User login
EMERGENCY MEDICINE is a practical, peer-reviewed monthly publication and Web site that meets the educational needs of emergency clinicians and urgent care clinicians for their practice.
COVID-19 guidance for children’s health care providers
We are in uncharted waters with national and local states of emergency, schools and most activities being shut down, and rapidly evolving strategies on managing the COVID-19 outbreak. Everyone’s anxiety is appropriately high. As health care providers for children, you are facing changes in your personal life at home and in practice, likely including setting up televisits, trying to assess which patients to see, managing staffing challenges, and facing potential cash flow issues as expenses continue but revenue may fall short. And, of course, you will address a host of novel questions and concerns from the families you care for.
Your top priorities are to stay calm while offering clear recommendations on testing, quarantine, and treatment with guidance from our federal and local public health agencies. By providing clear guidance on the medical issues, you will offer substantial reassurance to families. But even with a medical plan in place, this remains a confusing and anxiety-provoking moment, one without much precedent in most people’s lives or in our national experience. Our aim is to complement that guidance by offering you some principles to help families manage the stress and anxiety that the disruptions and uncertainties that this public health emergency has created.
Offer clear, open, regular, and child-centered communication
If you have an email mailing list of your parents, you may want to summarize information you are gathering with a note they can expect at a specified time each day. You could request them to email you questions that then can be included as an FAQ (frequently asked questions).
Most children will have noticed people wearing face masks, or dramatic scenes on the news with hospital workers in full protective gear, breathlessly reporting growing numbers of the infected and the deceased. At a minimum, they are being commanded to wash hands and to not touch their faces (which is challenging enough for adults!), and are probably overhearing conversations about quarantines and contagion as well as family concerns about jobs and family finances. Many children are managing extended school closures and some are even managing the quarantine or serious illness of a loved one. When children overhear frightening news from distressed adults, they are going to become anxious and afraid themselves. Parents should remember to find out what their children have seen, heard, or understood about what is going on, and they should correct misinformation or misunderstandings with clear explanations. They also should find out what their children are curious about. “What has you wondering about that?” is a great response when children have questions, in order to make sure you get at any underlying worry.
It is fine to not have an answer to every question. It is difficult to offer clear explanations about something that we don’t yet fully understand, and it is fine to acknowledge what we don’t know. “That’s a great question. Let’s look together at the CDC [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] website.” Offering to look for answers or information together can be a powerful way to model how to handle uncertainty. And always couch answers with appropriate (not false) reassurance: “Children and young adults appear to be very safe from this illness, but we want to take care to protect those that are older or already sick.”
Remember most children set their anxiety level based on their parent’s anxiety, and part of being child centered in your communication includes offering information in an age-appropriate manner. Preschool-aged children (up to 5 years) still have magical thinking. They are prone to finding masks and gowns scary and to assume that school stopping may be because they did something wrong. Tell them about the new illness, and about the doctors and officials working hard to keep people safe. Reassure them about all of the adults working hard together to understand the illness and take care of people who are sick. Their sense of time is less logical, so you may have to tell them more than once. Reassure them that children do not get very sick from this illness, but they can carry and spread it, like having paint on their hands, so they need to wash their hands often to take good care of other people.
School-age children (aged roughly 5-12 years) are better equipped cognitively to understand the seriousness of this outbreak. They are built to master new situations, but are prone to anxiety as they don’t yet have the emotional maturity to tolerate uncertainty or unfairness. Explain what is known without euphemisms, be truly curious about what their questions are, and look for answers together. Often what they need is to see you being calm in the face of uncertainty, bearing the strong feelings that may come, and preserving curiosity and compassion for others.
Adolescents also will need all of this support, and can be curious about more abstract implications (political, ethical, financial). Do not be surprised when they ask sophisticated questions, but still are focused on the personal disruptions or sacrifices (a canceled dance or sports meet, concerns about academic performance). Adolescence is a time of intense preoccupation with their emerging identity and relationships; it is normal for them to experience events in a way that may seem selfish, especially if it disrupts their time with friends. Remind parents to offer compassion and validation, while acknowledging that shared sacrifice and discomfort are a part of every individual’s experience when a society must respond to such a large challenge.
Be mindful of children’s vulnerabilities
Being child centered goes beyond thinking about their age and developmental stage. Parents are the experts on their children and will know about any particular vulnerabilities to the stresses of this serious outbreak. Children who are prone to anxiety or suffer from anxiety disorders may be more prone to silent worry. It is especially important to check in with them often, find out what they know and what they are worried about, and remind them to “never worry alone.” It also is important to continue with any recommended treatment, avoiding accommodation of their anxieties, except when it is required by public health protocols (i.e., staying home from school). Children with developmental disabilities may require additional support to change behaviors (hand washing) and may be more sensitive to changes in routine. And children with learning disabilities or special services in school may require additional support or structure during a prolonged period at home.
Preserve routines and structure
Routines and predictability are important to the sense of stability and well-being of most children (and adults). While disruptions are unavoidable, preserve what routines you can, and establish some new ones. For children who are out of school for several weeks, set up a consistent home routine, with a similar wake-up and bedtime, and a “school schedule.” There may be academic activities like reading or work sheets. If the parents’ work is disrupted, they can homeschool, shoring up weak academic areas or enhancing areas of interest. Be sure to preserve time for physical activity and social connections within this new framework. Social time does not require physical proximity, and can happen by screen or phone. Physical activity should be outside if at all possible. Predictability, preserved expectations (academic and otherwise), physical exercise, social connection, and consistent sleep will go a long way in protecting everyone’s ability to manage the disruptions of this epidemic.
Find opportunity in the disruption
Many families have been on a treadmill of work, school, and activities that have left little unscheduled time or spontaneity. Recommend looking at this disruption as a rare opportunity to slow down, spend time together, listen, learn more about one another, and even to have fun. Families could play board games, card games, watch movies together, or even read aloud. They might discover it is the time to try new hobbies (knitting, learning a new language or instrument), or to teach each other new skills. You might learn something new, or something new about your children. You also will offer a model of finding the opportunity in adversity, and even offer them some wonderful memories from a difficult time.
Take care of the vulnerable and ease others’ hardships
Without a doubt, this will be a difficult time for many people, medically, financially, and emotionally. One powerful strategy to build resilience in our children and strengthen our communities is to think with children about ways to help those who are most at risk or burdened by this challenge. Perhaps they want to make cards or FaceTime calls to older relatives who may be otherwise isolated. They may want to consider ways to support the work of first responders, even just with appreciation. They may want to reach out to elderly neighbors and offer to get groceries or other needed supplies for them. Balancing appropriate self-care with a focus on the needs of those who are more vulnerable or burdened than ourselves is a powerful way to show our children how communities pull together in a challenging time; enhance their feeling of connectedness; and build resilience in them, in our families, and in our communities.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected]
We are in uncharted waters with national and local states of emergency, schools and most activities being shut down, and rapidly evolving strategies on managing the COVID-19 outbreak. Everyone’s anxiety is appropriately high. As health care providers for children, you are facing changes in your personal life at home and in practice, likely including setting up televisits, trying to assess which patients to see, managing staffing challenges, and facing potential cash flow issues as expenses continue but revenue may fall short. And, of course, you will address a host of novel questions and concerns from the families you care for.
Your top priorities are to stay calm while offering clear recommendations on testing, quarantine, and treatment with guidance from our federal and local public health agencies. By providing clear guidance on the medical issues, you will offer substantial reassurance to families. But even with a medical plan in place, this remains a confusing and anxiety-provoking moment, one without much precedent in most people’s lives or in our national experience. Our aim is to complement that guidance by offering you some principles to help families manage the stress and anxiety that the disruptions and uncertainties that this public health emergency has created.
Offer clear, open, regular, and child-centered communication
If you have an email mailing list of your parents, you may want to summarize information you are gathering with a note they can expect at a specified time each day. You could request them to email you questions that then can be included as an FAQ (frequently asked questions).
Most children will have noticed people wearing face masks, or dramatic scenes on the news with hospital workers in full protective gear, breathlessly reporting growing numbers of the infected and the deceased. At a minimum, they are being commanded to wash hands and to not touch their faces (which is challenging enough for adults!), and are probably overhearing conversations about quarantines and contagion as well as family concerns about jobs and family finances. Many children are managing extended school closures and some are even managing the quarantine or serious illness of a loved one. When children overhear frightening news from distressed adults, they are going to become anxious and afraid themselves. Parents should remember to find out what their children have seen, heard, or understood about what is going on, and they should correct misinformation or misunderstandings with clear explanations. They also should find out what their children are curious about. “What has you wondering about that?” is a great response when children have questions, in order to make sure you get at any underlying worry.
It is fine to not have an answer to every question. It is difficult to offer clear explanations about something that we don’t yet fully understand, and it is fine to acknowledge what we don’t know. “That’s a great question. Let’s look together at the CDC [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] website.” Offering to look for answers or information together can be a powerful way to model how to handle uncertainty. And always couch answers with appropriate (not false) reassurance: “Children and young adults appear to be very safe from this illness, but we want to take care to protect those that are older or already sick.”
Remember most children set their anxiety level based on their parent’s anxiety, and part of being child centered in your communication includes offering information in an age-appropriate manner. Preschool-aged children (up to 5 years) still have magical thinking. They are prone to finding masks and gowns scary and to assume that school stopping may be because they did something wrong. Tell them about the new illness, and about the doctors and officials working hard to keep people safe. Reassure them about all of the adults working hard together to understand the illness and take care of people who are sick. Their sense of time is less logical, so you may have to tell them more than once. Reassure them that children do not get very sick from this illness, but they can carry and spread it, like having paint on their hands, so they need to wash their hands often to take good care of other people.
School-age children (aged roughly 5-12 years) are better equipped cognitively to understand the seriousness of this outbreak. They are built to master new situations, but are prone to anxiety as they don’t yet have the emotional maturity to tolerate uncertainty or unfairness. Explain what is known without euphemisms, be truly curious about what their questions are, and look for answers together. Often what they need is to see you being calm in the face of uncertainty, bearing the strong feelings that may come, and preserving curiosity and compassion for others.
Adolescents also will need all of this support, and can be curious about more abstract implications (political, ethical, financial). Do not be surprised when they ask sophisticated questions, but still are focused on the personal disruptions or sacrifices (a canceled dance or sports meet, concerns about academic performance). Adolescence is a time of intense preoccupation with their emerging identity and relationships; it is normal for them to experience events in a way that may seem selfish, especially if it disrupts their time with friends. Remind parents to offer compassion and validation, while acknowledging that shared sacrifice and discomfort are a part of every individual’s experience when a society must respond to such a large challenge.
Be mindful of children’s vulnerabilities
Being child centered goes beyond thinking about their age and developmental stage. Parents are the experts on their children and will know about any particular vulnerabilities to the stresses of this serious outbreak. Children who are prone to anxiety or suffer from anxiety disorders may be more prone to silent worry. It is especially important to check in with them often, find out what they know and what they are worried about, and remind them to “never worry alone.” It also is important to continue with any recommended treatment, avoiding accommodation of their anxieties, except when it is required by public health protocols (i.e., staying home from school). Children with developmental disabilities may require additional support to change behaviors (hand washing) and may be more sensitive to changes in routine. And children with learning disabilities or special services in school may require additional support or structure during a prolonged period at home.
Preserve routines and structure
Routines and predictability are important to the sense of stability and well-being of most children (and adults). While disruptions are unavoidable, preserve what routines you can, and establish some new ones. For children who are out of school for several weeks, set up a consistent home routine, with a similar wake-up and bedtime, and a “school schedule.” There may be academic activities like reading or work sheets. If the parents’ work is disrupted, they can homeschool, shoring up weak academic areas or enhancing areas of interest. Be sure to preserve time for physical activity and social connections within this new framework. Social time does not require physical proximity, and can happen by screen or phone. Physical activity should be outside if at all possible. Predictability, preserved expectations (academic and otherwise), physical exercise, social connection, and consistent sleep will go a long way in protecting everyone’s ability to manage the disruptions of this epidemic.
Find opportunity in the disruption
Many families have been on a treadmill of work, school, and activities that have left little unscheduled time or spontaneity. Recommend looking at this disruption as a rare opportunity to slow down, spend time together, listen, learn more about one another, and even to have fun. Families could play board games, card games, watch movies together, or even read aloud. They might discover it is the time to try new hobbies (knitting, learning a new language or instrument), or to teach each other new skills. You might learn something new, or something new about your children. You also will offer a model of finding the opportunity in adversity, and even offer them some wonderful memories from a difficult time.
Take care of the vulnerable and ease others’ hardships
Without a doubt, this will be a difficult time for many people, medically, financially, and emotionally. One powerful strategy to build resilience in our children and strengthen our communities is to think with children about ways to help those who are most at risk or burdened by this challenge. Perhaps they want to make cards or FaceTime calls to older relatives who may be otherwise isolated. They may want to consider ways to support the work of first responders, even just with appreciation. They may want to reach out to elderly neighbors and offer to get groceries or other needed supplies for them. Balancing appropriate self-care with a focus on the needs of those who are more vulnerable or burdened than ourselves is a powerful way to show our children how communities pull together in a challenging time; enhance their feeling of connectedness; and build resilience in them, in our families, and in our communities.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected]
We are in uncharted waters with national and local states of emergency, schools and most activities being shut down, and rapidly evolving strategies on managing the COVID-19 outbreak. Everyone’s anxiety is appropriately high. As health care providers for children, you are facing changes in your personal life at home and in practice, likely including setting up televisits, trying to assess which patients to see, managing staffing challenges, and facing potential cash flow issues as expenses continue but revenue may fall short. And, of course, you will address a host of novel questions and concerns from the families you care for.
Your top priorities are to stay calm while offering clear recommendations on testing, quarantine, and treatment with guidance from our federal and local public health agencies. By providing clear guidance on the medical issues, you will offer substantial reassurance to families. But even with a medical plan in place, this remains a confusing and anxiety-provoking moment, one without much precedent in most people’s lives or in our national experience. Our aim is to complement that guidance by offering you some principles to help families manage the stress and anxiety that the disruptions and uncertainties that this public health emergency has created.
Offer clear, open, regular, and child-centered communication
If you have an email mailing list of your parents, you may want to summarize information you are gathering with a note they can expect at a specified time each day. You could request them to email you questions that then can be included as an FAQ (frequently asked questions).
Most children will have noticed people wearing face masks, or dramatic scenes on the news with hospital workers in full protective gear, breathlessly reporting growing numbers of the infected and the deceased. At a minimum, they are being commanded to wash hands and to not touch their faces (which is challenging enough for adults!), and are probably overhearing conversations about quarantines and contagion as well as family concerns about jobs and family finances. Many children are managing extended school closures and some are even managing the quarantine or serious illness of a loved one. When children overhear frightening news from distressed adults, they are going to become anxious and afraid themselves. Parents should remember to find out what their children have seen, heard, or understood about what is going on, and they should correct misinformation or misunderstandings with clear explanations. They also should find out what their children are curious about. “What has you wondering about that?” is a great response when children have questions, in order to make sure you get at any underlying worry.
It is fine to not have an answer to every question. It is difficult to offer clear explanations about something that we don’t yet fully understand, and it is fine to acknowledge what we don’t know. “That’s a great question. Let’s look together at the CDC [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] website.” Offering to look for answers or information together can be a powerful way to model how to handle uncertainty. And always couch answers with appropriate (not false) reassurance: “Children and young adults appear to be very safe from this illness, but we want to take care to protect those that are older or already sick.”
Remember most children set their anxiety level based on their parent’s anxiety, and part of being child centered in your communication includes offering information in an age-appropriate manner. Preschool-aged children (up to 5 years) still have magical thinking. They are prone to finding masks and gowns scary and to assume that school stopping may be because they did something wrong. Tell them about the new illness, and about the doctors and officials working hard to keep people safe. Reassure them about all of the adults working hard together to understand the illness and take care of people who are sick. Their sense of time is less logical, so you may have to tell them more than once. Reassure them that children do not get very sick from this illness, but they can carry and spread it, like having paint on their hands, so they need to wash their hands often to take good care of other people.
School-age children (aged roughly 5-12 years) are better equipped cognitively to understand the seriousness of this outbreak. They are built to master new situations, but are prone to anxiety as they don’t yet have the emotional maturity to tolerate uncertainty or unfairness. Explain what is known without euphemisms, be truly curious about what their questions are, and look for answers together. Often what they need is to see you being calm in the face of uncertainty, bearing the strong feelings that may come, and preserving curiosity and compassion for others.
Adolescents also will need all of this support, and can be curious about more abstract implications (political, ethical, financial). Do not be surprised when they ask sophisticated questions, but still are focused on the personal disruptions or sacrifices (a canceled dance or sports meet, concerns about academic performance). Adolescence is a time of intense preoccupation with their emerging identity and relationships; it is normal for them to experience events in a way that may seem selfish, especially if it disrupts their time with friends. Remind parents to offer compassion and validation, while acknowledging that shared sacrifice and discomfort are a part of every individual’s experience when a society must respond to such a large challenge.
Be mindful of children’s vulnerabilities
Being child centered goes beyond thinking about their age and developmental stage. Parents are the experts on their children and will know about any particular vulnerabilities to the stresses of this serious outbreak. Children who are prone to anxiety or suffer from anxiety disorders may be more prone to silent worry. It is especially important to check in with them often, find out what they know and what they are worried about, and remind them to “never worry alone.” It also is important to continue with any recommended treatment, avoiding accommodation of their anxieties, except when it is required by public health protocols (i.e., staying home from school). Children with developmental disabilities may require additional support to change behaviors (hand washing) and may be more sensitive to changes in routine. And children with learning disabilities or special services in school may require additional support or structure during a prolonged period at home.
Preserve routines and structure
Routines and predictability are important to the sense of stability and well-being of most children (and adults). While disruptions are unavoidable, preserve what routines you can, and establish some new ones. For children who are out of school for several weeks, set up a consistent home routine, with a similar wake-up and bedtime, and a “school schedule.” There may be academic activities like reading or work sheets. If the parents’ work is disrupted, they can homeschool, shoring up weak academic areas or enhancing areas of interest. Be sure to preserve time for physical activity and social connections within this new framework. Social time does not require physical proximity, and can happen by screen or phone. Physical activity should be outside if at all possible. Predictability, preserved expectations (academic and otherwise), physical exercise, social connection, and consistent sleep will go a long way in protecting everyone’s ability to manage the disruptions of this epidemic.
Find opportunity in the disruption
Many families have been on a treadmill of work, school, and activities that have left little unscheduled time or spontaneity. Recommend looking at this disruption as a rare opportunity to slow down, spend time together, listen, learn more about one another, and even to have fun. Families could play board games, card games, watch movies together, or even read aloud. They might discover it is the time to try new hobbies (knitting, learning a new language or instrument), or to teach each other new skills. You might learn something new, or something new about your children. You also will offer a model of finding the opportunity in adversity, and even offer them some wonderful memories from a difficult time.
Take care of the vulnerable and ease others’ hardships
Without a doubt, this will be a difficult time for many people, medically, financially, and emotionally. One powerful strategy to build resilience in our children and strengthen our communities is to think with children about ways to help those who are most at risk or burdened by this challenge. Perhaps they want to make cards or FaceTime calls to older relatives who may be otherwise isolated. They may want to consider ways to support the work of first responders, even just with appreciation. They may want to reach out to elderly neighbors and offer to get groceries or other needed supplies for them. Balancing appropriate self-care with a focus on the needs of those who are more vulnerable or burdened than ourselves is a powerful way to show our children how communities pull together in a challenging time; enhance their feeling of connectedness; and build resilience in them, in our families, and in our communities.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected]
Physicians and health systems can reduce fear around COVID-19
A message from a Chief Wellness Officer
We are at a time, unfortunately, of significant public uncertainty and fear of “the coronavirus.” Mixed and inaccurate messages from national leaders in the setting of delayed testing availability have heightened fears and impeded a uniformity in responses, medical and preventive.
Despite this, physicians, nurses, and other health professionals across the country, and in many other countries, have been addressing the medical realities of this pandemic in a way that should make every one of us health professionals proud – from the Chinese doctors and nurses to the Italian intensivists and primary care physicians throughout many countries who have treated patients suffering from, or fearful of, a novel disease with uncertain transmission characteristics and unpredictable clinical outcomes.
It is now time for physicians and other health providers in the United States to step up to the plate and model appropriate transmission-reducing behavior for the general public. This will help reduce the overall morbidity and mortality associated with this pandemic and let us return to a more normal lifestyle as soon as possible. Physicians need to be reassuring but realistic, and there are concrete steps that we can take to demonstrate to the general public that there is a way forward.
First the basic facts. The United States does not have enough intensive care beds or ventilators to handle a major pandemic. We will also have insufficient physicians and nurses if many are quarantined. The tragic experience in Italy, where patients are dying from lack of ventilators, intensive care facilities, and staff, must not be repeated here.
Many health systems are canceling or reducing outpatient appointments and increasingly using video and other telehealth technologies, especially for assessing and triaging people who believe that they may have become infected and are relatively asymptomatic. While all of the disruptions may seem unsettling, they are actually good news for those of us in healthcare. Efforts to “flatten the curve” will slow the infection spread and help us better manage patients who become critical.
So, what can physicians do?
- Make sure you are getting good information about the situation. Access reliable information and data that are widely available through the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institutes of Health, and the World Health Organization. Listen to professional news organizations, local and national. Pass this information to your patients and community.
- Obviously, when practicing clinically, follow all infection control protocols, which will inevitably change over time. Make it clear to your patients why you are following these protocols and procedures.
- Support and actively promote the public health responses to this pandemic. Systematic reviews of the evidence base have found that isolating ill persons, testing and tracing contacts, quarantining exposed persons, closing schools and workplaces, and avoiding crowding are more effective if implemented immediately, simultaneously (ie, school closures combined with teleworking for parents), and with high community compliance.
- Practice social distancing so that you remain as much in control as you can. This will make you feel psychologically better and safer, as well as reduce the risk for transmission. Take the essential precautionary measures that we are all being asked to take. Wash your hands. Do not shake hands. Clean shared items. Do not go to large public gatherings. Minimize large group travel as much as you can. Use video to see your patients or your own doctor.
- Connect and reconnect with people you trust and love. See your family, your partner, your children, your friends. Speak to them on the phone and nourish those relationships. See how they feel and care for each other. They will be worried about you. Reassure them. Be in the moment with them and use the importance of these relationships to give yourself a chance not to overthink any fears you might have.
- Look after yourself physically. Physical fitness is good for your mental health. While White House guidelines suggest avoiding gyms, you can still enjoy long walks and outdoor activities. Take the weekend off and don’t work excessively. Sleep well – at least 7-8 hours. which has a series of really excellent meditation and relaxation tools.
- Do not panic. Uncertainty surrounding the pandemic makes all of us anxious and afraid. It is normal to become hypervigilant, especially with our nonstop media. It is normal to be concerned when we feel out of control and when we are hearing about a possible future catastrophe, especially when fed with differing sets of information from multiple sources and countries.
- Be careful with any large decisions you are making that may affect the lives of yourself and your loved ones. Think about your decisions and try to take the long view; and run them by your spouse, partner, or friends. This is not a time to be making sudden big decisions that may be driven unconsciously, in part at least, by fear and anxiety.
- Realize that all of these societal disruptions are actually good for us in health care, and they help your family and friends understand the importance of slowing the disease’s spread. That’s good for health care and good for everyone.
Finally, remember that “this is what we do,” to quote Doug Kirk, MD, chief medical officer of UC Davis Health. We must look after our patients. But we also have to look after ourselves so that we can look after our patients. We should all be proud of our work and our caring. And we should model our personal behavior to our patients and to our families and friends so that they will model it to their community networks. That way, more people will keep well, and we will have more chance of “flattening the curve” and reducing the morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19.
Peter M. Yellowlees, MBBS, MD, is a professor in the Department of Psychiatry at the University of California, Davis. He is a longtime Medscape contributor.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A message from a Chief Wellness Officer
We are at a time, unfortunately, of significant public uncertainty and fear of “the coronavirus.” Mixed and inaccurate messages from national leaders in the setting of delayed testing availability have heightened fears and impeded a uniformity in responses, medical and preventive.
Despite this, physicians, nurses, and other health professionals across the country, and in many other countries, have been addressing the medical realities of this pandemic in a way that should make every one of us health professionals proud – from the Chinese doctors and nurses to the Italian intensivists and primary care physicians throughout many countries who have treated patients suffering from, or fearful of, a novel disease with uncertain transmission characteristics and unpredictable clinical outcomes.
It is now time for physicians and other health providers in the United States to step up to the plate and model appropriate transmission-reducing behavior for the general public. This will help reduce the overall morbidity and mortality associated with this pandemic and let us return to a more normal lifestyle as soon as possible. Physicians need to be reassuring but realistic, and there are concrete steps that we can take to demonstrate to the general public that there is a way forward.
First the basic facts. The United States does not have enough intensive care beds or ventilators to handle a major pandemic. We will also have insufficient physicians and nurses if many are quarantined. The tragic experience in Italy, where patients are dying from lack of ventilators, intensive care facilities, and staff, must not be repeated here.
Many health systems are canceling or reducing outpatient appointments and increasingly using video and other telehealth technologies, especially for assessing and triaging people who believe that they may have become infected and are relatively asymptomatic. While all of the disruptions may seem unsettling, they are actually good news for those of us in healthcare. Efforts to “flatten the curve” will slow the infection spread and help us better manage patients who become critical.
So, what can physicians do?
- Make sure you are getting good information about the situation. Access reliable information and data that are widely available through the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institutes of Health, and the World Health Organization. Listen to professional news organizations, local and national. Pass this information to your patients and community.
- Obviously, when practicing clinically, follow all infection control protocols, which will inevitably change over time. Make it clear to your patients why you are following these protocols and procedures.
- Support and actively promote the public health responses to this pandemic. Systematic reviews of the evidence base have found that isolating ill persons, testing and tracing contacts, quarantining exposed persons, closing schools and workplaces, and avoiding crowding are more effective if implemented immediately, simultaneously (ie, school closures combined with teleworking for parents), and with high community compliance.
- Practice social distancing so that you remain as much in control as you can. This will make you feel psychologically better and safer, as well as reduce the risk for transmission. Take the essential precautionary measures that we are all being asked to take. Wash your hands. Do not shake hands. Clean shared items. Do not go to large public gatherings. Minimize large group travel as much as you can. Use video to see your patients or your own doctor.
- Connect and reconnect with people you trust and love. See your family, your partner, your children, your friends. Speak to them on the phone and nourish those relationships. See how they feel and care for each other. They will be worried about you. Reassure them. Be in the moment with them and use the importance of these relationships to give yourself a chance not to overthink any fears you might have.
- Look after yourself physically. Physical fitness is good for your mental health. While White House guidelines suggest avoiding gyms, you can still enjoy long walks and outdoor activities. Take the weekend off and don’t work excessively. Sleep well – at least 7-8 hours. which has a series of really excellent meditation and relaxation tools.
- Do not panic. Uncertainty surrounding the pandemic makes all of us anxious and afraid. It is normal to become hypervigilant, especially with our nonstop media. It is normal to be concerned when we feel out of control and when we are hearing about a possible future catastrophe, especially when fed with differing sets of information from multiple sources and countries.
- Be careful with any large decisions you are making that may affect the lives of yourself and your loved ones. Think about your decisions and try to take the long view; and run them by your spouse, partner, or friends. This is not a time to be making sudden big decisions that may be driven unconsciously, in part at least, by fear and anxiety.
- Realize that all of these societal disruptions are actually good for us in health care, and they help your family and friends understand the importance of slowing the disease’s spread. That’s good for health care and good for everyone.
Finally, remember that “this is what we do,” to quote Doug Kirk, MD, chief medical officer of UC Davis Health. We must look after our patients. But we also have to look after ourselves so that we can look after our patients. We should all be proud of our work and our caring. And we should model our personal behavior to our patients and to our families and friends so that they will model it to their community networks. That way, more people will keep well, and we will have more chance of “flattening the curve” and reducing the morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19.
Peter M. Yellowlees, MBBS, MD, is a professor in the Department of Psychiatry at the University of California, Davis. He is a longtime Medscape contributor.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A message from a Chief Wellness Officer
We are at a time, unfortunately, of significant public uncertainty and fear of “the coronavirus.” Mixed and inaccurate messages from national leaders in the setting of delayed testing availability have heightened fears and impeded a uniformity in responses, medical and preventive.
Despite this, physicians, nurses, and other health professionals across the country, and in many other countries, have been addressing the medical realities of this pandemic in a way that should make every one of us health professionals proud – from the Chinese doctors and nurses to the Italian intensivists and primary care physicians throughout many countries who have treated patients suffering from, or fearful of, a novel disease with uncertain transmission characteristics and unpredictable clinical outcomes.
It is now time for physicians and other health providers in the United States to step up to the plate and model appropriate transmission-reducing behavior for the general public. This will help reduce the overall morbidity and mortality associated with this pandemic and let us return to a more normal lifestyle as soon as possible. Physicians need to be reassuring but realistic, and there are concrete steps that we can take to demonstrate to the general public that there is a way forward.
First the basic facts. The United States does not have enough intensive care beds or ventilators to handle a major pandemic. We will also have insufficient physicians and nurses if many are quarantined. The tragic experience in Italy, where patients are dying from lack of ventilators, intensive care facilities, and staff, must not be repeated here.
Many health systems are canceling or reducing outpatient appointments and increasingly using video and other telehealth technologies, especially for assessing and triaging people who believe that they may have become infected and are relatively asymptomatic. While all of the disruptions may seem unsettling, they are actually good news for those of us in healthcare. Efforts to “flatten the curve” will slow the infection spread and help us better manage patients who become critical.
So, what can physicians do?
- Make sure you are getting good information about the situation. Access reliable information and data that are widely available through the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institutes of Health, and the World Health Organization. Listen to professional news organizations, local and national. Pass this information to your patients and community.
- Obviously, when practicing clinically, follow all infection control protocols, which will inevitably change over time. Make it clear to your patients why you are following these protocols and procedures.
- Support and actively promote the public health responses to this pandemic. Systematic reviews of the evidence base have found that isolating ill persons, testing and tracing contacts, quarantining exposed persons, closing schools and workplaces, and avoiding crowding are more effective if implemented immediately, simultaneously (ie, school closures combined with teleworking for parents), and with high community compliance.
- Practice social distancing so that you remain as much in control as you can. This will make you feel psychologically better and safer, as well as reduce the risk for transmission. Take the essential precautionary measures that we are all being asked to take. Wash your hands. Do not shake hands. Clean shared items. Do not go to large public gatherings. Minimize large group travel as much as you can. Use video to see your patients or your own doctor.
- Connect and reconnect with people you trust and love. See your family, your partner, your children, your friends. Speak to them on the phone and nourish those relationships. See how they feel and care for each other. They will be worried about you. Reassure them. Be in the moment with them and use the importance of these relationships to give yourself a chance not to overthink any fears you might have.
- Look after yourself physically. Physical fitness is good for your mental health. While White House guidelines suggest avoiding gyms, you can still enjoy long walks and outdoor activities. Take the weekend off and don’t work excessively. Sleep well – at least 7-8 hours. which has a series of really excellent meditation and relaxation tools.
- Do not panic. Uncertainty surrounding the pandemic makes all of us anxious and afraid. It is normal to become hypervigilant, especially with our nonstop media. It is normal to be concerned when we feel out of control and when we are hearing about a possible future catastrophe, especially when fed with differing sets of information from multiple sources and countries.
- Be careful with any large decisions you are making that may affect the lives of yourself and your loved ones. Think about your decisions and try to take the long view; and run them by your spouse, partner, or friends. This is not a time to be making sudden big decisions that may be driven unconsciously, in part at least, by fear and anxiety.
- Realize that all of these societal disruptions are actually good for us in health care, and they help your family and friends understand the importance of slowing the disease’s spread. That’s good for health care and good for everyone.
Finally, remember that “this is what we do,” to quote Doug Kirk, MD, chief medical officer of UC Davis Health. We must look after our patients. But we also have to look after ourselves so that we can look after our patients. We should all be proud of our work and our caring. And we should model our personal behavior to our patients and to our families and friends so that they will model it to their community networks. That way, more people will keep well, and we will have more chance of “flattening the curve” and reducing the morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19.
Peter M. Yellowlees, MBBS, MD, is a professor in the Department of Psychiatry at the University of California, Davis. He is a longtime Medscape contributor.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PARAGON-HF: Optimal systolic pressure in HFpEF is 120-129 mm Hg
A target systolic blood pressure (SBP) of 120-129 mm Hg in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction proved to be the sweet spot with the lowest rates of major adverse cardiovascular and renal events in a new analysis from the landmark PARAGON-HF trial.
This finding from the largest-ever randomized, controlled study in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) strengthens support for current U.S. joint hypertension guidelines, which call for a target SBP less than 130 mm Hg in patients with HFpEF (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017 Aug 8;70[6]:776-803), a recommendation based upon weak evidence until now. That’s because the SPRINT trial, the major impetus for adoption of intensive blood pressure control in the current guidelines, excluded patients with symptomatic HF, Scott D. Solomon, MD, and coinvestigators noted in their new analysis. The study was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and had been planned for presentation during the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. ACC organizers chose to present parts of the meeting virtually after COVID-19 concerns caused them to cancel the meeting.
The new analysis from PARAGON-HF (Prospective Comparison of ARNI with ARB Global Outcomes in HFpEF) also ruled out the SBP-lowering effect of sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto) as the explanation for the combination drug’s demonstrated beneficial impact on outcomes in the subgroup with an SBP of 120-129 mm Hg. That wasn’t actually a surprise. Indeed, the new study had two hypotheses: one, that the relationship between SBP and cardiovascular and renal outcomes in HFpEF would follow a J-shaped curve, and two, that sacubitril/valsartan’s blood pressure–lowering effect would not account for the drug’s outcome benefits in the subset of HFpEF patients with an SBP in the sweet spot of 120-129 mm Hg. Both hypotheses were borne out, noted Dr. Solomon, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of noninvasive cardiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston.
“These data strongly support that additional mechanisms other than blood pressure–lowering account for the benefit. But this is not surprising. The same can be said for most of the therapies that work in heart failure,” he said in an interview.
Take, for example, spironolactone. In TOPCAT (Treatment of Preserved Cardiac Function Heart Failure with an Aldosterone Antagonist), another major trial in which Dr. Solomon played a leadership role, the beneficial effect of spironolactone on clinical outcomes also proved unrelated to the drug’s blood pressure–lowering effect.
Other known effects of sacubitril/valsartan, a novel angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitor, or ARNI, might in theory account for the observed clinical benefits in ARNI-treated patients with an on-treatment SBP of 120-129 mm Hg in PARAGON-HF. These include improved left atrial remodeling, an increase in natriuretic peptides, and improved myocardial relaxation. However, the current lack of understanding of the basic mechanistic processes underlying the varied clinical expressions of HFpEF is a major factor contributing to the lack of any proven-effective therapy for this extremely common and costly disorder, according to Dr. Solomon and coinvestigators.
In contrast to HFpEF, for which to date there is no proven treatment, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction sacubitril/valsartan has a class I recommendation on the strength of its performance in significantly reducing cardiovascular deaths and heart failure hospitalizations in the PARADIGM-HF trial (N Engl J Med. 2014 Sep 11;371:993-1004).
PARAGON-HF included 4,822 patients with symptomatic HFpEF who were randomized to sacubitril/valsartan at 97/103 mg b.i.d. or valsartan at 160 mg b.i.d. As previously reported (N Engl J Med. 2019 Oct 24;381[17]:1609-20), at an average follow-up of 35 months, the primary outcome – a composite of total hospitalizations for heart failure and cardiovascular death – occurred at a rate of 12.8 events per 100 patient-years in the sacubitril/valsartan group and 14.6 per 100 patient-years in the valsartan arm, for a 13% relative risk reduction that narrowly missed statistical significance (P = .059).
However, sacubitril/valsartan showed significant benefit on some prespecified secondary endpoints, including worsening renal function, change in New York Heart Association class, and quality of life. Women, who notably accounted for 52% of study participants, appeared to benefit from sacubitril/valsartan more than men as evidenced by their 27% relative risk reduction in the primary endpoint. Also, in the roughly half of PARAGON-HF participants with a baseline left ventricular ejection fraction of 45%-57%, treatment with sacubitril/valsartan resulted in a statistically significant 22% relative risk reduction in the primary endpoint, compared with valsartan alone.
SBP and cardiovascular outcomes in HFpEF
In the new analysis, Dr. Solomon and coworkers examined outcomes based on baseline and mean achieved SBP quartiles regardless of treatment arm. In an unadjusted analysis, the primary composite endpoint occurred at a rate of 15.2 events/100 patient-years in HFpEF patients with an achieved SBP below 120 mm Hg, 11.4/100 patient-years at 120-129 mm Hg, 12.2/100 patient-years at 130-139 mm Hg, and 15.6/100 patient-years at 140 mm Hg or more. Further, in a multivariate regression analysis extensively adjusted for atrial fibrillation, sex, race, and numerous other potential confounders, the group with an achieved SBP of 120-129 mm Hg continued to fare best. The adjusted risks for the primary endpoint were 11% and 21% higher in patients in the first and third quartiles of achieved SBP, compared with those at 120-129 mm Hg, although neither trend reached statistical significance. But patients in the top quartile, with an achieved SBP of 140 mm Hg or more, had a highly significant 56% increase in risk, compared with patients in the second-lowest SBP quartile.
Change in blood pressure from baseline to week 48 had no impact on quality of life or high-sensitivity troponin T. However, each 10–mm Hg lowering of SBP was associated with a modest 2.1% reduction in log-transformed N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide.
Sacubitril/valsartan reduced SBP by an average of 5.2 mm Hg more than valsartan alone at 4 weeks regardless of baseline SBP. And the combo drug had a significantly greater SBP-lowering effect in women than men, by a margin of 6.3 mm Hg versus 4.0 mm Hg. But a Cox regression analysis showed that in women, as in the study population as a whole, sacubitril/valsartan’s SBP-lowering effects didn’t account for the drug’s impact on outcomes.
In an editorial accompanying publication of the new PARAGON-HF blood pressure analysis (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Mar 16. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.02.024), Hector O. Ventura, MD, and colleagues at the Ochsner Clinic in New Orleans observed that the study results “lend some credence to the prognostic relationship of blood pressure in HFpEF, but whether they should serve as a therapeutic target or are merely a prognostic surrogate determined by other pathogenic factors, such as vascular ventricular uncoupling or aortic stiffness on one hand when blood pressure is greater than 140 mm Hg, or a reduced cardiac performance indicated by reduced blood pressure to less than 120 mm Hg, remains uncertain.”
“What is certain, however, is that the relationship and contributions of hypertension in manifest HFpEF are complex, multifactorial and likely go well beyond a simplistic framework of hemodynamic influences,” they added.
Dr. Solomon has received research grants from and serves as a consultant to Novartis, which funded PARAGON-HF, and has similar financial relationships with more than a dozen other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Ventura reported having no relevant financial interests.
SOURCE: Solomon SD et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Mar 16. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.02.009.
A target systolic blood pressure (SBP) of 120-129 mm Hg in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction proved to be the sweet spot with the lowest rates of major adverse cardiovascular and renal events in a new analysis from the landmark PARAGON-HF trial.
This finding from the largest-ever randomized, controlled study in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) strengthens support for current U.S. joint hypertension guidelines, which call for a target SBP less than 130 mm Hg in patients with HFpEF (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017 Aug 8;70[6]:776-803), a recommendation based upon weak evidence until now. That’s because the SPRINT trial, the major impetus for adoption of intensive blood pressure control in the current guidelines, excluded patients with symptomatic HF, Scott D. Solomon, MD, and coinvestigators noted in their new analysis. The study was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and had been planned for presentation during the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. ACC organizers chose to present parts of the meeting virtually after COVID-19 concerns caused them to cancel the meeting.
The new analysis from PARAGON-HF (Prospective Comparison of ARNI with ARB Global Outcomes in HFpEF) also ruled out the SBP-lowering effect of sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto) as the explanation for the combination drug’s demonstrated beneficial impact on outcomes in the subgroup with an SBP of 120-129 mm Hg. That wasn’t actually a surprise. Indeed, the new study had two hypotheses: one, that the relationship between SBP and cardiovascular and renal outcomes in HFpEF would follow a J-shaped curve, and two, that sacubitril/valsartan’s blood pressure–lowering effect would not account for the drug’s outcome benefits in the subset of HFpEF patients with an SBP in the sweet spot of 120-129 mm Hg. Both hypotheses were borne out, noted Dr. Solomon, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of noninvasive cardiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston.
“These data strongly support that additional mechanisms other than blood pressure–lowering account for the benefit. But this is not surprising. The same can be said for most of the therapies that work in heart failure,” he said in an interview.
Take, for example, spironolactone. In TOPCAT (Treatment of Preserved Cardiac Function Heart Failure with an Aldosterone Antagonist), another major trial in which Dr. Solomon played a leadership role, the beneficial effect of spironolactone on clinical outcomes also proved unrelated to the drug’s blood pressure–lowering effect.
Other known effects of sacubitril/valsartan, a novel angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitor, or ARNI, might in theory account for the observed clinical benefits in ARNI-treated patients with an on-treatment SBP of 120-129 mm Hg in PARAGON-HF. These include improved left atrial remodeling, an increase in natriuretic peptides, and improved myocardial relaxation. However, the current lack of understanding of the basic mechanistic processes underlying the varied clinical expressions of HFpEF is a major factor contributing to the lack of any proven-effective therapy for this extremely common and costly disorder, according to Dr. Solomon and coinvestigators.
In contrast to HFpEF, for which to date there is no proven treatment, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction sacubitril/valsartan has a class I recommendation on the strength of its performance in significantly reducing cardiovascular deaths and heart failure hospitalizations in the PARADIGM-HF trial (N Engl J Med. 2014 Sep 11;371:993-1004).
PARAGON-HF included 4,822 patients with symptomatic HFpEF who were randomized to sacubitril/valsartan at 97/103 mg b.i.d. or valsartan at 160 mg b.i.d. As previously reported (N Engl J Med. 2019 Oct 24;381[17]:1609-20), at an average follow-up of 35 months, the primary outcome – a composite of total hospitalizations for heart failure and cardiovascular death – occurred at a rate of 12.8 events per 100 patient-years in the sacubitril/valsartan group and 14.6 per 100 patient-years in the valsartan arm, for a 13% relative risk reduction that narrowly missed statistical significance (P = .059).
However, sacubitril/valsartan showed significant benefit on some prespecified secondary endpoints, including worsening renal function, change in New York Heart Association class, and quality of life. Women, who notably accounted for 52% of study participants, appeared to benefit from sacubitril/valsartan more than men as evidenced by their 27% relative risk reduction in the primary endpoint. Also, in the roughly half of PARAGON-HF participants with a baseline left ventricular ejection fraction of 45%-57%, treatment with sacubitril/valsartan resulted in a statistically significant 22% relative risk reduction in the primary endpoint, compared with valsartan alone.
SBP and cardiovascular outcomes in HFpEF
In the new analysis, Dr. Solomon and coworkers examined outcomes based on baseline and mean achieved SBP quartiles regardless of treatment arm. In an unadjusted analysis, the primary composite endpoint occurred at a rate of 15.2 events/100 patient-years in HFpEF patients with an achieved SBP below 120 mm Hg, 11.4/100 patient-years at 120-129 mm Hg, 12.2/100 patient-years at 130-139 mm Hg, and 15.6/100 patient-years at 140 mm Hg or more. Further, in a multivariate regression analysis extensively adjusted for atrial fibrillation, sex, race, and numerous other potential confounders, the group with an achieved SBP of 120-129 mm Hg continued to fare best. The adjusted risks for the primary endpoint were 11% and 21% higher in patients in the first and third quartiles of achieved SBP, compared with those at 120-129 mm Hg, although neither trend reached statistical significance. But patients in the top quartile, with an achieved SBP of 140 mm Hg or more, had a highly significant 56% increase in risk, compared with patients in the second-lowest SBP quartile.
Change in blood pressure from baseline to week 48 had no impact on quality of life or high-sensitivity troponin T. However, each 10–mm Hg lowering of SBP was associated with a modest 2.1% reduction in log-transformed N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide.
Sacubitril/valsartan reduced SBP by an average of 5.2 mm Hg more than valsartan alone at 4 weeks regardless of baseline SBP. And the combo drug had a significantly greater SBP-lowering effect in women than men, by a margin of 6.3 mm Hg versus 4.0 mm Hg. But a Cox regression analysis showed that in women, as in the study population as a whole, sacubitril/valsartan’s SBP-lowering effects didn’t account for the drug’s impact on outcomes.
In an editorial accompanying publication of the new PARAGON-HF blood pressure analysis (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Mar 16. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.02.024), Hector O. Ventura, MD, and colleagues at the Ochsner Clinic in New Orleans observed that the study results “lend some credence to the prognostic relationship of blood pressure in HFpEF, but whether they should serve as a therapeutic target or are merely a prognostic surrogate determined by other pathogenic factors, such as vascular ventricular uncoupling or aortic stiffness on one hand when blood pressure is greater than 140 mm Hg, or a reduced cardiac performance indicated by reduced blood pressure to less than 120 mm Hg, remains uncertain.”
“What is certain, however, is that the relationship and contributions of hypertension in manifest HFpEF are complex, multifactorial and likely go well beyond a simplistic framework of hemodynamic influences,” they added.
Dr. Solomon has received research grants from and serves as a consultant to Novartis, which funded PARAGON-HF, and has similar financial relationships with more than a dozen other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Ventura reported having no relevant financial interests.
SOURCE: Solomon SD et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Mar 16. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.02.009.
A target systolic blood pressure (SBP) of 120-129 mm Hg in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction proved to be the sweet spot with the lowest rates of major adverse cardiovascular and renal events in a new analysis from the landmark PARAGON-HF trial.
This finding from the largest-ever randomized, controlled study in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) strengthens support for current U.S. joint hypertension guidelines, which call for a target SBP less than 130 mm Hg in patients with HFpEF (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017 Aug 8;70[6]:776-803), a recommendation based upon weak evidence until now. That’s because the SPRINT trial, the major impetus for adoption of intensive blood pressure control in the current guidelines, excluded patients with symptomatic HF, Scott D. Solomon, MD, and coinvestigators noted in their new analysis. The study was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and had been planned for presentation during the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. ACC organizers chose to present parts of the meeting virtually after COVID-19 concerns caused them to cancel the meeting.
The new analysis from PARAGON-HF (Prospective Comparison of ARNI with ARB Global Outcomes in HFpEF) also ruled out the SBP-lowering effect of sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto) as the explanation for the combination drug’s demonstrated beneficial impact on outcomes in the subgroup with an SBP of 120-129 mm Hg. That wasn’t actually a surprise. Indeed, the new study had two hypotheses: one, that the relationship between SBP and cardiovascular and renal outcomes in HFpEF would follow a J-shaped curve, and two, that sacubitril/valsartan’s blood pressure–lowering effect would not account for the drug’s outcome benefits in the subset of HFpEF patients with an SBP in the sweet spot of 120-129 mm Hg. Both hypotheses were borne out, noted Dr. Solomon, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of noninvasive cardiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston.
“These data strongly support that additional mechanisms other than blood pressure–lowering account for the benefit. But this is not surprising. The same can be said for most of the therapies that work in heart failure,” he said in an interview.
Take, for example, spironolactone. In TOPCAT (Treatment of Preserved Cardiac Function Heart Failure with an Aldosterone Antagonist), another major trial in which Dr. Solomon played a leadership role, the beneficial effect of spironolactone on clinical outcomes also proved unrelated to the drug’s blood pressure–lowering effect.
Other known effects of sacubitril/valsartan, a novel angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitor, or ARNI, might in theory account for the observed clinical benefits in ARNI-treated patients with an on-treatment SBP of 120-129 mm Hg in PARAGON-HF. These include improved left atrial remodeling, an increase in natriuretic peptides, and improved myocardial relaxation. However, the current lack of understanding of the basic mechanistic processes underlying the varied clinical expressions of HFpEF is a major factor contributing to the lack of any proven-effective therapy for this extremely common and costly disorder, according to Dr. Solomon and coinvestigators.
In contrast to HFpEF, for which to date there is no proven treatment, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction sacubitril/valsartan has a class I recommendation on the strength of its performance in significantly reducing cardiovascular deaths and heart failure hospitalizations in the PARADIGM-HF trial (N Engl J Med. 2014 Sep 11;371:993-1004).
PARAGON-HF included 4,822 patients with symptomatic HFpEF who were randomized to sacubitril/valsartan at 97/103 mg b.i.d. or valsartan at 160 mg b.i.d. As previously reported (N Engl J Med. 2019 Oct 24;381[17]:1609-20), at an average follow-up of 35 months, the primary outcome – a composite of total hospitalizations for heart failure and cardiovascular death – occurred at a rate of 12.8 events per 100 patient-years in the sacubitril/valsartan group and 14.6 per 100 patient-years in the valsartan arm, for a 13% relative risk reduction that narrowly missed statistical significance (P = .059).
However, sacubitril/valsartan showed significant benefit on some prespecified secondary endpoints, including worsening renal function, change in New York Heart Association class, and quality of life. Women, who notably accounted for 52% of study participants, appeared to benefit from sacubitril/valsartan more than men as evidenced by their 27% relative risk reduction in the primary endpoint. Also, in the roughly half of PARAGON-HF participants with a baseline left ventricular ejection fraction of 45%-57%, treatment with sacubitril/valsartan resulted in a statistically significant 22% relative risk reduction in the primary endpoint, compared with valsartan alone.
SBP and cardiovascular outcomes in HFpEF
In the new analysis, Dr. Solomon and coworkers examined outcomes based on baseline and mean achieved SBP quartiles regardless of treatment arm. In an unadjusted analysis, the primary composite endpoint occurred at a rate of 15.2 events/100 patient-years in HFpEF patients with an achieved SBP below 120 mm Hg, 11.4/100 patient-years at 120-129 mm Hg, 12.2/100 patient-years at 130-139 mm Hg, and 15.6/100 patient-years at 140 mm Hg or more. Further, in a multivariate regression analysis extensively adjusted for atrial fibrillation, sex, race, and numerous other potential confounders, the group with an achieved SBP of 120-129 mm Hg continued to fare best. The adjusted risks for the primary endpoint were 11% and 21% higher in patients in the first and third quartiles of achieved SBP, compared with those at 120-129 mm Hg, although neither trend reached statistical significance. But patients in the top quartile, with an achieved SBP of 140 mm Hg or more, had a highly significant 56% increase in risk, compared with patients in the second-lowest SBP quartile.
Change in blood pressure from baseline to week 48 had no impact on quality of life or high-sensitivity troponin T. However, each 10–mm Hg lowering of SBP was associated with a modest 2.1% reduction in log-transformed N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide.
Sacubitril/valsartan reduced SBP by an average of 5.2 mm Hg more than valsartan alone at 4 weeks regardless of baseline SBP. And the combo drug had a significantly greater SBP-lowering effect in women than men, by a margin of 6.3 mm Hg versus 4.0 mm Hg. But a Cox regression analysis showed that in women, as in the study population as a whole, sacubitril/valsartan’s SBP-lowering effects didn’t account for the drug’s impact on outcomes.
In an editorial accompanying publication of the new PARAGON-HF blood pressure analysis (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Mar 16. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.02.024), Hector O. Ventura, MD, and colleagues at the Ochsner Clinic in New Orleans observed that the study results “lend some credence to the prognostic relationship of blood pressure in HFpEF, but whether they should serve as a therapeutic target or are merely a prognostic surrogate determined by other pathogenic factors, such as vascular ventricular uncoupling or aortic stiffness on one hand when blood pressure is greater than 140 mm Hg, or a reduced cardiac performance indicated by reduced blood pressure to less than 120 mm Hg, remains uncertain.”
“What is certain, however, is that the relationship and contributions of hypertension in manifest HFpEF are complex, multifactorial and likely go well beyond a simplistic framework of hemodynamic influences,” they added.
Dr. Solomon has received research grants from and serves as a consultant to Novartis, which funded PARAGON-HF, and has similar financial relationships with more than a dozen other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Ventura reported having no relevant financial interests.
SOURCE: Solomon SD et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Mar 16. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.02.009.
FROM ACC 2020
CME in the time of COVID-19
As the COVID-19 pandemic spreads, it now seems like the norm is that large medical conferences are being canceled.
The American Psychiatric Association (APA) canceled its 2020 annual meeting, which was scheduled for late April. The cancellation disappointed many, because we will miss out on the camaraderie and professional invigoration that comes from gathering with psychiatrists and other mental health professionals from across the United States and around the world. After the APA’s decision was announced, the White House released guidelines advising Americans to avoid social gatherings of 10 or more people.
On a practical level, many psychiatrists will not be able to earn up to 35 continuing medical education credits (CME) from attending the meeting and fulfilling the administrative requirements to obtain a CME certificate. Not only have meetings been canceled, but events many other clinicians count on for CME, such as journal clubs and department grand rounds, have been canceled until they can be moved to a virtual space.
The CME requirements for state medical licenses vary widely. On average, most states require at least 25 credits per year or 60 to 100 credits every 2 years, and the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology requires diplomates to complete an average of 30 specialty and/or subspecialty CME credits per year, averaged over 3 years. Usually, annual medical conferences would be a great way to get an infusion of CME credits, brush up on cutting-edge treatments, and review the basics.
On top of everything else we have to worry about with COVID-19, getting enough CME credits has been added to the list for many psychiatrists and mental health clinicians. As our schedules and daily lives are disrupted, it’s important to find relief in routine activities that are not affected by social distancing and fears of isolation and quarantine. A routine activity to lean into might include learning or practicing a skill that we enjoy, such as psychiatry (hopefully!) and the practice of medicine. The CME could be focused on a psychiatric topic or perhaps learning about the specifics of COVID-19 or brushing up on medical knowledge that might be a bit rusty after many years of practicing solely psychiatry.
As you start to gather CME credits online, it’s helpful to sign up for a service that stores your CME credits and helps you keep track of the number. When it comes time to renew your medical license or apply for maintenance of certification (MOC), who wants to be the person searching through their email for PDFs of CME certificates or taking pictures or scanning paper certificates? The APA has a section under education and MOC to track certificates earned by watching online modules from its “Learning Center.” The website also allows users to upload external certificates. The American Medical Association offers a similar service on its “Ed Hub,” in which users can log in to watch, listen, or download articles to earn CME credits after finishing the associated quiz. Medscape, in the CME and Education section, also offers an easy-to-use CME dashboard, in which clinicians can filter by their specialty, topic, duration of learning activity – ranging from 0.25 to 3 CME credits. Clinicians also can track their credits as they complete activities.
If you’re someone who’s having trouble focusing on anything besides COVID-19, there are COVID-19-specific CME activities that are available and can help psychiatrists feel comfortable talking with patients, family, and their institutions about the risks of COVID-19. The AMA Ed Hub has a featured 8-credit CME course about the novel coronavirus with updates about diagnosis, treatment, and public health strategies.
For the psychiatrists who may have procrastinated in-depth learning about the opioid crisis or getting their buprenorphine waivers, AMA Ed Hub offers a 42-credit course about opioids and pain management covering guidelines, research, and treatment.
For fun refreshers on general medicine, the New England Journal of Medicine offers up to 20 online CME exams based on quizzes from interesting clinical cases ranging from “regular” medicine to rare clinical scenarios. The APA Learning Center has an easy-to-use search function allowing users to select content from more than 200 modules covering a wide range of general topics; from reviewing recent treatment guidelines to specialized psychiatric topics such as geriatric bipolar disorder. A psychiatrist who has been quickly pushed to telepsychiatry because of the current pandemic could use the APA Learning Center to find educational modules about risk management in telepsychiatry or learn the special considerations of using telepsychiatry to treat patients with serious mental illness.
Using podcasts to earn CME is becoming increasingly common, with such as outlets as JAMA Networks offering podcasts in many specialties in which subscribers can take a quiz through the JAMA app and obtain CME credits.
As our clinical boundaries as psychiatrists are pushed by an ever-changing public health situation, now is the time to earn CME focused on new topics to meet the demands placed on health care workers at the front lines of clinical care.
If the COVID-19 pandemic reaches the number of cases predicted by public health officials, our health care system is going to be under extreme stress. All specialties face the threat of losing part of their working capacity as clinicians get sick with the virus, or as they stay home because of exposure or to take care of a loved one. CME can be a way to empower ourselves by staying current on the cutting edge of our specialties, but also brushing up on the medicine that we may be asked to practice in a time of great need.
Dr. Posada is consultation-liaison psychiatry fellow with the Inova Fairfax Hospital/George Washington University program in Falls Church, Va. She also is associate producer of the MDedge Psychcast. Dr. Posada has no disclosures.
As the COVID-19 pandemic spreads, it now seems like the norm is that large medical conferences are being canceled.
The American Psychiatric Association (APA) canceled its 2020 annual meeting, which was scheduled for late April. The cancellation disappointed many, because we will miss out on the camaraderie and professional invigoration that comes from gathering with psychiatrists and other mental health professionals from across the United States and around the world. After the APA’s decision was announced, the White House released guidelines advising Americans to avoid social gatherings of 10 or more people.
On a practical level, many psychiatrists will not be able to earn up to 35 continuing medical education credits (CME) from attending the meeting and fulfilling the administrative requirements to obtain a CME certificate. Not only have meetings been canceled, but events many other clinicians count on for CME, such as journal clubs and department grand rounds, have been canceled until they can be moved to a virtual space.
The CME requirements for state medical licenses vary widely. On average, most states require at least 25 credits per year or 60 to 100 credits every 2 years, and the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology requires diplomates to complete an average of 30 specialty and/or subspecialty CME credits per year, averaged over 3 years. Usually, annual medical conferences would be a great way to get an infusion of CME credits, brush up on cutting-edge treatments, and review the basics.
On top of everything else we have to worry about with COVID-19, getting enough CME credits has been added to the list for many psychiatrists and mental health clinicians. As our schedules and daily lives are disrupted, it’s important to find relief in routine activities that are not affected by social distancing and fears of isolation and quarantine. A routine activity to lean into might include learning or practicing a skill that we enjoy, such as psychiatry (hopefully!) and the practice of medicine. The CME could be focused on a psychiatric topic or perhaps learning about the specifics of COVID-19 or brushing up on medical knowledge that might be a bit rusty after many years of practicing solely psychiatry.
As you start to gather CME credits online, it’s helpful to sign up for a service that stores your CME credits and helps you keep track of the number. When it comes time to renew your medical license or apply for maintenance of certification (MOC), who wants to be the person searching through their email for PDFs of CME certificates or taking pictures or scanning paper certificates? The APA has a section under education and MOC to track certificates earned by watching online modules from its “Learning Center.” The website also allows users to upload external certificates. The American Medical Association offers a similar service on its “Ed Hub,” in which users can log in to watch, listen, or download articles to earn CME credits after finishing the associated quiz. Medscape, in the CME and Education section, also offers an easy-to-use CME dashboard, in which clinicians can filter by their specialty, topic, duration of learning activity – ranging from 0.25 to 3 CME credits. Clinicians also can track their credits as they complete activities.
If you’re someone who’s having trouble focusing on anything besides COVID-19, there are COVID-19-specific CME activities that are available and can help psychiatrists feel comfortable talking with patients, family, and their institutions about the risks of COVID-19. The AMA Ed Hub has a featured 8-credit CME course about the novel coronavirus with updates about diagnosis, treatment, and public health strategies.
For the psychiatrists who may have procrastinated in-depth learning about the opioid crisis or getting their buprenorphine waivers, AMA Ed Hub offers a 42-credit course about opioids and pain management covering guidelines, research, and treatment.
For fun refreshers on general medicine, the New England Journal of Medicine offers up to 20 online CME exams based on quizzes from interesting clinical cases ranging from “regular” medicine to rare clinical scenarios. The APA Learning Center has an easy-to-use search function allowing users to select content from more than 200 modules covering a wide range of general topics; from reviewing recent treatment guidelines to specialized psychiatric topics such as geriatric bipolar disorder. A psychiatrist who has been quickly pushed to telepsychiatry because of the current pandemic could use the APA Learning Center to find educational modules about risk management in telepsychiatry or learn the special considerations of using telepsychiatry to treat patients with serious mental illness.
Using podcasts to earn CME is becoming increasingly common, with such as outlets as JAMA Networks offering podcasts in many specialties in which subscribers can take a quiz through the JAMA app and obtain CME credits.
As our clinical boundaries as psychiatrists are pushed by an ever-changing public health situation, now is the time to earn CME focused on new topics to meet the demands placed on health care workers at the front lines of clinical care.
If the COVID-19 pandemic reaches the number of cases predicted by public health officials, our health care system is going to be under extreme stress. All specialties face the threat of losing part of their working capacity as clinicians get sick with the virus, or as they stay home because of exposure or to take care of a loved one. CME can be a way to empower ourselves by staying current on the cutting edge of our specialties, but also brushing up on the medicine that we may be asked to practice in a time of great need.
Dr. Posada is consultation-liaison psychiatry fellow with the Inova Fairfax Hospital/George Washington University program in Falls Church, Va. She also is associate producer of the MDedge Psychcast. Dr. Posada has no disclosures.
As the COVID-19 pandemic spreads, it now seems like the norm is that large medical conferences are being canceled.
The American Psychiatric Association (APA) canceled its 2020 annual meeting, which was scheduled for late April. The cancellation disappointed many, because we will miss out on the camaraderie and professional invigoration that comes from gathering with psychiatrists and other mental health professionals from across the United States and around the world. After the APA’s decision was announced, the White House released guidelines advising Americans to avoid social gatherings of 10 or more people.
On a practical level, many psychiatrists will not be able to earn up to 35 continuing medical education credits (CME) from attending the meeting and fulfilling the administrative requirements to obtain a CME certificate. Not only have meetings been canceled, but events many other clinicians count on for CME, such as journal clubs and department grand rounds, have been canceled until they can be moved to a virtual space.
The CME requirements for state medical licenses vary widely. On average, most states require at least 25 credits per year or 60 to 100 credits every 2 years, and the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology requires diplomates to complete an average of 30 specialty and/or subspecialty CME credits per year, averaged over 3 years. Usually, annual medical conferences would be a great way to get an infusion of CME credits, brush up on cutting-edge treatments, and review the basics.
On top of everything else we have to worry about with COVID-19, getting enough CME credits has been added to the list for many psychiatrists and mental health clinicians. As our schedules and daily lives are disrupted, it’s important to find relief in routine activities that are not affected by social distancing and fears of isolation and quarantine. A routine activity to lean into might include learning or practicing a skill that we enjoy, such as psychiatry (hopefully!) and the practice of medicine. The CME could be focused on a psychiatric topic or perhaps learning about the specifics of COVID-19 or brushing up on medical knowledge that might be a bit rusty after many years of practicing solely psychiatry.
As you start to gather CME credits online, it’s helpful to sign up for a service that stores your CME credits and helps you keep track of the number. When it comes time to renew your medical license or apply for maintenance of certification (MOC), who wants to be the person searching through their email for PDFs of CME certificates or taking pictures or scanning paper certificates? The APA has a section under education and MOC to track certificates earned by watching online modules from its “Learning Center.” The website also allows users to upload external certificates. The American Medical Association offers a similar service on its “Ed Hub,” in which users can log in to watch, listen, or download articles to earn CME credits after finishing the associated quiz. Medscape, in the CME and Education section, also offers an easy-to-use CME dashboard, in which clinicians can filter by their specialty, topic, duration of learning activity – ranging from 0.25 to 3 CME credits. Clinicians also can track their credits as they complete activities.
If you’re someone who’s having trouble focusing on anything besides COVID-19, there are COVID-19-specific CME activities that are available and can help psychiatrists feel comfortable talking with patients, family, and their institutions about the risks of COVID-19. The AMA Ed Hub has a featured 8-credit CME course about the novel coronavirus with updates about diagnosis, treatment, and public health strategies.
For the psychiatrists who may have procrastinated in-depth learning about the opioid crisis or getting their buprenorphine waivers, AMA Ed Hub offers a 42-credit course about opioids and pain management covering guidelines, research, and treatment.
For fun refreshers on general medicine, the New England Journal of Medicine offers up to 20 online CME exams based on quizzes from interesting clinical cases ranging from “regular” medicine to rare clinical scenarios. The APA Learning Center has an easy-to-use search function allowing users to select content from more than 200 modules covering a wide range of general topics; from reviewing recent treatment guidelines to specialized psychiatric topics such as geriatric bipolar disorder. A psychiatrist who has been quickly pushed to telepsychiatry because of the current pandemic could use the APA Learning Center to find educational modules about risk management in telepsychiatry or learn the special considerations of using telepsychiatry to treat patients with serious mental illness.
Using podcasts to earn CME is becoming increasingly common, with such as outlets as JAMA Networks offering podcasts in many specialties in which subscribers can take a quiz through the JAMA app and obtain CME credits.
As our clinical boundaries as psychiatrists are pushed by an ever-changing public health situation, now is the time to earn CME focused on new topics to meet the demands placed on health care workers at the front lines of clinical care.
If the COVID-19 pandemic reaches the number of cases predicted by public health officials, our health care system is going to be under extreme stress. All specialties face the threat of losing part of their working capacity as clinicians get sick with the virus, or as they stay home because of exposure or to take care of a loved one. CME can be a way to empower ourselves by staying current on the cutting edge of our specialties, but also brushing up on the medicine that we may be asked to practice in a time of great need.
Dr. Posada is consultation-liaison psychiatry fellow with the Inova Fairfax Hospital/George Washington University program in Falls Church, Va. She also is associate producer of the MDedge Psychcast. Dr. Posada has no disclosures.
Coronavirus stays in aerosols for hours, on surfaces for days
according to a new study.
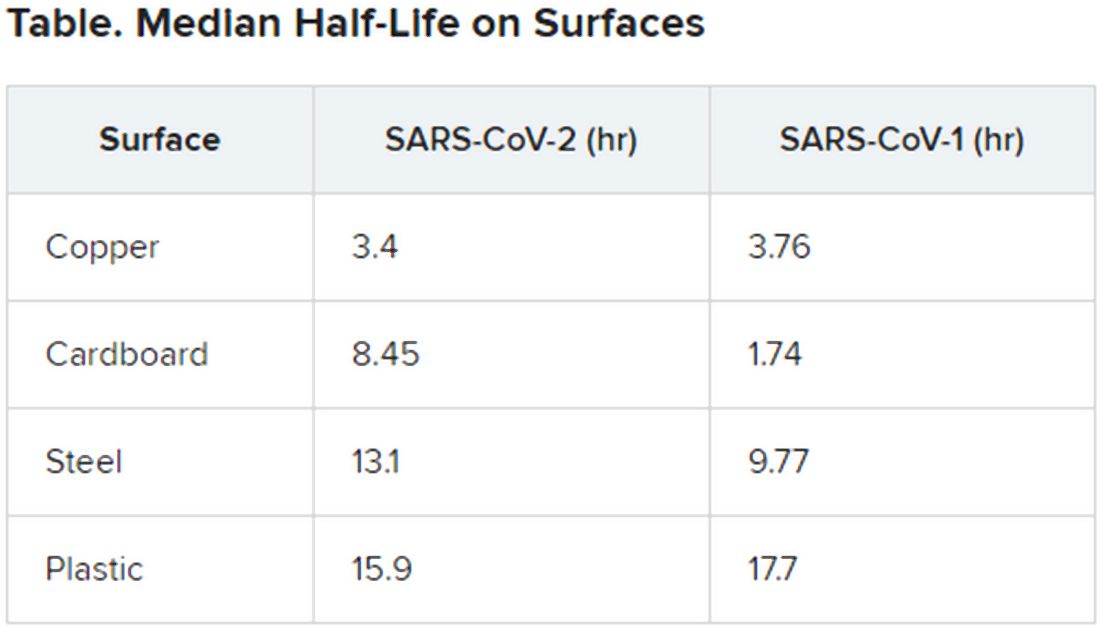
The data indicate that the stability of the new virus is similar to that of SARS-CoV-1, which caused the SARS epidemic, researchers report in an article published on the medRxivpreprint server. (The posted article has been submitted for journal publication but has not been peer reviewed.)
Transmission of SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19, has quickly outstripped the pace of the 2003 SARS epidemic. “Superspread” of the earlier disease arose from infection during medical procedures, in which a single infected individual seeded many secondary cases. In contrast, the novel coronavirus appears to be spread more through human-to-human transmission in a variety of settings.
However, it’s not yet known the extent to which asymptomatic or presymptomatic individuals spread the new virus through daily routine.
To investigate how long SARS-CoV-2 remains infective in the environment, Neeltje van Doremalen, PhD, of the Laboratory of Virology, Division of Intramural Research, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, in Hamilton, Montana, and colleagues conducted simulation experiments in which they compared the viability of SARS-CoV-2 with that of SARS-CoV-1 in aerosols and on surfaces.
Among patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, viral loads in the upper respiratory tract are high; as a consequence, respiratory secretion in the form of aerosols (<5 μm) or droplets (>5 mcm) is likely, the authors note.
van Doremalen and colleagues used nebulizers to generate aerosols. Samples of SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2 were collecting at 0, 30, 60, 120, and 180 minutes on a gelatin filter. The researchers then tested the infectivity of the viruses on Vero cells grown in culture.
They found that SARS-CoV-2 was largely stable through the full 180-minute test, with only a slight decline at 3 hours. This time course is similar to that of SARS-CoV-1; both viruses have a median half-life in aerosols of 2.7 hours (range, 1.65 hr for SARS-CoV-1, vs 7.24 hr for SARS-CoV-2).
The researchers then tested the viruses on a variety of surfaces for up to 7 days, using humidity values and temperatures designed to mimic “a variety of household and hospital situations.” The volumes of viral exposures that the team used were consistent with amounts found in the human upper and lower respiratory tracts.
For example, they applied 50 mcL of virus-containing solution to a piece of cardboard and then swabbed the surface, at different times, with an additional 1 mcL of medium. Each surface assay was replicated three times.
The novel coronavirus was most stable on plastic and stainless steel, with some virus remaining viable up to 72 hours. However, by that time the viral load had fallen by about three orders of magnitude, indicating exponential decay. This profile was remarkably similar to that of SARS-CoV-1, according to the authors.
However, the two viruses differed in staying power on copper and cardboard. No viable SARS-CoV-2 was detectable on copper after 4 hours or on cardboard after 24 hours. In contrast, SARS-CoV-1 was not viable beyond 8 hours for either copper or cardboard.
“Taken together, our results indicate that aerosol and fomite transmission of HCoV-19 [SARS-CoV-2] are plausible, as the virus can remain viable in aerosols for multiple hours and on surfaces up to days,” the authors conclude.
Andrew Pekosz, PhD, codirector of the Center of Excellence in Influenza Research and Surveillance and director of the Center for Emerging Viruses and Infectious Diseases at the Johns Hopkins Center for Global Health, Baltimore, Maryland, applauds the real-world value of the experiments.
“The PCR [polymerase chain reaction] test used [in other studies] to detect SARS-CoV-2 just detects the virus genome. It doesn’t tell you if the virus was still infectious, or ‘viable.’ That’s why this study is interesting,” Pekosz said. “It focuses on infectious virus, which is the virus that has the potential to transmit and infect another person. What we don’t know yet is how much infectious (viable) virus is needed to initiate infection in another person.”
He suggests that further investigations evaluate other types of environmental surfaces, including lacquered wood that is made into desks and ceramic tiles found in bathrooms and kitchens.
One limitation of the study is that the data for experiments on cardboard were more variable than the data for other surfaces tested.
The investigators and Pekosz have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a new study.

The data indicate that the stability of the new virus is similar to that of SARS-CoV-1, which caused the SARS epidemic, researchers report in an article published on the medRxivpreprint server. (The posted article has been submitted for journal publication but has not been peer reviewed.)
Transmission of SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19, has quickly outstripped the pace of the 2003 SARS epidemic. “Superspread” of the earlier disease arose from infection during medical procedures, in which a single infected individual seeded many secondary cases. In contrast, the novel coronavirus appears to be spread more through human-to-human transmission in a variety of settings.
However, it’s not yet known the extent to which asymptomatic or presymptomatic individuals spread the new virus through daily routine.
To investigate how long SARS-CoV-2 remains infective in the environment, Neeltje van Doremalen, PhD, of the Laboratory of Virology, Division of Intramural Research, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, in Hamilton, Montana, and colleagues conducted simulation experiments in which they compared the viability of SARS-CoV-2 with that of SARS-CoV-1 in aerosols and on surfaces.
Among patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, viral loads in the upper respiratory tract are high; as a consequence, respiratory secretion in the form of aerosols (<5 μm) or droplets (>5 mcm) is likely, the authors note.
van Doremalen and colleagues used nebulizers to generate aerosols. Samples of SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2 were collecting at 0, 30, 60, 120, and 180 minutes on a gelatin filter. The researchers then tested the infectivity of the viruses on Vero cells grown in culture.
They found that SARS-CoV-2 was largely stable through the full 180-minute test, with only a slight decline at 3 hours. This time course is similar to that of SARS-CoV-1; both viruses have a median half-life in aerosols of 2.7 hours (range, 1.65 hr for SARS-CoV-1, vs 7.24 hr for SARS-CoV-2).
The researchers then tested the viruses on a variety of surfaces for up to 7 days, using humidity values and temperatures designed to mimic “a variety of household and hospital situations.” The volumes of viral exposures that the team used were consistent with amounts found in the human upper and lower respiratory tracts.
For example, they applied 50 mcL of virus-containing solution to a piece of cardboard and then swabbed the surface, at different times, with an additional 1 mcL of medium. Each surface assay was replicated three times.
The novel coronavirus was most stable on plastic and stainless steel, with some virus remaining viable up to 72 hours. However, by that time the viral load had fallen by about three orders of magnitude, indicating exponential decay. This profile was remarkably similar to that of SARS-CoV-1, according to the authors.
However, the two viruses differed in staying power on copper and cardboard. No viable SARS-CoV-2 was detectable on copper after 4 hours or on cardboard after 24 hours. In contrast, SARS-CoV-1 was not viable beyond 8 hours for either copper or cardboard.
“Taken together, our results indicate that aerosol and fomite transmission of HCoV-19 [SARS-CoV-2] are plausible, as the virus can remain viable in aerosols for multiple hours and on surfaces up to days,” the authors conclude.
Andrew Pekosz, PhD, codirector of the Center of Excellence in Influenza Research and Surveillance and director of the Center for Emerging Viruses and Infectious Diseases at the Johns Hopkins Center for Global Health, Baltimore, Maryland, applauds the real-world value of the experiments.
“The PCR [polymerase chain reaction] test used [in other studies] to detect SARS-CoV-2 just detects the virus genome. It doesn’t tell you if the virus was still infectious, or ‘viable.’ That’s why this study is interesting,” Pekosz said. “It focuses on infectious virus, which is the virus that has the potential to transmit and infect another person. What we don’t know yet is how much infectious (viable) virus is needed to initiate infection in another person.”
He suggests that further investigations evaluate other types of environmental surfaces, including lacquered wood that is made into desks and ceramic tiles found in bathrooms and kitchens.
One limitation of the study is that the data for experiments on cardboard were more variable than the data for other surfaces tested.
The investigators and Pekosz have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a new study.

The data indicate that the stability of the new virus is similar to that of SARS-CoV-1, which caused the SARS epidemic, researchers report in an article published on the medRxivpreprint server. (The posted article has been submitted for journal publication but has not been peer reviewed.)
Transmission of SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19, has quickly outstripped the pace of the 2003 SARS epidemic. “Superspread” of the earlier disease arose from infection during medical procedures, in which a single infected individual seeded many secondary cases. In contrast, the novel coronavirus appears to be spread more through human-to-human transmission in a variety of settings.
However, it’s not yet known the extent to which asymptomatic or presymptomatic individuals spread the new virus through daily routine.
To investigate how long SARS-CoV-2 remains infective in the environment, Neeltje van Doremalen, PhD, of the Laboratory of Virology, Division of Intramural Research, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, in Hamilton, Montana, and colleagues conducted simulation experiments in which they compared the viability of SARS-CoV-2 with that of SARS-CoV-1 in aerosols and on surfaces.
Among patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, viral loads in the upper respiratory tract are high; as a consequence, respiratory secretion in the form of aerosols (<5 μm) or droplets (>5 mcm) is likely, the authors note.
van Doremalen and colleagues used nebulizers to generate aerosols. Samples of SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2 were collecting at 0, 30, 60, 120, and 180 minutes on a gelatin filter. The researchers then tested the infectivity of the viruses on Vero cells grown in culture.
They found that SARS-CoV-2 was largely stable through the full 180-minute test, with only a slight decline at 3 hours. This time course is similar to that of SARS-CoV-1; both viruses have a median half-life in aerosols of 2.7 hours (range, 1.65 hr for SARS-CoV-1, vs 7.24 hr for SARS-CoV-2).
The researchers then tested the viruses on a variety of surfaces for up to 7 days, using humidity values and temperatures designed to mimic “a variety of household and hospital situations.” The volumes of viral exposures that the team used were consistent with amounts found in the human upper and lower respiratory tracts.
For example, they applied 50 mcL of virus-containing solution to a piece of cardboard and then swabbed the surface, at different times, with an additional 1 mcL of medium. Each surface assay was replicated three times.
The novel coronavirus was most stable on plastic and stainless steel, with some virus remaining viable up to 72 hours. However, by that time the viral load had fallen by about three orders of magnitude, indicating exponential decay. This profile was remarkably similar to that of SARS-CoV-1, according to the authors.
However, the two viruses differed in staying power on copper and cardboard. No viable SARS-CoV-2 was detectable on copper after 4 hours or on cardboard after 24 hours. In contrast, SARS-CoV-1 was not viable beyond 8 hours for either copper or cardboard.
“Taken together, our results indicate that aerosol and fomite transmission of HCoV-19 [SARS-CoV-2] are plausible, as the virus can remain viable in aerosols for multiple hours and on surfaces up to days,” the authors conclude.
Andrew Pekosz, PhD, codirector of the Center of Excellence in Influenza Research and Surveillance and director of the Center for Emerging Viruses and Infectious Diseases at the Johns Hopkins Center for Global Health, Baltimore, Maryland, applauds the real-world value of the experiments.
“The PCR [polymerase chain reaction] test used [in other studies] to detect SARS-CoV-2 just detects the virus genome. It doesn’t tell you if the virus was still infectious, or ‘viable.’ That’s why this study is interesting,” Pekosz said. “It focuses on infectious virus, which is the virus that has the potential to transmit and infect another person. What we don’t know yet is how much infectious (viable) virus is needed to initiate infection in another person.”
He suggests that further investigations evaluate other types of environmental surfaces, including lacquered wood that is made into desks and ceramic tiles found in bathrooms and kitchens.
One limitation of the study is that the data for experiments on cardboard were more variable than the data for other surfaces tested.
The investigators and Pekosz have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sickle cell patients with vitamin D deficiency prone to more ED visits, longer stays
Patients with sickle cell disease (SCD) plus vitamin D deficiency were found to have more hospitalization outcomes, including number of emergency department (ED) visits, the number of hospital admissions for pain crisis, and the length of hospital admission, according to a study published online by researchers from New York-Presbyterian Brooklyn Methodist Hospital.
The researchers performed a retrospective chart review of all 134 pediatric patients with SCD (aged 1-21 years) from January 2015 to January 2016 in an urban-based hospital setting. Ninety patients with at least one reported vitamin D level who maintained follow-up during the time studied were enrolled. Hospitalization rates were compared between vitamin D deficiency (< 20 ng/mL) and sufficiency (> 20 ng/mL) patients.
When compared to patients with SCD and sufficient vitamin D levels, patients with both SCD and vitamin D deficiency were more likely to have at least one ED visit (P < .01), at least one admission for pain crisis (P < .01), and a longer length of admission (P < .0001), the researchers found.
“Screening and treatment for vitamin D deficiency is generally cost effective and readily available, potentially having a significant impact on the quality of life for those living with sickle cell disease,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that there was no study funding and that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Brown B et al. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2020.102415.
Patients with sickle cell disease (SCD) plus vitamin D deficiency were found to have more hospitalization outcomes, including number of emergency department (ED) visits, the number of hospital admissions for pain crisis, and the length of hospital admission, according to a study published online by researchers from New York-Presbyterian Brooklyn Methodist Hospital.
The researchers performed a retrospective chart review of all 134 pediatric patients with SCD (aged 1-21 years) from January 2015 to January 2016 in an urban-based hospital setting. Ninety patients with at least one reported vitamin D level who maintained follow-up during the time studied were enrolled. Hospitalization rates were compared between vitamin D deficiency (< 20 ng/mL) and sufficiency (> 20 ng/mL) patients.
When compared to patients with SCD and sufficient vitamin D levels, patients with both SCD and vitamin D deficiency were more likely to have at least one ED visit (P < .01), at least one admission for pain crisis (P < .01), and a longer length of admission (P < .0001), the researchers found.
“Screening and treatment for vitamin D deficiency is generally cost effective and readily available, potentially having a significant impact on the quality of life for those living with sickle cell disease,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that there was no study funding and that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Brown B et al. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2020.102415.
Patients with sickle cell disease (SCD) plus vitamin D deficiency were found to have more hospitalization outcomes, including number of emergency department (ED) visits, the number of hospital admissions for pain crisis, and the length of hospital admission, according to a study published online by researchers from New York-Presbyterian Brooklyn Methodist Hospital.
The researchers performed a retrospective chart review of all 134 pediatric patients with SCD (aged 1-21 years) from January 2015 to January 2016 in an urban-based hospital setting. Ninety patients with at least one reported vitamin D level who maintained follow-up during the time studied were enrolled. Hospitalization rates were compared between vitamin D deficiency (< 20 ng/mL) and sufficiency (> 20 ng/mL) patients.
When compared to patients with SCD and sufficient vitamin D levels, patients with both SCD and vitamin D deficiency were more likely to have at least one ED visit (P < .01), at least one admission for pain crisis (P < .01), and a longer length of admission (P < .0001), the researchers found.
“Screening and treatment for vitamin D deficiency is generally cost effective and readily available, potentially having a significant impact on the quality of life for those living with sickle cell disease,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that there was no study funding and that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Brown B et al. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2020.102415.
FROM BLOOD CELLS, MOLECULES, AND DISEASES
Some infected patients could show COVID-19 symptoms after quarantine
Although a 14-day quarantine after exposure to novel coronavirus is “well supported” by evidence, some infected individuals will not become symptomatic until after that period, according to authors of a recent analysis published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Most individuals infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) will develop symptoms by day 12 of the infection, which is within the 14-day period of active monitoring currently recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the authors wrote.
However, an estimated 101 out of 10,000 cases could become symptomatic after the end of that 14-day monitoring period, they cautioned.
“Our analyses do not preclude that estimate from being higher,” said the investigators, led by Stephen A. Lauer, PhD, MD, of Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore.
The analysis, based on 181 confirmed cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) that were documented outside of the outbreak epicenter, Wuhan, China, makes “more conservative assumptions” about the window of symptom onset and potential for continued exposure, compared with analyses in previous studies, the researchers wrote.
The estimated incubation period for SARS-CoV-2 in the 181-patient study was a median of 5.1 days, which is comparable with previous estimates based on COVID-19 cases outside of Wuhan and consistent with other known human coronavirus diseases, such as SARS, which had a reported mean incubation period of 5 days, Dr. Lauer and colleagues noted.
Symptoms developed within 11.5 days for 97.5% of patients in the study.
Whether it’s acceptable to have 101 out of 10,000 cases becoming symptomatic beyond the recommended quarantine window depends on two factors, according to the authors. The first is the expected infection risk in the population that is being monitored, and the second is “judgment about the cost of missing cases,” wrote the authors.
In an interview, Aaron Eli Glatt, MD, chair of medicine at Mount Sinai South Nassau, Oceanside, N.Y., said that in practical terms, the results suggest that the majority of patients with COVID-19 will be identified within 14 days, with an “outside chance” of an infected individual leaving quarantine and transmitting virus for a short period of time before becoming symptomatic.
“I think the proper message to give those patients [who are asymptomatic upon leaving quarantine] is, ‘after 14 days, we’re pretty sure you’re out of the woods, but should you get any symptoms, immediately requarantine yourself and seek medical care,” he said.
Study coauthor Kyra H. Grantz, a doctoral graduate student at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, said that extending a quarantine beyond 14 days might be considered in the highest-risk scenarios, though the benefits of doing so would have to be weighed against the costs to public health and to the individuals under quarantine.
“Our estimate of the incubation period definitely supports the 14-day recommendation that the CDC has been using,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Grantz emphasized that the estimate of 101 out of 10,000 cases developing symptoms after day 14 of active monitoring – representing the 99th percentile of cases – assumes the “most conservative, worst-case scenario” in a population that is fully infected.
“If you’re looking at a following a cohort of 1,000 people whom you think may have been exposed, only a certain percentage will be infected, and only a certain percentage of those will even develop symptoms – before we get to this idea of how many people would we miss,” she said.
The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. Four authors reported disclosures related to those entities, and the remaining five reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lauer SA et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Mar 9. doi:10.1101/2020.02.02.20020016.
Although a 14-day quarantine after exposure to novel coronavirus is “well supported” by evidence, some infected individuals will not become symptomatic until after that period, according to authors of a recent analysis published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Most individuals infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) will develop symptoms by day 12 of the infection, which is within the 14-day period of active monitoring currently recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the authors wrote.
However, an estimated 101 out of 10,000 cases could become symptomatic after the end of that 14-day monitoring period, they cautioned.
“Our analyses do not preclude that estimate from being higher,” said the investigators, led by Stephen A. Lauer, PhD, MD, of Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore.
The analysis, based on 181 confirmed cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) that were documented outside of the outbreak epicenter, Wuhan, China, makes “more conservative assumptions” about the window of symptom onset and potential for continued exposure, compared with analyses in previous studies, the researchers wrote.
The estimated incubation period for SARS-CoV-2 in the 181-patient study was a median of 5.1 days, which is comparable with previous estimates based on COVID-19 cases outside of Wuhan and consistent with other known human coronavirus diseases, such as SARS, which had a reported mean incubation period of 5 days, Dr. Lauer and colleagues noted.
Symptoms developed within 11.5 days for 97.5% of patients in the study.
Whether it’s acceptable to have 101 out of 10,000 cases becoming symptomatic beyond the recommended quarantine window depends on two factors, according to the authors. The first is the expected infection risk in the population that is being monitored, and the second is “judgment about the cost of missing cases,” wrote the authors.
In an interview, Aaron Eli Glatt, MD, chair of medicine at Mount Sinai South Nassau, Oceanside, N.Y., said that in practical terms, the results suggest that the majority of patients with COVID-19 will be identified within 14 days, with an “outside chance” of an infected individual leaving quarantine and transmitting virus for a short period of time before becoming symptomatic.
“I think the proper message to give those patients [who are asymptomatic upon leaving quarantine] is, ‘after 14 days, we’re pretty sure you’re out of the woods, but should you get any symptoms, immediately requarantine yourself and seek medical care,” he said.
Study coauthor Kyra H. Grantz, a doctoral graduate student at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, said that extending a quarantine beyond 14 days might be considered in the highest-risk scenarios, though the benefits of doing so would have to be weighed against the costs to public health and to the individuals under quarantine.
“Our estimate of the incubation period definitely supports the 14-day recommendation that the CDC has been using,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Grantz emphasized that the estimate of 101 out of 10,000 cases developing symptoms after day 14 of active monitoring – representing the 99th percentile of cases – assumes the “most conservative, worst-case scenario” in a population that is fully infected.
“If you’re looking at a following a cohort of 1,000 people whom you think may have been exposed, only a certain percentage will be infected, and only a certain percentage of those will even develop symptoms – before we get to this idea of how many people would we miss,” she said.
The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. Four authors reported disclosures related to those entities, and the remaining five reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lauer SA et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Mar 9. doi:10.1101/2020.02.02.20020016.
Although a 14-day quarantine after exposure to novel coronavirus is “well supported” by evidence, some infected individuals will not become symptomatic until after that period, according to authors of a recent analysis published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Most individuals infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) will develop symptoms by day 12 of the infection, which is within the 14-day period of active monitoring currently recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the authors wrote.
However, an estimated 101 out of 10,000 cases could become symptomatic after the end of that 14-day monitoring period, they cautioned.
“Our analyses do not preclude that estimate from being higher,” said the investigators, led by Stephen A. Lauer, PhD, MD, of Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore.
The analysis, based on 181 confirmed cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) that were documented outside of the outbreak epicenter, Wuhan, China, makes “more conservative assumptions” about the window of symptom onset and potential for continued exposure, compared with analyses in previous studies, the researchers wrote.
The estimated incubation period for SARS-CoV-2 in the 181-patient study was a median of 5.1 days, which is comparable with previous estimates based on COVID-19 cases outside of Wuhan and consistent with other known human coronavirus diseases, such as SARS, which had a reported mean incubation period of 5 days, Dr. Lauer and colleagues noted.
Symptoms developed within 11.5 days for 97.5% of patients in the study.
Whether it’s acceptable to have 101 out of 10,000 cases becoming symptomatic beyond the recommended quarantine window depends on two factors, according to the authors. The first is the expected infection risk in the population that is being monitored, and the second is “judgment about the cost of missing cases,” wrote the authors.
In an interview, Aaron Eli Glatt, MD, chair of medicine at Mount Sinai South Nassau, Oceanside, N.Y., said that in practical terms, the results suggest that the majority of patients with COVID-19 will be identified within 14 days, with an “outside chance” of an infected individual leaving quarantine and transmitting virus for a short period of time before becoming symptomatic.
“I think the proper message to give those patients [who are asymptomatic upon leaving quarantine] is, ‘after 14 days, we’re pretty sure you’re out of the woods, but should you get any symptoms, immediately requarantine yourself and seek medical care,” he said.
Study coauthor Kyra H. Grantz, a doctoral graduate student at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, said that extending a quarantine beyond 14 days might be considered in the highest-risk scenarios, though the benefits of doing so would have to be weighed against the costs to public health and to the individuals under quarantine.
“Our estimate of the incubation period definitely supports the 14-day recommendation that the CDC has been using,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Grantz emphasized that the estimate of 101 out of 10,000 cases developing symptoms after day 14 of active monitoring – representing the 99th percentile of cases – assumes the “most conservative, worst-case scenario” in a population that is fully infected.
“If you’re looking at a following a cohort of 1,000 people whom you think may have been exposed, only a certain percentage will be infected, and only a certain percentage of those will even develop symptoms – before we get to this idea of how many people would we miss,” she said.
The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. Four authors reported disclosures related to those entities, and the remaining five reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lauer SA et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Mar 9. doi:10.1101/2020.02.02.20020016.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Key clinical point: Some individuals who are infected with the novel coronavirus could become symptomatic after the active 14-day quarantine period.
Major finding: The median incubation period was 5.1 days, with 97.5% of patients developing symptoms within 11.5 days, implying that 101 of every 10,000 cases (99th percentile) would develop symptoms beyond the quarantine period.
Study details: Analysis of 181 confirmed COVID-19 cases identified outside of the outbreak epicenter, Wuhan, China.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. Four authors reported disclosures related to those entities, and the remaining five reported no conflicts of interest.
Source: Lauer SA et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Mar 9. doi: 10.1101/2020.02.02.20020016.
After PCI, stopping antiplatelet therapy for surgery appears safe
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – Following a percutaneous intervention with a second-generation drug-eluting stent, a judicious interruption of antiplatelet therapy for noncardiac surgery does not increase risk of net adverse clinical events, according to a large dataset presented at CRT 2020 sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute.
Drawn from a multicenter registry in South Korea, it is likely that those in whom antiplatelet therapy was stopped during the perioperative period were at a lower relative risk, but the data remain reassuring, according to Jung-Sun Kim, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at Yonsei University, Seoul, South Korea.
In the registry of patients with a second-generation drug-eluting stent (DES) undergoing noncardiac surgery, “antiplatelet therapy was discontinued in almost half of the patients,” Dr. Kim reported. When these patients were compared with those who did not discontinue antiplatelet therapy, the data, called an “exploratory analysis,” suggested “no increased risk” of a composite of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) or major bleeding.
The retrospective analysis involved 3,582 percutaneous intervention (PCI) patients who had received a second-generation DES and subsequently underwent noncardiac surgery. In 1,750 of these patients, antiplatelet therapy was temporarily discontinued. The remaining 1,832 remained on some form of antiplatelet treatment, whether aspirin, a P2Y12 inhibitor, or dual-antiplatelet therapy.
There were no significant differences in crude rates between groups in rates at 30 days of a composite endpoint of MACE, major bleeding as defined by the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis, or net adverse clinical events (NACE), a composite of adverse events that included MACE and major bleeding.
Relative risks for antiplatelet discontinuation remained generally low even after multiple stratifications performed to explore different variables, including the types of antiplatelet therapy being taken at the time of discontinuation, the types of noncardiac surgery performed, and the duration of discontinuation.
Of these variables, the interval of discontinuation appeared to be most relevant. Antiplatelet discontinuation of 3 days or less appeared to be associated with a higher risk of bleeding, although the difference did not reach significance. Discontinuations of 9 days or more were associated with increased risk of MACE, and this difference did reach statistical significance (hazard ratio, 3.38; 95% confidence interval, 1.36-8.38).
“Discontinuation of antiplatelet therapy for a period of 4-8 days appears to be optimal,” Dr. Kim said.
In general, risk of MACE, major bleeding, or NACE could not be linked to type of surgery, with the exception of intra-abdominal surgery. For this procedure, there appeared to be a lower risk of MACE in those who discontinued relative to those who remained on antiplatelet therapy, Dr. Kim reported.
Importantly, because of the fact that the decision to stop antiplatelet treatment was made by treating physicians, the characteristics of those who discontinued or remained on antiplatelet therapy differed meaningfully. Specifically, those in the discontinuation group were younger and were less likely to have additional risks for thrombotic events such as diabetes or chronic kidney disease. In those who discontinued antiplatelets, the average time since PCI was 23 months versus 16 months in the continuation group.
In addition, “more of the patients underwent higher-risk surgeries in the discontinuation group,” Dr. Kim added.
Relative rates of MACE and NACE remained similar even after risk adjustment, but Dr. Kim advised that the data should be “interpreted cautiously” because of the retrospective nature of the analysis.
A panel of experts invited to comment on the presentation agreed. These data were considered reassuring for clinicians considering an interruption of antiplatelet therapy following PCI with a second-generation DES, but there was uncertainty about their value for defining which patients are the best candidates.
The decision to discontinue antiplatelet drugs for noncardiac surgery is an important and common dilemma, but these data might be best characterized as “a testament to Korean cardiologists making good decisions,” said David J. Moliterno, MD, chairman of the department of medicine at University of Kentucky Health Care, Lexington.
Dr. Kim reported no potential financial conflicts of interest.
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – Following a percutaneous intervention with a second-generation drug-eluting stent, a judicious interruption of antiplatelet therapy for noncardiac surgery does not increase risk of net adverse clinical events, according to a large dataset presented at CRT 2020 sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute.
Drawn from a multicenter registry in South Korea, it is likely that those in whom antiplatelet therapy was stopped during the perioperative period were at a lower relative risk, but the data remain reassuring, according to Jung-Sun Kim, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at Yonsei University, Seoul, South Korea.
In the registry of patients with a second-generation drug-eluting stent (DES) undergoing noncardiac surgery, “antiplatelet therapy was discontinued in almost half of the patients,” Dr. Kim reported. When these patients were compared with those who did not discontinue antiplatelet therapy, the data, called an “exploratory analysis,” suggested “no increased risk” of a composite of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) or major bleeding.
The retrospective analysis involved 3,582 percutaneous intervention (PCI) patients who had received a second-generation DES and subsequently underwent noncardiac surgery. In 1,750 of these patients, antiplatelet therapy was temporarily discontinued. The remaining 1,832 remained on some form of antiplatelet treatment, whether aspirin, a P2Y12 inhibitor, or dual-antiplatelet therapy.
There were no significant differences in crude rates between groups in rates at 30 days of a composite endpoint of MACE, major bleeding as defined by the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis, or net adverse clinical events (NACE), a composite of adverse events that included MACE and major bleeding.
Relative risks for antiplatelet discontinuation remained generally low even after multiple stratifications performed to explore different variables, including the types of antiplatelet therapy being taken at the time of discontinuation, the types of noncardiac surgery performed, and the duration of discontinuation.
Of these variables, the interval of discontinuation appeared to be most relevant. Antiplatelet discontinuation of 3 days or less appeared to be associated with a higher risk of bleeding, although the difference did not reach significance. Discontinuations of 9 days or more were associated with increased risk of MACE, and this difference did reach statistical significance (hazard ratio, 3.38; 95% confidence interval, 1.36-8.38).
“Discontinuation of antiplatelet therapy for a period of 4-8 days appears to be optimal,” Dr. Kim said.
In general, risk of MACE, major bleeding, or NACE could not be linked to type of surgery, with the exception of intra-abdominal surgery. For this procedure, there appeared to be a lower risk of MACE in those who discontinued relative to those who remained on antiplatelet therapy, Dr. Kim reported.
Importantly, because of the fact that the decision to stop antiplatelet treatment was made by treating physicians, the characteristics of those who discontinued or remained on antiplatelet therapy differed meaningfully. Specifically, those in the discontinuation group were younger and were less likely to have additional risks for thrombotic events such as diabetes or chronic kidney disease. In those who discontinued antiplatelets, the average time since PCI was 23 months versus 16 months in the continuation group.
In addition, “more of the patients underwent higher-risk surgeries in the discontinuation group,” Dr. Kim added.
Relative rates of MACE and NACE remained similar even after risk adjustment, but Dr. Kim advised that the data should be “interpreted cautiously” because of the retrospective nature of the analysis.
A panel of experts invited to comment on the presentation agreed. These data were considered reassuring for clinicians considering an interruption of antiplatelet therapy following PCI with a second-generation DES, but there was uncertainty about their value for defining which patients are the best candidates.
The decision to discontinue antiplatelet drugs for noncardiac surgery is an important and common dilemma, but these data might be best characterized as “a testament to Korean cardiologists making good decisions,” said David J. Moliterno, MD, chairman of the department of medicine at University of Kentucky Health Care, Lexington.
Dr. Kim reported no potential financial conflicts of interest.
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – Following a percutaneous intervention with a second-generation drug-eluting stent, a judicious interruption of antiplatelet therapy for noncardiac surgery does not increase risk of net adverse clinical events, according to a large dataset presented at CRT 2020 sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute.
Drawn from a multicenter registry in South Korea, it is likely that those in whom antiplatelet therapy was stopped during the perioperative period were at a lower relative risk, but the data remain reassuring, according to Jung-Sun Kim, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at Yonsei University, Seoul, South Korea.
In the registry of patients with a second-generation drug-eluting stent (DES) undergoing noncardiac surgery, “antiplatelet therapy was discontinued in almost half of the patients,” Dr. Kim reported. When these patients were compared with those who did not discontinue antiplatelet therapy, the data, called an “exploratory analysis,” suggested “no increased risk” of a composite of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) or major bleeding.
The retrospective analysis involved 3,582 percutaneous intervention (PCI) patients who had received a second-generation DES and subsequently underwent noncardiac surgery. In 1,750 of these patients, antiplatelet therapy was temporarily discontinued. The remaining 1,832 remained on some form of antiplatelet treatment, whether aspirin, a P2Y12 inhibitor, or dual-antiplatelet therapy.
There were no significant differences in crude rates between groups in rates at 30 days of a composite endpoint of MACE, major bleeding as defined by the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis, or net adverse clinical events (NACE), a composite of adverse events that included MACE and major bleeding.
Relative risks for antiplatelet discontinuation remained generally low even after multiple stratifications performed to explore different variables, including the types of antiplatelet therapy being taken at the time of discontinuation, the types of noncardiac surgery performed, and the duration of discontinuation.
Of these variables, the interval of discontinuation appeared to be most relevant. Antiplatelet discontinuation of 3 days or less appeared to be associated with a higher risk of bleeding, although the difference did not reach significance. Discontinuations of 9 days or more were associated with increased risk of MACE, and this difference did reach statistical significance (hazard ratio, 3.38; 95% confidence interval, 1.36-8.38).
“Discontinuation of antiplatelet therapy for a period of 4-8 days appears to be optimal,” Dr. Kim said.
In general, risk of MACE, major bleeding, or NACE could not be linked to type of surgery, with the exception of intra-abdominal surgery. For this procedure, there appeared to be a lower risk of MACE in those who discontinued relative to those who remained on antiplatelet therapy, Dr. Kim reported.
Importantly, because of the fact that the decision to stop antiplatelet treatment was made by treating physicians, the characteristics of those who discontinued or remained on antiplatelet therapy differed meaningfully. Specifically, those in the discontinuation group were younger and were less likely to have additional risks for thrombotic events such as diabetes or chronic kidney disease. In those who discontinued antiplatelets, the average time since PCI was 23 months versus 16 months in the continuation group.
In addition, “more of the patients underwent higher-risk surgeries in the discontinuation group,” Dr. Kim added.
Relative rates of MACE and NACE remained similar even after risk adjustment, but Dr. Kim advised that the data should be “interpreted cautiously” because of the retrospective nature of the analysis.
A panel of experts invited to comment on the presentation agreed. These data were considered reassuring for clinicians considering an interruption of antiplatelet therapy following PCI with a second-generation DES, but there was uncertainty about their value for defining which patients are the best candidates.
The decision to discontinue antiplatelet drugs for noncardiac surgery is an important and common dilemma, but these data might be best characterized as “a testament to Korean cardiologists making good decisions,” said David J. Moliterno, MD, chairman of the department of medicine at University of Kentucky Health Care, Lexington.
Dr. Kim reported no potential financial conflicts of interest.
REPORTING FROM CRT 2020
ACIP advocates pre-exposure Ebola vaccination for high-risk groups
Vaccination against the Ebola virus is recommended for first responders, health care personnel, and laboratory workers deemed at high risk of exposure, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
The committee voted unanimously to recommended pre-exposure vaccination with the rVSVdeltaG-ZEBOV-GP vaccine for adults aged 18 years and older who are at potential risk of exposure to the Ebola species Zaire ebolavirus because they fall into any of the following three categories:
- They are responding to an outbreak of Ebola virus disease.
- They are working as health care personnel at a federally designated Ebola Treatment Center in the United States.
- The are working in laboratories or are other staff members at biosafety-level 4 facilities in the United States.
Mary Choi, MD, of the CDC’s National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID) presented data on the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine and the work group considerations in recommending vaccination in the three target populations.
In clinical trials, the most commonly reported adverse events associated with the vaccine were arthritis and arthralgia, Dr. Choi said, but the duration of those cases was limited to months and did not persist long term.
Pre-exposure vaccination for health care personnel, laboratory workers, and support staff would provide an additional layer of protection, she explained, in addition to existing safeguards such as personal protective equipment and engineering controls at the facility. The work group’s research showed that most of the target population believed that the desirable effects of that protection outweigh potentially undesirable effects, Dr. Choi noted.
Some committee members expressed concerns about vaccination of pregnant women. But the recommendations are presented as “population based, not shared decision making,” said Sharon E. Frey, MD, of Saint Louis University in St. Louis, Missouri.
Several members noted that pregnant women should not be automatically included or excluded from vaccination if they fall into a high-risk population. And the committee agreed that additional guidance in the policy note will help assess risk and that organizations will determine the risk for their employees and whether to offer the vaccine.
The FDA approved the currently available U.S. vaccine for Ebola in 2019. Merck manufactures that vaccine.
The ACIP members had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
Vaccination against the Ebola virus is recommended for first responders, health care personnel, and laboratory workers deemed at high risk of exposure, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
The committee voted unanimously to recommended pre-exposure vaccination with the rVSVdeltaG-ZEBOV-GP vaccine for adults aged 18 years and older who are at potential risk of exposure to the Ebola species Zaire ebolavirus because they fall into any of the following three categories:
- They are responding to an outbreak of Ebola virus disease.
- They are working as health care personnel at a federally designated Ebola Treatment Center in the United States.
- The are working in laboratories or are other staff members at biosafety-level 4 facilities in the United States.
Mary Choi, MD, of the CDC’s National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID) presented data on the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine and the work group considerations in recommending vaccination in the three target populations.
In clinical trials, the most commonly reported adverse events associated with the vaccine were arthritis and arthralgia, Dr. Choi said, but the duration of those cases was limited to months and did not persist long term.
Pre-exposure vaccination for health care personnel, laboratory workers, and support staff would provide an additional layer of protection, she explained, in addition to existing safeguards such as personal protective equipment and engineering controls at the facility. The work group’s research showed that most of the target population believed that the desirable effects of that protection outweigh potentially undesirable effects, Dr. Choi noted.
Some committee members expressed concerns about vaccination of pregnant women. But the recommendations are presented as “population based, not shared decision making,” said Sharon E. Frey, MD, of Saint Louis University in St. Louis, Missouri.
Several members noted that pregnant women should not be automatically included or excluded from vaccination if they fall into a high-risk population. And the committee agreed that additional guidance in the policy note will help assess risk and that organizations will determine the risk for their employees and whether to offer the vaccine.
The FDA approved the currently available U.S. vaccine for Ebola in 2019. Merck manufactures that vaccine.
The ACIP members had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
Vaccination against the Ebola virus is recommended for first responders, health care personnel, and laboratory workers deemed at high risk of exposure, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
The committee voted unanimously to recommended pre-exposure vaccination with the rVSVdeltaG-ZEBOV-GP vaccine for adults aged 18 years and older who are at potential risk of exposure to the Ebola species Zaire ebolavirus because they fall into any of the following three categories:
- They are responding to an outbreak of Ebola virus disease.
- They are working as health care personnel at a federally designated Ebola Treatment Center in the United States.
- The are working in laboratories or are other staff members at biosafety-level 4 facilities in the United States.
Mary Choi, MD, of the CDC’s National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID) presented data on the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine and the work group considerations in recommending vaccination in the three target populations.
In clinical trials, the most commonly reported adverse events associated with the vaccine were arthritis and arthralgia, Dr. Choi said, but the duration of those cases was limited to months and did not persist long term.
Pre-exposure vaccination for health care personnel, laboratory workers, and support staff would provide an additional layer of protection, she explained, in addition to existing safeguards such as personal protective equipment and engineering controls at the facility. The work group’s research showed that most of the target population believed that the desirable effects of that protection outweigh potentially undesirable effects, Dr. Choi noted.
Some committee members expressed concerns about vaccination of pregnant women. But the recommendations are presented as “population based, not shared decision making,” said Sharon E. Frey, MD, of Saint Louis University in St. Louis, Missouri.
Several members noted that pregnant women should not be automatically included or excluded from vaccination if they fall into a high-risk population. And the committee agreed that additional guidance in the policy note will help assess risk and that organizations will determine the risk for their employees and whether to offer the vaccine.
The FDA approved the currently available U.S. vaccine for Ebola in 2019. Merck manufactures that vaccine.
The ACIP members had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
AI algorithm finds diagnostic AFib signatures in normal ECGs
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – Researchers have created an artificial intelligence algorithm that can evaluate a 10-second ECG recording of a person in normal sinus rhythm and tell with a sensitivity and specificity of almost 80% whether or not that person ever had atrial fibrillation episodes some time in the past or will have a first arrhythmia episode in the near future.
Although this algorithm – derived from and then validated with a dataset of nearly 650,000 ECG recordings from more than 180,000 patients – still needs prospective validation, it offers the prospect for a potential revolution in screening for atrial fibrillation (AFib), Paul A. Friedman, MD, cautioned at the annual International AF Symposium. If initial clinical findings are confirmed, it would show that a 10-second, 12-lead ECG recording can provide the same screening scope as what otherwise takes weeks of ambulatory ECG recording with a Holter monitor or an implanted device, explained Dr. Friedman, professor of medicine and chair of the department of cardiovascular medicine at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
This finding “could have important implications for atrial fibrillation screening and for the management of patients with unexplained stroke,” Dr. Friedman and his associates noted in the published report of their study (Lancet. 2019 Sep 7;394[10201]:861-7). “We’re still working to define the window of ECG” recording time that provides the optimal assessment for a history of asymptomatic AFib, but the “possibilities this opens are huge,” Dr. Friedman said in his talk at the symposium. This work sprang from the premise that “subtle signatures” in a brief, apparently normal sinus rhythm ECG tracing can harbor reliable clues about AFib history or an imminent episode.
The 2019 report by Dr. Friedman and associates documented that in the validation phase of their study, the trained artificial intelligence (AI) program identified patients with a history of AFib or an impending arrhythmia event from a single, 10-second ECG that to the naked eye seemed to show normal sinus rhythm with a sensitivity of 79.0%, a specificity of 79.5%, and an accuracy of 79.4%. It also showed an area under a receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.87, meaning that screening for AFib by this method compared favorably with the area-under-the-curve (AUC) results tallied by several widely accepted screening tools, including Pap smears for cervical cancer (AUC of 0.70), mammograms for breast cancer (AUC of 0.85), and CHA2DS2-VASc scoring for estimating stroke risk in AFib patients (AUC of 0.57-0.72), Dr. Friedman said.
The researchers developed the AI algorithm with more than 450,000 10-second ECG tracings collected from roughly 126,000 patients who underwent at least one ECG recording as part of their routine care at the Mayo Clinic during 1993-2017. The goal was for the program to find and validate recurring characteristics in the ECG that consistently linked with a history of or an impending AFib episode and that did not appear in ECG recordings from people without any AFib history. The program this effort produced then underwent further adjustment with the use of more than 64,340 ECGs from an additional 18,116 patients, and then the final product underwent validation testing with a further 130,802 ECGs collected from an additional 36,280 people, the study phase that resulted in the reported sensitivity and specificity estimates.
It’s currently unclear to Dr. Friedman and associates what specific features the program uses to classify patients. It’s an important question, but if the results are reproducible and reliable, this uncertainty shouldn’t slow clinical adoption, he said in an interview.
While “this particular algorithm needs prospective vetting,” a similar algorithm developed by Dr. Friedman and the same research team that uses a 10-second ECG to identify patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction of 35% or less is further advanced in development, and a device that uses this algorithm will soon receive Food and Drug Administration review under a fast track designation that the agency approved in late 2019.
The researchers developed this algorithm for estimating left ventricular function using a strategy similar to their development of a tool for diagnosing AFib (Nat Med. 2019 Jan 7;25[1]:70-4), and results from 100 patients prospectively studied with this approach to ECG analysis and reported at the American Heart Association scientific sessions in November 2019 showed that the algorithm identified substantial left ventricular dysfunction with an AUC of 0.906 (Circulation. 2019 Nov 19;140[suppl 1]:A13447). The same team of investigators has developed an AI algorithm that can calculate a person’s physiologic age based on the ECG recording (Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2019 Sep;12[9]: 10.1161/CIRCEP.119.007284).
The study received no commercial funding, and Dr. Friedman and coauthors had no relevant disclosures. The Mayo Clinic has licensed a related artificial intelligence algorithm to EKO, and Dr. Friedman may benefit financially from this arrangement.
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – Researchers have created an artificial intelligence algorithm that can evaluate a 10-second ECG recording of a person in normal sinus rhythm and tell with a sensitivity and specificity of almost 80% whether or not that person ever had atrial fibrillation episodes some time in the past or will have a first arrhythmia episode in the near future.
Although this algorithm – derived from and then validated with a dataset of nearly 650,000 ECG recordings from more than 180,000 patients – still needs prospective validation, it offers the prospect for a potential revolution in screening for atrial fibrillation (AFib), Paul A. Friedman, MD, cautioned at the annual International AF Symposium. If initial clinical findings are confirmed, it would show that a 10-second, 12-lead ECG recording can provide the same screening scope as what otherwise takes weeks of ambulatory ECG recording with a Holter monitor or an implanted device, explained Dr. Friedman, professor of medicine and chair of the department of cardiovascular medicine at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
This finding “could have important implications for atrial fibrillation screening and for the management of patients with unexplained stroke,” Dr. Friedman and his associates noted in the published report of their study (Lancet. 2019 Sep 7;394[10201]:861-7). “We’re still working to define the window of ECG” recording time that provides the optimal assessment for a history of asymptomatic AFib, but the “possibilities this opens are huge,” Dr. Friedman said in his talk at the symposium. This work sprang from the premise that “subtle signatures” in a brief, apparently normal sinus rhythm ECG tracing can harbor reliable clues about AFib history or an imminent episode.
The 2019 report by Dr. Friedman and associates documented that in the validation phase of their study, the trained artificial intelligence (AI) program identified patients with a history of AFib or an impending arrhythmia event from a single, 10-second ECG that to the naked eye seemed to show normal sinus rhythm with a sensitivity of 79.0%, a specificity of 79.5%, and an accuracy of 79.4%. It also showed an area under a receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.87, meaning that screening for AFib by this method compared favorably with the area-under-the-curve (AUC) results tallied by several widely accepted screening tools, including Pap smears for cervical cancer (AUC of 0.70), mammograms for breast cancer (AUC of 0.85), and CHA2DS2-VASc scoring for estimating stroke risk in AFib patients (AUC of 0.57-0.72), Dr. Friedman said.
The researchers developed the AI algorithm with more than 450,000 10-second ECG tracings collected from roughly 126,000 patients who underwent at least one ECG recording as part of their routine care at the Mayo Clinic during 1993-2017. The goal was for the program to find and validate recurring characteristics in the ECG that consistently linked with a history of or an impending AFib episode and that did not appear in ECG recordings from people without any AFib history. The program this effort produced then underwent further adjustment with the use of more than 64,340 ECGs from an additional 18,116 patients, and then the final product underwent validation testing with a further 130,802 ECGs collected from an additional 36,280 people, the study phase that resulted in the reported sensitivity and specificity estimates.
It’s currently unclear to Dr. Friedman and associates what specific features the program uses to classify patients. It’s an important question, but if the results are reproducible and reliable, this uncertainty shouldn’t slow clinical adoption, he said in an interview.
While “this particular algorithm needs prospective vetting,” a similar algorithm developed by Dr. Friedman and the same research team that uses a 10-second ECG to identify patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction of 35% or less is further advanced in development, and a device that uses this algorithm will soon receive Food and Drug Administration review under a fast track designation that the agency approved in late 2019.
The researchers developed this algorithm for estimating left ventricular function using a strategy similar to their development of a tool for diagnosing AFib (Nat Med. 2019 Jan 7;25[1]:70-4), and results from 100 patients prospectively studied with this approach to ECG analysis and reported at the American Heart Association scientific sessions in November 2019 showed that the algorithm identified substantial left ventricular dysfunction with an AUC of 0.906 (Circulation. 2019 Nov 19;140[suppl 1]:A13447). The same team of investigators has developed an AI algorithm that can calculate a person’s physiologic age based on the ECG recording (Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2019 Sep;12[9]: 10.1161/CIRCEP.119.007284).
The study received no commercial funding, and Dr. Friedman and coauthors had no relevant disclosures. The Mayo Clinic has licensed a related artificial intelligence algorithm to EKO, and Dr. Friedman may benefit financially from this arrangement.
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – Researchers have created an artificial intelligence algorithm that can evaluate a 10-second ECG recording of a person in normal sinus rhythm and tell with a sensitivity and specificity of almost 80% whether or not that person ever had atrial fibrillation episodes some time in the past or will have a first arrhythmia episode in the near future.
Although this algorithm – derived from and then validated with a dataset of nearly 650,000 ECG recordings from more than 180,000 patients – still needs prospective validation, it offers the prospect for a potential revolution in screening for atrial fibrillation (AFib), Paul A. Friedman, MD, cautioned at the annual International AF Symposium. If initial clinical findings are confirmed, it would show that a 10-second, 12-lead ECG recording can provide the same screening scope as what otherwise takes weeks of ambulatory ECG recording with a Holter monitor or an implanted device, explained Dr. Friedman, professor of medicine and chair of the department of cardiovascular medicine at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
This finding “could have important implications for atrial fibrillation screening and for the management of patients with unexplained stroke,” Dr. Friedman and his associates noted in the published report of their study (Lancet. 2019 Sep 7;394[10201]:861-7). “We’re still working to define the window of ECG” recording time that provides the optimal assessment for a history of asymptomatic AFib, but the “possibilities this opens are huge,” Dr. Friedman said in his talk at the symposium. This work sprang from the premise that “subtle signatures” in a brief, apparently normal sinus rhythm ECG tracing can harbor reliable clues about AFib history or an imminent episode.
The 2019 report by Dr. Friedman and associates documented that in the validation phase of their study, the trained artificial intelligence (AI) program identified patients with a history of AFib or an impending arrhythmia event from a single, 10-second ECG that to the naked eye seemed to show normal sinus rhythm with a sensitivity of 79.0%, a specificity of 79.5%, and an accuracy of 79.4%. It also showed an area under a receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.87, meaning that screening for AFib by this method compared favorably with the area-under-the-curve (AUC) results tallied by several widely accepted screening tools, including Pap smears for cervical cancer (AUC of 0.70), mammograms for breast cancer (AUC of 0.85), and CHA2DS2-VASc scoring for estimating stroke risk in AFib patients (AUC of 0.57-0.72), Dr. Friedman said.
The researchers developed the AI algorithm with more than 450,000 10-second ECG tracings collected from roughly 126,000 patients who underwent at least one ECG recording as part of their routine care at the Mayo Clinic during 1993-2017. The goal was for the program to find and validate recurring characteristics in the ECG that consistently linked with a history of or an impending AFib episode and that did not appear in ECG recordings from people without any AFib history. The program this effort produced then underwent further adjustment with the use of more than 64,340 ECGs from an additional 18,116 patients, and then the final product underwent validation testing with a further 130,802 ECGs collected from an additional 36,280 people, the study phase that resulted in the reported sensitivity and specificity estimates.
It’s currently unclear to Dr. Friedman and associates what specific features the program uses to classify patients. It’s an important question, but if the results are reproducible and reliable, this uncertainty shouldn’t slow clinical adoption, he said in an interview.
While “this particular algorithm needs prospective vetting,” a similar algorithm developed by Dr. Friedman and the same research team that uses a 10-second ECG to identify patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction of 35% or less is further advanced in development, and a device that uses this algorithm will soon receive Food and Drug Administration review under a fast track designation that the agency approved in late 2019.
The researchers developed this algorithm for estimating left ventricular function using a strategy similar to their development of a tool for diagnosing AFib (Nat Med. 2019 Jan 7;25[1]:70-4), and results from 100 patients prospectively studied with this approach to ECG analysis and reported at the American Heart Association scientific sessions in November 2019 showed that the algorithm identified substantial left ventricular dysfunction with an AUC of 0.906 (Circulation. 2019 Nov 19;140[suppl 1]:A13447). The same team of investigators has developed an AI algorithm that can calculate a person’s physiologic age based on the ECG recording (Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2019 Sep;12[9]: 10.1161/CIRCEP.119.007284).
The study received no commercial funding, and Dr. Friedman and coauthors had no relevant disclosures. The Mayo Clinic has licensed a related artificial intelligence algorithm to EKO, and Dr. Friedman may benefit financially from this arrangement.
THE AF SYMPOSIUM 2020