User login
Steady VKA therapy beats switch to NOAC in frail AFib patients: FRAIL-AF
Switching frail patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) from anticoagulation therapy with vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) to a novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) resulted in more bleeding without any reduction in thromboembolic complications or all-cause mortality, randomized trial results show.
The study, FRAIL-AF, is the first randomized NOAC trial to exclusively include frail older patients, said lead author Linda P.T. Joosten, MD, Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care in Utrecht, the Netherlands, and these unexpected findings provide evidence that goes beyond what is currently available.
“Data from the FRAIL-AF trial showed that switching from a VKA to a NOAC should not be considered without a clear indication in frail older patients with AF[ib], as switching to a NOAC leads to 69% more bleeding,” she concluded, without any benefit on secondary clinical endpoints, including thromboembolic events and all-cause mortality.
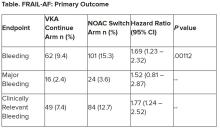
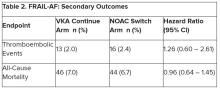
“The results turned out different than we expected,” Dr. Joosten said. “The hypothesis of this superiority trial was that switching from VKA therapy to a NOAC would result in less bleeding. However, we observed the opposite. After the interim analysis, the data and safety monitoring board advised to stop inclusion because switching from a VKA to a NOAC was clearly contraindicated with a hazard ratio of 1.69 and a highly significant P value of .001.”
Results of FRAIL-AF were presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and published online in the journal Circulation.
Session moderator Renate B. Schnabel, MD, interventional cardiologist with University Heart & Vascular Center Hamburg (Germany), congratulated the researchers on these “astonishing” data.
“The thing I want to emphasize here is that, in the absence of randomized controlled trial data, we should be very cautious in extrapolating data from the landmark trials to populations not enrolled in those, and to rely on observational data only,” Dr. Schnabel told Dr. Joosten. “We need randomized controlled trials that sometimes give astonishing results.”
Frailty a clinical syndrome
Frailty is “a lot more than just aging, multiple comorbidities and polypharmacy,” Dr. Joosten explained. “It’s really a clinical syndrome, with people with a high biological vulnerability, dependency on significant others, and a reduced capacity to resist stressors, all leading to a reduced homeostatic reserve.”
Frailty is common in the community, with a prevalence of about 12%, she noted, “and even more important, AF[ib] in frail older people is very common, with a prevalence of 18%. And “without any doubt, we have to adequately anticoagulate frail AF[ib] patients, as they have a high stroke risk, with an incidence of 12.4% per year,” Dr. Joosten noted, compared with 3.9% per year among nonfrail AFib patients.
NOACs are preferred over VKAs in nonfrail AFib patients, after four major trials, RE-LY with dabigatran, ROCKET-AF with rivaroxaban, ARISTOTLE with apixaban, and ENGAGE-AF with edoxaban, showed that NOAC treatment resulted in less major bleeding while stroke risk was comparable with treatment with warfarin, she noted.
The 2023 European Heart Rhythm Association consensus document on management of arrhythmias in frailty syndrome concludes that the advantages of NOACs relative to VKAs are “likely consistent” in frail and nonfrail AFib patients, but the level of evidence is low.
So it’s unknown if NOACs are preferred over VKAs in frail AFib patients, “and it’s even more questionable whether patients on VKAs should switch to NOAC therapy,” Dr. Joosten said.
This new trial aimed to answer the question of whether switching frail AFib patients currently managed on a VKA to a NOAC would reduce bleeding. FRAIL-AF was a pragmatic, multicenter, open-label, randomized, controlled superiority trial.
Older AFib patients were deemed frail if they were aged 75 years or older and had a score of 3 or more on the validated Groningen Frailty Indicator (GFI). Patients with a glomerular filtration rate of less than 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 or with valvular AFib were excluded.
Eligible patients were then assigned randomly to switch from their international normalized ratio (INR)–guided VKA treatment with either 1 mg acenocoumarol or 3 mg phenprocoumon, to a NOAC, or to continue VKA treatment. They were followed for 12 months for the primary outcome – major bleeding or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding complication, whichever came first – accounting for death as a competing risk.
A total of 1,330 patients were randomly assigned between January 2018 and June 2022. Their mean age was 83 years, and they had a median GFI of 4. After randomization, 6 patients in the switch-to-NOAC arm, and 1 in the continue-VKA arm were found to have exclusion criteria, so in the end, 662 patients were switched from a VKA to NOAC, while 661 continued on VKA therapy. The choice of NOAC was made by the treating physician.
Major bleeding was defined as a fatal bleeding; bleeding in a critical area or organ; bleeding leading to transfusion; and/or bleeding leading to a fall in hemoglobin level of 2 g/dL (1.24 mmol/L) or more. Nonmajor bleeding was bleeding not considered major but requiring face-to-face consultation, hospitalization or increased level of care, or medical intervention.
After a prespecified futility analysis planned after 163 primary outcome events, the trial was halted when it was seen that there were 101 primary outcome events in the switch arm compared to 62 in the continue arm, Dr. Joosten said. The difference appeared to be driven by clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding.
Secondary outcomes of thromboembolic events and all-cause mortality were similar between the groups.
Completely different patients
Discussant at the meeting for the presentation was Isabelle C. Van Gelder, MD, University Medical Centre Groningen (the Netherlands). She said the results are important and relevant because it “provides data on an important gap of knowledge in our AF[ib] guidelines, and a note for all the cardiologists – this study was not done in the hospital. This trial was done in general practitioner practices, so that’s important to consider.”
Comparing FRAIL-AF patients with those of the four previous NOAC trials, “you see that enormous difference in age,” with an average age of 83 years versus 70-73 years in those trials. “These are completely different patients than have been included previously,” she said.
That GFI score of 4 or more includes patients on four or more different types of medication, as well as memory complaints, an inability to walk around the house, and problems with vision or hearing.
The finding of a 69% increase in bleeding with NOACs in FRAIL-AF was “completely unexpected, and I think that we as cardiologists and as NOAC believers did not expect it at all, but it is as clear as it is.” The curves don’t diverge immediately, but rather after 3 months or thereafter, “so it has nothing to do with the switching process. So why did it occur?”
The Netherlands has dedicated thrombosis services that might improve time in therapeutic range for VKA patients, but there is no real difference in TTRs in FRAIL-AF versus the other NOAC trials, Dr. Van Gelder noted.
The most likely suspect in her view is frailty itself, in particular the tendency for patients to be on a high number of medications. A previous study showed, for example, that polypharmacy could be used as a proxy for the effect of frailty on bleeding risk; patients on 10 or more medications had a higher risk for bleeding on treatment with rivaroxaban versus those on 4 or fewer medications.
“Therefore, in my view, why was there such a high risk of bleeding? It’s because these are other patients than we are normally used to treat, we as cardiologists,” although general practitioners see these patients all the time. “It’s all about frailty.”
NOACs are still relatively new drugs, with possible unknown interactions, she added. Because of their frailty and polypharmacy, these patients may benefit from INR control, Dr. Van Gelder speculated. “Therefore, I agree with them that we should be careful; if such old, frail patients survive on VKA, do not change medications and do not switch!”
The study was supported by the Dutch government with additional and unrestricted educational grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, BMS-Pfizer, Bayer, and Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Joosten reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Van Gelder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Switching frail patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) from anticoagulation therapy with vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) to a novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) resulted in more bleeding without any reduction in thromboembolic complications or all-cause mortality, randomized trial results show.
The study, FRAIL-AF, is the first randomized NOAC trial to exclusively include frail older patients, said lead author Linda P.T. Joosten, MD, Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care in Utrecht, the Netherlands, and these unexpected findings provide evidence that goes beyond what is currently available.
“Data from the FRAIL-AF trial showed that switching from a VKA to a NOAC should not be considered without a clear indication in frail older patients with AF[ib], as switching to a NOAC leads to 69% more bleeding,” she concluded, without any benefit on secondary clinical endpoints, including thromboembolic events and all-cause mortality.
“The results turned out different than we expected,” Dr. Joosten said. “The hypothesis of this superiority trial was that switching from VKA therapy to a NOAC would result in less bleeding. However, we observed the opposite. After the interim analysis, the data and safety monitoring board advised to stop inclusion because switching from a VKA to a NOAC was clearly contraindicated with a hazard ratio of 1.69 and a highly significant P value of .001.”
Results of FRAIL-AF were presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and published online in the journal Circulation.
Session moderator Renate B. Schnabel, MD, interventional cardiologist with University Heart & Vascular Center Hamburg (Germany), congratulated the researchers on these “astonishing” data.
“The thing I want to emphasize here is that, in the absence of randomized controlled trial data, we should be very cautious in extrapolating data from the landmark trials to populations not enrolled in those, and to rely on observational data only,” Dr. Schnabel told Dr. Joosten. “We need randomized controlled trials that sometimes give astonishing results.”
Frailty a clinical syndrome
Frailty is “a lot more than just aging, multiple comorbidities and polypharmacy,” Dr. Joosten explained. “It’s really a clinical syndrome, with people with a high biological vulnerability, dependency on significant others, and a reduced capacity to resist stressors, all leading to a reduced homeostatic reserve.”
Frailty is common in the community, with a prevalence of about 12%, she noted, “and even more important, AF[ib] in frail older people is very common, with a prevalence of 18%. And “without any doubt, we have to adequately anticoagulate frail AF[ib] patients, as they have a high stroke risk, with an incidence of 12.4% per year,” Dr. Joosten noted, compared with 3.9% per year among nonfrail AFib patients.
NOACs are preferred over VKAs in nonfrail AFib patients, after four major trials, RE-LY with dabigatran, ROCKET-AF with rivaroxaban, ARISTOTLE with apixaban, and ENGAGE-AF with edoxaban, showed that NOAC treatment resulted in less major bleeding while stroke risk was comparable with treatment with warfarin, she noted.
The 2023 European Heart Rhythm Association consensus document on management of arrhythmias in frailty syndrome concludes that the advantages of NOACs relative to VKAs are “likely consistent” in frail and nonfrail AFib patients, but the level of evidence is low.
So it’s unknown if NOACs are preferred over VKAs in frail AFib patients, “and it’s even more questionable whether patients on VKAs should switch to NOAC therapy,” Dr. Joosten said.
This new trial aimed to answer the question of whether switching frail AFib patients currently managed on a VKA to a NOAC would reduce bleeding. FRAIL-AF was a pragmatic, multicenter, open-label, randomized, controlled superiority trial.
Older AFib patients were deemed frail if they were aged 75 years or older and had a score of 3 or more on the validated Groningen Frailty Indicator (GFI). Patients with a glomerular filtration rate of less than 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 or with valvular AFib were excluded.
Eligible patients were then assigned randomly to switch from their international normalized ratio (INR)–guided VKA treatment with either 1 mg acenocoumarol or 3 mg phenprocoumon, to a NOAC, or to continue VKA treatment. They were followed for 12 months for the primary outcome – major bleeding or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding complication, whichever came first – accounting for death as a competing risk.
A total of 1,330 patients were randomly assigned between January 2018 and June 2022. Their mean age was 83 years, and they had a median GFI of 4. After randomization, 6 patients in the switch-to-NOAC arm, and 1 in the continue-VKA arm were found to have exclusion criteria, so in the end, 662 patients were switched from a VKA to NOAC, while 661 continued on VKA therapy. The choice of NOAC was made by the treating physician.
Major bleeding was defined as a fatal bleeding; bleeding in a critical area or organ; bleeding leading to transfusion; and/or bleeding leading to a fall in hemoglobin level of 2 g/dL (1.24 mmol/L) or more. Nonmajor bleeding was bleeding not considered major but requiring face-to-face consultation, hospitalization or increased level of care, or medical intervention.
After a prespecified futility analysis planned after 163 primary outcome events, the trial was halted when it was seen that there were 101 primary outcome events in the switch arm compared to 62 in the continue arm, Dr. Joosten said. The difference appeared to be driven by clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding.
Secondary outcomes of thromboembolic events and all-cause mortality were similar between the groups.
Completely different patients
Discussant at the meeting for the presentation was Isabelle C. Van Gelder, MD, University Medical Centre Groningen (the Netherlands). She said the results are important and relevant because it “provides data on an important gap of knowledge in our AF[ib] guidelines, and a note for all the cardiologists – this study was not done in the hospital. This trial was done in general practitioner practices, so that’s important to consider.”
Comparing FRAIL-AF patients with those of the four previous NOAC trials, “you see that enormous difference in age,” with an average age of 83 years versus 70-73 years in those trials. “These are completely different patients than have been included previously,” she said.
That GFI score of 4 or more includes patients on four or more different types of medication, as well as memory complaints, an inability to walk around the house, and problems with vision or hearing.
The finding of a 69% increase in bleeding with NOACs in FRAIL-AF was “completely unexpected, and I think that we as cardiologists and as NOAC believers did not expect it at all, but it is as clear as it is.” The curves don’t diverge immediately, but rather after 3 months or thereafter, “so it has nothing to do with the switching process. So why did it occur?”
The Netherlands has dedicated thrombosis services that might improve time in therapeutic range for VKA patients, but there is no real difference in TTRs in FRAIL-AF versus the other NOAC trials, Dr. Van Gelder noted.
The most likely suspect in her view is frailty itself, in particular the tendency for patients to be on a high number of medications. A previous study showed, for example, that polypharmacy could be used as a proxy for the effect of frailty on bleeding risk; patients on 10 or more medications had a higher risk for bleeding on treatment with rivaroxaban versus those on 4 or fewer medications.
“Therefore, in my view, why was there such a high risk of bleeding? It’s because these are other patients than we are normally used to treat, we as cardiologists,” although general practitioners see these patients all the time. “It’s all about frailty.”
NOACs are still relatively new drugs, with possible unknown interactions, she added. Because of their frailty and polypharmacy, these patients may benefit from INR control, Dr. Van Gelder speculated. “Therefore, I agree with them that we should be careful; if such old, frail patients survive on VKA, do not change medications and do not switch!”
The study was supported by the Dutch government with additional and unrestricted educational grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, BMS-Pfizer, Bayer, and Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Joosten reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Van Gelder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Switching frail patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) from anticoagulation therapy with vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) to a novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) resulted in more bleeding without any reduction in thromboembolic complications or all-cause mortality, randomized trial results show.
The study, FRAIL-AF, is the first randomized NOAC trial to exclusively include frail older patients, said lead author Linda P.T. Joosten, MD, Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care in Utrecht, the Netherlands, and these unexpected findings provide evidence that goes beyond what is currently available.
“Data from the FRAIL-AF trial showed that switching from a VKA to a NOAC should not be considered without a clear indication in frail older patients with AF[ib], as switching to a NOAC leads to 69% more bleeding,” she concluded, without any benefit on secondary clinical endpoints, including thromboembolic events and all-cause mortality.
“The results turned out different than we expected,” Dr. Joosten said. “The hypothesis of this superiority trial was that switching from VKA therapy to a NOAC would result in less bleeding. However, we observed the opposite. After the interim analysis, the data and safety monitoring board advised to stop inclusion because switching from a VKA to a NOAC was clearly contraindicated with a hazard ratio of 1.69 and a highly significant P value of .001.”
Results of FRAIL-AF were presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and published online in the journal Circulation.
Session moderator Renate B. Schnabel, MD, interventional cardiologist with University Heart & Vascular Center Hamburg (Germany), congratulated the researchers on these “astonishing” data.
“The thing I want to emphasize here is that, in the absence of randomized controlled trial data, we should be very cautious in extrapolating data from the landmark trials to populations not enrolled in those, and to rely on observational data only,” Dr. Schnabel told Dr. Joosten. “We need randomized controlled trials that sometimes give astonishing results.”
Frailty a clinical syndrome
Frailty is “a lot more than just aging, multiple comorbidities and polypharmacy,” Dr. Joosten explained. “It’s really a clinical syndrome, with people with a high biological vulnerability, dependency on significant others, and a reduced capacity to resist stressors, all leading to a reduced homeostatic reserve.”
Frailty is common in the community, with a prevalence of about 12%, she noted, “and even more important, AF[ib] in frail older people is very common, with a prevalence of 18%. And “without any doubt, we have to adequately anticoagulate frail AF[ib] patients, as they have a high stroke risk, with an incidence of 12.4% per year,” Dr. Joosten noted, compared with 3.9% per year among nonfrail AFib patients.
NOACs are preferred over VKAs in nonfrail AFib patients, after four major trials, RE-LY with dabigatran, ROCKET-AF with rivaroxaban, ARISTOTLE with apixaban, and ENGAGE-AF with edoxaban, showed that NOAC treatment resulted in less major bleeding while stroke risk was comparable with treatment with warfarin, she noted.
The 2023 European Heart Rhythm Association consensus document on management of arrhythmias in frailty syndrome concludes that the advantages of NOACs relative to VKAs are “likely consistent” in frail and nonfrail AFib patients, but the level of evidence is low.
So it’s unknown if NOACs are preferred over VKAs in frail AFib patients, “and it’s even more questionable whether patients on VKAs should switch to NOAC therapy,” Dr. Joosten said.
This new trial aimed to answer the question of whether switching frail AFib patients currently managed on a VKA to a NOAC would reduce bleeding. FRAIL-AF was a pragmatic, multicenter, open-label, randomized, controlled superiority trial.
Older AFib patients were deemed frail if they were aged 75 years or older and had a score of 3 or more on the validated Groningen Frailty Indicator (GFI). Patients with a glomerular filtration rate of less than 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 or with valvular AFib were excluded.
Eligible patients were then assigned randomly to switch from their international normalized ratio (INR)–guided VKA treatment with either 1 mg acenocoumarol or 3 mg phenprocoumon, to a NOAC, or to continue VKA treatment. They were followed for 12 months for the primary outcome – major bleeding or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding complication, whichever came first – accounting for death as a competing risk.
A total of 1,330 patients were randomly assigned between January 2018 and June 2022. Their mean age was 83 years, and they had a median GFI of 4. After randomization, 6 patients in the switch-to-NOAC arm, and 1 in the continue-VKA arm were found to have exclusion criteria, so in the end, 662 patients were switched from a VKA to NOAC, while 661 continued on VKA therapy. The choice of NOAC was made by the treating physician.
Major bleeding was defined as a fatal bleeding; bleeding in a critical area or organ; bleeding leading to transfusion; and/or bleeding leading to a fall in hemoglobin level of 2 g/dL (1.24 mmol/L) or more. Nonmajor bleeding was bleeding not considered major but requiring face-to-face consultation, hospitalization or increased level of care, or medical intervention.
After a prespecified futility analysis planned after 163 primary outcome events, the trial was halted when it was seen that there were 101 primary outcome events in the switch arm compared to 62 in the continue arm, Dr. Joosten said. The difference appeared to be driven by clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding.
Secondary outcomes of thromboembolic events and all-cause mortality were similar between the groups.
Completely different patients
Discussant at the meeting for the presentation was Isabelle C. Van Gelder, MD, University Medical Centre Groningen (the Netherlands). She said the results are important and relevant because it “provides data on an important gap of knowledge in our AF[ib] guidelines, and a note for all the cardiologists – this study was not done in the hospital. This trial was done in general practitioner practices, so that’s important to consider.”
Comparing FRAIL-AF patients with those of the four previous NOAC trials, “you see that enormous difference in age,” with an average age of 83 years versus 70-73 years in those trials. “These are completely different patients than have been included previously,” she said.
That GFI score of 4 or more includes patients on four or more different types of medication, as well as memory complaints, an inability to walk around the house, and problems with vision or hearing.
The finding of a 69% increase in bleeding with NOACs in FRAIL-AF was “completely unexpected, and I think that we as cardiologists and as NOAC believers did not expect it at all, but it is as clear as it is.” The curves don’t diverge immediately, but rather after 3 months or thereafter, “so it has nothing to do with the switching process. So why did it occur?”
The Netherlands has dedicated thrombosis services that might improve time in therapeutic range for VKA patients, but there is no real difference in TTRs in FRAIL-AF versus the other NOAC trials, Dr. Van Gelder noted.
The most likely suspect in her view is frailty itself, in particular the tendency for patients to be on a high number of medications. A previous study showed, for example, that polypharmacy could be used as a proxy for the effect of frailty on bleeding risk; patients on 10 or more medications had a higher risk for bleeding on treatment with rivaroxaban versus those on 4 or fewer medications.
“Therefore, in my view, why was there such a high risk of bleeding? It’s because these are other patients than we are normally used to treat, we as cardiologists,” although general practitioners see these patients all the time. “It’s all about frailty.”
NOACs are still relatively new drugs, with possible unknown interactions, she added. Because of their frailty and polypharmacy, these patients may benefit from INR control, Dr. Van Gelder speculated. “Therefore, I agree with them that we should be careful; if such old, frail patients survive on VKA, do not change medications and do not switch!”
The study was supported by the Dutch government with additional and unrestricted educational grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, BMS-Pfizer, Bayer, and Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Joosten reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Van Gelder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE ESC CONGRESS 2023
‘New dawn’ for aldosterone as drug target in hypertension?
Once-daily treatment with the selective aldosterone synthase inhibitor lorundrostat (Mineralys Therapeutics) safely and significantly reduced blood pressure in adults with uncontrolled hypertension in a phase 2, randomized, controlled trial.
Eight weeks after adding lorundrostat (50 mg or 100 mg once daily) or placebo to background therapy, the medication lowered seated automated office systolic BP significantly more than placebo (−9.6 mm Hg with 50 mg; −7.8 mm Hg with 100 mg), with the greatest effects seen in adults with obesity.
“We need new drugs for treatment-resistant hypertension,” study investigator Steven Nissen, MD, chief academic officer at the Heart Vascular & Thoracic Institute at the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview. Lorundrostat represents a “new class” of antihypertensive that “looks to be safe and we’re seeing very large reductions in blood pressure.”
Results of the Target-HTN trial were published online in JAMA to coincide with presentation at the Hypertension Scientific Sessions, sponsored by the American Heart Association.
Aldosterone’s contribution ‘vastly underappreciated’
Excess aldosterone production contributes to uncontrolled BP in patients with obesity and other associated diseases, such as obstructive sleep apnea and metabolic syndrome.
“Aldosterone’s contribution to uncontrolled hypertension is vastly underappreciated,” first author and study presenter Luke Laffin, MD, also with the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
Aldosterone synthase inhibitors are a novel class of BP-lowering medications that decrease aldosterone production. Lorundrostat is one of two such agents in advanced clinical development. The other is baxdrostat (CinCor Pharma/AstraZeneca).
The Target-HTN randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial enrolled 200 adults (mean age, 66 years; 60% women) with uncontrolled hypertension while taking two or more antihypertensive medications; 42% of participants were taking three or more antihypertensive medications, 48% were obese and 40% had diabetes.
The study population was divided into two cohorts: an initial cohort of 163 adults with suppressed plasma renin activity at baseline (PRA ≤ 1.0 ng/mL per hour) and elevated plasma aldosterone (≥ 1.0 ng/dL) and a second cohort of 37 adults with PRA greater than 1.0 ng/mL per hour.
Participants were randomly assigned to placebo or one of five doses of lorundrostat in the initial cohort (12.5 mg, 50 mg, or 100 mg once daily or 12.5 mg or 25 mg twice daily).
In the second cohort, participants were randomly assigned (1:6) to placebo or lorundrostat 100 mg once daily. The primary endpoint was change in automated office systolic BP from baseline to week 8.
Among participants with suppressed PRA, following 8 weeks of treatment, changes in office systolic BP of −14.1, −13.2, and −6.9 mm Hg were observed with 100 mg, 50 mg, and 12.5 mg once-daily lorundrostat, respectively, compared with a change of −4.1 mm Hg with placebo.
Reductions in systolic BP in individuals receiving twice-daily doses of 25 mg and 12.5 mg of lorundrostat were −10.1 and −13.8 mm Hg, respectively.
Among participants without suppressed PRA, lorundrostat 100 mg once daily decreased systolic BP by 11.4 mm Hg, similar to BP reduction in those with suppressed PRA receiving the same dose.
A prespecified subgroup analysis showed that participants with obesity demonstrated greater BP lowering in response to lorundrostat.
No instances of cortisol insufficiency occurred. Six participants had increases in serum potassium above 6.0 mEq/L (6.0 mmol/L) that corrected with dose reduction or drug discontinuation.
The increase in serum potassium is “expected and manageable,” Dr. Laffin said in an interview. “Anytime you disrupt aldosterone production, you’re going to have to have an increase in serum potassium, but it’s very manageable and not something that is worrisome.”
A phase 2 trial in 300 adults with uncontrolled hypertension is currently underway. The trial will evaluate the BP-lowering effects of lorundrostat, administered on a background of a standardized antihypertensive medication regimen. A larger phase 3 study will start before the end of the year.
‘New dawn’ for therapies targeting aldosterone
The author of an editorial in JAMA noted that more 70 years after the first isolation of aldosterone, then called electrocortin, “there is a new dawn for therapies targeting aldosterone.”
“There is now real potential to provide better-targeted treatment for patients in whom aldosterone excess is known to contribute to their clinical condition and influence their clinical outcome, notably those with difficult-to-control hypertension, obesity, heart failure, chronic kidney disease, and the many with yet-to-be-diagnosed primary aldosteronism,” said Bryan Williams, MD, University College London.
The trial was funded by Mineralys Therapeutics, which is developing lorundrostat. Dr. Laffin reported that the Cleveland Clinic, his employer, was a study site for the Target-HTN trial and that C5Research, the academic research organization of the Cleveland Clinic, receives payment for services related to other Mineralys clinical trials. Dr. Laffin also reported receipt of personal fees from Medtronic, Lilly, and Crispr Therapeutics, grants from AstraZeneca, and stock options for LucidAct Health and Gordy Health. Dr. Nissen reported receipt of grants from Mineralys during the conduct of the study and grants from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Lilly, Esperion Therapeutics, Medtronic, grants from MyoKardia, New Amsterdam Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, and Silence Therapeutics. Dr. Williams reported being the unremunerated chair of the steering committee designing a phase 3 trial of the aldosterone synthase inhibitor baxdrostat for AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Once-daily treatment with the selective aldosterone synthase inhibitor lorundrostat (Mineralys Therapeutics) safely and significantly reduced blood pressure in adults with uncontrolled hypertension in a phase 2, randomized, controlled trial.
Eight weeks after adding lorundrostat (50 mg or 100 mg once daily) or placebo to background therapy, the medication lowered seated automated office systolic BP significantly more than placebo (−9.6 mm Hg with 50 mg; −7.8 mm Hg with 100 mg), with the greatest effects seen in adults with obesity.
“We need new drugs for treatment-resistant hypertension,” study investigator Steven Nissen, MD, chief academic officer at the Heart Vascular & Thoracic Institute at the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview. Lorundrostat represents a “new class” of antihypertensive that “looks to be safe and we’re seeing very large reductions in blood pressure.”
Results of the Target-HTN trial were published online in JAMA to coincide with presentation at the Hypertension Scientific Sessions, sponsored by the American Heart Association.
Aldosterone’s contribution ‘vastly underappreciated’
Excess aldosterone production contributes to uncontrolled BP in patients with obesity and other associated diseases, such as obstructive sleep apnea and metabolic syndrome.
“Aldosterone’s contribution to uncontrolled hypertension is vastly underappreciated,” first author and study presenter Luke Laffin, MD, also with the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
Aldosterone synthase inhibitors are a novel class of BP-lowering medications that decrease aldosterone production. Lorundrostat is one of two such agents in advanced clinical development. The other is baxdrostat (CinCor Pharma/AstraZeneca).
The Target-HTN randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial enrolled 200 adults (mean age, 66 years; 60% women) with uncontrolled hypertension while taking two or more antihypertensive medications; 42% of participants were taking three or more antihypertensive medications, 48% were obese and 40% had diabetes.
The study population was divided into two cohorts: an initial cohort of 163 adults with suppressed plasma renin activity at baseline (PRA ≤ 1.0 ng/mL per hour) and elevated plasma aldosterone (≥ 1.0 ng/dL) and a second cohort of 37 adults with PRA greater than 1.0 ng/mL per hour.
Participants were randomly assigned to placebo or one of five doses of lorundrostat in the initial cohort (12.5 mg, 50 mg, or 100 mg once daily or 12.5 mg or 25 mg twice daily).
In the second cohort, participants were randomly assigned (1:6) to placebo or lorundrostat 100 mg once daily. The primary endpoint was change in automated office systolic BP from baseline to week 8.
Among participants with suppressed PRA, following 8 weeks of treatment, changes in office systolic BP of −14.1, −13.2, and −6.9 mm Hg were observed with 100 mg, 50 mg, and 12.5 mg once-daily lorundrostat, respectively, compared with a change of −4.1 mm Hg with placebo.
Reductions in systolic BP in individuals receiving twice-daily doses of 25 mg and 12.5 mg of lorundrostat were −10.1 and −13.8 mm Hg, respectively.
Among participants without suppressed PRA, lorundrostat 100 mg once daily decreased systolic BP by 11.4 mm Hg, similar to BP reduction in those with suppressed PRA receiving the same dose.
A prespecified subgroup analysis showed that participants with obesity demonstrated greater BP lowering in response to lorundrostat.
No instances of cortisol insufficiency occurred. Six participants had increases in serum potassium above 6.0 mEq/L (6.0 mmol/L) that corrected with dose reduction or drug discontinuation.
The increase in serum potassium is “expected and manageable,” Dr. Laffin said in an interview. “Anytime you disrupt aldosterone production, you’re going to have to have an increase in serum potassium, but it’s very manageable and not something that is worrisome.”
A phase 2 trial in 300 adults with uncontrolled hypertension is currently underway. The trial will evaluate the BP-lowering effects of lorundrostat, administered on a background of a standardized antihypertensive medication regimen. A larger phase 3 study will start before the end of the year.
‘New dawn’ for therapies targeting aldosterone
The author of an editorial in JAMA noted that more 70 years after the first isolation of aldosterone, then called electrocortin, “there is a new dawn for therapies targeting aldosterone.”
“There is now real potential to provide better-targeted treatment for patients in whom aldosterone excess is known to contribute to their clinical condition and influence their clinical outcome, notably those with difficult-to-control hypertension, obesity, heart failure, chronic kidney disease, and the many with yet-to-be-diagnosed primary aldosteronism,” said Bryan Williams, MD, University College London.
The trial was funded by Mineralys Therapeutics, which is developing lorundrostat. Dr. Laffin reported that the Cleveland Clinic, his employer, was a study site for the Target-HTN trial and that C5Research, the academic research organization of the Cleveland Clinic, receives payment for services related to other Mineralys clinical trials. Dr. Laffin also reported receipt of personal fees from Medtronic, Lilly, and Crispr Therapeutics, grants from AstraZeneca, and stock options for LucidAct Health and Gordy Health. Dr. Nissen reported receipt of grants from Mineralys during the conduct of the study and grants from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Lilly, Esperion Therapeutics, Medtronic, grants from MyoKardia, New Amsterdam Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, and Silence Therapeutics. Dr. Williams reported being the unremunerated chair of the steering committee designing a phase 3 trial of the aldosterone synthase inhibitor baxdrostat for AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Once-daily treatment with the selective aldosterone synthase inhibitor lorundrostat (Mineralys Therapeutics) safely and significantly reduced blood pressure in adults with uncontrolled hypertension in a phase 2, randomized, controlled trial.
Eight weeks after adding lorundrostat (50 mg or 100 mg once daily) or placebo to background therapy, the medication lowered seated automated office systolic BP significantly more than placebo (−9.6 mm Hg with 50 mg; −7.8 mm Hg with 100 mg), with the greatest effects seen in adults with obesity.
“We need new drugs for treatment-resistant hypertension,” study investigator Steven Nissen, MD, chief academic officer at the Heart Vascular & Thoracic Institute at the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview. Lorundrostat represents a “new class” of antihypertensive that “looks to be safe and we’re seeing very large reductions in blood pressure.”
Results of the Target-HTN trial were published online in JAMA to coincide with presentation at the Hypertension Scientific Sessions, sponsored by the American Heart Association.
Aldosterone’s contribution ‘vastly underappreciated’
Excess aldosterone production contributes to uncontrolled BP in patients with obesity and other associated diseases, such as obstructive sleep apnea and metabolic syndrome.
“Aldosterone’s contribution to uncontrolled hypertension is vastly underappreciated,” first author and study presenter Luke Laffin, MD, also with the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
Aldosterone synthase inhibitors are a novel class of BP-lowering medications that decrease aldosterone production. Lorundrostat is one of two such agents in advanced clinical development. The other is baxdrostat (CinCor Pharma/AstraZeneca).
The Target-HTN randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial enrolled 200 adults (mean age, 66 years; 60% women) with uncontrolled hypertension while taking two or more antihypertensive medications; 42% of participants were taking three or more antihypertensive medications, 48% were obese and 40% had diabetes.
The study population was divided into two cohorts: an initial cohort of 163 adults with suppressed plasma renin activity at baseline (PRA ≤ 1.0 ng/mL per hour) and elevated plasma aldosterone (≥ 1.0 ng/dL) and a second cohort of 37 adults with PRA greater than 1.0 ng/mL per hour.
Participants were randomly assigned to placebo or one of five doses of lorundrostat in the initial cohort (12.5 mg, 50 mg, or 100 mg once daily or 12.5 mg or 25 mg twice daily).
In the second cohort, participants were randomly assigned (1:6) to placebo or lorundrostat 100 mg once daily. The primary endpoint was change in automated office systolic BP from baseline to week 8.
Among participants with suppressed PRA, following 8 weeks of treatment, changes in office systolic BP of −14.1, −13.2, and −6.9 mm Hg were observed with 100 mg, 50 mg, and 12.5 mg once-daily lorundrostat, respectively, compared with a change of −4.1 mm Hg with placebo.
Reductions in systolic BP in individuals receiving twice-daily doses of 25 mg and 12.5 mg of lorundrostat were −10.1 and −13.8 mm Hg, respectively.
Among participants without suppressed PRA, lorundrostat 100 mg once daily decreased systolic BP by 11.4 mm Hg, similar to BP reduction in those with suppressed PRA receiving the same dose.
A prespecified subgroup analysis showed that participants with obesity demonstrated greater BP lowering in response to lorundrostat.
No instances of cortisol insufficiency occurred. Six participants had increases in serum potassium above 6.0 mEq/L (6.0 mmol/L) that corrected with dose reduction or drug discontinuation.
The increase in serum potassium is “expected and manageable,” Dr. Laffin said in an interview. “Anytime you disrupt aldosterone production, you’re going to have to have an increase in serum potassium, but it’s very manageable and not something that is worrisome.”
A phase 2 trial in 300 adults with uncontrolled hypertension is currently underway. The trial will evaluate the BP-lowering effects of lorundrostat, administered on a background of a standardized antihypertensive medication regimen. A larger phase 3 study will start before the end of the year.
‘New dawn’ for therapies targeting aldosterone
The author of an editorial in JAMA noted that more 70 years after the first isolation of aldosterone, then called electrocortin, “there is a new dawn for therapies targeting aldosterone.”
“There is now real potential to provide better-targeted treatment for patients in whom aldosterone excess is known to contribute to their clinical condition and influence their clinical outcome, notably those with difficult-to-control hypertension, obesity, heart failure, chronic kidney disease, and the many with yet-to-be-diagnosed primary aldosteronism,” said Bryan Williams, MD, University College London.
The trial was funded by Mineralys Therapeutics, which is developing lorundrostat. Dr. Laffin reported that the Cleveland Clinic, his employer, was a study site for the Target-HTN trial and that C5Research, the academic research organization of the Cleveland Clinic, receives payment for services related to other Mineralys clinical trials. Dr. Laffin also reported receipt of personal fees from Medtronic, Lilly, and Crispr Therapeutics, grants from AstraZeneca, and stock options for LucidAct Health and Gordy Health. Dr. Nissen reported receipt of grants from Mineralys during the conduct of the study and grants from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Lilly, Esperion Therapeutics, Medtronic, grants from MyoKardia, New Amsterdam Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, and Silence Therapeutics. Dr. Williams reported being the unremunerated chair of the steering committee designing a phase 3 trial of the aldosterone synthase inhibitor baxdrostat for AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM HYPERTENSION 2023
Is AFib ablation the fifth pillar in heart failure care? CASTLE-HTx
Recorded Aug. 28, 2023. This transcript has been edited for clarity.
John M. Mandrola, MD: I’m here at the European Society of Cardiology meeting, and I’m very excited to have two colleagues whom I met at the Western Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (Western AFib) and who presented the CASTLE-HTx study. This is Christian Sohns and Philipp Sommer, and the CASTLE-HTx study is very exciting.
Before I get into that, I really want to introduce the concept of atrial fibrillation in heart failure. I like to say that there are two big populations of patients with atrial fibrillation, and the vast majority can be treated slowly with reassurance and education. There is a group of patients who have heart failure who, when they develop atrial fibrillation, can degenerate rapidly. The CASTLE-HTx study looked at catheter ablation versus medical therapy in patients with advanced heart failure.
Christian, why don’t you tell us the top-line results and what you found.
CASTLE-HTx key findings
Christian Sohns, MD, PhD: Thanks, first of all, for mentioning this special cohort of patients in end-stage heart failure, which is very important. The endpoint of the study was a composite of death from any cause or left ventricular assist device (LVAD) implantation and heart transplantation. These are very hard, strong clinical endpoints, not the rate of rehospitalization or something like that.
Catheter ablation was superior to medical therapy alone in terms of this composite endpoint. That was driven by cardiovascular death and all-cause mortality, which highlights the fact that you should always consider atrial fibrillation ablation in the end-stage heart failure cohort. The findings were driven by the fact that we saw left ventricular reverse remodeling and the reduction of atrial fibrillation in these patients.
Dr. Mandrola: Tell me about how it came about. It was conducted at your center. Who were these patients?
Philipp Sommer, MD: As one of the biggest centers for heart transplantations all over Europe, with roughly 100 transplants per year, we had many patients being referred to our center with the questions of whether those patients are eligible for a heart transplantation. Not all of the patients in our study were listed for a transplant, but all of them were admitted in that end-stage heart failure status to evaluate their eligibility for transplant.
If we look at the baseline data of those patients, they had an ejection fraction of 29%. They had a 6-minute walk test as a functional capacity parameter of around 300 m. Approximately two thirds of them were New York Heart Association class III and IV, which is significantly worse than what we saw in the previous studies dealing with heart failure patients.
I think overall, if you also look at NT-proBNP levels, this is a really sick patient population where some people might doubt if they should admit and refer those patients for an ablation procedure. Therefore, it’s really interesting and fascinating to see the results.
Dr. Mandrola: I did read in the manuscript, and I heard from you, that these were recruited as outpatients. So they were stable outpatients who were referred to the center for consideration of an LVAD or transplant?
Dr. Sohns: The definition of stability is very difficult in these patients because they have hospital stays, they have a history of drug therapy, and they have a history of interventions also behind them – not atrial fibrillation ablation, but others. I think these patients are referred because the referring physicians are done with the case. They can no longer offer any option to the patients other than surgical treatment, assist device, pump implantation, or transplantation.
If you look at the guidelines, they do not comment on atrial fibrillation ablation in this cohort of patients. Also, they have different recommendations between the American societies and the European societies regarding what is end-stage heart failure and how to treat these patients. Therefore, it was a big benefit of CASTLE-HTx that we randomized a cohort of patients with advanced end-stage heart failure.
How can AFib ablation have such big, early effects?
Dr. Mandrola: These are very clinically significant findings, with large effect sizes and very early separation of the Kaplan-Meier curves. How do you explain how dramatic an effect that is, and how early of an effect?
Dr. Sommer: That’s one of the key questions at the end of the day. I think our job basically was to provide the data and to ensure that the data are clean and that it’s all perfectly done. The interpretation of these data is really kind of difficult, although we do not have the 100% perfect and obvious explanation why the curves separated so early. Our view on that is that we are talking about a pretty fragile patient population, so little differences like having a tachyarrhythmia of 110 day in, day out or being in sinus rhythm of 60 can make a huge difference. That’s obviously pretty early.
The one that remains in tachyarrhythmia will deteriorate and will require an LVAD after a couple of months, and the one that you may keep in sinus rhythm, even with reduced atrial fibrillation burden – not zero, but reduced atrial fibrillation burden – and improved LV function, all of a sudden this patient will still remain on a low level of being stable, but he or she will remain stable and will not require any surgical interventions for the next 1.5-2 years. If we can manage to do this, just postponing the natural cause of the disease, I think that is a great benefit for the patient.
Dr. Mandrola: One of the things that comes up in our center is that I look at some of these patients and think, there’s no way I can put this patient under general anesthetic and do all of this. Your ablation procedure wasn’t that extensive, was it?
Dr. Sohns: On the one hand, no. On the other hand, yes. You need to take into consideration that it has been performed by experienced physicians with experience in heart failure treatment and atrial fibrillation in heart transplantation centers, though it›s not sure that we can transfer these results one-to-one to all other centers in the world.
It is very clear that we have almost no major complications in these patients. We were able to do these ablation procedures without general anesthesia. We have 60% of patients who had pulmonary vein isolation only and 40% of patients who have PVI and additional therapy. We have a procedure duration of almost 90 minutes during radiofrequency ablation.
We have different categories. When you talk about the different patient cohorts, we also see different stages of myocardial tissue damage, which will be part of another publication for sure. It is, in part, surprising how normal some of the atria were despite having a volume of 180 mL, but they had no fibrosis. That was very interesting.
Dr. Mandrola: How did the persistent vs paroxysmal atrial fibrillation sort out? Were these mostly patients with persistent atrial fibrillation?
Dr. Sommer: Two-thirds were persistent. It would be expected in this patient population that you would not find so many paroxysmal cases. I think it›s very important what Christian was just mentioning that when we discussed the trial design, we were anticipating problems with the sedation, for example. With the follow-up of those procedures, would they decompensate because of the fluid that you have to deliver during such a procedure.
We were quite surprised at the end of the day that the procedures were quite straightforward. Fortunately, we had no major complications. I think there were four complications in the 100 ablated patients. I think we were really positive about how the procedures turned out.
I should mention that one of the exclusion criteria was a left atrial diameter of about 60 mm. The huge ones may be very diseased, and maybe the hopeless ones were excluded from the study. Below 60 mm, we did the ablation.
Rhythm control
Dr. Mandrola: One of my colleagues, who is even more skeptical than me, wanted me to ask you, why wouldn’t you take a patient with persistent atrial fibrillation who had heart failure and just cardiovert and use amiodarone and try and maintain sinus rhythm that way?
Dr. Sohns: It is important to mention that 50% of the patients have already had amiodarone before they were randomized and enrolled for the trial. It might bring you a couple of minutes or a couple of hours [of relief], but the patients would get recurrence.
It was very interesting also, and this is in line with the data from Jason Andrade, who demonstrated that we were able to reduce the percentage of patients with persistent atrial fibrillation to paroxysmal. We did a down-staging of the underlying disease. This is not possible with cardioversion or drugs, for example.
Dr. Sommer: What I really like about that question and that comment is the idea that rhythm control in this subset of patients obviously has a role and an importance. It may be a cardioversion initially, giving amiodarone if they didn’t have that before, and you can keep the patient in sinus rhythm with this therapy, I think we’re reaching the same goal.
I think the critical point to get into the mind of physicians who treat heart failure is that sinus rhythm is beneficial, however you get there. Ablation, of course, as in other studies, is the most powerful tool to get there. Cardioversion can be a really good thing to do; you just have to think about it and consider it.
Dr. Mandrola: I do want to say to everybody that there is a tension sometimes between the heart failure community and the electrophysiology community. I think the ideal situation is that we work together, because I think that we can help with the maintenance of sinus rhythm. The control group mortality at 1 year was 20%, and I’ve heard people say that that’s not advanced heart failure. Advanced heart failure patients have much higher mortality than that. My colleague who is a heart failure specialist was criticizing a selection bias in picking the best patients. How would you answer that?
Dr. Sohns: There are data available from Eurotransplant, for example, that the waiting list mortality is 18%, so I think we are almost in line with this 20% mortality in this conservative group. You cannot generalize it. All these patients have different histories. We have 60% dilated cardiomyopathy and 40% ischemic cardiomyopathy. I think it is a very representative group in contrast to your friend who suggests that it is not.
Dr. Sommer: What I like about the discussion is that some approach us to say that the mortality in the control group is much too high – like, what are you doing with those patients that you create so many endpoints? Then others say that it’s not high enough because that is not end-stage heart failure. Come on! We have a patient cohort that is very well described and very well characterized.
If the label is end-stage heart failure, advanced heart failure, or whatever, they are sicker than the patients that we had in earlier trials. The patients that we treated were mostly excluded from all other trials. We opened the door. We found a clear result. I think everyone can see whatever you like to see.
Dr. Mandrola: What would your take-home message be after having done this trial design, the trial was conducted in your single center, and you come up with these amazing results? What would your message be to the whole community?
Dr. Sohns: Taking into consideration how severely sick these patients are, I can just repeat it: They are one step away from death, more or less, or from surgical intervention that can prolong their life. You should also consider that there are options like atrial fibrillation ablation that can buy time, postpone the natural course, or even in some patients replace the destination therapy. Therefore, in my opinion the next guidelines should recommend that every patient should carefully be checked for sinus rhythm before bringing these patients into the environment of transplantation.
Dr. Sommer: My interpretation is that we have to try to bring into physicians’ minds that besides a well-established and well-documented effect of drug therapy with the fabulous four, we may now have the fabulous five, including an ablation option for patients with atrial fibrillation.
Dr. Mandrola is a clinical electrophysiologist at Baptist Medical Associates, Louisville, Ky. Dr. Sohns is deputy director of the Heart and Diabetes Center NRW, Ruhr University Bochum, Bad Oeynhausen, Germany. Dr. Sommer is professor of cardiology at the Heart and Diabetes Center NRW. Dr. Mandrola reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Sohns reported receiving research funding from Else Kröner–Fresenius–Stiftung. Dr. Sommer reported consulting with Abbott, Biosense Webster, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic USA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Recorded Aug. 28, 2023. This transcript has been edited for clarity.
John M. Mandrola, MD: I’m here at the European Society of Cardiology meeting, and I’m very excited to have two colleagues whom I met at the Western Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (Western AFib) and who presented the CASTLE-HTx study. This is Christian Sohns and Philipp Sommer, and the CASTLE-HTx study is very exciting.
Before I get into that, I really want to introduce the concept of atrial fibrillation in heart failure. I like to say that there are two big populations of patients with atrial fibrillation, and the vast majority can be treated slowly with reassurance and education. There is a group of patients who have heart failure who, when they develop atrial fibrillation, can degenerate rapidly. The CASTLE-HTx study looked at catheter ablation versus medical therapy in patients with advanced heart failure.
Christian, why don’t you tell us the top-line results and what you found.
CASTLE-HTx key findings
Christian Sohns, MD, PhD: Thanks, first of all, for mentioning this special cohort of patients in end-stage heart failure, which is very important. The endpoint of the study was a composite of death from any cause or left ventricular assist device (LVAD) implantation and heart transplantation. These are very hard, strong clinical endpoints, not the rate of rehospitalization or something like that.
Catheter ablation was superior to medical therapy alone in terms of this composite endpoint. That was driven by cardiovascular death and all-cause mortality, which highlights the fact that you should always consider atrial fibrillation ablation in the end-stage heart failure cohort. The findings were driven by the fact that we saw left ventricular reverse remodeling and the reduction of atrial fibrillation in these patients.
Dr. Mandrola: Tell me about how it came about. It was conducted at your center. Who were these patients?
Philipp Sommer, MD: As one of the biggest centers for heart transplantations all over Europe, with roughly 100 transplants per year, we had many patients being referred to our center with the questions of whether those patients are eligible for a heart transplantation. Not all of the patients in our study were listed for a transplant, but all of them were admitted in that end-stage heart failure status to evaluate their eligibility for transplant.
If we look at the baseline data of those patients, they had an ejection fraction of 29%. They had a 6-minute walk test as a functional capacity parameter of around 300 m. Approximately two thirds of them were New York Heart Association class III and IV, which is significantly worse than what we saw in the previous studies dealing with heart failure patients.
I think overall, if you also look at NT-proBNP levels, this is a really sick patient population where some people might doubt if they should admit and refer those patients for an ablation procedure. Therefore, it’s really interesting and fascinating to see the results.
Dr. Mandrola: I did read in the manuscript, and I heard from you, that these were recruited as outpatients. So they were stable outpatients who were referred to the center for consideration of an LVAD or transplant?
Dr. Sohns: The definition of stability is very difficult in these patients because they have hospital stays, they have a history of drug therapy, and they have a history of interventions also behind them – not atrial fibrillation ablation, but others. I think these patients are referred because the referring physicians are done with the case. They can no longer offer any option to the patients other than surgical treatment, assist device, pump implantation, or transplantation.
If you look at the guidelines, they do not comment on atrial fibrillation ablation in this cohort of patients. Also, they have different recommendations between the American societies and the European societies regarding what is end-stage heart failure and how to treat these patients. Therefore, it was a big benefit of CASTLE-HTx that we randomized a cohort of patients with advanced end-stage heart failure.
How can AFib ablation have such big, early effects?
Dr. Mandrola: These are very clinically significant findings, with large effect sizes and very early separation of the Kaplan-Meier curves. How do you explain how dramatic an effect that is, and how early of an effect?
Dr. Sommer: That’s one of the key questions at the end of the day. I think our job basically was to provide the data and to ensure that the data are clean and that it’s all perfectly done. The interpretation of these data is really kind of difficult, although we do not have the 100% perfect and obvious explanation why the curves separated so early. Our view on that is that we are talking about a pretty fragile patient population, so little differences like having a tachyarrhythmia of 110 day in, day out or being in sinus rhythm of 60 can make a huge difference. That’s obviously pretty early.
The one that remains in tachyarrhythmia will deteriorate and will require an LVAD after a couple of months, and the one that you may keep in sinus rhythm, even with reduced atrial fibrillation burden – not zero, but reduced atrial fibrillation burden – and improved LV function, all of a sudden this patient will still remain on a low level of being stable, but he or she will remain stable and will not require any surgical interventions for the next 1.5-2 years. If we can manage to do this, just postponing the natural cause of the disease, I think that is a great benefit for the patient.
Dr. Mandrola: One of the things that comes up in our center is that I look at some of these patients and think, there’s no way I can put this patient under general anesthetic and do all of this. Your ablation procedure wasn’t that extensive, was it?
Dr. Sohns: On the one hand, no. On the other hand, yes. You need to take into consideration that it has been performed by experienced physicians with experience in heart failure treatment and atrial fibrillation in heart transplantation centers, though it›s not sure that we can transfer these results one-to-one to all other centers in the world.
It is very clear that we have almost no major complications in these patients. We were able to do these ablation procedures without general anesthesia. We have 60% of patients who had pulmonary vein isolation only and 40% of patients who have PVI and additional therapy. We have a procedure duration of almost 90 minutes during radiofrequency ablation.
We have different categories. When you talk about the different patient cohorts, we also see different stages of myocardial tissue damage, which will be part of another publication for sure. It is, in part, surprising how normal some of the atria were despite having a volume of 180 mL, but they had no fibrosis. That was very interesting.
Dr. Mandrola: How did the persistent vs paroxysmal atrial fibrillation sort out? Were these mostly patients with persistent atrial fibrillation?
Dr. Sommer: Two-thirds were persistent. It would be expected in this patient population that you would not find so many paroxysmal cases. I think it›s very important what Christian was just mentioning that when we discussed the trial design, we were anticipating problems with the sedation, for example. With the follow-up of those procedures, would they decompensate because of the fluid that you have to deliver during such a procedure.
We were quite surprised at the end of the day that the procedures were quite straightforward. Fortunately, we had no major complications. I think there were four complications in the 100 ablated patients. I think we were really positive about how the procedures turned out.
I should mention that one of the exclusion criteria was a left atrial diameter of about 60 mm. The huge ones may be very diseased, and maybe the hopeless ones were excluded from the study. Below 60 mm, we did the ablation.
Rhythm control
Dr. Mandrola: One of my colleagues, who is even more skeptical than me, wanted me to ask you, why wouldn’t you take a patient with persistent atrial fibrillation who had heart failure and just cardiovert and use amiodarone and try and maintain sinus rhythm that way?
Dr. Sohns: It is important to mention that 50% of the patients have already had amiodarone before they were randomized and enrolled for the trial. It might bring you a couple of minutes or a couple of hours [of relief], but the patients would get recurrence.
It was very interesting also, and this is in line with the data from Jason Andrade, who demonstrated that we were able to reduce the percentage of patients with persistent atrial fibrillation to paroxysmal. We did a down-staging of the underlying disease. This is not possible with cardioversion or drugs, for example.
Dr. Sommer: What I really like about that question and that comment is the idea that rhythm control in this subset of patients obviously has a role and an importance. It may be a cardioversion initially, giving amiodarone if they didn’t have that before, and you can keep the patient in sinus rhythm with this therapy, I think we’re reaching the same goal.
I think the critical point to get into the mind of physicians who treat heart failure is that sinus rhythm is beneficial, however you get there. Ablation, of course, as in other studies, is the most powerful tool to get there. Cardioversion can be a really good thing to do; you just have to think about it and consider it.
Dr. Mandrola: I do want to say to everybody that there is a tension sometimes between the heart failure community and the electrophysiology community. I think the ideal situation is that we work together, because I think that we can help with the maintenance of sinus rhythm. The control group mortality at 1 year was 20%, and I’ve heard people say that that’s not advanced heart failure. Advanced heart failure patients have much higher mortality than that. My colleague who is a heart failure specialist was criticizing a selection bias in picking the best patients. How would you answer that?
Dr. Sohns: There are data available from Eurotransplant, for example, that the waiting list mortality is 18%, so I think we are almost in line with this 20% mortality in this conservative group. You cannot generalize it. All these patients have different histories. We have 60% dilated cardiomyopathy and 40% ischemic cardiomyopathy. I think it is a very representative group in contrast to your friend who suggests that it is not.
Dr. Sommer: What I like about the discussion is that some approach us to say that the mortality in the control group is much too high – like, what are you doing with those patients that you create so many endpoints? Then others say that it’s not high enough because that is not end-stage heart failure. Come on! We have a patient cohort that is very well described and very well characterized.
If the label is end-stage heart failure, advanced heart failure, or whatever, they are sicker than the patients that we had in earlier trials. The patients that we treated were mostly excluded from all other trials. We opened the door. We found a clear result. I think everyone can see whatever you like to see.
Dr. Mandrola: What would your take-home message be after having done this trial design, the trial was conducted in your single center, and you come up with these amazing results? What would your message be to the whole community?
Dr. Sohns: Taking into consideration how severely sick these patients are, I can just repeat it: They are one step away from death, more or less, or from surgical intervention that can prolong their life. You should also consider that there are options like atrial fibrillation ablation that can buy time, postpone the natural course, or even in some patients replace the destination therapy. Therefore, in my opinion the next guidelines should recommend that every patient should carefully be checked for sinus rhythm before bringing these patients into the environment of transplantation.
Dr. Sommer: My interpretation is that we have to try to bring into physicians’ minds that besides a well-established and well-documented effect of drug therapy with the fabulous four, we may now have the fabulous five, including an ablation option for patients with atrial fibrillation.
Dr. Mandrola is a clinical electrophysiologist at Baptist Medical Associates, Louisville, Ky. Dr. Sohns is deputy director of the Heart and Diabetes Center NRW, Ruhr University Bochum, Bad Oeynhausen, Germany. Dr. Sommer is professor of cardiology at the Heart and Diabetes Center NRW. Dr. Mandrola reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Sohns reported receiving research funding from Else Kröner–Fresenius–Stiftung. Dr. Sommer reported consulting with Abbott, Biosense Webster, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic USA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Recorded Aug. 28, 2023. This transcript has been edited for clarity.
John M. Mandrola, MD: I’m here at the European Society of Cardiology meeting, and I’m very excited to have two colleagues whom I met at the Western Atrial Fibrillation Symposium (Western AFib) and who presented the CASTLE-HTx study. This is Christian Sohns and Philipp Sommer, and the CASTLE-HTx study is very exciting.
Before I get into that, I really want to introduce the concept of atrial fibrillation in heart failure. I like to say that there are two big populations of patients with atrial fibrillation, and the vast majority can be treated slowly with reassurance and education. There is a group of patients who have heart failure who, when they develop atrial fibrillation, can degenerate rapidly. The CASTLE-HTx study looked at catheter ablation versus medical therapy in patients with advanced heart failure.
Christian, why don’t you tell us the top-line results and what you found.
CASTLE-HTx key findings
Christian Sohns, MD, PhD: Thanks, first of all, for mentioning this special cohort of patients in end-stage heart failure, which is very important. The endpoint of the study was a composite of death from any cause or left ventricular assist device (LVAD) implantation and heart transplantation. These are very hard, strong clinical endpoints, not the rate of rehospitalization or something like that.
Catheter ablation was superior to medical therapy alone in terms of this composite endpoint. That was driven by cardiovascular death and all-cause mortality, which highlights the fact that you should always consider atrial fibrillation ablation in the end-stage heart failure cohort. The findings were driven by the fact that we saw left ventricular reverse remodeling and the reduction of atrial fibrillation in these patients.
Dr. Mandrola: Tell me about how it came about. It was conducted at your center. Who were these patients?
Philipp Sommer, MD: As one of the biggest centers for heart transplantations all over Europe, with roughly 100 transplants per year, we had many patients being referred to our center with the questions of whether those patients are eligible for a heart transplantation. Not all of the patients in our study were listed for a transplant, but all of them were admitted in that end-stage heart failure status to evaluate their eligibility for transplant.
If we look at the baseline data of those patients, they had an ejection fraction of 29%. They had a 6-minute walk test as a functional capacity parameter of around 300 m. Approximately two thirds of them were New York Heart Association class III and IV, which is significantly worse than what we saw in the previous studies dealing with heart failure patients.
I think overall, if you also look at NT-proBNP levels, this is a really sick patient population where some people might doubt if they should admit and refer those patients for an ablation procedure. Therefore, it’s really interesting and fascinating to see the results.
Dr. Mandrola: I did read in the manuscript, and I heard from you, that these were recruited as outpatients. So they were stable outpatients who were referred to the center for consideration of an LVAD or transplant?
Dr. Sohns: The definition of stability is very difficult in these patients because they have hospital stays, they have a history of drug therapy, and they have a history of interventions also behind them – not atrial fibrillation ablation, but others. I think these patients are referred because the referring physicians are done with the case. They can no longer offer any option to the patients other than surgical treatment, assist device, pump implantation, or transplantation.
If you look at the guidelines, they do not comment on atrial fibrillation ablation in this cohort of patients. Also, they have different recommendations between the American societies and the European societies regarding what is end-stage heart failure and how to treat these patients. Therefore, it was a big benefit of CASTLE-HTx that we randomized a cohort of patients with advanced end-stage heart failure.
How can AFib ablation have such big, early effects?
Dr. Mandrola: These are very clinically significant findings, with large effect sizes and very early separation of the Kaplan-Meier curves. How do you explain how dramatic an effect that is, and how early of an effect?
Dr. Sommer: That’s one of the key questions at the end of the day. I think our job basically was to provide the data and to ensure that the data are clean and that it’s all perfectly done. The interpretation of these data is really kind of difficult, although we do not have the 100% perfect and obvious explanation why the curves separated so early. Our view on that is that we are talking about a pretty fragile patient population, so little differences like having a tachyarrhythmia of 110 day in, day out or being in sinus rhythm of 60 can make a huge difference. That’s obviously pretty early.
The one that remains in tachyarrhythmia will deteriorate and will require an LVAD after a couple of months, and the one that you may keep in sinus rhythm, even with reduced atrial fibrillation burden – not zero, but reduced atrial fibrillation burden – and improved LV function, all of a sudden this patient will still remain on a low level of being stable, but he or she will remain stable and will not require any surgical interventions for the next 1.5-2 years. If we can manage to do this, just postponing the natural cause of the disease, I think that is a great benefit for the patient.
Dr. Mandrola: One of the things that comes up in our center is that I look at some of these patients and think, there’s no way I can put this patient under general anesthetic and do all of this. Your ablation procedure wasn’t that extensive, was it?
Dr. Sohns: On the one hand, no. On the other hand, yes. You need to take into consideration that it has been performed by experienced physicians with experience in heart failure treatment and atrial fibrillation in heart transplantation centers, though it›s not sure that we can transfer these results one-to-one to all other centers in the world.
It is very clear that we have almost no major complications in these patients. We were able to do these ablation procedures without general anesthesia. We have 60% of patients who had pulmonary vein isolation only and 40% of patients who have PVI and additional therapy. We have a procedure duration of almost 90 minutes during radiofrequency ablation.
We have different categories. When you talk about the different patient cohorts, we also see different stages of myocardial tissue damage, which will be part of another publication for sure. It is, in part, surprising how normal some of the atria were despite having a volume of 180 mL, but they had no fibrosis. That was very interesting.
Dr. Mandrola: How did the persistent vs paroxysmal atrial fibrillation sort out? Were these mostly patients with persistent atrial fibrillation?
Dr. Sommer: Two-thirds were persistent. It would be expected in this patient population that you would not find so many paroxysmal cases. I think it›s very important what Christian was just mentioning that when we discussed the trial design, we were anticipating problems with the sedation, for example. With the follow-up of those procedures, would they decompensate because of the fluid that you have to deliver during such a procedure.
We were quite surprised at the end of the day that the procedures were quite straightforward. Fortunately, we had no major complications. I think there were four complications in the 100 ablated patients. I think we were really positive about how the procedures turned out.
I should mention that one of the exclusion criteria was a left atrial diameter of about 60 mm. The huge ones may be very diseased, and maybe the hopeless ones were excluded from the study. Below 60 mm, we did the ablation.
Rhythm control
Dr. Mandrola: One of my colleagues, who is even more skeptical than me, wanted me to ask you, why wouldn’t you take a patient with persistent atrial fibrillation who had heart failure and just cardiovert and use amiodarone and try and maintain sinus rhythm that way?
Dr. Sohns: It is important to mention that 50% of the patients have already had amiodarone before they were randomized and enrolled for the trial. It might bring you a couple of minutes or a couple of hours [of relief], but the patients would get recurrence.
It was very interesting also, and this is in line with the data from Jason Andrade, who demonstrated that we were able to reduce the percentage of patients with persistent atrial fibrillation to paroxysmal. We did a down-staging of the underlying disease. This is not possible with cardioversion or drugs, for example.
Dr. Sommer: What I really like about that question and that comment is the idea that rhythm control in this subset of patients obviously has a role and an importance. It may be a cardioversion initially, giving amiodarone if they didn’t have that before, and you can keep the patient in sinus rhythm with this therapy, I think we’re reaching the same goal.
I think the critical point to get into the mind of physicians who treat heart failure is that sinus rhythm is beneficial, however you get there. Ablation, of course, as in other studies, is the most powerful tool to get there. Cardioversion can be a really good thing to do; you just have to think about it and consider it.
Dr. Mandrola: I do want to say to everybody that there is a tension sometimes between the heart failure community and the electrophysiology community. I think the ideal situation is that we work together, because I think that we can help with the maintenance of sinus rhythm. The control group mortality at 1 year was 20%, and I’ve heard people say that that’s not advanced heart failure. Advanced heart failure patients have much higher mortality than that. My colleague who is a heart failure specialist was criticizing a selection bias in picking the best patients. How would you answer that?
Dr. Sohns: There are data available from Eurotransplant, for example, that the waiting list mortality is 18%, so I think we are almost in line with this 20% mortality in this conservative group. You cannot generalize it. All these patients have different histories. We have 60% dilated cardiomyopathy and 40% ischemic cardiomyopathy. I think it is a very representative group in contrast to your friend who suggests that it is not.
Dr. Sommer: What I like about the discussion is that some approach us to say that the mortality in the control group is much too high – like, what are you doing with those patients that you create so many endpoints? Then others say that it’s not high enough because that is not end-stage heart failure. Come on! We have a patient cohort that is very well described and very well characterized.
If the label is end-stage heart failure, advanced heart failure, or whatever, they are sicker than the patients that we had in earlier trials. The patients that we treated were mostly excluded from all other trials. We opened the door. We found a clear result. I think everyone can see whatever you like to see.
Dr. Mandrola: What would your take-home message be after having done this trial design, the trial was conducted in your single center, and you come up with these amazing results? What would your message be to the whole community?
Dr. Sohns: Taking into consideration how severely sick these patients are, I can just repeat it: They are one step away from death, more or less, or from surgical intervention that can prolong their life. You should also consider that there are options like atrial fibrillation ablation that can buy time, postpone the natural course, or even in some patients replace the destination therapy. Therefore, in my opinion the next guidelines should recommend that every patient should carefully be checked for sinus rhythm before bringing these patients into the environment of transplantation.
Dr. Sommer: My interpretation is that we have to try to bring into physicians’ minds that besides a well-established and well-documented effect of drug therapy with the fabulous four, we may now have the fabulous five, including an ablation option for patients with atrial fibrillation.
Dr. Mandrola is a clinical electrophysiologist at Baptist Medical Associates, Louisville, Ky. Dr. Sohns is deputy director of the Heart and Diabetes Center NRW, Ruhr University Bochum, Bad Oeynhausen, Germany. Dr. Sommer is professor of cardiology at the Heart and Diabetes Center NRW. Dr. Mandrola reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Sohns reported receiving research funding from Else Kröner–Fresenius–Stiftung. Dr. Sommer reported consulting with Abbott, Biosense Webster, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic USA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is complete revascularization now compulsory? MULTISTARS-AMI and FIRE in context
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Michelle L. O’Donoghue, MD, MPH: Hi. This is Dr. Michelle O’Donoghue reporting for Medscape. Joining me today is Dr. Sahil Parikh, who’s a cardiologist and an interventionalist at Columbia University. He’s an associate professor of medicine.
We’ll be discussing two interesting trials that were presented at the ESC Congress here in Amsterdam. They do have the potential to be very practice-changing, so I think it’s worth talking about.
The FIRE trial
The first trial we’ll be talking about is the FIRE trial. Perhaps setting the stage, Sahil, I’d love to get your thoughts. We’ve had data in this space to suggest that, for patients with STEMI [ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction], a strategy of complete revascularization – and not only treating the culprit lesion but also treating additional lesions – may be of benefit. Where does that lead us in terms of what we didn’t know?
Sahil A. Parikh, MD: I think that the practice has moved, at least in the United States, over the past two decades, from staging percutaneous coronary interventions over 30 days from index to intervention to now trying to do patients in the same hospitalization whenever possible to achieve complete revascularization.
I think these data support not only that complete revascularization is compulsory now in these patients, but also doing it sooner rather than later, and that the benefit applies to most of the patients that we see in clinical practice. In the earlier data, the patients were relatively youthful – under Medicare age, less than 65 – and now this dataset has a median age of 80. This is more like the real-world clinical practice that most of us are encountering, and it extends the benefit, perhaps, greater than we’ve ever seen before.
O’Donoghue: The FIRE trial is interesting. As you say, it enrolled patients who were over the age of 75, where I think that some proceduralists are probably a little bit hesitant to think about complete revascularization due to concerns about any additional contrast load on their kidneys and other types of comorbidities. Of course, for any trial, there’s going to be some patient selection.
I think it’s very reassuring that even in this older patient group, a strategy of treating all the lesions – and not only in STEMI but also in non-STEMI patients – reduced cardiovascular events and mortality. I was really quite impressed by the mortality benefit.
Parikh: The mortality curve is almost surprising to me. On the other hand, it emboldens us now that we can treat these patients more completely and earlier in their clinical presentation. Certainly, we worried about contrast exposure and the duration of procedures in this older population, but it seems that the benefit that’s derived, which we saw in younger patients where we had a natural inclination to be more aggressive, extends also to this older population.
MULTISTARS AMI
O’Donoghue: To the question of timing, as you mentioned, prior to this, we had a study presented earlier this year, the BIOVASC trial, which also was suggestive that maybe earlier complete revascularization was better. But it wasn’t a significant difference, at least for the primary outcome. Now we have MULTISTARS AMI, which is very supportive of what we saw earlier this year, suggesting that complete revascularization really at the time that you’re treating the culprit may be the way to go.
Parikh: All of us, as interventionalists, are circumspect about what we might do in the middle of the night versus what we would do in the light of day. Certainly it seems clear, particularly if it’s straightforward anatomy, that taking care of it in the index procedure is not only saving contrast and fluoroscopy time, but it’s also providing a clinical benefit to the patients. That’s something that will also impact how clinicians interpret these data. Previously, there was always a question about whether we should just do it in the same hospitalization or do it at the same time. I think now, increasingly, we’re emboldened to do more in the index procedure.
O’Donoghue: When you’re thinking about nonculprit lesions and which ones to treat, do you always make that determination based on physiologic guidance of some kind? Are you using instantaneous wave-free ratio? What’s your practice?
Parikh: In the acute setting, imaging is superior for at least the assessment of which is a culprit. If you see a ruptured atherothrombotic situation on optical coherence tomography, for example, that’s fairly convincing and definitive. In the absence of that physiology, we are taught to avoid in the infarct-related artery because of potential spuriously false-negative findings.
In this situation, certainly, an imaging subgroup probably would be helpful because some of the benefit is almost certainly derived from identifying the infarct-related artery by accident – in other words, doing what you thought was the nonculprit artery, which is, in fact, the culprit. I think that probably is part of this. As somebody who uses imaging in the overwhelming number of my cases, I think that imaging would be an important surrogate to this.
Index procedure versus staged
O’Donoghue: For the operator who is coming in to do their STEMI case at 2:00 in the morning, would these data now push you toward doing complete revascularization at that time of night, or do you think that there is wiggle room in terms of interpreting these results regarding timing, where as long as you were doing it before hospital discharge and not, let’s say, 30 days out, that you may be able to derive the same benefit? What are some of the pros and cons?
Parikh: There’s definitely a fatigue factor in the middle of the night if it’s a particularly arduous intervention for the index infarct-related artery. I think there’s a human element where it may make sense just to stop and then bring the patient back in the same hospitalization. It’s clear, though, that doing complete revascularization is better and doing it sooner is better. How soon one actually does it is a judgment call, as ever.
In our practice, we’ve been pushing ourselves to get most of the patients done in their index hospitalization. If you have a left-sided culprit, the left anterior descending artery, for example, and there’s a high-grade stenosis in the circumflex, it may make sense to take care of that in the same index procedure. If, on the other hand, it’s in the right coronary artery where you have to put a new guide in and spend more time, that may be a patient whom you stage. I think those nuances will come up as interventionalists look at the subgroup analysis data more carefully.
O’Donoghue: Those are great points, and I think they also underscore that we always need to think about what type of patient was enrolled in these studies. Certainly, if you have somebody with renal dysfunction, there might be more concern about giving them a large contrast load all in one sitting, albeit hard to know whether they do or not. But spacing that out by just a couple of days would really have a big impact.
Parikh: Very often in the STEMI patient, you don’t have the benefit of knowing the creatinine. The patient will come in immediately, if not directly from the ambulance to the cath lab, and there are no laboratories at all to work with. If the patient has never been seen in the system before, you won’t know. Again, in those situations, one may have pause, particularly if it’s an older patient. I think what’s reassuring, though, is that the data are supportive of being more aggressive earlier, and certainly this is the dataset that we were looking for.
O’Donoghue: To summarize, the two key takeaways are that, one, we now have more data to support a complete revascularization strategy and even extending that now to non-STEMI patients. Two, sooner appears to be better, so ideally, all done at the time of the index procedure. I think this is very interesting science and we’ll see how it changes practice.
Thanks for joining me today. Signing off for Medscape, this is Dr. Michelle O’Donoghue.
Michelle O’Donoghue is a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and senior investigator with the TIMI Study Group.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Michelle L. O’Donoghue, MD, MPH: Hi. This is Dr. Michelle O’Donoghue reporting for Medscape. Joining me today is Dr. Sahil Parikh, who’s a cardiologist and an interventionalist at Columbia University. He’s an associate professor of medicine.
We’ll be discussing two interesting trials that were presented at the ESC Congress here in Amsterdam. They do have the potential to be very practice-changing, so I think it’s worth talking about.
The FIRE trial
The first trial we’ll be talking about is the FIRE trial. Perhaps setting the stage, Sahil, I’d love to get your thoughts. We’ve had data in this space to suggest that, for patients with STEMI [ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction], a strategy of complete revascularization – and not only treating the culprit lesion but also treating additional lesions – may be of benefit. Where does that lead us in terms of what we didn’t know?
Sahil A. Parikh, MD: I think that the practice has moved, at least in the United States, over the past two decades, from staging percutaneous coronary interventions over 30 days from index to intervention to now trying to do patients in the same hospitalization whenever possible to achieve complete revascularization.
I think these data support not only that complete revascularization is compulsory now in these patients, but also doing it sooner rather than later, and that the benefit applies to most of the patients that we see in clinical practice. In the earlier data, the patients were relatively youthful – under Medicare age, less than 65 – and now this dataset has a median age of 80. This is more like the real-world clinical practice that most of us are encountering, and it extends the benefit, perhaps, greater than we’ve ever seen before.
O’Donoghue: The FIRE trial is interesting. As you say, it enrolled patients who were over the age of 75, where I think that some proceduralists are probably a little bit hesitant to think about complete revascularization due to concerns about any additional contrast load on their kidneys and other types of comorbidities. Of course, for any trial, there’s going to be some patient selection.
I think it’s very reassuring that even in this older patient group, a strategy of treating all the lesions – and not only in STEMI but also in non-STEMI patients – reduced cardiovascular events and mortality. I was really quite impressed by the mortality benefit.
Parikh: The mortality curve is almost surprising to me. On the other hand, it emboldens us now that we can treat these patients more completely and earlier in their clinical presentation. Certainly, we worried about contrast exposure and the duration of procedures in this older population, but it seems that the benefit that’s derived, which we saw in younger patients where we had a natural inclination to be more aggressive, extends also to this older population.
MULTISTARS AMI
O’Donoghue: To the question of timing, as you mentioned, prior to this, we had a study presented earlier this year, the BIOVASC trial, which also was suggestive that maybe earlier complete revascularization was better. But it wasn’t a significant difference, at least for the primary outcome. Now we have MULTISTARS AMI, which is very supportive of what we saw earlier this year, suggesting that complete revascularization really at the time that you’re treating the culprit may be the way to go.
Parikh: All of us, as interventionalists, are circumspect about what we might do in the middle of the night versus what we would do in the light of day. Certainly it seems clear, particularly if it’s straightforward anatomy, that taking care of it in the index procedure is not only saving contrast and fluoroscopy time, but it’s also providing a clinical benefit to the patients. That’s something that will also impact how clinicians interpret these data. Previously, there was always a question about whether we should just do it in the same hospitalization or do it at the same time. I think now, increasingly, we’re emboldened to do more in the index procedure.
O’Donoghue: When you’re thinking about nonculprit lesions and which ones to treat, do you always make that determination based on physiologic guidance of some kind? Are you using instantaneous wave-free ratio? What’s your practice?
Parikh: In the acute setting, imaging is superior for at least the assessment of which is a culprit. If you see a ruptured atherothrombotic situation on optical coherence tomography, for example, that’s fairly convincing and definitive. In the absence of that physiology, we are taught to avoid in the infarct-related artery because of potential spuriously false-negative findings.
In this situation, certainly, an imaging subgroup probably would be helpful because some of the benefit is almost certainly derived from identifying the infarct-related artery by accident – in other words, doing what you thought was the nonculprit artery, which is, in fact, the culprit. I think that probably is part of this. As somebody who uses imaging in the overwhelming number of my cases, I think that imaging would be an important surrogate to this.
Index procedure versus staged
O’Donoghue: For the operator who is coming in to do their STEMI case at 2:00 in the morning, would these data now push you toward doing complete revascularization at that time of night, or do you think that there is wiggle room in terms of interpreting these results regarding timing, where as long as you were doing it before hospital discharge and not, let’s say, 30 days out, that you may be able to derive the same benefit? What are some of the pros and cons?
Parikh: There’s definitely a fatigue factor in the middle of the night if it’s a particularly arduous intervention for the index infarct-related artery. I think there’s a human element where it may make sense just to stop and then bring the patient back in the same hospitalization. It’s clear, though, that doing complete revascularization is better and doing it sooner is better. How soon one actually does it is a judgment call, as ever.
In our practice, we’ve been pushing ourselves to get most of the patients done in their index hospitalization. If you have a left-sided culprit, the left anterior descending artery, for example, and there’s a high-grade stenosis in the circumflex, it may make sense to take care of that in the same index procedure. If, on the other hand, it’s in the right coronary artery where you have to put a new guide in and spend more time, that may be a patient whom you stage. I think those nuances will come up as interventionalists look at the subgroup analysis data more carefully.
O’Donoghue: Those are great points, and I think they also underscore that we always need to think about what type of patient was enrolled in these studies. Certainly, if you have somebody with renal dysfunction, there might be more concern about giving them a large contrast load all in one sitting, albeit hard to know whether they do or not. But spacing that out by just a couple of days would really have a big impact.
Parikh: Very often in the STEMI patient, you don’t have the benefit of knowing the creatinine. The patient will come in immediately, if not directly from the ambulance to the cath lab, and there are no laboratories at all to work with. If the patient has never been seen in the system before, you won’t know. Again, in those situations, one may have pause, particularly if it’s an older patient. I think what’s reassuring, though, is that the data are supportive of being more aggressive earlier, and certainly this is the dataset that we were looking for.
O’Donoghue: To summarize, the two key takeaways are that, one, we now have more data to support a complete revascularization strategy and even extending that now to non-STEMI patients. Two, sooner appears to be better, so ideally, all done at the time of the index procedure. I think this is very interesting science and we’ll see how it changes practice.
Thanks for joining me today. Signing off for Medscape, this is Dr. Michelle O’Donoghue.
Michelle O’Donoghue is a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and senior investigator with the TIMI Study Group.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Michelle L. O’Donoghue, MD, MPH: Hi. This is Dr. Michelle O’Donoghue reporting for Medscape. Joining me today is Dr. Sahil Parikh, who’s a cardiologist and an interventionalist at Columbia University. He’s an associate professor of medicine.
We’ll be discussing two interesting trials that were presented at the ESC Congress here in Amsterdam. They do have the potential to be very practice-changing, so I think it’s worth talking about.
The FIRE trial
The first trial we’ll be talking about is the FIRE trial. Perhaps setting the stage, Sahil, I’d love to get your thoughts. We’ve had data in this space to suggest that, for patients with STEMI [ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction], a strategy of complete revascularization – and not only treating the culprit lesion but also treating additional lesions – may be of benefit. Where does that lead us in terms of what we didn’t know?
Sahil A. Parikh, MD: I think that the practice has moved, at least in the United States, over the past two decades, from staging percutaneous coronary interventions over 30 days from index to intervention to now trying to do patients in the same hospitalization whenever possible to achieve complete revascularization.
I think these data support not only that complete revascularization is compulsory now in these patients, but also doing it sooner rather than later, and that the benefit applies to most of the patients that we see in clinical practice. In the earlier data, the patients were relatively youthful – under Medicare age, less than 65 – and now this dataset has a median age of 80. This is more like the real-world clinical practice that most of us are encountering, and it extends the benefit, perhaps, greater than we’ve ever seen before.
O’Donoghue: The FIRE trial is interesting. As you say, it enrolled patients who were over the age of 75, where I think that some proceduralists are probably a little bit hesitant to think about complete revascularization due to concerns about any additional contrast load on their kidneys and other types of comorbidities. Of course, for any trial, there’s going to be some patient selection.
I think it’s very reassuring that even in this older patient group, a strategy of treating all the lesions – and not only in STEMI but also in non-STEMI patients – reduced cardiovascular events and mortality. I was really quite impressed by the mortality benefit.
Parikh: The mortality curve is almost surprising to me. On the other hand, it emboldens us now that we can treat these patients more completely and earlier in their clinical presentation. Certainly, we worried about contrast exposure and the duration of procedures in this older population, but it seems that the benefit that’s derived, which we saw in younger patients where we had a natural inclination to be more aggressive, extends also to this older population.
MULTISTARS AMI
O’Donoghue: To the question of timing, as you mentioned, prior to this, we had a study presented earlier this year, the BIOVASC trial, which also was suggestive that maybe earlier complete revascularization was better. But it wasn’t a significant difference, at least for the primary outcome. Now we have MULTISTARS AMI, which is very supportive of what we saw earlier this year, suggesting that complete revascularization really at the time that you’re treating the culprit may be the way to go.
Parikh: All of us, as interventionalists, are circumspect about what we might do in the middle of the night versus what we would do in the light of day. Certainly it seems clear, particularly if it’s straightforward anatomy, that taking care of it in the index procedure is not only saving contrast and fluoroscopy time, but it’s also providing a clinical benefit to the patients. That’s something that will also impact how clinicians interpret these data. Previously, there was always a question about whether we should just do it in the same hospitalization or do it at the same time. I think now, increasingly, we’re emboldened to do more in the index procedure.
O’Donoghue: When you’re thinking about nonculprit lesions and which ones to treat, do you always make that determination based on physiologic guidance of some kind? Are you using instantaneous wave-free ratio? What’s your practice?
Parikh: In the acute setting, imaging is superior for at least the assessment of which is a culprit. If you see a ruptured atherothrombotic situation on optical coherence tomography, for example, that’s fairly convincing and definitive. In the absence of that physiology, we are taught to avoid in the infarct-related artery because of potential spuriously false-negative findings.
In this situation, certainly, an imaging subgroup probably would be helpful because some of the benefit is almost certainly derived from identifying the infarct-related artery by accident – in other words, doing what you thought was the nonculprit artery, which is, in fact, the culprit. I think that probably is part of this. As somebody who uses imaging in the overwhelming number of my cases, I think that imaging would be an important surrogate to this.
Index procedure versus staged
O’Donoghue: For the operator who is coming in to do their STEMI case at 2:00 in the morning, would these data now push you toward doing complete revascularization at that time of night, or do you think that there is wiggle room in terms of interpreting these results regarding timing, where as long as you were doing it before hospital discharge and not, let’s say, 30 days out, that you may be able to derive the same benefit? What are some of the pros and cons?
Parikh: There’s definitely a fatigue factor in the middle of the night if it’s a particularly arduous intervention for the index infarct-related artery. I think there’s a human element where it may make sense just to stop and then bring the patient back in the same hospitalization. It’s clear, though, that doing complete revascularization is better and doing it sooner is better. How soon one actually does it is a judgment call, as ever.
In our practice, we’ve been pushing ourselves to get most of the patients done in their index hospitalization. If you have a left-sided culprit, the left anterior descending artery, for example, and there’s a high-grade stenosis in the circumflex, it may make sense to take care of that in the same index procedure. If, on the other hand, it’s in the right coronary artery where you have to put a new guide in and spend more time, that may be a patient whom you stage. I think those nuances will come up as interventionalists look at the subgroup analysis data more carefully.
O’Donoghue: Those are great points, and I think they also underscore that we always need to think about what type of patient was enrolled in these studies. Certainly, if you have somebody with renal dysfunction, there might be more concern about giving them a large contrast load all in one sitting, albeit hard to know whether they do or not. But spacing that out by just a couple of days would really have a big impact.
Parikh: Very often in the STEMI patient, you don’t have the benefit of knowing the creatinine. The patient will come in immediately, if not directly from the ambulance to the cath lab, and there are no laboratories at all to work with. If the patient has never been seen in the system before, you won’t know. Again, in those situations, one may have pause, particularly if it’s an older patient. I think what’s reassuring, though, is that the data are supportive of being more aggressive earlier, and certainly this is the dataset that we were looking for.
O’Donoghue: To summarize, the two key takeaways are that, one, we now have more data to support a complete revascularization strategy and even extending that now to non-STEMI patients. Two, sooner appears to be better, so ideally, all done at the time of the index procedure. I think this is very interesting science and we’ll see how it changes practice.
Thanks for joining me today. Signing off for Medscape, this is Dr. Michelle O’Donoghue.
Michelle O’Donoghue is a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and senior investigator with the TIMI Study Group.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Navigating chronic cough in primary care
Chronic cough took center stage at the European Respiratory Society Congress session titled “Conditions We Are Just Dealing With the Tip of the Iceberg in Primary Care: Frequently Mismanaged Conditions in Primary Health Care.”
“When it comes to chronic cough, general practitioners often feel lost,” Miguel Román Rodríguez, family doctor and an associate professor of family medicine at the University of the Balearic Islands, Palma, Mallorca, Spain, and one of the chairs of the session, said to this news organization.
“GPs are central in diagnosing conditions like chronic cough. We bring something that the specialists don’t bring: the knowledge of the context, of the family, the longitudinal history,” echoed the second chair of the session, Hilary Pinnock, family physician and professor of primary care respiratory medicine at the University of Edinburgh.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of chronic cough
Imran Satia, an assistant professor at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., guided attendees at the Milan, Italy, meeting through a comprehensive exploration of chronic cough. The first issue he addressed was the definition of the condition, emphasizing that it is defined by its duration, with chronic cough typically lasting for more than 8 weeks. Prof. Satia pointed out common associations of chronic cough, including asthma, nasal disease, and reflux disease.
Delving into epidemiology, he cited a meta-analysis indicating a global prevalence of approximately 10% in the adult population, with significant regional variability: from 18.1% in Australia to 2.3% in Africa. Notably, the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging found an overall prevalence of 16% at baseline. “The most common risk factor was smoke, but even in nonsmokers the prevalence reached 10%,” Prof. Satia added, highlighting that it increased with age and changed depending on location. “The most common associated comorbidities were heart failure and hypertension, but also conditions related to chronic pain, mood, and anxiety,” he explained.
Mental health was identified as a crucial factor in chronic cough, with psychological distress and depressive symptoms emerging as risk factors for developing chronic cough over the next 3 years, contributing to a 20% increased risk.
Effective management strategies
Prof. Satia proposed the use of algorithms to aid in the management of patients with chronic cough in primary care. He introduced a Canadian algorithm that offers specific recommendations for both primary and secondary care.
The algorithm’s primary care assessment, step 1, includes a comprehensive evaluation of the cough history (duration, severity, triggers, nature, location); cardiorespiratory, gastrointestinal, and nasal symptoms; and use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and smoking status. Essential diagnostic tests, such as chest radiography (to check for structural disease), complete blood cell count, and spirometry (with or without bronchodilator reversibility), were emphasized. Urgent referral criteria encompassed symptoms like hemoptysis, weight loss, fever, or abnormal chest radiography findings.
“When checking for cough history, GPs should always consider factors like the presence of dry or productive cough, mental health, presence of chronic pain, stroke, and swallowing,” said Prof. Satia, stressing the importance of documenting the impact of chronic cough on quality of life, work life, social life, and family life. “This is something that doctors sometimes do not ask about. They may think that these are not major problems, but acknowledging their importance can help the patient,” he added.
Step 2 of the algorithm focuses on treatment options tailored to specific diagnoses, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Prof. Satia urged caution, emphasizing that treatment should only be initiated when evidence of these conditions is present. Additionally, he encouraged early consideration of cough hypersensitivity syndrome when patients exhibit coughing in response to low levels of mechanical stimulation.
Current treatments and future prospects
Prof. Satia presented an overview of existing treatments for chronic cough, outlining their respective advantages and disadvantages. For instance, speech therapy is a patient-led approach with no side effects but entails challenges related to access, costs, and patient motivation. On the other hand, low-dose morphine offers rapid relief but is associated with issues like nausea, stigma, and constipation.
Looking ahead, Prof. Satia shared the results of COUGH-1 and COUGH-2, pivotal phase 3 trials evaluating the oral, peripherally acting P2X3-receptor antagonist gefapixant. This drug, currently approved in Switzerland and Japan, demonstrated a significant reduction in cough frequency, compared with placebo, with rapid and sustained effects. “The estimated relative reduction for 45 mg was 18.45% in COUGH-1 (12 weeks) and 14.64% in COUGH-2 (24 weeks). Of note, cough reduction is very quick and sustained with gefapixant, but a 40% reduction is observed in the placebo arm,” commented Prof. Satia.
Experts unanimously stressed the importance for specialists and GPs of effective communication in managing chronic cough, involving both patients and their families.
“As GPs, we are crucial to manage the common problems, but we are also crucial to spot the needle in the haystack: this is extremely difficult and challenging, and we need support from our colleagues,” Dr. Pinnock concluded.
Prof. Satia reported funding from Merck MSD, AstraZeneca, and GSK; consulting fees from Merck MSD, Genentech, and Respiplus; and speaker fees from AstraZeneca, GSK, and Merck MSD.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic cough took center stage at the European Respiratory Society Congress session titled “Conditions We Are Just Dealing With the Tip of the Iceberg in Primary Care: Frequently Mismanaged Conditions in Primary Health Care.”
“When it comes to chronic cough, general practitioners often feel lost,” Miguel Román Rodríguez, family doctor and an associate professor of family medicine at the University of the Balearic Islands, Palma, Mallorca, Spain, and one of the chairs of the session, said to this news organization.
“GPs are central in diagnosing conditions like chronic cough. We bring something that the specialists don’t bring: the knowledge of the context, of the family, the longitudinal history,” echoed the second chair of the session, Hilary Pinnock, family physician and professor of primary care respiratory medicine at the University of Edinburgh.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of chronic cough
Imran Satia, an assistant professor at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., guided attendees at the Milan, Italy, meeting through a comprehensive exploration of chronic cough. The first issue he addressed was the definition of the condition, emphasizing that it is defined by its duration, with chronic cough typically lasting for more than 8 weeks. Prof. Satia pointed out common associations of chronic cough, including asthma, nasal disease, and reflux disease.
Delving into epidemiology, he cited a meta-analysis indicating a global prevalence of approximately 10% in the adult population, with significant regional variability: from 18.1% in Australia to 2.3% in Africa. Notably, the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging found an overall prevalence of 16% at baseline. “The most common risk factor was smoke, but even in nonsmokers the prevalence reached 10%,” Prof. Satia added, highlighting that it increased with age and changed depending on location. “The most common associated comorbidities were heart failure and hypertension, but also conditions related to chronic pain, mood, and anxiety,” he explained.
Mental health was identified as a crucial factor in chronic cough, with psychological distress and depressive symptoms emerging as risk factors for developing chronic cough over the next 3 years, contributing to a 20% increased risk.
Effective management strategies
Prof. Satia proposed the use of algorithms to aid in the management of patients with chronic cough in primary care. He introduced a Canadian algorithm that offers specific recommendations for both primary and secondary care.
The algorithm’s primary care assessment, step 1, includes a comprehensive evaluation of the cough history (duration, severity, triggers, nature, location); cardiorespiratory, gastrointestinal, and nasal symptoms; and use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and smoking status. Essential diagnostic tests, such as chest radiography (to check for structural disease), complete blood cell count, and spirometry (with or without bronchodilator reversibility), were emphasized. Urgent referral criteria encompassed symptoms like hemoptysis, weight loss, fever, or abnormal chest radiography findings.
“When checking for cough history, GPs should always consider factors like the presence of dry or productive cough, mental health, presence of chronic pain, stroke, and swallowing,” said Prof. Satia, stressing the importance of documenting the impact of chronic cough on quality of life, work life, social life, and family life. “This is something that doctors sometimes do not ask about. They may think that these are not major problems, but acknowledging their importance can help the patient,” he added.
Step 2 of the algorithm focuses on treatment options tailored to specific diagnoses, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Prof. Satia urged caution, emphasizing that treatment should only be initiated when evidence of these conditions is present. Additionally, he encouraged early consideration of cough hypersensitivity syndrome when patients exhibit coughing in response to low levels of mechanical stimulation.
Current treatments and future prospects
Prof. Satia presented an overview of existing treatments for chronic cough, outlining their respective advantages and disadvantages. For instance, speech therapy is a patient-led approach with no side effects but entails challenges related to access, costs, and patient motivation. On the other hand, low-dose morphine offers rapid relief but is associated with issues like nausea, stigma, and constipation.
Looking ahead, Prof. Satia shared the results of COUGH-1 and COUGH-2, pivotal phase 3 trials evaluating the oral, peripherally acting P2X3-receptor antagonist gefapixant. This drug, currently approved in Switzerland and Japan, demonstrated a significant reduction in cough frequency, compared with placebo, with rapid and sustained effects. “The estimated relative reduction for 45 mg was 18.45% in COUGH-1 (12 weeks) and 14.64% in COUGH-2 (24 weeks). Of note, cough reduction is very quick and sustained with gefapixant, but a 40% reduction is observed in the placebo arm,” commented Prof. Satia.
Experts unanimously stressed the importance for specialists and GPs of effective communication in managing chronic cough, involving both patients and their families.
“As GPs, we are crucial to manage the common problems, but we are also crucial to spot the needle in the haystack: this is extremely difficult and challenging, and we need support from our colleagues,” Dr. Pinnock concluded.
Prof. Satia reported funding from Merck MSD, AstraZeneca, and GSK; consulting fees from Merck MSD, Genentech, and Respiplus; and speaker fees from AstraZeneca, GSK, and Merck MSD.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic cough took center stage at the European Respiratory Society Congress session titled “Conditions We Are Just Dealing With the Tip of the Iceberg in Primary Care: Frequently Mismanaged Conditions in Primary Health Care.”
“When it comes to chronic cough, general practitioners often feel lost,” Miguel Román Rodríguez, family doctor and an associate professor of family medicine at the University of the Balearic Islands, Palma, Mallorca, Spain, and one of the chairs of the session, said to this news organization.
“GPs are central in diagnosing conditions like chronic cough. We bring something that the specialists don’t bring: the knowledge of the context, of the family, the longitudinal history,” echoed the second chair of the session, Hilary Pinnock, family physician and professor of primary care respiratory medicine at the University of Edinburgh.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of chronic cough
Imran Satia, an assistant professor at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., guided attendees at the Milan, Italy, meeting through a comprehensive exploration of chronic cough. The first issue he addressed was the definition of the condition, emphasizing that it is defined by its duration, with chronic cough typically lasting for more than 8 weeks. Prof. Satia pointed out common associations of chronic cough, including asthma, nasal disease, and reflux disease.
Delving into epidemiology, he cited a meta-analysis indicating a global prevalence of approximately 10% in the adult population, with significant regional variability: from 18.1% in Australia to 2.3% in Africa. Notably, the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging found an overall prevalence of 16% at baseline. “The most common risk factor was smoke, but even in nonsmokers the prevalence reached 10%,” Prof. Satia added, highlighting that it increased with age and changed depending on location. “The most common associated comorbidities were heart failure and hypertension, but also conditions related to chronic pain, mood, and anxiety,” he explained.
Mental health was identified as a crucial factor in chronic cough, with psychological distress and depressive symptoms emerging as risk factors for developing chronic cough over the next 3 years, contributing to a 20% increased risk.
Effective management strategies
Prof. Satia proposed the use of algorithms to aid in the management of patients with chronic cough in primary care. He introduced a Canadian algorithm that offers specific recommendations for both primary and secondary care.
The algorithm’s primary care assessment, step 1, includes a comprehensive evaluation of the cough history (duration, severity, triggers, nature, location); cardiorespiratory, gastrointestinal, and nasal symptoms; and use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and smoking status. Essential diagnostic tests, such as chest radiography (to check for structural disease), complete blood cell count, and spirometry (with or without bronchodilator reversibility), were emphasized. Urgent referral criteria encompassed symptoms like hemoptysis, weight loss, fever, or abnormal chest radiography findings.
“When checking for cough history, GPs should always consider factors like the presence of dry or productive cough, mental health, presence of chronic pain, stroke, and swallowing,” said Prof. Satia, stressing the importance of documenting the impact of chronic cough on quality of life, work life, social life, and family life. “This is something that doctors sometimes do not ask about. They may think that these are not major problems, but acknowledging their importance can help the patient,” he added.
Step 2 of the algorithm focuses on treatment options tailored to specific diagnoses, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Prof. Satia urged caution, emphasizing that treatment should only be initiated when evidence of these conditions is present. Additionally, he encouraged early consideration of cough hypersensitivity syndrome when patients exhibit coughing in response to low levels of mechanical stimulation.
Current treatments and future prospects
Prof. Satia presented an overview of existing treatments for chronic cough, outlining their respective advantages and disadvantages. For instance, speech therapy is a patient-led approach with no side effects but entails challenges related to access, costs, and patient motivation. On the other hand, low-dose morphine offers rapid relief but is associated with issues like nausea, stigma, and constipation.
Looking ahead, Prof. Satia shared the results of COUGH-1 and COUGH-2, pivotal phase 3 trials evaluating the oral, peripherally acting P2X3-receptor antagonist gefapixant. This drug, currently approved in Switzerland and Japan, demonstrated a significant reduction in cough frequency, compared with placebo, with rapid and sustained effects. “The estimated relative reduction for 45 mg was 18.45% in COUGH-1 (12 weeks) and 14.64% in COUGH-2 (24 weeks). Of note, cough reduction is very quick and sustained with gefapixant, but a 40% reduction is observed in the placebo arm,” commented Prof. Satia.
Experts unanimously stressed the importance for specialists and GPs of effective communication in managing chronic cough, involving both patients and their families.
“As GPs, we are crucial to manage the common problems, but we are also crucial to spot the needle in the haystack: this is extremely difficult and challenging, and we need support from our colleagues,” Dr. Pinnock concluded.
Prof. Satia reported funding from Merck MSD, AstraZeneca, and GSK; consulting fees from Merck MSD, Genentech, and Respiplus; and speaker fees from AstraZeneca, GSK, and Merck MSD.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ERS 2023
Positive topline results for antihypertensive zilebesiran
Zilebesiran (Alnylam Pharmaceuticals), an investigational, subcutaneously administered small-interfering RNA (siRNA) therapeutic in development for the treatment of hypertension, met the primary and secondary endpoints, with an “encouraging” safety profile in the phase 2 KARDIA-1 study, the company announced.
KARDIA-1 is a phase 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study evaluating the efficacy and safety of zilebesiran as monotherapy in 394 adults with mild to moderate untreated hypertension or on stable therapy with one or more antihypertensive drugs.
Patients were randomly assigned to one of five treatment arms during a 12-month double-blind period and double-blind extension period: 150 mg or 300 mg zilebesiran subcutaneously once every 6 months, 300 mg or 600 mg zilebesiran subcutaneously once every 3 months, or placebo. Patients taking placebo were randomly assigned to one of the four initial zilebesiran dose regimens beginning at month 6.
The primary endpoint was change from baseline in systolic blood pressure (SBP) at 3 months assessed by 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring.
Topline data show a dose-dependent, clinically significant reduction in 24-hour mean SBP, with a placebo-subtracted reduction greater than 15 mm Hg (P < .0001) with both the 300 mg and 600 mg doses.
The study also met key secondary endpoints, showing “consistent and sustained reductions” in SBP at 6 months, which supports quarterly or biannual dosing, the company said.
There was one death due to cardiopulmonary arrest in a zilebesiran-treated patient that was considered unrelated to the drug. Serious adverse events were reported in 3.6% of zilebesiran-treated patients and 6.7% of placebo-treated patients. None was considered related to the study drug.
Adverse events occurring in 5% or more of zilebesiran-treated patients in any dose arm included COVID-19, injection-site reaction, hyperkalemia, hypertension, upper respiratory tract infection, arthralgia, and headache.
“As a physician, I believe these KARDIA-1 results, which demonstrate clinically significant reductions in systolic blood pressure of greater than 15 mm Hg, along with the ability to achieve durable tonic blood pressure control, provide hope that we may one day have access to a novel therapy with the potential to address the significant unmet needs of patients with uncontrolled hypertension who are at high risk of future cardiovascular events,” study investigator George L. Bakris, MD, director, American Heart Association Comprehensive Hypertension Center, University of Chicago Medicine, said in a statement.
The phase 2 results “further validate” the phase 1 results, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, Simon Fox, PhD, vice president, zilebesiran program lead at Alnylam, said in the statement.
The full KARDIA-1 results will be reported at an upcoming scientific conference, the statement notes. Topline results from the KARDIA-2 phase 2 study of zilebesiran in combination with one of three standard classes of antihypertensive medications in patients with mild to moderate hypertension are expected in early 2024.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Zilebesiran (Alnylam Pharmaceuticals), an investigational, subcutaneously administered small-interfering RNA (siRNA) therapeutic in development for the treatment of hypertension, met the primary and secondary endpoints, with an “encouraging” safety profile in the phase 2 KARDIA-1 study, the company announced.
KARDIA-1 is a phase 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study evaluating the efficacy and safety of zilebesiran as monotherapy in 394 adults with mild to moderate untreated hypertension or on stable therapy with one or more antihypertensive drugs.
Patients were randomly assigned to one of five treatment arms during a 12-month double-blind period and double-blind extension period: 150 mg or 300 mg zilebesiran subcutaneously once every 6 months, 300 mg or 600 mg zilebesiran subcutaneously once every 3 months, or placebo. Patients taking placebo were randomly assigned to one of the four initial zilebesiran dose regimens beginning at month 6.
The primary endpoint was change from baseline in systolic blood pressure (SBP) at 3 months assessed by 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring.
Topline data show a dose-dependent, clinically significant reduction in 24-hour mean SBP, with a placebo-subtracted reduction greater than 15 mm Hg (P < .0001) with both the 300 mg and 600 mg doses.
The study also met key secondary endpoints, showing “consistent and sustained reductions” in SBP at 6 months, which supports quarterly or biannual dosing, the company said.
There was one death due to cardiopulmonary arrest in a zilebesiran-treated patient that was considered unrelated to the drug. Serious adverse events were reported in 3.6% of zilebesiran-treated patients and 6.7% of placebo-treated patients. None was considered related to the study drug.
Adverse events occurring in 5% or more of zilebesiran-treated patients in any dose arm included COVID-19, injection-site reaction, hyperkalemia, hypertension, upper respiratory tract infection, arthralgia, and headache.
“As a physician, I believe these KARDIA-1 results, which demonstrate clinically significant reductions in systolic blood pressure of greater than 15 mm Hg, along with the ability to achieve durable tonic blood pressure control, provide hope that we may one day have access to a novel therapy with the potential to address the significant unmet needs of patients with uncontrolled hypertension who are at high risk of future cardiovascular events,” study investigator George L. Bakris, MD, director, American Heart Association Comprehensive Hypertension Center, University of Chicago Medicine, said in a statement.
The phase 2 results “further validate” the phase 1 results, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, Simon Fox, PhD, vice president, zilebesiran program lead at Alnylam, said in the statement.
The full KARDIA-1 results will be reported at an upcoming scientific conference, the statement notes. Topline results from the KARDIA-2 phase 2 study of zilebesiran in combination with one of three standard classes of antihypertensive medications in patients with mild to moderate hypertension are expected in early 2024.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Zilebesiran (Alnylam Pharmaceuticals), an investigational, subcutaneously administered small-interfering RNA (siRNA) therapeutic in development for the treatment of hypertension, met the primary and secondary endpoints, with an “encouraging” safety profile in the phase 2 KARDIA-1 study, the company announced.
KARDIA-1 is a phase 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study evaluating the efficacy and safety of zilebesiran as monotherapy in 394 adults with mild to moderate untreated hypertension or on stable therapy with one or more antihypertensive drugs.
Patients were randomly assigned to one of five treatment arms during a 12-month double-blind period and double-blind extension period: 150 mg or 300 mg zilebesiran subcutaneously once every 6 months, 300 mg or 600 mg zilebesiran subcutaneously once every 3 months, or placebo. Patients taking placebo were randomly assigned to one of the four initial zilebesiran dose regimens beginning at month 6.
The primary endpoint was change from baseline in systolic blood pressure (SBP) at 3 months assessed by 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring.
Topline data show a dose-dependent, clinically significant reduction in 24-hour mean SBP, with a placebo-subtracted reduction greater than 15 mm Hg (P < .0001) with both the 300 mg and 600 mg doses.
The study also met key secondary endpoints, showing “consistent and sustained reductions” in SBP at 6 months, which supports quarterly or biannual dosing, the company said.
There was one death due to cardiopulmonary arrest in a zilebesiran-treated patient that was considered unrelated to the drug. Serious adverse events were reported in 3.6% of zilebesiran-treated patients and 6.7% of placebo-treated patients. None was considered related to the study drug.
Adverse events occurring in 5% or more of zilebesiran-treated patients in any dose arm included COVID-19, injection-site reaction, hyperkalemia, hypertension, upper respiratory tract infection, arthralgia, and headache.
“As a physician, I believe these KARDIA-1 results, which demonstrate clinically significant reductions in systolic blood pressure of greater than 15 mm Hg, along with the ability to achieve durable tonic blood pressure control, provide hope that we may one day have access to a novel therapy with the potential to address the significant unmet needs of patients with uncontrolled hypertension who are at high risk of future cardiovascular events,” study investigator George L. Bakris, MD, director, American Heart Association Comprehensive Hypertension Center, University of Chicago Medicine, said in a statement.
The phase 2 results “further validate” the phase 1 results, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, Simon Fox, PhD, vice president, zilebesiran program lead at Alnylam, said in the statement.
The full KARDIA-1 results will be reported at an upcoming scientific conference, the statement notes. Topline results from the KARDIA-2 phase 2 study of zilebesiran in combination with one of three standard classes of antihypertensive medications in patients with mild to moderate hypertension are expected in early 2024.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A Case of Compound Heterozygous Factor V Leiden and Prothrombin G20210A Mutations With Recurrent Arterial Thromboembolism
BACKGROUND
There are 5 germline mutations that lead to hypercoagulability in the general population including: Factor V Leiden (FVL), Prothrombin G20210A (F2A), Protein C Deficiency (PCD), Protein S Deficiency (PSD), and Antithrombin Deficiency (ATD). Typical guidance is to defer testing, as it is thought not to change management.
CASE REPORT
We present a case of a patient who was found to be compound heterozygous mutations for FVL and F2A, who presented with two episodes of arterial thromboembolism resulting in cerebrovascular accident (CVA). A 63-year-old male with past medical history of hypertension, a CVA four years prior, and medication non-compliance presents with new onset left sided hemiparesis after an episode of convulsions. MRI and CT imaging of the head revealed ischemic CVA secondary to thromboembolism in the right posterior cerebral artery’s (PCA), P1 branch. Following administration of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) he had rapid symptom improvement. This second ischemic CVA prompted a workup which was notable for: negative echocardiogram, negative 30-day cardiac monitor, CT chest negative for malignancy, no significant vascular findings, negative for antiphospholipid syndrome, but genetic testing revealed the patient to be heterozygous for FVL and F2A mutations. He was started on apixaban 5 mg twice daily for ongoing secondary prevention. Though medication compliance continues to be difficult, after being placed on direct anticoagulant (DOAC), he has not had recurrent venous or arterial thrombotic events. A small case series found double heterozygosity for FVL and F2A further increases the risk of venous thromboembolism up to 17% or more in a lifetime.
CONCLUSIONS
Although current recommendations advocate against testing for specific mutations in most cases as it is likely not to change management1, this case suggests that it may be of some benefit in patients that have a workup that does not yield a clear etiology, especially in cryptogenic stroke which is typically managed with aspirin rather than direct oral anticoagulant.
BACKGROUND
There are 5 germline mutations that lead to hypercoagulability in the general population including: Factor V Leiden (FVL), Prothrombin G20210A (F2A), Protein C Deficiency (PCD), Protein S Deficiency (PSD), and Antithrombin Deficiency (ATD). Typical guidance is to defer testing, as it is thought not to change management.
CASE REPORT
We present a case of a patient who was found to be compound heterozygous mutations for FVL and F2A, who presented with two episodes of arterial thromboembolism resulting in cerebrovascular accident (CVA). A 63-year-old male with past medical history of hypertension, a CVA four years prior, and medication non-compliance presents with new onset left sided hemiparesis after an episode of convulsions. MRI and CT imaging of the head revealed ischemic CVA secondary to thromboembolism in the right posterior cerebral artery’s (PCA), P1 branch. Following administration of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) he had rapid symptom improvement. This second ischemic CVA prompted a workup which was notable for: negative echocardiogram, negative 30-day cardiac monitor, CT chest negative for malignancy, no significant vascular findings, negative for antiphospholipid syndrome, but genetic testing revealed the patient to be heterozygous for FVL and F2A mutations. He was started on apixaban 5 mg twice daily for ongoing secondary prevention. Though medication compliance continues to be difficult, after being placed on direct anticoagulant (DOAC), he has not had recurrent venous or arterial thrombotic events. A small case series found double heterozygosity for FVL and F2A further increases the risk of venous thromboembolism up to 17% or more in a lifetime.
CONCLUSIONS
Although current recommendations advocate against testing for specific mutations in most cases as it is likely not to change management1, this case suggests that it may be of some benefit in patients that have a workup that does not yield a clear etiology, especially in cryptogenic stroke which is typically managed with aspirin rather than direct oral anticoagulant.
BACKGROUND
There are 5 germline mutations that lead to hypercoagulability in the general population including: Factor V Leiden (FVL), Prothrombin G20210A (F2A), Protein C Deficiency (PCD), Protein S Deficiency (PSD), and Antithrombin Deficiency (ATD). Typical guidance is to defer testing, as it is thought not to change management.
CASE REPORT
We present a case of a patient who was found to be compound heterozygous mutations for FVL and F2A, who presented with two episodes of arterial thromboembolism resulting in cerebrovascular accident (CVA). A 63-year-old male with past medical history of hypertension, a CVA four years prior, and medication non-compliance presents with new onset left sided hemiparesis after an episode of convulsions. MRI and CT imaging of the head revealed ischemic CVA secondary to thromboembolism in the right posterior cerebral artery’s (PCA), P1 branch. Following administration of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) he had rapid symptom improvement. This second ischemic CVA prompted a workup which was notable for: negative echocardiogram, negative 30-day cardiac monitor, CT chest negative for malignancy, no significant vascular findings, negative for antiphospholipid syndrome, but genetic testing revealed the patient to be heterozygous for FVL and F2A mutations. He was started on apixaban 5 mg twice daily for ongoing secondary prevention. Though medication compliance continues to be difficult, after being placed on direct anticoagulant (DOAC), he has not had recurrent venous or arterial thrombotic events. A small case series found double heterozygosity for FVL and F2A further increases the risk of venous thromboembolism up to 17% or more in a lifetime.
CONCLUSIONS
Although current recommendations advocate against testing for specific mutations in most cases as it is likely not to change management1, this case suggests that it may be of some benefit in patients that have a workup that does not yield a clear etiology, especially in cryptogenic stroke which is typically managed with aspirin rather than direct oral anticoagulant.
Revision of a Massive Transfusion Protocol to Allow for Verbal Orders
PURPOSE
To improve the time to release of blood products for patients with severe or life-threatening bleeding.
BACKGROUND
Exsanguination, and the resultant coagulopathy, is the number one cause of trauma-related death. Massive transfusion protocols (MTP) improve mortality by shortening the time to transfusion and correcting coagulopathy. Many patients do not meet criteria for massive transfusion (> 10 units RBCs in 24 hours), yet present with clinical instability and require rapid release (RR) of uncrossmatched blood. A quality improvement initiative was performed to identify barriers to the MTP/RR protocol at a single institution.
METHODS/DATA
A multidisciplinary subcommittee was formed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the current MTP/RR process. Timed mock-MTP/RR trials were conducted to identify areas of delay with a goal to achieve a blood to bedside (B2B) time of under 10 minutes.
RESULTS
Timed mock-MTP/RR trials were conducted, which revealed a baseline B2B time of approximately 30 minutes. We identified problems and categorized them in terms of ordering (phase 1) and processing (phase 2). We found significant delays in phase 1. Reasons for delay were varied and included difficulty logging into the computer, staff unavailable to place orders (involved in resuscitation efforts), orders entered incorrectly, etc. Once orders were received, the blood bank could process them quickly in phase 2. Using root cause analysis, we discovered a critical step was to remove the barrier of electronic ordering. For this, a new process was developed in which the blood bank could accept verbal orders to release uncrossmatched blood during a medical emergency. Over the course of one year, a new policy for MTP/RR was drafted, an education training video was recorded, informational flyers were printed, and training drills were conducted. A repeat mock-MTP/RR scenario was performed after the change showing the B2B time was reduced by 90% from pre-intervention values to under 3 minutes. Since implementation, no new safety signals have been received, and the staff have reported improved satisfaction with the MTP/RR process.
IMPLICATIONS
A critical piece of any MTP/RR is the immediate availability of blood. Allowing verbal orders for blood products reduced time to transfusion by 90%. Through multidisciplinary effort, safe and efficient release of uncrossmatched blood products for nontraumatic massive transfusion can be achieved.
PURPOSE
To improve the time to release of blood products for patients with severe or life-threatening bleeding.
BACKGROUND
Exsanguination, and the resultant coagulopathy, is the number one cause of trauma-related death. Massive transfusion protocols (MTP) improve mortality by shortening the time to transfusion and correcting coagulopathy. Many patients do not meet criteria for massive transfusion (> 10 units RBCs in 24 hours), yet present with clinical instability and require rapid release (RR) of uncrossmatched blood. A quality improvement initiative was performed to identify barriers to the MTP/RR protocol at a single institution.
METHODS/DATA
A multidisciplinary subcommittee was formed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the current MTP/RR process. Timed mock-MTP/RR trials were conducted to identify areas of delay with a goal to achieve a blood to bedside (B2B) time of under 10 minutes.
RESULTS
Timed mock-MTP/RR trials were conducted, which revealed a baseline B2B time of approximately 30 minutes. We identified problems and categorized them in terms of ordering (phase 1) and processing (phase 2). We found significant delays in phase 1. Reasons for delay were varied and included difficulty logging into the computer, staff unavailable to place orders (involved in resuscitation efforts), orders entered incorrectly, etc. Once orders were received, the blood bank could process them quickly in phase 2. Using root cause analysis, we discovered a critical step was to remove the barrier of electronic ordering. For this, a new process was developed in which the blood bank could accept verbal orders to release uncrossmatched blood during a medical emergency. Over the course of one year, a new policy for MTP/RR was drafted, an education training video was recorded, informational flyers were printed, and training drills were conducted. A repeat mock-MTP/RR scenario was performed after the change showing the B2B time was reduced by 90% from pre-intervention values to under 3 minutes. Since implementation, no new safety signals have been received, and the staff have reported improved satisfaction with the MTP/RR process.
IMPLICATIONS
A critical piece of any MTP/RR is the immediate availability of blood. Allowing verbal orders for blood products reduced time to transfusion by 90%. Through multidisciplinary effort, safe and efficient release of uncrossmatched blood products for nontraumatic massive transfusion can be achieved.
PURPOSE
To improve the time to release of blood products for patients with severe or life-threatening bleeding.
BACKGROUND
Exsanguination, and the resultant coagulopathy, is the number one cause of trauma-related death. Massive transfusion protocols (MTP) improve mortality by shortening the time to transfusion and correcting coagulopathy. Many patients do not meet criteria for massive transfusion (> 10 units RBCs in 24 hours), yet present with clinical instability and require rapid release (RR) of uncrossmatched blood. A quality improvement initiative was performed to identify barriers to the MTP/RR protocol at a single institution.
METHODS/DATA
A multidisciplinary subcommittee was formed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the current MTP/RR process. Timed mock-MTP/RR trials were conducted to identify areas of delay with a goal to achieve a blood to bedside (B2B) time of under 10 minutes.
RESULTS
Timed mock-MTP/RR trials were conducted, which revealed a baseline B2B time of approximately 30 minutes. We identified problems and categorized them in terms of ordering (phase 1) and processing (phase 2). We found significant delays in phase 1. Reasons for delay were varied and included difficulty logging into the computer, staff unavailable to place orders (involved in resuscitation efforts), orders entered incorrectly, etc. Once orders were received, the blood bank could process them quickly in phase 2. Using root cause analysis, we discovered a critical step was to remove the barrier of electronic ordering. For this, a new process was developed in which the blood bank could accept verbal orders to release uncrossmatched blood during a medical emergency. Over the course of one year, a new policy for MTP/RR was drafted, an education training video was recorded, informational flyers were printed, and training drills were conducted. A repeat mock-MTP/RR scenario was performed after the change showing the B2B time was reduced by 90% from pre-intervention values to under 3 minutes. Since implementation, no new safety signals have been received, and the staff have reported improved satisfaction with the MTP/RR process.
IMPLICATIONS
A critical piece of any MTP/RR is the immediate availability of blood. Allowing verbal orders for blood products reduced time to transfusion by 90%. Through multidisciplinary effort, safe and efficient release of uncrossmatched blood products for nontraumatic massive transfusion can be achieved.
How do you prescribe exercise in primary prevention?
To avoid cardiovascular disease, the American Heart Association (AHA) recommends performing at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity every week, 75 minutes of intense aerobic activity every week, or a combination of both, preferably spread out throughout the week. But how knowledgeable are physicians when it comes to prescribing exercise, and how should patients be assessed so that appropriate physical activity can be recommended?
In a presentation titled, “Patient Evaluation and Exercise Prescription in Primary Prevention,”
“Exercise has cardioprotective, emotional, antiarrhythmic, and antithrombotic benefits, and it reduces stress,” she explained.
She also noted that the risk regarding cardiopulmonary and musculoskeletal components must be evaluated, because exercise can itself trigger coronary events, and the last thing intended when prescribing exercise is to cause complications. “We must recommend exercise progressively. We can’t suggest a high-intensity regimen to a patient if they haven’t had any preconditioning where collateral circulation could be developed and lung and cardiac capacity could be improved.”
Dr. Sánchez went on to say that, according to the AHA, patients should be classified as follows: those who exercise and those who don’t, those with a history of cardiovascular, metabolic, or renal disease, and those with symptomatic and asymptomatic diseases, in order to consider the parameters when recommending exercise.
“If the patient has symptoms and is doing light physical activity, like walking, they can keep doing this exercise and don’t need further assessments. But if they have a symptomatic disease and are not exercising, they need to be evaluated after exercise has been prescribed, and not just clinically, either. Some sort of diagnostic method should be considered. Also, for patients who are physically active and who desire to increase the intensity of their exercise, the recommendation is to perform a detailed clinical examination and, if necessary, perform additional imaging studies.”
Warning signs
- Dizziness.
- Orthopnea.
- Abnormal heart rate.
- Edema in the lower extremities.
- Chest pain, especially when occurring with exercise.
- Intermittent claudication.
- Heart murmurs.
- Dyspnea.
- Reduced output.
- Fatigue.
Calibrating exercise parameters
The parameters of frequency (number of sessions per week), intensity (perceived exertion measured by heart rate reached), time, and type (aerobic exercise vs. strength training) should be considered when forming an appropriate prescription for exercise, explained Dr. Sánchez.
“The big problem is that most physicians don’t know how to prescribe it properly. And beyond knowing how, the important thing is that, when we’re with the patient during the consultation, we ought to be doing more than just establishing a routine. We need to be motivators and we need to be identifying obstacles and the patient’s interest in exercise, because it’s clear that incorporating physical activity into our daily lives helps improve the quality and length of life,” the specialist added.
The recommendations are straightforward: for individuals aged 18-64 years, 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity per week, whether aerobic, strength training, or mixed, should be prescribed. “We need to encourage moving more and sitting less, and recommend comprehensive programs that include coordination, balance, and muscle strengthening. If a sedentary lifestyle is a risk factor, we need to encourage patients to start performing physical activity for 1-2 minutes every hour, because any exercise must be gradual and progressive to avoid complications,” she noted.
Evaluate, then recommend
The specialist emphasized the importance of making personalized prescriptions, exercising caution, and performing adequate assessments to know which exercise routine to recommend. “The patient should also be involved in their self-care and must have an adequate diet and hydration, and we need to remind them that they shouldn’t be exercising if they have an infection, due to the risk of myocarditis and sudden death,” she added.
Rafaelina Concepción, MD, cardiologist from the Dominican Republic and vice president of the Inter-American Society of Cardiology for Central America and the Caribbean, agreed with the importance of assessing risk and risk factors for patients who request an exercise routine. “For example, in patients with prediabetes, it has been shown that exercising can slow the progression to diabetes. The essential thing is to use stratification and know what kind of exercise to recommend, whether aerobic, strength training, or a combination of the two, to improve functional capacity without reaching the threshold heart rate while reducing the risk of other comorbidities like hypertension, obesity, and high lipids, and achieving lifestyle changes.”
Carlos Franco, MD, a cardiologist in El Salvador, emphasized that there is no such thing as zero risk when evaluating a patient. “Of course, there’s a difference between an athlete and someone who isn’t physically active, but we need to profile all patients correctly, evaluate risk factors in detail, not overlook subclinical cardiovascular disease, and check whether they need stress testing or additional imaging to assess cardiac functional capacity. Also, exercise must be prescribed gradually, and the patient’s nutritional status must be assessed.”
Dr. Franco ended by explaining that physicians must understand how to prescribe the basics of exercise and make small interventions of reasonable intensity, provide practical advice, and, to the extent possible, rely on specialists such as physiatrists, sports specialists, and physical therapists.
This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish Edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
To avoid cardiovascular disease, the American Heart Association (AHA) recommends performing at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity every week, 75 minutes of intense aerobic activity every week, or a combination of both, preferably spread out throughout the week. But how knowledgeable are physicians when it comes to prescribing exercise, and how should patients be assessed so that appropriate physical activity can be recommended?
In a presentation titled, “Patient Evaluation and Exercise Prescription in Primary Prevention,”
“Exercise has cardioprotective, emotional, antiarrhythmic, and antithrombotic benefits, and it reduces stress,” she explained.
She also noted that the risk regarding cardiopulmonary and musculoskeletal components must be evaluated, because exercise can itself trigger coronary events, and the last thing intended when prescribing exercise is to cause complications. “We must recommend exercise progressively. We can’t suggest a high-intensity regimen to a patient if they haven’t had any preconditioning where collateral circulation could be developed and lung and cardiac capacity could be improved.”
Dr. Sánchez went on to say that, according to the AHA, patients should be classified as follows: those who exercise and those who don’t, those with a history of cardiovascular, metabolic, or renal disease, and those with symptomatic and asymptomatic diseases, in order to consider the parameters when recommending exercise.
“If the patient has symptoms and is doing light physical activity, like walking, they can keep doing this exercise and don’t need further assessments. But if they have a symptomatic disease and are not exercising, they need to be evaluated after exercise has been prescribed, and not just clinically, either. Some sort of diagnostic method should be considered. Also, for patients who are physically active and who desire to increase the intensity of their exercise, the recommendation is to perform a detailed clinical examination and, if necessary, perform additional imaging studies.”
Warning signs
- Dizziness.
- Orthopnea.
- Abnormal heart rate.
- Edema in the lower extremities.
- Chest pain, especially when occurring with exercise.
- Intermittent claudication.
- Heart murmurs.
- Dyspnea.
- Reduced output.
- Fatigue.
Calibrating exercise parameters
The parameters of frequency (number of sessions per week), intensity (perceived exertion measured by heart rate reached), time, and type (aerobic exercise vs. strength training) should be considered when forming an appropriate prescription for exercise, explained Dr. Sánchez.
“The big problem is that most physicians don’t know how to prescribe it properly. And beyond knowing how, the important thing is that, when we’re with the patient during the consultation, we ought to be doing more than just establishing a routine. We need to be motivators and we need to be identifying obstacles and the patient’s interest in exercise, because it’s clear that incorporating physical activity into our daily lives helps improve the quality and length of life,” the specialist added.
The recommendations are straightforward: for individuals aged 18-64 years, 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity per week, whether aerobic, strength training, or mixed, should be prescribed. “We need to encourage moving more and sitting less, and recommend comprehensive programs that include coordination, balance, and muscle strengthening. If a sedentary lifestyle is a risk factor, we need to encourage patients to start performing physical activity for 1-2 minutes every hour, because any exercise must be gradual and progressive to avoid complications,” she noted.
Evaluate, then recommend
The specialist emphasized the importance of making personalized prescriptions, exercising caution, and performing adequate assessments to know which exercise routine to recommend. “The patient should also be involved in their self-care and must have an adequate diet and hydration, and we need to remind them that they shouldn’t be exercising if they have an infection, due to the risk of myocarditis and sudden death,” she added.
Rafaelina Concepción, MD, cardiologist from the Dominican Republic and vice president of the Inter-American Society of Cardiology for Central America and the Caribbean, agreed with the importance of assessing risk and risk factors for patients who request an exercise routine. “For example, in patients with prediabetes, it has been shown that exercising can slow the progression to diabetes. The essential thing is to use stratification and know what kind of exercise to recommend, whether aerobic, strength training, or a combination of the two, to improve functional capacity without reaching the threshold heart rate while reducing the risk of other comorbidities like hypertension, obesity, and high lipids, and achieving lifestyle changes.”
Carlos Franco, MD, a cardiologist in El Salvador, emphasized that there is no such thing as zero risk when evaluating a patient. “Of course, there’s a difference between an athlete and someone who isn’t physically active, but we need to profile all patients correctly, evaluate risk factors in detail, not overlook subclinical cardiovascular disease, and check whether they need stress testing or additional imaging to assess cardiac functional capacity. Also, exercise must be prescribed gradually, and the patient’s nutritional status must be assessed.”
Dr. Franco ended by explaining that physicians must understand how to prescribe the basics of exercise and make small interventions of reasonable intensity, provide practical advice, and, to the extent possible, rely on specialists such as physiatrists, sports specialists, and physical therapists.
This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish Edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
To avoid cardiovascular disease, the American Heart Association (AHA) recommends performing at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity every week, 75 minutes of intense aerobic activity every week, or a combination of both, preferably spread out throughout the week. But how knowledgeable are physicians when it comes to prescribing exercise, and how should patients be assessed so that appropriate physical activity can be recommended?
In a presentation titled, “Patient Evaluation and Exercise Prescription in Primary Prevention,”
“Exercise has cardioprotective, emotional, antiarrhythmic, and antithrombotic benefits, and it reduces stress,” she explained.
She also noted that the risk regarding cardiopulmonary and musculoskeletal components must be evaluated, because exercise can itself trigger coronary events, and the last thing intended when prescribing exercise is to cause complications. “We must recommend exercise progressively. We can’t suggest a high-intensity regimen to a patient if they haven’t had any preconditioning where collateral circulation could be developed and lung and cardiac capacity could be improved.”
Dr. Sánchez went on to say that, according to the AHA, patients should be classified as follows: those who exercise and those who don’t, those with a history of cardiovascular, metabolic, or renal disease, and those with symptomatic and asymptomatic diseases, in order to consider the parameters when recommending exercise.
“If the patient has symptoms and is doing light physical activity, like walking, they can keep doing this exercise and don’t need further assessments. But if they have a symptomatic disease and are not exercising, they need to be evaluated after exercise has been prescribed, and not just clinically, either. Some sort of diagnostic method should be considered. Also, for patients who are physically active and who desire to increase the intensity of their exercise, the recommendation is to perform a detailed clinical examination and, if necessary, perform additional imaging studies.”
Warning signs
- Dizziness.
- Orthopnea.
- Abnormal heart rate.
- Edema in the lower extremities.
- Chest pain, especially when occurring with exercise.
- Intermittent claudication.
- Heart murmurs.
- Dyspnea.
- Reduced output.
- Fatigue.
Calibrating exercise parameters
The parameters of frequency (number of sessions per week), intensity (perceived exertion measured by heart rate reached), time, and type (aerobic exercise vs. strength training) should be considered when forming an appropriate prescription for exercise, explained Dr. Sánchez.
“The big problem is that most physicians don’t know how to prescribe it properly. And beyond knowing how, the important thing is that, when we’re with the patient during the consultation, we ought to be doing more than just establishing a routine. We need to be motivators and we need to be identifying obstacles and the patient’s interest in exercise, because it’s clear that incorporating physical activity into our daily lives helps improve the quality and length of life,” the specialist added.
The recommendations are straightforward: for individuals aged 18-64 years, 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity per week, whether aerobic, strength training, or mixed, should be prescribed. “We need to encourage moving more and sitting less, and recommend comprehensive programs that include coordination, balance, and muscle strengthening. If a sedentary lifestyle is a risk factor, we need to encourage patients to start performing physical activity for 1-2 minutes every hour, because any exercise must be gradual and progressive to avoid complications,” she noted.
Evaluate, then recommend
The specialist emphasized the importance of making personalized prescriptions, exercising caution, and performing adequate assessments to know which exercise routine to recommend. “The patient should also be involved in their self-care and must have an adequate diet and hydration, and we need to remind them that they shouldn’t be exercising if they have an infection, due to the risk of myocarditis and sudden death,” she added.
Rafaelina Concepción, MD, cardiologist from the Dominican Republic and vice president of the Inter-American Society of Cardiology for Central America and the Caribbean, agreed with the importance of assessing risk and risk factors for patients who request an exercise routine. “For example, in patients with prediabetes, it has been shown that exercising can slow the progression to diabetes. The essential thing is to use stratification and know what kind of exercise to recommend, whether aerobic, strength training, or a combination of the two, to improve functional capacity without reaching the threshold heart rate while reducing the risk of other comorbidities like hypertension, obesity, and high lipids, and achieving lifestyle changes.”
Carlos Franco, MD, a cardiologist in El Salvador, emphasized that there is no such thing as zero risk when evaluating a patient. “Of course, there’s a difference between an athlete and someone who isn’t physically active, but we need to profile all patients correctly, evaluate risk factors in detail, not overlook subclinical cardiovascular disease, and check whether they need stress testing or additional imaging to assess cardiac functional capacity. Also, exercise must be prescribed gradually, and the patient’s nutritional status must be assessed.”
Dr. Franco ended by explaining that physicians must understand how to prescribe the basics of exercise and make small interventions of reasonable intensity, provide practical advice, and, to the extent possible, rely on specialists such as physiatrists, sports specialists, and physical therapists.
This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish Edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
No benefit of anti-inflammatory strategy in acute myocarditis
AMSTERDAM – A short course of the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, anakinra, appeared safe but did not reduce complications of acute myocarditis in the ARAMIS trial.
The trial was presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
Lead investigator, Mathieu Kerneis, MD, Pitie Salpetriere APHP University Hospital, Paris, said this was the largest randomized controlled trial of patients with acute myocarditis and probably the first ever study in the acute setting of myocarditis patients diagnosed with cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging, not on biopsy, who are mostly at low risk for events.
He suggested that one of the reasons for the neutral result could have been the low-risk population involved and the low complication rate. “We enrolled an all-comer acute myocarditis population diagnosed with CMR, who were mostly at a low risk of complications,” he noted.
“I don’t think the story of anti-inflammatory drugs in acute myocarditis is over. This is just the beginning. This was the first trial, and it was just a phase 2 trial. We need further randomized trials to explore the potential benefit of an anti-inflammatory strategy in acute myocarditis patients at higher risk of complications. In addition, larger studies are needed to evaluate prolonged anti-inflammatory strategies in acute myocarditis patients at low-to-moderate risk of complications,” Dr. Kerneis concluded.
“It is very challenging to do a trial in high-risk patients with myocarditis as these patients are quite rare,” he added.
Inflammation of the myocardium
Dr. Kerneis explained that acute myocarditis is an inflammation of the myocardium that can cause permanent damage to the heart muscle and lead to myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure, arrhythmias, and death. The condition can occur in individuals of all ages but is most frequent in young people. There is no specific treatment, but patients are generally treated with beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, and sometimes steroids.
Anakinra is an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist that works by targeting the interleukin-1β innate immune pathway. Anakinra is used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and has shown efficacy in pericarditis. Dr. Kerneis noted that there have been several case reports of successful treatment with anakinra in acute myocarditis.
The ARAMIS trial – conducted at six academic centers in France – was the first randomized study to evaluate inhibition of the interleukin-1β innate immune pathway in myocarditis patients. The trial enrolled 120 hospitalized, symptomatic patients with chest pain, increased cardiac troponin, and acute myocarditis diagnosed using CMR. More than half had had a recent bacterial or viral infection.
Patients were randomized within 72 hours of hospital admission to a daily subcutaneous dose of anakinra 100 mg or placebo until hospital discharge. Patients in both groups received standard-of-care treatments, including an ACE inhibitor, for at least 1 month. Consistent with prior data, the median age of participants was 28 years and 90% were men.
The primary endpoint was the number of days free of myocarditis complications (heart failure requiring hospitalization, chest pain requiring medication, left ventricular ejection fraction less than 50%, and ventricular arrhythmias) within 28 days postdischarge.
There was no significant difference in this endpoint between the two arms, with a median of 30 days for anakinra versus 31 days for placebo.
Overall, the rate of the composite endpoint of myocarditis complications occurred in 13.7% of patients, and there was a numerical reduction in the number of patients with these myocarditis complications with anakinra – 6 patients (10.5%) in the anakinra group versus 10 patients (16.5%) in the placebo group (odds ratio, 0.59; 95% confidence interval, 0.19-1.78). This was driven by fewer patients with chest pain requiring new medication (two patients versus six patients).
The safety endpoint was the number of serious adverse events within 28 days postdischarge. This endpoint occurred in seven patients (12.1%) in the anakinra arm and six patients (10.2%) in the placebo arm, with no significant difference between groups. Cases of severe infection within 28 days postdischarge were reported in both arms.
Low-risk population
Designated discussant of the study at the ESC Hotline session, Enrico Ammirati, MD, PhD, University of Milano-Bicocca, Monza, Italy, said that patients involved in ARAMIS fit the profile of acute myocarditis and that the CMR diagnosis was positive in all the patients enrolled.
Dr. Ammirati agreed with Dr. Kerneis that the neutral results of the study were probably caused by the low-risk population. “If we look at retrospective registries, at 30 days there are zero cardiac deaths or heart transplants at 30 days in patients with a low-risk presentation.
“The ARAMIS trial has shown the feasibility of conducting studies in the setting of acute myocarditis, and even if the primary endpoint was neutral, some important data are still missing, such as change in ejection fraction and troponin levels,” he noted.
“In terms of future perspective, we are moving to assessing efficacy of anakinra or other immunosuppressive drugs from acute low risk patients to higher risk patients with heart failure and severe dysfunction,” he said.
Dr. Ammirati is the lead investigator of another ongoing study in such a higher-risk population; the MYTHS trial is investigating the use of intravenous steroids in patients with suspected acute myocarditis complicated by acute heart failure or cardiogenic shock, and an ejection fraction below 41%.
“So, we will have more results on the best treatment in this higher risk group of patients,” he concluded.
The ARAMIS trial was an academic study funded by the French Health Ministry and coordinated by the ACTION Group. Dr. Kerneis reports having received consulting fees from Kiniksa, Sanofi, and Bayer, and holds a patent for use of abatacept in immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)–induced myocarditis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM – A short course of the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, anakinra, appeared safe but did not reduce complications of acute myocarditis in the ARAMIS trial.
The trial was presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
Lead investigator, Mathieu Kerneis, MD, Pitie Salpetriere APHP University Hospital, Paris, said this was the largest randomized controlled trial of patients with acute myocarditis and probably the first ever study in the acute setting of myocarditis patients diagnosed with cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging, not on biopsy, who are mostly at low risk for events.
He suggested that one of the reasons for the neutral result could have been the low-risk population involved and the low complication rate. “We enrolled an all-comer acute myocarditis population diagnosed with CMR, who were mostly at a low risk of complications,” he noted.
“I don’t think the story of anti-inflammatory drugs in acute myocarditis is over. This is just the beginning. This was the first trial, and it was just a phase 2 trial. We need further randomized trials to explore the potential benefit of an anti-inflammatory strategy in acute myocarditis patients at higher risk of complications. In addition, larger studies are needed to evaluate prolonged anti-inflammatory strategies in acute myocarditis patients at low-to-moderate risk of complications,” Dr. Kerneis concluded.
“It is very challenging to do a trial in high-risk patients with myocarditis as these patients are quite rare,” he added.
Inflammation of the myocardium
Dr. Kerneis explained that acute myocarditis is an inflammation of the myocardium that can cause permanent damage to the heart muscle and lead to myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure, arrhythmias, and death. The condition can occur in individuals of all ages but is most frequent in young people. There is no specific treatment, but patients are generally treated with beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, and sometimes steroids.
Anakinra is an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist that works by targeting the interleukin-1β innate immune pathway. Anakinra is used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and has shown efficacy in pericarditis. Dr. Kerneis noted that there have been several case reports of successful treatment with anakinra in acute myocarditis.
The ARAMIS trial – conducted at six academic centers in France – was the first randomized study to evaluate inhibition of the interleukin-1β innate immune pathway in myocarditis patients. The trial enrolled 120 hospitalized, symptomatic patients with chest pain, increased cardiac troponin, and acute myocarditis diagnosed using CMR. More than half had had a recent bacterial or viral infection.
Patients were randomized within 72 hours of hospital admission to a daily subcutaneous dose of anakinra 100 mg or placebo until hospital discharge. Patients in both groups received standard-of-care treatments, including an ACE inhibitor, for at least 1 month. Consistent with prior data, the median age of participants was 28 years and 90% were men.
The primary endpoint was the number of days free of myocarditis complications (heart failure requiring hospitalization, chest pain requiring medication, left ventricular ejection fraction less than 50%, and ventricular arrhythmias) within 28 days postdischarge.
There was no significant difference in this endpoint between the two arms, with a median of 30 days for anakinra versus 31 days for placebo.
Overall, the rate of the composite endpoint of myocarditis complications occurred in 13.7% of patients, and there was a numerical reduction in the number of patients with these myocarditis complications with anakinra – 6 patients (10.5%) in the anakinra group versus 10 patients (16.5%) in the placebo group (odds ratio, 0.59; 95% confidence interval, 0.19-1.78). This was driven by fewer patients with chest pain requiring new medication (two patients versus six patients).
The safety endpoint was the number of serious adverse events within 28 days postdischarge. This endpoint occurred in seven patients (12.1%) in the anakinra arm and six patients (10.2%) in the placebo arm, with no significant difference between groups. Cases of severe infection within 28 days postdischarge were reported in both arms.
Low-risk population
Designated discussant of the study at the ESC Hotline session, Enrico Ammirati, MD, PhD, University of Milano-Bicocca, Monza, Italy, said that patients involved in ARAMIS fit the profile of acute myocarditis and that the CMR diagnosis was positive in all the patients enrolled.
Dr. Ammirati agreed with Dr. Kerneis that the neutral results of the study were probably caused by the low-risk population. “If we look at retrospective registries, at 30 days there are zero cardiac deaths or heart transplants at 30 days in patients with a low-risk presentation.
“The ARAMIS trial has shown the feasibility of conducting studies in the setting of acute myocarditis, and even if the primary endpoint was neutral, some important data are still missing, such as change in ejection fraction and troponin levels,” he noted.
“In terms of future perspective, we are moving to assessing efficacy of anakinra or other immunosuppressive drugs from acute low risk patients to higher risk patients with heart failure and severe dysfunction,” he said.
Dr. Ammirati is the lead investigator of another ongoing study in such a higher-risk population; the MYTHS trial is investigating the use of intravenous steroids in patients with suspected acute myocarditis complicated by acute heart failure or cardiogenic shock, and an ejection fraction below 41%.
“So, we will have more results on the best treatment in this higher risk group of patients,” he concluded.
The ARAMIS trial was an academic study funded by the French Health Ministry and coordinated by the ACTION Group. Dr. Kerneis reports having received consulting fees from Kiniksa, Sanofi, and Bayer, and holds a patent for use of abatacept in immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)–induced myocarditis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM – A short course of the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, anakinra, appeared safe but did not reduce complications of acute myocarditis in the ARAMIS trial.
The trial was presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
Lead investigator, Mathieu Kerneis, MD, Pitie Salpetriere APHP University Hospital, Paris, said this was the largest randomized controlled trial of patients with acute myocarditis and probably the first ever study in the acute setting of myocarditis patients diagnosed with cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging, not on biopsy, who are mostly at low risk for events.
He suggested that one of the reasons for the neutral result could have been the low-risk population involved and the low complication rate. “We enrolled an all-comer acute myocarditis population diagnosed with CMR, who were mostly at a low risk of complications,” he noted.
“I don’t think the story of anti-inflammatory drugs in acute myocarditis is over. This is just the beginning. This was the first trial, and it was just a phase 2 trial. We need further randomized trials to explore the potential benefit of an anti-inflammatory strategy in acute myocarditis patients at higher risk of complications. In addition, larger studies are needed to evaluate prolonged anti-inflammatory strategies in acute myocarditis patients at low-to-moderate risk of complications,” Dr. Kerneis concluded.
“It is very challenging to do a trial in high-risk patients with myocarditis as these patients are quite rare,” he added.
Inflammation of the myocardium
Dr. Kerneis explained that acute myocarditis is an inflammation of the myocardium that can cause permanent damage to the heart muscle and lead to myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure, arrhythmias, and death. The condition can occur in individuals of all ages but is most frequent in young people. There is no specific treatment, but patients are generally treated with beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, and sometimes steroids.
Anakinra is an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist that works by targeting the interleukin-1β innate immune pathway. Anakinra is used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and has shown efficacy in pericarditis. Dr. Kerneis noted that there have been several case reports of successful treatment with anakinra in acute myocarditis.
The ARAMIS trial – conducted at six academic centers in France – was the first randomized study to evaluate inhibition of the interleukin-1β innate immune pathway in myocarditis patients. The trial enrolled 120 hospitalized, symptomatic patients with chest pain, increased cardiac troponin, and acute myocarditis diagnosed using CMR. More than half had had a recent bacterial or viral infection.
Patients were randomized within 72 hours of hospital admission to a daily subcutaneous dose of anakinra 100 mg or placebo until hospital discharge. Patients in both groups received standard-of-care treatments, including an ACE inhibitor, for at least 1 month. Consistent with prior data, the median age of participants was 28 years and 90% were men.
The primary endpoint was the number of days free of myocarditis complications (heart failure requiring hospitalization, chest pain requiring medication, left ventricular ejection fraction less than 50%, and ventricular arrhythmias) within 28 days postdischarge.
There was no significant difference in this endpoint between the two arms, with a median of 30 days for anakinra versus 31 days for placebo.
Overall, the rate of the composite endpoint of myocarditis complications occurred in 13.7% of patients, and there was a numerical reduction in the number of patients with these myocarditis complications with anakinra – 6 patients (10.5%) in the anakinra group versus 10 patients (16.5%) in the placebo group (odds ratio, 0.59; 95% confidence interval, 0.19-1.78). This was driven by fewer patients with chest pain requiring new medication (two patients versus six patients).
The safety endpoint was the number of serious adverse events within 28 days postdischarge. This endpoint occurred in seven patients (12.1%) in the anakinra arm and six patients (10.2%) in the placebo arm, with no significant difference between groups. Cases of severe infection within 28 days postdischarge were reported in both arms.
Low-risk population
Designated discussant of the study at the ESC Hotline session, Enrico Ammirati, MD, PhD, University of Milano-Bicocca, Monza, Italy, said that patients involved in ARAMIS fit the profile of acute myocarditis and that the CMR diagnosis was positive in all the patients enrolled.
Dr. Ammirati agreed with Dr. Kerneis that the neutral results of the study were probably caused by the low-risk population. “If we look at retrospective registries, at 30 days there are zero cardiac deaths or heart transplants at 30 days in patients with a low-risk presentation.
“The ARAMIS trial has shown the feasibility of conducting studies in the setting of acute myocarditis, and even if the primary endpoint was neutral, some important data are still missing, such as change in ejection fraction and troponin levels,” he noted.
“In terms of future perspective, we are moving to assessing efficacy of anakinra or other immunosuppressive drugs from acute low risk patients to higher risk patients with heart failure and severe dysfunction,” he said.
Dr. Ammirati is the lead investigator of another ongoing study in such a higher-risk population; the MYTHS trial is investigating the use of intravenous steroids in patients with suspected acute myocarditis complicated by acute heart failure or cardiogenic shock, and an ejection fraction below 41%.
“So, we will have more results on the best treatment in this higher risk group of patients,” he concluded.
The ARAMIS trial was an academic study funded by the French Health Ministry and coordinated by the ACTION Group. Dr. Kerneis reports having received consulting fees from Kiniksa, Sanofi, and Bayer, and holds a patent for use of abatacept in immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)–induced myocarditis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ESC CONGRESS 2023