User login
Detachment predicts worse posttraumatic outcomes
The results highlight the importance of screening for dissociation in patients who have experienced trauma, study investigator Lauren A.M. Lebois, PhD, director of the dissociative disorders and trauma research program at McLean Hospital in Belmont, Mass., told this news organization.
“Clinicians could identify individuals potentially at risk of a chronic, more severe psychiatric course before these people go down that road, and they have the opportunity to connect folks with a phased trauma treatment approach to speed their recovery,” said Dr. Lebois, who is also an assistant professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The study was published in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Underdiagnosed
Feelings of detachment or derealization are a type of dissociation. Patients with the syndrome report feeling foggy or as if they are in a dream. Dissociative diagnoses are not rare and, in fact, are more prevalent than schizophrenia.
Research supports a powerful relationship between dissociation and traumatic experiences. However, dissociation is among the most stigmatized of psychiatric conditions. Even among clinicians and researchers, beliefs about dissociation are often not based on the scientific literature, said Dr. Lebois.
“For instance, skepticism, misunderstanding, and lack of professional education about dissociation all contribute to striking rates of underdiagnosis and misdiagnoses,” she said.
Dr. Lebois and colleagues used data from the larger Advancing Understanding of Recovery After Trauma (AURORA) study and included 1,464 adults, mean age 35 years, appearing at 22 U.S. emergency departments. Patients experienced a traumatic event such as a motor vehicle crash or physical or sexual assault.
About 2 weeks after the trauma, participants reported symptoms of derealization as measured by a two-item version of the Brief Dissociative Experiences Scale.
Brain imaging data
A subset of 145 patients underwent functional MRI (fMRI), during which they completed an emotion reactivity task (viewing fearful-looking human faces) and a resting-state scan.
In addition to measuring history of childhood maltreatment, researchers assessed posttraumatic stress symptom severity at 2 weeks and again at 3 months using the posttraumatic stress disorder checklist. Also at 3 months, they measured depression and anxiety symptoms, pain, and functional impairment.
About 55% of self-report participants and 50% of MRI participants endorsed some level of persistent derealization at 2 weeks.
After controlling for potential confounders, including sex, age, childhood maltreatment, and current posttraumatic stress symptoms, researchers found persistent derealization was associated with increased ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) activity while viewing fearful faces.
The vmPFC helps to regulate emotional and physical reactions. “This region puts the ‘brakes’ on your emotional and physical reactivity – helping you to calm down” after a threatening or stressful experience has passed, said Dr. Lebois.
Researchers also found an association between higher self-reported derealization and decreased resting-state connectivity between the vmPFC and the orbitofrontal cortex and right lobule VIIIa – a region of the cerebellum involved in sensorimotor function.
“This may contribute to perceptual and affective distortions experienced during derealization – for example, feelings that surroundings are fading away, unreal, or strange,” said Dr. Lebois.
More pain, depression, anxiety
Higher levels of self-reported derealization at 2 weeks post trauma predicted higher levels of PTSD, anxiety, and depression as well as more bodily pain and impairment in work, family, and social life at 3 months.
“When we accounted for baseline levels of posttraumatic stress symptoms and trauma history, higher levels of self-reported derealization still predicted higher posttraumatic stress disorder and depression symptoms at 3 months,” said Dr. Lebois.
Additional adjusted analyses showed increased vmPFC activity during the fearful face task predicted 3-month self-reported PTSD symptoms.
Dr. Lebois “highly recommends” clinicians screen for dissociative symptoms, including derealization, in patients with trauma. Self-report screening tools are freely available online.
She noted patients with significant dissociative symptoms often do better with a “phase-oriented” approach to trauma treatment.
“In phase one, they learn emotional regulation skills to help them take more control over when they dissociate. Then they can successfully move on to trauma processing in phase two, which can involve exposure to trauma details.”
Although the field is not yet ready to use brain scans to diagnose dissociative symptoms, the new results “take us one step closer to being able to use objective neuroimaging biomarkers of derealization to augment subjective self-report measures,” said Dr. Lebois.
A limitation of the study was it could not determine a causal relationship, as some derealization may have been present before the traumatic event. The findings may not generalize to other types of dissociation, and the derealization assessment was measured only through a self-report 2 weeks after the trauma.
Another limitation was exclusion of patients with self-inflicted injuries or who were involved in domestic violence. The researchers noted the prevalence of derealization might have been even higher if such individuals were included.
An important investigation
In an accompanying editorial, Lisa M. Shin, PhD, department of psychology, Tufts University, and department of psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, notes having both clinical and neuroimaging variables as well as a large sample size makes the study “an important investigation” into predictors of psychiatric symptoms post-trauma.
Investigating a specific subtype of dissociation – persistent derealization – adds to the “novelty” of the study, she said.
The new findings “are certainly exciting for their potential clinical relevance and contributions to neurocircuitry models of PTSD,” she writes.
Some may argue administering a short, self-report measure of derealization “is far more efficient, cost-effective, and inclusive than conducting a specialized and expensive fMRI scan that is unlikely to be available to everyone,” notes Dr. Shin.
However, she added, a potential benefit of such a scan is identification of specific brain regions as potential targets for intervention. “For example, the results of this and other studies suggest that the vmPFC is a reasonable target for transcranial magnetic stimulation or its variants.”
The new results need to be replicated in a large, independent sample, said Dr. Shin. She added it would be helpful to know if other types of dissociation, and activation in other subregions of the vmPFC, also predict psychiatric outcomes after a trauma.
The study was supported by National Institute of Mental Health grants, the U.S. Army Medical Research and Material Command, One Mind, and the Mayday Fund. Dr. Lebois has received grant support from NIMH, and her spouse receives payments from Vanderbilt University for technology licensed to Acadia Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Shin receives textbook-related royalties from Pearson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The results highlight the importance of screening for dissociation in patients who have experienced trauma, study investigator Lauren A.M. Lebois, PhD, director of the dissociative disorders and trauma research program at McLean Hospital in Belmont, Mass., told this news organization.
“Clinicians could identify individuals potentially at risk of a chronic, more severe psychiatric course before these people go down that road, and they have the opportunity to connect folks with a phased trauma treatment approach to speed their recovery,” said Dr. Lebois, who is also an assistant professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The study was published in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Underdiagnosed
Feelings of detachment or derealization are a type of dissociation. Patients with the syndrome report feeling foggy or as if they are in a dream. Dissociative diagnoses are not rare and, in fact, are more prevalent than schizophrenia.
Research supports a powerful relationship between dissociation and traumatic experiences. However, dissociation is among the most stigmatized of psychiatric conditions. Even among clinicians and researchers, beliefs about dissociation are often not based on the scientific literature, said Dr. Lebois.
“For instance, skepticism, misunderstanding, and lack of professional education about dissociation all contribute to striking rates of underdiagnosis and misdiagnoses,” she said.
Dr. Lebois and colleagues used data from the larger Advancing Understanding of Recovery After Trauma (AURORA) study and included 1,464 adults, mean age 35 years, appearing at 22 U.S. emergency departments. Patients experienced a traumatic event such as a motor vehicle crash or physical or sexual assault.
About 2 weeks after the trauma, participants reported symptoms of derealization as measured by a two-item version of the Brief Dissociative Experiences Scale.
Brain imaging data
A subset of 145 patients underwent functional MRI (fMRI), during which they completed an emotion reactivity task (viewing fearful-looking human faces) and a resting-state scan.
In addition to measuring history of childhood maltreatment, researchers assessed posttraumatic stress symptom severity at 2 weeks and again at 3 months using the posttraumatic stress disorder checklist. Also at 3 months, they measured depression and anxiety symptoms, pain, and functional impairment.
About 55% of self-report participants and 50% of MRI participants endorsed some level of persistent derealization at 2 weeks.
After controlling for potential confounders, including sex, age, childhood maltreatment, and current posttraumatic stress symptoms, researchers found persistent derealization was associated with increased ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) activity while viewing fearful faces.
The vmPFC helps to regulate emotional and physical reactions. “This region puts the ‘brakes’ on your emotional and physical reactivity – helping you to calm down” after a threatening or stressful experience has passed, said Dr. Lebois.
Researchers also found an association between higher self-reported derealization and decreased resting-state connectivity between the vmPFC and the orbitofrontal cortex and right lobule VIIIa – a region of the cerebellum involved in sensorimotor function.
“This may contribute to perceptual and affective distortions experienced during derealization – for example, feelings that surroundings are fading away, unreal, or strange,” said Dr. Lebois.
More pain, depression, anxiety
Higher levels of self-reported derealization at 2 weeks post trauma predicted higher levels of PTSD, anxiety, and depression as well as more bodily pain and impairment in work, family, and social life at 3 months.
“When we accounted for baseline levels of posttraumatic stress symptoms and trauma history, higher levels of self-reported derealization still predicted higher posttraumatic stress disorder and depression symptoms at 3 months,” said Dr. Lebois.
Additional adjusted analyses showed increased vmPFC activity during the fearful face task predicted 3-month self-reported PTSD symptoms.
Dr. Lebois “highly recommends” clinicians screen for dissociative symptoms, including derealization, in patients with trauma. Self-report screening tools are freely available online.
She noted patients with significant dissociative symptoms often do better with a “phase-oriented” approach to trauma treatment.
“In phase one, they learn emotional regulation skills to help them take more control over when they dissociate. Then they can successfully move on to trauma processing in phase two, which can involve exposure to trauma details.”
Although the field is not yet ready to use brain scans to diagnose dissociative symptoms, the new results “take us one step closer to being able to use objective neuroimaging biomarkers of derealization to augment subjective self-report measures,” said Dr. Lebois.
A limitation of the study was it could not determine a causal relationship, as some derealization may have been present before the traumatic event. The findings may not generalize to other types of dissociation, and the derealization assessment was measured only through a self-report 2 weeks after the trauma.
Another limitation was exclusion of patients with self-inflicted injuries or who were involved in domestic violence. The researchers noted the prevalence of derealization might have been even higher if such individuals were included.
An important investigation
In an accompanying editorial, Lisa M. Shin, PhD, department of psychology, Tufts University, and department of psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, notes having both clinical and neuroimaging variables as well as a large sample size makes the study “an important investigation” into predictors of psychiatric symptoms post-trauma.
Investigating a specific subtype of dissociation – persistent derealization – adds to the “novelty” of the study, she said.
The new findings “are certainly exciting for their potential clinical relevance and contributions to neurocircuitry models of PTSD,” she writes.
Some may argue administering a short, self-report measure of derealization “is far more efficient, cost-effective, and inclusive than conducting a specialized and expensive fMRI scan that is unlikely to be available to everyone,” notes Dr. Shin.
However, she added, a potential benefit of such a scan is identification of specific brain regions as potential targets for intervention. “For example, the results of this and other studies suggest that the vmPFC is a reasonable target for transcranial magnetic stimulation or its variants.”
The new results need to be replicated in a large, independent sample, said Dr. Shin. She added it would be helpful to know if other types of dissociation, and activation in other subregions of the vmPFC, also predict psychiatric outcomes after a trauma.
The study was supported by National Institute of Mental Health grants, the U.S. Army Medical Research and Material Command, One Mind, and the Mayday Fund. Dr. Lebois has received grant support from NIMH, and her spouse receives payments from Vanderbilt University for technology licensed to Acadia Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Shin receives textbook-related royalties from Pearson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The results highlight the importance of screening for dissociation in patients who have experienced trauma, study investigator Lauren A.M. Lebois, PhD, director of the dissociative disorders and trauma research program at McLean Hospital in Belmont, Mass., told this news organization.
“Clinicians could identify individuals potentially at risk of a chronic, more severe psychiatric course before these people go down that road, and they have the opportunity to connect folks with a phased trauma treatment approach to speed their recovery,” said Dr. Lebois, who is also an assistant professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The study was published in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Underdiagnosed
Feelings of detachment or derealization are a type of dissociation. Patients with the syndrome report feeling foggy or as if they are in a dream. Dissociative diagnoses are not rare and, in fact, are more prevalent than schizophrenia.
Research supports a powerful relationship between dissociation and traumatic experiences. However, dissociation is among the most stigmatized of psychiatric conditions. Even among clinicians and researchers, beliefs about dissociation are often not based on the scientific literature, said Dr. Lebois.
“For instance, skepticism, misunderstanding, and lack of professional education about dissociation all contribute to striking rates of underdiagnosis and misdiagnoses,” she said.
Dr. Lebois and colleagues used data from the larger Advancing Understanding of Recovery After Trauma (AURORA) study and included 1,464 adults, mean age 35 years, appearing at 22 U.S. emergency departments. Patients experienced a traumatic event such as a motor vehicle crash or physical or sexual assault.
About 2 weeks after the trauma, participants reported symptoms of derealization as measured by a two-item version of the Brief Dissociative Experiences Scale.
Brain imaging data
A subset of 145 patients underwent functional MRI (fMRI), during which they completed an emotion reactivity task (viewing fearful-looking human faces) and a resting-state scan.
In addition to measuring history of childhood maltreatment, researchers assessed posttraumatic stress symptom severity at 2 weeks and again at 3 months using the posttraumatic stress disorder checklist. Also at 3 months, they measured depression and anxiety symptoms, pain, and functional impairment.
About 55% of self-report participants and 50% of MRI participants endorsed some level of persistent derealization at 2 weeks.
After controlling for potential confounders, including sex, age, childhood maltreatment, and current posttraumatic stress symptoms, researchers found persistent derealization was associated with increased ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) activity while viewing fearful faces.
The vmPFC helps to regulate emotional and physical reactions. “This region puts the ‘brakes’ on your emotional and physical reactivity – helping you to calm down” after a threatening or stressful experience has passed, said Dr. Lebois.
Researchers also found an association between higher self-reported derealization and decreased resting-state connectivity between the vmPFC and the orbitofrontal cortex and right lobule VIIIa – a region of the cerebellum involved in sensorimotor function.
“This may contribute to perceptual and affective distortions experienced during derealization – for example, feelings that surroundings are fading away, unreal, or strange,” said Dr. Lebois.
More pain, depression, anxiety
Higher levels of self-reported derealization at 2 weeks post trauma predicted higher levels of PTSD, anxiety, and depression as well as more bodily pain and impairment in work, family, and social life at 3 months.
“When we accounted for baseline levels of posttraumatic stress symptoms and trauma history, higher levels of self-reported derealization still predicted higher posttraumatic stress disorder and depression symptoms at 3 months,” said Dr. Lebois.
Additional adjusted analyses showed increased vmPFC activity during the fearful face task predicted 3-month self-reported PTSD symptoms.
Dr. Lebois “highly recommends” clinicians screen for dissociative symptoms, including derealization, in patients with trauma. Self-report screening tools are freely available online.
She noted patients with significant dissociative symptoms often do better with a “phase-oriented” approach to trauma treatment.
“In phase one, they learn emotional regulation skills to help them take more control over when they dissociate. Then they can successfully move on to trauma processing in phase two, which can involve exposure to trauma details.”
Although the field is not yet ready to use brain scans to diagnose dissociative symptoms, the new results “take us one step closer to being able to use objective neuroimaging biomarkers of derealization to augment subjective self-report measures,” said Dr. Lebois.
A limitation of the study was it could not determine a causal relationship, as some derealization may have been present before the traumatic event. The findings may not generalize to other types of dissociation, and the derealization assessment was measured only through a self-report 2 weeks after the trauma.
Another limitation was exclusion of patients with self-inflicted injuries or who were involved in domestic violence. The researchers noted the prevalence of derealization might have been even higher if such individuals were included.
An important investigation
In an accompanying editorial, Lisa M. Shin, PhD, department of psychology, Tufts University, and department of psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, notes having both clinical and neuroimaging variables as well as a large sample size makes the study “an important investigation” into predictors of psychiatric symptoms post-trauma.
Investigating a specific subtype of dissociation – persistent derealization – adds to the “novelty” of the study, she said.
The new findings “are certainly exciting for their potential clinical relevance and contributions to neurocircuitry models of PTSD,” she writes.
Some may argue administering a short, self-report measure of derealization “is far more efficient, cost-effective, and inclusive than conducting a specialized and expensive fMRI scan that is unlikely to be available to everyone,” notes Dr. Shin.
However, she added, a potential benefit of such a scan is identification of specific brain regions as potential targets for intervention. “For example, the results of this and other studies suggest that the vmPFC is a reasonable target for transcranial magnetic stimulation or its variants.”
The new results need to be replicated in a large, independent sample, said Dr. Shin. She added it would be helpful to know if other types of dissociation, and activation in other subregions of the vmPFC, also predict psychiatric outcomes after a trauma.
The study was supported by National Institute of Mental Health grants, the U.S. Army Medical Research and Material Command, One Mind, and the Mayday Fund. Dr. Lebois has received grant support from NIMH, and her spouse receives payments from Vanderbilt University for technology licensed to Acadia Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Shin receives textbook-related royalties from Pearson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHIATRY
Depression as a terminal illness
Is there a place for palliative care?
In 2020, there were 5,224 suicide deaths registered in England and Wales.1 The Mental Health Foundation, a London-based charitable organization, reports that approximately 70% of such deaths are in patients with depression.2 The number of attempted suicides is much higher – the South West London and St. George’s Mental Health Trust estimates that at least 140,000 people attempt suicide in England and Wales every year.3
In suicidal depression, the psychological pain is often unbearable and feels overwhelmingly incompatible with life. One is no longer living but merely surviving, and eventually the exhaustion will lead to decompensation. This is marked by suicide. The goal is to end the suffering permanently and this is achieved through death.
Depression, like all other physical and mental illnesses, runs a course. This is highly variable between individuals and can be the case even between separate relapse episodes in the same patient. Like many diagnoses, depression is known to lead to death in a significant number of people. Many suicidally depressed patients feel that death will be an inevitable result of the illness.
Suicide is often viewed as a symptom of severe depression, but what if we considered death as part of the disease process itself? Consequently, would it be justifiable to consider depression in these patients as a form of terminal illness, since without treatment, the condition would lead to death? Accordingly, could there be a place for palliative care in a small minority of suicidally depressed patients? Taking such a perspective would mean that instead of placing the focus on the prevention of deaths and prolonging of lifespan, the focus would be on making the patients comfortable as the disease progresses, maintaining their dignity, and promoting autonomy.
Suicidal depression and rights
The rationale for this is that psychiatric patients do not have the capacity to make such decisions in the acute setting, because of the direct effects of the unwell mind on their decision-making processes and cognitive faculties. While this may be true in some cases, there is limited evidence that this applies to all suicidally depressed patients in all cases.
Another argument against allowing suicidally depressed patients to decline treatment is the notion that the episode of depression can be successfully treated, and the patients can return to their normal level of functioning. However, in individuals with a previous history of severe depression, it is possible that they will relapse again at some point. In the same way, a cancer can be treated, and patients could return to their baseline level of functioning, only for the cancer to then return later in life. In both cases, these relapses are emotionally and physically exhausting and painful to get through. The difference is that a cancer patient can decline further treatment and opt for no treatment or for palliative treatment, knowing that the disease will shorten life expectancy. For suicidal depression, this is not an option. Such patients may be sectioned, admitted, and treated against their will. Suicide, which could be considered a natural endpoint of the depressive illness, is unacceptable.
Is it fair to confiscate one’s right to decline treatment, solely because that person suffers from a mental illness, as opposed to a physical one? Numerous studies have demonstrated clear structural, neurological, and neurochemical changes in suicidal depression. This is evidence that such a condition encompasses a clear physical property. Other conditions, such as dementia and chronic pain, have previously been accepted for euthanasia in certain countries. Pain is a subjective experience of nociceptive and neurochemical signaling. In the same way, depression is a subjective experience involving aberrant neurochemical signaling. The difference is that physical pain can often be localized. However, patients with suicidal depression often experience very severe and tangible pain that can be difficult to articulate and for others to understand if they have never experienced it themselves.
Like distinct forms of physical pain, suicidal depression creates a different form of pain, but it is pain, nonetheless. Is it therefore fair for suicidally depressed patients to be given lesser rights than those suffering from physical illnesses in determining their fate?
Suicidal depression and capacity
A patient is assumed to have capacity unless proven otherwise. This is often the reverse when managing psychiatric patients. However, if patients are able to fulfill all criteria required for demonstrating capacity (understanding the information, retaining, weighing up, and communicating the decision), surely they have demonstrated capacity to make their decisions, whether that is to receive or to refuse treatment.
For physical illnesses, adults with capacity are permitted to make decisions that their treating teams may not agree with, but this disagreement alone is generally insufficient to override the decisions. These patients, unlike in suicidal depression, have the right to refuse lifesaving or life-prolonging treatment.
An argument for this is that in terminal physical illnesses, death is a passive process and neither the patient nor the physician are actively causing it. However, in many palliative settings, patients can be given medications and treatment for symptomatic relief, even if these may hasten their death. The principle that makes this permissible is that the primary aim is to improve the symptoms and ensure comfort. The unintended effect includes side effects and hastened death. Similarly, in suicidal depression, one could argue that the patient should be permitted medications that may hasten or lead to death, so long as the primary aim is to improve the symptoms of the unbearable mental pain and suffering.
Let us consider an alternative scenario. What if previously suicidal patients are currently in remission from depression and make advanced directives? In their current healthy state, they assert that if, in the future, they were to relapse, they would not want any form of treatment. Instead, they wish for the disease to run its course, which may end in death through suicide.
In this case, the circumstances in which the statement was made would be entirely valid – the patients at that moment have capacity, are not under coercion, are able to articulate logical thought processes, and their reasoning would not be affected by a concurrent psychiatric pathology. Furthermore, they can demonstrate that suicide is not an impulsive decision and have considered the consequences of suicide on themselves and others. If the patients can demonstrate all the above, what would the ethical grounds be for refusing this advanced directive?
Medical ethics
Below, I consider this debate in the context of four pillars of medical ethics.
Non-maleficence
To determine whether an action is in line with non-maleficence, one must ask whether the proposed treatment will improve or resolve one’s condition. In the case of severe suicidal depression, the treatment may help patients in the short term, but what happens if or when they relapse? The treatment will likely prolong life, but also inadvertently prolong suffering. What if the patients do not wish to go through this again? The treatment regime can be profoundly taxing for the patients, the loved ones, and sometimes even for the treating team. Are we doing more harm by forcing these patients to stay alive against their will?
Beneficence
Beneficence is the moral duty to promote the action that is in the patient’s best interest. But who should determine what the patient’s best interests are if the patient and the doctor disagree? Usually, this decision is made by the treating doctor, who considers the patient’s past and present wishes, beliefs and values, and capacity assessment. Supposing that the law was not a restriction, could one’s psychiatrist ever agree on psychiatric grounds alone that it is indeed in the patient’s best interests to die?
Doctors play a central role in the duty of care. But care does not always mean active treatment. Caring encompasses physical, psychological, and spiritual welfare and includes considering an individual patient’s dignity, personal circumstances, and wishes. In certain circumstances, keeping patients with capacity alive against their wishes could be more harmful than caring.
Autonomy
Autonomy gives the patients ultimate decision-making responsibility for their own lives. It allows patients with capacity to decline treatment that is recommended by their physicians and to make decisions regarding their own death. However, in suicidally depressed patients, this autonomy is confiscated. Severely unwell patients, at high risk of committing suicide, are not permitted the autonomy to make the decision regarding their treatment, suicide, and death.
Justice
A justice-orientated and utilitarian view questions whether spending resources on these patients wastes time, resources, and expertise, and whether resources should instead be spent on patients who do want treatment.
For example, the British National Health Service holds an outstanding debt of £13.4 billion.4 The financial cost of treating mental illness in 2020/2021 was £14.31 billion.5 The NHS estimates that wider costs to national economy, including welfare benefits, housing support, social workers, community support, lost productivity at work, etc., amounts to approximately £77 billion annually.6 Many severely depressed patients are so unwell that their ability to contribute to society, financially, socially, and otherwise, is minimal. If patients with capacity genuinely want to die and society would benefit from a reduction in the pressures on health and social care services, would it not be in both their best interests to allow them to die? This way, resources could be redirected to service users who would appreciate and benefit from them the most.
A consequentialist view focuses on whether the action will benefit the patient overall; the action itself is not so relevant. According to this view, keeping suicidally depressed patients alive against their wishes would be ethical if the patients lack capacity. Keeping them safe and treating them until they are better would overall be in the patients’ best interests. However, if the patients do have capacity and wish to die, forcing them to stay alive and undergo treatment against their wishes would merely prolong their suffering and thus could be considered unethical.
When enough is enough
In suicidal treatment-resistant depression, where the patient has tried multiple treatments over time and carefully considered alternatives, when is it time to stop trying? For physical illness, patients can refuse treatment provided they can demonstrate capacity. In depression, they can refuse treatment only if they can demonstrate that they are not at serious risk to themselves or others. Most societies consider suicide as a serious risk to self and therefore unacceptable. However, if we considered suicide as a natural endpoint of the disease process, should the patient have the right to refuse treatment and allow the disease to progress to death?
The treatment regime can be a lengthy process and the repeated failures to improve can be physically and mentally exhausting and further compound the hopelessness. Treatments often have side effects, which further erode the patient’s physical and mental wellbeing. Is there a time when giving up and withdrawing active treatment is in the patient’s best interests, especially if that is what the patient wants?
Terminal diseases are incurable and likely to hasten one’s death. Severe suicidal treatment-resistant depression conforms to both conditions – it is unresponsive to treatment and has a high likelihood of precipitating premature death through suicide. Most terminal illnesses can be managed with palliative treatment. In the context of severe suicidal depression, euthanasia and assisted suicide could be considered as means of palliative care.
Palliative care involves managing the patient’s symptomatology, dignity, and comfort. Euthanasia and assisted suicide help to address all of these. Like palliative care, euthanasia and assisted suicide aim to improve symptoms of depression by alleviating pain and suffering, even if they may hasten death.
Euthanasia and assisted suicide in severe depression
Euthanasia and assisted suicide are legal in seven countries. Two countries (Belgium and the Netherlands) permit euthanasia for psychiatric illnesses. Passive euthanasia is practiced in most countries, e.g., withholding artificial life support. In suicidal depression, it could be considered that this withholding of treatment may directly lead to death by suicide.
In active euthanasia and assisted suicide, the patient is given a chemical that will directly lead to death. Euthanasia and assisted suicide allow individuals to die with dignity in a controlled and organized manner. It ends the patients’ suffering and allows them to finally find peace. The difficulties that led them to seek euthanasia/assisted suicide indicate a loss of control of the pain and suffering in life, and euthanasia allows them to regain this control and autonomy through death. It allows these individuals to properly say goodbye to their loved ones, and a chance to share their thoughts and feelings.
In contrast, suicide is often covert, clandestine, and planned in secret, and it frequently requires individuals to be dishonest with their closest loved ones. The suicide often comes as a shock to the loved ones and profound grief, questions, anger, pain, sorrow, and guilt follow. These are due to questions that have been left unanswered, thoughts that were never shared, regret that they had not done more to help, and anguish knowing that their loved one died alone, in unbearable mental agony, unable to speak to anyone about this final hurdle.
Euthanasia and assisted suicide provide a path to overcome all these issues. They encourage open conversations between the patients, their loved ones, and the treating team. They promote transparency, mutual support, and help prepare the loved ones for the death. In this way, euthanasia and assisted suicide can benefit both the patient and the loved ones.
A significant proportion of severely suicidally depressed patients will eventually go on to commit or attempt suicide. Thus, giving them the autonomy to choose euthanasia or assisted suicide could be considered a kind, fair, and compassionate course of action, as it respects their wishes, and allows them to escape their suffering and to die with dignity.
Conclusion
Depression has historically never been considered a terminal illness, but there is undeniable evidence that a significant number of deaths every year are directly caused by depression. Should we therefore shift the focus from lifesaving and life-prolonging treatment to ensuring comfort and maintaining dignity by exploring palliative options for extremely suicidally depressed patients with capacity, who are adamant on ending their lives?
Euthanasia and assisted suicide for depression pose a profound paradox when viewed through a deontological lens. According to this, the correct course of action directly corresponds to what the most “moral” action would be. The moral stance would be to help those who are suffering. But what exactly constitutes “help”? Are euthanasia and assisted suicide helping or harming? Likewise, is keeping patients with capacity alive against their wishes helping or harming? Many believe that euthanasia, assisted suicide, and suicide itself are intrinsically and morally wrong. But this poses another clear impasse. Who should be the ones to decide whether an action is moral or not? Should it be the individual? The treating physician? Or society?
Dr. Chang graduated from Imperial College London with an MBBS (medicine and surgery) and a BSc (gastroenterology and hepatology) degree.
References
1. Office for National Statistics. Suicides in England and Wales – Office for National Statistics, 2021.
2. Faulkner, A. Suicide and Deliberate Self Harm: The Fundamental Facts. Mental Health Foundation; 1997.
3. NHS. Suicide Factsheet. Southwest London and St. George’s Mental Health NHS Trust [ebook], 2022.
4. The King’s Fund. Financial debts and loans in the NHS. 2020.
5. NHS England. Mental Health Five Year Forward View Dashboard. 2018.
6. National Mental Health, Policy into Practice. The costs of mental ill health.
Is there a place for palliative care?
Is there a place for palliative care?
In 2020, there were 5,224 suicide deaths registered in England and Wales.1 The Mental Health Foundation, a London-based charitable organization, reports that approximately 70% of such deaths are in patients with depression.2 The number of attempted suicides is much higher – the South West London and St. George’s Mental Health Trust estimates that at least 140,000 people attempt suicide in England and Wales every year.3
In suicidal depression, the psychological pain is often unbearable and feels overwhelmingly incompatible with life. One is no longer living but merely surviving, and eventually the exhaustion will lead to decompensation. This is marked by suicide. The goal is to end the suffering permanently and this is achieved through death.
Depression, like all other physical and mental illnesses, runs a course. This is highly variable between individuals and can be the case even between separate relapse episodes in the same patient. Like many diagnoses, depression is known to lead to death in a significant number of people. Many suicidally depressed patients feel that death will be an inevitable result of the illness.
Suicide is often viewed as a symptom of severe depression, but what if we considered death as part of the disease process itself? Consequently, would it be justifiable to consider depression in these patients as a form of terminal illness, since without treatment, the condition would lead to death? Accordingly, could there be a place for palliative care in a small minority of suicidally depressed patients? Taking such a perspective would mean that instead of placing the focus on the prevention of deaths and prolonging of lifespan, the focus would be on making the patients comfortable as the disease progresses, maintaining their dignity, and promoting autonomy.
Suicidal depression and rights
The rationale for this is that psychiatric patients do not have the capacity to make such decisions in the acute setting, because of the direct effects of the unwell mind on their decision-making processes and cognitive faculties. While this may be true in some cases, there is limited evidence that this applies to all suicidally depressed patients in all cases.
Another argument against allowing suicidally depressed patients to decline treatment is the notion that the episode of depression can be successfully treated, and the patients can return to their normal level of functioning. However, in individuals with a previous history of severe depression, it is possible that they will relapse again at some point. In the same way, a cancer can be treated, and patients could return to their baseline level of functioning, only for the cancer to then return later in life. In both cases, these relapses are emotionally and physically exhausting and painful to get through. The difference is that a cancer patient can decline further treatment and opt for no treatment or for palliative treatment, knowing that the disease will shorten life expectancy. For suicidal depression, this is not an option. Such patients may be sectioned, admitted, and treated against their will. Suicide, which could be considered a natural endpoint of the depressive illness, is unacceptable.
Is it fair to confiscate one’s right to decline treatment, solely because that person suffers from a mental illness, as opposed to a physical one? Numerous studies have demonstrated clear structural, neurological, and neurochemical changes in suicidal depression. This is evidence that such a condition encompasses a clear physical property. Other conditions, such as dementia and chronic pain, have previously been accepted for euthanasia in certain countries. Pain is a subjective experience of nociceptive and neurochemical signaling. In the same way, depression is a subjective experience involving aberrant neurochemical signaling. The difference is that physical pain can often be localized. However, patients with suicidal depression often experience very severe and tangible pain that can be difficult to articulate and for others to understand if they have never experienced it themselves.
Like distinct forms of physical pain, suicidal depression creates a different form of pain, but it is pain, nonetheless. Is it therefore fair for suicidally depressed patients to be given lesser rights than those suffering from physical illnesses in determining their fate?
Suicidal depression and capacity
A patient is assumed to have capacity unless proven otherwise. This is often the reverse when managing psychiatric patients. However, if patients are able to fulfill all criteria required for demonstrating capacity (understanding the information, retaining, weighing up, and communicating the decision), surely they have demonstrated capacity to make their decisions, whether that is to receive or to refuse treatment.
For physical illnesses, adults with capacity are permitted to make decisions that their treating teams may not agree with, but this disagreement alone is generally insufficient to override the decisions. These patients, unlike in suicidal depression, have the right to refuse lifesaving or life-prolonging treatment.
An argument for this is that in terminal physical illnesses, death is a passive process and neither the patient nor the physician are actively causing it. However, in many palliative settings, patients can be given medications and treatment for symptomatic relief, even if these may hasten their death. The principle that makes this permissible is that the primary aim is to improve the symptoms and ensure comfort. The unintended effect includes side effects and hastened death. Similarly, in suicidal depression, one could argue that the patient should be permitted medications that may hasten or lead to death, so long as the primary aim is to improve the symptoms of the unbearable mental pain and suffering.
Let us consider an alternative scenario. What if previously suicidal patients are currently in remission from depression and make advanced directives? In their current healthy state, they assert that if, in the future, they were to relapse, they would not want any form of treatment. Instead, they wish for the disease to run its course, which may end in death through suicide.
In this case, the circumstances in which the statement was made would be entirely valid – the patients at that moment have capacity, are not under coercion, are able to articulate logical thought processes, and their reasoning would not be affected by a concurrent psychiatric pathology. Furthermore, they can demonstrate that suicide is not an impulsive decision and have considered the consequences of suicide on themselves and others. If the patients can demonstrate all the above, what would the ethical grounds be for refusing this advanced directive?
Medical ethics
Below, I consider this debate in the context of four pillars of medical ethics.
Non-maleficence
To determine whether an action is in line with non-maleficence, one must ask whether the proposed treatment will improve or resolve one’s condition. In the case of severe suicidal depression, the treatment may help patients in the short term, but what happens if or when they relapse? The treatment will likely prolong life, but also inadvertently prolong suffering. What if the patients do not wish to go through this again? The treatment regime can be profoundly taxing for the patients, the loved ones, and sometimes even for the treating team. Are we doing more harm by forcing these patients to stay alive against their will?
Beneficence
Beneficence is the moral duty to promote the action that is in the patient’s best interest. But who should determine what the patient’s best interests are if the patient and the doctor disagree? Usually, this decision is made by the treating doctor, who considers the patient’s past and present wishes, beliefs and values, and capacity assessment. Supposing that the law was not a restriction, could one’s psychiatrist ever agree on psychiatric grounds alone that it is indeed in the patient’s best interests to die?
Doctors play a central role in the duty of care. But care does not always mean active treatment. Caring encompasses physical, psychological, and spiritual welfare and includes considering an individual patient’s dignity, personal circumstances, and wishes. In certain circumstances, keeping patients with capacity alive against their wishes could be more harmful than caring.
Autonomy
Autonomy gives the patients ultimate decision-making responsibility for their own lives. It allows patients with capacity to decline treatment that is recommended by their physicians and to make decisions regarding their own death. However, in suicidally depressed patients, this autonomy is confiscated. Severely unwell patients, at high risk of committing suicide, are not permitted the autonomy to make the decision regarding their treatment, suicide, and death.
Justice
A justice-orientated and utilitarian view questions whether spending resources on these patients wastes time, resources, and expertise, and whether resources should instead be spent on patients who do want treatment.
For example, the British National Health Service holds an outstanding debt of £13.4 billion.4 The financial cost of treating mental illness in 2020/2021 was £14.31 billion.5 The NHS estimates that wider costs to national economy, including welfare benefits, housing support, social workers, community support, lost productivity at work, etc., amounts to approximately £77 billion annually.6 Many severely depressed patients are so unwell that their ability to contribute to society, financially, socially, and otherwise, is minimal. If patients with capacity genuinely want to die and society would benefit from a reduction in the pressures on health and social care services, would it not be in both their best interests to allow them to die? This way, resources could be redirected to service users who would appreciate and benefit from them the most.
A consequentialist view focuses on whether the action will benefit the patient overall; the action itself is not so relevant. According to this view, keeping suicidally depressed patients alive against their wishes would be ethical if the patients lack capacity. Keeping them safe and treating them until they are better would overall be in the patients’ best interests. However, if the patients do have capacity and wish to die, forcing them to stay alive and undergo treatment against their wishes would merely prolong their suffering and thus could be considered unethical.
When enough is enough
In suicidal treatment-resistant depression, where the patient has tried multiple treatments over time and carefully considered alternatives, when is it time to stop trying? For physical illness, patients can refuse treatment provided they can demonstrate capacity. In depression, they can refuse treatment only if they can demonstrate that they are not at serious risk to themselves or others. Most societies consider suicide as a serious risk to self and therefore unacceptable. However, if we considered suicide as a natural endpoint of the disease process, should the patient have the right to refuse treatment and allow the disease to progress to death?
The treatment regime can be a lengthy process and the repeated failures to improve can be physically and mentally exhausting and further compound the hopelessness. Treatments often have side effects, which further erode the patient’s physical and mental wellbeing. Is there a time when giving up and withdrawing active treatment is in the patient’s best interests, especially if that is what the patient wants?
Terminal diseases are incurable and likely to hasten one’s death. Severe suicidal treatment-resistant depression conforms to both conditions – it is unresponsive to treatment and has a high likelihood of precipitating premature death through suicide. Most terminal illnesses can be managed with palliative treatment. In the context of severe suicidal depression, euthanasia and assisted suicide could be considered as means of palliative care.
Palliative care involves managing the patient’s symptomatology, dignity, and comfort. Euthanasia and assisted suicide help to address all of these. Like palliative care, euthanasia and assisted suicide aim to improve symptoms of depression by alleviating pain and suffering, even if they may hasten death.
Euthanasia and assisted suicide in severe depression
Euthanasia and assisted suicide are legal in seven countries. Two countries (Belgium and the Netherlands) permit euthanasia for psychiatric illnesses. Passive euthanasia is practiced in most countries, e.g., withholding artificial life support. In suicidal depression, it could be considered that this withholding of treatment may directly lead to death by suicide.
In active euthanasia and assisted suicide, the patient is given a chemical that will directly lead to death. Euthanasia and assisted suicide allow individuals to die with dignity in a controlled and organized manner. It ends the patients’ suffering and allows them to finally find peace. The difficulties that led them to seek euthanasia/assisted suicide indicate a loss of control of the pain and suffering in life, and euthanasia allows them to regain this control and autonomy through death. It allows these individuals to properly say goodbye to their loved ones, and a chance to share their thoughts and feelings.
In contrast, suicide is often covert, clandestine, and planned in secret, and it frequently requires individuals to be dishonest with their closest loved ones. The suicide often comes as a shock to the loved ones and profound grief, questions, anger, pain, sorrow, and guilt follow. These are due to questions that have been left unanswered, thoughts that were never shared, regret that they had not done more to help, and anguish knowing that their loved one died alone, in unbearable mental agony, unable to speak to anyone about this final hurdle.
Euthanasia and assisted suicide provide a path to overcome all these issues. They encourage open conversations between the patients, their loved ones, and the treating team. They promote transparency, mutual support, and help prepare the loved ones for the death. In this way, euthanasia and assisted suicide can benefit both the patient and the loved ones.
A significant proportion of severely suicidally depressed patients will eventually go on to commit or attempt suicide. Thus, giving them the autonomy to choose euthanasia or assisted suicide could be considered a kind, fair, and compassionate course of action, as it respects their wishes, and allows them to escape their suffering and to die with dignity.
Conclusion
Depression has historically never been considered a terminal illness, but there is undeniable evidence that a significant number of deaths every year are directly caused by depression. Should we therefore shift the focus from lifesaving and life-prolonging treatment to ensuring comfort and maintaining dignity by exploring palliative options for extremely suicidally depressed patients with capacity, who are adamant on ending their lives?
Euthanasia and assisted suicide for depression pose a profound paradox when viewed through a deontological lens. According to this, the correct course of action directly corresponds to what the most “moral” action would be. The moral stance would be to help those who are suffering. But what exactly constitutes “help”? Are euthanasia and assisted suicide helping or harming? Likewise, is keeping patients with capacity alive against their wishes helping or harming? Many believe that euthanasia, assisted suicide, and suicide itself are intrinsically and morally wrong. But this poses another clear impasse. Who should be the ones to decide whether an action is moral or not? Should it be the individual? The treating physician? Or society?
Dr. Chang graduated from Imperial College London with an MBBS (medicine and surgery) and a BSc (gastroenterology and hepatology) degree.
References
1. Office for National Statistics. Suicides in England and Wales – Office for National Statistics, 2021.
2. Faulkner, A. Suicide and Deliberate Self Harm: The Fundamental Facts. Mental Health Foundation; 1997.
3. NHS. Suicide Factsheet. Southwest London and St. George’s Mental Health NHS Trust [ebook], 2022.
4. The King’s Fund. Financial debts and loans in the NHS. 2020.
5. NHS England. Mental Health Five Year Forward View Dashboard. 2018.
6. National Mental Health, Policy into Practice. The costs of mental ill health.
In 2020, there were 5,224 suicide deaths registered in England and Wales.1 The Mental Health Foundation, a London-based charitable organization, reports that approximately 70% of such deaths are in patients with depression.2 The number of attempted suicides is much higher – the South West London and St. George’s Mental Health Trust estimates that at least 140,000 people attempt suicide in England and Wales every year.3
In suicidal depression, the psychological pain is often unbearable and feels overwhelmingly incompatible with life. One is no longer living but merely surviving, and eventually the exhaustion will lead to decompensation. This is marked by suicide. The goal is to end the suffering permanently and this is achieved through death.
Depression, like all other physical and mental illnesses, runs a course. This is highly variable between individuals and can be the case even between separate relapse episodes in the same patient. Like many diagnoses, depression is known to lead to death in a significant number of people. Many suicidally depressed patients feel that death will be an inevitable result of the illness.
Suicide is often viewed as a symptom of severe depression, but what if we considered death as part of the disease process itself? Consequently, would it be justifiable to consider depression in these patients as a form of terminal illness, since without treatment, the condition would lead to death? Accordingly, could there be a place for palliative care in a small minority of suicidally depressed patients? Taking such a perspective would mean that instead of placing the focus on the prevention of deaths and prolonging of lifespan, the focus would be on making the patients comfortable as the disease progresses, maintaining their dignity, and promoting autonomy.
Suicidal depression and rights
The rationale for this is that psychiatric patients do not have the capacity to make such decisions in the acute setting, because of the direct effects of the unwell mind on their decision-making processes and cognitive faculties. While this may be true in some cases, there is limited evidence that this applies to all suicidally depressed patients in all cases.
Another argument against allowing suicidally depressed patients to decline treatment is the notion that the episode of depression can be successfully treated, and the patients can return to their normal level of functioning. However, in individuals with a previous history of severe depression, it is possible that they will relapse again at some point. In the same way, a cancer can be treated, and patients could return to their baseline level of functioning, only for the cancer to then return later in life. In both cases, these relapses are emotionally and physically exhausting and painful to get through. The difference is that a cancer patient can decline further treatment and opt for no treatment or for palliative treatment, knowing that the disease will shorten life expectancy. For suicidal depression, this is not an option. Such patients may be sectioned, admitted, and treated against their will. Suicide, which could be considered a natural endpoint of the depressive illness, is unacceptable.
Is it fair to confiscate one’s right to decline treatment, solely because that person suffers from a mental illness, as opposed to a physical one? Numerous studies have demonstrated clear structural, neurological, and neurochemical changes in suicidal depression. This is evidence that such a condition encompasses a clear physical property. Other conditions, such as dementia and chronic pain, have previously been accepted for euthanasia in certain countries. Pain is a subjective experience of nociceptive and neurochemical signaling. In the same way, depression is a subjective experience involving aberrant neurochemical signaling. The difference is that physical pain can often be localized. However, patients with suicidal depression often experience very severe and tangible pain that can be difficult to articulate and for others to understand if they have never experienced it themselves.
Like distinct forms of physical pain, suicidal depression creates a different form of pain, but it is pain, nonetheless. Is it therefore fair for suicidally depressed patients to be given lesser rights than those suffering from physical illnesses in determining their fate?
Suicidal depression and capacity
A patient is assumed to have capacity unless proven otherwise. This is often the reverse when managing psychiatric patients. However, if patients are able to fulfill all criteria required for demonstrating capacity (understanding the information, retaining, weighing up, and communicating the decision), surely they have demonstrated capacity to make their decisions, whether that is to receive or to refuse treatment.
For physical illnesses, adults with capacity are permitted to make decisions that their treating teams may not agree with, but this disagreement alone is generally insufficient to override the decisions. These patients, unlike in suicidal depression, have the right to refuse lifesaving or life-prolonging treatment.
An argument for this is that in terminal physical illnesses, death is a passive process and neither the patient nor the physician are actively causing it. However, in many palliative settings, patients can be given medications and treatment for symptomatic relief, even if these may hasten their death. The principle that makes this permissible is that the primary aim is to improve the symptoms and ensure comfort. The unintended effect includes side effects and hastened death. Similarly, in suicidal depression, one could argue that the patient should be permitted medications that may hasten or lead to death, so long as the primary aim is to improve the symptoms of the unbearable mental pain and suffering.
Let us consider an alternative scenario. What if previously suicidal patients are currently in remission from depression and make advanced directives? In their current healthy state, they assert that if, in the future, they were to relapse, they would not want any form of treatment. Instead, they wish for the disease to run its course, which may end in death through suicide.
In this case, the circumstances in which the statement was made would be entirely valid – the patients at that moment have capacity, are not under coercion, are able to articulate logical thought processes, and their reasoning would not be affected by a concurrent psychiatric pathology. Furthermore, they can demonstrate that suicide is not an impulsive decision and have considered the consequences of suicide on themselves and others. If the patients can demonstrate all the above, what would the ethical grounds be for refusing this advanced directive?
Medical ethics
Below, I consider this debate in the context of four pillars of medical ethics.
Non-maleficence
To determine whether an action is in line with non-maleficence, one must ask whether the proposed treatment will improve or resolve one’s condition. In the case of severe suicidal depression, the treatment may help patients in the short term, but what happens if or when they relapse? The treatment will likely prolong life, but also inadvertently prolong suffering. What if the patients do not wish to go through this again? The treatment regime can be profoundly taxing for the patients, the loved ones, and sometimes even for the treating team. Are we doing more harm by forcing these patients to stay alive against their will?
Beneficence
Beneficence is the moral duty to promote the action that is in the patient’s best interest. But who should determine what the patient’s best interests are if the patient and the doctor disagree? Usually, this decision is made by the treating doctor, who considers the patient’s past and present wishes, beliefs and values, and capacity assessment. Supposing that the law was not a restriction, could one’s psychiatrist ever agree on psychiatric grounds alone that it is indeed in the patient’s best interests to die?
Doctors play a central role in the duty of care. But care does not always mean active treatment. Caring encompasses physical, psychological, and spiritual welfare and includes considering an individual patient’s dignity, personal circumstances, and wishes. In certain circumstances, keeping patients with capacity alive against their wishes could be more harmful than caring.
Autonomy
Autonomy gives the patients ultimate decision-making responsibility for their own lives. It allows patients with capacity to decline treatment that is recommended by their physicians and to make decisions regarding their own death. However, in suicidally depressed patients, this autonomy is confiscated. Severely unwell patients, at high risk of committing suicide, are not permitted the autonomy to make the decision regarding their treatment, suicide, and death.
Justice
A justice-orientated and utilitarian view questions whether spending resources on these patients wastes time, resources, and expertise, and whether resources should instead be spent on patients who do want treatment.
For example, the British National Health Service holds an outstanding debt of £13.4 billion.4 The financial cost of treating mental illness in 2020/2021 was £14.31 billion.5 The NHS estimates that wider costs to national economy, including welfare benefits, housing support, social workers, community support, lost productivity at work, etc., amounts to approximately £77 billion annually.6 Many severely depressed patients are so unwell that their ability to contribute to society, financially, socially, and otherwise, is minimal. If patients with capacity genuinely want to die and society would benefit from a reduction in the pressures on health and social care services, would it not be in both their best interests to allow them to die? This way, resources could be redirected to service users who would appreciate and benefit from them the most.
A consequentialist view focuses on whether the action will benefit the patient overall; the action itself is not so relevant. According to this view, keeping suicidally depressed patients alive against their wishes would be ethical if the patients lack capacity. Keeping them safe and treating them until they are better would overall be in the patients’ best interests. However, if the patients do have capacity and wish to die, forcing them to stay alive and undergo treatment against their wishes would merely prolong their suffering and thus could be considered unethical.
When enough is enough
In suicidal treatment-resistant depression, where the patient has tried multiple treatments over time and carefully considered alternatives, when is it time to stop trying? For physical illness, patients can refuse treatment provided they can demonstrate capacity. In depression, they can refuse treatment only if they can demonstrate that they are not at serious risk to themselves or others. Most societies consider suicide as a serious risk to self and therefore unacceptable. However, if we considered suicide as a natural endpoint of the disease process, should the patient have the right to refuse treatment and allow the disease to progress to death?
The treatment regime can be a lengthy process and the repeated failures to improve can be physically and mentally exhausting and further compound the hopelessness. Treatments often have side effects, which further erode the patient’s physical and mental wellbeing. Is there a time when giving up and withdrawing active treatment is in the patient’s best interests, especially if that is what the patient wants?
Terminal diseases are incurable and likely to hasten one’s death. Severe suicidal treatment-resistant depression conforms to both conditions – it is unresponsive to treatment and has a high likelihood of precipitating premature death through suicide. Most terminal illnesses can be managed with palliative treatment. In the context of severe suicidal depression, euthanasia and assisted suicide could be considered as means of palliative care.
Palliative care involves managing the patient’s symptomatology, dignity, and comfort. Euthanasia and assisted suicide help to address all of these. Like palliative care, euthanasia and assisted suicide aim to improve symptoms of depression by alleviating pain and suffering, even if they may hasten death.
Euthanasia and assisted suicide in severe depression
Euthanasia and assisted suicide are legal in seven countries. Two countries (Belgium and the Netherlands) permit euthanasia for psychiatric illnesses. Passive euthanasia is practiced in most countries, e.g., withholding artificial life support. In suicidal depression, it could be considered that this withholding of treatment may directly lead to death by suicide.
In active euthanasia and assisted suicide, the patient is given a chemical that will directly lead to death. Euthanasia and assisted suicide allow individuals to die with dignity in a controlled and organized manner. It ends the patients’ suffering and allows them to finally find peace. The difficulties that led them to seek euthanasia/assisted suicide indicate a loss of control of the pain and suffering in life, and euthanasia allows them to regain this control and autonomy through death. It allows these individuals to properly say goodbye to their loved ones, and a chance to share their thoughts and feelings.
In contrast, suicide is often covert, clandestine, and planned in secret, and it frequently requires individuals to be dishonest with their closest loved ones. The suicide often comes as a shock to the loved ones and profound grief, questions, anger, pain, sorrow, and guilt follow. These are due to questions that have been left unanswered, thoughts that were never shared, regret that they had not done more to help, and anguish knowing that their loved one died alone, in unbearable mental agony, unable to speak to anyone about this final hurdle.
Euthanasia and assisted suicide provide a path to overcome all these issues. They encourage open conversations between the patients, their loved ones, and the treating team. They promote transparency, mutual support, and help prepare the loved ones for the death. In this way, euthanasia and assisted suicide can benefit both the patient and the loved ones.
A significant proportion of severely suicidally depressed patients will eventually go on to commit or attempt suicide. Thus, giving them the autonomy to choose euthanasia or assisted suicide could be considered a kind, fair, and compassionate course of action, as it respects their wishes, and allows them to escape their suffering and to die with dignity.
Conclusion
Depression has historically never been considered a terminal illness, but there is undeniable evidence that a significant number of deaths every year are directly caused by depression. Should we therefore shift the focus from lifesaving and life-prolonging treatment to ensuring comfort and maintaining dignity by exploring palliative options for extremely suicidally depressed patients with capacity, who are adamant on ending their lives?
Euthanasia and assisted suicide for depression pose a profound paradox when viewed through a deontological lens. According to this, the correct course of action directly corresponds to what the most “moral” action would be. The moral stance would be to help those who are suffering. But what exactly constitutes “help”? Are euthanasia and assisted suicide helping or harming? Likewise, is keeping patients with capacity alive against their wishes helping or harming? Many believe that euthanasia, assisted suicide, and suicide itself are intrinsically and morally wrong. But this poses another clear impasse. Who should be the ones to decide whether an action is moral or not? Should it be the individual? The treating physician? Or society?
Dr. Chang graduated from Imperial College London with an MBBS (medicine and surgery) and a BSc (gastroenterology and hepatology) degree.
References
1. Office for National Statistics. Suicides in England and Wales – Office for National Statistics, 2021.
2. Faulkner, A. Suicide and Deliberate Self Harm: The Fundamental Facts. Mental Health Foundation; 1997.
3. NHS. Suicide Factsheet. Southwest London and St. George’s Mental Health NHS Trust [ebook], 2022.
4. The King’s Fund. Financial debts and loans in the NHS. 2020.
5. NHS England. Mental Health Five Year Forward View Dashboard. 2018.
6. National Mental Health, Policy into Practice. The costs of mental ill health.
Mental health in America: ‘The kids are not alright’
A new report shines a light on the toll the pandemic and other stressors have taken on the mental health of U.S. children and adolescents over the last 6 years.
The report shows a dramatic increase in use of acute care services for depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions, especially among teens and preteens.
The report – The Kids Are Not Alright: Pediatric Mental Health Care Utilization from 2016-2021 – is the work of researchers at the Clarify Health Institute, the research arm of Clarify Health.
The results are “deeply concerning” and should “spark a conversation” around the need to improve access, utilization, and quality of pediatric behavioral health services, Niall Brennan, chief analytics and privacy officer for the Clarify Health Institute, told this news organization.
‘Startling’ trends
Leveraging an observational, national sample of insurance claims from more than 20 million children aged 1-19 years annually, the researchers observed several disturbing trends in mental health care.
From 2016 to 2021, inpatient (IP) admissions rose 61% (from 30 to 48 visits annually per 1,000) and emergency department visits rose 20% (from 55 to 66 visits annually per 1,000).
Mental health IP admissions ranged from a low of 27% in the West North Central region to a high of 137% in the Middle Atlantic region.
There were substantial increases from 2016 to 2021 in mental health IP admissions among children of all age groups, but particularly among adolescents 12 to 15 years old, increasing 84% among girls and 83% among boys in this age group.
There was also a sharp increase in mental health ED visits among girls and boys aged 12-15 years, increasing 20% overall during the study period.
Mental health IP use grew faster from 2016 to 2021 among children with commercial insurance than among those with Medicaid (103% vs. 40%).
In contrast, mental health–specific ED visits declined 10% among children with commercial insurance and increased by 20% among those with Medicaid.
ED utilization rates in 2021 were nearly twice as high in the Medicaid population, compared with those for children with commercial insurance.
These are “startling” increases, Mr. Brennan said in an interview.
These trends “reinforce health care leaders’ responsibility to address children’s mental health, especially when considering that half of all mental health conditions onset during adolescence and carry into adulthood,” Jean Drouin, MD, Clarify Health’s chief executive office and cofounder, adds in a news release.
“With a growing consensus that mental, behavioral, and physical health intersect, this research report aims to spark a conversation about the overall wellbeing of America’s next generation,” Dr. Drouin says.
Concern for the future
Commenting on the new report, Anish Dube, MD, chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Children, Adolescents, and their Families, said the findings are “concerning, though unsurprising.”
“They confirm what those of us in clinical practice have experienced in the last several years. The need for mental health services continues to rise every year, while access to adequate help remains lacking,” Dr. Dube said.
“With the recent COVID-19 pandemic, concerns about the effects of climate change, global political uncertainty, and a rapidly changing employment landscape, young people in particular are vulnerable to worries about their future and feelings of helplessness and hopelessness,” he added.
Dr. Dube said there is no one right solution, and addressing this problem must consider individual and local factors.
However, some of the broader interventions needed to tackle the problem include increasing access to care by enforcing mental health parity and increasing the number of trained and qualified mental health professionals, such as child and adolescent psychiatrists, who can assess and treat these conditions in young people before they become major crises and lead to acute interventions like inpatient hospitalization.
“Public health interventions aimed at schools and families in raising awareness of mental health and well-being, and simple, cost-effective interventions to practice mental wellness will also help reduce the burden of mental illness in young people,” Dr. Dube added.
“The APA continues to fight for mental health parity enforcement and for meaningful access to mental health care for children, adolescents, and their families,” Dr. Dube said.
This research was conducted by the Clarify Health Institute. Mr. Brennan and Dr. Dube report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new report shines a light on the toll the pandemic and other stressors have taken on the mental health of U.S. children and adolescents over the last 6 years.
The report shows a dramatic increase in use of acute care services for depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions, especially among teens and preteens.
The report – The Kids Are Not Alright: Pediatric Mental Health Care Utilization from 2016-2021 – is the work of researchers at the Clarify Health Institute, the research arm of Clarify Health.
The results are “deeply concerning” and should “spark a conversation” around the need to improve access, utilization, and quality of pediatric behavioral health services, Niall Brennan, chief analytics and privacy officer for the Clarify Health Institute, told this news organization.
‘Startling’ trends
Leveraging an observational, national sample of insurance claims from more than 20 million children aged 1-19 years annually, the researchers observed several disturbing trends in mental health care.
From 2016 to 2021, inpatient (IP) admissions rose 61% (from 30 to 48 visits annually per 1,000) and emergency department visits rose 20% (from 55 to 66 visits annually per 1,000).
Mental health IP admissions ranged from a low of 27% in the West North Central region to a high of 137% in the Middle Atlantic region.
There were substantial increases from 2016 to 2021 in mental health IP admissions among children of all age groups, but particularly among adolescents 12 to 15 years old, increasing 84% among girls and 83% among boys in this age group.
There was also a sharp increase in mental health ED visits among girls and boys aged 12-15 years, increasing 20% overall during the study period.
Mental health IP use grew faster from 2016 to 2021 among children with commercial insurance than among those with Medicaid (103% vs. 40%).
In contrast, mental health–specific ED visits declined 10% among children with commercial insurance and increased by 20% among those with Medicaid.
ED utilization rates in 2021 were nearly twice as high in the Medicaid population, compared with those for children with commercial insurance.
These are “startling” increases, Mr. Brennan said in an interview.
These trends “reinforce health care leaders’ responsibility to address children’s mental health, especially when considering that half of all mental health conditions onset during adolescence and carry into adulthood,” Jean Drouin, MD, Clarify Health’s chief executive office and cofounder, adds in a news release.
“With a growing consensus that mental, behavioral, and physical health intersect, this research report aims to spark a conversation about the overall wellbeing of America’s next generation,” Dr. Drouin says.
Concern for the future
Commenting on the new report, Anish Dube, MD, chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Children, Adolescents, and their Families, said the findings are “concerning, though unsurprising.”
“They confirm what those of us in clinical practice have experienced in the last several years. The need for mental health services continues to rise every year, while access to adequate help remains lacking,” Dr. Dube said.
“With the recent COVID-19 pandemic, concerns about the effects of climate change, global political uncertainty, and a rapidly changing employment landscape, young people in particular are vulnerable to worries about their future and feelings of helplessness and hopelessness,” he added.
Dr. Dube said there is no one right solution, and addressing this problem must consider individual and local factors.
However, some of the broader interventions needed to tackle the problem include increasing access to care by enforcing mental health parity and increasing the number of trained and qualified mental health professionals, such as child and adolescent psychiatrists, who can assess and treat these conditions in young people before they become major crises and lead to acute interventions like inpatient hospitalization.
“Public health interventions aimed at schools and families in raising awareness of mental health and well-being, and simple, cost-effective interventions to practice mental wellness will also help reduce the burden of mental illness in young people,” Dr. Dube added.
“The APA continues to fight for mental health parity enforcement and for meaningful access to mental health care for children, adolescents, and their families,” Dr. Dube said.
This research was conducted by the Clarify Health Institute. Mr. Brennan and Dr. Dube report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new report shines a light on the toll the pandemic and other stressors have taken on the mental health of U.S. children and adolescents over the last 6 years.
The report shows a dramatic increase in use of acute care services for depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions, especially among teens and preteens.
The report – The Kids Are Not Alright: Pediatric Mental Health Care Utilization from 2016-2021 – is the work of researchers at the Clarify Health Institute, the research arm of Clarify Health.
The results are “deeply concerning” and should “spark a conversation” around the need to improve access, utilization, and quality of pediatric behavioral health services, Niall Brennan, chief analytics and privacy officer for the Clarify Health Institute, told this news organization.
‘Startling’ trends
Leveraging an observational, national sample of insurance claims from more than 20 million children aged 1-19 years annually, the researchers observed several disturbing trends in mental health care.
From 2016 to 2021, inpatient (IP) admissions rose 61% (from 30 to 48 visits annually per 1,000) and emergency department visits rose 20% (from 55 to 66 visits annually per 1,000).
Mental health IP admissions ranged from a low of 27% in the West North Central region to a high of 137% in the Middle Atlantic region.
There were substantial increases from 2016 to 2021 in mental health IP admissions among children of all age groups, but particularly among adolescents 12 to 15 years old, increasing 84% among girls and 83% among boys in this age group.
There was also a sharp increase in mental health ED visits among girls and boys aged 12-15 years, increasing 20% overall during the study period.
Mental health IP use grew faster from 2016 to 2021 among children with commercial insurance than among those with Medicaid (103% vs. 40%).
In contrast, mental health–specific ED visits declined 10% among children with commercial insurance and increased by 20% among those with Medicaid.
ED utilization rates in 2021 were nearly twice as high in the Medicaid population, compared with those for children with commercial insurance.
These are “startling” increases, Mr. Brennan said in an interview.
These trends “reinforce health care leaders’ responsibility to address children’s mental health, especially when considering that half of all mental health conditions onset during adolescence and carry into adulthood,” Jean Drouin, MD, Clarify Health’s chief executive office and cofounder, adds in a news release.
“With a growing consensus that mental, behavioral, and physical health intersect, this research report aims to spark a conversation about the overall wellbeing of America’s next generation,” Dr. Drouin says.
Concern for the future
Commenting on the new report, Anish Dube, MD, chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Children, Adolescents, and their Families, said the findings are “concerning, though unsurprising.”
“They confirm what those of us in clinical practice have experienced in the last several years. The need for mental health services continues to rise every year, while access to adequate help remains lacking,” Dr. Dube said.
“With the recent COVID-19 pandemic, concerns about the effects of climate change, global political uncertainty, and a rapidly changing employment landscape, young people in particular are vulnerable to worries about their future and feelings of helplessness and hopelessness,” he added.
Dr. Dube said there is no one right solution, and addressing this problem must consider individual and local factors.
However, some of the broader interventions needed to tackle the problem include increasing access to care by enforcing mental health parity and increasing the number of trained and qualified mental health professionals, such as child and adolescent psychiatrists, who can assess and treat these conditions in young people before they become major crises and lead to acute interventions like inpatient hospitalization.
“Public health interventions aimed at schools and families in raising awareness of mental health and well-being, and simple, cost-effective interventions to practice mental wellness will also help reduce the burden of mental illness in young people,” Dr. Dube added.
“The APA continues to fight for mental health parity enforcement and for meaningful access to mental health care for children, adolescents, and their families,” Dr. Dube said.
This research was conducted by the Clarify Health Institute. Mr. Brennan and Dr. Dube report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Psychedelics may ease fear of death and dying
Psychedelics can produce positive changes in attitudes about death and dying – and may be a way to help ease anxiety and depression toward the end of life, new research suggests.
In a retrospective study of more than 3,000 participants,
“Individuals with existential anxiety and depression at end of life account for substantial suffering and significantly increased health care expenses from desperate and often futile seeking of intensive and expensive medical treatments,” co-investigator Roland Griffiths, PhD, Center for Psychedelics and Consciousness Research at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization.
“The present findings, which show that both psychedelic and non–drug-occasioned experiences can produce positive and enduring changes in attitudes about death, suggest the importance of future prospective experimental and clinical observational studies to better understand mechanisms of such changes as well as their potential clinical utility in ameliorating suffering related to fear of death,” Dr. Griffiths said.
The results were published online Aug. 24 in PLOS ONE.
Direct comparisons
Both psychedelic drug experiences and near-death experiences can alter perspectives on death and dying, but there have been few direct comparisons of these phenomena, the investigators note.
In the current study, they directly compared psychedelic-occasioned and nondrug experiences, which altered individuals’ beliefs about death.
The researchers surveyed 3,192 mostly White adults from the United States, including 933 who had a natural, nondrug near-death experience and 2,259 who had psychedelic near-death experiences induced with lysergic acid diethylamide, psilocybin, ayahuasca, or N,N-dimethyltryptamine.
The psychedelic group had more men than women and tended to be younger at the time of the experience than was the nondrug group.
Nearly 90% of individuals in both groups said that they were less afraid of death than they were before their experiences.
About half of both groups said they’d encountered something they might call “God” during the experience.
Three-quarters of the psychedelic group and 85% of the nondrug group rated their experiences as among the top five most personally meaningful and spiritually significant events of their life.
Individuals in both groups also reported moderate- to strong-lasting positive changes in personal well-being and life purpose and meaning after their experiences.
However, there were some differences between the groups.
More research needed
Compared with the psychedelic group, the nondrug group was more likely to report being unconscious, clinically dead, or that their life was in imminent danger.
The nonpsychedelic group was also more likely to report that their experience was very brief, lasting 5 minutes or less.
Both the psychedelic and nondrug participants showed robust increases on standardized measures of mystical and near-death experiences, but these measures were significantly greater in the psychedelic group.
The survey findings are in line with several recent clinical trials showing that a single treatment with the psychedelic psilocybin produced sustained decreases in anxiety and depression among patients with a life-threatening cancer diagnosis.
This includes a 2016 study by Dr. Griffiths and colleagues, which included 51 patients with late-stage cancer. As reported at the time, results showed a single, high dose of psilocybin had rapid, clinically significant, and lasting effects on mood and anxiety.
Limitations of the current survey cited by the researchers include the use of retrospective self-report to describe changes in death attitudes and the subjective features of the experiences. Also, respondents were a self-selected study population that may not be representative of all psychedelic or near-death experiences.
In addition, the study did not attempt to document worldview and other belief changes, such as increased belief in afterlife, that might help explain why death attitudes changed.
Looking ahead, the researchers note that future studies are needed to better understand the potential clinical use of psychedelics in ameliorating suffering related to fear of death.
Support through the Johns Hopkins Center for Psychedelic and Consciousness Research was provided by Tim Ferriss, Matt Mullenweg, Blake Mycoskie, Craig Nerenberg, and the Steven and Alexandra Cohen Foundation. Funding was also provided by the Y.C. Ho/Helen and Michael Chiang Foundation. The investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Psychedelics can produce positive changes in attitudes about death and dying – and may be a way to help ease anxiety and depression toward the end of life, new research suggests.
In a retrospective study of more than 3,000 participants,
“Individuals with existential anxiety and depression at end of life account for substantial suffering and significantly increased health care expenses from desperate and often futile seeking of intensive and expensive medical treatments,” co-investigator Roland Griffiths, PhD, Center for Psychedelics and Consciousness Research at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization.
“The present findings, which show that both psychedelic and non–drug-occasioned experiences can produce positive and enduring changes in attitudes about death, suggest the importance of future prospective experimental and clinical observational studies to better understand mechanisms of such changes as well as their potential clinical utility in ameliorating suffering related to fear of death,” Dr. Griffiths said.
The results were published online Aug. 24 in PLOS ONE.
Direct comparisons
Both psychedelic drug experiences and near-death experiences can alter perspectives on death and dying, but there have been few direct comparisons of these phenomena, the investigators note.
In the current study, they directly compared psychedelic-occasioned and nondrug experiences, which altered individuals’ beliefs about death.
The researchers surveyed 3,192 mostly White adults from the United States, including 933 who had a natural, nondrug near-death experience and 2,259 who had psychedelic near-death experiences induced with lysergic acid diethylamide, psilocybin, ayahuasca, or N,N-dimethyltryptamine.
The psychedelic group had more men than women and tended to be younger at the time of the experience than was the nondrug group.
Nearly 90% of individuals in both groups said that they were less afraid of death than they were before their experiences.
About half of both groups said they’d encountered something they might call “God” during the experience.
Three-quarters of the psychedelic group and 85% of the nondrug group rated their experiences as among the top five most personally meaningful and spiritually significant events of their life.
Individuals in both groups also reported moderate- to strong-lasting positive changes in personal well-being and life purpose and meaning after their experiences.
However, there were some differences between the groups.
More research needed
Compared with the psychedelic group, the nondrug group was more likely to report being unconscious, clinically dead, or that their life was in imminent danger.
The nonpsychedelic group was also more likely to report that their experience was very brief, lasting 5 minutes or less.
Both the psychedelic and nondrug participants showed robust increases on standardized measures of mystical and near-death experiences, but these measures were significantly greater in the psychedelic group.
The survey findings are in line with several recent clinical trials showing that a single treatment with the psychedelic psilocybin produced sustained decreases in anxiety and depression among patients with a life-threatening cancer diagnosis.
This includes a 2016 study by Dr. Griffiths and colleagues, which included 51 patients with late-stage cancer. As reported at the time, results showed a single, high dose of psilocybin had rapid, clinically significant, and lasting effects on mood and anxiety.
Limitations of the current survey cited by the researchers include the use of retrospective self-report to describe changes in death attitudes and the subjective features of the experiences. Also, respondents were a self-selected study population that may not be representative of all psychedelic or near-death experiences.
In addition, the study did not attempt to document worldview and other belief changes, such as increased belief in afterlife, that might help explain why death attitudes changed.
Looking ahead, the researchers note that future studies are needed to better understand the potential clinical use of psychedelics in ameliorating suffering related to fear of death.
Support through the Johns Hopkins Center for Psychedelic and Consciousness Research was provided by Tim Ferriss, Matt Mullenweg, Blake Mycoskie, Craig Nerenberg, and the Steven and Alexandra Cohen Foundation. Funding was also provided by the Y.C. Ho/Helen and Michael Chiang Foundation. The investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Psychedelics can produce positive changes in attitudes about death and dying – and may be a way to help ease anxiety and depression toward the end of life, new research suggests.
In a retrospective study of more than 3,000 participants,
“Individuals with existential anxiety and depression at end of life account for substantial suffering and significantly increased health care expenses from desperate and often futile seeking of intensive and expensive medical treatments,” co-investigator Roland Griffiths, PhD, Center for Psychedelics and Consciousness Research at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization.
“The present findings, which show that both psychedelic and non–drug-occasioned experiences can produce positive and enduring changes in attitudes about death, suggest the importance of future prospective experimental and clinical observational studies to better understand mechanisms of such changes as well as their potential clinical utility in ameliorating suffering related to fear of death,” Dr. Griffiths said.
The results were published online Aug. 24 in PLOS ONE.
Direct comparisons
Both psychedelic drug experiences and near-death experiences can alter perspectives on death and dying, but there have been few direct comparisons of these phenomena, the investigators note.
In the current study, they directly compared psychedelic-occasioned and nondrug experiences, which altered individuals’ beliefs about death.
The researchers surveyed 3,192 mostly White adults from the United States, including 933 who had a natural, nondrug near-death experience and 2,259 who had psychedelic near-death experiences induced with lysergic acid diethylamide, psilocybin, ayahuasca, or N,N-dimethyltryptamine.
The psychedelic group had more men than women and tended to be younger at the time of the experience than was the nondrug group.
Nearly 90% of individuals in both groups said that they were less afraid of death than they were before their experiences.
About half of both groups said they’d encountered something they might call “God” during the experience.
Three-quarters of the psychedelic group and 85% of the nondrug group rated their experiences as among the top five most personally meaningful and spiritually significant events of their life.
Individuals in both groups also reported moderate- to strong-lasting positive changes in personal well-being and life purpose and meaning after their experiences.
However, there were some differences between the groups.
More research needed
Compared with the psychedelic group, the nondrug group was more likely to report being unconscious, clinically dead, or that their life was in imminent danger.
The nonpsychedelic group was also more likely to report that their experience was very brief, lasting 5 minutes or less.
Both the psychedelic and nondrug participants showed robust increases on standardized measures of mystical and near-death experiences, but these measures were significantly greater in the psychedelic group.
The survey findings are in line with several recent clinical trials showing that a single treatment with the psychedelic psilocybin produced sustained decreases in anxiety and depression among patients with a life-threatening cancer diagnosis.
This includes a 2016 study by Dr. Griffiths and colleagues, which included 51 patients with late-stage cancer. As reported at the time, results showed a single, high dose of psilocybin had rapid, clinically significant, and lasting effects on mood and anxiety.
Limitations of the current survey cited by the researchers include the use of retrospective self-report to describe changes in death attitudes and the subjective features of the experiences. Also, respondents were a self-selected study population that may not be representative of all psychedelic or near-death experiences.
In addition, the study did not attempt to document worldview and other belief changes, such as increased belief in afterlife, that might help explain why death attitudes changed.
Looking ahead, the researchers note that future studies are needed to better understand the potential clinical use of psychedelics in ameliorating suffering related to fear of death.
Support through the Johns Hopkins Center for Psychedelic and Consciousness Research was provided by Tim Ferriss, Matt Mullenweg, Blake Mycoskie, Craig Nerenberg, and the Steven and Alexandra Cohen Foundation. Funding was also provided by the Y.C. Ho/Helen and Michael Chiang Foundation. The investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PLOS ONE
Prior psychological distress tied to ‘long-COVID’ conditions
In an analysis of almost 55,000 adult participants in three ongoing studies, having depression, anxiety, worry, perceived stress, or loneliness early in the pandemic, before SARS-CoV-2 infection, was associated with a 50% increased risk for developing long COVID. These types of psychological distress were also associated with a 15% to 51% greater risk for impairment in daily life among individuals with long COVID.
Psychological distress was even more strongly associated with developing long COVID than were physical health risk factors, and the increased risk was not explained by health behaviors such as smoking or physical comorbidities, researchers note.
“Our findings suggest the need to consider psychological health in addition to physical health as risk factors of long COVID-19,” lead author Siwen Wang, MD, postdoctoral fellow, department of nutrition, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, said in an interview.
“We need to increase public awareness of the importance of mental health and focus on getting mental health care for people who need it, increasing the supply of mental health clinicians and improving access to care,” she said.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
‘Poorly understood’
Postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (“long COVID”), which are “signs and symptoms consistent with COVID-19 that extend beyond 4 weeks from onset of infection” constitute “an emerging health issue,” the investigators write.
Dr. Wang noted that it has been estimated that 8-23 million Americans have developed long COVID. However, “despite the high prevalence and daily life impairment associated with long COVID, it is still poorly understood, and few risk factors have been established,” she said.
Although psychological distress may be implicated in long COVID, only three previous studies investigated psychological factors as potential contributors, the researchers note. Also, no study has investigated the potential role of other common manifestations of distress that have increased during the pandemic, such as loneliness and perceived stress, they add.
To investigate these issues, the researchers turned to three large ongoing longitudinal studies: the Nurses’ Health Study II (NSHII), the Nurses’ Health study 3 (NHS3), and the Growing Up Today Study (GUTS).
They analyzed data on 54,960 total participants (96.6% women; mean age, 57.5 years). Of the full group, 38% were active health care workers.
Participants completed an online COVID-19 questionnaire from April 2020 to Sept. 1, 2020 (baseline), and monthly surveys thereafter. Beginning in August 2020, surveys were administered quarterly. The end of follow-up was in November 2021.
The COVID questionnaires included questions about positive SARS-CoV-2 test results, COVID symptoms and hospitalization since March 1, 2020, and the presence of long-term COVID symptoms, such as fatigue, respiratory problems, persistent cough, muscle/joint/chest pain, smell/taste problems, confusion/disorientation/brain fog, depression/anxiety/changes in mood, headache, and memory problems.
Participants who reported these post-COVID conditions were asked about the frequency of symptoms and the degree of impairment in daily life.
Inflammation, immune dysregulation implicated?
The Patient Health Questionnaire–4 (PHQ-4) was used to assess for anxiety and depressive symptoms in the past 2 weeks. It consists of a two-item depression measure (PHQ-2) and a two-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale (GAD-2).
Non–health care providers completed two additional assessments of psychological distress: the four-item Perceived Stress Scale and the three-item UCLA Loneliness Scale.
The researchers included demographic factors, weight, smoking status, marital status, and medical conditions, including diabetes, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, asthma, and cancer, and socioeconomic factors as covariates.
For each participant, the investigators calculated the number of types of distress experienced at a high level, including probable depression, probable anxiety, worry about COVID-19, being in the top quartile of perceived stress, and loneliness.
During the 19 months of follow-up (1-47 weeks after baseline), 6% of respondents reported a positive result on a SARS-CoV-2 antibody, antigen, or polymerase chain reaction test.
Of these, 43.9% reported long-COVID conditions, with most reporting that symptoms lasted 2 months or longer; 55.8% reported at least occasional daily life impairment.
The most common post-COVID conditions were fatigue (reported by 56%), loss of smell or taste problems (44.6%), shortness of breath (25.5%), confusion/disorientation/ brain fog (24.5%), and memory issues (21.8%).
Among patients who had been infected, there was a considerably higher rate of preinfection psychological distress after adjusting for sociodemographic factors, health behaviors, and comorbidities. Each type of distress was associated with post-COVID conditions.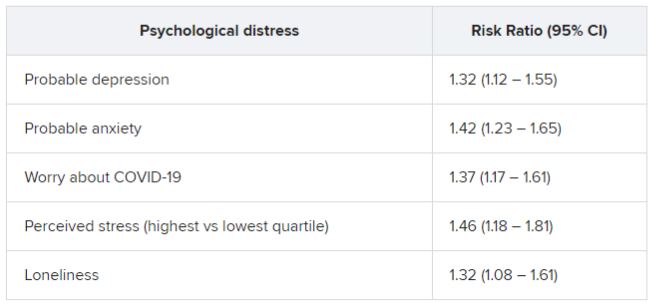
In addition, participants who had experienced at least two types of distress prior to infection were at nearly 50% increased risk for post–COVID conditions (risk ratio, 1.49; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-1.80).
Among those with post-COVID conditions, all types of distress were associated with increased risk for daily life impairment (RR range, 1.15-1.51).
Senior author Andrea Roberts, PhD, senior research scientist at the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, noted that the investigators did not examine biological mechanisms potentially underlying the association they found.
However, “based on prior research, it may be that inflammation and immune dysregulation related to psychological distress play a role in the association of distress with long COVID, but we can’t be sure,” Dr. Roberts said.
Contributes to the field
Commenting for this article, Yapeng Su, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, called the study “great work contributing to the long-COVID research field and revealing important connections” with psychological stress prior to infection.
Dr. Su, who was not involved with the study, was previously at the Institute for Systems Biology, also in Seattle, and has written about long COVID.
He noted that the “biological mechanism of such intriguing linkage is definitely the important next step, which will likely require deep phenotyping of biological specimens from these patients longitudinally.”
Dr. Wang pointed to past research suggesting that some patients with mental illness “sometimes develop autoantibodies that have also been associated with increased risk of long COVID.” In addition, depression “affects the brain in ways that may explain certain cognitive symptoms in long COVID,” she added.
More studies are now needed to understand how psychological distress increases the risk for long COVID, said Dr. Wang.
The research was supported by grants from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the National Institutes of Health, the Dean’s Fund for Scientific Advancement Acceleration Award from the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, the Massachusetts Consortium on Pathogen Readiness Evergrande COVID-19 Response Fund Award, and the Veterans Affairs Health Services Research and Development Service funds. Dr. Wang and Dr. Roberts have reported no relevant financial relationships. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Su reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In an analysis of almost 55,000 adult participants in three ongoing studies, having depression, anxiety, worry, perceived stress, or loneliness early in the pandemic, before SARS-CoV-2 infection, was associated with a 50% increased risk for developing long COVID. These types of psychological distress were also associated with a 15% to 51% greater risk for impairment in daily life among individuals with long COVID.
Psychological distress was even more strongly associated with developing long COVID than were physical health risk factors, and the increased risk was not explained by health behaviors such as smoking or physical comorbidities, researchers note.
“Our findings suggest the need to consider psychological health in addition to physical health as risk factors of long COVID-19,” lead author Siwen Wang, MD, postdoctoral fellow, department of nutrition, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, said in an interview.
“We need to increase public awareness of the importance of mental health and focus on getting mental health care for people who need it, increasing the supply of mental health clinicians and improving access to care,” she said.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
‘Poorly understood’
Postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (“long COVID”), which are “signs and symptoms consistent with COVID-19 that extend beyond 4 weeks from onset of infection” constitute “an emerging health issue,” the investigators write.
Dr. Wang noted that it has been estimated that 8-23 million Americans have developed long COVID. However, “despite the high prevalence and daily life impairment associated with long COVID, it is still poorly understood, and few risk factors have been established,” she said.
Although psychological distress may be implicated in long COVID, only three previous studies investigated psychological factors as potential contributors, the researchers note. Also, no study has investigated the potential role of other common manifestations of distress that have increased during the pandemic, such as loneliness and perceived stress, they add.
To investigate these issues, the researchers turned to three large ongoing longitudinal studies: the Nurses’ Health Study II (NSHII), the Nurses’ Health study 3 (NHS3), and the Growing Up Today Study (GUTS).
They analyzed data on 54,960 total participants (96.6% women; mean age, 57.5 years). Of the full group, 38% were active health care workers.
Participants completed an online COVID-19 questionnaire from April 2020 to Sept. 1, 2020 (baseline), and monthly surveys thereafter. Beginning in August 2020, surveys were administered quarterly. The end of follow-up was in November 2021.
The COVID questionnaires included questions about positive SARS-CoV-2 test results, COVID symptoms and hospitalization since March 1, 2020, and the presence of long-term COVID symptoms, such as fatigue, respiratory problems, persistent cough, muscle/joint/chest pain, smell/taste problems, confusion/disorientation/brain fog, depression/anxiety/changes in mood, headache, and memory problems.
Participants who reported these post-COVID conditions were asked about the frequency of symptoms and the degree of impairment in daily life.
Inflammation, immune dysregulation implicated?
The Patient Health Questionnaire–4 (PHQ-4) was used to assess for anxiety and depressive symptoms in the past 2 weeks. It consists of a two-item depression measure (PHQ-2) and a two-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale (GAD-2).
Non–health care providers completed two additional assessments of psychological distress: the four-item Perceived Stress Scale and the three-item UCLA Loneliness Scale.
The researchers included demographic factors, weight, smoking status, marital status, and medical conditions, including diabetes, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, asthma, and cancer, and socioeconomic factors as covariates.
For each participant, the investigators calculated the number of types of distress experienced at a high level, including probable depression, probable anxiety, worry about COVID-19, being in the top quartile of perceived stress, and loneliness.
During the 19 months of follow-up (1-47 weeks after baseline), 6% of respondents reported a positive result on a SARS-CoV-2 antibody, antigen, or polymerase chain reaction test.
Of these, 43.9% reported long-COVID conditions, with most reporting that symptoms lasted 2 months or longer; 55.8% reported at least occasional daily life impairment.
The most common post-COVID conditions were fatigue (reported by 56%), loss of smell or taste problems (44.6%), shortness of breath (25.5%), confusion/disorientation/ brain fog (24.5%), and memory issues (21.8%).
Among patients who had been infected, there was a considerably higher rate of preinfection psychological distress after adjusting for sociodemographic factors, health behaviors, and comorbidities. Each type of distress was associated with post-COVID conditions.
In addition, participants who had experienced at least two types of distress prior to infection were at nearly 50% increased risk for post–COVID conditions (risk ratio, 1.49; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-1.80).
Among those with post-COVID conditions, all types of distress were associated with increased risk for daily life impairment (RR range, 1.15-1.51).
Senior author Andrea Roberts, PhD, senior research scientist at the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, noted that the investigators did not examine biological mechanisms potentially underlying the association they found.
However, “based on prior research, it may be that inflammation and immune dysregulation related to psychological distress play a role in the association of distress with long COVID, but we can’t be sure,” Dr. Roberts said.
Contributes to the field
Commenting for this article, Yapeng Su, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, called the study “great work contributing to the long-COVID research field and revealing important connections” with psychological stress prior to infection.
Dr. Su, who was not involved with the study, was previously at the Institute for Systems Biology, also in Seattle, and has written about long COVID.
He noted that the “biological mechanism of such intriguing linkage is definitely the important next step, which will likely require deep phenotyping of biological specimens from these patients longitudinally.”
Dr. Wang pointed to past research suggesting that some patients with mental illness “sometimes develop autoantibodies that have also been associated with increased risk of long COVID.” In addition, depression “affects the brain in ways that may explain certain cognitive symptoms in long COVID,” she added.
More studies are now needed to understand how psychological distress increases the risk for long COVID, said Dr. Wang.
The research was supported by grants from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the National Institutes of Health, the Dean’s Fund for Scientific Advancement Acceleration Award from the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, the Massachusetts Consortium on Pathogen Readiness Evergrande COVID-19 Response Fund Award, and the Veterans Affairs Health Services Research and Development Service funds. Dr. Wang and Dr. Roberts have reported no relevant financial relationships. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Su reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In an analysis of almost 55,000 adult participants in three ongoing studies, having depression, anxiety, worry, perceived stress, or loneliness early in the pandemic, before SARS-CoV-2 infection, was associated with a 50% increased risk for developing long COVID. These types of psychological distress were also associated with a 15% to 51% greater risk for impairment in daily life among individuals with long COVID.
Psychological distress was even more strongly associated with developing long COVID than were physical health risk factors, and the increased risk was not explained by health behaviors such as smoking or physical comorbidities, researchers note.
“Our findings suggest the need to consider psychological health in addition to physical health as risk factors of long COVID-19,” lead author Siwen Wang, MD, postdoctoral fellow, department of nutrition, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, said in an interview.
“We need to increase public awareness of the importance of mental health and focus on getting mental health care for people who need it, increasing the supply of mental health clinicians and improving access to care,” she said.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
‘Poorly understood’
Postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (“long COVID”), which are “signs and symptoms consistent with COVID-19 that extend beyond 4 weeks from onset of infection” constitute “an emerging health issue,” the investigators write.
Dr. Wang noted that it has been estimated that 8-23 million Americans have developed long COVID. However, “despite the high prevalence and daily life impairment associated with long COVID, it is still poorly understood, and few risk factors have been established,” she said.
Although psychological distress may be implicated in long COVID, only three previous studies investigated psychological factors as potential contributors, the researchers note. Also, no study has investigated the potential role of other common manifestations of distress that have increased during the pandemic, such as loneliness and perceived stress, they add.
To investigate these issues, the researchers turned to three large ongoing longitudinal studies: the Nurses’ Health Study II (NSHII), the Nurses’ Health study 3 (NHS3), and the Growing Up Today Study (GUTS).
They analyzed data on 54,960 total participants (96.6% women; mean age, 57.5 years). Of the full group, 38% were active health care workers.
Participants completed an online COVID-19 questionnaire from April 2020 to Sept. 1, 2020 (baseline), and monthly surveys thereafter. Beginning in August 2020, surveys were administered quarterly. The end of follow-up was in November 2021.
The COVID questionnaires included questions about positive SARS-CoV-2 test results, COVID symptoms and hospitalization since March 1, 2020, and the presence of long-term COVID symptoms, such as fatigue, respiratory problems, persistent cough, muscle/joint/chest pain, smell/taste problems, confusion/disorientation/brain fog, depression/anxiety/changes in mood, headache, and memory problems.
Participants who reported these post-COVID conditions were asked about the frequency of symptoms and the degree of impairment in daily life.
Inflammation, immune dysregulation implicated?
The Patient Health Questionnaire–4 (PHQ-4) was used to assess for anxiety and depressive symptoms in the past 2 weeks. It consists of a two-item depression measure (PHQ-2) and a two-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale (GAD-2).
Non–health care providers completed two additional assessments of psychological distress: the four-item Perceived Stress Scale and the three-item UCLA Loneliness Scale.
The researchers included demographic factors, weight, smoking status, marital status, and medical conditions, including diabetes, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, asthma, and cancer, and socioeconomic factors as covariates.
For each participant, the investigators calculated the number of types of distress experienced at a high level, including probable depression, probable anxiety, worry about COVID-19, being in the top quartile of perceived stress, and loneliness.
During the 19 months of follow-up (1-47 weeks after baseline), 6% of respondents reported a positive result on a SARS-CoV-2 antibody, antigen, or polymerase chain reaction test.
Of these, 43.9% reported long-COVID conditions, with most reporting that symptoms lasted 2 months or longer; 55.8% reported at least occasional daily life impairment.
The most common post-COVID conditions were fatigue (reported by 56%), loss of smell or taste problems (44.6%), shortness of breath (25.5%), confusion/disorientation/ brain fog (24.5%), and memory issues (21.8%).
Among patients who had been infected, there was a considerably higher rate of preinfection psychological distress after adjusting for sociodemographic factors, health behaviors, and comorbidities. Each type of distress was associated with post-COVID conditions.
In addition, participants who had experienced at least two types of distress prior to infection were at nearly 50% increased risk for post–COVID conditions (risk ratio, 1.49; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-1.80).
Among those with post-COVID conditions, all types of distress were associated with increased risk for daily life impairment (RR range, 1.15-1.51).
Senior author Andrea Roberts, PhD, senior research scientist at the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, noted that the investigators did not examine biological mechanisms potentially underlying the association they found.
However, “based on prior research, it may be that inflammation and immune dysregulation related to psychological distress play a role in the association of distress with long COVID, but we can’t be sure,” Dr. Roberts said.
Contributes to the field
Commenting for this article, Yapeng Su, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, called the study “great work contributing to the long-COVID research field and revealing important connections” with psychological stress prior to infection.
Dr. Su, who was not involved with the study, was previously at the Institute for Systems Biology, also in Seattle, and has written about long COVID.
He noted that the “biological mechanism of such intriguing linkage is definitely the important next step, which will likely require deep phenotyping of biological specimens from these patients longitudinally.”
Dr. Wang pointed to past research suggesting that some patients with mental illness “sometimes develop autoantibodies that have also been associated with increased risk of long COVID.” In addition, depression “affects the brain in ways that may explain certain cognitive symptoms in long COVID,” she added.
More studies are now needed to understand how psychological distress increases the risk for long COVID, said Dr. Wang.
The research was supported by grants from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the National Institutes of Health, the Dean’s Fund for Scientific Advancement Acceleration Award from the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, the Massachusetts Consortium on Pathogen Readiness Evergrande COVID-19 Response Fund Award, and the Veterans Affairs Health Services Research and Development Service funds. Dr. Wang and Dr. Roberts have reported no relevant financial relationships. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Su reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA PSYCHIATRY
Psychiatrists’ views on psychoactive drugs clash with U.S. policy
“The consensus among experts, including psychiatrists, about specific drugs is not consistent or congruent with the schedule of these drugs” in the United States, lead author Adam Levin, MD, third-year psychiatry resident, Ohio State University, Columbus, and affiliate scholar at the Center for Psychedelic Drug Research and Education, Ohio State College of Social Work, told this news organization.
Dr. Levin stressed the importance of appropriate drug scheduling to improve access to treatments such as psilocybin (psychedelic mushrooms) and 4-methylenedioxy methamphetamine (MDMA), which are now being tested for psychiatric disorders.
“We are in the middle of a mental health crisis so having any new tools would be really important,” he said.
The survey findings were published online in the International Journal of Drug Policy.
Five drug schedules
The Controlled Substances Act of 1970 created five “schedules” that organized drugs from most to least dangerous (schedule I-V). However, Dr. Levin said that the schedules do not accurately reflect the harms or therapeutic benefits of the various drugs.
Some drugs in lower, less restrictive schedules have greater potential for harm than do those in higher schedules, he noted. For example, methamphetamine, which has been recalled in multiple formulations because of concerns about abuse and limited medical use, remains a schedule II drug.
In addition, several schedule I drugs, including psilocybin and MDMA that are deemed dangerous and of no medical value, have shown therapeutic potential and low rates of misuse, addiction, or physical harm, the investigators noted.
In fact, the Food and Drug Administration has granted breakthrough therapy status to psilocybin for treatment-resistant depression and major depressive disorder (MDD) and to MDMA for posttraumatic stress disorder. This has positioned these drugs for possible FDA approval within the next few years.
Access to schedule I drugs for research purposes is tightly controlled. “Once psilocybin was placed in schedule I, there was this massive drop-off in the research funding and amount of research; and we’re just now starting to understand the potential therapeutic value of this drug,” said Dr. Levin.
Even with a recent research resurgence, most studies are funded by charitable donations or for-profit companies because of continued hesitancy on the part of grant-making organizations, he added.
Apparent contradictions
Given the pending approval of several schedule I drugs and escalating abuse of drugs in lower schedules, there is a growing need to understand physician attitudes surrounding the apparent contradictions in the drug schedule, the investigators noted.
Their survey included a geographically diverse group of 181 mostly middle-aged psychiatrists (65.2% were men) with an average of 16.2 years of practice after residency.
Participants were randomly assigned to respond to a vignette depicting a clinical scenario where a patient wants one of four drugs to help treat severe depression: psilocybin, a schedule I drug; methamphetamine (Desoxyn), a schedule II drug; ketamine, a Schedule III drug; or alprazolam (Xanax), a schedule IV drug.
Each of these therapies has established antidepressant properties, but none are FDA approved for treatment of MDD. However, an intranasal formulation of the ketamine enantiomer Spravato (esketamine) was recently approved for treatment-resistant depression.
There were significant differences among the groups presented with different vignettes. Participants were more likely to warn against repeated use of and development of a new psychiatric problem with methamphetamine and alprazolam compared with psilocybin or ketamine.
Respondents were most concerned about increased suicide risk after the nonprescribed use of alprazolam compared with psilocybin and ketamine.
Compared with all other drugs, ketamine was more likely to be integrated into treatment plans.
Therapeutic value, abuse potential
Participants were asked to rate the safety, therapeutic value, and abuse potential of the four drugs as well as alcohol, a nonscheduled legal drug, if used properly or as directed.
Respondents viewed psilocybin and ketamine as similarly safe – and safer than methamphetamine and alprazolam. They considered ketamine as having the highest therapeutic potential, followed by psilocybin, and then alprazolam and methamphetamine. “Last was alcohol, which we expected because alcohol is not used therapeutically,” said Dr. Levin.
Survey completers viewed methamphetamine, alprazolam, and alcohol as having similarly high abuse potential, and ketamine as having mid-level abuse potential. Psilocybin was rated as having the lowest abuse potential, “which is exactly the opposite of what is implied by its schedule I status,” noted Dr. Levin.
The results provide evidence these drugs “are incorrectly scheduled,” he said.
“This suggests the schedule does not reflect current evidence, which I think is really important to understand because there are consequences to the drug schedule,” including criminal justice and research consequences, he added.
Dr. Levin pointed out that possession of drugs in more harmful schedules is linked to sometimes lengthy prison sentences.
The psychiatrists’ perceptions of the drugs “overlaps pretty significantly” with recent surveys of other mental health professionals, including psychologists and addiction experts, he noted.
The study was funded by the Drug Enforcement and Policy Center, Moritz College of Law, and The Ohio State University. Dr. Levin reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“The consensus among experts, including psychiatrists, about specific drugs is not consistent or congruent with the schedule of these drugs” in the United States, lead author Adam Levin, MD, third-year psychiatry resident, Ohio State University, Columbus, and affiliate scholar at the Center for Psychedelic Drug Research and Education, Ohio State College of Social Work, told this news organization.
Dr. Levin stressed the importance of appropriate drug scheduling to improve access to treatments such as psilocybin (psychedelic mushrooms) and 4-methylenedioxy methamphetamine (MDMA), which are now being tested for psychiatric disorders.
“We are in the middle of a mental health crisis so having any new tools would be really important,” he said.
The survey findings were published online in the International Journal of Drug Policy.
Five drug schedules
The Controlled Substances Act of 1970 created five “schedules” that organized drugs from most to least dangerous (schedule I-V). However, Dr. Levin said that the schedules do not accurately reflect the harms or therapeutic benefits of the various drugs.
Some drugs in lower, less restrictive schedules have greater potential for harm than do those in higher schedules, he noted. For example, methamphetamine, which has been recalled in multiple formulations because of concerns about abuse and limited medical use, remains a schedule II drug.
In addition, several schedule I drugs, including psilocybin and MDMA that are deemed dangerous and of no medical value, have shown therapeutic potential and low rates of misuse, addiction, or physical harm, the investigators noted.
In fact, the Food and Drug Administration has granted breakthrough therapy status to psilocybin for treatment-resistant depression and major depressive disorder (MDD) and to MDMA for posttraumatic stress disorder. This has positioned these drugs for possible FDA approval within the next few years.
Access to schedule I drugs for research purposes is tightly controlled. “Once psilocybin was placed in schedule I, there was this massive drop-off in the research funding and amount of research; and we’re just now starting to understand the potential therapeutic value of this drug,” said Dr. Levin.
Even with a recent research resurgence, most studies are funded by charitable donations or for-profit companies because of continued hesitancy on the part of grant-making organizations, he added.
Apparent contradictions
Given the pending approval of several schedule I drugs and escalating abuse of drugs in lower schedules, there is a growing need to understand physician attitudes surrounding the apparent contradictions in the drug schedule, the investigators noted.
Their survey included a geographically diverse group of 181 mostly middle-aged psychiatrists (65.2% were men) with an average of 16.2 years of practice after residency.
Participants were randomly assigned to respond to a vignette depicting a clinical scenario where a patient wants one of four drugs to help treat severe depression: psilocybin, a schedule I drug; methamphetamine (Desoxyn), a schedule II drug; ketamine, a Schedule III drug; or alprazolam (Xanax), a schedule IV drug.
Each of these therapies has established antidepressant properties, but none are FDA approved for treatment of MDD. However, an intranasal formulation of the ketamine enantiomer Spravato (esketamine) was recently approved for treatment-resistant depression.
There were significant differences among the groups presented with different vignettes. Participants were more likely to warn against repeated use of and development of a new psychiatric problem with methamphetamine and alprazolam compared with psilocybin or ketamine.
Respondents were most concerned about increased suicide risk after the nonprescribed use of alprazolam compared with psilocybin and ketamine.
Compared with all other drugs, ketamine was more likely to be integrated into treatment plans.
Therapeutic value, abuse potential
Participants were asked to rate the safety, therapeutic value, and abuse potential of the four drugs as well as alcohol, a nonscheduled legal drug, if used properly or as directed.
Respondents viewed psilocybin and ketamine as similarly safe – and safer than methamphetamine and alprazolam. They considered ketamine as having the highest therapeutic potential, followed by psilocybin, and then alprazolam and methamphetamine. “Last was alcohol, which we expected because alcohol is not used therapeutically,” said Dr. Levin.
Survey completers viewed methamphetamine, alprazolam, and alcohol as having similarly high abuse potential, and ketamine as having mid-level abuse potential. Psilocybin was rated as having the lowest abuse potential, “which is exactly the opposite of what is implied by its schedule I status,” noted Dr. Levin.
The results provide evidence these drugs “are incorrectly scheduled,” he said.
“This suggests the schedule does not reflect current evidence, which I think is really important to understand because there are consequences to the drug schedule,” including criminal justice and research consequences, he added.
Dr. Levin pointed out that possession of drugs in more harmful schedules is linked to sometimes lengthy prison sentences.
The psychiatrists’ perceptions of the drugs “overlaps pretty significantly” with recent surveys of other mental health professionals, including psychologists and addiction experts, he noted.
The study was funded by the Drug Enforcement and Policy Center, Moritz College of Law, and The Ohio State University. Dr. Levin reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“The consensus among experts, including psychiatrists, about specific drugs is not consistent or congruent with the schedule of these drugs” in the United States, lead author Adam Levin, MD, third-year psychiatry resident, Ohio State University, Columbus, and affiliate scholar at the Center for Psychedelic Drug Research and Education, Ohio State College of Social Work, told this news organization.
Dr. Levin stressed the importance of appropriate drug scheduling to improve access to treatments such as psilocybin (psychedelic mushrooms) and 4-methylenedioxy methamphetamine (MDMA), which are now being tested for psychiatric disorders.
“We are in the middle of a mental health crisis so having any new tools would be really important,” he said.
The survey findings were published online in the International Journal of Drug Policy.
Five drug schedules
The Controlled Substances Act of 1970 created five “schedules” that organized drugs from most to least dangerous (schedule I-V). However, Dr. Levin said that the schedules do not accurately reflect the harms or therapeutic benefits of the various drugs.
Some drugs in lower, less restrictive schedules have greater potential for harm than do those in higher schedules, he noted. For example, methamphetamine, which has been recalled in multiple formulations because of concerns about abuse and limited medical use, remains a schedule II drug.
In addition, several schedule I drugs, including psilocybin and MDMA that are deemed dangerous and of no medical value, have shown therapeutic potential and low rates of misuse, addiction, or physical harm, the investigators noted.
In fact, the Food and Drug Administration has granted breakthrough therapy status to psilocybin for treatment-resistant depression and major depressive disorder (MDD) and to MDMA for posttraumatic stress disorder. This has positioned these drugs for possible FDA approval within the next few years.
Access to schedule I drugs for research purposes is tightly controlled. “Once psilocybin was placed in schedule I, there was this massive drop-off in the research funding and amount of research; and we’re just now starting to understand the potential therapeutic value of this drug,” said Dr. Levin.
Even with a recent research resurgence, most studies are funded by charitable donations or for-profit companies because of continued hesitancy on the part of grant-making organizations, he added.
Apparent contradictions
Given the pending approval of several schedule I drugs and escalating abuse of drugs in lower schedules, there is a growing need to understand physician attitudes surrounding the apparent contradictions in the drug schedule, the investigators noted.
Their survey included a geographically diverse group of 181 mostly middle-aged psychiatrists (65.2% were men) with an average of 16.2 years of practice after residency.
Participants were randomly assigned to respond to a vignette depicting a clinical scenario where a patient wants one of four drugs to help treat severe depression: psilocybin, a schedule I drug; methamphetamine (Desoxyn), a schedule II drug; ketamine, a Schedule III drug; or alprazolam (Xanax), a schedule IV drug.
Each of these therapies has established antidepressant properties, but none are FDA approved for treatment of MDD. However, an intranasal formulation of the ketamine enantiomer Spravato (esketamine) was recently approved for treatment-resistant depression.
There were significant differences among the groups presented with different vignettes. Participants were more likely to warn against repeated use of and development of a new psychiatric problem with methamphetamine and alprazolam compared with psilocybin or ketamine.
Respondents were most concerned about increased suicide risk after the nonprescribed use of alprazolam compared with psilocybin and ketamine.
Compared with all other drugs, ketamine was more likely to be integrated into treatment plans.
Therapeutic value, abuse potential
Participants were asked to rate the safety, therapeutic value, and abuse potential of the four drugs as well as alcohol, a nonscheduled legal drug, if used properly or as directed.
Respondents viewed psilocybin and ketamine as similarly safe – and safer than methamphetamine and alprazolam. They considered ketamine as having the highest therapeutic potential, followed by psilocybin, and then alprazolam and methamphetamine. “Last was alcohol, which we expected because alcohol is not used therapeutically,” said Dr. Levin.
Survey completers viewed methamphetamine, alprazolam, and alcohol as having similarly high abuse potential, and ketamine as having mid-level abuse potential. Psilocybin was rated as having the lowest abuse potential, “which is exactly the opposite of what is implied by its schedule I status,” noted Dr. Levin.
The results provide evidence these drugs “are incorrectly scheduled,” he said.
“This suggests the schedule does not reflect current evidence, which I think is really important to understand because there are consequences to the drug schedule,” including criminal justice and research consequences, he added.
Dr. Levin pointed out that possession of drugs in more harmful schedules is linked to sometimes lengthy prison sentences.
The psychiatrists’ perceptions of the drugs “overlaps pretty significantly” with recent surveys of other mental health professionals, including psychologists and addiction experts, he noted.
The study was funded by the Drug Enforcement and Policy Center, Moritz College of Law, and The Ohio State University. Dr. Levin reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF DRUG POLICY
Robots better than humans at detecting mental well-being issues in children
Robots can be better at detecting mental well-being issues in children than parent-reported or self-reported testing, say U.K. researchers.
The researchers behind a new study, presented at the 31st IEEE International Conference on Robot & Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN) in Naples, Italy, have suggested that robots could be a useful addition to traditional methods of mental health assessment.
“There are times when traditional methods aren’t able to catch mental well-being lapses in children, as sometimes the changes are incredibly subtle,” said Nida Itrat Abbasi, a PhD student at Cambridge (England) Affective Computing and Robotics Group, University of Cambridge, and the study’s first author. “We wanted to see whether robots might be able to help with this process,” she explained.
The authors highlighted how, during the COVID-19 pandemic, home schooling, financial pressures, and isolation from peers and friends impacted the mental health of many children. Even before the pandemic however, anxiety and depression among children in the United Kingdom has been on the rise, but the resources and support to address mental well-being are severely limited.
Children engage with robots
For their study the research team – which comprised roboticists, computer scientists, and psychiatrists from the University of Cambridge – enrolled 28 participants between ages 8 and 13 years. While being observed from an adjacent room by a parent or guardian, along with members of the research team, the participants took part in a one-to-one 45-minute session with a Nao robot – a humanoid robot about 60 cm tall – that administered a series of standard psychological questionnaires to assess the mental well-being of each participant.
Participants interacted with the robot throughout the session by speaking with it or by touching sensors on the robot’s hands and feet. Additional sensors tracked participants’ heartbeat, head, and eye movements during the session.
Professor Hatice Gunes, affective intelligence and robotics laboratory, department of computer science, University of Cambridge, said: “Children are quite tactile, and they’re drawn to technology. If they’re using a screen-based tool, they’re withdrawn from the physical world,” she said. “But robots are perfect because they’re in the physical world – they’re more interactive, so the children are more engaged.”
Prior to each session the children and their parent or guardian completed standard online questionnaires to assess each child’s mental well-being.
During each session, the robot performed four different tasks:
- Asked open-ended questions about happy and sad memories over the last week.
- Administered the Short Mood and Feelings Questionnaire (SMFQ).
- Administered a picture task inspired by the Children’s Apperception Test (CAT), where children are asked to answer questions related to pictures shown.
- Administered the Revised Children’s Anxiety and Depression Scale (RCADS) for generalized anxiety, panic disorder, and low mood.
Following the SMFQ children were divided into three different groups according to how likely they were to be struggling with their mental well-being.
The researchers found that children with varying levels of well-being concerns interacted differently with the robot. For children that might not be experiencing mental well-being–related problems, the researchers found that interacting with the robot led to more positive response ratings to the questionnaires. However, for children that might be experiencing well-being–related concerns, the robot may have enabled them to divulge their true feelings and experiences, leading to more negative response ratings to the questionnaire.
Robots an addition not a replacement
“Since the robot we use is child-sized, and completely nonthreatening, children might see the robot as a confidant – they feel like they won’t get into trouble if they share secrets with it,” said Ms. Abbasi. “Other researchers have found that children are more likely to divulge private information – like that they’re being bullied, for example – to a robot than they would be to an adult,” she said.
Study participants all said they “enjoyed talking with the robot,” commented the authors, who added that, “the children were willing to confide in the robot, in some cases sharing information with the robot that they had not yet shared via the standard assessment method of online or in-person questionnaires.”
This is the first time that robots have been used to assess mental well-being in children, the researchers pointed out. “Robots could be a useful addition to traditional methods of mental health assessment,” they said, though they emphasized that robots are “not intended to be a substitute for professional mental health support.”
“We don’t have any intention of replacing psychologists or other mental health professionals with robots, since their expertise far surpasses anything a robot can do,” said Dr. Micol Spitale, affective computing and robotics laboratory, University of Cambridge, and study coauthor. “However, our work suggests that robots could be a useful tool in helping children to open up and share things they might not be comfortable sharing at first.”
The researchers say that they hope to expand their survey in future by including more participants and following them over time. They are also investigating whether similar results could be achieved if children interact with the robot via video chat.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
Robots can be better at detecting mental well-being issues in children than parent-reported or self-reported testing, say U.K. researchers.
The researchers behind a new study, presented at the 31st IEEE International Conference on Robot & Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN) in Naples, Italy, have suggested that robots could be a useful addition to traditional methods of mental health assessment.
“There are times when traditional methods aren’t able to catch mental well-being lapses in children, as sometimes the changes are incredibly subtle,” said Nida Itrat Abbasi, a PhD student at Cambridge (England) Affective Computing and Robotics Group, University of Cambridge, and the study’s first author. “We wanted to see whether robots might be able to help with this process,” she explained.
The authors highlighted how, during the COVID-19 pandemic, home schooling, financial pressures, and isolation from peers and friends impacted the mental health of many children. Even before the pandemic however, anxiety and depression among children in the United Kingdom has been on the rise, but the resources and support to address mental well-being are severely limited.
Children engage with robots
For their study the research team – which comprised roboticists, computer scientists, and psychiatrists from the University of Cambridge – enrolled 28 participants between ages 8 and 13 years. While being observed from an adjacent room by a parent or guardian, along with members of the research team, the participants took part in a one-to-one 45-minute session with a Nao robot – a humanoid robot about 60 cm tall – that administered a series of standard psychological questionnaires to assess the mental well-being of each participant.
Participants interacted with the robot throughout the session by speaking with it or by touching sensors on the robot’s hands and feet. Additional sensors tracked participants’ heartbeat, head, and eye movements during the session.
Professor Hatice Gunes, affective intelligence and robotics laboratory, department of computer science, University of Cambridge, said: “Children are quite tactile, and they’re drawn to technology. If they’re using a screen-based tool, they’re withdrawn from the physical world,” she said. “But robots are perfect because they’re in the physical world – they’re more interactive, so the children are more engaged.”
Prior to each session the children and their parent or guardian completed standard online questionnaires to assess each child’s mental well-being.
During each session, the robot performed four different tasks:
- Asked open-ended questions about happy and sad memories over the last week.
- Administered the Short Mood and Feelings Questionnaire (SMFQ).
- Administered a picture task inspired by the Children’s Apperception Test (CAT), where children are asked to answer questions related to pictures shown.
- Administered the Revised Children’s Anxiety and Depression Scale (RCADS) for generalized anxiety, panic disorder, and low mood.
Following the SMFQ children were divided into three different groups according to how likely they were to be struggling with their mental well-being.
The researchers found that children with varying levels of well-being concerns interacted differently with the robot. For children that might not be experiencing mental well-being–related problems, the researchers found that interacting with the robot led to more positive response ratings to the questionnaires. However, for children that might be experiencing well-being–related concerns, the robot may have enabled them to divulge their true feelings and experiences, leading to more negative response ratings to the questionnaire.
Robots an addition not a replacement
“Since the robot we use is child-sized, and completely nonthreatening, children might see the robot as a confidant – they feel like they won’t get into trouble if they share secrets with it,” said Ms. Abbasi. “Other researchers have found that children are more likely to divulge private information – like that they’re being bullied, for example – to a robot than they would be to an adult,” she said.
Study participants all said they “enjoyed talking with the robot,” commented the authors, who added that, “the children were willing to confide in the robot, in some cases sharing information with the robot that they had not yet shared via the standard assessment method of online or in-person questionnaires.”
This is the first time that robots have been used to assess mental well-being in children, the researchers pointed out. “Robots could be a useful addition to traditional methods of mental health assessment,” they said, though they emphasized that robots are “not intended to be a substitute for professional mental health support.”
“We don’t have any intention of replacing psychologists or other mental health professionals with robots, since their expertise far surpasses anything a robot can do,” said Dr. Micol Spitale, affective computing and robotics laboratory, University of Cambridge, and study coauthor. “However, our work suggests that robots could be a useful tool in helping children to open up and share things they might not be comfortable sharing at first.”
The researchers say that they hope to expand their survey in future by including more participants and following them over time. They are also investigating whether similar results could be achieved if children interact with the robot via video chat.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
Robots can be better at detecting mental well-being issues in children than parent-reported or self-reported testing, say U.K. researchers.
The researchers behind a new study, presented at the 31st IEEE International Conference on Robot & Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN) in Naples, Italy, have suggested that robots could be a useful addition to traditional methods of mental health assessment.
“There are times when traditional methods aren’t able to catch mental well-being lapses in children, as sometimes the changes are incredibly subtle,” said Nida Itrat Abbasi, a PhD student at Cambridge (England) Affective Computing and Robotics Group, University of Cambridge, and the study’s first author. “We wanted to see whether robots might be able to help with this process,” she explained.
The authors highlighted how, during the COVID-19 pandemic, home schooling, financial pressures, and isolation from peers and friends impacted the mental health of many children. Even before the pandemic however, anxiety and depression among children in the United Kingdom has been on the rise, but the resources and support to address mental well-being are severely limited.
Children engage with robots
For their study the research team – which comprised roboticists, computer scientists, and psychiatrists from the University of Cambridge – enrolled 28 participants between ages 8 and 13 years. While being observed from an adjacent room by a parent or guardian, along with members of the research team, the participants took part in a one-to-one 45-minute session with a Nao robot – a humanoid robot about 60 cm tall – that administered a series of standard psychological questionnaires to assess the mental well-being of each participant.
Participants interacted with the robot throughout the session by speaking with it or by touching sensors on the robot’s hands and feet. Additional sensors tracked participants’ heartbeat, head, and eye movements during the session.
Professor Hatice Gunes, affective intelligence and robotics laboratory, department of computer science, University of Cambridge, said: “Children are quite tactile, and they’re drawn to technology. If they’re using a screen-based tool, they’re withdrawn from the physical world,” she said. “But robots are perfect because they’re in the physical world – they’re more interactive, so the children are more engaged.”
Prior to each session the children and their parent or guardian completed standard online questionnaires to assess each child’s mental well-being.
During each session, the robot performed four different tasks:
- Asked open-ended questions about happy and sad memories over the last week.
- Administered the Short Mood and Feelings Questionnaire (SMFQ).
- Administered a picture task inspired by the Children’s Apperception Test (CAT), where children are asked to answer questions related to pictures shown.
- Administered the Revised Children’s Anxiety and Depression Scale (RCADS) for generalized anxiety, panic disorder, and low mood.
Following the SMFQ children were divided into three different groups according to how likely they were to be struggling with their mental well-being.
The researchers found that children with varying levels of well-being concerns interacted differently with the robot. For children that might not be experiencing mental well-being–related problems, the researchers found that interacting with the robot led to more positive response ratings to the questionnaires. However, for children that might be experiencing well-being–related concerns, the robot may have enabled them to divulge their true feelings and experiences, leading to more negative response ratings to the questionnaire.
Robots an addition not a replacement
“Since the robot we use is child-sized, and completely nonthreatening, children might see the robot as a confidant – they feel like they won’t get into trouble if they share secrets with it,” said Ms. Abbasi. “Other researchers have found that children are more likely to divulge private information – like that they’re being bullied, for example – to a robot than they would be to an adult,” she said.
Study participants all said they “enjoyed talking with the robot,” commented the authors, who added that, “the children were willing to confide in the robot, in some cases sharing information with the robot that they had not yet shared via the standard assessment method of online or in-person questionnaires.”
This is the first time that robots have been used to assess mental well-being in children, the researchers pointed out. “Robots could be a useful addition to traditional methods of mental health assessment,” they said, though they emphasized that robots are “not intended to be a substitute for professional mental health support.”
“We don’t have any intention of replacing psychologists or other mental health professionals with robots, since their expertise far surpasses anything a robot can do,” said Dr. Micol Spitale, affective computing and robotics laboratory, University of Cambridge, and study coauthor. “However, our work suggests that robots could be a useful tool in helping children to open up and share things they might not be comfortable sharing at first.”
The researchers say that they hope to expand their survey in future by including more participants and following them over time. They are also investigating whether similar results could be achieved if children interact with the robot via video chat.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
Borderline personality disorder raises relapse risk for MDD patients after ECT
ECT has demonstrated effectiveness for treatment of unipolar and bipolar major depression, but relapses within 6 months are frequent, and potential factors affecting relapse have not been well studied, wrote Matthieu Hein, MD, PhD, of Erasme Hospital, Université Libre de Bruxelles, and colleagues.
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a common comorbidity among individuals with major depressive disorder, and previous research suggests a possible negative effect of BPD on ECT response in MDD patients, they wrote.
In a study published in Psychiatry Research, the researchers recruited 68 females and 41 males aged 18 years and older with diagnosed MDD who had partial or complete response to ECT after receiving treatment at a single center. Approximately two-thirds of the patients were aged 50 years and older, and 22 met criteria for BPD. The ECT consisted of three sessions per week; the total number of sessions ranged from 6 to 18.
The primary outcome was relapse at 6 months after ECT treatment. Relapse was defined as a score of 16 or higher on the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale in combination with a mean absolute increase of at least 10 points from the psychiatric interview at the end of the ECT.
Relapse rates at 6 months were 37.6% for the study population overall, but significantly higher for those with BPD, compared with those without BPD (72.7% vs. 28.7%; P < .001).
In a multivariate analysis, adjusting for age, gender, and mood stabilizer use after ECT, relapse was approximately four times more likely among individuals with BPD, compared with those without (hazard ratio, 4.14). No significant association appeared between increased relapse and other comorbid personality disorders, anxiety disorders, alcohol or substance use disorders, or hospitalization during the ECT treatment period.
Potential reasons for the increased relapse risk among individuals with MDD and BPD include the younger age of the individuals with BPD, which has been shown to increase MDD relapse risk; the direct negative impact of BPD on mental functioning; and the documented tendency to poor treatment adherence, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
“Given these different elements, it seems important to screen more systematically for BPD in major depressed individuals treated with ECT in order to allow the implementation of more effective prevention strategies for relapse within 6 months in this particular subpopulation,” they emphasized.
“The demonstration of this higher risk of relapse within 6 months associated with BPD in major depressed individuals treated with ECT could open new therapeutic perspectives to allow better maintenance of euthymia in this particular subpopulation,” they added.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design and the focus on only BPD, which may not generalize to other personality disorders, the researchers noted.
However, the results support data from previous studies and highlight the need for more systematic BPD screening in MDD patients to prevent relapse after ECT, they said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
ECT has demonstrated effectiveness for treatment of unipolar and bipolar major depression, but relapses within 6 months are frequent, and potential factors affecting relapse have not been well studied, wrote Matthieu Hein, MD, PhD, of Erasme Hospital, Université Libre de Bruxelles, and colleagues.
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a common comorbidity among individuals with major depressive disorder, and previous research suggests a possible negative effect of BPD on ECT response in MDD patients, they wrote.
In a study published in Psychiatry Research, the researchers recruited 68 females and 41 males aged 18 years and older with diagnosed MDD who had partial or complete response to ECT after receiving treatment at a single center. Approximately two-thirds of the patients were aged 50 years and older, and 22 met criteria for BPD. The ECT consisted of three sessions per week; the total number of sessions ranged from 6 to 18.
The primary outcome was relapse at 6 months after ECT treatment. Relapse was defined as a score of 16 or higher on the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale in combination with a mean absolute increase of at least 10 points from the psychiatric interview at the end of the ECT.
Relapse rates at 6 months were 37.6% for the study population overall, but significantly higher for those with BPD, compared with those without BPD (72.7% vs. 28.7%; P < .001).
In a multivariate analysis, adjusting for age, gender, and mood stabilizer use after ECT, relapse was approximately four times more likely among individuals with BPD, compared with those without (hazard ratio, 4.14). No significant association appeared between increased relapse and other comorbid personality disorders, anxiety disorders, alcohol or substance use disorders, or hospitalization during the ECT treatment period.
Potential reasons for the increased relapse risk among individuals with MDD and BPD include the younger age of the individuals with BPD, which has been shown to increase MDD relapse risk; the direct negative impact of BPD on mental functioning; and the documented tendency to poor treatment adherence, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
“Given these different elements, it seems important to screen more systematically for BPD in major depressed individuals treated with ECT in order to allow the implementation of more effective prevention strategies for relapse within 6 months in this particular subpopulation,” they emphasized.
“The demonstration of this higher risk of relapse within 6 months associated with BPD in major depressed individuals treated with ECT could open new therapeutic perspectives to allow better maintenance of euthymia in this particular subpopulation,” they added.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design and the focus on only BPD, which may not generalize to other personality disorders, the researchers noted.
However, the results support data from previous studies and highlight the need for more systematic BPD screening in MDD patients to prevent relapse after ECT, they said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
ECT has demonstrated effectiveness for treatment of unipolar and bipolar major depression, but relapses within 6 months are frequent, and potential factors affecting relapse have not been well studied, wrote Matthieu Hein, MD, PhD, of Erasme Hospital, Université Libre de Bruxelles, and colleagues.
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a common comorbidity among individuals with major depressive disorder, and previous research suggests a possible negative effect of BPD on ECT response in MDD patients, they wrote.
In a study published in Psychiatry Research, the researchers recruited 68 females and 41 males aged 18 years and older with diagnosed MDD who had partial or complete response to ECT after receiving treatment at a single center. Approximately two-thirds of the patients were aged 50 years and older, and 22 met criteria for BPD. The ECT consisted of three sessions per week; the total number of sessions ranged from 6 to 18.
The primary outcome was relapse at 6 months after ECT treatment. Relapse was defined as a score of 16 or higher on the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale in combination with a mean absolute increase of at least 10 points from the psychiatric interview at the end of the ECT.
Relapse rates at 6 months were 37.6% for the study population overall, but significantly higher for those with BPD, compared with those without BPD (72.7% vs. 28.7%; P < .001).
In a multivariate analysis, adjusting for age, gender, and mood stabilizer use after ECT, relapse was approximately four times more likely among individuals with BPD, compared with those without (hazard ratio, 4.14). No significant association appeared between increased relapse and other comorbid personality disorders, anxiety disorders, alcohol or substance use disorders, or hospitalization during the ECT treatment period.
Potential reasons for the increased relapse risk among individuals with MDD and BPD include the younger age of the individuals with BPD, which has been shown to increase MDD relapse risk; the direct negative impact of BPD on mental functioning; and the documented tendency to poor treatment adherence, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
“Given these different elements, it seems important to screen more systematically for BPD in major depressed individuals treated with ECT in order to allow the implementation of more effective prevention strategies for relapse within 6 months in this particular subpopulation,” they emphasized.
“The demonstration of this higher risk of relapse within 6 months associated with BPD in major depressed individuals treated with ECT could open new therapeutic perspectives to allow better maintenance of euthymia in this particular subpopulation,” they added.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design and the focus on only BPD, which may not generalize to other personality disorders, the researchers noted.
However, the results support data from previous studies and highlight the need for more systematic BPD screening in MDD patients to prevent relapse after ECT, they said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM PSYCHIATRY RESEARCH
Neuropsychiatric symptoms after stroke
Many patients experience neuropsychiatric symptoms following stroke. There is tremendous variation in the type, severity, and timeline of these symptoms, which have the potential to significantly impact patients’ quality of life. Some symptoms occur as a direct result of ischemic injury to brain structures regulating behavior, executive function, perception, or affect. Other symptoms occur indirectly due to the patient’s often-difficult experiences with the health care system, disrupted routines, or altered poststroke functional abilities. Psychiatric symptoms are not as easily recognized as classic stroke symptoms (such as hemiparesis) and are frequently overlooked, especially in the acute phase. However, these symptoms can negatively influence patients’ interpersonal relationships, rehabilitation, and employment.
Patients and families may not realize certain symptoms are stroke-related and may not discuss them with their clinicians. It is important to ask about and recognize psychiatric symptoms in patients who have experienced a stroke so you can provide optimal education and treatment. In this article, we review the types of psychiatric symptoms associated with strokes in specific brain regions (Table1-10). We also describe symptoms that do not appear directly related to the anatomical structures affected by the infarct, including delirium, psychosis, depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress.
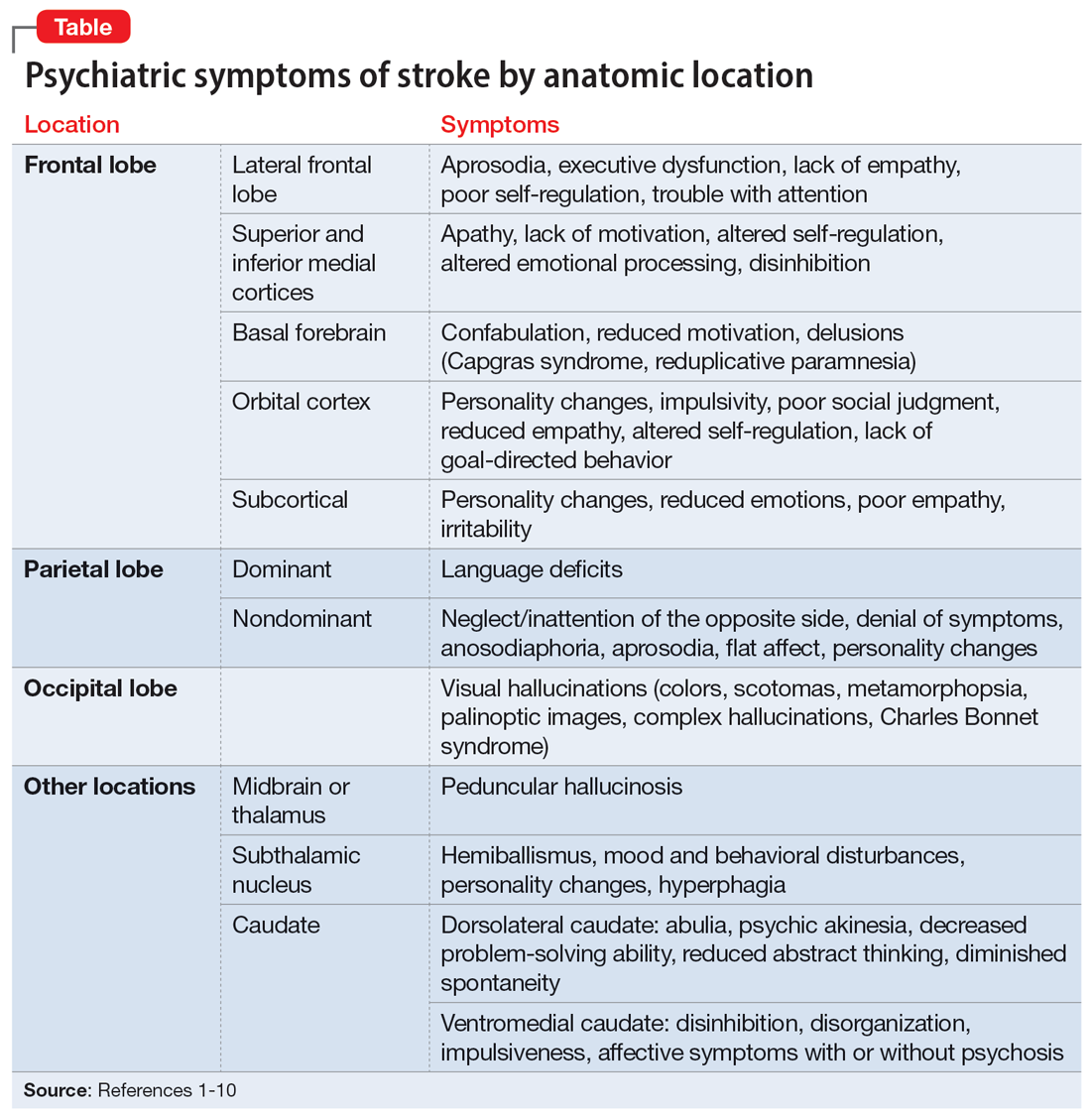
Symptoms associated with stroke in specific regions
Frontal lobe strokes
The frontal lobes are the largest lobes in the brain, and damage to areas within these lobes can cause behavioral and personality changes. Lesions in the lateral frontal cortex can cause aprosodia (difficulty expressing or comprehending variations in tone of voice), which can lead to communication errors. Lateral frontal cortex injury can cause executive dysfunction and a lack of empathy1 as well as trouble with attention, planning, and self-regulation that may affect daily functioning. Strokes affecting the superior and inferior mesial cortices may result in apathy, lack of motivation, altered self-regulation, altered emotional processing, and disinhibition. Patients who experience a basal forebrain stroke may exhibit confabulation, reduced motivation, and delusions such as Capgras syndrome (the belief that a person or place has been replaced by an exact copy) and reduplicative paramnesia (the belief that a place has been either moved, duplicated, or exists in 2 places simultaneously). Strokes involving the orbital cortex can be associated with personality changes, impulsivity, poor social judgment, reduced empathy, altered self-regulation, lack of goal-directed behavior, and environmental dependency.
Some strokes may occur primarily in the subcortical white matter within the frontal lobes. Symptoms may be due to a single stroke with sudden onset, or due to repeated ischemic events that accumulate over time, as seen with microvascular disease. In the case of microvascular disease, the onset of symptoms may be insidious and the course progressive. Infarcts in the subcortical area can also cause personality changes (though typically more subtle when compared to orbitofrontal strokes), reduced emotions, poor empathy, and irritability.1 Patients may lack insight into some of or all these symptoms following a frontal lobe infarct, which makes it critical to gather collateral information from the patient’s friends or family.
Parietal lobe strokes
Symptomatology from parietal strokes depends on whether the stroke affects the dominant or nondominant hemisphere. Dominant parietal lesions cause language deficits, and psychiatric symptoms may be difficult to elucidate due to the patient’s inability to communicate.2 On the other hand, patients with nondominant parietal stroke may have neglect of, or inattention to, the opposite (typically left) side.3 This often manifests as a reluctance to use the affected limb or limbs, in some cases despite a lack of true weakness or motor dysfunction. In addition, patients may also have visual and/or tactile inattention towards the affected side, despite a lack of gross visual or sensory impairment.2 In rare cases, a patient’s stroke may be misdiagnosed as a functional disorder due to the perceived unwillingness to use a neurologically intact limb. In severe cases, patients may not recognize an affected extremity as their own. Patients are also frequently unaware of deficits affecting their nondominant side and may argue with those attempting to explain their deficit. Anosodiaphoria—an abnormal lack of concern regarding their deficits—may also be observed. Additionally, aprosodia, flat affect, and personality changes may result from strokes affecting the nondominant hemisphere, which can impact the patient’s relationships and social functioning.3
Occipital lobe strokes
While negative or loss-of-function symptomatology is one of the hallmarks of stroke, occipital lobe infarcts can pose an exception. Although vision loss is the most common symptom with occipital lobe strokes, some patients experience visual hallucinations that may occur acutely or subacutely. In the acute phase, patients may report hallucinations of varied description,4 including poorly formed areas of color, scotomas, metamorphopsia (visual distortion in which straight lines appear curved), more complex and formed hallucinations and/or palinoptic images (images or brief scenes that continue to be perceived after looking away). These hallucinations, often referred to as release phenomena or release hallucinations, are thought to result from disinhibition of the visual cortex, which then fires spontaneously.
Hallucinations are associated with either infarction or hemorrhage in the posterior cerebral artery territory. In some cases, the hallucinations may take on a formed, complex appearance, and Charles Bonnet syndrome (visual hallucinations in the setting of vision loss, with insight into the hallucinations) has been identified in a small portion of patients.5
Continue to: The duration of these...
The duration of these hallucinations varies. Some patients describe very short periods of the disturbance, lasting minutes to hours and corresponding with the onset of their stroke. Others experience prolonged hallucinations, which frequently evolve into formed, complex images, lasting from days to months.6 In the setting of cortical stroke, patients may be at risk for seizures, which could manifest as visual hallucinations. It is essential to ensure that epileptic causes of hallucinations have been ruled out, because seizures may require treatment and other precautions.
Other stroke locations
Strokes in other locations also can result in psychiatric or behavioral symptoms. Acute stroke in the subcortical midbrain or thalamus may result in peduncular hallucinosis, a syndrome of vivid visual hallucinations.7 The midbrain (most commonly the reticular formation) is usually affected; however, certain lesions of the thalamus may also cause peduncular hallucinosis. This phenomenon is theorized to be due to an increase in serotonin activity relative to acetylcholine and is often accompanied by drowsiness.
The subthalamic nucleus is most frequently associated with disordered movement such as hemiballismus, but also causes disturbances in mood and behavior, including hyperphagia and personality changes.8 Irritability, aggressiveness, disinhibition, anxiety, and obscene speech may also be seen with lesions of the subthalamic nucleus.
Finally, the caudate nucleus may cause alterations in executive functioning and behavior.9 A stroke in the dorsolateral caudate may cause abulia and psychic akinesia, decreased problem-solving ability, reduced abstract thinking, and/or diminished spontaneity, whereas an infarct in the ventromedial region of the nucleus may cause disinhibition, disorganization, impulsiveness, and, in severe cases, affective symptoms with psychosis.10 Strokes in any of these areas are at risk for being misdiagnosed because patients may not have a hemiparesis, and isolated positive or psychiatric symptoms may not be recognized as stroke.
Symptoms not related to stroke location
Delirium and psychosis
Following a stroke, a patient may exhibit neuropsychiatric symptoms that do not appear to relate directly to the anatomical structures affected by the infarct. In the acute phase, factors such as older age and medical complications (including infection, metabolic derangement, and lack of sleep due to frequent neurologic checks) create a high risk of delirium.11 Differentiating delirium from alterations in mental status due to seizure, cerebral edema, or other medical complications is essential, and delirium precautions should be exercised to the greatest extent possible. Other neuropsychiatric symptoms may manifest following hospitalization.
Continue to: Poststroke psychosis...
Poststroke psychosis often presents subacutely. Among these patients, the most common psychosis is delusion disorder, followed by schizophrenia-like psychosis and mood disorder with psychotic features.12 Some evidence suggests antipsychotics may be highly effective for many of these patients.12 Poststroke psychosis does appear to correlate somewhat with nondominant hemisphere lesions, including the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and/or caudate nucleus. Because high mortality and poor functional outcomes have been associated with poststroke psychosis, early intervention is essential.
Depression
Depression is a common problem following stroke, affecting approximately 35% of stroke patients.13 In addition to impairing quality of life, depression negatively impacts rehabilitation and increases caregiver burden. There is significant variability regarding risk factors that increases the likelihood of poststroke depression; however, psychiatric history, dysphagia, and poor social support consistently correlate with a higher risk.14,15 Characteristics of a patient’s stroke, such as lesion volume and the ability to perform activities of daily living, are also risk factors. Identifying depression among patients who recently had a stroke is sometimes difficult due to a plethora of confounding factors. Patients may not communicate well due to aphasia, while strokes in other locations may result in an altered affect. Depending on the stroke location, patients may also suffer anosognosia (a lack of awareness of their deficits), which may impair their ability to learn and use adaptive strategies and equipment. An additional confounder is the significant overlap between depressive symptoms and those seen in the setting of a major medical event or hospitalization (decreased appetite, fatigue, etc). The prevalence of depression peaks approximately 3 to 6 months after stroke, with symptoms lasting 9 to 12 months on average, although many patients experience symptoms significantly longer.14 Because symptoms can begin within hours to days following a stroke, it is essential that both hospital and outpatient clinicians assess for depression when indicated. Patients with poststroke depression should receive prompt treatment because appropriate treatment correlates with improved rehabilitation, and most patients respond well to antidepressants.16 Early treatment reduces mortality and improves compliance with secondary stroke prevention measures, including pharmacotherapy.17
Anxiety and posttraumatic stress
Anxiety and anxiety-related disorders are additional potential complications following stroke that significantly influence patient outcomes and well-being. The abrupt, unexpected onset of stroke is often frightening to patients and families. The potential for life-altering deficits as well as intense, often invasive, interactions with the health care system does little to assuage patients’ fear. Stroke patients must contend with a change in neurologic function while processing their difficult experiences, and may develop profound fear of a recurrent stroke. As many as 22% of patients have an anxiety disorder 3 months after they have a stroke.18 Phobic disorder is the most prevalent subtype, followed by generalized anxiety disorder. Younger age and previous anxiety or depression place patients at greater risk of developing poststroke anxiety. Patients suffering from poststroke anxiety have a reduced quality of life, are more dependent, and show restricted participation in rehabilitation, all of which culminate in poorer outcomes.
Many patients describe their experiences surrounding their stroke as traumatic, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is increasingly acknowledged as a potential complication for patients with recent stroke.19 PTSD profoundly impacts patient quality of life. Interestingly, most patients who develop poststroke PTSD do not have a history of other psychiatric illness, and it is difficult to predict who may develop PTSD. Relatively little is known regarding optimal treatment strategies for poststroke PTSD, or the efficacy of pharmacotherapy and psychotherapeutic strategies to treat it.
Goals: Improve recovery and quality of life
Neuropsychiatric symptoms are common following a stroke and may manifest in a variety of ways. While some symptoms are a direct consequence of injury to a specific brain region, other symptoms may be a response to loss of independence, disability, experience with the medical system, or fear of recurrent stroke. The onset of psychiatric symptoms can be acute, beginning during hospitalization, or delayed. Understanding the association of psychiatric symptoms with the anatomical location of stroke may assist clinicians in identifying such symptoms. This knowledge informs conversations with patients and their caregivers, who may benefit from understanding that such symptoms are common after stroke. Furthermore, identifying psychiatric complications following stroke may affect rehabilitation. Additional investigation is necessary to find more effective treatment modalities and improve early intervention.
Continue to: Bottom Line
Bottom Line
Neuropsychiatric symptoms are frequently overlooked in patients with recent stroke. These symptoms include delirium, psychosis, depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder, and can be the direct result of injury to neuroanatomical structures or a consequence of the patient’s experience. Prompt treatment can maximize stroke recovery and quality of life.
Related Resources
- Zhang S, Xu M, Liu ZJ, et al. Neuropsychiatric issues after stroke: clinical significance and therapeutic implications. World J Psychiatry. 2020;10(6):125-138. doi:10.5498/wjp. v10.i6.125
- Saha G, Chakraborty K, Pattojoshi A. Management of psychiatric disorders in patients with stroke and traumatic brain injury. Indian J Psychiatry. 2022;64(Suppl 2): S344-S354.
1. Eslinger PJ, Reichwein RK. Frontal lobe stroke syndromes. In: Caplan LR, van Gijn J, eds. Stroke Syndromes. 3rd ed. Cambridge University Press; 2012:232-241.
2. Critchley M, Russell WR, Zangwill OL. Discussion on parietal lobe syndromes. Proc R Soc Med. 1951;44(4):337-346.
3. Hier DB, Mondlock J, Caplan LR. Behavioral abnormalities after right hemisphere stroke. Neurology. 1983;33(3):337-344.
4. Brust JC, Behrens MM. “Release hallucinations” as the major symptom of posterior cerebral artery occlusion: a report of 2 cases. Ann Neurol. 1977;2(5):432-436.
5. Kumral E, Uluakay A, Donmez A. Complex visual hallucinations following stroke: epileptic origin or a deafferentiation phenomenon? Austin J Cerebrovasc Dis & Stroke. 2014;1(1):1005.
6. Lee JS, Ko KH, Oh JH, et al. Charles Bonnet syndrome after occipital infarction. J Neurosonol Neuroimag. 2018;10(2):154-157.
7. Young JB. Peduncular hallucinosis. In: Aminoff MJ, Daroff RB, eds. Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2014:848.
8. Etemadifar M, Abtahi SH, Abtahi SM, et al. Hemiballismus, hyperphagia, and behavioral changes following subthalamic infarct. Case Rep Med. 2012;2012:768580. doi:10.1155/2012/768580
9. Kumral E, Evyapan D, Balkir K. Acute caudate vascular lesions. Stroke. 1999;30(1):100-108.
10. Wang PY. Neurobehavioral changes following caudate infarct: a case report with literature review. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Taipei). 1991;47(3):199-203.
11. Ahmed S, Leurent B, Sampson EL. Risk factors for incident delirium among older people in acute hospital medical units: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing. 2014;43(3):326-33.
12. Stangeland H, Orgeta V, Bell V. Poststroke psychosis: a systematic review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2018;89(8):879-885.
13. Lenzi GL, Altieri M, Maestrini I. Post-stroke depression. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2008;164(10):837-840.
14. Whyte EM, Mulsant BH. Post stroke depression: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and biological treatment. Biol Psychiatry. 2002;52(3):253-264.
15. Pritchard KT, Hreha KP, Hong I. Dysphagia associated with risk of depressive symptoms among stroke survivors after discharge from a cluster of inpatient rehabilitation facilities. Swallowing Rehabil. 2020;3(1):33-44.
16. Wiart L, Petit H, Joseph PA, et al. Fluoxetine in early poststroke depression: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Stroke. 2000;31(8):1829-1832.
17. Jorge RE, Robinson RG, Arndt S, et al. Mortality and poststroke depression: a placebo-controlled trial of antidepressants. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(10):1823-1829.
18. Chun HY, Whiteley WN, Dennis MS, et al. Anxiety after stroke: the importance of subtyping. Stroke. 2018;49(3):556-564.
19. Garton AL, Sisti JA, Gupta VP, et al. Poststroke post-traumatic stress disorder: a review. Stroke. 2017;48(2):507-512.
Many patients experience neuropsychiatric symptoms following stroke. There is tremendous variation in the type, severity, and timeline of these symptoms, which have the potential to significantly impact patients’ quality of life. Some symptoms occur as a direct result of ischemic injury to brain structures regulating behavior, executive function, perception, or affect. Other symptoms occur indirectly due to the patient’s often-difficult experiences with the health care system, disrupted routines, or altered poststroke functional abilities. Psychiatric symptoms are not as easily recognized as classic stroke symptoms (such as hemiparesis) and are frequently overlooked, especially in the acute phase. However, these symptoms can negatively influence patients’ interpersonal relationships, rehabilitation, and employment.
Patients and families may not realize certain symptoms are stroke-related and may not discuss them with their clinicians. It is important to ask about and recognize psychiatric symptoms in patients who have experienced a stroke so you can provide optimal education and treatment. In this article, we review the types of psychiatric symptoms associated with strokes in specific brain regions (Table1-10). We also describe symptoms that do not appear directly related to the anatomical structures affected by the infarct, including delirium, psychosis, depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress.

Symptoms associated with stroke in specific regions
Frontal lobe strokes
The frontal lobes are the largest lobes in the brain, and damage to areas within these lobes can cause behavioral and personality changes. Lesions in the lateral frontal cortex can cause aprosodia (difficulty expressing or comprehending variations in tone of voice), which can lead to communication errors. Lateral frontal cortex injury can cause executive dysfunction and a lack of empathy1 as well as trouble with attention, planning, and self-regulation that may affect daily functioning. Strokes affecting the superior and inferior mesial cortices may result in apathy, lack of motivation, altered self-regulation, altered emotional processing, and disinhibition. Patients who experience a basal forebrain stroke may exhibit confabulation, reduced motivation, and delusions such as Capgras syndrome (the belief that a person or place has been replaced by an exact copy) and reduplicative paramnesia (the belief that a place has been either moved, duplicated, or exists in 2 places simultaneously). Strokes involving the orbital cortex can be associated with personality changes, impulsivity, poor social judgment, reduced empathy, altered self-regulation, lack of goal-directed behavior, and environmental dependency.
Some strokes may occur primarily in the subcortical white matter within the frontal lobes. Symptoms may be due to a single stroke with sudden onset, or due to repeated ischemic events that accumulate over time, as seen with microvascular disease. In the case of microvascular disease, the onset of symptoms may be insidious and the course progressive. Infarcts in the subcortical area can also cause personality changes (though typically more subtle when compared to orbitofrontal strokes), reduced emotions, poor empathy, and irritability.1 Patients may lack insight into some of or all these symptoms following a frontal lobe infarct, which makes it critical to gather collateral information from the patient’s friends or family.
Parietal lobe strokes
Symptomatology from parietal strokes depends on whether the stroke affects the dominant or nondominant hemisphere. Dominant parietal lesions cause language deficits, and psychiatric symptoms may be difficult to elucidate due to the patient’s inability to communicate.2 On the other hand, patients with nondominant parietal stroke may have neglect of, or inattention to, the opposite (typically left) side.3 This often manifests as a reluctance to use the affected limb or limbs, in some cases despite a lack of true weakness or motor dysfunction. In addition, patients may also have visual and/or tactile inattention towards the affected side, despite a lack of gross visual or sensory impairment.2 In rare cases, a patient’s stroke may be misdiagnosed as a functional disorder due to the perceived unwillingness to use a neurologically intact limb. In severe cases, patients may not recognize an affected extremity as their own. Patients are also frequently unaware of deficits affecting their nondominant side and may argue with those attempting to explain their deficit. Anosodiaphoria—an abnormal lack of concern regarding their deficits—may also be observed. Additionally, aprosodia, flat affect, and personality changes may result from strokes affecting the nondominant hemisphere, which can impact the patient’s relationships and social functioning.3
Occipital lobe strokes
While negative or loss-of-function symptomatology is one of the hallmarks of stroke, occipital lobe infarcts can pose an exception. Although vision loss is the most common symptom with occipital lobe strokes, some patients experience visual hallucinations that may occur acutely or subacutely. In the acute phase, patients may report hallucinations of varied description,4 including poorly formed areas of color, scotomas, metamorphopsia (visual distortion in which straight lines appear curved), more complex and formed hallucinations and/or palinoptic images (images or brief scenes that continue to be perceived after looking away). These hallucinations, often referred to as release phenomena or release hallucinations, are thought to result from disinhibition of the visual cortex, which then fires spontaneously.
Hallucinations are associated with either infarction or hemorrhage in the posterior cerebral artery territory. In some cases, the hallucinations may take on a formed, complex appearance, and Charles Bonnet syndrome (visual hallucinations in the setting of vision loss, with insight into the hallucinations) has been identified in a small portion of patients.5
Continue to: The duration of these...
The duration of these hallucinations varies. Some patients describe very short periods of the disturbance, lasting minutes to hours and corresponding with the onset of their stroke. Others experience prolonged hallucinations, which frequently evolve into formed, complex images, lasting from days to months.6 In the setting of cortical stroke, patients may be at risk for seizures, which could manifest as visual hallucinations. It is essential to ensure that epileptic causes of hallucinations have been ruled out, because seizures may require treatment and other precautions.
Other stroke locations
Strokes in other locations also can result in psychiatric or behavioral symptoms. Acute stroke in the subcortical midbrain or thalamus may result in peduncular hallucinosis, a syndrome of vivid visual hallucinations.7 The midbrain (most commonly the reticular formation) is usually affected; however, certain lesions of the thalamus may also cause peduncular hallucinosis. This phenomenon is theorized to be due to an increase in serotonin activity relative to acetylcholine and is often accompanied by drowsiness.
The subthalamic nucleus is most frequently associated with disordered movement such as hemiballismus, but also causes disturbances in mood and behavior, including hyperphagia and personality changes.8 Irritability, aggressiveness, disinhibition, anxiety, and obscene speech may also be seen with lesions of the subthalamic nucleus.
Finally, the caudate nucleus may cause alterations in executive functioning and behavior.9 A stroke in the dorsolateral caudate may cause abulia and psychic akinesia, decreased problem-solving ability, reduced abstract thinking, and/or diminished spontaneity, whereas an infarct in the ventromedial region of the nucleus may cause disinhibition, disorganization, impulsiveness, and, in severe cases, affective symptoms with psychosis.10 Strokes in any of these areas are at risk for being misdiagnosed because patients may not have a hemiparesis, and isolated positive or psychiatric symptoms may not be recognized as stroke.
Symptoms not related to stroke location
Delirium and psychosis
Following a stroke, a patient may exhibit neuropsychiatric symptoms that do not appear to relate directly to the anatomical structures affected by the infarct. In the acute phase, factors such as older age and medical complications (including infection, metabolic derangement, and lack of sleep due to frequent neurologic checks) create a high risk of delirium.11 Differentiating delirium from alterations in mental status due to seizure, cerebral edema, or other medical complications is essential, and delirium precautions should be exercised to the greatest extent possible. Other neuropsychiatric symptoms may manifest following hospitalization.
Continue to: Poststroke psychosis...
Poststroke psychosis often presents subacutely. Among these patients, the most common psychosis is delusion disorder, followed by schizophrenia-like psychosis and mood disorder with psychotic features.12 Some evidence suggests antipsychotics may be highly effective for many of these patients.12 Poststroke psychosis does appear to correlate somewhat with nondominant hemisphere lesions, including the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and/or caudate nucleus. Because high mortality and poor functional outcomes have been associated with poststroke psychosis, early intervention is essential.
Depression
Depression is a common problem following stroke, affecting approximately 35% of stroke patients.13 In addition to impairing quality of life, depression negatively impacts rehabilitation and increases caregiver burden. There is significant variability regarding risk factors that increases the likelihood of poststroke depression; however, psychiatric history, dysphagia, and poor social support consistently correlate with a higher risk.14,15 Characteristics of a patient’s stroke, such as lesion volume and the ability to perform activities of daily living, are also risk factors. Identifying depression among patients who recently had a stroke is sometimes difficult due to a plethora of confounding factors. Patients may not communicate well due to aphasia, while strokes in other locations may result in an altered affect. Depending on the stroke location, patients may also suffer anosognosia (a lack of awareness of their deficits), which may impair their ability to learn and use adaptive strategies and equipment. An additional confounder is the significant overlap between depressive symptoms and those seen in the setting of a major medical event or hospitalization (decreased appetite, fatigue, etc). The prevalence of depression peaks approximately 3 to 6 months after stroke, with symptoms lasting 9 to 12 months on average, although many patients experience symptoms significantly longer.14 Because symptoms can begin within hours to days following a stroke, it is essential that both hospital and outpatient clinicians assess for depression when indicated. Patients with poststroke depression should receive prompt treatment because appropriate treatment correlates with improved rehabilitation, and most patients respond well to antidepressants.16 Early treatment reduces mortality and improves compliance with secondary stroke prevention measures, including pharmacotherapy.17
Anxiety and posttraumatic stress
Anxiety and anxiety-related disorders are additional potential complications following stroke that significantly influence patient outcomes and well-being. The abrupt, unexpected onset of stroke is often frightening to patients and families. The potential for life-altering deficits as well as intense, often invasive, interactions with the health care system does little to assuage patients’ fear. Stroke patients must contend with a change in neurologic function while processing their difficult experiences, and may develop profound fear of a recurrent stroke. As many as 22% of patients have an anxiety disorder 3 months after they have a stroke.18 Phobic disorder is the most prevalent subtype, followed by generalized anxiety disorder. Younger age and previous anxiety or depression place patients at greater risk of developing poststroke anxiety. Patients suffering from poststroke anxiety have a reduced quality of life, are more dependent, and show restricted participation in rehabilitation, all of which culminate in poorer outcomes.
Many patients describe their experiences surrounding their stroke as traumatic, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is increasingly acknowledged as a potential complication for patients with recent stroke.19 PTSD profoundly impacts patient quality of life. Interestingly, most patients who develop poststroke PTSD do not have a history of other psychiatric illness, and it is difficult to predict who may develop PTSD. Relatively little is known regarding optimal treatment strategies for poststroke PTSD, or the efficacy of pharmacotherapy and psychotherapeutic strategies to treat it.
Goals: Improve recovery and quality of life
Neuropsychiatric symptoms are common following a stroke and may manifest in a variety of ways. While some symptoms are a direct consequence of injury to a specific brain region, other symptoms may be a response to loss of independence, disability, experience with the medical system, or fear of recurrent stroke. The onset of psychiatric symptoms can be acute, beginning during hospitalization, or delayed. Understanding the association of psychiatric symptoms with the anatomical location of stroke may assist clinicians in identifying such symptoms. This knowledge informs conversations with patients and their caregivers, who may benefit from understanding that such symptoms are common after stroke. Furthermore, identifying psychiatric complications following stroke may affect rehabilitation. Additional investigation is necessary to find more effective treatment modalities and improve early intervention.
Continue to: Bottom Line
Bottom Line
Neuropsychiatric symptoms are frequently overlooked in patients with recent stroke. These symptoms include delirium, psychosis, depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder, and can be the direct result of injury to neuroanatomical structures or a consequence of the patient’s experience. Prompt treatment can maximize stroke recovery and quality of life.
Related Resources
- Zhang S, Xu M, Liu ZJ, et al. Neuropsychiatric issues after stroke: clinical significance and therapeutic implications. World J Psychiatry. 2020;10(6):125-138. doi:10.5498/wjp. v10.i6.125
- Saha G, Chakraborty K, Pattojoshi A. Management of psychiatric disorders in patients with stroke and traumatic brain injury. Indian J Psychiatry. 2022;64(Suppl 2): S344-S354.
Many patients experience neuropsychiatric symptoms following stroke. There is tremendous variation in the type, severity, and timeline of these symptoms, which have the potential to significantly impact patients’ quality of life. Some symptoms occur as a direct result of ischemic injury to brain structures regulating behavior, executive function, perception, or affect. Other symptoms occur indirectly due to the patient’s often-difficult experiences with the health care system, disrupted routines, or altered poststroke functional abilities. Psychiatric symptoms are not as easily recognized as classic stroke symptoms (such as hemiparesis) and are frequently overlooked, especially in the acute phase. However, these symptoms can negatively influence patients’ interpersonal relationships, rehabilitation, and employment.
Patients and families may not realize certain symptoms are stroke-related and may not discuss them with their clinicians. It is important to ask about and recognize psychiatric symptoms in patients who have experienced a stroke so you can provide optimal education and treatment. In this article, we review the types of psychiatric symptoms associated with strokes in specific brain regions (Table1-10). We also describe symptoms that do not appear directly related to the anatomical structures affected by the infarct, including delirium, psychosis, depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress.

Symptoms associated with stroke in specific regions
Frontal lobe strokes
The frontal lobes are the largest lobes in the brain, and damage to areas within these lobes can cause behavioral and personality changes. Lesions in the lateral frontal cortex can cause aprosodia (difficulty expressing or comprehending variations in tone of voice), which can lead to communication errors. Lateral frontal cortex injury can cause executive dysfunction and a lack of empathy1 as well as trouble with attention, planning, and self-regulation that may affect daily functioning. Strokes affecting the superior and inferior mesial cortices may result in apathy, lack of motivation, altered self-regulation, altered emotional processing, and disinhibition. Patients who experience a basal forebrain stroke may exhibit confabulation, reduced motivation, and delusions such as Capgras syndrome (the belief that a person or place has been replaced by an exact copy) and reduplicative paramnesia (the belief that a place has been either moved, duplicated, or exists in 2 places simultaneously). Strokes involving the orbital cortex can be associated with personality changes, impulsivity, poor social judgment, reduced empathy, altered self-regulation, lack of goal-directed behavior, and environmental dependency.
Some strokes may occur primarily in the subcortical white matter within the frontal lobes. Symptoms may be due to a single stroke with sudden onset, or due to repeated ischemic events that accumulate over time, as seen with microvascular disease. In the case of microvascular disease, the onset of symptoms may be insidious and the course progressive. Infarcts in the subcortical area can also cause personality changes (though typically more subtle when compared to orbitofrontal strokes), reduced emotions, poor empathy, and irritability.1 Patients may lack insight into some of or all these symptoms following a frontal lobe infarct, which makes it critical to gather collateral information from the patient’s friends or family.
Parietal lobe strokes
Symptomatology from parietal strokes depends on whether the stroke affects the dominant or nondominant hemisphere. Dominant parietal lesions cause language deficits, and psychiatric symptoms may be difficult to elucidate due to the patient’s inability to communicate.2 On the other hand, patients with nondominant parietal stroke may have neglect of, or inattention to, the opposite (typically left) side.3 This often manifests as a reluctance to use the affected limb or limbs, in some cases despite a lack of true weakness or motor dysfunction. In addition, patients may also have visual and/or tactile inattention towards the affected side, despite a lack of gross visual or sensory impairment.2 In rare cases, a patient’s stroke may be misdiagnosed as a functional disorder due to the perceived unwillingness to use a neurologically intact limb. In severe cases, patients may not recognize an affected extremity as their own. Patients are also frequently unaware of deficits affecting their nondominant side and may argue with those attempting to explain their deficit. Anosodiaphoria—an abnormal lack of concern regarding their deficits—may also be observed. Additionally, aprosodia, flat affect, and personality changes may result from strokes affecting the nondominant hemisphere, which can impact the patient’s relationships and social functioning.3
Occipital lobe strokes
While negative or loss-of-function symptomatology is one of the hallmarks of stroke, occipital lobe infarcts can pose an exception. Although vision loss is the most common symptom with occipital lobe strokes, some patients experience visual hallucinations that may occur acutely or subacutely. In the acute phase, patients may report hallucinations of varied description,4 including poorly formed areas of color, scotomas, metamorphopsia (visual distortion in which straight lines appear curved), more complex and formed hallucinations and/or palinoptic images (images or brief scenes that continue to be perceived after looking away). These hallucinations, often referred to as release phenomena or release hallucinations, are thought to result from disinhibition of the visual cortex, which then fires spontaneously.
Hallucinations are associated with either infarction or hemorrhage in the posterior cerebral artery territory. In some cases, the hallucinations may take on a formed, complex appearance, and Charles Bonnet syndrome (visual hallucinations in the setting of vision loss, with insight into the hallucinations) has been identified in a small portion of patients.5
Continue to: The duration of these...
The duration of these hallucinations varies. Some patients describe very short periods of the disturbance, lasting minutes to hours and corresponding with the onset of their stroke. Others experience prolonged hallucinations, which frequently evolve into formed, complex images, lasting from days to months.6 In the setting of cortical stroke, patients may be at risk for seizures, which could manifest as visual hallucinations. It is essential to ensure that epileptic causes of hallucinations have been ruled out, because seizures may require treatment and other precautions.
Other stroke locations
Strokes in other locations also can result in psychiatric or behavioral symptoms. Acute stroke in the subcortical midbrain or thalamus may result in peduncular hallucinosis, a syndrome of vivid visual hallucinations.7 The midbrain (most commonly the reticular formation) is usually affected; however, certain lesions of the thalamus may also cause peduncular hallucinosis. This phenomenon is theorized to be due to an increase in serotonin activity relative to acetylcholine and is often accompanied by drowsiness.
The subthalamic nucleus is most frequently associated with disordered movement such as hemiballismus, but also causes disturbances in mood and behavior, including hyperphagia and personality changes.8 Irritability, aggressiveness, disinhibition, anxiety, and obscene speech may also be seen with lesions of the subthalamic nucleus.
Finally, the caudate nucleus may cause alterations in executive functioning and behavior.9 A stroke in the dorsolateral caudate may cause abulia and psychic akinesia, decreased problem-solving ability, reduced abstract thinking, and/or diminished spontaneity, whereas an infarct in the ventromedial region of the nucleus may cause disinhibition, disorganization, impulsiveness, and, in severe cases, affective symptoms with psychosis.10 Strokes in any of these areas are at risk for being misdiagnosed because patients may not have a hemiparesis, and isolated positive or psychiatric symptoms may not be recognized as stroke.
Symptoms not related to stroke location
Delirium and psychosis
Following a stroke, a patient may exhibit neuropsychiatric symptoms that do not appear to relate directly to the anatomical structures affected by the infarct. In the acute phase, factors such as older age and medical complications (including infection, metabolic derangement, and lack of sleep due to frequent neurologic checks) create a high risk of delirium.11 Differentiating delirium from alterations in mental status due to seizure, cerebral edema, or other medical complications is essential, and delirium precautions should be exercised to the greatest extent possible. Other neuropsychiatric symptoms may manifest following hospitalization.
Continue to: Poststroke psychosis...
Poststroke psychosis often presents subacutely. Among these patients, the most common psychosis is delusion disorder, followed by schizophrenia-like psychosis and mood disorder with psychotic features.12 Some evidence suggests antipsychotics may be highly effective for many of these patients.12 Poststroke psychosis does appear to correlate somewhat with nondominant hemisphere lesions, including the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and/or caudate nucleus. Because high mortality and poor functional outcomes have been associated with poststroke psychosis, early intervention is essential.
Depression
Depression is a common problem following stroke, affecting approximately 35% of stroke patients.13 In addition to impairing quality of life, depression negatively impacts rehabilitation and increases caregiver burden. There is significant variability regarding risk factors that increases the likelihood of poststroke depression; however, psychiatric history, dysphagia, and poor social support consistently correlate with a higher risk.14,15 Characteristics of a patient’s stroke, such as lesion volume and the ability to perform activities of daily living, are also risk factors. Identifying depression among patients who recently had a stroke is sometimes difficult due to a plethora of confounding factors. Patients may not communicate well due to aphasia, while strokes in other locations may result in an altered affect. Depending on the stroke location, patients may also suffer anosognosia (a lack of awareness of their deficits), which may impair their ability to learn and use adaptive strategies and equipment. An additional confounder is the significant overlap between depressive symptoms and those seen in the setting of a major medical event or hospitalization (decreased appetite, fatigue, etc). The prevalence of depression peaks approximately 3 to 6 months after stroke, with symptoms lasting 9 to 12 months on average, although many patients experience symptoms significantly longer.14 Because symptoms can begin within hours to days following a stroke, it is essential that both hospital and outpatient clinicians assess for depression when indicated. Patients with poststroke depression should receive prompt treatment because appropriate treatment correlates with improved rehabilitation, and most patients respond well to antidepressants.16 Early treatment reduces mortality and improves compliance with secondary stroke prevention measures, including pharmacotherapy.17
Anxiety and posttraumatic stress
Anxiety and anxiety-related disorders are additional potential complications following stroke that significantly influence patient outcomes and well-being. The abrupt, unexpected onset of stroke is often frightening to patients and families. The potential for life-altering deficits as well as intense, often invasive, interactions with the health care system does little to assuage patients’ fear. Stroke patients must contend with a change in neurologic function while processing their difficult experiences, and may develop profound fear of a recurrent stroke. As many as 22% of patients have an anxiety disorder 3 months after they have a stroke.18 Phobic disorder is the most prevalent subtype, followed by generalized anxiety disorder. Younger age and previous anxiety or depression place patients at greater risk of developing poststroke anxiety. Patients suffering from poststroke anxiety have a reduced quality of life, are more dependent, and show restricted participation in rehabilitation, all of which culminate in poorer outcomes.
Many patients describe their experiences surrounding their stroke as traumatic, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is increasingly acknowledged as a potential complication for patients with recent stroke.19 PTSD profoundly impacts patient quality of life. Interestingly, most patients who develop poststroke PTSD do not have a history of other psychiatric illness, and it is difficult to predict who may develop PTSD. Relatively little is known regarding optimal treatment strategies for poststroke PTSD, or the efficacy of pharmacotherapy and psychotherapeutic strategies to treat it.
Goals: Improve recovery and quality of life
Neuropsychiatric symptoms are common following a stroke and may manifest in a variety of ways. While some symptoms are a direct consequence of injury to a specific brain region, other symptoms may be a response to loss of independence, disability, experience with the medical system, or fear of recurrent stroke. The onset of psychiatric symptoms can be acute, beginning during hospitalization, or delayed. Understanding the association of psychiatric symptoms with the anatomical location of stroke may assist clinicians in identifying such symptoms. This knowledge informs conversations with patients and their caregivers, who may benefit from understanding that such symptoms are common after stroke. Furthermore, identifying psychiatric complications following stroke may affect rehabilitation. Additional investigation is necessary to find more effective treatment modalities and improve early intervention.
Continue to: Bottom Line
Bottom Line
Neuropsychiatric symptoms are frequently overlooked in patients with recent stroke. These symptoms include delirium, psychosis, depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder, and can be the direct result of injury to neuroanatomical structures or a consequence of the patient’s experience. Prompt treatment can maximize stroke recovery and quality of life.
Related Resources
- Zhang S, Xu M, Liu ZJ, et al. Neuropsychiatric issues after stroke: clinical significance and therapeutic implications. World J Psychiatry. 2020;10(6):125-138. doi:10.5498/wjp. v10.i6.125
- Saha G, Chakraborty K, Pattojoshi A. Management of psychiatric disorders in patients with stroke and traumatic brain injury. Indian J Psychiatry. 2022;64(Suppl 2): S344-S354.
1. Eslinger PJ, Reichwein RK. Frontal lobe stroke syndromes. In: Caplan LR, van Gijn J, eds. Stroke Syndromes. 3rd ed. Cambridge University Press; 2012:232-241.
2. Critchley M, Russell WR, Zangwill OL. Discussion on parietal lobe syndromes. Proc R Soc Med. 1951;44(4):337-346.
3. Hier DB, Mondlock J, Caplan LR. Behavioral abnormalities after right hemisphere stroke. Neurology. 1983;33(3):337-344.
4. Brust JC, Behrens MM. “Release hallucinations” as the major symptom of posterior cerebral artery occlusion: a report of 2 cases. Ann Neurol. 1977;2(5):432-436.
5. Kumral E, Uluakay A, Donmez A. Complex visual hallucinations following stroke: epileptic origin or a deafferentiation phenomenon? Austin J Cerebrovasc Dis & Stroke. 2014;1(1):1005.
6. Lee JS, Ko KH, Oh JH, et al. Charles Bonnet syndrome after occipital infarction. J Neurosonol Neuroimag. 2018;10(2):154-157.
7. Young JB. Peduncular hallucinosis. In: Aminoff MJ, Daroff RB, eds. Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2014:848.
8. Etemadifar M, Abtahi SH, Abtahi SM, et al. Hemiballismus, hyperphagia, and behavioral changes following subthalamic infarct. Case Rep Med. 2012;2012:768580. doi:10.1155/2012/768580
9. Kumral E, Evyapan D, Balkir K. Acute caudate vascular lesions. Stroke. 1999;30(1):100-108.
10. Wang PY. Neurobehavioral changes following caudate infarct: a case report with literature review. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Taipei). 1991;47(3):199-203.
11. Ahmed S, Leurent B, Sampson EL. Risk factors for incident delirium among older people in acute hospital medical units: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing. 2014;43(3):326-33.
12. Stangeland H, Orgeta V, Bell V. Poststroke psychosis: a systematic review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2018;89(8):879-885.
13. Lenzi GL, Altieri M, Maestrini I. Post-stroke depression. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2008;164(10):837-840.
14. Whyte EM, Mulsant BH. Post stroke depression: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and biological treatment. Biol Psychiatry. 2002;52(3):253-264.
15. Pritchard KT, Hreha KP, Hong I. Dysphagia associated with risk of depressive symptoms among stroke survivors after discharge from a cluster of inpatient rehabilitation facilities. Swallowing Rehabil. 2020;3(1):33-44.
16. Wiart L, Petit H, Joseph PA, et al. Fluoxetine in early poststroke depression: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Stroke. 2000;31(8):1829-1832.
17. Jorge RE, Robinson RG, Arndt S, et al. Mortality and poststroke depression: a placebo-controlled trial of antidepressants. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(10):1823-1829.
18. Chun HY, Whiteley WN, Dennis MS, et al. Anxiety after stroke: the importance of subtyping. Stroke. 2018;49(3):556-564.
19. Garton AL, Sisti JA, Gupta VP, et al. Poststroke post-traumatic stress disorder: a review. Stroke. 2017;48(2):507-512.
1. Eslinger PJ, Reichwein RK. Frontal lobe stroke syndromes. In: Caplan LR, van Gijn J, eds. Stroke Syndromes. 3rd ed. Cambridge University Press; 2012:232-241.
2. Critchley M, Russell WR, Zangwill OL. Discussion on parietal lobe syndromes. Proc R Soc Med. 1951;44(4):337-346.
3. Hier DB, Mondlock J, Caplan LR. Behavioral abnormalities after right hemisphere stroke. Neurology. 1983;33(3):337-344.
4. Brust JC, Behrens MM. “Release hallucinations” as the major symptom of posterior cerebral artery occlusion: a report of 2 cases. Ann Neurol. 1977;2(5):432-436.
5. Kumral E, Uluakay A, Donmez A. Complex visual hallucinations following stroke: epileptic origin or a deafferentiation phenomenon? Austin J Cerebrovasc Dis & Stroke. 2014;1(1):1005.
6. Lee JS, Ko KH, Oh JH, et al. Charles Bonnet syndrome after occipital infarction. J Neurosonol Neuroimag. 2018;10(2):154-157.
7. Young JB. Peduncular hallucinosis. In: Aminoff MJ, Daroff RB, eds. Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2014:848.
8. Etemadifar M, Abtahi SH, Abtahi SM, et al. Hemiballismus, hyperphagia, and behavioral changes following subthalamic infarct. Case Rep Med. 2012;2012:768580. doi:10.1155/2012/768580
9. Kumral E, Evyapan D, Balkir K. Acute caudate vascular lesions. Stroke. 1999;30(1):100-108.
10. Wang PY. Neurobehavioral changes following caudate infarct: a case report with literature review. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Taipei). 1991;47(3):199-203.
11. Ahmed S, Leurent B, Sampson EL. Risk factors for incident delirium among older people in acute hospital medical units: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing. 2014;43(3):326-33.
12. Stangeland H, Orgeta V, Bell V. Poststroke psychosis: a systematic review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2018;89(8):879-885.
13. Lenzi GL, Altieri M, Maestrini I. Post-stroke depression. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2008;164(10):837-840.
14. Whyte EM, Mulsant BH. Post stroke depression: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and biological treatment. Biol Psychiatry. 2002;52(3):253-264.
15. Pritchard KT, Hreha KP, Hong I. Dysphagia associated with risk of depressive symptoms among stroke survivors after discharge from a cluster of inpatient rehabilitation facilities. Swallowing Rehabil. 2020;3(1):33-44.
16. Wiart L, Petit H, Joseph PA, et al. Fluoxetine in early poststroke depression: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Stroke. 2000;31(8):1829-1832.
17. Jorge RE, Robinson RG, Arndt S, et al. Mortality and poststroke depression: a placebo-controlled trial of antidepressants. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(10):1823-1829.
18. Chun HY, Whiteley WN, Dennis MS, et al. Anxiety after stroke: the importance of subtyping. Stroke. 2018;49(3):556-564.
19. Garton AL, Sisti JA, Gupta VP, et al. Poststroke post-traumatic stress disorder: a review. Stroke. 2017;48(2):507-512.
Hold or not to hold: Navigating involuntary commitment
CASE Depressed and suicidal
Police arrive at the home of Mr. H, age 50, after his wife calls 911. She reports he has depression and she saw him in bed brandishing a firearm as if he wanted to hurt himself. Upon arrival, the officers enter the house and find Mr. H in bed without a firearm. Mr. H says little to the officers about the alleged events, but acknowledges he has depression and is willing to go the hospital for further evaluation. Neither his wife nor the officers locate a firearm in the home.
EVALUATION Emergency detention
In the emergency department (ED), Mr. H’s laboratory results and physical examination findings are normal. He acknowledges feeling depressed over the past 2 weeks. Though he cannot identify any precipitants, he says he has experienced anhedonia, lack of appetite, decreased energy, and changes in his sleep patterns. When asked about the day’s events concerning the firearm, Mr. H becomes guarded and does not give a clear answer regarding having thoughts of suicide.
The evaluating psychiatrist obtains collateral from Mr. H’s wife and reviews his medical records. There are no active prescriptions on file and the psychiatrist notices that last year there was a suicide attempt involving a firearm. Following that episode, Mr. H was hospitalized, treated with sertraline 50 mg/d, and discharged with a diagnosis of major depressive disorder. There was no legal or substance abuse history.
In the ED, the psychiatrist conducts a psychiatric evaluation, including a suicide risk assessment, and determines Mr. H is at imminent risk of ending his life. Mr. H’s psychiatrist explains there are 2 treatment options: to be admitted to the hospital or to be discharged. The psychiatrist recommends hospital admission to Mr. H for his safety and stabilization. Mr. H says he prefers to return home.
Because the psychiatrist believes Mr. H is at imminent risk of ending his life and there is no less restrictive setting for treatment, he implements an emergency detention. In Ohio, this allows Mr. H to be held in the hospital for no more than 3 court days in accordance with state law. Before Mr. H’s emergency detention periods ends, the psychiatrist will need to decide whether Mr. H can be safely discharged. If the psychiatrist determines that Mr. H still needs treatment, the court will be petitioned for a civil commitment hearing.
[polldaddy:11189291]
The author’s observations
In some cases, courts allow information a psychiatrist does not directly obtain from a patient to be admitted as testimony in a civil commitment hearing. However, some jurisdictions consider sources of information not obtained directly from the patient as hearsay and thus inadmissible.1 Though each source listed may provide credible information that could be presented at a hearing, the psychiatrist should discuss with the patient the information obtained from these sources to ensure it is admissable.2 A discussion with Mr. H about the factors that led to his hospital arrival will avoid the psychiatrist’s reliance on what another person has heard or seen when providing testimony. Even when a psychiatrist is not faced with an issue of admissibility, caution must be taken with third-party reports.3
TREATMENT Civil commitment hearing
Before the emergency detention period expires, Mr. H’s psychiatrist determines that he remains at imminent risk of self-harm. To continue hospitalization, the psychiatrist files a petition for civil commitment and testifies at the commitment hearing. He reports that Mr. H suffers from a substantial mood disorder that grossly impairs his judgment and behavior. The psychiatrist also testifies that the least restrictive environment for treatment continues to be inpatient hospitalization, because Mr. H is still at imminent risk of harming himself.
Continue to: Following the psychiatrist's...
Following the psychiatrist’s testimony, the magistrate finds that Mr. H is a mentally ill person subject to hospitalization given his mood disorder that grossly impairs his judgment and behavior. The magistrate orders that Mr. H be civilly committed to the hospital.
[polldaddy:11189293]
The author’s observations
The psychiatrist’s testimony mirrors the language regarding civil commitment in the Ohio Revised Code.4 Other elements considered for mental illness in Ohio are a substantial disorder of memory, thought, orientation, or perception that grossly impairs one’s capacity to recognize reality or meet the demands of life.4 The definition of what constitutes a mental disorder varies by state, but the burden of persuasion—the standard by which the court must be convinced—is generally uniform.5 In the 1979 case Addington v Texas, the United States Supreme Court concluded that in a civil commitment hearing, the minimum standard of proof for involuntary commitment must be clear and convincing evidence.6 Neither medical certainty nor substantial probability are burdens of persuasions.6 Instead, these terms may be presented in a forensic report when an examiner outlines their opinion. Table 1 and the Figure provide more detail on burdens of persuasion.
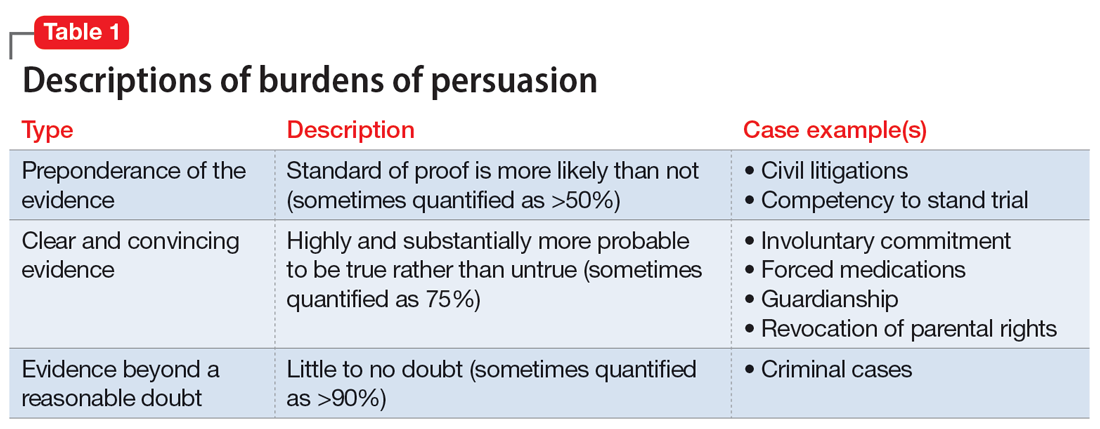
TREATMENT Civil commitment and patient rights
At a regularly scheduled treatment team meeting, the team informs Mr. H that he has been civilly committed for further treatment. Mr. H becomes upset and tells the team the decision is a complete violation of his rights. After a long rant, Mr. H walks out of the room, saying, “I did not even know when this hearing was.” A member of the treatment team becomes concerned that Mr. H may not have been notified of the hearing.
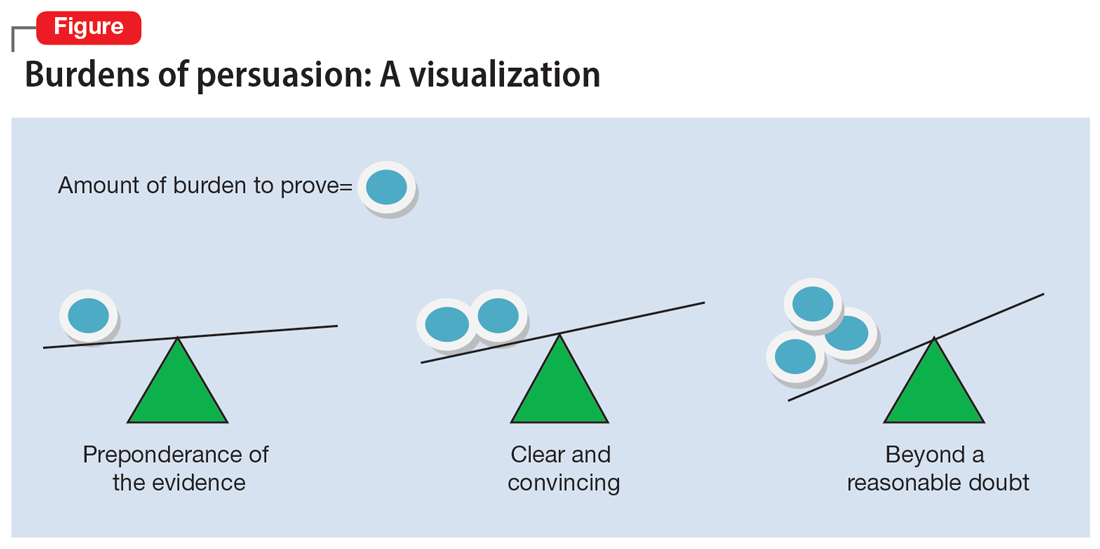
[polldaddy:11189294]
The author’s observations
It is not clear if Mr. H had been notified of his civil commitment hearing. If Mr. H had not been notified, his rights would have been compromised. Lessard v Schmidt (1972) outlined that individuals involved in a civil commitment hearing should be afforded the same rights as those involved in criminal proceedings.7 Mr. H should have been notified of his hearing and afforded the opportunity to have the assignment of counsel, the right to appear, the right to testify, the right to present witnesses and other evidence, and the right to confront witnesses.
Without notification of the hearing, the only right that would have remained intact for Mr. H would have been the assignment of counsel in his absence and without his knowledge. If Mr. H had been notified of the hearing and did not want to attend, yet still desired legal counsel, he could have waived his presence voluntarily after discussing this option with his attorney.8,9
Continue to: OUTCOME Stabilization and discharge
OUTCOME Stabilization and discharge
During his 10-day stay, Mr. H is treated with sertraline 50 mg/d and engages in individual and group therapy. He shows noticeable improvement in his depressive symptoms and reports having no thoughts of suicide or self-harm. The treatment team determines it is appropriate to discharge him home (the firearm was never found) and involves his wife in safety planning and follow-up care. On the day of his discharge, Mr. H reflects on his treatment and civil commitment. He says, “I did not know a judge could order me to be hospitalized.”
[polldaddy:11189297]
The author’s observations
The physician’s decision to pursue civil commitment is best described by the legal doctrines of police powers and parens patriae. Other relevant ethical principles are described in Table 2.10

Though ethical principles may play a role in civil commitment, parens patriae and police powers is the answer with respect to the State.11Parens patriae is Latin for the “parent of the country” and grants the State the power to protect those residents who are most vulnerable. Police power is the authority of the State to enact and enforce rules that limit the rights of individuals for the greater good of ensuring health, safety, and welfare of all citizens.
Bottom Line
Psychiatrists are entrusted with recognizing when a patient, due to mental illness, is a danger to themselves or others and in need of treatment. After an emergency detention period, if the patient remains a danger to themselves or others and does not want to voluntarily receive treatment, a court hearing is required. As an expert witness, the treating psychiatrist should know the factors of law in their jurisdiction that determine civil commitment.
Related Resources
- Extreme Risk Protection Orders. Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. https://www.jhsph.edu/research/ centers-and-institutes/johns-hopkins-center-for-gun-violenceprevention-and-policy/research/extreme-risk-protectionorders/
- Gutheil TG. The Psychiatrist as Expert Witness. 2nd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2009.
- Landmark Cases 2014. American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law. https://www.aapl.org/landmark-cases
Drug Brand Names
Sertraline • Zoloft
1. Pinals DA, Mossman D. Evaluation for Civil Commitment. Oxford University Press; 2012.
2. Thatcher BT, Mossman D. Testifying for civil commitment: help unwilling patients get the treatment they need. Current Psychiatry. 2009;8(11):51-56.
3. Marett CP, Mossman D. What is your liability for involuntary commitment based on faulty information? Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(3):21-25,33.
4. Ohio Rev Code § 5122.01 (2018).
5. The Burden of Proof. University of Minnesota. Accessed January 23, 2022. https://open.lib.umn.edu/criminallaw/chapter/2-4-the-burden-of-proof/
6. Gold LH, Frierson RL, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Forensic Psychiatry. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2018.
7. Gold LH, Frierson RL, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Suicide Assessment and Management. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2020.
8. Cook J. Good lawyering and bad role models: the role of respondent’s counsel in a civil commitment hearing. Georgetown Journal of Legal Ethics. 2000;14(1):179-195.
9. Ferris CE. The search for due process in civil commitment hearings: how procedural realities have altered substantive standards. Vanderbilt Law Rev. 2008;61(3):959-981.
10. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Civil Commitment and the Mental Health Care Continuum: Historical Trends and Principles for Law and Practice. 2019. Accessed January 23, 2022. https://www.samhsa.gov/resource/ebp/civil-commitment-mental-health-care-continuum-historical-trends-principles-law
11. Melton GB, Petrila J, Poythress NG, et al. Psychological Evaluations for the Courts: A Handbook for Mental Health Profession. 4th ed. Guilford Press; 2018.
CASE Depressed and suicidal
Police arrive at the home of Mr. H, age 50, after his wife calls 911. She reports he has depression and she saw him in bed brandishing a firearm as if he wanted to hurt himself. Upon arrival, the officers enter the house and find Mr. H in bed without a firearm. Mr. H says little to the officers about the alleged events, but acknowledges he has depression and is willing to go the hospital for further evaluation. Neither his wife nor the officers locate a firearm in the home.
EVALUATION Emergency detention
In the emergency department (ED), Mr. H’s laboratory results and physical examination findings are normal. He acknowledges feeling depressed over the past 2 weeks. Though he cannot identify any precipitants, he says he has experienced anhedonia, lack of appetite, decreased energy, and changes in his sleep patterns. When asked about the day’s events concerning the firearm, Mr. H becomes guarded and does not give a clear answer regarding having thoughts of suicide.
The evaluating psychiatrist obtains collateral from Mr. H’s wife and reviews his medical records. There are no active prescriptions on file and the psychiatrist notices that last year there was a suicide attempt involving a firearm. Following that episode, Mr. H was hospitalized, treated with sertraline 50 mg/d, and discharged with a diagnosis of major depressive disorder. There was no legal or substance abuse history.
In the ED, the psychiatrist conducts a psychiatric evaluation, including a suicide risk assessment, and determines Mr. H is at imminent risk of ending his life. Mr. H’s psychiatrist explains there are 2 treatment options: to be admitted to the hospital or to be discharged. The psychiatrist recommends hospital admission to Mr. H for his safety and stabilization. Mr. H says he prefers to return home.
Because the psychiatrist believes Mr. H is at imminent risk of ending his life and there is no less restrictive setting for treatment, he implements an emergency detention. In Ohio, this allows Mr. H to be held in the hospital for no more than 3 court days in accordance with state law. Before Mr. H’s emergency detention periods ends, the psychiatrist will need to decide whether Mr. H can be safely discharged. If the psychiatrist determines that Mr. H still needs treatment, the court will be petitioned for a civil commitment hearing.
[polldaddy:11189291]
The author’s observations
In some cases, courts allow information a psychiatrist does not directly obtain from a patient to be admitted as testimony in a civil commitment hearing. However, some jurisdictions consider sources of information not obtained directly from the patient as hearsay and thus inadmissible.1 Though each source listed may provide credible information that could be presented at a hearing, the psychiatrist should discuss with the patient the information obtained from these sources to ensure it is admissable.2 A discussion with Mr. H about the factors that led to his hospital arrival will avoid the psychiatrist’s reliance on what another person has heard or seen when providing testimony. Even when a psychiatrist is not faced with an issue of admissibility, caution must be taken with third-party reports.3
TREATMENT Civil commitment hearing
Before the emergency detention period expires, Mr. H’s psychiatrist determines that he remains at imminent risk of self-harm. To continue hospitalization, the psychiatrist files a petition for civil commitment and testifies at the commitment hearing. He reports that Mr. H suffers from a substantial mood disorder that grossly impairs his judgment and behavior. The psychiatrist also testifies that the least restrictive environment for treatment continues to be inpatient hospitalization, because Mr. H is still at imminent risk of harming himself.
Continue to: Following the psychiatrist's...
Following the psychiatrist’s testimony, the magistrate finds that Mr. H is a mentally ill person subject to hospitalization given his mood disorder that grossly impairs his judgment and behavior. The magistrate orders that Mr. H be civilly committed to the hospital.
[polldaddy:11189293]
The author’s observations
The psychiatrist’s testimony mirrors the language regarding civil commitment in the Ohio Revised Code.4 Other elements considered for mental illness in Ohio are a substantial disorder of memory, thought, orientation, or perception that grossly impairs one’s capacity to recognize reality or meet the demands of life.4 The definition of what constitutes a mental disorder varies by state, but the burden of persuasion—the standard by which the court must be convinced—is generally uniform.5 In the 1979 case Addington v Texas, the United States Supreme Court concluded that in a civil commitment hearing, the minimum standard of proof for involuntary commitment must be clear and convincing evidence.6 Neither medical certainty nor substantial probability are burdens of persuasions.6 Instead, these terms may be presented in a forensic report when an examiner outlines their opinion. Table 1 and the Figure provide more detail on burdens of persuasion.

TREATMENT Civil commitment and patient rights
At a regularly scheduled treatment team meeting, the team informs Mr. H that he has been civilly committed for further treatment. Mr. H becomes upset and tells the team the decision is a complete violation of his rights. After a long rant, Mr. H walks out of the room, saying, “I did not even know when this hearing was.” A member of the treatment team becomes concerned that Mr. H may not have been notified of the hearing.

[polldaddy:11189294]
The author’s observations
It is not clear if Mr. H had been notified of his civil commitment hearing. If Mr. H had not been notified, his rights would have been compromised. Lessard v Schmidt (1972) outlined that individuals involved in a civil commitment hearing should be afforded the same rights as those involved in criminal proceedings.7 Mr. H should have been notified of his hearing and afforded the opportunity to have the assignment of counsel, the right to appear, the right to testify, the right to present witnesses and other evidence, and the right to confront witnesses.
Without notification of the hearing, the only right that would have remained intact for Mr. H would have been the assignment of counsel in his absence and without his knowledge. If Mr. H had been notified of the hearing and did not want to attend, yet still desired legal counsel, he could have waived his presence voluntarily after discussing this option with his attorney.8,9
Continue to: OUTCOME Stabilization and discharge
OUTCOME Stabilization and discharge
During his 10-day stay, Mr. H is treated with sertraline 50 mg/d and engages in individual and group therapy. He shows noticeable improvement in his depressive symptoms and reports having no thoughts of suicide or self-harm. The treatment team determines it is appropriate to discharge him home (the firearm was never found) and involves his wife in safety planning and follow-up care. On the day of his discharge, Mr. H reflects on his treatment and civil commitment. He says, “I did not know a judge could order me to be hospitalized.”
[polldaddy:11189297]
The author’s observations
The physician’s decision to pursue civil commitment is best described by the legal doctrines of police powers and parens patriae. Other relevant ethical principles are described in Table 2.10

Though ethical principles may play a role in civil commitment, parens patriae and police powers is the answer with respect to the State.11Parens patriae is Latin for the “parent of the country” and grants the State the power to protect those residents who are most vulnerable. Police power is the authority of the State to enact and enforce rules that limit the rights of individuals for the greater good of ensuring health, safety, and welfare of all citizens.
Bottom Line
Psychiatrists are entrusted with recognizing when a patient, due to mental illness, is a danger to themselves or others and in need of treatment. After an emergency detention period, if the patient remains a danger to themselves or others and does not want to voluntarily receive treatment, a court hearing is required. As an expert witness, the treating psychiatrist should know the factors of law in their jurisdiction that determine civil commitment.
Related Resources
- Extreme Risk Protection Orders. Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. https://www.jhsph.edu/research/ centers-and-institutes/johns-hopkins-center-for-gun-violenceprevention-and-policy/research/extreme-risk-protectionorders/
- Gutheil TG. The Psychiatrist as Expert Witness. 2nd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2009.
- Landmark Cases 2014. American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law. https://www.aapl.org/landmark-cases
Drug Brand Names
Sertraline • Zoloft
CASE Depressed and suicidal
Police arrive at the home of Mr. H, age 50, after his wife calls 911. She reports he has depression and she saw him in bed brandishing a firearm as if he wanted to hurt himself. Upon arrival, the officers enter the house and find Mr. H in bed without a firearm. Mr. H says little to the officers about the alleged events, but acknowledges he has depression and is willing to go the hospital for further evaluation. Neither his wife nor the officers locate a firearm in the home.
EVALUATION Emergency detention
In the emergency department (ED), Mr. H’s laboratory results and physical examination findings are normal. He acknowledges feeling depressed over the past 2 weeks. Though he cannot identify any precipitants, he says he has experienced anhedonia, lack of appetite, decreased energy, and changes in his sleep patterns. When asked about the day’s events concerning the firearm, Mr. H becomes guarded and does not give a clear answer regarding having thoughts of suicide.
The evaluating psychiatrist obtains collateral from Mr. H’s wife and reviews his medical records. There are no active prescriptions on file and the psychiatrist notices that last year there was a suicide attempt involving a firearm. Following that episode, Mr. H was hospitalized, treated with sertraline 50 mg/d, and discharged with a diagnosis of major depressive disorder. There was no legal or substance abuse history.
In the ED, the psychiatrist conducts a psychiatric evaluation, including a suicide risk assessment, and determines Mr. H is at imminent risk of ending his life. Mr. H’s psychiatrist explains there are 2 treatment options: to be admitted to the hospital or to be discharged. The psychiatrist recommends hospital admission to Mr. H for his safety and stabilization. Mr. H says he prefers to return home.
Because the psychiatrist believes Mr. H is at imminent risk of ending his life and there is no less restrictive setting for treatment, he implements an emergency detention. In Ohio, this allows Mr. H to be held in the hospital for no more than 3 court days in accordance with state law. Before Mr. H’s emergency detention periods ends, the psychiatrist will need to decide whether Mr. H can be safely discharged. If the psychiatrist determines that Mr. H still needs treatment, the court will be petitioned for a civil commitment hearing.
[polldaddy:11189291]
The author’s observations
In some cases, courts allow information a psychiatrist does not directly obtain from a patient to be admitted as testimony in a civil commitment hearing. However, some jurisdictions consider sources of information not obtained directly from the patient as hearsay and thus inadmissible.1 Though each source listed may provide credible information that could be presented at a hearing, the psychiatrist should discuss with the patient the information obtained from these sources to ensure it is admissable.2 A discussion with Mr. H about the factors that led to his hospital arrival will avoid the psychiatrist’s reliance on what another person has heard or seen when providing testimony. Even when a psychiatrist is not faced with an issue of admissibility, caution must be taken with third-party reports.3
TREATMENT Civil commitment hearing
Before the emergency detention period expires, Mr. H’s psychiatrist determines that he remains at imminent risk of self-harm. To continue hospitalization, the psychiatrist files a petition for civil commitment and testifies at the commitment hearing. He reports that Mr. H suffers from a substantial mood disorder that grossly impairs his judgment and behavior. The psychiatrist also testifies that the least restrictive environment for treatment continues to be inpatient hospitalization, because Mr. H is still at imminent risk of harming himself.
Continue to: Following the psychiatrist's...
Following the psychiatrist’s testimony, the magistrate finds that Mr. H is a mentally ill person subject to hospitalization given his mood disorder that grossly impairs his judgment and behavior. The magistrate orders that Mr. H be civilly committed to the hospital.
[polldaddy:11189293]
The author’s observations
The psychiatrist’s testimony mirrors the language regarding civil commitment in the Ohio Revised Code.4 Other elements considered for mental illness in Ohio are a substantial disorder of memory, thought, orientation, or perception that grossly impairs one’s capacity to recognize reality or meet the demands of life.4 The definition of what constitutes a mental disorder varies by state, but the burden of persuasion—the standard by which the court must be convinced—is generally uniform.5 In the 1979 case Addington v Texas, the United States Supreme Court concluded that in a civil commitment hearing, the minimum standard of proof for involuntary commitment must be clear and convincing evidence.6 Neither medical certainty nor substantial probability are burdens of persuasions.6 Instead, these terms may be presented in a forensic report when an examiner outlines their opinion. Table 1 and the Figure provide more detail on burdens of persuasion.

TREATMENT Civil commitment and patient rights
At a regularly scheduled treatment team meeting, the team informs Mr. H that he has been civilly committed for further treatment. Mr. H becomes upset and tells the team the decision is a complete violation of his rights. After a long rant, Mr. H walks out of the room, saying, “I did not even know when this hearing was.” A member of the treatment team becomes concerned that Mr. H may not have been notified of the hearing.

[polldaddy:11189294]
The author’s observations
It is not clear if Mr. H had been notified of his civil commitment hearing. If Mr. H had not been notified, his rights would have been compromised. Lessard v Schmidt (1972) outlined that individuals involved in a civil commitment hearing should be afforded the same rights as those involved in criminal proceedings.7 Mr. H should have been notified of his hearing and afforded the opportunity to have the assignment of counsel, the right to appear, the right to testify, the right to present witnesses and other evidence, and the right to confront witnesses.
Without notification of the hearing, the only right that would have remained intact for Mr. H would have been the assignment of counsel in his absence and without his knowledge. If Mr. H had been notified of the hearing and did not want to attend, yet still desired legal counsel, he could have waived his presence voluntarily after discussing this option with his attorney.8,9
Continue to: OUTCOME Stabilization and discharge
OUTCOME Stabilization and discharge
During his 10-day stay, Mr. H is treated with sertraline 50 mg/d and engages in individual and group therapy. He shows noticeable improvement in his depressive symptoms and reports having no thoughts of suicide or self-harm. The treatment team determines it is appropriate to discharge him home (the firearm was never found) and involves his wife in safety planning and follow-up care. On the day of his discharge, Mr. H reflects on his treatment and civil commitment. He says, “I did not know a judge could order me to be hospitalized.”
[polldaddy:11189297]
The author’s observations
The physician’s decision to pursue civil commitment is best described by the legal doctrines of police powers and parens patriae. Other relevant ethical principles are described in Table 2.10

Though ethical principles may play a role in civil commitment, parens patriae and police powers is the answer with respect to the State.11Parens patriae is Latin for the “parent of the country” and grants the State the power to protect those residents who are most vulnerable. Police power is the authority of the State to enact and enforce rules that limit the rights of individuals for the greater good of ensuring health, safety, and welfare of all citizens.
Bottom Line
Psychiatrists are entrusted with recognizing when a patient, due to mental illness, is a danger to themselves or others and in need of treatment. After an emergency detention period, if the patient remains a danger to themselves or others and does not want to voluntarily receive treatment, a court hearing is required. As an expert witness, the treating psychiatrist should know the factors of law in their jurisdiction that determine civil commitment.
Related Resources
- Extreme Risk Protection Orders. Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. https://www.jhsph.edu/research/ centers-and-institutes/johns-hopkins-center-for-gun-violenceprevention-and-policy/research/extreme-risk-protectionorders/
- Gutheil TG. The Psychiatrist as Expert Witness. 2nd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2009.
- Landmark Cases 2014. American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law. https://www.aapl.org/landmark-cases
Drug Brand Names
Sertraline • Zoloft
1. Pinals DA, Mossman D. Evaluation for Civil Commitment. Oxford University Press; 2012.
2. Thatcher BT, Mossman D. Testifying for civil commitment: help unwilling patients get the treatment they need. Current Psychiatry. 2009;8(11):51-56.
3. Marett CP, Mossman D. What is your liability for involuntary commitment based on faulty information? Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(3):21-25,33.
4. Ohio Rev Code § 5122.01 (2018).
5. The Burden of Proof. University of Minnesota. Accessed January 23, 2022. https://open.lib.umn.edu/criminallaw/chapter/2-4-the-burden-of-proof/
6. Gold LH, Frierson RL, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Forensic Psychiatry. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2018.
7. Gold LH, Frierson RL, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Suicide Assessment and Management. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2020.
8. Cook J. Good lawyering and bad role models: the role of respondent’s counsel in a civil commitment hearing. Georgetown Journal of Legal Ethics. 2000;14(1):179-195.
9. Ferris CE. The search for due process in civil commitment hearings: how procedural realities have altered substantive standards. Vanderbilt Law Rev. 2008;61(3):959-981.
10. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Civil Commitment and the Mental Health Care Continuum: Historical Trends and Principles for Law and Practice. 2019. Accessed January 23, 2022. https://www.samhsa.gov/resource/ebp/civil-commitment-mental-health-care-continuum-historical-trends-principles-law
11. Melton GB, Petrila J, Poythress NG, et al. Psychological Evaluations for the Courts: A Handbook for Mental Health Profession. 4th ed. Guilford Press; 2018.
1. Pinals DA, Mossman D. Evaluation for Civil Commitment. Oxford University Press; 2012.
2. Thatcher BT, Mossman D. Testifying for civil commitment: help unwilling patients get the treatment they need. Current Psychiatry. 2009;8(11):51-56.
3. Marett CP, Mossman D. What is your liability for involuntary commitment based on faulty information? Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(3):21-25,33.
4. Ohio Rev Code § 5122.01 (2018).
5. The Burden of Proof. University of Minnesota. Accessed January 23, 2022. https://open.lib.umn.edu/criminallaw/chapter/2-4-the-burden-of-proof/
6. Gold LH, Frierson RL, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Forensic Psychiatry. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2018.
7. Gold LH, Frierson RL, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Suicide Assessment and Management. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2020.
8. Cook J. Good lawyering and bad role models: the role of respondent’s counsel in a civil commitment hearing. Georgetown Journal of Legal Ethics. 2000;14(1):179-195.
9. Ferris CE. The search for due process in civil commitment hearings: how procedural realities have altered substantive standards. Vanderbilt Law Rev. 2008;61(3):959-981.
10. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Civil Commitment and the Mental Health Care Continuum: Historical Trends and Principles for Law and Practice. 2019. Accessed January 23, 2022. https://www.samhsa.gov/resource/ebp/civil-commitment-mental-health-care-continuum-historical-trends-principles-law
11. Melton GB, Petrila J, Poythress NG, et al. Psychological Evaluations for the Courts: A Handbook for Mental Health Profession. 4th ed. Guilford Press; 2018.











