User login
Young and older athletes show similar arrhythmia patterns with fQRS
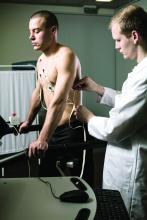
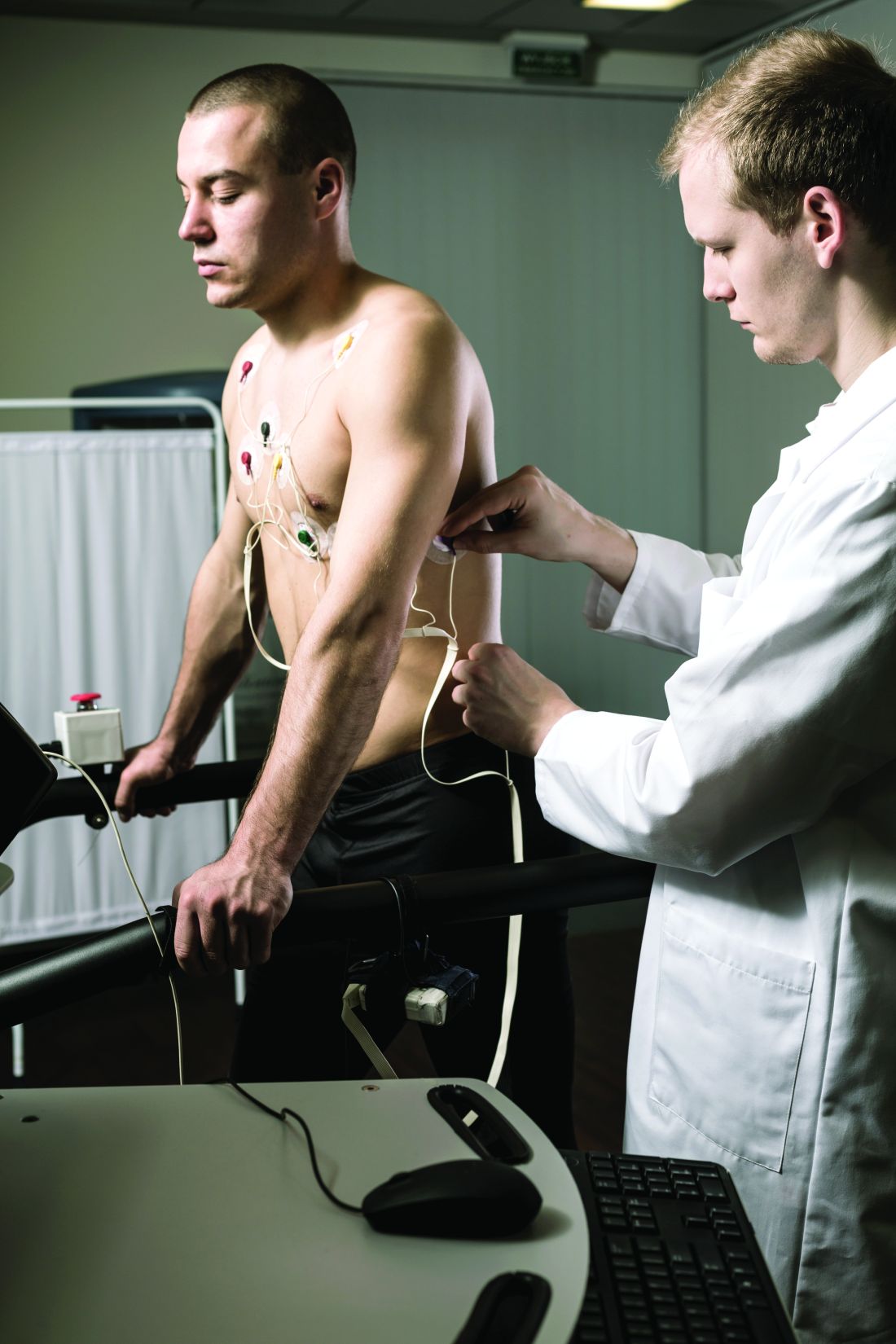
The prevalence of exercise-induced arrhythmias in young athletes with fragmented QRS (fQRS) patterns in lead V1 was 27%, similar to that seen in adult athletes, based on data from nearly 700 individuals.
Recent data suggest that fQRS complex in lead V1 (fQRSV1) in healthy athletes may promote arrhythmias in the context of training-induced right ventricular remodeling, but the prevalence and significance in young athletes has not been well studied, Guilia Quinto, MD, of the University of Padova (Italy) said in a presentation at the annual congress of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology.
Dr. Quinto and colleagues assessed data from of young athletes on ventricular arrhythmias during exercise tests.
The study population included 684 young athletes with a mean age of 15 years; 64% were male. Baseline data collection included medical history, physical exam, resting ECG, standardized maximum exercise tolerance, and echocardiography evaluation.
The overall prevalence of fQRSV1 was 27%. Individuals with fQRSV1 were significantly less likely than those without fQRSV1 to be female (22% vs. 43%), and to present with a lower resting heart rate (66.98 beats per minute vs. 70.08 beats per minute).
Echocardiographic data showed that individuals with fQRSV1 had significantly different morphological and functional right ventricular characteristics.
Notably, right ventricular end-diastolic diameter was 20.42 mm/m2 among individuals with fQRSV1 and 19.81 mm/m2 in those without, a significant difference (P = .019), Dr. Quinto said. Tricuspid annulus plain systolic excursion also differed significantly; 24.33 mm and 23.75 mm for individuals with and without fQRSV1, respectively (P = .013).
However, the individuals with fQRSV1 showed no increased occurrence of any type of exercise-induced arrhythmias regardless of morphology or complexity, said Dr. Quinto.
The prevalence of common and uncommon arrhythmias among individuals with and without fQRSV1 was 31% versus 34% and 13% versus 11%, respectively; these differences were not significant.
The study findings were limited by the relatively small size, but were strengthened by the review of echocardiographic data by two independent physicians, she said.
The results show that the overall prevalence of fQRSV1 in young athletes is comparable with patterns seen in studies of adult athletes, and no differences in exercise-induced arrhythmias occurred despite differences in right ventricular characteristics, she concluded.
Expanded insight into evaluation
The ECG pattern identified in the current study is often encountered in the evaluation of athletes, but its importance was unknown, Matthew Martinez, MD, a sports cardiologist at the Atlantic Health System in Morristown, N.J., said in an interview.
“Studies of ECG findings in athletes continues to inform us about which findings are important to evaluate. This study furthers our understanding of how to proceed,” and will serve as a guide for additional testing to reduce athlete risk, he said.
Looking ahead, “this study should guide clinicians about additional testing and evaluation when fQRS is present in adolescent athletes compared to adults,” Dr. Martinez noted. However, additional research is needed to determine which is the next best test, and whether the patient requires ongoing surveillance, or whether a single evaluation is sufficient, he said. “Further study should focus on best practices after fQRS is identified and whether outcomes can be linked to this finding.”
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Quinto and Dr. Martinez had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The prevalence of exercise-induced arrhythmias in young athletes with fragmented QRS (fQRS) patterns in lead V1 was 27%, similar to that seen in adult athletes, based on data from nearly 700 individuals.
Recent data suggest that fQRS complex in lead V1 (fQRSV1) in healthy athletes may promote arrhythmias in the context of training-induced right ventricular remodeling, but the prevalence and significance in young athletes has not been well studied, Guilia Quinto, MD, of the University of Padova (Italy) said in a presentation at the annual congress of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology.
Dr. Quinto and colleagues assessed data from of young athletes on ventricular arrhythmias during exercise tests.
The study population included 684 young athletes with a mean age of 15 years; 64% were male. Baseline data collection included medical history, physical exam, resting ECG, standardized maximum exercise tolerance, and echocardiography evaluation.
The overall prevalence of fQRSV1 was 27%. Individuals with fQRSV1 were significantly less likely than those without fQRSV1 to be female (22% vs. 43%), and to present with a lower resting heart rate (66.98 beats per minute vs. 70.08 beats per minute).
Echocardiographic data showed that individuals with fQRSV1 had significantly different morphological and functional right ventricular characteristics.
Notably, right ventricular end-diastolic diameter was 20.42 mm/m2 among individuals with fQRSV1 and 19.81 mm/m2 in those without, a significant difference (P = .019), Dr. Quinto said. Tricuspid annulus plain systolic excursion also differed significantly; 24.33 mm and 23.75 mm for individuals with and without fQRSV1, respectively (P = .013).
However, the individuals with fQRSV1 showed no increased occurrence of any type of exercise-induced arrhythmias regardless of morphology or complexity, said Dr. Quinto.
The prevalence of common and uncommon arrhythmias among individuals with and without fQRSV1 was 31% versus 34% and 13% versus 11%, respectively; these differences were not significant.
The study findings were limited by the relatively small size, but were strengthened by the review of echocardiographic data by two independent physicians, she said.
The results show that the overall prevalence of fQRSV1 in young athletes is comparable with patterns seen in studies of adult athletes, and no differences in exercise-induced arrhythmias occurred despite differences in right ventricular characteristics, she concluded.
Expanded insight into evaluation
The ECG pattern identified in the current study is often encountered in the evaluation of athletes, but its importance was unknown, Matthew Martinez, MD, a sports cardiologist at the Atlantic Health System in Morristown, N.J., said in an interview.
“Studies of ECG findings in athletes continues to inform us about which findings are important to evaluate. This study furthers our understanding of how to proceed,” and will serve as a guide for additional testing to reduce athlete risk, he said.
Looking ahead, “this study should guide clinicians about additional testing and evaluation when fQRS is present in adolescent athletes compared to adults,” Dr. Martinez noted. However, additional research is needed to determine which is the next best test, and whether the patient requires ongoing surveillance, or whether a single evaluation is sufficient, he said. “Further study should focus on best practices after fQRS is identified and whether outcomes can be linked to this finding.”
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Quinto and Dr. Martinez had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The prevalence of exercise-induced arrhythmias in young athletes with fragmented QRS (fQRS) patterns in lead V1 was 27%, similar to that seen in adult athletes, based on data from nearly 700 individuals.
Recent data suggest that fQRS complex in lead V1 (fQRSV1) in healthy athletes may promote arrhythmias in the context of training-induced right ventricular remodeling, but the prevalence and significance in young athletes has not been well studied, Guilia Quinto, MD, of the University of Padova (Italy) said in a presentation at the annual congress of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology.
Dr. Quinto and colleagues assessed data from of young athletes on ventricular arrhythmias during exercise tests.
The study population included 684 young athletes with a mean age of 15 years; 64% were male. Baseline data collection included medical history, physical exam, resting ECG, standardized maximum exercise tolerance, and echocardiography evaluation.
The overall prevalence of fQRSV1 was 27%. Individuals with fQRSV1 were significantly less likely than those without fQRSV1 to be female (22% vs. 43%), and to present with a lower resting heart rate (66.98 beats per minute vs. 70.08 beats per minute).
Echocardiographic data showed that individuals with fQRSV1 had significantly different morphological and functional right ventricular characteristics.
Notably, right ventricular end-diastolic diameter was 20.42 mm/m2 among individuals with fQRSV1 and 19.81 mm/m2 in those without, a significant difference (P = .019), Dr. Quinto said. Tricuspid annulus plain systolic excursion also differed significantly; 24.33 mm and 23.75 mm for individuals with and without fQRSV1, respectively (P = .013).
However, the individuals with fQRSV1 showed no increased occurrence of any type of exercise-induced arrhythmias regardless of morphology or complexity, said Dr. Quinto.
The prevalence of common and uncommon arrhythmias among individuals with and without fQRSV1 was 31% versus 34% and 13% versus 11%, respectively; these differences were not significant.
The study findings were limited by the relatively small size, but were strengthened by the review of echocardiographic data by two independent physicians, she said.
The results show that the overall prevalence of fQRSV1 in young athletes is comparable with patterns seen in studies of adult athletes, and no differences in exercise-induced arrhythmias occurred despite differences in right ventricular characteristics, she concluded.
Expanded insight into evaluation
The ECG pattern identified in the current study is often encountered in the evaluation of athletes, but its importance was unknown, Matthew Martinez, MD, a sports cardiologist at the Atlantic Health System in Morristown, N.J., said in an interview.
“Studies of ECG findings in athletes continues to inform us about which findings are important to evaluate. This study furthers our understanding of how to proceed,” and will serve as a guide for additional testing to reduce athlete risk, he said.
Looking ahead, “this study should guide clinicians about additional testing and evaluation when fQRS is present in adolescent athletes compared to adults,” Dr. Martinez noted. However, additional research is needed to determine which is the next best test, and whether the patient requires ongoing surveillance, or whether a single evaluation is sufficient, he said. “Further study should focus on best practices after fQRS is identified and whether outcomes can be linked to this finding.”
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Quinto and Dr. Martinez had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM ESC PREVENTIVE CARDIOLOGY 2022
Peripheral muscle fatigue limits post-COVID exercise
Peripheral muscle fatigue was the most common cause of exercise limitation in patients recovered from COVID-19 regardless of disease severity, in a study of nearly 300 individuals.
The source and magnitude of exercise intolerance in post–COVID-19 patients has not been well studied, said Mauricio Milani, MD, of Fitcordis Exercise Medicine Clinic, Brasilia, Brazil, in a presentation at the annual congress of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology.
To assess exercise intolerance, the researchers performed cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) on 144 adults who had recovered from COVID-19 and 144 matched controls who had not had COVID-19. The average age of the participants was 43 years, and 57% were male. COVID-19 was defined as mild, moderate, or severe in 60%, 21%, and 19% of the cases, respectively.
Residual symptoms were present in 41% of cases. CPET was performed at roughly 14 weeks after disease onset.
Among the COVID-19 patients, most of the CPET limitations (92%) were caused by muscle fatigue; cardiovascular limitations were noted in 2%, and pulmonary limitations were noted in 6%.
Data from the post-COVID CPET showed differences in peak oxygen consumption, as well as the first and second ventilatory thresholds (VT1 and VT2) between COVID-19 patients and controls, and with lower values related to higher illness severities, Dr. Milani said. Heart rate also varied according to illness severity, with lower values significantly related to higher illness severities and significant differences between COVID patients and controls.
A total of 42 individuals with COVID-19 had previous CPET data for comparison (27 with mild disease and 15 with moderate or severe disease), Dr. Milani said. In the subgroup with mild disease, the only significant difference in CPET results before and after COVID-19 was peak speed. In the moderate/severe group, the researchers observed higher reductions in peak speed and also reductions in oxygen consumption at peak and thresholds.
However, peak oxygen flows were not different before and after COVID-19 in either the mild or moderate/severe subgroups, Dr. Milani said.
The study findings were limited in part by the relatively small study population; however, the results indicate that peripheral muscle fatigue is the primary etiology in exercise limitation in post–COVID-19 patients.
“Our data suggest that treatment should emphasize comprehensive rehabilitation programs, including aerobic and muscle strengthening components,” Dr. Milani concluded.
COVID challenges remain unclear
“After COVID, patients often display a postviral syndrome with a wide range of symptoms,” Matthew Martinez, MD, a sports cardiologist at the Atlantic Health System in Morristown, N.J., in an interview said. “These conditions frequently lead to a sense of tiredness and weakness, pain, difficulty concentrating, and headaches that linger after the viral infection has cleared,” and these symptoms may continue for weeks.
However, this scenario is not unique to COVID-19: “This study confirms the importance of muscle fatigue in recovery,” said Dr. Martinez. “Recovery from viral illness requires hydration, sleep and slow progression return to exercise.” Consequently, Dr. Martinez said he was not surprised by the current study findings.
The take-home message for clinicians is to be aware that COVID-19 can have postviral syndrome, as is common after other infections, Dr. Martinez noted. The findings provide a starting point for discussing concerns with patients and explaining that a slow return to normal with usual care is expected. “Time to recovery will vary by individual,” he said. “Additional research is needed to identify which specific therapies are most important to help reduce time to recovery, and what new therapies could be developed to help facilitate muscle fatigue recovery and reduce time needed to recover.”
The study was supported by CAPES and CNPq. Dr. Milani had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Martinez had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Peripheral muscle fatigue was the most common cause of exercise limitation in patients recovered from COVID-19 regardless of disease severity, in a study of nearly 300 individuals.
The source and magnitude of exercise intolerance in post–COVID-19 patients has not been well studied, said Mauricio Milani, MD, of Fitcordis Exercise Medicine Clinic, Brasilia, Brazil, in a presentation at the annual congress of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology.
To assess exercise intolerance, the researchers performed cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) on 144 adults who had recovered from COVID-19 and 144 matched controls who had not had COVID-19. The average age of the participants was 43 years, and 57% were male. COVID-19 was defined as mild, moderate, or severe in 60%, 21%, and 19% of the cases, respectively.
Residual symptoms were present in 41% of cases. CPET was performed at roughly 14 weeks after disease onset.
Among the COVID-19 patients, most of the CPET limitations (92%) were caused by muscle fatigue; cardiovascular limitations were noted in 2%, and pulmonary limitations were noted in 6%.
Data from the post-COVID CPET showed differences in peak oxygen consumption, as well as the first and second ventilatory thresholds (VT1 and VT2) between COVID-19 patients and controls, and with lower values related to higher illness severities, Dr. Milani said. Heart rate also varied according to illness severity, with lower values significantly related to higher illness severities and significant differences between COVID patients and controls.
A total of 42 individuals with COVID-19 had previous CPET data for comparison (27 with mild disease and 15 with moderate or severe disease), Dr. Milani said. In the subgroup with mild disease, the only significant difference in CPET results before and after COVID-19 was peak speed. In the moderate/severe group, the researchers observed higher reductions in peak speed and also reductions in oxygen consumption at peak and thresholds.
However, peak oxygen flows were not different before and after COVID-19 in either the mild or moderate/severe subgroups, Dr. Milani said.
The study findings were limited in part by the relatively small study population; however, the results indicate that peripheral muscle fatigue is the primary etiology in exercise limitation in post–COVID-19 patients.
“Our data suggest that treatment should emphasize comprehensive rehabilitation programs, including aerobic and muscle strengthening components,” Dr. Milani concluded.
COVID challenges remain unclear
“After COVID, patients often display a postviral syndrome with a wide range of symptoms,” Matthew Martinez, MD, a sports cardiologist at the Atlantic Health System in Morristown, N.J., in an interview said. “These conditions frequently lead to a sense of tiredness and weakness, pain, difficulty concentrating, and headaches that linger after the viral infection has cleared,” and these symptoms may continue for weeks.
However, this scenario is not unique to COVID-19: “This study confirms the importance of muscle fatigue in recovery,” said Dr. Martinez. “Recovery from viral illness requires hydration, sleep and slow progression return to exercise.” Consequently, Dr. Martinez said he was not surprised by the current study findings.
The take-home message for clinicians is to be aware that COVID-19 can have postviral syndrome, as is common after other infections, Dr. Martinez noted. The findings provide a starting point for discussing concerns with patients and explaining that a slow return to normal with usual care is expected. “Time to recovery will vary by individual,” he said. “Additional research is needed to identify which specific therapies are most important to help reduce time to recovery, and what new therapies could be developed to help facilitate muscle fatigue recovery and reduce time needed to recover.”
The study was supported by CAPES and CNPq. Dr. Milani had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Martinez had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Peripheral muscle fatigue was the most common cause of exercise limitation in patients recovered from COVID-19 regardless of disease severity, in a study of nearly 300 individuals.
The source and magnitude of exercise intolerance in post–COVID-19 patients has not been well studied, said Mauricio Milani, MD, of Fitcordis Exercise Medicine Clinic, Brasilia, Brazil, in a presentation at the annual congress of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology.
To assess exercise intolerance, the researchers performed cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) on 144 adults who had recovered from COVID-19 and 144 matched controls who had not had COVID-19. The average age of the participants was 43 years, and 57% were male. COVID-19 was defined as mild, moderate, or severe in 60%, 21%, and 19% of the cases, respectively.
Residual symptoms were present in 41% of cases. CPET was performed at roughly 14 weeks after disease onset.
Among the COVID-19 patients, most of the CPET limitations (92%) were caused by muscle fatigue; cardiovascular limitations were noted in 2%, and pulmonary limitations were noted in 6%.
Data from the post-COVID CPET showed differences in peak oxygen consumption, as well as the first and second ventilatory thresholds (VT1 and VT2) between COVID-19 patients and controls, and with lower values related to higher illness severities, Dr. Milani said. Heart rate also varied according to illness severity, with lower values significantly related to higher illness severities and significant differences between COVID patients and controls.
A total of 42 individuals with COVID-19 had previous CPET data for comparison (27 with mild disease and 15 with moderate or severe disease), Dr. Milani said. In the subgroup with mild disease, the only significant difference in CPET results before and after COVID-19 was peak speed. In the moderate/severe group, the researchers observed higher reductions in peak speed and also reductions in oxygen consumption at peak and thresholds.
However, peak oxygen flows were not different before and after COVID-19 in either the mild or moderate/severe subgroups, Dr. Milani said.
The study findings were limited in part by the relatively small study population; however, the results indicate that peripheral muscle fatigue is the primary etiology in exercise limitation in post–COVID-19 patients.
“Our data suggest that treatment should emphasize comprehensive rehabilitation programs, including aerobic and muscle strengthening components,” Dr. Milani concluded.
COVID challenges remain unclear
“After COVID, patients often display a postviral syndrome with a wide range of symptoms,” Matthew Martinez, MD, a sports cardiologist at the Atlantic Health System in Morristown, N.J., in an interview said. “These conditions frequently lead to a sense of tiredness and weakness, pain, difficulty concentrating, and headaches that linger after the viral infection has cleared,” and these symptoms may continue for weeks.
However, this scenario is not unique to COVID-19: “This study confirms the importance of muscle fatigue in recovery,” said Dr. Martinez. “Recovery from viral illness requires hydration, sleep and slow progression return to exercise.” Consequently, Dr. Martinez said he was not surprised by the current study findings.
The take-home message for clinicians is to be aware that COVID-19 can have postviral syndrome, as is common after other infections, Dr. Martinez noted. The findings provide a starting point for discussing concerns with patients and explaining that a slow return to normal with usual care is expected. “Time to recovery will vary by individual,” he said. “Additional research is needed to identify which specific therapies are most important to help reduce time to recovery, and what new therapies could be developed to help facilitate muscle fatigue recovery and reduce time needed to recover.”
The study was supported by CAPES and CNPq. Dr. Milani had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Martinez had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM ESC PREVENTIVE CARDIOLOGY 2022
ILD progression, not diagnosis, triggers palliative care
Most health care providers are comfortable recommending palliative care (PC) for their patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD), but most do so at the time of disease progression, rather than diagnosis, as indicated on survey data from 128 clinicians.
ILD is associated with a high mortality rate and profound symptoms that contribute to poor quality of life, Rebecca A. Gersen, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote.
“Nevertheless, there is often a lack of preparedness for death by both patients and providers, contributing to increased distress,” they said. Clinician perspectives on the use of PC for ILD patients have not been well studied, although PC is not limited to end-of-life care and is recommended for ILD patients by professional organizations, including the American Thoracic Society. “PC is successful in improving breathlessness in chronic lung disease and can increase survival.”
In a study published in the journal CHEST®, the researchers surveyed health care providers at 68 Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation centers across the United States. The survey was sent and collected by email and a restricted social media platform. A total of 128 providers from 34 states completed the survey between October 2020 and January 2021. Of these, 61% were physicians, and 67% identified as White.
Overall, 95% of the respondents agreed or strongly agreed that addressing advance directives is important, but only 66% agreed or strongly agreed that they themselves addressed advance directives in the outpatient ILD clinic setting. A greater number (91%) agreed or strongly agreed that they had a high level of comfort in discussing prognosis, while 88% agreed or strongly agreed that they felt comfortable assessing a patient’s readiness for and acceptance of PC. Approximately two-thirds (67%) agreed or strongly agreed that they use PC services for ILD patients. There were no significant differences in responses from clinicians who had more than 10 years of experience and those who had less.
Of the providers who referred patients to PC, 54% did so at objective disease progression, and 80% did so at objective and/or symptomatic progress; 2% referred patients to PC at initial ILD diagnosis.
Lack of resources
Health care providers who reported that they rarely referred patients to palliative care were significantly more likely to cite a lack of local PC options (P < .01). Those who rarely referred patients for PC also were significantly less likely to feel comfortable discussing prognoses or advance directives in the ILD clinic (P = .03 and P = .02, respectively).
Among the 23% of responders who reported that they rarely referred patients, 66% said they did not have PC at their institution.
“In addition to understanding and addressing barriers to care, educational resources may be key to improving PC delivery to the ILD population,” the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including voluntary participation, lack of a validated questionnaire, and use of self-reports, which may not reflect physicians’ actual practice, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the use of U.S. data only, which may not generalize to countries with different health care models.
However, the results were strengthened by the use of data from providers at a range of institutions across the United States and by the high overall survey response rate, the researchers said.
“While ILD providers reassuringly demonstrate knowledge and interest in PC involvement, no current system exists to facilitate and monitor response to referral,” they noted. “Future research is desperately needed to address barriers to the provision of PC in order to enhance access to a critical service in the management and care of patients with ILD.”
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The researchers disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most health care providers are comfortable recommending palliative care (PC) for their patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD), but most do so at the time of disease progression, rather than diagnosis, as indicated on survey data from 128 clinicians.
ILD is associated with a high mortality rate and profound symptoms that contribute to poor quality of life, Rebecca A. Gersen, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote.
“Nevertheless, there is often a lack of preparedness for death by both patients and providers, contributing to increased distress,” they said. Clinician perspectives on the use of PC for ILD patients have not been well studied, although PC is not limited to end-of-life care and is recommended for ILD patients by professional organizations, including the American Thoracic Society. “PC is successful in improving breathlessness in chronic lung disease and can increase survival.”
In a study published in the journal CHEST®, the researchers surveyed health care providers at 68 Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation centers across the United States. The survey was sent and collected by email and a restricted social media platform. A total of 128 providers from 34 states completed the survey between October 2020 and January 2021. Of these, 61% were physicians, and 67% identified as White.
Overall, 95% of the respondents agreed or strongly agreed that addressing advance directives is important, but only 66% agreed or strongly agreed that they themselves addressed advance directives in the outpatient ILD clinic setting. A greater number (91%) agreed or strongly agreed that they had a high level of comfort in discussing prognosis, while 88% agreed or strongly agreed that they felt comfortable assessing a patient’s readiness for and acceptance of PC. Approximately two-thirds (67%) agreed or strongly agreed that they use PC services for ILD patients. There were no significant differences in responses from clinicians who had more than 10 years of experience and those who had less.
Of the providers who referred patients to PC, 54% did so at objective disease progression, and 80% did so at objective and/or symptomatic progress; 2% referred patients to PC at initial ILD diagnosis.
Lack of resources
Health care providers who reported that they rarely referred patients to palliative care were significantly more likely to cite a lack of local PC options (P < .01). Those who rarely referred patients for PC also were significantly less likely to feel comfortable discussing prognoses or advance directives in the ILD clinic (P = .03 and P = .02, respectively).
Among the 23% of responders who reported that they rarely referred patients, 66% said they did not have PC at their institution.
“In addition to understanding and addressing barriers to care, educational resources may be key to improving PC delivery to the ILD population,” the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including voluntary participation, lack of a validated questionnaire, and use of self-reports, which may not reflect physicians’ actual practice, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the use of U.S. data only, which may not generalize to countries with different health care models.
However, the results were strengthened by the use of data from providers at a range of institutions across the United States and by the high overall survey response rate, the researchers said.
“While ILD providers reassuringly demonstrate knowledge and interest in PC involvement, no current system exists to facilitate and monitor response to referral,” they noted. “Future research is desperately needed to address barriers to the provision of PC in order to enhance access to a critical service in the management and care of patients with ILD.”
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The researchers disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most health care providers are comfortable recommending palliative care (PC) for their patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD), but most do so at the time of disease progression, rather than diagnosis, as indicated on survey data from 128 clinicians.
ILD is associated with a high mortality rate and profound symptoms that contribute to poor quality of life, Rebecca A. Gersen, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote.
“Nevertheless, there is often a lack of preparedness for death by both patients and providers, contributing to increased distress,” they said. Clinician perspectives on the use of PC for ILD patients have not been well studied, although PC is not limited to end-of-life care and is recommended for ILD patients by professional organizations, including the American Thoracic Society. “PC is successful in improving breathlessness in chronic lung disease and can increase survival.”
In a study published in the journal CHEST®, the researchers surveyed health care providers at 68 Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation centers across the United States. The survey was sent and collected by email and a restricted social media platform. A total of 128 providers from 34 states completed the survey between October 2020 and January 2021. Of these, 61% were physicians, and 67% identified as White.
Overall, 95% of the respondents agreed or strongly agreed that addressing advance directives is important, but only 66% agreed or strongly agreed that they themselves addressed advance directives in the outpatient ILD clinic setting. A greater number (91%) agreed or strongly agreed that they had a high level of comfort in discussing prognosis, while 88% agreed or strongly agreed that they felt comfortable assessing a patient’s readiness for and acceptance of PC. Approximately two-thirds (67%) agreed or strongly agreed that they use PC services for ILD patients. There were no significant differences in responses from clinicians who had more than 10 years of experience and those who had less.
Of the providers who referred patients to PC, 54% did so at objective disease progression, and 80% did so at objective and/or symptomatic progress; 2% referred patients to PC at initial ILD diagnosis.
Lack of resources
Health care providers who reported that they rarely referred patients to palliative care were significantly more likely to cite a lack of local PC options (P < .01). Those who rarely referred patients for PC also were significantly less likely to feel comfortable discussing prognoses or advance directives in the ILD clinic (P = .03 and P = .02, respectively).
Among the 23% of responders who reported that they rarely referred patients, 66% said they did not have PC at their institution.
“In addition to understanding and addressing barriers to care, educational resources may be key to improving PC delivery to the ILD population,” the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including voluntary participation, lack of a validated questionnaire, and use of self-reports, which may not reflect physicians’ actual practice, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the use of U.S. data only, which may not generalize to countries with different health care models.
However, the results were strengthened by the use of data from providers at a range of institutions across the United States and by the high overall survey response rate, the researchers said.
“While ILD providers reassuringly demonstrate knowledge and interest in PC involvement, no current system exists to facilitate and monitor response to referral,” they noted. “Future research is desperately needed to address barriers to the provision of PC in order to enhance access to a critical service in the management and care of patients with ILD.”
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The researchers disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL CHEST®
Aspirin exposure fails to reduce cardiovascular event risk
The benefits of aspirin use for the primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) have been questioned in light of data showing neutral outcomes in low-risk patients and concerns about increased bleeding risk and mortality in healthy older adults, wrote Rita Del Pinto, MD, of University of L’Aquila (Italy) and colleagues in JAMA Network Open.
In the study, Dr. Del Pinto and colleagues conducted a post hoc analysis of data from more than 2,500 participants in SPRINT (Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial), a multicenter, randomized trial conducted from 2010 to 2013.
The goal of SPRINT was to compare intensive and standard blood pressure–lowering strategies for hypertension patients. The primary outcome of the current study was risk of a first cardiovascular event, which included adjudicated myocardial infarction, non–myocardial infarction acute coronary syndrome, stroke, acute heart failure, and CVD death.“There has been considerable improvement in the management of cardiovascular risk factors since the first reports on aspirin use for cardiovascular prevention,” Dr. Del Pinto said in an interview.
“As for hypertension, not only have more effective antihypertensive medications become available, but also evidence has recently emerged in support of a downwards redefinition of blood pressure targets during treatment,” she said. “In this context, in an era when great attention is paid to the personalization of treatment, no specific studies had addressed the association of aspirin use as a primary prevention strategy in a cohort of relatively old, high-risk individuals with treated systolic blood pressure steadily below the recommended target,” she added.
The researchers assessed whether aspirin use in addition to standard blood pressure management (a target of less than 140 mm Hg) decreased risk and improved survival.
The study population included 2,664 adult patients; 29.3% were women, and 24.5% were aged 75 years and older. Half of the patients (1,332) received aspirin and 1,332 did not.
In a multivariate analysis, 42 cardiovascular events occurred in the aspirin group, compared with 20 events in those not exposed to aspirin (hazard ratio, 2.30). The findings were consistent in subgroup analyses of younger individuals, current and former smokers, and patients on statins.
An additional subgroup analysis of individuals randomized to standard care or intensive care in the SPRINT study showed no significant difference in primary outcome rates between individuals who received aspirin and those who did not. The rates for aspirin use vs. non–aspirin use were 5.85% vs. 3.60% in the standard treatment group and 4.66% vs. 2.56% in the intensive treatment group.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the post hoc design, short follow-up period, and lack of data on the initiation of aspirin and bleeding events, the researchers wrote. However, the results suggest that modern management of hypertension may have redefined the potential benefits of aspirin in patients with hypertension, they concluded.
Findings confirm value of preventive care
“The study was conducted as a post-hoc analysis on an experimental cohort, which must be considered when interpreting the results,” Dr. Del Pinto said.
Despite the limitations, the study findings affirm that effective treatment of major cardiovascular risk factors, such as hypertension, with proven drugs is “a mainstay of the primary prevention of ASCVD,” she emphasized.
As for additional research, “Testing our findings in a dedicated setting with sufficiently long follow-up, where aspirin dose and indication, as well as any possible bleeding event, are reported could expand the clinical meaning of our observations,” said Dr. Del Pinto. “Also, the clinical impact of aspirin, even in combination with novel cardiovascular drugs such as direct oral anticoagulants, in populations exposed to combinations of risk factors, deserves further investigation.”
Data support shared decision-making
“While recent evidence has not shown a benefit of aspirin in the primary prevention of ASCVD in several populations, the subpopulation of patients with hypertension as an ASCVD risk factor is also of interest to the clinician,” Suman Pal, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, said in an interview. “The lack of benefit of aspirin in this study, despite its limitations, was surprising, and I would be eager to see how the role of aspirin in ASCVD prevention would continue to evolve in conjunction with improvement in other therapies for modification of risk factors.”
“The decision to continue aspirin in this subgroup of patients should warrant a discussion with patients and a reexamination of risks and benefits until further data are available,” Dr. Pal emphasized.
Larger studies with long-term follow-ups would be required to further clarify the role of aspirin in primary prevention of ASCVD in patients with hypertension without diabetes or chronic kidney disease, he added.
Data were supplied courtesy of BioLINCC. The study received no outside funding. The researchers and Dr. Pal had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The benefits of aspirin use for the primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) have been questioned in light of data showing neutral outcomes in low-risk patients and concerns about increased bleeding risk and mortality in healthy older adults, wrote Rita Del Pinto, MD, of University of L’Aquila (Italy) and colleagues in JAMA Network Open.
In the study, Dr. Del Pinto and colleagues conducted a post hoc analysis of data from more than 2,500 participants in SPRINT (Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial), a multicenter, randomized trial conducted from 2010 to 2013.
The goal of SPRINT was to compare intensive and standard blood pressure–lowering strategies for hypertension patients. The primary outcome of the current study was risk of a first cardiovascular event, which included adjudicated myocardial infarction, non–myocardial infarction acute coronary syndrome, stroke, acute heart failure, and CVD death.“There has been considerable improvement in the management of cardiovascular risk factors since the first reports on aspirin use for cardiovascular prevention,” Dr. Del Pinto said in an interview.
“As for hypertension, not only have more effective antihypertensive medications become available, but also evidence has recently emerged in support of a downwards redefinition of blood pressure targets during treatment,” she said. “In this context, in an era when great attention is paid to the personalization of treatment, no specific studies had addressed the association of aspirin use as a primary prevention strategy in a cohort of relatively old, high-risk individuals with treated systolic blood pressure steadily below the recommended target,” she added.
The researchers assessed whether aspirin use in addition to standard blood pressure management (a target of less than 140 mm Hg) decreased risk and improved survival.
The study population included 2,664 adult patients; 29.3% were women, and 24.5% were aged 75 years and older. Half of the patients (1,332) received aspirin and 1,332 did not.
In a multivariate analysis, 42 cardiovascular events occurred in the aspirin group, compared with 20 events in those not exposed to aspirin (hazard ratio, 2.30). The findings were consistent in subgroup analyses of younger individuals, current and former smokers, and patients on statins.
An additional subgroup analysis of individuals randomized to standard care or intensive care in the SPRINT study showed no significant difference in primary outcome rates between individuals who received aspirin and those who did not. The rates for aspirin use vs. non–aspirin use were 5.85% vs. 3.60% in the standard treatment group and 4.66% vs. 2.56% in the intensive treatment group.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the post hoc design, short follow-up period, and lack of data on the initiation of aspirin and bleeding events, the researchers wrote. However, the results suggest that modern management of hypertension may have redefined the potential benefits of aspirin in patients with hypertension, they concluded.
Findings confirm value of preventive care
“The study was conducted as a post-hoc analysis on an experimental cohort, which must be considered when interpreting the results,” Dr. Del Pinto said.
Despite the limitations, the study findings affirm that effective treatment of major cardiovascular risk factors, such as hypertension, with proven drugs is “a mainstay of the primary prevention of ASCVD,” she emphasized.
As for additional research, “Testing our findings in a dedicated setting with sufficiently long follow-up, where aspirin dose and indication, as well as any possible bleeding event, are reported could expand the clinical meaning of our observations,” said Dr. Del Pinto. “Also, the clinical impact of aspirin, even in combination with novel cardiovascular drugs such as direct oral anticoagulants, in populations exposed to combinations of risk factors, deserves further investigation.”
Data support shared decision-making
“While recent evidence has not shown a benefit of aspirin in the primary prevention of ASCVD in several populations, the subpopulation of patients with hypertension as an ASCVD risk factor is also of interest to the clinician,” Suman Pal, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, said in an interview. “The lack of benefit of aspirin in this study, despite its limitations, was surprising, and I would be eager to see how the role of aspirin in ASCVD prevention would continue to evolve in conjunction with improvement in other therapies for modification of risk factors.”
“The decision to continue aspirin in this subgroup of patients should warrant a discussion with patients and a reexamination of risks and benefits until further data are available,” Dr. Pal emphasized.
Larger studies with long-term follow-ups would be required to further clarify the role of aspirin in primary prevention of ASCVD in patients with hypertension without diabetes or chronic kidney disease, he added.
Data were supplied courtesy of BioLINCC. The study received no outside funding. The researchers and Dr. Pal had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The benefits of aspirin use for the primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) have been questioned in light of data showing neutral outcomes in low-risk patients and concerns about increased bleeding risk and mortality in healthy older adults, wrote Rita Del Pinto, MD, of University of L’Aquila (Italy) and colleagues in JAMA Network Open.
In the study, Dr. Del Pinto and colleagues conducted a post hoc analysis of data from more than 2,500 participants in SPRINT (Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial), a multicenter, randomized trial conducted from 2010 to 2013.
The goal of SPRINT was to compare intensive and standard blood pressure–lowering strategies for hypertension patients. The primary outcome of the current study was risk of a first cardiovascular event, which included adjudicated myocardial infarction, non–myocardial infarction acute coronary syndrome, stroke, acute heart failure, and CVD death.“There has been considerable improvement in the management of cardiovascular risk factors since the first reports on aspirin use for cardiovascular prevention,” Dr. Del Pinto said in an interview.
“As for hypertension, not only have more effective antihypertensive medications become available, but also evidence has recently emerged in support of a downwards redefinition of blood pressure targets during treatment,” she said. “In this context, in an era when great attention is paid to the personalization of treatment, no specific studies had addressed the association of aspirin use as a primary prevention strategy in a cohort of relatively old, high-risk individuals with treated systolic blood pressure steadily below the recommended target,” she added.
The researchers assessed whether aspirin use in addition to standard blood pressure management (a target of less than 140 mm Hg) decreased risk and improved survival.
The study population included 2,664 adult patients; 29.3% were women, and 24.5% were aged 75 years and older. Half of the patients (1,332) received aspirin and 1,332 did not.
In a multivariate analysis, 42 cardiovascular events occurred in the aspirin group, compared with 20 events in those not exposed to aspirin (hazard ratio, 2.30). The findings were consistent in subgroup analyses of younger individuals, current and former smokers, and patients on statins.
An additional subgroup analysis of individuals randomized to standard care or intensive care in the SPRINT study showed no significant difference in primary outcome rates between individuals who received aspirin and those who did not. The rates for aspirin use vs. non–aspirin use were 5.85% vs. 3.60% in the standard treatment group and 4.66% vs. 2.56% in the intensive treatment group.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the post hoc design, short follow-up period, and lack of data on the initiation of aspirin and bleeding events, the researchers wrote. However, the results suggest that modern management of hypertension may have redefined the potential benefits of aspirin in patients with hypertension, they concluded.
Findings confirm value of preventive care
“The study was conducted as a post-hoc analysis on an experimental cohort, which must be considered when interpreting the results,” Dr. Del Pinto said.
Despite the limitations, the study findings affirm that effective treatment of major cardiovascular risk factors, such as hypertension, with proven drugs is “a mainstay of the primary prevention of ASCVD,” she emphasized.
As for additional research, “Testing our findings in a dedicated setting with sufficiently long follow-up, where aspirin dose and indication, as well as any possible bleeding event, are reported could expand the clinical meaning of our observations,” said Dr. Del Pinto. “Also, the clinical impact of aspirin, even in combination with novel cardiovascular drugs such as direct oral anticoagulants, in populations exposed to combinations of risk factors, deserves further investigation.”
Data support shared decision-making
“While recent evidence has not shown a benefit of aspirin in the primary prevention of ASCVD in several populations, the subpopulation of patients with hypertension as an ASCVD risk factor is also of interest to the clinician,” Suman Pal, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, said in an interview. “The lack of benefit of aspirin in this study, despite its limitations, was surprising, and I would be eager to see how the role of aspirin in ASCVD prevention would continue to evolve in conjunction with improvement in other therapies for modification of risk factors.”
“The decision to continue aspirin in this subgroup of patients should warrant a discussion with patients and a reexamination of risks and benefits until further data are available,” Dr. Pal emphasized.
Larger studies with long-term follow-ups would be required to further clarify the role of aspirin in primary prevention of ASCVD in patients with hypertension without diabetes or chronic kidney disease, he added.
Data were supplied courtesy of BioLINCC. The study received no outside funding. The researchers and Dr. Pal had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Denosumab boosts bone strength in glucocorticoid users
Bone strength and microarchitecture remained stronger at 24 months after treatment with denosumab compared to risedronate, in a study of 110 adults using glucocorticoids.
Patients using glucocorticoids are at increased risk for vertebral and nonvertebral fractures at both the start of treatment or as treatment continues, wrote Piet Geusens, MD, of Maastricht University, the Netherlands, and colleagues.
Imaging data collected via high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) allow for the assessment of bone microarchitecture and strength, but specific data comparing the impact of bone treatment in patients using glucocorticoids are lacking, they said.
In a study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, the researchers identified a subset of 56 patients randomized to denosumab and 54 to risedronate patients out of a total of 590 patients who were enrolled in a phase 3 randomized, controlled trial of denosumab vs. risedronate for bone mineral density. The main results of the larger trial – presented at EULAR 2018 – showed greater increases in bone strength with denosumab over risedronate in patients receiving glucocorticoids.
In the current study, the researchers reviewed HR-pQCT scans of the distal radius and tibia at baseline, 12 months, and 24 months. Bone strength and microarchitecture were defined in terms of failure load (FL) as a primary outcome. Patients also were divided into subpopulations of those initiating glucocorticoid treatment (GC-I) and continuing treatment (GC-C).
Baseline characteristics were mainly balanced among the treatment groups within the GC-I and GC-C categories.
Among the GC-I patients, in the denosumab group, FL increased significantly from baseline to 12 months at the radius at tibia (1.8% and 1.7%, respectively) but did not change significantly in the risedronate group, which translated to a significant treatment difference between the drugs of 3.3% for radius and 2.5% for tibia.
At 24 months, the radius measure of FL was unchanged from baseline in denosumab patients but significantly decreased in risedronate patients, with a difference of –4.1%, which translated to a significant between-treatment difference at the radius of 5.6% (P < .001). Changes at the tibia were not significantly different between the groups at 24 months.
Among the GC-C patients, FL was unchanged from baseline to 12 months for both the denosumab and risedronate groups. However, FL significantly increased with denosumab (4.3%) and remained unchanged in the risedronate group.
The researchers also found significant differences between denosumab and risedronate in percentage changes in cortical bone mineral density, and less prominent changes and differences in trabecular bone mineral density.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of the HR-pQCT scanner, which limits the measurement of trabecular microarchitecture, and the use of only standard HR-pQCT parameters, which do not allow insight into endosteal changes, and the inability to correct for multiplicity of data, the researchers noted.
However, the results support the superiority of denosumab over risedronate for preventing FL and total bone mineral density loss at the radius and tibia in new glucocorticoid users, and for increasing FL and total bone mineral density at the radius in long-term glucocorticoid users, they said.
Denosumab therefore could be a useful therapeutic option and could inform decision-making in patients initiating GC-therapy or on long-term GC-therapy, they concluded.
The study was supported by Amgen. Dr. Geusens disclosed grants from Amgen, Celgene, Lilly, Merck, Pfizer, Roche, UCB, Fresenius, Mylan, and Sandoz, and grants and other funding from AbbVie, outside the current study.
Bone strength and microarchitecture remained stronger at 24 months after treatment with denosumab compared to risedronate, in a study of 110 adults using glucocorticoids.
Patients using glucocorticoids are at increased risk for vertebral and nonvertebral fractures at both the start of treatment or as treatment continues, wrote Piet Geusens, MD, of Maastricht University, the Netherlands, and colleagues.
Imaging data collected via high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) allow for the assessment of bone microarchitecture and strength, but specific data comparing the impact of bone treatment in patients using glucocorticoids are lacking, they said.
In a study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, the researchers identified a subset of 56 patients randomized to denosumab and 54 to risedronate patients out of a total of 590 patients who were enrolled in a phase 3 randomized, controlled trial of denosumab vs. risedronate for bone mineral density. The main results of the larger trial – presented at EULAR 2018 – showed greater increases in bone strength with denosumab over risedronate in patients receiving glucocorticoids.
In the current study, the researchers reviewed HR-pQCT scans of the distal radius and tibia at baseline, 12 months, and 24 months. Bone strength and microarchitecture were defined in terms of failure load (FL) as a primary outcome. Patients also were divided into subpopulations of those initiating glucocorticoid treatment (GC-I) and continuing treatment (GC-C).
Baseline characteristics were mainly balanced among the treatment groups within the GC-I and GC-C categories.
Among the GC-I patients, in the denosumab group, FL increased significantly from baseline to 12 months at the radius at tibia (1.8% and 1.7%, respectively) but did not change significantly in the risedronate group, which translated to a significant treatment difference between the drugs of 3.3% for radius and 2.5% for tibia.
At 24 months, the radius measure of FL was unchanged from baseline in denosumab patients but significantly decreased in risedronate patients, with a difference of –4.1%, which translated to a significant between-treatment difference at the radius of 5.6% (P < .001). Changes at the tibia were not significantly different between the groups at 24 months.
Among the GC-C patients, FL was unchanged from baseline to 12 months for both the denosumab and risedronate groups. However, FL significantly increased with denosumab (4.3%) and remained unchanged in the risedronate group.
The researchers also found significant differences between denosumab and risedronate in percentage changes in cortical bone mineral density, and less prominent changes and differences in trabecular bone mineral density.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of the HR-pQCT scanner, which limits the measurement of trabecular microarchitecture, and the use of only standard HR-pQCT parameters, which do not allow insight into endosteal changes, and the inability to correct for multiplicity of data, the researchers noted.
However, the results support the superiority of denosumab over risedronate for preventing FL and total bone mineral density loss at the radius and tibia in new glucocorticoid users, and for increasing FL and total bone mineral density at the radius in long-term glucocorticoid users, they said.
Denosumab therefore could be a useful therapeutic option and could inform decision-making in patients initiating GC-therapy or on long-term GC-therapy, they concluded.
The study was supported by Amgen. Dr. Geusens disclosed grants from Amgen, Celgene, Lilly, Merck, Pfizer, Roche, UCB, Fresenius, Mylan, and Sandoz, and grants and other funding from AbbVie, outside the current study.
Bone strength and microarchitecture remained stronger at 24 months after treatment with denosumab compared to risedronate, in a study of 110 adults using glucocorticoids.
Patients using glucocorticoids are at increased risk for vertebral and nonvertebral fractures at both the start of treatment or as treatment continues, wrote Piet Geusens, MD, of Maastricht University, the Netherlands, and colleagues.
Imaging data collected via high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) allow for the assessment of bone microarchitecture and strength, but specific data comparing the impact of bone treatment in patients using glucocorticoids are lacking, they said.
In a study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, the researchers identified a subset of 56 patients randomized to denosumab and 54 to risedronate patients out of a total of 590 patients who were enrolled in a phase 3 randomized, controlled trial of denosumab vs. risedronate for bone mineral density. The main results of the larger trial – presented at EULAR 2018 – showed greater increases in bone strength with denosumab over risedronate in patients receiving glucocorticoids.
In the current study, the researchers reviewed HR-pQCT scans of the distal radius and tibia at baseline, 12 months, and 24 months. Bone strength and microarchitecture were defined in terms of failure load (FL) as a primary outcome. Patients also were divided into subpopulations of those initiating glucocorticoid treatment (GC-I) and continuing treatment (GC-C).
Baseline characteristics were mainly balanced among the treatment groups within the GC-I and GC-C categories.
Among the GC-I patients, in the denosumab group, FL increased significantly from baseline to 12 months at the radius at tibia (1.8% and 1.7%, respectively) but did not change significantly in the risedronate group, which translated to a significant treatment difference between the drugs of 3.3% for radius and 2.5% for tibia.
At 24 months, the radius measure of FL was unchanged from baseline in denosumab patients but significantly decreased in risedronate patients, with a difference of –4.1%, which translated to a significant between-treatment difference at the radius of 5.6% (P < .001). Changes at the tibia were not significantly different between the groups at 24 months.
Among the GC-C patients, FL was unchanged from baseline to 12 months for both the denosumab and risedronate groups. However, FL significantly increased with denosumab (4.3%) and remained unchanged in the risedronate group.
The researchers also found significant differences between denosumab and risedronate in percentage changes in cortical bone mineral density, and less prominent changes and differences in trabecular bone mineral density.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of the HR-pQCT scanner, which limits the measurement of trabecular microarchitecture, and the use of only standard HR-pQCT parameters, which do not allow insight into endosteal changes, and the inability to correct for multiplicity of data, the researchers noted.
However, the results support the superiority of denosumab over risedronate for preventing FL and total bone mineral density loss at the radius and tibia in new glucocorticoid users, and for increasing FL and total bone mineral density at the radius in long-term glucocorticoid users, they said.
Denosumab therefore could be a useful therapeutic option and could inform decision-making in patients initiating GC-therapy or on long-term GC-therapy, they concluded.
The study was supported by Amgen. Dr. Geusens disclosed grants from Amgen, Celgene, Lilly, Merck, Pfizer, Roche, UCB, Fresenius, Mylan, and Sandoz, and grants and other funding from AbbVie, outside the current study.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH
TNF inhibitor treatment models promote personalized care in ankylosing spondylitis
A small number of patient and physician-reported outcomes, as well as laboratory and clinical factors, may help to predict the response of patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) to treatment with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors when they have never taken them before, according to an analysis of data from nearly 2,000 individuals in 10 clinical trials.
TNF inhibitors are recommended for patients with AS whose symptoms persist despite use of NSAIDs, Runsheng Wang, MD, adjunct assistant professor at Columbia University Medical Center, New York, and a practicing rheumatologist at Garden State Rheumatology Consultants, Union, N.J., and colleagues wrote. Randomized, controlled clinical trials have shown that TNF inhibitors are effective in treating AS, but approximately half of patients fail to achieve notable improvement, which suggests the need for a predictive model.
“In clinical practice, before starting a treatment, physicians and patients want to know how likely a patient would be to respond to the treatment, particularly when more than one treatment option is available,” Dr. Wang said in an interview. “In this study, we developed predictive models that can potentially answer this question.”
The results suggest that the models in the study can be used to personalize clinical decision-making for patients with AS, whether to promote confidence in choosing a TNF inhibitor or to terminate treatment in nonresponders who had a higher probability of nonresponse at baseline, the researchers wrote. Similar models for other biologic treatments can help prioritize treatment options.
The predictive models are practical for clinical use because the variables in the reduced models – can be collected easily during patient visits, Dr. Wang explained. However, data from clinical practice are needed to further validate the study findings.
In a retrospective cohort study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers analyzed data from 10 randomized, controlled clinical trials of TNF inhibitor treatment in patients with active AS conducted during 2002-2016. The study population included 1,899 adults with active AS who received an originator TNF inhibitor for at least 12 weeks, and the training set included 1,207 individuals. In the training set, the mean age of the participants was 39 years, and 75% were men.
The outcomes included major response and no response based on change in AS Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) from baseline to 12 weeks, and the researchers used machine-learning algorithms to estimate the probability of major response or no response. Major response was defined as a decrease in ASDAS of 2.0 or greater; no response was defined as a decrease in ASDAS of less than 1.1.
In the training set, a total of 407 patients (33.7%) had a major response, and 414 (34.3%) had no response.
The key features in the full, 21-variable model that increased the probability of a major response were higher C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, higher patient global assessment (PGA) of disease activity, and Bath AS Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) question 2 scores. (Question 2 asks for the overall level of back, hip, or neck pain associated with AS.) The probability of a major response decreased with higher body mass index and Bath AS Functional Index (BASFI) scores.
The key features in the model that increased the probability of no response were older age and higher BASFI scores. The probability of no response decreased with higher CRP levels, higher BASDAI question 2 scores, and higher PGA scores.
Overall, the researchers found that models using smaller subsets of variables (three or five variables in total) that would be easier to gather clinically yielded similar predictive performance.
The models were externally validated in a testing set of 692 individuals. Baseline characteristics were similar in the testing and training sets. In the testing set, the full models demonstrated moderate to high accuracy of 0.71 in the random forest model for major response and 0.76 in the random forest model for no response, with similar results in the reduced models.
At a prevalence of 25% for major response, the positive predictive values (PPVs) for random forest and logistic regression models ranged from 0.49 to 0.60, and the negative predictive values (NPVs) ranged from 0.82 to 0.84. At a prevalence of 25% for no response, PPVs ranged from 0.61 to 0.77, and NPVs ranged from 0.81 to 0.83.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of data on smoking, which has been linked both to shorter treatment adherence and worse response to TNF inhibitors; the inclusion of only TNF inhibitor–naive patients; and the exclusion of NSAIDs from the models, the researchers wrote.
Dr. Wang disclosed support from the Rheumatology Research Foundation. The study’s two other authors disclosed receiving support from the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. The study was based on an analysis of data from AbbVie and Pfizer that were made available through Vivli.
A small number of patient and physician-reported outcomes, as well as laboratory and clinical factors, may help to predict the response of patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) to treatment with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors when they have never taken them before, according to an analysis of data from nearly 2,000 individuals in 10 clinical trials.
TNF inhibitors are recommended for patients with AS whose symptoms persist despite use of NSAIDs, Runsheng Wang, MD, adjunct assistant professor at Columbia University Medical Center, New York, and a practicing rheumatologist at Garden State Rheumatology Consultants, Union, N.J., and colleagues wrote. Randomized, controlled clinical trials have shown that TNF inhibitors are effective in treating AS, but approximately half of patients fail to achieve notable improvement, which suggests the need for a predictive model.
“In clinical practice, before starting a treatment, physicians and patients want to know how likely a patient would be to respond to the treatment, particularly when more than one treatment option is available,” Dr. Wang said in an interview. “In this study, we developed predictive models that can potentially answer this question.”
The results suggest that the models in the study can be used to personalize clinical decision-making for patients with AS, whether to promote confidence in choosing a TNF inhibitor or to terminate treatment in nonresponders who had a higher probability of nonresponse at baseline, the researchers wrote. Similar models for other biologic treatments can help prioritize treatment options.
The predictive models are practical for clinical use because the variables in the reduced models – can be collected easily during patient visits, Dr. Wang explained. However, data from clinical practice are needed to further validate the study findings.
In a retrospective cohort study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers analyzed data from 10 randomized, controlled clinical trials of TNF inhibitor treatment in patients with active AS conducted during 2002-2016. The study population included 1,899 adults with active AS who received an originator TNF inhibitor for at least 12 weeks, and the training set included 1,207 individuals. In the training set, the mean age of the participants was 39 years, and 75% were men.
The outcomes included major response and no response based on change in AS Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) from baseline to 12 weeks, and the researchers used machine-learning algorithms to estimate the probability of major response or no response. Major response was defined as a decrease in ASDAS of 2.0 or greater; no response was defined as a decrease in ASDAS of less than 1.1.
In the training set, a total of 407 patients (33.7%) had a major response, and 414 (34.3%) had no response.
The key features in the full, 21-variable model that increased the probability of a major response were higher C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, higher patient global assessment (PGA) of disease activity, and Bath AS Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) question 2 scores. (Question 2 asks for the overall level of back, hip, or neck pain associated with AS.) The probability of a major response decreased with higher body mass index and Bath AS Functional Index (BASFI) scores.
The key features in the model that increased the probability of no response were older age and higher BASFI scores. The probability of no response decreased with higher CRP levels, higher BASDAI question 2 scores, and higher PGA scores.
Overall, the researchers found that models using smaller subsets of variables (three or five variables in total) that would be easier to gather clinically yielded similar predictive performance.
The models were externally validated in a testing set of 692 individuals. Baseline characteristics were similar in the testing and training sets. In the testing set, the full models demonstrated moderate to high accuracy of 0.71 in the random forest model for major response and 0.76 in the random forest model for no response, with similar results in the reduced models.
At a prevalence of 25% for major response, the positive predictive values (PPVs) for random forest and logistic regression models ranged from 0.49 to 0.60, and the negative predictive values (NPVs) ranged from 0.82 to 0.84. At a prevalence of 25% for no response, PPVs ranged from 0.61 to 0.77, and NPVs ranged from 0.81 to 0.83.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of data on smoking, which has been linked both to shorter treatment adherence and worse response to TNF inhibitors; the inclusion of only TNF inhibitor–naive patients; and the exclusion of NSAIDs from the models, the researchers wrote.
Dr. Wang disclosed support from the Rheumatology Research Foundation. The study’s two other authors disclosed receiving support from the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. The study was based on an analysis of data from AbbVie and Pfizer that were made available through Vivli.
A small number of patient and physician-reported outcomes, as well as laboratory and clinical factors, may help to predict the response of patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) to treatment with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors when they have never taken them before, according to an analysis of data from nearly 2,000 individuals in 10 clinical trials.
TNF inhibitors are recommended for patients with AS whose symptoms persist despite use of NSAIDs, Runsheng Wang, MD, adjunct assistant professor at Columbia University Medical Center, New York, and a practicing rheumatologist at Garden State Rheumatology Consultants, Union, N.J., and colleagues wrote. Randomized, controlled clinical trials have shown that TNF inhibitors are effective in treating AS, but approximately half of patients fail to achieve notable improvement, which suggests the need for a predictive model.
“In clinical practice, before starting a treatment, physicians and patients want to know how likely a patient would be to respond to the treatment, particularly when more than one treatment option is available,” Dr. Wang said in an interview. “In this study, we developed predictive models that can potentially answer this question.”
The results suggest that the models in the study can be used to personalize clinical decision-making for patients with AS, whether to promote confidence in choosing a TNF inhibitor or to terminate treatment in nonresponders who had a higher probability of nonresponse at baseline, the researchers wrote. Similar models for other biologic treatments can help prioritize treatment options.
The predictive models are practical for clinical use because the variables in the reduced models – can be collected easily during patient visits, Dr. Wang explained. However, data from clinical practice are needed to further validate the study findings.
In a retrospective cohort study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers analyzed data from 10 randomized, controlled clinical trials of TNF inhibitor treatment in patients with active AS conducted during 2002-2016. The study population included 1,899 adults with active AS who received an originator TNF inhibitor for at least 12 weeks, and the training set included 1,207 individuals. In the training set, the mean age of the participants was 39 years, and 75% were men.
The outcomes included major response and no response based on change in AS Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) from baseline to 12 weeks, and the researchers used machine-learning algorithms to estimate the probability of major response or no response. Major response was defined as a decrease in ASDAS of 2.0 or greater; no response was defined as a decrease in ASDAS of less than 1.1.
In the training set, a total of 407 patients (33.7%) had a major response, and 414 (34.3%) had no response.
The key features in the full, 21-variable model that increased the probability of a major response were higher C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, higher patient global assessment (PGA) of disease activity, and Bath AS Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) question 2 scores. (Question 2 asks for the overall level of back, hip, or neck pain associated with AS.) The probability of a major response decreased with higher body mass index and Bath AS Functional Index (BASFI) scores.
The key features in the model that increased the probability of no response were older age and higher BASFI scores. The probability of no response decreased with higher CRP levels, higher BASDAI question 2 scores, and higher PGA scores.
Overall, the researchers found that models using smaller subsets of variables (three or five variables in total) that would be easier to gather clinically yielded similar predictive performance.
The models were externally validated in a testing set of 692 individuals. Baseline characteristics were similar in the testing and training sets. In the testing set, the full models demonstrated moderate to high accuracy of 0.71 in the random forest model for major response and 0.76 in the random forest model for no response, with similar results in the reduced models.
At a prevalence of 25% for major response, the positive predictive values (PPVs) for random forest and logistic regression models ranged from 0.49 to 0.60, and the negative predictive values (NPVs) ranged from 0.82 to 0.84. At a prevalence of 25% for no response, PPVs ranged from 0.61 to 0.77, and NPVs ranged from 0.81 to 0.83.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of data on smoking, which has been linked both to shorter treatment adherence and worse response to TNF inhibitors; the inclusion of only TNF inhibitor–naive patients; and the exclusion of NSAIDs from the models, the researchers wrote.
Dr. Wang disclosed support from the Rheumatology Research Foundation. The study’s two other authors disclosed receiving support from the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. The study was based on an analysis of data from AbbVie and Pfizer that were made available through Vivli.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Adolescents are undertested for STIs
Approximately 20% of sexually active high schoolers reported testing for a sexually transmitted infection in the previous year, based on data from 2,501 respondents to the 2019 national Youth Risk Behavior Survey.
Data suggest that half of all new STIs in the United States occur in youth aged 15-24 years, and that 25% of sexually active young women in the United States have an STI, wrote Nicole Liddon, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues.
Although organizations including the American Academy of Pediatrics and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend varying degrees of routine STI screening for adolescents, data on the prevalence of testing in this population are limited, the researchers said.
However, the addition in 2019 of a question on STI testing to the national Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS) provided an opportunity to assess prevalence of STI testing, identify potential barriers, and increase screening rates, they wrote.
In a study published in Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed data from the 2019 national YRBS, an anonymous survey administered biannually to public and private high school students across the United States.
The study population included 2,501 individuals who reported sexual activity with at least one person during the 3 months prior to the survey.
Overall, 20.4% of the respondents reported being tested for an STI in the previous year, including significantly more females than males (26.1% vs. 13.7%).
The prevalence of testing among females was not significantly different according to race/ethnicity, sexual identity, or the sex of sexual contacts, but the prevalence increased with age; 12.6%, 22.8%, 28.5%, and 36.9% for females aged 15 years and younger, 16 years, 17 years, and 18 years, respectively.
Among males, no significant differences in STI testing were noted according to race/ethnicity, age, sexual identity, or sex of sexual contacts.
The researchers also analyzed prevalence of STI tested based on sexual behaviors. Among female students, the prevalence of STI testing was higher among those who reported the following behaviors, compared with those who did not: nonuse of condoms at last sexual intercourse (34.1% vs. 18.2%), substance use at last sexual intercourse (32.0% vs. 24.7%), and having four or more lifetime sex partners (31.9% vs. 24.7%).
Among male students, the prevalence of STI testing was higher among those who reported the following behaviors, compared with those who did not: sex before age 13 years (27.1% vs. 12.1%), having two or more recent sex partners (22.4% vs. 10.4%), having four or more lifetime sex partners (22.3% vs. 9.5%), and substance use at last sexual intercourse (19.2% vs. 12.1%).
The low prevalence of STI testing in teens has become more urgent in the wake of the coronavirus pandemic, the researchers wrote. “These prevalence estimates were derived before the possible profound impacts of the pandemic on adolescent sexual behavior and access to and use of health care services.”
Current guidelines allow health care providers the options for opt-out STI screening as a strategy to improve screening rates and testing; however, this option does not eliminate the need for conversations with adolescent patients about sexual activity, they emphasized.
The study findings were limited by several other factors including the inability to directly assess adherence to screening recommendations specifically, the inability to determine whether low testing rates resulted from limited access to health care or missed screening opportunities at visits, and the inclusion only of high school students but not out-of-school youth who may have more limited access to testing.
However, the results highlight the need to improve STI testing services for adolescents, and to address barriers at the individual and clinic level, they said. The addition of a question about past-year STI testing to the 2019 and future YRBS survey will promote ongoing monitoring of efforts to increase testing rates.
Teen sexual health goes beyond testing
The current study shows that routine testing for STIs according to published guidelines is low, Cynthia Holland-Hall, MD, and Andrea E. Bonny, MD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital and Ohio State University, both in Columbus, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Notably, sexually active females and males who had sex with male partners, two groups for whom annual testing is specifically recommended by multiple organizations, had testing rates of less than 30%, they said. The authors highlighted the study’s lack of information on which specific barriers, such as lack of access to the health care system, lack of knowledge, and fear of disclosure, contributed to overall low rates of testing.
However, STI testing is only one element of sexual and reproductive health care. Although opt-out testing may improve detection rates, the editorialists emphasized the need for patient-provider conversations about sex, citing recent studies showing that adolescents who spent some time alone with providers were more likely to receive sexual and reproductive health (SRH) services in the past year.
“Resources such as confidentiality policies, checklists, and written screening tools may facilitate SRH discussions,” Dr. Holland-Hall and Dr. Bonny said. “With a little practice, respect, and intention, a caring provider can take the awkward out of discussing sexual health but must not opt out of the conversation.”
Privacy and time issues exacerbate low testing rates
The current study is especially important at this time because many adolescents have likely missed well visits, and therefore important STI screens, because of disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, Karalyn Kinsella, MD, a pediatrician in private practice in Cheshire, Conn., said in an interview.
“I was surprised that the rate of screening was only one in five,” said Dr. Kinsella. “I knew it would be suboptimal, but not that low.”
According to Dr. Kinsella, there are two major barriers to increasing STI testing in adolescents in primary care. One barrier is that insurance companies will often state on the bill what the testing was for, which will lead to an uncomfortable conversation at a later date for the adolescent and parent when the bill arrives in the mail. A second barrier is when to test during a visit,. “If we obtain urine samples on all adolescents and many of them are not sexually active, we are wasting a lot of time in the short visit to obtain urine,” she explained. “If testing is scheduled for the end of the visit, they often leave without providing a urine sample.”
Overall, the study is an important reminder to general pediatricians about STI testing for sexually active teens, she emphasized.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. The editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kinsella had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
Approximately 20% of sexually active high schoolers reported testing for a sexually transmitted infection in the previous year, based on data from 2,501 respondents to the 2019 national Youth Risk Behavior Survey.
Data suggest that half of all new STIs in the United States occur in youth aged 15-24 years, and that 25% of sexually active young women in the United States have an STI, wrote Nicole Liddon, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues.
Although organizations including the American Academy of Pediatrics and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend varying degrees of routine STI screening for adolescents, data on the prevalence of testing in this population are limited, the researchers said.
However, the addition in 2019 of a question on STI testing to the national Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS) provided an opportunity to assess prevalence of STI testing, identify potential barriers, and increase screening rates, they wrote.
In a study published in Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed data from the 2019 national YRBS, an anonymous survey administered biannually to public and private high school students across the United States.
The study population included 2,501 individuals who reported sexual activity with at least one person during the 3 months prior to the survey.
Overall, 20.4% of the respondents reported being tested for an STI in the previous year, including significantly more females than males (26.1% vs. 13.7%).
The prevalence of testing among females was not significantly different according to race/ethnicity, sexual identity, or the sex of sexual contacts, but the prevalence increased with age; 12.6%, 22.8%, 28.5%, and 36.9% for females aged 15 years and younger, 16 years, 17 years, and 18 years, respectively.
Among males, no significant differences in STI testing were noted according to race/ethnicity, age, sexual identity, or sex of sexual contacts.
The researchers also analyzed prevalence of STI tested based on sexual behaviors. Among female students, the prevalence of STI testing was higher among those who reported the following behaviors, compared with those who did not: nonuse of condoms at last sexual intercourse (34.1% vs. 18.2%), substance use at last sexual intercourse (32.0% vs. 24.7%), and having four or more lifetime sex partners (31.9% vs. 24.7%).
Among male students, the prevalence of STI testing was higher among those who reported the following behaviors, compared with those who did not: sex before age 13 years (27.1% vs. 12.1%), having two or more recent sex partners (22.4% vs. 10.4%), having four or more lifetime sex partners (22.3% vs. 9.5%), and substance use at last sexual intercourse (19.2% vs. 12.1%).
The low prevalence of STI testing in teens has become more urgent in the wake of the coronavirus pandemic, the researchers wrote. “These prevalence estimates were derived before the possible profound impacts of the pandemic on adolescent sexual behavior and access to and use of health care services.”
Current guidelines allow health care providers the options for opt-out STI screening as a strategy to improve screening rates and testing; however, this option does not eliminate the need for conversations with adolescent patients about sexual activity, they emphasized.
The study findings were limited by several other factors including the inability to directly assess adherence to screening recommendations specifically, the inability to determine whether low testing rates resulted from limited access to health care or missed screening opportunities at visits, and the inclusion only of high school students but not out-of-school youth who may have more limited access to testing.
However, the results highlight the need to improve STI testing services for adolescents, and to address barriers at the individual and clinic level, they said. The addition of a question about past-year STI testing to the 2019 and future YRBS survey will promote ongoing monitoring of efforts to increase testing rates.
Teen sexual health goes beyond testing
The current study shows that routine testing for STIs according to published guidelines is low, Cynthia Holland-Hall, MD, and Andrea E. Bonny, MD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital and Ohio State University, both in Columbus, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Notably, sexually active females and males who had sex with male partners, two groups for whom annual testing is specifically recommended by multiple organizations, had testing rates of less than 30%, they said. The authors highlighted the study’s lack of information on which specific barriers, such as lack of access to the health care system, lack of knowledge, and fear of disclosure, contributed to overall low rates of testing.
However, STI testing is only one element of sexual and reproductive health care. Although opt-out testing may improve detection rates, the editorialists emphasized the need for patient-provider conversations about sex, citing recent studies showing that adolescents who spent some time alone with providers were more likely to receive sexual and reproductive health (SRH) services in the past year.
“Resources such as confidentiality policies, checklists, and written screening tools may facilitate SRH discussions,” Dr. Holland-Hall and Dr. Bonny said. “With a little practice, respect, and intention, a caring provider can take the awkward out of discussing sexual health but must not opt out of the conversation.”
Privacy and time issues exacerbate low testing rates
The current study is especially important at this time because many adolescents have likely missed well visits, and therefore important STI screens, because of disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, Karalyn Kinsella, MD, a pediatrician in private practice in Cheshire, Conn., said in an interview.
“I was surprised that the rate of screening was only one in five,” said Dr. Kinsella. “I knew it would be suboptimal, but not that low.”
According to Dr. Kinsella, there are two major barriers to increasing STI testing in adolescents in primary care. One barrier is that insurance companies will often state on the bill what the testing was for, which will lead to an uncomfortable conversation at a later date for the adolescent and parent when the bill arrives in the mail. A second barrier is when to test during a visit,. “If we obtain urine samples on all adolescents and many of them are not sexually active, we are wasting a lot of time in the short visit to obtain urine,” she explained. “If testing is scheduled for the end of the visit, they often leave without providing a urine sample.”
Overall, the study is an important reminder to general pediatricians about STI testing for sexually active teens, she emphasized.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. The editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kinsella had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
Approximately 20% of sexually active high schoolers reported testing for a sexually transmitted infection in the previous year, based on data from 2,501 respondents to the 2019 national Youth Risk Behavior Survey.
Data suggest that half of all new STIs in the United States occur in youth aged 15-24 years, and that 25% of sexually active young women in the United States have an STI, wrote Nicole Liddon, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues.
Although organizations including the American Academy of Pediatrics and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend varying degrees of routine STI screening for adolescents, data on the prevalence of testing in this population are limited, the researchers said.
However, the addition in 2019 of a question on STI testing to the national Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS) provided an opportunity to assess prevalence of STI testing, identify potential barriers, and increase screening rates, they wrote.
In a study published in Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed data from the 2019 national YRBS, an anonymous survey administered biannually to public and private high school students across the United States.
The study population included 2,501 individuals who reported sexual activity with at least one person during the 3 months prior to the survey.
Overall, 20.4% of the respondents reported being tested for an STI in the previous year, including significantly more females than males (26.1% vs. 13.7%).
The prevalence of testing among females was not significantly different according to race/ethnicity, sexual identity, or the sex of sexual contacts, but the prevalence increased with age; 12.6%, 22.8%, 28.5%, and 36.9% for females aged 15 years and younger, 16 years, 17 years, and 18 years, respectively.
Among males, no significant differences in STI testing were noted according to race/ethnicity, age, sexual identity, or sex of sexual contacts.
The researchers also analyzed prevalence of STI tested based on sexual behaviors. Among female students, the prevalence of STI testing was higher among those who reported the following behaviors, compared with those who did not: nonuse of condoms at last sexual intercourse (34.1% vs. 18.2%), substance use at last sexual intercourse (32.0% vs. 24.7%), and having four or more lifetime sex partners (31.9% vs. 24.7%).
Among male students, the prevalence of STI testing was higher among those who reported the following behaviors, compared with those who did not: sex before age 13 years (27.1% vs. 12.1%), having two or more recent sex partners (22.4% vs. 10.4%), having four or more lifetime sex partners (22.3% vs. 9.5%), and substance use at last sexual intercourse (19.2% vs. 12.1%).
The low prevalence of STI testing in teens has become more urgent in the wake of the coronavirus pandemic, the researchers wrote. “These prevalence estimates were derived before the possible profound impacts of the pandemic on adolescent sexual behavior and access to and use of health care services.”
Current guidelines allow health care providers the options for opt-out STI screening as a strategy to improve screening rates and testing; however, this option does not eliminate the need for conversations with adolescent patients about sexual activity, they emphasized.
The study findings were limited by several other factors including the inability to directly assess adherence to screening recommendations specifically, the inability to determine whether low testing rates resulted from limited access to health care or missed screening opportunities at visits, and the inclusion only of high school students but not out-of-school youth who may have more limited access to testing.
However, the results highlight the need to improve STI testing services for adolescents, and to address barriers at the individual and clinic level, they said. The addition of a question about past-year STI testing to the 2019 and future YRBS survey will promote ongoing monitoring of efforts to increase testing rates.
Teen sexual health goes beyond testing
The current study shows that routine testing for STIs according to published guidelines is low, Cynthia Holland-Hall, MD, and Andrea E. Bonny, MD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital and Ohio State University, both in Columbus, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Notably, sexually active females and males who had sex with male partners, two groups for whom annual testing is specifically recommended by multiple organizations, had testing rates of less than 30%, they said. The authors highlighted the study’s lack of information on which specific barriers, such as lack of access to the health care system, lack of knowledge, and fear of disclosure, contributed to overall low rates of testing.
However, STI testing is only one element of sexual and reproductive health care. Although opt-out testing may improve detection rates, the editorialists emphasized the need for patient-provider conversations about sex, citing recent studies showing that adolescents who spent some time alone with providers were more likely to receive sexual and reproductive health (SRH) services in the past year.
“Resources such as confidentiality policies, checklists, and written screening tools may facilitate SRH discussions,” Dr. Holland-Hall and Dr. Bonny said. “With a little practice, respect, and intention, a caring provider can take the awkward out of discussing sexual health but must not opt out of the conversation.”
Privacy and time issues exacerbate low testing rates
The current study is especially important at this time because many adolescents have likely missed well visits, and therefore important STI screens, because of disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, Karalyn Kinsella, MD, a pediatrician in private practice in Cheshire, Conn., said in an interview.
“I was surprised that the rate of screening was only one in five,” said Dr. Kinsella. “I knew it would be suboptimal, but not that low.”
According to Dr. Kinsella, there are two major barriers to increasing STI testing in adolescents in primary care. One barrier is that insurance companies will often state on the bill what the testing was for, which will lead to an uncomfortable conversation at a later date for the adolescent and parent when the bill arrives in the mail. A second barrier is when to test during a visit,. “If we obtain urine samples on all adolescents and many of them are not sexually active, we are wasting a lot of time in the short visit to obtain urine,” she explained. “If testing is scheduled for the end of the visit, they often leave without providing a urine sample.”
Overall, the study is an important reminder to general pediatricians about STI testing for sexually active teens, she emphasized.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. The editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kinsella had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Restless legs syndrome occurs often in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy
Patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD), a neurodegenerative disease, often experience gait and balance problems, as well as leg discomfort, sleep disturbances, and pain, wrote John W. Winkelman, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and colleagues. Restless legs syndrome (RLS) has been associated with neurological conditions including Parkinson’s disease, but the prevalence of RLS in ALD patients has not been examined, they said.
In a pilot study published in Sleep Medicine, the researchers identified 21 women and 11 men with ALD who were treated at a single center. The median age of the patients was 45.9 years. Twenty-seven patients had symptoms of myelopathy, with a median age of onset of 34 years.
The researchers assessed RLS severity using questionnaires and the Hopkins Telephone Diagnostic Interview (HTDI), a validated RLS assessment tool. They also reviewed patients’ charts for data on neurological examinations, functional gait measures, and laboratory assessments. Functional gait assessments included the 25-Foot Walk test (25-FW), the Timed Up and Go test (TUG), and Six Minute Walk test (6MW).
Thirteen patients (10 women and 3 men) met criteria for RLS based on the HTDI. The median age of RLS onset was 35 years. Six RLS patients (46.2%) reported using medication to relieve symptoms, and eight RLS patients had a history of antidepressant use.
In addition, six patients with RLS reported a history of anemia or iron deficiency. Ferritin levels were available for 14 patients: 8 women with RLS and 4 women and 2 men without RLS; the mean ferritin levels were 74.0 mcg/L in RLS patients and 99.5 mcg/L in those without RLS.
Of the seven ALD patients with brain lesions, all were men, only two were diagnosed with RLS, and all seven cases were mild, the researchers noted.
Overall, patients with RLS had more neurological signs and symptoms than those without RLS; the most significant were pain and gait difficulty. However, patients with RLS also were more likely than were those without RLS to report spasticity, muscle weakness, impaired coordination, hyperreflexia, impaired sensation, and paraesthesia, as well as bladder, bowel, and erectile dysfunction.
The 40.6% prevalence of RLS in patients with ALD is notably higher than that of the general population, in which the prevalence of RLS is 5%-10%, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
“Consistent with patterns observed in the general population, risk factors for RLS in this cohort of adults with ALD included female gender, increased age, lower iron indices, and use of serotonergic antidepressants,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the small size and the possible contribution of antidepressant use to the high rate of RLS, the researchers noted.
“Awareness of RLS in patients with ALD would allow for its effective treatment, which may improve the functional impairments as well as quality of life, mood, and anxiety issues in those with ALD,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding.
Dr. Winkelman disclosed ties with Advance Medical, Avadel, Disc Medicine, Eisai, Emalex, Idorsia, Noctrix, UpToDate, and Merck Pharmaceuticals, as well as research support from the National Institute on Drug Abuse and the Baszucki Brain Research Foundation. The study also was supported by grants from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the European Leukodystrophy Association, the Arrivederci Foundation, the Leblang Foundation, and the Hammer Family Fund Journal Preproof for ALD Research and Therapies for Women.
Patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD), a neurodegenerative disease, often experience gait and balance problems, as well as leg discomfort, sleep disturbances, and pain, wrote John W. Winkelman, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and colleagues. Restless legs syndrome (RLS) has been associated with neurological conditions including Parkinson’s disease, but the prevalence of RLS in ALD patients has not been examined, they said.
In a pilot study published in Sleep Medicine, the researchers identified 21 women and 11 men with ALD who were treated at a single center. The median age of the patients was 45.9 years. Twenty-seven patients had symptoms of myelopathy, with a median age of onset of 34 years.
The researchers assessed RLS severity using questionnaires and the Hopkins Telephone Diagnostic Interview (HTDI), a validated RLS assessment tool. They also reviewed patients’ charts for data on neurological examinations, functional gait measures, and laboratory assessments. Functional gait assessments included the 25-Foot Walk test (25-FW), the Timed Up and Go test (TUG), and Six Minute Walk test (6MW).
Thirteen patients (10 women and 3 men) met criteria for RLS based on the HTDI. The median age of RLS onset was 35 years. Six RLS patients (46.2%) reported using medication to relieve symptoms, and eight RLS patients had a history of antidepressant use.
In addition, six patients with RLS reported a history of anemia or iron deficiency. Ferritin levels were available for 14 patients: 8 women with RLS and 4 women and 2 men without RLS; the mean ferritin levels were 74.0 mcg/L in RLS patients and 99.5 mcg/L in those without RLS.
Of the seven ALD patients with brain lesions, all were men, only two were diagnosed with RLS, and all seven cases were mild, the researchers noted.
Overall, patients with RLS had more neurological signs and symptoms than those without RLS; the most significant were pain and gait difficulty. However, patients with RLS also were more likely than were those without RLS to report spasticity, muscle weakness, impaired coordination, hyperreflexia, impaired sensation, and paraesthesia, as well as bladder, bowel, and erectile dysfunction.
The 40.6% prevalence of RLS in patients with ALD is notably higher than that of the general population, in which the prevalence of RLS is 5%-10%, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
“Consistent with patterns observed in the general population, risk factors for RLS in this cohort of adults with ALD included female gender, increased age, lower iron indices, and use of serotonergic antidepressants,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the small size and the possible contribution of antidepressant use to the high rate of RLS, the researchers noted.
“Awareness of RLS in patients with ALD would allow for its effective treatment, which may improve the functional impairments as well as quality of life, mood, and anxiety issues in those with ALD,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding.
Dr. Winkelman disclosed ties with Advance Medical, Avadel, Disc Medicine, Eisai, Emalex, Idorsia, Noctrix, UpToDate, and Merck Pharmaceuticals, as well as research support from the National Institute on Drug Abuse and the Baszucki Brain Research Foundation. The study also was supported by grants from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the European Leukodystrophy Association, the Arrivederci Foundation, the Leblang Foundation, and the Hammer Family Fund Journal Preproof for ALD Research and Therapies for Women.
Patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD), a neurodegenerative disease, often experience gait and balance problems, as well as leg discomfort, sleep disturbances, and pain, wrote John W. Winkelman, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and colleagues. Restless legs syndrome (RLS) has been associated with neurological conditions including Parkinson’s disease, but the prevalence of RLS in ALD patients has not been examined, they said.
In a pilot study published in Sleep Medicine, the researchers identified 21 women and 11 men with ALD who were treated at a single center. The median age of the patients was 45.9 years. Twenty-seven patients had symptoms of myelopathy, with a median age of onset of 34 years.
The researchers assessed RLS severity using questionnaires and the Hopkins Telephone Diagnostic Interview (HTDI), a validated RLS assessment tool. They also reviewed patients’ charts for data on neurological examinations, functional gait measures, and laboratory assessments. Functional gait assessments included the 25-Foot Walk test (25-FW), the Timed Up and Go test (TUG), and Six Minute Walk test (6MW).
Thirteen patients (10 women and 3 men) met criteria for RLS based on the HTDI. The median age of RLS onset was 35 years. Six RLS patients (46.2%) reported using medication to relieve symptoms, and eight RLS patients had a history of antidepressant use.
In addition, six patients with RLS reported a history of anemia or iron deficiency. Ferritin levels were available for 14 patients: 8 women with RLS and 4 women and 2 men without RLS; the mean ferritin levels were 74.0 mcg/L in RLS patients and 99.5 mcg/L in those without RLS.
Of the seven ALD patients with brain lesions, all were men, only two were diagnosed with RLS, and all seven cases were mild, the researchers noted.
Overall, patients with RLS had more neurological signs and symptoms than those without RLS; the most significant were pain and gait difficulty. However, patients with RLS also were more likely than were those without RLS to report spasticity, muscle weakness, impaired coordination, hyperreflexia, impaired sensation, and paraesthesia, as well as bladder, bowel, and erectile dysfunction.
The 40.6% prevalence of RLS in patients with ALD is notably higher than that of the general population, in which the prevalence of RLS is 5%-10%, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
“Consistent with patterns observed in the general population, risk factors for RLS in this cohort of adults with ALD included female gender, increased age, lower iron indices, and use of serotonergic antidepressants,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the small size and the possible contribution of antidepressant use to the high rate of RLS, the researchers noted.
“Awareness of RLS in patients with ALD would allow for its effective treatment, which may improve the functional impairments as well as quality of life, mood, and anxiety issues in those with ALD,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding.
Dr. Winkelman disclosed ties with Advance Medical, Avadel, Disc Medicine, Eisai, Emalex, Idorsia, Noctrix, UpToDate, and Merck Pharmaceuticals, as well as research support from the National Institute on Drug Abuse and the Baszucki Brain Research Foundation. The study also was supported by grants from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the European Leukodystrophy Association, the Arrivederci Foundation, the Leblang Foundation, and the Hammer Family Fund Journal Preproof for ALD Research and Therapies for Women.
FROM SLEEP MEDICINE
Pneumonia shows strong connection to chronic otitis media
Individuals with a prior diagnosis of pneumonia were significantly more likely to develop chronic otitis media (COM) than were those without a history of pneumonia, based on data from a nationwide cohort study of more than 100,000 patients.
“Recently, middle ear diseases, including COM, have been recognized as respiratory tract diseases beyond the pathophysiological concepts of ventilation dysfunction, with recurrent infection that occurs from anatomically adjacent structures such as the middle ear, mastoid cavity, and eustachian tube,” but the potential link between pneumonia and chronic otitis media and adults in particular has not been examined, wrote Sung Kyun Kim, MD, of Hallym University, Dongtan, South Korea, and colleagues.
In a study recently published in the International Journal of Infectious Diseases, the researchers identified 23,436 adults with COM and 93,744 controls aged 40 years and older from a Korean health insurance database between 2002 and 2015.
The overall incidence of pneumonia in the study population was significantly higher in the COM group compared with controls (9.3% vs. 7.2%, P <.001). The odds ratios of pneumonia were significantly higher in the COM group compared with controls, and a history of pneumonia increased the odds of COM regardless of sex and across all ages.
Pneumonia was defined as when a patient had a diagnosis of pneumonia based on ICD-10 codes and underwent a chest x-ray or chest CT scan. Chronic otitis media was defined as when a patient had a diagnosis based on ICD-10 codes at least two times with one of the following conditions: chronic serous otitis media, chronic mucoid otitis media, other chronic nonsuppurative otitis media, unspecified nonsuppurative otitis media, chronic tubotympanic suppurative otitis media, chronic atticoantral suppurative otitis media, other chronic suppurative otitis media, or unspecified suppurative otitis media.
Age groups were divided into 5-year intervals, and patients were classified into income groups and rural vs. urban residence.
In a further sensitivity analysis, individuals who were diagnosed with pneumonia five or more times before the index date had a significantly higher odds ratio for COM compared with those with less than five diagnoses of pneumonia (adjusted odds ratio, 1.34; P < .001).
Microbiome dysbiosis may explain part of the connection between pneumonia and COM, the researchers wrote in their discussion. Pathogens in the lungs can prompt changes in the microbiome dynamics, as might the use of antibiotics, they said. In addition, “Mucus plugging in the airway caused by pneumonia induces hypoxic conditions and leads to the expression of inflammatory markers in the eustachian tube and middle ear mucosa,” they noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the retrospective design and lack of data on microbiological cultures for antibiotic susceptibility, radiologic findings on the severity of pneumonia, results of pulmonary function tests, and hearing thresholds, the researchers noted. Other limitations were the exclusion of the frequency of upper respiratory infections and antibiotic use due to lack of data, they said.
However, the results show an association between pneumonia diagnoses and increased incidence of COM, which suggests a novel perspective that “infection of the lower respiratory tract may affect the function of the eustachian tube and the middle ear to later cause COM,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Individuals with a prior diagnosis of pneumonia were significantly more likely to develop chronic otitis media (COM) than were those without a history of pneumonia, based on data from a nationwide cohort study of more than 100,000 patients.
“Recently, middle ear diseases, including COM, have been recognized as respiratory tract diseases beyond the pathophysiological concepts of ventilation dysfunction, with recurrent infection that occurs from anatomically adjacent structures such as the middle ear, mastoid cavity, and eustachian tube,” but the potential link between pneumonia and chronic otitis media and adults in particular has not been examined, wrote Sung Kyun Kim, MD, of Hallym University, Dongtan, South Korea, and colleagues.
In a study recently published in the International Journal of Infectious Diseases, the researchers identified 23,436 adults with COM and 93,744 controls aged 40 years and older from a Korean health insurance database between 2002 and 2015.
The overall incidence of pneumonia in the study population was significantly higher in the COM group compared with controls (9.3% vs. 7.2%, P <.001). The odds ratios of pneumonia were significantly higher in the COM group compared with controls, and a history of pneumonia increased the odds of COM regardless of sex and across all ages.
Pneumonia was defined as when a patient had a diagnosis of pneumonia based on ICD-10 codes and underwent a chest x-ray or chest CT scan. Chronic otitis media was defined as when a patient had a diagnosis based on ICD-10 codes at least two times with one of the following conditions: chronic serous otitis media, chronic mucoid otitis media, other chronic nonsuppurative otitis media, unspecified nonsuppurative otitis media, chronic tubotympanic suppurative otitis media, chronic atticoantral suppurative otitis media, other chronic suppurative otitis media, or unspecified suppurative otitis media.
Age groups were divided into 5-year intervals, and patients were classified into income groups and rural vs. urban residence.
In a further sensitivity analysis, individuals who were diagnosed with pneumonia five or more times before the index date had a significantly higher odds ratio for COM compared with those with less than five diagnoses of pneumonia (adjusted odds ratio, 1.34; P < .001).
Microbiome dysbiosis may explain part of the connection between pneumonia and COM, the researchers wrote in their discussion. Pathogens in the lungs can prompt changes in the microbiome dynamics, as might the use of antibiotics, they said. In addition, “Mucus plugging in the airway caused by pneumonia induces hypoxic conditions and leads to the expression of inflammatory markers in the eustachian tube and middle ear mucosa,” they noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the retrospective design and lack of data on microbiological cultures for antibiotic susceptibility, radiologic findings on the severity of pneumonia, results of pulmonary function tests, and hearing thresholds, the researchers noted. Other limitations were the exclusion of the frequency of upper respiratory infections and antibiotic use due to lack of data, they said.
However, the results show an association between pneumonia diagnoses and increased incidence of COM, which suggests a novel perspective that “infection of the lower respiratory tract may affect the function of the eustachian tube and the middle ear to later cause COM,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Individuals with a prior diagnosis of pneumonia were significantly more likely to develop chronic otitis media (COM) than were those without a history of pneumonia, based on data from a nationwide cohort study of more than 100,000 patients.
“Recently, middle ear diseases, including COM, have been recognized as respiratory tract diseases beyond the pathophysiological concepts of ventilation dysfunction, with recurrent infection that occurs from anatomically adjacent structures such as the middle ear, mastoid cavity, and eustachian tube,” but the potential link between pneumonia and chronic otitis media and adults in particular has not been examined, wrote Sung Kyun Kim, MD, of Hallym University, Dongtan, South Korea, and colleagues.
In a study recently published in the International Journal of Infectious Diseases, the researchers identified 23,436 adults with COM and 93,744 controls aged 40 years and older from a Korean health insurance database between 2002 and 2015.
The overall incidence of pneumonia in the study population was significantly higher in the COM group compared with controls (9.3% vs. 7.2%, P <.001). The odds ratios of pneumonia were significantly higher in the COM group compared with controls, and a history of pneumonia increased the odds of COM regardless of sex and across all ages.
Pneumonia was defined as when a patient had a diagnosis of pneumonia based on ICD-10 codes and underwent a chest x-ray or chest CT scan. Chronic otitis media was defined as when a patient had a diagnosis based on ICD-10 codes at least two times with one of the following conditions: chronic serous otitis media, chronic mucoid otitis media, other chronic nonsuppurative otitis media, unspecified nonsuppurative otitis media, chronic tubotympanic suppurative otitis media, chronic atticoantral suppurative otitis media, other chronic suppurative otitis media, or unspecified suppurative otitis media.
Age groups were divided into 5-year intervals, and patients were classified into income groups and rural vs. urban residence.
In a further sensitivity analysis, individuals who were diagnosed with pneumonia five or more times before the index date had a significantly higher odds ratio for COM compared with those with less than five diagnoses of pneumonia (adjusted odds ratio, 1.34; P < .001).
Microbiome dysbiosis may explain part of the connection between pneumonia and COM, the researchers wrote in their discussion. Pathogens in the lungs can prompt changes in the microbiome dynamics, as might the use of antibiotics, they said. In addition, “Mucus plugging in the airway caused by pneumonia induces hypoxic conditions and leads to the expression of inflammatory markers in the eustachian tube and middle ear mucosa,” they noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the retrospective design and lack of data on microbiological cultures for antibiotic susceptibility, radiologic findings on the severity of pneumonia, results of pulmonary function tests, and hearing thresholds, the researchers noted. Other limitations were the exclusion of the frequency of upper respiratory infections and antibiotic use due to lack of data, they said.
However, the results show an association between pneumonia diagnoses and increased incidence of COM, which suggests a novel perspective that “infection of the lower respiratory tract may affect the function of the eustachian tube and the middle ear to later cause COM,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Tebipenem pivoxil hydrobromide offers oral option for complex UTIs
“No new oral antibiotic alternative has emerged to treat these conditions in more than 25 years,” corresponding author Angela K. Talley, MD, said in an interview. The new research was published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Patients with complicated urinary tract infection (cUTI), including acute pyelonephritis (AP), are often hospitalized and treated with intravenous therapy because of the lack of oral options, especially in cases of antibiotic-resistant pathogens, explained Dr. Talley, of Spero Therapeutics.
In their new phase 3, double-blind randomized trial, the researchers evaluated the safety and effectiveness of oral TBP-PI-HBr, compared with intravenous ertapenem in hospitalized patients with cUTIs or AP. Oral tebipenem is an investigational carbapenem with demonstrated activity against uropathogenic Enterobacterales, and it has shown effectiveness in animal models, the researchers noted in their paper.
Methods and results
The researchers randomized 1,372 adult patients. The microbiologic intent-to-treat population included 449 patients who received TBP-PI-HBr (600 mg every 8 hours) and 419 who received ertapenem (1 g every 24 hours) for 7-10 days or up to 14 days for patients with bacteremia.
The primary endpoint was a composite of clinical cure and favorable microbiologic response, assessed at a test-of-cure visit on day 19. Clinical cure was defined as “complete resolution or clinically significant alleviation of baseline signs and symptoms of complicated urinary tract infection or acute pyelonephritis and no new symptoms, such that no further antimicrobial therapy was warranted,” the researchers wrote. Microbiologic response was defined as a reduction to less than 103 CFU per milliliter in uropathogen levels from baseline at day 19.
Overall, the clinical response occurred in 58.8% of patients who received TBP-PI-HBr and 61.6% of those who received ertapenem at the test-of-cure visit.
Clinical cure rates were similar in the TBP-PI-HBr and ertapenem groups (93.1% vs. 93.6%) at the test-of-cure visit.
Both treatment groups showed similar responses to Enterobacterales pathogens at the test-of-cure visit (62.7% for TBP-PI-HBr and 65.2% for ertapenem).
Among patients with bacteremia at baseline, overall response rates were 72.3% and 66.0% for TBP-PI-HBr and ertapenem, respectively, at the test-of-cure visit, and 93.6% and 96.2%, respectively, at the end-of-treatment visit on or around day 25.
The overall incidence of adverse events was approximately 26% in both treatment groups. Most adverse events were mild or moderate in severity and did not limit treatment, the researchers wrote.
The mean age of the patients was 58.1 years; 46.1% were aged 65 and older, and 11.5% had bacteremia at baseline.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the mandated 7- to 10-day course of antibiotics, which may not reflect the standard of care in other settings in the United States. The study’s trial sites were located in the United States, South Africa, and Europe. The study population was primarily White and from Central and Eastern Europe. Other limitations included the randomization of patients before confirming the baseline pathogen, although this was done to limit potential confounding from previous antibiotics, the researchers noted.
Safety and efficacy support application for approval
“To our knowledge, this is the first head-to-head evaluation of an IV vs. an oral drug for the treatment of cUTI and acute pyelonephritis,” Dr. Talley said in an interview.
“The findings demonstrate that almost all patients in the study achieved complete resolution of the signs and symptoms of their infection,” she said.
TBP-PI-HBr has not been approved by the Food and Drug Administration, but a new drug application that included data from the current study was submitted to the FDA and is currently under review, Dr. Talley noted.
As for additional research, the current study was conducted in hospitalized patients, and the use of TBP-PI-HBr in the outpatient setting has not yet been evaluated, she said.
Approval and use of oral carbapenem will change practice
The current study is very important because it provides a viable and effective alternative form of antibiotic delivery for the patients with complicated UTI, Noel N. Deep, MD, emphasized in an interview.
“Currently these patients have to be treated with IV carbapenem antibiotics either in a hospital or through a home health nurse,” Dr. Deep, a general internist in group practice in Antigo, Wisc., explained.
Current IV strategies also carry the inherent risk associated with the insertion of an IV catheter that is left in place for several days or replaced periodically. “The oral antibiotic eliminates these risks and higher health care costs and provides a safer and equally efficacious option,” Dr. Deep said.
In the current study, “I was definitely surprised at the effectiveness of the oral carbapenem,” Dr. Deep said. “I am absolutely delighted with this new treatment option that physicians can now add to their armamentarium [assuming FDA approval] as we provide care to our patients,” he said.
If approved, TBP-PI-HBr will definitely change the treatment spectrum for the multidrug-resistant bacterial UTIs, said Dr. Deep. “Carbapenems have continued to be effective and low antibiotic resistance to carbapenems has been recorded.”
As for additional research, “I would like to see studies done in other ethnicities and different countries to ascertain the effectiveness of this antibiotic in those populations and against other bacterial strains with potentially different resistance mechanisms,” Dr. Deep said.
The study was supported by Spero Therapeutics and the Department of Health and Human Services. Lead author Paul B. Eckburg, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and Dr. Talley are employees of Spero Therapeutics. Dr. Deep had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
“No new oral antibiotic alternative has emerged to treat these conditions in more than 25 years,” corresponding author Angela K. Talley, MD, said in an interview. The new research was published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Patients with complicated urinary tract infection (cUTI), including acute pyelonephritis (AP), are often hospitalized and treated with intravenous therapy because of the lack of oral options, especially in cases of antibiotic-resistant pathogens, explained Dr. Talley, of Spero Therapeutics.
In their new phase 3, double-blind randomized trial, the researchers evaluated the safety and effectiveness of oral TBP-PI-HBr, compared with intravenous ertapenem in hospitalized patients with cUTIs or AP. Oral tebipenem is an investigational carbapenem with demonstrated activity against uropathogenic Enterobacterales, and it has shown effectiveness in animal models, the researchers noted in their paper.
Methods and results
The researchers randomized 1,372 adult patients. The microbiologic intent-to-treat population included 449 patients who received TBP-PI-HBr (600 mg every 8 hours) and 419 who received ertapenem (1 g every 24 hours) for 7-10 days or up to 14 days for patients with bacteremia.
The primary endpoint was a composite of clinical cure and favorable microbiologic response, assessed at a test-of-cure visit on day 19. Clinical cure was defined as “complete resolution or clinically significant alleviation of baseline signs and symptoms of complicated urinary tract infection or acute pyelonephritis and no new symptoms, such that no further antimicrobial therapy was warranted,” the researchers wrote. Microbiologic response was defined as a reduction to less than 103 CFU per milliliter in uropathogen levels from baseline at day 19.
Overall, the clinical response occurred in 58.8% of patients who received TBP-PI-HBr and 61.6% of those who received ertapenem at the test-of-cure visit.
Clinical cure rates were similar in the TBP-PI-HBr and ertapenem groups (93.1% vs. 93.6%) at the test-of-cure visit.
Both treatment groups showed similar responses to Enterobacterales pathogens at the test-of-cure visit (62.7% for TBP-PI-HBr and 65.2% for ertapenem).
Among patients with bacteremia at baseline, overall response rates were 72.3% and 66.0% for TBP-PI-HBr and ertapenem, respectively, at the test-of-cure visit, and 93.6% and 96.2%, respectively, at the end-of-treatment visit on or around day 25.
The overall incidence of adverse events was approximately 26% in both treatment groups. Most adverse events were mild or moderate in severity and did not limit treatment, the researchers wrote.
The mean age of the patients was 58.1 years; 46.1% were aged 65 and older, and 11.5% had bacteremia at baseline.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the mandated 7- to 10-day course of antibiotics, which may not reflect the standard of care in other settings in the United States. The study’s trial sites were located in the United States, South Africa, and Europe. The study population was primarily White and from Central and Eastern Europe. Other limitations included the randomization of patients before confirming the baseline pathogen, although this was done to limit potential confounding from previous antibiotics, the researchers noted.
Safety and efficacy support application for approval
“To our knowledge, this is the first head-to-head evaluation of an IV vs. an oral drug for the treatment of cUTI and acute pyelonephritis,” Dr. Talley said in an interview.
“The findings demonstrate that almost all patients in the study achieved complete resolution of the signs and symptoms of their infection,” she said.
TBP-PI-HBr has not been approved by the Food and Drug Administration, but a new drug application that included data from the current study was submitted to the FDA and is currently under review, Dr. Talley noted.
As for additional research, the current study was conducted in hospitalized patients, and the use of TBP-PI-HBr in the outpatient setting has not yet been evaluated, she said.
Approval and use of oral carbapenem will change practice
The current study is very important because it provides a viable and effective alternative form of antibiotic delivery for the patients with complicated UTI, Noel N. Deep, MD, emphasized in an interview.
“Currently these patients have to be treated with IV carbapenem antibiotics either in a hospital or through a home health nurse,” Dr. Deep, a general internist in group practice in Antigo, Wisc., explained.
Current IV strategies also carry the inherent risk associated with the insertion of an IV catheter that is left in place for several days or replaced periodically. “The oral antibiotic eliminates these risks and higher health care costs and provides a safer and equally efficacious option,” Dr. Deep said.
In the current study, “I was definitely surprised at the effectiveness of the oral carbapenem,” Dr. Deep said. “I am absolutely delighted with this new treatment option that physicians can now add to their armamentarium [assuming FDA approval] as we provide care to our patients,” he said.
If approved, TBP-PI-HBr will definitely change the treatment spectrum for the multidrug-resistant bacterial UTIs, said Dr. Deep. “Carbapenems have continued to be effective and low antibiotic resistance to carbapenems has been recorded.”
As for additional research, “I would like to see studies done in other ethnicities and different countries to ascertain the effectiveness of this antibiotic in those populations and against other bacterial strains with potentially different resistance mechanisms,” Dr. Deep said.
The study was supported by Spero Therapeutics and the Department of Health and Human Services. Lead author Paul B. Eckburg, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and Dr. Talley are employees of Spero Therapeutics. Dr. Deep had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
“No new oral antibiotic alternative has emerged to treat these conditions in more than 25 years,” corresponding author Angela K. Talley, MD, said in an interview. The new research was published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Patients with complicated urinary tract infection (cUTI), including acute pyelonephritis (AP), are often hospitalized and treated with intravenous therapy because of the lack of oral options, especially in cases of antibiotic-resistant pathogens, explained Dr. Talley, of Spero Therapeutics.
In their new phase 3, double-blind randomized trial, the researchers evaluated the safety and effectiveness of oral TBP-PI-HBr, compared with intravenous ertapenem in hospitalized patients with cUTIs or AP. Oral tebipenem is an investigational carbapenem with demonstrated activity against uropathogenic Enterobacterales, and it has shown effectiveness in animal models, the researchers noted in their paper.
Methods and results
The researchers randomized 1,372 adult patients. The microbiologic intent-to-treat population included 449 patients who received TBP-PI-HBr (600 mg every 8 hours) and 419 who received ertapenem (1 g every 24 hours) for 7-10 days or up to 14 days for patients with bacteremia.
The primary endpoint was a composite of clinical cure and favorable microbiologic response, assessed at a test-of-cure visit on day 19. Clinical cure was defined as “complete resolution or clinically significant alleviation of baseline signs and symptoms of complicated urinary tract infection or acute pyelonephritis and no new symptoms, such that no further antimicrobial therapy was warranted,” the researchers wrote. Microbiologic response was defined as a reduction to less than 103 CFU per milliliter in uropathogen levels from baseline at day 19.
Overall, the clinical response occurred in 58.8% of patients who received TBP-PI-HBr and 61.6% of those who received ertapenem at the test-of-cure visit.
Clinical cure rates were similar in the TBP-PI-HBr and ertapenem groups (93.1% vs. 93.6%) at the test-of-cure visit.
Both treatment groups showed similar responses to Enterobacterales pathogens at the test-of-cure visit (62.7% for TBP-PI-HBr and 65.2% for ertapenem).
Among patients with bacteremia at baseline, overall response rates were 72.3% and 66.0% for TBP-PI-HBr and ertapenem, respectively, at the test-of-cure visit, and 93.6% and 96.2%, respectively, at the end-of-treatment visit on or around day 25.
The overall incidence of adverse events was approximately 26% in both treatment groups. Most adverse events were mild or moderate in severity and did not limit treatment, the researchers wrote.
The mean age of the patients was 58.1 years; 46.1% were aged 65 and older, and 11.5% had bacteremia at baseline.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the mandated 7- to 10-day course of antibiotics, which may not reflect the standard of care in other settings in the United States. The study’s trial sites were located in the United States, South Africa, and Europe. The study population was primarily White and from Central and Eastern Europe. Other limitations included the randomization of patients before confirming the baseline pathogen, although this was done to limit potential confounding from previous antibiotics, the researchers noted.
Safety and efficacy support application for approval
“To our knowledge, this is the first head-to-head evaluation of an IV vs. an oral drug for the treatment of cUTI and acute pyelonephritis,” Dr. Talley said in an interview.
“The findings demonstrate that almost all patients in the study achieved complete resolution of the signs and symptoms of their infection,” she said.
TBP-PI-HBr has not been approved by the Food and Drug Administration, but a new drug application that included data from the current study was submitted to the FDA and is currently under review, Dr. Talley noted.
As for additional research, the current study was conducted in hospitalized patients, and the use of TBP-PI-HBr in the outpatient setting has not yet been evaluated, she said.
Approval and use of oral carbapenem will change practice
The current study is very important because it provides a viable and effective alternative form of antibiotic delivery for the patients with complicated UTI, Noel N. Deep, MD, emphasized in an interview.
“Currently these patients have to be treated with IV carbapenem antibiotics either in a hospital or through a home health nurse,” Dr. Deep, a general internist in group practice in Antigo, Wisc., explained.
Current IV strategies also carry the inherent risk associated with the insertion of an IV catheter that is left in place for several days or replaced periodically. “The oral antibiotic eliminates these risks and higher health care costs and provides a safer and equally efficacious option,” Dr. Deep said.
In the current study, “I was definitely surprised at the effectiveness of the oral carbapenem,” Dr. Deep said. “I am absolutely delighted with this new treatment option that physicians can now add to their armamentarium [assuming FDA approval] as we provide care to our patients,” he said.
If approved, TBP-PI-HBr will definitely change the treatment spectrum for the multidrug-resistant bacterial UTIs, said Dr. Deep. “Carbapenems have continued to be effective and low antibiotic resistance to carbapenems has been recorded.”
As for additional research, “I would like to see studies done in other ethnicities and different countries to ascertain the effectiveness of this antibiotic in those populations and against other bacterial strains with potentially different resistance mechanisms,” Dr. Deep said.
The study was supported by Spero Therapeutics and the Department of Health and Human Services. Lead author Paul B. Eckburg, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and Dr. Talley are employees of Spero Therapeutics. Dr. Deep had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE