User login
Hairs With an Irregular Shape
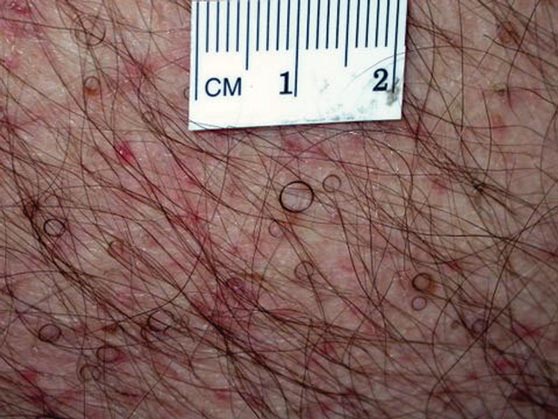
The Diagnosis: Circle Hairs
The patient’s hairs were visualized under dermoscopy (Figure 1). A skin biopsy showed a terminal hair in a horizontal distribution that was located beneath the stratum corneum (Figure 2). The patient was diagnosed with circle hairs.
Circle hairs were first described in 1963.1 These peculiar hairs grow in a circular horizontal distribution beneath the stratum corneum and are considered benign incidental findings. Their exact cause is unknown. If taken out and unrolled, their length and diameter tends to be smaller than surrounding hairs. It has been hypothesized that they are the result of hairs that lack the size necessary to perforate the stratum corneum.2 Others propose that they are vestigial remains that once had a part in preserving body heat.3 Circle hairs tend to grow in elderly, hairy, and obese males, predominantly on the torso and thighs.2,4
It is important to distinguish between circle hairs and rolled hairs. Rolled hairs may be found on the surface or beneath the stratum corneum and are associated with inflammation and keratinization abnormalities.2 If taken together, these latter findings can help differentiate between the two. The importance stands in recognizing that both circle hairs and rolled hairs are benign; however, rolled hairs can be related to other skin disorders that need additional treatment.

|

|
| Figure 2. A skin biopsy showed a terminal hair in a horizontal distribution that was located beneath the stratum corneum (A and B)(both Verhoeff-van Gieson, original magnifications ×40). |
1. Adatto R. Poils en spirale (poils enroules). Dermatologica. 1963;127:145-147.
2. Smith JB, Hogan DJ. Circle hairs are not rolled hairs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:634-635.
3. Contreras-Ruiz J, Duran-McKinster C, Tamayo-Sanchez L, et al. Circle hairs: a clinical curiosity. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2000;14:495-497.
4. Levit F, Scott MJ Jr. Circle hairs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8:423-425.
The Diagnosis: Circle Hairs
The patient’s hairs were visualized under dermoscopy (Figure 1). A skin biopsy showed a terminal hair in a horizontal distribution that was located beneath the stratum corneum (Figure 2). The patient was diagnosed with circle hairs.
Circle hairs were first described in 1963.1 These peculiar hairs grow in a circular horizontal distribution beneath the stratum corneum and are considered benign incidental findings. Their exact cause is unknown. If taken out and unrolled, their length and diameter tends to be smaller than surrounding hairs. It has been hypothesized that they are the result of hairs that lack the size necessary to perforate the stratum corneum.2 Others propose that they are vestigial remains that once had a part in preserving body heat.3 Circle hairs tend to grow in elderly, hairy, and obese males, predominantly on the torso and thighs.2,4
It is important to distinguish between circle hairs and rolled hairs. Rolled hairs may be found on the surface or beneath the stratum corneum and are associated with inflammation and keratinization abnormalities.2 If taken together, these latter findings can help differentiate between the two. The importance stands in recognizing that both circle hairs and rolled hairs are benign; however, rolled hairs can be related to other skin disorders that need additional treatment.

|

|
| Figure 2. A skin biopsy showed a terminal hair in a horizontal distribution that was located beneath the stratum corneum (A and B)(both Verhoeff-van Gieson, original magnifications ×40). |
The Diagnosis: Circle Hairs
The patient’s hairs were visualized under dermoscopy (Figure 1). A skin biopsy showed a terminal hair in a horizontal distribution that was located beneath the stratum corneum (Figure 2). The patient was diagnosed with circle hairs.
Circle hairs were first described in 1963.1 These peculiar hairs grow in a circular horizontal distribution beneath the stratum corneum and are considered benign incidental findings. Their exact cause is unknown. If taken out and unrolled, their length and diameter tends to be smaller than surrounding hairs. It has been hypothesized that they are the result of hairs that lack the size necessary to perforate the stratum corneum.2 Others propose that they are vestigial remains that once had a part in preserving body heat.3 Circle hairs tend to grow in elderly, hairy, and obese males, predominantly on the torso and thighs.2,4
It is important to distinguish between circle hairs and rolled hairs. Rolled hairs may be found on the surface or beneath the stratum corneum and are associated with inflammation and keratinization abnormalities.2 If taken together, these latter findings can help differentiate between the two. The importance stands in recognizing that both circle hairs and rolled hairs are benign; however, rolled hairs can be related to other skin disorders that need additional treatment.

|

|
| Figure 2. A skin biopsy showed a terminal hair in a horizontal distribution that was located beneath the stratum corneum (A and B)(both Verhoeff-van Gieson, original magnifications ×40). |
1. Adatto R. Poils en spirale (poils enroules). Dermatologica. 1963;127:145-147.
2. Smith JB, Hogan DJ. Circle hairs are not rolled hairs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:634-635.
3. Contreras-Ruiz J, Duran-McKinster C, Tamayo-Sanchez L, et al. Circle hairs: a clinical curiosity. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2000;14:495-497.
4. Levit F, Scott MJ Jr. Circle hairs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8:423-425.
1. Adatto R. Poils en spirale (poils enroules). Dermatologica. 1963;127:145-147.
2. Smith JB, Hogan DJ. Circle hairs are not rolled hairs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:634-635.
3. Contreras-Ruiz J, Duran-McKinster C, Tamayo-Sanchez L, et al. Circle hairs: a clinical curiosity. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2000;14:495-497.
4. Levit F, Scott MJ Jr. Circle hairs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8:423-425.
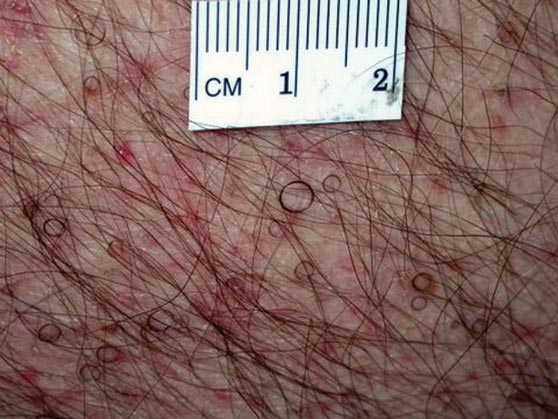
A 74-year-old man was evaluated for numerous peculiar hairs on the back that had been present for several years. He reported no other dermatologic concerns. The patient was obese and led a sedentary lifestyle, spending most of the day sitting or lying down. Physical examination revealed a hairy back with many irregularly shaped hairs.
Topical efinaconazole permeates nail to infection
Topical efinaconazole’s ability to permeate the nail to the infection in onychomycosis is not hampered by the presence of infection or nail thickness, according to data from a multicenter, open-label study.
Adult patients with onychomycosis treated with efinaconazole 10% solution for 4 weeks had drug concentrations in both big and second toenails much higher than minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values for common onychomycosis pathogens, the researchers reported in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology (J. Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:1388-92).
The topical triazole efinaconazole has a broad spectrum of activity that is particularly potent against the common onychomycosis pathogens Trichophyton rubrum,T. mentagrophytes, and Candida albicans, the investigators, led by Misao Sakamoto of Kaken Pharmaceutical in Tokyo, noted. The treatment is an alternative to oral antifungal therapy, which can have systemic side effects or drug interactions. However, transungual delivery of effective topical treatments has been hampered by low permeation rates. The goal of this study was to assess the transungual delivery of efinaconazole in onychomycosis and its fungicidal activity in the toenail.
A total of 40 patients treated their toenails with efinaconazole 5% or 10% topical solution once daily before bedtime for 28 days. Patients applied two drops of solution to both great toes and one drop to all other toenails. Nail samples were taken from the big toenails at weeks 2, 4, and 6. Fungicidal activity against T. rubrum in the ventral layer of the nails was assessed by using an in vitro human nail infection model. Concentrations of the antifungal in the toenail were similar at weeks 2 and 4 with 10% solution, whereas they were lower at week 2 than at week 4 with 5% treatment. For both doses, efinaconazole concentrations peaked at the end of week 4 and declined at week 6. Great-toenail concentrations at week 4 for the 5% and 10% solutions were 5.6 and 6.0 mg/g, respectively.
This finding might be explained by the drug diffusing into the nail bed, the study authors said. No differences in the concentrations were seen in normal or affected nails, suggesting that transungual delivery of efinaconazole was not influenced by the presence of disease.
Concentrations of the antifungal were similar in the great and second toenails, suggesting nail thickness did not affect drug accumulation. In the in vitro nail model, efinaconazole was effective in reducing fungal viability, which suggested that sufficient amounts of the antifungal were being delivered to the ventral layer of the nail plate, the researchers noted.
“The high efinaconazole concentrations in patients’ toenails and fungicidal activity in vitro potentially contribute to the clinical efficacy reported in phase III studies,” they concluded.
All authors work for Kaken Pharmaceutical or Dow Pharmaceutical Sciences (a division of Valeant Pharmaceuticals, manufacturer of efinaconazole). The study was funded by Kaken and Valeant.
Topical efinaconazole’s ability to permeate the nail to the infection in onychomycosis is not hampered by the presence of infection or nail thickness, according to data from a multicenter, open-label study.
Adult patients with onychomycosis treated with efinaconazole 10% solution for 4 weeks had drug concentrations in both big and second toenails much higher than minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values for common onychomycosis pathogens, the researchers reported in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology (J. Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:1388-92).
The topical triazole efinaconazole has a broad spectrum of activity that is particularly potent against the common onychomycosis pathogens Trichophyton rubrum,T. mentagrophytes, and Candida albicans, the investigators, led by Misao Sakamoto of Kaken Pharmaceutical in Tokyo, noted. The treatment is an alternative to oral antifungal therapy, which can have systemic side effects or drug interactions. However, transungual delivery of effective topical treatments has been hampered by low permeation rates. The goal of this study was to assess the transungual delivery of efinaconazole in onychomycosis and its fungicidal activity in the toenail.
A total of 40 patients treated their toenails with efinaconazole 5% or 10% topical solution once daily before bedtime for 28 days. Patients applied two drops of solution to both great toes and one drop to all other toenails. Nail samples were taken from the big toenails at weeks 2, 4, and 6. Fungicidal activity against T. rubrum in the ventral layer of the nails was assessed by using an in vitro human nail infection model. Concentrations of the antifungal in the toenail were similar at weeks 2 and 4 with 10% solution, whereas they were lower at week 2 than at week 4 with 5% treatment. For both doses, efinaconazole concentrations peaked at the end of week 4 and declined at week 6. Great-toenail concentrations at week 4 for the 5% and 10% solutions were 5.6 and 6.0 mg/g, respectively.
This finding might be explained by the drug diffusing into the nail bed, the study authors said. No differences in the concentrations were seen in normal or affected nails, suggesting that transungual delivery of efinaconazole was not influenced by the presence of disease.
Concentrations of the antifungal were similar in the great and second toenails, suggesting nail thickness did not affect drug accumulation. In the in vitro nail model, efinaconazole was effective in reducing fungal viability, which suggested that sufficient amounts of the antifungal were being delivered to the ventral layer of the nail plate, the researchers noted.
“The high efinaconazole concentrations in patients’ toenails and fungicidal activity in vitro potentially contribute to the clinical efficacy reported in phase III studies,” they concluded.
All authors work for Kaken Pharmaceutical or Dow Pharmaceutical Sciences (a division of Valeant Pharmaceuticals, manufacturer of efinaconazole). The study was funded by Kaken and Valeant.
Topical efinaconazole’s ability to permeate the nail to the infection in onychomycosis is not hampered by the presence of infection or nail thickness, according to data from a multicenter, open-label study.
Adult patients with onychomycosis treated with efinaconazole 10% solution for 4 weeks had drug concentrations in both big and second toenails much higher than minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values for common onychomycosis pathogens, the researchers reported in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology (J. Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:1388-92).
The topical triazole efinaconazole has a broad spectrum of activity that is particularly potent against the common onychomycosis pathogens Trichophyton rubrum,T. mentagrophytes, and Candida albicans, the investigators, led by Misao Sakamoto of Kaken Pharmaceutical in Tokyo, noted. The treatment is an alternative to oral antifungal therapy, which can have systemic side effects or drug interactions. However, transungual delivery of effective topical treatments has been hampered by low permeation rates. The goal of this study was to assess the transungual delivery of efinaconazole in onychomycosis and its fungicidal activity in the toenail.
A total of 40 patients treated their toenails with efinaconazole 5% or 10% topical solution once daily before bedtime for 28 days. Patients applied two drops of solution to both great toes and one drop to all other toenails. Nail samples were taken from the big toenails at weeks 2, 4, and 6. Fungicidal activity against T. rubrum in the ventral layer of the nails was assessed by using an in vitro human nail infection model. Concentrations of the antifungal in the toenail were similar at weeks 2 and 4 with 10% solution, whereas they were lower at week 2 than at week 4 with 5% treatment. For both doses, efinaconazole concentrations peaked at the end of week 4 and declined at week 6. Great-toenail concentrations at week 4 for the 5% and 10% solutions were 5.6 and 6.0 mg/g, respectively.
This finding might be explained by the drug diffusing into the nail bed, the study authors said. No differences in the concentrations were seen in normal or affected nails, suggesting that transungual delivery of efinaconazole was not influenced by the presence of disease.
Concentrations of the antifungal were similar in the great and second toenails, suggesting nail thickness did not affect drug accumulation. In the in vitro nail model, efinaconazole was effective in reducing fungal viability, which suggested that sufficient amounts of the antifungal were being delivered to the ventral layer of the nail plate, the researchers noted.
“The high efinaconazole concentrations in patients’ toenails and fungicidal activity in vitro potentially contribute to the clinical efficacy reported in phase III studies,” they concluded.
All authors work for Kaken Pharmaceutical or Dow Pharmaceutical Sciences (a division of Valeant Pharmaceuticals, manufacturer of efinaconazole). The study was funded by Kaken and Valeant.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF DRUGS IN DERMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Topical 10% efinaconazole was effective in permeating the nail to reach the infection site in patients with onychomycosis.
Major finding: Treatment with efinaconazole 10% solution resulted in drug concentrations much higher than MIC values of common onychomycosis pathogens in both the great toenails and second toenails of onychomycosis patients.
Data source: Multicenter, open-label study investigating the transungual delivery of efinaconazole in 40 patients with onychomycosis.
Disclosures: All authors work for Kaken Pharmaceutical or Dow Pharmaceutical Sciences (a division of Valeant Pharmaceuticals, manufacturer of efinaconazole). The study was funded by Kaken and Valeant.
Vehicle in topical efinaconazole hits the right spot in onychomycosis
The vehicle used in the topical antifungal efinaconazole 10% spread into the subungual space between the nail bed and nail plate, reaching the site of infection in patients with toenail onychomycosis, according to results from a small study.
Efinaconazole topical solution 10% has a broad spectrum of antifungal activity against the organisms most associated with toenail onychomycosis and has shown efficacy in two phase III trials, reported Dr. Boni E. Elweski of the University of Alabama, Birmingham, and her colleagues in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology (J. Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:1394-98). The vehicle for the topical solution was developed with low surface tension to create a greater probability of nail plate permeation and access through the subungual space, the study authors wrote.
To assess the effectiveness of the solution in reaching the site of infection, the researchers applied the vehicle to the toenails of 11 adult patients with moderate to severe onychomycosis. Two drops of test material (saturated fluorescein 0.6% in vehicle solution) were applied to the distal end of the toenail, and a brush was used to spread the solution below the surface of the nail and distal skin area in contact with the nail. Standard and UV pictures of the toenails were taken after 20-30 minutes, and the process was repeated 40-45 minutes later. Approximately 1-2 mm of the affected toenail was clipped, photographed, and clipped again.
The findings showed that the vehicle had spread into the subungual space, with deposition of fluorescein seen wherever the vehicle had reached, including the nail bed. Nail clippings also showed deposition to the underside of the nail plate. The data support the instructions for the use of efinaconazole topical solution 10%, which specifically state that the solution be brushed on the skin around the nail as well as the nail plate, the authors said. However, they noted that the study was performed without the active drug, and that results could differ if efinaconazole were included.
All of the study authors are either advisers for, or employees of, Valeant Pharmaceuticals, manufacturer of topical 10% efinaconazole.
The vehicle used in the topical antifungal efinaconazole 10% spread into the subungual space between the nail bed and nail plate, reaching the site of infection in patients with toenail onychomycosis, according to results from a small study.
Efinaconazole topical solution 10% has a broad spectrum of antifungal activity against the organisms most associated with toenail onychomycosis and has shown efficacy in two phase III trials, reported Dr. Boni E. Elweski of the University of Alabama, Birmingham, and her colleagues in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology (J. Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:1394-98). The vehicle for the topical solution was developed with low surface tension to create a greater probability of nail plate permeation and access through the subungual space, the study authors wrote.
To assess the effectiveness of the solution in reaching the site of infection, the researchers applied the vehicle to the toenails of 11 adult patients with moderate to severe onychomycosis. Two drops of test material (saturated fluorescein 0.6% in vehicle solution) were applied to the distal end of the toenail, and a brush was used to spread the solution below the surface of the nail and distal skin area in contact with the nail. Standard and UV pictures of the toenails were taken after 20-30 minutes, and the process was repeated 40-45 minutes later. Approximately 1-2 mm of the affected toenail was clipped, photographed, and clipped again.
The findings showed that the vehicle had spread into the subungual space, with deposition of fluorescein seen wherever the vehicle had reached, including the nail bed. Nail clippings also showed deposition to the underside of the nail plate. The data support the instructions for the use of efinaconazole topical solution 10%, which specifically state that the solution be brushed on the skin around the nail as well as the nail plate, the authors said. However, they noted that the study was performed without the active drug, and that results could differ if efinaconazole were included.
All of the study authors are either advisers for, or employees of, Valeant Pharmaceuticals, manufacturer of topical 10% efinaconazole.
The vehicle used in the topical antifungal efinaconazole 10% spread into the subungual space between the nail bed and nail plate, reaching the site of infection in patients with toenail onychomycosis, according to results from a small study.
Efinaconazole topical solution 10% has a broad spectrum of antifungal activity against the organisms most associated with toenail onychomycosis and has shown efficacy in two phase III trials, reported Dr. Boni E. Elweski of the University of Alabama, Birmingham, and her colleagues in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology (J. Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:1394-98). The vehicle for the topical solution was developed with low surface tension to create a greater probability of nail plate permeation and access through the subungual space, the study authors wrote.
To assess the effectiveness of the solution in reaching the site of infection, the researchers applied the vehicle to the toenails of 11 adult patients with moderate to severe onychomycosis. Two drops of test material (saturated fluorescein 0.6% in vehicle solution) were applied to the distal end of the toenail, and a brush was used to spread the solution below the surface of the nail and distal skin area in contact with the nail. Standard and UV pictures of the toenails were taken after 20-30 minutes, and the process was repeated 40-45 minutes later. Approximately 1-2 mm of the affected toenail was clipped, photographed, and clipped again.
The findings showed that the vehicle had spread into the subungual space, with deposition of fluorescein seen wherever the vehicle had reached, including the nail bed. Nail clippings also showed deposition to the underside of the nail plate. The data support the instructions for the use of efinaconazole topical solution 10%, which specifically state that the solution be brushed on the skin around the nail as well as the nail plate, the authors said. However, they noted that the study was performed without the active drug, and that results could differ if efinaconazole were included.
All of the study authors are either advisers for, or employees of, Valeant Pharmaceuticals, manufacturer of topical 10% efinaconazole.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF DRUGS IN DERMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: The vehicle used in the topical antifungal efinaconazole 10% might offer more opportunities for drugs to reach the infection site than traditional vehicle solutions.
Major finding: The vehicle used in topical 10% efinaconazole spread into the subungual space between the nail bed and nail plate, reaching the site of infection in patients with moderate to severe onychomycosis.
Data source: Single-center, 1-day study evaluating the spreading of the vehicle (without the active drug) used in efinaconazole under the nail plate in 11 patients with toenail onychomycosis.
Disclosures: All of the authors are either advisers for, or employees of, Valeant Pharmaceuticals, manufacturer of topical 10% efinaconazole.
Bilateral Onychodystrophy in a Boy With a History of Isolated Lichen Striatus
Lichen striatus (LS) is a relatively rare and self-limited linear dermatosis of unknown etiology. Lichen striatus primarily affects children, with more than 50% of cases occurring in patients aged 5 to 15 years.1,2 It presents clinically as a single unilateral linear band consisting of scaly, 1- to 3-mm papules that coalesce to form long streaks.3,4 The diagnosis usually is made clinically based on the characteristic appearance of skin lesions and a pattern of distribution that follows the lines of Blaschko.5,6 The papules usually are asymptomatic; however, if the patient is symptomatic, pruritus is the most common concern. Lichen striatus may resolve with postinflammatory hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation that may last for several months to years.
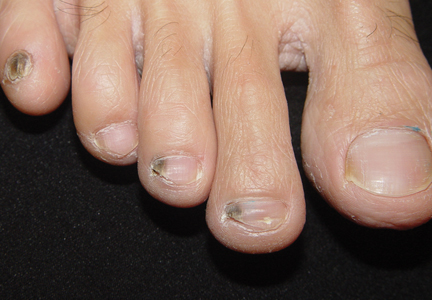
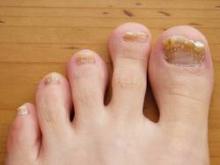
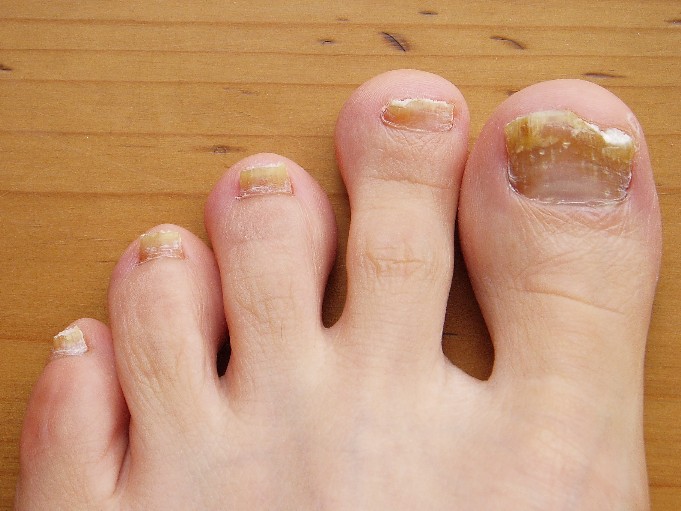
Nail involvement is uncommon in LS; a review of the literature has shown that 30 cases have been reported in the world literature since 1941.7 Nail changes may present before, after, or concurrently with the skin lesions.4,8 On rare occasions, nail involvement may be the only area of involvement without the presence of typical skin lesions.8 The involved nails may show longitudinal ridging, splitting, hyperkeratosis of the nail beds, thinning or thickening of the nail plate, nail pitting, and overcurvature of the nail plate, and rarely the nails may fall off completely.8-10
We report the case of a boy who was diagnosed with isolated LS at 2 years of age. The lesions spontaneously resolved within 6 months. Three years later the patient presented with a rare manifestation of LS in the form of bilateral onychodystrophy.
Case Report
An otherwise healthy 2-year-old boy presented for evaluation of a nonpruritic linear rash on the right lower side of the abdomen of 3 weeks’ duration. A review of systems was negative for any other constitutional signs or symptoms. No sick contacts were reported at the patient’s home, and his immunizations were up-to-date. His medical history was remarkable for a burn on the left hand from contact with a hot object at 11 months of age that required skin grafting.
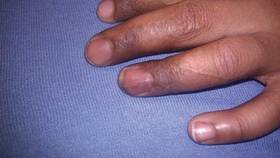
Dermatologic examination revealed a linear band of small, 1- to 3-mm, flesh-colored lichenoid papules. Many of the papules had a scaly appearance and some had a vesicular component or were flat topped. The band ranged from 2- to 3-cm wide and was 25 cm in length, extending from the right anterolateral part of the lower abdomen to the right upper lateral part of the buttocks (Figure 1). No abnormalities were noted on the rest of the skin. A diagnosis of LS was made.
|
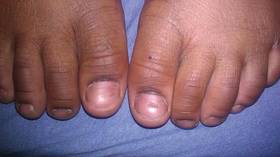
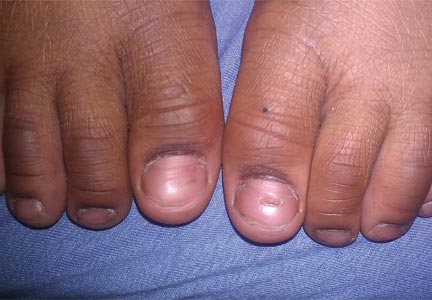
At 5 years of age, the patient returned for evaluation of bluish discoloration and thinning of the nails of the left middle and ring fingers of several months duration. The patient was afebrile and appeared to be healthy. There was no lymphadenopathy or hepatomegaly and the rest of the physical examination by a pediatrician was unremarkable. The nails of the 2 affected fingers had fallen off 2 months prior to presentation and had started to regrow. On dermatologic examination, it was noted that the regrown nails showed some residual longitudinal ridging, thinning, and dark discoloration of the proximal nail folds (Figure 2). On examination of the other toenails and fingernails there was evidence of bilateral pitting, ridging, and discoloration (Figure 3). The left great toenail was predominantly affected. The patient’s guardians were not aware of the toenail changes and denied any history of trauma to the fingers. When asked about the course of the prior abdominal linear rash, they reported that the lesions had completely resolved within 6 months. The rare diagnosis of isolated onychodystrophy as a late manifestation of the prior LS was made.
Comment
The etiology of LS remains unknown, but there have been several hypotheses suggesting environmental triggers such as trauma11 or infection.12 Others have suggested a possible autoimmune response13 or genetic components.6 Reports of simultaneous occurrences of LS in siblings as well as in a mother and her son14,15; outbreaks of LS among children who are not biologically related but in a shared living environment; and a possible seasonal variation suggest an environmental infectious agent (eg, a virus) as the possible triggering factor. However, laboratory testing for viral etiology in LS has not been helpful.
Many of the reported cases of LS have described a pattern of distribution along the lines of Blaschko.5,6,16,17 Lines of Blaschko are thought to be embryologic in origin and caused by the segmental growth of clones of cutaneous cells or the mutation-induced mosaicism of cutaneous cells, which led to the theory that mosaicism is involved in LS. Lichen striatus needs to be differentiated from other conditions with similar cutaneous appearances (eg, lichen nitidus, linear lichen planus of the digits, linear psoriasis, linear keratosis follicularis, linear epidermal nevus).
Skin biopsy to confirm the diagnosis rarely is necessary, as LS is a self-limited disorder and generally no treatment is recommended. Topical and intralesional steroids do not routinely impact the resolution of LS; however, emollients and topical steroids may be used to treat associated dryness and pruritus, if present.18 Immunomodulators such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus have been successfully used in treating persistent and pruritic LS lesions on the face and extremities.19,20 Tacrolimus also has been successfully used to treat nail abnormalities in LS.21
Guardians and family members should be reassured that LS is a benign condition that generally resolves spontaneously within 3 to 12 months. Also, guardians should be counseled regarding the possibility of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation, which may last for several months to years, particularly in children with darker skin types. Lichen striatus of the nails may have a more protracted course, lasting from 6 months to 5 years,22 but usually resolves spontaneously and without deformity.
Our patient developed a rare case of isolated LS at 2 years of age. Reports have suggested later onset of the condition, with more than 50% of all LS cases occurring in children aged 5 to 15 years.1,2 Despite the earlier onset in our case, the patient still presented with the classic nonpruritic single linear band of papules that is characteristic of LS.
The nail involvement in our case is quite intriguing because of its rarity, timing, and extent of involvement. Nail involvement is generally uncommon in LS, with approximately 30 cases reported worldwide since 1941.7 The nail changes in our patient were unique in their timing, with the isolated onychodystrophy developing 3 years after the initial skin lesion. This subtle timing may pose a diagnostic challenge in patients with LS if treating physicians are unable to link the presenting onychodystrophy to the earlier cutaneous component of the condition. Two reports have shown that nail changes in association with LS may occur at any time before, after, or concurrently with the skin lesions,4,8 suggesting that on rare occasions, as in our case, nail involvement may be the only area of involvement without the presence of typical LS skin lesions.8
The nail involvement in our patient also showed a greater severity than prior reports,8,9 as he lost 2 fingernails completely before regrowth. Also, the bilateral distribution of onychodystrophy in our patient involving both the fingernails and toenails appeared to be consistent with a report by Al-Niaimi and Cox.22
Nail involvement in cases of LS may be underreported when, as in our case, nail dystrophy presents as the only area of involvement without the presence of the typical skin lesions characteristic of LS. It is reasonable to recommend that clinicians facing similar presentations of isolated onychodystrophy should include the possibility of LS in the differential diagnosis before committing patients to a more common diagnosis (eg, onychomycosis). Clinicians should inquire about any history of cutaneous LS and counsel patients to return for treatment should skin lesions develop that are suggestive of LS.
1. Hofer T. Lichen striatus in adults or ‘adult blaschkitis’? there is no need for a new naming. Dermatology. 2003;207:89-92.
2. Taniguchi Abagge K, Parolin Marinoni L, Giraldi S, et al. Lichen striatus: description of 89 cases in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2004;21:440-443.
3. Hauber K, Rose C, Brocker EB, et al. Lichen striatus: clinical features and follow-up in 12 patients. Eur J Dermatol. 2000;10:536-539.
4. Karp DL, Cohen BA. Onychodystrophy in lichen striatus. Pediatr Dermatol. 1993;10:359-361.
5. Arias-Santiago SA, Sierra Girón-Prieto M, Fernández-Pugnarie MA, et al. Lichen striatus following Blaschko lines [published online ahead of print May 8, 2009]. An Pediatr (Barc). 2009;71:76-77.
6. Racette AJ, Adams AD, Kessler SE. Simultaneous lichen striatus in siblings along the same Blaschko line [published online ahead of print February 16, 2009]. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:50-54.
7. Markouch I, Clérici T, Saiag P, et al. Lichen striatus with nail dystrophy in an infant. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2009;136:883-886.
8. Tosti A, Peluso AM, Misciali C, et al. Nail lichen striatus: clinical features and long-term follow-up of five patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36:908-913.
9. Leposavic R, Belsito DV. Onychodystrophy and subungual hyperkeratosis due to lichen striatus. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1099-1100.
10. Baran R, Dupré A, Lauret P, et al. Lichen striatus with nail involvement. report of 4 cases and review of the 4 cases in the literature. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1979;106:885-891.
11. Shepherd V, Lun K, Strutton G. Lichen striatus in an adult following trauma. Australas J Dermatol. 2005;46:25-28.
12. Hafner C, Landthaler M, Vogt T. Lichen striatus (blaschkitis) following varicella infection. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:1345-1347.
13. Brennand S, Khan S, Chong AH. Lichen striatus in a pregnant woman. Australas J Dermatol. 2005;46:184-186.
14. Patrizi A, Neri I, Fiorentini C, et al. Simultaneous occurrence of lichen striatus in siblings. Pediatr Dermatol. 1997;14:293-295.
15. Yaosaka M, Sawamura D, Iitoyo M, et al. Lichen striatus affecting a mother and her son. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:352-353.
16. Keegan BR, Kamino H, Fangman W, et al. “Pediatric blaschkitis”: expanding the spectrum of childhood acquired Blaschko-linear dermatoses. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:621-627.
17. Taieb A, el Youbi A, Grosshans E, et al. Lichen striatus: a Blaschko linear acquired inflammatory skin eruption. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;25:637-642.
18. Tilly JJ, Drolet BA, Esterly NB. Lichenoid eruptions in children. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:606-624.
19. Vukićević J, Milobratović D, Vesić S, et al. Unilateral multiple lichen striatus treated with tacrolimus ointment: a case report. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Panonica Adriat. 2009;18:35-38.
20. Fujimoto N, Tajima S, Ishibashi A. Facial lichen striatus: successful treatment with tacrolimus ointment. Br J Dermatol. 2003;148:587-590.
21. Kim GW, Kim SH, Seo SH, et al. Lichen striatus with nail abnormality successfully treated with tacrolimus ointment. J Dermatol. 2009;36:616-617.
22. Al-Niaimi FA, Cox NH. Unilateral lichen striatus with bilateral onychodystrophy [published online ahead of print June 5, 2009]. Eur J Dermatol. 2009;19:511.
Lichen striatus (LS) is a relatively rare and self-limited linear dermatosis of unknown etiology. Lichen striatus primarily affects children, with more than 50% of cases occurring in patients aged 5 to 15 years.1,2 It presents clinically as a single unilateral linear band consisting of scaly, 1- to 3-mm papules that coalesce to form long streaks.3,4 The diagnosis usually is made clinically based on the characteristic appearance of skin lesions and a pattern of distribution that follows the lines of Blaschko.5,6 The papules usually are asymptomatic; however, if the patient is symptomatic, pruritus is the most common concern. Lichen striatus may resolve with postinflammatory hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation that may last for several months to years.
Nail involvement is uncommon in LS; a review of the literature has shown that 30 cases have been reported in the world literature since 1941.7 Nail changes may present before, after, or concurrently with the skin lesions.4,8 On rare occasions, nail involvement may be the only area of involvement without the presence of typical skin lesions.8 The involved nails may show longitudinal ridging, splitting, hyperkeratosis of the nail beds, thinning or thickening of the nail plate, nail pitting, and overcurvature of the nail plate, and rarely the nails may fall off completely.8-10
We report the case of a boy who was diagnosed with isolated LS at 2 years of age. The lesions spontaneously resolved within 6 months. Three years later the patient presented with a rare manifestation of LS in the form of bilateral onychodystrophy.
Case Report
An otherwise healthy 2-year-old boy presented for evaluation of a nonpruritic linear rash on the right lower side of the abdomen of 3 weeks’ duration. A review of systems was negative for any other constitutional signs or symptoms. No sick contacts were reported at the patient’s home, and his immunizations were up-to-date. His medical history was remarkable for a burn on the left hand from contact with a hot object at 11 months of age that required skin grafting.
Dermatologic examination revealed a linear band of small, 1- to 3-mm, flesh-colored lichenoid papules. Many of the papules had a scaly appearance and some had a vesicular component or were flat topped. The band ranged from 2- to 3-cm wide and was 25 cm in length, extending from the right anterolateral part of the lower abdomen to the right upper lateral part of the buttocks (Figure 1). No abnormalities were noted on the rest of the skin. A diagnosis of LS was made.
|
At 5 years of age, the patient returned for evaluation of bluish discoloration and thinning of the nails of the left middle and ring fingers of several months duration. The patient was afebrile and appeared to be healthy. There was no lymphadenopathy or hepatomegaly and the rest of the physical examination by a pediatrician was unremarkable. The nails of the 2 affected fingers had fallen off 2 months prior to presentation and had started to regrow. On dermatologic examination, it was noted that the regrown nails showed some residual longitudinal ridging, thinning, and dark discoloration of the proximal nail folds (Figure 2). On examination of the other toenails and fingernails there was evidence of bilateral pitting, ridging, and discoloration (Figure 3). The left great toenail was predominantly affected. The patient’s guardians were not aware of the toenail changes and denied any history of trauma to the fingers. When asked about the course of the prior abdominal linear rash, they reported that the lesions had completely resolved within 6 months. The rare diagnosis of isolated onychodystrophy as a late manifestation of the prior LS was made.
Comment
The etiology of LS remains unknown, but there have been several hypotheses suggesting environmental triggers such as trauma11 or infection.12 Others have suggested a possible autoimmune response13 or genetic components.6 Reports of simultaneous occurrences of LS in siblings as well as in a mother and her son14,15; outbreaks of LS among children who are not biologically related but in a shared living environment; and a possible seasonal variation suggest an environmental infectious agent (eg, a virus) as the possible triggering factor. However, laboratory testing for viral etiology in LS has not been helpful.
Many of the reported cases of LS have described a pattern of distribution along the lines of Blaschko.5,6,16,17 Lines of Blaschko are thought to be embryologic in origin and caused by the segmental growth of clones of cutaneous cells or the mutation-induced mosaicism of cutaneous cells, which led to the theory that mosaicism is involved in LS. Lichen striatus needs to be differentiated from other conditions with similar cutaneous appearances (eg, lichen nitidus, linear lichen planus of the digits, linear psoriasis, linear keratosis follicularis, linear epidermal nevus).
Skin biopsy to confirm the diagnosis rarely is necessary, as LS is a self-limited disorder and generally no treatment is recommended. Topical and intralesional steroids do not routinely impact the resolution of LS; however, emollients and topical steroids may be used to treat associated dryness and pruritus, if present.18 Immunomodulators such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus have been successfully used in treating persistent and pruritic LS lesions on the face and extremities.19,20 Tacrolimus also has been successfully used to treat nail abnormalities in LS.21
Guardians and family members should be reassured that LS is a benign condition that generally resolves spontaneously within 3 to 12 months. Also, guardians should be counseled regarding the possibility of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation, which may last for several months to years, particularly in children with darker skin types. Lichen striatus of the nails may have a more protracted course, lasting from 6 months to 5 years,22 but usually resolves spontaneously and without deformity.
Our patient developed a rare case of isolated LS at 2 years of age. Reports have suggested later onset of the condition, with more than 50% of all LS cases occurring in children aged 5 to 15 years.1,2 Despite the earlier onset in our case, the patient still presented with the classic nonpruritic single linear band of papules that is characteristic of LS.
The nail involvement in our case is quite intriguing because of its rarity, timing, and extent of involvement. Nail involvement is generally uncommon in LS, with approximately 30 cases reported worldwide since 1941.7 The nail changes in our patient were unique in their timing, with the isolated onychodystrophy developing 3 years after the initial skin lesion. This subtle timing may pose a diagnostic challenge in patients with LS if treating physicians are unable to link the presenting onychodystrophy to the earlier cutaneous component of the condition. Two reports have shown that nail changes in association with LS may occur at any time before, after, or concurrently with the skin lesions,4,8 suggesting that on rare occasions, as in our case, nail involvement may be the only area of involvement without the presence of typical LS skin lesions.8
The nail involvement in our patient also showed a greater severity than prior reports,8,9 as he lost 2 fingernails completely before regrowth. Also, the bilateral distribution of onychodystrophy in our patient involving both the fingernails and toenails appeared to be consistent with a report by Al-Niaimi and Cox.22
Nail involvement in cases of LS may be underreported when, as in our case, nail dystrophy presents as the only area of involvement without the presence of the typical skin lesions characteristic of LS. It is reasonable to recommend that clinicians facing similar presentations of isolated onychodystrophy should include the possibility of LS in the differential diagnosis before committing patients to a more common diagnosis (eg, onychomycosis). Clinicians should inquire about any history of cutaneous LS and counsel patients to return for treatment should skin lesions develop that are suggestive of LS.
Lichen striatus (LS) is a relatively rare and self-limited linear dermatosis of unknown etiology. Lichen striatus primarily affects children, with more than 50% of cases occurring in patients aged 5 to 15 years.1,2 It presents clinically as a single unilateral linear band consisting of scaly, 1- to 3-mm papules that coalesce to form long streaks.3,4 The diagnosis usually is made clinically based on the characteristic appearance of skin lesions and a pattern of distribution that follows the lines of Blaschko.5,6 The papules usually are asymptomatic; however, if the patient is symptomatic, pruritus is the most common concern. Lichen striatus may resolve with postinflammatory hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation that may last for several months to years.
Nail involvement is uncommon in LS; a review of the literature has shown that 30 cases have been reported in the world literature since 1941.7 Nail changes may present before, after, or concurrently with the skin lesions.4,8 On rare occasions, nail involvement may be the only area of involvement without the presence of typical skin lesions.8 The involved nails may show longitudinal ridging, splitting, hyperkeratosis of the nail beds, thinning or thickening of the nail plate, nail pitting, and overcurvature of the nail plate, and rarely the nails may fall off completely.8-10
We report the case of a boy who was diagnosed with isolated LS at 2 years of age. The lesions spontaneously resolved within 6 months. Three years later the patient presented with a rare manifestation of LS in the form of bilateral onychodystrophy.
Case Report
An otherwise healthy 2-year-old boy presented for evaluation of a nonpruritic linear rash on the right lower side of the abdomen of 3 weeks’ duration. A review of systems was negative for any other constitutional signs or symptoms. No sick contacts were reported at the patient’s home, and his immunizations were up-to-date. His medical history was remarkable for a burn on the left hand from contact with a hot object at 11 months of age that required skin grafting.
Dermatologic examination revealed a linear band of small, 1- to 3-mm, flesh-colored lichenoid papules. Many of the papules had a scaly appearance and some had a vesicular component or were flat topped. The band ranged from 2- to 3-cm wide and was 25 cm in length, extending from the right anterolateral part of the lower abdomen to the right upper lateral part of the buttocks (Figure 1). No abnormalities were noted on the rest of the skin. A diagnosis of LS was made.
|
At 5 years of age, the patient returned for evaluation of bluish discoloration and thinning of the nails of the left middle and ring fingers of several months duration. The patient was afebrile and appeared to be healthy. There was no lymphadenopathy or hepatomegaly and the rest of the physical examination by a pediatrician was unremarkable. The nails of the 2 affected fingers had fallen off 2 months prior to presentation and had started to regrow. On dermatologic examination, it was noted that the regrown nails showed some residual longitudinal ridging, thinning, and dark discoloration of the proximal nail folds (Figure 2). On examination of the other toenails and fingernails there was evidence of bilateral pitting, ridging, and discoloration (Figure 3). The left great toenail was predominantly affected. The patient’s guardians were not aware of the toenail changes and denied any history of trauma to the fingers. When asked about the course of the prior abdominal linear rash, they reported that the lesions had completely resolved within 6 months. The rare diagnosis of isolated onychodystrophy as a late manifestation of the prior LS was made.
Comment
The etiology of LS remains unknown, but there have been several hypotheses suggesting environmental triggers such as trauma11 or infection.12 Others have suggested a possible autoimmune response13 or genetic components.6 Reports of simultaneous occurrences of LS in siblings as well as in a mother and her son14,15; outbreaks of LS among children who are not biologically related but in a shared living environment; and a possible seasonal variation suggest an environmental infectious agent (eg, a virus) as the possible triggering factor. However, laboratory testing for viral etiology in LS has not been helpful.
Many of the reported cases of LS have described a pattern of distribution along the lines of Blaschko.5,6,16,17 Lines of Blaschko are thought to be embryologic in origin and caused by the segmental growth of clones of cutaneous cells or the mutation-induced mosaicism of cutaneous cells, which led to the theory that mosaicism is involved in LS. Lichen striatus needs to be differentiated from other conditions with similar cutaneous appearances (eg, lichen nitidus, linear lichen planus of the digits, linear psoriasis, linear keratosis follicularis, linear epidermal nevus).
Skin biopsy to confirm the diagnosis rarely is necessary, as LS is a self-limited disorder and generally no treatment is recommended. Topical and intralesional steroids do not routinely impact the resolution of LS; however, emollients and topical steroids may be used to treat associated dryness and pruritus, if present.18 Immunomodulators such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus have been successfully used in treating persistent and pruritic LS lesions on the face and extremities.19,20 Tacrolimus also has been successfully used to treat nail abnormalities in LS.21
Guardians and family members should be reassured that LS is a benign condition that generally resolves spontaneously within 3 to 12 months. Also, guardians should be counseled regarding the possibility of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation, which may last for several months to years, particularly in children with darker skin types. Lichen striatus of the nails may have a more protracted course, lasting from 6 months to 5 years,22 but usually resolves spontaneously and without deformity.
Our patient developed a rare case of isolated LS at 2 years of age. Reports have suggested later onset of the condition, with more than 50% of all LS cases occurring in children aged 5 to 15 years.1,2 Despite the earlier onset in our case, the patient still presented with the classic nonpruritic single linear band of papules that is characteristic of LS.
The nail involvement in our case is quite intriguing because of its rarity, timing, and extent of involvement. Nail involvement is generally uncommon in LS, with approximately 30 cases reported worldwide since 1941.7 The nail changes in our patient were unique in their timing, with the isolated onychodystrophy developing 3 years after the initial skin lesion. This subtle timing may pose a diagnostic challenge in patients with LS if treating physicians are unable to link the presenting onychodystrophy to the earlier cutaneous component of the condition. Two reports have shown that nail changes in association with LS may occur at any time before, after, or concurrently with the skin lesions,4,8 suggesting that on rare occasions, as in our case, nail involvement may be the only area of involvement without the presence of typical LS skin lesions.8
The nail involvement in our patient also showed a greater severity than prior reports,8,9 as he lost 2 fingernails completely before regrowth. Also, the bilateral distribution of onychodystrophy in our patient involving both the fingernails and toenails appeared to be consistent with a report by Al-Niaimi and Cox.22
Nail involvement in cases of LS may be underreported when, as in our case, nail dystrophy presents as the only area of involvement without the presence of the typical skin lesions characteristic of LS. It is reasonable to recommend that clinicians facing similar presentations of isolated onychodystrophy should include the possibility of LS in the differential diagnosis before committing patients to a more common diagnosis (eg, onychomycosis). Clinicians should inquire about any history of cutaneous LS and counsel patients to return for treatment should skin lesions develop that are suggestive of LS.
1. Hofer T. Lichen striatus in adults or ‘adult blaschkitis’? there is no need for a new naming. Dermatology. 2003;207:89-92.
2. Taniguchi Abagge K, Parolin Marinoni L, Giraldi S, et al. Lichen striatus: description of 89 cases in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2004;21:440-443.
3. Hauber K, Rose C, Brocker EB, et al. Lichen striatus: clinical features and follow-up in 12 patients. Eur J Dermatol. 2000;10:536-539.
4. Karp DL, Cohen BA. Onychodystrophy in lichen striatus. Pediatr Dermatol. 1993;10:359-361.
5. Arias-Santiago SA, Sierra Girón-Prieto M, Fernández-Pugnarie MA, et al. Lichen striatus following Blaschko lines [published online ahead of print May 8, 2009]. An Pediatr (Barc). 2009;71:76-77.
6. Racette AJ, Adams AD, Kessler SE. Simultaneous lichen striatus in siblings along the same Blaschko line [published online ahead of print February 16, 2009]. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:50-54.
7. Markouch I, Clérici T, Saiag P, et al. Lichen striatus with nail dystrophy in an infant. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2009;136:883-886.
8. Tosti A, Peluso AM, Misciali C, et al. Nail lichen striatus: clinical features and long-term follow-up of five patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36:908-913.
9. Leposavic R, Belsito DV. Onychodystrophy and subungual hyperkeratosis due to lichen striatus. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1099-1100.
10. Baran R, Dupré A, Lauret P, et al. Lichen striatus with nail involvement. report of 4 cases and review of the 4 cases in the literature. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1979;106:885-891.
11. Shepherd V, Lun K, Strutton G. Lichen striatus in an adult following trauma. Australas J Dermatol. 2005;46:25-28.
12. Hafner C, Landthaler M, Vogt T. Lichen striatus (blaschkitis) following varicella infection. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:1345-1347.
13. Brennand S, Khan S, Chong AH. Lichen striatus in a pregnant woman. Australas J Dermatol. 2005;46:184-186.
14. Patrizi A, Neri I, Fiorentini C, et al. Simultaneous occurrence of lichen striatus in siblings. Pediatr Dermatol. 1997;14:293-295.
15. Yaosaka M, Sawamura D, Iitoyo M, et al. Lichen striatus affecting a mother and her son. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:352-353.
16. Keegan BR, Kamino H, Fangman W, et al. “Pediatric blaschkitis”: expanding the spectrum of childhood acquired Blaschko-linear dermatoses. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:621-627.
17. Taieb A, el Youbi A, Grosshans E, et al. Lichen striatus: a Blaschko linear acquired inflammatory skin eruption. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;25:637-642.
18. Tilly JJ, Drolet BA, Esterly NB. Lichenoid eruptions in children. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:606-624.
19. Vukićević J, Milobratović D, Vesić S, et al. Unilateral multiple lichen striatus treated with tacrolimus ointment: a case report. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Panonica Adriat. 2009;18:35-38.
20. Fujimoto N, Tajima S, Ishibashi A. Facial lichen striatus: successful treatment with tacrolimus ointment. Br J Dermatol. 2003;148:587-590.
21. Kim GW, Kim SH, Seo SH, et al. Lichen striatus with nail abnormality successfully treated with tacrolimus ointment. J Dermatol. 2009;36:616-617.
22. Al-Niaimi FA, Cox NH. Unilateral lichen striatus with bilateral onychodystrophy [published online ahead of print June 5, 2009]. Eur J Dermatol. 2009;19:511.
1. Hofer T. Lichen striatus in adults or ‘adult blaschkitis’? there is no need for a new naming. Dermatology. 2003;207:89-92.
2. Taniguchi Abagge K, Parolin Marinoni L, Giraldi S, et al. Lichen striatus: description of 89 cases in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2004;21:440-443.
3. Hauber K, Rose C, Brocker EB, et al. Lichen striatus: clinical features and follow-up in 12 patients. Eur J Dermatol. 2000;10:536-539.
4. Karp DL, Cohen BA. Onychodystrophy in lichen striatus. Pediatr Dermatol. 1993;10:359-361.
5. Arias-Santiago SA, Sierra Girón-Prieto M, Fernández-Pugnarie MA, et al. Lichen striatus following Blaschko lines [published online ahead of print May 8, 2009]. An Pediatr (Barc). 2009;71:76-77.
6. Racette AJ, Adams AD, Kessler SE. Simultaneous lichen striatus in siblings along the same Blaschko line [published online ahead of print February 16, 2009]. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:50-54.
7. Markouch I, Clérici T, Saiag P, et al. Lichen striatus with nail dystrophy in an infant. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2009;136:883-886.
8. Tosti A, Peluso AM, Misciali C, et al. Nail lichen striatus: clinical features and long-term follow-up of five patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36:908-913.
9. Leposavic R, Belsito DV. Onychodystrophy and subungual hyperkeratosis due to lichen striatus. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1099-1100.
10. Baran R, Dupré A, Lauret P, et al. Lichen striatus with nail involvement. report of 4 cases and review of the 4 cases in the literature. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1979;106:885-891.
11. Shepherd V, Lun K, Strutton G. Lichen striatus in an adult following trauma. Australas J Dermatol. 2005;46:25-28.
12. Hafner C, Landthaler M, Vogt T. Lichen striatus (blaschkitis) following varicella infection. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:1345-1347.
13. Brennand S, Khan S, Chong AH. Lichen striatus in a pregnant woman. Australas J Dermatol. 2005;46:184-186.
14. Patrizi A, Neri I, Fiorentini C, et al. Simultaneous occurrence of lichen striatus in siblings. Pediatr Dermatol. 1997;14:293-295.
15. Yaosaka M, Sawamura D, Iitoyo M, et al. Lichen striatus affecting a mother and her son. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:352-353.
16. Keegan BR, Kamino H, Fangman W, et al. “Pediatric blaschkitis”: expanding the spectrum of childhood acquired Blaschko-linear dermatoses. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:621-627.
17. Taieb A, el Youbi A, Grosshans E, et al. Lichen striatus: a Blaschko linear acquired inflammatory skin eruption. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;25:637-642.
18. Tilly JJ, Drolet BA, Esterly NB. Lichenoid eruptions in children. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:606-624.
19. Vukićević J, Milobratović D, Vesić S, et al. Unilateral multiple lichen striatus treated with tacrolimus ointment: a case report. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Panonica Adriat. 2009;18:35-38.
20. Fujimoto N, Tajima S, Ishibashi A. Facial lichen striatus: successful treatment with tacrolimus ointment. Br J Dermatol. 2003;148:587-590.
21. Kim GW, Kim SH, Seo SH, et al. Lichen striatus with nail abnormality successfully treated with tacrolimus ointment. J Dermatol. 2009;36:616-617.
22. Al-Niaimi FA, Cox NH. Unilateral lichen striatus with bilateral onychodystrophy [published online ahead of print June 5, 2009]. Eur J Dermatol. 2009;19:511.
Practice Points
- Lichen striatus (LS) is a relatively rare and self-limited linear dermatosis of unknown etiology and diagnosis usually is made clinically.
- Nail involvement is uncommon in LS but also may be underreported. When present, nail changes may appear before, after, or concurrently with skin lesions.
- If a patient presents with a similar case of isolated onychodystrophy, the clinician should inquire about history of cutaneous LS and should consider the possibility of LS in the differential diagnosis.
Early treatment key to halting progression of cicatricial alopecia
VANCOUVER, B.C. – Cicatricial alopecia should be considered a "trichologic emergency," Dr. Jerry Shapiro advised at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association. The hair loss may be permanent, "so it’s important to get on top of this, and not just sit out the condition."
Cicatricial alopecia is characterized by a loss of follicular ostia with replacement by fibrous tissue. Primary cicatricial alopecia targets the hair follicle and involves preferential destruction of the follicular epithelium with sparing of interfollicular dermis. In secondary cicatricial alopecia, "the follicle is an innocent bystander" that is destroyed in the course of infectious tinea capitis, infiltrative diseases such as metastatic disease and sarcoidosis, trauma such as radiation exposure and burns, and inflammatory conditions such as pemphigus vulgaris.
The North American Hair Research Society consensus classification of cicatricial alopecia is based on the infiltrate: lymphocytic, neutrophilic, mixed, or nonspecific.
"We determine our treatment decisions based on the infiltrate," said Dr. Shapiro, whose New York– and Vancouver–based practices are devoted exclusively to hair and scalp disorders. "A biopsy can be crucial when you’re managing these patients, so you know how actively inflamed the lesions are and what the primary infiltrate is. We always take a 4-mm punch biopsy, and we may take two. We’ll do one for transverse sectioning and another one for longitudinal sectioning."
"Sometimes there’s (histologic) overlap between lupus erythematosus or lichen planopilaris," he said. The clinical and pathologic findings can be variable, so the differential diagnosis is difficult. "There are no cures, and the cause of these conditions is unknown."
Discoid lupus erythematosus often presents with atrophy and extensive hair loss. A hallmark feature is central follicular hyperkeratosis. If less than 10% of the scalp is involved, Dr. Shapiro uses ultrapotent topical corticosteroids such as clobetasol with or without triamcinolone acetonide (TCA) injections (10 mg/cc for a maximum total of 2 ccs per sitting once a month). "We inject into the areas that are red as well as the surrounding areas so that it doesn’t spread," he said.
If a patient responds to this regimen he continues to use it on an as-needed basis. For nonresponders, Dr. Shapiro resorts to hydroxychloroquine 200 mg b.i.d. or isotretinoin 40 mg b.i.d. Other alternatives can include topical tacrolimus. Others have used tazarotene and imiquimod, he said, but "I find the latter two too irritating."
For patients with 10% or greater scalp involvement, Dr. Shapiro uses hydroxychloroquine plus ultrapotent topical steroids, plus TCA injections, plus bridging therapy with prednisone, usually with 40 mg prednisone tapered.
Patients with lichen planopilaris typically present with peripheral hyperkeratosis, or frontal fibrosing alopecia, which is marked by loss of a strip of hair at the front and/or the sides of the scalp. Frontal fibrosing alopecia is "a silent epidemic. In Vancouver, I’m seeing about seven cases per day of this, and three to four cases per day in New York. Sometimes, the eyebrows are the first sign of hair loss. Many times it can go completely around the scalp, so it’s [considered] marginally fibrosing," Dr. Shapiro said.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia primarily affects postmenopausal women. "We think there is a hormonal component that is causing this, but there is also a trigger in the environment," Dr. Shapiro said. "We don’t know what the trigger is, but certain countries have less of it. China does not see that much of it, nor does Saudi Arabia."
Dr. Shapiro and his associates recently published a retrospective study of 62 cases of frontal fibrosing alopecia seen between January 2004 and March 2012. Of the 62 patients, 61 were women (Int. J. Dermatol. 2014 [doi:10.1111/ijd.12479]). Their average age was 61 years and the age of onset ranged from 18 to 81 years. In terms of symptoms, 22 (35%) patients were asymptomatic, 42 (68%) had a history of female pattern hair loss, and 50 (81%) patients’ eyebrows were affected.
In Dr. Shapiro’s experience, intralesional TCA with or without oral tetracycline or hydroxychloroquine may help to halt or slow the progression of frontal fibrosing alopecia. He typically uses intralesional Kenalog 2.5 mL/cc. "I do 30 injections for 3 ccs total: 0.1 cc/injection site and I go from one ear to the other," Dr. Shapiro said. "We’ll also use clobetasol solution at the beginning and taper to a betamethasone solution. Other things to consider are tacrolimus, Cetaphil cleanser, and finasteride."
Dr. Shapiro disclosed that he is a consultant to Johnson & Johnson, GSK/Stiefel, Allergan, MSD, and Applied Biology.
On Twitter @dougbrunk
VANCOUVER, B.C. – Cicatricial alopecia should be considered a "trichologic emergency," Dr. Jerry Shapiro advised at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association. The hair loss may be permanent, "so it’s important to get on top of this, and not just sit out the condition."
Cicatricial alopecia is characterized by a loss of follicular ostia with replacement by fibrous tissue. Primary cicatricial alopecia targets the hair follicle and involves preferential destruction of the follicular epithelium with sparing of interfollicular dermis. In secondary cicatricial alopecia, "the follicle is an innocent bystander" that is destroyed in the course of infectious tinea capitis, infiltrative diseases such as metastatic disease and sarcoidosis, trauma such as radiation exposure and burns, and inflammatory conditions such as pemphigus vulgaris.
The North American Hair Research Society consensus classification of cicatricial alopecia is based on the infiltrate: lymphocytic, neutrophilic, mixed, or nonspecific.
"We determine our treatment decisions based on the infiltrate," said Dr. Shapiro, whose New York– and Vancouver–based practices are devoted exclusively to hair and scalp disorders. "A biopsy can be crucial when you’re managing these patients, so you know how actively inflamed the lesions are and what the primary infiltrate is. We always take a 4-mm punch biopsy, and we may take two. We’ll do one for transverse sectioning and another one for longitudinal sectioning."
"Sometimes there’s (histologic) overlap between lupus erythematosus or lichen planopilaris," he said. The clinical and pathologic findings can be variable, so the differential diagnosis is difficult. "There are no cures, and the cause of these conditions is unknown."
Discoid lupus erythematosus often presents with atrophy and extensive hair loss. A hallmark feature is central follicular hyperkeratosis. If less than 10% of the scalp is involved, Dr. Shapiro uses ultrapotent topical corticosteroids such as clobetasol with or without triamcinolone acetonide (TCA) injections (10 mg/cc for a maximum total of 2 ccs per sitting once a month). "We inject into the areas that are red as well as the surrounding areas so that it doesn’t spread," he said.
If a patient responds to this regimen he continues to use it on an as-needed basis. For nonresponders, Dr. Shapiro resorts to hydroxychloroquine 200 mg b.i.d. or isotretinoin 40 mg b.i.d. Other alternatives can include topical tacrolimus. Others have used tazarotene and imiquimod, he said, but "I find the latter two too irritating."
For patients with 10% or greater scalp involvement, Dr. Shapiro uses hydroxychloroquine plus ultrapotent topical steroids, plus TCA injections, plus bridging therapy with prednisone, usually with 40 mg prednisone tapered.
Patients with lichen planopilaris typically present with peripheral hyperkeratosis, or frontal fibrosing alopecia, which is marked by loss of a strip of hair at the front and/or the sides of the scalp. Frontal fibrosing alopecia is "a silent epidemic. In Vancouver, I’m seeing about seven cases per day of this, and three to four cases per day in New York. Sometimes, the eyebrows are the first sign of hair loss. Many times it can go completely around the scalp, so it’s [considered] marginally fibrosing," Dr. Shapiro said.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia primarily affects postmenopausal women. "We think there is a hormonal component that is causing this, but there is also a trigger in the environment," Dr. Shapiro said. "We don’t know what the trigger is, but certain countries have less of it. China does not see that much of it, nor does Saudi Arabia."
Dr. Shapiro and his associates recently published a retrospective study of 62 cases of frontal fibrosing alopecia seen between January 2004 and March 2012. Of the 62 patients, 61 were women (Int. J. Dermatol. 2014 [doi:10.1111/ijd.12479]). Their average age was 61 years and the age of onset ranged from 18 to 81 years. In terms of symptoms, 22 (35%) patients were asymptomatic, 42 (68%) had a history of female pattern hair loss, and 50 (81%) patients’ eyebrows were affected.
In Dr. Shapiro’s experience, intralesional TCA with or without oral tetracycline or hydroxychloroquine may help to halt or slow the progression of frontal fibrosing alopecia. He typically uses intralesional Kenalog 2.5 mL/cc. "I do 30 injections for 3 ccs total: 0.1 cc/injection site and I go from one ear to the other," Dr. Shapiro said. "We’ll also use clobetasol solution at the beginning and taper to a betamethasone solution. Other things to consider are tacrolimus, Cetaphil cleanser, and finasteride."
Dr. Shapiro disclosed that he is a consultant to Johnson & Johnson, GSK/Stiefel, Allergan, MSD, and Applied Biology.
On Twitter @dougbrunk
VANCOUVER, B.C. – Cicatricial alopecia should be considered a "trichologic emergency," Dr. Jerry Shapiro advised at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association. The hair loss may be permanent, "so it’s important to get on top of this, and not just sit out the condition."
Cicatricial alopecia is characterized by a loss of follicular ostia with replacement by fibrous tissue. Primary cicatricial alopecia targets the hair follicle and involves preferential destruction of the follicular epithelium with sparing of interfollicular dermis. In secondary cicatricial alopecia, "the follicle is an innocent bystander" that is destroyed in the course of infectious tinea capitis, infiltrative diseases such as metastatic disease and sarcoidosis, trauma such as radiation exposure and burns, and inflammatory conditions such as pemphigus vulgaris.
The North American Hair Research Society consensus classification of cicatricial alopecia is based on the infiltrate: lymphocytic, neutrophilic, mixed, or nonspecific.
"We determine our treatment decisions based on the infiltrate," said Dr. Shapiro, whose New York– and Vancouver–based practices are devoted exclusively to hair and scalp disorders. "A biopsy can be crucial when you’re managing these patients, so you know how actively inflamed the lesions are and what the primary infiltrate is. We always take a 4-mm punch biopsy, and we may take two. We’ll do one for transverse sectioning and another one for longitudinal sectioning."
"Sometimes there’s (histologic) overlap between lupus erythematosus or lichen planopilaris," he said. The clinical and pathologic findings can be variable, so the differential diagnosis is difficult. "There are no cures, and the cause of these conditions is unknown."
Discoid lupus erythematosus often presents with atrophy and extensive hair loss. A hallmark feature is central follicular hyperkeratosis. If less than 10% of the scalp is involved, Dr. Shapiro uses ultrapotent topical corticosteroids such as clobetasol with or without triamcinolone acetonide (TCA) injections (10 mg/cc for a maximum total of 2 ccs per sitting once a month). "We inject into the areas that are red as well as the surrounding areas so that it doesn’t spread," he said.
If a patient responds to this regimen he continues to use it on an as-needed basis. For nonresponders, Dr. Shapiro resorts to hydroxychloroquine 200 mg b.i.d. or isotretinoin 40 mg b.i.d. Other alternatives can include topical tacrolimus. Others have used tazarotene and imiquimod, he said, but "I find the latter two too irritating."
For patients with 10% or greater scalp involvement, Dr. Shapiro uses hydroxychloroquine plus ultrapotent topical steroids, plus TCA injections, plus bridging therapy with prednisone, usually with 40 mg prednisone tapered.
Patients with lichen planopilaris typically present with peripheral hyperkeratosis, or frontal fibrosing alopecia, which is marked by loss of a strip of hair at the front and/or the sides of the scalp. Frontal fibrosing alopecia is "a silent epidemic. In Vancouver, I’m seeing about seven cases per day of this, and three to four cases per day in New York. Sometimes, the eyebrows are the first sign of hair loss. Many times it can go completely around the scalp, so it’s [considered] marginally fibrosing," Dr. Shapiro said.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia primarily affects postmenopausal women. "We think there is a hormonal component that is causing this, but there is also a trigger in the environment," Dr. Shapiro said. "We don’t know what the trigger is, but certain countries have less of it. China does not see that much of it, nor does Saudi Arabia."
Dr. Shapiro and his associates recently published a retrospective study of 62 cases of frontal fibrosing alopecia seen between January 2004 and March 2012. Of the 62 patients, 61 were women (Int. J. Dermatol. 2014 [doi:10.1111/ijd.12479]). Their average age was 61 years and the age of onset ranged from 18 to 81 years. In terms of symptoms, 22 (35%) patients were asymptomatic, 42 (68%) had a history of female pattern hair loss, and 50 (81%) patients’ eyebrows were affected.
In Dr. Shapiro’s experience, intralesional TCA with or without oral tetracycline or hydroxychloroquine may help to halt or slow the progression of frontal fibrosing alopecia. He typically uses intralesional Kenalog 2.5 mL/cc. "I do 30 injections for 3 ccs total: 0.1 cc/injection site and I go from one ear to the other," Dr. Shapiro said. "We’ll also use clobetasol solution at the beginning and taper to a betamethasone solution. Other things to consider are tacrolimus, Cetaphil cleanser, and finasteride."
Dr. Shapiro disclosed that he is a consultant to Johnson & Johnson, GSK/Stiefel, Allergan, MSD, and Applied Biology.
On Twitter @dougbrunk
EXPERT ANALYSIS AT THE PDA ANNUAL MEETING
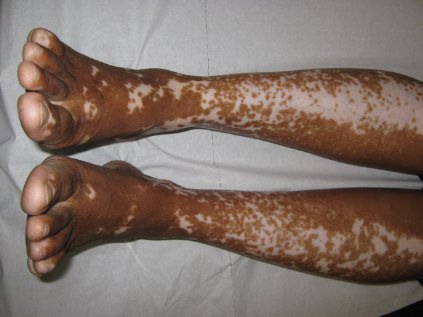
Vitiligo, alopecia more likely in GVHD when donor is female and recipient is male
The development of vitiligo or alopecia areata is not common in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease, but it is significantly more likely to occur when the donor was female, especially when the recipient was male, according to a report published online Sept. 10 in JAMA Dermatology.
Fifteen case reports and small series in the literature have reported the development of vitiligo or alopecia areata after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, most often among patients who first developed chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) after the procedure. To further explore the frequency of these two skin autoimmune manifestations in GVHD and to identify associated risk factors, researchers performed a retrospective cross-sectional analysis involving 282 adult and pediatric patients referred to the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center for GVHD in 2004-2013.
They identified 15 GVHD patients with vitiligo (4.9%) and 2 with alopecia areata (0.7%); one of these patients had both skin disorders. Most of the 15 patients had undergone stem-cell transplantation to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) (5 patients) or acute leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome (5 patients), and most had had a human leukocyte antigen–identical donor. Twelve of the 15 developed the skin disorder after having GVHD for more than 1 year, said Rena C. Zuo of the National Cancer Institute’s dermatology branch and her associates.
"Notably, CML accounts for only about 300 of 7,892 (3.8%) allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantations per year in the United States, a relative minority among indicated diseases," they said.
In what they described as the first study to identify an association between donor/recipient sex mismatch and the development of concomitant autoimmunity in patients with chronic GVHD, the investigators found that 14 of the 15 patients who developed vitiligo or alopecia areata had female donors, 2 of whom had previously given birth; the gender of the donor in the 15th case was unknown. Nine of these 14 recipients were male, "resulting in a female-to-male sex mismatch in [at least] 64% of cases," Ms. Zuo and her colleagues said (JAMA Dermatol. 2014 Sept. 10 [doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.1550]).
Both parous female donors and donor-recipient sex mismatch are known risk factors for GVHD. The risk of autoimmunity in female-to-male transplants "may reflect the activity of skin-homing donor T cells specific for recipient minor histocompatibility antigens encoded by Y-chromosome genes, a mechanism previously implicated in both GVHD and graft-versus-tumor responses," the investigators added.
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Cancer Institute. Ms. Zuo and her associates reported no financial conflicts of interest.
The development of vitiligo or alopecia areata is not common in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease, but it is significantly more likely to occur when the donor was female, especially when the recipient was male, according to a report published online Sept. 10 in JAMA Dermatology.
Fifteen case reports and small series in the literature have reported the development of vitiligo or alopecia areata after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, most often among patients who first developed chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) after the procedure. To further explore the frequency of these two skin autoimmune manifestations in GVHD and to identify associated risk factors, researchers performed a retrospective cross-sectional analysis involving 282 adult and pediatric patients referred to the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center for GVHD in 2004-2013.
They identified 15 GVHD patients with vitiligo (4.9%) and 2 with alopecia areata (0.7%); one of these patients had both skin disorders. Most of the 15 patients had undergone stem-cell transplantation to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) (5 patients) or acute leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome (5 patients), and most had had a human leukocyte antigen–identical donor. Twelve of the 15 developed the skin disorder after having GVHD for more than 1 year, said Rena C. Zuo of the National Cancer Institute’s dermatology branch and her associates.
"Notably, CML accounts for only about 300 of 7,892 (3.8%) allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantations per year in the United States, a relative minority among indicated diseases," they said.
In what they described as the first study to identify an association between donor/recipient sex mismatch and the development of concomitant autoimmunity in patients with chronic GVHD, the investigators found that 14 of the 15 patients who developed vitiligo or alopecia areata had female donors, 2 of whom had previously given birth; the gender of the donor in the 15th case was unknown. Nine of these 14 recipients were male, "resulting in a female-to-male sex mismatch in [at least] 64% of cases," Ms. Zuo and her colleagues said (JAMA Dermatol. 2014 Sept. 10 [doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.1550]).
Both parous female donors and donor-recipient sex mismatch are known risk factors for GVHD. The risk of autoimmunity in female-to-male transplants "may reflect the activity of skin-homing donor T cells specific for recipient minor histocompatibility antigens encoded by Y-chromosome genes, a mechanism previously implicated in both GVHD and graft-versus-tumor responses," the investigators added.
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Cancer Institute. Ms. Zuo and her associates reported no financial conflicts of interest.
The development of vitiligo or alopecia areata is not common in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease, but it is significantly more likely to occur when the donor was female, especially when the recipient was male, according to a report published online Sept. 10 in JAMA Dermatology.
Fifteen case reports and small series in the literature have reported the development of vitiligo or alopecia areata after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, most often among patients who first developed chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) after the procedure. To further explore the frequency of these two skin autoimmune manifestations in GVHD and to identify associated risk factors, researchers performed a retrospective cross-sectional analysis involving 282 adult and pediatric patients referred to the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center for GVHD in 2004-2013.
They identified 15 GVHD patients with vitiligo (4.9%) and 2 with alopecia areata (0.7%); one of these patients had both skin disorders. Most of the 15 patients had undergone stem-cell transplantation to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) (5 patients) or acute leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome (5 patients), and most had had a human leukocyte antigen–identical donor. Twelve of the 15 developed the skin disorder after having GVHD for more than 1 year, said Rena C. Zuo of the National Cancer Institute’s dermatology branch and her associates.
"Notably, CML accounts for only about 300 of 7,892 (3.8%) allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantations per year in the United States, a relative minority among indicated diseases," they said.
In what they described as the first study to identify an association between donor/recipient sex mismatch and the development of concomitant autoimmunity in patients with chronic GVHD, the investigators found that 14 of the 15 patients who developed vitiligo or alopecia areata had female donors, 2 of whom had previously given birth; the gender of the donor in the 15th case was unknown. Nine of these 14 recipients were male, "resulting in a female-to-male sex mismatch in [at least] 64% of cases," Ms. Zuo and her colleagues said (JAMA Dermatol. 2014 Sept. 10 [doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.1550]).
Both parous female donors and donor-recipient sex mismatch are known risk factors for GVHD. The risk of autoimmunity in female-to-male transplants "may reflect the activity of skin-homing donor T cells specific for recipient minor histocompatibility antigens encoded by Y-chromosome genes, a mechanism previously implicated in both GVHD and graft-versus-tumor responses," the investigators added.
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Cancer Institute. Ms. Zuo and her associates reported no financial conflicts of interest.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Female-to-male stem cell donation ups the risk for vitiligo in GVHD.
Major finding: 14 of the 15 patients who developed vitiligo or alopecia areata had female donors (the gender of the 15th donor was unknown), and 9 of these 14 recipients were male.
Data source: A retrospective cross-sectional analysis involving 282 adults and children with chronic GVHD, 15 of whom developed vitiligo or alopecia areata.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Zuo and her associates reported no financial conflicts of interest.
Fungal Melanonychia Caused by Trichophyton rubrum and the Value of Dermoscopy
To the Editor:
Longitudinal melanonychia encompasses a broad spectrum of diseases and often is a complex diagnostic problem. Differential diagnoses include ethnic-type nail pigmentation, which is more frequently seen in darker-skinned individuals; drug-induced pigmentation; subungual hemorrhage; fungal or bacterial infection; nevus; and melanoma.1,2 Fungal melan-onychia is an uncommon presentation of onychomycosis. Dermoscopy can assist in the evaluation of nail pigmentation caused by fungi to avoid unnecessary nail biopsies.
A 39-year-old man visited the dermatology clinic with a concern for melanoma because of blackish pigmentation of the toenails of 1 month’s duration. He denied history of trauma and was not taking any medications. On physical examination the second and third toenails revealed a 2-mm longitudinal band of black pigment on the lateral side; the fifth toenail showed diffuse black pigment (Figure 1A). The nail plates were thickened. Dermoscopy revealed prominent subungual hyperkeratosis, a homogeneous brown-black band with wide yellow streaks that were wider in the distal ends, and some focal reddish hue. No visible melanin inclusions were observed (Figure 2). These findings were suggestive of fungal infection. Cultures from the diseased nail grew a fungus identified as Trichophyton rubrum. The patient was treated with itraconazole 200 mg daily for 3 months. Clinical cure with disappearance of pigment was obtained at 5-month follow-up (Figure 1B).
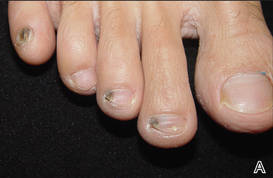
|
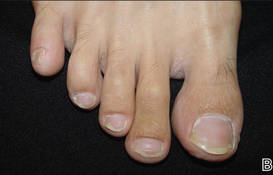
|
| Figure 1. Blackish discoloration of the right second, third, and fifth toenails (A). Resolution of pigmentation and subungual hyperkeratosis was achieved at 5-month follow-up after treatment (B). |
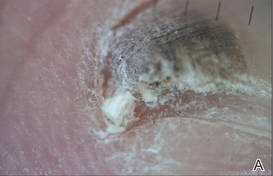
|
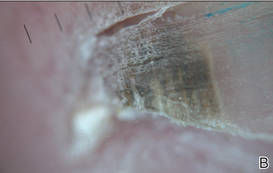
|
| Figure 2. Top view (A) and front view (B) of a homogeneous brown-black band with subungual hyperkeratosis and wide intervening yellow streaks. Each ruler mark denotes 1 mm. |
Our patient illustrates the value of dermoscopy in evaluating melanonychia. The pigmentation of adult-onset melanonychia involving multiple fingers can be divided into nonmelanocytic or melanocytic origin. Causes of the former include subungual hematoma, fungal or bacterial infection, and exogenous pigmentation. The nonmelanocytic pigment often is homogeneously distributed without melanin inclusions under the dermoscope.2
On the contrary, melanin inclusions can be detected as fine granules in pigmentation of melanocytic origin, either from focal melanocytic activation or melanocyte proliferation. Causes of focal melanocytic activation include ethnic-type nail hyperpigmentation; inflammatory nail diseases; or drug-, radiation-, and friction-induced hyperpigmentation. The characteristic dermoscopic features are thin longitudinal gray lines with regular thickness and spacing in a grayish background.1-3
Melanocyte proliferation can result in a nevus or melanoma of the nail apparatus. Both share dermoscopic features of brown-black longitudinal lines in a brown background. However, the longitudinal lines in melanoma are irregular in coloration, spacing, thickness, and parallelism, in contrast with the regular pattern of a nevus.1-4 Although patients often are concerned about melanoma, involvement of multiple fingers at the same time is less likely.
In our patient, the homogeneous deep brown color without melanin inclusions favored a nonmel-anocytic origin. The distally wider pigmentation suggested fungal infection because most ungual infections extend from the distal to the proximal part of the nail.5,6 The focal reddish hue may be related with traumatic hemorrhage from subungual hyperkeratosis.
Cases of fungal melanonychia are being reported at an increasing rate. Some fungal strains are capable of synthesizing melanin, which is associated with virulence and acts as a fungal armor against toxic insults.5 In T rubrum, the melanoid variant, the diffusible black pigment infiltrates the nail plate and attributes to the black nail clinically.4 The most frequently isolated fungi in fungal melanonychia are T rubrum and Scytalidium dimidiatum6; however, Candida species,7,8 dematiaceous fungus,9 and other dermatophytes such as Trichophyton soudanense10 have been reported to be the cause.5
Our patient presented with fungal melanonychia due to T rubrum with dermoscopic features. The prominent subungual hyperkeratosis, distally wider homogeneous brown-black pigmented band, and wide yellow streaks with focal reddish hue all suggested fungal melanonychia. The diagnosis was further confirmed by a good response to antifungal agents.
1. Ronger S, Touzet S, Ligeron C, et al. Dermoscopic examination of nail pigmentation. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1327-1333.
2. Braun RP, Baran R, Le Gal FA, et al. Diagnosis and management of nail pigmentations [published online ahead of print February 22, 2007]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:835-847.
3. Koga H, Saida T, Uhara H. Key point in dermoscopic differentiation between early nail apparatus melanoma and benign longitudinal melanonychia. J Dermatol. 2011;38:45-52.
4. Phan A, Dalle S, Touzet S, et al. Dermoscopic features of acral lentiginous melanoma in a large series of 110 cases in a white population [published online ahead of print November 18, 2009]. Br J Dermatol. 2010;162:765-771.
5. Finch J, Arenas R, Baran R. Fungal melanonychia [published online ahead of print January 17, 2012]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:830-841.
6. Lee SW, Kim YC, Kim DK, et al. Fungal melanonychia. J Dermatol. 2004;31:904-909.
7. Parlak AH, Goksugur N, Karabay O. A case of melanonychia due to Candida albicans. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;31:398-400.
8. Gautret P, Rodier MH, Kauffmann-Lacroix C, et al. Case report and review. onychomycosis due to Candida parapsilosis. Mycoses. 2000;43:433-435.
9. Barua P, Barua S, Borkakoty B, et al. Onychomycosis by Scytalidium dimidiatum in green tea leaf pluckers: report of two cases [published online ahead of print July 20, 2007]. Mycopathologia. 2007;164:193-195.
10. Ricci C, Monod M, Baudraz-Rosselet F. Onychomycosis due to Trichophyton soudanense in Switzerland. Dermatology. 1998;197:297-298.
To the Editor:
Longitudinal melanonychia encompasses a broad spectrum of diseases and often is a complex diagnostic problem. Differential diagnoses include ethnic-type nail pigmentation, which is more frequently seen in darker-skinned individuals; drug-induced pigmentation; subungual hemorrhage; fungal or bacterial infection; nevus; and melanoma.1,2 Fungal melan-onychia is an uncommon presentation of onychomycosis. Dermoscopy can assist in the evaluation of nail pigmentation caused by fungi to avoid unnecessary nail biopsies.
A 39-year-old man visited the dermatology clinic with a concern for melanoma because of blackish pigmentation of the toenails of 1 month’s duration. He denied history of trauma and was not taking any medications. On physical examination the second and third toenails revealed a 2-mm longitudinal band of black pigment on the lateral side; the fifth toenail showed diffuse black pigment (Figure 1A). The nail plates were thickened. Dermoscopy revealed prominent subungual hyperkeratosis, a homogeneous brown-black band with wide yellow streaks that were wider in the distal ends, and some focal reddish hue. No visible melanin inclusions were observed (Figure 2). These findings were suggestive of fungal infection. Cultures from the diseased nail grew a fungus identified as Trichophyton rubrum. The patient was treated with itraconazole 200 mg daily for 3 months. Clinical cure with disappearance of pigment was obtained at 5-month follow-up (Figure 1B).

|

|
| Figure 1. Blackish discoloration of the right second, third, and fifth toenails (A). Resolution of pigmentation and subungual hyperkeratosis was achieved at 5-month follow-up after treatment (B). |

|

|
| Figure 2. Top view (A) and front view (B) of a homogeneous brown-black band with subungual hyperkeratosis and wide intervening yellow streaks. Each ruler mark denotes 1 mm. |
Our patient illustrates the value of dermoscopy in evaluating melanonychia. The pigmentation of adult-onset melanonychia involving multiple fingers can be divided into nonmelanocytic or melanocytic origin. Causes of the former include subungual hematoma, fungal or bacterial infection, and exogenous pigmentation. The nonmelanocytic pigment often is homogeneously distributed without melanin inclusions under the dermoscope.2
On the contrary, melanin inclusions can be detected as fine granules in pigmentation of melanocytic origin, either from focal melanocytic activation or melanocyte proliferation. Causes of focal melanocytic activation include ethnic-type nail hyperpigmentation; inflammatory nail diseases; or drug-, radiation-, and friction-induced hyperpigmentation. The characteristic dermoscopic features are thin longitudinal gray lines with regular thickness and spacing in a grayish background.1-3
Melanocyte proliferation can result in a nevus or melanoma of the nail apparatus. Both share dermoscopic features of brown-black longitudinal lines in a brown background. However, the longitudinal lines in melanoma are irregular in coloration, spacing, thickness, and parallelism, in contrast with the regular pattern of a nevus.1-4 Although patients often are concerned about melanoma, involvement of multiple fingers at the same time is less likely.
In our patient, the homogeneous deep brown color without melanin inclusions favored a nonmel-anocytic origin. The distally wider pigmentation suggested fungal infection because most ungual infections extend from the distal to the proximal part of the nail.5,6 The focal reddish hue may be related with traumatic hemorrhage from subungual hyperkeratosis.
Cases of fungal melanonychia are being reported at an increasing rate. Some fungal strains are capable of synthesizing melanin, which is associated with virulence and acts as a fungal armor against toxic insults.5 In T rubrum, the melanoid variant, the diffusible black pigment infiltrates the nail plate and attributes to the black nail clinically.4 The most frequently isolated fungi in fungal melanonychia are T rubrum and Scytalidium dimidiatum6; however, Candida species,7,8 dematiaceous fungus,9 and other dermatophytes such as Trichophyton soudanense10 have been reported to be the cause.5
Our patient presented with fungal melanonychia due to T rubrum with dermoscopic features. The prominent subungual hyperkeratosis, distally wider homogeneous brown-black pigmented band, and wide yellow streaks with focal reddish hue all suggested fungal melanonychia. The diagnosis was further confirmed by a good response to antifungal agents.
To the Editor:
Longitudinal melanonychia encompasses a broad spectrum of diseases and often is a complex diagnostic problem. Differential diagnoses include ethnic-type nail pigmentation, which is more frequently seen in darker-skinned individuals; drug-induced pigmentation; subungual hemorrhage; fungal or bacterial infection; nevus; and melanoma.1,2 Fungal melan-onychia is an uncommon presentation of onychomycosis. Dermoscopy can assist in the evaluation of nail pigmentation caused by fungi to avoid unnecessary nail biopsies.
A 39-year-old man visited the dermatology clinic with a concern for melanoma because of blackish pigmentation of the toenails of 1 month’s duration. He denied history of trauma and was not taking any medications. On physical examination the second and third toenails revealed a 2-mm longitudinal band of black pigment on the lateral side; the fifth toenail showed diffuse black pigment (Figure 1A). The nail plates were thickened. Dermoscopy revealed prominent subungual hyperkeratosis, a homogeneous brown-black band with wide yellow streaks that were wider in the distal ends, and some focal reddish hue. No visible melanin inclusions were observed (Figure 2). These findings were suggestive of fungal infection. Cultures from the diseased nail grew a fungus identified as Trichophyton rubrum. The patient was treated with itraconazole 200 mg daily for 3 months. Clinical cure with disappearance of pigment was obtained at 5-month follow-up (Figure 1B).

|

|
| Figure 1. Blackish discoloration of the right second, third, and fifth toenails (A). Resolution of pigmentation and subungual hyperkeratosis was achieved at 5-month follow-up after treatment (B). |

|

|
| Figure 2. Top view (A) and front view (B) of a homogeneous brown-black band with subungual hyperkeratosis and wide intervening yellow streaks. Each ruler mark denotes 1 mm. |
Our patient illustrates the value of dermoscopy in evaluating melanonychia. The pigmentation of adult-onset melanonychia involving multiple fingers can be divided into nonmelanocytic or melanocytic origin. Causes of the former include subungual hematoma, fungal or bacterial infection, and exogenous pigmentation. The nonmelanocytic pigment often is homogeneously distributed without melanin inclusions under the dermoscope.2
On the contrary, melanin inclusions can be detected as fine granules in pigmentation of melanocytic origin, either from focal melanocytic activation or melanocyte proliferation. Causes of focal melanocytic activation include ethnic-type nail hyperpigmentation; inflammatory nail diseases; or drug-, radiation-, and friction-induced hyperpigmentation. The characteristic dermoscopic features are thin longitudinal gray lines with regular thickness and spacing in a grayish background.1-3
Melanocyte proliferation can result in a nevus or melanoma of the nail apparatus. Both share dermoscopic features of brown-black longitudinal lines in a brown background. However, the longitudinal lines in melanoma are irregular in coloration, spacing, thickness, and parallelism, in contrast with the regular pattern of a nevus.1-4 Although patients often are concerned about melanoma, involvement of multiple fingers at the same time is less likely.
In our patient, the homogeneous deep brown color without melanin inclusions favored a nonmel-anocytic origin. The distally wider pigmentation suggested fungal infection because most ungual infections extend from the distal to the proximal part of the nail.5,6 The focal reddish hue may be related with traumatic hemorrhage from subungual hyperkeratosis.
Cases of fungal melanonychia are being reported at an increasing rate. Some fungal strains are capable of synthesizing melanin, which is associated with virulence and acts as a fungal armor against toxic insults.5 In T rubrum, the melanoid variant, the diffusible black pigment infiltrates the nail plate and attributes to the black nail clinically.4 The most frequently isolated fungi in fungal melanonychia are T rubrum and Scytalidium dimidiatum6; however, Candida species,7,8 dematiaceous fungus,9 and other dermatophytes such as Trichophyton soudanense10 have been reported to be the cause.5
Our patient presented with fungal melanonychia due to T rubrum with dermoscopic features. The prominent subungual hyperkeratosis, distally wider homogeneous brown-black pigmented band, and wide yellow streaks with focal reddish hue all suggested fungal melanonychia. The diagnosis was further confirmed by a good response to antifungal agents.
1. Ronger S, Touzet S, Ligeron C, et al. Dermoscopic examination of nail pigmentation. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1327-1333.
2. Braun RP, Baran R, Le Gal FA, et al. Diagnosis and management of nail pigmentations [published online ahead of print February 22, 2007]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:835-847.
3. Koga H, Saida T, Uhara H. Key point in dermoscopic differentiation between early nail apparatus melanoma and benign longitudinal melanonychia. J Dermatol. 2011;38:45-52.
4. Phan A, Dalle S, Touzet S, et al. Dermoscopic features of acral lentiginous melanoma in a large series of 110 cases in a white population [published online ahead of print November 18, 2009]. Br J Dermatol. 2010;162:765-771.
5. Finch J, Arenas R, Baran R. Fungal melanonychia [published online ahead of print January 17, 2012]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:830-841.
6. Lee SW, Kim YC, Kim DK, et al. Fungal melanonychia. J Dermatol. 2004;31:904-909.
7. Parlak AH, Goksugur N, Karabay O. A case of melanonychia due to Candida albicans. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;31:398-400.
8. Gautret P, Rodier MH, Kauffmann-Lacroix C, et al. Case report and review. onychomycosis due to Candida parapsilosis. Mycoses. 2000;43:433-435.
9. Barua P, Barua S, Borkakoty B, et al. Onychomycosis by Scytalidium dimidiatum in green tea leaf pluckers: report of two cases [published online ahead of print July 20, 2007]. Mycopathologia. 2007;164:193-195.
10. Ricci C, Monod M, Baudraz-Rosselet F. Onychomycosis due to Trichophyton soudanense in Switzerland. Dermatology. 1998;197:297-298.
1. Ronger S, Touzet S, Ligeron C, et al. Dermoscopic examination of nail pigmentation. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1327-1333.
2. Braun RP, Baran R, Le Gal FA, et al. Diagnosis and management of nail pigmentations [published online ahead of print February 22, 2007]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:835-847.
3. Koga H, Saida T, Uhara H. Key point in dermoscopic differentiation between early nail apparatus melanoma and benign longitudinal melanonychia. J Dermatol. 2011;38:45-52.
4. Phan A, Dalle S, Touzet S, et al. Dermoscopic features of acral lentiginous melanoma in a large series of 110 cases in a white population [published online ahead of print November 18, 2009]. Br J Dermatol. 2010;162:765-771.
5. Finch J, Arenas R, Baran R. Fungal melanonychia [published online ahead of print January 17, 2012]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:830-841.
6. Lee SW, Kim YC, Kim DK, et al. Fungal melanonychia. J Dermatol. 2004;31:904-909.
7. Parlak AH, Goksugur N, Karabay O. A case of melanonychia due to Candida albicans. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;31:398-400.
8. Gautret P, Rodier MH, Kauffmann-Lacroix C, et al. Case report and review. onychomycosis due to Candida parapsilosis. Mycoses. 2000;43:433-435.
9. Barua P, Barua S, Borkakoty B, et al. Onychomycosis by Scytalidium dimidiatum in green tea leaf pluckers: report of two cases [published online ahead of print July 20, 2007]. Mycopathologia. 2007;164:193-195.
10. Ricci C, Monod M, Baudraz-Rosselet F. Onychomycosis due to Trichophyton soudanense in Switzerland. Dermatology. 1998;197:297-298.
Narrow-Toed Shoes and the Toe-to-Toe Sign
To the Editor:
Macro- or microtrauma to nails can cause and/or exacerbate chronic diseases such as ingrown nails, onycholysis, onychauxis, onychogryposis, and hallux valgus (bunions). This trauma also can break the anatomic barrier of the hyponychium, thereby creating a portal for dermatophytes and other organisms to penetrate the nail apparatus.1
For many years, one author (C.R.D.) has used the following demonstration to communicate to patients how improper shoe fit may cause toenail trauma. The patient’s shoe is flipped 180° and placed toe-to-toe with the patient’s foot (Figure). Most patients can comprehend the relationship between their shoe fit and their toenail disease when they see this demonstration. We have termed it toe-to-toe sign.
|
|
| The foot and shoe are toe-to-toe, demonstrating the narrow toe box in comparison to the actual toes (A). This comparison is accentuated when the shoe is placed over the foot with toes splayed from standing (B). |
Narrow toe box is the usual culprit. The toe-to-toe sign best emphasizes this relationship. This sign serves as a powerful tool when demonstrating how much the foot widens when bearing full weight, and how forces of ambulation and foot strike can damage the nails with narrow-toed footwear. This trauma is compounded with high-heeled shoes that force the toes forward. However, proper shoe fit may compete with idealized shoe style. It is not until patients realize the relationship between improper shoe fit, foot strike, and toe/toenail trauma that they can make long-term decisions that favorably impact their toes and toenails.
Reference
1. Daniel CR 3rd, Jellinek NJ. The pedal fungus reservoir. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:1344-1346.
To the Editor:
Macro- or microtrauma to nails can cause and/or exacerbate chronic diseases such as ingrown nails, onycholysis, onychauxis, onychogryposis, and hallux valgus (bunions). This trauma also can break the anatomic barrier of the hyponychium, thereby creating a portal for dermatophytes and other organisms to penetrate the nail apparatus.1
For many years, one author (C.R.D.) has used the following demonstration to communicate to patients how improper shoe fit may cause toenail trauma. The patient’s shoe is flipped 180° and placed toe-to-toe with the patient’s foot (Figure). Most patients can comprehend the relationship between their shoe fit and their toenail disease when they see this demonstration. We have termed it toe-to-toe sign.

|

|
| The foot and shoe are toe-to-toe, demonstrating the narrow toe box in comparison to the actual toes (A). This comparison is accentuated when the shoe is placed over the foot with toes splayed from standing (B). |
Narrow toe box is the usual culprit. The toe-to-toe sign best emphasizes this relationship. This sign serves as a powerful tool when demonstrating how much the foot widens when bearing full weight, and how forces of ambulation and foot strike can damage the nails with narrow-toed footwear. This trauma is compounded with high-heeled shoes that force the toes forward. However, proper shoe fit may compete with idealized shoe style. It is not until patients realize the relationship between improper shoe fit, foot strike, and toe/toenail trauma that they can make long-term decisions that favorably impact their toes and toenails.
To the Editor:
Macro- or microtrauma to nails can cause and/or exacerbate chronic diseases such as ingrown nails, onycholysis, onychauxis, onychogryposis, and hallux valgus (bunions). This trauma also can break the anatomic barrier of the hyponychium, thereby creating a portal for dermatophytes and other organisms to penetrate the nail apparatus.1
For many years, one author (C.R.D.) has used the following demonstration to communicate to patients how improper shoe fit may cause toenail trauma. The patient’s shoe is flipped 180° and placed toe-to-toe with the patient’s foot (Figure). Most patients can comprehend the relationship between their shoe fit and their toenail disease when they see this demonstration. We have termed it toe-to-toe sign.

|

|
| The foot and shoe are toe-to-toe, demonstrating the narrow toe box in comparison to the actual toes (A). This comparison is accentuated when the shoe is placed over the foot with toes splayed from standing (B). |
Narrow toe box is the usual culprit. The toe-to-toe sign best emphasizes this relationship. This sign serves as a powerful tool when demonstrating how much the foot widens when bearing full weight, and how forces of ambulation and foot strike can damage the nails with narrow-toed footwear. This trauma is compounded with high-heeled shoes that force the toes forward. However, proper shoe fit may compete with idealized shoe style. It is not until patients realize the relationship between improper shoe fit, foot strike, and toe/toenail trauma that they can make long-term decisions that favorably impact their toes and toenails.
Reference
1. Daniel CR 3rd, Jellinek NJ. The pedal fungus reservoir. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:1344-1346.
Reference
1. Daniel CR 3rd, Jellinek NJ. The pedal fungus reservoir. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:1344-1346.
Onychomycosis: Not just for adults
COEUR D’ALENE, IDAHO – Conventional wisdom holds that onychomycosis is rare in children. Not so.
Fully one-third of children and adolescents who presented with a nail complaint to a prominent dermatologic nail disorders center were diagnosed with mycologically confirmed onychomycosis, Dr. Julie Jefferson reported at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
That’s a substantially higher prevalence than the 15.5% figure reported by Spanish investigators in a 20-year retrospective study (Mycoses 2011;54:450-3). It’s also well below the 47% prevalence recently reported in Denver in a 5-year retrospective study, where Trychophyton rubrum was the most common pathogen, and the highest prevalence of onychomycosis in the pediatric population was seen in 6- to 10-year-olds (Pediatr. Dermatol. 2014;31:106-8), noted Dr. Jefferson of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
The investigators in both Span and Denver observed that the prevalence of pediatric onychomycosis appears to be increasing in recent years.
Dr. Jefferson presented a retrospective study that included 917 patients up to age 18 years who presented to the Oregon Dermatology and Research Center, Portland, in a recent 6-year period. One or more nail disorders were diagnosed in 11%. The mean age at presentation was 9.4 years, with a mean 2.4-year duration of the condition prior to presentation. Toenails were affected in 47 patients, fingernails in 37, and both in 18. Fourteen patients had two nail disorders, 9 had three, and 2 had four distinct nail disorders.
The etiologies ranged widely, from infections to congenital and hereditary malformations, tumors, inflammatory processes, and systemic diseases.
The most common nail condition was onychomycosis, diagnosed in 34 patients. Thus, 3.7% of all pediatric patients presenting to the dermatology center for any reason were diagnosed with onychomycosis, a higher rate than previously reported by others.
Other conditions included 13 cases of longitudinal melanonychia, 11 of disappearing nail bed, 9 of retronychia, 8 cases of congenital malalignment, 8 cases of trachyonychia, 7 of paronychia, 5 cases of psoriasis, and 2 of lichen planus.
Three of four patients with an ingrown toenail also had congenital malalignment of the affected great toenail, supporting the notion put forth by other investigators that congenital malalignment of the great toenail predisposes to ingrown toenails, according to Dr. Jefferson.
She reported having no financial conflicts related to this study.
COEUR D’ALENE, IDAHO – Conventional wisdom holds that onychomycosis is rare in children. Not so.
Fully one-third of children and adolescents who presented with a nail complaint to a prominent dermatologic nail disorders center were diagnosed with mycologically confirmed onychomycosis, Dr. Julie Jefferson reported at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
That’s a substantially higher prevalence than the 15.5% figure reported by Spanish investigators in a 20-year retrospective study (Mycoses 2011;54:450-3). It’s also well below the 47% prevalence recently reported in Denver in a 5-year retrospective study, where Trychophyton rubrum was the most common pathogen, and the highest prevalence of onychomycosis in the pediatric population was seen in 6- to 10-year-olds (Pediatr. Dermatol. 2014;31:106-8), noted Dr. Jefferson of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
The investigators in both Span and Denver observed that the prevalence of pediatric onychomycosis appears to be increasing in recent years.
Dr. Jefferson presented a retrospective study that included 917 patients up to age 18 years who presented to the Oregon Dermatology and Research Center, Portland, in a recent 6-year period. One or more nail disorders were diagnosed in 11%. The mean age at presentation was 9.4 years, with a mean 2.4-year duration of the condition prior to presentation. Toenails were affected in 47 patients, fingernails in 37, and both in 18. Fourteen patients had two nail disorders, 9 had three, and 2 had four distinct nail disorders.
The etiologies ranged widely, from infections to congenital and hereditary malformations, tumors, inflammatory processes, and systemic diseases.
The most common nail condition was onychomycosis, diagnosed in 34 patients. Thus, 3.7% of all pediatric patients presenting to the dermatology center for any reason were diagnosed with onychomycosis, a higher rate than previously reported by others.
Other conditions included 13 cases of longitudinal melanonychia, 11 of disappearing nail bed, 9 of retronychia, 8 cases of congenital malalignment, 8 cases of trachyonychia, 7 of paronychia, 5 cases of psoriasis, and 2 of lichen planus.
Three of four patients with an ingrown toenail also had congenital malalignment of the affected great toenail, supporting the notion put forth by other investigators that congenital malalignment of the great toenail predisposes to ingrown toenails, according to Dr. Jefferson.
She reported having no financial conflicts related to this study.
COEUR D’ALENE, IDAHO – Conventional wisdom holds that onychomycosis is rare in children. Not so.
Fully one-third of children and adolescents who presented with a nail complaint to a prominent dermatologic nail disorders center were diagnosed with mycologically confirmed onychomycosis, Dr. Julie Jefferson reported at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
That’s a substantially higher prevalence than the 15.5% figure reported by Spanish investigators in a 20-year retrospective study (Mycoses 2011;54:450-3). It’s also well below the 47% prevalence recently reported in Denver in a 5-year retrospective study, where Trychophyton rubrum was the most common pathogen, and the highest prevalence of onychomycosis in the pediatric population was seen in 6- to 10-year-olds (Pediatr. Dermatol. 2014;31:106-8), noted Dr. Jefferson of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
The investigators in both Span and Denver observed that the prevalence of pediatric onychomycosis appears to be increasing in recent years.
Dr. Jefferson presented a retrospective study that included 917 patients up to age 18 years who presented to the Oregon Dermatology and Research Center, Portland, in a recent 6-year period. One or more nail disorders were diagnosed in 11%. The mean age at presentation was 9.4 years, with a mean 2.4-year duration of the condition prior to presentation. Toenails were affected in 47 patients, fingernails in 37, and both in 18. Fourteen patients had two nail disorders, 9 had three, and 2 had four distinct nail disorders.
The etiologies ranged widely, from infections to congenital and hereditary malformations, tumors, inflammatory processes, and systemic diseases.
The most common nail condition was onychomycosis, diagnosed in 34 patients. Thus, 3.7% of all pediatric patients presenting to the dermatology center for any reason were diagnosed with onychomycosis, a higher rate than previously reported by others.
Other conditions included 13 cases of longitudinal melanonychia, 11 of disappearing nail bed, 9 of retronychia, 8 cases of congenital malalignment, 8 cases of trachyonychia, 7 of paronychia, 5 cases of psoriasis, and 2 of lichen planus.
Three of four patients with an ingrown toenail also had congenital malalignment of the affected great toenail, supporting the notion put forth by other investigators that congenital malalignment of the great toenail predisposes to ingrown toenails, according to Dr. Jefferson.
She reported having no financial conflicts related to this study.
AT THE SPD ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point: Onychomycosis appears to be rising in children and adolescents, and needs to be considered in the differential diagnosis of pediatric nail abnormalities.
Major finding: Onychomycosis was diagnosed in 3.7% of all children and adolescents who presented for any reason to a tertiary dermatology center, and in 33% of the 102 who presented for evaluation of a nail disorder.
Data source: This was a 6-year, single-center, retrospective study of 917 patients up to 18 years of age.
Disclosures: The presenter reported having no financial conflicts with regard to this study.
Maintenance therapy options for childhood alopecia areata
COEUR D’ALENE, IDAHO – Systemic corticosteroids usually bring an impressive initial response for children with alopecia areata. The big question is, ‘What do you try next?’
Children can’t safely remain on long-term systemic steroids. And the great majority of responders will relapse once steroids are discontinued. The challenge is to find a safe, well-tolerated drug with long-term effectiveness as a maintenance therapy.
"For me, when I look at the list of drugs for maintenance therapy in alopecia areata, which includes cyclosporine, azathioprine, and sulfasalazine, the drug I’m most comfortable giving to children for a prolonged time is methotrexate. That’s why this drug has really become my go-to maintenance therapy for patients with alopecia areata," Dr. Ruth Ann Vleugels said at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
"I will give them 2-3 months of systemic steroids as a boost while their methotrexate kicks in; but after that, it’s maintenance therapy with methotrexate at 1 mg/kg/week," added Dr. Vleugels, director of the Autoimmune Skin Disease Program at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
Of course, methotrexate doesn’t work as maintenance therapy for all children with alopecia areata. Patients who don’t respond to the initial several months of combination therapy with systemic steroids won’t respond to maintenance therapy with methotrexate alone.
For those few patients who need second-line maintenance therapy, Dr. Vleugels’ drug of choice is the transplant anti-rejection medication mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept), which is used off-label for alopecia areata. Mycophenolate mofetil also is her rescue agent as maintenance therapy for children with systemic lupus erythematosus, cutaneous lupus erythematosus, juvenile dermatomyositis, and linear morphea with progressive hemifacial atrophy.
In patients with progressive juvenile systemic sclerosis, Dr. Vleugels and her Boston colleagues now use mycophenolate mofetil, rather than methotrexate, as their first-line therapy based upon favorable results in their practice and prospective studies in adults (J. Rheumatol. 2012;39:1241-7).
The mycophenolate mofetil dosing in children with alopecia areata is 600 mg/m2 given twice daily, or 1 g twice daily in patients bigger than 1.5 m2. She uses half the dose for the first 2-3 weeks, then titrates up to full-dose therapy in order to minimize GI side effects, which she said are far and away the most common adverse effects. Smaller children do best with the liquid formulation.
A common clinical dilemma involves the child who experiences intolerable GI upset on mycophenolate mofetil. Dr. Vleugels offered two suggestions: One is to tell the parents to ignore the package insert and have their child take the drug with meals.
"No one can handle this drug on an empty stomach," she said.
A caveat: mycophenolate mofetil cannot be taken with antacids.
If mealtime dosing doesn’t solve the GI upset problem, the alternative is to switch to mycophenolic acid (Myfortic), which is enteric-coated, has better bioavailability, and is better tolerated. It’s also more expensive than mycophenolate mofetil and will require prior authorization from payers. The dose conversion is as follows: 500 mg mycophenolate mofetil equals 360 mg of mycophenolic acid.
Dr. Vleugels reported having no financial conflicts with regard to her presentation.
COEUR D’ALENE, IDAHO – Systemic corticosteroids usually bring an impressive initial response for children with alopecia areata. The big question is, ‘What do you try next?’
Children can’t safely remain on long-term systemic steroids. And the great majority of responders will relapse once steroids are discontinued. The challenge is to find a safe, well-tolerated drug with long-term effectiveness as a maintenance therapy.
"For me, when I look at the list of drugs for maintenance therapy in alopecia areata, which includes cyclosporine, azathioprine, and sulfasalazine, the drug I’m most comfortable giving to children for a prolonged time is methotrexate. That’s why this drug has really become my go-to maintenance therapy for patients with alopecia areata," Dr. Ruth Ann Vleugels said at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
"I will give them 2-3 months of systemic steroids as a boost while their methotrexate kicks in; but after that, it’s maintenance therapy with methotrexate at 1 mg/kg/week," added Dr. Vleugels, director of the Autoimmune Skin Disease Program at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
Of course, methotrexate doesn’t work as maintenance therapy for all children with alopecia areata. Patients who don’t respond to the initial several months of combination therapy with systemic steroids won’t respond to maintenance therapy with methotrexate alone.
For those few patients who need second-line maintenance therapy, Dr. Vleugels’ drug of choice is the transplant anti-rejection medication mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept), which is used off-label for alopecia areata. Mycophenolate mofetil also is her rescue agent as maintenance therapy for children with systemic lupus erythematosus, cutaneous lupus erythematosus, juvenile dermatomyositis, and linear morphea with progressive hemifacial atrophy.
In patients with progressive juvenile systemic sclerosis, Dr. Vleugels and her Boston colleagues now use mycophenolate mofetil, rather than methotrexate, as their first-line therapy based upon favorable results in their practice and prospective studies in adults (J. Rheumatol. 2012;39:1241-7).
The mycophenolate mofetil dosing in children with alopecia areata is 600 mg/m2 given twice daily, or 1 g twice daily in patients bigger than 1.5 m2. She uses half the dose for the first 2-3 weeks, then titrates up to full-dose therapy in order to minimize GI side effects, which she said are far and away the most common adverse effects. Smaller children do best with the liquid formulation.
A common clinical dilemma involves the child who experiences intolerable GI upset on mycophenolate mofetil. Dr. Vleugels offered two suggestions: One is to tell the parents to ignore the package insert and have their child take the drug with meals.
"No one can handle this drug on an empty stomach," she said.
A caveat: mycophenolate mofetil cannot be taken with antacids.
If mealtime dosing doesn’t solve the GI upset problem, the alternative is to switch to mycophenolic acid (Myfortic), which is enteric-coated, has better bioavailability, and is better tolerated. It’s also more expensive than mycophenolate mofetil and will require prior authorization from payers. The dose conversion is as follows: 500 mg mycophenolate mofetil equals 360 mg of mycophenolic acid.
Dr. Vleugels reported having no financial conflicts with regard to her presentation.
COEUR D’ALENE, IDAHO – Systemic corticosteroids usually bring an impressive initial response for children with alopecia areata. The big question is, ‘What do you try next?’
Children can’t safely remain on long-term systemic steroids. And the great majority of responders will relapse once steroids are discontinued. The challenge is to find a safe, well-tolerated drug with long-term effectiveness as a maintenance therapy.
"For me, when I look at the list of drugs for maintenance therapy in alopecia areata, which includes cyclosporine, azathioprine, and sulfasalazine, the drug I’m most comfortable giving to children for a prolonged time is methotrexate. That’s why this drug has really become my go-to maintenance therapy for patients with alopecia areata," Dr. Ruth Ann Vleugels said at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
"I will give them 2-3 months of systemic steroids as a boost while their methotrexate kicks in; but after that, it’s maintenance therapy with methotrexate at 1 mg/kg/week," added Dr. Vleugels, director of the Autoimmune Skin Disease Program at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
Of course, methotrexate doesn’t work as maintenance therapy for all children with alopecia areata. Patients who don’t respond to the initial several months of combination therapy with systemic steroids won’t respond to maintenance therapy with methotrexate alone.
For those few patients who need second-line maintenance therapy, Dr. Vleugels’ drug of choice is the transplant anti-rejection medication mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept), which is used off-label for alopecia areata. Mycophenolate mofetil also is her rescue agent as maintenance therapy for children with systemic lupus erythematosus, cutaneous lupus erythematosus, juvenile dermatomyositis, and linear morphea with progressive hemifacial atrophy.
In patients with progressive juvenile systemic sclerosis, Dr. Vleugels and her Boston colleagues now use mycophenolate mofetil, rather than methotrexate, as their first-line therapy based upon favorable results in their practice and prospective studies in adults (J. Rheumatol. 2012;39:1241-7).
The mycophenolate mofetil dosing in children with alopecia areata is 600 mg/m2 given twice daily, or 1 g twice daily in patients bigger than 1.5 m2. She uses half the dose for the first 2-3 weeks, then titrates up to full-dose therapy in order to minimize GI side effects, which she said are far and away the most common adverse effects. Smaller children do best with the liquid formulation.
A common clinical dilemma involves the child who experiences intolerable GI upset on mycophenolate mofetil. Dr. Vleugels offered two suggestions: One is to tell the parents to ignore the package insert and have their child take the drug with meals.
"No one can handle this drug on an empty stomach," she said.
A caveat: mycophenolate mofetil cannot be taken with antacids.
If mealtime dosing doesn’t solve the GI upset problem, the alternative is to switch to mycophenolic acid (Myfortic), which is enteric-coated, has better bioavailability, and is better tolerated. It’s also more expensive than mycophenolate mofetil and will require prior authorization from payers. The dose conversion is as follows: 500 mg mycophenolate mofetil equals 360 mg of mycophenolic acid.
Dr. Vleugels reported having no financial conflicts with regard to her presentation.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM THE SPD ANNUAL MEETING