User login
Statins’ effects on CVD outweigh risk for diabetes in RA
The use of statins by patients with rheumatoid arthritis appears to provide an overall net benefit on cardiovascular disease outcomes that outweighs the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) seen with the drugs in the general population, according to evidence from a cohort study of more than 16,000 people in the United Kingdom that was presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“Our study emphasizes that RA patients should be assessed for statin initiation to improve CVD risk,” lead study author Gulsen Ozen, MD, a third-year resident at the University of Nebraska, Omaha, said in an interview. Because the risk of T2DM with statin use is no worse in patients with RA than in the general population, statin initiation “is actually a great opportunity to address the risk factors for T2DM such as activity and exercise, obesity and weight loss, and [use of glucocorticoids], which have other important health effects,” she said.
“Also, importantly, even if [patients] develop T2DM, statins still work on CVD and mortality outcomes as in patients without diabetes,” Dr. Ozen added. “Given all, the benefits of statins way outweigh the hazards.”
Dr. Ozen said this was the first large cohort study to evaluate CVD mortality and T2DM risks with statins in patients with RA, a claim with which rheumatologist Elena Myasoedova, MD, PhD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., concurred.
Dr. Myasoedova, professor of rheumatology and epidemiology at Mayo, said in an interview that the study was “methodologically rigorous” using time-conditional propensity score (TCPS) matching and a prevalent new-user design, “thus addressing the immortal time bias” found in the design of studies in which patients enter a cohort but do not start a treatment before developing the outcome of interest and are assigned to the untreated group or when the period of delay from when patients enter the cohort to when they are treated is excluded from the analysis. An earlier study from the same authors did not use TCPS matching, she said.
“The study findings suggest that patients with RA can benefit from statin use in terms of CVD outcomes and mortality but physicians should use vigilance regarding increased T2DM risk and discuss this possibility with patients,” Dr. Myasoedova said. “Identifying patients who are at higher risk of developing T2DM after statin initiation would be important to personalize the approach to statin therapy.”
Study details
The study accessed records from the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink and linked Hospital Episode Statistics and Office of National Statistics databases. It analyzed adult patients with RA who were diagnosed during 1989-2018 in two cohorts: One for CVD and all-cause mortality, consisting of 1,768 statin initiators and 3,528 TCPS-matched nonusers; and a T2DM cohort with 3,608 statin initiators and 7,208 TCPS-matched nonusers.
In the entire cohort, statin use was associated with a 32% reduction in CV events (composite endpoint of the nonfatal or fatal MI, stroke, hospitalized heart failure, or CVD mortality), a 54% reduction in all-cause mortality, and a 33% increase in risk for T2DM, Dr. Ozen said. Results were similar in both sexes, although CV event reduction with statins in men did not reach statistical significance, likely because of a smaller sample size, she said.
Patients with and without a history of CVD had a similar reduction in CV events and all-cause mortality, and risk for T2DM increased with statins, but the latter reached statistical significance only in patients without a history of CVD, Dr. Ozen said.
Patients with RA who are at risk for T2DM and who are taking statins require blood glucose monitoring, which is typically done in patients with RA on disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and hemoglobin A1c testing when glucose levels are impaired, she said. “Any concerns for T2DM would be also communicated by the primary care providers of the patients to initiate further assessment and management,” she said.
But Dr. Ozen noted that confusion exists among primary care physicians and rheumatologists about who’s responsible for prescribing statins in these patients. “I would like to remind you that instead of assigning this role to a certain specialty, just good communication could improve this care gap of statin underutilization in RA,” she said. “Also, for rheumatologists, given that all-cause mortality reduction with statins was as high as CV event reduction, statins may be reducing other causes of mortality through improving disease activity.”
Bristol-Myers Squibb provided funding for the study. Dr. Ozen and Dr. Myasoedova have no relevant disclosures.
The use of statins by patients with rheumatoid arthritis appears to provide an overall net benefit on cardiovascular disease outcomes that outweighs the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) seen with the drugs in the general population, according to evidence from a cohort study of more than 16,000 people in the United Kingdom that was presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“Our study emphasizes that RA patients should be assessed for statin initiation to improve CVD risk,” lead study author Gulsen Ozen, MD, a third-year resident at the University of Nebraska, Omaha, said in an interview. Because the risk of T2DM with statin use is no worse in patients with RA than in the general population, statin initiation “is actually a great opportunity to address the risk factors for T2DM such as activity and exercise, obesity and weight loss, and [use of glucocorticoids], which have other important health effects,” she said.
“Also, importantly, even if [patients] develop T2DM, statins still work on CVD and mortality outcomes as in patients without diabetes,” Dr. Ozen added. “Given all, the benefits of statins way outweigh the hazards.”
Dr. Ozen said this was the first large cohort study to evaluate CVD mortality and T2DM risks with statins in patients with RA, a claim with which rheumatologist Elena Myasoedova, MD, PhD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., concurred.
Dr. Myasoedova, professor of rheumatology and epidemiology at Mayo, said in an interview that the study was “methodologically rigorous” using time-conditional propensity score (TCPS) matching and a prevalent new-user design, “thus addressing the immortal time bias” found in the design of studies in which patients enter a cohort but do not start a treatment before developing the outcome of interest and are assigned to the untreated group or when the period of delay from when patients enter the cohort to when they are treated is excluded from the analysis. An earlier study from the same authors did not use TCPS matching, she said.
“The study findings suggest that patients with RA can benefit from statin use in terms of CVD outcomes and mortality but physicians should use vigilance regarding increased T2DM risk and discuss this possibility with patients,” Dr. Myasoedova said. “Identifying patients who are at higher risk of developing T2DM after statin initiation would be important to personalize the approach to statin therapy.”
Study details
The study accessed records from the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink and linked Hospital Episode Statistics and Office of National Statistics databases. It analyzed adult patients with RA who were diagnosed during 1989-2018 in two cohorts: One for CVD and all-cause mortality, consisting of 1,768 statin initiators and 3,528 TCPS-matched nonusers; and a T2DM cohort with 3,608 statin initiators and 7,208 TCPS-matched nonusers.
In the entire cohort, statin use was associated with a 32% reduction in CV events (composite endpoint of the nonfatal or fatal MI, stroke, hospitalized heart failure, or CVD mortality), a 54% reduction in all-cause mortality, and a 33% increase in risk for T2DM, Dr. Ozen said. Results were similar in both sexes, although CV event reduction with statins in men did not reach statistical significance, likely because of a smaller sample size, she said.
Patients with and without a history of CVD had a similar reduction in CV events and all-cause mortality, and risk for T2DM increased with statins, but the latter reached statistical significance only in patients without a history of CVD, Dr. Ozen said.
Patients with RA who are at risk for T2DM and who are taking statins require blood glucose monitoring, which is typically done in patients with RA on disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and hemoglobin A1c testing when glucose levels are impaired, she said. “Any concerns for T2DM would be also communicated by the primary care providers of the patients to initiate further assessment and management,” she said.
But Dr. Ozen noted that confusion exists among primary care physicians and rheumatologists about who’s responsible for prescribing statins in these patients. “I would like to remind you that instead of assigning this role to a certain specialty, just good communication could improve this care gap of statin underutilization in RA,” she said. “Also, for rheumatologists, given that all-cause mortality reduction with statins was as high as CV event reduction, statins may be reducing other causes of mortality through improving disease activity.”
Bristol-Myers Squibb provided funding for the study. Dr. Ozen and Dr. Myasoedova have no relevant disclosures.
The use of statins by patients with rheumatoid arthritis appears to provide an overall net benefit on cardiovascular disease outcomes that outweighs the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) seen with the drugs in the general population, according to evidence from a cohort study of more than 16,000 people in the United Kingdom that was presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“Our study emphasizes that RA patients should be assessed for statin initiation to improve CVD risk,” lead study author Gulsen Ozen, MD, a third-year resident at the University of Nebraska, Omaha, said in an interview. Because the risk of T2DM with statin use is no worse in patients with RA than in the general population, statin initiation “is actually a great opportunity to address the risk factors for T2DM such as activity and exercise, obesity and weight loss, and [use of glucocorticoids], which have other important health effects,” she said.
“Also, importantly, even if [patients] develop T2DM, statins still work on CVD and mortality outcomes as in patients without diabetes,” Dr. Ozen added. “Given all, the benefits of statins way outweigh the hazards.”
Dr. Ozen said this was the first large cohort study to evaluate CVD mortality and T2DM risks with statins in patients with RA, a claim with which rheumatologist Elena Myasoedova, MD, PhD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., concurred.
Dr. Myasoedova, professor of rheumatology and epidemiology at Mayo, said in an interview that the study was “methodologically rigorous” using time-conditional propensity score (TCPS) matching and a prevalent new-user design, “thus addressing the immortal time bias” found in the design of studies in which patients enter a cohort but do not start a treatment before developing the outcome of interest and are assigned to the untreated group or when the period of delay from when patients enter the cohort to when they are treated is excluded from the analysis. An earlier study from the same authors did not use TCPS matching, she said.
“The study findings suggest that patients with RA can benefit from statin use in terms of CVD outcomes and mortality but physicians should use vigilance regarding increased T2DM risk and discuss this possibility with patients,” Dr. Myasoedova said. “Identifying patients who are at higher risk of developing T2DM after statin initiation would be important to personalize the approach to statin therapy.”
Study details
The study accessed records from the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink and linked Hospital Episode Statistics and Office of National Statistics databases. It analyzed adult patients with RA who were diagnosed during 1989-2018 in two cohorts: One for CVD and all-cause mortality, consisting of 1,768 statin initiators and 3,528 TCPS-matched nonusers; and a T2DM cohort with 3,608 statin initiators and 7,208 TCPS-matched nonusers.
In the entire cohort, statin use was associated with a 32% reduction in CV events (composite endpoint of the nonfatal or fatal MI, stroke, hospitalized heart failure, or CVD mortality), a 54% reduction in all-cause mortality, and a 33% increase in risk for T2DM, Dr. Ozen said. Results were similar in both sexes, although CV event reduction with statins in men did not reach statistical significance, likely because of a smaller sample size, she said.
Patients with and without a history of CVD had a similar reduction in CV events and all-cause mortality, and risk for T2DM increased with statins, but the latter reached statistical significance only in patients without a history of CVD, Dr. Ozen said.
Patients with RA who are at risk for T2DM and who are taking statins require blood glucose monitoring, which is typically done in patients with RA on disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and hemoglobin A1c testing when glucose levels are impaired, she said. “Any concerns for T2DM would be also communicated by the primary care providers of the patients to initiate further assessment and management,” she said.
But Dr. Ozen noted that confusion exists among primary care physicians and rheumatologists about who’s responsible for prescribing statins in these patients. “I would like to remind you that instead of assigning this role to a certain specialty, just good communication could improve this care gap of statin underutilization in RA,” she said. “Also, for rheumatologists, given that all-cause mortality reduction with statins was as high as CV event reduction, statins may be reducing other causes of mortality through improving disease activity.”
Bristol-Myers Squibb provided funding for the study. Dr. Ozen and Dr. Myasoedova have no relevant disclosures.
FROM ACR 2021
‘If obesity were diabetes or cancer, how would you approach it?’
“When considering the challenges of obesity, ask yourself: ‘If it were diabetes, cancer, HIV, or Alzheimer’s, how would you discuss it, approach it, assess it, treat it?’” Lee M. Kaplan, MD, PhD, asked the audience of health care professionals during ObesityWeek®, the annual meeting of The Obesity Society.
“And then do it for obesity, using the full spectrum of tools at our disposal,” he advised.
This was the takeaway that Dr. Kaplan, director of the Obesity, Metabolism, and Nutrition Institute at Massachusetts General Hospital and associate professor, Harvard Medical School, Boston, left the audience with at the end of his lecture entitled, “What does the future of obesity care look like?”
Invited to summarize his main points, Dr. Kaplan told this news organization in an interview that practitioners caring for patients with obesity need to first “recognize that obesity is a disease” caused by dysfunction of the metabolic system that regulates body fat – in the same way immune dysregulation can lead to asthma.
Second, “we are finally developing noninvasive therapies that are more effective,” he noted, referring to the recently approved semaglutide, and even more potent weight-loss therapies that could be on the market within 3 years, so that weight-loss outcomes with pharmacotherapy are approaching those with bariatric surgery.
Third, it is important that patients with obesity get “broad and equitable access” to treatment, and health care practitioners need to be on the same page and have a “shared understanding” of which treatments are appropriate for individual patients, “just as we do for other diseases.”
Need for a shared understanding
“Dr. Kaplan really brought home the idea that we all need a shared understanding of what obesity is – and what it is not,” agreed symposium moderator Donna H. Ryan, MD, in an email.
“He underscored the biologic basis of obesity,” noted Dr. Ryan, professor emerita at Pennington Biomedical Research Center in Baton Rouge, Louisiana, and associate editor-in-chief of Obesity, the official journal of The Obesity Society.
“It is a dysregulation of the body’s weight (especially adipose tissue) regulatory system,” she continued. “The body responds to powerful environmental pressures that produce excess energy balance, and we store that as fat and defend our highest fat mass. This makes obesity a disease, a chronic disease that requires a medical approach to reverse. It’s not a cosmetic problem, it’s a medical problem,” she emphasized.
There is so much misinformation out there about obesity, according to Dr. Ryan.
“People think it’s a lack of willpower, and even patients blame themselves for not being able to lose weight and keep it off. It’s not their fault! It’s biology.”
Although the supplement industry and fad diets falsely promise fast results, there is no magic diet, she continued.
“But we have made progress based on understanding the biologic basis of obesity and have new medications that offer real hope for patients.”
“With 42% of U.S. adults having a BMI that qualifies as obesity, we need a concerted and broad effort to address this problem, and that starts with everybody on the same page as to what obesity is ... a shared understanding of the biologic basis of obesity. It’s time to take obesity seriously,” she summarized, echoing Dr. Kaplan.
A question of biology
“Obesity results from inappropriate pathophysiological regulation of body fat mass,” when the body defends adiposity, Dr. Kaplan explained at the start of his lecture.
The treatment strategy for obesity has always been a stepwise approach starting with lifestyle changes, then pharmacotherapy, then possibly bariatric surgery – each step with a potentially greater chance of weight loss. But now, he explained, medicine is on the verge of having an armamentarium of more potent weight-loss medications.
Compared with phentermine/topiramate, orlistat, naltrexone/bupropion, and liraglutide – which roughly might provide 5% to 10% weight loss, the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist semaglutide 2.4 mg/week (Wegovy, Novo Nordisk), approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Association in June, provides almost double this potential weight loss.
And two new agents that could provide “never seen before weight loss” of 25% could potentially enter the marketplace by 2025: the amylin agonist cagrilintide (Novo Nordisk) and the twincretin tirzepatide (Eli Lilly) (a combined glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide [GIP] and GLP-1 receptor agonist).
In addition, when liraglutide comes off patent, a generic version could potentially be introduced, and combined generic liraglutide plus generic phentermine/topiramate could be a less expensive weight-loss treatment option in the future, he noted.
One size does not fit all
Importantly, weight loss varies widely among individual patients.
A graph of potential weight loss with different treatments (for example, bariatric surgery or liraglutide) versus the percentage of patients that attain the weight losses is roughly bell-shaped, Dr. Kaplan explained. For example, in the STEP1 trial of semaglutide, roughly 7.1% of patients lost less than 5% of their initial weight, 25% of patients lost 20% to 30%, and 10.8% of patients lost 30% or more; that is, patients at the higher end had weight loss comparable to that seen with bariatric surgery
Adding pharmacotherapy after bariatric surgery could be synergistic. For example, in the GRAVITAS study of patients with type 2 diabetes who had gastric bypass surgery, those who received liraglutide after surgery had augmented weight loss compared with those who received placebo.
People at a cocktail party might come up to him and say, “I’d like to lose 5 pounds, 10 pounds,” Dr. Kaplan related in the Q&A session.
“That’s not obesity,” he emphasized. Obesity is excess body fat that poses a risk to health. A person with obesity may have 50 or more excess pounds, and the body is trying to defend this weight.
“If we want to treat obesity more effectively, we have to fully understand why it is a disease and how that disease differs from the cultural desire for thinness,” he reiterated.
“We have to keep the needs and goals of all people living with obesity foremost in our minds, even if many of them have been previously misled by the bias, stigma, blame, and discrimination that surrounds them.”
“We need to re-evaluate what we think we know about obesity and open our minds to new ideas,” he added.
Dr. Kaplan has reported financial ties to Eli Lilly, Gelesis, GI Dynamics, IntelliHealth, Johnson & Johnson, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Rhythm Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Ryan has ties to numerous Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and several other pharmaceutical companies, including having an ownership interest in Gila Therapeutics, Xeno Biosciences, Epitomee, Calibrate, Roman, and Scientific Intake.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“When considering the challenges of obesity, ask yourself: ‘If it were diabetes, cancer, HIV, or Alzheimer’s, how would you discuss it, approach it, assess it, treat it?’” Lee M. Kaplan, MD, PhD, asked the audience of health care professionals during ObesityWeek®, the annual meeting of The Obesity Society.
“And then do it for obesity, using the full spectrum of tools at our disposal,” he advised.
This was the takeaway that Dr. Kaplan, director of the Obesity, Metabolism, and Nutrition Institute at Massachusetts General Hospital and associate professor, Harvard Medical School, Boston, left the audience with at the end of his lecture entitled, “What does the future of obesity care look like?”
Invited to summarize his main points, Dr. Kaplan told this news organization in an interview that practitioners caring for patients with obesity need to first “recognize that obesity is a disease” caused by dysfunction of the metabolic system that regulates body fat – in the same way immune dysregulation can lead to asthma.
Second, “we are finally developing noninvasive therapies that are more effective,” he noted, referring to the recently approved semaglutide, and even more potent weight-loss therapies that could be on the market within 3 years, so that weight-loss outcomes with pharmacotherapy are approaching those with bariatric surgery.
Third, it is important that patients with obesity get “broad and equitable access” to treatment, and health care practitioners need to be on the same page and have a “shared understanding” of which treatments are appropriate for individual patients, “just as we do for other diseases.”
Need for a shared understanding
“Dr. Kaplan really brought home the idea that we all need a shared understanding of what obesity is – and what it is not,” agreed symposium moderator Donna H. Ryan, MD, in an email.
“He underscored the biologic basis of obesity,” noted Dr. Ryan, professor emerita at Pennington Biomedical Research Center in Baton Rouge, Louisiana, and associate editor-in-chief of Obesity, the official journal of The Obesity Society.
“It is a dysregulation of the body’s weight (especially adipose tissue) regulatory system,” she continued. “The body responds to powerful environmental pressures that produce excess energy balance, and we store that as fat and defend our highest fat mass. This makes obesity a disease, a chronic disease that requires a medical approach to reverse. It’s not a cosmetic problem, it’s a medical problem,” she emphasized.
There is so much misinformation out there about obesity, according to Dr. Ryan.
“People think it’s a lack of willpower, and even patients blame themselves for not being able to lose weight and keep it off. It’s not their fault! It’s biology.”
Although the supplement industry and fad diets falsely promise fast results, there is no magic diet, she continued.
“But we have made progress based on understanding the biologic basis of obesity and have new medications that offer real hope for patients.”
“With 42% of U.S. adults having a BMI that qualifies as obesity, we need a concerted and broad effort to address this problem, and that starts with everybody on the same page as to what obesity is ... a shared understanding of the biologic basis of obesity. It’s time to take obesity seriously,” she summarized, echoing Dr. Kaplan.
A question of biology
“Obesity results from inappropriate pathophysiological regulation of body fat mass,” when the body defends adiposity, Dr. Kaplan explained at the start of his lecture.
The treatment strategy for obesity has always been a stepwise approach starting with lifestyle changes, then pharmacotherapy, then possibly bariatric surgery – each step with a potentially greater chance of weight loss. But now, he explained, medicine is on the verge of having an armamentarium of more potent weight-loss medications.
Compared with phentermine/topiramate, orlistat, naltrexone/bupropion, and liraglutide – which roughly might provide 5% to 10% weight loss, the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist semaglutide 2.4 mg/week (Wegovy, Novo Nordisk), approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Association in June, provides almost double this potential weight loss.
And two new agents that could provide “never seen before weight loss” of 25% could potentially enter the marketplace by 2025: the amylin agonist cagrilintide (Novo Nordisk) and the twincretin tirzepatide (Eli Lilly) (a combined glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide [GIP] and GLP-1 receptor agonist).
In addition, when liraglutide comes off patent, a generic version could potentially be introduced, and combined generic liraglutide plus generic phentermine/topiramate could be a less expensive weight-loss treatment option in the future, he noted.
One size does not fit all
Importantly, weight loss varies widely among individual patients.
A graph of potential weight loss with different treatments (for example, bariatric surgery or liraglutide) versus the percentage of patients that attain the weight losses is roughly bell-shaped, Dr. Kaplan explained. For example, in the STEP1 trial of semaglutide, roughly 7.1% of patients lost less than 5% of their initial weight, 25% of patients lost 20% to 30%, and 10.8% of patients lost 30% or more; that is, patients at the higher end had weight loss comparable to that seen with bariatric surgery
Adding pharmacotherapy after bariatric surgery could be synergistic. For example, in the GRAVITAS study of patients with type 2 diabetes who had gastric bypass surgery, those who received liraglutide after surgery had augmented weight loss compared with those who received placebo.
People at a cocktail party might come up to him and say, “I’d like to lose 5 pounds, 10 pounds,” Dr. Kaplan related in the Q&A session.
“That’s not obesity,” he emphasized. Obesity is excess body fat that poses a risk to health. A person with obesity may have 50 or more excess pounds, and the body is trying to defend this weight.
“If we want to treat obesity more effectively, we have to fully understand why it is a disease and how that disease differs from the cultural desire for thinness,” he reiterated.
“We have to keep the needs and goals of all people living with obesity foremost in our minds, even if many of them have been previously misled by the bias, stigma, blame, and discrimination that surrounds them.”
“We need to re-evaluate what we think we know about obesity and open our minds to new ideas,” he added.
Dr. Kaplan has reported financial ties to Eli Lilly, Gelesis, GI Dynamics, IntelliHealth, Johnson & Johnson, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Rhythm Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Ryan has ties to numerous Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and several other pharmaceutical companies, including having an ownership interest in Gila Therapeutics, Xeno Biosciences, Epitomee, Calibrate, Roman, and Scientific Intake.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“When considering the challenges of obesity, ask yourself: ‘If it were diabetes, cancer, HIV, or Alzheimer’s, how would you discuss it, approach it, assess it, treat it?’” Lee M. Kaplan, MD, PhD, asked the audience of health care professionals during ObesityWeek®, the annual meeting of The Obesity Society.
“And then do it for obesity, using the full spectrum of tools at our disposal,” he advised.
This was the takeaway that Dr. Kaplan, director of the Obesity, Metabolism, and Nutrition Institute at Massachusetts General Hospital and associate professor, Harvard Medical School, Boston, left the audience with at the end of his lecture entitled, “What does the future of obesity care look like?”
Invited to summarize his main points, Dr. Kaplan told this news organization in an interview that practitioners caring for patients with obesity need to first “recognize that obesity is a disease” caused by dysfunction of the metabolic system that regulates body fat – in the same way immune dysregulation can lead to asthma.
Second, “we are finally developing noninvasive therapies that are more effective,” he noted, referring to the recently approved semaglutide, and even more potent weight-loss therapies that could be on the market within 3 years, so that weight-loss outcomes with pharmacotherapy are approaching those with bariatric surgery.
Third, it is important that patients with obesity get “broad and equitable access” to treatment, and health care practitioners need to be on the same page and have a “shared understanding” of which treatments are appropriate for individual patients, “just as we do for other diseases.”
Need for a shared understanding
“Dr. Kaplan really brought home the idea that we all need a shared understanding of what obesity is – and what it is not,” agreed symposium moderator Donna H. Ryan, MD, in an email.
“He underscored the biologic basis of obesity,” noted Dr. Ryan, professor emerita at Pennington Biomedical Research Center in Baton Rouge, Louisiana, and associate editor-in-chief of Obesity, the official journal of The Obesity Society.
“It is a dysregulation of the body’s weight (especially adipose tissue) regulatory system,” she continued. “The body responds to powerful environmental pressures that produce excess energy balance, and we store that as fat and defend our highest fat mass. This makes obesity a disease, a chronic disease that requires a medical approach to reverse. It’s not a cosmetic problem, it’s a medical problem,” she emphasized.
There is so much misinformation out there about obesity, according to Dr. Ryan.
“People think it’s a lack of willpower, and even patients blame themselves for not being able to lose weight and keep it off. It’s not their fault! It’s biology.”
Although the supplement industry and fad diets falsely promise fast results, there is no magic diet, she continued.
“But we have made progress based on understanding the biologic basis of obesity and have new medications that offer real hope for patients.”
“With 42% of U.S. adults having a BMI that qualifies as obesity, we need a concerted and broad effort to address this problem, and that starts with everybody on the same page as to what obesity is ... a shared understanding of the biologic basis of obesity. It’s time to take obesity seriously,” she summarized, echoing Dr. Kaplan.
A question of biology
“Obesity results from inappropriate pathophysiological regulation of body fat mass,” when the body defends adiposity, Dr. Kaplan explained at the start of his lecture.
The treatment strategy for obesity has always been a stepwise approach starting with lifestyle changes, then pharmacotherapy, then possibly bariatric surgery – each step with a potentially greater chance of weight loss. But now, he explained, medicine is on the verge of having an armamentarium of more potent weight-loss medications.
Compared with phentermine/topiramate, orlistat, naltrexone/bupropion, and liraglutide – which roughly might provide 5% to 10% weight loss, the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist semaglutide 2.4 mg/week (Wegovy, Novo Nordisk), approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Association in June, provides almost double this potential weight loss.
And two new agents that could provide “never seen before weight loss” of 25% could potentially enter the marketplace by 2025: the amylin agonist cagrilintide (Novo Nordisk) and the twincretin tirzepatide (Eli Lilly) (a combined glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide [GIP] and GLP-1 receptor agonist).
In addition, when liraglutide comes off patent, a generic version could potentially be introduced, and combined generic liraglutide plus generic phentermine/topiramate could be a less expensive weight-loss treatment option in the future, he noted.
One size does not fit all
Importantly, weight loss varies widely among individual patients.
A graph of potential weight loss with different treatments (for example, bariatric surgery or liraglutide) versus the percentage of patients that attain the weight losses is roughly bell-shaped, Dr. Kaplan explained. For example, in the STEP1 trial of semaglutide, roughly 7.1% of patients lost less than 5% of their initial weight, 25% of patients lost 20% to 30%, and 10.8% of patients lost 30% or more; that is, patients at the higher end had weight loss comparable to that seen with bariatric surgery
Adding pharmacotherapy after bariatric surgery could be synergistic. For example, in the GRAVITAS study of patients with type 2 diabetes who had gastric bypass surgery, those who received liraglutide after surgery had augmented weight loss compared with those who received placebo.
People at a cocktail party might come up to him and say, “I’d like to lose 5 pounds, 10 pounds,” Dr. Kaplan related in the Q&A session.
“That’s not obesity,” he emphasized. Obesity is excess body fat that poses a risk to health. A person with obesity may have 50 or more excess pounds, and the body is trying to defend this weight.
“If we want to treat obesity more effectively, we have to fully understand why it is a disease and how that disease differs from the cultural desire for thinness,” he reiterated.
“We have to keep the needs and goals of all people living with obesity foremost in our minds, even if many of them have been previously misled by the bias, stigma, blame, and discrimination that surrounds them.”
“We need to re-evaluate what we think we know about obesity and open our minds to new ideas,” he added.
Dr. Kaplan has reported financial ties to Eli Lilly, Gelesis, GI Dynamics, IntelliHealth, Johnson & Johnson, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Rhythm Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Ryan has ties to numerous Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and several other pharmaceutical companies, including having an ownership interest in Gila Therapeutics, Xeno Biosciences, Epitomee, Calibrate, Roman, and Scientific Intake.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM OBESITY WEEK 2020
Pembrolizumab-Induced Type 1 Diabetes in a 95-Year-Old Veteran With Metastatic Melanoma
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (CPIs) have revolutionized cancer therapy and improved the prognosis for a variety of advanced solid tumors and Hodgkin lymphoma, but evidence is growing regarding severe endocrine disturbances.1,2 CPIs block inhibitory molecules on activated T cells to increase tumor cell destruction but also can breach normal tolerance, resulting in a spectrum of immune-related adverse events (irAE).1,2 Programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) inhibitors are one type of CPIs. Pembrolizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets the PD-1 checkpoint pathway and is approved for the treatment of malignant melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer.3,4 When the PD-1 checkpoint pathway is inhibited, T cells targeting cancer are activated, as are autoreactive T cells, such as those regulating pancreatic islet cell survival, which can lead to type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM).5
Case Presentation
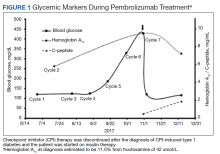
A 95-year-old male veteran with long-standing, stable prediabetes was treated with pembrolizumab for stage 4 melanoma. Four months after treatment initiation and 3 weeks after completion of his sixth treatment cycle of pembrolizumab (2 mg/kg every 3 weeks), he presented for surveillance positron emission tomography (PET) and was incidentally found to have a serum glucose of 423 mg/dL. Hypothesis-driven history taking revealed polyuria, polydipsia, and a 12-lb weight loss during the previous 3 months. The patient reported no abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting. He showed no evidence of pancreatic metastases on recent imaging. His family history was notable for a daughter with T1DM diagnosed at a young age.
On examination, the patient’s vital signs were normal aside from a blood pressure of 80/40 mm Hg. His body mass index was 30. He was alert and oriented with comfortable respirations and no Kussmaul breathing. He exhibited dry mucous membranes and poor skin turgor. Laboratory studies revealed 135 mmol/L sodium (reference, 135-145), 4.6 mmol/L potassium (reference, 3.6-5.2), 100 mmol/L chloride (reference, 99-106), bicarbonate of 26.5 mmol/L (reference, 23-29), serum blood urea nitrogen 27 mg/dL (reference, 6-24), 1.06 mg/dL creatinine (reference, 0.74-1.35), and 423 mg/dL glucose (reference, 70-100), with negative urine ketones. Further studies demonstrated 462 µmol/L fructosamine (reference, 190-270), correlating with hemoglobin A1c (
Dicussion
Immunotherapy is now an integral part of cancer treatment and can result in endocrine disturbances.1,2 Life-threatening irAEs are rare and may mimic more common conditions; thus, there is growing recognition of the need to educate health care professionals in appropriate screening and management of these conditions. CPI-induced T1DM is an uncommon but clinically significant event with an incidence of 0.4 to 1.27% and a median onset of 20 weeks after initiation of therapy (range, 1-228 weeks).8-12In case seriesfrom 3 academic centers, 59 to81% of patients with CPI-induced T1DM presented with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), and only 40 to 71% of patients were autoantibody positive.13-16 These patients are older than those presenting with classic T1DM, often require intensive care unit admission, and nearly invariably require exogenous insulin injections for metabolic control.13-16
Based on the later age of onset of cancers that may be treated with CPI, patients with CPI-induced T1DM may be misdiagnosed with T2DM or hyperglycemia from other causes, such as medications or acute illness in the outpatient setting, risking suboptimal treatment.
Given the infrequent incidence and lack of controlled trials, screening and treatment recommendations for CPI-induced T1DM are based on principles derived from case series and expert opinion. Development of polyuria, polydipsia, weight loss, nausea, and/or vomiting should prompt investigation for possible development or worsening of hyperglycemia, suggestive of development of T1DM.17 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) guidelines recommend that serum glucose be assessed at baseline and with each treatment cycle during induction for 12 weeks, then every 3 to 6 weeks thereafter.17 There is no reported association between the number of CPI treatments and the development of DM.8,9 Following our patient’s fifth pembrolizumab cycle, a random glucose reading was noted to be 186 mg/dL (Figure 1). Under the ASCO guidelines, ideally the patient would have received close clinical follow-up given the striking increase in plasma glucose compared with prior baseline lower values and perhaps been further evaluated with an anti-GAD antibody titer to screen for T1DM.17
This patient's case adds to the published reports of CPI-induced T1DM without DKA and represents the oldest patient experiencing this irAE in the literature.13-16 The degree of elevation of his initial fructosamine, which is comparable to an average plasma glucose of approximately 270 mg/dL, belied the rapid rate of rise of his recent plasma glucose. Given the trajectory of glycemic markers and symptoms, one could certainly be concerned about imminent decompensation to DKA. However, fortuitous point-of-care glucose reading prior to surveillance PET resulted in a new critical diagnosis and initiation of treatment.
Assessing the need for inpatient evaluation includes obtaining urine ketones and acid-base status as screening for DKA.17 Antibodies and C-peptide can be sent to support diagnosis of new onset T1DM, although the initiation of therapy should not be delayed for these results.17 As noted before, many of these patients also are antibody negative.13-16 Low C-peptide levels should prompt a high suspicion for CPI-induced T1DM, and initiation of insulin therapy should be strongly considered.17 In a case series of 27 patients, 85% exhibited a rapid loss of β-cell function, evidenced by the acute progression to hyperglycemia and low or undetectable levels of C-peptide at diagnosis.9 Likewise, our patient had a low C-peptide level and negative anti-GAD antibody titer but was treated before these results were available. Inpatient admission for close glycemic monitoring may be reasonable; several cases reported prompt diagnosis and avoidance of DKA in this setting.17
In contrast to other irAEs, there is no available evidence that high-dose corticosteroids alter the course of pembrolizumab-induced T2DM.18 Depending on the degree of hyperglycemia, endocrinology consultation and insulin treatment are appropriate where the diagnosis of T1DM is suspected even without evidence of DKA.17 For patients with T2DM, there may be a positive synergistic effect of metformin in combination with CPIs in tumor control.19 Our patient’s C-peptide improved with insulin treatment, consistent with correction of glucose toxicity and a honeymoon period in his course. However, in patients reported with pembrolizumab-induced T1DM, insulin requirement for treatment generally persists despite cessation of pembrolizumab therapy.13-16
Conclusions
Pembrolizumab-induced T1DM is a rare, but potentially life-threatening irAE. The acute risk of DKA requires early recognition and prompt treatment of patients taking CPIs. More than 90% of primary care physicians (PCPs) fulfill general medical care roles for patients with cancer; therefore, they play an essential role in evaluating symptoms during therapy.20 Further studies evaluating the role of PCPs and outcomes when PCPs are involved in oncologic care should be conducted.
With increased index of suspicion, this clinical scenario presents an opportunity for PCPs that may help reduce irAE-associated morbidity and mortality of patients on CPIs, like pembrolizumab. Figure 2 illustrates an example addendum that can be used to alert and tag a PCP of a mutual patient after initiation of CPI therapy. Determining the optimal interface between PCPs, oncologists, and endocrinologists in delivering and coordinating high-quality cancer care in the setting of immunotherapy is an important area for ongoing quality improvement.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank all the staff and health care professionals at VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System who were involved in the care of this patient.
1. Puzanov I, Diab A, Abdallah K, et al; Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer Toxicity Management Working Group. Managing toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: consensus recommendations from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Toxicity Management Working Group. J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5(1):95. doi:10.1186/s40425-017-0300-z
2. Villa NM, Farahmand A, Du L, et al. Endocrinopathies with use of cancer immunotherapies. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2018;88(2):327-332. doi:10.1111/cen.13483
3. Schachter J, Ribas A, Long GV, et al. Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab for advanced melanoma: final overall survival results of a multicentre, randomised, open-label phase 3 study (KEYNOTE-006). Lancet. 2017;390(10105):1853-1862. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31601-X
4. Garon EB, Hellmann MD, Rizvi NA, et al. Five-year overall survival for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with pembrolizumab: results from the phase I KEYNOTE-001 Study. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(28):2518-2527. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.00934
5. Ribas A. Tumor immunotherapy directed at PD-1. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(26):2517-2519. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1205943
6. Malmstrom H, Walldius G, Grill V, Jungner I, Gudbjomsdottir S, Hammar N. Frustosamine is a useful indicator of hyperglycemia and glucose control in clinical and epidemiological studies- cross-sectional and longitudinal experience from the AMORIS cohort. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e111463. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111463
7. Skinner S, Diaw M, Mbaye MN, et al. Evaluation of agreement between hemoglobin A1c, fasting glucose, and fructosamine in Senagalese individuals with and without sickle-cell trait. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0212552. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0212552
8. Byun DJ, Wolchok JD, Rosenberg LM, Girotra M. Cancer immunotherapy-immune checkpoint blockade and associated endocrinopathies. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13(4):195-207. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2016.205
9. Stamatouli AM, Quandt Z, Perdigoto AL, et al. Collateral damage: insulin-dependent diabetes induced with checkpoint inhibitors. Diabetes. 2018;67(8):1471-1480. doi:10.2337/dbi18-0002
10. Liu J, Zhou H, Zhang Y, et al. Reporting of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy-associated diabetes, 2015-2019. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(7):e79-e80. [Published online ahead of print, 2020 May 11]. doi:10.2337/dc20-0459
11. Barroso-Sousa R, Barry WT, Garrido-Castro AC, et al. Incidence of endocrine dysfunction following the use of different immune checkpoint inhibitor regimens: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(2):173-182. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3064
12. de Filette J, Andreescu CE, Cools F, Bravenboer B, Velkeniers B. A systematic review and meta-analysis of endocrine-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Horm Metab Res. 2019;51(3):145-156. doi:10.1055/a-0843-3366
13. Hughes J, Vudattu N, Sznol M, et al. Precipitation of autoimmune diabetes with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(4):e55-e57. doi:10.2337/dc14-2349
14. Clotman K, Janssens K, Specenier P, Weets I, De block CEM. Programmed cell death-1 inhibitor-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(9):3144-3154. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-00728
15. Kotwal A, Haddox C, Block M, Kudva YC. Immune checkpoint inhibitors: an emerging cause of insulin-dependent diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2019;7(1):e000591. doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2018-000591
16. Chang LS, Barroso-Sousa R, Tolaney SM, Hodi FS, Kaiser UB, Min L. Endocrine toxicity of cancer immunotherapy targeting immune checkpoints. Endocr Rev. 2019;40(1):17-65. doi:10.1210/er.2018-00006
17. Brahmer JR, Lacchetti C, Schneider BJ, et al; National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Management of immune-related adverse events in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(17):1714-1768. doi:10.1200/JCO.2017.77.6385
18. Aleksova J, Lau PK, Soldatos G, Mcarthur G. Glucocorticoids did not reverse type 1 diabetes mellitus secondary to pembrolizumab in a patient with metastatic melanoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2016;2016:bcr2016217454. doi:10.1136/bcr-2016-217454
19. Afzal MZ, Mercado RR, Shirai K. Efficacy of metformin in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors (anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA-4) in metastatic malignant melanoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6(1):64. doi:10.1186/s40425-018-0375-1
20. Klabunde CN, Ambs A, Keating NL, et al. The role of primary care physicians in cancer care. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(9):1029-1036. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1058-x
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (CPIs) have revolutionized cancer therapy and improved the prognosis for a variety of advanced solid tumors and Hodgkin lymphoma, but evidence is growing regarding severe endocrine disturbances.1,2 CPIs block inhibitory molecules on activated T cells to increase tumor cell destruction but also can breach normal tolerance, resulting in a spectrum of immune-related adverse events (irAE).1,2 Programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) inhibitors are one type of CPIs. Pembrolizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets the PD-1 checkpoint pathway and is approved for the treatment of malignant melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer.3,4 When the PD-1 checkpoint pathway is inhibited, T cells targeting cancer are activated, as are autoreactive T cells, such as those regulating pancreatic islet cell survival, which can lead to type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM).5
Case Presentation
A 95-year-old male veteran with long-standing, stable prediabetes was treated with pembrolizumab for stage 4 melanoma. Four months after treatment initiation and 3 weeks after completion of his sixth treatment cycle of pembrolizumab (2 mg/kg every 3 weeks), he presented for surveillance positron emission tomography (PET) and was incidentally found to have a serum glucose of 423 mg/dL. Hypothesis-driven history taking revealed polyuria, polydipsia, and a 12-lb weight loss during the previous 3 months. The patient reported no abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting. He showed no evidence of pancreatic metastases on recent imaging. His family history was notable for a daughter with T1DM diagnosed at a young age.
On examination, the patient’s vital signs were normal aside from a blood pressure of 80/40 mm Hg. His body mass index was 30. He was alert and oriented with comfortable respirations and no Kussmaul breathing. He exhibited dry mucous membranes and poor skin turgor. Laboratory studies revealed 135 mmol/L sodium (reference, 135-145), 4.6 mmol/L potassium (reference, 3.6-5.2), 100 mmol/L chloride (reference, 99-106), bicarbonate of 26.5 mmol/L (reference, 23-29), serum blood urea nitrogen 27 mg/dL (reference, 6-24), 1.06 mg/dL creatinine (reference, 0.74-1.35), and 423 mg/dL glucose (reference, 70-100), with negative urine ketones. Further studies demonstrated 462 µmol/L fructosamine (reference, 190-270), correlating with hemoglobin A1c (
Dicussion
Immunotherapy is now an integral part of cancer treatment and can result in endocrine disturbances.1,2 Life-threatening irAEs are rare and may mimic more common conditions; thus, there is growing recognition of the need to educate health care professionals in appropriate screening and management of these conditions. CPI-induced T1DM is an uncommon but clinically significant event with an incidence of 0.4 to 1.27% and a median onset of 20 weeks after initiation of therapy (range, 1-228 weeks).8-12In case seriesfrom 3 academic centers, 59 to81% of patients with CPI-induced T1DM presented with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), and only 40 to 71% of patients were autoantibody positive.13-16 These patients are older than those presenting with classic T1DM, often require intensive care unit admission, and nearly invariably require exogenous insulin injections for metabolic control.13-16
Based on the later age of onset of cancers that may be treated with CPI, patients with CPI-induced T1DM may be misdiagnosed with T2DM or hyperglycemia from other causes, such as medications or acute illness in the outpatient setting, risking suboptimal treatment.
Given the infrequent incidence and lack of controlled trials, screening and treatment recommendations for CPI-induced T1DM are based on principles derived from case series and expert opinion. Development of polyuria, polydipsia, weight loss, nausea, and/or vomiting should prompt investigation for possible development or worsening of hyperglycemia, suggestive of development of T1DM.17 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) guidelines recommend that serum glucose be assessed at baseline and with each treatment cycle during induction for 12 weeks, then every 3 to 6 weeks thereafter.17 There is no reported association between the number of CPI treatments and the development of DM.8,9 Following our patient’s fifth pembrolizumab cycle, a random glucose reading was noted to be 186 mg/dL (Figure 1). Under the ASCO guidelines, ideally the patient would have received close clinical follow-up given the striking increase in plasma glucose compared with prior baseline lower values and perhaps been further evaluated with an anti-GAD antibody titer to screen for T1DM.17
This patient's case adds to the published reports of CPI-induced T1DM without DKA and represents the oldest patient experiencing this irAE in the literature.13-16 The degree of elevation of his initial fructosamine, which is comparable to an average plasma glucose of approximately 270 mg/dL, belied the rapid rate of rise of his recent plasma glucose. Given the trajectory of glycemic markers and symptoms, one could certainly be concerned about imminent decompensation to DKA. However, fortuitous point-of-care glucose reading prior to surveillance PET resulted in a new critical diagnosis and initiation of treatment.
Assessing the need for inpatient evaluation includes obtaining urine ketones and acid-base status as screening for DKA.17 Antibodies and C-peptide can be sent to support diagnosis of new onset T1DM, although the initiation of therapy should not be delayed for these results.17 As noted before, many of these patients also are antibody negative.13-16 Low C-peptide levels should prompt a high suspicion for CPI-induced T1DM, and initiation of insulin therapy should be strongly considered.17 In a case series of 27 patients, 85% exhibited a rapid loss of β-cell function, evidenced by the acute progression to hyperglycemia and low or undetectable levels of C-peptide at diagnosis.9 Likewise, our patient had a low C-peptide level and negative anti-GAD antibody titer but was treated before these results were available. Inpatient admission for close glycemic monitoring may be reasonable; several cases reported prompt diagnosis and avoidance of DKA in this setting.17
In contrast to other irAEs, there is no available evidence that high-dose corticosteroids alter the course of pembrolizumab-induced T2DM.18 Depending on the degree of hyperglycemia, endocrinology consultation and insulin treatment are appropriate where the diagnosis of T1DM is suspected even without evidence of DKA.17 For patients with T2DM, there may be a positive synergistic effect of metformin in combination with CPIs in tumor control.19 Our patient’s C-peptide improved with insulin treatment, consistent with correction of glucose toxicity and a honeymoon period in his course. However, in patients reported with pembrolizumab-induced T1DM, insulin requirement for treatment generally persists despite cessation of pembrolizumab therapy.13-16
Conclusions
Pembrolizumab-induced T1DM is a rare, but potentially life-threatening irAE. The acute risk of DKA requires early recognition and prompt treatment of patients taking CPIs. More than 90% of primary care physicians (PCPs) fulfill general medical care roles for patients with cancer; therefore, they play an essential role in evaluating symptoms during therapy.20 Further studies evaluating the role of PCPs and outcomes when PCPs are involved in oncologic care should be conducted.
With increased index of suspicion, this clinical scenario presents an opportunity for PCPs that may help reduce irAE-associated morbidity and mortality of patients on CPIs, like pembrolizumab. Figure 2 illustrates an example addendum that can be used to alert and tag a PCP of a mutual patient after initiation of CPI therapy. Determining the optimal interface between PCPs, oncologists, and endocrinologists in delivering and coordinating high-quality cancer care in the setting of immunotherapy is an important area for ongoing quality improvement.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank all the staff and health care professionals at VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System who were involved in the care of this patient.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (CPIs) have revolutionized cancer therapy and improved the prognosis for a variety of advanced solid tumors and Hodgkin lymphoma, but evidence is growing regarding severe endocrine disturbances.1,2 CPIs block inhibitory molecules on activated T cells to increase tumor cell destruction but also can breach normal tolerance, resulting in a spectrum of immune-related adverse events (irAE).1,2 Programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) inhibitors are one type of CPIs. Pembrolizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets the PD-1 checkpoint pathway and is approved for the treatment of malignant melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer.3,4 When the PD-1 checkpoint pathway is inhibited, T cells targeting cancer are activated, as are autoreactive T cells, such as those regulating pancreatic islet cell survival, which can lead to type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM).5
Case Presentation
A 95-year-old male veteran with long-standing, stable prediabetes was treated with pembrolizumab for stage 4 melanoma. Four months after treatment initiation and 3 weeks after completion of his sixth treatment cycle of pembrolizumab (2 mg/kg every 3 weeks), he presented for surveillance positron emission tomography (PET) and was incidentally found to have a serum glucose of 423 mg/dL. Hypothesis-driven history taking revealed polyuria, polydipsia, and a 12-lb weight loss during the previous 3 months. The patient reported no abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting. He showed no evidence of pancreatic metastases on recent imaging. His family history was notable for a daughter with T1DM diagnosed at a young age.
On examination, the patient’s vital signs were normal aside from a blood pressure of 80/40 mm Hg. His body mass index was 30. He was alert and oriented with comfortable respirations and no Kussmaul breathing. He exhibited dry mucous membranes and poor skin turgor. Laboratory studies revealed 135 mmol/L sodium (reference, 135-145), 4.6 mmol/L potassium (reference, 3.6-5.2), 100 mmol/L chloride (reference, 99-106), bicarbonate of 26.5 mmol/L (reference, 23-29), serum blood urea nitrogen 27 mg/dL (reference, 6-24), 1.06 mg/dL creatinine (reference, 0.74-1.35), and 423 mg/dL glucose (reference, 70-100), with negative urine ketones. Further studies demonstrated 462 µmol/L fructosamine (reference, 190-270), correlating with hemoglobin A1c (
Dicussion
Immunotherapy is now an integral part of cancer treatment and can result in endocrine disturbances.1,2 Life-threatening irAEs are rare and may mimic more common conditions; thus, there is growing recognition of the need to educate health care professionals in appropriate screening and management of these conditions. CPI-induced T1DM is an uncommon but clinically significant event with an incidence of 0.4 to 1.27% and a median onset of 20 weeks after initiation of therapy (range, 1-228 weeks).8-12In case seriesfrom 3 academic centers, 59 to81% of patients with CPI-induced T1DM presented with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), and only 40 to 71% of patients were autoantibody positive.13-16 These patients are older than those presenting with classic T1DM, often require intensive care unit admission, and nearly invariably require exogenous insulin injections for metabolic control.13-16
Based on the later age of onset of cancers that may be treated with CPI, patients with CPI-induced T1DM may be misdiagnosed with T2DM or hyperglycemia from other causes, such as medications or acute illness in the outpatient setting, risking suboptimal treatment.
Given the infrequent incidence and lack of controlled trials, screening and treatment recommendations for CPI-induced T1DM are based on principles derived from case series and expert opinion. Development of polyuria, polydipsia, weight loss, nausea, and/or vomiting should prompt investigation for possible development or worsening of hyperglycemia, suggestive of development of T1DM.17 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) guidelines recommend that serum glucose be assessed at baseline and with each treatment cycle during induction for 12 weeks, then every 3 to 6 weeks thereafter.17 There is no reported association between the number of CPI treatments and the development of DM.8,9 Following our patient’s fifth pembrolizumab cycle, a random glucose reading was noted to be 186 mg/dL (Figure 1). Under the ASCO guidelines, ideally the patient would have received close clinical follow-up given the striking increase in plasma glucose compared with prior baseline lower values and perhaps been further evaluated with an anti-GAD antibody titer to screen for T1DM.17
This patient's case adds to the published reports of CPI-induced T1DM without DKA and represents the oldest patient experiencing this irAE in the literature.13-16 The degree of elevation of his initial fructosamine, which is comparable to an average plasma glucose of approximately 270 mg/dL, belied the rapid rate of rise of his recent plasma glucose. Given the trajectory of glycemic markers and symptoms, one could certainly be concerned about imminent decompensation to DKA. However, fortuitous point-of-care glucose reading prior to surveillance PET resulted in a new critical diagnosis and initiation of treatment.
Assessing the need for inpatient evaluation includes obtaining urine ketones and acid-base status as screening for DKA.17 Antibodies and C-peptide can be sent to support diagnosis of new onset T1DM, although the initiation of therapy should not be delayed for these results.17 As noted before, many of these patients also are antibody negative.13-16 Low C-peptide levels should prompt a high suspicion for CPI-induced T1DM, and initiation of insulin therapy should be strongly considered.17 In a case series of 27 patients, 85% exhibited a rapid loss of β-cell function, evidenced by the acute progression to hyperglycemia and low or undetectable levels of C-peptide at diagnosis.9 Likewise, our patient had a low C-peptide level and negative anti-GAD antibody titer but was treated before these results were available. Inpatient admission for close glycemic monitoring may be reasonable; several cases reported prompt diagnosis and avoidance of DKA in this setting.17
In contrast to other irAEs, there is no available evidence that high-dose corticosteroids alter the course of pembrolizumab-induced T2DM.18 Depending on the degree of hyperglycemia, endocrinology consultation and insulin treatment are appropriate where the diagnosis of T1DM is suspected even without evidence of DKA.17 For patients with T2DM, there may be a positive synergistic effect of metformin in combination with CPIs in tumor control.19 Our patient’s C-peptide improved with insulin treatment, consistent with correction of glucose toxicity and a honeymoon period in his course. However, in patients reported with pembrolizumab-induced T1DM, insulin requirement for treatment generally persists despite cessation of pembrolizumab therapy.13-16
Conclusions
Pembrolizumab-induced T1DM is a rare, but potentially life-threatening irAE. The acute risk of DKA requires early recognition and prompt treatment of patients taking CPIs. More than 90% of primary care physicians (PCPs) fulfill general medical care roles for patients with cancer; therefore, they play an essential role in evaluating symptoms during therapy.20 Further studies evaluating the role of PCPs and outcomes when PCPs are involved in oncologic care should be conducted.
With increased index of suspicion, this clinical scenario presents an opportunity for PCPs that may help reduce irAE-associated morbidity and mortality of patients on CPIs, like pembrolizumab. Figure 2 illustrates an example addendum that can be used to alert and tag a PCP of a mutual patient after initiation of CPI therapy. Determining the optimal interface between PCPs, oncologists, and endocrinologists in delivering and coordinating high-quality cancer care in the setting of immunotherapy is an important area for ongoing quality improvement.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank all the staff and health care professionals at VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System who were involved in the care of this patient.
1. Puzanov I, Diab A, Abdallah K, et al; Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer Toxicity Management Working Group. Managing toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: consensus recommendations from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Toxicity Management Working Group. J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5(1):95. doi:10.1186/s40425-017-0300-z
2. Villa NM, Farahmand A, Du L, et al. Endocrinopathies with use of cancer immunotherapies. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2018;88(2):327-332. doi:10.1111/cen.13483
3. Schachter J, Ribas A, Long GV, et al. Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab for advanced melanoma: final overall survival results of a multicentre, randomised, open-label phase 3 study (KEYNOTE-006). Lancet. 2017;390(10105):1853-1862. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31601-X
4. Garon EB, Hellmann MD, Rizvi NA, et al. Five-year overall survival for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with pembrolizumab: results from the phase I KEYNOTE-001 Study. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(28):2518-2527. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.00934
5. Ribas A. Tumor immunotherapy directed at PD-1. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(26):2517-2519. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1205943
6. Malmstrom H, Walldius G, Grill V, Jungner I, Gudbjomsdottir S, Hammar N. Frustosamine is a useful indicator of hyperglycemia and glucose control in clinical and epidemiological studies- cross-sectional and longitudinal experience from the AMORIS cohort. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e111463. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111463
7. Skinner S, Diaw M, Mbaye MN, et al. Evaluation of agreement between hemoglobin A1c, fasting glucose, and fructosamine in Senagalese individuals with and without sickle-cell trait. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0212552. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0212552
8. Byun DJ, Wolchok JD, Rosenberg LM, Girotra M. Cancer immunotherapy-immune checkpoint blockade and associated endocrinopathies. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13(4):195-207. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2016.205
9. Stamatouli AM, Quandt Z, Perdigoto AL, et al. Collateral damage: insulin-dependent diabetes induced with checkpoint inhibitors. Diabetes. 2018;67(8):1471-1480. doi:10.2337/dbi18-0002
10. Liu J, Zhou H, Zhang Y, et al. Reporting of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy-associated diabetes, 2015-2019. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(7):e79-e80. [Published online ahead of print, 2020 May 11]. doi:10.2337/dc20-0459
11. Barroso-Sousa R, Barry WT, Garrido-Castro AC, et al. Incidence of endocrine dysfunction following the use of different immune checkpoint inhibitor regimens: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(2):173-182. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3064
12. de Filette J, Andreescu CE, Cools F, Bravenboer B, Velkeniers B. A systematic review and meta-analysis of endocrine-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Horm Metab Res. 2019;51(3):145-156. doi:10.1055/a-0843-3366
13. Hughes J, Vudattu N, Sznol M, et al. Precipitation of autoimmune diabetes with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(4):e55-e57. doi:10.2337/dc14-2349
14. Clotman K, Janssens K, Specenier P, Weets I, De block CEM. Programmed cell death-1 inhibitor-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(9):3144-3154. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-00728
15. Kotwal A, Haddox C, Block M, Kudva YC. Immune checkpoint inhibitors: an emerging cause of insulin-dependent diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2019;7(1):e000591. doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2018-000591
16. Chang LS, Barroso-Sousa R, Tolaney SM, Hodi FS, Kaiser UB, Min L. Endocrine toxicity of cancer immunotherapy targeting immune checkpoints. Endocr Rev. 2019;40(1):17-65. doi:10.1210/er.2018-00006
17. Brahmer JR, Lacchetti C, Schneider BJ, et al; National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Management of immune-related adverse events in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(17):1714-1768. doi:10.1200/JCO.2017.77.6385
18. Aleksova J, Lau PK, Soldatos G, Mcarthur G. Glucocorticoids did not reverse type 1 diabetes mellitus secondary to pembrolizumab in a patient with metastatic melanoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2016;2016:bcr2016217454. doi:10.1136/bcr-2016-217454
19. Afzal MZ, Mercado RR, Shirai K. Efficacy of metformin in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors (anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA-4) in metastatic malignant melanoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6(1):64. doi:10.1186/s40425-018-0375-1
20. Klabunde CN, Ambs A, Keating NL, et al. The role of primary care physicians in cancer care. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(9):1029-1036. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1058-x
1. Puzanov I, Diab A, Abdallah K, et al; Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer Toxicity Management Working Group. Managing toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: consensus recommendations from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Toxicity Management Working Group. J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5(1):95. doi:10.1186/s40425-017-0300-z
2. Villa NM, Farahmand A, Du L, et al. Endocrinopathies with use of cancer immunotherapies. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2018;88(2):327-332. doi:10.1111/cen.13483
3. Schachter J, Ribas A, Long GV, et al. Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab for advanced melanoma: final overall survival results of a multicentre, randomised, open-label phase 3 study (KEYNOTE-006). Lancet. 2017;390(10105):1853-1862. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31601-X
4. Garon EB, Hellmann MD, Rizvi NA, et al. Five-year overall survival for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with pembrolizumab: results from the phase I KEYNOTE-001 Study. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(28):2518-2527. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.00934
5. Ribas A. Tumor immunotherapy directed at PD-1. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(26):2517-2519. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1205943
6. Malmstrom H, Walldius G, Grill V, Jungner I, Gudbjomsdottir S, Hammar N. Frustosamine is a useful indicator of hyperglycemia and glucose control in clinical and epidemiological studies- cross-sectional and longitudinal experience from the AMORIS cohort. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e111463. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111463
7. Skinner S, Diaw M, Mbaye MN, et al. Evaluation of agreement between hemoglobin A1c, fasting glucose, and fructosamine in Senagalese individuals with and without sickle-cell trait. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0212552. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0212552
8. Byun DJ, Wolchok JD, Rosenberg LM, Girotra M. Cancer immunotherapy-immune checkpoint blockade and associated endocrinopathies. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13(4):195-207. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2016.205
9. Stamatouli AM, Quandt Z, Perdigoto AL, et al. Collateral damage: insulin-dependent diabetes induced with checkpoint inhibitors. Diabetes. 2018;67(8):1471-1480. doi:10.2337/dbi18-0002
10. Liu J, Zhou H, Zhang Y, et al. Reporting of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy-associated diabetes, 2015-2019. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(7):e79-e80. [Published online ahead of print, 2020 May 11]. doi:10.2337/dc20-0459
11. Barroso-Sousa R, Barry WT, Garrido-Castro AC, et al. Incidence of endocrine dysfunction following the use of different immune checkpoint inhibitor regimens: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(2):173-182. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3064
12. de Filette J, Andreescu CE, Cools F, Bravenboer B, Velkeniers B. A systematic review and meta-analysis of endocrine-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Horm Metab Res. 2019;51(3):145-156. doi:10.1055/a-0843-3366
13. Hughes J, Vudattu N, Sznol M, et al. Precipitation of autoimmune diabetes with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(4):e55-e57. doi:10.2337/dc14-2349
14. Clotman K, Janssens K, Specenier P, Weets I, De block CEM. Programmed cell death-1 inhibitor-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(9):3144-3154. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-00728
15. Kotwal A, Haddox C, Block M, Kudva YC. Immune checkpoint inhibitors: an emerging cause of insulin-dependent diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2019;7(1):e000591. doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2018-000591
16. Chang LS, Barroso-Sousa R, Tolaney SM, Hodi FS, Kaiser UB, Min L. Endocrine toxicity of cancer immunotherapy targeting immune checkpoints. Endocr Rev. 2019;40(1):17-65. doi:10.1210/er.2018-00006
17. Brahmer JR, Lacchetti C, Schneider BJ, et al; National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Management of immune-related adverse events in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(17):1714-1768. doi:10.1200/JCO.2017.77.6385
18. Aleksova J, Lau PK, Soldatos G, Mcarthur G. Glucocorticoids did not reverse type 1 diabetes mellitus secondary to pembrolizumab in a patient with metastatic melanoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2016;2016:bcr2016217454. doi:10.1136/bcr-2016-217454
19. Afzal MZ, Mercado RR, Shirai K. Efficacy of metformin in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors (anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA-4) in metastatic malignant melanoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6(1):64. doi:10.1186/s40425-018-0375-1
20. Klabunde CN, Ambs A, Keating NL, et al. The role of primary care physicians in cancer care. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(9):1029-1036. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1058-x
SUGAR trial finds superior stent for those with diabetes and CAD
Superiority shown on TLF endpoint
Designed to show noninferiority for treatment of coronary artery disease (CAD) in patients with diabetes, a head-to-head comparison of contemporary stents ended up showing that one was superior to the for the primary endpoint of target lesion failure (TLF).
In the superiority analysis, the 35% relative reduction in the risk of TLF at 1 year for the Cre8 EVO (Alvimedica) stent relative to the Resolute Onyx (Medtronic) device reached significance, according to Rafael Romaguera, MD, PhD, an interventional cardiologist at the Bellvitge University Hospital, Barcelona.
At 1 year, the rates of TLF were 7.2% and 10.5% for the Cre8 EVO and Resolute Onyx stents, respectively. On the basis of noninferiority, the 3.73% reduction in TLF at 1 year among those receiving the Cre8 EVO device provided a highly significant confirmation of noninferiority (P < .001) and triggered the preplanned superiority analysis.
When the significant advantage on the TLF endpoint (P = .03) was broken down into its components, the Cre8 EVO stent was linked to numerically lower rates of cardiac death (2.1% vs. 2.7%), target vessel MI (5.3% vs. 7.2%), and target lesion revascularization (2.4% vs. 3.9%), according to the SUGAR (Second-Generation Drug-Eluting Stents in Diabetes) trial results presented at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting, held virtually and live in Orlando and sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
In a previous study comparing these devices, called the ReCre8 trial, the rates of TLF in an all-comer CAD population were similar at 1 year. When an updated 3-year analysis was presented earlier in 2021 at the Cardiovascular Research Technologies meeting, they remained similar.
Diabetes-centered trial was unmet need
The rationale for conducting a new trial limited to patients with diabetes was based on the greater risk in this population, according to Dr. Romaguera. He cited data that indicate the risk of major adverse cardiac events are about two times higher 2 years after stent implantation in patients with diabetes relative to those without, even when contemporary drug-eluting stents are used.
Both the Cre8 EVO and Resolute Onyx stent are drug eluting and employ contemporary architecture that provides the basis for marketing claims that they are suitable for complex patients; but they have differences.
“There are three features that I think differentiate the Cre8 EVO stent,” Dr. Romaguera reported at the meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
One is the absence of polymer, which contrasts with the permanent polymer of the Resolute device. This feature affects the dissolution of the anti-inflammatory drug and might be one explanation for the greater protection from ischemic events, according to Dr. Romaguera.
Another is the thickness of the struts, which range from 70 to 80 mm for the Cre8 EVO device and from 92 to 102 mm for the Resolute Onyx device. In experimental studies, strut thickness has been associated with greater risk of thrombus formation, although it is unclear if this modest difference is clinically significant.
Also important, the Cre8 EVO device employs sirolimus for an anti-inflammatory effect, while the Resolute Onyx elutes zotarolimus. Again, experimental evidence suggests a greater anti-inflammatory effect reduces the need for dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT); that might offer a relative advantage in patients with an elevated risk of bleeding.
It is not clear whether all of these features contribute to the better results observed in this trial in diabetes patients, but Dr. Romaguera indicated that the lower risk of TLF with Cre8 EVO is not just statistically significant but also clinically meaningful.
In SUGAR, which included 23 centers in Spain, 1,175 patients with confirmed diabetes scheduled for percutaneous intervention (PCI) were randomized to one of the two stents. The study was purposely designed with very few exclusion criteria.
SUGAR trial employed all-comer design
“This was an all-comer design and there was no limitation in regard to clinical presentation, complexity, number of lesions, or other disease features,” said Dr. Romaguera. The major exclusions were a life expectancy of less than 2 years and a contraindication to taking DAPT for at least 1 month,
The patients were almost equally divided between those who had a non–ST-segment elevation MI) and those with chronic coronary artery disease, but patients with a STEMI, representing about 12% of the population, were included. Almost all of the patients (about 95%) had type 2 diabetes; nearly one-third were on insulin at the time of randomization.
According to Dr. Romaguera, “SUGAR is the first powered trial to compare new-generation drug-eluting stents in patients with diabetes,” and he emphasized the all-comer design in supporting its clinical relevance.
Several of those participating in discussion of the trial during the late-breaker session agreed. Although the moderator, Gregg Stone, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, expressed surprise that the trial “actually demonstrated superiority” given the difficulty of showing a difference between modern stents, he called the findings “remarkable.”
Others seemed to suggest that it would alter their practice.
“This study is sweet like sugar for us, because now we have a stent that is dedicated and fitted for the diabetic population,” said Gennaro Sardella, MD, of Sapienza University of Rome.
For Marc Etienne Jolicoeur, MD, an interventional cardiologist associated with Duke University, Durham, N.C., one of the impressive findings was the early separation of the curves in favor of Cre8 EVO. Calling SUGAR a “fantastic trial,” he indicated that the progressive advantage over time reinforced his impression that the difference is real.
However, David Kandzari, MD, director of interventional cardiology, Piedmont Hart Institute, Atlanta, was more circumspect. He did not express any criticisms of the trial, but he called for “a larger evidence base” before declaring the Cre8 EVO device a standard of care for patients with diabetes undergoing PCI.
The SUGAR results were published in the European Heart Journal at the time of presentation at the meeting.
The trial was funded by the Spanish Society of Cardiology. Dr. Romaguera reported financial relationships with Biotronik and Boston Scientific. Dr. Stone, has financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies, including those developing devices used in PCI. Dr. Sardella and Dr. Jolicoeur reported no financial relationships relevant to this topic. Dr. Kandzari reported financial relationships with Ablative Solutions and Medtronic.
Superiority shown on TLF endpoint
Superiority shown on TLF endpoint
Designed to show noninferiority for treatment of coronary artery disease (CAD) in patients with diabetes, a head-to-head comparison of contemporary stents ended up showing that one was superior to the for the primary endpoint of target lesion failure (TLF).
In the superiority analysis, the 35% relative reduction in the risk of TLF at 1 year for the Cre8 EVO (Alvimedica) stent relative to the Resolute Onyx (Medtronic) device reached significance, according to Rafael Romaguera, MD, PhD, an interventional cardiologist at the Bellvitge University Hospital, Barcelona.
At 1 year, the rates of TLF were 7.2% and 10.5% for the Cre8 EVO and Resolute Onyx stents, respectively. On the basis of noninferiority, the 3.73% reduction in TLF at 1 year among those receiving the Cre8 EVO device provided a highly significant confirmation of noninferiority (P < .001) and triggered the preplanned superiority analysis.
When the significant advantage on the TLF endpoint (P = .03) was broken down into its components, the Cre8 EVO stent was linked to numerically lower rates of cardiac death (2.1% vs. 2.7%), target vessel MI (5.3% vs. 7.2%), and target lesion revascularization (2.4% vs. 3.9%), according to the SUGAR (Second-Generation Drug-Eluting Stents in Diabetes) trial results presented at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting, held virtually and live in Orlando and sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
In a previous study comparing these devices, called the ReCre8 trial, the rates of TLF in an all-comer CAD population were similar at 1 year. When an updated 3-year analysis was presented earlier in 2021 at the Cardiovascular Research Technologies meeting, they remained similar.
Diabetes-centered trial was unmet need
The rationale for conducting a new trial limited to patients with diabetes was based on the greater risk in this population, according to Dr. Romaguera. He cited data that indicate the risk of major adverse cardiac events are about two times higher 2 years after stent implantation in patients with diabetes relative to those without, even when contemporary drug-eluting stents are used.
Both the Cre8 EVO and Resolute Onyx stent are drug eluting and employ contemporary architecture that provides the basis for marketing claims that they are suitable for complex patients; but they have differences.
“There are three features that I think differentiate the Cre8 EVO stent,” Dr. Romaguera reported at the meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
One is the absence of polymer, which contrasts with the permanent polymer of the Resolute device. This feature affects the dissolution of the anti-inflammatory drug and might be one explanation for the greater protection from ischemic events, according to Dr. Romaguera.
Another is the thickness of the struts, which range from 70 to 80 mm for the Cre8 EVO device and from 92 to 102 mm for the Resolute Onyx device. In experimental studies, strut thickness has been associated with greater risk of thrombus formation, although it is unclear if this modest difference is clinically significant.
Also important, the Cre8 EVO device employs sirolimus for an anti-inflammatory effect, while the Resolute Onyx elutes zotarolimus. Again, experimental evidence suggests a greater anti-inflammatory effect reduces the need for dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT); that might offer a relative advantage in patients with an elevated risk of bleeding.
It is not clear whether all of these features contribute to the better results observed in this trial in diabetes patients, but Dr. Romaguera indicated that the lower risk of TLF with Cre8 EVO is not just statistically significant but also clinically meaningful.
In SUGAR, which included 23 centers in Spain, 1,175 patients with confirmed diabetes scheduled for percutaneous intervention (PCI) were randomized to one of the two stents. The study was purposely designed with very few exclusion criteria.
SUGAR trial employed all-comer design
“This was an all-comer design and there was no limitation in regard to clinical presentation, complexity, number of lesions, or other disease features,” said Dr. Romaguera. The major exclusions were a life expectancy of less than 2 years and a contraindication to taking DAPT for at least 1 month,
The patients were almost equally divided between those who had a non–ST-segment elevation MI) and those with chronic coronary artery disease, but patients with a STEMI, representing about 12% of the population, were included. Almost all of the patients (about 95%) had type 2 diabetes; nearly one-third were on insulin at the time of randomization.
According to Dr. Romaguera, “SUGAR is the first powered trial to compare new-generation drug-eluting stents in patients with diabetes,” and he emphasized the all-comer design in supporting its clinical relevance.
Several of those participating in discussion of the trial during the late-breaker session agreed. Although the moderator, Gregg Stone, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, expressed surprise that the trial “actually demonstrated superiority” given the difficulty of showing a difference between modern stents, he called the findings “remarkable.”
Others seemed to suggest that it would alter their practice.
“This study is sweet like sugar for us, because now we have a stent that is dedicated and fitted for the diabetic population,” said Gennaro Sardella, MD, of Sapienza University of Rome.
For Marc Etienne Jolicoeur, MD, an interventional cardiologist associated with Duke University, Durham, N.C., one of the impressive findings was the early separation of the curves in favor of Cre8 EVO. Calling SUGAR a “fantastic trial,” he indicated that the progressive advantage over time reinforced his impression that the difference is real.
However, David Kandzari, MD, director of interventional cardiology, Piedmont Hart Institute, Atlanta, was more circumspect. He did not express any criticisms of the trial, but he called for “a larger evidence base” before declaring the Cre8 EVO device a standard of care for patients with diabetes undergoing PCI.
The SUGAR results were published in the European Heart Journal at the time of presentation at the meeting.
The trial was funded by the Spanish Society of Cardiology. Dr. Romaguera reported financial relationships with Biotronik and Boston Scientific. Dr. Stone, has financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies, including those developing devices used in PCI. Dr. Sardella and Dr. Jolicoeur reported no financial relationships relevant to this topic. Dr. Kandzari reported financial relationships with Ablative Solutions and Medtronic.
Designed to show noninferiority for treatment of coronary artery disease (CAD) in patients with diabetes, a head-to-head comparison of contemporary stents ended up showing that one was superior to the for the primary endpoint of target lesion failure (TLF).
In the superiority analysis, the 35% relative reduction in the risk of TLF at 1 year for the Cre8 EVO (Alvimedica) stent relative to the Resolute Onyx (Medtronic) device reached significance, according to Rafael Romaguera, MD, PhD, an interventional cardiologist at the Bellvitge University Hospital, Barcelona.
At 1 year, the rates of TLF were 7.2% and 10.5% for the Cre8 EVO and Resolute Onyx stents, respectively. On the basis of noninferiority, the 3.73% reduction in TLF at 1 year among those receiving the Cre8 EVO device provided a highly significant confirmation of noninferiority (P < .001) and triggered the preplanned superiority analysis.
When the significant advantage on the TLF endpoint (P = .03) was broken down into its components, the Cre8 EVO stent was linked to numerically lower rates of cardiac death (2.1% vs. 2.7%), target vessel MI (5.3% vs. 7.2%), and target lesion revascularization (2.4% vs. 3.9%), according to the SUGAR (Second-Generation Drug-Eluting Stents in Diabetes) trial results presented at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting, held virtually and live in Orlando and sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
In a previous study comparing these devices, called the ReCre8 trial, the rates of TLF in an all-comer CAD population were similar at 1 year. When an updated 3-year analysis was presented earlier in 2021 at the Cardiovascular Research Technologies meeting, they remained similar.
Diabetes-centered trial was unmet need
The rationale for conducting a new trial limited to patients with diabetes was based on the greater risk in this population, according to Dr. Romaguera. He cited data that indicate the risk of major adverse cardiac events are about two times higher 2 years after stent implantation in patients with diabetes relative to those without, even when contemporary drug-eluting stents are used.
Both the Cre8 EVO and Resolute Onyx stent are drug eluting and employ contemporary architecture that provides the basis for marketing claims that they are suitable for complex patients; but they have differences.
“There are three features that I think differentiate the Cre8 EVO stent,” Dr. Romaguera reported at the meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
One is the absence of polymer, which contrasts with the permanent polymer of the Resolute device. This feature affects the dissolution of the anti-inflammatory drug and might be one explanation for the greater protection from ischemic events, according to Dr. Romaguera.
Another is the thickness of the struts, which range from 70 to 80 mm for the Cre8 EVO device and from 92 to 102 mm for the Resolute Onyx device. In experimental studies, strut thickness has been associated with greater risk of thrombus formation, although it is unclear if this modest difference is clinically significant.
Also important, the Cre8 EVO device employs sirolimus for an anti-inflammatory effect, while the Resolute Onyx elutes zotarolimus. Again, experimental evidence suggests a greater anti-inflammatory effect reduces the need for dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT); that might offer a relative advantage in patients with an elevated risk of bleeding.
It is not clear whether all of these features contribute to the better results observed in this trial in diabetes patients, but Dr. Romaguera indicated that the lower risk of TLF with Cre8 EVO is not just statistically significant but also clinically meaningful.
In SUGAR, which included 23 centers in Spain, 1,175 patients with confirmed diabetes scheduled for percutaneous intervention (PCI) were randomized to one of the two stents. The study was purposely designed with very few exclusion criteria.
SUGAR trial employed all-comer design
“This was an all-comer design and there was no limitation in regard to clinical presentation, complexity, number of lesions, or other disease features,” said Dr. Romaguera. The major exclusions were a life expectancy of less than 2 years and a contraindication to taking DAPT for at least 1 month,
The patients were almost equally divided between those who had a non–ST-segment elevation MI) and those with chronic coronary artery disease, but patients with a STEMI, representing about 12% of the population, were included. Almost all of the patients (about 95%) had type 2 diabetes; nearly one-third were on insulin at the time of randomization.
According to Dr. Romaguera, “SUGAR is the first powered trial to compare new-generation drug-eluting stents in patients with diabetes,” and he emphasized the all-comer design in supporting its clinical relevance.
Several of those participating in discussion of the trial during the late-breaker session agreed. Although the moderator, Gregg Stone, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, expressed surprise that the trial “actually demonstrated superiority” given the difficulty of showing a difference between modern stents, he called the findings “remarkable.”
Others seemed to suggest that it would alter their practice.
“This study is sweet like sugar for us, because now we have a stent that is dedicated and fitted for the diabetic population,” said Gennaro Sardella, MD, of Sapienza University of Rome.
For Marc Etienne Jolicoeur, MD, an interventional cardiologist associated with Duke University, Durham, N.C., one of the impressive findings was the early separation of the curves in favor of Cre8 EVO. Calling SUGAR a “fantastic trial,” he indicated that the progressive advantage over time reinforced his impression that the difference is real.
However, David Kandzari, MD, director of interventional cardiology, Piedmont Hart Institute, Atlanta, was more circumspect. He did not express any criticisms of the trial, but he called for “a larger evidence base” before declaring the Cre8 EVO device a standard of care for patients with diabetes undergoing PCI.
The SUGAR results were published in the European Heart Journal at the time of presentation at the meeting.
The trial was funded by the Spanish Society of Cardiology. Dr. Romaguera reported financial relationships with Biotronik and Boston Scientific. Dr. Stone, has financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies, including those developing devices used in PCI. Dr. Sardella and Dr. Jolicoeur reported no financial relationships relevant to this topic. Dr. Kandzari reported financial relationships with Ablative Solutions and Medtronic.
FROM TCT 2021
COVID-19 has brought more complex, longer office visits
Evidence of this came from the latest Primary Care Collaborative (PCC) survey, which found that primary care clinicians are seeing more complex patients requiring longer appointments in the wake of COVID-19.
The PCC with the Larry A. Green Center regularly surveys primary care clinicians. This round of questions came August 14-17 and included 1,263 respondents from 49 states, the District of Columbia, and two territories.
More than 7 in 10 (71%) respondents said their patients are more complex and nearly the same percentage said appointments are taking more time.
Ann Greiner, president and CEO of the PCC, said in an interview that 55% of respondents reported that clinicians are struggling to keep up with pent-up demand after patients have delayed or canceled care. Sixty-five percent in the survey said they had seen a rise in children’s mental health issues, and 58% said they were unsure how to help their patients with long COVID.
In addition, primary care clinicians are having repeated conversations with patients on why they should get a vaccine and which one.
“I think that’s adding to the complexity. There is a lot going on here with patient trust,” Ms. Greiner said.
‘We’re going to be playing catch-up’
Jacqueline Fincher, MD, an internist in Thompson, Ga., said in an interview that appointments have gotten longer and more complex in the wake of the pandemic – “no question.”
The immediate past president of the American College of Physicians is seeing patients with chronic disease that has gone untreated for sometimes a year or more, she said.
“Their blood pressure was not under good control, they were under more stress, their sugars were up and weren’t being followed as closely for conditions such as congestive heart failure,” she said.
Dr. Fincher, who works in a rural practice 40 miles from Augusta, Ga., with her physician husband and two other physicians, said patients are ready to come back in, “but I don’t have enough slots for them.”
She said she prioritizes what to help patients with first and schedules the next tier for the next appointment, but added, “honestly, over the next 2 years we’re going to be playing catch-up.”
At the same time, the CDC has estimated that 45% of U.S. adults are at increased risk for complications from COVID-19 because of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, respiratory disease, hypertension, or cancer. Rates ranged from 19.8% for people 18-29 years old to 80.7% for people over 80 years of age.
Long COVID could overwhelm existing health care capacity
Primary care physicians are also having to diagnose sometimes “invisible” symptoms after people have recovered from acute COVID-19 infection. Diagnosing takes intent listening to patients who describe symptoms that tests can’t confirm.
As this news organization has previously reported, half of COVID-19 survivors report postacute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) lasting longer than 6 months.
“These long-term PASC effects occur on a scale that could overwhelm existing health care capacity, particularly in low- and middle-income countries,” the authors wrote.
Anxiety, depression ‘have gone off the charts’
Danielle Loeb, MD, MPH, associate professor of internal medicine at the University of Colorado in Denver, who studies complexity in primary care, said in the wake of COVID-19, more patients have developed “new, serious anxiety.”
“That got extremely exacerbated during the pandemic. Anxiety and depression have gone off the charts,” said Dr. Loeb, who prefers the pronoun “they.”
Dr. Loeb cares for a large number of transgender patients. As offices reopen, some patients are having trouble reintegrating into the workplace and resuming social contacts. The primary care doctor says appointments can get longer because of the need to complete tasks, such as filling out forms for Family Medical Leave Act for those not yet ready to return to work.
COVID-19–related fears are keeping many patients from coming into the office, Dr. Loeb said, either from fear of exposure or because they have mental health issues that keep them from feeling safe leaving the house.
“That really affects my ability to care for them,” they said.
Loss of employment in the pandemic or fear of job loss and subsequent changing of insurance has complicated primary care in terms of treatment and administrative tasks, according to Dr. Loeb.
To help treat patients with acute mental health issues and manage other patients, Dr. Loeb’s practice has brought in a social worker and a therapist.
Team-based care is key in the survival of primary care practices, though providing that is difficult in the smaller clinics because of the critical mass of patients needed to make it viable, they said.
“It’s the only answer. It’s the only way you don’t drown,” Dr. Loeb added. “I’m not drowning, and I credit that to my clinic having the help to support the mental health piece of things.”
Rethinking workflow
Tricia McGinnis, MPP, MPH, executive vice president of the nonprofit Center for Health Care Strategies (CHCS) says complexity has forced rethinking workflow.
“A lot of the trends we’re seeing in primary care were there pre-COVID, but COVID has exacerbated those trends,” she said in an interview.
“The good news ... is that it was already becoming clear that primary care needed to provide basic mental health services and integrate with behavioral health. It had also become clear that effective primary care needed to address social issues that keep patients from accessing health care,” she said.
Expanding care teams, as Dr. Loeb mentioned, is a key strategy, according to Ms. McGinnis. Potential teams would include the clinical staff, but also social workers and community health workers – people who come from the community primary care is serving who can help build trust with patients and connect the patient to the primary care team.
“There’s a lot that needs to happen that the clinician doesn’t need to do,” she said.
Telehealth can be a big factor in coordinating the team, Ms. McGinnis added.
“It’s thinking less about who’s doing the work, but more about the work that needs to be done to keep people healthy. Then let’s think about the type of workers best suited to perform those tasks,” she said.
As for reimbursing more complex care, population-based, up-front capitated payments linked to high-quality care and better outcomes will need to replace fee-for-service models, according to Ms. McGinnis.
That will provide reliable incomes for primary care offices, but also flexibility in how each patient with different levels of complexity is managed, she said.
Ms. Greiner, Dr. Fincher, Dr. Loeb, and Ms. McGinnis have no relevant financial relationships.
Evidence of this came from the latest Primary Care Collaborative (PCC) survey, which found that primary care clinicians are seeing more complex patients requiring longer appointments in the wake of COVID-19.
The PCC with the Larry A. Green Center regularly surveys primary care clinicians. This round of questions came August 14-17 and included 1,263 respondents from 49 states, the District of Columbia, and two territories.
More than 7 in 10 (71%) respondents said their patients are more complex and nearly the same percentage said appointments are taking more time.
Ann Greiner, president and CEO of the PCC, said in an interview that 55% of respondents reported that clinicians are struggling to keep up with pent-up demand after patients have delayed or canceled care. Sixty-five percent in the survey said they had seen a rise in children’s mental health issues, and 58% said they were unsure how to help their patients with long COVID.
In addition, primary care clinicians are having repeated conversations with patients on why they should get a vaccine and which one.
“I think that’s adding to the complexity. There is a lot going on here with patient trust,” Ms. Greiner said.
‘We’re going to be playing catch-up’
Jacqueline Fincher, MD, an internist in Thompson, Ga., said in an interview that appointments have gotten longer and more complex in the wake of the pandemic – “no question.”
The immediate past president of the American College of Physicians is seeing patients with chronic disease that has gone untreated for sometimes a year or more, she said.
“Their blood pressure was not under good control, they were under more stress, their sugars were up and weren’t being followed as closely for conditions such as congestive heart failure,” she said.
Dr. Fincher, who works in a rural practice 40 miles from Augusta, Ga., with her physician husband and two other physicians, said patients are ready to come back in, “but I don’t have enough slots for them.”
She said she prioritizes what to help patients with first and schedules the next tier for the next appointment, but added, “honestly, over the next 2 years we’re going to be playing catch-up.”
At the same time, the CDC has estimated that 45% of U.S. adults are at increased risk for complications from COVID-19 because of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, respiratory disease, hypertension, or cancer. Rates ranged from 19.8% for people 18-29 years old to 80.7% for people over 80 years of age.
Long COVID could overwhelm existing health care capacity
Primary care physicians are also having to diagnose sometimes “invisible” symptoms after people have recovered from acute COVID-19 infection. Diagnosing takes intent listening to patients who describe symptoms that tests can’t confirm.
As this news organization has previously reported, half of COVID-19 survivors report postacute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) lasting longer than 6 months.
“These long-term PASC effects occur on a scale that could overwhelm existing health care capacity, particularly in low- and middle-income countries,” the authors wrote.
Anxiety, depression ‘have gone off the charts’
Danielle Loeb, MD, MPH, associate professor of internal medicine at the University of Colorado in Denver, who studies complexity in primary care, said in the wake of COVID-19, more patients have developed “new, serious anxiety.”
“That got extremely exacerbated during the pandemic. Anxiety and depression have gone off the charts,” said Dr. Loeb, who prefers the pronoun “they.”
Dr. Loeb cares for a large number of transgender patients. As offices reopen, some patients are having trouble reintegrating into the workplace and resuming social contacts. The primary care doctor says appointments can get longer because of the need to complete tasks, such as filling out forms for Family Medical Leave Act for those not yet ready to return to work.
COVID-19–related fears are keeping many patients from coming into the office, Dr. Loeb said, either from fear of exposure or because they have mental health issues that keep them from feeling safe leaving the house.
“That really affects my ability to care for them,” they said.
Loss of employment in the pandemic or fear of job loss and subsequent changing of insurance has complicated primary care in terms of treatment and administrative tasks, according to Dr. Loeb.
To help treat patients with acute mental health issues and manage other patients, Dr. Loeb’s practice has brought in a social worker and a therapist.
Team-based care is key in the survival of primary care practices, though providing that is difficult in the smaller clinics because of the critical mass of patients needed to make it viable, they said.
“It’s the only answer. It’s the only way you don’t drown,” Dr. Loeb added. “I’m not drowning, and I credit that to my clinic having the help to support the mental health piece of things.”
Rethinking workflow
Tricia McGinnis, MPP, MPH, executive vice president of the nonprofit Center for Health Care Strategies (CHCS) says complexity has forced rethinking workflow.
“A lot of the trends we’re seeing in primary care were there pre-COVID, but COVID has exacerbated those trends,” she said in an interview.
“The good news ... is that it was already becoming clear that primary care needed to provide basic mental health services and integrate with behavioral health. It had also become clear that effective primary care needed to address social issues that keep patients from accessing health care,” she said.
Expanding care teams, as Dr. Loeb mentioned, is a key strategy, according to Ms. McGinnis. Potential teams would include the clinical staff, but also social workers and community health workers – people who come from the community primary care is serving who can help build trust with patients and connect the patient to the primary care team.
“There’s a lot that needs to happen that the clinician doesn’t need to do,” she said.
Telehealth can be a big factor in coordinating the team, Ms. McGinnis added.
“It’s thinking less about who’s doing the work, but more about the work that needs to be done to keep people healthy. Then let’s think about the type of workers best suited to perform those tasks,” she said.
As for reimbursing more complex care, population-based, up-front capitated payments linked to high-quality care and better outcomes will need to replace fee-for-service models, according to Ms. McGinnis.
That will provide reliable incomes for primary care offices, but also flexibility in how each patient with different levels of complexity is managed, she said.
Ms. Greiner, Dr. Fincher, Dr. Loeb, and Ms. McGinnis have no relevant financial relationships.
Evidence of this came from the latest Primary Care Collaborative (PCC) survey, which found that primary care clinicians are seeing more complex patients requiring longer appointments in the wake of COVID-19.
The PCC with the Larry A. Green Center regularly surveys primary care clinicians. This round of questions came August 14-17 and included 1,263 respondents from 49 states, the District of Columbia, and two territories.
More than 7 in 10 (71%) respondents said their patients are more complex and nearly the same percentage said appointments are taking more time.
Ann Greiner, president and CEO of the PCC, said in an interview that 55% of respondents reported that clinicians are struggling to keep up with pent-up demand after patients have delayed or canceled care. Sixty-five percent in the survey said they had seen a rise in children’s mental health issues, and 58% said they were unsure how to help their patients with long COVID.
In addition, primary care clinicians are having repeated conversations with patients on why they should get a vaccine and which one.
“I think that’s adding to the complexity. There is a lot going on here with patient trust,” Ms. Greiner said.
‘We’re going to be playing catch-up’
Jacqueline Fincher, MD, an internist in Thompson, Ga., said in an interview that appointments have gotten longer and more complex in the wake of the pandemic – “no question.”
The immediate past president of the American College of Physicians is seeing patients with chronic disease that has gone untreated for sometimes a year or more, she said.
“Their blood pressure was not under good control, they were under more stress, their sugars were up and weren’t being followed as closely for conditions such as congestive heart failure,” she said.
Dr. Fincher, who works in a rural practice 40 miles from Augusta, Ga., with her physician husband and two other physicians, said patients are ready to come back in, “but I don’t have enough slots for them.”
She said she prioritizes what to help patients with first and schedules the next tier for the next appointment, but added, “honestly, over the next 2 years we’re going to be playing catch-up.”
At the same time, the CDC has estimated that 45% of U.S. adults are at increased risk for complications from COVID-19 because of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, respiratory disease, hypertension, or cancer. Rates ranged from 19.8% for people 18-29 years old to 80.7% for people over 80 years of age.
Long COVID could overwhelm existing health care capacity
Primary care physicians are also having to diagnose sometimes “invisible” symptoms after people have recovered from acute COVID-19 infection. Diagnosing takes intent listening to patients who describe symptoms that tests can’t confirm.
As this news organization has previously reported, half of COVID-19 survivors report postacute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) lasting longer than 6 months.
“These long-term PASC effects occur on a scale that could overwhelm existing health care capacity, particularly in low- and middle-income countries,” the authors wrote.
Anxiety, depression ‘have gone off the charts’
Danielle Loeb, MD, MPH, associate professor of internal medicine at the University of Colorado in Denver, who studies complexity in primary care, said in the wake of COVID-19, more patients have developed “new, serious anxiety.”
“That got extremely exacerbated during the pandemic. Anxiety and depression have gone off the charts,” said Dr. Loeb, who prefers the pronoun “they.”
Dr. Loeb cares for a large number of transgender patients. As offices reopen, some patients are having trouble reintegrating into the workplace and resuming social contacts. The primary care doctor says appointments can get longer because of the need to complete tasks, such as filling out forms for Family Medical Leave Act for those not yet ready to return to work.
COVID-19–related fears are keeping many patients from coming into the office, Dr. Loeb said, either from fear of exposure or because they have mental health issues that keep them from feeling safe leaving the house.
“That really affects my ability to care for them,” they said.
Loss of employment in the pandemic or fear of job loss and subsequent changing of insurance has complicated primary care in terms of treatment and administrative tasks, according to Dr. Loeb.
To help treat patients with acute mental health issues and manage other patients, Dr. Loeb’s practice has brought in a social worker and a therapist.
Team-based care is key in the survival of primary care practices, though providing that is difficult in the smaller clinics because of the critical mass of patients needed to make it viable, they said.
“It’s the only answer. It’s the only way you don’t drown,” Dr. Loeb added. “I’m not drowning, and I credit that to my clinic having the help to support the mental health piece of things.”
Rethinking workflow
Tricia McGinnis, MPP, MPH, executive vice president of the nonprofit Center for Health Care Strategies (CHCS) says complexity has forced rethinking workflow.
“A lot of the trends we’re seeing in primary care were there pre-COVID, but COVID has exacerbated those trends,” she said in an interview.
“The good news ... is that it was already becoming clear that primary care needed to provide basic mental health services and integrate with behavioral health. It had also become clear that effective primary care needed to address social issues that keep patients from accessing health care,” she said.
Expanding care teams, as Dr. Loeb mentioned, is a key strategy, according to Ms. McGinnis. Potential teams would include the clinical staff, but also social workers and community health workers – people who come from the community primary care is serving who can help build trust with patients and connect the patient to the primary care team.
“There’s a lot that needs to happen that the clinician doesn’t need to do,” she said.
Telehealth can be a big factor in coordinating the team, Ms. McGinnis added.
“It’s thinking less about who’s doing the work, but more about the work that needs to be done to keep people healthy. Then let’s think about the type of workers best suited to perform those tasks,” she said.
As for reimbursing more complex care, population-based, up-front capitated payments linked to high-quality care and better outcomes will need to replace fee-for-service models, according to Ms. McGinnis.
That will provide reliable incomes for primary care offices, but also flexibility in how each patient with different levels of complexity is managed, she said.
Ms. Greiner, Dr. Fincher, Dr. Loeb, and Ms. McGinnis have no relevant financial relationships.
New single-button blood glucose monitor available in U.S.
The POGO Automatic Blood Glucose Monitoring System (Intuity Medical) has been cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for people with diabetes aged 13 years and older.
It contains a 10-test cartridge, and once loaded and the monitor is turned on, the user only has to press their finger on a button to activate POGO Automatic, which then does all the work of lancing and blood collection, followed by a 4-second countdown and a result. Users only need to carry the monitor and not separate lancets or strips.
An app called Patterns is available for iOS and Android that allows the results from the device to automatically sync via Bluetooth. It visually presents glucose trends and enables data sharing with health care providers.
“We know that people with diabetes are more effective at managing their diabetes when they regularly check their blood glucose and use the information to take action,” said Daniel Einhorn, MD, medical director of Scripps Whittier Diabetes Institute, president of Diabetes and Endocrine Associates, and chairperson of the Intuity Medical Scientific Advisory Board, in a company statement.
“My patients and millions of others with diabetes have struggled for decades with the burden of checking their glucose because it’s complicated, there’s a lot to carry around, and it’s intrusive,” he added. “What they’ve needed is a simple, quick, and truly discreet way to check their blood glucose, so they’ll actually do it.”
How does POGO compare with CGM?
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), such as the Abbott FreeStyle Libre, Dexcom G6, and Eversense implant, are increasingly employed by people with type 1 diabetes, and some with type 2 diabetes, to keep a close eye on their blood glucose levels.
Asked how the POGO device compares with CGM systems, Intuity Chief Commercial Officer Dean Zikria said: “While [CGM] is certainly an important option for a subset of people with diabetes, CGM is a very different technology, requiring a user to wear a sensor and transmitter on their body.”
“Patients also need to obtain a prescription in order to use CGM.”
“Conversely, POGO Automatic is available with or without a prescription. POGO Automatic also gives people who do not want to wear a device on their body a new choice other than traditional blood glucose monitoring,” Mr. Zikria added.
The POGO system is available at U.S. pharmacies, including CVS and Walgreens, and can also be purchased online.
The device costs $68 from the company website and a pack of 5 cartridges (each containing 10 tests, with an aim of people performing 1-2 tests per day) costs a further $32 as a one-off, or $32 per month as a subscription.
The product is also eligible for purchase using Flexible Spending Accounts and Health Savings Accounts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The POGO Automatic Blood Glucose Monitoring System (Intuity Medical) has been cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for people with diabetes aged 13 years and older.
It contains a 10-test cartridge, and once loaded and the monitor is turned on, the user only has to press their finger on a button to activate POGO Automatic, which then does all the work of lancing and blood collection, followed by a 4-second countdown and a result. Users only need to carry the monitor and not separate lancets or strips.
An app called Patterns is available for iOS and Android that allows the results from the device to automatically sync via Bluetooth. It visually presents glucose trends and enables data sharing with health care providers.
“We know that people with diabetes are more effective at managing their diabetes when they regularly check their blood glucose and use the information to take action,” said Daniel Einhorn, MD, medical director of Scripps Whittier Diabetes Institute, president of Diabetes and Endocrine Associates, and chairperson of the Intuity Medical Scientific Advisory Board, in a company statement.
“My patients and millions of others with diabetes have struggled for decades with the burden of checking their glucose because it’s complicated, there’s a lot to carry around, and it’s intrusive,” he added. “What they’ve needed is a simple, quick, and truly discreet way to check their blood glucose, so they’ll actually do it.”
How does POGO compare with CGM?
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), such as the Abbott FreeStyle Libre, Dexcom G6, and Eversense implant, are increasingly employed by people with type 1 diabetes, and some with type 2 diabetes, to keep a close eye on their blood glucose levels.
Asked how the POGO device compares with CGM systems, Intuity Chief Commercial Officer Dean Zikria said: “While [CGM] is certainly an important option for a subset of people with diabetes, CGM is a very different technology, requiring a user to wear a sensor and transmitter on their body.”
“Patients also need to obtain a prescription in order to use CGM.”
“Conversely, POGO Automatic is available with or without a prescription. POGO Automatic also gives people who do not want to wear a device on their body a new choice other than traditional blood glucose monitoring,” Mr. Zikria added.
The POGO system is available at U.S. pharmacies, including CVS and Walgreens, and can also be purchased online.
The device costs $68 from the company website and a pack of 5 cartridges (each containing 10 tests, with an aim of people performing 1-2 tests per day) costs a further $32 as a one-off, or $32 per month as a subscription.
The product is also eligible for purchase using Flexible Spending Accounts and Health Savings Accounts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The POGO Automatic Blood Glucose Monitoring System (Intuity Medical) has been cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for people with diabetes aged 13 years and older.
It contains a 10-test cartridge, and once loaded and the monitor is turned on, the user only has to press their finger on a button to activate POGO Automatic, which then does all the work of lancing and blood collection, followed by a 4-second countdown and a result. Users only need to carry the monitor and not separate lancets or strips.
An app called Patterns is available for iOS and Android that allows the results from the device to automatically sync via Bluetooth. It visually presents glucose trends and enables data sharing with health care providers.
“We know that people with diabetes are more effective at managing their diabetes when they regularly check their blood glucose and use the information to take action,” said Daniel Einhorn, MD, medical director of Scripps Whittier Diabetes Institute, president of Diabetes and Endocrine Associates, and chairperson of the Intuity Medical Scientific Advisory Board, in a company statement.
“My patients and millions of others with diabetes have struggled for decades with the burden of checking their glucose because it’s complicated, there’s a lot to carry around, and it’s intrusive,” he added. “What they’ve needed is a simple, quick, and truly discreet way to check their blood glucose, so they’ll actually do it.”
How does POGO compare with CGM?
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), such as the Abbott FreeStyle Libre, Dexcom G6, and Eversense implant, are increasingly employed by people with type 1 diabetes, and some with type 2 diabetes, to keep a close eye on their blood glucose levels.
Asked how the POGO device compares with CGM systems, Intuity Chief Commercial Officer Dean Zikria said: “While [CGM] is certainly an important option for a subset of people with diabetes, CGM is a very different technology, requiring a user to wear a sensor and transmitter on their body.”
“Patients also need to obtain a prescription in order to use CGM.”
“Conversely, POGO Automatic is available with or without a prescription. POGO Automatic also gives people who do not want to wear a device on their body a new choice other than traditional blood glucose monitoring,” Mr. Zikria added.
The POGO system is available at U.S. pharmacies, including CVS and Walgreens, and can also be purchased online.
The device costs $68 from the company website and a pack of 5 cartridges (each containing 10 tests, with an aim of people performing 1-2 tests per day) costs a further $32 as a one-off, or $32 per month as a subscription.
The product is also eligible for purchase using Flexible Spending Accounts and Health Savings Accounts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AHA dietary guidance cites structural challenges to heart-healthy patterns
In a new scientific statement on diet and lifestyle recommendations, the American Heart Association is highlighting, for the first time, structural challenges that impede the adoption of heart-healthy dietary patterns.
This is in addition to stressing aspects of diet that improve cardiovascular health and reduce cardiovascular risk, with an emphasis on dietary patterns and food-based guidance beyond naming individual foods or nutrients.
The 2021 Dietary Guidance to Improve Cardiovascular Health scientific statement, developed under Alice H. Lichtenstein, DSc, chair of the AHA writing group, provides 10 evidence-based guidance recommendations to promote cardiometabolic health.
“The way to make heart-healthy choices every day,” said Dr. Lichtenstein, of the Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging at Tufts University in Boston, in a statement, “is to step back, look at the environment in which you eat, whether it be at home, at work, during social interaction, and then identify what the best choices are. And if there are no good choices, then think about how you can modify your environment so that there are good choices.”
The statement, published in Circulation, underscores growing evidence that nutrition-related chronic diseases have maternal-nutritional origins, and that prevention of pediatric obesity is a key to preserving and prolonging ideal cardiovascular health.
The features are as follows:
- Adjust energy intake and expenditure to achieve and maintain a healthy body weight. To counter the shift toward higher energy intake and more sedentary lifestyles over the past 3 decades, the statement recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate physical activity per week, adjusted for individual’s age, activity level, sex, and size.
- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables; choose a wide variety. Observational and intervention studies document that dietary patterns rich in varied fruits and vegetables, with the exception of white potatoes, are linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Also, whole fruits and vegetables, which more readily provide fiber and satiety, are preferred over juices.
- Choose whole grain foods and products made mostly with whole grains rather than refined grains. Evidence from observational, interventional, and clinical studies confirm the benefits of frequent consumption of whole grains over infrequent consumption or over refined grains in terms of CVD risk, coronary heart disease (CHD), stroke, metabolic syndrome, cardiometabolic risk factors, laxation, and gut microbiota.
- Choose healthy sources of protein, mostly from plants (legumes and nuts).
- Higher intake of legumes, which are rich in protein and fiber, is associated with lower CVD risk, while higher nut intake is associated with lower risks of CVD, CHD, and stroke mortality/incidence. Replacing animal-source foods with plant-source whole foods, beyond health benefits, lowers the diet’s carbon footprint. Meat alternatives are often ultraprocessed and evidence on their short- and long-term health effects is limited. Unsaturated fats are preferred, as are lean, nonprocessed meats.
- Use liquid plant oils rather than tropical oils (coconut, palm, and palm kernel), animal fats (butter and lard), and partially hydrogenated fats. Saturated and trans fats (animal and dairy fats, and partially hydrogenated fat) should be replaced with nontropical liquid plant oils. Evidence supports cardiovascular benefits of dietary unsaturated fats, especially polyunsaturated fats primarily from plant oils (e.g. soybean, corn, safflower and sunflower oils, walnuts, and flax seeds).
- Choose minimally processed foods instead of ultraprocessed foods. Because of their proven association with adverse health outcomes, including overweight and obesity, cardiometabolic disorders (type 2 diabetes, CVD), and all-cause mortality, the consumption of many ultraprocessed foods is of concern. Ultraprocessed foods include artificial colors and flavors and preservatives that promote shelf stability, preserve texture, and increase palatability. A general principle is to emphasize unprocessed or minimally processed foods.
- Minimize intake of beverages and foods with added sugars. Added sugars (commonly glucose, dextrose, sucrose, corn syrup, honey, maple syrup, and concentrated fruit juice) are tied to elevated risk for type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and excess body weight. Findings from meta-analyses on body weight and metabolic outcomes for replacing added sugars with low-energy sweeteners are mixed, and the possibility of reverse causality has been raised.
- Choose and prepare foods with little or no salt. In general, the effects of sodium reduction on blood pressure tend to be higher in Black people, middle-aged and older people, and those with hypertension. In the United States, the main combined sources of sodium intake are processed foods, those prepared outside the home, packaged foods, and restaurant foods. Potassium-enriched salts are a promising alternative.
- If you don’t drink alcohol, don’t start; if you choose to drink, limit intake.
- While relationships between alcohol intake and cardiovascular outcomes are complex, the 2020 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee recently concluded that those who do drink should consume no more than one drink per day and should not drink alcohol in binges; the 2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans continues to recommend no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
- Adhere to the guidance regardless in all settings. Food-based dietary guidance applies to all foods and beverages, regardless of where prepared, procured, and consumed. Policies should be enacted that encourage healthier default options (for example, whole grains, minimized sodium and sugar content).
Recognizing impediments
The AHA/ASA scientific statement closes with the declaration: “Creating an environment that facilitates, rather than impedes, adherence to heart-healthy dietary patterns among all individuals is a public health imperative.” It points to the National Institutes of Health’s 2020-2030 Strategic Plan for National Institutes of Health Nutrition Research, which focuses on precision nutrition as a means “to determine the impact on health of not only what individuals eat, but also of why, when, and how they eat throughout the life course.”
Ultimately, precision nutrition may provide personalized diets for CVD prevention. But the “food environment,” often conditioned by “rampant nutrition misinformation” through local, state, and federal practices and policies, may impede the adoption of heart-healthy dietary patterns. Factors such as targeted food marketing (for example, of processed food and beverages in minority neighborhoods), structural racism, neighborhood segregation, unhealthy built environments, and food insecurity create environments in which unhealthy foods are the default option.”
These factors compound adverse dietary and health effects, and underscore a need to “directly combat nutrition misinformation among the public and health care professionals.” They also explain why, despite widespread knowledge of heart-healthy dietary pattern components, little progress has been made in achieving dietary goals in the United States.
Dr. Lichtenstein’s office, in response to a request regarding AHA advocacy and consumer programs, provided the following links: Voices for Healthy Kids initiative site and choosing healthier processed foods and one on fresh, frozen, and canned fruits and vegetables.
Dr. Lichtenstein had no disclosures. Disclosures for the writing group members are included in the statement.
In a new scientific statement on diet and lifestyle recommendations, the American Heart Association is highlighting, for the first time, structural challenges that impede the adoption of heart-healthy dietary patterns.
This is in addition to stressing aspects of diet that improve cardiovascular health and reduce cardiovascular risk, with an emphasis on dietary patterns and food-based guidance beyond naming individual foods or nutrients.
The 2021 Dietary Guidance to Improve Cardiovascular Health scientific statement, developed under Alice H. Lichtenstein, DSc, chair of the AHA writing group, provides 10 evidence-based guidance recommendations to promote cardiometabolic health.
“The way to make heart-healthy choices every day,” said Dr. Lichtenstein, of the Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging at Tufts University in Boston, in a statement, “is to step back, look at the environment in which you eat, whether it be at home, at work, during social interaction, and then identify what the best choices are. And if there are no good choices, then think about how you can modify your environment so that there are good choices.”
The statement, published in Circulation, underscores growing evidence that nutrition-related chronic diseases have maternal-nutritional origins, and that prevention of pediatric obesity is a key to preserving and prolonging ideal cardiovascular health.
The features are as follows:
- Adjust energy intake and expenditure to achieve and maintain a healthy body weight. To counter the shift toward higher energy intake and more sedentary lifestyles over the past 3 decades, the statement recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate physical activity per week, adjusted for individual’s age, activity level, sex, and size.
- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables; choose a wide variety. Observational and intervention studies document that dietary patterns rich in varied fruits and vegetables, with the exception of white potatoes, are linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Also, whole fruits and vegetables, which more readily provide fiber and satiety, are preferred over juices.
- Choose whole grain foods and products made mostly with whole grains rather than refined grains. Evidence from observational, interventional, and clinical studies confirm the benefits of frequent consumption of whole grains over infrequent consumption or over refined grains in terms of CVD risk, coronary heart disease (CHD), stroke, metabolic syndrome, cardiometabolic risk factors, laxation, and gut microbiota.
- Choose healthy sources of protein, mostly from plants (legumes and nuts).
- Higher intake of legumes, which are rich in protein and fiber, is associated with lower CVD risk, while higher nut intake is associated with lower risks of CVD, CHD, and stroke mortality/incidence. Replacing animal-source foods with plant-source whole foods, beyond health benefits, lowers the diet’s carbon footprint. Meat alternatives are often ultraprocessed and evidence on their short- and long-term health effects is limited. Unsaturated fats are preferred, as are lean, nonprocessed meats.
- Use liquid plant oils rather than tropical oils (coconut, palm, and palm kernel), animal fats (butter and lard), and partially hydrogenated fats. Saturated and trans fats (animal and dairy fats, and partially hydrogenated fat) should be replaced with nontropical liquid plant oils. Evidence supports cardiovascular benefits of dietary unsaturated fats, especially polyunsaturated fats primarily from plant oils (e.g. soybean, corn, safflower and sunflower oils, walnuts, and flax seeds).
- Choose minimally processed foods instead of ultraprocessed foods. Because of their proven association with adverse health outcomes, including overweight and obesity, cardiometabolic disorders (type 2 diabetes, CVD), and all-cause mortality, the consumption of many ultraprocessed foods is of concern. Ultraprocessed foods include artificial colors and flavors and preservatives that promote shelf stability, preserve texture, and increase palatability. A general principle is to emphasize unprocessed or minimally processed foods.
- Minimize intake of beverages and foods with added sugars. Added sugars (commonly glucose, dextrose, sucrose, corn syrup, honey, maple syrup, and concentrated fruit juice) are tied to elevated risk for type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and excess body weight. Findings from meta-analyses on body weight and metabolic outcomes for replacing added sugars with low-energy sweeteners are mixed, and the possibility of reverse causality has been raised.
- Choose and prepare foods with little or no salt. In general, the effects of sodium reduction on blood pressure tend to be higher in Black people, middle-aged and older people, and those with hypertension. In the United States, the main combined sources of sodium intake are processed foods, those prepared outside the home, packaged foods, and restaurant foods. Potassium-enriched salts are a promising alternative.
- If you don’t drink alcohol, don’t start; if you choose to drink, limit intake.
- While relationships between alcohol intake and cardiovascular outcomes are complex, the 2020 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee recently concluded that those who do drink should consume no more than one drink per day and should not drink alcohol in binges; the 2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans continues to recommend no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
- Adhere to the guidance regardless in all settings. Food-based dietary guidance applies to all foods and beverages, regardless of where prepared, procured, and consumed. Policies should be enacted that encourage healthier default options (for example, whole grains, minimized sodium and sugar content).
Recognizing impediments
The AHA/ASA scientific statement closes with the declaration: “Creating an environment that facilitates, rather than impedes, adherence to heart-healthy dietary patterns among all individuals is a public health imperative.” It points to the National Institutes of Health’s 2020-2030 Strategic Plan for National Institutes of Health Nutrition Research, which focuses on precision nutrition as a means “to determine the impact on health of not only what individuals eat, but also of why, when, and how they eat throughout the life course.”
Ultimately, precision nutrition may provide personalized diets for CVD prevention. But the “food environment,” often conditioned by “rampant nutrition misinformation” through local, state, and federal practices and policies, may impede the adoption of heart-healthy dietary patterns. Factors such as targeted food marketing (for example, of processed food and beverages in minority neighborhoods), structural racism, neighborhood segregation, unhealthy built environments, and food insecurity create environments in which unhealthy foods are the default option.”
These factors compound adverse dietary and health effects, and underscore a need to “directly combat nutrition misinformation among the public and health care professionals.” They also explain why, despite widespread knowledge of heart-healthy dietary pattern components, little progress has been made in achieving dietary goals in the United States.
Dr. Lichtenstein’s office, in response to a request regarding AHA advocacy and consumer programs, provided the following links: Voices for Healthy Kids initiative site and choosing healthier processed foods and one on fresh, frozen, and canned fruits and vegetables.
Dr. Lichtenstein had no disclosures. Disclosures for the writing group members are included in the statement.
In a new scientific statement on diet and lifestyle recommendations, the American Heart Association is highlighting, for the first time, structural challenges that impede the adoption of heart-healthy dietary patterns.
This is in addition to stressing aspects of diet that improve cardiovascular health and reduce cardiovascular risk, with an emphasis on dietary patterns and food-based guidance beyond naming individual foods or nutrients.
The 2021 Dietary Guidance to Improve Cardiovascular Health scientific statement, developed under Alice H. Lichtenstein, DSc, chair of the AHA writing group, provides 10 evidence-based guidance recommendations to promote cardiometabolic health.
“The way to make heart-healthy choices every day,” said Dr. Lichtenstein, of the Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging at Tufts University in Boston, in a statement, “is to step back, look at the environment in which you eat, whether it be at home, at work, during social interaction, and then identify what the best choices are. And if there are no good choices, then think about how you can modify your environment so that there are good choices.”
The statement, published in Circulation, underscores growing evidence that nutrition-related chronic diseases have maternal-nutritional origins, and that prevention of pediatric obesity is a key to preserving and prolonging ideal cardiovascular health.
The features are as follows:
- Adjust energy intake and expenditure to achieve and maintain a healthy body weight. To counter the shift toward higher energy intake and more sedentary lifestyles over the past 3 decades, the statement recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate physical activity per week, adjusted for individual’s age, activity level, sex, and size.
- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables; choose a wide variety. Observational and intervention studies document that dietary patterns rich in varied fruits and vegetables, with the exception of white potatoes, are linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Also, whole fruits and vegetables, which more readily provide fiber and satiety, are preferred over juices.
- Choose whole grain foods and products made mostly with whole grains rather than refined grains. Evidence from observational, interventional, and clinical studies confirm the benefits of frequent consumption of whole grains over infrequent consumption or over refined grains in terms of CVD risk, coronary heart disease (CHD), stroke, metabolic syndrome, cardiometabolic risk factors, laxation, and gut microbiota.
- Choose healthy sources of protein, mostly from plants (legumes and nuts).
- Higher intake of legumes, which are rich in protein and fiber, is associated with lower CVD risk, while higher nut intake is associated with lower risks of CVD, CHD, and stroke mortality/incidence. Replacing animal-source foods with plant-source whole foods, beyond health benefits, lowers the diet’s carbon footprint. Meat alternatives are often ultraprocessed and evidence on their short- and long-term health effects is limited. Unsaturated fats are preferred, as are lean, nonprocessed meats.
- Use liquid plant oils rather than tropical oils (coconut, palm, and palm kernel), animal fats (butter and lard), and partially hydrogenated fats. Saturated and trans fats (animal and dairy fats, and partially hydrogenated fat) should be replaced with nontropical liquid plant oils. Evidence supports cardiovascular benefits of dietary unsaturated fats, especially polyunsaturated fats primarily from plant oils (e.g. soybean, corn, safflower and sunflower oils, walnuts, and flax seeds).
- Choose minimally processed foods instead of ultraprocessed foods. Because of their proven association with adverse health outcomes, including overweight and obesity, cardiometabolic disorders (type 2 diabetes, CVD), and all-cause mortality, the consumption of many ultraprocessed foods is of concern. Ultraprocessed foods include artificial colors and flavors and preservatives that promote shelf stability, preserve texture, and increase palatability. A general principle is to emphasize unprocessed or minimally processed foods.
- Minimize intake of beverages and foods with added sugars. Added sugars (commonly glucose, dextrose, sucrose, corn syrup, honey, maple syrup, and concentrated fruit juice) are tied to elevated risk for type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and excess body weight. Findings from meta-analyses on body weight and metabolic outcomes for replacing added sugars with low-energy sweeteners are mixed, and the possibility of reverse causality has been raised.
- Choose and prepare foods with little or no salt. In general, the effects of sodium reduction on blood pressure tend to be higher in Black people, middle-aged and older people, and those with hypertension. In the United States, the main combined sources of sodium intake are processed foods, those prepared outside the home, packaged foods, and restaurant foods. Potassium-enriched salts are a promising alternative.
- If you don’t drink alcohol, don’t start; if you choose to drink, limit intake.
- While relationships between alcohol intake and cardiovascular outcomes are complex, the 2020 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee recently concluded that those who do drink should consume no more than one drink per day and should not drink alcohol in binges; the 2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans continues to recommend no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
- Adhere to the guidance regardless in all settings. Food-based dietary guidance applies to all foods and beverages, regardless of where prepared, procured, and consumed. Policies should be enacted that encourage healthier default options (for example, whole grains, minimized sodium and sugar content).
Recognizing impediments
The AHA/ASA scientific statement closes with the declaration: “Creating an environment that facilitates, rather than impedes, adherence to heart-healthy dietary patterns among all individuals is a public health imperative.” It points to the National Institutes of Health’s 2020-2030 Strategic Plan for National Institutes of Health Nutrition Research, which focuses on precision nutrition as a means “to determine the impact on health of not only what individuals eat, but also of why, when, and how they eat throughout the life course.”
Ultimately, precision nutrition may provide personalized diets for CVD prevention. But the “food environment,” often conditioned by “rampant nutrition misinformation” through local, state, and federal practices and policies, may impede the adoption of heart-healthy dietary patterns. Factors such as targeted food marketing (for example, of processed food and beverages in minority neighborhoods), structural racism, neighborhood segregation, unhealthy built environments, and food insecurity create environments in which unhealthy foods are the default option.”
These factors compound adverse dietary and health effects, and underscore a need to “directly combat nutrition misinformation among the public and health care professionals.” They also explain why, despite widespread knowledge of heart-healthy dietary pattern components, little progress has been made in achieving dietary goals in the United States.
Dr. Lichtenstein’s office, in response to a request regarding AHA advocacy and consumer programs, provided the following links: Voices for Healthy Kids initiative site and choosing healthier processed foods and one on fresh, frozen, and canned fruits and vegetables.
Dr. Lichtenstein had no disclosures. Disclosures for the writing group members are included in the statement.
FROM CIRCULATION
Neighborhood fast food restaurants linked to type 2 diabetes
new research indicates.
The national study of more than 4 million U.S. veterans also found the opposite association with supermarkets in suburban and rural communities but not others.
“Neighborhood food environment was associated with type 2 diabetes risk among U.S. veterans in multiple community types, suggesting potential avenues for action to address the burden of type 2 diabetes,” say Rania Kanchi, MPH, of the department of population health, New York University Langone Health, and colleagues.
Restriction of fast food establishments could benefit all types of communities, while interventions to increase supermarket availability could help minimize diabetes risk in suburban and rural communities, they stress.
“These actions, combined with increasing awareness of the risk of type 2 diabetes and the importance of healthy diet intake, might be associated with a decrease in the burden of type 2 diabetes among adults in the U.S.,” the researchers add.
The data were published online Oct. 29 in JAMA Network Open.
“The more we learn about the relationship between the food environment and chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes, the more policymakers can act by improving the mix of healthy food options sold in restaurants and food outlets, or by creating better zoning laws that promote optimal food options for residents,” commented Lorna Thorpe, PhD, MPH, professor in the department of population health at NYU Langone and senior author of the study in a press release.
In an accompanying editorial, Elham Hatef, MD, MPH, of the Center for Population Health IT at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, calls the study “a great example of the capabilities of [health information technology] to provide a comprehensive assessment of a person’s health, which goes beyond just documenting clinical diseases and medical interventions.”
Research has large geographic breadth
The study is notable for its large geographic breadth, say the researchers.
“Most studies that examine the built food environment and its relationship to chronic diseases have been much smaller or conducted in localized areas,” Ms. Kanchi said in the press statement.
“Our study design is national in scope and allowed us to identify the types of communities that people are living in, characterize their food environment, and observe what happens to them over time. The size of our cohort allows for geographic generalizability in a way that other studies do not,” Ms. Kanchi continued.
The research included data for 4,100,650 individuals from the Veterans Affairs electronic health records (EHRs) who didn’t have type 2 diabetes at baseline, between 2008 and 2016. After a median follow-up of 5.5 person-years, 13.2% developed type 2 diabetes. Cumulative incidence was greater among those who were older, those who were non-Hispanic Black compared with other races, and those with disabilities and lower incomes.
The proportion of adults with type 2 diabetes was highest among those living in high-density urban communities (14.3%), followed by low-density urban (13.1%), rural (13.2%), and suburban (12.6%) communities.
Overall, a 10% increase in the number of fast food restaurants compared with other food establishments in a given neighborhood was associated with a 1% increased risk for incident type 2 diabetes in high-density urban, low-density urban, and rural communities and a 2% increased risk in suburban communities.
In contrast, a 10% increase in supermarket density compared with other food stores was associated with a lower risk for type 2 diabetes in suburban and rural communities, but the association wasn’t significant elsewhere.
“Taken together, our findings suggest that policies specific to fast food restaurants, such as [those] ... restricting the siting of fast food restaurants and healthy beverage default laws, may be effective in reducing type 2 diabetes risk in all community types,” say the authors.
“In urban areas where population and retail density are growing, it will be even more important to focus on these policies,” they emphasize.
Great example of capabilities of health information technology
In the editorial, Dr. Hatef notes that methodological advances, such as natural language processing and machine learning, have enabled health systems to use real-world data such as the free-text notes in the EHR to identify patient-level risk factors for diseases or disease complications.
Such methods could be further used to “evaluate the associations between social needs and place-based [social determinants of health] and type 2 diabetes incidence and management,” Dr. Hatef adds.
And linkage of data from the EHR to such community-level data “would help to comprehensively assess and identify patients likely to experience type 2 diabetes and its complications as a result of their risk factors or characteristics of the neighborhoods where they reside.”
“This approach could foster collaborations between the health systems and at-risk communities they serve and help to reallocate health system resources to those in most need in the community to reduce the burden of type 2 diabetes and other chronic conditions among racial minority groups and socioeconomically disadvantaged patients and to advance population health.”
The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Institute of Aging, the Commonwealth Universal Research Enhancement program funded by the Pennsylvania Department of Health, the Urban Health Collaborative at Drexel University, and the Built Environment and Health Research Group at Columbia University. Ms. Kanchi and Dr. Hatef have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research indicates.
The national study of more than 4 million U.S. veterans also found the opposite association with supermarkets in suburban and rural communities but not others.
“Neighborhood food environment was associated with type 2 diabetes risk among U.S. veterans in multiple community types, suggesting potential avenues for action to address the burden of type 2 diabetes,” say Rania Kanchi, MPH, of the department of population health, New York University Langone Health, and colleagues.
Restriction of fast food establishments could benefit all types of communities, while interventions to increase supermarket availability could help minimize diabetes risk in suburban and rural communities, they stress.
“These actions, combined with increasing awareness of the risk of type 2 diabetes and the importance of healthy diet intake, might be associated with a decrease in the burden of type 2 diabetes among adults in the U.S.,” the researchers add.
The data were published online Oct. 29 in JAMA Network Open.
“The more we learn about the relationship between the food environment and chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes, the more policymakers can act by improving the mix of healthy food options sold in restaurants and food outlets, or by creating better zoning laws that promote optimal food options for residents,” commented Lorna Thorpe, PhD, MPH, professor in the department of population health at NYU Langone and senior author of the study in a press release.
In an accompanying editorial, Elham Hatef, MD, MPH, of the Center for Population Health IT at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, calls the study “a great example of the capabilities of [health information technology] to provide a comprehensive assessment of a person’s health, which goes beyond just documenting clinical diseases and medical interventions.”
Research has large geographic breadth
The study is notable for its large geographic breadth, say the researchers.
“Most studies that examine the built food environment and its relationship to chronic diseases have been much smaller or conducted in localized areas,” Ms. Kanchi said in the press statement.
“Our study design is national in scope and allowed us to identify the types of communities that people are living in, characterize their food environment, and observe what happens to them over time. The size of our cohort allows for geographic generalizability in a way that other studies do not,” Ms. Kanchi continued.
The research included data for 4,100,650 individuals from the Veterans Affairs electronic health records (EHRs) who didn’t have type 2 diabetes at baseline, between 2008 and 2016. After a median follow-up of 5.5 person-years, 13.2% developed type 2 diabetes. Cumulative incidence was greater among those who were older, those who were non-Hispanic Black compared with other races, and those with disabilities and lower incomes.
The proportion of adults with type 2 diabetes was highest among those living in high-density urban communities (14.3%), followed by low-density urban (13.1%), rural (13.2%), and suburban (12.6%) communities.
Overall, a 10% increase in the number of fast food restaurants compared with other food establishments in a given neighborhood was associated with a 1% increased risk for incident type 2 diabetes in high-density urban, low-density urban, and rural communities and a 2% increased risk in suburban communities.
In contrast, a 10% increase in supermarket density compared with other food stores was associated with a lower risk for type 2 diabetes in suburban and rural communities, but the association wasn’t significant elsewhere.
“Taken together, our findings suggest that policies specific to fast food restaurants, such as [those] ... restricting the siting of fast food restaurants and healthy beverage default laws, may be effective in reducing type 2 diabetes risk in all community types,” say the authors.
“In urban areas where population and retail density are growing, it will be even more important to focus on these policies,” they emphasize.
Great example of capabilities of health information technology
In the editorial, Dr. Hatef notes that methodological advances, such as natural language processing and machine learning, have enabled health systems to use real-world data such as the free-text notes in the EHR to identify patient-level risk factors for diseases or disease complications.
Such methods could be further used to “evaluate the associations between social needs and place-based [social determinants of health] and type 2 diabetes incidence and management,” Dr. Hatef adds.
And linkage of data from the EHR to such community-level data “would help to comprehensively assess and identify patients likely to experience type 2 diabetes and its complications as a result of their risk factors or characteristics of the neighborhoods where they reside.”
“This approach could foster collaborations between the health systems and at-risk communities they serve and help to reallocate health system resources to those in most need in the community to reduce the burden of type 2 diabetes and other chronic conditions among racial minority groups and socioeconomically disadvantaged patients and to advance population health.”
The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Institute of Aging, the Commonwealth Universal Research Enhancement program funded by the Pennsylvania Department of Health, the Urban Health Collaborative at Drexel University, and the Built Environment and Health Research Group at Columbia University. Ms. Kanchi and Dr. Hatef have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research indicates.
The national study of more than 4 million U.S. veterans also found the opposite association with supermarkets in suburban and rural communities but not others.
“Neighborhood food environment was associated with type 2 diabetes risk among U.S. veterans in multiple community types, suggesting potential avenues for action to address the burden of type 2 diabetes,” say Rania Kanchi, MPH, of the department of population health, New York University Langone Health, and colleagues.
Restriction of fast food establishments could benefit all types of communities, while interventions to increase supermarket availability could help minimize diabetes risk in suburban and rural communities, they stress.
“These actions, combined with increasing awareness of the risk of type 2 diabetes and the importance of healthy diet intake, might be associated with a decrease in the burden of type 2 diabetes among adults in the U.S.,” the researchers add.
The data were published online Oct. 29 in JAMA Network Open.
“The more we learn about the relationship between the food environment and chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes, the more policymakers can act by improving the mix of healthy food options sold in restaurants and food outlets, or by creating better zoning laws that promote optimal food options for residents,” commented Lorna Thorpe, PhD, MPH, professor in the department of population health at NYU Langone and senior author of the study in a press release.
In an accompanying editorial, Elham Hatef, MD, MPH, of the Center for Population Health IT at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, calls the study “a great example of the capabilities of [health information technology] to provide a comprehensive assessment of a person’s health, which goes beyond just documenting clinical diseases and medical interventions.”
Research has large geographic breadth
The study is notable for its large geographic breadth, say the researchers.
“Most studies that examine the built food environment and its relationship to chronic diseases have been much smaller or conducted in localized areas,” Ms. Kanchi said in the press statement.
“Our study design is national in scope and allowed us to identify the types of communities that people are living in, characterize their food environment, and observe what happens to them over time. The size of our cohort allows for geographic generalizability in a way that other studies do not,” Ms. Kanchi continued.
The research included data for 4,100,650 individuals from the Veterans Affairs electronic health records (EHRs) who didn’t have type 2 diabetes at baseline, between 2008 and 2016. After a median follow-up of 5.5 person-years, 13.2% developed type 2 diabetes. Cumulative incidence was greater among those who were older, those who were non-Hispanic Black compared with other races, and those with disabilities and lower incomes.
The proportion of adults with type 2 diabetes was highest among those living in high-density urban communities (14.3%), followed by low-density urban (13.1%), rural (13.2%), and suburban (12.6%) communities.
Overall, a 10% increase in the number of fast food restaurants compared with other food establishments in a given neighborhood was associated with a 1% increased risk for incident type 2 diabetes in high-density urban, low-density urban, and rural communities and a 2% increased risk in suburban communities.
In contrast, a 10% increase in supermarket density compared with other food stores was associated with a lower risk for type 2 diabetes in suburban and rural communities, but the association wasn’t significant elsewhere.
“Taken together, our findings suggest that policies specific to fast food restaurants, such as [those] ... restricting the siting of fast food restaurants and healthy beverage default laws, may be effective in reducing type 2 diabetes risk in all community types,” say the authors.
“In urban areas where population and retail density are growing, it will be even more important to focus on these policies,” they emphasize.
Great example of capabilities of health information technology
In the editorial, Dr. Hatef notes that methodological advances, such as natural language processing and machine learning, have enabled health systems to use real-world data such as the free-text notes in the EHR to identify patient-level risk factors for diseases or disease complications.
Such methods could be further used to “evaluate the associations between social needs and place-based [social determinants of health] and type 2 diabetes incidence and management,” Dr. Hatef adds.
And linkage of data from the EHR to such community-level data “would help to comprehensively assess and identify patients likely to experience type 2 diabetes and its complications as a result of their risk factors or characteristics of the neighborhoods where they reside.”
“This approach could foster collaborations between the health systems and at-risk communities they serve and help to reallocate health system resources to those in most need in the community to reduce the burden of type 2 diabetes and other chronic conditions among racial minority groups and socioeconomically disadvantaged patients and to advance population health.”
The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Institute of Aging, the Commonwealth Universal Research Enhancement program funded by the Pennsylvania Department of Health, the Urban Health Collaborative at Drexel University, and the Built Environment and Health Research Group at Columbia University. Ms. Kanchi and Dr. Hatef have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Stem cell transplant seen as major type 1 diabetes advance
A novel investigational allogeneic stem cell–derived treatment resulted in near reversal of type 1 diabetes in a patient who had lived with the condition for about 40 years.
The patient was the first in Vertex Pharmaceuticals’ phase 1/2 multicenter, single-arm, open-label clinical trial of the insulin-producing islet cell therapy VX-880 for patients with type 1 diabetes who have impaired hypoglycemic awareness and severe hypoglycemia.
The cells are delivered by infusion into the hepatic portal vein. As of now, chronic immunosuppression is required to prevent rejection, but several approaches are being studied to overcome the limitation.
“There’s hope that this is a real advance. It’s been long awaited, and it looks really encouraging,” James Markmann, MD, PhD, the surgeon who performed the procedure, told this news organization.
The use of insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells derived from human pluripotent stem cells, first reported in 2014 by a team at the Harvard Stem Cell Institute, Boston, is seen as a major advance over use of cadaveric donor islet cells because stem cell–derived islets are available in unlimited and uncontaminated supplies.
Cadaveric donor islets are being used in products such as donislecel (CellTrans), which was endorsed by a Food and Drug Administration advisory committee in the summer for the treatment of type 1 diabetes that can’t be managed with current therapies.
The patient in the Vertex trial isn’t the first reported stem cell–derived islet recipient with type 1 diabetes, but these cells are the first to be transplanted into the liver.
“This Vertex patient stood out because the reduction in insulin requirement ... was so striking,” noted Dr. Markmann, chief of the division of transplant surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who has been transplanting islet cells from cadaveric donors into humans via the hepatic portal vein for over 20 years.
“Nobody knew what to expect, as it hadn’t been done before, but certainly the results in this patient are better than what I would have expected from a deceased donor islet transplant,” he added.
Asked to comment, A.M. James Shapiro, MD, agreed. “I think the most important finding is that a stem cell–derived islet is now transplanted into the liver of a patient safely, so far,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Shapiro is clinical director of the living donor and islet cell transplantation programs at the University of Alberta, Edmonton. He pioneered cadaveric donor islet cell transplantation more than 20 years ago with the watershed Edmonton Protocol.
‘Impressive finding ... bodes well for ongoing efforts’
Vertex announced the result by press release. The company plans to transplant another 16 patients, staggering them over time at multiple centers.
The first patient was treated with a single infusion of VX-880 at half the target dose (per protocol for the first two study subjects), along with standard immunosuppressive therapy. At 90 days, the patient’s C-peptide, a measure of endogenous insulin secretion, rose from undetectable to 280 pmol/L fasting and 560 pmol/L post mixed-meal tolerance testing.
Over the same period, the patient’s hemoglobin A1c dropped from 8.6% at baseline to 7.2%. And within 7 days, the individual’s daily exogenous insulin requirement dropped from an average of 34 units to just 2.9 units, a 91% decrease.
The patient had experienced five severe hypoglycemic episodes in the year prior to transplant. They experienced some mild hypoglycemia soon after the procedure while insulin doses were being adjusted, but none thereafter.
Dr. Shapiro said in an interview: “I was absolutely thrilled to see the first patient results with high C-peptide and a 91% reduction in insulin. That’s a pretty impressive finding for half dosing in the very first patient in a trial. I think it bodes really well for ongoing efforts in this area by Vertex and by others that have similar kinds of cells. It’s very exciting.”
However, he cautioned, “we do need some longer-term data to be sure there’s no off-target growth or other concerns. But based on the purity of this product, that risk is likely to be low.”
And he noted, “I think we still have to address the challenges of setting this process up. A huge amount of work has gone into manufacturing the cell product for a single patient. I think it remains to be seen whether the same technology can be delivered at a larger scale ... i.e., being able to treat hundreds or thousands of patients.”
A blog post on the website of diabetes charity JDRF called the result “outstanding.” “It’s a big deal,” they added. However, they also cautioned: “There are a few things to keep in mind while assessing the data. One is that these are only results from a single person. Data are needed from many more to fully evaluate the potential of this therapy. The second is that this person only received half the target dose of cells.”
Dr. Shapiro is working with another company, ViaCyte, which has also developed stem cell–derived islets. In contrast to the Vertex product, which is fully differentiated and delivered to the liver, ViaCyte’s PEC-Direct product is comprised of stem cell-derived pancreatic islet progenitor cells that are implanted subcutaneously in a pouch, allowing for vascularization.
In a late-breaking poster at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association in June 2021, ViaCyte reported on a patient given PEC-Direct. In that patient, stimulated C-peptide increased from 0.1 ng/mL at baseline to 0.8 ng/mL at week 39, and there was a drop in A1c from 7.4% to 6.6%, with no adverse events.
Immunosuppression: Which approach will come closer to cure?
Thus far, the requirement for lifelong immunosuppression has meant that any islet cell replacement approach, including with stem cell–derived islets, has been limited to use in people with type 1 diabetes who have hypoglycemic unawareness or severely unpredictable blood glucose levels.
Two broad approaches are simultaneously being explored to overcome the rejection problem: Encapsulation of the cells to protect them from the immune system, and genetic modification of the cells so that they don’t provoke the immune system in the first place.
In 2022, Vertex plans to file an investigational new drug application for an encapsulated islet cell program with the FDA.
Dr. Markmann believes the genetic modification approach is more promising. “I’m not a believer in encapsulation. I think the foreign body response is hard to overcome. I think the answer will ultimately be genetically modifying the [cell] lines. ... The cell could express something that would potentially turn off the lymphocytes or interfere with the lymphocytes trying to attack them.”
Moreover, he said, “you don’t have to get rid of immunosuppression completely. It’s all [a] risk-benefit [equation]. Even if you could get it down to a single less-toxic [immunosuppressive] agent that would be a huge step.”
Dr. Shapiro commented: “All efforts and eyes are laser-focused on developing cells or approaches that will allow transplantation of this kind of stem cell without any immunosuppression or with low-dose immunosuppression that could be regarded as being exceedingly low risk.”
“Then, and only then, I think we could offer this kind of treatment to children who are just diagnosed with diabetes or to [a bigger proportion of] patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. ... The science has to be done in a step-wise fashion,” he added.
Microencapsulation, Dr. Shapiro noted, “is a big challenge because the process of capturing the cells and putting them into a device is really injurious to their survival. ... That may or may not work.”
Dr. Shapiro and his Edmonton team are now embarking on a new trial with ViaCyte and CRISPR Therapeutics using gene-edited cells that contain two knock-in genes and two knock-out genes shown to be less immunogenic and anti-inflammatory in rodent models.
“They look to be promising. We’re going to start a first-in-human trial in the next few months with those cells to see if they really are able to withstand a transplant without the need for immunosuppression. That will be a very exciting trial in itself,” Dr. Shapiro said, noting that they expect to enroll the first patients in the next few months.
However, he cautioned, “first we have to make sure that the gene-edited product continues to function in patients in the way that the original product did, that the cells survive, and that the gene modifications are actually effective. ... Maybe other iterations will be needed.”
“I think, as we move forward, we will ultimately have a gene-edited stem cell–derived product that is immune evasive and will survive. So, I’m ... optimistic that this is not as long term as you might think, and it’s ... happening much more rapidly – at least in first-in-human trials to test safety and preliminary efficacy.”
Dr. Shapiro is a consultant for ViaCyte.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel investigational allogeneic stem cell–derived treatment resulted in near reversal of type 1 diabetes in a patient who had lived with the condition for about 40 years.
The patient was the first in Vertex Pharmaceuticals’ phase 1/2 multicenter, single-arm, open-label clinical trial of the insulin-producing islet cell therapy VX-880 for patients with type 1 diabetes who have impaired hypoglycemic awareness and severe hypoglycemia.
The cells are delivered by infusion into the hepatic portal vein. As of now, chronic immunosuppression is required to prevent rejection, but several approaches are being studied to overcome the limitation.
“There’s hope that this is a real advance. It’s been long awaited, and it looks really encouraging,” James Markmann, MD, PhD, the surgeon who performed the procedure, told this news organization.
The use of insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells derived from human pluripotent stem cells, first reported in 2014 by a team at the Harvard Stem Cell Institute, Boston, is seen as a major advance over use of cadaveric donor islet cells because stem cell–derived islets are available in unlimited and uncontaminated supplies.
Cadaveric donor islets are being used in products such as donislecel (CellTrans), which was endorsed by a Food and Drug Administration advisory committee in the summer for the treatment of type 1 diabetes that can’t be managed with current therapies.
The patient in the Vertex trial isn’t the first reported stem cell–derived islet recipient with type 1 diabetes, but these cells are the first to be transplanted into the liver.
“This Vertex patient stood out because the reduction in insulin requirement ... was so striking,” noted Dr. Markmann, chief of the division of transplant surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who has been transplanting islet cells from cadaveric donors into humans via the hepatic portal vein for over 20 years.
“Nobody knew what to expect, as it hadn’t been done before, but certainly the results in this patient are better than what I would have expected from a deceased donor islet transplant,” he added.
Asked to comment, A.M. James Shapiro, MD, agreed. “I think the most important finding is that a stem cell–derived islet is now transplanted into the liver of a patient safely, so far,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Shapiro is clinical director of the living donor and islet cell transplantation programs at the University of Alberta, Edmonton. He pioneered cadaveric donor islet cell transplantation more than 20 years ago with the watershed Edmonton Protocol.
‘Impressive finding ... bodes well for ongoing efforts’
Vertex announced the result by press release. The company plans to transplant another 16 patients, staggering them over time at multiple centers.
The first patient was treated with a single infusion of VX-880 at half the target dose (per protocol for the first two study subjects), along with standard immunosuppressive therapy. At 90 days, the patient’s C-peptide, a measure of endogenous insulin secretion, rose from undetectable to 280 pmol/L fasting and 560 pmol/L post mixed-meal tolerance testing.
Over the same period, the patient’s hemoglobin A1c dropped from 8.6% at baseline to 7.2%. And within 7 days, the individual’s daily exogenous insulin requirement dropped from an average of 34 units to just 2.9 units, a 91% decrease.
The patient had experienced five severe hypoglycemic episodes in the year prior to transplant. They experienced some mild hypoglycemia soon after the procedure while insulin doses were being adjusted, but none thereafter.
Dr. Shapiro said in an interview: “I was absolutely thrilled to see the first patient results with high C-peptide and a 91% reduction in insulin. That’s a pretty impressive finding for half dosing in the very first patient in a trial. I think it bodes really well for ongoing efforts in this area by Vertex and by others that have similar kinds of cells. It’s very exciting.”
However, he cautioned, “we do need some longer-term data to be sure there’s no off-target growth or other concerns. But based on the purity of this product, that risk is likely to be low.”
And he noted, “I think we still have to address the challenges of setting this process up. A huge amount of work has gone into manufacturing the cell product for a single patient. I think it remains to be seen whether the same technology can be delivered at a larger scale ... i.e., being able to treat hundreds or thousands of patients.”
A blog post on the website of diabetes charity JDRF called the result “outstanding.” “It’s a big deal,” they added. However, they also cautioned: “There are a few things to keep in mind while assessing the data. One is that these are only results from a single person. Data are needed from many more to fully evaluate the potential of this therapy. The second is that this person only received half the target dose of cells.”
Dr. Shapiro is working with another company, ViaCyte, which has also developed stem cell–derived islets. In contrast to the Vertex product, which is fully differentiated and delivered to the liver, ViaCyte’s PEC-Direct product is comprised of stem cell-derived pancreatic islet progenitor cells that are implanted subcutaneously in a pouch, allowing for vascularization.
In a late-breaking poster at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association in June 2021, ViaCyte reported on a patient given PEC-Direct. In that patient, stimulated C-peptide increased from 0.1 ng/mL at baseline to 0.8 ng/mL at week 39, and there was a drop in A1c from 7.4% to 6.6%, with no adverse events.
Immunosuppression: Which approach will come closer to cure?
Thus far, the requirement for lifelong immunosuppression has meant that any islet cell replacement approach, including with stem cell–derived islets, has been limited to use in people with type 1 diabetes who have hypoglycemic unawareness or severely unpredictable blood glucose levels.
Two broad approaches are simultaneously being explored to overcome the rejection problem: Encapsulation of the cells to protect them from the immune system, and genetic modification of the cells so that they don’t provoke the immune system in the first place.
In 2022, Vertex plans to file an investigational new drug application for an encapsulated islet cell program with the FDA.
Dr. Markmann believes the genetic modification approach is more promising. “I’m not a believer in encapsulation. I think the foreign body response is hard to overcome. I think the answer will ultimately be genetically modifying the [cell] lines. ... The cell could express something that would potentially turn off the lymphocytes or interfere with the lymphocytes trying to attack them.”
Moreover, he said, “you don’t have to get rid of immunosuppression completely. It’s all [a] risk-benefit [equation]. Even if you could get it down to a single less-toxic [immunosuppressive] agent that would be a huge step.”
Dr. Shapiro commented: “All efforts and eyes are laser-focused on developing cells or approaches that will allow transplantation of this kind of stem cell without any immunosuppression or with low-dose immunosuppression that could be regarded as being exceedingly low risk.”
“Then, and only then, I think we could offer this kind of treatment to children who are just diagnosed with diabetes or to [a bigger proportion of] patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. ... The science has to be done in a step-wise fashion,” he added.
Microencapsulation, Dr. Shapiro noted, “is a big challenge because the process of capturing the cells and putting them into a device is really injurious to their survival. ... That may or may not work.”
Dr. Shapiro and his Edmonton team are now embarking on a new trial with ViaCyte and CRISPR Therapeutics using gene-edited cells that contain two knock-in genes and two knock-out genes shown to be less immunogenic and anti-inflammatory in rodent models.
“They look to be promising. We’re going to start a first-in-human trial in the next few months with those cells to see if they really are able to withstand a transplant without the need for immunosuppression. That will be a very exciting trial in itself,” Dr. Shapiro said, noting that they expect to enroll the first patients in the next few months.
However, he cautioned, “first we have to make sure that the gene-edited product continues to function in patients in the way that the original product did, that the cells survive, and that the gene modifications are actually effective. ... Maybe other iterations will be needed.”
“I think, as we move forward, we will ultimately have a gene-edited stem cell–derived product that is immune evasive and will survive. So, I’m ... optimistic that this is not as long term as you might think, and it’s ... happening much more rapidly – at least in first-in-human trials to test safety and preliminary efficacy.”
Dr. Shapiro is a consultant for ViaCyte.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel investigational allogeneic stem cell–derived treatment resulted in near reversal of type 1 diabetes in a patient who had lived with the condition for about 40 years.
The patient was the first in Vertex Pharmaceuticals’ phase 1/2 multicenter, single-arm, open-label clinical trial of the insulin-producing islet cell therapy VX-880 for patients with type 1 diabetes who have impaired hypoglycemic awareness and severe hypoglycemia.
The cells are delivered by infusion into the hepatic portal vein. As of now, chronic immunosuppression is required to prevent rejection, but several approaches are being studied to overcome the limitation.
“There’s hope that this is a real advance. It’s been long awaited, and it looks really encouraging,” James Markmann, MD, PhD, the surgeon who performed the procedure, told this news organization.
The use of insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells derived from human pluripotent stem cells, first reported in 2014 by a team at the Harvard Stem Cell Institute, Boston, is seen as a major advance over use of cadaveric donor islet cells because stem cell–derived islets are available in unlimited and uncontaminated supplies.
Cadaveric donor islets are being used in products such as donislecel (CellTrans), which was endorsed by a Food and Drug Administration advisory committee in the summer for the treatment of type 1 diabetes that can’t be managed with current therapies.
The patient in the Vertex trial isn’t the first reported stem cell–derived islet recipient with type 1 diabetes, but these cells are the first to be transplanted into the liver.
“This Vertex patient stood out because the reduction in insulin requirement ... was so striking,” noted Dr. Markmann, chief of the division of transplant surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who has been transplanting islet cells from cadaveric donors into humans via the hepatic portal vein for over 20 years.
“Nobody knew what to expect, as it hadn’t been done before, but certainly the results in this patient are better than what I would have expected from a deceased donor islet transplant,” he added.
Asked to comment, A.M. James Shapiro, MD, agreed. “I think the most important finding is that a stem cell–derived islet is now transplanted into the liver of a patient safely, so far,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Shapiro is clinical director of the living donor and islet cell transplantation programs at the University of Alberta, Edmonton. He pioneered cadaveric donor islet cell transplantation more than 20 years ago with the watershed Edmonton Protocol.
‘Impressive finding ... bodes well for ongoing efforts’
Vertex announced the result by press release. The company plans to transplant another 16 patients, staggering them over time at multiple centers.
The first patient was treated with a single infusion of VX-880 at half the target dose (per protocol for the first two study subjects), along with standard immunosuppressive therapy. At 90 days, the patient’s C-peptide, a measure of endogenous insulin secretion, rose from undetectable to 280 pmol/L fasting and 560 pmol/L post mixed-meal tolerance testing.
Over the same period, the patient’s hemoglobin A1c dropped from 8.6% at baseline to 7.2%. And within 7 days, the individual’s daily exogenous insulin requirement dropped from an average of 34 units to just 2.9 units, a 91% decrease.
The patient had experienced five severe hypoglycemic episodes in the year prior to transplant. They experienced some mild hypoglycemia soon after the procedure while insulin doses were being adjusted, but none thereafter.
Dr. Shapiro said in an interview: “I was absolutely thrilled to see the first patient results with high C-peptide and a 91% reduction in insulin. That’s a pretty impressive finding for half dosing in the very first patient in a trial. I think it bodes really well for ongoing efforts in this area by Vertex and by others that have similar kinds of cells. It’s very exciting.”
However, he cautioned, “we do need some longer-term data to be sure there’s no off-target growth or other concerns. But based on the purity of this product, that risk is likely to be low.”
And he noted, “I think we still have to address the challenges of setting this process up. A huge amount of work has gone into manufacturing the cell product for a single patient. I think it remains to be seen whether the same technology can be delivered at a larger scale ... i.e., being able to treat hundreds or thousands of patients.”
A blog post on the website of diabetes charity JDRF called the result “outstanding.” “It’s a big deal,” they added. However, they also cautioned: “There are a few things to keep in mind while assessing the data. One is that these are only results from a single person. Data are needed from many more to fully evaluate the potential of this therapy. The second is that this person only received half the target dose of cells.”
Dr. Shapiro is working with another company, ViaCyte, which has also developed stem cell–derived islets. In contrast to the Vertex product, which is fully differentiated and delivered to the liver, ViaCyte’s PEC-Direct product is comprised of stem cell-derived pancreatic islet progenitor cells that are implanted subcutaneously in a pouch, allowing for vascularization.
In a late-breaking poster at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association in June 2021, ViaCyte reported on a patient given PEC-Direct. In that patient, stimulated C-peptide increased from 0.1 ng/mL at baseline to 0.8 ng/mL at week 39, and there was a drop in A1c from 7.4% to 6.6%, with no adverse events.
Immunosuppression: Which approach will come closer to cure?
Thus far, the requirement for lifelong immunosuppression has meant that any islet cell replacement approach, including with stem cell–derived islets, has been limited to use in people with type 1 diabetes who have hypoglycemic unawareness or severely unpredictable blood glucose levels.
Two broad approaches are simultaneously being explored to overcome the rejection problem: Encapsulation of the cells to protect them from the immune system, and genetic modification of the cells so that they don’t provoke the immune system in the first place.
In 2022, Vertex plans to file an investigational new drug application for an encapsulated islet cell program with the FDA.
Dr. Markmann believes the genetic modification approach is more promising. “I’m not a believer in encapsulation. I think the foreign body response is hard to overcome. I think the answer will ultimately be genetically modifying the [cell] lines. ... The cell could express something that would potentially turn off the lymphocytes or interfere with the lymphocytes trying to attack them.”
Moreover, he said, “you don’t have to get rid of immunosuppression completely. It’s all [a] risk-benefit [equation]. Even if you could get it down to a single less-toxic [immunosuppressive] agent that would be a huge step.”
Dr. Shapiro commented: “All efforts and eyes are laser-focused on developing cells or approaches that will allow transplantation of this kind of stem cell without any immunosuppression or with low-dose immunosuppression that could be regarded as being exceedingly low risk.”
“Then, and only then, I think we could offer this kind of treatment to children who are just diagnosed with diabetes or to [a bigger proportion of] patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. ... The science has to be done in a step-wise fashion,” he added.
Microencapsulation, Dr. Shapiro noted, “is a big challenge because the process of capturing the cells and putting them into a device is really injurious to their survival. ... That may or may not work.”
Dr. Shapiro and his Edmonton team are now embarking on a new trial with ViaCyte and CRISPR Therapeutics using gene-edited cells that contain two knock-in genes and two knock-out genes shown to be less immunogenic and anti-inflammatory in rodent models.
“They look to be promising. We’re going to start a first-in-human trial in the next few months with those cells to see if they really are able to withstand a transplant without the need for immunosuppression. That will be a very exciting trial in itself,” Dr. Shapiro said, noting that they expect to enroll the first patients in the next few months.
However, he cautioned, “first we have to make sure that the gene-edited product continues to function in patients in the way that the original product did, that the cells survive, and that the gene modifications are actually effective. ... Maybe other iterations will be needed.”
“I think, as we move forward, we will ultimately have a gene-edited stem cell–derived product that is immune evasive and will survive. So, I’m ... optimistic that this is not as long term as you might think, and it’s ... happening much more rapidly – at least in first-in-human trials to test safety and preliminary efficacy.”
Dr. Shapiro is a consultant for ViaCyte.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Green’ Mediterranean diet benefits may arise from ‘hunger hormone’
A “green” adaptation to the traditional Mediterranean diet could help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce visceral fat by increasing levels of ghrelin, the “hunger hormone,” new research suggests.
The current study is a new analysis of data from the randomized DIRECT-PLUS trial, which showed that the addition of green tea and substitution of red meat for a plant-based (Mankai) protein shake at dinner – dubbed the “green Mediterranean diet” – resulted in further improved cardiometabolic benefits compared with the traditional Mediterranean diet among people with baseline abdominal obesity and/or dyslipidemia, according to the researchers.
They specifically looked at ghrelin, nicknamed the “hunger hormone,” a neuropeptide mainly secreted by the gastric epithelium. It acts on the pituitary gland to release growth hormone. Ghrelin concentrations increase during fasting and decrease after eating. Lower levels are associated with insulin resistance and obesity.
Fasting ghrelin levels were elevated with weight loss, but those increases were associated with improved insulin sensitivity and regression of visceral adipose tissue even beyond weight loss.
Although the caloric restriction and weight loss were comparable with the two Mediterranean diets, the green Mediterranean diet group had double the increase in fasting ghrelin as the traditional Mediterranean diet group, the researchers point out in their report .
‘Hypothesis-generating’ study pushes many hot topic buttons
“This specific study is the first to show that ghrelin levels play an important role in metabolic adaptation to a dietary or lifestyle intervention and that ghrelin is an important player in the axis of adiposity, insulin resistance, and metabolic health,” lead researcher Gal Tsaban, MD, told this news organization.
The data partially explain some of the prior beneficial effects seen with the Green Mediterranean diet, even after adjustment for weight loss, he explained, noting that the revised version of the diet “could be considered as an alternative lifestyle intervention with possible metabolic benefits even beyond the Mediterranean diet, which is what we currently recommend for patients.”
Asked for comment, Christopher Gardner, PhD, was not as enthusiastic.
He took issue with the fact that ghrelin wasn’t a primary or even a prespecified secondary outcome of the DIRECT-PLUS trial and because the specific plant-based ingredients of the green Mediterranean diet used in the study may not be widely available or desirable and therefore limit the study’s generalizability.
Dr. Gardner, who is director of nutrition studies at the Stanford Prevention Research Center, California, also said: “They’re tying lots of interesting things together. The Mediterranean diet is a cool thing, ghrelin is a cool thing, and insulin resistance is hugely important in this day and age, even though we don’t all agree on how to measure it.”
“But it gets tough as you try to link them all together for an exploratory outcome. ... To me it’s an interesting hypothesis-generating study that pushes a lot of interesting buttons that are hot topics in the field.”
Green Mediterranean diet led to higher ghrelin, metabolic benefits
In DIRECT-PLUS, a total of 294 adults (88% men) older than 30 years of age with abdominal obesity (waist circumference >102 cm for men or >88 cm for women), or dyslipidemia (triglycerides >150 mg/dL and HDL-cholesterol ≤40 mg/dL for men or ≤50 mg/dL for women) were included. Half had prediabetes or type 2 diabetes.
They were randomized to one of three diets: a diet based on standard healthy dietary guidelines; a traditional Mediterranean diet low in simple carbohydrates, rich in vegetables, with poultry and fish replacing beef and lamb and 28 g/day of walnuts; or the Green-Mediterranean diet, including 3-4 cups/day of green tea and 100 g/day of a green shake made from the Mankai strain of Wolffia globosa (also known as duckweed) replacing dinner, and 28 g/day of walnuts.
The Green Mediterranean diet included 800 mg more polyphenols than the traditional Mediterranean diet. Both were equally calorie-restricted, at about 1,500-1,800 kcal/day for men and 1,200-1,400 kcal/day for women. All three groups were instructed to engage in regular physical activity and were given free gym memberships.
The retention rate was 98.3% after 6 months and 89.8% after 18 months.
Weight loss was similar between the two Mediterranean diet groups (2.9% and 3.9% for the traditional and green versions, respectively) compared with the standard healthy diet (0.6%) (P < .05 for both Mediterranean diet groups vs. control).
After 6 months, fasting ghrelin increased in the traditional (8.0%; P = .015) and green (10.5%; P = 0.031) Mediterranean groups versus baseline, with no significant change in the control group.
By 18 months, fasting ghrelin was significantly greater compared with baseline only in the green Mediterranean group (P = .012).
Because the differences in fasting ghrelin trajectories were only significant in men – likely due to the small sample size of women – a subsequent 18-month analysis was limited to the men. In a multivariate model adjusted for age, intervention group, baseline biomarker values, and 18-month weight changes, the 18-month change in fasting ghrelin remained a significant predictor for changes in A1c and homeostatic model of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR; P = .022).
Because weight loss remained the most significant predictor of improved insulin resistance, a further analysis examined the association between changes in fasting ghrelin levels with changes in the fraction of insulin resistance marker that were not attributed to weight loss, per se. With the other adjustments, fasting ghrelin was associated with residual reductions in A1c (P = .003), HOMA-IR (P = .021), increased HDL-cholesterol (P = .024), and relative visceral adipose tissue loss (P = .003).
No specific product needed to push Mediterranean diet towards vegan
Dr. Tsaban, a nutritional researcher and cardiologist at Ben-Gurion University and Soroka University Medical Center, Be’er-Sheva, Israel, said the Mankai shake is commonly consumed in Israel but is also available worldwide. The study participants, all employees at an isolated nuclear research facility in the Negev, were particularly motivated. “They didn’t have a satiety problem with the drink. It made them very full,” he said. The manufacturer supplied the shakes but didn’t fund the study, he added.
However, Dr. Tsaban said that the “green Mediterranean diet” doesn’t depend on specific products.
Rather, “the concept is to push the Mediterranean diet a bit further and to replace the animal-based protein with vegetable-based protein, to shift your dietary habits towards a more vegan lifestyle. It’s not completely vegan, but it’s trending there. ... Our main goal was to increase the polyphenol intake, the antioxidant intake from vegetables. ... I think it can be replicated.”
Dr. Gardner said, “At the end of the day, it’s an exploratory study. ... It raises some interesting points that give the rest of us room to follow-up on.”
The study was funded by grants from the German Research Foundation, the Israel Ministry of Health, the Israel Ministry of Science and Technology, and the California Walnut Commission. Dr. Tsaban has reported no further relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gardner has reported receiving study funding from Beyond Meat.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A “green” adaptation to the traditional Mediterranean diet could help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce visceral fat by increasing levels of ghrelin, the “hunger hormone,” new research suggests.
The current study is a new analysis of data from the randomized DIRECT-PLUS trial, which showed that the addition of green tea and substitution of red meat for a plant-based (Mankai) protein shake at dinner – dubbed the “green Mediterranean diet” – resulted in further improved cardiometabolic benefits compared with the traditional Mediterranean diet among people with baseline abdominal obesity and/or dyslipidemia, according to the researchers.
They specifically looked at ghrelin, nicknamed the “hunger hormone,” a neuropeptide mainly secreted by the gastric epithelium. It acts on the pituitary gland to release growth hormone. Ghrelin concentrations increase during fasting and decrease after eating. Lower levels are associated with insulin resistance and obesity.
Fasting ghrelin levels were elevated with weight loss, but those increases were associated with improved insulin sensitivity and regression of visceral adipose tissue even beyond weight loss.
Although the caloric restriction and weight loss were comparable with the two Mediterranean diets, the green Mediterranean diet group had double the increase in fasting ghrelin as the traditional Mediterranean diet group, the researchers point out in their report .
‘Hypothesis-generating’ study pushes many hot topic buttons
“This specific study is the first to show that ghrelin levels play an important role in metabolic adaptation to a dietary or lifestyle intervention and that ghrelin is an important player in the axis of adiposity, insulin resistance, and metabolic health,” lead researcher Gal Tsaban, MD, told this news organization.
The data partially explain some of the prior beneficial effects seen with the Green Mediterranean diet, even after adjustment for weight loss, he explained, noting that the revised version of the diet “could be considered as an alternative lifestyle intervention with possible metabolic benefits even beyond the Mediterranean diet, which is what we currently recommend for patients.”
Asked for comment, Christopher Gardner, PhD, was not as enthusiastic.
He took issue with the fact that ghrelin wasn’t a primary or even a prespecified secondary outcome of the DIRECT-PLUS trial and because the specific plant-based ingredients of the green Mediterranean diet used in the study may not be widely available or desirable and therefore limit the study’s generalizability.
Dr. Gardner, who is director of nutrition studies at the Stanford Prevention Research Center, California, also said: “They’re tying lots of interesting things together. The Mediterranean diet is a cool thing, ghrelin is a cool thing, and insulin resistance is hugely important in this day and age, even though we don’t all agree on how to measure it.”
“But it gets tough as you try to link them all together for an exploratory outcome. ... To me it’s an interesting hypothesis-generating study that pushes a lot of interesting buttons that are hot topics in the field.”
Green Mediterranean diet led to higher ghrelin, metabolic benefits
In DIRECT-PLUS, a total of 294 adults (88% men) older than 30 years of age with abdominal obesity (waist circumference >102 cm for men or >88 cm for women), or dyslipidemia (triglycerides >150 mg/dL and HDL-cholesterol ≤40 mg/dL for men or ≤50 mg/dL for women) were included. Half had prediabetes or type 2 diabetes.
They were randomized to one of three diets: a diet based on standard healthy dietary guidelines; a traditional Mediterranean diet low in simple carbohydrates, rich in vegetables, with poultry and fish replacing beef and lamb and 28 g/day of walnuts; or the Green-Mediterranean diet, including 3-4 cups/day of green tea and 100 g/day of a green shake made from the Mankai strain of Wolffia globosa (also known as duckweed) replacing dinner, and 28 g/day of walnuts.
The Green Mediterranean diet included 800 mg more polyphenols than the traditional Mediterranean diet. Both were equally calorie-restricted, at about 1,500-1,800 kcal/day for men and 1,200-1,400 kcal/day for women. All three groups were instructed to engage in regular physical activity and were given free gym memberships.
The retention rate was 98.3% after 6 months and 89.8% after 18 months.
Weight loss was similar between the two Mediterranean diet groups (2.9% and 3.9% for the traditional and green versions, respectively) compared with the standard healthy diet (0.6%) (P < .05 for both Mediterranean diet groups vs. control).
After 6 months, fasting ghrelin increased in the traditional (8.0%; P = .015) and green (10.5%; P = 0.031) Mediterranean groups versus baseline, with no significant change in the control group.
By 18 months, fasting ghrelin was significantly greater compared with baseline only in the green Mediterranean group (P = .012).
Because the differences in fasting ghrelin trajectories were only significant in men – likely due to the small sample size of women – a subsequent 18-month analysis was limited to the men. In a multivariate model adjusted for age, intervention group, baseline biomarker values, and 18-month weight changes, the 18-month change in fasting ghrelin remained a significant predictor for changes in A1c and homeostatic model of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR; P = .022).
Because weight loss remained the most significant predictor of improved insulin resistance, a further analysis examined the association between changes in fasting ghrelin levels with changes in the fraction of insulin resistance marker that were not attributed to weight loss, per se. With the other adjustments, fasting ghrelin was associated with residual reductions in A1c (P = .003), HOMA-IR (P = .021), increased HDL-cholesterol (P = .024), and relative visceral adipose tissue loss (P = .003).
No specific product needed to push Mediterranean diet towards vegan
Dr. Tsaban, a nutritional researcher and cardiologist at Ben-Gurion University and Soroka University Medical Center, Be’er-Sheva, Israel, said the Mankai shake is commonly consumed in Israel but is also available worldwide. The study participants, all employees at an isolated nuclear research facility in the Negev, were particularly motivated. “They didn’t have a satiety problem with the drink. It made them very full,” he said. The manufacturer supplied the shakes but didn’t fund the study, he added.
However, Dr. Tsaban said that the “green Mediterranean diet” doesn’t depend on specific products.
Rather, “the concept is to push the Mediterranean diet a bit further and to replace the animal-based protein with vegetable-based protein, to shift your dietary habits towards a more vegan lifestyle. It’s not completely vegan, but it’s trending there. ... Our main goal was to increase the polyphenol intake, the antioxidant intake from vegetables. ... I think it can be replicated.”
Dr. Gardner said, “At the end of the day, it’s an exploratory study. ... It raises some interesting points that give the rest of us room to follow-up on.”
The study was funded by grants from the German Research Foundation, the Israel Ministry of Health, the Israel Ministry of Science and Technology, and the California Walnut Commission. Dr. Tsaban has reported no further relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gardner has reported receiving study funding from Beyond Meat.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A “green” adaptation to the traditional Mediterranean diet could help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce visceral fat by increasing levels of ghrelin, the “hunger hormone,” new research suggests.
The current study is a new analysis of data from the randomized DIRECT-PLUS trial, which showed that the addition of green tea and substitution of red meat for a plant-based (Mankai) protein shake at dinner – dubbed the “green Mediterranean diet” – resulted in further improved cardiometabolic benefits compared with the traditional Mediterranean diet among people with baseline abdominal obesity and/or dyslipidemia, according to the researchers.
They specifically looked at ghrelin, nicknamed the “hunger hormone,” a neuropeptide mainly secreted by the gastric epithelium. It acts on the pituitary gland to release growth hormone. Ghrelin concentrations increase during fasting and decrease after eating. Lower levels are associated with insulin resistance and obesity.
Fasting ghrelin levels were elevated with weight loss, but those increases were associated with improved insulin sensitivity and regression of visceral adipose tissue even beyond weight loss.
Although the caloric restriction and weight loss were comparable with the two Mediterranean diets, the green Mediterranean diet group had double the increase in fasting ghrelin as the traditional Mediterranean diet group, the researchers point out in their report .
‘Hypothesis-generating’ study pushes many hot topic buttons
“This specific study is the first to show that ghrelin levels play an important role in metabolic adaptation to a dietary or lifestyle intervention and that ghrelin is an important player in the axis of adiposity, insulin resistance, and metabolic health,” lead researcher Gal Tsaban, MD, told this news organization.
The data partially explain some of the prior beneficial effects seen with the Green Mediterranean diet, even after adjustment for weight loss, he explained, noting that the revised version of the diet “could be considered as an alternative lifestyle intervention with possible metabolic benefits even beyond the Mediterranean diet, which is what we currently recommend for patients.”
Asked for comment, Christopher Gardner, PhD, was not as enthusiastic.
He took issue with the fact that ghrelin wasn’t a primary or even a prespecified secondary outcome of the DIRECT-PLUS trial and because the specific plant-based ingredients of the green Mediterranean diet used in the study may not be widely available or desirable and therefore limit the study’s generalizability.
Dr. Gardner, who is director of nutrition studies at the Stanford Prevention Research Center, California, also said: “They’re tying lots of interesting things together. The Mediterranean diet is a cool thing, ghrelin is a cool thing, and insulin resistance is hugely important in this day and age, even though we don’t all agree on how to measure it.”
“But it gets tough as you try to link them all together for an exploratory outcome. ... To me it’s an interesting hypothesis-generating study that pushes a lot of interesting buttons that are hot topics in the field.”
Green Mediterranean diet led to higher ghrelin, metabolic benefits
In DIRECT-PLUS, a total of 294 adults (88% men) older than 30 years of age with abdominal obesity (waist circumference >102 cm for men or >88 cm for women), or dyslipidemia (triglycerides >150 mg/dL and HDL-cholesterol ≤40 mg/dL for men or ≤50 mg/dL for women) were included. Half had prediabetes or type 2 diabetes.
They were randomized to one of three diets: a diet based on standard healthy dietary guidelines; a traditional Mediterranean diet low in simple carbohydrates, rich in vegetables, with poultry and fish replacing beef and lamb and 28 g/day of walnuts; or the Green-Mediterranean diet, including 3-4 cups/day of green tea and 100 g/day of a green shake made from the Mankai strain of Wolffia globosa (also known as duckweed) replacing dinner, and 28 g/day of walnuts.
The Green Mediterranean diet included 800 mg more polyphenols than the traditional Mediterranean diet. Both were equally calorie-restricted, at about 1,500-1,800 kcal/day for men and 1,200-1,400 kcal/day for women. All three groups were instructed to engage in regular physical activity and were given free gym memberships.
The retention rate was 98.3% after 6 months and 89.8% after 18 months.
Weight loss was similar between the two Mediterranean diet groups (2.9% and 3.9% for the traditional and green versions, respectively) compared with the standard healthy diet (0.6%) (P < .05 for both Mediterranean diet groups vs. control).
After 6 months, fasting ghrelin increased in the traditional (8.0%; P = .015) and green (10.5%; P = 0.031) Mediterranean groups versus baseline, with no significant change in the control group.
By 18 months, fasting ghrelin was significantly greater compared with baseline only in the green Mediterranean group (P = .012).
Because the differences in fasting ghrelin trajectories were only significant in men – likely due to the small sample size of women – a subsequent 18-month analysis was limited to the men. In a multivariate model adjusted for age, intervention group, baseline biomarker values, and 18-month weight changes, the 18-month change in fasting ghrelin remained a significant predictor for changes in A1c and homeostatic model of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR; P = .022).
Because weight loss remained the most significant predictor of improved insulin resistance, a further analysis examined the association between changes in fasting ghrelin levels with changes in the fraction of insulin resistance marker that were not attributed to weight loss, per se. With the other adjustments, fasting ghrelin was associated with residual reductions in A1c (P = .003), HOMA-IR (P = .021), increased HDL-cholesterol (P = .024), and relative visceral adipose tissue loss (P = .003).
No specific product needed to push Mediterranean diet towards vegan
Dr. Tsaban, a nutritional researcher and cardiologist at Ben-Gurion University and Soroka University Medical Center, Be’er-Sheva, Israel, said the Mankai shake is commonly consumed in Israel but is also available worldwide. The study participants, all employees at an isolated nuclear research facility in the Negev, were particularly motivated. “They didn’t have a satiety problem with the drink. It made them very full,” he said. The manufacturer supplied the shakes but didn’t fund the study, he added.
However, Dr. Tsaban said that the “green Mediterranean diet” doesn’t depend on specific products.
Rather, “the concept is to push the Mediterranean diet a bit further and to replace the animal-based protein with vegetable-based protein, to shift your dietary habits towards a more vegan lifestyle. It’s not completely vegan, but it’s trending there. ... Our main goal was to increase the polyphenol intake, the antioxidant intake from vegetables. ... I think it can be replicated.”
Dr. Gardner said, “At the end of the day, it’s an exploratory study. ... It raises some interesting points that give the rest of us room to follow-up on.”
The study was funded by grants from the German Research Foundation, the Israel Ministry of Health, the Israel Ministry of Science and Technology, and the California Walnut Commission. Dr. Tsaban has reported no further relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gardner has reported receiving study funding from Beyond Meat.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.