User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Should you tell your doctor that you’re a doctor?
The question drew spirited debate when urologist Ashley Winter, MD, made a simple, straightforward request on Twitter: “If you are a doctor & you come to an appointment please tell me you are a doctor, not because I will treat you differently but because it’s easier to speak in jargon.”
She later added, “This doesn’t’ mean I would be less patient-focused or emotional with a physician or other [healthcare worker]. Just means that, instead of saying ‘you will have a catheter draining your urine to a bag,’ I can say, ‘you will have a Foley.’ ”
The Tweet followed an encounter with a patient who told Dr. Winter that he was a doctor only after she had gone to some length explaining a surgical procedure in lay terms.
“I explained the surgery, obviously assuming he was an intelligent adult, but using fully layman’s terms,” she said in an interview. The patient then told her that he was a doctor. “I guess I felt this embarrassment — I wouldn’t have treated him differently, but I just could have discussed the procedure with him in more professional terms.”
“To some extent, it was my own fault,” she commented in an interview. “I didn’t take the time to ask [about his work] at the beginning of the consultation, but that’s a fine line, also,” added Dr. Winter, a urologist and sexual medicine physician in Portland, Ore.
“You know that patient is there because they want care from you and it’s not necessarily always at the forefront of importance to be asking them what they do for their work, but alternatively, if you don’t ask then you put them in this position where they have to find a way to go ahead and tell you.”
Several people chimed in on the thread to voice their thoughts on the matter. Some commiserated with Dr. Winter’s experience:
“I took care of a retired cardiologist in the hospital as a second-year resident and honest to god he let me ramble on ‘explaining’ his echo result and never told me. I found out a couple days later and wanted to die,” posted @MaddyAndrewsMD.
Another recalled a similarly embarrassing experience when she “went on and on” discussing headaches with a patient whose husband “was in the corner smirking.”
“They told my attending later [that the] husband was a retired FM doc who practiced medicine longer than I’ve been alive. I wanted to die,” posted @JSinghDO.
Many on the thread, though, were doctors and other healthcare professionals speaking as patients. Some said they didn’t want to disclose their status as a healthcare provider because they felt it affected the care they received.
For example, @drhelenrainford commented: “In my experience my care is less ‘caring’ when they know I am a [doctor]. I get spoken to like they are discussing a patient with me — no empathy just facts and difficult results just blurted out without consideration. Awful awful time as an inpatient …but that’s another story!”
@Dr_B_Ring said: “Nope – You and I speak different jargon – I would want you to speak to me like a human that doesn’t know your jargon. My ego would get in the way of asking about the acronyms I don’t know if you knew I was a fellow physician.”
Conversely, @lozzlemcfozzle said: “Honestly I prefer not to tell my Doctors — I’ve found people skip explanations assuming I ‘know,’ or seem a little nervous when I tell them!”
Others said they felt uncomfortable — pretentious, even — in announcing their status, or worried that they might come across as expecting special care.
“It’s such a tough needle to thread. Want to tell people early but not come off as demanding special treatment, but don’t want to wait too long and it seems like a trap,” said @MDaware.
Twitter user @MsBabyCatcher wrote: “I have a hard time doing this because I don’t want people to think I’m being pretentious or going to micromanage/dictate care.”
Replying to @MsBabyCatcher, @RedStethoscope wrote: “I used to think this too until I got [very poor] care a few times, and was advised by other doctor moms to ‘play the doctor card.’ I have gotten better/more compassionate care by making sure it’s clear that I’m a physician (which is junk, but here we are).”
Several of those responding used the words “tricky” and “awkward,” suggesting a common theme for doctors presenting as patients.
“I struggle with this. My 5-year-old broke her arm this weekend, we spent hours in the ED, of my own hospital, I never mentioned it because I didn’t want to get preferential care. But as they were explaining her type of fracture, it felt awkward and inefficient,” said @lindsay_petty.
To avoid the awkwardness, a number of respondents said they purposefully use medical jargon to open up a conversation rather than just offering up the information that they are a doctor.
Still others offered suggestions on how to broach the subject more directly when presenting as a patient:
‘”Just FYI I’m a X doc but I’m here because I really want your help and advice!” That’s what I usually do,” wrote @drcakefm.
@BeeSting14618 Tweeted: “I usually say ‘I know some of this but I’m here because I want YOUR guidance. Also I may ask dumb questions, and I’ll tell you if a question is asking your opinion or making a request.’”
A few others injected a bit of humor: “I just do the 14-part handshake that only doctors know. Is that not customary?” quipped @Branmiz25.
“Ah yes, that transmits the entire [history of present illness],” replied Dr. Winter.
Jokes aside, the topic is obviously one that touched on a shared experience among healthcare providers, Dr. Winter commented. The Twitter thread she started just “blew up.”
That’s typically a sign that the Tweet is relatable for a lot of people, she said.
“It’s definitely something that all of us as care providers and as patients understand. It’s a funny, awkward thing that can really change an interaction, so we probably all feel pretty strongly about our experiences related to that,” she added.
The debate begs the question: Is there a duty or ethical reason to disclose?
“I definitely think it is very reasonable to disclose that one is a medical professional to another doctor,” medical ethicist Charlotte Blease, PhD, said in an interview. “There are good reasons to believe doing so might make a difference to the quality of communication and transparency.”
If the ability to use medical terminology or jargon more freely improves patient understanding, autonomy, and shared decision-making, then it may be of benefit, said Dr. Blease, a Keane OpenNotes Scholar at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston.
“Since doctors should strive to communicate effectively with every patient and to respect their unique needs and level of understanding, then I see no reason to deny that one is a medic,” she added.”
Knowing how to share the information is another story.
“This is something that affects all of us as physicians — we’re going to be patients at some point, right?” Dr. Winter commented. “But I don’t think how to disclose that is something that was ever brought up in my medical training.”
“Maybe there should just be a discussion of this one day when people are in medical school — maybe in a professionalism course — to broach this topic or look at if there’s any literature on outcomes related to disclosure of status or what are best practices,” she suggested.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The question drew spirited debate when urologist Ashley Winter, MD, made a simple, straightforward request on Twitter: “If you are a doctor & you come to an appointment please tell me you are a doctor, not because I will treat you differently but because it’s easier to speak in jargon.”
She later added, “This doesn’t’ mean I would be less patient-focused or emotional with a physician or other [healthcare worker]. Just means that, instead of saying ‘you will have a catheter draining your urine to a bag,’ I can say, ‘you will have a Foley.’ ”
The Tweet followed an encounter with a patient who told Dr. Winter that he was a doctor only after she had gone to some length explaining a surgical procedure in lay terms.
“I explained the surgery, obviously assuming he was an intelligent adult, but using fully layman’s terms,” she said in an interview. The patient then told her that he was a doctor. “I guess I felt this embarrassment — I wouldn’t have treated him differently, but I just could have discussed the procedure with him in more professional terms.”
“To some extent, it was my own fault,” she commented in an interview. “I didn’t take the time to ask [about his work] at the beginning of the consultation, but that’s a fine line, also,” added Dr. Winter, a urologist and sexual medicine physician in Portland, Ore.
“You know that patient is there because they want care from you and it’s not necessarily always at the forefront of importance to be asking them what they do for their work, but alternatively, if you don’t ask then you put them in this position where they have to find a way to go ahead and tell you.”
Several people chimed in on the thread to voice their thoughts on the matter. Some commiserated with Dr. Winter’s experience:
“I took care of a retired cardiologist in the hospital as a second-year resident and honest to god he let me ramble on ‘explaining’ his echo result and never told me. I found out a couple days later and wanted to die,” posted @MaddyAndrewsMD.
Another recalled a similarly embarrassing experience when she “went on and on” discussing headaches with a patient whose husband “was in the corner smirking.”
“They told my attending later [that the] husband was a retired FM doc who practiced medicine longer than I’ve been alive. I wanted to die,” posted @JSinghDO.
Many on the thread, though, were doctors and other healthcare professionals speaking as patients. Some said they didn’t want to disclose their status as a healthcare provider because they felt it affected the care they received.
For example, @drhelenrainford commented: “In my experience my care is less ‘caring’ when they know I am a [doctor]. I get spoken to like they are discussing a patient with me — no empathy just facts and difficult results just blurted out without consideration. Awful awful time as an inpatient …but that’s another story!”
@Dr_B_Ring said: “Nope – You and I speak different jargon – I would want you to speak to me like a human that doesn’t know your jargon. My ego would get in the way of asking about the acronyms I don’t know if you knew I was a fellow physician.”
Conversely, @lozzlemcfozzle said: “Honestly I prefer not to tell my Doctors — I’ve found people skip explanations assuming I ‘know,’ or seem a little nervous when I tell them!”
Others said they felt uncomfortable — pretentious, even — in announcing their status, or worried that they might come across as expecting special care.
“It’s such a tough needle to thread. Want to tell people early but not come off as demanding special treatment, but don’t want to wait too long and it seems like a trap,” said @MDaware.
Twitter user @MsBabyCatcher wrote: “I have a hard time doing this because I don’t want people to think I’m being pretentious or going to micromanage/dictate care.”
Replying to @MsBabyCatcher, @RedStethoscope wrote: “I used to think this too until I got [very poor] care a few times, and was advised by other doctor moms to ‘play the doctor card.’ I have gotten better/more compassionate care by making sure it’s clear that I’m a physician (which is junk, but here we are).”
Several of those responding used the words “tricky” and “awkward,” suggesting a common theme for doctors presenting as patients.
“I struggle with this. My 5-year-old broke her arm this weekend, we spent hours in the ED, of my own hospital, I never mentioned it because I didn’t want to get preferential care. But as they were explaining her type of fracture, it felt awkward and inefficient,” said @lindsay_petty.
To avoid the awkwardness, a number of respondents said they purposefully use medical jargon to open up a conversation rather than just offering up the information that they are a doctor.
Still others offered suggestions on how to broach the subject more directly when presenting as a patient:
‘”Just FYI I’m a X doc but I’m here because I really want your help and advice!” That’s what I usually do,” wrote @drcakefm.
@BeeSting14618 Tweeted: “I usually say ‘I know some of this but I’m here because I want YOUR guidance. Also I may ask dumb questions, and I’ll tell you if a question is asking your opinion or making a request.’”
A few others injected a bit of humor: “I just do the 14-part handshake that only doctors know. Is that not customary?” quipped @Branmiz25.
“Ah yes, that transmits the entire [history of present illness],” replied Dr. Winter.
Jokes aside, the topic is obviously one that touched on a shared experience among healthcare providers, Dr. Winter commented. The Twitter thread she started just “blew up.”
That’s typically a sign that the Tweet is relatable for a lot of people, she said.
“It’s definitely something that all of us as care providers and as patients understand. It’s a funny, awkward thing that can really change an interaction, so we probably all feel pretty strongly about our experiences related to that,” she added.
The debate begs the question: Is there a duty or ethical reason to disclose?
“I definitely think it is very reasonable to disclose that one is a medical professional to another doctor,” medical ethicist Charlotte Blease, PhD, said in an interview. “There are good reasons to believe doing so might make a difference to the quality of communication and transparency.”
If the ability to use medical terminology or jargon more freely improves patient understanding, autonomy, and shared decision-making, then it may be of benefit, said Dr. Blease, a Keane OpenNotes Scholar at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston.
“Since doctors should strive to communicate effectively with every patient and to respect their unique needs and level of understanding, then I see no reason to deny that one is a medic,” she added.”
Knowing how to share the information is another story.
“This is something that affects all of us as physicians — we’re going to be patients at some point, right?” Dr. Winter commented. “But I don’t think how to disclose that is something that was ever brought up in my medical training.”
“Maybe there should just be a discussion of this one day when people are in medical school — maybe in a professionalism course — to broach this topic or look at if there’s any literature on outcomes related to disclosure of status or what are best practices,” she suggested.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The question drew spirited debate when urologist Ashley Winter, MD, made a simple, straightforward request on Twitter: “If you are a doctor & you come to an appointment please tell me you are a doctor, not because I will treat you differently but because it’s easier to speak in jargon.”
She later added, “This doesn’t’ mean I would be less patient-focused or emotional with a physician or other [healthcare worker]. Just means that, instead of saying ‘you will have a catheter draining your urine to a bag,’ I can say, ‘you will have a Foley.’ ”
The Tweet followed an encounter with a patient who told Dr. Winter that he was a doctor only after she had gone to some length explaining a surgical procedure in lay terms.
“I explained the surgery, obviously assuming he was an intelligent adult, but using fully layman’s terms,” she said in an interview. The patient then told her that he was a doctor. “I guess I felt this embarrassment — I wouldn’t have treated him differently, but I just could have discussed the procedure with him in more professional terms.”
“To some extent, it was my own fault,” she commented in an interview. “I didn’t take the time to ask [about his work] at the beginning of the consultation, but that’s a fine line, also,” added Dr. Winter, a urologist and sexual medicine physician in Portland, Ore.
“You know that patient is there because they want care from you and it’s not necessarily always at the forefront of importance to be asking them what they do for their work, but alternatively, if you don’t ask then you put them in this position where they have to find a way to go ahead and tell you.”
Several people chimed in on the thread to voice their thoughts on the matter. Some commiserated with Dr. Winter’s experience:
“I took care of a retired cardiologist in the hospital as a second-year resident and honest to god he let me ramble on ‘explaining’ his echo result and never told me. I found out a couple days later and wanted to die,” posted @MaddyAndrewsMD.
Another recalled a similarly embarrassing experience when she “went on and on” discussing headaches with a patient whose husband “was in the corner smirking.”
“They told my attending later [that the] husband was a retired FM doc who practiced medicine longer than I’ve been alive. I wanted to die,” posted @JSinghDO.
Many on the thread, though, were doctors and other healthcare professionals speaking as patients. Some said they didn’t want to disclose their status as a healthcare provider because they felt it affected the care they received.
For example, @drhelenrainford commented: “In my experience my care is less ‘caring’ when they know I am a [doctor]. I get spoken to like they are discussing a patient with me — no empathy just facts and difficult results just blurted out without consideration. Awful awful time as an inpatient …but that’s another story!”
@Dr_B_Ring said: “Nope – You and I speak different jargon – I would want you to speak to me like a human that doesn’t know your jargon. My ego would get in the way of asking about the acronyms I don’t know if you knew I was a fellow physician.”
Conversely, @lozzlemcfozzle said: “Honestly I prefer not to tell my Doctors — I’ve found people skip explanations assuming I ‘know,’ or seem a little nervous when I tell them!”
Others said they felt uncomfortable — pretentious, even — in announcing their status, or worried that they might come across as expecting special care.
“It’s such a tough needle to thread. Want to tell people early but not come off as demanding special treatment, but don’t want to wait too long and it seems like a trap,” said @MDaware.
Twitter user @MsBabyCatcher wrote: “I have a hard time doing this because I don’t want people to think I’m being pretentious or going to micromanage/dictate care.”
Replying to @MsBabyCatcher, @RedStethoscope wrote: “I used to think this too until I got [very poor] care a few times, and was advised by other doctor moms to ‘play the doctor card.’ I have gotten better/more compassionate care by making sure it’s clear that I’m a physician (which is junk, but here we are).”
Several of those responding used the words “tricky” and “awkward,” suggesting a common theme for doctors presenting as patients.
“I struggle with this. My 5-year-old broke her arm this weekend, we spent hours in the ED, of my own hospital, I never mentioned it because I didn’t want to get preferential care. But as they were explaining her type of fracture, it felt awkward and inefficient,” said @lindsay_petty.
To avoid the awkwardness, a number of respondents said they purposefully use medical jargon to open up a conversation rather than just offering up the information that they are a doctor.
Still others offered suggestions on how to broach the subject more directly when presenting as a patient:
‘”Just FYI I’m a X doc but I’m here because I really want your help and advice!” That’s what I usually do,” wrote @drcakefm.
@BeeSting14618 Tweeted: “I usually say ‘I know some of this but I’m here because I want YOUR guidance. Also I may ask dumb questions, and I’ll tell you if a question is asking your opinion or making a request.’”
A few others injected a bit of humor: “I just do the 14-part handshake that only doctors know. Is that not customary?” quipped @Branmiz25.
“Ah yes, that transmits the entire [history of present illness],” replied Dr. Winter.
Jokes aside, the topic is obviously one that touched on a shared experience among healthcare providers, Dr. Winter commented. The Twitter thread she started just “blew up.”
That’s typically a sign that the Tweet is relatable for a lot of people, she said.
“It’s definitely something that all of us as care providers and as patients understand. It’s a funny, awkward thing that can really change an interaction, so we probably all feel pretty strongly about our experiences related to that,” she added.
The debate begs the question: Is there a duty or ethical reason to disclose?
“I definitely think it is very reasonable to disclose that one is a medical professional to another doctor,” medical ethicist Charlotte Blease, PhD, said in an interview. “There are good reasons to believe doing so might make a difference to the quality of communication and transparency.”
If the ability to use medical terminology or jargon more freely improves patient understanding, autonomy, and shared decision-making, then it may be of benefit, said Dr. Blease, a Keane OpenNotes Scholar at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston.
“Since doctors should strive to communicate effectively with every patient and to respect their unique needs and level of understanding, then I see no reason to deny that one is a medic,” she added.”
Knowing how to share the information is another story.
“This is something that affects all of us as physicians — we’re going to be patients at some point, right?” Dr. Winter commented. “But I don’t think how to disclose that is something that was ever brought up in my medical training.”
“Maybe there should just be a discussion of this one day when people are in medical school — maybe in a professionalism course — to broach this topic or look at if there’s any literature on outcomes related to disclosure of status or what are best practices,” she suggested.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Unvaccinated people 20 times more likely to die from COVID: Texas study
During the month of September, , according to a new study from the Texas Department of State Health Services.
The data also showed that unvaccinated people were 13 times more likely to test positive for COVID-19 than people who were fully vaccinated.
“This analysis quantifies what we’ve known for months,” Jennifer Shuford, MD, the state’s chief epidemiologist, told The Dallas Morning News.
“The COVID-19 vaccines are doing an excellent job of protecting people from getting sick and from dying from COVID-19,” she said. “Vaccination remains the best way to keep yourself and the people close to you safe from this deadly disease.”
As part of the study, researchers analyzed electronic lab reports, death certificates, and state immunization records, with a particular focus on September when the contagious Delta variant surged across Texas. The research marks the state’s first statistical analysis of COVID-19 vaccinations in Texas and the effects, the newspaper reported.
The protective effect of vaccination was most noticeable among younger groups. During September, the risk of COVID-19 death was 23 times higher in unvaccinated people in their 30s and 55 times higher for unvaccinated people in their 40s.
In addition, there were fewer than 10 COVID-19 deaths in September among fully vaccinated people between ages 18-29, as compared with 339 deaths among unvaccinated people in the same age group.
Then, looking at a longer time period -- from Jan. 15 to Oct. 1 -- the researchers found that unvaccinated people were 45 times more likely to contract COVID-19 than fully vaccinated people. The protective effect of vaccination against infection was strong across all adult age groups but greatest among ages 12-17.
“All authorized COVID-19 vaccines in the United States are highly effective at protecting people from getting sick or severely ill with COVID-19, including those infected with Delta and other known variants,” the study authors wrote. “Real world data from Texas clearly shows these benefits.”
About 15.6 million people in Texas have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19 in a state of about 29 million residents, according to state data. About 66% of the population has received at least one dose, while 58% is fully vaccinated.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
During the month of September, , according to a new study from the Texas Department of State Health Services.
The data also showed that unvaccinated people were 13 times more likely to test positive for COVID-19 than people who were fully vaccinated.
“This analysis quantifies what we’ve known for months,” Jennifer Shuford, MD, the state’s chief epidemiologist, told The Dallas Morning News.
“The COVID-19 vaccines are doing an excellent job of protecting people from getting sick and from dying from COVID-19,” she said. “Vaccination remains the best way to keep yourself and the people close to you safe from this deadly disease.”
As part of the study, researchers analyzed electronic lab reports, death certificates, and state immunization records, with a particular focus on September when the contagious Delta variant surged across Texas. The research marks the state’s first statistical analysis of COVID-19 vaccinations in Texas and the effects, the newspaper reported.
The protective effect of vaccination was most noticeable among younger groups. During September, the risk of COVID-19 death was 23 times higher in unvaccinated people in their 30s and 55 times higher for unvaccinated people in their 40s.
In addition, there were fewer than 10 COVID-19 deaths in September among fully vaccinated people between ages 18-29, as compared with 339 deaths among unvaccinated people in the same age group.
Then, looking at a longer time period -- from Jan. 15 to Oct. 1 -- the researchers found that unvaccinated people were 45 times more likely to contract COVID-19 than fully vaccinated people. The protective effect of vaccination against infection was strong across all adult age groups but greatest among ages 12-17.
“All authorized COVID-19 vaccines in the United States are highly effective at protecting people from getting sick or severely ill with COVID-19, including those infected with Delta and other known variants,” the study authors wrote. “Real world data from Texas clearly shows these benefits.”
About 15.6 million people in Texas have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19 in a state of about 29 million residents, according to state data. About 66% of the population has received at least one dose, while 58% is fully vaccinated.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
During the month of September, , according to a new study from the Texas Department of State Health Services.
The data also showed that unvaccinated people were 13 times more likely to test positive for COVID-19 than people who were fully vaccinated.
“This analysis quantifies what we’ve known for months,” Jennifer Shuford, MD, the state’s chief epidemiologist, told The Dallas Morning News.
“The COVID-19 vaccines are doing an excellent job of protecting people from getting sick and from dying from COVID-19,” she said. “Vaccination remains the best way to keep yourself and the people close to you safe from this deadly disease.”
As part of the study, researchers analyzed electronic lab reports, death certificates, and state immunization records, with a particular focus on September when the contagious Delta variant surged across Texas. The research marks the state’s first statistical analysis of COVID-19 vaccinations in Texas and the effects, the newspaper reported.
The protective effect of vaccination was most noticeable among younger groups. During September, the risk of COVID-19 death was 23 times higher in unvaccinated people in their 30s and 55 times higher for unvaccinated people in their 40s.
In addition, there were fewer than 10 COVID-19 deaths in September among fully vaccinated people between ages 18-29, as compared with 339 deaths among unvaccinated people in the same age group.
Then, looking at a longer time period -- from Jan. 15 to Oct. 1 -- the researchers found that unvaccinated people were 45 times more likely to contract COVID-19 than fully vaccinated people. The protective effect of vaccination against infection was strong across all adult age groups but greatest among ages 12-17.
“All authorized COVID-19 vaccines in the United States are highly effective at protecting people from getting sick or severely ill with COVID-19, including those infected with Delta and other known variants,” the study authors wrote. “Real world data from Texas clearly shows these benefits.”
About 15.6 million people in Texas have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19 in a state of about 29 million residents, according to state data. About 66% of the population has received at least one dose, while 58% is fully vaccinated.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Electronic ‘nose’ sniffs out sarcoidosis
An electronic nose (eNose) that measures volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted from the lungs successfully distinguished sarcoidosis from interstitial lung disease (ILD) and healthy controls, according to a report in the journal CHEST.
The approach has the potential to generate clinical data that can’t be achieved through other noninvasive means, such as the serum biomarker soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R). sIL-2R is often used to track disease activity, but it isn’t specific for diagnosing sarcoidosis, and it isn’t available worldwide.
Sarcoidosis is a granulomatous inflammatory disease with no known cause and can affect most organs, but an estimated 89%-99% of cases affect the lungs. There is no simple noninvasive diagnostic test, leaving physicians to rely on clinical features, biopsies to obtain tissue pathology, and the ruling out of other granulomatous diagnoses.
The challenge is more difficult because sarcoidosis is a heterogeneous disease, with great variation in the number of organs affected, severity, rate of progression, and response to therapy.
Previous researchers have used VOCs in an attempt to diagnose diseases, since the compounds reflect pathophysiological processes. Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GCMS) is one method to identify the individual VOCs, but the process is time consuming and complex. Some nevertheless showed potential in sarcoidosis, but failed to reproduce their performance in validation cohorts.
In the new study, a cross-sectional analysis showed that exhaled breath analysis using an eNose had excellent sensitivity and specificity for distinguishing sarcoidosis from ILD and healthy controls, and identified sarcoidosis regardless of pulmonary involvement, pulmonary fibrosis, multiple organ involvement, immunosuppressive treatment, or whether or not pathology supported the diagnosis.
The eNose technology produces a “breath-print” after combining information from a broad range of VOCs. The information originates from an array of metal-oxide semiconductor sensors with partial specificity that artificial intelligence processes to discern patterns. Overall, the system functions similarly to the mammalian olfactory system. The artificial intelligence instead views it as a “breath-print” that it can compare against previously learned patterns.
“It is a quite easy, simple, and quick procedure, which is noninvasive. We can collect a lot of data from the VOCs in the exhaled breath because there are several sensors that cross-react. We can create breath profiles and group patients to see if profiles differ. Ultimately, we can use the profiles to diagnose or detect disease in the earlier stage and more accurately,” said Iris van der Sar, MD. Dr. van der Sar is the lead author on the study and a PhD candidate at Erasmus Medical Center in Rotterdam.
The study requires further prospective validation, but the technology could have important clinical benefits, said senior author and principal investigator Marlies Wijsenbeek, MD, PhD, pulmonologist and head of the Interstitial Lung Disease Center at Erasmus Medical Center. “If we in future can avoid a biopsy, that would be most attractive,” said Dr. Wijsenbeek.
“We hope to come to a point-of-care device that can be used to facilitate early diagnosis at low burden for the patient and health care system,” said Karen Moor, MD, PhD, and post-doc on this project. The researchers also hope to determine if the eNose can help evaluate a patient’s response to therapy.
Studies of eNose technology in other chronic diseases have shown promising results, but not all results have been validated yet in independent or external cohorts.
The current study included 569 outpatients, 252 with sarcoidosis and 317 with ILD, along with 48 healthy controls. The researchers constructed a training set using 168 patients with sarcoidosis and 32 healthy controls, and a validation set using 84 patients with sarcoidosis and 16 healthy controls. The eNose differentiated between patients and controls in both groups, with an area under the curve of 1.00 for each regardless of pulmonary involvement or treatment.
It also distinguished those with sarcoidosis and pulmonary involvement from those with ILD, with an AUC of 0.90 (95% confidence interval, 0.87-0.94) in the training set, and an AUC of 0.87 (95% CI, 0.82-0.93) in the validation set.
It differentiated between pulmonary sarcoidosis and hypersensitivity pneumonitis in the training set (AUC 0.95; 95% CI, 0.90-0.99) and the validation set (AUC, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.75-1.00).
The study received no funding. Dr. Wijsenbeek, Dr. van der Sar, and Dr. Moor have no relevant financial disclosures.
An electronic nose (eNose) that measures volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted from the lungs successfully distinguished sarcoidosis from interstitial lung disease (ILD) and healthy controls, according to a report in the journal CHEST.
The approach has the potential to generate clinical data that can’t be achieved through other noninvasive means, such as the serum biomarker soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R). sIL-2R is often used to track disease activity, but it isn’t specific for diagnosing sarcoidosis, and it isn’t available worldwide.
Sarcoidosis is a granulomatous inflammatory disease with no known cause and can affect most organs, but an estimated 89%-99% of cases affect the lungs. There is no simple noninvasive diagnostic test, leaving physicians to rely on clinical features, biopsies to obtain tissue pathology, and the ruling out of other granulomatous diagnoses.
The challenge is more difficult because sarcoidosis is a heterogeneous disease, with great variation in the number of organs affected, severity, rate of progression, and response to therapy.
Previous researchers have used VOCs in an attempt to diagnose diseases, since the compounds reflect pathophysiological processes. Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GCMS) is one method to identify the individual VOCs, but the process is time consuming and complex. Some nevertheless showed potential in sarcoidosis, but failed to reproduce their performance in validation cohorts.
In the new study, a cross-sectional analysis showed that exhaled breath analysis using an eNose had excellent sensitivity and specificity for distinguishing sarcoidosis from ILD and healthy controls, and identified sarcoidosis regardless of pulmonary involvement, pulmonary fibrosis, multiple organ involvement, immunosuppressive treatment, or whether or not pathology supported the diagnosis.
The eNose technology produces a “breath-print” after combining information from a broad range of VOCs. The information originates from an array of metal-oxide semiconductor sensors with partial specificity that artificial intelligence processes to discern patterns. Overall, the system functions similarly to the mammalian olfactory system. The artificial intelligence instead views it as a “breath-print” that it can compare against previously learned patterns.
“It is a quite easy, simple, and quick procedure, which is noninvasive. We can collect a lot of data from the VOCs in the exhaled breath because there are several sensors that cross-react. We can create breath profiles and group patients to see if profiles differ. Ultimately, we can use the profiles to diagnose or detect disease in the earlier stage and more accurately,” said Iris van der Sar, MD. Dr. van der Sar is the lead author on the study and a PhD candidate at Erasmus Medical Center in Rotterdam.
The study requires further prospective validation, but the technology could have important clinical benefits, said senior author and principal investigator Marlies Wijsenbeek, MD, PhD, pulmonologist and head of the Interstitial Lung Disease Center at Erasmus Medical Center. “If we in future can avoid a biopsy, that would be most attractive,” said Dr. Wijsenbeek.
“We hope to come to a point-of-care device that can be used to facilitate early diagnosis at low burden for the patient and health care system,” said Karen Moor, MD, PhD, and post-doc on this project. The researchers also hope to determine if the eNose can help evaluate a patient’s response to therapy.
Studies of eNose technology in other chronic diseases have shown promising results, but not all results have been validated yet in independent or external cohorts.
The current study included 569 outpatients, 252 with sarcoidosis and 317 with ILD, along with 48 healthy controls. The researchers constructed a training set using 168 patients with sarcoidosis and 32 healthy controls, and a validation set using 84 patients with sarcoidosis and 16 healthy controls. The eNose differentiated between patients and controls in both groups, with an area under the curve of 1.00 for each regardless of pulmonary involvement or treatment.
It also distinguished those with sarcoidosis and pulmonary involvement from those with ILD, with an AUC of 0.90 (95% confidence interval, 0.87-0.94) in the training set, and an AUC of 0.87 (95% CI, 0.82-0.93) in the validation set.
It differentiated between pulmonary sarcoidosis and hypersensitivity pneumonitis in the training set (AUC 0.95; 95% CI, 0.90-0.99) and the validation set (AUC, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.75-1.00).
The study received no funding. Dr. Wijsenbeek, Dr. van der Sar, and Dr. Moor have no relevant financial disclosures.
An electronic nose (eNose) that measures volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted from the lungs successfully distinguished sarcoidosis from interstitial lung disease (ILD) and healthy controls, according to a report in the journal CHEST.
The approach has the potential to generate clinical data that can’t be achieved through other noninvasive means, such as the serum biomarker soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R). sIL-2R is often used to track disease activity, but it isn’t specific for diagnosing sarcoidosis, and it isn’t available worldwide.
Sarcoidosis is a granulomatous inflammatory disease with no known cause and can affect most organs, but an estimated 89%-99% of cases affect the lungs. There is no simple noninvasive diagnostic test, leaving physicians to rely on clinical features, biopsies to obtain tissue pathology, and the ruling out of other granulomatous diagnoses.
The challenge is more difficult because sarcoidosis is a heterogeneous disease, with great variation in the number of organs affected, severity, rate of progression, and response to therapy.
Previous researchers have used VOCs in an attempt to diagnose diseases, since the compounds reflect pathophysiological processes. Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GCMS) is one method to identify the individual VOCs, but the process is time consuming and complex. Some nevertheless showed potential in sarcoidosis, but failed to reproduce their performance in validation cohorts.
In the new study, a cross-sectional analysis showed that exhaled breath analysis using an eNose had excellent sensitivity and specificity for distinguishing sarcoidosis from ILD and healthy controls, and identified sarcoidosis regardless of pulmonary involvement, pulmonary fibrosis, multiple organ involvement, immunosuppressive treatment, or whether or not pathology supported the diagnosis.
The eNose technology produces a “breath-print” after combining information from a broad range of VOCs. The information originates from an array of metal-oxide semiconductor sensors with partial specificity that artificial intelligence processes to discern patterns. Overall, the system functions similarly to the mammalian olfactory system. The artificial intelligence instead views it as a “breath-print” that it can compare against previously learned patterns.
“It is a quite easy, simple, and quick procedure, which is noninvasive. We can collect a lot of data from the VOCs in the exhaled breath because there are several sensors that cross-react. We can create breath profiles and group patients to see if profiles differ. Ultimately, we can use the profiles to diagnose or detect disease in the earlier stage and more accurately,” said Iris van der Sar, MD. Dr. van der Sar is the lead author on the study and a PhD candidate at Erasmus Medical Center in Rotterdam.
The study requires further prospective validation, but the technology could have important clinical benefits, said senior author and principal investigator Marlies Wijsenbeek, MD, PhD, pulmonologist and head of the Interstitial Lung Disease Center at Erasmus Medical Center. “If we in future can avoid a biopsy, that would be most attractive,” said Dr. Wijsenbeek.
“We hope to come to a point-of-care device that can be used to facilitate early diagnosis at low burden for the patient and health care system,” said Karen Moor, MD, PhD, and post-doc on this project. The researchers also hope to determine if the eNose can help evaluate a patient’s response to therapy.
Studies of eNose technology in other chronic diseases have shown promising results, but not all results have been validated yet in independent or external cohorts.
The current study included 569 outpatients, 252 with sarcoidosis and 317 with ILD, along with 48 healthy controls. The researchers constructed a training set using 168 patients with sarcoidosis and 32 healthy controls, and a validation set using 84 patients with sarcoidosis and 16 healthy controls. The eNose differentiated between patients and controls in both groups, with an area under the curve of 1.00 for each regardless of pulmonary involvement or treatment.
It also distinguished those with sarcoidosis and pulmonary involvement from those with ILD, with an AUC of 0.90 (95% confidence interval, 0.87-0.94) in the training set, and an AUC of 0.87 (95% CI, 0.82-0.93) in the validation set.
It differentiated between pulmonary sarcoidosis and hypersensitivity pneumonitis in the training set (AUC 0.95; 95% CI, 0.90-0.99) and the validation set (AUC, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.75-1.00).
The study received no funding. Dr. Wijsenbeek, Dr. van der Sar, and Dr. Moor have no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM CHEST
As constituents clamor for ivermectin, Republican politicians embrace the cause
When state senators in South Carolina held two hearings in September about COVID-19 treatments, they got an earful on the benefits of ivermectin — which many of the lawmakers echoed, sharing experiences of their own loved ones.
The demands for access to the drug were loud and insistent, despite federal regulators’ recent warning against using the drug to treat COVID.
Ivermectin is a generic drug that has been used for decades to treat river blindness, scabies, and even head lice. Veterinarians also use it, in different formulations and dosages, to treat animals for parasites like worms.
At one of the South Carolina hearings, Pressley Stutts III reminded the panel that his father, a prominent GOP leader in the state, had died of COVID a month earlier. He believed ivermectin could have helped him. But doctors at the hospital wouldn’t discuss it.
“I went every bit as far as I could without getting myself thrown in jail trying to save my father’s life,” he told the panel, as lawmakers offered condolences.
“What is going on here?” he asked, with the passion in his voice growing. “My dad’s dead!”
After the pandemic began, scientists launched clinical trials to see if ivermectin could help as a treatment for COVID. Some are still ongoing. But providers in mainstream medicine have rejected it as a COVID treatment, citing the poor quality of the studies to date, and two notorious “preprint” studies that were circulated before they were peer-reviewed, and later taken off the internet because of inaccurate and flawed data.
On Aug. 26, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advised clinicians not to use ivermectin, citing insufficient evidence of benefit and pointing out that unauthorized use had led to accidental poisonings. Vaccination, the CDC reiterated, is still the best way to avoid serious illness and death from the coronavirus.
But many Americans remain convinced ivermectin could be beneficial, and some politicians appear to be listening to them.
“If we have medications out here that are working — or seem to be working — I think it’s absolutely horrible that we’re not trying them,” said Republican state Sen. Tom Corbin in South Carolina. He questioned doctors who had come to the Statehouse to counter efforts to move ivermectin into mainstream use.
The doctors challenged the implied insult that they weren’t following best practices: “Any implication that any of us would do anything to withhold effective treatments from our patients is really insulting to our profession,” said Dr. Annie Andrews, a professor at the Medical University of South Carolina who has cared for COVID patients throughout the pandemic.
Instead of listening to the medical consensus, some politicians in states like South Carolina seem to be taking cues from doctors on the fringe. During one September hearing, state senators patched in a call from Dr. Pierre Kory.
Last year, Dr. Kory started a nonprofit called the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance, which promotes ivermectin. He said he’s not making money by prescribing the drug, though the nonprofit does solicit donations and has not yet filed required financial documents with the IRS.
Dr. Kory acknowledged his medical opinions have landed him on “an island.”
He first testified about ivermectin to a U.S. Senate committee in December. That video went viral. Although it was taken down by YouTube, his Senate testimony prompted patients across the country to ask for ivermectin when they fell ill.
By late August, outpatient prescriptions had jumped 24-fold. Calls to poison control hotlines had tripled, mostly related to people taking ivermectin formulations meant for livestock.
Dr. Kory said he has effectively lost two jobs over his views on ivermectin. At his current hospital in Wisconsin, where he runs the intensive care unit two weeks a month, managers called him to a meeting in September, where he was informed he could no longer prescribe ivermectin. He’d been giving it to “every patient with COVID,” he said.
“After the pharma-geddon that was unleashed, yeah, they shut it down,” he told the South Carolina lawmakers. “And I will tell you that many hospitals across the country had already shut it down months ago.”
Framing the ivermectin fight as a battle against faceless federal agencies and big pharmaceutical corporations appealed to Americans already suspicious of the science behind the pandemic and the approved COVID vaccines.
Dr. Kory suggests success stories with COVID treatments in other parts of the world have been suppressed to instead promote the vaccines.
In an interview with NPR, Dr. Kory said he regrets the flashpoint he helped ignite.
“I feel really bad for the patients, and I feel really bad for the doctors,” he told NPR. “Both of them — both the patients and doctors — are trapped.”
Patients are still demanding the treatment, but doctors sympathetic to their wishes are being told by their health systems not to try it.
Now conservatives in elected office are sensing political payoff if they step in to help patients get the drug. State legislatures, including those in Tennessee and Alaska, are debating various ways to increase access to ivermectin — with proposals such as shielding doctors from repercussions for prescribing it, or forcing pharmacists to fill questionable prescriptions.
The Montana State News Bureau reported that the state’s Republican attorney general dispatched a state trooper to a hospital in Helena where a politically connected patient was dying of COVID. Her family was asking for ivermectin.
In a statement, St. Peter’s Hospital said doctors and nurses were “harassed and threatened by three public officials.”
“These officials have no medical training or experience, yet they were insisting our providers give treatments for COVID-19 that are not authorized, clinically approved, or within the guidelines established by the FDA and the CDC,” the statement added.
On Oct. 14, the Republican attorney general in Nebraska addressed the controversy, issuing a nearly 50-page legal opinion arguing that doctors who consider the “off-label” use of ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine for COVID are acting within the parameters of their state medical licenses, as long as the physician obtains appropriate informed consent from a patient.
Some patients have filed lawsuits to obtain ivermectin, with mixed success. A patient in Illinois was denied. But other hospitals, including one in Ohio, have been forced to administer the drug against the objections of their physicians.
Even as they gain powerful political supporters, some ivermectin fans say they’re now avoiding the health care system — because they’ve lost faith in it.
Lesa Berry, of Richmond, Va., had a friend who died earlier this year of COVID. The doctors refused to use ivermectin, despite requests from Ms. Berry and the patient’s daughter.
They know better now, she said.
“My first attempt would have been to keep her out of the hospital,” Ms. Berry said. “Because right now when you go to the hospital, they only give you what’s on the CDC protocol.”
Ms. Berry and her husband have purchased their own supply of ivermectin, which they keep at home.
This story is from a partnership that includes NPR, Nashville Public Radio and KHN. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
When state senators in South Carolina held two hearings in September about COVID-19 treatments, they got an earful on the benefits of ivermectin — which many of the lawmakers echoed, sharing experiences of their own loved ones.
The demands for access to the drug were loud and insistent, despite federal regulators’ recent warning against using the drug to treat COVID.
Ivermectin is a generic drug that has been used for decades to treat river blindness, scabies, and even head lice. Veterinarians also use it, in different formulations and dosages, to treat animals for parasites like worms.
At one of the South Carolina hearings, Pressley Stutts III reminded the panel that his father, a prominent GOP leader in the state, had died of COVID a month earlier. He believed ivermectin could have helped him. But doctors at the hospital wouldn’t discuss it.
“I went every bit as far as I could without getting myself thrown in jail trying to save my father’s life,” he told the panel, as lawmakers offered condolences.
“What is going on here?” he asked, with the passion in his voice growing. “My dad’s dead!”
After the pandemic began, scientists launched clinical trials to see if ivermectin could help as a treatment for COVID. Some are still ongoing. But providers in mainstream medicine have rejected it as a COVID treatment, citing the poor quality of the studies to date, and two notorious “preprint” studies that were circulated before they were peer-reviewed, and later taken off the internet because of inaccurate and flawed data.
On Aug. 26, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advised clinicians not to use ivermectin, citing insufficient evidence of benefit and pointing out that unauthorized use had led to accidental poisonings. Vaccination, the CDC reiterated, is still the best way to avoid serious illness and death from the coronavirus.
But many Americans remain convinced ivermectin could be beneficial, and some politicians appear to be listening to them.
“If we have medications out here that are working — or seem to be working — I think it’s absolutely horrible that we’re not trying them,” said Republican state Sen. Tom Corbin in South Carolina. He questioned doctors who had come to the Statehouse to counter efforts to move ivermectin into mainstream use.
The doctors challenged the implied insult that they weren’t following best practices: “Any implication that any of us would do anything to withhold effective treatments from our patients is really insulting to our profession,” said Dr. Annie Andrews, a professor at the Medical University of South Carolina who has cared for COVID patients throughout the pandemic.
Instead of listening to the medical consensus, some politicians in states like South Carolina seem to be taking cues from doctors on the fringe. During one September hearing, state senators patched in a call from Dr. Pierre Kory.
Last year, Dr. Kory started a nonprofit called the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance, which promotes ivermectin. He said he’s not making money by prescribing the drug, though the nonprofit does solicit donations and has not yet filed required financial documents with the IRS.
Dr. Kory acknowledged his medical opinions have landed him on “an island.”
He first testified about ivermectin to a U.S. Senate committee in December. That video went viral. Although it was taken down by YouTube, his Senate testimony prompted patients across the country to ask for ivermectin when they fell ill.
By late August, outpatient prescriptions had jumped 24-fold. Calls to poison control hotlines had tripled, mostly related to people taking ivermectin formulations meant for livestock.
Dr. Kory said he has effectively lost two jobs over his views on ivermectin. At his current hospital in Wisconsin, where he runs the intensive care unit two weeks a month, managers called him to a meeting in September, where he was informed he could no longer prescribe ivermectin. He’d been giving it to “every patient with COVID,” he said.
“After the pharma-geddon that was unleashed, yeah, they shut it down,” he told the South Carolina lawmakers. “And I will tell you that many hospitals across the country had already shut it down months ago.”
Framing the ivermectin fight as a battle against faceless federal agencies and big pharmaceutical corporations appealed to Americans already suspicious of the science behind the pandemic and the approved COVID vaccines.
Dr. Kory suggests success stories with COVID treatments in other parts of the world have been suppressed to instead promote the vaccines.
In an interview with NPR, Dr. Kory said he regrets the flashpoint he helped ignite.
“I feel really bad for the patients, and I feel really bad for the doctors,” he told NPR. “Both of them — both the patients and doctors — are trapped.”
Patients are still demanding the treatment, but doctors sympathetic to their wishes are being told by their health systems not to try it.
Now conservatives in elected office are sensing political payoff if they step in to help patients get the drug. State legislatures, including those in Tennessee and Alaska, are debating various ways to increase access to ivermectin — with proposals such as shielding doctors from repercussions for prescribing it, or forcing pharmacists to fill questionable prescriptions.
The Montana State News Bureau reported that the state’s Republican attorney general dispatched a state trooper to a hospital in Helena where a politically connected patient was dying of COVID. Her family was asking for ivermectin.
In a statement, St. Peter’s Hospital said doctors and nurses were “harassed and threatened by three public officials.”
“These officials have no medical training or experience, yet they were insisting our providers give treatments for COVID-19 that are not authorized, clinically approved, or within the guidelines established by the FDA and the CDC,” the statement added.
On Oct. 14, the Republican attorney general in Nebraska addressed the controversy, issuing a nearly 50-page legal opinion arguing that doctors who consider the “off-label” use of ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine for COVID are acting within the parameters of their state medical licenses, as long as the physician obtains appropriate informed consent from a patient.
Some patients have filed lawsuits to obtain ivermectin, with mixed success. A patient in Illinois was denied. But other hospitals, including one in Ohio, have been forced to administer the drug against the objections of their physicians.
Even as they gain powerful political supporters, some ivermectin fans say they’re now avoiding the health care system — because they’ve lost faith in it.
Lesa Berry, of Richmond, Va., had a friend who died earlier this year of COVID. The doctors refused to use ivermectin, despite requests from Ms. Berry and the patient’s daughter.
They know better now, she said.
“My first attempt would have been to keep her out of the hospital,” Ms. Berry said. “Because right now when you go to the hospital, they only give you what’s on the CDC protocol.”
Ms. Berry and her husband have purchased their own supply of ivermectin, which they keep at home.
This story is from a partnership that includes NPR, Nashville Public Radio and KHN. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
When state senators in South Carolina held two hearings in September about COVID-19 treatments, they got an earful on the benefits of ivermectin — which many of the lawmakers echoed, sharing experiences of their own loved ones.
The demands for access to the drug were loud and insistent, despite federal regulators’ recent warning against using the drug to treat COVID.
Ivermectin is a generic drug that has been used for decades to treat river blindness, scabies, and even head lice. Veterinarians also use it, in different formulations and dosages, to treat animals for parasites like worms.
At one of the South Carolina hearings, Pressley Stutts III reminded the panel that his father, a prominent GOP leader in the state, had died of COVID a month earlier. He believed ivermectin could have helped him. But doctors at the hospital wouldn’t discuss it.
“I went every bit as far as I could without getting myself thrown in jail trying to save my father’s life,” he told the panel, as lawmakers offered condolences.
“What is going on here?” he asked, with the passion in his voice growing. “My dad’s dead!”
After the pandemic began, scientists launched clinical trials to see if ivermectin could help as a treatment for COVID. Some are still ongoing. But providers in mainstream medicine have rejected it as a COVID treatment, citing the poor quality of the studies to date, and two notorious “preprint” studies that were circulated before they were peer-reviewed, and later taken off the internet because of inaccurate and flawed data.
On Aug. 26, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advised clinicians not to use ivermectin, citing insufficient evidence of benefit and pointing out that unauthorized use had led to accidental poisonings. Vaccination, the CDC reiterated, is still the best way to avoid serious illness and death from the coronavirus.
But many Americans remain convinced ivermectin could be beneficial, and some politicians appear to be listening to them.
“If we have medications out here that are working — or seem to be working — I think it’s absolutely horrible that we’re not trying them,” said Republican state Sen. Tom Corbin in South Carolina. He questioned doctors who had come to the Statehouse to counter efforts to move ivermectin into mainstream use.
The doctors challenged the implied insult that they weren’t following best practices: “Any implication that any of us would do anything to withhold effective treatments from our patients is really insulting to our profession,” said Dr. Annie Andrews, a professor at the Medical University of South Carolina who has cared for COVID patients throughout the pandemic.
Instead of listening to the medical consensus, some politicians in states like South Carolina seem to be taking cues from doctors on the fringe. During one September hearing, state senators patched in a call from Dr. Pierre Kory.
Last year, Dr. Kory started a nonprofit called the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance, which promotes ivermectin. He said he’s not making money by prescribing the drug, though the nonprofit does solicit donations and has not yet filed required financial documents with the IRS.
Dr. Kory acknowledged his medical opinions have landed him on “an island.”
He first testified about ivermectin to a U.S. Senate committee in December. That video went viral. Although it was taken down by YouTube, his Senate testimony prompted patients across the country to ask for ivermectin when they fell ill.
By late August, outpatient prescriptions had jumped 24-fold. Calls to poison control hotlines had tripled, mostly related to people taking ivermectin formulations meant for livestock.
Dr. Kory said he has effectively lost two jobs over his views on ivermectin. At his current hospital in Wisconsin, where he runs the intensive care unit two weeks a month, managers called him to a meeting in September, where he was informed he could no longer prescribe ivermectin. He’d been giving it to “every patient with COVID,” he said.
“After the pharma-geddon that was unleashed, yeah, they shut it down,” he told the South Carolina lawmakers. “And I will tell you that many hospitals across the country had already shut it down months ago.”
Framing the ivermectin fight as a battle against faceless federal agencies and big pharmaceutical corporations appealed to Americans already suspicious of the science behind the pandemic and the approved COVID vaccines.
Dr. Kory suggests success stories with COVID treatments in other parts of the world have been suppressed to instead promote the vaccines.
In an interview with NPR, Dr. Kory said he regrets the flashpoint he helped ignite.
“I feel really bad for the patients, and I feel really bad for the doctors,” he told NPR. “Both of them — both the patients and doctors — are trapped.”
Patients are still demanding the treatment, but doctors sympathetic to their wishes are being told by their health systems not to try it.
Now conservatives in elected office are sensing political payoff if they step in to help patients get the drug. State legislatures, including those in Tennessee and Alaska, are debating various ways to increase access to ivermectin — with proposals such as shielding doctors from repercussions for prescribing it, or forcing pharmacists to fill questionable prescriptions.
The Montana State News Bureau reported that the state’s Republican attorney general dispatched a state trooper to a hospital in Helena where a politically connected patient was dying of COVID. Her family was asking for ivermectin.
In a statement, St. Peter’s Hospital said doctors and nurses were “harassed and threatened by three public officials.”
“These officials have no medical training or experience, yet they were insisting our providers give treatments for COVID-19 that are not authorized, clinically approved, or within the guidelines established by the FDA and the CDC,” the statement added.
On Oct. 14, the Republican attorney general in Nebraska addressed the controversy, issuing a nearly 50-page legal opinion arguing that doctors who consider the “off-label” use of ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine for COVID are acting within the parameters of their state medical licenses, as long as the physician obtains appropriate informed consent from a patient.
Some patients have filed lawsuits to obtain ivermectin, with mixed success. A patient in Illinois was denied. But other hospitals, including one in Ohio, have been forced to administer the drug against the objections of their physicians.
Even as they gain powerful political supporters, some ivermectin fans say they’re now avoiding the health care system — because they’ve lost faith in it.
Lesa Berry, of Richmond, Va., had a friend who died earlier this year of COVID. The doctors refused to use ivermectin, despite requests from Ms. Berry and the patient’s daughter.
They know better now, she said.
“My first attempt would have been to keep her out of the hospital,” Ms. Berry said. “Because right now when you go to the hospital, they only give you what’s on the CDC protocol.”
Ms. Berry and her husband have purchased their own supply of ivermectin, which they keep at home.
This story is from a partnership that includes NPR, Nashville Public Radio and KHN. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Genotype, need for transfusion predict death in VEXAS syndrome
Among patients with the recently defined severe autoinflammatory syndrome VEXAS, those who are transfusion dependent or have a specific amino acid substitution are at highest risk for death, whereas those with ear chondritis are at significantly lower risk, a multinational team of investigators has found.
Their study of mortality and predictors of survival among patients with genetically confirmed VEXAS showed that patients with a VEXAS variant resulting in an amino acid substitution of a methionine for a valine had a 3.5-fold higher risk for death, compared with patients with either a methionine-to-threonine substitution or a methionine-to-leucine swap.
Transfusion dependence was an independent predictor of mortality. Patients who became dependent on transfusions after symptom onset had a nearly threefold higher risk for death, reported Marcela A. Ferrada, MD, a clinical fellow at the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases.
“These findings should inform risk assessment and clinical management in patients with VEXAS syndrome,” she said in an oral abstract presentation during the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“These genetic findings have proven right now to be not only diagnostic, but we have shown that they’re also prognostic, and we hope that this is going to help us identify patients who could have more aggressive treatment,” Dr. Ferrada said.
She also discussed her findings in a media briefing held 2 days prior to her plenary presentation. At that briefing, this news organization asked participating clinicians whether they had patients who they suspected may have had undiagnosed VEXAS.
“My answer to that is interesting,” replied moderator Vaneet Sandhu, MD, from Loma Linda (Calif.) University and Riverside University Health System.
“In the last couple of days, I’ve been reading about VEXAS, and actually texted one of my colleagues yesterday and said, ‘Hey, you know these patients we’ve been seeing who have these strange rashes and chondritis and have maybe a diagnosis of leukocytoclastic vasculitis or something else – are we not diagnosing these patients?’ ” she said.
“I think we are looking at every patient with chondritis and reexamining their phenotype. We had dismissed certain symptoms because they didn’t fit the archetype for relapsing polychondritis, for example, but it could be VEXAS,” said Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, of Washington University in St. Louis, who also presented data during the briefing.
Three variants
VEXAS is caused by somatic mutations in UBA1, a gene that initiates cytoplasmic ubiquitylation, a process by which misfolded proteins are tagged for degradation.
The syndrome’s name is an acronym descriptive of the major features:
- Vacuoles in bone marrow cells.
- E-1 activating enzyme that UBA1 encodes for.
- X-linked.
- Autoinflammatory.
- Somatic mutation featuring hematologic mosaicism.
VEXAS results in rheumatologic, dermatologic, and hematologic symptoms that are often misdiagnosed as being caused by treatment-refractory relapsing polychondritis, polyarteritis nodosa, Sweet syndrome, giant cell arteritis, or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS).
VEXAS was identified as a distinct syndrome within the past year by Dr. Ferrada and other investigators at NIAMS, the National Human Genome Research Institute, and other institutions.
In the study reported at ACR 2021, Dr. Ferrada and colleagues assessed 83 men who had been referred for genetic testing for VEXAS at the National Institutes of Health, in Bethesda, Md., and at Leeds (England) Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust.
All patients were confirmed to have VEXAS-defining genetic mutations in UBA1 by Sanger sequencing of peripheral blood samples. Only those patients with mutations at codon p.Met41 were included in the investigators’ analysis. Mutations at that site account for nearly all cases of VEXAS that have been identified to date.
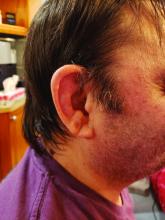
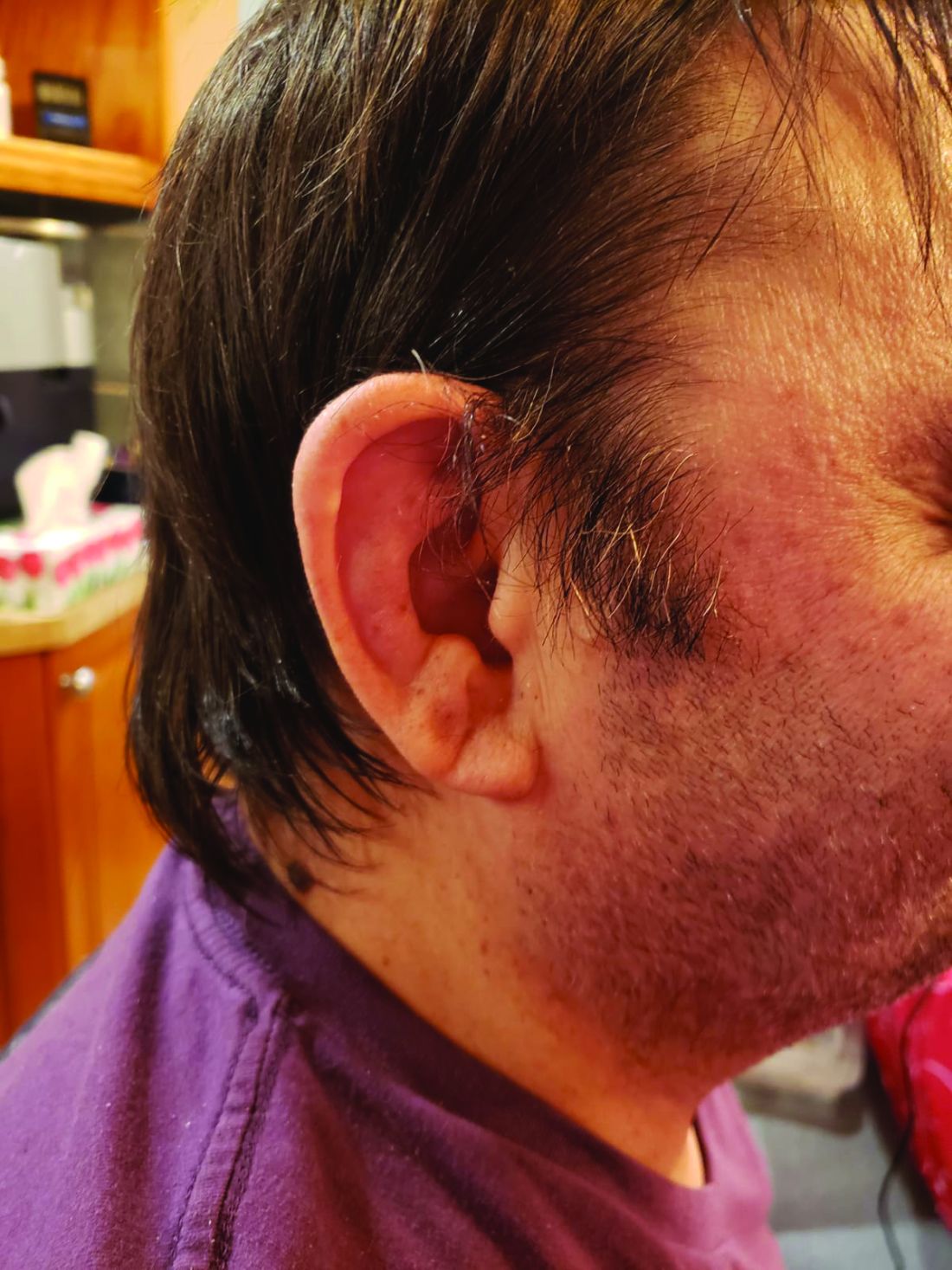
The most common clinical manifestation of VEXAS was skin involvement, which occurred in all but one of the 83 patients. Other common manifestations included arthritis (58 patients), pulmonary infiltrates (57 patients), and ear chondritis (54 patients).
Fifteen patients were found to have the leucine variant, 18 had the valine variant, and 50 had the threonine variant. The median age at disease onset was 66 years in the leucine and threonine variant groups and 65 in the valine variant group.
The clinical diagnosis differed according to genotype: 4 of 18 patients (22%) with the valine variant were diagnosed with relapsing polychondritis, compared with 8 of 15 (53%) with the leucine variant and 31 of 50 (62%) with the threonine variant (P = .01).
In contrast, 55% of patients with valine genotype were diagnosed with undifferentiated fever, compared with 6% of those with the leucine and 16% with the threonine genotypes (P = .001). More patients with the leucine variant (60%) were diagnosed with Sweet syndrome, compared with 11% and 14% of patients with the valine and threonine variants, respectively (P = .001).
There was no significant difference among the three genotypes in the percentage of patients diagnosed with MDS.
The follow-up period ranged from 1 to 18 years (median, 4.7 years). The median survival time from disease onset for all patients was 10 years.
Among patients with the valine variant, median survival was 9 years, which was significantly less than among patients with the other two variants (P = .01).
In univariable analysis, independent predictors of mortality were ear chondritis (hazard ratio, 0.26; P = .005), transfusion dependence, a time-dependent variable (HR, 2.59; P = .03), and the valine variant (HR, 3.5; P = .008).
The association between VEXAS genotype and phenotype could be explained by the finding that, among patients with the valine variant, there was significantly less translation of the catalytically proficient UBA1b isoform than in patients with the other two variants, Dr. Ferrada said.
Therapeutic options
Dr. Ferrada noted that to date no drugs have been shown to provide consistent therapeutic benefits for patients with VEXAS, but evidence as to the etiology of the syndrome points to possible treatment approaches.
“All of these findings I think are extremely important to help us guide management of these patients, as we know that the mutation is located in the stem cells in the bone marrow. So we suspect that doing a bone marrow transplant in these patients is going to be curative,” Dr. Ferrada said during the briefing.
Investigators are planning a phase 2 trial of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant for patients with VEXAS.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Ferrada, Dr. Sandhu, and Dr. Kim have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among patients with the recently defined severe autoinflammatory syndrome VEXAS, those who are transfusion dependent or have a specific amino acid substitution are at highest risk for death, whereas those with ear chondritis are at significantly lower risk, a multinational team of investigators has found.
Their study of mortality and predictors of survival among patients with genetically confirmed VEXAS showed that patients with a VEXAS variant resulting in an amino acid substitution of a methionine for a valine had a 3.5-fold higher risk for death, compared with patients with either a methionine-to-threonine substitution or a methionine-to-leucine swap.
Transfusion dependence was an independent predictor of mortality. Patients who became dependent on transfusions after symptom onset had a nearly threefold higher risk for death, reported Marcela A. Ferrada, MD, a clinical fellow at the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases.
“These findings should inform risk assessment and clinical management in patients with VEXAS syndrome,” she said in an oral abstract presentation during the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“These genetic findings have proven right now to be not only diagnostic, but we have shown that they’re also prognostic, and we hope that this is going to help us identify patients who could have more aggressive treatment,” Dr. Ferrada said.
She also discussed her findings in a media briefing held 2 days prior to her plenary presentation. At that briefing, this news organization asked participating clinicians whether they had patients who they suspected may have had undiagnosed VEXAS.
“My answer to that is interesting,” replied moderator Vaneet Sandhu, MD, from Loma Linda (Calif.) University and Riverside University Health System.
“In the last couple of days, I’ve been reading about VEXAS, and actually texted one of my colleagues yesterday and said, ‘Hey, you know these patients we’ve been seeing who have these strange rashes and chondritis and have maybe a diagnosis of leukocytoclastic vasculitis or something else – are we not diagnosing these patients?’ ” she said.
“I think we are looking at every patient with chondritis and reexamining their phenotype. We had dismissed certain symptoms because they didn’t fit the archetype for relapsing polychondritis, for example, but it could be VEXAS,” said Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, of Washington University in St. Louis, who also presented data during the briefing.
Three variants
VEXAS is caused by somatic mutations in UBA1, a gene that initiates cytoplasmic ubiquitylation, a process by which misfolded proteins are tagged for degradation.
The syndrome’s name is an acronym descriptive of the major features:
- Vacuoles in bone marrow cells.
- E-1 activating enzyme that UBA1 encodes for.
- X-linked.
- Autoinflammatory.
- Somatic mutation featuring hematologic mosaicism.
VEXAS results in rheumatologic, dermatologic, and hematologic symptoms that are often misdiagnosed as being caused by treatment-refractory relapsing polychondritis, polyarteritis nodosa, Sweet syndrome, giant cell arteritis, or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS).
VEXAS was identified as a distinct syndrome within the past year by Dr. Ferrada and other investigators at NIAMS, the National Human Genome Research Institute, and other institutions.
In the study reported at ACR 2021, Dr. Ferrada and colleagues assessed 83 men who had been referred for genetic testing for VEXAS at the National Institutes of Health, in Bethesda, Md., and at Leeds (England) Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust.
All patients were confirmed to have VEXAS-defining genetic mutations in UBA1 by Sanger sequencing of peripheral blood samples. Only those patients with mutations at codon p.Met41 were included in the investigators’ analysis. Mutations at that site account for nearly all cases of VEXAS that have been identified to date.
The most common clinical manifestation of VEXAS was skin involvement, which occurred in all but one of the 83 patients. Other common manifestations included arthritis (58 patients), pulmonary infiltrates (57 patients), and ear chondritis (54 patients).
Fifteen patients were found to have the leucine variant, 18 had the valine variant, and 50 had the threonine variant. The median age at disease onset was 66 years in the leucine and threonine variant groups and 65 in the valine variant group.
The clinical diagnosis differed according to genotype: 4 of 18 patients (22%) with the valine variant were diagnosed with relapsing polychondritis, compared with 8 of 15 (53%) with the leucine variant and 31 of 50 (62%) with the threonine variant (P = .01).
In contrast, 55% of patients with valine genotype were diagnosed with undifferentiated fever, compared with 6% of those with the leucine and 16% with the threonine genotypes (P = .001). More patients with the leucine variant (60%) were diagnosed with Sweet syndrome, compared with 11% and 14% of patients with the valine and threonine variants, respectively (P = .001).
There was no significant difference among the three genotypes in the percentage of patients diagnosed with MDS.
The follow-up period ranged from 1 to 18 years (median, 4.7 years). The median survival time from disease onset for all patients was 10 years.
Among patients with the valine variant, median survival was 9 years, which was significantly less than among patients with the other two variants (P = .01).
In univariable analysis, independent predictors of mortality were ear chondritis (hazard ratio, 0.26; P = .005), transfusion dependence, a time-dependent variable (HR, 2.59; P = .03), and the valine variant (HR, 3.5; P = .008).
The association between VEXAS genotype and phenotype could be explained by the finding that, among patients with the valine variant, there was significantly less translation of the catalytically proficient UBA1b isoform than in patients with the other two variants, Dr. Ferrada said.
Therapeutic options
Dr. Ferrada noted that to date no drugs have been shown to provide consistent therapeutic benefits for patients with VEXAS, but evidence as to the etiology of the syndrome points to possible treatment approaches.
“All of these findings I think are extremely important to help us guide management of these patients, as we know that the mutation is located in the stem cells in the bone marrow. So we suspect that doing a bone marrow transplant in these patients is going to be curative,” Dr. Ferrada said during the briefing.
Investigators are planning a phase 2 trial of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant for patients with VEXAS.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Ferrada, Dr. Sandhu, and Dr. Kim have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among patients with the recently defined severe autoinflammatory syndrome VEXAS, those who are transfusion dependent or have a specific amino acid substitution are at highest risk for death, whereas those with ear chondritis are at significantly lower risk, a multinational team of investigators has found.
Their study of mortality and predictors of survival among patients with genetically confirmed VEXAS showed that patients with a VEXAS variant resulting in an amino acid substitution of a methionine for a valine had a 3.5-fold higher risk for death, compared with patients with either a methionine-to-threonine substitution or a methionine-to-leucine swap.
Transfusion dependence was an independent predictor of mortality. Patients who became dependent on transfusions after symptom onset had a nearly threefold higher risk for death, reported Marcela A. Ferrada, MD, a clinical fellow at the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases.
“These findings should inform risk assessment and clinical management in patients with VEXAS syndrome,” she said in an oral abstract presentation during the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“These genetic findings have proven right now to be not only diagnostic, but we have shown that they’re also prognostic, and we hope that this is going to help us identify patients who could have more aggressive treatment,” Dr. Ferrada said.
She also discussed her findings in a media briefing held 2 days prior to her plenary presentation. At that briefing, this news organization asked participating clinicians whether they had patients who they suspected may have had undiagnosed VEXAS.
“My answer to that is interesting,” replied moderator Vaneet Sandhu, MD, from Loma Linda (Calif.) University and Riverside University Health System.
“In the last couple of days, I’ve been reading about VEXAS, and actually texted one of my colleagues yesterday and said, ‘Hey, you know these patients we’ve been seeing who have these strange rashes and chondritis and have maybe a diagnosis of leukocytoclastic vasculitis or something else – are we not diagnosing these patients?’ ” she said.
“I think we are looking at every patient with chondritis and reexamining their phenotype. We had dismissed certain symptoms because they didn’t fit the archetype for relapsing polychondritis, for example, but it could be VEXAS,” said Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, of Washington University in St. Louis, who also presented data during the briefing.
Three variants
VEXAS is caused by somatic mutations in UBA1, a gene that initiates cytoplasmic ubiquitylation, a process by which misfolded proteins are tagged for degradation.
The syndrome’s name is an acronym descriptive of the major features:
- Vacuoles in bone marrow cells.
- E-1 activating enzyme that UBA1 encodes for.
- X-linked.
- Autoinflammatory.
- Somatic mutation featuring hematologic mosaicism.
VEXAS results in rheumatologic, dermatologic, and hematologic symptoms that are often misdiagnosed as being caused by treatment-refractory relapsing polychondritis, polyarteritis nodosa, Sweet syndrome, giant cell arteritis, or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS).
VEXAS was identified as a distinct syndrome within the past year by Dr. Ferrada and other investigators at NIAMS, the National Human Genome Research Institute, and other institutions.
In the study reported at ACR 2021, Dr. Ferrada and colleagues assessed 83 men who had been referred for genetic testing for VEXAS at the National Institutes of Health, in Bethesda, Md., and at Leeds (England) Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust.
All patients were confirmed to have VEXAS-defining genetic mutations in UBA1 by Sanger sequencing of peripheral blood samples. Only those patients with mutations at codon p.Met41 were included in the investigators’ analysis. Mutations at that site account for nearly all cases of VEXAS that have been identified to date.
The most common clinical manifestation of VEXAS was skin involvement, which occurred in all but one of the 83 patients. Other common manifestations included arthritis (58 patients), pulmonary infiltrates (57 patients), and ear chondritis (54 patients).
Fifteen patients were found to have the leucine variant, 18 had the valine variant, and 50 had the threonine variant. The median age at disease onset was 66 years in the leucine and threonine variant groups and 65 in the valine variant group.
The clinical diagnosis differed according to genotype: 4 of 18 patients (22%) with the valine variant were diagnosed with relapsing polychondritis, compared with 8 of 15 (53%) with the leucine variant and 31 of 50 (62%) with the threonine variant (P = .01).
In contrast, 55% of patients with valine genotype were diagnosed with undifferentiated fever, compared with 6% of those with the leucine and 16% with the threonine genotypes (P = .001). More patients with the leucine variant (60%) were diagnosed with Sweet syndrome, compared with 11% and 14% of patients with the valine and threonine variants, respectively (P = .001).
There was no significant difference among the three genotypes in the percentage of patients diagnosed with MDS.
The follow-up period ranged from 1 to 18 years (median, 4.7 years). The median survival time from disease onset for all patients was 10 years.
Among patients with the valine variant, median survival was 9 years, which was significantly less than among patients with the other two variants (P = .01).
In univariable analysis, independent predictors of mortality were ear chondritis (hazard ratio, 0.26; P = .005), transfusion dependence, a time-dependent variable (HR, 2.59; P = .03), and the valine variant (HR, 3.5; P = .008).
The association between VEXAS genotype and phenotype could be explained by the finding that, among patients with the valine variant, there was significantly less translation of the catalytically proficient UBA1b isoform than in patients with the other two variants, Dr. Ferrada said.
Therapeutic options
Dr. Ferrada noted that to date no drugs have been shown to provide consistent therapeutic benefits for patients with VEXAS, but evidence as to the etiology of the syndrome points to possible treatment approaches.
“All of these findings I think are extremely important to help us guide management of these patients, as we know that the mutation is located in the stem cells in the bone marrow. So we suspect that doing a bone marrow transplant in these patients is going to be curative,” Dr. Ferrada said during the briefing.
Investigators are planning a phase 2 trial of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant for patients with VEXAS.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Ferrada, Dr. Sandhu, and Dr. Kim have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2021
Lupus patients in remission see more flares with HCQ reduction, discontinuation
Continuation of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) when a patient’s systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is in remission or has very low disease activity is linked to a lower risk of flares than is reducing or stopping the antimalarial drug, according to new research presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“Though HCQ is a cornerstone SLE drug, physicians and patients often consider lowering or stopping the drug during remission or low disease activity in order to limit long-term toxicity,” Sasha Bernatsky, MD, PhD, a professor of rheumatology at McGill University in Montreal, told attendees. Her group’s findings revealed a 20% increased risk of flares in those who reduced their HCQ dose and a 56% greater risk of flares in those who discontinued HCQ, compared with those who continued on a maintenance dose.
“I’m going to be using these results in discussions with my patients regarding what the potential implications are of lowering or stopping hydroxychloroquine,” Dr. Bernatsky told attendees. “I think, in the end, this information should be in their hands so that they can be the ones to make these decisions with us, and, of course, given the significant flare rates even in remission, we need to keep on working on optimizing lupus treatments.”
Study details
The researchers analyzed prospective data from 1,460 patients enrolled in the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC) cohort, which includes 33 sites across Europe, Asia, and North America. Patients in this cohort undergo annual follow-ups after enrollment within 15 months of their diagnosis. The study population was 89% female and 52% white. All participants either had low disease activity, defined as a score of 4 or lower on the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000 (SLEDAI-2K) and/or as a prednisone dose no greater than 7.5 mg/day, or were in complete remission, defined as a 0 on SLEDAI-2K while receiving no therapy, including no prednisone or immunosuppressives in the past year.
In addition to adjusting for sex, race/ethnicity, age, education, and geographic residence, the researchers took into account baseline SLE duration, renal damage, body mass index, smoking status, and use of prednisone, immunosuppressives, and biologics. For the outcome of time to first flare, the researchers analyzed those who discontinued HCQ separately from those who reduced the dose, comparing each to those who continued HCQ maintenance therapy. The researchers defined first flare as either hospitalization because of SLE, increased disease activity (at least 4 points on the SLEDAI-2K), or therapy augmentation with steroids, immunosuppressives, antimalarials, or biologics.
Within each cohort, patients who reduced or stopped HCQ therapy were matched to patients who continued HCQ maintenance therapy based on duration of HCQ since time zero, the point at which participants were considered at risk for SLE flares. In the reduction cohort, time zero was the date of a participant’s first HCQ reduction; in the discontinuation cohort, time zero was the date a participant stopped the therapy. Because of the study’s design and reliance on person-years of exposure, it was possible for a single participant to contribute data to more than one cohort.
Results
The overall cohort examining reduction of HCQ dose included 564 patients who reduced their dose, contributing 1,063 person-years of data, and 778 matched patients who started HCQ at the same time but continued HCQ maintenance therapy without a dose reduction, contributing 1,242 person-years. The average duration of HCQ use since time zero in this cohort was 3.4 years.
Before stratifying for disease activity, the group who reduced their therapy experienced 40 first flares per 100 person-years, compared with 31.9 first flares per 100 person-years on maintenance therapy. Those who reduced HCQ had a 20% greater risk of flares than did those who continued it (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.2). However, when those in remission were compared with those not in remission – independent of disease activity level – patients in remission were twice as likely to experience a flare if they reduced their HCQ dose (aHR, 2.14).
In the discontinuation cohort, 389 patients who stopped HCQ therapy contributed 657 person-years, and 577 matched patients who continued HCQ maintenance therapy contributed 924 person-years. The average duration of HCQ use since time zero in this cohort was 4.2 years. Before stratifying for disease activity, the average number of first flares per 100 person-years was 41.3 in the HCQ discontinuation group and 30 in the HCQ maintenance group, resulting in a 56% higher risk of flares for those who stopped HCQ, compared with patients who continued HCQ (aHR, 1.56). Looking only at those in remission, patients were nearly three times more likely to experience a flare if they stopped HCQ than were patients not in remission who continued a maintenance dose (aHR, 2.77).
Patient age is an important consideration
Overall, these findings are not surprising, said Jill P. Buyon, MD, director of the division of rheumatology and of the Lupus Center at NYU-Langone Health in New York. Dr. Buyon is not involved in the current study but is studying discontinuation of HCQ in older adults with lupus.
“It has been already shown that when lupus patients discontinue HCQ, flares are more likely, but does this apply to all age groups?” Dr. Buyon asked in an interview. “Data are essential to more accurately weigh the balance between accumulating ocular exposure, the explosion of new tools to assess retinal injury, and the risk of disease flare in a population that may have more stable/quiescent disease than younger patients.”
Although HCQ’s track record with infection risk is consistently better than that of more immunosuppressive drugs and is very safe during pregnancy, Dr. Buyon said her “ophthalmology colleagues persistently emphasize the risk of retinal accumulation of drug and ocular toxicity over time.” She referenced a recent case-control study in which overall prevalence of HCQ retinopathy was 7.5%, and greater for patients taking more than 5 mg/kg of HCQ or who used HCQ for more than 10 years.
”Risk escalates with continued use, and evaluation by sensitive approaches such as multifocal electroretinography suggests nearly a third of patients accrue retinal damage,” Dr. Buyon said. “As the longevity of patients improves and comorbidities such as renal insufficiency (which affects HCQ clearance) may increase, the ratio of efficacy to toxicity would be expected to decrease.” Further, the fact that disease activity may wane as people age means that rheumatologists treating older adults need to address a critical question, she said: “Can HCQ be safely withdrawn? This question is important in the context of an even broader concern regarding management of SLE in the elderly population, a topic which has received minimal attention.”
The study is limited by its observational design and the fact that the intervention was not randomly allocated, although the researchers attempted to adjust for confounders. Dr. Bernatsky also noted that mild flares might have been missed, and the researchers did not evaluate HCQ levels or adherence, nor did the data set include physicians’ or patients’ explicitly stated reasons for HCQ reduction or discontinuation.
”We estimated that 5% of patients may have reduced HCQ therapy as result of the AAO [American Academy of Ophthalmology] guidelines, 55% because of low disease activity state, and the remainder (40%) for other reasons, possibly intolerance or patient preference,” the researchers noted in their abstract. “Among those who discontinued HCQ, 4% had retinal changes of concern, 15% were in clinical remission, and the remainder stopped for unknown reasons, possibly intolerance or patient preference.”
Dr. Buyon also pointed out that the cohort was initially intended for studying cardiovascular risk and not designed to capture all visits during each year of follow-up.
“Thus, while hospitalizations would be well captured, not all flares, particularly those not severe, would be captured, and thus we may not have the complete picture,” she said, reiterating Dr. Bernatsky’s point that mild flares may have been missed.
”Clearly, this is a very important topic for the management of our patients, particularly those who are elderly and may have already reaped the benefits of hydroxychloroquine,” Dr. Buyon said. “Of course, we have to be mindful of the potential benefit with regard to blood clotting and lipid lowering. Nevertheless, accumulated ocular toxicity and cardiac issues such as cardiomyopathy may emerge to tip the balance after years of accumulated drug exposure.”
The research was funded by the Canadian Institute of Health Research, the Singer Family Fund for Lupus Research, and the SLICC Group. Dr. Bernatsky had no disclosures. Dr. Buyon noted that she has an R34 NIH planning grant to study the safety of withdrawal of hydroxychloroquine in elderly lupus patients that is relevant to this study.
Continuation of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) when a patient’s systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is in remission or has very low disease activity is linked to a lower risk of flares than is reducing or stopping the antimalarial drug, according to new research presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“Though HCQ is a cornerstone SLE drug, physicians and patients often consider lowering or stopping the drug during remission or low disease activity in order to limit long-term toxicity,” Sasha Bernatsky, MD, PhD, a professor of rheumatology at McGill University in Montreal, told attendees. Her group’s findings revealed a 20% increased risk of flares in those who reduced their HCQ dose and a 56% greater risk of flares in those who discontinued HCQ, compared with those who continued on a maintenance dose.
“I’m going to be using these results in discussions with my patients regarding what the potential implications are of lowering or stopping hydroxychloroquine,” Dr. Bernatsky told attendees. “I think, in the end, this information should be in their hands so that they can be the ones to make these decisions with us, and, of course, given the significant flare rates even in remission, we need to keep on working on optimizing lupus treatments.”
Study details
The researchers analyzed prospective data from 1,460 patients enrolled in the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC) cohort, which includes 33 sites across Europe, Asia, and North America. Patients in this cohort undergo annual follow-ups after enrollment within 15 months of their diagnosis. The study population was 89% female and 52% white. All participants either had low disease activity, defined as a score of 4 or lower on the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000 (SLEDAI-2K) and/or as a prednisone dose no greater than 7.5 mg/day, or were in complete remission, defined as a 0 on SLEDAI-2K while receiving no therapy, including no prednisone or immunosuppressives in the past year.
In addition to adjusting for sex, race/ethnicity, age, education, and geographic residence, the researchers took into account baseline SLE duration, renal damage, body mass index, smoking status, and use of prednisone, immunosuppressives, and biologics. For the outcome of time to first flare, the researchers analyzed those who discontinued HCQ separately from those who reduced the dose, comparing each to those who continued HCQ maintenance therapy. The researchers defined first flare as either hospitalization because of SLE, increased disease activity (at least 4 points on the SLEDAI-2K), or therapy augmentation with steroids, immunosuppressives, antimalarials, or biologics.
Within each cohort, patients who reduced or stopped HCQ therapy were matched to patients who continued HCQ maintenance therapy based on duration of HCQ since time zero, the point at which participants were considered at risk for SLE flares. In the reduction cohort, time zero was the date of a participant’s first HCQ reduction; in the discontinuation cohort, time zero was the date a participant stopped the therapy. Because of the study’s design and reliance on person-years of exposure, it was possible for a single participant to contribute data to more than one cohort.
Results
The overall cohort examining reduction of HCQ dose included 564 patients who reduced their dose, contributing 1,063 person-years of data, and 778 matched patients who started HCQ at the same time but continued HCQ maintenance therapy without a dose reduction, contributing 1,242 person-years. The average duration of HCQ use since time zero in this cohort was 3.4 years.
Before stratifying for disease activity, the group who reduced their therapy experienced 40 first flares per 100 person-years, compared with 31.9 first flares per 100 person-years on maintenance therapy. Those who reduced HCQ had a 20% greater risk of flares than did those who continued it (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.2). However, when those in remission were compared with those not in remission – independent of disease activity level – patients in remission were twice as likely to experience a flare if they reduced their HCQ dose (aHR, 2.14).
In the discontinuation cohort, 389 patients who stopped HCQ therapy contributed 657 person-years, and 577 matched patients who continued HCQ maintenance therapy contributed 924 person-years. The average duration of HCQ use since time zero in this cohort was 4.2 years. Before stratifying for disease activity, the average number of first flares per 100 person-years was 41.3 in the HCQ discontinuation group and 30 in the HCQ maintenance group, resulting in a 56% higher risk of flares for those who stopped HCQ, compared with patients who continued HCQ (aHR, 1.56). Looking only at those in remission, patients were nearly three times more likely to experience a flare if they stopped HCQ than were patients not in remission who continued a maintenance dose (aHR, 2.77).
Patient age is an important consideration
Overall, these findings are not surprising, said Jill P. Buyon, MD, director of the division of rheumatology and of the Lupus Center at NYU-Langone Health in New York. Dr. Buyon is not involved in the current study but is studying discontinuation of HCQ in older adults with lupus.
“It has been already shown that when lupus patients discontinue HCQ, flares are more likely, but does this apply to all age groups?” Dr. Buyon asked in an interview. “Data are essential to more accurately weigh the balance between accumulating ocular exposure, the explosion of new tools to assess retinal injury, and the risk of disease flare in a population that may have more stable/quiescent disease than younger patients.”
Although HCQ’s track record with infection risk is consistently better than that of more immunosuppressive drugs and is very safe during pregnancy, Dr. Buyon said her “ophthalmology colleagues persistently emphasize the risk of retinal accumulation of drug and ocular toxicity over time.” She referenced a recent case-control study in which overall prevalence of HCQ retinopathy was 7.5%, and greater for patients taking more than 5 mg/kg of HCQ or who used HCQ for more than 10 years.
”Risk escalates with continued use, and evaluation by sensitive approaches such as multifocal electroretinography suggests nearly a third of patients accrue retinal damage,” Dr. Buyon said. “As the longevity of patients improves and comorbidities such as renal insufficiency (which affects HCQ clearance) may increase, the ratio of efficacy to toxicity would be expected to decrease.” Further, the fact that disease activity may wane as people age means that rheumatologists treating older adults need to address a critical question, she said: “Can HCQ be safely withdrawn? This question is important in the context of an even broader concern regarding management of SLE in the elderly population, a topic which has received minimal attention.”
The study is limited by its observational design and the fact that the intervention was not randomly allocated, although the researchers attempted to adjust for confounders. Dr. Bernatsky also noted that mild flares might have been missed, and the researchers did not evaluate HCQ levels or adherence, nor did the data set include physicians’ or patients’ explicitly stated reasons for HCQ reduction or discontinuation.
”We estimated that 5% of patients may have reduced HCQ therapy as result of the AAO [American Academy of Ophthalmology] guidelines, 55% because of low disease activity state, and the remainder (40%) for other reasons, possibly intolerance or patient preference,” the researchers noted in their abstract. “Among those who discontinued HCQ, 4% had retinal changes of concern, 15% were in clinical remission, and the remainder stopped for unknown reasons, possibly intolerance or patient preference.”
Dr. Buyon also pointed out that the cohort was initially intended for studying cardiovascular risk and not designed to capture all visits during each year of follow-up.
“Thus, while hospitalizations would be well captured, not all flares, particularly those not severe, would be captured, and thus we may not have the complete picture,” she said, reiterating Dr. Bernatsky’s point that mild flares may have been missed.
”Clearly, this is a very important topic for the management of our patients, particularly those who are elderly and may have already reaped the benefits of hydroxychloroquine,” Dr. Buyon said. “Of course, we have to be mindful of the potential benefit with regard to blood clotting and lipid lowering. Nevertheless, accumulated ocular toxicity and cardiac issues such as cardiomyopathy may emerge to tip the balance after years of accumulated drug exposure.”
The research was funded by the Canadian Institute of Health Research, the Singer Family Fund for Lupus Research, and the SLICC Group. Dr. Bernatsky had no disclosures. Dr. Buyon noted that she has an R34 NIH planning grant to study the safety of withdrawal of hydroxychloroquine in elderly lupus patients that is relevant to this study.
Continuation of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) when a patient’s systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is in remission or has very low disease activity is linked to a lower risk of flares than is reducing or stopping the antimalarial drug, according to new research presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“Though HCQ is a cornerstone SLE drug, physicians and patients often consider lowering or stopping the drug during remission or low disease activity in order to limit long-term toxicity,” Sasha Bernatsky, MD, PhD, a professor of rheumatology at McGill University in Montreal, told attendees. Her group’s findings revealed a 20% increased risk of flares in those who reduced their HCQ dose and a 56% greater risk of flares in those who discontinued HCQ, compared with those who continued on a maintenance dose.
“I’m going to be using these results in discussions with my patients regarding what the potential implications are of lowering or stopping hydroxychloroquine,” Dr. Bernatsky told attendees. “I think, in the end, this information should be in their hands so that they can be the ones to make these decisions with us, and, of course, given the significant flare rates even in remission, we need to keep on working on optimizing lupus treatments.”
Study details
The researchers analyzed prospective data from 1,460 patients enrolled in the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC) cohort, which includes 33 sites across Europe, Asia, and North America. Patients in this cohort undergo annual follow-ups after enrollment within 15 months of their diagnosis. The study population was 89% female and 52% white. All participants either had low disease activity, defined as a score of 4 or lower on the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000 (SLEDAI-2K) and/or as a prednisone dose no greater than 7.5 mg/day, or were in complete remission, defined as a 0 on SLEDAI-2K while receiving no therapy, including no prednisone or immunosuppressives in the past year.
In addition to adjusting for sex, race/ethnicity, age, education, and geographic residence, the researchers took into account baseline SLE duration, renal damage, body mass index, smoking status, and use of prednisone, immunosuppressives, and biologics. For the outcome of time to first flare, the researchers analyzed those who discontinued HCQ separately from those who reduced the dose, comparing each to those who continued HCQ maintenance therapy. The researchers defined first flare as either hospitalization because of SLE, increased disease activity (at least 4 points on the SLEDAI-2K), or therapy augmentation with steroids, immunosuppressives, antimalarials, or biologics.
Within each cohort, patients who reduced or stopped HCQ therapy were matched to patients who continued HCQ maintenance therapy based on duration of HCQ since time zero, the point at which participants were considered at risk for SLE flares. In the reduction cohort, time zero was the date of a participant’s first HCQ reduction; in the discontinuation cohort, time zero was the date a participant stopped the therapy. Because of the study’s design and reliance on person-years of exposure, it was possible for a single participant to contribute data to more than one cohort.
Results
The overall cohort examining reduction of HCQ dose included 564 patients who reduced their dose, contributing 1,063 person-years of data, and 778 matched patients who started HCQ at the same time but continued HCQ maintenance therapy without a dose reduction, contributing 1,242 person-years. The average duration of HCQ use since time zero in this cohort was 3.4 years.
Before stratifying for disease activity, the group who reduced their therapy experienced 40 first flares per 100 person-years, compared with 31.9 first flares per 100 person-years on maintenance therapy. Those who reduced HCQ had a 20% greater risk of flares than did those who continued it (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.2). However, when those in remission were compared with those not in remission – independent of disease activity level – patients in remission were twice as likely to experience a flare if they reduced their HCQ dose (aHR, 2.14).
In the discontinuation cohort, 389 patients who stopped HCQ therapy contributed 657 person-years, and 577 matched patients who continued HCQ maintenance therapy contributed 924 person-years. The average duration of HCQ use since time zero in this cohort was 4.2 years. Before stratifying for disease activity, the average number of first flares per 100 person-years was 41.3 in the HCQ discontinuation group and 30 in the HCQ maintenance group, resulting in a 56% higher risk of flares for those who stopped HCQ, compared with patients who continued HCQ (aHR, 1.56). Looking only at those in remission, patients were nearly three times more likely to experience a flare if they stopped HCQ than were patients not in remission who continued a maintenance dose (aHR, 2.77).
Patient age is an important consideration
Overall, these findings are not surprising, said Jill P. Buyon, MD, director of the division of rheumatology and of the Lupus Center at NYU-Langone Health in New York. Dr. Buyon is not involved in the current study but is studying discontinuation of HCQ in older adults with lupus.
“It has been already shown that when lupus patients discontinue HCQ, flares are more likely, but does this apply to all age groups?” Dr. Buyon asked in an interview. “Data are essential to more accurately weigh the balance between accumulating ocular exposure, the explosion of new tools to assess retinal injury, and the risk of disease flare in a population that may have more stable/quiescent disease than younger patients.”
Although HCQ’s track record with infection risk is consistently better than that of more immunosuppressive drugs and is very safe during pregnancy, Dr. Buyon said her “ophthalmology colleagues persistently emphasize the risk of retinal accumulation of drug and ocular toxicity over time.” She referenced a recent case-control study in which overall prevalence of HCQ retinopathy was 7.5%, and greater for patients taking more than 5 mg/kg of HCQ or who used HCQ for more than 10 years.
”Risk escalates with continued use, and evaluation by sensitive approaches such as multifocal electroretinography suggests nearly a third of patients accrue retinal damage,” Dr. Buyon said. “As the longevity of patients improves and comorbidities such as renal insufficiency (which affects HCQ clearance) may increase, the ratio of efficacy to toxicity would be expected to decrease.” Further, the fact that disease activity may wane as people age means that rheumatologists treating older adults need to address a critical question, she said: “Can HCQ be safely withdrawn? This question is important in the context of an even broader concern regarding management of SLE in the elderly population, a topic which has received minimal attention.”
The study is limited by its observational design and the fact that the intervention was not randomly allocated, although the researchers attempted to adjust for confounders. Dr. Bernatsky also noted that mild flares might have been missed, and the researchers did not evaluate HCQ levels or adherence, nor did the data set include physicians’ or patients’ explicitly stated reasons for HCQ reduction or discontinuation.
”We estimated that 5% of patients may have reduced HCQ therapy as result of the AAO [American Academy of Ophthalmology] guidelines, 55% because of low disease activity state, and the remainder (40%) for other reasons, possibly intolerance or patient preference,” the researchers noted in their abstract. “Among those who discontinued HCQ, 4% had retinal changes of concern, 15% were in clinical remission, and the remainder stopped for unknown reasons, possibly intolerance or patient preference.”
Dr. Buyon also pointed out that the cohort was initially intended for studying cardiovascular risk and not designed to capture all visits during each year of follow-up.
“Thus, while hospitalizations would be well captured, not all flares, particularly those not severe, would be captured, and thus we may not have the complete picture,” she said, reiterating Dr. Bernatsky’s point that mild flares may have been missed.
”Clearly, this is a very important topic for the management of our patients, particularly those who are elderly and may have already reaped the benefits of hydroxychloroquine,” Dr. Buyon said. “Of course, we have to be mindful of the potential benefit with regard to blood clotting and lipid lowering. Nevertheless, accumulated ocular toxicity and cardiac issues such as cardiomyopathy may emerge to tip the balance after years of accumulated drug exposure.”
The research was funded by the Canadian Institute of Health Research, the Singer Family Fund for Lupus Research, and the SLICC Group. Dr. Bernatsky had no disclosures. Dr. Buyon noted that she has an R34 NIH planning grant to study the safety of withdrawal of hydroxychloroquine in elderly lupus patients that is relevant to this study.
FROM ACR 2021
More eczema in children exposed to toxic metals in utero
published Oct. 27, 2021, in JAMA Network Open.
In this multicenter cohort study, led by epidemiologist Shu-Li Wang, PhD, of the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, in Taiwan, each twofold increase in prenatal arsenic level correlated with a 2.4-fold higher rate of atopic dermatitis in 4-year-olds.
Atopic diseases have been on the rise. Eczema (atopic dermatitis) is the first stage of the so-called atopic march, followed by food allergies, allergic rhinitis, and asthma later in childhood. Previous research has linked heavy metal exposure to allergic diseases in adults. In another study by Dr. Wang and colleagues that was published in 2021, prenatal and early-life arsenic exposure was found to correlate with higher rates of allergic rhinitis and asthma in children. In that study, the participants were followed every 2-3 years through the age of 14 as part of the Taiwan Maternal and Infant Cohort Study.
The new study included 370 mother and child pairs who were enrolled in that birth cohort study between October 2012 and May 2015. During their third trimester of pregnancy, women completed questionnaires about their lifestyle, diet, and living environment. In addition, their height, weight, and blood pressure were recorded, and urine samples were taken. In follow-up interviews 3-4 years later, the mothers were asked whether their child had ever been diagnosed with atopic dermatitis.
The researchers used an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer to analyze the participants’ urine samples. They assessed for exposures in utero to eight metals: arsenic, cadmium, lead, cobalt, copper, nickel, thallium, and zinc.
Each unit increase of an index that estimates the combined exposure to these metals during pregnancy was associated with 63% higher odds of atopic dermatitis in the children by age 4. The researchers adjusted for parental allergies (yes or no), mother’s educational level (<12 years, 13-16 years, or >16 years), geographic area (central or eastern Taiwan), exposure to tobacco smoke during pregnancy, and the child’s gender. Arsenic (40.1%) and cadmium (20.5%) accounted for most of the metal coexposure index.
A wealth of previous research links arsenic exposure during adulthood to skin disease and immune dysfunction. Early-life arsenic exposure has been linked with elevated risk for various adult disorders, including cancer, diabetes, and heart disease, years later. In light of such research, “the findings in this paper are not surprising,” J. Christopher States, PhD, director of the Center for Integrative Environmental Health Science at the University of Louisville (Ky.), told this news organization. “Low-level arsenic exposure does not cause disease immediately, but it does appear to have long-lasting effects, making individuals susceptible to ‘second hits’ with another environmental agent.”
Research into the molecular mechanisms for these links has shown that arsenic and cadmium exposure can promote allergic phenotypes in immune cells. “We think the toxic metals activate the alarmin pathway, thus inducing innate lymphoid cells, then activating T-helper 2 cells, which drive immunoglobulin E production and breakdown of the epithelium and promotion of allergies,” said Kari Nadeau, MD, PhD, director of the Sean N. Parker Center for Allergy and Asthma Research at Stanford University. Dr. Nadeau led that study, published in 2017 in PLOS One, along with epidemiologist Margaret Karagas, PhD, of Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H.
As for what pregnant women can do to minimize their exposure to heavy metals, “that is a difficult problem and primarily a function of where one lives,” said Dr. States.
Drinking water and food are major sources of arsenic exposure. Groundwater is naturally contaminated with arsenic deposits that seep in from bedrock, said Dr. States. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency regulates arsenic levels in public drinking water that is supplied to more than a few thousand people. However, small water supplies and private wells are unregulated, he said, and having these water sources tested for arsenic or fitted with systems to reduce arsenic can be very expensive.
Among foods, rice can have high concentrations of arsenic, Dr. Karagas told this news organization. To minimize arsenic exposure through the diet, women can limit rice-based foods, according to a web-based tool developed by her and coworkers.
In addition, tobacco smoke is a major source of cadmium exposure and a moderate source of arsenic exposure, Dr. States noted. Women can reduce their exposure to these metals by avoiding tobacco and secondhand smoke.
The study was supported by grants from the National Health Research Institutes, Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, Taiwan Ministry of Science and Technology, and the Taiwan Environmental Protection Administration. The authors and quoted experts report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
published Oct. 27, 2021, in JAMA Network Open.
In this multicenter cohort study, led by epidemiologist Shu-Li Wang, PhD, of the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, in Taiwan, each twofold increase in prenatal arsenic level correlated with a 2.4-fold higher rate of atopic dermatitis in 4-year-olds.
Atopic diseases have been on the rise. Eczema (atopic dermatitis) is the first stage of the so-called atopic march, followed by food allergies, allergic rhinitis, and asthma later in childhood. Previous research has linked heavy metal exposure to allergic diseases in adults. In another study by Dr. Wang and colleagues that was published in 2021, prenatal and early-life arsenic exposure was found to correlate with higher rates of allergic rhinitis and asthma in children. In that study, the participants were followed every 2-3 years through the age of 14 as part of the Taiwan Maternal and Infant Cohort Study.
The new study included 370 mother and child pairs who were enrolled in that birth cohort study between October 2012 and May 2015. During their third trimester of pregnancy, women completed questionnaires about their lifestyle, diet, and living environment. In addition, their height, weight, and blood pressure were recorded, and urine samples were taken. In follow-up interviews 3-4 years later, the mothers were asked whether their child had ever been diagnosed with atopic dermatitis.
The researchers used an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer to analyze the participants’ urine samples. They assessed for exposures in utero to eight metals: arsenic, cadmium, lead, cobalt, copper, nickel, thallium, and zinc.
Each unit increase of an index that estimates the combined exposure to these metals during pregnancy was associated with 63% higher odds of atopic dermatitis in the children by age 4. The researchers adjusted for parental allergies (yes or no), mother’s educational level (<12 years, 13-16 years, or >16 years), geographic area (central or eastern Taiwan), exposure to tobacco smoke during pregnancy, and the child’s gender. Arsenic (40.1%) and cadmium (20.5%) accounted for most of the metal coexposure index.
A wealth of previous research links arsenic exposure during adulthood to skin disease and immune dysfunction. Early-life arsenic exposure has been linked with elevated risk for various adult disorders, including cancer, diabetes, and heart disease, years later. In light of such research, “the findings in this paper are not surprising,” J. Christopher States, PhD, director of the Center for Integrative Environmental Health Science at the University of Louisville (Ky.), told this news organization. “Low-level arsenic exposure does not cause disease immediately, but it does appear to have long-lasting effects, making individuals susceptible to ‘second hits’ with another environmental agent.”
Research into the molecular mechanisms for these links has shown that arsenic and cadmium exposure can promote allergic phenotypes in immune cells. “We think the toxic metals activate the alarmin pathway, thus inducing innate lymphoid cells, then activating T-helper 2 cells, which drive immunoglobulin E production and breakdown of the epithelium and promotion of allergies,” said Kari Nadeau, MD, PhD, director of the Sean N. Parker Center for Allergy and Asthma Research at Stanford University. Dr. Nadeau led that study, published in 2017 in PLOS One, along with epidemiologist Margaret Karagas, PhD, of Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H.
As for what pregnant women can do to minimize their exposure to heavy metals, “that is a difficult problem and primarily a function of where one lives,” said Dr. States.
Drinking water and food are major sources of arsenic exposure. Groundwater is naturally contaminated with arsenic deposits that seep in from bedrock, said Dr. States. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency regulates arsenic levels in public drinking water that is supplied to more than a few thousand people. However, small water supplies and private wells are unregulated, he said, and having these water sources tested for arsenic or fitted with systems to reduce arsenic can be very expensive.
Among foods, rice can have high concentrations of arsenic, Dr. Karagas told this news organization. To minimize arsenic exposure through the diet, women can limit rice-based foods, according to a web-based tool developed by her and coworkers.
In addition, tobacco smoke is a major source of cadmium exposure and a moderate source of arsenic exposure, Dr. States noted. Women can reduce their exposure to these metals by avoiding tobacco and secondhand smoke.
The study was supported by grants from the National Health Research Institutes, Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, Taiwan Ministry of Science and Technology, and the Taiwan Environmental Protection Administration. The authors and quoted experts report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
published Oct. 27, 2021, in JAMA Network Open.
In this multicenter cohort study, led by epidemiologist Shu-Li Wang, PhD, of the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, in Taiwan, each twofold increase in prenatal arsenic level correlated with a 2.4-fold higher rate of atopic dermatitis in 4-year-olds.
Atopic diseases have been on the rise. Eczema (atopic dermatitis) is the first stage of the so-called atopic march, followed by food allergies, allergic rhinitis, and asthma later in childhood. Previous research has linked heavy metal exposure to allergic diseases in adults. In another study by Dr. Wang and colleagues that was published in 2021, prenatal and early-life arsenic exposure was found to correlate with higher rates of allergic rhinitis and asthma in children. In that study, the participants were followed every 2-3 years through the age of 14 as part of the Taiwan Maternal and Infant Cohort Study.
The new study included 370 mother and child pairs who were enrolled in that birth cohort study between October 2012 and May 2015. During their third trimester of pregnancy, women completed questionnaires about their lifestyle, diet, and living environment. In addition, their height, weight, and blood pressure were recorded, and urine samples were taken. In follow-up interviews 3-4 years later, the mothers were asked whether their child had ever been diagnosed with atopic dermatitis.
The researchers used an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer to analyze the participants’ urine samples. They assessed for exposures in utero to eight metals: arsenic, cadmium, lead, cobalt, copper, nickel, thallium, and zinc.
Each unit increase of an index that estimates the combined exposure to these metals during pregnancy was associated with 63% higher odds of atopic dermatitis in the children by age 4. The researchers adjusted for parental allergies (yes or no), mother’s educational level (<12 years, 13-16 years, or >16 years), geographic area (central or eastern Taiwan), exposure to tobacco smoke during pregnancy, and the child’s gender. Arsenic (40.1%) and cadmium (20.5%) accounted for most of the metal coexposure index.
A wealth of previous research links arsenic exposure during adulthood to skin disease and immune dysfunction. Early-life arsenic exposure has been linked with elevated risk for various adult disorders, including cancer, diabetes, and heart disease, years later. In light of such research, “the findings in this paper are not surprising,” J. Christopher States, PhD, director of the Center for Integrative Environmental Health Science at the University of Louisville (Ky.), told this news organization. “Low-level arsenic exposure does not cause disease immediately, but it does appear to have long-lasting effects, making individuals susceptible to ‘second hits’ with another environmental agent.”
Research into the molecular mechanisms for these links has shown that arsenic and cadmium exposure can promote allergic phenotypes in immune cells. “We think the toxic metals activate the alarmin pathway, thus inducing innate lymphoid cells, then activating T-helper 2 cells, which drive immunoglobulin E production and breakdown of the epithelium and promotion of allergies,” said Kari Nadeau, MD, PhD, director of the Sean N. Parker Center for Allergy and Asthma Research at Stanford University. Dr. Nadeau led that study, published in 2017 in PLOS One, along with epidemiologist Margaret Karagas, PhD, of Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H.
As for what pregnant women can do to minimize their exposure to heavy metals, “that is a difficult problem and primarily a function of where one lives,” said Dr. States.
Drinking water and food are major sources of arsenic exposure. Groundwater is naturally contaminated with arsenic deposits that seep in from bedrock, said Dr. States. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency regulates arsenic levels in public drinking water that is supplied to more than a few thousand people. However, small water supplies and private wells are unregulated, he said, and having these water sources tested for arsenic or fitted with systems to reduce arsenic can be very expensive.
Among foods, rice can have high concentrations of arsenic, Dr. Karagas told this news organization. To minimize arsenic exposure through the diet, women can limit rice-based foods, according to a web-based tool developed by her and coworkers.
In addition, tobacco smoke is a major source of cadmium exposure and a moderate source of arsenic exposure, Dr. States noted. Women can reduce their exposure to these metals by avoiding tobacco and secondhand smoke.
The study was supported by grants from the National Health Research Institutes, Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, Taiwan Ministry of Science and Technology, and the Taiwan Environmental Protection Administration. The authors and quoted experts report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Does the use of frankincense make sense in dermatology?
The Boswellia serrata exudate or gum (known in India as “guggulu”) that forms an aromatic resin traditionally used as incense – and known as frankincense (especially when retrieved from Boswellia species found in Eritrea and Somalia but also from the Indian variety) – has been considered for thousands of years to possess therapeutic properties. It is used in Ayurvedic medicine, as well as in traditional medicine in China and the Middle East, particularly for its anti-inflammatory effects to treat chronic conditions.1-8 In fact, such essential oils have been used since 2800 BC to treat various inflammatory conditions, including skin sores and wounds, as well as in perfumes and incense.2,9 In the West, use of frankincense dates back to thousands of years as well, more often found in the form of incense for religious and cultural ceremonies.7 Over the past 2 decades, .3 This column focuses on some of the emerging data on this ancient botanical agent.
Chemical constituents
Terpenoids and essential oils are the primary components of frankincense and are known to impart anti-inflammatory and anticancer activity. The same is true for myrrh, which has been combined with frankincense in traditional Chinese medicine as a single medication for millennia, with the two acting synergistically and considered still to be a potent combination in conferring various biological benefits.7
In 2010, in a systematic review of the anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities of Boswellia species and their chemical ingredients, Efferth and Oesch found that frankincense blocks the production of leukotrienes, cyclooxygenase (COX) 1 and 2, as well as 5-lipoxygenase; and oxidative stress. It also contributes to regulation of immune cells from the innate and acquired immune systems and exerts anticancer activity by influencing signaling transduction responsible for cell cycle arrest, as well as inhibition of proliferation, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. The investigators also reported on clinical trial results that have found efficacy of frankincense and its constituents in ameliorating symptoms of psoriasis and erythematous eczema, among other disorders.3
Anti-inflammatory activity
Li et al. completed a study in 2016 to identify the active ingredients responsible for the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of frankincense. They found that alpha-pinene, linalool, and 1-octanol were key contributors. These constituents were noted for suppressing COX-2 overexpression in mice, as well as nociceptive stimulus-induced inflammatory infiltrates.10
Noting the increasing popularity of frankincense essential oil in skin care, despite a paucity of data, in 2017, Han et al. evaluated the biological activities of the essential oil in pre-inflamed human dermal fibroblasts using 17 key protein biomarkers. Frankincense essential oil displayed significant antiproliferative activity and suppressed collagen III, interferon gamma-induced protein 10, and intracellular adhesion molecule 1. The investigators referred to the overall encouraging potential of frankincense essential oil to exert influence over inflammation and tissue remodeling in human skin and called for additional research into its mechanisms of action and active constituents.11
Anticancer activity
The main active ingredient in frankincense, boswellic acid, has been shown to promote apoptosis, suppress matrix metalloproteinase secretion, and hinder migration in metastatic melanoma cell lines in mice.6,12
In 2019, Hakkim et al. demonstrated that frankincense essential oil yielded substantial antimelanoma activity in vitro and in vivo and ameliorated hepatotoxicity caused by acetaminophen.13
There is one case report in the literature on the use of frankincense as a treatment for skin cancer. A 56-year-old man received frankincense oil multiple times a day for 4 months to treat a nodular basal cell carcinoma on one arm (which resolved) and an infiltrative BCC on the chest (some focal residual tumor remained).6,14 Topical frankincense or boswellic acid has been given a grade D recommendation for treating skin cancer, however, because of only one level-of-evidence-5 study.6
Antimicrobial activity
In 2012, de Rapper et al. collected samples of three essential oils of frankincense (Boswellia rivae, Boswellia neglecta, and Boswellia papyrifera) and two essential oil samples of myrrh and sweet myrrh from different regions of Ethiopia to study their anti-infective properties alone and in combination. The investigators observed synergistic and additive effects, particularly between B. papyrifera and Commiphora myrrha. While noting the long history of the combined use of frankincense and myrrh essential oils since 1500 BC, the investigators highlighted their study as the first antimicrobial work to verify the effectiveness of this combination, validating the use of this combination to thwart particular pathogens.15
Just 2 years ago, Ljaljević Grbić et al. evaluated the in vitro antimicrobial potential of the liquid and vapor phases of B. carteri and C. myrrha (frankincense and myrrh, respectively) essential oils, finding that frankincense demonstrated marked capacity to act as a natural antimicrobial agent.9
Transdermal delivery
In 2017, Zhu et al. showed that frankincense and myrrh essential oils promoted the permeability of the Chinese herb Chuanxiong and may facilitate drug elimination from the epidermis via dermal capillaries by dint of improved cutaneous blood flow, thereby augmenting transdermal drug delivery.16 The same team also showed that frankincense and myrrh essential oils, by fostering permeation by enhancing drug delivery across the stratum corneum, can also alter the structure of the stratum corneum.17
Conclusion
The use of frankincense in traditional medicine has a long and impressive track record. Recent research provides reason for optimism, and further investigating the possible incorporation of this botanical agent into modern dermatologic therapies appears warranted. Clearly, however, much more research is needed.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur who practices in Miami. She founded the Cosmetic Dermatology Center at the University of Miami in 1997. Dr. Baumann has written two textbooks and a New York Times Best Sellers book for consumers. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Revance, Evolus, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions Inc., a company that independently tests skin care products and makes recommendations to physicians on which skin care technologies are best. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Kimmatkar N et al. Phytomedicine. 2003 Jan;10(1):3-7.
2. Ammon HP. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2002;152(15-16):373-8.
3. Efferth T & Oesch F. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020 Feb 4;S1044-579X(20)30034-1.
4. Banno N et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006 Sep 19;107(2):249-53.
5. Poeckel D & Werz O. Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(28):3359-69.
6. Li JY, Kampp JT. Dermatol Surg. 2019 Jan;45(1):58-67.
7. Cao B et al. Molecules. 2019 Aug 24;24(17): 3076.
8. Mertens M et al. Flavour Fragr J. 2009;24:279-300.
9. Ljaljević Grbić M et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jun 12;219:1-14.
10. Li XJ et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Feb 17;179:22-6.
11. Han X et al. Biochim Open. 2017 Feb 3;4:31-5.
12. Zhao W et al. Cancer Detect Prev. 2003;27:67-75.
13. Hakkim FL et al. Oncotarget. 2019 May 28;10(37):3472-90.
14. Fung K et al. OA Altern Med 2013;1:14.
15. de Rapper S et al. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2012 Apr;54(4):352-8.
16. Zhu XF et al. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Feb;42(4):680-5.
17. Guan YM et al. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Sep;42(17):3350-5.
The Boswellia serrata exudate or gum (known in India as “guggulu”) that forms an aromatic resin traditionally used as incense – and known as frankincense (especially when retrieved from Boswellia species found in Eritrea and Somalia but also from the Indian variety) – has been considered for thousands of years to possess therapeutic properties. It is used in Ayurvedic medicine, as well as in traditional medicine in China and the Middle East, particularly for its anti-inflammatory effects to treat chronic conditions.1-8 In fact, such essential oils have been used since 2800 BC to treat various inflammatory conditions, including skin sores and wounds, as well as in perfumes and incense.2,9 In the West, use of frankincense dates back to thousands of years as well, more often found in the form of incense for religious and cultural ceremonies.7 Over the past 2 decades, .3 This column focuses on some of the emerging data on this ancient botanical agent.
Chemical constituents
Terpenoids and essential oils are the primary components of frankincense and are known to impart anti-inflammatory and anticancer activity. The same is true for myrrh, which has been combined with frankincense in traditional Chinese medicine as a single medication for millennia, with the two acting synergistically and considered still to be a potent combination in conferring various biological benefits.7
In 2010, in a systematic review of the anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities of Boswellia species and their chemical ingredients, Efferth and Oesch found that frankincense blocks the production of leukotrienes, cyclooxygenase (COX) 1 and 2, as well as 5-lipoxygenase; and oxidative stress. It also contributes to regulation of immune cells from the innate and acquired immune systems and exerts anticancer activity by influencing signaling transduction responsible for cell cycle arrest, as well as inhibition of proliferation, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. The investigators also reported on clinical trial results that have found efficacy of frankincense and its constituents in ameliorating symptoms of psoriasis and erythematous eczema, among other disorders.3
Anti-inflammatory activity
Li et al. completed a study in 2016 to identify the active ingredients responsible for the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of frankincense. They found that alpha-pinene, linalool, and 1-octanol were key contributors. These constituents were noted for suppressing COX-2 overexpression in mice, as well as nociceptive stimulus-induced inflammatory infiltrates.10
Noting the increasing popularity of frankincense essential oil in skin care, despite a paucity of data, in 2017, Han et al. evaluated the biological activities of the essential oil in pre-inflamed human dermal fibroblasts using 17 key protein biomarkers. Frankincense essential oil displayed significant antiproliferative activity and suppressed collagen III, interferon gamma-induced protein 10, and intracellular adhesion molecule 1. The investigators referred to the overall encouraging potential of frankincense essential oil to exert influence over inflammation and tissue remodeling in human skin and called for additional research into its mechanisms of action and active constituents.11
Anticancer activity
The main active ingredient in frankincense, boswellic acid, has been shown to promote apoptosis, suppress matrix metalloproteinase secretion, and hinder migration in metastatic melanoma cell lines in mice.6,12
In 2019, Hakkim et al. demonstrated that frankincense essential oil yielded substantial antimelanoma activity in vitro and in vivo and ameliorated hepatotoxicity caused by acetaminophen.13
There is one case report in the literature on the use of frankincense as a treatment for skin cancer. A 56-year-old man received frankincense oil multiple times a day for 4 months to treat a nodular basal cell carcinoma on one arm (which resolved) and an infiltrative BCC on the chest (some focal residual tumor remained).6,14 Topical frankincense or boswellic acid has been given a grade D recommendation for treating skin cancer, however, because of only one level-of-evidence-5 study.6
Antimicrobial activity
In 2012, de Rapper et al. collected samples of three essential oils of frankincense (Boswellia rivae, Boswellia neglecta, and Boswellia papyrifera) and two essential oil samples of myrrh and sweet myrrh from different regions of Ethiopia to study their anti-infective properties alone and in combination. The investigators observed synergistic and additive effects, particularly between B. papyrifera and Commiphora myrrha. While noting the long history of the combined use of frankincense and myrrh essential oils since 1500 BC, the investigators highlighted their study as the first antimicrobial work to verify the effectiveness of this combination, validating the use of this combination to thwart particular pathogens.15
Just 2 years ago, Ljaljević Grbić et al. evaluated the in vitro antimicrobial potential of the liquid and vapor phases of B. carteri and C. myrrha (frankincense and myrrh, respectively) essential oils, finding that frankincense demonstrated marked capacity to act as a natural antimicrobial agent.9
Transdermal delivery
In 2017, Zhu et al. showed that frankincense and myrrh essential oils promoted the permeability of the Chinese herb Chuanxiong and may facilitate drug elimination from the epidermis via dermal capillaries by dint of improved cutaneous blood flow, thereby augmenting transdermal drug delivery.16 The same team also showed that frankincense and myrrh essential oils, by fostering permeation by enhancing drug delivery across the stratum corneum, can also alter the structure of the stratum corneum.17
Conclusion
The use of frankincense in traditional medicine has a long and impressive track record. Recent research provides reason for optimism, and further investigating the possible incorporation of this botanical agent into modern dermatologic therapies appears warranted. Clearly, however, much more research is needed.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur who practices in Miami. She founded the Cosmetic Dermatology Center at the University of Miami in 1997. Dr. Baumann has written two textbooks and a New York Times Best Sellers book for consumers. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Revance, Evolus, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions Inc., a company that independently tests skin care products and makes recommendations to physicians on which skin care technologies are best. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Kimmatkar N et al. Phytomedicine. 2003 Jan;10(1):3-7.
2. Ammon HP. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2002;152(15-16):373-8.
3. Efferth T & Oesch F. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020 Feb 4;S1044-579X(20)30034-1.
4. Banno N et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006 Sep 19;107(2):249-53.
5. Poeckel D & Werz O. Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(28):3359-69.
6. Li JY, Kampp JT. Dermatol Surg. 2019 Jan;45(1):58-67.
7. Cao B et al. Molecules. 2019 Aug 24;24(17): 3076.
8. Mertens M et al. Flavour Fragr J. 2009;24:279-300.
9. Ljaljević Grbić M et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jun 12;219:1-14.
10. Li XJ et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Feb 17;179:22-6.
11. Han X et al. Biochim Open. 2017 Feb 3;4:31-5.
12. Zhao W et al. Cancer Detect Prev. 2003;27:67-75.
13. Hakkim FL et al. Oncotarget. 2019 May 28;10(37):3472-90.
14. Fung K et al. OA Altern Med 2013;1:14.
15. de Rapper S et al. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2012 Apr;54(4):352-8.
16. Zhu XF et al. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Feb;42(4):680-5.
17. Guan YM et al. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Sep;42(17):3350-5.
The Boswellia serrata exudate or gum (known in India as “guggulu”) that forms an aromatic resin traditionally used as incense – and known as frankincense (especially when retrieved from Boswellia species found in Eritrea and Somalia but also from the Indian variety) – has been considered for thousands of years to possess therapeutic properties. It is used in Ayurvedic medicine, as well as in traditional medicine in China and the Middle East, particularly for its anti-inflammatory effects to treat chronic conditions.1-8 In fact, such essential oils have been used since 2800 BC to treat various inflammatory conditions, including skin sores and wounds, as well as in perfumes and incense.2,9 In the West, use of frankincense dates back to thousands of years as well, more often found in the form of incense for religious and cultural ceremonies.7 Over the past 2 decades, .3 This column focuses on some of the emerging data on this ancient botanical agent.
Chemical constituents
Terpenoids and essential oils are the primary components of frankincense and are known to impart anti-inflammatory and anticancer activity. The same is true for myrrh, which has been combined with frankincense in traditional Chinese medicine as a single medication for millennia, with the two acting synergistically and considered still to be a potent combination in conferring various biological benefits.7
In 2010, in a systematic review of the anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities of Boswellia species and their chemical ingredients, Efferth and Oesch found that frankincense blocks the production of leukotrienes, cyclooxygenase (COX) 1 and 2, as well as 5-lipoxygenase; and oxidative stress. It also contributes to regulation of immune cells from the innate and acquired immune systems and exerts anticancer activity by influencing signaling transduction responsible for cell cycle arrest, as well as inhibition of proliferation, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. The investigators also reported on clinical trial results that have found efficacy of frankincense and its constituents in ameliorating symptoms of psoriasis and erythematous eczema, among other disorders.3
Anti-inflammatory activity
Li et al. completed a study in 2016 to identify the active ingredients responsible for the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of frankincense. They found that alpha-pinene, linalool, and 1-octanol were key contributors. These constituents were noted for suppressing COX-2 overexpression in mice, as well as nociceptive stimulus-induced inflammatory infiltrates.10
Noting the increasing popularity of frankincense essential oil in skin care, despite a paucity of data, in 2017, Han et al. evaluated the biological activities of the essential oil in pre-inflamed human dermal fibroblasts using 17 key protein biomarkers. Frankincense essential oil displayed significant antiproliferative activity and suppressed collagen III, interferon gamma-induced protein 10, and intracellular adhesion molecule 1. The investigators referred to the overall encouraging potential of frankincense essential oil to exert influence over inflammation and tissue remodeling in human skin and called for additional research into its mechanisms of action and active constituents.11
Anticancer activity
The main active ingredient in frankincense, boswellic acid, has been shown to promote apoptosis, suppress matrix metalloproteinase secretion, and hinder migration in metastatic melanoma cell lines in mice.6,12
In 2019, Hakkim et al. demonstrated that frankincense essential oil yielded substantial antimelanoma activity in vitro and in vivo and ameliorated hepatotoxicity caused by acetaminophen.13
There is one case report in the literature on the use of frankincense as a treatment for skin cancer. A 56-year-old man received frankincense oil multiple times a day for 4 months to treat a nodular basal cell carcinoma on one arm (which resolved) and an infiltrative BCC on the chest (some focal residual tumor remained).6,14 Topical frankincense or boswellic acid has been given a grade D recommendation for treating skin cancer, however, because of only one level-of-evidence-5 study.6
Antimicrobial activity
In 2012, de Rapper et al. collected samples of three essential oils of frankincense (Boswellia rivae, Boswellia neglecta, and Boswellia papyrifera) and two essential oil samples of myrrh and sweet myrrh from different regions of Ethiopia to study their anti-infective properties alone and in combination. The investigators observed synergistic and additive effects, particularly between B. papyrifera and Commiphora myrrha. While noting the long history of the combined use of frankincense and myrrh essential oils since 1500 BC, the investigators highlighted their study as the first antimicrobial work to verify the effectiveness of this combination, validating the use of this combination to thwart particular pathogens.15
Just 2 years ago, Ljaljević Grbić et al. evaluated the in vitro antimicrobial potential of the liquid and vapor phases of B. carteri and C. myrrha (frankincense and myrrh, respectively) essential oils, finding that frankincense demonstrated marked capacity to act as a natural antimicrobial agent.9
Transdermal delivery
In 2017, Zhu et al. showed that frankincense and myrrh essential oils promoted the permeability of the Chinese herb Chuanxiong and may facilitate drug elimination from the epidermis via dermal capillaries by dint of improved cutaneous blood flow, thereby augmenting transdermal drug delivery.16 The same team also showed that frankincense and myrrh essential oils, by fostering permeation by enhancing drug delivery across the stratum corneum, can also alter the structure of the stratum corneum.17
Conclusion
The use of frankincense in traditional medicine has a long and impressive track record. Recent research provides reason for optimism, and further investigating the possible incorporation of this botanical agent into modern dermatologic therapies appears warranted. Clearly, however, much more research is needed.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur who practices in Miami. She founded the Cosmetic Dermatology Center at the University of Miami in 1997. Dr. Baumann has written two textbooks and a New York Times Best Sellers book for consumers. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Revance, Evolus, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions Inc., a company that independently tests skin care products and makes recommendations to physicians on which skin care technologies are best. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Kimmatkar N et al. Phytomedicine. 2003 Jan;10(1):3-7.
2. Ammon HP. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2002;152(15-16):373-8.
3. Efferth T & Oesch F. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020 Feb 4;S1044-579X(20)30034-1.
4. Banno N et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006 Sep 19;107(2):249-53.
5. Poeckel D & Werz O. Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(28):3359-69.
6. Li JY, Kampp JT. Dermatol Surg. 2019 Jan;45(1):58-67.
7. Cao B et al. Molecules. 2019 Aug 24;24(17): 3076.
8. Mertens M et al. Flavour Fragr J. 2009;24:279-300.
9. Ljaljević Grbić M et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jun 12;219:1-14.
10. Li XJ et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Feb 17;179:22-6.
11. Han X et al. Biochim Open. 2017 Feb 3;4:31-5.
12. Zhao W et al. Cancer Detect Prev. 2003;27:67-75.
13. Hakkim FL et al. Oncotarget. 2019 May 28;10(37):3472-90.
14. Fung K et al. OA Altern Med 2013;1:14.
15. de Rapper S et al. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2012 Apr;54(4):352-8.
16. Zhu XF et al. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Feb;42(4):680-5.
17. Guan YM et al. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Sep;42(17):3350-5.
Early peanut feeding guidelines still not reaching families
Four years after new infant feeding guidelines were issued to prevent allergies to peanut and other foods, 70% of surveyed parents and caregivers in the United States said they had never heard about the new recommendation.
Food allergies in developed countries have doubled in each of the last decades and now affect 7.6% of U.S. children. About 1 in 50 are allergic to peanut. Data from the 2015 LEAP study and other research has convincingly shown that early, sustained feeding of peanuts, eggs, and other allergens can prevent babies from developing allergies to these foods.
Based on those findings, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) updated its feeding guidelines in 2017, urging parents to introduce these foods to babies around 4-6 months of age rather than wait until 1-3 years of age, as previously recommended. The American Academy of Pediatrics approved those guidelines too, and in 2019 changed its own feeding recommendations.
To assess awareness of this new guidance and to what extent these recommendations are being translated into clinical practice, researchers surveyed a demographically representative U.S. sample of 3,062 parents and caregivers with children between 7 months and 3½ years old. The survey was conducted in English and Spanish over the web or by phone.
More than one-third reported that their child’s primary care physician never discussed when to start feeding peanut-containing foods. And among those whose doctors did offer guidance, fewer than 1 in 4 specifically recommended introducing peanut by 6 months of age.
These data show that “despite strong evidence that early introduction of peanut within the first year of life can prevent the development of peanut allergy, this evidence is simply not making its way to parents of infants,” said Christopher Warren, PhD, assistant professor of preventive medicine at the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago. Dr. Warren led the study and presented the findings on a poster at this year’s American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology annual meeting in New Orleans.
In addition to caregivers, the Northwestern team surveyed U.S. allergists and pediatricians about the new feeding guidelines. Uptake was fairly good among allergists, with 65% reporting full implementation. On the other hand, while most pediatricians seemed familiar with the 2017 recommendations, fewer than one-third said they were following them.
“What’s unique about this challenge is that it’s not just a guideline change – it’s a guideline reversal,” said Wendy Sue Swanson, MD, chief medical officer for SpoonfulONE, a company that makes mix-ins and other products for multi-allergen feeding. After telling families for years to avoid these allergens in early life because food allergies were rising, “it’s harder advice to say, actually, we were wrong. Not only should you not wait, you should get peanut in while your baby’s immune system has this critical moment to learn and develop, and you should keep getting it in,” Dr. Swanson said in an interview.
Making matters worse, pediatricians are time pressed. Typically, at 4- to 6-month-old well-check visits, “they’re talking about sleep and development and feeding and milestones,” said Ruchi Gupta, MD, MPH, professor of pediatrics and medicine at Northwestern Feinberg, who led the allergist and pediatrician analyses.
Another challenge: Guidelines differ depending on the child’s level of food allergy risk, so it’s hard to explain them clearly and quickly. Babies at highest risk – as judged by having severe eczema, egg allergy, or both – should get peanut IgE blood testing and, if negative, begin regular consumption of peanut by 4-6 months. Intermediate-risk babies who have mild-to-moderate eczema are recommended to start peanut-containing foods by 6 months. And for low-risk babies with no eczema or known food allergies, the guidance is simply to introduce peanut-containing foods “in accordance with family preferences and cultural practices.”
As for pediatricians who say it’s hard to distinguish mild-to-moderate from severe eczema, “any eczema puts you at some risk,” Dr. Gupta told this news organization. “If they’ve required steroid creams to clear up their skin, or if you look at their skin, and you think it’s severe, don’t hesitate. Go ahead and draw the IgE and send them to an allergist.”
Australia, which has the highest rate of confirmed food allergy, has had more success implementing early feeding guidelines, said Dr. Swanson. Unlike the United States’ tiered approach, she said, they “had a national guideline that very crisply, years ago, told parents what to do.” Australia also has nurse educators that follow up with new moms to make sure they understand and follow the recommendations.
Dr. Gupta receives research support from the National Institutes of Health, Food Allergy Research and Education, the Melchiorre Family Foundation, the Sunshine Charitable Foundation, the Walder Foundation, the UnitedHealth Group, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Genentech. She serves as a medical consultant/advisor for Genentech, Novartis, and Food Allergy Research and Education. Dr. Swanson serves as chief medical officer for SpoonfulONE.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Four years after new infant feeding guidelines were issued to prevent allergies to peanut and other foods, 70% of surveyed parents and caregivers in the United States said they had never heard about the new recommendation.
Food allergies in developed countries have doubled in each of the last decades and now affect 7.6% of U.S. children. About 1 in 50 are allergic to peanut. Data from the 2015 LEAP study and other research has convincingly shown that early, sustained feeding of peanuts, eggs, and other allergens can prevent babies from developing allergies to these foods.
Based on those findings, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) updated its feeding guidelines in 2017, urging parents to introduce these foods to babies around 4-6 months of age rather than wait until 1-3 years of age, as previously recommended. The American Academy of Pediatrics approved those guidelines too, and in 2019 changed its own feeding recommendations.
To assess awareness of this new guidance and to what extent these recommendations are being translated into clinical practice, researchers surveyed a demographically representative U.S. sample of 3,062 parents and caregivers with children between 7 months and 3½ years old. The survey was conducted in English and Spanish over the web or by phone.
More than one-third reported that their child’s primary care physician never discussed when to start feeding peanut-containing foods. And among those whose doctors did offer guidance, fewer than 1 in 4 specifically recommended introducing peanut by 6 months of age.
These data show that “despite strong evidence that early introduction of peanut within the first year of life can prevent the development of peanut allergy, this evidence is simply not making its way to parents of infants,” said Christopher Warren, PhD, assistant professor of preventive medicine at the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago. Dr. Warren led the study and presented the findings on a poster at this year’s American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology annual meeting in New Orleans.
In addition to caregivers, the Northwestern team surveyed U.S. allergists and pediatricians about the new feeding guidelines. Uptake was fairly good among allergists, with 65% reporting full implementation. On the other hand, while most pediatricians seemed familiar with the 2017 recommendations, fewer than one-third said they were following them.
“What’s unique about this challenge is that it’s not just a guideline change – it’s a guideline reversal,” said Wendy Sue Swanson, MD, chief medical officer for SpoonfulONE, a company that makes mix-ins and other products for multi-allergen feeding. After telling families for years to avoid these allergens in early life because food allergies were rising, “it’s harder advice to say, actually, we were wrong. Not only should you not wait, you should get peanut in while your baby’s immune system has this critical moment to learn and develop, and you should keep getting it in,” Dr. Swanson said in an interview.
Making matters worse, pediatricians are time pressed. Typically, at 4- to 6-month-old well-check visits, “they’re talking about sleep and development and feeding and milestones,” said Ruchi Gupta, MD, MPH, professor of pediatrics and medicine at Northwestern Feinberg, who led the allergist and pediatrician analyses.
Another challenge: Guidelines differ depending on the child’s level of food allergy risk, so it’s hard to explain them clearly and quickly. Babies at highest risk – as judged by having severe eczema, egg allergy, or both – should get peanut IgE blood testing and, if negative, begin regular consumption of peanut by 4-6 months. Intermediate-risk babies who have mild-to-moderate eczema are recommended to start peanut-containing foods by 6 months. And for low-risk babies with no eczema or known food allergies, the guidance is simply to introduce peanut-containing foods “in accordance with family preferences and cultural practices.”
As for pediatricians who say it’s hard to distinguish mild-to-moderate from severe eczema, “any eczema puts you at some risk,” Dr. Gupta told this news organization. “If they’ve required steroid creams to clear up their skin, or if you look at their skin, and you think it’s severe, don’t hesitate. Go ahead and draw the IgE and send them to an allergist.”
Australia, which has the highest rate of confirmed food allergy, has had more success implementing early feeding guidelines, said Dr. Swanson. Unlike the United States’ tiered approach, she said, they “had a national guideline that very crisply, years ago, told parents what to do.” Australia also has nurse educators that follow up with new moms to make sure they understand and follow the recommendations.
Dr. Gupta receives research support from the National Institutes of Health, Food Allergy Research and Education, the Melchiorre Family Foundation, the Sunshine Charitable Foundation, the Walder Foundation, the UnitedHealth Group, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Genentech. She serves as a medical consultant/advisor for Genentech, Novartis, and Food Allergy Research and Education. Dr. Swanson serves as chief medical officer for SpoonfulONE.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Four years after new infant feeding guidelines were issued to prevent allergies to peanut and other foods, 70% of surveyed parents and caregivers in the United States said they had never heard about the new recommendation.
Food allergies in developed countries have doubled in each of the last decades and now affect 7.6% of U.S. children. About 1 in 50 are allergic to peanut. Data from the 2015 LEAP study and other research has convincingly shown that early, sustained feeding of peanuts, eggs, and other allergens can prevent babies from developing allergies to these foods.
Based on those findings, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) updated its feeding guidelines in 2017, urging parents to introduce these foods to babies around 4-6 months of age rather than wait until 1-3 years of age, as previously recommended. The American Academy of Pediatrics approved those guidelines too, and in 2019 changed its own feeding recommendations.
To assess awareness of this new guidance and to what extent these recommendations are being translated into clinical practice, researchers surveyed a demographically representative U.S. sample of 3,062 parents and caregivers with children between 7 months and 3½ years old. The survey was conducted in English and Spanish over the web or by phone.
More than one-third reported that their child’s primary care physician never discussed when to start feeding peanut-containing foods. And among those whose doctors did offer guidance, fewer than 1 in 4 specifically recommended introducing peanut by 6 months of age.
These data show that “despite strong evidence that early introduction of peanut within the first year of life can prevent the development of peanut allergy, this evidence is simply not making its way to parents of infants,” said Christopher Warren, PhD, assistant professor of preventive medicine at the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago. Dr. Warren led the study and presented the findings on a poster at this year’s American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology annual meeting in New Orleans.
In addition to caregivers, the Northwestern team surveyed U.S. allergists and pediatricians about the new feeding guidelines. Uptake was fairly good among allergists, with 65% reporting full implementation. On the other hand, while most pediatricians seemed familiar with the 2017 recommendations, fewer than one-third said they were following them.
“What’s unique about this challenge is that it’s not just a guideline change – it’s a guideline reversal,” said Wendy Sue Swanson, MD, chief medical officer for SpoonfulONE, a company that makes mix-ins and other products for multi-allergen feeding. After telling families for years to avoid these allergens in early life because food allergies were rising, “it’s harder advice to say, actually, we were wrong. Not only should you not wait, you should get peanut in while your baby’s immune system has this critical moment to learn and develop, and you should keep getting it in,” Dr. Swanson said in an interview.
Making matters worse, pediatricians are time pressed. Typically, at 4- to 6-month-old well-check visits, “they’re talking about sleep and development and feeding and milestones,” said Ruchi Gupta, MD, MPH, professor of pediatrics and medicine at Northwestern Feinberg, who led the allergist and pediatrician analyses.
Another challenge: Guidelines differ depending on the child’s level of food allergy risk, so it’s hard to explain them clearly and quickly. Babies at highest risk – as judged by having severe eczema, egg allergy, or both – should get peanut IgE blood testing and, if negative, begin regular consumption of peanut by 4-6 months. Intermediate-risk babies who have mild-to-moderate eczema are recommended to start peanut-containing foods by 6 months. And for low-risk babies with no eczema or known food allergies, the guidance is simply to introduce peanut-containing foods “in accordance with family preferences and cultural practices.”
As for pediatricians who say it’s hard to distinguish mild-to-moderate from severe eczema, “any eczema puts you at some risk,” Dr. Gupta told this news organization. “If they’ve required steroid creams to clear up their skin, or if you look at their skin, and you think it’s severe, don’t hesitate. Go ahead and draw the IgE and send them to an allergist.”
Australia, which has the highest rate of confirmed food allergy, has had more success implementing early feeding guidelines, said Dr. Swanson. Unlike the United States’ tiered approach, she said, they “had a national guideline that very crisply, years ago, told parents what to do.” Australia also has nurse educators that follow up with new moms to make sure they understand and follow the recommendations.
Dr. Gupta receives research support from the National Institutes of Health, Food Allergy Research and Education, the Melchiorre Family Foundation, the Sunshine Charitable Foundation, the Walder Foundation, the UnitedHealth Group, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Genentech. She serves as a medical consultant/advisor for Genentech, Novartis, and Food Allergy Research and Education. Dr. Swanson serves as chief medical officer for SpoonfulONE.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID vaccines’ protection dropped sharply over 6 months: Study
, a study of almost 800,000 veterans found.
The study, published in the journal Science ., says the three vaccines offered about the same protection against the virus in March, when the Delta variant was first detected in the United States, but that changed 6 months later.
The Moderna two-dose vaccine went from being 89% effective in March to 58% effective in September, according to a story about the study in theLos Angeles Times.
Meanwhile, the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine went from being 87% effective to 45% effective over the same time period.
The Johnson & Johnson vaccine showed the biggest drop -- from 86% effectiveness to 13% over those 6 months.
“In summary, although vaccination remains protective against SARS-CoV-2 infection, protection waned as the Delta variant emerged in the U.S., and this decline did not differ by age,” the study said.
The three vaccines also lost effectiveness in the ability to protect against death in veterans 65 and over after only 3 months, the Los Angeles Times reported.
Compared to unvaccinated veterans in that age group, veterans who got the Moderna vaccine and had a breakthrough case were 76% less likely to die of COVID-19 by July.
The protection was 70% for Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine recipients and 52% for J&J vaccine recipients for the same age group, compared to unvaccinated veterans, according to the newspaper.
For veterans under 65, the protectiveness against a fatal case of COVID was 84% for Pfizer/BioNTech recipients, 82% for Moderna recipients, and 73% for J&J recipients, compared to unvaccinated veterans in that age group.
The study confirms the need for booster vaccines and protective measures such as vaccine passports, vaccine mandates, masking, hand-washing, and social distancing, the researchers said.
Of the veterans studied, about 500,000 were vaccinated and 300,000 were not. Researchers noted that the study population had 6 times as many men as women. About 48% of the study group was 65 or older, 29% was 50-64, while 24% was under 50.
Researchers from the Public Health Institute in Oakland, the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in San Francisco, and the University of Texas Health Science Center conducted the study.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, a study of almost 800,000 veterans found.
The study, published in the journal Science ., says the three vaccines offered about the same protection against the virus in March, when the Delta variant was first detected in the United States, but that changed 6 months later.
The Moderna two-dose vaccine went from being 89% effective in March to 58% effective in September, according to a story about the study in theLos Angeles Times.
Meanwhile, the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine went from being 87% effective to 45% effective over the same time period.
The Johnson & Johnson vaccine showed the biggest drop -- from 86% effectiveness to 13% over those 6 months.
“In summary, although vaccination remains protective against SARS-CoV-2 infection, protection waned as the Delta variant emerged in the U.S., and this decline did not differ by age,” the study said.
The three vaccines also lost effectiveness in the ability to protect against death in veterans 65 and over after only 3 months, the Los Angeles Times reported.
Compared to unvaccinated veterans in that age group, veterans who got the Moderna vaccine and had a breakthrough case were 76% less likely to die of COVID-19 by July.
The protection was 70% for Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine recipients and 52% for J&J vaccine recipients for the same age group, compared to unvaccinated veterans, according to the newspaper.
For veterans under 65, the protectiveness against a fatal case of COVID was 84% for Pfizer/BioNTech recipients, 82% for Moderna recipients, and 73% for J&J recipients, compared to unvaccinated veterans in that age group.
The study confirms the need for booster vaccines and protective measures such as vaccine passports, vaccine mandates, masking, hand-washing, and social distancing, the researchers said.
Of the veterans studied, about 500,000 were vaccinated and 300,000 were not. Researchers noted that the study population had 6 times as many men as women. About 48% of the study group was 65 or older, 29% was 50-64, while 24% was under 50.
Researchers from the Public Health Institute in Oakland, the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in San Francisco, and the University of Texas Health Science Center conducted the study.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, a study of almost 800,000 veterans found.
The study, published in the journal Science ., says the three vaccines offered about the same protection against the virus in March, when the Delta variant was first detected in the United States, but that changed 6 months later.
The Moderna two-dose vaccine went from being 89% effective in March to 58% effective in September, according to a story about the study in theLos Angeles Times.
Meanwhile, the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine went from being 87% effective to 45% effective over the same time period.
The Johnson & Johnson vaccine showed the biggest drop -- from 86% effectiveness to 13% over those 6 months.
“In summary, although vaccination remains protective against SARS-CoV-2 infection, protection waned as the Delta variant emerged in the U.S., and this decline did not differ by age,” the study said.
The three vaccines also lost effectiveness in the ability to protect against death in veterans 65 and over after only 3 months, the Los Angeles Times reported.
Compared to unvaccinated veterans in that age group, veterans who got the Moderna vaccine and had a breakthrough case were 76% less likely to die of COVID-19 by July.
The protection was 70% for Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine recipients and 52% for J&J vaccine recipients for the same age group, compared to unvaccinated veterans, according to the newspaper.
For veterans under 65, the protectiveness against a fatal case of COVID was 84% for Pfizer/BioNTech recipients, 82% for Moderna recipients, and 73% for J&J recipients, compared to unvaccinated veterans in that age group.
The study confirms the need for booster vaccines and protective measures such as vaccine passports, vaccine mandates, masking, hand-washing, and social distancing, the researchers said.
Of the veterans studied, about 500,000 were vaccinated and 300,000 were not. Researchers noted that the study population had 6 times as many men as women. About 48% of the study group was 65 or older, 29% was 50-64, while 24% was under 50.
Researchers from the Public Health Institute in Oakland, the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in San Francisco, and the University of Texas Health Science Center conducted the study.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM SCIENCE