User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Case reports underscore risk of cerebral edema, AFCE in children with COVID-19
according to pediatric neurologists who are urging colleagues to watch out for similar cases.
At least one other child in the United States has died after becoming infected with the virus and developing cerebral edema. “The rapid and devastating clinical course in both of these cases highlights the need for early recognition of a cerebral edema and AFCE as potential complications of COVID-19 in pediatric patients,” the neurologists wrote.
The case was highlighted in a poster presented at the annual meeting of the Child Neurology Society and in a report published earlier this year in Child Neurology Open.
According to pediatric neurologist Timothy Gershon, MD, PhD , of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, the child appeared in clinic in July 2020. She had been healthy but was suffering from 1 day of fever, seizure-like activity (generalized convulsions and drooling), anorexia, and lethargy.
The girl, who was subsequently diagnosed with COVID-19, deteriorated in the hospital. “She received IV dexamethasone in attempts to reduce cerebral edema,” the neurologists wrote. “Regarding immunomodulatory therapy, she received intravenous immunoglobulin (2 g/kg), anakinra, and hydrocortisone; despite approval for remdesivir and COVID-19 convalescent plasma, these were ultimately withheld due to poor prognosis.”
Brain death examinations at 24 and 48 hours after cardiac arrest were consistent with brain death, they reported.
Neurologists believe the patient suffered from AFCE, “an often fatal pediatric clinical entity consisting of fever, encephalopathy, and new-onset seizures followed by rapid, diffuse, and medically-refractory cerebral edema.” They add that “AFCE occurs as a rare complication of a variety of common pediatric infections, and a CNS [central nervous system] pathogen is identified in only a minority of cases, suggesting a para-infectious mechanism of edema.”
Neurologists offered a case definition of the “recently recognized” AFCE earlier this year.
“This was an extremely rare rapid progression to cerebral edema. I think it was related to the patient’s COVID infection, but why this patient got it and others don’t is unknown,” Dr. Gershon said in an interview. “The full spectrum of neurological complications of COVID were not yet known [at the time]. We didn’t know, and still don’t know, what the causative links are between COVID and suddenly having seizures and brain swelling.”
He said he’d treat a similar patient differently now and give dexamethasone earlier in the clinical course, although “there is no data to tell us if any therapy could have reversed it.” Specifically, he said, “I’d give dexamethasone at the first sign of brain involvement, using the dosing recommended for cerebral edema, and try to get the MRI earlier in the course.”
Dr. Gershon and colleagues noted another case of fatal cerebral edema in a child, a 7-year-old boy who was treated in New York state. That case “shows that fatal cerebral edema may complicate pediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome,” they wrote.
Pediatric critical care specialist Preetha Krishnan, MD, of Randall Children’s Hospital at Legacy Emanuel in Portland, Ore., helped develop the new definition of AFCE. In an interview, she said AFCE is difficult to diagnose because the signs/symptoms – such as fever, altered sensorium, and seizures – are found in other conditions such as febrile status epilepticus with a viral illness.
“The key to recognition of AFCE is that unlike other disease processes, these children have rapid neurologic progression,” she said. “In addition, many of our AFCE patients also had vomiting and/or headache, which in retrospect was likely an indication of elevated ICP [intracranial pressure] rather than viral infection.”
She added that “if a child with fever, seizures, and encephalopathy has cerebral edema on imaging and/or has neurologic progression, AFCE should be considered. Most of our cases of AFCE had fulminant progression within the first 3 days of their head imaging noting cerebral edema. There are other neurologic diseases, such as acute necrotizing encephalopathy of childhood, that also have progressive signs/symptoms, but head imaging and lab work should help differentiate many of these etiologies.”
In regard to treatment, she said, “our unit would likely err on the side of providing as much neuroprotective measures as is reasonable, such as maintaining normothermia, consideration of hyperosmolar therapy, maintaining normocarbia and normoxemia, managing seizures, etc. I would recommend getting the entire neurocritical care team involved in the management discussion. This varies by center, but will likely include neurology, ID [infectious disease], possibly neurosurgery, and PICU.”
As for the new case report, Krishnan said COVID-19 has been linked to neurologic complications, “so it does not surprise me that AFCE is part of the neurologic spectrum of disease.”
No funding was reported, and the authors report no relevant disclosures. Dr. Krishnan has no disclosures.
according to pediatric neurologists who are urging colleagues to watch out for similar cases.
At least one other child in the United States has died after becoming infected with the virus and developing cerebral edema. “The rapid and devastating clinical course in both of these cases highlights the need for early recognition of a cerebral edema and AFCE as potential complications of COVID-19 in pediatric patients,” the neurologists wrote.
The case was highlighted in a poster presented at the annual meeting of the Child Neurology Society and in a report published earlier this year in Child Neurology Open.
According to pediatric neurologist Timothy Gershon, MD, PhD , of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, the child appeared in clinic in July 2020. She had been healthy but was suffering from 1 day of fever, seizure-like activity (generalized convulsions and drooling), anorexia, and lethargy.
The girl, who was subsequently diagnosed with COVID-19, deteriorated in the hospital. “She received IV dexamethasone in attempts to reduce cerebral edema,” the neurologists wrote. “Regarding immunomodulatory therapy, she received intravenous immunoglobulin (2 g/kg), anakinra, and hydrocortisone; despite approval for remdesivir and COVID-19 convalescent plasma, these were ultimately withheld due to poor prognosis.”
Brain death examinations at 24 and 48 hours after cardiac arrest were consistent with brain death, they reported.
Neurologists believe the patient suffered from AFCE, “an often fatal pediatric clinical entity consisting of fever, encephalopathy, and new-onset seizures followed by rapid, diffuse, and medically-refractory cerebral edema.” They add that “AFCE occurs as a rare complication of a variety of common pediatric infections, and a CNS [central nervous system] pathogen is identified in only a minority of cases, suggesting a para-infectious mechanism of edema.”
Neurologists offered a case definition of the “recently recognized” AFCE earlier this year.
“This was an extremely rare rapid progression to cerebral edema. I think it was related to the patient’s COVID infection, but why this patient got it and others don’t is unknown,” Dr. Gershon said in an interview. “The full spectrum of neurological complications of COVID were not yet known [at the time]. We didn’t know, and still don’t know, what the causative links are between COVID and suddenly having seizures and brain swelling.”
He said he’d treat a similar patient differently now and give dexamethasone earlier in the clinical course, although “there is no data to tell us if any therapy could have reversed it.” Specifically, he said, “I’d give dexamethasone at the first sign of brain involvement, using the dosing recommended for cerebral edema, and try to get the MRI earlier in the course.”
Dr. Gershon and colleagues noted another case of fatal cerebral edema in a child, a 7-year-old boy who was treated in New York state. That case “shows that fatal cerebral edema may complicate pediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome,” they wrote.
Pediatric critical care specialist Preetha Krishnan, MD, of Randall Children’s Hospital at Legacy Emanuel in Portland, Ore., helped develop the new definition of AFCE. In an interview, she said AFCE is difficult to diagnose because the signs/symptoms – such as fever, altered sensorium, and seizures – are found in other conditions such as febrile status epilepticus with a viral illness.
“The key to recognition of AFCE is that unlike other disease processes, these children have rapid neurologic progression,” she said. “In addition, many of our AFCE patients also had vomiting and/or headache, which in retrospect was likely an indication of elevated ICP [intracranial pressure] rather than viral infection.”
She added that “if a child with fever, seizures, and encephalopathy has cerebral edema on imaging and/or has neurologic progression, AFCE should be considered. Most of our cases of AFCE had fulminant progression within the first 3 days of their head imaging noting cerebral edema. There are other neurologic diseases, such as acute necrotizing encephalopathy of childhood, that also have progressive signs/symptoms, but head imaging and lab work should help differentiate many of these etiologies.”
In regard to treatment, she said, “our unit would likely err on the side of providing as much neuroprotective measures as is reasonable, such as maintaining normothermia, consideration of hyperosmolar therapy, maintaining normocarbia and normoxemia, managing seizures, etc. I would recommend getting the entire neurocritical care team involved in the management discussion. This varies by center, but will likely include neurology, ID [infectious disease], possibly neurosurgery, and PICU.”
As for the new case report, Krishnan said COVID-19 has been linked to neurologic complications, “so it does not surprise me that AFCE is part of the neurologic spectrum of disease.”
No funding was reported, and the authors report no relevant disclosures. Dr. Krishnan has no disclosures.
according to pediatric neurologists who are urging colleagues to watch out for similar cases.
At least one other child in the United States has died after becoming infected with the virus and developing cerebral edema. “The rapid and devastating clinical course in both of these cases highlights the need for early recognition of a cerebral edema and AFCE as potential complications of COVID-19 in pediatric patients,” the neurologists wrote.
The case was highlighted in a poster presented at the annual meeting of the Child Neurology Society and in a report published earlier this year in Child Neurology Open.
According to pediatric neurologist Timothy Gershon, MD, PhD , of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, the child appeared in clinic in July 2020. She had been healthy but was suffering from 1 day of fever, seizure-like activity (generalized convulsions and drooling), anorexia, and lethargy.
The girl, who was subsequently diagnosed with COVID-19, deteriorated in the hospital. “She received IV dexamethasone in attempts to reduce cerebral edema,” the neurologists wrote. “Regarding immunomodulatory therapy, she received intravenous immunoglobulin (2 g/kg), anakinra, and hydrocortisone; despite approval for remdesivir and COVID-19 convalescent plasma, these were ultimately withheld due to poor prognosis.”
Brain death examinations at 24 and 48 hours after cardiac arrest were consistent with brain death, they reported.
Neurologists believe the patient suffered from AFCE, “an often fatal pediatric clinical entity consisting of fever, encephalopathy, and new-onset seizures followed by rapid, diffuse, and medically-refractory cerebral edema.” They add that “AFCE occurs as a rare complication of a variety of common pediatric infections, and a CNS [central nervous system] pathogen is identified in only a minority of cases, suggesting a para-infectious mechanism of edema.”
Neurologists offered a case definition of the “recently recognized” AFCE earlier this year.
“This was an extremely rare rapid progression to cerebral edema. I think it was related to the patient’s COVID infection, but why this patient got it and others don’t is unknown,” Dr. Gershon said in an interview. “The full spectrum of neurological complications of COVID were not yet known [at the time]. We didn’t know, and still don’t know, what the causative links are between COVID and suddenly having seizures and brain swelling.”
He said he’d treat a similar patient differently now and give dexamethasone earlier in the clinical course, although “there is no data to tell us if any therapy could have reversed it.” Specifically, he said, “I’d give dexamethasone at the first sign of brain involvement, using the dosing recommended for cerebral edema, and try to get the MRI earlier in the course.”
Dr. Gershon and colleagues noted another case of fatal cerebral edema in a child, a 7-year-old boy who was treated in New York state. That case “shows that fatal cerebral edema may complicate pediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome,” they wrote.
Pediatric critical care specialist Preetha Krishnan, MD, of Randall Children’s Hospital at Legacy Emanuel in Portland, Ore., helped develop the new definition of AFCE. In an interview, she said AFCE is difficult to diagnose because the signs/symptoms – such as fever, altered sensorium, and seizures – are found in other conditions such as febrile status epilepticus with a viral illness.
“The key to recognition of AFCE is that unlike other disease processes, these children have rapid neurologic progression,” she said. “In addition, many of our AFCE patients also had vomiting and/or headache, which in retrospect was likely an indication of elevated ICP [intracranial pressure] rather than viral infection.”
She added that “if a child with fever, seizures, and encephalopathy has cerebral edema on imaging and/or has neurologic progression, AFCE should be considered. Most of our cases of AFCE had fulminant progression within the first 3 days of their head imaging noting cerebral edema. There are other neurologic diseases, such as acute necrotizing encephalopathy of childhood, that also have progressive signs/symptoms, but head imaging and lab work should help differentiate many of these etiologies.”
In regard to treatment, she said, “our unit would likely err on the side of providing as much neuroprotective measures as is reasonable, such as maintaining normothermia, consideration of hyperosmolar therapy, maintaining normocarbia and normoxemia, managing seizures, etc. I would recommend getting the entire neurocritical care team involved in the management discussion. This varies by center, but will likely include neurology, ID [infectious disease], possibly neurosurgery, and PICU.”
As for the new case report, Krishnan said COVID-19 has been linked to neurologic complications, “so it does not surprise me that AFCE is part of the neurologic spectrum of disease.”
No funding was reported, and the authors report no relevant disclosures. Dr. Krishnan has no disclosures.
FROM CNS 2021
Merck’s new COVID-19 pill: ‘Game changer’ or just one more tool?
Soon after Merck announced on Oct. 1 that it would ask federal regulators for emergency use authorization (EUA) for its auspicious new COVID-19 pill, the accolades began.
Former Food and Drug Administration chief Scott Gottlieb, MD, told CNBC the drug was “a profound game changer.” Top infectious disease expert Anthony S. Fauci, MD, called the early data “impressive.” The World Health Organization termed it “certainly good news,” while saying it awaits more data.
Merck, partnering with Ridgeback Biotherapeutics on the investigational oral antiviral medicine molnupiravir, plans to submit applications to regulatory agencies worldwide, hoping to deliver the first oral antiviral medication for COVID-19.
Interim clinical trial results show that the drug may slash the risk for hospitalization or death by 50% in those with mild to moderate COVID-19.
When the results were found to be so favorable, the study was halted at the recommendation of an independent data-monitoring committee and in consultation with the FDA.
“This anticipated drug has gotten a little more hype than it deserves,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn. He and others suggest a reality check.
“It’s not exactly a home run, like penicillin for strep throat,” agreed Carl Fichtenbaum, MD, professor of infectious diseases at the University of Cincinnati, who is investigating a similar pill for a rival company, Atea, partnering with Roche.
“But it is encouraging,” he said. “It will probably be an incremental improvement on what we have.” The fact that it can be taken at home is a plus: “Anything we can do to keep people from getting sicker is a good thing.”
“The data show in this higher risk group [those who were studied had at least one risk factor for severe COVID-19, such as age or a medical condition], it reduces the risk of advancing to severe disease by 50%,” Dr. Schaffner said. While that’s a clear benefit for half, it of course leaves the other half without benefit, he said.
Others critiqued the predicted cost of the drug. The U.S. government has already agreed to pay about $700 per patient, according to a new report from Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, and King’s College Hospital, London. That analysis concluded that the actual cost of production for the 5-day course is $17.74.
“We fully expect that having an oral treatment that reduces the risk of hospitalizations will be significantly cost effective for society,” Melissa Moody, a Merck spokesperson, told this news organization. “We are optimistic that molnupiravir can become an important medicine as part of the global effort to fight the pandemic.”
Merck expects to produce 10 million courses of treatment by the end of the year, with additional doses expected to be produced in 2022, according to a company press release. Earlier in 2021, Merck finalized its agreement with the U.S. government to supply about 1.7 million courses of the drug at the $700 price, once an EUA or FDA approval is given.
Merck also has supply and purchase agreements with other governments worldwide, pending regulatory approval.
Study details
Details about the study findings came from a Merck press release. In the planned interim analysis, Merck and Ridgeback evaluated data from 775 patients initially enrolled in the phase 3 MOVe-OUT trial.
All adults had lab-confirmed mild to moderate COVID-19, and reported onset of symptoms within 5 days of being randomly assigned to the drug or placebo. All had at least one risk factor linked with poor disease outcome (such as older age or obesity).
The drug is a ribonucleoside and works by creating mutations in the virus’s genome, halting the ability of the virus to replicate.
Through day 29 of the study, the drug reduced the risk or hospitalization or death by about 50%. While 7.3% of those who received the drug either died or were hospitalized by day 29, 14.1% of those on placebo did, a statistically significant difference (P = .0012).
Side effects were similar in both groups, with 35% of the drug-treated and 40% of the placebo group reporting some side effect, Merck reported. Adverse drug-related events were 12% in the drug group and 11% in the placebo group. While 1.3% of the drug-treated group quit the study because of an adverse event, 3.4% of the placebo group quit.
Pros, cons, and unknowns
The ability to take the drug orally, and at home, is a definite plus, Dr. Schaffner said, compared with the monoclonal antibody treatment currently approved that must be given intravenously or subcutaneously and in certain locations.
More people could be reached and helped with the option of an at-home, oral medicine, he and others agreed.
The regimen for molnupiravir is four pills, two times daily, for 5 days, even if symptoms are mild. As with other prescription drugs, “there will always be folks who don’t comply completely” with the prescribed regimen, Dr. Schaffner said. With this pill, that might be especially true if the symptoms are very mild.
The 50% reduction is not as effective as the benefit often quoted for monoclonal antibody treatment. In clinical trials of Regeneron’s monoclonal antibody treatment, the regimen reduced COVID-19–related hospitalization or death in high-risk patients by 70%.
Even so, the new pill could change the pandemic’s course, others say. “I think molnupiravir has the potential to change how we take care of people who have COVID and risk factors for developing severe disease,” Rajesh Tim Gandhi, MD, an infectious disease physician at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, told this news organization.
“What we’ll need to do, however, is make sure that people get tested quickly after they develop symptoms and, if they’re confirmed to have COVID, start on the pills within 5 days of developing symptoms,” he said, while warning that more data are needed about the drug and the trial results.
Another concern is that the promise of a pill will stall vaccination rates, with some people figuring why get vaccinated when they can obtain the pill if they do get sick.
Relying on treatment alone won’t work, Dr. Schaffner said. “Let’s [also] focus on prevention, which is the vaccine. We have to keep working both sides of the street.”
Dr. Gandhi added: “It’s important to remember that even though molnupiravir reduced the likelihood of hospitalization and death, a number of people who received the drug still got sick enough to end up in the hospital.”
Also unknown, he said, is how severe their disease was and whether they will develop long COVID.
The Merck study included only unvaccinated people. Might it work for those vaccinated people who get a breakthrough infection? “From a purely scientific perspective, there is no reason to believe molnupiravir would not work in people who are vaccinated, but the overall efficacy on top of the vaccine is likely dependent on how well they were able to mount a protective immune response to the vaccine,” Ms. Moody said. Still, Merck believes the pill could be of benefit for these infections too, she added.
As for the expected cost, Ms. Moody said that the company takes into account a number of factors in setting pricing, “but fundamentally we look at the impact of the disease, the benefits that the drug delivers to patients and to society, and at supporting ongoing drug development.”
On Merck’s heels: Pfizer, Roche, Atea
Pfizer is studying an antiviral pill, PF-07321332, a protease inhibitor that blocks the protease enzymes and halts replication of the virus.
In addition to studying the drug in infected patients at high risk of severe illness and in those at typical risk, Pfizer launched a phase 2-3 study in late September that will enroll people who live in the same household as a person with a confirmed, symptomatic COVID-19 infection to see if the drug can prevent disease in those who have been exposed.
Atea and Roche’s COVID pill, AT527, is in phase 3 trials as well. AT527 is an inhibitor of polymerase, an enzyme many viruses have, to stop replications. Atea is evaluating the drug to reduce disease “burden” and for both pre- and postexposure prevention.
Big picture: Role of COVID-19 pills
It may be necessary to target the coronavirus with more than one antiviral agent, said Dr. Fichtenbaum, a principal investigator for the AT527 trials.
“Sometimes viruses require two or three active agents to control their replication,” he said, citing information gleaned from other viral research, such as HIV. For control of HIV infection, a cocktail or combination of antivirals is often recommended.
That may well be the case for COVID-19, Dr. Fichtenbaum said. The goal would be to attack the virus at more than one pathway.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Soon after Merck announced on Oct. 1 that it would ask federal regulators for emergency use authorization (EUA) for its auspicious new COVID-19 pill, the accolades began.
Former Food and Drug Administration chief Scott Gottlieb, MD, told CNBC the drug was “a profound game changer.” Top infectious disease expert Anthony S. Fauci, MD, called the early data “impressive.” The World Health Organization termed it “certainly good news,” while saying it awaits more data.
Merck, partnering with Ridgeback Biotherapeutics on the investigational oral antiviral medicine molnupiravir, plans to submit applications to regulatory agencies worldwide, hoping to deliver the first oral antiviral medication for COVID-19.
Interim clinical trial results show that the drug may slash the risk for hospitalization or death by 50% in those with mild to moderate COVID-19.
When the results were found to be so favorable, the study was halted at the recommendation of an independent data-monitoring committee and in consultation with the FDA.
“This anticipated drug has gotten a little more hype than it deserves,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn. He and others suggest a reality check.
“It’s not exactly a home run, like penicillin for strep throat,” agreed Carl Fichtenbaum, MD, professor of infectious diseases at the University of Cincinnati, who is investigating a similar pill for a rival company, Atea, partnering with Roche.
“But it is encouraging,” he said. “It will probably be an incremental improvement on what we have.” The fact that it can be taken at home is a plus: “Anything we can do to keep people from getting sicker is a good thing.”
“The data show in this higher risk group [those who were studied had at least one risk factor for severe COVID-19, such as age or a medical condition], it reduces the risk of advancing to severe disease by 50%,” Dr. Schaffner said. While that’s a clear benefit for half, it of course leaves the other half without benefit, he said.
Others critiqued the predicted cost of the drug. The U.S. government has already agreed to pay about $700 per patient, according to a new report from Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, and King’s College Hospital, London. That analysis concluded that the actual cost of production for the 5-day course is $17.74.
“We fully expect that having an oral treatment that reduces the risk of hospitalizations will be significantly cost effective for society,” Melissa Moody, a Merck spokesperson, told this news organization. “We are optimistic that molnupiravir can become an important medicine as part of the global effort to fight the pandemic.”
Merck expects to produce 10 million courses of treatment by the end of the year, with additional doses expected to be produced in 2022, according to a company press release. Earlier in 2021, Merck finalized its agreement with the U.S. government to supply about 1.7 million courses of the drug at the $700 price, once an EUA or FDA approval is given.
Merck also has supply and purchase agreements with other governments worldwide, pending regulatory approval.
Study details
Details about the study findings came from a Merck press release. In the planned interim analysis, Merck and Ridgeback evaluated data from 775 patients initially enrolled in the phase 3 MOVe-OUT trial.
All adults had lab-confirmed mild to moderate COVID-19, and reported onset of symptoms within 5 days of being randomly assigned to the drug or placebo. All had at least one risk factor linked with poor disease outcome (such as older age or obesity).
The drug is a ribonucleoside and works by creating mutations in the virus’s genome, halting the ability of the virus to replicate.
Through day 29 of the study, the drug reduced the risk or hospitalization or death by about 50%. While 7.3% of those who received the drug either died or were hospitalized by day 29, 14.1% of those on placebo did, a statistically significant difference (P = .0012).
Side effects were similar in both groups, with 35% of the drug-treated and 40% of the placebo group reporting some side effect, Merck reported. Adverse drug-related events were 12% in the drug group and 11% in the placebo group. While 1.3% of the drug-treated group quit the study because of an adverse event, 3.4% of the placebo group quit.
Pros, cons, and unknowns
The ability to take the drug orally, and at home, is a definite plus, Dr. Schaffner said, compared with the monoclonal antibody treatment currently approved that must be given intravenously or subcutaneously and in certain locations.
More people could be reached and helped with the option of an at-home, oral medicine, he and others agreed.
The regimen for molnupiravir is four pills, two times daily, for 5 days, even if symptoms are mild. As with other prescription drugs, “there will always be folks who don’t comply completely” with the prescribed regimen, Dr. Schaffner said. With this pill, that might be especially true if the symptoms are very mild.
The 50% reduction is not as effective as the benefit often quoted for monoclonal antibody treatment. In clinical trials of Regeneron’s monoclonal antibody treatment, the regimen reduced COVID-19–related hospitalization or death in high-risk patients by 70%.
Even so, the new pill could change the pandemic’s course, others say. “I think molnupiravir has the potential to change how we take care of people who have COVID and risk factors for developing severe disease,” Rajesh Tim Gandhi, MD, an infectious disease physician at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, told this news organization.
“What we’ll need to do, however, is make sure that people get tested quickly after they develop symptoms and, if they’re confirmed to have COVID, start on the pills within 5 days of developing symptoms,” he said, while warning that more data are needed about the drug and the trial results.
Another concern is that the promise of a pill will stall vaccination rates, with some people figuring why get vaccinated when they can obtain the pill if they do get sick.
Relying on treatment alone won’t work, Dr. Schaffner said. “Let’s [also] focus on prevention, which is the vaccine. We have to keep working both sides of the street.”
Dr. Gandhi added: “It’s important to remember that even though molnupiravir reduced the likelihood of hospitalization and death, a number of people who received the drug still got sick enough to end up in the hospital.”
Also unknown, he said, is how severe their disease was and whether they will develop long COVID.
The Merck study included only unvaccinated people. Might it work for those vaccinated people who get a breakthrough infection? “From a purely scientific perspective, there is no reason to believe molnupiravir would not work in people who are vaccinated, but the overall efficacy on top of the vaccine is likely dependent on how well they were able to mount a protective immune response to the vaccine,” Ms. Moody said. Still, Merck believes the pill could be of benefit for these infections too, she added.
As for the expected cost, Ms. Moody said that the company takes into account a number of factors in setting pricing, “but fundamentally we look at the impact of the disease, the benefits that the drug delivers to patients and to society, and at supporting ongoing drug development.”
On Merck’s heels: Pfizer, Roche, Atea
Pfizer is studying an antiviral pill, PF-07321332, a protease inhibitor that blocks the protease enzymes and halts replication of the virus.
In addition to studying the drug in infected patients at high risk of severe illness and in those at typical risk, Pfizer launched a phase 2-3 study in late September that will enroll people who live in the same household as a person with a confirmed, symptomatic COVID-19 infection to see if the drug can prevent disease in those who have been exposed.
Atea and Roche’s COVID pill, AT527, is in phase 3 trials as well. AT527 is an inhibitor of polymerase, an enzyme many viruses have, to stop replications. Atea is evaluating the drug to reduce disease “burden” and for both pre- and postexposure prevention.
Big picture: Role of COVID-19 pills
It may be necessary to target the coronavirus with more than one antiviral agent, said Dr. Fichtenbaum, a principal investigator for the AT527 trials.
“Sometimes viruses require two or three active agents to control their replication,” he said, citing information gleaned from other viral research, such as HIV. For control of HIV infection, a cocktail or combination of antivirals is often recommended.
That may well be the case for COVID-19, Dr. Fichtenbaum said. The goal would be to attack the virus at more than one pathway.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Soon after Merck announced on Oct. 1 that it would ask federal regulators for emergency use authorization (EUA) for its auspicious new COVID-19 pill, the accolades began.
Former Food and Drug Administration chief Scott Gottlieb, MD, told CNBC the drug was “a profound game changer.” Top infectious disease expert Anthony S. Fauci, MD, called the early data “impressive.” The World Health Organization termed it “certainly good news,” while saying it awaits more data.
Merck, partnering with Ridgeback Biotherapeutics on the investigational oral antiviral medicine molnupiravir, plans to submit applications to regulatory agencies worldwide, hoping to deliver the first oral antiviral medication for COVID-19.
Interim clinical trial results show that the drug may slash the risk for hospitalization or death by 50% in those with mild to moderate COVID-19.
When the results were found to be so favorable, the study was halted at the recommendation of an independent data-monitoring committee and in consultation with the FDA.
“This anticipated drug has gotten a little more hype than it deserves,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn. He and others suggest a reality check.
“It’s not exactly a home run, like penicillin for strep throat,” agreed Carl Fichtenbaum, MD, professor of infectious diseases at the University of Cincinnati, who is investigating a similar pill for a rival company, Atea, partnering with Roche.
“But it is encouraging,” he said. “It will probably be an incremental improvement on what we have.” The fact that it can be taken at home is a plus: “Anything we can do to keep people from getting sicker is a good thing.”
“The data show in this higher risk group [those who were studied had at least one risk factor for severe COVID-19, such as age or a medical condition], it reduces the risk of advancing to severe disease by 50%,” Dr. Schaffner said. While that’s a clear benefit for half, it of course leaves the other half without benefit, he said.
Others critiqued the predicted cost of the drug. The U.S. government has already agreed to pay about $700 per patient, according to a new report from Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, and King’s College Hospital, London. That analysis concluded that the actual cost of production for the 5-day course is $17.74.
“We fully expect that having an oral treatment that reduces the risk of hospitalizations will be significantly cost effective for society,” Melissa Moody, a Merck spokesperson, told this news organization. “We are optimistic that molnupiravir can become an important medicine as part of the global effort to fight the pandemic.”
Merck expects to produce 10 million courses of treatment by the end of the year, with additional doses expected to be produced in 2022, according to a company press release. Earlier in 2021, Merck finalized its agreement with the U.S. government to supply about 1.7 million courses of the drug at the $700 price, once an EUA or FDA approval is given.
Merck also has supply and purchase agreements with other governments worldwide, pending regulatory approval.
Study details
Details about the study findings came from a Merck press release. In the planned interim analysis, Merck and Ridgeback evaluated data from 775 patients initially enrolled in the phase 3 MOVe-OUT trial.
All adults had lab-confirmed mild to moderate COVID-19, and reported onset of symptoms within 5 days of being randomly assigned to the drug or placebo. All had at least one risk factor linked with poor disease outcome (such as older age or obesity).
The drug is a ribonucleoside and works by creating mutations in the virus’s genome, halting the ability of the virus to replicate.
Through day 29 of the study, the drug reduced the risk or hospitalization or death by about 50%. While 7.3% of those who received the drug either died or were hospitalized by day 29, 14.1% of those on placebo did, a statistically significant difference (P = .0012).
Side effects were similar in both groups, with 35% of the drug-treated and 40% of the placebo group reporting some side effect, Merck reported. Adverse drug-related events were 12% in the drug group and 11% in the placebo group. While 1.3% of the drug-treated group quit the study because of an adverse event, 3.4% of the placebo group quit.
Pros, cons, and unknowns
The ability to take the drug orally, and at home, is a definite plus, Dr. Schaffner said, compared with the monoclonal antibody treatment currently approved that must be given intravenously or subcutaneously and in certain locations.
More people could be reached and helped with the option of an at-home, oral medicine, he and others agreed.
The regimen for molnupiravir is four pills, two times daily, for 5 days, even if symptoms are mild. As with other prescription drugs, “there will always be folks who don’t comply completely” with the prescribed regimen, Dr. Schaffner said. With this pill, that might be especially true if the symptoms are very mild.
The 50% reduction is not as effective as the benefit often quoted for monoclonal antibody treatment. In clinical trials of Regeneron’s monoclonal antibody treatment, the regimen reduced COVID-19–related hospitalization or death in high-risk patients by 70%.
Even so, the new pill could change the pandemic’s course, others say. “I think molnupiravir has the potential to change how we take care of people who have COVID and risk factors for developing severe disease,” Rajesh Tim Gandhi, MD, an infectious disease physician at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, told this news organization.
“What we’ll need to do, however, is make sure that people get tested quickly after they develop symptoms and, if they’re confirmed to have COVID, start on the pills within 5 days of developing symptoms,” he said, while warning that more data are needed about the drug and the trial results.
Another concern is that the promise of a pill will stall vaccination rates, with some people figuring why get vaccinated when they can obtain the pill if they do get sick.
Relying on treatment alone won’t work, Dr. Schaffner said. “Let’s [also] focus on prevention, which is the vaccine. We have to keep working both sides of the street.”
Dr. Gandhi added: “It’s important to remember that even though molnupiravir reduced the likelihood of hospitalization and death, a number of people who received the drug still got sick enough to end up in the hospital.”
Also unknown, he said, is how severe their disease was and whether they will develop long COVID.
The Merck study included only unvaccinated people. Might it work for those vaccinated people who get a breakthrough infection? “From a purely scientific perspective, there is no reason to believe molnupiravir would not work in people who are vaccinated, but the overall efficacy on top of the vaccine is likely dependent on how well they were able to mount a protective immune response to the vaccine,” Ms. Moody said. Still, Merck believes the pill could be of benefit for these infections too, she added.
As for the expected cost, Ms. Moody said that the company takes into account a number of factors in setting pricing, “but fundamentally we look at the impact of the disease, the benefits that the drug delivers to patients and to society, and at supporting ongoing drug development.”
On Merck’s heels: Pfizer, Roche, Atea
Pfizer is studying an antiviral pill, PF-07321332, a protease inhibitor that blocks the protease enzymes and halts replication of the virus.
In addition to studying the drug in infected patients at high risk of severe illness and in those at typical risk, Pfizer launched a phase 2-3 study in late September that will enroll people who live in the same household as a person with a confirmed, symptomatic COVID-19 infection to see if the drug can prevent disease in those who have been exposed.
Atea and Roche’s COVID pill, AT527, is in phase 3 trials as well. AT527 is an inhibitor of polymerase, an enzyme many viruses have, to stop replications. Atea is evaluating the drug to reduce disease “burden” and for both pre- and postexposure prevention.
Big picture: Role of COVID-19 pills
It may be necessary to target the coronavirus with more than one antiviral agent, said Dr. Fichtenbaum, a principal investigator for the AT527 trials.
“Sometimes viruses require two or three active agents to control their replication,” he said, citing information gleaned from other viral research, such as HIV. For control of HIV infection, a cocktail or combination of antivirals is often recommended.
That may well be the case for COVID-19, Dr. Fichtenbaum said. The goal would be to attack the virus at more than one pathway.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Painful Psoriasiform Plaques
The Diagnosis: Acquired Acrodermatitis Enteropathica
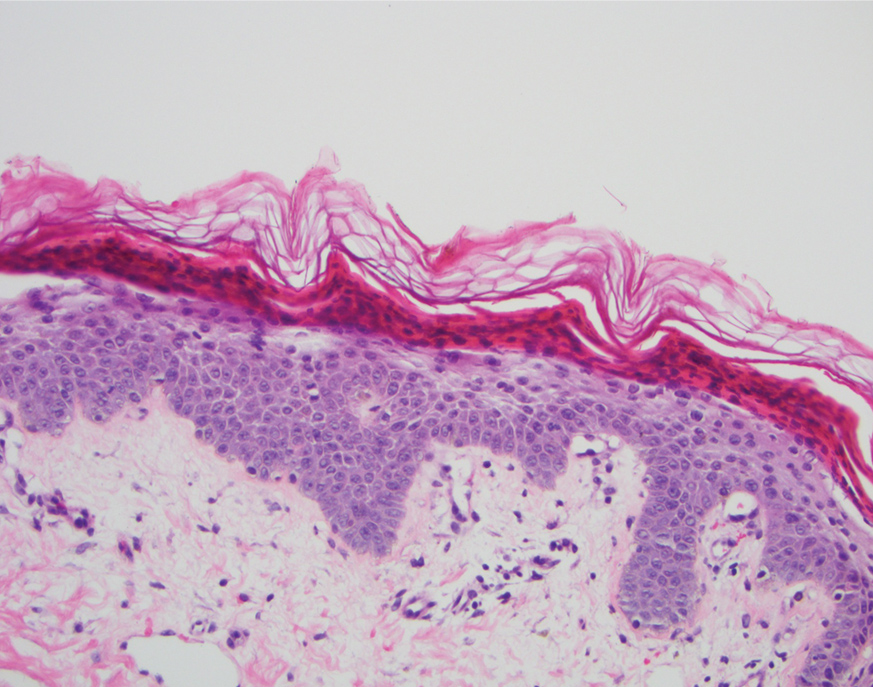
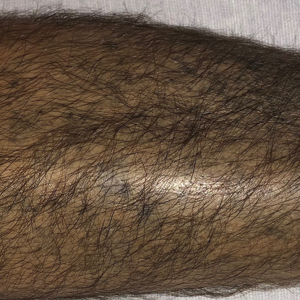
A punch biopsy of an elevated scaly border of the rash on the thigh revealed parakeratosis, absence of the granular layer, and epidermal pallor with psoriasiform and spongiotic dermatitis (Figure). Serum zinc levels were 60.1 μg/dL (reference range, 75.0–120.0 μg/dL), suggestive of a nutritional deficiency dermatitis. Laboratory and histopathologic findings were most consistent with a diagnosis of acquired acrodermatitis enteropathica (AE).
Acrodermatitis enteropathica has been associated with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and alcohol use disorder working synergistically to cause malabsorption and malnutrition, respectively.1 Zinc functions in the structural integrity, wound healing, and anti-inflammatory properties of the skin. There is a 17.3% risk for hypozincemia worldwide; in developed nations there is an estimated 3% to 10% occurrence rate.2 Acrodermatitis enteropathica can be classified as either acquired or hereditary. Both classically present as a triad of acral dermatitis, diarrhea, and alopecia, though the complete triad is seen in 20% of cases.3,4
Hereditary AE is an autosomal-recessive disorder presenting in infancy that results in the loss of a zinc transporter. In contrast, acquired AE occurs later in life and usually is seen in patients who have decreased intake, malabsorption, or excessive loss of zinc.4 Acrodermatitis enteropathica is observed in individuals with conditions such as anorexia nervosa, pancreatic insufficiency, celiac disease, Crohn disease, or gastric bypass surgery (as in our case) and alcohol recidivism. In early disease, AE often presents with angular cheilitis and paronychia, but if left untreated, it can progress to mental status changes, hypogonadism, and depression.4 Acrodermatitis enteropathica presents as erythematous, erosive, scaly plaques or a papulosquamous psoriasiform rash with well-demarcated borders typically involving the orificial, acral, and intertriginous areas of the body.1,4
Acrodermatitis enteropathica belongs to a family of deficiency dermatoses that includes pellagra, necrolytic acral erythema (NAE), and necrolytic migratory erythema (NME).5 It is important to distinguish AE from NAE, as they can present similarly with well-defined and tender psoriasiform lesions peripherally. Histologically, NAE mimics AE with psoriasiform hyperplasia with parakeratosis.6 Necrolytic acral erythema characteristically is associated with active hepatitis C infection, which was absent in our patient.7
Similar to AE, NME affects the perineal and intertriginous surfaces.8 However, necrolytic migratory erythema has cutaneous manifestations in up to 70% of patients with glucagonoma syndrome, which classically presents as a triad of NME, weight loss, and diabetes mellitus.5 Laboratory studies show marked hyperglucagonemia, and imaging reveals enteropancreatic neoplasia. Necrolytic migratory erythema will rapidly resolve once the glucagonoma has been surgically removed.5 Bazex syndrome, or acrokeratosis paraneoplastica, is a paraneoplastic skin disease that is linked to underlying aerodigestive tract malignancies.
Bazex syndrome clinically is characterized by hyperkeratotic and psoriasiform lesions favoring the ears, nails, and nose.9
Psoriasis vulgaris is a common chronic inflammatory skin condition that usually presents as well-demarcated plaques with silvery scale and observed pinpoint bleeding when layers of scale are removed (Auspitz sign). Lesions typically are found on the extensor surfaces of the body in addition to the neck, feet, hands, and trunk. Treatment of psoriasis vulgaris ranges from topical steroids for mild cases to systemic biologics for moderate to severe circumstances.10 In our patient, topical triamcinolone offered little relief.
Acrodermatitis enteropathica displays clinical and histologic characteristics analogous to many deficiency dermatoses and may represent a spectrum of disease. Because the clinicopathologic findings are nonspecific, it is critical to obtain a comprehensive history and maintain a high index of suspicion in patients with risk factors for malnutrition. The treatment for AE is supplemental oral zinc usually initiated at 0.5 to 1 mg/kg daily in children and 30 to 45 mg daily in adults.3 Our patient initially was prescribed oral zinc supplementation; however, at 1-month follow-up, the rash had not improved. Failure of zinc monotherapy supports a multifactorial nutritional deficiency, which necessitated comprehensive nutritional appraisal and supplementation in our patient. Due to the steatorrhea, fecal pancreatic elastase levels were evaluated and were less than 15 μg/g (reference range, ≥201 μg/g), confirming pancreatic exocrine insufficiency, a known complication of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.11 Pancrelipase 500 U/kg per meal was added in addition to zinc oxide 40% paste to apply to the rash twice daily, with more frequent applications to the anogenital regions after bowel movements. The patient had substantial clinical improvement after 2 months.
- Shahsavari D, Ahmed Z, Karikkineth A, et al. Zinc-deficiency acrodermatitis in a patient with chronic alcoholism and gastric bypass: a case report. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2014. doi:10.3402/jchimp.v4.24707
- Kelly S, Stelzer JW, Esplin N, et al. Acquired acrodermatitis enteropathica: a case study. Cureus. 2017;9:E1667.
- Guliani A, Bishnoi A. Acquired acrodermatitis enteropathica. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1305.
- Baruch D, Naga L, Driscoll M, et al. Acrodermatitis enteropathica from zinc-deficient total parenteral nutrition. Cutis. 2018;101:450-453.
- van Beek AP, de Haas ER, van Vloten WA, et al. The glucagonoma syndrome and necrolytic migratory erythema: a clinical review. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004;151:531-537.
- Botelho LF, Enokihara MM, Enokihara MY. Necrolytic acral erythema: a rare skin disease associated with hepatitis C virus infection. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:649-651.
- Abdallah MA, Ghozzi MY, Monib HA, et al. Necrolytic acral erythema: a cutaneous sign of hepatitis C virus infection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:247-251.
- Tolliver S, Graham J, Kaffenberger BH. A review of cutaneous manifestations within glucagonoma syndrome: necrolytic migratory erythema. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:642-645.
- Poligone B, Christensen SR, Lazova R, et al. Bazex syndrome (acrokeratosis paraneoplastica). Lancet. 2007;369:530. 10. Kupetsky EA, Keller M. Psoriasis vulgaris: an evidencebased guide for primary care. J Am Board Fam Med. 2013; 26:787-801.
- Borbély Y, Plebani A, Kröll D, et al. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016;12:790-794.
The Diagnosis: Acquired Acrodermatitis Enteropathica
A punch biopsy of an elevated scaly border of the rash on the thigh revealed parakeratosis, absence of the granular layer, and epidermal pallor with psoriasiform and spongiotic dermatitis (Figure). Serum zinc levels were 60.1 μg/dL (reference range, 75.0–120.0 μg/dL), suggestive of a nutritional deficiency dermatitis. Laboratory and histopathologic findings were most consistent with a diagnosis of acquired acrodermatitis enteropathica (AE).
Acrodermatitis enteropathica has been associated with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and alcohol use disorder working synergistically to cause malabsorption and malnutrition, respectively.1 Zinc functions in the structural integrity, wound healing, and anti-inflammatory properties of the skin. There is a 17.3% risk for hypozincemia worldwide; in developed nations there is an estimated 3% to 10% occurrence rate.2 Acrodermatitis enteropathica can be classified as either acquired or hereditary. Both classically present as a triad of acral dermatitis, diarrhea, and alopecia, though the complete triad is seen in 20% of cases.3,4
Hereditary AE is an autosomal-recessive disorder presenting in infancy that results in the loss of a zinc transporter. In contrast, acquired AE occurs later in life and usually is seen in patients who have decreased intake, malabsorption, or excessive loss of zinc.4 Acrodermatitis enteropathica is observed in individuals with conditions such as anorexia nervosa, pancreatic insufficiency, celiac disease, Crohn disease, or gastric bypass surgery (as in our case) and alcohol recidivism. In early disease, AE often presents with angular cheilitis and paronychia, but if left untreated, it can progress to mental status changes, hypogonadism, and depression.4 Acrodermatitis enteropathica presents as erythematous, erosive, scaly plaques or a papulosquamous psoriasiform rash with well-demarcated borders typically involving the orificial, acral, and intertriginous areas of the body.1,4
Acrodermatitis enteropathica belongs to a family of deficiency dermatoses that includes pellagra, necrolytic acral erythema (NAE), and necrolytic migratory erythema (NME).5 It is important to distinguish AE from NAE, as they can present similarly with well-defined and tender psoriasiform lesions peripherally. Histologically, NAE mimics AE with psoriasiform hyperplasia with parakeratosis.6 Necrolytic acral erythema characteristically is associated with active hepatitis C infection, which was absent in our patient.7
Similar to AE, NME affects the perineal and intertriginous surfaces.8 However, necrolytic migratory erythema has cutaneous manifestations in up to 70% of patients with glucagonoma syndrome, which classically presents as a triad of NME, weight loss, and diabetes mellitus.5 Laboratory studies show marked hyperglucagonemia, and imaging reveals enteropancreatic neoplasia. Necrolytic migratory erythema will rapidly resolve once the glucagonoma has been surgically removed.5 Bazex syndrome, or acrokeratosis paraneoplastica, is a paraneoplastic skin disease that is linked to underlying aerodigestive tract malignancies.
Bazex syndrome clinically is characterized by hyperkeratotic and psoriasiform lesions favoring the ears, nails, and nose.9
Psoriasis vulgaris is a common chronic inflammatory skin condition that usually presents as well-demarcated plaques with silvery scale and observed pinpoint bleeding when layers of scale are removed (Auspitz sign). Lesions typically are found on the extensor surfaces of the body in addition to the neck, feet, hands, and trunk. Treatment of psoriasis vulgaris ranges from topical steroids for mild cases to systemic biologics for moderate to severe circumstances.10 In our patient, topical triamcinolone offered little relief.
Acrodermatitis enteropathica displays clinical and histologic characteristics analogous to many deficiency dermatoses and may represent a spectrum of disease. Because the clinicopathologic findings are nonspecific, it is critical to obtain a comprehensive history and maintain a high index of suspicion in patients with risk factors for malnutrition. The treatment for AE is supplemental oral zinc usually initiated at 0.5 to 1 mg/kg daily in children and 30 to 45 mg daily in adults.3 Our patient initially was prescribed oral zinc supplementation; however, at 1-month follow-up, the rash had not improved. Failure of zinc monotherapy supports a multifactorial nutritional deficiency, which necessitated comprehensive nutritional appraisal and supplementation in our patient. Due to the steatorrhea, fecal pancreatic elastase levels were evaluated and were less than 15 μg/g (reference range, ≥201 μg/g), confirming pancreatic exocrine insufficiency, a known complication of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.11 Pancrelipase 500 U/kg per meal was added in addition to zinc oxide 40% paste to apply to the rash twice daily, with more frequent applications to the anogenital regions after bowel movements. The patient had substantial clinical improvement after 2 months.
The Diagnosis: Acquired Acrodermatitis Enteropathica
A punch biopsy of an elevated scaly border of the rash on the thigh revealed parakeratosis, absence of the granular layer, and epidermal pallor with psoriasiform and spongiotic dermatitis (Figure). Serum zinc levels were 60.1 μg/dL (reference range, 75.0–120.0 μg/dL), suggestive of a nutritional deficiency dermatitis. Laboratory and histopathologic findings were most consistent with a diagnosis of acquired acrodermatitis enteropathica (AE).
Acrodermatitis enteropathica has been associated with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and alcohol use disorder working synergistically to cause malabsorption and malnutrition, respectively.1 Zinc functions in the structural integrity, wound healing, and anti-inflammatory properties of the skin. There is a 17.3% risk for hypozincemia worldwide; in developed nations there is an estimated 3% to 10% occurrence rate.2 Acrodermatitis enteropathica can be classified as either acquired or hereditary. Both classically present as a triad of acral dermatitis, diarrhea, and alopecia, though the complete triad is seen in 20% of cases.3,4
Hereditary AE is an autosomal-recessive disorder presenting in infancy that results in the loss of a zinc transporter. In contrast, acquired AE occurs later in life and usually is seen in patients who have decreased intake, malabsorption, or excessive loss of zinc.4 Acrodermatitis enteropathica is observed in individuals with conditions such as anorexia nervosa, pancreatic insufficiency, celiac disease, Crohn disease, or gastric bypass surgery (as in our case) and alcohol recidivism. In early disease, AE often presents with angular cheilitis and paronychia, but if left untreated, it can progress to mental status changes, hypogonadism, and depression.4 Acrodermatitis enteropathica presents as erythematous, erosive, scaly plaques or a papulosquamous psoriasiform rash with well-demarcated borders typically involving the orificial, acral, and intertriginous areas of the body.1,4
Acrodermatitis enteropathica belongs to a family of deficiency dermatoses that includes pellagra, necrolytic acral erythema (NAE), and necrolytic migratory erythema (NME).5 It is important to distinguish AE from NAE, as they can present similarly with well-defined and tender psoriasiform lesions peripherally. Histologically, NAE mimics AE with psoriasiform hyperplasia with parakeratosis.6 Necrolytic acral erythema characteristically is associated with active hepatitis C infection, which was absent in our patient.7
Similar to AE, NME affects the perineal and intertriginous surfaces.8 However, necrolytic migratory erythema has cutaneous manifestations in up to 70% of patients with glucagonoma syndrome, which classically presents as a triad of NME, weight loss, and diabetes mellitus.5 Laboratory studies show marked hyperglucagonemia, and imaging reveals enteropancreatic neoplasia. Necrolytic migratory erythema will rapidly resolve once the glucagonoma has been surgically removed.5 Bazex syndrome, or acrokeratosis paraneoplastica, is a paraneoplastic skin disease that is linked to underlying aerodigestive tract malignancies.
Bazex syndrome clinically is characterized by hyperkeratotic and psoriasiform lesions favoring the ears, nails, and nose.9
Psoriasis vulgaris is a common chronic inflammatory skin condition that usually presents as well-demarcated plaques with silvery scale and observed pinpoint bleeding when layers of scale are removed (Auspitz sign). Lesions typically are found on the extensor surfaces of the body in addition to the neck, feet, hands, and trunk. Treatment of psoriasis vulgaris ranges from topical steroids for mild cases to systemic biologics for moderate to severe circumstances.10 In our patient, topical triamcinolone offered little relief.
Acrodermatitis enteropathica displays clinical and histologic characteristics analogous to many deficiency dermatoses and may represent a spectrum of disease. Because the clinicopathologic findings are nonspecific, it is critical to obtain a comprehensive history and maintain a high index of suspicion in patients with risk factors for malnutrition. The treatment for AE is supplemental oral zinc usually initiated at 0.5 to 1 mg/kg daily in children and 30 to 45 mg daily in adults.3 Our patient initially was prescribed oral zinc supplementation; however, at 1-month follow-up, the rash had not improved. Failure of zinc monotherapy supports a multifactorial nutritional deficiency, which necessitated comprehensive nutritional appraisal and supplementation in our patient. Due to the steatorrhea, fecal pancreatic elastase levels were evaluated and were less than 15 μg/g (reference range, ≥201 μg/g), confirming pancreatic exocrine insufficiency, a known complication of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.11 Pancrelipase 500 U/kg per meal was added in addition to zinc oxide 40% paste to apply to the rash twice daily, with more frequent applications to the anogenital regions after bowel movements. The patient had substantial clinical improvement after 2 months.
- Shahsavari D, Ahmed Z, Karikkineth A, et al. Zinc-deficiency acrodermatitis in a patient with chronic alcoholism and gastric bypass: a case report. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2014. doi:10.3402/jchimp.v4.24707
- Kelly S, Stelzer JW, Esplin N, et al. Acquired acrodermatitis enteropathica: a case study. Cureus. 2017;9:E1667.
- Guliani A, Bishnoi A. Acquired acrodermatitis enteropathica. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1305.
- Baruch D, Naga L, Driscoll M, et al. Acrodermatitis enteropathica from zinc-deficient total parenteral nutrition. Cutis. 2018;101:450-453.
- van Beek AP, de Haas ER, van Vloten WA, et al. The glucagonoma syndrome and necrolytic migratory erythema: a clinical review. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004;151:531-537.
- Botelho LF, Enokihara MM, Enokihara MY. Necrolytic acral erythema: a rare skin disease associated with hepatitis C virus infection. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:649-651.
- Abdallah MA, Ghozzi MY, Monib HA, et al. Necrolytic acral erythema: a cutaneous sign of hepatitis C virus infection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:247-251.
- Tolliver S, Graham J, Kaffenberger BH. A review of cutaneous manifestations within glucagonoma syndrome: necrolytic migratory erythema. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:642-645.
- Poligone B, Christensen SR, Lazova R, et al. Bazex syndrome (acrokeratosis paraneoplastica). Lancet. 2007;369:530. 10. Kupetsky EA, Keller M. Psoriasis vulgaris: an evidencebased guide for primary care. J Am Board Fam Med. 2013; 26:787-801.
- Borbély Y, Plebani A, Kröll D, et al. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016;12:790-794.
- Shahsavari D, Ahmed Z, Karikkineth A, et al. Zinc-deficiency acrodermatitis in a patient with chronic alcoholism and gastric bypass: a case report. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2014. doi:10.3402/jchimp.v4.24707
- Kelly S, Stelzer JW, Esplin N, et al. Acquired acrodermatitis enteropathica: a case study. Cureus. 2017;9:E1667.
- Guliani A, Bishnoi A. Acquired acrodermatitis enteropathica. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1305.
- Baruch D, Naga L, Driscoll M, et al. Acrodermatitis enteropathica from zinc-deficient total parenteral nutrition. Cutis. 2018;101:450-453.
- van Beek AP, de Haas ER, van Vloten WA, et al. The glucagonoma syndrome and necrolytic migratory erythema: a clinical review. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004;151:531-537.
- Botelho LF, Enokihara MM, Enokihara MY. Necrolytic acral erythema: a rare skin disease associated with hepatitis C virus infection. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:649-651.
- Abdallah MA, Ghozzi MY, Monib HA, et al. Necrolytic acral erythema: a cutaneous sign of hepatitis C virus infection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:247-251.
- Tolliver S, Graham J, Kaffenberger BH. A review of cutaneous manifestations within glucagonoma syndrome: necrolytic migratory erythema. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:642-645.
- Poligone B, Christensen SR, Lazova R, et al. Bazex syndrome (acrokeratosis paraneoplastica). Lancet. 2007;369:530. 10. Kupetsky EA, Keller M. Psoriasis vulgaris: an evidencebased guide for primary care. J Am Board Fam Med. 2013; 26:787-801.
- Borbély Y, Plebani A, Kröll D, et al. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016;12:790-794.
A 45-year-old woman presented to the emergency department with a painful skin eruption and malaise of 5 weeks’ duration. She had an orthotopic liver transplant 5 years prior for end-stage liver disease due to mixed nonalcoholic and alcoholic steatohepatitis and was on mycophenolate mofetil and tacrolimus for graft rejection prophylaxis. Her medical history also included Roux-en-Y gastric bypass 15 years prior, alcohol use disorder, hypothyroidism, and depression.
The exanthem began on the legs as pruritic, red, raised, exudative lesions that gradually crusted. Over the 2 weeks prior to the current presentation, the rash became tender as it spread to the feet, thighs, perianal skin, buttocks, and elbows. Triamcinolone ointment prescribed for a presumed nummular dermatitis effected marginal benefit. A review of systems was notable for a 15-pound weight loss over several weeks; lowgrade fever of 3 days’ duration; epigastric abdominal pain; and long-standing, frequent defecation of oily, foul-smelling feces.
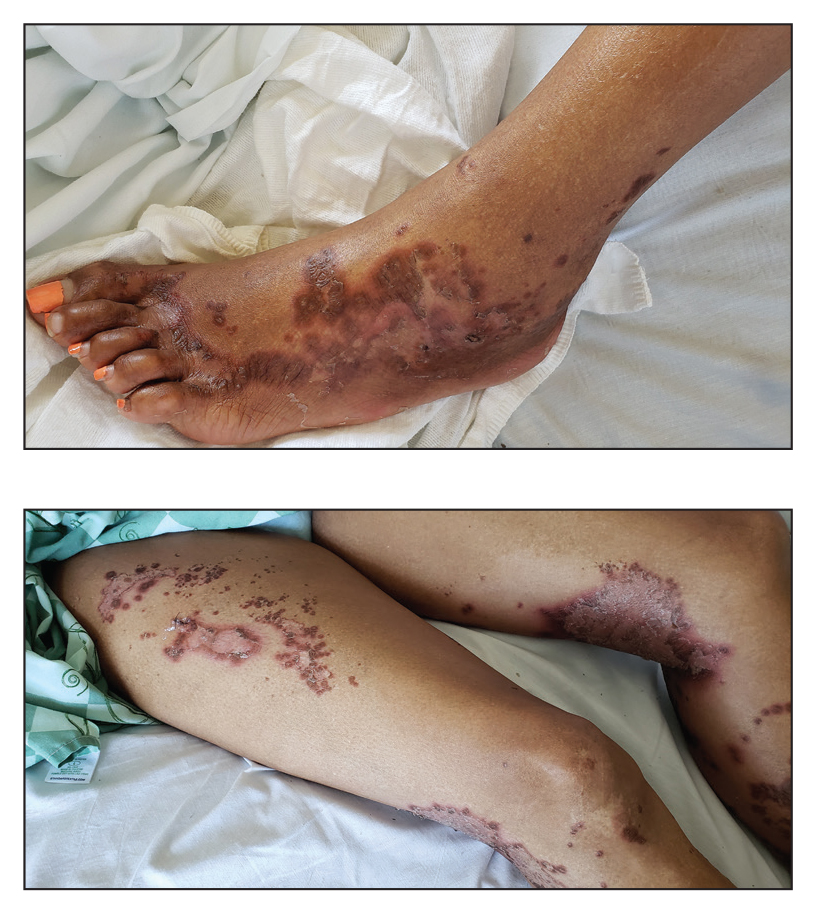
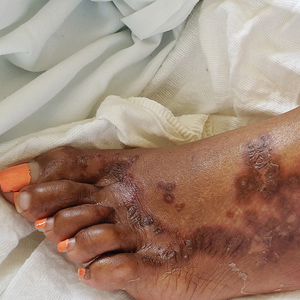
Physical examination revealed a combination of flat-topped, violaceous papules and serpiginous, polycyclic, annular plaques coalescing to form larger psoriasiform plaques with hyperkeratotic rims and dusky borders on the dorsal aspect of the feet (top), lateral ankles, legs (bottom), lateral thighs, buttocks, perianal skin, and elbows. Bilateral angular cheilitis, a smooth and fissured tongue, and pitting of all fingernails were noted.
Exercise appears to improve bone structure, not density
“Postmenopausal women with low bone mass should obtain adequate calcium and vitamin D and participate in bone-loading exercises,” researchers noted in a recent study published in Osteoporosis International.
“Additional use of bisphosphonates will increase bone mineral density (BMD), especially at the spine,” wrote Nancy Waltman, PhD, College of Nursing, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, and colleagues.
The findings are partial results from the Heartland Osteoporosis Prevention Study (HOPS), which randomized women who had entered menopause within the previous 6 months and had osteopenia (low bone mass, T score –1.0 to –2.49) to receive one of three treatments for 12 months:
- Bone-loading and resistance exercise plus calcium and vitamin D supplements.
- Risedronate plus calcium and vitamin D supplements.
- Calcium and vitamin D supplements alone (control).
At 1 year, “risedronate significantly increased BMD at the spine, compared to exercise and control, and serum biomarkers of bone turnover also significantly reduced in the risedronate group,” Laura Bilek, PT, PhD, said during an oral presentation of the research at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
However, the results also showed that, importantly, “in postmenopausal women, exercise appears to improve strength at the hip through changes in structure, not BMD,” stressed Dr. Bilek, of the College of Allied Health Professionals, University of Nebraska Medical Center.
Bone health is about more than just bone mineral density
“The key takeaway for clinicians is that bone health is about more than just density!” she noted in an email.
Current guidelines don’t recommend prescribing risedronate until a woman has overt osteoporosis, she said.
On the other hand, many studies have shown that, to be most effective, bone-loading exercises should be a lifelong habit and women should begin to do them at least during menopause and should not wait until bone loss occurs.
Other studies have shown that exercise changes bone structure (size or geometry), which improves bone strength. The current study supports both prior observations.
And exercise also improves muscle strength and decreases the risk of falls and fractures, Dr. Bilek noted.
Invited to comment, Pauline M. Camacho, MD, cochair of the task force for the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE) guidelines for osteoporosis, noted that all three measures – pharmacotherapy, exercise, and calcium/vitamin D – are important in the successful management of osteoporosis.
This study showed that risedronate is superior to calcium/vitamin D supplementation as well as exercise for BMD and for bone turnover in these women with osteopenia, said Dr. Camacho, professor of medicine and director of the Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Center, Loyola University Medical Center, Chicago.
“Most women with osteopenia do not receive pharmacologic therapy,” she noted, and receive it only “if there is a history of fractures or they have other features that change that diagnosis to osteoporosis.
“There is no downside to exercise, and this needs to be advised to all patients,” she said. “The other aspect of exercise that was not assessed in this study is its effect on balance. Patients who exercise will have improved balance, which should translate into fewer falls, and thus fewer fractures.”
How can women with osteopenia maintain bone health?
In their article, Dr. Waltman and colleagues say the Lifting Intervention for Training Muscle and Osteoporosis Rehabilitation (LIFTMOR) clinical trial is one of the first to address clinician concerns about the safety and effectiveness of exercise to improve bone health.
In that trial of 101 postmenopausal women with low bone mass, 8 months of 30-minute, twice-weekly, supervised high-intensity resistance and impact training was safe and BMD increased by 2.9% at the lumbar spine and 0.3% at the femoral neck.
“Our [HOPS] study,” Dr. Waltman and colleagues explained, “builds on the LIFTMOR clinical trial and adds further data to inform whether postmenopausal women with low bone mass can effectively maintain or even improve BMD with bone-loading exercises prior to prescriptions for medication.
“Our long-term goal is to contribute to the development of clinical practice guidelines for the prevention of fractures in postmenopausal women with low bone mass,” they said.
They randomized 276 postmenopausal women who were a mean age of 54 (range, 44-63); most were White (78%) or Hispanic (6%).
Women were excluded from the study if they had a diagnosis of osteoporosis (T-score < −2.5); had an increased risk of a major fracture or hip fracture; had been on bisphosphonates within the last 6 months; were currently on estrogen, tamoxifen, or aromatase inhibitors; had a serum vitamin D level < 10 mg/mL or > 100 mg/mL; had any conditions that prohibited prescriptions for calcium and vitamin D supplements, risedronate, or exercise; or weighed more than 300 pounds.
All women received 1,200 mg/day of calcium (from supplements or diet) and 1,000-3,000 IU/day of vitamin D supplements, based on their serum 25(OH) vitamin D levels.
The exercise program consisted of visiting a gym three times a week for 45 minutes of bone-loading exercise – jogging with a weighted vest – and resistance exercises, which were supervised by a trainer for the first 2 weeks.
Women in the risedronate group received a 150-mg tablet of risedronate every 4 weeks.
At baseline, 6 months, and 12 months, the women had DXA scans to determine BMD and hip structure, and had blood tests to determine levels of serum markers for bone formation (bone specific alkaline phosphatase [Alkphase B]) and bone resorption (N-terminal telopeptide [NTx]).
Compared with baseline, at 12 months, the women had the following changes in BMD at the following sites:
- Spine: +1.9%, +0.9%, and –0.4%, in the risedronate, exercise, and control groups.
- Total hip: +0.9%, +0.5%, and +0.5%, in the risedronate, exercise, and control groups.
- Femoral neck: +0.09%, –0.4%, and –0.5%, in the risedronate, exercise, and control groups.
These improvements in BMD were significantly greater in the risedronate group than in the exercise or control groups (P < .01 for both).
The decreases in serum levels of NtX and Alkphase B were also greater with risedronate than in the exercise or control groups (P < .01 for all).
The most frequent adverse effect with the calcium supplement was constipation (n = 4). Some women taking risedronate had gastrointestinal disturbances (n = 4), muscle or joint pain (n = 11), or chest pain and dizziness (n = 2). None of the women had adverse effects from vitamin D. A few women had muscle soreness from exercise that went away after the exercises were adapted. None of the women had a serious injury or fracture from exercise.
More women in the exercise group withdrew from the study (n = 20), with most citing lack of time as the reason; 13 women withdrew from the risedronate group, and 16 withdrew from the control group.
Of the 276 participants who completed the 12-month study, treatment adherence was 92% for calcium, 94% for vitamin D, 75% for risedronate, and 59% for exercise.
Exercise was associated with positive changes in intertrochanter hip structural analysis measures, which will be described in an upcoming study, Dr. Bilek said.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Nursing Research of the National Institutes of Health. The researchers have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Postmenopausal women with low bone mass should obtain adequate calcium and vitamin D and participate in bone-loading exercises,” researchers noted in a recent study published in Osteoporosis International.
“Additional use of bisphosphonates will increase bone mineral density (BMD), especially at the spine,” wrote Nancy Waltman, PhD, College of Nursing, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, and colleagues.
The findings are partial results from the Heartland Osteoporosis Prevention Study (HOPS), which randomized women who had entered menopause within the previous 6 months and had osteopenia (low bone mass, T score –1.0 to –2.49) to receive one of three treatments for 12 months:
- Bone-loading and resistance exercise plus calcium and vitamin D supplements.
- Risedronate plus calcium and vitamin D supplements.
- Calcium and vitamin D supplements alone (control).
At 1 year, “risedronate significantly increased BMD at the spine, compared to exercise and control, and serum biomarkers of bone turnover also significantly reduced in the risedronate group,” Laura Bilek, PT, PhD, said during an oral presentation of the research at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
However, the results also showed that, importantly, “in postmenopausal women, exercise appears to improve strength at the hip through changes in structure, not BMD,” stressed Dr. Bilek, of the College of Allied Health Professionals, University of Nebraska Medical Center.
Bone health is about more than just bone mineral density
“The key takeaway for clinicians is that bone health is about more than just density!” she noted in an email.
Current guidelines don’t recommend prescribing risedronate until a woman has overt osteoporosis, she said.
On the other hand, many studies have shown that, to be most effective, bone-loading exercises should be a lifelong habit and women should begin to do them at least during menopause and should not wait until bone loss occurs.
Other studies have shown that exercise changes bone structure (size or geometry), which improves bone strength. The current study supports both prior observations.
And exercise also improves muscle strength and decreases the risk of falls and fractures, Dr. Bilek noted.
Invited to comment, Pauline M. Camacho, MD, cochair of the task force for the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE) guidelines for osteoporosis, noted that all three measures – pharmacotherapy, exercise, and calcium/vitamin D – are important in the successful management of osteoporosis.
This study showed that risedronate is superior to calcium/vitamin D supplementation as well as exercise for BMD and for bone turnover in these women with osteopenia, said Dr. Camacho, professor of medicine and director of the Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Center, Loyola University Medical Center, Chicago.
“Most women with osteopenia do not receive pharmacologic therapy,” she noted, and receive it only “if there is a history of fractures or they have other features that change that diagnosis to osteoporosis.
“There is no downside to exercise, and this needs to be advised to all patients,” she said. “The other aspect of exercise that was not assessed in this study is its effect on balance. Patients who exercise will have improved balance, which should translate into fewer falls, and thus fewer fractures.”
How can women with osteopenia maintain bone health?
In their article, Dr. Waltman and colleagues say the Lifting Intervention for Training Muscle and Osteoporosis Rehabilitation (LIFTMOR) clinical trial is one of the first to address clinician concerns about the safety and effectiveness of exercise to improve bone health.
In that trial of 101 postmenopausal women with low bone mass, 8 months of 30-minute, twice-weekly, supervised high-intensity resistance and impact training was safe and BMD increased by 2.9% at the lumbar spine and 0.3% at the femoral neck.
“Our [HOPS] study,” Dr. Waltman and colleagues explained, “builds on the LIFTMOR clinical trial and adds further data to inform whether postmenopausal women with low bone mass can effectively maintain or even improve BMD with bone-loading exercises prior to prescriptions for medication.
“Our long-term goal is to contribute to the development of clinical practice guidelines for the prevention of fractures in postmenopausal women with low bone mass,” they said.
They randomized 276 postmenopausal women who were a mean age of 54 (range, 44-63); most were White (78%) or Hispanic (6%).
Women were excluded from the study if they had a diagnosis of osteoporosis (T-score < −2.5); had an increased risk of a major fracture or hip fracture; had been on bisphosphonates within the last 6 months; were currently on estrogen, tamoxifen, or aromatase inhibitors; had a serum vitamin D level < 10 mg/mL or > 100 mg/mL; had any conditions that prohibited prescriptions for calcium and vitamin D supplements, risedronate, or exercise; or weighed more than 300 pounds.
All women received 1,200 mg/day of calcium (from supplements or diet) and 1,000-3,000 IU/day of vitamin D supplements, based on their serum 25(OH) vitamin D levels.
The exercise program consisted of visiting a gym three times a week for 45 minutes of bone-loading exercise – jogging with a weighted vest – and resistance exercises, which were supervised by a trainer for the first 2 weeks.
Women in the risedronate group received a 150-mg tablet of risedronate every 4 weeks.
At baseline, 6 months, and 12 months, the women had DXA scans to determine BMD and hip structure, and had blood tests to determine levels of serum markers for bone formation (bone specific alkaline phosphatase [Alkphase B]) and bone resorption (N-terminal telopeptide [NTx]).
Compared with baseline, at 12 months, the women had the following changes in BMD at the following sites:
- Spine: +1.9%, +0.9%, and –0.4%, in the risedronate, exercise, and control groups.
- Total hip: +0.9%, +0.5%, and +0.5%, in the risedronate, exercise, and control groups.
- Femoral neck: +0.09%, –0.4%, and –0.5%, in the risedronate, exercise, and control groups.
These improvements in BMD were significantly greater in the risedronate group than in the exercise or control groups (P < .01 for both).
The decreases in serum levels of NtX and Alkphase B were also greater with risedronate than in the exercise or control groups (P < .01 for all).
The most frequent adverse effect with the calcium supplement was constipation (n = 4). Some women taking risedronate had gastrointestinal disturbances (n = 4), muscle or joint pain (n = 11), or chest pain and dizziness (n = 2). None of the women had adverse effects from vitamin D. A few women had muscle soreness from exercise that went away after the exercises were adapted. None of the women had a serious injury or fracture from exercise.
More women in the exercise group withdrew from the study (n = 20), with most citing lack of time as the reason; 13 women withdrew from the risedronate group, and 16 withdrew from the control group.
Of the 276 participants who completed the 12-month study, treatment adherence was 92% for calcium, 94% for vitamin D, 75% for risedronate, and 59% for exercise.
Exercise was associated with positive changes in intertrochanter hip structural analysis measures, which will be described in an upcoming study, Dr. Bilek said.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Nursing Research of the National Institutes of Health. The researchers have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Postmenopausal women with low bone mass should obtain adequate calcium and vitamin D and participate in bone-loading exercises,” researchers noted in a recent study published in Osteoporosis International.
“Additional use of bisphosphonates will increase bone mineral density (BMD), especially at the spine,” wrote Nancy Waltman, PhD, College of Nursing, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, and colleagues.
The findings are partial results from the Heartland Osteoporosis Prevention Study (HOPS), which randomized women who had entered menopause within the previous 6 months and had osteopenia (low bone mass, T score –1.0 to –2.49) to receive one of three treatments for 12 months:
- Bone-loading and resistance exercise plus calcium and vitamin D supplements.
- Risedronate plus calcium and vitamin D supplements.
- Calcium and vitamin D supplements alone (control).
At 1 year, “risedronate significantly increased BMD at the spine, compared to exercise and control, and serum biomarkers of bone turnover also significantly reduced in the risedronate group,” Laura Bilek, PT, PhD, said during an oral presentation of the research at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
However, the results also showed that, importantly, “in postmenopausal women, exercise appears to improve strength at the hip through changes in structure, not BMD,” stressed Dr. Bilek, of the College of Allied Health Professionals, University of Nebraska Medical Center.
Bone health is about more than just bone mineral density
“The key takeaway for clinicians is that bone health is about more than just density!” she noted in an email.
Current guidelines don’t recommend prescribing risedronate until a woman has overt osteoporosis, she said.
On the other hand, many studies have shown that, to be most effective, bone-loading exercises should be a lifelong habit and women should begin to do them at least during menopause and should not wait until bone loss occurs.
Other studies have shown that exercise changes bone structure (size or geometry), which improves bone strength. The current study supports both prior observations.
And exercise also improves muscle strength and decreases the risk of falls and fractures, Dr. Bilek noted.
Invited to comment, Pauline M. Camacho, MD, cochair of the task force for the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE) guidelines for osteoporosis, noted that all three measures – pharmacotherapy, exercise, and calcium/vitamin D – are important in the successful management of osteoporosis.
This study showed that risedronate is superior to calcium/vitamin D supplementation as well as exercise for BMD and for bone turnover in these women with osteopenia, said Dr. Camacho, professor of medicine and director of the Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Center, Loyola University Medical Center, Chicago.
“Most women with osteopenia do not receive pharmacologic therapy,” she noted, and receive it only “if there is a history of fractures or they have other features that change that diagnosis to osteoporosis.
“There is no downside to exercise, and this needs to be advised to all patients,” she said. “The other aspect of exercise that was not assessed in this study is its effect on balance. Patients who exercise will have improved balance, which should translate into fewer falls, and thus fewer fractures.”
How can women with osteopenia maintain bone health?
In their article, Dr. Waltman and colleagues say the Lifting Intervention for Training Muscle and Osteoporosis Rehabilitation (LIFTMOR) clinical trial is one of the first to address clinician concerns about the safety and effectiveness of exercise to improve bone health.
In that trial of 101 postmenopausal women with low bone mass, 8 months of 30-minute, twice-weekly, supervised high-intensity resistance and impact training was safe and BMD increased by 2.9% at the lumbar spine and 0.3% at the femoral neck.
“Our [HOPS] study,” Dr. Waltman and colleagues explained, “builds on the LIFTMOR clinical trial and adds further data to inform whether postmenopausal women with low bone mass can effectively maintain or even improve BMD with bone-loading exercises prior to prescriptions for medication.
“Our long-term goal is to contribute to the development of clinical practice guidelines for the prevention of fractures in postmenopausal women with low bone mass,” they said.
They randomized 276 postmenopausal women who were a mean age of 54 (range, 44-63); most were White (78%) or Hispanic (6%).
Women were excluded from the study if they had a diagnosis of osteoporosis (T-score < −2.5); had an increased risk of a major fracture or hip fracture; had been on bisphosphonates within the last 6 months; were currently on estrogen, tamoxifen, or aromatase inhibitors; had a serum vitamin D level < 10 mg/mL or > 100 mg/mL; had any conditions that prohibited prescriptions for calcium and vitamin D supplements, risedronate, or exercise; or weighed more than 300 pounds.
All women received 1,200 mg/day of calcium (from supplements or diet) and 1,000-3,000 IU/day of vitamin D supplements, based on their serum 25(OH) vitamin D levels.
The exercise program consisted of visiting a gym three times a week for 45 minutes of bone-loading exercise – jogging with a weighted vest – and resistance exercises, which were supervised by a trainer for the first 2 weeks.
Women in the risedronate group received a 150-mg tablet of risedronate every 4 weeks.
At baseline, 6 months, and 12 months, the women had DXA scans to determine BMD and hip structure, and had blood tests to determine levels of serum markers for bone formation (bone specific alkaline phosphatase [Alkphase B]) and bone resorption (N-terminal telopeptide [NTx]).
Compared with baseline, at 12 months, the women had the following changes in BMD at the following sites:
- Spine: +1.9%, +0.9%, and –0.4%, in the risedronate, exercise, and control groups.
- Total hip: +0.9%, +0.5%, and +0.5%, in the risedronate, exercise, and control groups.
- Femoral neck: +0.09%, –0.4%, and –0.5%, in the risedronate, exercise, and control groups.
These improvements in BMD were significantly greater in the risedronate group than in the exercise or control groups (P < .01 for both).
The decreases in serum levels of NtX and Alkphase B were also greater with risedronate than in the exercise or control groups (P < .01 for all).
The most frequent adverse effect with the calcium supplement was constipation (n = 4). Some women taking risedronate had gastrointestinal disturbances (n = 4), muscle or joint pain (n = 11), or chest pain and dizziness (n = 2). None of the women had adverse effects from vitamin D. A few women had muscle soreness from exercise that went away after the exercises were adapted. None of the women had a serious injury or fracture from exercise.
More women in the exercise group withdrew from the study (n = 20), with most citing lack of time as the reason; 13 women withdrew from the risedronate group, and 16 withdrew from the control group.
Of the 276 participants who completed the 12-month study, treatment adherence was 92% for calcium, 94% for vitamin D, 75% for risedronate, and 59% for exercise.
Exercise was associated with positive changes in intertrochanter hip structural analysis measures, which will be described in an upcoming study, Dr. Bilek said.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Nursing Research of the National Institutes of Health. The researchers have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ASBMR 2021
New York’s largest health care provider fires 1,400 unvaccinated employees
The employees represented less than 2% of Northwell’s 76,000 employees, who are now all fully vaccinated against COVID-19, Joe Kemp, the assistant vice president of public relations for the company, told The Hill.
“Northwell Health is proud to announce that our workforce -- the largest in New York State -- is 100% vaccinated,” the company said in a statement to several news outlets.
“This allows us to continue to provide exceptional care at all of our facilities, without interruption and remain open and fully operational,” Northwell Health said.
Having a fully vaccinated workforce is part of the health system’s duty to protect others, the company said. Northwell Health includes 23 hospitals and more than 830 outpatient facilities, according to ABC News.
“Northwell regrets losing any employee under such circumstances,” the company said. “We owe it to our staff, our patients, and the communities we serve to be 100% vaccinated against COVID-19.”
Former New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo announced in August that the state would require health care workers to receive at least one COVID-19 vaccine shot by Sept. 27. Employees didn’t have the option for weekly testing or religious exemptions, which is being challenged in several lawsuits, according to The New York Times.
The order went into effect last week, prompting tens of thousands of employees to get vaccinated. As of last week, 87% of hospital staff were fully vaccinated, and 92% of hospital and retirement home workers had received at least one dose, according to state health data.
Northwell announced its own vaccine mandate in August as well, which sparked protests among some workers. The order applied to both clinical and non-clinical staff.
A few thousand Northwell employees got vaccinated as the deadline approached, Mr. Kemp told The New York Times. Some who lost their jobs at first were able to return to work, and those who have been terminated can interview for reinstatement for 30 days. The hospital system is also “openly recruiting” for the vacant positions.
“The goal was to get people vaccinated, not to get people terminated,” Mr. Kemp said.
Hospitalized COVID-19 patients in New York hit a low of 350 in mid-July, according to state hospitalization data. Now, about 2,200 people are hospitalized throughout the state, most of whom are unvaccinated.
As of Oct. 3, nearly 72% of New York residents had received at least one vaccine dose, according to the latest state data. About 64% are fully vaccinated.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The employees represented less than 2% of Northwell’s 76,000 employees, who are now all fully vaccinated against COVID-19, Joe Kemp, the assistant vice president of public relations for the company, told The Hill.
“Northwell Health is proud to announce that our workforce -- the largest in New York State -- is 100% vaccinated,” the company said in a statement to several news outlets.
“This allows us to continue to provide exceptional care at all of our facilities, without interruption and remain open and fully operational,” Northwell Health said.
Having a fully vaccinated workforce is part of the health system’s duty to protect others, the company said. Northwell Health includes 23 hospitals and more than 830 outpatient facilities, according to ABC News.
“Northwell regrets losing any employee under such circumstances,” the company said. “We owe it to our staff, our patients, and the communities we serve to be 100% vaccinated against COVID-19.”
Former New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo announced in August that the state would require health care workers to receive at least one COVID-19 vaccine shot by Sept. 27. Employees didn’t have the option for weekly testing or religious exemptions, which is being challenged in several lawsuits, according to The New York Times.
The order went into effect last week, prompting tens of thousands of employees to get vaccinated. As of last week, 87% of hospital staff were fully vaccinated, and 92% of hospital and retirement home workers had received at least one dose, according to state health data.
Northwell announced its own vaccine mandate in August as well, which sparked protests among some workers. The order applied to both clinical and non-clinical staff.
A few thousand Northwell employees got vaccinated as the deadline approached, Mr. Kemp told The New York Times. Some who lost their jobs at first were able to return to work, and those who have been terminated can interview for reinstatement for 30 days. The hospital system is also “openly recruiting” for the vacant positions.
“The goal was to get people vaccinated, not to get people terminated,” Mr. Kemp said.
Hospitalized COVID-19 patients in New York hit a low of 350 in mid-July, according to state hospitalization data. Now, about 2,200 people are hospitalized throughout the state, most of whom are unvaccinated.
As of Oct. 3, nearly 72% of New York residents had received at least one vaccine dose, according to the latest state data. About 64% are fully vaccinated.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The employees represented less than 2% of Northwell’s 76,000 employees, who are now all fully vaccinated against COVID-19, Joe Kemp, the assistant vice president of public relations for the company, told The Hill.
“Northwell Health is proud to announce that our workforce -- the largest in New York State -- is 100% vaccinated,” the company said in a statement to several news outlets.
“This allows us to continue to provide exceptional care at all of our facilities, without interruption and remain open and fully operational,” Northwell Health said.
Having a fully vaccinated workforce is part of the health system’s duty to protect others, the company said. Northwell Health includes 23 hospitals and more than 830 outpatient facilities, according to ABC News.
“Northwell regrets losing any employee under such circumstances,” the company said. “We owe it to our staff, our patients, and the communities we serve to be 100% vaccinated against COVID-19.”
Former New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo announced in August that the state would require health care workers to receive at least one COVID-19 vaccine shot by Sept. 27. Employees didn’t have the option for weekly testing or religious exemptions, which is being challenged in several lawsuits, according to The New York Times.
The order went into effect last week, prompting tens of thousands of employees to get vaccinated. As of last week, 87% of hospital staff were fully vaccinated, and 92% of hospital and retirement home workers had received at least one dose, according to state health data.
Northwell announced its own vaccine mandate in August as well, which sparked protests among some workers. The order applied to both clinical and non-clinical staff.
A few thousand Northwell employees got vaccinated as the deadline approached, Mr. Kemp told The New York Times. Some who lost their jobs at first were able to return to work, and those who have been terminated can interview for reinstatement for 30 days. The hospital system is also “openly recruiting” for the vacant positions.
“The goal was to get people vaccinated, not to get people terminated,” Mr. Kemp said.
Hospitalized COVID-19 patients in New York hit a low of 350 in mid-July, according to state hospitalization data. Now, about 2,200 people are hospitalized throughout the state, most of whom are unvaccinated.
As of Oct. 3, nearly 72% of New York residents had received at least one vaccine dose, according to the latest state data. About 64% are fully vaccinated.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Chronic Hyperpigmented Patches on the Legs
The Diagnosis: Drug-Induced Hyperpigmentation
Additional history provided by the patient’s caretaker elucidated an extensive list of medications including chlorpromazine and minocycline, among several others. The caretaker revealed that the patient began treatment for acne vulgaris 2 years prior; despite the acne resolving, therapy was not discontinued. The blue-gray and brown pigmentation on our patient’s shins likely was attributed to a medication he was taking.
Both chlorpromazine and minocycline, among many other medications, are known to cause abnormal pigmentation of the skin.1 Minocycline is a tetracycline antibiotic prescribed for acne and other inflammatory cutaneous conditions. It is highly lipophilic, allowing it to reach high drug concentrations in the skin and nail unit.2 Patients taking minocycline long term and at high doses are at greatest risk for pigment deposition.3,4
Minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation is classified into 3 types. Type I describes blue-black deposition of pigment in acne scars and areas of inflammation, typically on facial skin.1,5 Histologically, type I stains positive for Perls Prussian blue, indicating an increased deposition of iron as hemosiderin,1 which likely occurs because minocycline is thought to play a role in defective clearance of hemosiderin from the dermis of injured tissue.5 Type II hyperpigmentation presents as bluegray pigment on the lower legs and occasionally the arms.6,7 Type II stains positive for both Perls Prussian blue and Fontana-Masson, demonstrating hemosiderin and melanin, respectively.6 The third form of hyperpigmentation results in diffuse, dark brown to gray pigmentation with a predilection for sun-exposed areas.8 Histology of type III shows increased pigment in the basal portion of the epidermis and brown-black pigment in macrophages of the dermis. Type III stains positive for Fontana-Masson and negative for Perls Prussian blue. The etiology of hyperpigmentation has been suspected to be caused by minocycline stimulating melanin production and/or deposition of minocycline-melanin complexes in dermal macrophages after a certain drug level; this largely is seen in patients receiving 100 to 200 mg daily as early as 1 year into treatment.8
Chlorpromazine is a typical antipsychotic that causes abnormal skin pigmentation in sun-exposed areas due to increased melanogenesis.9 Similar to type III minocyclineinduced hyperpigmentation, a histologic specimen may stain positive for Fontana-Masson yet negative for Perls Prussian blue. Lal et al10 demonstrated complete resolution of abnormal skin pigmentation within 5 years after stopping chlorpromazine. In contrast, minocyclineinduced hyperpigmentation may be permanent in some cases. There is substantial clinical and histologic overlap for drug-induced hyperpigmentation etiologies; it would behoove the clinician to focus on the most common locations affected and the generalized coloration.
Treatment of minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation includes the use of Q-switched lasers, specifically Q-switched ruby and Q-switched alexandrite.11 The use of the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser appears to be ineffective at clearing minocycline-induced pigmentation.7,11 In our patient, minocycline was discontinued immediately. Due to the patient’s critical condition, he deferred all other therapy. Erythema dyschromicum perstans, also referred to as ashy dermatosis, is an idiopathic form of hyperpigmentation.12 Lesions start as blue-gray to ashy gray macules, occasionally surrounded by a slightly erythematous, raised border.
Erythema dyschromicum perstans typically presents on the trunk, face, and arms of patients with Fitzpatrick skin types III and IV; it is considered a variant of lichen planus actinicus.12 Histologically, erythema dyschromicum perstans may mimic lichen planus pigmentosus (LPP); however, subtle differences exist to distinguish the 2 conditions. Erythema dyschromicum perstans demonstrates a mild lichenoid infiltrate, focal basal vacuolization at the dermoepidermal junction, and melanophage deposition.13 In contrast, LPP demonstrates pigmentary incontinence and a more severe inflammatory infiltrate. A perifollicular infiltrate and fibrosis also can be seen in LPP, which may explain the frontal fibrosing alopecia that often precedes LPP.13
Addison disease, also known as primary adrenal insufficiency, can cause diffuse hyperpigmentation in the skin, mucosae, and nail beds. The pigmentation is prominent in regions of naturally increased pigmentation, such as the flexural surfaces and intertriginous areas.14 Patients with adrenal insufficiency will have accompanying weight loss, hypotension, and fatigue, among other symptoms related to deficiency of cortisol and aldosterone. Skin biopsy shows acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, focal parakeratosis, spongiosis, superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate, basal melanin deposition, and superficial dermal macrophages.15
Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis is an uncommon dermatosis that presents with multiple hyperpigmented macules and papules that coalesce to form patches and plaques centrally with reticulation in the periphery.16 Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis commonly presents on the upper trunk, axillae, and neck, though involvement can include flexural surfaces as well as the lower trunk and legs.16,17 Biopsy demonstrates undulating hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, acanthosis, and negative fungal staining.16
Pretibial myxedema most commonly is associated with Graves disease and presents as well-defined thickening and induration with overlying pink or purple-brown papules in the pretibial region.18 An acral surface and mucin deposition within the entire dermis may be appreciated on histology with staining for colloidal iron or Alcian blue.
- Fenske NA, Millns JL, Greer KE. Minocycline-induced pigmentation at sites of cutaneous inflammation. JAMA. 1980;244:1103-1106. doi:10.1001/jama.1980.03310100021021
- Snodgrass A, Motaparthi K. Systemic antibacterial agents. In: Wolverton SE, Wu JJ, eds. Comprehensive Dermatologic Drug Therapy. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2020:69-98.
- Eisen D, Hakim MD. Minocycline-induced pigmentation. incidence, prevention and management. Drug Saf. 1998;18:431-440. doi:10.2165/00002018-199818060-00004
- Goulden V, Glass D, Cunliffe WJ. Safety of long-term high-dose minocycline in the treatment of acne. Br J Dermatol. 1996;134:693-695. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1996.tb06972.x
- Basler RS, Kohnen PW. Localized hemosiderosis as a sequela of acne. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114:1695-1697.
- Ridgway HA, Sonnex TS, Kennedy CT, et al. Hyperpigmentation associated with oral minocycline. Br J Dermatol. 1982;107:95-102. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1982.tb00296.x
- Nisar MS, Iyer K, Brodell RT, et al. Minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation: comparison of 3 Q-switched lasers to reverse its effects. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013;6:159-162. doi:10.2147/CCID.S42166
- Simons JJ, Morales A. Minocycline and generalized cutaneous pigmentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1980;3:244-247. doi:10.1016/s0190 -9622(80)80186-1
- Perry TL, Culling CF, Berry K, et al. 7-Hydroxychlorpromazine: potential toxic drug metabolite in psychiatric patients. Science. 1964;146:81-83. doi:10.1126/science.146.3640.81
- Lal S, Bloom D, Silver B, et al. Replacement of chlorpromazine with other neuroleptics: effect on abnormal skin pigmentation and ocular changes. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 1993;18:173-177.
- Tsao H, Busam K, Barnhill RL, et al. Treatment of minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation with the Q-switched ruby laser. Arch Dermatol. 1996;132:1250-1251.
- Knox JM, Dodge BG, Freeman RG. Erythema dyschromicum perstans. Arch Dermatol. 1968;97:262-272. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1968.01610090034006
- Rutnin S, Udompanich S, Pratumchart N, et al. Ashy dermatosis and lichen planus pigmentosus: the histopathological differences. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:5829185. doi:10.1155/2019/5829185
- Montgomery H, O’Leary PA. Pigmentation of the skin in Addison’s disease, acanthosis nigricans and hemochromatosis. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1930;21:970-984. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1930.01440120072005
- Fernandez-Flores A, Cassarino DS. Histopathologic findings of cutaneous hyperpigmentation in Addison disease and immunostain of the melanocytic population. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:924-927. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000937
- Davis MD, Weenig RH, Camilleri MJ. Confluent and reticulate papillomatosis (Gougerot-Carteaud syndrome): a minocycline-responsive dermatosis without evidence for yeast in pathogenesis. a study of 39 patients and a proposal of diagnostic criteria. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154:287-293. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06955.x
- Jo S, Park HS, Cho S, et al. Updated diagnosis criteria for confluent and reticulated papillomatosis: a case report. Ann Dermatol. 2014; 26:409-410. doi:10.5021/ad.2014.26.3.409
- Lause M, Kamboj A, Fernandez Faith E. Dermatologic manifestations of endocrine disorders. Transl Pediatr. 2017;6:300-312. doi:10.21037 /tp.2017.09.08
The Diagnosis: Drug-Induced Hyperpigmentation
Additional history provided by the patient’s caretaker elucidated an extensive list of medications including chlorpromazine and minocycline, among several others. The caretaker revealed that the patient began treatment for acne vulgaris 2 years prior; despite the acne resolving, therapy was not discontinued. The blue-gray and brown pigmentation on our patient’s shins likely was attributed to a medication he was taking.
Both chlorpromazine and minocycline, among many other medications, are known to cause abnormal pigmentation of the skin.1 Minocycline is a tetracycline antibiotic prescribed for acne and other inflammatory cutaneous conditions. It is highly lipophilic, allowing it to reach high drug concentrations in the skin and nail unit.2 Patients taking minocycline long term and at high doses are at greatest risk for pigment deposition.3,4
Minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation is classified into 3 types. Type I describes blue-black deposition of pigment in acne scars and areas of inflammation, typically on facial skin.1,5 Histologically, type I stains positive for Perls Prussian blue, indicating an increased deposition of iron as hemosiderin,1 which likely occurs because minocycline is thought to play a role in defective clearance of hemosiderin from the dermis of injured tissue.5 Type II hyperpigmentation presents as bluegray pigment on the lower legs and occasionally the arms.6,7 Type II stains positive for both Perls Prussian blue and Fontana-Masson, demonstrating hemosiderin and melanin, respectively.6 The third form of hyperpigmentation results in diffuse, dark brown to gray pigmentation with a predilection for sun-exposed areas.8 Histology of type III shows increased pigment in the basal portion of the epidermis and brown-black pigment in macrophages of the dermis. Type III stains positive for Fontana-Masson and negative for Perls Prussian blue. The etiology of hyperpigmentation has been suspected to be caused by minocycline stimulating melanin production and/or deposition of minocycline-melanin complexes in dermal macrophages after a certain drug level; this largely is seen in patients receiving 100 to 200 mg daily as early as 1 year into treatment.8
Chlorpromazine is a typical antipsychotic that causes abnormal skin pigmentation in sun-exposed areas due to increased melanogenesis.9 Similar to type III minocyclineinduced hyperpigmentation, a histologic specimen may stain positive for Fontana-Masson yet negative for Perls Prussian blue. Lal et al10 demonstrated complete resolution of abnormal skin pigmentation within 5 years after stopping chlorpromazine. In contrast, minocyclineinduced hyperpigmentation may be permanent in some cases. There is substantial clinical and histologic overlap for drug-induced hyperpigmentation etiologies; it would behoove the clinician to focus on the most common locations affected and the generalized coloration.
Treatment of minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation includes the use of Q-switched lasers, specifically Q-switched ruby and Q-switched alexandrite.11 The use of the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser appears to be ineffective at clearing minocycline-induced pigmentation.7,11 In our patient, minocycline was discontinued immediately. Due to the patient’s critical condition, he deferred all other therapy. Erythema dyschromicum perstans, also referred to as ashy dermatosis, is an idiopathic form of hyperpigmentation.12 Lesions start as blue-gray to ashy gray macules, occasionally surrounded by a slightly erythematous, raised border.
Erythema dyschromicum perstans typically presents on the trunk, face, and arms of patients with Fitzpatrick skin types III and IV; it is considered a variant of lichen planus actinicus.12 Histologically, erythema dyschromicum perstans may mimic lichen planus pigmentosus (LPP); however, subtle differences exist to distinguish the 2 conditions. Erythema dyschromicum perstans demonstrates a mild lichenoid infiltrate, focal basal vacuolization at the dermoepidermal junction, and melanophage deposition.13 In contrast, LPP demonstrates pigmentary incontinence and a more severe inflammatory infiltrate. A perifollicular infiltrate and fibrosis also can be seen in LPP, which may explain the frontal fibrosing alopecia that often precedes LPP.13
Addison disease, also known as primary adrenal insufficiency, can cause diffuse hyperpigmentation in the skin, mucosae, and nail beds. The pigmentation is prominent in regions of naturally increased pigmentation, such as the flexural surfaces and intertriginous areas.14 Patients with adrenal insufficiency will have accompanying weight loss, hypotension, and fatigue, among other symptoms related to deficiency of cortisol and aldosterone. Skin biopsy shows acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, focal parakeratosis, spongiosis, superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate, basal melanin deposition, and superficial dermal macrophages.15
Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis is an uncommon dermatosis that presents with multiple hyperpigmented macules and papules that coalesce to form patches and plaques centrally with reticulation in the periphery.16 Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis commonly presents on the upper trunk, axillae, and neck, though involvement can include flexural surfaces as well as the lower trunk and legs.16,17 Biopsy demonstrates undulating hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, acanthosis, and negative fungal staining.16
Pretibial myxedema most commonly is associated with Graves disease and presents as well-defined thickening and induration with overlying pink or purple-brown papules in the pretibial region.18 An acral surface and mucin deposition within the entire dermis may be appreciated on histology with staining for colloidal iron or Alcian blue.
The Diagnosis: Drug-Induced Hyperpigmentation
Additional history provided by the patient’s caretaker elucidated an extensive list of medications including chlorpromazine and minocycline, among several others. The caretaker revealed that the patient began treatment for acne vulgaris 2 years prior; despite the acne resolving, therapy was not discontinued. The blue-gray and brown pigmentation on our patient’s shins likely was attributed to a medication he was taking.
Both chlorpromazine and minocycline, among many other medications, are known to cause abnormal pigmentation of the skin.1 Minocycline is a tetracycline antibiotic prescribed for acne and other inflammatory cutaneous conditions. It is highly lipophilic, allowing it to reach high drug concentrations in the skin and nail unit.2 Patients taking minocycline long term and at high doses are at greatest risk for pigment deposition.3,4
Minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation is classified into 3 types. Type I describes blue-black deposition of pigment in acne scars and areas of inflammation, typically on facial skin.1,5 Histologically, type I stains positive for Perls Prussian blue, indicating an increased deposition of iron as hemosiderin,1 which likely occurs because minocycline is thought to play a role in defective clearance of hemosiderin from the dermis of injured tissue.5 Type II hyperpigmentation presents as bluegray pigment on the lower legs and occasionally the arms.6,7 Type II stains positive for both Perls Prussian blue and Fontana-Masson, demonstrating hemosiderin and melanin, respectively.6 The third form of hyperpigmentation results in diffuse, dark brown to gray pigmentation with a predilection for sun-exposed areas.8 Histology of type III shows increased pigment in the basal portion of the epidermis and brown-black pigment in macrophages of the dermis. Type III stains positive for Fontana-Masson and negative for Perls Prussian blue. The etiology of hyperpigmentation has been suspected to be caused by minocycline stimulating melanin production and/or deposition of minocycline-melanin complexes in dermal macrophages after a certain drug level; this largely is seen in patients receiving 100 to 200 mg daily as early as 1 year into treatment.8
Chlorpromazine is a typical antipsychotic that causes abnormal skin pigmentation in sun-exposed areas due to increased melanogenesis.9 Similar to type III minocyclineinduced hyperpigmentation, a histologic specimen may stain positive for Fontana-Masson yet negative for Perls Prussian blue. Lal et al10 demonstrated complete resolution of abnormal skin pigmentation within 5 years after stopping chlorpromazine. In contrast, minocyclineinduced hyperpigmentation may be permanent in some cases. There is substantial clinical and histologic overlap for drug-induced hyperpigmentation etiologies; it would behoove the clinician to focus on the most common locations affected and the generalized coloration.
Treatment of minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation includes the use of Q-switched lasers, specifically Q-switched ruby and Q-switched alexandrite.11 The use of the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser appears to be ineffective at clearing minocycline-induced pigmentation.7,11 In our patient, minocycline was discontinued immediately. Due to the patient’s critical condition, he deferred all other therapy. Erythema dyschromicum perstans, also referred to as ashy dermatosis, is an idiopathic form of hyperpigmentation.12 Lesions start as blue-gray to ashy gray macules, occasionally surrounded by a slightly erythematous, raised border.
Erythema dyschromicum perstans typically presents on the trunk, face, and arms of patients with Fitzpatrick skin types III and IV; it is considered a variant of lichen planus actinicus.12 Histologically, erythema dyschromicum perstans may mimic lichen planus pigmentosus (LPP); however, subtle differences exist to distinguish the 2 conditions. Erythema dyschromicum perstans demonstrates a mild lichenoid infiltrate, focal basal vacuolization at the dermoepidermal junction, and melanophage deposition.13 In contrast, LPP demonstrates pigmentary incontinence and a more severe inflammatory infiltrate. A perifollicular infiltrate and fibrosis also can be seen in LPP, which may explain the frontal fibrosing alopecia that often precedes LPP.13
Addison disease, also known as primary adrenal insufficiency, can cause diffuse hyperpigmentation in the skin, mucosae, and nail beds. The pigmentation is prominent in regions of naturally increased pigmentation, such as the flexural surfaces and intertriginous areas.14 Patients with adrenal insufficiency will have accompanying weight loss, hypotension, and fatigue, among other symptoms related to deficiency of cortisol and aldosterone. Skin biopsy shows acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, focal parakeratosis, spongiosis, superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate, basal melanin deposition, and superficial dermal macrophages.15
Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis is an uncommon dermatosis that presents with multiple hyperpigmented macules and papules that coalesce to form patches and plaques centrally with reticulation in the periphery.16 Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis commonly presents on the upper trunk, axillae, and neck, though involvement can include flexural surfaces as well as the lower trunk and legs.16,17 Biopsy demonstrates undulating hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, acanthosis, and negative fungal staining.16
Pretibial myxedema most commonly is associated with Graves disease and presents as well-defined thickening and induration with overlying pink or purple-brown papules in the pretibial region.18 An acral surface and mucin deposition within the entire dermis may be appreciated on histology with staining for colloidal iron or Alcian blue.
- Fenske NA, Millns JL, Greer KE. Minocycline-induced pigmentation at sites of cutaneous inflammation. JAMA. 1980;244:1103-1106. doi:10.1001/jama.1980.03310100021021
- Snodgrass A, Motaparthi K. Systemic antibacterial agents. In: Wolverton SE, Wu JJ, eds. Comprehensive Dermatologic Drug Therapy. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2020:69-98.
- Eisen D, Hakim MD. Minocycline-induced pigmentation. incidence, prevention and management. Drug Saf. 1998;18:431-440. doi:10.2165/00002018-199818060-00004
- Goulden V, Glass D, Cunliffe WJ. Safety of long-term high-dose minocycline in the treatment of acne. Br J Dermatol. 1996;134:693-695. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1996.tb06972.x
- Basler RS, Kohnen PW. Localized hemosiderosis as a sequela of acne. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114:1695-1697.
- Ridgway HA, Sonnex TS, Kennedy CT, et al. Hyperpigmentation associated with oral minocycline. Br J Dermatol. 1982;107:95-102. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1982.tb00296.x
- Nisar MS, Iyer K, Brodell RT, et al. Minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation: comparison of 3 Q-switched lasers to reverse its effects. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013;6:159-162. doi:10.2147/CCID.S42166
- Simons JJ, Morales A. Minocycline and generalized cutaneous pigmentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1980;3:244-247. doi:10.1016/s0190 -9622(80)80186-1
- Perry TL, Culling CF, Berry K, et al. 7-Hydroxychlorpromazine: potential toxic drug metabolite in psychiatric patients. Science. 1964;146:81-83. doi:10.1126/science.146.3640.81
- Lal S, Bloom D, Silver B, et al. Replacement of chlorpromazine with other neuroleptics: effect on abnormal skin pigmentation and ocular changes. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 1993;18:173-177.
- Tsao H, Busam K, Barnhill RL, et al. Treatment of minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation with the Q-switched ruby laser. Arch Dermatol. 1996;132:1250-1251.
- Knox JM, Dodge BG, Freeman RG. Erythema dyschromicum perstans. Arch Dermatol. 1968;97:262-272. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1968.01610090034006
- Rutnin S, Udompanich S, Pratumchart N, et al. Ashy dermatosis and lichen planus pigmentosus: the histopathological differences. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:5829185. doi:10.1155/2019/5829185
- Montgomery H, O’Leary PA. Pigmentation of the skin in Addison’s disease, acanthosis nigricans and hemochromatosis. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1930;21:970-984. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1930.01440120072005
- Fernandez-Flores A, Cassarino DS. Histopathologic findings of cutaneous hyperpigmentation in Addison disease and immunostain of the melanocytic population. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:924-927. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000937
- Davis MD, Weenig RH, Camilleri MJ. Confluent and reticulate papillomatosis (Gougerot-Carteaud syndrome): a minocycline-responsive dermatosis without evidence for yeast in pathogenesis. a study of 39 patients and a proposal of diagnostic criteria. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154:287-293. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06955.x
- Jo S, Park HS, Cho S, et al. Updated diagnosis criteria for confluent and reticulated papillomatosis: a case report. Ann Dermatol. 2014; 26:409-410. doi:10.5021/ad.2014.26.3.409
- Lause M, Kamboj A, Fernandez Faith E. Dermatologic manifestations of endocrine disorders. Transl Pediatr. 2017;6:300-312. doi:10.21037 /tp.2017.09.08
- Fenske NA, Millns JL, Greer KE. Minocycline-induced pigmentation at sites of cutaneous inflammation. JAMA. 1980;244:1103-1106. doi:10.1001/jama.1980.03310100021021
- Snodgrass A, Motaparthi K. Systemic antibacterial agents. In: Wolverton SE, Wu JJ, eds. Comprehensive Dermatologic Drug Therapy. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2020:69-98.
- Eisen D, Hakim MD. Minocycline-induced pigmentation. incidence, prevention and management. Drug Saf. 1998;18:431-440. doi:10.2165/00002018-199818060-00004
- Goulden V, Glass D, Cunliffe WJ. Safety of long-term high-dose minocycline in the treatment of acne. Br J Dermatol. 1996;134:693-695. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1996.tb06972.x
- Basler RS, Kohnen PW. Localized hemosiderosis as a sequela of acne. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114:1695-1697.
- Ridgway HA, Sonnex TS, Kennedy CT, et al. Hyperpigmentation associated with oral minocycline. Br J Dermatol. 1982;107:95-102. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1982.tb00296.x
- Nisar MS, Iyer K, Brodell RT, et al. Minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation: comparison of 3 Q-switched lasers to reverse its effects. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013;6:159-162. doi:10.2147/CCID.S42166
- Simons JJ, Morales A. Minocycline and generalized cutaneous pigmentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1980;3:244-247. doi:10.1016/s0190 -9622(80)80186-1
- Perry TL, Culling CF, Berry K, et al. 7-Hydroxychlorpromazine: potential toxic drug metabolite in psychiatric patients. Science. 1964;146:81-83. doi:10.1126/science.146.3640.81
- Lal S, Bloom D, Silver B, et al. Replacement of chlorpromazine with other neuroleptics: effect on abnormal skin pigmentation and ocular changes. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 1993;18:173-177.
- Tsao H, Busam K, Barnhill RL, et al. Treatment of minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation with the Q-switched ruby laser. Arch Dermatol. 1996;132:1250-1251.
- Knox JM, Dodge BG, Freeman RG. Erythema dyschromicum perstans. Arch Dermatol. 1968;97:262-272. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1968.01610090034006
- Rutnin S, Udompanich S, Pratumchart N, et al. Ashy dermatosis and lichen planus pigmentosus: the histopathological differences. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:5829185. doi:10.1155/2019/5829185
- Montgomery H, O’Leary PA. Pigmentation of the skin in Addison’s disease, acanthosis nigricans and hemochromatosis. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1930;21:970-984. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1930.01440120072005
- Fernandez-Flores A, Cassarino DS. Histopathologic findings of cutaneous hyperpigmentation in Addison disease and immunostain of the melanocytic population. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:924-927. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000937
- Davis MD, Weenig RH, Camilleri MJ. Confluent and reticulate papillomatosis (Gougerot-Carteaud syndrome): a minocycline-responsive dermatosis without evidence for yeast in pathogenesis. a study of 39 patients and a proposal of diagnostic criteria. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154:287-293. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06955.x
- Jo S, Park HS, Cho S, et al. Updated diagnosis criteria for confluent and reticulated papillomatosis: a case report. Ann Dermatol. 2014; 26:409-410. doi:10.5021/ad.2014.26.3.409
- Lause M, Kamboj A, Fernandez Faith E. Dermatologic manifestations of endocrine disorders. Transl Pediatr. 2017;6:300-312. doi:10.21037 /tp.2017.09.08
A 37-year-old man with a history of cerebral palsy, bipolar disorder, and impulse control disorder presented to the emergency department with breathing difficulty and worsening malaise. The patient subsequently was intubated due to hypoxic respiratory failure and was found to be positive for SARS-CoV-2. He was admitted to the intensive care unit, and dermatology was consulted due to concern that the cutaneous findings were demonstrative of a vasculitic process. Physical examination revealed diffuse, symmetric, dark brown to blue-gray macules coalescing into patches on the anterior tibia (top) and covering the entire lower leg (bottom). The patches were mottled and did not blanch with pressure. According to the patient’s caretaker, the leg hyperpigmentation had been present for 2 years.
Medtronic expands recall of MiniMed 600 insulin pumps
Medtronic has updated a previous recall of its MiniMed 600 series insulin pumps to include all with a potentially problematic clear retainer ring, not just those that appear damaged.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced on Oct. 5 that Medtronic will now replace any MiniMed 600 series pump that has a clear retainer ring with an updated pump that includes a black retainer ring at no extra charge, regardless of warranty status.
In November 2019, Medtronic first advised patients to examine their pumps for potential damage to the ring, and to contact the company if it appeared to be loose, damaged, or missing. In February 2020, the FDA designated the recall as class 1, “the most serious type of recall,” for which use of the devices “may cause serious injuries or death.”
In this case, one potential risk is hyperglycemia. This can occur if the reservoir isn’t properly locked into place by the retainer ring, and insulin isn’t infused into the body. That, in turn, can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis. Another risk is hypoglycemia, which could result from over-delivery of insulin if the retainer ring breaks or detaches and the user inserts the reservoir back into the pump with the infusion set still connected to the body.
While serious injuries and deaths have been reported with the use of Minimed series 600 insulin pumps, “those adverse events may not have been directly related to the damaged clear retainer rings that are the basis for this recall,” according to the FDA notice. Nonetheless, lawsuits have reportedly been filed.
The new update is not a result of any new issues, Medtronic spokesperson Pamela Reese told this news organization. “Medtronic will proactively replace all MiniMed 600 series insulin pumps with the clear retainer ring design with an equivalent pump that has an updated black retainer ring design, which is designed to better withstand damage sustained by an accidental drop or bump on a hard surface.”
She added, “As we analyze the information that we continuously collect on the safety and performance of our insulin pumps, we recognize that patients who are still using the clear retainer ring could potentially encounter future problems. Therefore, we are currently accelerating our replacement as inventory allows over the coming months to eliminate any potential performance concerns and optimize patient safety and experience.”
The company has replaced nearly half of the clear retainer ring pumps that were in use since November 2019, she said.
The specific insulin pump products are the model 630G, distributed between September 2016 and February 2020; and the 670G, distributed between May 2015 and December 2020. The 630G is approved for people aged 16 years and older, and the 670G – which works with a continuous glucose monitor in a “hybrid closed-loop system – is available for people with type 1 diabetes as young as 7 years of age.
Medtronic has updated a previous recall of its MiniMed 600 series insulin pumps to include all with a potentially problematic clear retainer ring, not just those that appear damaged.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced on Oct. 5 that Medtronic will now replace any MiniMed 600 series pump that has a clear retainer ring with an updated pump that includes a black retainer ring at no extra charge, regardless of warranty status.
In November 2019, Medtronic first advised patients to examine their pumps for potential damage to the ring, and to contact the company if it appeared to be loose, damaged, or missing. In February 2020, the FDA designated the recall as class 1, “the most serious type of recall,” for which use of the devices “may cause serious injuries or death.”
In this case, one potential risk is hyperglycemia. This can occur if the reservoir isn’t properly locked into place by the retainer ring, and insulin isn’t infused into the body. That, in turn, can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis. Another risk is hypoglycemia, which could result from over-delivery of insulin if the retainer ring breaks or detaches and the user inserts the reservoir back into the pump with the infusion set still connected to the body.
While serious injuries and deaths have been reported with the use of Minimed series 600 insulin pumps, “those adverse events may not have been directly related to the damaged clear retainer rings that are the basis for this recall,” according to the FDA notice. Nonetheless, lawsuits have reportedly been filed.
The new update is not a result of any new issues, Medtronic spokesperson Pamela Reese told this news organization. “Medtronic will proactively replace all MiniMed 600 series insulin pumps with the clear retainer ring design with an equivalent pump that has an updated black retainer ring design, which is designed to better withstand damage sustained by an accidental drop or bump on a hard surface.”
She added, “As we analyze the information that we continuously collect on the safety and performance of our insulin pumps, we recognize that patients who are still using the clear retainer ring could potentially encounter future problems. Therefore, we are currently accelerating our replacement as inventory allows over the coming months to eliminate any potential performance concerns and optimize patient safety and experience.”
The company has replaced nearly half of the clear retainer ring pumps that were in use since November 2019, she said.
The specific insulin pump products are the model 630G, distributed between September 2016 and February 2020; and the 670G, distributed between May 2015 and December 2020. The 630G is approved for people aged 16 years and older, and the 670G – which works with a continuous glucose monitor in a “hybrid closed-loop system – is available for people with type 1 diabetes as young as 7 years of age.
Medtronic has updated a previous recall of its MiniMed 600 series insulin pumps to include all with a potentially problematic clear retainer ring, not just those that appear damaged.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced on Oct. 5 that Medtronic will now replace any MiniMed 600 series pump that has a clear retainer ring with an updated pump that includes a black retainer ring at no extra charge, regardless of warranty status.
In November 2019, Medtronic first advised patients to examine their pumps for potential damage to the ring, and to contact the company if it appeared to be loose, damaged, or missing. In February 2020, the FDA designated the recall as class 1, “the most serious type of recall,” for which use of the devices “may cause serious injuries or death.”
In this case, one potential risk is hyperglycemia. This can occur if the reservoir isn’t properly locked into place by the retainer ring, and insulin isn’t infused into the body. That, in turn, can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis. Another risk is hypoglycemia, which could result from over-delivery of insulin if the retainer ring breaks or detaches and the user inserts the reservoir back into the pump with the infusion set still connected to the body.
While serious injuries and deaths have been reported with the use of Minimed series 600 insulin pumps, “those adverse events may not have been directly related to the damaged clear retainer rings that are the basis for this recall,” according to the FDA notice. Nonetheless, lawsuits have reportedly been filed.
The new update is not a result of any new issues, Medtronic spokesperson Pamela Reese told this news organization. “Medtronic will proactively replace all MiniMed 600 series insulin pumps with the clear retainer ring design with an equivalent pump that has an updated black retainer ring design, which is designed to better withstand damage sustained by an accidental drop or bump on a hard surface.”
She added, “As we analyze the information that we continuously collect on the safety and performance of our insulin pumps, we recognize that patients who are still using the clear retainer ring could potentially encounter future problems. Therefore, we are currently accelerating our replacement as inventory allows over the coming months to eliminate any potential performance concerns and optimize patient safety and experience.”
The company has replaced nearly half of the clear retainer ring pumps that were in use since November 2019, she said.
The specific insulin pump products are the model 630G, distributed between September 2016 and February 2020; and the 670G, distributed between May 2015 and December 2020. The 630G is approved for people aged 16 years and older, and the 670G – which works with a continuous glucose monitor in a “hybrid closed-loop system – is available for people with type 1 diabetes as young as 7 years of age.
Children and COVID: Decline of summer surge continues
The continuing decline in COVID-19 incidence suggests the latest surge has peaked as new cases in children dropped for the 4th consecutive week, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
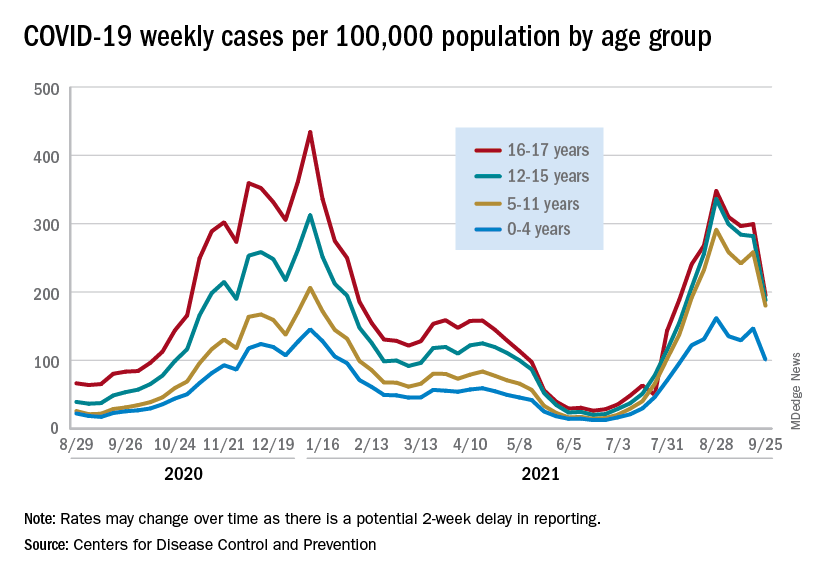
Preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, however, show an uptick in new cases in late September, largely among younger children, that may indicate otherwise. Those data have a potential 2-week reporting delay, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker, so the most recent points on the graph (see above) could still go up.
. Those new cases made up almost 27% of all cases for the week, and the nearly 5.9 million child cases that have been reported since the start of the pandemic represent 16.2% of cases among Americans of all ages, the two groups said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The CDC data on new cases by age group suggest that younger children have borne a heavier burden in the summer surge of COVID than they did last winter. The rate of new cases was not as high for 16- and 17-year-olds in the summer, but the other age groups all reached higher peaks than in the winter, including the 12- to 15-year-olds, who have been getting vaccinated since May, according to the COVID Data Tracker.
With vaccination approval getting closer for children under age 12 years, initiation in those already eligible continues to slide. Those aged 12-15 made up just 6.9% of new vaccinations during the 2 weeks from Sept. 21 to Oct. 4, and that figure has been dropping since July 13-26, when it was 14.1%. Vaccine initiation among 16- and 17-year-olds over that time has dropped by almost half, from 5.4% to 2.9%, the CDC data show.
All the vaccinations so far add up to this: Almost 55% of those aged 12-15 have gotten at least one dose of COVID vaccine, as have over 62% of those aged 16-17, and 52% of the older group is fully vaccinated, as is 44% of the younger group. Altogether, 10.8 million children were fully vaccinated as of Oct. 4, including those under 12 who may be participating in clinical trials or had a birth date entered incorrectly, the CDC said.
The continuing decline in COVID-19 incidence suggests the latest surge has peaked as new cases in children dropped for the 4th consecutive week, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, however, show an uptick in new cases in late September, largely among younger children, that may indicate otherwise. Those data have a potential 2-week reporting delay, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker, so the most recent points on the graph (see above) could still go up.
. Those new cases made up almost 27% of all cases for the week, and the nearly 5.9 million child cases that have been reported since the start of the pandemic represent 16.2% of cases among Americans of all ages, the two groups said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The CDC data on new cases by age group suggest that younger children have borne a heavier burden in the summer surge of COVID than they did last winter. The rate of new cases was not as high for 16- and 17-year-olds in the summer, but the other age groups all reached higher peaks than in the winter, including the 12- to 15-year-olds, who have been getting vaccinated since May, according to the COVID Data Tracker.
With vaccination approval getting closer for children under age 12 years, initiation in those already eligible continues to slide. Those aged 12-15 made up just 6.9% of new vaccinations during the 2 weeks from Sept. 21 to Oct. 4, and that figure has been dropping since July 13-26, when it was 14.1%. Vaccine initiation among 16- and 17-year-olds over that time has dropped by almost half, from 5.4% to 2.9%, the CDC data show.
All the vaccinations so far add up to this: Almost 55% of those aged 12-15 have gotten at least one dose of COVID vaccine, as have over 62% of those aged 16-17, and 52% of the older group is fully vaccinated, as is 44% of the younger group. Altogether, 10.8 million children were fully vaccinated as of Oct. 4, including those under 12 who may be participating in clinical trials or had a birth date entered incorrectly, the CDC said.
The continuing decline in COVID-19 incidence suggests the latest surge has peaked as new cases in children dropped for the 4th consecutive week, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, however, show an uptick in new cases in late September, largely among younger children, that may indicate otherwise. Those data have a potential 2-week reporting delay, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker, so the most recent points on the graph (see above) could still go up.
. Those new cases made up almost 27% of all cases for the week, and the nearly 5.9 million child cases that have been reported since the start of the pandemic represent 16.2% of cases among Americans of all ages, the two groups said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The CDC data on new cases by age group suggest that younger children have borne a heavier burden in the summer surge of COVID than they did last winter. The rate of new cases was not as high for 16- and 17-year-olds in the summer, but the other age groups all reached higher peaks than in the winter, including the 12- to 15-year-olds, who have been getting vaccinated since May, according to the COVID Data Tracker.
With vaccination approval getting closer for children under age 12 years, initiation in those already eligible continues to slide. Those aged 12-15 made up just 6.9% of new vaccinations during the 2 weeks from Sept. 21 to Oct. 4, and that figure has been dropping since July 13-26, when it was 14.1%. Vaccine initiation among 16- and 17-year-olds over that time has dropped by almost half, from 5.4% to 2.9%, the CDC data show.
All the vaccinations so far add up to this: Almost 55% of those aged 12-15 have gotten at least one dose of COVID vaccine, as have over 62% of those aged 16-17, and 52% of the older group is fully vaccinated, as is 44% of the younger group. Altogether, 10.8 million children were fully vaccinated as of Oct. 4, including those under 12 who may be participating in clinical trials or had a birth date entered incorrectly, the CDC said.
Hypoglycemia awareness program helps tricky-to-treat T1D
People with insulin-treated type 1 diabetes who had problems avoiding hypoglycemic episodes despite optimal care were helped significantly by a new psychoeducational program called HARPdoc, it was reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
In a randomized controlled trial (RCT), both HARPdoc and the more established Blood Glucose Awareness Training (BGAT) were effective at reducing the number of severe hypoglycemia episodes seen, from five episodes at baseline to one at 1 year in both groups, and one and none at 2-years’ follow-up, respectively.
“HARPdoc is not superior to BGAT in its ability to restore hypoglycemia awareness and reduce severe hypoglycemia,” said Stephanie Amiel, MD, FRCP, the chief investigator for the trial. However, “it does reduce cognitive barriers to hypoglycemia avoidance, so it achieves what it set out to do.”
Dr. Amiel, professor of diabetes research at Kings College London, added that it was important to note that HARPdoc was better than BGAT at improving participants’ mental health, “producing a clinically important and sustainable reduction in diabetes distress, anxiety, and depression.”
What’s HARPdoc?
The Hypoglycaemia Awareness Restoration Programme for people with type 1 diabetes and problematic hypoglycaemia persisting despite optimised self-care (HARPdoc) was designed to specifically address why some people with type 1 diabetes find it difficult to avoid recurrent hypoglycemia.
“It’s a psychoeducational program with clinical knowledge about hypoglycemia and group learning, but also explicit topics on mindset and behavior change,” explained Nicole de Zoysa, DClinPsych, one of the clinical psychologists involved in the trial.
Over the course of the 6-week program, there are four group sessions (weeks 1-3, and week 6) and two individual sessions (weeks 4 and 5) that address important “cognitive barriers” or “thinking traps” to avoiding hypoglycemia that were identified during prior qualitative research.
HARPdoc is thus “an attempt to make sense of people’s reluctance or seeming reluctance to take action around hypoglycemia, Dr. de Zoysa said. The intervention draws on both cognitive behavioral theory “to work with the beliefs” and motivational interviewing “to work with the resistance.”
The HARPdoc RCT
Starting in 2017 and ending earlier this year, the HARPdoc RCT was a parallel group study conducted at three specialist diabetes centers in the United Kingdom and one in the United States.
A total of 99 adults with insulin-treated type 1 diabetes and impaired hypoglycemia awareness were enrolled – with 49 randomized to the HARPdoc arm and 50 to the BGAT arm. All had been offered technologies to help them potentially bring their hypoglycemia under better control, such as continuous glucose monitoring, insulin pumps, or closed loop systems, and received structured education on flexible insulin dosing.
The aim was to show superiority of the HARPdoc program over BGAT, in helping people avoid episodes of severe hypoglycemia, defined as episodes that needed other people’s intervention to help resolve.
BGAT is also a psychoeducation program that has been around since the 1980s but barely used in the United Kingdom, Dr. Amiel noted.
Baseline demographic characteristics were similar for the HARPdoc and BGAT arms: The mean age was 57 versus 52 years, there was a long (30+ years) duration of diabetes, over half of the participants were male, and almost all were White.
Primary endpoint not met, but still ‘impressive’
Although the primary endpoint of the trial was not met, the reductions in severe hypoglycemia seen are still “impressive,” said Ramzi Ajjan, MD, FRCP, of Leeds (England) University and Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust.
“I was really blown away,” by the improvement in both study arms, said Dr. Ajjan, who was not involved in the trial. “These people have had proper clinical input,” he stressed, noting that both interventions worked, with no difference between them in terms of severe hypoglycemia.
Dr. Ajjan was not surprised by the better cognition scores measured using the A2A questionnaire seen with HARPdoc versus BGAT, as “this is what the intervention was designed to address.”
In terms of the mental health benefits seen, HARPdoc significantly reduced the level of diabetes distress as measured using the Problem Areas In Diabetes (PAID) questionnaire versus the BGAT intervention.
The PAID score was around 30 in both groups at baseline, this fell to about 26 at 1 year, and around 20 at 2 years in the HARPdoc group, which was significantly lower than the score seen in the BGAT group which rose slightly then fell back to baseline levels.
A similar pattern was seen in the levels of depression and anxiety, which were measured by the HADS-D and HADS-A instruments. So HARPdoc was more effective at improving psychological and mental health outcomes than BGAT, Dr. Ajjan observed.
The HARPdoc project is funded by the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation with additional support from the UK’s National Institute of Health Research. The HARPdoc RCT was jointly sponsored by King’s College London and King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. Dr. Amiel has served on advisory panels for Roche, Medtronic, and Novo Nordisk. Dr. de Zoysa did not state having any conflicts of interest. Dr. Ajjan disclosed that he has financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies.
People with insulin-treated type 1 diabetes who had problems avoiding hypoglycemic episodes despite optimal care were helped significantly by a new psychoeducational program called HARPdoc, it was reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
In a randomized controlled trial (RCT), both HARPdoc and the more established Blood Glucose Awareness Training (BGAT) were effective at reducing the number of severe hypoglycemia episodes seen, from five episodes at baseline to one at 1 year in both groups, and one and none at 2-years’ follow-up, respectively.
“HARPdoc is not superior to BGAT in its ability to restore hypoglycemia awareness and reduce severe hypoglycemia,” said Stephanie Amiel, MD, FRCP, the chief investigator for the trial. However, “it does reduce cognitive barriers to hypoglycemia avoidance, so it achieves what it set out to do.”
Dr. Amiel, professor of diabetes research at Kings College London, added that it was important to note that HARPdoc was better than BGAT at improving participants’ mental health, “producing a clinically important and sustainable reduction in diabetes distress, anxiety, and depression.”
What’s HARPdoc?
The Hypoglycaemia Awareness Restoration Programme for people with type 1 diabetes and problematic hypoglycaemia persisting despite optimised self-care (HARPdoc) was designed to specifically address why some people with type 1 diabetes find it difficult to avoid recurrent hypoglycemia.
“It’s a psychoeducational program with clinical knowledge about hypoglycemia and group learning, but also explicit topics on mindset and behavior change,” explained Nicole de Zoysa, DClinPsych, one of the clinical psychologists involved in the trial.
Over the course of the 6-week program, there are four group sessions (weeks 1-3, and week 6) and two individual sessions (weeks 4 and 5) that address important “cognitive barriers” or “thinking traps” to avoiding hypoglycemia that were identified during prior qualitative research.
HARPdoc is thus “an attempt to make sense of people’s reluctance or seeming reluctance to take action around hypoglycemia, Dr. de Zoysa said. The intervention draws on both cognitive behavioral theory “to work with the beliefs” and motivational interviewing “to work with the resistance.”
The HARPdoc RCT
Starting in 2017 and ending earlier this year, the HARPdoc RCT was a parallel group study conducted at three specialist diabetes centers in the United Kingdom and one in the United States.
A total of 99 adults with insulin-treated type 1 diabetes and impaired hypoglycemia awareness were enrolled – with 49 randomized to the HARPdoc arm and 50 to the BGAT arm. All had been offered technologies to help them potentially bring their hypoglycemia under better control, such as continuous glucose monitoring, insulin pumps, or closed loop systems, and received structured education on flexible insulin dosing.
The aim was to show superiority of the HARPdoc program over BGAT, in helping people avoid episodes of severe hypoglycemia, defined as episodes that needed other people’s intervention to help resolve.
BGAT is also a psychoeducation program that has been around since the 1980s but barely used in the United Kingdom, Dr. Amiel noted.
Baseline demographic characteristics were similar for the HARPdoc and BGAT arms: The mean age was 57 versus 52 years, there was a long (30+ years) duration of diabetes, over half of the participants were male, and almost all were White.
Primary endpoint not met, but still ‘impressive’
Although the primary endpoint of the trial was not met, the reductions in severe hypoglycemia seen are still “impressive,” said Ramzi Ajjan, MD, FRCP, of Leeds (England) University and Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust.
“I was really blown away,” by the improvement in both study arms, said Dr. Ajjan, who was not involved in the trial. “These people have had proper clinical input,” he stressed, noting that both interventions worked, with no difference between them in terms of severe hypoglycemia.
Dr. Ajjan was not surprised by the better cognition scores measured using the A2A questionnaire seen with HARPdoc versus BGAT, as “this is what the intervention was designed to address.”
In terms of the mental health benefits seen, HARPdoc significantly reduced the level of diabetes distress as measured using the Problem Areas In Diabetes (PAID) questionnaire versus the BGAT intervention.
The PAID score was around 30 in both groups at baseline, this fell to about 26 at 1 year, and around 20 at 2 years in the HARPdoc group, which was significantly lower than the score seen in the BGAT group which rose slightly then fell back to baseline levels.
A similar pattern was seen in the levels of depression and anxiety, which were measured by the HADS-D and HADS-A instruments. So HARPdoc was more effective at improving psychological and mental health outcomes than BGAT, Dr. Ajjan observed.
The HARPdoc project is funded by the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation with additional support from the UK’s National Institute of Health Research. The HARPdoc RCT was jointly sponsored by King’s College London and King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. Dr. Amiel has served on advisory panels for Roche, Medtronic, and Novo Nordisk. Dr. de Zoysa did not state having any conflicts of interest. Dr. Ajjan disclosed that he has financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies.
People with insulin-treated type 1 diabetes who had problems avoiding hypoglycemic episodes despite optimal care were helped significantly by a new psychoeducational program called HARPdoc, it was reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
In a randomized controlled trial (RCT), both HARPdoc and the more established Blood Glucose Awareness Training (BGAT) were effective at reducing the number of severe hypoglycemia episodes seen, from five episodes at baseline to one at 1 year in both groups, and one and none at 2-years’ follow-up, respectively.
“HARPdoc is not superior to BGAT in its ability to restore hypoglycemia awareness and reduce severe hypoglycemia,” said Stephanie Amiel, MD, FRCP, the chief investigator for the trial. However, “it does reduce cognitive barriers to hypoglycemia avoidance, so it achieves what it set out to do.”
Dr. Amiel, professor of diabetes research at Kings College London, added that it was important to note that HARPdoc was better than BGAT at improving participants’ mental health, “producing a clinically important and sustainable reduction in diabetes distress, anxiety, and depression.”
What’s HARPdoc?
The Hypoglycaemia Awareness Restoration Programme for people with type 1 diabetes and problematic hypoglycaemia persisting despite optimised self-care (HARPdoc) was designed to specifically address why some people with type 1 diabetes find it difficult to avoid recurrent hypoglycemia.
“It’s a psychoeducational program with clinical knowledge about hypoglycemia and group learning, but also explicit topics on mindset and behavior change,” explained Nicole de Zoysa, DClinPsych, one of the clinical psychologists involved in the trial.
Over the course of the 6-week program, there are four group sessions (weeks 1-3, and week 6) and two individual sessions (weeks 4 and 5) that address important “cognitive barriers” or “thinking traps” to avoiding hypoglycemia that were identified during prior qualitative research.
HARPdoc is thus “an attempt to make sense of people’s reluctance or seeming reluctance to take action around hypoglycemia, Dr. de Zoysa said. The intervention draws on both cognitive behavioral theory “to work with the beliefs” and motivational interviewing “to work with the resistance.”
The HARPdoc RCT
Starting in 2017 and ending earlier this year, the HARPdoc RCT was a parallel group study conducted at three specialist diabetes centers in the United Kingdom and one in the United States.
A total of 99 adults with insulin-treated type 1 diabetes and impaired hypoglycemia awareness were enrolled – with 49 randomized to the HARPdoc arm and 50 to the BGAT arm. All had been offered technologies to help them potentially bring their hypoglycemia under better control, such as continuous glucose monitoring, insulin pumps, or closed loop systems, and received structured education on flexible insulin dosing.
The aim was to show superiority of the HARPdoc program over BGAT, in helping people avoid episodes of severe hypoglycemia, defined as episodes that needed other people’s intervention to help resolve.
BGAT is also a psychoeducation program that has been around since the 1980s but barely used in the United Kingdom, Dr. Amiel noted.
Baseline demographic characteristics were similar for the HARPdoc and BGAT arms: The mean age was 57 versus 52 years, there was a long (30+ years) duration of diabetes, over half of the participants were male, and almost all were White.
Primary endpoint not met, but still ‘impressive’
Although the primary endpoint of the trial was not met, the reductions in severe hypoglycemia seen are still “impressive,” said Ramzi Ajjan, MD, FRCP, of Leeds (England) University and Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust.
“I was really blown away,” by the improvement in both study arms, said Dr. Ajjan, who was not involved in the trial. “These people have had proper clinical input,” he stressed, noting that both interventions worked, with no difference between them in terms of severe hypoglycemia.
Dr. Ajjan was not surprised by the better cognition scores measured using the A2A questionnaire seen with HARPdoc versus BGAT, as “this is what the intervention was designed to address.”
In terms of the mental health benefits seen, HARPdoc significantly reduced the level of diabetes distress as measured using the Problem Areas In Diabetes (PAID) questionnaire versus the BGAT intervention.
The PAID score was around 30 in both groups at baseline, this fell to about 26 at 1 year, and around 20 at 2 years in the HARPdoc group, which was significantly lower than the score seen in the BGAT group which rose slightly then fell back to baseline levels.
A similar pattern was seen in the levels of depression and anxiety, which were measured by the HADS-D and HADS-A instruments. So HARPdoc was more effective at improving psychological and mental health outcomes than BGAT, Dr. Ajjan observed.
The HARPdoc project is funded by the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation with additional support from the UK’s National Institute of Health Research. The HARPdoc RCT was jointly sponsored by King’s College London and King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. Dr. Amiel has served on advisory panels for Roche, Medtronic, and Novo Nordisk. Dr. de Zoysa did not state having any conflicts of interest. Dr. Ajjan disclosed that he has financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies.
FROM EASD 2021
Johnson & Johnson requests FDA approval for vaccine booster doses
The company said it filed a request for people ages 18 and older who have received the one-shot vaccine. Johnson & Johnson submitted data for several different booster intervals -- ranging from 2 months to 6 months -- but didn’t formally recommend one to the FDA, The Associated Press reported.
“We’re describing the data to them,” Mathai Mammen, MD, head of global research and development for Janssen, the company’s vaccine division, told CNN.
“The process is not that we asked for a very specific interval -- we’re providing them data and we’re going to be presenting to the committee,” he said. “They’ll take all that into consideration when they ultimately decide on an appropriate interval.”
The FDA’s independent vaccine advisory committee meets next week to review data on booster shots from both Johnson & Johnson and Moderna. It’s the first step in the review process, which then requires approval from leaders at the FDA and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. If both agencies authorize the extra shots, Americans could receive boosters from Johnson & Johnson and Moderna later this month, the AP reported.
Johnson & Johnson previously released data that showed the vaccine remains highly effective against COVID-19 at least 5 months after vaccination, with 81% efficacy against hospitalizations in the United States.
Two weeks ago, the company reported that a booster dose at 2 months or 6 months further lifted immunity, with a booster at 2 months providing 94% protection against moderate and severe COVID-19. The company said the 6-month booster raised antibodies by 12 times but didn’t release additional data at that time.
In September, the FDA authorized booster shots of the Pfizer vaccine for ages 65 and older, those who live in long-term care facilities, and those with higher risks for contracting COVID-19. The Biden administration is supporting a booster campaign to address potential waning vaccine immunity and remaining surges of the more contagious Delta variant, the AP reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The company said it filed a request for people ages 18 and older who have received the one-shot vaccine. Johnson & Johnson submitted data for several different booster intervals -- ranging from 2 months to 6 months -- but didn’t formally recommend one to the FDA, The Associated Press reported.
“We’re describing the data to them,” Mathai Mammen, MD, head of global research and development for Janssen, the company’s vaccine division, told CNN.
“The process is not that we asked for a very specific interval -- we’re providing them data and we’re going to be presenting to the committee,” he said. “They’ll take all that into consideration when they ultimately decide on an appropriate interval.”
The FDA’s independent vaccine advisory committee meets next week to review data on booster shots from both Johnson & Johnson and Moderna. It’s the first step in the review process, which then requires approval from leaders at the FDA and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. If both agencies authorize the extra shots, Americans could receive boosters from Johnson & Johnson and Moderna later this month, the AP reported.
Johnson & Johnson previously released data that showed the vaccine remains highly effective against COVID-19 at least 5 months after vaccination, with 81% efficacy against hospitalizations in the United States.
Two weeks ago, the company reported that a booster dose at 2 months or 6 months further lifted immunity, with a booster at 2 months providing 94% protection against moderate and severe COVID-19. The company said the 6-month booster raised antibodies by 12 times but didn’t release additional data at that time.
In September, the FDA authorized booster shots of the Pfizer vaccine for ages 65 and older, those who live in long-term care facilities, and those with higher risks for contracting COVID-19. The Biden administration is supporting a booster campaign to address potential waning vaccine immunity and remaining surges of the more contagious Delta variant, the AP reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The company said it filed a request for people ages 18 and older who have received the one-shot vaccine. Johnson & Johnson submitted data for several different booster intervals -- ranging from 2 months to 6 months -- but didn’t formally recommend one to the FDA, The Associated Press reported.
“We’re describing the data to them,” Mathai Mammen, MD, head of global research and development for Janssen, the company’s vaccine division, told CNN.
“The process is not that we asked for a very specific interval -- we’re providing them data and we’re going to be presenting to the committee,” he said. “They’ll take all that into consideration when they ultimately decide on an appropriate interval.”
The FDA’s independent vaccine advisory committee meets next week to review data on booster shots from both Johnson & Johnson and Moderna. It’s the first step in the review process, which then requires approval from leaders at the FDA and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. If both agencies authorize the extra shots, Americans could receive boosters from Johnson & Johnson and Moderna later this month, the AP reported.
Johnson & Johnson previously released data that showed the vaccine remains highly effective against COVID-19 at least 5 months after vaccination, with 81% efficacy against hospitalizations in the United States.
Two weeks ago, the company reported that a booster dose at 2 months or 6 months further lifted immunity, with a booster at 2 months providing 94% protection against moderate and severe COVID-19. The company said the 6-month booster raised antibodies by 12 times but didn’t release additional data at that time.
In September, the FDA authorized booster shots of the Pfizer vaccine for ages 65 and older, those who live in long-term care facilities, and those with higher risks for contracting COVID-19. The Biden administration is supporting a booster campaign to address potential waning vaccine immunity and remaining surges of the more contagious Delta variant, the AP reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.