS – Rhonda Voskuhl, MD, delivered the Kenneth P. Johnson Memorial lecture at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis. In an hour-long talk, Dr. Voskuhl outlined her research approach, which she terms the “bedside to bench to bedside” strategy.
“My view has been that, when we start out research based on a molecule, we don’t really know for sure its clinical relevance. It’s kind of high risk, because you could go through a lot of work, for many years,” she said in a video interview. When work begins in vitro, the researcher runs the risk of proceeding from test tubes, to animal experiments, and then to people, “and then ultimately finding out that it’s not relevant,” said Dr. Voskuhl, director of the multiple sclerosis (MS) program and Jack H. Skirball Chair of Multiple Sclerosis Research at the University of California, Los Angeles.
“And so I just thought, to derisk this whole thing, I think I want to start at the end and then work backwards,” by choosing a physiologically relevant manifestation of MS, she said. “We know that there’s something there. ... All we have to do is figure it out.”
In iterative fashion, Dr. Voskuhl proceeds from the clinical observation, “which we know is true, and then go to the laboratory bench and figure it out by doing a lot of manipulation and isolation of one thing versus another.”
“When you put this in the context of cell-specific and region-specific gene expression, to find disability-specific treatments,” Dr. Voskuhl said, this targeted approach helps address the fact that MS patients differ so much in their presentations and disease course.
“We know that, for example, the neuronal cells differ, and some of the neurotrophic cells differ from pathway to pathway; furthermore, what’s important is that oligocytes and astrocytes and dendrocytes have been shown to differ from one region of the brain and spinal cord to another. So these clearly would have different gene expression signatures, potentially posing different targets for treatment,” Dr. Voskuhl said.
DALLAS – Rhonda Voskuhl, MD, delivered the Kenneth P. Johnson Memorial lecture at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis. In an hour-long talk, Dr. Voskuhl outlined her research approach, which she terms the “bedside to bench to bedside” strategy.
“My view has been that, when we start out research based on a molecule, we don’t really know for sure its clinical relevance. It’s kind of high risk, because you could go through a lot of work, for many years,” she said in a video interview. When work begins in vitro, the researcher runs the risk of proceeding from test tubes, to animal experiments, and then to people, “and then ultimately finding out that it’s not relevant,” said Dr. Voskuhl, director of the multiple sclerosis (MS) program and Jack H. Skirball Chair of Multiple Sclerosis Research at the University of California, Los Angeles.
“And so I just thought, to derisk this whole thing, I think I want to start at the end and then work backwards,” by choosing a physiologically relevant manifestation of MS, she said. “We know that there’s something there. ... All we have to do is figure it out.”
In iterative fashion, Dr. Voskuhl proceeds from the clinical observation, “which we know is true, and then go to the laboratory bench and figure it out by doing a lot of manipulation and isolation of one thing versus another.”
“When you put this in the context of cell-specific and region-specific gene expression, to find disability-specific treatments,” Dr. Voskuhl said, this targeted approach helps address the fact that MS patients differ so much in their presentations and disease course.
“We know that, for example, the neuronal cells differ, and some of the neurotrophic cells differ from pathway to pathway; furthermore, what’s important is that oligocytes and astrocytes and dendrocytes have been shown to differ from one region of the brain and spinal cord to another. So these clearly would have different gene expression signatures, potentially posing different targets for treatment,” Dr. Voskuhl said.
DALLAS – Rhonda Voskuhl, MD, delivered the Kenneth P. Johnson Memorial lecture at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis. In an hour-long talk, Dr. Voskuhl outlined her research approach, which she terms the “bedside to bench to bedside” strategy.
“My view has been that, when we start out research based on a molecule, we don’t really know for sure its clinical relevance. It’s kind of high risk, because you could go through a lot of work, for many years,” she said in a video interview. When work begins in vitro, the researcher runs the risk of proceeding from test tubes, to animal experiments, and then to people, “and then ultimately finding out that it’s not relevant,” said Dr. Voskuhl, director of the multiple sclerosis (MS) program and Jack H. Skirball Chair of Multiple Sclerosis Research at the University of California, Los Angeles.
“And so I just thought, to derisk this whole thing, I think I want to start at the end and then work backwards,” by choosing a physiologically relevant manifestation of MS, she said. “We know that there’s something there. ... All we have to do is figure it out.”
In iterative fashion, Dr. Voskuhl proceeds from the clinical observation, “which we know is true, and then go to the laboratory bench and figure it out by doing a lot of manipulation and isolation of one thing versus another.”
“When you put this in the context of cell-specific and region-specific gene expression, to find disability-specific treatments,” Dr. Voskuhl said, this targeted approach helps address the fact that MS patients differ so much in their presentations and disease course.
“We know that, for example, the neuronal cells differ, and some of the neurotrophic cells differ from pathway to pathway; furthermore, what’s important is that oligocytes and astrocytes and dendrocytes have been shown to differ from one region of the brain and spinal cord to another. So these clearly would have different gene expression signatures, potentially posing different targets for treatment,” Dr. Voskuhl said.
REPORTING FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2019
Food allergies and atopic dermatitis: What is the evidence?
WASHINGTON – The and brings up an interesting discussion, Peter Lio, MD, said in a video interview at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Patients are often convinced that food is the main driver of their AD, or parents believe it is a trigger in their children with AD, according to Dr. Lio of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics at Northwestern University, Chicago.

There is an increased risk of true food allergy in patients with AD, which “seems to get worse with increasing severity of the disease,” he pointed out. However, he added, many patients believe that food allergy is what is driving their eczema, “and that’s the part we don’t really think bears out” in clinical trials.
In the interview, Dr. Lio reviewed some of the clinical trial data and discussed other issues, including foods that seem to have an inflammatory effect in the body, the concepts of “transcutaneous sensitization” in children with AD and the “leaky gut,” and why he tends to recommend probiotics for patients with AD.
Dr. Lio spoke on diet and AD during a session titled “Dietary Triggers and Modifications of Common Dermatologic Conditions – An Evidence Based Approach,” at the meeting, He had no relevant disclosures.
WASHINGTON – The and brings up an interesting discussion, Peter Lio, MD, said in a video interview at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Patients are often convinced that food is the main driver of their AD, or parents believe it is a trigger in their children with AD, according to Dr. Lio of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics at Northwestern University, Chicago.

There is an increased risk of true food allergy in patients with AD, which “seems to get worse with increasing severity of the disease,” he pointed out. However, he added, many patients believe that food allergy is what is driving their eczema, “and that’s the part we don’t really think bears out” in clinical trials.
In the interview, Dr. Lio reviewed some of the clinical trial data and discussed other issues, including foods that seem to have an inflammatory effect in the body, the concepts of “transcutaneous sensitization” in children with AD and the “leaky gut,” and why he tends to recommend probiotics for patients with AD.
Dr. Lio spoke on diet and AD during a session titled “Dietary Triggers and Modifications of Common Dermatologic Conditions – An Evidence Based Approach,” at the meeting, He had no relevant disclosures.
WASHINGTON – The and brings up an interesting discussion, Peter Lio, MD, said in a video interview at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Patients are often convinced that food is the main driver of their AD, or parents believe it is a trigger in their children with AD, according to Dr. Lio of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics at Northwestern University, Chicago.

There is an increased risk of true food allergy in patients with AD, which “seems to get worse with increasing severity of the disease,” he pointed out. However, he added, many patients believe that food allergy is what is driving their eczema, “and that’s the part we don’t really think bears out” in clinical trials.
In the interview, Dr. Lio reviewed some of the clinical trial data and discussed other issues, including foods that seem to have an inflammatory effect in the body, the concepts of “transcutaneous sensitization” in children with AD and the “leaky gut,” and why he tends to recommend probiotics for patients with AD.
Dr. Lio spoke on diet and AD during a session titled “Dietary Triggers and Modifications of Common Dermatologic Conditions – An Evidence Based Approach,” at the meeting, He had no relevant disclosures.
REPORTING FROM AAD 2019
MS research: “Our patients can’t wait” for conventional techniques
DALLAS – The time is right to bring big data and high-horsepower computation to the thorniest problems in multiple sclerosis (MS) research, said Jennifer Graves, MD, who cochaired the closing session at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Research and Treatment in Multiple Sclerosis. The session focused on harnessing machine learning, deep learning, and the newest noninvasive observational techniques to move research and clinical care forward.
“We’ve reached a point in MS research where we’re hitting some stumbling blocks. And a lot of those stumbling blocks are related to how well and how precisely we can measure phenotype in MS. The reason that’s important is that our next frontier is treating progressive MS – and what that requires is finding things that let us know what’s happening at the biological level, so that we can screen drugs faster. We can’t afford to have 3- to 5-year clinical trials. ... Because our patients can’t wait,” said Dr. Graves, an associate professor of neuroscience at the University of California, San Diego.
“We can use all sorts of big data sources, whether it’s the rich imaging data we get on patients when they go into the MRI scanner, whether it’s wearable sensors,” or even newer technology, Dr. Graves said. “We can use technology to give us the sensitivity that we’ve been missing.”
Wearable technology, including accelerometers, can track physical activity that tracks with outcomes in MS, she added. As the tech armament increases, so will data available for analysis and correlation.
However, the key to progress will be to focus on technology that measures change over time. “This is the key: sensitivity to change over time. A lot of things can be associated with disability,” said Dr. Graves, but the key is tracking what changes in an individual patient with disease progression, “so that we can detect treatment effects or side effects.”
DALLAS – The time is right to bring big data and high-horsepower computation to the thorniest problems in multiple sclerosis (MS) research, said Jennifer Graves, MD, who cochaired the closing session at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Research and Treatment in Multiple Sclerosis. The session focused on harnessing machine learning, deep learning, and the newest noninvasive observational techniques to move research and clinical care forward.
“We’ve reached a point in MS research where we’re hitting some stumbling blocks. And a lot of those stumbling blocks are related to how well and how precisely we can measure phenotype in MS. The reason that’s important is that our next frontier is treating progressive MS – and what that requires is finding things that let us know what’s happening at the biological level, so that we can screen drugs faster. We can’t afford to have 3- to 5-year clinical trials. ... Because our patients can’t wait,” said Dr. Graves, an associate professor of neuroscience at the University of California, San Diego.
“We can use all sorts of big data sources, whether it’s the rich imaging data we get on patients when they go into the MRI scanner, whether it’s wearable sensors,” or even newer technology, Dr. Graves said. “We can use technology to give us the sensitivity that we’ve been missing.”
Wearable technology, including accelerometers, can track physical activity that tracks with outcomes in MS, she added. As the tech armament increases, so will data available for analysis and correlation.
However, the key to progress will be to focus on technology that measures change over time. “This is the key: sensitivity to change over time. A lot of things can be associated with disability,” said Dr. Graves, but the key is tracking what changes in an individual patient with disease progression, “so that we can detect treatment effects or side effects.”
DALLAS – The time is right to bring big data and high-horsepower computation to the thorniest problems in multiple sclerosis (MS) research, said Jennifer Graves, MD, who cochaired the closing session at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Research and Treatment in Multiple Sclerosis. The session focused on harnessing machine learning, deep learning, and the newest noninvasive observational techniques to move research and clinical care forward.
“We’ve reached a point in MS research where we’re hitting some stumbling blocks. And a lot of those stumbling blocks are related to how well and how precisely we can measure phenotype in MS. The reason that’s important is that our next frontier is treating progressive MS – and what that requires is finding things that let us know what’s happening at the biological level, so that we can screen drugs faster. We can’t afford to have 3- to 5-year clinical trials. ... Because our patients can’t wait,” said Dr. Graves, an associate professor of neuroscience at the University of California, San Diego.
“We can use all sorts of big data sources, whether it’s the rich imaging data we get on patients when they go into the MRI scanner, whether it’s wearable sensors,” or even newer technology, Dr. Graves said. “We can use technology to give us the sensitivity that we’ve been missing.”
Wearable technology, including accelerometers, can track physical activity that tracks with outcomes in MS, she added. As the tech armament increases, so will data available for analysis and correlation.
However, the key to progress will be to focus on technology that measures change over time. “This is the key: sensitivity to change over time. A lot of things can be associated with disability,” said Dr. Graves, but the key is tracking what changes in an individual patient with disease progression, “so that we can detect treatment effects or side effects.”
REPORTING FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2019
Medical tourism for MS stem cell therapy is common
DALLAS – “Stem cell therapy is something that has been a topic of interest for neurologists for a while,” said Wijdan Rai, MD, speaking at the meeting presented by the American Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis.
However, “stem cell tourism is notoriously difficult to study, because it’s not regulated; there’s no database we can access to try to figure out what exactly is going on in these clinics,” said Dr. Rai.
Dr. Rai, a neurology resident at the Ohio State University, Columbus, said that she and her colleagues had noticed patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) were asking more frequently about stem cell therapies, and mesenchymal stem cell therapy in particular.
To translate these anecdotal observations into more concrete data, Dr. Rai and her colleagues surveyed academic neurologists in the outpatient setting to see if their patients were asking them about medical tourism for stem cell therapy. Additionally, they were asked about patients who actually had sought out the therapy and if there were adverse reactions from stem cell therapy.
The 25-item questionnaire was sent to academic neurologists via an online survey tool called Synapse through the American Academy of Neurology. Dr. Rai and her colleagues found that over 90% of respondents had been asked about stem cell therapies and that 25% of respondents said their patients had some kind of complication from the treatment.
“Most commonly, it was some variation of an infection, like meningitis, encephalitis, or hepatitis C,” said Dr. Rai. Other physicians reported that their patients had spinal cord tumors, deterioration of MS, or stroke.
with this evidence in hand, she hopes that a fact sheet can be developed and hosted on a website so physicians can point their patients to evidence-based information about stem cell therapies in MS.
DALLAS – “Stem cell therapy is something that has been a topic of interest for neurologists for a while,” said Wijdan Rai, MD, speaking at the meeting presented by the American Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis.
However, “stem cell tourism is notoriously difficult to study, because it’s not regulated; there’s no database we can access to try to figure out what exactly is going on in these clinics,” said Dr. Rai.
Dr. Rai, a neurology resident at the Ohio State University, Columbus, said that she and her colleagues had noticed patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) were asking more frequently about stem cell therapies, and mesenchymal stem cell therapy in particular.
To translate these anecdotal observations into more concrete data, Dr. Rai and her colleagues surveyed academic neurologists in the outpatient setting to see if their patients were asking them about medical tourism for stem cell therapy. Additionally, they were asked about patients who actually had sought out the therapy and if there were adverse reactions from stem cell therapy.
The 25-item questionnaire was sent to academic neurologists via an online survey tool called Synapse through the American Academy of Neurology. Dr. Rai and her colleagues found that over 90% of respondents had been asked about stem cell therapies and that 25% of respondents said their patients had some kind of complication from the treatment.
“Most commonly, it was some variation of an infection, like meningitis, encephalitis, or hepatitis C,” said Dr. Rai. Other physicians reported that their patients had spinal cord tumors, deterioration of MS, or stroke.
with this evidence in hand, she hopes that a fact sheet can be developed and hosted on a website so physicians can point their patients to evidence-based information about stem cell therapies in MS.
DALLAS – “Stem cell therapy is something that has been a topic of interest for neurologists for a while,” said Wijdan Rai, MD, speaking at the meeting presented by the American Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis.
However, “stem cell tourism is notoriously difficult to study, because it’s not regulated; there’s no database we can access to try to figure out what exactly is going on in these clinics,” said Dr. Rai.
Dr. Rai, a neurology resident at the Ohio State University, Columbus, said that she and her colleagues had noticed patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) were asking more frequently about stem cell therapies, and mesenchymal stem cell therapy in particular.
To translate these anecdotal observations into more concrete data, Dr. Rai and her colleagues surveyed academic neurologists in the outpatient setting to see if their patients were asking them about medical tourism for stem cell therapy. Additionally, they were asked about patients who actually had sought out the therapy and if there were adverse reactions from stem cell therapy.
The 25-item questionnaire was sent to academic neurologists via an online survey tool called Synapse through the American Academy of Neurology. Dr. Rai and her colleagues found that over 90% of respondents had been asked about stem cell therapies and that 25% of respondents said their patients had some kind of complication from the treatment.
“Most commonly, it was some variation of an infection, like meningitis, encephalitis, or hepatitis C,” said Dr. Rai. Other physicians reported that their patients had spinal cord tumors, deterioration of MS, or stroke.
with this evidence in hand, she hopes that a fact sheet can be developed and hosted on a website so physicians can point their patients to evidence-based information about stem cell therapies in MS.
REPORTING FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2019
Smartphone assessment of motor, cognitive function in MS extends clinicians’ reach
DALLAS –
Alexandra Boukhvalova, a medical student at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, and her collaborators developed an interactive smartphone app to assess some aspects of cognitive and motor function for patients with multiple sclerosis (MS). Their findings were reported during a poster session at the meeting held by the American Society for Prevention and Treatment in Multiple Sclerosis.
“The clinician assessment is an hour-long assessment; it requires a trained neurologist,” Ms. Boukhvalova pointed out. In thinking about how app-based assessment could augment the clinical exam, she and her collaborators realized that “a lot of the neurologic exam is still quite subjective – so is there a way that we can make that exam more objective and quantifiable and also add a little bit of ease with accessibility and mobility?
“We created a suite of test apps ... to assess different neurological systems, ranging from motor function, cognitive and visual dysfunction, general fatigue, and strength,” she said. The apps included tapping tests and balloon-popping tasks, along with measures to give some indication of spasticity by assessing the smoothness of movements.
Participants completed the testing both in the clinic and from home. “We did not need an investigator present for patients to be able to complete the tests,” said Ms. Boukhvalova.
Ms. Boukhvalova and her colleagues compared performance on the gamified tasks between patients with MS and healthy controls. For all tasks, the participants with MS could clearly be differentiated from the healthy participants.
A further plus was that “The patients almost viewed these tests as games.” They reported that they enjoyed completing them, said Ms. Boukhvalova, adding that app-based assessments also offer an additional point of connection between MS patients and specialists, whom they may only see annually or semiannually.
Further app development may focus on utilizing sensor and accelerometer functions in smartphones to perform more natural and sophisticated motor analysis to look at gait and gross motor functioning, she said.
DALLAS –
Alexandra Boukhvalova, a medical student at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, and her collaborators developed an interactive smartphone app to assess some aspects of cognitive and motor function for patients with multiple sclerosis (MS). Their findings were reported during a poster session at the meeting held by the American Society for Prevention and Treatment in Multiple Sclerosis.
“The clinician assessment is an hour-long assessment; it requires a trained neurologist,” Ms. Boukhvalova pointed out. In thinking about how app-based assessment could augment the clinical exam, she and her collaborators realized that “a lot of the neurologic exam is still quite subjective – so is there a way that we can make that exam more objective and quantifiable and also add a little bit of ease with accessibility and mobility?
“We created a suite of test apps ... to assess different neurological systems, ranging from motor function, cognitive and visual dysfunction, general fatigue, and strength,” she said. The apps included tapping tests and balloon-popping tasks, along with measures to give some indication of spasticity by assessing the smoothness of movements.
Participants completed the testing both in the clinic and from home. “We did not need an investigator present for patients to be able to complete the tests,” said Ms. Boukhvalova.
Ms. Boukhvalova and her colleagues compared performance on the gamified tasks between patients with MS and healthy controls. For all tasks, the participants with MS could clearly be differentiated from the healthy participants.
A further plus was that “The patients almost viewed these tests as games.” They reported that they enjoyed completing them, said Ms. Boukhvalova, adding that app-based assessments also offer an additional point of connection between MS patients and specialists, whom they may only see annually or semiannually.
Further app development may focus on utilizing sensor and accelerometer functions in smartphones to perform more natural and sophisticated motor analysis to look at gait and gross motor functioning, she said.
DALLAS –
Alexandra Boukhvalova, a medical student at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, and her collaborators developed an interactive smartphone app to assess some aspects of cognitive and motor function for patients with multiple sclerosis (MS). Their findings were reported during a poster session at the meeting held by the American Society for Prevention and Treatment in Multiple Sclerosis.
“The clinician assessment is an hour-long assessment; it requires a trained neurologist,” Ms. Boukhvalova pointed out. In thinking about how app-based assessment could augment the clinical exam, she and her collaborators realized that “a lot of the neurologic exam is still quite subjective – so is there a way that we can make that exam more objective and quantifiable and also add a little bit of ease with accessibility and mobility?
“We created a suite of test apps ... to assess different neurological systems, ranging from motor function, cognitive and visual dysfunction, general fatigue, and strength,” she said. The apps included tapping tests and balloon-popping tasks, along with measures to give some indication of spasticity by assessing the smoothness of movements.
Participants completed the testing both in the clinic and from home. “We did not need an investigator present for patients to be able to complete the tests,” said Ms. Boukhvalova.
Ms. Boukhvalova and her colleagues compared performance on the gamified tasks between patients with MS and healthy controls. For all tasks, the participants with MS could clearly be differentiated from the healthy participants.
A further plus was that “The patients almost viewed these tests as games.” They reported that they enjoyed completing them, said Ms. Boukhvalova, adding that app-based assessments also offer an additional point of connection between MS patients and specialists, whom they may only see annually or semiannually.
Further app development may focus on utilizing sensor and accelerometer functions in smartphones to perform more natural and sophisticated motor analysis to look at gait and gross motor functioning, she said.
REPORTING FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2019
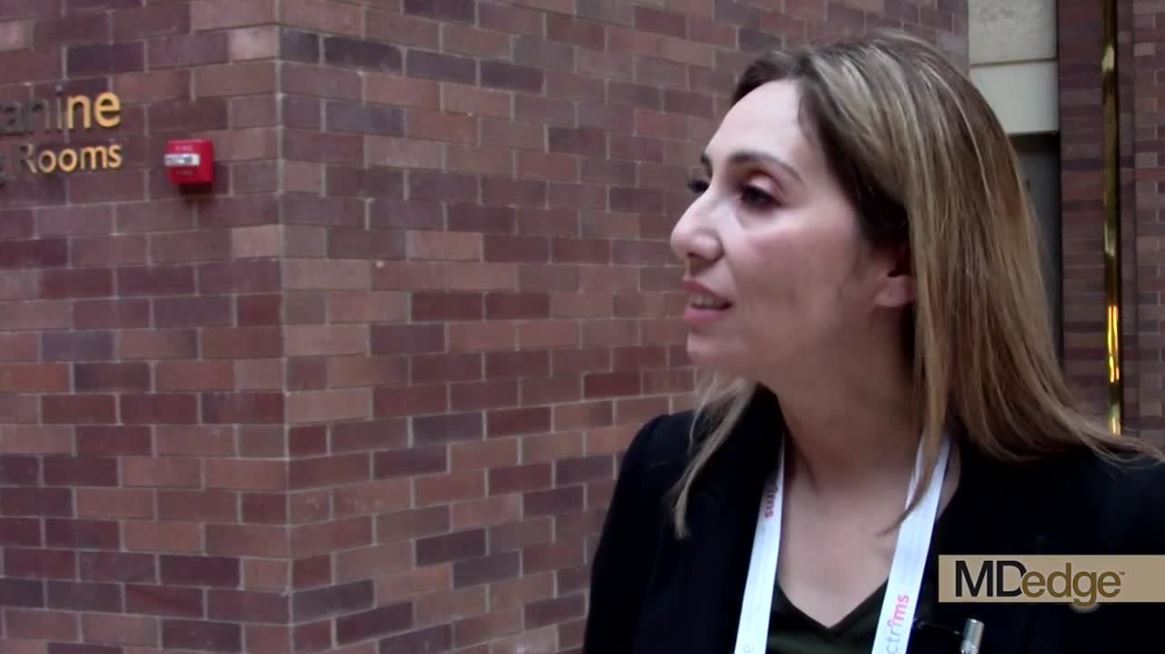
Don’t forget social determinants of health in minority MS patients
DALLAS – The way Lilyana Amezcua, MD, sees it, clinicians should view race and ethnicity as health disparities when assessing individuals with multiple sclerosis.
Whites are predominately affected with MS, “but we have seen changing demographics,” said Dr. Amezcua, of the University of Southern California MS Comprehensive Care and Research Group. “Why are African Americans now at higher risk ... and why do African Americans appear to have more severe disease? Is it a biological difference ... or is it because of poor access” to health care?
At the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis, Dr. Amezcua delivered a presentation entitled “Effect of Race and Ethnicity on MS Presentation and Disease Course.” She called on researchers in the field “to not just take race and ethnicity as any small variable. We need to be cognizant and use the correct methodology, depending on what [question] we want to answer. We need to better define how we ascertain race, how we ascertain ethnicity.”
Dr. Amezcua, who is also the MS fellowship program director at the Keck School of Medicine, disclosed that she receives funding from the National MS Society, the National Institutes of Health, the California Community Foundation, and Biogen.
DALLAS – The way Lilyana Amezcua, MD, sees it, clinicians should view race and ethnicity as health disparities when assessing individuals with multiple sclerosis.
Whites are predominately affected with MS, “but we have seen changing demographics,” said Dr. Amezcua, of the University of Southern California MS Comprehensive Care and Research Group. “Why are African Americans now at higher risk ... and why do African Americans appear to have more severe disease? Is it a biological difference ... or is it because of poor access” to health care?
At the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis, Dr. Amezcua delivered a presentation entitled “Effect of Race and Ethnicity on MS Presentation and Disease Course.” She called on researchers in the field “to not just take race and ethnicity as any small variable. We need to be cognizant and use the correct methodology, depending on what [question] we want to answer. We need to better define how we ascertain race, how we ascertain ethnicity.”
Dr. Amezcua, who is also the MS fellowship program director at the Keck School of Medicine, disclosed that she receives funding from the National MS Society, the National Institutes of Health, the California Community Foundation, and Biogen.
DALLAS – The way Lilyana Amezcua, MD, sees it, clinicians should view race and ethnicity as health disparities when assessing individuals with multiple sclerosis.
Whites are predominately affected with MS, “but we have seen changing demographics,” said Dr. Amezcua, of the University of Southern California MS Comprehensive Care and Research Group. “Why are African Americans now at higher risk ... and why do African Americans appear to have more severe disease? Is it a biological difference ... or is it because of poor access” to health care?
At the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis, Dr. Amezcua delivered a presentation entitled “Effect of Race and Ethnicity on MS Presentation and Disease Course.” She called on researchers in the field “to not just take race and ethnicity as any small variable. We need to be cognizant and use the correct methodology, depending on what [question] we want to answer. We need to better define how we ascertain race, how we ascertain ethnicity.”
Dr. Amezcua, who is also the MS fellowship program director at the Keck School of Medicine, disclosed that she receives funding from the National MS Society, the National Institutes of Health, the California Community Foundation, and Biogen.
REPORTING FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2019