User login
ID Practitioner is an independent news source that provides infectious disease specialists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on the infectious disease specialist’s practice. Specialty focus topics include antimicrobial resistance, emerging infections, global ID, hepatitis, HIV, hospital-acquired infections, immunizations and vaccines, influenza, mycoses, pediatric infections, and STIs. Infectious Diseases News is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
sofosbuvir
ritonavir with dasabuvir
discount
support path
program
ritonavir
greedy
ledipasvir
assistance
viekira pak
vpak
advocacy
needy
protest
abbvie
paritaprevir
ombitasvir
direct-acting antivirals
dasabuvir
gilead
fake-ovir
support
v pak
oasis
harvoni
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-idp')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-medstat-latest-articles-articles-section')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-idp')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-idp')]
The power of an odd couple
The time has come for good men and women to unite and rise up against a common foe. For too long nurses and doctors have labored under the tyranny of a dictator who claimed to help them provide high-quality care for their patients while at the same time cutting their paperwork to nil. But like most autocrats he failed to engage his subjects in a meaningful dialogue as each new version of his promised improvements rolled off the drawing board. When the caregivers were slow to adopt these new nonsystems he offered them financial incentives and issued threats to their survival. Although they were warned that there might be uncomfortable adjustment periods, the caregivers were promised that the steep learning curves would level out and their professional lives would again be valued and productive.
Of course, the dictator is not a single person but a motley and disorganized conglomerate of user- and patient-unfriendly electronic health record nonsystems. Ask almost any nurse or physician for her feelings about computer-based medical record systems, and you will hear tales of long hours, disengagement, and frustration. Caregivers are unhappy at all levels, and patients have grown tired of their nurses and physicians spending most of their time looking at computer screens.
You certainly have heard this all before. But you are hearing it in hospital hallways and grocery store checkout lines as a low rumble of discontent emerging from separate individuals, not as a well-articulated and widely distributed voice of physicians as a group. To some extent this relative silence is because there is no such group, at least not in same mold as a labor union. The term “labor union” may make you uncomfortable. But given the current climate in medicine, unionizing may be the best and only way to effect change.
But organizing to effect change in the workplace isn’t part of the physician genome. In the 1960s, a group of house officers in Boston engaged in a heal-in to successfully improve their salaries and working conditions. But over the ensuing half century physicians have remained tragically silent in the face of a changing workplace landscape in which they have gone from being independent owner operators in control of their destinies to becoming employees feeling powerless to improve their working conditions. This perceived impotence has escalated in the face of the challenge posed by the introduction of dysfunctional EHRs.
Ironically, a solution is at almost every physician’s elbow. In a recent New York Times opinion piece Theresa Brown and Stephen Bergman acknowledge that physicians don’t seem prepared to mount a meaningful response to the challenge to the failed promise of EHRs (“Doctors, Nurses and the Paperwork Crisis That Could Unite Them,” Dec. 31, 2019). They point out that, over the last half century, physicians have remained isolated on the sidelines, finding just enough voice to grumble. Nurses have in a variety of situations organized to effect change in their working conditions – in some cases by forming labor unions.
The authors of this op-ed piece, a physician and a nurse, make a strong argument that the time has come for nurses and doctors shake off the shackles of their stereotypic roles and join in creating a loud, forceful, and effective voice to demand a working environment in which the computer functions as an asset and no longer as the terrible burden it has become. Neither group has the power to do it alone, but together they may be able to turn the tide. For physicians it will probably mean venturing several steps outside of their comfort zone. But working shoulder to shoulder with nurses may provide the courage to speak out.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
The time has come for good men and women to unite and rise up against a common foe. For too long nurses and doctors have labored under the tyranny of a dictator who claimed to help them provide high-quality care for their patients while at the same time cutting their paperwork to nil. But like most autocrats he failed to engage his subjects in a meaningful dialogue as each new version of his promised improvements rolled off the drawing board. When the caregivers were slow to adopt these new nonsystems he offered them financial incentives and issued threats to their survival. Although they were warned that there might be uncomfortable adjustment periods, the caregivers were promised that the steep learning curves would level out and their professional lives would again be valued and productive.
Of course, the dictator is not a single person but a motley and disorganized conglomerate of user- and patient-unfriendly electronic health record nonsystems. Ask almost any nurse or physician for her feelings about computer-based medical record systems, and you will hear tales of long hours, disengagement, and frustration. Caregivers are unhappy at all levels, and patients have grown tired of their nurses and physicians spending most of their time looking at computer screens.
You certainly have heard this all before. But you are hearing it in hospital hallways and grocery store checkout lines as a low rumble of discontent emerging from separate individuals, not as a well-articulated and widely distributed voice of physicians as a group. To some extent this relative silence is because there is no such group, at least not in same mold as a labor union. The term “labor union” may make you uncomfortable. But given the current climate in medicine, unionizing may be the best and only way to effect change.
But organizing to effect change in the workplace isn’t part of the physician genome. In the 1960s, a group of house officers in Boston engaged in a heal-in to successfully improve their salaries and working conditions. But over the ensuing half century physicians have remained tragically silent in the face of a changing workplace landscape in which they have gone from being independent owner operators in control of their destinies to becoming employees feeling powerless to improve their working conditions. This perceived impotence has escalated in the face of the challenge posed by the introduction of dysfunctional EHRs.
Ironically, a solution is at almost every physician’s elbow. In a recent New York Times opinion piece Theresa Brown and Stephen Bergman acknowledge that physicians don’t seem prepared to mount a meaningful response to the challenge to the failed promise of EHRs (“Doctors, Nurses and the Paperwork Crisis That Could Unite Them,” Dec. 31, 2019). They point out that, over the last half century, physicians have remained isolated on the sidelines, finding just enough voice to grumble. Nurses have in a variety of situations organized to effect change in their working conditions – in some cases by forming labor unions.
The authors of this op-ed piece, a physician and a nurse, make a strong argument that the time has come for nurses and doctors shake off the shackles of their stereotypic roles and join in creating a loud, forceful, and effective voice to demand a working environment in which the computer functions as an asset and no longer as the terrible burden it has become. Neither group has the power to do it alone, but together they may be able to turn the tide. For physicians it will probably mean venturing several steps outside of their comfort zone. But working shoulder to shoulder with nurses may provide the courage to speak out.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
The time has come for good men and women to unite and rise up against a common foe. For too long nurses and doctors have labored under the tyranny of a dictator who claimed to help them provide high-quality care for their patients while at the same time cutting their paperwork to nil. But like most autocrats he failed to engage his subjects in a meaningful dialogue as each new version of his promised improvements rolled off the drawing board. When the caregivers were slow to adopt these new nonsystems he offered them financial incentives and issued threats to their survival. Although they were warned that there might be uncomfortable adjustment periods, the caregivers were promised that the steep learning curves would level out and their professional lives would again be valued and productive.
Of course, the dictator is not a single person but a motley and disorganized conglomerate of user- and patient-unfriendly electronic health record nonsystems. Ask almost any nurse or physician for her feelings about computer-based medical record systems, and you will hear tales of long hours, disengagement, and frustration. Caregivers are unhappy at all levels, and patients have grown tired of their nurses and physicians spending most of their time looking at computer screens.
You certainly have heard this all before. But you are hearing it in hospital hallways and grocery store checkout lines as a low rumble of discontent emerging from separate individuals, not as a well-articulated and widely distributed voice of physicians as a group. To some extent this relative silence is because there is no such group, at least not in same mold as a labor union. The term “labor union” may make you uncomfortable. But given the current climate in medicine, unionizing may be the best and only way to effect change.
But organizing to effect change in the workplace isn’t part of the physician genome. In the 1960s, a group of house officers in Boston engaged in a heal-in to successfully improve their salaries and working conditions. But over the ensuing half century physicians have remained tragically silent in the face of a changing workplace landscape in which they have gone from being independent owner operators in control of their destinies to becoming employees feeling powerless to improve their working conditions. This perceived impotence has escalated in the face of the challenge posed by the introduction of dysfunctional EHRs.
Ironically, a solution is at almost every physician’s elbow. In a recent New York Times opinion piece Theresa Brown and Stephen Bergman acknowledge that physicians don’t seem prepared to mount a meaningful response to the challenge to the failed promise of EHRs (“Doctors, Nurses and the Paperwork Crisis That Could Unite Them,” Dec. 31, 2019). They point out that, over the last half century, physicians have remained isolated on the sidelines, finding just enough voice to grumble. Nurses have in a variety of situations organized to effect change in their working conditions – in some cases by forming labor unions.
The authors of this op-ed piece, a physician and a nurse, make a strong argument that the time has come for nurses and doctors shake off the shackles of their stereotypic roles and join in creating a loud, forceful, and effective voice to demand a working environment in which the computer functions as an asset and no longer as the terrible burden it has become. Neither group has the power to do it alone, but together they may be able to turn the tide. For physicians it will probably mean venturing several steps outside of their comfort zone. But working shoulder to shoulder with nurses may provide the courage to speak out.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
CDC begins coronavirus diagnostic test kit distribution; new case confirmed in Wisconsin
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Wisconsin Department of Health Services confirmed a new case of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) on Feb. 5, 2020, bringing the total number of cases in the United States to 12.*
Earlier in the day, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, told reporters that 206 individuals under investigation had tested negative for infection with the novel virus and that tests were pending on another 76 individuals.
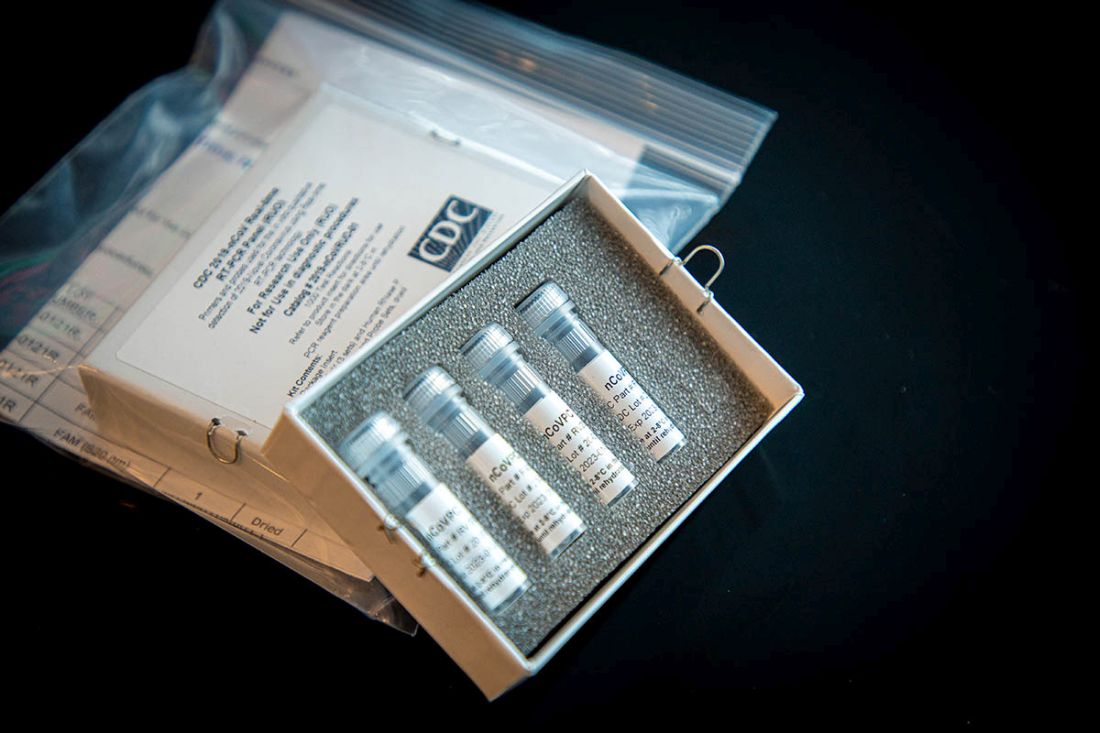
The agency also announced during a press briefing call that diagnostic test kits will begin shipping on Feb. 5, less than 24 hours after receiving an emergency use authorization from the Food and Drug Administration. Full information is available in an article published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The emergency use authorization will allow for broader use of the CDC’s 2019-nCoV Real Time RT-PCR Diagnostic Panel, which to date has been limited for use at CDC laboratories. Under the emergency use authorization, the diagnostic kit is authorized for patients who meed the CDC criteria for 2019-nCoV testing. The diagnostic test is a reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction test that provides presumptive detection of 2019-nCoV from respiratory secretions, such as nasal or oral swabs. A positive test indicates likely infection, although a negative test does not preclude infection and should not be the sole determination for patient management decisions.
“Today, the test kits will start shipping to over 100 U.S. public health labs,” she said. “Each of these labs is required to perform international verification for [Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments] compliance prior to reporting out. This process is expected to take a few days.”
Dr. Messonnier said that 200 test kits will be distributed to domestic labs and another 200 test kits will go to select international labs. Each kit can perform diagnostics on 700-800 patient samples.
“What that means is that, by the start of next week, we expect there to be much enhanced capacity for laboratory testing closer to our patients,” she said, adding that additional test kits are being produced and will be available for ordering in the future. Each laboratory that places an order will receive one test kit.
“Distribution of these tests will improve the global capacity to detect and respond to this new virus,” Dr. Messonnier said. “Availability of this test is a starting place for greater commercial availability of diagnostic testing for nCoV.”
The CDC also said that the next batch of passengers arriving from Wuhan, China, will be arriving in one of four locations: Travis Air Force Base, Fairfield, Calif.; Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, San Diego; Lackland Air Force Base, San Antonio; and Eppley Airfield, Omaha, Neb. Passengers will be quarantined for up to 14 days from the day the flight left Wuhan and medical care will be provided if needed.
“We do not believe these people pose a threat to the communities where they are being housed as we are taking measures to minimize any contact,” she said, adding that confirmed infections are expected among these and other returning travelers.
Dr. Messonnier warned that the quarantine measures “may not catch every single returning traveler returning with novel coronavirus, given the nature of this virus and how it is spreading. But if we can catch the majority of them, that will slow the entry of this virus into the United States.”
*This story was updated on 02/05/2020.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Wisconsin Department of Health Services confirmed a new case of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) on Feb. 5, 2020, bringing the total number of cases in the United States to 12.*
Earlier in the day, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, told reporters that 206 individuals under investigation had tested negative for infection with the novel virus and that tests were pending on another 76 individuals.
The agency also announced during a press briefing call that diagnostic test kits will begin shipping on Feb. 5, less than 24 hours after receiving an emergency use authorization from the Food and Drug Administration. Full information is available in an article published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The emergency use authorization will allow for broader use of the CDC’s 2019-nCoV Real Time RT-PCR Diagnostic Panel, which to date has been limited for use at CDC laboratories. Under the emergency use authorization, the diagnostic kit is authorized for patients who meed the CDC criteria for 2019-nCoV testing. The diagnostic test is a reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction test that provides presumptive detection of 2019-nCoV from respiratory secretions, such as nasal or oral swabs. A positive test indicates likely infection, although a negative test does not preclude infection and should not be the sole determination for patient management decisions.
“Today, the test kits will start shipping to over 100 U.S. public health labs,” she said. “Each of these labs is required to perform international verification for [Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments] compliance prior to reporting out. This process is expected to take a few days.”
Dr. Messonnier said that 200 test kits will be distributed to domestic labs and another 200 test kits will go to select international labs. Each kit can perform diagnostics on 700-800 patient samples.
“What that means is that, by the start of next week, we expect there to be much enhanced capacity for laboratory testing closer to our patients,” she said, adding that additional test kits are being produced and will be available for ordering in the future. Each laboratory that places an order will receive one test kit.
“Distribution of these tests will improve the global capacity to detect and respond to this new virus,” Dr. Messonnier said. “Availability of this test is a starting place for greater commercial availability of diagnostic testing for nCoV.”
The CDC also said that the next batch of passengers arriving from Wuhan, China, will be arriving in one of four locations: Travis Air Force Base, Fairfield, Calif.; Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, San Diego; Lackland Air Force Base, San Antonio; and Eppley Airfield, Omaha, Neb. Passengers will be quarantined for up to 14 days from the day the flight left Wuhan and medical care will be provided if needed.
“We do not believe these people pose a threat to the communities where they are being housed as we are taking measures to minimize any contact,” she said, adding that confirmed infections are expected among these and other returning travelers.
Dr. Messonnier warned that the quarantine measures “may not catch every single returning traveler returning with novel coronavirus, given the nature of this virus and how it is spreading. But if we can catch the majority of them, that will slow the entry of this virus into the United States.”
*This story was updated on 02/05/2020.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Wisconsin Department of Health Services confirmed a new case of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) on Feb. 5, 2020, bringing the total number of cases in the United States to 12.*
Earlier in the day, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, told reporters that 206 individuals under investigation had tested negative for infection with the novel virus and that tests were pending on another 76 individuals.
The agency also announced during a press briefing call that diagnostic test kits will begin shipping on Feb. 5, less than 24 hours after receiving an emergency use authorization from the Food and Drug Administration. Full information is available in an article published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The emergency use authorization will allow for broader use of the CDC’s 2019-nCoV Real Time RT-PCR Diagnostic Panel, which to date has been limited for use at CDC laboratories. Under the emergency use authorization, the diagnostic kit is authorized for patients who meed the CDC criteria for 2019-nCoV testing. The diagnostic test is a reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction test that provides presumptive detection of 2019-nCoV from respiratory secretions, such as nasal or oral swabs. A positive test indicates likely infection, although a negative test does not preclude infection and should not be the sole determination for patient management decisions.
“Today, the test kits will start shipping to over 100 U.S. public health labs,” she said. “Each of these labs is required to perform international verification for [Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments] compliance prior to reporting out. This process is expected to take a few days.”
Dr. Messonnier said that 200 test kits will be distributed to domestic labs and another 200 test kits will go to select international labs. Each kit can perform diagnostics on 700-800 patient samples.
“What that means is that, by the start of next week, we expect there to be much enhanced capacity for laboratory testing closer to our patients,” she said, adding that additional test kits are being produced and will be available for ordering in the future. Each laboratory that places an order will receive one test kit.
“Distribution of these tests will improve the global capacity to detect and respond to this new virus,” Dr. Messonnier said. “Availability of this test is a starting place for greater commercial availability of diagnostic testing for nCoV.”
The CDC also said that the next batch of passengers arriving from Wuhan, China, will be arriving in one of four locations: Travis Air Force Base, Fairfield, Calif.; Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, San Diego; Lackland Air Force Base, San Antonio; and Eppley Airfield, Omaha, Neb. Passengers will be quarantined for up to 14 days from the day the flight left Wuhan and medical care will be provided if needed.
“We do not believe these people pose a threat to the communities where they are being housed as we are taking measures to minimize any contact,” she said, adding that confirmed infections are expected among these and other returning travelers.
Dr. Messonnier warned that the quarantine measures “may not catch every single returning traveler returning with novel coronavirus, given the nature of this virus and how it is spreading. But if we can catch the majority of them, that will slow the entry of this virus into the United States.”
*This story was updated on 02/05/2020.
The 2019 novel coronavirus: Case review IDs clinical characteristics
A group of physicians in Wuhan, China, who are treating patients with the 2019 novel coronavirus have gone the extra mile to share their clinical experiences with colleagues around the world.
Nanshan Chen, MD, of Jinyintan Hospital, Wuhan, and his team conducted a retrospective study on 99 cases and, in very short order, published their initial findings in the Lancet online on Jan. 29. These findings could guide action in other cases and help clinicians all over the world create treatment plans for patients of the 2019-nCoV.
The findings show that and characteristics of those with fatal infections align with the MuLBSTA score – an early warning model for predicting viral pneumonia–related mortality, according to a case review.
Of 99 patients who presented with 2019-nCoV pneumonia at Jinyintan Hospital between Jan. 1 and Jan. 20, 67 were men, the mean age was 55.5 years, and 50 patients had chronic diseases.
“All the data of included cases have been shared with [the World Health Organization]. The study was approved by Jinyintan Hospital Ethics Committee and written informed consent was obtained from patients involved before enrollment when data were collected retrospectively,” the researchers noted.
Nearly half of the patients (49%) lived or worked near a specific seafood market, suggesting disease clustering.
Clinical manifestations affecting the majority of patients included fever and cough in 83% and 82% of patients, respectively. Other symptoms included shortness of breath in 31%, muscle aches in 11%, confusion in 9%, headache in 8%, sore throat in 5%, and rhinorrhea, chest pain, diarrhea, and nausea and vomiting in 1%-4% of patients, the investigators found.
Imaging showed bilateral pneumonia in 75% of cases, multiple mottling and ground-glass opacity in 14%, and pneumothorax in 1%. Organ function damage was present in a third of patients at admission: 17% had acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) – including 11 patients who worsened quickly and died of multiple organ failure. Eight percent had acute respiratory injury, 3% had acute renal injury, 4% had septic shock, and 1% had ventilator-associated pneumonia, they said, noting that all cases were confirmed by real-time polymerase chain reaction.
A notable laboratory finding was reduced absolute lymphocyte counts in most patients, the investigators said.
All patients were treated in isolation and 76% received antiviral treatment with oseltamivir, ganciclovir, lopinavir, or ritonavir for 3-14 days (median, 3 days). Most patients also received antibiotic treatment, including a single antibiotic in 25% of cases and combination therapy in 45%, with most antibiotics used to cover “common pathogens and some atypical pathogens,” they said, adding that “when secondary bacterial infection occurred, medication was administered according to the results of bacterial culture and drug sensitivity.”
Cephalosporins, quinolones, carbapenems, tigecycline against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, linezolid, and antifungal drugs were used, and duration ranged from 3 to 17 days (median, 5 days).
Nineteen patients also received steroid treatments.
As of Jan. 25, 31 patients had been discharged and 57 remained hospitalized. Of the 11 who died, the first 2 were a 61-year-old man and a 69-year-old man, each diagnosed with severe pneumonia and ARDS. The first experienced sudden cardiac arrest and died on admission day 11, and the second died of severe pneumonia, septic shock, and respiratory failure on admission day 9. Neither had underlying disease, but both had a long history of smoking, the investigators noted.
“The deaths of these two patients were consistent with the MuLBSTA score,” they wrote, explaining that the scoring system takes into account multilobular infiltration, lymphopenia, bacterial coinfection, smoking history, hypertension, and age.
Eight of the nine other patients who died had lymphopenia, seven had bilateral pneumonia, five were over age 60 years, three had hypertension, and one was a heavy smoker, they added.
Most coronavirus infections cause mild symptoms and have good prognosis, but some patients with the 2019-nCoV, which was identified Jan. 7 following the development of several cases of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, develop fatal disease. The paucity of data regarding epidemiology and clinical features of pneumonia associated with 2019-nCoV prompted the current retrospective study at the center where the first cases were admitted, the investigators explained.
They noted that the sequence of 2019-nCoV “is relatively different from the six other coronavirus subtypes, including the highly pathogenic severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)-CoV, as well as the human coronaviruses (HCoV)-OC43, -229E, -NL63, and -HKU1 that induce mild upper respiratory disease, but can be classified as a betacoronavirus with evidence of human-to-human transmission.
Mortality associated with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV have been reported as more than 10% and more than 35%, respectively; at data cutoff for the current study, mortality among the 99 included cases was 11%, which is similar to that in another recent 2019-nCoV report, they said.
The finding of greater risk among older men also has been seen with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, and the high rate among individuals with chronic diseases, mainly cerebrovascular disease, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, also has been reported with MERS-CoV, they added.
“Our results suggest that 2019-nCoV is more likely to infect older adult males with chronic comorbidities as a result of the weaker immune functions of these patients,” they wrote.
Coinfection with bacteria and fungi occurred in some patients, particularly those with severe illness, and cultures most often showed A. baumannii, K. pneumoniae, A. flavus, C. glabrata, and C. albicans, and the findings of reduced absolute lymphocyte values in most patients suggests that “2019-nCoV might mainly act on lymphocytes, especially T lymphocytes, as does SARS-CoV,” they noted.
Given the rapid progression with ARDS and septic shock in some patients in this review, “early identification and timely treatment of critical cases is of crucial importance,” they said.
“Use of intravenous immunoglobulin is recommended to enhance the ability of anti-infection for severely ill patients, and steroids (methylprednisolone 1-2 mg/kg per day) are recommended for patients with ARDS, for as short a duration of treatment as possible,” they added.
Further, since some studies suggest that a substantial decrease in lymphocyte count indicates consumption of many immune cells by coronavirus, thereby inhibiting cellular immune function, damage to T lymphocytes might be “an important factor leading to exacerbations of patients,” they wrote, adding that “[t]he low absolute value of lymphocytes could be used as a reference index in the diagnosis of new coronavirus infections in the clinic.”
The MuLBSTA score also should be investigated to determine its applicability for predicting mortality risk in patients with 2019-nCoV infection, they added.
The current study is limited by its small sample size; additional studies are needed to include “as many patients as possible in Wuhan, in other cities in China, and even in other countries to get a more comprehensive understanding of 2019-nCoV,” they said.
The National Key R&D Program of China funded the study. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Chen N et al. Lancet. 2020 Jan 29. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7.
A group of physicians in Wuhan, China, who are treating patients with the 2019 novel coronavirus have gone the extra mile to share their clinical experiences with colleagues around the world.
Nanshan Chen, MD, of Jinyintan Hospital, Wuhan, and his team conducted a retrospective study on 99 cases and, in very short order, published their initial findings in the Lancet online on Jan. 29. These findings could guide action in other cases and help clinicians all over the world create treatment plans for patients of the 2019-nCoV.
The findings show that and characteristics of those with fatal infections align with the MuLBSTA score – an early warning model for predicting viral pneumonia–related mortality, according to a case review.
Of 99 patients who presented with 2019-nCoV pneumonia at Jinyintan Hospital between Jan. 1 and Jan. 20, 67 were men, the mean age was 55.5 years, and 50 patients had chronic diseases.
“All the data of included cases have been shared with [the World Health Organization]. The study was approved by Jinyintan Hospital Ethics Committee and written informed consent was obtained from patients involved before enrollment when data were collected retrospectively,” the researchers noted.
Nearly half of the patients (49%) lived or worked near a specific seafood market, suggesting disease clustering.
Clinical manifestations affecting the majority of patients included fever and cough in 83% and 82% of patients, respectively. Other symptoms included shortness of breath in 31%, muscle aches in 11%, confusion in 9%, headache in 8%, sore throat in 5%, and rhinorrhea, chest pain, diarrhea, and nausea and vomiting in 1%-4% of patients, the investigators found.
Imaging showed bilateral pneumonia in 75% of cases, multiple mottling and ground-glass opacity in 14%, and pneumothorax in 1%. Organ function damage was present in a third of patients at admission: 17% had acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) – including 11 patients who worsened quickly and died of multiple organ failure. Eight percent had acute respiratory injury, 3% had acute renal injury, 4% had septic shock, and 1% had ventilator-associated pneumonia, they said, noting that all cases were confirmed by real-time polymerase chain reaction.
A notable laboratory finding was reduced absolute lymphocyte counts in most patients, the investigators said.
All patients were treated in isolation and 76% received antiviral treatment with oseltamivir, ganciclovir, lopinavir, or ritonavir for 3-14 days (median, 3 days). Most patients also received antibiotic treatment, including a single antibiotic in 25% of cases and combination therapy in 45%, with most antibiotics used to cover “common pathogens and some atypical pathogens,” they said, adding that “when secondary bacterial infection occurred, medication was administered according to the results of bacterial culture and drug sensitivity.”
Cephalosporins, quinolones, carbapenems, tigecycline against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, linezolid, and antifungal drugs were used, and duration ranged from 3 to 17 days (median, 5 days).
Nineteen patients also received steroid treatments.
As of Jan. 25, 31 patients had been discharged and 57 remained hospitalized. Of the 11 who died, the first 2 were a 61-year-old man and a 69-year-old man, each diagnosed with severe pneumonia and ARDS. The first experienced sudden cardiac arrest and died on admission day 11, and the second died of severe pneumonia, septic shock, and respiratory failure on admission day 9. Neither had underlying disease, but both had a long history of smoking, the investigators noted.
“The deaths of these two patients were consistent with the MuLBSTA score,” they wrote, explaining that the scoring system takes into account multilobular infiltration, lymphopenia, bacterial coinfection, smoking history, hypertension, and age.
Eight of the nine other patients who died had lymphopenia, seven had bilateral pneumonia, five were over age 60 years, three had hypertension, and one was a heavy smoker, they added.
Most coronavirus infections cause mild symptoms and have good prognosis, but some patients with the 2019-nCoV, which was identified Jan. 7 following the development of several cases of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, develop fatal disease. The paucity of data regarding epidemiology and clinical features of pneumonia associated with 2019-nCoV prompted the current retrospective study at the center where the first cases were admitted, the investigators explained.
They noted that the sequence of 2019-nCoV “is relatively different from the six other coronavirus subtypes, including the highly pathogenic severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)-CoV, as well as the human coronaviruses (HCoV)-OC43, -229E, -NL63, and -HKU1 that induce mild upper respiratory disease, but can be classified as a betacoronavirus with evidence of human-to-human transmission.
Mortality associated with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV have been reported as more than 10% and more than 35%, respectively; at data cutoff for the current study, mortality among the 99 included cases was 11%, which is similar to that in another recent 2019-nCoV report, they said.
The finding of greater risk among older men also has been seen with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, and the high rate among individuals with chronic diseases, mainly cerebrovascular disease, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, also has been reported with MERS-CoV, they added.
“Our results suggest that 2019-nCoV is more likely to infect older adult males with chronic comorbidities as a result of the weaker immune functions of these patients,” they wrote.
Coinfection with bacteria and fungi occurred in some patients, particularly those with severe illness, and cultures most often showed A. baumannii, K. pneumoniae, A. flavus, C. glabrata, and C. albicans, and the findings of reduced absolute lymphocyte values in most patients suggests that “2019-nCoV might mainly act on lymphocytes, especially T lymphocytes, as does SARS-CoV,” they noted.
Given the rapid progression with ARDS and septic shock in some patients in this review, “early identification and timely treatment of critical cases is of crucial importance,” they said.
“Use of intravenous immunoglobulin is recommended to enhance the ability of anti-infection for severely ill patients, and steroids (methylprednisolone 1-2 mg/kg per day) are recommended for patients with ARDS, for as short a duration of treatment as possible,” they added.
Further, since some studies suggest that a substantial decrease in lymphocyte count indicates consumption of many immune cells by coronavirus, thereby inhibiting cellular immune function, damage to T lymphocytes might be “an important factor leading to exacerbations of patients,” they wrote, adding that “[t]he low absolute value of lymphocytes could be used as a reference index in the diagnosis of new coronavirus infections in the clinic.”
The MuLBSTA score also should be investigated to determine its applicability for predicting mortality risk in patients with 2019-nCoV infection, they added.
The current study is limited by its small sample size; additional studies are needed to include “as many patients as possible in Wuhan, in other cities in China, and even in other countries to get a more comprehensive understanding of 2019-nCoV,” they said.
The National Key R&D Program of China funded the study. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Chen N et al. Lancet. 2020 Jan 29. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7.
A group of physicians in Wuhan, China, who are treating patients with the 2019 novel coronavirus have gone the extra mile to share their clinical experiences with colleagues around the world.
Nanshan Chen, MD, of Jinyintan Hospital, Wuhan, and his team conducted a retrospective study on 99 cases and, in very short order, published their initial findings in the Lancet online on Jan. 29. These findings could guide action in other cases and help clinicians all over the world create treatment plans for patients of the 2019-nCoV.
The findings show that and characteristics of those with fatal infections align with the MuLBSTA score – an early warning model for predicting viral pneumonia–related mortality, according to a case review.
Of 99 patients who presented with 2019-nCoV pneumonia at Jinyintan Hospital between Jan. 1 and Jan. 20, 67 were men, the mean age was 55.5 years, and 50 patients had chronic diseases.
“All the data of included cases have been shared with [the World Health Organization]. The study was approved by Jinyintan Hospital Ethics Committee and written informed consent was obtained from patients involved before enrollment when data were collected retrospectively,” the researchers noted.
Nearly half of the patients (49%) lived or worked near a specific seafood market, suggesting disease clustering.
Clinical manifestations affecting the majority of patients included fever and cough in 83% and 82% of patients, respectively. Other symptoms included shortness of breath in 31%, muscle aches in 11%, confusion in 9%, headache in 8%, sore throat in 5%, and rhinorrhea, chest pain, diarrhea, and nausea and vomiting in 1%-4% of patients, the investigators found.
Imaging showed bilateral pneumonia in 75% of cases, multiple mottling and ground-glass opacity in 14%, and pneumothorax in 1%. Organ function damage was present in a third of patients at admission: 17% had acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) – including 11 patients who worsened quickly and died of multiple organ failure. Eight percent had acute respiratory injury, 3% had acute renal injury, 4% had septic shock, and 1% had ventilator-associated pneumonia, they said, noting that all cases were confirmed by real-time polymerase chain reaction.
A notable laboratory finding was reduced absolute lymphocyte counts in most patients, the investigators said.
All patients were treated in isolation and 76% received antiviral treatment with oseltamivir, ganciclovir, lopinavir, or ritonavir for 3-14 days (median, 3 days). Most patients also received antibiotic treatment, including a single antibiotic in 25% of cases and combination therapy in 45%, with most antibiotics used to cover “common pathogens and some atypical pathogens,” they said, adding that “when secondary bacterial infection occurred, medication was administered according to the results of bacterial culture and drug sensitivity.”
Cephalosporins, quinolones, carbapenems, tigecycline against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, linezolid, and antifungal drugs were used, and duration ranged from 3 to 17 days (median, 5 days).
Nineteen patients also received steroid treatments.
As of Jan. 25, 31 patients had been discharged and 57 remained hospitalized. Of the 11 who died, the first 2 were a 61-year-old man and a 69-year-old man, each diagnosed with severe pneumonia and ARDS. The first experienced sudden cardiac arrest and died on admission day 11, and the second died of severe pneumonia, septic shock, and respiratory failure on admission day 9. Neither had underlying disease, but both had a long history of smoking, the investigators noted.
“The deaths of these two patients were consistent with the MuLBSTA score,” they wrote, explaining that the scoring system takes into account multilobular infiltration, lymphopenia, bacterial coinfection, smoking history, hypertension, and age.
Eight of the nine other patients who died had lymphopenia, seven had bilateral pneumonia, five were over age 60 years, three had hypertension, and one was a heavy smoker, they added.
Most coronavirus infections cause mild symptoms and have good prognosis, but some patients with the 2019-nCoV, which was identified Jan. 7 following the development of several cases of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, develop fatal disease. The paucity of data regarding epidemiology and clinical features of pneumonia associated with 2019-nCoV prompted the current retrospective study at the center where the first cases were admitted, the investigators explained.
They noted that the sequence of 2019-nCoV “is relatively different from the six other coronavirus subtypes, including the highly pathogenic severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)-CoV, as well as the human coronaviruses (HCoV)-OC43, -229E, -NL63, and -HKU1 that induce mild upper respiratory disease, but can be classified as a betacoronavirus with evidence of human-to-human transmission.
Mortality associated with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV have been reported as more than 10% and more than 35%, respectively; at data cutoff for the current study, mortality among the 99 included cases was 11%, which is similar to that in another recent 2019-nCoV report, they said.
The finding of greater risk among older men also has been seen with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, and the high rate among individuals with chronic diseases, mainly cerebrovascular disease, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, also has been reported with MERS-CoV, they added.
“Our results suggest that 2019-nCoV is more likely to infect older adult males with chronic comorbidities as a result of the weaker immune functions of these patients,” they wrote.
Coinfection with bacteria and fungi occurred in some patients, particularly those with severe illness, and cultures most often showed A. baumannii, K. pneumoniae, A. flavus, C. glabrata, and C. albicans, and the findings of reduced absolute lymphocyte values in most patients suggests that “2019-nCoV might mainly act on lymphocytes, especially T lymphocytes, as does SARS-CoV,” they noted.
Given the rapid progression with ARDS and septic shock in some patients in this review, “early identification and timely treatment of critical cases is of crucial importance,” they said.
“Use of intravenous immunoglobulin is recommended to enhance the ability of anti-infection for severely ill patients, and steroids (methylprednisolone 1-2 mg/kg per day) are recommended for patients with ARDS, for as short a duration of treatment as possible,” they added.
Further, since some studies suggest that a substantial decrease in lymphocyte count indicates consumption of many immune cells by coronavirus, thereby inhibiting cellular immune function, damage to T lymphocytes might be “an important factor leading to exacerbations of patients,” they wrote, adding that “[t]he low absolute value of lymphocytes could be used as a reference index in the diagnosis of new coronavirus infections in the clinic.”
The MuLBSTA score also should be investigated to determine its applicability for predicting mortality risk in patients with 2019-nCoV infection, they added.
The current study is limited by its small sample size; additional studies are needed to include “as many patients as possible in Wuhan, in other cities in China, and even in other countries to get a more comprehensive understanding of 2019-nCoV,” they said.
The National Key R&D Program of China funded the study. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Chen N et al. Lancet. 2020 Jan 29. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7.
FROM THE LANCET
Trump takes on multiple health topics in State of the Union
President Donald J. Trump took on multiple health care issues in his State of the Union address, imploring Congress to avoid the “socialism” of Medicare-for-all, to pass legislation banning late-term abortions, and to protect insurance coverage for preexisting conditions while joining together to reduce rising drug prices.
Mr. Trump said his administration has already been “taking on the big pharmaceutical companies,” claiming that, in 2019, “for the first time in 51 years, the cost of prescription drugs actually went down.”
That statement was called “misleading” by the New York Times because such efforts have excluded some high-cost drugs, and prices had risen by the end of the year, the publication noted in a fact-check of the president’s speech.
A survey issued in December 2019 found that the United States pays the highest prices in the world for pharmaceuticals, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
But the president did throw down a gauntlet for Congress. “Working together, the Congress can reduce drug prices substantially from current levels,” he said, stating that he had been “speaking to Sen. Chuck Grassley of Iowa and others in the Congress in order to get something on drug pricing done, and done properly.
“Get a bill to my desk, and I will sign it into law without delay,” Mr. Trump said.
A group of House Democrats then stood up in the chamber and loudly chanted, “HR3, HR3,” referring to the Lower Drug Costs Now Act, which the House passed in December 2019.
The bill would give the Department of Health & Human Services the power to negotiate directly with drug companies on up to 250 drugs per year, in particular, the highest-costing and most-utilized drugs.
The Senate has not taken up the legislation, but Sen. Grassley (R) and Sen. Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) introduced a similar bill, the Prescription Drug Pricing Reduction Act. It has been approved by the Senate Finance Committee but has not been moved to the Senate floor.
“I appreciate President Trump recognizing the work we’re doing to lower prescription drug prices,” Sen. Grassley said in a statement after the State of the Union. “Iowans and Americans across the country are demanding reforms that lower sky-high drug costs. A recent poll showed 70% of Americans want Congress to make lowering drug prices its top priority.”
Rep. Greg Walden (R-Ore.), the ranking Republican on the House Energy and Commerce Committee, said he believed Trump was committed to lowering drug costs. “I’ve never seen a president lean in further than President Donald Trump on lowering health care costs,” said Rep. Walden in a statement after the speech.
Trump touted his price transparency rule, which he said would go into effect next January, as a key way to cut health care costs.
Preexisting conditions
The president said that since he’d taken office, insurance had become more affordable and that the quality of health care had improved. He also said that he was making what he called an “iron-clad pledge” to American families.
“We will always protect patients with preexisting conditions – that is a guarantee,” Mr. Trump said.
In a press conference before the speech, Speaker of the House Nancy Pelosi (D-Calif.) took issue with that pledge. “The president swears that he supports protections for people with preexisting conditions, but right now, he is fighting in federal court to eliminate these lifesaving protections and every last protection and benefit of the Affordable Care Act,” she said.
During the speech, Rep. G. K. Butterfield (D-N.C.) tweeted “#FactCheck: Claiming to protect Americans with preexisting conditions, Trump and his administration have repeatedly sought to undermine protections offered by the ACA through executive orders and the courts. He is seeking to strike down the law and its protections entirely.”
Larry Levitt, executive vice president for health policy at the Kaiser Family Foundation, pointed out in a tweet that insurance plans that Trump touted as “affordable alternatives” are in fact missing those protections.
“Ironically, the cheaper health insurance plans that President Trump has expanded are short-term plans that don’t cover preexisting conditions,” Mr. Levitt said.
Socialist takeover
Mr. Trump condemned the Medicare-for-all proposals that have been introduced in Congress and that are being backed in whole or in part by all of the Democratic candidates for president.
“As we work to improve Americans’ health care, there are those who want to take away your health care, take away your doctor, and abolish private insurance entirely,” said Mr. Trump.
He said that 132 members of Congress “have endorsed legislation to impose a socialist takeover of our health care system, wiping out the private health insurance plans of 180 million Americans.”
Added Mr. Trump: “We will never let socialism destroy American health care!”
Medicare-for-all has waxed and waned in popularity among voters, with generally more Democrats than Republicans favoring a single-payer system, with or without a public option.
Preliminary exit polls in Iowa that were conducted during Monday’s caucus found that 57% of Iowa Democratic caucus-goers supported a single-payer plan; 38% opposed such a plan, according to the Washington Post.
Opioids, the coronavirus, and abortion
In some of his final remarks on health care, Mr. Trump cited progress in the opioid crisis, noting that, in 2019, drug overdose deaths declined for the first time in 30 years.
He said that his administration was coordinating with the Chinese government regarding the coronavirus outbreak and noted the launch of initiatives to improve care for people with kidney disease, Alzheimer’s, and mental health problems.
Mr. Trump repeated his 2019 State of the Union claim that the government would help end AIDS in America by the end of the decade.
The president also announced that he was asking Congress for “an additional $50 million” to fund neonatal research. He followed that up with a plea about abortion.
“I am calling upon the members of Congress here tonight to pass legislation finally banning the late-term abortion of babies,” he said.
Insulin costs?
In the days before the speech, some news outlets had reported that Mr. Trump and the HHS were working on a plan to lower insulin prices for Medicare beneficiaries, and there were suggestions it would come up in the speech.
At least 13 members of Congress invited people advocating for lower insulin costs as their guests for the State of the Union, Stat reported. Rep. Pelosi invited twins from San Francisco with type 1 diabetes as her guests.
But Mr. Trump never mentioned insulin in his speech.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
President Donald J. Trump took on multiple health care issues in his State of the Union address, imploring Congress to avoid the “socialism” of Medicare-for-all, to pass legislation banning late-term abortions, and to protect insurance coverage for preexisting conditions while joining together to reduce rising drug prices.
Mr. Trump said his administration has already been “taking on the big pharmaceutical companies,” claiming that, in 2019, “for the first time in 51 years, the cost of prescription drugs actually went down.”
That statement was called “misleading” by the New York Times because such efforts have excluded some high-cost drugs, and prices had risen by the end of the year, the publication noted in a fact-check of the president’s speech.
A survey issued in December 2019 found that the United States pays the highest prices in the world for pharmaceuticals, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
But the president did throw down a gauntlet for Congress. “Working together, the Congress can reduce drug prices substantially from current levels,” he said, stating that he had been “speaking to Sen. Chuck Grassley of Iowa and others in the Congress in order to get something on drug pricing done, and done properly.
“Get a bill to my desk, and I will sign it into law without delay,” Mr. Trump said.
A group of House Democrats then stood up in the chamber and loudly chanted, “HR3, HR3,” referring to the Lower Drug Costs Now Act, which the House passed in December 2019.
The bill would give the Department of Health & Human Services the power to negotiate directly with drug companies on up to 250 drugs per year, in particular, the highest-costing and most-utilized drugs.
The Senate has not taken up the legislation, but Sen. Grassley (R) and Sen. Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) introduced a similar bill, the Prescription Drug Pricing Reduction Act. It has been approved by the Senate Finance Committee but has not been moved to the Senate floor.
“I appreciate President Trump recognizing the work we’re doing to lower prescription drug prices,” Sen. Grassley said in a statement after the State of the Union. “Iowans and Americans across the country are demanding reforms that lower sky-high drug costs. A recent poll showed 70% of Americans want Congress to make lowering drug prices its top priority.”
Rep. Greg Walden (R-Ore.), the ranking Republican on the House Energy and Commerce Committee, said he believed Trump was committed to lowering drug costs. “I’ve never seen a president lean in further than President Donald Trump on lowering health care costs,” said Rep. Walden in a statement after the speech.
Trump touted his price transparency rule, which he said would go into effect next January, as a key way to cut health care costs.
Preexisting conditions
The president said that since he’d taken office, insurance had become more affordable and that the quality of health care had improved. He also said that he was making what he called an “iron-clad pledge” to American families.
“We will always protect patients with preexisting conditions – that is a guarantee,” Mr. Trump said.
In a press conference before the speech, Speaker of the House Nancy Pelosi (D-Calif.) took issue with that pledge. “The president swears that he supports protections for people with preexisting conditions, but right now, he is fighting in federal court to eliminate these lifesaving protections and every last protection and benefit of the Affordable Care Act,” she said.
During the speech, Rep. G. K. Butterfield (D-N.C.) tweeted “#FactCheck: Claiming to protect Americans with preexisting conditions, Trump and his administration have repeatedly sought to undermine protections offered by the ACA through executive orders and the courts. He is seeking to strike down the law and its protections entirely.”
Larry Levitt, executive vice president for health policy at the Kaiser Family Foundation, pointed out in a tweet that insurance plans that Trump touted as “affordable alternatives” are in fact missing those protections.
“Ironically, the cheaper health insurance plans that President Trump has expanded are short-term plans that don’t cover preexisting conditions,” Mr. Levitt said.
Socialist takeover
Mr. Trump condemned the Medicare-for-all proposals that have been introduced in Congress and that are being backed in whole or in part by all of the Democratic candidates for president.
“As we work to improve Americans’ health care, there are those who want to take away your health care, take away your doctor, and abolish private insurance entirely,” said Mr. Trump.
He said that 132 members of Congress “have endorsed legislation to impose a socialist takeover of our health care system, wiping out the private health insurance plans of 180 million Americans.”
Added Mr. Trump: “We will never let socialism destroy American health care!”
Medicare-for-all has waxed and waned in popularity among voters, with generally more Democrats than Republicans favoring a single-payer system, with or without a public option.
Preliminary exit polls in Iowa that were conducted during Monday’s caucus found that 57% of Iowa Democratic caucus-goers supported a single-payer plan; 38% opposed such a plan, according to the Washington Post.
Opioids, the coronavirus, and abortion
In some of his final remarks on health care, Mr. Trump cited progress in the opioid crisis, noting that, in 2019, drug overdose deaths declined for the first time in 30 years.
He said that his administration was coordinating with the Chinese government regarding the coronavirus outbreak and noted the launch of initiatives to improve care for people with kidney disease, Alzheimer’s, and mental health problems.
Mr. Trump repeated his 2019 State of the Union claim that the government would help end AIDS in America by the end of the decade.
The president also announced that he was asking Congress for “an additional $50 million” to fund neonatal research. He followed that up with a plea about abortion.
“I am calling upon the members of Congress here tonight to pass legislation finally banning the late-term abortion of babies,” he said.
Insulin costs?
In the days before the speech, some news outlets had reported that Mr. Trump and the HHS were working on a plan to lower insulin prices for Medicare beneficiaries, and there were suggestions it would come up in the speech.
At least 13 members of Congress invited people advocating for lower insulin costs as their guests for the State of the Union, Stat reported. Rep. Pelosi invited twins from San Francisco with type 1 diabetes as her guests.
But Mr. Trump never mentioned insulin in his speech.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
President Donald J. Trump took on multiple health care issues in his State of the Union address, imploring Congress to avoid the “socialism” of Medicare-for-all, to pass legislation banning late-term abortions, and to protect insurance coverage for preexisting conditions while joining together to reduce rising drug prices.
Mr. Trump said his administration has already been “taking on the big pharmaceutical companies,” claiming that, in 2019, “for the first time in 51 years, the cost of prescription drugs actually went down.”
That statement was called “misleading” by the New York Times because such efforts have excluded some high-cost drugs, and prices had risen by the end of the year, the publication noted in a fact-check of the president’s speech.
A survey issued in December 2019 found that the United States pays the highest prices in the world for pharmaceuticals, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
But the president did throw down a gauntlet for Congress. “Working together, the Congress can reduce drug prices substantially from current levels,” he said, stating that he had been “speaking to Sen. Chuck Grassley of Iowa and others in the Congress in order to get something on drug pricing done, and done properly.
“Get a bill to my desk, and I will sign it into law without delay,” Mr. Trump said.
A group of House Democrats then stood up in the chamber and loudly chanted, “HR3, HR3,” referring to the Lower Drug Costs Now Act, which the House passed in December 2019.
The bill would give the Department of Health & Human Services the power to negotiate directly with drug companies on up to 250 drugs per year, in particular, the highest-costing and most-utilized drugs.
The Senate has not taken up the legislation, but Sen. Grassley (R) and Sen. Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) introduced a similar bill, the Prescription Drug Pricing Reduction Act. It has been approved by the Senate Finance Committee but has not been moved to the Senate floor.
“I appreciate President Trump recognizing the work we’re doing to lower prescription drug prices,” Sen. Grassley said in a statement after the State of the Union. “Iowans and Americans across the country are demanding reforms that lower sky-high drug costs. A recent poll showed 70% of Americans want Congress to make lowering drug prices its top priority.”
Rep. Greg Walden (R-Ore.), the ranking Republican on the House Energy and Commerce Committee, said he believed Trump was committed to lowering drug costs. “I’ve never seen a president lean in further than President Donald Trump on lowering health care costs,” said Rep. Walden in a statement after the speech.
Trump touted his price transparency rule, which he said would go into effect next January, as a key way to cut health care costs.
Preexisting conditions
The president said that since he’d taken office, insurance had become more affordable and that the quality of health care had improved. He also said that he was making what he called an “iron-clad pledge” to American families.
“We will always protect patients with preexisting conditions – that is a guarantee,” Mr. Trump said.
In a press conference before the speech, Speaker of the House Nancy Pelosi (D-Calif.) took issue with that pledge. “The president swears that he supports protections for people with preexisting conditions, but right now, he is fighting in federal court to eliminate these lifesaving protections and every last protection and benefit of the Affordable Care Act,” she said.
During the speech, Rep. G. K. Butterfield (D-N.C.) tweeted “#FactCheck: Claiming to protect Americans with preexisting conditions, Trump and his administration have repeatedly sought to undermine protections offered by the ACA through executive orders and the courts. He is seeking to strike down the law and its protections entirely.”
Larry Levitt, executive vice president for health policy at the Kaiser Family Foundation, pointed out in a tweet that insurance plans that Trump touted as “affordable alternatives” are in fact missing those protections.
“Ironically, the cheaper health insurance plans that President Trump has expanded are short-term plans that don’t cover preexisting conditions,” Mr. Levitt said.
Socialist takeover
Mr. Trump condemned the Medicare-for-all proposals that have been introduced in Congress and that are being backed in whole or in part by all of the Democratic candidates for president.
“As we work to improve Americans’ health care, there are those who want to take away your health care, take away your doctor, and abolish private insurance entirely,” said Mr. Trump.
He said that 132 members of Congress “have endorsed legislation to impose a socialist takeover of our health care system, wiping out the private health insurance plans of 180 million Americans.”
Added Mr. Trump: “We will never let socialism destroy American health care!”
Medicare-for-all has waxed and waned in popularity among voters, with generally more Democrats than Republicans favoring a single-payer system, with or without a public option.
Preliminary exit polls in Iowa that were conducted during Monday’s caucus found that 57% of Iowa Democratic caucus-goers supported a single-payer plan; 38% opposed such a plan, according to the Washington Post.
Opioids, the coronavirus, and abortion
In some of his final remarks on health care, Mr. Trump cited progress in the opioid crisis, noting that, in 2019, drug overdose deaths declined for the first time in 30 years.
He said that his administration was coordinating with the Chinese government regarding the coronavirus outbreak and noted the launch of initiatives to improve care for people with kidney disease, Alzheimer’s, and mental health problems.
Mr. Trump repeated his 2019 State of the Union claim that the government would help end AIDS in America by the end of the decade.
The president also announced that he was asking Congress for “an additional $50 million” to fund neonatal research. He followed that up with a plea about abortion.
“I am calling upon the members of Congress here tonight to pass legislation finally banning the late-term abortion of babies,” he said.
Insulin costs?
In the days before the speech, some news outlets had reported that Mr. Trump and the HHS were working on a plan to lower insulin prices for Medicare beneficiaries, and there were suggestions it would come up in the speech.
At least 13 members of Congress invited people advocating for lower insulin costs as their guests for the State of the Union, Stat reported. Rep. Pelosi invited twins from San Francisco with type 1 diabetes as her guests.
But Mr. Trump never mentioned insulin in his speech.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves novel pandemic influenza vaccine
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the first and only adjuvanted, cell-based pandemic vaccine to provide active immunization against the influenza A virus H5N1 strain.
Influenza A (H5N1) monovalent vaccine, adjuvanted (Audenz, Seqirus) is for use in individuals aged 6 months and older. It’s designed to be rapidly deployed to help protect the U.S. population and can be stockpiled for first responders in the event of a pandemic.
The vaccine and formulated prefilled syringes used in the vaccine are produced in a state-of-the-art production facility built and supported through a multiyear public-private partnership between Seqirus and the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA), part of the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response at the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services.
“Pandemic influenza viruses can be deadly and spread rapidly, making production of safe, effective vaccines essential in saving lives,” BARDA Director Rick Bright, PhD, said in a company news release.
“With this licensure – the latest FDA-approved vaccine to prevent H5N1 influenza — we celebrate a decade-long partnership to achieve health security goals set by the National Strategy for Pandemic Influenza and the 2019 Executive Order to speed the availability of influenza vaccine. Ultimately, this latest licensure means we can protect more people in an influenza pandemic,” said Bright.
“The approval of Audenz represents a key advance in influenza prevention and pandemic preparedness, combining leading-edge, cell-based manufacturing and adjuvant technologies,” Russell Basser, MD, chief scientist and senior vice president of research and development at Seqirus, said in the news release. “This pandemic influenza vaccine exemplifies our commitment to developing innovative technologies that can help provide rapid response during a pandemic emergency.”
Audenz had FDA fast track designation, a process designed to facilitate the development and expedite the review of drugs to treat serious conditions and fill an unmet medical need.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the first and only adjuvanted, cell-based pandemic vaccine to provide active immunization against the influenza A virus H5N1 strain.
Influenza A (H5N1) monovalent vaccine, adjuvanted (Audenz, Seqirus) is for use in individuals aged 6 months and older. It’s designed to be rapidly deployed to help protect the U.S. population and can be stockpiled for first responders in the event of a pandemic.
The vaccine and formulated prefilled syringes used in the vaccine are produced in a state-of-the-art production facility built and supported through a multiyear public-private partnership between Seqirus and the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA), part of the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response at the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services.
“Pandemic influenza viruses can be deadly and spread rapidly, making production of safe, effective vaccines essential in saving lives,” BARDA Director Rick Bright, PhD, said in a company news release.
“With this licensure – the latest FDA-approved vaccine to prevent H5N1 influenza — we celebrate a decade-long partnership to achieve health security goals set by the National Strategy for Pandemic Influenza and the 2019 Executive Order to speed the availability of influenza vaccine. Ultimately, this latest licensure means we can protect more people in an influenza pandemic,” said Bright.
“The approval of Audenz represents a key advance in influenza prevention and pandemic preparedness, combining leading-edge, cell-based manufacturing and adjuvant technologies,” Russell Basser, MD, chief scientist and senior vice president of research and development at Seqirus, said in the news release. “This pandemic influenza vaccine exemplifies our commitment to developing innovative technologies that can help provide rapid response during a pandemic emergency.”
Audenz had FDA fast track designation, a process designed to facilitate the development and expedite the review of drugs to treat serious conditions and fill an unmet medical need.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the first and only adjuvanted, cell-based pandemic vaccine to provide active immunization against the influenza A virus H5N1 strain.
Influenza A (H5N1) monovalent vaccine, adjuvanted (Audenz, Seqirus) is for use in individuals aged 6 months and older. It’s designed to be rapidly deployed to help protect the U.S. population and can be stockpiled for first responders in the event of a pandemic.
The vaccine and formulated prefilled syringes used in the vaccine are produced in a state-of-the-art production facility built and supported through a multiyear public-private partnership between Seqirus and the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA), part of the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response at the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services.
“Pandemic influenza viruses can be deadly and spread rapidly, making production of safe, effective vaccines essential in saving lives,” BARDA Director Rick Bright, PhD, said in a company news release.
“With this licensure – the latest FDA-approved vaccine to prevent H5N1 influenza — we celebrate a decade-long partnership to achieve health security goals set by the National Strategy for Pandemic Influenza and the 2019 Executive Order to speed the availability of influenza vaccine. Ultimately, this latest licensure means we can protect more people in an influenza pandemic,” said Bright.
“The approval of Audenz represents a key advance in influenza prevention and pandemic preparedness, combining leading-edge, cell-based manufacturing and adjuvant technologies,” Russell Basser, MD, chief scientist and senior vice president of research and development at Seqirus, said in the news release. “This pandemic influenza vaccine exemplifies our commitment to developing innovative technologies that can help provide rapid response during a pandemic emergency.”
Audenz had FDA fast track designation, a process designed to facilitate the development and expedite the review of drugs to treat serious conditions and fill an unmet medical need.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ACIP updates recommendations for adult vaccines
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has released an updated schedule for adult vaccines. The update includes changes regarding the administration of several vaccines, including those for influenza, human papillomavirus (HPV), hepatitis A and B, and meningitis B, as well as the pneumococcal 13-valent conjugate (PCV13) vaccine.
The schedule, revised annually by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the CDC, was simultaneously published online February 3, 2020, in the Annals of Internal Medicine and on the CDC website.
Perhaps the change most likely to raise questions is that concerning the PCV13 vaccine. “Owing to a decline in prevalence of the types covered by the PCV13 vaccine, this is no longer routinely recommended for all persons age 65 and older,” senior author Mark Freedman, DVM, MPH, of the immunization services division at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Disease, said in an interview.
For purposes of shared clinical decision, however, it should be discussed with previously unvaccinated seniors who do not have risk factors, such as an immunocompromising condition, a cerebrospinal fluid leak, or a cochlear implant.
“But the circumstances for use of the vaccine are not always clear even based on the detailed list of considerations provided, because it’s impossible to think of every conceivable combination of risk factors,” Mr. Freedman added.
Possible beneficiaries of this vaccine are vulnerable elderly people living in nursing homes and long-term care facilities and those living in or traveling to settings in which the rate of pediatric PCV13 uptake is low or zero.
All adults in this age group should continue to receive a single dose of the pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine.*
HPV
The advisory committee now recommends catch-up immunization for women and men through age 26 years (the previous cutoff for men was 21). And in another new recommendation, the ACIP advises considering vaccination for some patients aged 27-45 years who have not been adequately vaccinated.
“Most people ages 27-45 do not need vaccination, but some may benefit,” Mr. Freedman said. “For example, somebody who’s been in a prior long-term monogamous relationship and suddenly finds himself with a new sexual partner.”
“That makes very good sense for older people who haven’t been vaccinated and might continue to be exposed to HPV,” Daniel M. Musher, MD, a professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine and an infectious diseases physician at the Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center, both in Houston, said in an interview.
Here again, the ACIP advises taking a shared decision-making approach, with clinicians discussing the merits of vaccination in this and other scenarios with patients according to the talking points outlined in the HPV section.
Influenza, hepatitis A and B
For the 2019-2020 influenza season, routine influenza vaccination is recommended for all persons aged 6 months or older who have no contraindications. Where more than one appropriate option is available, the ACIP does not recommend any product over another.
Routine hepatitis A vaccination is recommended for all persons aged 1 year or older who have HIV infection regardless of their level of immune suppression.
For hepatitis B, a new addition to the list of vulnerable patients who may possibly benefit from vaccination is pregnant women at risk for infection or an adverse infection-related pregnancy outcome. Whereas older formulations are safe, the ACIP does not recommend the HepB-CpG (Heplisav-B) vaccine during pregnancy, owing to the fact that safety data are lacking.
Meningitis B
Individuals aged 10 years or older who have complement deficiency, who use a complement inhibitor, who have asplenia, or who are microbiologists should receive a meningitis B booster dose 1 year following completion of a primary series. After that, they should receive booster doses every 2-3 years for as long they are at elevated risk.
Vaccination should be discussed with individuals aged 16-23 years even if they are not at increased risk for meningococcal disease. Persons aged 10 years or older whom public health authorities deem to be at increased risk during an outbreak should have a one-time booster dose if at least 1 year has elapsed since completion of a meningitis B primary series.
Td/Tdap, varicella
The ACIP now recommends that either the Td or Tdap vaccine be given in cases in which currently just the Td vaccine is recommended; that is, for the 10-year booster shot as well as for tetanus prophylaxis in wound management and the catch-up immunization schedule, including that for pregnant women.
Vaccination against varicella should be considered for HIV-infected individuals who are without evidence of varicella immunity and whose CD4 counts are at least 200 cells/mL.
Dr. Musher, who was not involved in drafting the recommendations, takes issue generally with the addition of shared clinical decision making on vaccination. “Shared decision making is a problem for anyone practicing medicine. It places a terrible burden [on] the doctors to discuss these options with patients at great length. Most patients want the doctor to make the decision.”
In his view, this approach makes little sense in the case of the PCV13 vaccine because the strains it covers have disappeared from the population through the widespread vaccination of children. “But discussions are important for some vaccines, such as the herpes zoster vaccine, since patients can have a terrible reaction to the first dose and refuse to have the second,” he said.
Some of these new recommendations were released in 2019 after ACIP members met to vote on them in February, June, and October.
As in previous years, the schedule has been streamlined for easier reference. Physicians are reminded to closely read the details in the vaccine notes, as these specify who needs what vaccine, when, and at what dose.
The ACIP develops its recommendations after reviewing vaccine-related data, including the data regarding the epidemiology and burden of the vaccine-preventable disease, vaccine effectiveness and safety, the quality of evidence, implementability, and the economics of immunization policy.
The authors have received grants and expense payments from public and not-for-profit institutions. One coauthor has received fees from ACI Clinical for data and safety monitoring in an immunization trial. Dr. Musher has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Correction, 3/31/20: An earlier version of this article misstated the recommendation for administration of the pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine. All adults in this age group should continue to receive a single dose of this vaccine.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has released an updated schedule for adult vaccines. The update includes changes regarding the administration of several vaccines, including those for influenza, human papillomavirus (HPV), hepatitis A and B, and meningitis B, as well as the pneumococcal 13-valent conjugate (PCV13) vaccine.
The schedule, revised annually by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the CDC, was simultaneously published online February 3, 2020, in the Annals of Internal Medicine and on the CDC website.
Perhaps the change most likely to raise questions is that concerning the PCV13 vaccine. “Owing to a decline in prevalence of the types covered by the PCV13 vaccine, this is no longer routinely recommended for all persons age 65 and older,” senior author Mark Freedman, DVM, MPH, of the immunization services division at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Disease, said in an interview.
For purposes of shared clinical decision, however, it should be discussed with previously unvaccinated seniors who do not have risk factors, such as an immunocompromising condition, a cerebrospinal fluid leak, or a cochlear implant.
“But the circumstances for use of the vaccine are not always clear even based on the detailed list of considerations provided, because it’s impossible to think of every conceivable combination of risk factors,” Mr. Freedman added.
Possible beneficiaries of this vaccine are vulnerable elderly people living in nursing homes and long-term care facilities and those living in or traveling to settings in which the rate of pediatric PCV13 uptake is low or zero.
All adults in this age group should continue to receive a single dose of the pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine.*
HPV
The advisory committee now recommends catch-up immunization for women and men through age 26 years (the previous cutoff for men was 21). And in another new recommendation, the ACIP advises considering vaccination for some patients aged 27-45 years who have not been adequately vaccinated.
“Most people ages 27-45 do not need vaccination, but some may benefit,” Mr. Freedman said. “For example, somebody who’s been in a prior long-term monogamous relationship and suddenly finds himself with a new sexual partner.”
“That makes very good sense for older people who haven’t been vaccinated and might continue to be exposed to HPV,” Daniel M. Musher, MD, a professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine and an infectious diseases physician at the Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center, both in Houston, said in an interview.
Here again, the ACIP advises taking a shared decision-making approach, with clinicians discussing the merits of vaccination in this and other scenarios with patients according to the talking points outlined in the HPV section.
Influenza, hepatitis A and B
For the 2019-2020 influenza season, routine influenza vaccination is recommended for all persons aged 6 months or older who have no contraindications. Where more than one appropriate option is available, the ACIP does not recommend any product over another.
Routine hepatitis A vaccination is recommended for all persons aged 1 year or older who have HIV infection regardless of their level of immune suppression.
For hepatitis B, a new addition to the list of vulnerable patients who may possibly benefit from vaccination is pregnant women at risk for infection or an adverse infection-related pregnancy outcome. Whereas older formulations are safe, the ACIP does not recommend the HepB-CpG (Heplisav-B) vaccine during pregnancy, owing to the fact that safety data are lacking.
Meningitis B
Individuals aged 10 years or older who have complement deficiency, who use a complement inhibitor, who have asplenia, or who are microbiologists should receive a meningitis B booster dose 1 year following completion of a primary series. After that, they should receive booster doses every 2-3 years for as long they are at elevated risk.
Vaccination should be discussed with individuals aged 16-23 years even if they are not at increased risk for meningococcal disease. Persons aged 10 years or older whom public health authorities deem to be at increased risk during an outbreak should have a one-time booster dose if at least 1 year has elapsed since completion of a meningitis B primary series.
Td/Tdap, varicella
The ACIP now recommends that either the Td or Tdap vaccine be given in cases in which currently just the Td vaccine is recommended; that is, for the 10-year booster shot as well as for tetanus prophylaxis in wound management and the catch-up immunization schedule, including that for pregnant women.
Vaccination against varicella should be considered for HIV-infected individuals who are without evidence of varicella immunity and whose CD4 counts are at least 200 cells/mL.
Dr. Musher, who was not involved in drafting the recommendations, takes issue generally with the addition of shared clinical decision making on vaccination. “Shared decision making is a problem for anyone practicing medicine. It places a terrible burden [on] the doctors to discuss these options with patients at great length. Most patients want the doctor to make the decision.”
In his view, this approach makes little sense in the case of the PCV13 vaccine because the strains it covers have disappeared from the population through the widespread vaccination of children. “But discussions are important for some vaccines, such as the herpes zoster vaccine, since patients can have a terrible reaction to the first dose and refuse to have the second,” he said.
Some of these new recommendations were released in 2019 after ACIP members met to vote on them in February, June, and October.
As in previous years, the schedule has been streamlined for easier reference. Physicians are reminded to closely read the details in the vaccine notes, as these specify who needs what vaccine, when, and at what dose.
The ACIP develops its recommendations after reviewing vaccine-related data, including the data regarding the epidemiology and burden of the vaccine-preventable disease, vaccine effectiveness and safety, the quality of evidence, implementability, and the economics of immunization policy.
The authors have received grants and expense payments from public and not-for-profit institutions. One coauthor has received fees from ACI Clinical for data and safety monitoring in an immunization trial. Dr. Musher has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Correction, 3/31/20: An earlier version of this article misstated the recommendation for administration of the pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine. All adults in this age group should continue to receive a single dose of this vaccine.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has released an updated schedule for adult vaccines. The update includes changes regarding the administration of several vaccines, including those for influenza, human papillomavirus (HPV), hepatitis A and B, and meningitis B, as well as the pneumococcal 13-valent conjugate (PCV13) vaccine.
The schedule, revised annually by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the CDC, was simultaneously published online February 3, 2020, in the Annals of Internal Medicine and on the CDC website.
Perhaps the change most likely to raise questions is that concerning the PCV13 vaccine. “Owing to a decline in prevalence of the types covered by the PCV13 vaccine, this is no longer routinely recommended for all persons age 65 and older,” senior author Mark Freedman, DVM, MPH, of the immunization services division at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Disease, said in an interview.
For purposes of shared clinical decision, however, it should be discussed with previously unvaccinated seniors who do not have risk factors, such as an immunocompromising condition, a cerebrospinal fluid leak, or a cochlear implant.
“But the circumstances for use of the vaccine are not always clear even based on the detailed list of considerations provided, because it’s impossible to think of every conceivable combination of risk factors,” Mr. Freedman added.
Possible beneficiaries of this vaccine are vulnerable elderly people living in nursing homes and long-term care facilities and those living in or traveling to settings in which the rate of pediatric PCV13 uptake is low or zero.
All adults in this age group should continue to receive a single dose of the pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine.*
HPV
The advisory committee now recommends catch-up immunization for women and men through age 26 years (the previous cutoff for men was 21). And in another new recommendation, the ACIP advises considering vaccination for some patients aged 27-45 years who have not been adequately vaccinated.
“Most people ages 27-45 do not need vaccination, but some may benefit,” Mr. Freedman said. “For example, somebody who’s been in a prior long-term monogamous relationship and suddenly finds himself with a new sexual partner.”
“That makes very good sense for older people who haven’t been vaccinated and might continue to be exposed to HPV,” Daniel M. Musher, MD, a professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine and an infectious diseases physician at the Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center, both in Houston, said in an interview.
Here again, the ACIP advises taking a shared decision-making approach, with clinicians discussing the merits of vaccination in this and other scenarios with patients according to the talking points outlined in the HPV section.
Influenza, hepatitis A and B
For the 2019-2020 influenza season, routine influenza vaccination is recommended for all persons aged 6 months or older who have no contraindications. Where more than one appropriate option is available, the ACIP does not recommend any product over another.
Routine hepatitis A vaccination is recommended for all persons aged 1 year or older who have HIV infection regardless of their level of immune suppression.
For hepatitis B, a new addition to the list of vulnerable patients who may possibly benefit from vaccination is pregnant women at risk for infection or an adverse infection-related pregnancy outcome. Whereas older formulations are safe, the ACIP does not recommend the HepB-CpG (Heplisav-B) vaccine during pregnancy, owing to the fact that safety data are lacking.
Meningitis B
Individuals aged 10 years or older who have complement deficiency, who use a complement inhibitor, who have asplenia, or who are microbiologists should receive a meningitis B booster dose 1 year following completion of a primary series. After that, they should receive booster doses every 2-3 years for as long they are at elevated risk.
Vaccination should be discussed with individuals aged 16-23 years even if they are not at increased risk for meningococcal disease. Persons aged 10 years or older whom public health authorities deem to be at increased risk during an outbreak should have a one-time booster dose if at least 1 year has elapsed since completion of a meningitis B primary series.
Td/Tdap, varicella
The ACIP now recommends that either the Td or Tdap vaccine be given in cases in which currently just the Td vaccine is recommended; that is, for the 10-year booster shot as well as for tetanus prophylaxis in wound management and the catch-up immunization schedule, including that for pregnant women.
Vaccination against varicella should be considered for HIV-infected individuals who are without evidence of varicella immunity and whose CD4 counts are at least 200 cells/mL.
Dr. Musher, who was not involved in drafting the recommendations, takes issue generally with the addition of shared clinical decision making on vaccination. “Shared decision making is a problem for anyone practicing medicine. It places a terrible burden [on] the doctors to discuss these options with patients at great length. Most patients want the doctor to make the decision.”
In his view, this approach makes little sense in the case of the PCV13 vaccine because the strains it covers have disappeared from the population through the widespread vaccination of children. “But discussions are important for some vaccines, such as the herpes zoster vaccine, since patients can have a terrible reaction to the first dose and refuse to have the second,” he said.
Some of these new recommendations were released in 2019 after ACIP members met to vote on them in February, June, and October.
As in previous years, the schedule has been streamlined for easier reference. Physicians are reminded to closely read the details in the vaccine notes, as these specify who needs what vaccine, when, and at what dose.
The ACIP develops its recommendations after reviewing vaccine-related data, including the data regarding the epidemiology and burden of the vaccine-preventable disease, vaccine effectiveness and safety, the quality of evidence, implementability, and the economics of immunization policy.
The authors have received grants and expense payments from public and not-for-profit institutions. One coauthor has received fees from ACI Clinical for data and safety monitoring in an immunization trial. Dr. Musher has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Correction, 3/31/20: An earlier version of this article misstated the recommendation for administration of the pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine. All adults in this age group should continue to receive a single dose of this vaccine.
Novel coronavirus cases now at 11; entry ban and quarantine measures begin
, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said during a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention press briefing.
Four of the new cases are in California, and one in Massachusetts. Although four of the new cases have recent travel history to Wuhan, China, the epicenter of the 2019-nCoV outbreak, the fifth is a close household contact of one of the other California patients, said Dr. Messonnier. This last case is the second instance of person-to-person spread of 2019-nCoV in the United States.
“We expect to find additional cases of the novel coronavirus in the United States,” she said. “We expect to see more cases of person-to-person spread among close contacts. And we continue to expect this will happen given the explosive nature of this outbreak in China.”
As of the morning of Feb. 3, 167 persons under investigation, or PUIs, for possible 2019-nCoV have tested negative for the virus, and an additional 82 PUIs have testing pending – this latter figure includes some tests that are still in transit to the CDC, said Dr. Messonnier.
During the briefing, Dr. Messonnier emphasized both the aggressive nature of the U.S. public health response and the rationale for quick and assertive action. “The goal of our public health response is to protect and contain,” she said. “Strong measures now may blunt the impact of this virus on the United States.”
She cited the intensity of transmission in Hubei Province, the expansion of transmission to other provinces in China, the expansion of cases outside of China, and sporadic ongoing deaths from 2019-nCoV as drivers of the aggressive U.S. public health response.
A presidential proclamation is currently in place that bars U.S. entry to foreign nationals who have visited mainland China within the past 14 days; the ban does not apply to travelers from Hong Kong and Macao. Immediate family members of U.S. citizens and individuals who have U.S. permanent resident status are exempted from the entry ban and will be allowed entry into the United States.
However, explained Dr. Messonnier, those who have traveled to China recently and are permitted entry will be subject to screening. All passengers with such recent travel will be directed to one of 11 U.S. airports set up to perform additional screening.
As of Feb 3, the list of airports includes:
- San Francisco International Airport in California.
- Los Angeles International Airport in California.
- Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport in Georgia.
- Daniel K. Inouye International Airport in Hawaii.
- O’Hare International Airport in Illinois.
- Detroit Metropolitan Airport in Michigan.
- Newark Liberty International Airport in New Jersey.
- John F. Kennedy International Airport in New York.
- Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport in Texas.
- Washington Dulles International Airport in Virginia.
- Seattle-Tacoma International Airport in Washington.
Travelers who have been to Hubei Province in the previous 14 days will have an additional health assessment at which they will be screened for fever, cough, or difficulty breathing. Any American citizens or exempt individuals who are symptomatic would then be transferred for further medical evaluation. Asymptomatic travelers in this category will be subject to a mandatory 14-day quarantine near their point of entry, rather than continuing on to their final destinations.
Dr. Messonnier emphasized that the mandatory 14-day quarantine is specifically for Americans or exempt individuals returning from Hubei Province, adding that the CDC is presently working with individual states to determine the exact venues for quarantine.
American citizens and exempt individuals returning from other parts of mainland China will be routed to one of the 11 airports and will also receive additional health screening. Symptomatic individuals in this travel category would be referred for further evaluation before being able to complete their itinerary.
Asymptomatic American citizens and exempt individuals who are returning from mainland China – but not Hubei Province – will be allowed to travel on to their final destinations, but will be asked to stay home as much as possible and to monitor their health during the 14 days after their return.
The U.S. Department of State is bringing back more Americans from Wuhan province this week, and these individuals will also be kept under federal quarantine for 14 days.
“There are likely to be confirmed infections among returning travelers,” said Dr. Messonnier. “It is important to note that this strategy is not meant to catch every single traveler returning from China with novel coronavirus; given the nature of this virus and how it’s spreading, that would be impossible, but working together we can catch the majority of them.
“The goal here is to slow the entry of this virus into the United States,” she said, adding that the nation’s health care and public health systems stand on high alert to detect the virus in community settings. In response to questioning from the press, Dr. Messonnier defended the stringent quarantine measures, noting that they are in line with those taken by some other nations, and with the aggressive action being taken by the Chinese government itself. “These actions are science based and aimed at protecting the health of all Americans,” she said.
The real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) assay that the CDC has developed detects 2019-nCoV in both respiratory and serum specimens. Dr. Messonnier reported that the CDC is today filing an emergency use authorization (EUA) application to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to expedite access to the assay for public health laboratories across the country. “This will greatly enhance our capacity to test for this virus,” she said, noting that EUA approval may come as soon as the end of this week.
Although the CDC is poised to send an expert team to China, it’s still awaiting favorable results from the international negotiations currently underway. “This is a horrible situation in China,” said Dr. Messonnier. “Our presence on the ground in China would be a help to China. ... Science should trump everything else; that’s what we’re hoping – that the scientific expertise of the global community can be brought to bear on the incredibly complicated, difficult situation that our colleagues in China are dealing with.”
, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said during a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention press briefing.
Four of the new cases are in California, and one in Massachusetts. Although four of the new cases have recent travel history to Wuhan, China, the epicenter of the 2019-nCoV outbreak, the fifth is a close household contact of one of the other California patients, said Dr. Messonnier. This last case is the second instance of person-to-person spread of 2019-nCoV in the United States.
“We expect to find additional cases of the novel coronavirus in the United States,” she said. “We expect to see more cases of person-to-person spread among close contacts. And we continue to expect this will happen given the explosive nature of this outbreak in China.”
As of the morning of Feb. 3, 167 persons under investigation, or PUIs, for possible 2019-nCoV have tested negative for the virus, and an additional 82 PUIs have testing pending – this latter figure includes some tests that are still in transit to the CDC, said Dr. Messonnier.
During the briefing, Dr. Messonnier emphasized both the aggressive nature of the U.S. public health response and the rationale for quick and assertive action. “The goal of our public health response is to protect and contain,” she said. “Strong measures now may blunt the impact of this virus on the United States.”
She cited the intensity of transmission in Hubei Province, the expansion of transmission to other provinces in China, the expansion of cases outside of China, and sporadic ongoing deaths from 2019-nCoV as drivers of the aggressive U.S. public health response.
A presidential proclamation is currently in place that bars U.S. entry to foreign nationals who have visited mainland China within the past 14 days; the ban does not apply to travelers from Hong Kong and Macao. Immediate family members of U.S. citizens and individuals who have U.S. permanent resident status are exempted from the entry ban and will be allowed entry into the United States.
However, explained Dr. Messonnier, those who have traveled to China recently and are permitted entry will be subject to screening. All passengers with such recent travel will be directed to one of 11 U.S. airports set up to perform additional screening.
As of Feb 3, the list of airports includes:
- San Francisco International Airport in California.
- Los Angeles International Airport in California.
- Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport in Georgia.
- Daniel K. Inouye International Airport in Hawaii.
- O’Hare International Airport in Illinois.
- Detroit Metropolitan Airport in Michigan.
- Newark Liberty International Airport in New Jersey.
- John F. Kennedy International Airport in New York.
- Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport in Texas.
- Washington Dulles International Airport in Virginia.
- Seattle-Tacoma International Airport in Washington.
Travelers who have been to Hubei Province in the previous 14 days will have an additional health assessment at which they will be screened for fever, cough, or difficulty breathing. Any American citizens or exempt individuals who are symptomatic would then be transferred for further medical evaluation. Asymptomatic travelers in this category will be subject to a mandatory 14-day quarantine near their point of entry, rather than continuing on to their final destinations.
Dr. Messonnier emphasized that the mandatory 14-day quarantine is specifically for Americans or exempt individuals returning from Hubei Province, adding that the CDC is presently working with individual states to determine the exact venues for quarantine.
American citizens and exempt individuals returning from other parts of mainland China will be routed to one of the 11 airports and will also receive additional health screening. Symptomatic individuals in this travel category would be referred for further evaluation before being able to complete their itinerary.
Asymptomatic American citizens and exempt individuals who are returning from mainland China – but not Hubei Province – will be allowed to travel on to their final destinations, but will be asked to stay home as much as possible and to monitor their health during the 14 days after their return.
The U.S. Department of State is bringing back more Americans from Wuhan province this week, and these individuals will also be kept under federal quarantine for 14 days.
“There are likely to be confirmed infections among returning travelers,” said Dr. Messonnier. “It is important to note that this strategy is not meant to catch every single traveler returning from China with novel coronavirus; given the nature of this virus and how it’s spreading, that would be impossible, but working together we can catch the majority of them.
“The goal here is to slow the entry of this virus into the United States,” she said, adding that the nation’s health care and public health systems stand on high alert to detect the virus in community settings. In response to questioning from the press, Dr. Messonnier defended the stringent quarantine measures, noting that they are in line with those taken by some other nations, and with the aggressive action being taken by the Chinese government itself. “These actions are science based and aimed at protecting the health of all Americans,” she said.
The real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) assay that the CDC has developed detects 2019-nCoV in both respiratory and serum specimens. Dr. Messonnier reported that the CDC is today filing an emergency use authorization (EUA) application to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to expedite access to the assay for public health laboratories across the country. “This will greatly enhance our capacity to test for this virus,” she said, noting that EUA approval may come as soon as the end of this week.
Although the CDC is poised to send an expert team to China, it’s still awaiting favorable results from the international negotiations currently underway. “This is a horrible situation in China,” said Dr. Messonnier. “Our presence on the ground in China would be a help to China. ... Science should trump everything else; that’s what we’re hoping – that the scientific expertise of the global community can be brought to bear on the incredibly complicated, difficult situation that our colleagues in China are dealing with.”
, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said during a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention press briefing.
Four of the new cases are in California, and one in Massachusetts. Although four of the new cases have recent travel history to Wuhan, China, the epicenter of the 2019-nCoV outbreak, the fifth is a close household contact of one of the other California patients, said Dr. Messonnier. This last case is the second instance of person-to-person spread of 2019-nCoV in the United States.
“We expect to find additional cases of the novel coronavirus in the United States,” she said. “We expect to see more cases of person-to-person spread among close contacts. And we continue to expect this will happen given the explosive nature of this outbreak in China.”
As of the morning of Feb. 3, 167 persons under investigation, or PUIs, for possible 2019-nCoV have tested negative for the virus, and an additional 82 PUIs have testing pending – this latter figure includes some tests that are still in transit to the CDC, said Dr. Messonnier.
During the briefing, Dr. Messonnier emphasized both the aggressive nature of the U.S. public health response and the rationale for quick and assertive action. “The goal of our public health response is to protect and contain,” she said. “Strong measures now may blunt the impact of this virus on the United States.”
She cited the intensity of transmission in Hubei Province, the expansion of transmission to other provinces in China, the expansion of cases outside of China, and sporadic ongoing deaths from 2019-nCoV as drivers of the aggressive U.S. public health response.
A presidential proclamation is currently in place that bars U.S. entry to foreign nationals who have visited mainland China within the past 14 days; the ban does not apply to travelers from Hong Kong and Macao. Immediate family members of U.S. citizens and individuals who have U.S. permanent resident status are exempted from the entry ban and will be allowed entry into the United States.
However, explained Dr. Messonnier, those who have traveled to China recently and are permitted entry will be subject to screening. All passengers with such recent travel will be directed to one of 11 U.S. airports set up to perform additional screening.
As of Feb 3, the list of airports includes:
- San Francisco International Airport in California.
- Los Angeles International Airport in California.
- Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport in Georgia.
- Daniel K. Inouye International Airport in Hawaii.
- O’Hare International Airport in Illinois.
- Detroit Metropolitan Airport in Michigan.
- Newark Liberty International Airport in New Jersey.
- John F. Kennedy International Airport in New York.
- Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport in Texas.
- Washington Dulles International Airport in Virginia.
- Seattle-Tacoma International Airport in Washington.
Travelers who have been to Hubei Province in the previous 14 days will have an additional health assessment at which they will be screened for fever, cough, or difficulty breathing. Any American citizens or exempt individuals who are symptomatic would then be transferred for further medical evaluation. Asymptomatic travelers in this category will be subject to a mandatory 14-day quarantine near their point of entry, rather than continuing on to their final destinations.
Dr. Messonnier emphasized that the mandatory 14-day quarantine is specifically for Americans or exempt individuals returning from Hubei Province, adding that the CDC is presently working with individual states to determine the exact venues for quarantine.
American citizens and exempt individuals returning from other parts of mainland China will be routed to one of the 11 airports and will also receive additional health screening. Symptomatic individuals in this travel category would be referred for further evaluation before being able to complete their itinerary.
Asymptomatic American citizens and exempt individuals who are returning from mainland China – but not Hubei Province – will be allowed to travel on to their final destinations, but will be asked to stay home as much as possible and to monitor their health during the 14 days after their return.
The U.S. Department of State is bringing back more Americans from Wuhan province this week, and these individuals will also be kept under federal quarantine for 14 days.
“There are likely to be confirmed infections among returning travelers,” said Dr. Messonnier. “It is important to note that this strategy is not meant to catch every single traveler returning from China with novel coronavirus; given the nature of this virus and how it’s spreading, that would be impossible, but working together we can catch the majority of them.
“The goal here is to slow the entry of this virus into the United States,” she said, adding that the nation’s health care and public health systems stand on high alert to detect the virus in community settings. In response to questioning from the press, Dr. Messonnier defended the stringent quarantine measures, noting that they are in line with those taken by some other nations, and with the aggressive action being taken by the Chinese government itself. “These actions are science based and aimed at protecting the health of all Americans,” she said.
The real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) assay that the CDC has developed detects 2019-nCoV in both respiratory and serum specimens. Dr. Messonnier reported that the CDC is today filing an emergency use authorization (EUA) application to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to expedite access to the assay for public health laboratories across the country. “This will greatly enhance our capacity to test for this virus,” she said, noting that EUA approval may come as soon as the end of this week.
Although the CDC is poised to send an expert team to China, it’s still awaiting favorable results from the international negotiations currently underway. “This is a horrible situation in China,” said Dr. Messonnier. “Our presence on the ground in China would be a help to China. ... Science should trump everything else; that’s what we’re hoping – that the scientific expertise of the global community can be brought to bear on the incredibly complicated, difficult situation that our colleagues in China are dealing with.”
FROM A CDC PRESS BRIEFING
Physician groups push back on Medicaid block grant plan
It took less than a day for physician groups to start pushing back at the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services over its new Medicaid block grant plan, which was introduced on Jan. 30.
Dubbed “Healthy Adult Opportunity,” the agency is offering all states the chance to participate in a block grant program through the 1115 waiver process.
According to a fact sheet issued by the agency, the program will focus on “adults under age 65 who are not eligible for Medicaid on the basis of disability or their need for long term care services and supports, and who are not eligible under a state plan. Other very low-income parents, children, pregnant women, elderly adults, and people eligible on the basis of a disability will not be directly affected – except from the improvement that results from states reinvesting savings into strengthening their overall programs.”
States will be operating within a defined budget when participating in the program and expenditures exceeding that defined budget will not be eligible for additional federal funding. Budgets will be based on a state’s historic costs, as well as national and regional trends, and will be tied to inflation with the potential to have adjustments made for extraordinary events. States can set their baseline using the prior year’s total spending or a per-enrollee spending model.
A Jan. 30 letter to state Medicaid directors notes that states participating in the program “will be granted extensive flexibility to test alternative approaches to implementing their Medicaid programs, including the ability to make many ongoing program adjustments without the need for demonstration or state plan amendments that require prior approval.”
Among the activities states can engage in under this plan are adjusting cost-sharing requirements, adopting a closed formulary, and applying additional conditions of eligibility. Requests, if approved, will be approved for a 5-year initial period, with a renewal option of up to 10 years.
But physician groups are not seeing a benefit with this new block grant program.
“Moving to a block grant system will likely limit the ability of Medicaid patients to receive preventive and needed medical care from their family physicians, and it will only increase the health disparities that exist in these communities, worsen overall health outcomes, and ultimately increase costs,” Gary LeRoy, MD, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said in a statement.
The American Medical Association concurred.
“The AMA opposes caps on federal Medicaid funding, such as block grants, because they would increase the number of uninsured and undermine Medicaid’s role as an indispensable safety net,” Patrice Harris, MD, the AMA’s president, said in a statement. “The AMA supports flexibility in Medicaid and encourages CMS to work with states to develop and test new Medicaid models that best meet the needs and priorities of low-income patients. While encouraging flexibility, the AMA is mindful that expanding Medicaid has been a literal lifesaver for low-income patients. We need to find ways to build on this success. We look forward to reviewing the proposal in detail.”
Officials at the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists said the changes have the potential to harm women and children’s health, as well as negatively impact physician reimbursement and ultimately access to care.
“Limits on the federal contribution to the Medicaid program would negatively impact patients by forcing states to reduce the number of people who are eligible for Medicaid coverage, eliminate covered services, and increase beneficiary cost-sharing,” ACOG President Ted Anderson, MD, said in a statement. “ACOG is also concerned that this block grant opportunity could lower physician reimbursement for certain services, forcing providers out of the program and jeopardizing patients’ ability to access health care services. Given our nation’s stark rates of maternal mortality and severe maternal morbidity, we are alarmed by the Administration’s willingness to weaken physician payment in Medicaid.”
It took less than a day for physician groups to start pushing back at the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services over its new Medicaid block grant plan, which was introduced on Jan. 30.
Dubbed “Healthy Adult Opportunity,” the agency is offering all states the chance to participate in a block grant program through the 1115 waiver process.
According to a fact sheet issued by the agency, the program will focus on “adults under age 65 who are not eligible for Medicaid on the basis of disability or their need for long term care services and supports, and who are not eligible under a state plan. Other very low-income parents, children, pregnant women, elderly adults, and people eligible on the basis of a disability will not be directly affected – except from the improvement that results from states reinvesting savings into strengthening their overall programs.”
States will be operating within a defined budget when participating in the program and expenditures exceeding that defined budget will not be eligible for additional federal funding. Budgets will be based on a state’s historic costs, as well as national and regional trends, and will be tied to inflation with the potential to have adjustments made for extraordinary events. States can set their baseline using the prior year’s total spending or a per-enrollee spending model.
A Jan. 30 letter to state Medicaid directors notes that states participating in the program “will be granted extensive flexibility to test alternative approaches to implementing their Medicaid programs, including the ability to make many ongoing program adjustments without the need for demonstration or state plan amendments that require prior approval.”
Among the activities states can engage in under this plan are adjusting cost-sharing requirements, adopting a closed formulary, and applying additional conditions of eligibility. Requests, if approved, will be approved for a 5-year initial period, with a renewal option of up to 10 years.
But physician groups are not seeing a benefit with this new block grant program.
“Moving to a block grant system will likely limit the ability of Medicaid patients to receive preventive and needed medical care from their family physicians, and it will only increase the health disparities that exist in these communities, worsen overall health outcomes, and ultimately increase costs,” Gary LeRoy, MD, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said in a statement.
The American Medical Association concurred.
“The AMA opposes caps on federal Medicaid funding, such as block grants, because they would increase the number of uninsured and undermine Medicaid’s role as an indispensable safety net,” Patrice Harris, MD, the AMA’s president, said in a statement. “The AMA supports flexibility in Medicaid and encourages CMS to work with states to develop and test new Medicaid models that best meet the needs and priorities of low-income patients. While encouraging flexibility, the AMA is mindful that expanding Medicaid has been a literal lifesaver for low-income patients. We need to find ways to build on this success. We look forward to reviewing the proposal in detail.”
Officials at the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists said the changes have the potential to harm women and children’s health, as well as negatively impact physician reimbursement and ultimately access to care.
“Limits on the federal contribution to the Medicaid program would negatively impact patients by forcing states to reduce the number of people who are eligible for Medicaid coverage, eliminate covered services, and increase beneficiary cost-sharing,” ACOG President Ted Anderson, MD, said in a statement. “ACOG is also concerned that this block grant opportunity could lower physician reimbursement for certain services, forcing providers out of the program and jeopardizing patients’ ability to access health care services. Given our nation’s stark rates of maternal mortality and severe maternal morbidity, we are alarmed by the Administration’s willingness to weaken physician payment in Medicaid.”
It took less than a day for physician groups to start pushing back at the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services over its new Medicaid block grant plan, which was introduced on Jan. 30.
Dubbed “Healthy Adult Opportunity,” the agency is offering all states the chance to participate in a block grant program through the 1115 waiver process.
According to a fact sheet issued by the agency, the program will focus on “adults under age 65 who are not eligible for Medicaid on the basis of disability or their need for long term care services and supports, and who are not eligible under a state plan. Other very low-income parents, children, pregnant women, elderly adults, and people eligible on the basis of a disability will not be directly affected – except from the improvement that results from states reinvesting savings into strengthening their overall programs.”
States will be operating within a defined budget when participating in the program and expenditures exceeding that defined budget will not be eligible for additional federal funding. Budgets will be based on a state’s historic costs, as well as national and regional trends, and will be tied to inflation with the potential to have adjustments made for extraordinary events. States can set their baseline using the prior year’s total spending or a per-enrollee spending model.
A Jan. 30 letter to state Medicaid directors notes that states participating in the program “will be granted extensive flexibility to test alternative approaches to implementing their Medicaid programs, including the ability to make many ongoing program adjustments without the need for demonstration or state plan amendments that require prior approval.”
Among the activities states can engage in under this plan are adjusting cost-sharing requirements, adopting a closed formulary, and applying additional conditions of eligibility. Requests, if approved, will be approved for a 5-year initial period, with a renewal option of up to 10 years.
But physician groups are not seeing a benefit with this new block grant program.
“Moving to a block grant system will likely limit the ability of Medicaid patients to receive preventive and needed medical care from their family physicians, and it will only increase the health disparities that exist in these communities, worsen overall health outcomes, and ultimately increase costs,” Gary LeRoy, MD, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said in a statement.
The American Medical Association concurred.
“The AMA opposes caps on federal Medicaid funding, such as block grants, because they would increase the number of uninsured and undermine Medicaid’s role as an indispensable safety net,” Patrice Harris, MD, the AMA’s president, said in a statement. “The AMA supports flexibility in Medicaid and encourages CMS to work with states to develop and test new Medicaid models that best meet the needs and priorities of low-income patients. While encouraging flexibility, the AMA is mindful that expanding Medicaid has been a literal lifesaver for low-income patients. We need to find ways to build on this success. We look forward to reviewing the proposal in detail.”
Officials at the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists said the changes have the potential to harm women and children’s health, as well as negatively impact physician reimbursement and ultimately access to care.
“Limits on the federal contribution to the Medicaid program would negatively impact patients by forcing states to reduce the number of people who are eligible for Medicaid coverage, eliminate covered services, and increase beneficiary cost-sharing,” ACOG President Ted Anderson, MD, said in a statement. “ACOG is also concerned that this block grant opportunity could lower physician reimbursement for certain services, forcing providers out of the program and jeopardizing patients’ ability to access health care services. Given our nation’s stark rates of maternal mortality and severe maternal morbidity, we are alarmed by the Administration’s willingness to weaken physician payment in Medicaid.”
Don’t forget about the flu: 2019-2010 season is not over
Nationally, an estimated 5.7% of all outpatients visiting health care providers had influenza-like illness (ILI) for the week ending Jan. 25, which was up from 5.1% the previous week but still lower than the current seasonal high of 7.1% recorded during the week of Dec. 22-28, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
Another key indicator of influenza activity, the percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive, also remains high as it rose from 25.7% the week before to 27.7% for the week ending Jan. 25, the influenza division said. That is the highest rate of the 2019-2020 season so far, surpassing the 26.8% reached during Dec. 22-28.
Another new seasonal high involves the number of states, 33 plus Puerto Rico, at the highest level of ILI activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale for the latest reporting week, topping the 32 jurisdictions from the last full week of December. Another eight states and the District of Columbia were in the “high” range with activity levels of 8 and 9, and no state with available data was lower than level 6, the CDC data show.
Going along with the recent 2-week increase in activity is a large increase in the number of ILI-related pediatric deaths, which rose from 39 on Jan. 11 to the current count of 68, the CDC said. At the same point last year, there had been 36 pediatric deaths.
Other indicators of ILI severity, however, “are not high at this point in the season,” the influenza division noted. “Overall, hospitalization rates remain similar to what has been seen at this time during recent seasons, but rates among children and young adults are higher at this time than in recent seasons.” Overall pneumonia and influenza mortality is also low, the CDC added.

Nationally, an estimated 5.7% of all outpatients visiting health care providers had influenza-like illness (ILI) for the week ending Jan. 25, which was up from 5.1% the previous week but still lower than the current seasonal high of 7.1% recorded during the week of Dec. 22-28, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
Another key indicator of influenza activity, the percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive, also remains high as it rose from 25.7% the week before to 27.7% for the week ending Jan. 25, the influenza division said. That is the highest rate of the 2019-2020 season so far, surpassing the 26.8% reached during Dec. 22-28.
Another new seasonal high involves the number of states, 33 plus Puerto Rico, at the highest level of ILI activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale for the latest reporting week, topping the 32 jurisdictions from the last full week of December. Another eight states and the District of Columbia were in the “high” range with activity levels of 8 and 9, and no state with available data was lower than level 6, the CDC data show.
Going along with the recent 2-week increase in activity is a large increase in the number of ILI-related pediatric deaths, which rose from 39 on Jan. 11 to the current count of 68, the CDC said. At the same point last year, there had been 36 pediatric deaths.
Other indicators of ILI severity, however, “are not high at this point in the season,” the influenza division noted. “Overall, hospitalization rates remain similar to what has been seen at this time during recent seasons, but rates among children and young adults are higher at this time than in recent seasons.” Overall pneumonia and influenza mortality is also low, the CDC added.

Nationally, an estimated 5.7% of all outpatients visiting health care providers had influenza-like illness (ILI) for the week ending Jan. 25, which was up from 5.1% the previous week but still lower than the current seasonal high of 7.1% recorded during the week of Dec. 22-28, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
Another key indicator of influenza activity, the percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive, also remains high as it rose from 25.7% the week before to 27.7% for the week ending Jan. 25, the influenza division said. That is the highest rate of the 2019-2020 season so far, surpassing the 26.8% reached during Dec. 22-28.
Another new seasonal high involves the number of states, 33 plus Puerto Rico, at the highest level of ILI activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale for the latest reporting week, topping the 32 jurisdictions from the last full week of December. Another eight states and the District of Columbia were in the “high” range with activity levels of 8 and 9, and no state with available data was lower than level 6, the CDC data show.
Going along with the recent 2-week increase in activity is a large increase in the number of ILI-related pediatric deaths, which rose from 39 on Jan. 11 to the current count of 68, the CDC said. At the same point last year, there had been 36 pediatric deaths.
Other indicators of ILI severity, however, “are not high at this point in the season,” the influenza division noted. “Overall, hospitalization rates remain similar to what has been seen at this time during recent seasons, but rates among children and young adults are higher at this time than in recent seasons.” Overall pneumonia and influenza mortality is also low, the CDC added.
Next-generation sequencing can expedite surveillance/discovery of new bat coronaviruses
Enrichment next-generation sequencing (NGS) provides a more cost-efficient and sensitive method for detecting and sequencing novel coronaviruses from wild bat populations, according to a study reported in mSphere, an open-access journal from the American Society for Microbiology.
With the appearance of the new zoonotic Wuhan coronavirus, the importance of monitoring the likelihood of new virus risks in wildlife reservoirs has been heightened. Bats in particular have been found to be the most common reservoir of coronaviruses, including being a probable source or mixing vessel for two previous modern epidemic coronaviruses: SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome) and MERS (Middle East respiratory syndrome).
“We should be alert and vigilant with the knowledge that bat CoVs [coronaviruses] are likely to cause another disease outbreak, not only because of their prevalence but also because the high frequency of recombination between viruses may lead to the generation of viruses with changes in virulence,” according to Bei Li, MD, of the Wuhan (China) Institute of Virology, and colleagues.
“We previously provided serological evidence that [HKU8-related] CoV had jumped over from bats to camels and recombined with MERS-CoV, alerting other researchers that the CoV species could be dangerous. ... Genome-level comparison is needed to monitor the risk of alterations in species tropism and pathogenesis,” according to study authors. They performed a study to develop a more effective and cost efficient method for detecting and sequencing novel coronaviruses in the bat population.
The taxonomy of coronaviruses is particularly complex and may be too narrowly defined, given the high level of genetic plasticity found. There are four genera (Alpha-, Beta-, Gamma-, and Deltacoronavirus) consisting of 38 unique species in the CoV subfamily Orthocoronavirinae, and the number is increasing. Viral taxomists rely on the open reading frame 1b (ORF1b) gene for classification, but viruses in the same species may show great diversity in regions outside ORF1b, confounding the species designation. In particular, bat CoVs classed as the same species can differ significantly in terms of receptor usage or virus-host interaction, as observed in bat SARS-related CoVs, according to the researchers.
The researchers obtained RNA from previous bat CoV surveillance projects, which used bat rectal swabs. Libraries for NGS were constructed from total RNA and processed to generate RNA fragments larger than 300 nucleotides. Following first- and second-strand cDNA synthesis, double-stranded cDNA was purified and the library was amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology.
Targeted CoV genome enrichment was achieved using 4,303 customized biotinylated 120-mer baits. These baits were designed from 90 representative CoV genomes, and in silico analysis determined that these baits should target the known CoV species tested. These baits were added and hybridized to the libraries. To capture virus-specific library fragments, streptavidin magnetic beads (which bind to biotin) were added to the hybridization reaction mixture. The beads were then washed to remove unbound DNA. The postcapture virus-specific library fragments were then amplified using a subsequent round of PCR.
The enrichment NGS were retrospectively complemented with unbiased NGS and/or additional Sanger sequencing to obtain full-length genomes. The study showed that enrichment NGS not only decreased the amount of data requiring analysis but produced full-length genome coverage in both laboratory and clinical samples.
Using this technology, the researchers “effectively reduced sequencing costs by increasing the sensitivity of detection. We discovered nine full genomes of bat CoVs in this study and revealed great genetic diversity for eight of them.” In addition, they noted that using standard targeted PCR, which is common practice for many surveillance studies, would not have discovered this diversity.
“We should be alert and vigilant with the knowledge that bat CoVs are likely to cause another disease outbreak, not only because of their prevalence but also because the high frequency of recombination between viruses may lead to the generation of viruses with changes in virulence,” according to the researchers.
“We have provided a cost-effective methodology for bat CoV surveillance. The high genetic diversity observed in our newly sequenced samples suggests further work is needed to characterize these bat CoVs prior to or in the early stages of spillover to humans,” the authors concluded.
This study was supported by the Chinese government. The authors reported that they had no conflicts.
Viral genome data for new CoVs from this study are available in GenBank under accession numbers MN611517 to MN611525.
SOURCE: Li B et al. mSphere 2020 Jan 29;5:e00807-19.
Enrichment next-generation sequencing (NGS) provides a more cost-efficient and sensitive method for detecting and sequencing novel coronaviruses from wild bat populations, according to a study reported in mSphere, an open-access journal from the American Society for Microbiology.
With the appearance of the new zoonotic Wuhan coronavirus, the importance of monitoring the likelihood of new virus risks in wildlife reservoirs has been heightened. Bats in particular have been found to be the most common reservoir of coronaviruses, including being a probable source or mixing vessel for two previous modern epidemic coronaviruses: SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome) and MERS (Middle East respiratory syndrome).
“We should be alert and vigilant with the knowledge that bat CoVs [coronaviruses] are likely to cause another disease outbreak, not only because of their prevalence but also because the high frequency of recombination between viruses may lead to the generation of viruses with changes in virulence,” according to Bei Li, MD, of the Wuhan (China) Institute of Virology, and colleagues.
“We previously provided serological evidence that [HKU8-related] CoV had jumped over from bats to camels and recombined with MERS-CoV, alerting other researchers that the CoV species could be dangerous. ... Genome-level comparison is needed to monitor the risk of alterations in species tropism and pathogenesis,” according to study authors. They performed a study to develop a more effective and cost efficient method for detecting and sequencing novel coronaviruses in the bat population.
The taxonomy of coronaviruses is particularly complex and may be too narrowly defined, given the high level of genetic plasticity found. There are four genera (Alpha-, Beta-, Gamma-, and Deltacoronavirus) consisting of 38 unique species in the CoV subfamily Orthocoronavirinae, and the number is increasing. Viral taxomists rely on the open reading frame 1b (ORF1b) gene for classification, but viruses in the same species may show great diversity in regions outside ORF1b, confounding the species designation. In particular, bat CoVs classed as the same species can differ significantly in terms of receptor usage or virus-host interaction, as observed in bat SARS-related CoVs, according to the researchers.
The researchers obtained RNA from previous bat CoV surveillance projects, which used bat rectal swabs. Libraries for NGS were constructed from total RNA and processed to generate RNA fragments larger than 300 nucleotides. Following first- and second-strand cDNA synthesis, double-stranded cDNA was purified and the library was amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology.
Targeted CoV genome enrichment was achieved using 4,303 customized biotinylated 120-mer baits. These baits were designed from 90 representative CoV genomes, and in silico analysis determined that these baits should target the known CoV species tested. These baits were added and hybridized to the libraries. To capture virus-specific library fragments, streptavidin magnetic beads (which bind to biotin) were added to the hybridization reaction mixture. The beads were then washed to remove unbound DNA. The postcapture virus-specific library fragments were then amplified using a subsequent round of PCR.
The enrichment NGS were retrospectively complemented with unbiased NGS and/or additional Sanger sequencing to obtain full-length genomes. The study showed that enrichment NGS not only decreased the amount of data requiring analysis but produced full-length genome coverage in both laboratory and clinical samples.
Using this technology, the researchers “effectively reduced sequencing costs by increasing the sensitivity of detection. We discovered nine full genomes of bat CoVs in this study and revealed great genetic diversity for eight of them.” In addition, they noted that using standard targeted PCR, which is common practice for many surveillance studies, would not have discovered this diversity.
“We should be alert and vigilant with the knowledge that bat CoVs are likely to cause another disease outbreak, not only because of their prevalence but also because the high frequency of recombination between viruses may lead to the generation of viruses with changes in virulence,” according to the researchers.
“We have provided a cost-effective methodology for bat CoV surveillance. The high genetic diversity observed in our newly sequenced samples suggests further work is needed to characterize these bat CoVs prior to or in the early stages of spillover to humans,” the authors concluded.
This study was supported by the Chinese government. The authors reported that they had no conflicts.
Viral genome data for new CoVs from this study are available in GenBank under accession numbers MN611517 to MN611525.
SOURCE: Li B et al. mSphere 2020 Jan 29;5:e00807-19.
Enrichment next-generation sequencing (NGS) provides a more cost-efficient and sensitive method for detecting and sequencing novel coronaviruses from wild bat populations, according to a study reported in mSphere, an open-access journal from the American Society for Microbiology.
With the appearance of the new zoonotic Wuhan coronavirus, the importance of monitoring the likelihood of new virus risks in wildlife reservoirs has been heightened. Bats in particular have been found to be the most common reservoir of coronaviruses, including being a probable source or mixing vessel for two previous modern epidemic coronaviruses: SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome) and MERS (Middle East respiratory syndrome).
“We should be alert and vigilant with the knowledge that bat CoVs [coronaviruses] are likely to cause another disease outbreak, not only because of their prevalence but also because the high frequency of recombination between viruses may lead to the generation of viruses with changes in virulence,” according to Bei Li, MD, of the Wuhan (China) Institute of Virology, and colleagues.
“We previously provided serological evidence that [HKU8-related] CoV had jumped over from bats to camels and recombined with MERS-CoV, alerting other researchers that the CoV species could be dangerous. ... Genome-level comparison is needed to monitor the risk of alterations in species tropism and pathogenesis,” according to study authors. They performed a study to develop a more effective and cost efficient method for detecting and sequencing novel coronaviruses in the bat population.
The taxonomy of coronaviruses is particularly complex and may be too narrowly defined, given the high level of genetic plasticity found. There are four genera (Alpha-, Beta-, Gamma-, and Deltacoronavirus) consisting of 38 unique species in the CoV subfamily Orthocoronavirinae, and the number is increasing. Viral taxomists rely on the open reading frame 1b (ORF1b) gene for classification, but viruses in the same species may show great diversity in regions outside ORF1b, confounding the species designation. In particular, bat CoVs classed as the same species can differ significantly in terms of receptor usage or virus-host interaction, as observed in bat SARS-related CoVs, according to the researchers.
The researchers obtained RNA from previous bat CoV surveillance projects, which used bat rectal swabs. Libraries for NGS were constructed from total RNA and processed to generate RNA fragments larger than 300 nucleotides. Following first- and second-strand cDNA synthesis, double-stranded cDNA was purified and the library was amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology.
Targeted CoV genome enrichment was achieved using 4,303 customized biotinylated 120-mer baits. These baits were designed from 90 representative CoV genomes, and in silico analysis determined that these baits should target the known CoV species tested. These baits were added and hybridized to the libraries. To capture virus-specific library fragments, streptavidin magnetic beads (which bind to biotin) were added to the hybridization reaction mixture. The beads were then washed to remove unbound DNA. The postcapture virus-specific library fragments were then amplified using a subsequent round of PCR.
The enrichment NGS were retrospectively complemented with unbiased NGS and/or additional Sanger sequencing to obtain full-length genomes. The study showed that enrichment NGS not only decreased the amount of data requiring analysis but produced full-length genome coverage in both laboratory and clinical samples.
Using this technology, the researchers “effectively reduced sequencing costs by increasing the sensitivity of detection. We discovered nine full genomes of bat CoVs in this study and revealed great genetic diversity for eight of them.” In addition, they noted that using standard targeted PCR, which is common practice for many surveillance studies, would not have discovered this diversity.
“We should be alert and vigilant with the knowledge that bat CoVs are likely to cause another disease outbreak, not only because of their prevalence but also because the high frequency of recombination between viruses may lead to the generation of viruses with changes in virulence,” according to the researchers.
“We have provided a cost-effective methodology for bat CoV surveillance. The high genetic diversity observed in our newly sequenced samples suggests further work is needed to characterize these bat CoVs prior to or in the early stages of spillover to humans,” the authors concluded.
This study was supported by the Chinese government. The authors reported that they had no conflicts.
Viral genome data for new CoVs from this study are available in GenBank under accession numbers MN611517 to MN611525.
SOURCE: Li B et al. mSphere 2020 Jan 29;5:e00807-19.
FROM MSPHERE