User login
Young children with neuromuscular disease are vulnerable to respiratory viruses
This highlights the need for new vaccines
Influenza gets a lot of attention each winter, but respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and other respiratory viruses have as much or more impact on pediatric populations, particularly certain high-risk groups. But currently there are no vaccines for noninfluenza respiratory viruses. That said, several are under development, for RSV and parainfluenza.
Which groups are likely to get the most benefit from these newer vaccines?
We all are aware of the extra vulnerability to respiratory viruses (RSV being the most frequent) in premature infants, those with chronic lung disease, or those with congenital heart syndromes; such vulnerable patients are not infrequently seen in routine practice. A recent report shined a brighter light on such a group.
Real-world data from a nationwide Canadian surveillance system (CARESS) was used to analyze relative risks of categories of young children who are thought to be vulnerable to respiratory viruses, with a particular focus on those with neuromuscular disease. The CARESS investigators analyzed 12 years’ data on respiratory hospitalizations from among palivizumab-prophylaxed patients (including specific data on RSV when patients were tested for RSV per standard of care).1 Unfortunately, RSV testing was not universal despite hospitalization, so the true incidence of RSV-specific hospitalizations was likely underestimated.
Nevertheless, more than 25,000 children from 2005 through 2017 were grouped into three categories of palivizumab-prophylaxed high-risk children: standard indications (SI), n = 20,335; chronic medical conditions (CMD), n = 4,063; and neuromuscular disease (NMD), n = 605. This study is notable for having a relatively large number of neuromuscular disease subjects. Two-thirds of each group were fully palivizumab adherent.
The SI group included the standard American Academy of Pediatrics–recommended groups, such as premature infants, congenital heart disease, etc.
The CMD group included conditions that lead clinicians to use palivizumab off label, such as cystic fibrosis, congenital airway anomalies, immunodeficiency, and pulmonary disorders.
The NMD participants were subdivided into two groups. Group 1 comprised general hypotonic neuromuscular diseases such as hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, Prader-Willi syndrome, chromosomal disorders, and migration/demyelinating diseases. Group 2 included more severe infantile neuromuscular disorders, such as spinal muscular atrophy, myotonic dystrophy, centronuclear and nemaline myopathy, mitochondrial and glycogen storage myopathies, or arthrogryposis.
Overall, 6.9% of CARESS RSV-prophylaxed subjects were hospitalized. About one in five hospitalized patients from each group was hospitalized more than once. Specific respiratory hospitalization rates for each group were 6% (n = 1,228) for SI subjects and 9.4% (n = 380) for CMD, compared with 19.2% (n = 116) for NMD subjects.
It is unclear what proportion underwent RSV testing, but a total of 334 were confirmed RSV positive: 261 were SI, 54 were CMD and 19 were NMD. The RSV-test-positive rate was 1.5% for SI, 1.6% for CMD and 3.3% for NMD; so while a higher number of SI children were RSV positive, the rate of RSV positivity was actually highest with NMD.
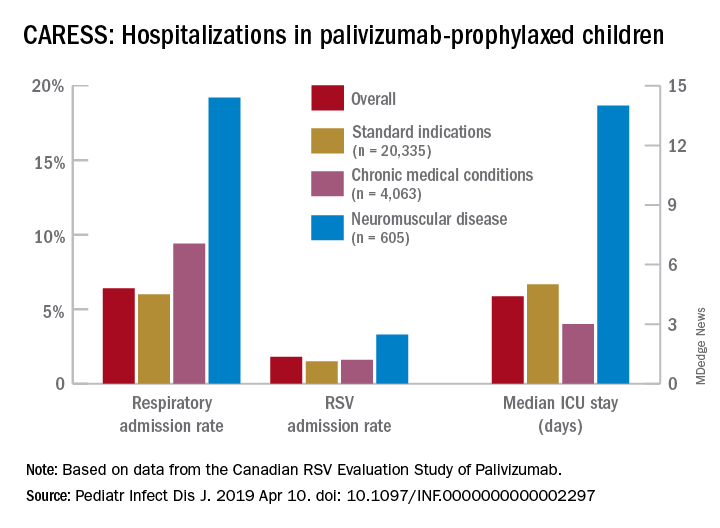
RSV-positive subjects needing ICU care among NMD patients also had longer ICU stays (median 14 days), compared with RSV-positive CMD or SI subjects (median 3 and 5 days, respectively). Further, hospitalized RSV-positive NMD subjects presented more frequently with pneumonia (42% vs. 30% for CMD and 20% for SI) while hospitalized RSV-positive SI subjects more often had apnea (17% vs. 10% for NMD and 5% for CMD, P less than .05).
These differences in the courses of NMD patients raise the question as to whether the NMD group was somehow different from the SI and CMD groups, other than muscular weakness that likely leads to less ability to clear secretions and a less efficient cough. It turns out that NMD children were older and had worse neonatal medical courses (longer hospital stays, more often ventilated, and used oxygen longer). It could be argued that these differences may have been in part due to the muscular weakness inherent in their underlying disease, but they appear to be predictors of worse respiratory infectious disease than other vulnerable populations as the NMD children get older.
Indeed, the overall risk of any respiratory admission among NMD subjects was nearly twice as high, compared with SI (hazard ratio, 1.90, P less than .0005); but the somewhat higher risk for NMD vs. CMD was not significant (HR, 1.33, P = .090). However, when looking specifically at RSV confirmed admissions, NMD had more than twice the hospitalization risk than either other group (HR, 2.26, P = .001 vs. SI; and HR, 2.74, P = .001 vs. CMD).
Further, an NMD subgroup analysis showed 1.69 times the overall respiratory hospitalization risk among the more severe vs. less severe NMD group, but a similar risk of RSV admission. The authors point out that one reason for this discrepancy may be a higher probability of aspiration causing hospitalization because of more dramatic acute events during respiratory infections in patients with more severe NMD. It also may be that palivizumab evened the playing field for RSV but not for other viruses such as parainfluenza, adenovirus, or even rhinovirus.
Nevertheless, these data tell us that risk of respiratory disease severe enough to need hospitalization continues to an older age in NMD than SI or CMD patients, well past 2 years of age. And the risk is not only from RSV. That said, RSV remains a player in some patients (particularly NMD patients) despite palivizumab prophylaxis, highlighting the need for RSV as well as parainfluenza vaccines. While these vaccines should help all young children, they seem likely to be even more beneficial for high-risk children including those with NMD, and particularly those with more severe NMD.
Eleven among 60 total candidate RSV vaccines (live attenuated, particle based, or vector based) are currently in clinical trials.2 Fewer parainfluenza vaccines are in the pipeline, but clinical trials also are underway.3-5 Approval of such vaccines is not expected until the mid-2020s, so at present we are left with providing palivizumab to our vulnerable patients while emphasizing nonmedical strategies that may help prevent respiratory viruses. These only partially successful preventive interventions include breastfeeding, avoiding secondhand smoke, and avoiding known high-risk exposures, such as large day care centers.
My hope is for quicker than projected progress on the vaccine front so that winter admissions for respiratory viruses might decrease in numbers similar to the decrease we have noted with another vaccine successful against a seasonally active pathogen – rotavirus.
Dr. Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospital–Kansas City, Mo. Children’s Mercy Hospital receives grant funding to study two candidate RSV vaccines. The hospital also receives CDC funding under the New Vaccine Surveillance Network for multicenter surveillance of acute respiratory infections, including influenza, RSV, and parainfluenza virus. Email Dr. Harrison at [email protected].
References
1. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2019 Apr 10. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000002297.
2. “Advances in RSV Vaccine Research and Development – A Global Agenda.”
3. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2015 Dec;4(4): e143-6.
4. J Virol. 2015 Oct;89(20):10319-32.
5. Vaccine. 2017 Dec 18;35(51):7139-46.
This highlights the need for new vaccines
This highlights the need for new vaccines
Influenza gets a lot of attention each winter, but respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and other respiratory viruses have as much or more impact on pediatric populations, particularly certain high-risk groups. But currently there are no vaccines for noninfluenza respiratory viruses. That said, several are under development, for RSV and parainfluenza.
Which groups are likely to get the most benefit from these newer vaccines?
We all are aware of the extra vulnerability to respiratory viruses (RSV being the most frequent) in premature infants, those with chronic lung disease, or those with congenital heart syndromes; such vulnerable patients are not infrequently seen in routine practice. A recent report shined a brighter light on such a group.
Real-world data from a nationwide Canadian surveillance system (CARESS) was used to analyze relative risks of categories of young children who are thought to be vulnerable to respiratory viruses, with a particular focus on those with neuromuscular disease. The CARESS investigators analyzed 12 years’ data on respiratory hospitalizations from among palivizumab-prophylaxed patients (including specific data on RSV when patients were tested for RSV per standard of care).1 Unfortunately, RSV testing was not universal despite hospitalization, so the true incidence of RSV-specific hospitalizations was likely underestimated.
Nevertheless, more than 25,000 children from 2005 through 2017 were grouped into three categories of palivizumab-prophylaxed high-risk children: standard indications (SI), n = 20,335; chronic medical conditions (CMD), n = 4,063; and neuromuscular disease (NMD), n = 605. This study is notable for having a relatively large number of neuromuscular disease subjects. Two-thirds of each group were fully palivizumab adherent.
The SI group included the standard American Academy of Pediatrics–recommended groups, such as premature infants, congenital heart disease, etc.
The CMD group included conditions that lead clinicians to use palivizumab off label, such as cystic fibrosis, congenital airway anomalies, immunodeficiency, and pulmonary disorders.
The NMD participants were subdivided into two groups. Group 1 comprised general hypotonic neuromuscular diseases such as hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, Prader-Willi syndrome, chromosomal disorders, and migration/demyelinating diseases. Group 2 included more severe infantile neuromuscular disorders, such as spinal muscular atrophy, myotonic dystrophy, centronuclear and nemaline myopathy, mitochondrial and glycogen storage myopathies, or arthrogryposis.
Overall, 6.9% of CARESS RSV-prophylaxed subjects were hospitalized. About one in five hospitalized patients from each group was hospitalized more than once. Specific respiratory hospitalization rates for each group were 6% (n = 1,228) for SI subjects and 9.4% (n = 380) for CMD, compared with 19.2% (n = 116) for NMD subjects.
It is unclear what proportion underwent RSV testing, but a total of 334 were confirmed RSV positive: 261 were SI, 54 were CMD and 19 were NMD. The RSV-test-positive rate was 1.5% for SI, 1.6% for CMD and 3.3% for NMD; so while a higher number of SI children were RSV positive, the rate of RSV positivity was actually highest with NMD.

RSV-positive subjects needing ICU care among NMD patients also had longer ICU stays (median 14 days), compared with RSV-positive CMD or SI subjects (median 3 and 5 days, respectively). Further, hospitalized RSV-positive NMD subjects presented more frequently with pneumonia (42% vs. 30% for CMD and 20% for SI) while hospitalized RSV-positive SI subjects more often had apnea (17% vs. 10% for NMD and 5% for CMD, P less than .05).
These differences in the courses of NMD patients raise the question as to whether the NMD group was somehow different from the SI and CMD groups, other than muscular weakness that likely leads to less ability to clear secretions and a less efficient cough. It turns out that NMD children were older and had worse neonatal medical courses (longer hospital stays, more often ventilated, and used oxygen longer). It could be argued that these differences may have been in part due to the muscular weakness inherent in their underlying disease, but they appear to be predictors of worse respiratory infectious disease than other vulnerable populations as the NMD children get older.
Indeed, the overall risk of any respiratory admission among NMD subjects was nearly twice as high, compared with SI (hazard ratio, 1.90, P less than .0005); but the somewhat higher risk for NMD vs. CMD was not significant (HR, 1.33, P = .090). However, when looking specifically at RSV confirmed admissions, NMD had more than twice the hospitalization risk than either other group (HR, 2.26, P = .001 vs. SI; and HR, 2.74, P = .001 vs. CMD).
Further, an NMD subgroup analysis showed 1.69 times the overall respiratory hospitalization risk among the more severe vs. less severe NMD group, but a similar risk of RSV admission. The authors point out that one reason for this discrepancy may be a higher probability of aspiration causing hospitalization because of more dramatic acute events during respiratory infections in patients with more severe NMD. It also may be that palivizumab evened the playing field for RSV but not for other viruses such as parainfluenza, adenovirus, or even rhinovirus.
Nevertheless, these data tell us that risk of respiratory disease severe enough to need hospitalization continues to an older age in NMD than SI or CMD patients, well past 2 years of age. And the risk is not only from RSV. That said, RSV remains a player in some patients (particularly NMD patients) despite palivizumab prophylaxis, highlighting the need for RSV as well as parainfluenza vaccines. While these vaccines should help all young children, they seem likely to be even more beneficial for high-risk children including those with NMD, and particularly those with more severe NMD.
Eleven among 60 total candidate RSV vaccines (live attenuated, particle based, or vector based) are currently in clinical trials.2 Fewer parainfluenza vaccines are in the pipeline, but clinical trials also are underway.3-5 Approval of such vaccines is not expected until the mid-2020s, so at present we are left with providing palivizumab to our vulnerable patients while emphasizing nonmedical strategies that may help prevent respiratory viruses. These only partially successful preventive interventions include breastfeeding, avoiding secondhand smoke, and avoiding known high-risk exposures, such as large day care centers.
My hope is for quicker than projected progress on the vaccine front so that winter admissions for respiratory viruses might decrease in numbers similar to the decrease we have noted with another vaccine successful against a seasonally active pathogen – rotavirus.
Dr. Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospital–Kansas City, Mo. Children’s Mercy Hospital receives grant funding to study two candidate RSV vaccines. The hospital also receives CDC funding under the New Vaccine Surveillance Network for multicenter surveillance of acute respiratory infections, including influenza, RSV, and parainfluenza virus. Email Dr. Harrison at [email protected].
References
1. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2019 Apr 10. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000002297.
2. “Advances in RSV Vaccine Research and Development – A Global Agenda.”
3. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2015 Dec;4(4): e143-6.
4. J Virol. 2015 Oct;89(20):10319-32.
5. Vaccine. 2017 Dec 18;35(51):7139-46.
Influenza gets a lot of attention each winter, but respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and other respiratory viruses have as much or more impact on pediatric populations, particularly certain high-risk groups. But currently there are no vaccines for noninfluenza respiratory viruses. That said, several are under development, for RSV and parainfluenza.
Which groups are likely to get the most benefit from these newer vaccines?
We all are aware of the extra vulnerability to respiratory viruses (RSV being the most frequent) in premature infants, those with chronic lung disease, or those with congenital heart syndromes; such vulnerable patients are not infrequently seen in routine practice. A recent report shined a brighter light on such a group.
Real-world data from a nationwide Canadian surveillance system (CARESS) was used to analyze relative risks of categories of young children who are thought to be vulnerable to respiratory viruses, with a particular focus on those with neuromuscular disease. The CARESS investigators analyzed 12 years’ data on respiratory hospitalizations from among palivizumab-prophylaxed patients (including specific data on RSV when patients were tested for RSV per standard of care).1 Unfortunately, RSV testing was not universal despite hospitalization, so the true incidence of RSV-specific hospitalizations was likely underestimated.
Nevertheless, more than 25,000 children from 2005 through 2017 were grouped into three categories of palivizumab-prophylaxed high-risk children: standard indications (SI), n = 20,335; chronic medical conditions (CMD), n = 4,063; and neuromuscular disease (NMD), n = 605. This study is notable for having a relatively large number of neuromuscular disease subjects. Two-thirds of each group were fully palivizumab adherent.
The SI group included the standard American Academy of Pediatrics–recommended groups, such as premature infants, congenital heart disease, etc.
The CMD group included conditions that lead clinicians to use palivizumab off label, such as cystic fibrosis, congenital airway anomalies, immunodeficiency, and pulmonary disorders.
The NMD participants were subdivided into two groups. Group 1 comprised general hypotonic neuromuscular diseases such as hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, Prader-Willi syndrome, chromosomal disorders, and migration/demyelinating diseases. Group 2 included more severe infantile neuromuscular disorders, such as spinal muscular atrophy, myotonic dystrophy, centronuclear and nemaline myopathy, mitochondrial and glycogen storage myopathies, or arthrogryposis.
Overall, 6.9% of CARESS RSV-prophylaxed subjects were hospitalized. About one in five hospitalized patients from each group was hospitalized more than once. Specific respiratory hospitalization rates for each group were 6% (n = 1,228) for SI subjects and 9.4% (n = 380) for CMD, compared with 19.2% (n = 116) for NMD subjects.
It is unclear what proportion underwent RSV testing, but a total of 334 were confirmed RSV positive: 261 were SI, 54 were CMD and 19 were NMD. The RSV-test-positive rate was 1.5% for SI, 1.6% for CMD and 3.3% for NMD; so while a higher number of SI children were RSV positive, the rate of RSV positivity was actually highest with NMD.

RSV-positive subjects needing ICU care among NMD patients also had longer ICU stays (median 14 days), compared with RSV-positive CMD or SI subjects (median 3 and 5 days, respectively). Further, hospitalized RSV-positive NMD subjects presented more frequently with pneumonia (42% vs. 30% for CMD and 20% for SI) while hospitalized RSV-positive SI subjects more often had apnea (17% vs. 10% for NMD and 5% for CMD, P less than .05).
These differences in the courses of NMD patients raise the question as to whether the NMD group was somehow different from the SI and CMD groups, other than muscular weakness that likely leads to less ability to clear secretions and a less efficient cough. It turns out that NMD children were older and had worse neonatal medical courses (longer hospital stays, more often ventilated, and used oxygen longer). It could be argued that these differences may have been in part due to the muscular weakness inherent in their underlying disease, but they appear to be predictors of worse respiratory infectious disease than other vulnerable populations as the NMD children get older.
Indeed, the overall risk of any respiratory admission among NMD subjects was nearly twice as high, compared with SI (hazard ratio, 1.90, P less than .0005); but the somewhat higher risk for NMD vs. CMD was not significant (HR, 1.33, P = .090). However, when looking specifically at RSV confirmed admissions, NMD had more than twice the hospitalization risk than either other group (HR, 2.26, P = .001 vs. SI; and HR, 2.74, P = .001 vs. CMD).
Further, an NMD subgroup analysis showed 1.69 times the overall respiratory hospitalization risk among the more severe vs. less severe NMD group, but a similar risk of RSV admission. The authors point out that one reason for this discrepancy may be a higher probability of aspiration causing hospitalization because of more dramatic acute events during respiratory infections in patients with more severe NMD. It also may be that palivizumab evened the playing field for RSV but not for other viruses such as parainfluenza, adenovirus, or even rhinovirus.
Nevertheless, these data tell us that risk of respiratory disease severe enough to need hospitalization continues to an older age in NMD than SI or CMD patients, well past 2 years of age. And the risk is not only from RSV. That said, RSV remains a player in some patients (particularly NMD patients) despite palivizumab prophylaxis, highlighting the need for RSV as well as parainfluenza vaccines. While these vaccines should help all young children, they seem likely to be even more beneficial for high-risk children including those with NMD, and particularly those with more severe NMD.
Eleven among 60 total candidate RSV vaccines (live attenuated, particle based, or vector based) are currently in clinical trials.2 Fewer parainfluenza vaccines are in the pipeline, but clinical trials also are underway.3-5 Approval of such vaccines is not expected until the mid-2020s, so at present we are left with providing palivizumab to our vulnerable patients while emphasizing nonmedical strategies that may help prevent respiratory viruses. These only partially successful preventive interventions include breastfeeding, avoiding secondhand smoke, and avoiding known high-risk exposures, such as large day care centers.
My hope is for quicker than projected progress on the vaccine front so that winter admissions for respiratory viruses might decrease in numbers similar to the decrease we have noted with another vaccine successful against a seasonally active pathogen – rotavirus.
Dr. Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospital–Kansas City, Mo. Children’s Mercy Hospital receives grant funding to study two candidate RSV vaccines. The hospital also receives CDC funding under the New Vaccine Surveillance Network for multicenter surveillance of acute respiratory infections, including influenza, RSV, and parainfluenza virus. Email Dr. Harrison at [email protected].
References
1. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2019 Apr 10. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000002297.
2. “Advances in RSV Vaccine Research and Development – A Global Agenda.”
3. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2015 Dec;4(4): e143-6.
4. J Virol. 2015 Oct;89(20):10319-32.
5. Vaccine. 2017 Dec 18;35(51):7139-46.
Measles complications in the U.S. unchanged in posteradication era
CHICAGO – An evaluation of the measles threat in the modern era gives no indication that the risk of complications or death is any different than it was before a vaccine became available, according to an analysis of inpatient complications between 2002 and 2013.
In 2000, measles was declared eliminated in the United States, but for those who have been infected since that time, the risk of serious complications and death has not diminished, noted Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, in a session at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology.
By eliminated, the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention – which reported 86 confirmed cases of measles in 2000 – was referring to a technical definition of no new endemic or continuous transmissions in the previous 12 months. It was expected that a modest number of cases of this reportable disease would continue to accrue for an infection that remains common elsewhere in the world.
“Worldwide there are about 20 million cases of measles annually with an estimated 100,000 deaths attributed to this cause,” said Dr. Chovatiya, who is a dermatology resident at Northwestern University, Chicago.
In the United States, posteradication infection rates remained at low levels for several years but were already rising from 2002 to 2013, when Dr. Chovatiya and his coinvestigators sought to describe the incidence, associations, comorbidities, and outcomes of hospitalizations for measles. Toward the end of the period the researchers were examining the incidence rates climbed more steeply.
“So far this year, 764 CDC cases of measles [were] reported. That is the most we have seen in the U.S. since 1994,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
Based on his analysis of hospitalizations from 2002 to 2013, the threat of these outbreaks is no different then that before the disease was declared eliminated or before a vaccine became available.
The cross-sectional study was conducted with data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample, an all-payer database that is considered to be a representative of national trends.
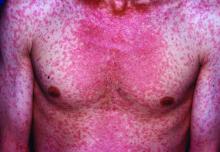
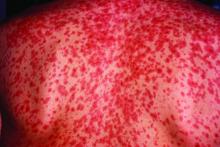
Characteristic of measles, the majority of the 582 hospitalizations evaluated over this period occurred in children aged between 1 and 9 years. The proportion of patients with preexisting chronic comorbid conditions was low. Rather, “most were pretty healthy” prior to admission, according to Dr. Chovatiya, who said that the majority of admissions were from an emergency department.
Measles, which targets epithelial cells and depresses the immune system, is a potentially serious disease because of its ability to produce complications in essentially every organ of the body, including the lungs, kidneys, blood, and central nervous system. Consistent with past studies, the most common complication in this series was pneumonia, observed in 20% of patients. The list of other serious complications identified in this study period, including encephalitis and acute renal failure, was long.
“We observed death in 4.3% of our 582 cases, or about 25 cases,” reported Dr. Chovatiya. He indicated that this is a high percentage among a population composed largely of children who were well before hospitalization.
The mortality rate from measles was numerically but not statistically higher than that of overall hospital admissions during this period, but an admission for measles was associated with significantly longer average length of stay (3.7 vs. 3.5 days) and slightly but significantly higher direct costs ($18,907 vs. $18,474).
“I want to point out that these are just direct inpatient costs,” Dr. Chovatiya said. Extrapolating from published data about indirect expenses, he said that the total health cost burden “is absolutely staggering.”
Previous studies have suggested that about 25% of patients with measles require hospitalization and 1 in every 1,000 patients will die. The data collected by Dr. Chovatiya support these often-cited figures, indicating that they remain unchanged in the modern era.
particularly insufficient penetration of vaccination in many communities.
The vaccine “is inexpensive, extremely effective, and lifesaving,” said Dr. Chovatiya, making the point that all of the morbidity, mortality, and costs he described are largely avoidable.
Attempting to provide perspective of the measles threat and the impact of the vaccine, Dr. Chovatiya cited a hypothetical calculation that 732,000 deaths from measles would have been expected in the United States among the pool of children born between 1994 and 2013 had no vaccine been offered. Again, most of these deaths would have occurred in otherwise healthy children.
Dr. Chovatiya reported no potential conflicts of interest.
CHICAGO – An evaluation of the measles threat in the modern era gives no indication that the risk of complications or death is any different than it was before a vaccine became available, according to an analysis of inpatient complications between 2002 and 2013.
In 2000, measles was declared eliminated in the United States, but for those who have been infected since that time, the risk of serious complications and death has not diminished, noted Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, in a session at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology.
By eliminated, the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention – which reported 86 confirmed cases of measles in 2000 – was referring to a technical definition of no new endemic or continuous transmissions in the previous 12 months. It was expected that a modest number of cases of this reportable disease would continue to accrue for an infection that remains common elsewhere in the world.
“Worldwide there are about 20 million cases of measles annually with an estimated 100,000 deaths attributed to this cause,” said Dr. Chovatiya, who is a dermatology resident at Northwestern University, Chicago.
In the United States, posteradication infection rates remained at low levels for several years but were already rising from 2002 to 2013, when Dr. Chovatiya and his coinvestigators sought to describe the incidence, associations, comorbidities, and outcomes of hospitalizations for measles. Toward the end of the period the researchers were examining the incidence rates climbed more steeply.
“So far this year, 764 CDC cases of measles [were] reported. That is the most we have seen in the U.S. since 1994,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
Based on his analysis of hospitalizations from 2002 to 2013, the threat of these outbreaks is no different then that before the disease was declared eliminated or before a vaccine became available.
The cross-sectional study was conducted with data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample, an all-payer database that is considered to be a representative of national trends.
Characteristic of measles, the majority of the 582 hospitalizations evaluated over this period occurred in children aged between 1 and 9 years. The proportion of patients with preexisting chronic comorbid conditions was low. Rather, “most were pretty healthy” prior to admission, according to Dr. Chovatiya, who said that the majority of admissions were from an emergency department.
Measles, which targets epithelial cells and depresses the immune system, is a potentially serious disease because of its ability to produce complications in essentially every organ of the body, including the lungs, kidneys, blood, and central nervous system. Consistent with past studies, the most common complication in this series was pneumonia, observed in 20% of patients. The list of other serious complications identified in this study period, including encephalitis and acute renal failure, was long.
“We observed death in 4.3% of our 582 cases, or about 25 cases,” reported Dr. Chovatiya. He indicated that this is a high percentage among a population composed largely of children who were well before hospitalization.
The mortality rate from measles was numerically but not statistically higher than that of overall hospital admissions during this period, but an admission for measles was associated with significantly longer average length of stay (3.7 vs. 3.5 days) and slightly but significantly higher direct costs ($18,907 vs. $18,474).
“I want to point out that these are just direct inpatient costs,” Dr. Chovatiya said. Extrapolating from published data about indirect expenses, he said that the total health cost burden “is absolutely staggering.”
Previous studies have suggested that about 25% of patients with measles require hospitalization and 1 in every 1,000 patients will die. The data collected by Dr. Chovatiya support these often-cited figures, indicating that they remain unchanged in the modern era.
particularly insufficient penetration of vaccination in many communities.
The vaccine “is inexpensive, extremely effective, and lifesaving,” said Dr. Chovatiya, making the point that all of the morbidity, mortality, and costs he described are largely avoidable.
Attempting to provide perspective of the measles threat and the impact of the vaccine, Dr. Chovatiya cited a hypothetical calculation that 732,000 deaths from measles would have been expected in the United States among the pool of children born between 1994 and 2013 had no vaccine been offered. Again, most of these deaths would have occurred in otherwise healthy children.
Dr. Chovatiya reported no potential conflicts of interest.
CHICAGO – An evaluation of the measles threat in the modern era gives no indication that the risk of complications or death is any different than it was before a vaccine became available, according to an analysis of inpatient complications between 2002 and 2013.
In 2000, measles was declared eliminated in the United States, but for those who have been infected since that time, the risk of serious complications and death has not diminished, noted Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, in a session at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology.
By eliminated, the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention – which reported 86 confirmed cases of measles in 2000 – was referring to a technical definition of no new endemic or continuous transmissions in the previous 12 months. It was expected that a modest number of cases of this reportable disease would continue to accrue for an infection that remains common elsewhere in the world.
“Worldwide there are about 20 million cases of measles annually with an estimated 100,000 deaths attributed to this cause,” said Dr. Chovatiya, who is a dermatology resident at Northwestern University, Chicago.
In the United States, posteradication infection rates remained at low levels for several years but were already rising from 2002 to 2013, when Dr. Chovatiya and his coinvestigators sought to describe the incidence, associations, comorbidities, and outcomes of hospitalizations for measles. Toward the end of the period the researchers were examining the incidence rates climbed more steeply.
“So far this year, 764 CDC cases of measles [were] reported. That is the most we have seen in the U.S. since 1994,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
Based on his analysis of hospitalizations from 2002 to 2013, the threat of these outbreaks is no different then that before the disease was declared eliminated or before a vaccine became available.
The cross-sectional study was conducted with data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample, an all-payer database that is considered to be a representative of national trends.
Characteristic of measles, the majority of the 582 hospitalizations evaluated over this period occurred in children aged between 1 and 9 years. The proportion of patients with preexisting chronic comorbid conditions was low. Rather, “most were pretty healthy” prior to admission, according to Dr. Chovatiya, who said that the majority of admissions were from an emergency department.
Measles, which targets epithelial cells and depresses the immune system, is a potentially serious disease because of its ability to produce complications in essentially every organ of the body, including the lungs, kidneys, blood, and central nervous system. Consistent with past studies, the most common complication in this series was pneumonia, observed in 20% of patients. The list of other serious complications identified in this study period, including encephalitis and acute renal failure, was long.
“We observed death in 4.3% of our 582 cases, or about 25 cases,” reported Dr. Chovatiya. He indicated that this is a high percentage among a population composed largely of children who were well before hospitalization.
The mortality rate from measles was numerically but not statistically higher than that of overall hospital admissions during this period, but an admission for measles was associated with significantly longer average length of stay (3.7 vs. 3.5 days) and slightly but significantly higher direct costs ($18,907 vs. $18,474).
“I want to point out that these are just direct inpatient costs,” Dr. Chovatiya said. Extrapolating from published data about indirect expenses, he said that the total health cost burden “is absolutely staggering.”
Previous studies have suggested that about 25% of patients with measles require hospitalization and 1 in every 1,000 patients will die. The data collected by Dr. Chovatiya support these often-cited figures, indicating that they remain unchanged in the modern era.
particularly insufficient penetration of vaccination in many communities.
The vaccine “is inexpensive, extremely effective, and lifesaving,” said Dr. Chovatiya, making the point that all of the morbidity, mortality, and costs he described are largely avoidable.
Attempting to provide perspective of the measles threat and the impact of the vaccine, Dr. Chovatiya cited a hypothetical calculation that 732,000 deaths from measles would have been expected in the United States among the pool of children born between 1994 and 2013 had no vaccine been offered. Again, most of these deaths would have occurred in otherwise healthy children.
Dr. Chovatiya reported no potential conflicts of interest.
REPORTING FROM SID 2019
Maternal immunization protects against serious RSV infection in infancy
LJUBLJANA, SLOVENIA – Passive protection of infants from severe respiratory syncytial virus lower respiratory tract infection during the first 6 months of life has convincingly been achieved through maternal immunization using a novel nanoparticle vaccine in the landmark PREPARE trial.
“I think it’s important for everyone, especially people like myself who’ve been working on maternal immunization for about 20 years, to realize that this is a historic study,” Flor M. Munoz, MD, declared in reporting the study results at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
“We have here for the first time a phase-3, global, randomized, placebo-controlled, observer-blinded clinical trial looking at an experimental vaccine in pregnant women for the protection of infants from a disease for which we really don’t have other potential solutions quite yet, and in a period of high vulnerability,” said Dr. Munoz, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
Indeed, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the No. 2 cause of mortality worldwide during the first year of life. Moreover, most cases of severe RSV lower respiratory tract infection occur in otherwise healthy infants aged less than 5 months, when active immunization presents daunting challenges.
“While certainly mortality is uncommon in high-income countries, we do see significant hospitalization there due to severe RSV lower respiratory tract infection in the first year of life, sometimes more than other common diseases, like influenza,” she noted.
PREPARE included 4,636 women with low-risk pregnancies who were randomized 2:1 to a single intramuscular injection of the investigational RSV vaccine or placebo during gestational weeks 28-36, with efficacy assessed through the first 180 days of life. The study took place at 87 sites in 11 countries during 4 years worth of RSV seasons. Roughly half of participants were South African, one-quarter were in the United States, and the rest were drawn from nine other low-, middle-, or high-income countries in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. The median gestational age at vaccination was 32 weeks.
The primary efficacy endpoint specified by the Food and Drug Administration – but not other regulatory agencies – was the placebo-subtracted rate of RSV lower respiratory tract infection as defined by RSV detected by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, along with at least one clinical manifestation of lower respiratory tract infection, oxygen saturation below 95%, and/or tachypnea. The risk of this outcome was reduced by 39% during the first 90 days of life and by 27% through 180 days in infants in the maternal immunization group, a difference which didn’t achieve statistical significance.
However, prespecified major secondary endpoints arguably of greater clinical relevance were consistently positive. Notably, when levels of transplacentally transferred neutralizing antibodies against RSV A and B were highest, with events occurring in 57 of 2,765 evaluable infants in the active treatment arm and in 53 of 1,430 controls. Similarly, there was a 40% reduction through day 180. Moreover, rates of another key secondary endpoint – RSV lower respiratory tract infection plus severe hypoxemia with an oxygen saturation below 92% – were reduced by 48% and 42% through days 90 and 180, respectively. Thus, the vaccine’s protective effect was greatest against the most severe outcomes of RSV infection in infancy, according to Dr. Munoz.
No safety signals related to this immunization strategy were seen during 1 year of follow-up of infants and 6 months for the mothers. Side effects were essentially limited to mild, self-limited injection site reactions, with zero impact on pregnancy and delivery.
An intriguing finding in an exploratory analysis was that the vaccine appeared to have ancillary benefits beyond prevention of medically significant RSV disease in the young infants. For example, the rate of all lower respiratory tract infections with severe hypoxemia – with no requirement for demonstration of RSV infection – was reduced by 46% during the first 90 days of life in the immunized group. Similarly, the rate of all-cause lower respiratory tract infection resulting in hospitalization was reduced by 28%.
“This is actually quite interesting, because these are unexpected benefits in terms of all-cause effects,” the pediatrician commented, adding that she and her coinvestigators are delving into this phenomenon in order to gain better understanding.
Additional analyses of the recently completed PREPARE study are ongoing but already have yielded some important findings. For example, women immunized before 33 weeks’ gestation had significantly greater transplacental antibody transfer than those immunized later in pregnancy, with resultant markedly greater vaccine efficacy in their offspring as well: A placebo-subtracted 70% reduction in RSV lower respiratory tract infection with severe hypoxemia through 90 days, compared with a 44% reduction associated with immunization at gestational week 33 or later. And when the interval between immunization and delivery was at least 30 days, the risk of this endpoint was reduced by 65%; in contrast, there was no significant difference between vaccine and placebo groups when time from immunization to delivery was less than 30 days.
Also noteworthy was that maternal immunization afforded no infant protection in the United States. This unanticipated finding is still under investigation, although suspicion centers around the fact that RSV seasons were generally milder there, and American women were vaccinated at a later gestational age, with a corresponding shorter interval to delivery.
The novel recombinant nanoparticle vaccine tested in PREPARE contains a nearly full-length RSV fusion protein produced in insect cells. The nanoparticles express both prefusion epitopes and epitopes common to pre- and postfusion conformations. Aluminum phosphate is employed as the adjuvant.
Novavax’s stock price has been kicked to the curb since the company earlier reported that a large phase 3 trial of the vaccine failed to meet its primary endpoint for prevention of RSV lower respiratory tract infection in older adults. Now the vaccine’s failure to meet its prespecified FDA-mandated primary endpoint in the maternal immunization study will doubtless spawn further financially dismissive headlines in the business press as well.
But pediatricians are famously advocates for children, and PREPARE received a warm welcome from the pediatric infectious disease community, regardless of investor response. Indeed, PREPARE was the only clinical trial deemed of sufficient import to be featured in the opening plenary session of ESPID 2019.
Ulrich Heininger, MD, professor of pediatrics at the University of Basel (Switzerland), who cochaired the session, jointly sponsored by ESPID and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, declared, “These findings, I think, are a great step forward.”
Dr. Munoz reported receiving research grants from Janssen, the National Institutes of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and Novavax, which sponsored the PREPARE trial, assisted by an $89 million grant from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
LJUBLJANA, SLOVENIA – Passive protection of infants from severe respiratory syncytial virus lower respiratory tract infection during the first 6 months of life has convincingly been achieved through maternal immunization using a novel nanoparticle vaccine in the landmark PREPARE trial.
“I think it’s important for everyone, especially people like myself who’ve been working on maternal immunization for about 20 years, to realize that this is a historic study,” Flor M. Munoz, MD, declared in reporting the study results at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
“We have here for the first time a phase-3, global, randomized, placebo-controlled, observer-blinded clinical trial looking at an experimental vaccine in pregnant women for the protection of infants from a disease for which we really don’t have other potential solutions quite yet, and in a period of high vulnerability,” said Dr. Munoz, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
Indeed, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the No. 2 cause of mortality worldwide during the first year of life. Moreover, most cases of severe RSV lower respiratory tract infection occur in otherwise healthy infants aged less than 5 months, when active immunization presents daunting challenges.
“While certainly mortality is uncommon in high-income countries, we do see significant hospitalization there due to severe RSV lower respiratory tract infection in the first year of life, sometimes more than other common diseases, like influenza,” she noted.
PREPARE included 4,636 women with low-risk pregnancies who were randomized 2:1 to a single intramuscular injection of the investigational RSV vaccine or placebo during gestational weeks 28-36, with efficacy assessed through the first 180 days of life. The study took place at 87 sites in 11 countries during 4 years worth of RSV seasons. Roughly half of participants were South African, one-quarter were in the United States, and the rest were drawn from nine other low-, middle-, or high-income countries in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. The median gestational age at vaccination was 32 weeks.
The primary efficacy endpoint specified by the Food and Drug Administration – but not other regulatory agencies – was the placebo-subtracted rate of RSV lower respiratory tract infection as defined by RSV detected by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, along with at least one clinical manifestation of lower respiratory tract infection, oxygen saturation below 95%, and/or tachypnea. The risk of this outcome was reduced by 39% during the first 90 days of life and by 27% through 180 days in infants in the maternal immunization group, a difference which didn’t achieve statistical significance.
However, prespecified major secondary endpoints arguably of greater clinical relevance were consistently positive. Notably, when levels of transplacentally transferred neutralizing antibodies against RSV A and B were highest, with events occurring in 57 of 2,765 evaluable infants in the active treatment arm and in 53 of 1,430 controls. Similarly, there was a 40% reduction through day 180. Moreover, rates of another key secondary endpoint – RSV lower respiratory tract infection plus severe hypoxemia with an oxygen saturation below 92% – were reduced by 48% and 42% through days 90 and 180, respectively. Thus, the vaccine’s protective effect was greatest against the most severe outcomes of RSV infection in infancy, according to Dr. Munoz.
No safety signals related to this immunization strategy were seen during 1 year of follow-up of infants and 6 months for the mothers. Side effects were essentially limited to mild, self-limited injection site reactions, with zero impact on pregnancy and delivery.
An intriguing finding in an exploratory analysis was that the vaccine appeared to have ancillary benefits beyond prevention of medically significant RSV disease in the young infants. For example, the rate of all lower respiratory tract infections with severe hypoxemia – with no requirement for demonstration of RSV infection – was reduced by 46% during the first 90 days of life in the immunized group. Similarly, the rate of all-cause lower respiratory tract infection resulting in hospitalization was reduced by 28%.
“This is actually quite interesting, because these are unexpected benefits in terms of all-cause effects,” the pediatrician commented, adding that she and her coinvestigators are delving into this phenomenon in order to gain better understanding.
Additional analyses of the recently completed PREPARE study are ongoing but already have yielded some important findings. For example, women immunized before 33 weeks’ gestation had significantly greater transplacental antibody transfer than those immunized later in pregnancy, with resultant markedly greater vaccine efficacy in their offspring as well: A placebo-subtracted 70% reduction in RSV lower respiratory tract infection with severe hypoxemia through 90 days, compared with a 44% reduction associated with immunization at gestational week 33 or later. And when the interval between immunization and delivery was at least 30 days, the risk of this endpoint was reduced by 65%; in contrast, there was no significant difference between vaccine and placebo groups when time from immunization to delivery was less than 30 days.
Also noteworthy was that maternal immunization afforded no infant protection in the United States. This unanticipated finding is still under investigation, although suspicion centers around the fact that RSV seasons were generally milder there, and American women were vaccinated at a later gestational age, with a corresponding shorter interval to delivery.
The novel recombinant nanoparticle vaccine tested in PREPARE contains a nearly full-length RSV fusion protein produced in insect cells. The nanoparticles express both prefusion epitopes and epitopes common to pre- and postfusion conformations. Aluminum phosphate is employed as the adjuvant.
Novavax’s stock price has been kicked to the curb since the company earlier reported that a large phase 3 trial of the vaccine failed to meet its primary endpoint for prevention of RSV lower respiratory tract infection in older adults. Now the vaccine’s failure to meet its prespecified FDA-mandated primary endpoint in the maternal immunization study will doubtless spawn further financially dismissive headlines in the business press as well.
But pediatricians are famously advocates for children, and PREPARE received a warm welcome from the pediatric infectious disease community, regardless of investor response. Indeed, PREPARE was the only clinical trial deemed of sufficient import to be featured in the opening plenary session of ESPID 2019.
Ulrich Heininger, MD, professor of pediatrics at the University of Basel (Switzerland), who cochaired the session, jointly sponsored by ESPID and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, declared, “These findings, I think, are a great step forward.”
Dr. Munoz reported receiving research grants from Janssen, the National Institutes of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and Novavax, which sponsored the PREPARE trial, assisted by an $89 million grant from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
LJUBLJANA, SLOVENIA – Passive protection of infants from severe respiratory syncytial virus lower respiratory tract infection during the first 6 months of life has convincingly been achieved through maternal immunization using a novel nanoparticle vaccine in the landmark PREPARE trial.
“I think it’s important for everyone, especially people like myself who’ve been working on maternal immunization for about 20 years, to realize that this is a historic study,” Flor M. Munoz, MD, declared in reporting the study results at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
“We have here for the first time a phase-3, global, randomized, placebo-controlled, observer-blinded clinical trial looking at an experimental vaccine in pregnant women for the protection of infants from a disease for which we really don’t have other potential solutions quite yet, and in a period of high vulnerability,” said Dr. Munoz, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
Indeed, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the No. 2 cause of mortality worldwide during the first year of life. Moreover, most cases of severe RSV lower respiratory tract infection occur in otherwise healthy infants aged less than 5 months, when active immunization presents daunting challenges.
“While certainly mortality is uncommon in high-income countries, we do see significant hospitalization there due to severe RSV lower respiratory tract infection in the first year of life, sometimes more than other common diseases, like influenza,” she noted.
PREPARE included 4,636 women with low-risk pregnancies who were randomized 2:1 to a single intramuscular injection of the investigational RSV vaccine or placebo during gestational weeks 28-36, with efficacy assessed through the first 180 days of life. The study took place at 87 sites in 11 countries during 4 years worth of RSV seasons. Roughly half of participants were South African, one-quarter were in the United States, and the rest were drawn from nine other low-, middle-, or high-income countries in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. The median gestational age at vaccination was 32 weeks.
The primary efficacy endpoint specified by the Food and Drug Administration – but not other regulatory agencies – was the placebo-subtracted rate of RSV lower respiratory tract infection as defined by RSV detected by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, along with at least one clinical manifestation of lower respiratory tract infection, oxygen saturation below 95%, and/or tachypnea. The risk of this outcome was reduced by 39% during the first 90 days of life and by 27% through 180 days in infants in the maternal immunization group, a difference which didn’t achieve statistical significance.
However, prespecified major secondary endpoints arguably of greater clinical relevance were consistently positive. Notably, when levels of transplacentally transferred neutralizing antibodies against RSV A and B were highest, with events occurring in 57 of 2,765 evaluable infants in the active treatment arm and in 53 of 1,430 controls. Similarly, there was a 40% reduction through day 180. Moreover, rates of another key secondary endpoint – RSV lower respiratory tract infection plus severe hypoxemia with an oxygen saturation below 92% – were reduced by 48% and 42% through days 90 and 180, respectively. Thus, the vaccine’s protective effect was greatest against the most severe outcomes of RSV infection in infancy, according to Dr. Munoz.
No safety signals related to this immunization strategy were seen during 1 year of follow-up of infants and 6 months for the mothers. Side effects were essentially limited to mild, self-limited injection site reactions, with zero impact on pregnancy and delivery.
An intriguing finding in an exploratory analysis was that the vaccine appeared to have ancillary benefits beyond prevention of medically significant RSV disease in the young infants. For example, the rate of all lower respiratory tract infections with severe hypoxemia – with no requirement for demonstration of RSV infection – was reduced by 46% during the first 90 days of life in the immunized group. Similarly, the rate of all-cause lower respiratory tract infection resulting in hospitalization was reduced by 28%.
“This is actually quite interesting, because these are unexpected benefits in terms of all-cause effects,” the pediatrician commented, adding that she and her coinvestigators are delving into this phenomenon in order to gain better understanding.
Additional analyses of the recently completed PREPARE study are ongoing but already have yielded some important findings. For example, women immunized before 33 weeks’ gestation had significantly greater transplacental antibody transfer than those immunized later in pregnancy, with resultant markedly greater vaccine efficacy in their offspring as well: A placebo-subtracted 70% reduction in RSV lower respiratory tract infection with severe hypoxemia through 90 days, compared with a 44% reduction associated with immunization at gestational week 33 or later. And when the interval between immunization and delivery was at least 30 days, the risk of this endpoint was reduced by 65%; in contrast, there was no significant difference between vaccine and placebo groups when time from immunization to delivery was less than 30 days.
Also noteworthy was that maternal immunization afforded no infant protection in the United States. This unanticipated finding is still under investigation, although suspicion centers around the fact that RSV seasons were generally milder there, and American women were vaccinated at a later gestational age, with a corresponding shorter interval to delivery.
The novel recombinant nanoparticle vaccine tested in PREPARE contains a nearly full-length RSV fusion protein produced in insect cells. The nanoparticles express both prefusion epitopes and epitopes common to pre- and postfusion conformations. Aluminum phosphate is employed as the adjuvant.
Novavax’s stock price has been kicked to the curb since the company earlier reported that a large phase 3 trial of the vaccine failed to meet its primary endpoint for prevention of RSV lower respiratory tract infection in older adults. Now the vaccine’s failure to meet its prespecified FDA-mandated primary endpoint in the maternal immunization study will doubtless spawn further financially dismissive headlines in the business press as well.
But pediatricians are famously advocates for children, and PREPARE received a warm welcome from the pediatric infectious disease community, regardless of investor response. Indeed, PREPARE was the only clinical trial deemed of sufficient import to be featured in the opening plenary session of ESPID 2019.
Ulrich Heininger, MD, professor of pediatrics at the University of Basel (Switzerland), who cochaired the session, jointly sponsored by ESPID and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, declared, “These findings, I think, are a great step forward.”
Dr. Munoz reported receiving research grants from Janssen, the National Institutes of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and Novavax, which sponsored the PREPARE trial, assisted by an $89 million grant from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
REPORTING FROM ESPID 2019
Flu vaccine visits reveal missed opportunities for HPV vaccination
BALTIMORE – according to a study.
“Overall in preventive visits, missed opportunities were much higher for HPV, compared to the other two vaccines” recommended for adolescents, MenACWY (meningococcal conjugate vaccine) and Tdap, Mary Kate Kelly, MPH, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, told attendees at the Pediatric Academic Societies annual meeting. “In order to increase vaccination rates, it’s essential to implement efforts to reduce missed opportunities.”
According to 2018 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, Ms. Kelly said, vaccine coverage for the HPV vaccine is approximately 66%, compared with 85% for the MenACWY vaccine and 89% for the Tdap vaccine.
Ms. Kelly and her colleagues investigated how often children or adolescents missed an opportunity to get an HPV vaccine when they received an influenza vaccine during an office visit. This study was part of the larger STOP HPV trial funded by the National Institutes of Health and aimed at implementing evidence-based interventions to reduce missed opportunities for HPV vaccination in primary care.
The researchers retrospectively reviewed EHRs from 2015 to 2018 for 48 pediatric practices across 19 states. All practices were part of the American Academy of Pediatrics’ Pediatric Research in Office Settings (PROS) national pediatric primary care network. The researchers isolated all visits for patients aged 11-17 years who received their flu vaccine and were eligible to receive the HPV vaccine.
The investigators defined a missed opportunity as one in which a patient was due for the HPV vaccine but did not receive one at the visit when they received their flu vaccine.
The study involved 40,129 patients who received the flu vaccine at 52,818 visits when they also were eligible to receive the HPV vaccine. The median age of patients was 12 years old, and 47% were female.
In 68% of visits, the patient could have received an HPV vaccine but did not – even though they were due and eligible for one. The rate was the same for boys and for girls. By contrast, only 38% of visits involved a missed opportunity for the MenACWY vaccines and 39% for the Tdap vaccine.
Rates of missed opportunities for HPV vaccination ranged among individual practices from 22% to 81% of overall visits. Patients were more than twice as likely to miss the opportunity for an HPV vaccine dose if it would have been their first dose – 70% of missed opportunities – versus being a second or third dose, which comprised 30% of missed opportunities (adjusted relative risk, 2.48; P less than .001)).
“However, missed opportunities were also common for subsequent HPV doses when vaccine hesitancy is less likely to be an issue,” Ms. Kelly added.
It also was much more likely that missed opportunities occurred during nurse visits or visits for an acute or chronic condition rather than preventive visits, which made up about half (51%) of all visits analyzed. While 48% of preventive visits involved a missed opportunity, 93% of nurse visits (aRR compared with preventive, 2.18; P less than.001) and 89% of acute or chronic visits (aRR, 2.11; P less than .001) did.
Percentages of missed opportunities were similarly high for the MenACWY and Tdap vaccines at nurse visits and acute/chronic visits, but much lower at preventive visits for the MenACWY (12%) and Tdap (15%) vaccines.
“Increasing simultaneous administration of HPV and other adolescent vaccines with the influenza vaccine may help to improve coverage,” Ms. Kelly concluded.
The study was limited by its use of a convenience sample from practices that were interested in participating and willing to stock the HPV vaccine. Additionally, the researchers could not detect or adjust for EHR errors or inaccurate or incomplete vaccine histories, and they were unable to look at vaccine hesitancy or refusal with the EHRs.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, and the National Research Network to Improve Children’s Health. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
BALTIMORE – according to a study.
“Overall in preventive visits, missed opportunities were much higher for HPV, compared to the other two vaccines” recommended for adolescents, MenACWY (meningococcal conjugate vaccine) and Tdap, Mary Kate Kelly, MPH, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, told attendees at the Pediatric Academic Societies annual meeting. “In order to increase vaccination rates, it’s essential to implement efforts to reduce missed opportunities.”
According to 2018 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, Ms. Kelly said, vaccine coverage for the HPV vaccine is approximately 66%, compared with 85% for the MenACWY vaccine and 89% for the Tdap vaccine.
Ms. Kelly and her colleagues investigated how often children or adolescents missed an opportunity to get an HPV vaccine when they received an influenza vaccine during an office visit. This study was part of the larger STOP HPV trial funded by the National Institutes of Health and aimed at implementing evidence-based interventions to reduce missed opportunities for HPV vaccination in primary care.
The researchers retrospectively reviewed EHRs from 2015 to 2018 for 48 pediatric practices across 19 states. All practices were part of the American Academy of Pediatrics’ Pediatric Research in Office Settings (PROS) national pediatric primary care network. The researchers isolated all visits for patients aged 11-17 years who received their flu vaccine and were eligible to receive the HPV vaccine.
The investigators defined a missed opportunity as one in which a patient was due for the HPV vaccine but did not receive one at the visit when they received their flu vaccine.
The study involved 40,129 patients who received the flu vaccine at 52,818 visits when they also were eligible to receive the HPV vaccine. The median age of patients was 12 years old, and 47% were female.
In 68% of visits, the patient could have received an HPV vaccine but did not – even though they were due and eligible for one. The rate was the same for boys and for girls. By contrast, only 38% of visits involved a missed opportunity for the MenACWY vaccines and 39% for the Tdap vaccine.
Rates of missed opportunities for HPV vaccination ranged among individual practices from 22% to 81% of overall visits. Patients were more than twice as likely to miss the opportunity for an HPV vaccine dose if it would have been their first dose – 70% of missed opportunities – versus being a second or third dose, which comprised 30% of missed opportunities (adjusted relative risk, 2.48; P less than .001)).
“However, missed opportunities were also common for subsequent HPV doses when vaccine hesitancy is less likely to be an issue,” Ms. Kelly added.
It also was much more likely that missed opportunities occurred during nurse visits or visits for an acute or chronic condition rather than preventive visits, which made up about half (51%) of all visits analyzed. While 48% of preventive visits involved a missed opportunity, 93% of nurse visits (aRR compared with preventive, 2.18; P less than.001) and 89% of acute or chronic visits (aRR, 2.11; P less than .001) did.
Percentages of missed opportunities were similarly high for the MenACWY and Tdap vaccines at nurse visits and acute/chronic visits, but much lower at preventive visits for the MenACWY (12%) and Tdap (15%) vaccines.
“Increasing simultaneous administration of HPV and other adolescent vaccines with the influenza vaccine may help to improve coverage,” Ms. Kelly concluded.
The study was limited by its use of a convenience sample from practices that were interested in participating and willing to stock the HPV vaccine. Additionally, the researchers could not detect or adjust for EHR errors or inaccurate or incomplete vaccine histories, and they were unable to look at vaccine hesitancy or refusal with the EHRs.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, and the National Research Network to Improve Children’s Health. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
BALTIMORE – according to a study.
“Overall in preventive visits, missed opportunities were much higher for HPV, compared to the other two vaccines” recommended for adolescents, MenACWY (meningococcal conjugate vaccine) and Tdap, Mary Kate Kelly, MPH, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, told attendees at the Pediatric Academic Societies annual meeting. “In order to increase vaccination rates, it’s essential to implement efforts to reduce missed opportunities.”
According to 2018 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, Ms. Kelly said, vaccine coverage for the HPV vaccine is approximately 66%, compared with 85% for the MenACWY vaccine and 89% for the Tdap vaccine.
Ms. Kelly and her colleagues investigated how often children or adolescents missed an opportunity to get an HPV vaccine when they received an influenza vaccine during an office visit. This study was part of the larger STOP HPV trial funded by the National Institutes of Health and aimed at implementing evidence-based interventions to reduce missed opportunities for HPV vaccination in primary care.
The researchers retrospectively reviewed EHRs from 2015 to 2018 for 48 pediatric practices across 19 states. All practices were part of the American Academy of Pediatrics’ Pediatric Research in Office Settings (PROS) national pediatric primary care network. The researchers isolated all visits for patients aged 11-17 years who received their flu vaccine and were eligible to receive the HPV vaccine.
The investigators defined a missed opportunity as one in which a patient was due for the HPV vaccine but did not receive one at the visit when they received their flu vaccine.
The study involved 40,129 patients who received the flu vaccine at 52,818 visits when they also were eligible to receive the HPV vaccine. The median age of patients was 12 years old, and 47% were female.
In 68% of visits, the patient could have received an HPV vaccine but did not – even though they were due and eligible for one. The rate was the same for boys and for girls. By contrast, only 38% of visits involved a missed opportunity for the MenACWY vaccines and 39% for the Tdap vaccine.
Rates of missed opportunities for HPV vaccination ranged among individual practices from 22% to 81% of overall visits. Patients were more than twice as likely to miss the opportunity for an HPV vaccine dose if it would have been their first dose – 70% of missed opportunities – versus being a second or third dose, which comprised 30% of missed opportunities (adjusted relative risk, 2.48; P less than .001)).
“However, missed opportunities were also common for subsequent HPV doses when vaccine hesitancy is less likely to be an issue,” Ms. Kelly added.
It also was much more likely that missed opportunities occurred during nurse visits or visits for an acute or chronic condition rather than preventive visits, which made up about half (51%) of all visits analyzed. While 48% of preventive visits involved a missed opportunity, 93% of nurse visits (aRR compared with preventive, 2.18; P less than.001) and 89% of acute or chronic visits (aRR, 2.11; P less than .001) did.
Percentages of missed opportunities were similarly high for the MenACWY and Tdap vaccines at nurse visits and acute/chronic visits, but much lower at preventive visits for the MenACWY (12%) and Tdap (15%) vaccines.
“Increasing simultaneous administration of HPV and other adolescent vaccines with the influenza vaccine may help to improve coverage,” Ms. Kelly concluded.
The study was limited by its use of a convenience sample from practices that were interested in participating and willing to stock the HPV vaccine. Additionally, the researchers could not detect or adjust for EHR errors or inaccurate or incomplete vaccine histories, and they were unable to look at vaccine hesitancy or refusal with the EHRs.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, and the National Research Network to Improve Children’s Health. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
REPORTING FROM PAS 2019
U.S. measles cases climb to over 800 for the year
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
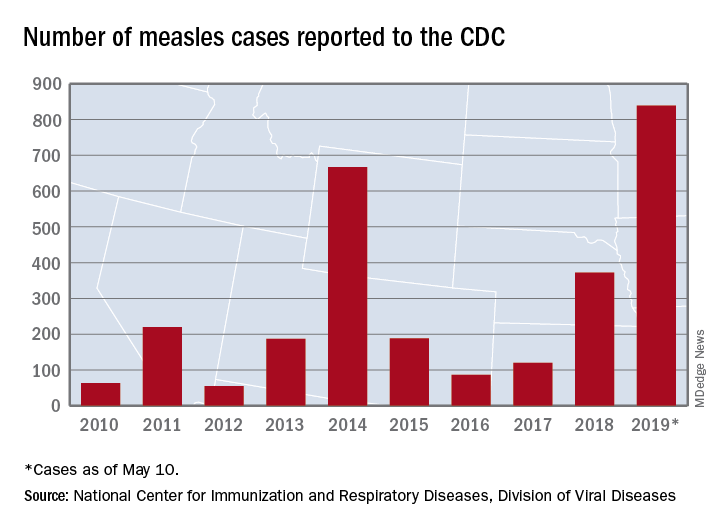
There are 10 states dealing with ongoing outbreaks now that Pennsylvania has been added to the list, the CDC reported May 13. The state has had five cases so far, all in Allegheny County. New York City continued to have the most active outbreak, adding 43 more cases in Brooklyn last week for a total of 410 in the city since the beginning of 2019, NYC Health said.
Several of this year’s outbreaks were predicted in an analysis published in the Lancet Infectious Diseases (2019 May 9. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30231-2). Investigators identified the 25 counties most likely to experience a measles outbreak in 2019 – a list that includes Queens, N.Y. (adjacent to Brooklyn), Multnomah, Ore. (adjacent to Clark County, Wash., where 71 people were infected earlier this year), and San Mateo, Calif., where 4 cases have been reported.
“We recommend that public health officials and policymakers prioritize monitoring the counties we identify to be at high risk that have not yet reported cases, especially those that lie adjacent to counties with ongoing outbreaks and those that house large international airports,” senior author Lauren Gardner of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in a written statement.
The outbreak in Clark County was declared over in late April, but Gov. Jay Inslee signed a bill on May 10 that removes the personal/philosophical exemption for the MMR vaccine from the state’s school and child care immunization requirements. “We must step up our leadership to educate the public about the critical role vaccines have in keeping us healthy and safe, and continue working with communities to improve vaccination rates,” Washington State Secretary of Health John Wiesman said in a written statement.
In Oregon, a bill that would eliminate religious and philosophical exemptions to child vaccination requirements passed the state house of representatives by a 35-25 vote and is moving to the senate. Gov. Kate Brown has said that she plans to sign the bill, according to OregonLive.com.
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

There are 10 states dealing with ongoing outbreaks now that Pennsylvania has been added to the list, the CDC reported May 13. The state has had five cases so far, all in Allegheny County. New York City continued to have the most active outbreak, adding 43 more cases in Brooklyn last week for a total of 410 in the city since the beginning of 2019, NYC Health said.
Several of this year’s outbreaks were predicted in an analysis published in the Lancet Infectious Diseases (2019 May 9. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30231-2). Investigators identified the 25 counties most likely to experience a measles outbreak in 2019 – a list that includes Queens, N.Y. (adjacent to Brooklyn), Multnomah, Ore. (adjacent to Clark County, Wash., where 71 people were infected earlier this year), and San Mateo, Calif., where 4 cases have been reported.
“We recommend that public health officials and policymakers prioritize monitoring the counties we identify to be at high risk that have not yet reported cases, especially those that lie adjacent to counties with ongoing outbreaks and those that house large international airports,” senior author Lauren Gardner of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in a written statement.
The outbreak in Clark County was declared over in late April, but Gov. Jay Inslee signed a bill on May 10 that removes the personal/philosophical exemption for the MMR vaccine from the state’s school and child care immunization requirements. “We must step up our leadership to educate the public about the critical role vaccines have in keeping us healthy and safe, and continue working with communities to improve vaccination rates,” Washington State Secretary of Health John Wiesman said in a written statement.
In Oregon, a bill that would eliminate religious and philosophical exemptions to child vaccination requirements passed the state house of representatives by a 35-25 vote and is moving to the senate. Gov. Kate Brown has said that she plans to sign the bill, according to OregonLive.com.
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

There are 10 states dealing with ongoing outbreaks now that Pennsylvania has been added to the list, the CDC reported May 13. The state has had five cases so far, all in Allegheny County. New York City continued to have the most active outbreak, adding 43 more cases in Brooklyn last week for a total of 410 in the city since the beginning of 2019, NYC Health said.
Several of this year’s outbreaks were predicted in an analysis published in the Lancet Infectious Diseases (2019 May 9. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30231-2). Investigators identified the 25 counties most likely to experience a measles outbreak in 2019 – a list that includes Queens, N.Y. (adjacent to Brooklyn), Multnomah, Ore. (adjacent to Clark County, Wash., where 71 people were infected earlier this year), and San Mateo, Calif., where 4 cases have been reported.
“We recommend that public health officials and policymakers prioritize monitoring the counties we identify to be at high risk that have not yet reported cases, especially those that lie adjacent to counties with ongoing outbreaks and those that house large international airports,” senior author Lauren Gardner of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in a written statement.
The outbreak in Clark County was declared over in late April, but Gov. Jay Inslee signed a bill on May 10 that removes the personal/philosophical exemption for the MMR vaccine from the state’s school and child care immunization requirements. “We must step up our leadership to educate the public about the critical role vaccines have in keeping us healthy and safe, and continue working with communities to improve vaccination rates,” Washington State Secretary of Health John Wiesman said in a written statement.
In Oregon, a bill that would eliminate religious and philosophical exemptions to child vaccination requirements passed the state house of representatives by a 35-25 vote and is moving to the senate. Gov. Kate Brown has said that she plans to sign the bill, according to OregonLive.com.
Rotavirus vaccine had strong protective effect in routine U.K. practice
Oral rotavirus vaccination had a strong protective effect against laboratory-confirmed rotavirus infection in the first 2 years of the U.K. infant immunization program, investigators are reporting.
The estimated effectiveness was 77% for all infants with confirmed infection, and greater than 80% for those under 12 months of age, according to the report. The vaccine did not demonstrate efficacy against all-cause acute gastroenteritis, although this was likely because of high, sustained vaccine coverage coupled with the “substantial impact” of the rotavirus vaccine, wrote investigators led by Sara L. Thomas, MB BS, PhD, of the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine.
Taken together, these findings provide “reassurance” that rotavirus vaccine is effective in a real-world setting and set the stage for future analyses of cost effectiveness, Dr. Thomas and coauthors said in a report on the study appearing in Vaccine: X, the open access mirror journal of Vaccine.
“As data accumulate in the post-vaccination era, more detailed assessment of waning of effectiveness over time can be undertaken, and investigation of rotavirus strain-specific protection,” they wrote.
Oral live-attenuated rotavirus vaccine (Rotarix) was introduced in the U.K. in 2013 as a two-dose schedule at 2 and 3 months of age. Vaccine uptake by the age of 25 weeks was rapid and sustained, exceeding 90%, according to previous reports. Declines in hospital admissions and primary care for all-cause acute gastroenteritis were substantial, associated with an estimated reduction of £12.5 million in health care costs in the first year of the program for children 5 years of age and younger.
To assess rotavirus vaccine effectiveness in the public health setting, Dr. Thomas and colleagues conducted a pair of studies: one designed to evaluate vaccine effectiveness against laboratory-confirmed rotavirus infections using laboratory surveillance data for 1,869 children and 1,032 controls and another to estimate vaccine effectiveness against all-cause acute gastroenteritis using electronic health data on 40,723 children.
Stratified by age, the data showed that vaccine effectiveness was 85% in those younger than 12 months, and 54% for older children.
By contrast, they found no evidence that the rotavirus vaccine protected against all-cause acute gastroenteritis in an analysis that adjusted for age and other factors. Analysis also suggested a lack of effectiveness against hospitalized acute gastroenteritis, according to the study authors.
In prelicensure trials, oral live-attenuated rotavirus vaccine in middle- and high-income settings had efficacy against severe rotavirus-confirmed gastroenteritis of greater than 85% and efficacy against severe all-cause gastroenteritis up to 40%, investigators noted.
The lack of vaccine efficacy on all-cause acute gastroenteritis is likely because of “highly effective implementation” of the vaccine program and rapid attainment of coverage, plus high vaccine effectiveness against rotavirus-specific acute gastroenteritis, the investigators said.
“As a result, almost all AGE in the study population in the post-vaccine era was likely to have been due to nonrotavirus organisms or non-infectious causes,” said Dr. Thomas and coauthors.
This highlights the importance of choosing “specific outcomes” to study when vaccine coverage and effectiveness are both high, they concluded.
Funding for this research came from the National Institute for Health Research Health Protection Research Unit in Immunisation at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine in partnership with Public Health England. The Immunisation and Countermeasures Division of Public Health England provided vaccine manufacturers with postmarketing surveillance reports, according to the article’s disclosure section.
SOURCE: Walker JL et al. Vaccine: X. 2019 Apr 11. doi: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2019.100005.
Oral rotavirus vaccination had a strong protective effect against laboratory-confirmed rotavirus infection in the first 2 years of the U.K. infant immunization program, investigators are reporting.
The estimated effectiveness was 77% for all infants with confirmed infection, and greater than 80% for those under 12 months of age, according to the report. The vaccine did not demonstrate efficacy against all-cause acute gastroenteritis, although this was likely because of high, sustained vaccine coverage coupled with the “substantial impact” of the rotavirus vaccine, wrote investigators led by Sara L. Thomas, MB BS, PhD, of the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine.
Taken together, these findings provide “reassurance” that rotavirus vaccine is effective in a real-world setting and set the stage for future analyses of cost effectiveness, Dr. Thomas and coauthors said in a report on the study appearing in Vaccine: X, the open access mirror journal of Vaccine.
“As data accumulate in the post-vaccination era, more detailed assessment of waning of effectiveness over time can be undertaken, and investigation of rotavirus strain-specific protection,” they wrote.
Oral live-attenuated rotavirus vaccine (Rotarix) was introduced in the U.K. in 2013 as a two-dose schedule at 2 and 3 months of age. Vaccine uptake by the age of 25 weeks was rapid and sustained, exceeding 90%, according to previous reports. Declines in hospital admissions and primary care for all-cause acute gastroenteritis were substantial, associated with an estimated reduction of £12.5 million in health care costs in the first year of the program for children 5 years of age and younger.
To assess rotavirus vaccine effectiveness in the public health setting, Dr. Thomas and colleagues conducted a pair of studies: one designed to evaluate vaccine effectiveness against laboratory-confirmed rotavirus infections using laboratory surveillance data for 1,869 children and 1,032 controls and another to estimate vaccine effectiveness against all-cause acute gastroenteritis using electronic health data on 40,723 children.
Stratified by age, the data showed that vaccine effectiveness was 85% in those younger than 12 months, and 54% for older children.
By contrast, they found no evidence that the rotavirus vaccine protected against all-cause acute gastroenteritis in an analysis that adjusted for age and other factors. Analysis also suggested a lack of effectiveness against hospitalized acute gastroenteritis, according to the study authors.
In prelicensure trials, oral live-attenuated rotavirus vaccine in middle- and high-income settings had efficacy against severe rotavirus-confirmed gastroenteritis of greater than 85% and efficacy against severe all-cause gastroenteritis up to 40%, investigators noted.
The lack of vaccine efficacy on all-cause acute gastroenteritis is likely because of “highly effective implementation” of the vaccine program and rapid attainment of coverage, plus high vaccine effectiveness against rotavirus-specific acute gastroenteritis, the investigators said.
“As a result, almost all AGE in the study population in the post-vaccine era was likely to have been due to nonrotavirus organisms or non-infectious causes,” said Dr. Thomas and coauthors.
This highlights the importance of choosing “specific outcomes” to study when vaccine coverage and effectiveness are both high, they concluded.
Funding for this research came from the National Institute for Health Research Health Protection Research Unit in Immunisation at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine in partnership with Public Health England. The Immunisation and Countermeasures Division of Public Health England provided vaccine manufacturers with postmarketing surveillance reports, according to the article’s disclosure section.
SOURCE: Walker JL et al. Vaccine: X. 2019 Apr 11. doi: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2019.100005.
Oral rotavirus vaccination had a strong protective effect against laboratory-confirmed rotavirus infection in the first 2 years of the U.K. infant immunization program, investigators are reporting.
The estimated effectiveness was 77% for all infants with confirmed infection, and greater than 80% for those under 12 months of age, according to the report. The vaccine did not demonstrate efficacy against all-cause acute gastroenteritis, although this was likely because of high, sustained vaccine coverage coupled with the “substantial impact” of the rotavirus vaccine, wrote investigators led by Sara L. Thomas, MB BS, PhD, of the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine.
Taken together, these findings provide “reassurance” that rotavirus vaccine is effective in a real-world setting and set the stage for future analyses of cost effectiveness, Dr. Thomas and coauthors said in a report on the study appearing in Vaccine: X, the open access mirror journal of Vaccine.
“As data accumulate in the post-vaccination era, more detailed assessment of waning of effectiveness over time can be undertaken, and investigation of rotavirus strain-specific protection,” they wrote.
Oral live-attenuated rotavirus vaccine (Rotarix) was introduced in the U.K. in 2013 as a two-dose schedule at 2 and 3 months of age. Vaccine uptake by the age of 25 weeks was rapid and sustained, exceeding 90%, according to previous reports. Declines in hospital admissions and primary care for all-cause acute gastroenteritis were substantial, associated with an estimated reduction of £12.5 million in health care costs in the first year of the program for children 5 years of age and younger.
To assess rotavirus vaccine effectiveness in the public health setting, Dr. Thomas and colleagues conducted a pair of studies: one designed to evaluate vaccine effectiveness against laboratory-confirmed rotavirus infections using laboratory surveillance data for 1,869 children and 1,032 controls and another to estimate vaccine effectiveness against all-cause acute gastroenteritis using electronic health data on 40,723 children.
Stratified by age, the data showed that vaccine effectiveness was 85% in those younger than 12 months, and 54% for older children.
By contrast, they found no evidence that the rotavirus vaccine protected against all-cause acute gastroenteritis in an analysis that adjusted for age and other factors. Analysis also suggested a lack of effectiveness against hospitalized acute gastroenteritis, according to the study authors.
In prelicensure trials, oral live-attenuated rotavirus vaccine in middle- and high-income settings had efficacy against severe rotavirus-confirmed gastroenteritis of greater than 85% and efficacy against severe all-cause gastroenteritis up to 40%, investigators noted.
The lack of vaccine efficacy on all-cause acute gastroenteritis is likely because of “highly effective implementation” of the vaccine program and rapid attainment of coverage, plus high vaccine effectiveness against rotavirus-specific acute gastroenteritis, the investigators said.
“As a result, almost all AGE in the study population in the post-vaccine era was likely to have been due to nonrotavirus organisms or non-infectious causes,” said Dr. Thomas and coauthors.
This highlights the importance of choosing “specific outcomes” to study when vaccine coverage and effectiveness are both high, they concluded.
Funding for this research came from the National Institute for Health Research Health Protection Research Unit in Immunisation at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine in partnership with Public Health England. The Immunisation and Countermeasures Division of Public Health England provided vaccine manufacturers with postmarketing surveillance reports, according to the article’s disclosure section.
SOURCE: Walker JL et al. Vaccine: X. 2019 Apr 11. doi: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2019.100005.
FROM VACCINE
Why we should vaccinate early for measles
Since the measles outbreak in the Pacific Northwest (where I did my training and remain in touch with colleagues and patients), parents with infants ages 6 to 11 months are requesting vaccinations before 12 months—the standard age to start immunizations.1 But physicians decline to provide inoculation, citing institutional policy on the risks of early vaccination. What are these risks, and how should we respond when parents ask about early vaccination?
The safety and efficacy of early vaccination are well documented. Early vaccination is a technique employed to curb outbreaks both in the United States and worldwide. Guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend vaccinating infants at 6 months of age if they will be traveling,2 and the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends vaccinations during a measles outbreak as part of intensified service delivery or in settings, such as daycare facilities, in which there is an increased risk for disease exposure during an outbreak.3 Any dose given before 12 months is considered supplemental, and the child must still complete the regular 2-dose vaccine schedule. Studies on the adverse effect profiles of vaccines show that the younger the infant, the fewer adverse events occur—because adverse events reflect the increasingly robust immune response that comes with age.4
Many physicians are concerned about adequate immune response. In vaccine research, this is gauged by the proportion of patients with seroconversion after vaccination. This is also reflected in vaccine efficacy (VE), which gradually increases with age and maturity of the immune system. For example, measles VE is 60% to 70% in 6-to-8-month cohorts5 and 70% to 80% in 9-to-11-month cohorts.6 VE at 12 months is in the 90% range, and completion of the 2-dose series yields a VE of ≥ 95%.7 Thus, while the vaccine is more effective at later ages, it still provides protection to younger cohorts.
“Blunting” (ie, a reduced immune response to the second dose of vaccine3) is another concern with early measles vaccination, but a WHO meta-analysis proved this concern to be unfounded.1,3 Twelve papers examining seropositivity in children who received a second measles vaccine after early primary vaccination found a pooled proportion of seropositivity of 97%.1,8,9 Furthermore, evidence shows that children have sustained measles-specific T-cell responses after early primary measles immunization.10
Early vaccination has few risks and significant benefit. Therefore, in light of the recent measles outbreak, relaxing the lower boundary for the measles vaccine is appropriate. In addition to physically protecting the patient and general population, honoring parents’ requests for vaccination respects their autonomy and fosters trust. Synthesis of good science with a trusting doctor–patient relationship is key to ending the measles outbreak.
Rachel Roth, MD
Tel Aviv, Israel
1. Conclusions of the SAGE Working Group on Measles and Rubella. 21-22 June 2017. Geneva WHO Policy Recommendation on administration of MCV to infants. SAGE. https://www.who.int/immunization/sage/meetings/2017/october/2_measles_vaccination_before_6_months_for_yellow_book_FINAL.pdf. Accessed April 24, 2019.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles (Rubeola). For healthcare professionals. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/hcp/index.html. Accessed April 24, 2019.
3. World Health Organization. Measles vaccines: WHO position paper, April 2017 - recommendations. Vaccine. 2017;92:205-227.
4. van der Maas NA, Woudenberg T, Hahné SJ, et al. Tolerability of early measles-mumps-rubella vaccination in infants aged 6-14 months during a measles outbreak in the Netherlands in 2013-2014. J Infect Dis. 2016;213:1466-1471.
5. Lochlainn LN, de Gier B, van der Maas NA, et al. Measles vaccination below 9 months of age: systematic literature review and meta-analyses of effects and safety. National Institute for Public Health and the Environment. https://www.who.int/immunization/sage/meetings/2015/october/2_MCV1_below_9_months_Effect_safety_28092015.pdf. Published September 28, 2015. Accessed April 24, 2019.
6. Uzicanin A, Zimmerman L. Field effectiveness of live attenuated measles-containing vaccines: a review of published literature. J Infect Dis. 2011;204(suppl 1):S133-S149.
7. Woudenberg T, van der Maas NA, Knol MJ, et al. Effectiveness of early measles, mumps, and rubella vaccination among 6-14-month-old infants during an epidemic in the Netherlands: an observational cohort study. J Infect Dis. 2017;215:1181-1187.
8. Martins C, Garly ML, Bale C, et al. Measles virus antibody responses in children randomly assigned to receive standard-titer edmonston-zagreb measles vaccine at 4.5 and 9 months of age, 9 months of age, or 9 and 18 months of age. J Infect Dis. 2014;210:693-700.
9. Njie-Jobe J, Nyamweya S, Miles DJ, et al. Immunological impact of an additional early measles vaccine in Gambian children: responses to a boost at 3 years. Vaccine. 2012;30:2543-2550.
10. Gans HA, Yasukawa LL, Sung P, et al. Measles humoral and cell-mediated immunity in children aged 5–10 years after primary measles immunization administered at 6 or 9 months of age. J Infect Dis. 2013;207:574-582.
Since the measles outbreak in the Pacific Northwest (where I did my training and remain in touch with colleagues and patients), parents with infants ages 6 to 11 months are requesting vaccinations before 12 months—the standard age to start immunizations.1 But physicians decline to provide inoculation, citing institutional policy on the risks of early vaccination. What are these risks, and how should we respond when parents ask about early vaccination?
The safety and efficacy of early vaccination are well documented. Early vaccination is a technique employed to curb outbreaks both in the United States and worldwide. Guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend vaccinating infants at 6 months of age if they will be traveling,2 and the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends vaccinations during a measles outbreak as part of intensified service delivery or in settings, such as daycare facilities, in which there is an increased risk for disease exposure during an outbreak.3 Any dose given before 12 months is considered supplemental, and the child must still complete the regular 2-dose vaccine schedule. Studies on the adverse effect profiles of vaccines show that the younger the infant, the fewer adverse events occur—because adverse events reflect the increasingly robust immune response that comes with age.4
Many physicians are concerned about adequate immune response. In vaccine research, this is gauged by the proportion of patients with seroconversion after vaccination. This is also reflected in vaccine efficacy (VE), which gradually increases with age and maturity of the immune system. For example, measles VE is 60% to 70% in 6-to-8-month cohorts5 and 70% to 80% in 9-to-11-month cohorts.6 VE at 12 months is in the 90% range, and completion of the 2-dose series yields a VE of ≥ 95%.7 Thus, while the vaccine is more effective at later ages, it still provides protection to younger cohorts.
“Blunting” (ie, a reduced immune response to the second dose of vaccine3) is another concern with early measles vaccination, but a WHO meta-analysis proved this concern to be unfounded.1,3 Twelve papers examining seropositivity in children who received a second measles vaccine after early primary vaccination found a pooled proportion of seropositivity of 97%.1,8,9 Furthermore, evidence shows that children have sustained measles-specific T-cell responses after early primary measles immunization.10
Early vaccination has few risks and significant benefit. Therefore, in light of the recent measles outbreak, relaxing the lower boundary for the measles vaccine is appropriate. In addition to physically protecting the patient and general population, honoring parents’ requests for vaccination respects their autonomy and fosters trust. Synthesis of good science with a trusting doctor–patient relationship is key to ending the measles outbreak.
Rachel Roth, MD
Tel Aviv, Israel
Since the measles outbreak in the Pacific Northwest (where I did my training and remain in touch with colleagues and patients), parents with infants ages 6 to 11 months are requesting vaccinations before 12 months—the standard age to start immunizations.1 But physicians decline to provide inoculation, citing institutional policy on the risks of early vaccination. What are these risks, and how should we respond when parents ask about early vaccination?
The safety and efficacy of early vaccination are well documented. Early vaccination is a technique employed to curb outbreaks both in the United States and worldwide. Guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend vaccinating infants at 6 months of age if they will be traveling,2 and the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends vaccinations during a measles outbreak as part of intensified service delivery or in settings, such as daycare facilities, in which there is an increased risk for disease exposure during an outbreak.3 Any dose given before 12 months is considered supplemental, and the child must still complete the regular 2-dose vaccine schedule. Studies on the adverse effect profiles of vaccines show that the younger the infant, the fewer adverse events occur—because adverse events reflect the increasingly robust immune response that comes with age.4
Many physicians are concerned about adequate immune response. In vaccine research, this is gauged by the proportion of patients with seroconversion after vaccination. This is also reflected in vaccine efficacy (VE), which gradually increases with age and maturity of the immune system. For example, measles VE is 60% to 70% in 6-to-8-month cohorts5 and 70% to 80% in 9-to-11-month cohorts.6 VE at 12 months is in the 90% range, and completion of the 2-dose series yields a VE of ≥ 95%.7 Thus, while the vaccine is more effective at later ages, it still provides protection to younger cohorts.
“Blunting” (ie, a reduced immune response to the second dose of vaccine3) is another concern with early measles vaccination, but a WHO meta-analysis proved this concern to be unfounded.1,3 Twelve papers examining seropositivity in children who received a second measles vaccine after early primary vaccination found a pooled proportion of seropositivity of 97%.1,8,9 Furthermore, evidence shows that children have sustained measles-specific T-cell responses after early primary measles immunization.10
Early vaccination has few risks and significant benefit. Therefore, in light of the recent measles outbreak, relaxing the lower boundary for the measles vaccine is appropriate. In addition to physically protecting the patient and general population, honoring parents’ requests for vaccination respects their autonomy and fosters trust. Synthesis of good science with a trusting doctor–patient relationship is key to ending the measles outbreak.
Rachel Roth, MD
Tel Aviv, Israel
1. Conclusions of the SAGE Working Group on Measles and Rubella. 21-22 June 2017. Geneva WHO Policy Recommendation on administration of MCV to infants. SAGE. https://www.who.int/immunization/sage/meetings/2017/october/2_measles_vaccination_before_6_months_for_yellow_book_FINAL.pdf. Accessed April 24, 2019.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles (Rubeola). For healthcare professionals. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/hcp/index.html. Accessed April 24, 2019.
3. World Health Organization. Measles vaccines: WHO position paper, April 2017 - recommendations. Vaccine. 2017;92:205-227.
4. van der Maas NA, Woudenberg T, Hahné SJ, et al. Tolerability of early measles-mumps-rubella vaccination in infants aged 6-14 months during a measles outbreak in the Netherlands in 2013-2014. J Infect Dis. 2016;213:1466-1471.
5. Lochlainn LN, de Gier B, van der Maas NA, et al. Measles vaccination below 9 months of age: systematic literature review and meta-analyses of effects and safety. National Institute for Public Health and the Environment. https://www.who.int/immunization/sage/meetings/2015/october/2_MCV1_below_9_months_Effect_safety_28092015.pdf. Published September 28, 2015. Accessed April 24, 2019.
6. Uzicanin A, Zimmerman L. Field effectiveness of live attenuated measles-containing vaccines: a review of published literature. J Infect Dis. 2011;204(suppl 1):S133-S149.
7. Woudenberg T, van der Maas NA, Knol MJ, et al. Effectiveness of early measles, mumps, and rubella vaccination among 6-14-month-old infants during an epidemic in the Netherlands: an observational cohort study. J Infect Dis. 2017;215:1181-1187.
8. Martins C, Garly ML, Bale C, et al. Measles virus antibody responses in children randomly assigned to receive standard-titer edmonston-zagreb measles vaccine at 4.5 and 9 months of age, 9 months of age, or 9 and 18 months of age. J Infect Dis. 2014;210:693-700.
9. Njie-Jobe J, Nyamweya S, Miles DJ, et al. Immunological impact of an additional early measles vaccine in Gambian children: responses to a boost at 3 years. Vaccine. 2012;30:2543-2550.
10. Gans HA, Yasukawa LL, Sung P, et al. Measles humoral and cell-mediated immunity in children aged 5–10 years after primary measles immunization administered at 6 or 9 months of age. J Infect Dis. 2013;207:574-582.
1. Conclusions of the SAGE Working Group on Measles and Rubella. 21-22 June 2017. Geneva WHO Policy Recommendation on administration of MCV to infants. SAGE. https://www.who.int/immunization/sage/meetings/2017/october/2_measles_vaccination_before_6_months_for_yellow_book_FINAL.pdf. Accessed April 24, 2019.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles (Rubeola). For healthcare professionals. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/hcp/index.html. Accessed April 24, 2019.
3. World Health Organization. Measles vaccines: WHO position paper, April 2017 - recommendations. Vaccine. 2017;92:205-227.
4. van der Maas NA, Woudenberg T, Hahné SJ, et al. Tolerability of early measles-mumps-rubella vaccination in infants aged 6-14 months during a measles outbreak in the Netherlands in 2013-2014. J Infect Dis. 2016;213:1466-1471.
5. Lochlainn LN, de Gier B, van der Maas NA, et al. Measles vaccination below 9 months of age: systematic literature review and meta-analyses of effects and safety. National Institute for Public Health and the Environment. https://www.who.int/immunization/sage/meetings/2015/october/2_MCV1_below_9_months_Effect_safety_28092015.pdf. Published September 28, 2015. Accessed April 24, 2019.
6. Uzicanin A, Zimmerman L. Field effectiveness of live attenuated measles-containing vaccines: a review of published literature. J Infect Dis. 2011;204(suppl 1):S133-S149.
7. Woudenberg T, van der Maas NA, Knol MJ, et al. Effectiveness of early measles, mumps, and rubella vaccination among 6-14-month-old infants during an epidemic in the Netherlands: an observational cohort study. J Infect Dis. 2017;215:1181-1187.
8. Martins C, Garly ML, Bale C, et al. Measles virus antibody responses in children randomly assigned to receive standard-titer edmonston-zagreb measles vaccine at 4.5 and 9 months of age, 9 months of age, or 9 and 18 months of age. J Infect Dis. 2014;210:693-700.
9. Njie-Jobe J, Nyamweya S, Miles DJ, et al. Immunological impact of an additional early measles vaccine in Gambian children: responses to a boost at 3 years. Vaccine. 2012;30:2543-2550.
10. Gans HA, Yasukawa LL, Sung P, et al. Measles humoral and cell-mediated immunity in children aged 5–10 years after primary measles immunization administered at 6 or 9 months of age. J Infect Dis. 2013;207:574-582.
PCV13 vaccine reduces frequency of otitis media visits
The mean number of office visits for otitis media in children younger than 5 years dropped significantly after the introduction of the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, according to findings published in the International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology.
Previous studies have shown that more than half of children with otitis media (OM) have serotypes included in the PCV7 vaccine (4, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F, and 23F), wrote Xiaofeng Zhou, MD, of Pfizer, New York, and colleagues.
To assess the impact of PCV13, with the additional serotypes 1, 3, 5, 6A, 7F, and 19A, the researchers analyzed data from the U.S. National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey and National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey for three time periods: pre-PCV7 (1997-1999), after the introduction of PCV7 (2001-2009), and after the introduction of PCV13 (2011-2013).
Between the pre-PCV7 and PCV13 time periods, the researchers found significant reductions in the mean rates of OM visits of 48% and 41% among children younger than 2 years and younger than 5 years, respectively; reductions were 24% and 22%, respectively, when comparing PCV13 and PCV7. Ambulatory care visits for skin rash and trauma were not significantly different among the study periods.
Comparing the PCV7 and PCV13 time periods, the mean number of OM visits per 100 children declined from 84 to 64 per 100 children younger than 2 years, 41 to 34 per 100 children between ages 2 and 5 years, and from 59 to 46 per 100 children younger than 5 years.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of an ecologic study design, which was chosen to help reduce selection bias, but that did not show evidence of the field effectiveness of the PCV13 vaccine. Another limitation was the potential misclassification of patients with OM given clinician variability in diagnostic criteria, the researchers noted.
“Our results in this study, while not providing direct evidence of causality, nonetheless suggest a significant and positive impact of the PCV13 vaccination program on otitis media for children less than 5 years of age in the U.S., with further reductions in OM visits observed in PCV13 period following a decade of PCV7 use,” Dr. Zhou and associates said.
The investigators are employed by Pfizer, which funded the study.
SOURCE: Zhou X et al. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Apr. 119:96-102.
The mean number of office visits for otitis media in children younger than 5 years dropped significantly after the introduction of the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, according to findings published in the International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology.
Previous studies have shown that more than half of children with otitis media (OM) have serotypes included in the PCV7 vaccine (4, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F, and 23F), wrote Xiaofeng Zhou, MD, of Pfizer, New York, and colleagues.
To assess the impact of PCV13, with the additional serotypes 1, 3, 5, 6A, 7F, and 19A, the researchers analyzed data from the U.S. National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey and National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey for three time periods: pre-PCV7 (1997-1999), after the introduction of PCV7 (2001-2009), and after the introduction of PCV13 (2011-2013).
Between the pre-PCV7 and PCV13 time periods, the researchers found significant reductions in the mean rates of OM visits of 48% and 41% among children younger than 2 years and younger than 5 years, respectively; reductions were 24% and 22%, respectively, when comparing PCV13 and PCV7. Ambulatory care visits for skin rash and trauma were not significantly different among the study periods.
Comparing the PCV7 and PCV13 time periods, the mean number of OM visits per 100 children declined from 84 to 64 per 100 children younger than 2 years, 41 to 34 per 100 children between ages 2 and 5 years, and from 59 to 46 per 100 children younger than 5 years.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of an ecologic study design, which was chosen to help reduce selection bias, but that did not show evidence of the field effectiveness of the PCV13 vaccine. Another limitation was the potential misclassification of patients with OM given clinician variability in diagnostic criteria, the researchers noted.
“Our results in this study, while not providing direct evidence of causality, nonetheless suggest a significant and positive impact of the PCV13 vaccination program on otitis media for children less than 5 years of age in the U.S., with further reductions in OM visits observed in PCV13 period following a decade of PCV7 use,” Dr. Zhou and associates said.
The investigators are employed by Pfizer, which funded the study.
SOURCE: Zhou X et al. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Apr. 119:96-102.
The mean number of office visits for otitis media in children younger than 5 years dropped significantly after the introduction of the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, according to findings published in the International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology.
Previous studies have shown that more than half of children with otitis media (OM) have serotypes included in the PCV7 vaccine (4, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F, and 23F), wrote Xiaofeng Zhou, MD, of Pfizer, New York, and colleagues.
To assess the impact of PCV13, with the additional serotypes 1, 3, 5, 6A, 7F, and 19A, the researchers analyzed data from the U.S. National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey and National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey for three time periods: pre-PCV7 (1997-1999), after the introduction of PCV7 (2001-2009), and after the introduction of PCV13 (2011-2013).
Between the pre-PCV7 and PCV13 time periods, the researchers found significant reductions in the mean rates of OM visits of 48% and 41% among children younger than 2 years and younger than 5 years, respectively; reductions were 24% and 22%, respectively, when comparing PCV13 and PCV7. Ambulatory care visits for skin rash and trauma were not significantly different among the study periods.
Comparing the PCV7 and PCV13 time periods, the mean number of OM visits per 100 children declined from 84 to 64 per 100 children younger than 2 years, 41 to 34 per 100 children between ages 2 and 5 years, and from 59 to 46 per 100 children younger than 5 years.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of an ecologic study design, which was chosen to help reduce selection bias, but that did not show evidence of the field effectiveness of the PCV13 vaccine. Another limitation was the potential misclassification of patients with OM given clinician variability in diagnostic criteria, the researchers noted.
“Our results in this study, while not providing direct evidence of causality, nonetheless suggest a significant and positive impact of the PCV13 vaccination program on otitis media for children less than 5 years of age in the U.S., with further reductions in OM visits observed in PCV13 period following a decade of PCV7 use,” Dr. Zhou and associates said.
The investigators are employed by Pfizer, which funded the study.
SOURCE: Zhou X et al. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Apr. 119:96-102.
FROM THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PEDIATRIC OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY
United States up to 764 measles cases for the year
The number of U.S. measles cases in 2019 rose by 60 during the week ending May 3, which puts the new postelimination high at 764 cases for the year, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
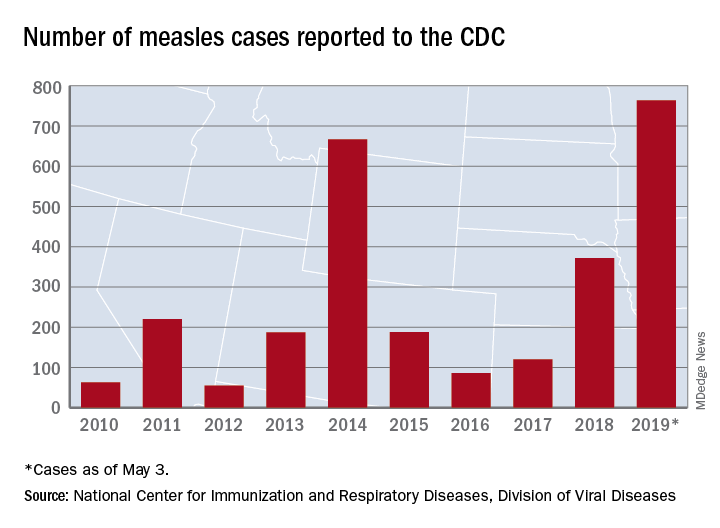
The CDC is currently tracking nine measles outbreaks in six states. The largest outbreak this year has been in New York City, mainly Brooklyn, which has almost half (367) of all cases in the country. An outbreak in New York’s Rockland County has resulted in another 109 cases so far this year. California is experiencing outbreaks in three counties – Butte, Los Angeles, and Sacramento – and the state was up to 40 confirmed cases as of May 1. The other states with outbreaks are Michigan, New Jersey, Georgia, and Maryland.
Twenty-three states now have reported measles cases in 2019, as officials in Pittsburgh reported Pennsylvania’s first case on April 30. Four additional cases in the area were reported on May 2 by the Allegheny County Health Department. A measles outbreak is “defined as three or more cases” by the CDC, but the situation in Pennsylvania is not yet being reported as such.
One Pennsylvania legislator in the state, Rep. Daryl Metcalfe (R) of Butler County, has authored a bill that would “bar health care practitioners and facilities and insurance companies from denying care if parents refuse or delay” recommended vaccinations, PennLive.com reported.
Pennsylvania Governor Tom Wolf (D) said that the “bill would put children, pregnant women, and vulnerable patients at risk of being exposed to horrific diseases – at the doctor’s office.”
The number of U.S. measles cases in 2019 rose by 60 during the week ending May 3, which puts the new postelimination high at 764 cases for the year, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The CDC is currently tracking nine measles outbreaks in six states. The largest outbreak this year has been in New York City, mainly Brooklyn, which has almost half (367) of all cases in the country. An outbreak in New York’s Rockland County has resulted in another 109 cases so far this year. California is experiencing outbreaks in three counties – Butte, Los Angeles, and Sacramento – and the state was up to 40 confirmed cases as of May 1. The other states with outbreaks are Michigan, New Jersey, Georgia, and Maryland.
Twenty-three states now have reported measles cases in 2019, as officials in Pittsburgh reported Pennsylvania’s first case on April 30. Four additional cases in the area were reported on May 2 by the Allegheny County Health Department. A measles outbreak is “defined as three or more cases” by the CDC, but the situation in Pennsylvania is not yet being reported as such.
One Pennsylvania legislator in the state, Rep. Daryl Metcalfe (R) of Butler County, has authored a bill that would “bar health care practitioners and facilities and insurance companies from denying care if parents refuse or delay” recommended vaccinations, PennLive.com reported.
Pennsylvania Governor Tom Wolf (D) said that the “bill would put children, pregnant women, and vulnerable patients at risk of being exposed to horrific diseases – at the doctor’s office.”
The number of U.S. measles cases in 2019 rose by 60 during the week ending May 3, which puts the new postelimination high at 764 cases for the year, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The CDC is currently tracking nine measles outbreaks in six states. The largest outbreak this year has been in New York City, mainly Brooklyn, which has almost half (367) of all cases in the country. An outbreak in New York’s Rockland County has resulted in another 109 cases so far this year. California is experiencing outbreaks in three counties – Butte, Los Angeles, and Sacramento – and the state was up to 40 confirmed cases as of May 1. The other states with outbreaks are Michigan, New Jersey, Georgia, and Maryland.
Twenty-three states now have reported measles cases in 2019, as officials in Pittsburgh reported Pennsylvania’s first case on April 30. Four additional cases in the area were reported on May 2 by the Allegheny County Health Department. A measles outbreak is “defined as three or more cases” by the CDC, but the situation in Pennsylvania is not yet being reported as such.
One Pennsylvania legislator in the state, Rep. Daryl Metcalfe (R) of Butler County, has authored a bill that would “bar health care practitioners and facilities and insurance companies from denying care if parents refuse or delay” recommended vaccinations, PennLive.com reported.
Pennsylvania Governor Tom Wolf (D) said that the “bill would put children, pregnant women, and vulnerable patients at risk of being exposed to horrific diseases – at the doctor’s office.”
FDA approves first vaccine for prevention of dengue disease
The vaccine was approved for children aged 9-16 years who live in endemic areas and have previously had laboratory-confirmed dengue disease.
Dengue is endemic in the U.S. territories of American Samoa, Guam, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands, according to an FDA statement announcing the approval.
While the first infection with dengue virus typically results in either no symptoms or a mild illness that can be mistaken for the flu, a second infection can lead to a more severe form of the disease, including dengue hemorrhagic fever, which can be fatal. About 95% of hospitalized patients with dengue disease have a second dengue virus infection.
FDA approval of Dengvaxia is based on results from three randomized, placebo-controlled studies of 35,000 individuals in dengue-endemic areas. The vaccine was about 76% effective in preventing symptomatic, laboratory-confirmed dengue disease in people aged 9-16 years with a previous dengue diagnosis. The most common adverse events were headache, muscle pain, joint pain, fatigue, injection site pain, and low-grade fever; the frequency of adverse events decreased after each subsequent dose.
“Infection by one type of dengue virus usually provides immunity against that specific serotype, but a subsequent infection by any of the other three serotypes of the virus increases the risk of developing severe dengue disease. ... The FDA’s approval of this vaccine will help protect people previously infected with dengue virus from subsequent development of dengue disease,” Peter Marks, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in the FDA statement.
The vaccine was approved for children aged 9-16 years who live in endemic areas and have previously had laboratory-confirmed dengue disease.
Dengue is endemic in the U.S. territories of American Samoa, Guam, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands, according to an FDA statement announcing the approval.
While the first infection with dengue virus typically results in either no symptoms or a mild illness that can be mistaken for the flu, a second infection can lead to a more severe form of the disease, including dengue hemorrhagic fever, which can be fatal. About 95% of hospitalized patients with dengue disease have a second dengue virus infection.
FDA approval of Dengvaxia is based on results from three randomized, placebo-controlled studies of 35,000 individuals in dengue-endemic areas. The vaccine was about 76% effective in preventing symptomatic, laboratory-confirmed dengue disease in people aged 9-16 years with a previous dengue diagnosis. The most common adverse events were headache, muscle pain, joint pain, fatigue, injection site pain, and low-grade fever; the frequency of adverse events decreased after each subsequent dose.
“Infection by one type of dengue virus usually provides immunity against that specific serotype, but a subsequent infection by any of the other three serotypes of the virus increases the risk of developing severe dengue disease. ... The FDA’s approval of this vaccine will help protect people previously infected with dengue virus from subsequent development of dengue disease,” Peter Marks, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in the FDA statement.
The vaccine was approved for children aged 9-16 years who live in endemic areas and have previously had laboratory-confirmed dengue disease.
Dengue is endemic in the U.S. territories of American Samoa, Guam, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands, according to an FDA statement announcing the approval.
While the first infection with dengue virus typically results in either no symptoms or a mild illness that can be mistaken for the flu, a second infection can lead to a more severe form of the disease, including dengue hemorrhagic fever, which can be fatal. About 95% of hospitalized patients with dengue disease have a second dengue virus infection.
FDA approval of Dengvaxia is based on results from three randomized, placebo-controlled studies of 35,000 individuals in dengue-endemic areas. The vaccine was about 76% effective in preventing symptomatic, laboratory-confirmed dengue disease in people aged 9-16 years with a previous dengue diagnosis. The most common adverse events were headache, muscle pain, joint pain, fatigue, injection site pain, and low-grade fever; the frequency of adverse events decreased after each subsequent dose.
“Infection by one type of dengue virus usually provides immunity against that specific serotype, but a subsequent infection by any of the other three serotypes of the virus increases the risk of developing severe dengue disease. ... The FDA’s approval of this vaccine will help protect people previously infected with dengue virus from subsequent development of dengue disease,” Peter Marks, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in the FDA statement.