User login
Tocilizumab shortage continues as pandemic wears on
With worldwide supplies of tocilizumab dwindling as the COVID-19 pandemic rages on, a shortage of the agent will persist “for at least the next several weeks,” according to Genentech, the Roche unit that manufactures tocilizumab under the trade name Actemra IV.
The World Health Organization and Unitaid have called on Genentech to guarantee equitable distribution of the biologic agent globally and to ease up on technology transfer restrictions to make the treatment more accessible.
At this point, supplies of tocilizumab for subcutaneous use to treat rheumatoid arthritis and its other approved indications for inflammatory conditions aren’t as dire, but Genentech is watching them as well, the company says.
In June, the Food and Drug Administration issued an emergency use authorization for intravenous tocilizumab for hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Since then, it has been included in the WHO Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline. And on the same day Genentech and Roche reported the tocilizumab shortage, the European Medicines Agency posted a statement that it had started evaluating RoActemra, the European brand name for tocilizumab, for hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
The FDA authorization has caused an unprecedented run on supplies for the biologic agent, which is FDA approved to treat RA, giant cell arteritis, systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease, polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis, systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and cytokine release syndrome.
Depleted stocks
In the United States, stocks of the 200- and 400-mg units were unavailable, according to an FDA update in mid-August on its website, and the 80-mg/4-mL unit is available by drop ship only. Supplies of 80-mg units were expected to be depleted by the end of the third week in August, Genentech said in a press release.
The company expects to resupply stocks by the end of August. “However,” the Genentech statement added, “if the pandemic continues to spread at its current pace, we anticipate additional periods of stockout in the weeks and months ahead.”
For patients with RA or other approved indications taking the subcutaneous formulation – pens and prefilled syringes – supplies continue to be available, but, the company added, “the supply situation continues to evolve.” The subcutaneous formulations aren’t authorized for use in COVID-19 patients. However, the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists’ website lists the 162-mg/0.9-mL prefilled syringe as one of the products affected by the shortage.
In a separate statement, Roche said that demand for tocilizumab increased 300% in developing countries over prepandemic orders, and that U.S. demand spiked more than 400% in the first 2 weeks of August.
Roche laid out four reasons for the shortage: global manufacturing capacity limits; raw material shortages; the overall complex process of manufacturing biologic agents; and “the dynamically evolving nature of the pandemic.”
The Roche statement noted the company ramped up manufacturing of tocilizumab more than 100% over prepandemic capacity.
With regard to issues WHO and Unitaid raised in their statement, Roche stated that about 60% of its COVID-19 supplies have gone to developing countries, and that Roche and partner Chugai – both of whom hold tocilizumab-related patents – won’t assert any patents over its use for COVID-19 in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) during the pandemic.
“Roche is in the midst of discussions with WHO and we are committed to support access in LMICs as much as we can,” a Roche spokesperson said in an interview.
Blair Solow, MD, chair of the American College of Rheumatology’s government affairs committee, said the organization supports the equitable distribution of tocilizumab. “We will work to ensure that our patients continue to have access to the medications they need,” she said. “We will continue to engage with the FDA and others to address shortages and ensure patient access to critical therapies.”
The ACR said that any health care professionals having difficulty getting tocilizumab IV or any other COVID-19-related issues can contact the organization at [email protected].
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With worldwide supplies of tocilizumab dwindling as the COVID-19 pandemic rages on, a shortage of the agent will persist “for at least the next several weeks,” according to Genentech, the Roche unit that manufactures tocilizumab under the trade name Actemra IV.
The World Health Organization and Unitaid have called on Genentech to guarantee equitable distribution of the biologic agent globally and to ease up on technology transfer restrictions to make the treatment more accessible.
At this point, supplies of tocilizumab for subcutaneous use to treat rheumatoid arthritis and its other approved indications for inflammatory conditions aren’t as dire, but Genentech is watching them as well, the company says.
In June, the Food and Drug Administration issued an emergency use authorization for intravenous tocilizumab for hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Since then, it has been included in the WHO Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline. And on the same day Genentech and Roche reported the tocilizumab shortage, the European Medicines Agency posted a statement that it had started evaluating RoActemra, the European brand name for tocilizumab, for hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
The FDA authorization has caused an unprecedented run on supplies for the biologic agent, which is FDA approved to treat RA, giant cell arteritis, systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease, polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis, systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and cytokine release syndrome.
Depleted stocks
In the United States, stocks of the 200- and 400-mg units were unavailable, according to an FDA update in mid-August on its website, and the 80-mg/4-mL unit is available by drop ship only. Supplies of 80-mg units were expected to be depleted by the end of the third week in August, Genentech said in a press release.
The company expects to resupply stocks by the end of August. “However,” the Genentech statement added, “if the pandemic continues to spread at its current pace, we anticipate additional periods of stockout in the weeks and months ahead.”
For patients with RA or other approved indications taking the subcutaneous formulation – pens and prefilled syringes – supplies continue to be available, but, the company added, “the supply situation continues to evolve.” The subcutaneous formulations aren’t authorized for use in COVID-19 patients. However, the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists’ website lists the 162-mg/0.9-mL prefilled syringe as one of the products affected by the shortage.
In a separate statement, Roche said that demand for tocilizumab increased 300% in developing countries over prepandemic orders, and that U.S. demand spiked more than 400% in the first 2 weeks of August.
Roche laid out four reasons for the shortage: global manufacturing capacity limits; raw material shortages; the overall complex process of manufacturing biologic agents; and “the dynamically evolving nature of the pandemic.”
The Roche statement noted the company ramped up manufacturing of tocilizumab more than 100% over prepandemic capacity.
With regard to issues WHO and Unitaid raised in their statement, Roche stated that about 60% of its COVID-19 supplies have gone to developing countries, and that Roche and partner Chugai – both of whom hold tocilizumab-related patents – won’t assert any patents over its use for COVID-19 in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) during the pandemic.
“Roche is in the midst of discussions with WHO and we are committed to support access in LMICs as much as we can,” a Roche spokesperson said in an interview.
Blair Solow, MD, chair of the American College of Rheumatology’s government affairs committee, said the organization supports the equitable distribution of tocilizumab. “We will work to ensure that our patients continue to have access to the medications they need,” she said. “We will continue to engage with the FDA and others to address shortages and ensure patient access to critical therapies.”
The ACR said that any health care professionals having difficulty getting tocilizumab IV or any other COVID-19-related issues can contact the organization at [email protected].
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With worldwide supplies of tocilizumab dwindling as the COVID-19 pandemic rages on, a shortage of the agent will persist “for at least the next several weeks,” according to Genentech, the Roche unit that manufactures tocilizumab under the trade name Actemra IV.
The World Health Organization and Unitaid have called on Genentech to guarantee equitable distribution of the biologic agent globally and to ease up on technology transfer restrictions to make the treatment more accessible.
At this point, supplies of tocilizumab for subcutaneous use to treat rheumatoid arthritis and its other approved indications for inflammatory conditions aren’t as dire, but Genentech is watching them as well, the company says.
In June, the Food and Drug Administration issued an emergency use authorization for intravenous tocilizumab for hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Since then, it has been included in the WHO Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline. And on the same day Genentech and Roche reported the tocilizumab shortage, the European Medicines Agency posted a statement that it had started evaluating RoActemra, the European brand name for tocilizumab, for hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
The FDA authorization has caused an unprecedented run on supplies for the biologic agent, which is FDA approved to treat RA, giant cell arteritis, systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease, polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis, systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and cytokine release syndrome.
Depleted stocks
In the United States, stocks of the 200- and 400-mg units were unavailable, according to an FDA update in mid-August on its website, and the 80-mg/4-mL unit is available by drop ship only. Supplies of 80-mg units were expected to be depleted by the end of the third week in August, Genentech said in a press release.
The company expects to resupply stocks by the end of August. “However,” the Genentech statement added, “if the pandemic continues to spread at its current pace, we anticipate additional periods of stockout in the weeks and months ahead.”
For patients with RA or other approved indications taking the subcutaneous formulation – pens and prefilled syringes – supplies continue to be available, but, the company added, “the supply situation continues to evolve.” The subcutaneous formulations aren’t authorized for use in COVID-19 patients. However, the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists’ website lists the 162-mg/0.9-mL prefilled syringe as one of the products affected by the shortage.
In a separate statement, Roche said that demand for tocilizumab increased 300% in developing countries over prepandemic orders, and that U.S. demand spiked more than 400% in the first 2 weeks of August.
Roche laid out four reasons for the shortage: global manufacturing capacity limits; raw material shortages; the overall complex process of manufacturing biologic agents; and “the dynamically evolving nature of the pandemic.”
The Roche statement noted the company ramped up manufacturing of tocilizumab more than 100% over prepandemic capacity.
With regard to issues WHO and Unitaid raised in their statement, Roche stated that about 60% of its COVID-19 supplies have gone to developing countries, and that Roche and partner Chugai – both of whom hold tocilizumab-related patents – won’t assert any patents over its use for COVID-19 in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) during the pandemic.
“Roche is in the midst of discussions with WHO and we are committed to support access in LMICs as much as we can,” a Roche spokesperson said in an interview.
Blair Solow, MD, chair of the American College of Rheumatology’s government affairs committee, said the organization supports the equitable distribution of tocilizumab. “We will work to ensure that our patients continue to have access to the medications they need,” she said. “We will continue to engage with the FDA and others to address shortages and ensure patient access to critical therapies.”
The ACR said that any health care professionals having difficulty getting tocilizumab IV or any other COVID-19-related issues can contact the organization at [email protected].
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Preterm and early term birth linked to an increased risk of autism
Preterm and early birth is associated with an increased risk of autism independent of genetic or environmental factors, according to new research published in Pediatrics.
Although previous studies have linked preterm births to an increased risk of autism – one 2017 study published in Cerebral Cortex found that 27.4% of the children born extremely preterm were diagnosed with autism – Casey Crump, MD, PhD, said potential causality, sex-specific differences, and association with early-term births were still unclear.
“Preterm birth had previously been linked with higher risk of autism; however, several important questions remained unanswered,” said Dr. Crump, professor and vice chair for research at the department of family medicine and community health and professor of epidemiology in the department of population health science and policy at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai New York. “To our knowledge, [our study] is the largest to date of gestational age at birth in relation to autism, and one of the first to investigate sex-specific differences, early term birth, or the influence of shared familial factors.”
Dr. Crump and colleagues examined data from more than 4 million infants born in Sweden between 1973 and 2013 who were followed-up for autism spectrum disorder identified from nationwide outpatient and inpatient diagnoses through December 2015. Children born between 22 and 27 weeks were considered extremely preterm, those born between 28 and 33 week were characterized as very to moderate preterm, and those born between 34 and 36 weeks were considered late preterm. Early-term births are characterized as infants born between 37 and 38 weeks and children born between 39 and 41 weeks were considered term births.
They found that 6.1% of those born extremely preterm were diagnosed with autism. Meanwhile, autism spectrum disorder prevalences were 2.6% for very to moderate preterm, 1.9% for late preterm, 2.1% for all preterm, and 1.6% for early term, compared with 1.4% for term birth.
The researchers’ analysis showed that preterm and early birth were associated with a significantly increased risk of autism in males and females. Children who were born extremely preterm had an approximately fourfold increased risk of autism. Researchers also found that each additional week of gestation was associated with a 5% lower prevalence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) on average.
“The elevated risk even in [late preterm] infants is not completely surprising because a number of investigators have shown higher incidences of early cognitive, language motor and impairment, and school problems ... and psychiatric disorders, some of which may extend to adulthood,” Elisabeth McGowan, MD, who was not involved in the study, said in a solicited editorial commentary about the study.
Dr. Crump believes the association between preterm birth and autism may be because of increased inflammatory marker levels. A 2009 study published in Reproductive Sciences found that increased proinflammatory cytokine levels have been associated with the timing and initiation of preterm birth, and also have been detected in the brain and cerebrospinal fluid of individuals with autism “and may play a key role in its pathogenesis,” Dr. Crump said.
“Inflammatory-driven alteration of neuronal connections during critical periods of brain development may be central to the development of autism,” Dr. Crump explained.
However, Dr. Crump said that, although the relative risks of autism were higher in those born preterm, the absolute risk of the condition is low.
“The report by Crump is in many ways a definitive accounting of the elevated rates of ASD in preterm infants,” said Dr. McGowan, associate professor of pediatrics at the Women and Infants Hospital, Providence, R.I. “And although the impact of prematurity on brain development may be part of the causal chain resulting in ASD (or other neurodevelopmental outcomes), these factors are operating in a complex biological landscape, with pathways to ASD outcomes that can be expected to be heterogeneous.”
ASD is a developmental condition that affects about 1 in 54 children, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Many children are not diagnosed with ASD until later in childhood, which in some cases delays treatment and early intervention. ASD may be detected as early as 18 months, but the average age of diagnosis for ASD is 4.3 years, according to the CDC.
“Children born prematurely need early evaluation and long-term follow-up to facilitate timely detection and treatment of autism, especially those born at the earliest gestational ages,” Dr. Crump said in an interview. “In patients of all ages, gestational age at birth should be routinely included in history-taking and medical records to help identify in clinical practice those born preterm or early term. Such information can provide additional valuable context for understanding patients’ health and may facilitate earlier evaluation for autism and other neurodevelopmental conditions in those born prematurely.”
Dr. Crump and colleagues said more research is needed to understand the biologic mechanisms linking preterm birth with higher risks of autism, which “may reveal new targets for intervention at critical windows of neurodevelopment to improve the disease trajectory.”
Experts interviewed did not disclose any relevant financial relationships.
Preterm and early birth is associated with an increased risk of autism independent of genetic or environmental factors, according to new research published in Pediatrics.
Although previous studies have linked preterm births to an increased risk of autism – one 2017 study published in Cerebral Cortex found that 27.4% of the children born extremely preterm were diagnosed with autism – Casey Crump, MD, PhD, said potential causality, sex-specific differences, and association with early-term births were still unclear.
“Preterm birth had previously been linked with higher risk of autism; however, several important questions remained unanswered,” said Dr. Crump, professor and vice chair for research at the department of family medicine and community health and professor of epidemiology in the department of population health science and policy at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai New York. “To our knowledge, [our study] is the largest to date of gestational age at birth in relation to autism, and one of the first to investigate sex-specific differences, early term birth, or the influence of shared familial factors.”
Dr. Crump and colleagues examined data from more than 4 million infants born in Sweden between 1973 and 2013 who were followed-up for autism spectrum disorder identified from nationwide outpatient and inpatient diagnoses through December 2015. Children born between 22 and 27 weeks were considered extremely preterm, those born between 28 and 33 week were characterized as very to moderate preterm, and those born between 34 and 36 weeks were considered late preterm. Early-term births are characterized as infants born between 37 and 38 weeks and children born between 39 and 41 weeks were considered term births.
They found that 6.1% of those born extremely preterm were diagnosed with autism. Meanwhile, autism spectrum disorder prevalences were 2.6% for very to moderate preterm, 1.9% for late preterm, 2.1% for all preterm, and 1.6% for early term, compared with 1.4% for term birth.
The researchers’ analysis showed that preterm and early birth were associated with a significantly increased risk of autism in males and females. Children who were born extremely preterm had an approximately fourfold increased risk of autism. Researchers also found that each additional week of gestation was associated with a 5% lower prevalence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) on average.
“The elevated risk even in [late preterm] infants is not completely surprising because a number of investigators have shown higher incidences of early cognitive, language motor and impairment, and school problems ... and psychiatric disorders, some of which may extend to adulthood,” Elisabeth McGowan, MD, who was not involved in the study, said in a solicited editorial commentary about the study.
Dr. Crump believes the association between preterm birth and autism may be because of increased inflammatory marker levels. A 2009 study published in Reproductive Sciences found that increased proinflammatory cytokine levels have been associated with the timing and initiation of preterm birth, and also have been detected in the brain and cerebrospinal fluid of individuals with autism “and may play a key role in its pathogenesis,” Dr. Crump said.
“Inflammatory-driven alteration of neuronal connections during critical periods of brain development may be central to the development of autism,” Dr. Crump explained.
However, Dr. Crump said that, although the relative risks of autism were higher in those born preterm, the absolute risk of the condition is low.
“The report by Crump is in many ways a definitive accounting of the elevated rates of ASD in preterm infants,” said Dr. McGowan, associate professor of pediatrics at the Women and Infants Hospital, Providence, R.I. “And although the impact of prematurity on brain development may be part of the causal chain resulting in ASD (or other neurodevelopmental outcomes), these factors are operating in a complex biological landscape, with pathways to ASD outcomes that can be expected to be heterogeneous.”
ASD is a developmental condition that affects about 1 in 54 children, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Many children are not diagnosed with ASD until later in childhood, which in some cases delays treatment and early intervention. ASD may be detected as early as 18 months, but the average age of diagnosis for ASD is 4.3 years, according to the CDC.
“Children born prematurely need early evaluation and long-term follow-up to facilitate timely detection and treatment of autism, especially those born at the earliest gestational ages,” Dr. Crump said in an interview. “In patients of all ages, gestational age at birth should be routinely included in history-taking and medical records to help identify in clinical practice those born preterm or early term. Such information can provide additional valuable context for understanding patients’ health and may facilitate earlier evaluation for autism and other neurodevelopmental conditions in those born prematurely.”
Dr. Crump and colleagues said more research is needed to understand the biologic mechanisms linking preterm birth with higher risks of autism, which “may reveal new targets for intervention at critical windows of neurodevelopment to improve the disease trajectory.”
Experts interviewed did not disclose any relevant financial relationships.
Preterm and early birth is associated with an increased risk of autism independent of genetic or environmental factors, according to new research published in Pediatrics.
Although previous studies have linked preterm births to an increased risk of autism – one 2017 study published in Cerebral Cortex found that 27.4% of the children born extremely preterm were diagnosed with autism – Casey Crump, MD, PhD, said potential causality, sex-specific differences, and association with early-term births were still unclear.
“Preterm birth had previously been linked with higher risk of autism; however, several important questions remained unanswered,” said Dr. Crump, professor and vice chair for research at the department of family medicine and community health and professor of epidemiology in the department of population health science and policy at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai New York. “To our knowledge, [our study] is the largest to date of gestational age at birth in relation to autism, and one of the first to investigate sex-specific differences, early term birth, or the influence of shared familial factors.”
Dr. Crump and colleagues examined data from more than 4 million infants born in Sweden between 1973 and 2013 who were followed-up for autism spectrum disorder identified from nationwide outpatient and inpatient diagnoses through December 2015. Children born between 22 and 27 weeks were considered extremely preterm, those born between 28 and 33 week were characterized as very to moderate preterm, and those born between 34 and 36 weeks were considered late preterm. Early-term births are characterized as infants born between 37 and 38 weeks and children born between 39 and 41 weeks were considered term births.
They found that 6.1% of those born extremely preterm were diagnosed with autism. Meanwhile, autism spectrum disorder prevalences were 2.6% for very to moderate preterm, 1.9% for late preterm, 2.1% for all preterm, and 1.6% for early term, compared with 1.4% for term birth.
The researchers’ analysis showed that preterm and early birth were associated with a significantly increased risk of autism in males and females. Children who were born extremely preterm had an approximately fourfold increased risk of autism. Researchers also found that each additional week of gestation was associated with a 5% lower prevalence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) on average.
“The elevated risk even in [late preterm] infants is not completely surprising because a number of investigators have shown higher incidences of early cognitive, language motor and impairment, and school problems ... and psychiatric disorders, some of which may extend to adulthood,” Elisabeth McGowan, MD, who was not involved in the study, said in a solicited editorial commentary about the study.
Dr. Crump believes the association between preterm birth and autism may be because of increased inflammatory marker levels. A 2009 study published in Reproductive Sciences found that increased proinflammatory cytokine levels have been associated with the timing and initiation of preterm birth, and also have been detected in the brain and cerebrospinal fluid of individuals with autism “and may play a key role in its pathogenesis,” Dr. Crump said.
“Inflammatory-driven alteration of neuronal connections during critical periods of brain development may be central to the development of autism,” Dr. Crump explained.
However, Dr. Crump said that, although the relative risks of autism were higher in those born preterm, the absolute risk of the condition is low.
“The report by Crump is in many ways a definitive accounting of the elevated rates of ASD in preterm infants,” said Dr. McGowan, associate professor of pediatrics at the Women and Infants Hospital, Providence, R.I. “And although the impact of prematurity on brain development may be part of the causal chain resulting in ASD (or other neurodevelopmental outcomes), these factors are operating in a complex biological landscape, with pathways to ASD outcomes that can be expected to be heterogeneous.”
ASD is a developmental condition that affects about 1 in 54 children, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Many children are not diagnosed with ASD until later in childhood, which in some cases delays treatment and early intervention. ASD may be detected as early as 18 months, but the average age of diagnosis for ASD is 4.3 years, according to the CDC.
“Children born prematurely need early evaluation and long-term follow-up to facilitate timely detection and treatment of autism, especially those born at the earliest gestational ages,” Dr. Crump said in an interview. “In patients of all ages, gestational age at birth should be routinely included in history-taking and medical records to help identify in clinical practice those born preterm or early term. Such information can provide additional valuable context for understanding patients’ health and may facilitate earlier evaluation for autism and other neurodevelopmental conditions in those born prematurely.”
Dr. Crump and colleagues said more research is needed to understand the biologic mechanisms linking preterm birth with higher risks of autism, which “may reveal new targets for intervention at critical windows of neurodevelopment to improve the disease trajectory.”
Experts interviewed did not disclose any relevant financial relationships.
FROM PEDIATRICS
AAP ‘silencing debate’ on gender dysphoria, says doctor group
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) is at the center of a row with an international group of doctors who question whether hormone treatment is the most appropriate way to treat adolescents with gender dysphoria.
After initially accepting the application and payment from the Society for Evidence-Based Gender Medicine (SEGM) for the organization to have an information booth at the AAP annual meeting in October, the AAP did a U-turn earlier this month and canceled the registration, with no explanation as to why.
“Just days earlier,” says SEGM in a statement on its website, “over 80% of AAP members” had indicated they wanted more discussion on the topic of “addressing alternatives to the use of hormone therapies for gender dysphoric youth.”
“This rejection sends a strong signal that the AAP does not want to see any debate on what constitutes evidence-based care for gender-diverse youth,” they add.
Asked for an explanation as to why it accepted but later rescinded SEGM’s application for a booth, the AAP has given no response to date.
A Wall Street Journal article on the furor, published last week, has clocked up 785 comments to date.
There has been an exponential increase in the number of adolescents who identify as transgender – reporting discomfort with their birth sex – in Western countries, and the debate has been covered in detail, having intensified worldwide in the last 12 months, regarding how best to treat youth with gender dysphoria.
Although “affirmative” medical care, defined as treatment with puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones to transition to the opposite sex, is supported by the AAP and other medical organizations, there is growing concern among many doctors and other health care professionals as to whether this is, in fact, the best way to proceed, given that there are a number of irreversible changes associated with treatment. There is also a growing number of “detransitioners” – mostly young people who transitioned and then changed their minds, and “detransitioned” back to their birth sex.
“Because of the low quality of the available evidence and the marked change in the presentation of gender dysphoria in youth in the last several years (many more adolescents with recently emerging transgender identities and significant mental health comorbidities are presenting for care), what constitutes good health care for this patient group is far from clear,” notes SEGM.
“Quelling the debate will not help America’s pediatricians guide patients and their families based on best available evidence. The politicization of the field of gender medicine must end, if we care about gender-variant youth and their long-term health,” they conclude.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) is at the center of a row with an international group of doctors who question whether hormone treatment is the most appropriate way to treat adolescents with gender dysphoria.
After initially accepting the application and payment from the Society for Evidence-Based Gender Medicine (SEGM) for the organization to have an information booth at the AAP annual meeting in October, the AAP did a U-turn earlier this month and canceled the registration, with no explanation as to why.
“Just days earlier,” says SEGM in a statement on its website, “over 80% of AAP members” had indicated they wanted more discussion on the topic of “addressing alternatives to the use of hormone therapies for gender dysphoric youth.”
“This rejection sends a strong signal that the AAP does not want to see any debate on what constitutes evidence-based care for gender-diverse youth,” they add.
Asked for an explanation as to why it accepted but later rescinded SEGM’s application for a booth, the AAP has given no response to date.
A Wall Street Journal article on the furor, published last week, has clocked up 785 comments to date.
There has been an exponential increase in the number of adolescents who identify as transgender – reporting discomfort with their birth sex – in Western countries, and the debate has been covered in detail, having intensified worldwide in the last 12 months, regarding how best to treat youth with gender dysphoria.
Although “affirmative” medical care, defined as treatment with puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones to transition to the opposite sex, is supported by the AAP and other medical organizations, there is growing concern among many doctors and other health care professionals as to whether this is, in fact, the best way to proceed, given that there are a number of irreversible changes associated with treatment. There is also a growing number of “detransitioners” – mostly young people who transitioned and then changed their minds, and “detransitioned” back to their birth sex.
“Because of the low quality of the available evidence and the marked change in the presentation of gender dysphoria in youth in the last several years (many more adolescents with recently emerging transgender identities and significant mental health comorbidities are presenting for care), what constitutes good health care for this patient group is far from clear,” notes SEGM.
“Quelling the debate will not help America’s pediatricians guide patients and their families based on best available evidence. The politicization of the field of gender medicine must end, if we care about gender-variant youth and their long-term health,” they conclude.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) is at the center of a row with an international group of doctors who question whether hormone treatment is the most appropriate way to treat adolescents with gender dysphoria.
After initially accepting the application and payment from the Society for Evidence-Based Gender Medicine (SEGM) for the organization to have an information booth at the AAP annual meeting in October, the AAP did a U-turn earlier this month and canceled the registration, with no explanation as to why.
“Just days earlier,” says SEGM in a statement on its website, “over 80% of AAP members” had indicated they wanted more discussion on the topic of “addressing alternatives to the use of hormone therapies for gender dysphoric youth.”
“This rejection sends a strong signal that the AAP does not want to see any debate on what constitutes evidence-based care for gender-diverse youth,” they add.
Asked for an explanation as to why it accepted but later rescinded SEGM’s application for a booth, the AAP has given no response to date.
A Wall Street Journal article on the furor, published last week, has clocked up 785 comments to date.
There has been an exponential increase in the number of adolescents who identify as transgender – reporting discomfort with their birth sex – in Western countries, and the debate has been covered in detail, having intensified worldwide in the last 12 months, regarding how best to treat youth with gender dysphoria.
Although “affirmative” medical care, defined as treatment with puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones to transition to the opposite sex, is supported by the AAP and other medical organizations, there is growing concern among many doctors and other health care professionals as to whether this is, in fact, the best way to proceed, given that there are a number of irreversible changes associated with treatment. There is also a growing number of “detransitioners” – mostly young people who transitioned and then changed their minds, and “detransitioned” back to their birth sex.
“Because of the low quality of the available evidence and the marked change in the presentation of gender dysphoria in youth in the last several years (many more adolescents with recently emerging transgender identities and significant mental health comorbidities are presenting for care), what constitutes good health care for this patient group is far from clear,” notes SEGM.
“Quelling the debate will not help America’s pediatricians guide patients and their families based on best available evidence. The politicization of the field of gender medicine must end, if we care about gender-variant youth and their long-term health,” they conclude.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: New cases rise to winter levels
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children topped 100,000 for the first time since early February, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
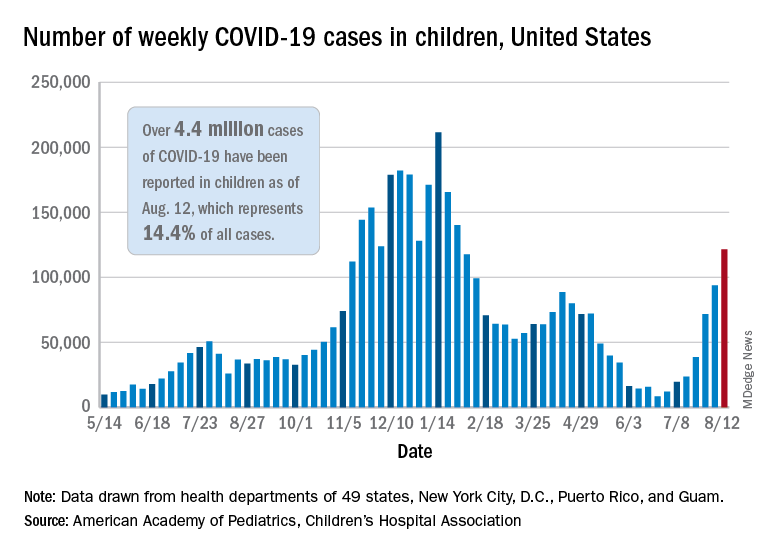
the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVD-19 report. The recent surge in child COVID has also brought a record high in hospitalizations and shortages of pediatric ICU beds in some areas.
The 121,000 new cases represent an increase of almost 1,400% since June 18-24, when the weekly tally was just 8,447 and at its lowest point in over a year, the AAP/CHA data show.
On the vaccination front in the last week (Aug. 10-16), vaccine initiation for 12- to 17-year-olds was fairly robust but still down slightly, compared with the previous week. Just over 402,000 children aged 12-15 years received a first vaccination, which was down slightly from 411,000 the week before but still higher than any of the 6 weeks from June 22 to Aug. 2, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Vaccinations were down by a similar margin for 15- to-17-year-olds.
Over 10.9 million children aged 12-17 have had at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine administered, of whom 8.1 million are fully vaccinated. Among those aged 12-15 years, 44.5% have gotten at least one dose and 31.8% are fully vaccinated, with corresponding figures of 53.9% and 42.5% for 16- and 17-year-olds, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The number of COVID-19 cases reported in children since the start of the pandemic is up to 4.4 million, which makes up 14.4% of all cases in the United States, the AAP and CHA said. Other cumulative figures through Aug. 12 include almost 18,000 hospitalizations – reported by 23 states and New York City – and 378 deaths – reported by 43 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
In the latest edition of their ongoing report, compiled using state data since the summer of 2020, the two groups noted that, “in the summer of 2021, some states have revised cases counts previously reported, begun reporting less frequently, or dropped metrics previously reported.” Among those states are Nebraska, which shut down its online COVID dashboard in late June, and Alabama, which stopped reporting cumulative cases and deaths after July 29.
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children topped 100,000 for the first time since early February, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVD-19 report. The recent surge in child COVID has also brought a record high in hospitalizations and shortages of pediatric ICU beds in some areas.
The 121,000 new cases represent an increase of almost 1,400% since June 18-24, when the weekly tally was just 8,447 and at its lowest point in over a year, the AAP/CHA data show.
On the vaccination front in the last week (Aug. 10-16), vaccine initiation for 12- to 17-year-olds was fairly robust but still down slightly, compared with the previous week. Just over 402,000 children aged 12-15 years received a first vaccination, which was down slightly from 411,000 the week before but still higher than any of the 6 weeks from June 22 to Aug. 2, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Vaccinations were down by a similar margin for 15- to-17-year-olds.
Over 10.9 million children aged 12-17 have had at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine administered, of whom 8.1 million are fully vaccinated. Among those aged 12-15 years, 44.5% have gotten at least one dose and 31.8% are fully vaccinated, with corresponding figures of 53.9% and 42.5% for 16- and 17-year-olds, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The number of COVID-19 cases reported in children since the start of the pandemic is up to 4.4 million, which makes up 14.4% of all cases in the United States, the AAP and CHA said. Other cumulative figures through Aug. 12 include almost 18,000 hospitalizations – reported by 23 states and New York City – and 378 deaths – reported by 43 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
In the latest edition of their ongoing report, compiled using state data since the summer of 2020, the two groups noted that, “in the summer of 2021, some states have revised cases counts previously reported, begun reporting less frequently, or dropped metrics previously reported.” Among those states are Nebraska, which shut down its online COVID dashboard in late June, and Alabama, which stopped reporting cumulative cases and deaths after July 29.
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children topped 100,000 for the first time since early February, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVD-19 report. The recent surge in child COVID has also brought a record high in hospitalizations and shortages of pediatric ICU beds in some areas.
The 121,000 new cases represent an increase of almost 1,400% since June 18-24, when the weekly tally was just 8,447 and at its lowest point in over a year, the AAP/CHA data show.
On the vaccination front in the last week (Aug. 10-16), vaccine initiation for 12- to 17-year-olds was fairly robust but still down slightly, compared with the previous week. Just over 402,000 children aged 12-15 years received a first vaccination, which was down slightly from 411,000 the week before but still higher than any of the 6 weeks from June 22 to Aug. 2, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Vaccinations were down by a similar margin for 15- to-17-year-olds.
Over 10.9 million children aged 12-17 have had at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine administered, of whom 8.1 million are fully vaccinated. Among those aged 12-15 years, 44.5% have gotten at least one dose and 31.8% are fully vaccinated, with corresponding figures of 53.9% and 42.5% for 16- and 17-year-olds, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The number of COVID-19 cases reported in children since the start of the pandemic is up to 4.4 million, which makes up 14.4% of all cases in the United States, the AAP and CHA said. Other cumulative figures through Aug. 12 include almost 18,000 hospitalizations – reported by 23 states and New York City – and 378 deaths – reported by 43 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
In the latest edition of their ongoing report, compiled using state data since the summer of 2020, the two groups noted that, “in the summer of 2021, some states have revised cases counts previously reported, begun reporting less frequently, or dropped metrics previously reported.” Among those states are Nebraska, which shut down its online COVID dashboard in late June, and Alabama, which stopped reporting cumulative cases and deaths after July 29.
U.S. reports record COVID-19 hospitalizations of children
The number of children hospitalized with COVID-19 in the U.S. hit a record high on Aug. 14, with more than 1,900 in hospitals.
Hospitals across the South are running out of beds as the contagious Delta variant spreads, mostly among unvaccinated people. Children make up about 2.4% of the country’s COVID-19 hospitalizations, and those under 12 are particularly vulnerable since they’re not eligible to receive a vaccine.
“This is not last year’s COVID,” Sally Goza, MD, former president of the American Academy of Pediatrics, told CNN on Aug. 14.
“This one is worse, and our children are the ones that are going to be affected by it the most,” she said.
The number of newly hospitalized COVID-19 patients for ages 18-49 also hit record highs during the week of Aug. 9. A fifth of the nation’s hospitalizations are in Florida, where the number of COVID-19 patients hit a record high of 16,100 on Aug. 14. More than 90% of the state’s intensive care unit beds are filled.
More than 90% of the ICU beds in Texas are full as well. On Aug. 13, there were no pediatric ICU beds available in Dallas or the 19 surrounding counties, which means that young patients would be transported father away for care – even Oklahoma City.
“That means if your child’s in a car wreck, if your child has a congenital heart defect or something and needs an ICU bed, or more likely, if they have COVID and need an ICU bed, we don’t have one,” Clay Jenkins, a Dallas County judge, said on Aug. 13.
“Your child will wait for another child to die,” he said.
As children return to classes, educators are talking about the possibility of vaccine mandates. The National Education Association announced its support of mandatory vaccination for its members.
“Our students under 12 can’t get vaccinated,” Becky Pringle, president of the association, told CNN.
“It’s our responsibility to keep them safe,” she said. “Keeping them safe means that everyone who can be vaccinated should be vaccinated.”
The U.S. now has an average of about 129,000 new COVID-19 cases per day, Reuters reported, which has doubled in about 2 weeks. The number of hospitalized patients is at a 6-month high, and about 600 people are dying each day.
Arkansas, Florida, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Oregon have reported record numbers of COVID-19 hospitalizations.
In addition, eight states make up half of all the COVID-19 hospitalizations in the U.S. but only 24% of the nation’s population – Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, Nevada, and Texas. These states have vaccination rates lower than the national average, and their COVID-19 patients account for at least 15% of their overall hospitalizations.
To address the surge in hospitalizations, Oregon Gov. Kate Brown has ordered the deployment of up to 1,500 Oregon National Guard members to help health care workers.
“I know this is not the summer many of us envisioned,” Gov. Brown said Aug. 13. “The harsh and frustrating reality is that the Delta variant has changed everything. Delta is highly contagious, and we must take action now.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The number of children hospitalized with COVID-19 in the U.S. hit a record high on Aug. 14, with more than 1,900 in hospitals.
Hospitals across the South are running out of beds as the contagious Delta variant spreads, mostly among unvaccinated people. Children make up about 2.4% of the country’s COVID-19 hospitalizations, and those under 12 are particularly vulnerable since they’re not eligible to receive a vaccine.
“This is not last year’s COVID,” Sally Goza, MD, former president of the American Academy of Pediatrics, told CNN on Aug. 14.
“This one is worse, and our children are the ones that are going to be affected by it the most,” she said.
The number of newly hospitalized COVID-19 patients for ages 18-49 also hit record highs during the week of Aug. 9. A fifth of the nation’s hospitalizations are in Florida, where the number of COVID-19 patients hit a record high of 16,100 on Aug. 14. More than 90% of the state’s intensive care unit beds are filled.
More than 90% of the ICU beds in Texas are full as well. On Aug. 13, there were no pediatric ICU beds available in Dallas or the 19 surrounding counties, which means that young patients would be transported father away for care – even Oklahoma City.
“That means if your child’s in a car wreck, if your child has a congenital heart defect or something and needs an ICU bed, or more likely, if they have COVID and need an ICU bed, we don’t have one,” Clay Jenkins, a Dallas County judge, said on Aug. 13.
“Your child will wait for another child to die,” he said.
As children return to classes, educators are talking about the possibility of vaccine mandates. The National Education Association announced its support of mandatory vaccination for its members.
“Our students under 12 can’t get vaccinated,” Becky Pringle, president of the association, told CNN.
“It’s our responsibility to keep them safe,” she said. “Keeping them safe means that everyone who can be vaccinated should be vaccinated.”
The U.S. now has an average of about 129,000 new COVID-19 cases per day, Reuters reported, which has doubled in about 2 weeks. The number of hospitalized patients is at a 6-month high, and about 600 people are dying each day.
Arkansas, Florida, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Oregon have reported record numbers of COVID-19 hospitalizations.
In addition, eight states make up half of all the COVID-19 hospitalizations in the U.S. but only 24% of the nation’s population – Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, Nevada, and Texas. These states have vaccination rates lower than the national average, and their COVID-19 patients account for at least 15% of their overall hospitalizations.
To address the surge in hospitalizations, Oregon Gov. Kate Brown has ordered the deployment of up to 1,500 Oregon National Guard members to help health care workers.
“I know this is not the summer many of us envisioned,” Gov. Brown said Aug. 13. “The harsh and frustrating reality is that the Delta variant has changed everything. Delta is highly contagious, and we must take action now.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The number of children hospitalized with COVID-19 in the U.S. hit a record high on Aug. 14, with more than 1,900 in hospitals.
Hospitals across the South are running out of beds as the contagious Delta variant spreads, mostly among unvaccinated people. Children make up about 2.4% of the country’s COVID-19 hospitalizations, and those under 12 are particularly vulnerable since they’re not eligible to receive a vaccine.
“This is not last year’s COVID,” Sally Goza, MD, former president of the American Academy of Pediatrics, told CNN on Aug. 14.
“This one is worse, and our children are the ones that are going to be affected by it the most,” she said.
The number of newly hospitalized COVID-19 patients for ages 18-49 also hit record highs during the week of Aug. 9. A fifth of the nation’s hospitalizations are in Florida, where the number of COVID-19 patients hit a record high of 16,100 on Aug. 14. More than 90% of the state’s intensive care unit beds are filled.
More than 90% of the ICU beds in Texas are full as well. On Aug. 13, there were no pediatric ICU beds available in Dallas or the 19 surrounding counties, which means that young patients would be transported father away for care – even Oklahoma City.
“That means if your child’s in a car wreck, if your child has a congenital heart defect or something and needs an ICU bed, or more likely, if they have COVID and need an ICU bed, we don’t have one,” Clay Jenkins, a Dallas County judge, said on Aug. 13.
“Your child will wait for another child to die,” he said.
As children return to classes, educators are talking about the possibility of vaccine mandates. The National Education Association announced its support of mandatory vaccination for its members.
“Our students under 12 can’t get vaccinated,” Becky Pringle, president of the association, told CNN.
“It’s our responsibility to keep them safe,” she said. “Keeping them safe means that everyone who can be vaccinated should be vaccinated.”
The U.S. now has an average of about 129,000 new COVID-19 cases per day, Reuters reported, which has doubled in about 2 weeks. The number of hospitalized patients is at a 6-month high, and about 600 people are dying each day.
Arkansas, Florida, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Oregon have reported record numbers of COVID-19 hospitalizations.
In addition, eight states make up half of all the COVID-19 hospitalizations in the U.S. but only 24% of the nation’s population – Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, Nevada, and Texas. These states have vaccination rates lower than the national average, and their COVID-19 patients account for at least 15% of their overall hospitalizations.
To address the surge in hospitalizations, Oregon Gov. Kate Brown has ordered the deployment of up to 1,500 Oregon National Guard members to help health care workers.
“I know this is not the summer many of us envisioned,” Gov. Brown said Aug. 13. “The harsh and frustrating reality is that the Delta variant has changed everything. Delta is highly contagious, and we must take action now.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Universal masking is the key to safe school attendance
“I want my child to go back to school,” the mother said to me. “I just want you to tell me it will be safe.”
As the summer break winds down for children across the United States, pediatric COVID-19 cases are rising. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, nearly 94,000 cases were reported for the week ending Aug. 5, more than double the case count from 2 weeks earlier.1
Anecdotally, some children’s hospitals are reporting an increase in pediatric COVID-19 admissions. In the hospital in which I practice, we are seeing numbers similar to those we saw in December and January: a typical daily census of 10 kids admitted with COVID-19, with 4 of them in the intensive care unit. It is a stark contrast to June when, most days, we had no patients with COVID-19 in the hospital. About half of our hospitalized patients are too young to be vaccinated against COVID-19, while the rest are unvaccinated children 12 years and older.
Vaccination of eligible children and teachers is an essential strategy for preventing the spread of COVID-19 in schools, but as children head back to school, immunization rates of educators are largely unknown and are suboptimal among students in most states. As of Aug. 11, 10.7 million U.S. children had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine, representing 43% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 53% of 16- to 17-year-olds.2 Rates vary substantially by state, with more than 70% of kids in Vermont receiving at least one dose of vaccine, compared with less than 25% in Wyoming and Alabama.
Still, in the absence of robust immunization rates, we have data that schools can still reopen successfully. We need to follow the science and implement universal masking, a safe, effective, and practical mitigation strategy.
It worked in Wisconsin. Seventeen K-12 schools in rural Wisconsin opened last fall for in-person instruction.3 Reported compliance with masking was high, ranging from 92.1% to 97.4%, and in-school transmission of COVID-19 was low, with seven cases among 4,876 students.
It worked in Salt Lake City.4 In 20 elementary schools open for in-person instruction Dec. 3, 2020, to Jan. 31, 2021, compliance with mask-wearing was high and in-school transmission was very low, despite a high community incidence of COVID-19. Notably, students’ classroom seats were less than 6 feet apart, suggesting that consistent mask-wearing works even when physical distancing is challenging.
One of the best examples of successful school reopening happened in North Carolina, where pediatricians, pediatric infectious disease specialists, and other experts affiliated with Duke University formed the ABC Science Collaborative to support school districts that requested scientific input to help guide return-to-school policies during the COVID-19 pandemic. From Oct. 26, 2020, to Feb. 28, 2021, the ABC Science Collaborative worked with 13 school districts that were open for in-person instruction using basic mitigation strategies, including universal masking.5 During this time period, there were 4,969 community-acquired SARS-CoV-2 infections in the more than 100,000 students and staff present in schools. Transmission to school contacts was identified in only 209 individuals for a secondary attack rate of less than 1%.
Duke investigator Kanecia Zimmerman, MD, told Duke Today, “We know that, if our goal is to reduce transmission of COVID-19 in schools, there are two effective ways to do that: 1. vaccination, 2. masking. In the setting of schools ... the science suggests masking can be extremely effective, particularly for those who can’t get vaccinated while COVID-19 is still circulating.”
Both the AAP6 and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society7 have emphasized the importance of in-person instruction and endorsed universal masking in school. Mask-optional policies or “mask-if-you-are-unvaccinated” policies don’t work, as we have seen in society at large. They are likely to be especially challenging in school settings. Given an option, many, if not most kids, will take off their masks. Kids who leave them on run the risk of stigmatization or bullying.
On Aug. 4, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention updated its guidance to recommend universal indoor masking for all students, staff, teachers, and visitors to K-12 schools, regardless of vaccination status. Now we’ll have to wait and see if school districts, elected officials, and parents will get on board with masks. ... and we’ll be left to count the number of rising COVID-19 cases that occur until they do.
Case in point: Kids in Greater Clark County, Ind., headed back to school on July 28. Masks were not required on school property, although unvaccinated students and teachers were “strongly encouraged” to wear them.8
Over the first 8 days of in-person instruction, schools in Greater Clark County identified 70 cases of COVID-19 in students and quarantined more than 1,100 of the district’s 10,300 students. Only the unvaccinated were required to quarantine. The district began requiring masks in all school buildings on Aug. 9.9
The worried mother had one last question for me. “What’s the best mask for a child to wear?” For most kids, a simple, well-fitting cloth mask is fine. The best mask is ultimately the mask a child will wear. A toolkit with practical tips for helping children successfully wear a mask is available on the ABC Science Collaborative website.
Dr. Bryant, president of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, is a pediatrician at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. American Academy of Pediatrics. “Children and COVID-19: State-level data report.”
2. American Academy of Pediatrics. “Children and COVID-19 vaccination trends.”
3. Falk A et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:136-40.
4. Hershow RB et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021;70:442-8.
5. Zimmerman KO et al. Pediatrics. 2021 Jul;e2021052686. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052686.
6. American Academy of Pediatrics. “American Academy of Pediatrics updates recommendations for opening schools in fall 2021.”
7. Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society. “PIDS supports universal masking for students, school staff.”
8. Courtney Hayden. WHAS11. “Greater Clark County Schools return to class July 28.”
9. Dustin Vogt. WAVE3 News. “Greater Clark Country Schools to require masks amid 70 positive cases.”
“I want my child to go back to school,” the mother said to me. “I just want you to tell me it will be safe.”
As the summer break winds down for children across the United States, pediatric COVID-19 cases are rising. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, nearly 94,000 cases were reported for the week ending Aug. 5, more than double the case count from 2 weeks earlier.1
Anecdotally, some children’s hospitals are reporting an increase in pediatric COVID-19 admissions. In the hospital in which I practice, we are seeing numbers similar to those we saw in December and January: a typical daily census of 10 kids admitted with COVID-19, with 4 of them in the intensive care unit. It is a stark contrast to June when, most days, we had no patients with COVID-19 in the hospital. About half of our hospitalized patients are too young to be vaccinated against COVID-19, while the rest are unvaccinated children 12 years and older.
Vaccination of eligible children and teachers is an essential strategy for preventing the spread of COVID-19 in schools, but as children head back to school, immunization rates of educators are largely unknown and are suboptimal among students in most states. As of Aug. 11, 10.7 million U.S. children had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine, representing 43% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 53% of 16- to 17-year-olds.2 Rates vary substantially by state, with more than 70% of kids in Vermont receiving at least one dose of vaccine, compared with less than 25% in Wyoming and Alabama.
Still, in the absence of robust immunization rates, we have data that schools can still reopen successfully. We need to follow the science and implement universal masking, a safe, effective, and practical mitigation strategy.
It worked in Wisconsin. Seventeen K-12 schools in rural Wisconsin opened last fall for in-person instruction.3 Reported compliance with masking was high, ranging from 92.1% to 97.4%, and in-school transmission of COVID-19 was low, with seven cases among 4,876 students.
It worked in Salt Lake City.4 In 20 elementary schools open for in-person instruction Dec. 3, 2020, to Jan. 31, 2021, compliance with mask-wearing was high and in-school transmission was very low, despite a high community incidence of COVID-19. Notably, students’ classroom seats were less than 6 feet apart, suggesting that consistent mask-wearing works even when physical distancing is challenging.
One of the best examples of successful school reopening happened in North Carolina, where pediatricians, pediatric infectious disease specialists, and other experts affiliated with Duke University formed the ABC Science Collaborative to support school districts that requested scientific input to help guide return-to-school policies during the COVID-19 pandemic. From Oct. 26, 2020, to Feb. 28, 2021, the ABC Science Collaborative worked with 13 school districts that were open for in-person instruction using basic mitigation strategies, including universal masking.5 During this time period, there were 4,969 community-acquired SARS-CoV-2 infections in the more than 100,000 students and staff present in schools. Transmission to school contacts was identified in only 209 individuals for a secondary attack rate of less than 1%.
Duke investigator Kanecia Zimmerman, MD, told Duke Today, “We know that, if our goal is to reduce transmission of COVID-19 in schools, there are two effective ways to do that: 1. vaccination, 2. masking. In the setting of schools ... the science suggests masking can be extremely effective, particularly for those who can’t get vaccinated while COVID-19 is still circulating.”
Both the AAP6 and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society7 have emphasized the importance of in-person instruction and endorsed universal masking in school. Mask-optional policies or “mask-if-you-are-unvaccinated” policies don’t work, as we have seen in society at large. They are likely to be especially challenging in school settings. Given an option, many, if not most kids, will take off their masks. Kids who leave them on run the risk of stigmatization or bullying.
On Aug. 4, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention updated its guidance to recommend universal indoor masking for all students, staff, teachers, and visitors to K-12 schools, regardless of vaccination status. Now we’ll have to wait and see if school districts, elected officials, and parents will get on board with masks. ... and we’ll be left to count the number of rising COVID-19 cases that occur until they do.
Case in point: Kids in Greater Clark County, Ind., headed back to school on July 28. Masks were not required on school property, although unvaccinated students and teachers were “strongly encouraged” to wear them.8
Over the first 8 days of in-person instruction, schools in Greater Clark County identified 70 cases of COVID-19 in students and quarantined more than 1,100 of the district’s 10,300 students. Only the unvaccinated were required to quarantine. The district began requiring masks in all school buildings on Aug. 9.9
The worried mother had one last question for me. “What’s the best mask for a child to wear?” For most kids, a simple, well-fitting cloth mask is fine. The best mask is ultimately the mask a child will wear. A toolkit with practical tips for helping children successfully wear a mask is available on the ABC Science Collaborative website.
Dr. Bryant, president of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, is a pediatrician at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. American Academy of Pediatrics. “Children and COVID-19: State-level data report.”
2. American Academy of Pediatrics. “Children and COVID-19 vaccination trends.”
3. Falk A et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:136-40.
4. Hershow RB et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021;70:442-8.
5. Zimmerman KO et al. Pediatrics. 2021 Jul;e2021052686. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052686.
6. American Academy of Pediatrics. “American Academy of Pediatrics updates recommendations for opening schools in fall 2021.”
7. Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society. “PIDS supports universal masking for students, school staff.”
8. Courtney Hayden. WHAS11. “Greater Clark County Schools return to class July 28.”
9. Dustin Vogt. WAVE3 News. “Greater Clark Country Schools to require masks amid 70 positive cases.”
“I want my child to go back to school,” the mother said to me. “I just want you to tell me it will be safe.”
As the summer break winds down for children across the United States, pediatric COVID-19 cases are rising. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, nearly 94,000 cases were reported for the week ending Aug. 5, more than double the case count from 2 weeks earlier.1
Anecdotally, some children’s hospitals are reporting an increase in pediatric COVID-19 admissions. In the hospital in which I practice, we are seeing numbers similar to those we saw in December and January: a typical daily census of 10 kids admitted with COVID-19, with 4 of them in the intensive care unit. It is a stark contrast to June when, most days, we had no patients with COVID-19 in the hospital. About half of our hospitalized patients are too young to be vaccinated against COVID-19, while the rest are unvaccinated children 12 years and older.
Vaccination of eligible children and teachers is an essential strategy for preventing the spread of COVID-19 in schools, but as children head back to school, immunization rates of educators are largely unknown and are suboptimal among students in most states. As of Aug. 11, 10.7 million U.S. children had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine, representing 43% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 53% of 16- to 17-year-olds.2 Rates vary substantially by state, with more than 70% of kids in Vermont receiving at least one dose of vaccine, compared with less than 25% in Wyoming and Alabama.
Still, in the absence of robust immunization rates, we have data that schools can still reopen successfully. We need to follow the science and implement universal masking, a safe, effective, and practical mitigation strategy.
It worked in Wisconsin. Seventeen K-12 schools in rural Wisconsin opened last fall for in-person instruction.3 Reported compliance with masking was high, ranging from 92.1% to 97.4%, and in-school transmission of COVID-19 was low, with seven cases among 4,876 students.
It worked in Salt Lake City.4 In 20 elementary schools open for in-person instruction Dec. 3, 2020, to Jan. 31, 2021, compliance with mask-wearing was high and in-school transmission was very low, despite a high community incidence of COVID-19. Notably, students’ classroom seats were less than 6 feet apart, suggesting that consistent mask-wearing works even when physical distancing is challenging.
One of the best examples of successful school reopening happened in North Carolina, where pediatricians, pediatric infectious disease specialists, and other experts affiliated with Duke University formed the ABC Science Collaborative to support school districts that requested scientific input to help guide return-to-school policies during the COVID-19 pandemic. From Oct. 26, 2020, to Feb. 28, 2021, the ABC Science Collaborative worked with 13 school districts that were open for in-person instruction using basic mitigation strategies, including universal masking.5 During this time period, there were 4,969 community-acquired SARS-CoV-2 infections in the more than 100,000 students and staff present in schools. Transmission to school contacts was identified in only 209 individuals for a secondary attack rate of less than 1%.
Duke investigator Kanecia Zimmerman, MD, told Duke Today, “We know that, if our goal is to reduce transmission of COVID-19 in schools, there are two effective ways to do that: 1. vaccination, 2. masking. In the setting of schools ... the science suggests masking can be extremely effective, particularly for those who can’t get vaccinated while COVID-19 is still circulating.”
Both the AAP6 and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society7 have emphasized the importance of in-person instruction and endorsed universal masking in school. Mask-optional policies or “mask-if-you-are-unvaccinated” policies don’t work, as we have seen in society at large. They are likely to be especially challenging in school settings. Given an option, many, if not most kids, will take off their masks. Kids who leave them on run the risk of stigmatization or bullying.
On Aug. 4, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention updated its guidance to recommend universal indoor masking for all students, staff, teachers, and visitors to K-12 schools, regardless of vaccination status. Now we’ll have to wait and see if school districts, elected officials, and parents will get on board with masks. ... and we’ll be left to count the number of rising COVID-19 cases that occur until they do.
Case in point: Kids in Greater Clark County, Ind., headed back to school on July 28. Masks were not required on school property, although unvaccinated students and teachers were “strongly encouraged” to wear them.8
Over the first 8 days of in-person instruction, schools in Greater Clark County identified 70 cases of COVID-19 in students and quarantined more than 1,100 of the district’s 10,300 students. Only the unvaccinated were required to quarantine. The district began requiring masks in all school buildings on Aug. 9.9
The worried mother had one last question for me. “What’s the best mask for a child to wear?” For most kids, a simple, well-fitting cloth mask is fine. The best mask is ultimately the mask a child will wear. A toolkit with practical tips for helping children successfully wear a mask is available on the ABC Science Collaborative website.
Dr. Bryant, president of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, is a pediatrician at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. American Academy of Pediatrics. “Children and COVID-19: State-level data report.”
2. American Academy of Pediatrics. “Children and COVID-19 vaccination trends.”
3. Falk A et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:136-40.
4. Hershow RB et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021;70:442-8.
5. Zimmerman KO et al. Pediatrics. 2021 Jul;e2021052686. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052686.
6. American Academy of Pediatrics. “American Academy of Pediatrics updates recommendations for opening schools in fall 2021.”
7. Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society. “PIDS supports universal masking for students, school staff.”
8. Courtney Hayden. WHAS11. “Greater Clark County Schools return to class July 28.”
9. Dustin Vogt. WAVE3 News. “Greater Clark Country Schools to require masks amid 70 positive cases.”
Is this a psychiatric emergency? How to screen, assess, and triage safety concerns from the primary care office
Case vignette: Laura is a 14-year-old biological girl who presents to your office for a routine well-child visit. She is doing well medically but notes that over the past 3 months she has been having increasing thoughts of suicide and has self-harmed via cutting on her wrists with a blade removed from a shaving razor. You contemplate what the most salient questions are in order to determine the best disposition for your patient.
The case vignette above may sound like one that you have heard before, and if not, you undoubtedly will encounter such a situation moving forward. The rate of suicidal ideation amongst youth ages 10-24 has increased by 57.4% between 2007 and 2018.1 Furthermore, suicide is the second leading cause of death in those aged 10 through young adulthood.2 According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s 2019 High School Youth Risk Behavior Survey, 18.8% of high school students seriously considered attempting suicide, 15.7% made a plan about how they would attempt suicide, and 8.9% actually attempted suicide, with 2.5% having a suicide attempt that resulted in an injury, poisoning, or overdose that had to be treated by a doctor or nurse during the 12 months before the survey.3 Children often present first to their primary care provider, and they may be the first individual who the child shares their suicidal or self-harm thoughts with. It may be useful to have a standardized approach, while using your own clinical judgment, to determine best next steps. Given the significant recent surge in children presenting to the emergency department for psychiatric needs and that environment having its own limitations (for example, long wait times, nontherapeutic space, etc.), a simple screen and brief assessment may lead to being able to maintain a patient safely outside of the hospital.
Screen all appropriate patients for suicide
There are, at minimum, three validated screening tools that can be used as to determine what the best next step should be. They include the Ask Suicide-Screening Questions (ASQ) developed by the National Institute of Mental Health, the Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS), and the PHQ-9 (modified for adolescents). We can highlight one of the screening tools here as noted below, but the choice of screener may be based on facility and/or clinician preference.
The Ask Suicide-Screening Questions
The ASQ, developed by the National Institute of Mental Health, include the following four binary questions plus a fifth acuity question, as follows:
1. In the past few weeks, have you wished you were dead?
2. In the past few weeks, have you felt that you or your family would be better off if you were dead?
3. In the past week, have you been having thoughts about killing yourself?
4. Have you ever tried to kill yourself?
a. If yes, how?
b. When?
The following acuity question is to be asked if any of the above are answered “yes”:
5. Are you having thoughts of killing yourself right now?
a. If yes, please describe.
Assess the level of risk
Once you have screened a patient, you need to assess the level of risk to help determine the level of care required. Returning to our original case vignette, does the patient warrant outpatient management, crisis evaluation, or an emergency psychiatric evaluation? You may have already decided that the patient needs an emergency mental health evaluation from a local crisis clinician evaluation and/or the emergency department. However, you may also find that the screen did not elicit imminent concern, but it does warrant a brief assessment to further elucidate the level of risk and proper disposition. One such instrument that may be helpful is the Brief Suicide Safety Assessment (BSSA) – also developed by the NIMH as a tool linked to the ASQ. There are clear and specific instructions in the BSSA with suggestions on how to ask questions. Important components to the BSSA include:
- A focus on a more thorough clinical history – including frequency of suicidal ideation, suicide plan, past behavior, associated symptoms, and social support/stressors
- Collateral information (e.g., further details from those who know the patient such as family/friends).
- Safety planning.
- Determining disposition.
The BSSA may suggest that a crisis/psychiatric evaluation is warranted or suggest that a safety plan with a mental health referral will likely be sufficient.
Triage and safety planning
A safety plan should be created if you determine that a patient can be safely maintained as an outpatient based on your screening, assessment, and triaging. Traditional safety plans come in many different forms and can be found online (Example of a Safety Plan Template). However, most safety plans include some version of the following:
- Increased supervision: 24/7 supervision with doors open/unlocked.
- Reduced access: medications (prescription and OTC) locked away; sharps and firearms secured.
- Adaptive coping strategies (e.g., relaxation techniques such as drawing or listening to music).
- Reliable persons for support (e.g., parent, therapist, school counselor).
- Outpatient mental health provider follow-up and/or referral.
- Provision of local crisis and national hotline contact information.
- Use of a safety plan phone app completed with patient.
Envision a safety plan as a living document that evolves, grows, and changes with your patient/family – one that can be easily reviewed/updated at each visit.
Returning to our case vignette
Laura returns to your office for a follow-up after a 10-day stay at a hospital-diversion program or inpatient psychiatric unit. The decision is made to use the primary care NIMH ASQ/BSSA algorithm, and you determine the patient to not be at imminent risk following the screen and assessment. Laura is triaged as appropriate for outpatient care, you collaborate to update the safety plan, regular follow-ups are scheduled, and a mental health referral has been placed. Thus, there are tools to assist with screening, assessing, and triaging pediatric patients with suicidal ideation that provide the patient with appropriate care and treatment and may help alleviate the need to have a patient present to the emergency department.
Dr. Abdul-Karim is a child psychiatrist at the University of Vermont University Children’s Hospital in Burlington.
Additional resources
The American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry has developed information that can be provided to families about suicide safety precautions that can be taken at home, which can be found here: Facts for Families. Suicide Safety: Precautions at Home.
Screening tools listed above can be found here:
ASQ Toolkit.
C-SSRS.
PHQ-9 Modified for Adolescents (PHQ-A).
References
1. Curtin SC. National Center for Health Statistics. “State Suicide Rates Among Adolescents and Young Adults Aged 10-24: United States, 2000-2018” National Vital Statistics Reports..
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. “Underlying Cause of Death 2018-2019” CDC WONDER Online Database. Accessed 2021 Jul 31, 6:57:39 p.m.
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1991-2019 High School Youth Risk Behavior Survey Data.
Case vignette: Laura is a 14-year-old biological girl who presents to your office for a routine well-child visit. She is doing well medically but notes that over the past 3 months she has been having increasing thoughts of suicide and has self-harmed via cutting on her wrists with a blade removed from a shaving razor. You contemplate what the most salient questions are in order to determine the best disposition for your patient.
The case vignette above may sound like one that you have heard before, and if not, you undoubtedly will encounter such a situation moving forward. The rate of suicidal ideation amongst youth ages 10-24 has increased by 57.4% between 2007 and 2018.1 Furthermore, suicide is the second leading cause of death in those aged 10 through young adulthood.2 According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s 2019 High School Youth Risk Behavior Survey, 18.8% of high school students seriously considered attempting suicide, 15.7% made a plan about how they would attempt suicide, and 8.9% actually attempted suicide, with 2.5% having a suicide attempt that resulted in an injury, poisoning, or overdose that had to be treated by a doctor or nurse during the 12 months before the survey.3 Children often present first to their primary care provider, and they may be the first individual who the child shares their suicidal or self-harm thoughts with. It may be useful to have a standardized approach, while using your own clinical judgment, to determine best next steps. Given the significant recent surge in children presenting to the emergency department for psychiatric needs and that environment having its own limitations (for example, long wait times, nontherapeutic space, etc.), a simple screen and brief assessment may lead to being able to maintain a patient safely outside of the hospital.
Screen all appropriate patients for suicide
There are, at minimum, three validated screening tools that can be used as to determine what the best next step should be. They include the Ask Suicide-Screening Questions (ASQ) developed by the National Institute of Mental Health, the Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS), and the PHQ-9 (modified for adolescents). We can highlight one of the screening tools here as noted below, but the choice of screener may be based on facility and/or clinician preference.
The Ask Suicide-Screening Questions
The ASQ, developed by the National Institute of Mental Health, include the following four binary questions plus a fifth acuity question, as follows:
1. In the past few weeks, have you wished you were dead?
2. In the past few weeks, have you felt that you or your family would be better off if you were dead?
3. In the past week, have you been having thoughts about killing yourself?
4. Have you ever tried to kill yourself?
a. If yes, how?
b. When?
The following acuity question is to be asked if any of the above are answered “yes”:
5. Are you having thoughts of killing yourself right now?
a. If yes, please describe.
Assess the level of risk
Once you have screened a patient, you need to assess the level of risk to help determine the level of care required. Returning to our original case vignette, does the patient warrant outpatient management, crisis evaluation, or an emergency psychiatric evaluation? You may have already decided that the patient needs an emergency mental health evaluation from a local crisis clinician evaluation and/or the emergency department. However, you may also find that the screen did not elicit imminent concern, but it does warrant a brief assessment to further elucidate the level of risk and proper disposition. One such instrument that may be helpful is the Brief Suicide Safety Assessment (BSSA) – also developed by the NIMH as a tool linked to the ASQ. There are clear and specific instructions in the BSSA with suggestions on how to ask questions. Important components to the BSSA include:
- A focus on a more thorough clinical history – including frequency of suicidal ideation, suicide plan, past behavior, associated symptoms, and social support/stressors
- Collateral information (e.g., further details from those who know the patient such as family/friends).
- Safety planning.
- Determining disposition.
The BSSA may suggest that a crisis/psychiatric evaluation is warranted or suggest that a safety plan with a mental health referral will likely be sufficient.
Triage and safety planning
A safety plan should be created if you determine that a patient can be safely maintained as an outpatient based on your screening, assessment, and triaging. Traditional safety plans come in many different forms and can be found online (Example of a Safety Plan Template). However, most safety plans include some version of the following:
- Increased supervision: 24/7 supervision with doors open/unlocked.
- Reduced access: medications (prescription and OTC) locked away; sharps and firearms secured.
- Adaptive coping strategies (e.g., relaxation techniques such as drawing or listening to music).
- Reliable persons for support (e.g., parent, therapist, school counselor).
- Outpatient mental health provider follow-up and/or referral.
- Provision of local crisis and national hotline contact information.
- Use of a safety plan phone app completed with patient.
Envision a safety plan as a living document that evolves, grows, and changes with your patient/family – one that can be easily reviewed/updated at each visit.
Returning to our case vignette
Laura returns to your office for a follow-up after a 10-day stay at a hospital-diversion program or inpatient psychiatric unit. The decision is made to use the primary care NIMH ASQ/BSSA algorithm, and you determine the patient to not be at imminent risk following the screen and assessment. Laura is triaged as appropriate for outpatient care, you collaborate to update the safety plan, regular follow-ups are scheduled, and a mental health referral has been placed. Thus, there are tools to assist with screening, assessing, and triaging pediatric patients with suicidal ideation that provide the patient with appropriate care and treatment and may help alleviate the need to have a patient present to the emergency department.
Dr. Abdul-Karim is a child psychiatrist at the University of Vermont University Children’s Hospital in Burlington.
Additional resources
The American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry has developed information that can be provided to families about suicide safety precautions that can be taken at home, which can be found here: Facts for Families. Suicide Safety: Precautions at Home.
Screening tools listed above can be found here:
ASQ Toolkit.
C-SSRS.
PHQ-9 Modified for Adolescents (PHQ-A).
References
1. Curtin SC. National Center for Health Statistics. “State Suicide Rates Among Adolescents and Young Adults Aged 10-24: United States, 2000-2018” National Vital Statistics Reports..
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. “Underlying Cause of Death 2018-2019” CDC WONDER Online Database. Accessed 2021 Jul 31, 6:57:39 p.m.
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1991-2019 High School Youth Risk Behavior Survey Data.
Case vignette: Laura is a 14-year-old biological girl who presents to your office for a routine well-child visit. She is doing well medically but notes that over the past 3 months she has been having increasing thoughts of suicide and has self-harmed via cutting on her wrists with a blade removed from a shaving razor. You contemplate what the most salient questions are in order to determine the best disposition for your patient.
The case vignette above may sound like one that you have heard before, and if not, you undoubtedly will encounter such a situation moving forward. The rate of suicidal ideation amongst youth ages 10-24 has increased by 57.4% between 2007 and 2018.1 Furthermore, suicide is the second leading cause of death in those aged 10 through young adulthood.2 According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s 2019 High School Youth Risk Behavior Survey, 18.8% of high school students seriously considered attempting suicide, 15.7% made a plan about how they would attempt suicide, and 8.9% actually attempted suicide, with 2.5% having a suicide attempt that resulted in an injury, poisoning, or overdose that had to be treated by a doctor or nurse during the 12 months before the survey.3 Children often present first to their primary care provider, and they may be the first individual who the child shares their suicidal or self-harm thoughts with. It may be useful to have a standardized approach, while using your own clinical judgment, to determine best next steps. Given the significant recent surge in children presenting to the emergency department for psychiatric needs and that environment having its own limitations (for example, long wait times, nontherapeutic space, etc.), a simple screen and brief assessment may lead to being able to maintain a patient safely outside of the hospital.
Screen all appropriate patients for suicide
There are, at minimum, three validated screening tools that can be used as to determine what the best next step should be. They include the Ask Suicide-Screening Questions (ASQ) developed by the National Institute of Mental Health, the Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS), and the PHQ-9 (modified for adolescents). We can highlight one of the screening tools here as noted below, but the choice of screener may be based on facility and/or clinician preference.
The Ask Suicide-Screening Questions
The ASQ, developed by the National Institute of Mental Health, include the following four binary questions plus a fifth acuity question, as follows:
1. In the past few weeks, have you wished you were dead?
2. In the past few weeks, have you felt that you or your family would be better off if you were dead?
3. In the past week, have you been having thoughts about killing yourself?
4. Have you ever tried to kill yourself?
a. If yes, how?
b. When?
The following acuity question is to be asked if any of the above are answered “yes”:
5. Are you having thoughts of killing yourself right now?
a. If yes, please describe.
Assess the level of risk
Once you have screened a patient, you need to assess the level of risk to help determine the level of care required. Returning to our original case vignette, does the patient warrant outpatient management, crisis evaluation, or an emergency psychiatric evaluation? You may have already decided that the patient needs an emergency mental health evaluation from a local crisis clinician evaluation and/or the emergency department. However, you may also find that the screen did not elicit imminent concern, but it does warrant a brief assessment to further elucidate the level of risk and proper disposition. One such instrument that may be helpful is the Brief Suicide Safety Assessment (BSSA) – also developed by the NIMH as a tool linked to the ASQ. There are clear and specific instructions in the BSSA with suggestions on how to ask questions. Important components to the BSSA include:
- A focus on a more thorough clinical history – including frequency of suicidal ideation, suicide plan, past behavior, associated symptoms, and social support/stressors
- Collateral information (e.g., further details from those who know the patient such as family/friends).
- Safety planning.
- Determining disposition.
The BSSA may suggest that a crisis/psychiatric evaluation is warranted or suggest that a safety plan with a mental health referral will likely be sufficient.
Triage and safety planning
A safety plan should be created if you determine that a patient can be safely maintained as an outpatient based on your screening, assessment, and triaging. Traditional safety plans come in many different forms and can be found online (Example of a Safety Plan Template). However, most safety plans include some version of the following:
- Increased supervision: 24/7 supervision with doors open/unlocked.
- Reduced access: medications (prescription and OTC) locked away; sharps and firearms secured.
- Adaptive coping strategies (e.g., relaxation techniques such as drawing or listening to music).
- Reliable persons for support (e.g., parent, therapist, school counselor).
- Outpatient mental health provider follow-up and/or referral.
- Provision of local crisis and national hotline contact information.
- Use of a safety plan phone app completed with patient.
Envision a safety plan as a living document that evolves, grows, and changes with your patient/family – one that can be easily reviewed/updated at each visit.
Returning to our case vignette
Laura returns to your office for a follow-up after a 10-day stay at a hospital-diversion program or inpatient psychiatric unit. The decision is made to use the primary care NIMH ASQ/BSSA algorithm, and you determine the patient to not be at imminent risk following the screen and assessment. Laura is triaged as appropriate for outpatient care, you collaborate to update the safety plan, regular follow-ups are scheduled, and a mental health referral has been placed. Thus, there are tools to assist with screening, assessing, and triaging pediatric patients with suicidal ideation that provide the patient with appropriate care and treatment and may help alleviate the need to have a patient present to the emergency department.
Dr. Abdul-Karim is a child psychiatrist at the University of Vermont University Children’s Hospital in Burlington.
Additional resources
The American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry has developed information that can be provided to families about suicide safety precautions that can be taken at home, which can be found here: Facts for Families. Suicide Safety: Precautions at Home.
Screening tools listed above can be found here:
ASQ Toolkit.
C-SSRS.
PHQ-9 Modified for Adolescents (PHQ-A).
References
1. Curtin SC. National Center for Health Statistics. “State Suicide Rates Among Adolescents and Young Adults Aged 10-24: United States, 2000-2018” National Vital Statistics Reports..
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. “Underlying Cause of Death 2018-2019” CDC WONDER Online Database. Accessed 2021 Jul 31, 6:57:39 p.m.
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1991-2019 High School Youth Risk Behavior Survey Data.
Specific COVID-19 antibodies found in breast milk of vaccinated women
The breast milk of women who had received Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine contained specific antibodies against the infectious disease, new research found.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has raised questions among individuals who are breastfeeding, both because of the possibility of viral transmission to infants during breastfeeding and, more recently, of the potential risks and benefits of vaccination in this specific population,” researchers wrote.
In August, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, and most recently, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, recommended that pregnant people receive the COVID-19 vaccine.
The study, published Aug. 11 in JAMA Network Open, adds to a growing collection of research that has found COVID-19 antibodies in the breast milk of women who were vaccinated against or have been infected with the illness.
Study author Erika Esteve-Palau, MD, PhD, and her colleagues collected blood and milk samples from 33 people who were on average 37 years old and who were on average 17.5 months post partum to examine the correlation of the levels of immunoglobulin G antibodies against the spike protein (S1 subunit) and against the nucleocapsid (NC) of SARS-CoV-2.
Blood and milk samples were taken from each study participant at three time points – 2 weeks after receiving the first dose of the vaccine, 2 weeks after receiving the second dose, and 4 weeks after the second dose. No participants had confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection prior to vaccination or during the study period.
Researchers found that, after the second dose of the vaccine, IgG(S1) levels in breast milk increased and were positively associated with corresponding levels in the blood samples. The median range of IgG(S1) levels for serum-milk pairs at each time point were 519 to 1 arbitrary units (AU) per mL 2 weeks after receiving the first dose of the vaccine, 8,644 to 78 AU/mL 2 weeks after receiving the second dose, and 12,478 to 50.4 AU/mL 4 weeks after receiving the second dose.
Lisette D. Tanner, MD, MPH, FACOG, who was not involved in the study, said she was not surprised by the findings as previous studies have shown the passage of antibodies in breast milk in vaccinated women. One 2021 study published in JAMA found SARS-CoV-2–specific IgA and IgG antibodies in breast milk for 6 weeks after vaccination. IgA secretion was evident as early as 2 weeks after vaccination followed by a spike in IgG after 4 weeks (a week after the second vaccine). Meanwhile, another 2021 study published in mBio found that breast milk produced by parents with COVID-19 is a source of SARS-CoV-2 IgA and IgG antibodies and can neutralize COVID-19 activity.
“While the data from this and other studies is promising in regards to the passage of antibodies, it is currently unclear what the long-term effects for children will be,” said Dr. Tanner of the department of gynecology and obstetrics at Emory University, Atlanta. “It is not yet known what level of antibodies is necessary to convey protection to either neonates or children. This is an active area of investigation at multiple institutions.”
Dr. Tanner said she wished the study “evaluated neonatal cord blood or serum levels to better understand the immune response mounted by the children of women who received vaccination.”
Researchers of the current study said larger prospective studies are needed to confirm the safety of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in individuals who are breastfeeding and further assess the association of vaccination with infants’ health and SARS-CoV-2–specific immunity.
Dr. Palau and Dr. Tanner had no relevant financial disclosures.
The breast milk of women who had received Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine contained specific antibodies against the infectious disease, new research found.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has raised questions among individuals who are breastfeeding, both because of the possibility of viral transmission to infants during breastfeeding and, more recently, of the potential risks and benefits of vaccination in this specific population,” researchers wrote.
In August, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, and most recently, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, recommended that pregnant people receive the COVID-19 vaccine.
The study, published Aug. 11 in JAMA Network Open, adds to a growing collection of research that has found COVID-19 antibodies in the breast milk of women who were vaccinated against or have been infected with the illness.
Study author Erika Esteve-Palau, MD, PhD, and her colleagues collected blood and milk samples from 33 people who were on average 37 years old and who were on average 17.5 months post partum to examine the correlation of the levels of immunoglobulin G antibodies against the spike protein (S1 subunit) and against the nucleocapsid (NC) of SARS-CoV-2.
Blood and milk samples were taken from each study participant at three time points – 2 weeks after receiving the first dose of the vaccine, 2 weeks after receiving the second dose, and 4 weeks after the second dose. No participants had confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection prior to vaccination or during the study period.
Researchers found that, after the second dose of the vaccine, IgG(S1) levels in breast milk increased and were positively associated with corresponding levels in the blood samples. The median range of IgG(S1) levels for serum-milk pairs at each time point were 519 to 1 arbitrary units (AU) per mL 2 weeks after receiving the first dose of the vaccine, 8,644 to 78 AU/mL 2 weeks after receiving the second dose, and 12,478 to 50.4 AU/mL 4 weeks after receiving the second dose.
Lisette D. Tanner, MD, MPH, FACOG, who was not involved in the study, said she was not surprised by the findings as previous studies have shown the passage of antibodies in breast milk in vaccinated women. One 2021 study published in JAMA found SARS-CoV-2–specific IgA and IgG antibodies in breast milk for 6 weeks after vaccination. IgA secretion was evident as early as 2 weeks after vaccination followed by a spike in IgG after 4 weeks (a week after the second vaccine). Meanwhile, another 2021 study published in mBio found that breast milk produced by parents with COVID-19 is a source of SARS-CoV-2 IgA and IgG antibodies and can neutralize COVID-19 activity.
“While the data from this and other studies is promising in regards to the passage of antibodies, it is currently unclear what the long-term effects for children will be,” said Dr. Tanner of the department of gynecology and obstetrics at Emory University, Atlanta. “It is not yet known what level of antibodies is necessary to convey protection to either neonates or children. This is an active area of investigation at multiple institutions.”
Dr. Tanner said she wished the study “evaluated neonatal cord blood or serum levels to better understand the immune response mounted by the children of women who received vaccination.”
Researchers of the current study said larger prospective studies are needed to confirm the safety of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in individuals who are breastfeeding and further assess the association of vaccination with infants’ health and SARS-CoV-2–specific immunity.
Dr. Palau and Dr. Tanner had no relevant financial disclosures.
The breast milk of women who had received Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine contained specific antibodies against the infectious disease, new research found.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has raised questions among individuals who are breastfeeding, both because of the possibility of viral transmission to infants during breastfeeding and, more recently, of the potential risks and benefits of vaccination in this specific population,” researchers wrote.
In August, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, and most recently, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, recommended that pregnant people receive the COVID-19 vaccine.
The study, published Aug. 11 in JAMA Network Open, adds to a growing collection of research that has found COVID-19 antibodies in the breast milk of women who were vaccinated against or have been infected with the illness.
Study author Erika Esteve-Palau, MD, PhD, and her colleagues collected blood and milk samples from 33 people who were on average 37 years old and who were on average 17.5 months post partum to examine the correlation of the levels of immunoglobulin G antibodies against the spike protein (S1 subunit) and against the nucleocapsid (NC) of SARS-CoV-2.
Blood and milk samples were taken from each study participant at three time points – 2 weeks after receiving the first dose of the vaccine, 2 weeks after receiving the second dose, and 4 weeks after the second dose. No participants had confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection prior to vaccination or during the study period.
Researchers found that, after the second dose of the vaccine, IgG(S1) levels in breast milk increased and were positively associated with corresponding levels in the blood samples. The median range of IgG(S1) levels for serum-milk pairs at each time point were 519 to 1 arbitrary units (AU) per mL 2 weeks after receiving the first dose of the vaccine, 8,644 to 78 AU/mL 2 weeks after receiving the second dose, and 12,478 to 50.4 AU/mL 4 weeks after receiving the second dose.
Lisette D. Tanner, MD, MPH, FACOG, who was not involved in the study, said she was not surprised by the findings as previous studies have shown the passage of antibodies in breast milk in vaccinated women. One 2021 study published in JAMA found SARS-CoV-2–specific IgA and IgG antibodies in breast milk for 6 weeks after vaccination. IgA secretion was evident as early as 2 weeks after vaccination followed by a spike in IgG after 4 weeks (a week after the second vaccine). Meanwhile, another 2021 study published in mBio found that breast milk produced by parents with COVID-19 is a source of SARS-CoV-2 IgA and IgG antibodies and can neutralize COVID-19 activity.
“While the data from this and other studies is promising in regards to the passage of antibodies, it is currently unclear what the long-term effects for children will be,” said Dr. Tanner of the department of gynecology and obstetrics at Emory University, Atlanta. “It is not yet known what level of antibodies is necessary to convey protection to either neonates or children. This is an active area of investigation at multiple institutions.”
Dr. Tanner said she wished the study “evaluated neonatal cord blood or serum levels to better understand the immune response mounted by the children of women who received vaccination.”
Researchers of the current study said larger prospective studies are needed to confirm the safety of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in individuals who are breastfeeding and further assess the association of vaccination with infants’ health and SARS-CoV-2–specific immunity.
Dr. Palau and Dr. Tanner had no relevant financial disclosures.
JAMA NETWORK OPEN
No more encopresis!
Wishful thinking. “Repeated involuntary passage of stool in the underwear after the acquisition of toileting skills (typically > 4 years of age) in the absence of overt neuromuscular anorectal dysfunction,” formerly called encopresis, certainly still exists, renamed functional fecal incontinence (FFI). You have surely cared for many children with FFI over the years, mostly the 80% retentive (constipated) type but newer information may make your management more successful!
The first step in managing FFI is detecting it. This may seem easy as we get a whiff of its presence, even if the child and parents are unaware because of habituation to the odor. Children lose sensation from rectal dilation by the stool mass and become unaware of leakage. But they also are ashamed of and deny “accidents,” hide soiled underwear, and keep distance from parents and peers. Our physical exam may reveal an abdominal mass or perianal stool. While there, check the anal wink, anus placement, lower spine integrity, and ankle reflexes for rare neurological causes. A rectal exam is not required if the story fits but, if not, may show a dilated rectal vault and hard mass. Blood work, x-ray, ultrasound, barium enemas, or manometry are rarely indicated.
Instead of counting on expressed concern, we should routinely ask children about large, painful, or infrequent poops. There are even Rome IV criteria for constipation – at least two of the following without organic pathology and with duration of at least 1 month: less than 2 defecations/week, a history of hard or painful stools, retentive posturing or excessive stool retention, large stools blocking the toilet, large rectal fecal mass, or at least 1 episode of incontinence/week. Our history should request this but parents are often unaware of their child’s patterns except for that blocked toilet!
Other actionable history includes struggles over toilet training, early anal fissure or painful stools, a history of “straining”, crying, or crossing legs (attempts to withhold), short stature and/or diarrhea (possible celiac disease), abdominal pain, poor appetite, or a diet high in milk products or low in fiber. Family history may suggest rare organic causes such as hypothyroidism, Hirschsprung disease, multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2, or celiac disease, but also constipation (in 55%). After the newborn period (imperforate anus or meconium ileus), 95% of constipation is functional.
While constipation has a worldwide prevalence of 9.5%, low exercise and low-fiber diet are particularly American. Low total food intake as a cause is uncommon in the United States but another reason to screen for food insecurity.
Patterns of behavior can predispose to constipation and FFI. For the child, oppositionality, social anxiety, depression, or eating disorders may interfere with sufficient stool frequency and relaxation needed to fully evacuate at home, daycare, or school. Query every child with ADHD about stool patterns as inattention to urge plus impatience with completing defection (and ODD) are common disorders leading to FFI. Parents who are overly demanding, intrusive, rushing, irritable, anxious, or obsessive may also make routine toileting stressful. When caregivers are neglectful, fail to maintain routines for eating, or ignore dirty diapers, toilet training is more likely to fail and constipation ensue.
Clean out and maintenance using medication are needed for FFI, but child and family behavior change are also critical; the combination has proven more successful. Both the child and parents need clear a explanation of how constipation develops from withholding, regardless of the reason (pain, anxiety, conflict, diet), leading to larger stools more difficult to pass as water is absorbed in the colon. The large mass stretches the bowel so that sensation and strength for motility is impaired and softer stool leaks by and out the rectum unbeknownst to the child. I find drawing “the rock of poop” in a dilated thin walled colon with nerves sparse and “liquid stool sneaking by” compared to a “muscular” colon with soft poop animates and objectifies this explanation. Making it clear that leaking is involuntary is key to having the parent and child directly forgive each other for prior anger, blaming, sneaking, or punishment. While the school-aged child needs to be in charge of toileting, resolving the conflict is essential.
The critical next step is cleaning out “the rocks,” which should only rarely be omitted. Polyethylene glycol (PEG, for example, Miralax) has the best evidence, tastes better (without electrolytes), and dosing 1-1.5 g/kg per day premixed in 10 mL/kg fluid of the child’s choice kept cold and swallowed within 30 minutes daily for 3-6 days until feces have no more chunks. This process disimpacts 95% of the time. Reassure parents of the long-term safety despite the warning on the label that it is intended for adult users. Lactulose or sorbitol (1 mL/kg, once or twice daily), magnesium hydroxide, bisacodyl, or senna are long second choices. Only if these fail should mineral oil 15-30 mL per year of age, up to 240 mL per day be used and then not in infants or if there is aspiration risk. While enemas (mineral oil, sodium phosphate, or saline) and p.o. PEG are equally effective, enemas are very intrusive and unnecessary. There is insufficient evidence for probiotics, prebiotics, or synbiotics.
It is crucial to be honest with the child and parents that clean out can be uncomfortable as cramping or leaking may occur. Thus, starting PEG after school on Friday and being prepared to stay home Monday (if rocks are still emerging) may be needed to avoid accidents.
After clean out, maintenance using daily PEG 0.4-0.8 g/kg per day (best) or lactulose needs to be continued for 2-6 or even 12 months to prevent relapse as the bowel recovers. Bowels need to produce 1-2 soft stools per day for 1 month before considering weaning off PEG. High-fiber (age of child plus 5-10 g/day) diet perpetually is more acceptable if we suggest Frosted Mini-Wheats, Fig Newtons, cookies or muffins baked with wheat bran, popcorn, or fruits with “p” in the name (for example, prunes, pears, apricots), Raisin Bran, or methylcellulose in juice or Popsicles, wafers (with jelly or frosting), or tablets. Infant diet can include brown sugar, or prune/apple/pear juice (Karo is no longer reliably osmotic). Diet needs to include 32-64 ounces of nonmilk fluids, although this will not serve as treatment alone. Limit cow milk to 16 oz. or consider eliminating it entirely if other treatments fail as cow milk is constipating.
Maintenance also requires coaching the child to commence “exercises” to “strengthen the bowel.” These consist of sitting with feet supported to elevate at the hip for 10 minutes by a timer after meals 2-3 times per day and pushing. Entertainment such as music, books, small toys, or a noncompetitive video game and/or rewards of cash, tokens, or treats may lighten the routine. These “exercises” need to be continued indefinitely and monitored with a stool diary. Monthly check-ins are essential to adherence and success, especially in the first 3-4 months, to address any relapses.
While constipation has consequences besides FFI: physical (abdominal pain, anal fissure, rectal prolapse, enuresis, UTI, vesicoureteral reflux, and upper urinary tract dilatation, poor appetite, or poor growth), emotional problems (lability, depression, anxiety, aggression, and low self-esteem), social problems (peer humiliation, teasing, rejection, parent upset, anger, shaming, and punishment), and school absence, we can be supportive and effective coaches for this chronic condition.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS (www.CHADIS.com). She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
Wishful thinking. “Repeated involuntary passage of stool in the underwear after the acquisition of toileting skills (typically > 4 years of age) in the absence of overt neuromuscular anorectal dysfunction,” formerly called encopresis, certainly still exists, renamed functional fecal incontinence (FFI). You have surely cared for many children with FFI over the years, mostly the 80% retentive (constipated) type but newer information may make your management more successful!
The first step in managing FFI is detecting it. This may seem easy as we get a whiff of its presence, even if the child and parents are unaware because of habituation to the odor. Children lose sensation from rectal dilation by the stool mass and become unaware of leakage. But they also are ashamed of and deny “accidents,” hide soiled underwear, and keep distance from parents and peers. Our physical exam may reveal an abdominal mass or perianal stool. While there, check the anal wink, anus placement, lower spine integrity, and ankle reflexes for rare neurological causes. A rectal exam is not required if the story fits but, if not, may show a dilated rectal vault and hard mass. Blood work, x-ray, ultrasound, barium enemas, or manometry are rarely indicated.
Instead of counting on expressed concern, we should routinely ask children about large, painful, or infrequent poops. There are even Rome IV criteria for constipation – at least two of the following without organic pathology and with duration of at least 1 month: less than 2 defecations/week, a history of hard or painful stools, retentive posturing or excessive stool retention, large stools blocking the toilet, large rectal fecal mass, or at least 1 episode of incontinence/week. Our history should request this but parents are often unaware of their child’s patterns except for that blocked toilet!
Other actionable history includes struggles over toilet training, early anal fissure or painful stools, a history of “straining”, crying, or crossing legs (attempts to withhold), short stature and/or diarrhea (possible celiac disease), abdominal pain, poor appetite, or a diet high in milk products or low in fiber. Family history may suggest rare organic causes such as hypothyroidism, Hirschsprung disease, multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2, or celiac disease, but also constipation (in 55%). After the newborn period (imperforate anus or meconium ileus), 95% of constipation is functional.
While constipation has a worldwide prevalence of 9.5%, low exercise and low-fiber diet are particularly American. Low total food intake as a cause is uncommon in the United States but another reason to screen for food insecurity.
Patterns of behavior can predispose to constipation and FFI. For the child, oppositionality, social anxiety, depression, or eating disorders may interfere with sufficient stool frequency and relaxation needed to fully evacuate at home, daycare, or school. Query every child with ADHD about stool patterns as inattention to urge plus impatience with completing defection (and ODD) are common disorders leading to FFI. Parents who are overly demanding, intrusive, rushing, irritable, anxious, or obsessive may also make routine toileting stressful. When caregivers are neglectful, fail to maintain routines for eating, or ignore dirty diapers, toilet training is more likely to fail and constipation ensue.
Clean out and maintenance using medication are needed for FFI, but child and family behavior change are also critical; the combination has proven more successful. Both the child and parents need clear a explanation of how constipation develops from withholding, regardless of the reason (pain, anxiety, conflict, diet), leading to larger stools more difficult to pass as water is absorbed in the colon. The large mass stretches the bowel so that sensation and strength for motility is impaired and softer stool leaks by and out the rectum unbeknownst to the child. I find drawing “the rock of poop” in a dilated thin walled colon with nerves sparse and “liquid stool sneaking by” compared to a “muscular” colon with soft poop animates and objectifies this explanation. Making it clear that leaking is involuntary is key to having the parent and child directly forgive each other for prior anger, blaming, sneaking, or punishment. While the school-aged child needs to be in charge of toileting, resolving the conflict is essential.
The critical next step is cleaning out “the rocks,” which should only rarely be omitted. Polyethylene glycol (PEG, for example, Miralax) has the best evidence, tastes better (without electrolytes), and dosing 1-1.5 g/kg per day premixed in 10 mL/kg fluid of the child’s choice kept cold and swallowed within 30 minutes daily for 3-6 days until feces have no more chunks. This process disimpacts 95% of the time. Reassure parents of the long-term safety despite the warning on the label that it is intended for adult users. Lactulose or sorbitol (1 mL/kg, once or twice daily), magnesium hydroxide, bisacodyl, or senna are long second choices. Only if these fail should mineral oil 15-30 mL per year of age, up to 240 mL per day be used and then not in infants or if there is aspiration risk. While enemas (mineral oil, sodium phosphate, or saline) and p.o. PEG are equally effective, enemas are very intrusive and unnecessary. There is insufficient evidence for probiotics, prebiotics, or synbiotics.
It is crucial to be honest with the child and parents that clean out can be uncomfortable as cramping or leaking may occur. Thus, starting PEG after school on Friday and being prepared to stay home Monday (if rocks are still emerging) may be needed to avoid accidents.
After clean out, maintenance using daily PEG 0.4-0.8 g/kg per day (best) or lactulose needs to be continued for 2-6 or even 12 months to prevent relapse as the bowel recovers. Bowels need to produce 1-2 soft stools per day for 1 month before considering weaning off PEG. High-fiber (age of child plus 5-10 g/day) diet perpetually is more acceptable if we suggest Frosted Mini-Wheats, Fig Newtons, cookies or muffins baked with wheat bran, popcorn, or fruits with “p” in the name (for example, prunes, pears, apricots), Raisin Bran, or methylcellulose in juice or Popsicles, wafers (with jelly or frosting), or tablets. Infant diet can include brown sugar, or prune/apple/pear juice (Karo is no longer reliably osmotic). Diet needs to include 32-64 ounces of nonmilk fluids, although this will not serve as treatment alone. Limit cow milk to 16 oz. or consider eliminating it entirely if other treatments fail as cow milk is constipating.
Maintenance also requires coaching the child to commence “exercises” to “strengthen the bowel.” These consist of sitting with feet supported to elevate at the hip for 10 minutes by a timer after meals 2-3 times per day and pushing. Entertainment such as music, books, small toys, or a noncompetitive video game and/or rewards of cash, tokens, or treats may lighten the routine. These “exercises” need to be continued indefinitely and monitored with a stool diary. Monthly check-ins are essential to adherence and success, especially in the first 3-4 months, to address any relapses.
While constipation has consequences besides FFI: physical (abdominal pain, anal fissure, rectal prolapse, enuresis, UTI, vesicoureteral reflux, and upper urinary tract dilatation, poor appetite, or poor growth), emotional problems (lability, depression, anxiety, aggression, and low self-esteem), social problems (peer humiliation, teasing, rejection, parent upset, anger, shaming, and punishment), and school absence, we can be supportive and effective coaches for this chronic condition.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS (www.CHADIS.com). She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
Wishful thinking. “Repeated involuntary passage of stool in the underwear after the acquisition of toileting skills (typically > 4 years of age) in the absence of overt neuromuscular anorectal dysfunction,” formerly called encopresis, certainly still exists, renamed functional fecal incontinence (FFI). You have surely cared for many children with FFI over the years, mostly the 80% retentive (constipated) type but newer information may make your management more successful!
The first step in managing FFI is detecting it. This may seem easy as we get a whiff of its presence, even if the child and parents are unaware because of habituation to the odor. Children lose sensation from rectal dilation by the stool mass and become unaware of leakage. But they also are ashamed of and deny “accidents,” hide soiled underwear, and keep distance from parents and peers. Our physical exam may reveal an abdominal mass or perianal stool. While there, check the anal wink, anus placement, lower spine integrity, and ankle reflexes for rare neurological causes. A rectal exam is not required if the story fits but, if not, may show a dilated rectal vault and hard mass. Blood work, x-ray, ultrasound, barium enemas, or manometry are rarely indicated.
Instead of counting on expressed concern, we should routinely ask children about large, painful, or infrequent poops. There are even Rome IV criteria for constipation – at least two of the following without organic pathology and with duration of at least 1 month: less than 2 defecations/week, a history of hard or painful stools, retentive posturing or excessive stool retention, large stools blocking the toilet, large rectal fecal mass, or at least 1 episode of incontinence/week. Our history should request this but parents are often unaware of their child’s patterns except for that blocked toilet!
Other actionable history includes struggles over toilet training, early anal fissure or painful stools, a history of “straining”, crying, or crossing legs (attempts to withhold), short stature and/or diarrhea (possible celiac disease), abdominal pain, poor appetite, or a diet high in milk products or low in fiber. Family history may suggest rare organic causes such as hypothyroidism, Hirschsprung disease, multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2, or celiac disease, but also constipation (in 55%). After the newborn period (imperforate anus or meconium ileus), 95% of constipation is functional.
While constipation has a worldwide prevalence of 9.5%, low exercise and low-fiber diet are particularly American. Low total food intake as a cause is uncommon in the United States but another reason to screen for food insecurity.
Patterns of behavior can predispose to constipation and FFI. For the child, oppositionality, social anxiety, depression, or eating disorders may interfere with sufficient stool frequency and relaxation needed to fully evacuate at home, daycare, or school. Query every child with ADHD about stool patterns as inattention to urge plus impatience with completing defection (and ODD) are common disorders leading to FFI. Parents who are overly demanding, intrusive, rushing, irritable, anxious, or obsessive may also make routine toileting stressful. When caregivers are neglectful, fail to maintain routines for eating, or ignore dirty diapers, toilet training is more likely to fail and constipation ensue.
Clean out and maintenance using medication are needed for FFI, but child and family behavior change are also critical; the combination has proven more successful. Both the child and parents need clear a explanation of how constipation develops from withholding, regardless of the reason (pain, anxiety, conflict, diet), leading to larger stools more difficult to pass as water is absorbed in the colon. The large mass stretches the bowel so that sensation and strength for motility is impaired and softer stool leaks by and out the rectum unbeknownst to the child. I find drawing “the rock of poop” in a dilated thin walled colon with nerves sparse and “liquid stool sneaking by” compared to a “muscular” colon with soft poop animates and objectifies this explanation. Making it clear that leaking is involuntary is key to having the parent and child directly forgive each other for prior anger, blaming, sneaking, or punishment. While the school-aged child needs to be in charge of toileting, resolving the conflict is essential.
The critical next step is cleaning out “the rocks,” which should only rarely be omitted. Polyethylene glycol (PEG, for example, Miralax) has the best evidence, tastes better (without electrolytes), and dosing 1-1.5 g/kg per day premixed in 10 mL/kg fluid of the child’s choice kept cold and swallowed within 30 minutes daily for 3-6 days until feces have no more chunks. This process disimpacts 95% of the time. Reassure parents of the long-term safety despite the warning on the label that it is intended for adult users. Lactulose or sorbitol (1 mL/kg, once or twice daily), magnesium hydroxide, bisacodyl, or senna are long second choices. Only if these fail should mineral oil 15-30 mL per year of age, up to 240 mL per day be used and then not in infants or if there is aspiration risk. While enemas (mineral oil, sodium phosphate, or saline) and p.o. PEG are equally effective, enemas are very intrusive and unnecessary. There is insufficient evidence for probiotics, prebiotics, or synbiotics.
It is crucial to be honest with the child and parents that clean out can be uncomfortable as cramping or leaking may occur. Thus, starting PEG after school on Friday and being prepared to stay home Monday (if rocks are still emerging) may be needed to avoid accidents.
After clean out, maintenance using daily PEG 0.4-0.8 g/kg per day (best) or lactulose needs to be continued for 2-6 or even 12 months to prevent relapse as the bowel recovers. Bowels need to produce 1-2 soft stools per day for 1 month before considering weaning off PEG. High-fiber (age of child plus 5-10 g/day) diet perpetually is more acceptable if we suggest Frosted Mini-Wheats, Fig Newtons, cookies or muffins baked with wheat bran, popcorn, or fruits with “p” in the name (for example, prunes, pears, apricots), Raisin Bran, or methylcellulose in juice or Popsicles, wafers (with jelly or frosting), or tablets. Infant diet can include brown sugar, or prune/apple/pear juice (Karo is no longer reliably osmotic). Diet needs to include 32-64 ounces of nonmilk fluids, although this will not serve as treatment alone. Limit cow milk to 16 oz. or consider eliminating it entirely if other treatments fail as cow milk is constipating.
Maintenance also requires coaching the child to commence “exercises” to “strengthen the bowel.” These consist of sitting with feet supported to elevate at the hip for 10 minutes by a timer after meals 2-3 times per day and pushing. Entertainment such as music, books, small toys, or a noncompetitive video game and/or rewards of cash, tokens, or treats may lighten the routine. These “exercises” need to be continued indefinitely and monitored with a stool diary. Monthly check-ins are essential to adherence and success, especially in the first 3-4 months, to address any relapses.
While constipation has consequences besides FFI: physical (abdominal pain, anal fissure, rectal prolapse, enuresis, UTI, vesicoureteral reflux, and upper urinary tract dilatation, poor appetite, or poor growth), emotional problems (lability, depression, anxiety, aggression, and low self-esteem), social problems (peer humiliation, teasing, rejection, parent upset, anger, shaming, and punishment), and school absence, we can be supportive and effective coaches for this chronic condition.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS (www.CHADIS.com). She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
Move from awareness to action to combat racism in medicine
Structural racism and implicit bias are connected, and both must be addressed to move from awareness of racism to action, said Nathan Chomilo, MD, of HealthPartners/Park Nicollet, Brooklyn Center, Minn., in a presentation at the virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine annual conference.
“We need pediatricians with the courage to address racism head on,” he said.
One step in moving from awareness to action against structural and institutional racism in medicine is examining policies, Dr. Chomilo said. He cited the creation of Medicare and Medicaid in 1965 as examples of how policy changes can make a difference, illustrated by data from 1955-1975 that showed a significant decrease in infant deaths among Black infants in Mississippi after 1965.
Medicaid expansion has helped to narrow, but not eliminate, racial disparities in health care, Dr. Chomilo said. The impact of Medicare and Medicaid is evident in the current COVID-19 pandemic, as county level data show that areas where more than 25% of the population are uninsured have higher rates of COVID-19 infections, said Dr. Chomilo. Policies that impact access to care also impact their incidence of chronic diseases and risk for severe disease, he noted.
“If you don’t have ready access to a health care provider, you don’t have access to the vaccine, and you don’t have information that would inform your getting the vaccine,” he added.
Prioritizing the power of voting
“Voting is one of many ways we can impact structural racism in health care policy,” Dr. Chomilo emphasized.
However, voting inequity remains a challenge, Dr. Chomilo noted. Community level disparities lead to inequity in voting access and subsequent disparities in voter participation, he said. “Leaders are less responsive to nonvoting constituents,” which can result in policies that impact health inequitably, and loop back to community level health disparities, he explained.
Historically, physicians have had an 8%-9% lower voter turnout than the general public, although this may have changed in recent elections, Dr. Chomilo said. He encouraged all clinicians to set an example and vote, and to empower their patients to vote. Evidence shows that enfranchisement of Black voters is associated with reductions in education gaps for Blacks and Whites, and that enfranchisement of women is associated with increased spending on children and lower child mortality, he said. Dr. Chomilo encouraged pediatricians and all clinicians to take advantage of the resources on voting available from the American Academy of Pediatrics (aap.org/votekids).
“When we see more people in a community vote, leaders are more responsive to their needs,” he said.
Informing racial identity
“Racial identity is informed by racial socialization,” Dr. Chomilo said. “All of us are socialized along the lines of race; it happens in conversations with parents, family, peers, community.” Another point in moving from awareness to action in eliminating structural racism is recognizing that children are not too young to talk about race, Dr. Chomilo emphasized.
Children start to navigate racial identity and to take note of other differences at an early age. For example, a 3-year-old might ask, “why does that person talk funny, why is that person being pushed in a chair?” Dr. Chomilo said, and it is important for parents and as pediatricians to be prepared for these questions, which are part of normal development. As children get older, they start to reflect on what differences mean for them, which is not rooted in anything negative, he noted.
Children first develop racial identity at home, but children solidify their identities in child care and school settings, Dr. Chomilo said. The American Academy of Pediatrics has acknowledged the potential for racial bias in education and child care, and said in a statement that, “it is critical for pediatricians to recognize the institutional personally mediated, and internalized levels of racism that occur in the educational setting, because education is a critical social determinant of health for children.” In fact, data from children in preschool show that they use racial categories to identify themselves and others, to include or exclude children from activities, and to negotiate power in their social and play networks.
Early intervention matters in educating children about racism, Dr. Chomilo said. “If we were not taught to talk about race, it is on us to learn about it ourselves as well,” he said.
Ultimately, the goal is to create active antiracism among adults and children, said Dr. Chomilo. He encouraged pediatricians and parents not to shut down or discourage children when they raise questions of race, but to take the opportunity to teach. “There may be hurt feelings around what a child said, even if they didn’t mean to offend someone,” he noted. Take the topic seriously, and make racism conversations ongoing; teach children to safely oppose negative messages and behaviors in others, and replace them with something positive, he emphasized.
Addressing bias in clinical settings
Dr. Chomilo also encouraged hospitalists to consider internalized racism in clinical settings and take action to build confidence and cultural pride in all patients by ensuring that a pediatric hospital unit is welcoming and representative of the diversity in a given community, with appropriate options for books, movies, and toys. He also encouraged pediatric hospitalists to assess children for experiences of racism as part of a social assessment. Be aware of signs of posttraumatic stress, anxiety, depression, or grief that might have a racial component, he said.
Dr. Chomilo had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Structural racism and implicit bias are connected, and both must be addressed to move from awareness of racism to action, said Nathan Chomilo, MD, of HealthPartners/Park Nicollet, Brooklyn Center, Minn., in a presentation at the virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine annual conference.
“We need pediatricians with the courage to address racism head on,” he said.
One step in moving from awareness to action against structural and institutional racism in medicine is examining policies, Dr. Chomilo said. He cited the creation of Medicare and Medicaid in 1965 as examples of how policy changes can make a difference, illustrated by data from 1955-1975 that showed a significant decrease in infant deaths among Black infants in Mississippi after 1965.
Medicaid expansion has helped to narrow, but not eliminate, racial disparities in health care, Dr. Chomilo said. The impact of Medicare and Medicaid is evident in the current COVID-19 pandemic, as county level data show that areas where more than 25% of the population are uninsured have higher rates of COVID-19 infections, said Dr. Chomilo. Policies that impact access to care also impact their incidence of chronic diseases and risk for severe disease, he noted.
“If you don’t have ready access to a health care provider, you don’t have access to the vaccine, and you don’t have information that would inform your getting the vaccine,” he added.
Prioritizing the power of voting
“Voting is one of many ways we can impact structural racism in health care policy,” Dr. Chomilo emphasized.
However, voting inequity remains a challenge, Dr. Chomilo noted. Community level disparities lead to inequity in voting access and subsequent disparities in voter participation, he said. “Leaders are less responsive to nonvoting constituents,” which can result in policies that impact health inequitably, and loop back to community level health disparities, he explained.
Historically, physicians have had an 8%-9% lower voter turnout than the general public, although this may have changed in recent elections, Dr. Chomilo said. He encouraged all clinicians to set an example and vote, and to empower their patients to vote. Evidence shows that enfranchisement of Black voters is associated with reductions in education gaps for Blacks and Whites, and that enfranchisement of women is associated with increased spending on children and lower child mortality, he said. Dr. Chomilo encouraged pediatricians and all clinicians to take advantage of the resources on voting available from the American Academy of Pediatrics (aap.org/votekids).
“When we see more people in a community vote, leaders are more responsive to their needs,” he said.
Informing racial identity
“Racial identity is informed by racial socialization,” Dr. Chomilo said. “All of us are socialized along the lines of race; it happens in conversations with parents, family, peers, community.” Another point in moving from awareness to action in eliminating structural racism is recognizing that children are not too young to talk about race, Dr. Chomilo emphasized.
Children start to navigate racial identity and to take note of other differences at an early age. For example, a 3-year-old might ask, “why does that person talk funny, why is that person being pushed in a chair?” Dr. Chomilo said, and it is important for parents and as pediatricians to be prepared for these questions, which are part of normal development. As children get older, they start to reflect on what differences mean for them, which is not rooted in anything negative, he noted.
Children first develop racial identity at home, but children solidify their identities in child care and school settings, Dr. Chomilo said. The American Academy of Pediatrics has acknowledged the potential for racial bias in education and child care, and said in a statement that, “it is critical for pediatricians to recognize the institutional personally mediated, and internalized levels of racism that occur in the educational setting, because education is a critical social determinant of health for children.” In fact, data from children in preschool show that they use racial categories to identify themselves and others, to include or exclude children from activities, and to negotiate power in their social and play networks.
Early intervention matters in educating children about racism, Dr. Chomilo said. “If we were not taught to talk about race, it is on us to learn about it ourselves as well,” he said.
Ultimately, the goal is to create active antiracism among adults and children, said Dr. Chomilo. He encouraged pediatricians and parents not to shut down or discourage children when they raise questions of race, but to take the opportunity to teach. “There may be hurt feelings around what a child said, even if they didn’t mean to offend someone,” he noted. Take the topic seriously, and make racism conversations ongoing; teach children to safely oppose negative messages and behaviors in others, and replace them with something positive, he emphasized.
Addressing bias in clinical settings
Dr. Chomilo also encouraged hospitalists to consider internalized racism in clinical settings and take action to build confidence and cultural pride in all patients by ensuring that a pediatric hospital unit is welcoming and representative of the diversity in a given community, with appropriate options for books, movies, and toys. He also encouraged pediatric hospitalists to assess children for experiences of racism as part of a social assessment. Be aware of signs of posttraumatic stress, anxiety, depression, or grief that might have a racial component, he said.
Dr. Chomilo had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Structural racism and implicit bias are connected, and both must be addressed to move from awareness of racism to action, said Nathan Chomilo, MD, of HealthPartners/Park Nicollet, Brooklyn Center, Minn., in a presentation at the virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine annual conference.
“We need pediatricians with the courage to address racism head on,” he said.
One step in moving from awareness to action against structural and institutional racism in medicine is examining policies, Dr. Chomilo said. He cited the creation of Medicare and Medicaid in 1965 as examples of how policy changes can make a difference, illustrated by data from 1955-1975 that showed a significant decrease in infant deaths among Black infants in Mississippi after 1965.
Medicaid expansion has helped to narrow, but not eliminate, racial disparities in health care, Dr. Chomilo said. The impact of Medicare and Medicaid is evident in the current COVID-19 pandemic, as county level data show that areas where more than 25% of the population are uninsured have higher rates of COVID-19 infections, said Dr. Chomilo. Policies that impact access to care also impact their incidence of chronic diseases and risk for severe disease, he noted.
“If you don’t have ready access to a health care provider, you don’t have access to the vaccine, and you don’t have information that would inform your getting the vaccine,” he added.
Prioritizing the power of voting
“Voting is one of many ways we can impact structural racism in health care policy,” Dr. Chomilo emphasized.
However, voting inequity remains a challenge, Dr. Chomilo noted. Community level disparities lead to inequity in voting access and subsequent disparities in voter participation, he said. “Leaders are less responsive to nonvoting constituents,” which can result in policies that impact health inequitably, and loop back to community level health disparities, he explained.
Historically, physicians have had an 8%-9% lower voter turnout than the general public, although this may have changed in recent elections, Dr. Chomilo said. He encouraged all clinicians to set an example and vote, and to empower their patients to vote. Evidence shows that enfranchisement of Black voters is associated with reductions in education gaps for Blacks and Whites, and that enfranchisement of women is associated with increased spending on children and lower child mortality, he said. Dr. Chomilo encouraged pediatricians and all clinicians to take advantage of the resources on voting available from the American Academy of Pediatrics (aap.org/votekids).
“When we see more people in a community vote, leaders are more responsive to their needs,” he said.
Informing racial identity
“Racial identity is informed by racial socialization,” Dr. Chomilo said. “All of us are socialized along the lines of race; it happens in conversations with parents, family, peers, community.” Another point in moving from awareness to action in eliminating structural racism is recognizing that children are not too young to talk about race, Dr. Chomilo emphasized.
Children start to navigate racial identity and to take note of other differences at an early age. For example, a 3-year-old might ask, “why does that person talk funny, why is that person being pushed in a chair?” Dr. Chomilo said, and it is important for parents and as pediatricians to be prepared for these questions, which are part of normal development. As children get older, they start to reflect on what differences mean for them, which is not rooted in anything negative, he noted.
Children first develop racial identity at home, but children solidify their identities in child care and school settings, Dr. Chomilo said. The American Academy of Pediatrics has acknowledged the potential for racial bias in education and child care, and said in a statement that, “it is critical for pediatricians to recognize the institutional personally mediated, and internalized levels of racism that occur in the educational setting, because education is a critical social determinant of health for children.” In fact, data from children in preschool show that they use racial categories to identify themselves and others, to include or exclude children from activities, and to negotiate power in their social and play networks.
Early intervention matters in educating children about racism, Dr. Chomilo said. “If we were not taught to talk about race, it is on us to learn about it ourselves as well,” he said.
Ultimately, the goal is to create active antiracism among adults and children, said Dr. Chomilo. He encouraged pediatricians and parents not to shut down or discourage children when they raise questions of race, but to take the opportunity to teach. “There may be hurt feelings around what a child said, even if they didn’t mean to offend someone,” he noted. Take the topic seriously, and make racism conversations ongoing; teach children to safely oppose negative messages and behaviors in others, and replace them with something positive, he emphasized.
Addressing bias in clinical settings
Dr. Chomilo also encouraged hospitalists to consider internalized racism in clinical settings and take action to build confidence and cultural pride in all patients by ensuring that a pediatric hospital unit is welcoming and representative of the diversity in a given community, with appropriate options for books, movies, and toys. He also encouraged pediatric hospitalists to assess children for experiences of racism as part of a social assessment. Be aware of signs of posttraumatic stress, anxiety, depression, or grief that might have a racial component, he said.
Dr. Chomilo had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM PHM 2021







