User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
What are the risk factors for Mohs surgery–related anxiety?
confirmed by a health care provider (HCP), results from a single-center survey demonstrated.
“Higher patient-reported anxiety in hospital settings is significantly linked to lower patient satisfaction with the quality of care and higher patient-reported postoperative pain,” corresponding author Ally-Khan Somani, MD, PhD, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online in Dermatologic Surgery. “Identifying factors associated with perioperative patient anxiety could improve outcomes and patient satisfaction.”
Dr. Somani, director of dermatologic surgery and cutaneous oncology in the department of dermatology at the University of Indiana, Indianapolis, and coauthors surveyed 145 patients who underwent Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) at the university from February 2018 to March 2020. They collected patient self-reported demographics, medical history, and administered a 10-point visual analog scale assessment of anxiety at multiple stages. They also sought HCP-perceived assessments of anxiety and used a stepwise regression mode to explore factors that potentially contributed to anxiety outcomes. The mean age of the 145 patients was 63 years, 60% were female, and 77% had no self-reported anxiety confirmed by a prior HCP’s diagnosis.
Two-thirds of patients (66%) received a pre-MMS consultation with the surgeon, 59% had a history of skin cancer removal surgery, and 86% had 1-2 layers removed during the current MMS.
Prior to MMS, the researchers found that significant risk factors for increased anxiety included younger age, female sex, and self-reported history of anxiety confirmed by an HCP (P < .05), while intraoperatively, HCP-perceived patient anxiety increased with younger patient age and more layers removed. Following MMS, patient anxiety increased significantly with more layers removed and higher self-reported preoperative anxiety levels. “Although existing research is divided regarding the efficacy of pre-MMS consultation for anxiety reduction, these findings suggest that patient-reported and HCP-perceived anxiety were not significantly affected by in-person pre-MMS consultation with the surgeon,” Dr. Somani and colleagues wrote. “Thus, routinely recommending consultations may not be the best approach for improving anxiety outcomes.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of their analysis, including its single-center design, enrollment of demographically similar patients, and the fact that no objective measurements of anxiety such as heart rate or blood pressure were taken.
“One of the main benefits of Mohs surgery is that we are able to operate under local anesthesia, but this also means that our patients are acutely aware of everything going on around them,” said Patricia M. Richey, MD, who practices Mohs surgery and cosmetic dermatology in Washington, D.C., and was asked to comment on the study.
“I think it is so important that this study is primarily focusing on the patient experience,” she said. “While this study did not find that a pre-op consult impacted patient anxiety levels, I do think we can infer that it is critical to connect with your patients on some level prior to surgery, as it helps you tailor your process to make the day more tolerable for them [such as] playing music, determining the need for an oral anxiolytic, etc.”
Neither the researchers nor Dr. Richey reported having financial disclosures.
confirmed by a health care provider (HCP), results from a single-center survey demonstrated.
“Higher patient-reported anxiety in hospital settings is significantly linked to lower patient satisfaction with the quality of care and higher patient-reported postoperative pain,” corresponding author Ally-Khan Somani, MD, PhD, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online in Dermatologic Surgery. “Identifying factors associated with perioperative patient anxiety could improve outcomes and patient satisfaction.”
Dr. Somani, director of dermatologic surgery and cutaneous oncology in the department of dermatology at the University of Indiana, Indianapolis, and coauthors surveyed 145 patients who underwent Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) at the university from February 2018 to March 2020. They collected patient self-reported demographics, medical history, and administered a 10-point visual analog scale assessment of anxiety at multiple stages. They also sought HCP-perceived assessments of anxiety and used a stepwise regression mode to explore factors that potentially contributed to anxiety outcomes. The mean age of the 145 patients was 63 years, 60% were female, and 77% had no self-reported anxiety confirmed by a prior HCP’s diagnosis.
Two-thirds of patients (66%) received a pre-MMS consultation with the surgeon, 59% had a history of skin cancer removal surgery, and 86% had 1-2 layers removed during the current MMS.
Prior to MMS, the researchers found that significant risk factors for increased anxiety included younger age, female sex, and self-reported history of anxiety confirmed by an HCP (P < .05), while intraoperatively, HCP-perceived patient anxiety increased with younger patient age and more layers removed. Following MMS, patient anxiety increased significantly with more layers removed and higher self-reported preoperative anxiety levels. “Although existing research is divided regarding the efficacy of pre-MMS consultation for anxiety reduction, these findings suggest that patient-reported and HCP-perceived anxiety were not significantly affected by in-person pre-MMS consultation with the surgeon,” Dr. Somani and colleagues wrote. “Thus, routinely recommending consultations may not be the best approach for improving anxiety outcomes.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of their analysis, including its single-center design, enrollment of demographically similar patients, and the fact that no objective measurements of anxiety such as heart rate or blood pressure were taken.
“One of the main benefits of Mohs surgery is that we are able to operate under local anesthesia, but this also means that our patients are acutely aware of everything going on around them,” said Patricia M. Richey, MD, who practices Mohs surgery and cosmetic dermatology in Washington, D.C., and was asked to comment on the study.
“I think it is so important that this study is primarily focusing on the patient experience,” she said. “While this study did not find that a pre-op consult impacted patient anxiety levels, I do think we can infer that it is critical to connect with your patients on some level prior to surgery, as it helps you tailor your process to make the day more tolerable for them [such as] playing music, determining the need for an oral anxiolytic, etc.”
Neither the researchers nor Dr. Richey reported having financial disclosures.
confirmed by a health care provider (HCP), results from a single-center survey demonstrated.
“Higher patient-reported anxiety in hospital settings is significantly linked to lower patient satisfaction with the quality of care and higher patient-reported postoperative pain,” corresponding author Ally-Khan Somani, MD, PhD, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online in Dermatologic Surgery. “Identifying factors associated with perioperative patient anxiety could improve outcomes and patient satisfaction.”
Dr. Somani, director of dermatologic surgery and cutaneous oncology in the department of dermatology at the University of Indiana, Indianapolis, and coauthors surveyed 145 patients who underwent Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) at the university from February 2018 to March 2020. They collected patient self-reported demographics, medical history, and administered a 10-point visual analog scale assessment of anxiety at multiple stages. They also sought HCP-perceived assessments of anxiety and used a stepwise regression mode to explore factors that potentially contributed to anxiety outcomes. The mean age of the 145 patients was 63 years, 60% were female, and 77% had no self-reported anxiety confirmed by a prior HCP’s diagnosis.
Two-thirds of patients (66%) received a pre-MMS consultation with the surgeon, 59% had a history of skin cancer removal surgery, and 86% had 1-2 layers removed during the current MMS.
Prior to MMS, the researchers found that significant risk factors for increased anxiety included younger age, female sex, and self-reported history of anxiety confirmed by an HCP (P < .05), while intraoperatively, HCP-perceived patient anxiety increased with younger patient age and more layers removed. Following MMS, patient anxiety increased significantly with more layers removed and higher self-reported preoperative anxiety levels. “Although existing research is divided regarding the efficacy of pre-MMS consultation for anxiety reduction, these findings suggest that patient-reported and HCP-perceived anxiety were not significantly affected by in-person pre-MMS consultation with the surgeon,” Dr. Somani and colleagues wrote. “Thus, routinely recommending consultations may not be the best approach for improving anxiety outcomes.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of their analysis, including its single-center design, enrollment of demographically similar patients, and the fact that no objective measurements of anxiety such as heart rate or blood pressure were taken.
“One of the main benefits of Mohs surgery is that we are able to operate under local anesthesia, but this also means that our patients are acutely aware of everything going on around them,” said Patricia M. Richey, MD, who practices Mohs surgery and cosmetic dermatology in Washington, D.C., and was asked to comment on the study.
“I think it is so important that this study is primarily focusing on the patient experience,” she said. “While this study did not find that a pre-op consult impacted patient anxiety levels, I do think we can infer that it is critical to connect with your patients on some level prior to surgery, as it helps you tailor your process to make the day more tolerable for them [such as] playing music, determining the need for an oral anxiolytic, etc.”
Neither the researchers nor Dr. Richey reported having financial disclosures.
FROM DERMATOLOGIC SURGERY
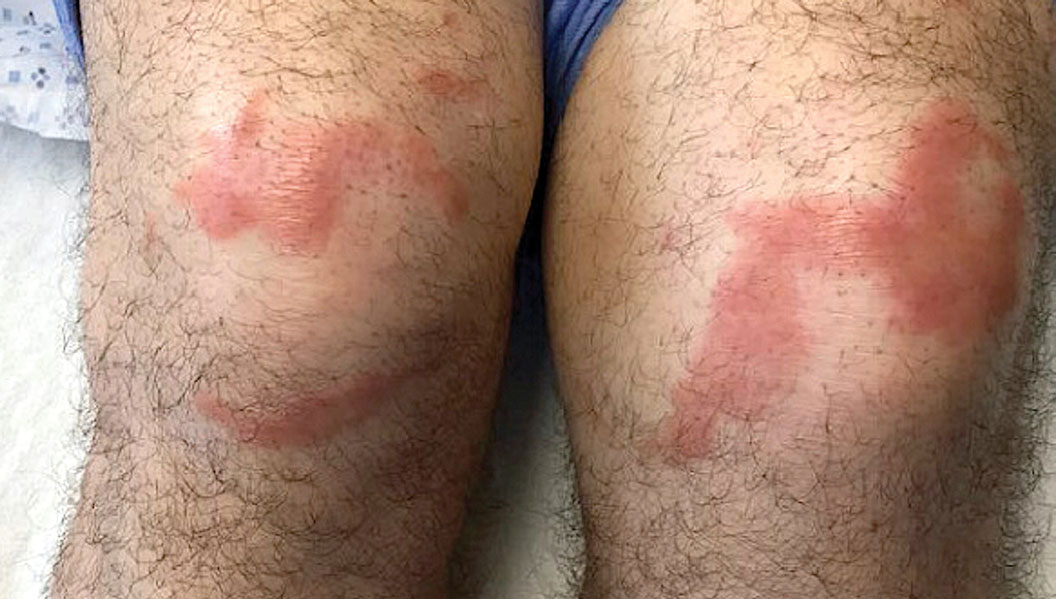
Multiple Annular Erythematous Plaques
The Diagnosis: Mid-Borderline Multibacillary Leprosy
The biopsies showed a granulomatous dermatitis involving the dermis and subcutaneous adipose tissue (Figure, A). Fite staining also revealed numerous acid-fast bacilli (AFB) throughout the dermis (Figure, B); however, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for Mycobacterium tuberculosis was negative, and concomitant AFB tissue culture showed no growth after 8 weeks of incubation from the left wrist biopsy (Table). Interestingly, a left inguinal lymph node biopsy performed 6 months prior to presentation that helped to establish the diagnosis of follicular lymphoma also revealed nonnecrotizing granulomas and the presence of rare AFB; this formalin-fixed specimen subsequently tested negative for M tuberculosis and nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) by broad-range PCR. Due to a high index of suspicion, another unpreserved skin biopsy of the right knee was sent for NTM testing with PCR. Primers to 16S ribosomal RNA and the beta subunit of RNA polymerase, rpoB, gene detected Mycobacterium leprae DNA, leading to the diagnosis of mid-borderline (or borderline-borderline) multibacillary leprosy. Our patient subsequently reported subtle hypoesthesia of the plaques on the knees. He recalled eating undercooked armadillo meat in the southern United States more than 30 years prior to admission. In addition, he had a history of being incarcerated in the northeastern United States. This case was reported to the National Hansen’s Disease Program, and our patient was started on a 2-year course of daily clarithromycin, daily minocycline, and once-monthly moxifloxacin. His family also was evaluated and did not have any skin lesions concerning for leprosy.
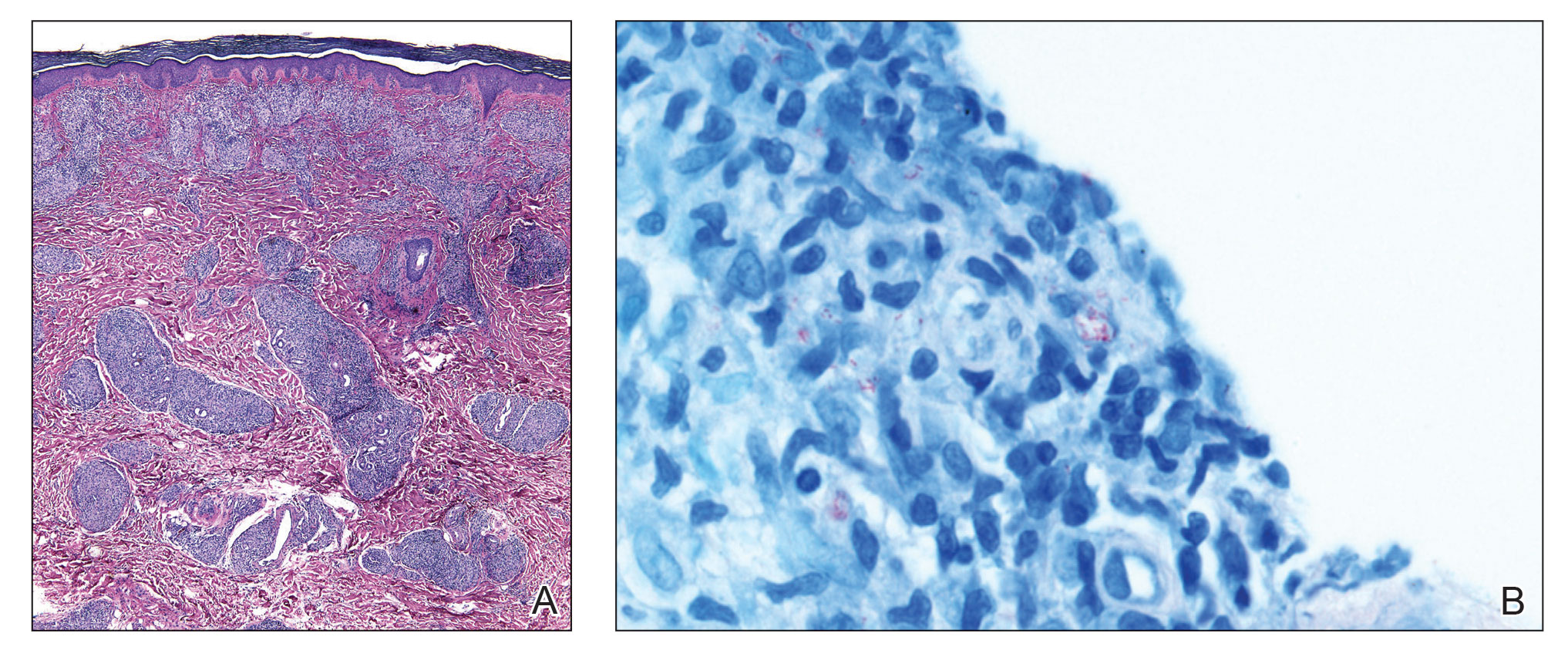
Leprosy is a major global health concern, transmitted via breaks in the skin, respiratory secretions, and contact with armadillos. It continues to be endemic in India, Brazil, and Indonesia.1 In the United States where leprosy is nonendemic, 159 new cases were detected in 2020; the most notable risk factors in the United States are armadillo exposure and travel history.2,3 Mycobacterium leprae are intracellular bacilli that preferentially infect macrophages and Schwann cells, resulting in erythematous or hypopigmented skin lesions that often are anesthetic. Mycobacterium leprae has the longest doubling time of all bacteria with unknown in vitro growth requirements and a typical in vivo incubation period of 2 to 10 years.4 Therefore, in vitro cultures will yield no growth, as seen in our case. In our patient, Fite stain showed acid-fast organisms in multiple tissue specimens, but AFB cultures demonstrated no growth after 8 weeks of incubation. Although clinicopathologic correlation is most important, PCR analysis can help to assist in the diagnosis of leprosy. Unpreserved tissue should be used when possible, as the fixation process may adversely affect the analytic sensitivity of subsequent PCR-based assays.5 In our case, NTM were not detected by PCR in the inguinal lymph node specimen despite demonstrating rare AFB staining. This result likely was multifactorial, including the effect of formalin fixation and paraffin embedding as well as concomitant low biomass.
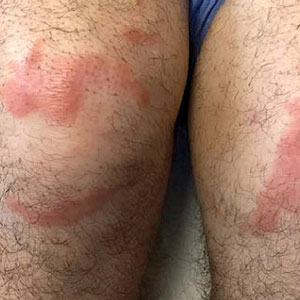
Leprosy is known as a great imitator, and clinical manifestations (both neurologic and cutaneous) depend on host immune response to the mycobacteria. Although tuberculoid leprosy (associated with T helper type 1 immune response) is distinguished by few asymmetric, well-demarcated, and often hypopigmented plaques, lepromatous leprosy (associated with T helper type 2 response) is characterized by numerous symmetric and poorly defined lesions. Borderline leprosy, as seen in our patient, is the most common type of leprosy and shows features of both tuberculoid and lepromatous leprosy.4 It also may be particularly difficult to diagnose.6,7 Borderline-borderline leprosy involves lesions that mostly are of the lepromatous type and symmetric but also may include raised plaques, as in tuberculoid leprosy.4 Plaques in an annular configuration with central clearing, as seen in our patient, are considered suggestive.8 Histopathology of borderline-borderline leprosy lesions shows subepidermal clear zones, and granulomas are more diffuse than in tuberculoid leprosy.4
Given the noncaseating granulomatous dermatitis seen on histopathology and the relatively higher incidence of sarcoidosis in our region of practice, our initial differential included sarcoidosis and other granulomatous disorders such as granuloma annulare. Interestingly, sarcoidosis has been misdiagnosed as leprosy on multiple occasions in countries where leprosy is endemic.9,10 Localized cutaneous leishmaniasis typically presents with infiltrated plaques and nodules that may ulcerate; diffuse and disseminated as well as mucocutaneous presentations may occur depending on the species and severity of infection. Parasitized macrophages containing amastigotes may be seen in the dermis highlighted by CD1a immunostaining. Mycosis fungoides presents as papulosquamous patches or plaques, often favoring sunprotected sites; the hypopigmented variant may mimic the central clearing seen in leprosy.
The diagnosis of leprosy can be challenging due to varying clinical presentation; indolent growth of the causative organism; and indeterminate nature of stains, including the Fite stain. Although leprosy is an uncommon diagnosis, this case underscores the need to keep it in the differential of granulomatous dermatoses in the appropriate clinical setting, particularly in patients with risk factors for exposure.8
- Blok DJ, De Vlas SJ, Richardus JH. Global elimination of leprosy by 2020: are we on track? Parasit Vectors. 2015;8:548. doi:10.1186/s13071-015-1143-4
- National Hansen’s disease (leprosy) program caring and curing since 1894. Health Resources and Services Administration website. Published April 13, 2017. Accessed November 17, 2022. https://www.hrsa.gov/hansens-disease/index.html
- Aslam S, Peraza J, Mekaiel A, et al. Major risk factors for leprosy in a non-endemic area of the United States: a case series. IDCases. 2019;17:E00557. doi:10.1016/j.idcr.2019.e00557
- Kundakci N, Erdem C. Leprosy: a great imitator. Clin Dermatol. 2019;37:200-212. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2019.01.002
- Marchetti G, Gori A, Catozzi L, et al. Evaluation of PCR in detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues: comparison of four amplification assays. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36:1512-1517.
- Pawar M, Zawar V. Mid-borderline leprosy masquerading as an overlap syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018;57:1686-1688. doi:10.1093 /rheumatology/key125
- Day W, Prodanovic E. Borderline lepromatous leprosy masking as tinea versicolor. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:E125-E126. doi:10.1111/ijd.14439
- Lastória JC, de Abreu MAMM. Leprosy: review of the epidemiological, clinical, and etiopathogenic aspects: part 1. An Bras Dermatol. 2014;89:205-218. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20142450
- Kaushik A, Vinay K, Narang T, et al. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis: a mimic of leprosy? Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:677-680. doi:10.1111/ced.13863
- Chowdhary KN, Rao R, Priya P, et al. Cutaneous sarcoidosis misdiagnosed as leprosy. report of two cases and review of literature. Indian J Lepr. 2016;88:177-183.
The Diagnosis: Mid-Borderline Multibacillary Leprosy
The biopsies showed a granulomatous dermatitis involving the dermis and subcutaneous adipose tissue (Figure, A). Fite staining also revealed numerous acid-fast bacilli (AFB) throughout the dermis (Figure, B); however, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for Mycobacterium tuberculosis was negative, and concomitant AFB tissue culture showed no growth after 8 weeks of incubation from the left wrist biopsy (Table). Interestingly, a left inguinal lymph node biopsy performed 6 months prior to presentation that helped to establish the diagnosis of follicular lymphoma also revealed nonnecrotizing granulomas and the presence of rare AFB; this formalin-fixed specimen subsequently tested negative for M tuberculosis and nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) by broad-range PCR. Due to a high index of suspicion, another unpreserved skin biopsy of the right knee was sent for NTM testing with PCR. Primers to 16S ribosomal RNA and the beta subunit of RNA polymerase, rpoB, gene detected Mycobacterium leprae DNA, leading to the diagnosis of mid-borderline (or borderline-borderline) multibacillary leprosy. Our patient subsequently reported subtle hypoesthesia of the plaques on the knees. He recalled eating undercooked armadillo meat in the southern United States more than 30 years prior to admission. In addition, he had a history of being incarcerated in the northeastern United States. This case was reported to the National Hansen’s Disease Program, and our patient was started on a 2-year course of daily clarithromycin, daily minocycline, and once-monthly moxifloxacin. His family also was evaluated and did not have any skin lesions concerning for leprosy.

Leprosy is a major global health concern, transmitted via breaks in the skin, respiratory secretions, and contact with armadillos. It continues to be endemic in India, Brazil, and Indonesia.1 In the United States where leprosy is nonendemic, 159 new cases were detected in 2020; the most notable risk factors in the United States are armadillo exposure and travel history.2,3 Mycobacterium leprae are intracellular bacilli that preferentially infect macrophages and Schwann cells, resulting in erythematous or hypopigmented skin lesions that often are anesthetic. Mycobacterium leprae has the longest doubling time of all bacteria with unknown in vitro growth requirements and a typical in vivo incubation period of 2 to 10 years.4 Therefore, in vitro cultures will yield no growth, as seen in our case. In our patient, Fite stain showed acid-fast organisms in multiple tissue specimens, but AFB cultures demonstrated no growth after 8 weeks of incubation. Although clinicopathologic correlation is most important, PCR analysis can help to assist in the diagnosis of leprosy. Unpreserved tissue should be used when possible, as the fixation process may adversely affect the analytic sensitivity of subsequent PCR-based assays.5 In our case, NTM were not detected by PCR in the inguinal lymph node specimen despite demonstrating rare AFB staining. This result likely was multifactorial, including the effect of formalin fixation and paraffin embedding as well as concomitant low biomass.

Leprosy is known as a great imitator, and clinical manifestations (both neurologic and cutaneous) depend on host immune response to the mycobacteria. Although tuberculoid leprosy (associated with T helper type 1 immune response) is distinguished by few asymmetric, well-demarcated, and often hypopigmented plaques, lepromatous leprosy (associated with T helper type 2 response) is characterized by numerous symmetric and poorly defined lesions. Borderline leprosy, as seen in our patient, is the most common type of leprosy and shows features of both tuberculoid and lepromatous leprosy.4 It also may be particularly difficult to diagnose.6,7 Borderline-borderline leprosy involves lesions that mostly are of the lepromatous type and symmetric but also may include raised plaques, as in tuberculoid leprosy.4 Plaques in an annular configuration with central clearing, as seen in our patient, are considered suggestive.8 Histopathology of borderline-borderline leprosy lesions shows subepidermal clear zones, and granulomas are more diffuse than in tuberculoid leprosy.4
Given the noncaseating granulomatous dermatitis seen on histopathology and the relatively higher incidence of sarcoidosis in our region of practice, our initial differential included sarcoidosis and other granulomatous disorders such as granuloma annulare. Interestingly, sarcoidosis has been misdiagnosed as leprosy on multiple occasions in countries where leprosy is endemic.9,10 Localized cutaneous leishmaniasis typically presents with infiltrated plaques and nodules that may ulcerate; diffuse and disseminated as well as mucocutaneous presentations may occur depending on the species and severity of infection. Parasitized macrophages containing amastigotes may be seen in the dermis highlighted by CD1a immunostaining. Mycosis fungoides presents as papulosquamous patches or plaques, often favoring sunprotected sites; the hypopigmented variant may mimic the central clearing seen in leprosy.
The diagnosis of leprosy can be challenging due to varying clinical presentation; indolent growth of the causative organism; and indeterminate nature of stains, including the Fite stain. Although leprosy is an uncommon diagnosis, this case underscores the need to keep it in the differential of granulomatous dermatoses in the appropriate clinical setting, particularly in patients with risk factors for exposure.8
The Diagnosis: Mid-Borderline Multibacillary Leprosy
The biopsies showed a granulomatous dermatitis involving the dermis and subcutaneous adipose tissue (Figure, A). Fite staining also revealed numerous acid-fast bacilli (AFB) throughout the dermis (Figure, B); however, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for Mycobacterium tuberculosis was negative, and concomitant AFB tissue culture showed no growth after 8 weeks of incubation from the left wrist biopsy (Table). Interestingly, a left inguinal lymph node biopsy performed 6 months prior to presentation that helped to establish the diagnosis of follicular lymphoma also revealed nonnecrotizing granulomas and the presence of rare AFB; this formalin-fixed specimen subsequently tested negative for M tuberculosis and nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) by broad-range PCR. Due to a high index of suspicion, another unpreserved skin biopsy of the right knee was sent for NTM testing with PCR. Primers to 16S ribosomal RNA and the beta subunit of RNA polymerase, rpoB, gene detected Mycobacterium leprae DNA, leading to the diagnosis of mid-borderline (or borderline-borderline) multibacillary leprosy. Our patient subsequently reported subtle hypoesthesia of the plaques on the knees. He recalled eating undercooked armadillo meat in the southern United States more than 30 years prior to admission. In addition, he had a history of being incarcerated in the northeastern United States. This case was reported to the National Hansen’s Disease Program, and our patient was started on a 2-year course of daily clarithromycin, daily minocycline, and once-monthly moxifloxacin. His family also was evaluated and did not have any skin lesions concerning for leprosy.

Leprosy is a major global health concern, transmitted via breaks in the skin, respiratory secretions, and contact with armadillos. It continues to be endemic in India, Brazil, and Indonesia.1 In the United States where leprosy is nonendemic, 159 new cases were detected in 2020; the most notable risk factors in the United States are armadillo exposure and travel history.2,3 Mycobacterium leprae are intracellular bacilli that preferentially infect macrophages and Schwann cells, resulting in erythematous or hypopigmented skin lesions that often are anesthetic. Mycobacterium leprae has the longest doubling time of all bacteria with unknown in vitro growth requirements and a typical in vivo incubation period of 2 to 10 years.4 Therefore, in vitro cultures will yield no growth, as seen in our case. In our patient, Fite stain showed acid-fast organisms in multiple tissue specimens, but AFB cultures demonstrated no growth after 8 weeks of incubation. Although clinicopathologic correlation is most important, PCR analysis can help to assist in the diagnosis of leprosy. Unpreserved tissue should be used when possible, as the fixation process may adversely affect the analytic sensitivity of subsequent PCR-based assays.5 In our case, NTM were not detected by PCR in the inguinal lymph node specimen despite demonstrating rare AFB staining. This result likely was multifactorial, including the effect of formalin fixation and paraffin embedding as well as concomitant low biomass.

Leprosy is known as a great imitator, and clinical manifestations (both neurologic and cutaneous) depend on host immune response to the mycobacteria. Although tuberculoid leprosy (associated with T helper type 1 immune response) is distinguished by few asymmetric, well-demarcated, and often hypopigmented plaques, lepromatous leprosy (associated with T helper type 2 response) is characterized by numerous symmetric and poorly defined lesions. Borderline leprosy, as seen in our patient, is the most common type of leprosy and shows features of both tuberculoid and lepromatous leprosy.4 It also may be particularly difficult to diagnose.6,7 Borderline-borderline leprosy involves lesions that mostly are of the lepromatous type and symmetric but also may include raised plaques, as in tuberculoid leprosy.4 Plaques in an annular configuration with central clearing, as seen in our patient, are considered suggestive.8 Histopathology of borderline-borderline leprosy lesions shows subepidermal clear zones, and granulomas are more diffuse than in tuberculoid leprosy.4
Given the noncaseating granulomatous dermatitis seen on histopathology and the relatively higher incidence of sarcoidosis in our region of practice, our initial differential included sarcoidosis and other granulomatous disorders such as granuloma annulare. Interestingly, sarcoidosis has been misdiagnosed as leprosy on multiple occasions in countries where leprosy is endemic.9,10 Localized cutaneous leishmaniasis typically presents with infiltrated plaques and nodules that may ulcerate; diffuse and disseminated as well as mucocutaneous presentations may occur depending on the species and severity of infection. Parasitized macrophages containing amastigotes may be seen in the dermis highlighted by CD1a immunostaining. Mycosis fungoides presents as papulosquamous patches or plaques, often favoring sunprotected sites; the hypopigmented variant may mimic the central clearing seen in leprosy.
The diagnosis of leprosy can be challenging due to varying clinical presentation; indolent growth of the causative organism; and indeterminate nature of stains, including the Fite stain. Although leprosy is an uncommon diagnosis, this case underscores the need to keep it in the differential of granulomatous dermatoses in the appropriate clinical setting, particularly in patients with risk factors for exposure.8
- Blok DJ, De Vlas SJ, Richardus JH. Global elimination of leprosy by 2020: are we on track? Parasit Vectors. 2015;8:548. doi:10.1186/s13071-015-1143-4
- National Hansen’s disease (leprosy) program caring and curing since 1894. Health Resources and Services Administration website. Published April 13, 2017. Accessed November 17, 2022. https://www.hrsa.gov/hansens-disease/index.html
- Aslam S, Peraza J, Mekaiel A, et al. Major risk factors for leprosy in a non-endemic area of the United States: a case series. IDCases. 2019;17:E00557. doi:10.1016/j.idcr.2019.e00557
- Kundakci N, Erdem C. Leprosy: a great imitator. Clin Dermatol. 2019;37:200-212. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2019.01.002
- Marchetti G, Gori A, Catozzi L, et al. Evaluation of PCR in detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues: comparison of four amplification assays. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36:1512-1517.
- Pawar M, Zawar V. Mid-borderline leprosy masquerading as an overlap syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018;57:1686-1688. doi:10.1093 /rheumatology/key125
- Day W, Prodanovic E. Borderline lepromatous leprosy masking as tinea versicolor. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:E125-E126. doi:10.1111/ijd.14439
- Lastória JC, de Abreu MAMM. Leprosy: review of the epidemiological, clinical, and etiopathogenic aspects: part 1. An Bras Dermatol. 2014;89:205-218. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20142450
- Kaushik A, Vinay K, Narang T, et al. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis: a mimic of leprosy? Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:677-680. doi:10.1111/ced.13863
- Chowdhary KN, Rao R, Priya P, et al. Cutaneous sarcoidosis misdiagnosed as leprosy. report of two cases and review of literature. Indian J Lepr. 2016;88:177-183.
- Blok DJ, De Vlas SJ, Richardus JH. Global elimination of leprosy by 2020: are we on track? Parasit Vectors. 2015;8:548. doi:10.1186/s13071-015-1143-4
- National Hansen’s disease (leprosy) program caring and curing since 1894. Health Resources and Services Administration website. Published April 13, 2017. Accessed November 17, 2022. https://www.hrsa.gov/hansens-disease/index.html
- Aslam S, Peraza J, Mekaiel A, et al. Major risk factors for leprosy in a non-endemic area of the United States: a case series. IDCases. 2019;17:E00557. doi:10.1016/j.idcr.2019.e00557
- Kundakci N, Erdem C. Leprosy: a great imitator. Clin Dermatol. 2019;37:200-212. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2019.01.002
- Marchetti G, Gori A, Catozzi L, et al. Evaluation of PCR in detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues: comparison of four amplification assays. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36:1512-1517.
- Pawar M, Zawar V. Mid-borderline leprosy masquerading as an overlap syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018;57:1686-1688. doi:10.1093 /rheumatology/key125
- Day W, Prodanovic E. Borderline lepromatous leprosy masking as tinea versicolor. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:E125-E126. doi:10.1111/ijd.14439
- Lastória JC, de Abreu MAMM. Leprosy: review of the epidemiological, clinical, and etiopathogenic aspects: part 1. An Bras Dermatol. 2014;89:205-218. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20142450
- Kaushik A, Vinay K, Narang T, et al. Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis: a mimic of leprosy? Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:677-680. doi:10.1111/ced.13863
- Chowdhary KN, Rao R, Priya P, et al. Cutaneous sarcoidosis misdiagnosed as leprosy. report of two cases and review of literature. Indian J Lepr. 2016;88:177-183.
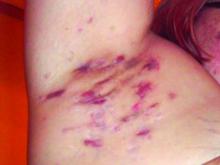
A 59-year-old man was admitted to the medical ward with multiple annular erythematous plaques and polyarthralgia of several months’ duration. His medical history included low-grade stage IIA follicular lymphoma diagnosed 6 months prior to presentation, substance abuse with opiates and cocaine, coronary artery disease, ascending aortic aneurysm, and chronic lower back pain. Physical examination revealed multiple red to red-brown papules and plaques, some in an annular configuration, that were distributed on the cheeks, left wrist, knees, dorsal feet, and soles. Bilateral inguinal lymphadenopathy also was noted. Serological testing for HIV, hepatitis B and C viruses, Treponema pallidum, Borrelia burgdorferi, and tuberculosis assay were negative. Arthrocentesis of the left wrist 1 week prior to admission noted 5333 nucleated cells/μL (reference range, <3000 cells/μL) and no crystals; culture of the fluid was sterile. Skin biopsies of plaques on the left wrist, left dorsal foot, and right knee were obtained for histopathologic analysis.
Consider quality of life, comorbidities in hidradenitis suppurativa
LAS VEGAS – , Robert G. Micheletti, MD, said in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
For patients with HS, “the quality-of-life impact is profound, greater than any other systematically studied dermatologic condition,” said Dr. Micheletti, associate professor of dermatology at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylavnia, and chief of hospital dermatology, and chief of dermatology at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia.
Two key aspects of quality of life that affect HS patients are sexual health and overall pain, he said. The female-to-male ratio of HS is approximately 3:1, and data show that approximately 40% of female HS patients experience fertility issues and have unaddressed questions about HS and pregnancy, said Dr. Micheletti. Additionally, data from a systematic review showed that 50%-60% of patients with HS reported sexual dysfunction. Impaired sexual function is also associated with both overall impaired quality of life ratings and the presence of mood disorders, he noted.
Pain also has a significant impact on quality of life for HS patients. When these patients present in an emergency department, 70% report severe pain, and approximately 60% receive opioids, said Dr. Micheletti.
Data from a 2021 study showed that HS patients are significantly more likely to receive opioids compared with controls, and also more likely to be diagnosed with opioid use disorder than controls, especially if they are seen by nondermatologists, he noted.
For acute pain, Dr. Micheletti recommended starting with acetaminophen 500 mg every 4 to 6 hours as needed, and topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). “It still makes sense to do topical care,” said Dr. Micheletti, but he added that he also prescribes medications for anxiety for these patients.
Patients with increased pain severity or refractory disease may benefit from systemic NSAIDs, or intralesional triamcinolone, he noted. Incision and draining of abscesses may provide temporary symptomatic relief, but keep in mind that lesions will recur, he noted.
For the most severe cases, Dr. Micheletti advised adding tramadol as a first-line opioid, or another short-acting opioid for breakthrough pain.
To manage patients with HS who have chronic pain, Dr. Micheletti recommended starting with HS disease–directed therapy, but also screening for pain severity and psychological comorbidities.
His strategies in these cases include nonpharmacological pain management in the form of physical therapy, wound care, and behavioral health. His algorithm for nociceptive pain is NSAIDs with or without acetaminophen; duloxetine or nortriptyline are other options. For neuropathic pain, gabapentin and/or duloxetine are top choices, but pregabalin, venlafaxine, and nortriptyline are on the list as well.
Topical NSAIDs or topical lidocaine may serve as add-ons to systemic therapy in more severe cases, or as first-line therapy for milder chronic pain, Dr. Micheletti noted. Patients who have failed treatment with at least two pharmacologic agents, suffer medically refractory HS with debilitating pain, or use opioids on an ongoing basis should be referred to a pain management specialist, he said.
Don’t forget lifestyle
Although data on the impact of diet on patients with HS are limited, “we know anecdotally that dairy and refined carbohydrates are associated with exacerbations,” said Dr. Micheletti.
In addition, many patients use complementary medicine “and they aren’t always telling us,” he emphasized. Smoking is prevalent among patients with HS, and is a risk factor for the disease in general, and for more severe and refractory disease, he added. Consequently, screening for tobacco smoking is recommended for patients with HS not only because of the impact on disease, but because it is a potentially modifiable cardiovascular risk factor, he explained.
Consider comorbidities
Cardiovascular disease is among several comorbidities associated with HS, said Dr. Micheletti. HS foundations in the United States and Canada recently published evidence-based recommendations for comorbidity screening. The recommendations included screening for 19 specific comorbidities: acne, dissecting cellulitis, pilonidal disease, pyoderma gangrenosum, depression, anxiety, suicide, smoking, substance abuse, polycystic ovary syndrome, obesity, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, inflammatory bowel disease, spondyloarthritis, and sexual dysfunction.
Dr. Micheletti highlighted cardiovascular comorbidities, and noted the association between HS and modifiable cardiovascular risk factors: smoking, obesity, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia. “HS is also independently associated with cardiovascular disease leading to myocardial infarction, stroke, cardiovascular-associated death, and all-cause mortality compared to controls,” he said. Studies show an incidence rate ratio of 1.53 for major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with HS compared with controls, with the highest relative risk among those aged 18-29 years, he added.
Medical management
Depending on the patient, medical management of HS may involve antibiotics, hormonal agents, and biologics, said Dr. Micheletti. Some of the most commonly used antibiotic regimens for HS are those recommended in treatment guidelines, including doxycycline and a clindamycin/rifampin combination, he said. However, the use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or ciprofloxacin has been associated with increased antibiotic resistance and is not supported by available evidence, he noted.
Hormonal therapies may help some women with HS, said Dr. Micheletti. Options include spironolactone, metformin, or estrogen-containing hormonal contraceptives, he said.
When it comes to biologics, only 33% of HS patients meet criteria for their use (Hurley stage II or III, moderate or severe HS), he noted. However, research suggests “a huge gap” in the use of anti-TNF therapy even among patients for whom it is recommended, he said.
Of the TNF-alpha inhibitors, data on adalimumab, which is FDA-approved for HS, are the most recent. Adalimumab “is our gold standard biologic and our gateway biologic, for HS at this time,” Dr. Micheletti said.
However, those who respond to adalimumab “can continue to do better, but they can wax and wane and flare,” he cautioned. Infliximab, while not approved for HS, has been studied in patients with HS and is prescribed by some providers. Although no comparative studies have been done for infliximab versus adalimumab, “anecdotally, response to infliximab tends to be better, and it is the most effective biologic in common use for severe HS,” he noted.
Dr. Micheletti’s top treatment recommendations for using biologics start with considering biosimilars. Most patients on biosimilars do fine, but some patients who previously responded to infliximab will unpredictably lose efficacy or have reactions when switched to a biosimilar, he said.
Patients on biologics also may experience waning efficacy in the wake of an immune response stimulated by foreign antibodies, said Dr. Micheletti. “Anti-drug antibody formation is more likely to occur when treatment is interrupted,” he noted. Minimize the risk of antibody formation by paying attention to adherence issues and dosing frequency, he advised.
If patients fail both adalimumab and infliximab, Dr. Micheletti tells them not to lose hope, and that treatment is a trial-and-error process that may involve more than one therapy. Other biologics in active use for HS include ustekinumab, anakinra, secukinumab, brodalumab, golimumab, and JAK inhibitors, any of which might be effective in any given patient, he said.
Surgical solutions
For HS patients with chronic, recurring inflammation and drainage associated with a sinus tract, surgical deroofing may the best treatment option, Dr. Micheletti said. “Deroofing involves the use of a probe to trace the extent of the subcutaneous tract, followed by incision and removal of the tract ‘roof,’ ’’ he explained. The deroofing procedure involves local anesthesia and has a low morbidity rate, as well as a low recurrence rate and high levels of patient satisfaction, he said.
“The acute role for surgery is to remove active foci of inflammation and relieve pain,” which is achieved more effectively with deroofing, said Dr. Micheletti. By contrast, incision and drainage is associated with an almost 100% recurrence rate, he added.
When planning elective surgery for HS, Dr. Micheletti noted that holding infliximab for less than 4 weeks does not affect postoperative infection rates in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and a recent randomized, controlled trial showed that adalimumab can be continued safely through HS surgeries.
In fact, “continuing TNF inhibitors through elective surgery does not increase infection risk and results in better disease control,” and dermatologists should work with surgery to balance infection and disease flare concerns in HS patients, he said.
Dr. Micheletti disclosed serving as a consultant or advisor for Adaptimmune and Vertex, and research funding from Amgen and Cabaletta Bio. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – , Robert G. Micheletti, MD, said in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
For patients with HS, “the quality-of-life impact is profound, greater than any other systematically studied dermatologic condition,” said Dr. Micheletti, associate professor of dermatology at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylavnia, and chief of hospital dermatology, and chief of dermatology at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia.
Two key aspects of quality of life that affect HS patients are sexual health and overall pain, he said. The female-to-male ratio of HS is approximately 3:1, and data show that approximately 40% of female HS patients experience fertility issues and have unaddressed questions about HS and pregnancy, said Dr. Micheletti. Additionally, data from a systematic review showed that 50%-60% of patients with HS reported sexual dysfunction. Impaired sexual function is also associated with both overall impaired quality of life ratings and the presence of mood disorders, he noted.
Pain also has a significant impact on quality of life for HS patients. When these patients present in an emergency department, 70% report severe pain, and approximately 60% receive opioids, said Dr. Micheletti.
Data from a 2021 study showed that HS patients are significantly more likely to receive opioids compared with controls, and also more likely to be diagnosed with opioid use disorder than controls, especially if they are seen by nondermatologists, he noted.
For acute pain, Dr. Micheletti recommended starting with acetaminophen 500 mg every 4 to 6 hours as needed, and topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). “It still makes sense to do topical care,” said Dr. Micheletti, but he added that he also prescribes medications for anxiety for these patients.
Patients with increased pain severity or refractory disease may benefit from systemic NSAIDs, or intralesional triamcinolone, he noted. Incision and draining of abscesses may provide temporary symptomatic relief, but keep in mind that lesions will recur, he noted.
For the most severe cases, Dr. Micheletti advised adding tramadol as a first-line opioid, or another short-acting opioid for breakthrough pain.
To manage patients with HS who have chronic pain, Dr. Micheletti recommended starting with HS disease–directed therapy, but also screening for pain severity and psychological comorbidities.
His strategies in these cases include nonpharmacological pain management in the form of physical therapy, wound care, and behavioral health. His algorithm for nociceptive pain is NSAIDs with or without acetaminophen; duloxetine or nortriptyline are other options. For neuropathic pain, gabapentin and/or duloxetine are top choices, but pregabalin, venlafaxine, and nortriptyline are on the list as well.
Topical NSAIDs or topical lidocaine may serve as add-ons to systemic therapy in more severe cases, or as first-line therapy for milder chronic pain, Dr. Micheletti noted. Patients who have failed treatment with at least two pharmacologic agents, suffer medically refractory HS with debilitating pain, or use opioids on an ongoing basis should be referred to a pain management specialist, he said.
Don’t forget lifestyle
Although data on the impact of diet on patients with HS are limited, “we know anecdotally that dairy and refined carbohydrates are associated with exacerbations,” said Dr. Micheletti.
In addition, many patients use complementary medicine “and they aren’t always telling us,” he emphasized. Smoking is prevalent among patients with HS, and is a risk factor for the disease in general, and for more severe and refractory disease, he added. Consequently, screening for tobacco smoking is recommended for patients with HS not only because of the impact on disease, but because it is a potentially modifiable cardiovascular risk factor, he explained.
Consider comorbidities
Cardiovascular disease is among several comorbidities associated with HS, said Dr. Micheletti. HS foundations in the United States and Canada recently published evidence-based recommendations for comorbidity screening. The recommendations included screening for 19 specific comorbidities: acne, dissecting cellulitis, pilonidal disease, pyoderma gangrenosum, depression, anxiety, suicide, smoking, substance abuse, polycystic ovary syndrome, obesity, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, inflammatory bowel disease, spondyloarthritis, and sexual dysfunction.
Dr. Micheletti highlighted cardiovascular comorbidities, and noted the association between HS and modifiable cardiovascular risk factors: smoking, obesity, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia. “HS is also independently associated with cardiovascular disease leading to myocardial infarction, stroke, cardiovascular-associated death, and all-cause mortality compared to controls,” he said. Studies show an incidence rate ratio of 1.53 for major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with HS compared with controls, with the highest relative risk among those aged 18-29 years, he added.
Medical management
Depending on the patient, medical management of HS may involve antibiotics, hormonal agents, and biologics, said Dr. Micheletti. Some of the most commonly used antibiotic regimens for HS are those recommended in treatment guidelines, including doxycycline and a clindamycin/rifampin combination, he said. However, the use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or ciprofloxacin has been associated with increased antibiotic resistance and is not supported by available evidence, he noted.
Hormonal therapies may help some women with HS, said Dr. Micheletti. Options include spironolactone, metformin, or estrogen-containing hormonal contraceptives, he said.
When it comes to biologics, only 33% of HS patients meet criteria for their use (Hurley stage II or III, moderate or severe HS), he noted. However, research suggests “a huge gap” in the use of anti-TNF therapy even among patients for whom it is recommended, he said.
Of the TNF-alpha inhibitors, data on adalimumab, which is FDA-approved for HS, are the most recent. Adalimumab “is our gold standard biologic and our gateway biologic, for HS at this time,” Dr. Micheletti said.
However, those who respond to adalimumab “can continue to do better, but they can wax and wane and flare,” he cautioned. Infliximab, while not approved for HS, has been studied in patients with HS and is prescribed by some providers. Although no comparative studies have been done for infliximab versus adalimumab, “anecdotally, response to infliximab tends to be better, and it is the most effective biologic in common use for severe HS,” he noted.
Dr. Micheletti’s top treatment recommendations for using biologics start with considering biosimilars. Most patients on biosimilars do fine, but some patients who previously responded to infliximab will unpredictably lose efficacy or have reactions when switched to a biosimilar, he said.
Patients on biologics also may experience waning efficacy in the wake of an immune response stimulated by foreign antibodies, said Dr. Micheletti. “Anti-drug antibody formation is more likely to occur when treatment is interrupted,” he noted. Minimize the risk of antibody formation by paying attention to adherence issues and dosing frequency, he advised.
If patients fail both adalimumab and infliximab, Dr. Micheletti tells them not to lose hope, and that treatment is a trial-and-error process that may involve more than one therapy. Other biologics in active use for HS include ustekinumab, anakinra, secukinumab, brodalumab, golimumab, and JAK inhibitors, any of which might be effective in any given patient, he said.
Surgical solutions
For HS patients with chronic, recurring inflammation and drainage associated with a sinus tract, surgical deroofing may the best treatment option, Dr. Micheletti said. “Deroofing involves the use of a probe to trace the extent of the subcutaneous tract, followed by incision and removal of the tract ‘roof,’ ’’ he explained. The deroofing procedure involves local anesthesia and has a low morbidity rate, as well as a low recurrence rate and high levels of patient satisfaction, he said.
“The acute role for surgery is to remove active foci of inflammation and relieve pain,” which is achieved more effectively with deroofing, said Dr. Micheletti. By contrast, incision and drainage is associated with an almost 100% recurrence rate, he added.
When planning elective surgery for HS, Dr. Micheletti noted that holding infliximab for less than 4 weeks does not affect postoperative infection rates in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and a recent randomized, controlled trial showed that adalimumab can be continued safely through HS surgeries.
In fact, “continuing TNF inhibitors through elective surgery does not increase infection risk and results in better disease control,” and dermatologists should work with surgery to balance infection and disease flare concerns in HS patients, he said.
Dr. Micheletti disclosed serving as a consultant or advisor for Adaptimmune and Vertex, and research funding from Amgen and Cabaletta Bio. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – , Robert G. Micheletti, MD, said in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
For patients with HS, “the quality-of-life impact is profound, greater than any other systematically studied dermatologic condition,” said Dr. Micheletti, associate professor of dermatology at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylavnia, and chief of hospital dermatology, and chief of dermatology at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia.
Two key aspects of quality of life that affect HS patients are sexual health and overall pain, he said. The female-to-male ratio of HS is approximately 3:1, and data show that approximately 40% of female HS patients experience fertility issues and have unaddressed questions about HS and pregnancy, said Dr. Micheletti. Additionally, data from a systematic review showed that 50%-60% of patients with HS reported sexual dysfunction. Impaired sexual function is also associated with both overall impaired quality of life ratings and the presence of mood disorders, he noted.
Pain also has a significant impact on quality of life for HS patients. When these patients present in an emergency department, 70% report severe pain, and approximately 60% receive opioids, said Dr. Micheletti.
Data from a 2021 study showed that HS patients are significantly more likely to receive opioids compared with controls, and also more likely to be diagnosed with opioid use disorder than controls, especially if they are seen by nondermatologists, he noted.
For acute pain, Dr. Micheletti recommended starting with acetaminophen 500 mg every 4 to 6 hours as needed, and topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). “It still makes sense to do topical care,” said Dr. Micheletti, but he added that he also prescribes medications for anxiety for these patients.
Patients with increased pain severity or refractory disease may benefit from systemic NSAIDs, or intralesional triamcinolone, he noted. Incision and draining of abscesses may provide temporary symptomatic relief, but keep in mind that lesions will recur, he noted.
For the most severe cases, Dr. Micheletti advised adding tramadol as a first-line opioid, or another short-acting opioid for breakthrough pain.
To manage patients with HS who have chronic pain, Dr. Micheletti recommended starting with HS disease–directed therapy, but also screening for pain severity and psychological comorbidities.
His strategies in these cases include nonpharmacological pain management in the form of physical therapy, wound care, and behavioral health. His algorithm for nociceptive pain is NSAIDs with or without acetaminophen; duloxetine or nortriptyline are other options. For neuropathic pain, gabapentin and/or duloxetine are top choices, but pregabalin, venlafaxine, and nortriptyline are on the list as well.
Topical NSAIDs or topical lidocaine may serve as add-ons to systemic therapy in more severe cases, or as first-line therapy for milder chronic pain, Dr. Micheletti noted. Patients who have failed treatment with at least two pharmacologic agents, suffer medically refractory HS with debilitating pain, or use opioids on an ongoing basis should be referred to a pain management specialist, he said.
Don’t forget lifestyle
Although data on the impact of diet on patients with HS are limited, “we know anecdotally that dairy and refined carbohydrates are associated with exacerbations,” said Dr. Micheletti.
In addition, many patients use complementary medicine “and they aren’t always telling us,” he emphasized. Smoking is prevalent among patients with HS, and is a risk factor for the disease in general, and for more severe and refractory disease, he added. Consequently, screening for tobacco smoking is recommended for patients with HS not only because of the impact on disease, but because it is a potentially modifiable cardiovascular risk factor, he explained.
Consider comorbidities
Cardiovascular disease is among several comorbidities associated with HS, said Dr. Micheletti. HS foundations in the United States and Canada recently published evidence-based recommendations for comorbidity screening. The recommendations included screening for 19 specific comorbidities: acne, dissecting cellulitis, pilonidal disease, pyoderma gangrenosum, depression, anxiety, suicide, smoking, substance abuse, polycystic ovary syndrome, obesity, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, inflammatory bowel disease, spondyloarthritis, and sexual dysfunction.
Dr. Micheletti highlighted cardiovascular comorbidities, and noted the association between HS and modifiable cardiovascular risk factors: smoking, obesity, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia. “HS is also independently associated with cardiovascular disease leading to myocardial infarction, stroke, cardiovascular-associated death, and all-cause mortality compared to controls,” he said. Studies show an incidence rate ratio of 1.53 for major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with HS compared with controls, with the highest relative risk among those aged 18-29 years, he added.
Medical management
Depending on the patient, medical management of HS may involve antibiotics, hormonal agents, and biologics, said Dr. Micheletti. Some of the most commonly used antibiotic regimens for HS are those recommended in treatment guidelines, including doxycycline and a clindamycin/rifampin combination, he said. However, the use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or ciprofloxacin has been associated with increased antibiotic resistance and is not supported by available evidence, he noted.
Hormonal therapies may help some women with HS, said Dr. Micheletti. Options include spironolactone, metformin, or estrogen-containing hormonal contraceptives, he said.
When it comes to biologics, only 33% of HS patients meet criteria for their use (Hurley stage II or III, moderate or severe HS), he noted. However, research suggests “a huge gap” in the use of anti-TNF therapy even among patients for whom it is recommended, he said.
Of the TNF-alpha inhibitors, data on adalimumab, which is FDA-approved for HS, are the most recent. Adalimumab “is our gold standard biologic and our gateway biologic, for HS at this time,” Dr. Micheletti said.
However, those who respond to adalimumab “can continue to do better, but they can wax and wane and flare,” he cautioned. Infliximab, while not approved for HS, has been studied in patients with HS and is prescribed by some providers. Although no comparative studies have been done for infliximab versus adalimumab, “anecdotally, response to infliximab tends to be better, and it is the most effective biologic in common use for severe HS,” he noted.
Dr. Micheletti’s top treatment recommendations for using biologics start with considering biosimilars. Most patients on biosimilars do fine, but some patients who previously responded to infliximab will unpredictably lose efficacy or have reactions when switched to a biosimilar, he said.
Patients on biologics also may experience waning efficacy in the wake of an immune response stimulated by foreign antibodies, said Dr. Micheletti. “Anti-drug antibody formation is more likely to occur when treatment is interrupted,” he noted. Minimize the risk of antibody formation by paying attention to adherence issues and dosing frequency, he advised.
If patients fail both adalimumab and infliximab, Dr. Micheletti tells them not to lose hope, and that treatment is a trial-and-error process that may involve more than one therapy. Other biologics in active use for HS include ustekinumab, anakinra, secukinumab, brodalumab, golimumab, and JAK inhibitors, any of which might be effective in any given patient, he said.
Surgical solutions
For HS patients with chronic, recurring inflammation and drainage associated with a sinus tract, surgical deroofing may the best treatment option, Dr. Micheletti said. “Deroofing involves the use of a probe to trace the extent of the subcutaneous tract, followed by incision and removal of the tract ‘roof,’ ’’ he explained. The deroofing procedure involves local anesthesia and has a low morbidity rate, as well as a low recurrence rate and high levels of patient satisfaction, he said.
“The acute role for surgery is to remove active foci of inflammation and relieve pain,” which is achieved more effectively with deroofing, said Dr. Micheletti. By contrast, incision and drainage is associated with an almost 100% recurrence rate, he added.
When planning elective surgery for HS, Dr. Micheletti noted that holding infliximab for less than 4 weeks does not affect postoperative infection rates in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and a recent randomized, controlled trial showed that adalimumab can be continued safely through HS surgeries.
In fact, “continuing TNF inhibitors through elective surgery does not increase infection risk and results in better disease control,” and dermatologists should work with surgery to balance infection and disease flare concerns in HS patients, he said.
Dr. Micheletti disclosed serving as a consultant or advisor for Adaptimmune and Vertex, and research funding from Amgen and Cabaletta Bio. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT INNOVATIONS IN DERMATOLOGY
Women docs: How your next job contract can reflect your real goals
Rebecca Chester, MD, an Arizona-based interventional cardiologist, recently left her position in a private practice and started employment at a hospital system.
“When I was negotiating my previous contract with the private practice, I found that navigating contracts from the standpoint of a woman still in childbearing years was a little disappointing and challenging,” Dr. Chester told this news organization.
“I wanted to have more children and hired a lawyer recommended by a male colleague to help me not only understand the contract but also negotiate time off and maternity leave, but the lawyer discouraged me from advocating for maternity leave, feeling that it might stigmatize me and prevent me from getting a job,” she says.
He also didn’t explain very much. “He just said it falls under ‘disability leave’ and left it at that.”
Fortunately, Dr. Chester had a good experience with the group. “As things turned out, I did have a child later that year, and they treated me well – I actually got time off – and they didn’t make me take extra call. But it might have turned out very differently because I didn’t know what I was getting into. If I hadn’t worked for such a conscientious group, I might have been in a much tougher situation.”
Since then, Dr. Chester has spoken to female colleagues who received “more support from their legal advisors regarding maternity leave.” She suggests turning to female physicians for recommendations to a lawyer.
Although the central components of a contract (for example, noncompete covenants, malpractice “tail” coverage, bonus structure, vacation time, disability, and call) are relevant to physicians of all genders, the needs of women and men are often different.
Dennis Hursh, managing partner of Physician Agreements Health Law, a Pennsylvania-based law firm that represents physicians, told this news organization that women physicians have “several issues that need special attention when negotiating their physician employment agreements.”
It starts with the interview
“Women have to be sensitive to the interviewer’s casual ‘let’s-get-to-know-each-other’ types of questions that may seem natural but really are unlawful to bring into an employment interview,” said Mr. Hursh.
He warned women to beware of questions such as “Are you married? Do you have kids? Are you planning to start a family?” These may be friendly chit-chat for male interviewees but there may be other agendas when asked to a prospective female employee.
Many of Mr. Hursh’s female clients have been asked this type of question, which “should be regarded as a ‘red flag.’ Yes, it may be an innocent, well-intentioned ice-breaker, but it’s actually unlawful to bring that up in an employment setting and, according to the Equal Opportunity Commission, can be seen as a form of discrimination.” He advises female physicians not to engage with the question and simply to refocus the discussion.
Know your worth and go for it
Medscape’s Physician Compensation surveys have consistently found discrepancies in earnings between male and female physicians, both in primary care and in specialties. In 2022, male primary care physicians earned 23% more than their female counterparts, whereas male specialists earned 31% more.
One reason may be that women tend to be more timid about negotiating for better compensation packages. Amanda Hill of Hill Health Law, a health care practice based in Austin, Tex., told this news organization that in her experience one of the most “overarching” features of female physicians is “that they either don’t know what they’re worth or they undersell themselves.”
In contrast to men, “many women are afraid of coming across as greedy or crass, or even demanding or bossy. But it’s a misperception that if you ask for more money, your future employer will hate you or won’t hire you,” said Ms. Hill.
Ms. Hill and Mr. Hursh encourage physicians to find out what they’re worth, which varies by region and specialty, by consulting benchmarks provided by companies such as Medical Group Management Association.
Jon Appino, MBA, principal and founder of Contract Diagnostics, a Kansas City–based consulting company that specializes in physician employment contract reviews, told this news organization that it’s important to look beyond the salary at other aspects of the position. For example, some figures “don’t take into account how much call a physician is taking. You may know what the average ob.gyn. is making, but an ob.gyn. may be working 3 days a week, while another one is working 6 days a week, one may be on call 15 times per month and another may be on call 15 times a quarter.” Other components of compensation include relative value unit (RVU) thresholds and bonuses.
Once you have that information, “don’t be intimidated, even if you’re sitting in front of several executives who are savvy about negotiations, and don’t worry about coming across as ‘high-maintenance’ or ‘all about money,’ ” Mr. Appino says. Proceed with confidence, knowing your worth and pursuing it.
Part-time vs. full-time
Mr. Appino has seen “more female than male physicians who want to work less than full-time. So it’s important to clarify whether that’s a possibility now or in the future and to understand the implications of working part-time.”
He explained that a full-time employee typically puts in a 40-hour work week, which translates into 1.0 Full-Time Equivalent (FTE), or one unit of work. “For example, if a person wants to work 0.8 FTEs – 4 days a week – is vacation time pro-rated? At what point is there a medical insurance fall-off or a higher monthly premium?”
In medical settings, FTEs may be tied to different metrics rather than the number of weekly hours – for example, for a hospitalist, it might be a certain number of shifts and might also vary by specialty. And it affects the call schedule too. “Call is hard to pro-rate. Many hospital bylaws mandate that call be divided equally, but if one surgeon is working 1.0 FTEs and another is working 0.8 FTEs, how does that call schedule get divided?”
Maternity leave: A tricky question
Many attorneys counsel against raising the question out of fear of scaring away potential employers.
“On the one hand, it is and should be absolutely reasonable to ask about the maternity leave policy or even negotiate for paid leave or additional leave, but it also highlights that you’re planning to have a baby and be out for months,” said Ms. Hill.
“And as much as we want people to be fair and reasonable, on the side of the employer, bias still very much exists, especially in a situation where revenue is based on group numbers. So suddenly, the employer thinks up some ‘nondiscriminatory’ reason why that person isn’t a great fit for the organization.”
Andrew Knoll, MD, JD, a former hospitalist who is now a partner with Cohen Compagni Beckman Appler & Knoll PLLC in Syracuse, N.Y., said that maternity leave is “rare” in an employment agreement, except sometimes in small private practice groups, because it often falls under the purview of “disability leave,” and “from a legal perspective, it’s no different than any other type of disability leave.”
The Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA), which applies if a group is large enough, allows employees 12 weeks of unpaid leave, during which time their job is protected and their benefits maintained. And some states require employers to offer paid family leave.
“During this time, the woman can take time off – albeit without pay sometimes – to bond with the baby,” Dr. Knoll says. “Since there are statutory laws that protect the employee’s job, offering specific paid maternity leave is very unlikely.”
Ms. Hill advises carefully examining the employer’s comprehensive benefits plan to ascertain if paid maternity leave is included in the benefits. “But unless you’re currently pregnant and want to start off the relationship with true transparency – ‘I’m due in April and curious how we can handle that if you hire me now’ – I would keep the family planning questions to yourself before you get the job.”
Mr. Hursh, author of “The Final Hurdle: A Physician’s Guide to Negotiating a Fair Employment Agreement” (Charleston, S.C.: Advantage, 2012), has a different perspective. “I think all women, no matter how old they are, should ask about maternity leave, whether or not they’re planning a family,” he said.
“The employer may say, ‘We treat maternity leave like any other disability; our policy is such-and-such.’ If they cite an unacceptable policy, it’s a red flag about how they treat women, and should give a woman pause before accepting a position at that organization. Even if your rights are protected under the law and the organization’s policy is violating the law, no one wants to go to battle with HR or to have to go to court.”
Do you want partnership?
Not all female physicians entering a private practice want to advance to becoming partners. Many who are balancing family and work commitments “would prefer to just go into the office, perform their clinical responsibilities, go home, and be done” without the extra headaches, tasks, and time involved with business leadership, says Mr. Appino.
Some private practices have different contracts for those on partnership vs. nonpartnership tracks, so “you should ascertain this information and make sure it’s not automatically assumed that you would like to be on a partnership track,” says Mr. Appino.
On the other hand, you may want to become a partner. “I always suggest asking about the possibility of obtaining a leadership position in an organization or becoming an owner in a private practice,” says Mr. Hursh. “You may be told, ‘We’ve never had a woman in leadership before.’ This might be innocent if you’re the first woman hired, but it might be a red flag as to how women are regarded.” Either way, it’s important to have the information and know what your options are.
The impact of shift schedule
Mr. Hursh advises drilling down into the specifics of the schedule if you’re considering becoming a hospitalist. “Does a ‘week-on/week-off’ shift schedule assume you’ll be taking your vacation time or completing your CME requirements during the week off? This is important for all physicians, but especially for women who might want to use their weeks off to attend to children and family.”
Moreover, “there should be limits on shifts. You shouldn’t have a full day shift followed by a night shift. And there should be a limit on the number of shifts you work without time off. Twelve would be a brutal schedule. Seven is a reasonable amount. Make sure this is in writing and that the contract protects you. Don’t allow the employer to say, ‘We expect you to do the work we assign’ and leave it vague.”
Often, hospitalists will receive an annual salary under the assumption that a certain minimum number of shifts will be completed, but there is no maximum. “It’s important that the salary includes the minimum number of shifts, but that a compensation structure is created so that additional shifts receive additional compensation,” Mr. Hursh said.
Removing the ‘golden handcuffs’
Ms. Hill observes that there are some “really terrible contracts out there, which physicians – especially women – often feel pressured into signing.” They’re told, “This is our standard contract. You won’t find anything better.” Or, “Don’t worry about the small print and legalese.” The physician “gets scared or is artificially reassured, signs an overwhelmingly unfair contract, and then feels stuck.”
Being stuck in a bad contract “is debilitating and adds to burnout, feeling of depression, and the sense that there is no recourse and nowhere to go, especially if your family depends on you,” Ms. Hill said.
“More women than men feel hamstrung or are resigned to being harassed – which is not uncommon in the medical setting, especially in surgical specialties – or just accept poor treatment,” Ms. Hill added. Yes, you can “fight the system and go to HR, but fighting the system is very hard.”
She urges women “not to feel stuck or imprisoned by the ‘golden handcuffs’ but to consult a good lawyer, even if you have to break the contract.” Be aware of the reasons for your unhappiness and bring them to your lawyer – perhaps the system has engaged in fraud, perhaps there has been sexual or racial harassment, perhaps the organization hasn’t followed its own compliance policies.
Dr. Chester consulted Ms. Hill before signing the contract for her current position. “I wanted someone who could give me personalized advice, not only generic advice, and who understood my needs as a woman.”
Ms. Hill helped her to understand “what was and wasn’t fair and reasonable, what changes I could request based on my goals and whether they were realistic, and how to pick my battles. For example, I tried to negotiate tail coverage up front in my previous job but was unsuccessful. The new employer paid tail for me, both from my previous employment and for my current employment.”
Dr. Chester advises other female physicians “never to sign anything without having a lawyer review it and to make sure that the lawyer is sensitive to their specific needs.”
It can be hard to be a female physician. Having the right knowledge and ammunition and knowing how to negotiate well paves the way for success and thriving in an often male-dominated market.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rebecca Chester, MD, an Arizona-based interventional cardiologist, recently left her position in a private practice and started employment at a hospital system.
“When I was negotiating my previous contract with the private practice, I found that navigating contracts from the standpoint of a woman still in childbearing years was a little disappointing and challenging,” Dr. Chester told this news organization.
“I wanted to have more children and hired a lawyer recommended by a male colleague to help me not only understand the contract but also negotiate time off and maternity leave, but the lawyer discouraged me from advocating for maternity leave, feeling that it might stigmatize me and prevent me from getting a job,” she says.
He also didn’t explain very much. “He just said it falls under ‘disability leave’ and left it at that.”
Fortunately, Dr. Chester had a good experience with the group. “As things turned out, I did have a child later that year, and they treated me well – I actually got time off – and they didn’t make me take extra call. But it might have turned out very differently because I didn’t know what I was getting into. If I hadn’t worked for such a conscientious group, I might have been in a much tougher situation.”
Since then, Dr. Chester has spoken to female colleagues who received “more support from their legal advisors regarding maternity leave.” She suggests turning to female physicians for recommendations to a lawyer.
Although the central components of a contract (for example, noncompete covenants, malpractice “tail” coverage, bonus structure, vacation time, disability, and call) are relevant to physicians of all genders, the needs of women and men are often different.
Dennis Hursh, managing partner of Physician Agreements Health Law, a Pennsylvania-based law firm that represents physicians, told this news organization that women physicians have “several issues that need special attention when negotiating their physician employment agreements.”
It starts with the interview
“Women have to be sensitive to the interviewer’s casual ‘let’s-get-to-know-each-other’ types of questions that may seem natural but really are unlawful to bring into an employment interview,” said Mr. Hursh.
He warned women to beware of questions such as “Are you married? Do you have kids? Are you planning to start a family?” These may be friendly chit-chat for male interviewees but there may be other agendas when asked to a prospective female employee.
Many of Mr. Hursh’s female clients have been asked this type of question, which “should be regarded as a ‘red flag.’ Yes, it may be an innocent, well-intentioned ice-breaker, but it’s actually unlawful to bring that up in an employment setting and, according to the Equal Opportunity Commission, can be seen as a form of discrimination.” He advises female physicians not to engage with the question and simply to refocus the discussion.
Know your worth and go for it
Medscape’s Physician Compensation surveys have consistently found discrepancies in earnings between male and female physicians, both in primary care and in specialties. In 2022, male primary care physicians earned 23% more than their female counterparts, whereas male specialists earned 31% more.
One reason may be that women tend to be more timid about negotiating for better compensation packages. Amanda Hill of Hill Health Law, a health care practice based in Austin, Tex., told this news organization that in her experience one of the most “overarching” features of female physicians is “that they either don’t know what they’re worth or they undersell themselves.”
In contrast to men, “many women are afraid of coming across as greedy or crass, or even demanding or bossy. But it’s a misperception that if you ask for more money, your future employer will hate you or won’t hire you,” said Ms. Hill.
Ms. Hill and Mr. Hursh encourage physicians to find out what they’re worth, which varies by region and specialty, by consulting benchmarks provided by companies such as Medical Group Management Association.
Jon Appino, MBA, principal and founder of Contract Diagnostics, a Kansas City–based consulting company that specializes in physician employment contract reviews, told this news organization that it’s important to look beyond the salary at other aspects of the position. For example, some figures “don’t take into account how much call a physician is taking. You may know what the average ob.gyn. is making, but an ob.gyn. may be working 3 days a week, while another one is working 6 days a week, one may be on call 15 times per month and another may be on call 15 times a quarter.” Other components of compensation include relative value unit (RVU) thresholds and bonuses.
Once you have that information, “don’t be intimidated, even if you’re sitting in front of several executives who are savvy about negotiations, and don’t worry about coming across as ‘high-maintenance’ or ‘all about money,’ ” Mr. Appino says. Proceed with confidence, knowing your worth and pursuing it.
Part-time vs. full-time
Mr. Appino has seen “more female than male physicians who want to work less than full-time. So it’s important to clarify whether that’s a possibility now or in the future and to understand the implications of working part-time.”
He explained that a full-time employee typically puts in a 40-hour work week, which translates into 1.0 Full-Time Equivalent (FTE), or one unit of work. “For example, if a person wants to work 0.8 FTEs – 4 days a week – is vacation time pro-rated? At what point is there a medical insurance fall-off or a higher monthly premium?”
In medical settings, FTEs may be tied to different metrics rather than the number of weekly hours – for example, for a hospitalist, it might be a certain number of shifts and might also vary by specialty. And it affects the call schedule too. “Call is hard to pro-rate. Many hospital bylaws mandate that call be divided equally, but if one surgeon is working 1.0 FTEs and another is working 0.8 FTEs, how does that call schedule get divided?”
Maternity leave: A tricky question
Many attorneys counsel against raising the question out of fear of scaring away potential employers.
“On the one hand, it is and should be absolutely reasonable to ask about the maternity leave policy or even negotiate for paid leave or additional leave, but it also highlights that you’re planning to have a baby and be out for months,” said Ms. Hill.
“And as much as we want people to be fair and reasonable, on the side of the employer, bias still very much exists, especially in a situation where revenue is based on group numbers. So suddenly, the employer thinks up some ‘nondiscriminatory’ reason why that person isn’t a great fit for the organization.”
Andrew Knoll, MD, JD, a former hospitalist who is now a partner with Cohen Compagni Beckman Appler & Knoll PLLC in Syracuse, N.Y., said that maternity leave is “rare” in an employment agreement, except sometimes in small private practice groups, because it often falls under the purview of “disability leave,” and “from a legal perspective, it’s no different than any other type of disability leave.”
The Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA), which applies if a group is large enough, allows employees 12 weeks of unpaid leave, during which time their job is protected and their benefits maintained. And some states require employers to offer paid family leave.
“During this time, the woman can take time off – albeit without pay sometimes – to bond with the baby,” Dr. Knoll says. “Since there are statutory laws that protect the employee’s job, offering specific paid maternity leave is very unlikely.”
Ms. Hill advises carefully examining the employer’s comprehensive benefits plan to ascertain if paid maternity leave is included in the benefits. “But unless you’re currently pregnant and want to start off the relationship with true transparency – ‘I’m due in April and curious how we can handle that if you hire me now’ – I would keep the family planning questions to yourself before you get the job.”
Mr. Hursh, author of “The Final Hurdle: A Physician’s Guide to Negotiating a Fair Employment Agreement” (Charleston, S.C.: Advantage, 2012), has a different perspective. “I think all women, no matter how old they are, should ask about maternity leave, whether or not they’re planning a family,” he said.
“The employer may say, ‘We treat maternity leave like any other disability; our policy is such-and-such.’ If they cite an unacceptable policy, it’s a red flag about how they treat women, and should give a woman pause before accepting a position at that organization. Even if your rights are protected under the law and the organization’s policy is violating the law, no one wants to go to battle with HR or to have to go to court.”
Do you want partnership?
Not all female physicians entering a private practice want to advance to becoming partners. Many who are balancing family and work commitments “would prefer to just go into the office, perform their clinical responsibilities, go home, and be done” without the extra headaches, tasks, and time involved with business leadership, says Mr. Appino.
Some private practices have different contracts for those on partnership vs. nonpartnership tracks, so “you should ascertain this information and make sure it’s not automatically assumed that you would like to be on a partnership track,” says Mr. Appino.
On the other hand, you may want to become a partner. “I always suggest asking about the possibility of obtaining a leadership position in an organization or becoming an owner in a private practice,” says Mr. Hursh. “You may be told, ‘We’ve never had a woman in leadership before.’ This might be innocent if you’re the first woman hired, but it might be a red flag as to how women are regarded.” Either way, it’s important to have the information and know what your options are.
The impact of shift schedule
Mr. Hursh advises drilling down into the specifics of the schedule if you’re considering becoming a hospitalist. “Does a ‘week-on/week-off’ shift schedule assume you’ll be taking your vacation time or completing your CME requirements during the week off? This is important for all physicians, but especially for women who might want to use their weeks off to attend to children and family.”
Moreover, “there should be limits on shifts. You shouldn’t have a full day shift followed by a night shift. And there should be a limit on the number of shifts you work without time off. Twelve would be a brutal schedule. Seven is a reasonable amount. Make sure this is in writing and that the contract protects you. Don’t allow the employer to say, ‘We expect you to do the work we assign’ and leave it vague.”
Often, hospitalists will receive an annual salary under the assumption that a certain minimum number of shifts will be completed, but there is no maximum. “It’s important that the salary includes the minimum number of shifts, but that a compensation structure is created so that additional shifts receive additional compensation,” Mr. Hursh said.
Removing the ‘golden handcuffs’
Ms. Hill observes that there are some “really terrible contracts out there, which physicians – especially women – often feel pressured into signing.” They’re told, “This is our standard contract. You won’t find anything better.” Or, “Don’t worry about the small print and legalese.” The physician “gets scared or is artificially reassured, signs an overwhelmingly unfair contract, and then feels stuck.”
Being stuck in a bad contract “is debilitating and adds to burnout, feeling of depression, and the sense that there is no recourse and nowhere to go, especially if your family depends on you,” Ms. Hill said.
“More women than men feel hamstrung or are resigned to being harassed – which is not uncommon in the medical setting, especially in surgical specialties – or just accept poor treatment,” Ms. Hill added. Yes, you can “fight the system and go to HR, but fighting the system is very hard.”
She urges women “not to feel stuck or imprisoned by the ‘golden handcuffs’ but to consult a good lawyer, even if you have to break the contract.” Be aware of the reasons for your unhappiness and bring them to your lawyer – perhaps the system has engaged in fraud, perhaps there has been sexual or racial harassment, perhaps the organization hasn’t followed its own compliance policies.
Dr. Chester consulted Ms. Hill before signing the contract for her current position. “I wanted someone who could give me personalized advice, not only generic advice, and who understood my needs as a woman.”
Ms. Hill helped her to understand “what was and wasn’t fair and reasonable, what changes I could request based on my goals and whether they were realistic, and how to pick my battles. For example, I tried to negotiate tail coverage up front in my previous job but was unsuccessful. The new employer paid tail for me, both from my previous employment and for my current employment.”
Dr. Chester advises other female physicians “never to sign anything without having a lawyer review it and to make sure that the lawyer is sensitive to their specific needs.”
It can be hard to be a female physician. Having the right knowledge and ammunition and knowing how to negotiate well paves the way for success and thriving in an often male-dominated market.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rebecca Chester, MD, an Arizona-based interventional cardiologist, recently left her position in a private practice and started employment at a hospital system.
“When I was negotiating my previous contract with the private practice, I found that navigating contracts from the standpoint of a woman still in childbearing years was a little disappointing and challenging,” Dr. Chester told this news organization.
“I wanted to have more children and hired a lawyer recommended by a male colleague to help me not only understand the contract but also negotiate time off and maternity leave, but the lawyer discouraged me from advocating for maternity leave, feeling that it might stigmatize me and prevent me from getting a job,” she says.
He also didn’t explain very much. “He just said it falls under ‘disability leave’ and left it at that.”
Fortunately, Dr. Chester had a good experience with the group. “As things turned out, I did have a child later that year, and they treated me well – I actually got time off – and they didn’t make me take extra call. But it might have turned out very differently because I didn’t know what I was getting into. If I hadn’t worked for such a conscientious group, I might have been in a much tougher situation.”
Since then, Dr. Chester has spoken to female colleagues who received “more support from their legal advisors regarding maternity leave.” She suggests turning to female physicians for recommendations to a lawyer.
Although the central components of a contract (for example, noncompete covenants, malpractice “tail” coverage, bonus structure, vacation time, disability, and call) are relevant to physicians of all genders, the needs of women and men are often different.
Dennis Hursh, managing partner of Physician Agreements Health Law, a Pennsylvania-based law firm that represents physicians, told this news organization that women physicians have “several issues that need special attention when negotiating their physician employment agreements.”
It starts with the interview
“Women have to be sensitive to the interviewer’s casual ‘let’s-get-to-know-each-other’ types of questions that may seem natural but really are unlawful to bring into an employment interview,” said Mr. Hursh.
He warned women to beware of questions such as “Are you married? Do you have kids? Are you planning to start a family?” These may be friendly chit-chat for male interviewees but there may be other agendas when asked to a prospective female employee.
Many of Mr. Hursh’s female clients have been asked this type of question, which “should be regarded as a ‘red flag.’ Yes, it may be an innocent, well-intentioned ice-breaker, but it’s actually unlawful to bring that up in an employment setting and, according to the Equal Opportunity Commission, can be seen as a form of discrimination.” He advises female physicians not to engage with the question and simply to refocus the discussion.
Know your worth and go for it
Medscape’s Physician Compensation surveys have consistently found discrepancies in earnings between male and female physicians, both in primary care and in specialties. In 2022, male primary care physicians earned 23% more than their female counterparts, whereas male specialists earned 31% more.
One reason may be that women tend to be more timid about negotiating for better compensation packages. Amanda Hill of Hill Health Law, a health care practice based in Austin, Tex., told this news organization that in her experience one of the most “overarching” features of female physicians is “that they either don’t know what they’re worth or they undersell themselves.”
In contrast to men, “many women are afraid of coming across as greedy or crass, or even demanding or bossy. But it’s a misperception that if you ask for more money, your future employer will hate you or won’t hire you,” said Ms. Hill.
Ms. Hill and Mr. Hursh encourage physicians to find out what they’re worth, which varies by region and specialty, by consulting benchmarks provided by companies such as Medical Group Management Association.
Jon Appino, MBA, principal and founder of Contract Diagnostics, a Kansas City–based consulting company that specializes in physician employment contract reviews, told this news organization that it’s important to look beyond the salary at other aspects of the position. For example, some figures “don’t take into account how much call a physician is taking. You may know what the average ob.gyn. is making, but an ob.gyn. may be working 3 days a week, while another one is working 6 days a week, one may be on call 15 times per month and another may be on call 15 times a quarter.” Other components of compensation include relative value unit (RVU) thresholds and bonuses.
Once you have that information, “don’t be intimidated, even if you’re sitting in front of several executives who are savvy about negotiations, and don’t worry about coming across as ‘high-maintenance’ or ‘all about money,’ ” Mr. Appino says. Proceed with confidence, knowing your worth and pursuing it.
Part-time vs. full-time
Mr. Appino has seen “more female than male physicians who want to work less than full-time. So it’s important to clarify whether that’s a possibility now or in the future and to understand the implications of working part-time.”
He explained that a full-time employee typically puts in a 40-hour work week, which translates into 1.0 Full-Time Equivalent (FTE), or one unit of work. “For example, if a person wants to work 0.8 FTEs – 4 days a week – is vacation time pro-rated? At what point is there a medical insurance fall-off or a higher monthly premium?”
In medical settings, FTEs may be tied to different metrics rather than the number of weekly hours – for example, for a hospitalist, it might be a certain number of shifts and might also vary by specialty. And it affects the call schedule too. “Call is hard to pro-rate. Many hospital bylaws mandate that call be divided equally, but if one surgeon is working 1.0 FTEs and another is working 0.8 FTEs, how does that call schedule get divided?”
Maternity leave: A tricky question
Many attorneys counsel against raising the question out of fear of scaring away potential employers.
“On the one hand, it is and should be absolutely reasonable to ask about the maternity leave policy or even negotiate for paid leave or additional leave, but it also highlights that you’re planning to have a baby and be out for months,” said Ms. Hill.
“And as much as we want people to be fair and reasonable, on the side of the employer, bias still very much exists, especially in a situation where revenue is based on group numbers. So suddenly, the employer thinks up some ‘nondiscriminatory’ reason why that person isn’t a great fit for the organization.”
Andrew Knoll, MD, JD, a former hospitalist who is now a partner with Cohen Compagni Beckman Appler & Knoll PLLC in Syracuse, N.Y., said that maternity leave is “rare” in an employment agreement, except sometimes in small private practice groups, because it often falls under the purview of “disability leave,” and “from a legal perspective, it’s no different than any other type of disability leave.”
The Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA), which applies if a group is large enough, allows employees 12 weeks of unpaid leave, during which time their job is protected and their benefits maintained. And some states require employers to offer paid family leave.
“During this time, the woman can take time off – albeit without pay sometimes – to bond with the baby,” Dr. Knoll says. “Since there are statutory laws that protect the employee’s job, offering specific paid maternity leave is very unlikely.”
Ms. Hill advises carefully examining the employer’s comprehensive benefits plan to ascertain if paid maternity leave is included in the benefits. “But unless you’re currently pregnant and want to start off the relationship with true transparency – ‘I’m due in April and curious how we can handle that if you hire me now’ – I would keep the family planning questions to yourself before you get the job.”
Mr. Hursh, author of “The Final Hurdle: A Physician’s Guide to Negotiating a Fair Employment Agreement” (Charleston, S.C.: Advantage, 2012), has a different perspective. “I think all women, no matter how old they are, should ask about maternity leave, whether or not they’re planning a family,” he said.
“The employer may say, ‘We treat maternity leave like any other disability; our policy is such-and-such.’ If they cite an unacceptable policy, it’s a red flag about how they treat women, and should give a woman pause before accepting a position at that organization. Even if your rights are protected under the law and the organization’s policy is violating the law, no one wants to go to battle with HR or to have to go to court.”
Do you want partnership?
Not all female physicians entering a private practice want to advance to becoming partners. Many who are balancing family and work commitments “would prefer to just go into the office, perform their clinical responsibilities, go home, and be done” without the extra headaches, tasks, and time involved with business leadership, says Mr. Appino.
Some private practices have different contracts for those on partnership vs. nonpartnership tracks, so “you should ascertain this information and make sure it’s not automatically assumed that you would like to be on a partnership track,” says Mr. Appino.
On the other hand, you may want to become a partner. “I always suggest asking about the possibility of obtaining a leadership position in an organization or becoming an owner in a private practice,” says Mr. Hursh. “You may be told, ‘We’ve never had a woman in leadership before.’ This might be innocent if you’re the first woman hired, but it might be a red flag as to how women are regarded.” Either way, it’s important to have the information and know what your options are.
The impact of shift schedule
Mr. Hursh advises drilling down into the specifics of the schedule if you’re considering becoming a hospitalist. “Does a ‘week-on/week-off’ shift schedule assume you’ll be taking your vacation time or completing your CME requirements during the week off? This is important for all physicians, but especially for women who might want to use their weeks off to attend to children and family.”
Moreover, “there should be limits on shifts. You shouldn’t have a full day shift followed by a night shift. And there should be a limit on the number of shifts you work without time off. Twelve would be a brutal schedule. Seven is a reasonable amount. Make sure this is in writing and that the contract protects you. Don’t allow the employer to say, ‘We expect you to do the work we assign’ and leave it vague.”
Often, hospitalists will receive an annual salary under the assumption that a certain minimum number of shifts will be completed, but there is no maximum. “It’s important that the salary includes the minimum number of shifts, but that a compensation structure is created so that additional shifts receive additional compensation,” Mr. Hursh said.
Removing the ‘golden handcuffs’
Ms. Hill observes that there are some “really terrible contracts out there, which physicians – especially women – often feel pressured into signing.” They’re told, “This is our standard contract. You won’t find anything better.” Or, “Don’t worry about the small print and legalese.” The physician “gets scared or is artificially reassured, signs an overwhelmingly unfair contract, and then feels stuck.”
Being stuck in a bad contract “is debilitating and adds to burnout, feeling of depression, and the sense that there is no recourse and nowhere to go, especially if your family depends on you,” Ms. Hill said.
“More women than men feel hamstrung or are resigned to being harassed – which is not uncommon in the medical setting, especially in surgical specialties – or just accept poor treatment,” Ms. Hill added. Yes, you can “fight the system and go to HR, but fighting the system is very hard.”
She urges women “not to feel stuck or imprisoned by the ‘golden handcuffs’ but to consult a good lawyer, even if you have to break the contract.” Be aware of the reasons for your unhappiness and bring them to your lawyer – perhaps the system has engaged in fraud, perhaps there has been sexual or racial harassment, perhaps the organization hasn’t followed its own compliance policies.
Dr. Chester consulted Ms. Hill before signing the contract for her current position. “I wanted someone who could give me personalized advice, not only generic advice, and who understood my needs as a woman.”
Ms. Hill helped her to understand “what was and wasn’t fair and reasonable, what changes I could request based on my goals and whether they were realistic, and how to pick my battles. For example, I tried to negotiate tail coverage up front in my previous job but was unsuccessful. The new employer paid tail for me, both from my previous employment and for my current employment.”
Dr. Chester advises other female physicians “never to sign anything without having a lawyer review it and to make sure that the lawyer is sensitive to their specific needs.”
It can be hard to be a female physician. Having the right knowledge and ammunition and knowing how to negotiate well paves the way for success and thriving in an often male-dominated market.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pandemic caused treatment delay for half of patients with CTCL, study finds
showed. However, among patients with CTCL diagnosed with COVID-19 during that time, no cases were acquired from outpatient visits.
“Delays in therapy for patients with cutaneous lymphomas should likely be avoided,” two of the study authors, Larisa J. Geskin, MD, of the department of dermatology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, and Bradley D. Kwinta, a medical student at Columbia University, told this news organization in a combined response via email.
“Continuing treatment and maintenance therapy appears critical to avoiding disease progression, highlighting the importance of maintenance therapy in CTCL,” they said. “These patients can be safely treated according to established treatment protocols while practicing physical distancing and using personal protective equipment without significantly increasing their risk of COVID-19 infection.”
The United States Cutaneous Lymphoma Consortium and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer developed emergency guidelines for the management of patients with cutaneous lymphomas during the pandemic to ensure patient safety, and the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas created an International Cutaneous Lymphomas Pandemic Section to collect data to assess the impact of these guidelines.
“Using this data, we can determine if these measures were effective in preventing COVID-19 infection, what the impact was of maintenance therapy, and how delays in treatment affected disease outcomes in CTCL patients,” the authors and their colleagues wrote in the study, which was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
They retrospectively analyzed data from the electronic medical records of 149 patients with CTCL who were being managed at one of nine international academic medical centers in seven countries from March to October 2020. Slightly more than half (56%) were male, 70% were White, 18% were Black, 52% had stage IA-IIA disease, and 19% acquired COVID-19 during the study period.
Of the 149 patients, 79 (53%) experienced a mean treatment delay of 3.2 months (range, 10 days to 10 months). After adjusting for age, race, biological sex, COVID-19 status, and disease stage, treatment delay was associated with a significant risk of disease relapse or progression across all stages (odds ratio, 5.00; P < .001). Specifically, for each additional month that a patient experienced treatment delay, the odds of disease progression increased by 37% (OR, 1.37; P < .001).
A total of 28 patients with CTCL (19%) were diagnosed with COVID-19, but none were acquired from outpatient office visits. Patients who contracted COVID-19 did not have a statistically significant increase in odds of disease progression, compared with COVID-negative patients (OR, 0.41; P = .07).
According to Dr. Geskin, who is also director of the Comprehensive Skin Cancer Center in the division of cutaneous oncology in the department of dermatology at Columbia, and Mr. Kwinta, no clinical trials exist to inform maintenance protocols in patients with cutaneous lymphomas. “There are also no randomized and controlled observational studies that demonstrate the impact that therapy delay may have on disease outcomes,” they said in the email. “In fact, the need for maintenance therapy for CTCL is often debated. Our findings demonstrate the importance of continuing treatment and the use of maintenance therapy in avoiding disease progression in these incurable lymphomas.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its retrospective observational design. “Therefore, we cannot establish a definitive causal link between treatment delay and disease progression,” they said. “Our cohort of patients were on various and often multiple therapies, making it hard to extrapolate our data to discern which maintenance therapies were most effective in preventing disease progression.”
In addition, their data only includes patients from March to October 2020, “before the discovery of new variants and the development of COVID-19 vaccines,” they added. “Additional studies would be required to draw conclusions on how COVID-19 vaccines may affect patients with CTCL, including outcomes in the setting of new variants.”
The authors reported having no financial disclosures.
showed. However, among patients with CTCL diagnosed with COVID-19 during that time, no cases were acquired from outpatient visits.
“Delays in therapy for patients with cutaneous lymphomas should likely be avoided,” two of the study authors, Larisa J. Geskin, MD, of the department of dermatology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, and Bradley D. Kwinta, a medical student at Columbia University, told this news organization in a combined response via email.
“Continuing treatment and maintenance therapy appears critical to avoiding disease progression, highlighting the importance of maintenance therapy in CTCL,” they said. “These patients can be safely treated according to established treatment protocols while practicing physical distancing and using personal protective equipment without significantly increasing their risk of COVID-19 infection.”
The United States Cutaneous Lymphoma Consortium and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer developed emergency guidelines for the management of patients with cutaneous lymphomas during the pandemic to ensure patient safety, and the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas created an International Cutaneous Lymphomas Pandemic Section to collect data to assess the impact of these guidelines.
“Using this data, we can determine if these measures were effective in preventing COVID-19 infection, what the impact was of maintenance therapy, and how delays in treatment affected disease outcomes in CTCL patients,” the authors and their colleagues wrote in the study, which was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
They retrospectively analyzed data from the electronic medical records of 149 patients with CTCL who were being managed at one of nine international academic medical centers in seven countries from March to October 2020. Slightly more than half (56%) were male, 70% were White, 18% were Black, 52% had stage IA-IIA disease, and 19% acquired COVID-19 during the study period.
Of the 149 patients, 79 (53%) experienced a mean treatment delay of 3.2 months (range, 10 days to 10 months). After adjusting for age, race, biological sex, COVID-19 status, and disease stage, treatment delay was associated with a significant risk of disease relapse or progression across all stages (odds ratio, 5.00; P < .001). Specifically, for each additional month that a patient experienced treatment delay, the odds of disease progression increased by 37% (OR, 1.37; P < .001).
A total of 28 patients with CTCL (19%) were diagnosed with COVID-19, but none were acquired from outpatient office visits. Patients who contracted COVID-19 did not have a statistically significant increase in odds of disease progression, compared with COVID-negative patients (OR, 0.41; P = .07).
According to Dr. Geskin, who is also director of the Comprehensive Skin Cancer Center in the division of cutaneous oncology in the department of dermatology at Columbia, and Mr. Kwinta, no clinical trials exist to inform maintenance protocols in patients with cutaneous lymphomas. “There are also no randomized and controlled observational studies that demonstrate the impact that therapy delay may have on disease outcomes,” they said in the email. “In fact, the need for maintenance therapy for CTCL is often debated. Our findings demonstrate the importance of continuing treatment and the use of maintenance therapy in avoiding disease progression in these incurable lymphomas.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its retrospective observational design. “Therefore, we cannot establish a definitive causal link between treatment delay and disease progression,” they said. “Our cohort of patients were on various and often multiple therapies, making it hard to extrapolate our data to discern which maintenance therapies were most effective in preventing disease progression.”
In addition, their data only includes patients from March to October 2020, “before the discovery of new variants and the development of COVID-19 vaccines,” they added. “Additional studies would be required to draw conclusions on how COVID-19 vaccines may affect patients with CTCL, including outcomes in the setting of new variants.”
The authors reported having no financial disclosures.
showed. However, among patients with CTCL diagnosed with COVID-19 during that time, no cases were acquired from outpatient visits.
“Delays in therapy for patients with cutaneous lymphomas should likely be avoided,” two of the study authors, Larisa J. Geskin, MD, of the department of dermatology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, and Bradley D. Kwinta, a medical student at Columbia University, told this news organization in a combined response via email.
“Continuing treatment and maintenance therapy appears critical to avoiding disease progression, highlighting the importance of maintenance therapy in CTCL,” they said. “These patients can be safely treated according to established treatment protocols while practicing physical distancing and using personal protective equipment without significantly increasing their risk of COVID-19 infection.”
The United States Cutaneous Lymphoma Consortium and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer developed emergency guidelines for the management of patients with cutaneous lymphomas during the pandemic to ensure patient safety, and the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas created an International Cutaneous Lymphomas Pandemic Section to collect data to assess the impact of these guidelines.
“Using this data, we can determine if these measures were effective in preventing COVID-19 infection, what the impact was of maintenance therapy, and how delays in treatment affected disease outcomes in CTCL patients,” the authors and their colleagues wrote in the study, which was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
They retrospectively analyzed data from the electronic medical records of 149 patients with CTCL who were being managed at one of nine international academic medical centers in seven countries from March to October 2020. Slightly more than half (56%) were male, 70% were White, 18% were Black, 52% had stage IA-IIA disease, and 19% acquired COVID-19 during the study period.
Of the 149 patients, 79 (53%) experienced a mean treatment delay of 3.2 months (range, 10 days to 10 months). After adjusting for age, race, biological sex, COVID-19 status, and disease stage, treatment delay was associated with a significant risk of disease relapse or progression across all stages (odds ratio, 5.00; P < .001). Specifically, for each additional month that a patient experienced treatment delay, the odds of disease progression increased by 37% (OR, 1.37; P < .001).
A total of 28 patients with CTCL (19%) were diagnosed with COVID-19, but none were acquired from outpatient office visits. Patients who contracted COVID-19 did not have a statistically significant increase in odds of disease progression, compared with COVID-negative patients (OR, 0.41; P = .07).
According to Dr. Geskin, who is also director of the Comprehensive Skin Cancer Center in the division of cutaneous oncology in the department of dermatology at Columbia, and Mr. Kwinta, no clinical trials exist to inform maintenance protocols in patients with cutaneous lymphomas. “There are also no randomized and controlled observational studies that demonstrate the impact that therapy delay may have on disease outcomes,” they said in the email. “In fact, the need for maintenance therapy for CTCL is often debated. Our findings demonstrate the importance of continuing treatment and the use of maintenance therapy in avoiding disease progression in these incurable lymphomas.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its retrospective observational design. “Therefore, we cannot establish a definitive causal link between treatment delay and disease progression,” they said. “Our cohort of patients were on various and often multiple therapies, making it hard to extrapolate our data to discern which maintenance therapies were most effective in preventing disease progression.”
In addition, their data only includes patients from March to October 2020, “before the discovery of new variants and the development of COVID-19 vaccines,” they added. “Additional studies would be required to draw conclusions on how COVID-19 vaccines may affect patients with CTCL, including outcomes in the setting of new variants.”
The authors reported having no financial disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Who’s more likely to develop a second primary melanoma?
Individuals with a primary melanoma may be more likely to develop a second primary melanoma if they have certain characteristics, a new study suggests.
for melanoma.
Notably, the researchers also found only limited evidence that elevated levels of sun exposure contributed to second melanoma risk.
Overall, the findings suggest that “within the general population, the presence of many nevi and having a high genetic predisposition to melanoma were associated with the highest risks of developing second primary melanoma,” Catherine M. Olsen, PhD, of the University of Queensland, Australia, and colleagues concluded.
The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
People with melanoma are believed to be at high risk for developing subsequent tumors, yet most never do. Population-based studies indicate that only about 8%-18% of patients are diagnosed with a second primary melanoma.
Previous studies using modified case-control design have identified several factors associated with developing multiple primary melanomas, including older age, male sex, a family history of melanoma, high nevus counts or presence of atypical nevi, higher ambient UV radiation and personal sun exposure, as well as certain inherited genetic variants.
However, these studies aren’t equipped to assess the magnitude of risk of developing multiple melanomas among those who have not yet had melanoma.
In the current analysis, Dr. Olsen and colleagues set out to understand the level of risk using a prospective cohort study design. The cohort comprised participants in the QSkin Sun and Health Study and included 38,845 patients with a baseline median age of 56 years, followed for a median of 7.4 years. Among these participants, 1,212 (3.1%) had only one primary melanoma diagnosis, and 245 (0.6%) had two or more primary melanomas. Of those with more primary melanomas, 59 had synchronous primary melanoma, meaning first and second primary melanomas were diagnosed on the same day.
The investigators compared the clinical characteristics of patients with first and second melanomas, looking at demographic, phenotypic, sun exposure, and genetic factors. The team found that the median time between first and second melanoma, excluding cases of synchronous primary melanoma, was 18.4 months.
Those who developed second melanomas were older at baseline than those who developed only one (59.3 years vs. 58.2 years, respectively; P < .001), and were more likely to have a sun-sensitive phenotype, a self-reported history of excisions for nonmelanoma skin cancers, and a high polygenic risk score for melanoma. Among people who developed second primary melanomas, the second melanomas were more likely to be in situ and of the lentigo maligna subtype.
Notably, factors including age, sex, sunburn tendency, and family history of melanoma had similarly elevated effect sizes among those diagnosed with first and second melanomas. The authors also found similar associations with baseline measures for personal sun exposure – including sunburns and cumulative sun exposure; however, the number of past skin cancer excisions was more strongly associated with second primaries (P = .05).
The team did identify two factors associated with a higher risk of developing a second primary melanoma. A nevus phenotype was more strongly associated with developing a second primary melanoma (hazard ratio, 6.36) than the initial one (HR, 3.46). And second primary melanomas had stronger associations with high melanoma polygenic risk scores than first primary melanomas (HR, 3.28 vs HR, 2.06; P = .03).
The authors noted several limitations to the study, including the generalizability of the findings outside of Australia and the relatively small number of people with second primary melanomas.
Still, the investigators note that the data “offer unique insights that differ from earlier efforts.” Namely, the “findings showed that many of the classic phenotypic risk factors for melanoma were similarly associated with risk of first and second melanomas; however, high numbers of nevi and high genetic predisposition were more strongly associated with second [rather] than first primary melanomas.”
This work was supported by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. Dr. Olsen reports no relevant financial relationships. Coauthor Rachel Neale, PhD, reported grants from Viatris and the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia outside the submitted work. Coauthor David Whiteman, MBBS, PhD, reported personal fees from Pierre Fabre (speaker fees for conference presentation) outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Individuals with a primary melanoma may be more likely to develop a second primary melanoma if they have certain characteristics, a new study suggests.
for melanoma.
Notably, the researchers also found only limited evidence that elevated levels of sun exposure contributed to second melanoma risk.
Overall, the findings suggest that “within the general population, the presence of many nevi and having a high genetic predisposition to melanoma were associated with the highest risks of developing second primary melanoma,” Catherine M. Olsen, PhD, of the University of Queensland, Australia, and colleagues concluded.
The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
People with melanoma are believed to be at high risk for developing subsequent tumors, yet most never do. Population-based studies indicate that only about 8%-18% of patients are diagnosed with a second primary melanoma.
Previous studies using modified case-control design have identified several factors associated with developing multiple primary melanomas, including older age, male sex, a family history of melanoma, high nevus counts or presence of atypical nevi, higher ambient UV radiation and personal sun exposure, as well as certain inherited genetic variants.
However, these studies aren’t equipped to assess the magnitude of risk of developing multiple melanomas among those who have not yet had melanoma.
In the current analysis, Dr. Olsen and colleagues set out to understand the level of risk using a prospective cohort study design. The cohort comprised participants in the QSkin Sun and Health Study and included 38,845 patients with a baseline median age of 56 years, followed for a median of 7.4 years. Among these participants, 1,212 (3.1%) had only one primary melanoma diagnosis, and 245 (0.6%) had two or more primary melanomas. Of those with more primary melanomas, 59 had synchronous primary melanoma, meaning first and second primary melanomas were diagnosed on the same day.
The investigators compared the clinical characteristics of patients with first and second melanomas, looking at demographic, phenotypic, sun exposure, and genetic factors. The team found that the median time between first and second melanoma, excluding cases of synchronous primary melanoma, was 18.4 months.
Those who developed second melanomas were older at baseline than those who developed only one (59.3 years vs. 58.2 years, respectively; P < .001), and were more likely to have a sun-sensitive phenotype, a self-reported history of excisions for nonmelanoma skin cancers, and a high polygenic risk score for melanoma. Among people who developed second primary melanomas, the second melanomas were more likely to be in situ and of the lentigo maligna subtype.
Notably, factors including age, sex, sunburn tendency, and family history of melanoma had similarly elevated effect sizes among those diagnosed with first and second melanomas. The authors also found similar associations with baseline measures for personal sun exposure – including sunburns and cumulative sun exposure; however, the number of past skin cancer excisions was more strongly associated with second primaries (P = .05).
The team did identify two factors associated with a higher risk of developing a second primary melanoma. A nevus phenotype was more strongly associated with developing a second primary melanoma (hazard ratio, 6.36) than the initial one (HR, 3.46). And second primary melanomas had stronger associations with high melanoma polygenic risk scores than first primary melanomas (HR, 3.28 vs HR, 2.06; P = .03).
The authors noted several limitations to the study, including the generalizability of the findings outside of Australia and the relatively small number of people with second primary melanomas.
Still, the investigators note that the data “offer unique insights that differ from earlier efforts.” Namely, the “findings showed that many of the classic phenotypic risk factors for melanoma were similarly associated with risk of first and second melanomas; however, high numbers of nevi and high genetic predisposition were more strongly associated with second [rather] than first primary melanomas.”
This work was supported by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. Dr. Olsen reports no relevant financial relationships. Coauthor Rachel Neale, PhD, reported grants from Viatris and the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia outside the submitted work. Coauthor David Whiteman, MBBS, PhD, reported personal fees from Pierre Fabre (speaker fees for conference presentation) outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Individuals with a primary melanoma may be more likely to develop a second primary melanoma if they have certain characteristics, a new study suggests.
for melanoma.
Notably, the researchers also found only limited evidence that elevated levels of sun exposure contributed to second melanoma risk.
Overall, the findings suggest that “within the general population, the presence of many nevi and having a high genetic predisposition to melanoma were associated with the highest risks of developing second primary melanoma,” Catherine M. Olsen, PhD, of the University of Queensland, Australia, and colleagues concluded.
The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
People with melanoma are believed to be at high risk for developing subsequent tumors, yet most never do. Population-based studies indicate that only about 8%-18% of patients are diagnosed with a second primary melanoma.
Previous studies using modified case-control design have identified several factors associated with developing multiple primary melanomas, including older age, male sex, a family history of melanoma, high nevus counts or presence of atypical nevi, higher ambient UV radiation and personal sun exposure, as well as certain inherited genetic variants.
However, these studies aren’t equipped to assess the magnitude of risk of developing multiple melanomas among those who have not yet had melanoma.
In the current analysis, Dr. Olsen and colleagues set out to understand the level of risk using a prospective cohort study design. The cohort comprised participants in the QSkin Sun and Health Study and included 38,845 patients with a baseline median age of 56 years, followed for a median of 7.4 years. Among these participants, 1,212 (3.1%) had only one primary melanoma diagnosis, and 245 (0.6%) had two or more primary melanomas. Of those with more primary melanomas, 59 had synchronous primary melanoma, meaning first and second primary melanomas were diagnosed on the same day.
The investigators compared the clinical characteristics of patients with first and second melanomas, looking at demographic, phenotypic, sun exposure, and genetic factors. The team found that the median time between first and second melanoma, excluding cases of synchronous primary melanoma, was 18.4 months.
Those who developed second melanomas were older at baseline than those who developed only one (59.3 years vs. 58.2 years, respectively; P < .001), and were more likely to have a sun-sensitive phenotype, a self-reported history of excisions for nonmelanoma skin cancers, and a high polygenic risk score for melanoma. Among people who developed second primary melanomas, the second melanomas were more likely to be in situ and of the lentigo maligna subtype.
Notably, factors including age, sex, sunburn tendency, and family history of melanoma had similarly elevated effect sizes among those diagnosed with first and second melanomas. The authors also found similar associations with baseline measures for personal sun exposure – including sunburns and cumulative sun exposure; however, the number of past skin cancer excisions was more strongly associated with second primaries (P = .05).
The team did identify two factors associated with a higher risk of developing a second primary melanoma. A nevus phenotype was more strongly associated with developing a second primary melanoma (hazard ratio, 6.36) than the initial one (HR, 3.46). And second primary melanomas had stronger associations with high melanoma polygenic risk scores than first primary melanomas (HR, 3.28 vs HR, 2.06; P = .03).
The authors noted several limitations to the study, including the generalizability of the findings outside of Australia and the relatively small number of people with second primary melanomas.
Still, the investigators note that the data “offer unique insights that differ from earlier efforts.” Namely, the “findings showed that many of the classic phenotypic risk factors for melanoma were similarly associated with risk of first and second melanomas; however, high numbers of nevi and high genetic predisposition were more strongly associated with second [rather] than first primary melanomas.”
This work was supported by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. Dr. Olsen reports no relevant financial relationships. Coauthor Rachel Neale, PhD, reported grants from Viatris and the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia outside the submitted work. Coauthor David Whiteman, MBBS, PhD, reported personal fees from Pierre Fabre (speaker fees for conference presentation) outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
How blunt is too blunt for informed consent?
Sitting across from a patient explaining a complicated treatment proposal, protocol, or medication may be one of the most complex yet crucial tasks you have as a physician. Although informed consent is at the forefront of shared decisions between you and your patient, there’s a fine line between providing enough information on the risks and benefits of a particular treatment and knowing you’ve explained it well enough to fully educate your patient about their choices.
“It is a bit of a fine line because unless your patient happens to be a health care provider, medicine is complicated for patients to understand,” said David L. Feldman, MD, chief medical officer at The Doctors Company, the nation’s largest medical malpractice insurer in New York.
In addition, documenting the interaction is critical, said James Giordano, PhD, MPhil, professor in the departments of neurology and biochemistry and chief of the neuroethics studies program at the Pellegrino Center for Clinical Bioethics at Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington.
“As with anything in medicine, the key rule is that if it’s not documented, it’s not done,” he said. “This also means diligent documentation in all aspects of the medical record, including the electronic medical record and the written one.”
That said, it’s important to know what’s enough and what’s too granular when you discuss a procedure with your patients, said Erum N. Ilyas, MD, a board-certified dermatologist at Schweiger Dermatology and a bioethicist near Philadelphia.
“One of the most challenging aspects of informed consent, especially for young physicians, is how to discuss a procedure or a medication in a manner that is both relevant and concise,” Dr. llyas said. “I’ve had residents about to perform a skin biopsy spend several minutes covering every aspect of every potential outcome of a routine skin biopsy. The patient is left traumatized and confused as to whether they should proceed with the small procedure.”
Instead, the goal of informed consent is to ensure that the patient has a general overview of the procedure and is empowered, knowing that the decision to proceed is, indeed, part of their decision-making process.
How long an informed consent discussion takes depends on the procedure.
“When I was in practice as a plastic surgeon, the conversations varied from the straightforward ‘I’m taking this mole off your cheek, and there’s a risk of scarring and bleeding’ to talking about a mastectomy and breast reconstruction, which could take an hour or more to discuss,” Dr. Feldman said.
Ultimately, it’s as essential for doctors to explain the risks associated with a procedure as it is for patients to understand precisely what’s involved, Dr. Ilyas added.
She also recommends creating a flow to the conversation that places the discussion of risks within the context of why the procedure is being performed. This way, clarity about both the risks and the need for the treatment or procedure can be achieved.
When doing so, it’s critical to make sure you’re speaking your patient’s language – literally.
“Have a translator in the room if needed,” Dr. Feldman added. “If your patient is hearing or sight impaired, you need to have every contingency ready to ensure that everyone is in complete communication.”
Document, document, document!
To best protect yourself, the patient must consent to each procedure and intervention via active, informed consent, said Dr. Giordano.
“It’s not enough to hand a patient a piece of paper and say sign it,” he said. “There should be some documented evidence that the patient has not only read the document but that the key parts of the document have been explained and that the patient’s level of comprehension has been assessed and verified.”
It is vital if the patient has a disability, a neurological impairment, or a neurocognitive or psychiatric condition that might impede his or her ability to understand the consent that’s being sought.
In addition, it’s best if a ‘clinical proxy’ handles the consent (for example, a nurse, office worker, or case manager).
“This can be very helpful because it means you’ve had third-party documentation of informed consent,” Dr. Giordano said. “It should then be re-documented with you as the clinician and stated that the patient has affirmatively and actively agreed to treatment.”
What happens when things go wrong?
If you’re sued over informed consent, with the patient claiming that you didn’t fully explain the potential risks, the first thing to consider is why this happened.
“Very often, these situations occur if there was some difficulty or competency of communication,” Dr. Giordano said. “You may have done everything right, but somehow the patient hasn’t gained an understanding of the procedure required.”
Physicians must take a hard look at how they’re explaining risks and possible side effects. For doctors who perform these procedures regularly, the risks may seem small, and they may unconsciously minimize them to the patient. But when something goes wrong, the patient may then feel that they didn’t fully understand the frequency of poor outcomes, or the potential severity.
Next, it’s important to perform a ‘gap analysis’ to assess why something went awry. That means, look at all the potential factors involved to identify which one was the weak link.
“It might be that the patient was on a signing frenzy and signed away but didn’t receive active and informed content,” Dr. Giordano said. “The goal is to learn how to close the gap for this case and for future cases.”
To protect yourself, consider using technology to your advantage, especially since lawsuits over informed consent usually happen several years after the procedure. This is when a patient might argue that you didn’t tell them about possible complications and that they might have opted out of the procedure if they had known about those issues ahead of time.
“Even before the statute of limitations is up for a lawsuit, it could be five years from the time the procedure occurred due to the length of time a lawsuit can take,” Dr. Feldman said. “That’s why it’s important to take a video of your conversation or make a recording of the informed consent conversation. This way if there’s a question of what you said, there’s a video of it.”
For many physicians, this would be a big change – to video record and then store all their informed consent conversations. It could most likely help you if a lawsuit occurs, but some physicians may feel that process to be cumbersome and time-consuming, and they’d rather find another way to ensure that patients understand the risks.
Ultimately, however, if there’s a legal question involved with informed consent, the general thinking is that the effect on the patient must be harmful for it to stand up.
“The question becomes whether the outcome rendered that gap in the consenting process forgivable,” Dr. Giordano said. “The hope is that there was nothing harmful to the patient and that the benefit of the procedure was demonstrable despite any gaps in the informed consent process.”
In the end, informed consent should be a matter of good communication before, during, and after any treatment or procedure.
“When you form a relationship with a patient who needs any procedure, small or large, you’re going to be guiding them through a very scary thing,” Dr. Feldman said. “You want to make patients feel like you care about them and that, while neither you nor the system is perfect, you’ll take care of them. That’s the bottom line.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sitting across from a patient explaining a complicated treatment proposal, protocol, or medication may be one of the most complex yet crucial tasks you have as a physician. Although informed consent is at the forefront of shared decisions between you and your patient, there’s a fine line between providing enough information on the risks and benefits of a particular treatment and knowing you’ve explained it well enough to fully educate your patient about their choices.
“It is a bit of a fine line because unless your patient happens to be a health care provider, medicine is complicated for patients to understand,” said David L. Feldman, MD, chief medical officer at The Doctors Company, the nation’s largest medical malpractice insurer in New York.
In addition, documenting the interaction is critical, said James Giordano, PhD, MPhil, professor in the departments of neurology and biochemistry and chief of the neuroethics studies program at the Pellegrino Center for Clinical Bioethics at Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington.
“As with anything in medicine, the key rule is that if it’s not documented, it’s not done,” he said. “This also means diligent documentation in all aspects of the medical record, including the electronic medical record and the written one.”
That said, it’s important to know what’s enough and what’s too granular when you discuss a procedure with your patients, said Erum N. Ilyas, MD, a board-certified dermatologist at Schweiger Dermatology and a bioethicist near Philadelphia.
“One of the most challenging aspects of informed consent, especially for young physicians, is how to discuss a procedure or a medication in a manner that is both relevant and concise,” Dr. llyas said. “I’ve had residents about to perform a skin biopsy spend several minutes covering every aspect of every potential outcome of a routine skin biopsy. The patient is left traumatized and confused as to whether they should proceed with the small procedure.”
Instead, the goal of informed consent is to ensure that the patient has a general overview of the procedure and is empowered, knowing that the decision to proceed is, indeed, part of their decision-making process.
How long an informed consent discussion takes depends on the procedure.
“When I was in practice as a plastic surgeon, the conversations varied from the straightforward ‘I’m taking this mole off your cheek, and there’s a risk of scarring and bleeding’ to talking about a mastectomy and breast reconstruction, which could take an hour or more to discuss,” Dr. Feldman said.
Ultimately, it’s as essential for doctors to explain the risks associated with a procedure as it is for patients to understand precisely what’s involved, Dr. Ilyas added.
She also recommends creating a flow to the conversation that places the discussion of risks within the context of why the procedure is being performed. This way, clarity about both the risks and the need for the treatment or procedure can be achieved.
When doing so, it’s critical to make sure you’re speaking your patient’s language – literally.
“Have a translator in the room if needed,” Dr. Feldman added. “If your patient is hearing or sight impaired, you need to have every contingency ready to ensure that everyone is in complete communication.”
Document, document, document!
To best protect yourself, the patient must consent to each procedure and intervention via active, informed consent, said Dr. Giordano.
“It’s not enough to hand a patient a piece of paper and say sign it,” he said. “There should be some documented evidence that the patient has not only read the document but that the key parts of the document have been explained and that the patient’s level of comprehension has been assessed and verified.”
It is vital if the patient has a disability, a neurological impairment, or a neurocognitive or psychiatric condition that might impede his or her ability to understand the consent that’s being sought.
In addition, it’s best if a ‘clinical proxy’ handles the consent (for example, a nurse, office worker, or case manager).
“This can be very helpful because it means you’ve had third-party documentation of informed consent,” Dr. Giordano said. “It should then be re-documented with you as the clinician and stated that the patient has affirmatively and actively agreed to treatment.”
What happens when things go wrong?
If you’re sued over informed consent, with the patient claiming that you didn’t fully explain the potential risks, the first thing to consider is why this happened.
“Very often, these situations occur if there was some difficulty or competency of communication,” Dr. Giordano said. “You may have done everything right, but somehow the patient hasn’t gained an understanding of the procedure required.”
Physicians must take a hard look at how they’re explaining risks and possible side effects. For doctors who perform these procedures regularly, the risks may seem small, and they may unconsciously minimize them to the patient. But when something goes wrong, the patient may then feel that they didn’t fully understand the frequency of poor outcomes, or the potential severity.
Next, it’s important to perform a ‘gap analysis’ to assess why something went awry. That means, look at all the potential factors involved to identify which one was the weak link.
“It might be that the patient was on a signing frenzy and signed away but didn’t receive active and informed content,” Dr. Giordano said. “The goal is to learn how to close the gap for this case and for future cases.”
To protect yourself, consider using technology to your advantage, especially since lawsuits over informed consent usually happen several years after the procedure. This is when a patient might argue that you didn’t tell them about possible complications and that they might have opted out of the procedure if they had known about those issues ahead of time.
“Even before the statute of limitations is up for a lawsuit, it could be five years from the time the procedure occurred due to the length of time a lawsuit can take,” Dr. Feldman said. “That’s why it’s important to take a video of your conversation or make a recording of the informed consent conversation. This way if there’s a question of what you said, there’s a video of it.”
For many physicians, this would be a big change – to video record and then store all their informed consent conversations. It could most likely help you if a lawsuit occurs, but some physicians may feel that process to be cumbersome and time-consuming, and they’d rather find another way to ensure that patients understand the risks.
Ultimately, however, if there’s a legal question involved with informed consent, the general thinking is that the effect on the patient must be harmful for it to stand up.
“The question becomes whether the outcome rendered that gap in the consenting process forgivable,” Dr. Giordano said. “The hope is that there was nothing harmful to the patient and that the benefit of the procedure was demonstrable despite any gaps in the informed consent process.”
In the end, informed consent should be a matter of good communication before, during, and after any treatment or procedure.
“When you form a relationship with a patient who needs any procedure, small or large, you’re going to be guiding them through a very scary thing,” Dr. Feldman said. “You want to make patients feel like you care about them and that, while neither you nor the system is perfect, you’ll take care of them. That’s the bottom line.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sitting across from a patient explaining a complicated treatment proposal, protocol, or medication may be one of the most complex yet crucial tasks you have as a physician. Although informed consent is at the forefront of shared decisions between you and your patient, there’s a fine line between providing enough information on the risks and benefits of a particular treatment and knowing you’ve explained it well enough to fully educate your patient about their choices.
“It is a bit of a fine line because unless your patient happens to be a health care provider, medicine is complicated for patients to understand,” said David L. Feldman, MD, chief medical officer at The Doctors Company, the nation’s largest medical malpractice insurer in New York.
In addition, documenting the interaction is critical, said James Giordano, PhD, MPhil, professor in the departments of neurology and biochemistry and chief of the neuroethics studies program at the Pellegrino Center for Clinical Bioethics at Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington.
“As with anything in medicine, the key rule is that if it’s not documented, it’s not done,” he said. “This also means diligent documentation in all aspects of the medical record, including the electronic medical record and the written one.”
That said, it’s important to know what’s enough and what’s too granular when you discuss a procedure with your patients, said Erum N. Ilyas, MD, a board-certified dermatologist at Schweiger Dermatology and a bioethicist near Philadelphia.
“One of the most challenging aspects of informed consent, especially for young physicians, is how to discuss a procedure or a medication in a manner that is both relevant and concise,” Dr. llyas said. “I’ve had residents about to perform a skin biopsy spend several minutes covering every aspect of every potential outcome of a routine skin biopsy. The patient is left traumatized and confused as to whether they should proceed with the small procedure.”
Instead, the goal of informed consent is to ensure that the patient has a general overview of the procedure and is empowered, knowing that the decision to proceed is, indeed, part of their decision-making process.
How long an informed consent discussion takes depends on the procedure.
“When I was in practice as a plastic surgeon, the conversations varied from the straightforward ‘I’m taking this mole off your cheek, and there’s a risk of scarring and bleeding’ to talking about a mastectomy and breast reconstruction, which could take an hour or more to discuss,” Dr. Feldman said.
Ultimately, it’s as essential for doctors to explain the risks associated with a procedure as it is for patients to understand precisely what’s involved, Dr. Ilyas added.
She also recommends creating a flow to the conversation that places the discussion of risks within the context of why the procedure is being performed. This way, clarity about both the risks and the need for the treatment or procedure can be achieved.
When doing so, it’s critical to make sure you’re speaking your patient’s language – literally.
“Have a translator in the room if needed,” Dr. Feldman added. “If your patient is hearing or sight impaired, you need to have every contingency ready to ensure that everyone is in complete communication.”
Document, document, document!
To best protect yourself, the patient must consent to each procedure and intervention via active, informed consent, said Dr. Giordano.
“It’s not enough to hand a patient a piece of paper and say sign it,” he said. “There should be some documented evidence that the patient has not only read the document but that the key parts of the document have been explained and that the patient’s level of comprehension has been assessed and verified.”
It is vital if the patient has a disability, a neurological impairment, or a neurocognitive or psychiatric condition that might impede his or her ability to understand the consent that’s being sought.
In addition, it’s best if a ‘clinical proxy’ handles the consent (for example, a nurse, office worker, or case manager).
“This can be very helpful because it means you’ve had third-party documentation of informed consent,” Dr. Giordano said. “It should then be re-documented with you as the clinician and stated that the patient has affirmatively and actively agreed to treatment.”
What happens when things go wrong?
If you’re sued over informed consent, with the patient claiming that you didn’t fully explain the potential risks, the first thing to consider is why this happened.
“Very often, these situations occur if there was some difficulty or competency of communication,” Dr. Giordano said. “You may have done everything right, but somehow the patient hasn’t gained an understanding of the procedure required.”
Physicians must take a hard look at how they’re explaining risks and possible side effects. For doctors who perform these procedures regularly, the risks may seem small, and they may unconsciously minimize them to the patient. But when something goes wrong, the patient may then feel that they didn’t fully understand the frequency of poor outcomes, or the potential severity.
Next, it’s important to perform a ‘gap analysis’ to assess why something went awry. That means, look at all the potential factors involved to identify which one was the weak link.
“It might be that the patient was on a signing frenzy and signed away but didn’t receive active and informed content,” Dr. Giordano said. “The goal is to learn how to close the gap for this case and for future cases.”
To protect yourself, consider using technology to your advantage, especially since lawsuits over informed consent usually happen several years after the procedure. This is when a patient might argue that you didn’t tell them about possible complications and that they might have opted out of the procedure if they had known about those issues ahead of time.
“Even before the statute of limitations is up for a lawsuit, it could be five years from the time the procedure occurred due to the length of time a lawsuit can take,” Dr. Feldman said. “That’s why it’s important to take a video of your conversation or make a recording of the informed consent conversation. This way if there’s a question of what you said, there’s a video of it.”
For many physicians, this would be a big change – to video record and then store all their informed consent conversations. It could most likely help you if a lawsuit occurs, but some physicians may feel that process to be cumbersome and time-consuming, and they’d rather find another way to ensure that patients understand the risks.
Ultimately, however, if there’s a legal question involved with informed consent, the general thinking is that the effect on the patient must be harmful for it to stand up.
“The question becomes whether the outcome rendered that gap in the consenting process forgivable,” Dr. Giordano said. “The hope is that there was nothing harmful to the patient and that the benefit of the procedure was demonstrable despite any gaps in the informed consent process.”
In the end, informed consent should be a matter of good communication before, during, and after any treatment or procedure.
“When you form a relationship with a patient who needs any procedure, small or large, you’re going to be guiding them through a very scary thing,” Dr. Feldman said. “You want to make patients feel like you care about them and that, while neither you nor the system is perfect, you’ll take care of them. That’s the bottom line.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Analysis of doctors’ EHR email finds infrequent but notable hostility
Among the emails, 43% were from patients; the remainder were mostly from other physicians or clinicians, or automated. The content of the messages wasn’t associated with doctor burnout, as the researchers had hypothesized. And only about 5% of the messages had negative sentiment.
But the researchers were struck by the hostility of that sentiment, displayed in messages like these that surely would be distressing for physicians to read:
“I hope and expect that you will spend eternity in he**. You are an abusive, nasty, cheap person.”
“Your office is full of liars, hypocrites and I will do everything in my power to prevent anyone from going to your bullsh** office again.”
About 5% of emails had an overall negative sentiment, with high-frequency words like “cancel,” “pain,” or “problem.” Among patient messages, 3% were negative and contained words and expletives suggesting hatred, hostility, or violence.
“F***” was the most common expletive used by patients.
Researchers provided examples of profanity-laced messages, including one patient who said, “I am so upset that I was told the blood work would include the gender of the baby. I have been waiting 5 [days] to find it, and it wasn’t even fu**ing tested!!!! What a disappointment in your office and the bullsh** I was told. I will be switching plans because this is sh**!”
Researchers also noted some high-frequency words associated with violence, such as “shoot,” “fight,” and “kill.”
“This is concerning, especially given documentation of patient-inflicted violence against physicians. Health systems should be proactive in ensuring that the in-basket does not become a venue for physician abuse and cyberbullying,” the researchers wrote in JAMA Network Open.
“Posting reminders in EHR patient portals to use kind language when sending messages, applying filters for expletives or threatening words, and creating frameworks for identifying patients who frequently send negative messages are potential strategies for mitigating this risk.”
Using a form of artificial intelligence technology called natural language processing (NLP), researchers at the University of California, San Diego, analyzed the characteristics of more than 1.4 million emails received by the university’s physicians, 43% of them from patients. They specifically looked at the volume of messages, word count, and overall sentiment.
Whereas other studies have examined the growing burden of EHR messaging for doctors, this type of email sentiment analysis could help in creating solutions. Researchers say that one such solution could involve applying filters for expletives or threatening words. It also could help identify fixable health system issues that make patients so angry, the researchers say.
Among the emails from physicians to physicians, just over half reported burnout, which correlated to the following phrases: “I am beginning to burn out and have one or more symptoms of burnout” and “I feel completely burned out [and] am at the point where I may need to seek help.”
On average, physicians who reported burnout received a greater volume of patient messages. The odds of burnout were significantly higher among Hispanic/Latinx physicians and females. Physicians with more than 15 years of clinical practice had markedly lower burnout.
Despite physicians now spending more time on EHR in-basket tasks than they did before the pandemic, the study found no significant associations between message characteristics and burnout.
Data for the cross-sectional study were collected from multiple specialties from April to September 2020. Physicians then completed a survey and assessed their burnout on a 5-point scale. Of the 609 physician responses, approximately 49% of participants were women, 56% were White, and 64% worked in outpatient settings. About 70% of the doctors had been in practice for 15 years or less.
The sentiment score was based on word content as well as the use of negation, punctuation, degree modifiers, all caps, emoticons, emojis, and acronyms. Positive patient messages were more likely to convey gratitude and thanks, along with casual expressions, such as “fyi” and “lol.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among the emails, 43% were from patients; the remainder were mostly from other physicians or clinicians, or automated. The content of the messages wasn’t associated with doctor burnout, as the researchers had hypothesized. And only about 5% of the messages had negative sentiment.
But the researchers were struck by the hostility of that sentiment, displayed in messages like these that surely would be distressing for physicians to read:
“I hope and expect that you will spend eternity in he**. You are an abusive, nasty, cheap person.”
“Your office is full of liars, hypocrites and I will do everything in my power to prevent anyone from going to your bullsh** office again.”
About 5% of emails had an overall negative sentiment, with high-frequency words like “cancel,” “pain,” or “problem.” Among patient messages, 3% were negative and contained words and expletives suggesting hatred, hostility, or violence.
“F***” was the most common expletive used by patients.
Researchers provided examples of profanity-laced messages, including one patient who said, “I am so upset that I was told the blood work would include the gender of the baby. I have been waiting 5 [days] to find it, and it wasn’t even fu**ing tested!!!! What a disappointment in your office and the bullsh** I was told. I will be switching plans because this is sh**!”
Researchers also noted some high-frequency words associated with violence, such as “shoot,” “fight,” and “kill.”
“This is concerning, especially given documentation of patient-inflicted violence against physicians. Health systems should be proactive in ensuring that the in-basket does not become a venue for physician abuse and cyberbullying,” the researchers wrote in JAMA Network Open.
“Posting reminders in EHR patient portals to use kind language when sending messages, applying filters for expletives or threatening words, and creating frameworks for identifying patients who frequently send negative messages are potential strategies for mitigating this risk.”
Using a form of artificial intelligence technology called natural language processing (NLP), researchers at the University of California, San Diego, analyzed the characteristics of more than 1.4 million emails received by the university’s physicians, 43% of them from patients. They specifically looked at the volume of messages, word count, and overall sentiment.
Whereas other studies have examined the growing burden of EHR messaging for doctors, this type of email sentiment analysis could help in creating solutions. Researchers say that one such solution could involve applying filters for expletives or threatening words. It also could help identify fixable health system issues that make patients so angry, the researchers say.
Among the emails from physicians to physicians, just over half reported burnout, which correlated to the following phrases: “I am beginning to burn out and have one or more symptoms of burnout” and “I feel completely burned out [and] am at the point where I may need to seek help.”
On average, physicians who reported burnout received a greater volume of patient messages. The odds of burnout were significantly higher among Hispanic/Latinx physicians and females. Physicians with more than 15 years of clinical practice had markedly lower burnout.
Despite physicians now spending more time on EHR in-basket tasks than they did before the pandemic, the study found no significant associations between message characteristics and burnout.
Data for the cross-sectional study were collected from multiple specialties from April to September 2020. Physicians then completed a survey and assessed their burnout on a 5-point scale. Of the 609 physician responses, approximately 49% of participants were women, 56% were White, and 64% worked in outpatient settings. About 70% of the doctors had been in practice for 15 years or less.
The sentiment score was based on word content as well as the use of negation, punctuation, degree modifiers, all caps, emoticons, emojis, and acronyms. Positive patient messages were more likely to convey gratitude and thanks, along with casual expressions, such as “fyi” and “lol.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among the emails, 43% were from patients; the remainder were mostly from other physicians or clinicians, or automated. The content of the messages wasn’t associated with doctor burnout, as the researchers had hypothesized. And only about 5% of the messages had negative sentiment.
But the researchers were struck by the hostility of that sentiment, displayed in messages like these that surely would be distressing for physicians to read:
“I hope and expect that you will spend eternity in he**. You are an abusive, nasty, cheap person.”
“Your office is full of liars, hypocrites and I will do everything in my power to prevent anyone from going to your bullsh** office again.”
About 5% of emails had an overall negative sentiment, with high-frequency words like “cancel,” “pain,” or “problem.” Among patient messages, 3% were negative and contained words and expletives suggesting hatred, hostility, or violence.
“F***” was the most common expletive used by patients.
Researchers provided examples of profanity-laced messages, including one patient who said, “I am so upset that I was told the blood work would include the gender of the baby. I have been waiting 5 [days] to find it, and it wasn’t even fu**ing tested!!!! What a disappointment in your office and the bullsh** I was told. I will be switching plans because this is sh**!”
Researchers also noted some high-frequency words associated with violence, such as “shoot,” “fight,” and “kill.”
“This is concerning, especially given documentation of patient-inflicted violence against physicians. Health systems should be proactive in ensuring that the in-basket does not become a venue for physician abuse and cyberbullying,” the researchers wrote in JAMA Network Open.
“Posting reminders in EHR patient portals to use kind language when sending messages, applying filters for expletives or threatening words, and creating frameworks for identifying patients who frequently send negative messages are potential strategies for mitigating this risk.”
Using a form of artificial intelligence technology called natural language processing (NLP), researchers at the University of California, San Diego, analyzed the characteristics of more than 1.4 million emails received by the university’s physicians, 43% of them from patients. They specifically looked at the volume of messages, word count, and overall sentiment.
Whereas other studies have examined the growing burden of EHR messaging for doctors, this type of email sentiment analysis could help in creating solutions. Researchers say that one such solution could involve applying filters for expletives or threatening words. It also could help identify fixable health system issues that make patients so angry, the researchers say.
Among the emails from physicians to physicians, just over half reported burnout, which correlated to the following phrases: “I am beginning to burn out and have one or more symptoms of burnout” and “I feel completely burned out [and] am at the point where I may need to seek help.”
On average, physicians who reported burnout received a greater volume of patient messages. The odds of burnout were significantly higher among Hispanic/Latinx physicians and females. Physicians with more than 15 years of clinical practice had markedly lower burnout.
Despite physicians now spending more time on EHR in-basket tasks than they did before the pandemic, the study found no significant associations between message characteristics and burnout.
Data for the cross-sectional study were collected from multiple specialties from April to September 2020. Physicians then completed a survey and assessed their burnout on a 5-point scale. Of the 609 physician responses, approximately 49% of participants were women, 56% were White, and 64% worked in outpatient settings. About 70% of the doctors had been in practice for 15 years or less.
The sentiment score was based on word content as well as the use of negation, punctuation, degree modifiers, all caps, emoticons, emojis, and acronyms. Positive patient messages were more likely to convey gratitude and thanks, along with casual expressions, such as “fyi” and “lol.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
U.S. biosimilar competition, use, and availability still lags behind European countries
The uptake and treatment costs of biosimilar drugs in the United States from 2011 to 2020 were significantly higher than in both Germany and Switzerland, based on data from a cohort study of publicly available commercial databases.
Biologics remain the fastest growing segment of drug research and development, but their costs remain high, David L. Carl, MSc, of the University of Zurich, and colleagues wrote in their study, published online in JAMA Network Open.
As patents and regulatory exclusivity periods expire, biologics face competition from biosimilars, which may drive competition and lower prices, they said.
“However, studies have shown that there are varying policies and biosimilar uptake in European countries and that the observed levels of competition and uptake have not reached the expected levels in the U.S.,” the researchers said.
To assist the discussions of policy makers in the United States and Europe as they consider legislative and regulatory reforms that are intended to promote the competition of biosimilars, the researchers reviewed data from 15 biosimilars and 6 biologics in the United States, 52 biosimilars and 15 biologics in Germany, and 28 biosimilars and 13 biologics in Switzerland.
They analyzed temporal trends in the uptake of biosimilars and their relative prices, compared with the prices of biologics in each country, by obtaining wholesale acquisition costs from online drug pricing databases. They extracted quarterly sales volume data for 2011-2020 from the IQVIA database. In the case of confidential rebates in Switzerland, the researchers obtained list prices.
Overall, the uptake of biosimilars increased in all three countries during the study period. However, the prices of biosimilars and the reference products were significantly higher in the United States, compared with Germany and Switzerland, both of which have national mechanisms for drug price negotiation. The monthly treatment cost of biosimilars was a median of 1.94 and 2.74 times higher in the United States than in Germany and Switzerland, respectively.
On average, the biosimilar market share at launch was highest in Germany; however, it increased at the fastest rate in the United States.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the sample size and the inclusion only of sales data provided by IQVIA, and by the use of list prices only without accounting for drug rebates, the researchers noted. Other limitations were the inability to compare conclusions from the United States and European Union directly because the drugs entered markets at different times, and not all the same drugs have been approved or designated as biosimilars, they said.
However, the results illustrate a difference in uptake of biosimilars in the United States with a reduced impact on drug costs, they said.
Looking ahead, “Policies for drug pricing negotiations in the U.S. against anticompetitive practices of exclusionary contracts could allow biosimilars to enter the market sooner and at lower costs, which could result in lower health care costs and improved patient access,” they concluded.
The study was partially funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation. Lead author Mr. Carl had no financial conflicts to disclose; several coauthors disclosed funding from organizations including The Health Foundation, the U.K. National Institute for Health Research, and the Pharmaceutical Group of the European Union; all were unrelated to the current study.
The uptake and treatment costs of biosimilar drugs in the United States from 2011 to 2020 were significantly higher than in both Germany and Switzerland, based on data from a cohort study of publicly available commercial databases.
Biologics remain the fastest growing segment of drug research and development, but their costs remain high, David L. Carl, MSc, of the University of Zurich, and colleagues wrote in their study, published online in JAMA Network Open.
As patents and regulatory exclusivity periods expire, biologics face competition from biosimilars, which may drive competition and lower prices, they said.
“However, studies have shown that there are varying policies and biosimilar uptake in European countries and that the observed levels of competition and uptake have not reached the expected levels in the U.S.,” the researchers said.
To assist the discussions of policy makers in the United States and Europe as they consider legislative and regulatory reforms that are intended to promote the competition of biosimilars, the researchers reviewed data from 15 biosimilars and 6 biologics in the United States, 52 biosimilars and 15 biologics in Germany, and 28 biosimilars and 13 biologics in Switzerland.
They analyzed temporal trends in the uptake of biosimilars and their relative prices, compared with the prices of biologics in each country, by obtaining wholesale acquisition costs from online drug pricing databases. They extracted quarterly sales volume data for 2011-2020 from the IQVIA database. In the case of confidential rebates in Switzerland, the researchers obtained list prices.
Overall, the uptake of biosimilars increased in all three countries during the study period. However, the prices of biosimilars and the reference products were significantly higher in the United States, compared with Germany and Switzerland, both of which have national mechanisms for drug price negotiation. The monthly treatment cost of biosimilars was a median of 1.94 and 2.74 times higher in the United States than in Germany and Switzerland, respectively.
On average, the biosimilar market share at launch was highest in Germany; however, it increased at the fastest rate in the United States.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the sample size and the inclusion only of sales data provided by IQVIA, and by the use of list prices only without accounting for drug rebates, the researchers noted. Other limitations were the inability to compare conclusions from the United States and European Union directly because the drugs entered markets at different times, and not all the same drugs have been approved or designated as biosimilars, they said.
However, the results illustrate a difference in uptake of biosimilars in the United States with a reduced impact on drug costs, they said.
Looking ahead, “Policies for drug pricing negotiations in the U.S. against anticompetitive practices of exclusionary contracts could allow biosimilars to enter the market sooner and at lower costs, which could result in lower health care costs and improved patient access,” they concluded.
The study was partially funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation. Lead author Mr. Carl had no financial conflicts to disclose; several coauthors disclosed funding from organizations including The Health Foundation, the U.K. National Institute for Health Research, and the Pharmaceutical Group of the European Union; all were unrelated to the current study.
The uptake and treatment costs of biosimilar drugs in the United States from 2011 to 2020 were significantly higher than in both Germany and Switzerland, based on data from a cohort study of publicly available commercial databases.
Biologics remain the fastest growing segment of drug research and development, but their costs remain high, David L. Carl, MSc, of the University of Zurich, and colleagues wrote in their study, published online in JAMA Network Open.
As patents and regulatory exclusivity periods expire, biologics face competition from biosimilars, which may drive competition and lower prices, they said.
“However, studies have shown that there are varying policies and biosimilar uptake in European countries and that the observed levels of competition and uptake have not reached the expected levels in the U.S.,” the researchers said.
To assist the discussions of policy makers in the United States and Europe as they consider legislative and regulatory reforms that are intended to promote the competition of biosimilars, the researchers reviewed data from 15 biosimilars and 6 biologics in the United States, 52 biosimilars and 15 biologics in Germany, and 28 biosimilars and 13 biologics in Switzerland.
They analyzed temporal trends in the uptake of biosimilars and their relative prices, compared with the prices of biologics in each country, by obtaining wholesale acquisition costs from online drug pricing databases. They extracted quarterly sales volume data for 2011-2020 from the IQVIA database. In the case of confidential rebates in Switzerland, the researchers obtained list prices.
Overall, the uptake of biosimilars increased in all three countries during the study period. However, the prices of biosimilars and the reference products were significantly higher in the United States, compared with Germany and Switzerland, both of which have national mechanisms for drug price negotiation. The monthly treatment cost of biosimilars was a median of 1.94 and 2.74 times higher in the United States than in Germany and Switzerland, respectively.
On average, the biosimilar market share at launch was highest in Germany; however, it increased at the fastest rate in the United States.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the sample size and the inclusion only of sales data provided by IQVIA, and by the use of list prices only without accounting for drug rebates, the researchers noted. Other limitations were the inability to compare conclusions from the United States and European Union directly because the drugs entered markets at different times, and not all the same drugs have been approved or designated as biosimilars, they said.
However, the results illustrate a difference in uptake of biosimilars in the United States with a reduced impact on drug costs, they said.
Looking ahead, “Policies for drug pricing negotiations in the U.S. against anticompetitive practices of exclusionary contracts could allow biosimilars to enter the market sooner and at lower costs, which could result in lower health care costs and improved patient access,” they concluded.
The study was partially funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation. Lead author Mr. Carl had no financial conflicts to disclose; several coauthors disclosed funding from organizations including The Health Foundation, the U.K. National Institute for Health Research, and the Pharmaceutical Group of the European Union; all were unrelated to the current study.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
A new use for dating apps: Chasing STDs
Heather Meador and Anna Herber-Downey use dating apps on the job – and their boss knows it.
Both are public health nurses employed by Linn County Public Health in eastern Iowa. They’ve learned that dating apps are the most efficient way to inform users that people they previously met on the sites may have exposed them to sexually transmitted infections.
A nationwide surge in STIs, also known as STDs – with reported cases of gonorrhea and syphilis increasing 10% and 7%, respectively, from 2019 to 2020, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – isn’t sparing Iowa. The duo has found that the telephone call, a traditional method of contact tracing, no longer works well.
“When I started 12 years ago, we called everyone,” said Ms. Meador, the county health department’s clinical branch supervisor. “It’s getting harder and harder to just call someone on the phone.”
Even texting is ineffective, they said. And people aren’t necessarily answering messages on Facebook. The dating apps are where they’re at.
Because many people are meeting sex partners online – via sites like Grindr or Snapchat, which are headquartered in West Hollywood and Santa Monica, Calif., respectively – contact tracers often don’t have much information to go on, just a screen name or a picture.
So, about a year ago, Ms. Meador and her colleagues got approval from their bosses at the local level to build profiles on the app, through which they can contact the sex partners of infected people.
Traditionally, contact tracers interview people infected with an STI about their recent encounters and then reach out to those partners to tell them about the potential exposure.
Linn County contact tracers use the apps throughout their workday. Grindr, in particular, relies on geolocation, showing users matches who are close by. So the tracers use the apps when they’re out and about, hoping to wander into the same neighborhoods as the person diagnosed with an STI. Sometimes users “tap” the contract tracers to see whether they’re interested – in dating, that is.
When the public health officials spot someone they’re looking for, they send a message asking for a call. It’s a successful method: Ms. Herber-Downey estimated they make an initial contact 75% of the time.
Linn County’s decision to move online comes as STI rates rise nationally, funding to fight them falls, and people adopt new technologies to meet people and seek fun. “STIs are increasing way faster than the funding we have,” said Leo Parker, director of prevention programs for the National Coalition of STD Directors, all while public health departments – many underfunded – are grappling with new behaviors.
“Social media companies have billions; we have tens of thousands,” said Jeffrey Klausner, MD, MPH, a University of Southern California, Los Angeles, public health professor, who previously served as San Francisco’s director of STD prevention and control services. That funding disparity means few public health departments have staff members who can go online. “It’s only really in major cities that they have anyone who’s tasked for that,” Dr. Klausner said.
Even when departments have enough employees to take on the challenge, institutional support can be lacking. Some public health officials question employees who log into the apps. Dr. Klausner once testified on behalf of a Ventura County, Calif., contact tracer who was fired for using sex sites for work.
But with people migrating online to meet partners, following them there makes sense. “We’re now in a digital age,” Mr. Parker said. Individuals might not be out, or might be questioning their identity, making online venues comfortable, anonymous spaces for romance – which, in turn, means people are harder to reach face-to-face, at least at first.
What’s more, online spaces like Grindr are effective public health tools beyond contact tracing. They can be useful ways to get the word out about public health concerns.
Mr. Parker and the Linn County officials said public service announcements on dating apps – advocating for condom use or sharing the business hours for sexual health clinics – do seem to lead people to services. “We do have individuals coming in, saying, ‘I saw you had free testing. I saw it on Grindr,’ ” Mr. Parker said.
Grindr, which touts itself as the biggest dating app focused on LGBTQ+ people, pushes out messages and information to its members, said Jack Harrison-Quintana, director of Grindr for Equality. That engagement intensified during a 2015 meningitis outbreak among LGBTQ+ communities in Chicago, for example.
During that outbreak, the app sent citywide messages about vaccination. Then Mr. Harrison-Quintana took advantage of the service’s design: Using the site’s geolocating capabilities, Grindr workers targeted messages to specific neighborhoods. “We could go in and really go block to block and say, ‘Is this where the cases are showing up?’ ” he said. If so, they sent more messages to that area.
That campaign encouraged further efforts from the app, which regularly sends public health messages about everything from COVID-19 to monkeypox to the platform’s base of roughly 11 million monthly users. Grindr also allows users to display their HIV status and indicate whether they’re vaccinated against COVID, monkeypox, and meningitis.
There are a couple of things Grindr won’t do, however. The company won’t allow public health departments to create institutional accounts. And it won’t allow automated notifications about STI exposures to be sent to users.
That’s due to privacy concerns, the company said, despite calls from public health advocates to deploy better messaging features. Grindr believes that a government presence on the app would be too intrusive and that even anonymous notifications would allow users to trace infections back to their source. (When asked about public health officials who join the site on their own, company spokesperson Patrick Lenihan said: “Individuals are free to say something like ‘I’m a public health professional – ask me about my work!’ in their profile and are free to discuss sexual and public health matters however they see fit.”)
Grindr’s position – however disappointing to some in the public health world – reflects a longtime balancing act attempted by the private sector, which aims to square government concerns with users’ privacy interests.
Dr. Klausner pointed to a 1999 syphilis outbreak in San Francisco as one of the first times he saw how those interests could be at odds. The outbreak was traced to an AOL chatroom. Based on his research, Dr. Klausner said it seemed as though people could go online and “get a sex partner faster than you can get a pizza delivered.”
But persuading New York–based Time Warner, eventually AOL’s corporate parent, to cooperate was time-intensive and tricky – gaining entrée into the chatroom required help from the New York attorney general’s office.
The online industry has advanced since then, Dr. Klausner said. He helped one service develop a system to send digital postcards to potentially exposed people. “Congratulations, you got syphilis,” the postcards read. “They were edgy postcards,” he said, although some options were less “snarky.”
Overall, however, the dating app world is still “bifurcated,” he said. For public health efforts, apps that appeal to LGBTQ+ users are generally more helpful than those that predominantly cater to heterosexual clients.
That’s due to the community’s history with sexual health, explained Jen Hecht, a leader of Building Healthy Online Communities, a public health group partnering with dating apps. “Folks in the queer community have – what – 30, 40 years of thinking about HIV?” she said.
Even though STIs affect everyone, “the norm and the expectation is not there” for straight-focused dating apps, she said. Indeed, neither Match Group nor Bumble – the corporations with the biggest apps focused on heterosexual dating, both based in Texas – responded to multiple requests for comment from KHN.
But users, at least so far, seem to appreciate the app-based interventions. Mr. Harrison-Quintana said Grindr has landed on a just-the-facts approach to conveying health information. He has never received any backlash, “which has been very nice.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Heather Meador and Anna Herber-Downey use dating apps on the job – and their boss knows it.
Both are public health nurses employed by Linn County Public Health in eastern Iowa. They’ve learned that dating apps are the most efficient way to inform users that people they previously met on the sites may have exposed them to sexually transmitted infections.
A nationwide surge in STIs, also known as STDs – with reported cases of gonorrhea and syphilis increasing 10% and 7%, respectively, from 2019 to 2020, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – isn’t sparing Iowa. The duo has found that the telephone call, a traditional method of contact tracing, no longer works well.
“When I started 12 years ago, we called everyone,” said Ms. Meador, the county health department’s clinical branch supervisor. “It’s getting harder and harder to just call someone on the phone.”
Even texting is ineffective, they said. And people aren’t necessarily answering messages on Facebook. The dating apps are where they’re at.
Because many people are meeting sex partners online – via sites like Grindr or Snapchat, which are headquartered in West Hollywood and Santa Monica, Calif., respectively – contact tracers often don’t have much information to go on, just a screen name or a picture.
So, about a year ago, Ms. Meador and her colleagues got approval from their bosses at the local level to build profiles on the app, through which they can contact the sex partners of infected people.
Traditionally, contact tracers interview people infected with an STI about their recent encounters and then reach out to those partners to tell them about the potential exposure.
Linn County contact tracers use the apps throughout their workday. Grindr, in particular, relies on geolocation, showing users matches who are close by. So the tracers use the apps when they’re out and about, hoping to wander into the same neighborhoods as the person diagnosed with an STI. Sometimes users “tap” the contract tracers to see whether they’re interested – in dating, that is.
When the public health officials spot someone they’re looking for, they send a message asking for a call. It’s a successful method: Ms. Herber-Downey estimated they make an initial contact 75% of the time.
Linn County’s decision to move online comes as STI rates rise nationally, funding to fight them falls, and people adopt new technologies to meet people and seek fun. “STIs are increasing way faster than the funding we have,” said Leo Parker, director of prevention programs for the National Coalition of STD Directors, all while public health departments – many underfunded – are grappling with new behaviors.
“Social media companies have billions; we have tens of thousands,” said Jeffrey Klausner, MD, MPH, a University of Southern California, Los Angeles, public health professor, who previously served as San Francisco’s director of STD prevention and control services. That funding disparity means few public health departments have staff members who can go online. “It’s only really in major cities that they have anyone who’s tasked for that,” Dr. Klausner said.
Even when departments have enough employees to take on the challenge, institutional support can be lacking. Some public health officials question employees who log into the apps. Dr. Klausner once testified on behalf of a Ventura County, Calif., contact tracer who was fired for using sex sites for work.
But with people migrating online to meet partners, following them there makes sense. “We’re now in a digital age,” Mr. Parker said. Individuals might not be out, or might be questioning their identity, making online venues comfortable, anonymous spaces for romance – which, in turn, means people are harder to reach face-to-face, at least at first.
What’s more, online spaces like Grindr are effective public health tools beyond contact tracing. They can be useful ways to get the word out about public health concerns.
Mr. Parker and the Linn County officials said public service announcements on dating apps – advocating for condom use or sharing the business hours for sexual health clinics – do seem to lead people to services. “We do have individuals coming in, saying, ‘I saw you had free testing. I saw it on Grindr,’ ” Mr. Parker said.
Grindr, which touts itself as the biggest dating app focused on LGBTQ+ people, pushes out messages and information to its members, said Jack Harrison-Quintana, director of Grindr for Equality. That engagement intensified during a 2015 meningitis outbreak among LGBTQ+ communities in Chicago, for example.
During that outbreak, the app sent citywide messages about vaccination. Then Mr. Harrison-Quintana took advantage of the service’s design: Using the site’s geolocating capabilities, Grindr workers targeted messages to specific neighborhoods. “We could go in and really go block to block and say, ‘Is this where the cases are showing up?’ ” he said. If so, they sent more messages to that area.
That campaign encouraged further efforts from the app, which regularly sends public health messages about everything from COVID-19 to monkeypox to the platform’s base of roughly 11 million monthly users. Grindr also allows users to display their HIV status and indicate whether they’re vaccinated against COVID, monkeypox, and meningitis.
There are a couple of things Grindr won’t do, however. The company won’t allow public health departments to create institutional accounts. And it won’t allow automated notifications about STI exposures to be sent to users.
That’s due to privacy concerns, the company said, despite calls from public health advocates to deploy better messaging features. Grindr believes that a government presence on the app would be too intrusive and that even anonymous notifications would allow users to trace infections back to their source. (When asked about public health officials who join the site on their own, company spokesperson Patrick Lenihan said: “Individuals are free to say something like ‘I’m a public health professional – ask me about my work!’ in their profile and are free to discuss sexual and public health matters however they see fit.”)
Grindr’s position – however disappointing to some in the public health world – reflects a longtime balancing act attempted by the private sector, which aims to square government concerns with users’ privacy interests.
Dr. Klausner pointed to a 1999 syphilis outbreak in San Francisco as one of the first times he saw how those interests could be at odds. The outbreak was traced to an AOL chatroom. Based on his research, Dr. Klausner said it seemed as though people could go online and “get a sex partner faster than you can get a pizza delivered.”
But persuading New York–based Time Warner, eventually AOL’s corporate parent, to cooperate was time-intensive and tricky – gaining entrée into the chatroom required help from the New York attorney general’s office.
The online industry has advanced since then, Dr. Klausner said. He helped one service develop a system to send digital postcards to potentially exposed people. “Congratulations, you got syphilis,” the postcards read. “They were edgy postcards,” he said, although some options were less “snarky.”
Overall, however, the dating app world is still “bifurcated,” he said. For public health efforts, apps that appeal to LGBTQ+ users are generally more helpful than those that predominantly cater to heterosexual clients.
That’s due to the community’s history with sexual health, explained Jen Hecht, a leader of Building Healthy Online Communities, a public health group partnering with dating apps. “Folks in the queer community have – what – 30, 40 years of thinking about HIV?” she said.
Even though STIs affect everyone, “the norm and the expectation is not there” for straight-focused dating apps, she said. Indeed, neither Match Group nor Bumble – the corporations with the biggest apps focused on heterosexual dating, both based in Texas – responded to multiple requests for comment from KHN.
But users, at least so far, seem to appreciate the app-based interventions. Mr. Harrison-Quintana said Grindr has landed on a just-the-facts approach to conveying health information. He has never received any backlash, “which has been very nice.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Heather Meador and Anna Herber-Downey use dating apps on the job – and their boss knows it.
Both are public health nurses employed by Linn County Public Health in eastern Iowa. They’ve learned that dating apps are the most efficient way to inform users that people they previously met on the sites may have exposed them to sexually transmitted infections.
A nationwide surge in STIs, also known as STDs – with reported cases of gonorrhea and syphilis increasing 10% and 7%, respectively, from 2019 to 2020, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – isn’t sparing Iowa. The duo has found that the telephone call, a traditional method of contact tracing, no longer works well.
“When I started 12 years ago, we called everyone,” said Ms. Meador, the county health department’s clinical branch supervisor. “It’s getting harder and harder to just call someone on the phone.”
Even texting is ineffective, they said. And people aren’t necessarily answering messages on Facebook. The dating apps are where they’re at.
Because many people are meeting sex partners online – via sites like Grindr or Snapchat, which are headquartered in West Hollywood and Santa Monica, Calif., respectively – contact tracers often don’t have much information to go on, just a screen name or a picture.
So, about a year ago, Ms. Meador and her colleagues got approval from their bosses at the local level to build profiles on the app, through which they can contact the sex partners of infected people.
Traditionally, contact tracers interview people infected with an STI about their recent encounters and then reach out to those partners to tell them about the potential exposure.
Linn County contact tracers use the apps throughout their workday. Grindr, in particular, relies on geolocation, showing users matches who are close by. So the tracers use the apps when they’re out and about, hoping to wander into the same neighborhoods as the person diagnosed with an STI. Sometimes users “tap” the contract tracers to see whether they’re interested – in dating, that is.
When the public health officials spot someone they’re looking for, they send a message asking for a call. It’s a successful method: Ms. Herber-Downey estimated they make an initial contact 75% of the time.
Linn County’s decision to move online comes as STI rates rise nationally, funding to fight them falls, and people adopt new technologies to meet people and seek fun. “STIs are increasing way faster than the funding we have,” said Leo Parker, director of prevention programs for the National Coalition of STD Directors, all while public health departments – many underfunded – are grappling with new behaviors.
“Social media companies have billions; we have tens of thousands,” said Jeffrey Klausner, MD, MPH, a University of Southern California, Los Angeles, public health professor, who previously served as San Francisco’s director of STD prevention and control services. That funding disparity means few public health departments have staff members who can go online. “It’s only really in major cities that they have anyone who’s tasked for that,” Dr. Klausner said.
Even when departments have enough employees to take on the challenge, institutional support can be lacking. Some public health officials question employees who log into the apps. Dr. Klausner once testified on behalf of a Ventura County, Calif., contact tracer who was fired for using sex sites for work.
But with people migrating online to meet partners, following them there makes sense. “We’re now in a digital age,” Mr. Parker said. Individuals might not be out, or might be questioning their identity, making online venues comfortable, anonymous spaces for romance – which, in turn, means people are harder to reach face-to-face, at least at first.
What’s more, online spaces like Grindr are effective public health tools beyond contact tracing. They can be useful ways to get the word out about public health concerns.
Mr. Parker and the Linn County officials said public service announcements on dating apps – advocating for condom use or sharing the business hours for sexual health clinics – do seem to lead people to services. “We do have individuals coming in, saying, ‘I saw you had free testing. I saw it on Grindr,’ ” Mr. Parker said.
Grindr, which touts itself as the biggest dating app focused on LGBTQ+ people, pushes out messages and information to its members, said Jack Harrison-Quintana, director of Grindr for Equality. That engagement intensified during a 2015 meningitis outbreak among LGBTQ+ communities in Chicago, for example.
During that outbreak, the app sent citywide messages about vaccination. Then Mr. Harrison-Quintana took advantage of the service’s design: Using the site’s geolocating capabilities, Grindr workers targeted messages to specific neighborhoods. “We could go in and really go block to block and say, ‘Is this where the cases are showing up?’ ” he said. If so, they sent more messages to that area.
That campaign encouraged further efforts from the app, which regularly sends public health messages about everything from COVID-19 to monkeypox to the platform’s base of roughly 11 million monthly users. Grindr also allows users to display their HIV status and indicate whether they’re vaccinated against COVID, monkeypox, and meningitis.
There are a couple of things Grindr won’t do, however. The company won’t allow public health departments to create institutional accounts. And it won’t allow automated notifications about STI exposures to be sent to users.
That’s due to privacy concerns, the company said, despite calls from public health advocates to deploy better messaging features. Grindr believes that a government presence on the app would be too intrusive and that even anonymous notifications would allow users to trace infections back to their source. (When asked about public health officials who join the site on their own, company spokesperson Patrick Lenihan said: “Individuals are free to say something like ‘I’m a public health professional – ask me about my work!’ in their profile and are free to discuss sexual and public health matters however they see fit.”)
Grindr’s position – however disappointing to some in the public health world – reflects a longtime balancing act attempted by the private sector, which aims to square government concerns with users’ privacy interests.
Dr. Klausner pointed to a 1999 syphilis outbreak in San Francisco as one of the first times he saw how those interests could be at odds. The outbreak was traced to an AOL chatroom. Based on his research, Dr. Klausner said it seemed as though people could go online and “get a sex partner faster than you can get a pizza delivered.”
But persuading New York–based Time Warner, eventually AOL’s corporate parent, to cooperate was time-intensive and tricky – gaining entrée into the chatroom required help from the New York attorney general’s office.
The online industry has advanced since then, Dr. Klausner said. He helped one service develop a system to send digital postcards to potentially exposed people. “Congratulations, you got syphilis,” the postcards read. “They were edgy postcards,” he said, although some options were less “snarky.”
Overall, however, the dating app world is still “bifurcated,” he said. For public health efforts, apps that appeal to LGBTQ+ users are generally more helpful than those that predominantly cater to heterosexual clients.
That’s due to the community’s history with sexual health, explained Jen Hecht, a leader of Building Healthy Online Communities, a public health group partnering with dating apps. “Folks in the queer community have – what – 30, 40 years of thinking about HIV?” she said.
Even though STIs affect everyone, “the norm and the expectation is not there” for straight-focused dating apps, she said. Indeed, neither Match Group nor Bumble – the corporations with the biggest apps focused on heterosexual dating, both based in Texas – responded to multiple requests for comment from KHN.
But users, at least so far, seem to appreciate the app-based interventions. Mr. Harrison-Quintana said Grindr has landed on a just-the-facts approach to conveying health information. He has never received any backlash, “which has been very nice.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.