User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
FDA Approves IL-13 inhibitor for Atopic Dermatitis
The that is not well controlled, despite treatment with topical prescription therapies.
The recommended initial starting dose of lebrikizumab consists of 500 mg (two 250 mg injections) at baseline and week 2, followed by 250 mg every 2 weeks until week 16 or later when adequate clinical response is achieved. Then, maintenance dosing is recommended with one monthly injection (250 mg every 4 weeks). Children aged 12-17 years must weigh at least 88 pounds (40 kg) to be eligible for lebrikizumab treatment.
According to a press release from Lilly, which has been developing lebrikizumab, approval was based on results from the ADvocate 1, ADvocate 2, and ADhere studies, which included over 1000 adults and children aged 12 and older with moderate to severe AD. The primary endpoint for these studies was evaluated at 16 weeks and measured clear or almost clear skin (IGA score of 0 or 1).
According to Lilly, 38% of people in ADvocate 1 and 2 who took lebrikizumab achieved clear or almost-clear skin at 16 weeks, compared with 12% of those in the placebo arm, and 10% experienced these results as early as 4 weeks. Of those treated with lebrikizumab who experienced clear or almost-clear skin at week 16, 77% maintained those results at 1 year on the once-monthly dose. In addition, on average, 43% of those on lebrikizumab experienced relief of itch at 16 weeks, compared with 12% of those on placebo, according to the press release.
The most common side effects of lebrikizumab observed in the clinical trials include eye and eyelid inflammation, such as redness, swelling, and itching; injection-site reactions; and herpes zoster (shingles).
Lebrikizumab was approved in Japan in January 2024, and by the European Commission in 2023.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The that is not well controlled, despite treatment with topical prescription therapies.
The recommended initial starting dose of lebrikizumab consists of 500 mg (two 250 mg injections) at baseline and week 2, followed by 250 mg every 2 weeks until week 16 or later when adequate clinical response is achieved. Then, maintenance dosing is recommended with one monthly injection (250 mg every 4 weeks). Children aged 12-17 years must weigh at least 88 pounds (40 kg) to be eligible for lebrikizumab treatment.
According to a press release from Lilly, which has been developing lebrikizumab, approval was based on results from the ADvocate 1, ADvocate 2, and ADhere studies, which included over 1000 adults and children aged 12 and older with moderate to severe AD. The primary endpoint for these studies was evaluated at 16 weeks and measured clear or almost clear skin (IGA score of 0 or 1).
According to Lilly, 38% of people in ADvocate 1 and 2 who took lebrikizumab achieved clear or almost-clear skin at 16 weeks, compared with 12% of those in the placebo arm, and 10% experienced these results as early as 4 weeks. Of those treated with lebrikizumab who experienced clear or almost-clear skin at week 16, 77% maintained those results at 1 year on the once-monthly dose. In addition, on average, 43% of those on lebrikizumab experienced relief of itch at 16 weeks, compared with 12% of those on placebo, according to the press release.
The most common side effects of lebrikizumab observed in the clinical trials include eye and eyelid inflammation, such as redness, swelling, and itching; injection-site reactions; and herpes zoster (shingles).
Lebrikizumab was approved in Japan in January 2024, and by the European Commission in 2023.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The that is not well controlled, despite treatment with topical prescription therapies.
The recommended initial starting dose of lebrikizumab consists of 500 mg (two 250 mg injections) at baseline and week 2, followed by 250 mg every 2 weeks until week 16 or later when adequate clinical response is achieved. Then, maintenance dosing is recommended with one monthly injection (250 mg every 4 weeks). Children aged 12-17 years must weigh at least 88 pounds (40 kg) to be eligible for lebrikizumab treatment.
According to a press release from Lilly, which has been developing lebrikizumab, approval was based on results from the ADvocate 1, ADvocate 2, and ADhere studies, which included over 1000 adults and children aged 12 and older with moderate to severe AD. The primary endpoint for these studies was evaluated at 16 weeks and measured clear or almost clear skin (IGA score of 0 or 1).
According to Lilly, 38% of people in ADvocate 1 and 2 who took lebrikizumab achieved clear or almost-clear skin at 16 weeks, compared with 12% of those in the placebo arm, and 10% experienced these results as early as 4 weeks. Of those treated with lebrikizumab who experienced clear or almost-clear skin at week 16, 77% maintained those results at 1 year on the once-monthly dose. In addition, on average, 43% of those on lebrikizumab experienced relief of itch at 16 weeks, compared with 12% of those on placebo, according to the press release.
The most common side effects of lebrikizumab observed in the clinical trials include eye and eyelid inflammation, such as redness, swelling, and itching; injection-site reactions; and herpes zoster (shingles).
Lebrikizumab was approved in Japan in January 2024, and by the European Commission in 2023.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A 14-Year-Old Female Presents With a Growth Under Her Toenail
BY XOCHITL LONGSTAFF, BS; ANGELINA LABIB, MD; AND DAWN EICHENFIELD, MD, PHD
Diagnosis: Subungual bony exostosis
The patient was referred to orthopedics for further evaluation and ultimately underwent excisional surgery. At her most recent follow-up visit with orthopedic surgery, her new nail was observed to be growing well.
Subungual exostosis, also known as Dupuytren’s exostosis, is a benign osteocartilaginous tumor that classically presents as a bony growth at the dorsal aspect of the distal phalanx of the great toe, near the nail bed. The pathogenesis remains unclear, but suggested etiologies include prior trauma, infection, and hereditary abnormalities.1
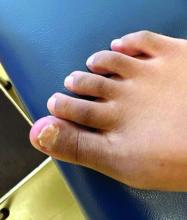
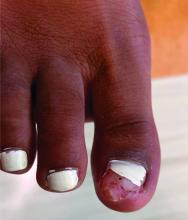
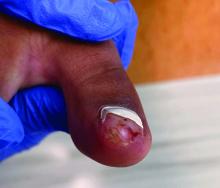
Clinically, lesions can be painful and may be associated with skin ulceration. The location at the dorsal distal great toe is a key distinguishing feature. Physical exam reveals a firm, fixed nodule with a hyperkeratotic smooth surface.2
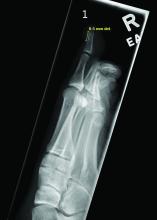
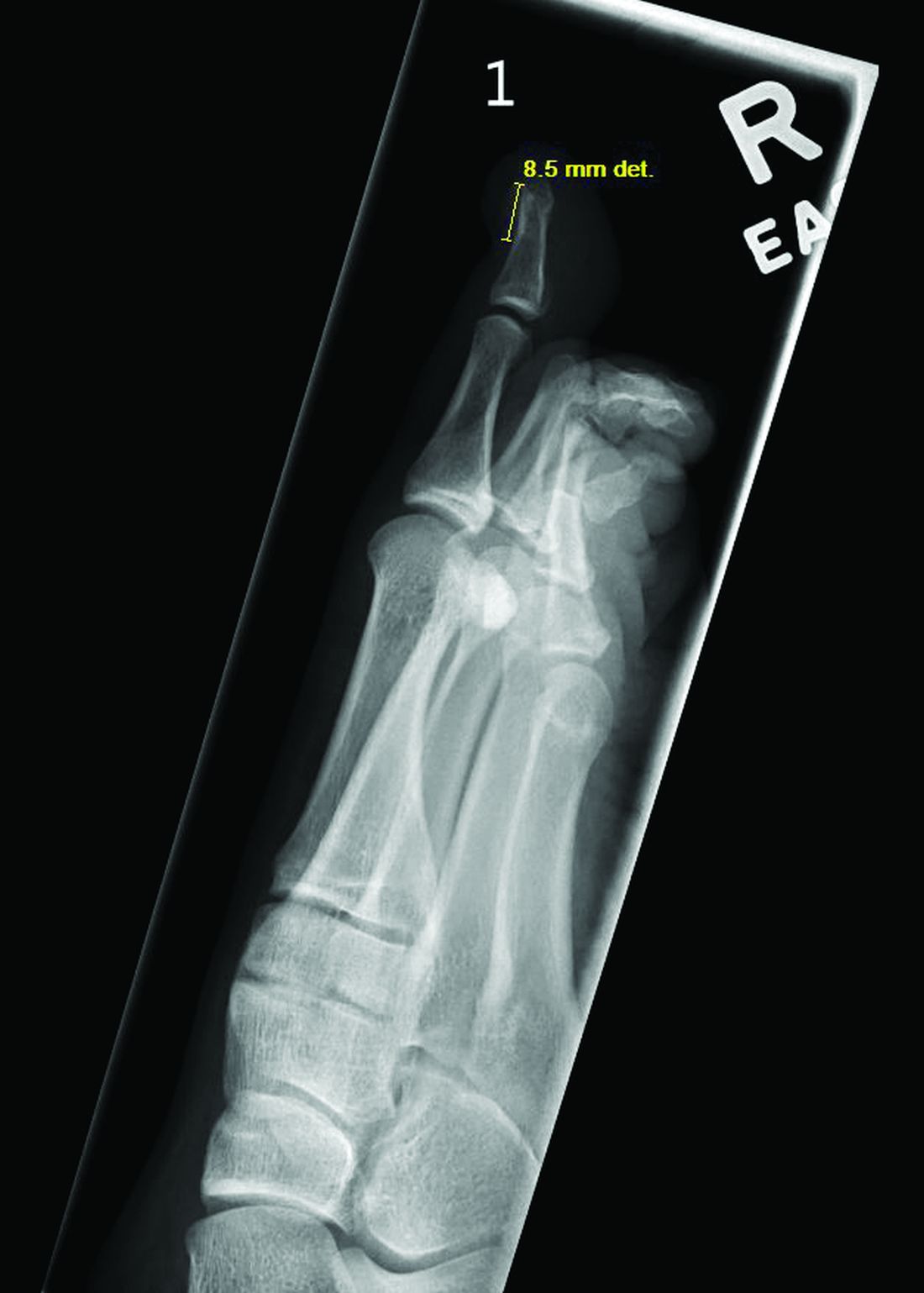
Radiographic evaluation, particularly with a lateral view, is often diagnostic. The classic radiographic finding in subungual exostosis is an osseous structure connected to the distal phalanx, with a hazy periphery representing a fibrocartilage cap.
Treatment involves complete marginal excision. The complications from surgical excision are minimal, with the most common being recurrence.3 However, the recurrence rate is also generally low, around 4%.1
Ms. Longstaff is currently completing a research year as a Pediatric Clinical Research Fellow at University of California San Diego (UCSD) Rady Children’s Hospital prior to finishing her final year at the David Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles. Dr. Labib is the Post-Doctoral Pediatric Clinical Research Fellow at UCSD Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield is a dermatologist at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego and assistant clinical professor at UCSD.
References
1. Alabdullrahman LW et al. Osteochondroma. In: StatPearls [Internet]. 2024 Feb 26. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544296/#.
2. DaCambra MP et al. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Apr;472(4):1251-9. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3345-4.
3. Womack ME et al. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2022 Mar 22;6(3):e21.00239. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-21-00239.
BY XOCHITL LONGSTAFF, BS; ANGELINA LABIB, MD; AND DAWN EICHENFIELD, MD, PHD
Diagnosis: Subungual bony exostosis
The patient was referred to orthopedics for further evaluation and ultimately underwent excisional surgery. At her most recent follow-up visit with orthopedic surgery, her new nail was observed to be growing well.
Subungual exostosis, also known as Dupuytren’s exostosis, is a benign osteocartilaginous tumor that classically presents as a bony growth at the dorsal aspect of the distal phalanx of the great toe, near the nail bed. The pathogenesis remains unclear, but suggested etiologies include prior trauma, infection, and hereditary abnormalities.1
Clinically, lesions can be painful and may be associated with skin ulceration. The location at the dorsal distal great toe is a key distinguishing feature. Physical exam reveals a firm, fixed nodule with a hyperkeratotic smooth surface.2
Radiographic evaluation, particularly with a lateral view, is often diagnostic. The classic radiographic finding in subungual exostosis is an osseous structure connected to the distal phalanx, with a hazy periphery representing a fibrocartilage cap.
Treatment involves complete marginal excision. The complications from surgical excision are minimal, with the most common being recurrence.3 However, the recurrence rate is also generally low, around 4%.1
Ms. Longstaff is currently completing a research year as a Pediatric Clinical Research Fellow at University of California San Diego (UCSD) Rady Children’s Hospital prior to finishing her final year at the David Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles. Dr. Labib is the Post-Doctoral Pediatric Clinical Research Fellow at UCSD Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield is a dermatologist at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego and assistant clinical professor at UCSD.
References
1. Alabdullrahman LW et al. Osteochondroma. In: StatPearls [Internet]. 2024 Feb 26. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544296/#.
2. DaCambra MP et al. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Apr;472(4):1251-9. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3345-4.
3. Womack ME et al. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2022 Mar 22;6(3):e21.00239. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-21-00239.
BY XOCHITL LONGSTAFF, BS; ANGELINA LABIB, MD; AND DAWN EICHENFIELD, MD, PHD
Diagnosis: Subungual bony exostosis
The patient was referred to orthopedics for further evaluation and ultimately underwent excisional surgery. At her most recent follow-up visit with orthopedic surgery, her new nail was observed to be growing well.
Subungual exostosis, also known as Dupuytren’s exostosis, is a benign osteocartilaginous tumor that classically presents as a bony growth at the dorsal aspect of the distal phalanx of the great toe, near the nail bed. The pathogenesis remains unclear, but suggested etiologies include prior trauma, infection, and hereditary abnormalities.1
Clinically, lesions can be painful and may be associated with skin ulceration. The location at the dorsal distal great toe is a key distinguishing feature. Physical exam reveals a firm, fixed nodule with a hyperkeratotic smooth surface.2
Radiographic evaluation, particularly with a lateral view, is often diagnostic. The classic radiographic finding in subungual exostosis is an osseous structure connected to the distal phalanx, with a hazy periphery representing a fibrocartilage cap.
Treatment involves complete marginal excision. The complications from surgical excision are minimal, with the most common being recurrence.3 However, the recurrence rate is also generally low, around 4%.1
Ms. Longstaff is currently completing a research year as a Pediatric Clinical Research Fellow at University of California San Diego (UCSD) Rady Children’s Hospital prior to finishing her final year at the David Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles. Dr. Labib is the Post-Doctoral Pediatric Clinical Research Fellow at UCSD Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield is a dermatologist at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego and assistant clinical professor at UCSD.
References
1. Alabdullrahman LW et al. Osteochondroma. In: StatPearls [Internet]. 2024 Feb 26. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544296/#.
2. DaCambra MP et al. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Apr;472(4):1251-9. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3345-4.
3. Womack ME et al. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2022 Mar 22;6(3):e21.00239. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-21-00239.
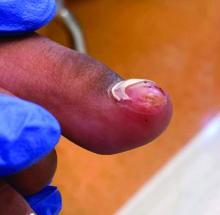
A 14-year-old healthy female presents with a painful nodule under her great toenail. The nodule had been present for 2 months and there was no preceding trauma. Three days prior to presentation, her nail cracked and bled after bumping her toe. The toe is painful to palpation. Given the associated pain, the patient visited urgent care and was prescribed cephalexin and acetaminophen.
Physical examination reveals a skin-colored subungual nodule with hypertrophic tissue originating from the nail bed of the right great toe, but no thickening of the nail plate (Figures 1-3).
Are Pharmacy Deserts Worsening Health Disparities?
TOPLINE:
Pharmacy closures in the United States are creating “pharmacy deserts,” disproportionately affecting socially vulnerable communities. High social vulnerability and low primary care practitioner (PCP) density are linked to increased pharmacy desert density.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data through 2020 on communities located 10 or more miles from the nearest retail pharmacy were sourced from TelePharm Map.
- Counties were stratified as having a high pharmacy desert density if the number of pharmacy deserts per 1000 inhabitants was in the 80th percentile or higher.
- Social vulnerability index and healthcare practitioner data were obtained from the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry and the Area Health Resources Files.
- PCP density was calculated as the number of PCPs per 10,000 inhabitants.
- A total of 3143 counties were analyzed, with 1447 (46%) having at least one pharmacy desert.
TAKEAWAY:
- Counties with a high pharmacy desert density had a higher social vulnerability index than those with a low pharmacy desert density (P = .006).
- Areas with a high pharmacy desert density had lower median PCP density than those with low or no pharmacy desert density (P < .001).
- High social vulnerability index (odds ratio [OR], 1.35; 95% CI, 1.07-1.70; P = .01) and low PCP density (OR, 2.27; 95% CI, 1.80-2.86; P < .001) were associated with a higher likelihood for a county to have a high pharmacy desert density.
- Pharmacy closures are leaving more individuals without easy access to medications, with disproportionate consequences for certain communities.
IN PRACTICE:
“As high pharmacy desert density counties also have a lower PCP density, patients residing in these regions face increased barriers to accessing primary healthcare needs,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Giovanni Catalano, MD, Muhammad Muntazir Mehdi Khan, MBBS, and Timothy M. Pawlik, MD, PhD, MPH, MTS, MBA, Department of Surgery, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus, Ohio. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design of the study limited the ability to draw causal inferences. The study relied on public county-level data, which may not have captured all relevant variables. The use of the social vulnerability index and PCP density as proxies did not fully represent the complexity of pharmacy access issues. The study’s findings were not generalizable to regions outside the United States.
DISCLOSURES:
No relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Pharmacy closures in the United States are creating “pharmacy deserts,” disproportionately affecting socially vulnerable communities. High social vulnerability and low primary care practitioner (PCP) density are linked to increased pharmacy desert density.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data through 2020 on communities located 10 or more miles from the nearest retail pharmacy were sourced from TelePharm Map.
- Counties were stratified as having a high pharmacy desert density if the number of pharmacy deserts per 1000 inhabitants was in the 80th percentile or higher.
- Social vulnerability index and healthcare practitioner data were obtained from the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry and the Area Health Resources Files.
- PCP density was calculated as the number of PCPs per 10,000 inhabitants.
- A total of 3143 counties were analyzed, with 1447 (46%) having at least one pharmacy desert.
TAKEAWAY:
- Counties with a high pharmacy desert density had a higher social vulnerability index than those with a low pharmacy desert density (P = .006).
- Areas with a high pharmacy desert density had lower median PCP density than those with low or no pharmacy desert density (P < .001).
- High social vulnerability index (odds ratio [OR], 1.35; 95% CI, 1.07-1.70; P = .01) and low PCP density (OR, 2.27; 95% CI, 1.80-2.86; P < .001) were associated with a higher likelihood for a county to have a high pharmacy desert density.
- Pharmacy closures are leaving more individuals without easy access to medications, with disproportionate consequences for certain communities.
IN PRACTICE:
“As high pharmacy desert density counties also have a lower PCP density, patients residing in these regions face increased barriers to accessing primary healthcare needs,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Giovanni Catalano, MD, Muhammad Muntazir Mehdi Khan, MBBS, and Timothy M. Pawlik, MD, PhD, MPH, MTS, MBA, Department of Surgery, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus, Ohio. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design of the study limited the ability to draw causal inferences. The study relied on public county-level data, which may not have captured all relevant variables. The use of the social vulnerability index and PCP density as proxies did not fully represent the complexity of pharmacy access issues. The study’s findings were not generalizable to regions outside the United States.
DISCLOSURES:
No relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Pharmacy closures in the United States are creating “pharmacy deserts,” disproportionately affecting socially vulnerable communities. High social vulnerability and low primary care practitioner (PCP) density are linked to increased pharmacy desert density.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data through 2020 on communities located 10 or more miles from the nearest retail pharmacy were sourced from TelePharm Map.
- Counties were stratified as having a high pharmacy desert density if the number of pharmacy deserts per 1000 inhabitants was in the 80th percentile or higher.
- Social vulnerability index and healthcare practitioner data were obtained from the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry and the Area Health Resources Files.
- PCP density was calculated as the number of PCPs per 10,000 inhabitants.
- A total of 3143 counties were analyzed, with 1447 (46%) having at least one pharmacy desert.
TAKEAWAY:
- Counties with a high pharmacy desert density had a higher social vulnerability index than those with a low pharmacy desert density (P = .006).
- Areas with a high pharmacy desert density had lower median PCP density than those with low or no pharmacy desert density (P < .001).
- High social vulnerability index (odds ratio [OR], 1.35; 95% CI, 1.07-1.70; P = .01) and low PCP density (OR, 2.27; 95% CI, 1.80-2.86; P < .001) were associated with a higher likelihood for a county to have a high pharmacy desert density.
- Pharmacy closures are leaving more individuals without easy access to medications, with disproportionate consequences for certain communities.
IN PRACTICE:
“As high pharmacy desert density counties also have a lower PCP density, patients residing in these regions face increased barriers to accessing primary healthcare needs,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Giovanni Catalano, MD, Muhammad Muntazir Mehdi Khan, MBBS, and Timothy M. Pawlik, MD, PhD, MPH, MTS, MBA, Department of Surgery, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus, Ohio. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design of the study limited the ability to draw causal inferences. The study relied on public county-level data, which may not have captured all relevant variables. The use of the social vulnerability index and PCP density as proxies did not fully represent the complexity of pharmacy access issues. The study’s findings were not generalizable to regions outside the United States.
DISCLOSURES:
No relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
UVA Defends Medical School Dean, Hospital CEO After Docs Call for Their Removal
The University of Virginia (UVA) is defending the CEO of its health system and its medical school dean in the wake of a very public call for their removal.
At least 128 members of the University of Virginia faculty who are employed by both the medical school and the UVA Physicians Group wrote to the UVA Board of Visitors and its peer-elected faculty leaders, expressing no confidence in K. Craig Kent, MD, CEO of UVA Health and executive vice president for health affairs, and Melina Kibbe, MD, dean of the medical school and chief health affairs officer.
Dr. Kibbe, a vascular surgeon and researcher, is also the editor in chief of JAMA Surgery.
“We call for the immediate removal of Craig Kent and Melina Kibbe,” wrote the physicians.
The letter alleged that patient safety was compromised because doctors, nurses, and other staff were pressured to abstain from reporting safety concerns and that physicians had been hired “despite concerns regarding integrity and quality.” Those who raised safety concerns faced “explicit and implicit threats and retaliation,” including delays and denials of promotion and tenure, said the letter.
The September 5 letter did not include signatures. The authors said that names were being protected, but that they would share the names with a limited audience.
UVA President Jim Ryan took issue with the notion that the signees were anonymous. He said in his own letter to medical school faculty that some of the accusations were about matters that had already been addressed or that were being worked on. As far as allegations that he was not previously aware of, “we will do our best to investigate,” he said.
The faculty who signed the letter “have besmirched the reputations of not just Melina and Craig,” wrote Mr. Ryan. “They have unfairly — and I trust unwittingly — cast a shadow over the great work of the entire health system and medical school.”
The authors claimed that reports about bullying and harassment of trainees had been “suppressed, minimized, and subsequently altered.”
And they said that spending on leadership was prioritized over addressing clinical and technical staff shortages. Whistleblowers who reported fraud were not protected, and clinicians were pressured to modify patient records to “obfuscate adverse outcomes and boost productivity metrics,” they wrote.
The 128 members of the UVA Physicians Group who signed the letter represent about 10% of the 1400 medical school faculty members.
It is not the first time that Dr. Kent has been given a vote of no confidence. In 2017, when he was the dean of the College of Medicine at the Ohio State University, Dr. Kent was accused in a “no confidence” letter from 25 physicians and faculty of helping to undermine the school’s mission and taking actions that led to resignations and early retirements of many staff, the Columbus Dispatch reported.
William G. Crutchfield Jr., a member of the UVA Health System Board, defended Dr. Kent and Dr. Kibbe in a lengthy statement shared with this news organization. He said that UVA Health’s four hospitals had received “A” ratings for safety, and that the system has a 5.1% turnover rate compared with a national average of 8.3%.
Dr. Kent and Dr. Kibbe have recruited faculty from top academic medical centers, Mr. Crutchfield wrote.
“If our work environment were so toxic, these people would not have joined our faculty,” he wrote.
Mr. Crutchfield credited Dr. Kent and Dr. Kibbe with crafting a new 10-year strategic plan and for hiring a chief strategy officer to lead the plan — a move that replaced “expensive outside consultants.”
Mr. Ryan said in his letter that his inbox “is overflowing with testimonials from some of the 1200-plus faculty who did not sign the letter, who attest that the health system today — under Melina and Craig’s leadership — is in the best shape it has ever been in, and that they have addressed changes that have needed to be made for more than two decades.”
A request to see some of these positive testimonials was not answered by press time.
Mr. Crutchfield, like Mr. Ryan, said that the letter writers were doing more harm than good.
“If a small cabal of people hiding behind anonymity can force outstanding leaders out of UVA, it will make it extremely difficult to recruit outstanding new physicians, nurses, technicians, and administrators,” he wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The University of Virginia (UVA) is defending the CEO of its health system and its medical school dean in the wake of a very public call for their removal.
At least 128 members of the University of Virginia faculty who are employed by both the medical school and the UVA Physicians Group wrote to the UVA Board of Visitors and its peer-elected faculty leaders, expressing no confidence in K. Craig Kent, MD, CEO of UVA Health and executive vice president for health affairs, and Melina Kibbe, MD, dean of the medical school and chief health affairs officer.
Dr. Kibbe, a vascular surgeon and researcher, is also the editor in chief of JAMA Surgery.
“We call for the immediate removal of Craig Kent and Melina Kibbe,” wrote the physicians.
The letter alleged that patient safety was compromised because doctors, nurses, and other staff were pressured to abstain from reporting safety concerns and that physicians had been hired “despite concerns regarding integrity and quality.” Those who raised safety concerns faced “explicit and implicit threats and retaliation,” including delays and denials of promotion and tenure, said the letter.
The September 5 letter did not include signatures. The authors said that names were being protected, but that they would share the names with a limited audience.
UVA President Jim Ryan took issue with the notion that the signees were anonymous. He said in his own letter to medical school faculty that some of the accusations were about matters that had already been addressed or that were being worked on. As far as allegations that he was not previously aware of, “we will do our best to investigate,” he said.
The faculty who signed the letter “have besmirched the reputations of not just Melina and Craig,” wrote Mr. Ryan. “They have unfairly — and I trust unwittingly — cast a shadow over the great work of the entire health system and medical school.”
The authors claimed that reports about bullying and harassment of trainees had been “suppressed, minimized, and subsequently altered.”
And they said that spending on leadership was prioritized over addressing clinical and technical staff shortages. Whistleblowers who reported fraud were not protected, and clinicians were pressured to modify patient records to “obfuscate adverse outcomes and boost productivity metrics,” they wrote.
The 128 members of the UVA Physicians Group who signed the letter represent about 10% of the 1400 medical school faculty members.
It is not the first time that Dr. Kent has been given a vote of no confidence. In 2017, when he was the dean of the College of Medicine at the Ohio State University, Dr. Kent was accused in a “no confidence” letter from 25 physicians and faculty of helping to undermine the school’s mission and taking actions that led to resignations and early retirements of many staff, the Columbus Dispatch reported.
William G. Crutchfield Jr., a member of the UVA Health System Board, defended Dr. Kent and Dr. Kibbe in a lengthy statement shared with this news organization. He said that UVA Health’s four hospitals had received “A” ratings for safety, and that the system has a 5.1% turnover rate compared with a national average of 8.3%.
Dr. Kent and Dr. Kibbe have recruited faculty from top academic medical centers, Mr. Crutchfield wrote.
“If our work environment were so toxic, these people would not have joined our faculty,” he wrote.
Mr. Crutchfield credited Dr. Kent and Dr. Kibbe with crafting a new 10-year strategic plan and for hiring a chief strategy officer to lead the plan — a move that replaced “expensive outside consultants.”
Mr. Ryan said in his letter that his inbox “is overflowing with testimonials from some of the 1200-plus faculty who did not sign the letter, who attest that the health system today — under Melina and Craig’s leadership — is in the best shape it has ever been in, and that they have addressed changes that have needed to be made for more than two decades.”
A request to see some of these positive testimonials was not answered by press time.
Mr. Crutchfield, like Mr. Ryan, said that the letter writers were doing more harm than good.
“If a small cabal of people hiding behind anonymity can force outstanding leaders out of UVA, it will make it extremely difficult to recruit outstanding new physicians, nurses, technicians, and administrators,” he wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The University of Virginia (UVA) is defending the CEO of its health system and its medical school dean in the wake of a very public call for their removal.
At least 128 members of the University of Virginia faculty who are employed by both the medical school and the UVA Physicians Group wrote to the UVA Board of Visitors and its peer-elected faculty leaders, expressing no confidence in K. Craig Kent, MD, CEO of UVA Health and executive vice president for health affairs, and Melina Kibbe, MD, dean of the medical school and chief health affairs officer.
Dr. Kibbe, a vascular surgeon and researcher, is also the editor in chief of JAMA Surgery.
“We call for the immediate removal of Craig Kent and Melina Kibbe,” wrote the physicians.
The letter alleged that patient safety was compromised because doctors, nurses, and other staff were pressured to abstain from reporting safety concerns and that physicians had been hired “despite concerns regarding integrity and quality.” Those who raised safety concerns faced “explicit and implicit threats and retaliation,” including delays and denials of promotion and tenure, said the letter.
The September 5 letter did not include signatures. The authors said that names were being protected, but that they would share the names with a limited audience.
UVA President Jim Ryan took issue with the notion that the signees were anonymous. He said in his own letter to medical school faculty that some of the accusations were about matters that had already been addressed or that were being worked on. As far as allegations that he was not previously aware of, “we will do our best to investigate,” he said.
The faculty who signed the letter “have besmirched the reputations of not just Melina and Craig,” wrote Mr. Ryan. “They have unfairly — and I trust unwittingly — cast a shadow over the great work of the entire health system and medical school.”
The authors claimed that reports about bullying and harassment of trainees had been “suppressed, minimized, and subsequently altered.”
And they said that spending on leadership was prioritized over addressing clinical and technical staff shortages. Whistleblowers who reported fraud were not protected, and clinicians were pressured to modify patient records to “obfuscate adverse outcomes and boost productivity metrics,” they wrote.
The 128 members of the UVA Physicians Group who signed the letter represent about 10% of the 1400 medical school faculty members.
It is not the first time that Dr. Kent has been given a vote of no confidence. In 2017, when he was the dean of the College of Medicine at the Ohio State University, Dr. Kent was accused in a “no confidence” letter from 25 physicians and faculty of helping to undermine the school’s mission and taking actions that led to resignations and early retirements of many staff, the Columbus Dispatch reported.
William G. Crutchfield Jr., a member of the UVA Health System Board, defended Dr. Kent and Dr. Kibbe in a lengthy statement shared with this news organization. He said that UVA Health’s four hospitals had received “A” ratings for safety, and that the system has a 5.1% turnover rate compared with a national average of 8.3%.
Dr. Kent and Dr. Kibbe have recruited faculty from top academic medical centers, Mr. Crutchfield wrote.
“If our work environment were so toxic, these people would not have joined our faculty,” he wrote.
Mr. Crutchfield credited Dr. Kent and Dr. Kibbe with crafting a new 10-year strategic plan and for hiring a chief strategy officer to lead the plan — a move that replaced “expensive outside consultants.”
Mr. Ryan said in his letter that his inbox “is overflowing with testimonials from some of the 1200-plus faculty who did not sign the letter, who attest that the health system today — under Melina and Craig’s leadership — is in the best shape it has ever been in, and that they have addressed changes that have needed to be made for more than two decades.”
A request to see some of these positive testimonials was not answered by press time.
Mr. Crutchfield, like Mr. Ryan, said that the letter writers were doing more harm than good.
“If a small cabal of people hiding behind anonymity can force outstanding leaders out of UVA, it will make it extremely difficult to recruit outstanding new physicians, nurses, technicians, and administrators,” he wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Current Hydroxychloroquine Use in Lupus May Provide Protection Against Cardiovascular Events
TOPLINE:
Current use of hydroxychloroquine is associated with a lower risk for myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and other thromboembolic events in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). This protective effect diminishes after discontinuation of hydroxychloroquine treatment.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers used a nested case-control design to evaluate the association between exposure to hydroxychloroquine and the risk for cardiovascular events in patients with SLE.
- They included 52,883 adults with SLE (mean age, 44.23 years; 86.6% women) identified from the National System of Health Databases, which includes 99% of the French population.
- Among these, 1981 individuals with composite cardiovascular conditions were matched with 16,892 control individuals without cardiovascular conditions.
- Patients were categorized on the basis of hydroxychloroquine exposure into current users (last exposure within 90 days before a cardiovascular event), remote users (91-365 days before), and nonusers (no exposure within 365 days).
- The study outcomes included a composite of cardiovascular events, including MI, stroke (including transient ischemic attack), and other thromboembolic events such as phlebitis, thrombophlebitis, venous thrombosis, venous thromboembolism, and pulmonary embolism.
TAKEAWAY:
- Current hydroxychloroquine users had lower odds of experiencing a composite cardiovascular outcome than nonusers (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 0.63; 95% CI, 0.57-0.70).
- The odds of MI (aOR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.60-0.87), stroke (aOR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.61-0.83), and other thromboembolic events (aOR, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.48-0.69) were also lower among current users than among nonusers.
- No significant association was found for remote hydroxychloroquine exposure and the risk for composite cardiovascular events, MI, stroke, and other thromboembolic events.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings support the protective association of hydroxychloroquine against CV [cardiovascular] events and underscore the importance of continuous hydroxychloroquine therapy for patients diagnosed with SLE,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Lamiae Grimaldi-Bensouda, PharmD, PhD, Department of Pharmacology, Hospital Group Paris-Saclay, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, France. It was published online on August 30, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The observational nature of the study may have introduced confounding. Current hydroxychloroquine users were younger than nonusers, with an average age difference of almost 5 years. Current hydroxychloroquine users had a twofold longer duration of onset of SLE and had a higher prevalence of chronic kidney disease compared with nonusers.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the Banque pour l’Investissement, Deeptech. Some authors declared having financial ties with various institutions and companies outside of the current study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Current use of hydroxychloroquine is associated with a lower risk for myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and other thromboembolic events in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). This protective effect diminishes after discontinuation of hydroxychloroquine treatment.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers used a nested case-control design to evaluate the association between exposure to hydroxychloroquine and the risk for cardiovascular events in patients with SLE.
- They included 52,883 adults with SLE (mean age, 44.23 years; 86.6% women) identified from the National System of Health Databases, which includes 99% of the French population.
- Among these, 1981 individuals with composite cardiovascular conditions were matched with 16,892 control individuals without cardiovascular conditions.
- Patients were categorized on the basis of hydroxychloroquine exposure into current users (last exposure within 90 days before a cardiovascular event), remote users (91-365 days before), and nonusers (no exposure within 365 days).
- The study outcomes included a composite of cardiovascular events, including MI, stroke (including transient ischemic attack), and other thromboembolic events such as phlebitis, thrombophlebitis, venous thrombosis, venous thromboembolism, and pulmonary embolism.
TAKEAWAY:
- Current hydroxychloroquine users had lower odds of experiencing a composite cardiovascular outcome than nonusers (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 0.63; 95% CI, 0.57-0.70).
- The odds of MI (aOR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.60-0.87), stroke (aOR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.61-0.83), and other thromboembolic events (aOR, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.48-0.69) were also lower among current users than among nonusers.
- No significant association was found for remote hydroxychloroquine exposure and the risk for composite cardiovascular events, MI, stroke, and other thromboembolic events.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings support the protective association of hydroxychloroquine against CV [cardiovascular] events and underscore the importance of continuous hydroxychloroquine therapy for patients diagnosed with SLE,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Lamiae Grimaldi-Bensouda, PharmD, PhD, Department of Pharmacology, Hospital Group Paris-Saclay, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, France. It was published online on August 30, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The observational nature of the study may have introduced confounding. Current hydroxychloroquine users were younger than nonusers, with an average age difference of almost 5 years. Current hydroxychloroquine users had a twofold longer duration of onset of SLE and had a higher prevalence of chronic kidney disease compared with nonusers.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the Banque pour l’Investissement, Deeptech. Some authors declared having financial ties with various institutions and companies outside of the current study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Current use of hydroxychloroquine is associated with a lower risk for myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and other thromboembolic events in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). This protective effect diminishes after discontinuation of hydroxychloroquine treatment.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers used a nested case-control design to evaluate the association between exposure to hydroxychloroquine and the risk for cardiovascular events in patients with SLE.
- They included 52,883 adults with SLE (mean age, 44.23 years; 86.6% women) identified from the National System of Health Databases, which includes 99% of the French population.
- Among these, 1981 individuals with composite cardiovascular conditions were matched with 16,892 control individuals without cardiovascular conditions.
- Patients were categorized on the basis of hydroxychloroquine exposure into current users (last exposure within 90 days before a cardiovascular event), remote users (91-365 days before), and nonusers (no exposure within 365 days).
- The study outcomes included a composite of cardiovascular events, including MI, stroke (including transient ischemic attack), and other thromboembolic events such as phlebitis, thrombophlebitis, venous thrombosis, venous thromboembolism, and pulmonary embolism.
TAKEAWAY:
- Current hydroxychloroquine users had lower odds of experiencing a composite cardiovascular outcome than nonusers (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 0.63; 95% CI, 0.57-0.70).
- The odds of MI (aOR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.60-0.87), stroke (aOR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.61-0.83), and other thromboembolic events (aOR, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.48-0.69) were also lower among current users than among nonusers.
- No significant association was found for remote hydroxychloroquine exposure and the risk for composite cardiovascular events, MI, stroke, and other thromboembolic events.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings support the protective association of hydroxychloroquine against CV [cardiovascular] events and underscore the importance of continuous hydroxychloroquine therapy for patients diagnosed with SLE,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Lamiae Grimaldi-Bensouda, PharmD, PhD, Department of Pharmacology, Hospital Group Paris-Saclay, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, France. It was published online on August 30, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The observational nature of the study may have introduced confounding. Current hydroxychloroquine users were younger than nonusers, with an average age difference of almost 5 years. Current hydroxychloroquine users had a twofold longer duration of onset of SLE and had a higher prevalence of chronic kidney disease compared with nonusers.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the Banque pour l’Investissement, Deeptech. Some authors declared having financial ties with various institutions and companies outside of the current study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Unlocking the Potential of Baricitinib for Vitiligo
Vitiligo, the most common skin pigmentation disorder, has affected patients for thousands of years.1 The psychological and social impacts on patients include sleep and sexual disorders, low self-esteem, low quality of life, anxiety, and depression when compared to those without vitiligo.2,3 There have been substantial therapeutic advancements in the treatment of vitiligo, with the recent approval of ruxolitinib cream 1.5% by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2022 and by the European Medicines Agency in 2023.4 Ruxolitinib is the first topical Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor approved by the FDA for the treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo in patients 12 years and older, ushering in the era of JAK inhibitors for patients affected by vitiligo. The efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib was supported by 2 randomized clinical trials.4 It also is FDA approved for the intermittent and short-term treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in nonimmunocompromised patients 12 years and older whose disease is not adequately controlled with other topical medications.5
Vitiligo is characterized by an important inflammatory component, with the JAK/STAT (signal transducer and activator of transcription) pathway playing a crucial role in transmitting signals of inflammatory cytokines. In particular, IFN-γ and chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10 are major contributors to the development of vitiligo, acting through the JAK/STAT pathway in local keratinocytes. Inhibiting JAK activity helps mitigate the effects of IFN-γ and downstream chemokines.6
Currently, baricitinib is not FDA approved for the treatment of vitiligo; it is FDA approved for moderate to severe active rheumatoid arthritis, severe alopecia areata, and in specific cases for COVID-19.7 Mumford et al8 first reported the use of oral baricitinib for the treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo. This patient experienced poor improvement using the oral JAK inhibitor tofacitinib for 5 months but achieved near-complete repigmentation after switching to baricitinib for 8 months (4 mg daily).8 Furthermore, a recent study found that in vitro baricitinib could increase tyrosinase activity and melanin content as well as stimulate the expression of genes related to tyrosinase in damaged melanocytes.9
A recent study by Li et al10 has shown satisfactory repigmentation and good tolerance in 2 cases of vitiligo treated with oral baricitinib in combination with narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) phototherapy. These findings are supported by a prior study of oral tofacitinib and NB-UVB phototherapy in 10 cases; the JAK inhibitor treatment demonstrated enhanced effectiveness when combined with light exposure.11
Large-scale randomized clinical trials are needed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of oral baricitinib for vitiligo treatment. Currently, a clinical trial is underway (recruiting phase) to compare the efficacy and safety of combining baricitinib and excimer lamp phototherapy vs phototherapy alone.12 The results of this trial can provide valuable information about whether baricitinib is promising as part of the therapeutic arsenal for vitiligo treatment in the future. A recently completed multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial assessed the efficacy and tolerability of oral baricitinib in combination with NB-UVB phototherapy for the treatment of vitiligo. The trial included 49 patients and may provide valuable insights for the potential future application of baricitinib in the treatment of vitiligo.13 If the results of these clinical trials are favorable, approval of the first orally administered JAK inhibitor for repigmentation treatment in patients with vitiligo could follow, which would be a major breakthrough.
The off-label use of baricitinib—alone or in combination with phototherapy—appears to be promising in studies with a small sample size (an important limitation). The results of clinical trials will help us elucidate the efficacy and safety of baricitinib for vitiligo treatment, which could be a subject of debate. Recently, the FDA issued a warning due to findings showing that the use of tofacitinib has been associated with an increased risk of serious heart-related events, such heart attack, stroke, cancer, blood clots, and death.14 In response, the FDA issued warnings for 2 other JAK inhibitors—baricitinib and upadacitinib. Unlike tofacitinib, baricitinib and upadacitinib have not been studied in large safety clinical trials, and as a result, their risks have not been adequately evaluated. However, due to the shared mechanisms of action of these drugs, the FDA believes that these medications may pose similar risks as those observed in the tofacitinib safety trial.14
Disadvantages of JAK inhibitors include the high cost, immune-related side effects, potential cardiovascular adverse effects, and limited availability worldwide. If current and future clinical trials obtain objective evidence with a large sample size that yields positive outcomes with tolerable or acceptable side effects, and if the drug is affordable for hospitals and patients, the use of oral or topical baricitinib will be embraced and may be approved for vitiligo.
- Berger BJ, Rudolph RI, Leyden JJ. Letter: transient acantholytic dermatosis. Arch Dermatol. 1974;109:913. doi:10.1001/archderm.1974.01630060081033
- Hu Z, Wang T. Beyond skin white spots: vitiligo and associated comorbidities. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1072837. doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1072837
- Rzepecki AK, McLellan BN, Elbuluk N. Beyond traditional treatment: the importance of psychosocial therapy in vitiligo. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:688-691.
- Topical ruxolitinib evaluation in vitiligo study 1 (TRuE-V1). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04052425. Updated September 21, 2022. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04052425
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves topical treatment addressing repigmentation in vitiligo in patients aged 12 and older. July 19, 2022. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/news-events-human-drugs/fda-approves-topical-treatment-addressing-repigmentation-vitiligo-patients-aged-12-and-older
- Harris JE, Harris TH, Weninger W, et al. A mouse model of vitiligo with focused epidermal depigmentation requires IFN-γ for autoreactive CD8+ T-cell accumulation in the skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:1869-1876. doi:10.1038/jid.2011.463
- Garcia-Melendo C, Cubiró X, Puig L. Janus kinase inhibitors in dermatology: part 1—general considerations and applications in vitiligo and alopecia areata. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2021;112:503-515. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2020.12.003
- Mumford BP, Gibson A, Chong AH. Repigmentation of vitiligo with oral baricitinib. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:374-376. doi:10.1111/ajd.13348
- Dong J, Huang X, Ma LP, et al. Baricitinib is effective in treating progressing vitiligo in vivo and in vitro. Dose Response. 2022;20:15593258221105370. doi:10.1177/15593258221105370
- Li X, Sun Y, Du J, et al. Excellent repigmentation of generalized vitiligo with oral baricitinib combined with NB-UVB phototherapy. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:635-638. doi:10.2147/CCID.S396430
- Liu LY, Strassner JP, Refat MA, et al. Repigmentation in vitiligo using the Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib may require concomitant light exposure. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:675-682.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.05.043
- Evaluation safety, efficacy baricitinib plus excimer light versus excimer light alone in non segmental vitiligo. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05950542. Updated July 18, 2023. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05950542
- Evaluation of effect and tolerance of the association of baricitinib and phototherapy versus phototherapy in adults with progressive vitiligo (BARVIT). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04822584. Updated June 13, 2023. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04822584
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA requires warnings about increased risk of serious heart-related events, cancer, blood clots, and death for JAK inhibitors that treat certain chronic inflammatory conditions. December 7, 2021. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-requires-warnings-about-increased-risk-serious-heart-related-events-cancer-blood-clots-and-death
Vitiligo, the most common skin pigmentation disorder, has affected patients for thousands of years.1 The psychological and social impacts on patients include sleep and sexual disorders, low self-esteem, low quality of life, anxiety, and depression when compared to those without vitiligo.2,3 There have been substantial therapeutic advancements in the treatment of vitiligo, with the recent approval of ruxolitinib cream 1.5% by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2022 and by the European Medicines Agency in 2023.4 Ruxolitinib is the first topical Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor approved by the FDA for the treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo in patients 12 years and older, ushering in the era of JAK inhibitors for patients affected by vitiligo. The efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib was supported by 2 randomized clinical trials.4 It also is FDA approved for the intermittent and short-term treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in nonimmunocompromised patients 12 years and older whose disease is not adequately controlled with other topical medications.5
Vitiligo is characterized by an important inflammatory component, with the JAK/STAT (signal transducer and activator of transcription) pathway playing a crucial role in transmitting signals of inflammatory cytokines. In particular, IFN-γ and chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10 are major contributors to the development of vitiligo, acting through the JAK/STAT pathway in local keratinocytes. Inhibiting JAK activity helps mitigate the effects of IFN-γ and downstream chemokines.6
Currently, baricitinib is not FDA approved for the treatment of vitiligo; it is FDA approved for moderate to severe active rheumatoid arthritis, severe alopecia areata, and in specific cases for COVID-19.7 Mumford et al8 first reported the use of oral baricitinib for the treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo. This patient experienced poor improvement using the oral JAK inhibitor tofacitinib for 5 months but achieved near-complete repigmentation after switching to baricitinib for 8 months (4 mg daily).8 Furthermore, a recent study found that in vitro baricitinib could increase tyrosinase activity and melanin content as well as stimulate the expression of genes related to tyrosinase in damaged melanocytes.9
A recent study by Li et al10 has shown satisfactory repigmentation and good tolerance in 2 cases of vitiligo treated with oral baricitinib in combination with narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) phototherapy. These findings are supported by a prior study of oral tofacitinib and NB-UVB phototherapy in 10 cases; the JAK inhibitor treatment demonstrated enhanced effectiveness when combined with light exposure.11
Large-scale randomized clinical trials are needed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of oral baricitinib for vitiligo treatment. Currently, a clinical trial is underway (recruiting phase) to compare the efficacy and safety of combining baricitinib and excimer lamp phototherapy vs phototherapy alone.12 The results of this trial can provide valuable information about whether baricitinib is promising as part of the therapeutic arsenal for vitiligo treatment in the future. A recently completed multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial assessed the efficacy and tolerability of oral baricitinib in combination with NB-UVB phototherapy for the treatment of vitiligo. The trial included 49 patients and may provide valuable insights for the potential future application of baricitinib in the treatment of vitiligo.13 If the results of these clinical trials are favorable, approval of the first orally administered JAK inhibitor for repigmentation treatment in patients with vitiligo could follow, which would be a major breakthrough.
The off-label use of baricitinib—alone or in combination with phototherapy—appears to be promising in studies with a small sample size (an important limitation). The results of clinical trials will help us elucidate the efficacy and safety of baricitinib for vitiligo treatment, which could be a subject of debate. Recently, the FDA issued a warning due to findings showing that the use of tofacitinib has been associated with an increased risk of serious heart-related events, such heart attack, stroke, cancer, blood clots, and death.14 In response, the FDA issued warnings for 2 other JAK inhibitors—baricitinib and upadacitinib. Unlike tofacitinib, baricitinib and upadacitinib have not been studied in large safety clinical trials, and as a result, their risks have not been adequately evaluated. However, due to the shared mechanisms of action of these drugs, the FDA believes that these medications may pose similar risks as those observed in the tofacitinib safety trial.14
Disadvantages of JAK inhibitors include the high cost, immune-related side effects, potential cardiovascular adverse effects, and limited availability worldwide. If current and future clinical trials obtain objective evidence with a large sample size that yields positive outcomes with tolerable or acceptable side effects, and if the drug is affordable for hospitals and patients, the use of oral or topical baricitinib will be embraced and may be approved for vitiligo.
Vitiligo, the most common skin pigmentation disorder, has affected patients for thousands of years.1 The psychological and social impacts on patients include sleep and sexual disorders, low self-esteem, low quality of life, anxiety, and depression when compared to those without vitiligo.2,3 There have been substantial therapeutic advancements in the treatment of vitiligo, with the recent approval of ruxolitinib cream 1.5% by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2022 and by the European Medicines Agency in 2023.4 Ruxolitinib is the first topical Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor approved by the FDA for the treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo in patients 12 years and older, ushering in the era of JAK inhibitors for patients affected by vitiligo. The efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib was supported by 2 randomized clinical trials.4 It also is FDA approved for the intermittent and short-term treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in nonimmunocompromised patients 12 years and older whose disease is not adequately controlled with other topical medications.5
Vitiligo is characterized by an important inflammatory component, with the JAK/STAT (signal transducer and activator of transcription) pathway playing a crucial role in transmitting signals of inflammatory cytokines. In particular, IFN-γ and chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10 are major contributors to the development of vitiligo, acting through the JAK/STAT pathway in local keratinocytes. Inhibiting JAK activity helps mitigate the effects of IFN-γ and downstream chemokines.6
Currently, baricitinib is not FDA approved for the treatment of vitiligo; it is FDA approved for moderate to severe active rheumatoid arthritis, severe alopecia areata, and in specific cases for COVID-19.7 Mumford et al8 first reported the use of oral baricitinib for the treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo. This patient experienced poor improvement using the oral JAK inhibitor tofacitinib for 5 months but achieved near-complete repigmentation after switching to baricitinib for 8 months (4 mg daily).8 Furthermore, a recent study found that in vitro baricitinib could increase tyrosinase activity and melanin content as well as stimulate the expression of genes related to tyrosinase in damaged melanocytes.9
A recent study by Li et al10 has shown satisfactory repigmentation and good tolerance in 2 cases of vitiligo treated with oral baricitinib in combination with narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) phototherapy. These findings are supported by a prior study of oral tofacitinib and NB-UVB phototherapy in 10 cases; the JAK inhibitor treatment demonstrated enhanced effectiveness when combined with light exposure.11
Large-scale randomized clinical trials are needed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of oral baricitinib for vitiligo treatment. Currently, a clinical trial is underway (recruiting phase) to compare the efficacy and safety of combining baricitinib and excimer lamp phototherapy vs phototherapy alone.12 The results of this trial can provide valuable information about whether baricitinib is promising as part of the therapeutic arsenal for vitiligo treatment in the future. A recently completed multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial assessed the efficacy and tolerability of oral baricitinib in combination with NB-UVB phototherapy for the treatment of vitiligo. The trial included 49 patients and may provide valuable insights for the potential future application of baricitinib in the treatment of vitiligo.13 If the results of these clinical trials are favorable, approval of the first orally administered JAK inhibitor for repigmentation treatment in patients with vitiligo could follow, which would be a major breakthrough.
The off-label use of baricitinib—alone or in combination with phototherapy—appears to be promising in studies with a small sample size (an important limitation). The results of clinical trials will help us elucidate the efficacy and safety of baricitinib for vitiligo treatment, which could be a subject of debate. Recently, the FDA issued a warning due to findings showing that the use of tofacitinib has been associated with an increased risk of serious heart-related events, such heart attack, stroke, cancer, blood clots, and death.14 In response, the FDA issued warnings for 2 other JAK inhibitors—baricitinib and upadacitinib. Unlike tofacitinib, baricitinib and upadacitinib have not been studied in large safety clinical trials, and as a result, their risks have not been adequately evaluated. However, due to the shared mechanisms of action of these drugs, the FDA believes that these medications may pose similar risks as those observed in the tofacitinib safety trial.14
Disadvantages of JAK inhibitors include the high cost, immune-related side effects, potential cardiovascular adverse effects, and limited availability worldwide. If current and future clinical trials obtain objective evidence with a large sample size that yields positive outcomes with tolerable or acceptable side effects, and if the drug is affordable for hospitals and patients, the use of oral or topical baricitinib will be embraced and may be approved for vitiligo.
- Berger BJ, Rudolph RI, Leyden JJ. Letter: transient acantholytic dermatosis. Arch Dermatol. 1974;109:913. doi:10.1001/archderm.1974.01630060081033
- Hu Z, Wang T. Beyond skin white spots: vitiligo and associated comorbidities. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1072837. doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1072837
- Rzepecki AK, McLellan BN, Elbuluk N. Beyond traditional treatment: the importance of psychosocial therapy in vitiligo. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:688-691.
- Topical ruxolitinib evaluation in vitiligo study 1 (TRuE-V1). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04052425. Updated September 21, 2022. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04052425
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves topical treatment addressing repigmentation in vitiligo in patients aged 12 and older. July 19, 2022. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/news-events-human-drugs/fda-approves-topical-treatment-addressing-repigmentation-vitiligo-patients-aged-12-and-older
- Harris JE, Harris TH, Weninger W, et al. A mouse model of vitiligo with focused epidermal depigmentation requires IFN-γ for autoreactive CD8+ T-cell accumulation in the skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:1869-1876. doi:10.1038/jid.2011.463
- Garcia-Melendo C, Cubiró X, Puig L. Janus kinase inhibitors in dermatology: part 1—general considerations and applications in vitiligo and alopecia areata. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2021;112:503-515. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2020.12.003
- Mumford BP, Gibson A, Chong AH. Repigmentation of vitiligo with oral baricitinib. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:374-376. doi:10.1111/ajd.13348
- Dong J, Huang X, Ma LP, et al. Baricitinib is effective in treating progressing vitiligo in vivo and in vitro. Dose Response. 2022;20:15593258221105370. doi:10.1177/15593258221105370
- Li X, Sun Y, Du J, et al. Excellent repigmentation of generalized vitiligo with oral baricitinib combined with NB-UVB phototherapy. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:635-638. doi:10.2147/CCID.S396430
- Liu LY, Strassner JP, Refat MA, et al. Repigmentation in vitiligo using the Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib may require concomitant light exposure. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:675-682.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.05.043
- Evaluation safety, efficacy baricitinib plus excimer light versus excimer light alone in non segmental vitiligo. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05950542. Updated July 18, 2023. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05950542
- Evaluation of effect and tolerance of the association of baricitinib and phototherapy versus phototherapy in adults with progressive vitiligo (BARVIT). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04822584. Updated June 13, 2023. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04822584
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA requires warnings about increased risk of serious heart-related events, cancer, blood clots, and death for JAK inhibitors that treat certain chronic inflammatory conditions. December 7, 2021. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-requires-warnings-about-increased-risk-serious-heart-related-events-cancer-blood-clots-and-death
- Berger BJ, Rudolph RI, Leyden JJ. Letter: transient acantholytic dermatosis. Arch Dermatol. 1974;109:913. doi:10.1001/archderm.1974.01630060081033
- Hu Z, Wang T. Beyond skin white spots: vitiligo and associated comorbidities. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1072837. doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1072837
- Rzepecki AK, McLellan BN, Elbuluk N. Beyond traditional treatment: the importance of psychosocial therapy in vitiligo. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:688-691.
- Topical ruxolitinib evaluation in vitiligo study 1 (TRuE-V1). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04052425. Updated September 21, 2022. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04052425
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves topical treatment addressing repigmentation in vitiligo in patients aged 12 and older. July 19, 2022. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/news-events-human-drugs/fda-approves-topical-treatment-addressing-repigmentation-vitiligo-patients-aged-12-and-older
- Harris JE, Harris TH, Weninger W, et al. A mouse model of vitiligo with focused epidermal depigmentation requires IFN-γ for autoreactive CD8+ T-cell accumulation in the skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:1869-1876. doi:10.1038/jid.2011.463
- Garcia-Melendo C, Cubiró X, Puig L. Janus kinase inhibitors in dermatology: part 1—general considerations and applications in vitiligo and alopecia areata. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2021;112:503-515. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2020.12.003
- Mumford BP, Gibson A, Chong AH. Repigmentation of vitiligo with oral baricitinib. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:374-376. doi:10.1111/ajd.13348
- Dong J, Huang X, Ma LP, et al. Baricitinib is effective in treating progressing vitiligo in vivo and in vitro. Dose Response. 2022;20:15593258221105370. doi:10.1177/15593258221105370
- Li X, Sun Y, Du J, et al. Excellent repigmentation of generalized vitiligo with oral baricitinib combined with NB-UVB phototherapy. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:635-638. doi:10.2147/CCID.S396430
- Liu LY, Strassner JP, Refat MA, et al. Repigmentation in vitiligo using the Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib may require concomitant light exposure. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:675-682.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.05.043
- Evaluation safety, efficacy baricitinib plus excimer light versus excimer light alone in non segmental vitiligo. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05950542. Updated July 18, 2023. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05950542
- Evaluation of effect and tolerance of the association of baricitinib and phototherapy versus phototherapy in adults with progressive vitiligo (BARVIT). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04822584. Updated June 13, 2023. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04822584
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA requires warnings about increased risk of serious heart-related events, cancer, blood clots, and death for JAK inhibitors that treat certain chronic inflammatory conditions. December 7, 2021. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-requires-warnings-about-increased-risk-serious-heart-related-events-cancer-blood-clots-and-death
Do Cannabis Users Need More Anesthesia During Surgery?
TOPLINE:
However, the clinical relevance of this difference remains unclear.
METHODOLOGY:
- To assess if cannabis use leads to higher doses of inhalational anesthesia during surgery, the researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study comparing the average intraoperative minimum alveolar concentrations of volatile anesthetics (isoflurane and sevoflurane) between older adults who used cannabis products and those who did not.
- The researchers reviewed electronic health records of 22,476 patients aged 65 years or older who underwent surgery at the University of Florida Health System between 2018 and 2020.
- Overall, 268 patients who reported using cannabis within 60 days of surgery (median age, 69 years; 35% women) were matched to 1072 nonusers.
- The median duration of anesthesia was 175 minutes.
- The primary outcome was the intraoperative time-weighted average of isoflurane or sevoflurane minimum alveolar concentration equivalents.
TAKEAWAY:
- Cannabis users had significantly higher average minimum alveolar concentrations of isoflurane or sevoflurane than nonusers (mean, 0.58 vs 0.54; mean difference, 0.04; P = .021).
- The findings were confirmed in a sensitivity analysis that revealed higher mean average minimum alveolar concentrations of anesthesia in cannabis users than in nonusers (0.57 vs 0.53; P = .029).
- Although the 0.04 difference in minimum alveolar concentration between cannabis users and nonusers was statistically significant, its clinical importance is unclear.
IN PRACTICE:
“While recent guidelines underscore the importance of universal screening for cannabinoids before surgery, caution is paramount to prevent clinical bias leading to the administration of unnecessary higher doses of inhalational anesthesia, especially as robust evidence supporting such practices remains lacking,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Ruba Sajdeya, MD, PhD, of the Department of Epidemiology at the University of Florida, Gainesville, and was published online in August 2024 in Anesthesiology.
LIMITATIONS:
This study lacked access to prescription or dispensed medications, including opioids, which may have introduced residual confounding. Potential underdocumentation of cannabis use in medical records could have led to exposure misclassification. The causality between cannabis usage and increased anesthetic dosing could not be established due to the observational nature of this study.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the National Institute on Aging, the National Institutes of Health, and in part by the University of Florida Clinical and Translational Science Institute. Some authors declared receiving research support, consulting fees, and honoraria and having other ties with pharmaceutical companies and various other sources.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
However, the clinical relevance of this difference remains unclear.
METHODOLOGY:
- To assess if cannabis use leads to higher doses of inhalational anesthesia during surgery, the researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study comparing the average intraoperative minimum alveolar concentrations of volatile anesthetics (isoflurane and sevoflurane) between older adults who used cannabis products and those who did not.
- The researchers reviewed electronic health records of 22,476 patients aged 65 years or older who underwent surgery at the University of Florida Health System between 2018 and 2020.
- Overall, 268 patients who reported using cannabis within 60 days of surgery (median age, 69 years; 35% women) were matched to 1072 nonusers.
- The median duration of anesthesia was 175 minutes.
- The primary outcome was the intraoperative time-weighted average of isoflurane or sevoflurane minimum alveolar concentration equivalents.
TAKEAWAY:
- Cannabis users had significantly higher average minimum alveolar concentrations of isoflurane or sevoflurane than nonusers (mean, 0.58 vs 0.54; mean difference, 0.04; P = .021).
- The findings were confirmed in a sensitivity analysis that revealed higher mean average minimum alveolar concentrations of anesthesia in cannabis users than in nonusers (0.57 vs 0.53; P = .029).
- Although the 0.04 difference in minimum alveolar concentration between cannabis users and nonusers was statistically significant, its clinical importance is unclear.
IN PRACTICE:
“While recent guidelines underscore the importance of universal screening for cannabinoids before surgery, caution is paramount to prevent clinical bias leading to the administration of unnecessary higher doses of inhalational anesthesia, especially as robust evidence supporting such practices remains lacking,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Ruba Sajdeya, MD, PhD, of the Department of Epidemiology at the University of Florida, Gainesville, and was published online in August 2024 in Anesthesiology.
LIMITATIONS:
This study lacked access to prescription or dispensed medications, including opioids, which may have introduced residual confounding. Potential underdocumentation of cannabis use in medical records could have led to exposure misclassification. The causality between cannabis usage and increased anesthetic dosing could not be established due to the observational nature of this study.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the National Institute on Aging, the National Institutes of Health, and in part by the University of Florida Clinical and Translational Science Institute. Some authors declared receiving research support, consulting fees, and honoraria and having other ties with pharmaceutical companies and various other sources.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
However, the clinical relevance of this difference remains unclear.
METHODOLOGY:
- To assess if cannabis use leads to higher doses of inhalational anesthesia during surgery, the researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study comparing the average intraoperative minimum alveolar concentrations of volatile anesthetics (isoflurane and sevoflurane) between older adults who used cannabis products and those who did not.
- The researchers reviewed electronic health records of 22,476 patients aged 65 years or older who underwent surgery at the University of Florida Health System between 2018 and 2020.
- Overall, 268 patients who reported using cannabis within 60 days of surgery (median age, 69 years; 35% women) were matched to 1072 nonusers.
- The median duration of anesthesia was 175 minutes.
- The primary outcome was the intraoperative time-weighted average of isoflurane or sevoflurane minimum alveolar concentration equivalents.
TAKEAWAY:
- Cannabis users had significantly higher average minimum alveolar concentrations of isoflurane or sevoflurane than nonusers (mean, 0.58 vs 0.54; mean difference, 0.04; P = .021).
- The findings were confirmed in a sensitivity analysis that revealed higher mean average minimum alveolar concentrations of anesthesia in cannabis users than in nonusers (0.57 vs 0.53; P = .029).
- Although the 0.04 difference in minimum alveolar concentration between cannabis users and nonusers was statistically significant, its clinical importance is unclear.
IN PRACTICE:
“While recent guidelines underscore the importance of universal screening for cannabinoids before surgery, caution is paramount to prevent clinical bias leading to the administration of unnecessary higher doses of inhalational anesthesia, especially as robust evidence supporting such practices remains lacking,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Ruba Sajdeya, MD, PhD, of the Department of Epidemiology at the University of Florida, Gainesville, and was published online in August 2024 in Anesthesiology.
LIMITATIONS:
This study lacked access to prescription or dispensed medications, including opioids, which may have introduced residual confounding. Potential underdocumentation of cannabis use in medical records could have led to exposure misclassification. The causality between cannabis usage and increased anesthetic dosing could not be established due to the observational nature of this study.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the National Institute on Aging, the National Institutes of Health, and in part by the University of Florida Clinical and Translational Science Institute. Some authors declared receiving research support, consulting fees, and honoraria and having other ties with pharmaceutical companies and various other sources.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Enhanced Care for Pediatric Patients With Generalized Lichen Planus: Diagnosis and Treatment Tips
Practice Gap
Lichen planus (LP) is an inflammatory cutaneous disorder. Although it often is characterized by the 6 Ps—pruritic, polygonal, planar, purple, papules, and plaques with a predilection for the wrists and ankles—the presentation can vary in morphology and distribution.1-5 With an incidence of approximately 1% in the general population, LP is undoubtedly uncommon.1 Its prevalence in the pediatric population is especially low, with only 2% to 3% of cases manifesting in individuals younger than 20 years.2
Generalized LP (also referred to as eruptive or exanthematous LP) is a rarely reported clinical subtype in which lesions are disseminated or spread rapidly.5 The rarity of generalized LP in children often leads to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment, impacting the patient’s quality of life. Thus, there is a need for heightened awareness among clinicians on the variable presentation of LP in the pediatric population. Incorporating a punch biopsy for the diagnosis of LP when lesions manifest as widespread, erythematous to violaceous, flat-topped papules or plaques, along with the addition of an intramuscular (IM) injection in the treatment plan, improves overall patient outcomes.
Tools and Techniques
A detailed physical examination followed by a punch biopsy was critical for the diagnosis of generalized LP in a 7-year-old Black girl. The examination revealed a widespread distribution of dark, violaceous, polygonal, shiny, flat-topped, firm papules coalescing into plaques across the entire body, with a greater predilection for the legs and overlying joints (Figure, A). Some lesions exhibited fine, silver-white, reticular patterns consistent with Wickham striae. Notably, there was no involvement of the scalp, nails, or mucosal surfaces.
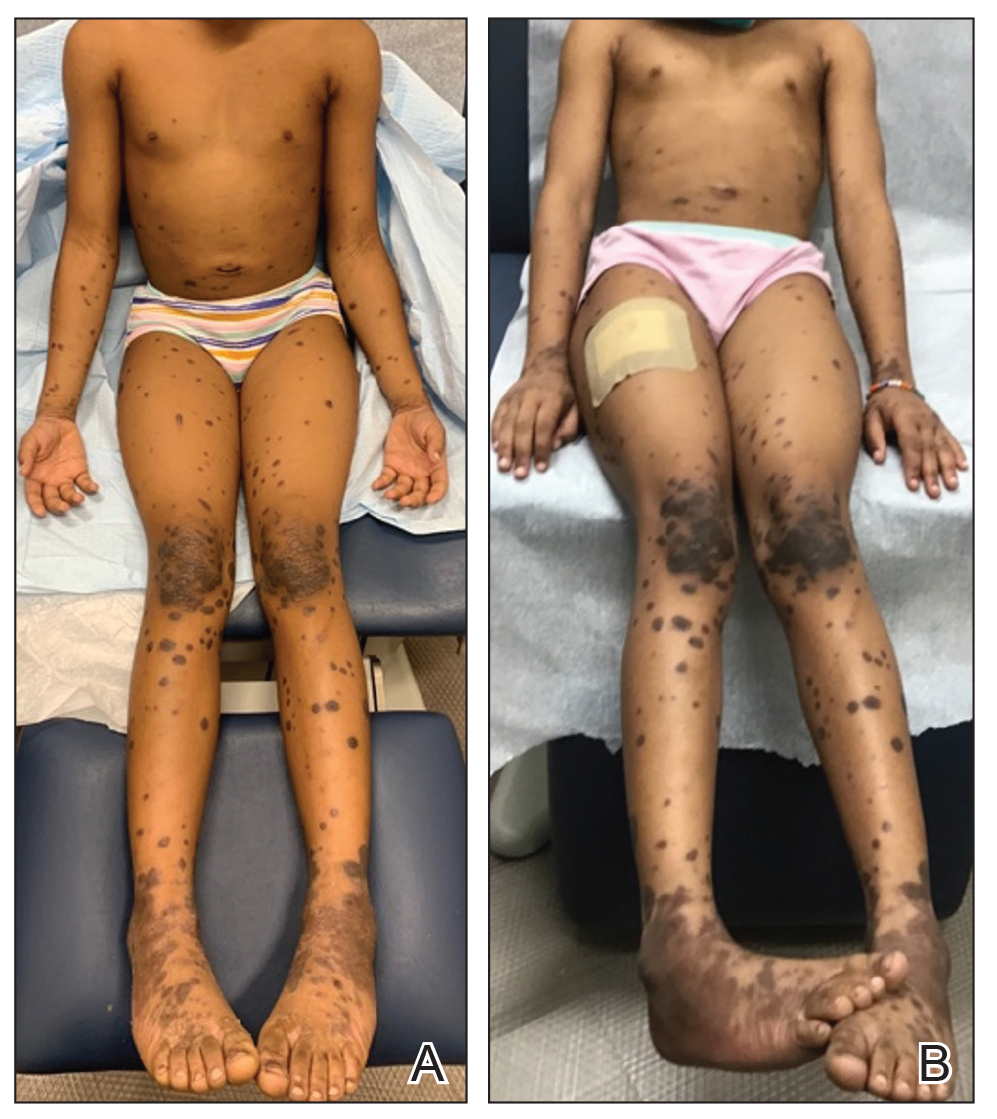
The patient had no relevant medical or family history of skin disease and no recent history of illness. She previously was treated by a pediatrician with triamcinolone cream 0.1%, a course of oral cephalexin, and oral cetirizine 10 mg once daily without relief of symptoms.
Although the clinical presentation was consistent with LP, the differential diagnosis included lichen simplex chronicus, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and generalized granuloma annulare. To address the need for early recognition of LP in pediatric patients, a punch biopsy of a lesion on the left anterior thigh was performed and showed lichenoid interface dermatitis—a pivotal finding in distinguishing LP from other conditions in the differential.
Given the patient’s age and severity of the LP, a combination of topical and systemic therapies was prescribed—clobetasol cream 0.025% twice daily and 1 injection of 0.5 cc of IM triamcinolone acetonide 40 mg/mL. This regimen was guided by the efficacy of IM injections in providing prompt symptomatic relief, particularly for patients with extensive disease or for those whose condition is refractory to topical treatments.6 Our patient achieved remarkable improvement at 2-week follow-up (Figure, B), without any observed adverse effects. At that time, the patient’s mother refused further systemic treatment and opted for only the topical therapy as well as natural light therapy.
Practice Implications
Timely and accurate diagnosis of LP in pediatric patients, especially those with skin of color, is crucial. Early intervention is especially important in mitigating the risk for chronic symptoms and preventing potential scarring, which tends to be more pronounced and challenging to treat in individuals with darker skin tones.7 Although not present in our patient, it is important to note that LP can affect the face (including the eyelids) as well as the palms and soles in pediatric patients with skin of color.
The most common approach to management of pediatric LP involves the use of a topical corticosteroid and an oral antihistamine, but the recalcitrant and generalized distribution of lesions warrants the administration of a systemic corticosteroid regardless of the patient’s age.6 In our patient, prompt administration of low-dose IM triamcinolone was both crucial and beneficial. Although an underutilized approach, IM triamcinolone helps to prevent the progression of lesions to the scalp, nails, and mucosa while also reducing inflammation and pruritus in glabrous skin.8
Triamcinolone acetonide injections—administered at concentrations of 5 to 40 mg/mL—directly into the lesion (0.5–1 cc per 2 cm2) are highly effective in managing recalcitrant thickened lesions such as those seen in hypertrophic LP and palmoplantar LP.6 This treatment is particularly beneficial when lesions are unresponsive to topical therapies. Administered every 3 to 6 weeks, these injections provide rapid symptom relief, typically within 72 hours,6 while also contributing to the reduction of lesion size and thickness over time. The concentration of triamcinolone acetonide should be selected based on the lesion’s severity, with higher concentrations reserved for thicker, more resistant lesions. More frequent injections may be warranted in cases in which rapid lesion reduction is necessary, while less frequent sessions may suffice for maintenance therapy. It is important to follow patients closely for adverse effects, such as signs of local skin atrophy or hypopigmentation, and to adjust the dose or frequency accordingly. To mitigate these risks, consider using the lowest effective concentration and rotating injection sites if treating multiple lesions. Additionally, combining intralesional corticosteroids with topical therapies can enhance outcomes, particularly in cases in which monotherapy is insufficient.
Patients should be monitored vigilantly for complications of LP. The risk for postinflammatory hyperpigmentation is a particular concern for patients with skin of color. Other complications of untreated LP include nail deformities and scarring alopecia.9 Regular and thorough follow-ups every few months to monitor scalp, mucosal, and genital involvement are essential to manage this risk effectively.
Furthermore, patient education is key. Informing patients and their caregivers about the nature of LP, the available treatment options, and the importance of ongoing follow-up can help to enhance treatment adherence and improve overall outcomes.
- Le Cleach L, Chosidow O. Clinical practice. Lichen planus. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:723-732. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1103641
- Handa S, Sahoo B. Childhood lichen planus: a study of 87 cases. Int J Dermatol. 2002;41:423-427. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2002.01522.x
- George J, Murray T, Bain M. Generalized, eruptive lichen planus in a pediatric patient. Contemp Pediatr. 2022;39:32-34.
- Arnold DL, Krishnamurthy K. Lichen planus. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated June 1, 2023. Accessed August 12, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526126/
- Weston G, Payette M. Update on lichen planus and its clinical variants. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2015;1:140-149. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2015.04.001
- Mutalik SD, Belgaumkar VA, Rasal YD. Current perspectives in the treatment of childhood lichen planus. Indian J Paediatr Dermatol. 2021;22:316-325. doi:10.4103/ijpd.ijpd_165_20
- Usatine RP, Tinitigan M. Diagnosis and treatment of lichen planus. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84:53-60.
- Thomas LW, Elsensohn A, Bergheim T, et al. Intramuscular steroids in the treatment of dermatologic disease: a systematic review. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:323-329.
- Gorouhi F, Davari P, Fazel N. Cutaneous and mucosal lichen planus: a comprehensive review of clinical subtypes, risk factors, diagnosis, and prognosis. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:742826. doi:10.1155/2014/742826
Practice Gap
Lichen planus (LP) is an inflammatory cutaneous disorder. Although it often is characterized by the 6 Ps—pruritic, polygonal, planar, purple, papules, and plaques with a predilection for the wrists and ankles—the presentation can vary in morphology and distribution.1-5 With an incidence of approximately 1% in the general population, LP is undoubtedly uncommon.1 Its prevalence in the pediatric population is especially low, with only 2% to 3% of cases manifesting in individuals younger than 20 years.2
Generalized LP (also referred to as eruptive or exanthematous LP) is a rarely reported clinical subtype in which lesions are disseminated or spread rapidly.5 The rarity of generalized LP in children often leads to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment, impacting the patient’s quality of life. Thus, there is a need for heightened awareness among clinicians on the variable presentation of LP in the pediatric population. Incorporating a punch biopsy for the diagnosis of LP when lesions manifest as widespread, erythematous to violaceous, flat-topped papules or plaques, along with the addition of an intramuscular (IM) injection in the treatment plan, improves overall patient outcomes.
Tools and Techniques
A detailed physical examination followed by a punch biopsy was critical for the diagnosis of generalized LP in a 7-year-old Black girl. The examination revealed a widespread distribution of dark, violaceous, polygonal, shiny, flat-topped, firm papules coalescing into plaques across the entire body, with a greater predilection for the legs and overlying joints (Figure, A). Some lesions exhibited fine, silver-white, reticular patterns consistent with Wickham striae. Notably, there was no involvement of the scalp, nails, or mucosal surfaces.

The patient had no relevant medical or family history of skin disease and no recent history of illness. She previously was treated by a pediatrician with triamcinolone cream 0.1%, a course of oral cephalexin, and oral cetirizine 10 mg once daily without relief of symptoms.
Although the clinical presentation was consistent with LP, the differential diagnosis included lichen simplex chronicus, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and generalized granuloma annulare. To address the need for early recognition of LP in pediatric patients, a punch biopsy of a lesion on the left anterior thigh was performed and showed lichenoid interface dermatitis—a pivotal finding in distinguishing LP from other conditions in the differential.
Given the patient’s age and severity of the LP, a combination of topical and systemic therapies was prescribed—clobetasol cream 0.025% twice daily and 1 injection of 0.5 cc of IM triamcinolone acetonide 40 mg/mL. This regimen was guided by the efficacy of IM injections in providing prompt symptomatic relief, particularly for patients with extensive disease or for those whose condition is refractory to topical treatments.6 Our patient achieved remarkable improvement at 2-week follow-up (Figure, B), without any observed adverse effects. At that time, the patient’s mother refused further systemic treatment and opted for only the topical therapy as well as natural light therapy.
Practice Implications
Timely and accurate diagnosis of LP in pediatric patients, especially those with skin of color, is crucial. Early intervention is especially important in mitigating the risk for chronic symptoms and preventing potential scarring, which tends to be more pronounced and challenging to treat in individuals with darker skin tones.7 Although not present in our patient, it is important to note that LP can affect the face (including the eyelids) as well as the palms and soles in pediatric patients with skin of color.
The most common approach to management of pediatric LP involves the use of a topical corticosteroid and an oral antihistamine, but the recalcitrant and generalized distribution of lesions warrants the administration of a systemic corticosteroid regardless of the patient’s age.6 In our patient, prompt administration of low-dose IM triamcinolone was both crucial and beneficial. Although an underutilized approach, IM triamcinolone helps to prevent the progression of lesions to the scalp, nails, and mucosa while also reducing inflammation and pruritus in glabrous skin.8
Triamcinolone acetonide injections—administered at concentrations of 5 to 40 mg/mL—directly into the lesion (0.5–1 cc per 2 cm2) are highly effective in managing recalcitrant thickened lesions such as those seen in hypertrophic LP and palmoplantar LP.6 This treatment is particularly beneficial when lesions are unresponsive to topical therapies. Administered every 3 to 6 weeks, these injections provide rapid symptom relief, typically within 72 hours,6 while also contributing to the reduction of lesion size and thickness over time. The concentration of triamcinolone acetonide should be selected based on the lesion’s severity, with higher concentrations reserved for thicker, more resistant lesions. More frequent injections may be warranted in cases in which rapid lesion reduction is necessary, while less frequent sessions may suffice for maintenance therapy. It is important to follow patients closely for adverse effects, such as signs of local skin atrophy or hypopigmentation, and to adjust the dose or frequency accordingly. To mitigate these risks, consider using the lowest effective concentration and rotating injection sites if treating multiple lesions. Additionally, combining intralesional corticosteroids with topical therapies can enhance outcomes, particularly in cases in which monotherapy is insufficient.
Patients should be monitored vigilantly for complications of LP. The risk for postinflammatory hyperpigmentation is a particular concern for patients with skin of color. Other complications of untreated LP include nail deformities and scarring alopecia.9 Regular and thorough follow-ups every few months to monitor scalp, mucosal, and genital involvement are essential to manage this risk effectively.
Furthermore, patient education is key. Informing patients and their caregivers about the nature of LP, the available treatment options, and the importance of ongoing follow-up can help to enhance treatment adherence and improve overall outcomes.
Practice Gap
Lichen planus (LP) is an inflammatory cutaneous disorder. Although it often is characterized by the 6 Ps—pruritic, polygonal, planar, purple, papules, and plaques with a predilection for the wrists and ankles—the presentation can vary in morphology and distribution.1-5 With an incidence of approximately 1% in the general population, LP is undoubtedly uncommon.1 Its prevalence in the pediatric population is especially low, with only 2% to 3% of cases manifesting in individuals younger than 20 years.2
Generalized LP (also referred to as eruptive or exanthematous LP) is a rarely reported clinical subtype in which lesions are disseminated or spread rapidly.5 The rarity of generalized LP in children often leads to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment, impacting the patient’s quality of life. Thus, there is a need for heightened awareness among clinicians on the variable presentation of LP in the pediatric population. Incorporating a punch biopsy for the diagnosis of LP when lesions manifest as widespread, erythematous to violaceous, flat-topped papules or plaques, along with the addition of an intramuscular (IM) injection in the treatment plan, improves overall patient outcomes.
Tools and Techniques
A detailed physical examination followed by a punch biopsy was critical for the diagnosis of generalized LP in a 7-year-old Black girl. The examination revealed a widespread distribution of dark, violaceous, polygonal, shiny, flat-topped, firm papules coalescing into plaques across the entire body, with a greater predilection for the legs and overlying joints (Figure, A). Some lesions exhibited fine, silver-white, reticular patterns consistent with Wickham striae. Notably, there was no involvement of the scalp, nails, or mucosal surfaces.

The patient had no relevant medical or family history of skin disease and no recent history of illness. She previously was treated by a pediatrician with triamcinolone cream 0.1%, a course of oral cephalexin, and oral cetirizine 10 mg once daily without relief of symptoms.
Although the clinical presentation was consistent with LP, the differential diagnosis included lichen simplex chronicus, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and generalized granuloma annulare. To address the need for early recognition of LP in pediatric patients, a punch biopsy of a lesion on the left anterior thigh was performed and showed lichenoid interface dermatitis—a pivotal finding in distinguishing LP from other conditions in the differential.
Given the patient’s age and severity of the LP, a combination of topical and systemic therapies was prescribed—clobetasol cream 0.025% twice daily and 1 injection of 0.5 cc of IM triamcinolone acetonide 40 mg/mL. This regimen was guided by the efficacy of IM injections in providing prompt symptomatic relief, particularly for patients with extensive disease or for those whose condition is refractory to topical treatments.6 Our patient achieved remarkable improvement at 2-week follow-up (Figure, B), without any observed adverse effects. At that time, the patient’s mother refused further systemic treatment and opted for only the topical therapy as well as natural light therapy.
Practice Implications
Timely and accurate diagnosis of LP in pediatric patients, especially those with skin of color, is crucial. Early intervention is especially important in mitigating the risk for chronic symptoms and preventing potential scarring, which tends to be more pronounced and challenging to treat in individuals with darker skin tones.7 Although not present in our patient, it is important to note that LP can affect the face (including the eyelids) as well as the palms and soles in pediatric patients with skin of color.
The most common approach to management of pediatric LP involves the use of a topical corticosteroid and an oral antihistamine, but the recalcitrant and generalized distribution of lesions warrants the administration of a systemic corticosteroid regardless of the patient’s age.6 In our patient, prompt administration of low-dose IM triamcinolone was both crucial and beneficial. Although an underutilized approach, IM triamcinolone helps to prevent the progression of lesions to the scalp, nails, and mucosa while also reducing inflammation and pruritus in glabrous skin.8
Triamcinolone acetonide injections—administered at concentrations of 5 to 40 mg/mL—directly into the lesion (0.5–1 cc per 2 cm2) are highly effective in managing recalcitrant thickened lesions such as those seen in hypertrophic LP and palmoplantar LP.6 This treatment is particularly beneficial when lesions are unresponsive to topical therapies. Administered every 3 to 6 weeks, these injections provide rapid symptom relief, typically within 72 hours,6 while also contributing to the reduction of lesion size and thickness over time. The concentration of triamcinolone acetonide should be selected based on the lesion’s severity, with higher concentrations reserved for thicker, more resistant lesions. More frequent injections may be warranted in cases in which rapid lesion reduction is necessary, while less frequent sessions may suffice for maintenance therapy. It is important to follow patients closely for adverse effects, such as signs of local skin atrophy or hypopigmentation, and to adjust the dose or frequency accordingly. To mitigate these risks, consider using the lowest effective concentration and rotating injection sites if treating multiple lesions. Additionally, combining intralesional corticosteroids with topical therapies can enhance outcomes, particularly in cases in which monotherapy is insufficient.
Patients should be monitored vigilantly for complications of LP. The risk for postinflammatory hyperpigmentation is a particular concern for patients with skin of color. Other complications of untreated LP include nail deformities and scarring alopecia.9 Regular and thorough follow-ups every few months to monitor scalp, mucosal, and genital involvement are essential to manage this risk effectively.
Furthermore, patient education is key. Informing patients and their caregivers about the nature of LP, the available treatment options, and the importance of ongoing follow-up can help to enhance treatment adherence and improve overall outcomes.
- Le Cleach L, Chosidow O. Clinical practice. Lichen planus. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:723-732. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1103641
- Handa S, Sahoo B. Childhood lichen planus: a study of 87 cases. Int J Dermatol. 2002;41:423-427. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2002.01522.x
- George J, Murray T, Bain M. Generalized, eruptive lichen planus in a pediatric patient. Contemp Pediatr. 2022;39:32-34.
- Arnold DL, Krishnamurthy K. Lichen planus. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated June 1, 2023. Accessed August 12, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526126/
- Weston G, Payette M. Update on lichen planus and its clinical variants. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2015;1:140-149. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2015.04.001
- Mutalik SD, Belgaumkar VA, Rasal YD. Current perspectives in the treatment of childhood lichen planus. Indian J Paediatr Dermatol. 2021;22:316-325. doi:10.4103/ijpd.ijpd_165_20
- Usatine RP, Tinitigan M. Diagnosis and treatment of lichen planus. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84:53-60.
- Thomas LW, Elsensohn A, Bergheim T, et al. Intramuscular steroids in the treatment of dermatologic disease: a systematic review. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:323-329.
- Gorouhi F, Davari P, Fazel N. Cutaneous and mucosal lichen planus: a comprehensive review of clinical subtypes, risk factors, diagnosis, and prognosis. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:742826. doi:10.1155/2014/742826
- Le Cleach L, Chosidow O. Clinical practice. Lichen planus. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:723-732. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1103641
- Handa S, Sahoo B. Childhood lichen planus: a study of 87 cases. Int J Dermatol. 2002;41:423-427. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2002.01522.x
- George J, Murray T, Bain M. Generalized, eruptive lichen planus in a pediatric patient. Contemp Pediatr. 2022;39:32-34.
- Arnold DL, Krishnamurthy K. Lichen planus. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated June 1, 2023. Accessed August 12, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526126/
- Weston G, Payette M. Update on lichen planus and its clinical variants. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2015;1:140-149. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2015.04.001
- Mutalik SD, Belgaumkar VA, Rasal YD. Current perspectives in the treatment of childhood lichen planus. Indian J Paediatr Dermatol. 2021;22:316-325. doi:10.4103/ijpd.ijpd_165_20
- Usatine RP, Tinitigan M. Diagnosis and treatment of lichen planus. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84:53-60.
- Thomas LW, Elsensohn A, Bergheim T, et al. Intramuscular steroids in the treatment of dermatologic disease: a systematic review. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:323-329.
- Gorouhi F, Davari P, Fazel N. Cutaneous and mucosal lichen planus: a comprehensive review of clinical subtypes, risk factors, diagnosis, and prognosis. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:742826. doi:10.1155/2014/742826
Top DEI Topics to Incorporate Into Dermatology Residency Training: An Electronic Delphi Consensus Study
Diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) programs seek to improve dermatologic education and clinical care for an increasingly diverse patient population as well as to recruit and sustain a physician workforce that reflects the diversity of the patients they serve.1,2 In dermatology, only 4.2% and 3.0% of practicing dermatologists self-identify as being of Hispanic and African American ethnicity, respectively, compared with 18.5% and 13.4% of the general population, respectively.3 Creating an educational system that works to meet the goals of DEI is essential to improve health outcomes and address disparities. The lack of robust DEI-related curricula during residency training may limit the ability of practicing dermatologists to provide comprehensive and culturally sensitive care. It has been shown that racial concordance between patients and physicians has a positive impact on patient satisfaction by fostering a trusting patient-physician relationship.4
It is the responsibility of all dermatologists to create an environment where patients from any background can feel comfortable, which can be cultivated by establishing patient-centered communication and cultural humility.5 These skills can be strengthened via the implementation of DEI-related curricula during residency training. Augmenting exposure of these topics during training can optimize the delivery of dermatologic care by providing residents with the tools and confidence needed to care for patients of culturally diverse backgrounds. Enhancing DEI education is crucial to not only improve the recognition and treatment of dermatologic conditions in all skin and hair types but also to minimize misconceptions, stigma, health disparities, and discrimination faced by historically marginalized communities. Creating a culture of inclusion is of paramount importance to build successful relationships with patients and colleagues of culturally diverse backgrounds.6
There are multiple efforts underway to increase DEI education across the field of dermatology, including the development of DEI task forces in professional organizations and societies that serve to expand DEI-related research, mentorship, and education. The American Academy of Dermatology has been leading efforts to create a curriculum focused on skin of color, particularly addressing inadequate educational training on how dermatologic conditions manifest in this population.7 The Skin of Color Society has similar efforts underway and is developing a speakers bureau to give leading experts a platform to lecture dermatology trainees as well as patient and community audiences on various topics in skin of color.8 These are just 2 of many professional dermatology organizations that are advocating for expanded education on DEI; however, consistently integrating DEI-related topics into dermatology residency training curricula remains a gap in pedagogy. To identify the DEI-related topics of greatest relevance to the dermatology resident curricula, we implemented a modified electronic Delphi (e-Delphi) consensus process to provide standardized recommendations.
Methods
A 2-round modified e-Delphi method was utilized (Figure). An initial list of potential curricular topics was formulated by an expert panel consisting of 5 dermatologists from the Association of Professors of Dermatology DEI subcommittee and the American Academy of Dermatology Diversity Task Force (A.M.A., S.B., R.V., S.D.W., J.I.S.). Initial topics were selected via several meetings among the panel members to discuss existing DEI concerns and issues that were deemed relevant due to education gaps in residency training. The list of topics was further expanded with recommendations obtained via an email sent to dermatology program directors on the Association of Professors of Dermatology listserve, which solicited voluntary participation of academic dermatologists, including program directors and dermatology residents.
There were 2 voting rounds, with each round consisting of questions scored on a Likert scale ranging from 1 to 5 (1=not essential, 2=probably not essential, 3=neutral, 4=probably essential, 5=definitely essential). The inclusion criteria to classify a topic as necessary for integration into the dermatology residency curriculum included 95% (18/19) or more of respondents rating the topic as probably essential or definitely essential; if more than 90% (17/19) of respondents rated the topic as probably essential or definitely essential and less than 10% (2/19) rated it as not essential or probably not essential, the topic was still included as part of the suggested curriculum. Topics that received ratings of probably essential or definitely essential by less than 80% (15/19) of respondents were removed from consideration. The topics that did not meet inclusion or exclusion criteria during the first round of voting were refined by the e-Delphi steering committee (V.S.E-C. and F-A.R.) based on open-ended feedback from the voting group provided at the end of the survey and subsequently passed to the second round of voting.
Results
Participants—A total of 19 respondents participated in both voting rounds, the majority (80% [15/19]) of whom were program directors or dermatologists affiliated with academia or development of DEI education; the remaining 20% [4/19]) were dermatology residents.
Open-Ended Feedback—Voting group members were able to provide open-ended feedback for each of the sets of topics after the survey, which the steering committee utilized to modify the topics as needed for the final voting round. For example, “structural racism/discrimination” was originally mentioned as a topic, but several participants suggested including specific types of racism; therefore, the wording was changed to “racism: types, definitions” to encompass broader definitions and types of racism.
Survey Results—Two genres of topics were surveyed in each voting round: clinical and nonclinical. Participants voted on a total of 61 topics, with 23 ultimately selected in the final list of consensus curricular topics. Of those, 9 were clinical and 14 nonclinical. All topics deemed necessary for inclusion in residency curricula are presented in eTables 1 and 2.
During the first round of voting, the e-Delphi panel reached a consensus to include the following 17 topics as essential to dermatology residency training (along with the percentage of voters who classified them as probably essential or definitely essential): how to mitigate bias in clinical and workplace settings (100% [40/40]); social determinants of health-related disparities in dermatology (100% [40/40]); hairstyling practices across different hair textures (100% [40/40]); definitions and examples of microaggressions (97.50% [39/40]); definition, background, and types of bias (97.50% [39/40]); manifestations of bias in the clinical setting (97.44% [38/39]); racial and ethnic disparities in dermatology (97.44% [38/39]); keloids (97.37% [37/38]); differences in dermoscopic presentations in skin of color (97.30% [36/37]); skin cancer in patients with skin of color (97.30% [36/37]); disparities due to bias (95.00% [38/40]); how to apply cultural humility and safety to patients of different cultural backgrounds (94.87% [37/40]); best practices in providing care to patients with limited English proficiency (94.87% [37/40]); hair loss in patients with textured hair (94.74% [36/38]); pseudofolliculitis barbae and acne keloidalis nuchae (94.60% [35/37]); disparities regarding people experiencing homelessness (92.31% [36/39]); and definitions and types of racism and other forms of discrimination (92.31% [36/39]). eTable 1 provides a list of suggested resources to incorporate these topics into the educational components of residency curricula. The resources provided were not part of the voting process, and they were not considered in the consensus analysis; they are included here as suggested educational catalysts.
During the second round of voting, 25 topics were evaluated. Of those, the following 6 topics were proposed to be included as essential in residency training: differences in prevalence and presentation of common inflammatory disorders (100% [29/29]); manifestations of bias in the learning environment (96.55%); antiracist action and how to decrease the effects of structural racism in clinical and educational settings (96.55% [28/29]); diversity of images in dermatology education (96.55% [28/29]); pigmentary disorders and their psychological effects (96.55% [28/29]); and LGBTQ (lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer) dermatologic health care (96.55% [28/29]). eTable 2 includes these topics as well as suggested resources to help incorporate them into training.
Comment
This study utilized a modified e-Delphi technique to identify relevant clinical and nonclinical DEI topics that should be incorporated into dermatology residency curricula. The panel members reached a consensus for 9 clinical DEI-related topics. The respondents agreed that the topics related to skin and hair conditions in patients with skin of color as well as textured hair were crucial to residency education. Skin cancer, hair loss, pseudofolliculitis barbae, acne keloidalis nuchae, keloids, pigmentary disorders, and their varying presentations in patients with skin of color were among the recommended topics. The panel also recommended educating residents on the variable visual presentations of inflammatory conditions in skin of color. Addressing the needs of diverse patients—for example, those belonging to the LGBTQ community—also was deemed important for inclusion.
The remaining 14 chosen topics were nonclinical items addressing concepts such as bias and health care disparities as well as cultural humility and safety.9 Cultural humility and safety focus on developing cultural awareness by creating a safe setting for patients rather than encouraging power relationships between them and their physicians. Various topics related to racism also were recommended to be included in residency curricula, including education on implementation of antiracist action in the workplace.
Many of the nonclinical topics are intertwined; for instance, learning about health care disparities in patients with limited English proficiency allows for improved best practices in delivering care to patients from this population. The first step in overcoming bias and subsequent disparities is acknowledging how the perpetuation of bias leads to disparities after being taught tools to recognize it.
Our group’s guidance on DEI topics should help dermatology residency program leaders as they design and refine program curricula. There are multiple avenues for incorporating education on these topics, including lectures, interactive workshops, role-playing sessions, book or journal clubs, and discussion circles. Many of these topics/programs may already be included in programs’ didactic curricula, which would minimize the burden of finding space to educate on these topics. Institutional cultural change is key to ensuring truly diverse, equitable, and inclusive workplaces. Educating tomorrow’s dermatologists on these topics is a first step toward achieving that cultural change.
Limitations—A limitation of this e-Delphi survey is that only a selection of experts in this field was included. Additionally, we were concerned that the Likert scale format and the bar we set for inclusion and exclusion may have failed to adequately capture participants’ nuanced opinions. As such, participants were able to provide open-ended feedback, and suggestions for alternate wording or other changes were considered by the steering committee. Finally, inclusion recommendations identified in this survey were developed specifically for US dermatology residents.
Conclusion
In this e-Delphi consensus assessment of DEI-related topics, we recommend the inclusion of 23 topics into dermatology residency program curricula to improve medical training and the patient-physician relationship as well as to create better health outcomes. We also provide specific sample resource recommendations in eTables 1 and 2 to facilitate inclusion of these topics into residency curricula across the country.
- US Census Bureau projections show a slower growing, older, more diverse nation a half century from now. News release. US Census Bureau. December 12, 2012. Accessed August 14, 2024. https://www.census.gov/newsroom/releases/archives/population/cb12243.html#:~:text=12%2C%202012,U.S.%20Census%20Bureau%20Projections%20Show%20a%20Slower%20Growing%2C%20Older%2C%20More,by%20the%20U.S.%20Census%20Bureau
- Lopez S, Lourido JO, Lim HW, et al. The call to action to increase racial and ethnic diversity in dermatology: a retrospective, cross-sectional study to monitor progress. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;86:E121-E123. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.10.011
- El-Kashlan N, Alexis A. Disparities in dermatology: a reflection. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022;15:27-29.
- Laveist TA, Nuru-Jeter A. Is doctor-patient race concordance associated with greater satisfaction with care? J Health Soc Behav. 2002;43:296-306.
- Street RL Jr, O’Malley KJ, Cooper LA, et al. Understanding concordance in patient-physician relationships: personal and ethnic dimensions of shared identity. Ann Fam Med. 2008;6:198-205. doi:10.1370/afm.821
- Dadrass F, Bowers S, Shinkai K, et al. Diversity, equity, and inclusion in dermatology residency. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41:257-263. doi:10.1016/j.det.2022.10.006
- Diversity and the Academy. American Academy of Dermatology website. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://www.aad.org/member/career/diversity
- SOCS speaks. Skin of Color Society website. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://skinofcolorsociety.org/news-media/socs-speaks
- Solchanyk D, Ekeh O, Saffran L, et al. Integrating cultural humility into the medical education curriculum: strategies for educators. Teach Learn Med. 2021;33:554-560. doi:10.1080/10401334.2021.1877711
Diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) programs seek to improve dermatologic education and clinical care for an increasingly diverse patient population as well as to recruit and sustain a physician workforce that reflects the diversity of the patients they serve.1,2 In dermatology, only 4.2% and 3.0% of practicing dermatologists self-identify as being of Hispanic and African American ethnicity, respectively, compared with 18.5% and 13.4% of the general population, respectively.3 Creating an educational system that works to meet the goals of DEI is essential to improve health outcomes and address disparities. The lack of robust DEI-related curricula during residency training may limit the ability of practicing dermatologists to provide comprehensive and culturally sensitive care. It has been shown that racial concordance between patients and physicians has a positive impact on patient satisfaction by fostering a trusting patient-physician relationship.4
It is the responsibility of all dermatologists to create an environment where patients from any background can feel comfortable, which can be cultivated by establishing patient-centered communication and cultural humility.5 These skills can be strengthened via the implementation of DEI-related curricula during residency training. Augmenting exposure of these topics during training can optimize the delivery of dermatologic care by providing residents with the tools and confidence needed to care for patients of culturally diverse backgrounds. Enhancing DEI education is crucial to not only improve the recognition and treatment of dermatologic conditions in all skin and hair types but also to minimize misconceptions, stigma, health disparities, and discrimination faced by historically marginalized communities. Creating a culture of inclusion is of paramount importance to build successful relationships with patients and colleagues of culturally diverse backgrounds.6
There are multiple efforts underway to increase DEI education across the field of dermatology, including the development of DEI task forces in professional organizations and societies that serve to expand DEI-related research, mentorship, and education. The American Academy of Dermatology has been leading efforts to create a curriculum focused on skin of color, particularly addressing inadequate educational training on how dermatologic conditions manifest in this population.7 The Skin of Color Society has similar efforts underway and is developing a speakers bureau to give leading experts a platform to lecture dermatology trainees as well as patient and community audiences on various topics in skin of color.8 These are just 2 of many professional dermatology organizations that are advocating for expanded education on DEI; however, consistently integrating DEI-related topics into dermatology residency training curricula remains a gap in pedagogy. To identify the DEI-related topics of greatest relevance to the dermatology resident curricula, we implemented a modified electronic Delphi (e-Delphi) consensus process to provide standardized recommendations.
Methods
A 2-round modified e-Delphi method was utilized (Figure). An initial list of potential curricular topics was formulated by an expert panel consisting of 5 dermatologists from the Association of Professors of Dermatology DEI subcommittee and the American Academy of Dermatology Diversity Task Force (A.M.A., S.B., R.V., S.D.W., J.I.S.). Initial topics were selected via several meetings among the panel members to discuss existing DEI concerns and issues that were deemed relevant due to education gaps in residency training. The list of topics was further expanded with recommendations obtained via an email sent to dermatology program directors on the Association of Professors of Dermatology listserve, which solicited voluntary participation of academic dermatologists, including program directors and dermatology residents.

There were 2 voting rounds, with each round consisting of questions scored on a Likert scale ranging from 1 to 5 (1=not essential, 2=probably not essential, 3=neutral, 4=probably essential, 5=definitely essential). The inclusion criteria to classify a topic as necessary for integration into the dermatology residency curriculum included 95% (18/19) or more of respondents rating the topic as probably essential or definitely essential; if more than 90% (17/19) of respondents rated the topic as probably essential or definitely essential and less than 10% (2/19) rated it as not essential or probably not essential, the topic was still included as part of the suggested curriculum. Topics that received ratings of probably essential or definitely essential by less than 80% (15/19) of respondents were removed from consideration. The topics that did not meet inclusion or exclusion criteria during the first round of voting were refined by the e-Delphi steering committee (V.S.E-C. and F-A.R.) based on open-ended feedback from the voting group provided at the end of the survey and subsequently passed to the second round of voting.
Results
Participants—A total of 19 respondents participated in both voting rounds, the majority (80% [15/19]) of whom were program directors or dermatologists affiliated with academia or development of DEI education; the remaining 20% [4/19]) were dermatology residents.
Open-Ended Feedback—Voting group members were able to provide open-ended feedback for each of the sets of topics after the survey, which the steering committee utilized to modify the topics as needed for the final voting round. For example, “structural racism/discrimination” was originally mentioned as a topic, but several participants suggested including specific types of racism; therefore, the wording was changed to “racism: types, definitions” to encompass broader definitions and types of racism.
Survey Results—Two genres of topics were surveyed in each voting round: clinical and nonclinical. Participants voted on a total of 61 topics, with 23 ultimately selected in the final list of consensus curricular topics. Of those, 9 were clinical and 14 nonclinical. All topics deemed necessary for inclusion in residency curricula are presented in eTables 1 and 2.
During the first round of voting, the e-Delphi panel reached a consensus to include the following 17 topics as essential to dermatology residency training (along with the percentage of voters who classified them as probably essential or definitely essential): how to mitigate bias in clinical and workplace settings (100% [40/40]); social determinants of health-related disparities in dermatology (100% [40/40]); hairstyling practices across different hair textures (100% [40/40]); definitions and examples of microaggressions (97.50% [39/40]); definition, background, and types of bias (97.50% [39/40]); manifestations of bias in the clinical setting (97.44% [38/39]); racial and ethnic disparities in dermatology (97.44% [38/39]); keloids (97.37% [37/38]); differences in dermoscopic presentations in skin of color (97.30% [36/37]); skin cancer in patients with skin of color (97.30% [36/37]); disparities due to bias (95.00% [38/40]); how to apply cultural humility and safety to patients of different cultural backgrounds (94.87% [37/40]); best practices in providing care to patients with limited English proficiency (94.87% [37/40]); hair loss in patients with textured hair (94.74% [36/38]); pseudofolliculitis barbae and acne keloidalis nuchae (94.60% [35/37]); disparities regarding people experiencing homelessness (92.31% [36/39]); and definitions and types of racism and other forms of discrimination (92.31% [36/39]). eTable 1 provides a list of suggested resources to incorporate these topics into the educational components of residency curricula. The resources provided were not part of the voting process, and they were not considered in the consensus analysis; they are included here as suggested educational catalysts.
During the second round of voting, 25 topics were evaluated. Of those, the following 6 topics were proposed to be included as essential in residency training: differences in prevalence and presentation of common inflammatory disorders (100% [29/29]); manifestations of bias in the learning environment (96.55%); antiracist action and how to decrease the effects of structural racism in clinical and educational settings (96.55% [28/29]); diversity of images in dermatology education (96.55% [28/29]); pigmentary disorders and their psychological effects (96.55% [28/29]); and LGBTQ (lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer) dermatologic health care (96.55% [28/29]). eTable 2 includes these topics as well as suggested resources to help incorporate them into training.
Comment
This study utilized a modified e-Delphi technique to identify relevant clinical and nonclinical DEI topics that should be incorporated into dermatology residency curricula. The panel members reached a consensus for 9 clinical DEI-related topics. The respondents agreed that the topics related to skin and hair conditions in patients with skin of color as well as textured hair were crucial to residency education. Skin cancer, hair loss, pseudofolliculitis barbae, acne keloidalis nuchae, keloids, pigmentary disorders, and their varying presentations in patients with skin of color were among the recommended topics. The panel also recommended educating residents on the variable visual presentations of inflammatory conditions in skin of color. Addressing the needs of diverse patients—for example, those belonging to the LGBTQ community—also was deemed important for inclusion.
The remaining 14 chosen topics were nonclinical items addressing concepts such as bias and health care disparities as well as cultural humility and safety.9 Cultural humility and safety focus on developing cultural awareness by creating a safe setting for patients rather than encouraging power relationships between them and their physicians. Various topics related to racism also were recommended to be included in residency curricula, including education on implementation of antiracist action in the workplace.
Many of the nonclinical topics are intertwined; for instance, learning about health care disparities in patients with limited English proficiency allows for improved best practices in delivering care to patients from this population. The first step in overcoming bias and subsequent disparities is acknowledging how the perpetuation of bias leads to disparities after being taught tools to recognize it.
Our group’s guidance on DEI topics should help dermatology residency program leaders as they design and refine program curricula. There are multiple avenues for incorporating education on these topics, including lectures, interactive workshops, role-playing sessions, book or journal clubs, and discussion circles. Many of these topics/programs may already be included in programs’ didactic curricula, which would minimize the burden of finding space to educate on these topics. Institutional cultural change is key to ensuring truly diverse, equitable, and inclusive workplaces. Educating tomorrow’s dermatologists on these topics is a first step toward achieving that cultural change.
Limitations—A limitation of this e-Delphi survey is that only a selection of experts in this field was included. Additionally, we were concerned that the Likert scale format and the bar we set for inclusion and exclusion may have failed to adequately capture participants’ nuanced opinions. As such, participants were able to provide open-ended feedback, and suggestions for alternate wording or other changes were considered by the steering committee. Finally, inclusion recommendations identified in this survey were developed specifically for US dermatology residents.
Conclusion
In this e-Delphi consensus assessment of DEI-related topics, we recommend the inclusion of 23 topics into dermatology residency program curricula to improve medical training and the patient-physician relationship as well as to create better health outcomes. We also provide specific sample resource recommendations in eTables 1 and 2 to facilitate inclusion of these topics into residency curricula across the country.
Diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) programs seek to improve dermatologic education and clinical care for an increasingly diverse patient population as well as to recruit and sustain a physician workforce that reflects the diversity of the patients they serve.1,2 In dermatology, only 4.2% and 3.0% of practicing dermatologists self-identify as being of Hispanic and African American ethnicity, respectively, compared with 18.5% and 13.4% of the general population, respectively.3 Creating an educational system that works to meet the goals of DEI is essential to improve health outcomes and address disparities. The lack of robust DEI-related curricula during residency training may limit the ability of practicing dermatologists to provide comprehensive and culturally sensitive care. It has been shown that racial concordance between patients and physicians has a positive impact on patient satisfaction by fostering a trusting patient-physician relationship.4
It is the responsibility of all dermatologists to create an environment where patients from any background can feel comfortable, which can be cultivated by establishing patient-centered communication and cultural humility.5 These skills can be strengthened via the implementation of DEI-related curricula during residency training. Augmenting exposure of these topics during training can optimize the delivery of dermatologic care by providing residents with the tools and confidence needed to care for patients of culturally diverse backgrounds. Enhancing DEI education is crucial to not only improve the recognition and treatment of dermatologic conditions in all skin and hair types but also to minimize misconceptions, stigma, health disparities, and discrimination faced by historically marginalized communities. Creating a culture of inclusion is of paramount importance to build successful relationships with patients and colleagues of culturally diverse backgrounds.6
There are multiple efforts underway to increase DEI education across the field of dermatology, including the development of DEI task forces in professional organizations and societies that serve to expand DEI-related research, mentorship, and education. The American Academy of Dermatology has been leading efforts to create a curriculum focused on skin of color, particularly addressing inadequate educational training on how dermatologic conditions manifest in this population.7 The Skin of Color Society has similar efforts underway and is developing a speakers bureau to give leading experts a platform to lecture dermatology trainees as well as patient and community audiences on various topics in skin of color.8 These are just 2 of many professional dermatology organizations that are advocating for expanded education on DEI; however, consistently integrating DEI-related topics into dermatology residency training curricula remains a gap in pedagogy. To identify the DEI-related topics of greatest relevance to the dermatology resident curricula, we implemented a modified electronic Delphi (e-Delphi) consensus process to provide standardized recommendations.
Methods
A 2-round modified e-Delphi method was utilized (Figure). An initial list of potential curricular topics was formulated by an expert panel consisting of 5 dermatologists from the Association of Professors of Dermatology DEI subcommittee and the American Academy of Dermatology Diversity Task Force (A.M.A., S.B., R.V., S.D.W., J.I.S.). Initial topics were selected via several meetings among the panel members to discuss existing DEI concerns and issues that were deemed relevant due to education gaps in residency training. The list of topics was further expanded with recommendations obtained via an email sent to dermatology program directors on the Association of Professors of Dermatology listserve, which solicited voluntary participation of academic dermatologists, including program directors and dermatology residents.

There were 2 voting rounds, with each round consisting of questions scored on a Likert scale ranging from 1 to 5 (1=not essential, 2=probably not essential, 3=neutral, 4=probably essential, 5=definitely essential). The inclusion criteria to classify a topic as necessary for integration into the dermatology residency curriculum included 95% (18/19) or more of respondents rating the topic as probably essential or definitely essential; if more than 90% (17/19) of respondents rated the topic as probably essential or definitely essential and less than 10% (2/19) rated it as not essential or probably not essential, the topic was still included as part of the suggested curriculum. Topics that received ratings of probably essential or definitely essential by less than 80% (15/19) of respondents were removed from consideration. The topics that did not meet inclusion or exclusion criteria during the first round of voting were refined by the e-Delphi steering committee (V.S.E-C. and F-A.R.) based on open-ended feedback from the voting group provided at the end of the survey and subsequently passed to the second round of voting.
Results
Participants—A total of 19 respondents participated in both voting rounds, the majority (80% [15/19]) of whom were program directors or dermatologists affiliated with academia or development of DEI education; the remaining 20% [4/19]) were dermatology residents.
Open-Ended Feedback—Voting group members were able to provide open-ended feedback for each of the sets of topics after the survey, which the steering committee utilized to modify the topics as needed for the final voting round. For example, “structural racism/discrimination” was originally mentioned as a topic, but several participants suggested including specific types of racism; therefore, the wording was changed to “racism: types, definitions” to encompass broader definitions and types of racism.
Survey Results—Two genres of topics were surveyed in each voting round: clinical and nonclinical. Participants voted on a total of 61 topics, with 23 ultimately selected in the final list of consensus curricular topics. Of those, 9 were clinical and 14 nonclinical. All topics deemed necessary for inclusion in residency curricula are presented in eTables 1 and 2.
During the first round of voting, the e-Delphi panel reached a consensus to include the following 17 topics as essential to dermatology residency training (along with the percentage of voters who classified them as probably essential or definitely essential): how to mitigate bias in clinical and workplace settings (100% [40/40]); social determinants of health-related disparities in dermatology (100% [40/40]); hairstyling practices across different hair textures (100% [40/40]); definitions and examples of microaggressions (97.50% [39/40]); definition, background, and types of bias (97.50% [39/40]); manifestations of bias in the clinical setting (97.44% [38/39]); racial and ethnic disparities in dermatology (97.44% [38/39]); keloids (97.37% [37/38]); differences in dermoscopic presentations in skin of color (97.30% [36/37]); skin cancer in patients with skin of color (97.30% [36/37]); disparities due to bias (95.00% [38/40]); how to apply cultural humility and safety to patients of different cultural backgrounds (94.87% [37/40]); best practices in providing care to patients with limited English proficiency (94.87% [37/40]); hair loss in patients with textured hair (94.74% [36/38]); pseudofolliculitis barbae and acne keloidalis nuchae (94.60% [35/37]); disparities regarding people experiencing homelessness (92.31% [36/39]); and definitions and types of racism and other forms of discrimination (92.31% [36/39]). eTable 1 provides a list of suggested resources to incorporate these topics into the educational components of residency curricula. The resources provided were not part of the voting process, and they were not considered in the consensus analysis; they are included here as suggested educational catalysts.
During the second round of voting, 25 topics were evaluated. Of those, the following 6 topics were proposed to be included as essential in residency training: differences in prevalence and presentation of common inflammatory disorders (100% [29/29]); manifestations of bias in the learning environment (96.55%); antiracist action and how to decrease the effects of structural racism in clinical and educational settings (96.55% [28/29]); diversity of images in dermatology education (96.55% [28/29]); pigmentary disorders and their psychological effects (96.55% [28/29]); and LGBTQ (lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer) dermatologic health care (96.55% [28/29]). eTable 2 includes these topics as well as suggested resources to help incorporate them into training.
Comment
This study utilized a modified e-Delphi technique to identify relevant clinical and nonclinical DEI topics that should be incorporated into dermatology residency curricula. The panel members reached a consensus for 9 clinical DEI-related topics. The respondents agreed that the topics related to skin and hair conditions in patients with skin of color as well as textured hair were crucial to residency education. Skin cancer, hair loss, pseudofolliculitis barbae, acne keloidalis nuchae, keloids, pigmentary disorders, and their varying presentations in patients with skin of color were among the recommended topics. The panel also recommended educating residents on the variable visual presentations of inflammatory conditions in skin of color. Addressing the needs of diverse patients—for example, those belonging to the LGBTQ community—also was deemed important for inclusion.
The remaining 14 chosen topics were nonclinical items addressing concepts such as bias and health care disparities as well as cultural humility and safety.9 Cultural humility and safety focus on developing cultural awareness by creating a safe setting for patients rather than encouraging power relationships between them and their physicians. Various topics related to racism also were recommended to be included in residency curricula, including education on implementation of antiracist action in the workplace.
Many of the nonclinical topics are intertwined; for instance, learning about health care disparities in patients with limited English proficiency allows for improved best practices in delivering care to patients from this population. The first step in overcoming bias and subsequent disparities is acknowledging how the perpetuation of bias leads to disparities after being taught tools to recognize it.
Our group’s guidance on DEI topics should help dermatology residency program leaders as they design and refine program curricula. There are multiple avenues for incorporating education on these topics, including lectures, interactive workshops, role-playing sessions, book or journal clubs, and discussion circles. Many of these topics/programs may already be included in programs’ didactic curricula, which would minimize the burden of finding space to educate on these topics. Institutional cultural change is key to ensuring truly diverse, equitable, and inclusive workplaces. Educating tomorrow’s dermatologists on these topics is a first step toward achieving that cultural change.
Limitations—A limitation of this e-Delphi survey is that only a selection of experts in this field was included. Additionally, we were concerned that the Likert scale format and the bar we set for inclusion and exclusion may have failed to adequately capture participants’ nuanced opinions. As such, participants were able to provide open-ended feedback, and suggestions for alternate wording or other changes were considered by the steering committee. Finally, inclusion recommendations identified in this survey were developed specifically for US dermatology residents.
Conclusion
In this e-Delphi consensus assessment of DEI-related topics, we recommend the inclusion of 23 topics into dermatology residency program curricula to improve medical training and the patient-physician relationship as well as to create better health outcomes. We also provide specific sample resource recommendations in eTables 1 and 2 to facilitate inclusion of these topics into residency curricula across the country.
- US Census Bureau projections show a slower growing, older, more diverse nation a half century from now. News release. US Census Bureau. December 12, 2012. Accessed August 14, 2024. https://www.census.gov/newsroom/releases/archives/population/cb12243.html#:~:text=12%2C%202012,U.S.%20Census%20Bureau%20Projections%20Show%20a%20Slower%20Growing%2C%20Older%2C%20More,by%20the%20U.S.%20Census%20Bureau
- Lopez S, Lourido JO, Lim HW, et al. The call to action to increase racial and ethnic diversity in dermatology: a retrospective, cross-sectional study to monitor progress. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;86:E121-E123. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.10.011
- El-Kashlan N, Alexis A. Disparities in dermatology: a reflection. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022;15:27-29.
- Laveist TA, Nuru-Jeter A. Is doctor-patient race concordance associated with greater satisfaction with care? J Health Soc Behav. 2002;43:296-306.
- Street RL Jr, O’Malley KJ, Cooper LA, et al. Understanding concordance in patient-physician relationships: personal and ethnic dimensions of shared identity. Ann Fam Med. 2008;6:198-205. doi:10.1370/afm.821
- Dadrass F, Bowers S, Shinkai K, et al. Diversity, equity, and inclusion in dermatology residency. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41:257-263. doi:10.1016/j.det.2022.10.006
- Diversity and the Academy. American Academy of Dermatology website. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://www.aad.org/member/career/diversity
- SOCS speaks. Skin of Color Society website. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://skinofcolorsociety.org/news-media/socs-speaks
- Solchanyk D, Ekeh O, Saffran L, et al. Integrating cultural humility into the medical education curriculum: strategies for educators. Teach Learn Med. 2021;33:554-560. doi:10.1080/10401334.2021.1877711
- US Census Bureau projections show a slower growing, older, more diverse nation a half century from now. News release. US Census Bureau. December 12, 2012. Accessed August 14, 2024. https://www.census.gov/newsroom/releases/archives/population/cb12243.html#:~:text=12%2C%202012,U.S.%20Census%20Bureau%20Projections%20Show%20a%20Slower%20Growing%2C%20Older%2C%20More,by%20the%20U.S.%20Census%20Bureau
- Lopez S, Lourido JO, Lim HW, et al. The call to action to increase racial and ethnic diversity in dermatology: a retrospective, cross-sectional study to monitor progress. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;86:E121-E123. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.10.011
- El-Kashlan N, Alexis A. Disparities in dermatology: a reflection. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022;15:27-29.
- Laveist TA, Nuru-Jeter A. Is doctor-patient race concordance associated with greater satisfaction with care? J Health Soc Behav. 2002;43:296-306.
- Street RL Jr, O’Malley KJ, Cooper LA, et al. Understanding concordance in patient-physician relationships: personal and ethnic dimensions of shared identity. Ann Fam Med. 2008;6:198-205. doi:10.1370/afm.821
- Dadrass F, Bowers S, Shinkai K, et al. Diversity, equity, and inclusion in dermatology residency. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41:257-263. doi:10.1016/j.det.2022.10.006
- Diversity and the Academy. American Academy of Dermatology website. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://www.aad.org/member/career/diversity
- SOCS speaks. Skin of Color Society website. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://skinofcolorsociety.org/news-media/socs-speaks
- Solchanyk D, Ekeh O, Saffran L, et al. Integrating cultural humility into the medical education curriculum: strategies for educators. Teach Learn Med. 2021;33:554-560. doi:10.1080/10401334.2021.1877711
PRACTICE POINTS
- Advancing curricula related to diversity, equity, and inclusion in dermatology training can improve health outcomes, address health care workforce disparities, and enhance clinical care for diverse patient populations.
- Education on patient-centered communication, cultural humility, and the impact of social determinants of health results in dermatology residents who are better equipped with the necessary tools to effectively care for patients from diverse backgrounds.
Melasma Risk Factors: A Matched Cohort Study Using Data From the All of Us Research Program
To the Editor:
Melasma (also known as chloasma) is characterized by symmetric hyperpigmented patches affecting sun-exposed areas. Women commonly develop this condition during pregnancy, suggesting a connection between melasma and increased female sex hormone levels.1 Other hypothesized risk factors include sun exposure, genetic susceptibility, estrogen and/or progesterone therapy, and thyroid abnormalities but have not been corroborated.2 Treatment options are limited because the pathogenesis is poorly understood; thus, we aimed to analyze melasma risk factors using a national database with a nested case-control approach.
We conducted a matched case-control study using the Registered Tier dataset (version 7) from the National Institute of Health’s All of Us Research Program (https://allofus.nih.gov/), which is available to authorized users through the program’s Researcher Workbench and includes more than 413,000 total participants enrolled from May 1, 2018, through July 1, 2022. Cases included patients 18 years and older with a diagnosis of melasma (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification code L81.1 [Chloasma]; concept ID 4264234 [Chloasma]; and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine [SNOMED] code 36209000 [Chloasma]), and controls without a diagnosis of melasma were matched in a 1:10 ratio based on age, sex, and self-reported race. Concept IDs and SNOMED codes were used to identify individuals in each cohort with a diagnosis of alcohol dependence (concept IDs 433753, 435243, 4218106; SNOMED codes 15167005, 66590003, 7200002), depression (concept ID 440383; SNOMED code 35489007), hypothyroidism (concept ID 140673; SNOMED code 40930008), hyperthyroidism (concept ID 4142479; SNOMED code 34486009), anxiety (concept IDs 441542, 442077, 434613; SNOMED codes 48694002, 197480006, 21897009), tobacco dependence (concept IDs 37109023, 437264, 4099811; SNOMED codes 16077091000119107, 89765005, 191887008), or obesity (concept IDs 433736 and 434005; SNOMED codes 414916001 and 238136002), or with a history of radiation therapy (concept IDs 4085340, 4311117, 4061844, 4029715; SNOMED codes 24803000, 85983004, 200861004, 108290001) or hormonal medications containing estrogen and/or progesterone, including oral medications and implants (concept IDs 21602445, 40254009, 21602514, 21603814, 19049228, 21602529, 1549080, 1551673, 1549254, 21602472, 21602446, 21602450, 21602515, 21602566, 21602473, 21602567, 21602488, 21602585, 1596779, 1586808, 21602524). In our case cohort, diagnoses and exposures to treatments were only considered for analysis if they occurred prior to melasma diagnosis.
Multivariate logistic regression was performed to calculate odds ratios and P values between melasma and each comorbidity or exposure to the treatments specified. Statistical significance was set at P<.05.
We identified 744 melasma cases (mean age, 55.20 years; 95.43% female; 12.10% Black) and 7440 controls with similar demographics (ie, age, sex, race/ethnicity) between groups (all P>.05 [Table 1]). Patients with a melasma diagnosis were more likely to have a pre-existing diagnosis of depression (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.51-2.31 [P<.001]) or hypothyroidism (OR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.04-1.65 [P<.05]), or a history of radiation therapy (OR, 19.08; 95% CI, 10.20-35.69 [P<.001]) and/or estrogen and/or progesterone therapy (OR, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.69-2.40 [P<.001]) prior to melasma diagnosis. A diagnosis of anxiety prior to melasma diagnosis trended toward an association with melasma (P=.067). Pre-existing alcohol dependence, obesity, and hyperthyroidism were not associated with melasma (P=.98, P=.28, and P=.29, respectively). A diagnosis of tobacco dependence was associated with a decreased melasma risk (OR, 0.53, 95% CI, 0.37-0.76)[P<.001])(Table 2).
Our study results suggest that pre-existing depression was a risk factor for subsequent melasma diagnosis. Depression may exacerbate stress, leading to increased activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis as well as increased levels of cortisol and adrenocorticotropic hormone, which subsequently act on melanocytes to increase melanogenesis.3 A retrospective study of 254 participants, including 127 with melasma, showed that increased melasma severity was associated with higher rates of depression (P=.002)2; however, the risk for melasma following a depression diagnosis has not been reported.
Our results also showed that hypothyroidism was associated with an increased risk for melasma. On a cellular level, hypothyroidism can cause systemic inflammation, potentailly leading to increased stress and melanogenesis via activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.4 These findings are similar to a systematic review and meta-analysis reporting increased thyroid-stimulating hormone, anti–thyroid peroxidase, and antithyroglobulin antibody levels associated with increased melasma risk (mean difference between cases and controls, 0.33 [95% CI, 0.18-0.47]; pooled association, P=.020; mean difference between cases and controls, 0.28 [95% CI, 0.01-0.55], respectively).5
Patients in our cohort who had a history of radiation therapy were 19 times more likely to develop melasma, similar to findings of a survey-based study of 421 breast cancer survivors in which 336 (79.81%) reported hyperpigmentation in irradiated areas.6 Patients in our cohort who had a history of estrogen and/or progesterone therapy were 2 times more likely to develop melasma, similar to a case-control study of 207 patients with melasma and 207 controls that showed combined oral contraceptives increased risk for melasma (OR, 1.23 [95% CI, 1.08-1.41; P<.01).3
Tobacco use is not a well-known protective factor against melasma. Prior studies have indicated that tobacco smoking activates melanocytes via the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway, leading to hyperpigmentation.7 Although exposure to cigarette smoke decreases angiogenesis and would more likely lead to hyperpigmentation, nicotine exposure has been shown to increase angiogenesis, which could lead to increased blood flow and partially explain the protection against melasma demonstrated in our cohort.8 Future studies are needed to explore this relationship.
Limitations of our study include lack of information about melasma severity and information about prior melasma treatment in our cohort as well as possible misdiagnosis reported in the dataset.
Our results demonstrated that pre-existing depression and hypothyroidism as well as a history of radiation or estrogen and/or progesterone therapies are potential risk factors for melasma. Therefore, we recommend that patients with melasma be screened for depression and thyroid dysfunction, and patients undergoing radiation therapy or starting estrogen and/or progesterone therapy should be counseled on their increased risk for melasma. Future studies are needed to determine whether treatment of comorbidities such as hypothyroidism and depression improve melasma severity. The decreased risk for melasma associated with tobacco use also requires further investigation.
Acknowledgments—The All of Us Research Program is supported by the National Institutes of Health, Office of the Director: Regional Medical Centers: 1 OT2 OD026549; 1 OT2 OD026554; 1 OT2 OD026557; 1 OT2 OD026556; 1 OT2 OD026550; 1 OT2 OD 026552; 1 OT2 OD026553; 1 OT2 OD026548; 1 OT2 OD026551; 1 OT2 OD026555; IAA #: AOD 16037; Federally Qualified Health Centers: HHSN 263201600085U; Data and Research Center: 5 U2C OD023196; Biobank: 1 U24 OD023121; The Participant Center: U24 OD023176; Participant Technology Systems Center: 1 U24 OD023163; Communications and Engagement: 3 OT2 OD023205; 3 OT2 OD023206; and Community Partners: 1 OT2 OD025277; 3 OT2 OD025315; 1 OT2 OD025337; 1 OT2 OD025276.
In addition, the All of Us Research Program would not be possible without the partnership of its participants, who we gratefully acknowledge for their contributions and without whom this research would not have been possible. We also thank the All of Us Research Program for making the participant data examined in this study available to us.
- Filoni A, Mariano M, Cameli N. Melasma: how hormones can modulate skin pigmentation. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019;18:458-463. doi:10.1111/jocd.12877
- Platsidaki E, Efstathiou V, Markantoni V, et al. Self-esteem, depression, anxiety and quality of life in patients with melasma living in a sunny mediterranean area: results from a prospective cross-sectional study. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023;13:1127-1136. doi:10.1007/s13555-023-00915-1
- Handel AC, Lima PB, Tonolli VM, et al. Risk factors for facial melasma in women: a case-control study. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:588-594. doi:10.1111/bjd.13059
- Erge E, Kiziltunc C, Balci SB, et al. A novel inflammatory marker for the diagnosis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: platelet-count-to-lymphocyte-count ratio (published January 22, 2023). Diseases. 2023;11:15. doi:10.3390/diseases11010015
- Kheradmand M, Afshari M, Damiani G, et al. Melasma and thyroid disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:1231-1238. doi:10.1111/ijd.14497
- Chu CN, Hu KC, Wu RS, et al. Radiation-irritated skin and hyperpigmentation may impact the quality of life of breast cancer patients after whole breast radiotherapy (published March 31, 2021). BMC Cancer. 2021;21:330. doi:10.1186/s12885-021-08047-5
- Nakamura M, Ueda Y, Hayashi M, et al. Tobacco smoke-induced skin pigmentation is mediated by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Exp Dermatol. 2013;22:556-558. doi:10.1111/exd.12170
- Ejaz S, Lim CW. Toxicological overview of cigarette smoking on angiogenesis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2005;20:335-344. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2005.03.011
To the Editor:
Melasma (also known as chloasma) is characterized by symmetric hyperpigmented patches affecting sun-exposed areas. Women commonly develop this condition during pregnancy, suggesting a connection between melasma and increased female sex hormone levels.1 Other hypothesized risk factors include sun exposure, genetic susceptibility, estrogen and/or progesterone therapy, and thyroid abnormalities but have not been corroborated.2 Treatment options are limited because the pathogenesis is poorly understood; thus, we aimed to analyze melasma risk factors using a national database with a nested case-control approach.
We conducted a matched case-control study using the Registered Tier dataset (version 7) from the National Institute of Health’s All of Us Research Program (https://allofus.nih.gov/), which is available to authorized users through the program’s Researcher Workbench and includes more than 413,000 total participants enrolled from May 1, 2018, through July 1, 2022. Cases included patients 18 years and older with a diagnosis of melasma (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification code L81.1 [Chloasma]; concept ID 4264234 [Chloasma]; and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine [SNOMED] code 36209000 [Chloasma]), and controls without a diagnosis of melasma were matched in a 1:10 ratio based on age, sex, and self-reported race. Concept IDs and SNOMED codes were used to identify individuals in each cohort with a diagnosis of alcohol dependence (concept IDs 433753, 435243, 4218106; SNOMED codes 15167005, 66590003, 7200002), depression (concept ID 440383; SNOMED code 35489007), hypothyroidism (concept ID 140673; SNOMED code 40930008), hyperthyroidism (concept ID 4142479; SNOMED code 34486009), anxiety (concept IDs 441542, 442077, 434613; SNOMED codes 48694002, 197480006, 21897009), tobacco dependence (concept IDs 37109023, 437264, 4099811; SNOMED codes 16077091000119107, 89765005, 191887008), or obesity (concept IDs 433736 and 434005; SNOMED codes 414916001 and 238136002), or with a history of radiation therapy (concept IDs 4085340, 4311117, 4061844, 4029715; SNOMED codes 24803000, 85983004, 200861004, 108290001) or hormonal medications containing estrogen and/or progesterone, including oral medications and implants (concept IDs 21602445, 40254009, 21602514, 21603814, 19049228, 21602529, 1549080, 1551673, 1549254, 21602472, 21602446, 21602450, 21602515, 21602566, 21602473, 21602567, 21602488, 21602585, 1596779, 1586808, 21602524). In our case cohort, diagnoses and exposures to treatments were only considered for analysis if they occurred prior to melasma diagnosis.
Multivariate logistic regression was performed to calculate odds ratios and P values between melasma and each comorbidity or exposure to the treatments specified. Statistical significance was set at P<.05.
We identified 744 melasma cases (mean age, 55.20 years; 95.43% female; 12.10% Black) and 7440 controls with similar demographics (ie, age, sex, race/ethnicity) between groups (all P>.05 [Table 1]). Patients with a melasma diagnosis were more likely to have a pre-existing diagnosis of depression (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.51-2.31 [P<.001]) or hypothyroidism (OR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.04-1.65 [P<.05]), or a history of radiation therapy (OR, 19.08; 95% CI, 10.20-35.69 [P<.001]) and/or estrogen and/or progesterone therapy (OR, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.69-2.40 [P<.001]) prior to melasma diagnosis. A diagnosis of anxiety prior to melasma diagnosis trended toward an association with melasma (P=.067). Pre-existing alcohol dependence, obesity, and hyperthyroidism were not associated with melasma (P=.98, P=.28, and P=.29, respectively). A diagnosis of tobacco dependence was associated with a decreased melasma risk (OR, 0.53, 95% CI, 0.37-0.76)[P<.001])(Table 2).
Our study results suggest that pre-existing depression was a risk factor for subsequent melasma diagnosis. Depression may exacerbate stress, leading to increased activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis as well as increased levels of cortisol and adrenocorticotropic hormone, which subsequently act on melanocytes to increase melanogenesis.3 A retrospective study of 254 participants, including 127 with melasma, showed that increased melasma severity was associated with higher rates of depression (P=.002)2; however, the risk for melasma following a depression diagnosis has not been reported.
Our results also showed that hypothyroidism was associated with an increased risk for melasma. On a cellular level, hypothyroidism can cause systemic inflammation, potentailly leading to increased stress and melanogenesis via activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.4 These findings are similar to a systematic review and meta-analysis reporting increased thyroid-stimulating hormone, anti–thyroid peroxidase, and antithyroglobulin antibody levels associated with increased melasma risk (mean difference between cases and controls, 0.33 [95% CI, 0.18-0.47]; pooled association, P=.020; mean difference between cases and controls, 0.28 [95% CI, 0.01-0.55], respectively).5
Patients in our cohort who had a history of radiation therapy were 19 times more likely to develop melasma, similar to findings of a survey-based study of 421 breast cancer survivors in which 336 (79.81%) reported hyperpigmentation in irradiated areas.6 Patients in our cohort who had a history of estrogen and/or progesterone therapy were 2 times more likely to develop melasma, similar to a case-control study of 207 patients with melasma and 207 controls that showed combined oral contraceptives increased risk for melasma (OR, 1.23 [95% CI, 1.08-1.41; P<.01).3
Tobacco use is not a well-known protective factor against melasma. Prior studies have indicated that tobacco smoking activates melanocytes via the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway, leading to hyperpigmentation.7 Although exposure to cigarette smoke decreases angiogenesis and would more likely lead to hyperpigmentation, nicotine exposure has been shown to increase angiogenesis, which could lead to increased blood flow and partially explain the protection against melasma demonstrated in our cohort.8 Future studies are needed to explore this relationship.


Limitations of our study include lack of information about melasma severity and information about prior melasma treatment in our cohort as well as possible misdiagnosis reported in the dataset.
Our results demonstrated that pre-existing depression and hypothyroidism as well as a history of radiation or estrogen and/or progesterone therapies are potential risk factors for melasma. Therefore, we recommend that patients with melasma be screened for depression and thyroid dysfunction, and patients undergoing radiation therapy or starting estrogen and/or progesterone therapy should be counseled on their increased risk for melasma. Future studies are needed to determine whether treatment of comorbidities such as hypothyroidism and depression improve melasma severity. The decreased risk for melasma associated with tobacco use also requires further investigation.
Acknowledgments—The All of Us Research Program is supported by the National Institutes of Health, Office of the Director: Regional Medical Centers: 1 OT2 OD026549; 1 OT2 OD026554; 1 OT2 OD026557; 1 OT2 OD026556; 1 OT2 OD026550; 1 OT2 OD 026552; 1 OT2 OD026553; 1 OT2 OD026548; 1 OT2 OD026551; 1 OT2 OD026555; IAA #: AOD 16037; Federally Qualified Health Centers: HHSN 263201600085U; Data and Research Center: 5 U2C OD023196; Biobank: 1 U24 OD023121; The Participant Center: U24 OD023176; Participant Technology Systems Center: 1 U24 OD023163; Communications and Engagement: 3 OT2 OD023205; 3 OT2 OD023206; and Community Partners: 1 OT2 OD025277; 3 OT2 OD025315; 1 OT2 OD025337; 1 OT2 OD025276.
In addition, the All of Us Research Program would not be possible without the partnership of its participants, who we gratefully acknowledge for their contributions and without whom this research would not have been possible. We also thank the All of Us Research Program for making the participant data examined in this study available to us.
To the Editor:
Melasma (also known as chloasma) is characterized by symmetric hyperpigmented patches affecting sun-exposed areas. Women commonly develop this condition during pregnancy, suggesting a connection between melasma and increased female sex hormone levels.1 Other hypothesized risk factors include sun exposure, genetic susceptibility, estrogen and/or progesterone therapy, and thyroid abnormalities but have not been corroborated.2 Treatment options are limited because the pathogenesis is poorly understood; thus, we aimed to analyze melasma risk factors using a national database with a nested case-control approach.
We conducted a matched case-control study using the Registered Tier dataset (version 7) from the National Institute of Health’s All of Us Research Program (https://allofus.nih.gov/), which is available to authorized users through the program’s Researcher Workbench and includes more than 413,000 total participants enrolled from May 1, 2018, through July 1, 2022. Cases included patients 18 years and older with a diagnosis of melasma (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification code L81.1 [Chloasma]; concept ID 4264234 [Chloasma]; and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine [SNOMED] code 36209000 [Chloasma]), and controls without a diagnosis of melasma were matched in a 1:10 ratio based on age, sex, and self-reported race. Concept IDs and SNOMED codes were used to identify individuals in each cohort with a diagnosis of alcohol dependence (concept IDs 433753, 435243, 4218106; SNOMED codes 15167005, 66590003, 7200002), depression (concept ID 440383; SNOMED code 35489007), hypothyroidism (concept ID 140673; SNOMED code 40930008), hyperthyroidism (concept ID 4142479; SNOMED code 34486009), anxiety (concept IDs 441542, 442077, 434613; SNOMED codes 48694002, 197480006, 21897009), tobacco dependence (concept IDs 37109023, 437264, 4099811; SNOMED codes 16077091000119107, 89765005, 191887008), or obesity (concept IDs 433736 and 434005; SNOMED codes 414916001 and 238136002), or with a history of radiation therapy (concept IDs 4085340, 4311117, 4061844, 4029715; SNOMED codes 24803000, 85983004, 200861004, 108290001) or hormonal medications containing estrogen and/or progesterone, including oral medications and implants (concept IDs 21602445, 40254009, 21602514, 21603814, 19049228, 21602529, 1549080, 1551673, 1549254, 21602472, 21602446, 21602450, 21602515, 21602566, 21602473, 21602567, 21602488, 21602585, 1596779, 1586808, 21602524). In our case cohort, diagnoses and exposures to treatments were only considered for analysis if they occurred prior to melasma diagnosis.
Multivariate logistic regression was performed to calculate odds ratios and P values between melasma and each comorbidity or exposure to the treatments specified. Statistical significance was set at P<.05.
We identified 744 melasma cases (mean age, 55.20 years; 95.43% female; 12.10% Black) and 7440 controls with similar demographics (ie, age, sex, race/ethnicity) between groups (all P>.05 [Table 1]). Patients with a melasma diagnosis were more likely to have a pre-existing diagnosis of depression (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.51-2.31 [P<.001]) or hypothyroidism (OR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.04-1.65 [P<.05]), or a history of radiation therapy (OR, 19.08; 95% CI, 10.20-35.69 [P<.001]) and/or estrogen and/or progesterone therapy (OR, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.69-2.40 [P<.001]) prior to melasma diagnosis. A diagnosis of anxiety prior to melasma diagnosis trended toward an association with melasma (P=.067). Pre-existing alcohol dependence, obesity, and hyperthyroidism were not associated with melasma (P=.98, P=.28, and P=.29, respectively). A diagnosis of tobacco dependence was associated with a decreased melasma risk (OR, 0.53, 95% CI, 0.37-0.76)[P<.001])(Table 2).
Our study results suggest that pre-existing depression was a risk factor for subsequent melasma diagnosis. Depression may exacerbate stress, leading to increased activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis as well as increased levels of cortisol and adrenocorticotropic hormone, which subsequently act on melanocytes to increase melanogenesis.3 A retrospective study of 254 participants, including 127 with melasma, showed that increased melasma severity was associated with higher rates of depression (P=.002)2; however, the risk for melasma following a depression diagnosis has not been reported.
Our results also showed that hypothyroidism was associated with an increased risk for melasma. On a cellular level, hypothyroidism can cause systemic inflammation, potentailly leading to increased stress and melanogenesis via activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.4 These findings are similar to a systematic review and meta-analysis reporting increased thyroid-stimulating hormone, anti–thyroid peroxidase, and antithyroglobulin antibody levels associated with increased melasma risk (mean difference between cases and controls, 0.33 [95% CI, 0.18-0.47]; pooled association, P=.020; mean difference between cases and controls, 0.28 [95% CI, 0.01-0.55], respectively).5
Patients in our cohort who had a history of radiation therapy were 19 times more likely to develop melasma, similar to findings of a survey-based study of 421 breast cancer survivors in which 336 (79.81%) reported hyperpigmentation in irradiated areas.6 Patients in our cohort who had a history of estrogen and/or progesterone therapy were 2 times more likely to develop melasma, similar to a case-control study of 207 patients with melasma and 207 controls that showed combined oral contraceptives increased risk for melasma (OR, 1.23 [95% CI, 1.08-1.41; P<.01).3
Tobacco use is not a well-known protective factor against melasma. Prior studies have indicated that tobacco smoking activates melanocytes via the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway, leading to hyperpigmentation.7 Although exposure to cigarette smoke decreases angiogenesis and would more likely lead to hyperpigmentation, nicotine exposure has been shown to increase angiogenesis, which could lead to increased blood flow and partially explain the protection against melasma demonstrated in our cohort.8 Future studies are needed to explore this relationship.


Limitations of our study include lack of information about melasma severity and information about prior melasma treatment in our cohort as well as possible misdiagnosis reported in the dataset.
Our results demonstrated that pre-existing depression and hypothyroidism as well as a history of radiation or estrogen and/or progesterone therapies are potential risk factors for melasma. Therefore, we recommend that patients with melasma be screened for depression and thyroid dysfunction, and patients undergoing radiation therapy or starting estrogen and/or progesterone therapy should be counseled on their increased risk for melasma. Future studies are needed to determine whether treatment of comorbidities such as hypothyroidism and depression improve melasma severity. The decreased risk for melasma associated with tobacco use also requires further investigation.
Acknowledgments—The All of Us Research Program is supported by the National Institutes of Health, Office of the Director: Regional Medical Centers: 1 OT2 OD026549; 1 OT2 OD026554; 1 OT2 OD026557; 1 OT2 OD026556; 1 OT2 OD026550; 1 OT2 OD 026552; 1 OT2 OD026553; 1 OT2 OD026548; 1 OT2 OD026551; 1 OT2 OD026555; IAA #: AOD 16037; Federally Qualified Health Centers: HHSN 263201600085U; Data and Research Center: 5 U2C OD023196; Biobank: 1 U24 OD023121; The Participant Center: U24 OD023176; Participant Technology Systems Center: 1 U24 OD023163; Communications and Engagement: 3 OT2 OD023205; 3 OT2 OD023206; and Community Partners: 1 OT2 OD025277; 3 OT2 OD025315; 1 OT2 OD025337; 1 OT2 OD025276.
In addition, the All of Us Research Program would not be possible without the partnership of its participants, who we gratefully acknowledge for their contributions and without whom this research would not have been possible. We also thank the All of Us Research Program for making the participant data examined in this study available to us.
- Filoni A, Mariano M, Cameli N. Melasma: how hormones can modulate skin pigmentation. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019;18:458-463. doi:10.1111/jocd.12877
- Platsidaki E, Efstathiou V, Markantoni V, et al. Self-esteem, depression, anxiety and quality of life in patients with melasma living in a sunny mediterranean area: results from a prospective cross-sectional study. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023;13:1127-1136. doi:10.1007/s13555-023-00915-1
- Handel AC, Lima PB, Tonolli VM, et al. Risk factors for facial melasma in women: a case-control study. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:588-594. doi:10.1111/bjd.13059
- Erge E, Kiziltunc C, Balci SB, et al. A novel inflammatory marker for the diagnosis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: platelet-count-to-lymphocyte-count ratio (published January 22, 2023). Diseases. 2023;11:15. doi:10.3390/diseases11010015
- Kheradmand M, Afshari M, Damiani G, et al. Melasma and thyroid disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:1231-1238. doi:10.1111/ijd.14497
- Chu CN, Hu KC, Wu RS, et al. Radiation-irritated skin and hyperpigmentation may impact the quality of life of breast cancer patients after whole breast radiotherapy (published March 31, 2021). BMC Cancer. 2021;21:330. doi:10.1186/s12885-021-08047-5
- Nakamura M, Ueda Y, Hayashi M, et al. Tobacco smoke-induced skin pigmentation is mediated by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Exp Dermatol. 2013;22:556-558. doi:10.1111/exd.12170
- Ejaz S, Lim CW. Toxicological overview of cigarette smoking on angiogenesis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2005;20:335-344. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2005.03.011
- Filoni A, Mariano M, Cameli N. Melasma: how hormones can modulate skin pigmentation. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019;18:458-463. doi:10.1111/jocd.12877
- Platsidaki E, Efstathiou V, Markantoni V, et al. Self-esteem, depression, anxiety and quality of life in patients with melasma living in a sunny mediterranean area: results from a prospective cross-sectional study. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023;13:1127-1136. doi:10.1007/s13555-023-00915-1
- Handel AC, Lima PB, Tonolli VM, et al. Risk factors for facial melasma in women: a case-control study. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:588-594. doi:10.1111/bjd.13059
- Erge E, Kiziltunc C, Balci SB, et al. A novel inflammatory marker for the diagnosis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: platelet-count-to-lymphocyte-count ratio (published January 22, 2023). Diseases. 2023;11:15. doi:10.3390/diseases11010015
- Kheradmand M, Afshari M, Damiani G, et al. Melasma and thyroid disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:1231-1238. doi:10.1111/ijd.14497
- Chu CN, Hu KC, Wu RS, et al. Radiation-irritated skin and hyperpigmentation may impact the quality of life of breast cancer patients after whole breast radiotherapy (published March 31, 2021). BMC Cancer. 2021;21:330. doi:10.1186/s12885-021-08047-5
- Nakamura M, Ueda Y, Hayashi M, et al. Tobacco smoke-induced skin pigmentation is mediated by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Exp Dermatol. 2013;22:556-558. doi:10.1111/exd.12170
- Ejaz S, Lim CW. Toxicological overview of cigarette smoking on angiogenesis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2005;20:335-344. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2005.03.011
Practice Points
- Treatment options for melasma are limited due to its poorly understood pathogenesis.
- Depression and hypothyroidism and/or history of exposure to radiation and hormonal therapies may increase melasma risk.
- We recommend that patients with melasma be screened for depression and thyroid dysfunction. Patients undergoing radiation therapy or starting estrogen and/ or progesterone therapy should be counseled on the increased risk for melasma.