User login
FDA OKs low-dose colchicine for broad CV indication
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the anti-inflammatory drug colchicine 0.5 mg tablets (Lodoco) as the first specific anti-inflammatory drug demonstrated to reduce the risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, coronary revascularization, and cardiovascular death in adult patients with established atherosclerotic disease or with multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
The drug, which targets residual inflammation as an underlying cause of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, has a dosage of 0.5 mg once daily, and can be used alone or in combination with cholesterol-lowering medications.
The drug’s manufacturer, Agepha Pharma, said it anticipates that Lodoco will be available for prescription in the second half of 2023.
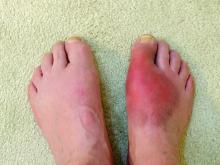
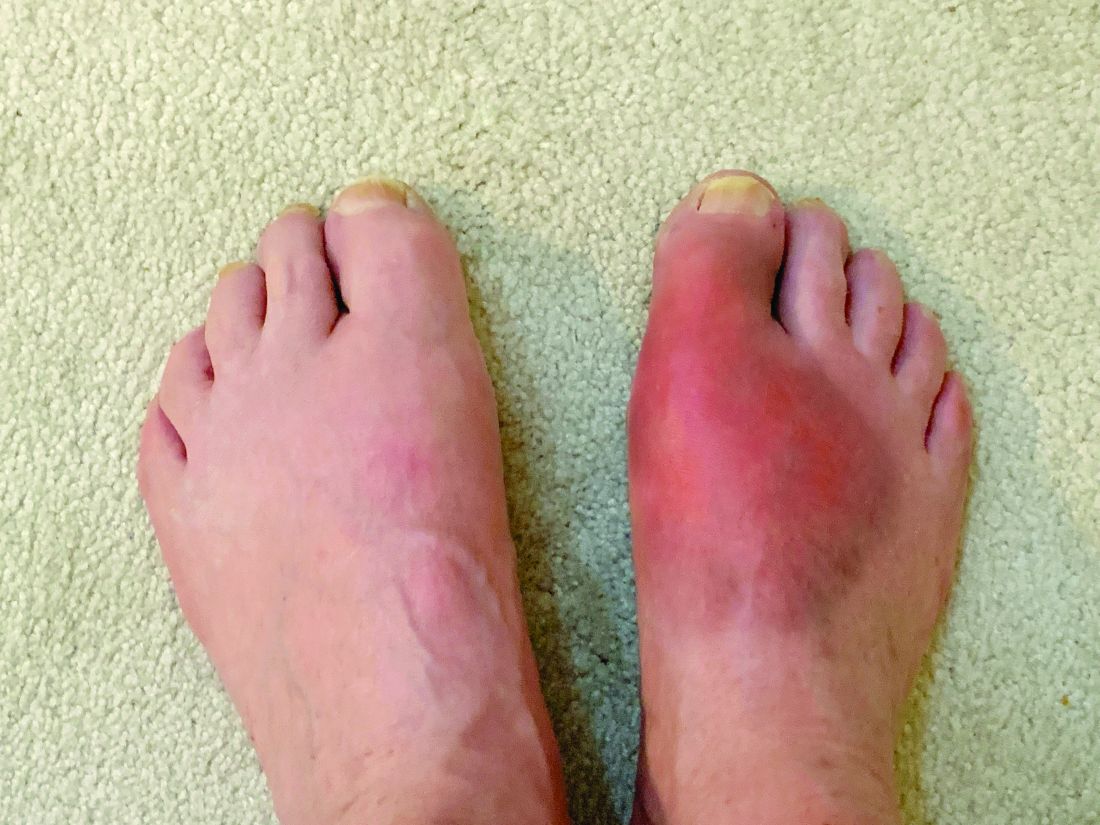
Colchicine has been available for many years and used at higher doses for the acute treatment of gout and pericarditis, but the current formulation is a much lower dose for long-term use in patients with atherosclerotic heart disease.
Data supporting the approval has come from two major randomized trials, LoDoCo-2 and COLCOT.
In the LoDoCo-2 trial, the anti-inflammatory drug cut the risk of cardiovascular events by one third when added to standard prevention therapies in patients with chronic coronary disease. And in the COLCOT study, use of colchicine reduced cardiovascular events by 23% compared with placebo in patients with a recent MI.
Paul Ridker, MD, director of the Center for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, who has been a pioneer in establishing inflammation as an underlying cause of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, welcomed the Lodoco approval.
‘A very big day for cardiology’
“This is a very big day for cardiology,” Dr. Ridker said in an interview.
“The FDA approval of colchicine for patients with atherosclerotic disease is a huge signal that physicians need to be aware of inflammation as a key player in cardiovascular disease,” he said.
Dr. Ridker was the lead author of a recent study showing that among patients receiving contemporary statins, inflammation assessed by high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) was a stronger predictor for risk of future cardiovascular events and death than LDL cholesterol.
He pointed out that
“That is virtually identical to the indication approved for statin therapy. That shows just how important the FDA thinks this is,” he commented.
But Dr. Ridker added that, while the label does not specify that Lodoco has to be used in addition to statin therapy, he believes that it will be used as additional therapy to statins in the vast majority of patients.
“This is not an alternative to statin therapy. In the randomized trials, the benefits were seen on top of statins,” he stressed.
Dr. Ridker believes that physicians will need time to feel comfortable with this new approach.
“Initially, I think, it will be used mainly by cardiologists who know about inflammation, but I believe over time it will be widely prescribed by internists, in much the same way as statins are used today,” he commented.
Dr. Ridker said he already uses low dose colchicine in his high-risk patients who have high levels of inflammation as seen on hsCRP testing. He believes this is where the drug will mostly be used initially, as this is where it is likely to be most effective.
The prescribing information states that Lodoco is contraindicated in patients who are taking strong CYP3A4 inhibitors or P-glycoprotein inhibitors, such as ketoconazole, fluconazole, and clarithromycin, and in patients with preexisting blood dyscrasias, renal failure, and severe hepatic impairment.
Common side effects reported in published clinical studies and literature with the use of colchicine are gastrointestinal symptoms (diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal cramping) and myalgia.
More serious adverse effects are listed as blood dyscrasias such as myelosuppression, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, and aplastic anemia; and neuromuscular toxicity in the form of myotoxicity including rhabdomyolysis, which may occur, especially in combination with other drugs known to cause this effect. If these adverse effects occur, it is recommended that the drug be stopped.
The prescribing information also notes that Lodoco may rarely and transiently impair fertility in males; and that patients with renal or hepatic impairment should be monitored closely for adverse effects of colchicine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the anti-inflammatory drug colchicine 0.5 mg tablets (Lodoco) as the first specific anti-inflammatory drug demonstrated to reduce the risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, coronary revascularization, and cardiovascular death in adult patients with established atherosclerotic disease or with multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
The drug, which targets residual inflammation as an underlying cause of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, has a dosage of 0.5 mg once daily, and can be used alone or in combination with cholesterol-lowering medications.
The drug’s manufacturer, Agepha Pharma, said it anticipates that Lodoco will be available for prescription in the second half of 2023.
Colchicine has been available for many years and used at higher doses for the acute treatment of gout and pericarditis, but the current formulation is a much lower dose for long-term use in patients with atherosclerotic heart disease.
Data supporting the approval has come from two major randomized trials, LoDoCo-2 and COLCOT.
In the LoDoCo-2 trial, the anti-inflammatory drug cut the risk of cardiovascular events by one third when added to standard prevention therapies in patients with chronic coronary disease. And in the COLCOT study, use of colchicine reduced cardiovascular events by 23% compared with placebo in patients with a recent MI.
Paul Ridker, MD, director of the Center for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, who has been a pioneer in establishing inflammation as an underlying cause of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, welcomed the Lodoco approval.
‘A very big day for cardiology’
“This is a very big day for cardiology,” Dr. Ridker said in an interview.
“The FDA approval of colchicine for patients with atherosclerotic disease is a huge signal that physicians need to be aware of inflammation as a key player in cardiovascular disease,” he said.
Dr. Ridker was the lead author of a recent study showing that among patients receiving contemporary statins, inflammation assessed by high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) was a stronger predictor for risk of future cardiovascular events and death than LDL cholesterol.
He pointed out that
“That is virtually identical to the indication approved for statin therapy. That shows just how important the FDA thinks this is,” he commented.
But Dr. Ridker added that, while the label does not specify that Lodoco has to be used in addition to statin therapy, he believes that it will be used as additional therapy to statins in the vast majority of patients.
“This is not an alternative to statin therapy. In the randomized trials, the benefits were seen on top of statins,” he stressed.
Dr. Ridker believes that physicians will need time to feel comfortable with this new approach.
“Initially, I think, it will be used mainly by cardiologists who know about inflammation, but I believe over time it will be widely prescribed by internists, in much the same way as statins are used today,” he commented.
Dr. Ridker said he already uses low dose colchicine in his high-risk patients who have high levels of inflammation as seen on hsCRP testing. He believes this is where the drug will mostly be used initially, as this is where it is likely to be most effective.
The prescribing information states that Lodoco is contraindicated in patients who are taking strong CYP3A4 inhibitors or P-glycoprotein inhibitors, such as ketoconazole, fluconazole, and clarithromycin, and in patients with preexisting blood dyscrasias, renal failure, and severe hepatic impairment.
Common side effects reported in published clinical studies and literature with the use of colchicine are gastrointestinal symptoms (diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal cramping) and myalgia.
More serious adverse effects are listed as blood dyscrasias such as myelosuppression, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, and aplastic anemia; and neuromuscular toxicity in the form of myotoxicity including rhabdomyolysis, which may occur, especially in combination with other drugs known to cause this effect. If these adverse effects occur, it is recommended that the drug be stopped.
The prescribing information also notes that Lodoco may rarely and transiently impair fertility in males; and that patients with renal or hepatic impairment should be monitored closely for adverse effects of colchicine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the anti-inflammatory drug colchicine 0.5 mg tablets (Lodoco) as the first specific anti-inflammatory drug demonstrated to reduce the risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, coronary revascularization, and cardiovascular death in adult patients with established atherosclerotic disease or with multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
The drug, which targets residual inflammation as an underlying cause of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, has a dosage of 0.5 mg once daily, and can be used alone or in combination with cholesterol-lowering medications.
The drug’s manufacturer, Agepha Pharma, said it anticipates that Lodoco will be available for prescription in the second half of 2023.
Colchicine has been available for many years and used at higher doses for the acute treatment of gout and pericarditis, but the current formulation is a much lower dose for long-term use in patients with atherosclerotic heart disease.
Data supporting the approval has come from two major randomized trials, LoDoCo-2 and COLCOT.
In the LoDoCo-2 trial, the anti-inflammatory drug cut the risk of cardiovascular events by one third when added to standard prevention therapies in patients with chronic coronary disease. And in the COLCOT study, use of colchicine reduced cardiovascular events by 23% compared with placebo in patients with a recent MI.
Paul Ridker, MD, director of the Center for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, who has been a pioneer in establishing inflammation as an underlying cause of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, welcomed the Lodoco approval.
‘A very big day for cardiology’
“This is a very big day for cardiology,” Dr. Ridker said in an interview.
“The FDA approval of colchicine for patients with atherosclerotic disease is a huge signal that physicians need to be aware of inflammation as a key player in cardiovascular disease,” he said.
Dr. Ridker was the lead author of a recent study showing that among patients receiving contemporary statins, inflammation assessed by high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) was a stronger predictor for risk of future cardiovascular events and death than LDL cholesterol.
He pointed out that
“That is virtually identical to the indication approved for statin therapy. That shows just how important the FDA thinks this is,” he commented.
But Dr. Ridker added that, while the label does not specify that Lodoco has to be used in addition to statin therapy, he believes that it will be used as additional therapy to statins in the vast majority of patients.
“This is not an alternative to statin therapy. In the randomized trials, the benefits were seen on top of statins,” he stressed.
Dr. Ridker believes that physicians will need time to feel comfortable with this new approach.
“Initially, I think, it will be used mainly by cardiologists who know about inflammation, but I believe over time it will be widely prescribed by internists, in much the same way as statins are used today,” he commented.
Dr. Ridker said he already uses low dose colchicine in his high-risk patients who have high levels of inflammation as seen on hsCRP testing. He believes this is where the drug will mostly be used initially, as this is where it is likely to be most effective.
The prescribing information states that Lodoco is contraindicated in patients who are taking strong CYP3A4 inhibitors or P-glycoprotein inhibitors, such as ketoconazole, fluconazole, and clarithromycin, and in patients with preexisting blood dyscrasias, renal failure, and severe hepatic impairment.
Common side effects reported in published clinical studies and literature with the use of colchicine are gastrointestinal symptoms (diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal cramping) and myalgia.
More serious adverse effects are listed as blood dyscrasias such as myelosuppression, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, and aplastic anemia; and neuromuscular toxicity in the form of myotoxicity including rhabdomyolysis, which may occur, especially in combination with other drugs known to cause this effect. If these adverse effects occur, it is recommended that the drug be stopped.
The prescribing information also notes that Lodoco may rarely and transiently impair fertility in males; and that patients with renal or hepatic impairment should be monitored closely for adverse effects of colchicine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Gout linked to smaller brain volume, higher likelihood of neurodegenerative diseases
Patients with gout may have smaller brain volumes and higher brain iron markers than people without gout, and also be more likely to develop Parkinson’s disease, probable essential tremor, and dementia, researchers in the United Kingdom report.
“We were surprised about the regions of the brain affected by gout, several of which are important for motor function. The other intriguing finding was that the risk of dementia amongst gout patients was strongly time-dependent: highest in the first 3 years after their gout diagnosis,” lead study author Anya Topiwala, BMBCh, DPhil, said in an interview.
“Our combination of traditional and genetic approaches increases the confidence that gout is causing the brain findings,” said Dr. Topiwala, a clinical research fellow and consultant psychiatrist in the Nuffield Department of Population Health at the University of Oxford, England.
“We suggest that clinicians be vigilant for cognitive and motor problems after gout diagnosis, particularly in the early stages,” she added.
Links between gout and neurodegenerative diseases debated in earlier studies
Gout, the most common inflammatory arthritis, affects around 1%-4% of people, the authors wrote, with monosodium urate crystal deposits causing acute flares of pain and swelling in joints and periarticular tissues.
Whether and how gout may affect the brain has been debated in the literature. Gout and hyperuricemia have been linked with elevated stroke risk; and although observational studies have linked hyperuricemia with lower dementia risk, especially Alzheimer’s disease, Mendelian randomization studies have had conflicting results in Alzheimer’s disease.
A novel approach that analyzes brain structure and genetics
In a study published in Nature Communications, Dr. Topiwala and her colleagues combined observational and Mendelian randomization techniques to explore relationships between gout and neurodegenerative diseases. They analyzed data from over 303,000 volunteer participants between 40 and 69 years of age recruited between 2006 and 2010 to contribute their detailed genetic and health information to the U.K. Biobank, a large-scale biomedical database and research resource.
Patients with gout tended to be older and male. At baseline, all participants’ serum urate levels were measured, and 30.8% of patients with gout reported that they currently used urate-lowering therapy.
MRI shows brain changes in patients with gout
In what the authors said is the first investigation of neuroimaging markers in patients with gout, they compared differences in gray matter volumes found in the 1,165 participants with gout and the 32,202 controls without gout who had MRI data.
They found no marked sex differences in associations. Urate was inversely linked with global brain volume and with gray and white matter volumes, and gout appeared to age global gray matter by 2 years.
Patients with gout and higher urate showed significant differences in regional gray matter volumes, especially in the cerebellum, pons, and midbrain, as well as subcortical differences in the nucleus accumbens, putamen, and caudate. They also showed significant differences in white matter tract microstructure in the fornix.
Patients with gout were more likely to develop dementia (average hazard ratio [HR] over study = 1.60), especially in the first 3 years after gout diagnosis (HR = 7.40). They were also at higher risk for vascular dementia (average HR = 2.41), compared with all-cause dementia, but not for Alzheimer’s disease (average HR = 1.62).
In asymptomatic participants though, urate and dementia were inversely linked (HR = 0.85), with no time dependence.
Gout was linked with higher incidence of Parkinson’s disease (HR = 1.43) and probable essential tremor (HR = 6.75). In asymptomatic participants, urate and Parkinson’s disease (HR = 0.89), but not probable essential tremor, were inversely linked.
Genetic analyses reinforce MRI results
Using Mendelian randomization estimates, the authors found that genetic links generally reflected their observational findings. Both genetically predicted gout and serum urate were significantly linked with regional gray matter volumes, including cerebellar, midbrain, pons, and brainstem.
They also found significant links with higher magnetic susceptibility in the putamen and caudate, markers of higher iron. But while genetically predicted gout was significantly linked with global gray matter volume, urate was not.
In males, but not in females, urate was positively linked with alcohol intake and lower socioeconomic status.
Dr. Topiwala acknowledged several limitations to the study, writing that “the results from the volunteer participants may not apply to other populations; the cross-sectional serum urate measurements may not reflect chronic exposure; and Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor may have been diagnostically confounded.”
A novel approach that suggests further related research
Asked to comment on the study, Puja Khanna, MD, MPH, a rheumatologist and clinical associate professor of medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, called its novel use of neuroimaging interesting.
Dr. Khanna, who was not involved in the study, said she would like to know more about the role that horizontal pleiotropy – one genetic variant having independent effects on multiple traits – plays in this disease process, and about the impact of the antioxidative properties of urate in maintaining neuroprotection.
“[The] U.K. Biobank is an excellent database to look at questions of association,” John D. FitzGerald, MD, PhD, MPH, MBA, professor and clinical chief of rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
“This is a fairly rigorous study,” added Dr. FitzGerald, also not involved in the study. “While it has lots of strengths,” including its large sample size and Mendelian randomization, it also has “abundant weaknesses,” he added. “It is largely cross-sectional, with single urate measurement and single brain MRI.”
“Causation is the big question,” Dr. FitzGerald noted. “Does treating gout (or urate) help prevent dementia or neurodegenerative decline?”
Early diagnosis benefits patients
Dr. Khanna and Dr. FitzGerald joined the authors in advising doctors to monitor their gout patients for cognitive and motor symptoms of neurodegenerative disease.
“It is clearly important to pay close attention to the neurologic exam and history in gout, especially because it is a disease of the aging population,” Dr. Khanna advised. “Addressing dementia when gout is diagnosed can lead to prompt mitigation strategies that can hugely impact patients.”
Dr. Topiwala and her colleagues would like to investigate why the dementia risk was time-dependent. “Is this because of the acute inflammatory response in gout, or could it just be that patients with gout visit their doctors more frequently, so any cognitive problems are picked up sooner?” she asked.
The authors, and Dr. Khanna and Dr. FitzGerald, report no relevant financial relationships. The Wellcome Trust; the U.K. Medical Research Council; the European Commission Horizon 2020 research and innovation program; the British Heart Foundation; the U.S. National Institutes of Health; the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council; and the National Institute for Health and Care Research funded the study.
Patients with gout may have smaller brain volumes and higher brain iron markers than people without gout, and also be more likely to develop Parkinson’s disease, probable essential tremor, and dementia, researchers in the United Kingdom report.
“We were surprised about the regions of the brain affected by gout, several of which are important for motor function. The other intriguing finding was that the risk of dementia amongst gout patients was strongly time-dependent: highest in the first 3 years after their gout diagnosis,” lead study author Anya Topiwala, BMBCh, DPhil, said in an interview.
“Our combination of traditional and genetic approaches increases the confidence that gout is causing the brain findings,” said Dr. Topiwala, a clinical research fellow and consultant psychiatrist in the Nuffield Department of Population Health at the University of Oxford, England.
“We suggest that clinicians be vigilant for cognitive and motor problems after gout diagnosis, particularly in the early stages,” she added.
Links between gout and neurodegenerative diseases debated in earlier studies
Gout, the most common inflammatory arthritis, affects around 1%-4% of people, the authors wrote, with monosodium urate crystal deposits causing acute flares of pain and swelling in joints and periarticular tissues.
Whether and how gout may affect the brain has been debated in the literature. Gout and hyperuricemia have been linked with elevated stroke risk; and although observational studies have linked hyperuricemia with lower dementia risk, especially Alzheimer’s disease, Mendelian randomization studies have had conflicting results in Alzheimer’s disease.
A novel approach that analyzes brain structure and genetics
In a study published in Nature Communications, Dr. Topiwala and her colleagues combined observational and Mendelian randomization techniques to explore relationships between gout and neurodegenerative diseases. They analyzed data from over 303,000 volunteer participants between 40 and 69 years of age recruited between 2006 and 2010 to contribute their detailed genetic and health information to the U.K. Biobank, a large-scale biomedical database and research resource.
Patients with gout tended to be older and male. At baseline, all participants’ serum urate levels were measured, and 30.8% of patients with gout reported that they currently used urate-lowering therapy.
MRI shows brain changes in patients with gout
In what the authors said is the first investigation of neuroimaging markers in patients with gout, they compared differences in gray matter volumes found in the 1,165 participants with gout and the 32,202 controls without gout who had MRI data.
They found no marked sex differences in associations. Urate was inversely linked with global brain volume and with gray and white matter volumes, and gout appeared to age global gray matter by 2 years.
Patients with gout and higher urate showed significant differences in regional gray matter volumes, especially in the cerebellum, pons, and midbrain, as well as subcortical differences in the nucleus accumbens, putamen, and caudate. They also showed significant differences in white matter tract microstructure in the fornix.
Patients with gout were more likely to develop dementia (average hazard ratio [HR] over study = 1.60), especially in the first 3 years after gout diagnosis (HR = 7.40). They were also at higher risk for vascular dementia (average HR = 2.41), compared with all-cause dementia, but not for Alzheimer’s disease (average HR = 1.62).
In asymptomatic participants though, urate and dementia were inversely linked (HR = 0.85), with no time dependence.
Gout was linked with higher incidence of Parkinson’s disease (HR = 1.43) and probable essential tremor (HR = 6.75). In asymptomatic participants, urate and Parkinson’s disease (HR = 0.89), but not probable essential tremor, were inversely linked.
Genetic analyses reinforce MRI results
Using Mendelian randomization estimates, the authors found that genetic links generally reflected their observational findings. Both genetically predicted gout and serum urate were significantly linked with regional gray matter volumes, including cerebellar, midbrain, pons, and brainstem.
They also found significant links with higher magnetic susceptibility in the putamen and caudate, markers of higher iron. But while genetically predicted gout was significantly linked with global gray matter volume, urate was not.
In males, but not in females, urate was positively linked with alcohol intake and lower socioeconomic status.
Dr. Topiwala acknowledged several limitations to the study, writing that “the results from the volunteer participants may not apply to other populations; the cross-sectional serum urate measurements may not reflect chronic exposure; and Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor may have been diagnostically confounded.”
A novel approach that suggests further related research
Asked to comment on the study, Puja Khanna, MD, MPH, a rheumatologist and clinical associate professor of medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, called its novel use of neuroimaging interesting.
Dr. Khanna, who was not involved in the study, said she would like to know more about the role that horizontal pleiotropy – one genetic variant having independent effects on multiple traits – plays in this disease process, and about the impact of the antioxidative properties of urate in maintaining neuroprotection.
“[The] U.K. Biobank is an excellent database to look at questions of association,” John D. FitzGerald, MD, PhD, MPH, MBA, professor and clinical chief of rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
“This is a fairly rigorous study,” added Dr. FitzGerald, also not involved in the study. “While it has lots of strengths,” including its large sample size and Mendelian randomization, it also has “abundant weaknesses,” he added. “It is largely cross-sectional, with single urate measurement and single brain MRI.”
“Causation is the big question,” Dr. FitzGerald noted. “Does treating gout (or urate) help prevent dementia or neurodegenerative decline?”
Early diagnosis benefits patients
Dr. Khanna and Dr. FitzGerald joined the authors in advising doctors to monitor their gout patients for cognitive and motor symptoms of neurodegenerative disease.
“It is clearly important to pay close attention to the neurologic exam and history in gout, especially because it is a disease of the aging population,” Dr. Khanna advised. “Addressing dementia when gout is diagnosed can lead to prompt mitigation strategies that can hugely impact patients.”
Dr. Topiwala and her colleagues would like to investigate why the dementia risk was time-dependent. “Is this because of the acute inflammatory response in gout, or could it just be that patients with gout visit their doctors more frequently, so any cognitive problems are picked up sooner?” she asked.
The authors, and Dr. Khanna and Dr. FitzGerald, report no relevant financial relationships. The Wellcome Trust; the U.K. Medical Research Council; the European Commission Horizon 2020 research and innovation program; the British Heart Foundation; the U.S. National Institutes of Health; the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council; and the National Institute for Health and Care Research funded the study.
Patients with gout may have smaller brain volumes and higher brain iron markers than people without gout, and also be more likely to develop Parkinson’s disease, probable essential tremor, and dementia, researchers in the United Kingdom report.
“We were surprised about the regions of the brain affected by gout, several of which are important for motor function. The other intriguing finding was that the risk of dementia amongst gout patients was strongly time-dependent: highest in the first 3 years after their gout diagnosis,” lead study author Anya Topiwala, BMBCh, DPhil, said in an interview.
“Our combination of traditional and genetic approaches increases the confidence that gout is causing the brain findings,” said Dr. Topiwala, a clinical research fellow and consultant psychiatrist in the Nuffield Department of Population Health at the University of Oxford, England.
“We suggest that clinicians be vigilant for cognitive and motor problems after gout diagnosis, particularly in the early stages,” she added.
Links between gout and neurodegenerative diseases debated in earlier studies
Gout, the most common inflammatory arthritis, affects around 1%-4% of people, the authors wrote, with monosodium urate crystal deposits causing acute flares of pain and swelling in joints and periarticular tissues.
Whether and how gout may affect the brain has been debated in the literature. Gout and hyperuricemia have been linked with elevated stroke risk; and although observational studies have linked hyperuricemia with lower dementia risk, especially Alzheimer’s disease, Mendelian randomization studies have had conflicting results in Alzheimer’s disease.
A novel approach that analyzes brain structure and genetics
In a study published in Nature Communications, Dr. Topiwala and her colleagues combined observational and Mendelian randomization techniques to explore relationships between gout and neurodegenerative diseases. They analyzed data from over 303,000 volunteer participants between 40 and 69 years of age recruited between 2006 and 2010 to contribute their detailed genetic and health information to the U.K. Biobank, a large-scale biomedical database and research resource.
Patients with gout tended to be older and male. At baseline, all participants’ serum urate levels were measured, and 30.8% of patients with gout reported that they currently used urate-lowering therapy.
MRI shows brain changes in patients with gout
In what the authors said is the first investigation of neuroimaging markers in patients with gout, they compared differences in gray matter volumes found in the 1,165 participants with gout and the 32,202 controls without gout who had MRI data.
They found no marked sex differences in associations. Urate was inversely linked with global brain volume and with gray and white matter volumes, and gout appeared to age global gray matter by 2 years.
Patients with gout and higher urate showed significant differences in regional gray matter volumes, especially in the cerebellum, pons, and midbrain, as well as subcortical differences in the nucleus accumbens, putamen, and caudate. They also showed significant differences in white matter tract microstructure in the fornix.
Patients with gout were more likely to develop dementia (average hazard ratio [HR] over study = 1.60), especially in the first 3 years after gout diagnosis (HR = 7.40). They were also at higher risk for vascular dementia (average HR = 2.41), compared with all-cause dementia, but not for Alzheimer’s disease (average HR = 1.62).
In asymptomatic participants though, urate and dementia were inversely linked (HR = 0.85), with no time dependence.
Gout was linked with higher incidence of Parkinson’s disease (HR = 1.43) and probable essential tremor (HR = 6.75). In asymptomatic participants, urate and Parkinson’s disease (HR = 0.89), but not probable essential tremor, were inversely linked.
Genetic analyses reinforce MRI results
Using Mendelian randomization estimates, the authors found that genetic links generally reflected their observational findings. Both genetically predicted gout and serum urate were significantly linked with regional gray matter volumes, including cerebellar, midbrain, pons, and brainstem.
They also found significant links with higher magnetic susceptibility in the putamen and caudate, markers of higher iron. But while genetically predicted gout was significantly linked with global gray matter volume, urate was not.
In males, but not in females, urate was positively linked with alcohol intake and lower socioeconomic status.
Dr. Topiwala acknowledged several limitations to the study, writing that “the results from the volunteer participants may not apply to other populations; the cross-sectional serum urate measurements may not reflect chronic exposure; and Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor may have been diagnostically confounded.”
A novel approach that suggests further related research
Asked to comment on the study, Puja Khanna, MD, MPH, a rheumatologist and clinical associate professor of medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, called its novel use of neuroimaging interesting.
Dr. Khanna, who was not involved in the study, said she would like to know more about the role that horizontal pleiotropy – one genetic variant having independent effects on multiple traits – plays in this disease process, and about the impact of the antioxidative properties of urate in maintaining neuroprotection.
“[The] U.K. Biobank is an excellent database to look at questions of association,” John D. FitzGerald, MD, PhD, MPH, MBA, professor and clinical chief of rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
“This is a fairly rigorous study,” added Dr. FitzGerald, also not involved in the study. “While it has lots of strengths,” including its large sample size and Mendelian randomization, it also has “abundant weaknesses,” he added. “It is largely cross-sectional, with single urate measurement and single brain MRI.”
“Causation is the big question,” Dr. FitzGerald noted. “Does treating gout (or urate) help prevent dementia or neurodegenerative decline?”
Early diagnosis benefits patients
Dr. Khanna and Dr. FitzGerald joined the authors in advising doctors to monitor their gout patients for cognitive and motor symptoms of neurodegenerative disease.
“It is clearly important to pay close attention to the neurologic exam and history in gout, especially because it is a disease of the aging population,” Dr. Khanna advised. “Addressing dementia when gout is diagnosed can lead to prompt mitigation strategies that can hugely impact patients.”
Dr. Topiwala and her colleagues would like to investigate why the dementia risk was time-dependent. “Is this because of the acute inflammatory response in gout, or could it just be that patients with gout visit their doctors more frequently, so any cognitive problems are picked up sooner?” she asked.
The authors, and Dr. Khanna and Dr. FitzGerald, report no relevant financial relationships. The Wellcome Trust; the U.K. Medical Research Council; the European Commission Horizon 2020 research and innovation program; the British Heart Foundation; the U.S. National Institutes of Health; the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council; and the National Institute for Health and Care Research funded the study.
FROM NATURE COMMUNICATIONS
Investigational uricase-based gout drug meets primary endpoints in phase 3 trials
MILAN – Serum uric acid of less than 6 mg/dL was achieved and maintained for a substantial period of time with a once-monthly infusion of SEL-212 in patients with refractory gout, according to results of the two phase 3 DISSOLVE I and II trials.
Both trials met their primary endpoints. In DISSOLVE I – the U.S. study – 56% of patients on SEL-212 at 0.15 mg/kg (high dose) achieved a response, defined as achievement and maintenance of a reduction in serum urate to less than 6 mg/dL for at least 80% of the time during month 6 of treatment. In DISSOLVE II – the global study – 46% of patients on SEL-212 on the 0.15-mg/kg dose achieved response.
In participants aged 50 years or older, there was a statistically significant higher response rate at the high dose of SEL-212 in both DISSOLVE I and II of 65% and 47%, respectively, compared with placebo.
Herbert S.B. Baraf, MD, clinical professor of medicine at George Washington University, Washington, and principal investigator of the DISSOLVE program, presented results of the two phase 3 trials during a late-breaking session at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
“The top-line data from the two SEL-212 phase 3 studies are encouraging. They show that induction of immunotolerance with an infusion of a rapamycin-containing nanoparticle (SEL-110), followed immediately by an infusion of pegadricase, a potent but immunogenic uricase, allows for a strong and sustained uric acid–lowering effect without the development of anti-drug antibodies,” Dr. Baraf said in an interview.
SEL-212 is a monthly two-part infusion therapy – a combination of Selecta Biosciences’s ImmTOR immune tolerance platform, and a therapeutic uricase enzyme (pegadricase), designed to treat refractory gout. SEL-110 (ImmTOR) is an immune-tolerizing, nanoencapsulated rapamycin administered 30 minutes before pegadricase and inhibits anti-pegadricase antibodies. SEL-37 is a pegylated uricase (pegadricase) that converts uric acid to excretable allantoin.
SEL-212 was originally developed by Selecta. Swedish Orphan Biovitrum (Sobi) licensed SEL-212 from Selecta in June 2020 and is responsible for development, regulatory, and commercial activities in all markets outside of China. Selecta is responsible for ImmTOR manufacturing. The phase 3 program for SEL-212 was run by Selecta and funded by Sobi.
It is understood that a biologic license application will be submitted to the Food and Drug Administration, most likely next year, and if approved, “the SEL-212 two-component infusion treatment would provide a monthly alternative to twice-monthly pegloticase, for patients with refractory gout,” Dr. Baraf added.
Details of the trials
The two DISSOLVE studies replicate double-blind, placebo-controlled trials in patients with chronic refractory gout. DISSOLVE I was carried out in 112 patients across 29 sites in the United States, and DISSOLVE II tested the two-part treatment in 153 patients across 37 sites in the United States, Russia, Ukraine, Georgia, and Serbia.
Both studies randomized patients 1:1:1 to a high dose (SEL-110 of 0.15 mg/kg plus SEL-037 of 0.2 mg/kg), low dose (SEL-110 of 0.1 mg/kg plus SEL-037 of 0.2 mg/kg), or placebo (saline) infused every 28 days for 6 months. Prophylaxis against infusion reactions and gout flares were given to all participants.
Adult patients had a 10- to 14-year history of symptomatic gout, with three or more flares over the 18 months prior to screening, or one or more tophus, or a diagnosis of gouty arthritis. They were also required to have chronic refractory gout with a failure to normalize serum uric acid with any xanthine oxidase inhibitor (for example, allopurinol) and to have not been previously exposed to uricase-based therapy. Serum uric acid had to be at least 7 mg/dL. Participants were balanced for age, body mass index, and sex across treatment groups. Gout severity was greater in DISSOLVE II, Dr. Baraf reported.
Both studies treated patients for 6 months, but DISSOLVE 1 continued with a 6-month, blinded safety extension. The primary endpoint in both studies was serum urate control during month 6, and secondary endpoints included tender and swollen joint counts, tophus burden, patient-reported outcomes of activity limitation, quality of life, and gout flare incidence.
In DISSOLVE I, patients on SEL-212 had a statistically significant higher response rate during month 6 of 56% with the high dose (P < .0001) and 48% with the low dose (P < .0001), compared with 4% of patients randomized to receive placebo. In DISSOLVE II, participants on SEL-212 had a statistically significant higher response rate during month 6 of 46% with the high dose (P = .0002) and 40% with the low dose (P = .0008), compared with 11% of patients randomized to receive placebo.
“We also saw significant reductions in serum uric acid for all treatment groups, compared with placebo,” Dr. Baraf reported. Mean percentage change was –62.3% and –58.3% in the high- and low-dose groups, respectively, in DISSOLVE I, and –58.1% and –52.2% in DISSOLVE II, respectively.
SEL-212 had a favorable safety profile with adverse events as expected across both doses, including mild to moderate stomatitis (3.4% in the low-dose group and 9.2% in the high-dose group versus 0% in the placebo group), and a greater number of infusion reactions at 24 hours and 1 hour after drug administration in both treatment groups versus placebo. Six patients had treatment-related serious adverse events, including two cases of anaphylaxis and one gout flare in both the high- and low-dose treatment groups. The 6-month extension period in the DISSOLVE I trial showed that the majority (75%) of patients who completed 6 months of SEL-212 treatment as a responder continued to be successfully treated through 12 months with no infusion reactions or safety signals.
“I expect more data will be forthcoming on the important clinical secondary endpoints targeted by SEL-212 therapy,” Dr. Baraf noted.
Need control arm taking allopurinol?
Roy Fleischmann, MD, clinical professor of medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center and codirector of the Metroplex Clinical Research Center, both in Dallas, commented on the study methods after the presentation. “The major problem with this study is that they say the patients had had insufficient response to allopurinol, and my guess is most had received 100-200 mg of allopurinol but were not titrated up to the maximum tolerated dose,” he said, adding: “they should have had a control arm of patients on allopurinol and titrated to the maximum tolerated dose. So, I don’t know what this is really telling us with respect to allopurinol, which is a relatively cheap drug.”
Dr. Baraf reported consulting with Horizon, Sobi, and Selecta; serving on Horizon’s speakers bureau, and receiving grant/research support from Horizon and Sobi. Dr. Fleischmann reported no financial relationship of relevance to this study.
MILAN – Serum uric acid of less than 6 mg/dL was achieved and maintained for a substantial period of time with a once-monthly infusion of SEL-212 in patients with refractory gout, according to results of the two phase 3 DISSOLVE I and II trials.
Both trials met their primary endpoints. In DISSOLVE I – the U.S. study – 56% of patients on SEL-212 at 0.15 mg/kg (high dose) achieved a response, defined as achievement and maintenance of a reduction in serum urate to less than 6 mg/dL for at least 80% of the time during month 6 of treatment. In DISSOLVE II – the global study – 46% of patients on SEL-212 on the 0.15-mg/kg dose achieved response.
In participants aged 50 years or older, there was a statistically significant higher response rate at the high dose of SEL-212 in both DISSOLVE I and II of 65% and 47%, respectively, compared with placebo.
Herbert S.B. Baraf, MD, clinical professor of medicine at George Washington University, Washington, and principal investigator of the DISSOLVE program, presented results of the two phase 3 trials during a late-breaking session at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
“The top-line data from the two SEL-212 phase 3 studies are encouraging. They show that induction of immunotolerance with an infusion of a rapamycin-containing nanoparticle (SEL-110), followed immediately by an infusion of pegadricase, a potent but immunogenic uricase, allows for a strong and sustained uric acid–lowering effect without the development of anti-drug antibodies,” Dr. Baraf said in an interview.
SEL-212 is a monthly two-part infusion therapy – a combination of Selecta Biosciences’s ImmTOR immune tolerance platform, and a therapeutic uricase enzyme (pegadricase), designed to treat refractory gout. SEL-110 (ImmTOR) is an immune-tolerizing, nanoencapsulated rapamycin administered 30 minutes before pegadricase and inhibits anti-pegadricase antibodies. SEL-37 is a pegylated uricase (pegadricase) that converts uric acid to excretable allantoin.
SEL-212 was originally developed by Selecta. Swedish Orphan Biovitrum (Sobi) licensed SEL-212 from Selecta in June 2020 and is responsible for development, regulatory, and commercial activities in all markets outside of China. Selecta is responsible for ImmTOR manufacturing. The phase 3 program for SEL-212 was run by Selecta and funded by Sobi.
It is understood that a biologic license application will be submitted to the Food and Drug Administration, most likely next year, and if approved, “the SEL-212 two-component infusion treatment would provide a monthly alternative to twice-monthly pegloticase, for patients with refractory gout,” Dr. Baraf added.
Details of the trials
The two DISSOLVE studies replicate double-blind, placebo-controlled trials in patients with chronic refractory gout. DISSOLVE I was carried out in 112 patients across 29 sites in the United States, and DISSOLVE II tested the two-part treatment in 153 patients across 37 sites in the United States, Russia, Ukraine, Georgia, and Serbia.
Both studies randomized patients 1:1:1 to a high dose (SEL-110 of 0.15 mg/kg plus SEL-037 of 0.2 mg/kg), low dose (SEL-110 of 0.1 mg/kg plus SEL-037 of 0.2 mg/kg), or placebo (saline) infused every 28 days for 6 months. Prophylaxis against infusion reactions and gout flares were given to all participants.
Adult patients had a 10- to 14-year history of symptomatic gout, with three or more flares over the 18 months prior to screening, or one or more tophus, or a diagnosis of gouty arthritis. They were also required to have chronic refractory gout with a failure to normalize serum uric acid with any xanthine oxidase inhibitor (for example, allopurinol) and to have not been previously exposed to uricase-based therapy. Serum uric acid had to be at least 7 mg/dL. Participants were balanced for age, body mass index, and sex across treatment groups. Gout severity was greater in DISSOLVE II, Dr. Baraf reported.
Both studies treated patients for 6 months, but DISSOLVE 1 continued with a 6-month, blinded safety extension. The primary endpoint in both studies was serum urate control during month 6, and secondary endpoints included tender and swollen joint counts, tophus burden, patient-reported outcomes of activity limitation, quality of life, and gout flare incidence.
In DISSOLVE I, patients on SEL-212 had a statistically significant higher response rate during month 6 of 56% with the high dose (P < .0001) and 48% with the low dose (P < .0001), compared with 4% of patients randomized to receive placebo. In DISSOLVE II, participants on SEL-212 had a statistically significant higher response rate during month 6 of 46% with the high dose (P = .0002) and 40% with the low dose (P = .0008), compared with 11% of patients randomized to receive placebo.
“We also saw significant reductions in serum uric acid for all treatment groups, compared with placebo,” Dr. Baraf reported. Mean percentage change was –62.3% and –58.3% in the high- and low-dose groups, respectively, in DISSOLVE I, and –58.1% and –52.2% in DISSOLVE II, respectively.
SEL-212 had a favorable safety profile with adverse events as expected across both doses, including mild to moderate stomatitis (3.4% in the low-dose group and 9.2% in the high-dose group versus 0% in the placebo group), and a greater number of infusion reactions at 24 hours and 1 hour after drug administration in both treatment groups versus placebo. Six patients had treatment-related serious adverse events, including two cases of anaphylaxis and one gout flare in both the high- and low-dose treatment groups. The 6-month extension period in the DISSOLVE I trial showed that the majority (75%) of patients who completed 6 months of SEL-212 treatment as a responder continued to be successfully treated through 12 months with no infusion reactions or safety signals.
“I expect more data will be forthcoming on the important clinical secondary endpoints targeted by SEL-212 therapy,” Dr. Baraf noted.
Need control arm taking allopurinol?
Roy Fleischmann, MD, clinical professor of medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center and codirector of the Metroplex Clinical Research Center, both in Dallas, commented on the study methods after the presentation. “The major problem with this study is that they say the patients had had insufficient response to allopurinol, and my guess is most had received 100-200 mg of allopurinol but were not titrated up to the maximum tolerated dose,” he said, adding: “they should have had a control arm of patients on allopurinol and titrated to the maximum tolerated dose. So, I don’t know what this is really telling us with respect to allopurinol, which is a relatively cheap drug.”
Dr. Baraf reported consulting with Horizon, Sobi, and Selecta; serving on Horizon’s speakers bureau, and receiving grant/research support from Horizon and Sobi. Dr. Fleischmann reported no financial relationship of relevance to this study.
MILAN – Serum uric acid of less than 6 mg/dL was achieved and maintained for a substantial period of time with a once-monthly infusion of SEL-212 in patients with refractory gout, according to results of the two phase 3 DISSOLVE I and II trials.
Both trials met their primary endpoints. In DISSOLVE I – the U.S. study – 56% of patients on SEL-212 at 0.15 mg/kg (high dose) achieved a response, defined as achievement and maintenance of a reduction in serum urate to less than 6 mg/dL for at least 80% of the time during month 6 of treatment. In DISSOLVE II – the global study – 46% of patients on SEL-212 on the 0.15-mg/kg dose achieved response.
In participants aged 50 years or older, there was a statistically significant higher response rate at the high dose of SEL-212 in both DISSOLVE I and II of 65% and 47%, respectively, compared with placebo.
Herbert S.B. Baraf, MD, clinical professor of medicine at George Washington University, Washington, and principal investigator of the DISSOLVE program, presented results of the two phase 3 trials during a late-breaking session at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
“The top-line data from the two SEL-212 phase 3 studies are encouraging. They show that induction of immunotolerance with an infusion of a rapamycin-containing nanoparticle (SEL-110), followed immediately by an infusion of pegadricase, a potent but immunogenic uricase, allows for a strong and sustained uric acid–lowering effect without the development of anti-drug antibodies,” Dr. Baraf said in an interview.
SEL-212 is a monthly two-part infusion therapy – a combination of Selecta Biosciences’s ImmTOR immune tolerance platform, and a therapeutic uricase enzyme (pegadricase), designed to treat refractory gout. SEL-110 (ImmTOR) is an immune-tolerizing, nanoencapsulated rapamycin administered 30 minutes before pegadricase and inhibits anti-pegadricase antibodies. SEL-37 is a pegylated uricase (pegadricase) that converts uric acid to excretable allantoin.
SEL-212 was originally developed by Selecta. Swedish Orphan Biovitrum (Sobi) licensed SEL-212 from Selecta in June 2020 and is responsible for development, regulatory, and commercial activities in all markets outside of China. Selecta is responsible for ImmTOR manufacturing. The phase 3 program for SEL-212 was run by Selecta and funded by Sobi.
It is understood that a biologic license application will be submitted to the Food and Drug Administration, most likely next year, and if approved, “the SEL-212 two-component infusion treatment would provide a monthly alternative to twice-monthly pegloticase, for patients with refractory gout,” Dr. Baraf added.
Details of the trials
The two DISSOLVE studies replicate double-blind, placebo-controlled trials in patients with chronic refractory gout. DISSOLVE I was carried out in 112 patients across 29 sites in the United States, and DISSOLVE II tested the two-part treatment in 153 patients across 37 sites in the United States, Russia, Ukraine, Georgia, and Serbia.
Both studies randomized patients 1:1:1 to a high dose (SEL-110 of 0.15 mg/kg plus SEL-037 of 0.2 mg/kg), low dose (SEL-110 of 0.1 mg/kg plus SEL-037 of 0.2 mg/kg), or placebo (saline) infused every 28 days for 6 months. Prophylaxis against infusion reactions and gout flares were given to all participants.
Adult patients had a 10- to 14-year history of symptomatic gout, with three or more flares over the 18 months prior to screening, or one or more tophus, or a diagnosis of gouty arthritis. They were also required to have chronic refractory gout with a failure to normalize serum uric acid with any xanthine oxidase inhibitor (for example, allopurinol) and to have not been previously exposed to uricase-based therapy. Serum uric acid had to be at least 7 mg/dL. Participants were balanced for age, body mass index, and sex across treatment groups. Gout severity was greater in DISSOLVE II, Dr. Baraf reported.
Both studies treated patients for 6 months, but DISSOLVE 1 continued with a 6-month, blinded safety extension. The primary endpoint in both studies was serum urate control during month 6, and secondary endpoints included tender and swollen joint counts, tophus burden, patient-reported outcomes of activity limitation, quality of life, and gout flare incidence.
In DISSOLVE I, patients on SEL-212 had a statistically significant higher response rate during month 6 of 56% with the high dose (P < .0001) and 48% with the low dose (P < .0001), compared with 4% of patients randomized to receive placebo. In DISSOLVE II, participants on SEL-212 had a statistically significant higher response rate during month 6 of 46% with the high dose (P = .0002) and 40% with the low dose (P = .0008), compared with 11% of patients randomized to receive placebo.
“We also saw significant reductions in serum uric acid for all treatment groups, compared with placebo,” Dr. Baraf reported. Mean percentage change was –62.3% and –58.3% in the high- and low-dose groups, respectively, in DISSOLVE I, and –58.1% and –52.2% in DISSOLVE II, respectively.
SEL-212 had a favorable safety profile with adverse events as expected across both doses, including mild to moderate stomatitis (3.4% in the low-dose group and 9.2% in the high-dose group versus 0% in the placebo group), and a greater number of infusion reactions at 24 hours and 1 hour after drug administration in both treatment groups versus placebo. Six patients had treatment-related serious adverse events, including two cases of anaphylaxis and one gout flare in both the high- and low-dose treatment groups. The 6-month extension period in the DISSOLVE I trial showed that the majority (75%) of patients who completed 6 months of SEL-212 treatment as a responder continued to be successfully treated through 12 months with no infusion reactions or safety signals.
“I expect more data will be forthcoming on the important clinical secondary endpoints targeted by SEL-212 therapy,” Dr. Baraf noted.
Need control arm taking allopurinol?
Roy Fleischmann, MD, clinical professor of medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center and codirector of the Metroplex Clinical Research Center, both in Dallas, commented on the study methods after the presentation. “The major problem with this study is that they say the patients had had insufficient response to allopurinol, and my guess is most had received 100-200 mg of allopurinol but were not titrated up to the maximum tolerated dose,” he said, adding: “they should have had a control arm of patients on allopurinol and titrated to the maximum tolerated dose. So, I don’t know what this is really telling us with respect to allopurinol, which is a relatively cheap drug.”
Dr. Baraf reported consulting with Horizon, Sobi, and Selecta; serving on Horizon’s speakers bureau, and receiving grant/research support from Horizon and Sobi. Dr. Fleischmann reported no financial relationship of relevance to this study.
AT EULAR 2023
URAT1 inhibitor shows ‘substantial’ uric acid reduction in phase 2 gout trial
MILAN – About 80% of patients with gout who took the investigational selective uric acid transporter 1 (URAT1) inhibitor AR882 over 3 months reduced their serum uric acid levels to below recommended thresholds (below 5 or 4 mg/dL) for better flare and tophi reduction in a phase 2b study.
The drug was well tolerated, and patients with comorbidities did not require any adjustments in disease management.
At 75 mg, the highest tested dose of AR882, 73% of patients had serum uric acid levels < 5 mg/dL and 55% had < 4 mg/dL by week 12 of therapy in the intent-to-treat population, whereas in the per-protocol analysis, 82% had serum uric acid levels < 5 mg/dL and 63% < 4 mg/dL.
“These efficacy results are not typically what you see with a once-daily oral medication, so it is really exciting,” Robert Keenan, MD, chief medical officer of Arthrosi Therapeutics, San Diego, said in presenting the results at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
“Regardless of whether you’re treating subclinical, hidden crystal deposition, versus clinically visible tophi, versus chronic, debilitating gout, we believe that AR882 has the potential to treat the entire gout spectrum with a once-daily monotherapy,” Dr. Keenan asserted.
“Currently, most gout patients around the world do not have a safe, effective, and easy to use alternative to allopurinol or febuxostat, which decrease the production of uric acid,” he said. “AR882 is a URAT1 inhibitor that goes to the root of the problem in over 90% of gout patients, helping the kidneys eliminate uric acid to levels similar to all those without hyperuricemia and gout.”
Abhishek Abhishek, MD, professor of rheumatology at the University of Nottingham (England), welcomed the study. “It’s a promising study and the reduction in uric acid was substantial. It was a small study and a larger phase 3 study is needed, but it does offer real hope for patients with gout as a third treatment option because we only have allopurinol and febuxostat, so if it is shown efficacious and safe and gets approved, then it’ll help more patients with gout.”
Anne-Kathrin Tausche, MD, a rheumatologist from University Clinic Dresden (Germany), said: “These results are really impressive. We’ve lost lesinurad now because Grünenthal no longer produces it, so this might be a good alternative for patients with severe gout.
“It is favorable with [few] side effects. With allopurinol, we have to titrate it in patients with poor renal function, but it doesn’t seem to be the case with this drug. I really hope they start phase 3 soon,” she added.
Phase 2 study, but promising results
Results of the global phase 2b, randomized, double-blind trial compared the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of AR882 against placebo in patients with gout.
A total of 140 patients with gout, aged 18-75 years with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) > 30 mL/min, were recruited across the United States, Australia, and Taiwan. Patients received either once-daily AR882 50 mg (n = 46) for 12 weeks, AR882 50 mg for 2 weeks and then AR882 75 mg (n = 47) for 10 weeks, or matching placebo for 12 weeks (n = 47). Flare prophylaxis with daily colchicine started 10 days prior to the first dose and continued throughout the study.
“Patient characteristics were typical for gout trials except for having a very diverse population,” he said. The trial included 57.9% White, 27.9% Asian, and 15% Black patients. They had a mean age of 55 years, body mass index 31-32 kg/m2. There was a range of comorbidities including hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, evenly distributed across placebo and AR882 treatment groups.
The efficacy endpoints were the proportion of patients who reached serum uric acid below 6, 5, 4, and 3 mg/dL, at 6 weeks of therapy, while safety was also monitored throughout the study. Reductions in serum uric acid at weeks 2, 4, 6, 12 were exploratory endpoints.
The primary endpoint of the percentage of patients below < 6 mg/dL at 6 weeks in the intent-to-treat population was met by 66% with AR882 at the lower dose (50 mg) and 84% at the higher dose (75 mg).
With the 50-mg dose, serum uric acid was reduced at week 6 to < 5mg/dL by 41%, < 4mg/dL by 12%, and < 3mg/dL by 2%, whereas these percentages were 68%, 52%, and 23%, respectively, with the 75-mg dose.
Exploratory endpoints showed that by week 12, serum uric acid levels dropped from baseline 8.6 mg/dL to about 5.0 mg/dL with AR882 50 mg and from baseline 8.6 mg/dL to about 3.5 mg/dL with AR882 75 mg. Also at week 12, 55% and 23% reached serum uric acid levels of < 4mg/dL and < 3mg/dL in the intent-to-treat population. No change was observed in the placebo group.
All adverse events were mild to moderate, with the most prevalent being gout flares. There was little difference between doses. There were no clinically significant changes in a total of 778 post-dose measurements of alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) and 723 post-dose triplicated electrocardiogram (ECG) measurements.
Dr. Keenan is chief medical officer of Arthrosi Therapeutics. Dr. Tausche and Dr. Abhishek have no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
MILAN – About 80% of patients with gout who took the investigational selective uric acid transporter 1 (URAT1) inhibitor AR882 over 3 months reduced their serum uric acid levels to below recommended thresholds (below 5 or 4 mg/dL) for better flare and tophi reduction in a phase 2b study.
The drug was well tolerated, and patients with comorbidities did not require any adjustments in disease management.
At 75 mg, the highest tested dose of AR882, 73% of patients had serum uric acid levels < 5 mg/dL and 55% had < 4 mg/dL by week 12 of therapy in the intent-to-treat population, whereas in the per-protocol analysis, 82% had serum uric acid levels < 5 mg/dL and 63% < 4 mg/dL.
“These efficacy results are not typically what you see with a once-daily oral medication, so it is really exciting,” Robert Keenan, MD, chief medical officer of Arthrosi Therapeutics, San Diego, said in presenting the results at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
“Regardless of whether you’re treating subclinical, hidden crystal deposition, versus clinically visible tophi, versus chronic, debilitating gout, we believe that AR882 has the potential to treat the entire gout spectrum with a once-daily monotherapy,” Dr. Keenan asserted.
“Currently, most gout patients around the world do not have a safe, effective, and easy to use alternative to allopurinol or febuxostat, which decrease the production of uric acid,” he said. “AR882 is a URAT1 inhibitor that goes to the root of the problem in over 90% of gout patients, helping the kidneys eliminate uric acid to levels similar to all those without hyperuricemia and gout.”
Abhishek Abhishek, MD, professor of rheumatology at the University of Nottingham (England), welcomed the study. “It’s a promising study and the reduction in uric acid was substantial. It was a small study and a larger phase 3 study is needed, but it does offer real hope for patients with gout as a third treatment option because we only have allopurinol and febuxostat, so if it is shown efficacious and safe and gets approved, then it’ll help more patients with gout.”
Anne-Kathrin Tausche, MD, a rheumatologist from University Clinic Dresden (Germany), said: “These results are really impressive. We’ve lost lesinurad now because Grünenthal no longer produces it, so this might be a good alternative for patients with severe gout.
“It is favorable with [few] side effects. With allopurinol, we have to titrate it in patients with poor renal function, but it doesn’t seem to be the case with this drug. I really hope they start phase 3 soon,” she added.
Phase 2 study, but promising results
Results of the global phase 2b, randomized, double-blind trial compared the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of AR882 against placebo in patients with gout.
A total of 140 patients with gout, aged 18-75 years with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) > 30 mL/min, were recruited across the United States, Australia, and Taiwan. Patients received either once-daily AR882 50 mg (n = 46) for 12 weeks, AR882 50 mg for 2 weeks and then AR882 75 mg (n = 47) for 10 weeks, or matching placebo for 12 weeks (n = 47). Flare prophylaxis with daily colchicine started 10 days prior to the first dose and continued throughout the study.
“Patient characteristics were typical for gout trials except for having a very diverse population,” he said. The trial included 57.9% White, 27.9% Asian, and 15% Black patients. They had a mean age of 55 years, body mass index 31-32 kg/m2. There was a range of comorbidities including hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, evenly distributed across placebo and AR882 treatment groups.
The efficacy endpoints were the proportion of patients who reached serum uric acid below 6, 5, 4, and 3 mg/dL, at 6 weeks of therapy, while safety was also monitored throughout the study. Reductions in serum uric acid at weeks 2, 4, 6, 12 were exploratory endpoints.
The primary endpoint of the percentage of patients below < 6 mg/dL at 6 weeks in the intent-to-treat population was met by 66% with AR882 at the lower dose (50 mg) and 84% at the higher dose (75 mg).
With the 50-mg dose, serum uric acid was reduced at week 6 to < 5mg/dL by 41%, < 4mg/dL by 12%, and < 3mg/dL by 2%, whereas these percentages were 68%, 52%, and 23%, respectively, with the 75-mg dose.
Exploratory endpoints showed that by week 12, serum uric acid levels dropped from baseline 8.6 mg/dL to about 5.0 mg/dL with AR882 50 mg and from baseline 8.6 mg/dL to about 3.5 mg/dL with AR882 75 mg. Also at week 12, 55% and 23% reached serum uric acid levels of < 4mg/dL and < 3mg/dL in the intent-to-treat population. No change was observed in the placebo group.
All adverse events were mild to moderate, with the most prevalent being gout flares. There was little difference between doses. There were no clinically significant changes in a total of 778 post-dose measurements of alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) and 723 post-dose triplicated electrocardiogram (ECG) measurements.
Dr. Keenan is chief medical officer of Arthrosi Therapeutics. Dr. Tausche and Dr. Abhishek have no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
MILAN – About 80% of patients with gout who took the investigational selective uric acid transporter 1 (URAT1) inhibitor AR882 over 3 months reduced their serum uric acid levels to below recommended thresholds (below 5 or 4 mg/dL) for better flare and tophi reduction in a phase 2b study.
The drug was well tolerated, and patients with comorbidities did not require any adjustments in disease management.
At 75 mg, the highest tested dose of AR882, 73% of patients had serum uric acid levels < 5 mg/dL and 55% had < 4 mg/dL by week 12 of therapy in the intent-to-treat population, whereas in the per-protocol analysis, 82% had serum uric acid levels < 5 mg/dL and 63% < 4 mg/dL.
“These efficacy results are not typically what you see with a once-daily oral medication, so it is really exciting,” Robert Keenan, MD, chief medical officer of Arthrosi Therapeutics, San Diego, said in presenting the results at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
“Regardless of whether you’re treating subclinical, hidden crystal deposition, versus clinically visible tophi, versus chronic, debilitating gout, we believe that AR882 has the potential to treat the entire gout spectrum with a once-daily monotherapy,” Dr. Keenan asserted.
“Currently, most gout patients around the world do not have a safe, effective, and easy to use alternative to allopurinol or febuxostat, which decrease the production of uric acid,” he said. “AR882 is a URAT1 inhibitor that goes to the root of the problem in over 90% of gout patients, helping the kidneys eliminate uric acid to levels similar to all those without hyperuricemia and gout.”
Abhishek Abhishek, MD, professor of rheumatology at the University of Nottingham (England), welcomed the study. “It’s a promising study and the reduction in uric acid was substantial. It was a small study and a larger phase 3 study is needed, but it does offer real hope for patients with gout as a third treatment option because we only have allopurinol and febuxostat, so if it is shown efficacious and safe and gets approved, then it’ll help more patients with gout.”
Anne-Kathrin Tausche, MD, a rheumatologist from University Clinic Dresden (Germany), said: “These results are really impressive. We’ve lost lesinurad now because Grünenthal no longer produces it, so this might be a good alternative for patients with severe gout.
“It is favorable with [few] side effects. With allopurinol, we have to titrate it in patients with poor renal function, but it doesn’t seem to be the case with this drug. I really hope they start phase 3 soon,” she added.
Phase 2 study, but promising results
Results of the global phase 2b, randomized, double-blind trial compared the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of AR882 against placebo in patients with gout.
A total of 140 patients with gout, aged 18-75 years with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) > 30 mL/min, were recruited across the United States, Australia, and Taiwan. Patients received either once-daily AR882 50 mg (n = 46) for 12 weeks, AR882 50 mg for 2 weeks and then AR882 75 mg (n = 47) for 10 weeks, or matching placebo for 12 weeks (n = 47). Flare prophylaxis with daily colchicine started 10 days prior to the first dose and continued throughout the study.
“Patient characteristics were typical for gout trials except for having a very diverse population,” he said. The trial included 57.9% White, 27.9% Asian, and 15% Black patients. They had a mean age of 55 years, body mass index 31-32 kg/m2. There was a range of comorbidities including hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, evenly distributed across placebo and AR882 treatment groups.
The efficacy endpoints were the proportion of patients who reached serum uric acid below 6, 5, 4, and 3 mg/dL, at 6 weeks of therapy, while safety was also monitored throughout the study. Reductions in serum uric acid at weeks 2, 4, 6, 12 were exploratory endpoints.
The primary endpoint of the percentage of patients below < 6 mg/dL at 6 weeks in the intent-to-treat population was met by 66% with AR882 at the lower dose (50 mg) and 84% at the higher dose (75 mg).
With the 50-mg dose, serum uric acid was reduced at week 6 to < 5mg/dL by 41%, < 4mg/dL by 12%, and < 3mg/dL by 2%, whereas these percentages were 68%, 52%, and 23%, respectively, with the 75-mg dose.
Exploratory endpoints showed that by week 12, serum uric acid levels dropped from baseline 8.6 mg/dL to about 5.0 mg/dL with AR882 50 mg and from baseline 8.6 mg/dL to about 3.5 mg/dL with AR882 75 mg. Also at week 12, 55% and 23% reached serum uric acid levels of < 4mg/dL and < 3mg/dL in the intent-to-treat population. No change was observed in the placebo group.
All adverse events were mild to moderate, with the most prevalent being gout flares. There was little difference between doses. There were no clinically significant changes in a total of 778 post-dose measurements of alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) and 723 post-dose triplicated electrocardiogram (ECG) measurements.
Dr. Keenan is chief medical officer of Arthrosi Therapeutics. Dr. Tausche and Dr. Abhishek have no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
AT EULAR 2023
Colchicine’s 2010 price spike had major impact on gout care
A large price increase for colchicine in 2010 led to a significant falloff in its use for gout that persisted for the next decade while emergency and rheumatology visits for gout rose, suggesting poorer disease control, a retrospective cohort study reported.
The price of colchicine, commonly prescribed for acute gout attacks, climbed from $11.25 per prescription in 2009 to $190.49 in 2011, with the average out-of-pocket cost more than quadrupling, from $7.37 to $29.42, the study noted. Colchicine prescriptions for gout declined 27% over the next decade, according to adjusted analyses that the study authors performed.
“A roughly 16-fold increase in colchicine prices appeared to have lowered colchicine use over the next decade,” senior author Zirui Song, MD, PhD, an associate professor of health care policy and medicine at Harvard Medical School and an internist at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, told this news organization in written comments. “Over the same period, patients with gout used more of other medications that could treat gout. They also had more emergency department visits for gout and rheumatologist visits for gout, which potentially signals poorer disease control.”
The study, published online in JAMA Internal Medicine, examined MarketScan data from a longitudinal cohort of patients who had employer-sponsored health insurance and a diagnosis of gout from 2007 to 2019. MarketScan is an IBM database of medical and drug data from employers and health plans. The study examined more than 2.7 million patient-year observations over the 13-year period.
How the price increase happened
After 2011, a large percentage of patients shifted to less effective but more affordable drugs to treat gout. Prescriptions for allopurinol increased 32% (P < .001) and oral corticosteroids 8.3% over the decade. “These are imperfect substitutes,” Dr. Song said. “Allopurinol is used to prevent gout, while oral corticosteroids can be used to treat a gout flare.”
At the same time, visits for gout-related complaints to emergency departments and rheumatology offices increased through the ensuing years: 39.8% and 10.5% on an adjusted analysis, respectively (P < .001 for both).
Colchicine is actually a drug that predates the creation of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 1938 and had been grandfathered under its Unapproved Drug Initiative. Then in 2009, the FDA determined that colchicine was effective for treating arthritis-related gout flares after the manufacturer, URL Pharma, presented results of a randomized, controlled trial of 185 patients with gout.
The next year, the FDA granted URL Pharma 3 years of market exclusivity for the drug under the brand name Colcrys, now trademarked by Takeda Pharmaceuticals.
The latest study noted that longer-term analysis of the impact of the FDA’s decision had been lacking. The goal, said Dr. Song, was “to better understand the long-run implications of large drug price increases in the U.S. by studying the case of colchicine.”
He added, “For drugs that lack competition, large price increases can have large economic and clinical consequences over many years.”
Absorbing the cost
Lead author Dan P. Ly, MD, PhD, MPP, assistant professor at the University of California, Los Angeles, added, “Our study has large implications [for] when generic medications or other medications experience large price increases. Use of the medication in question drops or patients have to pay more out of pocket, and patient health can suffer as a result.”
The dropoff in colchicine use in this patient population could have been worse, Dr. Song said. “Despite colchicine use decreasing by 27% over nearly a decade, the fact that it did not decline more suggests that for patients with gout, the large price increase was mostly absorbed by their insurers, employers, or themselves – e.g., passed through to higher premiums, lower wages, or higher cost-sharing.”
Aaron Kesselheim, MD, JD, MPH, a professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, reported previously on the price consequences of colchicine early on after the FDA granted the manufacturer market exclusivity.
“In our past research, we looked at how the massive increase in the price of colchicine increased spending on the drug and reduced use in a relatively short time period after the price hike,” said Dr. Kesselheim, who was not involved in this current study by Dr. Ly, Dr. Song, and Mia Giuriato, BBA, MA, from Harvard Medical School. “This study evaluated the experiences of patients with gout over multiple years and showed that the reductions in use persisted and were associated with increases in ED and rheumatology visits, suggesting worsening control of gout due to the relative inaccessibility of the drug at the new high price.”
The latest findings have public policy implications, Dr. Kesselheim said. “In the case of colchicine, the FDA made a bad pitch, leading to a home run for the manufacturer and a shutout for patients.”
“The FDA needs to make sure to take into account the quite predictable patient effects that can result from disruptions to competition when it considers taking steps like it did in the colchicine case to disrupt the market and create an artificial monopoly, even if the FDA acted in the best of intentions in this case,” Dr. Kesselheim added.
Dr. Song received funding for the study from the National Institutes of Health and Arnold Ventures. He also disclosed receiving personal fees from the Research Triangle Institute, Google Ventures, VBID Health, and the International Foundation of Employee Benefit Plans. Dr. Ly, Ms. Giuriato, and Dr. Kesselheim report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A large price increase for colchicine in 2010 led to a significant falloff in its use for gout that persisted for the next decade while emergency and rheumatology visits for gout rose, suggesting poorer disease control, a retrospective cohort study reported.
The price of colchicine, commonly prescribed for acute gout attacks, climbed from $11.25 per prescription in 2009 to $190.49 in 2011, with the average out-of-pocket cost more than quadrupling, from $7.37 to $29.42, the study noted. Colchicine prescriptions for gout declined 27% over the next decade, according to adjusted analyses that the study authors performed.
“A roughly 16-fold increase in colchicine prices appeared to have lowered colchicine use over the next decade,” senior author Zirui Song, MD, PhD, an associate professor of health care policy and medicine at Harvard Medical School and an internist at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, told this news organization in written comments. “Over the same period, patients with gout used more of other medications that could treat gout. They also had more emergency department visits for gout and rheumatologist visits for gout, which potentially signals poorer disease control.”
The study, published online in JAMA Internal Medicine, examined MarketScan data from a longitudinal cohort of patients who had employer-sponsored health insurance and a diagnosis of gout from 2007 to 2019. MarketScan is an IBM database of medical and drug data from employers and health plans. The study examined more than 2.7 million patient-year observations over the 13-year period.
How the price increase happened
After 2011, a large percentage of patients shifted to less effective but more affordable drugs to treat gout. Prescriptions for allopurinol increased 32% (P < .001) and oral corticosteroids 8.3% over the decade. “These are imperfect substitutes,” Dr. Song said. “Allopurinol is used to prevent gout, while oral corticosteroids can be used to treat a gout flare.”
At the same time, visits for gout-related complaints to emergency departments and rheumatology offices increased through the ensuing years: 39.8% and 10.5% on an adjusted analysis, respectively (P < .001 for both).
Colchicine is actually a drug that predates the creation of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 1938 and had been grandfathered under its Unapproved Drug Initiative. Then in 2009, the FDA determined that colchicine was effective for treating arthritis-related gout flares after the manufacturer, URL Pharma, presented results of a randomized, controlled trial of 185 patients with gout.
The next year, the FDA granted URL Pharma 3 years of market exclusivity for the drug under the brand name Colcrys, now trademarked by Takeda Pharmaceuticals.
The latest study noted that longer-term analysis of the impact of the FDA’s decision had been lacking. The goal, said Dr. Song, was “to better understand the long-run implications of large drug price increases in the U.S. by studying the case of colchicine.”
He added, “For drugs that lack competition, large price increases can have large economic and clinical consequences over many years.”
Absorbing the cost
Lead author Dan P. Ly, MD, PhD, MPP, assistant professor at the University of California, Los Angeles, added, “Our study has large implications [for] when generic medications or other medications experience large price increases. Use of the medication in question drops or patients have to pay more out of pocket, and patient health can suffer as a result.”
The dropoff in colchicine use in this patient population could have been worse, Dr. Song said. “Despite colchicine use decreasing by 27% over nearly a decade, the fact that it did not decline more suggests that for patients with gout, the large price increase was mostly absorbed by their insurers, employers, or themselves – e.g., passed through to higher premiums, lower wages, or higher cost-sharing.”
Aaron Kesselheim, MD, JD, MPH, a professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, reported previously on the price consequences of colchicine early on after the FDA granted the manufacturer market exclusivity.
“In our past research, we looked at how the massive increase in the price of colchicine increased spending on the drug and reduced use in a relatively short time period after the price hike,” said Dr. Kesselheim, who was not involved in this current study by Dr. Ly, Dr. Song, and Mia Giuriato, BBA, MA, from Harvard Medical School. “This study evaluated the experiences of patients with gout over multiple years and showed that the reductions in use persisted and were associated with increases in ED and rheumatology visits, suggesting worsening control of gout due to the relative inaccessibility of the drug at the new high price.”
The latest findings have public policy implications, Dr. Kesselheim said. “In the case of colchicine, the FDA made a bad pitch, leading to a home run for the manufacturer and a shutout for patients.”
“The FDA needs to make sure to take into account the quite predictable patient effects that can result from disruptions to competition when it considers taking steps like it did in the colchicine case to disrupt the market and create an artificial monopoly, even if the FDA acted in the best of intentions in this case,” Dr. Kesselheim added.
Dr. Song received funding for the study from the National Institutes of Health and Arnold Ventures. He also disclosed receiving personal fees from the Research Triangle Institute, Google Ventures, VBID Health, and the International Foundation of Employee Benefit Plans. Dr. Ly, Ms. Giuriato, and Dr. Kesselheim report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A large price increase for colchicine in 2010 led to a significant falloff in its use for gout that persisted for the next decade while emergency and rheumatology visits for gout rose, suggesting poorer disease control, a retrospective cohort study reported.
The price of colchicine, commonly prescribed for acute gout attacks, climbed from $11.25 per prescription in 2009 to $190.49 in 2011, with the average out-of-pocket cost more than quadrupling, from $7.37 to $29.42, the study noted. Colchicine prescriptions for gout declined 27% over the next decade, according to adjusted analyses that the study authors performed.
“A roughly 16-fold increase in colchicine prices appeared to have lowered colchicine use over the next decade,” senior author Zirui Song, MD, PhD, an associate professor of health care policy and medicine at Harvard Medical School and an internist at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, told this news organization in written comments. “Over the same period, patients with gout used more of other medications that could treat gout. They also had more emergency department visits for gout and rheumatologist visits for gout, which potentially signals poorer disease control.”
The study, published online in JAMA Internal Medicine, examined MarketScan data from a longitudinal cohort of patients who had employer-sponsored health insurance and a diagnosis of gout from 2007 to 2019. MarketScan is an IBM database of medical and drug data from employers and health plans. The study examined more than 2.7 million patient-year observations over the 13-year period.
How the price increase happened
After 2011, a large percentage of patients shifted to less effective but more affordable drugs to treat gout. Prescriptions for allopurinol increased 32% (P < .001) and oral corticosteroids 8.3% over the decade. “These are imperfect substitutes,” Dr. Song said. “Allopurinol is used to prevent gout, while oral corticosteroids can be used to treat a gout flare.”
At the same time, visits for gout-related complaints to emergency departments and rheumatology offices increased through the ensuing years: 39.8% and 10.5% on an adjusted analysis, respectively (P < .001 for both).
Colchicine is actually a drug that predates the creation of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 1938 and had been grandfathered under its Unapproved Drug Initiative. Then in 2009, the FDA determined that colchicine was effective for treating arthritis-related gout flares after the manufacturer, URL Pharma, presented results of a randomized, controlled trial of 185 patients with gout.
The next year, the FDA granted URL Pharma 3 years of market exclusivity for the drug under the brand name Colcrys, now trademarked by Takeda Pharmaceuticals.
The latest study noted that longer-term analysis of the impact of the FDA’s decision had been lacking. The goal, said Dr. Song, was “to better understand the long-run implications of large drug price increases in the U.S. by studying the case of colchicine.”
He added, “For drugs that lack competition, large price increases can have large economic and clinical consequences over many years.”
Absorbing the cost
Lead author Dan P. Ly, MD, PhD, MPP, assistant professor at the University of California, Los Angeles, added, “Our study has large implications [for] when generic medications or other medications experience large price increases. Use of the medication in question drops or patients have to pay more out of pocket, and patient health can suffer as a result.”
The dropoff in colchicine use in this patient population could have been worse, Dr. Song said. “Despite colchicine use decreasing by 27% over nearly a decade, the fact that it did not decline more suggests that for patients with gout, the large price increase was mostly absorbed by their insurers, employers, or themselves – e.g., passed through to higher premiums, lower wages, or higher cost-sharing.”
Aaron Kesselheim, MD, JD, MPH, a professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, reported previously on the price consequences of colchicine early on after the FDA granted the manufacturer market exclusivity.
“In our past research, we looked at how the massive increase in the price of colchicine increased spending on the drug and reduced use in a relatively short time period after the price hike,” said Dr. Kesselheim, who was not involved in this current study by Dr. Ly, Dr. Song, and Mia Giuriato, BBA, MA, from Harvard Medical School. “This study evaluated the experiences of patients with gout over multiple years and showed that the reductions in use persisted and were associated with increases in ED and rheumatology visits, suggesting worsening control of gout due to the relative inaccessibility of the drug at the new high price.”
The latest findings have public policy implications, Dr. Kesselheim said. “In the case of colchicine, the FDA made a bad pitch, leading to a home run for the manufacturer and a shutout for patients.”
“The FDA needs to make sure to take into account the quite predictable patient effects that can result from disruptions to competition when it considers taking steps like it did in the colchicine case to disrupt the market and create an artificial monopoly, even if the FDA acted in the best of intentions in this case,” Dr. Kesselheim added.
Dr. Song received funding for the study from the National Institutes of Health and Arnold Ventures. He also disclosed receiving personal fees from the Research Triangle Institute, Google Ventures, VBID Health, and the International Foundation of Employee Benefit Plans. Dr. Ly, Ms. Giuriato, and Dr. Kesselheim report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Care for patients with gout needs improvement, says doctor
said a presenter at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians. Failure to understand the disease process and goals of urate-lowering therapy (ULT) is a key barrier to achieving optimal gout therapy.
“There’s too much focus on the flare and too little focus on the urate burden of the disease. Regardless of the clinical setting, the goal should be to manage [high] serum uric acid levels,” said Lawrence Edwards, MD, professor at the University of Florida, Gainesville, during his talk.
Dr. Edwards, who specializes in treating patients with gout and rheumatoid arthritis, discussed the role of primary care providers in the treatment of gout. “We can and must do better,” he said.
Understanding the pathology of gout is key to effective treatment
Knowledge of the molecular pathology of gout has advanced drastically over the last few years. “The improved understanding of the molecules involved in disease initiation and progression can help us make better treatment decisions depending on the stage of the disease,” Dr. Edwards said.
Gout is caused by the deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals, which starts as asymptomatic hyperuricemia, he said. Inflammatory responses to MSU crystals are responsible for gout flares, the frequency of which increases as the disease progresses.
Innate immune responses driven by macrophages and neutrophils play a crucial role in acute gout attacks. In the molecular pathway, proinflammatory cytokines IL-1 beta and IL-6 are the mediators of gout flares, whereas IL-8 accumulates over time and contributes to disease progression and systemic illness. If left untreated or undertreated, the repeated inflammatory reaction leads to advanced gout. The urate burden also increases with disease progression.
“Physicians need to better educate themselves on the destructive nature of this inflammatory arthritis and the need for effective urate-lowering therapy in the management of gout,” Dr. Edwards said.
Management of acute gout attacks
The management of gout flares involves the use of pharmacological agents to control pain and inflammation. The three most common anti-inflammatory therapies are colchicine, NSAIDs, and corticosteroids (either oral or intramuscular).
The choice of which of these should be used alone or in combination for a flare is based on previous tolerance of the medication or the presence of diabetes, kidney disease, heart disease, or a history of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Dr. Edwards referred internists to the 2020 American College of Rheumatology gout management guideline.
“Regardless of which therapy is chosen, the more important consideration is how quickly the patients can start treatment after the flare begins,” said Dr. Edwards when asked about priorities in the management of gout flares. “This means that the patient should have ready access to whichever the chosen approach is. We call this the ‘pill-in-the-pocket’ approach,” he added.
Reducing the urate burden is also important for effective treatment. The serum urate level is the primary marker of how well a patient’s gout is being managed. ULT should be initiated in patients with subcutaneous tophi, gout-related radiographic damage, or frequent flares (≥ 2 per year). Allopurinol is typically the first-line ULT of choice.
Dr. Edwards noted that far too much focus is placed on flare treatment rather than addressing the underlying sources of gouty symptoms – the elevated serum levels of urate.
Management of advanced gout
“The management of advanced gout is challenging, and the dissolution of MSU is slow unless you take an aggressive approach,” Dr. Edwards said.
Switching to pegloticase is recommended for patients with frequent flares, nonresolving tophi, or high serum urate levels that persist despite treatment with xanthine oxidase inhibitors or other ULT agents.
“The frequency and severity of gout flares are what patients focus on, but if that’s the only focus of the treating physicians, then they are leaving the job less than halfway done. Getting the serum urate to below a level of 6.0 mg/dL is the most important aspect in the lifelong management of gout,” said Dr. Edwards.
Barriers to effective gout treatment
When asked during an interview after the session about the most important barriers to successful gout management, Allison M. Mays, MD, a geriatric medicine subspecialist at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said that “the fact that gout mostly impacts quality of life and not necessarily mortality means that other things may take precedent.” She explained that gout typically coexists with other comorbidities, often multiple ones. Patients may also defer taking an additional medication for a disease like gout, which has only episodic discomfort.
She added that gout management involves shared decision-making between patients and the medical team – including the primary care physician, rheumatologist, orthopedist, and emergency physician. Following a visit to the urgent care or the ED for an acute flare of gout, the patient may not follow up with their primary care doctor or bring it up at their next visit for chronic management, she noted.
Dr. Edwards serves as a consultant to Horizon Pharmaceuticals, Atom Biosciences, Shanton Biosciences, and Aclaris Therapeutics. Horizon marketed pegloticase up until last month when Amgen bought the drug. Dr. Edwards is also president of Gout Education Society, and he has no financial agreement with any of the multiple companies that produce colchicine and allopurinol. Dr. Mays reported no conflicts.
said a presenter at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians. Failure to understand the disease process and goals of urate-lowering therapy (ULT) is a key barrier to achieving optimal gout therapy.
“There’s too much focus on the flare and too little focus on the urate burden of the disease. Regardless of the clinical setting, the goal should be to manage [high] serum uric acid levels,” said Lawrence Edwards, MD, professor at the University of Florida, Gainesville, during his talk.
Dr. Edwards, who specializes in treating patients with gout and rheumatoid arthritis, discussed the role of primary care providers in the treatment of gout. “We can and must do better,” he said.
Understanding the pathology of gout is key to effective treatment
Knowledge of the molecular pathology of gout has advanced drastically over the last few years. “The improved understanding of the molecules involved in disease initiation and progression can help us make better treatment decisions depending on the stage of the disease,” Dr. Edwards said.
Gout is caused by the deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals, which starts as asymptomatic hyperuricemia, he said. Inflammatory responses to MSU crystals are responsible for gout flares, the frequency of which increases as the disease progresses.
Innate immune responses driven by macrophages and neutrophils play a crucial role in acute gout attacks. In the molecular pathway, proinflammatory cytokines IL-1 beta and IL-6 are the mediators of gout flares, whereas IL-8 accumulates over time and contributes to disease progression and systemic illness. If left untreated or undertreated, the repeated inflammatory reaction leads to advanced gout. The urate burden also increases with disease progression.
“Physicians need to better educate themselves on the destructive nature of this inflammatory arthritis and the need for effective urate-lowering therapy in the management of gout,” Dr. Edwards said.
Management of acute gout attacks
The management of gout flares involves the use of pharmacological agents to control pain and inflammation. The three most common anti-inflammatory therapies are colchicine, NSAIDs, and corticosteroids (either oral or intramuscular).
The choice of which of these should be used alone or in combination for a flare is based on previous tolerance of the medication or the presence of diabetes, kidney disease, heart disease, or a history of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Dr. Edwards referred internists to the 2020 American College of Rheumatology gout management guideline.
“Regardless of which therapy is chosen, the more important consideration is how quickly the patients can start treatment after the flare begins,” said Dr. Edwards when asked about priorities in the management of gout flares. “This means that the patient should have ready access to whichever the chosen approach is. We call this the ‘pill-in-the-pocket’ approach,” he added.
Reducing the urate burden is also important for effective treatment. The serum urate level is the primary marker of how well a patient’s gout is being managed. ULT should be initiated in patients with subcutaneous tophi, gout-related radiographic damage, or frequent flares (≥ 2 per year). Allopurinol is typically the first-line ULT of choice.
Dr. Edwards noted that far too much focus is placed on flare treatment rather than addressing the underlying sources of gouty symptoms – the elevated serum levels of urate.
Management of advanced gout
“The management of advanced gout is challenging, and the dissolution of MSU is slow unless you take an aggressive approach,” Dr. Edwards said.
Switching to pegloticase is recommended for patients with frequent flares, nonresolving tophi, or high serum urate levels that persist despite treatment with xanthine oxidase inhibitors or other ULT agents.
“The frequency and severity of gout flares are what patients focus on, but if that’s the only focus of the treating physicians, then they are leaving the job less than halfway done. Getting the serum urate to below a level of 6.0 mg/dL is the most important aspect in the lifelong management of gout,” said Dr. Edwards.
Barriers to effective gout treatment
When asked during an interview after the session about the most important barriers to successful gout management, Allison M. Mays, MD, a geriatric medicine subspecialist at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said that “the fact that gout mostly impacts quality of life and not necessarily mortality means that other things may take precedent.” She explained that gout typically coexists with other comorbidities, often multiple ones. Patients may also defer taking an additional medication for a disease like gout, which has only episodic discomfort.
She added that gout management involves shared decision-making between patients and the medical team – including the primary care physician, rheumatologist, orthopedist, and emergency physician. Following a visit to the urgent care or the ED for an acute flare of gout, the patient may not follow up with their primary care doctor or bring it up at their next visit for chronic management, she noted.
Dr. Edwards serves as a consultant to Horizon Pharmaceuticals, Atom Biosciences, Shanton Biosciences, and Aclaris Therapeutics. Horizon marketed pegloticase up until last month when Amgen bought the drug. Dr. Edwards is also president of Gout Education Society, and he has no financial agreement with any of the multiple companies that produce colchicine and allopurinol. Dr. Mays reported no conflicts.
said a presenter at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians. Failure to understand the disease process and goals of urate-lowering therapy (ULT) is a key barrier to achieving optimal gout therapy.
“There’s too much focus on the flare and too little focus on the urate burden of the disease. Regardless of the clinical setting, the goal should be to manage [high] serum uric acid levels,” said Lawrence Edwards, MD, professor at the University of Florida, Gainesville, during his talk.
Dr. Edwards, who specializes in treating patients with gout and rheumatoid arthritis, discussed the role of primary care providers in the treatment of gout. “We can and must do better,” he said.
Understanding the pathology of gout is key to effective treatment
Knowledge of the molecular pathology of gout has advanced drastically over the last few years. “The improved understanding of the molecules involved in disease initiation and progression can help us make better treatment decisions depending on the stage of the disease,” Dr. Edwards said.
Gout is caused by the deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals, which starts as asymptomatic hyperuricemia, he said. Inflammatory responses to MSU crystals are responsible for gout flares, the frequency of which increases as the disease progresses.
Innate immune responses driven by macrophages and neutrophils play a crucial role in acute gout attacks. In the molecular pathway, proinflammatory cytokines IL-1 beta and IL-6 are the mediators of gout flares, whereas IL-8 accumulates over time and contributes to disease progression and systemic illness. If left untreated or undertreated, the repeated inflammatory reaction leads to advanced gout. The urate burden also increases with disease progression.
“Physicians need to better educate themselves on the destructive nature of this inflammatory arthritis and the need for effective urate-lowering therapy in the management of gout,” Dr. Edwards said.
Management of acute gout attacks
The management of gout flares involves the use of pharmacological agents to control pain and inflammation. The three most common anti-inflammatory therapies are colchicine, NSAIDs, and corticosteroids (either oral or intramuscular).
The choice of which of these should be used alone or in combination for a flare is based on previous tolerance of the medication or the presence of diabetes, kidney disease, heart disease, or a history of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Dr. Edwards referred internists to the 2020 American College of Rheumatology gout management guideline.
“Regardless of which therapy is chosen, the more important consideration is how quickly the patients can start treatment after the flare begins,” said Dr. Edwards when asked about priorities in the management of gout flares. “This means that the patient should have ready access to whichever the chosen approach is. We call this the ‘pill-in-the-pocket’ approach,” he added.
Reducing the urate burden is also important for effective treatment. The serum urate level is the primary marker of how well a patient’s gout is being managed. ULT should be initiated in patients with subcutaneous tophi, gout-related radiographic damage, or frequent flares (≥ 2 per year). Allopurinol is typically the first-line ULT of choice.
Dr. Edwards noted that far too much focus is placed on flare treatment rather than addressing the underlying sources of gouty symptoms – the elevated serum levels of urate.
Management of advanced gout
“The management of advanced gout is challenging, and the dissolution of MSU is slow unless you take an aggressive approach,” Dr. Edwards said.
Switching to pegloticase is recommended for patients with frequent flares, nonresolving tophi, or high serum urate levels that persist despite treatment with xanthine oxidase inhibitors or other ULT agents.
“The frequency and severity of gout flares are what patients focus on, but if that’s the only focus of the treating physicians, then they are leaving the job less than halfway done. Getting the serum urate to below a level of 6.0 mg/dL is the most important aspect in the lifelong management of gout,” said Dr. Edwards.
Barriers to effective gout treatment
When asked during an interview after the session about the most important barriers to successful gout management, Allison M. Mays, MD, a geriatric medicine subspecialist at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said that “the fact that gout mostly impacts quality of life and not necessarily mortality means that other things may take precedent.” She explained that gout typically coexists with other comorbidities, often multiple ones. Patients may also defer taking an additional medication for a disease like gout, which has only episodic discomfort.
She added that gout management involves shared decision-making between patients and the medical team – including the primary care physician, rheumatologist, orthopedist, and emergency physician. Following a visit to the urgent care or the ED for an acute flare of gout, the patient may not follow up with their primary care doctor or bring it up at their next visit for chronic management, she noted.
Dr. Edwards serves as a consultant to Horizon Pharmaceuticals, Atom Biosciences, Shanton Biosciences, and Aclaris Therapeutics. Horizon marketed pegloticase up until last month when Amgen bought the drug. Dr. Edwards is also president of Gout Education Society, and he has no financial agreement with any of the multiple companies that produce colchicine and allopurinol. Dr. Mays reported no conflicts.
AT INTERNAL MEDICINE 2023
In families with gout, obesity and alcohol add to personal risk
Gout-associated genetic factors increase the risk of gout by nearly two and a half times among people with a close family history of the disease. The risk is approximately three times higher among people with a family history of gout who are also heavy drinkers; for people with a family history of gout who are also overweight, the risk is four times higher, according to a large population-based study from South Korea.
The increased familial risk of gout (hazard ratio, 2.42) dropped only slightly after adjustment for lifestyle and biological risk factors (HR, 2.29), suggesting that genes are the key drivers for the risk of gout among first-degree relatives.
Risk was highest among individuals with an affected brother (HR, 3.00), followed by father (HR, 2.33), sister (HR, 1.97), and mother (HR, 1.68).
“Although the familial aggregation of gout [where a first-degree relative has the disease] is influenced by both genetic and lifestyle/biological factors, our findings suggest that a genetic predisposition is the predominant driver of familial aggregation,” first author Kyoung-Hoon Kim, PhD, from Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service, Wonju-si, South Korea, and colleagues wrote in Arthritis Care and Research.
However, lifestyle is still important, as suggested by comparisons with members of the general population who do not have a family history of gout or a high body mass index (BMI). The risk increased for persons with a family history of gout who were also overweight (HR, 4.39), and it increased further for people with obesity (HR, 6.62), suggesting a dose-response interaction, the authors wrote.
When family history was combined with heavy alcohol consumption, the risk rose (HR, 2.95) in comparison with the general population who had neither risk factor.
The study fills a gap in evidence on “familial risk of gout as opposed to hereditary risk of gout, which has long been recognized,” the researchers wrote.
In addition, the findings suggest the possibility of a dose-dependent gene-environment interaction, “as the combination of both a family history of gout and either high BMI or heavy alcohol consumption was associated with a markedly increased risk of disease, which was even further elevated among obese individuals.”
Abhishek Abhishek, MD, professor of rheumatology and honorary consultant rheumatologist at Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust, reflected on the minimal attenuation after adjustment for lifestyle and demographic factors. “This suggests that most of the familial impact is, in fact, genetic rather than due to shared environmental factors and is an important finding.”
He said in an interview that the findings also confirmed the synergistic effect of genetic and lifestyle factors in causing gout. “Lifestyle factors such as alcohol excess and obesity should be addressed more aggressively in those with a first-degree relative with gout.
“Although not directly evaluated in this study, aggressive management of excess weight and high alcohol consumption may prevent the onset of gout or improve its outcomes in those who already have this condition,” he added.
Study of over 5 million individuals with familial aggregation of gout
The researchers drew on data from the government-operated mandatory insurance service that provides for South Korea’s entire population of over 50 million people (the National Health Insurance database), as well as the National Health Screening Program database. Information on familial relationships and risk factor data were identified for 5,524,403 individuals from 2002 to 2018 who had a blood-related first-degree relative.
Familial risk was calculated by comparing the risk of individuals with and those without affected first-degree relatives. Interactions between family history and obesity or alcohol consumption were assessed using a scale that measured gout risk due to interaction of two factors.
Initially, adjustments to familial risk were made with respect to age and sex. Subsequently, possible risk factors included smoking, BMI, hypertension, and hyperglycemia.
Alcohol consumption levels were noted and categorized as nondrinker, moderate drinker, or heavy drinker, with different consumption levels for men and women. For men, heavy drinking was defined as having at least two drinks per week and at least five drinks on any day; for women, heavy drinking was defined as having at least two drinks per week and at least four drinks on any day.
Overweight and obesity were determined on the basis of BMI, using standard categories: overweight was defined as BMI of 25 to less than 30 kg/m2, and obesity was defined as BMI of 30 or higher.
Dr. Kim and coauthors noted that both high BMI and heavy drinking were associated with an increased risk of gout, regardless of whether there was a family history of the disease, and that the findings suggest “a dose-dependent interactive relationship in which genetic factors and obesity potentiate each other rather than operating independently.”
People who are both overweight and have a family history of disease had a combined risk of gout that was significantly higher than the sum of their individual risk factors (HR, 4.39 vs. 3.43). This risk was accentuated among people with obesity (HR, 6.62 vs. 4.74) and was more pronounced in men than in women.
In other risk analyses in which familial and nonfamilial gout risk groups were compared, the risk associated with obesity was higher in the familial, compared with the nonfamilial group (HR, 5.50 vs. 5.36).
Bruce Rothschild, MD, a rheumatologist with Indiana University Health, Muncie, and research associate at Carnegie Museum of Natural History, Pittsburgh, shared his thoughts on the study in an interview and noted some limitations. “The findings of this study do not conflict with what is generally believed, but there are several issues that complicate interpretation,” he began. “The first is how gout is diagnosed. Since crystal presence confirmation is rare in clinical practice, and by assumption of the database used, diagnosis is based on fulfillment of a certain number of criteria, one of which is hyperuricemia – this is not actual confirmation of diagnosis.”
He pointed out that the incidence of gout depends on who received treatment, and the study excluded those who were not receiving treatment and those who were not prescribed allopurinol or febuxostat. “Single parents were also excluded, and this may also have affected results.
“Overweight and obesity were not adjusted for age, and the interpretation is age dependent,” he added. “It really comes down to the way gout is diagnosed, and this is a worldwide problem because the diagnosis has been so dumbed down that we don’t really know what is claimed as gout.”
Dr. Kim and coauthors disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Abhishek has received institutional research grants from AstraZeneca and Oxford Immunotech and personal fees from UpToDate, Springer, Cadilla Pharmaceuticals, NGM Bio, Limbic, and Inflazome. Dr. Rothschild disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Gout-associated genetic factors increase the risk of gout by nearly two and a half times among people with a close family history of the disease. The risk is approximately three times higher among people with a family history of gout who are also heavy drinkers; for people with a family history of gout who are also overweight, the risk is four times higher, according to a large population-based study from South Korea.
The increased familial risk of gout (hazard ratio, 2.42) dropped only slightly after adjustment for lifestyle and biological risk factors (HR, 2.29), suggesting that genes are the key drivers for the risk of gout among first-degree relatives.
Risk was highest among individuals with an affected brother (HR, 3.00), followed by father (HR, 2.33), sister (HR, 1.97), and mother (HR, 1.68).
“Although the familial aggregation of gout [where a first-degree relative has the disease] is influenced by both genetic and lifestyle/biological factors, our findings suggest that a genetic predisposition is the predominant driver of familial aggregation,” first author Kyoung-Hoon Kim, PhD, from Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service, Wonju-si, South Korea, and colleagues wrote in Arthritis Care and Research.
However, lifestyle is still important, as suggested by comparisons with members of the general population who do not have a family history of gout or a high body mass index (BMI). The risk increased for persons with a family history of gout who were also overweight (HR, 4.39), and it increased further for people with obesity (HR, 6.62), suggesting a dose-response interaction, the authors wrote.
When family history was combined with heavy alcohol consumption, the risk rose (HR, 2.95) in comparison with the general population who had neither risk factor.
The study fills a gap in evidence on “familial risk of gout as opposed to hereditary risk of gout, which has long been recognized,” the researchers wrote.
In addition, the findings suggest the possibility of a dose-dependent gene-environment interaction, “as the combination of both a family history of gout and either high BMI or heavy alcohol consumption was associated with a markedly increased risk of disease, which was even further elevated among obese individuals.”
Abhishek Abhishek, MD, professor of rheumatology and honorary consultant rheumatologist at Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust, reflected on the minimal attenuation after adjustment for lifestyle and demographic factors. “This suggests that most of the familial impact is, in fact, genetic rather than due to shared environmental factors and is an important finding.”
He said in an interview that the findings also confirmed the synergistic effect of genetic and lifestyle factors in causing gout. “Lifestyle factors such as alcohol excess and obesity should be addressed more aggressively in those with a first-degree relative with gout.
“Although not directly evaluated in this study, aggressive management of excess weight and high alcohol consumption may prevent the onset of gout or improve its outcomes in those who already have this condition,” he added.
Study of over 5 million individuals with familial aggregation of gout
The researchers drew on data from the government-operated mandatory insurance service that provides for South Korea’s entire population of over 50 million people (the National Health Insurance database), as well as the National Health Screening Program database. Information on familial relationships and risk factor data were identified for 5,524,403 individuals from 2002 to 2018 who had a blood-related first-degree relative.
Familial risk was calculated by comparing the risk of individuals with and those without affected first-degree relatives. Interactions between family history and obesity or alcohol consumption were assessed using a scale that measured gout risk due to interaction of two factors.
Initially, adjustments to familial risk were made with respect to age and sex. Subsequently, possible risk factors included smoking, BMI, hypertension, and hyperglycemia.
Alcohol consumption levels were noted and categorized as nondrinker, moderate drinker, or heavy drinker, with different consumption levels for men and women. For men, heavy drinking was defined as having at least two drinks per week and at least five drinks on any day; for women, heavy drinking was defined as having at least two drinks per week and at least four drinks on any day.
Overweight and obesity were determined on the basis of BMI, using standard categories: overweight was defined as BMI of 25 to less than 30 kg/m2, and obesity was defined as BMI of 30 or higher.
Dr. Kim and coauthors noted that both high BMI and heavy drinking were associated with an increased risk of gout, regardless of whether there was a family history of the disease, and that the findings suggest “a dose-dependent interactive relationship in which genetic factors and obesity potentiate each other rather than operating independently.”
People who are both overweight and have a family history of disease had a combined risk of gout that was significantly higher than the sum of their individual risk factors (HR, 4.39 vs. 3.43). This risk was accentuated among people with obesity (HR, 6.62 vs. 4.74) and was more pronounced in men than in women.
In other risk analyses in which familial and nonfamilial gout risk groups were compared, the risk associated with obesity was higher in the familial, compared with the nonfamilial group (HR, 5.50 vs. 5.36).
Bruce Rothschild, MD, a rheumatologist with Indiana University Health, Muncie, and research associate at Carnegie Museum of Natural History, Pittsburgh, shared his thoughts on the study in an interview and noted some limitations. “The findings of this study do not conflict with what is generally believed, but there are several issues that complicate interpretation,” he began. “The first is how gout is diagnosed. Since crystal presence confirmation is rare in clinical practice, and by assumption of the database used, diagnosis is based on fulfillment of a certain number of criteria, one of which is hyperuricemia – this is not actual confirmation of diagnosis.”
He pointed out that the incidence of gout depends on who received treatment, and the study excluded those who were not receiving treatment and those who were not prescribed allopurinol or febuxostat. “Single parents were also excluded, and this may also have affected results.
“Overweight and obesity were not adjusted for age, and the interpretation is age dependent,” he added. “It really comes down to the way gout is diagnosed, and this is a worldwide problem because the diagnosis has been so dumbed down that we don’t really know what is claimed as gout.”
Dr. Kim and coauthors disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Abhishek has received institutional research grants from AstraZeneca and Oxford Immunotech and personal fees from UpToDate, Springer, Cadilla Pharmaceuticals, NGM Bio, Limbic, and Inflazome. Dr. Rothschild disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Gout-associated genetic factors increase the risk of gout by nearly two and a half times among people with a close family history of the disease. The risk is approximately three times higher among people with a family history of gout who are also heavy drinkers; for people with a family history of gout who are also overweight, the risk is four times higher, according to a large population-based study from South Korea.
The increased familial risk of gout (hazard ratio, 2.42) dropped only slightly after adjustment for lifestyle and biological risk factors (HR, 2.29), suggesting that genes are the key drivers for the risk of gout among first-degree relatives.
Risk was highest among individuals with an affected brother (HR, 3.00), followed by father (HR, 2.33), sister (HR, 1.97), and mother (HR, 1.68).
“Although the familial aggregation of gout [where a first-degree relative has the disease] is influenced by both genetic and lifestyle/biological factors, our findings suggest that a genetic predisposition is the predominant driver of familial aggregation,” first author Kyoung-Hoon Kim, PhD, from Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service, Wonju-si, South Korea, and colleagues wrote in Arthritis Care and Research.
However, lifestyle is still important, as suggested by comparisons with members of the general population who do not have a family history of gout or a high body mass index (BMI). The risk increased for persons with a family history of gout who were also overweight (HR, 4.39), and it increased further for people with obesity (HR, 6.62), suggesting a dose-response interaction, the authors wrote.
When family history was combined with heavy alcohol consumption, the risk rose (HR, 2.95) in comparison with the general population who had neither risk factor.
The study fills a gap in evidence on “familial risk of gout as opposed to hereditary risk of gout, which has long been recognized,” the researchers wrote.
In addition, the findings suggest the possibility of a dose-dependent gene-environment interaction, “as the combination of both a family history of gout and either high BMI or heavy alcohol consumption was associated with a markedly increased risk of disease, which was even further elevated among obese individuals.”
Abhishek Abhishek, MD, professor of rheumatology and honorary consultant rheumatologist at Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust, reflected on the minimal attenuation after adjustment for lifestyle and demographic factors. “This suggests that most of the familial impact is, in fact, genetic rather than due to shared environmental factors and is an important finding.”
He said in an interview that the findings also confirmed the synergistic effect of genetic and lifestyle factors in causing gout. “Lifestyle factors such as alcohol excess and obesity should be addressed more aggressively in those with a first-degree relative with gout.
“Although not directly evaluated in this study, aggressive management of excess weight and high alcohol consumption may prevent the onset of gout or improve its outcomes in those who already have this condition,” he added.
Study of over 5 million individuals with familial aggregation of gout
The researchers drew on data from the government-operated mandatory insurance service that provides for South Korea’s entire population of over 50 million people (the National Health Insurance database), as well as the National Health Screening Program database. Information on familial relationships and risk factor data were identified for 5,524,403 individuals from 2002 to 2018 who had a blood-related first-degree relative.
Familial risk was calculated by comparing the risk of individuals with and those without affected first-degree relatives. Interactions between family history and obesity or alcohol consumption were assessed using a scale that measured gout risk due to interaction of two factors.
Initially, adjustments to familial risk were made with respect to age and sex. Subsequently, possible risk factors included smoking, BMI, hypertension, and hyperglycemia.
Alcohol consumption levels were noted and categorized as nondrinker, moderate drinker, or heavy drinker, with different consumption levels for men and women. For men, heavy drinking was defined as having at least two drinks per week and at least five drinks on any day; for women, heavy drinking was defined as having at least two drinks per week and at least four drinks on any day.
Overweight and obesity were determined on the basis of BMI, using standard categories: overweight was defined as BMI of 25 to less than 30 kg/m2, and obesity was defined as BMI of 30 or higher.
Dr. Kim and coauthors noted that both high BMI and heavy drinking were associated with an increased risk of gout, regardless of whether there was a family history of the disease, and that the findings suggest “a dose-dependent interactive relationship in which genetic factors and obesity potentiate each other rather than operating independently.”
People who are both overweight and have a family history of disease had a combined risk of gout that was significantly higher than the sum of their individual risk factors (HR, 4.39 vs. 3.43). This risk was accentuated among people with obesity (HR, 6.62 vs. 4.74) and was more pronounced in men than in women.
In other risk analyses in which familial and nonfamilial gout risk groups were compared, the risk associated with obesity was higher in the familial, compared with the nonfamilial group (HR, 5.50 vs. 5.36).
Bruce Rothschild, MD, a rheumatologist with Indiana University Health, Muncie, and research associate at Carnegie Museum of Natural History, Pittsburgh, shared his thoughts on the study in an interview and noted some limitations. “The findings of this study do not conflict with what is generally believed, but there are several issues that complicate interpretation,” he began. “The first is how gout is diagnosed. Since crystal presence confirmation is rare in clinical practice, and by assumption of the database used, diagnosis is based on fulfillment of a certain number of criteria, one of which is hyperuricemia – this is not actual confirmation of diagnosis.”
He pointed out that the incidence of gout depends on who received treatment, and the study excluded those who were not receiving treatment and those who were not prescribed allopurinol or febuxostat. “Single parents were also excluded, and this may also have affected results.
“Overweight and obesity were not adjusted for age, and the interpretation is age dependent,” he added. “It really comes down to the way gout is diagnosed, and this is a worldwide problem because the diagnosis has been so dumbed down that we don’t really know what is claimed as gout.”
Dr. Kim and coauthors disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Abhishek has received institutional research grants from AstraZeneca and Oxford Immunotech and personal fees from UpToDate, Springer, Cadilla Pharmaceuticals, NGM Bio, Limbic, and Inflazome. Dr. Rothschild disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ARTHRITIS CARE AND RESEARCH
Teamwork guides cardio-rheumatology clinics that care for unique patient population
Clinical cardiologist Heba Wassif, MD, MPH, knows the value of working with her fellow rheumatologists, surgeons, and other clinicians to establish a care plan for her patients with cardiac conditions and autoimmune diseases.
She is the cofounder of the Cleveland Clinic’s new cardio-rheumatology program, which places an emphasis on multidisciplinary care. In her role, Dr. Wassif closely follows her patients, and if she sees any inflammation or any other condition that requires the rheumatologist, she reaches out to her colleagues to adjust medications if needed.
Collaboration with a rheumatologist was important when a patient with valvular disease was prepping for surgery. The patient was on significant immunosuppressants and the surgery had to be timed appropriately, accounting for any decreases in her immunosuppression, explained Dr. Wassif, director of inpatient clinical cardiology at Cleveland Clinic in Ohio.
Cardio-rheumatology programs are “the newest child” in a series of cardiology offshoots focusing on different populations. Cardio-oncology and cardio-obstetrics took off about 6 years ago, with cardio-rheumatology clinics and interested physicians rising in number over the last several years, Dr. Wassif noted.
The relationship between cardiovascular diseases and rheumatologic conditions is certainly recognized more often, “which means more literature is being published to discuss the link,” according to Rekha Mankad, MD, a trailblazer of this model of care. She directs the Women’s Heart Clinic at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., which was one of the earliest adopters of a cardio-rheumatology clinic.
Ten years ago, “nobody was talking about the link between rheumatologic conditions and cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Mankad said. “I’ve been asked to speak on this topic, and programs have asked me to speak about establishing cardio-rheumatology practices. So, there’s been an evolution as far as a recognition that these two conditions overlap.”
Patients have come to her independent of internal referrals, which means they have done Google searches on cardiology and rheumatology. “I think that it has made a splash, at least in the world of cardiology,” Dr. Mankad observed in an interview.
Other institutions such as NYU-Langone, Yale, Stanford, Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and Women’s College Hospital in Toronto have formed similar clinics whose focus is to address the specific needs of rheumatology patients with cardiac conditions through a teamwork approach.
Challenges of treating cardiac, rheumatologic conditions
The rise in clinics addresses the longstanding connection between autoimmune disorders and cardiac conditions.
Cardiologists have known that there is an element of inflammation that contributes to atherosclerosis, said Dr. Wassif, who has researched this topic extensively. A recent study she led found a strong association between rheumatic immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) and high risk of acute coronary syndrome in Medicare patients.
“This particular population has a very clear increased risk for cardiovascular conditions, including valve disease and heart failure,” she emphasized.
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis and lupus have up to a twofold and eightfold higher risk of heart disease, respectively, noted Michael S. Garshick, MD, a cardiovascular disease specialist who directs the cardio-rheumatology program at NYU-Langone Health, in New York. Cardiologists “have really developed an understanding that the immune system can impact the heart, and that there’s a need for people to understand the nuance behind how the immune system can affect them and what to do about it,” Dr. Garshick said.
Caring for patients with both afflictions comes with specific challenges. Many physicians are not well trained on managing and treating patients with these dual conditions.
The “lipid paradox,” in which lipids are reduced with active inflammation in some rheumatologic conditions, can make treatment more nuanced. In addition, the traditional ASCVD (atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease) score often underestimates the cardiovascular risk of these patients, noted cardiologist Margaret Furman, MD, MPH, assistant professor and codirector of Yale’s Cardio-Rheumatology Program, New Haven, Conn.
Newer biologic medications used to treat rheumatologic diseases can alter a patient’s lipid profile, she said in an interview.
“It can be difficult to assess each individual patient’s cardiovascular risk as their disease state and treatment can vary throughout their lifetime based on their degree of inflammation. The importance of aggressive lipid management is often underestimated,” Dr. Furman added.
Cardiology and rheumatology partnerships can address gaps in care of this unique group of patients, said Vaidehi R. Chowdhary, MBBS, MD, clinical chief of the Yale Section of Rheumatology, Allergy, and Immunology at Yale University.
“The role of the rheumatologist in this dyad is to educate patients on this risk, work toward adequate control of inflammation, and minimize use of medications that contribute to increased cardiovascular risks,” said Dr. Chowdhary, who cofounded Yale’s cardio-rheumatology program with Dr. Furman.
Cardiologists in turn can assert their knowledge about medications and their impact on lipids and inflammation, Dr. Wassif said.
Many anti-inflammatory therapies are now within the cardiologist’s purview, Dr. Garshick noted. “For example, specifically with pericarditis, there’s [Food and Drug Administration]–approved anti-inflammatories or biologics. We’re the ones who feel the most comfortable giving them right now.” Cardiologists quite often are consulted about medications that are efficacious in rheumatologic conditions but could negatively impact the cardiovascular system, such as Janus kinase inhibitors, he added.
‘Reading the tea leaves’
Each program has its own unique story. For the Cleveland Clinic, the concept of a cardio-rheumatology program began during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020. Developing such a concept and gaining institutional acceptance is always a work in process, Dr. Wassif said. “It’s not that you decide one day that you’re going to build a center, and that center is going to come into fruition overnight. You first gauge interest within your division. Who are the individuals that are interested in this area?”
Cleveland Clinic’s center is seeking to build relations between medical disciplines while spotlighting the concept of cardio-rheumatology, said Dr. Wassif, who has been providing education within the clinic and at other health institutions to ensure that patients receive appropriate attention early.
NYU-Langone launched its program amid this heightened awareness that the immune system could affect atherosclerosis, “kind of reading of the tea leaves, so to speak,” Dr. Garshick said.
Several clinical trials served as a catalyst for this movement. “A lot of clinical cardiologists were never 100% convinced that targeting the immune system reduced cardiovascular disease,” he said. Then the CANTOS clinical trial came along and showed for the first time that a therapeutic monoclonal antibody targeting interleukin-1beta, a cytokine central to inflammatory response, could in fact reduce cardiovascular disease.
Trials like this, along with epidemiologic literature connecting the rheumatologic and the autoimmune conditions with cardiovascular disease, pushed this concept to the forefront, Dr. Garshick said.
The notion that a clinic could successfully address cardiac problems in patients with rheumatic diseases yielded promising returns at Women’s College Hospital in Toronto, according to a report presented at the 2018 American College of Rheumatology annual meeting. Researchers reported that patients with rheumatologic conditions who attended a cardio-rheumatology clinic at this center saw improvements in care. The clinic identified increased cardiovascular risk and early atherosclerosis, and 53.8% of patients altered their medications after being seen in the clinic.
A total of 39.7% and 32.1% received lipid lowering and antiplatelet therapies, respectively, and 14% received antihypertensive therapy. A small percentage were treated for heart failure or placed on lifelong anticoagulation therapy for atrial fibrillation, and one patient received a percutaneous coronary stent.
Ins and outs of the referral process
Initially designed for preventive cardiac risk assessment, Yale’s program evolved into a multidisciplinary, patient-centered approach for the management of complex cardiovascular conditions in patients with autoimmune rheumatologic diseases.
The program is open to anyone who carries a diagnosis of rheumatologic disease or has elevated inflammatory markers. “Every patient, regardless of the reason for the referral, receives a cardiovascular risk assessment,” Dr. Furman said.
Most referrals come from rheumatologists, although cardiology colleagues and pulmonologists have also sent referrals. A pulmonologist, for example, may want to rule out a cardiac cause to shortness of breath. The patient’s workup, care, and follow-up are based on the reason for referral.
“We are currently referring patients with established cardiac disease, traditional risk factors, or for better risk assessment for primary prevention of coronary artery disease,” Dr. Chowdhary said. “We communicate very frequently about medication changes, and patients are aware of goals of care from both sides.”
Dr. Furman works closely with several of the rheumatology specialists taking care of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and scleroderma.
Rheumatology follows patients every 3-6 months or more frequently based on their disease activity.
Dr. Mankad uses her sleuthing skills at Mayo Clinic to determine what the patients need. If they come in for a preventive assessment, she looks more closely at their cardiovascular risks and may order additional imaging to look for subclinical atherosclerosis. “We’re more aggressive with statin therapy in this population because of that,” she said.
If it’s valve disease, she pays extra attention to the patients’ valves in the echocardiograms and follows them a bit more regularly than someone without a rheumatologic condition and valve disease.
For patients with heart failure signs or symptoms, “it depends on how symptomatic they are,” Dr. Mankad said. In some instances, she may look for evidence of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in patients who have rheumatoid arthritis who happen to be short of breath. “There’s so many different manifestations that patients with rheumatologic conditions can have as far as what could be affected in the heart,” she noted.
Quite frequently, Dr. Mankad identifies subclinical disease in her patients with rheumatoid arthritis. “I’ve seen many patients whose risk scores would not dictate statin therapy. But I went looking for subclinical disease by either doing coronary assessment or carotid assessment and have found atherosclerosis that would be enough to warrant statin therapy.”
A personalized assessment to reduce cardiac risk
NYU-Langone’s program offers opportunities to educate patients about the link between cardiac and rheumatologic disease.
“Their rheumatologist or their dermatologist will say, ‘Hey, have you heard about the connection between psoriasis, psoriatic or rheumatoid arthritis, and heart disease and the risk of heart attack or stroke?’ ” Dr. Garshick said.
The patients will often say they know nothing about these connections and want to learn more about how to treat it.
“We’ll say, ‘we have someone here that can help you.’ They’ll send them to myself or other colleagues like me across the country. We’ll assess blood pressure, weight, lipids, hemoglobin A1c, and other serologic and oftentimes imaging biomarkers of cardiovascular risk.” The patients will receive a personalized assessment, listing things they can do to lower their risk, whether it’s diet, exercise, or lifestyle. “Many times it can involve medications to reduce heart disease risk,” said Dr. Garshick.
In some instances, a rheumatologist or dermatologist may be concerned about starting a patient on a specific medication for the disease such as a JAK inhibitor. “We’ll help assess their risk because there’s been a lot of literature out in the rheumatology world about the risk of JAK inhibitors and heart disease and blood clots,” said Dr. Garshick.
Dr. Garshick also sees patients with rheumatologic conditions who have a specific cardiovascular concern or complaint such as shortness of breath or chest pain. “We’ll work that up with a specific knowledge of the underlying immune condition and how that may impact their heart,” he said.
Advances in research
As they continue to see patients and devise specific care plans, developers of cardio-rheumatology programs have been supplementing their work with ongoing research.
Yale’s clinic is expanding this year to include a new attending physician, Attila Feher, MD, PhD, who has conducted research in autoimmunity and microcirculation using molecular imaging and multimodality imaging techniques. Prevalence of coronary microvascular dysfunction appears to be increased in this patient population, Dr. Furman said.
Dr. Wassif recently coauthored a paper that examined patients with underlying rheumatologic conditions who undergo valvular and aortic valve replacement. “To our surprise, there was really no difference between patients with autoimmune conditions and others with nonautoimmune conditions,” she said, adding that the study had its limitations.
Other work includes data on Medicare patients with ST- and non-ST-elevation myocardial infarctions who have an underlying autoimmune disorder. Dr. Wassif and her colleagues found that their long-term outcomes are worse than those of patients without these conditions. “It’s unclear if worse outcomes are related to complications of autoimmunity versus the extent of their underlying disease. This is a work in progress and certainly an area that is ripe for research.”
Dr. Garshick and other collaborators at NYU have been focusing on the endothelium, specifically platelet biology in patients with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and lupus. “We’re about to start the same research with gout as well,” he said.
“The process we’re most interested in is understanding how these diseases impact the early stages of cholesterol. And the way we’re doing that is evaluating the vasculature, specifically the endothelium,” he said.
He has finished two clinical trials that evaluate how standard heart disease medications such as aspirin and statins impact or can potentially benefit patients with psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis. “We have a whole list of other trials in the pipeline with other institutions across the country.”
Through a grant, Dr. Mankad is assessing whether a PET scan could detect inflammation in the hearts of rheumatoid arthritis patients. “We’re looking to see if the reason these patients have heart failure later in life is because their heart muscle actually shows evidence of inflammation, even when they have no symptoms,” she explained.
Other tests such as echocardiogram and CT scans will be used to evaluate coronary disease in about 40-50 patients. The goal of using these multiple imaging tools is to find markers indicating that the heart is affected by rheumatoid arthritis, which may indicate a higher likelihood of developing heart failure, she said.
Clinics are popping up
Through these new clinics, some collaborations have emerged. Dr. Garshick works closely with Brigham and Women’s Hospital, which has a similar cardio-rheumatology program, run by Brittany Weber, MD, to exchange ideas, discuss challenging cases, and collaborate.
“There are a lot of clinics like us popping up across the country,” he observed. Every so often, he hears from other institutions that are interested in starting their own cardio-rheumatology programs. “They ask us: How do you start, what should we look for?”
It’s an education process for both patients and providers, Dr. Garshick emphasized. “I also think it’s a bandwidth issue. Many of our rheumatology and dermatology colleagues are acutely aware of the connection, but there may not be enough time at a clinic visit to really go in depth” with these dual conditions, he said.
NYU-Langone Health for the past several years has been holding a symposium to educate people on the cardio-rheumatology connection and treating inflammation in cardiovascular disease. This year’s symposium, held in conjunction with Brigham and Women’s Hospital, is scheduled for April 28. For more information, visit the course website: nyulmc.org/cvinflammationcme.
“What we’re trying to do is help [other institutions] get that bandwidth” to adequately help and serve these patients, he said.
Dr. Garshick has received consultant fees from Abbvie and Horizon therapeutics and an unrestricted research grant from Pfizer. No other sources had relevant financial disclosures.
Clinical cardiologist Heba Wassif, MD, MPH, knows the value of working with her fellow rheumatologists, surgeons, and other clinicians to establish a care plan for her patients with cardiac conditions and autoimmune diseases.
She is the cofounder of the Cleveland Clinic’s new cardio-rheumatology program, which places an emphasis on multidisciplinary care. In her role, Dr. Wassif closely follows her patients, and if she sees any inflammation or any other condition that requires the rheumatologist, she reaches out to her colleagues to adjust medications if needed.
Collaboration with a rheumatologist was important when a patient with valvular disease was prepping for surgery. The patient was on significant immunosuppressants and the surgery had to be timed appropriately, accounting for any decreases in her immunosuppression, explained Dr. Wassif, director of inpatient clinical cardiology at Cleveland Clinic in Ohio.
Cardio-rheumatology programs are “the newest child” in a series of cardiology offshoots focusing on different populations. Cardio-oncology and cardio-obstetrics took off about 6 years ago, with cardio-rheumatology clinics and interested physicians rising in number over the last several years, Dr. Wassif noted.
The relationship between cardiovascular diseases and rheumatologic conditions is certainly recognized more often, “which means more literature is being published to discuss the link,” according to Rekha Mankad, MD, a trailblazer of this model of care. She directs the Women’s Heart Clinic at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., which was one of the earliest adopters of a cardio-rheumatology clinic.
Ten years ago, “nobody was talking about the link between rheumatologic conditions and cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Mankad said. “I’ve been asked to speak on this topic, and programs have asked me to speak about establishing cardio-rheumatology practices. So, there’s been an evolution as far as a recognition that these two conditions overlap.”
Patients have come to her independent of internal referrals, which means they have done Google searches on cardiology and rheumatology. “I think that it has made a splash, at least in the world of cardiology,” Dr. Mankad observed in an interview.
Other institutions such as NYU-Langone, Yale, Stanford, Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and Women’s College Hospital in Toronto have formed similar clinics whose focus is to address the specific needs of rheumatology patients with cardiac conditions through a teamwork approach.
Challenges of treating cardiac, rheumatologic conditions
The rise in clinics addresses the longstanding connection between autoimmune disorders and cardiac conditions.
Cardiologists have known that there is an element of inflammation that contributes to atherosclerosis, said Dr. Wassif, who has researched this topic extensively. A recent study she led found a strong association between rheumatic immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) and high risk of acute coronary syndrome in Medicare patients.
“This particular population has a very clear increased risk for cardiovascular conditions, including valve disease and heart failure,” she emphasized.
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis and lupus have up to a twofold and eightfold higher risk of heart disease, respectively, noted Michael S. Garshick, MD, a cardiovascular disease specialist who directs the cardio-rheumatology program at NYU-Langone Health, in New York. Cardiologists “have really developed an understanding that the immune system can impact the heart, and that there’s a need for people to understand the nuance behind how the immune system can affect them and what to do about it,” Dr. Garshick said.
Caring for patients with both afflictions comes with specific challenges. Many physicians are not well trained on managing and treating patients with these dual conditions.
The “lipid paradox,” in which lipids are reduced with active inflammation in some rheumatologic conditions, can make treatment more nuanced. In addition, the traditional ASCVD (atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease) score often underestimates the cardiovascular risk of these patients, noted cardiologist Margaret Furman, MD, MPH, assistant professor and codirector of Yale’s Cardio-Rheumatology Program, New Haven, Conn.
Newer biologic medications used to treat rheumatologic diseases can alter a patient’s lipid profile, she said in an interview.
“It can be difficult to assess each individual patient’s cardiovascular risk as their disease state and treatment can vary throughout their lifetime based on their degree of inflammation. The importance of aggressive lipid management is often underestimated,” Dr. Furman added.
Cardiology and rheumatology partnerships can address gaps in care of this unique group of patients, said Vaidehi R. Chowdhary, MBBS, MD, clinical chief of the Yale Section of Rheumatology, Allergy, and Immunology at Yale University.
“The role of the rheumatologist in this dyad is to educate patients on this risk, work toward adequate control of inflammation, and minimize use of medications that contribute to increased cardiovascular risks,” said Dr. Chowdhary, who cofounded Yale’s cardio-rheumatology program with Dr. Furman.
Cardiologists in turn can assert their knowledge about medications and their impact on lipids and inflammation, Dr. Wassif said.
Many anti-inflammatory therapies are now within the cardiologist’s purview, Dr. Garshick noted. “For example, specifically with pericarditis, there’s [Food and Drug Administration]–approved anti-inflammatories or biologics. We’re the ones who feel the most comfortable giving them right now.” Cardiologists quite often are consulted about medications that are efficacious in rheumatologic conditions but could negatively impact the cardiovascular system, such as Janus kinase inhibitors, he added.
‘Reading the tea leaves’
Each program has its own unique story. For the Cleveland Clinic, the concept of a cardio-rheumatology program began during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020. Developing such a concept and gaining institutional acceptance is always a work in process, Dr. Wassif said. “It’s not that you decide one day that you’re going to build a center, and that center is going to come into fruition overnight. You first gauge interest within your division. Who are the individuals that are interested in this area?”
Cleveland Clinic’s center is seeking to build relations between medical disciplines while spotlighting the concept of cardio-rheumatology, said Dr. Wassif, who has been providing education within the clinic and at other health institutions to ensure that patients receive appropriate attention early.
NYU-Langone launched its program amid this heightened awareness that the immune system could affect atherosclerosis, “kind of reading of the tea leaves, so to speak,” Dr. Garshick said.
Several clinical trials served as a catalyst for this movement. “A lot of clinical cardiologists were never 100% convinced that targeting the immune system reduced cardiovascular disease,” he said. Then the CANTOS clinical trial came along and showed for the first time that a therapeutic monoclonal antibody targeting interleukin-1beta, a cytokine central to inflammatory response, could in fact reduce cardiovascular disease.
Trials like this, along with epidemiologic literature connecting the rheumatologic and the autoimmune conditions with cardiovascular disease, pushed this concept to the forefront, Dr. Garshick said.
The notion that a clinic could successfully address cardiac problems in patients with rheumatic diseases yielded promising returns at Women’s College Hospital in Toronto, according to a report presented at the 2018 American College of Rheumatology annual meeting. Researchers reported that patients with rheumatologic conditions who attended a cardio-rheumatology clinic at this center saw improvements in care. The clinic identified increased cardiovascular risk and early atherosclerosis, and 53.8% of patients altered their medications after being seen in the clinic.
A total of 39.7% and 32.1% received lipid lowering and antiplatelet therapies, respectively, and 14% received antihypertensive therapy. A small percentage were treated for heart failure or placed on lifelong anticoagulation therapy for atrial fibrillation, and one patient received a percutaneous coronary stent.
Ins and outs of the referral process
Initially designed for preventive cardiac risk assessment, Yale’s program evolved into a multidisciplinary, patient-centered approach for the management of complex cardiovascular conditions in patients with autoimmune rheumatologic diseases.
The program is open to anyone who carries a diagnosis of rheumatologic disease or has elevated inflammatory markers. “Every patient, regardless of the reason for the referral, receives a cardiovascular risk assessment,” Dr. Furman said.
Most referrals come from rheumatologists, although cardiology colleagues and pulmonologists have also sent referrals. A pulmonologist, for example, may want to rule out a cardiac cause to shortness of breath. The patient’s workup, care, and follow-up are based on the reason for referral.
“We are currently referring patients with established cardiac disease, traditional risk factors, or for better risk assessment for primary prevention of coronary artery disease,” Dr. Chowdhary said. “We communicate very frequently about medication changes, and patients are aware of goals of care from both sides.”
Dr. Furman works closely with several of the rheumatology specialists taking care of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and scleroderma.
Rheumatology follows patients every 3-6 months or more frequently based on their disease activity.
Dr. Mankad uses her sleuthing skills at Mayo Clinic to determine what the patients need. If they come in for a preventive assessment, she looks more closely at their cardiovascular risks and may order additional imaging to look for subclinical atherosclerosis. “We’re more aggressive with statin therapy in this population because of that,” she said.
If it’s valve disease, she pays extra attention to the patients’ valves in the echocardiograms and follows them a bit more regularly than someone without a rheumatologic condition and valve disease.
For patients with heart failure signs or symptoms, “it depends on how symptomatic they are,” Dr. Mankad said. In some instances, she may look for evidence of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in patients who have rheumatoid arthritis who happen to be short of breath. “There’s so many different manifestations that patients with rheumatologic conditions can have as far as what could be affected in the heart,” she noted.
Quite frequently, Dr. Mankad identifies subclinical disease in her patients with rheumatoid arthritis. “I’ve seen many patients whose risk scores would not dictate statin therapy. But I went looking for subclinical disease by either doing coronary assessment or carotid assessment and have found atherosclerosis that would be enough to warrant statin therapy.”
A personalized assessment to reduce cardiac risk
NYU-Langone’s program offers opportunities to educate patients about the link between cardiac and rheumatologic disease.
“Their rheumatologist or their dermatologist will say, ‘Hey, have you heard about the connection between psoriasis, psoriatic or rheumatoid arthritis, and heart disease and the risk of heart attack or stroke?’ ” Dr. Garshick said.
The patients will often say they know nothing about these connections and want to learn more about how to treat it.
“We’ll say, ‘we have someone here that can help you.’ They’ll send them to myself or other colleagues like me across the country. We’ll assess blood pressure, weight, lipids, hemoglobin A1c, and other serologic and oftentimes imaging biomarkers of cardiovascular risk.” The patients will receive a personalized assessment, listing things they can do to lower their risk, whether it’s diet, exercise, or lifestyle. “Many times it can involve medications to reduce heart disease risk,” said Dr. Garshick.
In some instances, a rheumatologist or dermatologist may be concerned about starting a patient on a specific medication for the disease such as a JAK inhibitor. “We’ll help assess their risk because there’s been a lot of literature out in the rheumatology world about the risk of JAK inhibitors and heart disease and blood clots,” said Dr. Garshick.
Dr. Garshick also sees patients with rheumatologic conditions who have a specific cardiovascular concern or complaint such as shortness of breath or chest pain. “We’ll work that up with a specific knowledge of the underlying immune condition and how that may impact their heart,” he said.
Advances in research
As they continue to see patients and devise specific care plans, developers of cardio-rheumatology programs have been supplementing their work with ongoing research.
Yale’s clinic is expanding this year to include a new attending physician, Attila Feher, MD, PhD, who has conducted research in autoimmunity and microcirculation using molecular imaging and multimodality imaging techniques. Prevalence of coronary microvascular dysfunction appears to be increased in this patient population, Dr. Furman said.
Dr. Wassif recently coauthored a paper that examined patients with underlying rheumatologic conditions who undergo valvular and aortic valve replacement. “To our surprise, there was really no difference between patients with autoimmune conditions and others with nonautoimmune conditions,” she said, adding that the study had its limitations.
Other work includes data on Medicare patients with ST- and non-ST-elevation myocardial infarctions who have an underlying autoimmune disorder. Dr. Wassif and her colleagues found that their long-term outcomes are worse than those of patients without these conditions. “It’s unclear if worse outcomes are related to complications of autoimmunity versus the extent of their underlying disease. This is a work in progress and certainly an area that is ripe for research.”
Dr. Garshick and other collaborators at NYU have been focusing on the endothelium, specifically platelet biology in patients with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and lupus. “We’re about to start the same research with gout as well,” he said.
“The process we’re most interested in is understanding how these diseases impact the early stages of cholesterol. And the way we’re doing that is evaluating the vasculature, specifically the endothelium,” he said.
He has finished two clinical trials that evaluate how standard heart disease medications such as aspirin and statins impact or can potentially benefit patients with psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis. “We have a whole list of other trials in the pipeline with other institutions across the country.”
Through a grant, Dr. Mankad is assessing whether a PET scan could detect inflammation in the hearts of rheumatoid arthritis patients. “We’re looking to see if the reason these patients have heart failure later in life is because their heart muscle actually shows evidence of inflammation, even when they have no symptoms,” she explained.
Other tests such as echocardiogram and CT scans will be used to evaluate coronary disease in about 40-50 patients. The goal of using these multiple imaging tools is to find markers indicating that the heart is affected by rheumatoid arthritis, which may indicate a higher likelihood of developing heart failure, she said.
Clinics are popping up
Through these new clinics, some collaborations have emerged. Dr. Garshick works closely with Brigham and Women’s Hospital, which has a similar cardio-rheumatology program, run by Brittany Weber, MD, to exchange ideas, discuss challenging cases, and collaborate.
“There are a lot of clinics like us popping up across the country,” he observed. Every so often, he hears from other institutions that are interested in starting their own cardio-rheumatology programs. “They ask us: How do you start, what should we look for?”
It’s an education process for both patients and providers, Dr. Garshick emphasized. “I also think it’s a bandwidth issue. Many of our rheumatology and dermatology colleagues are acutely aware of the connection, but there may not be enough time at a clinic visit to really go in depth” with these dual conditions, he said.
NYU-Langone Health for the past several years has been holding a symposium to educate people on the cardio-rheumatology connection and treating inflammation in cardiovascular disease. This year’s symposium, held in conjunction with Brigham and Women’s Hospital, is scheduled for April 28. For more information, visit the course website: nyulmc.org/cvinflammationcme.
“What we’re trying to do is help [other institutions] get that bandwidth” to adequately help and serve these patients, he said.
Dr. Garshick has received consultant fees from Abbvie and Horizon therapeutics and an unrestricted research grant from Pfizer. No other sources had relevant financial disclosures.
Clinical cardiologist Heba Wassif, MD, MPH, knows the value of working with her fellow rheumatologists, surgeons, and other clinicians to establish a care plan for her patients with cardiac conditions and autoimmune diseases.
She is the cofounder of the Cleveland Clinic’s new cardio-rheumatology program, which places an emphasis on multidisciplinary care. In her role, Dr. Wassif closely follows her patients, and if she sees any inflammation or any other condition that requires the rheumatologist, she reaches out to her colleagues to adjust medications if needed.
Collaboration with a rheumatologist was important when a patient with valvular disease was prepping for surgery. The patient was on significant immunosuppressants and the surgery had to be timed appropriately, accounting for any decreases in her immunosuppression, explained Dr. Wassif, director of inpatient clinical cardiology at Cleveland Clinic in Ohio.
Cardio-rheumatology programs are “the newest child” in a series of cardiology offshoots focusing on different populations. Cardio-oncology and cardio-obstetrics took off about 6 years ago, with cardio-rheumatology clinics and interested physicians rising in number over the last several years, Dr. Wassif noted.
The relationship between cardiovascular diseases and rheumatologic conditions is certainly recognized more often, “which means more literature is being published to discuss the link,” according to Rekha Mankad, MD, a trailblazer of this model of care. She directs the Women’s Heart Clinic at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., which was one of the earliest adopters of a cardio-rheumatology clinic.
Ten years ago, “nobody was talking about the link between rheumatologic conditions and cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Mankad said. “I’ve been asked to speak on this topic, and programs have asked me to speak about establishing cardio-rheumatology practices. So, there’s been an evolution as far as a recognition that these two conditions overlap.”
Patients have come to her independent of internal referrals, which means they have done Google searches on cardiology and rheumatology. “I think that it has made a splash, at least in the world of cardiology,” Dr. Mankad observed in an interview.
Other institutions such as NYU-Langone, Yale, Stanford, Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and Women’s College Hospital in Toronto have formed similar clinics whose focus is to address the specific needs of rheumatology patients with cardiac conditions through a teamwork approach.
Challenges of treating cardiac, rheumatologic conditions
The rise in clinics addresses the longstanding connection between autoimmune disorders and cardiac conditions.
Cardiologists have known that there is an element of inflammation that contributes to atherosclerosis, said Dr. Wassif, who has researched this topic extensively. A recent study she led found a strong association between rheumatic immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) and high risk of acute coronary syndrome in Medicare patients.
“This particular population has a very clear increased risk for cardiovascular conditions, including valve disease and heart failure,” she emphasized.
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis and lupus have up to a twofold and eightfold higher risk of heart disease, respectively, noted Michael S. Garshick, MD, a cardiovascular disease specialist who directs the cardio-rheumatology program at NYU-Langone Health, in New York. Cardiologists “have really developed an understanding that the immune system can impact the heart, and that there’s a need for people to understand the nuance behind how the immune system can affect them and what to do about it,” Dr. Garshick said.
Caring for patients with both afflictions comes with specific challenges. Many physicians are not well trained on managing and treating patients with these dual conditions.
The “lipid paradox,” in which lipids are reduced with active inflammation in some rheumatologic conditions, can make treatment more nuanced. In addition, the traditional ASCVD (atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease) score often underestimates the cardiovascular risk of these patients, noted cardiologist Margaret Furman, MD, MPH, assistant professor and codirector of Yale’s Cardio-Rheumatology Program, New Haven, Conn.
Newer biologic medications used to treat rheumatologic diseases can alter a patient’s lipid profile, she said in an interview.
“It can be difficult to assess each individual patient’s cardiovascular risk as their disease state and treatment can vary throughout their lifetime based on their degree of inflammation. The importance of aggressive lipid management is often underestimated,” Dr. Furman added.
Cardiology and rheumatology partnerships can address gaps in care of this unique group of patients, said Vaidehi R. Chowdhary, MBBS, MD, clinical chief of the Yale Section of Rheumatology, Allergy, and Immunology at Yale University.
“The role of the rheumatologist in this dyad is to educate patients on this risk, work toward adequate control of inflammation, and minimize use of medications that contribute to increased cardiovascular risks,” said Dr. Chowdhary, who cofounded Yale’s cardio-rheumatology program with Dr. Furman.
Cardiologists in turn can assert their knowledge about medications and their impact on lipids and inflammation, Dr. Wassif said.
Many anti-inflammatory therapies are now within the cardiologist’s purview, Dr. Garshick noted. “For example, specifically with pericarditis, there’s [Food and Drug Administration]–approved anti-inflammatories or biologics. We’re the ones who feel the most comfortable giving them right now.” Cardiologists quite often are consulted about medications that are efficacious in rheumatologic conditions but could negatively impact the cardiovascular system, such as Janus kinase inhibitors, he added.
‘Reading the tea leaves’
Each program has its own unique story. For the Cleveland Clinic, the concept of a cardio-rheumatology program began during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020. Developing such a concept and gaining institutional acceptance is always a work in process, Dr. Wassif said. “It’s not that you decide one day that you’re going to build a center, and that center is going to come into fruition overnight. You first gauge interest within your division. Who are the individuals that are interested in this area?”
Cleveland Clinic’s center is seeking to build relations between medical disciplines while spotlighting the concept of cardio-rheumatology, said Dr. Wassif, who has been providing education within the clinic and at other health institutions to ensure that patients receive appropriate attention early.
NYU-Langone launched its program amid this heightened awareness that the immune system could affect atherosclerosis, “kind of reading of the tea leaves, so to speak,” Dr. Garshick said.
Several clinical trials served as a catalyst for this movement. “A lot of clinical cardiologists were never 100% convinced that targeting the immune system reduced cardiovascular disease,” he said. Then the CANTOS clinical trial came along and showed for the first time that a therapeutic monoclonal antibody targeting interleukin-1beta, a cytokine central to inflammatory response, could in fact reduce cardiovascular disease.
Trials like this, along with epidemiologic literature connecting the rheumatologic and the autoimmune conditions with cardiovascular disease, pushed this concept to the forefront, Dr. Garshick said.
The notion that a clinic could successfully address cardiac problems in patients with rheumatic diseases yielded promising returns at Women’s College Hospital in Toronto, according to a report presented at the 2018 American College of Rheumatology annual meeting. Researchers reported that patients with rheumatologic conditions who attended a cardio-rheumatology clinic at this center saw improvements in care. The clinic identified increased cardiovascular risk and early atherosclerosis, and 53.8% of patients altered their medications after being seen in the clinic.
A total of 39.7% and 32.1% received lipid lowering and antiplatelet therapies, respectively, and 14% received antihypertensive therapy. A small percentage were treated for heart failure or placed on lifelong anticoagulation therapy for atrial fibrillation, and one patient received a percutaneous coronary stent.
Ins and outs of the referral process
Initially designed for preventive cardiac risk assessment, Yale’s program evolved into a multidisciplinary, patient-centered approach for the management of complex cardiovascular conditions in patients with autoimmune rheumatologic diseases.
The program is open to anyone who carries a diagnosis of rheumatologic disease or has elevated inflammatory markers. “Every patient, regardless of the reason for the referral, receives a cardiovascular risk assessment,” Dr. Furman said.
Most referrals come from rheumatologists, although cardiology colleagues and pulmonologists have also sent referrals. A pulmonologist, for example, may want to rule out a cardiac cause to shortness of breath. The patient’s workup, care, and follow-up are based on the reason for referral.
“We are currently referring patients with established cardiac disease, traditional risk factors, or for better risk assessment for primary prevention of coronary artery disease,” Dr. Chowdhary said. “We communicate very frequently about medication changes, and patients are aware of goals of care from both sides.”
Dr. Furman works closely with several of the rheumatology specialists taking care of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and scleroderma.
Rheumatology follows patients every 3-6 months or more frequently based on their disease activity.
Dr. Mankad uses her sleuthing skills at Mayo Clinic to determine what the patients need. If they come in for a preventive assessment, she looks more closely at their cardiovascular risks and may order additional imaging to look for subclinical atherosclerosis. “We’re more aggressive with statin therapy in this population because of that,” she said.
If it’s valve disease, she pays extra attention to the patients’ valves in the echocardiograms and follows them a bit more regularly than someone without a rheumatologic condition and valve disease.
For patients with heart failure signs or symptoms, “it depends on how symptomatic they are,” Dr. Mankad said. In some instances, she may look for evidence of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in patients who have rheumatoid arthritis who happen to be short of breath. “There’s so many different manifestations that patients with rheumatologic conditions can have as far as what could be affected in the heart,” she noted.
Quite frequently, Dr. Mankad identifies subclinical disease in her patients with rheumatoid arthritis. “I’ve seen many patients whose risk scores would not dictate statin therapy. But I went looking for subclinical disease by either doing coronary assessment or carotid assessment and have found atherosclerosis that would be enough to warrant statin therapy.”
A personalized assessment to reduce cardiac risk
NYU-Langone’s program offers opportunities to educate patients about the link between cardiac and rheumatologic disease.
“Their rheumatologist or their dermatologist will say, ‘Hey, have you heard about the connection between psoriasis, psoriatic or rheumatoid arthritis, and heart disease and the risk of heart attack or stroke?’ ” Dr. Garshick said.
The patients will often say they know nothing about these connections and want to learn more about how to treat it.
“We’ll say, ‘we have someone here that can help you.’ They’ll send them to myself or other colleagues like me across the country. We’ll assess blood pressure, weight, lipids, hemoglobin A1c, and other serologic and oftentimes imaging biomarkers of cardiovascular risk.” The patients will receive a personalized assessment, listing things they can do to lower their risk, whether it’s diet, exercise, or lifestyle. “Many times it can involve medications to reduce heart disease risk,” said Dr. Garshick.
In some instances, a rheumatologist or dermatologist may be concerned about starting a patient on a specific medication for the disease such as a JAK inhibitor. “We’ll help assess their risk because there’s been a lot of literature out in the rheumatology world about the risk of JAK inhibitors and heart disease and blood clots,” said Dr. Garshick.
Dr. Garshick also sees patients with rheumatologic conditions who have a specific cardiovascular concern or complaint such as shortness of breath or chest pain. “We’ll work that up with a specific knowledge of the underlying immune condition and how that may impact their heart,” he said.
Advances in research
As they continue to see patients and devise specific care plans, developers of cardio-rheumatology programs have been supplementing their work with ongoing research.
Yale’s clinic is expanding this year to include a new attending physician, Attila Feher, MD, PhD, who has conducted research in autoimmunity and microcirculation using molecular imaging and multimodality imaging techniques. Prevalence of coronary microvascular dysfunction appears to be increased in this patient population, Dr. Furman said.
Dr. Wassif recently coauthored a paper that examined patients with underlying rheumatologic conditions who undergo valvular and aortic valve replacement. “To our surprise, there was really no difference between patients with autoimmune conditions and others with nonautoimmune conditions,” she said, adding that the study had its limitations.
Other work includes data on Medicare patients with ST- and non-ST-elevation myocardial infarctions who have an underlying autoimmune disorder. Dr. Wassif and her colleagues found that their long-term outcomes are worse than those of patients without these conditions. “It’s unclear if worse outcomes are related to complications of autoimmunity versus the extent of their underlying disease. This is a work in progress and certainly an area that is ripe for research.”
Dr. Garshick and other collaborators at NYU have been focusing on the endothelium, specifically platelet biology in patients with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and lupus. “We’re about to start the same research with gout as well,” he said.
“The process we’re most interested in is understanding how these diseases impact the early stages of cholesterol. And the way we’re doing that is evaluating the vasculature, specifically the endothelium,” he said.
He has finished two clinical trials that evaluate how standard heart disease medications such as aspirin and statins impact or can potentially benefit patients with psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis. “We have a whole list of other trials in the pipeline with other institutions across the country.”
Through a grant, Dr. Mankad is assessing whether a PET scan could detect inflammation in the hearts of rheumatoid arthritis patients. “We’re looking to see if the reason these patients have heart failure later in life is because their heart muscle actually shows evidence of inflammation, even when they have no symptoms,” she explained.
Other tests such as echocardiogram and CT scans will be used to evaluate coronary disease in about 40-50 patients. The goal of using these multiple imaging tools is to find markers indicating that the heart is affected by rheumatoid arthritis, which may indicate a higher likelihood of developing heart failure, she said.
Clinics are popping up
Through these new clinics, some collaborations have emerged. Dr. Garshick works closely with Brigham and Women’s Hospital, which has a similar cardio-rheumatology program, run by Brittany Weber, MD, to exchange ideas, discuss challenging cases, and collaborate.
“There are a lot of clinics like us popping up across the country,” he observed. Every so often, he hears from other institutions that are interested in starting their own cardio-rheumatology programs. “They ask us: How do you start, what should we look for?”
It’s an education process for both patients and providers, Dr. Garshick emphasized. “I also think it’s a bandwidth issue. Many of our rheumatology and dermatology colleagues are acutely aware of the connection, but there may not be enough time at a clinic visit to really go in depth” with these dual conditions, he said.
NYU-Langone Health for the past several years has been holding a symposium to educate people on the cardio-rheumatology connection and treating inflammation in cardiovascular disease. This year’s symposium, held in conjunction with Brigham and Women’s Hospital, is scheduled for April 28. For more information, visit the course website: nyulmc.org/cvinflammationcme.
“What we’re trying to do is help [other institutions] get that bandwidth” to adequately help and serve these patients, he said.
Dr. Garshick has received consultant fees from Abbvie and Horizon therapeutics and an unrestricted research grant from Pfizer. No other sources had relevant financial disclosures.
Phil Robinson: Rheumatologist, colleague, huntsman spider rescuer
Helen Tanner remembers stealing glimpses of her husband, Philip (“Phil”) Robinson, MBChB, PhD, associate professor at the University of Queensland (Australia), catching and rehoming huge Huntsman spiders. Robinson made the extra effort because he didn’t want to hurt them; he wasn’t a big fan of the large spider with a potential leg span of 6 inches that’s commonly found in Australia, per the Australian Museum.
Robinson also relished taking his children, Eddie, 4, and Tommy, 7, on roller coaster rides, which they enjoyed, despite the experience typically giving him motion sickness, Tanner said.
“He would do anything to make the children happy,” she said. “His children meant the world to him.”
Robinson died Jan. 3 as a result of diffuse gastric adenocarcinoma, according to his wife, who added that it was a short, 2-week-long illness.
A leader of global effort to understand COVID-19 and rheumatic disease
Jinoos Yazdany, MD, MPH, chief of the division of rheumatology at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, described Robinson as “one of the hardest-working people I have ever known. ... [still] his deep love and dedication for his family and kids was always present.”
Robinson would wake up early, even on weekends, to lead international calls across multiple time zones, Yazdany said. “He was driven by a deep curiosity and an intense desire to generate scholarship that would help people with rheumatic diseases.”
Yazdany added that Robinson had a full research portfolio in gout and spondyloarthritis and a busy clinical practice.
She often caught glimpses of Robinson’s young children during Zoom calls. “He was also a talented baker and loved to bake with his kids, often posting pictures of his creations on social media,” Yazdany said.
A mutual colleague compiled some of Robinson’s baking successes. That includes “ ‘probably about to be locked down’ cookies” on July 17, 2021, and “Queensland lockdown cookies!!!” on July 2, 2021. Reuters reported on July 21, 2021, that Australia was witnessing an alarming increase in COVID-19 cases.
Robinson also worked his social media skills to rally support for the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance, according to an article published by his colleagues in The Rheumatologist. Yazdany collaborated with him in this effort.
Launched on March 12, 2020, the Global Rheumatology Alliance’s mission is to “collect, analyze, and disseminate information about COVID-19 and rheumatology to patients, physicians, and other relevant groups to improve the care of patients with rheumatic disease.” Robinson served as chair of governance and policy for the collaborative effort.
Inspired by a conversation on Twitter by Leonard Calabrese, DO, a rheumatologist at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, about an outcomes registry created by gastroenterologists specific to patients with inflammatory bowel disease, Robinson launched a discussion about a similar effort for rheumatology on Twitter, they write.
Along with colleagues and within a single Zoom conference call, Yazdany and Robinson had a plan to organize the registry, Robinson’s colleagues write.
Two projects of the Global Rheumatology Alliance are a health care provider–entered registry for providers to enter data about rheumatology patients with COVID-19 infections, and their COVID-19 Vax Survey, which is available in 12 languages, including English.
Yazdany had never met Robinson before she started working with him on the Global Rheumatology Alliance. They started chatting on Twitter, then moved to Zoom conference calls, and subsequently had weeks when they talked by phone and “emailed constantly,” she said.
“As I reflect on our initial interactions, I am struck by how brilliantly we got along and trusted each other,” Yazdany told this news organization. “We both liked to think big, believed in inclusive collaborations, and were committed to helping people with rheumatic diseases during a scary and uncertain time.”
Still, Yazdany noted that she and Phil brought different strengths to their collaborations. She brought her skills related to the technical aspects of research databases, while “Phil worked his magic in mobilizing friends and colleagues from all over the world,” she said. “He served as a wonderful leader, one whom people believed in and would follow.”
The two colleagues, who spent much of their collaborations over Zoom calls, email, and Slack, while living more than 7,000 miles apart, finally met in person at ACR Convergence 2022, which took place in Philadelphia that year. “It felt like the best kind of reunion with a dear friend,” Yazdany remembered.
A mentor who created a platform for ‘good people to do great things’
David Liew, MBBS, PhD, consultant rheumatologist and clinical pharmacologist at Austin Health in Melbourne, marveled at Robinson’s ability to “distill things simply and cleanly, with clarity but without losing detail.” Liew, who collaborated with Robinson throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, likens the experience to “jamming with [jazz musician John] Coltrane.”
“What I think was particularly remarkable was the capacity to not only have those thoughts himself, but to facilitate others to have that springboard,” said Liew, who added that Robinson “took enormous pleasure in facilitating others’ success.”
“I think the greatest joy he drew out of the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance, apart from facing up to the challenge that needed to be faced, was creating a platform for good people to do great things,” said Liew, who recalled one situation where Robinson gently challenged him. Looking back now, Liew can “now see he very clearly was laying me up, giving me the best chance to shine.”
He describes Robinson as “a deep soul who loved his wife and two sons enormously” and “a whiskey aficionado.” “[Whiskey] suited his contemplative style,” Liew recalled. “Some of my fondest conversations with him were over a whiskey, either in person or virtually, pondering the ‘big issues.’”
A ‘friend and a colleague and so much more’
Claire Barrett, MBBS, president of the Australian Rheumatology Association, described Robinson as a “friend and a colleague and so much more. ... [He was] someone who I worked, laughed, ate, drank, danced, and had fun with,” she told this news organization. They served together as volunteers for the Australian Rheumatology Association and its Queensland branch, as well as Arthritis Queensland; they were also colleagues at Metro North Hospital and Health Service in Brisbane, Queensland.
Robinson was her “go to” for insightful comment on a variety of topics, she said. That could be advice on managing a patient with difficult gout, challenging spondyloarthritis, or the best treatment for a patient with COVID-19.
“[Phil] was a friend I could ask about anything, knowing I would not be judged,” Barrett said. “His kids and our grandkids are similar ages, so we would swap stories and photos and laugh about how cute/funny/cuddly/busy/etc. they were. My heart is broken he won’t get the chance to enjoy their future and the excitement of having Phil continuing to be such an active dad.”
Tanner, Robinson’s wife, said, “he loved everything.” That included the academic side of medicine, and working out what was wrong with his patients and helping them get better. “He was dedicated to this,” she added.
“He also loved the camaraderie of the job – all the people he met and interacted with. [Phil] loved sharing his ideas for research and also discussing complex patients with colleagues. He was driven by finding the answers to problems and doing this as part of a team of researchers/clinicians. He wasn’t interested in personal success.”
Robinson received his medical degree from Otago Medical School in Dunedin, New Zealand, according to the University of Queensland. His specialty training in general and acute care medicine and rheumatology was completed in Wellington, New Zealand, and Dunedin. Robinson also achieved a PhD in human genetics at the University of Queensland Diamantina Institute and had a postdoctoral fellowship at the Queensland Brain Institute at the University of Queensland.
Before his death, he worked at the Royal Brisbane and Women’s Hospital in Herston, Queensland, and at St. Andrew’s War Memorial Hospital in Spring Hill in Brisbane.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Helen Tanner remembers stealing glimpses of her husband, Philip (“Phil”) Robinson, MBChB, PhD, associate professor at the University of Queensland (Australia), catching and rehoming huge Huntsman spiders. Robinson made the extra effort because he didn’t want to hurt them; he wasn’t a big fan of the large spider with a potential leg span of 6 inches that’s commonly found in Australia, per the Australian Museum.
Robinson also relished taking his children, Eddie, 4, and Tommy, 7, on roller coaster rides, which they enjoyed, despite the experience typically giving him motion sickness, Tanner said.
“He would do anything to make the children happy,” she said. “His children meant the world to him.”
Robinson died Jan. 3 as a result of diffuse gastric adenocarcinoma, according to his wife, who added that it was a short, 2-week-long illness.
A leader of global effort to understand COVID-19 and rheumatic disease
Jinoos Yazdany, MD, MPH, chief of the division of rheumatology at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, described Robinson as “one of the hardest-working people I have ever known. ... [still] his deep love and dedication for his family and kids was always present.”
Robinson would wake up early, even on weekends, to lead international calls across multiple time zones, Yazdany said. “He was driven by a deep curiosity and an intense desire to generate scholarship that would help people with rheumatic diseases.”
Yazdany added that Robinson had a full research portfolio in gout and spondyloarthritis and a busy clinical practice.
She often caught glimpses of Robinson’s young children during Zoom calls. “He was also a talented baker and loved to bake with his kids, often posting pictures of his creations on social media,” Yazdany said.
A mutual colleague compiled some of Robinson’s baking successes. That includes “ ‘probably about to be locked down’ cookies” on July 17, 2021, and “Queensland lockdown cookies!!!” on July 2, 2021. Reuters reported on July 21, 2021, that Australia was witnessing an alarming increase in COVID-19 cases.
Robinson also worked his social media skills to rally support for the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance, according to an article published by his colleagues in The Rheumatologist. Yazdany collaborated with him in this effort.
Launched on March 12, 2020, the Global Rheumatology Alliance’s mission is to “collect, analyze, and disseminate information about COVID-19 and rheumatology to patients, physicians, and other relevant groups to improve the care of patients with rheumatic disease.” Robinson served as chair of governance and policy for the collaborative effort.
Inspired by a conversation on Twitter by Leonard Calabrese, DO, a rheumatologist at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, about an outcomes registry created by gastroenterologists specific to patients with inflammatory bowel disease, Robinson launched a discussion about a similar effort for rheumatology on Twitter, they write.
Along with colleagues and within a single Zoom conference call, Yazdany and Robinson had a plan to organize the registry, Robinson’s colleagues write.
Two projects of the Global Rheumatology Alliance are a health care provider–entered registry for providers to enter data about rheumatology patients with COVID-19 infections, and their COVID-19 Vax Survey, which is available in 12 languages, including English.
Yazdany had never met Robinson before she started working with him on the Global Rheumatology Alliance. They started chatting on Twitter, then moved to Zoom conference calls, and subsequently had weeks when they talked by phone and “emailed constantly,” she said.
“As I reflect on our initial interactions, I am struck by how brilliantly we got along and trusted each other,” Yazdany told this news organization. “We both liked to think big, believed in inclusive collaborations, and were committed to helping people with rheumatic diseases during a scary and uncertain time.”
Still, Yazdany noted that she and Phil brought different strengths to their collaborations. She brought her skills related to the technical aspects of research databases, while “Phil worked his magic in mobilizing friends and colleagues from all over the world,” she said. “He served as a wonderful leader, one whom people believed in and would follow.”
The two colleagues, who spent much of their collaborations over Zoom calls, email, and Slack, while living more than 7,000 miles apart, finally met in person at ACR Convergence 2022, which took place in Philadelphia that year. “It felt like the best kind of reunion with a dear friend,” Yazdany remembered.
A mentor who created a platform for ‘good people to do great things’
David Liew, MBBS, PhD, consultant rheumatologist and clinical pharmacologist at Austin Health in Melbourne, marveled at Robinson’s ability to “distill things simply and cleanly, with clarity but without losing detail.” Liew, who collaborated with Robinson throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, likens the experience to “jamming with [jazz musician John] Coltrane.”
“What I think was particularly remarkable was the capacity to not only have those thoughts himself, but to facilitate others to have that springboard,” said Liew, who added that Robinson “took enormous pleasure in facilitating others’ success.”
“I think the greatest joy he drew out of the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance, apart from facing up to the challenge that needed to be faced, was creating a platform for good people to do great things,” said Liew, who recalled one situation where Robinson gently challenged him. Looking back now, Liew can “now see he very clearly was laying me up, giving me the best chance to shine.”
He describes Robinson as “a deep soul who loved his wife and two sons enormously” and “a whiskey aficionado.” “[Whiskey] suited his contemplative style,” Liew recalled. “Some of my fondest conversations with him were over a whiskey, either in person or virtually, pondering the ‘big issues.’”
A ‘friend and a colleague and so much more’
Claire Barrett, MBBS, president of the Australian Rheumatology Association, described Robinson as a “friend and a colleague and so much more. ... [He was] someone who I worked, laughed, ate, drank, danced, and had fun with,” she told this news organization. They served together as volunteers for the Australian Rheumatology Association and its Queensland branch, as well as Arthritis Queensland; they were also colleagues at Metro North Hospital and Health Service in Brisbane, Queensland.
Robinson was her “go to” for insightful comment on a variety of topics, she said. That could be advice on managing a patient with difficult gout, challenging spondyloarthritis, or the best treatment for a patient with COVID-19.
“[Phil] was a friend I could ask about anything, knowing I would not be judged,” Barrett said. “His kids and our grandkids are similar ages, so we would swap stories and photos and laugh about how cute/funny/cuddly/busy/etc. they were. My heart is broken he won’t get the chance to enjoy their future and the excitement of having Phil continuing to be such an active dad.”
Tanner, Robinson’s wife, said, “he loved everything.” That included the academic side of medicine, and working out what was wrong with his patients and helping them get better. “He was dedicated to this,” she added.
“He also loved the camaraderie of the job – all the people he met and interacted with. [Phil] loved sharing his ideas for research and also discussing complex patients with colleagues. He was driven by finding the answers to problems and doing this as part of a team of researchers/clinicians. He wasn’t interested in personal success.”
Robinson received his medical degree from Otago Medical School in Dunedin, New Zealand, according to the University of Queensland. His specialty training in general and acute care medicine and rheumatology was completed in Wellington, New Zealand, and Dunedin. Robinson also achieved a PhD in human genetics at the University of Queensland Diamantina Institute and had a postdoctoral fellowship at the Queensland Brain Institute at the University of Queensland.
Before his death, he worked at the Royal Brisbane and Women’s Hospital in Herston, Queensland, and at St. Andrew’s War Memorial Hospital in Spring Hill in Brisbane.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Helen Tanner remembers stealing glimpses of her husband, Philip (“Phil”) Robinson, MBChB, PhD, associate professor at the University of Queensland (Australia), catching and rehoming huge Huntsman spiders. Robinson made the extra effort because he didn’t want to hurt them; he wasn’t a big fan of the large spider with a potential leg span of 6 inches that’s commonly found in Australia, per the Australian Museum.
Robinson also relished taking his children, Eddie, 4, and Tommy, 7, on roller coaster rides, which they enjoyed, despite the experience typically giving him motion sickness, Tanner said.
“He would do anything to make the children happy,” she said. “His children meant the world to him.”
Robinson died Jan. 3 as a result of diffuse gastric adenocarcinoma, according to his wife, who added that it was a short, 2-week-long illness.
A leader of global effort to understand COVID-19 and rheumatic disease
Jinoos Yazdany, MD, MPH, chief of the division of rheumatology at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, described Robinson as “one of the hardest-working people I have ever known. ... [still] his deep love and dedication for his family and kids was always present.”
Robinson would wake up early, even on weekends, to lead international calls across multiple time zones, Yazdany said. “He was driven by a deep curiosity and an intense desire to generate scholarship that would help people with rheumatic diseases.”
Yazdany added that Robinson had a full research portfolio in gout and spondyloarthritis and a busy clinical practice.
She often caught glimpses of Robinson’s young children during Zoom calls. “He was also a talented baker and loved to bake with his kids, often posting pictures of his creations on social media,” Yazdany said.
A mutual colleague compiled some of Robinson’s baking successes. That includes “ ‘probably about to be locked down’ cookies” on July 17, 2021, and “Queensland lockdown cookies!!!” on July 2, 2021. Reuters reported on July 21, 2021, that Australia was witnessing an alarming increase in COVID-19 cases.
Robinson also worked his social media skills to rally support for the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance, according to an article published by his colleagues in The Rheumatologist. Yazdany collaborated with him in this effort.
Launched on March 12, 2020, the Global Rheumatology Alliance’s mission is to “collect, analyze, and disseminate information about COVID-19 and rheumatology to patients, physicians, and other relevant groups to improve the care of patients with rheumatic disease.” Robinson served as chair of governance and policy for the collaborative effort.
Inspired by a conversation on Twitter by Leonard Calabrese, DO, a rheumatologist at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, about an outcomes registry created by gastroenterologists specific to patients with inflammatory bowel disease, Robinson launched a discussion about a similar effort for rheumatology on Twitter, they write.
Along with colleagues and within a single Zoom conference call, Yazdany and Robinson had a plan to organize the registry, Robinson’s colleagues write.
Two projects of the Global Rheumatology Alliance are a health care provider–entered registry for providers to enter data about rheumatology patients with COVID-19 infections, and their COVID-19 Vax Survey, which is available in 12 languages, including English.
Yazdany had never met Robinson before she started working with him on the Global Rheumatology Alliance. They started chatting on Twitter, then moved to Zoom conference calls, and subsequently had weeks when they talked by phone and “emailed constantly,” she said.
“As I reflect on our initial interactions, I am struck by how brilliantly we got along and trusted each other,” Yazdany told this news organization. “We both liked to think big, believed in inclusive collaborations, and were committed to helping people with rheumatic diseases during a scary and uncertain time.”
Still, Yazdany noted that she and Phil brought different strengths to their collaborations. She brought her skills related to the technical aspects of research databases, while “Phil worked his magic in mobilizing friends and colleagues from all over the world,” she said. “He served as a wonderful leader, one whom people believed in and would follow.”
The two colleagues, who spent much of their collaborations over Zoom calls, email, and Slack, while living more than 7,000 miles apart, finally met in person at ACR Convergence 2022, which took place in Philadelphia that year. “It felt like the best kind of reunion with a dear friend,” Yazdany remembered.
A mentor who created a platform for ‘good people to do great things’
David Liew, MBBS, PhD, consultant rheumatologist and clinical pharmacologist at Austin Health in Melbourne, marveled at Robinson’s ability to “distill things simply and cleanly, with clarity but without losing detail.” Liew, who collaborated with Robinson throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, likens the experience to “jamming with [jazz musician John] Coltrane.”
“What I think was particularly remarkable was the capacity to not only have those thoughts himself, but to facilitate others to have that springboard,” said Liew, who added that Robinson “took enormous pleasure in facilitating others’ success.”
“I think the greatest joy he drew out of the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance, apart from facing up to the challenge that needed to be faced, was creating a platform for good people to do great things,” said Liew, who recalled one situation where Robinson gently challenged him. Looking back now, Liew can “now see he very clearly was laying me up, giving me the best chance to shine.”
He describes Robinson as “a deep soul who loved his wife and two sons enormously” and “a whiskey aficionado.” “[Whiskey] suited his contemplative style,” Liew recalled. “Some of my fondest conversations with him were over a whiskey, either in person or virtually, pondering the ‘big issues.’”
A ‘friend and a colleague and so much more’
Claire Barrett, MBBS, president of the Australian Rheumatology Association, described Robinson as a “friend and a colleague and so much more. ... [He was] someone who I worked, laughed, ate, drank, danced, and had fun with,” she told this news organization. They served together as volunteers for the Australian Rheumatology Association and its Queensland branch, as well as Arthritis Queensland; they were also colleagues at Metro North Hospital and Health Service in Brisbane, Queensland.
Robinson was her “go to” for insightful comment on a variety of topics, she said. That could be advice on managing a patient with difficult gout, challenging spondyloarthritis, or the best treatment for a patient with COVID-19.
“[Phil] was a friend I could ask about anything, knowing I would not be judged,” Barrett said. “His kids and our grandkids are similar ages, so we would swap stories and photos and laugh about how cute/funny/cuddly/busy/etc. they were. My heart is broken he won’t get the chance to enjoy their future and the excitement of having Phil continuing to be such an active dad.”
Tanner, Robinson’s wife, said, “he loved everything.” That included the academic side of medicine, and working out what was wrong with his patients and helping them get better. “He was dedicated to this,” she added.
“He also loved the camaraderie of the job – all the people he met and interacted with. [Phil] loved sharing his ideas for research and also discussing complex patients with colleagues. He was driven by finding the answers to problems and doing this as part of a team of researchers/clinicians. He wasn’t interested in personal success.”
Robinson received his medical degree from Otago Medical School in Dunedin, New Zealand, according to the University of Queensland. His specialty training in general and acute care medicine and rheumatology was completed in Wellington, New Zealand, and Dunedin. Robinson also achieved a PhD in human genetics at the University of Queensland Diamantina Institute and had a postdoctoral fellowship at the Queensland Brain Institute at the University of Queensland.
Before his death, he worked at the Royal Brisbane and Women’s Hospital in Herston, Queensland, and at St. Andrew’s War Memorial Hospital in Spring Hill in Brisbane.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Metabolic syndrome may promote gout in young men
Metabolic syndrome is associated with a significantly increased risk for gout in young men, but the risk can be mitigated by improvement in individual components of the syndrome, based on data from a pair of population-based studies totaling more than 4 million individuals.
Gout remains the most common type of inflammatory arthritis in men, and the rate has been rising among younger adults, Yeonghee Eun, MD, PhD, of Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, South Korea, and colleagues wrote. An increasing body of evidence suggests a link between gout and metabolic syndrome (MetS), but large studies have been lacking, especially in younger adults.
In a study published in Frontiers in Medicine, the researchers reviewed data from 3,569,104 men aged 20-39 years who underwent a health checkup between 2009 and 2012 in South Korea, based on the Korean National Health Insurance Service. The primary outcome of incident gout was identified using claims data. The mean age of the participants was 31.5 years.
Over a mean follow-up of 7.4 years, the incidence of gout was 3.36 per 1,000 person-years. The risk of developing gout was more than twice as high among individuals who met MetS criteria than in those who did not (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.44).
MetS was defined as the presence of at least two of the following components: hypertriglyceridemia, abdominal obesity, reduced HDL cholesterol, elevated blood pressure, and elevated fasting glucose.
Overall, individuals with all five MetS components had a fivefold increase in gout risk, compared with people who did not have MetS (aHR, 5.24). In an analysis of each component of MetS, hypertriglyceridemia and abdominal obesity showed the strongest association with gout (aHRs of 2.08 and 2.33, respectively).
The impact of MetS on risk of incident gout was greater in younger participants, which suggests that the management of MetS in young people should be emphasized, the researchers said.
In a further analysis of body mass index subgroups, MetS had the greatest impact on gout risk for individuals who were underweight (aHR, 3.82). “In particular, in the underweight group, the risk of gout increased 10-fold when abdominal obesity was present,” the researchers said.
The study was limited by several factors including potential selection bias and potential overestimation of gout incidence because of the use of diagnostic codes, the researchers noted. Other limitations included lack of control for nutritional or dietary risk factors and the inability to include cases that occurred after the study period.
However, findings were strengthened by the large number of participants with MetS who were underweight or normal weight, the researchers wrote. More research on the mechanism of action is needed, but the data suggest that MetS is a key risk factor in the development of gout in young men.
In a second study, published in Arthritis & Rheumatology, Dr. Eun and colleagues examined associations between MetS changes and incident gout in young men. Although previous studies have shown that changes in MetS status can alter the risk of cardiovascular events, atrial fibrillation, end-stage renal disease, and all-cause mortality, the impact of these changes on gout has not been well studied, they said. The researchers used the same study cohort, the National Health Insurance Service database in South Korea. They reviewed data from 1,293,166 individuals aged 20-39 years. Of these, 18,473 were diagnosed with gout for an incidence rate 3.36/1,000 person-years. The researchers compared gout incidence for men who met criteria for MetS at three health checkups and those without MetS.
Overall, patients with MetS at all three checkups had a nearly fourfold higher risk of gout than those who never had MetS, with an adjusted hazard ratio of 3.82, the researchers wrote. The development of MetS over the study period more than doubled the risk of gout, but recovery from MetS reduced incident gout risk by approximately 50% (aHR, 0.52).
In findings similar to the Frontiers in Medicine study, the greatest associations with gout were noted for changes in elevated triglycerides and changes in abdominal obesity; aHRs for development and recovery for elevated triglycerides were 1.74 and 0.56, respectively, and for abdominal obesity, 1.94 and 0.69, respectively.
More research is needed to explore the mechanism by which both abdominal obesity and elevated triglycerides drive the development of gout, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
Also similar to the Frontiers study, the associations among changes in MetS and incident gout were greater for the youngest participants (in their 20s) and in the underweight or normal weight BMI groups.
Limitations of the second study included possible selection bias because of the study population of workplace employees who participated in regular health checks and the lack of data on women or on men aged 40 years and older, the researchers noted. Other limitations included possible misclassification of MetS because of varying health checkup results and drug claims, and lack of data on serum urate, which prevented assessment of hyperuricemia as a cause of gout.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and suggest that MetS is a modifiable risk factor for gout, the researchers concluded.
Neither of the studies received outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Metabolic syndrome is associated with a significantly increased risk for gout in young men, but the risk can be mitigated by improvement in individual components of the syndrome, based on data from a pair of population-based studies totaling more than 4 million individuals.
Gout remains the most common type of inflammatory arthritis in men, and the rate has been rising among younger adults, Yeonghee Eun, MD, PhD, of Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, South Korea, and colleagues wrote. An increasing body of evidence suggests a link between gout and metabolic syndrome (MetS), but large studies have been lacking, especially in younger adults.
In a study published in Frontiers in Medicine, the researchers reviewed data from 3,569,104 men aged 20-39 years who underwent a health checkup between 2009 and 2012 in South Korea, based on the Korean National Health Insurance Service. The primary outcome of incident gout was identified using claims data. The mean age of the participants was 31.5 years.
Over a mean follow-up of 7.4 years, the incidence of gout was 3.36 per 1,000 person-years. The risk of developing gout was more than twice as high among individuals who met MetS criteria than in those who did not (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.44).
MetS was defined as the presence of at least two of the following components: hypertriglyceridemia, abdominal obesity, reduced HDL cholesterol, elevated blood pressure, and elevated fasting glucose.
Overall, individuals with all five MetS components had a fivefold increase in gout risk, compared with people who did not have MetS (aHR, 5.24). In an analysis of each component of MetS, hypertriglyceridemia and abdominal obesity showed the strongest association with gout (aHRs of 2.08 and 2.33, respectively).
The impact of MetS on risk of incident gout was greater in younger participants, which suggests that the management of MetS in young people should be emphasized, the researchers said.
In a further analysis of body mass index subgroups, MetS had the greatest impact on gout risk for individuals who were underweight (aHR, 3.82). “In particular, in the underweight group, the risk of gout increased 10-fold when abdominal obesity was present,” the researchers said.
The study was limited by several factors including potential selection bias and potential overestimation of gout incidence because of the use of diagnostic codes, the researchers noted. Other limitations included lack of control for nutritional or dietary risk factors and the inability to include cases that occurred after the study period.
However, findings were strengthened by the large number of participants with MetS who were underweight or normal weight, the researchers wrote. More research on the mechanism of action is needed, but the data suggest that MetS is a key risk factor in the development of gout in young men.
In a second study, published in Arthritis & Rheumatology, Dr. Eun and colleagues examined associations between MetS changes and incident gout in young men. Although previous studies have shown that changes in MetS status can alter the risk of cardiovascular events, atrial fibrillation, end-stage renal disease, and all-cause mortality, the impact of these changes on gout has not been well studied, they said. The researchers used the same study cohort, the National Health Insurance Service database in South Korea. They reviewed data from 1,293,166 individuals aged 20-39 years. Of these, 18,473 were diagnosed with gout for an incidence rate 3.36/1,000 person-years. The researchers compared gout incidence for men who met criteria for MetS at three health checkups and those without MetS.
Overall, patients with MetS at all three checkups had a nearly fourfold higher risk of gout than those who never had MetS, with an adjusted hazard ratio of 3.82, the researchers wrote. The development of MetS over the study period more than doubled the risk of gout, but recovery from MetS reduced incident gout risk by approximately 50% (aHR, 0.52).
In findings similar to the Frontiers in Medicine study, the greatest associations with gout were noted for changes in elevated triglycerides and changes in abdominal obesity; aHRs for development and recovery for elevated triglycerides were 1.74 and 0.56, respectively, and for abdominal obesity, 1.94 and 0.69, respectively.
More research is needed to explore the mechanism by which both abdominal obesity and elevated triglycerides drive the development of gout, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
Also similar to the Frontiers study, the associations among changes in MetS and incident gout were greater for the youngest participants (in their 20s) and in the underweight or normal weight BMI groups.
Limitations of the second study included possible selection bias because of the study population of workplace employees who participated in regular health checks and the lack of data on women or on men aged 40 years and older, the researchers noted. Other limitations included possible misclassification of MetS because of varying health checkup results and drug claims, and lack of data on serum urate, which prevented assessment of hyperuricemia as a cause of gout.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and suggest that MetS is a modifiable risk factor for gout, the researchers concluded.
Neither of the studies received outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Metabolic syndrome is associated with a significantly increased risk for gout in young men, but the risk can be mitigated by improvement in individual components of the syndrome, based on data from a pair of population-based studies totaling more than 4 million individuals.
Gout remains the most common type of inflammatory arthritis in men, and the rate has been rising among younger adults, Yeonghee Eun, MD, PhD, of Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, South Korea, and colleagues wrote. An increasing body of evidence suggests a link between gout and metabolic syndrome (MetS), but large studies have been lacking, especially in younger adults.
In a study published in Frontiers in Medicine, the researchers reviewed data from 3,569,104 men aged 20-39 years who underwent a health checkup between 2009 and 2012 in South Korea, based on the Korean National Health Insurance Service. The primary outcome of incident gout was identified using claims data. The mean age of the participants was 31.5 years.
Over a mean follow-up of 7.4 years, the incidence of gout was 3.36 per 1,000 person-years. The risk of developing gout was more than twice as high among individuals who met MetS criteria than in those who did not (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.44).
MetS was defined as the presence of at least two of the following components: hypertriglyceridemia, abdominal obesity, reduced HDL cholesterol, elevated blood pressure, and elevated fasting glucose.
Overall, individuals with all five MetS components had a fivefold increase in gout risk, compared with people who did not have MetS (aHR, 5.24). In an analysis of each component of MetS, hypertriglyceridemia and abdominal obesity showed the strongest association with gout (aHRs of 2.08 and 2.33, respectively).
The impact of MetS on risk of incident gout was greater in younger participants, which suggests that the management of MetS in young people should be emphasized, the researchers said.
In a further analysis of body mass index subgroups, MetS had the greatest impact on gout risk for individuals who were underweight (aHR, 3.82). “In particular, in the underweight group, the risk of gout increased 10-fold when abdominal obesity was present,” the researchers said.
The study was limited by several factors including potential selection bias and potential overestimation of gout incidence because of the use of diagnostic codes, the researchers noted. Other limitations included lack of control for nutritional or dietary risk factors and the inability to include cases that occurred after the study period.
However, findings were strengthened by the large number of participants with MetS who were underweight or normal weight, the researchers wrote. More research on the mechanism of action is needed, but the data suggest that MetS is a key risk factor in the development of gout in young men.
In a second study, published in Arthritis & Rheumatology, Dr. Eun and colleagues examined associations between MetS changes and incident gout in young men. Although previous studies have shown that changes in MetS status can alter the risk of cardiovascular events, atrial fibrillation, end-stage renal disease, and all-cause mortality, the impact of these changes on gout has not been well studied, they said. The researchers used the same study cohort, the National Health Insurance Service database in South Korea. They reviewed data from 1,293,166 individuals aged 20-39 years. Of these, 18,473 were diagnosed with gout for an incidence rate 3.36/1,000 person-years. The researchers compared gout incidence for men who met criteria for MetS at three health checkups and those without MetS.
Overall, patients with MetS at all three checkups had a nearly fourfold higher risk of gout than those who never had MetS, with an adjusted hazard ratio of 3.82, the researchers wrote. The development of MetS over the study period more than doubled the risk of gout, but recovery from MetS reduced incident gout risk by approximately 50% (aHR, 0.52).
In findings similar to the Frontiers in Medicine study, the greatest associations with gout were noted for changes in elevated triglycerides and changes in abdominal obesity; aHRs for development and recovery for elevated triglycerides were 1.74 and 0.56, respectively, and for abdominal obesity, 1.94 and 0.69, respectively.
More research is needed to explore the mechanism by which both abdominal obesity and elevated triglycerides drive the development of gout, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
Also similar to the Frontiers study, the associations among changes in MetS and incident gout were greater for the youngest participants (in their 20s) and in the underweight or normal weight BMI groups.
Limitations of the second study included possible selection bias because of the study population of workplace employees who participated in regular health checks and the lack of data on women or on men aged 40 years and older, the researchers noted. Other limitations included possible misclassification of MetS because of varying health checkup results and drug claims, and lack of data on serum urate, which prevented assessment of hyperuricemia as a cause of gout.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and suggest that MetS is a modifiable risk factor for gout, the researchers concluded.
Neither of the studies received outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM FRONTIERS IN MEDICINE AND ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY