User login
Hospitalist comanagement reduced odds of MI, shortened vascular surgery stays
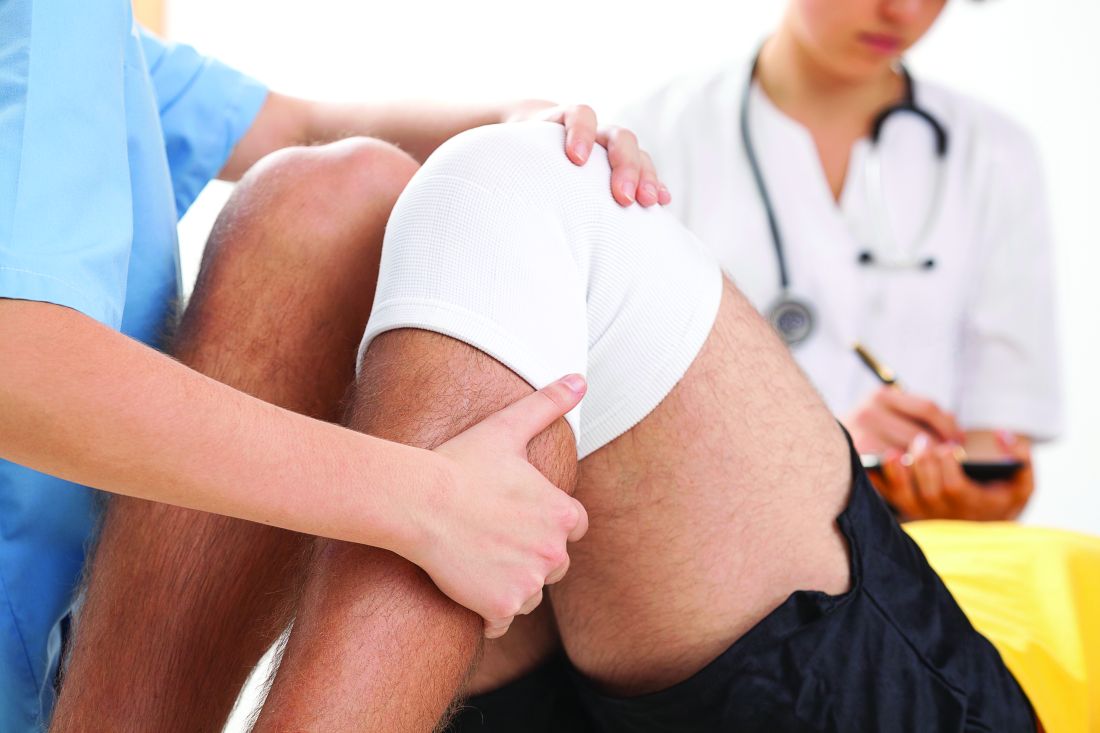
CHICAGO – A care model that uses hospitalists to comanage vascular surgery patients cut myocardial infarction rates by more than half and reduced hospital stays by about 12%, according to results of a study of the hospitalist comanagement model from Loyola University Chicago, Maywood, Ill., presented at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
“Hospitalist comanagement was associated with decreased length of stay without affecting readmission for patients undergoing amputation, embolectomy, and infected graft,” said Kaavya Adam, a third-year medical student at Loyola University Chicago. “In the overall population, there was a reduction in cases of MI, 30-day readmissions, and overall length of stay.”
In 2014, Loyola implemented a program that used 11 hospitalists to rotate through the vascular surgery service. The hospitalists call on any patient who stays more than 24 hours on the non-ICU floors. Adam said hospitalist duties include evaluating patient comorbidities, adjusting medication, talking with family about medical management, seeing patients on the day of surgery, ordering preoperative labs, and meeting with the anesthesiology and vascular surgery teams.
The study compared outcomes in 866 patients admitted during 2007-2013, before the comanagement model was put into place, and 572 admitted during 2014-2017.
Rates of diabetes, hypertension, chronic kidney disease, coronary artery disease, hyperlipidemia, and malnutrition were similar between the groups. However, the pre-comanagement group had significantly higher rates of ischemic pain (27.8% vs. 10.7%), gangrene (21.3% vs. 13.6%) and ulceration (30.6% vs. 21.9%), while the comanaged group had significantly higher rates of claudication (34.3% vs. 13.2%). The statistical analysis accounted for these variations, Adam said.
“We did find significant results for the reduction in the odds of MI at 30 days; there was a 61% reduction,” he said.
The reduction in hospital stay was even more pronounced for patients with complex cases, Adam said. In amputation, the length of stay was reduced by 3.77 days (P = .01); in embolectomy, by 7.35 (P = .004); and in infected graft, by 8.35 (P = .007).
Continuing research will evaluate the cost effectiveness of the hospitalist model and define a comanagement model that is most beneficial, Mr. Adam said. He had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Adam K et al. Midwestern Vascular 2019, Abstract 14.
CHICAGO – A care model that uses hospitalists to comanage vascular surgery patients cut myocardial infarction rates by more than half and reduced hospital stays by about 12%, according to results of a study of the hospitalist comanagement model from Loyola University Chicago, Maywood, Ill., presented at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
“Hospitalist comanagement was associated with decreased length of stay without affecting readmission for patients undergoing amputation, embolectomy, and infected graft,” said Kaavya Adam, a third-year medical student at Loyola University Chicago. “In the overall population, there was a reduction in cases of MI, 30-day readmissions, and overall length of stay.”
In 2014, Loyola implemented a program that used 11 hospitalists to rotate through the vascular surgery service. The hospitalists call on any patient who stays more than 24 hours on the non-ICU floors. Adam said hospitalist duties include evaluating patient comorbidities, adjusting medication, talking with family about medical management, seeing patients on the day of surgery, ordering preoperative labs, and meeting with the anesthesiology and vascular surgery teams.
The study compared outcomes in 866 patients admitted during 2007-2013, before the comanagement model was put into place, and 572 admitted during 2014-2017.
Rates of diabetes, hypertension, chronic kidney disease, coronary artery disease, hyperlipidemia, and malnutrition were similar between the groups. However, the pre-comanagement group had significantly higher rates of ischemic pain (27.8% vs. 10.7%), gangrene (21.3% vs. 13.6%) and ulceration (30.6% vs. 21.9%), while the comanaged group had significantly higher rates of claudication (34.3% vs. 13.2%). The statistical analysis accounted for these variations, Adam said.
“We did find significant results for the reduction in the odds of MI at 30 days; there was a 61% reduction,” he said.
The reduction in hospital stay was even more pronounced for patients with complex cases, Adam said. In amputation, the length of stay was reduced by 3.77 days (P = .01); in embolectomy, by 7.35 (P = .004); and in infected graft, by 8.35 (P = .007).
Continuing research will evaluate the cost effectiveness of the hospitalist model and define a comanagement model that is most beneficial, Mr. Adam said. He had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Adam K et al. Midwestern Vascular 2019, Abstract 14.
CHICAGO – A care model that uses hospitalists to comanage vascular surgery patients cut myocardial infarction rates by more than half and reduced hospital stays by about 12%, according to results of a study of the hospitalist comanagement model from Loyola University Chicago, Maywood, Ill., presented at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
“Hospitalist comanagement was associated with decreased length of stay without affecting readmission for patients undergoing amputation, embolectomy, and infected graft,” said Kaavya Adam, a third-year medical student at Loyola University Chicago. “In the overall population, there was a reduction in cases of MI, 30-day readmissions, and overall length of stay.”
In 2014, Loyola implemented a program that used 11 hospitalists to rotate through the vascular surgery service. The hospitalists call on any patient who stays more than 24 hours on the non-ICU floors. Adam said hospitalist duties include evaluating patient comorbidities, adjusting medication, talking with family about medical management, seeing patients on the day of surgery, ordering preoperative labs, and meeting with the anesthesiology and vascular surgery teams.
The study compared outcomes in 866 patients admitted during 2007-2013, before the comanagement model was put into place, and 572 admitted during 2014-2017.
Rates of diabetes, hypertension, chronic kidney disease, coronary artery disease, hyperlipidemia, and malnutrition were similar between the groups. However, the pre-comanagement group had significantly higher rates of ischemic pain (27.8% vs. 10.7%), gangrene (21.3% vs. 13.6%) and ulceration (30.6% vs. 21.9%), while the comanaged group had significantly higher rates of claudication (34.3% vs. 13.2%). The statistical analysis accounted for these variations, Adam said.
“We did find significant results for the reduction in the odds of MI at 30 days; there was a 61% reduction,” he said.
The reduction in hospital stay was even more pronounced for patients with complex cases, Adam said. In amputation, the length of stay was reduced by 3.77 days (P = .01); in embolectomy, by 7.35 (P = .004); and in infected graft, by 8.35 (P = .007).
Continuing research will evaluate the cost effectiveness of the hospitalist model and define a comanagement model that is most beneficial, Mr. Adam said. He had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Adam K et al. Midwestern Vascular 2019, Abstract 14.
REPORTING FROM MIDWESTERN VASCULAR 2019
Key clinical point: Hospitalist comanagement of vascular surgery patients reduced hospital stays.
Major finding: Hospitalist comanagement significantly reduced the odds of MI at 30 days; a 61% reduction.
Study details: Database query of 1,438 vascular surgery admissions during 2007-2017.
Disclosures: Mr. Adam had no relevant financial disclosures.
Source: Adam K et al. Midwestern Vascular 2019, Abstract 14.
TAVR, SAVR share same infective endocarditis risk
PARIS – The risk of infective endocarditis following transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) for the treatment of severe aortic stenosis proved to be the same as after surgical replacement in a French national propensity score–matched study.
This finding from what is believed to be the largest-ever study of infective endocarditis following TAVR will come as a surprise to many physicians. It’s easy to mistakenly assume the risk of this feared complication is lower – and perhaps even negligible – in TAVR patients since the procedure doesn’t involve a significant surgical wound, it’s briefer, the hospital length of stay is shorter, and recovery time is markedly less than with surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR).
Not so, Laurent Fauchier, MD, PhD, said in presenting the study findings at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“Do not think there is a lower risk of infective endocarditis. Be aware, be careful, and provide appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis, just as surgeons do in SAVR. Don’t think, as I did, that with TAVR with no pacemaker implantation there is no risk of infective endocarditis. The TAVR valve is a device, it’s a prosthesis, and the risk is very similar to that of surgery,” advised Dr. Fauchier, a cardiologist at Francois Rabelais University in Tours, France.
He presented a study of all of the nearly 108,000 patients who underwent isolated TAVR or SAVR in France during 2010-2018. The data source was the French national administrative hospital discharge record system. Since the TAVR patients were overall markedly older and sicker than the SAVR patients, especially during the first years of the study, he and his coinvestigators performed propensity score matching using 30 variables, which enabled them to narrow the field of inquiry down to a carefully selected study population of 16,291 TAVR patients and an equal number of closely similar SAVR patients.
A total of 1,070 cases of infective endocarditis occurred during a mean follow-up of just over 2 years. The rate of hospital admission for this complication was 1.89% per year in the TAVR group and similar at 1.71% per year in the SAVR cohort.
Of note, all-cause mortality in TAVR patients who developed infective endocarditis was 1.32-fold greater than it was in SAVR patients with infective endocarditis, a statistically significant difference. The explanation for the increased mortality risk in the TAVR group probably has to do at least in part with an inability on the part of the investigators to fully capture and control for the TAVR group’s greater frailty, according to the cardiologist.
Risk factors for infective endocarditis shared in common by TAVR and SAVR patients included male gender, a higher Charlson Comorbidity Index score, and a greater frailty index. The main predictors unique to the TAVR patients were atrial fibrillation, anemia, and tricuspid regurgitation. And although pacemaker and defibrillator implantation were risk factors for infective endocarditis in the SAVR patients, it wasn’t predictive of increased risk in the TAVR population. Dr. Fauchier called this finding “quite reassuring” given that roughly 20% of the TAVR group received a pacemaker.
The causative microorganisms for infective endocarditis were essentially the same in the TAVR and SAVR groups, simplifying antimicrobial prophylaxis decision making.
Dr. Fauchier reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, conducted free of commercial support. He serves as a consultant to and/or on speakers’ bureaus for Bayer, BMS Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medtronic, and Novartis.
PARIS – The risk of infective endocarditis following transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) for the treatment of severe aortic stenosis proved to be the same as after surgical replacement in a French national propensity score–matched study.
This finding from what is believed to be the largest-ever study of infective endocarditis following TAVR will come as a surprise to many physicians. It’s easy to mistakenly assume the risk of this feared complication is lower – and perhaps even negligible – in TAVR patients since the procedure doesn’t involve a significant surgical wound, it’s briefer, the hospital length of stay is shorter, and recovery time is markedly less than with surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR).
Not so, Laurent Fauchier, MD, PhD, said in presenting the study findings at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“Do not think there is a lower risk of infective endocarditis. Be aware, be careful, and provide appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis, just as surgeons do in SAVR. Don’t think, as I did, that with TAVR with no pacemaker implantation there is no risk of infective endocarditis. The TAVR valve is a device, it’s a prosthesis, and the risk is very similar to that of surgery,” advised Dr. Fauchier, a cardiologist at Francois Rabelais University in Tours, France.
He presented a study of all of the nearly 108,000 patients who underwent isolated TAVR or SAVR in France during 2010-2018. The data source was the French national administrative hospital discharge record system. Since the TAVR patients were overall markedly older and sicker than the SAVR patients, especially during the first years of the study, he and his coinvestigators performed propensity score matching using 30 variables, which enabled them to narrow the field of inquiry down to a carefully selected study population of 16,291 TAVR patients and an equal number of closely similar SAVR patients.
A total of 1,070 cases of infective endocarditis occurred during a mean follow-up of just over 2 years. The rate of hospital admission for this complication was 1.89% per year in the TAVR group and similar at 1.71% per year in the SAVR cohort.
Of note, all-cause mortality in TAVR patients who developed infective endocarditis was 1.32-fold greater than it was in SAVR patients with infective endocarditis, a statistically significant difference. The explanation for the increased mortality risk in the TAVR group probably has to do at least in part with an inability on the part of the investigators to fully capture and control for the TAVR group’s greater frailty, according to the cardiologist.
Risk factors for infective endocarditis shared in common by TAVR and SAVR patients included male gender, a higher Charlson Comorbidity Index score, and a greater frailty index. The main predictors unique to the TAVR patients were atrial fibrillation, anemia, and tricuspid regurgitation. And although pacemaker and defibrillator implantation were risk factors for infective endocarditis in the SAVR patients, it wasn’t predictive of increased risk in the TAVR population. Dr. Fauchier called this finding “quite reassuring” given that roughly 20% of the TAVR group received a pacemaker.
The causative microorganisms for infective endocarditis were essentially the same in the TAVR and SAVR groups, simplifying antimicrobial prophylaxis decision making.
Dr. Fauchier reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, conducted free of commercial support. He serves as a consultant to and/or on speakers’ bureaus for Bayer, BMS Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medtronic, and Novartis.
PARIS – The risk of infective endocarditis following transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) for the treatment of severe aortic stenosis proved to be the same as after surgical replacement in a French national propensity score–matched study.
This finding from what is believed to be the largest-ever study of infective endocarditis following TAVR will come as a surprise to many physicians. It’s easy to mistakenly assume the risk of this feared complication is lower – and perhaps even negligible – in TAVR patients since the procedure doesn’t involve a significant surgical wound, it’s briefer, the hospital length of stay is shorter, and recovery time is markedly less than with surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR).
Not so, Laurent Fauchier, MD, PhD, said in presenting the study findings at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“Do not think there is a lower risk of infective endocarditis. Be aware, be careful, and provide appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis, just as surgeons do in SAVR. Don’t think, as I did, that with TAVR with no pacemaker implantation there is no risk of infective endocarditis. The TAVR valve is a device, it’s a prosthesis, and the risk is very similar to that of surgery,” advised Dr. Fauchier, a cardiologist at Francois Rabelais University in Tours, France.
He presented a study of all of the nearly 108,000 patients who underwent isolated TAVR or SAVR in France during 2010-2018. The data source was the French national administrative hospital discharge record system. Since the TAVR patients were overall markedly older and sicker than the SAVR patients, especially during the first years of the study, he and his coinvestigators performed propensity score matching using 30 variables, which enabled them to narrow the field of inquiry down to a carefully selected study population of 16,291 TAVR patients and an equal number of closely similar SAVR patients.
A total of 1,070 cases of infective endocarditis occurred during a mean follow-up of just over 2 years. The rate of hospital admission for this complication was 1.89% per year in the TAVR group and similar at 1.71% per year in the SAVR cohort.
Of note, all-cause mortality in TAVR patients who developed infective endocarditis was 1.32-fold greater than it was in SAVR patients with infective endocarditis, a statistically significant difference. The explanation for the increased mortality risk in the TAVR group probably has to do at least in part with an inability on the part of the investigators to fully capture and control for the TAVR group’s greater frailty, according to the cardiologist.
Risk factors for infective endocarditis shared in common by TAVR and SAVR patients included male gender, a higher Charlson Comorbidity Index score, and a greater frailty index. The main predictors unique to the TAVR patients were atrial fibrillation, anemia, and tricuspid regurgitation. And although pacemaker and defibrillator implantation were risk factors for infective endocarditis in the SAVR patients, it wasn’t predictive of increased risk in the TAVR population. Dr. Fauchier called this finding “quite reassuring” given that roughly 20% of the TAVR group received a pacemaker.
The causative microorganisms for infective endocarditis were essentially the same in the TAVR and SAVR groups, simplifying antimicrobial prophylaxis decision making.
Dr. Fauchier reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, conducted free of commercial support. He serves as a consultant to and/or on speakers’ bureaus for Bayer, BMS Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medtronic, and Novartis.
REPORTING FROM THE ESC CONGRESS 2019
Post-TAVR anticoagulation alone fails to cut stroke risk in AFib
In patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) who have undergone transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) and had a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2, oral anticoagulant (OAC) therapy alone was not linked to reduced stroke risk.
By contrast, antiplatelet therapy was linked to a reduced risk of stroke in those AFib-TAVR patients, regardless of whether an oral anticoagulant was on board, according to results of a substudy of the randomized PARTNER II (Placement of Aortic Transcatheter Valve II) trial and its associated registries.
“Anticoagulant therapy was associated with a reduced risk of stroke and the composite of death or stroke when used concomitantly with uninterrupted antiplatelet therapy following TAVR,” concluded authors of the analysis, led by Ioanna Kosmidou, MD, PhD, of Columbia University in New York.
Taken together, these findings suggest OAC alone is “not sufficient” to prevent cerebrovascular events after TAVR in patients with AFib, Dr. Kosmidou and colleagues reported in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
The analysis of the PARTNER II substudy included a total of 1,621 patients with aortic stenosis treated with TAVR who had a history of AFib and an absolute indication for anticoagulation as evidenced by a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2.
Despite the absolute indication for anticoagulation, more than 40% of these patients were not prescribed an OAC upon discharge, investigators wrote, though the rate of nonprescribing decreased over the 5-year enrollment period of 2011-2015.
OAC therapy alone was not linked to reduced stroke risk in this cohort, investigators said. After 2 years, the rate of stroke was 6.6% for AFib-TAVR patients on anticoagulant therapy, and 5.6% for those who were not on anticoagulant therapy, a nonsignificant difference at P = 0.53, according to the reported data.
By contrast, uninterrupted antiplatelet therapy reduced both risk of stroke and risk of the composite endpoint of stroke and death at 2 years “irrespective of concomitant anticoagulation,” Dr. Kosmidou and coinvestigators wrote in the report.
The stroke rates were 5.4% for antiplatelet therapy plus OAC, versus 11.1% for those receiving neither antithrombotic treatment (P = 0.03), while the rates of stroke or death were 29.7% and 40.1%, respectively (P = 0.01), according to investigators.
After adjustment, stroke risk was not significantly reduced for OAC when compared with no OAC or antiplatelet therapy (HR, 0.61; P = .16), whereas stroke risk was indeed reduced for antiplatelet therapy alone (HR, 0.32; P = .002) and antiplatelet therapy with oral anticoagulation (HR, 0.44; P = .018).
The PARTNER II study was funded by Edwards Lifesciences. Senior author Martin B. Leon, MD, and several other study coauthors reported disclosures related to Edwards Lifesciences, in addition to Abbott Vascular, Cordis, Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and other companies. Dr. Kosmidou reported no disclosures.
SOURCE: Kosmidou I et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12:1580-9.
Results of this PARTNER II substudy investigation by Kosmidou and colleagues are timely and thought provoking because they imply that some current recommendations may be insufficient for preventing stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
Specifically, the results showed no difference in risk of stroke or the composite of death and stroke at 2 years in oral anticoagulant (OAC) and non-OAC patient groups, whereas by contrast, antiplatelet therapy was linked with reduced stroke risk versus no antithrombotic therapy, whether or not the patients received OAC.
The substudy reinforces the understanding that TAVR itself is a determinant of stroke because of mechanisms that go beyond thrombus formation in the left atrial appendage and are essentially platelet mediated.
How to manage antithrombotic therapy in patients with AFib who undergo TAVR remains a residual field of ambiguity.
However, observational studies cannot be conclusive, they said, so results of relevant prospective, randomized trials are eagerly awaited.
For example, the effects of novel oral anticoagulants versus vitamin K antagonists will be evaluated in the ENVISAGE-TAVI study, as well as the ATLANTIS trial, which will additionally include non-OAC patients.
The relative benefits of OAC alone versus OAC plus antiplatelet therapy will be evaluated in the AVATAR study, which will include AFib-TAVR patients randomized to OAC versus OAC plus aspirin, while the POPular-TAVI and CLOE trials will also include cohorts that help provide a more eloquent answer regarding the benefit-risk ratio of combining antiplatelet therapy and OAC in these patients.
Davide Capodanno, MD, PhD, and Antonio Greco, MD, of the University of Catania (Italy) made these comments in an accompanying editorial (JACC: Cardiovasc Interv. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2019.07.004). Dr. Capodanno reported disclosures related to Abbott Vascular, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi-Sankyo, and Sanofi. Dr. Greco reported having no relevant disclosures.
Results of this PARTNER II substudy investigation by Kosmidou and colleagues are timely and thought provoking because they imply that some current recommendations may be insufficient for preventing stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
Specifically, the results showed no difference in risk of stroke or the composite of death and stroke at 2 years in oral anticoagulant (OAC) and non-OAC patient groups, whereas by contrast, antiplatelet therapy was linked with reduced stroke risk versus no antithrombotic therapy, whether or not the patients received OAC.
The substudy reinforces the understanding that TAVR itself is a determinant of stroke because of mechanisms that go beyond thrombus formation in the left atrial appendage and are essentially platelet mediated.
How to manage antithrombotic therapy in patients with AFib who undergo TAVR remains a residual field of ambiguity.
However, observational studies cannot be conclusive, they said, so results of relevant prospective, randomized trials are eagerly awaited.
For example, the effects of novel oral anticoagulants versus vitamin K antagonists will be evaluated in the ENVISAGE-TAVI study, as well as the ATLANTIS trial, which will additionally include non-OAC patients.
The relative benefits of OAC alone versus OAC plus antiplatelet therapy will be evaluated in the AVATAR study, which will include AFib-TAVR patients randomized to OAC versus OAC plus aspirin, while the POPular-TAVI and CLOE trials will also include cohorts that help provide a more eloquent answer regarding the benefit-risk ratio of combining antiplatelet therapy and OAC in these patients.
Davide Capodanno, MD, PhD, and Antonio Greco, MD, of the University of Catania (Italy) made these comments in an accompanying editorial (JACC: Cardiovasc Interv. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2019.07.004). Dr. Capodanno reported disclosures related to Abbott Vascular, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi-Sankyo, and Sanofi. Dr. Greco reported having no relevant disclosures.
Results of this PARTNER II substudy investigation by Kosmidou and colleagues are timely and thought provoking because they imply that some current recommendations may be insufficient for preventing stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
Specifically, the results showed no difference in risk of stroke or the composite of death and stroke at 2 years in oral anticoagulant (OAC) and non-OAC patient groups, whereas by contrast, antiplatelet therapy was linked with reduced stroke risk versus no antithrombotic therapy, whether or not the patients received OAC.
The substudy reinforces the understanding that TAVR itself is a determinant of stroke because of mechanisms that go beyond thrombus formation in the left atrial appendage and are essentially platelet mediated.
How to manage antithrombotic therapy in patients with AFib who undergo TAVR remains a residual field of ambiguity.
However, observational studies cannot be conclusive, they said, so results of relevant prospective, randomized trials are eagerly awaited.
For example, the effects of novel oral anticoagulants versus vitamin K antagonists will be evaluated in the ENVISAGE-TAVI study, as well as the ATLANTIS trial, which will additionally include non-OAC patients.
The relative benefits of OAC alone versus OAC plus antiplatelet therapy will be evaluated in the AVATAR study, which will include AFib-TAVR patients randomized to OAC versus OAC plus aspirin, while the POPular-TAVI and CLOE trials will also include cohorts that help provide a more eloquent answer regarding the benefit-risk ratio of combining antiplatelet therapy and OAC in these patients.
Davide Capodanno, MD, PhD, and Antonio Greco, MD, of the University of Catania (Italy) made these comments in an accompanying editorial (JACC: Cardiovasc Interv. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2019.07.004). Dr. Capodanno reported disclosures related to Abbott Vascular, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi-Sankyo, and Sanofi. Dr. Greco reported having no relevant disclosures.
In patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) who have undergone transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) and had a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2, oral anticoagulant (OAC) therapy alone was not linked to reduced stroke risk.
By contrast, antiplatelet therapy was linked to a reduced risk of stroke in those AFib-TAVR patients, regardless of whether an oral anticoagulant was on board, according to results of a substudy of the randomized PARTNER II (Placement of Aortic Transcatheter Valve II) trial and its associated registries.
“Anticoagulant therapy was associated with a reduced risk of stroke and the composite of death or stroke when used concomitantly with uninterrupted antiplatelet therapy following TAVR,” concluded authors of the analysis, led by Ioanna Kosmidou, MD, PhD, of Columbia University in New York.
Taken together, these findings suggest OAC alone is “not sufficient” to prevent cerebrovascular events after TAVR in patients with AFib, Dr. Kosmidou and colleagues reported in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
The analysis of the PARTNER II substudy included a total of 1,621 patients with aortic stenosis treated with TAVR who had a history of AFib and an absolute indication for anticoagulation as evidenced by a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2.
Despite the absolute indication for anticoagulation, more than 40% of these patients were not prescribed an OAC upon discharge, investigators wrote, though the rate of nonprescribing decreased over the 5-year enrollment period of 2011-2015.
OAC therapy alone was not linked to reduced stroke risk in this cohort, investigators said. After 2 years, the rate of stroke was 6.6% for AFib-TAVR patients on anticoagulant therapy, and 5.6% for those who were not on anticoagulant therapy, a nonsignificant difference at P = 0.53, according to the reported data.
By contrast, uninterrupted antiplatelet therapy reduced both risk of stroke and risk of the composite endpoint of stroke and death at 2 years “irrespective of concomitant anticoagulation,” Dr. Kosmidou and coinvestigators wrote in the report.
The stroke rates were 5.4% for antiplatelet therapy plus OAC, versus 11.1% for those receiving neither antithrombotic treatment (P = 0.03), while the rates of stroke or death were 29.7% and 40.1%, respectively (P = 0.01), according to investigators.
After adjustment, stroke risk was not significantly reduced for OAC when compared with no OAC or antiplatelet therapy (HR, 0.61; P = .16), whereas stroke risk was indeed reduced for antiplatelet therapy alone (HR, 0.32; P = .002) and antiplatelet therapy with oral anticoagulation (HR, 0.44; P = .018).
The PARTNER II study was funded by Edwards Lifesciences. Senior author Martin B. Leon, MD, and several other study coauthors reported disclosures related to Edwards Lifesciences, in addition to Abbott Vascular, Cordis, Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and other companies. Dr. Kosmidou reported no disclosures.
SOURCE: Kosmidou I et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12:1580-9.
In patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) who have undergone transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) and had a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2, oral anticoagulant (OAC) therapy alone was not linked to reduced stroke risk.
By contrast, antiplatelet therapy was linked to a reduced risk of stroke in those AFib-TAVR patients, regardless of whether an oral anticoagulant was on board, according to results of a substudy of the randomized PARTNER II (Placement of Aortic Transcatheter Valve II) trial and its associated registries.
“Anticoagulant therapy was associated with a reduced risk of stroke and the composite of death or stroke when used concomitantly with uninterrupted antiplatelet therapy following TAVR,” concluded authors of the analysis, led by Ioanna Kosmidou, MD, PhD, of Columbia University in New York.
Taken together, these findings suggest OAC alone is “not sufficient” to prevent cerebrovascular events after TAVR in patients with AFib, Dr. Kosmidou and colleagues reported in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
The analysis of the PARTNER II substudy included a total of 1,621 patients with aortic stenosis treated with TAVR who had a history of AFib and an absolute indication for anticoagulation as evidenced by a CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2.
Despite the absolute indication for anticoagulation, more than 40% of these patients were not prescribed an OAC upon discharge, investigators wrote, though the rate of nonprescribing decreased over the 5-year enrollment period of 2011-2015.
OAC therapy alone was not linked to reduced stroke risk in this cohort, investigators said. After 2 years, the rate of stroke was 6.6% for AFib-TAVR patients on anticoagulant therapy, and 5.6% for those who were not on anticoagulant therapy, a nonsignificant difference at P = 0.53, according to the reported data.
By contrast, uninterrupted antiplatelet therapy reduced both risk of stroke and risk of the composite endpoint of stroke and death at 2 years “irrespective of concomitant anticoagulation,” Dr. Kosmidou and coinvestigators wrote in the report.
The stroke rates were 5.4% for antiplatelet therapy plus OAC, versus 11.1% for those receiving neither antithrombotic treatment (P = 0.03), while the rates of stroke or death were 29.7% and 40.1%, respectively (P = 0.01), according to investigators.
After adjustment, stroke risk was not significantly reduced for OAC when compared with no OAC or antiplatelet therapy (HR, 0.61; P = .16), whereas stroke risk was indeed reduced for antiplatelet therapy alone (HR, 0.32; P = .002) and antiplatelet therapy with oral anticoagulation (HR, 0.44; P = .018).
The PARTNER II study was funded by Edwards Lifesciences. Senior author Martin B. Leon, MD, and several other study coauthors reported disclosures related to Edwards Lifesciences, in addition to Abbott Vascular, Cordis, Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and other companies. Dr. Kosmidou reported no disclosures.
SOURCE: Kosmidou I et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12:1580-9.
FROM JACC: CARDIOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS
Opioid use curbed with patient education and lower prescription quantities
Patients given lower prescription quantities of opioid tablets with and without opioid education used significantly less of the medication compared with those given more tablets and no education, according to data from 264 adults and adolescents who underwent anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) surgery.
Although lower default prescription programs have been shown to reduce the number of tablets prescribed, “the effect of reduced prescription quantities on actual patient opioid consumption remains undetermined,” wrote Kevin X. Farley, BS, of Emory University, Atlanta, and colleagues.
In a study published in JAMA, the researchers examined whether patients took fewer tablets if given fewer, and whether patient education about opioids further reduced the number of tablets taken.
The study population included adults and adolescents who underwent ACL surgery at a single center. The patients were divided into three groups: 109 patients received 50 opioid tablets after surgery, 78 received 30 tablets plus education prior to surgery about appropriate opioid use and alternative pain management, and 77 received 30 tablets but no education on opioid use.
Patients given 50 tablets consumed an average of 25 tablets for an average of 5.8 days. By contrast, patients given 30 tablets but no opioid education consumed an average of 16 tablets for an average of 4.5 days, and those given 30 tablets and preoperative education consumed an average of 12 tablets for an average of 3.5 days.
In addition, patients given 30 tablets reported lower levels of constipation and fatigue compared with patients given 50 tablets. No differences were seen in medication refills among the groups.
The findings were limited by several factors including the use of data from a single center, the lack of randomization, and the potential for recall bias, the researchers noted. However, the results suggest that prescribing fewer tablets may further reduce use, as each group consumed approximately half of the tablets given, the researchers added.
“Further investigation should evaluate whether similar opioid stewardship and education protocols would be successful in other patient populations,” they said.
Corresponding author John Xerogeanes, MD, disclosed personal fees from Arthrex and stock options from Trice. The other researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Patients given lower prescription quantities of opioid tablets with and without opioid education used significantly less of the medication compared with those given more tablets and no education, according to data from 264 adults and adolescents who underwent anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) surgery.
Although lower default prescription programs have been shown to reduce the number of tablets prescribed, “the effect of reduced prescription quantities on actual patient opioid consumption remains undetermined,” wrote Kevin X. Farley, BS, of Emory University, Atlanta, and colleagues.
In a study published in JAMA, the researchers examined whether patients took fewer tablets if given fewer, and whether patient education about opioids further reduced the number of tablets taken.
The study population included adults and adolescents who underwent ACL surgery at a single center. The patients were divided into three groups: 109 patients received 50 opioid tablets after surgery, 78 received 30 tablets plus education prior to surgery about appropriate opioid use and alternative pain management, and 77 received 30 tablets but no education on opioid use.
Patients given 50 tablets consumed an average of 25 tablets for an average of 5.8 days. By contrast, patients given 30 tablets but no opioid education consumed an average of 16 tablets for an average of 4.5 days, and those given 30 tablets and preoperative education consumed an average of 12 tablets for an average of 3.5 days.
In addition, patients given 30 tablets reported lower levels of constipation and fatigue compared with patients given 50 tablets. No differences were seen in medication refills among the groups.
The findings were limited by several factors including the use of data from a single center, the lack of randomization, and the potential for recall bias, the researchers noted. However, the results suggest that prescribing fewer tablets may further reduce use, as each group consumed approximately half of the tablets given, the researchers added.
“Further investigation should evaluate whether similar opioid stewardship and education protocols would be successful in other patient populations,” they said.
Corresponding author John Xerogeanes, MD, disclosed personal fees from Arthrex and stock options from Trice. The other researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Patients given lower prescription quantities of opioid tablets with and without opioid education used significantly less of the medication compared with those given more tablets and no education, according to data from 264 adults and adolescents who underwent anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) surgery.
Although lower default prescription programs have been shown to reduce the number of tablets prescribed, “the effect of reduced prescription quantities on actual patient opioid consumption remains undetermined,” wrote Kevin X. Farley, BS, of Emory University, Atlanta, and colleagues.
In a study published in JAMA, the researchers examined whether patients took fewer tablets if given fewer, and whether patient education about opioids further reduced the number of tablets taken.
The study population included adults and adolescents who underwent ACL surgery at a single center. The patients were divided into three groups: 109 patients received 50 opioid tablets after surgery, 78 received 30 tablets plus education prior to surgery about appropriate opioid use and alternative pain management, and 77 received 30 tablets but no education on opioid use.
Patients given 50 tablets consumed an average of 25 tablets for an average of 5.8 days. By contrast, patients given 30 tablets but no opioid education consumed an average of 16 tablets for an average of 4.5 days, and those given 30 tablets and preoperative education consumed an average of 12 tablets for an average of 3.5 days.
In addition, patients given 30 tablets reported lower levels of constipation and fatigue compared with patients given 50 tablets. No differences were seen in medication refills among the groups.
The findings were limited by several factors including the use of data from a single center, the lack of randomization, and the potential for recall bias, the researchers noted. However, the results suggest that prescribing fewer tablets may further reduce use, as each group consumed approximately half of the tablets given, the researchers added.
“Further investigation should evaluate whether similar opioid stewardship and education protocols would be successful in other patient populations,” they said.
Corresponding author John Xerogeanes, MD, disclosed personal fees from Arthrex and stock options from Trice. The other researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM JAMA
Key clinical point: Patient education and fewer tablets prescribed significantly reduced the amount of opioid tablets taken compared with no education and more tablets prescribed.
Major finding: Patients given 50 tablets and no patient education, 30 tablets and no patient education, and 30 tablets plus education consumed an average of 25, 16, and 12 tablets, respectively.
Study details: The data come from 264 adolescents and adults who underwent ACL surgery at a single center.
Disclosures: Corresponding author John Xerogeanes, MD, disclosed personal fees from Arthrex and stock options from Trice. The other researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Source: Farley KX et al. JAMA. 2019 June 25.321(24):2465-7.
Severe OSA increases cardiovascular risk after surgery
Unrecognized severe obstructive sleep apnea is a risk factor for cardiovascular complications after major noncardiac surgery, according to a study published in JAMA.
The researchers state that perioperative mismanagement of obstructive sleep apnea can lead to serious medical consequences. “General anesthetics, sedatives, and postoperative analgesics are potent respiratory depressants that relax the upper airway dilator muscles and impair ventilatory response to hypoxemia and hypercapnia. Each of these events exacerbates [obstructive sleep apnea] and may predispose patients to postoperative cardiovascular complications,” said researchers who conducted the The Postoperative vascular complications in unrecognised Obstructive Sleep apnoea (POSA) study (NCT01494181).
They undertook a prospective observational cohort study involving 1,218 patients undergoing major noncardiac surgery, who were already considered at high risk of postoperative cardiovascular events – having, for example, a history of coronary artery disease, stroke, diabetes, or renal impairment. However, none had a prior diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea.
Preoperative sleep monitoring revealed that two-thirds of the cohort had unrecognized and untreated obstructive sleep apnea, including 11.2% with severe obstructive sleep apnea.
At 30 days after surgery, patients with obstructive sleep apnea had a 49% higher risk of the primary outcome of myocardial injury, cardiac death, heart failure, thromboembolism, atrial fibrillation, or stroke, compared with those without obstructive sleep apnea.
However, this association was largely due to a significant 2.23-fold higher risk among patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea, while those with only moderate or mild sleep apnea did not show a significant increased risk of cardiovascular complications.
Patients in this study with severe obstructive sleep apnea had a 13-fold higher risk of cardiac death, 80% higher risk of myocardial injury, more than sixfold higher risk of heart failure, and nearly fourfold higher risk of atrial fibrillation.
Researchers also saw an association between obstructive sleep apnea and increased risk of infective outcomes, unplanned tracheal intubation, postoperative lung ventilation, and readmission to the ICU.
The majority of patients received nocturnal oximetry monitoring during their first 3 nights after surgery. This revealed that patients without obstructive sleep apnea had significant increases in oxygen desaturation index during their first night after surgery, while those with sleep apnea did not return to their baseline oxygen desaturation index until the third night after surgery.
“Despite a substantial decrease in ODI [oxygen desaturation index] with oxygen therapy in patients with OSA during the first 3 postoperative nights, supplemental oxygen did not modify the association between OSA and postoperative cardiovascular event,” wrote Matthew T.V. Chan, MD, of Chinese University of Hong Kong, Prince of Wales Hospital, and coauthors.
Given that the events were associated with longer durations of severe oxyhemoglobin desaturation, more aggressive interventions such as positive airway pressure or oral appliances may be required, they noted.
“However, high-level evidence demonstrating the effect of these measures on perioperative outcomes is lacking [and] further clinical trials are now required to test if additional monitoring or alternative interventions would reduce the risk,” they wrote.
The study was supported by the Health and Medical Research Fund (Hong Kong), National Healthcare Group–Khoo Teck Puat Hospital, University Health Network Foundation, University of Malaya, Malaysian Society of Anaesthesiologists, Auckland Medical Research Foundation, and ResMed. One author declared grants from private industry and a patent pending on an obstructive sleep apnea risk questionnaire used in the study.
SOURCE: Chan M et al. JAMA 2019;321[18]:1788-98. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.4783.
This study is large, prospective, and rigorous and adds important new information to the puzzle of the impact of sleep apnea on postoperative risk, Dennis Auckley, MD, and Stavros Memtsoudis, MD, wrote in an editorial accompanying this study. The study focused on predetermined clinically significant and measurable events, used standardized and objective sleep apnea testing, and attempted to control for many of the confounders that might have influenced outcomes.
The results suggest that obstructive sleep apnea should be recognized as a major perioperative risk factor, and it should receive the same attention and optimization efforts as comorbidities such as diabetes.
Dr. Auckley is from the division of pulmonary, critical care and sleep medicine at MetroHealth Medical Center, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and Dr. Memtsoudis is clinical professor of anesthesiology at Cornell University, New York. These comments are adapted from an editorial (JAMA 2019;231[18]:1775-6). Both declared board and executive positions with the Society of Anesthesia and Sleep Medicine. Dr. Auckley declared research funding from Medtronic, and Dr. Memtsoudis declared personal fees from Teikoku and Sandoz.
This study is large, prospective, and rigorous and adds important new information to the puzzle of the impact of sleep apnea on postoperative risk, Dennis Auckley, MD, and Stavros Memtsoudis, MD, wrote in an editorial accompanying this study. The study focused on predetermined clinically significant and measurable events, used standardized and objective sleep apnea testing, and attempted to control for many of the confounders that might have influenced outcomes.
The results suggest that obstructive sleep apnea should be recognized as a major perioperative risk factor, and it should receive the same attention and optimization efforts as comorbidities such as diabetes.
Dr. Auckley is from the division of pulmonary, critical care and sleep medicine at MetroHealth Medical Center, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and Dr. Memtsoudis is clinical professor of anesthesiology at Cornell University, New York. These comments are adapted from an editorial (JAMA 2019;231[18]:1775-6). Both declared board and executive positions with the Society of Anesthesia and Sleep Medicine. Dr. Auckley declared research funding from Medtronic, and Dr. Memtsoudis declared personal fees from Teikoku and Sandoz.
This study is large, prospective, and rigorous and adds important new information to the puzzle of the impact of sleep apnea on postoperative risk, Dennis Auckley, MD, and Stavros Memtsoudis, MD, wrote in an editorial accompanying this study. The study focused on predetermined clinically significant and measurable events, used standardized and objective sleep apnea testing, and attempted to control for many of the confounders that might have influenced outcomes.
The results suggest that obstructive sleep apnea should be recognized as a major perioperative risk factor, and it should receive the same attention and optimization efforts as comorbidities such as diabetes.
Dr. Auckley is from the division of pulmonary, critical care and sleep medicine at MetroHealth Medical Center, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and Dr. Memtsoudis is clinical professor of anesthesiology at Cornell University, New York. These comments are adapted from an editorial (JAMA 2019;231[18]:1775-6). Both declared board and executive positions with the Society of Anesthesia and Sleep Medicine. Dr. Auckley declared research funding from Medtronic, and Dr. Memtsoudis declared personal fees from Teikoku and Sandoz.
Unrecognized severe obstructive sleep apnea is a risk factor for cardiovascular complications after major noncardiac surgery, according to a study published in JAMA.
The researchers state that perioperative mismanagement of obstructive sleep apnea can lead to serious medical consequences. “General anesthetics, sedatives, and postoperative analgesics are potent respiratory depressants that relax the upper airway dilator muscles and impair ventilatory response to hypoxemia and hypercapnia. Each of these events exacerbates [obstructive sleep apnea] and may predispose patients to postoperative cardiovascular complications,” said researchers who conducted the The Postoperative vascular complications in unrecognised Obstructive Sleep apnoea (POSA) study (NCT01494181).
They undertook a prospective observational cohort study involving 1,218 patients undergoing major noncardiac surgery, who were already considered at high risk of postoperative cardiovascular events – having, for example, a history of coronary artery disease, stroke, diabetes, or renal impairment. However, none had a prior diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea.
Preoperative sleep monitoring revealed that two-thirds of the cohort had unrecognized and untreated obstructive sleep apnea, including 11.2% with severe obstructive sleep apnea.
At 30 days after surgery, patients with obstructive sleep apnea had a 49% higher risk of the primary outcome of myocardial injury, cardiac death, heart failure, thromboembolism, atrial fibrillation, or stroke, compared with those without obstructive sleep apnea.
However, this association was largely due to a significant 2.23-fold higher risk among patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea, while those with only moderate or mild sleep apnea did not show a significant increased risk of cardiovascular complications.
Patients in this study with severe obstructive sleep apnea had a 13-fold higher risk of cardiac death, 80% higher risk of myocardial injury, more than sixfold higher risk of heart failure, and nearly fourfold higher risk of atrial fibrillation.
Researchers also saw an association between obstructive sleep apnea and increased risk of infective outcomes, unplanned tracheal intubation, postoperative lung ventilation, and readmission to the ICU.
The majority of patients received nocturnal oximetry monitoring during their first 3 nights after surgery. This revealed that patients without obstructive sleep apnea had significant increases in oxygen desaturation index during their first night after surgery, while those with sleep apnea did not return to their baseline oxygen desaturation index until the third night after surgery.
“Despite a substantial decrease in ODI [oxygen desaturation index] with oxygen therapy in patients with OSA during the first 3 postoperative nights, supplemental oxygen did not modify the association between OSA and postoperative cardiovascular event,” wrote Matthew T.V. Chan, MD, of Chinese University of Hong Kong, Prince of Wales Hospital, and coauthors.
Given that the events were associated with longer durations of severe oxyhemoglobin desaturation, more aggressive interventions such as positive airway pressure or oral appliances may be required, they noted.
“However, high-level evidence demonstrating the effect of these measures on perioperative outcomes is lacking [and] further clinical trials are now required to test if additional monitoring or alternative interventions would reduce the risk,” they wrote.
The study was supported by the Health and Medical Research Fund (Hong Kong), National Healthcare Group–Khoo Teck Puat Hospital, University Health Network Foundation, University of Malaya, Malaysian Society of Anaesthesiologists, Auckland Medical Research Foundation, and ResMed. One author declared grants from private industry and a patent pending on an obstructive sleep apnea risk questionnaire used in the study.
SOURCE: Chan M et al. JAMA 2019;321[18]:1788-98. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.4783.
Unrecognized severe obstructive sleep apnea is a risk factor for cardiovascular complications after major noncardiac surgery, according to a study published in JAMA.
The researchers state that perioperative mismanagement of obstructive sleep apnea can lead to serious medical consequences. “General anesthetics, sedatives, and postoperative analgesics are potent respiratory depressants that relax the upper airway dilator muscles and impair ventilatory response to hypoxemia and hypercapnia. Each of these events exacerbates [obstructive sleep apnea] and may predispose patients to postoperative cardiovascular complications,” said researchers who conducted the The Postoperative vascular complications in unrecognised Obstructive Sleep apnoea (POSA) study (NCT01494181).
They undertook a prospective observational cohort study involving 1,218 patients undergoing major noncardiac surgery, who were already considered at high risk of postoperative cardiovascular events – having, for example, a history of coronary artery disease, stroke, diabetes, or renal impairment. However, none had a prior diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea.
Preoperative sleep monitoring revealed that two-thirds of the cohort had unrecognized and untreated obstructive sleep apnea, including 11.2% with severe obstructive sleep apnea.
At 30 days after surgery, patients with obstructive sleep apnea had a 49% higher risk of the primary outcome of myocardial injury, cardiac death, heart failure, thromboembolism, atrial fibrillation, or stroke, compared with those without obstructive sleep apnea.
However, this association was largely due to a significant 2.23-fold higher risk among patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea, while those with only moderate or mild sleep apnea did not show a significant increased risk of cardiovascular complications.
Patients in this study with severe obstructive sleep apnea had a 13-fold higher risk of cardiac death, 80% higher risk of myocardial injury, more than sixfold higher risk of heart failure, and nearly fourfold higher risk of atrial fibrillation.
Researchers also saw an association between obstructive sleep apnea and increased risk of infective outcomes, unplanned tracheal intubation, postoperative lung ventilation, and readmission to the ICU.
The majority of patients received nocturnal oximetry monitoring during their first 3 nights after surgery. This revealed that patients without obstructive sleep apnea had significant increases in oxygen desaturation index during their first night after surgery, while those with sleep apnea did not return to their baseline oxygen desaturation index until the third night after surgery.
“Despite a substantial decrease in ODI [oxygen desaturation index] with oxygen therapy in patients with OSA during the first 3 postoperative nights, supplemental oxygen did not modify the association between OSA and postoperative cardiovascular event,” wrote Matthew T.V. Chan, MD, of Chinese University of Hong Kong, Prince of Wales Hospital, and coauthors.
Given that the events were associated with longer durations of severe oxyhemoglobin desaturation, more aggressive interventions such as positive airway pressure or oral appliances may be required, they noted.
“However, high-level evidence demonstrating the effect of these measures on perioperative outcomes is lacking [and] further clinical trials are now required to test if additional monitoring or alternative interventions would reduce the risk,” they wrote.
The study was supported by the Health and Medical Research Fund (Hong Kong), National Healthcare Group–Khoo Teck Puat Hospital, University Health Network Foundation, University of Malaya, Malaysian Society of Anaesthesiologists, Auckland Medical Research Foundation, and ResMed. One author declared grants from private industry and a patent pending on an obstructive sleep apnea risk questionnaire used in the study.
SOURCE: Chan M et al. JAMA 2019;321[18]:1788-98. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.4783.
FROM JAMA
Novel strategies may help curb bariatric SSI
BALTIMORE – While rates of surgical site infections after bariatric surgery have been reported in the low single digits, SSIs have continued to be a persistent complication.
At the annual meeting of the Society of American Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Surgeons, researchers reported on two strategies to reduce SSI in bariatric surgery: a predictive tool that identifies risk factors for wound infection, allowing surgeons to employ protective measures before and during surgery, and a change in surgical practice leading to a 78% reduction in wound infection rates that resulted from a single-center study.
Jerry Dang, MD, of the University of Alberta, Edmonton, reported that the BariWound predictive tool designed to stratify patients into risk categories showed a high level of accuracy with an area under the curve of 0.73. Cynthia Weber, MD, of University Hospitals, Cleveland, reported that changing the method for performing circular-stapled gastrojejunostomy (GJ) from the transoral to the transabdominal approach along with more vigilant use of wound protection reduced wound infection rates from 6% to 1.3%.
Dr. Dang noted that SSI has been reported as the most common hospital-acquired complication in bariatric surgery, with reported rates of between 1% and 10%. A 2014 analysis of the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database reported an SSI rate of 1.8% (Surg Endosc. 2014;28:3285-92). Although these rates are low, Dr. Dang explained that his group wanted to identify factors associated with SSI within 30 days of bariatric surgery. They analyzed outcomes data of 274,187 patients in the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program database who had bariatric surgery in 2015 and 2016 (196,608 by laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy [SG] and 77,579 laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass [RYGB]). Their analysis determined an incisional SSI rate of 0.47% (n = 1,291). “Incisional SSI rates were four times higher for laparoscopic RYGB: 1.04% vs. 0.25%,” Dr. Dang said.
On multivariable logistic regression, the adjusted odds ratio of SSI after RYGB vs. SG was 3.13 (P less than .001). Other significant risk factors were chronic steroid or immunosuppressant use (odds ratio, 1.75; P = .001), female sex (OR, 1.48; P less than .001) and history of gastroesophageal reflux disease (OR, 1.45; P less than .001). Other factors with a 21%-31% greater risk of SSI were white race (P = .002), history of diabetes (P less than .001), hypertension (P less than .001), obstructive sleep apnea (P = .001), and longer operation times (P less than .001). Each single-digit increase in body mass index increased risk by 3%, and older age actually had a protective effect for unknown reasons, Dr. Dang noted.
The BariWound tool assigns points to each risk factor. Each hour of operation time and each 10 kg/m2 of weight carry a value of 1 point, with partial points allowed. RYGB equals 5 points, and chronic steroid/immunosuppressant use, 4 points. The tool assigns risk to four categories based on score and 30-day SSI rate:
- Low, less than 15 (1% risk of SSI).
- Moderate, 15-21.9 (1%-5%).
- High, 22-26.9 (5%-10%).
- Very high, greater than 27 (greater than 10%).
“The BariWound tool can help to inform clinical decision making so patients can know they’re at higher risk, and this could allow for us to target high-risk patients with preventive packages, such as the Cleveland Clinic Technique of wound protection, wound irrigation, and wound packing as a resource-saving measure,” Dr. Dang said. “Targeting high-risk populations can reduce cost and operating time.”
Dr. Weber reported on her institution’s study of SSIs using two different methods for circular stapling of GJ that involved two different surgeons who performed 333 RYGB procedures from January 2016 to March 2018. Surgeon “A” had traditionally used the transoral technique without wound protection to insert the anvil of the stapler; surgeon “B” used wound protection and the transabdominal technique for stapler insertion. Wound protection involves draping of the stapler with sterile plastic.
“In a quarterly review, we detected a higher than expected wound complication rate of 6%,” Dr. Weber said. “Of particular concern was the development of five recent wound infection cases, which all occurred in the transoral group for a rate of 8.9% in that cohort.”
That left the quality team questioning the safety profile of the transoral technique, Dr. Weber said. “We wanted to know why and whether or not the main contributor to the development of a wound infection was the technique for the anvil introduction or was it the difference between surgeons using wound protection.”
Halfway through the study period, surgeon A made two modifications: He adopted the transabdominal technique for a subset of patients; and because of the surgeon’s comfort level and expertise with the transoral approach, he continued using that approach but added wound protection. Surgeon B continued with the transabdominal approach with wound protection. The share of transabdominal insertions in the study population increased from 69.2% before the change to 75% after. Demographics between the pre- and postchange patient populations were similar, as were the rates of revision surgery between the two groups.
“We noticed a significant reduction in total wound complications from 6% to 1.3%, and we noticed a complete elimination of surgical site infections after adding wound protection to the transoral technique,” Dr. Weber said.
Dr. Weber noted a number of limitations with the study: its retrospective nature; the lack of control for other intraoperative factors that contribute to SSIs; relatively low incidence of SSI; and surgeon’s choice to determine the technique of anvil insertion.
“We found that our quality improvement intervention was efficacious and decided that it was not the technique of anvil insertion, but it was the wound protection that was key to preventing wound infections, as we saw complete elimination after we added wound protection to the transoral technique,” Dr. Weber said. “Using proper precautions with the circular stapler and anastomosis can be done using either technique for anvil insertion. Overall self-assessment of outcomes leads to best practice.”
Dr. Dang had no financial relationships to disclose. Dr. Weber’s coauthor Leena Khatian, MD, MPH, disclosed relationships with Torax Medical, Medtronic, and Gore.
SOURCES: Weber C et al. SAGES 2109, Presentation S049; Dang J et al. SAGES 2019, Presentation S050.
BALTIMORE – While rates of surgical site infections after bariatric surgery have been reported in the low single digits, SSIs have continued to be a persistent complication.
At the annual meeting of the Society of American Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Surgeons, researchers reported on two strategies to reduce SSI in bariatric surgery: a predictive tool that identifies risk factors for wound infection, allowing surgeons to employ protective measures before and during surgery, and a change in surgical practice leading to a 78% reduction in wound infection rates that resulted from a single-center study.
Jerry Dang, MD, of the University of Alberta, Edmonton, reported that the BariWound predictive tool designed to stratify patients into risk categories showed a high level of accuracy with an area under the curve of 0.73. Cynthia Weber, MD, of University Hospitals, Cleveland, reported that changing the method for performing circular-stapled gastrojejunostomy (GJ) from the transoral to the transabdominal approach along with more vigilant use of wound protection reduced wound infection rates from 6% to 1.3%.
Dr. Dang noted that SSI has been reported as the most common hospital-acquired complication in bariatric surgery, with reported rates of between 1% and 10%. A 2014 analysis of the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database reported an SSI rate of 1.8% (Surg Endosc. 2014;28:3285-92). Although these rates are low, Dr. Dang explained that his group wanted to identify factors associated with SSI within 30 days of bariatric surgery. They analyzed outcomes data of 274,187 patients in the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program database who had bariatric surgery in 2015 and 2016 (196,608 by laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy [SG] and 77,579 laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass [RYGB]). Their analysis determined an incisional SSI rate of 0.47% (n = 1,291). “Incisional SSI rates were four times higher for laparoscopic RYGB: 1.04% vs. 0.25%,” Dr. Dang said.
On multivariable logistic regression, the adjusted odds ratio of SSI after RYGB vs. SG was 3.13 (P less than .001). Other significant risk factors were chronic steroid or immunosuppressant use (odds ratio, 1.75; P = .001), female sex (OR, 1.48; P less than .001) and history of gastroesophageal reflux disease (OR, 1.45; P less than .001). Other factors with a 21%-31% greater risk of SSI were white race (P = .002), history of diabetes (P less than .001), hypertension (P less than .001), obstructive sleep apnea (P = .001), and longer operation times (P less than .001). Each single-digit increase in body mass index increased risk by 3%, and older age actually had a protective effect for unknown reasons, Dr. Dang noted.
The BariWound tool assigns points to each risk factor. Each hour of operation time and each 10 kg/m2 of weight carry a value of 1 point, with partial points allowed. RYGB equals 5 points, and chronic steroid/immunosuppressant use, 4 points. The tool assigns risk to four categories based on score and 30-day SSI rate:
- Low, less than 15 (1% risk of SSI).
- Moderate, 15-21.9 (1%-5%).
- High, 22-26.9 (5%-10%).
- Very high, greater than 27 (greater than 10%).
“The BariWound tool can help to inform clinical decision making so patients can know they’re at higher risk, and this could allow for us to target high-risk patients with preventive packages, such as the Cleveland Clinic Technique of wound protection, wound irrigation, and wound packing as a resource-saving measure,” Dr. Dang said. “Targeting high-risk populations can reduce cost and operating time.”
Dr. Weber reported on her institution’s study of SSIs using two different methods for circular stapling of GJ that involved two different surgeons who performed 333 RYGB procedures from January 2016 to March 2018. Surgeon “A” had traditionally used the transoral technique without wound protection to insert the anvil of the stapler; surgeon “B” used wound protection and the transabdominal technique for stapler insertion. Wound protection involves draping of the stapler with sterile plastic.
“In a quarterly review, we detected a higher than expected wound complication rate of 6%,” Dr. Weber said. “Of particular concern was the development of five recent wound infection cases, which all occurred in the transoral group for a rate of 8.9% in that cohort.”
That left the quality team questioning the safety profile of the transoral technique, Dr. Weber said. “We wanted to know why and whether or not the main contributor to the development of a wound infection was the technique for the anvil introduction or was it the difference between surgeons using wound protection.”
Halfway through the study period, surgeon A made two modifications: He adopted the transabdominal technique for a subset of patients; and because of the surgeon’s comfort level and expertise with the transoral approach, he continued using that approach but added wound protection. Surgeon B continued with the transabdominal approach with wound protection. The share of transabdominal insertions in the study population increased from 69.2% before the change to 75% after. Demographics between the pre- and postchange patient populations were similar, as were the rates of revision surgery between the two groups.
“We noticed a significant reduction in total wound complications from 6% to 1.3%, and we noticed a complete elimination of surgical site infections after adding wound protection to the transoral technique,” Dr. Weber said.
Dr. Weber noted a number of limitations with the study: its retrospective nature; the lack of control for other intraoperative factors that contribute to SSIs; relatively low incidence of SSI; and surgeon’s choice to determine the technique of anvil insertion.
“We found that our quality improvement intervention was efficacious and decided that it was not the technique of anvil insertion, but it was the wound protection that was key to preventing wound infections, as we saw complete elimination after we added wound protection to the transoral technique,” Dr. Weber said. “Using proper precautions with the circular stapler and anastomosis can be done using either technique for anvil insertion. Overall self-assessment of outcomes leads to best practice.”
Dr. Dang had no financial relationships to disclose. Dr. Weber’s coauthor Leena Khatian, MD, MPH, disclosed relationships with Torax Medical, Medtronic, and Gore.
SOURCES: Weber C et al. SAGES 2109, Presentation S049; Dang J et al. SAGES 2019, Presentation S050.
BALTIMORE – While rates of surgical site infections after bariatric surgery have been reported in the low single digits, SSIs have continued to be a persistent complication.
At the annual meeting of the Society of American Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Surgeons, researchers reported on two strategies to reduce SSI in bariatric surgery: a predictive tool that identifies risk factors for wound infection, allowing surgeons to employ protective measures before and during surgery, and a change in surgical practice leading to a 78% reduction in wound infection rates that resulted from a single-center study.
Jerry Dang, MD, of the University of Alberta, Edmonton, reported that the BariWound predictive tool designed to stratify patients into risk categories showed a high level of accuracy with an area under the curve of 0.73. Cynthia Weber, MD, of University Hospitals, Cleveland, reported that changing the method for performing circular-stapled gastrojejunostomy (GJ) from the transoral to the transabdominal approach along with more vigilant use of wound protection reduced wound infection rates from 6% to 1.3%.
Dr. Dang noted that SSI has been reported as the most common hospital-acquired complication in bariatric surgery, with reported rates of between 1% and 10%. A 2014 analysis of the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database reported an SSI rate of 1.8% (Surg Endosc. 2014;28:3285-92). Although these rates are low, Dr. Dang explained that his group wanted to identify factors associated with SSI within 30 days of bariatric surgery. They analyzed outcomes data of 274,187 patients in the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program database who had bariatric surgery in 2015 and 2016 (196,608 by laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy [SG] and 77,579 laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass [RYGB]). Their analysis determined an incisional SSI rate of 0.47% (n = 1,291). “Incisional SSI rates were four times higher for laparoscopic RYGB: 1.04% vs. 0.25%,” Dr. Dang said.
On multivariable logistic regression, the adjusted odds ratio of SSI after RYGB vs. SG was 3.13 (P less than .001). Other significant risk factors were chronic steroid or immunosuppressant use (odds ratio, 1.75; P = .001), female sex (OR, 1.48; P less than .001) and history of gastroesophageal reflux disease (OR, 1.45; P less than .001). Other factors with a 21%-31% greater risk of SSI were white race (P = .002), history of diabetes (P less than .001), hypertension (P less than .001), obstructive sleep apnea (P = .001), and longer operation times (P less than .001). Each single-digit increase in body mass index increased risk by 3%, and older age actually had a protective effect for unknown reasons, Dr. Dang noted.
The BariWound tool assigns points to each risk factor. Each hour of operation time and each 10 kg/m2 of weight carry a value of 1 point, with partial points allowed. RYGB equals 5 points, and chronic steroid/immunosuppressant use, 4 points. The tool assigns risk to four categories based on score and 30-day SSI rate:
- Low, less than 15 (1% risk of SSI).
- Moderate, 15-21.9 (1%-5%).
- High, 22-26.9 (5%-10%).
- Very high, greater than 27 (greater than 10%).
“The BariWound tool can help to inform clinical decision making so patients can know they’re at higher risk, and this could allow for us to target high-risk patients with preventive packages, such as the Cleveland Clinic Technique of wound protection, wound irrigation, and wound packing as a resource-saving measure,” Dr. Dang said. “Targeting high-risk populations can reduce cost and operating time.”
Dr. Weber reported on her institution’s study of SSIs using two different methods for circular stapling of GJ that involved two different surgeons who performed 333 RYGB procedures from January 2016 to March 2018. Surgeon “A” had traditionally used the transoral technique without wound protection to insert the anvil of the stapler; surgeon “B” used wound protection and the transabdominal technique for stapler insertion. Wound protection involves draping of the stapler with sterile plastic.
“In a quarterly review, we detected a higher than expected wound complication rate of 6%,” Dr. Weber said. “Of particular concern was the development of five recent wound infection cases, which all occurred in the transoral group for a rate of 8.9% in that cohort.”
That left the quality team questioning the safety profile of the transoral technique, Dr. Weber said. “We wanted to know why and whether or not the main contributor to the development of a wound infection was the technique for the anvil introduction or was it the difference between surgeons using wound protection.”
Halfway through the study period, surgeon A made two modifications: He adopted the transabdominal technique for a subset of patients; and because of the surgeon’s comfort level and expertise with the transoral approach, he continued using that approach but added wound protection. Surgeon B continued with the transabdominal approach with wound protection. The share of transabdominal insertions in the study population increased from 69.2% before the change to 75% after. Demographics between the pre- and postchange patient populations were similar, as were the rates of revision surgery between the two groups.
“We noticed a significant reduction in total wound complications from 6% to 1.3%, and we noticed a complete elimination of surgical site infections after adding wound protection to the transoral technique,” Dr. Weber said.
Dr. Weber noted a number of limitations with the study: its retrospective nature; the lack of control for other intraoperative factors that contribute to SSIs; relatively low incidence of SSI; and surgeon’s choice to determine the technique of anvil insertion.
“We found that our quality improvement intervention was efficacious and decided that it was not the technique of anvil insertion, but it was the wound protection that was key to preventing wound infections, as we saw complete elimination after we added wound protection to the transoral technique,” Dr. Weber said. “Using proper precautions with the circular stapler and anastomosis can be done using either technique for anvil insertion. Overall self-assessment of outcomes leads to best practice.”
Dr. Dang had no financial relationships to disclose. Dr. Weber’s coauthor Leena Khatian, MD, MPH, disclosed relationships with Torax Medical, Medtronic, and Gore.
SOURCES: Weber C et al. SAGES 2109, Presentation S049; Dang J et al. SAGES 2019, Presentation S050.
REPORTING FROM SAGES 2019
Key clinical point: .
Major findings: The BariWound predictive model had an accuracy of area under the curve of 0.73; wound infection rates decreased from 6% to 1.3% after the change in practice.
Study details: Analysis of 274,187 cases from the 2015 MBSAQIP database; and a retrospective analysis of 333 bariatric cases performed from January 2016 to March 2018 at a single center.
Disclosures: Dr. Dang has no relationships to disclose. Dr. Weber has no disclosures, although coauthor Leena Khatian, MD, MPH, disclosed relationships with Torax Medical, Medtronic, and Gore.
Sources: Weber C et al. SAGES 2109, Presentation S049; Dang J et al. SAGES 2019, Presentation S050.
HM19 Day One highlights: Pulmonary, critical care, and perioperative care updates (VIDEO)
Marina Farah, MD, MHA, and Kranthi Sitammagari, MD, editorial board members for The Hospitalist, discuss Day One highlights from HM19.

Marina Farah, MD, MHA, and Kranthi Sitammagari, MD, editorial board members for The Hospitalist, discuss Day One highlights from HM19.

Marina Farah, MD, MHA, and Kranthi Sitammagari, MD, editorial board members for The Hospitalist, discuss Day One highlights from HM19.

Better communication with pharmacists can improve postop pain control
LAS VEGAS – . Watch out for overlapping medication orders. Beware of gabapentin mishaps, and embrace Tylenol – but not always.
April Smith, PharmD, associate professor of pharmacy practice at Creighton University, Omaha, offered these tips about postoperative care to surgeons at the 2019 Annual Minimally Invasive Surgery Symposium by Global Academy for Medical Education.
“We’re probably one of the most underutilized professions you have on your team,” she said, adding that “we have to know what you’re doing to help you.”
As she explained, “if you’re going to have a new order set, let us know that, so we can be your allies in helping nurses and other people understand why we’re doing what we’re doing. I’m on the same floor, and the nurses are coming up to me and asking me questions. If I can explain to them why we’re doing these things, they’ll get on board a lot faster and save you a lot of phone calls. I know you’re surgeons and you hate that [phone calls].”
Better communication with pharmacists can also boost the stocking of enhanced-recovery medications in automatic dispensing machines, she said, so they’re ready when patients need them.
Dr. Smith offered these tips about specific postsurgery medications:
- Scopolamine is a “great drug for post-op vomiting and nausea,” Dr. Smith said. But do not use it in patients over 65, and it’s contraindicated in glaucoma. Beware of these notable side effects: Blurry vision, constipation, and urinary retention. Dexamethasone and ondansetron can be used as an alternative, she said.
- Use of the blood thinner enoxaparin after discharge may become more common as surgical stays become shorter, Dr. Smith said. She urged surgeons to keep its cost in mind: a 10-day course can be as little as $2 with Medicaid or as much as $140 (a cash price for patients without coverage).
- Make sure to adjust medications based on preoperative or intraoperative doses, she said, to avoid endangering patients by inadvertently doubling up on doses. And watch out for previous use of gabapentin, which is part of enhanced-recovery protocols. Patients who take the drug at home should be put back on their typical dose.
- Also, she warned, “don’t give gabapentin to someone who’s never had it before plus an opioid.” This, she said, can cause delirium.
- Consider starting liquids the night of surgery so patients can begin taking their home medications such as sleep, chronic pain, and psychiatric drugs. Patients will be more stable and satisfied, Dr. Smith said.
- Don’t prescribe hard-to-find medications like oxycodone oral solution or oral ketorolac. These drugs will send patients from pharmacy to pharmacy in search of them, Dr. Smith said.
- Embrace a “Meds to Beds” program if possible. These programs enlist on-site pharmacies to deliver medications to bedside for patients to take home.
- Consider Tylenol as a postoperative painkiller with scheduled doses and be aware that you can prescribe the over-the-counter adult liquid form. However, Dr. Smith cautioned that Tylenol is “not great” on an as-needed basis. Gabapentin and celecoxib (unless contraindicated) are also helpful for postop pain relief, and they’re inexpensive, she said. Three to five days should be enough in most minimally invasive surgeries.
- Don’t overprescribe opioids. “The more we prescribe, the more they will consume,” Dr. Smith said. Check the American College of Surgeons guidelines regarding the ideal number of postsurgery, 5-mg doses of oxycodone to prescribe to opioid-naive patients at discharge. No more than 10 or 15 pills are recommended for several types of general surgery (J Amer Coll Surg. 2018;227:411-8).
Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Smith reports no relevant disclosures.
LAS VEGAS – . Watch out for overlapping medication orders. Beware of gabapentin mishaps, and embrace Tylenol – but not always.
April Smith, PharmD, associate professor of pharmacy practice at Creighton University, Omaha, offered these tips about postoperative care to surgeons at the 2019 Annual Minimally Invasive Surgery Symposium by Global Academy for Medical Education.
“We’re probably one of the most underutilized professions you have on your team,” she said, adding that “we have to know what you’re doing to help you.”
As she explained, “if you’re going to have a new order set, let us know that, so we can be your allies in helping nurses and other people understand why we’re doing what we’re doing. I’m on the same floor, and the nurses are coming up to me and asking me questions. If I can explain to them why we’re doing these things, they’ll get on board a lot faster and save you a lot of phone calls. I know you’re surgeons and you hate that [phone calls].”
Better communication with pharmacists can also boost the stocking of enhanced-recovery medications in automatic dispensing machines, she said, so they’re ready when patients need them.
Dr. Smith offered these tips about specific postsurgery medications:
- Scopolamine is a “great drug for post-op vomiting and nausea,” Dr. Smith said. But do not use it in patients over 65, and it’s contraindicated in glaucoma. Beware of these notable side effects: Blurry vision, constipation, and urinary retention. Dexamethasone and ondansetron can be used as an alternative, she said.
- Use of the blood thinner enoxaparin after discharge may become more common as surgical stays become shorter, Dr. Smith said. She urged surgeons to keep its cost in mind: a 10-day course can be as little as $2 with Medicaid or as much as $140 (a cash price for patients without coverage).
- Make sure to adjust medications based on preoperative or intraoperative doses, she said, to avoid endangering patients by inadvertently doubling up on doses. And watch out for previous use of gabapentin, which is part of enhanced-recovery protocols. Patients who take the drug at home should be put back on their typical dose.
- Also, she warned, “don’t give gabapentin to someone who’s never had it before plus an opioid.” This, she said, can cause delirium.
- Consider starting liquids the night of surgery so patients can begin taking their home medications such as sleep, chronic pain, and psychiatric drugs. Patients will be more stable and satisfied, Dr. Smith said.
- Don’t prescribe hard-to-find medications like oxycodone oral solution or oral ketorolac. These drugs will send patients from pharmacy to pharmacy in search of them, Dr. Smith said.
- Embrace a “Meds to Beds” program if possible. These programs enlist on-site pharmacies to deliver medications to bedside for patients to take home.
- Consider Tylenol as a postoperative painkiller with scheduled doses and be aware that you can prescribe the over-the-counter adult liquid form. However, Dr. Smith cautioned that Tylenol is “not great” on an as-needed basis. Gabapentin and celecoxib (unless contraindicated) are also helpful for postop pain relief, and they’re inexpensive, she said. Three to five days should be enough in most minimally invasive surgeries.
- Don’t overprescribe opioids. “The more we prescribe, the more they will consume,” Dr. Smith said. Check the American College of Surgeons guidelines regarding the ideal number of postsurgery, 5-mg doses of oxycodone to prescribe to opioid-naive patients at discharge. No more than 10 or 15 pills are recommended for several types of general surgery (J Amer Coll Surg. 2018;227:411-8).
Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Smith reports no relevant disclosures.
LAS VEGAS – . Watch out for overlapping medication orders. Beware of gabapentin mishaps, and embrace Tylenol – but not always.
April Smith, PharmD, associate professor of pharmacy practice at Creighton University, Omaha, offered these tips about postoperative care to surgeons at the 2019 Annual Minimally Invasive Surgery Symposium by Global Academy for Medical Education.
“We’re probably one of the most underutilized professions you have on your team,” she said, adding that “we have to know what you’re doing to help you.”
As she explained, “if you’re going to have a new order set, let us know that, so we can be your allies in helping nurses and other people understand why we’re doing what we’re doing. I’m on the same floor, and the nurses are coming up to me and asking me questions. If I can explain to them why we’re doing these things, they’ll get on board a lot faster and save you a lot of phone calls. I know you’re surgeons and you hate that [phone calls].”
Better communication with pharmacists can also boost the stocking of enhanced-recovery medications in automatic dispensing machines, she said, so they’re ready when patients need them.
Dr. Smith offered these tips about specific postsurgery medications:
- Scopolamine is a “great drug for post-op vomiting and nausea,” Dr. Smith said. But do not use it in patients over 65, and it’s contraindicated in glaucoma. Beware of these notable side effects: Blurry vision, constipation, and urinary retention. Dexamethasone and ondansetron can be used as an alternative, she said.
- Use of the blood thinner enoxaparin after discharge may become more common as surgical stays become shorter, Dr. Smith said. She urged surgeons to keep its cost in mind: a 10-day course can be as little as $2 with Medicaid or as much as $140 (a cash price for patients without coverage).
- Make sure to adjust medications based on preoperative or intraoperative doses, she said, to avoid endangering patients by inadvertently doubling up on doses. And watch out for previous use of gabapentin, which is part of enhanced-recovery protocols. Patients who take the drug at home should be put back on their typical dose.
- Also, she warned, “don’t give gabapentin to someone who’s never had it before plus an opioid.” This, she said, can cause delirium.
- Consider starting liquids the night of surgery so patients can begin taking their home medications such as sleep, chronic pain, and psychiatric drugs. Patients will be more stable and satisfied, Dr. Smith said.
- Don’t prescribe hard-to-find medications like oxycodone oral solution or oral ketorolac. These drugs will send patients from pharmacy to pharmacy in search of them, Dr. Smith said.
- Embrace a “Meds to Beds” program if possible. These programs enlist on-site pharmacies to deliver medications to bedside for patients to take home.
- Consider Tylenol as a postoperative painkiller with scheduled doses and be aware that you can prescribe the over-the-counter adult liquid form. However, Dr. Smith cautioned that Tylenol is “not great” on an as-needed basis. Gabapentin and celecoxib (unless contraindicated) are also helpful for postop pain relief, and they’re inexpensive, she said. Three to five days should be enough in most minimally invasive surgeries.
- Don’t overprescribe opioids. “The more we prescribe, the more they will consume,” Dr. Smith said. Check the American College of Surgeons guidelines regarding the ideal number of postsurgery, 5-mg doses of oxycodone to prescribe to opioid-naive patients at discharge. No more than 10 or 15 pills are recommended for several types of general surgery (J Amer Coll Surg. 2018;227:411-8).
Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Smith reports no relevant disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM MISS
The ever-evolving scope of hospitalists’ clinical services
More care ‘beyond the walls’ of the hospital
The 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) Report provides indispensable data about the scope of clinical services routinely provided by adult and pediatric hospitalists. This year’s SoHM report reveals that a growing number of Hospital Medicine Groups (HMGs) serving adults are involved in roles beyond the inpatient medical wards, including various surgical comanagement programs, outpatient care, and post-acute care services.
The survey also compares services provided by academic and nonacademic HMGs, which remain markedly different in some areas. As the landscape of health care continues to evolve, hospitalists transform their scope of services to meet the needs of the institutions and communities they serve.
In the previous three SoHM reports, it was well established that more than 87% of adult hospital medicine groups play some role in comanaging surgical patients. In this year’s SoHM report, that role was further stratified to capture the various subspecialties represented, and to identify whether the hospitalists generally served as admitting/attending physician or consultant.
Hospitalists’ roles in comanagement are most prominent for care of orthopedic and general surgery patients, but more than 50% of surveyed HMGs reported being involved in comanagement in some capacity with neurosurgery, obstetrics, and cardiovascular surgery. Additionally, almost 95% of surveyed adult HMGs reported that they provided comanagement services for at least one other surgical specialty that was not listed in the survey.
The report also displays comanagement services provided to various medical subspecialties, including neurology, GI/liver, oncology, and more. Of the medical subspecialties represented, adult HMGs comanaged GI/liver (98.2%) and oncology (97.7%) services more often than others.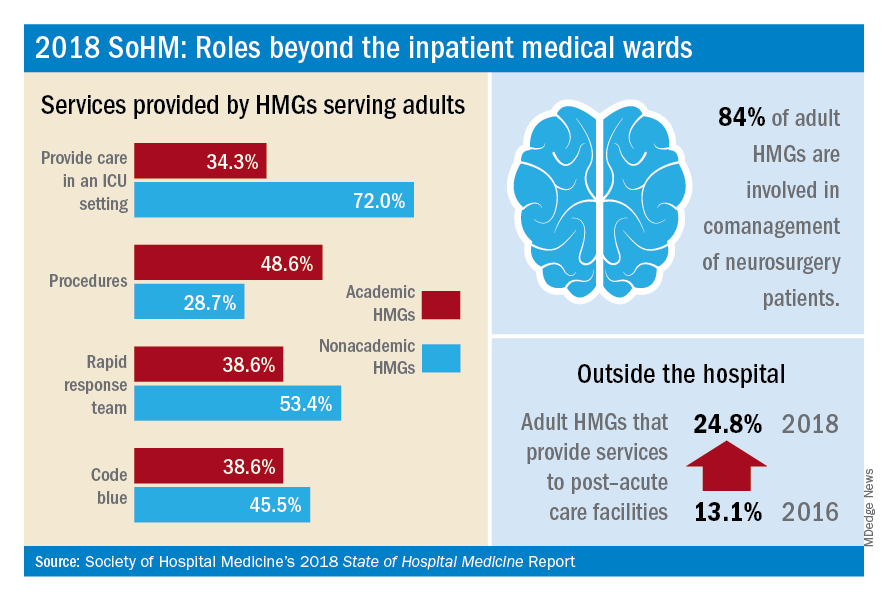
Interestingly, more HMGs are providing care for patients beyond the walls of the hospital. In the 2018 SoHM report, over 17% of surveyed HMG respondents reported providing care in an outpatient setting, representing an increase of 6.5 percentage points over 2016. Most strikingly, from 2016 to 2018, there was a 12 percentage point increase in adult HMGs reporting services provided to post-acute care facilities (from 13.1% to 24.8%).
These trends were most notable in the Midwest region where nearly 28% of HMGs provide patient care in an outpatient setting and up to 34% in post-acute care facilities. In part, this trend may result from the increased emphasis on improving transitions of care, by providing prehospital preoperative services, postdischarge follow-up encounters, or offering posthospitalization extensivist care.
Within the hospital itself, there remain striking differences in certain services provided by academic and nonacademic HMGs serving adults. Nonacademic HMGs are far more likely to cover patients in an ICU than their academic counterparts (72.0% vs. 34.3%). In contrast, academic hospitalist groups were significantly more inclined to perform procedures. However, the report also showed that there was an overall downtrend of percentage of HMGs that cover patients in an ICU or perform procedures.
As the scope of hospitalist services continues to change over time, should there be concern for scope creep? It depends on how one might view the change. As health care becomes ever more complex, high-functioning HMGs are needed to navigate it, both within and beyond the hospital. Some might consider scope evolution to be a reflection of hospitalists being recognized for their ability to provide high-quality, efficient, and comprehensive care. Hospital medicine groups will likely continue to evolve to meet the needs of an ever-changing health care environment.
Dr. Kurian is chief of the academic division of hospital medicine at Northwell Health in New York. She is a member of the SHM Practice Analysis Committee.
More care ‘beyond the walls’ of the hospital
More care ‘beyond the walls’ of the hospital
The 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) Report provides indispensable data about the scope of clinical services routinely provided by adult and pediatric hospitalists. This year’s SoHM report reveals that a growing number of Hospital Medicine Groups (HMGs) serving adults are involved in roles beyond the inpatient medical wards, including various surgical comanagement programs, outpatient care, and post-acute care services.
The survey also compares services provided by academic and nonacademic HMGs, which remain markedly different in some areas. As the landscape of health care continues to evolve, hospitalists transform their scope of services to meet the needs of the institutions and communities they serve.
In the previous three SoHM reports, it was well established that more than 87% of adult hospital medicine groups play some role in comanaging surgical patients. In this year’s SoHM report, that role was further stratified to capture the various subspecialties represented, and to identify whether the hospitalists generally served as admitting/attending physician or consultant.
Hospitalists’ roles in comanagement are most prominent for care of orthopedic and general surgery patients, but more than 50% of surveyed HMGs reported being involved in comanagement in some capacity with neurosurgery, obstetrics, and cardiovascular surgery. Additionally, almost 95% of surveyed adult HMGs reported that they provided comanagement services for at least one other surgical specialty that was not listed in the survey.
The report also displays comanagement services provided to various medical subspecialties, including neurology, GI/liver, oncology, and more. Of the medical subspecialties represented, adult HMGs comanaged GI/liver (98.2%) and oncology (97.7%) services more often than others.
Interestingly, more HMGs are providing care for patients beyond the walls of the hospital. In the 2018 SoHM report, over 17% of surveyed HMG respondents reported providing care in an outpatient setting, representing an increase of 6.5 percentage points over 2016. Most strikingly, from 2016 to 2018, there was a 12 percentage point increase in adult HMGs reporting services provided to post-acute care facilities (from 13.1% to 24.8%).
These trends were most notable in the Midwest region where nearly 28% of HMGs provide patient care in an outpatient setting and up to 34% in post-acute care facilities. In part, this trend may result from the increased emphasis on improving transitions of care, by providing prehospital preoperative services, postdischarge follow-up encounters, or offering posthospitalization extensivist care.
Within the hospital itself, there remain striking differences in certain services provided by academic and nonacademic HMGs serving adults. Nonacademic HMGs are far more likely to cover patients in an ICU than their academic counterparts (72.0% vs. 34.3%). In contrast, academic hospitalist groups were significantly more inclined to perform procedures. However, the report also showed that there was an overall downtrend of percentage of HMGs that cover patients in an ICU or perform procedures.
As the scope of hospitalist services continues to change over time, should there be concern for scope creep? It depends on how one might view the change. As health care becomes ever more complex, high-functioning HMGs are needed to navigate it, both within and beyond the hospital. Some might consider scope evolution to be a reflection of hospitalists being recognized for their ability to provide high-quality, efficient, and comprehensive care. Hospital medicine groups will likely continue to evolve to meet the needs of an ever-changing health care environment.
Dr. Kurian is chief of the academic division of hospital medicine at Northwell Health in New York. She is a member of the SHM Practice Analysis Committee.
The 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) Report provides indispensable data about the scope of clinical services routinely provided by adult and pediatric hospitalists. This year’s SoHM report reveals that a growing number of Hospital Medicine Groups (HMGs) serving adults are involved in roles beyond the inpatient medical wards, including various surgical comanagement programs, outpatient care, and post-acute care services.
The survey also compares services provided by academic and nonacademic HMGs, which remain markedly different in some areas. As the landscape of health care continues to evolve, hospitalists transform their scope of services to meet the needs of the institutions and communities they serve.
In the previous three SoHM reports, it was well established that more than 87% of adult hospital medicine groups play some role in comanaging surgical patients. In this year’s SoHM report, that role was further stratified to capture the various subspecialties represented, and to identify whether the hospitalists generally served as admitting/attending physician or consultant.
Hospitalists’ roles in comanagement are most prominent for care of orthopedic and general surgery patients, but more than 50% of surveyed HMGs reported being involved in comanagement in some capacity with neurosurgery, obstetrics, and cardiovascular surgery. Additionally, almost 95% of surveyed adult HMGs reported that they provided comanagement services for at least one other surgical specialty that was not listed in the survey.
The report also displays comanagement services provided to various medical subspecialties, including neurology, GI/liver, oncology, and more. Of the medical subspecialties represented, adult HMGs comanaged GI/liver (98.2%) and oncology (97.7%) services more often than others.
Interestingly, more HMGs are providing care for patients beyond the walls of the hospital. In the 2018 SoHM report, over 17% of surveyed HMG respondents reported providing care in an outpatient setting, representing an increase of 6.5 percentage points over 2016. Most strikingly, from 2016 to 2018, there was a 12 percentage point increase in adult HMGs reporting services provided to post-acute care facilities (from 13.1% to 24.8%).
These trends were most notable in the Midwest region where nearly 28% of HMGs provide patient care in an outpatient setting and up to 34% in post-acute care facilities. In part, this trend may result from the increased emphasis on improving transitions of care, by providing prehospital preoperative services, postdischarge follow-up encounters, or offering posthospitalization extensivist care.
Within the hospital itself, there remain striking differences in certain services provided by academic and nonacademic HMGs serving adults. Nonacademic HMGs are far more likely to cover patients in an ICU than their academic counterparts (72.0% vs. 34.3%). In contrast, academic hospitalist groups were significantly more inclined to perform procedures. However, the report also showed that there was an overall downtrend of percentage of HMGs that cover patients in an ICU or perform procedures.
As the scope of hospitalist services continues to change over time, should there be concern for scope creep? It depends on how one might view the change. As health care becomes ever more complex, high-functioning HMGs are needed to navigate it, both within and beyond the hospital. Some might consider scope evolution to be a reflection of hospitalists being recognized for their ability to provide high-quality, efficient, and comprehensive care. Hospital medicine groups will likely continue to evolve to meet the needs of an ever-changing health care environment.
Dr. Kurian is chief of the academic division of hospital medicine at Northwell Health in New York. She is a member of the SHM Practice Analysis Committee.
Noncardiac surgery has 7% covert stroke rate in elderly
HONOLULU – Covert strokes are relatively common in elderly patients who undergo noncardiac surgery, with a 7% incidence among a group of prospectively followed but generally unselected patients in a multicenter, international study.
By definition, these covert strokes were acutely asymptomatic, but showed evidence of clinical effects during the subsequent year. Twelve months after surgery, patients with acute, perioperative covert strokes found by systematic collection of postoperative MRI brain scans had a twofold increased rate of cognitive decline and a greater than twofold increased rate of delirium, compared with the patients who did not have evidence of a covert stroke, Marko Mrkobrada, MD, said at the International Stroke Conference sponsored by the American Heart Association.
The message from these findings is that, when elderly patients exhibit confusion or delirium after noncardiac surgery, their physicians should have a high index of suspicion that a covert stroke may have occurred, Dr. Mrkobrada said in a video interview. It’s possible that typical stroke symptoms do not appear in many of the covert stroke patients because they are masked in the immediate postoperative period, he added.
Right now, the only way to screen for a covert stroke is with a brain MR, a test that generally costs several hundred dollars, which is too expensive for routine screening. Dr. Mrkobrada said that his team hopes further study will identify a biomarker that can flag patients with a covert stroke at a lower cost. For example, colleagues of Dr. Mrkobrada have successfully used high-sensitivity troponin T, a biomarker of myocardial injury, to identify patients who have myocardial injury after noncardiac surgery (MINS; JAMA. 2017 April 25;371[16]:1642-51). Study results also established that treating MINS patients with dabigatran improved their long-term clinical outcomes (Lancet. 2018 June 9;391[10137]:2325-34).
Covert stroke after noncardiac surgery “is the same concept” as MINS, said Dr. Mrkobrada, a researcher at the London Health Sciences Centre in Canada. “We find strokes that do not get picked up after noncardiac surgery just like MIs that are not picked up,” he said. It’s also possible that certain interventions may improve outcomes in patients with covert strokes, just as they have helped MINS patients, he suggested. Potentially helpful interventions could include aspirin, a statin, and improved blood pressure control. A major goal for his research group is finding a biomarker that makes diagnosing covert stroke as easy as using high sensitivity troponin T to diagnose MINS.
The NeuroVISION (Detection and Neurological Impact of Cerebrovascular Events In Noncardiac Surgery Patients: A Cohort EvaluatioN) study enrolled and tested 1,114 people aged 65 years or older scheduled for elective noncardiac surgery anticipated to keep them hospitalized for at least 2 days at any of 12 participating centers in nine countries. Patients underwent cognitive function testing before surgery and had a brain MR scan 2-9 days after surgery, and they were excluded if they developed an overt stroke prior to the scan. Patients underwent a second round of cognitive testing a year after surgery. Patients averaged 73 years old.
The screening MR scans identified covert strokes in 78 of the study subjects (7%). The 1-year cognitive tests showed measurable drops in cognitive function in 42% of those who had experience covert strokes and in 29% of everyone else. Those rates translated to a doubled odds ratio for cognitive decline after covert stroke, compared with people without covert stroke after adjustment for baseline between-group differences, a highly statistically significant between-group difference for the study’s primary endpoint. Delirium occurred 2.2-fold more often in the covert stroke patients after adjustment, and overt strokes during 1-year follow-up were 4.1-fold more common patients who’d experienced a covert stroke, compared with everyone else, after adjustment, Dr. Mrkobrada reported. NeuroVISION is the first large-scale study to assess the incidence and associations of covert strokes after noncardiac surgery, he noted.
SOURCE: Mrkobrada M. ISC 2019, Late-Breaking Abstract LB18.
HONOLULU – Covert strokes are relatively common in elderly patients who undergo noncardiac surgery, with a 7% incidence among a group of prospectively followed but generally unselected patients in a multicenter, international study.
By definition, these covert strokes were acutely asymptomatic, but showed evidence of clinical effects during the subsequent year. Twelve months after surgery, patients with acute, perioperative covert strokes found by systematic collection of postoperative MRI brain scans had a twofold increased rate of cognitive decline and a greater than twofold increased rate of delirium, compared with the patients who did not have evidence of a covert stroke, Marko Mrkobrada, MD, said at the International Stroke Conference sponsored by the American Heart Association.
The message from these findings is that, when elderly patients exhibit confusion or delirium after noncardiac surgery, their physicians should have a high index of suspicion that a covert stroke may have occurred, Dr. Mrkobrada said in a video interview. It’s possible that typical stroke symptoms do not appear in many of the covert stroke patients because they are masked in the immediate postoperative period, he added.
Right now, the only way to screen for a covert stroke is with a brain MR, a test that generally costs several hundred dollars, which is too expensive for routine screening. Dr. Mrkobrada said that his team hopes further study will identify a biomarker that can flag patients with a covert stroke at a lower cost. For example, colleagues of Dr. Mrkobrada have successfully used high-sensitivity troponin T, a biomarker of myocardial injury, to identify patients who have myocardial injury after noncardiac surgery (MINS; JAMA. 2017 April 25;371[16]:1642-51). Study results also established that treating MINS patients with dabigatran improved their long-term clinical outcomes (Lancet. 2018 June 9;391[10137]:2325-34).
Covert stroke after noncardiac surgery “is the same concept” as MINS, said Dr. Mrkobrada, a researcher at the London Health Sciences Centre in Canada. “We find strokes that do not get picked up after noncardiac surgery just like MIs that are not picked up,” he said. It’s also possible that certain interventions may improve outcomes in patients with covert strokes, just as they have helped MINS patients, he suggested. Potentially helpful interventions could include aspirin, a statin, and improved blood pressure control. A major goal for his research group is finding a biomarker that makes diagnosing covert stroke as easy as using high sensitivity troponin T to diagnose MINS.
The NeuroVISION (Detection and Neurological Impact of Cerebrovascular Events In Noncardiac Surgery Patients: A Cohort EvaluatioN) study enrolled and tested 1,114 people aged 65 years or older scheduled for elective noncardiac surgery anticipated to keep them hospitalized for at least 2 days at any of 12 participating centers in nine countries. Patients underwent cognitive function testing before surgery and had a brain MR scan 2-9 days after surgery, and they were excluded if they developed an overt stroke prior to the scan. Patients underwent a second round of cognitive testing a year after surgery. Patients averaged 73 years old.
The screening MR scans identified covert strokes in 78 of the study subjects (7%). The 1-year cognitive tests showed measurable drops in cognitive function in 42% of those who had experience covert strokes and in 29% of everyone else. Those rates translated to a doubled odds ratio for cognitive decline after covert stroke, compared with people without covert stroke after adjustment for baseline between-group differences, a highly statistically significant between-group difference for the study’s primary endpoint. Delirium occurred 2.2-fold more often in the covert stroke patients after adjustment, and overt strokes during 1-year follow-up were 4.1-fold more common patients who’d experienced a covert stroke, compared with everyone else, after adjustment, Dr. Mrkobrada reported. NeuroVISION is the first large-scale study to assess the incidence and associations of covert strokes after noncardiac surgery, he noted.
SOURCE: Mrkobrada M. ISC 2019, Late-Breaking Abstract LB18.
HONOLULU – Covert strokes are relatively common in elderly patients who undergo noncardiac surgery, with a 7% incidence among a group of prospectively followed but generally unselected patients in a multicenter, international study.
By definition, these covert strokes were acutely asymptomatic, but showed evidence of clinical effects during the subsequent year. Twelve months after surgery, patients with acute, perioperative covert strokes found by systematic collection of postoperative MRI brain scans had a twofold increased rate of cognitive decline and a greater than twofold increased rate of delirium, compared with the patients who did not have evidence of a covert stroke, Marko Mrkobrada, MD, said at the International Stroke Conference sponsored by the American Heart Association.
The message from these findings is that, when elderly patients exhibit confusion or delirium after noncardiac surgery, their physicians should have a high index of suspicion that a covert stroke may have occurred, Dr. Mrkobrada said in a video interview. It’s possible that typical stroke symptoms do not appear in many of the covert stroke patients because they are masked in the immediate postoperative period, he added.
Right now, the only way to screen for a covert stroke is with a brain MR, a test that generally costs several hundred dollars, which is too expensive for routine screening. Dr. Mrkobrada said that his team hopes further study will identify a biomarker that can flag patients with a covert stroke at a lower cost. For example, colleagues of Dr. Mrkobrada have successfully used high-sensitivity troponin T, a biomarker of myocardial injury, to identify patients who have myocardial injury after noncardiac surgery (MINS; JAMA. 2017 April 25;371[16]:1642-51). Study results also established that treating MINS patients with dabigatran improved their long-term clinical outcomes (Lancet. 2018 June 9;391[10137]:2325-34).
Covert stroke after noncardiac surgery “is the same concept” as MINS, said Dr. Mrkobrada, a researcher at the London Health Sciences Centre in Canada. “We find strokes that do not get picked up after noncardiac surgery just like MIs that are not picked up,” he said. It’s also possible that certain interventions may improve outcomes in patients with covert strokes, just as they have helped MINS patients, he suggested. Potentially helpful interventions could include aspirin, a statin, and improved blood pressure control. A major goal for his research group is finding a biomarker that makes diagnosing covert stroke as easy as using high sensitivity troponin T to diagnose MINS.
The NeuroVISION (Detection and Neurological Impact of Cerebrovascular Events In Noncardiac Surgery Patients: A Cohort EvaluatioN) study enrolled and tested 1,114 people aged 65 years or older scheduled for elective noncardiac surgery anticipated to keep them hospitalized for at least 2 days at any of 12 participating centers in nine countries. Patients underwent cognitive function testing before surgery and had a brain MR scan 2-9 days after surgery, and they were excluded if they developed an overt stroke prior to the scan. Patients underwent a second round of cognitive testing a year after surgery. Patients averaged 73 years old.
The screening MR scans identified covert strokes in 78 of the study subjects (7%). The 1-year cognitive tests showed measurable drops in cognitive function in 42% of those who had experience covert strokes and in 29% of everyone else. Those rates translated to a doubled odds ratio for cognitive decline after covert stroke, compared with people without covert stroke after adjustment for baseline between-group differences, a highly statistically significant between-group difference for the study’s primary endpoint. Delirium occurred 2.2-fold more often in the covert stroke patients after adjustment, and overt strokes during 1-year follow-up were 4.1-fold more common patients who’d experienced a covert stroke, compared with everyone else, after adjustment, Dr. Mrkobrada reported. NeuroVISION is the first large-scale study to assess the incidence and associations of covert strokes after noncardiac surgery, he noted.
SOURCE: Mrkobrada M. ISC 2019, Late-Breaking Abstract LB18.
REPORTING FROM ISC 2019
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Elderly patients who underwent noncardiac surgery had a 7% incidence of covert stroke.
Study details: NeuroVISION, a prospective, multicenter, observational study with 1,114 patients.
Disclosures: NeuroVISION did not receive commercial funding. Dr. Mrkobrada had no disclosures.
Source: Mrkobrada M. ISC 2019, Late-Breaking Abstract LB18.