User login
Single Session Mindfulness Intervention Linked to Reduced Depression
TOPLINE:
One session of a telehealth intervention combining mindfulness and compassion significantly lowered self-perceived stress and symptoms of depression and anxiety compared with a waitlist control group, results of a new trial showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- The randomized clinical trial (RCT) included 91 participants aged 18-70 years recruited from the community and the University of Texas at Austin and followed from 2020 to 2021.
- To be included in the trial, participants had to be sheltering at home during the pandemic and endorse loneliness as one of the top issues affecting them.
- Participants were randomized to one of three groups that received single-session online interventions. These included mindfulness-only (MO), mindfulness and compassion (MC), and a waitlist control (WL) group.
- During the compassion component, participants were instructed to focus on a person, place, object, or spiritual figure that evoked feelings of warmth, love, and kindness in them. The primary outcome was self-reported loneliness and secondary outcomes were self-reported stress, depression, and anxiety.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 1-week follow-up, the MC group led to reductions in perceived stress (b = −3.75), anxiety (b = −3.79), and depression (b = −3.01) but not loneliness compared with control individuals.
- Compared with the MO group alone, the MC group had no meaningful differences in perceived depression (b = −1.08) or anxiety (b = −1.50), and the same was true at the 2-week follow-up.
- Researchers speculated that the lack of difference between outcomes in the two mindfulness groups probably meant that the MC group may have only been effective in reducing self-perceived symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression compared with the control group.
IN PRACTICE:
“This brief single session mindfulness intervention offers an approach that can be easily adopted in a range of contexts. It is important for future research to evaluate this approach with larger samples and to examine whether changes in symptoms are maintained over longer periods of time,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
Mikael Rubin, PhD, of Palo Alto University in Palo Alto, California, led the study, which was published online in PLOS ONE.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by its small sample size and short follow-up period.
DISCLOSURES:
There was no funding listed for the study nor were there any reported disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
One session of a telehealth intervention combining mindfulness and compassion significantly lowered self-perceived stress and symptoms of depression and anxiety compared with a waitlist control group, results of a new trial showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- The randomized clinical trial (RCT) included 91 participants aged 18-70 years recruited from the community and the University of Texas at Austin and followed from 2020 to 2021.
- To be included in the trial, participants had to be sheltering at home during the pandemic and endorse loneliness as one of the top issues affecting them.
- Participants were randomized to one of three groups that received single-session online interventions. These included mindfulness-only (MO), mindfulness and compassion (MC), and a waitlist control (WL) group.
- During the compassion component, participants were instructed to focus on a person, place, object, or spiritual figure that evoked feelings of warmth, love, and kindness in them. The primary outcome was self-reported loneliness and secondary outcomes were self-reported stress, depression, and anxiety.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 1-week follow-up, the MC group led to reductions in perceived stress (b = −3.75), anxiety (b = −3.79), and depression (b = −3.01) but not loneliness compared with control individuals.
- Compared with the MO group alone, the MC group had no meaningful differences in perceived depression (b = −1.08) or anxiety (b = −1.50), and the same was true at the 2-week follow-up.
- Researchers speculated that the lack of difference between outcomes in the two mindfulness groups probably meant that the MC group may have only been effective in reducing self-perceived symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression compared with the control group.
IN PRACTICE:
“This brief single session mindfulness intervention offers an approach that can be easily adopted in a range of contexts. It is important for future research to evaluate this approach with larger samples and to examine whether changes in symptoms are maintained over longer periods of time,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
Mikael Rubin, PhD, of Palo Alto University in Palo Alto, California, led the study, which was published online in PLOS ONE.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by its small sample size and short follow-up period.
DISCLOSURES:
There was no funding listed for the study nor were there any reported disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
One session of a telehealth intervention combining mindfulness and compassion significantly lowered self-perceived stress and symptoms of depression and anxiety compared with a waitlist control group, results of a new trial showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- The randomized clinical trial (RCT) included 91 participants aged 18-70 years recruited from the community and the University of Texas at Austin and followed from 2020 to 2021.
- To be included in the trial, participants had to be sheltering at home during the pandemic and endorse loneliness as one of the top issues affecting them.
- Participants were randomized to one of three groups that received single-session online interventions. These included mindfulness-only (MO), mindfulness and compassion (MC), and a waitlist control (WL) group.
- During the compassion component, participants were instructed to focus on a person, place, object, or spiritual figure that evoked feelings of warmth, love, and kindness in them. The primary outcome was self-reported loneliness and secondary outcomes were self-reported stress, depression, and anxiety.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 1-week follow-up, the MC group led to reductions in perceived stress (b = −3.75), anxiety (b = −3.79), and depression (b = −3.01) but not loneliness compared with control individuals.
- Compared with the MO group alone, the MC group had no meaningful differences in perceived depression (b = −1.08) or anxiety (b = −1.50), and the same was true at the 2-week follow-up.
- Researchers speculated that the lack of difference between outcomes in the two mindfulness groups probably meant that the MC group may have only been effective in reducing self-perceived symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression compared with the control group.
IN PRACTICE:
“This brief single session mindfulness intervention offers an approach that can be easily adopted in a range of contexts. It is important for future research to evaluate this approach with larger samples and to examine whether changes in symptoms are maintained over longer periods of time,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
Mikael Rubin, PhD, of Palo Alto University in Palo Alto, California, led the study, which was published online in PLOS ONE.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by its small sample size and short follow-up period.
DISCLOSURES:
There was no funding listed for the study nor were there any reported disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ADHD Meds Linked to Lower Suicide, Hospitalization Risk
TOPLINE:
Certain stimulants prescribed for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are associated with a decreased risk for psychiatric and nonpsychiatric hospitalization and suicide, new data from a national cohort study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators used various medical and administrative databases in Sweden to identify individuals aged 16-65 years who were diagnosed with ADHD between January 2006 and December 2021.
- Participants were followed for up to 15 years (mean duration, 7 years) from date of diagnosis until death, emigration, or end of data linkage in December 2021.
- Researchers wanted to explore the link between ADHD meds and psychiatric hospitalization, nonpsychiatric hospitalization, and suicidal behavior.
TAKEAWAY:
- The cohort included 221,700 individuals with ADHD (mean age, 25 years; 54% male), and 56% had a psychiatric comorbidity such as an anxiety or stress-related disorder (24%), and depression or bipolar disorder (20%).
- Investigators found significantly lower risk for psychiatric hospitalization for the several medications. These included amphetamine (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.74), lisdexamphetamine (aHR, 0.80), dexamphetamine (aHR, 0.88), methylphenidate (aHR, 0.93), and polytherapy (aHR, 0.85). All but atomoxetine was significant at the P < .001 level.
- ADHD medications associated with a significantly lower risk for nonpsychiatric hospitalization included amphetamine (aHR, 0.62), lisdexamphetamine (aHR, 0.64), polytherapy (aHR, 0.67), dexamphetamine (aHR, 0.72), methylphenidate (aHR, 0.80), and atomoxetine (aHR, 0.84). All but atomoxetine was significant at the P < .001 level.
- Use of dexamphetamine (aHR, 0.69; P < .001), lisdexamphetamine (aHR, 0.76; P = .43), polytherapy (aHR, 0.85; P = .02), and methylphenidate (aHR, 0.92; P = .007) were associated with a significantly lower risk for suicidal behavior.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although concerns have been raised about the potential of amphetamines and methylphenidate for increasing the risk of adverse psychiatric outcomes, such as psychosis and mania, our results show that overall, the net effect on psychiatric outcomes is positive,” study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Heidi Taipale, PhD, of Karolinska Institutet, led the study, which was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Due to the use of nationwide registers, there was a lack of detailed clinical data, including type and severity of symptoms. There was also no data on nonpharmacologic treatments.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the AFA Insurance Agency. Dr. Taipale reported receiving personal fees from Gedeon Richter, Janssen, Lundbeck, and Otsuka and grants from Janssen and Eli Lilly outside of the submitted work. Other disclosures are noted in the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Certain stimulants prescribed for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are associated with a decreased risk for psychiatric and nonpsychiatric hospitalization and suicide, new data from a national cohort study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators used various medical and administrative databases in Sweden to identify individuals aged 16-65 years who were diagnosed with ADHD between January 2006 and December 2021.
- Participants were followed for up to 15 years (mean duration, 7 years) from date of diagnosis until death, emigration, or end of data linkage in December 2021.
- Researchers wanted to explore the link between ADHD meds and psychiatric hospitalization, nonpsychiatric hospitalization, and suicidal behavior.
TAKEAWAY:
- The cohort included 221,700 individuals with ADHD (mean age, 25 years; 54% male), and 56% had a psychiatric comorbidity such as an anxiety or stress-related disorder (24%), and depression or bipolar disorder (20%).
- Investigators found significantly lower risk for psychiatric hospitalization for the several medications. These included amphetamine (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.74), lisdexamphetamine (aHR, 0.80), dexamphetamine (aHR, 0.88), methylphenidate (aHR, 0.93), and polytherapy (aHR, 0.85). All but atomoxetine was significant at the P < .001 level.
- ADHD medications associated with a significantly lower risk for nonpsychiatric hospitalization included amphetamine (aHR, 0.62), lisdexamphetamine (aHR, 0.64), polytherapy (aHR, 0.67), dexamphetamine (aHR, 0.72), methylphenidate (aHR, 0.80), and atomoxetine (aHR, 0.84). All but atomoxetine was significant at the P < .001 level.
- Use of dexamphetamine (aHR, 0.69; P < .001), lisdexamphetamine (aHR, 0.76; P = .43), polytherapy (aHR, 0.85; P = .02), and methylphenidate (aHR, 0.92; P = .007) were associated with a significantly lower risk for suicidal behavior.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although concerns have been raised about the potential of amphetamines and methylphenidate for increasing the risk of adverse psychiatric outcomes, such as psychosis and mania, our results show that overall, the net effect on psychiatric outcomes is positive,” study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Heidi Taipale, PhD, of Karolinska Institutet, led the study, which was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Due to the use of nationwide registers, there was a lack of detailed clinical data, including type and severity of symptoms. There was also no data on nonpharmacologic treatments.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the AFA Insurance Agency. Dr. Taipale reported receiving personal fees from Gedeon Richter, Janssen, Lundbeck, and Otsuka and grants from Janssen and Eli Lilly outside of the submitted work. Other disclosures are noted in the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Certain stimulants prescribed for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are associated with a decreased risk for psychiatric and nonpsychiatric hospitalization and suicide, new data from a national cohort study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators used various medical and administrative databases in Sweden to identify individuals aged 16-65 years who were diagnosed with ADHD between January 2006 and December 2021.
- Participants were followed for up to 15 years (mean duration, 7 years) from date of diagnosis until death, emigration, or end of data linkage in December 2021.
- Researchers wanted to explore the link between ADHD meds and psychiatric hospitalization, nonpsychiatric hospitalization, and suicidal behavior.
TAKEAWAY:
- The cohort included 221,700 individuals with ADHD (mean age, 25 years; 54% male), and 56% had a psychiatric comorbidity such as an anxiety or stress-related disorder (24%), and depression or bipolar disorder (20%).
- Investigators found significantly lower risk for psychiatric hospitalization for the several medications. These included amphetamine (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.74), lisdexamphetamine (aHR, 0.80), dexamphetamine (aHR, 0.88), methylphenidate (aHR, 0.93), and polytherapy (aHR, 0.85). All but atomoxetine was significant at the P < .001 level.
- ADHD medications associated with a significantly lower risk for nonpsychiatric hospitalization included amphetamine (aHR, 0.62), lisdexamphetamine (aHR, 0.64), polytherapy (aHR, 0.67), dexamphetamine (aHR, 0.72), methylphenidate (aHR, 0.80), and atomoxetine (aHR, 0.84). All but atomoxetine was significant at the P < .001 level.
- Use of dexamphetamine (aHR, 0.69; P < .001), lisdexamphetamine (aHR, 0.76; P = .43), polytherapy (aHR, 0.85; P = .02), and methylphenidate (aHR, 0.92; P = .007) were associated with a significantly lower risk for suicidal behavior.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although concerns have been raised about the potential of amphetamines and methylphenidate for increasing the risk of adverse psychiatric outcomes, such as psychosis and mania, our results show that overall, the net effect on psychiatric outcomes is positive,” study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Heidi Taipale, PhD, of Karolinska Institutet, led the study, which was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Due to the use of nationwide registers, there was a lack of detailed clinical data, including type and severity of symptoms. There was also no data on nonpharmacologic treatments.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the AFA Insurance Agency. Dr. Taipale reported receiving personal fees from Gedeon Richter, Janssen, Lundbeck, and Otsuka and grants from Janssen and Eli Lilly outside of the submitted work. Other disclosures are noted in the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Evaluation of Anti-Agitation Medication Prescribing Patterns by Age in the Emergency Department
Each year, about 2.6% of emergency department (ED) visits involve agitation.1 ED clinicians are especially prone to workplace violence and assault, facing the challenge of caring for patients while maintaining safety. A 2013 prospective study found an average of 4.15 violent events per employee in 9 months; nurses and patient care assistants were most frequently affected.2 A 2022 survey from the American College of Emergency Physicians found 55% of respondents reported being physically assaulted in the ED and 79% of respondents reported witnessing another assault. Most of these assaults (98%) were committed by the patients.3 Appropriate management of patients experiencing acute agitation is critical for the safety of all parties involved.
The initial approach to acute agitation management involves nonpharmacologic measures in an attempt to avoid coercive actions, such as physical restraints. Reducing environmental stimulation and verbal de-escalation are effective and help the patients with agitation regain control over their behavior.4
When these measures fail, however, pharmacologic therapy is often administered to ensure safety. The goal of pharmacologic therapy is to calm the patient without causing sedation.5 This allows the patient to continue participating in their care and allows the care team to accurately assess them, which is critical in determining the underlying etiology of agitation. Historically, haloperidol has commonly been used to manage acute agitation. It is frequently administered with lorazepam and diphenhydramine to reduce the incidence of haloperidol’s extrapyramidal adverse effects. However, there are several potential concerns with this method, including oversedation, QTc prolongation, potential drug interactions, and polypharmacy.5,6
The American Association of Emergency Psychiatry Project BETA Psychopharmacology Workgroup published a Consensus Statement in 2012 regarding the psychopharmacology of agitation.5 When considering medication for agitation management, clinicians must first determine a provisional diagnosis outlining the most probable etiology of the patient’s behavior, such as delirium, intoxication, or a psychiatric disorder. Apart from alcohol intoxication, benzodiazepines (BZDs) or second-generation antipsychotics as monotherapy are generally preferred over haloperidol for acute agitation.5 Second-generation antipsychotics have demonstrated to be as effective as haloperidol but are thought to be safer options. Quetiapine is not recommended for use in the ED due to the risk of orthostatic hypotension, as patients are often volume depleted.5The Veterans Affairs Southern Nevada Healthcare System (VASNHS) serves veterans in the Las Vegas area. Among the nearly 220,000 veterans in Nevada, about 100,000 veterans are aged ≥ 65 years.7 The 2012 consensus statement on psychopharmacology for agitation offers no specific age-related guidance. However, there are safety concerns in older adults both with antipsychotics and BZDs, even with acute use. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a boxed warning for all antipsychotics due to increased mortality in older adult patients with dementia-related psychosis.8 The 2023 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria provides guidance on pharmacological therapy for adults aged ≥ 65 years and recommends avoiding antipsychotics and BZDs.9 In addition to the FDA boxed warning, data suggest increased mortality with antipsychotic use independent of dementia. With BZDs, changes in pharmacodynamics make older adults more prone to adverse effects, including cognitive impairment, delirium, falls, and fractures. A retrospective chart review evaluated risperidone use in the ED and found that adults aged ≥ 65 years experienced higher rates of hypotension, even though this age group received about half the dose of risperidone compared with younger patients.10 For this patient population, the general approach in treating acute agitation has been to avoid the use of medications, but prescribe lower doses when necessary.11
With limited research on acute agitation management in older adults, the purpose of this study was to compare current prescribing practices of anti-agitation medications between adults aged 18 to 64 years and adults aged ≥ 65 years in the VASNHS ED. This study was also conducted to better understand the anti-agitation prescribing practices at VASNHS, as no order sets or protocols existed at the time of the study to guide medication selection in agitation management. To our knowledge, this is the first observational study evaluating pharmacologic acute agitation management in the ED based on age.
Methods
This study was a retrospective chart review of patients aged ≥ 18 years who presented to the VASNHS ED and received medication for acute agitation. Patients were identified through active orders for a formulary agitation medication from August 1, 2019, to July 31, 2022. Formulary medication options included intravenous, oral, and intramuscular routes for haloperidol, droperidol, lorazepam, olanzapine, or ziprasidone. Veterans were excluded if they presented with alcohol intoxication, alcohol or BZD withdrawal, if the medication administration was unrelated to agitation, or whether the medication was not administered. While alcohol and/or BZDs can contribute to acute agitation, these patients were excluded due to a clear indication for BZD therapy and the challenge in a retrospective chart review to determine whether patients received medication for agitation vs other withdrawal-related symptoms.
Endpoints
The primary endpoint was the medication selection between 2 age groups: 18 to 64 years and ≥ 65 years. The secondary endpoints included ordered medication dose by regimen, additional anti-agitation medication use within 3 hours of initial medication administration, and disposition. Safety outcomes included incidence of newly occurring oxygen desaturation < 95%, supplemental oxygen requirement, intubation, QTc prolongation, and hypotension with systolic blood pressure < 90 mm Hg within 1 hour of medication administration. Data collected included patient demographics, substance use, conditions contributing to altered mental status, active psychotropic medication prescriptions, medication adherence, agitation medication prescriber, and doses. Adherence to psychotropic medication in the past 6 months was defined as ≥ 80% of days covered with medication and based on fill history. This was only calculated for applicable patients and did not include patients with only as-needed medications, such as hydroxyzine for anxiety.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS. Baseline characteristics were analyzed using descriptive statistics. χ2 and Fisher exact tests were used to analyze categorical data. A student t test was used for continuous variables and a 2-sided P value of < .05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
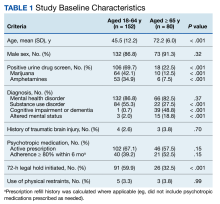
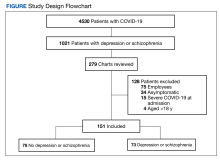
During the study period, 2342 unique patient encounters with active anti-agitation medication orders in the ED were identified and 232 encounters met the inclusion criteria. Of those excluded, 605 encounters had alcohol involvement. The study included 152 patient encounters for 128 patients aged 18 to 64 years of whom 16 patients had > 1 encounter with a mean (SD) 2.5 (1.1) visits. The study included 80 patient encounters for 72 patients aged ≥ 65 years of whom 7 patients had > 1 encounter with a mean (SD) 2.1 (0.3) visits. The mean age was 45.5 years in the younger cohort and 72.2 years in the older cohort. For data analysis and characterization of the ED population, each patient encounter was treated as a unique patient.
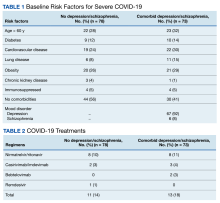
Baseline characteristics significantly differed between the 2 groups (Table 1). When comparing patients aged 18 to 64 years and those aged ≥ 65 years, the younger cohort had higher rates of substance use disorder diagnosis (55.3% vs 27.5%, P < .001), positive urine drug screen (69.7% vs 22.5%, P < .001), and 72-hour legal hold (59.9% vs 32.5%, P < .001) and lower rates of cognitive impairment or dementia (0.7% vs 48.8%, P < .001), and altered mental status-related diagnosis (2.0% vs 18.8%, P < .001). Diagnoses in the younger cohort included 1 each for hyperglycemia, urinary tract infection, and hyponatremia. Diagnoses in the older cohort included 4 for urinary tract infections, 4 for sepsis, 2 for encephalopathy, 2, for hyperglycemia, 1 gastrointestinal bleed, 1 thyrotoxicosis, and 1 respiratory failure.
Endpoints
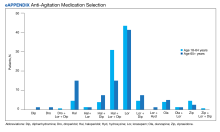
The primary outcome of anti-agitation medication selection significantly differed between the younger cohort and older cohort (P = .02). All medication combinations ordered are shown in the eAppendix based on patient age and the percentage of patients in the age cohort that received that medication combination. Lorazepam monotherapy was the most common anti-agitation medication regimen ordered: 43.4% in patients aged 18 to 64 years and 41.3% in patients aged ≥ 65 years. Second-generation antipsychotic use was low.
Only 10.5% of patients aged 18 to 64 years and 8.8% of patients aged ≥ 65 years received a medication combination including a second-generation antipsychotic. Intramuscular administration (41.4%) was most common followed by intravenous (37.5%), oral (19.8%), and oral disintegrating tablets (1.3%). The median (IQR) number of anti-agitation medications ordered by a prescriber was 6 (3-11) and 18 of 28 prescribers did not prescribe second-generation antipsychotics.
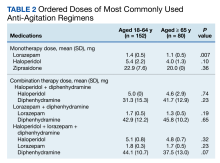
Medication doses ordered did not significantly differ except lorazepam monotherapy, as patients aged ≥ 65 received a lower dose (P = .007) (Table 2). Given the limited data within 1 hour, the first set of vital signs available after medication administration was used for analysis of safety outcomes. Vital signs were documented within 1 hour after medication administration for only 28.3% of patients aged 18 to 64 years and 42.5% of patients aged ≥ 65 years. The median (IQR) time to documentation for vital signs after medication administration was 96 minutes (56-177) for patients aged 18 to 64 years and 64 minutes (25-121) for patients aged ≥ 65 years. Electrocardiogram measurement after medication administration only occurred in 7.9% of patients aged 18 to 64 years and 5% of patients aged ≥ 65 years.
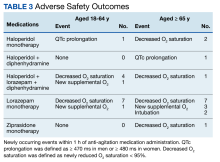
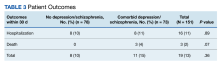
Fourteen patients (7.9%) aged 18 to 64 years and 17 patients (15.0%) aged ≥ 65 years experienced an adverse outcome (P = .09) (Table 3). Most patients who had an adverse safety outcome experienced new oxygen desaturation < 95%. Of those patients, only a small proportion required new supplemental oxygen or intubation. The 2 patients intubated had ongoing medical issues complicating their course in the ED. New QTc prolongation was only documented in haloperidol-containing regimens.
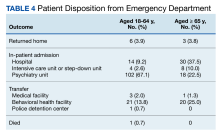
The proportion of patients requiring additional anti-agitation medication doses within 3 hours following initial administration was similar between the 2 groups. The mean (SD) amount of time to administration of subsequent dose was 55 minutes (30) in the younger cohort and 64 minutes (36) in the older cohort. Patient disposition from the ED, significantly differed based on age (P < .001) (Table 4). Patients aged 18 to 64 years were more frequently admitted to the psychiatry unit, while patients aged ≥ 65 years were primarily admitted to the hospital. One patient in the younger cohort died due to hyponatremia.
Discussion
The most likely causes of acute agitation significantly differed between patients aged 18 to 64 years and patients aged ≥ 65 years. Patients in the younger cohort were more likely to present with a history of substance use disorder or a positive urine drug screen for illicit substances. They were also more likely to have a 72-hour legal hold initiated, suggesting higher rates of suicidal and/or homicidal ideations. Patients in the older cohort were likely to present with a history of cognitive impairment or be diagnosed with a condition contributing to an altered mental status. To our knowledge, this is the first study that has assessed characteristics of patients experiencing acute agitation in the ED based on age and demonstrated significant differences in potential contributing factors to acute agitation. These findings may have important implications in helping guide the selection of empiric regimens, especially when the cause of agitation cannot immediately be elucidated.
Lorazepam monotherapy, haloperidol monotherapy, and a combination of haloperidol, lorazepam, and diphenhydramine were the 3 most frequently prescribed regimens for acute agitation. There was low second-generation antipsychotic use. Outside of the VASNHS formulary, there were no policies or restrictions that would have prevented clinicians from ordering a particular anti-agitation medication during the study period.
Since the end of the period assessed in this study, VASNHS clinicians have been educated on the guidelines for anti-agitation medication regimens to encourage higher use of second-generation antipsychotics when appropriate. Training has been developed to prevent unnecessary delays when using these products. Barriers to second-generation antipsychotic use at VASNHS have also been identified and addressed. Previously, second-generation antipsychotics and the sterile water required for medication reconstitution were not overridable in Pyxis machines, often resulting in delays in administering these medications to acutely agitated patients. As of February 2023, olanzapine, ziprasidone, and sterile water are overridable, making them more accessible in situations when medication is urgently needed. Clinicians also expressed concern regarding a lack of familiarity with reconstituting and administering intramuscular second-generation antipsychotics.
While the general guidance has been to use lower doses of anti-agitation medications in patients aged ≥ 65 years, no significant differences were seen in doses ordered other than for lorazepam. In our study, however, there were no significant differences in adverse safety outcomes, though a higher proportion of patients in the older cohort experienced new respiratory-related outcomes after medication administration. Given the retrospective nature of this study and limited documentation of vital signs after medication administration, we cannot conclude the adverse safety outcomes were directly related to the anti-agitation medications. Most patients in both groups did not require additional doses of anti-agitation medications. The results of this study have been used to guide the development of an order set for anti-agitation medications.
Limitations
As a retrospective chart review, this study is unable to prove any differences in prescribing patterns for anti-agitation medications based on age. As a single-center study, the prescribing patterns and baseline characteristics are unique to the facility and not generalizable to all patients with acute agitation in the ED. Future, higher-quality studies with adequate power in diverse patient populations are needed to further elucidate differences in acute agitation etiology and anti-agitation medications based on patient age.
The anti-agitation medication used may have been skewed for patients with multiple and/or previous ED encounters. If information was available on previous causes of agitation and/or previous efficacy of regimens, this may have influenced selection. Additionally, clinical pharmacy specialists began providing daytime coverage in the ED in April 2022. As a part of their role, these pharmacists provide recommendations for medication selection in the management of acute agitation and can order anti-agitation medications. While no pharmacist prescriptions were identified in the study, their recommendations may have influenced medication selection toward the end of the study period.
Given the retrospective nature of the study, it is unclear whether medication selection may have been guided by the patient’s presentation or comorbidities to avoid adverse effects. This may have influenced the safety outcomes observed. Another limitation to this data is vital signs documentation. Vital signs were rarely documented in the ED within 1 hour of medication administration, meaning the vital signs captured may not be related to the agitation medication. Among the patients with documented vital signs, 20 patients were documented within 10 minutes, likely prior to when the medication had taken full effect. This time variability further limits the ability to link safety outcomes to medications and demonstrates a need for additional research. Very few patients had electrocardiogram data after medication administration. If patients did have an electrocardiogram measured in the ED, this more commonly occurred prior to any medication administration, which may have also guided clinicians in initial medication selection.
This study may have also overlooked risperidone use. Though risperidone is on the VASNHS formulary, it was not expected to be commonly used in the ED setting due to it only being available by mouth. However, oral medication use was higher than expected, and there were instances where clinicians initially ordered 1 of the included anti-agitation medications but patients ultimately received risperidone. Based on these findings, the current study may have overlooked this as an anti-agitation medication regimen. In addition, by excluding alcohol intoxication, alcohol withdrawal, and BZD withdrawal, this study did not fully capture the agitated population in our ED.
Conclusions
Anti-agitation medication prescribing patterns may differ between adults aged 18 to 64 years and those aged ≥ 65 years. The findings of this study also suggest that the most common agitation etiologies may differ based on patient age. Future studies should further explore anti-agitation medication use and agitation etiologies among older adults to guide medication prescribing.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Ted Turner, PharmD, BCPP, and Phong Ly, PharmD, BCPS, for their support and assistance on this project.
1. Miner JR, Klein LR, Cole JB, Driver BE, Moore JC, Ho JD. The characteristics and prevalence of agitation in an urban county emergency department. Ann Emerg Med. 2018;72(4):361-370. doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2018.06.001
2. Kowalenko T, Gates D, Gillespie GL, Succop P, Mentzel TK. Prospective study of violence against ED workers. Am J Emerg Med. 2013;31(1):197-205. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2012.07.010
3. Marketing General Incorporated. ACEP emergency department violence poll results. American College of Emergency Physicians. August 2022. Accessed January 10, 2024. https://www.emergencyphysicians.org/siteassets/emphysicians/all-pdfs/acep-emergency-department-violence-report-2022-abridged.pdf
4. Richmond JS, Berlin JS, Fishkind AB, et al. Verbal de-escalation of the agitated patient: consensus statement of the American Association for Emergency Psychiatry Project BETA De-escalation Workgroup. West J Emerg Med. 2012;13(1):17-25. doi:10.5811/westjem.2011.9.6864
5. Wilson MP, Pepper D, Currier GW, Holloman GH Jr, Feifel D. The psychopharmacology of agitation: consensus statement of the American Association for Emergency Psychiatry Project BETA Psychopharmacology Workgroup. West J Emerg Med. 2012;13(1):26-34. doi:10.5811/westjem.2011.9.6866
6. Pierre JM. Time to retire haloperidol? Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(5):18-28.
7. US Department of Veteran Affairs. National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. Updated September 7, 2022. Accessed January 10, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/Veteran_Population.asp
8. Yan J. FDA extends black-box warning to all antipsychotics. Psychiatric News. 2008;43(14):1-27. doi:10.1176/pn.43.14.0001
9. 2023 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2023 updated AGS Beers Criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2023;71(7):2052-2081. doi:10.1111/jgs.18372
10. Wilson MP, Nordstrom K, Hopper A, Porter A, Castillo EM, Vilke GM. Risperidone in the emergency setting is associated with more hypotension in elderly patients. J Emerg Med. 2017;53(5):735-739. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2017.06.026
11. Gottlieb M, Long B, Koyfman A. Approach to the agitated emergency department patient. J Emerg Med. 2018;54(4):447-457. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2017.12.049
Each year, about 2.6% of emergency department (ED) visits involve agitation.1 ED clinicians are especially prone to workplace violence and assault, facing the challenge of caring for patients while maintaining safety. A 2013 prospective study found an average of 4.15 violent events per employee in 9 months; nurses and patient care assistants were most frequently affected.2 A 2022 survey from the American College of Emergency Physicians found 55% of respondents reported being physically assaulted in the ED and 79% of respondents reported witnessing another assault. Most of these assaults (98%) were committed by the patients.3 Appropriate management of patients experiencing acute agitation is critical for the safety of all parties involved.
The initial approach to acute agitation management involves nonpharmacologic measures in an attempt to avoid coercive actions, such as physical restraints. Reducing environmental stimulation and verbal de-escalation are effective and help the patients with agitation regain control over their behavior.4
When these measures fail, however, pharmacologic therapy is often administered to ensure safety. The goal of pharmacologic therapy is to calm the patient without causing sedation.5 This allows the patient to continue participating in their care and allows the care team to accurately assess them, which is critical in determining the underlying etiology of agitation. Historically, haloperidol has commonly been used to manage acute agitation. It is frequently administered with lorazepam and diphenhydramine to reduce the incidence of haloperidol’s extrapyramidal adverse effects. However, there are several potential concerns with this method, including oversedation, QTc prolongation, potential drug interactions, and polypharmacy.5,6
The American Association of Emergency Psychiatry Project BETA Psychopharmacology Workgroup published a Consensus Statement in 2012 regarding the psychopharmacology of agitation.5 When considering medication for agitation management, clinicians must first determine a provisional diagnosis outlining the most probable etiology of the patient’s behavior, such as delirium, intoxication, or a psychiatric disorder. Apart from alcohol intoxication, benzodiazepines (BZDs) or second-generation antipsychotics as monotherapy are generally preferred over haloperidol for acute agitation.5 Second-generation antipsychotics have demonstrated to be as effective as haloperidol but are thought to be safer options. Quetiapine is not recommended for use in the ED due to the risk of orthostatic hypotension, as patients are often volume depleted.5The Veterans Affairs Southern Nevada Healthcare System (VASNHS) serves veterans in the Las Vegas area. Among the nearly 220,000 veterans in Nevada, about 100,000 veterans are aged ≥ 65 years.7 The 2012 consensus statement on psychopharmacology for agitation offers no specific age-related guidance. However, there are safety concerns in older adults both with antipsychotics and BZDs, even with acute use. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a boxed warning for all antipsychotics due to increased mortality in older adult patients with dementia-related psychosis.8 The 2023 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria provides guidance on pharmacological therapy for adults aged ≥ 65 years and recommends avoiding antipsychotics and BZDs.9 In addition to the FDA boxed warning, data suggest increased mortality with antipsychotic use independent of dementia. With BZDs, changes in pharmacodynamics make older adults more prone to adverse effects, including cognitive impairment, delirium, falls, and fractures. A retrospective chart review evaluated risperidone use in the ED and found that adults aged ≥ 65 years experienced higher rates of hypotension, even though this age group received about half the dose of risperidone compared with younger patients.10 For this patient population, the general approach in treating acute agitation has been to avoid the use of medications, but prescribe lower doses when necessary.11
With limited research on acute agitation management in older adults, the purpose of this study was to compare current prescribing practices of anti-agitation medications between adults aged 18 to 64 years and adults aged ≥ 65 years in the VASNHS ED. This study was also conducted to better understand the anti-agitation prescribing practices at VASNHS, as no order sets or protocols existed at the time of the study to guide medication selection in agitation management. To our knowledge, this is the first observational study evaluating pharmacologic acute agitation management in the ED based on age.
Methods
This study was a retrospective chart review of patients aged ≥ 18 years who presented to the VASNHS ED and received medication for acute agitation. Patients were identified through active orders for a formulary agitation medication from August 1, 2019, to July 31, 2022. Formulary medication options included intravenous, oral, and intramuscular routes for haloperidol, droperidol, lorazepam, olanzapine, or ziprasidone. Veterans were excluded if they presented with alcohol intoxication, alcohol or BZD withdrawal, if the medication administration was unrelated to agitation, or whether the medication was not administered. While alcohol and/or BZDs can contribute to acute agitation, these patients were excluded due to a clear indication for BZD therapy and the challenge in a retrospective chart review to determine whether patients received medication for agitation vs other withdrawal-related symptoms.
Endpoints
The primary endpoint was the medication selection between 2 age groups: 18 to 64 years and ≥ 65 years. The secondary endpoints included ordered medication dose by regimen, additional anti-agitation medication use within 3 hours of initial medication administration, and disposition. Safety outcomes included incidence of newly occurring oxygen desaturation < 95%, supplemental oxygen requirement, intubation, QTc prolongation, and hypotension with systolic blood pressure < 90 mm Hg within 1 hour of medication administration. Data collected included patient demographics, substance use, conditions contributing to altered mental status, active psychotropic medication prescriptions, medication adherence, agitation medication prescriber, and doses. Adherence to psychotropic medication in the past 6 months was defined as ≥ 80% of days covered with medication and based on fill history. This was only calculated for applicable patients and did not include patients with only as-needed medications, such as hydroxyzine for anxiety.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS. Baseline characteristics were analyzed using descriptive statistics. χ2 and Fisher exact tests were used to analyze categorical data. A student t test was used for continuous variables and a 2-sided P value of < .05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
During the study period, 2342 unique patient encounters with active anti-agitation medication orders in the ED were identified and 232 encounters met the inclusion criteria. Of those excluded, 605 encounters had alcohol involvement. The study included 152 patient encounters for 128 patients aged 18 to 64 years of whom 16 patients had > 1 encounter with a mean (SD) 2.5 (1.1) visits. The study included 80 patient encounters for 72 patients aged ≥ 65 years of whom 7 patients had > 1 encounter with a mean (SD) 2.1 (0.3) visits. The mean age was 45.5 years in the younger cohort and 72.2 years in the older cohort. For data analysis and characterization of the ED population, each patient encounter was treated as a unique patient.
Baseline characteristics significantly differed between the 2 groups (Table 1). When comparing patients aged 18 to 64 years and those aged ≥ 65 years, the younger cohort had higher rates of substance use disorder diagnosis (55.3% vs 27.5%, P < .001), positive urine drug screen (69.7% vs 22.5%, P < .001), and 72-hour legal hold (59.9% vs 32.5%, P < .001) and lower rates of cognitive impairment or dementia (0.7% vs 48.8%, P < .001), and altered mental status-related diagnosis (2.0% vs 18.8%, P < .001). Diagnoses in the younger cohort included 1 each for hyperglycemia, urinary tract infection, and hyponatremia. Diagnoses in the older cohort included 4 for urinary tract infections, 4 for sepsis, 2 for encephalopathy, 2, for hyperglycemia, 1 gastrointestinal bleed, 1 thyrotoxicosis, and 1 respiratory failure.
Endpoints
The primary outcome of anti-agitation medication selection significantly differed between the younger cohort and older cohort (P = .02). All medication combinations ordered are shown in the eAppendix based on patient age and the percentage of patients in the age cohort that received that medication combination. Lorazepam monotherapy was the most common anti-agitation medication regimen ordered: 43.4% in patients aged 18 to 64 years and 41.3% in patients aged ≥ 65 years. Second-generation antipsychotic use was low.
Only 10.5% of patients aged 18 to 64 years and 8.8% of patients aged ≥ 65 years received a medication combination including a second-generation antipsychotic. Intramuscular administration (41.4%) was most common followed by intravenous (37.5%), oral (19.8%), and oral disintegrating tablets (1.3%). The median (IQR) number of anti-agitation medications ordered by a prescriber was 6 (3-11) and 18 of 28 prescribers did not prescribe second-generation antipsychotics.
Medication doses ordered did not significantly differ except lorazepam monotherapy, as patients aged ≥ 65 received a lower dose (P = .007) (Table 2). Given the limited data within 1 hour, the first set of vital signs available after medication administration was used for analysis of safety outcomes. Vital signs were documented within 1 hour after medication administration for only 28.3% of patients aged 18 to 64 years and 42.5% of patients aged ≥ 65 years. The median (IQR) time to documentation for vital signs after medication administration was 96 minutes (56-177) for patients aged 18 to 64 years and 64 minutes (25-121) for patients aged ≥ 65 years. Electrocardiogram measurement after medication administration only occurred in 7.9% of patients aged 18 to 64 years and 5% of patients aged ≥ 65 years.
Fourteen patients (7.9%) aged 18 to 64 years and 17 patients (15.0%) aged ≥ 65 years experienced an adverse outcome (P = .09) (Table 3). Most patients who had an adverse safety outcome experienced new oxygen desaturation < 95%. Of those patients, only a small proportion required new supplemental oxygen or intubation. The 2 patients intubated had ongoing medical issues complicating their course in the ED. New QTc prolongation was only documented in haloperidol-containing regimens.
The proportion of patients requiring additional anti-agitation medication doses within 3 hours following initial administration was similar between the 2 groups. The mean (SD) amount of time to administration of subsequent dose was 55 minutes (30) in the younger cohort and 64 minutes (36) in the older cohort. Patient disposition from the ED, significantly differed based on age (P < .001) (Table 4). Patients aged 18 to 64 years were more frequently admitted to the psychiatry unit, while patients aged ≥ 65 years were primarily admitted to the hospital. One patient in the younger cohort died due to hyponatremia.
Discussion
The most likely causes of acute agitation significantly differed between patients aged 18 to 64 years and patients aged ≥ 65 years. Patients in the younger cohort were more likely to present with a history of substance use disorder or a positive urine drug screen for illicit substances. They were also more likely to have a 72-hour legal hold initiated, suggesting higher rates of suicidal and/or homicidal ideations. Patients in the older cohort were likely to present with a history of cognitive impairment or be diagnosed with a condition contributing to an altered mental status. To our knowledge, this is the first study that has assessed characteristics of patients experiencing acute agitation in the ED based on age and demonstrated significant differences in potential contributing factors to acute agitation. These findings may have important implications in helping guide the selection of empiric regimens, especially when the cause of agitation cannot immediately be elucidated.
Lorazepam monotherapy, haloperidol monotherapy, and a combination of haloperidol, lorazepam, and diphenhydramine were the 3 most frequently prescribed regimens for acute agitation. There was low second-generation antipsychotic use. Outside of the VASNHS formulary, there were no policies or restrictions that would have prevented clinicians from ordering a particular anti-agitation medication during the study period.
Since the end of the period assessed in this study, VASNHS clinicians have been educated on the guidelines for anti-agitation medication regimens to encourage higher use of second-generation antipsychotics when appropriate. Training has been developed to prevent unnecessary delays when using these products. Barriers to second-generation antipsychotic use at VASNHS have also been identified and addressed. Previously, second-generation antipsychotics and the sterile water required for medication reconstitution were not overridable in Pyxis machines, often resulting in delays in administering these medications to acutely agitated patients. As of February 2023, olanzapine, ziprasidone, and sterile water are overridable, making them more accessible in situations when medication is urgently needed. Clinicians also expressed concern regarding a lack of familiarity with reconstituting and administering intramuscular second-generation antipsychotics.
While the general guidance has been to use lower doses of anti-agitation medications in patients aged ≥ 65 years, no significant differences were seen in doses ordered other than for lorazepam. In our study, however, there were no significant differences in adverse safety outcomes, though a higher proportion of patients in the older cohort experienced new respiratory-related outcomes after medication administration. Given the retrospective nature of this study and limited documentation of vital signs after medication administration, we cannot conclude the adverse safety outcomes were directly related to the anti-agitation medications. Most patients in both groups did not require additional doses of anti-agitation medications. The results of this study have been used to guide the development of an order set for anti-agitation medications.
Limitations
As a retrospective chart review, this study is unable to prove any differences in prescribing patterns for anti-agitation medications based on age. As a single-center study, the prescribing patterns and baseline characteristics are unique to the facility and not generalizable to all patients with acute agitation in the ED. Future, higher-quality studies with adequate power in diverse patient populations are needed to further elucidate differences in acute agitation etiology and anti-agitation medications based on patient age.
The anti-agitation medication used may have been skewed for patients with multiple and/or previous ED encounters. If information was available on previous causes of agitation and/or previous efficacy of regimens, this may have influenced selection. Additionally, clinical pharmacy specialists began providing daytime coverage in the ED in April 2022. As a part of their role, these pharmacists provide recommendations for medication selection in the management of acute agitation and can order anti-agitation medications. While no pharmacist prescriptions were identified in the study, their recommendations may have influenced medication selection toward the end of the study period.
Given the retrospective nature of the study, it is unclear whether medication selection may have been guided by the patient’s presentation or comorbidities to avoid adverse effects. This may have influenced the safety outcomes observed. Another limitation to this data is vital signs documentation. Vital signs were rarely documented in the ED within 1 hour of medication administration, meaning the vital signs captured may not be related to the agitation medication. Among the patients with documented vital signs, 20 patients were documented within 10 minutes, likely prior to when the medication had taken full effect. This time variability further limits the ability to link safety outcomes to medications and demonstrates a need for additional research. Very few patients had electrocardiogram data after medication administration. If patients did have an electrocardiogram measured in the ED, this more commonly occurred prior to any medication administration, which may have also guided clinicians in initial medication selection.
This study may have also overlooked risperidone use. Though risperidone is on the VASNHS formulary, it was not expected to be commonly used in the ED setting due to it only being available by mouth. However, oral medication use was higher than expected, and there were instances where clinicians initially ordered 1 of the included anti-agitation medications but patients ultimately received risperidone. Based on these findings, the current study may have overlooked this as an anti-agitation medication regimen. In addition, by excluding alcohol intoxication, alcohol withdrawal, and BZD withdrawal, this study did not fully capture the agitated population in our ED.
Conclusions
Anti-agitation medication prescribing patterns may differ between adults aged 18 to 64 years and those aged ≥ 65 years. The findings of this study also suggest that the most common agitation etiologies may differ based on patient age. Future studies should further explore anti-agitation medication use and agitation etiologies among older adults to guide medication prescribing.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Ted Turner, PharmD, BCPP, and Phong Ly, PharmD, BCPS, for their support and assistance on this project.
Each year, about 2.6% of emergency department (ED) visits involve agitation.1 ED clinicians are especially prone to workplace violence and assault, facing the challenge of caring for patients while maintaining safety. A 2013 prospective study found an average of 4.15 violent events per employee in 9 months; nurses and patient care assistants were most frequently affected.2 A 2022 survey from the American College of Emergency Physicians found 55% of respondents reported being physically assaulted in the ED and 79% of respondents reported witnessing another assault. Most of these assaults (98%) were committed by the patients.3 Appropriate management of patients experiencing acute agitation is critical for the safety of all parties involved.
The initial approach to acute agitation management involves nonpharmacologic measures in an attempt to avoid coercive actions, such as physical restraints. Reducing environmental stimulation and verbal de-escalation are effective and help the patients with agitation regain control over their behavior.4
When these measures fail, however, pharmacologic therapy is often administered to ensure safety. The goal of pharmacologic therapy is to calm the patient without causing sedation.5 This allows the patient to continue participating in their care and allows the care team to accurately assess them, which is critical in determining the underlying etiology of agitation. Historically, haloperidol has commonly been used to manage acute agitation. It is frequently administered with lorazepam and diphenhydramine to reduce the incidence of haloperidol’s extrapyramidal adverse effects. However, there are several potential concerns with this method, including oversedation, QTc prolongation, potential drug interactions, and polypharmacy.5,6
The American Association of Emergency Psychiatry Project BETA Psychopharmacology Workgroup published a Consensus Statement in 2012 regarding the psychopharmacology of agitation.5 When considering medication for agitation management, clinicians must first determine a provisional diagnosis outlining the most probable etiology of the patient’s behavior, such as delirium, intoxication, or a psychiatric disorder. Apart from alcohol intoxication, benzodiazepines (BZDs) or second-generation antipsychotics as monotherapy are generally preferred over haloperidol for acute agitation.5 Second-generation antipsychotics have demonstrated to be as effective as haloperidol but are thought to be safer options. Quetiapine is not recommended for use in the ED due to the risk of orthostatic hypotension, as patients are often volume depleted.5The Veterans Affairs Southern Nevada Healthcare System (VASNHS) serves veterans in the Las Vegas area. Among the nearly 220,000 veterans in Nevada, about 100,000 veterans are aged ≥ 65 years.7 The 2012 consensus statement on psychopharmacology for agitation offers no specific age-related guidance. However, there are safety concerns in older adults both with antipsychotics and BZDs, even with acute use. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a boxed warning for all antipsychotics due to increased mortality in older adult patients with dementia-related psychosis.8 The 2023 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria provides guidance on pharmacological therapy for adults aged ≥ 65 years and recommends avoiding antipsychotics and BZDs.9 In addition to the FDA boxed warning, data suggest increased mortality with antipsychotic use independent of dementia. With BZDs, changes in pharmacodynamics make older adults more prone to adverse effects, including cognitive impairment, delirium, falls, and fractures. A retrospective chart review evaluated risperidone use in the ED and found that adults aged ≥ 65 years experienced higher rates of hypotension, even though this age group received about half the dose of risperidone compared with younger patients.10 For this patient population, the general approach in treating acute agitation has been to avoid the use of medications, but prescribe lower doses when necessary.11
With limited research on acute agitation management in older adults, the purpose of this study was to compare current prescribing practices of anti-agitation medications between adults aged 18 to 64 years and adults aged ≥ 65 years in the VASNHS ED. This study was also conducted to better understand the anti-agitation prescribing practices at VASNHS, as no order sets or protocols existed at the time of the study to guide medication selection in agitation management. To our knowledge, this is the first observational study evaluating pharmacologic acute agitation management in the ED based on age.
Methods
This study was a retrospective chart review of patients aged ≥ 18 years who presented to the VASNHS ED and received medication for acute agitation. Patients were identified through active orders for a formulary agitation medication from August 1, 2019, to July 31, 2022. Formulary medication options included intravenous, oral, and intramuscular routes for haloperidol, droperidol, lorazepam, olanzapine, or ziprasidone. Veterans were excluded if they presented with alcohol intoxication, alcohol or BZD withdrawal, if the medication administration was unrelated to agitation, or whether the medication was not administered. While alcohol and/or BZDs can contribute to acute agitation, these patients were excluded due to a clear indication for BZD therapy and the challenge in a retrospective chart review to determine whether patients received medication for agitation vs other withdrawal-related symptoms.
Endpoints
The primary endpoint was the medication selection between 2 age groups: 18 to 64 years and ≥ 65 years. The secondary endpoints included ordered medication dose by regimen, additional anti-agitation medication use within 3 hours of initial medication administration, and disposition. Safety outcomes included incidence of newly occurring oxygen desaturation < 95%, supplemental oxygen requirement, intubation, QTc prolongation, and hypotension with systolic blood pressure < 90 mm Hg within 1 hour of medication administration. Data collected included patient demographics, substance use, conditions contributing to altered mental status, active psychotropic medication prescriptions, medication adherence, agitation medication prescriber, and doses. Adherence to psychotropic medication in the past 6 months was defined as ≥ 80% of days covered with medication and based on fill history. This was only calculated for applicable patients and did not include patients with only as-needed medications, such as hydroxyzine for anxiety.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS. Baseline characteristics were analyzed using descriptive statistics. χ2 and Fisher exact tests were used to analyze categorical data. A student t test was used for continuous variables and a 2-sided P value of < .05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
During the study period, 2342 unique patient encounters with active anti-agitation medication orders in the ED were identified and 232 encounters met the inclusion criteria. Of those excluded, 605 encounters had alcohol involvement. The study included 152 patient encounters for 128 patients aged 18 to 64 years of whom 16 patients had > 1 encounter with a mean (SD) 2.5 (1.1) visits. The study included 80 patient encounters for 72 patients aged ≥ 65 years of whom 7 patients had > 1 encounter with a mean (SD) 2.1 (0.3) visits. The mean age was 45.5 years in the younger cohort and 72.2 years in the older cohort. For data analysis and characterization of the ED population, each patient encounter was treated as a unique patient.
Baseline characteristics significantly differed between the 2 groups (Table 1). When comparing patients aged 18 to 64 years and those aged ≥ 65 years, the younger cohort had higher rates of substance use disorder diagnosis (55.3% vs 27.5%, P < .001), positive urine drug screen (69.7% vs 22.5%, P < .001), and 72-hour legal hold (59.9% vs 32.5%, P < .001) and lower rates of cognitive impairment or dementia (0.7% vs 48.8%, P < .001), and altered mental status-related diagnosis (2.0% vs 18.8%, P < .001). Diagnoses in the younger cohort included 1 each for hyperglycemia, urinary tract infection, and hyponatremia. Diagnoses in the older cohort included 4 for urinary tract infections, 4 for sepsis, 2 for encephalopathy, 2, for hyperglycemia, 1 gastrointestinal bleed, 1 thyrotoxicosis, and 1 respiratory failure.
Endpoints
The primary outcome of anti-agitation medication selection significantly differed between the younger cohort and older cohort (P = .02). All medication combinations ordered are shown in the eAppendix based on patient age and the percentage of patients in the age cohort that received that medication combination. Lorazepam monotherapy was the most common anti-agitation medication regimen ordered: 43.4% in patients aged 18 to 64 years and 41.3% in patients aged ≥ 65 years. Second-generation antipsychotic use was low.
Only 10.5% of patients aged 18 to 64 years and 8.8% of patients aged ≥ 65 years received a medication combination including a second-generation antipsychotic. Intramuscular administration (41.4%) was most common followed by intravenous (37.5%), oral (19.8%), and oral disintegrating tablets (1.3%). The median (IQR) number of anti-agitation medications ordered by a prescriber was 6 (3-11) and 18 of 28 prescribers did not prescribe second-generation antipsychotics.
Medication doses ordered did not significantly differ except lorazepam monotherapy, as patients aged ≥ 65 received a lower dose (P = .007) (Table 2). Given the limited data within 1 hour, the first set of vital signs available after medication administration was used for analysis of safety outcomes. Vital signs were documented within 1 hour after medication administration for only 28.3% of patients aged 18 to 64 years and 42.5% of patients aged ≥ 65 years. The median (IQR) time to documentation for vital signs after medication administration was 96 minutes (56-177) for patients aged 18 to 64 years and 64 minutes (25-121) for patients aged ≥ 65 years. Electrocardiogram measurement after medication administration only occurred in 7.9% of patients aged 18 to 64 years and 5% of patients aged ≥ 65 years.
Fourteen patients (7.9%) aged 18 to 64 years and 17 patients (15.0%) aged ≥ 65 years experienced an adverse outcome (P = .09) (Table 3). Most patients who had an adverse safety outcome experienced new oxygen desaturation < 95%. Of those patients, only a small proportion required new supplemental oxygen or intubation. The 2 patients intubated had ongoing medical issues complicating their course in the ED. New QTc prolongation was only documented in haloperidol-containing regimens.
The proportion of patients requiring additional anti-agitation medication doses within 3 hours following initial administration was similar between the 2 groups. The mean (SD) amount of time to administration of subsequent dose was 55 minutes (30) in the younger cohort and 64 minutes (36) in the older cohort. Patient disposition from the ED, significantly differed based on age (P < .001) (Table 4). Patients aged 18 to 64 years were more frequently admitted to the psychiatry unit, while patients aged ≥ 65 years were primarily admitted to the hospital. One patient in the younger cohort died due to hyponatremia.
Discussion
The most likely causes of acute agitation significantly differed between patients aged 18 to 64 years and patients aged ≥ 65 years. Patients in the younger cohort were more likely to present with a history of substance use disorder or a positive urine drug screen for illicit substances. They were also more likely to have a 72-hour legal hold initiated, suggesting higher rates of suicidal and/or homicidal ideations. Patients in the older cohort were likely to present with a history of cognitive impairment or be diagnosed with a condition contributing to an altered mental status. To our knowledge, this is the first study that has assessed characteristics of patients experiencing acute agitation in the ED based on age and demonstrated significant differences in potential contributing factors to acute agitation. These findings may have important implications in helping guide the selection of empiric regimens, especially when the cause of agitation cannot immediately be elucidated.
Lorazepam monotherapy, haloperidol monotherapy, and a combination of haloperidol, lorazepam, and diphenhydramine were the 3 most frequently prescribed regimens for acute agitation. There was low second-generation antipsychotic use. Outside of the VASNHS formulary, there were no policies or restrictions that would have prevented clinicians from ordering a particular anti-agitation medication during the study period.
Since the end of the period assessed in this study, VASNHS clinicians have been educated on the guidelines for anti-agitation medication regimens to encourage higher use of second-generation antipsychotics when appropriate. Training has been developed to prevent unnecessary delays when using these products. Barriers to second-generation antipsychotic use at VASNHS have also been identified and addressed. Previously, second-generation antipsychotics and the sterile water required for medication reconstitution were not overridable in Pyxis machines, often resulting in delays in administering these medications to acutely agitated patients. As of February 2023, olanzapine, ziprasidone, and sterile water are overridable, making them more accessible in situations when medication is urgently needed. Clinicians also expressed concern regarding a lack of familiarity with reconstituting and administering intramuscular second-generation antipsychotics.
While the general guidance has been to use lower doses of anti-agitation medications in patients aged ≥ 65 years, no significant differences were seen in doses ordered other than for lorazepam. In our study, however, there were no significant differences in adverse safety outcomes, though a higher proportion of patients in the older cohort experienced new respiratory-related outcomes after medication administration. Given the retrospective nature of this study and limited documentation of vital signs after medication administration, we cannot conclude the adverse safety outcomes were directly related to the anti-agitation medications. Most patients in both groups did not require additional doses of anti-agitation medications. The results of this study have been used to guide the development of an order set for anti-agitation medications.
Limitations
As a retrospective chart review, this study is unable to prove any differences in prescribing patterns for anti-agitation medications based on age. As a single-center study, the prescribing patterns and baseline characteristics are unique to the facility and not generalizable to all patients with acute agitation in the ED. Future, higher-quality studies with adequate power in diverse patient populations are needed to further elucidate differences in acute agitation etiology and anti-agitation medications based on patient age.
The anti-agitation medication used may have been skewed for patients with multiple and/or previous ED encounters. If information was available on previous causes of agitation and/or previous efficacy of regimens, this may have influenced selection. Additionally, clinical pharmacy specialists began providing daytime coverage in the ED in April 2022. As a part of their role, these pharmacists provide recommendations for medication selection in the management of acute agitation and can order anti-agitation medications. While no pharmacist prescriptions were identified in the study, their recommendations may have influenced medication selection toward the end of the study period.
Given the retrospective nature of the study, it is unclear whether medication selection may have been guided by the patient’s presentation or comorbidities to avoid adverse effects. This may have influenced the safety outcomes observed. Another limitation to this data is vital signs documentation. Vital signs were rarely documented in the ED within 1 hour of medication administration, meaning the vital signs captured may not be related to the agitation medication. Among the patients with documented vital signs, 20 patients were documented within 10 minutes, likely prior to when the medication had taken full effect. This time variability further limits the ability to link safety outcomes to medications and demonstrates a need for additional research. Very few patients had electrocardiogram data after medication administration. If patients did have an electrocardiogram measured in the ED, this more commonly occurred prior to any medication administration, which may have also guided clinicians in initial medication selection.
This study may have also overlooked risperidone use. Though risperidone is on the VASNHS formulary, it was not expected to be commonly used in the ED setting due to it only being available by mouth. However, oral medication use was higher than expected, and there were instances where clinicians initially ordered 1 of the included anti-agitation medications but patients ultimately received risperidone. Based on these findings, the current study may have overlooked this as an anti-agitation medication regimen. In addition, by excluding alcohol intoxication, alcohol withdrawal, and BZD withdrawal, this study did not fully capture the agitated population in our ED.
Conclusions
Anti-agitation medication prescribing patterns may differ between adults aged 18 to 64 years and those aged ≥ 65 years. The findings of this study also suggest that the most common agitation etiologies may differ based on patient age. Future studies should further explore anti-agitation medication use and agitation etiologies among older adults to guide medication prescribing.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Ted Turner, PharmD, BCPP, and Phong Ly, PharmD, BCPS, for their support and assistance on this project.
1. Miner JR, Klein LR, Cole JB, Driver BE, Moore JC, Ho JD. The characteristics and prevalence of agitation in an urban county emergency department. Ann Emerg Med. 2018;72(4):361-370. doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2018.06.001
2. Kowalenko T, Gates D, Gillespie GL, Succop P, Mentzel TK. Prospective study of violence against ED workers. Am J Emerg Med. 2013;31(1):197-205. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2012.07.010
3. Marketing General Incorporated. ACEP emergency department violence poll results. American College of Emergency Physicians. August 2022. Accessed January 10, 2024. https://www.emergencyphysicians.org/siteassets/emphysicians/all-pdfs/acep-emergency-department-violence-report-2022-abridged.pdf
4. Richmond JS, Berlin JS, Fishkind AB, et al. Verbal de-escalation of the agitated patient: consensus statement of the American Association for Emergency Psychiatry Project BETA De-escalation Workgroup. West J Emerg Med. 2012;13(1):17-25. doi:10.5811/westjem.2011.9.6864
5. Wilson MP, Pepper D, Currier GW, Holloman GH Jr, Feifel D. The psychopharmacology of agitation: consensus statement of the American Association for Emergency Psychiatry Project BETA Psychopharmacology Workgroup. West J Emerg Med. 2012;13(1):26-34. doi:10.5811/westjem.2011.9.6866
6. Pierre JM. Time to retire haloperidol? Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(5):18-28.
7. US Department of Veteran Affairs. National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. Updated September 7, 2022. Accessed January 10, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/Veteran_Population.asp
8. Yan J. FDA extends black-box warning to all antipsychotics. Psychiatric News. 2008;43(14):1-27. doi:10.1176/pn.43.14.0001
9. 2023 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2023 updated AGS Beers Criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2023;71(7):2052-2081. doi:10.1111/jgs.18372
10. Wilson MP, Nordstrom K, Hopper A, Porter A, Castillo EM, Vilke GM. Risperidone in the emergency setting is associated with more hypotension in elderly patients. J Emerg Med. 2017;53(5):735-739. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2017.06.026
11. Gottlieb M, Long B, Koyfman A. Approach to the agitated emergency department patient. J Emerg Med. 2018;54(4):447-457. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2017.12.049
1. Miner JR, Klein LR, Cole JB, Driver BE, Moore JC, Ho JD. The characteristics and prevalence of agitation in an urban county emergency department. Ann Emerg Med. 2018;72(4):361-370. doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2018.06.001
2. Kowalenko T, Gates D, Gillespie GL, Succop P, Mentzel TK. Prospective study of violence against ED workers. Am J Emerg Med. 2013;31(1):197-205. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2012.07.010
3. Marketing General Incorporated. ACEP emergency department violence poll results. American College of Emergency Physicians. August 2022. Accessed January 10, 2024. https://www.emergencyphysicians.org/siteassets/emphysicians/all-pdfs/acep-emergency-department-violence-report-2022-abridged.pdf
4. Richmond JS, Berlin JS, Fishkind AB, et al. Verbal de-escalation of the agitated patient: consensus statement of the American Association for Emergency Psychiatry Project BETA De-escalation Workgroup. West J Emerg Med. 2012;13(1):17-25. doi:10.5811/westjem.2011.9.6864
5. Wilson MP, Pepper D, Currier GW, Holloman GH Jr, Feifel D. The psychopharmacology of agitation: consensus statement of the American Association for Emergency Psychiatry Project BETA Psychopharmacology Workgroup. West J Emerg Med. 2012;13(1):26-34. doi:10.5811/westjem.2011.9.6866
6. Pierre JM. Time to retire haloperidol? Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(5):18-28.
7. US Department of Veteran Affairs. National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. Updated September 7, 2022. Accessed January 10, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/Veteran_Population.asp
8. Yan J. FDA extends black-box warning to all antipsychotics. Psychiatric News. 2008;43(14):1-27. doi:10.1176/pn.43.14.0001
9. 2023 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2023 updated AGS Beers Criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2023;71(7):2052-2081. doi:10.1111/jgs.18372
10. Wilson MP, Nordstrom K, Hopper A, Porter A, Castillo EM, Vilke GM. Risperidone in the emergency setting is associated with more hypotension in elderly patients. J Emerg Med. 2017;53(5):735-739. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2017.06.026
11. Gottlieb M, Long B, Koyfman A. Approach to the agitated emergency department patient. J Emerg Med. 2018;54(4):447-457. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2017.12.049
Preparing Veterans Health Administration Psychologists to Meet the Complex Needs of Aging Veterans
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is understaffed for clinical psychologists who have specialty training in geriatrics (ie, geropsychologists) to meet the needs of aging veterans. Though only 16.8% of US adults are aged ≥ 65 years,1 this age group comprises 45.9% of patients within the VHA.2 The needs of older adults are complex and warrant specialized services from mental health clinicians trained to understand lifespan developmental processes, biological changes associated with aging, and changes in psychosocial functioning.
Older veterans (aged ≥ 65 years) present with higher rates of combined medical and mental health diagnoses compared to both younger veterans and older adults who are not veterans.3 Nearly 1 of 5 (18.1%) older veterans who use VHA services have confirmed mental health diagnoses, and an additional 25.5% have documented mental health concerns without a formal diagnosis in their health record.4 The clinical presentations of older veterans frequently differ from younger adults and include greater complexity. For example, older veterans face an increased risk of cognitive impairment compared to the general population, due in part to higher prevalence of posttraumatic stress, which doubles their risk of developing dementia.5 Additional examples of multicomplexity among older veterans may include co-occurring medical and psychiatric diagnoses, the presence of delirium, social isolation/loneliness, and concerns related to polypharmacy. These complex presentations result in significant challenges for mental health clinicians in areas like assessment (eg, accuracy of case conceptualization), intervention (eg, selection and prioritization), and consultation (eg, coordination among multiple medical and mental health specialists).
Older veterans also present with substantial resilience. Research has found that aging veterans exposed to trauma during their military service often review their memories and past experiences, which is known as later-adulthood trauma reengagement.6 Through this normative life review process, veterans engage with memories and experiences from their past that they previously avoided, which could lead to posttraumatic growth for some. Unfortunately, others may experience an increase in psychological distress. Mental health clinicians with specialty expertise and training in aging and lifespan development can facilitate positive outcomes to reduce distress.7
The United States in general, and the VHA specifically, face a growing shortage of geriatric mental health clinicians.
The Geriatric Scholars Program (GSP) was developed in 2008 to address the training gap and provide education in geriatrics to VHA clinicians that treat older veterans, particularly in rural areas.11,12 The GSP initially focused on primary care physicians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and pharmacists. It was later expanded to include other disciplines (ie, social work, rehabilitation therapists, and psychiatrists). In 2013, the GSP – Psychology Track (GSP-P) was developed with funding from the VHA Offices of Rural Health and Geriatrics and Extended Care specifically for psychologists.
This article describes the multicomponent longitudinal GSP-P, which has evolved to meet the target audience’s ongoing needs for knowledge, skills, and opportunities to refine practice behaviors. GSP-P received the 2020 Award for Excellence in Geropsychology Training from the Council of Professional Geropsychology Training Programs. GSP-P has grown within the context of the larger GSP and aligns with the other existing elective learning opportunities (Figure 1).
Program description
Introductory Course
Psychologist subject matter experts (SMEs) developed an intensive course in geropsychology in the absence of a similar course in the geriatric medicine board review curriculum. SMEs reviewed the guidelines for practice by professional organizations like the Pikes Peak Geropsychology Competencies, which outline knowledge and skills in various domains.13 SMEs integrated this review with findings from a needs assessment for postlicensed VHA psychology staff in 4 health care systems, drafted a syllabus, and circulated it to geropsychology experts for feedback. The resulting multiday course covered general mental health as well as topics particularly salient for mental health clinicians treating older veterans including suicide prevention and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).14 This Geropsychology Competencies Review Course was piloted in 1 region initially before being offered nationally in 2014.
Quality Improvement
Introductory course attendees also participate in an intensive day-long interactive workshop in quality improvement (QI). After completing these trainings, they apply what they have learned at their home facility by embarking on a QI project related to geriatrics. The QI projects reinforce learning and initiate practice changes not only for attendees but at times the larger health care system. Topics are selected by scholars in response to the needs they observe in their clinics. Recent GSP projects include efforts to increase screenings for depression and anxiety, improve adherence to VHA dementia policy, increase access to virtual care, and increase referrals to programs such as whole health or cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia, a first-line treatment for insomnia in older adults.17 Another project targeted the improvement of referrals to the Compassionate Contact Corps in an effort to reduce social isolation and loneliness among older veterans.18 Evaluations demonstrate significant improvement in scholars’ confidence in related program development and management from precourse to 3 months postcourse.15
Webinars
The Addressing Geriatric Mental Health webinar series was created to introduce learners to topics that could not be covered in the introductory course. Topics were suggested by the expert reviewers of the curriculum or identified by the scholars themselves (eg, chronic pain, sexuality, or serious mental illness). A secondary function of the webinars was to reach a broader audience. Over time, scholars and webinar attendees requested opportunities to explore topics in greater depth (eg, PTSD later in life). These requests led the webinars to focus on annual themes.
The series is open to all disciplines of geriatric scholars, VHA staff, and non-VHA staff through the Veterans Affairs Talent Management System and the TRAIN Learning Network (train.org). Attendance for the 37 webinars was captured from logins to the virtual learning platform and may underestimate attendance if a group attended on a single screen. Average attendance increased from 157 attendees/webinar in 2015 to 418 attendees/webinar in 2023 (Figure 2). This may have been related to the increase in virtual learning during the COVID-19 pandemic, but represents a 166% increase in audience from the inaugural year of the series.
Advanced Learning Opportunities
To invest in the ongoing growth and development of introductory course graduates, GSP-P developed and offered an advanced workshop in 2019. This multiday workshop focused on further enhancement of geropsychology competencies, with an emphasis on treating older veterans with mental and physical comorbidities. Didactics and experiential learning exercises led by SMEs covered topics such as adjusting to chronic illness, capacity assessment, PTSD, insomnia and sleep changes, chronic pain, and psychological interventions in palliative care and hospice settings. Evaluation findings demonstrated significant improvements from precourse to 6 months postcourse in confidence and knowledge as
To facilitate ongoing and individually tailored learning following the advanced workshop, scholars also developed and executed independent learning plans (ILPs) during a 6-month window with consultation from an experienced geropsychologist. Fifteen of 19 scholars (78.9%) completed ILPs with an average of 3 learning goals listed. After completing the ILPs, scholars endorsed their clinical and/or personal usefulness, citing increased confidence, enhanced skills for use with patients with complex needs, personal fulfillment, and career advancement. Most scholars noted ILPs were feasible and learning resources were accessible. Overall, the evaluation found ILPs to be a valuable way to enhance psychologists’ learning and effectiveness in treating older veterans with complex health needs.20
Clinical Practica
All geriatric scholars who completed the program have additional opportunities for professional development through practicum experiences focused on specific clinical approaches to the care of older veterans, such as dementia care, pain management, geriatric assessment, and palliative care. These practica provide scholars with individualized learning experiences in an individualized or small group setting and may be conducted either in-person or virtually.
In response to an expressed need from those who completed the program, the GSP-P planning committee collaborated with an SME to develop a virtual practicum to assess patients’ decision making capacity. Evaluating capacities among older adults is a common request, yet clinicians report little to no formal training in how to conceptualize and approach these complex questions.21,22 Utilizing an evidence-informed and structured approach promotes the balancing of an older adult’s autonomy and professional ethics. Learning capacity evaluation skills could better position psychologists to not only navigate complex ethical, legal, and clinical situations, but also serve as expert consultants to interdisciplinary teams. This virtual practicum was initiated in 2022 and to date has included 10 scholars. The practicum includes multiple modalities of learning: (1) self-directed review of core concepts; (2) attendance at 4 capacity didactics focused on introduction to evaluating capacities, medical consent and decision making, financial decision making and management, and independent living; and (3) participation in 5 group consultations on capacity evaluations conducted at their home sites. During these group consultations, additional case examples were shared to reinforce capacity concepts.
Discussion
The objective of GSP-P is to enhance geropsychology practice competencies among VHA psychologists given the outsized representation of older adults within the VHA system and their complex care needs. The curricula have significantly evolved to accomplish this, expanding the reach and investing in the continuing growth and development of scholars.
There are several elements that set GSP apart from other geriatric and geropsychology continuing medical education programs. The first is that the training is veteran focused, allowing us to discuss the unique impact military service has on aging. Similarly, because all scholars work within the integrated health care system, we can introduce and review key resources and programs that benefit all veterans and their families/care partners across the system. Through the GSP, the VA invests in ongoing professional development. Scholars can participate in additional experiential practica, webinars, and advanced workshops tailored to their individual learning needs. Lastly, the GSP works to create a community among its scholars where they can not only continue to consult with presenters/instructors, but also one another. A planned future direction for the GSP-P is to incorporate quarterly office hours and discussions for alumni to develop an increased sense of community. This may strengthen commitment to the overall VA mission, leading to increased retainment of talent who now have the knowledge, skills, and confidence to care for aging veterans.
Limitations
GSP is limited by its available funding. Additionally, the number of participants who can enroll each year in GSP-P (not including webinars) is capped by policy. Another limitation is the number of QI coaches available to mentor scholars on their projects.
Conclusions
Outcomes of GSP-P have been extremely favorable. Following participation in the program, we have found a significant increase in confidence in geropsychology practice among clinicians, as well as enhanced knowledge and skills across competency domains.15,19 We have observed rising attendance in our annual webinar series and graduates of our introductory courses participate in subsequent trainings (eg, advanced workshop or virtual practicum). Several graduates of GSP-P have become board certified in geropsychology by the American Board of Geropsychology and many proceed to supervise geropsychology-focused clinical rotations for psychology practicum students, predoctoral interns, and postdoctoral fellows. This suggests that the reach of GSP-P programming may extend farther than reported in this article.
The needs of aging veterans have also changed based on cohort differences, as the population of World War II and Korean War era veterans has declined and the number of older Vietnam era veterans has grown. We expect different challenges with older Gulf War and post-9/11 era veterans. For instance, 17% of troops deployed to Iraq or Afghanistan following 9/11 experienced mild traumatic brain injury (TBI), and 59% of those experienced > 1 mild TBI.23 Research indicates that younger post-9/11 veterans have a 3-fold risk of developing early onset dementia after experiencing a TBI.24 Therefore, even though post-9/11 veterans are not older in terms of chronological age, some may experience symptoms and conditions more often occurring in older veterans. As a result, it would be beneficial for clinicians to learn about the presentation and treatment of geriatric conditions such as dementia.
Moving forward, the GSP-P should identify potential opportunities to collaborate with the non-VHA mental health community–which also faces a shortage of geriatric mental health clinicians–to extend educational opportunities to improve care for veterans in all settings (eg, cosponsor training opportunities open to both VHA and non-VHA clinicians).8,25 Many aging veterans may receive portions of their health care outside the VHA, particularly those who reside in rural areas. Additionally, as veterans age, so do their support systems (eg, family members, friends, spouses, caregivers, and even clinicians), most of whom will receive care outside of the VHA. Community education collaborations will not only improve the care of older veterans, but also the care of older adults in the general population.
Promising directions include the adoption of the GSP model in other health care settings. Recently, Indian Health Service has adapted the model, beginning with primary care clinicians and pharmacists and is beginning to expand to other disciplines. Additional investments in VHA workforce training include the availability of geropsychology internship and fellowship training opportunities through the Office of Academic Affiliations, which provide earlier opportunities to specialize in geropsychology. Continued investment in both prelicensure and postpsychology licensure training efforts are needed within the VHA to meet the geriatric mental health needs of veterans.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Terri Huh, PhD, for her contributions to the development and initiation of the GSP-P. The authors also appreciate the collaboration and quality initiative training led by Carol Callaway-Lane, DNP, ACNP-BC, and her team.
1. Caplan Z, Rabe M; US Department of Commerce, US Census Bureau. The Older Population: 2020 (Census Brief No. C2020BR-07). May 2023. Accessed February 27, 2024. https://www2.census.gov/library/publications/decennial/2020/census-briefs/c2020br-07.pdf
2. US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. VA benefits & health care utilization. Updated February 2023. Accessed February 27, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/docs/pocketcards/fy2023q2.PDF
3. O’Malley KA, Vinson L, Pless Kaiser A, Sager Z, Hinrichs K. Mental health and aging veterans: How the Veterans Health Administration meets the needs of aging veterans. Public Policy Aging Rep. 2020;30(1):19-23. doi:10.1093/ppar/prz027
4. Greenberg G, Hoff R. FY 2021 Older Adult (65+ on October 1st) Veteran Data Sheet: National, VISN, and Healthcare System Tables. West Haven, CT: U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Northeast Program Evaluation Center. 2022.
5. Yaffe K, Vittinghoff E, Lindquist K, et al. Posttraumatic stress disorder and risk of dementia among US veterans. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67(6):608-613. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.61
6. Davison EH, Kaiser AP, Spiro A 3rd, Moye J, King LA, King DW. From late-onset stress symptomatology to later-adulthood trauma reengagement in aging combat veterans: Taking a broader view. Gerontologist. 2016;56(1):14-21. doi:10.1093/geront/gnv097
7. Kaiser AP, Boyle JT, Bamonti PM, O’Malley K, Moye J. Development, adaptation, and clinical implementation of the Later-Adulthood Trauma Reengagement (LATR) group intervention for older veterans. Psychol Serv. 2023;20(4):863-875. doi:10.1037/ser0000736
8. Moye J, Karel MJ, Stamm KE, et al. Workforce analysis of psychological practice with older adults: Growing crisis requires urgent action. Train Educ Prof Psychol. 2019;13(1):46-55. doi:10.1037/tep0000206
9. Stamm K, Lin L, Conroy J. Critical needs in geropsychology. Monitor on Psychology. 2021;52(4):21.
10. American Board of Geropsychology. Specialists. 2024. Accessed February 6, 2024. https://abgero.org/board-members/specialists/
11. Kramer BJ. The VA Geriatric Scholars Program. Fed Pract. 2015;32(5):46-48.
12. Kramer BJ, Creekmur B, Howe JL, et al. Veterans Affairs Geriatric Scholars Program: Enhancing existing primary care clinician skills in caring for older veterans. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2016;64(11):2343-2348. doi:10.1111/jgs.14382
13. Knight BG, Karel MJ, Hinrichsen GA, Qualls SH, Duffy M. Pikes Peak model for training in professional geropsychology. Am Psychol. 2009;64(3):205-14. doi:10.1037/a0015059
14. Huh JWT, Rodriguez R, Gould CE, R Brunskill S, Melendez L, Kramer BJ. Developing a program to increase geropsychology competencies of Veterans Health Administration (VHA) psychologists. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2020;41(4):463-479. doi:10.1080/02701960.2018.1491402
15. Huh JWT, Rodriguez RL, Gregg JJ, Scales AN, Kramer BJ, Gould CE. Improving geropsychology competencies of Veterans Affairs psychologists. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021;69(3):798-805. doi:10.1111/jgs.17029
16. Karel MJ, Emery EE, Molinari V; CoPGTP Task Force on the Assessment of Geropsychology Competencies. Development of a tool to evaluate geropsychology knowledge and skill competencies. Int Psychogeriatr. 2010;22(6):886-896. doi:10.1017/S1041610209991736
17. Morgenthaler T, Kramer M, Alessi C, et al. Practice parameters for the psychological and behavioral treatment of insomnia: an update. An American Academy of Sleep Medicine report. Sleep. 2006;29(11):1415-1419.
18. Sullivan J, Gualtieri L, Campbell M, Davila H, Pendergast J, Taylor P. VA Compassionate Contact Corps: a phone-based intervention for veterans interested in speaking with peers. Innov Aging. 2021;5(Suppl 1):204. doi:10.1093/geroni/igab046.788
19. Gregg JJ, Rodriguez RL, Mehta PS, Kramer BJ, Gould CE. Enhancing specialty training in geropsychology competencies: an evaluation of a VA Geriatric Scholars Program advanced topics workshop. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2023;44(3):329-338. doi:10.1080/02701960.2022.2069764
20. Gould CE, Rodriguez RL, Gregg J, Mehta PS, Kramer J. Mentored independent learning plans among psychologists: a mixed methods investigation. J Amer Geriatr Soc. 2023;71(S1):S53.
21. Mullaly E, Kinsella G, Berberovic N, et al. Assessment of decision-making capacity: exploration of common practices among neuropsychologists. Aust Psychol. 2007;42:178-186. doi:10.1080/00050060601187142
22. Seyfried L, Ryan KA, Kim SYH. Assessment of decision-making capacity: Views and experiences of consultation psychiatrists. Psychosomatics. 2013;54(2):115-123. doi:10.1016/j.psym.2012.08.001
23. Wilk JE, Herrell RK, Wynn GH, Riviere LA, Hoge CW. Mild traumatic brain injury (concussion), posttraumatic stress disorder, and depression in U.S. soldiers involved in combat deployments: association with postdeployment symptoms. Psychosom Med. 2012;74(3):249-257. doi:10.1097/PSY.0b013e318244c604
24. Kennedy E, Panahi S, Stewart IJ, et al. Traumatic brain injury and early onset dementia in post 9-11 veterans. Brain Inj. 2022;36(5):620-627.doi:10.1080/02699052.2022.2033846
25. Merz CC, Koh D, Sakai EY, et al. The big shortage: Geropsychologists discuss facilitators and barriers to working in the field of aging. Transl Issues Psychol Sci. 2017;3(4):388-399. doi:10.1037/tps0000137
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is understaffed for clinical psychologists who have specialty training in geriatrics (ie, geropsychologists) to meet the needs of aging veterans. Though only 16.8% of US adults are aged ≥ 65 years,1 this age group comprises 45.9% of patients within the VHA.2 The needs of older adults are complex and warrant specialized services from mental health clinicians trained to understand lifespan developmental processes, biological changes associated with aging, and changes in psychosocial functioning.
Older veterans (aged ≥ 65 years) present with higher rates of combined medical and mental health diagnoses compared to both younger veterans and older adults who are not veterans.3 Nearly 1 of 5 (18.1%) older veterans who use VHA services have confirmed mental health diagnoses, and an additional 25.5% have documented mental health concerns without a formal diagnosis in their health record.4 The clinical presentations of older veterans frequently differ from younger adults and include greater complexity. For example, older veterans face an increased risk of cognitive impairment compared to the general population, due in part to higher prevalence of posttraumatic stress, which doubles their risk of developing dementia.5 Additional examples of multicomplexity among older veterans may include co-occurring medical and psychiatric diagnoses, the presence of delirium, social isolation/loneliness, and concerns related to polypharmacy. These complex presentations result in significant challenges for mental health clinicians in areas like assessment (eg, accuracy of case conceptualization), intervention (eg, selection and prioritization), and consultation (eg, coordination among multiple medical and mental health specialists).
Older veterans also present with substantial resilience. Research has found that aging veterans exposed to trauma during their military service often review their memories and past experiences, which is known as later-adulthood trauma reengagement.6 Through this normative life review process, veterans engage with memories and experiences from their past that they previously avoided, which could lead to posttraumatic growth for some. Unfortunately, others may experience an increase in psychological distress. Mental health clinicians with specialty expertise and training in aging and lifespan development can facilitate positive outcomes to reduce distress.7
The United States in general, and the VHA specifically, face a growing shortage of geriatric mental health clinicians.
The Geriatric Scholars Program (GSP) was developed in 2008 to address the training gap and provide education in geriatrics to VHA clinicians that treat older veterans, particularly in rural areas.11,12 The GSP initially focused on primary care physicians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and pharmacists. It was later expanded to include other disciplines (ie, social work, rehabilitation therapists, and psychiatrists). In 2013, the GSP – Psychology Track (GSP-P) was developed with funding from the VHA Offices of Rural Health and Geriatrics and Extended Care specifically for psychologists.
This article describes the multicomponent longitudinal GSP-P, which has evolved to meet the target audience’s ongoing needs for knowledge, skills, and opportunities to refine practice behaviors. GSP-P received the 2020 Award for Excellence in Geropsychology Training from the Council of Professional Geropsychology Training Programs. GSP-P has grown within the context of the larger GSP and aligns with the other existing elective learning opportunities (Figure 1).
Program description
Introductory Course
Psychologist subject matter experts (SMEs) developed an intensive course in geropsychology in the absence of a similar course in the geriatric medicine board review curriculum. SMEs reviewed the guidelines for practice by professional organizations like the Pikes Peak Geropsychology Competencies, which outline knowledge and skills in various domains.13 SMEs integrated this review with findings from a needs assessment for postlicensed VHA psychology staff in 4 health care systems, drafted a syllabus, and circulated it to geropsychology experts for feedback. The resulting multiday course covered general mental health as well as topics particularly salient for mental health clinicians treating older veterans including suicide prevention and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).14 This Geropsychology Competencies Review Course was piloted in 1 region initially before being offered nationally in 2014.
Quality Improvement
Introductory course attendees also participate in an intensive day-long interactive workshop in quality improvement (QI). After completing these trainings, they apply what they have learned at their home facility by embarking on a QI project related to geriatrics. The QI projects reinforce learning and initiate practice changes not only for attendees but at times the larger health care system. Topics are selected by scholars in response to the needs they observe in their clinics. Recent GSP projects include efforts to increase screenings for depression and anxiety, improve adherence to VHA dementia policy, increase access to virtual care, and increase referrals to programs such as whole health or cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia, a first-line treatment for insomnia in older adults.17 Another project targeted the improvement of referrals to the Compassionate Contact Corps in an effort to reduce social isolation and loneliness among older veterans.18 Evaluations demonstrate significant improvement in scholars’ confidence in related program development and management from precourse to 3 months postcourse.15
Webinars
The Addressing Geriatric Mental Health webinar series was created to introduce learners to topics that could not be covered in the introductory course. Topics were suggested by the expert reviewers of the curriculum or identified by the scholars themselves (eg, chronic pain, sexuality, or serious mental illness). A secondary function of the webinars was to reach a broader audience. Over time, scholars and webinar attendees requested opportunities to explore topics in greater depth (eg, PTSD later in life). These requests led the webinars to focus on annual themes.
The series is open to all disciplines of geriatric scholars, VHA staff, and non-VHA staff through the Veterans Affairs Talent Management System and the TRAIN Learning Network (train.org). Attendance for the 37 webinars was captured from logins to the virtual learning platform and may underestimate attendance if a group attended on a single screen. Average attendance increased from 157 attendees/webinar in 2015 to 418 attendees/webinar in 2023 (Figure 2). This may have been related to the increase in virtual learning during the COVID-19 pandemic, but represents a 166% increase in audience from the inaugural year of the series.
Advanced Learning Opportunities
To invest in the ongoing growth and development of introductory course graduates, GSP-P developed and offered an advanced workshop in 2019. This multiday workshop focused on further enhancement of geropsychology competencies, with an emphasis on treating older veterans with mental and physical comorbidities. Didactics and experiential learning exercises led by SMEs covered topics such as adjusting to chronic illness, capacity assessment, PTSD, insomnia and sleep changes, chronic pain, and psychological interventions in palliative care and hospice settings. Evaluation findings demonstrated significant improvements from precourse to 6 months postcourse in confidence and knowledge as
To facilitate ongoing and individually tailored learning following the advanced workshop, scholars also developed and executed independent learning plans (ILPs) during a 6-month window with consultation from an experienced geropsychologist. Fifteen of 19 scholars (78.9%) completed ILPs with an average of 3 learning goals listed. After completing the ILPs, scholars endorsed their clinical and/or personal usefulness, citing increased confidence, enhanced skills for use with patients with complex needs, personal fulfillment, and career advancement. Most scholars noted ILPs were feasible and learning resources were accessible. Overall, the evaluation found ILPs to be a valuable way to enhance psychologists’ learning and effectiveness in treating older veterans with complex health needs.20
Clinical Practica
All geriatric scholars who completed the program have additional opportunities for professional development through practicum experiences focused on specific clinical approaches to the care of older veterans, such as dementia care, pain management, geriatric assessment, and palliative care. These practica provide scholars with individualized learning experiences in an individualized or small group setting and may be conducted either in-person or virtually.
In response to an expressed need from those who completed the program, the GSP-P planning committee collaborated with an SME to develop a virtual practicum to assess patients’ decision making capacity. Evaluating capacities among older adults is a common request, yet clinicians report little to no formal training in how to conceptualize and approach these complex questions.21,22 Utilizing an evidence-informed and structured approach promotes the balancing of an older adult’s autonomy and professional ethics. Learning capacity evaluation skills could better position psychologists to not only navigate complex ethical, legal, and clinical situations, but also serve as expert consultants to interdisciplinary teams. This virtual practicum was initiated in 2022 and to date has included 10 scholars. The practicum includes multiple modalities of learning: (1) self-directed review of core concepts; (2) attendance at 4 capacity didactics focused on introduction to evaluating capacities, medical consent and decision making, financial decision making and management, and independent living; and (3) participation in 5 group consultations on capacity evaluations conducted at their home sites. During these group consultations, additional case examples were shared to reinforce capacity concepts.
Discussion
The objective of GSP-P is to enhance geropsychology practice competencies among VHA psychologists given the outsized representation of older adults within the VHA system and their complex care needs. The curricula have significantly evolved to accomplish this, expanding the reach and investing in the continuing growth and development of scholars.
There are several elements that set GSP apart from other geriatric and geropsychology continuing medical education programs. The first is that the training is veteran focused, allowing us to discuss the unique impact military service has on aging. Similarly, because all scholars work within the integrated health care system, we can introduce and review key resources and programs that benefit all veterans and their families/care partners across the system. Through the GSP, the VA invests in ongoing professional development. Scholars can participate in additional experiential practica, webinars, and advanced workshops tailored to their individual learning needs. Lastly, the GSP works to create a community among its scholars where they can not only continue to consult with presenters/instructors, but also one another. A planned future direction for the GSP-P is to incorporate quarterly office hours and discussions for alumni to develop an increased sense of community. This may strengthen commitment to the overall VA mission, leading to increased retainment of talent who now have the knowledge, skills, and confidence to care for aging veterans.
Limitations
GSP is limited by its available funding. Additionally, the number of participants who can enroll each year in GSP-P (not including webinars) is capped by policy. Another limitation is the number of QI coaches available to mentor scholars on their projects.
Conclusions
Outcomes of GSP-P have been extremely favorable. Following participation in the program, we have found a significant increase in confidence in geropsychology practice among clinicians, as well as enhanced knowledge and skills across competency domains.15,19 We have observed rising attendance in our annual webinar series and graduates of our introductory courses participate in subsequent trainings (eg, advanced workshop or virtual practicum). Several graduates of GSP-P have become board certified in geropsychology by the American Board of Geropsychology and many proceed to supervise geropsychology-focused clinical rotations for psychology practicum students, predoctoral interns, and postdoctoral fellows. This suggests that the reach of GSP-P programming may extend farther than reported in this article.
The needs of aging veterans have also changed based on cohort differences, as the population of World War II and Korean War era veterans has declined and the number of older Vietnam era veterans has grown. We expect different challenges with older Gulf War and post-9/11 era veterans. For instance, 17% of troops deployed to Iraq or Afghanistan following 9/11 experienced mild traumatic brain injury (TBI), and 59% of those experienced > 1 mild TBI.23 Research indicates that younger post-9/11 veterans have a 3-fold risk of developing early onset dementia after experiencing a TBI.24 Therefore, even though post-9/11 veterans are not older in terms of chronological age, some may experience symptoms and conditions more often occurring in older veterans. As a result, it would be beneficial for clinicians to learn about the presentation and treatment of geriatric conditions such as dementia.
Moving forward, the GSP-P should identify potential opportunities to collaborate with the non-VHA mental health community–which also faces a shortage of geriatric mental health clinicians–to extend educational opportunities to improve care for veterans in all settings (eg, cosponsor training opportunities open to both VHA and non-VHA clinicians).8,25 Many aging veterans may receive portions of their health care outside the VHA, particularly those who reside in rural areas. Additionally, as veterans age, so do their support systems (eg, family members, friends, spouses, caregivers, and even clinicians), most of whom will receive care outside of the VHA. Community education collaborations will not only improve the care of older veterans, but also the care of older adults in the general population.
Promising directions include the adoption of the GSP model in other health care settings. Recently, Indian Health Service has adapted the model, beginning with primary care clinicians and pharmacists and is beginning to expand to other disciplines. Additional investments in VHA workforce training include the availability of geropsychology internship and fellowship training opportunities through the Office of Academic Affiliations, which provide earlier opportunities to specialize in geropsychology. Continued investment in both prelicensure and postpsychology licensure training efforts are needed within the VHA to meet the geriatric mental health needs of veterans.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Terri Huh, PhD, for her contributions to the development and initiation of the GSP-P. The authors also appreciate the collaboration and quality initiative training led by Carol Callaway-Lane, DNP, ACNP-BC, and her team.
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is understaffed for clinical psychologists who have specialty training in geriatrics (ie, geropsychologists) to meet the needs of aging veterans. Though only 16.8% of US adults are aged ≥ 65 years,1 this age group comprises 45.9% of patients within the VHA.2 The needs of older adults are complex and warrant specialized services from mental health clinicians trained to understand lifespan developmental processes, biological changes associated with aging, and changes in psychosocial functioning.
Older veterans (aged ≥ 65 years) present with higher rates of combined medical and mental health diagnoses compared to both younger veterans and older adults who are not veterans.3 Nearly 1 of 5 (18.1%) older veterans who use VHA services have confirmed mental health diagnoses, and an additional 25.5% have documented mental health concerns without a formal diagnosis in their health record.4 The clinical presentations of older veterans frequently differ from younger adults and include greater complexity. For example, older veterans face an increased risk of cognitive impairment compared to the general population, due in part to higher prevalence of posttraumatic stress, which doubles their risk of developing dementia.5 Additional examples of multicomplexity among older veterans may include co-occurring medical and psychiatric diagnoses, the presence of delirium, social isolation/loneliness, and concerns related to polypharmacy. These complex presentations result in significant challenges for mental health clinicians in areas like assessment (eg, accuracy of case conceptualization), intervention (eg, selection and prioritization), and consultation (eg, coordination among multiple medical and mental health specialists).
Older veterans also present with substantial resilience. Research has found that aging veterans exposed to trauma during their military service often review their memories and past experiences, which is known as later-adulthood trauma reengagement.6 Through this normative life review process, veterans engage with memories and experiences from their past that they previously avoided, which could lead to posttraumatic growth for some. Unfortunately, others may experience an increase in psychological distress. Mental health clinicians with specialty expertise and training in aging and lifespan development can facilitate positive outcomes to reduce distress.7
The United States in general, and the VHA specifically, face a growing shortage of geriatric mental health clinicians.
The Geriatric Scholars Program (GSP) was developed in 2008 to address the training gap and provide education in geriatrics to VHA clinicians that treat older veterans, particularly in rural areas.11,12 The GSP initially focused on primary care physicians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and pharmacists. It was later expanded to include other disciplines (ie, social work, rehabilitation therapists, and psychiatrists). In 2013, the GSP – Psychology Track (GSP-P) was developed with funding from the VHA Offices of Rural Health and Geriatrics and Extended Care specifically for psychologists.
This article describes the multicomponent longitudinal GSP-P, which has evolved to meet the target audience’s ongoing needs for knowledge, skills, and opportunities to refine practice behaviors. GSP-P received the 2020 Award for Excellence in Geropsychology Training from the Council of Professional Geropsychology Training Programs. GSP-P has grown within the context of the larger GSP and aligns with the other existing elective learning opportunities (Figure 1).
Program description
Introductory Course
Psychologist subject matter experts (SMEs) developed an intensive course in geropsychology in the absence of a similar course in the geriatric medicine board review curriculum. SMEs reviewed the guidelines for practice by professional organizations like the Pikes Peak Geropsychology Competencies, which outline knowledge and skills in various domains.13 SMEs integrated this review with findings from a needs assessment for postlicensed VHA psychology staff in 4 health care systems, drafted a syllabus, and circulated it to geropsychology experts for feedback. The resulting multiday course covered general mental health as well as topics particularly salient for mental health clinicians treating older veterans including suicide prevention and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).14 This Geropsychology Competencies Review Course was piloted in 1 region initially before being offered nationally in 2014.
Quality Improvement
Introductory course attendees also participate in an intensive day-long interactive workshop in quality improvement (QI). After completing these trainings, they apply what they have learned at their home facility by embarking on a QI project related to geriatrics. The QI projects reinforce learning and initiate practice changes not only for attendees but at times the larger health care system. Topics are selected by scholars in response to the needs they observe in their clinics. Recent GSP projects include efforts to increase screenings for depression and anxiety, improve adherence to VHA dementia policy, increase access to virtual care, and increase referrals to programs such as whole health or cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia, a first-line treatment for insomnia in older adults.17 Another project targeted the improvement of referrals to the Compassionate Contact Corps in an effort to reduce social isolation and loneliness among older veterans.18 Evaluations demonstrate significant improvement in scholars’ confidence in related program development and management from precourse to 3 months postcourse.15
Webinars
The Addressing Geriatric Mental Health webinar series was created to introduce learners to topics that could not be covered in the introductory course. Topics were suggested by the expert reviewers of the curriculum or identified by the scholars themselves (eg, chronic pain, sexuality, or serious mental illness). A secondary function of the webinars was to reach a broader audience. Over time, scholars and webinar attendees requested opportunities to explore topics in greater depth (eg, PTSD later in life). These requests led the webinars to focus on annual themes.
The series is open to all disciplines of geriatric scholars, VHA staff, and non-VHA staff through the Veterans Affairs Talent Management System and the TRAIN Learning Network (train.org). Attendance for the 37 webinars was captured from logins to the virtual learning platform and may underestimate attendance if a group attended on a single screen. Average attendance increased from 157 attendees/webinar in 2015 to 418 attendees/webinar in 2023 (Figure 2). This may have been related to the increase in virtual learning during the COVID-19 pandemic, but represents a 166% increase in audience from the inaugural year of the series.
Advanced Learning Opportunities
To invest in the ongoing growth and development of introductory course graduates, GSP-P developed and offered an advanced workshop in 2019. This multiday workshop focused on further enhancement of geropsychology competencies, with an emphasis on treating older veterans with mental and physical comorbidities. Didactics and experiential learning exercises led by SMEs covered topics such as adjusting to chronic illness, capacity assessment, PTSD, insomnia and sleep changes, chronic pain, and psychological interventions in palliative care and hospice settings. Evaluation findings demonstrated significant improvements from precourse to 6 months postcourse in confidence and knowledge as
To facilitate ongoing and individually tailored learning following the advanced workshop, scholars also developed and executed independent learning plans (ILPs) during a 6-month window with consultation from an experienced geropsychologist. Fifteen of 19 scholars (78.9%) completed ILPs with an average of 3 learning goals listed. After completing the ILPs, scholars endorsed their clinical and/or personal usefulness, citing increased confidence, enhanced skills for use with patients with complex needs, personal fulfillment, and career advancement. Most scholars noted ILPs were feasible and learning resources were accessible. Overall, the evaluation found ILPs to be a valuable way to enhance psychologists’ learning and effectiveness in treating older veterans with complex health needs.20
Clinical Practica
All geriatric scholars who completed the program have additional opportunities for professional development through practicum experiences focused on specific clinical approaches to the care of older veterans, such as dementia care, pain management, geriatric assessment, and palliative care. These practica provide scholars with individualized learning experiences in an individualized or small group setting and may be conducted either in-person or virtually.
In response to an expressed need from those who completed the program, the GSP-P planning committee collaborated with an SME to develop a virtual practicum to assess patients’ decision making capacity. Evaluating capacities among older adults is a common request, yet clinicians report little to no formal training in how to conceptualize and approach these complex questions.21,22 Utilizing an evidence-informed and structured approach promotes the balancing of an older adult’s autonomy and professional ethics. Learning capacity evaluation skills could better position psychologists to not only navigate complex ethical, legal, and clinical situations, but also serve as expert consultants to interdisciplinary teams. This virtual practicum was initiated in 2022 and to date has included 10 scholars. The practicum includes multiple modalities of learning: (1) self-directed review of core concepts; (2) attendance at 4 capacity didactics focused on introduction to evaluating capacities, medical consent and decision making, financial decision making and management, and independent living; and (3) participation in 5 group consultations on capacity evaluations conducted at their home sites. During these group consultations, additional case examples were shared to reinforce capacity concepts.
Discussion
The objective of GSP-P is to enhance geropsychology practice competencies among VHA psychologists given the outsized representation of older adults within the VHA system and their complex care needs. The curricula have significantly evolved to accomplish this, expanding the reach and investing in the continuing growth and development of scholars.
There are several elements that set GSP apart from other geriatric and geropsychology continuing medical education programs. The first is that the training is veteran focused, allowing us to discuss the unique impact military service has on aging. Similarly, because all scholars work within the integrated health care system, we can introduce and review key resources and programs that benefit all veterans and their families/care partners across the system. Through the GSP, the VA invests in ongoing professional development. Scholars can participate in additional experiential practica, webinars, and advanced workshops tailored to their individual learning needs. Lastly, the GSP works to create a community among its scholars where they can not only continue to consult with presenters/instructors, but also one another. A planned future direction for the GSP-P is to incorporate quarterly office hours and discussions for alumni to develop an increased sense of community. This may strengthen commitment to the overall VA mission, leading to increased retainment of talent who now have the knowledge, skills, and confidence to care for aging veterans.
Limitations
GSP is limited by its available funding. Additionally, the number of participants who can enroll each year in GSP-P (not including webinars) is capped by policy. Another limitation is the number of QI coaches available to mentor scholars on their projects.
Conclusions
Outcomes of GSP-P have been extremely favorable. Following participation in the program, we have found a significant increase in confidence in geropsychology practice among clinicians, as well as enhanced knowledge and skills across competency domains.15,19 We have observed rising attendance in our annual webinar series and graduates of our introductory courses participate in subsequent trainings (eg, advanced workshop or virtual practicum). Several graduates of GSP-P have become board certified in geropsychology by the American Board of Geropsychology and many proceed to supervise geropsychology-focused clinical rotations for psychology practicum students, predoctoral interns, and postdoctoral fellows. This suggests that the reach of GSP-P programming may extend farther than reported in this article.
The needs of aging veterans have also changed based on cohort differences, as the population of World War II and Korean War era veterans has declined and the number of older Vietnam era veterans has grown. We expect different challenges with older Gulf War and post-9/11 era veterans. For instance, 17% of troops deployed to Iraq or Afghanistan following 9/11 experienced mild traumatic brain injury (TBI), and 59% of those experienced > 1 mild TBI.23 Research indicates that younger post-9/11 veterans have a 3-fold risk of developing early onset dementia after experiencing a TBI.24 Therefore, even though post-9/11 veterans are not older in terms of chronological age, some may experience symptoms and conditions more often occurring in older veterans. As a result, it would be beneficial for clinicians to learn about the presentation and treatment of geriatric conditions such as dementia.
Moving forward, the GSP-P should identify potential opportunities to collaborate with the non-VHA mental health community–which also faces a shortage of geriatric mental health clinicians–to extend educational opportunities to improve care for veterans in all settings (eg, cosponsor training opportunities open to both VHA and non-VHA clinicians).8,25 Many aging veterans may receive portions of their health care outside the VHA, particularly those who reside in rural areas. Additionally, as veterans age, so do their support systems (eg, family members, friends, spouses, caregivers, and even clinicians), most of whom will receive care outside of the VHA. Community education collaborations will not only improve the care of older veterans, but also the care of older adults in the general population.
Promising directions include the adoption of the GSP model in other health care settings. Recently, Indian Health Service has adapted the model, beginning with primary care clinicians and pharmacists and is beginning to expand to other disciplines. Additional investments in VHA workforce training include the availability of geropsychology internship and fellowship training opportunities through the Office of Academic Affiliations, which provide earlier opportunities to specialize in geropsychology. Continued investment in both prelicensure and postpsychology licensure training efforts are needed within the VHA to meet the geriatric mental health needs of veterans.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Terri Huh, PhD, for her contributions to the development and initiation of the GSP-P. The authors also appreciate the collaboration and quality initiative training led by Carol Callaway-Lane, DNP, ACNP-BC, and her team.
1. Caplan Z, Rabe M; US Department of Commerce, US Census Bureau. The Older Population: 2020 (Census Brief No. C2020BR-07). May 2023. Accessed February 27, 2024. https://www2.census.gov/library/publications/decennial/2020/census-briefs/c2020br-07.pdf
2. US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. VA benefits & health care utilization. Updated February 2023. Accessed February 27, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/docs/pocketcards/fy2023q2.PDF
3. O’Malley KA, Vinson L, Pless Kaiser A, Sager Z, Hinrichs K. Mental health and aging veterans: How the Veterans Health Administration meets the needs of aging veterans. Public Policy Aging Rep. 2020;30(1):19-23. doi:10.1093/ppar/prz027
4. Greenberg G, Hoff R. FY 2021 Older Adult (65+ on October 1st) Veteran Data Sheet: National, VISN, and Healthcare System Tables. West Haven, CT: U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Northeast Program Evaluation Center. 2022.
5. Yaffe K, Vittinghoff E, Lindquist K, et al. Posttraumatic stress disorder and risk of dementia among US veterans. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67(6):608-613. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.61
6. Davison EH, Kaiser AP, Spiro A 3rd, Moye J, King LA, King DW. From late-onset stress symptomatology to later-adulthood trauma reengagement in aging combat veterans: Taking a broader view. Gerontologist. 2016;56(1):14-21. doi:10.1093/geront/gnv097
7. Kaiser AP, Boyle JT, Bamonti PM, O’Malley K, Moye J. Development, adaptation, and clinical implementation of the Later-Adulthood Trauma Reengagement (LATR) group intervention for older veterans. Psychol Serv. 2023;20(4):863-875. doi:10.1037/ser0000736
8. Moye J, Karel MJ, Stamm KE, et al. Workforce analysis of psychological practice with older adults: Growing crisis requires urgent action. Train Educ Prof Psychol. 2019;13(1):46-55. doi:10.1037/tep0000206
9. Stamm K, Lin L, Conroy J. Critical needs in geropsychology. Monitor on Psychology. 2021;52(4):21.
10. American Board of Geropsychology. Specialists. 2024. Accessed February 6, 2024. https://abgero.org/board-members/specialists/
11. Kramer BJ. The VA Geriatric Scholars Program. Fed Pract. 2015;32(5):46-48.
12. Kramer BJ, Creekmur B, Howe JL, et al. Veterans Affairs Geriatric Scholars Program: Enhancing existing primary care clinician skills in caring for older veterans. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2016;64(11):2343-2348. doi:10.1111/jgs.14382
13. Knight BG, Karel MJ, Hinrichsen GA, Qualls SH, Duffy M. Pikes Peak model for training in professional geropsychology. Am Psychol. 2009;64(3):205-14. doi:10.1037/a0015059
14. Huh JWT, Rodriguez R, Gould CE, R Brunskill S, Melendez L, Kramer BJ. Developing a program to increase geropsychology competencies of Veterans Health Administration (VHA) psychologists. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2020;41(4):463-479. doi:10.1080/02701960.2018.1491402
15. Huh JWT, Rodriguez RL, Gregg JJ, Scales AN, Kramer BJ, Gould CE. Improving geropsychology competencies of Veterans Affairs psychologists. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021;69(3):798-805. doi:10.1111/jgs.17029
16. Karel MJ, Emery EE, Molinari V; CoPGTP Task Force on the Assessment of Geropsychology Competencies. Development of a tool to evaluate geropsychology knowledge and skill competencies. Int Psychogeriatr. 2010;22(6):886-896. doi:10.1017/S1041610209991736
17. Morgenthaler T, Kramer M, Alessi C, et al. Practice parameters for the psychological and behavioral treatment of insomnia: an update. An American Academy of Sleep Medicine report. Sleep. 2006;29(11):1415-1419.
18. Sullivan J, Gualtieri L, Campbell M, Davila H, Pendergast J, Taylor P. VA Compassionate Contact Corps: a phone-based intervention for veterans interested in speaking with peers. Innov Aging. 2021;5(Suppl 1):204. doi:10.1093/geroni/igab046.788
19. Gregg JJ, Rodriguez RL, Mehta PS, Kramer BJ, Gould CE. Enhancing specialty training in geropsychology competencies: an evaluation of a VA Geriatric Scholars Program advanced topics workshop. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2023;44(3):329-338. doi:10.1080/02701960.2022.2069764
20. Gould CE, Rodriguez RL, Gregg J, Mehta PS, Kramer J. Mentored independent learning plans among psychologists: a mixed methods investigation. J Amer Geriatr Soc. 2023;71(S1):S53.
21. Mullaly E, Kinsella G, Berberovic N, et al. Assessment of decision-making capacity: exploration of common practices among neuropsychologists. Aust Psychol. 2007;42:178-186. doi:10.1080/00050060601187142
22. Seyfried L, Ryan KA, Kim SYH. Assessment of decision-making capacity: Views and experiences of consultation psychiatrists. Psychosomatics. 2013;54(2):115-123. doi:10.1016/j.psym.2012.08.001
23. Wilk JE, Herrell RK, Wynn GH, Riviere LA, Hoge CW. Mild traumatic brain injury (concussion), posttraumatic stress disorder, and depression in U.S. soldiers involved in combat deployments: association with postdeployment symptoms. Psychosom Med. 2012;74(3):249-257. doi:10.1097/PSY.0b013e318244c604
24. Kennedy E, Panahi S, Stewart IJ, et al. Traumatic brain injury and early onset dementia in post 9-11 veterans. Brain Inj. 2022;36(5):620-627.doi:10.1080/02699052.2022.2033846
25. Merz CC, Koh D, Sakai EY, et al. The big shortage: Geropsychologists discuss facilitators and barriers to working in the field of aging. Transl Issues Psychol Sci. 2017;3(4):388-399. doi:10.1037/tps0000137
1. Caplan Z, Rabe M; US Department of Commerce, US Census Bureau. The Older Population: 2020 (Census Brief No. C2020BR-07). May 2023. Accessed February 27, 2024. https://www2.census.gov/library/publications/decennial/2020/census-briefs/c2020br-07.pdf
2. US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. VA benefits & health care utilization. Updated February 2023. Accessed February 27, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/docs/pocketcards/fy2023q2.PDF
3. O’Malley KA, Vinson L, Pless Kaiser A, Sager Z, Hinrichs K. Mental health and aging veterans: How the Veterans Health Administration meets the needs of aging veterans. Public Policy Aging Rep. 2020;30(1):19-23. doi:10.1093/ppar/prz027
4. Greenberg G, Hoff R. FY 2021 Older Adult (65+ on October 1st) Veteran Data Sheet: National, VISN, and Healthcare System Tables. West Haven, CT: U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Northeast Program Evaluation Center. 2022.
5. Yaffe K, Vittinghoff E, Lindquist K, et al. Posttraumatic stress disorder and risk of dementia among US veterans. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67(6):608-613. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.61
6. Davison EH, Kaiser AP, Spiro A 3rd, Moye J, King LA, King DW. From late-onset stress symptomatology to later-adulthood trauma reengagement in aging combat veterans: Taking a broader view. Gerontologist. 2016;56(1):14-21. doi:10.1093/geront/gnv097
7. Kaiser AP, Boyle JT, Bamonti PM, O’Malley K, Moye J. Development, adaptation, and clinical implementation of the Later-Adulthood Trauma Reengagement (LATR) group intervention for older veterans. Psychol Serv. 2023;20(4):863-875. doi:10.1037/ser0000736
8. Moye J, Karel MJ, Stamm KE, et al. Workforce analysis of psychological practice with older adults: Growing crisis requires urgent action. Train Educ Prof Psychol. 2019;13(1):46-55. doi:10.1037/tep0000206
9. Stamm K, Lin L, Conroy J. Critical needs in geropsychology. Monitor on Psychology. 2021;52(4):21.
10. American Board of Geropsychology. Specialists. 2024. Accessed February 6, 2024. https://abgero.org/board-members/specialists/
11. Kramer BJ. The VA Geriatric Scholars Program. Fed Pract. 2015;32(5):46-48.
12. Kramer BJ, Creekmur B, Howe JL, et al. Veterans Affairs Geriatric Scholars Program: Enhancing existing primary care clinician skills in caring for older veterans. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2016;64(11):2343-2348. doi:10.1111/jgs.14382
13. Knight BG, Karel MJ, Hinrichsen GA, Qualls SH, Duffy M. Pikes Peak model for training in professional geropsychology. Am Psychol. 2009;64(3):205-14. doi:10.1037/a0015059
14. Huh JWT, Rodriguez R, Gould CE, R Brunskill S, Melendez L, Kramer BJ. Developing a program to increase geropsychology competencies of Veterans Health Administration (VHA) psychologists. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2020;41(4):463-479. doi:10.1080/02701960.2018.1491402
15. Huh JWT, Rodriguez RL, Gregg JJ, Scales AN, Kramer BJ, Gould CE. Improving geropsychology competencies of Veterans Affairs psychologists. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021;69(3):798-805. doi:10.1111/jgs.17029
16. Karel MJ, Emery EE, Molinari V; CoPGTP Task Force on the Assessment of Geropsychology Competencies. Development of a tool to evaluate geropsychology knowledge and skill competencies. Int Psychogeriatr. 2010;22(6):886-896. doi:10.1017/S1041610209991736
17. Morgenthaler T, Kramer M, Alessi C, et al. Practice parameters for the psychological and behavioral treatment of insomnia: an update. An American Academy of Sleep Medicine report. Sleep. 2006;29(11):1415-1419.
18. Sullivan J, Gualtieri L, Campbell M, Davila H, Pendergast J, Taylor P. VA Compassionate Contact Corps: a phone-based intervention for veterans interested in speaking with peers. Innov Aging. 2021;5(Suppl 1):204. doi:10.1093/geroni/igab046.788
19. Gregg JJ, Rodriguez RL, Mehta PS, Kramer BJ, Gould CE. Enhancing specialty training in geropsychology competencies: an evaluation of a VA Geriatric Scholars Program advanced topics workshop. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2023;44(3):329-338. doi:10.1080/02701960.2022.2069764
20. Gould CE, Rodriguez RL, Gregg J, Mehta PS, Kramer J. Mentored independent learning plans among psychologists: a mixed methods investigation. J Amer Geriatr Soc. 2023;71(S1):S53.
21. Mullaly E, Kinsella G, Berberovic N, et al. Assessment of decision-making capacity: exploration of common practices among neuropsychologists. Aust Psychol. 2007;42:178-186. doi:10.1080/00050060601187142
22. Seyfried L, Ryan KA, Kim SYH. Assessment of decision-making capacity: Views and experiences of consultation psychiatrists. Psychosomatics. 2013;54(2):115-123. doi:10.1016/j.psym.2012.08.001
23. Wilk JE, Herrell RK, Wynn GH, Riviere LA, Hoge CW. Mild traumatic brain injury (concussion), posttraumatic stress disorder, and depression in U.S. soldiers involved in combat deployments: association with postdeployment symptoms. Psychosom Med. 2012;74(3):249-257. doi:10.1097/PSY.0b013e318244c604
24. Kennedy E, Panahi S, Stewart IJ, et al. Traumatic brain injury and early onset dementia in post 9-11 veterans. Brain Inj. 2022;36(5):620-627.doi:10.1080/02699052.2022.2033846
25. Merz CC, Koh D, Sakai EY, et al. The big shortage: Geropsychologists discuss facilitators and barriers to working in the field of aging. Transl Issues Psychol Sci. 2017;3(4):388-399. doi:10.1037/tps0000137
Underlying Mental Illness and Risk of Severe Outcomes Associated With COVID-19
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has identified factors that put patients at a higher risk of severe COVID-19 infection, which include advanced age, obesity, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, lung disease, and immunocompromising conditions. The CDC also acknowledges that mood disorders, including depression and schizophrenia, contribute to the progression to severe COVID-19.1 Antiviral therapies, such as nirmatrelvir and ritonavir combination, remdesivir, and molnupiravir, and monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapies, have been used to prevent hospitalization and mortality from COVID-19 infection for individuals with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 who are at high risk of progressing to severe infection.2 Although antiviral and mAb therapies likely have mitigated many infections, poor prognoses are prevalent. It is important to identify all patients at risk of progressing to severe COVID-19 infection.
Although the CDC considers depression and schizophrenia to be risk factors for severe COVID-19 infection, the Captain James A. Lovell Federal Health Care Center (FHCC) in North Chicago, Illinois, does not, making these patients ineligible for antiviral or mAb therapies unless they have another risk factor. As a result, these patients could be at risk of severe COVID-19 infection, but might not be treated appropriately. Psychiatric diagnoses are common among veterans, with 19.7% experiencing a mental illness in 2020.3 It is imperative to determine whether depression or schizophrenia play a role in the progression of COVID-19 to expand access to individuals who are eligible for antiviral or mAb therapies.
Because COVID-19 is a novel virus, there are few studies of psychiatric disorders and COVID-19 prognosis. A 2020 case control study determined that those with a recent mental illness diagnosis were at higher risk of COVID-19 infection with worse outcomes compared with those without psychiatric diagnoses. This effect was most prevalent among individuals with depression and schizophrenia.4 However, these individuals also were found to have additional comorbidities that could have contributed to poorer outcomes. A meta-analysis determined that psychiatric disorders were associated with increased COVID-19-related mortality.5 A 2022 cohort study that included vaccinated US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) patients determined that having a psychiatric diagnosis was associated with increased incidence of breakthrough infections.6 Individuals with psychiatric conditions are thought to be at higher risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes because of poor access to care and higher incidence of untreated underlying health conditions.7 Lifestyle factors also could play a role. Because there is minimal data on COVID-19 prognosis and mental illness, further research is warranted to determine whether psychiatric diagnoses could contribute to more severe COVID-19 infections.
Methods
This was a retrospective cohort chart review study at FHCC that compared COVID-19 outcomes in individuals with depression or schizophrenia with those without these diagnoses. FHCC patients with the International Classification of Diseases code for COVID-19 (U07.1) from fiscal years 2020 to 2022 were included. We then selected patients with a depression or schizophrenia diagnosis noted in the electronic health record (EHR). These 2 patient lists were consolidated to identify every individual with a COVID-19 diagnosis and a diagnosis of depression or schizophrenia.
Patients were included if they were aged ≥ 18 years with a positive COVID-19 infection confirmed via polymerase chain reaction or blood test. Patients also had to have mild-to-moderate COVID-19 with ≥ 1 symptom such as fever, cough, sore throat, malaise, headache, muscle pain, loss of taste and smell, or shortness of breath. Patients were excluded if they had an asymptomatic infection, presented with severe COVID-19 infection, or were an FHCC employee. Severe COVID-19 was defined as having oxygen saturation < 94%, a respiratory rate > 30 breaths per minute, or supplemental oxygen requirement.
Patient EHRs were reviewed and analyzed using the VA Computerized Patient Record System and Joint Legacy Viewer. Collected data included age, medical history, use of antiviral or mAb therapy, and admission or death within 30 days of a positive COVID-19 test. The primary outcome of this study was severe COVID-19 outcomes defined as hospitalization, admission to the intensive care unit, intubation or mechanical ventilation, or death within 30 days of infection. The primary outcome was analyzed with a student t test; P < .05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
More than 5000 individuals had a COVID-19 diagnosis during the study period. Among these patients, 4530 had no depression or schizophrenia diagnosis; 1021 individuals had COVID-19 and a preexisting diagnosis of depression or schizophrenia. Among these 1021 patients, 279 charts were reviewed due to time constraints; 128 patients met exclusion criteria and 151 patients were included in the study. Of the 151 patients with COVID-19, 78 had no depression or schizophrenia and 73 patients with COVID-19 had a preexisting depression or schizophrenia diagnosis (Figure).
The 2 groups were similar at baseline. The most common risk factors for severe COVID-19 included age > 60 years, obesity, and cardiovascular disease. However, more than half of the individuals analyzed had no risk factors (Table 1). Some patients with risk factors received antiviral or mAb therapy to prevent severe COVID-19 infection; combination nirmatrelvir and ritonavir was the most common agent (Table 2). Of the 73 individuals with a psychiatric diagnosis, 67 had depression (91.8%), and 6 had schizophrenia (8.2%).
Hospitalization or death within 30 days of COVID-19 infection between patients with depression or schizophrenia and patients without these psychiatric diagnoses was not statistically significant (P = .36). Sixteen individuals were hospitalized, 8 in each group. Three individuals died within 30 days; death only occurred in patients who had depression or schizophrenia (Table 3).
Discussion
This study found that hospitalization or death within 30 days of COVID-19 infection occurred more frequently among individuals with depression or schizophrenia compared with those without these psychiatric comorbidities. However, this difference was not statistically significant.
This study had several limitations. It was a retrospective, chart review study, which relied on accurate documentation. In addition, we reviewed COVID-19 cases from fiscal years 2020 to 2022 and as a result, several viral variants were analyzed. This made it difficult to draw conclusions, especially because the omicron variant is thought to be less deadly, which may have skewed the data. Vaccinations and COVID-19 treatments became available in late 2020, which likely affected the progression to severe disease. Our study did not assess vaccination status, therefore it is unclear whether COVID-19 vaccination played a role in mitigating infection. When the pandemic began, many individuals were afraid to come to the hospital and did not receive care until they progressed to severe COVID-19, which would have excluded them from the study. Many individuals had additional comorbidities that likely impacted their COVID-19 outcomes. It is not possible to conclude if the depression or schizophrenia diagnoses were responsible for hospitalization or death within 30 days of infection or if it was because of other known risk factors. Future research is needed to address these limitations.
Conclusions
More COVID-19 hospitalizations and deaths occurred within 30 days of infection among those with depression and schizophrenia compared with individuals without these comorbidities. However, this effect was not statistically significant. Many limitations could have contributed to this finding, which should be addressed in future studies. Because the sample size was small, further research with a larger patient population is warranted to explore the association between psychiatric comorbidities such as depression and schizophrenia and COVID-19 disease progression. Future studies also could include assessment of vaccination status and exclude individuals with other high-risk comorbidities for severe COVID-19 outcomes. These studies could determine if depression and schizophrenia are correlated with worse COVID-19 outcomes and ensure that all high-risk patients are identified and treated appropriately to prevent morbidity and mortality.
Acknowledgements
Thank you to the research committee at the Captain James A. Lovell Federal Health Care Center who assisted in the completion of this project, including Shaiza Khan, PharmD, BCPS; Yinka Alaka, PharmD; and Hong-Yen Vi, PharmD, BCPS, BCCCP.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Underlying medical conditions associated with higher risk for severe COVID-19: information for healthcare professionals. Updated February 9, 2023. Accessed February 27, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care/underlyingconditions.html
2. National Institutes of Health. Therapeutic management of nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19. Updated November 2, 2023. Accessed February 27, 2024. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/management/clinical-management-of-adults/nonhospitalized-adults-therapeutic-management
3. National Alliance on Mental Illness. Mental health by the numbers. Updated April 2023. Accessed February 27, 2024. https://www.nami.org/mhstats
4. Wang Q, Xu R, Volkow ND. Increased risk of COVID-19 infection and mortality in people with mental disorders: analysis from electronic health records in the United States. World Psychiatry . 2021;20(1):124-130. doi:10.1002/wps.20806
5. Fond G, Nemani K, Etchecopar-Etchart D, et al. Association Between Mental Health Disorders and Mortality Among Patients With COVID-19 in 7 Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry . 2021;78(11):1208-1217. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.2274
6. Nishimi K, Neylan TC, Bertenthal D, Seal KH, O’Donovan A. Association of Psychiatric Disorders With Incidence of SARS-CoV-2 Breakthrough Infection Among Vaccinated Adults. JAMA Netw Open . 2022;5(4):e227287. Published 2022 Apr 1. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.7287
7. Koyama AK, Koumans EH, Sircar K, et al. Mental Health Conditions and Severe COVID-19 Outcomes after Hospitalization, United States. Emerg Infect Dis . 2022;28(7):1533-1536. doi:10.3201/eid2807.212208
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has identified factors that put patients at a higher risk of severe COVID-19 infection, which include advanced age, obesity, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, lung disease, and immunocompromising conditions. The CDC also acknowledges that mood disorders, including depression and schizophrenia, contribute to the progression to severe COVID-19.1 Antiviral therapies, such as nirmatrelvir and ritonavir combination, remdesivir, and molnupiravir, and monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapies, have been used to prevent hospitalization and mortality from COVID-19 infection for individuals with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 who are at high risk of progressing to severe infection.2 Although antiviral and mAb therapies likely have mitigated many infections, poor prognoses are prevalent. It is important to identify all patients at risk of progressing to severe COVID-19 infection.
Although the CDC considers depression and schizophrenia to be risk factors for severe COVID-19 infection, the Captain James A. Lovell Federal Health Care Center (FHCC) in North Chicago, Illinois, does not, making these patients ineligible for antiviral or mAb therapies unless they have another risk factor. As a result, these patients could be at risk of severe COVID-19 infection, but might not be treated appropriately. Psychiatric diagnoses are common among veterans, with 19.7% experiencing a mental illness in 2020.3 It is imperative to determine whether depression or schizophrenia play a role in the progression of COVID-19 to expand access to individuals who are eligible for antiviral or mAb therapies.
Because COVID-19 is a novel virus, there are few studies of psychiatric disorders and COVID-19 prognosis. A 2020 case control study determined that those with a recent mental illness diagnosis were at higher risk of COVID-19 infection with worse outcomes compared with those without psychiatric diagnoses. This effect was most prevalent among individuals with depression and schizophrenia.4 However, these individuals also were found to have additional comorbidities that could have contributed to poorer outcomes. A meta-analysis determined that psychiatric disorders were associated with increased COVID-19-related mortality.5 A 2022 cohort study that included vaccinated US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) patients determined that having a psychiatric diagnosis was associated with increased incidence of breakthrough infections.6 Individuals with psychiatric conditions are thought to be at higher risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes because of poor access to care and higher incidence of untreated underlying health conditions.7 Lifestyle factors also could play a role. Because there is minimal data on COVID-19 prognosis and mental illness, further research is warranted to determine whether psychiatric diagnoses could contribute to more severe COVID-19 infections.
Methods
This was a retrospective cohort chart review study at FHCC that compared COVID-19 outcomes in individuals with depression or schizophrenia with those without these diagnoses. FHCC patients with the International Classification of Diseases code for COVID-19 (U07.1) from fiscal years 2020 to 2022 were included. We then selected patients with a depression or schizophrenia diagnosis noted in the electronic health record (EHR). These 2 patient lists were consolidated to identify every individual with a COVID-19 diagnosis and a diagnosis of depression or schizophrenia.
Patients were included if they were aged ≥ 18 years with a positive COVID-19 infection confirmed via polymerase chain reaction or blood test. Patients also had to have mild-to-moderate COVID-19 with ≥ 1 symptom such as fever, cough, sore throat, malaise, headache, muscle pain, loss of taste and smell, or shortness of breath. Patients were excluded if they had an asymptomatic infection, presented with severe COVID-19 infection, or were an FHCC employee. Severe COVID-19 was defined as having oxygen saturation < 94%, a respiratory rate > 30 breaths per minute, or supplemental oxygen requirement.
Patient EHRs were reviewed and analyzed using the VA Computerized Patient Record System and Joint Legacy Viewer. Collected data included age, medical history, use of antiviral or mAb therapy, and admission or death within 30 days of a positive COVID-19 test. The primary outcome of this study was severe COVID-19 outcomes defined as hospitalization, admission to the intensive care unit, intubation or mechanical ventilation, or death within 30 days of infection. The primary outcome was analyzed with a student t test; P < .05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
More than 5000 individuals had a COVID-19 diagnosis during the study period. Among these patients, 4530 had no depression or schizophrenia diagnosis; 1021 individuals had COVID-19 and a preexisting diagnosis of depression or schizophrenia. Among these 1021 patients, 279 charts were reviewed due to time constraints; 128 patients met exclusion criteria and 151 patients were included in the study. Of the 151 patients with COVID-19, 78 had no depression or schizophrenia and 73 patients with COVID-19 had a preexisting depression or schizophrenia diagnosis (Figure).
The 2 groups were similar at baseline. The most common risk factors for severe COVID-19 included age > 60 years, obesity, and cardiovascular disease. However, more than half of the individuals analyzed had no risk factors (Table 1). Some patients with risk factors received antiviral or mAb therapy to prevent severe COVID-19 infection; combination nirmatrelvir and ritonavir was the most common agent (Table 2). Of the 73 individuals with a psychiatric diagnosis, 67 had depression (91.8%), and 6 had schizophrenia (8.2%).
Hospitalization or death within 30 days of COVID-19 infection between patients with depression or schizophrenia and patients without these psychiatric diagnoses was not statistically significant (P = .36). Sixteen individuals were hospitalized, 8 in each group. Three individuals died within 30 days; death only occurred in patients who had depression or schizophrenia (Table 3).
Discussion
This study found that hospitalization or death within 30 days of COVID-19 infection occurred more frequently among individuals with depression or schizophrenia compared with those without these psychiatric comorbidities. However, this difference was not statistically significant.
This study had several limitations. It was a retrospective, chart review study, which relied on accurate documentation. In addition, we reviewed COVID-19 cases from fiscal years 2020 to 2022 and as a result, several viral variants were analyzed. This made it difficult to draw conclusions, especially because the omicron variant is thought to be less deadly, which may have skewed the data. Vaccinations and COVID-19 treatments became available in late 2020, which likely affected the progression to severe disease. Our study did not assess vaccination status, therefore it is unclear whether COVID-19 vaccination played a role in mitigating infection. When the pandemic began, many individuals were afraid to come to the hospital and did not receive care until they progressed to severe COVID-19, which would have excluded them from the study. Many individuals had additional comorbidities that likely impacted their COVID-19 outcomes. It is not possible to conclude if the depression or schizophrenia diagnoses were responsible for hospitalization or death within 30 days of infection or if it was because of other known risk factors. Future research is needed to address these limitations.
Conclusions
More COVID-19 hospitalizations and deaths occurred within 30 days of infection among those with depression and schizophrenia compared with individuals without these comorbidities. However, this effect was not statistically significant. Many limitations could have contributed to this finding, which should be addressed in future studies. Because the sample size was small, further research with a larger patient population is warranted to explore the association between psychiatric comorbidities such as depression and schizophrenia and COVID-19 disease progression. Future studies also could include assessment of vaccination status and exclude individuals with other high-risk comorbidities for severe COVID-19 outcomes. These studies could determine if depression and schizophrenia are correlated with worse COVID-19 outcomes and ensure that all high-risk patients are identified and treated appropriately to prevent morbidity and mortality.
Acknowledgements
Thank you to the research committee at the Captain James A. Lovell Federal Health Care Center who assisted in the completion of this project, including Shaiza Khan, PharmD, BCPS; Yinka Alaka, PharmD; and Hong-Yen Vi, PharmD, BCPS, BCCCP.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has identified factors that put patients at a higher risk of severe COVID-19 infection, which include advanced age, obesity, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, lung disease, and immunocompromising conditions. The CDC also acknowledges that mood disorders, including depression and schizophrenia, contribute to the progression to severe COVID-19.1 Antiviral therapies, such as nirmatrelvir and ritonavir combination, remdesivir, and molnupiravir, and monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapies, have been used to prevent hospitalization and mortality from COVID-19 infection for individuals with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 who are at high risk of progressing to severe infection.2 Although antiviral and mAb therapies likely have mitigated many infections, poor prognoses are prevalent. It is important to identify all patients at risk of progressing to severe COVID-19 infection.
Although the CDC considers depression and schizophrenia to be risk factors for severe COVID-19 infection, the Captain James A. Lovell Federal Health Care Center (FHCC) in North Chicago, Illinois, does not, making these patients ineligible for antiviral or mAb therapies unless they have another risk factor. As a result, these patients could be at risk of severe COVID-19 infection, but might not be treated appropriately. Psychiatric diagnoses are common among veterans, with 19.7% experiencing a mental illness in 2020.3 It is imperative to determine whether depression or schizophrenia play a role in the progression of COVID-19 to expand access to individuals who are eligible for antiviral or mAb therapies.
Because COVID-19 is a novel virus, there are few studies of psychiatric disorders and COVID-19 prognosis. A 2020 case control study determined that those with a recent mental illness diagnosis were at higher risk of COVID-19 infection with worse outcomes compared with those without psychiatric diagnoses. This effect was most prevalent among individuals with depression and schizophrenia.4 However, these individuals also were found to have additional comorbidities that could have contributed to poorer outcomes. A meta-analysis determined that psychiatric disorders were associated with increased COVID-19-related mortality.5 A 2022 cohort study that included vaccinated US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) patients determined that having a psychiatric diagnosis was associated with increased incidence of breakthrough infections.6 Individuals with psychiatric conditions are thought to be at higher risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes because of poor access to care and higher incidence of untreated underlying health conditions.7 Lifestyle factors also could play a role. Because there is minimal data on COVID-19 prognosis and mental illness, further research is warranted to determine whether psychiatric diagnoses could contribute to more severe COVID-19 infections.
Methods
This was a retrospective cohort chart review study at FHCC that compared COVID-19 outcomes in individuals with depression or schizophrenia with those without these diagnoses. FHCC patients with the International Classification of Diseases code for COVID-19 (U07.1) from fiscal years 2020 to 2022 were included. We then selected patients with a depression or schizophrenia diagnosis noted in the electronic health record (EHR). These 2 patient lists were consolidated to identify every individual with a COVID-19 diagnosis and a diagnosis of depression or schizophrenia.
Patients were included if they were aged ≥ 18 years with a positive COVID-19 infection confirmed via polymerase chain reaction or blood test. Patients also had to have mild-to-moderate COVID-19 with ≥ 1 symptom such as fever, cough, sore throat, malaise, headache, muscle pain, loss of taste and smell, or shortness of breath. Patients were excluded if they had an asymptomatic infection, presented with severe COVID-19 infection, or were an FHCC employee. Severe COVID-19 was defined as having oxygen saturation < 94%, a respiratory rate > 30 breaths per minute, or supplemental oxygen requirement.
Patient EHRs were reviewed and analyzed using the VA Computerized Patient Record System and Joint Legacy Viewer. Collected data included age, medical history, use of antiviral or mAb therapy, and admission or death within 30 days of a positive COVID-19 test. The primary outcome of this study was severe COVID-19 outcomes defined as hospitalization, admission to the intensive care unit, intubation or mechanical ventilation, or death within 30 days of infection. The primary outcome was analyzed with a student t test; P < .05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
More than 5000 individuals had a COVID-19 diagnosis during the study period. Among these patients, 4530 had no depression or schizophrenia diagnosis; 1021 individuals had COVID-19 and a preexisting diagnosis of depression or schizophrenia. Among these 1021 patients, 279 charts were reviewed due to time constraints; 128 patients met exclusion criteria and 151 patients were included in the study. Of the 151 patients with COVID-19, 78 had no depression or schizophrenia and 73 patients with COVID-19 had a preexisting depression or schizophrenia diagnosis (Figure).
The 2 groups were similar at baseline. The most common risk factors for severe COVID-19 included age > 60 years, obesity, and cardiovascular disease. However, more than half of the individuals analyzed had no risk factors (Table 1). Some patients with risk factors received antiviral or mAb therapy to prevent severe COVID-19 infection; combination nirmatrelvir and ritonavir was the most common agent (Table 2). Of the 73 individuals with a psychiatric diagnosis, 67 had depression (91.8%), and 6 had schizophrenia (8.2%).
Hospitalization or death within 30 days of COVID-19 infection between patients with depression or schizophrenia and patients without these psychiatric diagnoses was not statistically significant (P = .36). Sixteen individuals were hospitalized, 8 in each group. Three individuals died within 30 days; death only occurred in patients who had depression or schizophrenia (Table 3).
Discussion
This study found that hospitalization or death within 30 days of COVID-19 infection occurred more frequently among individuals with depression or schizophrenia compared with those without these psychiatric comorbidities. However, this difference was not statistically significant.
This study had several limitations. It was a retrospective, chart review study, which relied on accurate documentation. In addition, we reviewed COVID-19 cases from fiscal years 2020 to 2022 and as a result, several viral variants were analyzed. This made it difficult to draw conclusions, especially because the omicron variant is thought to be less deadly, which may have skewed the data. Vaccinations and COVID-19 treatments became available in late 2020, which likely affected the progression to severe disease. Our study did not assess vaccination status, therefore it is unclear whether COVID-19 vaccination played a role in mitigating infection. When the pandemic began, many individuals were afraid to come to the hospital and did not receive care until they progressed to severe COVID-19, which would have excluded them from the study. Many individuals had additional comorbidities that likely impacted their COVID-19 outcomes. It is not possible to conclude if the depression or schizophrenia diagnoses were responsible for hospitalization or death within 30 days of infection or if it was because of other known risk factors. Future research is needed to address these limitations.
Conclusions
More COVID-19 hospitalizations and deaths occurred within 30 days of infection among those with depression and schizophrenia compared with individuals without these comorbidities. However, this effect was not statistically significant. Many limitations could have contributed to this finding, which should be addressed in future studies. Because the sample size was small, further research with a larger patient population is warranted to explore the association between psychiatric comorbidities such as depression and schizophrenia and COVID-19 disease progression. Future studies also could include assessment of vaccination status and exclude individuals with other high-risk comorbidities for severe COVID-19 outcomes. These studies could determine if depression and schizophrenia are correlated with worse COVID-19 outcomes and ensure that all high-risk patients are identified and treated appropriately to prevent morbidity and mortality.
Acknowledgements
Thank you to the research committee at the Captain James A. Lovell Federal Health Care Center who assisted in the completion of this project, including Shaiza Khan, PharmD, BCPS; Yinka Alaka, PharmD; and Hong-Yen Vi, PharmD, BCPS, BCCCP.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Underlying medical conditions associated with higher risk for severe COVID-19: information for healthcare professionals. Updated February 9, 2023. Accessed February 27, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care/underlyingconditions.html
2. National Institutes of Health. Therapeutic management of nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19. Updated November 2, 2023. Accessed February 27, 2024. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/management/clinical-management-of-adults/nonhospitalized-adults-therapeutic-management
3. National Alliance on Mental Illness. Mental health by the numbers. Updated April 2023. Accessed February 27, 2024. https://www.nami.org/mhstats
4. Wang Q, Xu R, Volkow ND. Increased risk of COVID-19 infection and mortality in people with mental disorders: analysis from electronic health records in the United States. World Psychiatry . 2021;20(1):124-130. doi:10.1002/wps.20806
5. Fond G, Nemani K, Etchecopar-Etchart D, et al. Association Between Mental Health Disorders and Mortality Among Patients With COVID-19 in 7 Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry . 2021;78(11):1208-1217. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.2274
6. Nishimi K, Neylan TC, Bertenthal D, Seal KH, O’Donovan A. Association of Psychiatric Disorders With Incidence of SARS-CoV-2 Breakthrough Infection Among Vaccinated Adults. JAMA Netw Open . 2022;5(4):e227287. Published 2022 Apr 1. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.7287
7. Koyama AK, Koumans EH, Sircar K, et al. Mental Health Conditions and Severe COVID-19 Outcomes after Hospitalization, United States. Emerg Infect Dis . 2022;28(7):1533-1536. doi:10.3201/eid2807.212208
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Underlying medical conditions associated with higher risk for severe COVID-19: information for healthcare professionals. Updated February 9, 2023. Accessed February 27, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care/underlyingconditions.html
2. National Institutes of Health. Therapeutic management of nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19. Updated November 2, 2023. Accessed February 27, 2024. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/management/clinical-management-of-adults/nonhospitalized-adults-therapeutic-management
3. National Alliance on Mental Illness. Mental health by the numbers. Updated April 2023. Accessed February 27, 2024. https://www.nami.org/mhstats
4. Wang Q, Xu R, Volkow ND. Increased risk of COVID-19 infection and mortality in people with mental disorders: analysis from electronic health records in the United States. World Psychiatry . 2021;20(1):124-130. doi:10.1002/wps.20806
5. Fond G, Nemani K, Etchecopar-Etchart D, et al. Association Between Mental Health Disorders and Mortality Among Patients With COVID-19 in 7 Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry . 2021;78(11):1208-1217. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.2274
6. Nishimi K, Neylan TC, Bertenthal D, Seal KH, O’Donovan A. Association of Psychiatric Disorders With Incidence of SARS-CoV-2 Breakthrough Infection Among Vaccinated Adults. JAMA Netw Open . 2022;5(4):e227287. Published 2022 Apr 1. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.7287
7. Koyama AK, Koumans EH, Sircar K, et al. Mental Health Conditions and Severe COVID-19 Outcomes after Hospitalization, United States. Emerg Infect Dis . 2022;28(7):1533-1536. doi:10.3201/eid2807.212208
AI and Suicide Prevention in Primary Care: A Q&A
Primary care physicians play a critical role in identifying patients at risk for serious mental health issues, including suicidality. But the ever-increasing demands on their clinical time can hinder the ability to identify emotional distress in time to intervene. Can artificial intelligence (AI) help?
This news organization spoke with Tom Zaubler, MD, a psychiatrist and chief medical officer of NeuroFlow, about how AI can improve the ability of primary care physicians and other clinicians to screen their patients for suicidal ideation and boost rates of treatment for mental health issues in their patients. This interview has been edited for clarity and length.
Question: How can AI help in suicide prevention and mental health screening in primary care?
Answer: Recent studies have demonstrated the potential of AI in mental health screening and suicide prevention. One method is natural language processing (NLP), which can analyze patients› journal entries for signs of suicidal thoughts or behaviors. This technology has shown promise in detecting suicidal ideation in patients who may not report such thoughts on traditional screening tools like the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9). AI can be part of an integrated approach to identify and provide support to individuals at risk for suicide or those without a psychiatric history but who may still be at risk.
Q: A recent study by [Maria] Oquendo and colleagues found that one fifth of patients who attempt suicide do not meet the criteria for a mental health disorder.
Improved screening is obviously important, but in some ways it’s not the most important part of the problem. The lack of accessibility to specialized mental health care is a critical obstacle to treating patients with acute psychiatric needs.
How can primary care doctors effectively connect patients with mental health support, given the scarcity of mental health professionals?
A: Primary care doctors can leverage technology to extend mental health support. This includes using platforms for safety screening and providing patients with immediate access to local and national resources and digital interventions. Alerts can be sent to professionals within the practice or employed by technology companies to offer immediate support, including suicide safety planning and counseling. Users can hit a button to “Find a Therapist.” Also, if they acknowledge feelings of self-harm, these keywords are detected within the app by NLP. “Urgent alerts” are then sent to clinicians who are overseeing patient care. If someone is flagged, a social worker or member of a response services team intervenes and calls the person at risk to tailor care. These interventions do not always require a psychiatrist or masters-prepared clinician but can be effectively managed by trained paraprofessionals. These staff members can provide suicide safety planning and lethal-means-restriction counseling, and can assess the need for escalation of care.
Q: How is technology likely to manifest in physician practices in the near future to support mental health care?
A: Automated screening platforms for depression and anxiety, alerts for physicians when patients screen positively, and integration with collaborative care models are a few of the ways technology will become part of clinical practice. Additionally, advanced data analytics and predictive modeling using electronic health records and claims data will help identify high-risk patients. Technologies like voice recognition and machine learning can analyze patient journals and possibly, in the future, social media feeds to detect mental health issues. These technologies aim to extend and augment the capabilities of healthcare practices, improving the identification and management of patients at risk for mental health issues.
Q: Are these technologies as effective in pediatric populations, and are there any specific challenges?
A: Technologies for mental health screening and support are effective in pediatric populations, with certain age-specific considerations and legal restrictions on technology use. For adolescents and older children comfortable with technology, digital tools can significantly impact mental health care. For younger children, technology must facilitate information-gathering from various sources, including parents and teachers. Despite challenges, technology is crucial for early identification and intervention in pediatric mental health, potentially shortening the time to diagnosis and improving outcomes.
The statistics are horrifying. One third of adolescent girls have seriously thought about suicide over the past year; 13% attempt suicide. So there’s a need in the adolescent population and in the preadolescent population, too, because there’s an 8- to 10-year lag between onset of symptoms and diagnosis of mental illness. If we can shorten that lag, you see improved performance in schools; you see decreased truancy; you see greater economic achievement and so on. It makes such a profound difference. Not to mention it saves lives. So, yes, technology is critical in a pediatric population. It exists and it’s happening right now. There are challenges, but the goal can be met.
Q: A 2014 study found that 45% of people who completed suicide visited a primary care physician in the preceding month. And only 23% of people who attempt suicide have not seen a primary care physician within the past year. What does that say about the importance of screening at the primary care level?
A: The fact that a significant percentage of individuals who die by suicide have visited a primary care physician within a month or year prior to their death underscores the critical role of primary care in suicide prevention. This highlights the potential for primary care settings to identify and intervene with individuals at risk for suicide, making the case for the importance of integrating effective mental health screenings and support technologies in primary care practices.
Q: In other words, we’re not talking about a marginal benefit.
A: No, the potential benefit is huge. The United States Preventive Services Task Force did not endorse universal screening for suicide in its 2023 recommendations; they felt — and I accept that conclusion — there wasn›t enough evidence [at the time] to really support that recommendation. I think when you talk to a lot of suicide researchers, what you will hear is that providing suicide assessments as far upstream as possible is critical, especially when you start seeing more and more research showing that 20% of the population who die by suicide are not likely to have any psychiatric pathology at all. I believe the evidence base will soon support a recommendation for universal screening for adults. I believe it is especially important to screen for suicidal ideation in kids, given the high rates of suicide in this population.
Dr. Zaubler has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: chief medical officer, NeuroFlow.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary care physicians play a critical role in identifying patients at risk for serious mental health issues, including suicidality. But the ever-increasing demands on their clinical time can hinder the ability to identify emotional distress in time to intervene. Can artificial intelligence (AI) help?
This news organization spoke with Tom Zaubler, MD, a psychiatrist and chief medical officer of NeuroFlow, about how AI can improve the ability of primary care physicians and other clinicians to screen their patients for suicidal ideation and boost rates of treatment for mental health issues in their patients. This interview has been edited for clarity and length.
Question: How can AI help in suicide prevention and mental health screening in primary care?
Answer: Recent studies have demonstrated the potential of AI in mental health screening and suicide prevention. One method is natural language processing (NLP), which can analyze patients› journal entries for signs of suicidal thoughts or behaviors. This technology has shown promise in detecting suicidal ideation in patients who may not report such thoughts on traditional screening tools like the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9). AI can be part of an integrated approach to identify and provide support to individuals at risk for suicide or those without a psychiatric history but who may still be at risk.
Q: A recent study by [Maria] Oquendo and colleagues found that one fifth of patients who attempt suicide do not meet the criteria for a mental health disorder.
Improved screening is obviously important, but in some ways it’s not the most important part of the problem. The lack of accessibility to specialized mental health care is a critical obstacle to treating patients with acute psychiatric needs.
How can primary care doctors effectively connect patients with mental health support, given the scarcity of mental health professionals?
A: Primary care doctors can leverage technology to extend mental health support. This includes using platforms for safety screening and providing patients with immediate access to local and national resources and digital interventions. Alerts can be sent to professionals within the practice or employed by technology companies to offer immediate support, including suicide safety planning and counseling. Users can hit a button to “Find a Therapist.” Also, if they acknowledge feelings of self-harm, these keywords are detected within the app by NLP. “Urgent alerts” are then sent to clinicians who are overseeing patient care. If someone is flagged, a social worker or member of a response services team intervenes and calls the person at risk to tailor care. These interventions do not always require a psychiatrist or masters-prepared clinician but can be effectively managed by trained paraprofessionals. These staff members can provide suicide safety planning and lethal-means-restriction counseling, and can assess the need for escalation of care.
Q: How is technology likely to manifest in physician practices in the near future to support mental health care?
A: Automated screening platforms for depression and anxiety, alerts for physicians when patients screen positively, and integration with collaborative care models are a few of the ways technology will become part of clinical practice. Additionally, advanced data analytics and predictive modeling using electronic health records and claims data will help identify high-risk patients. Technologies like voice recognition and machine learning can analyze patient journals and possibly, in the future, social media feeds to detect mental health issues. These technologies aim to extend and augment the capabilities of healthcare practices, improving the identification and management of patients at risk for mental health issues.
Q: Are these technologies as effective in pediatric populations, and are there any specific challenges?
A: Technologies for mental health screening and support are effective in pediatric populations, with certain age-specific considerations and legal restrictions on technology use. For adolescents and older children comfortable with technology, digital tools can significantly impact mental health care. For younger children, technology must facilitate information-gathering from various sources, including parents and teachers. Despite challenges, technology is crucial for early identification and intervention in pediatric mental health, potentially shortening the time to diagnosis and improving outcomes.
The statistics are horrifying. One third of adolescent girls have seriously thought about suicide over the past year; 13% attempt suicide. So there’s a need in the adolescent population and in the preadolescent population, too, because there’s an 8- to 10-year lag between onset of symptoms and diagnosis of mental illness. If we can shorten that lag, you see improved performance in schools; you see decreased truancy; you see greater economic achievement and so on. It makes such a profound difference. Not to mention it saves lives. So, yes, technology is critical in a pediatric population. It exists and it’s happening right now. There are challenges, but the goal can be met.
Q: A 2014 study found that 45% of people who completed suicide visited a primary care physician in the preceding month. And only 23% of people who attempt suicide have not seen a primary care physician within the past year. What does that say about the importance of screening at the primary care level?
A: The fact that a significant percentage of individuals who die by suicide have visited a primary care physician within a month or year prior to their death underscores the critical role of primary care in suicide prevention. This highlights the potential for primary care settings to identify and intervene with individuals at risk for suicide, making the case for the importance of integrating effective mental health screenings and support technologies in primary care practices.
Q: In other words, we’re not talking about a marginal benefit.
A: No, the potential benefit is huge. The United States Preventive Services Task Force did not endorse universal screening for suicide in its 2023 recommendations; they felt — and I accept that conclusion — there wasn›t enough evidence [at the time] to really support that recommendation. I think when you talk to a lot of suicide researchers, what you will hear is that providing suicide assessments as far upstream as possible is critical, especially when you start seeing more and more research showing that 20% of the population who die by suicide are not likely to have any psychiatric pathology at all. I believe the evidence base will soon support a recommendation for universal screening for adults. I believe it is especially important to screen for suicidal ideation in kids, given the high rates of suicide in this population.
Dr. Zaubler has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: chief medical officer, NeuroFlow.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary care physicians play a critical role in identifying patients at risk for serious mental health issues, including suicidality. But the ever-increasing demands on their clinical time can hinder the ability to identify emotional distress in time to intervene. Can artificial intelligence (AI) help?
This news organization spoke with Tom Zaubler, MD, a psychiatrist and chief medical officer of NeuroFlow, about how AI can improve the ability of primary care physicians and other clinicians to screen their patients for suicidal ideation and boost rates of treatment for mental health issues in their patients. This interview has been edited for clarity and length.
Question: How can AI help in suicide prevention and mental health screening in primary care?
Answer: Recent studies have demonstrated the potential of AI in mental health screening and suicide prevention. One method is natural language processing (NLP), which can analyze patients› journal entries for signs of suicidal thoughts or behaviors. This technology has shown promise in detecting suicidal ideation in patients who may not report such thoughts on traditional screening tools like the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9). AI can be part of an integrated approach to identify and provide support to individuals at risk for suicide or those without a psychiatric history but who may still be at risk.
Q: A recent study by [Maria] Oquendo and colleagues found that one fifth of patients who attempt suicide do not meet the criteria for a mental health disorder.
Improved screening is obviously important, but in some ways it’s not the most important part of the problem. The lack of accessibility to specialized mental health care is a critical obstacle to treating patients with acute psychiatric needs.
How can primary care doctors effectively connect patients with mental health support, given the scarcity of mental health professionals?
A: Primary care doctors can leverage technology to extend mental health support. This includes using platforms for safety screening and providing patients with immediate access to local and national resources and digital interventions. Alerts can be sent to professionals within the practice or employed by technology companies to offer immediate support, including suicide safety planning and counseling. Users can hit a button to “Find a Therapist.” Also, if they acknowledge feelings of self-harm, these keywords are detected within the app by NLP. “Urgent alerts” are then sent to clinicians who are overseeing patient care. If someone is flagged, a social worker or member of a response services team intervenes and calls the person at risk to tailor care. These interventions do not always require a psychiatrist or masters-prepared clinician but can be effectively managed by trained paraprofessionals. These staff members can provide suicide safety planning and lethal-means-restriction counseling, and can assess the need for escalation of care.
Q: How is technology likely to manifest in physician practices in the near future to support mental health care?
A: Automated screening platforms for depression and anxiety, alerts for physicians when patients screen positively, and integration with collaborative care models are a few of the ways technology will become part of clinical practice. Additionally, advanced data analytics and predictive modeling using electronic health records and claims data will help identify high-risk patients. Technologies like voice recognition and machine learning can analyze patient journals and possibly, in the future, social media feeds to detect mental health issues. These technologies aim to extend and augment the capabilities of healthcare practices, improving the identification and management of patients at risk for mental health issues.
Q: Are these technologies as effective in pediatric populations, and are there any specific challenges?
A: Technologies for mental health screening and support are effective in pediatric populations, with certain age-specific considerations and legal restrictions on technology use. For adolescents and older children comfortable with technology, digital tools can significantly impact mental health care. For younger children, technology must facilitate information-gathering from various sources, including parents and teachers. Despite challenges, technology is crucial for early identification and intervention in pediatric mental health, potentially shortening the time to diagnosis and improving outcomes.
The statistics are horrifying. One third of adolescent girls have seriously thought about suicide over the past year; 13% attempt suicide. So there’s a need in the adolescent population and in the preadolescent population, too, because there’s an 8- to 10-year lag between onset of symptoms and diagnosis of mental illness. If we can shorten that lag, you see improved performance in schools; you see decreased truancy; you see greater economic achievement and so on. It makes such a profound difference. Not to mention it saves lives. So, yes, technology is critical in a pediatric population. It exists and it’s happening right now. There are challenges, but the goal can be met.
Q: A 2014 study found that 45% of people who completed suicide visited a primary care physician in the preceding month. And only 23% of people who attempt suicide have not seen a primary care physician within the past year. What does that say about the importance of screening at the primary care level?
A: The fact that a significant percentage of individuals who die by suicide have visited a primary care physician within a month or year prior to their death underscores the critical role of primary care in suicide prevention. This highlights the potential for primary care settings to identify and intervene with individuals at risk for suicide, making the case for the importance of integrating effective mental health screenings and support technologies in primary care practices.
Q: In other words, we’re not talking about a marginal benefit.
A: No, the potential benefit is huge. The United States Preventive Services Task Force did not endorse universal screening for suicide in its 2023 recommendations; they felt — and I accept that conclusion — there wasn›t enough evidence [at the time] to really support that recommendation. I think when you talk to a lot of suicide researchers, what you will hear is that providing suicide assessments as far upstream as possible is critical, especially when you start seeing more and more research showing that 20% of the population who die by suicide are not likely to have any psychiatric pathology at all. I believe the evidence base will soon support a recommendation for universal screening for adults. I believe it is especially important to screen for suicidal ideation in kids, given the high rates of suicide in this population.
Dr. Zaubler has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: chief medical officer, NeuroFlow.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Perinatal Mood and Anxiety Disorder Increasing Rapidly
The number of women with perinatal mood and anxiety disorder (PMAD) has spiked sharply in the United States. A new study explores trends by state and time period.
Between 2008 and 2020, in a national cohort of 750,004 commercially insured women with a live birth, nearly 1 in 5 (144,037 [19.2%]) were diagnosed with PMAD, according to a paper published in Health Affairs. PMAD diagnoses among privately insured women increased by 93.3% over those years, wrote lead author Kara Zivin, PhD, of the University of Michigan, Veterans Affairs Ann Arbor Healthcare System, and colleagues.
PMAD describes a spectrum of emotional complications with mild to severe symptoms that can affect women while pregnant and through the first year after giving birth.
The total number of perinatal women decreased from a high of 64,842 in 2008 to a low of 52,479 in 2020, a 19.1% decrease, but over the same time, women with diagnosed PMAD increased 56.4% from 9,520 in 2008 to 14,890 in 2020. Prevalence of PMAD doubled from 1,468 per 10,000 deliveries to 2,837 per 10,000 deliveries in 2020, according to the analysis.
Differences by State
Increases differed substantially by state. Though average annual changes across all states reached 109 additional PMAD diagnoses per 10,000 deliveries, Iowa had the greatest increase with an additional 163 PMAD diagnoses per 10,000 deliveries annually. New Mexico had the smallest annual growth, at an additional 49 per 10,000 deliveries.
The increases were accompanied by maternal health improvement efforts. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) required insurance companies to cover maternity and preventive services, which likely increased PMAD screening and detection, the researchers noted.
“Diagnosis of PMAD is rising due to increased awareness and in all likelihood, decrease in stigma, but availability of providers is so challenging,” said Lee S. Cohen, MD, who was not part of the study. Dr. Cohen is director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health and Perinatal and Reproductive Psychiatry at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. “The navigation to providers by women who are suffering is beyond challenging,” he said.
The authors reported that all states except Vermont saw increasing rates of PMAD diagnoses post-ACA vs. pre-ACA. The researchers also found that relative to the period from 2008 to 2014, psychotherapy rates continued rising from 2015 to 2020 and suicidality (suicidal ideation or self-harm diagnoses) rates declined.
States’ Suicidality Rates Vary Widely
“Overall, access to psychotherapy may have stemmed suicidality despite increasing PMAD diagnoses. But although more PMAD diagnoses may have led to increased psychotherapy, therapy access depends on provider availability, which varies by geographic region and insurance coverage network,” the authors wrote.
Suicidality rates differed greatly by state. Louisiana’s annual rate of increase was greatest, at 22 per 10,000 while Maryland had the greatest negative annual rate of change, at −15 per 10,000 deliveries, the authors explained.
“Observed trends in PMAD diagnoses among privately insured people during 2008-2020 and in associated suicidality and psychotherapy use suggest an increasingly rapid worsening of US maternal mental health,” the authors wrote.
The authors noted that this study did not include those on public insurance, a group that may experience disproportionate maternal morbidity and mortality burden, and urged that future studies include them.
Strengths of Study
Kimberly McKee, PhD, MPH, assistant professor in the department of family medicine at University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, who was not part of this research, said this paper gives a broader look than prior work because it includes the year before and after birth, rather than delivery and hospitalization.
“It’s really important to look out at least 12 months postpartum,” she noted.
Another strength is that the study was able to look at use of services such as psychotherapy before and post ACA. She noted the increased use of psychotherapy and the decrease in suicidal ideation was an association, but said, “I think it’s reasonable to assume that there was a benefit.”
She noted that these data go through 2020 and the COVID-19 pandemic has even further stressed the healthcare system, which could affect these numbers.
Primary Care’s Role
“The opportunity for primary care to really be the medical home for reproductive-age women is key here,” Dr. McKee said, adding that primary care can provide the continuity if women go off and on insurance around pregnancy and make sure the women get follow-up care and referrals to specialty care.
Models that integrate behavioral health and primary care are particularly promising, she said. Inclusion of social workers at the point of care can also help meet needs regarding social determinants of health.
Telehealth is another avenue for expansion extending the reach for following perinatal women, she said. “Using every tool we have to reach individuals where they are can allow for more frequent check-ins, which is really important here.”
Dr. McKee said the paper highlights an important reality: Mental health is a leading cause and contributor to maternal mortality, which “is 100% preventable.” Yet, current literature continues to show increases.
“This is a fairly common problem that affects not just women, but the fetus, their children, their families,” she noted.
The authors and Dr. Cohen and Dr. McKee reported no relevant financial relationships.
The number of women with perinatal mood and anxiety disorder (PMAD) has spiked sharply in the United States. A new study explores trends by state and time period.
Between 2008 and 2020, in a national cohort of 750,004 commercially insured women with a live birth, nearly 1 in 5 (144,037 [19.2%]) were diagnosed with PMAD, according to a paper published in Health Affairs. PMAD diagnoses among privately insured women increased by 93.3% over those years, wrote lead author Kara Zivin, PhD, of the University of Michigan, Veterans Affairs Ann Arbor Healthcare System, and colleagues.
PMAD describes a spectrum of emotional complications with mild to severe symptoms that can affect women while pregnant and through the first year after giving birth.
The total number of perinatal women decreased from a high of 64,842 in 2008 to a low of 52,479 in 2020, a 19.1% decrease, but over the same time, women with diagnosed PMAD increased 56.4% from 9,520 in 2008 to 14,890 in 2020. Prevalence of PMAD doubled from 1,468 per 10,000 deliveries to 2,837 per 10,000 deliveries in 2020, according to the analysis.
Differences by State
Increases differed substantially by state. Though average annual changes across all states reached 109 additional PMAD diagnoses per 10,000 deliveries, Iowa had the greatest increase with an additional 163 PMAD diagnoses per 10,000 deliveries annually. New Mexico had the smallest annual growth, at an additional 49 per 10,000 deliveries.
The increases were accompanied by maternal health improvement efforts. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) required insurance companies to cover maternity and preventive services, which likely increased PMAD screening and detection, the researchers noted.
“Diagnosis of PMAD is rising due to increased awareness and in all likelihood, decrease in stigma, but availability of providers is so challenging,” said Lee S. Cohen, MD, who was not part of the study. Dr. Cohen is director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health and Perinatal and Reproductive Psychiatry at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. “The navigation to providers by women who are suffering is beyond challenging,” he said.
The authors reported that all states except Vermont saw increasing rates of PMAD diagnoses post-ACA vs. pre-ACA. The researchers also found that relative to the period from 2008 to 2014, psychotherapy rates continued rising from 2015 to 2020 and suicidality (suicidal ideation or self-harm diagnoses) rates declined.
States’ Suicidality Rates Vary Widely
“Overall, access to psychotherapy may have stemmed suicidality despite increasing PMAD diagnoses. But although more PMAD diagnoses may have led to increased psychotherapy, therapy access depends on provider availability, which varies by geographic region and insurance coverage network,” the authors wrote.
Suicidality rates differed greatly by state. Louisiana’s annual rate of increase was greatest, at 22 per 10,000 while Maryland had the greatest negative annual rate of change, at −15 per 10,000 deliveries, the authors explained.
“Observed trends in PMAD diagnoses among privately insured people during 2008-2020 and in associated suicidality and psychotherapy use suggest an increasingly rapid worsening of US maternal mental health,” the authors wrote.
The authors noted that this study did not include those on public insurance, a group that may experience disproportionate maternal morbidity and mortality burden, and urged that future studies include them.
Strengths of Study
Kimberly McKee, PhD, MPH, assistant professor in the department of family medicine at University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, who was not part of this research, said this paper gives a broader look than prior work because it includes the year before and after birth, rather than delivery and hospitalization.
“It’s really important to look out at least 12 months postpartum,” she noted.
Another strength is that the study was able to look at use of services such as psychotherapy before and post ACA. She noted the increased use of psychotherapy and the decrease in suicidal ideation was an association, but said, “I think it’s reasonable to assume that there was a benefit.”
She noted that these data go through 2020 and the COVID-19 pandemic has even further stressed the healthcare system, which could affect these numbers.
Primary Care’s Role
“The opportunity for primary care to really be the medical home for reproductive-age women is key here,” Dr. McKee said, adding that primary care can provide the continuity if women go off and on insurance around pregnancy and make sure the women get follow-up care and referrals to specialty care.
Models that integrate behavioral health and primary care are particularly promising, she said. Inclusion of social workers at the point of care can also help meet needs regarding social determinants of health.
Telehealth is another avenue for expansion extending the reach for following perinatal women, she said. “Using every tool we have to reach individuals where they are can allow for more frequent check-ins, which is really important here.”
Dr. McKee said the paper highlights an important reality: Mental health is a leading cause and contributor to maternal mortality, which “is 100% preventable.” Yet, current literature continues to show increases.
“This is a fairly common problem that affects not just women, but the fetus, their children, their families,” she noted.
The authors and Dr. Cohen and Dr. McKee reported no relevant financial relationships.
The number of women with perinatal mood and anxiety disorder (PMAD) has spiked sharply in the United States. A new study explores trends by state and time period.
Between 2008 and 2020, in a national cohort of 750,004 commercially insured women with a live birth, nearly 1 in 5 (144,037 [19.2%]) were diagnosed with PMAD, according to a paper published in Health Affairs. PMAD diagnoses among privately insured women increased by 93.3% over those years, wrote lead author Kara Zivin, PhD, of the University of Michigan, Veterans Affairs Ann Arbor Healthcare System, and colleagues.
PMAD describes a spectrum of emotional complications with mild to severe symptoms that can affect women while pregnant and through the first year after giving birth.
The total number of perinatal women decreased from a high of 64,842 in 2008 to a low of 52,479 in 2020, a 19.1% decrease, but over the same time, women with diagnosed PMAD increased 56.4% from 9,520 in 2008 to 14,890 in 2020. Prevalence of PMAD doubled from 1,468 per 10,000 deliveries to 2,837 per 10,000 deliveries in 2020, according to the analysis.
Differences by State
Increases differed substantially by state. Though average annual changes across all states reached 109 additional PMAD diagnoses per 10,000 deliveries, Iowa had the greatest increase with an additional 163 PMAD diagnoses per 10,000 deliveries annually. New Mexico had the smallest annual growth, at an additional 49 per 10,000 deliveries.
The increases were accompanied by maternal health improvement efforts. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) required insurance companies to cover maternity and preventive services, which likely increased PMAD screening and detection, the researchers noted.
“Diagnosis of PMAD is rising due to increased awareness and in all likelihood, decrease in stigma, but availability of providers is so challenging,” said Lee S. Cohen, MD, who was not part of the study. Dr. Cohen is director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health and Perinatal and Reproductive Psychiatry at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. “The navigation to providers by women who are suffering is beyond challenging,” he said.
The authors reported that all states except Vermont saw increasing rates of PMAD diagnoses post-ACA vs. pre-ACA. The researchers also found that relative to the period from 2008 to 2014, psychotherapy rates continued rising from 2015 to 2020 and suicidality (suicidal ideation or self-harm diagnoses) rates declined.
States’ Suicidality Rates Vary Widely
“Overall, access to psychotherapy may have stemmed suicidality despite increasing PMAD diagnoses. But although more PMAD diagnoses may have led to increased psychotherapy, therapy access depends on provider availability, which varies by geographic region and insurance coverage network,” the authors wrote.
Suicidality rates differed greatly by state. Louisiana’s annual rate of increase was greatest, at 22 per 10,000 while Maryland had the greatest negative annual rate of change, at −15 per 10,000 deliveries, the authors explained.
“Observed trends in PMAD diagnoses among privately insured people during 2008-2020 and in associated suicidality and psychotherapy use suggest an increasingly rapid worsening of US maternal mental health,” the authors wrote.
The authors noted that this study did not include those on public insurance, a group that may experience disproportionate maternal morbidity and mortality burden, and urged that future studies include them.
Strengths of Study
Kimberly McKee, PhD, MPH, assistant professor in the department of family medicine at University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, who was not part of this research, said this paper gives a broader look than prior work because it includes the year before and after birth, rather than delivery and hospitalization.
“It’s really important to look out at least 12 months postpartum,” she noted.
Another strength is that the study was able to look at use of services such as psychotherapy before and post ACA. She noted the increased use of psychotherapy and the decrease in suicidal ideation was an association, but said, “I think it’s reasonable to assume that there was a benefit.”
She noted that these data go through 2020 and the COVID-19 pandemic has even further stressed the healthcare system, which could affect these numbers.
Primary Care’s Role
“The opportunity for primary care to really be the medical home for reproductive-age women is key here,” Dr. McKee said, adding that primary care can provide the continuity if women go off and on insurance around pregnancy and make sure the women get follow-up care and referrals to specialty care.
Models that integrate behavioral health and primary care are particularly promising, she said. Inclusion of social workers at the point of care can also help meet needs regarding social determinants of health.
Telehealth is another avenue for expansion extending the reach for following perinatal women, she said. “Using every tool we have to reach individuals where they are can allow for more frequent check-ins, which is really important here.”
Dr. McKee said the paper highlights an important reality: Mental health is a leading cause and contributor to maternal mortality, which “is 100% preventable.” Yet, current literature continues to show increases.
“This is a fairly common problem that affects not just women, but the fetus, their children, their families,” she noted.
The authors and Dr. Cohen and Dr. McKee reported no relevant financial relationships.
FROM HEALTH AFFAIRS
Childhood Adversity Robustly Linked to Adult Mental Illness
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) are associated with a significantly increased risk for adult depressive, anxiety, and stress-related disorders, new data from a large registry study of twins showed.
Researchers found that each additional adverse event placed children at a 52% greater risk for a psychiatric disorder as an adult, with sexual abuse associated with the greatest risk.
The findings showed that the association held even after controlling for shared genetic and environmental factors.
The results suggested that “interventions targeting ACEs, including primary prevention and enhanced access to evidence-based trauma therapies to individuals who experienced ACEs, may be associated with reduced risk of future psychopathology,” the investigators, with first author Hilda Björk Daníelsdóttir, MSc, of the University of Iceland, Reykjavik, Iceland, wrote.
The findings were published online on March 6 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Dose-Dependent Effect
Previous research has shown a robust link between childhood abuse and an increased risk for psychiatric disorders in adulthood, but evidence of this association in studies that adjust for familial confounding is “completely lacking,” the investigators wrote.
To learn more about how genetic factors may affect the relationship between ACEs and later psychiatric diagnoses, the investigators used data from the nationwide Swedish Twin Registry, which includes data on more than 25,000 identical and nonidentical twins.
The twin registry is linked to the Swedish National Patient Registry, which includes information on inpatient or outpatient psychiatric diagnoses after age 19.
The twins responded to a large web-based questionnaire about past-week depressive symptoms as a measure of current mental health and distinct types of ACEs including family violence, emotional abuse or neglect, physical neglect, physical abuse, sexual abuse, rape, and hate crime.
Three birth cohorts from the twin registry were surveyed between 2005 and 2016 and followed up in the national registry from age 19 until the end of 2016.
Among the sample of 25,000 twin pairs (15,000 female; mean age at assessment, 29 years), 9750 (39%) participants reported exposure to at least one ACE, while 2000 (8%) reported exposure to three or more ACEs. Most respondents — 61% — reported no ACE exposure.
More than 2300 participants received a psychiatric diagnosis as an adult. The incidence of any psychiatric disorder increased from 503 individuals (6.4%) among participants without any ACEs to 993 individuals (24.6%) among those reporting three or more.
At the cohort level, a greater number of ACEs was associated with increased odds of any psychiatric disorder in a dose-dependent manner, the investigators noted (odds ratio [OR], 1.52; 95% CI, 1.48-1.57).
Untangling Genes and Environment
To determine how much of the increased risk for adult mental illness is due to ACEs and how much can be attributed to genetics and environment, the researchers focused on twin pairs where one had exposure to one type of ACEs and the other did not. This analysis revealed that the association remained but was attenuated. In identical twins, the effect of each ACE raised the odds of having a psychiatric condition by 20% (1.20; 95% CI, 1.02-1.40), and for nonidentical twins, the odds increased by 29% (1.29; 95% CI, 1.14-1.47).
The weakening of the risk “suggests that familial confounding contributed to the association between ACEs and adult mental health outcomes,” the authors wrote.
Of all the ACEs, sexual abuse carried the highest risk for adult psychiatric disorders. Children who were exposed to sexual abuse, compared with those who were not, had up to a 200% higher risk for any psychiatric disorder in the following comparisons: Full cohort (OR, 3.09; 95% CI, 2.68-3.56), dizygotic twin pairs (OR, 2.10; 95% CI, 1.33-3.32), and monozygotic twin pairs (1.80; 95% CI, 1.04-3.11).
“Our results demonstrated that familial factors contributed to a lesser extent to the association between sexual abuse and adult psychiatric disorders,” the authors wrote.
One major limitation of the study was that ACEs were based on retrospective report and thus may be subject to recall bias. Also, the findings cannot be generalized to other countries or cultures.
The study was funded by the European Research Council, the Icelandic Center for Research, and the European Union Horizon 2020. Disclosures are noted in the original article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) are associated with a significantly increased risk for adult depressive, anxiety, and stress-related disorders, new data from a large registry study of twins showed.
Researchers found that each additional adverse event placed children at a 52% greater risk for a psychiatric disorder as an adult, with sexual abuse associated with the greatest risk.
The findings showed that the association held even after controlling for shared genetic and environmental factors.
The results suggested that “interventions targeting ACEs, including primary prevention and enhanced access to evidence-based trauma therapies to individuals who experienced ACEs, may be associated with reduced risk of future psychopathology,” the investigators, with first author Hilda Björk Daníelsdóttir, MSc, of the University of Iceland, Reykjavik, Iceland, wrote.
The findings were published online on March 6 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Dose-Dependent Effect
Previous research has shown a robust link between childhood abuse and an increased risk for psychiatric disorders in adulthood, but evidence of this association in studies that adjust for familial confounding is “completely lacking,” the investigators wrote.
To learn more about how genetic factors may affect the relationship between ACEs and later psychiatric diagnoses, the investigators used data from the nationwide Swedish Twin Registry, which includes data on more than 25,000 identical and nonidentical twins.
The twin registry is linked to the Swedish National Patient Registry, which includes information on inpatient or outpatient psychiatric diagnoses after age 19.
The twins responded to a large web-based questionnaire about past-week depressive symptoms as a measure of current mental health and distinct types of ACEs including family violence, emotional abuse or neglect, physical neglect, physical abuse, sexual abuse, rape, and hate crime.
Three birth cohorts from the twin registry were surveyed between 2005 and 2016 and followed up in the national registry from age 19 until the end of 2016.
Among the sample of 25,000 twin pairs (15,000 female; mean age at assessment, 29 years), 9750 (39%) participants reported exposure to at least one ACE, while 2000 (8%) reported exposure to three or more ACEs. Most respondents — 61% — reported no ACE exposure.
More than 2300 participants received a psychiatric diagnosis as an adult. The incidence of any psychiatric disorder increased from 503 individuals (6.4%) among participants without any ACEs to 993 individuals (24.6%) among those reporting three or more.
At the cohort level, a greater number of ACEs was associated with increased odds of any psychiatric disorder in a dose-dependent manner, the investigators noted (odds ratio [OR], 1.52; 95% CI, 1.48-1.57).
Untangling Genes and Environment
To determine how much of the increased risk for adult mental illness is due to ACEs and how much can be attributed to genetics and environment, the researchers focused on twin pairs where one had exposure to one type of ACEs and the other did not. This analysis revealed that the association remained but was attenuated. In identical twins, the effect of each ACE raised the odds of having a psychiatric condition by 20% (1.20; 95% CI, 1.02-1.40), and for nonidentical twins, the odds increased by 29% (1.29; 95% CI, 1.14-1.47).
The weakening of the risk “suggests that familial confounding contributed to the association between ACEs and adult mental health outcomes,” the authors wrote.
Of all the ACEs, sexual abuse carried the highest risk for adult psychiatric disorders. Children who were exposed to sexual abuse, compared with those who were not, had up to a 200% higher risk for any psychiatric disorder in the following comparisons: Full cohort (OR, 3.09; 95% CI, 2.68-3.56), dizygotic twin pairs (OR, 2.10; 95% CI, 1.33-3.32), and monozygotic twin pairs (1.80; 95% CI, 1.04-3.11).
“Our results demonstrated that familial factors contributed to a lesser extent to the association between sexual abuse and adult psychiatric disorders,” the authors wrote.
One major limitation of the study was that ACEs were based on retrospective report and thus may be subject to recall bias. Also, the findings cannot be generalized to other countries or cultures.
The study was funded by the European Research Council, the Icelandic Center for Research, and the European Union Horizon 2020. Disclosures are noted in the original article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) are associated with a significantly increased risk for adult depressive, anxiety, and stress-related disorders, new data from a large registry study of twins showed.
Researchers found that each additional adverse event placed children at a 52% greater risk for a psychiatric disorder as an adult, with sexual abuse associated with the greatest risk.
The findings showed that the association held even after controlling for shared genetic and environmental factors.
The results suggested that “interventions targeting ACEs, including primary prevention and enhanced access to evidence-based trauma therapies to individuals who experienced ACEs, may be associated with reduced risk of future psychopathology,” the investigators, with first author Hilda Björk Daníelsdóttir, MSc, of the University of Iceland, Reykjavik, Iceland, wrote.
The findings were published online on March 6 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Dose-Dependent Effect
Previous research has shown a robust link between childhood abuse and an increased risk for psychiatric disorders in adulthood, but evidence of this association in studies that adjust for familial confounding is “completely lacking,” the investigators wrote.
To learn more about how genetic factors may affect the relationship between ACEs and later psychiatric diagnoses, the investigators used data from the nationwide Swedish Twin Registry, which includes data on more than 25,000 identical and nonidentical twins.
The twin registry is linked to the Swedish National Patient Registry, which includes information on inpatient or outpatient psychiatric diagnoses after age 19.
The twins responded to a large web-based questionnaire about past-week depressive symptoms as a measure of current mental health and distinct types of ACEs including family violence, emotional abuse or neglect, physical neglect, physical abuse, sexual abuse, rape, and hate crime.
Three birth cohorts from the twin registry were surveyed between 2005 and 2016 and followed up in the national registry from age 19 until the end of 2016.
Among the sample of 25,000 twin pairs (15,000 female; mean age at assessment, 29 years), 9750 (39%) participants reported exposure to at least one ACE, while 2000 (8%) reported exposure to three or more ACEs. Most respondents — 61% — reported no ACE exposure.
More than 2300 participants received a psychiatric diagnosis as an adult. The incidence of any psychiatric disorder increased from 503 individuals (6.4%) among participants without any ACEs to 993 individuals (24.6%) among those reporting three or more.
At the cohort level, a greater number of ACEs was associated with increased odds of any psychiatric disorder in a dose-dependent manner, the investigators noted (odds ratio [OR], 1.52; 95% CI, 1.48-1.57).
Untangling Genes and Environment
To determine how much of the increased risk for adult mental illness is due to ACEs and how much can be attributed to genetics and environment, the researchers focused on twin pairs where one had exposure to one type of ACEs and the other did not. This analysis revealed that the association remained but was attenuated. In identical twins, the effect of each ACE raised the odds of having a psychiatric condition by 20% (1.20; 95% CI, 1.02-1.40), and for nonidentical twins, the odds increased by 29% (1.29; 95% CI, 1.14-1.47).
The weakening of the risk “suggests that familial confounding contributed to the association between ACEs and adult mental health outcomes,” the authors wrote.
Of all the ACEs, sexual abuse carried the highest risk for adult psychiatric disorders. Children who were exposed to sexual abuse, compared with those who were not, had up to a 200% higher risk for any psychiatric disorder in the following comparisons: Full cohort (OR, 3.09; 95% CI, 2.68-3.56), dizygotic twin pairs (OR, 2.10; 95% CI, 1.33-3.32), and monozygotic twin pairs (1.80; 95% CI, 1.04-3.11).
“Our results demonstrated that familial factors contributed to a lesser extent to the association between sexual abuse and adult psychiatric disorders,” the authors wrote.
One major limitation of the study was that ACEs were based on retrospective report and thus may be subject to recall bias. Also, the findings cannot be generalized to other countries or cultures.
The study was funded by the European Research Council, the Icelandic Center for Research, and the European Union Horizon 2020. Disclosures are noted in the original article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Mental Health and Slow Concussion Recovery
Those of you who are regular readers of Letters from Maine have probably noticed that concussion is one of my favorite topics. The explanation for this perseveration is personal and may lie in the fact that I played two contact sports in college. In high school we still wore leather helmets and in college the lacrosse helmets were constructed of plastic-coated cardboard. I can recall just a few of what might be now labeled as sports-related concussions. Ironically, my only loss of consciousness came on the first dinner date with the woman who would eventually become my wife. A hypotensive episode resulting from the combination of sweat loss (2 hours of basketball) and blood loss from selling some platelets earlier in the day (to pay for the dinner) led to the unfortunate meeting of my head and the beautifully tiled floor at the restaurant.
Postconcussion Recovery
The phenomenon of delayed symptomatic recovery has been a particular interest of mine. Within the last 12 months I have written about an excellent companion commentary in Pediatricsby Talin Babikian PhD, a psychologist at University of California, Los Angeles, in which he urges us to “Consider the comorbidities or premorbidities,” including, among others, anxiety and/or depression, post-traumatic stress, and poor sleep when we are faced with a patient who is slow in shedding his postconcussion symptoms. A short 6 months after reading Dr. Babikian’s prescient commentary, I have encountered some evidence supporting his advice.
Investigators at the Sports Medicine and Performance Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia have recently published a study in which they have found “Preexisting mental health diagnoses are associated with greater postinjury emotional symptom burden and longer concussion recovery in a dose-response fashion.” In their prospective study of over 3000 children and adolescents, they found that, although patients with more mental health diagnoses were at greater risk of increased emotional symptoms after concussion, “Children and adolescents with any preexisting mental health diagnosis took longer to recover.”
Female patients and those with abnormal visio-vestibular test results at the initial postinjury evaluation took longer to recover, although boys with prolonged recovery had more emotional symptoms. In general, patients with preexisting mental health diagnoses returned to exercise later, a known factor in delayed concussion recovery.
Making Sense of It All
There are a couple of ways to look at this paper’s findings. The first is through the lens that focuses on the population of children and adolescents who have known mental health conditions. If our patient has a mental health diagnosis, we shouldn’t be surprised that he/she is taking longer to recover from his/her concussion and is experiencing an increase in symptoms. Most of us probably suspected this already. However, we should be particularly aware of this phenomenon if the patient is male.
The other perspective is probably more valuable to us as primary care physicians. Even one diagnosis so subtle that we may have overlooked it is likely to slow his/her progress toward recovery. And, of course, it may be that injury has triggered an underlying condition that none — not even the most astute diagnostician — would have found without a focused investigation.
I can’t leave this subject without wondering whether the findings in this paper should be extrapolated to other conditions of delayed recovery, including Lyme disease and COVID 19. Patients with these conditions are understandably resistant to the suggestion that their mental health may be contributing to the situation. Too many have been told too often it is “all in their head.” However, I think we as clinicians should keep open minds when symptoms are resolving more slowly than we would expect.
Finally, in their conclusion the authors of this paper reinforce a principle that has unfortunately taken some of us a while to accept. Early introduction of symptom-limited exercise should be a standard of postconcussion management, especially for patients with a mental health diagnosis.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Those of you who are regular readers of Letters from Maine have probably noticed that concussion is one of my favorite topics. The explanation for this perseveration is personal and may lie in the fact that I played two contact sports in college. In high school we still wore leather helmets and in college the lacrosse helmets were constructed of plastic-coated cardboard. I can recall just a few of what might be now labeled as sports-related concussions. Ironically, my only loss of consciousness came on the first dinner date with the woman who would eventually become my wife. A hypotensive episode resulting from the combination of sweat loss (2 hours of basketball) and blood loss from selling some platelets earlier in the day (to pay for the dinner) led to the unfortunate meeting of my head and the beautifully tiled floor at the restaurant.
Postconcussion Recovery
The phenomenon of delayed symptomatic recovery has been a particular interest of mine. Within the last 12 months I have written about an excellent companion commentary in Pediatricsby Talin Babikian PhD, a psychologist at University of California, Los Angeles, in which he urges us to “Consider the comorbidities or premorbidities,” including, among others, anxiety and/or depression, post-traumatic stress, and poor sleep when we are faced with a patient who is slow in shedding his postconcussion symptoms. A short 6 months after reading Dr. Babikian’s prescient commentary, I have encountered some evidence supporting his advice.
Investigators at the Sports Medicine and Performance Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia have recently published a study in which they have found “Preexisting mental health diagnoses are associated with greater postinjury emotional symptom burden and longer concussion recovery in a dose-response fashion.” In their prospective study of over 3000 children and adolescents, they found that, although patients with more mental health diagnoses were at greater risk of increased emotional symptoms after concussion, “Children and adolescents with any preexisting mental health diagnosis took longer to recover.”
Female patients and those with abnormal visio-vestibular test results at the initial postinjury evaluation took longer to recover, although boys with prolonged recovery had more emotional symptoms. In general, patients with preexisting mental health diagnoses returned to exercise later, a known factor in delayed concussion recovery.
Making Sense of It All
There are a couple of ways to look at this paper’s findings. The first is through the lens that focuses on the population of children and adolescents who have known mental health conditions. If our patient has a mental health diagnosis, we shouldn’t be surprised that he/she is taking longer to recover from his/her concussion and is experiencing an increase in symptoms. Most of us probably suspected this already. However, we should be particularly aware of this phenomenon if the patient is male.
The other perspective is probably more valuable to us as primary care physicians. Even one diagnosis so subtle that we may have overlooked it is likely to slow his/her progress toward recovery. And, of course, it may be that injury has triggered an underlying condition that none — not even the most astute diagnostician — would have found without a focused investigation.
I can’t leave this subject without wondering whether the findings in this paper should be extrapolated to other conditions of delayed recovery, including Lyme disease and COVID 19. Patients with these conditions are understandably resistant to the suggestion that their mental health may be contributing to the situation. Too many have been told too often it is “all in their head.” However, I think we as clinicians should keep open minds when symptoms are resolving more slowly than we would expect.
Finally, in their conclusion the authors of this paper reinforce a principle that has unfortunately taken some of us a while to accept. Early introduction of symptom-limited exercise should be a standard of postconcussion management, especially for patients with a mental health diagnosis.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Those of you who are regular readers of Letters from Maine have probably noticed that concussion is one of my favorite topics. The explanation for this perseveration is personal and may lie in the fact that I played two contact sports in college. In high school we still wore leather helmets and in college the lacrosse helmets were constructed of plastic-coated cardboard. I can recall just a few of what might be now labeled as sports-related concussions. Ironically, my only loss of consciousness came on the first dinner date with the woman who would eventually become my wife. A hypotensive episode resulting from the combination of sweat loss (2 hours of basketball) and blood loss from selling some platelets earlier in the day (to pay for the dinner) led to the unfortunate meeting of my head and the beautifully tiled floor at the restaurant.
Postconcussion Recovery
The phenomenon of delayed symptomatic recovery has been a particular interest of mine. Within the last 12 months I have written about an excellent companion commentary in Pediatricsby Talin Babikian PhD, a psychologist at University of California, Los Angeles, in which he urges us to “Consider the comorbidities or premorbidities,” including, among others, anxiety and/or depression, post-traumatic stress, and poor sleep when we are faced with a patient who is slow in shedding his postconcussion symptoms. A short 6 months after reading Dr. Babikian’s prescient commentary, I have encountered some evidence supporting his advice.
Investigators at the Sports Medicine and Performance Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia have recently published a study in which they have found “Preexisting mental health diagnoses are associated with greater postinjury emotional symptom burden and longer concussion recovery in a dose-response fashion.” In their prospective study of over 3000 children and adolescents, they found that, although patients with more mental health diagnoses were at greater risk of increased emotional symptoms after concussion, “Children and adolescents with any preexisting mental health diagnosis took longer to recover.”
Female patients and those with abnormal visio-vestibular test results at the initial postinjury evaluation took longer to recover, although boys with prolonged recovery had more emotional symptoms. In general, patients with preexisting mental health diagnoses returned to exercise later, a known factor in delayed concussion recovery.
Making Sense of It All
There are a couple of ways to look at this paper’s findings. The first is through the lens that focuses on the population of children and adolescents who have known mental health conditions. If our patient has a mental health diagnosis, we shouldn’t be surprised that he/she is taking longer to recover from his/her concussion and is experiencing an increase in symptoms. Most of us probably suspected this already. However, we should be particularly aware of this phenomenon if the patient is male.
The other perspective is probably more valuable to us as primary care physicians. Even one diagnosis so subtle that we may have overlooked it is likely to slow his/her progress toward recovery. And, of course, it may be that injury has triggered an underlying condition that none — not even the most astute diagnostician — would have found without a focused investigation.
I can’t leave this subject without wondering whether the findings in this paper should be extrapolated to other conditions of delayed recovery, including Lyme disease and COVID 19. Patients with these conditions are understandably resistant to the suggestion that their mental health may be contributing to the situation. Too many have been told too often it is “all in their head.” However, I think we as clinicians should keep open minds when symptoms are resolving more slowly than we would expect.
Finally, in their conclusion the authors of this paper reinforce a principle that has unfortunately taken some of us a while to accept. Early introduction of symptom-limited exercise should be a standard of postconcussion management, especially for patients with a mental health diagnosis.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Methylphenidate Linked to Small Increase in CV Event Risk
TOPLINE:
Methylphenidate was associated with a small increased risk for cardiovascular events in individuals taking the drug for more than 6 months in a new cohort study.
METHODOLOGY:
- The retrospective, population-based cohort study was based on national Swedish registry data and included 26,710 patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) aged 12-60 years (median age 20) who had been prescribed methylphenidate between 2007 and 2012. They were each matched on birth date, sex, and county with up to 10 nonusers without ADHD (a total of 225,672 controls).
- Rates of cardiovascular events, including ischemic heart disease, venous thromboembolism, heart failure, or tachyarrhythmias 1 year before methylphenidate treatment and 6 months after treatment initiation were compared between individuals receiving methylphenidate and matched controls using a Bayesian within-individual design.
TAKEAWAY:
- The overall incidence of cardiovascular events was 1.51 per 10,000 person-weeks for individuals receiving methylphenidate and 0.77 for the matched controls.
- Individuals taking methylphenidate had a 70% posterior probability for a greater than 10% increased risk for cardiovascular events than controls and a 49% posterior probability for an increased risk larger than 20%.
- No difference was found in this risk between individuals with and without a history of cardiovascular disease.
IN PRACTICE:
The researchers concluded that these results support a small (10%) increased risk for cardiovascular events in individuals receiving methylphenidate compared with matched controls after 6 months of treatment. The probability of finding a difference in risk between users and nonusers decreased when considering risk for 20% or larger, with no evidence of differences between those with and without a history of cardiovascular disease. They said the findings suggest the decision to initiate methylphenidate should incorporate considerations of potential adverse cardiovascular effects among the broader benefits and risks for treatment for individual patients.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Miguel Garcia-Argibay, PhD, Örebro University, Örebro, Sweden, was published online in JAMA Network Open on March 6.
LIMITATIONS:
The data were observational, and thus, causality could not be inferred. Lack of information on methylphenidate dose meant that it was not possible to assess a dose effect. Compliance with the medication was also not known, and the association may therefore have been underestimated. The findings of this study were based on data collected from a Swedish population, which may not be representative of other populations.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program and the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life, and Welfare.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Methylphenidate was associated with a small increased risk for cardiovascular events in individuals taking the drug for more than 6 months in a new cohort study.
METHODOLOGY:
- The retrospective, population-based cohort study was based on national Swedish registry data and included 26,710 patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) aged 12-60 years (median age 20) who had been prescribed methylphenidate between 2007 and 2012. They were each matched on birth date, sex, and county with up to 10 nonusers without ADHD (a total of 225,672 controls).
- Rates of cardiovascular events, including ischemic heart disease, venous thromboembolism, heart failure, or tachyarrhythmias 1 year before methylphenidate treatment and 6 months after treatment initiation were compared between individuals receiving methylphenidate and matched controls using a Bayesian within-individual design.
TAKEAWAY:
- The overall incidence of cardiovascular events was 1.51 per 10,000 person-weeks for individuals receiving methylphenidate and 0.77 for the matched controls.
- Individuals taking methylphenidate had a 70% posterior probability for a greater than 10% increased risk for cardiovascular events than controls and a 49% posterior probability for an increased risk larger than 20%.
- No difference was found in this risk between individuals with and without a history of cardiovascular disease.
IN PRACTICE:
The researchers concluded that these results support a small (10%) increased risk for cardiovascular events in individuals receiving methylphenidate compared with matched controls after 6 months of treatment. The probability of finding a difference in risk between users and nonusers decreased when considering risk for 20% or larger, with no evidence of differences between those with and without a history of cardiovascular disease. They said the findings suggest the decision to initiate methylphenidate should incorporate considerations of potential adverse cardiovascular effects among the broader benefits and risks for treatment for individual patients.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Miguel Garcia-Argibay, PhD, Örebro University, Örebro, Sweden, was published online in JAMA Network Open on March 6.
LIMITATIONS:
The data were observational, and thus, causality could not be inferred. Lack of information on methylphenidate dose meant that it was not possible to assess a dose effect. Compliance with the medication was also not known, and the association may therefore have been underestimated. The findings of this study were based on data collected from a Swedish population, which may not be representative of other populations.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program and the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life, and Welfare.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Methylphenidate was associated with a small increased risk for cardiovascular events in individuals taking the drug for more than 6 months in a new cohort study.
METHODOLOGY:
- The retrospective, population-based cohort study was based on national Swedish registry data and included 26,710 patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) aged 12-60 years (median age 20) who had been prescribed methylphenidate between 2007 and 2012. They were each matched on birth date, sex, and county with up to 10 nonusers without ADHD (a total of 225,672 controls).
- Rates of cardiovascular events, including ischemic heart disease, venous thromboembolism, heart failure, or tachyarrhythmias 1 year before methylphenidate treatment and 6 months after treatment initiation were compared between individuals receiving methylphenidate and matched controls using a Bayesian within-individual design.
TAKEAWAY:
- The overall incidence of cardiovascular events was 1.51 per 10,000 person-weeks for individuals receiving methylphenidate and 0.77 for the matched controls.
- Individuals taking methylphenidate had a 70% posterior probability for a greater than 10% increased risk for cardiovascular events than controls and a 49% posterior probability for an increased risk larger than 20%.
- No difference was found in this risk between individuals with and without a history of cardiovascular disease.
IN PRACTICE:
The researchers concluded that these results support a small (10%) increased risk for cardiovascular events in individuals receiving methylphenidate compared with matched controls after 6 months of treatment. The probability of finding a difference in risk between users and nonusers decreased when considering risk for 20% or larger, with no evidence of differences between those with and without a history of cardiovascular disease. They said the findings suggest the decision to initiate methylphenidate should incorporate considerations of potential adverse cardiovascular effects among the broader benefits and risks for treatment for individual patients.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Miguel Garcia-Argibay, PhD, Örebro University, Örebro, Sweden, was published online in JAMA Network Open on March 6.
LIMITATIONS:
The data were observational, and thus, causality could not be inferred. Lack of information on methylphenidate dose meant that it was not possible to assess a dose effect. Compliance with the medication was also not known, and the association may therefore have been underestimated. The findings of this study were based on data collected from a Swedish population, which may not be representative of other populations.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program and the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life, and Welfare.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.