User login
COVID hospitalizations climb for fourth straight week
Weekly new hospitalizations for COVID-19 have climbed for the fourth straight week.
according to newly updated Centers for Disease Control and Prevention figures. Hospitalizations reached an all-time low of about 6,300 per week in July.
The CDC stopped tracking the number of people infected by the virus earlier in 2023, and now relies on hospitalization data to gauge the current impact of COVID-19.
“We have to remember that we’re still dealing with numbers that are far less than what we’ve seen for the pandemic,” John Brownstein, PhD, a professor of biomedical informatics at Harvard Medical School, Boston, told ABC News. “We have to zoom out to look at our experience for the entire pandemic, to understand that what we’re dealing with now is far from any crisis that we’ve experienced with previous waves.”
The current predominant strain remains EG.5, and experts believe it is not more severe or more contagious than other recent variants.
Dr. Brownstein told ABC News that one reason for the concern about rising COVID metrics, despite their overall low levels, is that a surge occurred in the summer of 2021 with the dangerous Delta variant.
“But each new variant so far that has come through has subsequently had less of a population impact,” he said. “Now, is it possible we may see one in the future that is worthy, a real concern? Absolutely. But overall, we’ve seen a dampening of effect over the last several variants that have come through.”
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Weekly new hospitalizations for COVID-19 have climbed for the fourth straight week.
according to newly updated Centers for Disease Control and Prevention figures. Hospitalizations reached an all-time low of about 6,300 per week in July.
The CDC stopped tracking the number of people infected by the virus earlier in 2023, and now relies on hospitalization data to gauge the current impact of COVID-19.
“We have to remember that we’re still dealing with numbers that are far less than what we’ve seen for the pandemic,” John Brownstein, PhD, a professor of biomedical informatics at Harvard Medical School, Boston, told ABC News. “We have to zoom out to look at our experience for the entire pandemic, to understand that what we’re dealing with now is far from any crisis that we’ve experienced with previous waves.”
The current predominant strain remains EG.5, and experts believe it is not more severe or more contagious than other recent variants.
Dr. Brownstein told ABC News that one reason for the concern about rising COVID metrics, despite their overall low levels, is that a surge occurred in the summer of 2021 with the dangerous Delta variant.
“But each new variant so far that has come through has subsequently had less of a population impact,” he said. “Now, is it possible we may see one in the future that is worthy, a real concern? Absolutely. But overall, we’ve seen a dampening of effect over the last several variants that have come through.”
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Weekly new hospitalizations for COVID-19 have climbed for the fourth straight week.
according to newly updated Centers for Disease Control and Prevention figures. Hospitalizations reached an all-time low of about 6,300 per week in July.
The CDC stopped tracking the number of people infected by the virus earlier in 2023, and now relies on hospitalization data to gauge the current impact of COVID-19.
“We have to remember that we’re still dealing with numbers that are far less than what we’ve seen for the pandemic,” John Brownstein, PhD, a professor of biomedical informatics at Harvard Medical School, Boston, told ABC News. “We have to zoom out to look at our experience for the entire pandemic, to understand that what we’re dealing with now is far from any crisis that we’ve experienced with previous waves.”
The current predominant strain remains EG.5, and experts believe it is not more severe or more contagious than other recent variants.
Dr. Brownstein told ABC News that one reason for the concern about rising COVID metrics, despite their overall low levels, is that a surge occurred in the summer of 2021 with the dangerous Delta variant.
“But each new variant so far that has come through has subsequently had less of a population impact,” he said. “Now, is it possible we may see one in the future that is worthy, a real concern? Absolutely. But overall, we’ve seen a dampening of effect over the last several variants that have come through.”
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
New COVID shots will be available in September
The updated vaccine still needs final sign-offs from the Food and Drug Administration and the CDC.
“We anticipate that they are going to be available for most folks by the third or fourth week of September,” Director Mandy Cohen, MD, MPH, said on a podcast hosted by former White House COVID adviser Andy Slavitt. “We are likely to see this as a recommendation as an annual COVID shot, just as we have an annual flu shot. I think that will give folks more clarity on whether they should get one or not.”
For people who are considering now whether they should get the currently available COVID vaccine or wait until the new one comes out, Dr. Cohen said that depends on a person’s individual risk. People who are 65 or older or who have multiple health conditions should go ahead and get the currently available shot if it’s been more than 6-8 months since their last dose. For all other people, it’s OK to wait for the new version.
Analysts expect low demand for the updated vaccine. About 240 million people in the United States got at least one dose when vaccines first became available in 2021, Reuters reported, but that number dropped to less than 50 million getting the most updated shot in the fall of 2022.
“Take a look at what happened last winter. It was 50 million in the U.S., and it seems likely to be lower than that, given that there’s less concern about COVID this year than last year,” Michael Yee, a health care industry analyst for the firm Jefferies, told Reuters.
Dr. Cohen noted during the podcast that the recent uptick in virus activity should be taken in context.
“What we’re seeing right now in August of 2023 are small increases of folks getting COVID. We are still at some of the lowest hospitalizations that we’ve been at in the past 3 years,” she said. “Even a 10% increase on a very, very small number is still very small. My level of concern continues to be low.”
A version of this article was first published on WebMD.com .
The updated vaccine still needs final sign-offs from the Food and Drug Administration and the CDC.
“We anticipate that they are going to be available for most folks by the third or fourth week of September,” Director Mandy Cohen, MD, MPH, said on a podcast hosted by former White House COVID adviser Andy Slavitt. “We are likely to see this as a recommendation as an annual COVID shot, just as we have an annual flu shot. I think that will give folks more clarity on whether they should get one or not.”
For people who are considering now whether they should get the currently available COVID vaccine or wait until the new one comes out, Dr. Cohen said that depends on a person’s individual risk. People who are 65 or older or who have multiple health conditions should go ahead and get the currently available shot if it’s been more than 6-8 months since their last dose. For all other people, it’s OK to wait for the new version.
Analysts expect low demand for the updated vaccine. About 240 million people in the United States got at least one dose when vaccines first became available in 2021, Reuters reported, but that number dropped to less than 50 million getting the most updated shot in the fall of 2022.
“Take a look at what happened last winter. It was 50 million in the U.S., and it seems likely to be lower than that, given that there’s less concern about COVID this year than last year,” Michael Yee, a health care industry analyst for the firm Jefferies, told Reuters.
Dr. Cohen noted during the podcast that the recent uptick in virus activity should be taken in context.
“What we’re seeing right now in August of 2023 are small increases of folks getting COVID. We are still at some of the lowest hospitalizations that we’ve been at in the past 3 years,” she said. “Even a 10% increase on a very, very small number is still very small. My level of concern continues to be low.”
A version of this article was first published on WebMD.com .
The updated vaccine still needs final sign-offs from the Food and Drug Administration and the CDC.
“We anticipate that they are going to be available for most folks by the third or fourth week of September,” Director Mandy Cohen, MD, MPH, said on a podcast hosted by former White House COVID adviser Andy Slavitt. “We are likely to see this as a recommendation as an annual COVID shot, just as we have an annual flu shot. I think that will give folks more clarity on whether they should get one or not.”
For people who are considering now whether they should get the currently available COVID vaccine or wait until the new one comes out, Dr. Cohen said that depends on a person’s individual risk. People who are 65 or older or who have multiple health conditions should go ahead and get the currently available shot if it’s been more than 6-8 months since their last dose. For all other people, it’s OK to wait for the new version.
Analysts expect low demand for the updated vaccine. About 240 million people in the United States got at least one dose when vaccines first became available in 2021, Reuters reported, but that number dropped to less than 50 million getting the most updated shot in the fall of 2022.
“Take a look at what happened last winter. It was 50 million in the U.S., and it seems likely to be lower than that, given that there’s less concern about COVID this year than last year,” Michael Yee, a health care industry analyst for the firm Jefferies, told Reuters.
Dr. Cohen noted during the podcast that the recent uptick in virus activity should be taken in context.
“What we’re seeing right now in August of 2023 are small increases of folks getting COVID. We are still at some of the lowest hospitalizations that we’ve been at in the past 3 years,” she said. “Even a 10% increase on a very, very small number is still very small. My level of concern continues to be low.”
A version of this article was first published on WebMD.com .
It may be time to pay attention to COVID again
More than 3 years into the COVID-19 era, most Americans have settled back into their prepandemic lifestyles.
Since April, a new COVID variant has cropped up. According to recent Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, EG.5 – from the Omicron family – now makes up 17% of all cases in the United States, up from 7.5% in the first week of July.
A summary from the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota says that EG.5, nicknamed “Eris” by health trackers, is nearly the same as its parent strain, XBB.1.9.2, but has one extra spike mutation.
Along with the news of EG.5’s growing prevalence, COVID-related hospitalization rates have increased by 12.5% during the week ending on July 29 – the most significant uptick since December. Still, no connection has been made between the new variant and rising hospital admissions. And so far, experts have found no difference in the severity of illness or symptoms between Eris and the strains that came before it.
Cause for concern?
The COVID virus has a great tendency to mutate, said William Schaffner, MD, a professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
“Fortunately, these are relatively minor mutations.” Even so, SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, continues to be highly contagious. “There isn’t any doubt that it’s spreading – but it’s not more serious.”
So, Dr. Schaffner doesn’t think it’s time to panic. He prefers calling it an “uptick” in cases instead of a “surge,” because a surge “sounds too big.”
While the numbers are still low, compared with 2022’s summer surge, experts still urge people to stay aware of changes in the virus. “I do not think that there is any cause for alarm,” agreed Bernard Camins, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York.
So why the higher number of cases? “There has been an increase in COVID cases this summer, probably related to travel, socializing, and dwindling masking,” said Anne Liu, MD, an allergy, immunology, and infectious disease specialist at Stanford (Calif.) University. Even so, “because of an existing level of immunity from vaccination and prior infections, it has been limited and case severity has been lower than in prior surges.”
What the official numbers say
The CDC no longer updates its COVID Data Tracker Weekly Review. They stopped in May 2023 when the federal public health emergency ended.
But the agency continues to track COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, ED visits, and deaths in different ways. The key takeaways include 9,056 new hospitalizations reported for the week ending July 29, 2023. That is relatively low, compared with July 30, 2022, when the weekly new hospitalization numbers topped 44,000.
“Last year, we saw a summer wave with cases peaking around mid-July. In that sense, our summer wave is coming a bit later than last year,” said Pavitra Roychoudhury, PhD, an assistant professor and researcher in the vaccine and infectious disease division at the University of Washington, Seattle.
“It’s unclear how high the peak will be during this current wave. Levels of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater, as well as the number of hospitalizations, are currently lower than this time last year.”
For part of the pandemic, the CDC recommended people monitor COVID numbers in their own communities. But the agency’s local guidance on COVID is tied to hospital admission levels, which are currently low for more than 99% of the country, even if they are increasing.
So, while it’s good news that hospitalization numbers are smaller, it means the agency’s ability to identify local outbreaks or hot spots of SARS-CoV-2 is now more limited.
It’s not just an uptick in hospitalizations nationwide, as other COVID-19 indicators, including ED visits, positive tests, and wastewater levels, are increasing across the United States.
In terms of other metrics:
- On June 19, 0.47% of ED visits resulted in a positive COVID diagnosis. On Aug. 4, that rate had more than doubled to 1.1%.
- On July 29, 8.9% of people who took a COVID test reported a positive result. The positivity rate has been increasing since June 10, when 4.1% of tests came back positive. This figure only includes test results reported to the CDC. Results of home testing remain largely unknown.
- The weekly percentage of deaths related to COVID-19 was 1% as of July 29. That’s low, compared with previous rates. For example, for the week ending July 30, 2022, it was 5.8%.
What about new COVID vaccines?
As long as the general public continue to make informed decisions and get the new Omicron vaccine or booster once it’s available, experts predict lower hospitalization rates this winter.
“Everyone should get the Omicron booster when it becomes available,” recommended Dean Winslow, MD, a professor of medicine at Stanford University.
In the meantime, “it is important to emphasize that COVID-19 is going to be with us for the foreseeable future,” he said. Since the symptoms linked to these newer Omicron subvariants are generally milder than with earlier variants, “if one has even mild cold symptoms, it is a good idea to test yourself for COVID-19 and start treatment early if one is elderly or otherwise at high risk for severe disease.”
Dr. Schaffner remains optimistic for now. “We anticipate that the vaccines we currently have available, and certainly the vaccine that is being developed for this fall, will continue to prevent severe disease associated with this virus.”
Although it’s difficult to predict an exact time line, Dr. Schaffner said they could be available by the end of September.
His predictions assume “that we don’t have a new nasty variant that crops up somewhere in the world,” he said. “[If] things continue to move the way they have been, we anticipate that this vaccine ... will be really effective and help us keep out of the hospital during this winter, when we expect more of an increase of COVID once again.”
Asked for his outlook on vaccine recommendations, Dr. Camins was less certain. “It is too soon to tell.” Guidance on COVID shots will be based on results of ongoing studies. “It would be prudent, however, for everyone to plan on getting the flu shot in September.”
Stay alert and stay realistic
Cautious optimism and a call to remain vigilant seem like the consensus at the moment. While the numbers remain low so far and the uptick in new cases and hospitalizations are relatively small, compared with past scenarios, “it makes sense to boost our anti-Omicron antibody levels with immunizations before fall and winter,” Dr. Liu said.
“It’s just advisable for everyone – especially those who are at higher risk for hospitalization or death – to be aware,” Dr. Camins said, “so they can form their own decisions to participate in activities that may put them at risk for contracting COVID-19.”
While respiratory virus work best at keeping people with the flu, COVID, or RSV out of the hospital, they’re not as good at preventing milder infections. Dr. Schaffner said: “If we don’t expect perfection, we won’t be so disappointed.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
More than 3 years into the COVID-19 era, most Americans have settled back into their prepandemic lifestyles.
Since April, a new COVID variant has cropped up. According to recent Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, EG.5 – from the Omicron family – now makes up 17% of all cases in the United States, up from 7.5% in the first week of July.
A summary from the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota says that EG.5, nicknamed “Eris” by health trackers, is nearly the same as its parent strain, XBB.1.9.2, but has one extra spike mutation.
Along with the news of EG.5’s growing prevalence, COVID-related hospitalization rates have increased by 12.5% during the week ending on July 29 – the most significant uptick since December. Still, no connection has been made between the new variant and rising hospital admissions. And so far, experts have found no difference in the severity of illness or symptoms between Eris and the strains that came before it.
Cause for concern?
The COVID virus has a great tendency to mutate, said William Schaffner, MD, a professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
“Fortunately, these are relatively minor mutations.” Even so, SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, continues to be highly contagious. “There isn’t any doubt that it’s spreading – but it’s not more serious.”
So, Dr. Schaffner doesn’t think it’s time to panic. He prefers calling it an “uptick” in cases instead of a “surge,” because a surge “sounds too big.”
While the numbers are still low, compared with 2022’s summer surge, experts still urge people to stay aware of changes in the virus. “I do not think that there is any cause for alarm,” agreed Bernard Camins, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York.
So why the higher number of cases? “There has been an increase in COVID cases this summer, probably related to travel, socializing, and dwindling masking,” said Anne Liu, MD, an allergy, immunology, and infectious disease specialist at Stanford (Calif.) University. Even so, “because of an existing level of immunity from vaccination and prior infections, it has been limited and case severity has been lower than in prior surges.”
What the official numbers say
The CDC no longer updates its COVID Data Tracker Weekly Review. They stopped in May 2023 when the federal public health emergency ended.
But the agency continues to track COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, ED visits, and deaths in different ways. The key takeaways include 9,056 new hospitalizations reported for the week ending July 29, 2023. That is relatively low, compared with July 30, 2022, when the weekly new hospitalization numbers topped 44,000.
“Last year, we saw a summer wave with cases peaking around mid-July. In that sense, our summer wave is coming a bit later than last year,” said Pavitra Roychoudhury, PhD, an assistant professor and researcher in the vaccine and infectious disease division at the University of Washington, Seattle.
“It’s unclear how high the peak will be during this current wave. Levels of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater, as well as the number of hospitalizations, are currently lower than this time last year.”
For part of the pandemic, the CDC recommended people monitor COVID numbers in their own communities. But the agency’s local guidance on COVID is tied to hospital admission levels, which are currently low for more than 99% of the country, even if they are increasing.
So, while it’s good news that hospitalization numbers are smaller, it means the agency’s ability to identify local outbreaks or hot spots of SARS-CoV-2 is now more limited.
It’s not just an uptick in hospitalizations nationwide, as other COVID-19 indicators, including ED visits, positive tests, and wastewater levels, are increasing across the United States.
In terms of other metrics:
- On June 19, 0.47% of ED visits resulted in a positive COVID diagnosis. On Aug. 4, that rate had more than doubled to 1.1%.
- On July 29, 8.9% of people who took a COVID test reported a positive result. The positivity rate has been increasing since June 10, when 4.1% of tests came back positive. This figure only includes test results reported to the CDC. Results of home testing remain largely unknown.
- The weekly percentage of deaths related to COVID-19 was 1% as of July 29. That’s low, compared with previous rates. For example, for the week ending July 30, 2022, it was 5.8%.
What about new COVID vaccines?
As long as the general public continue to make informed decisions and get the new Omicron vaccine or booster once it’s available, experts predict lower hospitalization rates this winter.
“Everyone should get the Omicron booster when it becomes available,” recommended Dean Winslow, MD, a professor of medicine at Stanford University.
In the meantime, “it is important to emphasize that COVID-19 is going to be with us for the foreseeable future,” he said. Since the symptoms linked to these newer Omicron subvariants are generally milder than with earlier variants, “if one has even mild cold symptoms, it is a good idea to test yourself for COVID-19 and start treatment early if one is elderly or otherwise at high risk for severe disease.”
Dr. Schaffner remains optimistic for now. “We anticipate that the vaccines we currently have available, and certainly the vaccine that is being developed for this fall, will continue to prevent severe disease associated with this virus.”
Although it’s difficult to predict an exact time line, Dr. Schaffner said they could be available by the end of September.
His predictions assume “that we don’t have a new nasty variant that crops up somewhere in the world,” he said. “[If] things continue to move the way they have been, we anticipate that this vaccine ... will be really effective and help us keep out of the hospital during this winter, when we expect more of an increase of COVID once again.”
Asked for his outlook on vaccine recommendations, Dr. Camins was less certain. “It is too soon to tell.” Guidance on COVID shots will be based on results of ongoing studies. “It would be prudent, however, for everyone to plan on getting the flu shot in September.”
Stay alert and stay realistic
Cautious optimism and a call to remain vigilant seem like the consensus at the moment. While the numbers remain low so far and the uptick in new cases and hospitalizations are relatively small, compared with past scenarios, “it makes sense to boost our anti-Omicron antibody levels with immunizations before fall and winter,” Dr. Liu said.
“It’s just advisable for everyone – especially those who are at higher risk for hospitalization or death – to be aware,” Dr. Camins said, “so they can form their own decisions to participate in activities that may put them at risk for contracting COVID-19.”
While respiratory virus work best at keeping people with the flu, COVID, or RSV out of the hospital, they’re not as good at preventing milder infections. Dr. Schaffner said: “If we don’t expect perfection, we won’t be so disappointed.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
More than 3 years into the COVID-19 era, most Americans have settled back into their prepandemic lifestyles.
Since April, a new COVID variant has cropped up. According to recent Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, EG.5 – from the Omicron family – now makes up 17% of all cases in the United States, up from 7.5% in the first week of July.
A summary from the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota says that EG.5, nicknamed “Eris” by health trackers, is nearly the same as its parent strain, XBB.1.9.2, but has one extra spike mutation.
Along with the news of EG.5’s growing prevalence, COVID-related hospitalization rates have increased by 12.5% during the week ending on July 29 – the most significant uptick since December. Still, no connection has been made between the new variant and rising hospital admissions. And so far, experts have found no difference in the severity of illness or symptoms between Eris and the strains that came before it.
Cause for concern?
The COVID virus has a great tendency to mutate, said William Schaffner, MD, a professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
“Fortunately, these are relatively minor mutations.” Even so, SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, continues to be highly contagious. “There isn’t any doubt that it’s spreading – but it’s not more serious.”
So, Dr. Schaffner doesn’t think it’s time to panic. He prefers calling it an “uptick” in cases instead of a “surge,” because a surge “sounds too big.”
While the numbers are still low, compared with 2022’s summer surge, experts still urge people to stay aware of changes in the virus. “I do not think that there is any cause for alarm,” agreed Bernard Camins, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York.
So why the higher number of cases? “There has been an increase in COVID cases this summer, probably related to travel, socializing, and dwindling masking,” said Anne Liu, MD, an allergy, immunology, and infectious disease specialist at Stanford (Calif.) University. Even so, “because of an existing level of immunity from vaccination and prior infections, it has been limited and case severity has been lower than in prior surges.”
What the official numbers say
The CDC no longer updates its COVID Data Tracker Weekly Review. They stopped in May 2023 when the federal public health emergency ended.
But the agency continues to track COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, ED visits, and deaths in different ways. The key takeaways include 9,056 new hospitalizations reported for the week ending July 29, 2023. That is relatively low, compared with July 30, 2022, when the weekly new hospitalization numbers topped 44,000.
“Last year, we saw a summer wave with cases peaking around mid-July. In that sense, our summer wave is coming a bit later than last year,” said Pavitra Roychoudhury, PhD, an assistant professor and researcher in the vaccine and infectious disease division at the University of Washington, Seattle.
“It’s unclear how high the peak will be during this current wave. Levels of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater, as well as the number of hospitalizations, are currently lower than this time last year.”
For part of the pandemic, the CDC recommended people monitor COVID numbers in their own communities. But the agency’s local guidance on COVID is tied to hospital admission levels, which are currently low for more than 99% of the country, even if they are increasing.
So, while it’s good news that hospitalization numbers are smaller, it means the agency’s ability to identify local outbreaks or hot spots of SARS-CoV-2 is now more limited.
It’s not just an uptick in hospitalizations nationwide, as other COVID-19 indicators, including ED visits, positive tests, and wastewater levels, are increasing across the United States.
In terms of other metrics:
- On June 19, 0.47% of ED visits resulted in a positive COVID diagnosis. On Aug. 4, that rate had more than doubled to 1.1%.
- On July 29, 8.9% of people who took a COVID test reported a positive result. The positivity rate has been increasing since June 10, when 4.1% of tests came back positive. This figure only includes test results reported to the CDC. Results of home testing remain largely unknown.
- The weekly percentage of deaths related to COVID-19 was 1% as of July 29. That’s low, compared with previous rates. For example, for the week ending July 30, 2022, it was 5.8%.
What about new COVID vaccines?
As long as the general public continue to make informed decisions and get the new Omicron vaccine or booster once it’s available, experts predict lower hospitalization rates this winter.
“Everyone should get the Omicron booster when it becomes available,” recommended Dean Winslow, MD, a professor of medicine at Stanford University.
In the meantime, “it is important to emphasize that COVID-19 is going to be with us for the foreseeable future,” he said. Since the symptoms linked to these newer Omicron subvariants are generally milder than with earlier variants, “if one has even mild cold symptoms, it is a good idea to test yourself for COVID-19 and start treatment early if one is elderly or otherwise at high risk for severe disease.”
Dr. Schaffner remains optimistic for now. “We anticipate that the vaccines we currently have available, and certainly the vaccine that is being developed for this fall, will continue to prevent severe disease associated with this virus.”
Although it’s difficult to predict an exact time line, Dr. Schaffner said they could be available by the end of September.
His predictions assume “that we don’t have a new nasty variant that crops up somewhere in the world,” he said. “[If] things continue to move the way they have been, we anticipate that this vaccine ... will be really effective and help us keep out of the hospital during this winter, when we expect more of an increase of COVID once again.”
Asked for his outlook on vaccine recommendations, Dr. Camins was less certain. “It is too soon to tell.” Guidance on COVID shots will be based on results of ongoing studies. “It would be prudent, however, for everyone to plan on getting the flu shot in September.”
Stay alert and stay realistic
Cautious optimism and a call to remain vigilant seem like the consensus at the moment. While the numbers remain low so far and the uptick in new cases and hospitalizations are relatively small, compared with past scenarios, “it makes sense to boost our anti-Omicron antibody levels with immunizations before fall and winter,” Dr. Liu said.
“It’s just advisable for everyone – especially those who are at higher risk for hospitalization or death – to be aware,” Dr. Camins said, “so they can form their own decisions to participate in activities that may put them at risk for contracting COVID-19.”
While respiratory virus work best at keeping people with the flu, COVID, or RSV out of the hospital, they’re not as good at preventing milder infections. Dr. Schaffner said: “If we don’t expect perfection, we won’t be so disappointed.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
U.S. has new dominant COVID variant called EG.5
Called “Eris” among avid COVID trackers, the strain EG.5 now accounts for 17% of all U.S. COVID infections, according to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates. That’s up from 12% the week prior.
EG.5 has been rising worldwide, just weeks after the World Health Organization added the strain to its official monitoring list. In the United Kingdom, it now accounts for 1 in 10 COVID cases, The Independent reported.
EG.5 is a descendant of the XBB strains that have dominated tracking lists in recent months. It has the same makeup as XBB.1.9.2 but carries an extra spike mutation, according to a summary published by the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota. The spike protein is the part of the virus that allows it to enter human cells. But there’s no indication so far that EG.5 is more contagious or severe than other recent variants, according to the CIDRAP summary and a recent podcast from the American Medical Association. The CDC said that current vaccines protect against the variant.
U.S. hospitals saw a 12% increase in COVID admissions during the week ending on July 22, with 8,047 people being admitted because of the virus, up from an all-time low of 6,306 the week of June 24. In 17 states, the past-week increase in hospitalizations was 20% or greater. In Minnesota, the rate jumped by 50%, and in West Virginia, it jumped by 63%. Meanwhile, deaths reached their lowest weekly rate ever for the week of data ending July 29, with just 176 deaths reported by the CDC.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Called “Eris” among avid COVID trackers, the strain EG.5 now accounts for 17% of all U.S. COVID infections, according to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates. That’s up from 12% the week prior.
EG.5 has been rising worldwide, just weeks after the World Health Organization added the strain to its official monitoring list. In the United Kingdom, it now accounts for 1 in 10 COVID cases, The Independent reported.
EG.5 is a descendant of the XBB strains that have dominated tracking lists in recent months. It has the same makeup as XBB.1.9.2 but carries an extra spike mutation, according to a summary published by the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota. The spike protein is the part of the virus that allows it to enter human cells. But there’s no indication so far that EG.5 is more contagious or severe than other recent variants, according to the CIDRAP summary and a recent podcast from the American Medical Association. The CDC said that current vaccines protect against the variant.
U.S. hospitals saw a 12% increase in COVID admissions during the week ending on July 22, with 8,047 people being admitted because of the virus, up from an all-time low of 6,306 the week of June 24. In 17 states, the past-week increase in hospitalizations was 20% or greater. In Minnesota, the rate jumped by 50%, and in West Virginia, it jumped by 63%. Meanwhile, deaths reached their lowest weekly rate ever for the week of data ending July 29, with just 176 deaths reported by the CDC.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Called “Eris” among avid COVID trackers, the strain EG.5 now accounts for 17% of all U.S. COVID infections, according to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates. That’s up from 12% the week prior.
EG.5 has been rising worldwide, just weeks after the World Health Organization added the strain to its official monitoring list. In the United Kingdom, it now accounts for 1 in 10 COVID cases, The Independent reported.
EG.5 is a descendant of the XBB strains that have dominated tracking lists in recent months. It has the same makeup as XBB.1.9.2 but carries an extra spike mutation, according to a summary published by the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota. The spike protein is the part of the virus that allows it to enter human cells. But there’s no indication so far that EG.5 is more contagious or severe than other recent variants, according to the CIDRAP summary and a recent podcast from the American Medical Association. The CDC said that current vaccines protect against the variant.
U.S. hospitals saw a 12% increase in COVID admissions during the week ending on July 22, with 8,047 people being admitted because of the virus, up from an all-time low of 6,306 the week of June 24. In 17 states, the past-week increase in hospitalizations was 20% or greater. In Minnesota, the rate jumped by 50%, and in West Virginia, it jumped by 63%. Meanwhile, deaths reached their lowest weekly rate ever for the week of data ending July 29, with just 176 deaths reported by the CDC.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
New air monitor can detect COVID virus in 5 minutes
The project was a collaboration among researchers from the university’s engineering and medical schools; the results were published in Nature Communications.
One of the challenges the team had to overcome is that detecting the virus in a roomful of air “is like finding a needle in a haystack,” researcher and associate engineering professor Rajan Chakrabarty, PhD, said in a statement.
The team overcame that challenge using a technology called wet cyclone that samples the equivalent of 176 cubic feet of air in 5 minutes. A light on the device turns from green to red when the virus is detected, which the researchers said indicates that increased air circulation is needed.
The device stands just 10 inches tall and 1 foot wide and is considered a proof of concept. The next step would be to implement the technology into a prototype to see how a commercial or household design could be achieved. The researchers foresee potential for the device to be used in hospitals and schools, as well as to be able to detect other respiratory viruses such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus.
Current methods used for detecting viruses in the air take between 1 and 24 hours to collect and analyze samples. The existing methods usually require skilled labor, resulting in a process that doesn’t allow for real-time information that could translate into reducing risk or the spread of the virus, the researchers wrote.
The team tested their device both in laboratory experiments where they released aerosolized SARS-CoV-2 into a room-sized chamber, as well as in the apartments of two people who were COVID positive.
“There is nothing at the moment that tells us how safe a room is,” Washington University neurology professor John Cirrito, PhD, said in a statement. “If you are in a room with 100 people, you don’t want to find out 5 days later whether you could be sick or not. The idea with this device is that you can know essentially in real time, or every 5 minutes, if there is a live virus in the air.”
Their goal is to develop a commercially available air quality monitor, the researchers said.
The study authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
The project was a collaboration among researchers from the university’s engineering and medical schools; the results were published in Nature Communications.
One of the challenges the team had to overcome is that detecting the virus in a roomful of air “is like finding a needle in a haystack,” researcher and associate engineering professor Rajan Chakrabarty, PhD, said in a statement.
The team overcame that challenge using a technology called wet cyclone that samples the equivalent of 176 cubic feet of air in 5 minutes. A light on the device turns from green to red when the virus is detected, which the researchers said indicates that increased air circulation is needed.
The device stands just 10 inches tall and 1 foot wide and is considered a proof of concept. The next step would be to implement the technology into a prototype to see how a commercial or household design could be achieved. The researchers foresee potential for the device to be used in hospitals and schools, as well as to be able to detect other respiratory viruses such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus.
Current methods used for detecting viruses in the air take between 1 and 24 hours to collect and analyze samples. The existing methods usually require skilled labor, resulting in a process that doesn’t allow for real-time information that could translate into reducing risk or the spread of the virus, the researchers wrote.
The team tested their device both in laboratory experiments where they released aerosolized SARS-CoV-2 into a room-sized chamber, as well as in the apartments of two people who were COVID positive.
“There is nothing at the moment that tells us how safe a room is,” Washington University neurology professor John Cirrito, PhD, said in a statement. “If you are in a room with 100 people, you don’t want to find out 5 days later whether you could be sick or not. The idea with this device is that you can know essentially in real time, or every 5 minutes, if there is a live virus in the air.”
Their goal is to develop a commercially available air quality monitor, the researchers said.
The study authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
The project was a collaboration among researchers from the university’s engineering and medical schools; the results were published in Nature Communications.
One of the challenges the team had to overcome is that detecting the virus in a roomful of air “is like finding a needle in a haystack,” researcher and associate engineering professor Rajan Chakrabarty, PhD, said in a statement.
The team overcame that challenge using a technology called wet cyclone that samples the equivalent of 176 cubic feet of air in 5 minutes. A light on the device turns from green to red when the virus is detected, which the researchers said indicates that increased air circulation is needed.
The device stands just 10 inches tall and 1 foot wide and is considered a proof of concept. The next step would be to implement the technology into a prototype to see how a commercial or household design could be achieved. The researchers foresee potential for the device to be used in hospitals and schools, as well as to be able to detect other respiratory viruses such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus.
Current methods used for detecting viruses in the air take between 1 and 24 hours to collect and analyze samples. The existing methods usually require skilled labor, resulting in a process that doesn’t allow for real-time information that could translate into reducing risk or the spread of the virus, the researchers wrote.
The team tested their device both in laboratory experiments where they released aerosolized SARS-CoV-2 into a room-sized chamber, as well as in the apartments of two people who were COVID positive.
“There is nothing at the moment that tells us how safe a room is,” Washington University neurology professor John Cirrito, PhD, said in a statement. “If you are in a room with 100 people, you don’t want to find out 5 days later whether you could be sick or not. The idea with this device is that you can know essentially in real time, or every 5 minutes, if there is a live virus in the air.”
Their goal is to develop a commercially available air quality monitor, the researchers said.
The study authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM NATURE COMMUNICATIONS
Pigmenting Purpuric Dermatoses: Striking But Not a Manifestation of COVID-19 Infection
Pigmented purpuric dermatoses (PPDs) are characterized by petechiae, dusky macules representative of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation and dermal hemosiderin, and purpura generally localized to the lower extremities. They typically represent a spectrum of lymphocytic capillaritis, variable erythrocyte extravasation from papillary dermal blood vessels, and deposition of hemosiderin, yielding the classic red to orange to golden-brown findings on gross examination. Clinical overlap exists, but variants include Schamberg disease (SD), Majocchi purpura, Gougerot-Blum purpura, eczematoid purpura of Doucas and Kapetanakis (DK), and lichen aureus.1 Other forms are rarer, including linear, granulomatous, quadrantic, transitory, and familial variants. It remains controversial whether PPD may precede or have an association with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.2 Dermoscopy usually shows copper-red pigmentation in the background, oval red dots, linear vessels, brown globules, and follicular openings. Although these findings may be useful in PPD diagnosis, they are not applicable in differentiating among the variants.
Pigmented purpuric dermatoses can easily be mistaken for stasis dermatitis or cellulitis, as these may occur concomitantly or in populations at risk for all 3 conditions, such as women older than 50 years with recent trauma or infection in the affected area. Tissue biopsy and clinical laboratory evaluation may be required to differentiate between PPD from leukocytoclastic vasculitis or the myriad causes of retiform purpura. Importantly, clinicians also should differentiate PPD from the purpuric eruptions of the lower extremities associated with COVID-19 infection.
Pigmented Purpuric Dermatoses
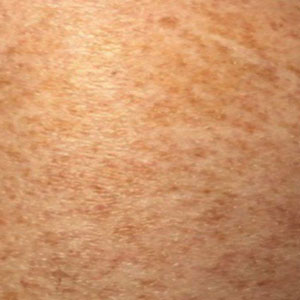
Schamberg Disease—In 1901, Jay Frank Schamberg, a distinguished professor of dermatology in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, described “a peculiar progressive pigmentary disease of the skin” in a 15-year-old adolescent boy.3 Schamberg disease is the most common PPD, characterized by pruritic spots resembling cayenne pepper (Figure 1) with orange-brown pigmented macules on the legs and feet.4 Although platelet dysfunction, coagulation deficiencies, or dermal atrophy may contribute to hemorrhaging that manifests as petechiae or ecchymoses, SD typically is not associated with any laboratory abnormalities, and petechial eruption is not widespread.5 Capillary fragility can be assessed by the tourniquet test, in which pressure is applied to the forearm with a blood pressure cuff inflated between systolic and diastolic blood pressure for 5 to 10 minutes. Upon removing the cuff, a positive test is indicated by 15 or more petechiae in an area 5 cm in diameter due to poor platelet function. A positive result may be seen in SD.6
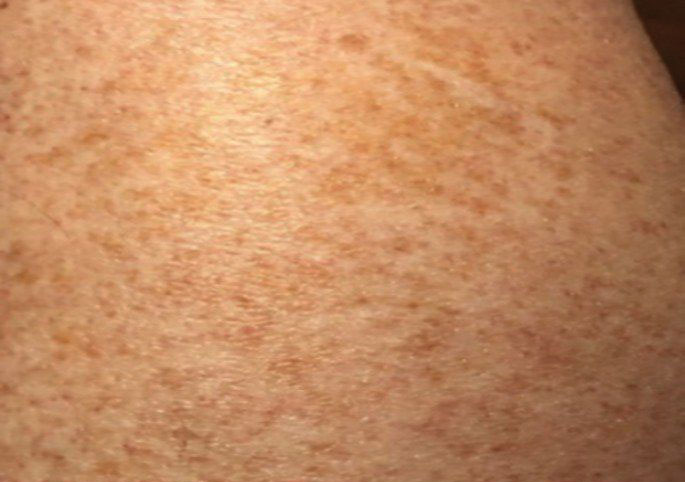
Histologically, SD is characterized by patchy parakeratosis, mild spongiosis of the stratum Malpighi, and lymphoid capillaritis (Figure 2).7 In addition to CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, CD1a+, and CD36+ lymphocytes, histology also may contain dendritic cells and cellular adhesion molecules (intercellular adhesion molecule 1, epithelial cell adhesion molecule 1) within the superficial perivascular infiltrate.8 There is no definitive therapy, but first-line interventions include emollients, topical steroids, and oral antihistamines. Nonpharmacologic management includes compression or support stockings, elevation of the lower extremities, and avoidance of offending medications (if identifiable).1
Majocchi Purpura—Domenico Majocchi was a renowned Italian dermatologist who described an entity in 1898 that he called purpura annularis telangiectodes, now also known as Majocchi purpura.9 It is more common in females, young adults, and children. Majocchi purpura has rarely been reported in families with a possible autosomal-dominant inheritance.10 Typically, bluish-red annular macules with central atrophy surrounded by hyperpigmentation may be seen on the lower extremities, potentially extending to the upper extremities.1 Treatment of Majocchi purpura remains a challenge but may respond to narrowband UVB phototherapy. Emollients and topical steroids also are used as first-line treatments. Biopsy demonstrates telangiectasia, pericapillary infiltration of mononuclear lymphocytes, and papillary dermal hemosiderin.11
Gougerot-Blum Purpura—In 1925, French dermatologists Henri Gougerot and Paul Blum described a pigmented purpuric lichenoid dermatitis known as Gougerot-Blum purpura,12 a rare PPD characterized by lichenoid papules that eventually coalesce into plaques of various colors, along with red-brown hyperpigmentation.4 As with other PPD variants, the legs are most involved, with rare extension to the trunk or thighs. The plaques may resemble and be mistaken for Kaposi sarcoma, cutaneous vasculitis, traumatic purpura, or mycosis fungoides. Dermoscopic examination reveals small, polygonal or round, red dots underlying brown scaly patches.13 Gougerot-Blum purpura is found more commonly in adult men and rarely affects children.4 Histologically, a lichenoid and superficial perivascular infiltrate composed of lymphocytes and macrophages is seen. Various therapies have been described, including topical steroids, antihistamines, psoralen plus UVA phototherapy, and cyclosporin A.14
Eczematoid Purpura of Doucas and Kapetanakis—In 1949, Greek dermatologists Christopher Doucas and John Kapetanakis observed several cases of purpuric dermatosis similar in form to the “pigmented purpuric lichenoid dermatitis” of Gougerot-Blum purpura12 and to the “progressive pigmentary dermatitis” of Schamberg disease.3 After observing a gradual disappearance of the classic yellow color from hemosiderin deposition, Doucas and Kapetanakis described a new bright red eruption with lichenification.15 Eczematoid purpura of Doucas and Kapetanakis is rare and predominantly seen in middle-aged males. Hyperpigmented or dark brown macules may develop bilaterally on the legs, progressing to the thighs and upper extremities. Unlike the other types of PPD, DK is extensive and severely pruritic.4
Although most PPD can be drug induced, DK has shown the greatest tendency for pruritic erythematous plaques following drug usage including but not limited to amlodipine, aspirin, acetaminophen, thiamine, interferon alfa, chlordiazepoxide, and isotretinoin. Additionally, DK has been associated with a contact allergy to clothing dyes and rubber.4 On histology, epidermal spongiosis may be seen, correlating with the eczematoid clinical findings. Spontaneous remission also is more common compared to the other PPDs. Treatment consists of topical corticosteroids and antihistamines.16
Lichen Aureus—Lichen aureus was first observed by the dermatologist R.H. Martin in 1958.17 It is clinically characterized by closely aggregated purpuric papules with a distinctive golden-brown color more often localized to the lower extremities and sometimes in a dermatomal distribution. Lichen aureus affects males and females equally, and similar to Majocchi purpura can be seen in children.4 Histopathologic examination reveals a prominent lichenoid plus superficial and deep perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate, extravasated erythrocytes, papillary dermal edema, hemosiderophages, and an unaffected epidermis. In rare cases, perineural infiltrates may be seen. Topical steroids usually are ineffective in lichen aureus treatment, but responses to psoralen plus UVA therapy also have been noted.17
Differential Diagnosis
COVID-19–Related Cutaneous Changes—Because COVID-19–related pathology is now a common differential diagnosis for many cutaneous eruptions, one must be mindful of the possibility for patients to have PPD, cutaneous changes from underlying COVID-19, or both.18 The microvascular changes from COVID-19 infection can be variable.19 Besides the presence of erythema along a distal digit, manifestations can include reticulated dusky erythema mimicking livedoid vasculopathy or inflammatory purpura.19
Retiform Purpura—Retiform purpura may occur in the setting of microvascular occlusion and can represent the pattern of underlying dermal vasculature. It is nonblanching and typically stellate or branching.20 The microvascular occlusion may be a result of hypercoagulability or may be secondary to cutaneous vasculitis, resulting in thrombosis and subsequent vascular occlusion.21 There are many reasons for hypercoagulability in retiform purpura, including disseminated intravascular coagulation in the setting of COVID-19 infection.22 The treatment of retiform purpura is aimed at alleviating the underlying cause and providing symptomatic relief. Conversely, the PPDs generally are benign and require minimal workup.
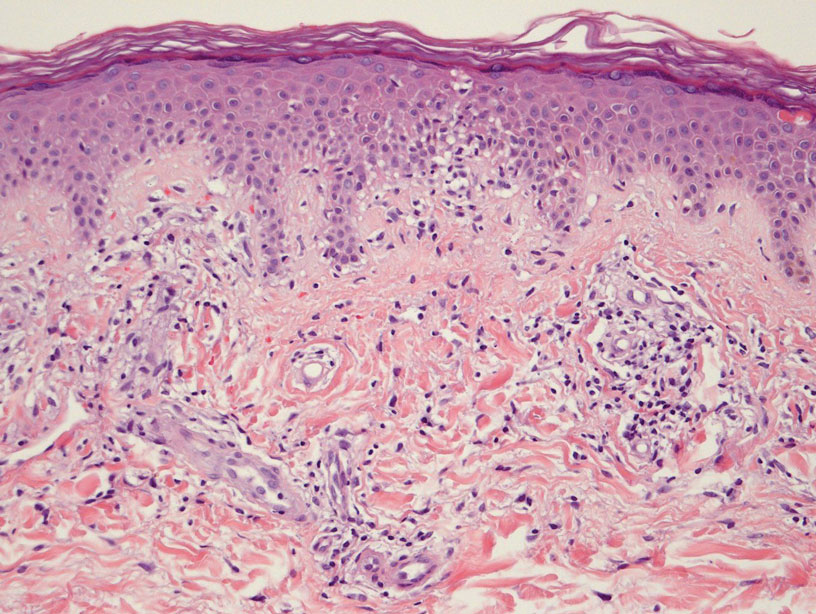
Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis—The hallmark of leukocytoclastic vasculitis is palpable purpura, often appearing as nonblanchable papules, typically in a dependent distribution such as the lower extremities (Figure 3). Although it primarily affects children, Henoch-Schönlein purpura is a type of leukocytoclastic vasculitis with lesions potentially similar in appearance to those of PPD.23 Palpable purpura may be painful and may ulcerate but rarely is pruritic. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis represents perivascular infiltrates composed of neutrophils, lymphocytes, and occasionally eosinophils, along with karyorrhexis, luminal fibrin, and fibrinoid degeneration of blood vessel walls, often resulting from immune complex deposition. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis may affect blood vessels of any size and requires further clinical and laboratory evaluation for infection (including COVID-19), hypercoagulability, autoimmune disease, or medication-related reactions.24
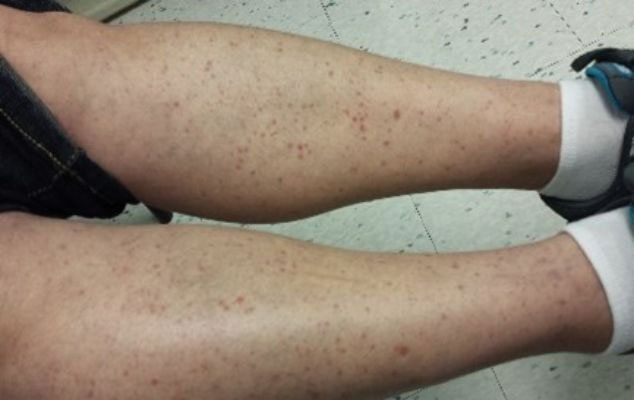
Stasis Dermatitis—Stasis dermatitis, a chronic inflammatory condition stemming from retrograde venous flow due to incompetent venous valves, mimics PPD. Stasis dermatitis initially appears as demarcated erythematous plaques, fissures, and scaling of the lower legs bilaterally, usually involving the medial malleolus.25 With time, the affected region develops overlying brawny hyperpigmentation and fibrosis (Figure 4). Pruritus or pain are common features, while fissures and superficial erosions may heal and recur, leading to lichenification.
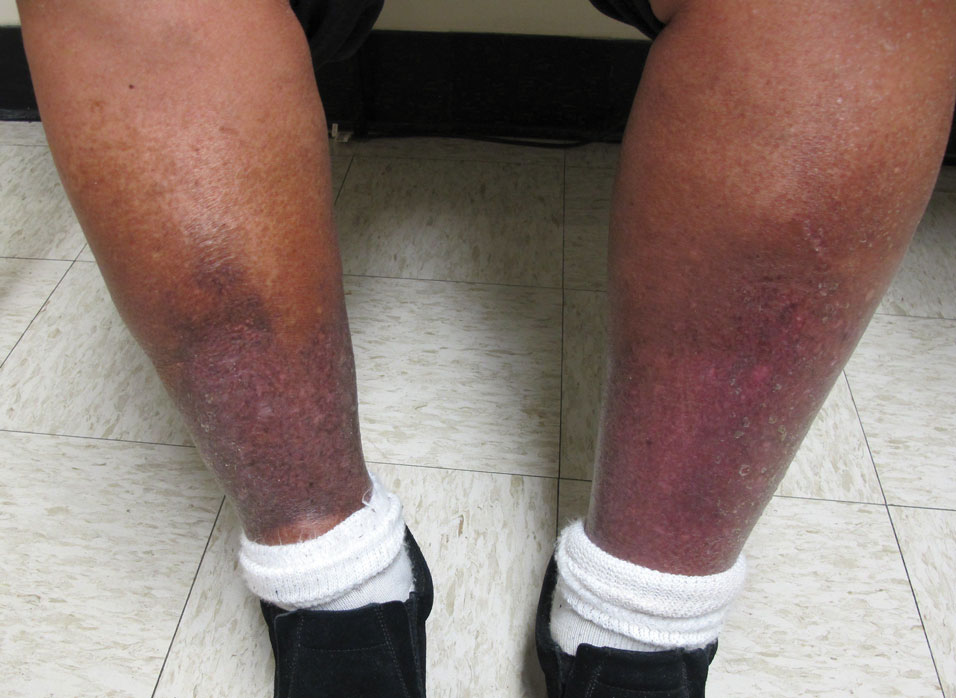
Although both commonly appear on the lower extremities, duplex ultrasonography may be helpful to distinguish PPDs from stasis dermatitis since the latter occurs in the context of chronic venous insufficiency, varicose veins, soft tissue edema, and lymphedema.25 Additionally, pruritus, lichenification, and edema often are not seen in most PPD variants, although stasis dermatitis and PPD may occur in tandem. Conservative treatment involves elevation of the extremities, compression, and topical steroids for symptomatic relief.
Cellulitis—The key characteristics of cellulitis are redness, swelling, warmth, tenderness, fever, and leukocytosis. A history of trauma, such as a prior break in the skin, and pain in the affected area suggest cellulitis. Several skin conditions present similarly to cellulitis, including PPD, and thus approximately 30% of cases are misdiagnosed.26 Cellulitis rarely presents in a bilateral or diffusely scattered pattern as seen in PPDs. Rather, it is unilateral with smooth indistinct borders. Variables suggestive of cellulitis include immunosuppression, rapid progression, and previous occurrences. Hyperpigmented plaques or thickening of the skin are more indicative of a chronic process such as stasis dermatitis or lipodermatosclerosis rather than acute cellulitis. Purpura is not a typical finding in most cases of soft tissue cellulitis. Treatment may be case specific depending on severity, presence or absence of sepsis, findings on blood cultures, or other pathologic evaluation. Antibiotics are directed to the causative organism, typically Streptococcus and Staphylococcus species, although coverage against various gram-negative organisms may be indicated.27
Caution With Teledermatology
COVID-19 has established the value of telemedicine in providing access to health care services for at-risk or underserved individuals. The PPDs are benign, often asymptomatic, and potentially identifiable with teledermatology alone; however, they also can easily be mistaken for COVID-19–related eruptions, vasculitis, other types of purpura, stasis dermatitis, or other complications of lower extremity stasis and lymphedema, especially in an aging population. If tissue biopsy is required, as in the workup of vasculitis, the efficacy of telemedicine becomes more questionable. It is important to delineate the potentially confusing PPDs from other potentially dangerous or life-threatening inflammatory dermatoses.28
- Sardana K, Sarkar R , Sehgal VN. Pigmented purpuric dermatoses: an overview. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:482-488.
- Çaytemel C, Baykut B, Ag˘ırgöl S¸, et al. Pigmented purpuric dermatosis: ten years of experience in a tertiary hospital and awareness of mycosis fungoides in differential diagnosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:611-616.
- Schamberg JF. A peculiar progressive pigmentary disease of the skin. Br J Dermatol. 1901;13:1-5.
- Martínez Pallás I, Conejero Del Mazo R, Lezcano Biosca V. Pigmented purpuric dermatosis: a review of the literature. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2020;111:196-204.
- Ozkaya DB, Emiroglu N, Su O, et al. Dermatoscopic findings of pigmented purpuric dermatosis. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:584-587.
- Lava SAG, Milani GP, Fossali EF, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of small-vessel leukocytoclastic vasculitides in childhood. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017;53:439-451.
- Bonnet U, Selle C, Isbruch K, et al. Recurrent purpura due to alcohol-related Schamberg’s disease and its association with serum immunoglobulins: a longitudinal observation of a heavy drinker. J Med Case Rep. 2016;10:301.
- Zaldivar Fujigaki JL, Anjum F. Schamberg Disease. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
- Majocchi J. Purpura annularis telangiectodes. Arch Dermatol Syph. 1898;43:447.
- Sethuraman G, Sugandhan S, Bansal A, et al. Familial pigmented purpuric dermatoses. J Dermatol. 2006;33:639-641.
- Miller K, Fischer M, Kamino H, et al. Purpura annularis telangiectoides. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:5.
- Coulombe J, Jean SE, Hatami A, et al. Pigmented purpuric dermatosis: clinicopathologic characterization in a pediatric series. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:358-362.
- Park MY, Shim WH, Kim JM, et al. Dermoscopic finding in pigmented purpuric lichenoid dermatosis of Gougerot-Blum: a useful tool for clinical diagnosis. Ann Dermatol. 2018;30:245-247.
- Risikesan J, Sommerlund M, Ramsing M, et al. Successful topical treatment of pigmented purpuric lichenoid dermatitis of Gougerot-Blum in a young patient: a case report and summary of the most common pigmented purpuric dermatoses. Case Rep Dermatol. 2017;9:169-176.
- Doucas C, Kapetanakis J. Eczematid-like purpura. Dermatologica. 1953;106:86-95.
- Kim DH, Seo SH, Ahn HH, et al. Characteristics and clinical manifestations of pigmented purpuric dermatosis. Ann Dermatol. 2015;27:404-410.
- Aung PP, Burns SJ, Bhawan J. Lichen aureus: an unusual histopathological presentation: a case report and a review of literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36:E1-E4.
- Singh P, Schwartz RA. Disseminated intravascular coagulation: a devastating systemic disorder of special concern with COVID-19. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E14053.
- Almutairi N, Schwartz RA. COVID-19 with dermatologic manifestations and implications: an unfolding conundrum. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E13544.
- Georgesen C, Fox LP, Harp J. Retiform purpura: a diagnostic approach. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:783-796.
- Torregrosa Calatayud JL, Garcías Ladaria J, De Unamuno Bustos B, et al. Retiform purpura caused by the use of cocaine, that was probably adulterated with levamisole. Ann Dermatol. 2015;27:117-119.
- Keim CK, Schwartz RA, Kapila R. Levamisole-induced and COVID-19-induced retiform purpura: two overlapping, emerging clinical syndromes. Arch Dermatol Res. 2021;22:1-9.
- González LM, Janniger CK, Schwartz RA. Pediatric Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:1157-1165.
- Yıldırım Bay E, Moustafa E, Semiz Y, et al. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis secondary to COVID-19 infection presenting with inclusion bodies: a histopathological correlation. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022;21:27-29.
- Sundaresan S, Migden MR, Silapunt S. Stasis dermatitis: pathophysiology, evaluation, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:383-390.
- Hirschmann JV, Raugi GJ. Lower limb cellulitis and its mimics: part I. lower limb cellulitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:163.E1-E12; quiz 75-76.
- Keller EC, Tomecki KJ, Alraies MC. Distinguishing cellulitis from its mimics. Cleveland Clin J Med. 2012;79:547-552.
- Georgesen C, Fox LP, Harp J. Retiform purpura: workup and therapeutic considerations in select conditions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:799-816.
Pigmented purpuric dermatoses (PPDs) are characterized by petechiae, dusky macules representative of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation and dermal hemosiderin, and purpura generally localized to the lower extremities. They typically represent a spectrum of lymphocytic capillaritis, variable erythrocyte extravasation from papillary dermal blood vessels, and deposition of hemosiderin, yielding the classic red to orange to golden-brown findings on gross examination. Clinical overlap exists, but variants include Schamberg disease (SD), Majocchi purpura, Gougerot-Blum purpura, eczematoid purpura of Doucas and Kapetanakis (DK), and lichen aureus.1 Other forms are rarer, including linear, granulomatous, quadrantic, transitory, and familial variants. It remains controversial whether PPD may precede or have an association with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.2 Dermoscopy usually shows copper-red pigmentation in the background, oval red dots, linear vessels, brown globules, and follicular openings. Although these findings may be useful in PPD diagnosis, they are not applicable in differentiating among the variants.
Pigmented purpuric dermatoses can easily be mistaken for stasis dermatitis or cellulitis, as these may occur concomitantly or in populations at risk for all 3 conditions, such as women older than 50 years with recent trauma or infection in the affected area. Tissue biopsy and clinical laboratory evaluation may be required to differentiate between PPD from leukocytoclastic vasculitis or the myriad causes of retiform purpura. Importantly, clinicians also should differentiate PPD from the purpuric eruptions of the lower extremities associated with COVID-19 infection.
Pigmented Purpuric Dermatoses
Schamberg Disease—In 1901, Jay Frank Schamberg, a distinguished professor of dermatology in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, described “a peculiar progressive pigmentary disease of the skin” in a 15-year-old adolescent boy.3 Schamberg disease is the most common PPD, characterized by pruritic spots resembling cayenne pepper (Figure 1) with orange-brown pigmented macules on the legs and feet.4 Although platelet dysfunction, coagulation deficiencies, or dermal atrophy may contribute to hemorrhaging that manifests as petechiae or ecchymoses, SD typically is not associated with any laboratory abnormalities, and petechial eruption is not widespread.5 Capillary fragility can be assessed by the tourniquet test, in which pressure is applied to the forearm with a blood pressure cuff inflated between systolic and diastolic blood pressure for 5 to 10 minutes. Upon removing the cuff, a positive test is indicated by 15 or more petechiae in an area 5 cm in diameter due to poor platelet function. A positive result may be seen in SD.6

Histologically, SD is characterized by patchy parakeratosis, mild spongiosis of the stratum Malpighi, and lymphoid capillaritis (Figure 2).7 In addition to CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, CD1a+, and CD36+ lymphocytes, histology also may contain dendritic cells and cellular adhesion molecules (intercellular adhesion molecule 1, epithelial cell adhesion molecule 1) within the superficial perivascular infiltrate.8 There is no definitive therapy, but first-line interventions include emollients, topical steroids, and oral antihistamines. Nonpharmacologic management includes compression or support stockings, elevation of the lower extremities, and avoidance of offending medications (if identifiable).1

Majocchi Purpura—Domenico Majocchi was a renowned Italian dermatologist who described an entity in 1898 that he called purpura annularis telangiectodes, now also known as Majocchi purpura.9 It is more common in females, young adults, and children. Majocchi purpura has rarely been reported in families with a possible autosomal-dominant inheritance.10 Typically, bluish-red annular macules with central atrophy surrounded by hyperpigmentation may be seen on the lower extremities, potentially extending to the upper extremities.1 Treatment of Majocchi purpura remains a challenge but may respond to narrowband UVB phototherapy. Emollients and topical steroids also are used as first-line treatments. Biopsy demonstrates telangiectasia, pericapillary infiltration of mononuclear lymphocytes, and papillary dermal hemosiderin.11
Gougerot-Blum Purpura—In 1925, French dermatologists Henri Gougerot and Paul Blum described a pigmented purpuric lichenoid dermatitis known as Gougerot-Blum purpura,12 a rare PPD characterized by lichenoid papules that eventually coalesce into plaques of various colors, along with red-brown hyperpigmentation.4 As with other PPD variants, the legs are most involved, with rare extension to the trunk or thighs. The plaques may resemble and be mistaken for Kaposi sarcoma, cutaneous vasculitis, traumatic purpura, or mycosis fungoides. Dermoscopic examination reveals small, polygonal or round, red dots underlying brown scaly patches.13 Gougerot-Blum purpura is found more commonly in adult men and rarely affects children.4 Histologically, a lichenoid and superficial perivascular infiltrate composed of lymphocytes and macrophages is seen. Various therapies have been described, including topical steroids, antihistamines, psoralen plus UVA phototherapy, and cyclosporin A.14
Eczematoid Purpura of Doucas and Kapetanakis—In 1949, Greek dermatologists Christopher Doucas and John Kapetanakis observed several cases of purpuric dermatosis similar in form to the “pigmented purpuric lichenoid dermatitis” of Gougerot-Blum purpura12 and to the “progressive pigmentary dermatitis” of Schamberg disease.3 After observing a gradual disappearance of the classic yellow color from hemosiderin deposition, Doucas and Kapetanakis described a new bright red eruption with lichenification.15 Eczematoid purpura of Doucas and Kapetanakis is rare and predominantly seen in middle-aged males. Hyperpigmented or dark brown macules may develop bilaterally on the legs, progressing to the thighs and upper extremities. Unlike the other types of PPD, DK is extensive and severely pruritic.4
Although most PPD can be drug induced, DK has shown the greatest tendency for pruritic erythematous plaques following drug usage including but not limited to amlodipine, aspirin, acetaminophen, thiamine, interferon alfa, chlordiazepoxide, and isotretinoin. Additionally, DK has been associated with a contact allergy to clothing dyes and rubber.4 On histology, epidermal spongiosis may be seen, correlating with the eczematoid clinical findings. Spontaneous remission also is more common compared to the other PPDs. Treatment consists of topical corticosteroids and antihistamines.16
Lichen Aureus—Lichen aureus was first observed by the dermatologist R.H. Martin in 1958.17 It is clinically characterized by closely aggregated purpuric papules with a distinctive golden-brown color more often localized to the lower extremities and sometimes in a dermatomal distribution. Lichen aureus affects males and females equally, and similar to Majocchi purpura can be seen in children.4 Histopathologic examination reveals a prominent lichenoid plus superficial and deep perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate, extravasated erythrocytes, papillary dermal edema, hemosiderophages, and an unaffected epidermis. In rare cases, perineural infiltrates may be seen. Topical steroids usually are ineffective in lichen aureus treatment, but responses to psoralen plus UVA therapy also have been noted.17
Differential Diagnosis
COVID-19–Related Cutaneous Changes—Because COVID-19–related pathology is now a common differential diagnosis for many cutaneous eruptions, one must be mindful of the possibility for patients to have PPD, cutaneous changes from underlying COVID-19, or both.18 The microvascular changes from COVID-19 infection can be variable.19 Besides the presence of erythema along a distal digit, manifestations can include reticulated dusky erythema mimicking livedoid vasculopathy or inflammatory purpura.19
Retiform Purpura—Retiform purpura may occur in the setting of microvascular occlusion and can represent the pattern of underlying dermal vasculature. It is nonblanching and typically stellate or branching.20 The microvascular occlusion may be a result of hypercoagulability or may be secondary to cutaneous vasculitis, resulting in thrombosis and subsequent vascular occlusion.21 There are many reasons for hypercoagulability in retiform purpura, including disseminated intravascular coagulation in the setting of COVID-19 infection.22 The treatment of retiform purpura is aimed at alleviating the underlying cause and providing symptomatic relief. Conversely, the PPDs generally are benign and require minimal workup.
Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis—The hallmark of leukocytoclastic vasculitis is palpable purpura, often appearing as nonblanchable papules, typically in a dependent distribution such as the lower extremities (Figure 3). Although it primarily affects children, Henoch-Schönlein purpura is a type of leukocytoclastic vasculitis with lesions potentially similar in appearance to those of PPD.23 Palpable purpura may be painful and may ulcerate but rarely is pruritic. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis represents perivascular infiltrates composed of neutrophils, lymphocytes, and occasionally eosinophils, along with karyorrhexis, luminal fibrin, and fibrinoid degeneration of blood vessel walls, often resulting from immune complex deposition. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis may affect blood vessels of any size and requires further clinical and laboratory evaluation for infection (including COVID-19), hypercoagulability, autoimmune disease, or medication-related reactions.24

Stasis Dermatitis—Stasis dermatitis, a chronic inflammatory condition stemming from retrograde venous flow due to incompetent venous valves, mimics PPD. Stasis dermatitis initially appears as demarcated erythematous plaques, fissures, and scaling of the lower legs bilaterally, usually involving the medial malleolus.25 With time, the affected region develops overlying brawny hyperpigmentation and fibrosis (Figure 4). Pruritus or pain are common features, while fissures and superficial erosions may heal and recur, leading to lichenification.

Although both commonly appear on the lower extremities, duplex ultrasonography may be helpful to distinguish PPDs from stasis dermatitis since the latter occurs in the context of chronic venous insufficiency, varicose veins, soft tissue edema, and lymphedema.25 Additionally, pruritus, lichenification, and edema often are not seen in most PPD variants, although stasis dermatitis and PPD may occur in tandem. Conservative treatment involves elevation of the extremities, compression, and topical steroids for symptomatic relief.
Cellulitis—The key characteristics of cellulitis are redness, swelling, warmth, tenderness, fever, and leukocytosis. A history of trauma, such as a prior break in the skin, and pain in the affected area suggest cellulitis. Several skin conditions present similarly to cellulitis, including PPD, and thus approximately 30% of cases are misdiagnosed.26 Cellulitis rarely presents in a bilateral or diffusely scattered pattern as seen in PPDs. Rather, it is unilateral with smooth indistinct borders. Variables suggestive of cellulitis include immunosuppression, rapid progression, and previous occurrences. Hyperpigmented plaques or thickening of the skin are more indicative of a chronic process such as stasis dermatitis or lipodermatosclerosis rather than acute cellulitis. Purpura is not a typical finding in most cases of soft tissue cellulitis. Treatment may be case specific depending on severity, presence or absence of sepsis, findings on blood cultures, or other pathologic evaluation. Antibiotics are directed to the causative organism, typically Streptococcus and Staphylococcus species, although coverage against various gram-negative organisms may be indicated.27
Caution With Teledermatology
COVID-19 has established the value of telemedicine in providing access to health care services for at-risk or underserved individuals. The PPDs are benign, often asymptomatic, and potentially identifiable with teledermatology alone; however, they also can easily be mistaken for COVID-19–related eruptions, vasculitis, other types of purpura, stasis dermatitis, or other complications of lower extremity stasis and lymphedema, especially in an aging population. If tissue biopsy is required, as in the workup of vasculitis, the efficacy of telemedicine becomes more questionable. It is important to delineate the potentially confusing PPDs from other potentially dangerous or life-threatening inflammatory dermatoses.28
Pigmented purpuric dermatoses (PPDs) are characterized by petechiae, dusky macules representative of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation and dermal hemosiderin, and purpura generally localized to the lower extremities. They typically represent a spectrum of lymphocytic capillaritis, variable erythrocyte extravasation from papillary dermal blood vessels, and deposition of hemosiderin, yielding the classic red to orange to golden-brown findings on gross examination. Clinical overlap exists, but variants include Schamberg disease (SD), Majocchi purpura, Gougerot-Blum purpura, eczematoid purpura of Doucas and Kapetanakis (DK), and lichen aureus.1 Other forms are rarer, including linear, granulomatous, quadrantic, transitory, and familial variants. It remains controversial whether PPD may precede or have an association with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.2 Dermoscopy usually shows copper-red pigmentation in the background, oval red dots, linear vessels, brown globules, and follicular openings. Although these findings may be useful in PPD diagnosis, they are not applicable in differentiating among the variants.
Pigmented purpuric dermatoses can easily be mistaken for stasis dermatitis or cellulitis, as these may occur concomitantly or in populations at risk for all 3 conditions, such as women older than 50 years with recent trauma or infection in the affected area. Tissue biopsy and clinical laboratory evaluation may be required to differentiate between PPD from leukocytoclastic vasculitis or the myriad causes of retiform purpura. Importantly, clinicians also should differentiate PPD from the purpuric eruptions of the lower extremities associated with COVID-19 infection.
Pigmented Purpuric Dermatoses
Schamberg Disease—In 1901, Jay Frank Schamberg, a distinguished professor of dermatology in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, described “a peculiar progressive pigmentary disease of the skin” in a 15-year-old adolescent boy.3 Schamberg disease is the most common PPD, characterized by pruritic spots resembling cayenne pepper (Figure 1) with orange-brown pigmented macules on the legs and feet.4 Although platelet dysfunction, coagulation deficiencies, or dermal atrophy may contribute to hemorrhaging that manifests as petechiae or ecchymoses, SD typically is not associated with any laboratory abnormalities, and petechial eruption is not widespread.5 Capillary fragility can be assessed by the tourniquet test, in which pressure is applied to the forearm with a blood pressure cuff inflated between systolic and diastolic blood pressure for 5 to 10 minutes. Upon removing the cuff, a positive test is indicated by 15 or more petechiae in an area 5 cm in diameter due to poor platelet function. A positive result may be seen in SD.6

Histologically, SD is characterized by patchy parakeratosis, mild spongiosis of the stratum Malpighi, and lymphoid capillaritis (Figure 2).7 In addition to CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, CD1a+, and CD36+ lymphocytes, histology also may contain dendritic cells and cellular adhesion molecules (intercellular adhesion molecule 1, epithelial cell adhesion molecule 1) within the superficial perivascular infiltrate.8 There is no definitive therapy, but first-line interventions include emollients, topical steroids, and oral antihistamines. Nonpharmacologic management includes compression or support stockings, elevation of the lower extremities, and avoidance of offending medications (if identifiable).1

Majocchi Purpura—Domenico Majocchi was a renowned Italian dermatologist who described an entity in 1898 that he called purpura annularis telangiectodes, now also known as Majocchi purpura.9 It is more common in females, young adults, and children. Majocchi purpura has rarely been reported in families with a possible autosomal-dominant inheritance.10 Typically, bluish-red annular macules with central atrophy surrounded by hyperpigmentation may be seen on the lower extremities, potentially extending to the upper extremities.1 Treatment of Majocchi purpura remains a challenge but may respond to narrowband UVB phototherapy. Emollients and topical steroids also are used as first-line treatments. Biopsy demonstrates telangiectasia, pericapillary infiltration of mononuclear lymphocytes, and papillary dermal hemosiderin.11
Gougerot-Blum Purpura—In 1925, French dermatologists Henri Gougerot and Paul Blum described a pigmented purpuric lichenoid dermatitis known as Gougerot-Blum purpura,12 a rare PPD characterized by lichenoid papules that eventually coalesce into plaques of various colors, along with red-brown hyperpigmentation.4 As with other PPD variants, the legs are most involved, with rare extension to the trunk or thighs. The plaques may resemble and be mistaken for Kaposi sarcoma, cutaneous vasculitis, traumatic purpura, or mycosis fungoides. Dermoscopic examination reveals small, polygonal or round, red dots underlying brown scaly patches.13 Gougerot-Blum purpura is found more commonly in adult men and rarely affects children.4 Histologically, a lichenoid and superficial perivascular infiltrate composed of lymphocytes and macrophages is seen. Various therapies have been described, including topical steroids, antihistamines, psoralen plus UVA phototherapy, and cyclosporin A.14
Eczematoid Purpura of Doucas and Kapetanakis—In 1949, Greek dermatologists Christopher Doucas and John Kapetanakis observed several cases of purpuric dermatosis similar in form to the “pigmented purpuric lichenoid dermatitis” of Gougerot-Blum purpura12 and to the “progressive pigmentary dermatitis” of Schamberg disease.3 After observing a gradual disappearance of the classic yellow color from hemosiderin deposition, Doucas and Kapetanakis described a new bright red eruption with lichenification.15 Eczematoid purpura of Doucas and Kapetanakis is rare and predominantly seen in middle-aged males. Hyperpigmented or dark brown macules may develop bilaterally on the legs, progressing to the thighs and upper extremities. Unlike the other types of PPD, DK is extensive and severely pruritic.4
Although most PPD can be drug induced, DK has shown the greatest tendency for pruritic erythematous plaques following drug usage including but not limited to amlodipine, aspirin, acetaminophen, thiamine, interferon alfa, chlordiazepoxide, and isotretinoin. Additionally, DK has been associated with a contact allergy to clothing dyes and rubber.4 On histology, epidermal spongiosis may be seen, correlating with the eczematoid clinical findings. Spontaneous remission also is more common compared to the other PPDs. Treatment consists of topical corticosteroids and antihistamines.16
Lichen Aureus—Lichen aureus was first observed by the dermatologist R.H. Martin in 1958.17 It is clinically characterized by closely aggregated purpuric papules with a distinctive golden-brown color more often localized to the lower extremities and sometimes in a dermatomal distribution. Lichen aureus affects males and females equally, and similar to Majocchi purpura can be seen in children.4 Histopathologic examination reveals a prominent lichenoid plus superficial and deep perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate, extravasated erythrocytes, papillary dermal edema, hemosiderophages, and an unaffected epidermis. In rare cases, perineural infiltrates may be seen. Topical steroids usually are ineffective in lichen aureus treatment, but responses to psoralen plus UVA therapy also have been noted.17
Differential Diagnosis
COVID-19–Related Cutaneous Changes—Because COVID-19–related pathology is now a common differential diagnosis for many cutaneous eruptions, one must be mindful of the possibility for patients to have PPD, cutaneous changes from underlying COVID-19, or both.18 The microvascular changes from COVID-19 infection can be variable.19 Besides the presence of erythema along a distal digit, manifestations can include reticulated dusky erythema mimicking livedoid vasculopathy or inflammatory purpura.19
Retiform Purpura—Retiform purpura may occur in the setting of microvascular occlusion and can represent the pattern of underlying dermal vasculature. It is nonblanching and typically stellate or branching.20 The microvascular occlusion may be a result of hypercoagulability or may be secondary to cutaneous vasculitis, resulting in thrombosis and subsequent vascular occlusion.21 There are many reasons for hypercoagulability in retiform purpura, including disseminated intravascular coagulation in the setting of COVID-19 infection.22 The treatment of retiform purpura is aimed at alleviating the underlying cause and providing symptomatic relief. Conversely, the PPDs generally are benign and require minimal workup.
Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis—The hallmark of leukocytoclastic vasculitis is palpable purpura, often appearing as nonblanchable papules, typically in a dependent distribution such as the lower extremities (Figure 3). Although it primarily affects children, Henoch-Schönlein purpura is a type of leukocytoclastic vasculitis with lesions potentially similar in appearance to those of PPD.23 Palpable purpura may be painful and may ulcerate but rarely is pruritic. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis represents perivascular infiltrates composed of neutrophils, lymphocytes, and occasionally eosinophils, along with karyorrhexis, luminal fibrin, and fibrinoid degeneration of blood vessel walls, often resulting from immune complex deposition. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis may affect blood vessels of any size and requires further clinical and laboratory evaluation for infection (including COVID-19), hypercoagulability, autoimmune disease, or medication-related reactions.24

Stasis Dermatitis—Stasis dermatitis, a chronic inflammatory condition stemming from retrograde venous flow due to incompetent venous valves, mimics PPD. Stasis dermatitis initially appears as demarcated erythematous plaques, fissures, and scaling of the lower legs bilaterally, usually involving the medial malleolus.25 With time, the affected region develops overlying brawny hyperpigmentation and fibrosis (Figure 4). Pruritus or pain are common features, while fissures and superficial erosions may heal and recur, leading to lichenification.

Although both commonly appear on the lower extremities, duplex ultrasonography may be helpful to distinguish PPDs from stasis dermatitis since the latter occurs in the context of chronic venous insufficiency, varicose veins, soft tissue edema, and lymphedema.25 Additionally, pruritus, lichenification, and edema often are not seen in most PPD variants, although stasis dermatitis and PPD may occur in tandem. Conservative treatment involves elevation of the extremities, compression, and topical steroids for symptomatic relief.
Cellulitis—The key characteristics of cellulitis are redness, swelling, warmth, tenderness, fever, and leukocytosis. A history of trauma, such as a prior break in the skin, and pain in the affected area suggest cellulitis. Several skin conditions present similarly to cellulitis, including PPD, and thus approximately 30% of cases are misdiagnosed.26 Cellulitis rarely presents in a bilateral or diffusely scattered pattern as seen in PPDs. Rather, it is unilateral with smooth indistinct borders. Variables suggestive of cellulitis include immunosuppression, rapid progression, and previous occurrences. Hyperpigmented plaques or thickening of the skin are more indicative of a chronic process such as stasis dermatitis or lipodermatosclerosis rather than acute cellulitis. Purpura is not a typical finding in most cases of soft tissue cellulitis. Treatment may be case specific depending on severity, presence or absence of sepsis, findings on blood cultures, or other pathologic evaluation. Antibiotics are directed to the causative organism, typically Streptococcus and Staphylococcus species, although coverage against various gram-negative organisms may be indicated.27
Caution With Teledermatology
COVID-19 has established the value of telemedicine in providing access to health care services for at-risk or underserved individuals. The PPDs are benign, often asymptomatic, and potentially identifiable with teledermatology alone; however, they also can easily be mistaken for COVID-19–related eruptions, vasculitis, other types of purpura, stasis dermatitis, or other complications of lower extremity stasis and lymphedema, especially in an aging population. If tissue biopsy is required, as in the workup of vasculitis, the efficacy of telemedicine becomes more questionable. It is important to delineate the potentially confusing PPDs from other potentially dangerous or life-threatening inflammatory dermatoses.28
- Sardana K, Sarkar R , Sehgal VN. Pigmented purpuric dermatoses: an overview. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:482-488.
- Çaytemel C, Baykut B, Ag˘ırgöl S¸, et al. Pigmented purpuric dermatosis: ten years of experience in a tertiary hospital and awareness of mycosis fungoides in differential diagnosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:611-616.
- Schamberg JF. A peculiar progressive pigmentary disease of the skin. Br J Dermatol. 1901;13:1-5.
- Martínez Pallás I, Conejero Del Mazo R, Lezcano Biosca V. Pigmented purpuric dermatosis: a review of the literature. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2020;111:196-204.
- Ozkaya DB, Emiroglu N, Su O, et al. Dermatoscopic findings of pigmented purpuric dermatosis. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:584-587.
- Lava SAG, Milani GP, Fossali EF, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of small-vessel leukocytoclastic vasculitides in childhood. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017;53:439-451.
- Bonnet U, Selle C, Isbruch K, et al. Recurrent purpura due to alcohol-related Schamberg’s disease and its association with serum immunoglobulins: a longitudinal observation of a heavy drinker. J Med Case Rep. 2016;10:301.
- Zaldivar Fujigaki JL, Anjum F. Schamberg Disease. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
- Majocchi J. Purpura annularis telangiectodes. Arch Dermatol Syph. 1898;43:447.
- Sethuraman G, Sugandhan S, Bansal A, et al. Familial pigmented purpuric dermatoses. J Dermatol. 2006;33:639-641.
- Miller K, Fischer M, Kamino H, et al. Purpura annularis telangiectoides. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:5.
- Coulombe J, Jean SE, Hatami A, et al. Pigmented purpuric dermatosis: clinicopathologic characterization in a pediatric series. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:358-362.
- Park MY, Shim WH, Kim JM, et al. Dermoscopic finding in pigmented purpuric lichenoid dermatosis of Gougerot-Blum: a useful tool for clinical diagnosis. Ann Dermatol. 2018;30:245-247.
- Risikesan J, Sommerlund M, Ramsing M, et al. Successful topical treatment of pigmented purpuric lichenoid dermatitis of Gougerot-Blum in a young patient: a case report and summary of the most common pigmented purpuric dermatoses. Case Rep Dermatol. 2017;9:169-176.
- Doucas C, Kapetanakis J. Eczematid-like purpura. Dermatologica. 1953;106:86-95.
- Kim DH, Seo SH, Ahn HH, et al. Characteristics and clinical manifestations of pigmented purpuric dermatosis. Ann Dermatol. 2015;27:404-410.
- Aung PP, Burns SJ, Bhawan J. Lichen aureus: an unusual histopathological presentation: a case report and a review of literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36:E1-E4.
- Singh P, Schwartz RA. Disseminated intravascular coagulation: a devastating systemic disorder of special concern with COVID-19. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E14053.
- Almutairi N, Schwartz RA. COVID-19 with dermatologic manifestations and implications: an unfolding conundrum. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E13544.
- Georgesen C, Fox LP, Harp J. Retiform purpura: a diagnostic approach. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:783-796.
- Torregrosa Calatayud JL, Garcías Ladaria J, De Unamuno Bustos B, et al. Retiform purpura caused by the use of cocaine, that was probably adulterated with levamisole. Ann Dermatol. 2015;27:117-119.
- Keim CK, Schwartz RA, Kapila R. Levamisole-induced and COVID-19-induced retiform purpura: two overlapping, emerging clinical syndromes. Arch Dermatol Res. 2021;22:1-9.
- González LM, Janniger CK, Schwartz RA. Pediatric Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:1157-1165.
- Yıldırım Bay E, Moustafa E, Semiz Y, et al. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis secondary to COVID-19 infection presenting with inclusion bodies: a histopathological correlation. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022;21:27-29.
- Sundaresan S, Migden MR, Silapunt S. Stasis dermatitis: pathophysiology, evaluation, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:383-390.
- Hirschmann JV, Raugi GJ. Lower limb cellulitis and its mimics: part I. lower limb cellulitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:163.E1-E12; quiz 75-76.
- Keller EC, Tomecki KJ, Alraies MC. Distinguishing cellulitis from its mimics. Cleveland Clin J Med. 2012;79:547-552.
- Georgesen C, Fox LP, Harp J. Retiform purpura: workup and therapeutic considerations in select conditions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:799-816.
- Sardana K, Sarkar R , Sehgal VN. Pigmented purpuric dermatoses: an overview. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:482-488.
- Çaytemel C, Baykut B, Ag˘ırgöl S¸, et al. Pigmented purpuric dermatosis: ten years of experience in a tertiary hospital and awareness of mycosis fungoides in differential diagnosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:611-616.
- Schamberg JF. A peculiar progressive pigmentary disease of the skin. Br J Dermatol. 1901;13:1-5.
- Martínez Pallás I, Conejero Del Mazo R, Lezcano Biosca V. Pigmented purpuric dermatosis: a review of the literature. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2020;111:196-204.
- Ozkaya DB, Emiroglu N, Su O, et al. Dermatoscopic findings of pigmented purpuric dermatosis. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:584-587.
- Lava SAG, Milani GP, Fossali EF, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of small-vessel leukocytoclastic vasculitides in childhood. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017;53:439-451.
- Bonnet U, Selle C, Isbruch K, et al. Recurrent purpura due to alcohol-related Schamberg’s disease and its association with serum immunoglobulins: a longitudinal observation of a heavy drinker. J Med Case Rep. 2016;10:301.
- Zaldivar Fujigaki JL, Anjum F. Schamberg Disease. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
- Majocchi J. Purpura annularis telangiectodes. Arch Dermatol Syph. 1898;43:447.
- Sethuraman G, Sugandhan S, Bansal A, et al. Familial pigmented purpuric dermatoses. J Dermatol. 2006;33:639-641.
- Miller K, Fischer M, Kamino H, et al. Purpura annularis telangiectoides. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:5.
- Coulombe J, Jean SE, Hatami A, et al. Pigmented purpuric dermatosis: clinicopathologic characterization in a pediatric series. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:358-362.
- Park MY, Shim WH, Kim JM, et al. Dermoscopic finding in pigmented purpuric lichenoid dermatosis of Gougerot-Blum: a useful tool for clinical diagnosis. Ann Dermatol. 2018;30:245-247.
- Risikesan J, Sommerlund M, Ramsing M, et al. Successful topical treatment of pigmented purpuric lichenoid dermatitis of Gougerot-Blum in a young patient: a case report and summary of the most common pigmented purpuric dermatoses. Case Rep Dermatol. 2017;9:169-176.
- Doucas C, Kapetanakis J. Eczematid-like purpura. Dermatologica. 1953;106:86-95.
- Kim DH, Seo SH, Ahn HH, et al. Characteristics and clinical manifestations of pigmented purpuric dermatosis. Ann Dermatol. 2015;27:404-410.
- Aung PP, Burns SJ, Bhawan J. Lichen aureus: an unusual histopathological presentation: a case report and a review of literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36:E1-E4.
- Singh P, Schwartz RA. Disseminated intravascular coagulation: a devastating systemic disorder of special concern with COVID-19. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E14053.
- Almutairi N, Schwartz RA. COVID-19 with dermatologic manifestations and implications: an unfolding conundrum. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E13544.
- Georgesen C, Fox LP, Harp J. Retiform purpura: a diagnostic approach. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:783-796.
- Torregrosa Calatayud JL, Garcías Ladaria J, De Unamuno Bustos B, et al. Retiform purpura caused by the use of cocaine, that was probably adulterated with levamisole. Ann Dermatol. 2015;27:117-119.
- Keim CK, Schwartz RA, Kapila R. Levamisole-induced and COVID-19-induced retiform purpura: two overlapping, emerging clinical syndromes. Arch Dermatol Res. 2021;22:1-9.
- González LM, Janniger CK, Schwartz RA. Pediatric Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:1157-1165.
- Yıldırım Bay E, Moustafa E, Semiz Y, et al. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis secondary to COVID-19 infection presenting with inclusion bodies: a histopathological correlation. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022;21:27-29.
- Sundaresan S, Migden MR, Silapunt S. Stasis dermatitis: pathophysiology, evaluation, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:383-390.
- Hirschmann JV, Raugi GJ. Lower limb cellulitis and its mimics: part I. lower limb cellulitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:163.E1-E12; quiz 75-76.
- Keller EC, Tomecki KJ, Alraies MC. Distinguishing cellulitis from its mimics. Cleveland Clin J Med. 2012;79:547-552.
- Georgesen C, Fox LP, Harp J. Retiform purpura: workup and therapeutic considerations in select conditions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:799-816.
Practice Points
- Dermatologists should be aware of the clinical presentations of pigmenting purpuric dermatoses (PPDs).
- Certain PPDs may resemble the thromboembolic events seen in COVID-19. Clinicians should especially be aware of how to differentiate these benign pigmentary disorders from other serious conditions.
- Teledermatology is widely utilized, but caution may be prudent when evaluating erythematous or purpuric dermatoses, especially those of the lower extremities.
- Pigmenting purpuric dermatoses generally are benign and do not require immediate treatment.
Long COVID and vaccines: Separating facts from falsehoods
The COVID-19 vaccines have been a game changer for millions of people worldwide in preventing death or disability from the virus. Research suggests that they offer significant protection against long COVID.
False and unfounded claims made by some antivaccine groups that the vaccines themselves may cause long COVID persist and serve as barriers to vaccination.
To help separate the facts from falsehoods, here’s a checklist for doctors on what scientific studies have determined about vaccination and long COVID.
What the research shows
Doctors who work in long COVID clinics have for years suspected that vaccination may help protect against the development of long COVID, noted Lawrence Purpura, MD, MPH, an infectious disease specialist at New York–Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, who treats patients with long COVID in his clinic.
Over the past year, several large, well-conducted studies have borne out that theory, including the following studies:
- In the RECOVER study, published in May in the journal Nature Communications, researchers examined the electronic health records of more than 5 million people who had been diagnosed with COVID and found that vaccination reduced the risk that they would develop long COVID. Although the researchers didn’t compare the effects of having boosters to being fully vaccinated without them, experts have suggested that having a full round of recommended shots may offer the most protection. “My thoughts are that more shots are better, and other work has shown compelling evidence that the protective effect of vaccination on COVID-19 wanes over time,” said study coauthor Daniel Brannock, MS, a research scientist at RTI International in Research Triangle Park, N.C. “It stands to reason that the same is true for long COVID.”
- A review published in February in BMJ Medicine concluded that 10 studies showed a significant reduction in the incidence of long COVID among vaccinated patients. Even one dose of a vaccine was protective.
- A meta-analysis of six studies published last December in Antimicrobial Stewardship and Healthcare Epidemiology found that one or more doses of a COVID-19 vaccine were 29% effective in preventing symptoms of long COVID.
- In a June meta-analysis published in JAMA Internal Medicine, researchers analyzed more than 40 studies that included 860,000 patients and found that two doses of a COVID-19 vaccine reduced the risk of long COVID by almost half.
The message? COVID vaccination is very effective in reducing the risk of long COVID.
“It’s important to emphasize that many of the risk factors [for long COVID] cannot be changed, or at least cannot be changed easily, but vaccination is a decision that can be taken by everyone,” said Vassilios Vassiliou, MBBS, PhD, clinical professor of cardiac medicine at Norwich Medical School in England, who coauthored the article in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Why vaccines may be protective
The COVID-19 vaccines work well to prevent serious illness from the virus, noted Aaron Friedberg, MD, clinical coleader of the Post COVID Recovery Program at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center. That may be a clue to why the vaccines help prevent long COVID symptoms.
“When you get COVID and you’ve been vaccinated, the virus may still attach in your nose and respiratory tract, but it’s less likely to spread throughout your body,” he explained. “It’s like a forest fire – if the ground is wet or it starts to rain, it’s less likely to create a great blaze. As a result, your body is less likely to experience inflammation and damage that makes it more likely that you’ll develop long COVID.”
Dr. Friedberg stressed that even for patients who have had COVID, it’s important to get vaccinated – a message he consistently delivers to his own patients.
“There is some protection that comes from having COVID before, but for some people, that’s not enough,” he said. “It’s true that after infection, your body creates antibodies that help protect you against the virus. But I explain to patients that these may be like old Velcro: They barely grab on enough to stay on for the moment, but they don’t last long term. You’re much more likely to get a reliable immune response from the vaccine.”
In addition, a second or third bout of COVID could be the one that gives patients long COVID, Dr. Friedberg adds.
“I have a number of patients in my clinic who were fine after their first bout of COVID but experienced debilitating long COVID symptoms after they developed COVID again,” he said. “Why leave it to chance?”
Vaccines and ‘long vax’
The COVID vaccines are considered very safe but have been linked to very rare side effects, such as blood clots and heart inflammation. There have also been anecdotal reports of symptoms that resemble long COVID – a syndrome that has come to be known as “long Vax” – an extremely rare condition that may or may not be tied to vaccination.
“I have seen people in my clinic who developed symptoms suggestive of long COVID that linger for months – brain fog, fatigue, heart palpitations – soon after they got the COVID-19 vaccine,” said Dr. Purpura. But no published studies have suggested a link, he cautions.
A study called LISTEN is being organized at Yale in an effort to better understand postvaccine adverse events and a potential link to long COVID.
Talking to patients
Discussions of vaccination with patients, including those with COVID or long COVID, are often fraught and challenging, said Dr. Purpura.
“There’s a lot of fear that they will have a worsening of their symptoms,” he explained. The conversation he has with his patients mirrors the conversation all physicians should have with their patients about COVID-19 vaccination, even if they don’t have long COVID. He stresses the importance of highlighting the following components:
- Show compassion and empathy. “A lot of people have strongly held opinions – it’s worth it to try to find out why they feel the way that they do,” said Dr. Friedberg.
- Walk them through side effects. “Many people are afraid of the side effects of the vaccine, especially if they already have long COVID,” explained Dr. Purpura. Such patients can be asked how they felt after their last vaccination, such a shingles or flu shot. Then explain that the COVID-19 vaccine is not much different and that they may experience temporary side effects such as fatigue, headache, or a mild fever for 24-48 hours.
- Explain the benefits. Eighty-five percent of people say their health care provider is a trusted source of information on COVID-19 vaccines, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation. That trust is conducive to talks about the vaccine’s benefits, including its ability to protect against long COVID.
Other ways to reduce risk of long COVID
Vaccines can lower the chances of a patient’s developing long COVID. So can the antiviral medication nirmatrelvir (Paxlovid). A March 2023 study published in JAMA Internal Medicine included more than 280,000 people with COVID. The researchers found that vaccination reduced the risk for developing the condition by about 25%.
“I mention that study to all of my long COVID patients who become reinfected with the virus,” said Dr. Purpura. “It not only appears protective against long COVID, but since it lowers levels of virus circulating in their body, it seems to help prevent a flare-up of symptoms.”
Another treatment that may help is the diabetes drug metformin, he added.
A June 2023 study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases found that when metformin was given within 3 days of symptom onset, the incidence of long COVID was reduced by about 41%.
“We’re still trying to wrap our brains around this one, but the thought is it may help to lower inflammation, which plays a role in long COVID,” Dr. Purpura explained. More studies need to be conducted, though, before recommending its use.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 vaccines have been a game changer for millions of people worldwide in preventing death or disability from the virus. Research suggests that they offer significant protection against long COVID.
False and unfounded claims made by some antivaccine groups that the vaccines themselves may cause long COVID persist and serve as barriers to vaccination.
To help separate the facts from falsehoods, here’s a checklist for doctors on what scientific studies have determined about vaccination and long COVID.
What the research shows
Doctors who work in long COVID clinics have for years suspected that vaccination may help protect against the development of long COVID, noted Lawrence Purpura, MD, MPH, an infectious disease specialist at New York–Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, who treats patients with long COVID in his clinic.
Over the past year, several large, well-conducted studies have borne out that theory, including the following studies:
- In the RECOVER study, published in May in the journal Nature Communications, researchers examined the electronic health records of more than 5 million people who had been diagnosed with COVID and found that vaccination reduced the risk that they would develop long COVID. Although the researchers didn’t compare the effects of having boosters to being fully vaccinated without them, experts have suggested that having a full round of recommended shots may offer the most protection. “My thoughts are that more shots are better, and other work has shown compelling evidence that the protective effect of vaccination on COVID-19 wanes over time,” said study coauthor Daniel Brannock, MS, a research scientist at RTI International in Research Triangle Park, N.C. “It stands to reason that the same is true for long COVID.”
- A review published in February in BMJ Medicine concluded that 10 studies showed a significant reduction in the incidence of long COVID among vaccinated patients. Even one dose of a vaccine was protective.
- A meta-analysis of six studies published last December in Antimicrobial Stewardship and Healthcare Epidemiology found that one or more doses of a COVID-19 vaccine were 29% effective in preventing symptoms of long COVID.
- In a June meta-analysis published in JAMA Internal Medicine, researchers analyzed more than 40 studies that included 860,000 patients and found that two doses of a COVID-19 vaccine reduced the risk of long COVID by almost half.
The message? COVID vaccination is very effective in reducing the risk of long COVID.
“It’s important to emphasize that many of the risk factors [for long COVID] cannot be changed, or at least cannot be changed easily, but vaccination is a decision that can be taken by everyone,” said Vassilios Vassiliou, MBBS, PhD, clinical professor of cardiac medicine at Norwich Medical School in England, who coauthored the article in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Why vaccines may be protective
The COVID-19 vaccines work well to prevent serious illness from the virus, noted Aaron Friedberg, MD, clinical coleader of the Post COVID Recovery Program at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center. That may be a clue to why the vaccines help prevent long COVID symptoms.
“When you get COVID and you’ve been vaccinated, the virus may still attach in your nose and respiratory tract, but it’s less likely to spread throughout your body,” he explained. “It’s like a forest fire – if the ground is wet or it starts to rain, it’s less likely to create a great blaze. As a result, your body is less likely to experience inflammation and damage that makes it more likely that you’ll develop long COVID.”
Dr. Friedberg stressed that even for patients who have had COVID, it’s important to get vaccinated – a message he consistently delivers to his own patients.
“There is some protection that comes from having COVID before, but for some people, that’s not enough,” he said. “It’s true that after infection, your body creates antibodies that help protect you against the virus. But I explain to patients that these may be like old Velcro: They barely grab on enough to stay on for the moment, but they don’t last long term. You’re much more likely to get a reliable immune response from the vaccine.”
In addition, a second or third bout of COVID could be the one that gives patients long COVID, Dr. Friedberg adds.
“I have a number of patients in my clinic who were fine after their first bout of COVID but experienced debilitating long COVID symptoms after they developed COVID again,” he said. “Why leave it to chance?”
Vaccines and ‘long vax’
The COVID vaccines are considered very safe but have been linked to very rare side effects, such as blood clots and heart inflammation. There have also been anecdotal reports of symptoms that resemble long COVID – a syndrome that has come to be known as “long Vax” – an extremely rare condition that may or may not be tied to vaccination.
“I have seen people in my clinic who developed symptoms suggestive of long COVID that linger for months – brain fog, fatigue, heart palpitations – soon after they got the COVID-19 vaccine,” said Dr. Purpura. But no published studies have suggested a link, he cautions.
A study called LISTEN is being organized at Yale in an effort to better understand postvaccine adverse events and a potential link to long COVID.
Talking to patients
Discussions of vaccination with patients, including those with COVID or long COVID, are often fraught and challenging, said Dr. Purpura.
“There’s a lot of fear that they will have a worsening of their symptoms,” he explained. The conversation he has with his patients mirrors the conversation all physicians should have with their patients about COVID-19 vaccination, even if they don’t have long COVID. He stresses the importance of highlighting the following components:
- Show compassion and empathy. “A lot of people have strongly held opinions – it’s worth it to try to find out why they feel the way that they do,” said Dr. Friedberg.
- Walk them through side effects. “Many people are afraid of the side effects of the vaccine, especially if they already have long COVID,” explained Dr. Purpura. Such patients can be asked how they felt after their last vaccination, such a shingles or flu shot. Then explain that the COVID-19 vaccine is not much different and that they may experience temporary side effects such as fatigue, headache, or a mild fever for 24-48 hours.
- Explain the benefits. Eighty-five percent of people say their health care provider is a trusted source of information on COVID-19 vaccines, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation. That trust is conducive to talks about the vaccine’s benefits, including its ability to protect against long COVID.
Other ways to reduce risk of long COVID
Vaccines can lower the chances of a patient’s developing long COVID. So can the antiviral medication nirmatrelvir (Paxlovid). A March 2023 study published in JAMA Internal Medicine included more than 280,000 people with COVID. The researchers found that vaccination reduced the risk for developing the condition by about 25%.
“I mention that study to all of my long COVID patients who become reinfected with the virus,” said Dr. Purpura. “It not only appears protective against long COVID, but since it lowers levels of virus circulating in their body, it seems to help prevent a flare-up of symptoms.”
Another treatment that may help is the diabetes drug metformin, he added.
A June 2023 study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases found that when metformin was given within 3 days of symptom onset, the incidence of long COVID was reduced by about 41%.
“We’re still trying to wrap our brains around this one, but the thought is it may help to lower inflammation, which plays a role in long COVID,” Dr. Purpura explained. More studies need to be conducted, though, before recommending its use.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 vaccines have been a game changer for millions of people worldwide in preventing death or disability from the virus. Research suggests that they offer significant protection against long COVID.
False and unfounded claims made by some antivaccine groups that the vaccines themselves may cause long COVID persist and serve as barriers to vaccination.
To help separate the facts from falsehoods, here’s a checklist for doctors on what scientific studies have determined about vaccination and long COVID.
What the research shows
Doctors who work in long COVID clinics have for years suspected that vaccination may help protect against the development of long COVID, noted Lawrence Purpura, MD, MPH, an infectious disease specialist at New York–Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, who treats patients with long COVID in his clinic.
Over the past year, several large, well-conducted studies have borne out that theory, including the following studies:
- In the RECOVER study, published in May in the journal Nature Communications, researchers examined the electronic health records of more than 5 million people who had been diagnosed with COVID and found that vaccination reduced the risk that they would develop long COVID. Although the researchers didn’t compare the effects of having boosters to being fully vaccinated without them, experts have suggested that having a full round of recommended shots may offer the most protection. “My thoughts are that more shots are better, and other work has shown compelling evidence that the protective effect of vaccination on COVID-19 wanes over time,” said study coauthor Daniel Brannock, MS, a research scientist at RTI International in Research Triangle Park, N.C. “It stands to reason that the same is true for long COVID.”
- A review published in February in BMJ Medicine concluded that 10 studies showed a significant reduction in the incidence of long COVID among vaccinated patients. Even one dose of a vaccine was protective.
- A meta-analysis of six studies published last December in Antimicrobial Stewardship and Healthcare Epidemiology found that one or more doses of a COVID-19 vaccine were 29% effective in preventing symptoms of long COVID.
- In a June meta-analysis published in JAMA Internal Medicine, researchers analyzed more than 40 studies that included 860,000 patients and found that two doses of a COVID-19 vaccine reduced the risk of long COVID by almost half.
The message? COVID vaccination is very effective in reducing the risk of long COVID.
“It’s important to emphasize that many of the risk factors [for long COVID] cannot be changed, or at least cannot be changed easily, but vaccination is a decision that can be taken by everyone,” said Vassilios Vassiliou, MBBS, PhD, clinical professor of cardiac medicine at Norwich Medical School in England, who coauthored the article in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Why vaccines may be protective
The COVID-19 vaccines work well to prevent serious illness from the virus, noted Aaron Friedberg, MD, clinical coleader of the Post COVID Recovery Program at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center. That may be a clue to why the vaccines help prevent long COVID symptoms.
“When you get COVID and you’ve been vaccinated, the virus may still attach in your nose and respiratory tract, but it’s less likely to spread throughout your body,” he explained. “It’s like a forest fire – if the ground is wet or it starts to rain, it’s less likely to create a great blaze. As a result, your body is less likely to experience inflammation and damage that makes it more likely that you’ll develop long COVID.”
Dr. Friedberg stressed that even for patients who have had COVID, it’s important to get vaccinated – a message he consistently delivers to his own patients.
“There is some protection that comes from having COVID before, but for some people, that’s not enough,” he said. “It’s true that after infection, your body creates antibodies that help protect you against the virus. But I explain to patients that these may be like old Velcro: They barely grab on enough to stay on for the moment, but they don’t last long term. You’re much more likely to get a reliable immune response from the vaccine.”
In addition, a second or third bout of COVID could be the one that gives patients long COVID, Dr. Friedberg adds.
“I have a number of patients in my clinic who were fine after their first bout of COVID but experienced debilitating long COVID symptoms after they developed COVID again,” he said. “Why leave it to chance?”
Vaccines and ‘long vax’
The COVID vaccines are considered very safe but have been linked to very rare side effects, such as blood clots and heart inflammation. There have also been anecdotal reports of symptoms that resemble long COVID – a syndrome that has come to be known as “long Vax” – an extremely rare condition that may or may not be tied to vaccination.
“I have seen people in my clinic who developed symptoms suggestive of long COVID that linger for months – brain fog, fatigue, heart palpitations – soon after they got the COVID-19 vaccine,” said Dr. Purpura. But no published studies have suggested a link, he cautions.
A study called LISTEN is being organized at Yale in an effort to better understand postvaccine adverse events and a potential link to long COVID.
Talking to patients
Discussions of vaccination with patients, including those with COVID or long COVID, are often fraught and challenging, said Dr. Purpura.
“There’s a lot of fear that they will have a worsening of their symptoms,” he explained. The conversation he has with his patients mirrors the conversation all physicians should have with their patients about COVID-19 vaccination, even if they don’t have long COVID. He stresses the importance of highlighting the following components:
- Show compassion and empathy. “A lot of people have strongly held opinions – it’s worth it to try to find out why they feel the way that they do,” said Dr. Friedberg.
- Walk them through side effects. “Many people are afraid of the side effects of the vaccine, especially if they already have long COVID,” explained Dr. Purpura. Such patients can be asked how they felt after their last vaccination, such a shingles or flu shot. Then explain that the COVID-19 vaccine is not much different and that they may experience temporary side effects such as fatigue, headache, or a mild fever for 24-48 hours.
- Explain the benefits. Eighty-five percent of people say their health care provider is a trusted source of information on COVID-19 vaccines, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation. That trust is conducive to talks about the vaccine’s benefits, including its ability to protect against long COVID.
Other ways to reduce risk of long COVID
Vaccines can lower the chances of a patient’s developing long COVID. So can the antiviral medication nirmatrelvir (Paxlovid). A March 2023 study published in JAMA Internal Medicine included more than 280,000 people with COVID. The researchers found that vaccination reduced the risk for developing the condition by about 25%.
“I mention that study to all of my long COVID patients who become reinfected with the virus,” said Dr. Purpura. “It not only appears protective against long COVID, but since it lowers levels of virus circulating in their body, it seems to help prevent a flare-up of symptoms.”
Another treatment that may help is the diabetes drug metformin, he added.
A June 2023 study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases found that when metformin was given within 3 days of symptom onset, the incidence of long COVID was reduced by about 41%.
“We’re still trying to wrap our brains around this one, but the thought is it may help to lower inflammation, which plays a role in long COVID,” Dr. Purpura explained. More studies need to be conducted, though, before recommending its use.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Deer populations pose COVID risk to humans: Study
According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, which led the research project, humans transmitted the virus to deer at least 100 times. The virus then spread widely among free-ranging deer populations, and there were three possible cases of the deer transmitting the virus to humans.
The data comes from tests done between November 2021 and April 2022 on more than 12,000 deer found across half of the United States. Sequencing of the virus found in the deer showed that deer had been exposed to all of the prominent variants, including Alpha, Gamma, Delta, and Omicron.
Some of the findings about transmission were published in the journal Nature Communications, in which researchers noted that in addition to being identified in deer, the virus has been found in wild and domestic animals, including mink, rats, otters, ferrets, hamsters, gorillas, cats, dogs, lions, and tigers. Animal-to-human transmission has been documented or suspected in mink and domestic cats, in addition to white-tailed deer.
The findings are important because the animal populations can become “reservoirs ... in which the virus circulates covertly, persisting in the population and can be transmitted to other animals or humans potentially causing disease outbreaks,” according to the paper, which was a collaboration among scientists from the U.S. Department of Agriculture, CDC, and the University of Missouri–Columbia.
In the three cases of possible deer-to-human transmission, researchers said that mutated versions of the virus previously found only in deer had been found in COVID test samples taken from one person in North Carolina and two people in Massachusetts. Those deer-specific mutated versions of the virus have not been found in any other human samples, lending evidence that the mutations occurred within deer.
“Deer regularly interact with humans and are commonly found in human environments – near our homes, pets, wastewater, and trash,” researcher and University of Missouri–Columbia professor Xiu-Feng “Henry” Wan, PhD, said in a statement. “The potential for SARS-CoV-2, or any zoonotic disease, to persist and evolve in wildlife populations can pose unique public health risks.”
In the Nature Communications paper, the researchers suggested that deer may be exposed to the virus from human food waste, masks, or other waste products. The authors concluded that further study is needed to determine how virus transmission occurs between deer and humans.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, which led the research project, humans transmitted the virus to deer at least 100 times. The virus then spread widely among free-ranging deer populations, and there were three possible cases of the deer transmitting the virus to humans.
The data comes from tests done between November 2021 and April 2022 on more than 12,000 deer found across half of the United States. Sequencing of the virus found in the deer showed that deer had been exposed to all of the prominent variants, including Alpha, Gamma, Delta, and Omicron.
Some of the findings about transmission were published in the journal Nature Communications, in which researchers noted that in addition to being identified in deer, the virus has been found in wild and domestic animals, including mink, rats, otters, ferrets, hamsters, gorillas, cats, dogs, lions, and tigers. Animal-to-human transmission has been documented or suspected in mink and domestic cats, in addition to white-tailed deer.
The findings are important because the animal populations can become “reservoirs ... in which the virus circulates covertly, persisting in the population and can be transmitted to other animals or humans potentially causing disease outbreaks,” according to the paper, which was a collaboration among scientists from the U.S. Department of Agriculture, CDC, and the University of Missouri–Columbia.
In the three cases of possible deer-to-human transmission, researchers said that mutated versions of the virus previously found only in deer had been found in COVID test samples taken from one person in North Carolina and two people in Massachusetts. Those deer-specific mutated versions of the virus have not been found in any other human samples, lending evidence that the mutations occurred within deer.
“Deer regularly interact with humans and are commonly found in human environments – near our homes, pets, wastewater, and trash,” researcher and University of Missouri–Columbia professor Xiu-Feng “Henry” Wan, PhD, said in a statement. “The potential for SARS-CoV-2, or any zoonotic disease, to persist and evolve in wildlife populations can pose unique public health risks.”
In the Nature Communications paper, the researchers suggested that deer may be exposed to the virus from human food waste, masks, or other waste products. The authors concluded that further study is needed to determine how virus transmission occurs between deer and humans.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, which led the research project, humans transmitted the virus to deer at least 100 times. The virus then spread widely among free-ranging deer populations, and there were three possible cases of the deer transmitting the virus to humans.
The data comes from tests done between November 2021 and April 2022 on more than 12,000 deer found across half of the United States. Sequencing of the virus found in the deer showed that deer had been exposed to all of the prominent variants, including Alpha, Gamma, Delta, and Omicron.
Some of the findings about transmission were published in the journal Nature Communications, in which researchers noted that in addition to being identified in deer, the virus has been found in wild and domestic animals, including mink, rats, otters, ferrets, hamsters, gorillas, cats, dogs, lions, and tigers. Animal-to-human transmission has been documented or suspected in mink and domestic cats, in addition to white-tailed deer.
The findings are important because the animal populations can become “reservoirs ... in which the virus circulates covertly, persisting in the population and can be transmitted to other animals or humans potentially causing disease outbreaks,” according to the paper, which was a collaboration among scientists from the U.S. Department of Agriculture, CDC, and the University of Missouri–Columbia.
In the three cases of possible deer-to-human transmission, researchers said that mutated versions of the virus previously found only in deer had been found in COVID test samples taken from one person in North Carolina and two people in Massachusetts. Those deer-specific mutated versions of the virus have not been found in any other human samples, lending evidence that the mutations occurred within deer.
“Deer regularly interact with humans and are commonly found in human environments – near our homes, pets, wastewater, and trash,” researcher and University of Missouri–Columbia professor Xiu-Feng “Henry” Wan, PhD, said in a statement. “The potential for SARS-CoV-2, or any zoonotic disease, to persist and evolve in wildlife populations can pose unique public health risks.”
In the Nature Communications paper, the researchers suggested that deer may be exposed to the virus from human food waste, masks, or other waste products. The authors concluded that further study is needed to determine how virus transmission occurs between deer and humans.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM NATURE COMMUNICATIONS
Long COVID patients turn to doctors for help with disability claims
As millions of Americans face another year of long COVID, some are finding they are unable to return to work or cannot work as they did before they got sick and are turning to doctors for help with documenting their disability.
For those who can return to work, a doctor’s diagnosis of long COVID is key to gaining access to workplace accommodations, such as working flex hours or remotely. For those who cannot work, a note from the doctor is the first step to collecting disability payments.
With no definitive blood tests or scans for long COVID that could confirm a diagnosis, some say doctors may feel uncomfortable in this role, which puts them in a tough spot, said Wes Ely, MD, MPH, codirector of the critical illness, brain dysfunction and survivorship center at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
Doctors typically are not taught to deal with vagueness in diagnostics.
“Long COVID falls straight into the gray zone,” he said. There are no tests and a long list of common symptoms. “It makes a lot of doctors feel super insecure,” he said.
Now, patients and their advocates are calling for doctors to be more open-minded about how they assess those with long COVID and other chronic illnesses. Although their disability may not be visible, many with long COVID struggle to function. If they need help, they say, they need a doctor to confirm their limitations – test results or no test results.
Better documentation of patient-reported symptoms would go a long way, according to a perspective published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“There’s a long history of people with disabilities being forced to ask doctors to legitimize their symptoms,” said study author Zackary Berger, MD, PhD, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Md. Dr. Berger believes doctors should learn to listen more closely to patients, turn their narratives into patient notes, and use the new International Classification of Diseases 10 (ICD-10) code, a worldwide system for identifying and generating data on diseases, when they diagnose long COVID. He also thinks doctors should become advocates for their patients.
The Americans With Disabilities Act allows employers to request medical proof of disability, “and thereby assigns physicians the gate-keeping role of determining patients’ eligibility for reasonable accommodations,” according to the analysis. Those accommodations may mean a handicapped parking space or extra days working remotely.
Without a definitive diagnostic test, long COVID joins fibromyalgia and ME/CFS (myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome), which lack biomarkers or imaging tests to support a diagnosis, they write.
“These diagnoses are therefore contentious, and government agencies, employers, and many physicians do not accept these conditions as real,” they write.
Physicians make a good faith effort in trying to understand long COVID, but both doctors and the courts like to see evidence, said Michael Ashley Stein, JD, PHD, director of the Harvard Law School Project on Disability. Dr. Stein and others say that doctors should listen closely to their patients’ descriptions of their symptoms.
“In the absence of agreed-upon biomarkers, doctors need to listen to their patients and look for other [indications] and other consistent evidence of conditions, and then work from there rather than dismiss the existence of these conditions,” he said.
Dr. Ely said he and others were taught in medical school that if it doesn’t come up on a diagnostic test, there’s no problem. “I am absolutely complicit,” he said. “I’m part of the community that did that for so many years.”
Dr. Ely agreed that the demand for clinical test results does not work for long COVID and chronic diseases such as ME/CFS. People come in with complaints and they get a typical medical workup with labs, he said, and the labs look normal on paper.
“And [the doctor is] thinking: ‘I don’t know what is wrong with this person and there’s nothing on paper I can treat. I don’t know if I even believe in long COVID.’ ”
At the same time, patients might need support from a doctor to get accommodations at work under the ADA, such as flexible hours. Or doctors’ notes may be required if a patient is trying to collect private disability insurance, workers compensation, or federal disability payments through Social Security.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines on diagnosing long COVID, updated last December, point out that normal laboratory or imaging findings do not rule out long COVID.
In addition, 12 key symptoms of long COVID were identified in May by scientists working with the RECOVER Initiative, the federal government’s long COVID research program. These symptoms include fatigue, brain fog, dizziness, gastrointestinal symptoms, loss of or change in smell or taste, chest pain, and abnormal movements.
Still, patients with long COVID seeking help also face the “disability con,” a term coined by the second author of the NEJM article, Doron Dorfman, a professor at Seton Hall Law School in Newark, N.J.
“Nowadays, when people think disability, they immediately think fraud,” he said.
Prof. Dorfman thinks the perception that many people are faking disabilities to gain an unfair advantage is the biggest barrier for anyone seeking help. The disability system is “preventing people who deserve legal rights from actually obtaining them,” he said.
He urged doctors to believe their patients. One way is to try to “translate the person’s narrative into medical language.”
His coauthor Dr. Berger did not agree with the argument that doctors cannot diagnose without tests.
“Any clinician knows that lab tests are not everything,” he said. “There are conditions that don’t have specific biomarkers that we diagnose all the time.” He cited acquired pneumonia and urinary tract infections as examples.
Benefits lawyers have taken note of the complexities for people with long COVID who seek help through the ADA and federal disability program.
One law firm noted: “The government safety net is not designed to help an emerging disease with no clear diagnosis or treatment plans. Insurance carriers are denying claims, and long-term disability benefits are being denied.”
About 16 million working-age Americans have long COVID, according to an update of a 2022 report by the Brookings Institute. Up to 4 million of these people are out of work because of the condition, the study found. The research is based on newly collected U.S. Census Bureau data that show 24% of those with long COVID report “significant activity limitations.”
Dr. Ely said he sees progress in this area. Many of these issues have come up at the committee convened by the National Academy of Science to look at the working definition of long COVID. NAS, a Washington research group, held a public meeting on their findings on June 22.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As millions of Americans face another year of long COVID, some are finding they are unable to return to work or cannot work as they did before they got sick and are turning to doctors for help with documenting their disability.
For those who can return to work, a doctor’s diagnosis of long COVID is key to gaining access to workplace accommodations, such as working flex hours or remotely. For those who cannot work, a note from the doctor is the first step to collecting disability payments.
With no definitive blood tests or scans for long COVID that could confirm a diagnosis, some say doctors may feel uncomfortable in this role, which puts them in a tough spot, said Wes Ely, MD, MPH, codirector of the critical illness, brain dysfunction and survivorship center at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
Doctors typically are not taught to deal with vagueness in diagnostics.
“Long COVID falls straight into the gray zone,” he said. There are no tests and a long list of common symptoms. “It makes a lot of doctors feel super insecure,” he said.
Now, patients and their advocates are calling for doctors to be more open-minded about how they assess those with long COVID and other chronic illnesses. Although their disability may not be visible, many with long COVID struggle to function. If they need help, they say, they need a doctor to confirm their limitations – test results or no test results.
Better documentation of patient-reported symptoms would go a long way, according to a perspective published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“There’s a long history of people with disabilities being forced to ask doctors to legitimize their symptoms,” said study author Zackary Berger, MD, PhD, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Md. Dr. Berger believes doctors should learn to listen more closely to patients, turn their narratives into patient notes, and use the new International Classification of Diseases 10 (ICD-10) code, a worldwide system for identifying and generating data on diseases, when they diagnose long COVID. He also thinks doctors should become advocates for their patients.
The Americans With Disabilities Act allows employers to request medical proof of disability, “and thereby assigns physicians the gate-keeping role of determining patients’ eligibility for reasonable accommodations,” according to the analysis. Those accommodations may mean a handicapped parking space or extra days working remotely.
Without a definitive diagnostic test, long COVID joins fibromyalgia and ME/CFS (myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome), which lack biomarkers or imaging tests to support a diagnosis, they write.
“These diagnoses are therefore contentious, and government agencies, employers, and many physicians do not accept these conditions as real,” they write.
Physicians make a good faith effort in trying to understand long COVID, but both doctors and the courts like to see evidence, said Michael Ashley Stein, JD, PHD, director of the Harvard Law School Project on Disability. Dr. Stein and others say that doctors should listen closely to their patients’ descriptions of their symptoms.
“In the absence of agreed-upon biomarkers, doctors need to listen to their patients and look for other [indications] and other consistent evidence of conditions, and then work from there rather than dismiss the existence of these conditions,” he said.
Dr. Ely said he and others were taught in medical school that if it doesn’t come up on a diagnostic test, there’s no problem. “I am absolutely complicit,” he said. “I’m part of the community that did that for so many years.”
Dr. Ely agreed that the demand for clinical test results does not work for long COVID and chronic diseases such as ME/CFS. People come in with complaints and they get a typical medical workup with labs, he said, and the labs look normal on paper.
“And [the doctor is] thinking: ‘I don’t know what is wrong with this person and there’s nothing on paper I can treat. I don’t know if I even believe in long COVID.’ ”
At the same time, patients might need support from a doctor to get accommodations at work under the ADA, such as flexible hours. Or doctors’ notes may be required if a patient is trying to collect private disability insurance, workers compensation, or federal disability payments through Social Security.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines on diagnosing long COVID, updated last December, point out that normal laboratory or imaging findings do not rule out long COVID.
In addition, 12 key symptoms of long COVID were identified in May by scientists working with the RECOVER Initiative, the federal government’s long COVID research program. These symptoms include fatigue, brain fog, dizziness, gastrointestinal symptoms, loss of or change in smell or taste, chest pain, and abnormal movements.
Still, patients with long COVID seeking help also face the “disability con,” a term coined by the second author of the NEJM article, Doron Dorfman, a professor at Seton Hall Law School in Newark, N.J.
“Nowadays, when people think disability, they immediately think fraud,” he said.
Prof. Dorfman thinks the perception that many people are faking disabilities to gain an unfair advantage is the biggest barrier for anyone seeking help. The disability system is “preventing people who deserve legal rights from actually obtaining them,” he said.
He urged doctors to believe their patients. One way is to try to “translate the person’s narrative into medical language.”
His coauthor Dr. Berger did not agree with the argument that doctors cannot diagnose without tests.
“Any clinician knows that lab tests are not everything,” he said. “There are conditions that don’t have specific biomarkers that we diagnose all the time.” He cited acquired pneumonia and urinary tract infections as examples.
Benefits lawyers have taken note of the complexities for people with long COVID who seek help through the ADA and federal disability program.
One law firm noted: “The government safety net is not designed to help an emerging disease with no clear diagnosis or treatment plans. Insurance carriers are denying claims, and long-term disability benefits are being denied.”
About 16 million working-age Americans have long COVID, according to an update of a 2022 report by the Brookings Institute. Up to 4 million of these people are out of work because of the condition, the study found. The research is based on newly collected U.S. Census Bureau data that show 24% of those with long COVID report “significant activity limitations.”
Dr. Ely said he sees progress in this area. Many of these issues have come up at the committee convened by the National Academy of Science to look at the working definition of long COVID. NAS, a Washington research group, held a public meeting on their findings on June 22.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As millions of Americans face another year of long COVID, some are finding they are unable to return to work or cannot work as they did before they got sick and are turning to doctors for help with documenting their disability.
For those who can return to work, a doctor’s diagnosis of long COVID is key to gaining access to workplace accommodations, such as working flex hours or remotely. For those who cannot work, a note from the doctor is the first step to collecting disability payments.
With no definitive blood tests or scans for long COVID that could confirm a diagnosis, some say doctors may feel uncomfortable in this role, which puts them in a tough spot, said Wes Ely, MD, MPH, codirector of the critical illness, brain dysfunction and survivorship center at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
Doctors typically are not taught to deal with vagueness in diagnostics.
“Long COVID falls straight into the gray zone,” he said. There are no tests and a long list of common symptoms. “It makes a lot of doctors feel super insecure,” he said.
Now, patients and their advocates are calling for doctors to be more open-minded about how they assess those with long COVID and other chronic illnesses. Although their disability may not be visible, many with long COVID struggle to function. If they need help, they say, they need a doctor to confirm their limitations – test results or no test results.
Better documentation of patient-reported symptoms would go a long way, according to a perspective published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“There’s a long history of people with disabilities being forced to ask doctors to legitimize their symptoms,” said study author Zackary Berger, MD, PhD, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Md. Dr. Berger believes doctors should learn to listen more closely to patients, turn their narratives into patient notes, and use the new International Classification of Diseases 10 (ICD-10) code, a worldwide system for identifying and generating data on diseases, when they diagnose long COVID. He also thinks doctors should become advocates for their patients.
The Americans With Disabilities Act allows employers to request medical proof of disability, “and thereby assigns physicians the gate-keeping role of determining patients’ eligibility for reasonable accommodations,” according to the analysis. Those accommodations may mean a handicapped parking space or extra days working remotely.
Without a definitive diagnostic test, long COVID joins fibromyalgia and ME/CFS (myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome), which lack biomarkers or imaging tests to support a diagnosis, they write.
“These diagnoses are therefore contentious, and government agencies, employers, and many physicians do not accept these conditions as real,” they write.
Physicians make a good faith effort in trying to understand long COVID, but both doctors and the courts like to see evidence, said Michael Ashley Stein, JD, PHD, director of the Harvard Law School Project on Disability. Dr. Stein and others say that doctors should listen closely to their patients’ descriptions of their symptoms.
“In the absence of agreed-upon biomarkers, doctors need to listen to their patients and look for other [indications] and other consistent evidence of conditions, and then work from there rather than dismiss the existence of these conditions,” he said.
Dr. Ely said he and others were taught in medical school that if it doesn’t come up on a diagnostic test, there’s no problem. “I am absolutely complicit,” he said. “I’m part of the community that did that for so many years.”
Dr. Ely agreed that the demand for clinical test results does not work for long COVID and chronic diseases such as ME/CFS. People come in with complaints and they get a typical medical workup with labs, he said, and the labs look normal on paper.
“And [the doctor is] thinking: ‘I don’t know what is wrong with this person and there’s nothing on paper I can treat. I don’t know if I even believe in long COVID.’ ”
At the same time, patients might need support from a doctor to get accommodations at work under the ADA, such as flexible hours. Or doctors’ notes may be required if a patient is trying to collect private disability insurance, workers compensation, or federal disability payments through Social Security.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines on diagnosing long COVID, updated last December, point out that normal laboratory or imaging findings do not rule out long COVID.
In addition, 12 key symptoms of long COVID were identified in May by scientists working with the RECOVER Initiative, the federal government’s long COVID research program. These symptoms include fatigue, brain fog, dizziness, gastrointestinal symptoms, loss of or change in smell or taste, chest pain, and abnormal movements.
Still, patients with long COVID seeking help also face the “disability con,” a term coined by the second author of the NEJM article, Doron Dorfman, a professor at Seton Hall Law School in Newark, N.J.
“Nowadays, when people think disability, they immediately think fraud,” he said.
Prof. Dorfman thinks the perception that many people are faking disabilities to gain an unfair advantage is the biggest barrier for anyone seeking help. The disability system is “preventing people who deserve legal rights from actually obtaining them,” he said.
He urged doctors to believe their patients. One way is to try to “translate the person’s narrative into medical language.”
His coauthor Dr. Berger did not agree with the argument that doctors cannot diagnose without tests.
“Any clinician knows that lab tests are not everything,” he said. “There are conditions that don’t have specific biomarkers that we diagnose all the time.” He cited acquired pneumonia and urinary tract infections as examples.
Benefits lawyers have taken note of the complexities for people with long COVID who seek help through the ADA and federal disability program.
One law firm noted: “The government safety net is not designed to help an emerging disease with no clear diagnosis or treatment plans. Insurance carriers are denying claims, and long-term disability benefits are being denied.”
About 16 million working-age Americans have long COVID, according to an update of a 2022 report by the Brookings Institute. Up to 4 million of these people are out of work because of the condition, the study found. The research is based on newly collected U.S. Census Bureau data that show 24% of those with long COVID report “significant activity limitations.”
Dr. Ely said he sees progress in this area. Many of these issues have come up at the committee convened by the National Academy of Science to look at the working definition of long COVID. NAS, a Washington research group, held a public meeting on their findings on June 22.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Nearly one in five in U.S. still hadn’t gotten COVID by end of 2022
, according to a new estimate.
The findings came from an analysis of blood donations. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention analyzed donor blood from 143,000 people every 3 months during 2022, looking for the presence of COVID antibodies that meant a person had previously been infected with the virus. The prevalence of antibodies from previous infections steadily rose throughout the year. Antibodies from prior infection were found in 49% of donors as of Feb. 15, 2022, 59% of donors as of May 15, 2022, 70% of donors as of Aug. 15, 2022, and 78% of donors as of Nov. 15, 2022.
Donor blood also was analyzed for the presence of antibodies known to come from COVID vaccination. When the vaccine-induced and infection-induced antibody data were combined, the CDC estimated that 97% of people had antibodies as of the end of the 2022.
In the report, CDC authors explained that while the presence of antibodies is related to protection from infection and to less severe disease, the level of antibodies that a person has can vary. The authors said that no standards have yet been set that show a minimum level of antibodies needed to provide protection.
As of July 3, more than 1.1 million people had died in the United States from COVID-19, according to CDC data. Deaths for the first half of 2023 are down dramatically, compared with the first 3 years of the pandemic, with just 41,538 death certificates this year listing the virus as an underlying or contributing cause. About two in three COVID deaths this year occurred in a hospital or nursing home, and 89% of people who died from the virus this year have been age 65 or older.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new estimate.
The findings came from an analysis of blood donations. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention analyzed donor blood from 143,000 people every 3 months during 2022, looking for the presence of COVID antibodies that meant a person had previously been infected with the virus. The prevalence of antibodies from previous infections steadily rose throughout the year. Antibodies from prior infection were found in 49% of donors as of Feb. 15, 2022, 59% of donors as of May 15, 2022, 70% of donors as of Aug. 15, 2022, and 78% of donors as of Nov. 15, 2022.
Donor blood also was analyzed for the presence of antibodies known to come from COVID vaccination. When the vaccine-induced and infection-induced antibody data were combined, the CDC estimated that 97% of people had antibodies as of the end of the 2022.
In the report, CDC authors explained that while the presence of antibodies is related to protection from infection and to less severe disease, the level of antibodies that a person has can vary. The authors said that no standards have yet been set that show a minimum level of antibodies needed to provide protection.
As of July 3, more than 1.1 million people had died in the United States from COVID-19, according to CDC data. Deaths for the first half of 2023 are down dramatically, compared with the first 3 years of the pandemic, with just 41,538 death certificates this year listing the virus as an underlying or contributing cause. About two in three COVID deaths this year occurred in a hospital or nursing home, and 89% of people who died from the virus this year have been age 65 or older.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new estimate.
The findings came from an analysis of blood donations. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention analyzed donor blood from 143,000 people every 3 months during 2022, looking for the presence of COVID antibodies that meant a person had previously been infected with the virus. The prevalence of antibodies from previous infections steadily rose throughout the year. Antibodies from prior infection were found in 49% of donors as of Feb. 15, 2022, 59% of donors as of May 15, 2022, 70% of donors as of Aug. 15, 2022, and 78% of donors as of Nov. 15, 2022.
Donor blood also was analyzed for the presence of antibodies known to come from COVID vaccination. When the vaccine-induced and infection-induced antibody data were combined, the CDC estimated that 97% of people had antibodies as of the end of the 2022.
In the report, CDC authors explained that while the presence of antibodies is related to protection from infection and to less severe disease, the level of antibodies that a person has can vary. The authors said that no standards have yet been set that show a minimum level of antibodies needed to provide protection.
As of July 3, more than 1.1 million people had died in the United States from COVID-19, according to CDC data. Deaths for the first half of 2023 are down dramatically, compared with the first 3 years of the pandemic, with just 41,538 death certificates this year listing the virus as an underlying or contributing cause. About two in three COVID deaths this year occurred in a hospital or nursing home, and 89% of people who died from the virus this year have been age 65 or older.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.